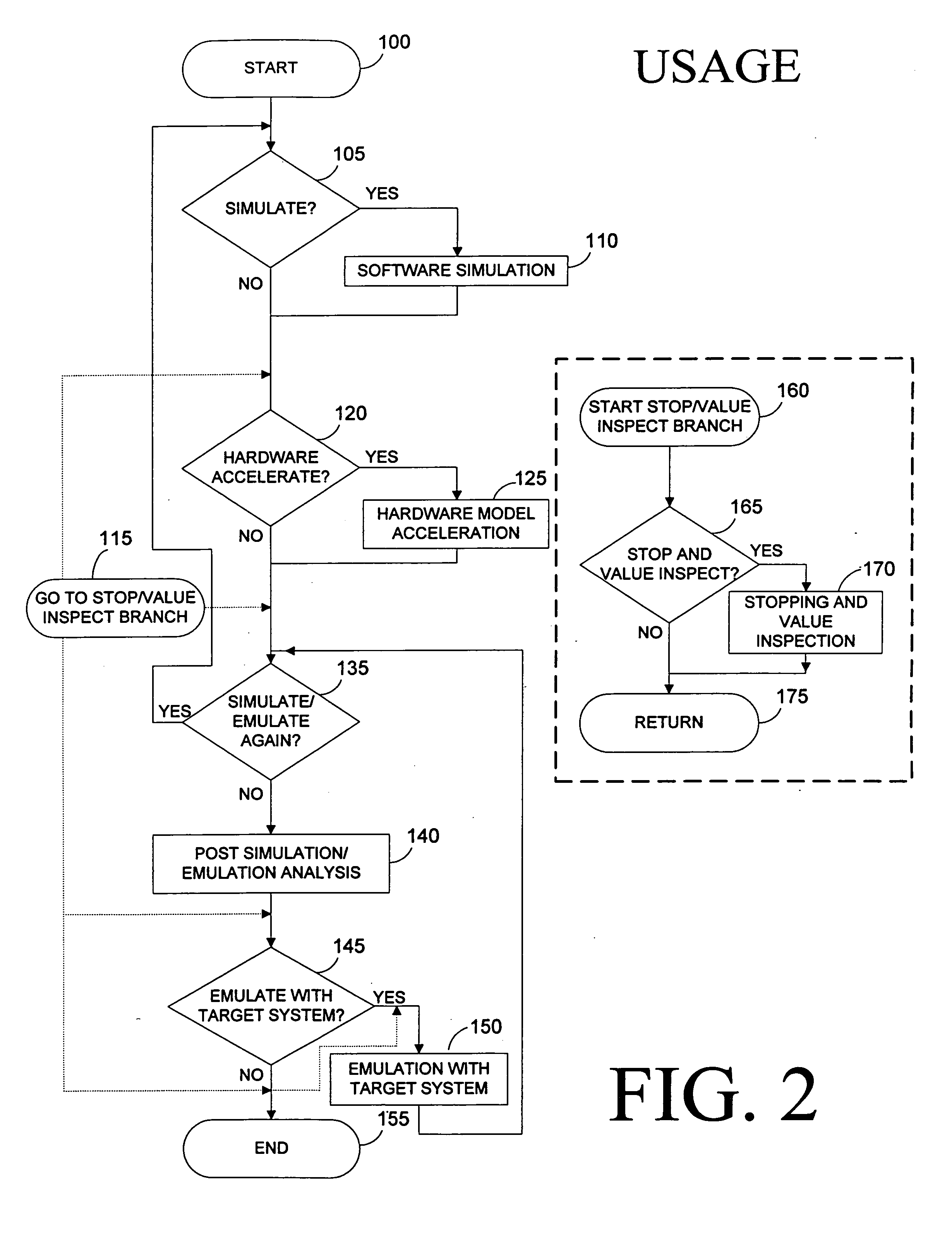
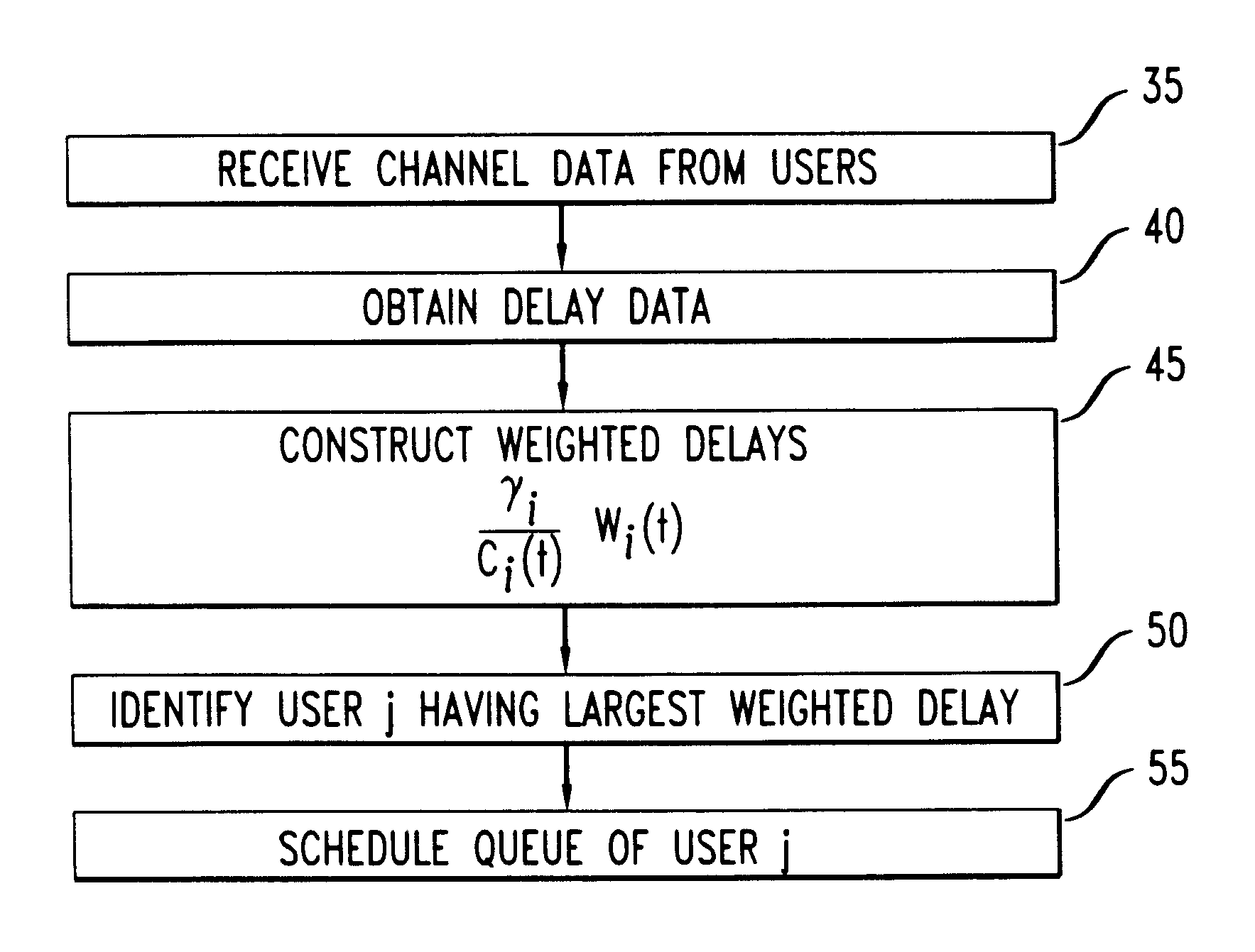
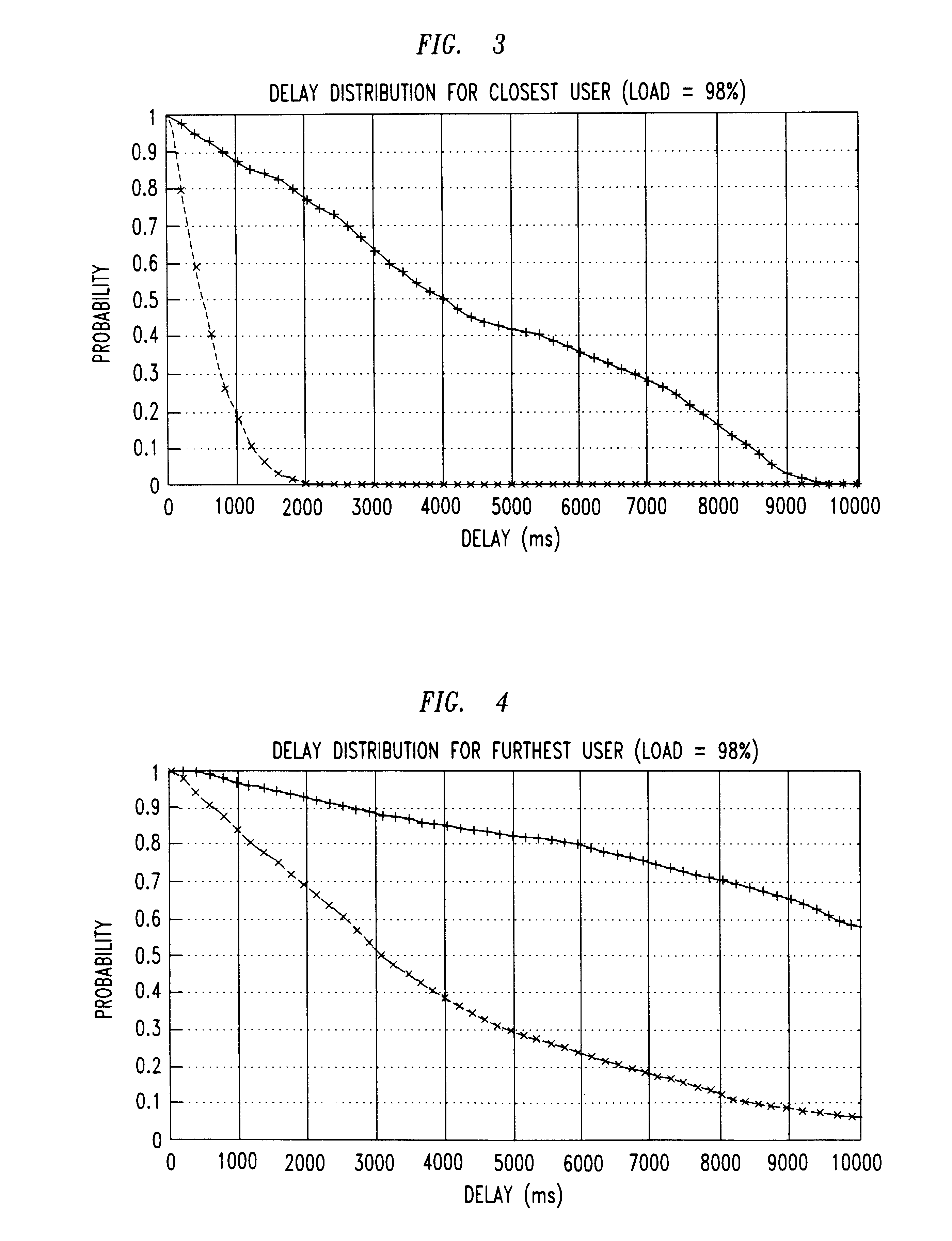
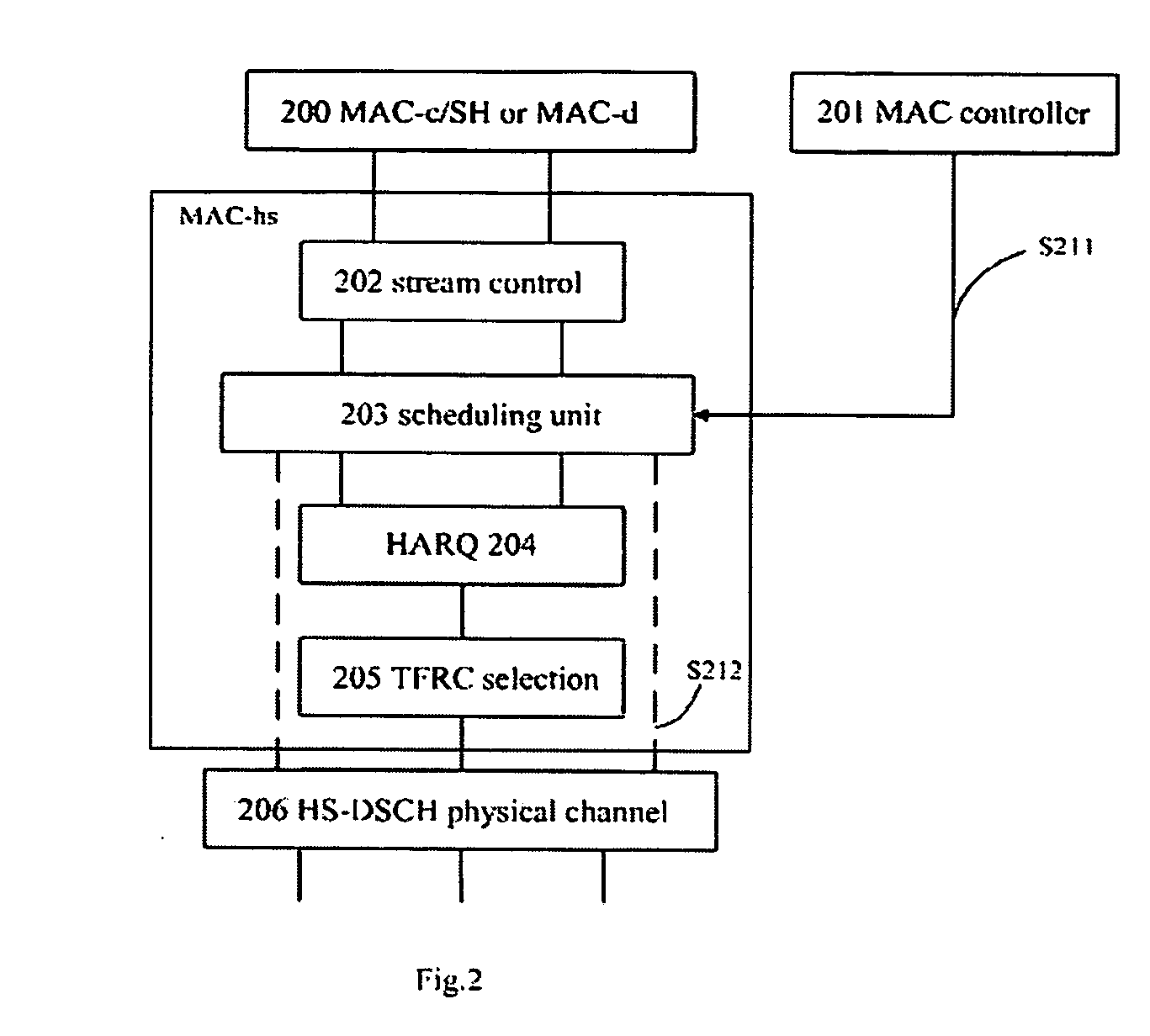
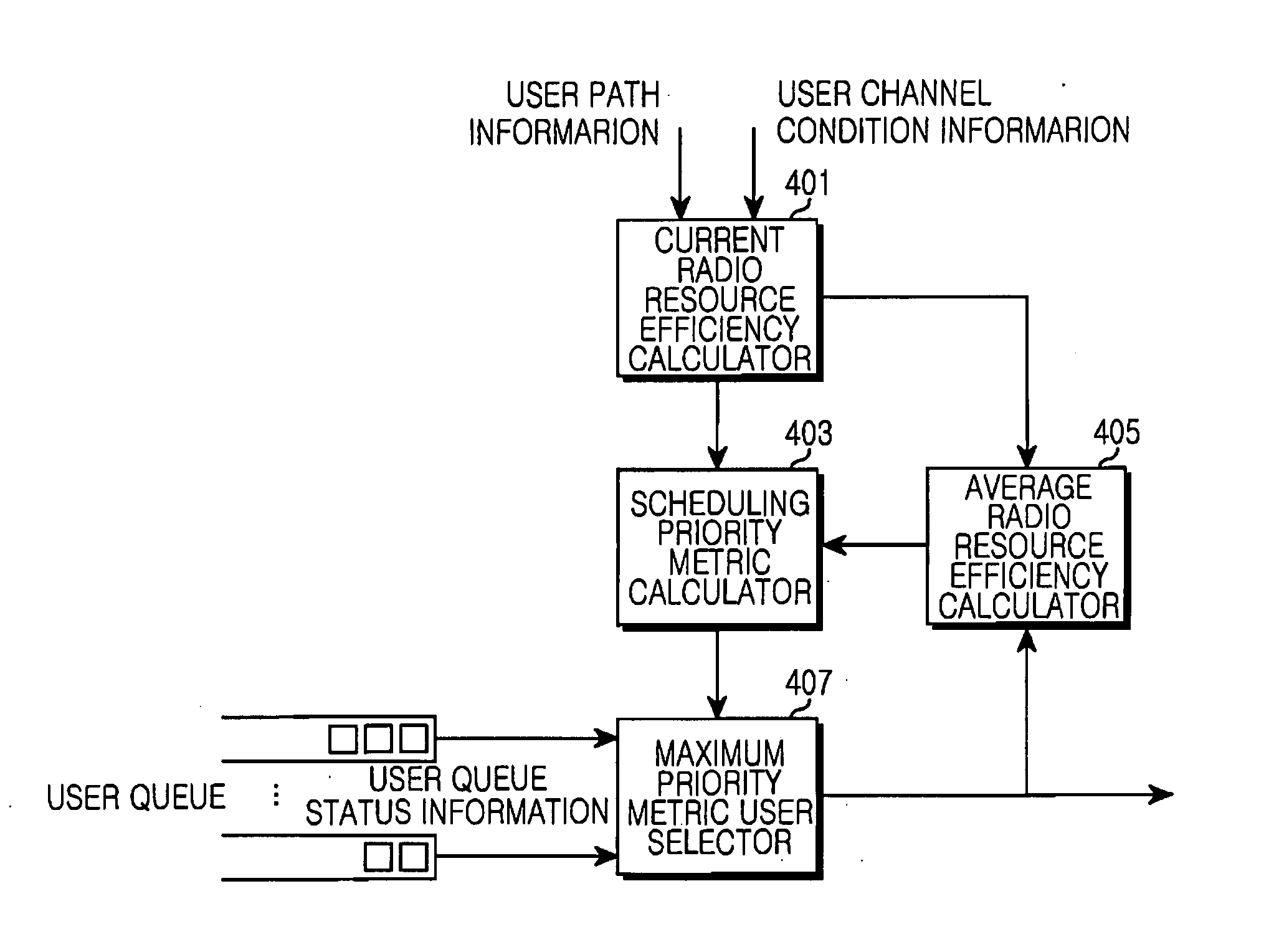
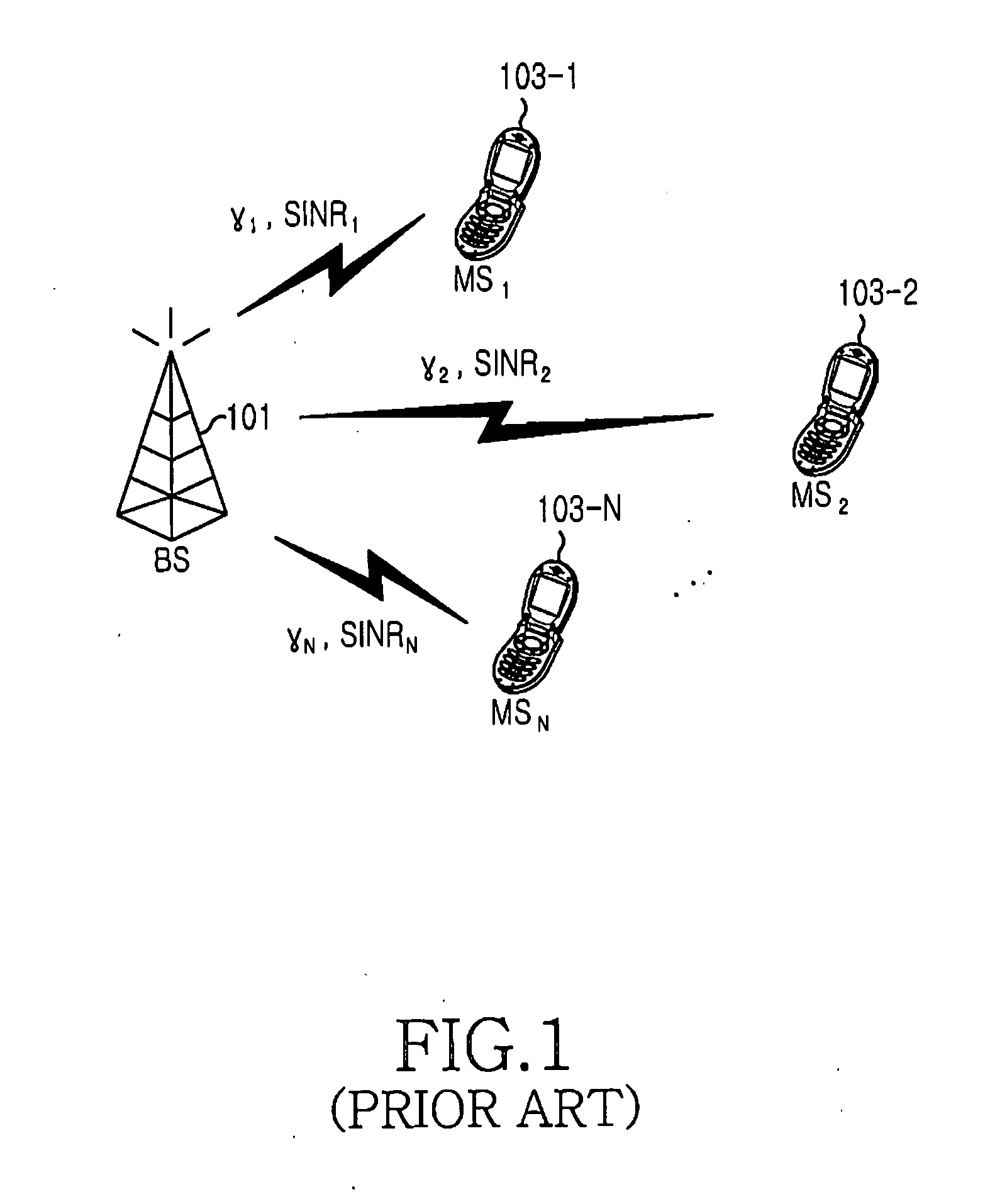
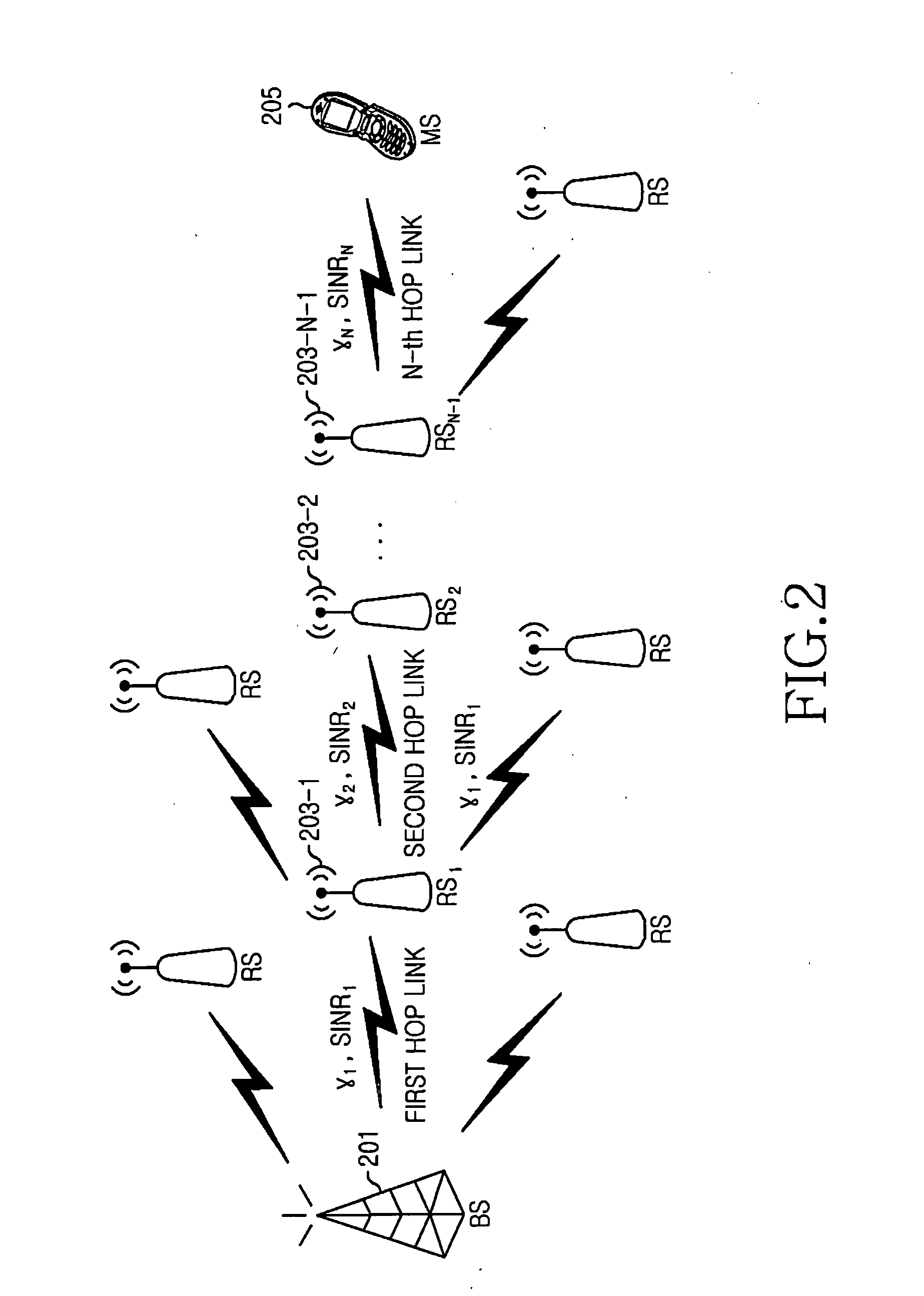
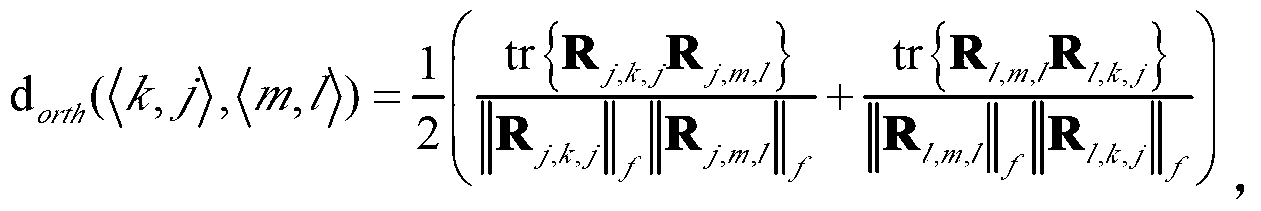Patents
Literature
477 results about "Packet scheduling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
