Patents
Literature
540 results about "Link adaptation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
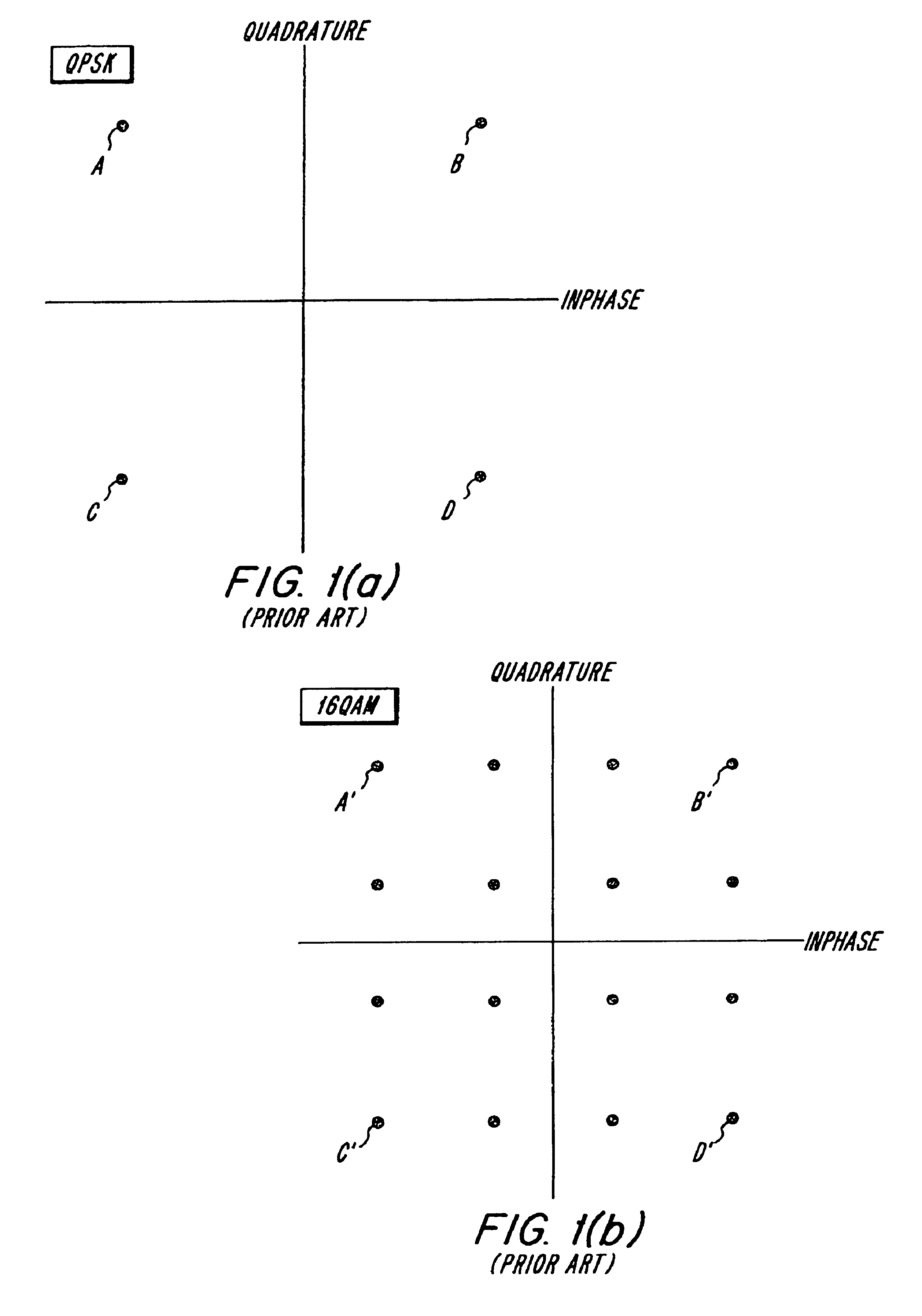
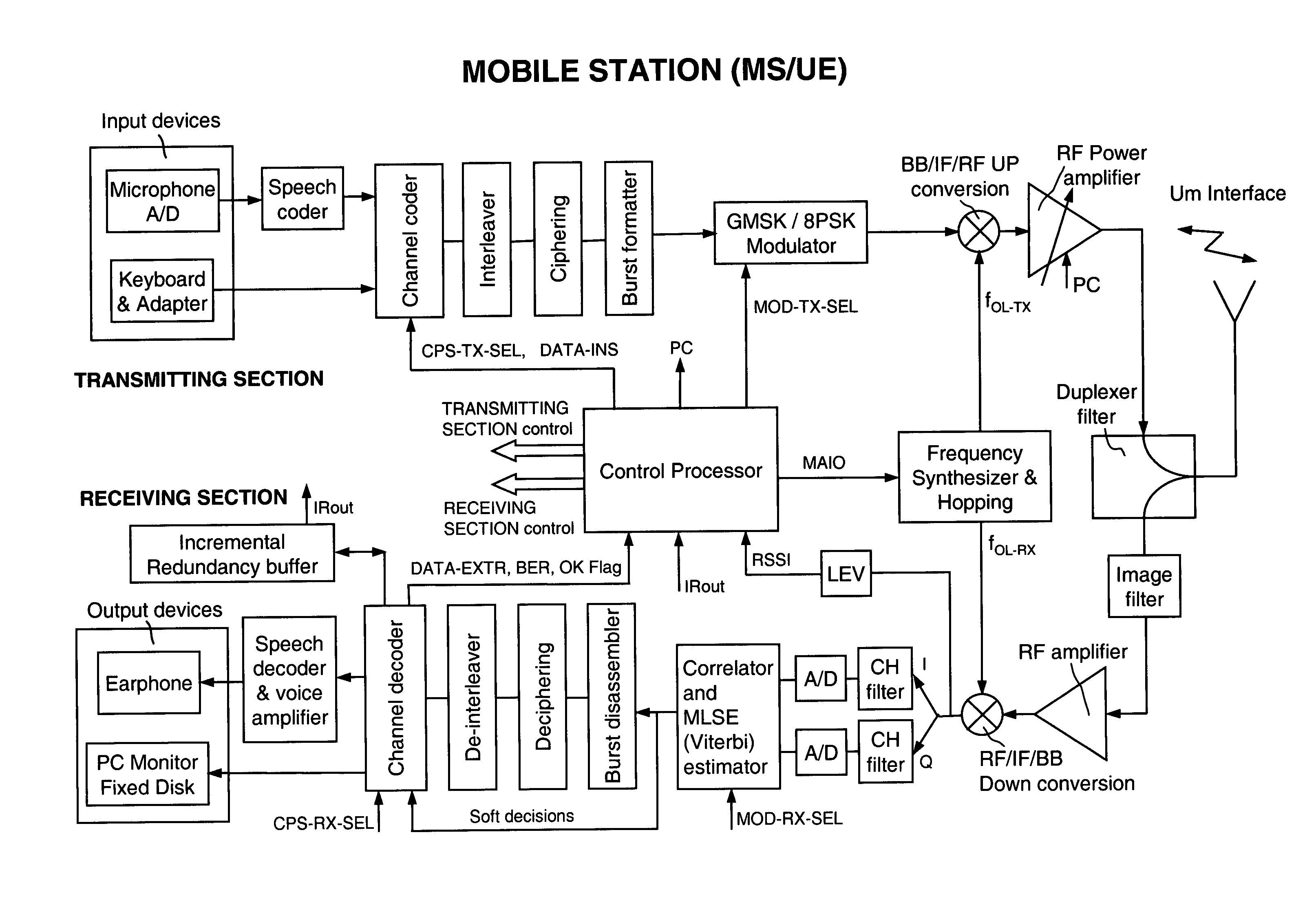
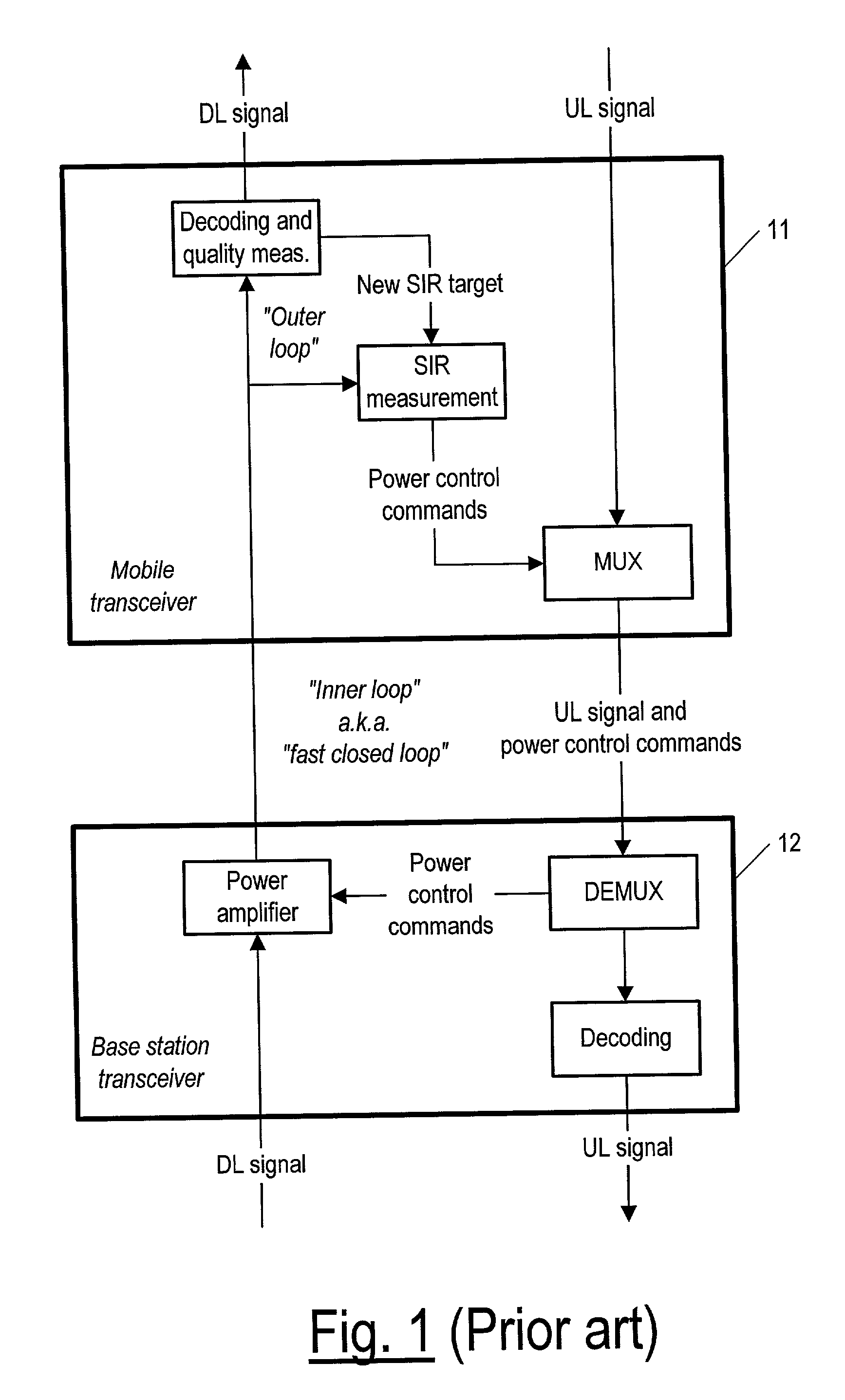
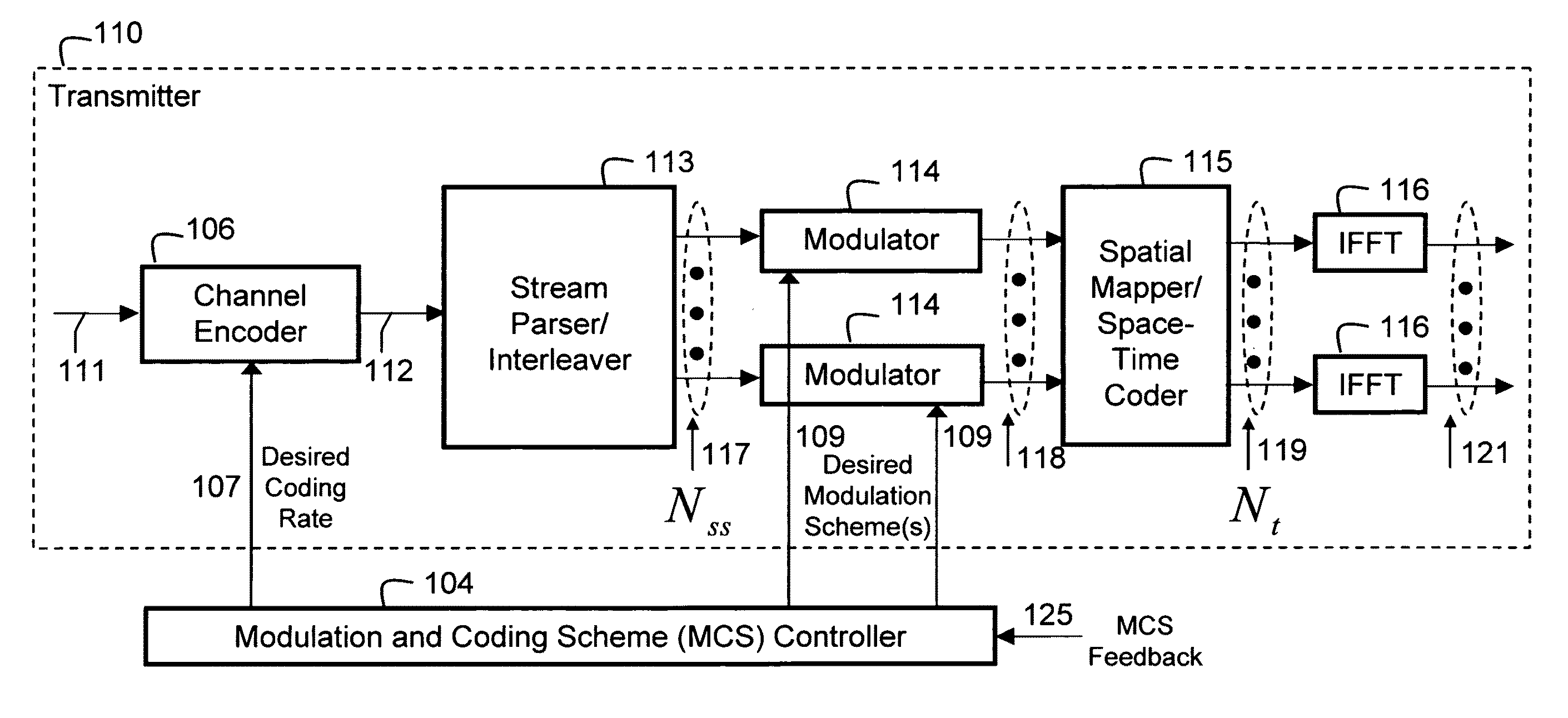
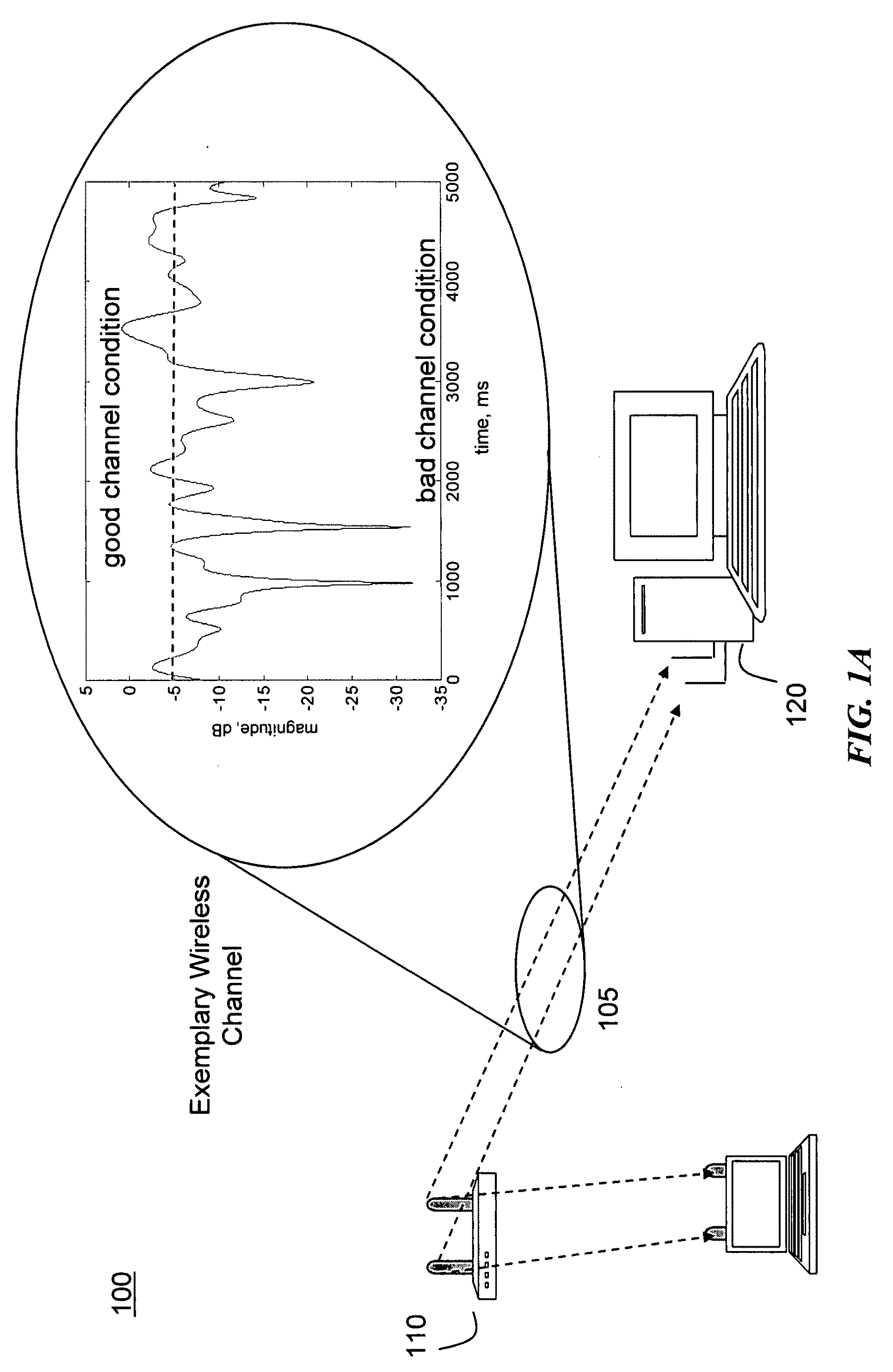
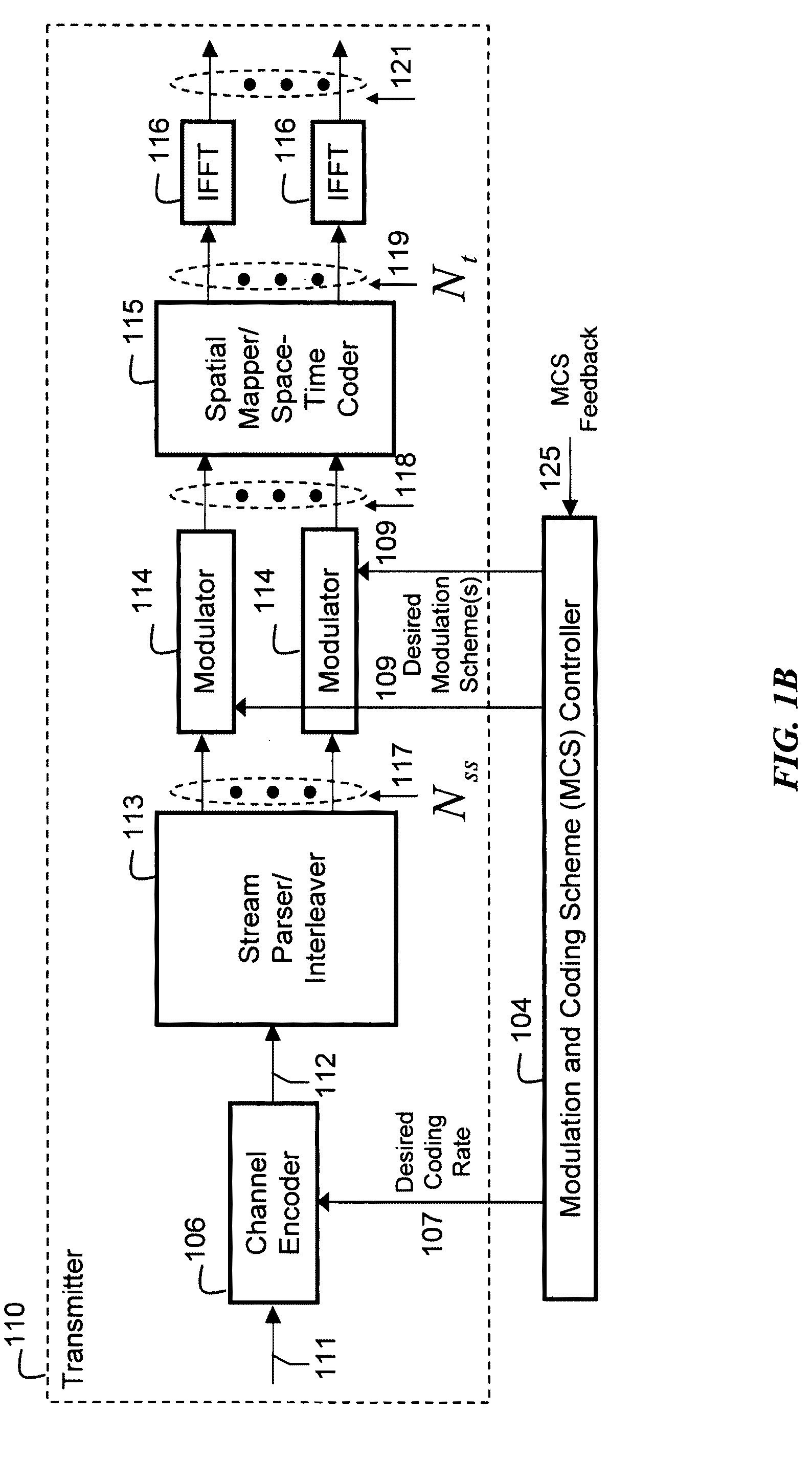
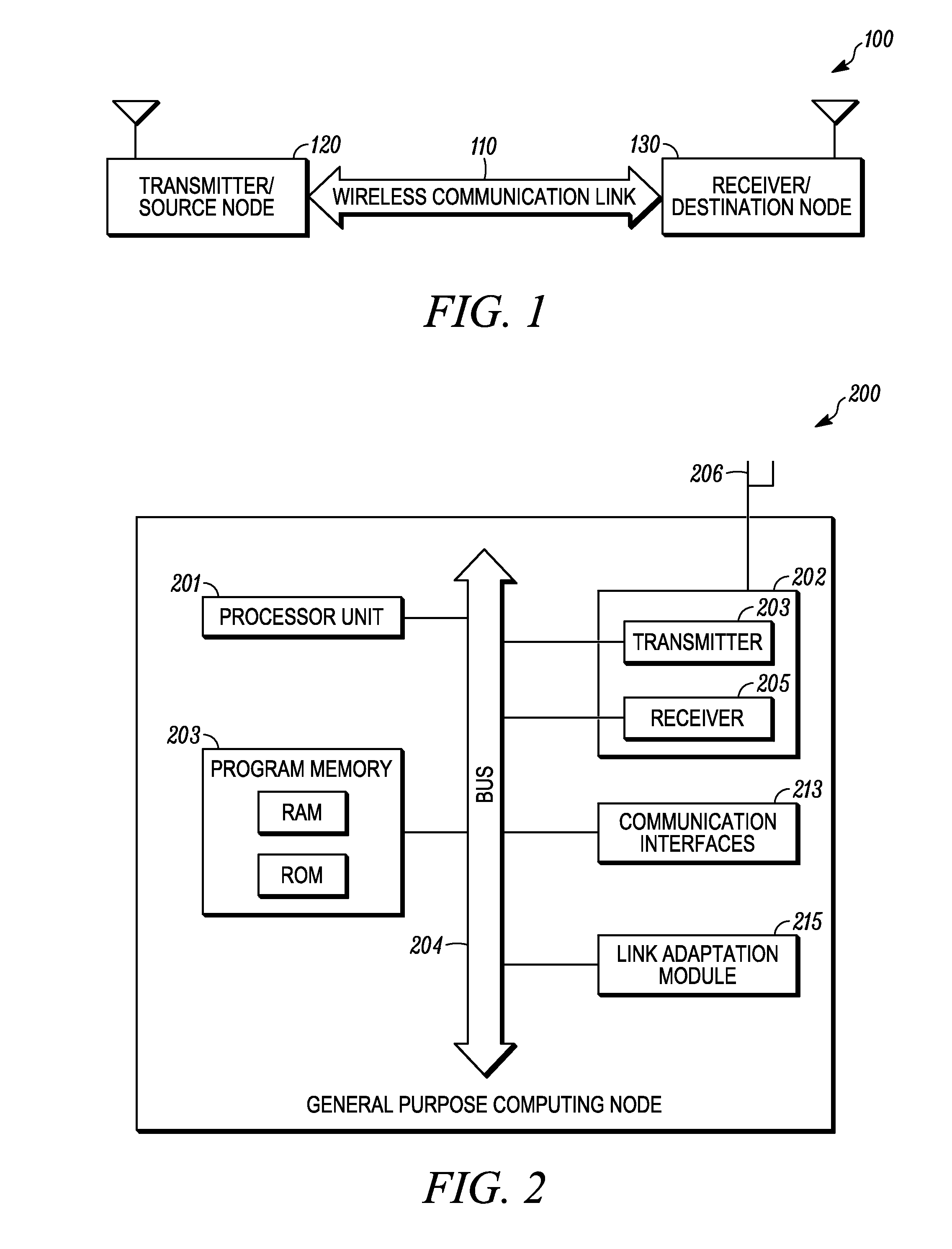
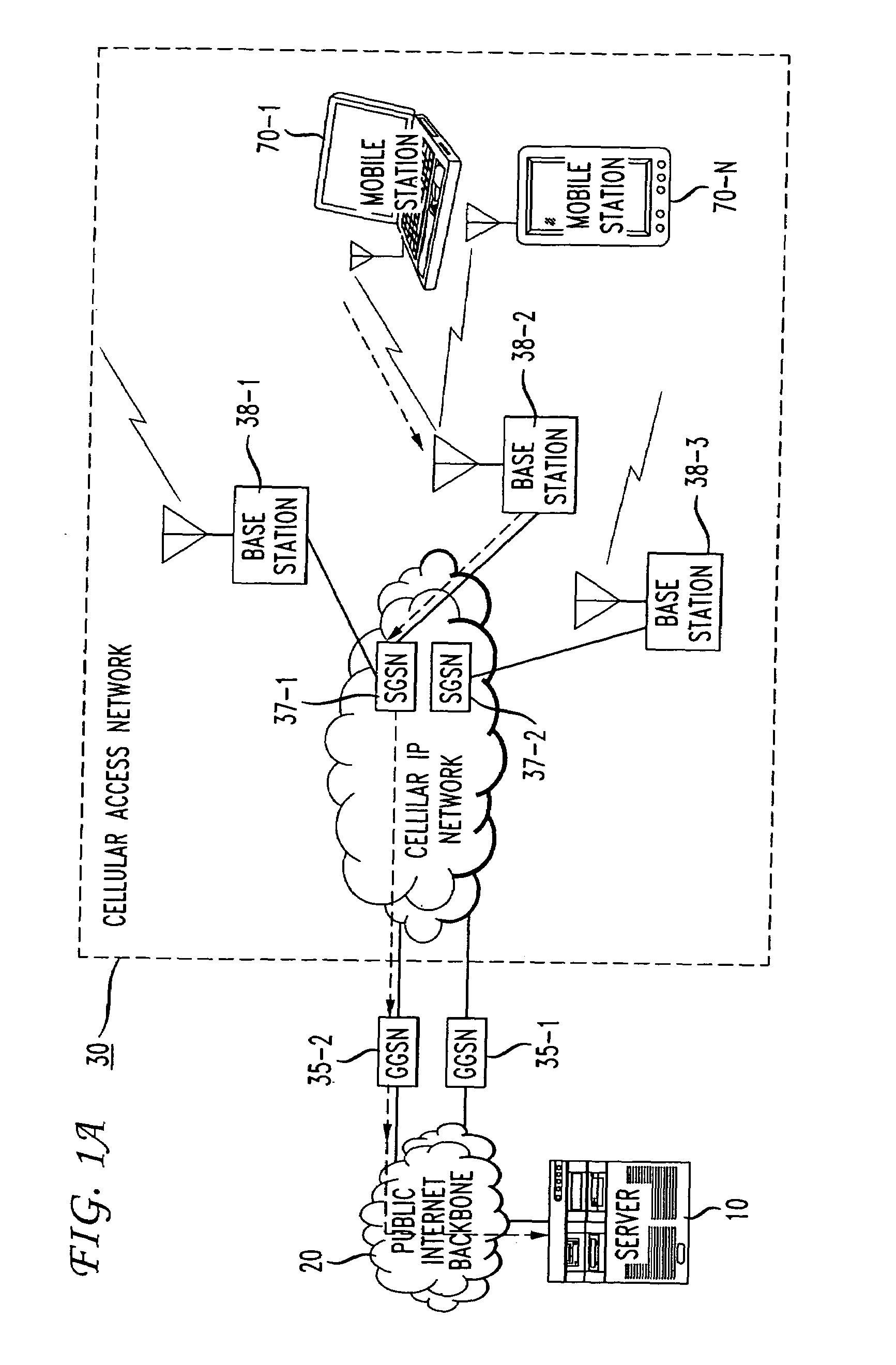
Link adaptation, or adaptive coding and modulation (ACM), is a term used in wireless communications to denote the matching of the modulation, coding and other signal and protocol parameters to the conditions on the radio link (e.g. the pathloss, the interference due to signals coming from other transmitters, the sensitivity of the receiver, the available transmitter power margin, etc.). For example, WiMAX uses a rate adaptation algorithm that adapts the modulation and coding scheme (MCS) according to the quality of the radio channel, and thus the bit rate and robustness of data transmission. The process of link adaptation is a dynamic one and the signal and protocol parameters change as the radio link conditions change—for example in High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) in Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) this can take place every 2 ms.
