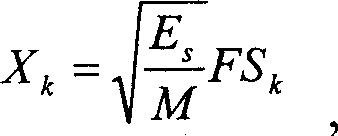Patents
Literature
144 results about "Coherence time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
For an electromagnetic wave, the coherence time is the time over which a propagating wave (especially a laser or maser beam) may be considered coherent, meaning that its phase is, on average, predictable. In long-distance transmission systems, the coherence time may be reduced by propagation factors such as dispersion, scattering, and diffraction. The coherence time, usually designated τ, is calculated by dividing the coherence length by the phase velocity of light in a medium; approximately given by τ=1/Δν≈λ²/(c Δλ) where λ is the central wavelength of the source, Δν and Δλ is the spectral width of the source in units of frequency and wavelength respectively, and c is the speed of light in vacuum.
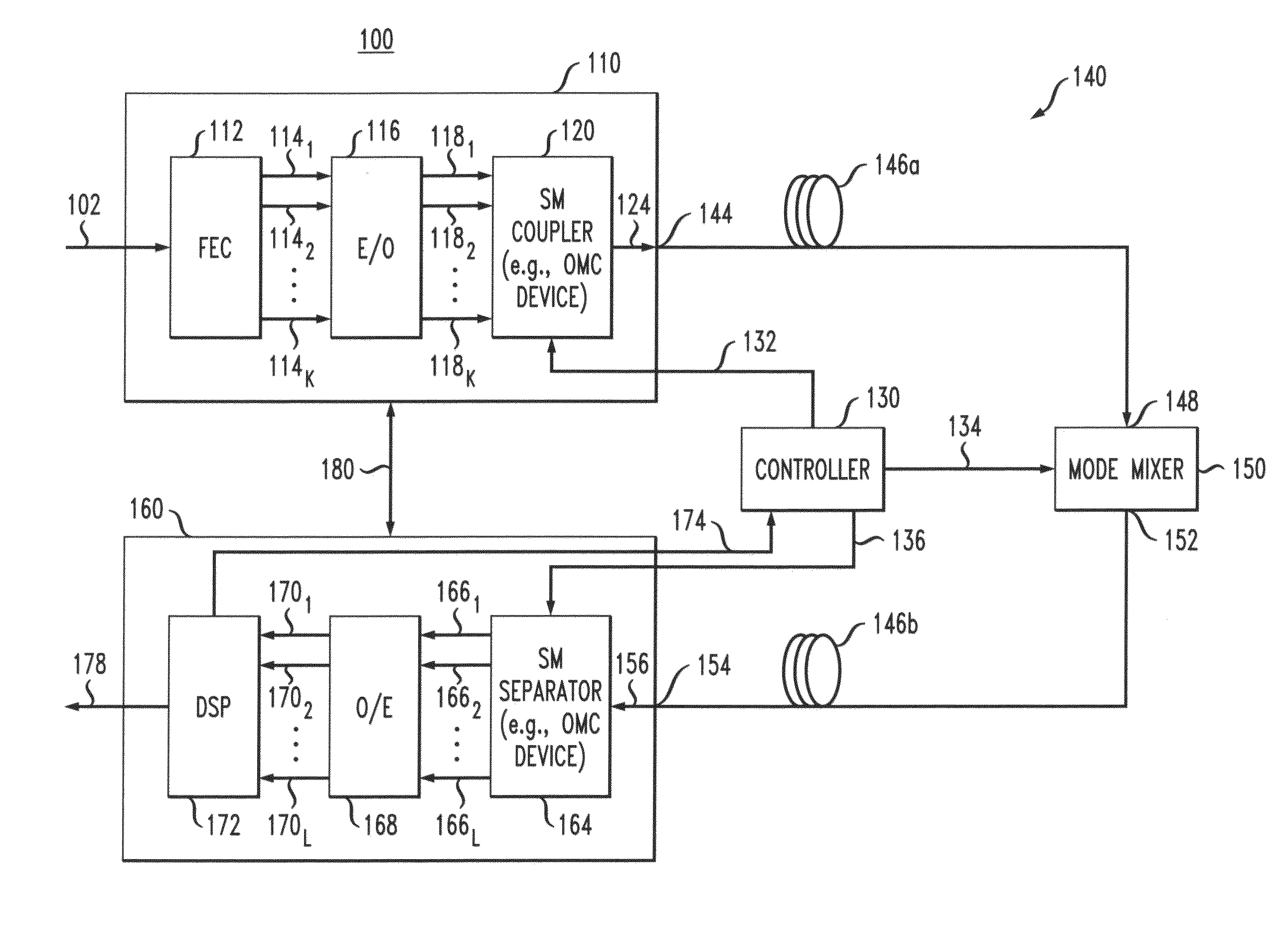
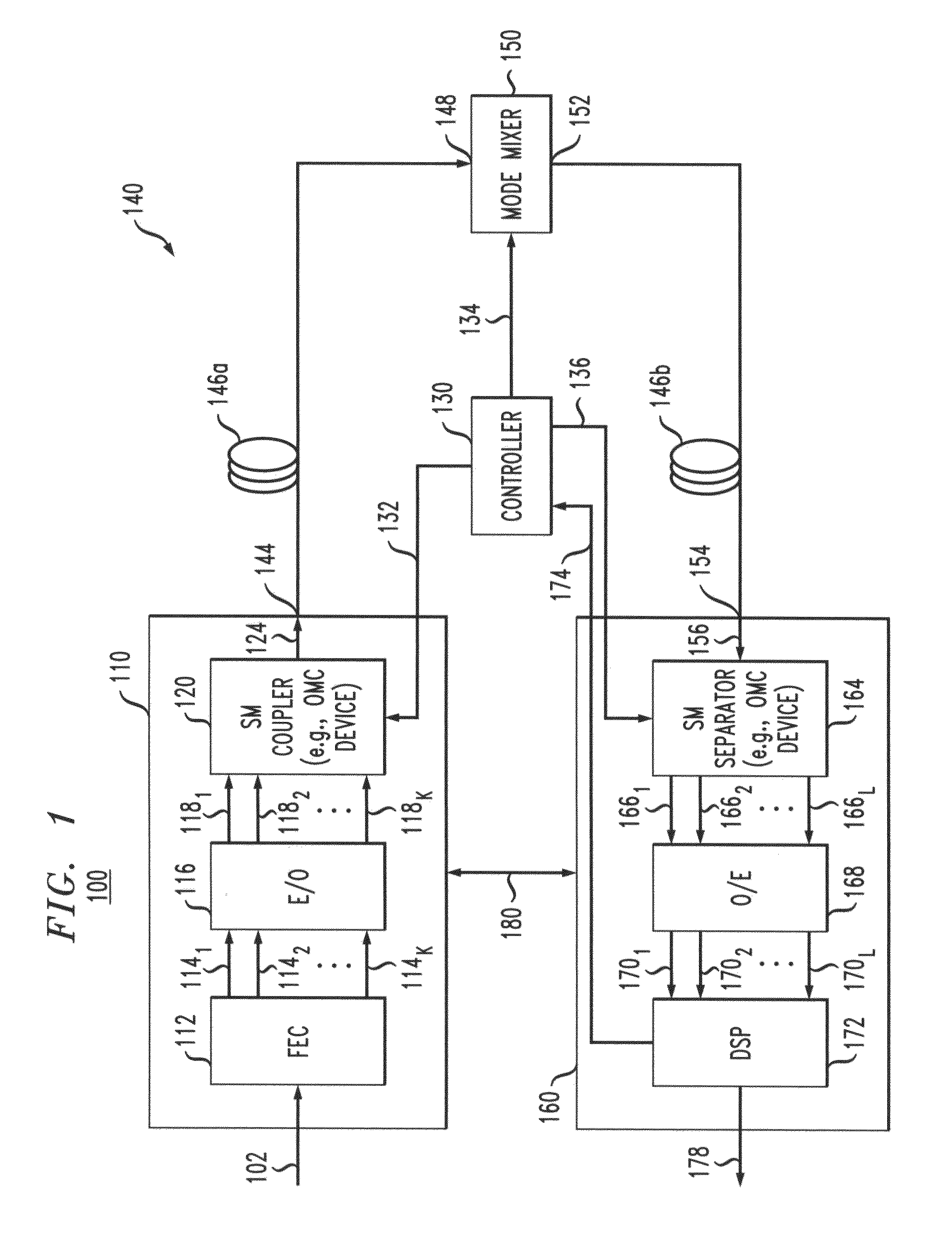
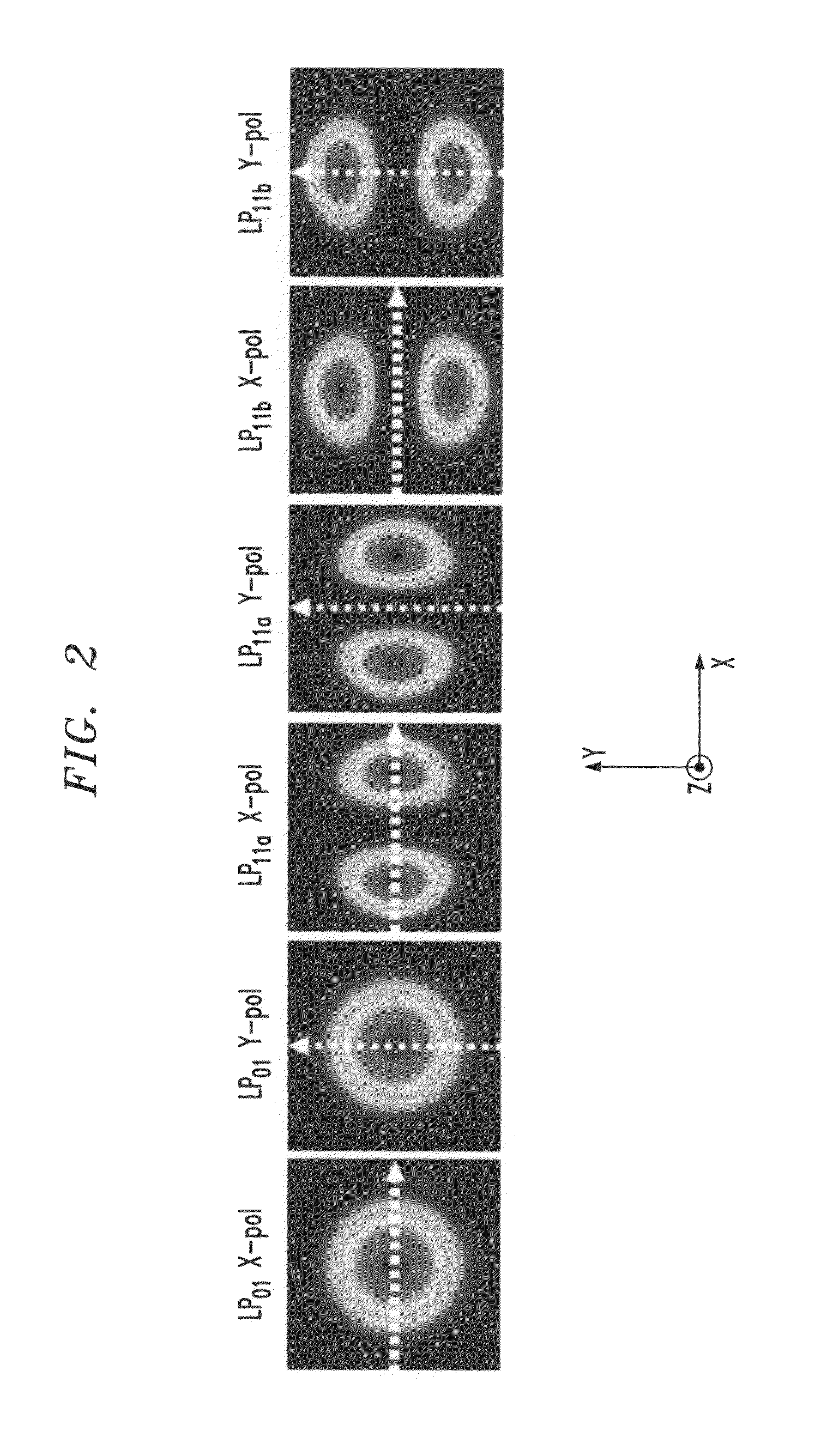
Intra-link spatial-mode mixing in an under-addressed optical MIMO system
ActiveUS20120224807A1Reduce frequencyReduce outage rateOptical mode multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesCoherence timeError correcting
The outage probability in an under-addressed optical MIMO system may