Patents
Literature
2002results about "Register arrangements" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
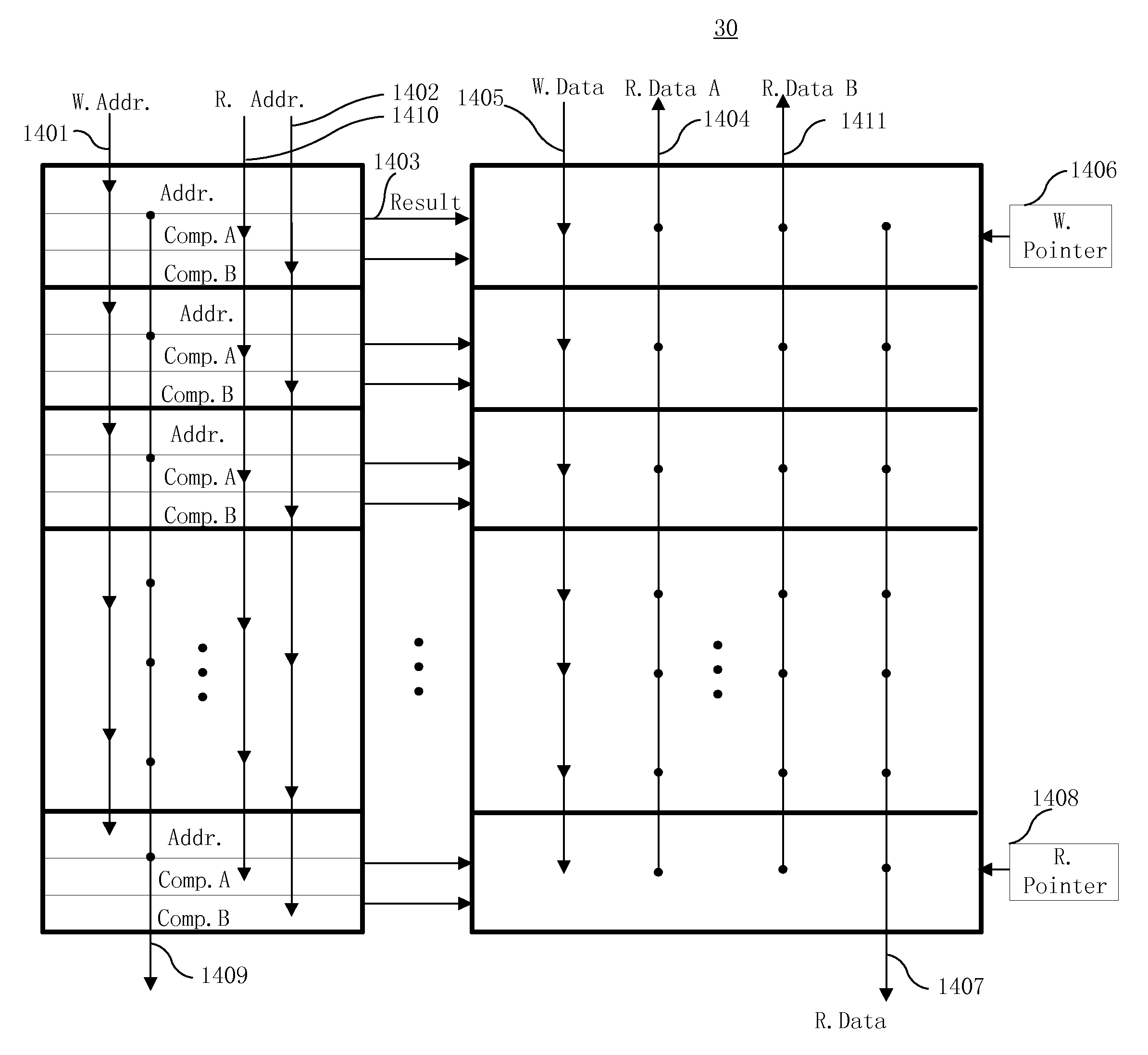
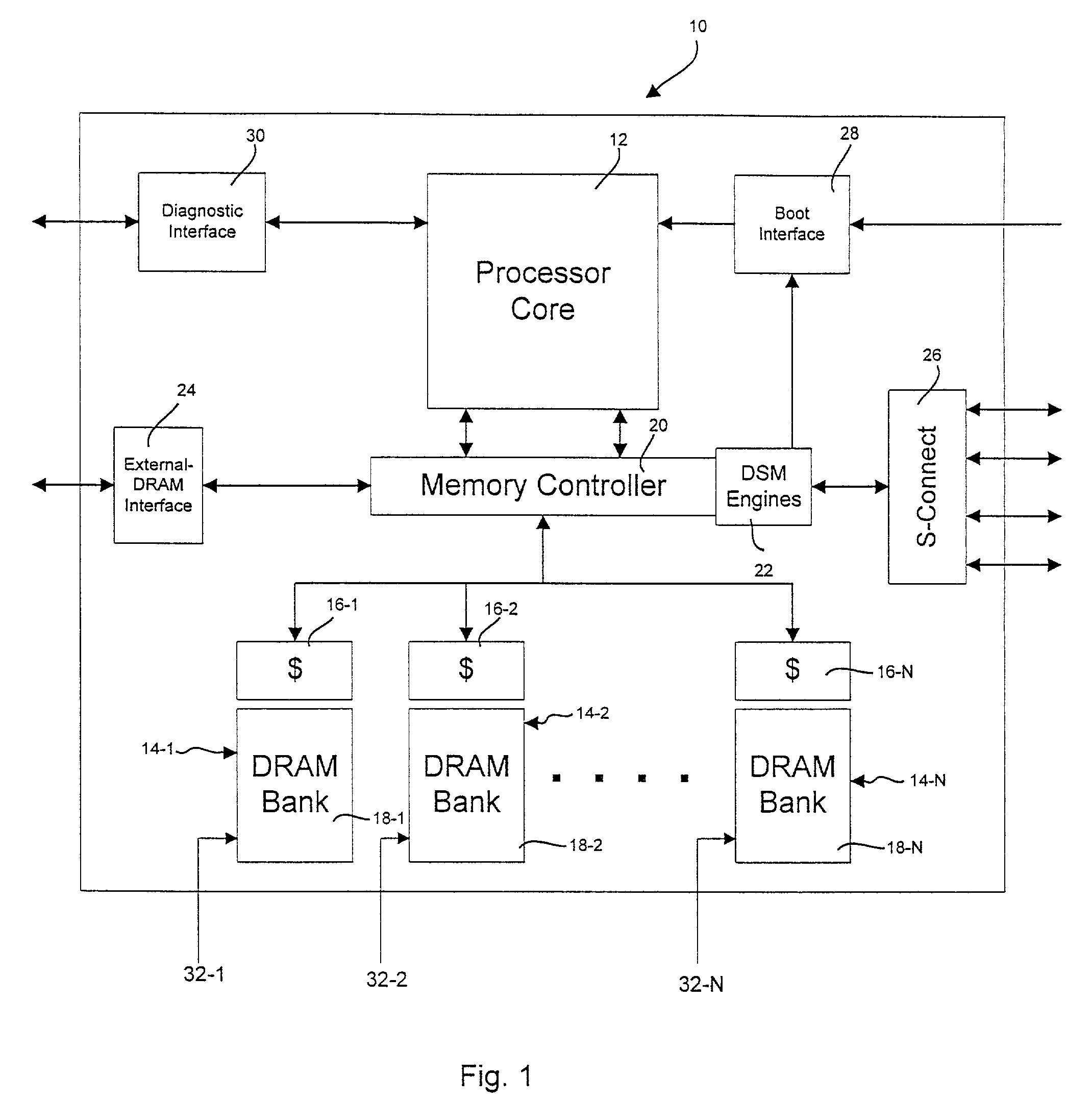
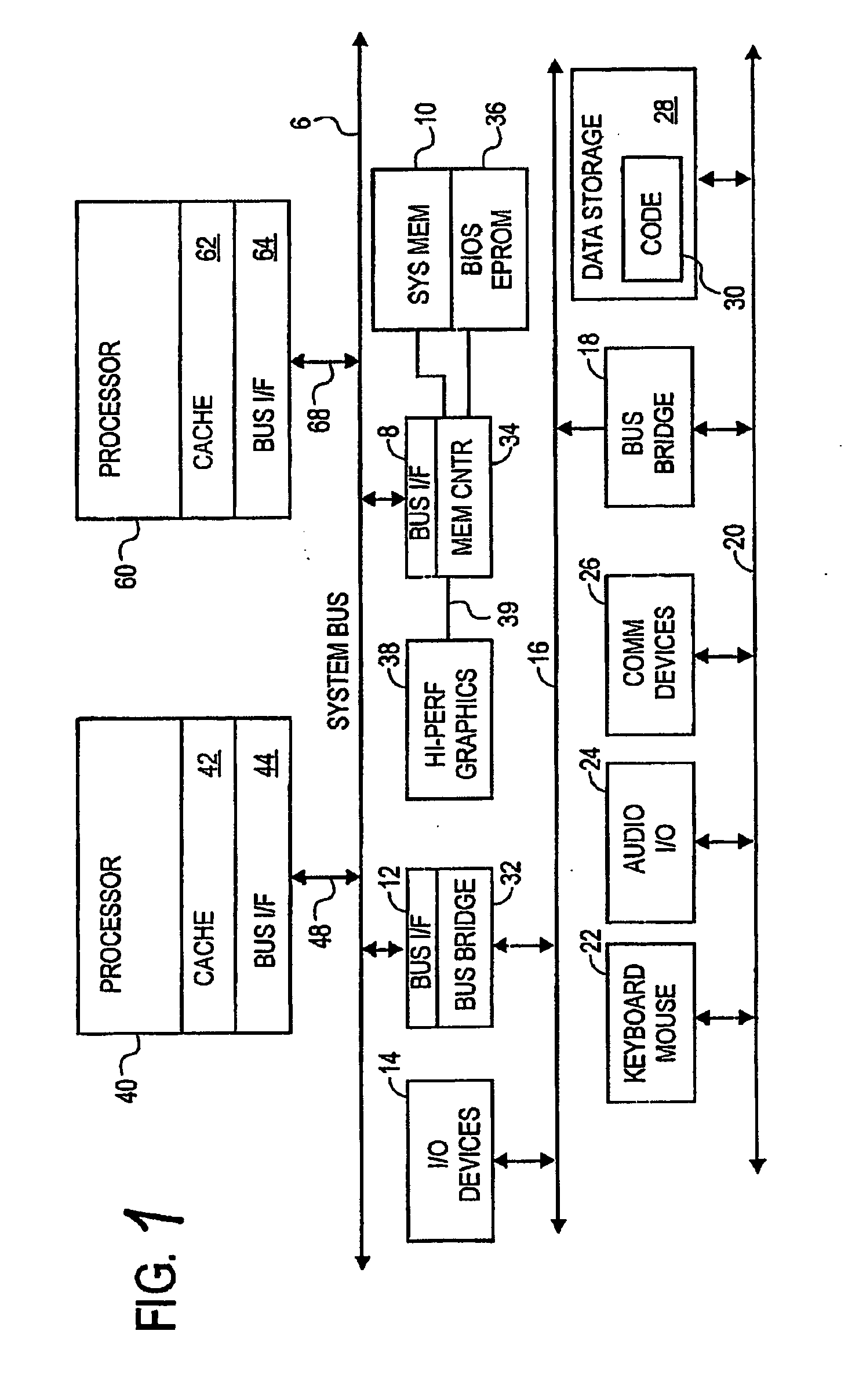
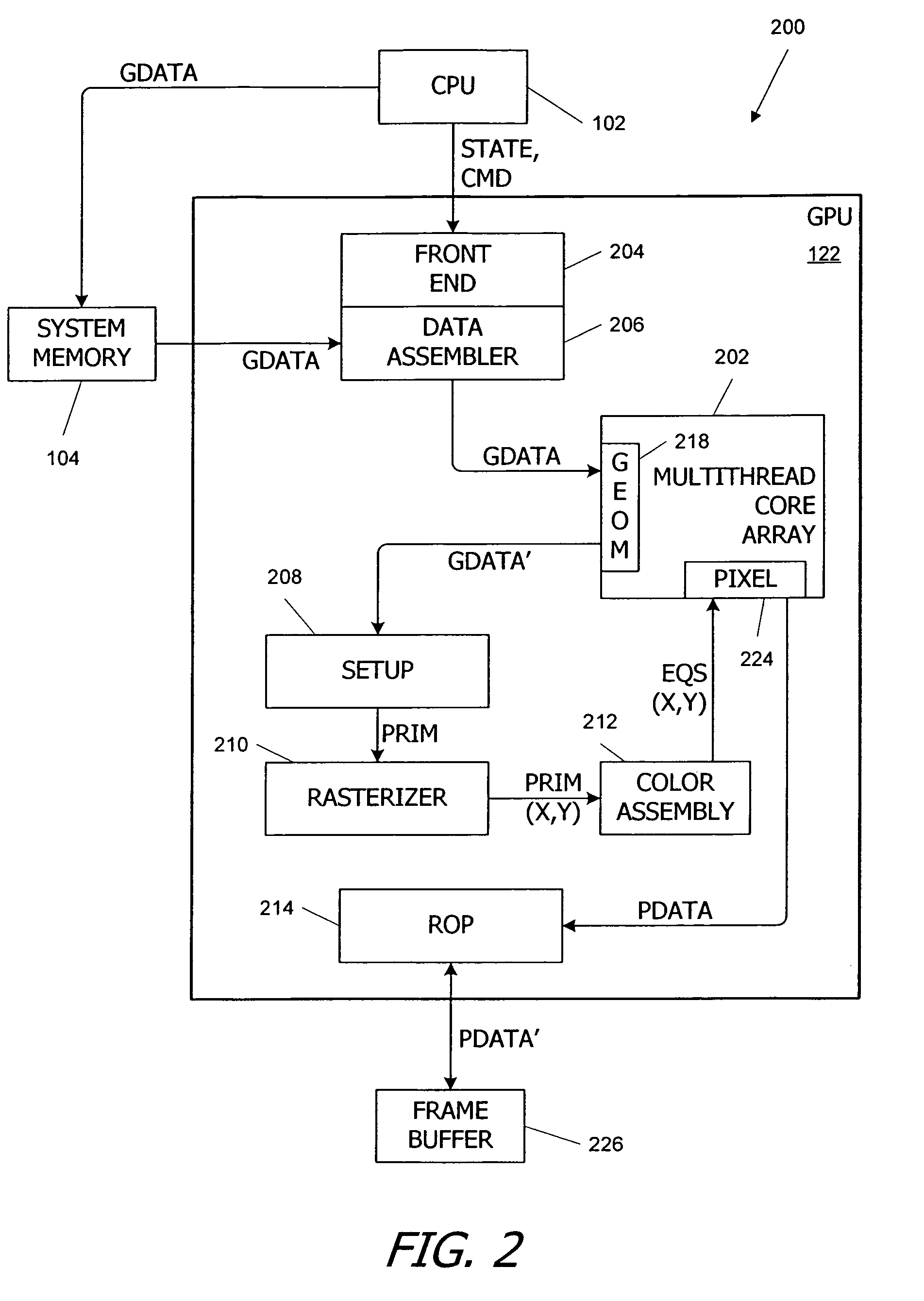
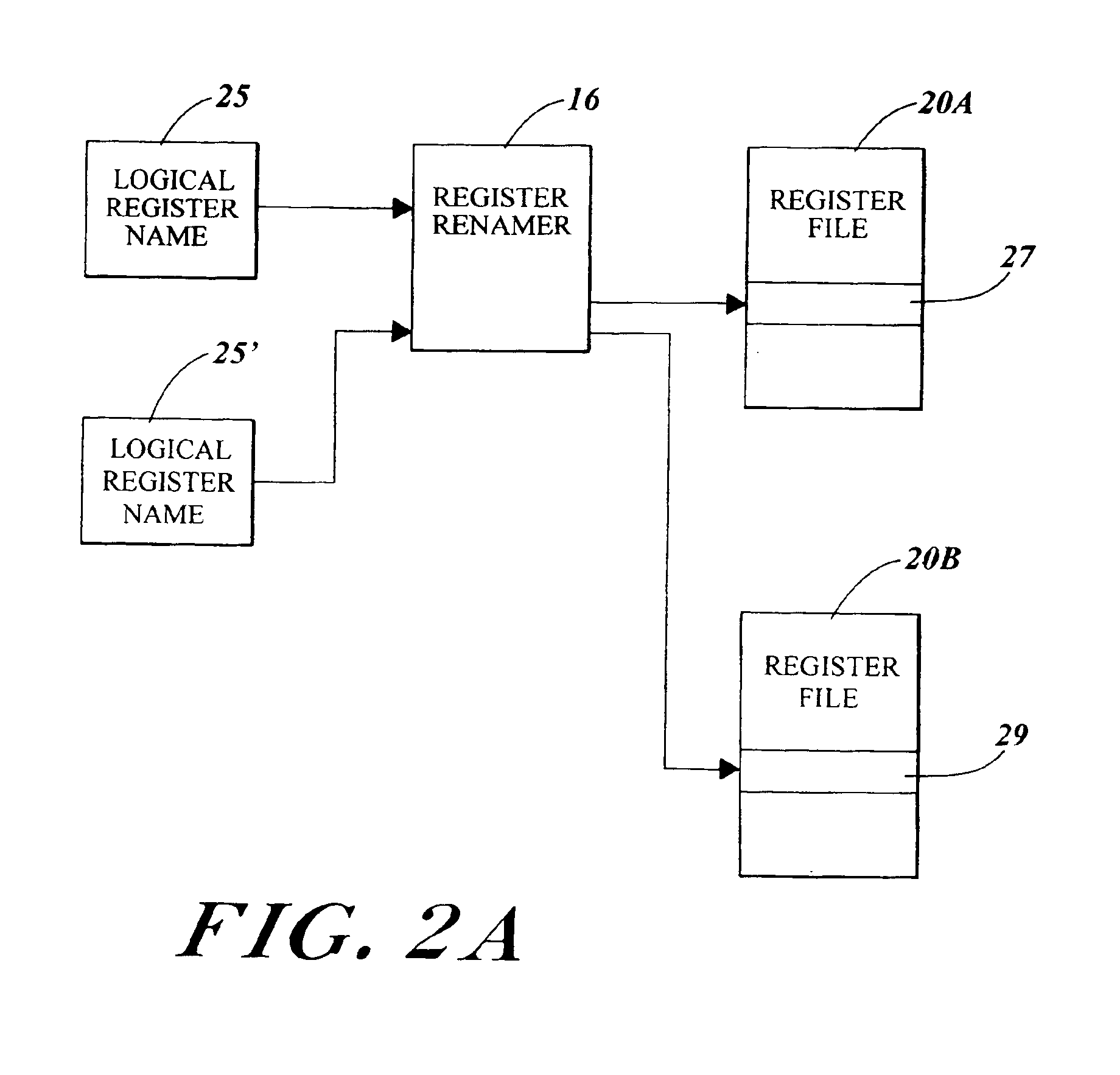
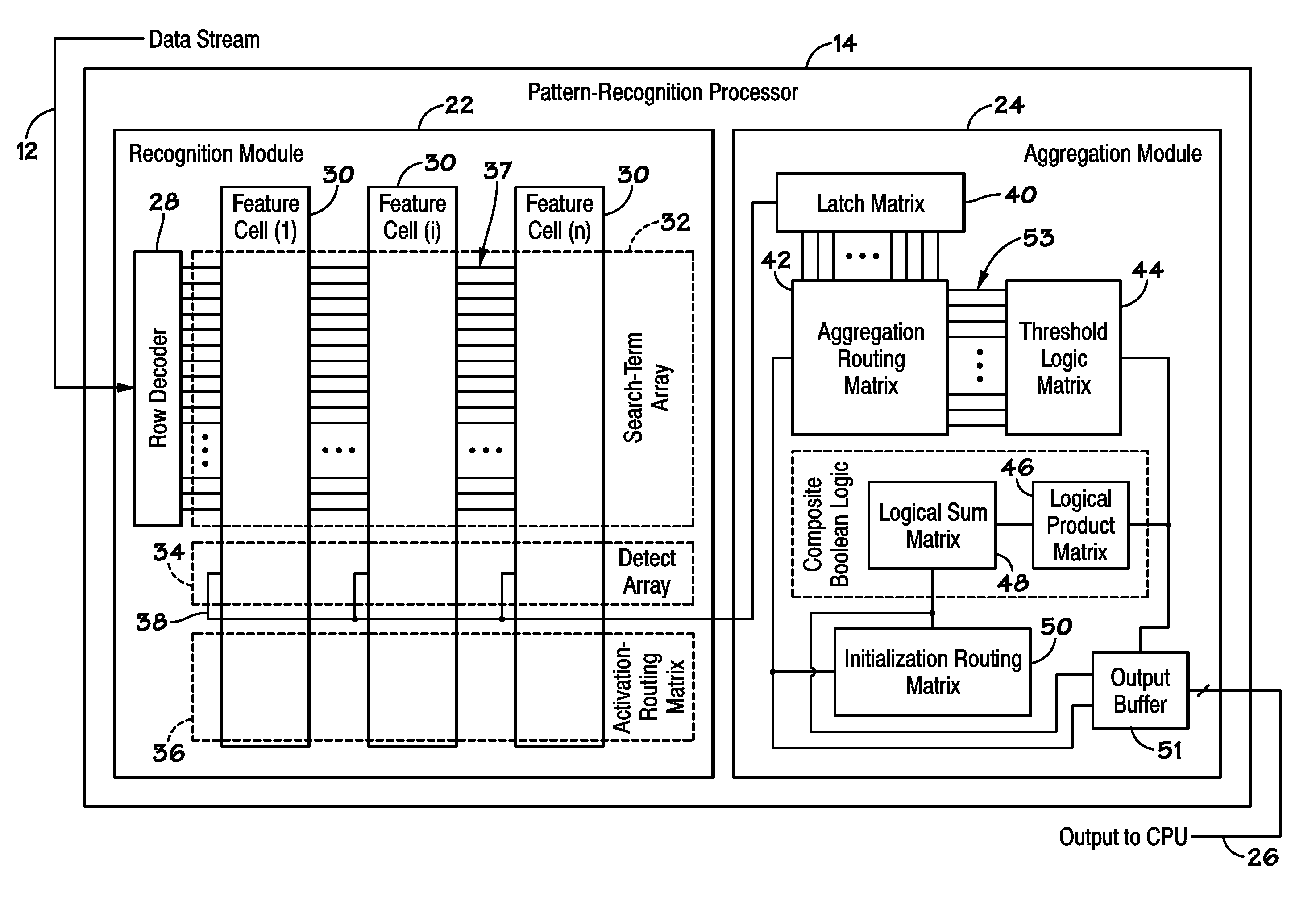
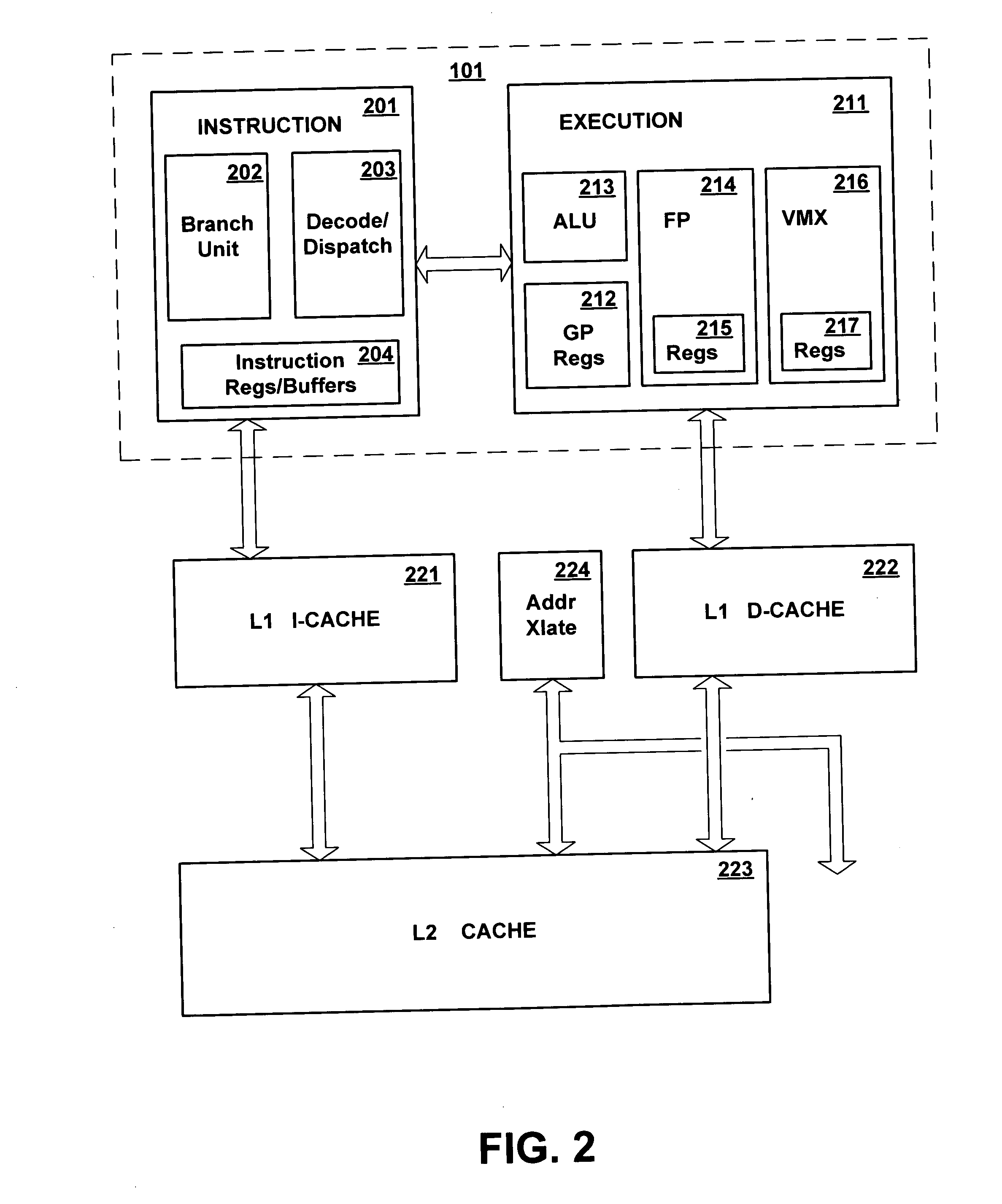
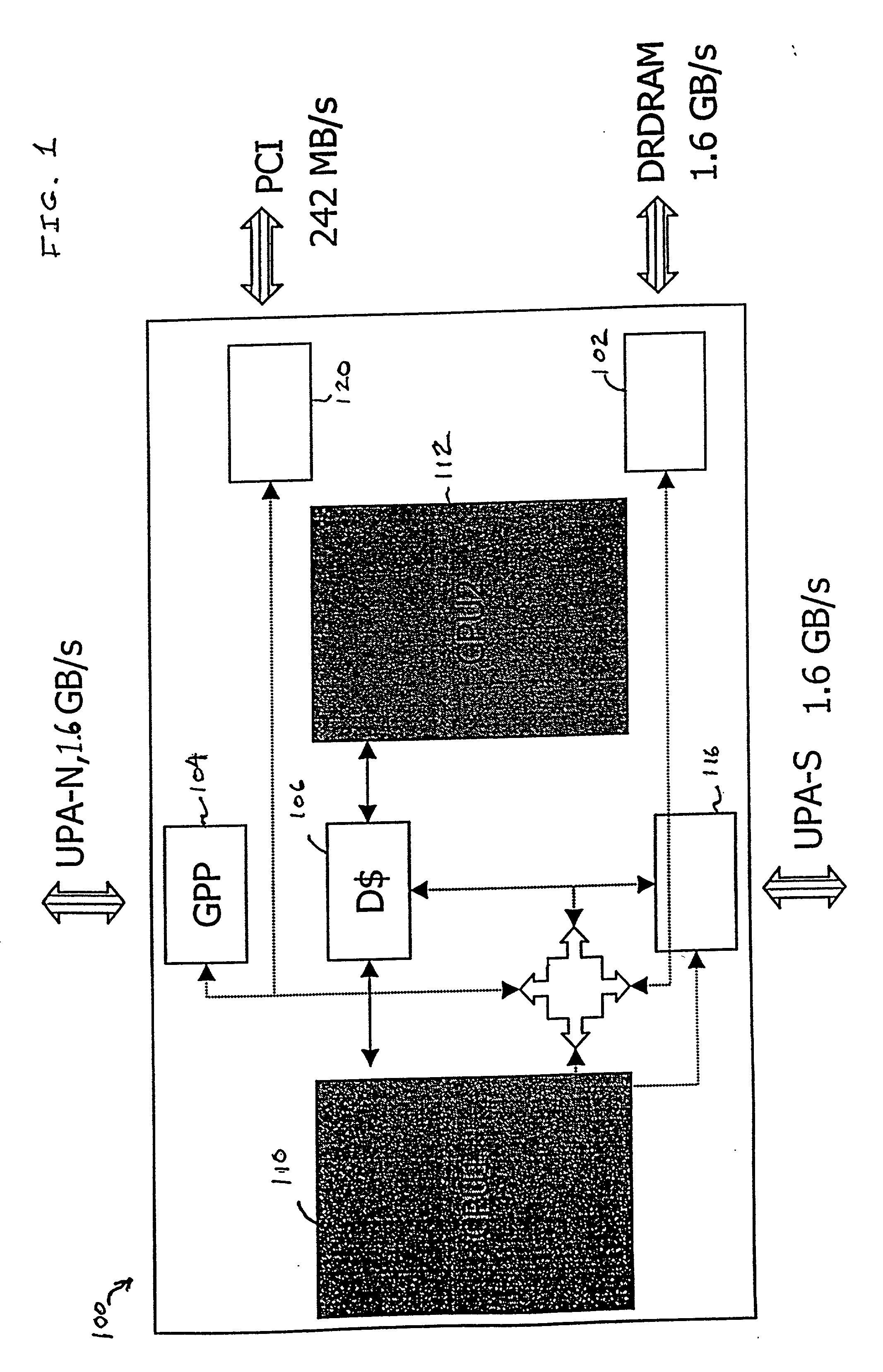
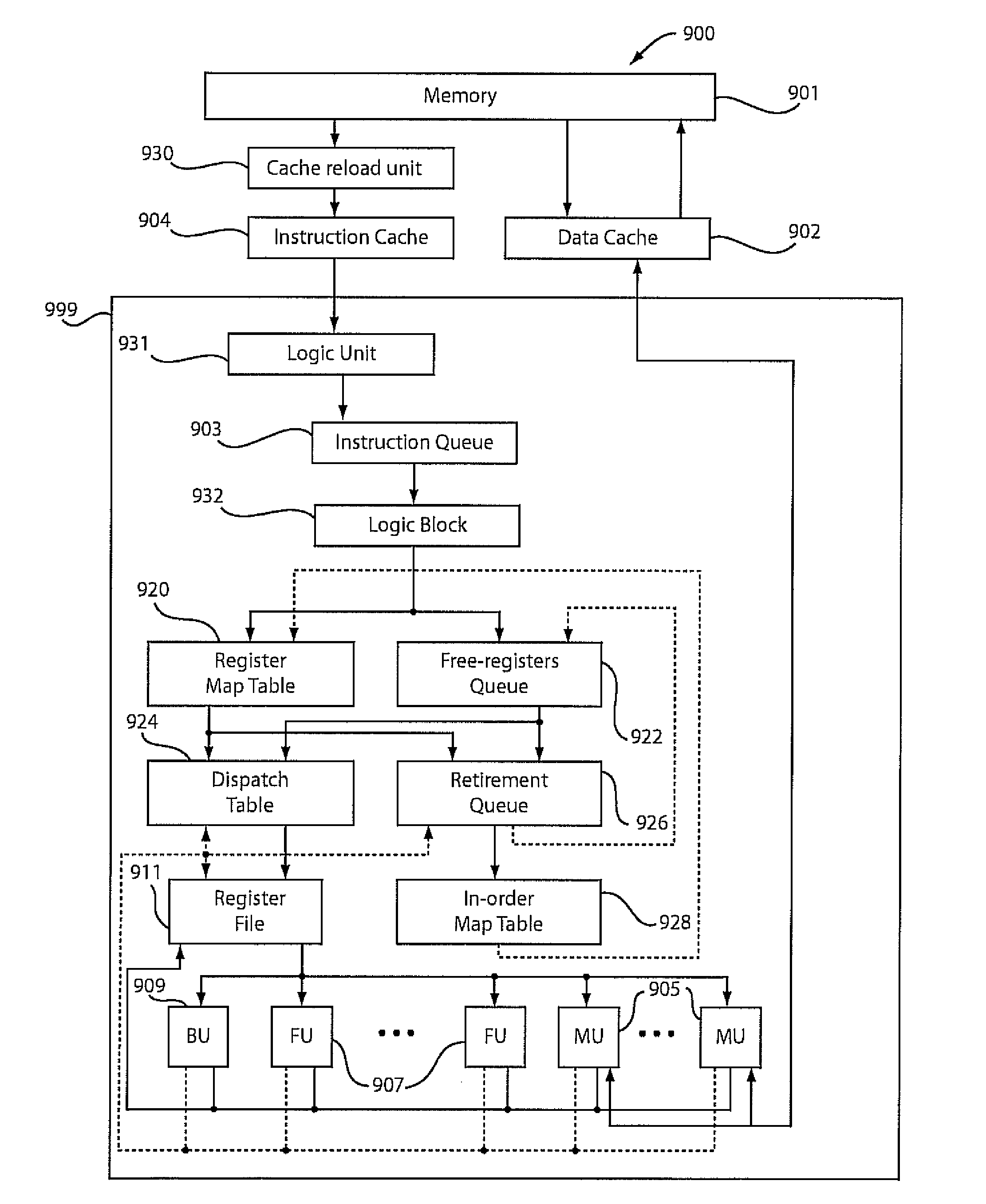
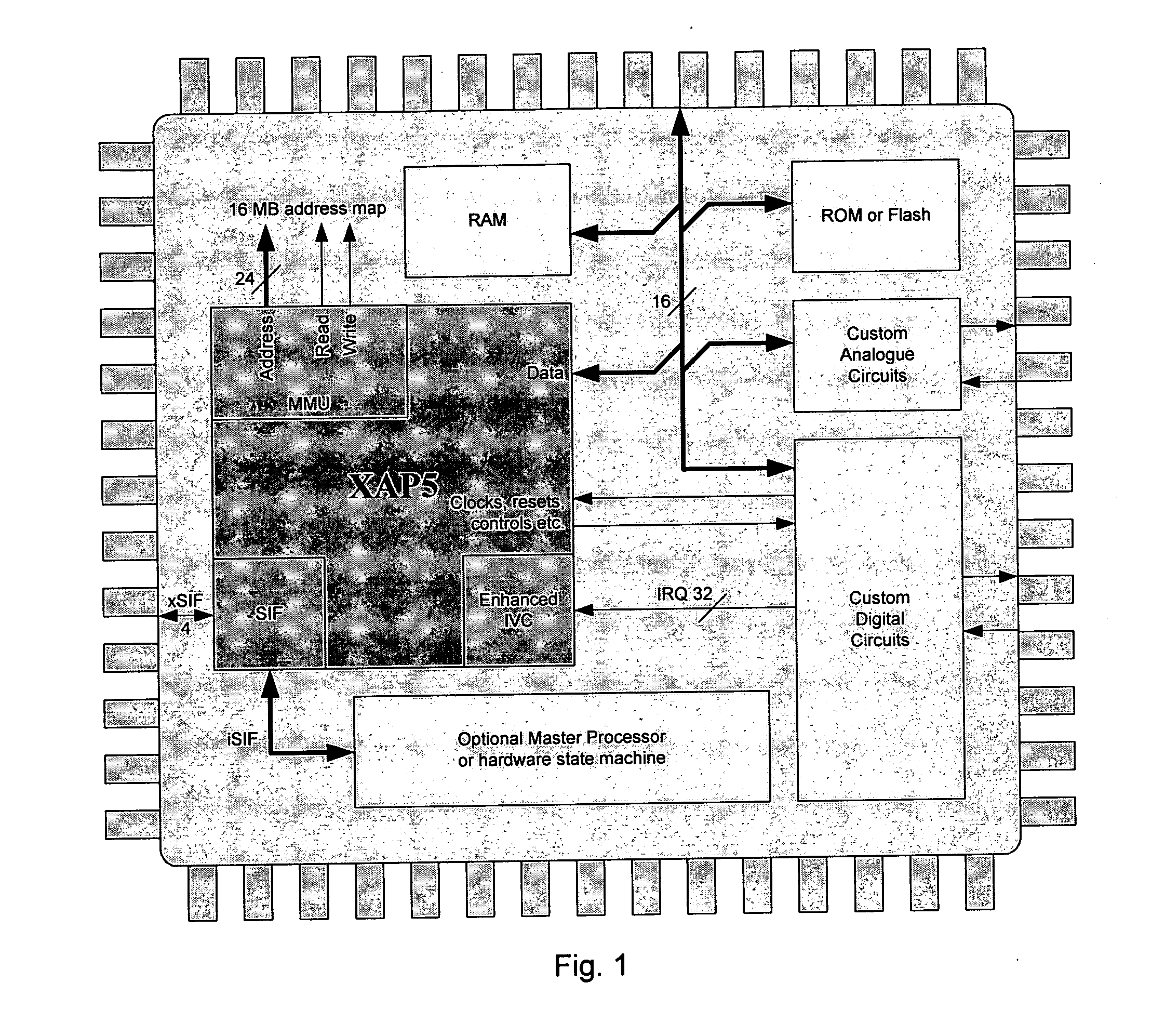
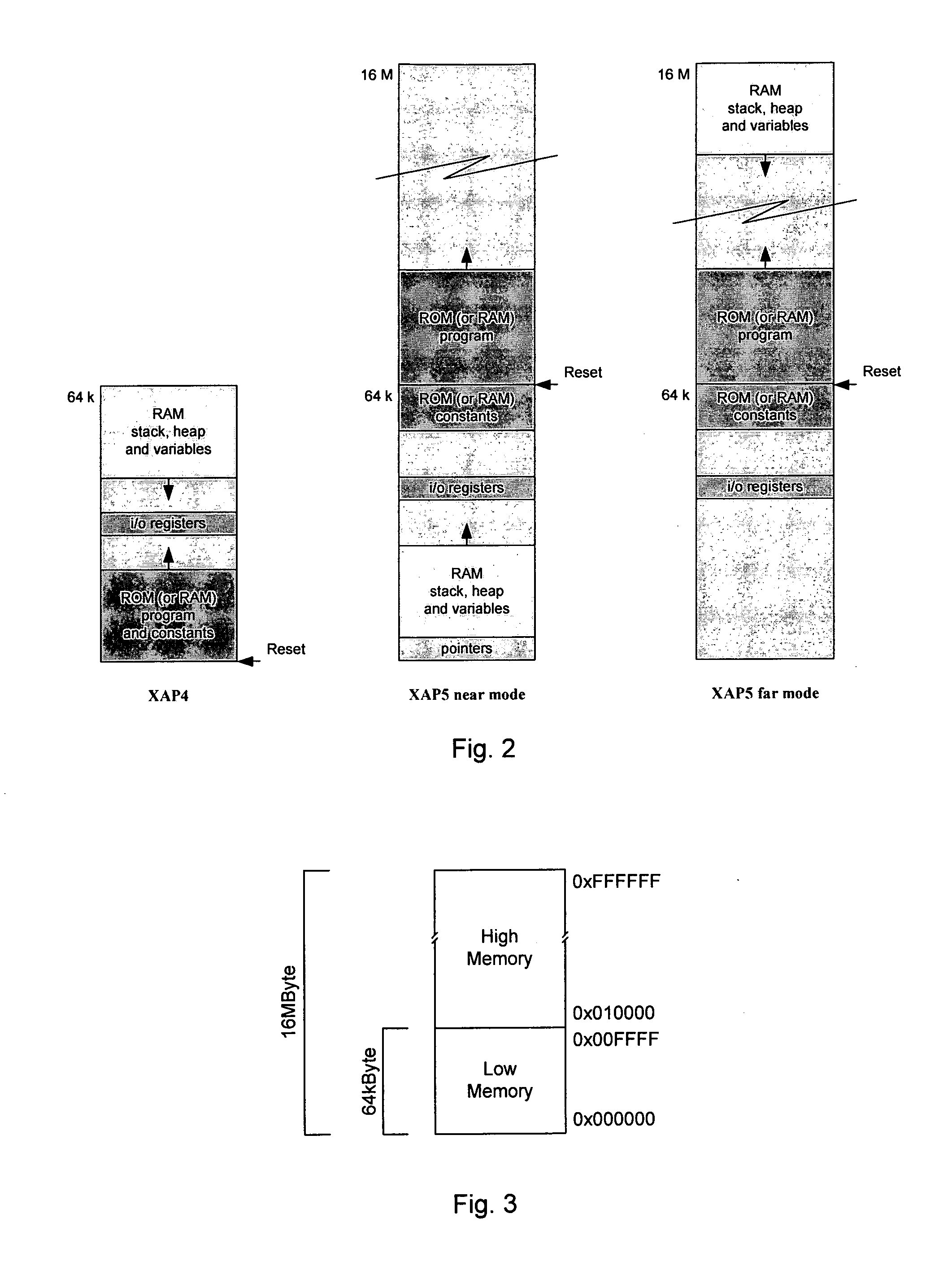
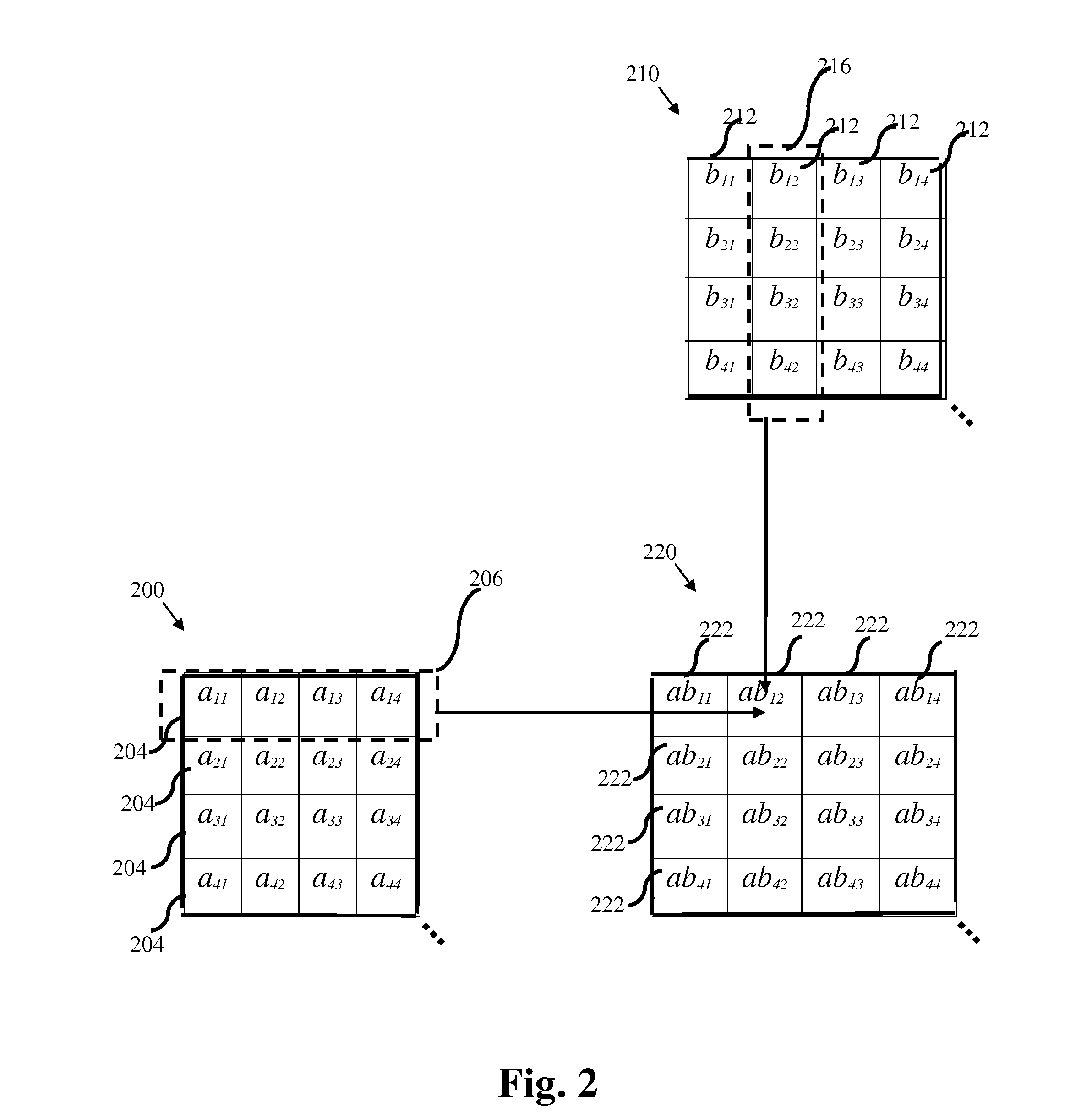
Processor-cache system and method
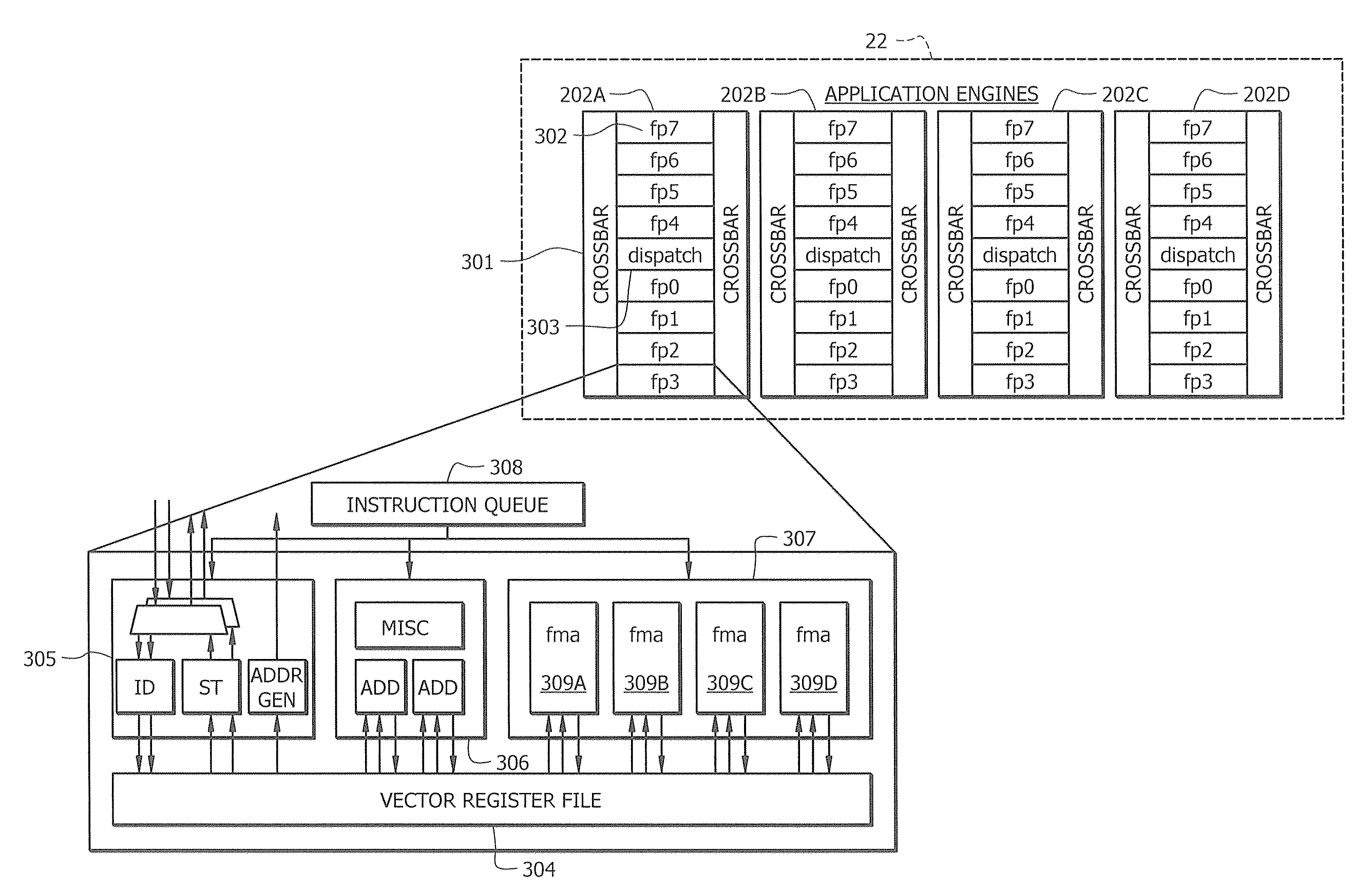
ActiveUS9047193B2Shorten the counting processEfficient and uniform structureEnergy efficient ICTRegister arrangementsAddress generation unitProcessor register
A digital system is provided. The digital system includes an execution unit, a level-zero (L0) memory, and an address generation unit. The execution unit is coupled to a data memory containing data to be used in operations of the execution unit. The L0 memory is coupled between the execution unit and the data memory and configured to receive a part of the data in the data memory. The address generation unit is configured to generate address information for addressing the L0 memory. Further, the L0 memory provides at least two operands of a single instruction from the part of the data to the execution unit directly, without loading the at least two operands into one or more registers, using the address information from the address generation unit.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINHAO MICROELECTRONICS
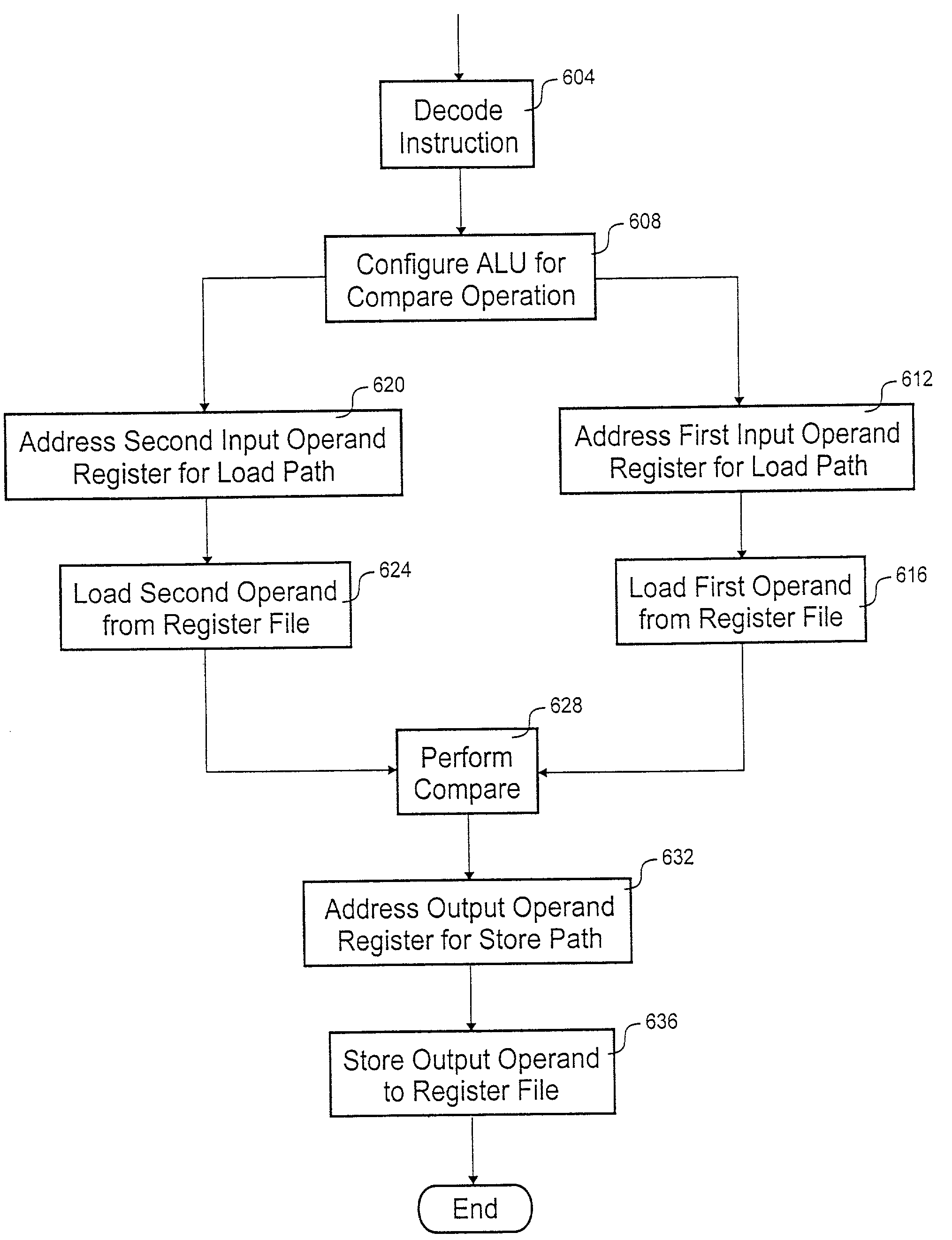
Processing architecture having a compare capability
According to the invention, a processing core that executes a compare instruction is disclosed. The processing core includes a register file, comparison logic, decode logic, and a store path. Included in the register file are a number of general-purpose registers. The general-purpose registers include a first input operand register, a second input operand register and an output operand register. Comparison logic is coupled to the register file. The comparison logic tests for at least two of the following relationships: less than, equal to, greater than and no valid relationship. The decode logic selects the output operand register from the plurality of general-purpose registers. The store path extends between the comparison logic and the selected output operand register.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