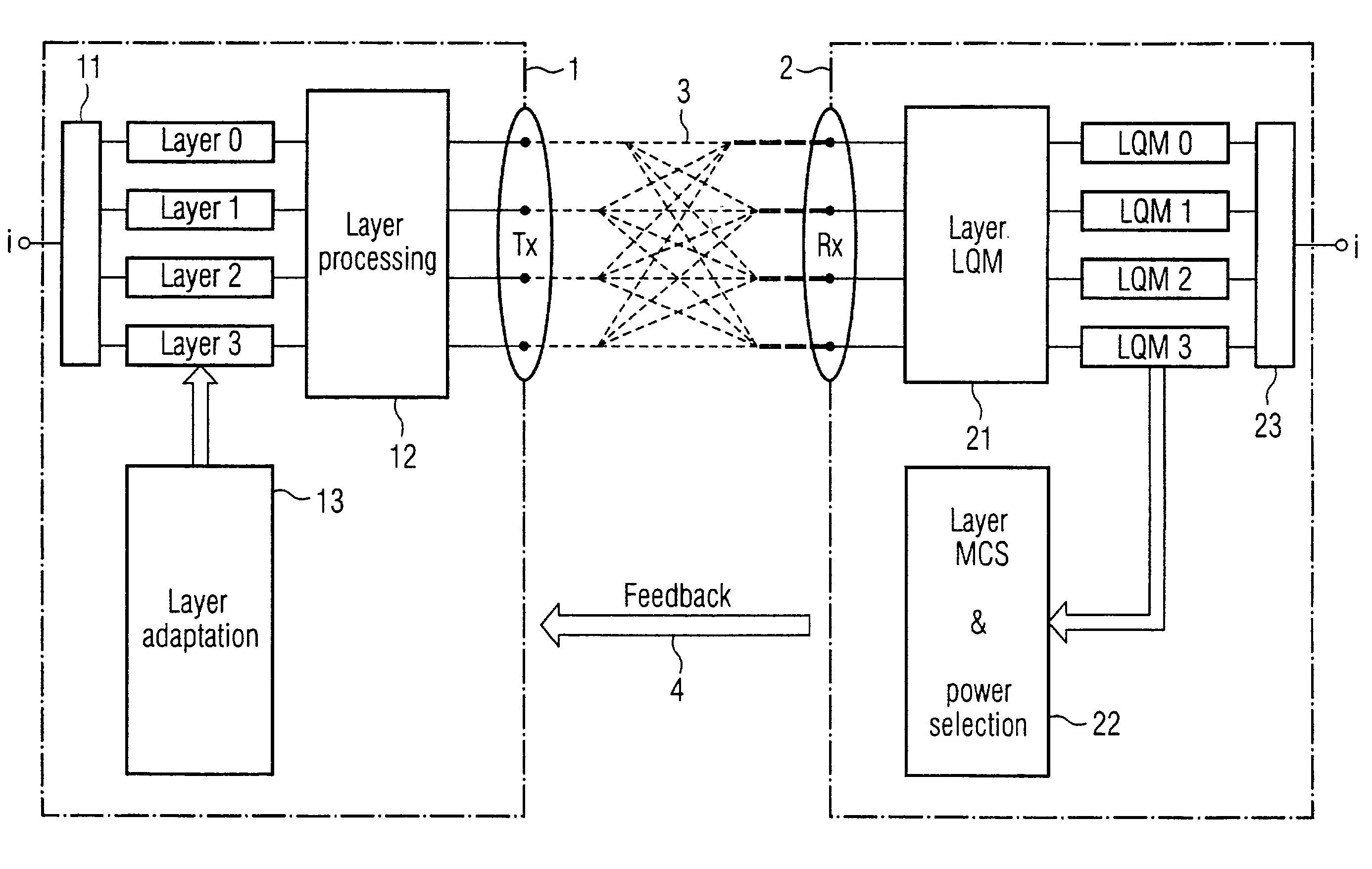
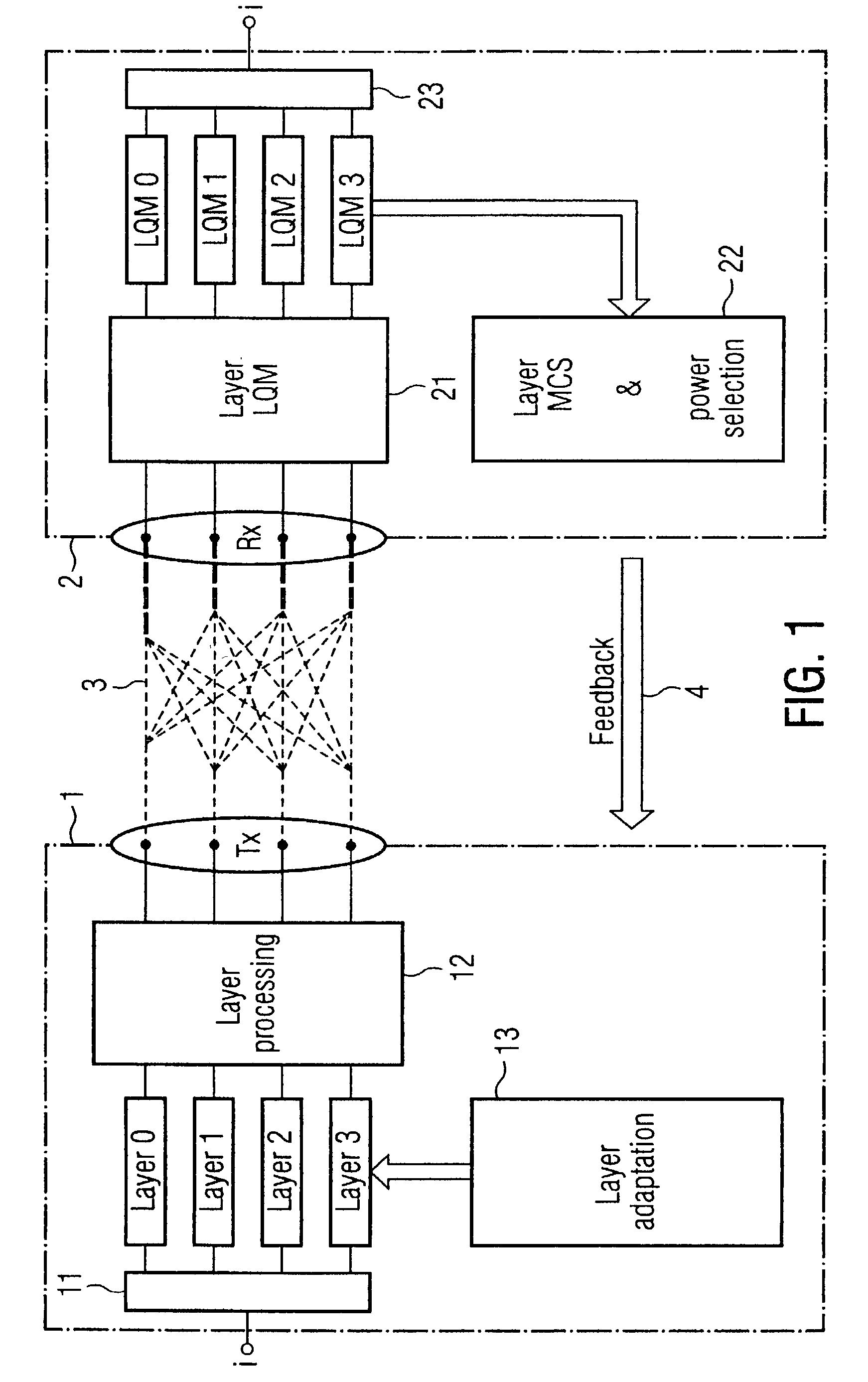
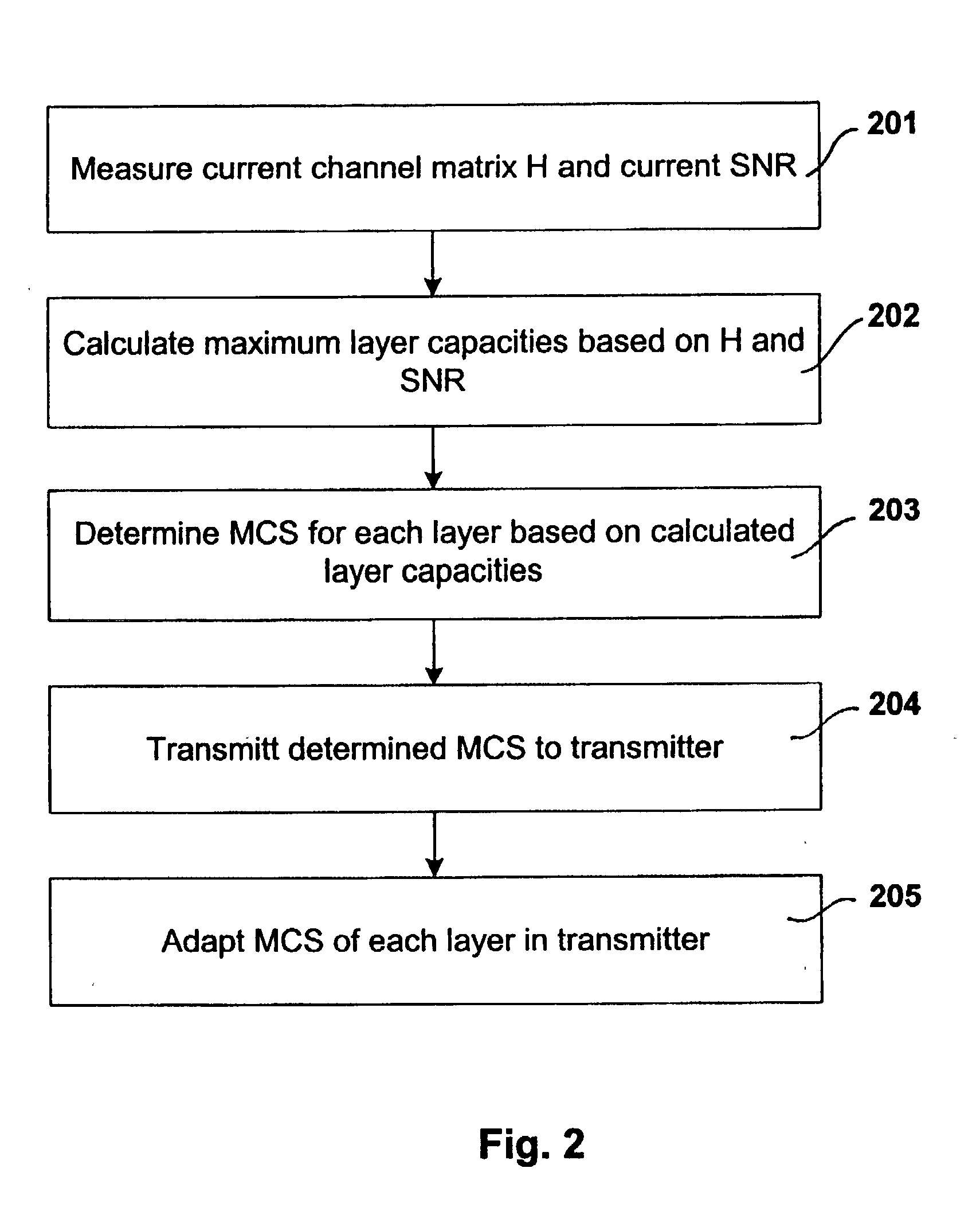
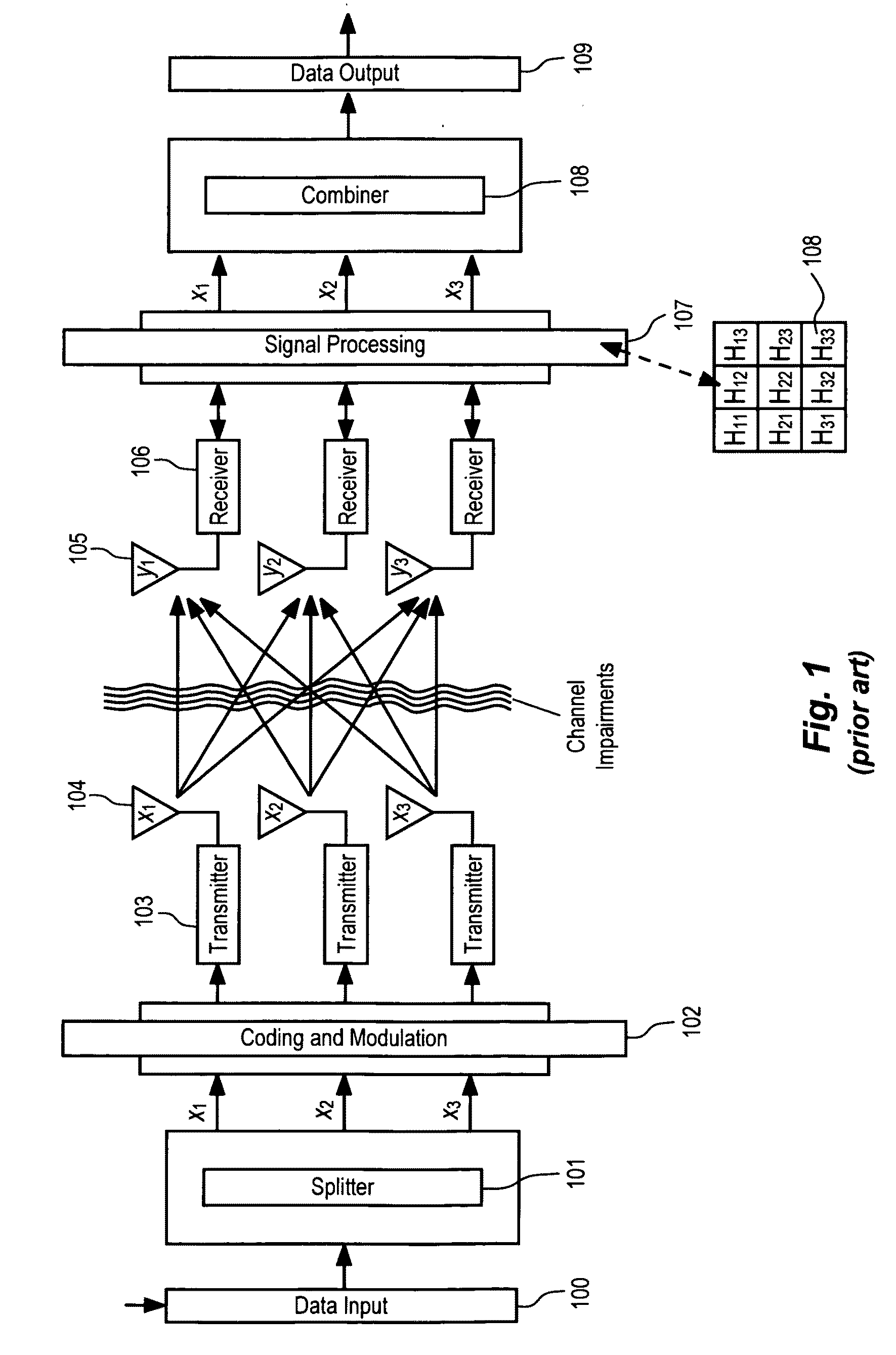
Link adaptation for MIMO transmission schemes
ActiveUS20030003863A1Reduce in quantitySmall rateError prevention/detection by using return channelSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemMimo transmission
MIMO transmission methods are applied to communicaiton systems in which a transmitter has more than one transmit antenna and a receiver has more than one receive antenna. Information to be transmitted is divided into a plurality of subsignals according to the number of used transmit antennas and each subsignal is processed separately before it is emitted by the respective transmit antenna. In the receiver the different receive signals are processed thus that subsignals are detected and decoded and the contribution of each detected and decoded subsignal is subtracted from the receive signals and whereby a feedback channel from receiver to transmitter is used to send control information to the transmitter depending on the receive situation. In order to optimize the usage of the MIMO channel the invention proposes the in the receiver the link quality of each subsignal is determined and information of each subsignal is transmitted to the receiver via the feedback channel and that in the transmitter properties of the subsignals are controlled by the link quality information.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
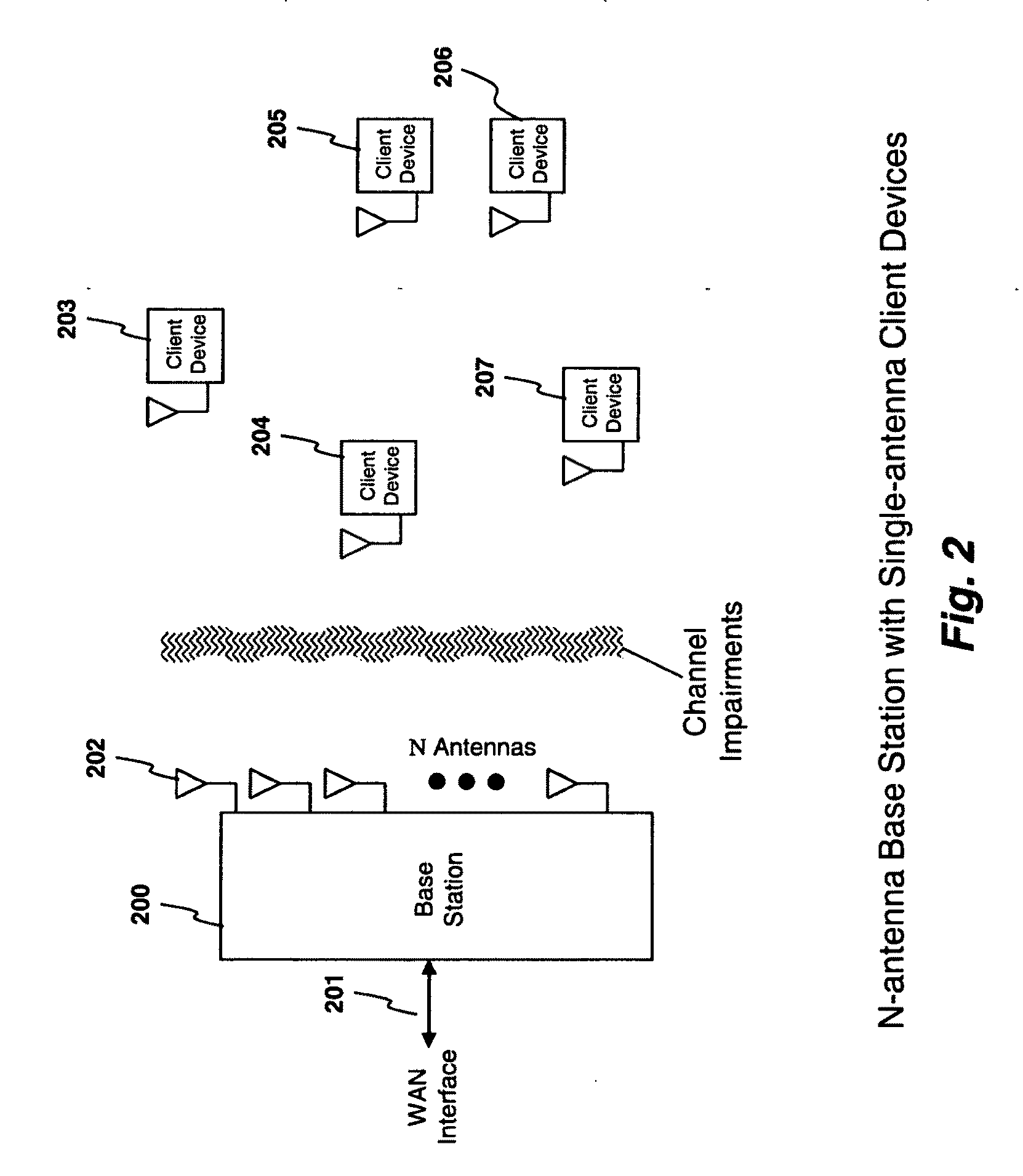
Interference management, handoff, power control and link adaptation in distributed-input distributed-output (DIDO) communication systems
ActiveUS20110003607A1Reduce distractionsImprove downlink throughputDiversity/multi-antenna systemsTransmission noise suppressionPrecodingCommunications system
A system and method are described herein employing a plurality of distributed transmitting antennas to create locations in space with zero RF energy. In one embodiment, when M transmit antennas are employed, it is possible to create up to (M−1) points of zero RF energy in predefined locations. In one embodiment of the invention, the points of zero RF energy are wireless devices and the transmit antennas are aware of the channel state information (CSI) between the transmitters and the receivers. In one embodiment, the CSI is computed at the receivers and fed back to the transmitters. In another embodiment, the CSI is computed at the transmitter via training from the receivers, assuming channel reciprocity is exploited. The transmitters may utilize the CSI to determine the interfering signals to be simultaneously transmitted. In one embodiment, block diagonalization (BD) precoding is employed at the transmit antennas to generate points of zero RF energy.
Owner:REARDEN
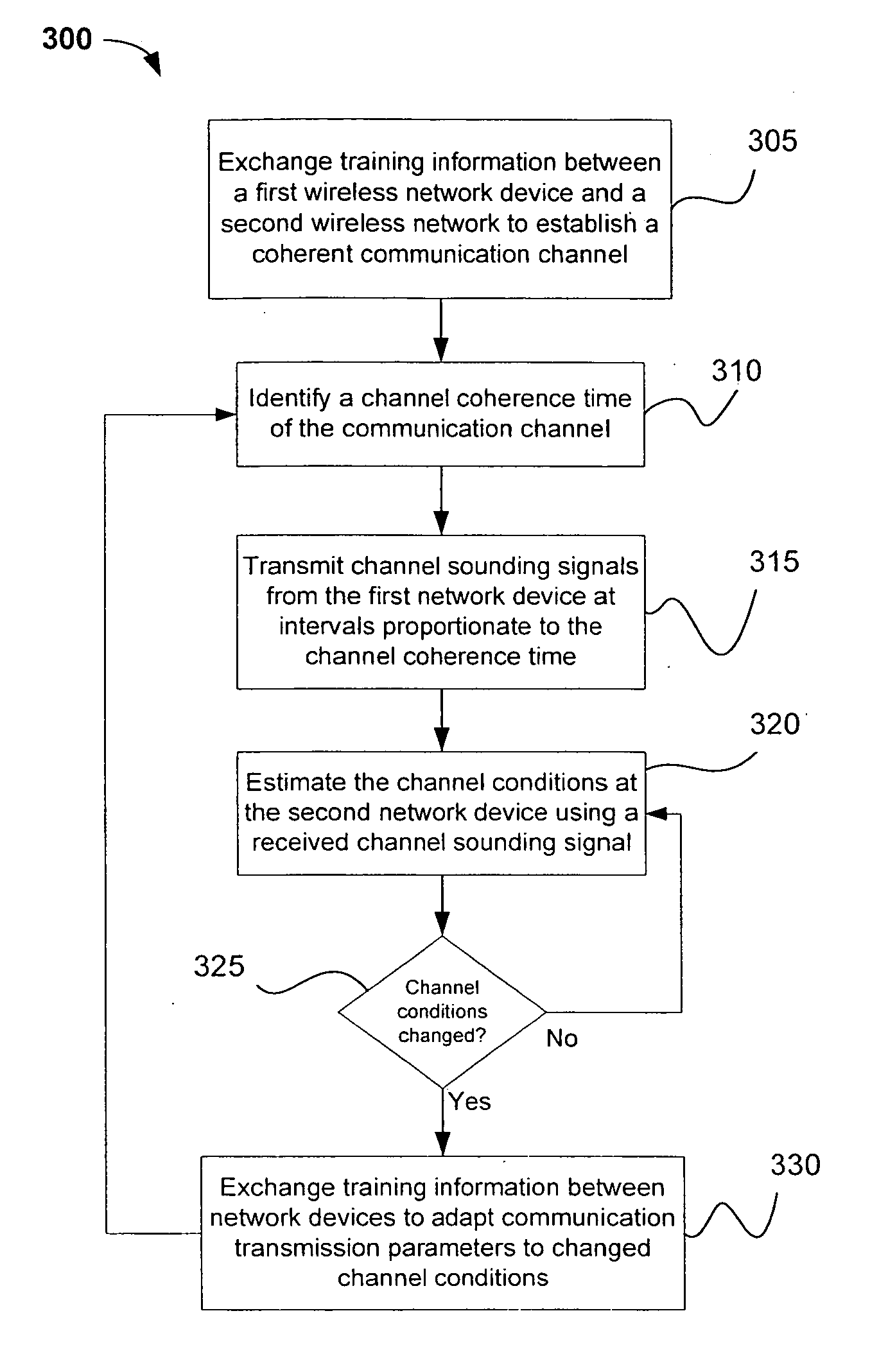
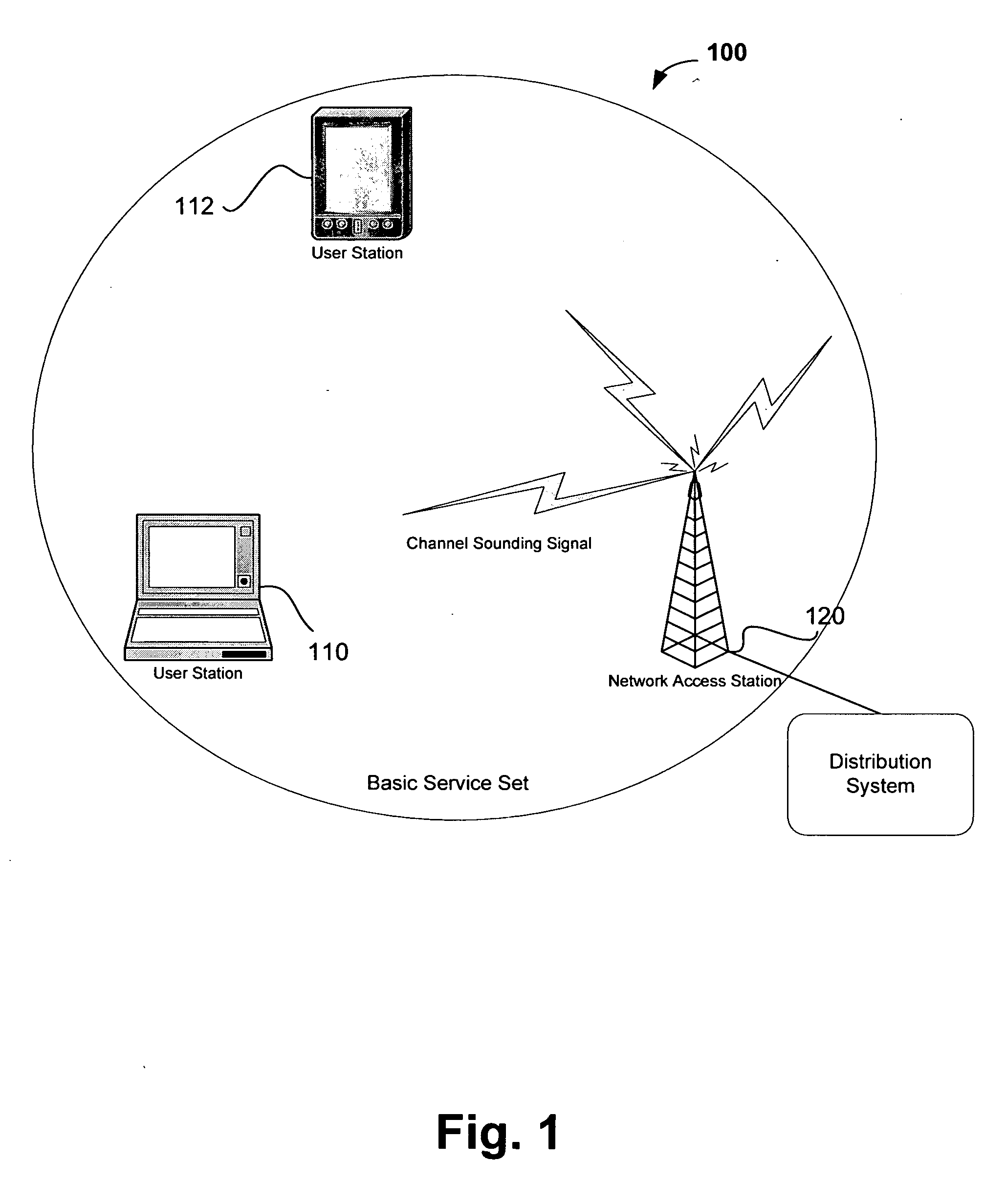
Channel adaptation using variable sounding signal rates
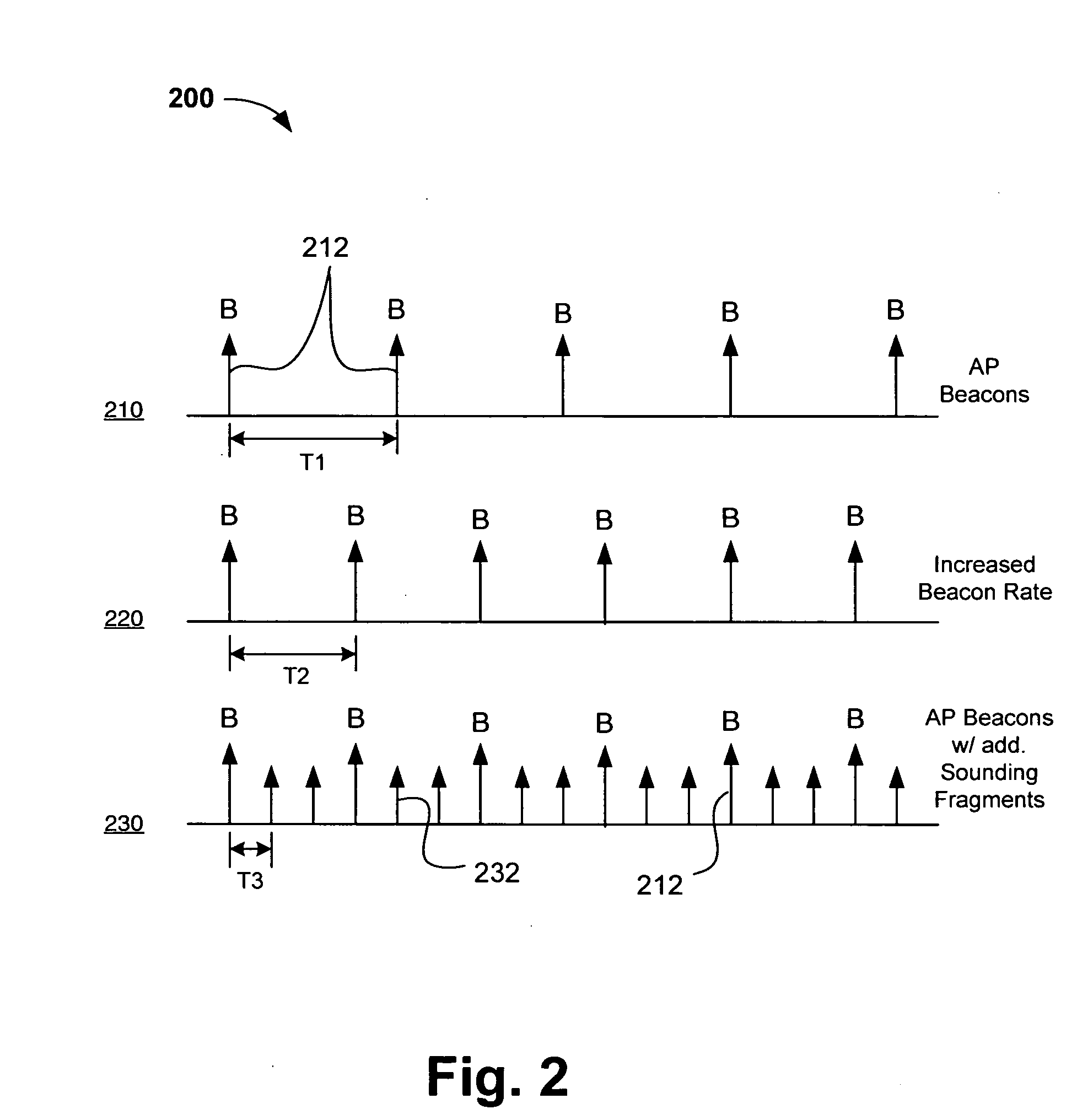
InactiveUS20050170781A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsCoherence timeLink adaptation
Systems, devices and methods for updating link adaptations in multi-carrier modulated signals between an access point (AP) and a wireless local area network (WLAN) station (STA) include (are configured for) periodically transmitting a channel sounding signal from the AP. The STA receives each unsolicited channel sounding signal and evaluates the current channel conditions between the AP and STA. The AP adjusts a rate of transmission of the channel sounding signals in accordance with the channel coherence time so that the channel estimates performed by the STA will be valid within the time varying characteristics of the channel. Depending on the length of the coherence time for network environment, the channel sounding signals may be AP beacons, low overhead signal fragments with no payload, or a combination of both.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dynamic radio link adaptation
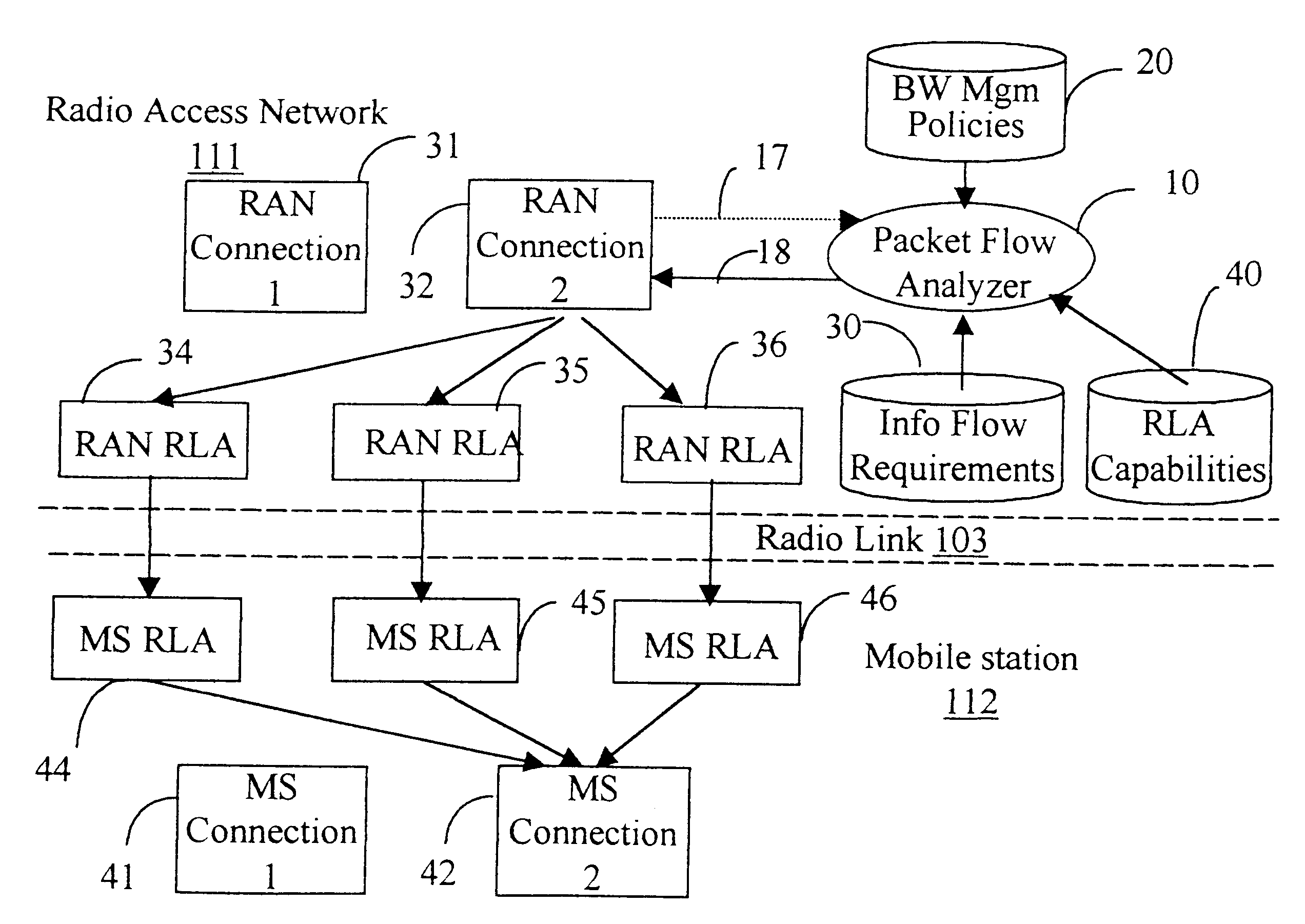
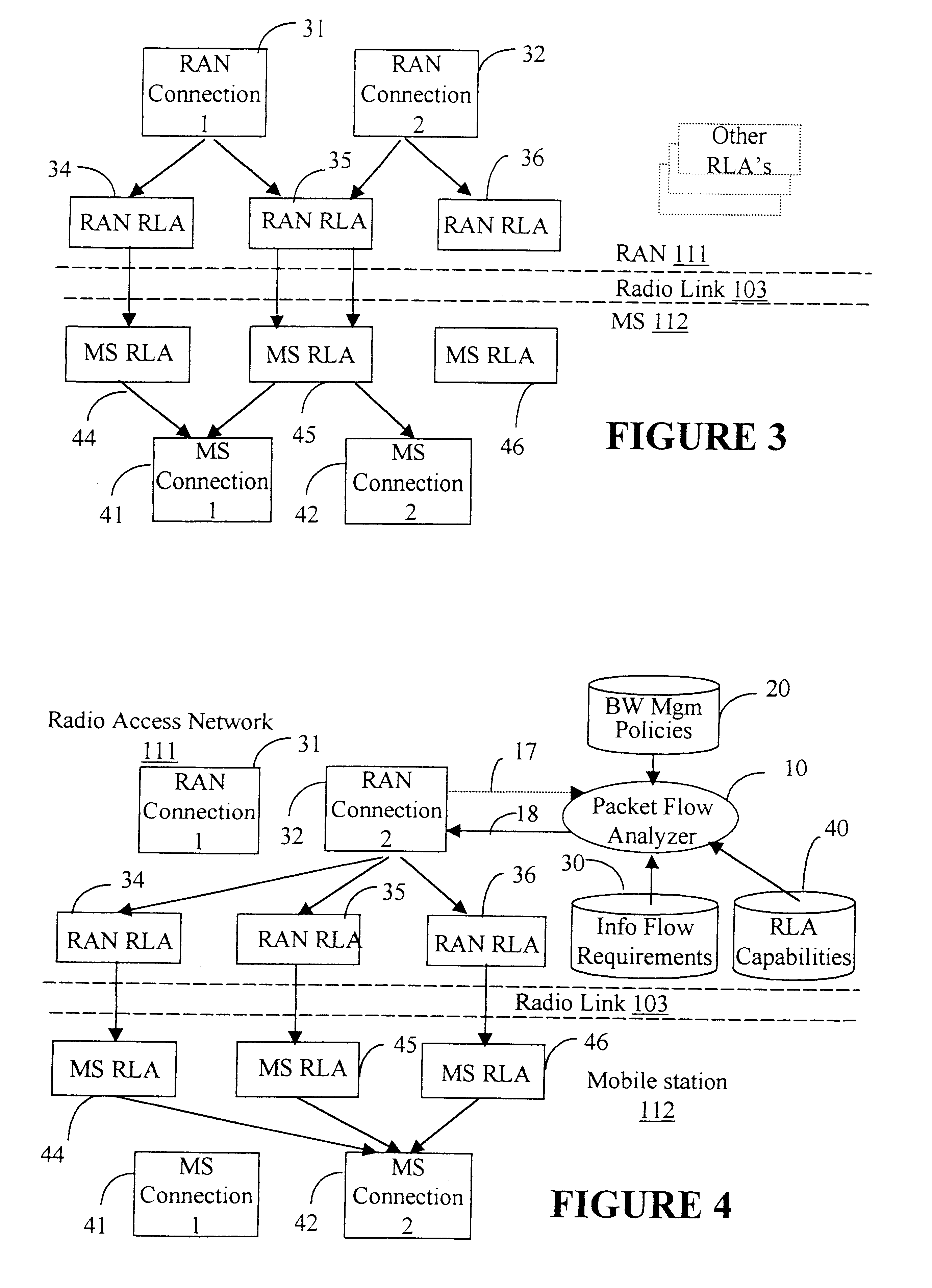
InactiveUS6515972B1Network traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexQuality of serviceAccess network
A radio link adapter for wireless transmission of multimedia data through a communication link between a radio access network (RAN) and a mobile station (MS), is provided. The information flow is constantly monitored to determine an information element (IE) type of service requirements and for allocating paired radio link adapters (RLAs) designed to fit the respective type of service requirements. A connection end may be initially established in the RAN or in the MS. An analyser monitors the link, detects the type of service (ToS) required, and dynamically allocates the appropriate type of RLA to the connection. There is no need to recreate the connection when selecting the adapter for transporting various types of services and therefore, the transport of the information flow of a specific ToS over the communication link is optimized, while maintaining the end-to-end quality of service (QoS).