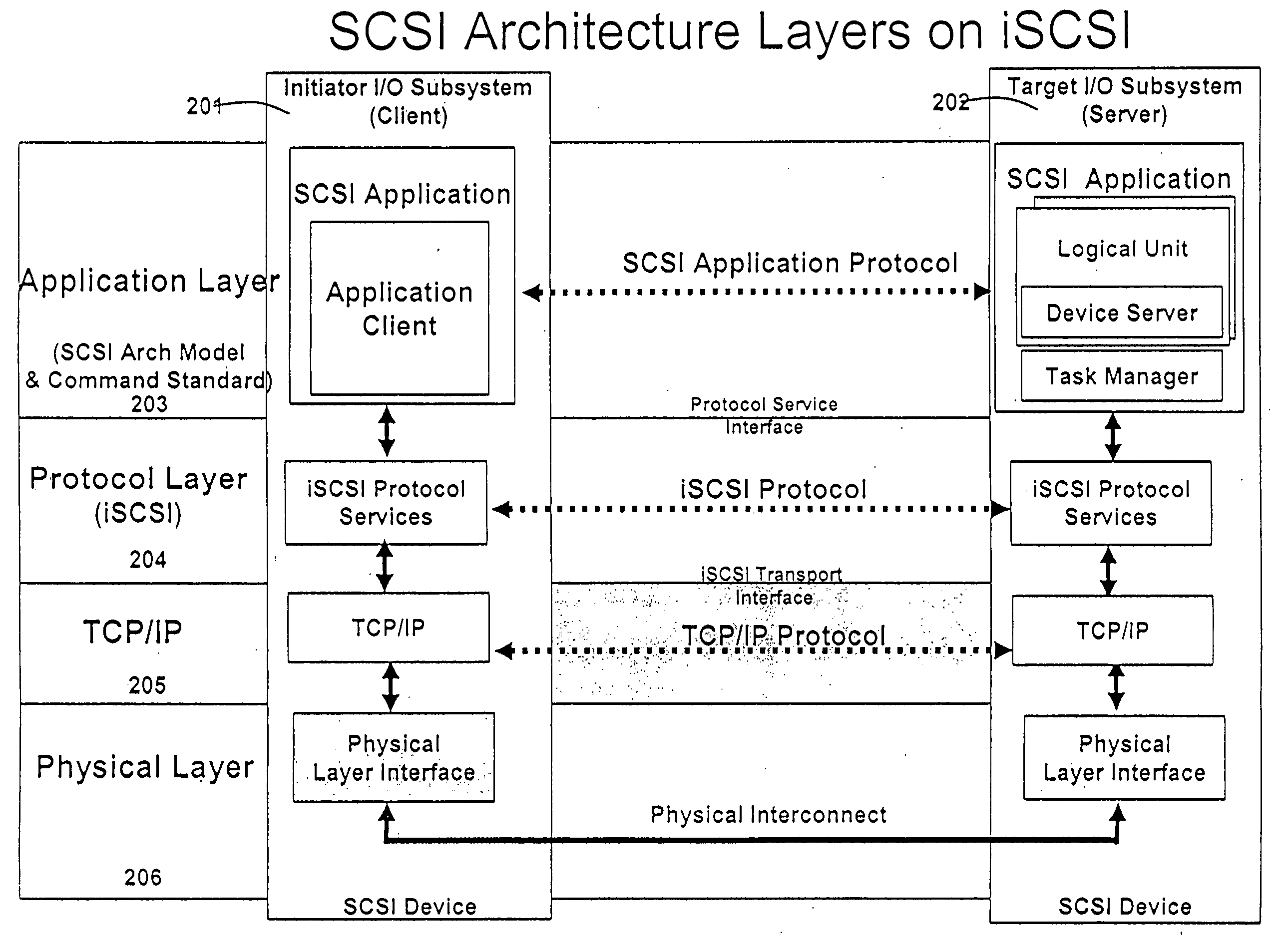
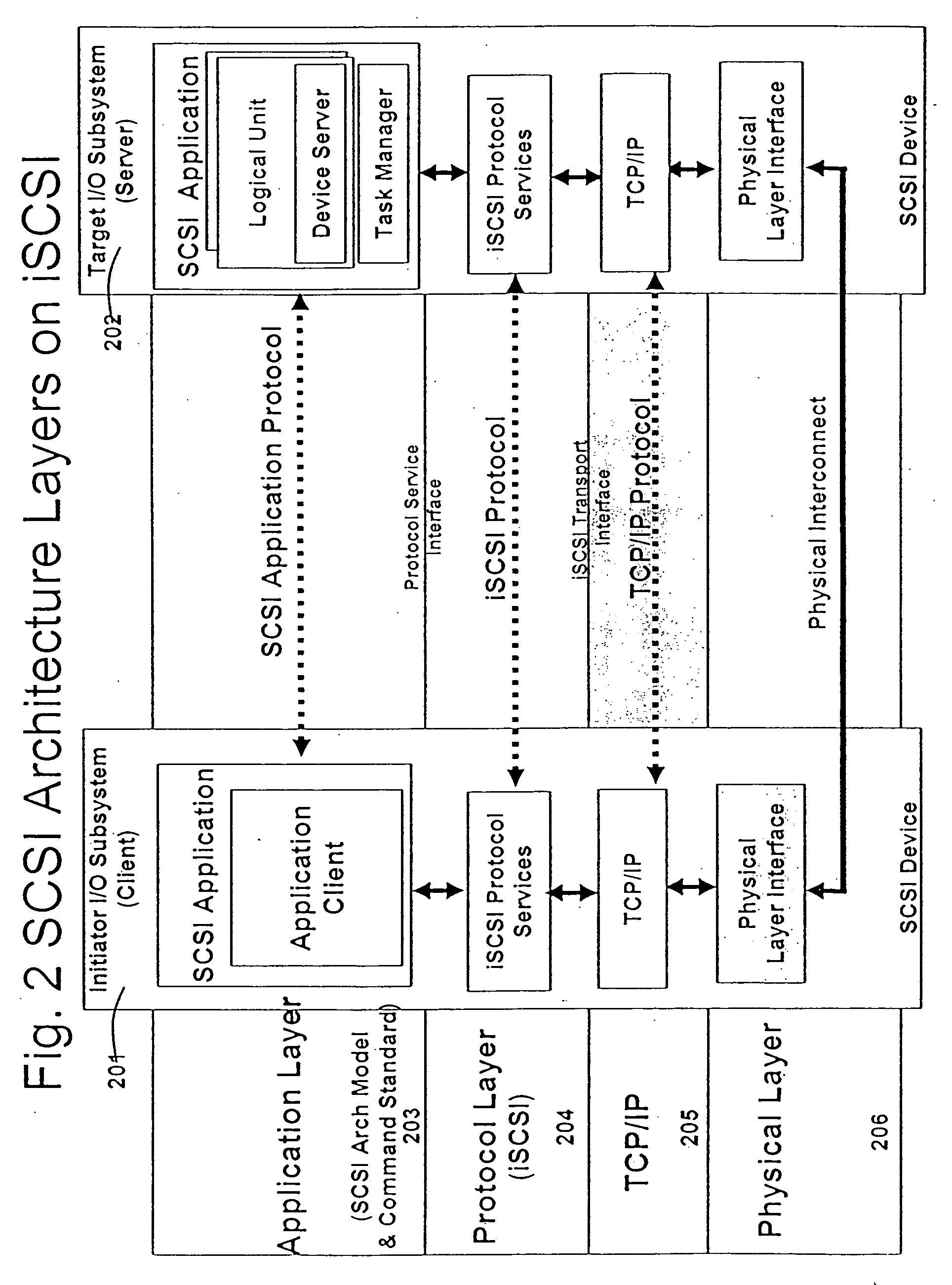
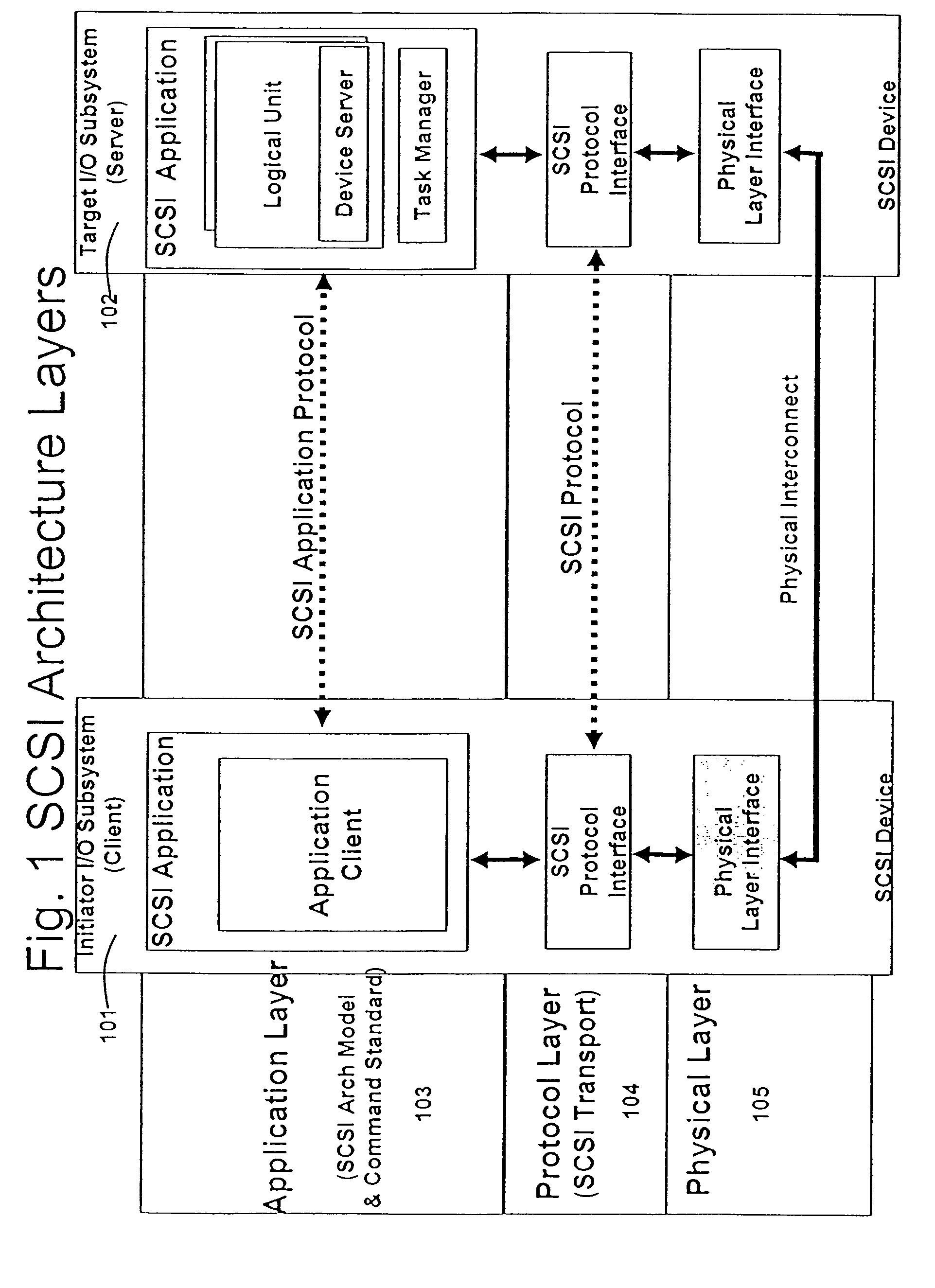
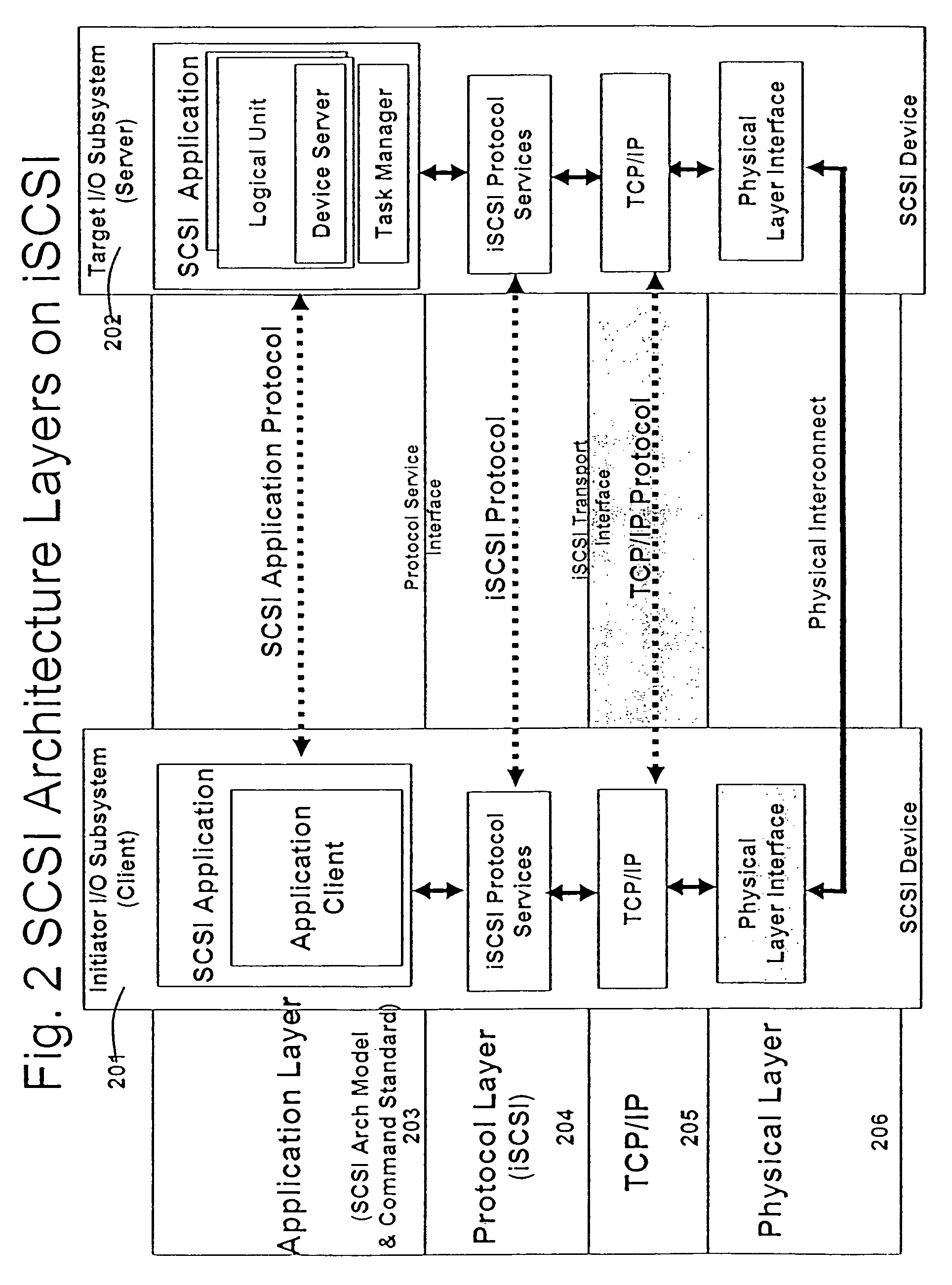
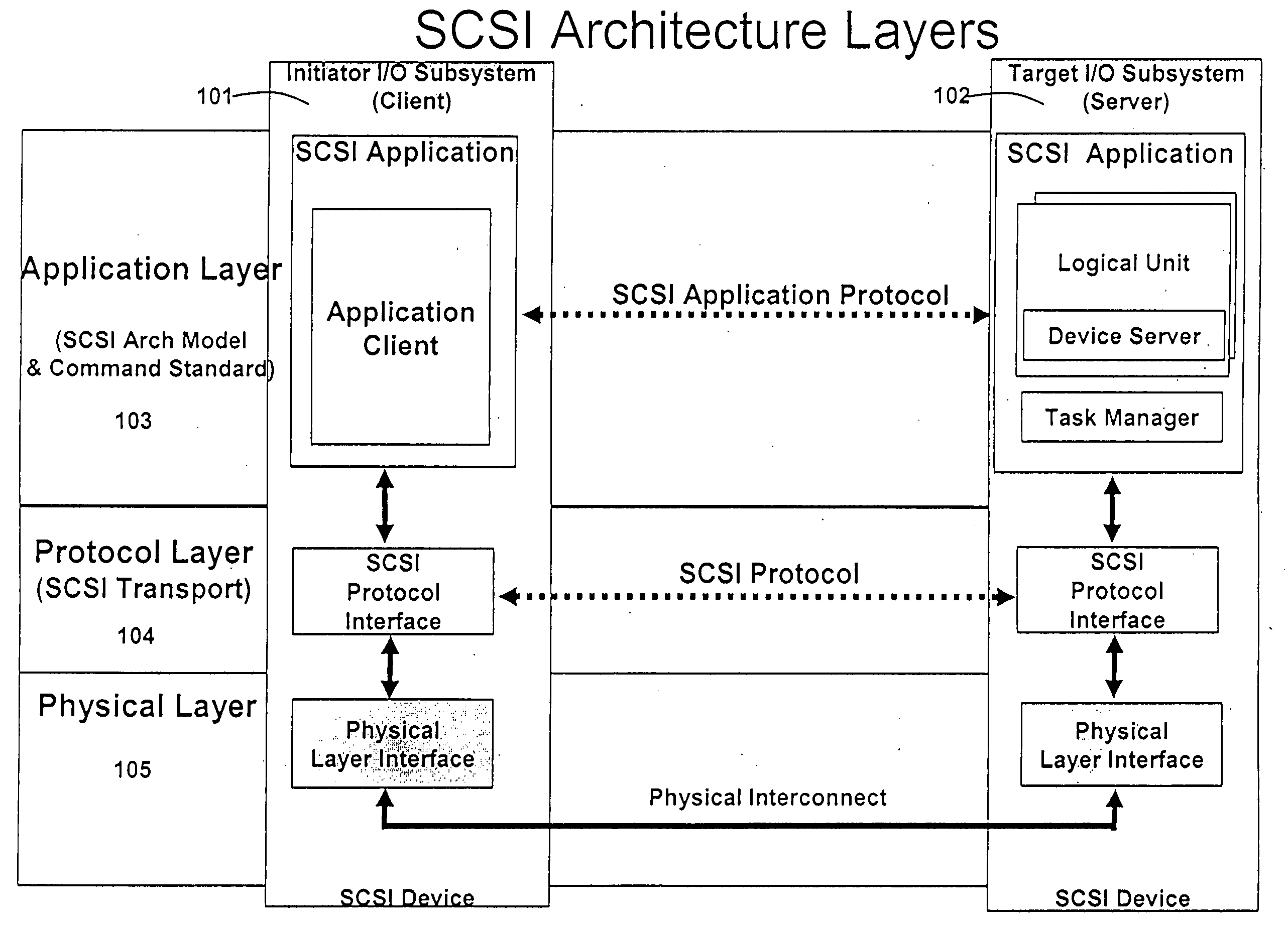
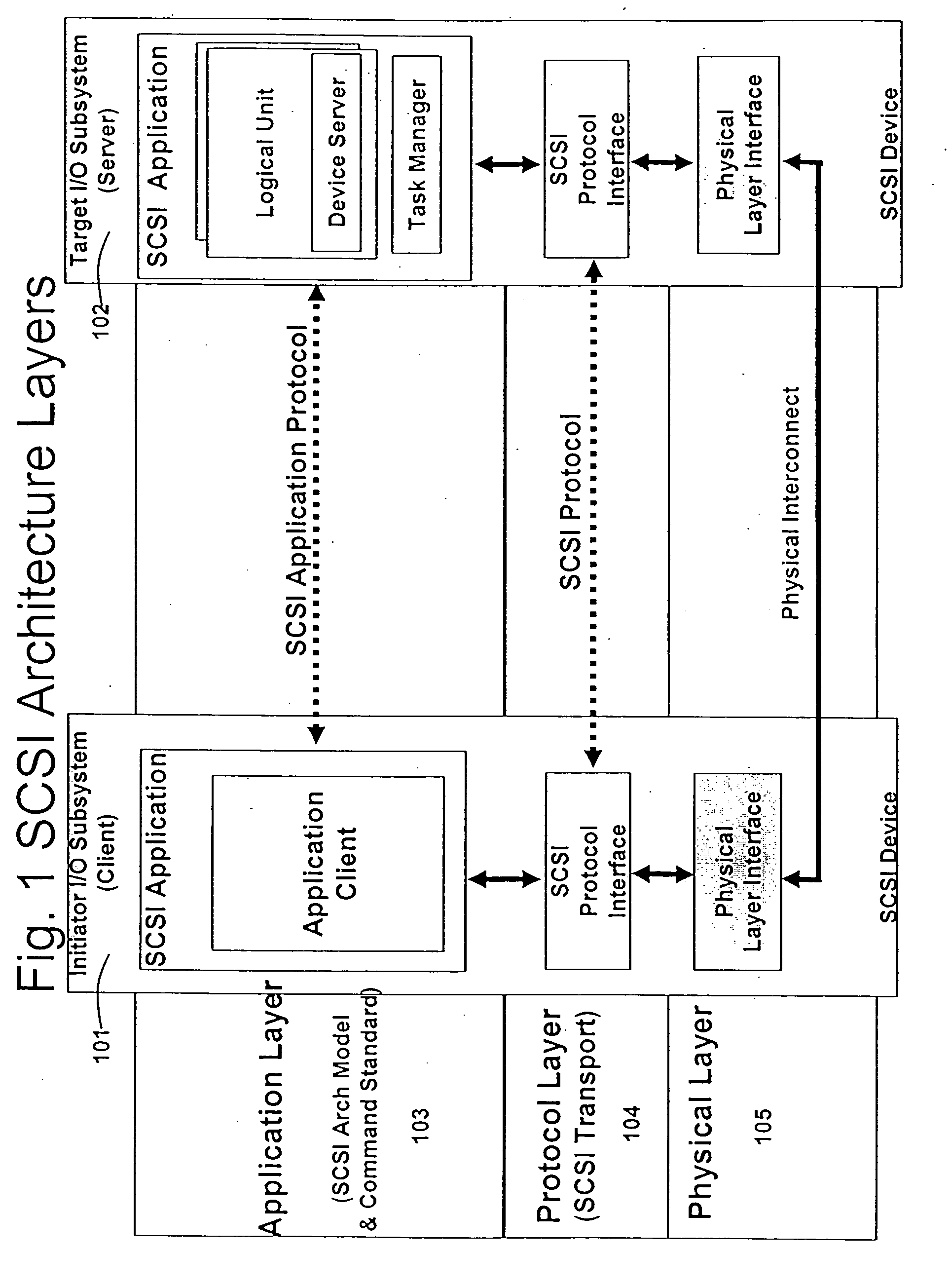
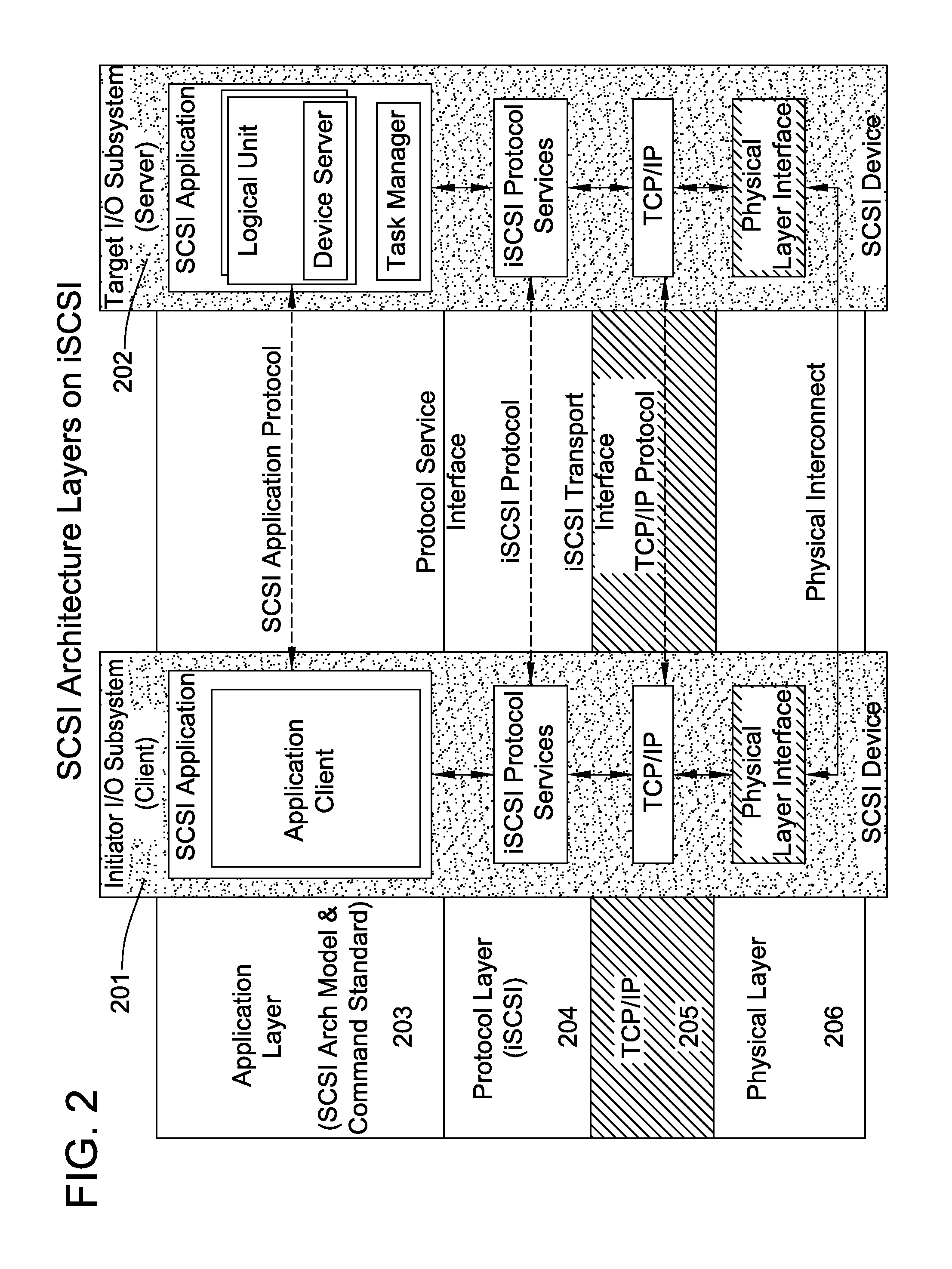
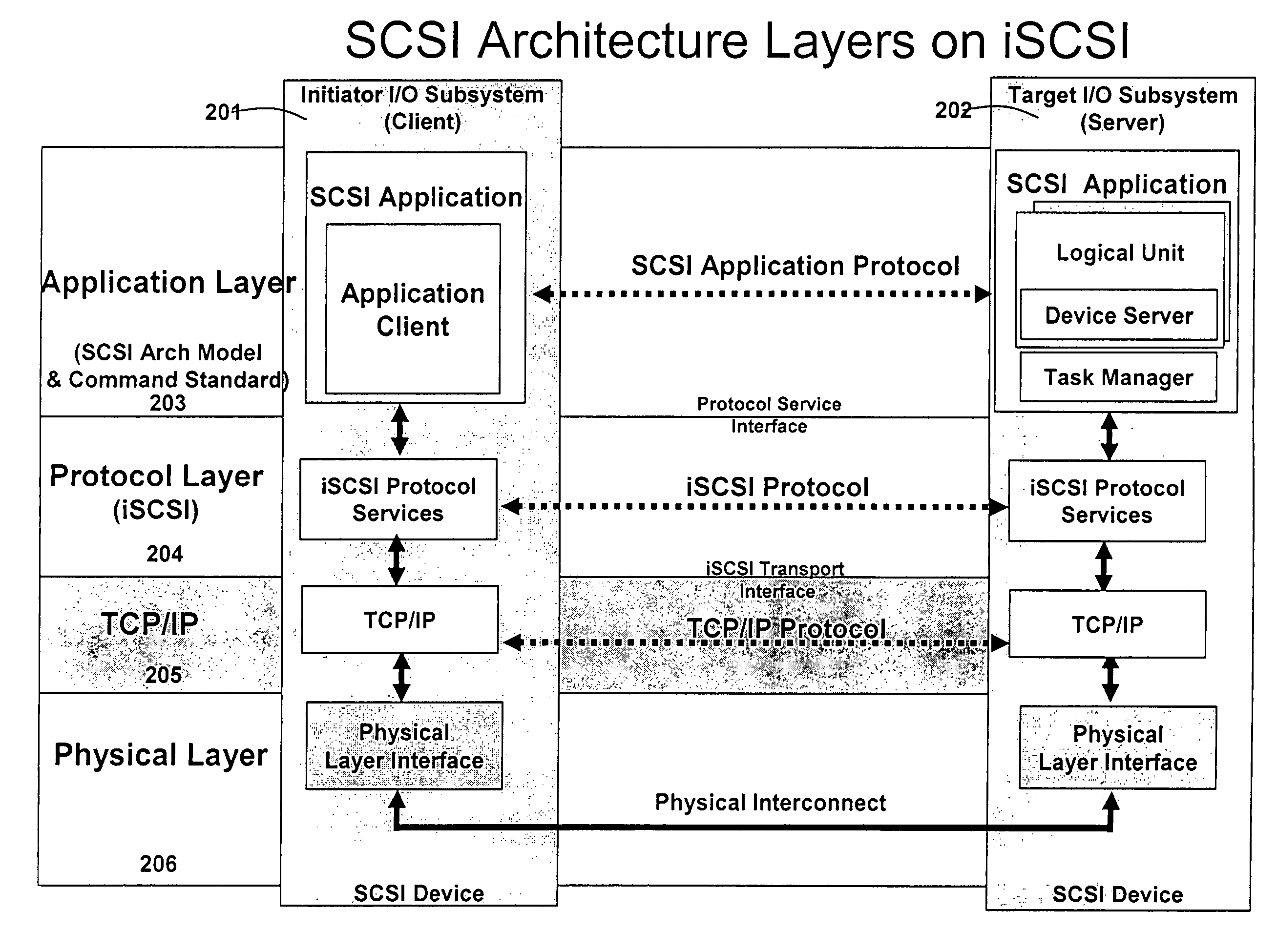
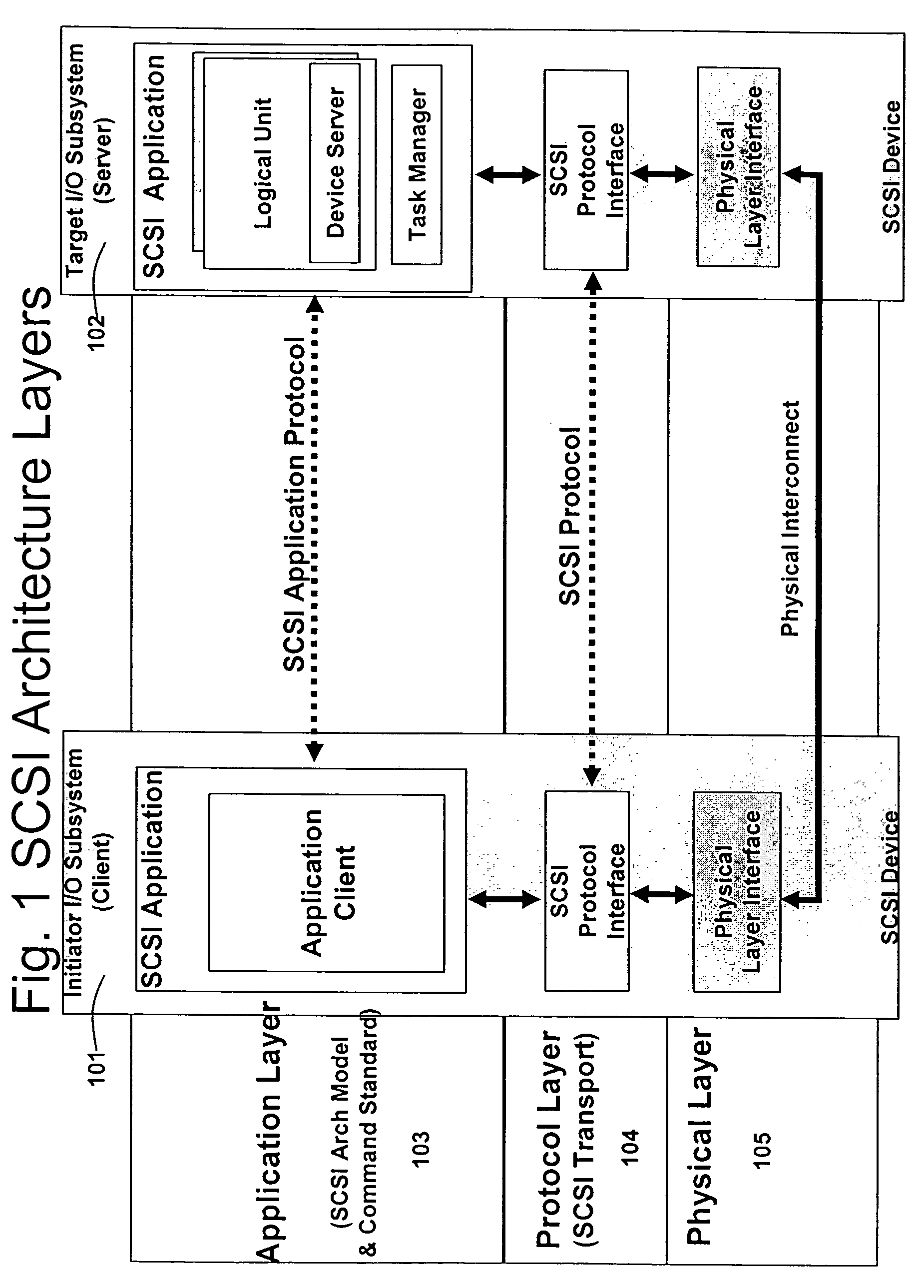
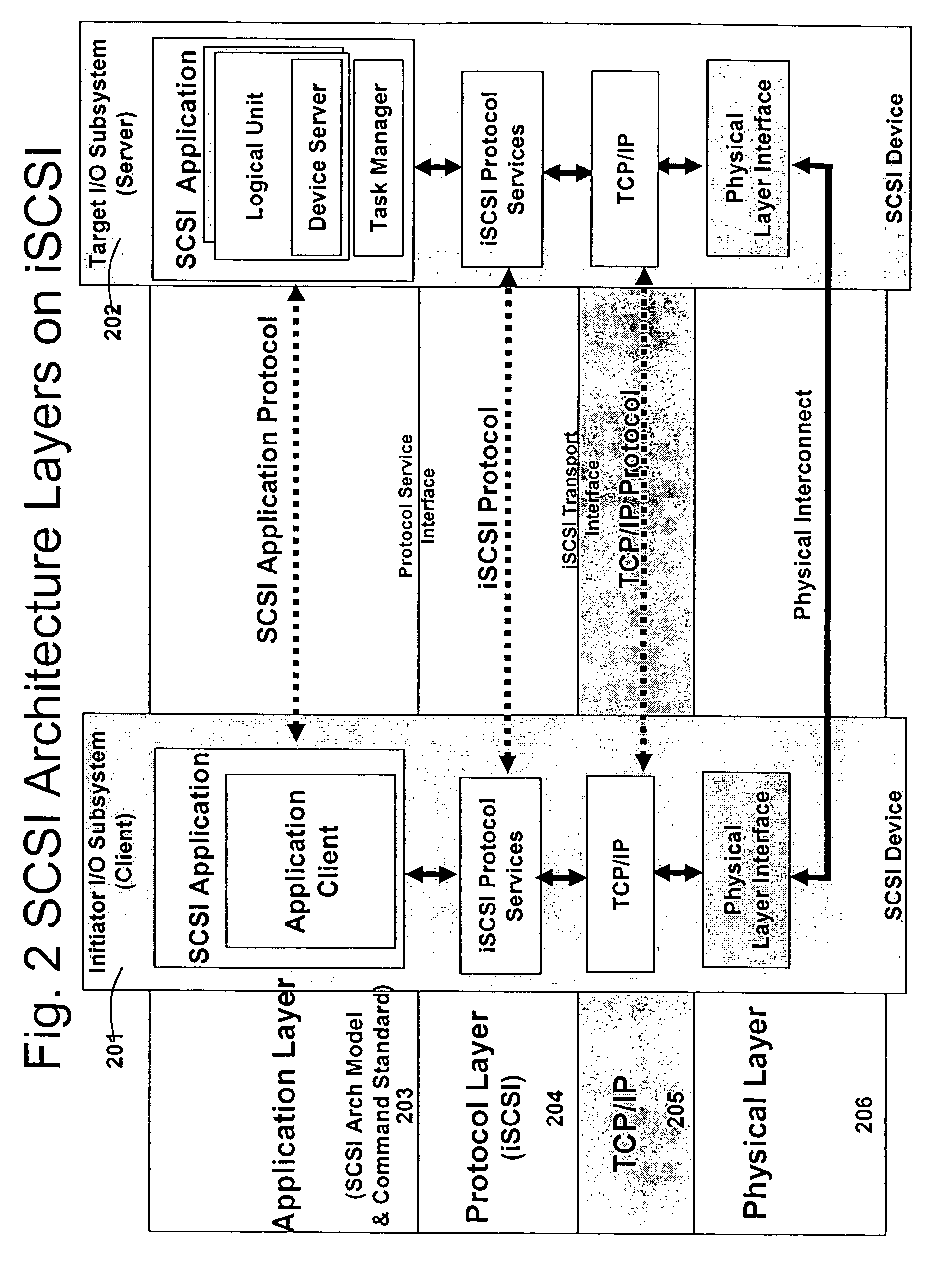
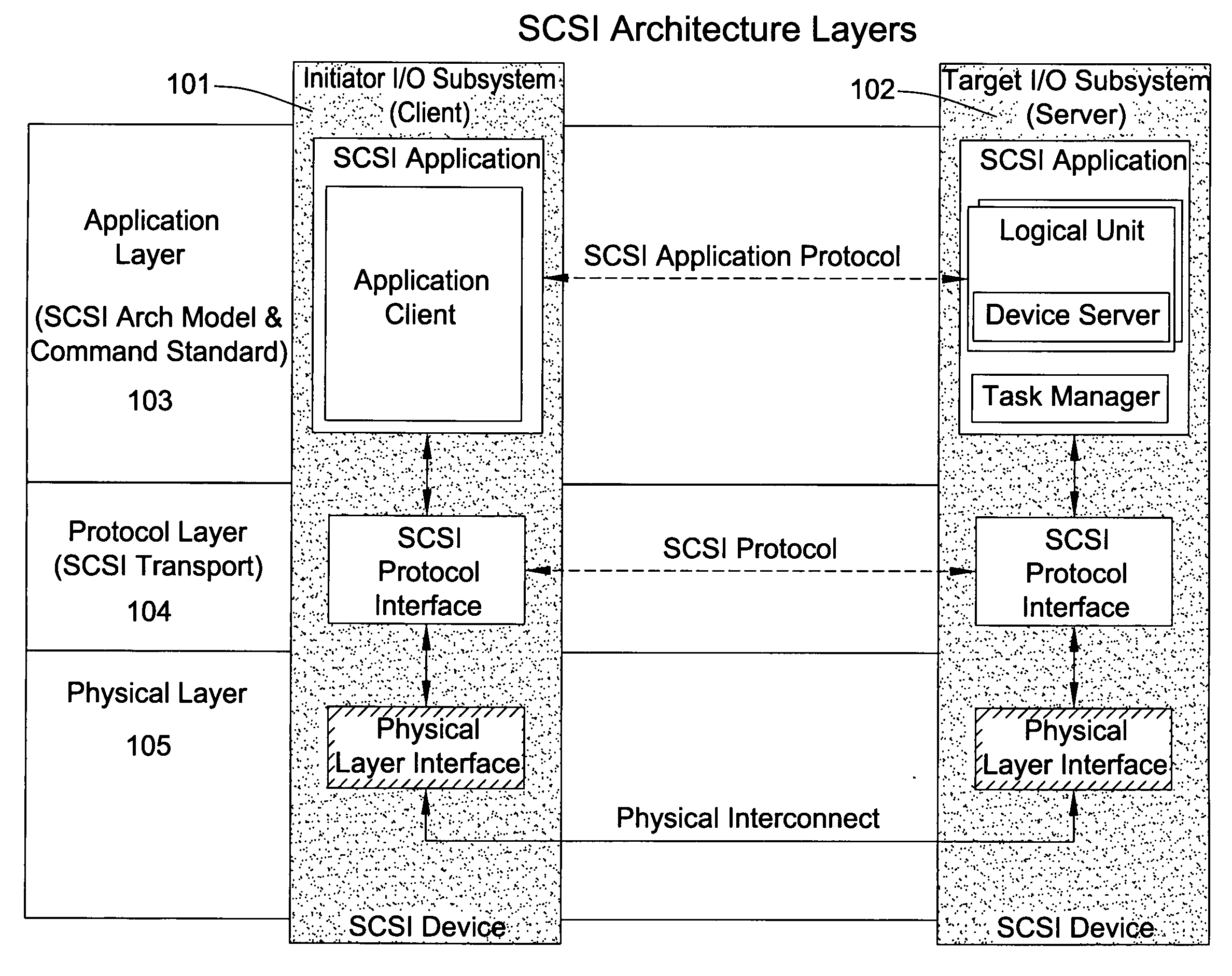