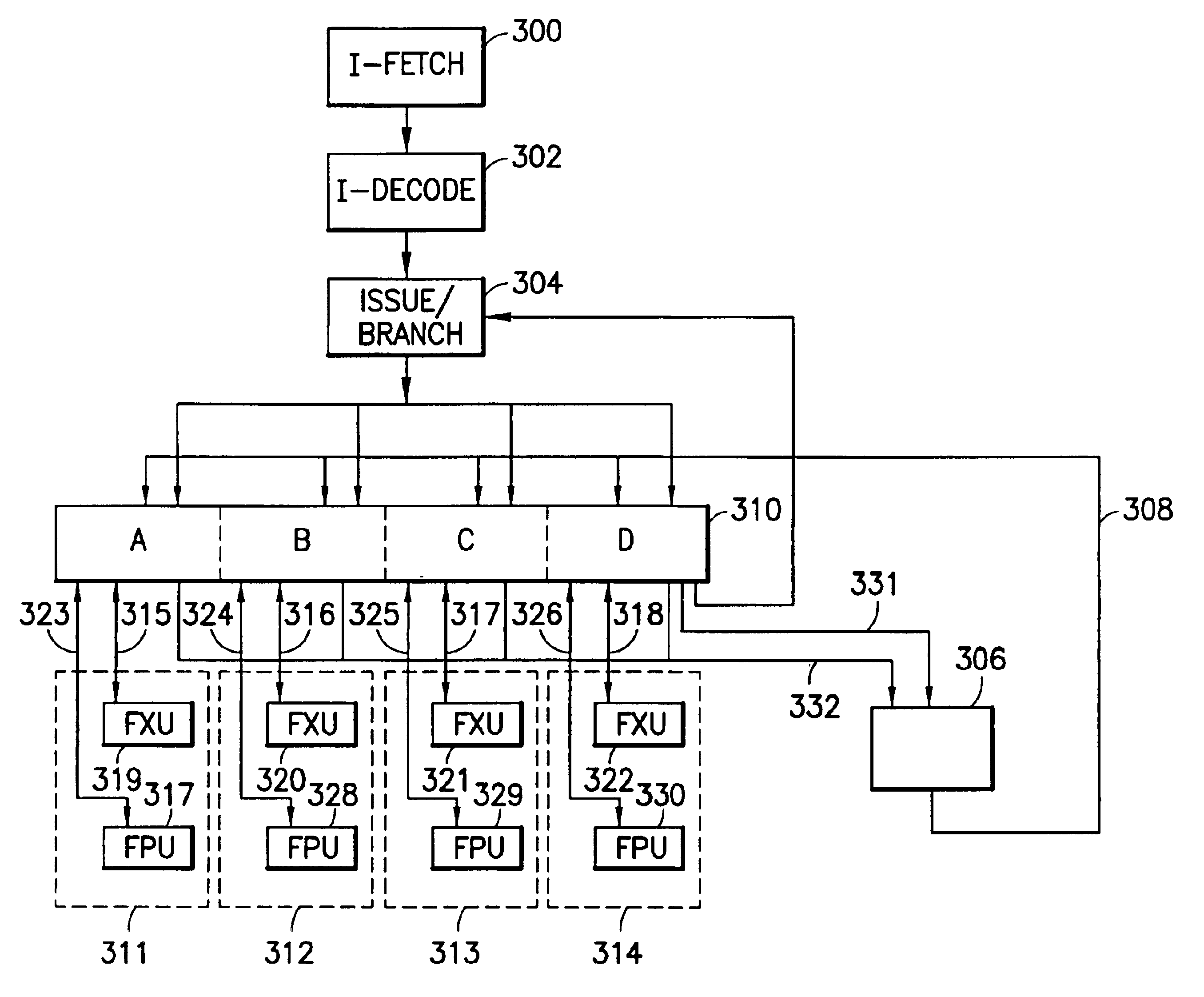
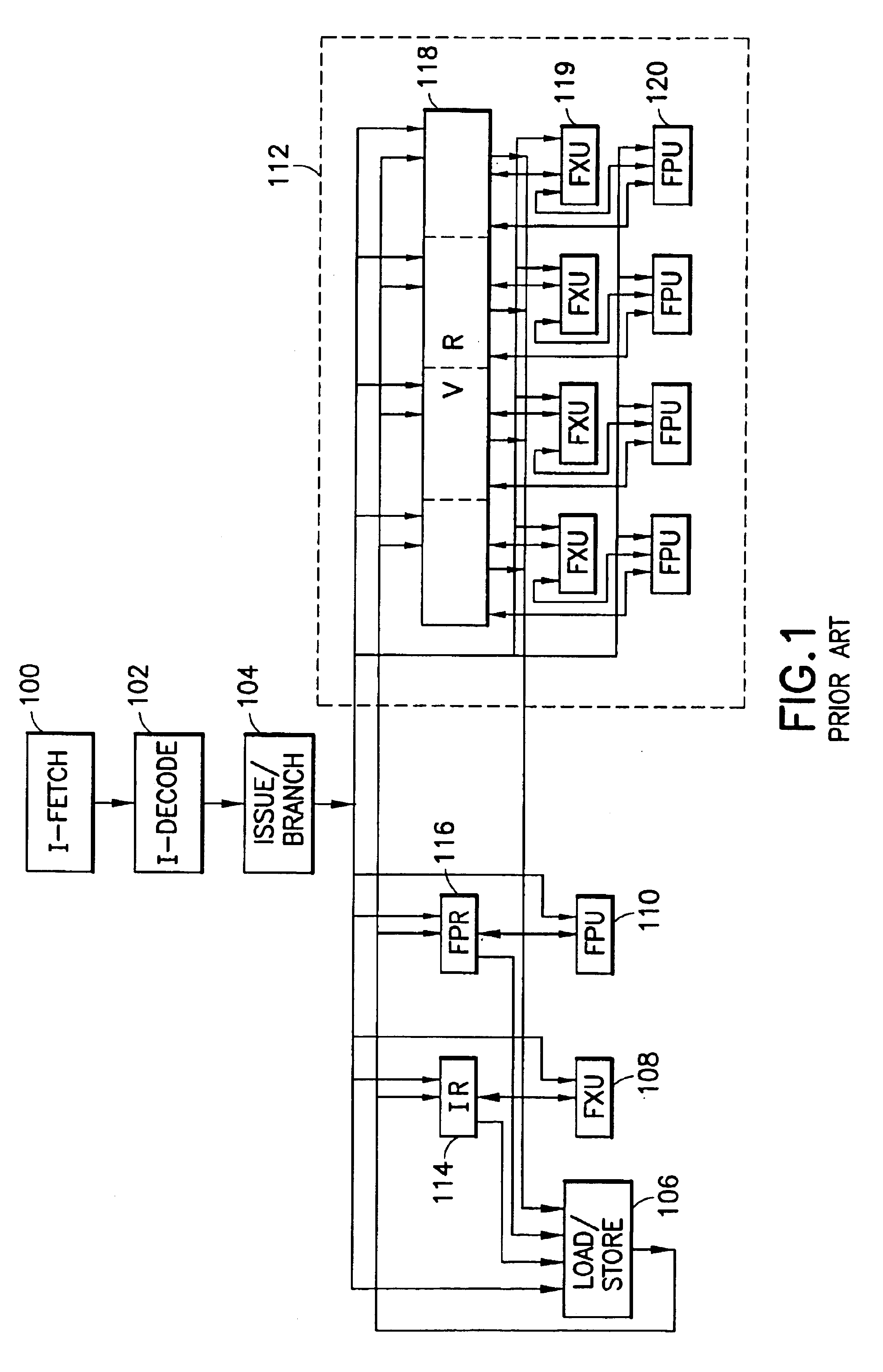
Microprocessors
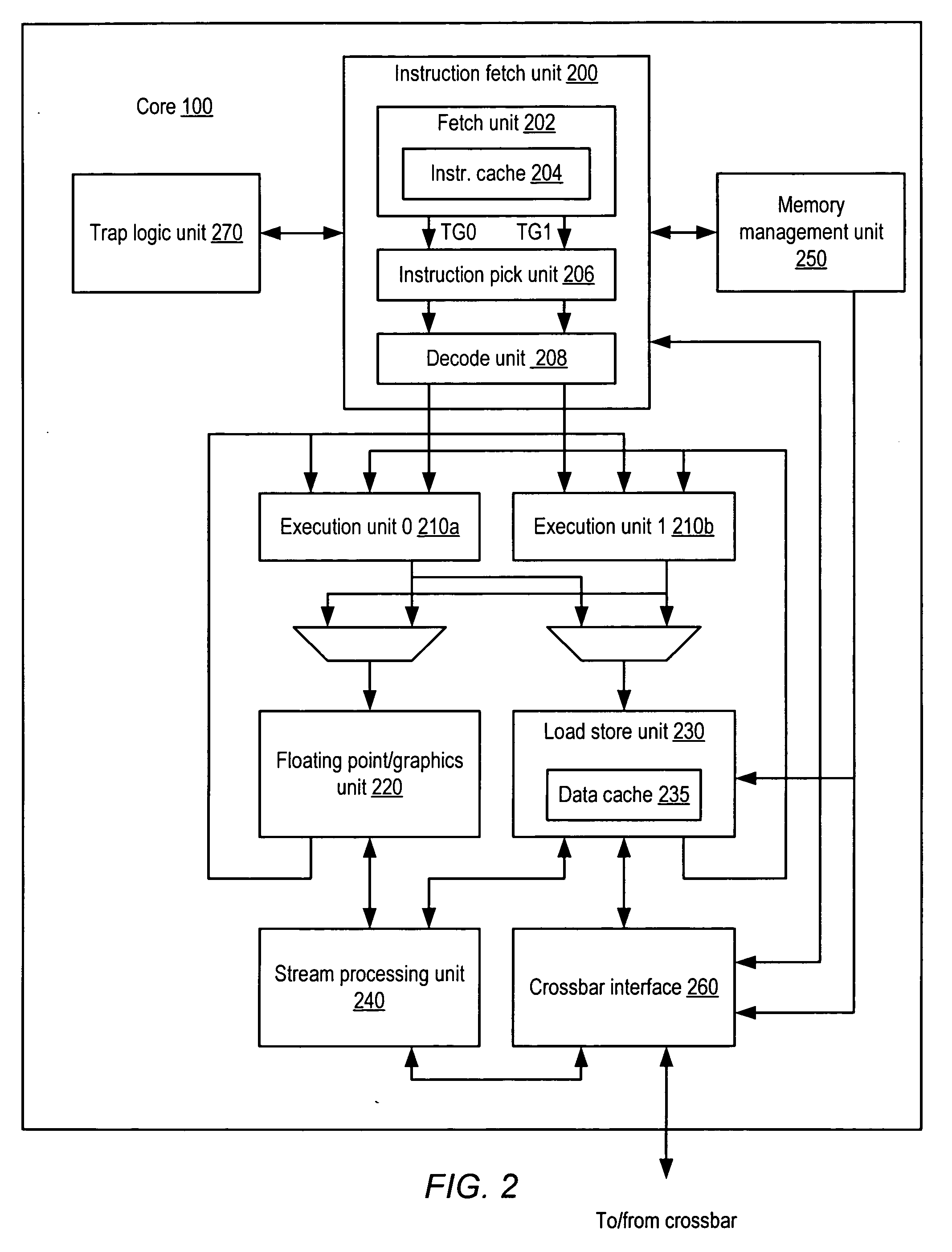
A processor (100) is provided that is a programmable fixed point digital signal processor (DSP) with variable instruction length, offering both high code density and easy programming. Architecture and instruction set are optimized for low power consumption and high efficiency execution of DSP algorithms, such as for wireless telephones, as well as pure control tasks. The processor includes an instruction buffer unit (106), a program flow control unit (108), an address / data flow unit (110), a data computation unit (112), and multiple interconnecting busses. Dual multiply-accumulate blocks improve processing performance. A memory interface unit (104) provides parallel access to data and instruction memories. The instruction buffer is operable to buffer single and compound instructions pending execution thereof. A decode mechanism is configured to decode instructions from the instruction buffer. The use of compound instructions enables effective use of the bandwidth available within the processor. A soft dual memory instruction can be compiled from separate first and second programmed memory instructions. Instructions can be conditionally executed or repeatedly executed. Bit field processing and various addressing modes, such as circular buffer addressing, further support execution of DSP algorithms. The processor includes a multistage execution pipeline with pipeline protection features. Various functional modules can be separately powered down to conserve power. The processor includes emulation and code debugging facilities with support for cache analysis.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
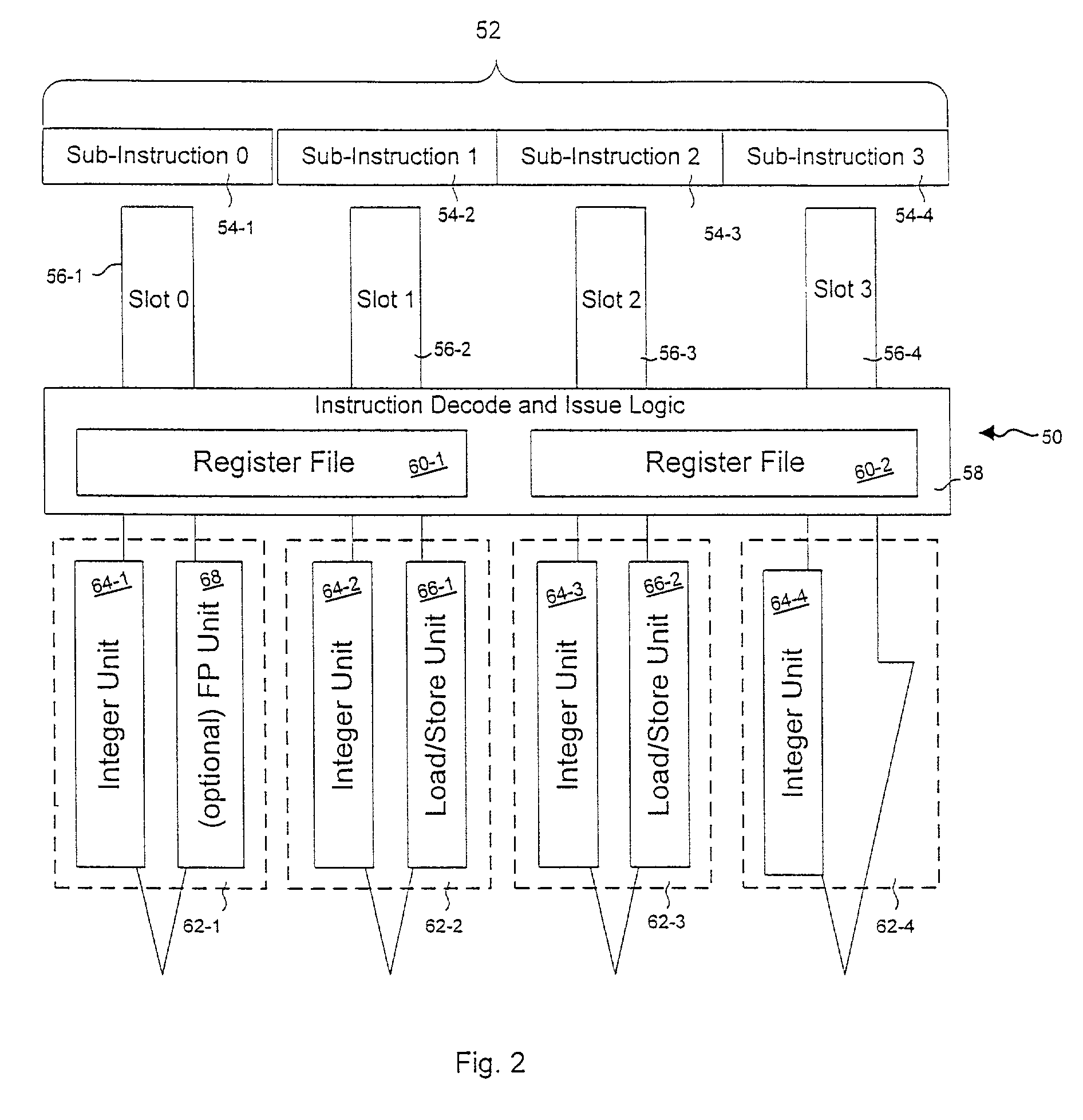
SIMD datapath coupled to scalar/vector/address/conditional data register file with selective subpath scalar processing mode
InactiveUS6839828B2Not compromise SIMD data processing performanceReduce consumptionRegister arrangementsDigital data processing detailsProcessor registerOperation mode