Owner:APPLE INC
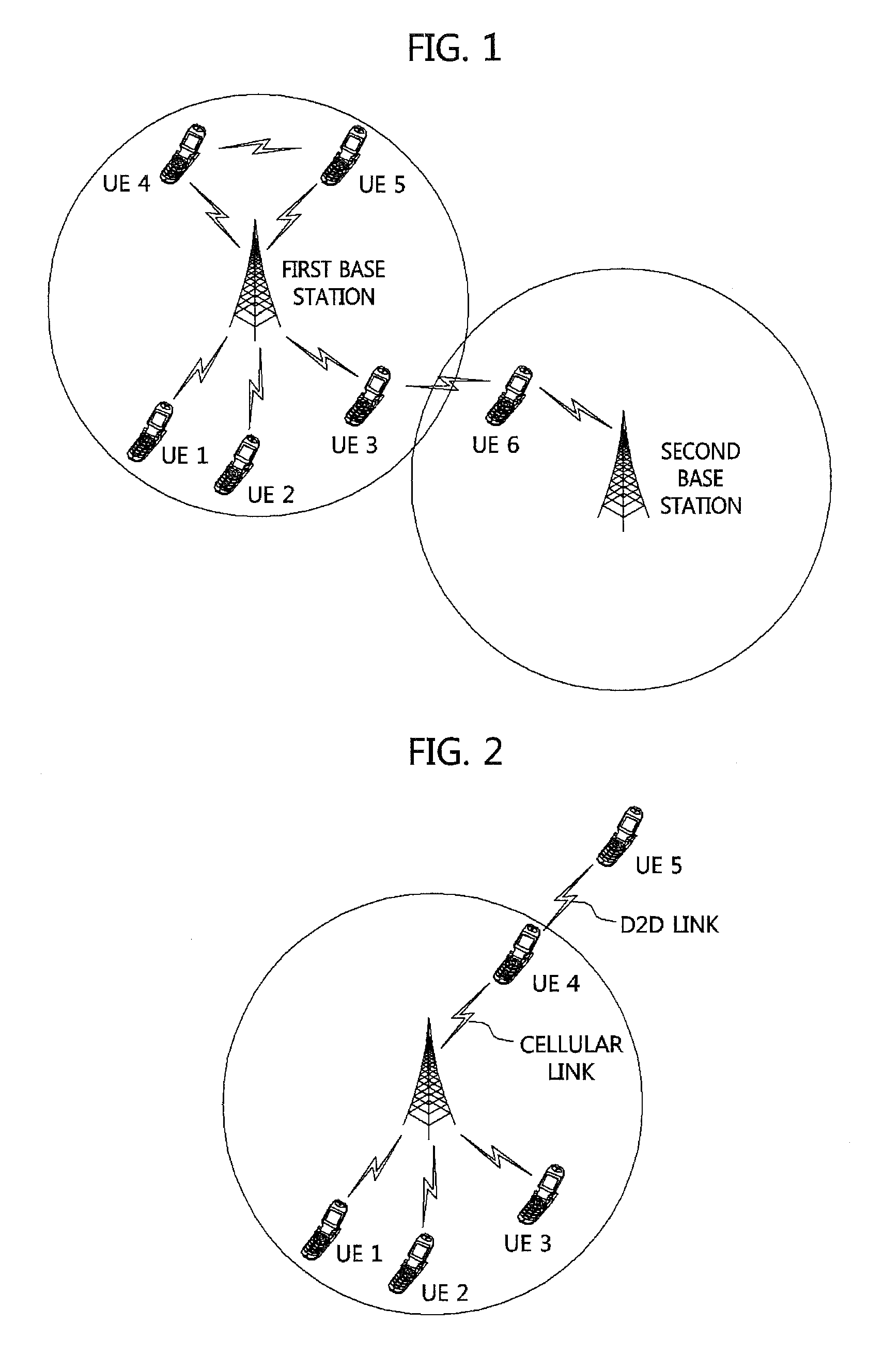
Device to device communication method using partial device control
ActiveUS20150078279A1Efficient executionPower managementReceivers monitoringLink adaptationResource allocation
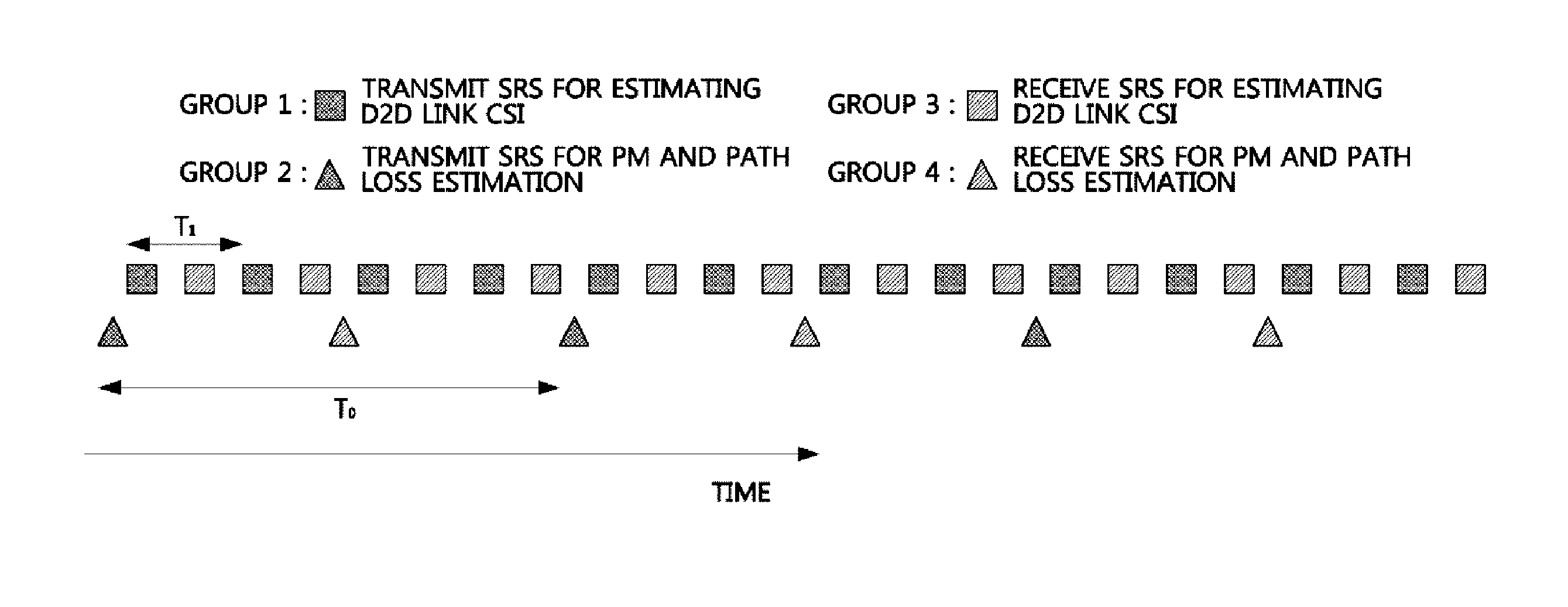
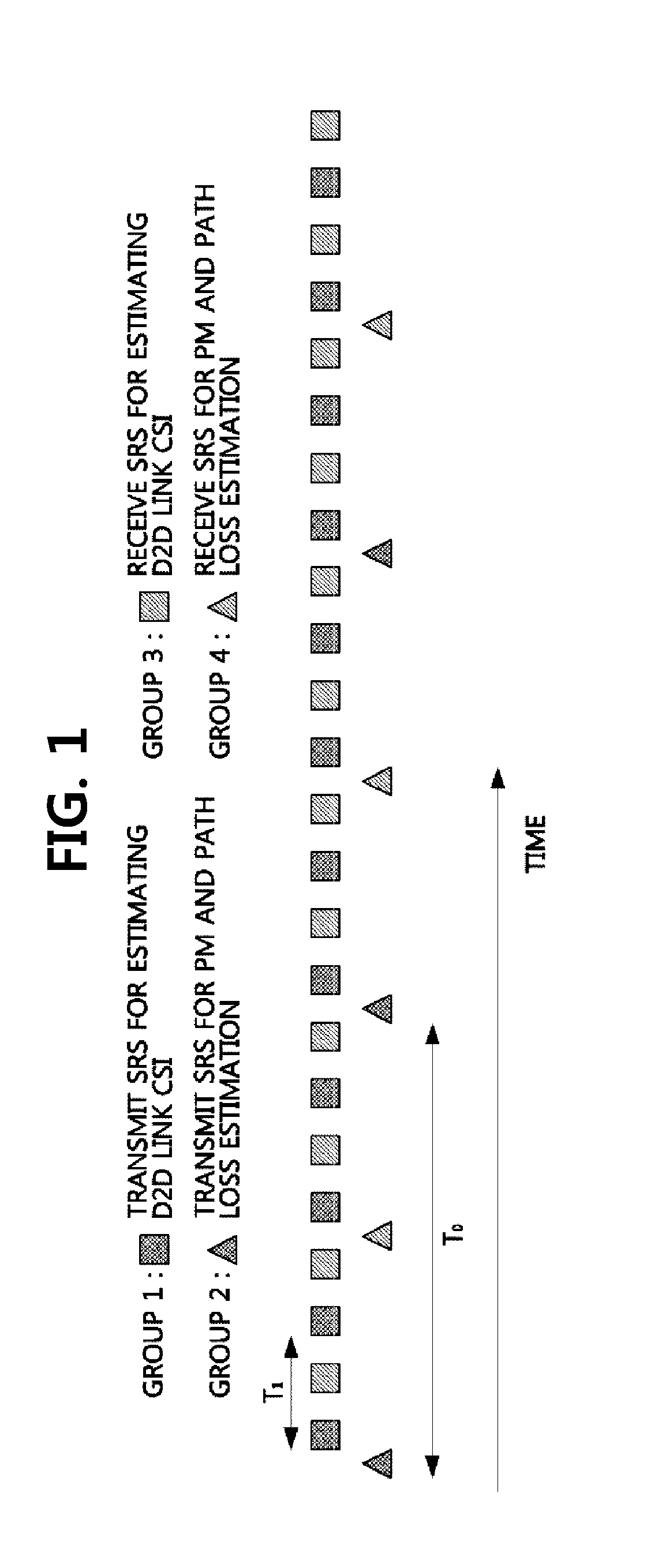
A device to device (D2D) communication method based on a partial device control is disclosed. According to the present invention, the D2D communication method and, particularly, to a partial device control method for D2D communication a relates to, and provides a D2D resource allocation and release method, a D2D HARQ process operating method, a link adaptation method comprising D2D link power control and adaptive modulation and coding (AMC), a D2D control information signaling method, a CSI reporting method for D2D communication, and contents of a CSI report. The present invention can enhance the advantages of and compensate for the disadvantages of both methods through the combination of a base station control a base station control type D2D communication method and a device control type D2D communication method.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
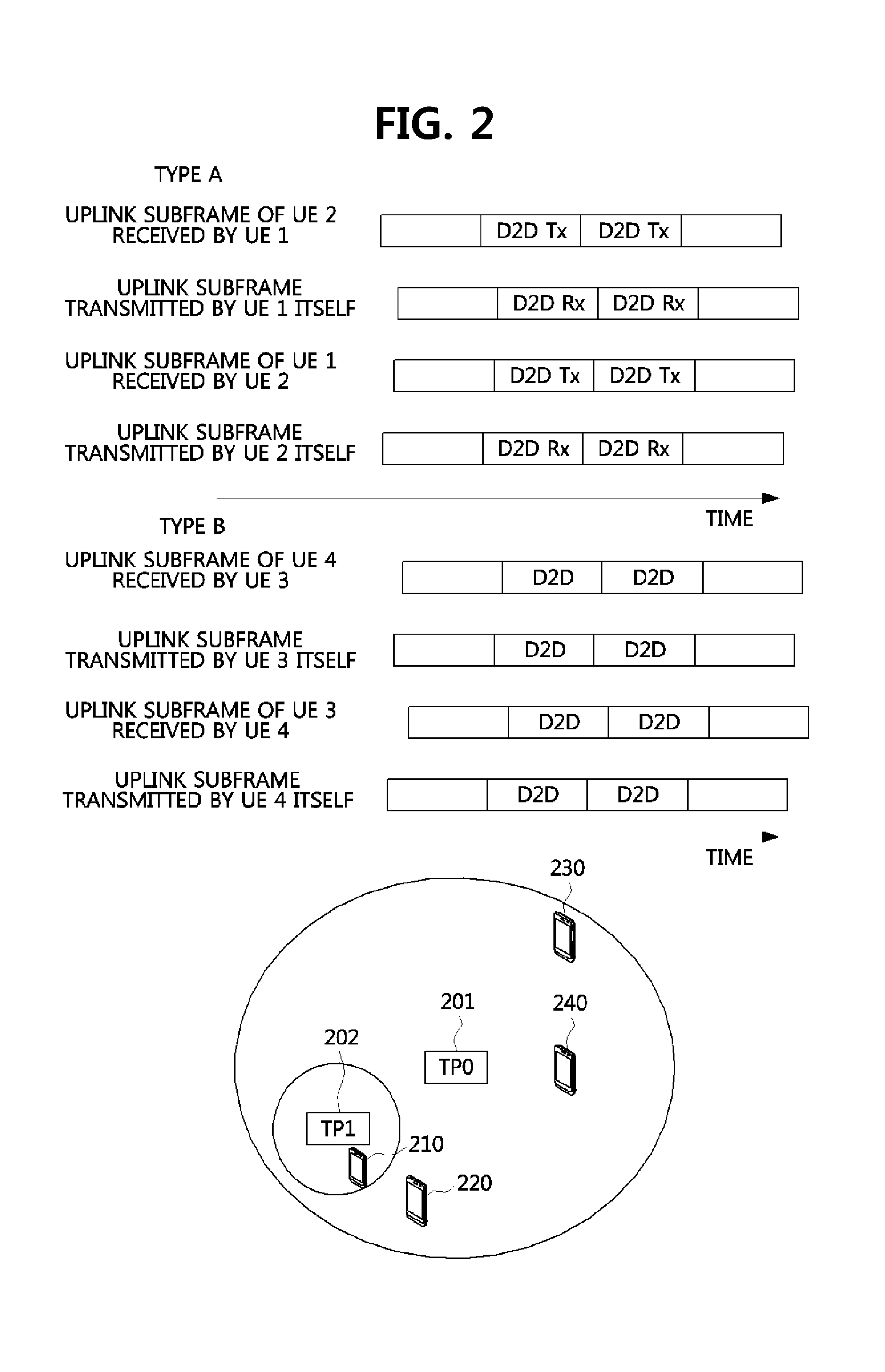
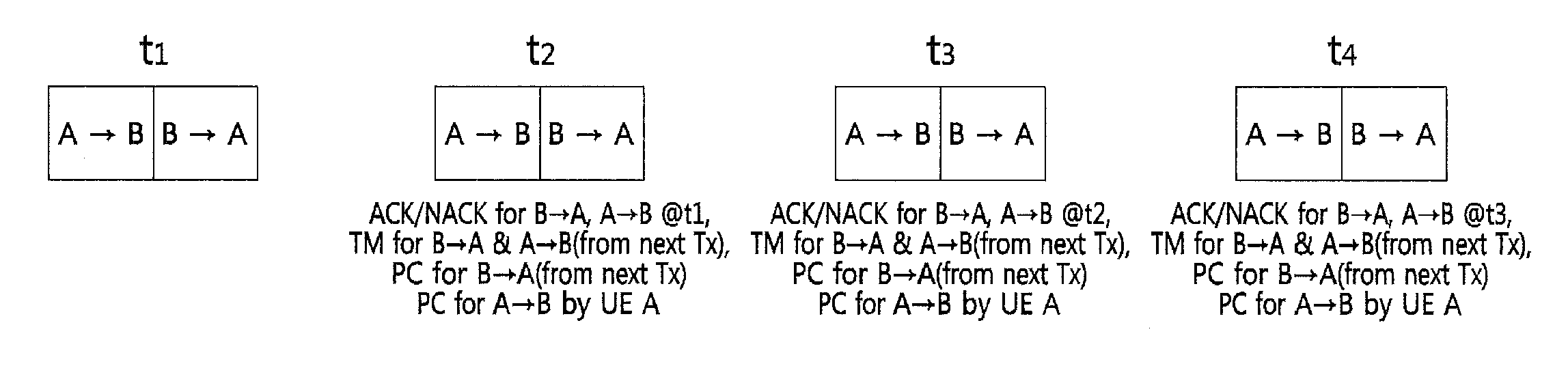
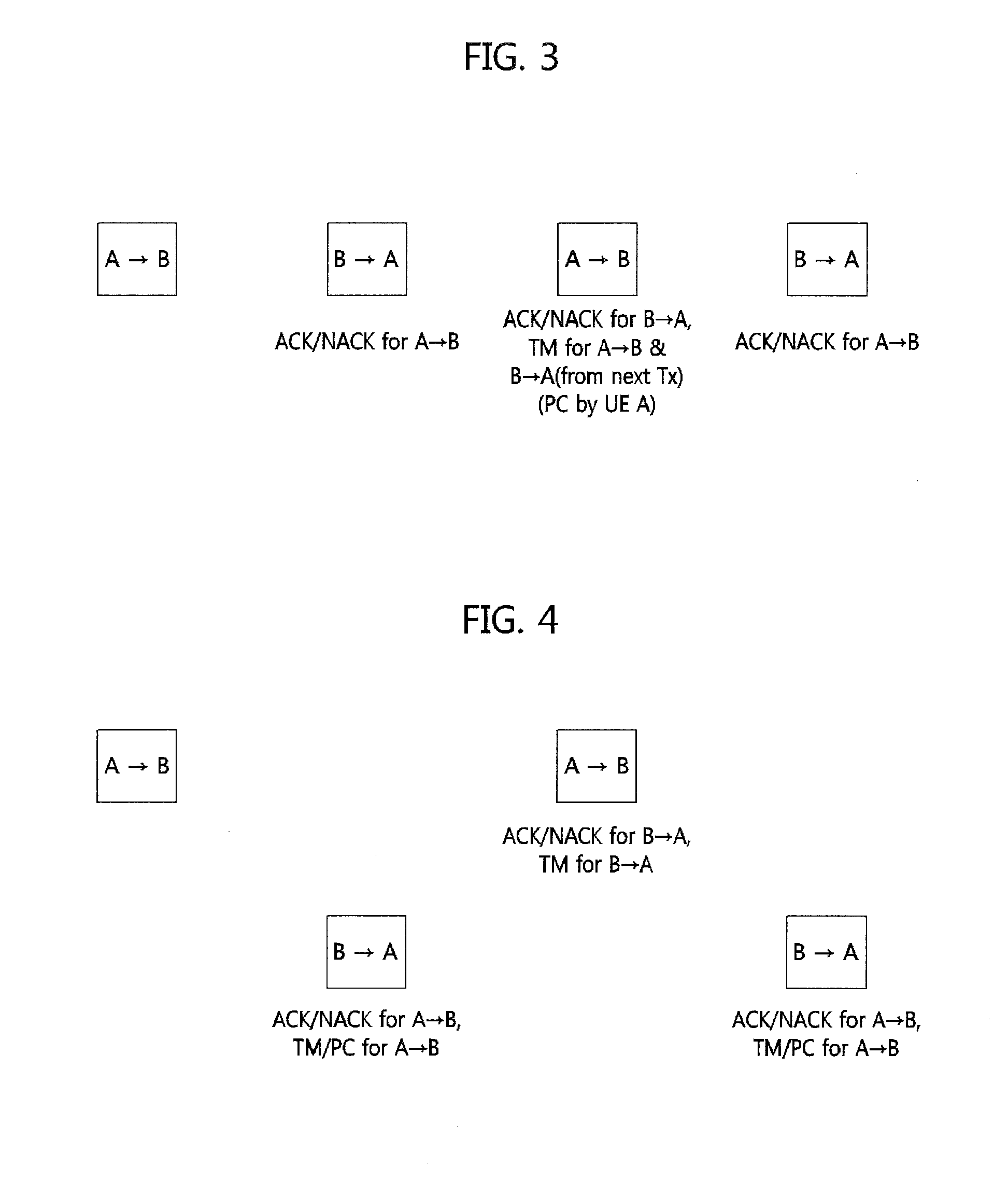
Method for HARQ and link adaptation of device to device link in direct communication between user equipments and relaying by user equipment
Provided is a method of processing hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) and adaptive transmission of a device-to-device (D2D) link. In the method, an operation method of user equipment (UE) includes (a) receiving an initial transmission mode (TM) and transmission power for the D2D link from a base station, and performing data transmission through the D2D link, (b) determining, at the UE, a TM and transmission power of a succeeding subframe, or receiving a TM control value and a transmission power control value from counterpart UE of the D2D link and determining the TM and the transmission power of the succeeding subframe, and (c) performing the data transmission to the counterpart UE using the determined TM and transmission power. Here, (b) and (c) are repeated.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
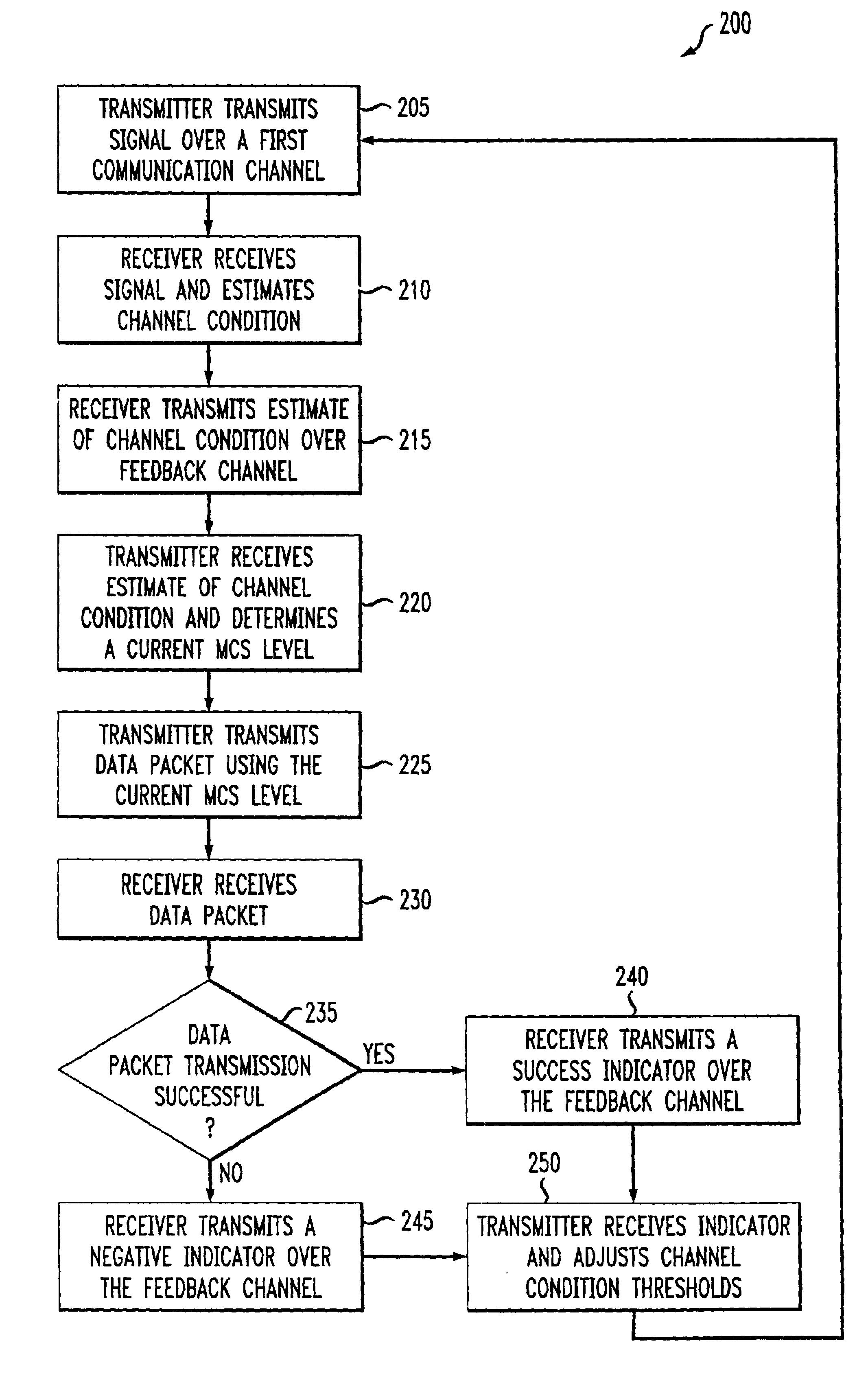
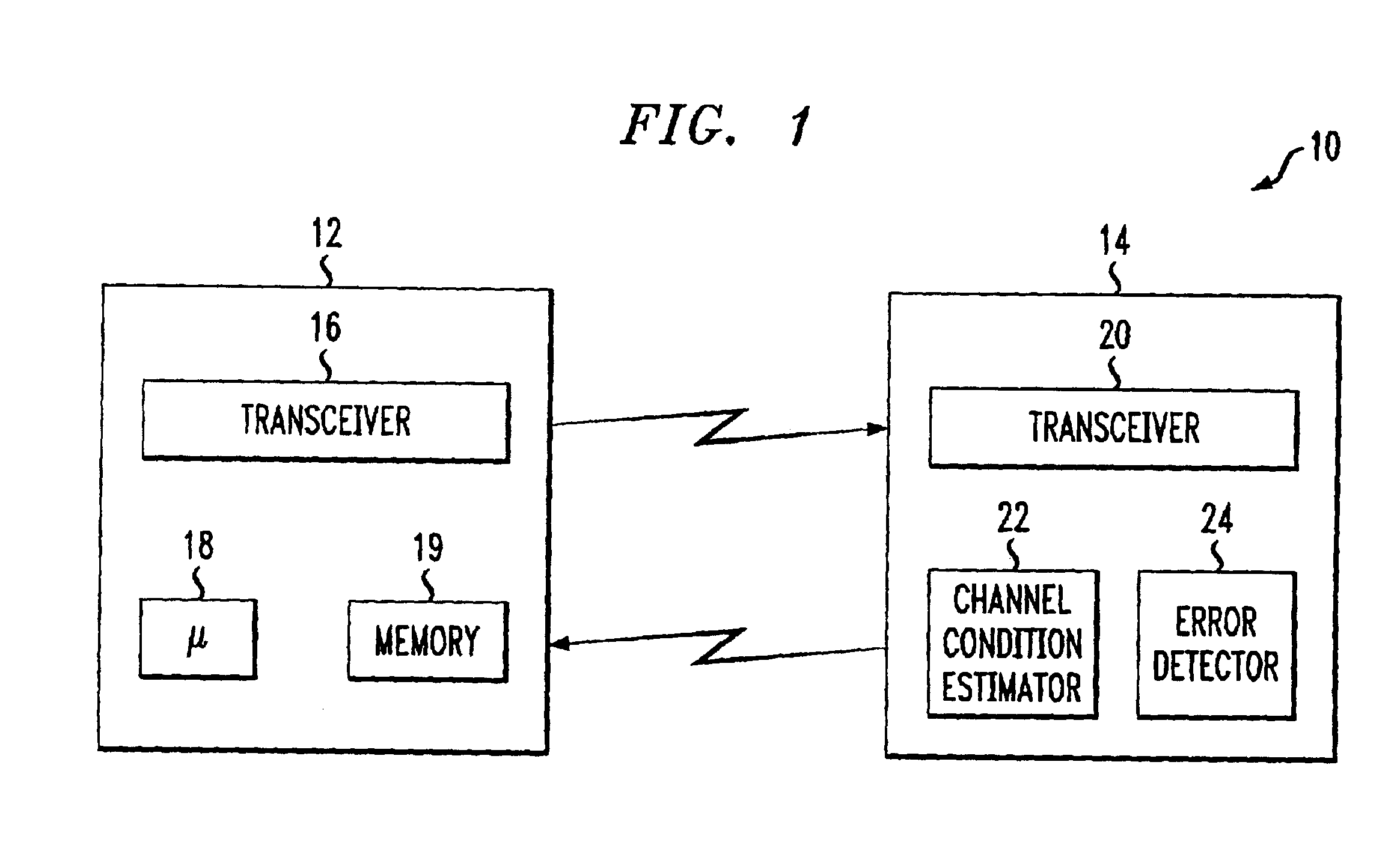
Delay sensitive adaptive quality control loop for rate adaptation
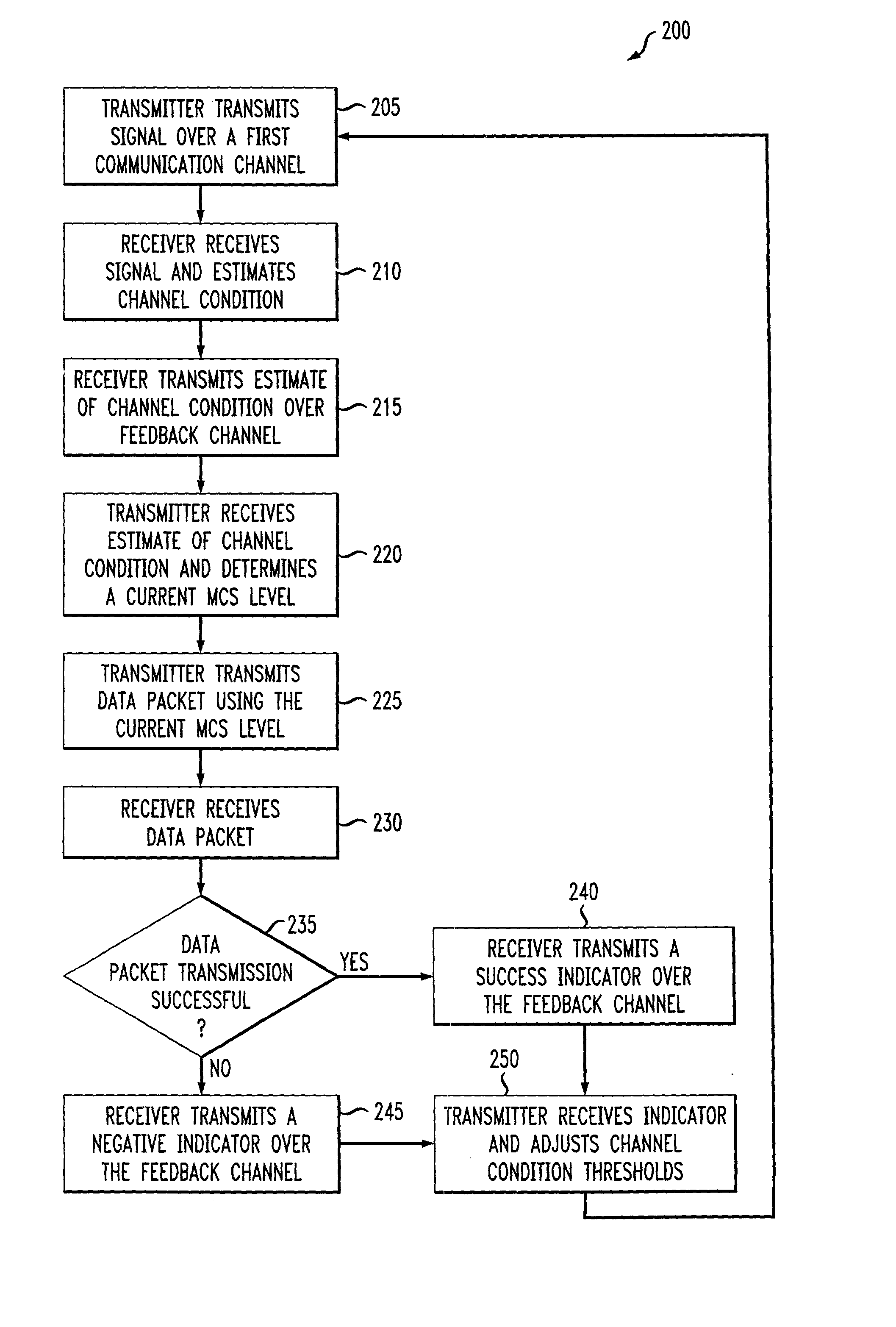
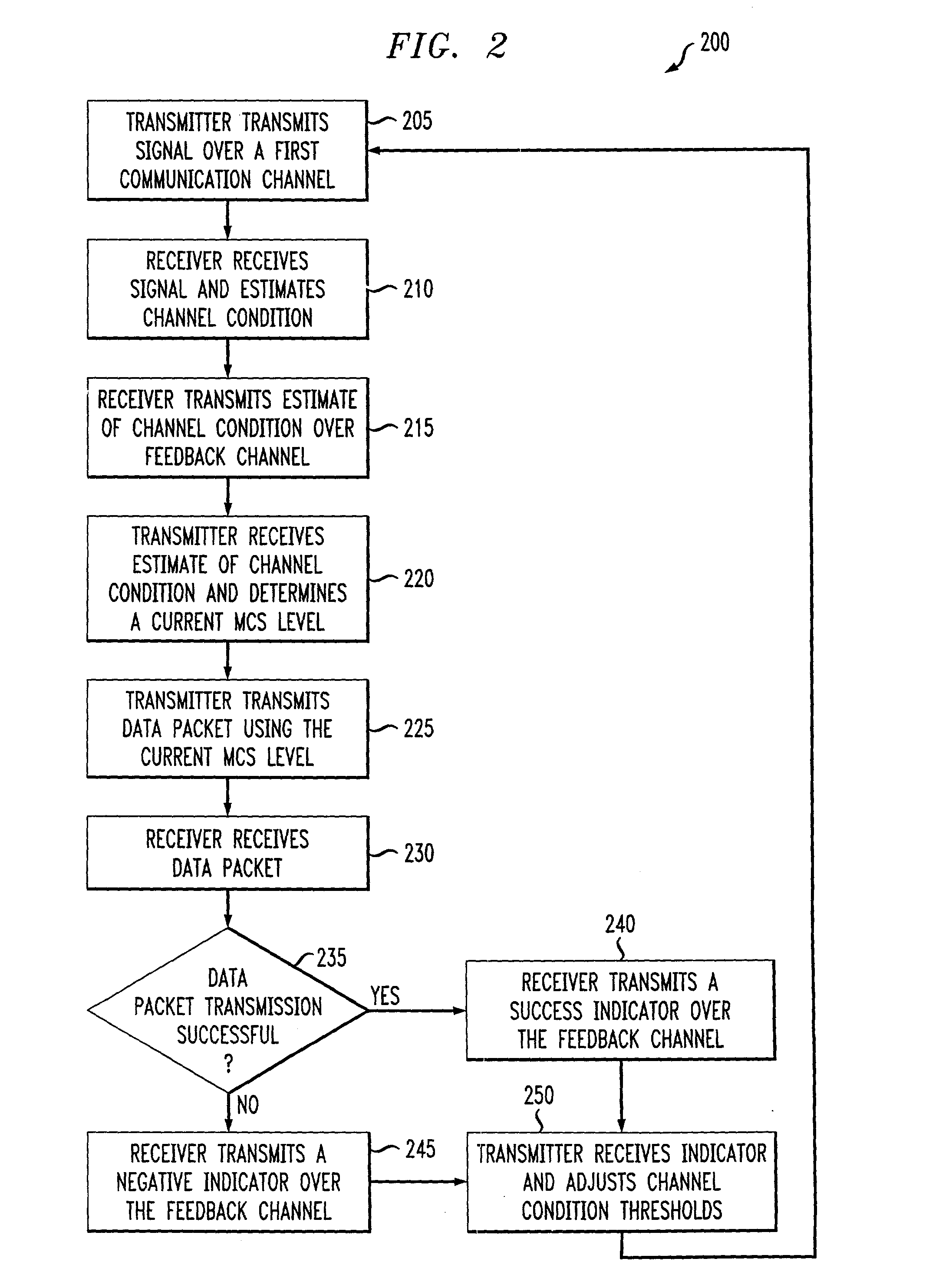
InactiveUS6915477B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelMultiple-port networksCommunications systemRate adaptation
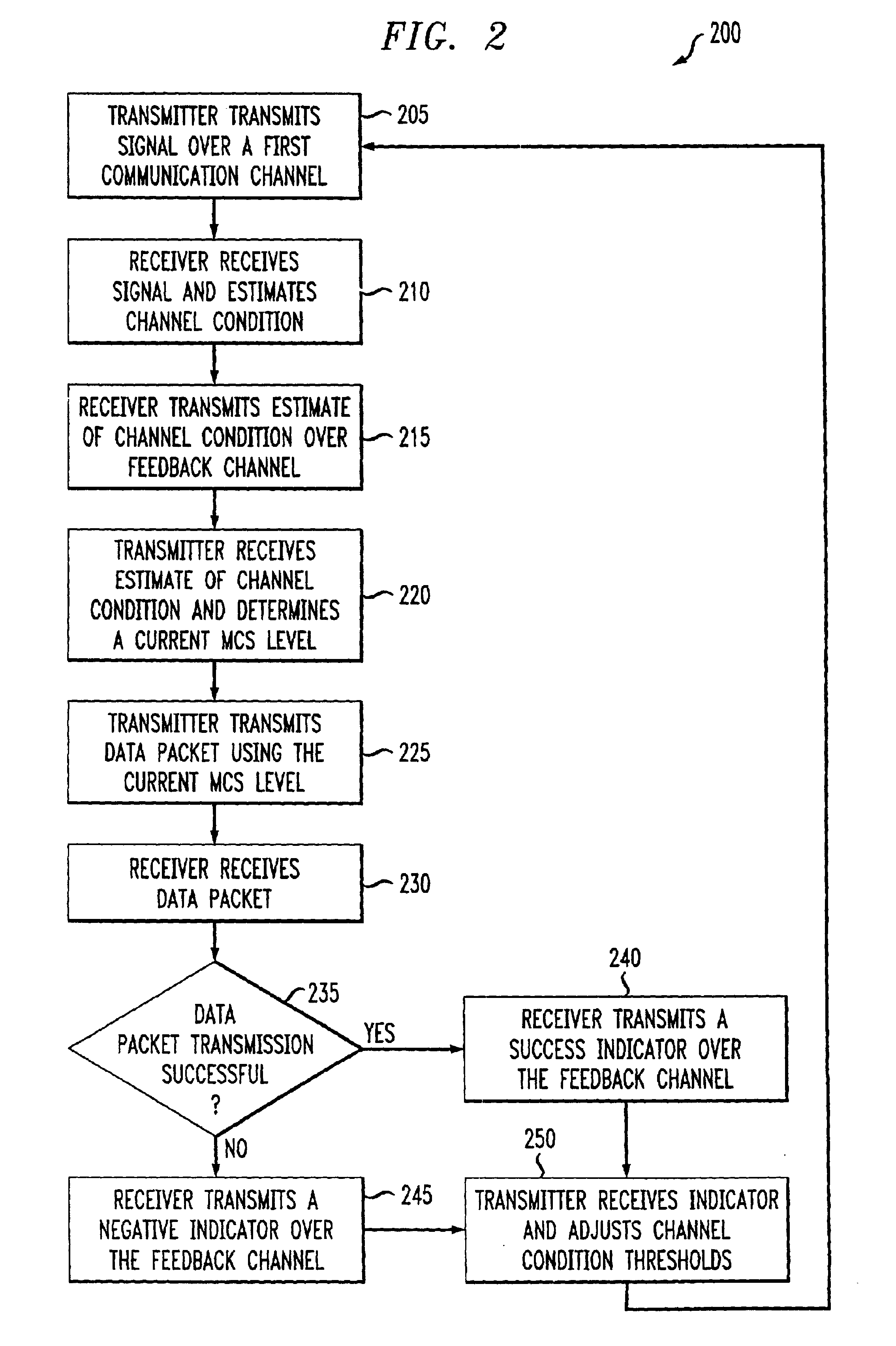
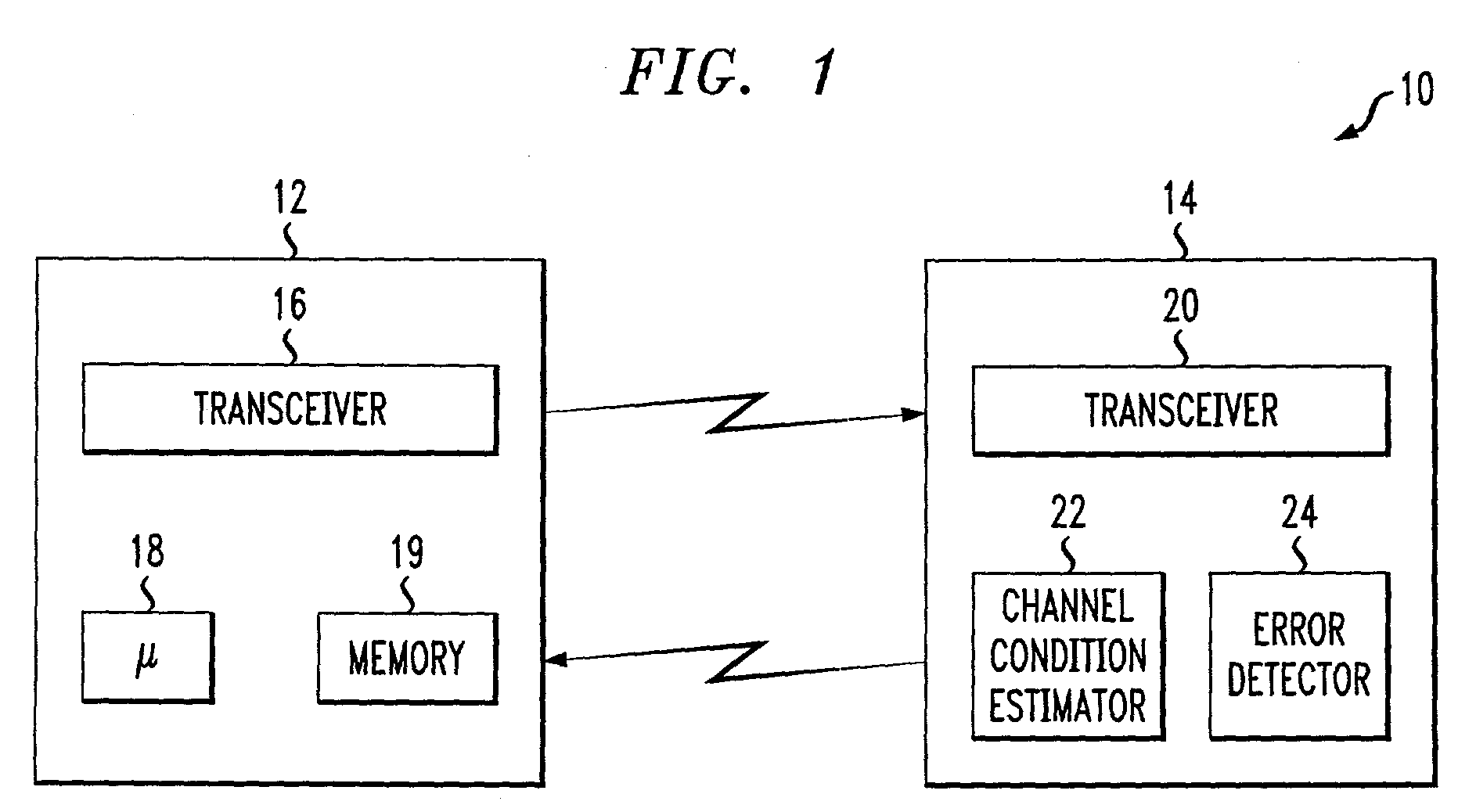
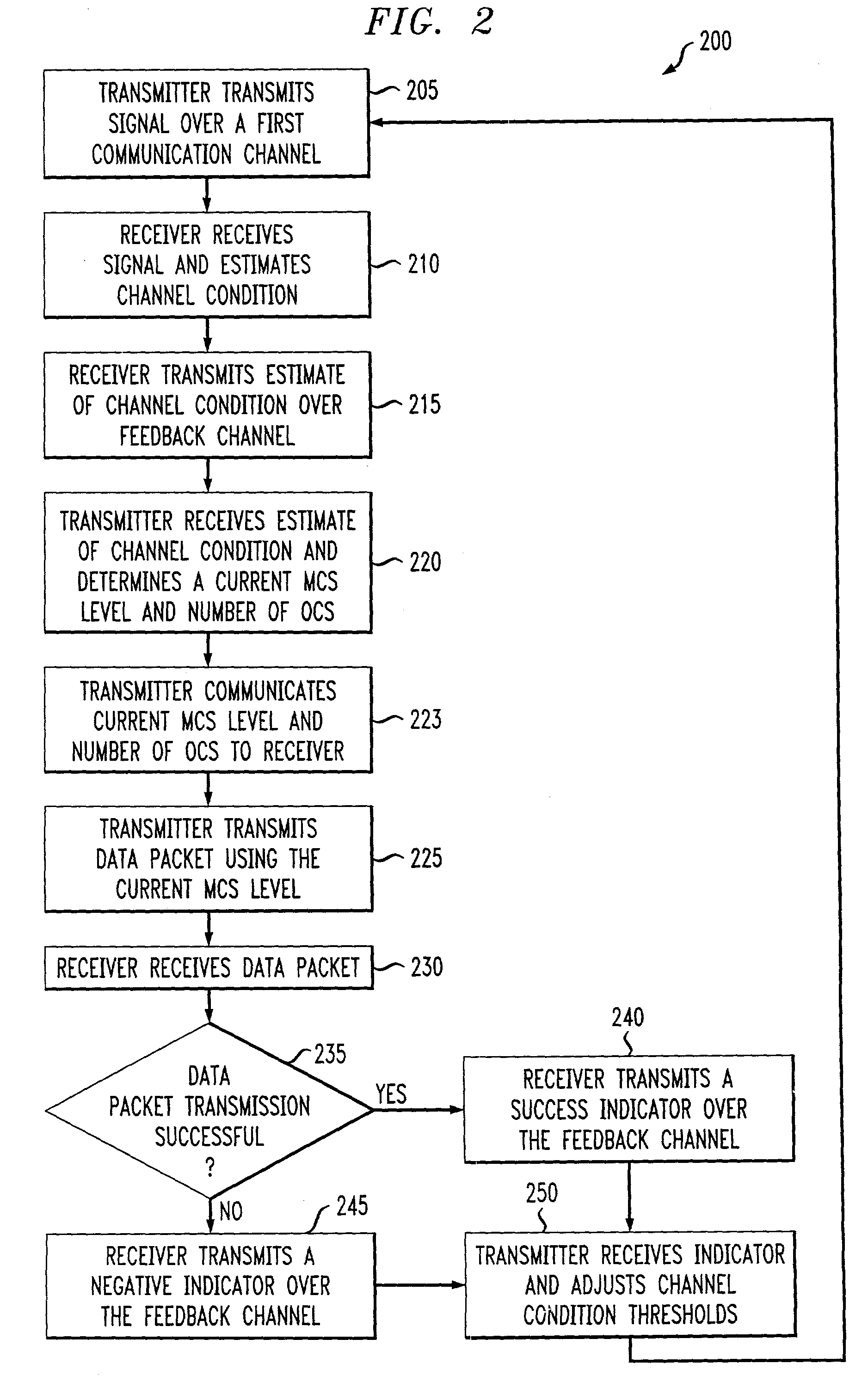