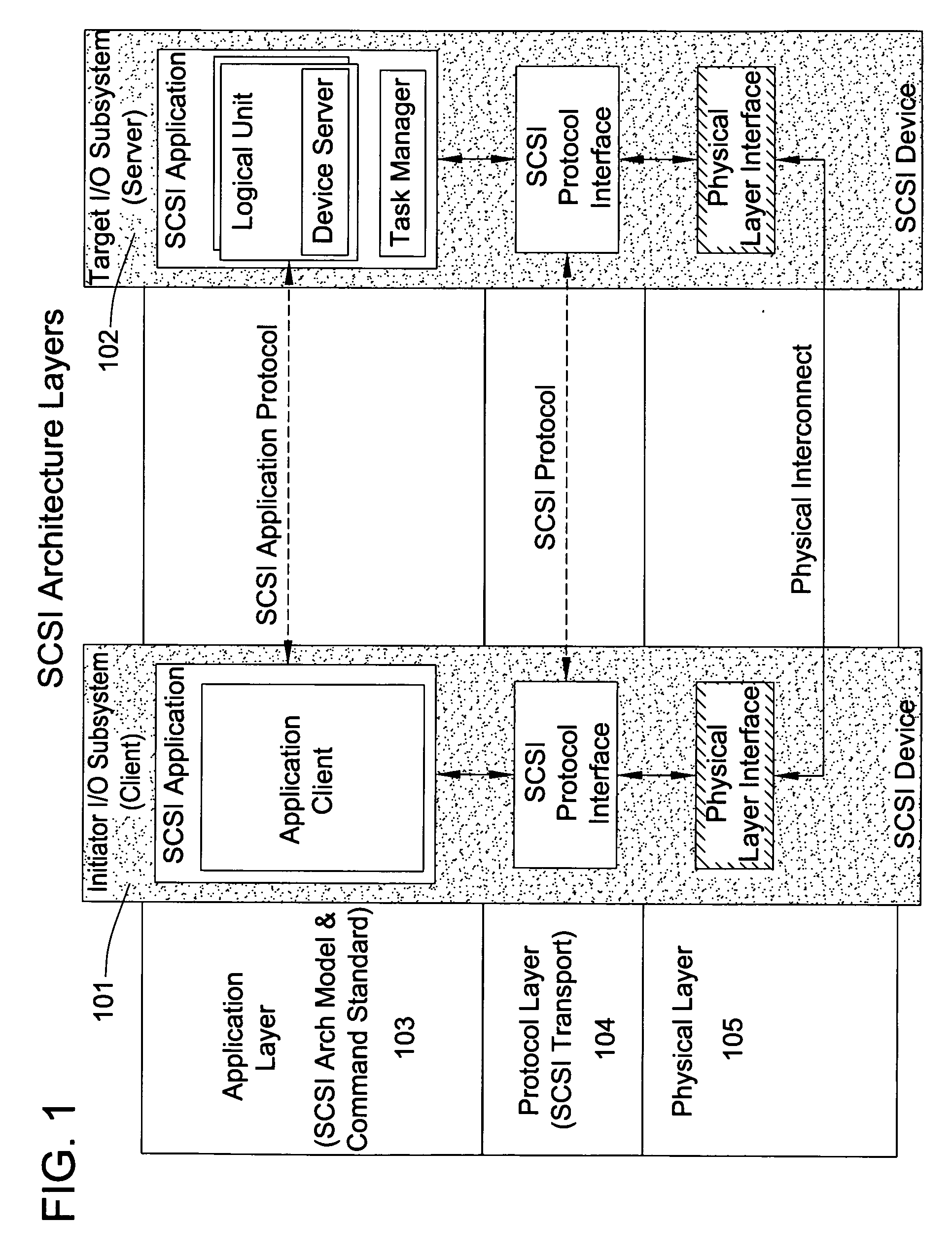
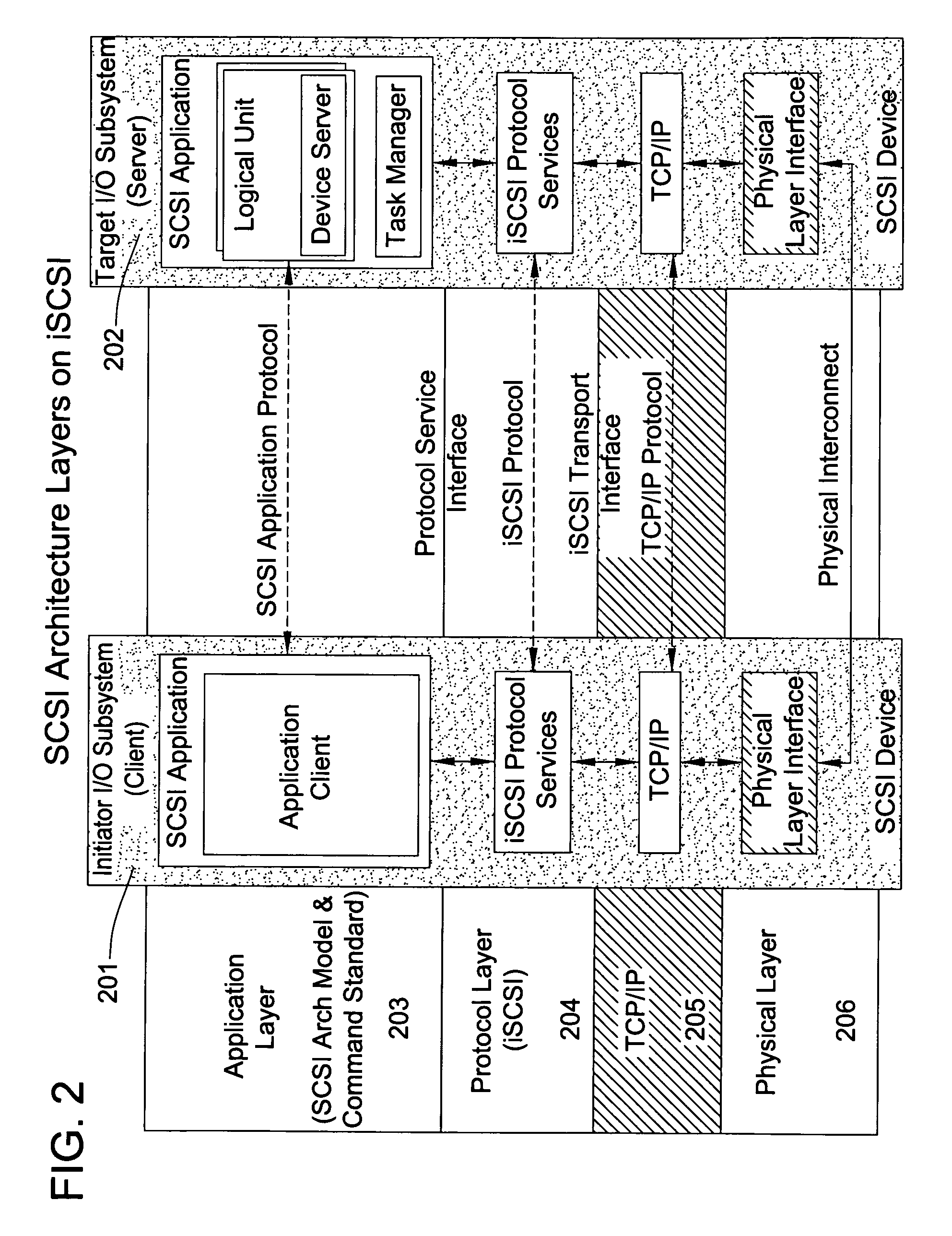
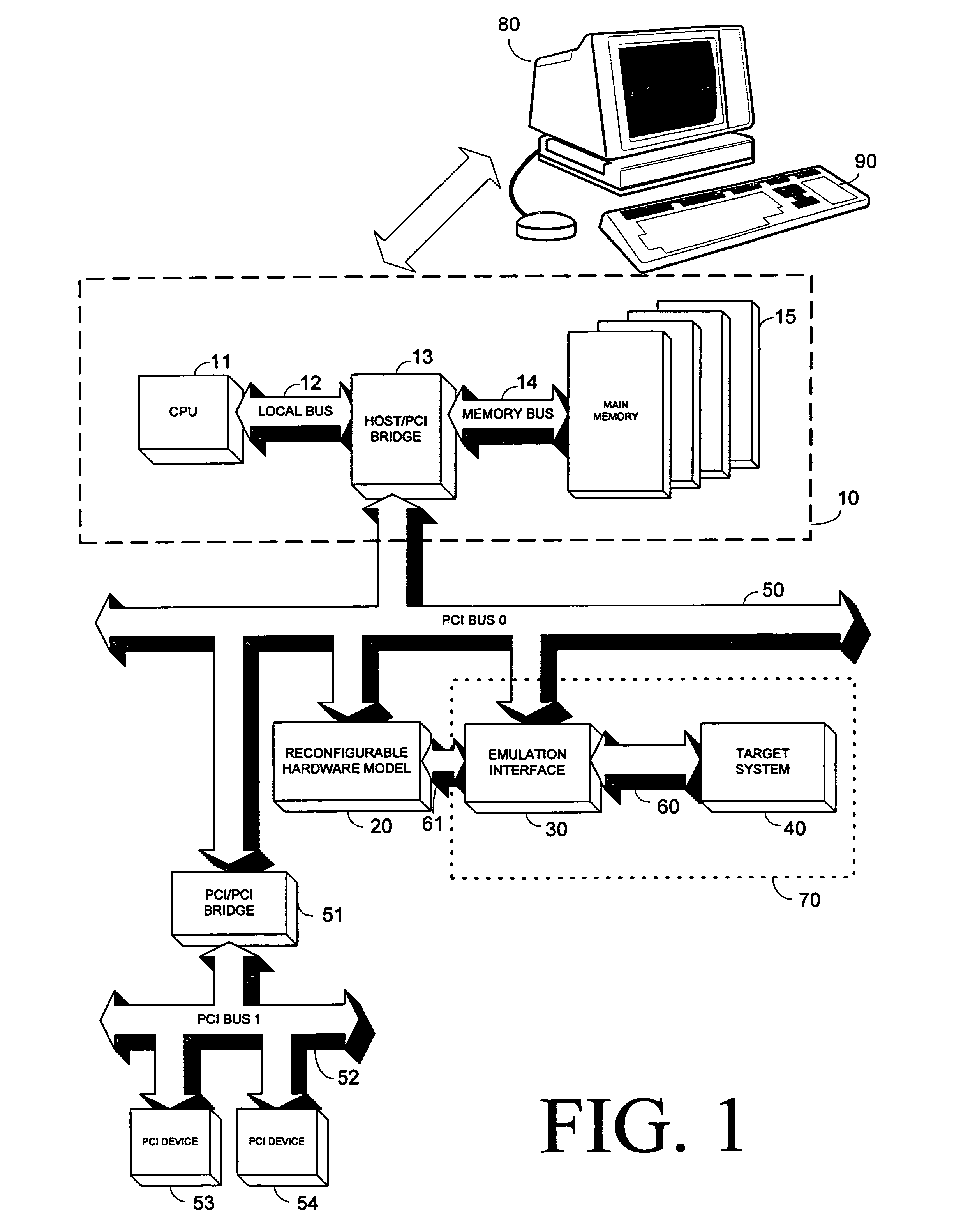
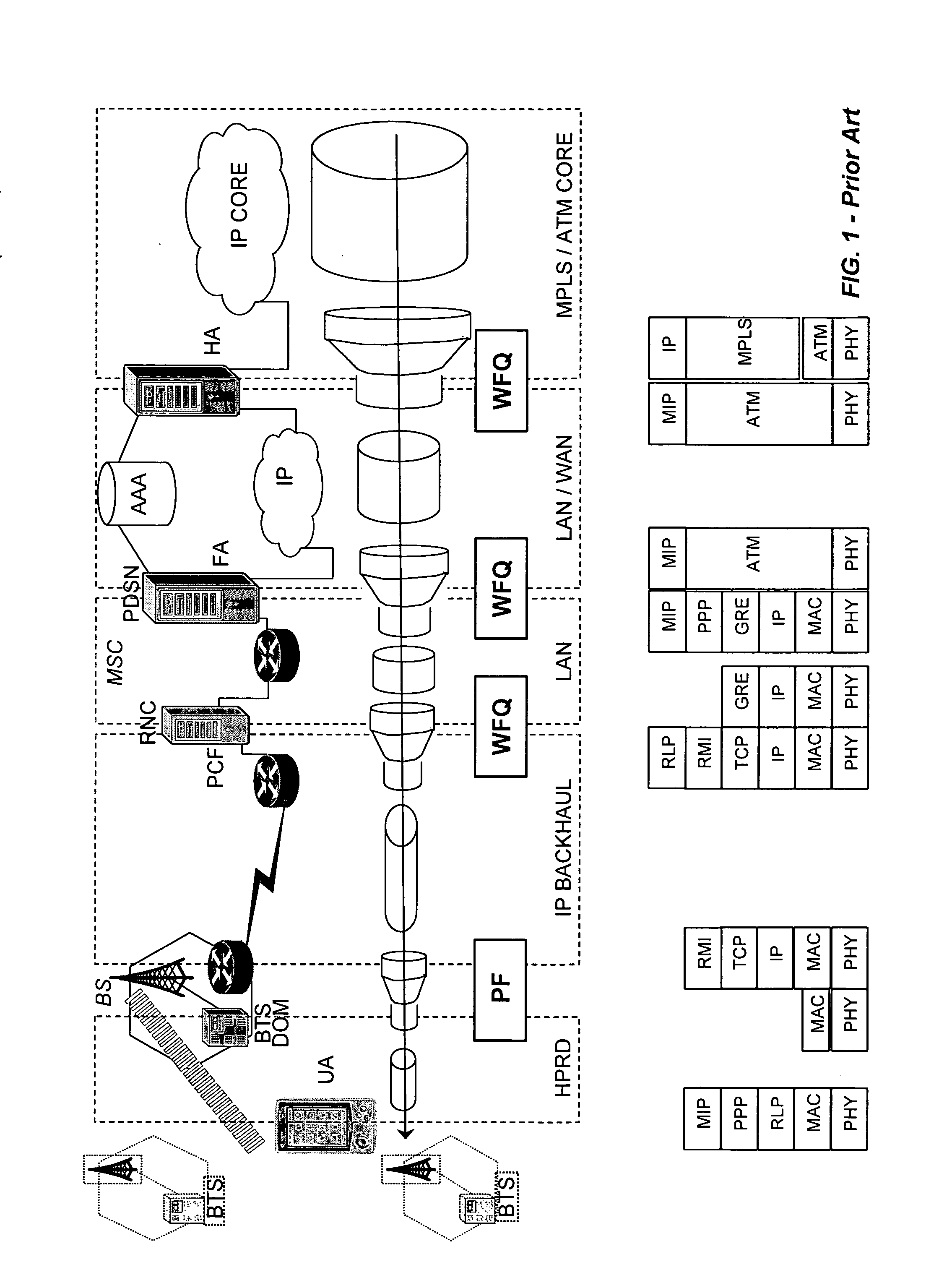
A packet scheduling algorithm is employed by the server to schedule the appropriate forwarding order to the outgoing link to meet a variety of QoS requirements associated to each packet. For wireline systems, the physical medium is in general regarded as stable and robust.