There is provided a processor designed to operate in a plurality of modes for processing vector and scalar instructions. Register files are each for storing scalar and vector data and address information. A parallel vector unit, coupled to the register files, includes functional units configurable to operate in a vector operation mode and a scalar operation mode. The vector unit includes an apparatus for tightly coupling the functional units to perform an operation specified by a current instruction. Under a vector operation mode, the vector unit performs, in parallel, a single vector operation on a plurality of data elements. The operations performed on the plurality of data elements are each performed by a different functional unit of the vector unit. Under a scalar operation mode, the vector unit performs a scalar operation on a data element received from the register files in a functional unit within the vector unit.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Digital signal processor containing scalar processor and a plurality of vector processors operating from a single instruction
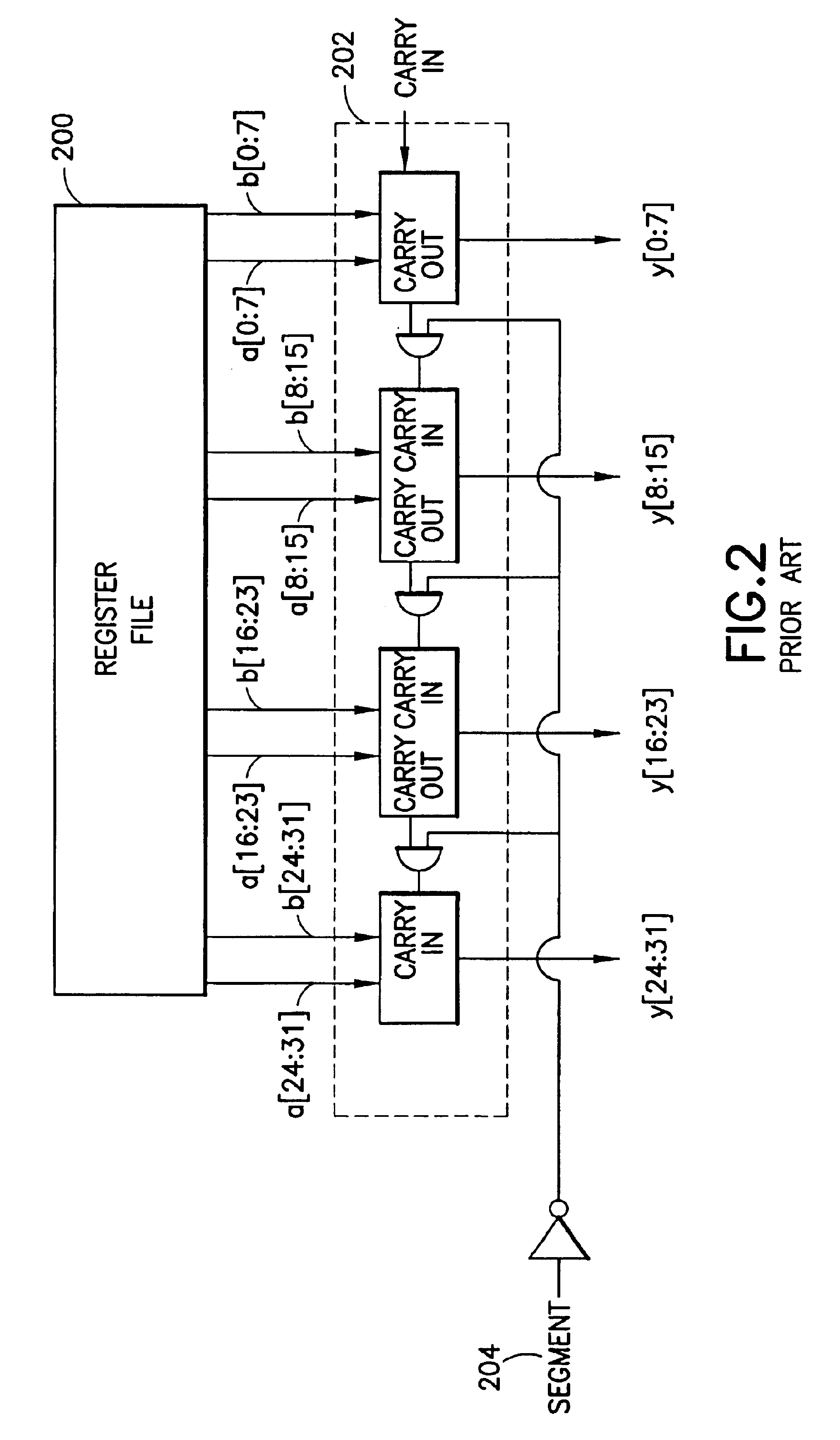
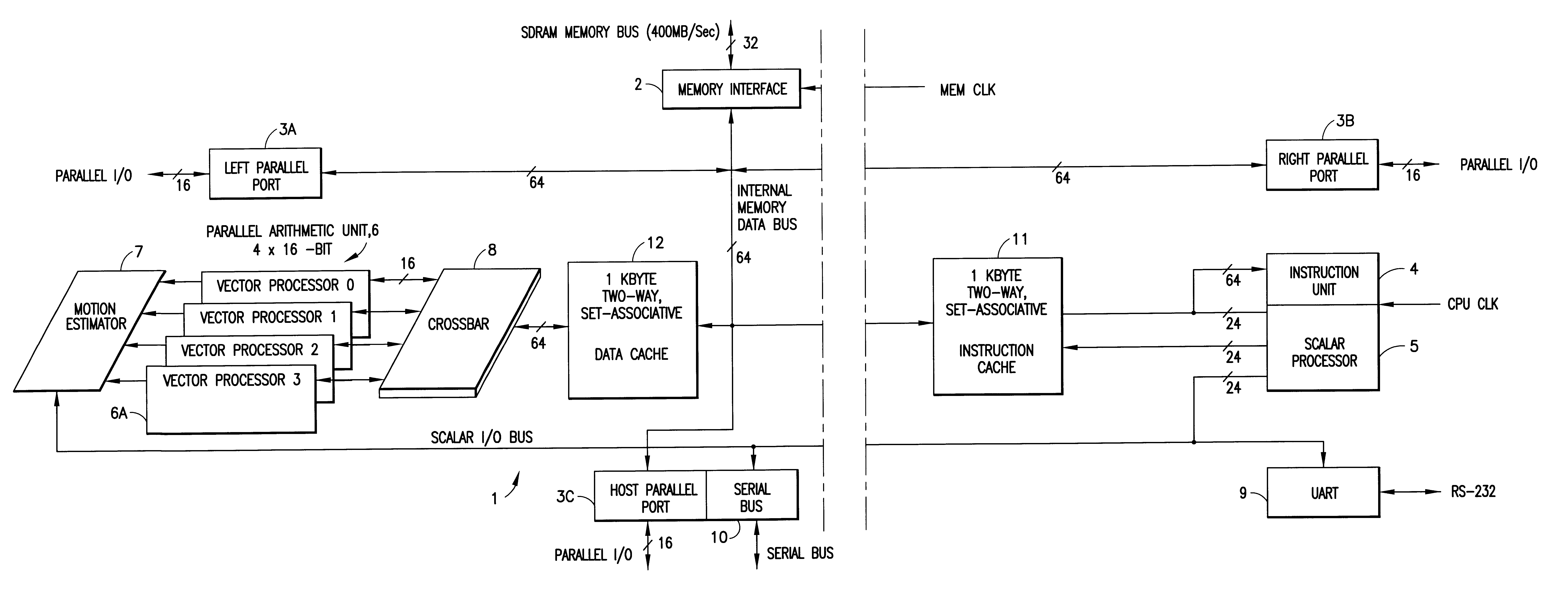
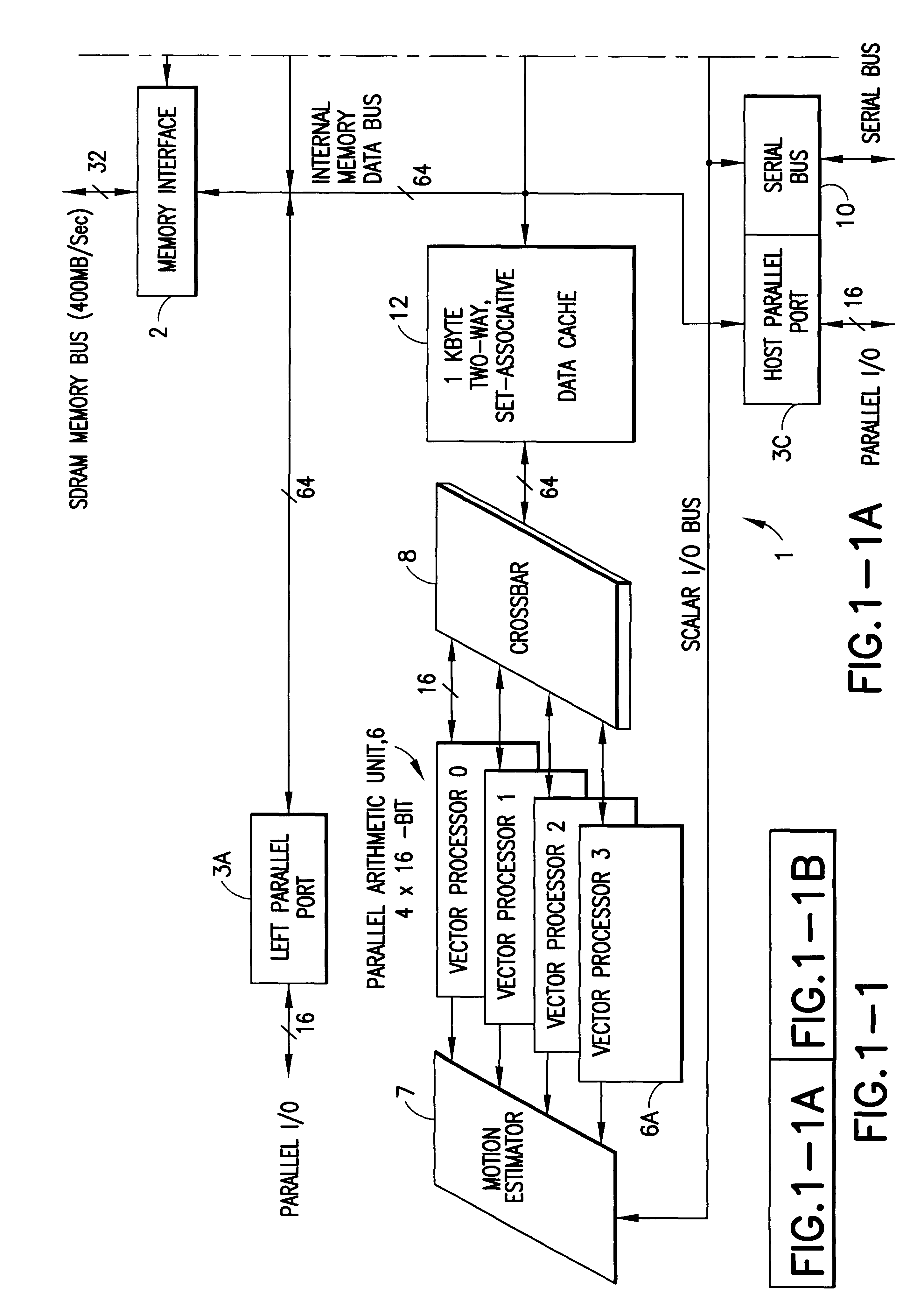
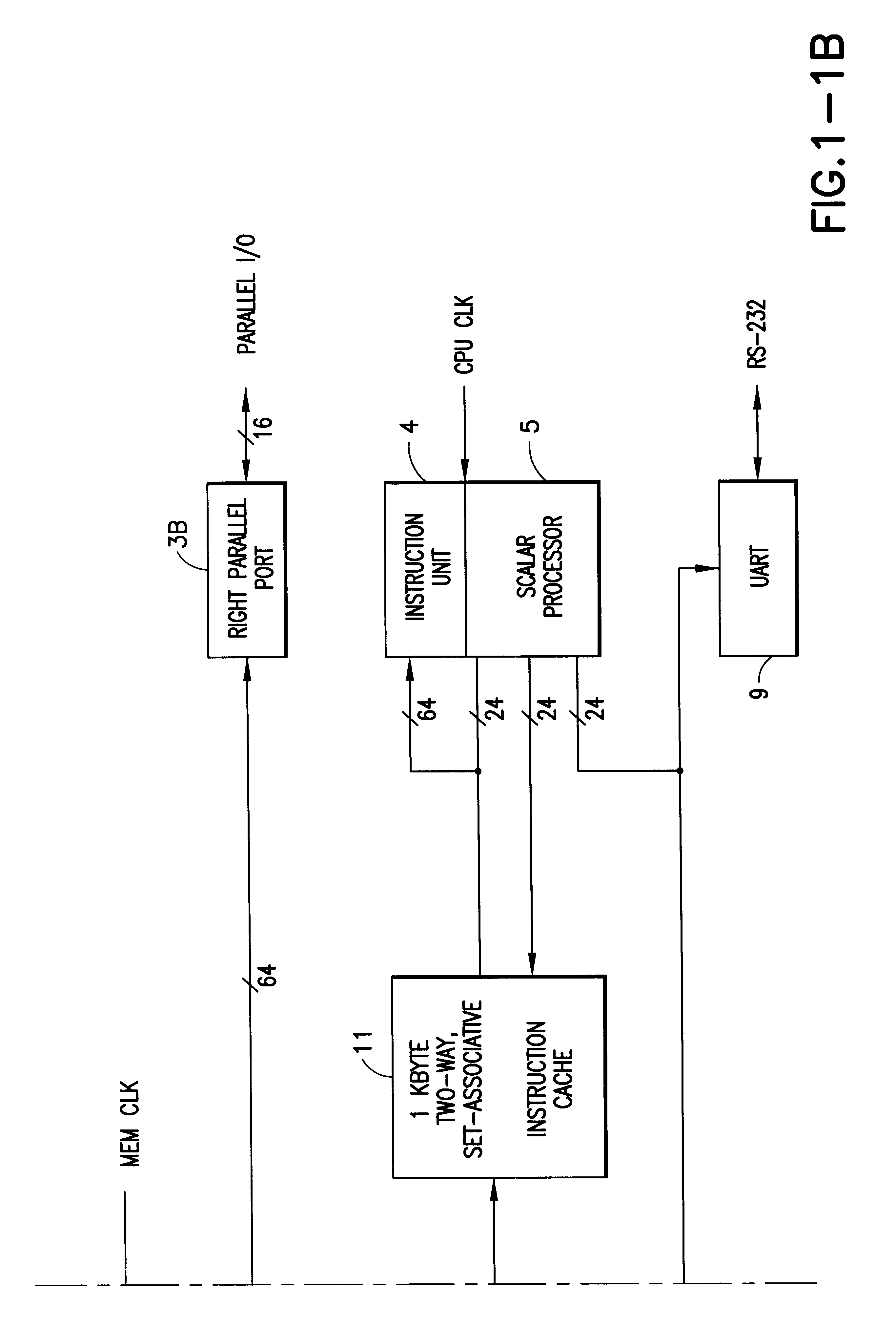
InactiveUS6317819B1Register arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationCrossbar switchDigital data
A digital data processor integrated circuit (1) includes a plurality of functionally identical first processor elements (6A) and a second processor element (5). The first processor elements are bidirectionally coupled to a first cache (12) via a crossbar switch matrix (8). The second processor element is coupled to a second cache (11). Each of the first cache and the second cache contain a two-way, set-associative cache memory that uses a least-recently-used (LRU) replacement algorithm and that operates with a use-as-fill mode to minimize a number of wait states said processor elements need experience before continuing execution after a cache-miss. An operation of each of the first processor elements and an operation of the second processor element are locked together during an execution of a single instruction read from the second cache. The instruction specifies, in a first portion that is coupled in common to each of the plurality of first processor elements, the operation of each of the plurality of first processor elements in parallel. A second portion of the instruction specifies the operation of the second processor element. Also included is a motion estimator (7) and an internal data bus coupling together a first parallel port (3A), a second parallel port (3B), a third parallel port (3C), an external memory interface (2), and a data input / output of the first cache and the second cache.