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation that selectively adjusts channel condition thresholds based on delay sensitivity of data packets being transmitted. For wireless communication systems incorporating an error correction scheme using re-transmissions, the quality control loop adaptively adjusts channel condition thresholds more frequently for delay sensitive data packets, such as video, and less frequently for delay insensitive data packets, such as text messaging. Channel condition thresholds may be adjusted using fixed or variable steps based on error detection results.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Quality of service controlled link adaptation
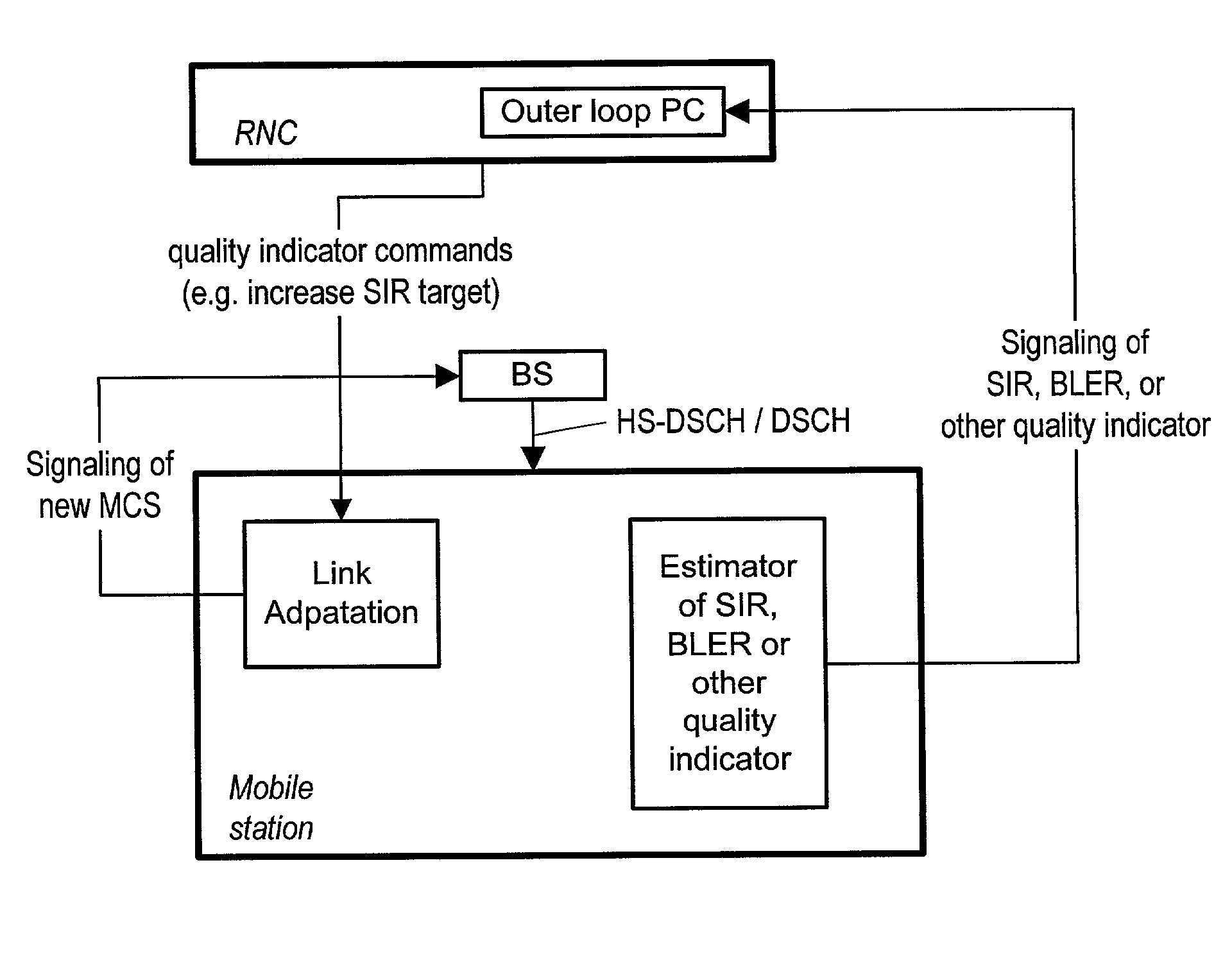
InactiveUS20050159166A1Increase data capacityImprove throughputNetwork traffic/resource managementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsQuality of serviceQuality control
A quality of service profile for a mobile communication subscriber unit is determined and includes one or more mobile-specific desired quality of service parameters. Actual values for the service parameter(s) is(are) determined and fed back to a link quality controller to determine whether they are in an acceptable range or relationship with corresponding actual quality of service parameter values. A modulation and / or coding scheme for transmitting the information over the radio link is selected or adjusted based on whether the desired and actual quality of service parameters are in an acceptable range or acceptable relationship. A combined “desired” quality of service parameter using the first and second quality of service parameters (or more if desired) may be determined. A combined “actual” quality of service parameter using first and second actual quality service parameter values is determined. Those combined desired and actual quality of service parameters are compared to determine whether they are in an acceptable range or relationship. The modulation or coding scheme (or both) is (are) selected or adjusted based thereon.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Link Adaptation In Grant-Free Multiple Access Systems
ActiveUS20170034845A1Well formedNetwork traffic/resource managementChannel coding adaptationUplink transmissionLink adaptation
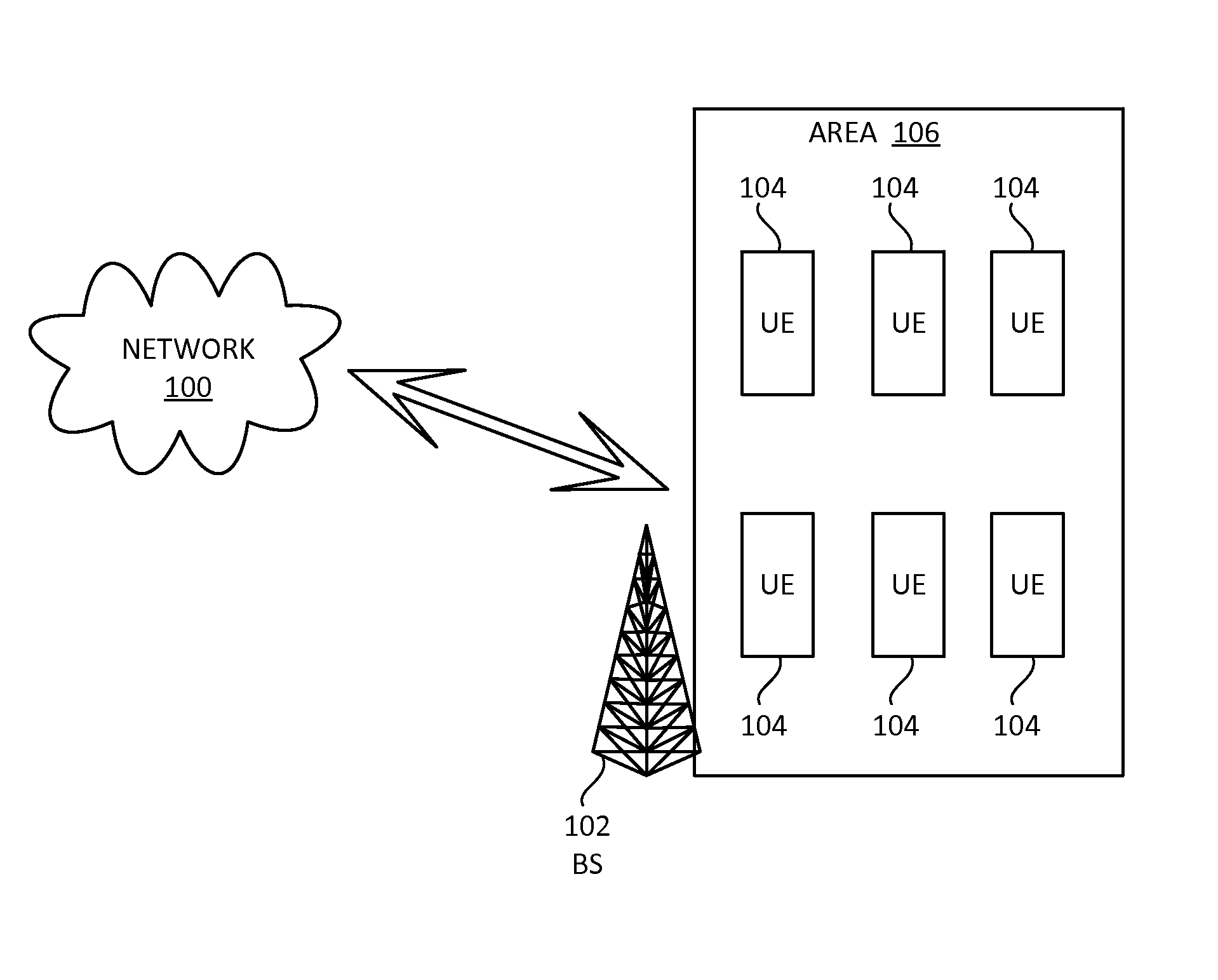
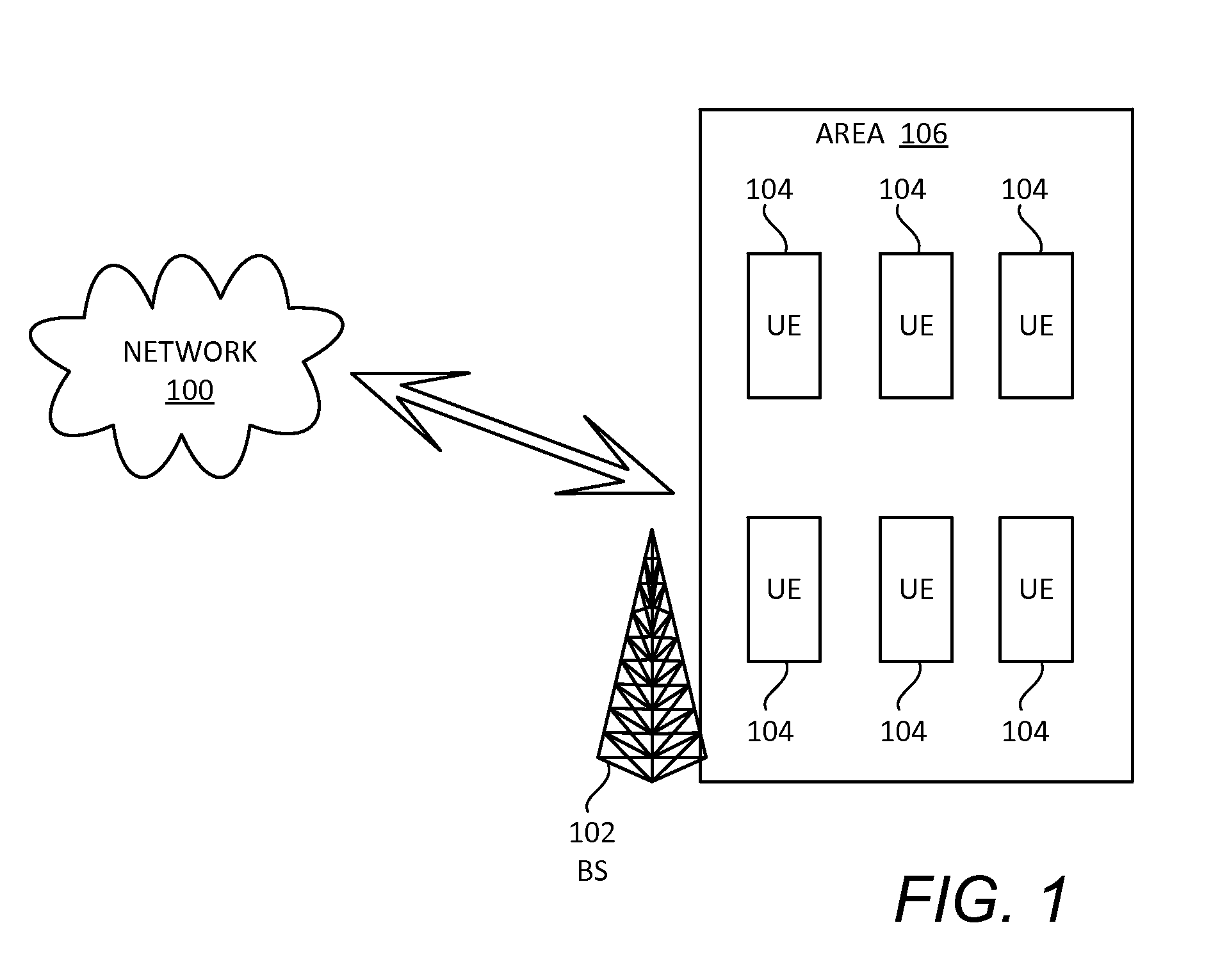
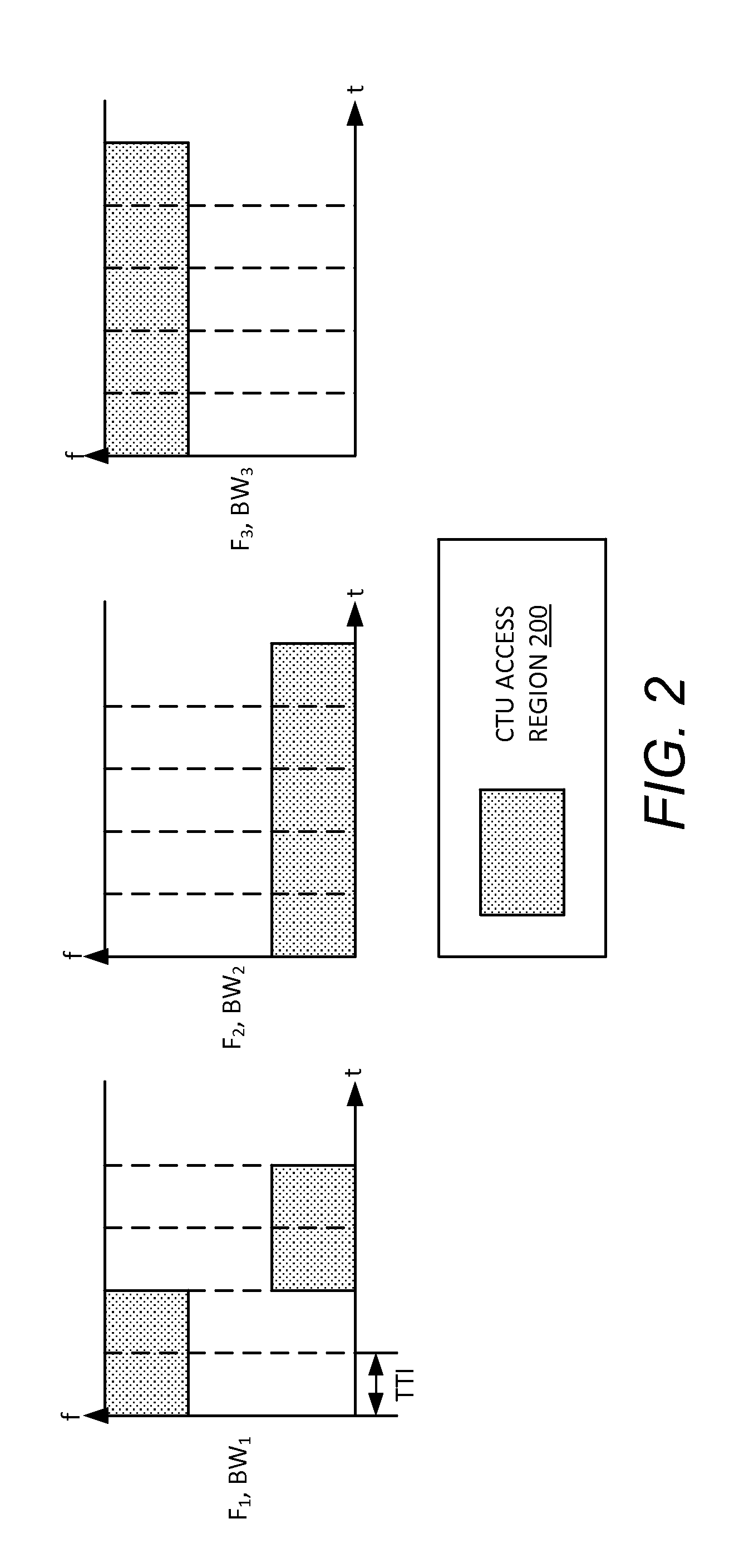
A BS determines an amount of resource overloading for a contention transmission unit (CTU) access region associated with a grant-free uplink transmission scheme in a multiple access system. The BS determines a modulation and coding scheme (MCS) limit indicating a maximum MCS level for the CTU access region. The BS sends the MCS limit to a plurality of user equipments (UEs) associated with the first CTU access region. A UE receives from the base station the MCS limit and determines a first MCS index within the MCS limit for a first uplink transmission. The UE sends the first uplink transmission to the base station using a CTU in the CTU access region. The first uplink transmission includes user data and the first MCS index determined at the first UE.