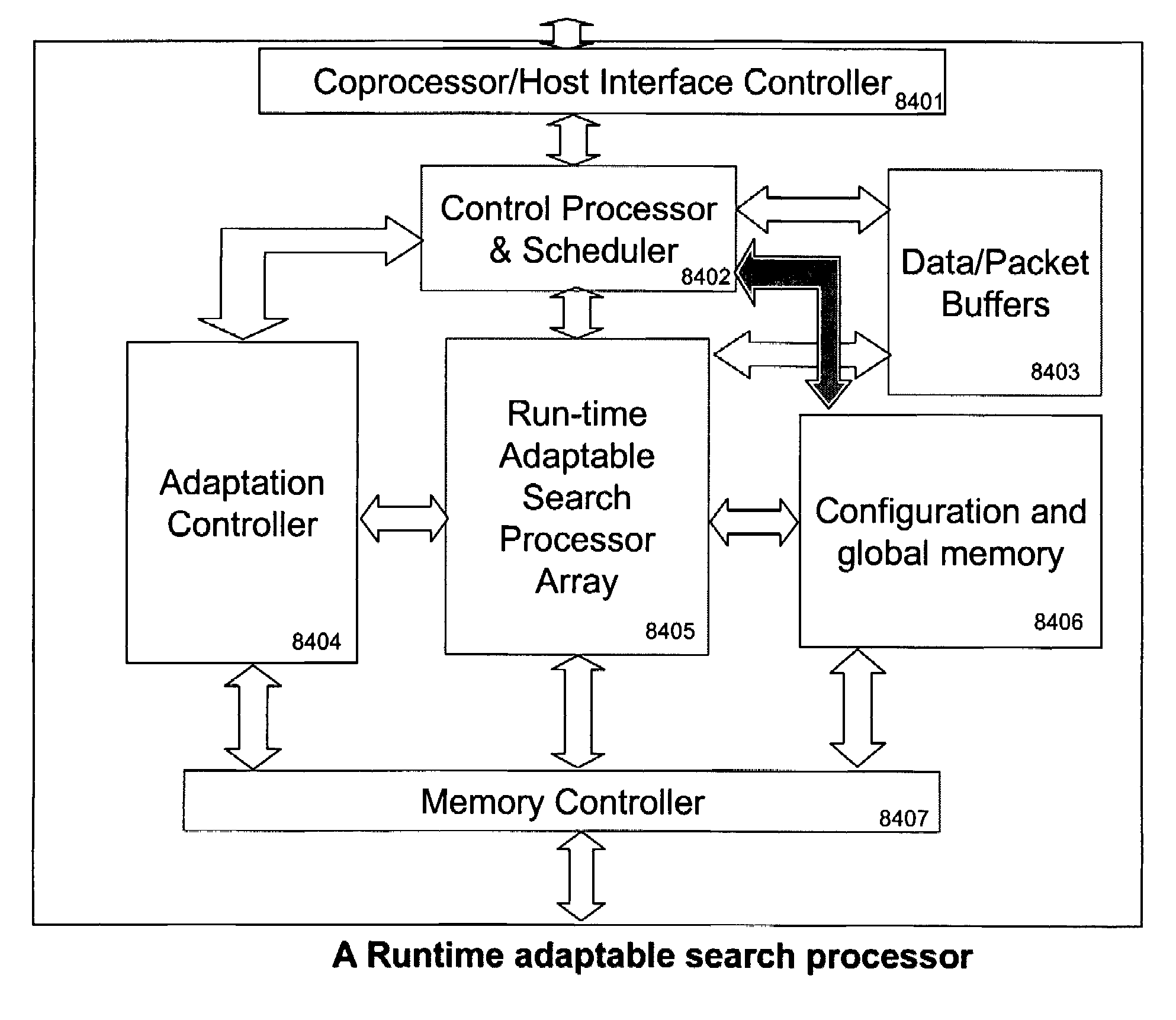
Runtime adaptable search processor
ActiveUS20060136570A1Reduce stacking processImproving host CPU performanceWeb data indexingMultiple digital computer combinationsData packInternal memory
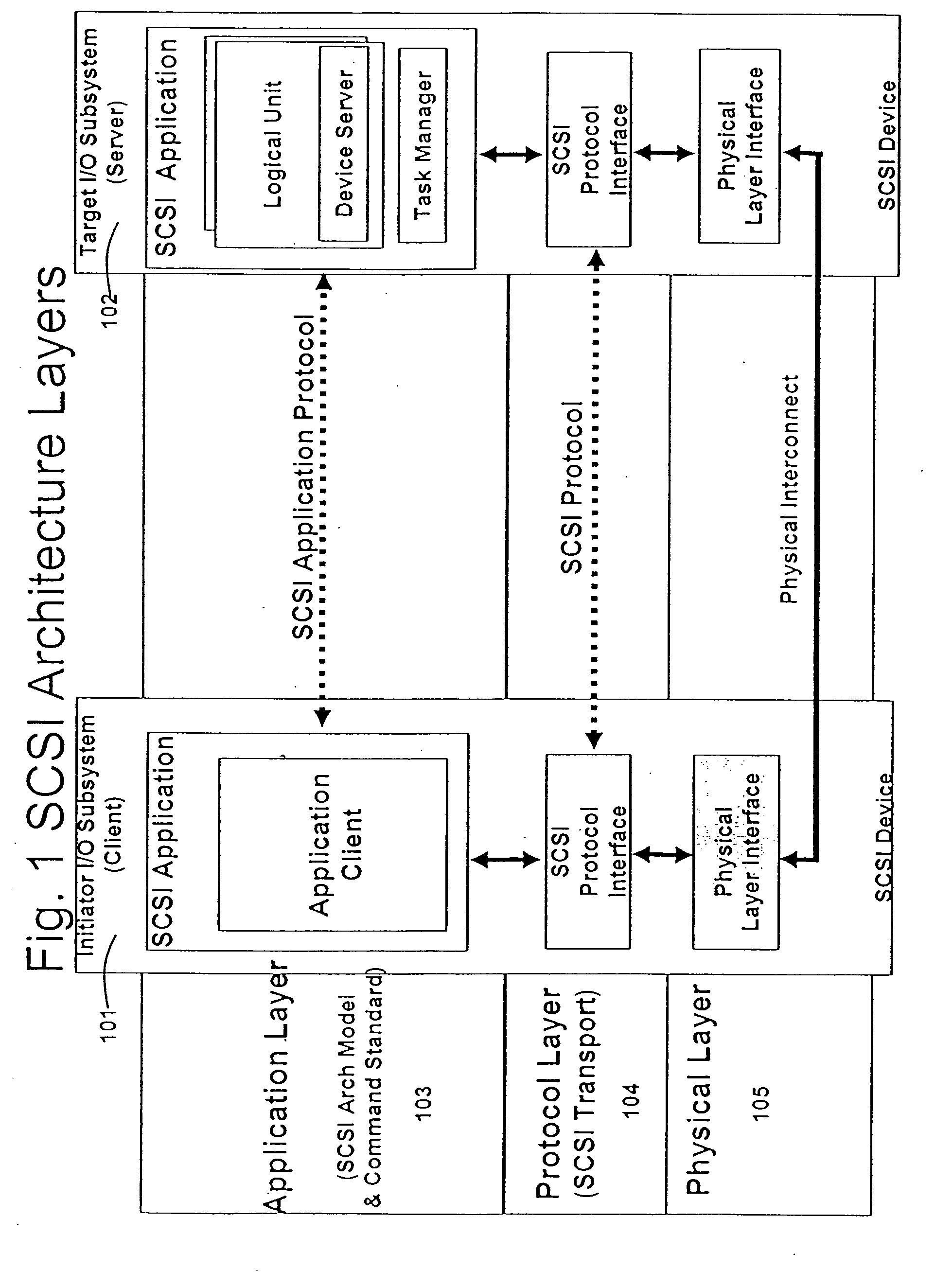
A runtime adaptable search processor is disclosed. The search processor provides high speed content search capability to meet the performance need of network line rates growing to 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps and higher. he search processor provides a unique combination of NFA and DFA based search engines that can process incoming data in parallel to perform the search against the specific rules programmed in the search engines. The processor architecture also provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Runtime adaptable search processor
ActiveUS7685254B2Improve application performanceLarge capacityWeb data indexingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPacket schedulingSchema for Object-Oriented XML
A runtime adaptable search processor is disclosed. The search processor provides high speed content search capability to meet the performance need of network line rates growing to 1 Gbps, 10 Gbps and higher. The search processor provides a unique combination of NFA and DFA based search engines that can process incoming data in parallel to perform the search against the specific rules programmed in the search engines. The processor architecture also provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. Scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Runtime adaptable security processor
InactiveUS20050108518A1Improve performanceReduce overheadSecuring communicationInternal memoryPacket scheduling
A runtime adaptable security processor is disclosed. The processor architecture provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Packet scheduling for video transmission with sender queue control
InactiveUS20060095943A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTransport systemVideo transmission
Owner:SHARP KK
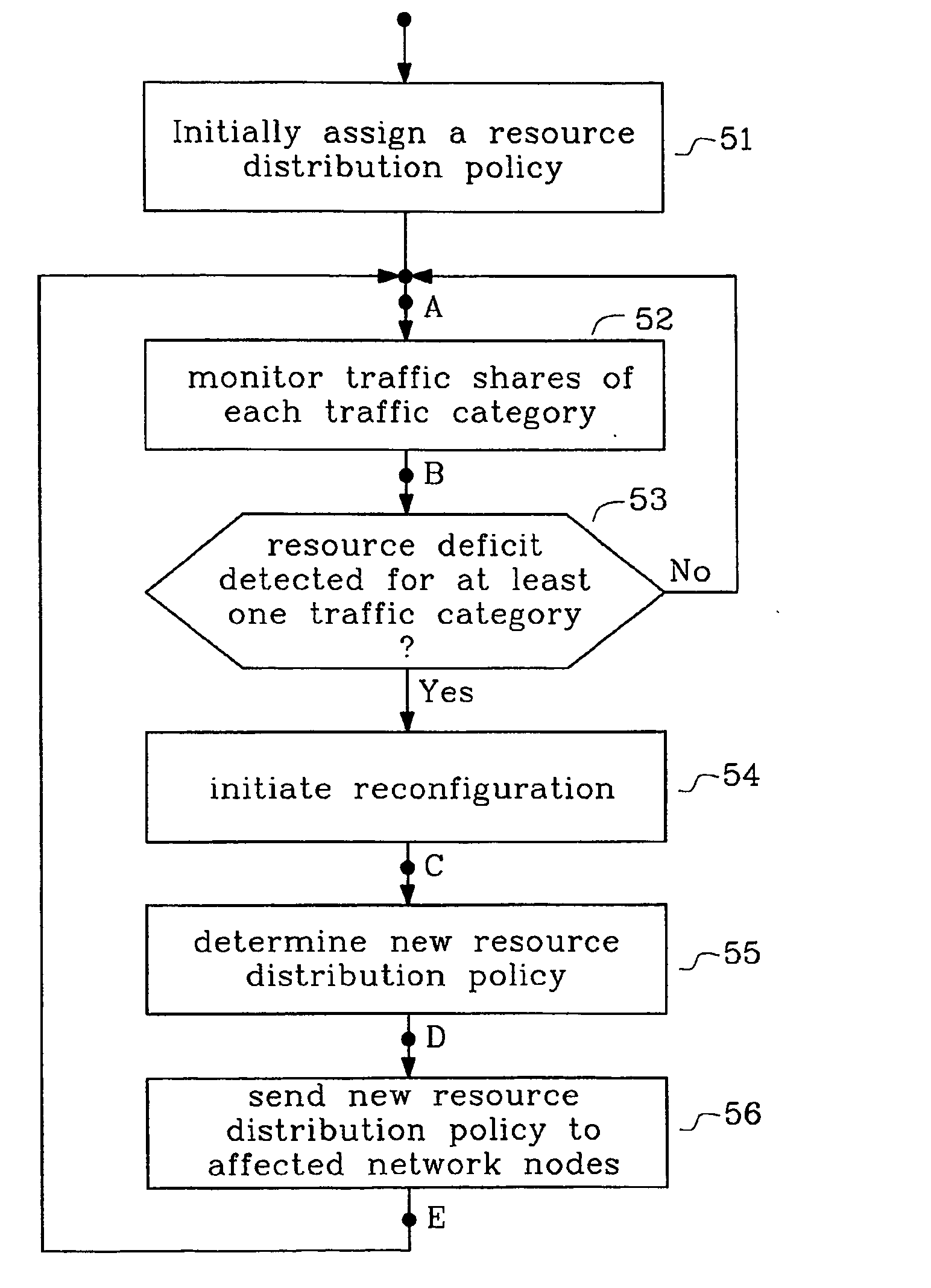
Method and arrangements to achieve a dynamic resource distribution policy in packet based communication networks
InactiveUS20050044206A1Available network resources can be used more efficientlyEasy to useNetwork traffic/resource managementDigital computer detailsDynamic resourcePacket scheduling
The present invention relates to a method and arrangements to achieve a dynamic and efficient resource distribution policy in packet based communication networks applying service differentiation and packet scheduling. The method initially allocates for each traffic class a certain share of the available resources, e.g. in terms of a share of the transmission bandwidth. The actual traffic shares for each of the traffic classes are monitored and compared to the assigned shares. If the monitored traffic shares does not correspond to the assigned shares a reconfiguration algorithm is started that equalizes resources according to the actual need. The new resource distribution policy is then distributed to the affected network nodes by means of a sequence of Load Control refresh packets where the shares of packets that belong to the various traffic classes correspond to the resource shares that are assigned to these traffic classes in the new resource distribution policy.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Packet scheduling system and method for multimedia data
InactiveUS6988144B1Time-division multiplexMultiple digital computer combinationsPacket schedulingClient-side
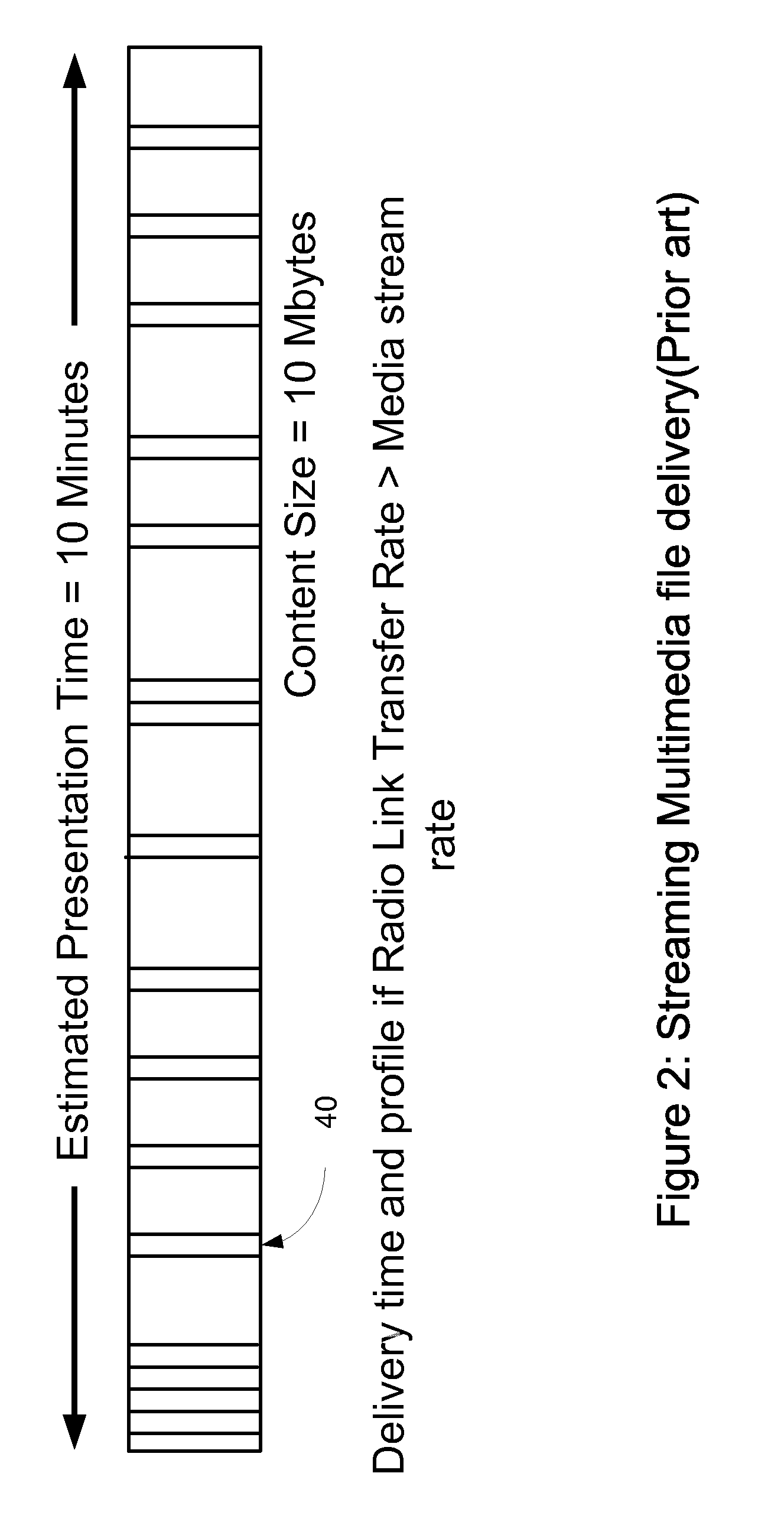
A method for scheduling the delivery of multimedia data packets over a communications medium with a limited bandwidth. The packets may contain data representing images, sounds, or other media which are to be delivered from a source or server to a recipient or client. The 6 method described here minimizes the delay between the point in time when a client requests the multimedia data and the point in time when the client may start presenting the data without risk of interruption, for a given communications bandwidth. This method also determines the minimum buffer sizes needed by the client in order to present this multimedia data subject to the specified bandwidth limit.
Owner:IBM CORP
Runtime adaptable security processor
InactiveUS20120117610A1Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceComputer security arrangementsSpecial data processing applicationsInternal memoryApplication software
A runtime adaptable security processor is disclosed. The processor architecture provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. A high performance content search and rules processing security processor is disclosed which may be used for application layer and network layer security. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
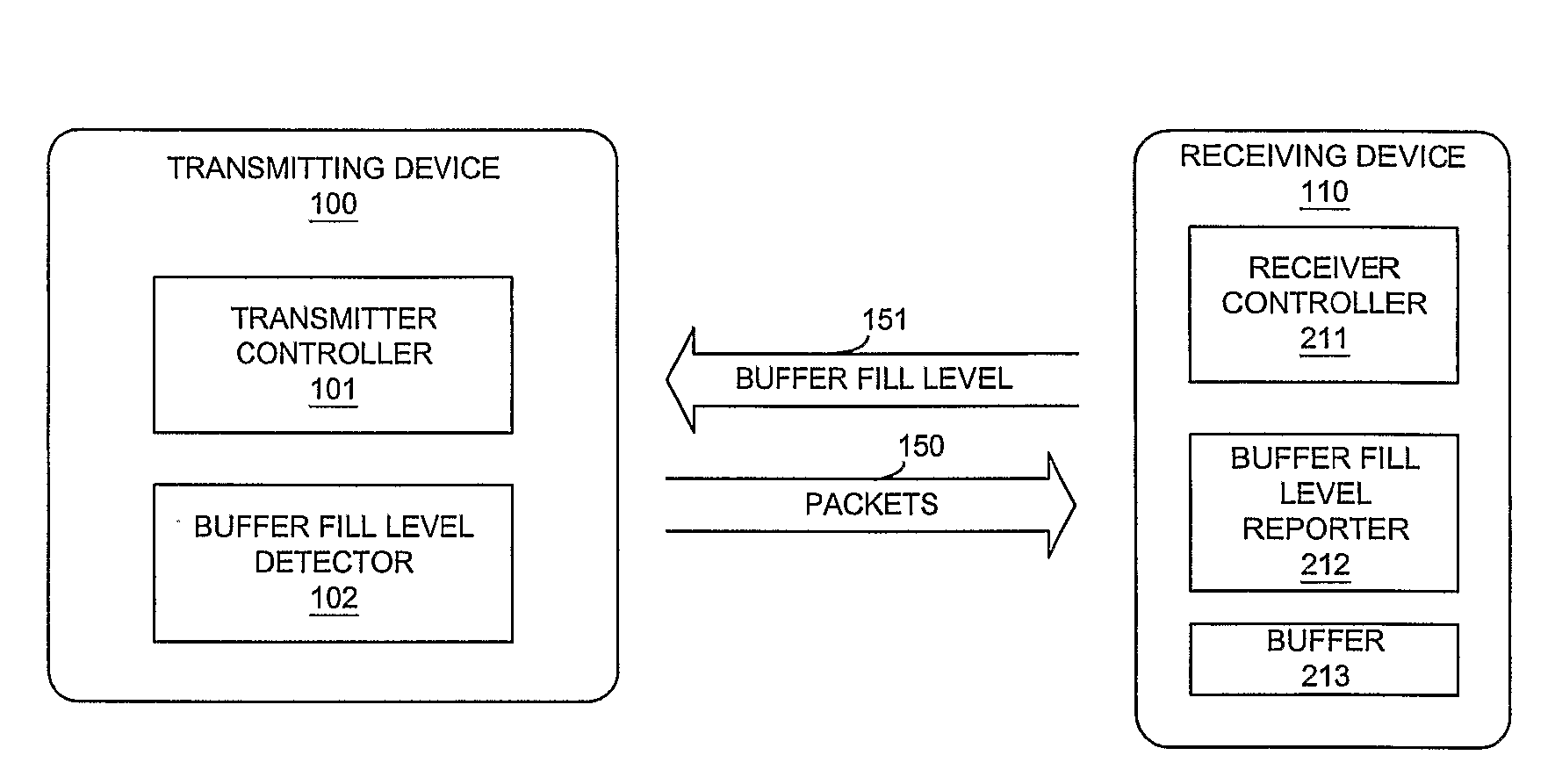
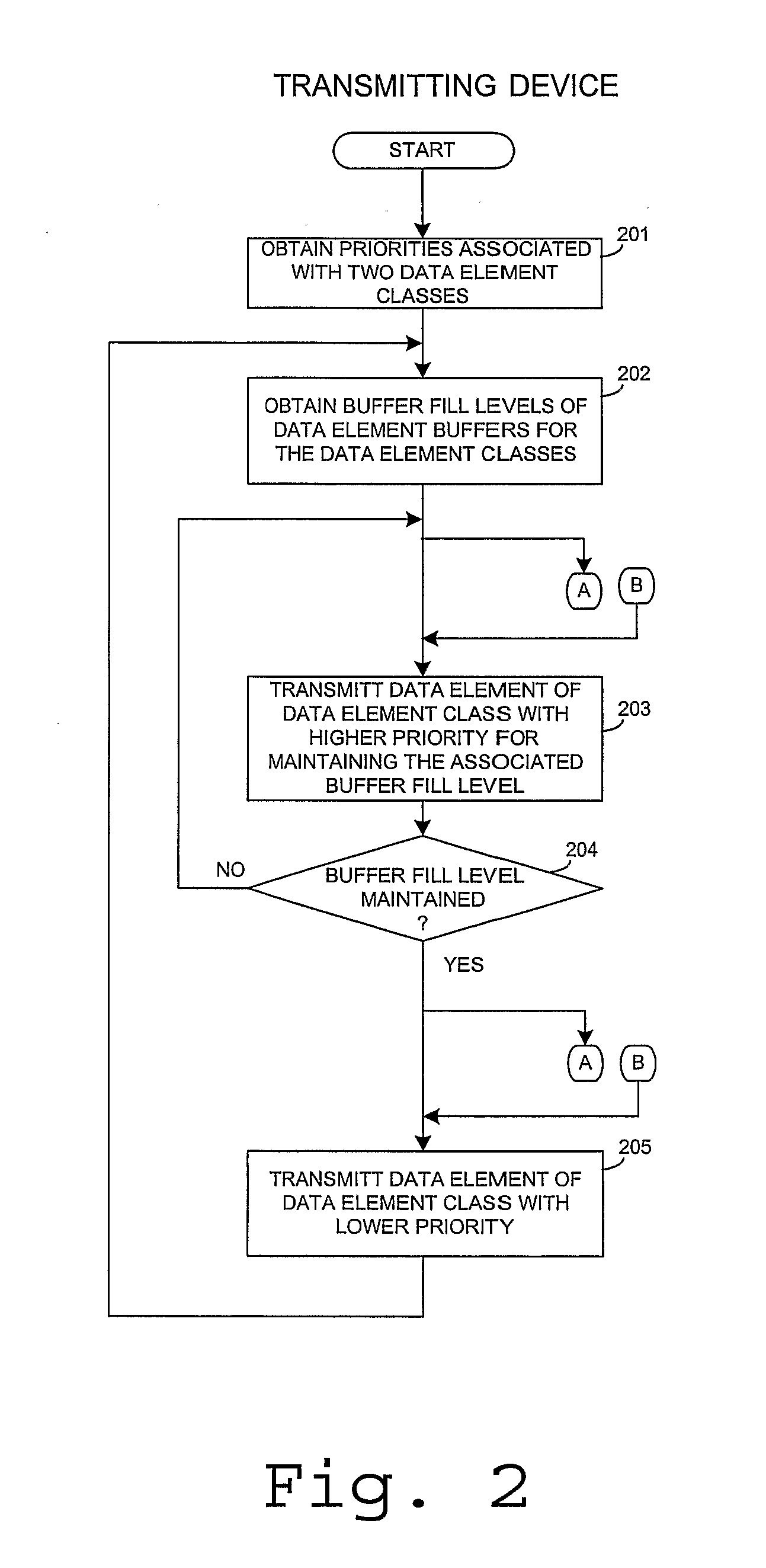
Packet Scheduling for Data Stream Transmission
ActiveUS20080256272A1Optimize schedulingRaise priorityData switching networksInput/output processes for data processingData streamPacket scheduling
The invention relates to transmitting data elements of a data stream based on a priority and target buffer fill levels at a receiving device. A transmitter controller transmits data elements of a data element class with a highest priority first, for reaching an associated buffer fill level and then turns to data elements of successively lower priorities, until the available bandwidth is exhausted.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Runtime adaptable protocol processor
ActiveUS7631107B2Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceComputer controlTime-division multiplexInternal memoryData pack
A runtime adaptable protocol processor is disclosed. The processor architecture provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. Further, a runtime adaptable processor is coupled to the protocol processing hardware and may be dynamically adapted to perform hardware tasks as per the needs of the network traffic being sent or received and / or the policies programmed or services or applications being supported. A set of engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a session information database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer. A security system is also disclosed that enables a new way of implementing security capabilities inside enterprise networks in a distributed manner using a protocol processing hardware with appropriate security features.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
Tcp/ip processor and engine using rdma
InactiveUS20080253395A1Sharply reduces TCP/IP protocol stack overheadImprove performanceDigital computer detailsTime-division multiplexInternal memoryTransmission protocol
A TCP / IP processor and data processing engines for use in the TCP / IP processor is disclosed. The TCP / IP processor can transport data payloads of Internet Protocol (IP) data packets using an architecture that provides capabilities to transport and process Internet Protocol (IP) packets from Layer 2 through transport protocol layer and may also provide packet inspection through Layer 7. The engines may perform pass-through packet classification, policy processing and / or security processing enabling packet streaming through the architecture at nearly the full line rate. A scheduler schedules packets to packet processors for processing. An internal memory or local session database cache stores a TCP / IP session information database and may also store a storage information session database for a certain number of active sessions. The session information that is not in the internal memory is stored and retrieved to / from an additional memory. An application running on an initiator or target can in certain instantiations register a region of memory, which is made available to its peer(s) for access directly without substantial host intervention through RDMA data transfer.