Owner:CUFER ASSET LTD LLC
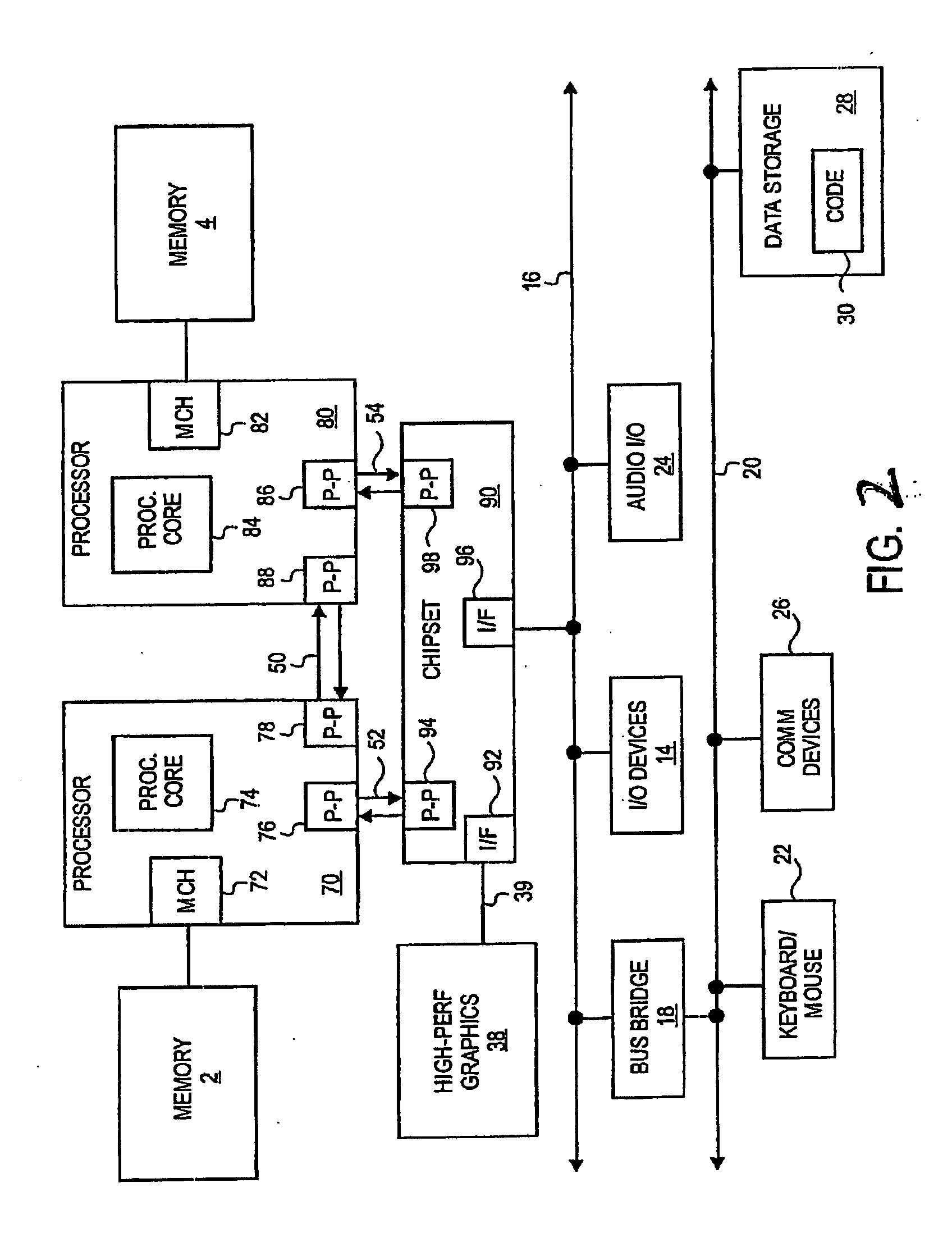
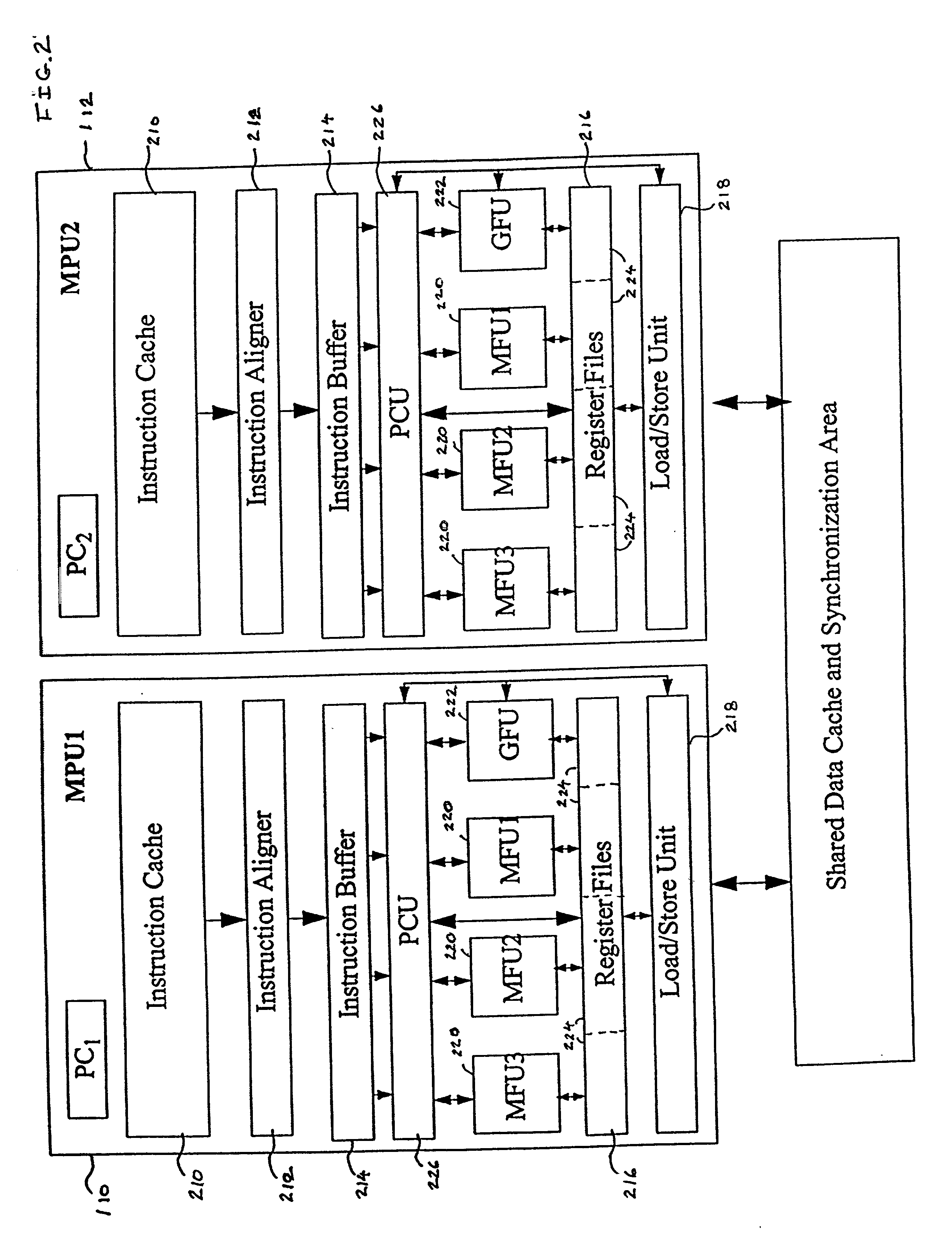
Multi-core multi-thread processor
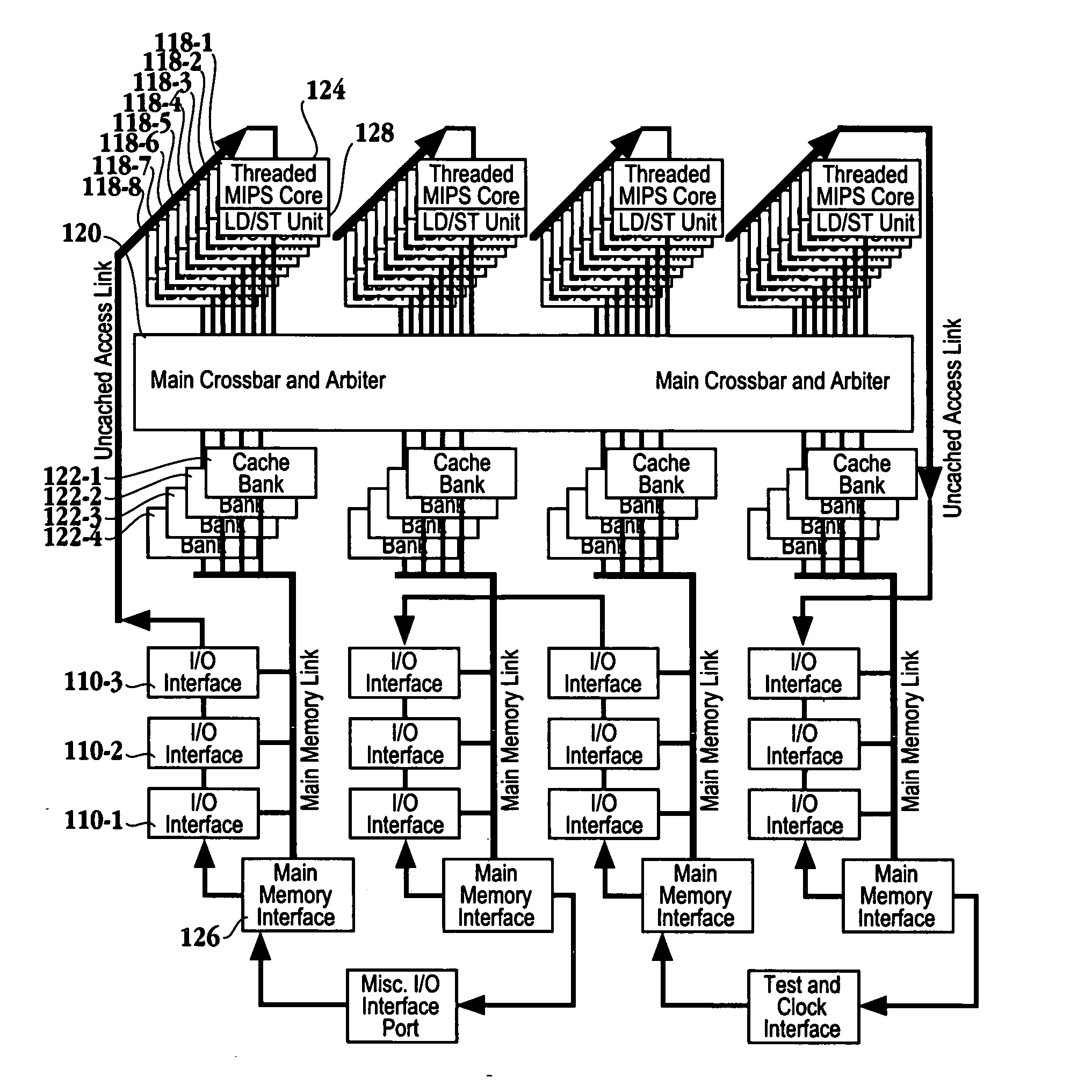
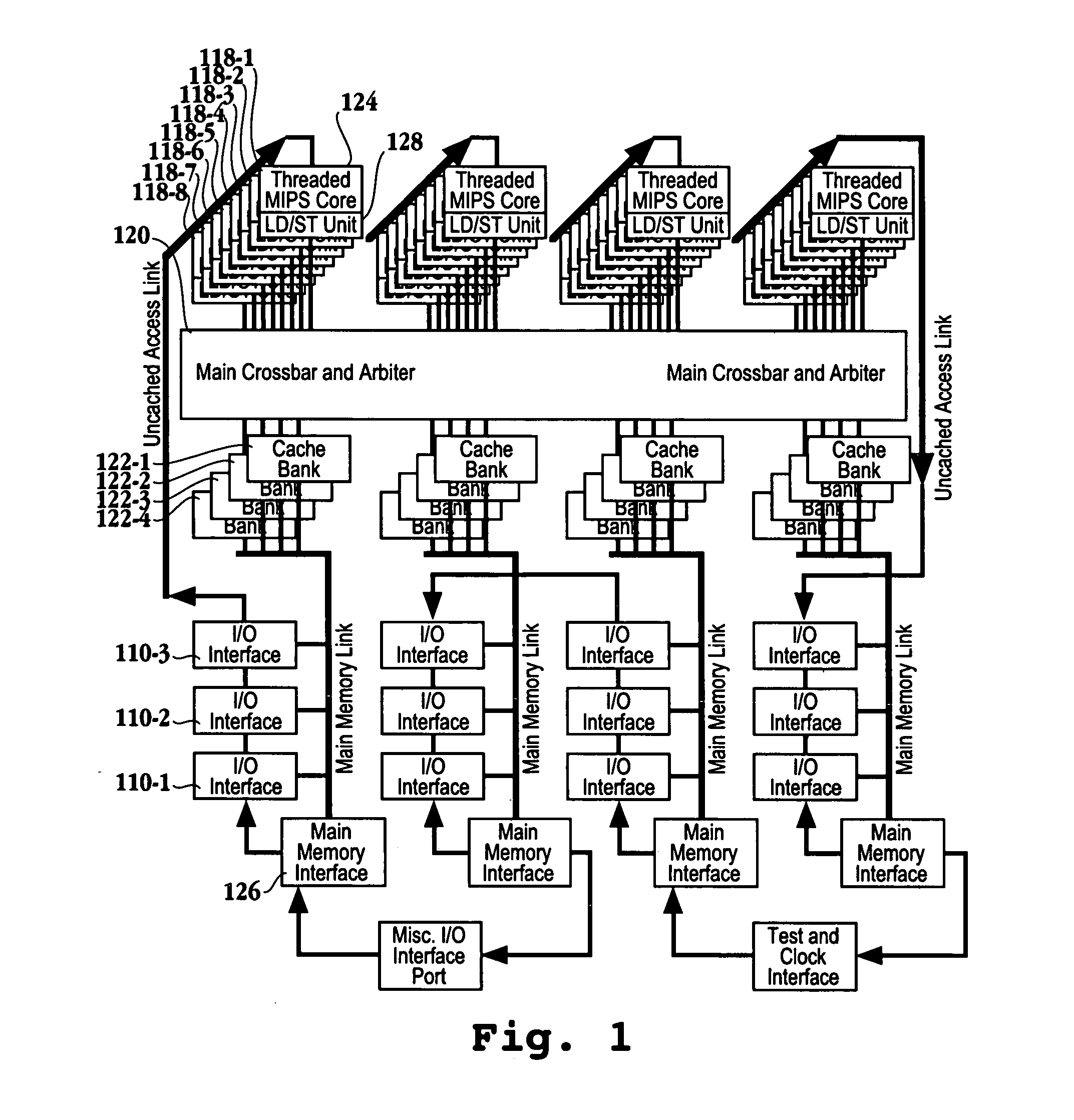
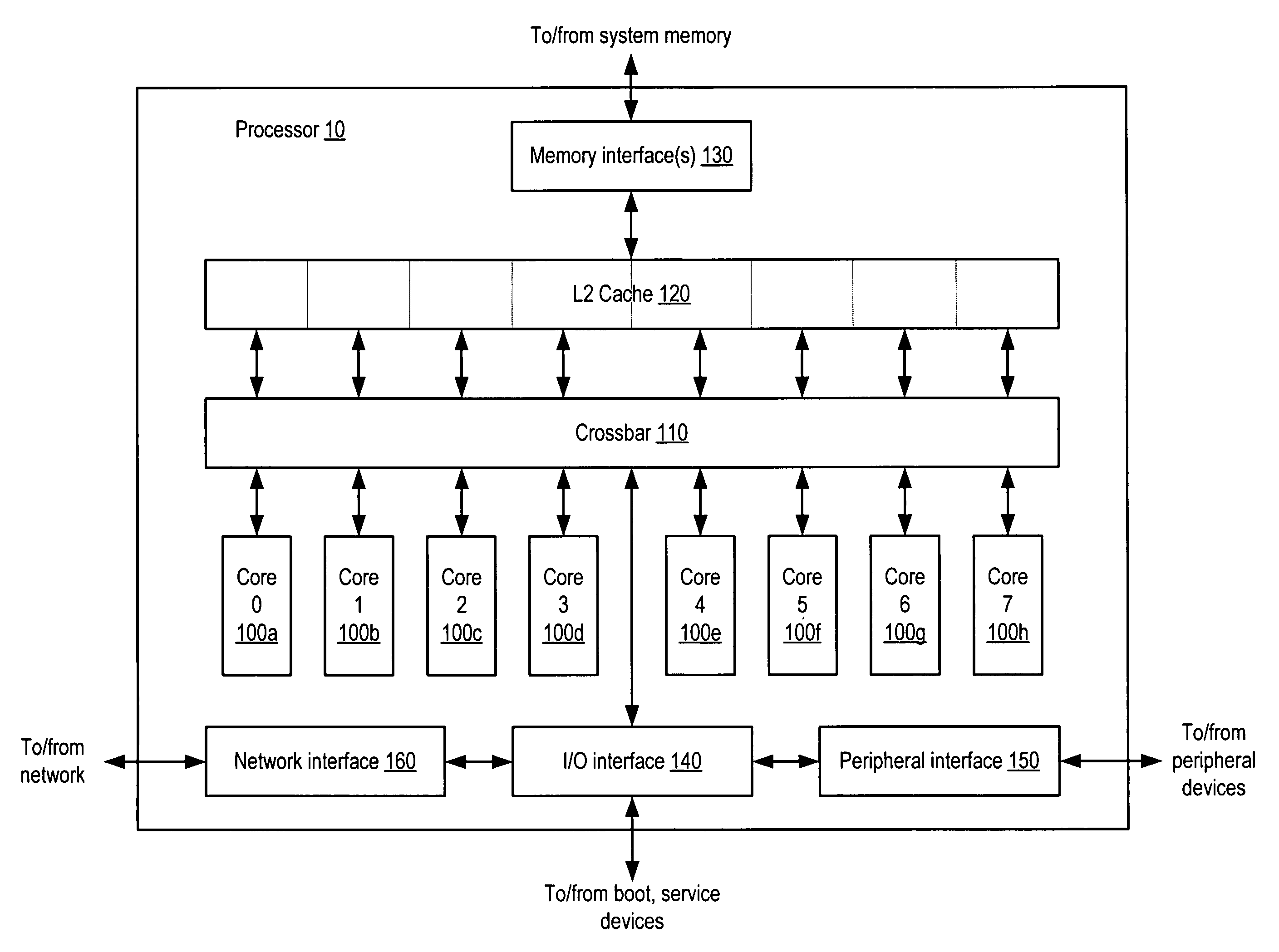
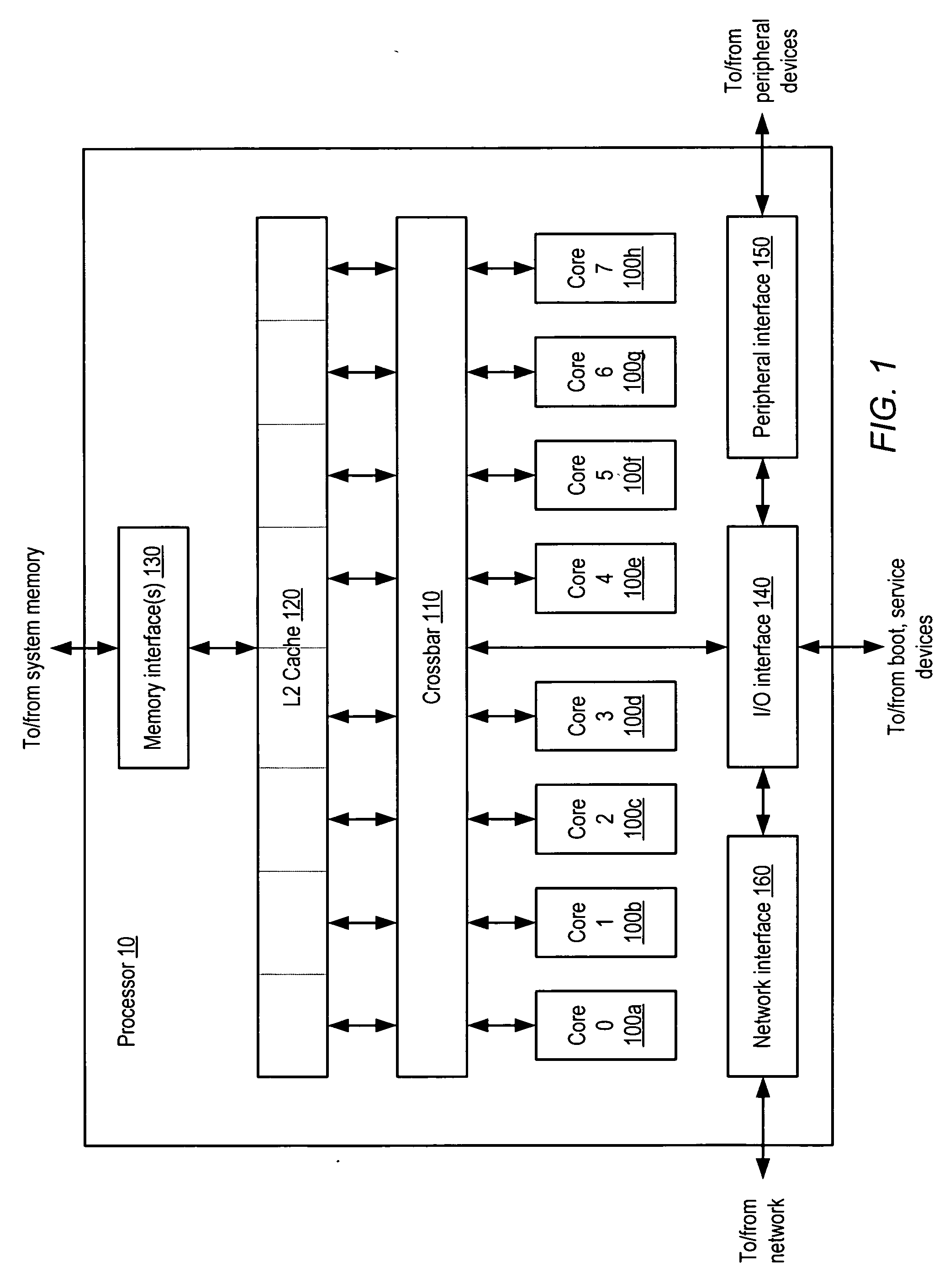
ActiveUS20050044319A1Easy accessRegister arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory interfaceParallel computing
A processor is provided. The processor includes at least two cores. The at least two cores have a first level cache memory and are multi-threaded. A crossbar is included. A plurality of cache bank memories in communication with the at least two cores through the crossbar is provided. Each of the plurality of cache bank memories communicates with a main memory interface. A plurality of input / output interface modules in communication with the main memory interface and providing a link to the at least two cores are included. The link bypasses the plurality of cache bank memories and the crossbar. Threading hardware configured to enable the at least two cores to switch from a first thread to a second thread in a manner hiding delays caused by cache accesses is included. A server and a method for determining when to switch threads in a multi-core multi-thread environment are included.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
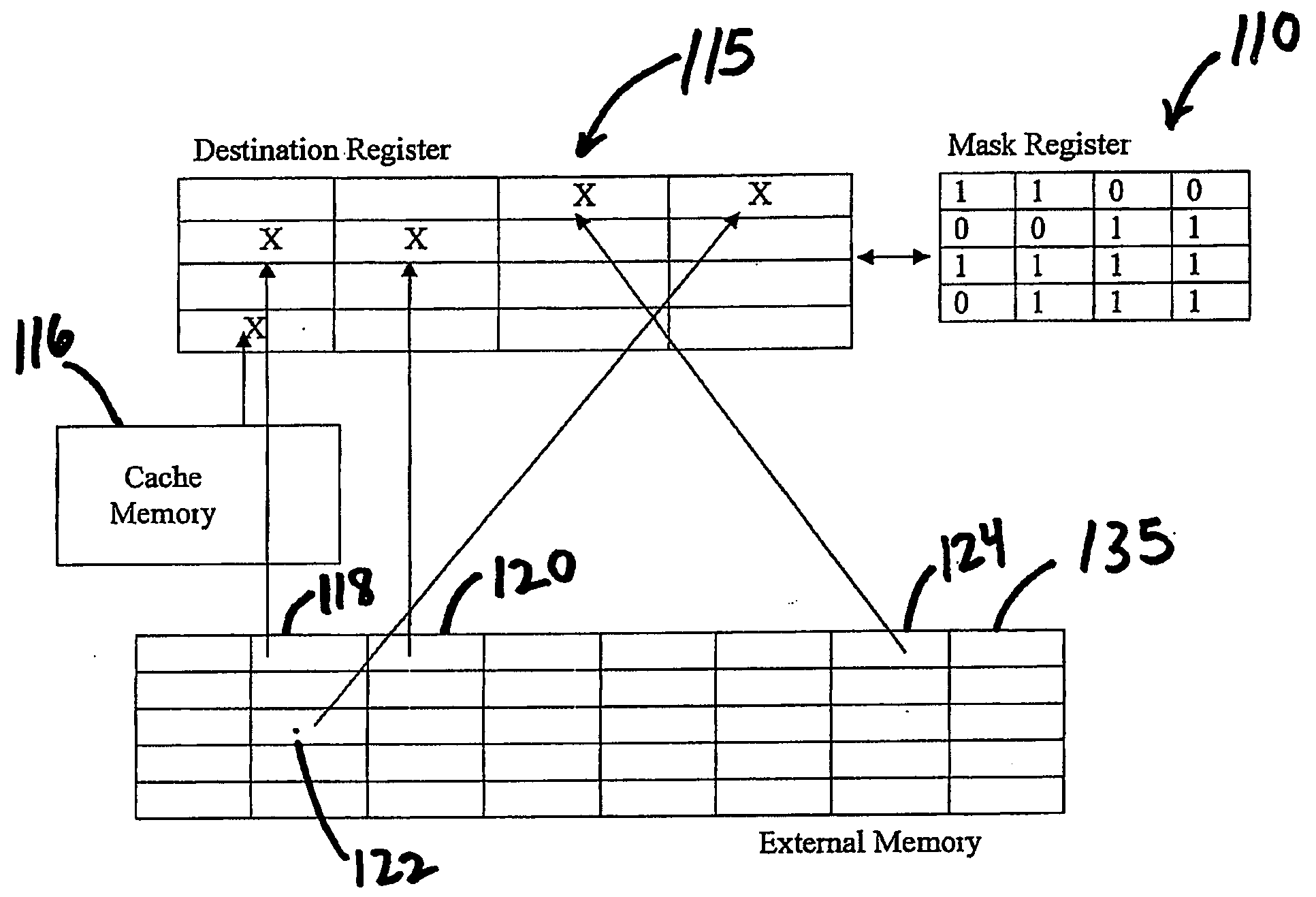
Device, system, and method for gathering elements from memory
InactiveUS20090172364A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRegister arrangementsData fieldData element
A system and method for assigning values to elements in a first register, where each data field in a first register corresponds to a data element to be written into a second register, and where for each data field in the first register, a first value may indicate that the corresponding data element has not been written into the second register and a second value indicates that the corresponding data element has been written into the second register, reading the values of each of the data fields in the first register, and for each data field in the first register having the first value, gathering the corresponding data element and writing the corresponding data element into the second register, and changing the value of the data field in the first register from the first value to the second value. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
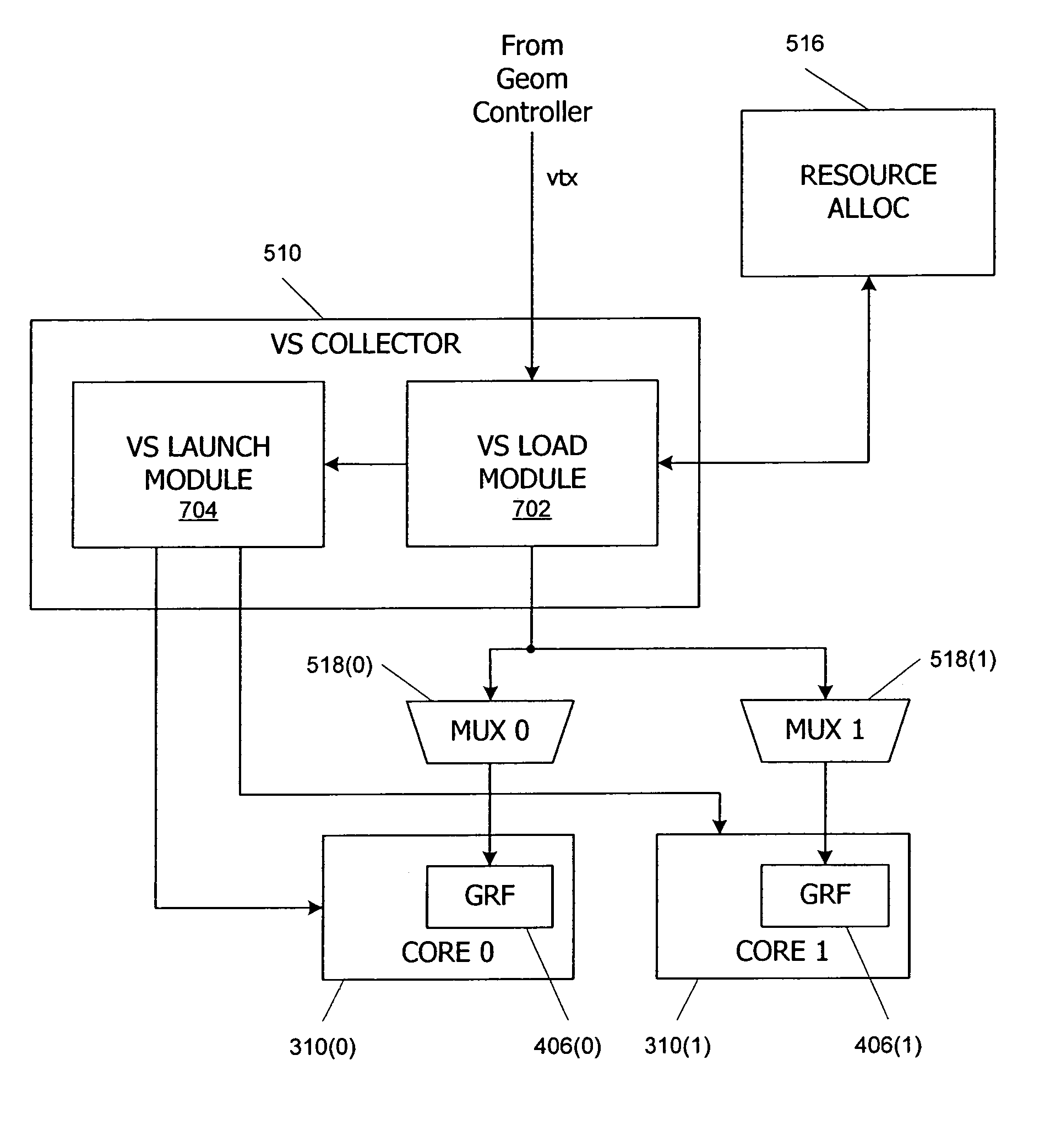
Multithreaded SIMD parallel processor with loading of groups of threads
ActiveUS7447873B1Management loadRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerProcessing coreProcessor register
In a multithreaded processing core, groups of threads are executed using single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) parallelism by a set of parallel processing engines. Input data defining objects to be processed received as a stream of input data blocks, and the input data blocks are loaded into a local register file in the core such that all of the data for one of the input objects is accessible to one of the processing engines. The input data can be loaded directly into the local register file, or the data can be accumulated in a buffer and loaded after accumulation, for instance during a launch operation for a SIMD group. Shared input data can also be loaded into a shared memory in the processing core.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Coprocessor opcode division by data type
InactiveUS6247113B1Easy to scaleReduced hardware coprocessorRegister arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemCoprocessor
A data processing system having a main processor and a coprocessor. The main processor responsds to coprocessor instructions within its instruction stream by issuing the coprocessor instructions upon a coprocessor bus and detecting if the coprocessor accepts them by returning an accept signal. The coprocessor instructions include a coprocessor number and the coprocessor checks this number to see if it matches its own number(s) to determine whether or not it should accept the coprocessor instruction. A data type field within the coprocessor number in the coprocessor instruction also serves to specify one of multiple data types to be used in the coprocessor operation; particular coprocessors can interpret this part of the coprocessor number to determine data type. If the coprocessor supports multiple data types, then it has multiple coprocessor numbers for which it will issue accept signals and then uses the data type field to control the data type used. If a coprocessor does not support a particular data type then it will not issue an accept signal for coprocessor instructions that specify that data type. The main processor can then use emulation code to provide support for that coprocessor instruction.