Owner:FUTUREWEI TECH INC
Method and apparatus for link adaptation
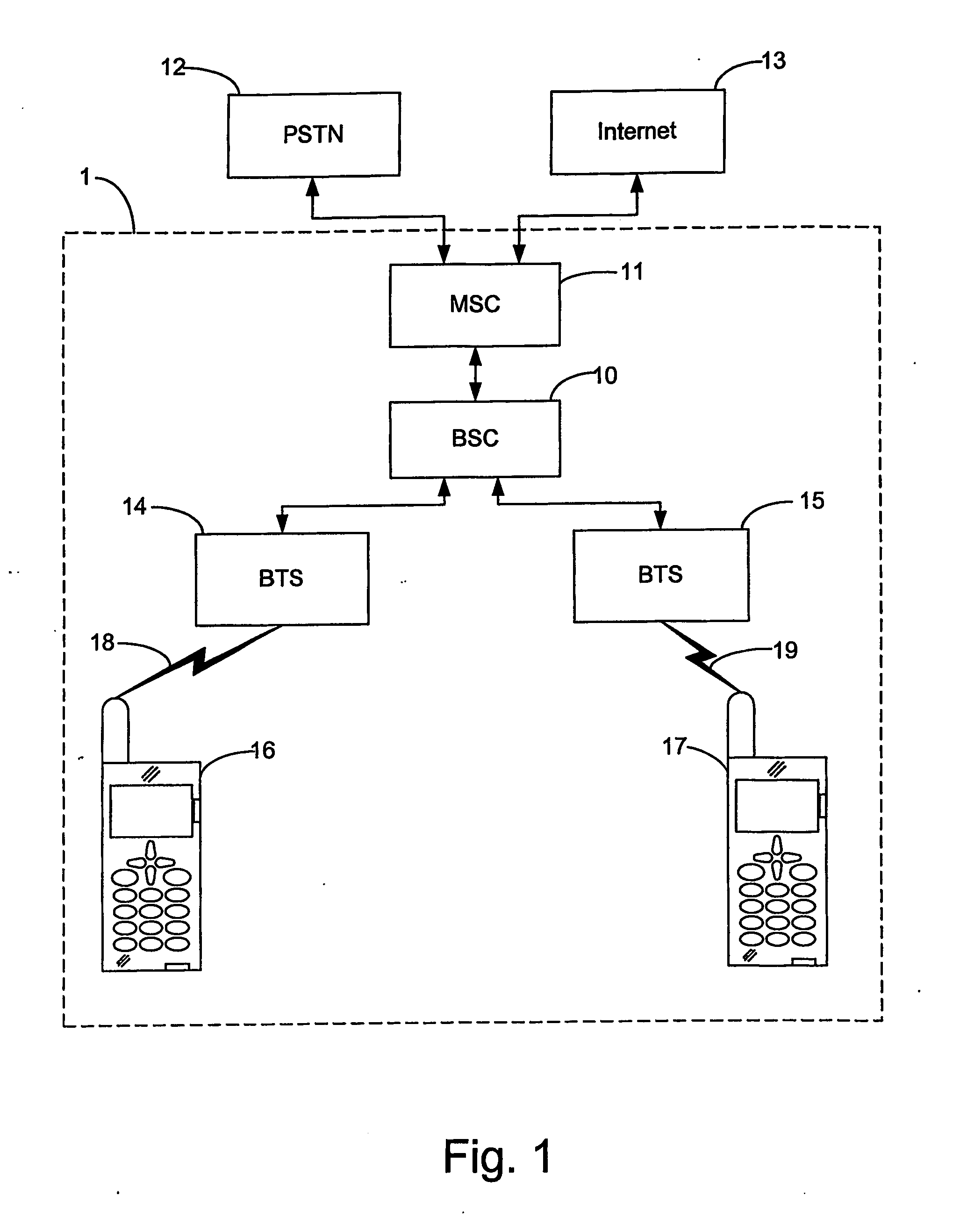
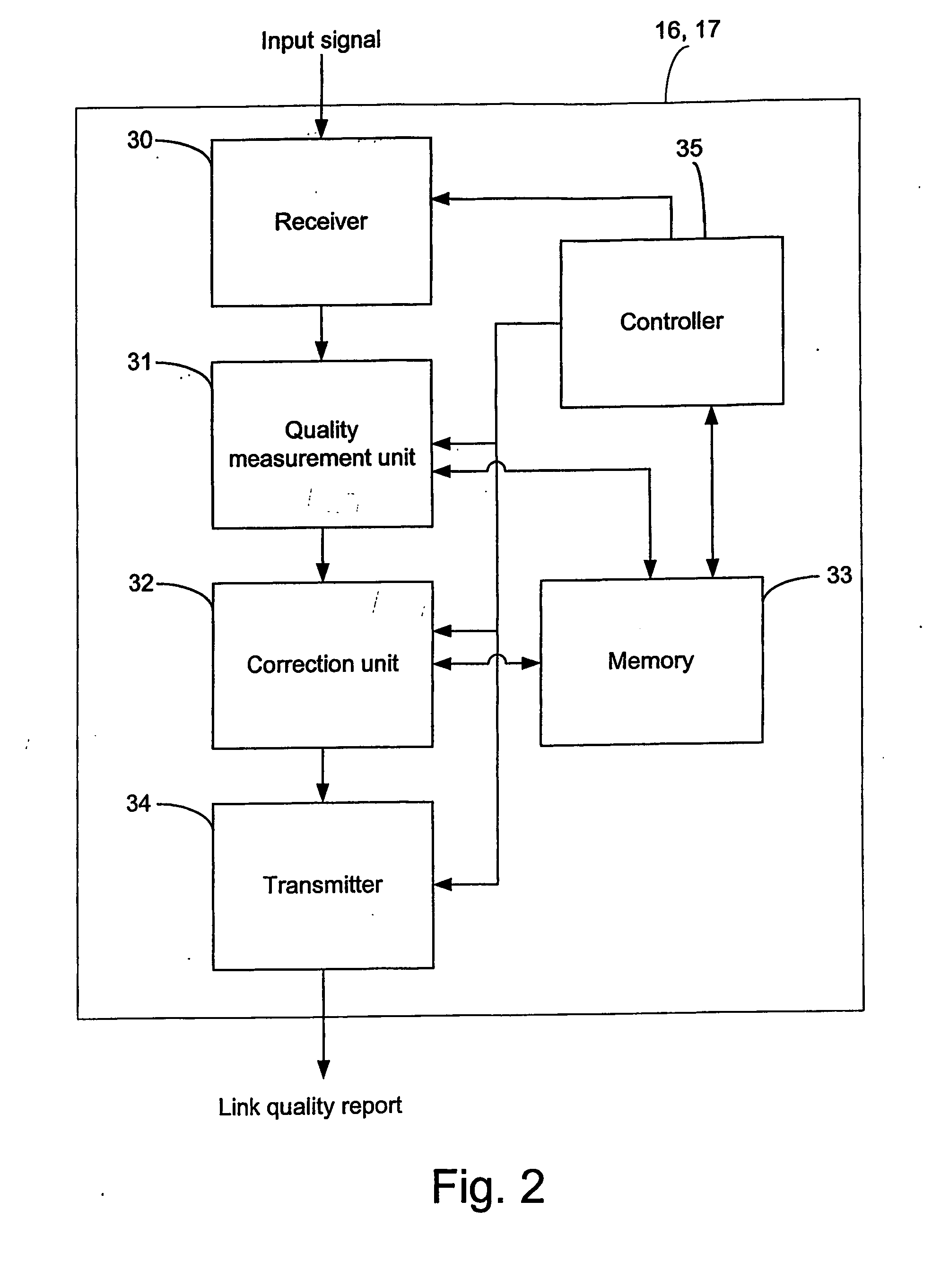
InactiveUS20070026803A1Improve link performanceImprove performancePower managementReceivers monitoringCommunications systemSignal quality
A method and apparatus for providing a link quality report in a wireless communication system supporting link adaptation. An input signal carrying data blocks in one or several transmission intervals of a reporting interval is received by a receiver of the apparatus. A quality measurement unit provides a link quality measure of the current reporting interval. A correction unit corrects the link quality measure by determining a SIR loss of the link, which is induced by unmatched transmission parameter settings of a physical layer. Then, a link quality report for the current reporting interval is based on the corrected link quality measure and transmitted by the transmitter to the transmitting unit, which will adapt the setting of physical layer parameters accordingly.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
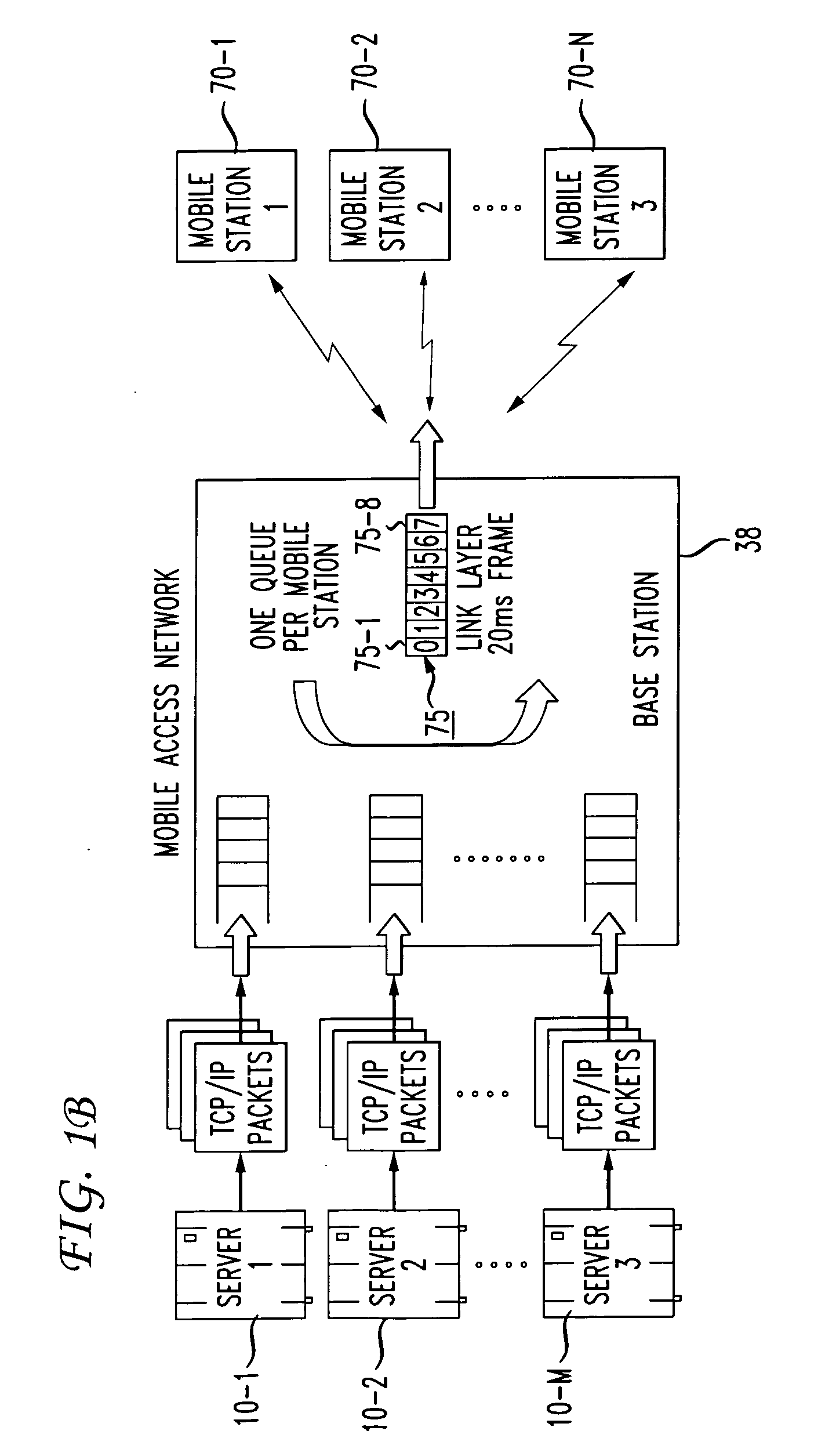
Apparatus and Method for Radio Transmission of Real-Time Ip Packets Using Header Compression Technique
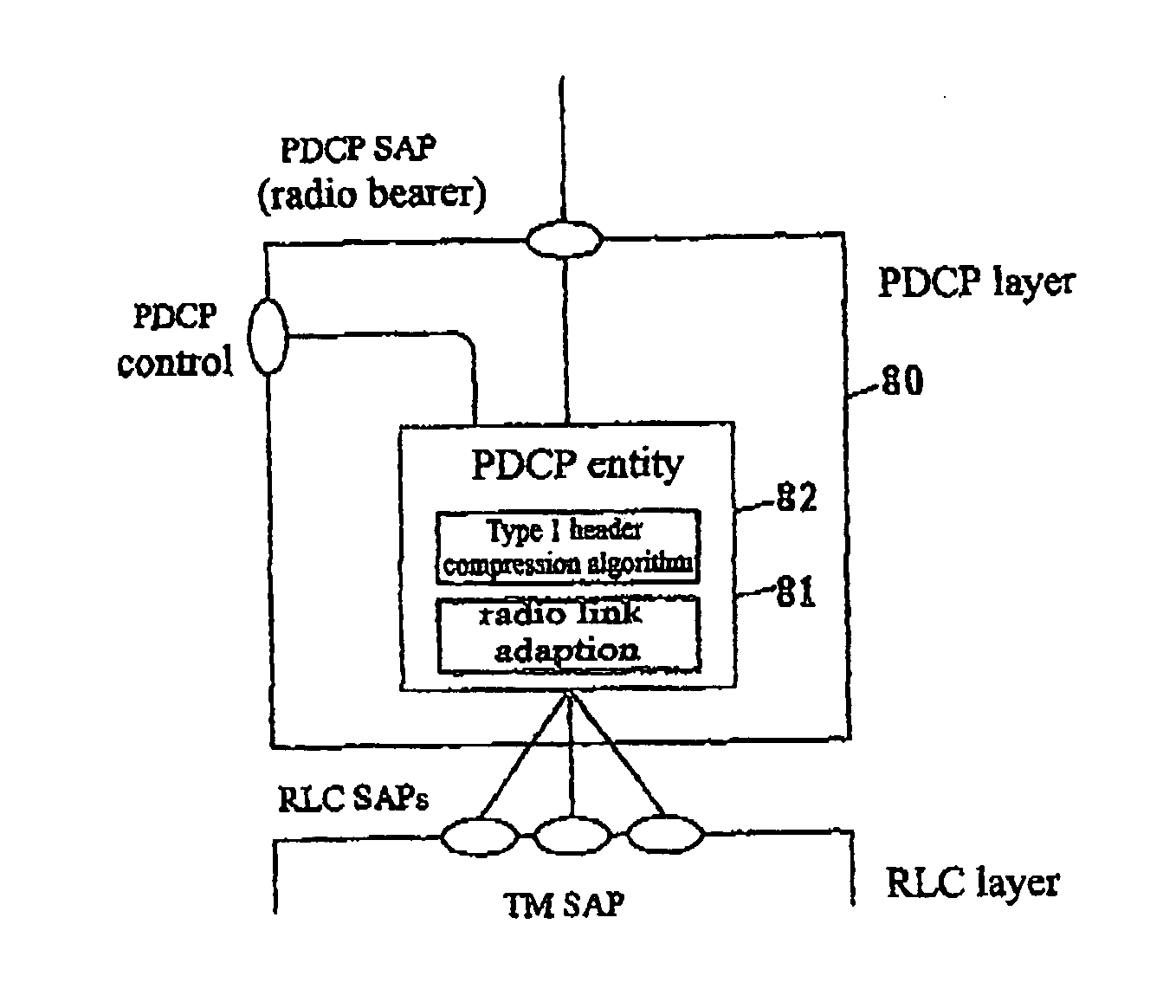
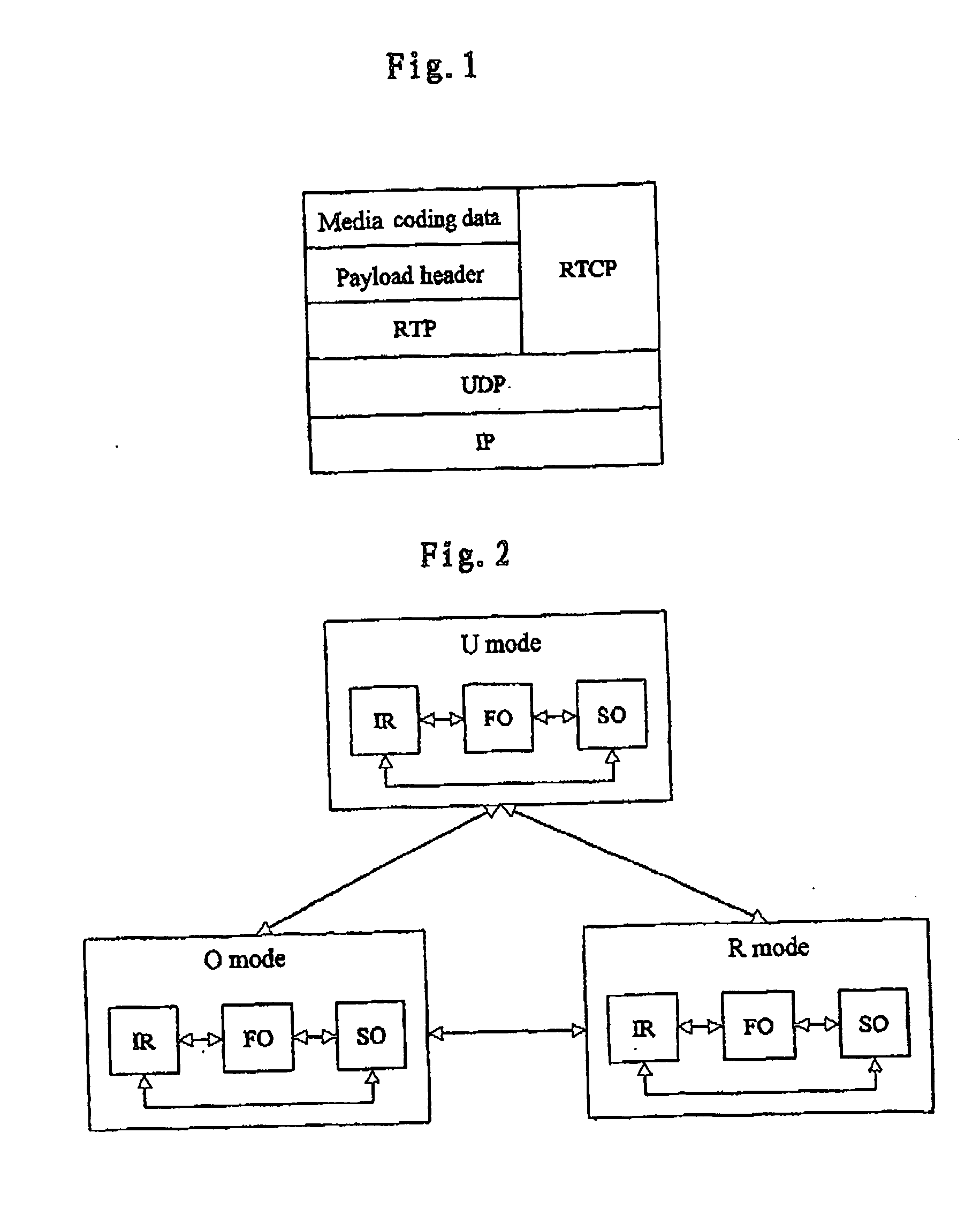
InactiveUS20070248075A1Efficient use ofSuitably delayedTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationData packWireless transmission
The present invention provides an apparatus and method of radio transmission of real-time IP packets using header compression technique. In the present invention, the size of a compressed header of an RTP packet can be adapted to length types required by the system by adding a radio link adaptation unit to the existing PDCP entity. The method comprises header-compressing the RTP packets, to obtain header-compressed RTP packets having a plurality of different header compression lengths; pre-configuring header compression lengths and length types required by the system; and PDU-size adapting the plurality of different header compression lengths of the header-compressed RTP packets, so as to comply with said lengths and length types required by the system.