Owner:MEMORY ACCESS TECH LLC
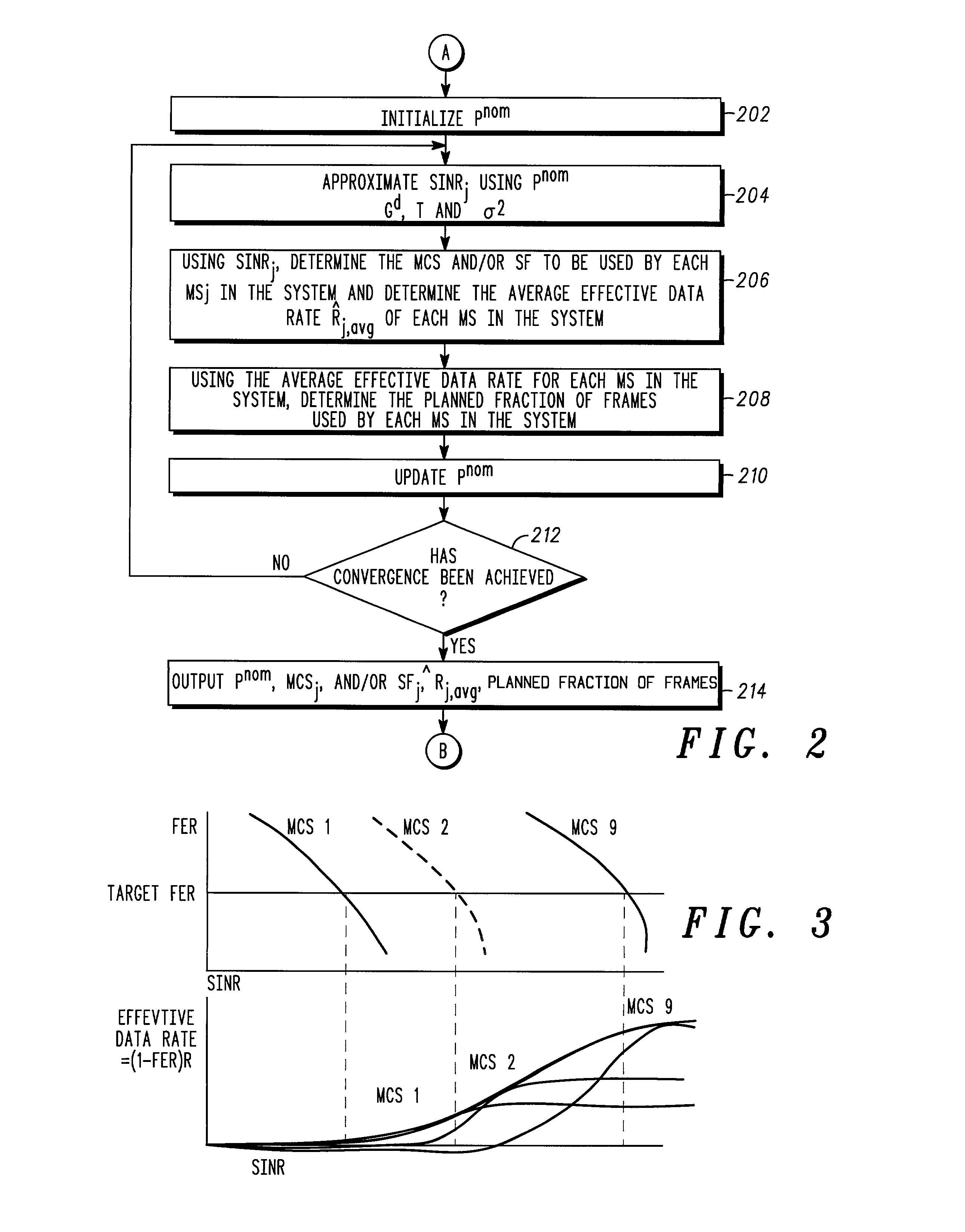
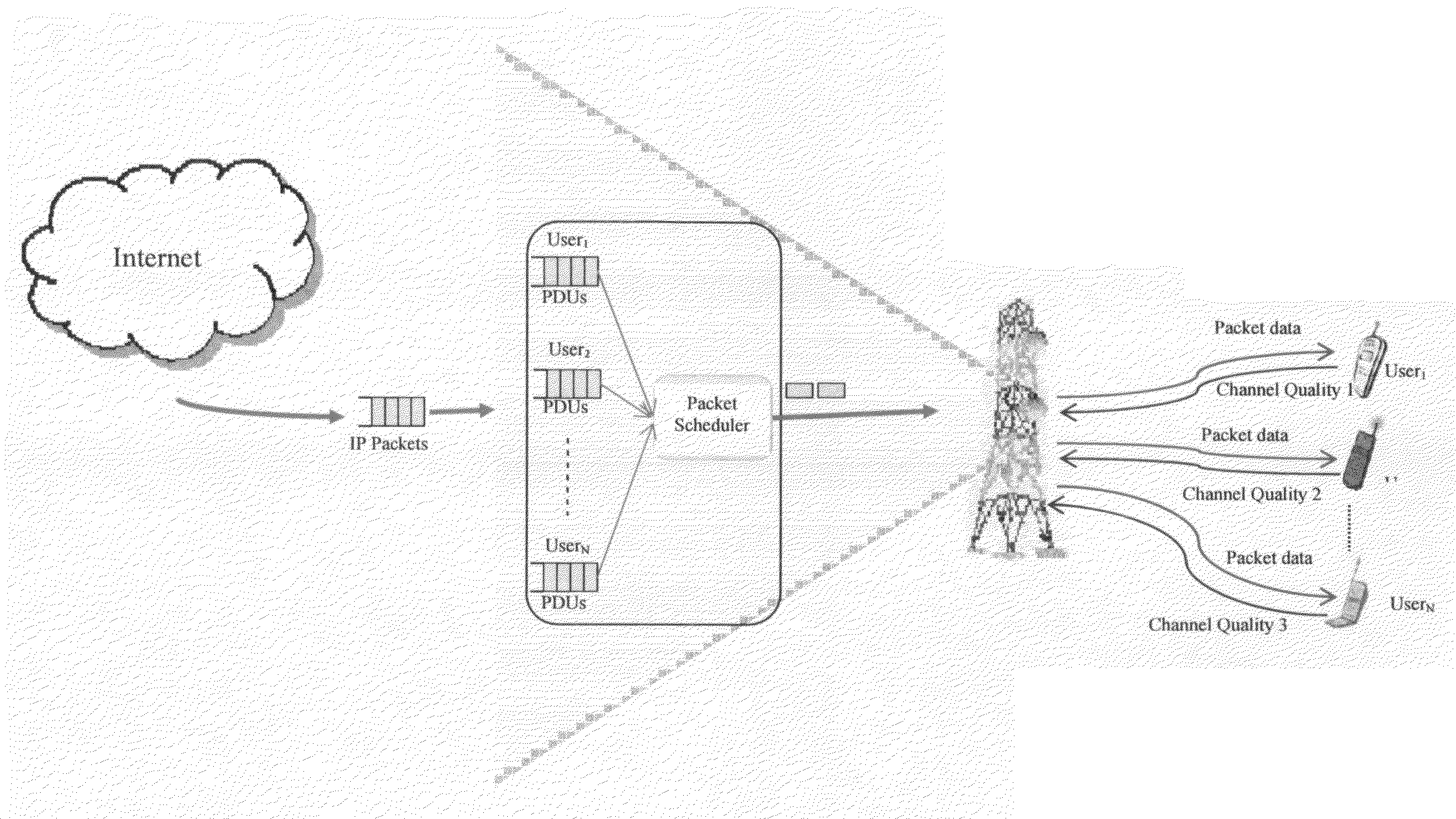
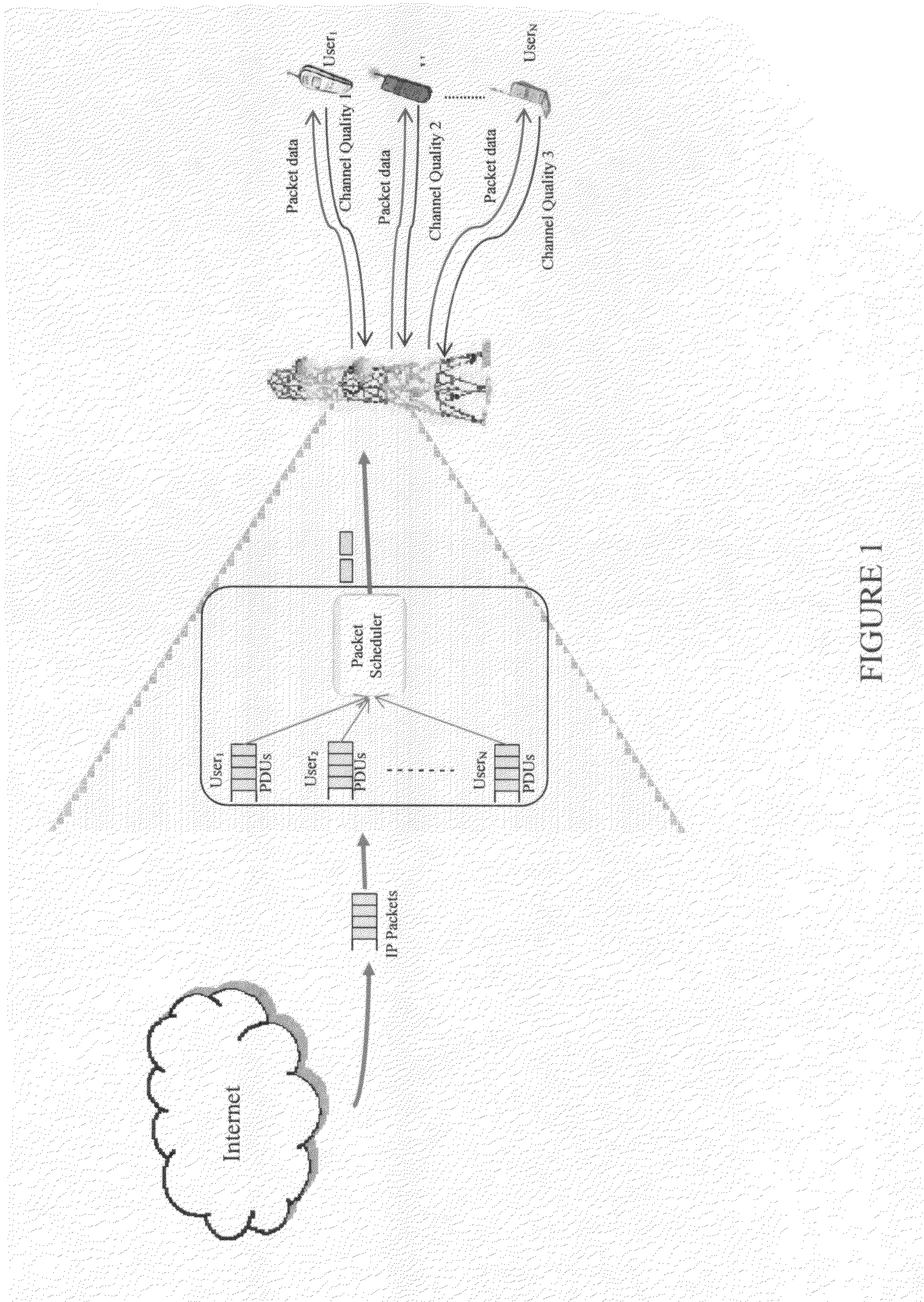
Method for packet scheduling and radio resource allocation in a wireless communication system
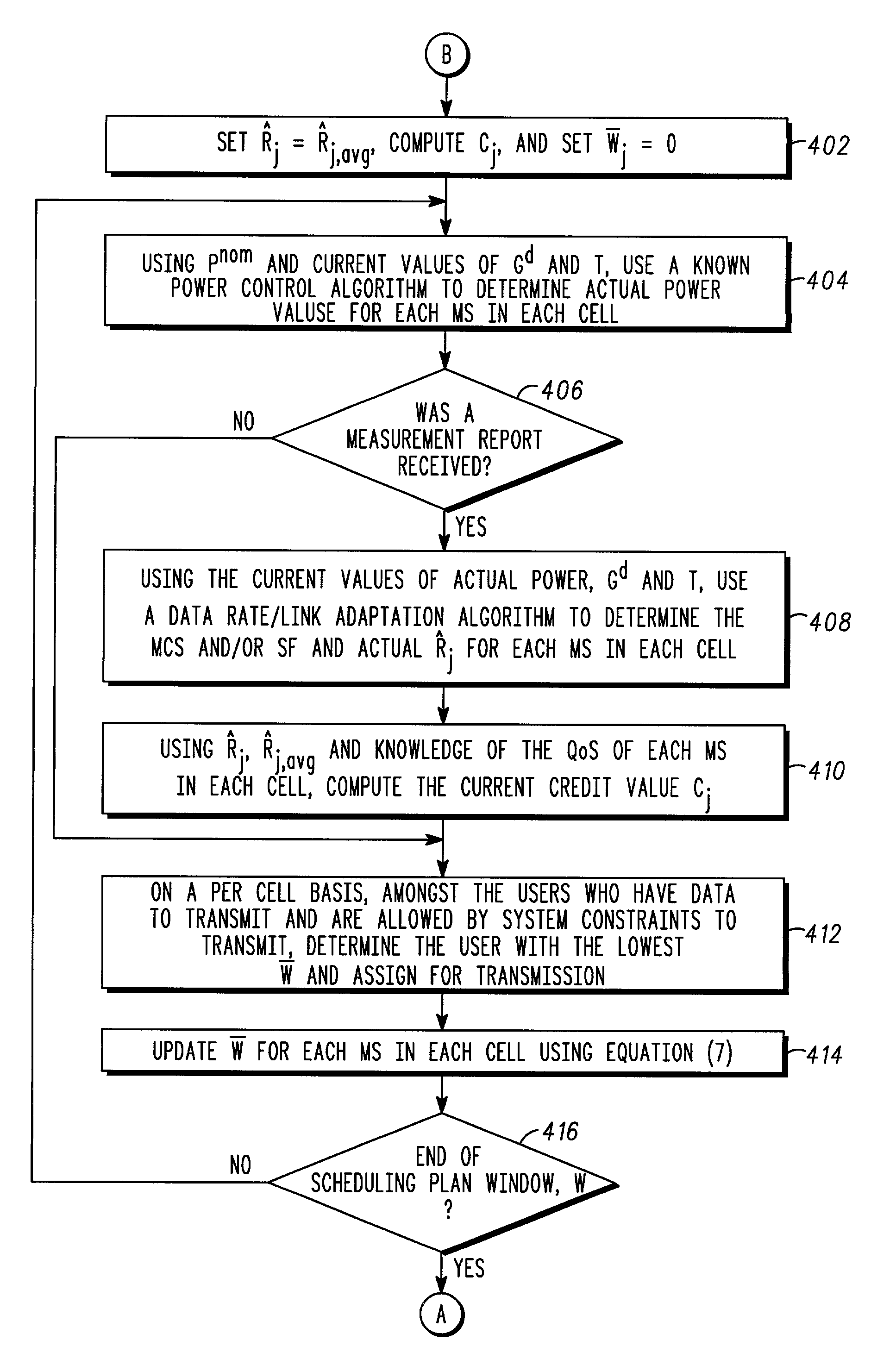
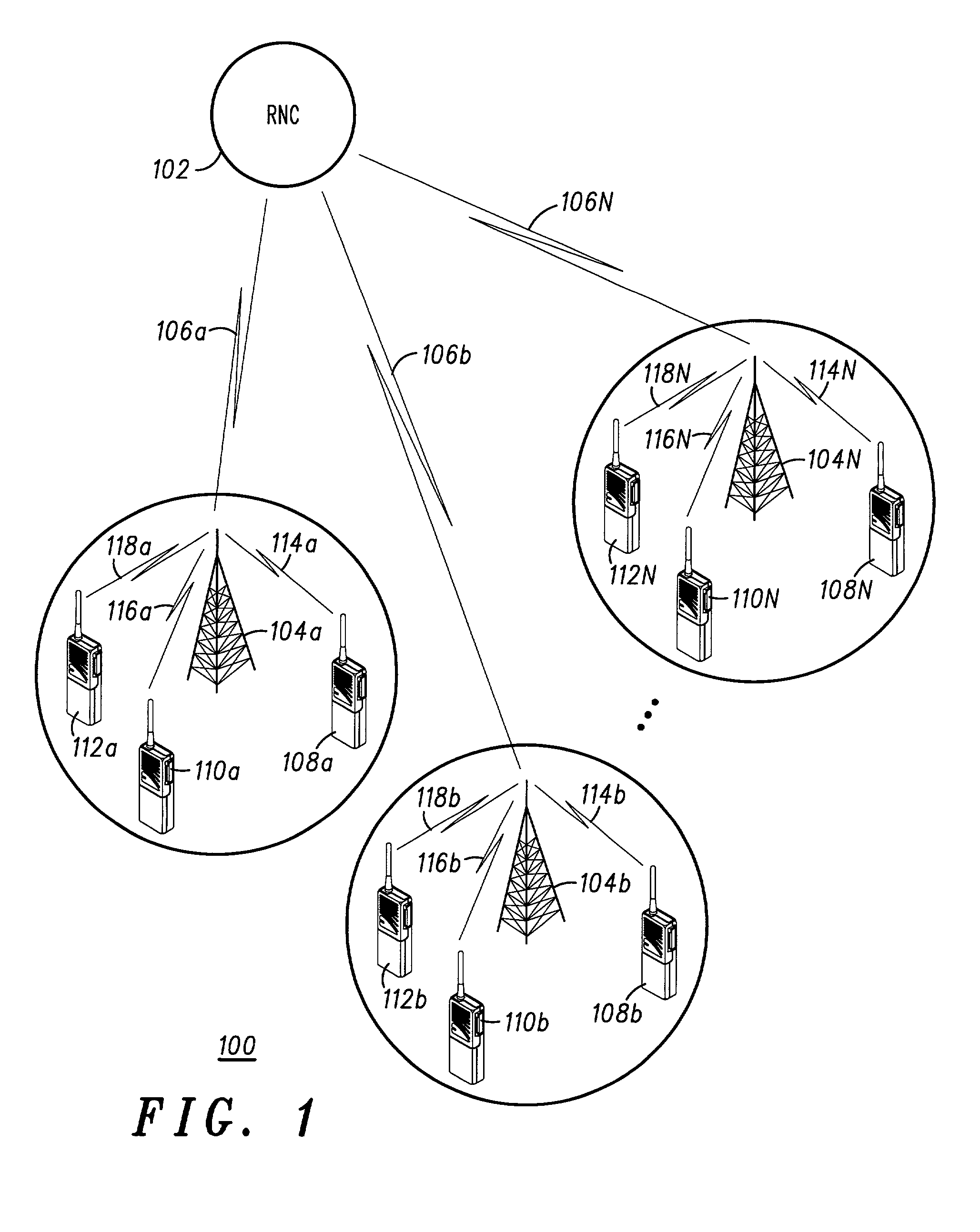
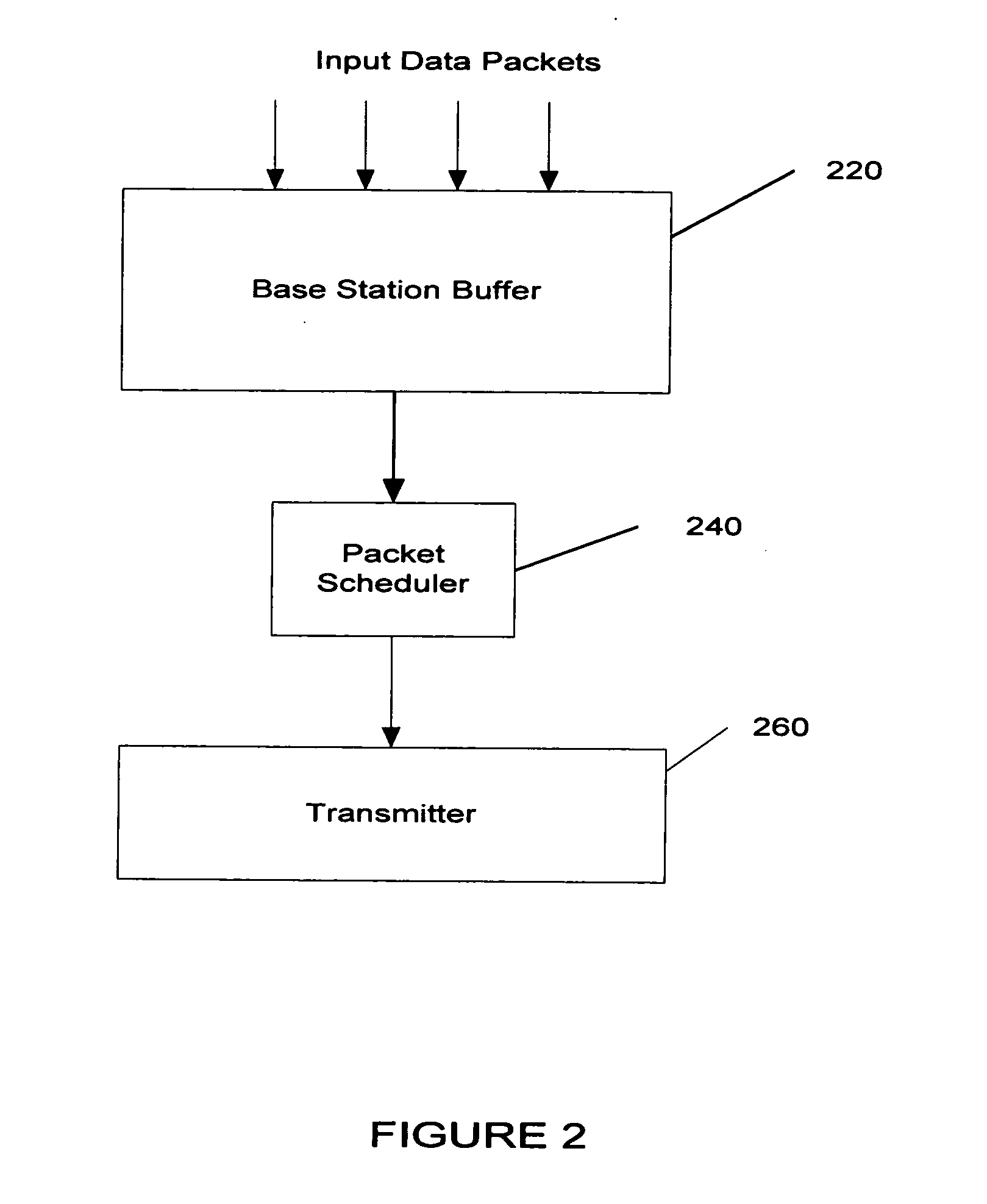
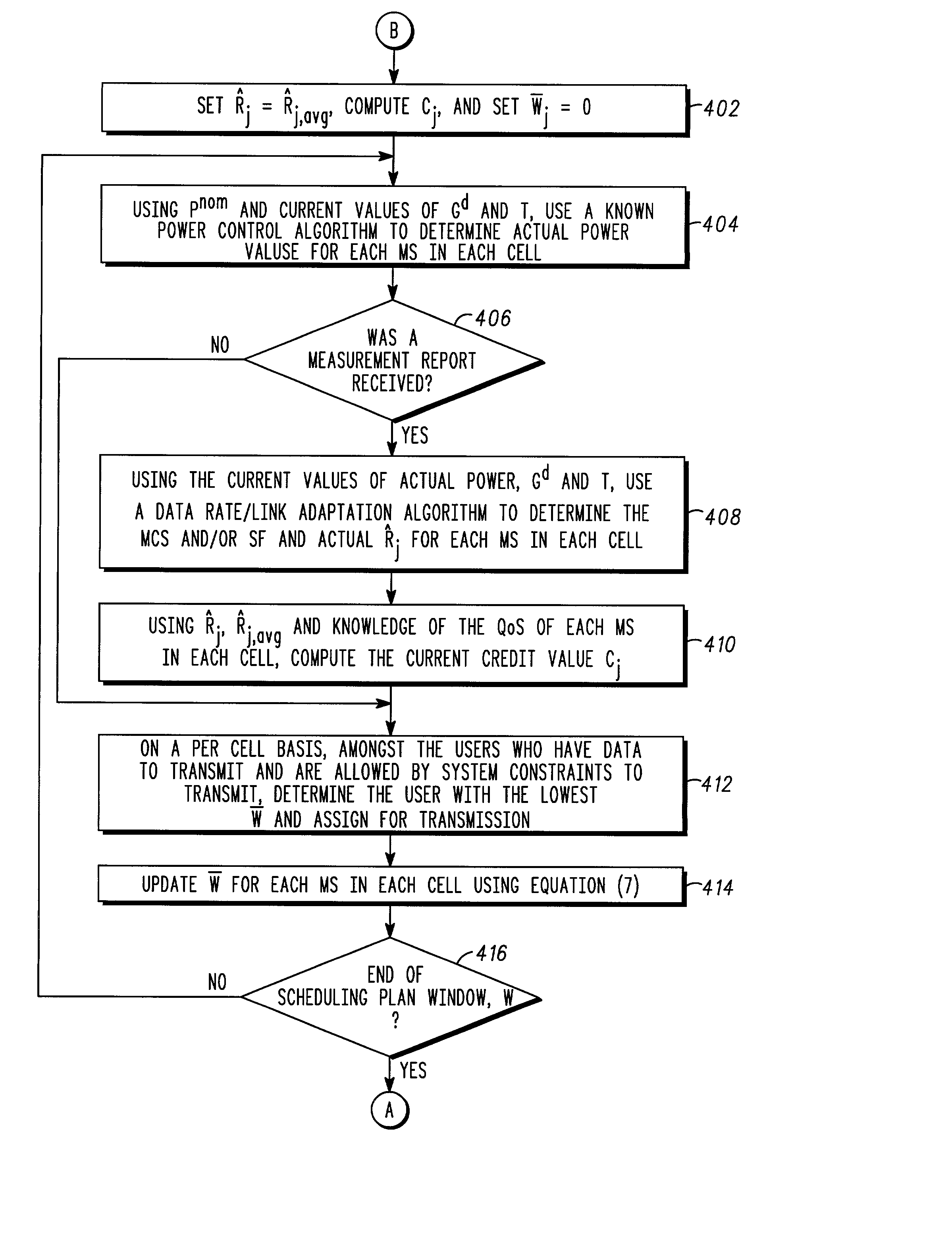
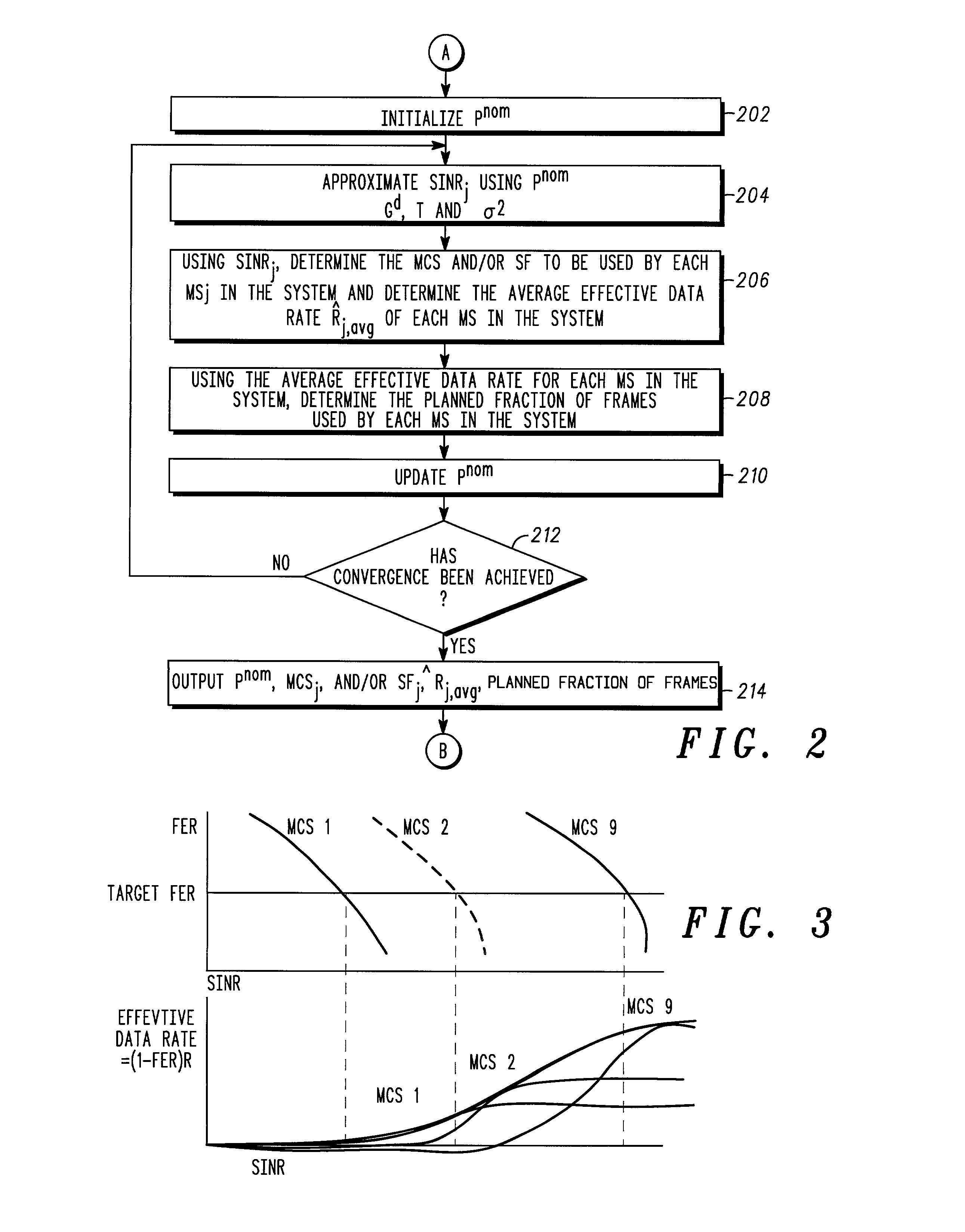
A method of performing packet level transmission scheduling in a communications systems including a plurality of cells, each cell including a base station and plurarity of mobile stations. The method performs scheduling while considering radio resource allocation at the wireless access node. In a schedule plan phase of the method, average power and average effective data rate are determined for all mobile stations in the system. In addition, the planned fractions of frames ρ that each mobile in the system will transmit is determined so that resources are allocated fairly. In the actual schedule phase of the method, current power and effective data rate values are compared to the average power values. This information along with the ρ values is used to determine the actual schedule of packet transmissions for all mobiles in a particular cell.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
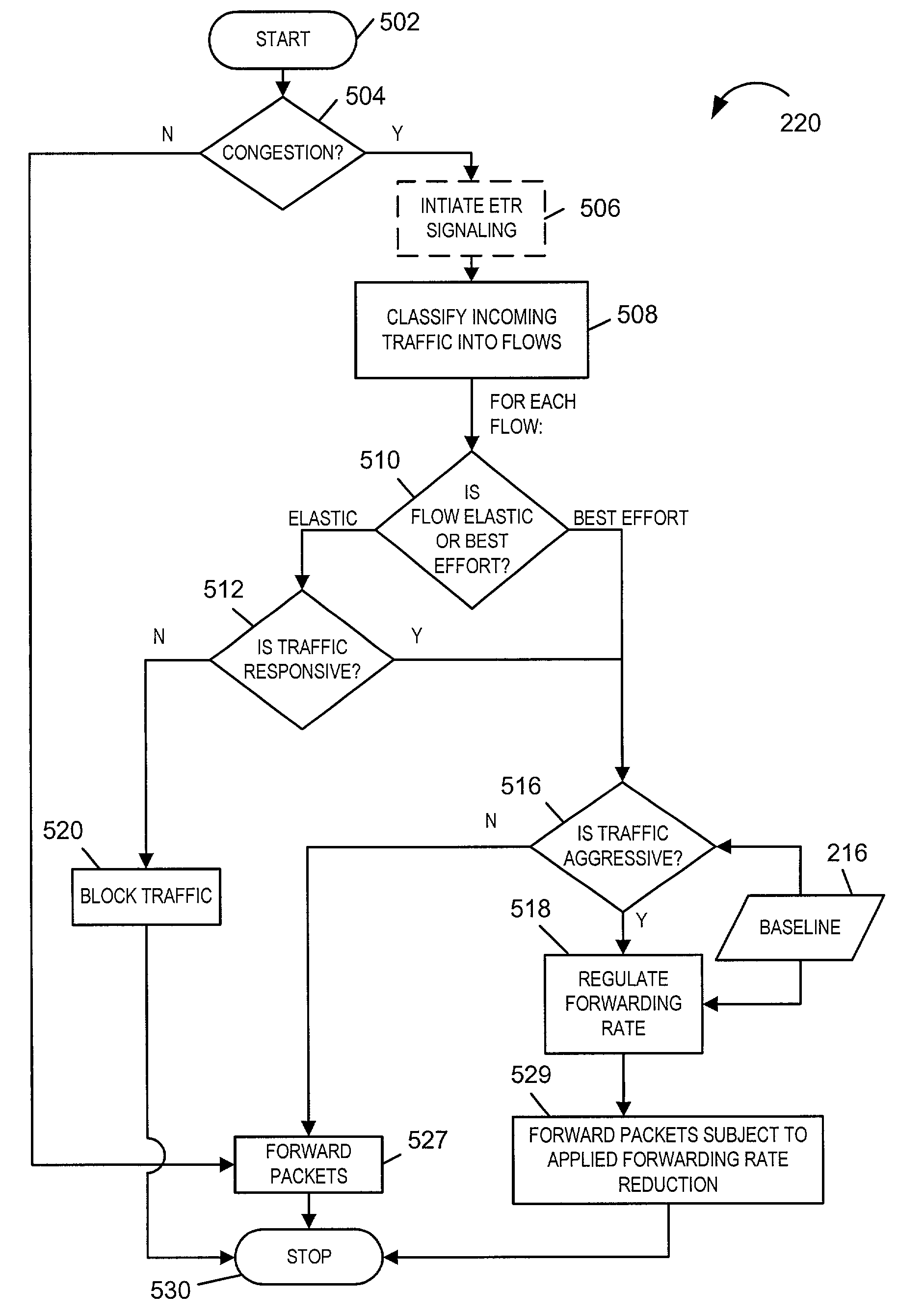
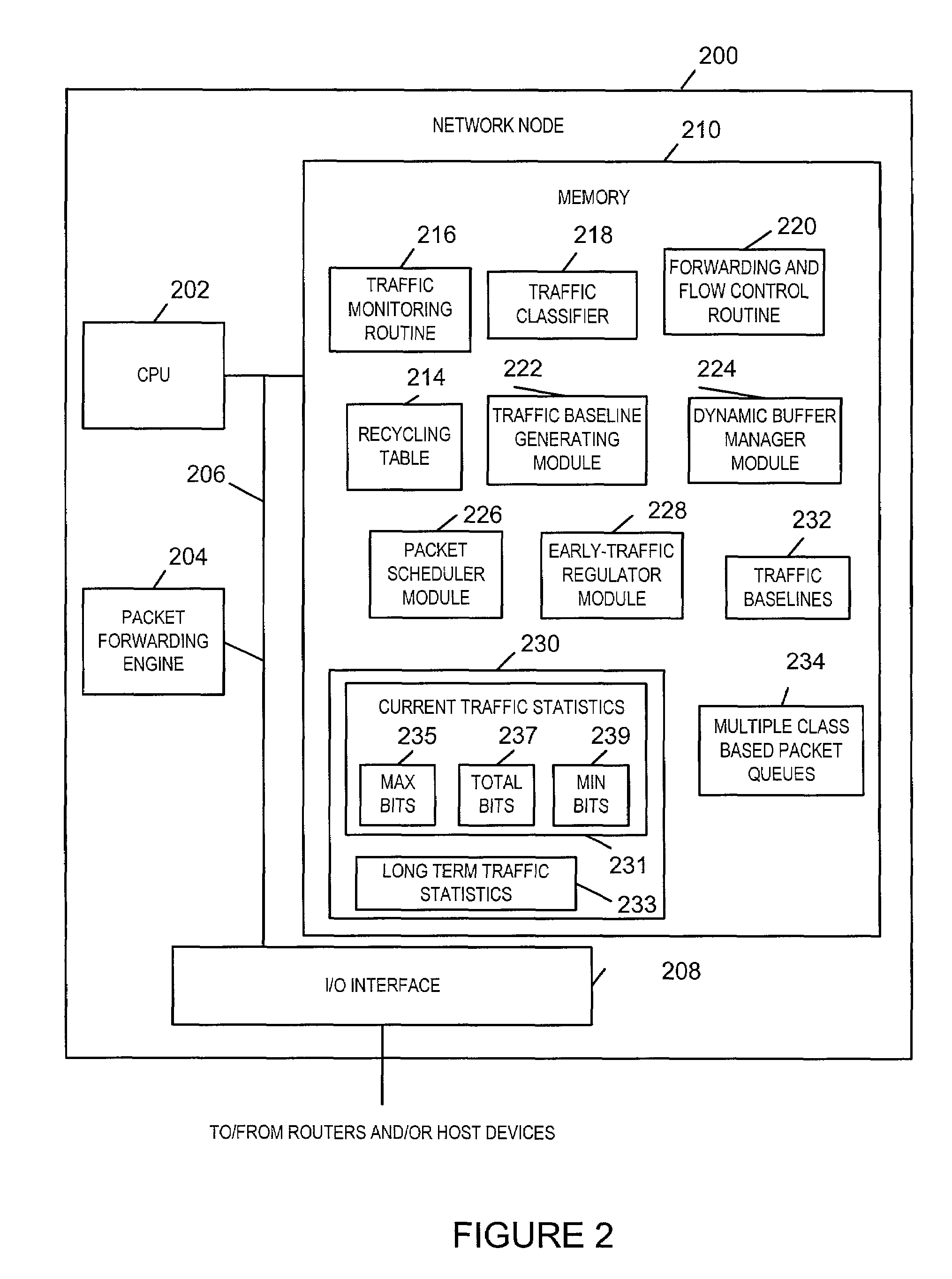
Anti-flooding flow-control methods and apparatus
ActiveUS7092357B1Reducing flow of trafficReduce processing burdenError preventionTransmission systemsTraffic capacityData stream
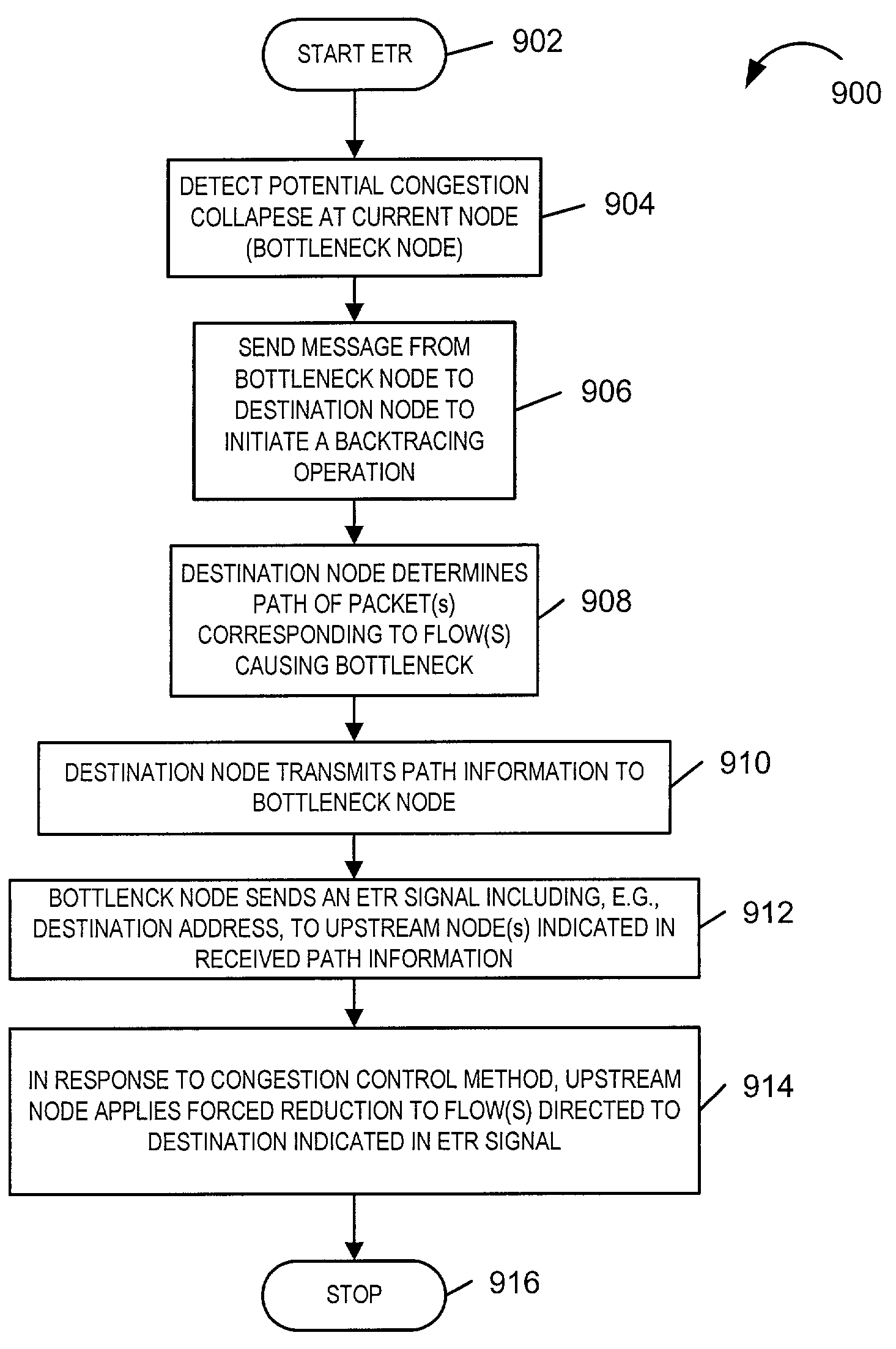
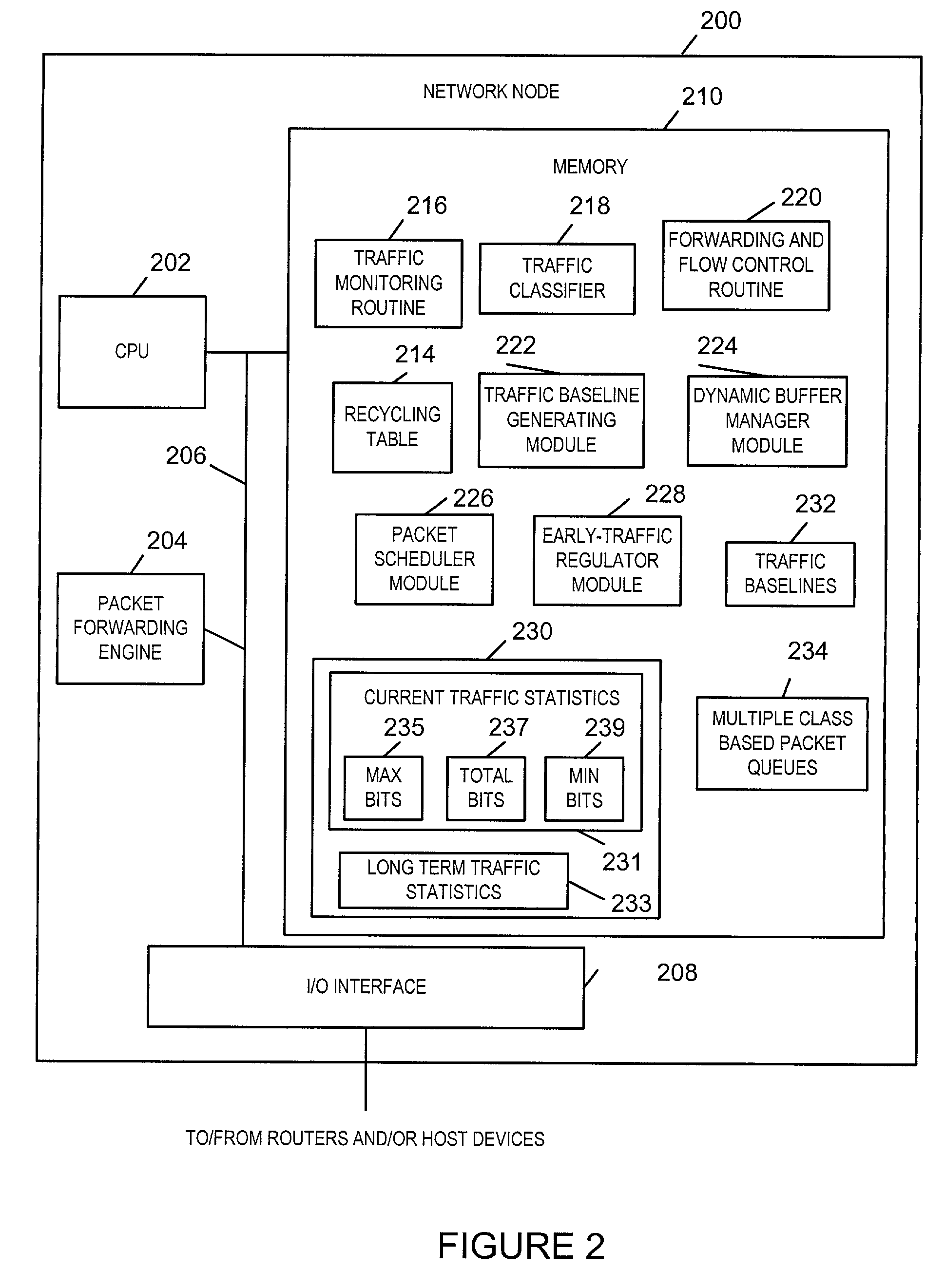
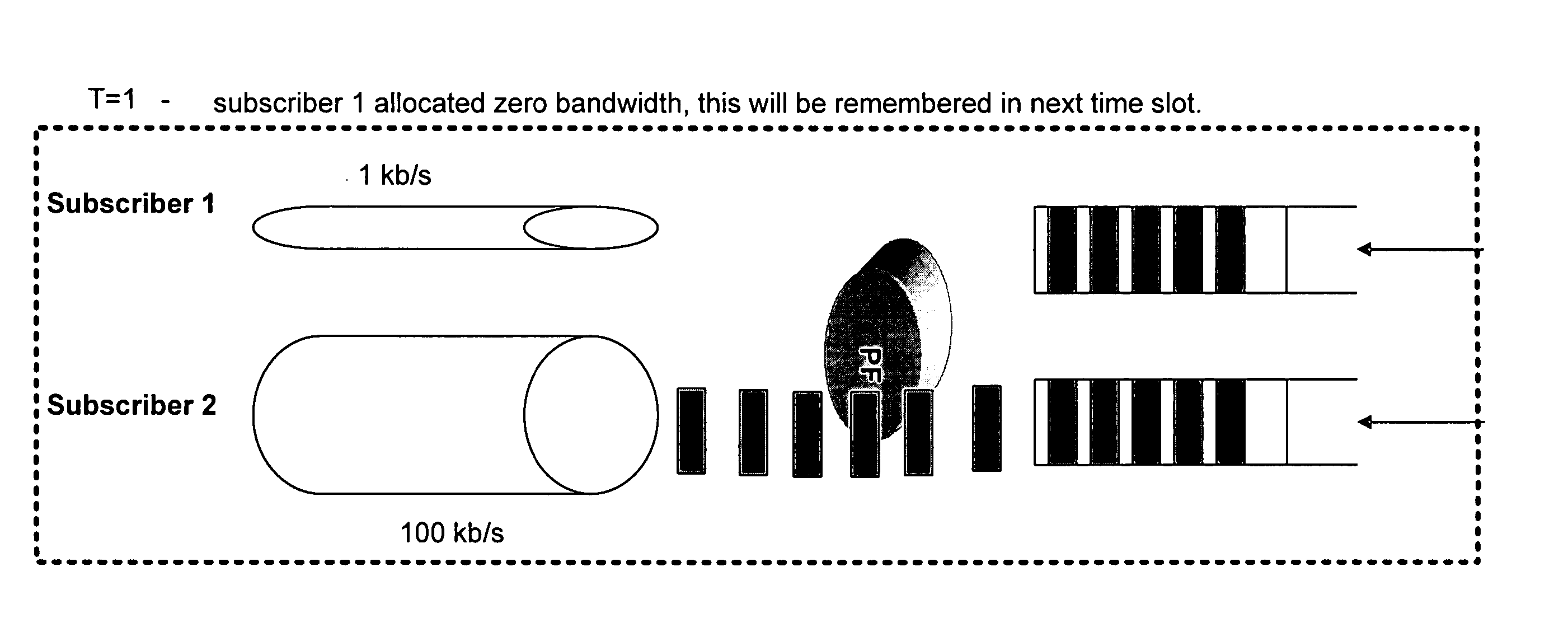
Methods and apparatus for providing an Anti-Flooding Flow-Control (AFFC) mechanism suitable for use in defending against flooding network Denial-of-Service (N-DoS) attacks is described. Features of the AFFC mechanism include (1) traffic baseline generation, (2) dynamic buffer management, (3) packet scheduling, and (4) optional early traffic regulation. Baseline statistics on the flow rates for flows of data corresponding to different classes of packets are generated. When a router senses congestion, it activates the AFFC mechanism of the present invention. Traffic flows are classified. Elastic traffic is examined to determine if it is responsive to flow control signals. Flows of non-responsive elastic traffic is dropped. The remaining flows are compared to corresponding class baseline flow rates. Flows exceeding the baseline flow rates are subject to forced flow rate reductions, e.g., dropping of packets.
Owner:PALO ALTO NETWORKS INC
Systems, processes and integrated circuits for improved packet scheduling of media over packet
InactiveUS20060007871A1Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime informationPacket scheduling
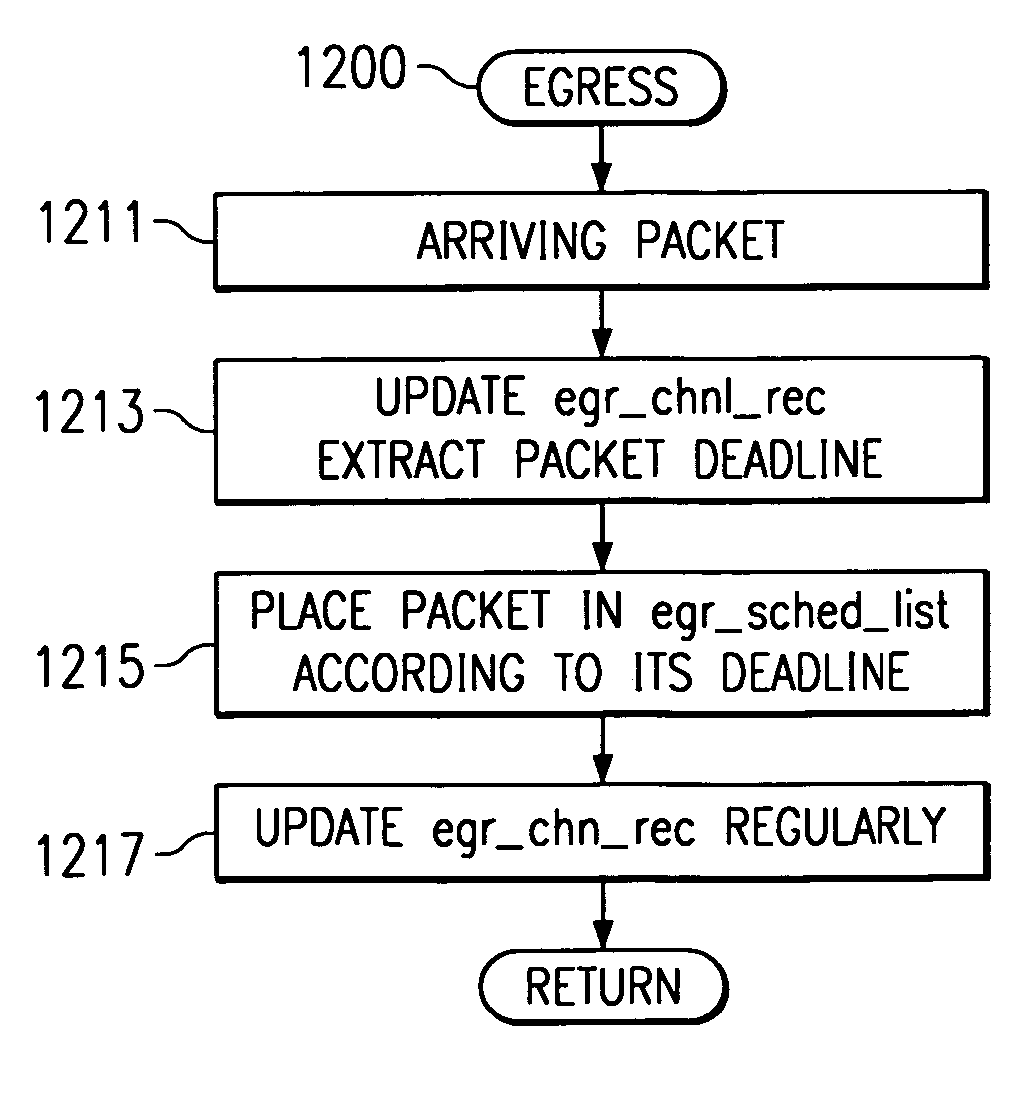
A method of processing first and second record packets of real-time information includes computing for each packet a deadline interval and ordering processing of the packets according to the respective deadline intervals. A single-chip integrated circuit has a processor circuit and embedded electronic instructions forming an egress packet control establishing an egress scheduling list structure and operations in the processor circuit that extract a packet deadline intervals, place packets in the egress scheduling list according to deadline intervals; and embed a decoder that decodes the packets according to a priority depending to their deadline intervals.