Owner:ARM LTD
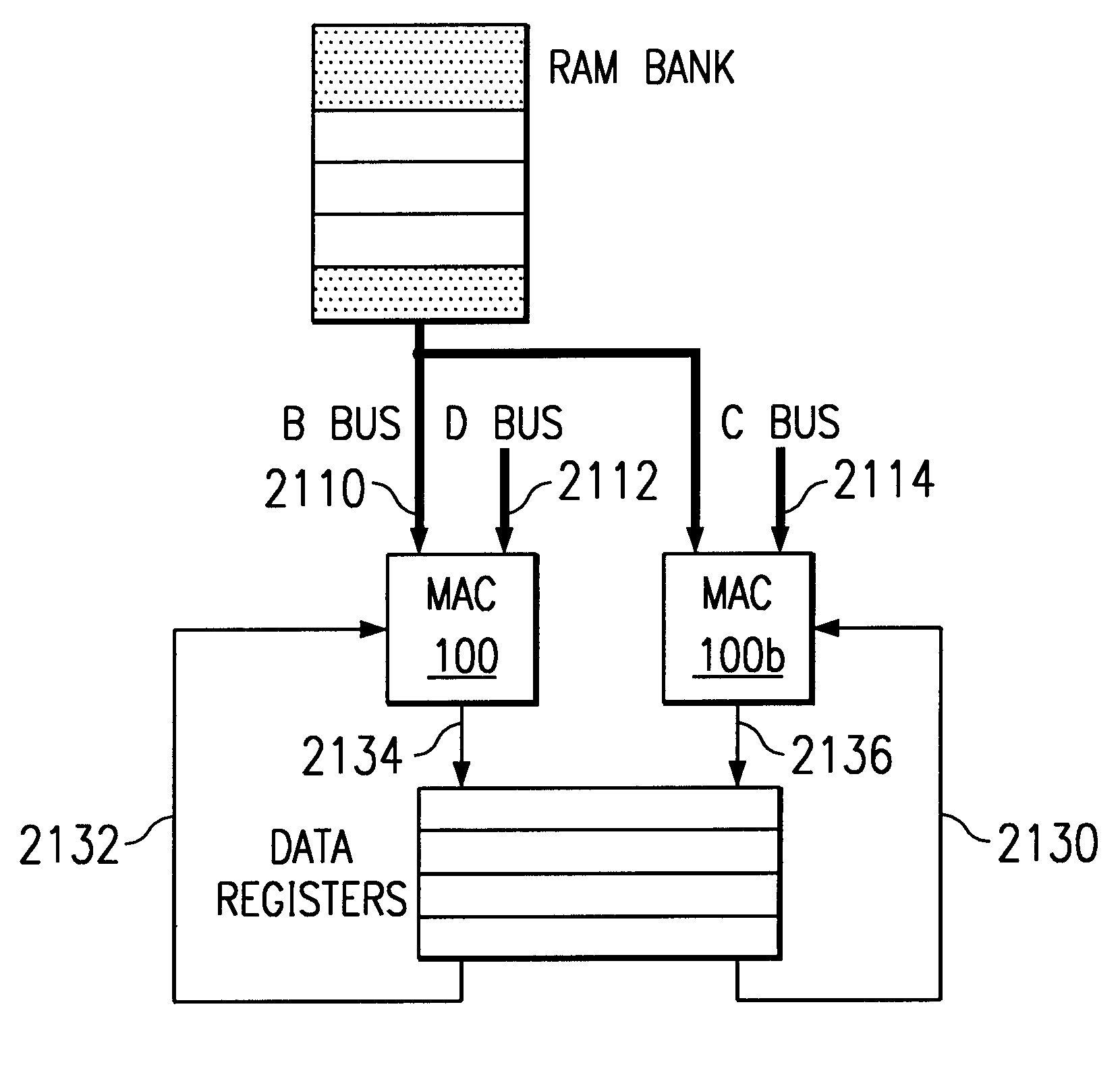
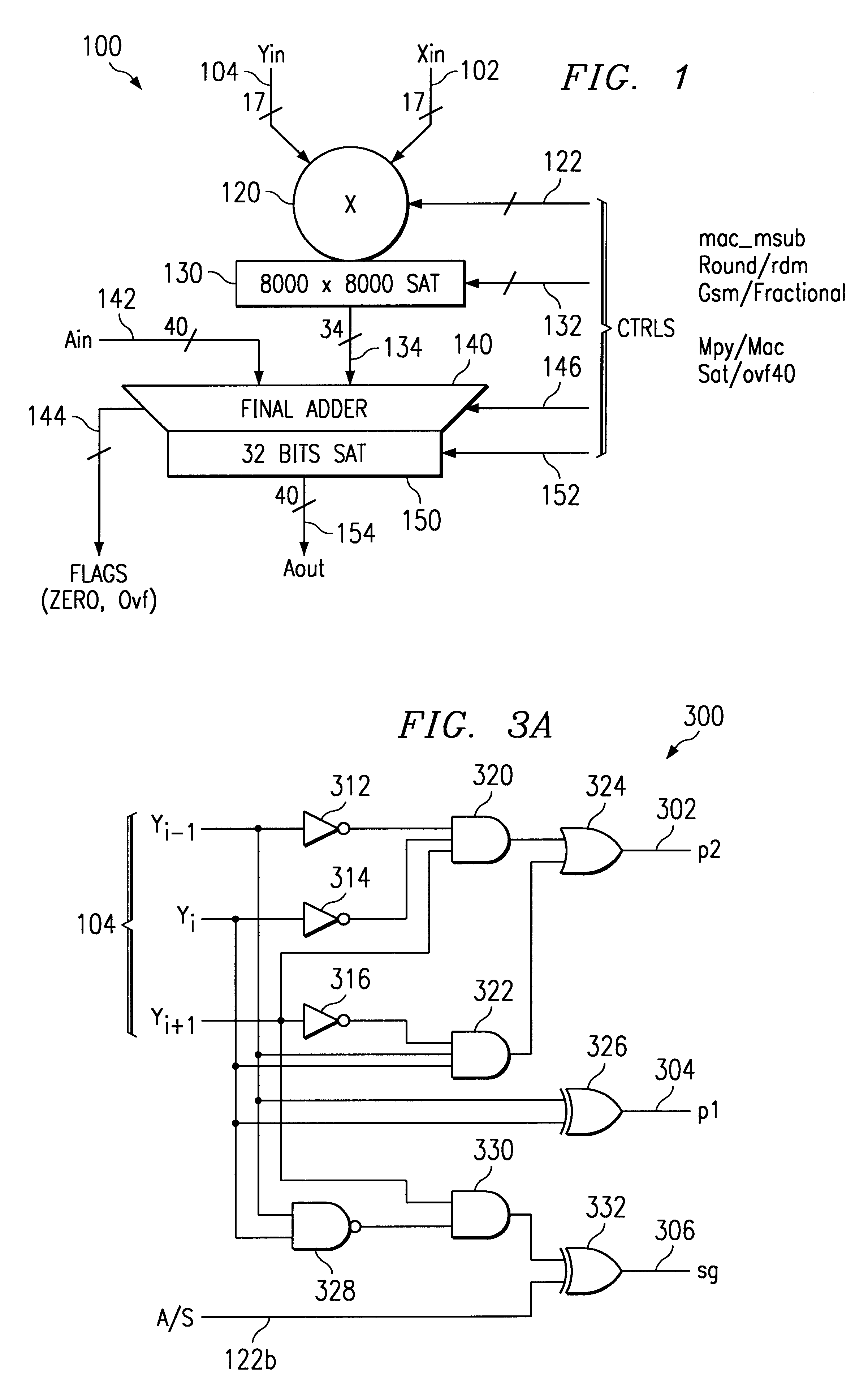
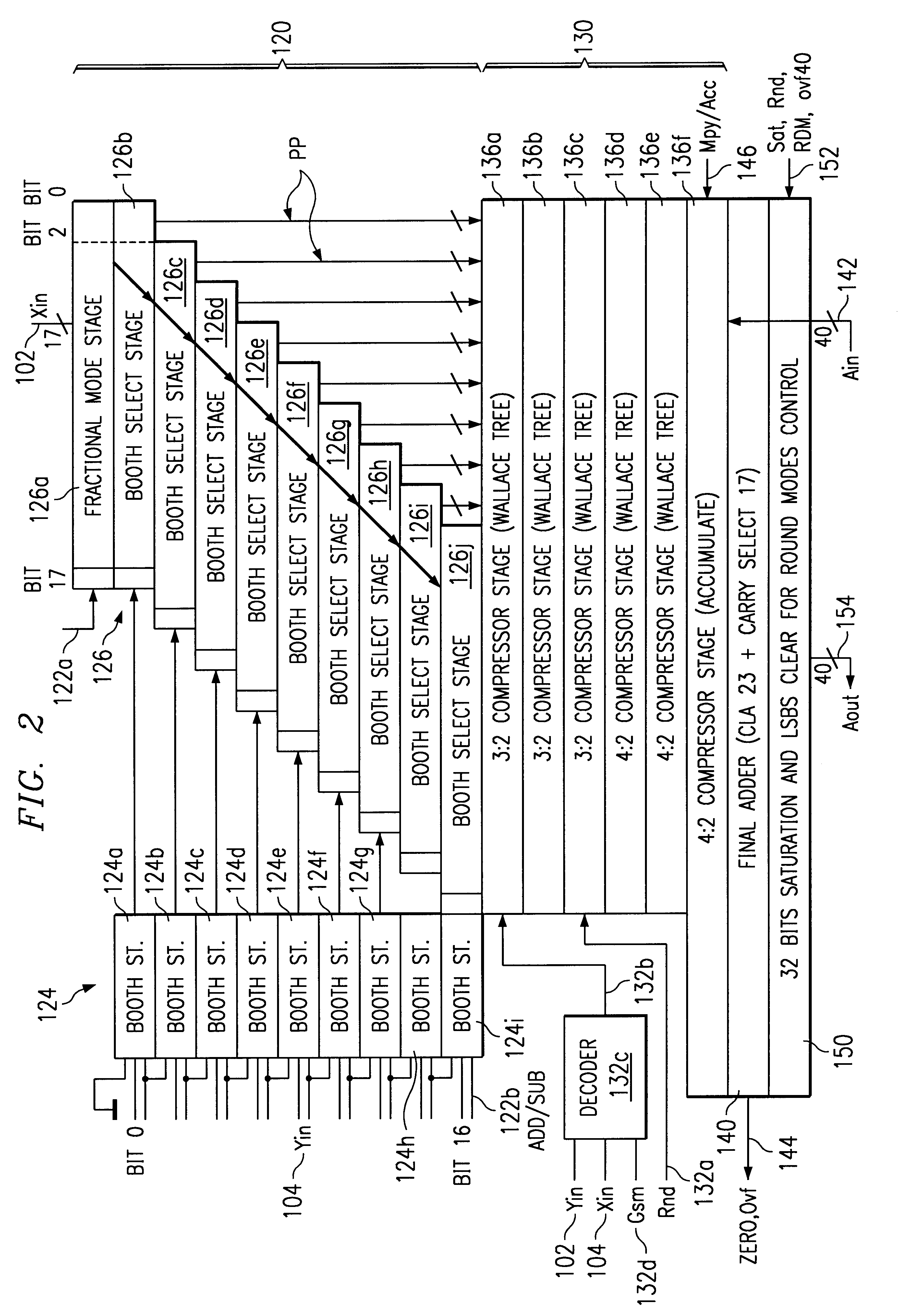
Multiplier accumulator circuits
A multiply-accumulate (MAC) unit, having a first binary operand X, a second binary operand Y, a third binary operand, Booth recode logic for generating a plurality of partial products from said first and second operands, a Wallace tree adder for reducing the partial products and for selectively arithmetically combining the reduced partial products with said third operand, a final adder for generating a final sum, and a saturation circuitry for selectively rounding or saturating said final sum is provided. A dual MAC unit is also provided.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
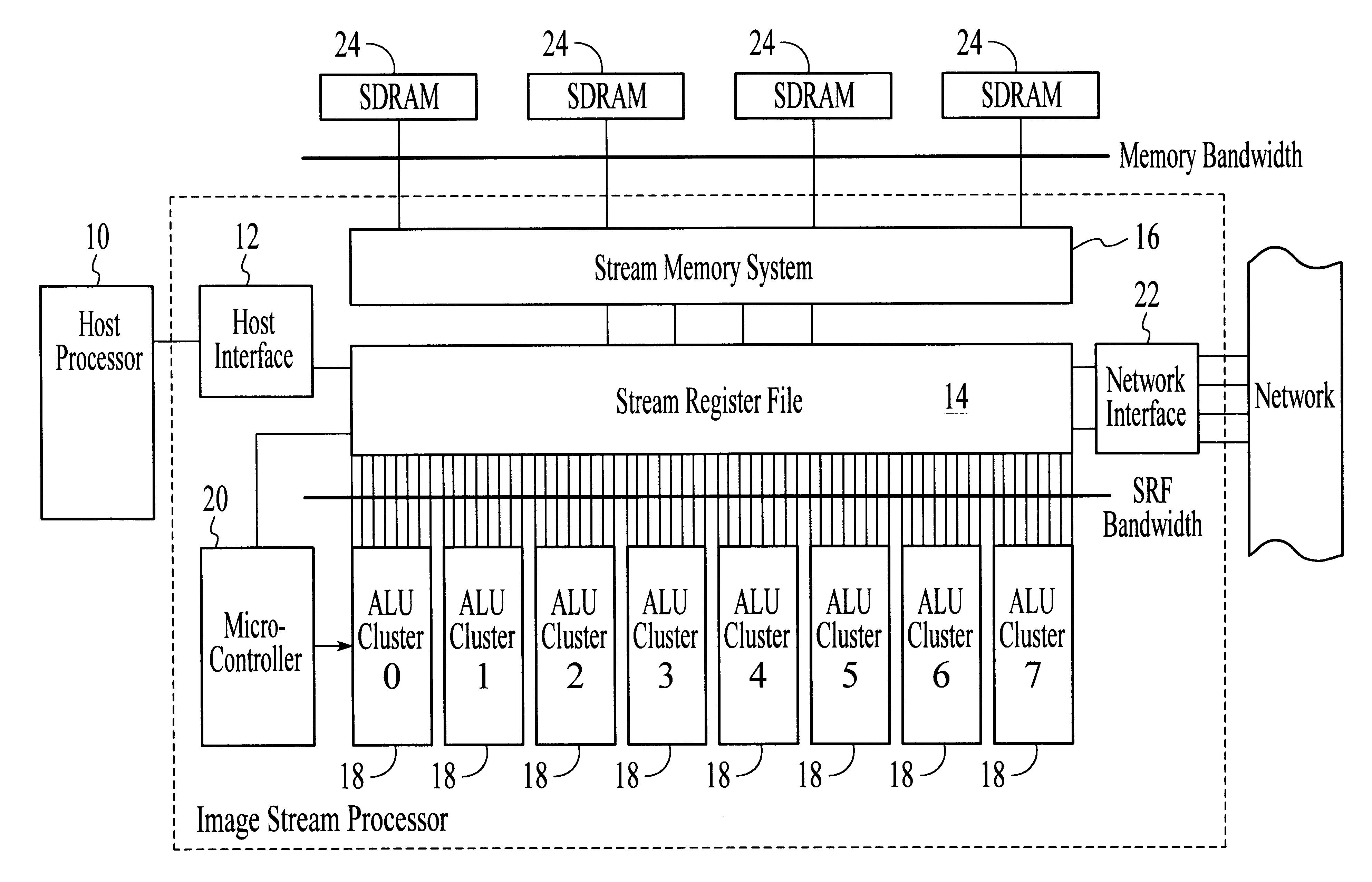
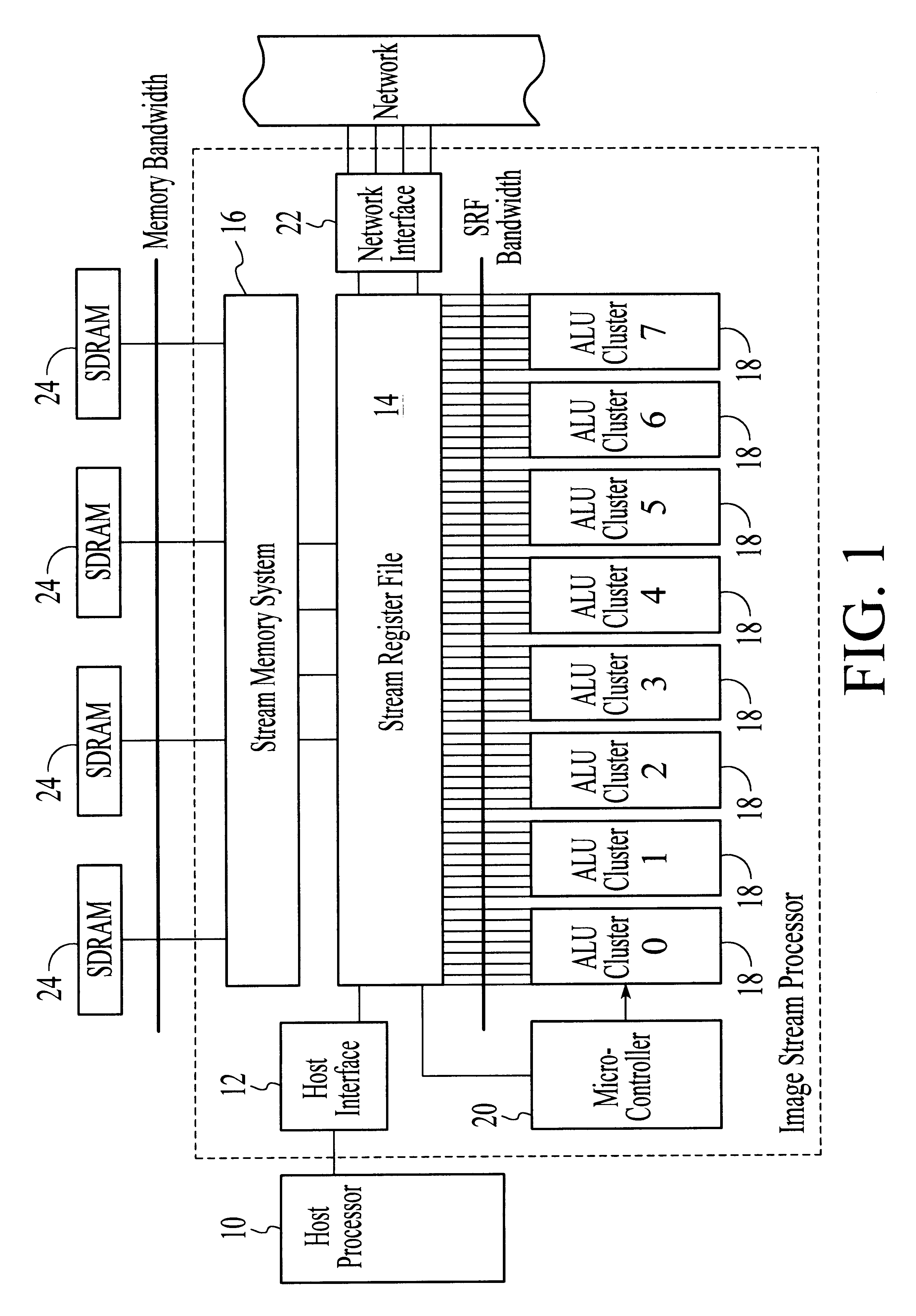
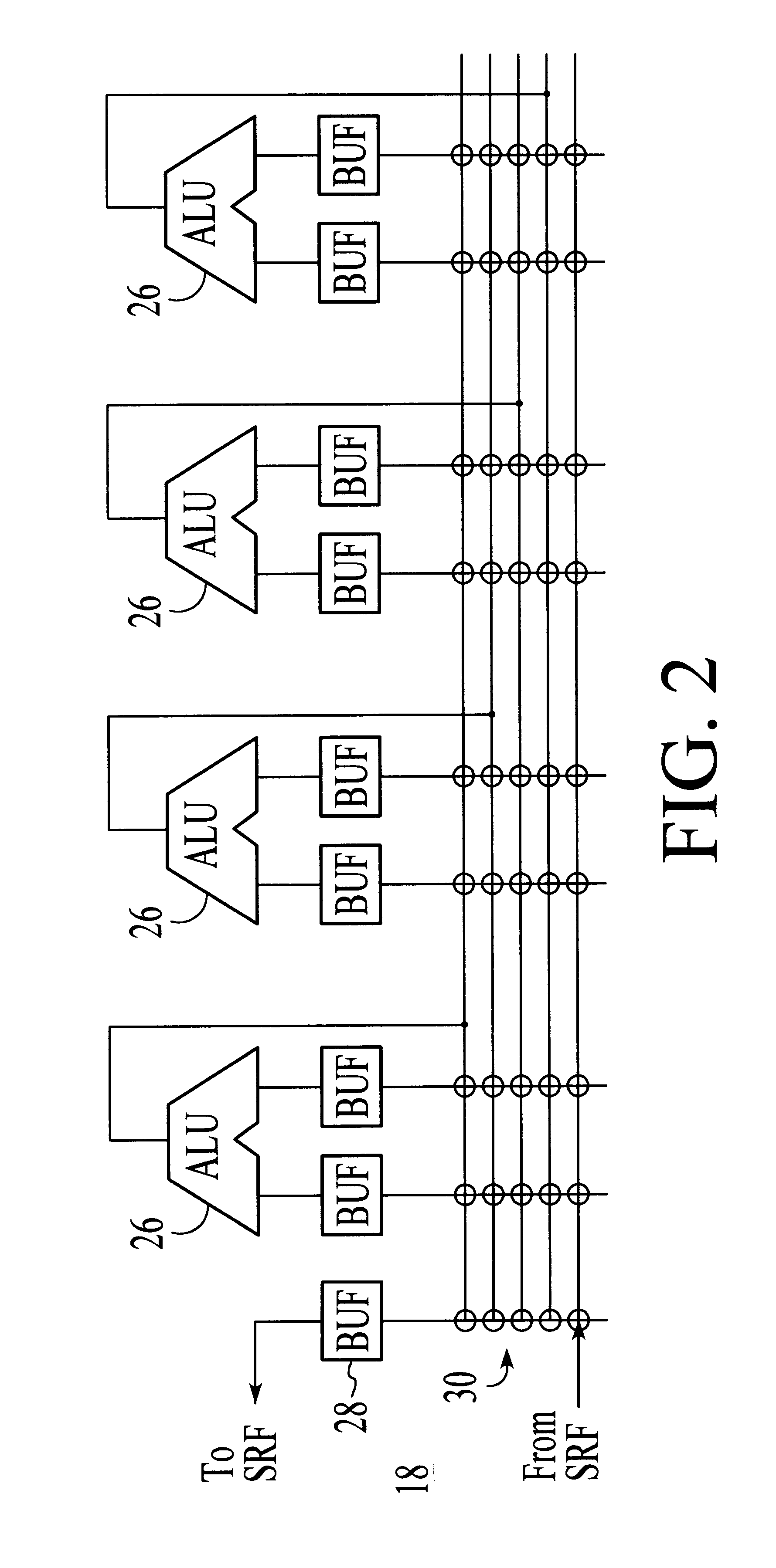
System and method for performing compound vector operations
InactiveUS6192384B1Reduce bandwidth requirementsMinimize the numberOperational speed enhancementRegister arrangementsOperating instructionImaging processing
A processor particularly useful in multimedia applications such as image processing is based on a stream programming model and has a tiered storage architecture to minimize global bandwidth requirements. The processor has a stream register file through which the processor's functional units transfer streams to execute processor operations. Load and store instructions transfer streams between the stream register file and a stream memory; send and receive instructions transfer streams between stream register files of different processors; and operate instructions pass streams between the stream register file and computational kernels. Each of the computational kernels is capable of performing compound vector operations. A compound vector operation performs a sequence of arithmetic operations on data read from the stream register file, i.e., a global storage resource, and generates a result that is written back to the stream register file. Each function or compound vector operation is specified by an instruction sequence that specifies the arithmetic operations and data movements that are performed each cycle to carry out the compound operation. This sequence can, for example, be specified using microcode.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND +1
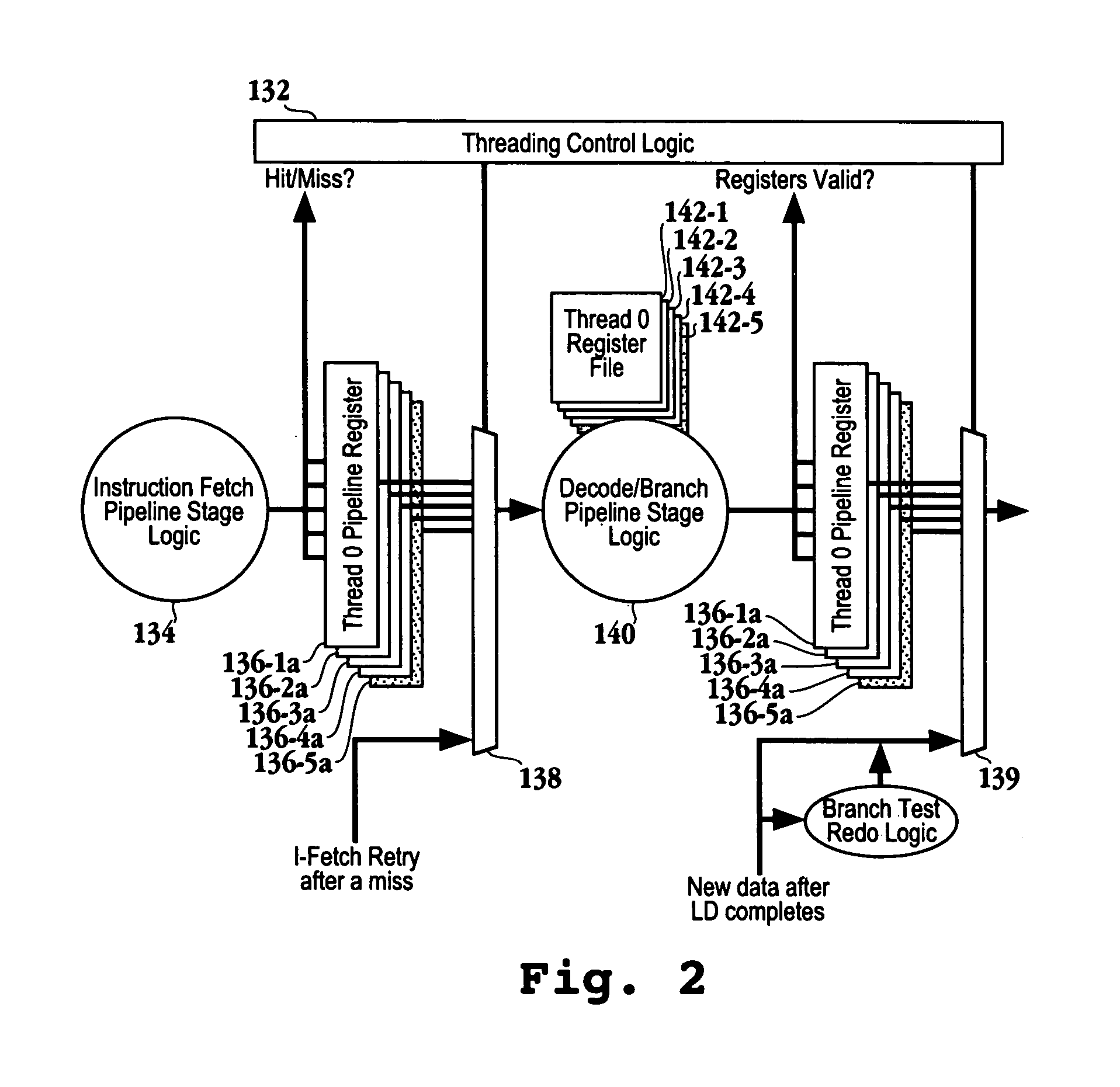
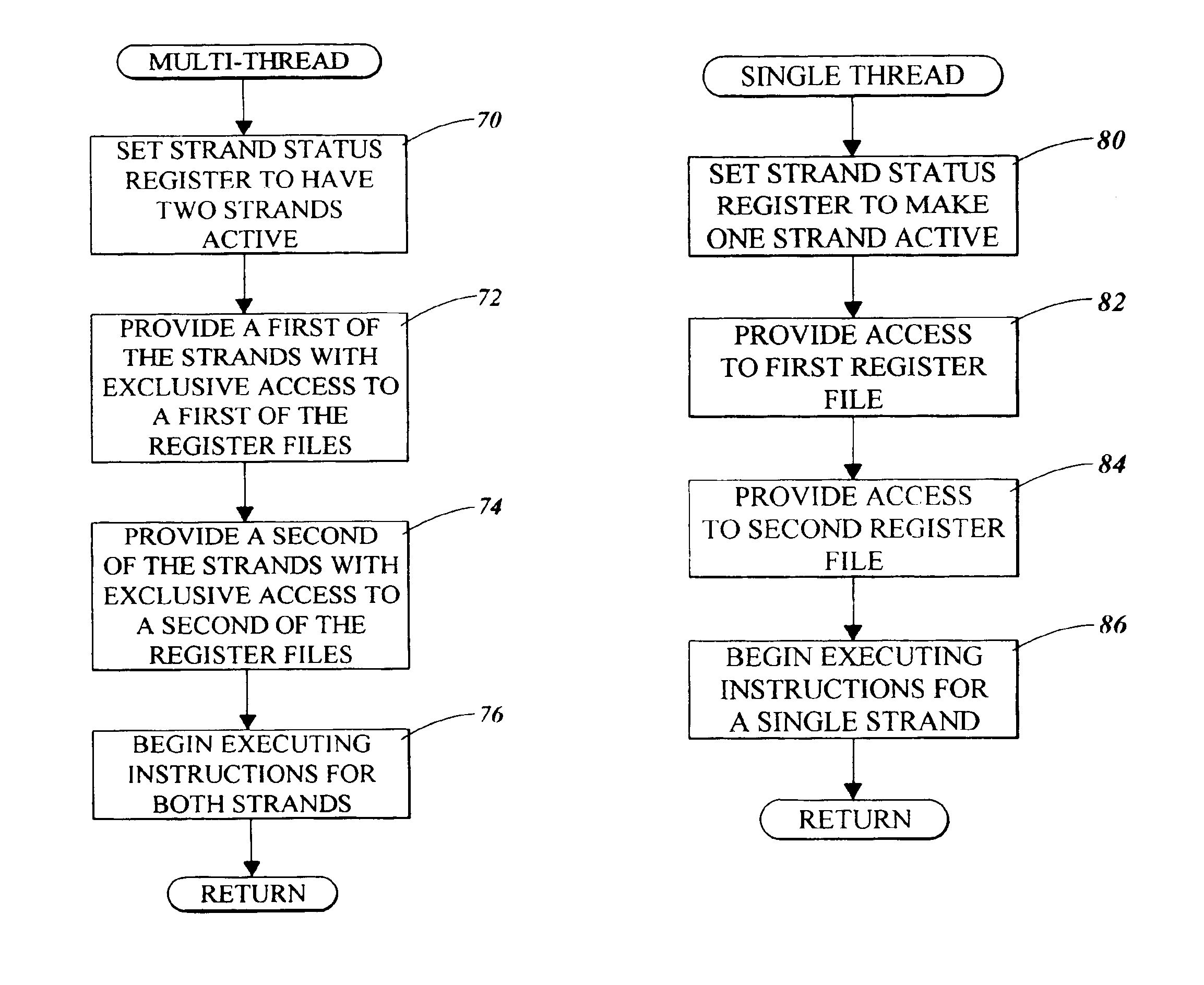
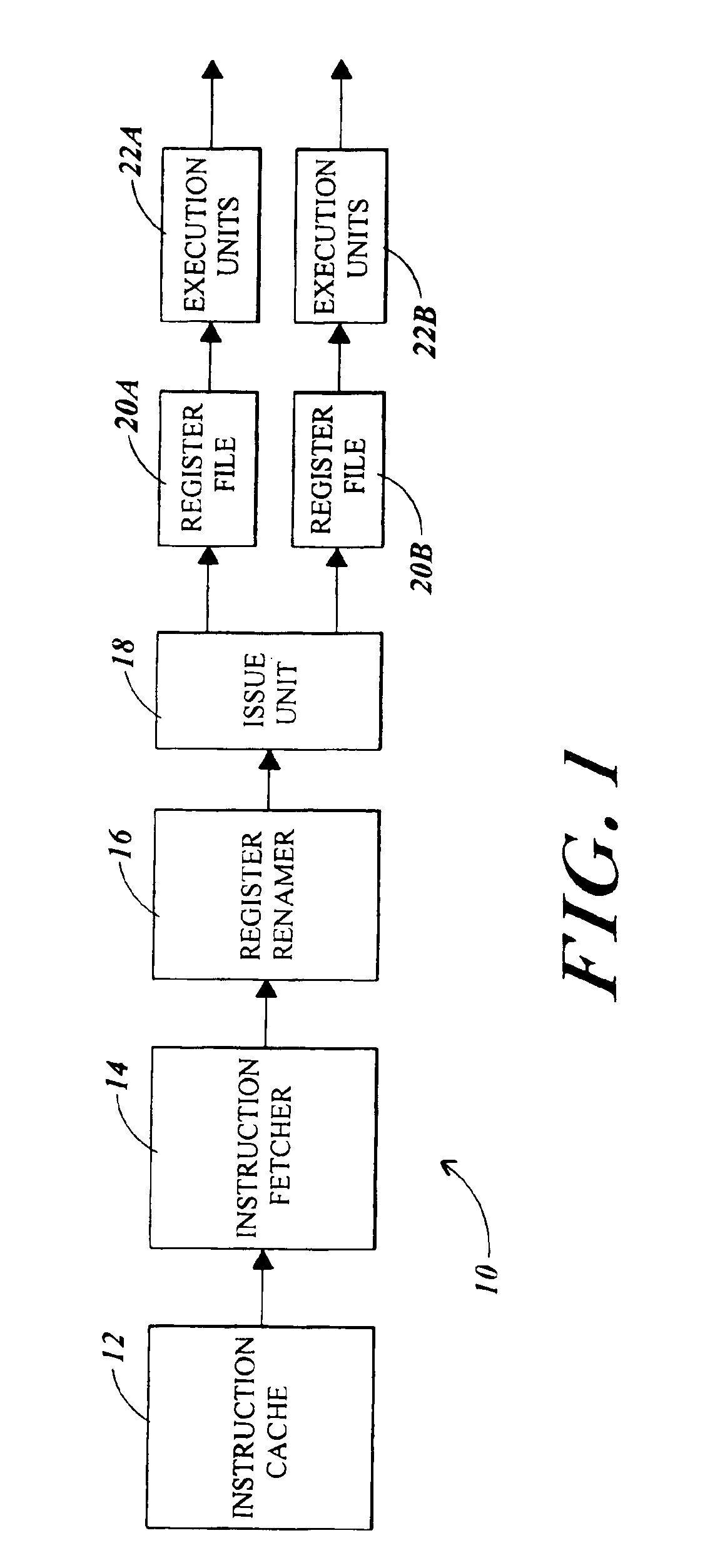
Microprocessor and method for giving each thread exclusive access to one register file in a multi-threading mode and for giving an active thread access to multiple register files in a single thread mode
InactiveUS6954846B2Maximize issue rateRegister arrangementsUnauthorized memory use protectionMicroprocessorExclusive access
A microprocessor includes multiple register files. In a single thread mode, the microprocessor allows a single thread to have access to multiple ones of the register files. In a multi-thread mode, each thread has access to respective ones of the register files. In the multi-thread mode, multiple threads are simultaneously executing. Circuitry and hardware are provided to facilitate the respective modes and to facilitate transitions between the modes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Vector register addressing
InactiveUS6332186B1Without complexityWithout costRegister arrangementsInstruction analysisMemory addressProcessing Instruction
A floating point unit 26 is provided with a register bank 38 comprising 32 registers that may be used as either vector registers V or scalar registers S. Data values are transferred between memory 30 and the registers within the register bank 38 using contiguous block memory access instructions. Vector processing instructions specify a sequence of processing operations to be performed upon data values within a sequence of registers. The register address is incremented between each operation by an amount controlled by a stride value. Accordingly, the register address can be incremented by values such as 0, 1, 2 or 4 between each iteration. This provides a mechanism for retaining block memory access instructions to contiguous memory addresses whilst supporting vector matrix and / or complex operations in which the data values needed for each iteration are not adjacent to one another in the memory 30.
Owner:ARM LTD
Indirect Register Access Method and System
ActiveUS20100100691A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationRegister arrangementsAccess methodProcessor register
Systems and methods are provided for managing access to registers. In one embodiment, a system may include a processor and a plurality of registers. The processor and the plurality of registers may be integrated into a single device, or may be in separate devices. The plurality of registers may include a first set of registers that are directly accessible by the processor, and a second set of registers that are not directly accessible by the processor. The second set of registers may, however, be accessed indirectly by the processor via the first set of registers. In one embodiment, the first set of registers may include a register for selecting a register bank from the second set of registers, and a register for selecting a particular address within the register bank, to allow indirect access by the processor to the registers of the second set.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Apparatus and Method for Processing an Instruction Matrix Specifying Parallel and Dependent Operations