Owner:USRCOM CHINA
Multi-channel adapative quality control loop for link rate adaptation in data packet communications
InactiveUS20030123598A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission monitoringPacket communicationRate adaptation
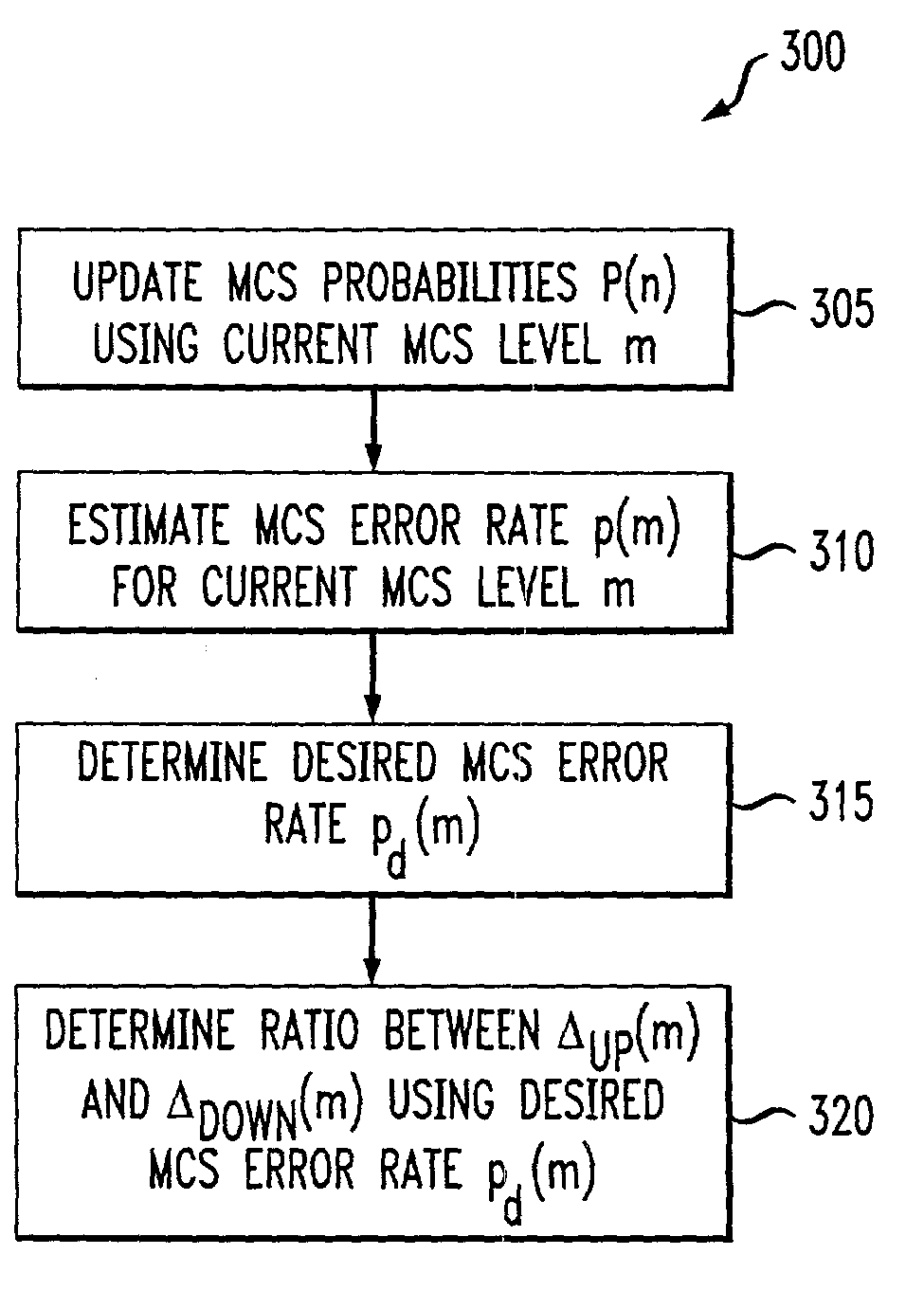
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation based on modulation and / or coding schemes (also referred to as "MCS levels") and one or more spreading codes that adaptively selects channel condition thresholds in real-time without measuring all the factors that affect selecting optimal channel condition thresholds. The adaptive quality control loop involves adjusting the channel condition thresholds with variable up and down steps based on target quality metrics along with measurements such as error detection results, relative frequencies of visiting each MCS level, and transmitted data rates, wherein the target quality metrics can be a block error rate or bit error rate target criterion. If the target quality metric is a block error rate target criterion, the variable step is determined using a desired MCS error rate based on MCS probabilities, MCS error rates and the block error rate target criterion. If the target quality metric is a bit error rate target criterion, the variable step is determined using a desired MCS error rate based on MCS probabilities, MCS error rates, average rate of bit errors, data rate, and the bit error rate target criterion.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Method and apparatus for transmitting and receiving different signal types in communication systems
ActiveUS20090034505A1Without consuming additional bandwidth resourcesWithout consuming additional bandwidth resourceModulated-carrier systemsTransmission path divisionCommunications systemSounding reference signal
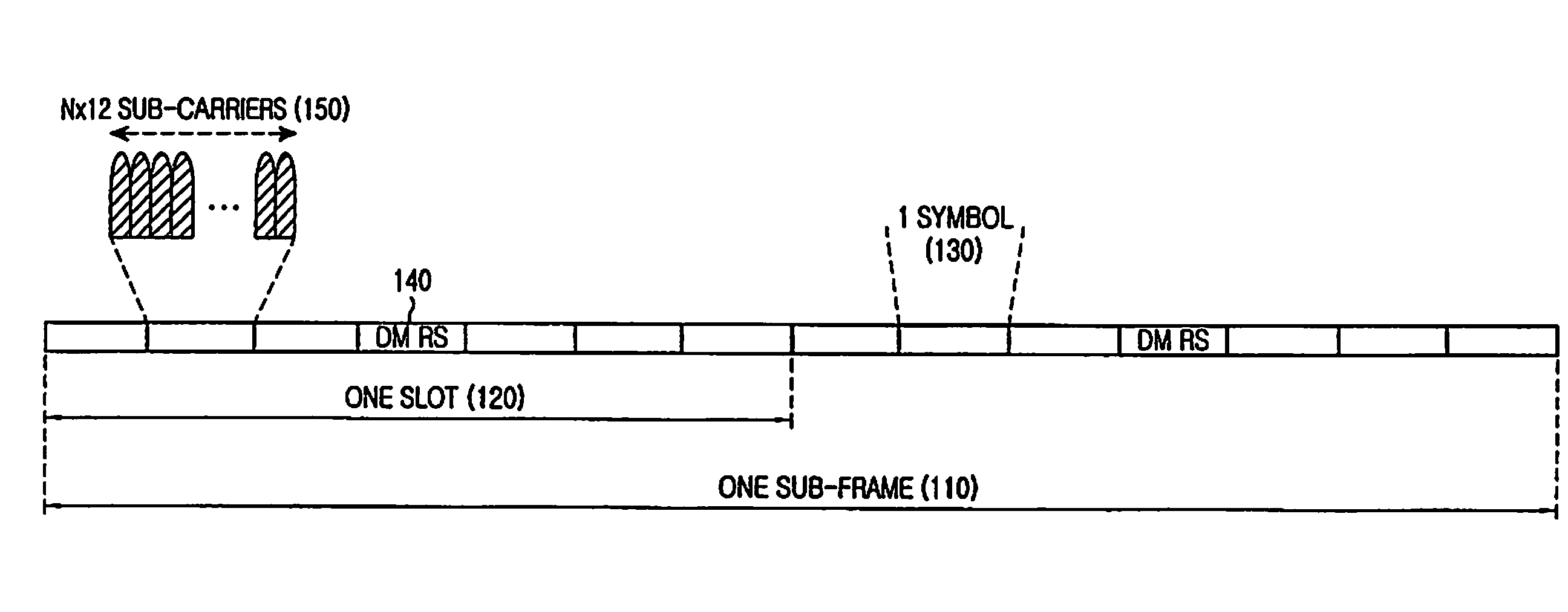
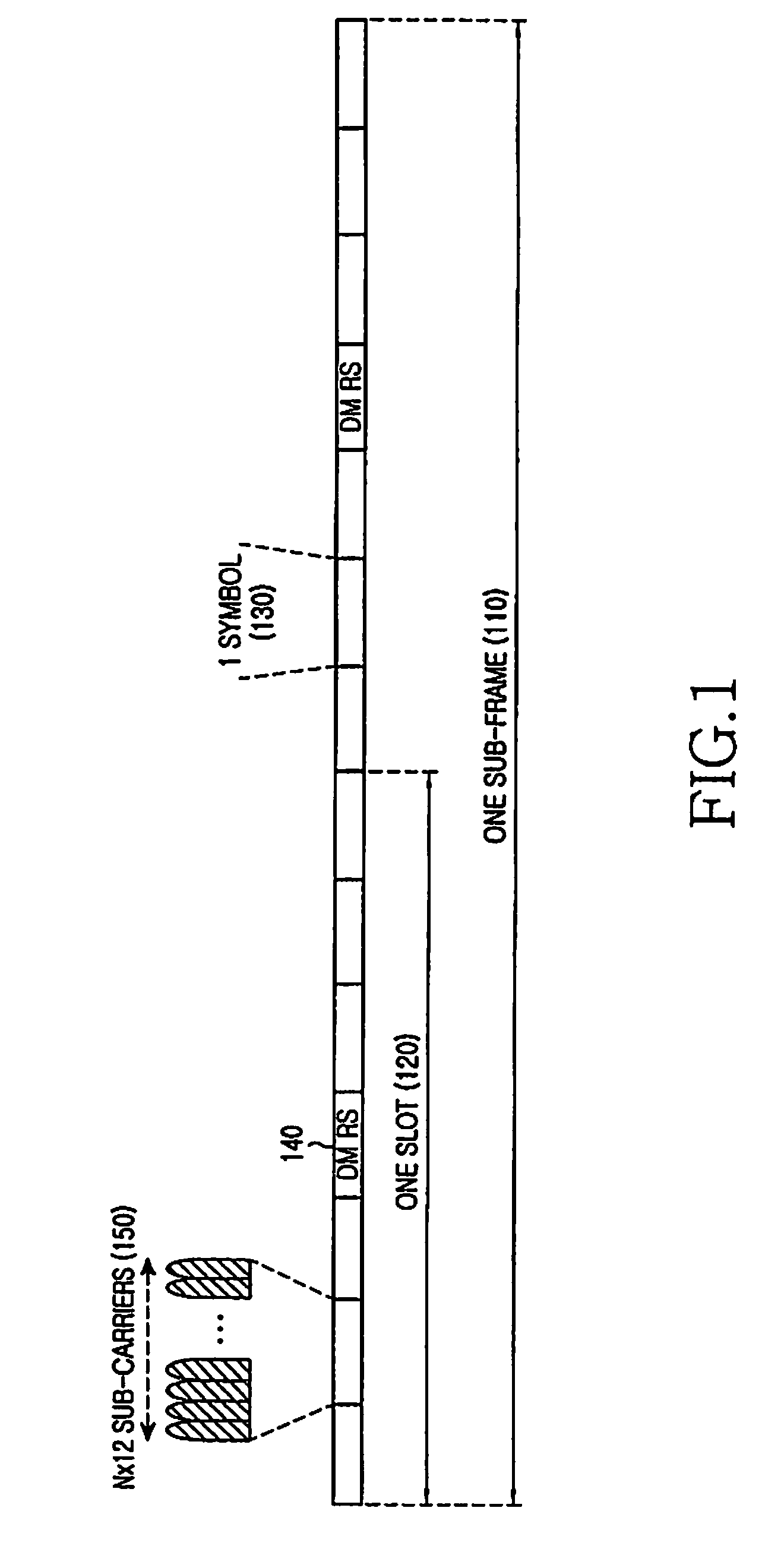
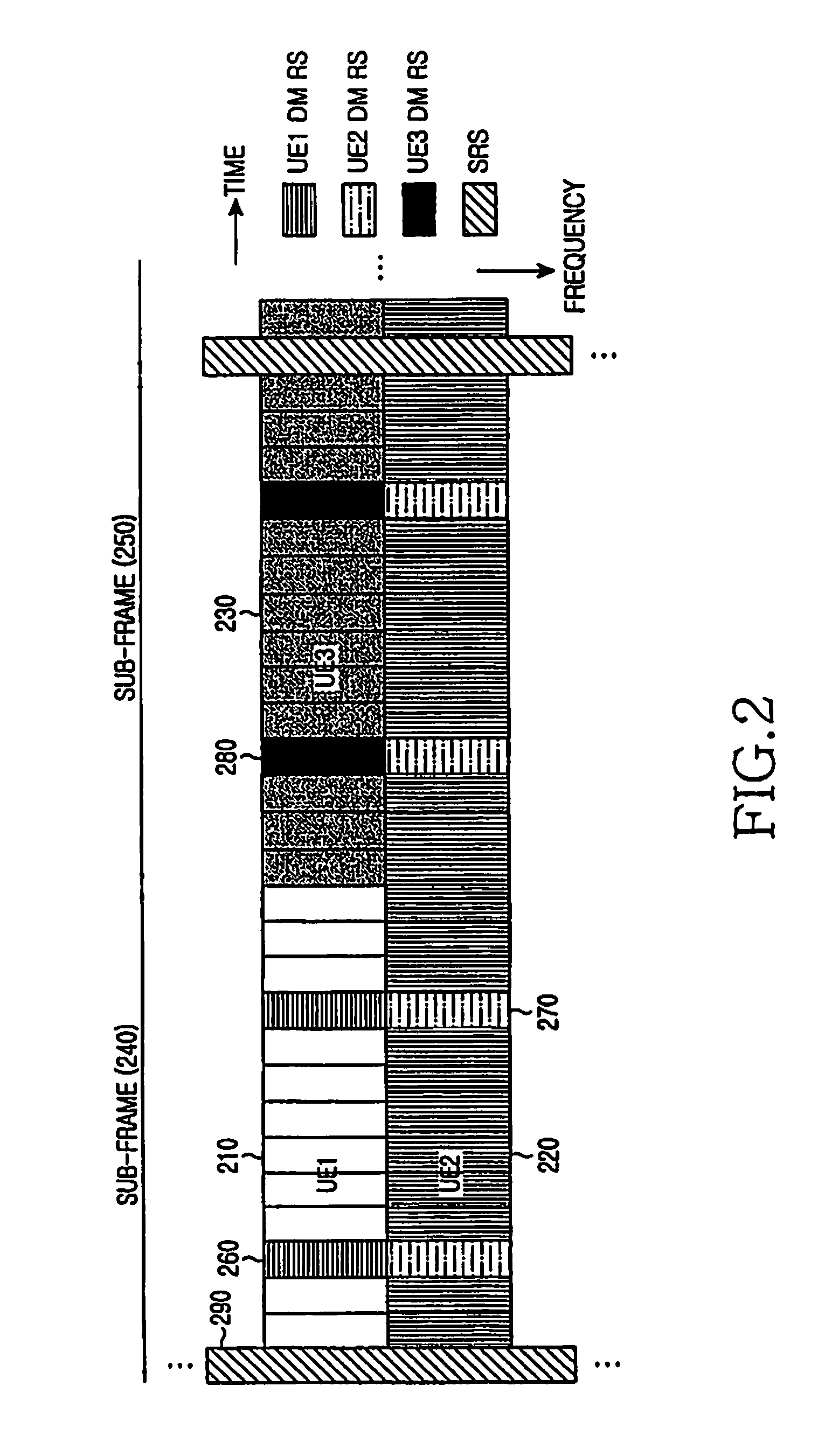
A method and apparatus for multiplexing a reference signal from a User Equipment (UE), not having any other signal transmission in the respective Transmission Time Interval (TTI), with a reference signal from another UE also having data transmission in the respective TTI, or with the control signal and reference signal from another UE transmitted in the respective TTI. The multiplexed reference signal from the UE not having any other signal transmission in the respective TTI can serve as a sounding reference signal to enable the serving base station to apply link adaptation to a subsequent signal transmitted by the UE or it can serve as a reference signal conveying state information, such as resource request or service request.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET INT LTD
Method and system for control signalling enabling flexible link adaptation in a radiocommunication system
InactiveUS6865233B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelChannel coding adaptationControl signalOriginal data
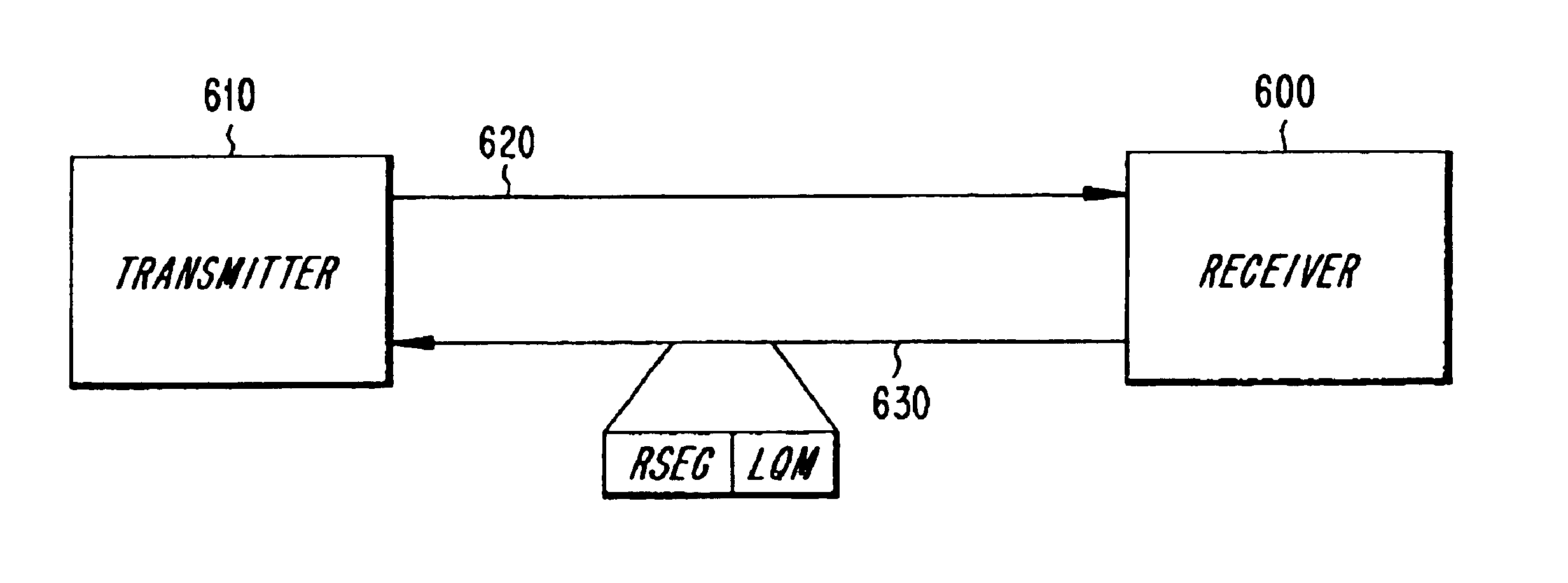
Control signalling for systems employing link adaptation and incremental redundancy is described. A link adaptation / incremental redundancy message can be transmitted from a receiving entity to a transmitting entity to inform the transmitting entity of the receiving entity's incremental redundancy status or preference. Another message, which indicates whether resegmentation should be performed for retransmitted blocks can also be transmitted from a receiving entity to a transmitting entity. Both of these messages can be used by the transmitting entity to determine an appropriate modulation / coding scheme for subsequent transmissions of both original data blocks and retransmitted data blocks. The messages can be used together or independently in either link (uplink or downlink) between a base station and a mobile station in a radiocommunication system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method and system for wireless packet scheduling with per packet QoS support and link adaptation
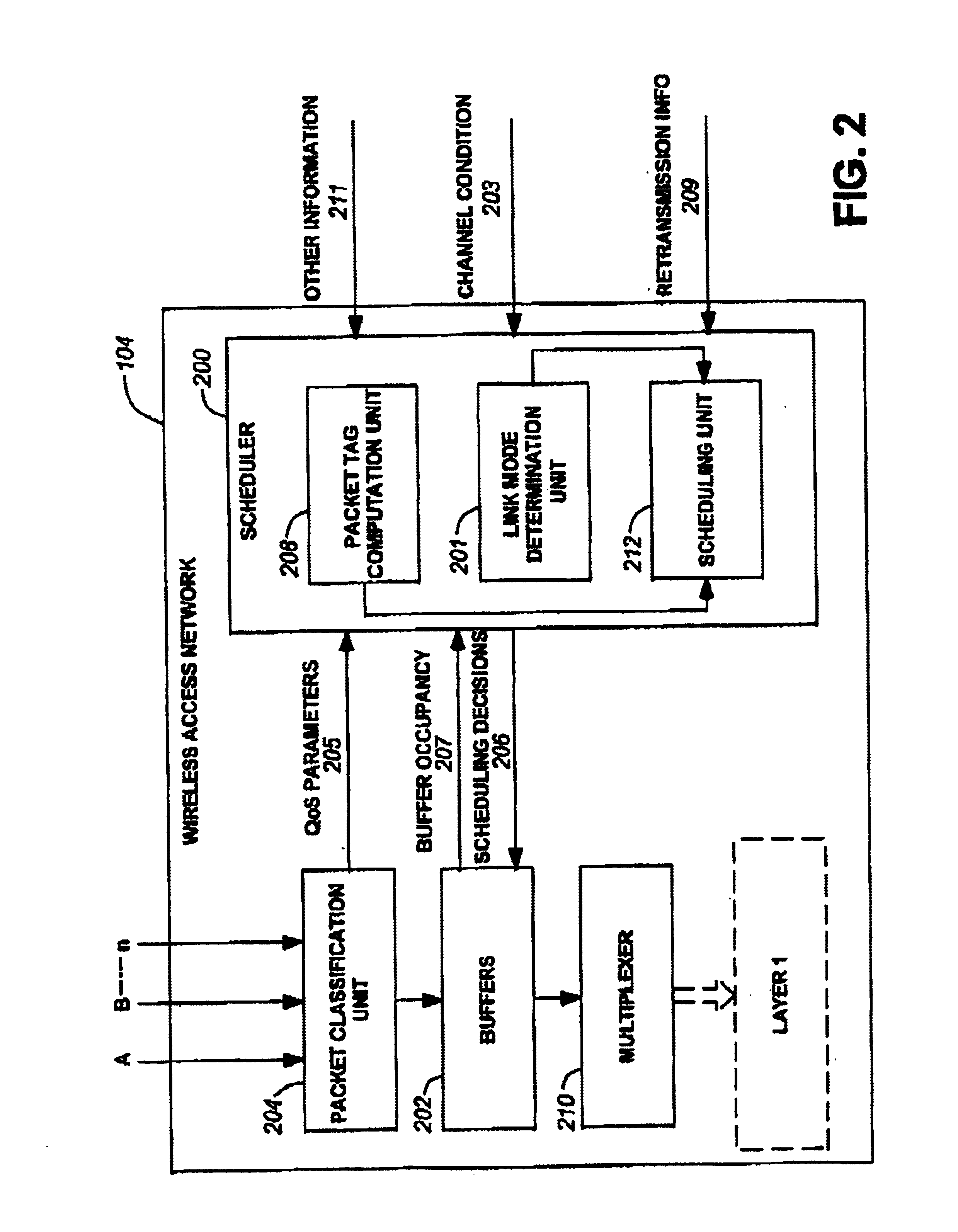
InactiveUS6879561B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsTransmission systemsTelecommunications networkPacket scheduling
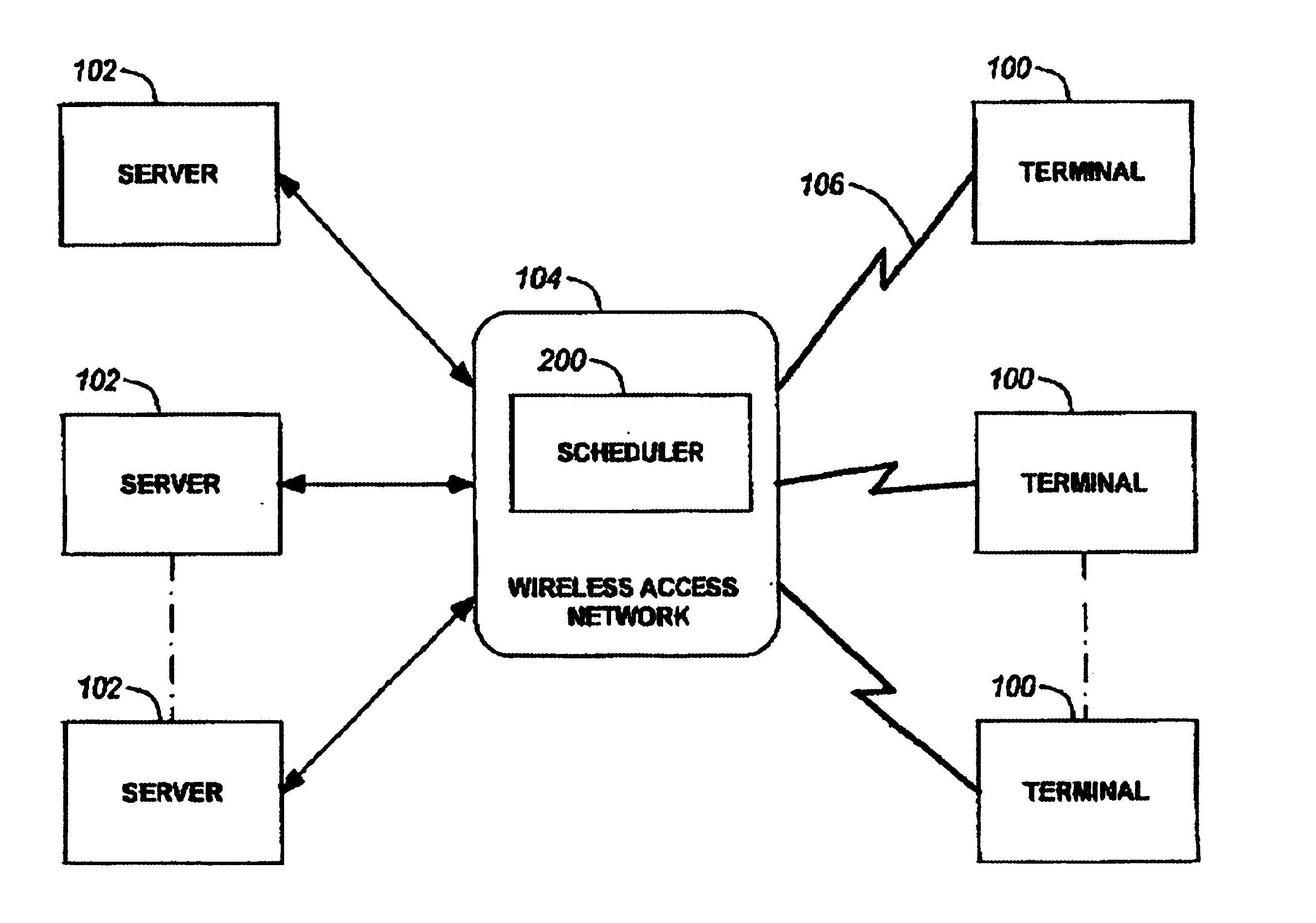
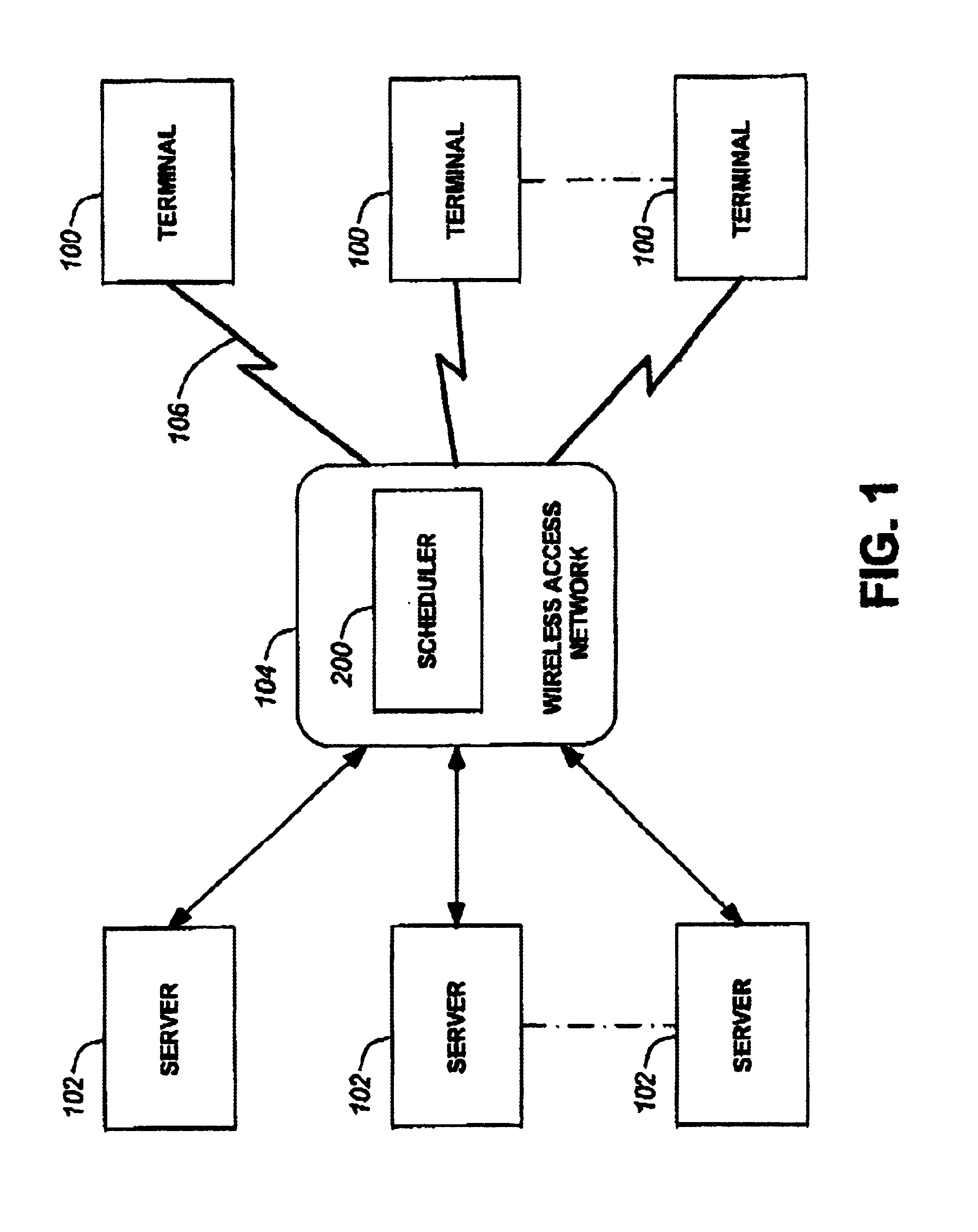
A method and system for scheduling data in the down, or forward, link, on a per packet basis in a wireless telecommunications network. The scheduler determines the order of packets to be sent from multiple queues based on per IP QoS, real time channel condition and real time buffer occupancy. The scheduler determines the necessary support link adaptation on a per packet basis based on per packet QoS and the channel condition. The scheduling system and method take into consideration both upper layer per packet QoS, for example packet delay bound, and the real time channel condition (C / I) for each mobile terminal. The method of the present invention also determines the layer 2 frame length for each scheduled packet.
Owner:APPLE INC
Delay sensitive adapative quality control loop for rate adaptation
InactiveUS20030126536A1Multiple-port networksError prevention/detection by using return channelRate adaptationCommunications system
An adaptive quality control loop for link rate adaptation that selectively adjusts channel condition thresholds based on delay sensitivity of data packets being transmitted. For wireless communication systems incorporating an error correction scheme using retransmissions, the quality control loop adaptively adjusts channel condition thresholds more frequently for delay sensitive data packets, such as video, and less frequently for delay insensitive data packets, such as text messaging. Channel condition thresholds may be adjusted using fixed or variable steps based on error detection results.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Method of link adaptation in enhanced cellular systems to discriminate between high and low variability
ActiveUS7289574B2Quick and easy changeReduce capacityError prevention/detection by using return channelEnergy efficient ICTDependabilityLink adaptation
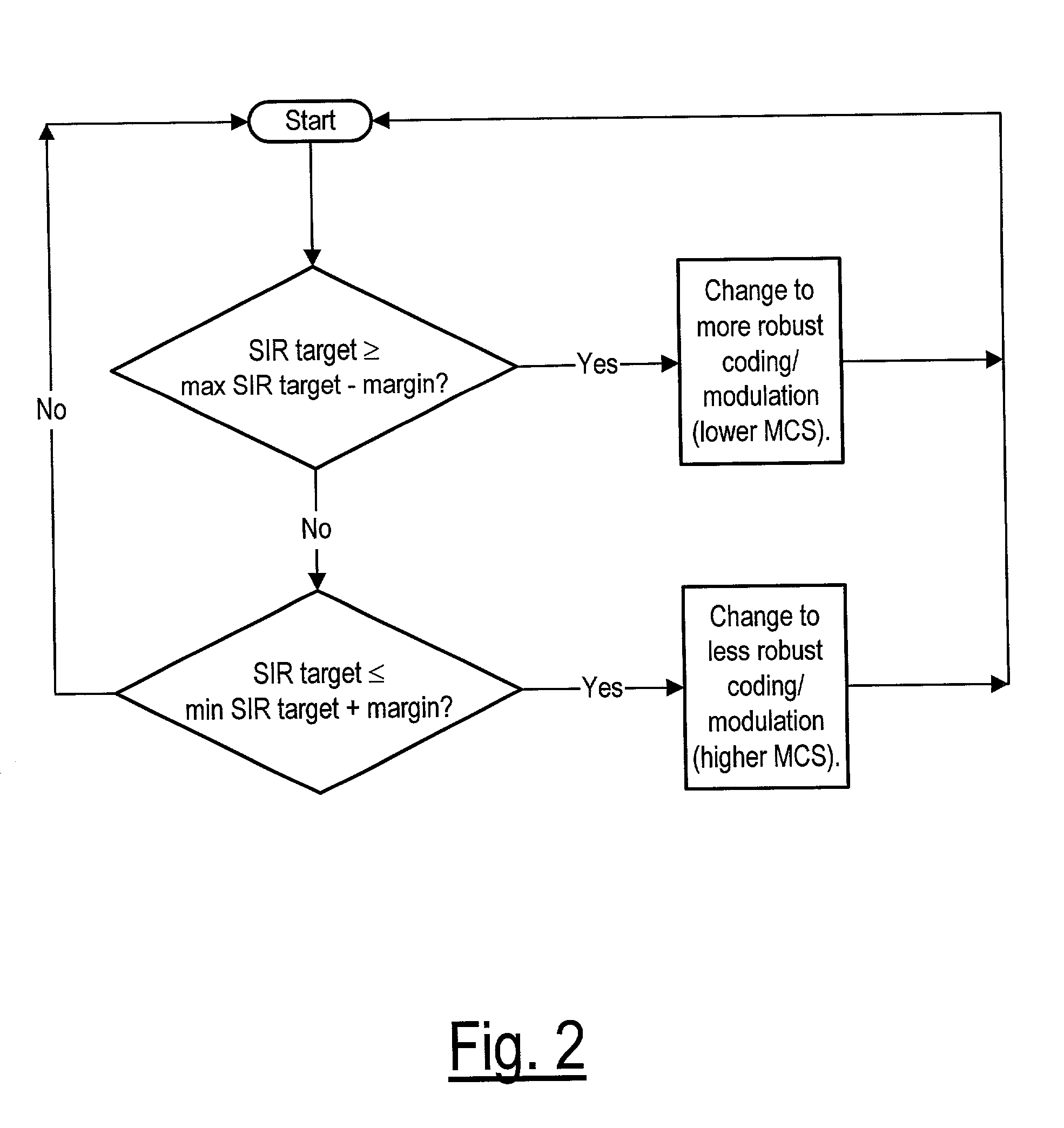
To perform link adaptation at radio interfaces of an enhanced packet data cellular network the system behavior is simulated for different C / I conditions. Two sets of tables are obtained, each table including upgrade and downgrade thresholds expressed in terms of Block Error Rate (BLER). The tables are specialized for taking into account EGPRS type II hybrid ARQ, Incremental Redundancy (IR). Transmitted blocks are checked for FEC and results are sent to the network that continuously updates BLER. A reliability filter output is used to decide the weight between new and old measurements. IR efficiency is tested for each incoming block and an indicative variable IR_status is filtered. Each threshold of BLER to be used is obtained by linear interpolation between the tabulated threshold without IR and with perfect IR, both weighed with filtered IR_status. Filtered BLER is compared with interpolated thresholds for testing the incoming of a MCS switching condition.