Owner:WELIN ANDREW M
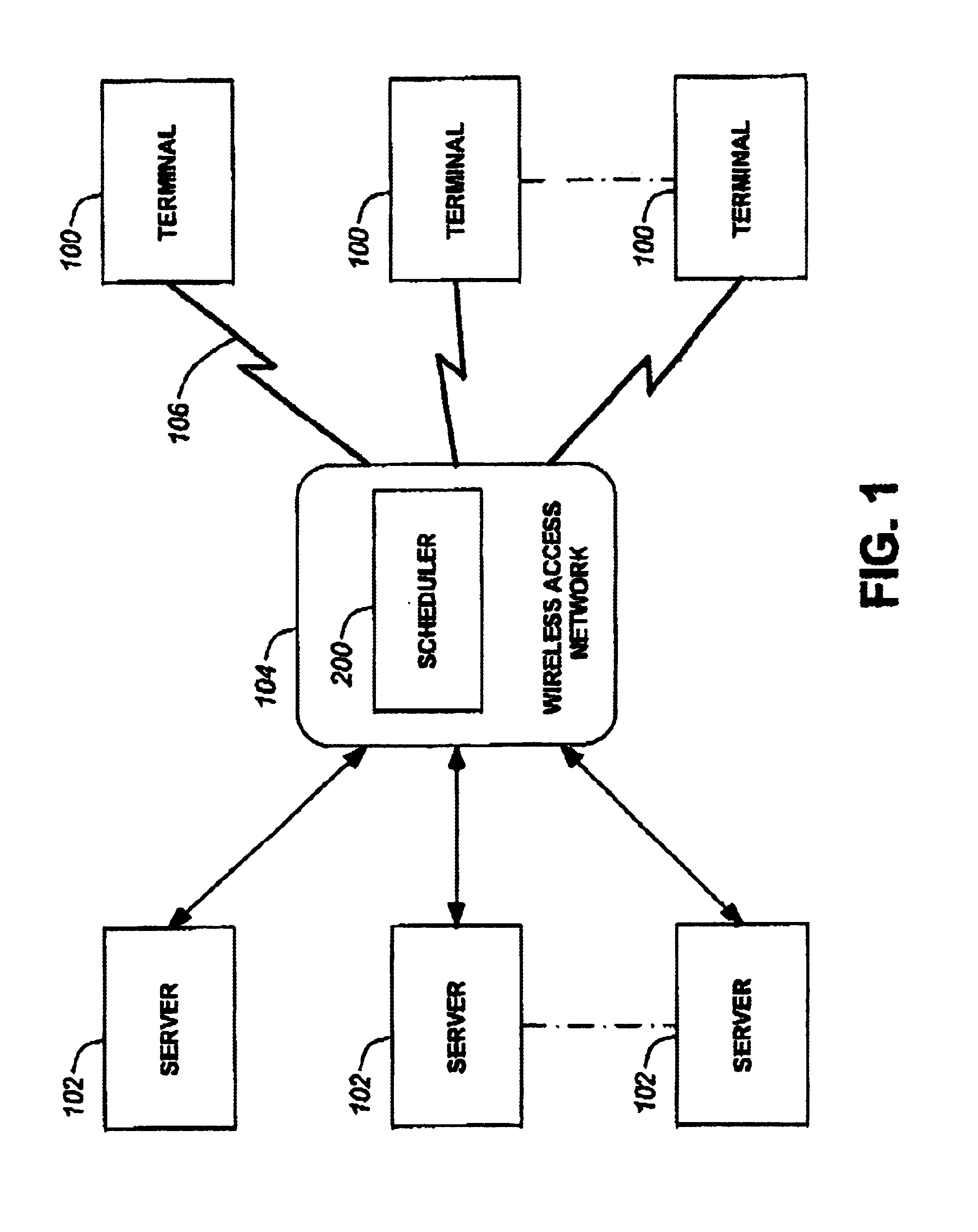
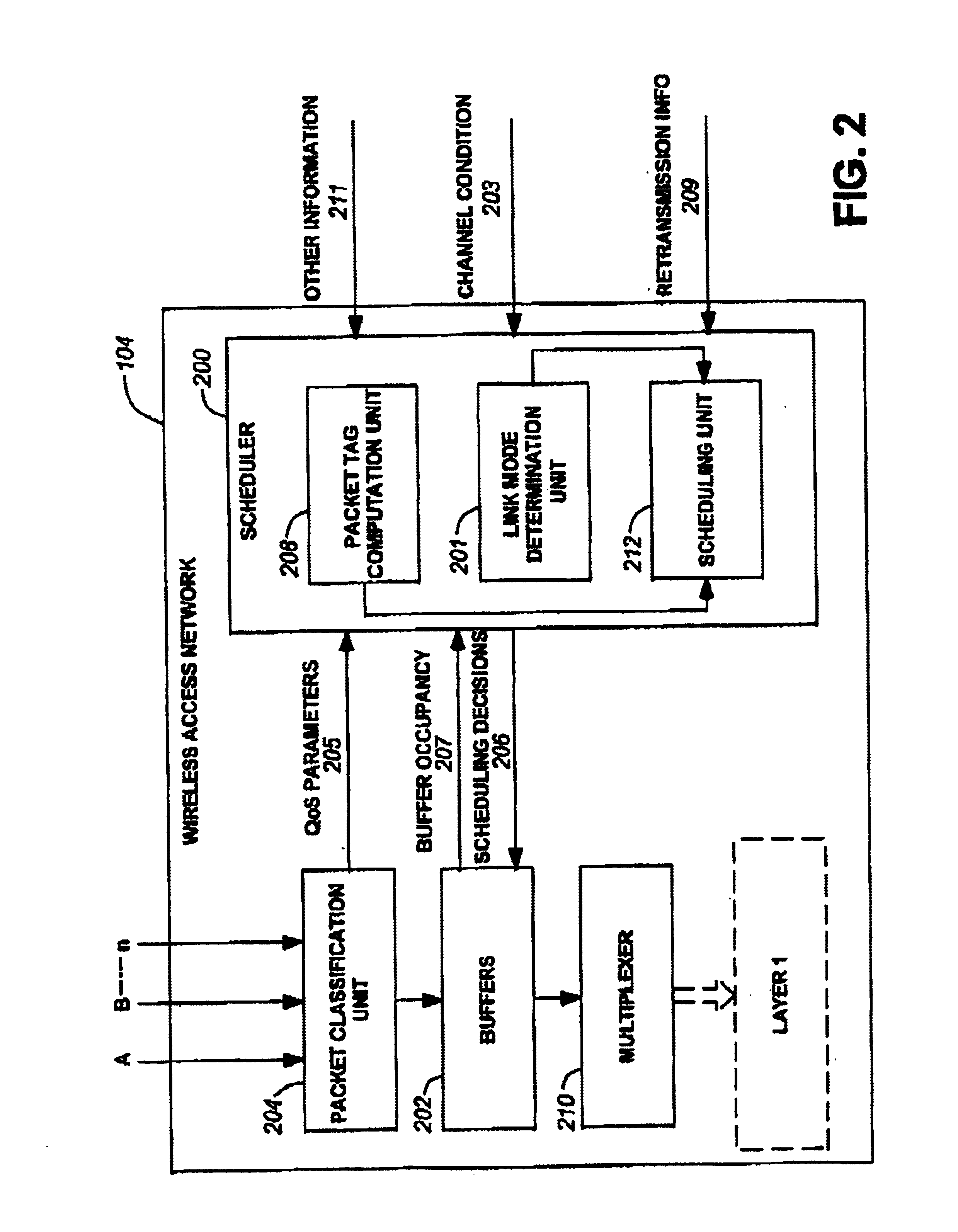
Method and system for wireless packet scheduling with per packet QoS support and link adaptation
InactiveUS6879561B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsTelecommunications networkPacket scheduling
A method and system for scheduling data in the down, or forward, link, on a per packet basis in a wireless telecommunications network. The scheduler determines the order of packets to be sent from multiple queues based on per IP QoS, real time channel condition and real time buffer occupancy. The scheduler determines the necessary support link adaptation on a per packet basis based on per packet QoS and the channel condition. The scheduling system and method take into consideration both upper layer per packet QoS, for example packet delay bound, and the real time channel condition (C / I) for each mobile terminal. The method of the present invention also determines the layer 2 frame length for each scheduled packet.
Owner:APPLE INC
Inter-chip communication system
InactiveUS20050102125A1Decrease in performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsCAD circuit designData packCommunications system
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Method of packet scheduling, with improved delay performance, for wireless networks
InactiveUS6590890B1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexTraffic capacityWireless mesh network
A new scheduling discipline is disclosed for the forward link of a wireless network such as a CDMA network. The new discipline, which we denominate Modified LWDF (M-LWDF), resembles the known LWDF discipline in that only one queue is served at a time, and the queue to be served is that having the largest weighted delay. According to M-LWDF, the weighted delay of the i'th queue is defined aswherein Wi(t) is a packet delay, a queue length, or an increasing function of packet delay or queue length for the i'th queue, ci(t) is a weight coefficient descriptive of channel conditions for the i'th user, and gammai is a fixed constant that can be chosen arbitrarily. We have found that if any scheduling discipline can yield stable queues for a given traffic pattern of arriving packets, then M-LWDF can, even under changing channel conditions. Moreover, we have found that M-LWDF can provide favorable QoS in terms of delay bounds.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
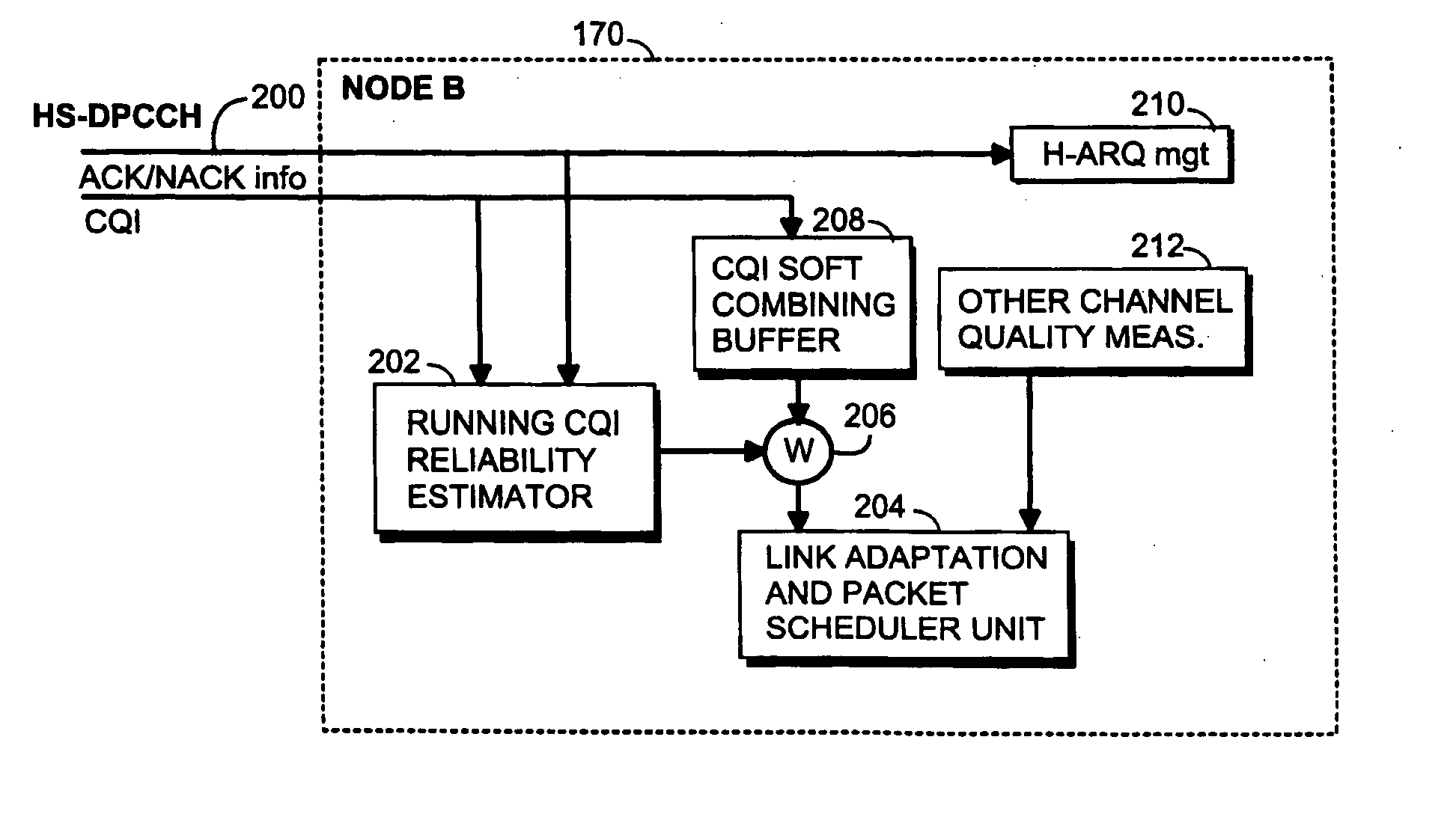
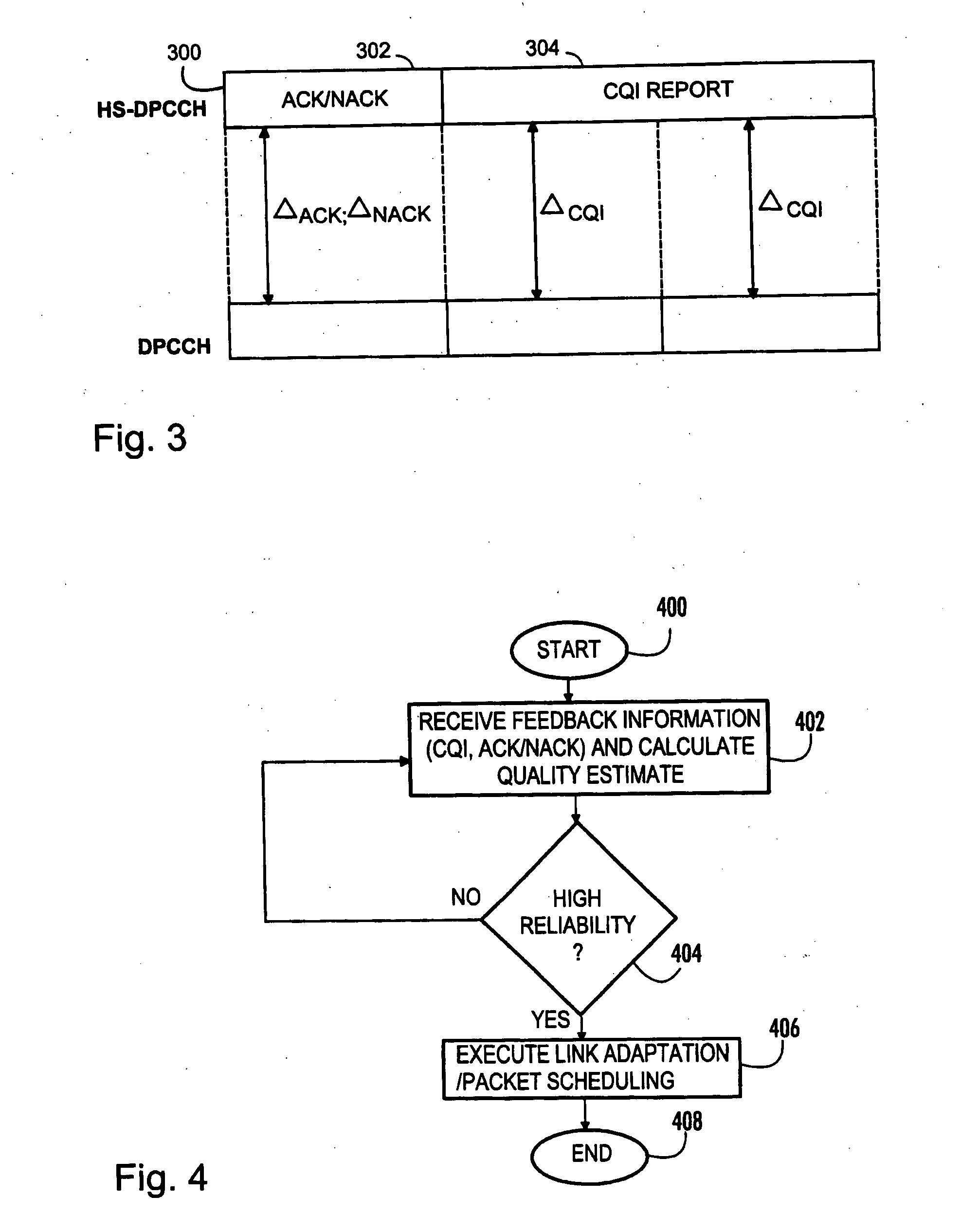
Method and base station for controlling link adaptation and packet scheduling in high speed downlink packet access (HSDPA) radio system
ActiveUS20050047387A1Improve estimation accuracyReduce delaysError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket schedulingControl channel
A method of controlling link adaptation and packet scheduling in an HSDPA (High Speed Downlink Packet Access) radio system and an HSDPA base station communicating over a control channel with one or more user equipment units is provided. According to one embodiment the base station includes a device for receiving feedback information from the user equipment. The base station further includes a device for calculating a quality estimate related to the feedback information and executing link adaptation and packet scheduling based on the calculated quality estimate.