ActiveUS20090113170A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsRegister arrangementsParallel computingMatrix manipulation
Owner:INTEL CORP
Digital data processing apparatus having multi-level register file
InactiveUS20050289299A1Faster access latency timeSlow access latency timeRegister arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDigital dataMemory bank
A processor contains multiple levels of registers having different access latency. A relatively smaller set of registers is contained in a relatively faster higher level register bank, and a larger, more complete set of the registers is contained in a relatively slower lower level register bank. Physically, the higher level register bank is placed closer to functional logic which receives inputs from the registers. Preferably, the lower level bank includes a complete set of all processor registers, and the higher level bank includes a smaller subset of the registers, duplicating information in the lower level bank. The higher level bank is preferably accessible in a single clock cycle.
Owner:IBM CORP
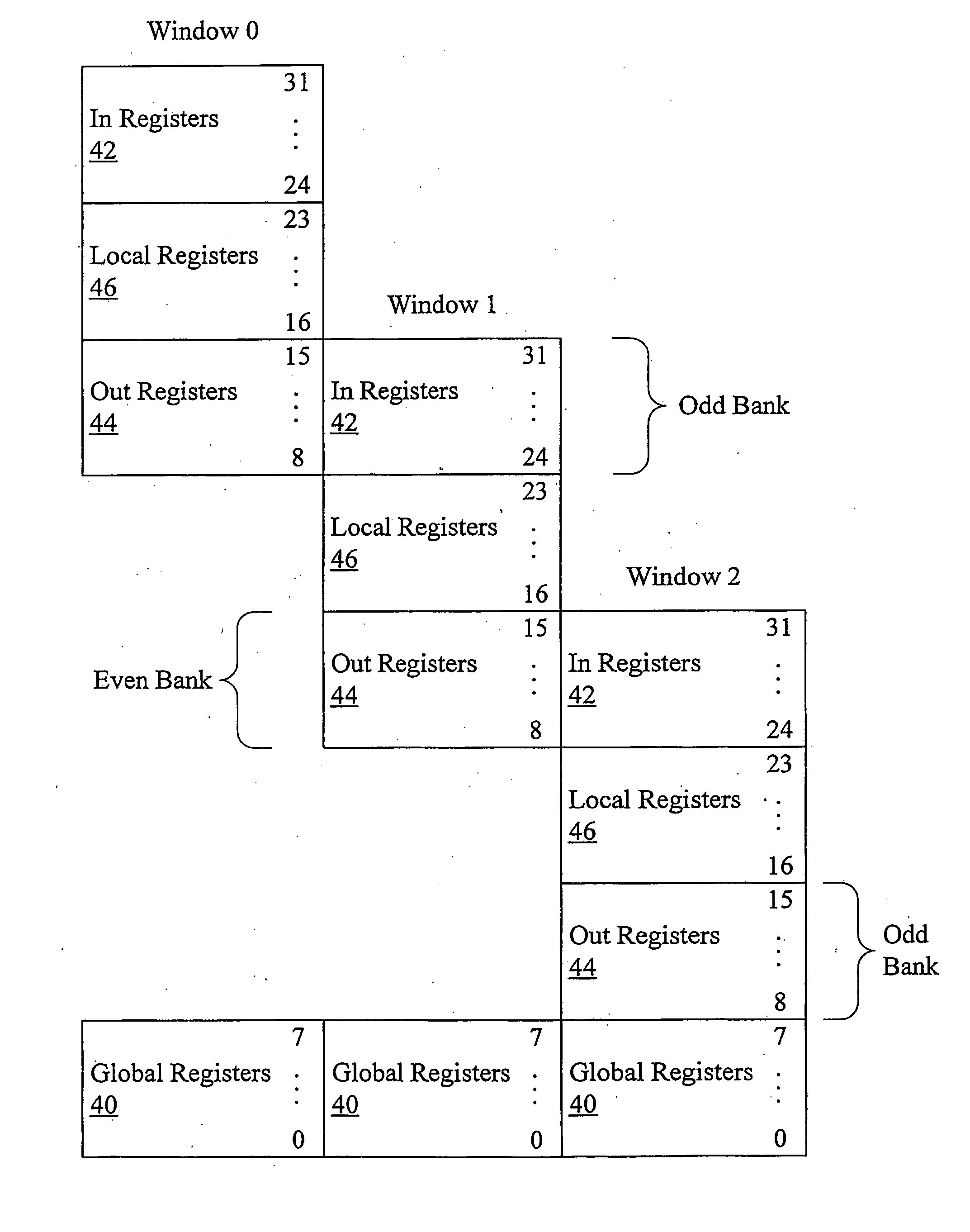
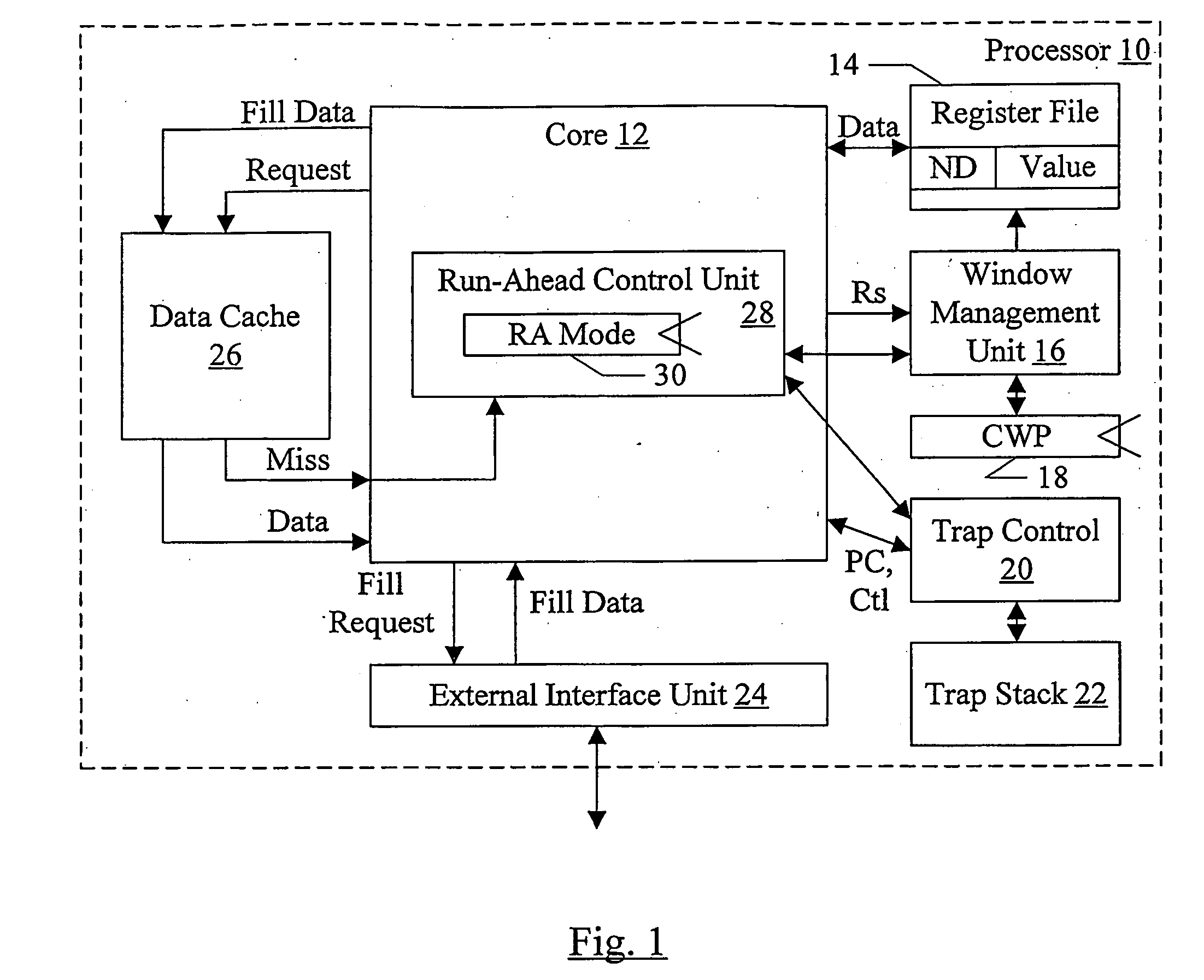
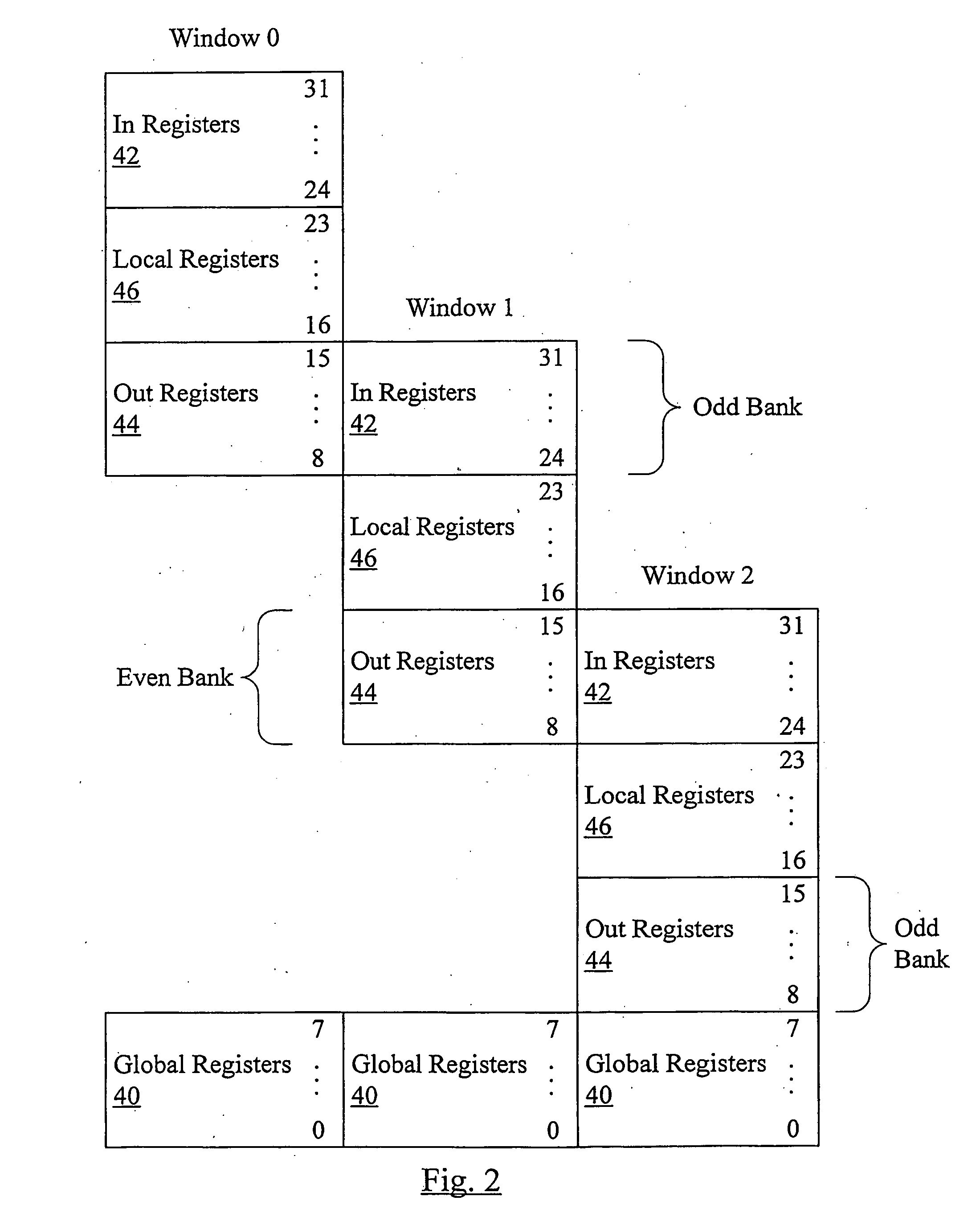
Using windowed register file to checkpoint register state
InactiveUS20080016325A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsSpeculative executionManagement unit
In one embodiment, a processor comprises a core configured to execute instructions; a register file comprising a plurality of storage locations; and a window management unit. The window management unit is configured to operate the plurality of storage locations as a plurality of windows, wherein register addresses encoded into the instructions identify storage locations among a subset of the plurality of storage locations that are within a current window. Additionally, the window management unit is configured to allocate a second window in response to a predetermined event. One of the current window and the second window serves as a checkpoint of register state, and the other one of the current window and the second window is updated in response to instructions processed subsequent to the checkpoint. The checkpoint may be restored if the speculative execution results are discarded.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
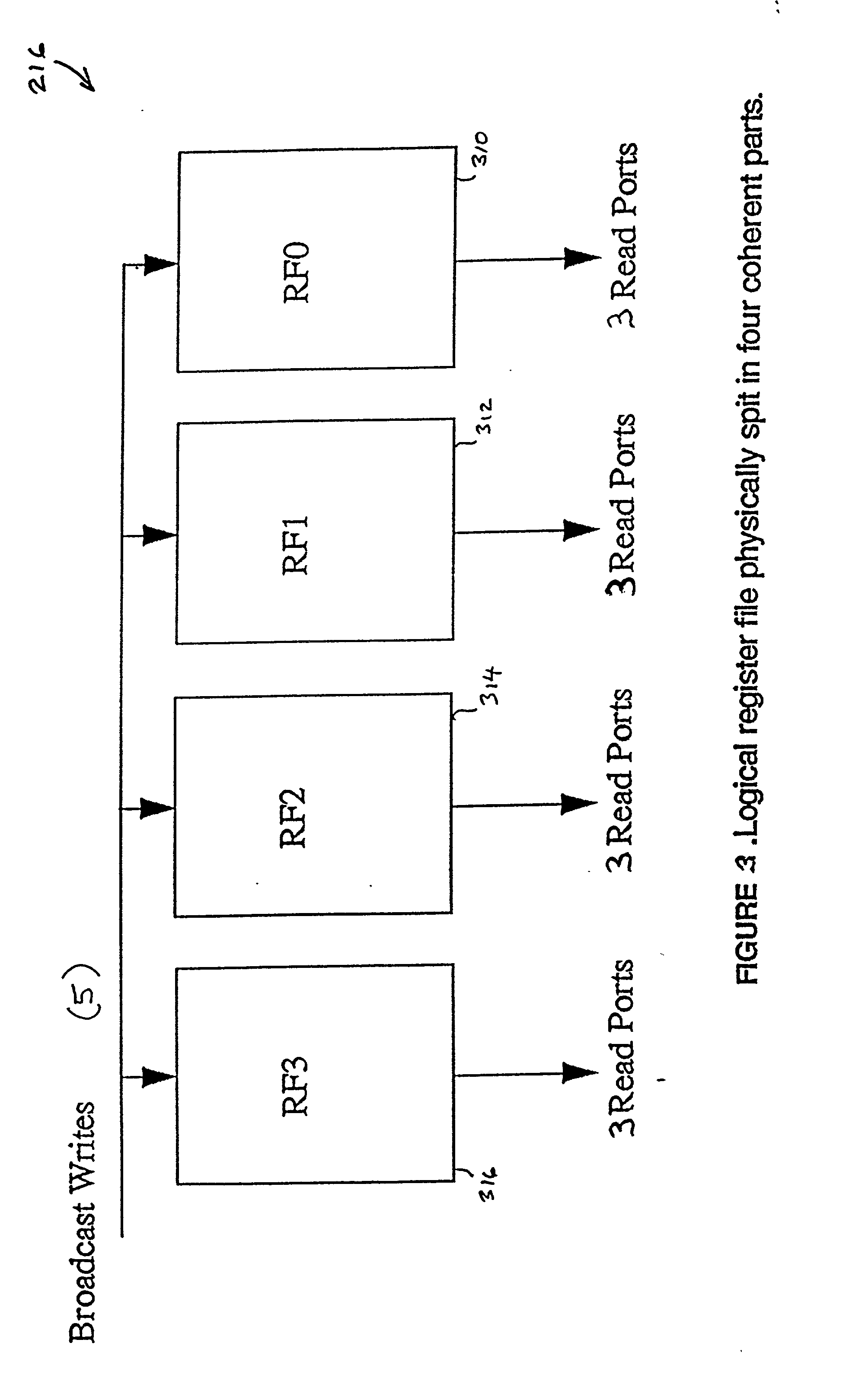
Local and global register partitioning in a vliw processor
InactiveUS20010042190A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsProcessor registerVery long instruction word
A Very Long Instruction Word (VLIW) processor having a plurality of functional units includes a multi-ported register file that is divided into a plurality of separate register file segments, each of the register file segments being associated to one of the plurality of functional units. The register file segments are partitioned into local registers and global registers. The global registers are read and written by all functional units. The local registers are read and written only by a functional unit associated with a particular register file segment. The local registers and global registers are addressed using register addresses in an address space that is separately defined for a register file segment / functional unit pair. The global registers are addressed within a selected global register range using the same register addresses for the plurality of register file segment / functional unit pairs. The local registers in a register file segment are addressed using register addresses in a local register range outside the global register range that are assigned within a single register file segment / functional unit pair. Register addresses in the local register range are the same for the plurality of register file segment / functional unit pairs and address registers locally within a register file segment / functional unit pair.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
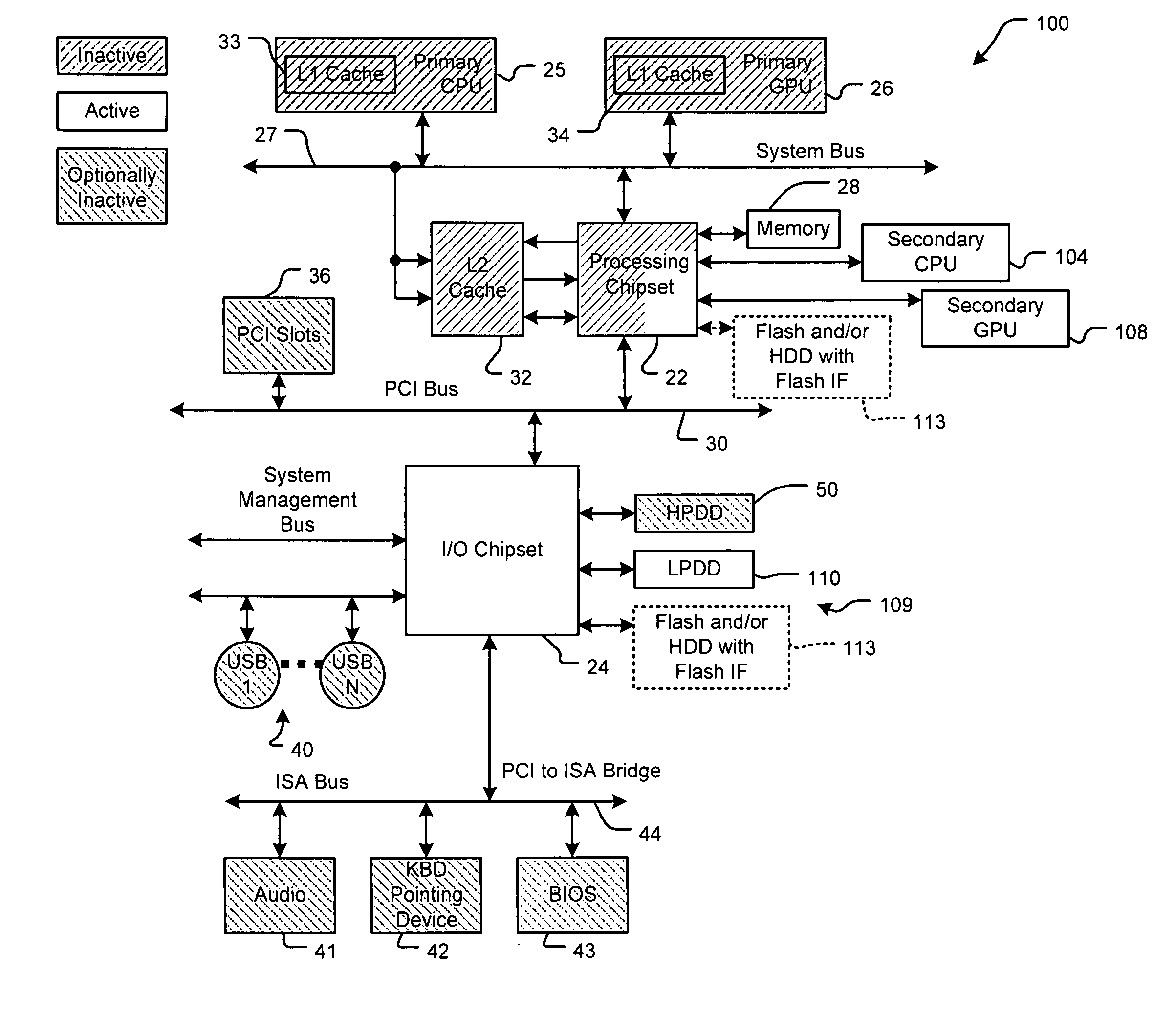
System with high power and low power processors and thread transfer
A processing system comprises a first processor that has active and inactive states and that processes at least one thread during the active state. A second processor has active and inactive states. The second processor consumes less power when operating in the active state than the first processor operating in the active state. A control module communicates with the first and second processors and selectively transfers the at least one thread from the first processor to the second processor and selects the inactive state of the first processor. The second processor processes the at least one thread.