be reduced by configuring an intra-link optical mode mixer to dynamically change the spatial-mode mixing characteristics of the link on a time scale that is faster than the channel coherence time. Provided that the MIMO system employs an FEC code that has a sufficient error-correcting capacity for correcting the amount of errors corresponding to an average state of the MIMO channel, this relatively fast dynamic change tends to reduce the frequency of events during which the number of errors per FEC-encoded block of data exceeds the error-correcting capacity of the FEC code.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
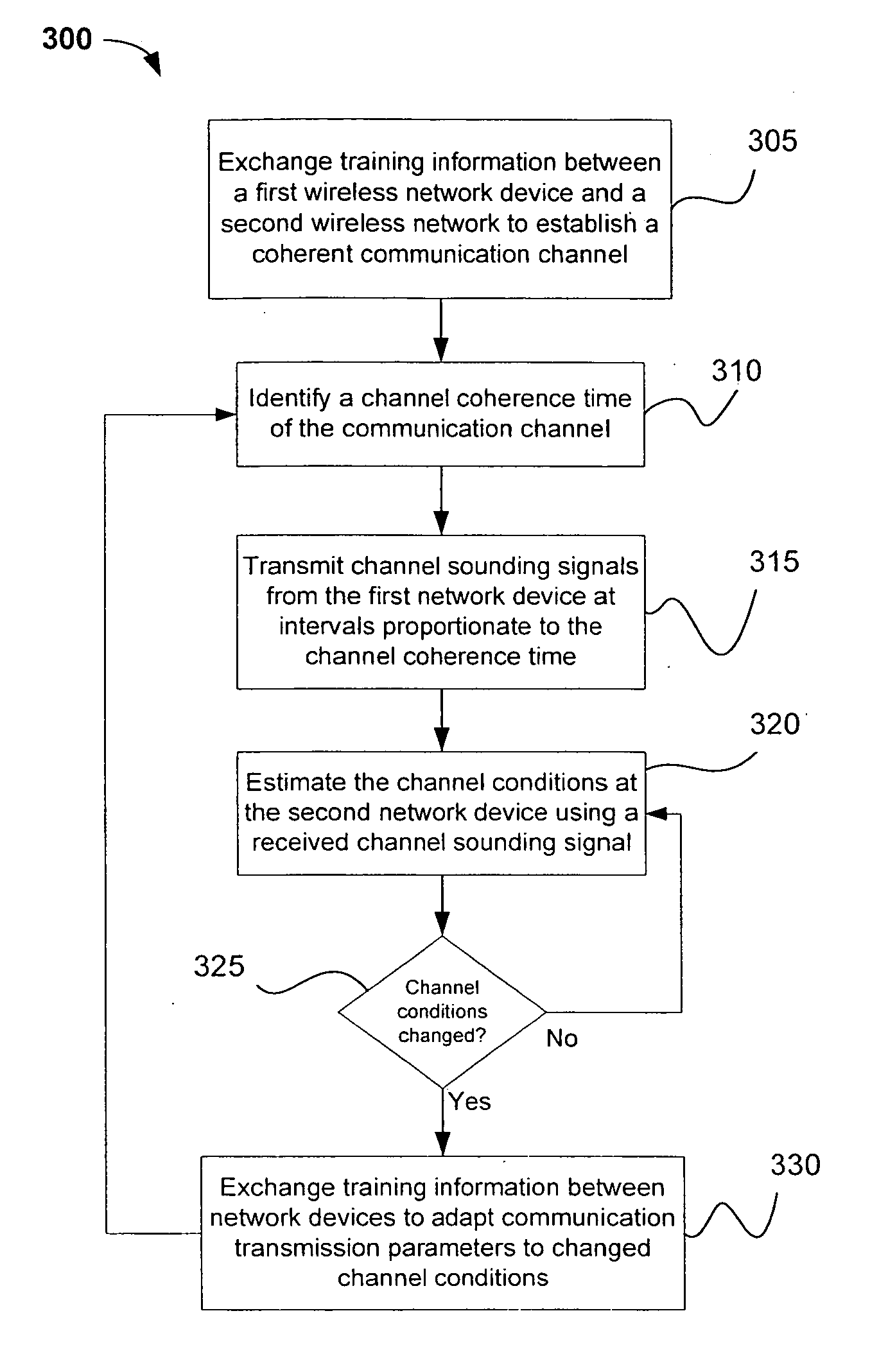
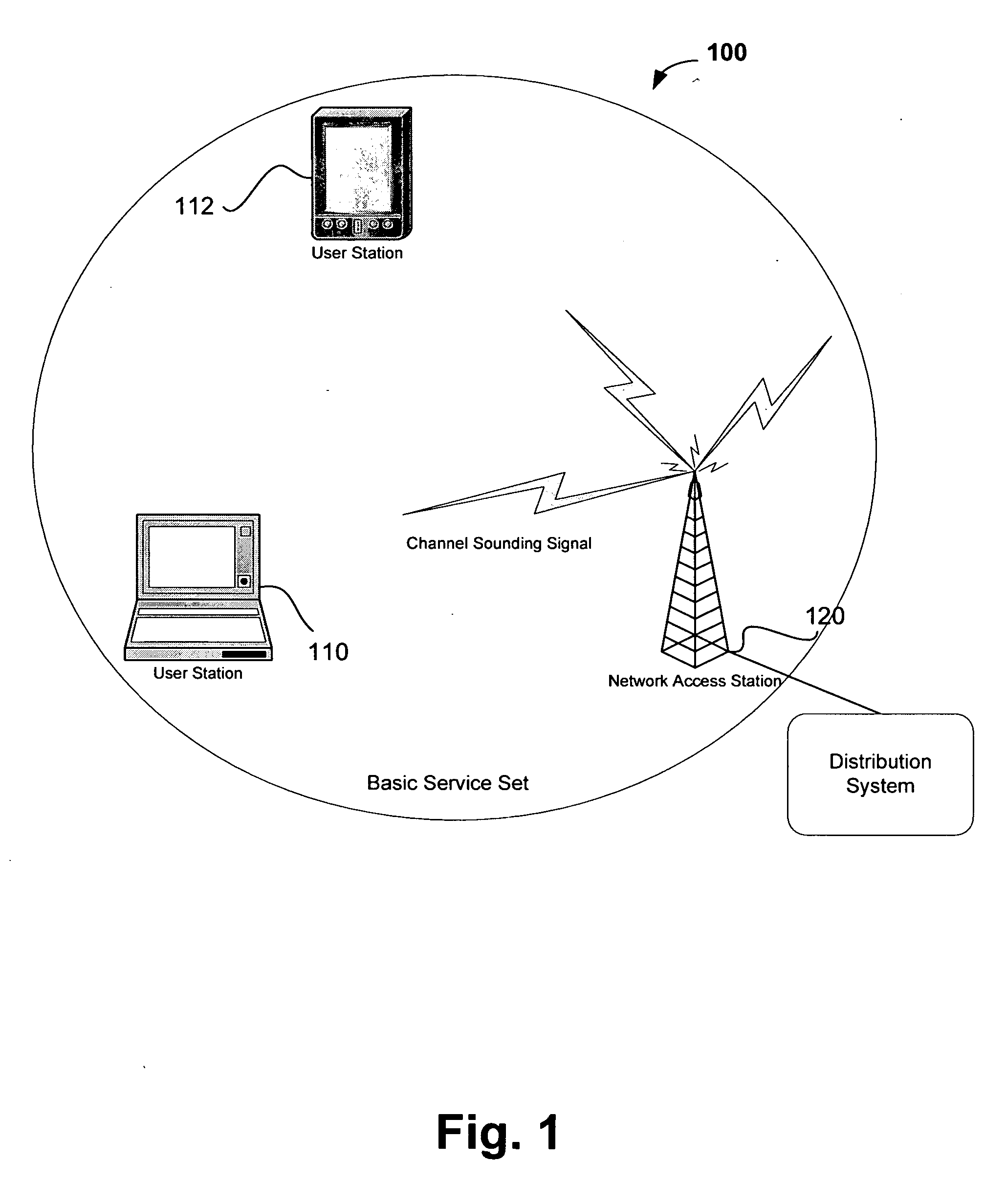
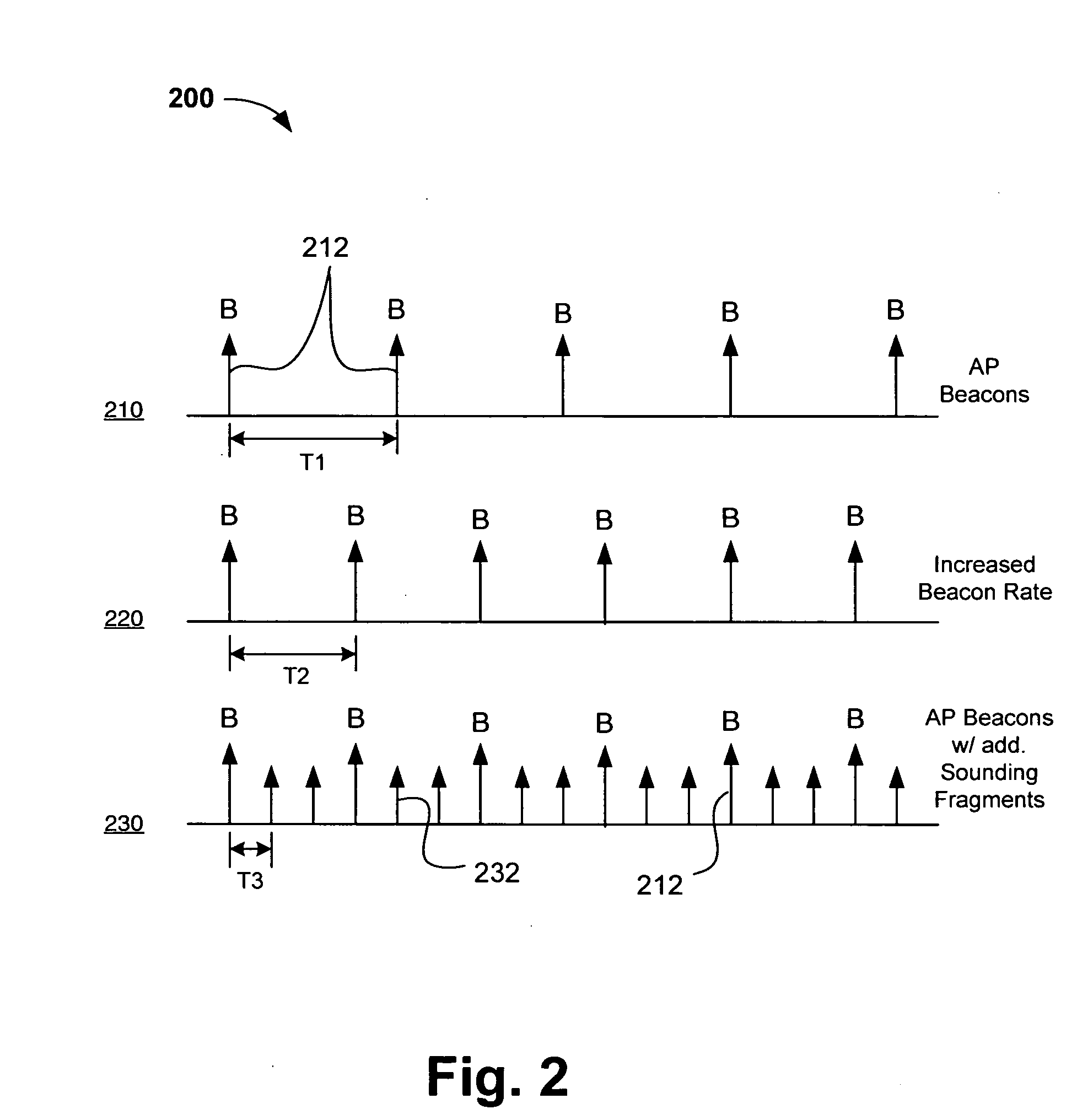
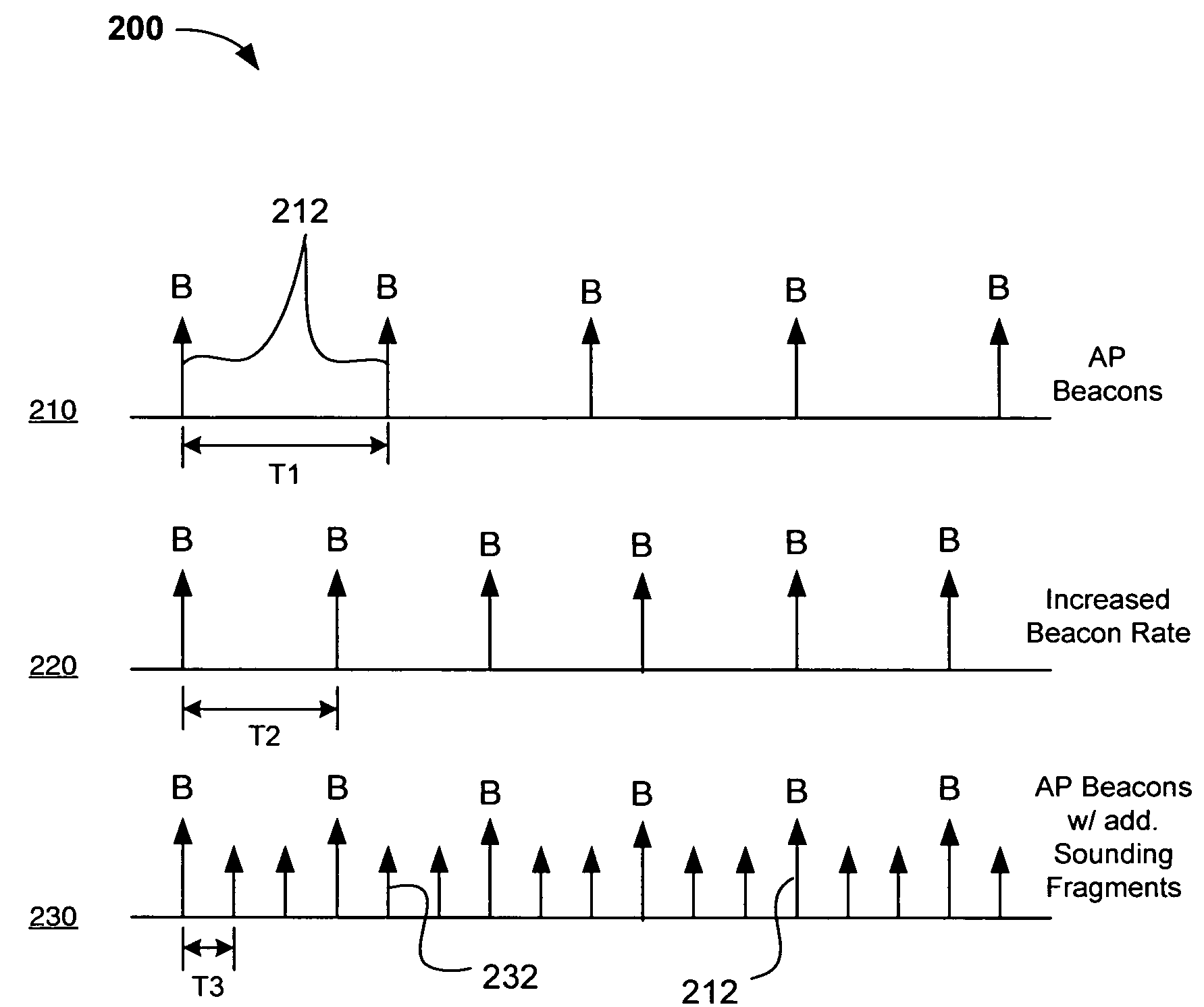
Channel adaptation using variable sounding signal rates