Owner:RPX CORP
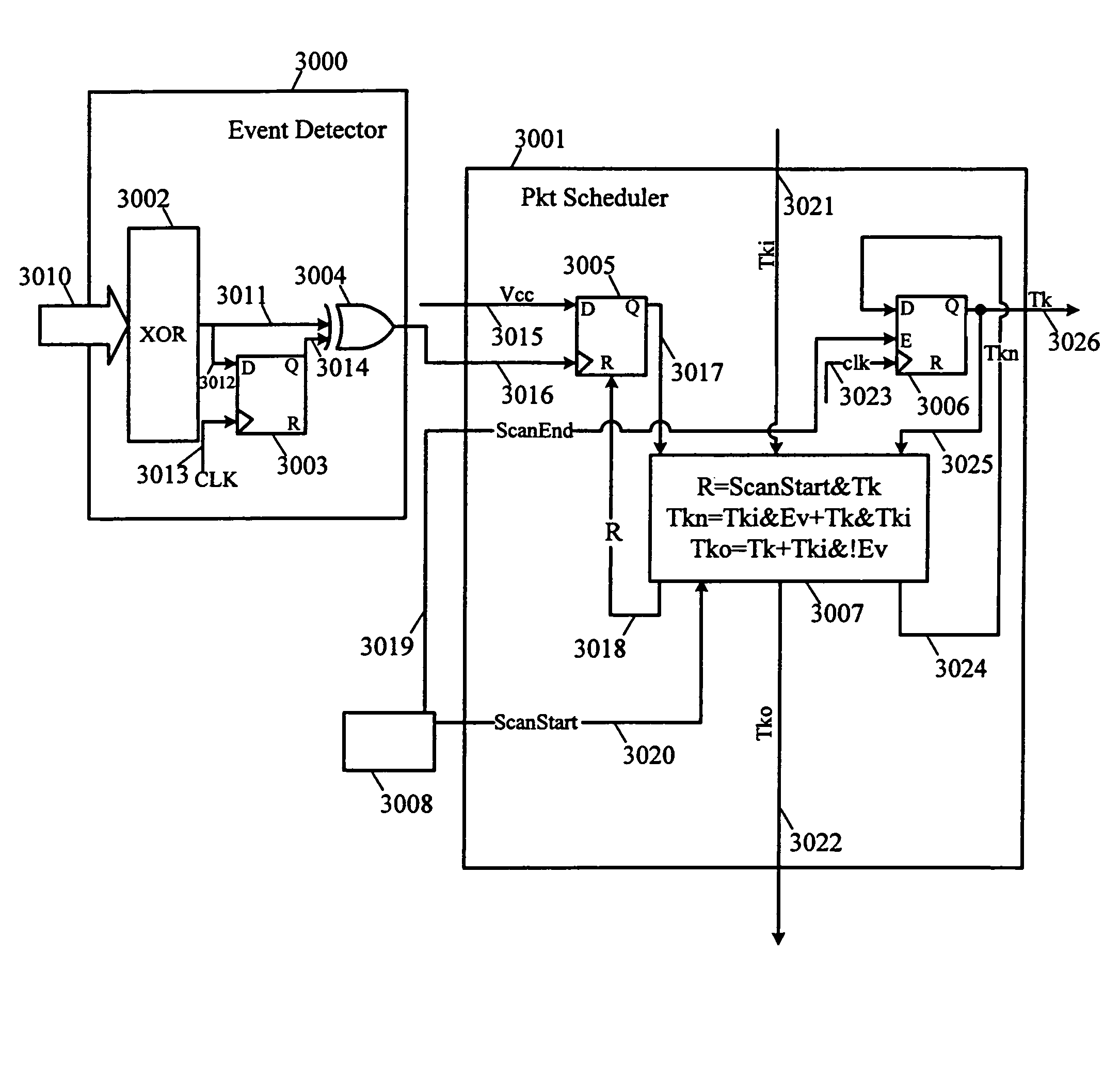
Inter-chip communication system
InactiveUS7512728B2Decrease in performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsCAD circuit designCommunications systemPacket scheduling
The complexity of user designs, the limited capacity of FPGA chips, and the limited number of chip pinouts have resulted in the development of inter-chip communication technology that necessitates the transfer of a large amount of data across a limited number of pins in the shortest amount of time. The inter-chip communication system transfers signals across FPGA chip boundaries only when these signals change values. Thus, no cycles are wasted and every event signal has a fair chance of achieving communication across chip boundaries. The inter-chip communication system includes a series of event detectors that detect changes in signal values and packet schedulers which can then schedule the transfer of these changed signal values to another designated chip. Working with a plurality of signal groups that represents signals at the separated connections, the event detector detects events (or changes in signal values). When an event has been detected, the event detector alerts the packet scheduler. The packet scheduler employs a token ring scheme as follows. When the packet scheduler receives a token and detects an event, the packet scheduler “grabs” the token and schedules the transmission of this packet in the next packet cycle. If, however, the packet scheduler receives the token but does not detect an event, it will pass the token to the next packet scheduler. At the end of each packet cycle, the packet scheduler that grabbed the token will pass the token to the next logic associated with another packet.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
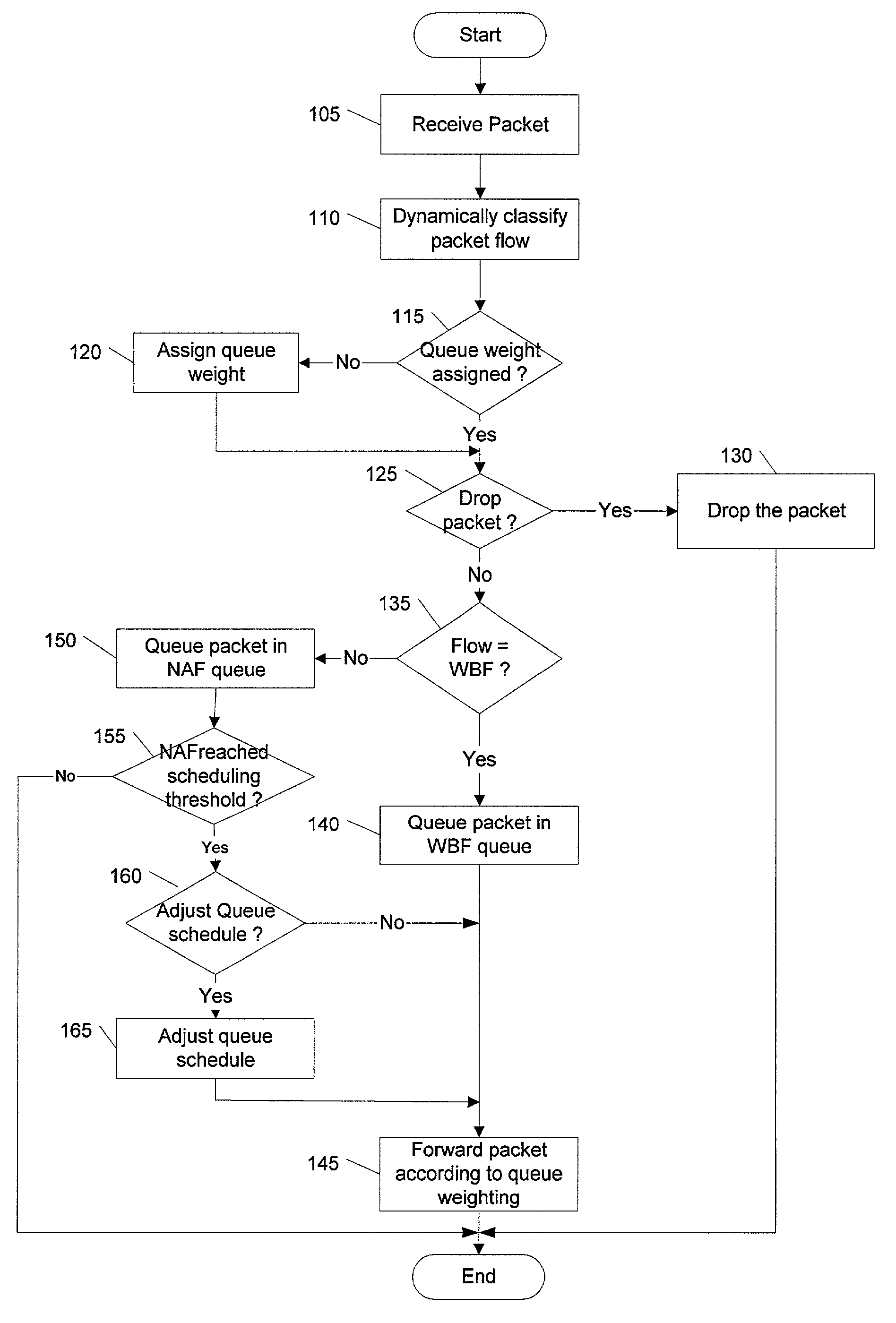
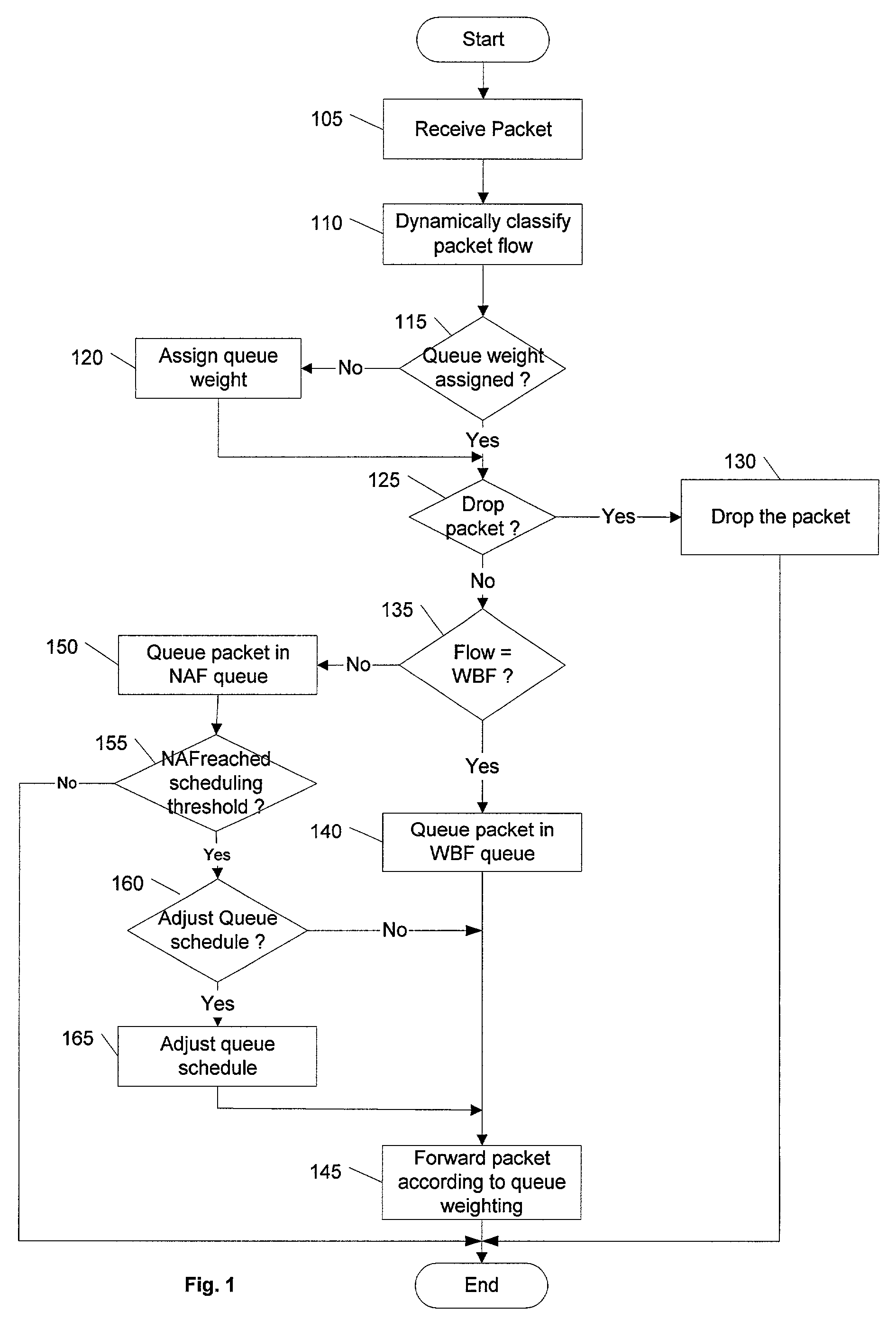
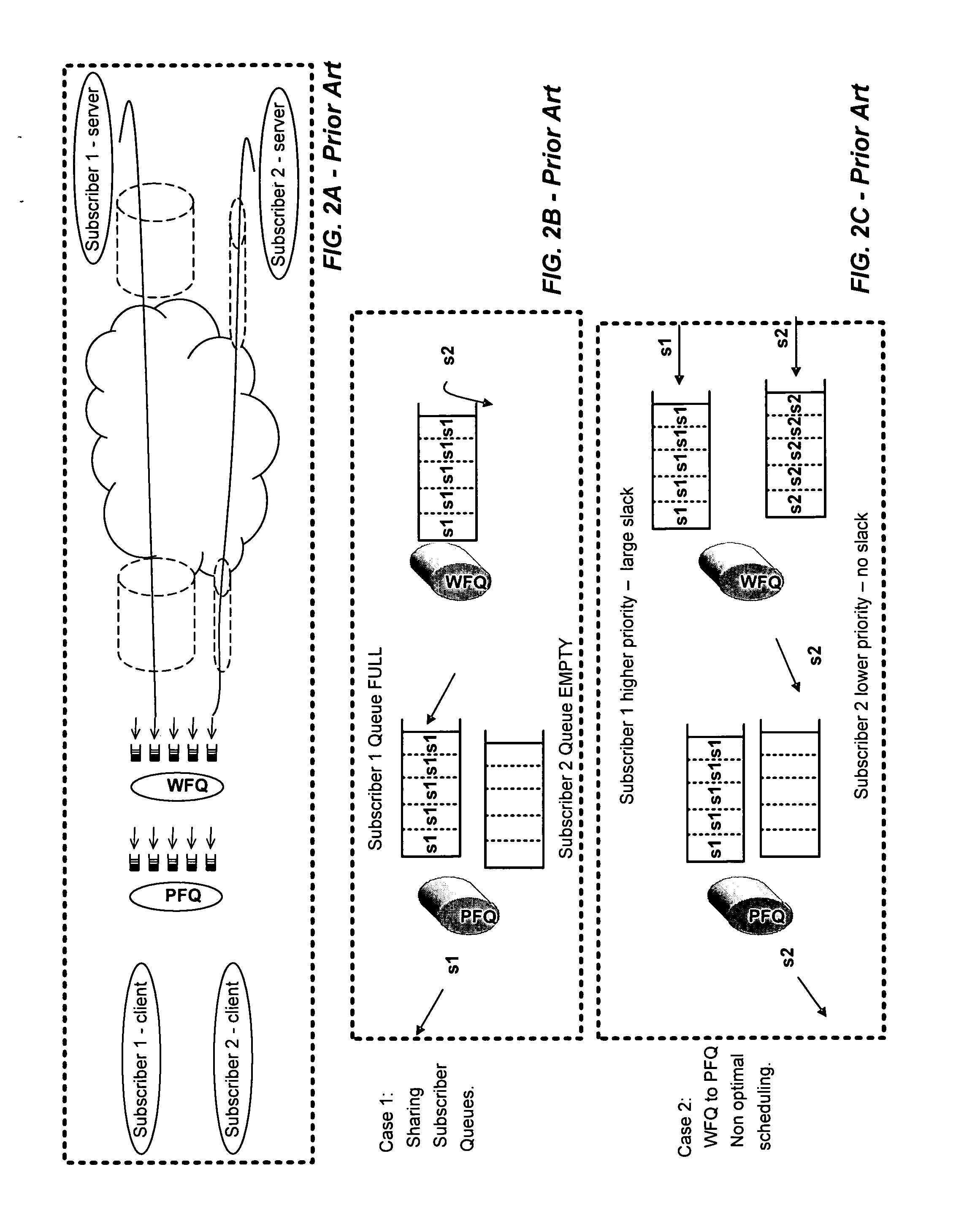
Dynamic behavioral queue classification and weighting
The present invention defines a method and apparatus to extend class-based queuing (CBQ) with multiple “behavioral” queues per class, to include a dynamic weighting mechanism between these queues. The packets are forwarded from the behavioral queues according to the weighting assigned to each queue. The weighting for packet scheduling of the queues is adjusted to account for additional flow going through the queues. The weight of a queue is controlled relative to the weight available to other queues. When a flow is reclassified, the queue weights is readjusted accordingly. Well behaved flows experience low delay and can thus achieve a fair bandwidth allocation without having to have multiple packets queued to compete with non-adaptive aggressive flows.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Apparatus and method for packet scheduling
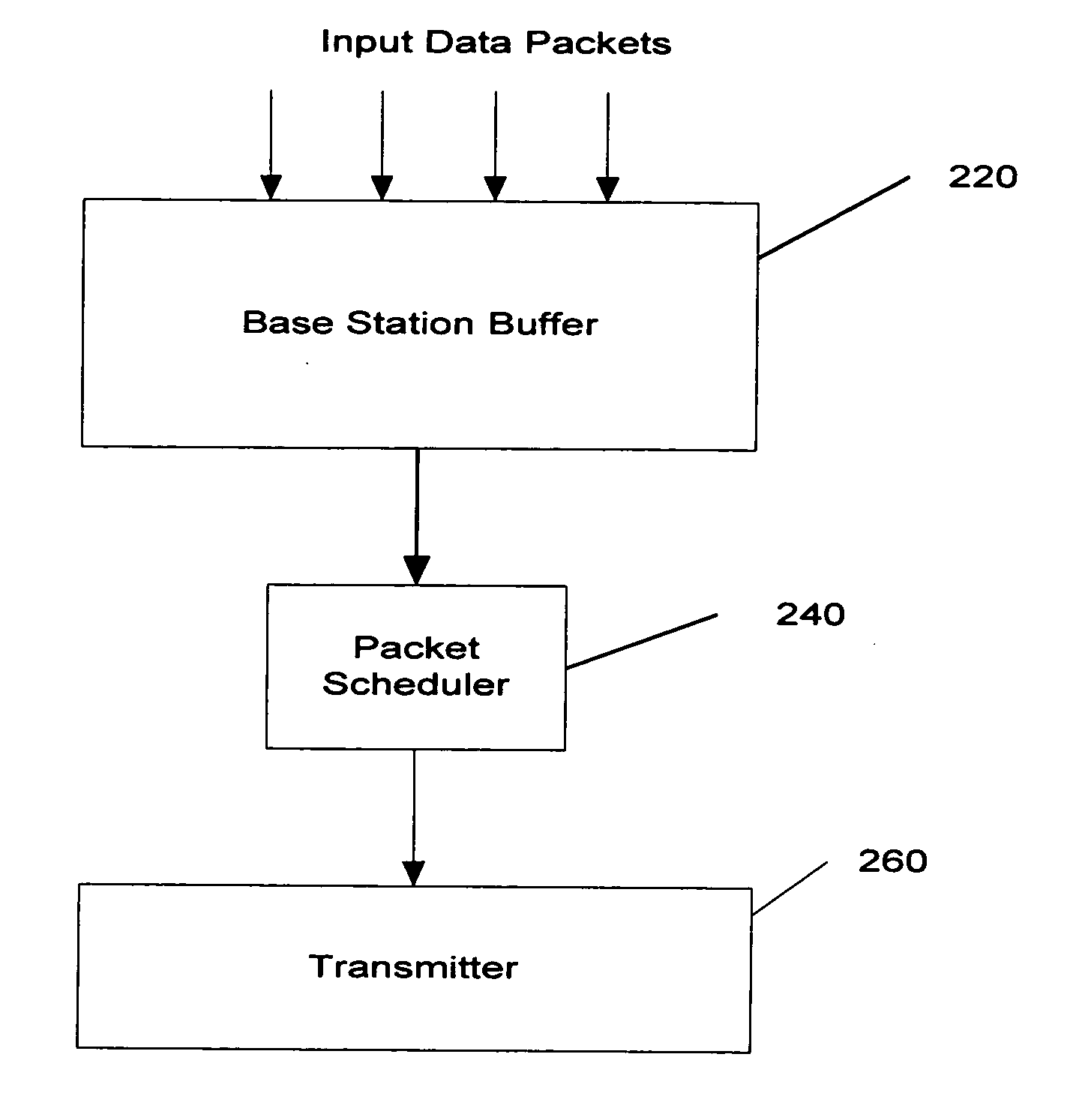
InactiveUS6891834B1Quick dispatchData switching by path configurationStore-and-forward switching systemsPacket schedulingByte
In a network router, a tree structure or a sorting network is used to compare scheduling values and select a packet to be forwarded from an appropriate queue. In the tree structure, each leaf represents the scheduling value of a queue and internal nodes of the structure represent winners in comparisons of scheduling values of sibling nodes of the tree structure. CBR scheduling values may first be compared to select a queue and, if transmission from a CBR queue is not timely, a packet may be selected using WFQ scheduling values. The scheduling values are updated to reflect variable packet lengths and byte stuffing in the prior packet. Scheduling may be performed in multiple stages.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Application, Usage & Radio Link Aware Transport Network Scheduler
ActiveUS20100195602A1Reduce wasteFacilitates optimal sharingNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless commuication servicesTransit networkThird generation
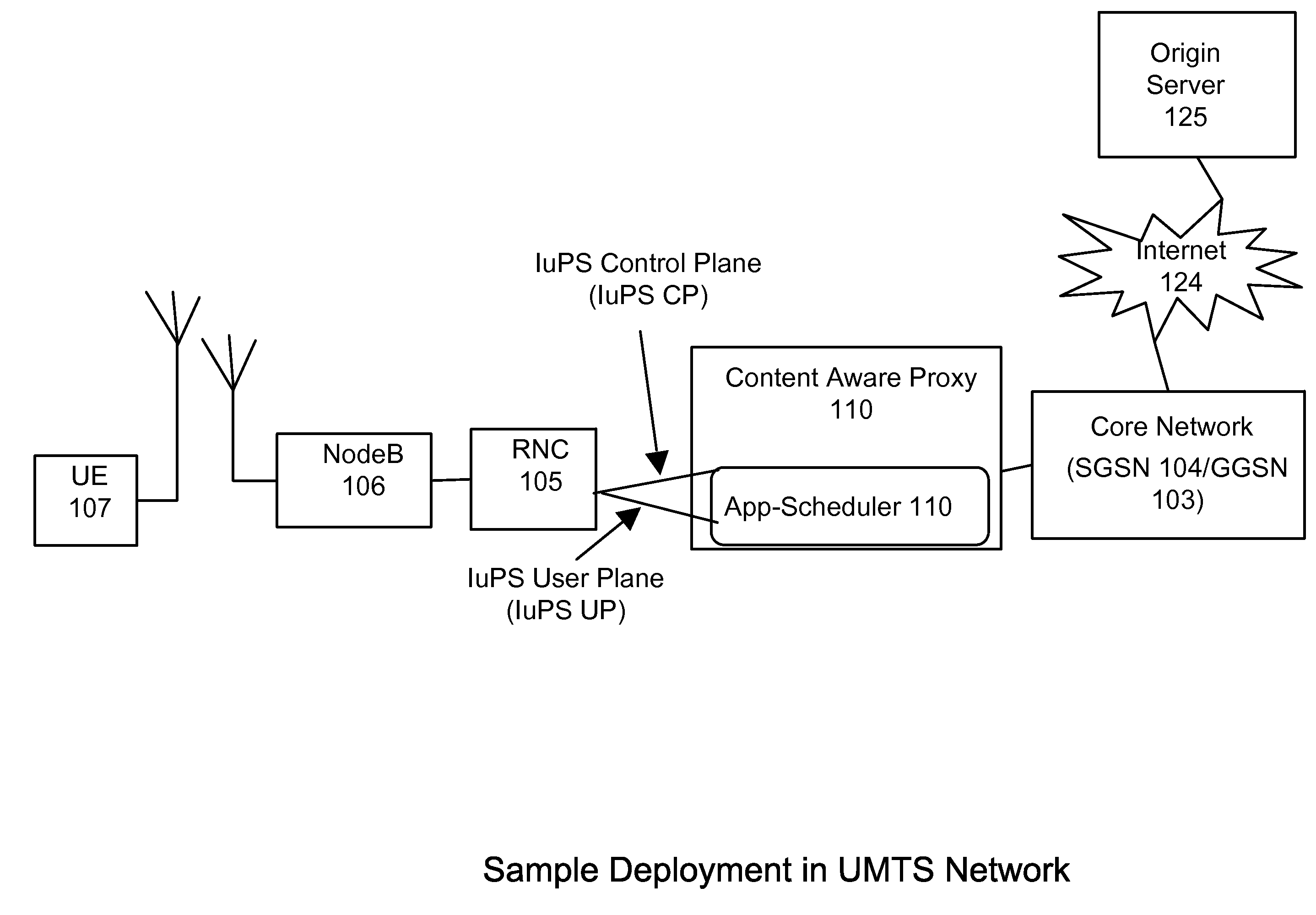
A packet scheduling method and apparatus with the knowledge of application behavior, anticipated usage / behavior based on the type of content, and underlying transport conditions during the time of delivery, is disclosed. This type of scheduling is applicable to a content server or a transit network device in wireless (e.g., 3G, WIMAX, LTE, WIFI) or wire-line networks. Methods for identifying or estimating rendering times of multi-media objects, segmenting a large media content, and automatically pausing or delaying delivery are disclosed. The scheduling reduces transit network bandwidth wastage, and facilitates optimal sharing of network resources such as in a wireless network.
Owner:RIBBON COMM SECURITIES CORP
Method and apparatus to facilitate real-time packet scheduling in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS20060227796A1Network traffic/resource managementData switching by path configurationData packCommunications system
A method, apparatus and system for scheduling data packets in a wireless communications system. The invention includes determining a priority for at least one data packet, wherein determining the priority of the data packet is based at least on a plurality of quality of service factors, wherein each of the plurality of QoS factors has a corresponding weighting factor and the determined priority includes minimum-performance guarantees. The invention further includes scheduling transmission of the at least one data packet based at least on the determined priority.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
Method for packet scheduling and radio resource allocation in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20020147022A1Energy efficient ICTNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemData rate
A method of performing packet level transmission scheduling in a communications systems including a plurality of cells,each cell including a base station and plurarity of mobile stations. The method performs scheduling while considering radio resource allocation at the wireless access node. In a schedule plan phase of the method, average power and average effective data rate are determined for all mobile stations in the system. In addition, the planned fractions of frames rho that each mobile in the system will transmit is determined so that resources are allocated fairly. In the actual schedule phase of the method, current power and effective data rate values are compared to the average power values. This information along with the rho values is used to determine the actual schedule of packet transmissions for all mobiles in a particular cell.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Early traffic regulation techniques to protect against network flooding
ActiveUS7295516B1Reducing flow of trafficReduce processing burdenError preventionTransmission systemsRoad traffic controlTraffic capacity
Methods and apparatus for providing an Anti-Flooding Flow-Control (AFFC) mechanism suitable for use in defending against flooding network Denial-of-Service (N-DoS) attacks is described. Features of the AFFC mechanism include (1) traffic baseline generation, (2) dynamic buffer management, (3) packet scheduling, and (4) optional early traffic regulation. Baseline statistics on the flow rates for flows of data corresponding to different classes of packets are generated. When a router senses congestion, it activates the AFFC mechanism of the present invention. Traffic flows are classified. Elastic traffic is examined to determine if it is responsive to flow control signals. Flows of non-responsive elastic traffic is dropped. The remaining flows are compared to corresponding class baseline flow rates. Flows exceeding the baseline flow rates are subject to forced flow rate reductions, e.g., dropping of packets.