Owner:SUTARDJA SEHAT
Vertically and horizontally threaded processor with multidimensional storage for storing thread data
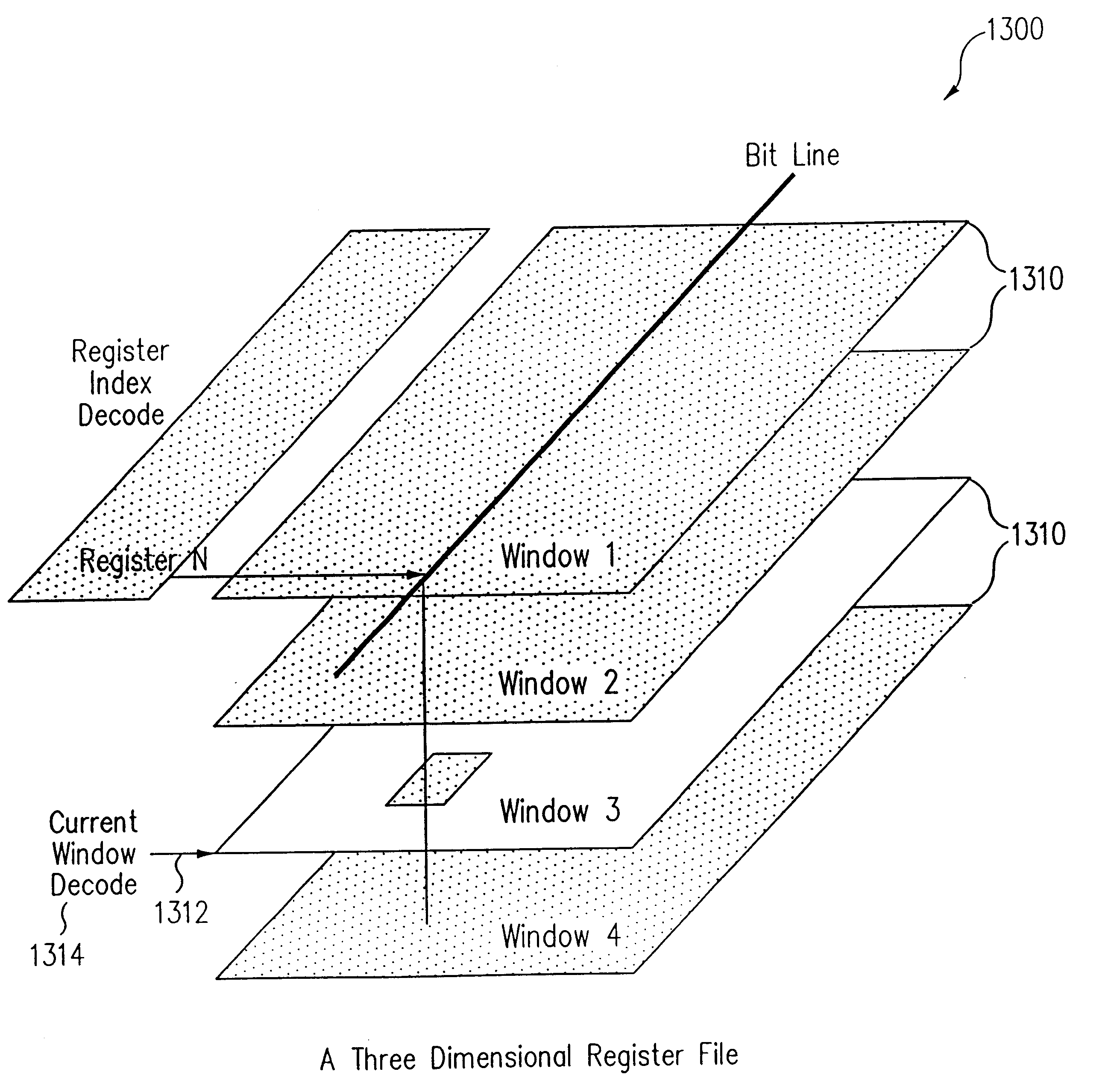
InactiveUS6351808B1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsMultidimensional scalingProcessor register
A processor includes a "four-dimensional" register structure in which register file structures are replicated by N for vertical threading in combination with a three-dimensional storage circuit. The multi-dimensional storage is formed by constructing a storage, such as a register file or memory, as a plurality of two-dimensional storage planes.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and Method of Indirect Register Access
ActiveUS20100100714A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsProcessor registerComputer science
Systems and methods are provided for managing access to registers. A system may include a set of direct registers and a set of indirect registers. The indirect registers may be accessed through the direct registers, and the direct registers may provide various features to provide faster access to the indirect registers. One of the direct registers may indicate access modes for accessing the indirect registers. The access modes may include auto-increment, auto-decrement, auto-reset, and no change modes. Based on the access mode, the currently accessed address may be automatically modified after accessing the indirect register at the address.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Implementing instruction set architectures with non-contiguous register file specifiers
ActiveUS20080189519A1Register arrangementsInstruction analysisProcessing InstructionProcessor register
There are provided methods and computer program products for implementing instruction set architectures with non-contiguous register file specifiers. A method for processing instruction code includes processing a fixed-width instruction of a fixed-width instruction set using a non-contiguous register specifier of a non-contiguous register specification. The fixed-width instruction includes the non-contiguous register specifier.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Data processing apparatus
ActiveUS20100293342A1Simple structureSmall spacingConditional code generationRegister arrangementsInstruction setContent-addressable memory
Apparatus comprises a processor configured for operation under a sequence of instructions from an instruction set, wherein said processor comprises: means for conditionally inhibiting at least one type of trap, interrupt or exception (TIE) event, wherein, when operating under a sequence of instructions, said inhibition means is inaccessible by said instructions to inhibit the or each type of TIE event, without interrupting said sequence. A data processing apparatus includes a processor adapted to operate under control of program code comprising instructions selected from an instruction set, the apparatus comprising: a predefined memory space providing a predefined addressable memory for storing program code and data, a larger memory space providing a larger addressable memory, means for accessing program code and data within the predefined memory space, and means for controlling the access means so as to enable the access means to access program code located within the larger memory space.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE CONSULTANTS LTD
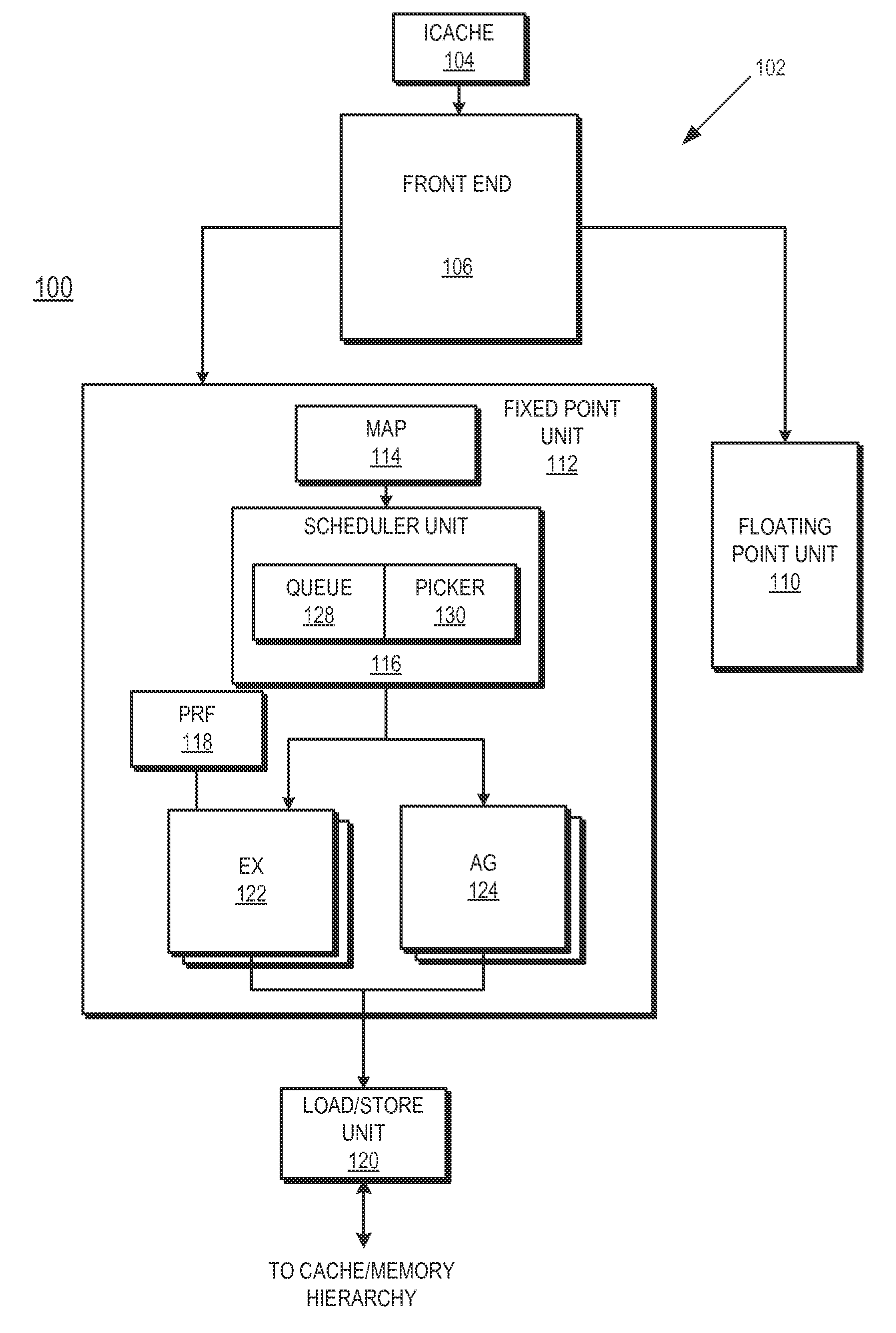
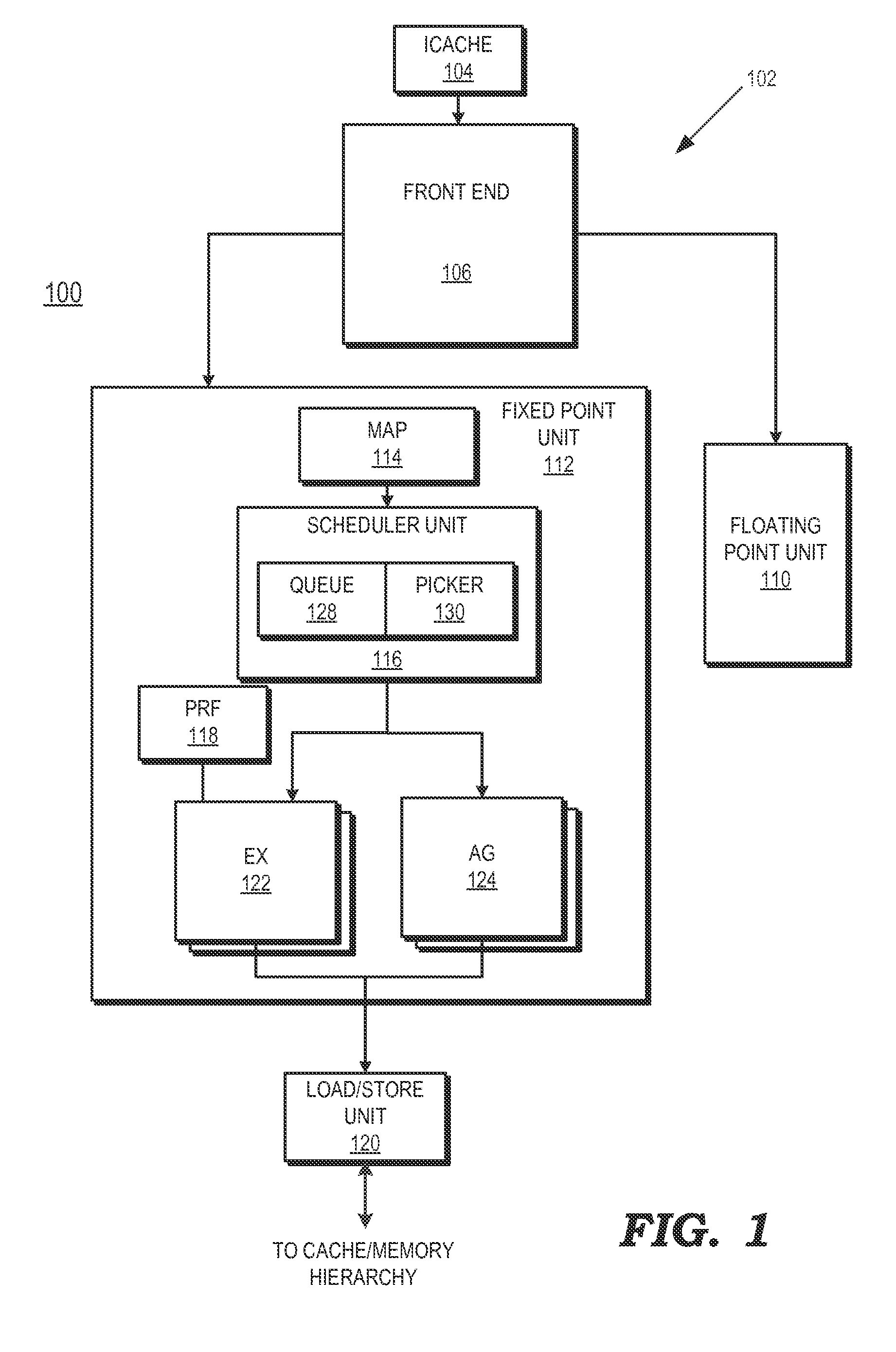
Dependent instruction suppression
ActiveUS20140380024A1Register arrangementsDigital computer detailsDependency informationLoad instruction
A method includes suppressing execution of at least one dependent instruction of a load instruction by a processor using stored dependency information responsive to an invalid status of the load instruction. A processor includes an execution unit to execute instructions and a scheduler. The scheduler is to select for execution in the execution unit a load instruction having at least one dependent instruction and suppress execution of the at least one dependent instruction using stored dependency information responsive to an invalid status of the load instruction.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
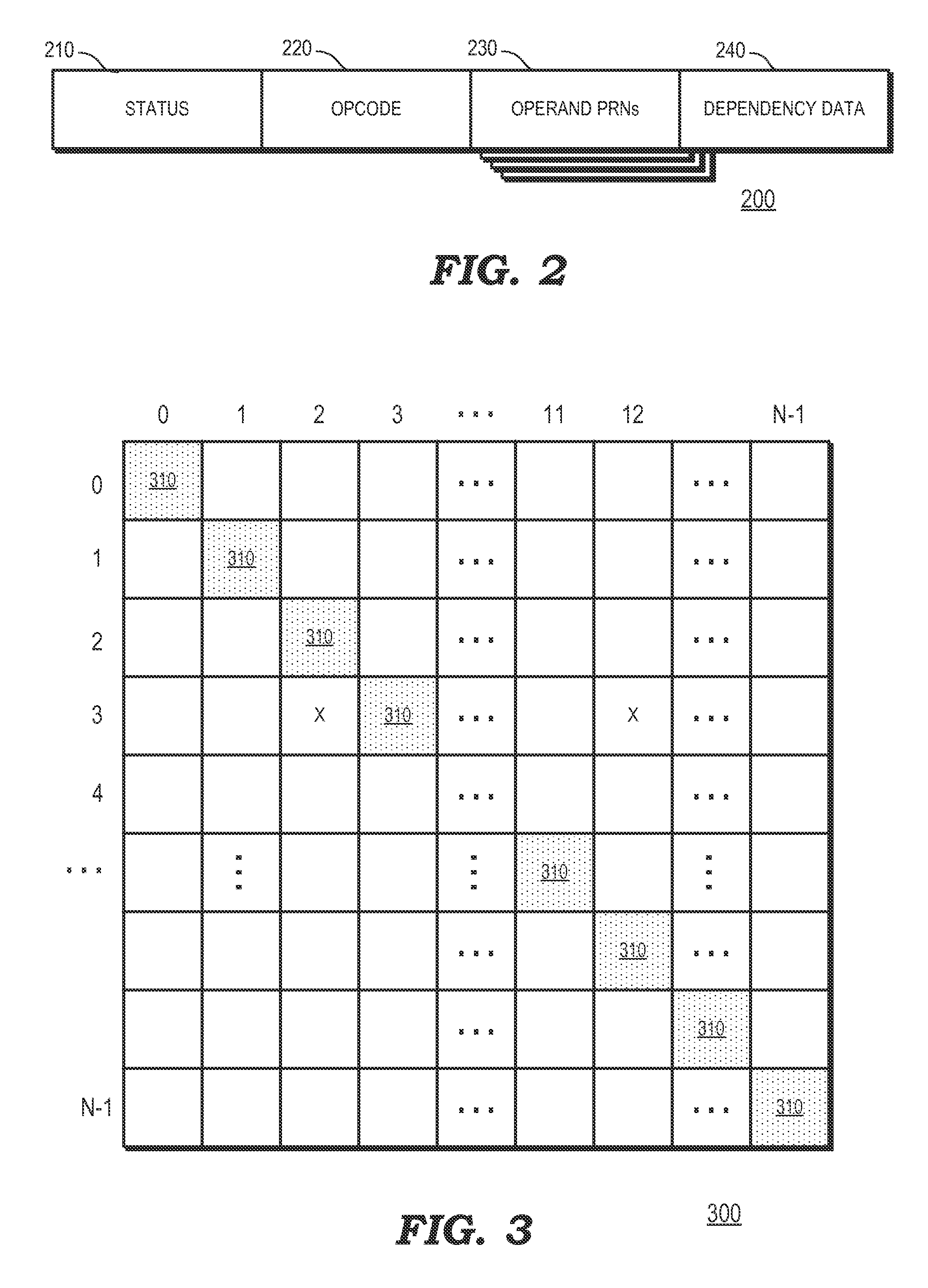
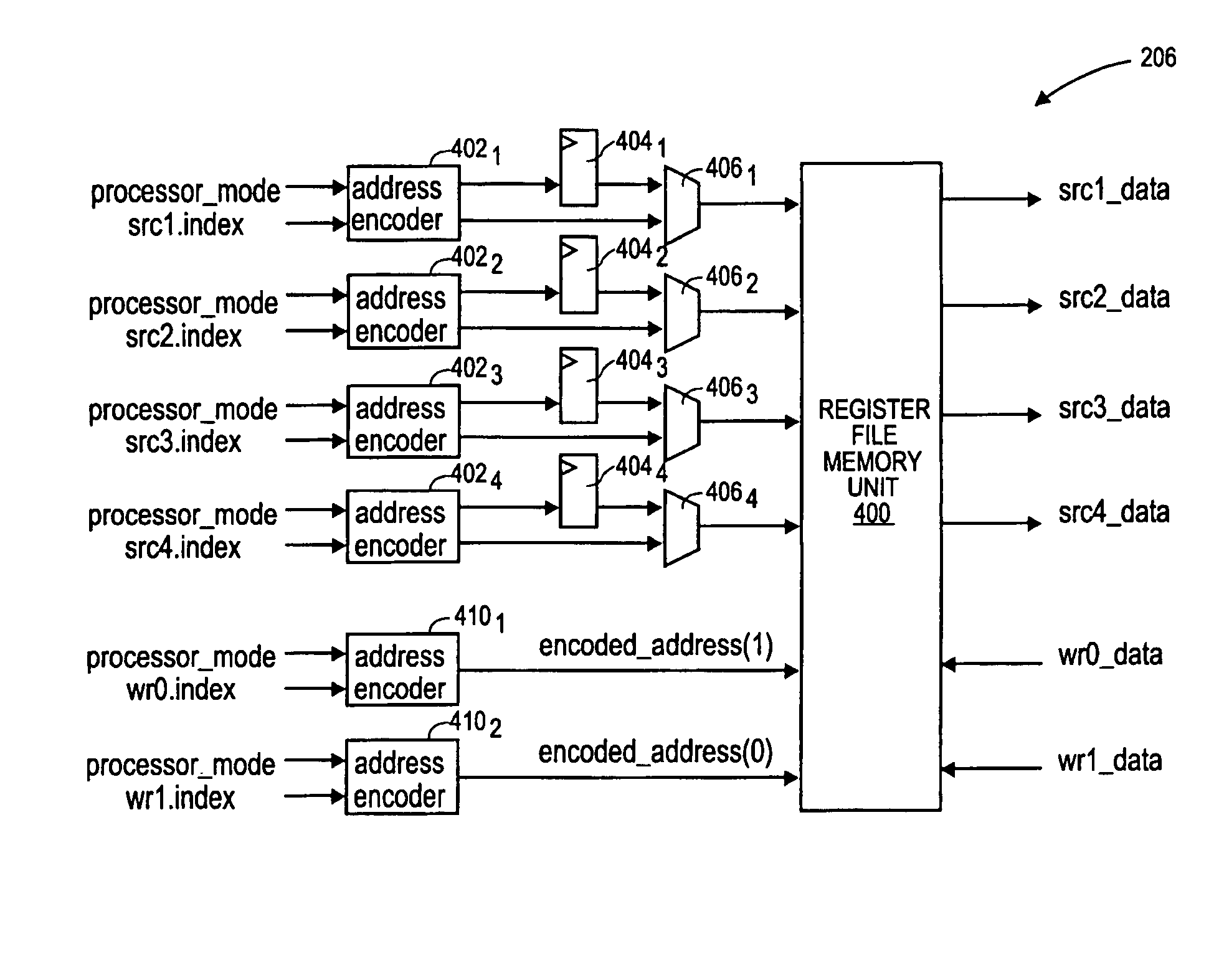
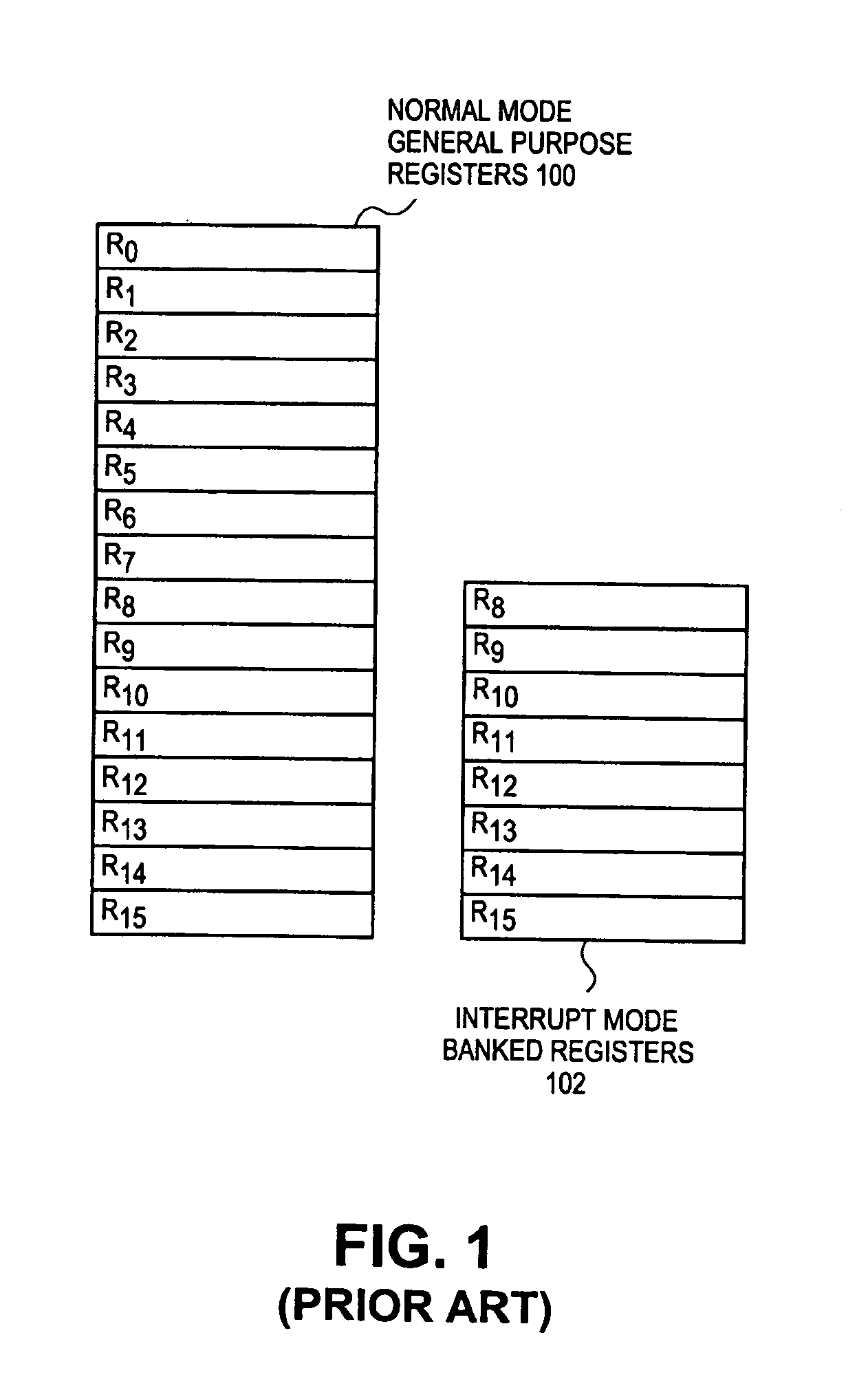
Memory mapped register file and method for accessing the same
InactiveUS7558942B1Register arrangementsGeneral purpose stored program computerData processing systemProcessing Instruction
A data processing system comprises a processor to process instructions. A plurality of pipeline stages to execute instructions including a register file. The register file includes a memory unit having a plurality of memory locations, each memory location being addressable by an encoded address. The encoded address corresponds to at least one register and processing mode. Input ports receive inputs for addressing at least one of the memory locations using an encoded address. Output ports to output data from at least one of the memory locations using an encoded address.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method and appratus for power throttling in a multi-thread processor
ActiveUS20060020831A1Save powerRegister arrangementsVolume/mass flow measurementControl powerParallel computing
A method and apparatus for controlling power consumption in a processor. In one embodiment, a processor includes a pipeline. The pipeline includes logic for fetching instructions, issuing instructions, and executing instructions. The processor also includes a power management unit. The power management unit is configured to input M stalls into the pipeline every N instruction cycles (where M and N are integer value and wherein M is less than N).