Owner:RPX CORP +2
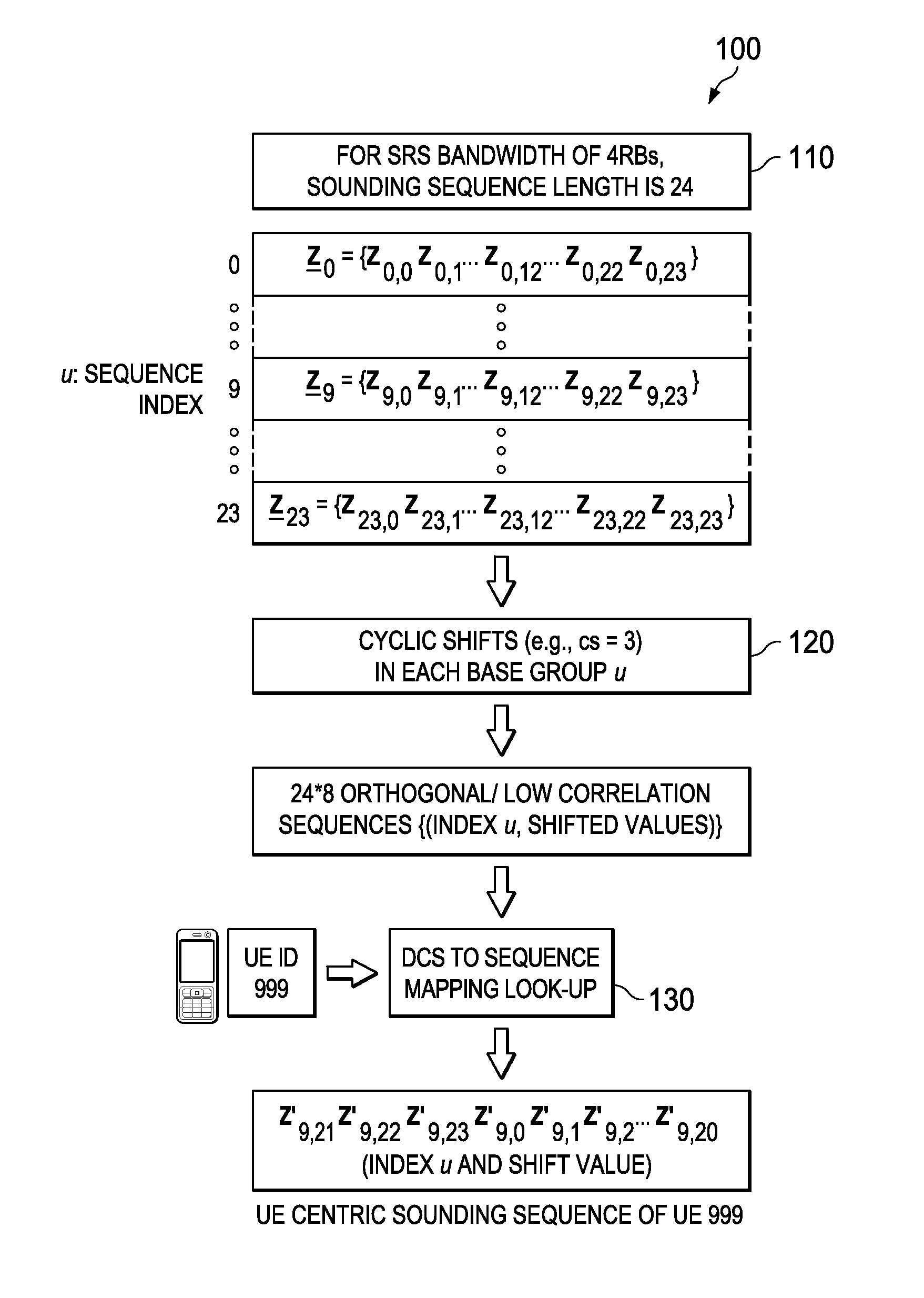
System and Method for Network Uplink Measurement Based Operation Using UE Centric Sounding
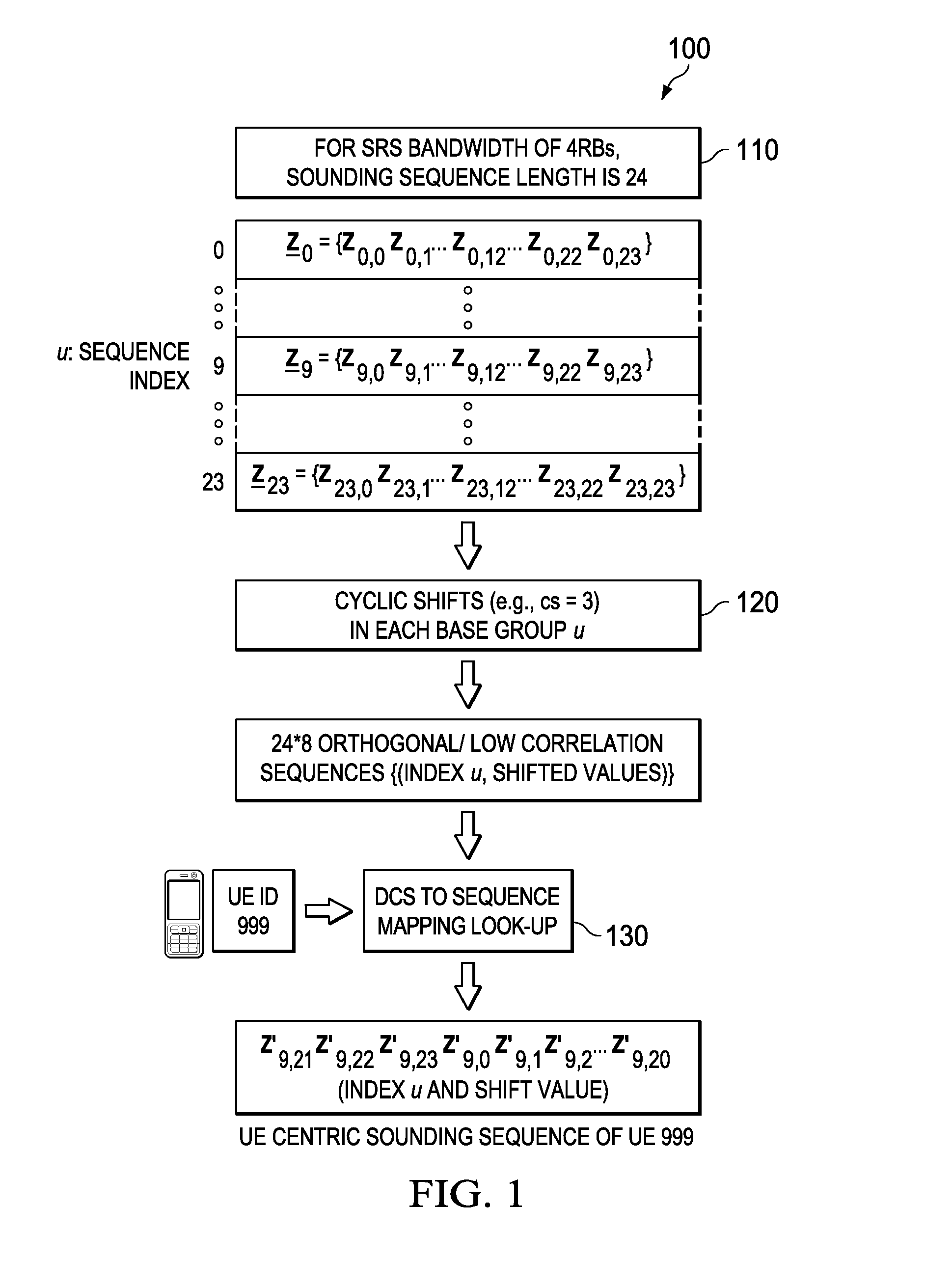
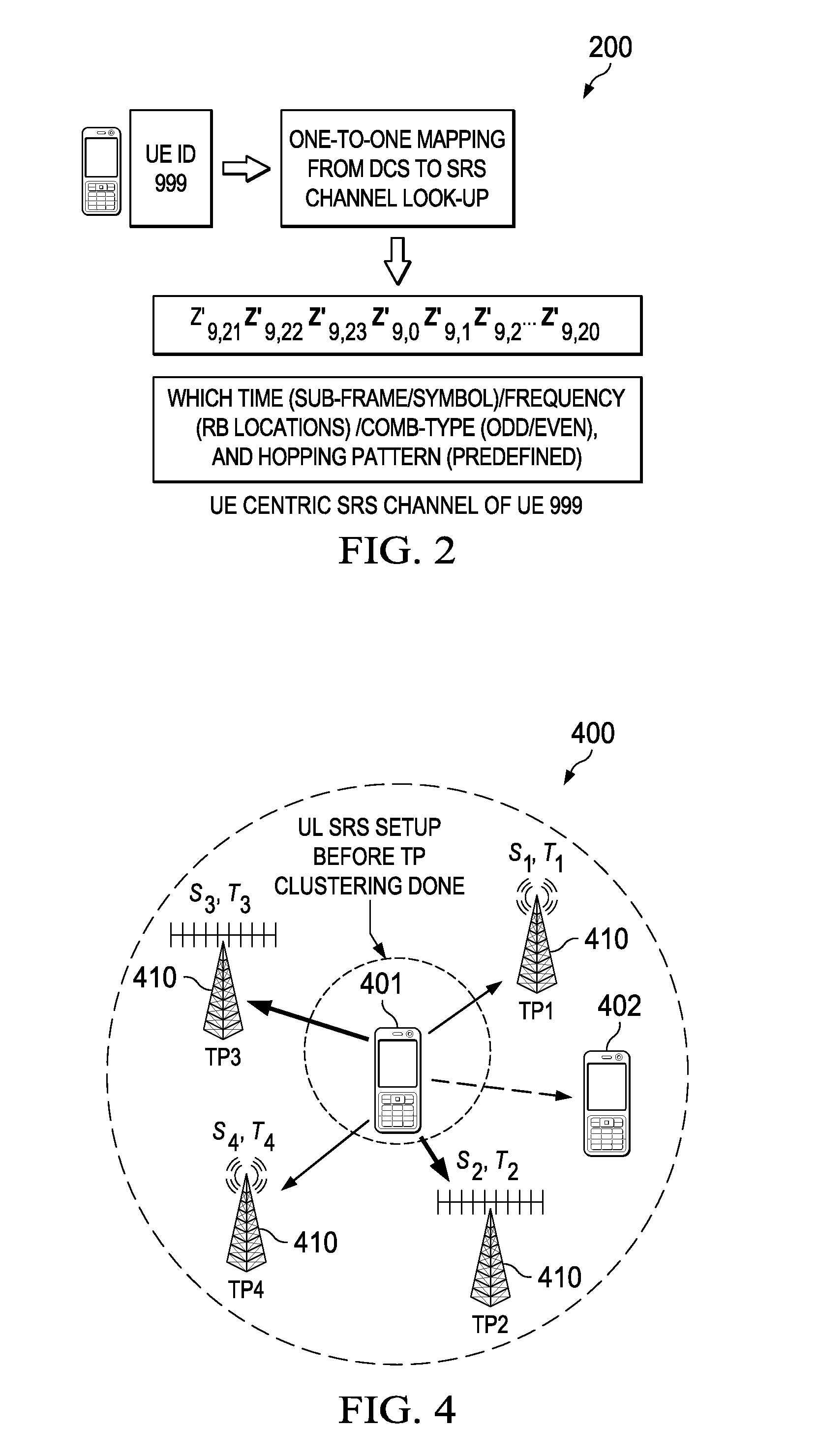
ActiveUS20150003263A1Slow link adaptationEasy to useSite diversityError preventionSounding reference signalLink adaptation
Embodiments are provided for uplink measurement based mechanism and control using user equipment (UE) centric sounding signals. The mechanism provides an alternative to DL-measurement dominated system control. Based on UL-measurements at TPs, the network obtains knowledge of users' channel and timing information, traffic, and interference, and is thus able to perform better control, including TP and UE clustering and optimization, and power control and link adaptation. In an embodiment method, a TP receives one-to-one mapping information indicating a plurality of UE IDs and a plurality of sounding channels assigned to the corresponding UE IDs. When the TP detects a sounding reference signal (SRS) from a UE, the TP is able to identify the UE using the detected SRS and the one-to-one mapping information. The TP then obtains measurement information for the identified UE, enabling better control and communications for uplink and downlink transmissions between multiple TPs and the UE.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
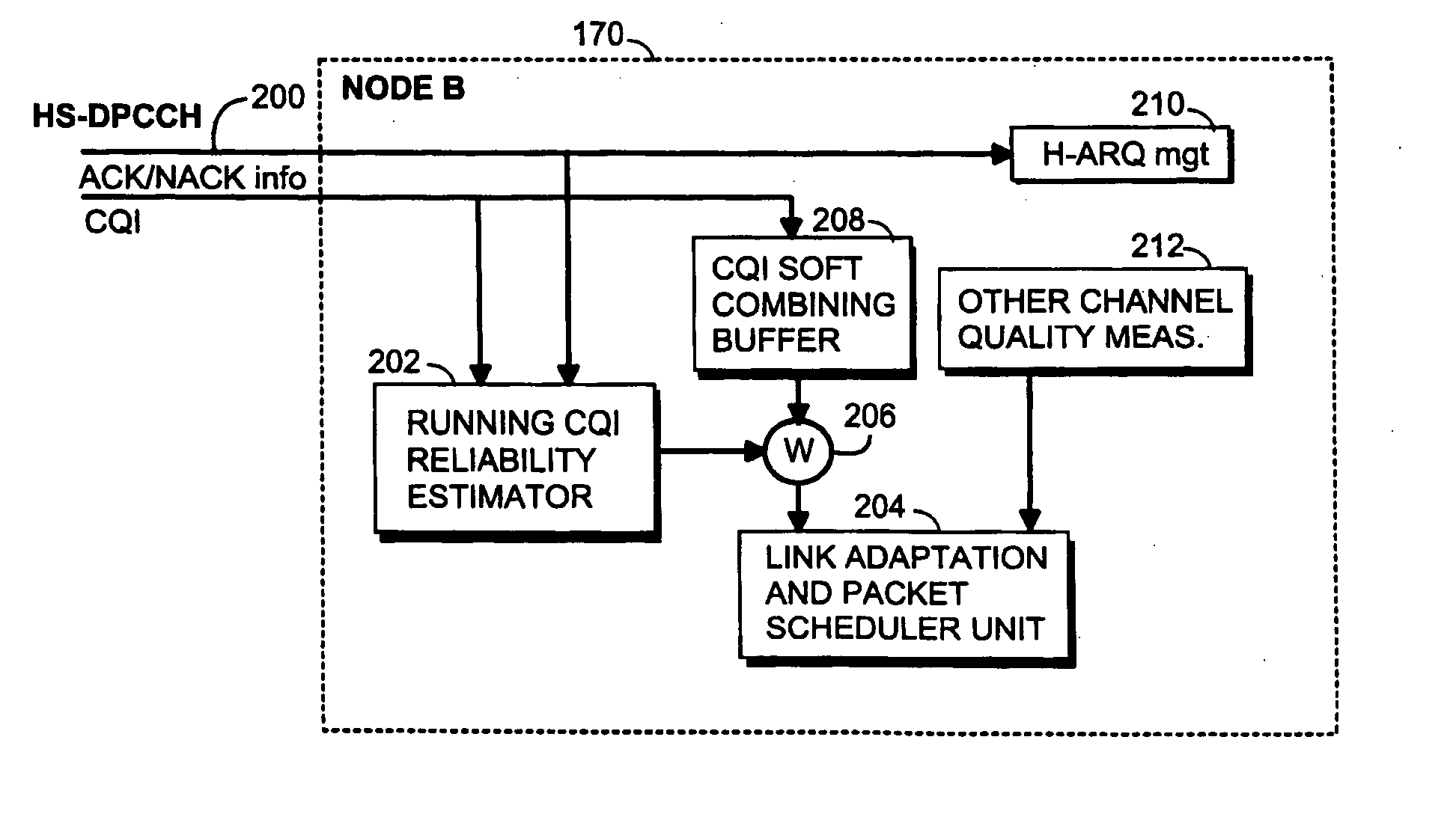
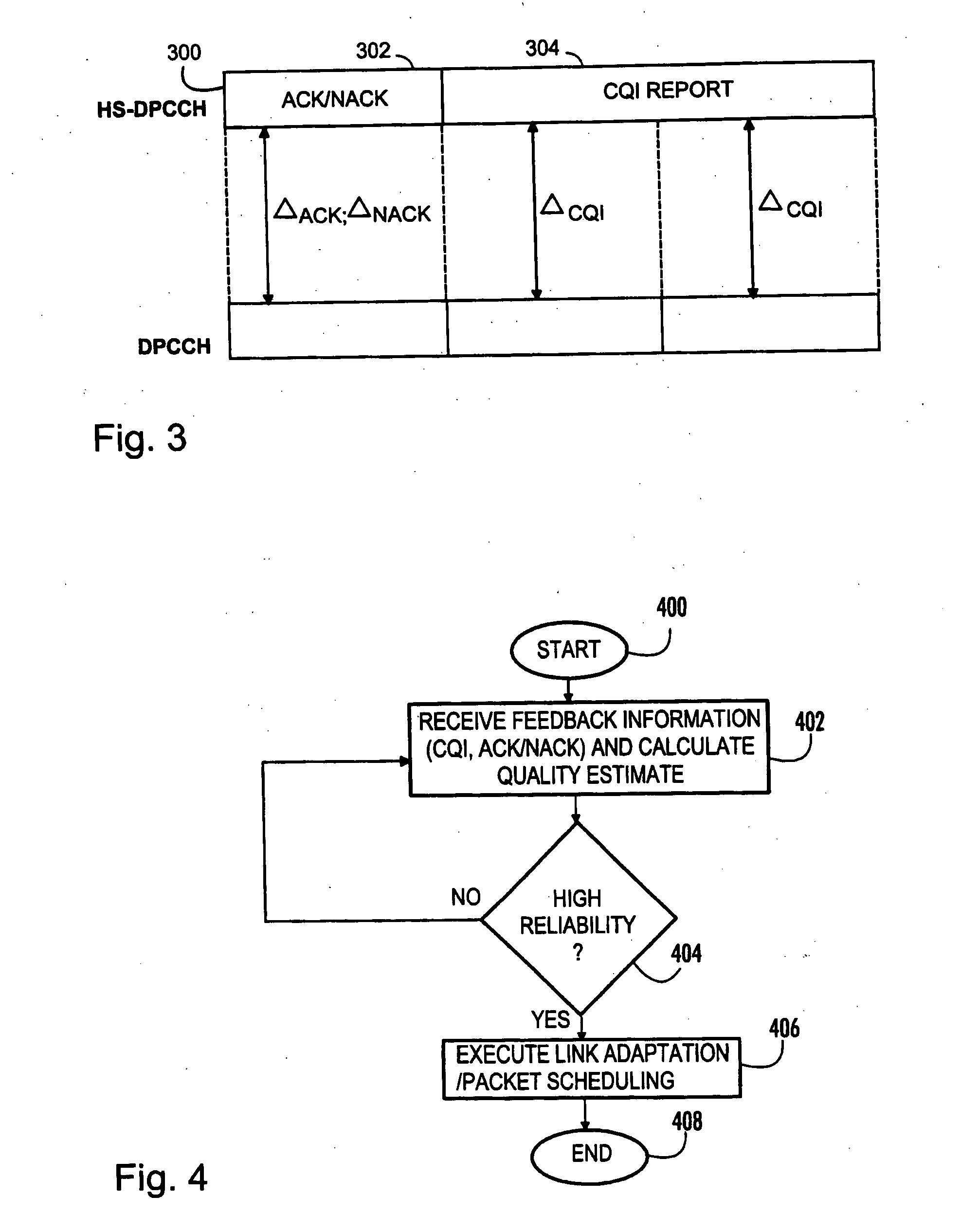
Method and base station for controlling link adaptation and packet scheduling in high speed downlink packet access (HSDPA) radio system
ActiveUS20050047387A1Improve estimation accuracyReduce delaysError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsPacket schedulingControl channel
A method of controlling link adaptation and packet scheduling in an HSDPA (High Speed Downlink Packet Access) radio system and an HSDPA base station communicating over a control channel with one or more user equipment units is provided. According to one embodiment the base station includes a device for receiving feedback information from the user equipment. The base station further includes a device for calculating a quality estimate related to the feedback information and executing link adaptation and packet scheduling based on the calculated quality estimate.
Owner:RPX CORP
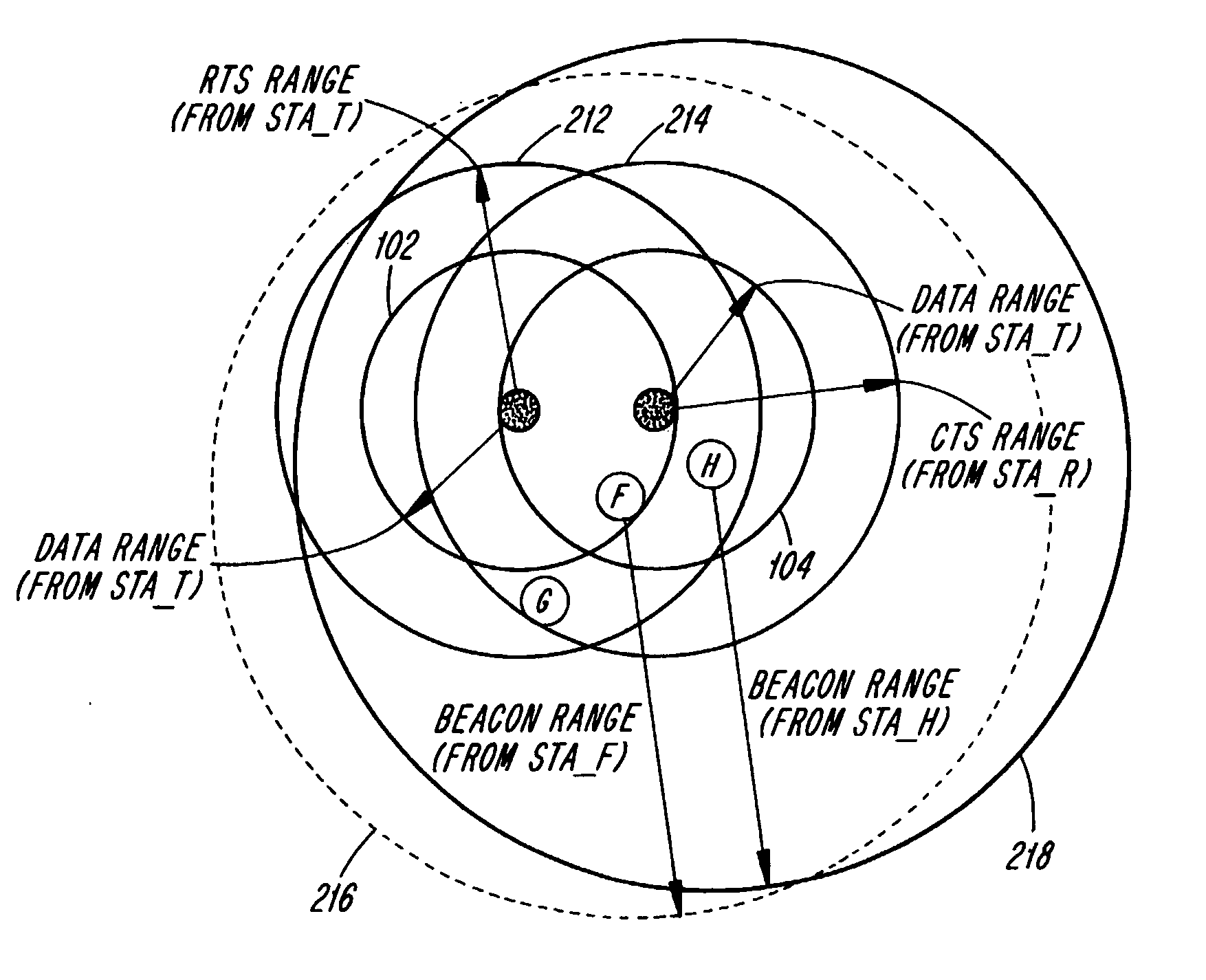
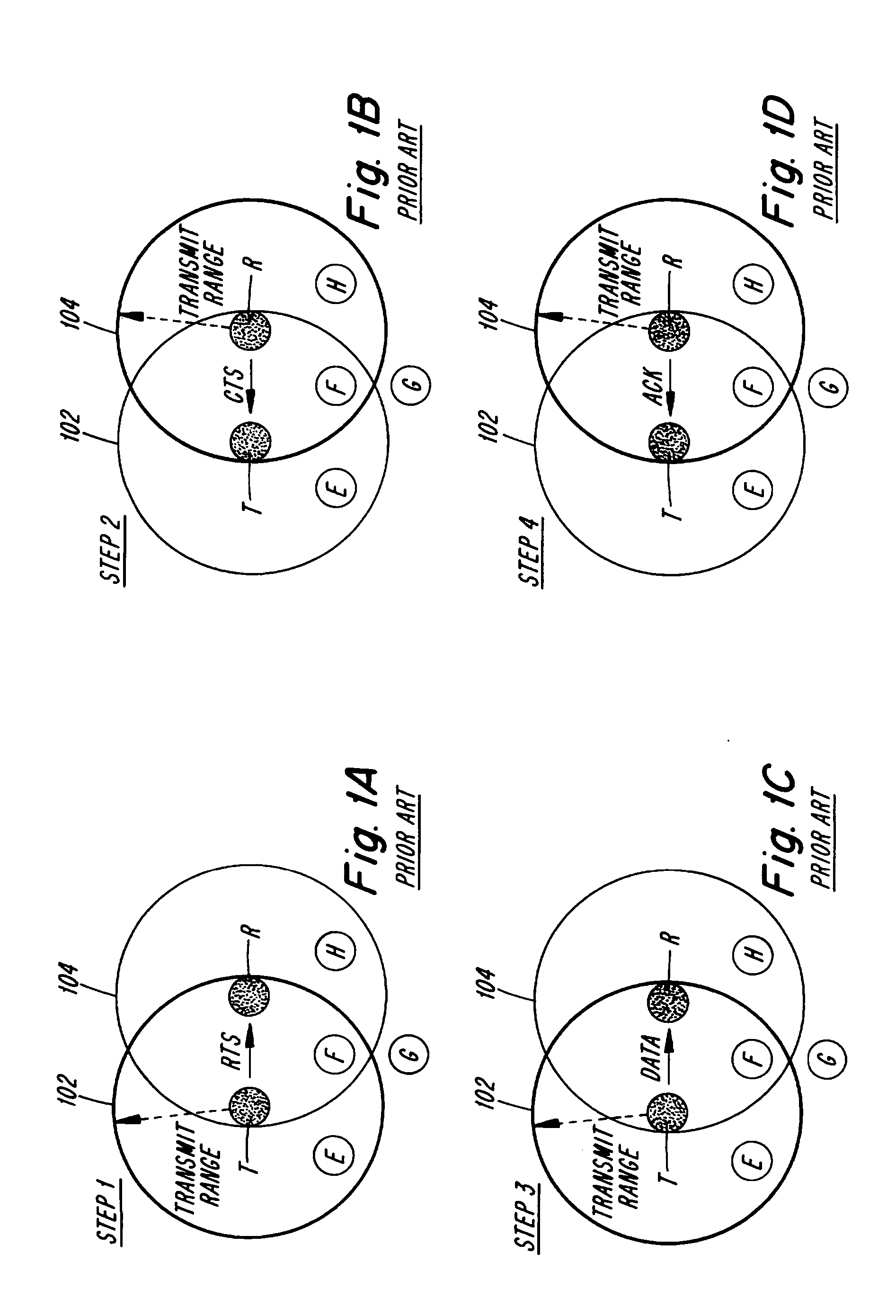
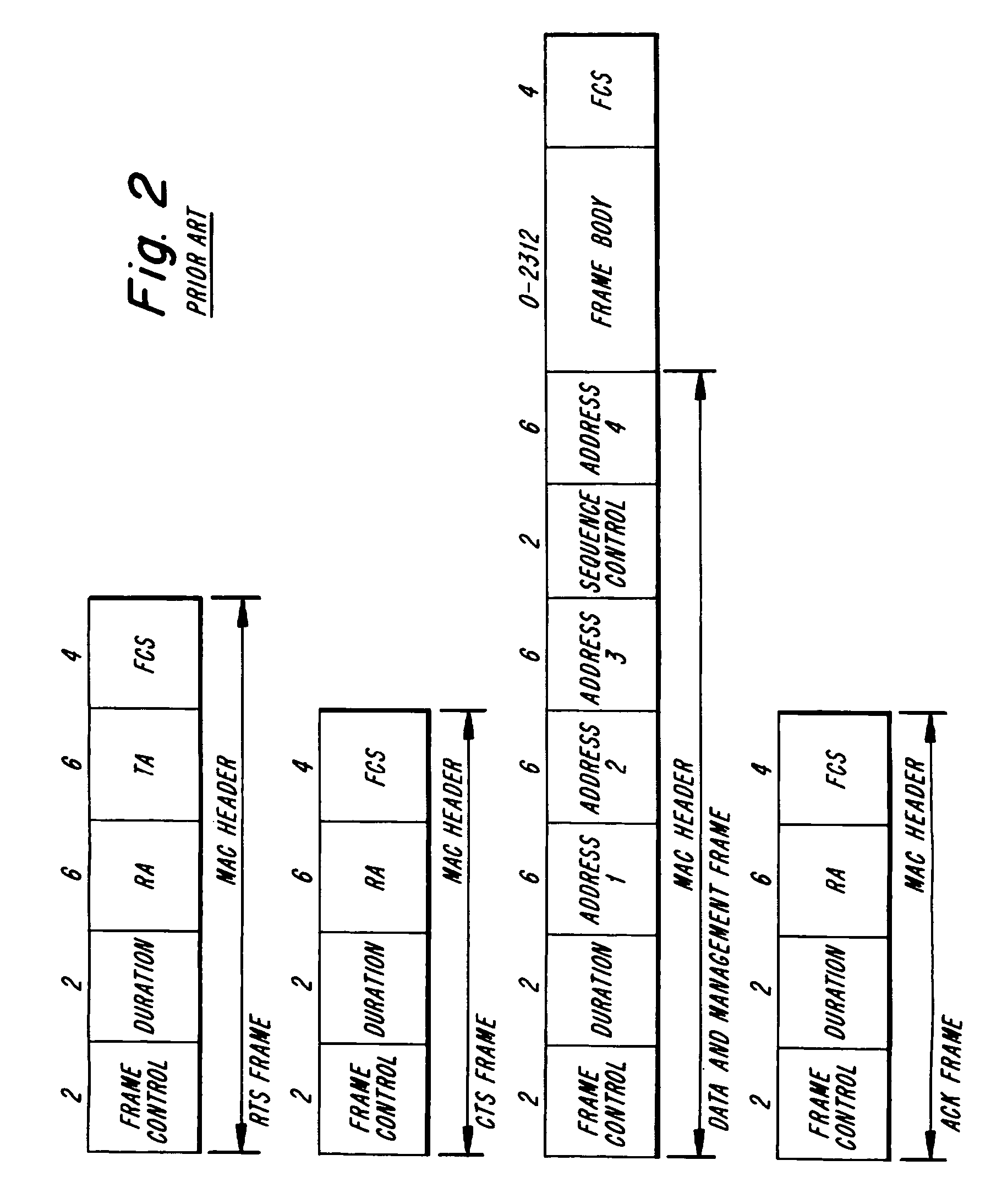
Instantaneous joint transmit power control and link adaptation for RTS/CTS based channel access
InactiveUS20080076466A1Improve system performancePower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementClear to sendStation
A method for closed loop link adjustment based on a Request To Send-Clear To Send (RTS-CTS) channel access scheme includes the following steps. Designating a station as an originating station. Transmitting a RTS frame with predetermined transmit power from an originating station, prior to an intended DATA transmission, sounding the channel such that reception characteristics can be evaluated at a designated receiving station. Transmitting, in response to the originating station, a CTS frame with a predetermined transmit power from the receiving station with directives of link adjustments. Transmitting a DATA frame from the originating station to the receiving station frame complying with link adjustment directives to the extent of the originating stations capabilities. And, transmitting an acknowledge (ACK) frame in response to the originating stations from the receiving station indicating result of DATA frame reception.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
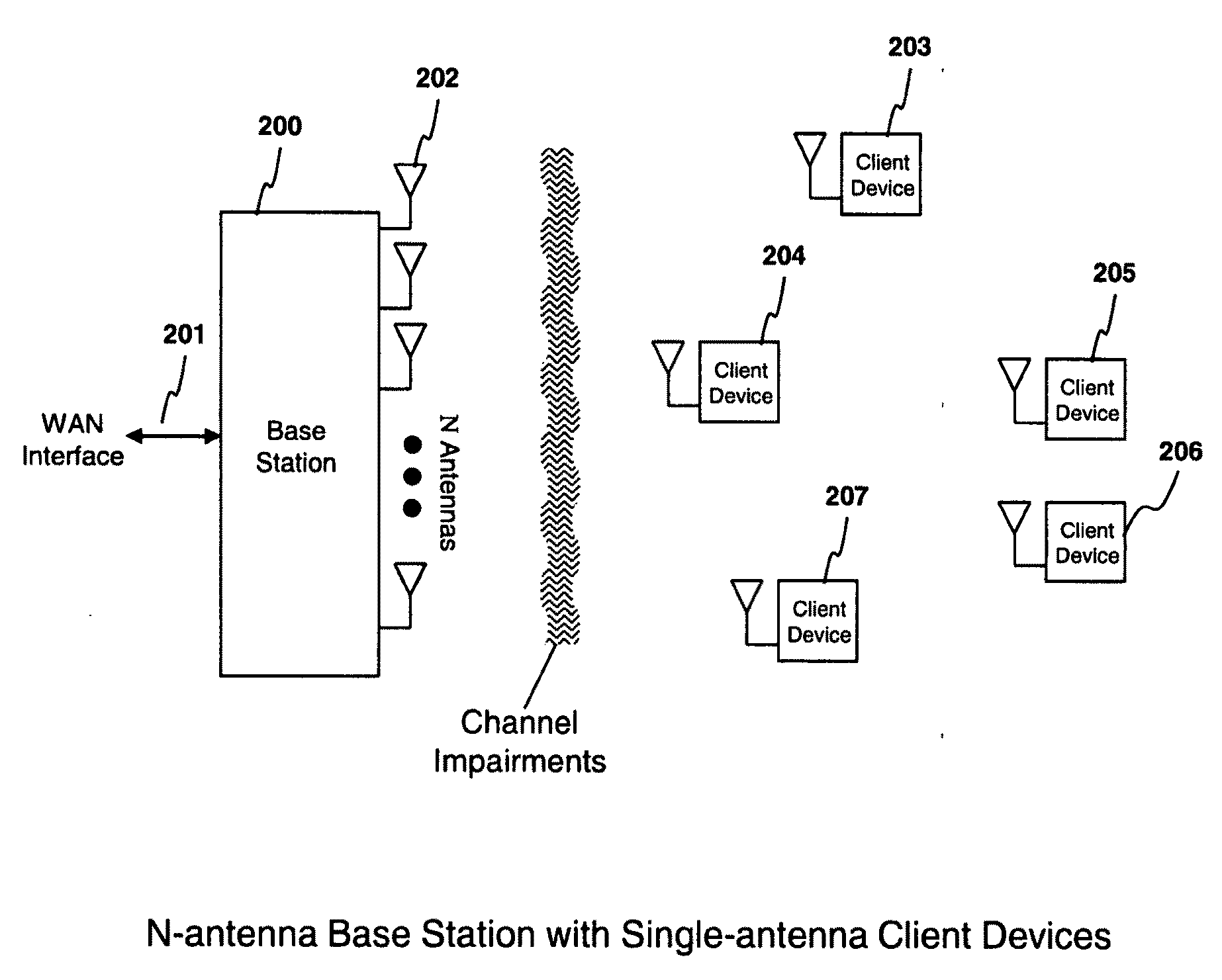
Adaptive channel bandwidth selection for MIMO wireless systems
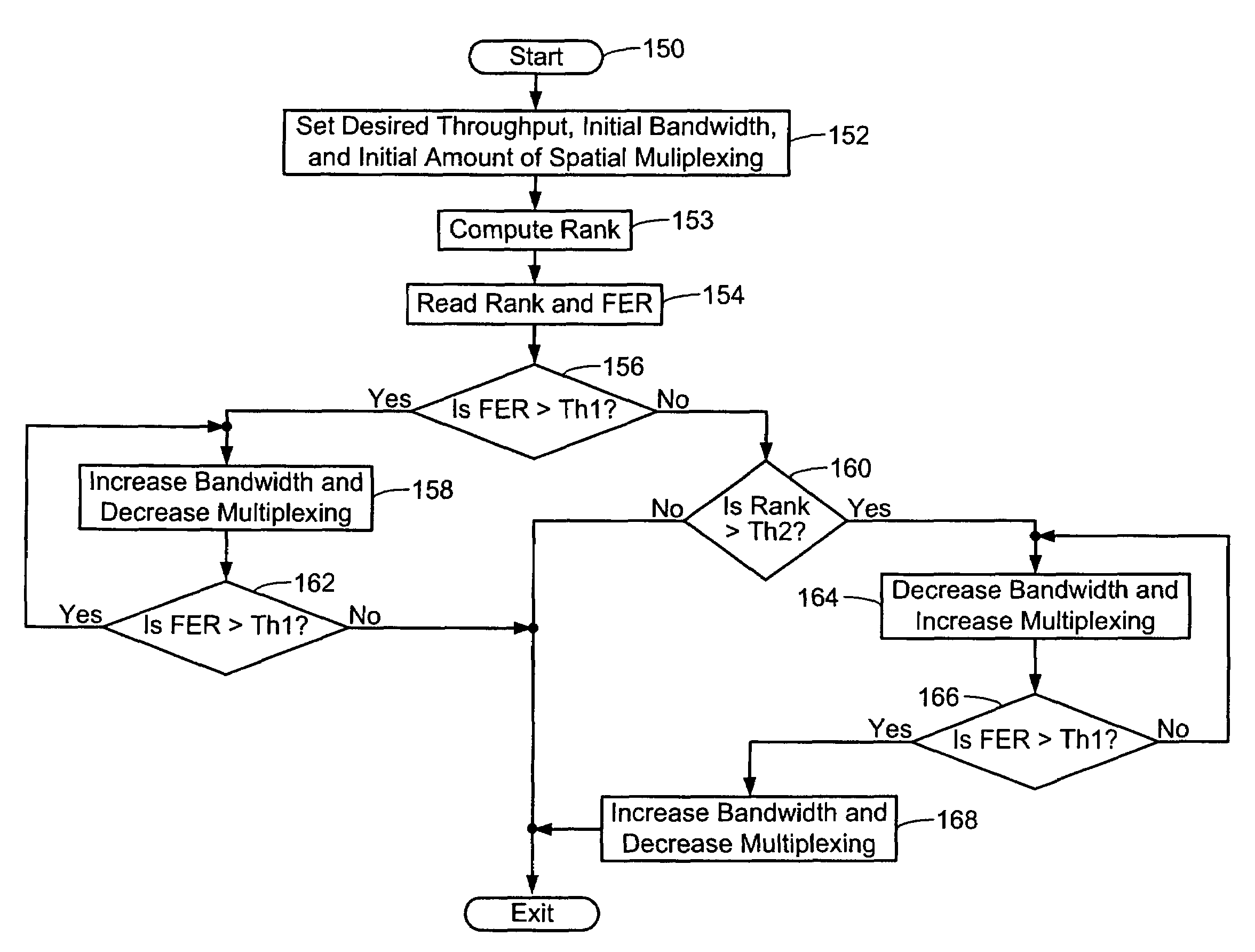
A wireless communications device for a multiple input multiple output wireless communications system includes a radio frequency transceiver that includes at least two antennae and a medium access control device that includes a link adaptation module. The link adaptation module dynamically adjusts a bandwidth of the wireless communications device based on a transmission error rate and a correlation measurement at a remote wireless communications device. A transmission error module receives the transmission error rate from the remote wireless communications device and generates a transmission error control signal. A signal correlation module receives the correlation measurement from the remote wireless communication device and generates a signal correlation control signal. The link adaptation module adjusts at least one of the bandwidth and an amount of spatial multiplexing that is executed by a space-time processor based on the transmission error control signal and the signal correlation control signal.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Method for determining whether to perform link adaptation in WCDMA communications
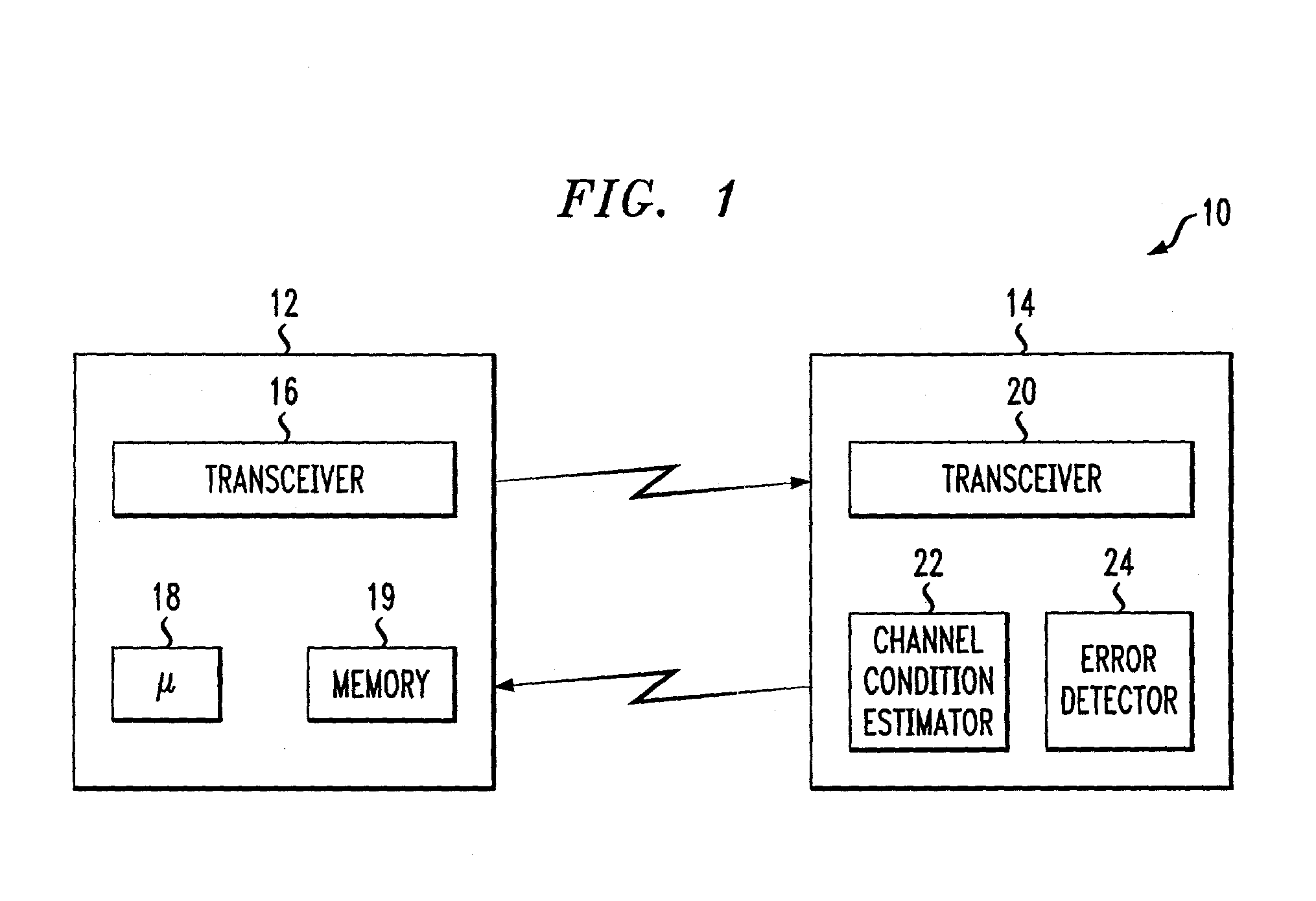
InactiveUS7027420B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorSignal qualityLink adaptation
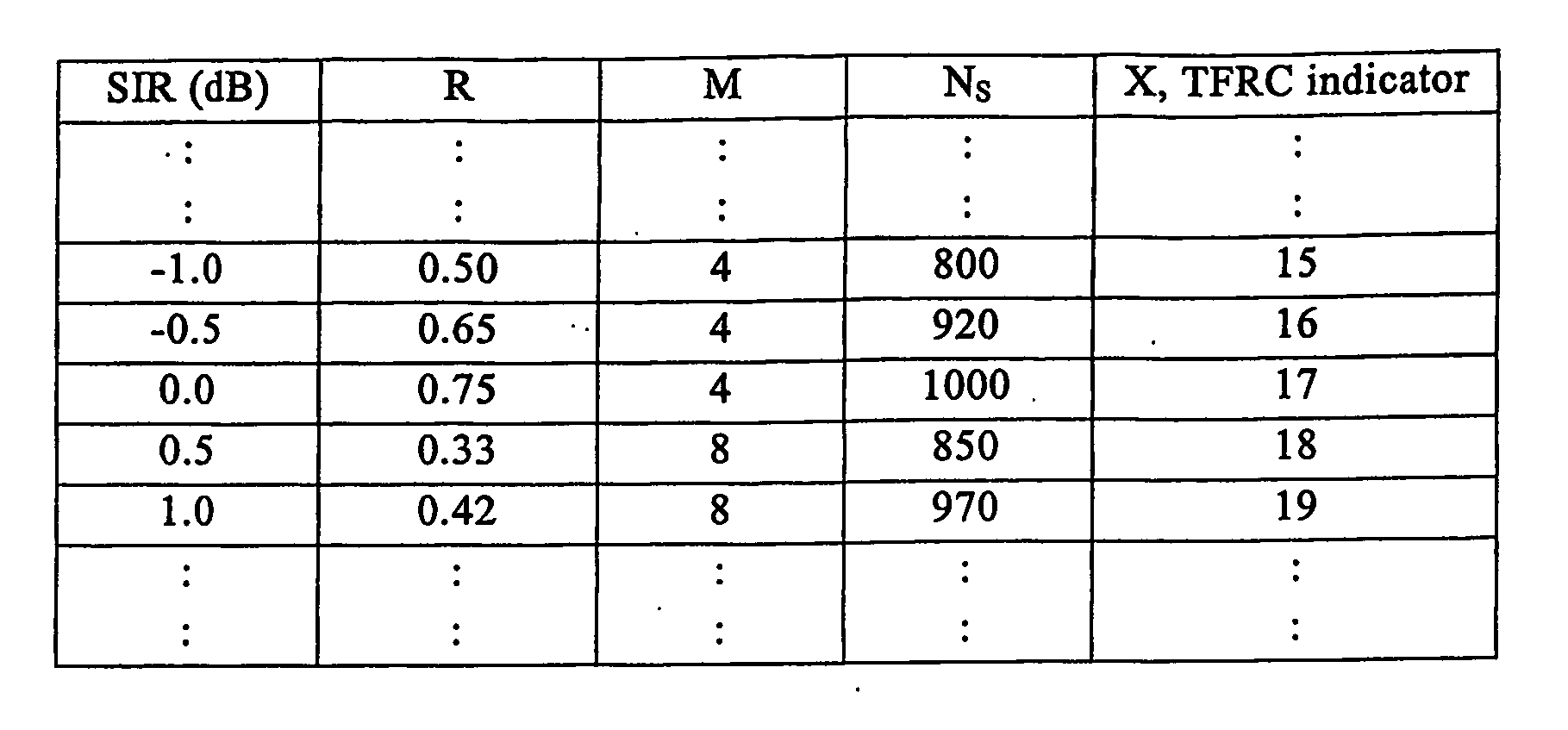
An apparatus and corresponding method for deciding whether to perform link adaptation for communication transmitted from a first communication device to a second communication device, where the second communication device examines a signal received from the first communication device and provides a first indication of the quality of the signal. The method includes the steps of: recording at least one first indication of the quality of the signal as received by the second communication device; providing a second indication of the quality of the signal based on the at least one first indication of the quality of the signal; and deciding to perform link adaptation based on the second indication of the quality of the signal. The first indication of the quality of the signal is for example a signal to interference ratio (SIR) estimate. Often, the second indication of the quality of the signal is a changed SIR target value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus of link adaptation in wireless local area network
ActiveUS20130250904A1Reduce overheadAvoid confictSpatial transmit diversityNetwork topologiesTelecommunicationsMimo transmission
A method of link adaptation performed by an access point supporting multi user(MU) multiple input multiple output(MIMO) in wireless local area network system is provided. The method includes transmitting, to a first station, a physical layer convergence procedure (PLCP) protocol data unit (PPDU) containing a modulation and coding scheme(MCS) request(MRQ) and receiving, from the first station, a MCS feedback(MFB) in response to the MRQ, wherein the first station is one of destination stations of MU-MIMO transmission performed by the access point, and the MFB includes a recommended MCS value computed, by the first station, on the assumption that the first station, as a member of the destination stations, receives data transmitted over at least one spatial stream allocated to the first station in MU-MIMO transmission.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
Link adaptation in general packet radio service networks
ActiveUS20030198312A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorGeneral Packet Radio ServiceTelecommunications network