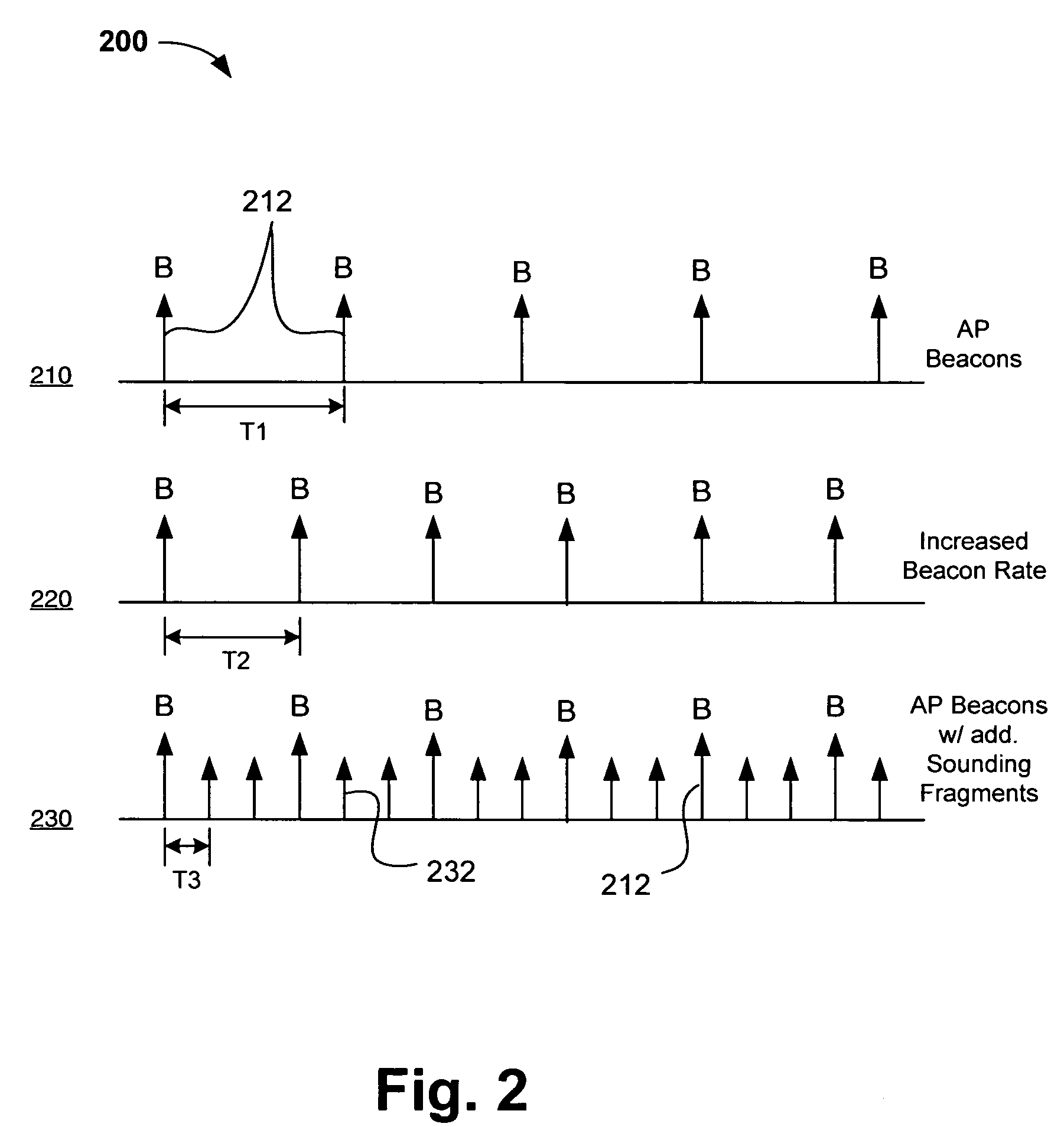
InactiveUS20050170781A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorFrequency-division multiplex detailsCoherence timeLink adaptation
Systems, devices and methods for updating link adaptations in multi-carrier modulated signals between an access point (AP) and a wireless local area network (WLAN) station (STA) include (are configured for) periodically transmitting a