Owner:PALO ALTO NETWORKS INC
Integrated packet latency aware QoS scheduling using proportional fairness and weighted fair queuing for wireless integrated multimedia packet services
ActiveUS20070041364A1Network traffic/resource managementIn VoIP networksPacket communicationPacket scheduling
Packet communication networks for transmission to wireless subscriber devices utilize both wireline and wireless packet routing components. The routing elements of these two different types often implement different packet scheduling algorithms, typically a form of Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ) in the wireline portion of the network and Proportional Fairness (PF) queuing in the wireless domain. To improve resource allocation and thus end to end quality of service for time sensitive communications, such as integrated multimedia services, the present disclosure suggests adding the notion of slack time into either one or both of the packet scheduling algorithms. By modifying one or more of these algorithms, e.g. to reorder or shuffle packets based on slack times, global optimal resource allocations are possible, at least in certain cases.
Owner:CELLCO PARTNERSHIP INC
Packet scheduling method for wireless communication system
ActiveUS20070116024A1Reduce loss rateEnsures comparative fairnessError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsData packCommunications system
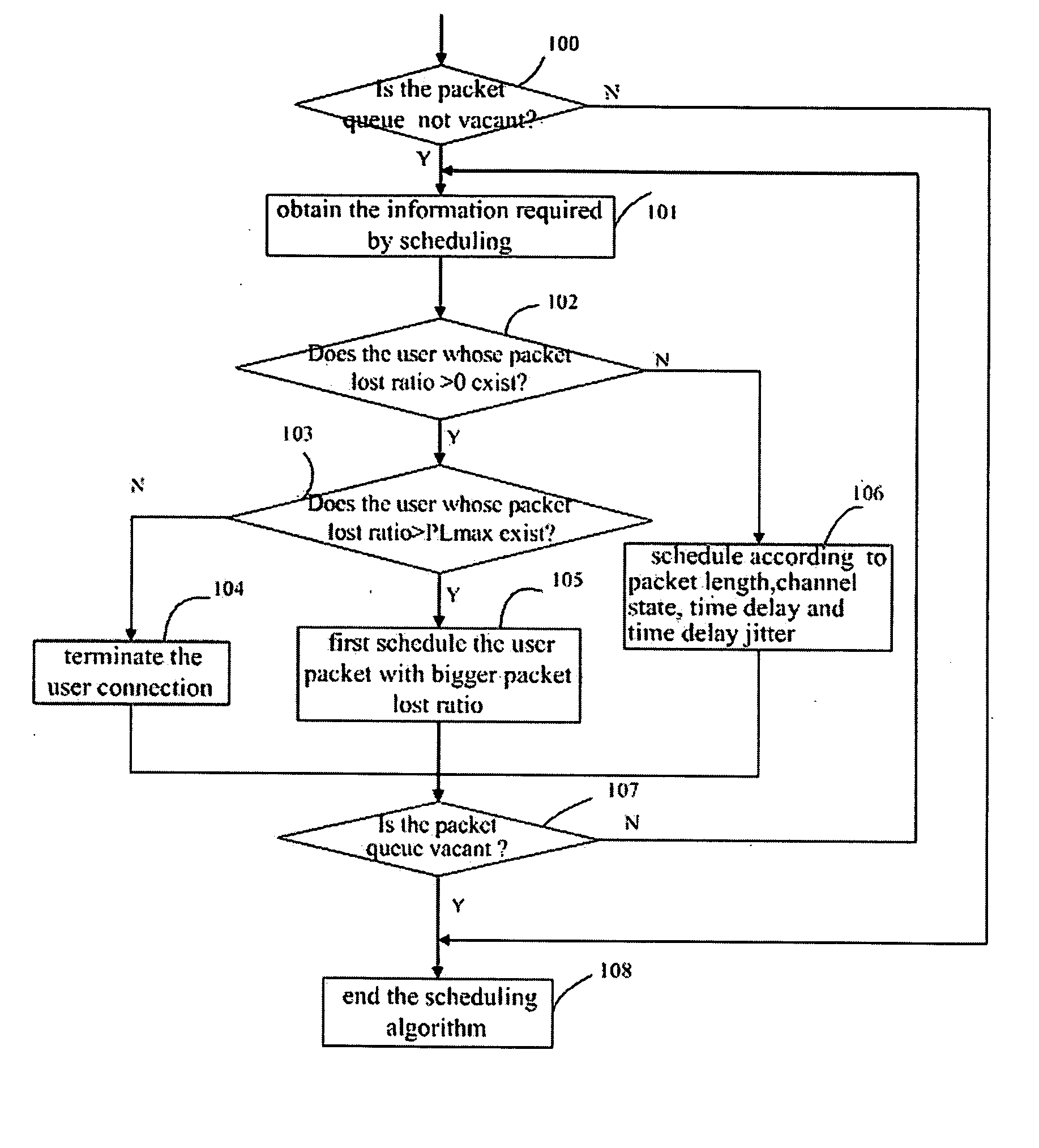
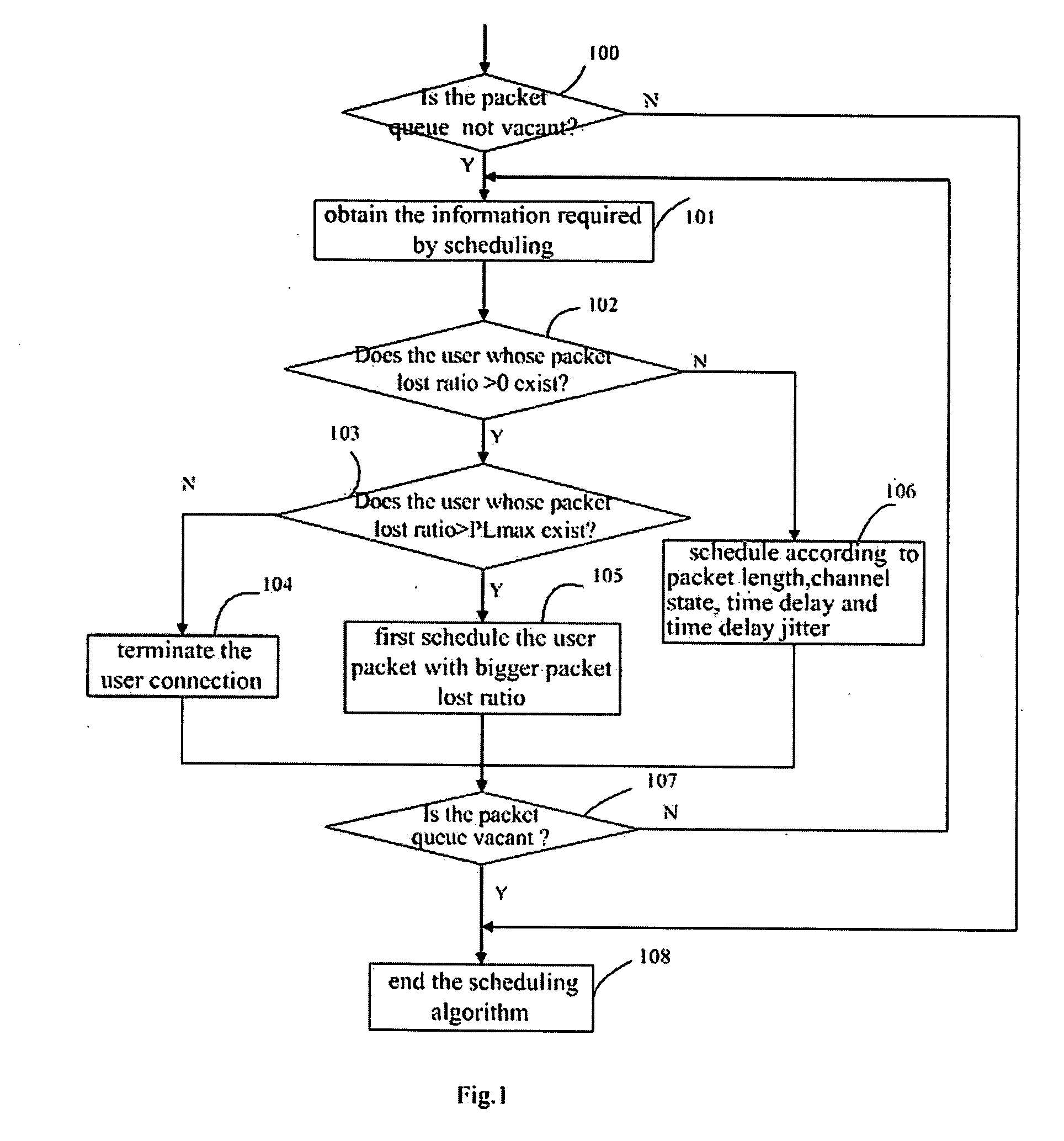
The present invention provides a method of scheduling packet in a wireless telecommunication system, in which the user packet queues to be transmitted are divided into the user packet queues with lost packet and the user packet queues without lost packet; for the user packet queues with lost packet, if a real time lost ratio of packet for the user excesses a predetermined lost ratio threshold of packet, terminate a connection to the user; if the real time lost ratio of packet for the user does not excess the predetermined lost ratio threshold of packet, schedule the user packet queues according to a volume of the lost ratio of packet; for the user packet queues without lost packet, schedule according to packet lengths, channel quality states, time delays and time delay jitters. The present invention decreases the packet lost ratio by giving priority to scheduling users with high packet lost ratio under the condition of existing a certain extent of packet lost, takes the requirements of user packet service sensitive to the time delay jitter into full consideration, and controls the time delay jitter to maintain invariable, therefore improves the telecommunication quality of those users.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Opportunistic packet scheduling apparatus and method in multihop relay wireless access communication system
Opportunistic packet scheduling apparatus and method in a multihop relay wireless access communication system are provided. The method includes aggregating channel condition information which are estimated and reported by Mobile Stations (MSs) and a Relay Station (RS) for each MS path in a cell, determining a Modulation and Coding Scheme (MCS) level which corresponds to the aggregated channel condition information for a corresponding hop of each MS path, determining a transmittable coded packet size and a number of subchannels required for the packet transmission depending on the determined MCS level, and calculating a current radio resource efficiency of the corresponding MS path using the determined coded packet size and the determined number of the subchannels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
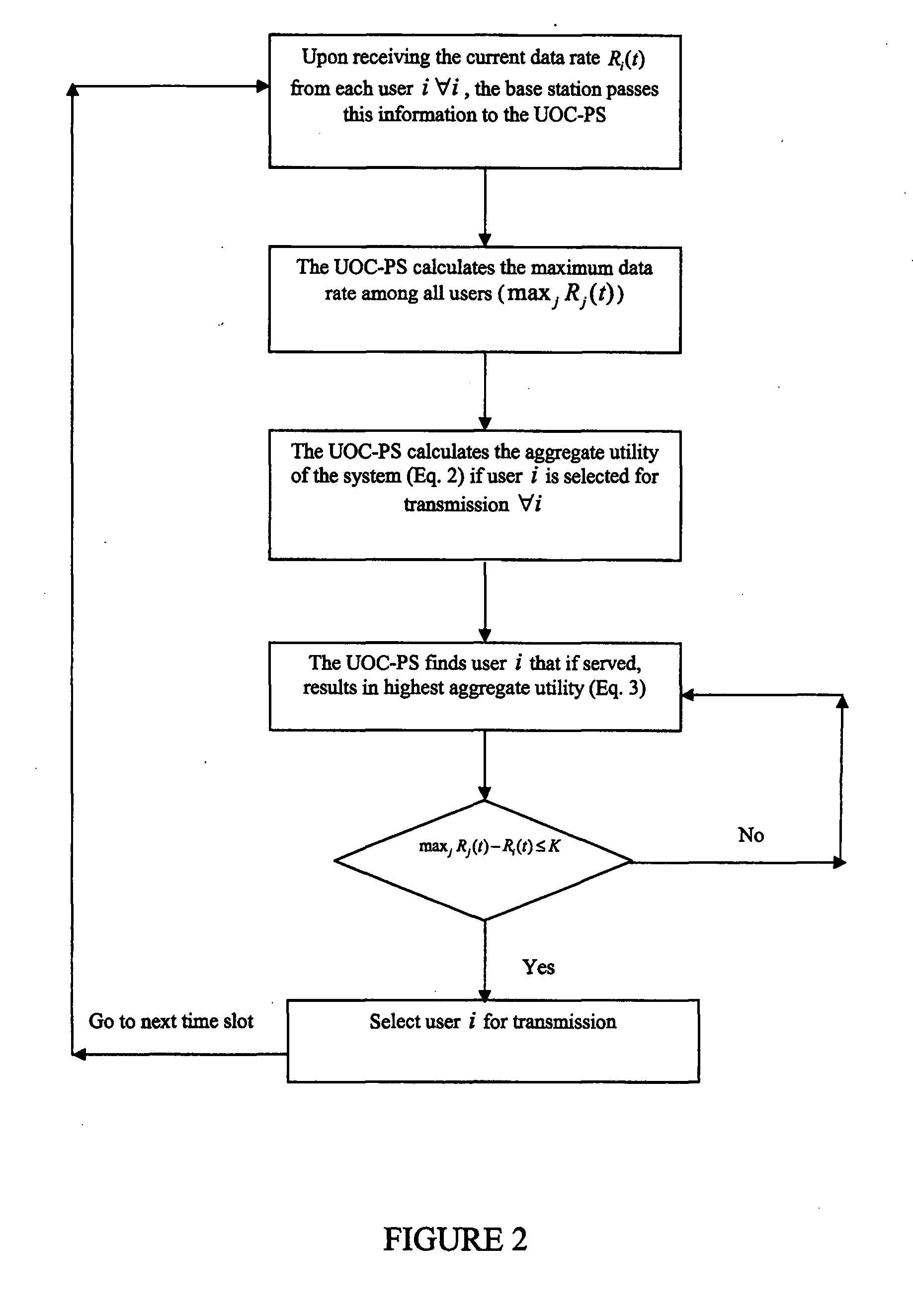
Method for optimal packet scheduling for wireless and mobile communications networks
InactiveUS20080137537A1Increase opportunitiesChannel quality conditionError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsSystem capacityControl system
This invention relates to a centralized packet scheduler for a wireless communications network such as HSDPA, 1×EV-DO Revisions 0, A and B, WiMAX, infrastructure-mode WiFi and any other type of network where centralized packet scheduling is applicable. The invention provides a utility-opportunity cost packet scheduling scheme for high-speed access that simultaneously achieves efficiency, fairness, user satisfaction, and flexibility. The scheme employs a flexible utility function that incorporates the channel quality conditions of the users as well as a fairness measure. The utility function maximizes user satisfaction as perceived by the service provider while ensuring that users with favourable instantaneous channel quality conditions do not monopolize the radio resources. In addition, the scheme uses an opportunity cost function to allow the service provider to optimize fairness in the context of network throughput and hence, to control the system capacity. The scheme combines the requirements of users (e.g., throughput, delay, fairness, etc.) with the requirements of the service provider (e.g., revenue) in making scheduling decisions.
Owner:QUEENS UNIV OF KINGSTON
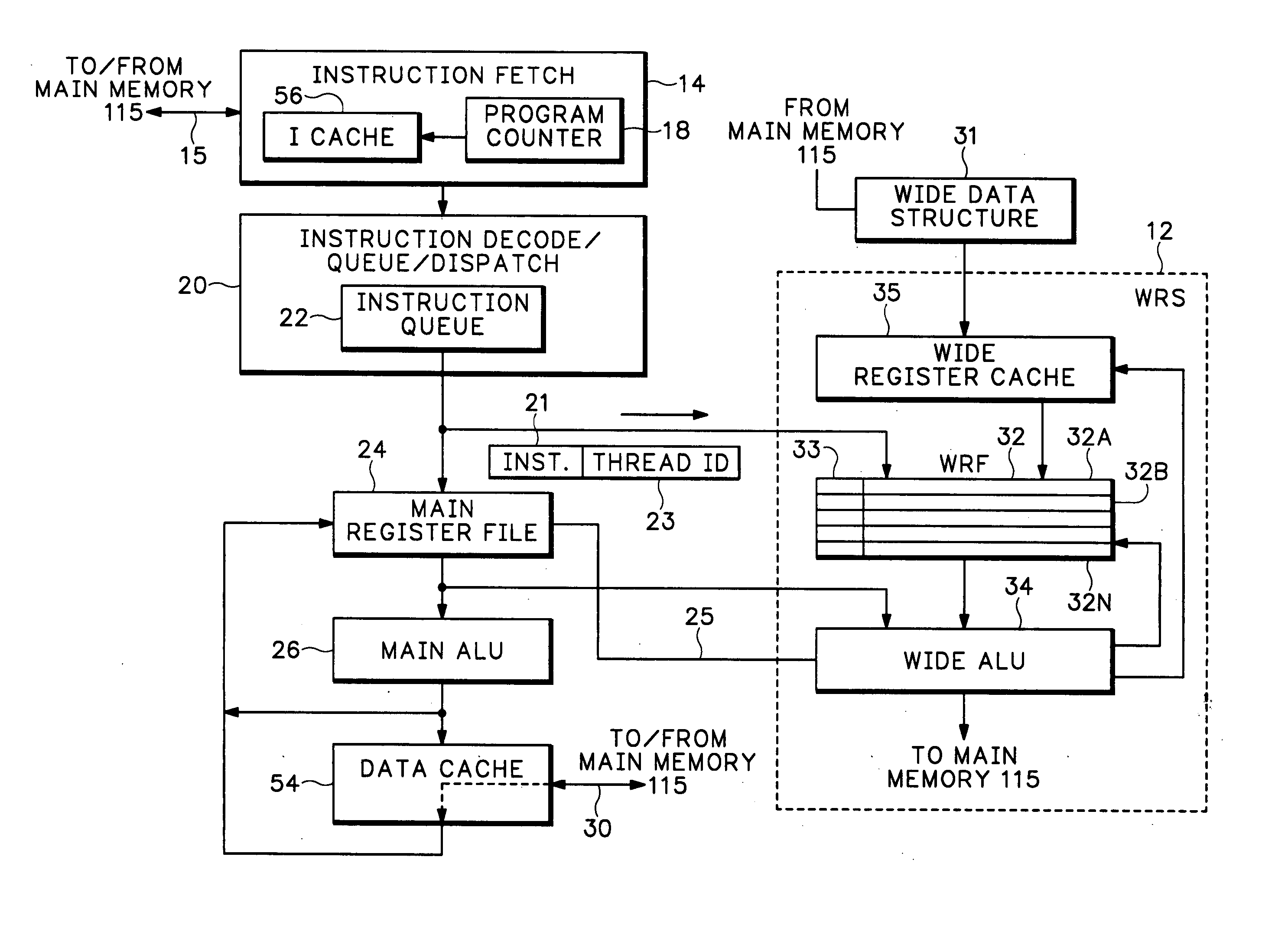
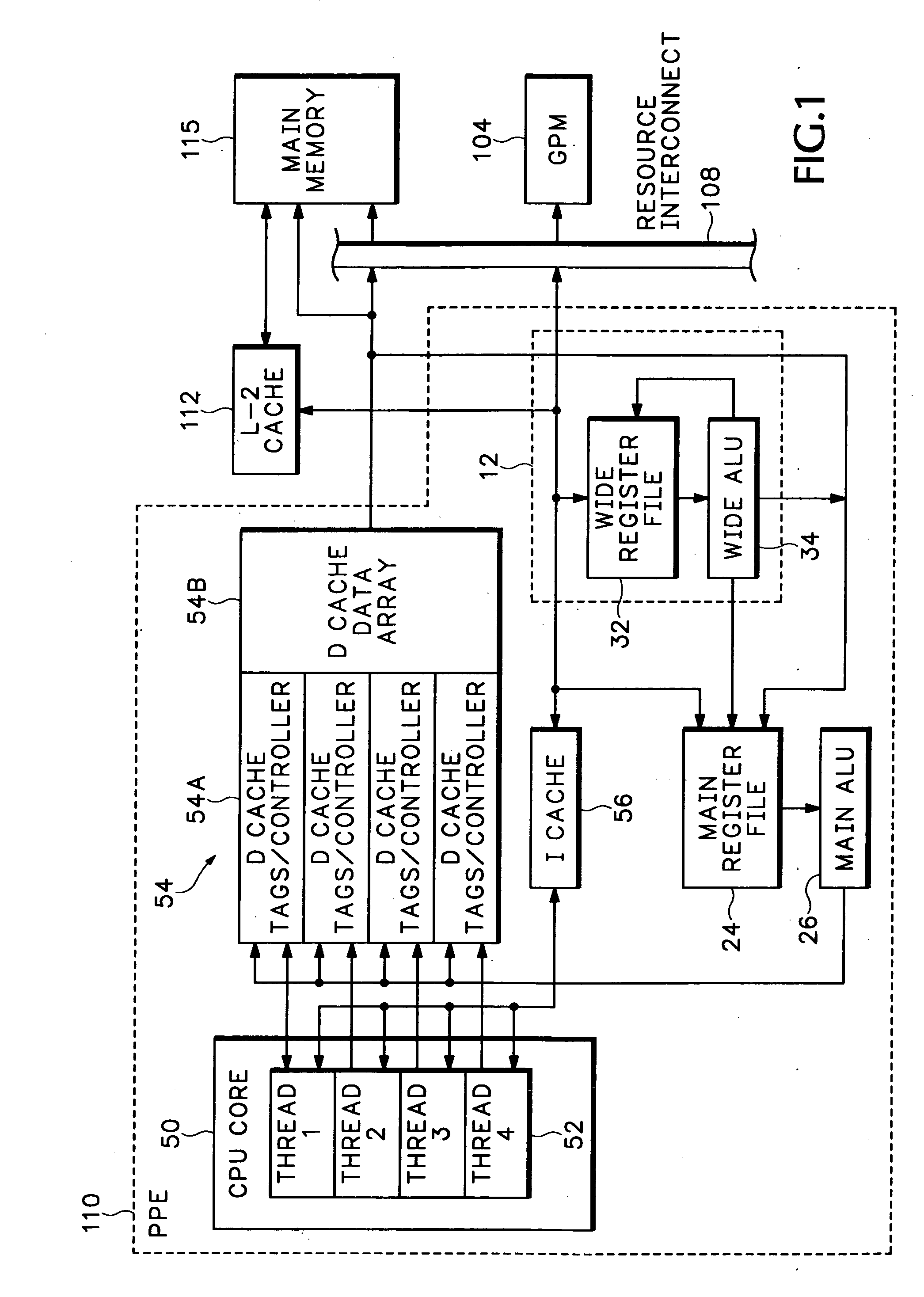
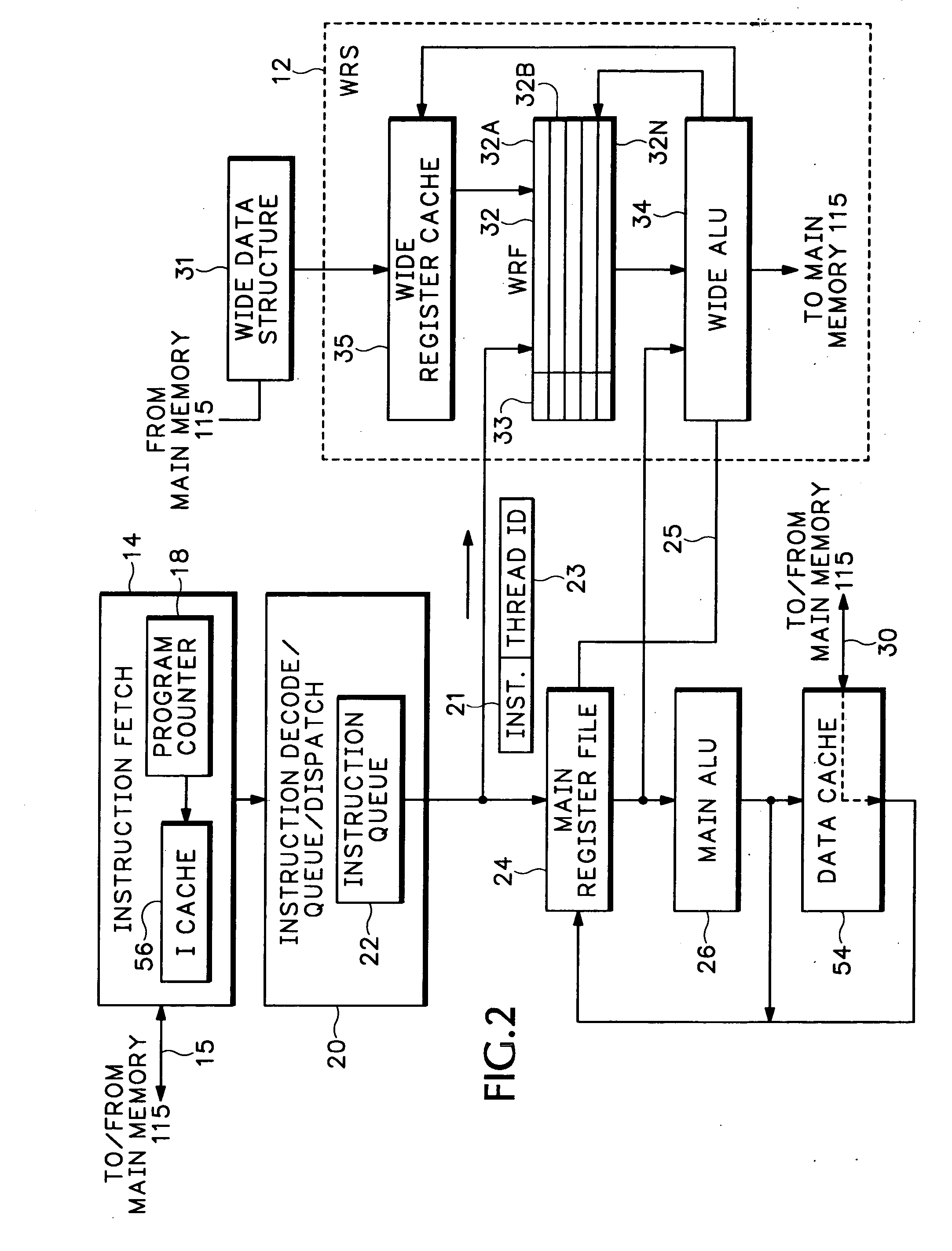
Packet processor with wide register set architecture
InactiveUS20060200647A1Improve performanceWider bitRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerData packLogic cell
A Wide Register Set (WRS) is used in a packet processor to increase performance for certain packet processing operations. The registers in the WRS have wider bit lengths than the main registers used for primary packet processing operations. A wide logic unit is configured to conduct logic operations on the wide register set and in one implementation includes hardware primitives specifically configured for packet scheduling operations. A special interlocking mechanism is additionally used to coordinate accesses among multiple processors or threads to the same wide register address locations. The WRS produces a scheduling engine that is much cheaper than previous hardware solutions with higher performance than previous software solutions. The WRS provides a small, compact, flexible, and scalable scheduling sub-system and can tolerate long memory latencies by using cheaper memory while sharing memory with other uses. The result is a new packet processing architecture that has a wide range of cost / performance points, based on desired scheduling requirements.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
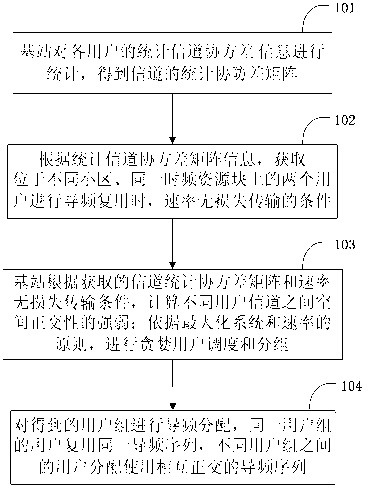
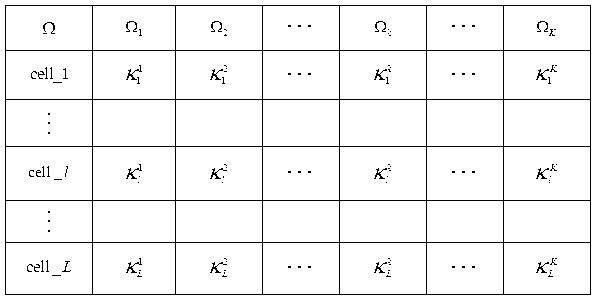
Spatial-orthogonality-based large-scale MIMO (multiple input multiple output) system pilot frequency distribution method
ActiveCN103298124ATake advantage ofReduce Feedback OverheadBaseband system detailsTransmission path multiple useChannel state informationMultiplexing
The invention relates to a spatial-orthogonality-based large-scale MIMO system pilot frequency distribution method. The method comprises the following steps: 1) obtaining the statistical covariance matrix information of every user terminal channel through a base station; 2) under the condition that the statistical covariance matrix information is known, obtaining the condition for achieving no-speed-loss transmission when two users located in different cells on the same time-frequency block perform pilot frequency multiplexing; 3) according to the information obtained in step 1), contrasting and calculating the spatial orthogonality degree among the channels of different users through the base station, and utilizing the condition of achieving the no-speed-loss transmission in step 2) to perform greedy packet scheduling on the users under the principle of maximizing the system sum speed; and 4) performing pilot frequency distribution on every user group. Under the condition that the user side does not know instantaneous channel state information, the spatial-orthogonality-based large-scale MIMO system pilot frequency distribution method can achieve the pilot frequency multiplexing and meanwhile effectively reduce the influence caused by the problem of pilot frequency pollution and improve the system throughput performance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com