In one embodiment of the method of adaptively selecting an airlink coding scheme in a telecommunications network, a coding scheme operating region is determined based on a currently used coding scheme and measurements representative of a block error rate. A block error coding scheme is determined based on the determined coding scheme operating region. In another embodiment of the method of adaptively selecting an airlink coding scheme in a telecommunications network, a first coding scheme is determined based on measurements representative of one or more conditional channel quality metrics, and a second coding scheme is determined based on measurements representative of a block error rate. One of the first and second coding schemes is selected as the coding scheme.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
Performance-based link adaptation techniques
InactiveUS20090116589A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringChannel state informationCommunications system
A multiple carrier wireless communications system includes a channel predictor, a performance predictor, and a link adapter. The channel predictor is configured to predict channel state information for a next packet based on channel state information for the current packet. The performance predictor includes an uncoded performance predictor configured to predict system performance at an input of a decoder based on a modulation type and the predicted channel state information for the next packet, and a decoder input-output performance mapper configured to determine a required coding rate based on a requested system performance and the predicted system performance at the input of the decoder. The link adapter includes a modulation and coding scheme (MCS) updater configured to identify a MCS based on the required coding rate.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
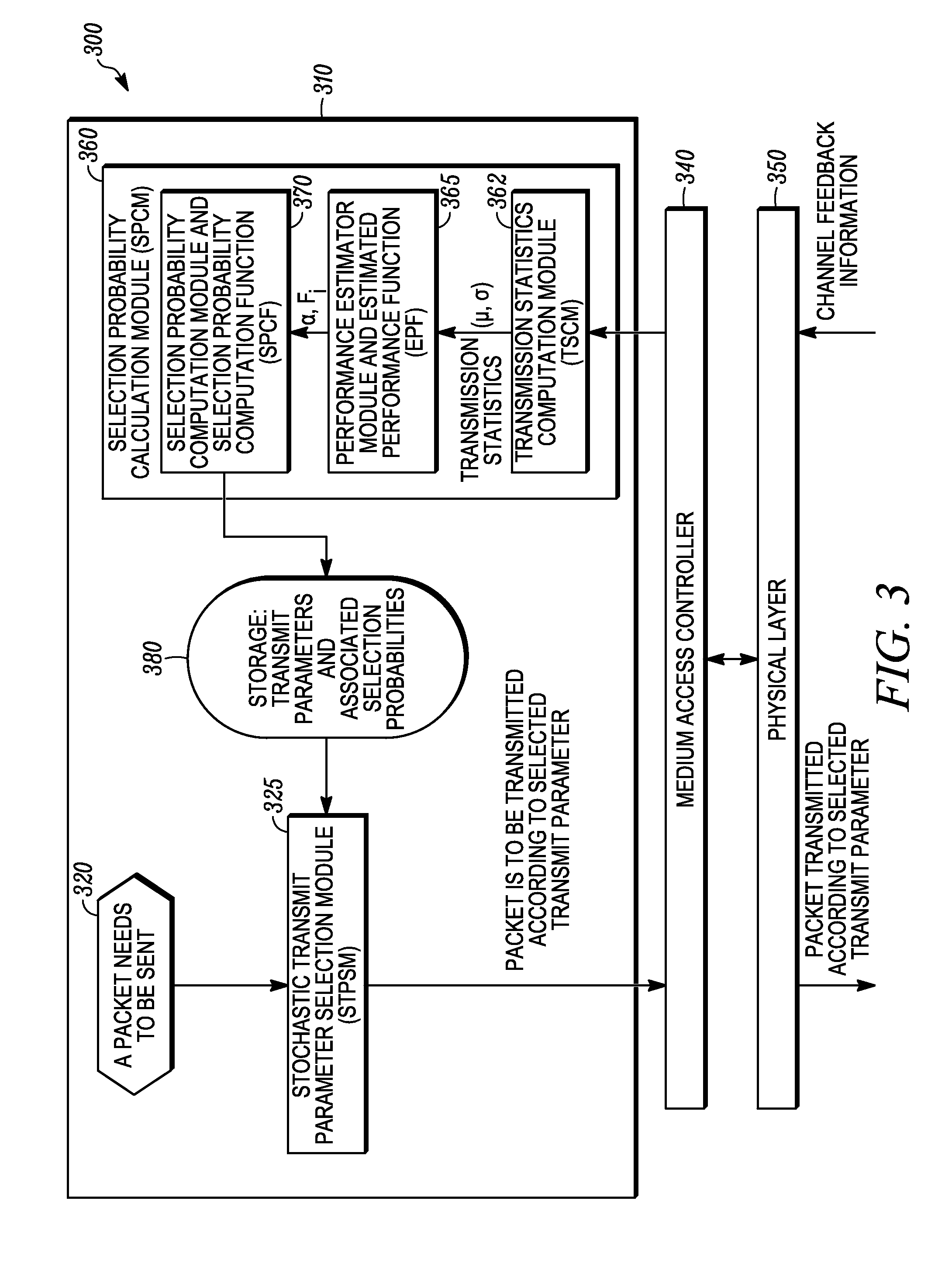
Method and apparatus for link adaptation by stochastically selecting a transmit parameter
A method and apparatus for link adaptation is provided. A node stores a set of transmit parameters and corresponding selection probabilities for each of the transmit parameters. The node stochastically selects a particular transmit parameter based on the selection probabilities, and then transmits a packet according to the particular selected transmit parameter. From received transmission feedback information, the node derives performance statistics, and uses the performance statistics to specify an estimated performance function for the particular transmit parameter. The node updates a selection probability computation function (SPCF), and uses the SPCF to generate updated selection probabilities corresponding to each transmit parameter in the set of available transmit parameters.
Owner:ARRIS ENTERPRISES LLC
Method of link adaptation in wireless local area network and apparatus for the same
ActiveUS20130188630A1Improve throughputNetwork topologiesSignalling characterisationTelecommunicationsWireless lan
A method of link adaptation in a wireless local area network is provided. The method includes requesting, by a requester, modulation and coding scheme (MCS) feedback to a plurality of responders, by transmitting a MCS request (MRQ) indicator, and, receiving, by the requester, feedback frames from each of the plurality of responders, wherein each of the feedback frame comprises MCS feedback (MFB) information.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
System and method for link adaptation in communication systems
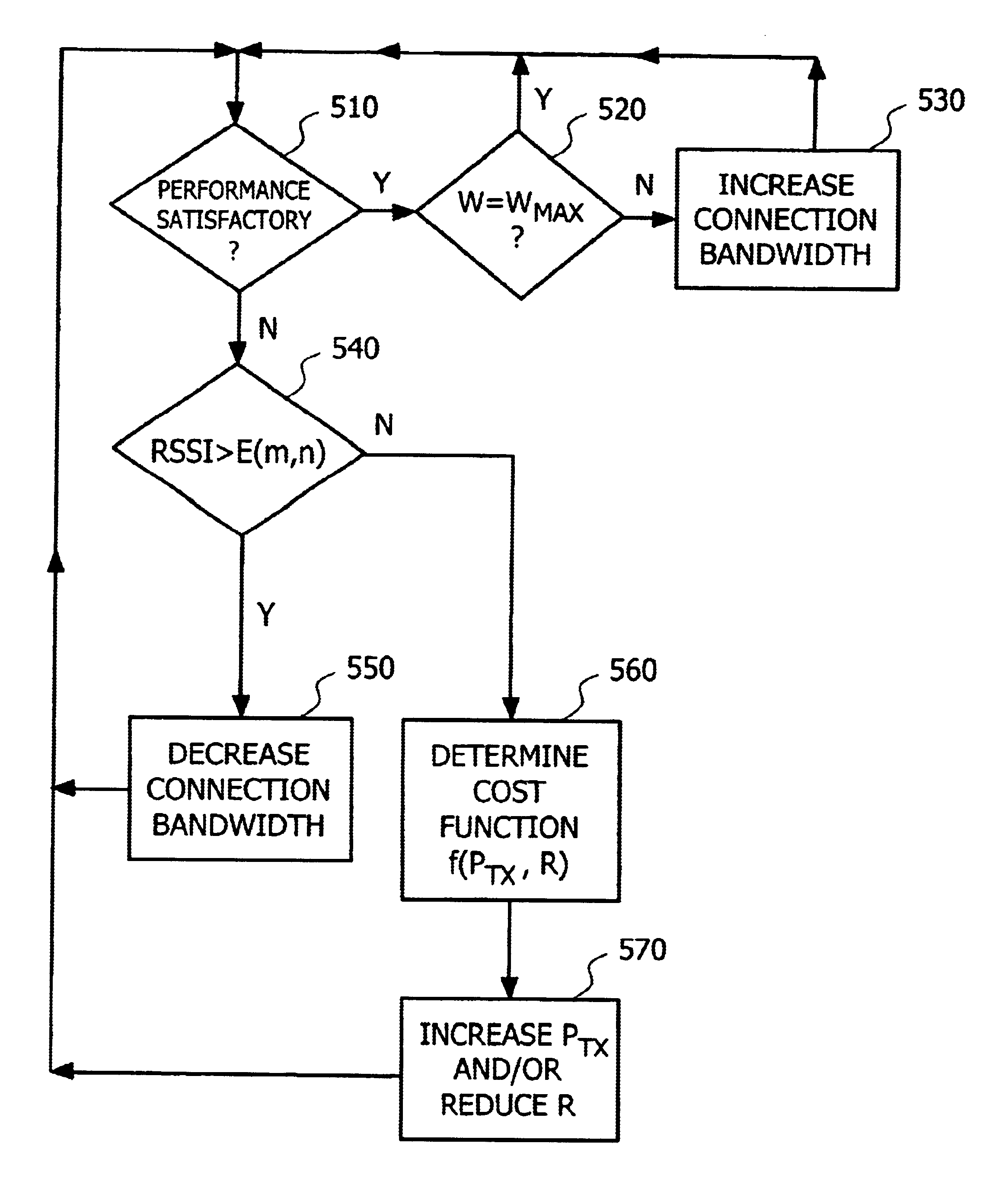
InactiveUS6944460B2Increase channel bandwidthSignal rate can be loweredEnergy efficient ICTPower managementTelecommunications linkCommunications system
A system, method, and computer program product for allocating resources to a communication channel between a transmitter and a receiver are disclosed. The receiver implements a procedure that instructs the transmitter to utilize the maximum available bandwidth, consistent with maintaining satisfactory communication channel performance. When the performance of the communication channel degrades, the receiver measures the strength of a communication signal received from the transmitter. If the communication signal strength satisfies a threshold, then the bandwidth dedicated to the communication channel may be decreased, and at least one of the number of bits per symbol and coding rate may be increased. By contrast, if the communication signal strength fails to satisfy a threshold, then the transmitter may increase the transmission power and / or reduce the user rate of the communication link.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Channel efficiency based packet scheduling for interactive data in cellular networks
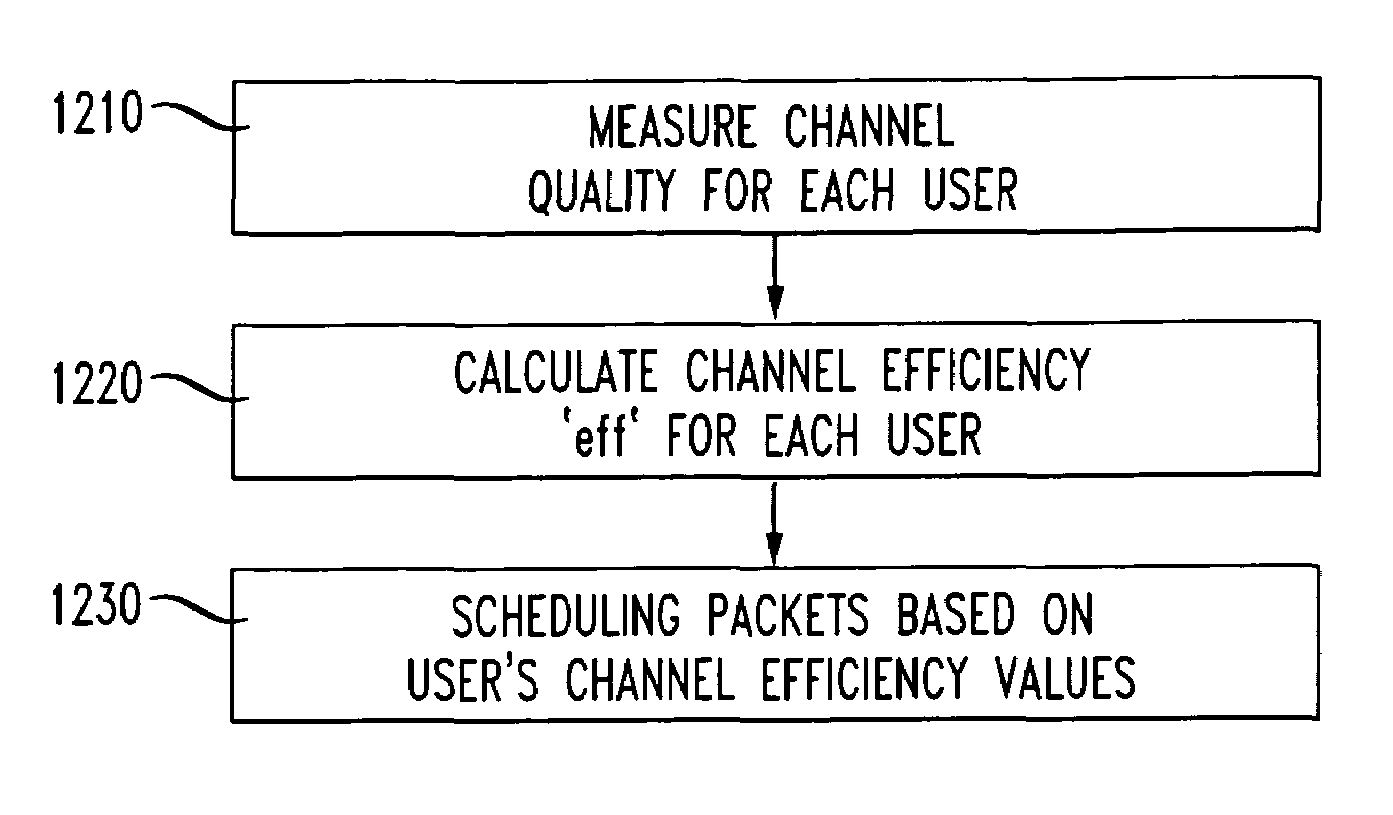
InactiveUS7046678B2More modulation schemeEffectively channelError preventionTransmission systemsTrade offsLink adaptation
The present packet scheduling algorithm gives cellular network operators greater flexibility in adjusting the way resources are allocated among interactive best-effort data users. Best effort data users with different radio link qualities may have different amounts of data delivered to them using the same amount of radio resource. In the context of link adaptation, this characteristic complicates the fairness issue in cellular environments and has a profound impact on the overall system performance. As a result, the present packet scheduling algorithm is capable of allocating radio resource dynamically, not only based on channel conditions, but also to achieve different performance trade-offs among users with different link qualities. According to the algorithm, channel quality is determined for each user, channel efficiency is calculated and the channel efficiency value is used as the primary factor in weighting the delivery of packets to (or from) a given user. In a packet schedule weighting equation, a value of exponent may be varied from negative to positive to give good (or bad) users better service. However, performance of users with bad channel qualities degrades the performance of good channel users in a disproportionate manner. It is shown that it is frequently preferable to favor users with good channel qualities.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
Method and arrangement for transmitting cq1 on the uplink
ActiveUS20090323541A1Reduce resultReduce wastePower managementFrequency-division multiplex detailsData streamEngineering
A method for transmitting data flows between a network element and a number of receivers over a first channel. The method comprises the steps of: performing a link adaptation for the transmission of a data flow by said network element, and transmitting the data flow, transmitting an indication of a channel quality required for reception of the data flow on a second channel, receiving by said receivers said indication of channel quality, measuring a link quality by said receivers by monitoring a pilot channel, comparing said measured link quality with said received indication of the channel quality, and transmitting to said network element result of said comparison of said measured link quality with said received indication of the channel quality, if said result is lower than a predetermined value. The invention also relates to a network element and a user equipment.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com