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Protected function calling
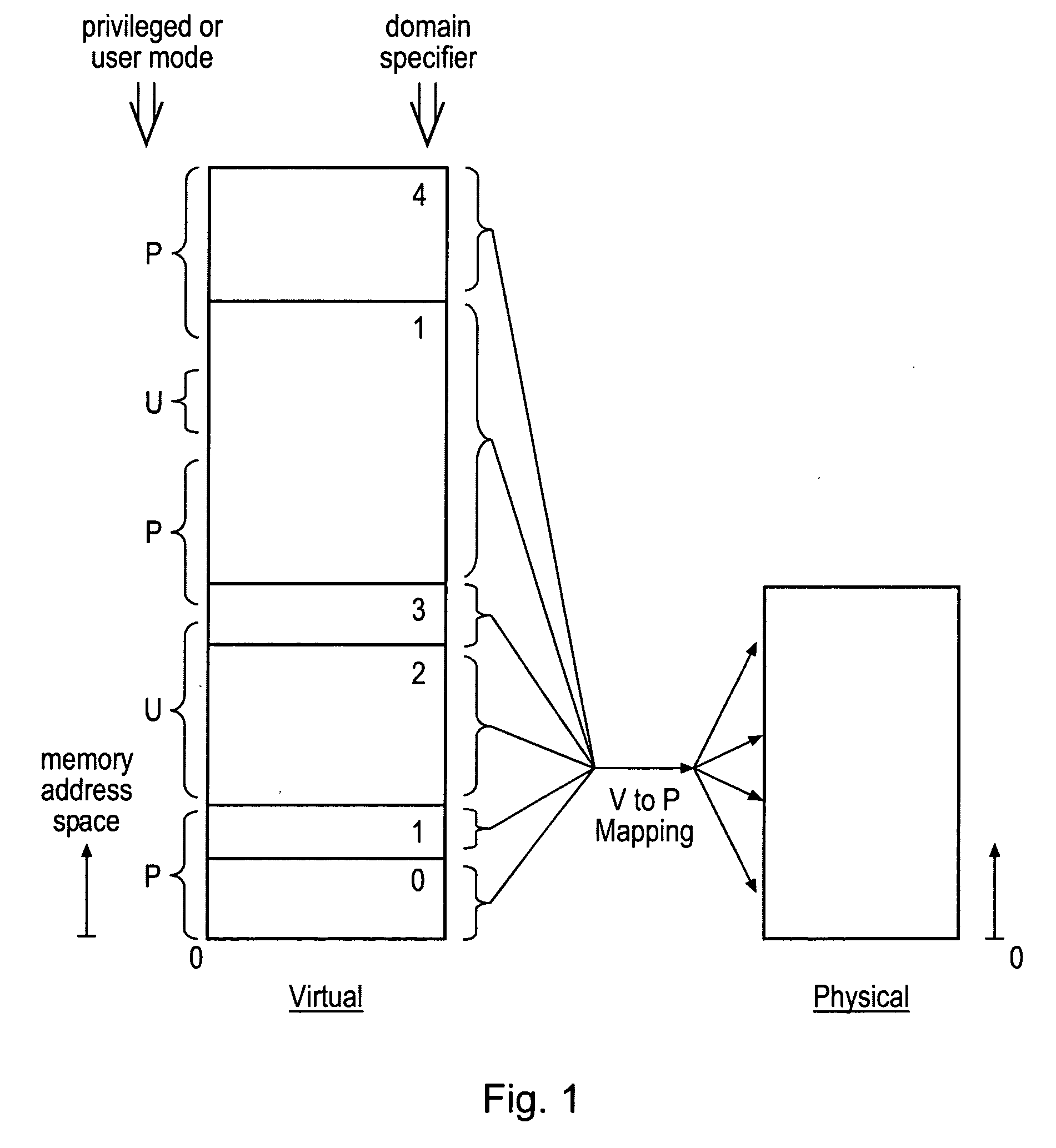
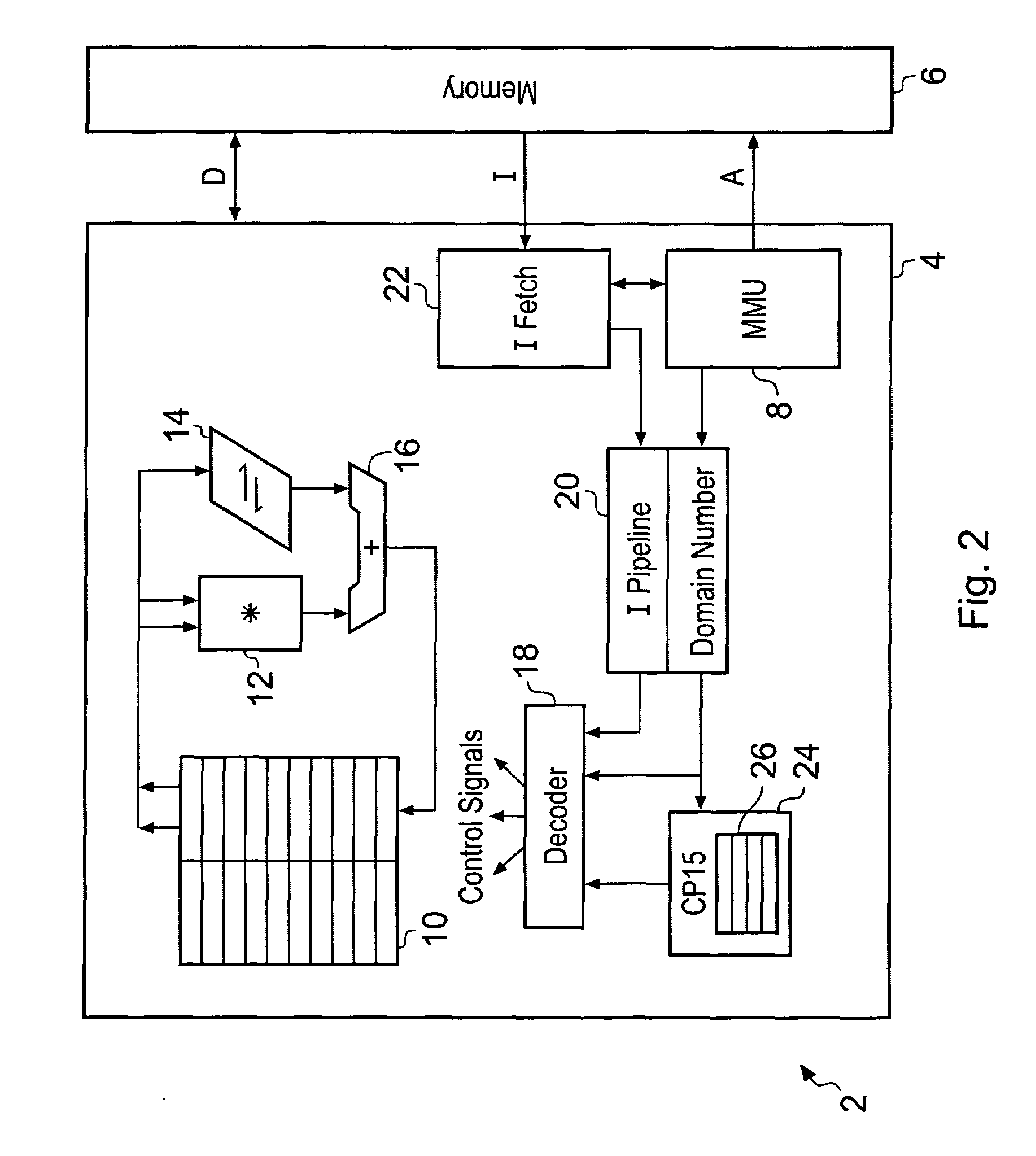
ActiveUS20080250216A1Improve securityAchieve backward compatibilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationRegister arrangementsMemory addressParallel computing
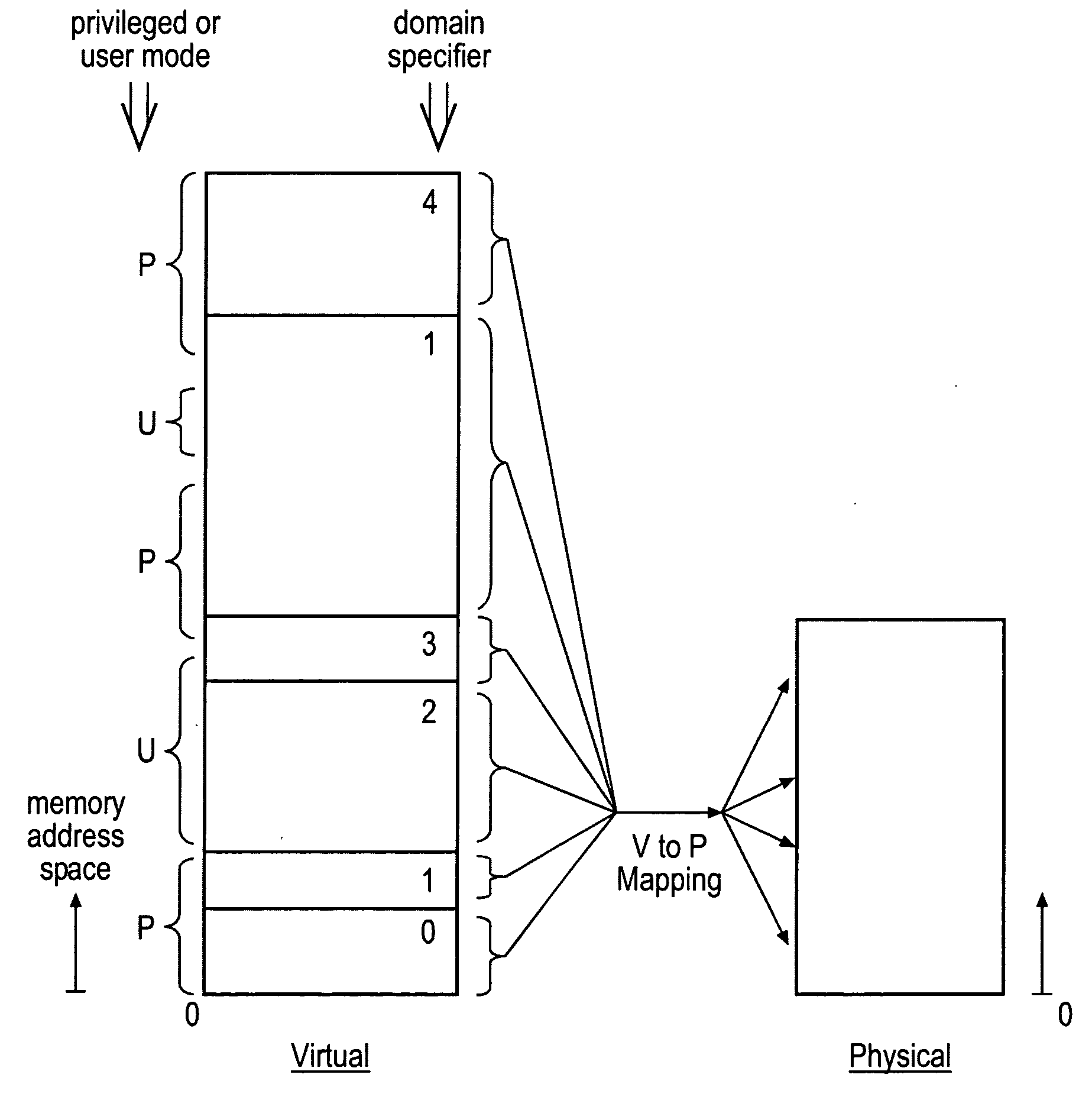
Memory address space is divided into domains and instruction access control circuitry is used to detect when the memory address from which an instruction to be executed is fetched has crossed a domain boundary and changed and in such cases to conduct a check to ensure that the instruction within the new domain is a permitted instruction of a permitted form. The permitted instruction can be arranged to be a no operation instruction other than in respect of the instruction access control circuitry, in order to assist backward compatibility.
Owner:ARM LTD
System, device, and method for multiplying multi-dimensional data arrays
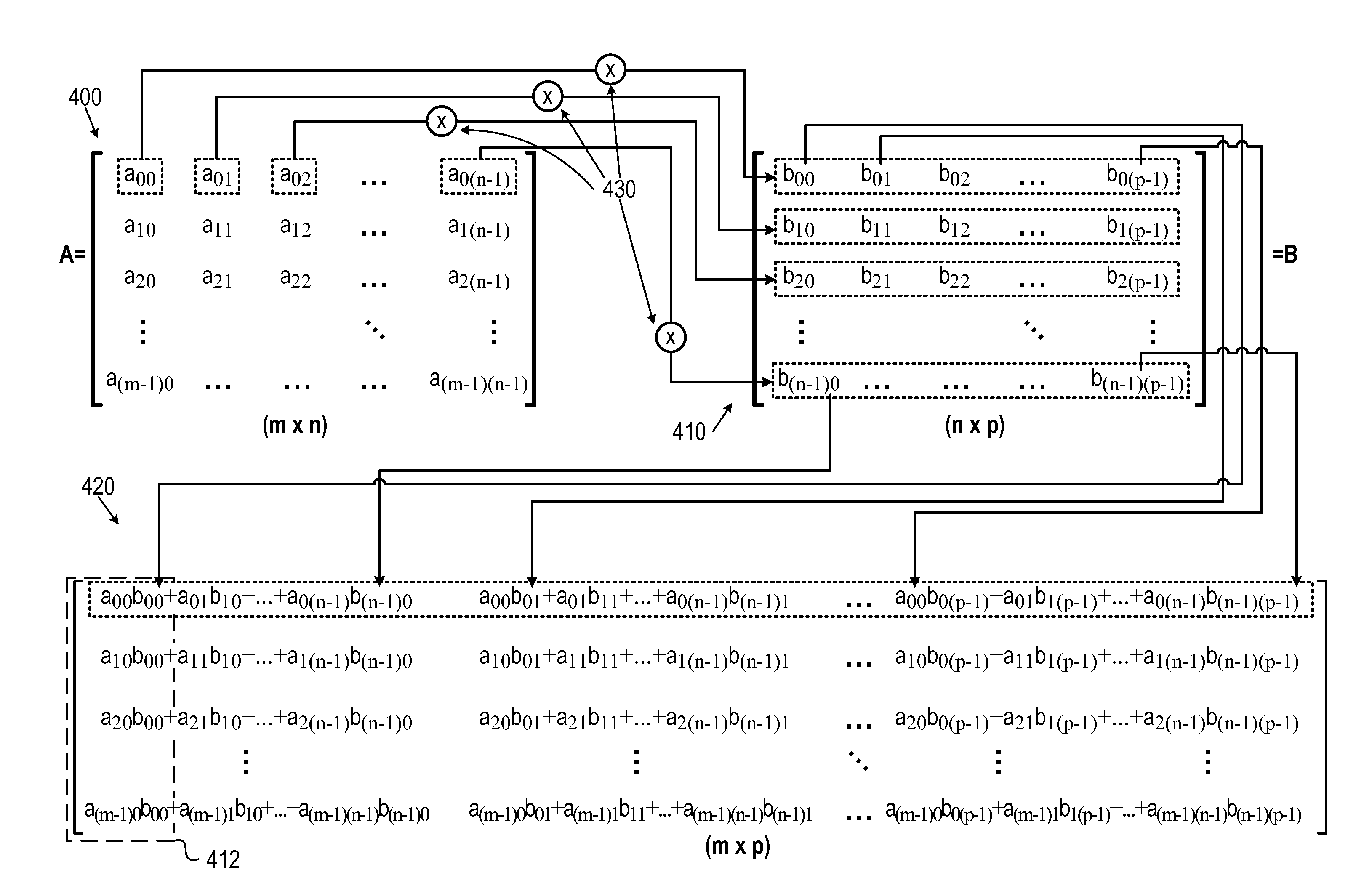
InactiveUS20120113133A1Register arrangementsComputation using non-contact making devicesArray data structureSingle element
A system, processor, and method for multiplying multi-dimensional data, for example, matrices, stored in vector memories. Each data element in a vector memory representing a sequential single element in a row of a left operand data array may be multiplied with a respective vector in a vector memory representing a sequential row in the right operand data array. The memory element representing the left operand element may be multiplied with the memory vector representing the right operand row that is in the same sequential order. A plurality of vectors of product elements may be generated by the multiplying. A single product element from each of the plurality of vectors of product elements may be added to a sum of product elements to generate each respective element in the same sequential order in a row of a product data array to generate a vector of a complete row of elements of the product data array.
Owner:CEVA D S P LTD
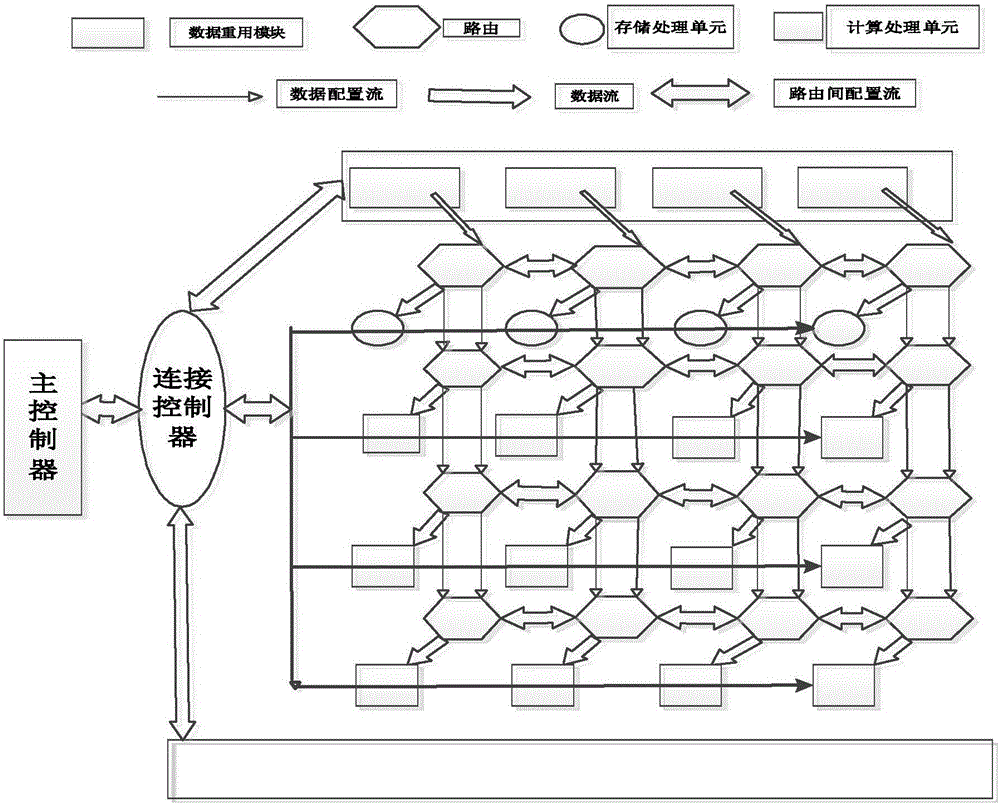
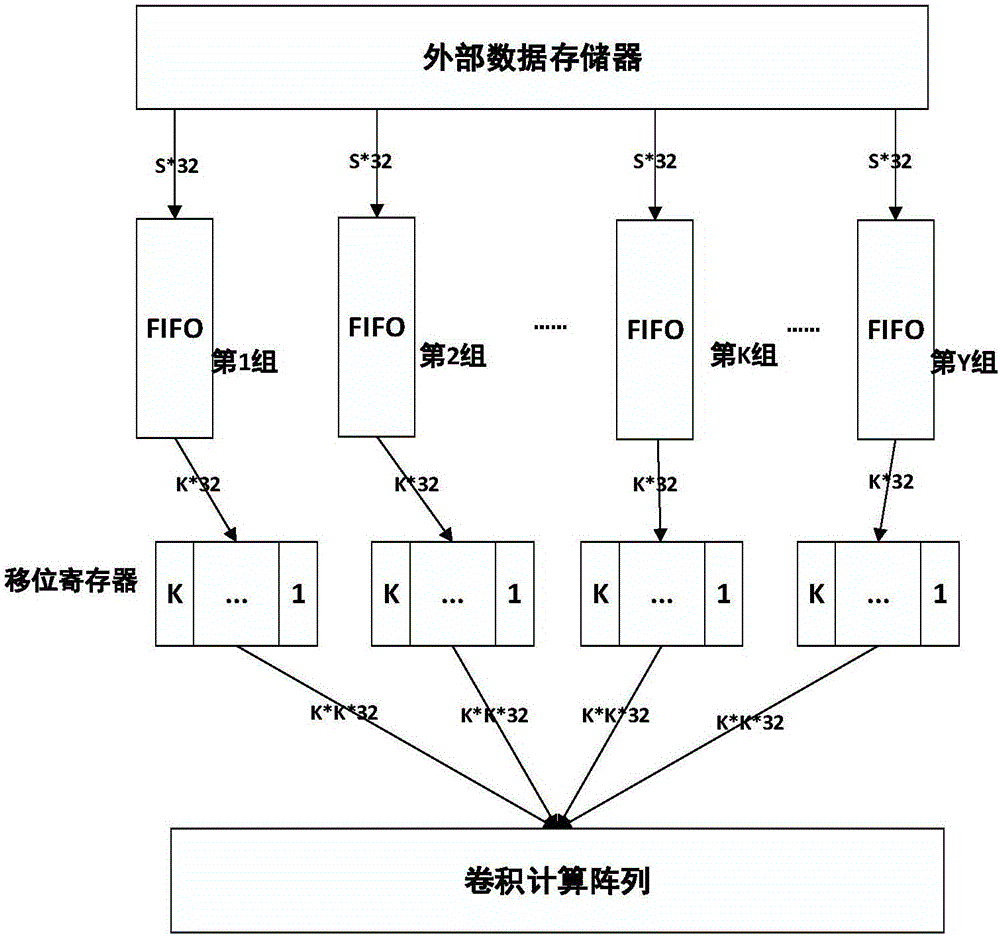
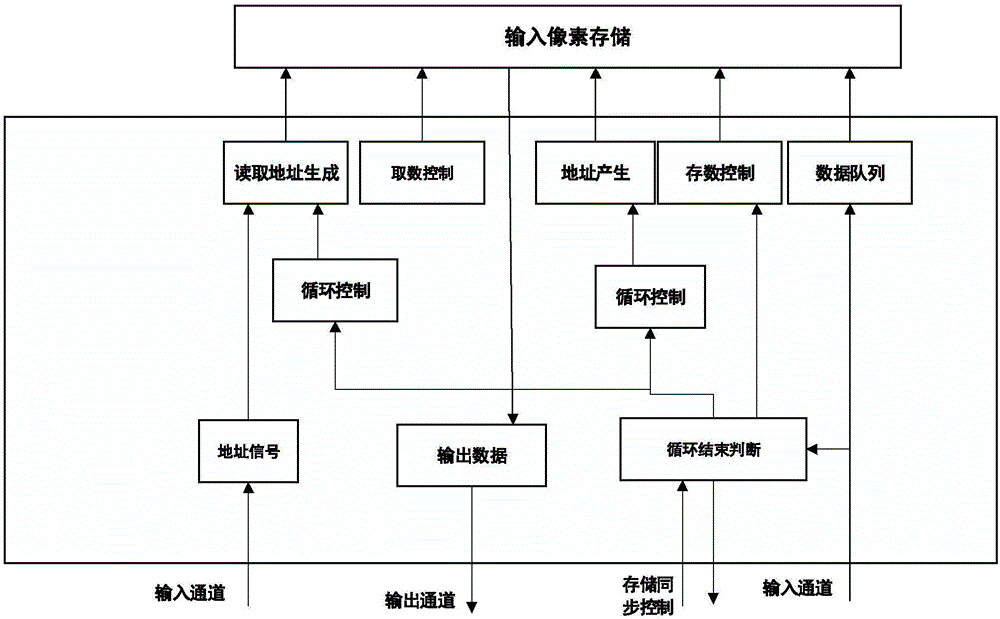
System for circular convolution calculation data reuse of convolutional neural network
InactiveCN106250103ARegister arrangementsConcurrent instruction executionProcessor registerComputation process
The invention discloses a coarse-grained reconfigurable system-oriented convolution neural network loop convolution calculation data reuse system, including a main controller and a connection control module, an input data reuse module, a convolution loop operation processing array, and a data transmission Pathways in four parts. During the convolution cycle operation, the essence is to multiply multiple two-dimensional input data matrices with multiple two-dimensional weight matrices. Generally, these matrices are large in size, and the multiplication takes up most of the time of the entire convolution calculation. The present invention utilizes a coarse-grained reconfigurable array system to complete the convolution calculation process. After receiving the convolution operation request instruction, the register rotation method is used to fully explore the reusability of the input data in the convolution cycle calculation process, which improves the data utilization rate. It also reduces the bandwidth access pressure, and the designed array unit is configurable, and can complete convolution operations with different cyclic convolution scales and step sizes.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Dynamically-selectable vector register partitioning
InactiveUS20100115233A1Register arrangementsProgram control using wired connectionsProcessor registerMulti processor
The present invention is directed generally to dynamically-selectable vector register partitioning, and more specifically to a processor infrastructure (e.g., co-processor infrastructure in a multi-processor system) that supports dynamic setting of vector register partitioning to any of a plurality of different vector partitioning modes. Thus, rather than being restricted to a fixed vector register partitioning mode, embodiments of the present invention enable a processor to be dynamically set to any of a plurality of different vector partitioning modes. Thus, for instance, different vector register partitioning modes may be employed for different applications being executed by the processor, and / or different vector register partitioning modes may even be employed for use in processing different vector oriented operations within a given applications being executed by the processor, in accordance with certain embodiments of the present invention.
Owner:CONVEY COMP
Popular searches
Energy efficient computing Comparison of digital values Specific program execution arrangements Memory systems Computation using denominational number representation Handling data according to predetermined rules Current supply arrangements Number-of-one counters Next instruction address formation Power supply for data processing
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com