channel sounding signal from the AP. The STA receives each unsolicited channel sounding signal and evaluates the current channel conditions between the AP and STA. The AP adjusts a rate of transmission of the channel sounding signals in accordance with the channel coherence time so that the channel estimates performed by the STA will be valid within the time varying characteristics of the channel. Depending on the length of the coherence time for network environment, the channel sounding signals may be AP beacons, low overhead signal fragments with no payload, or a combination of both.
Owner:INTEL CORP
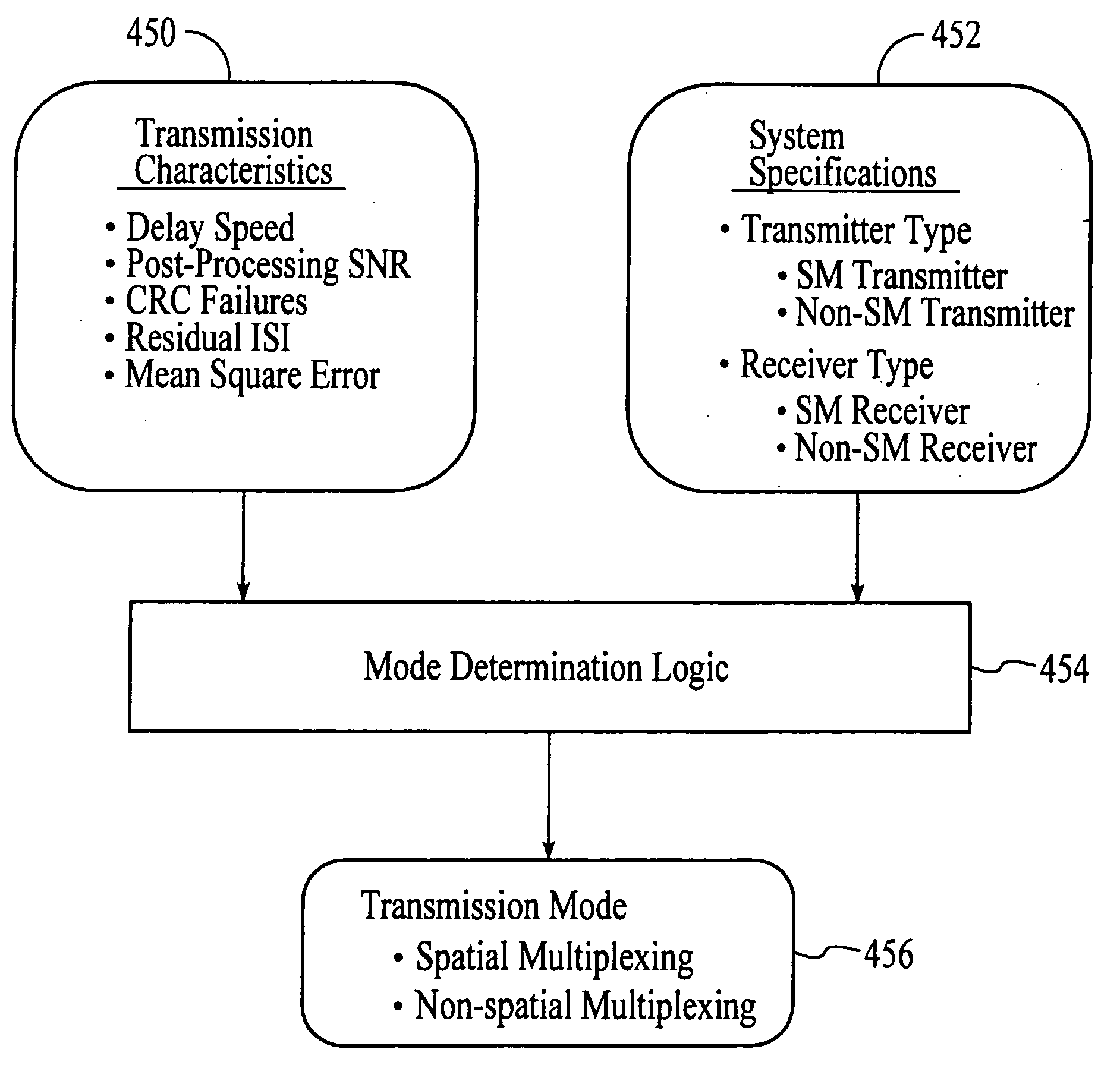
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
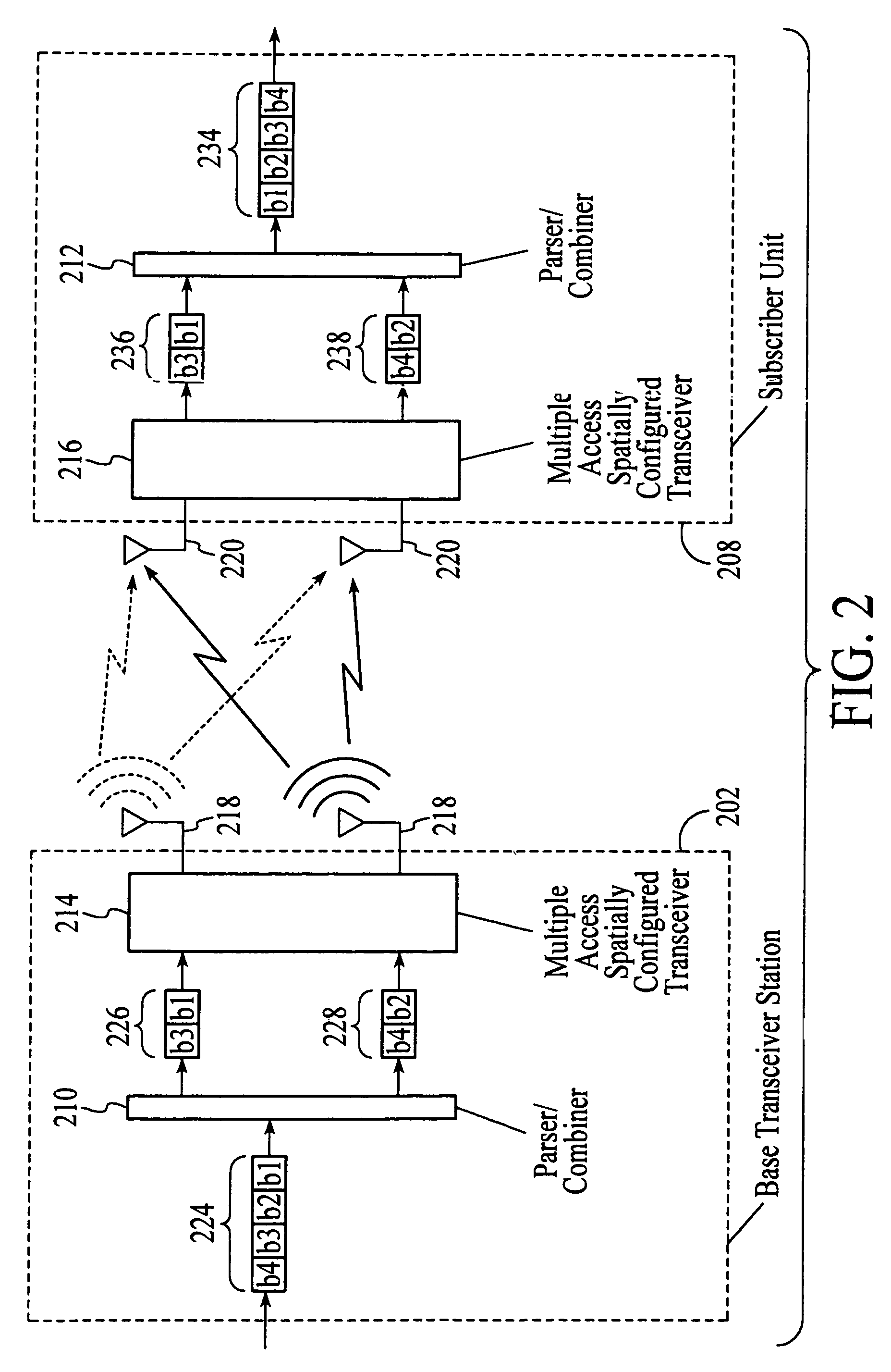
InactiveUS20050174981A1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionTransceiverMultiple modes
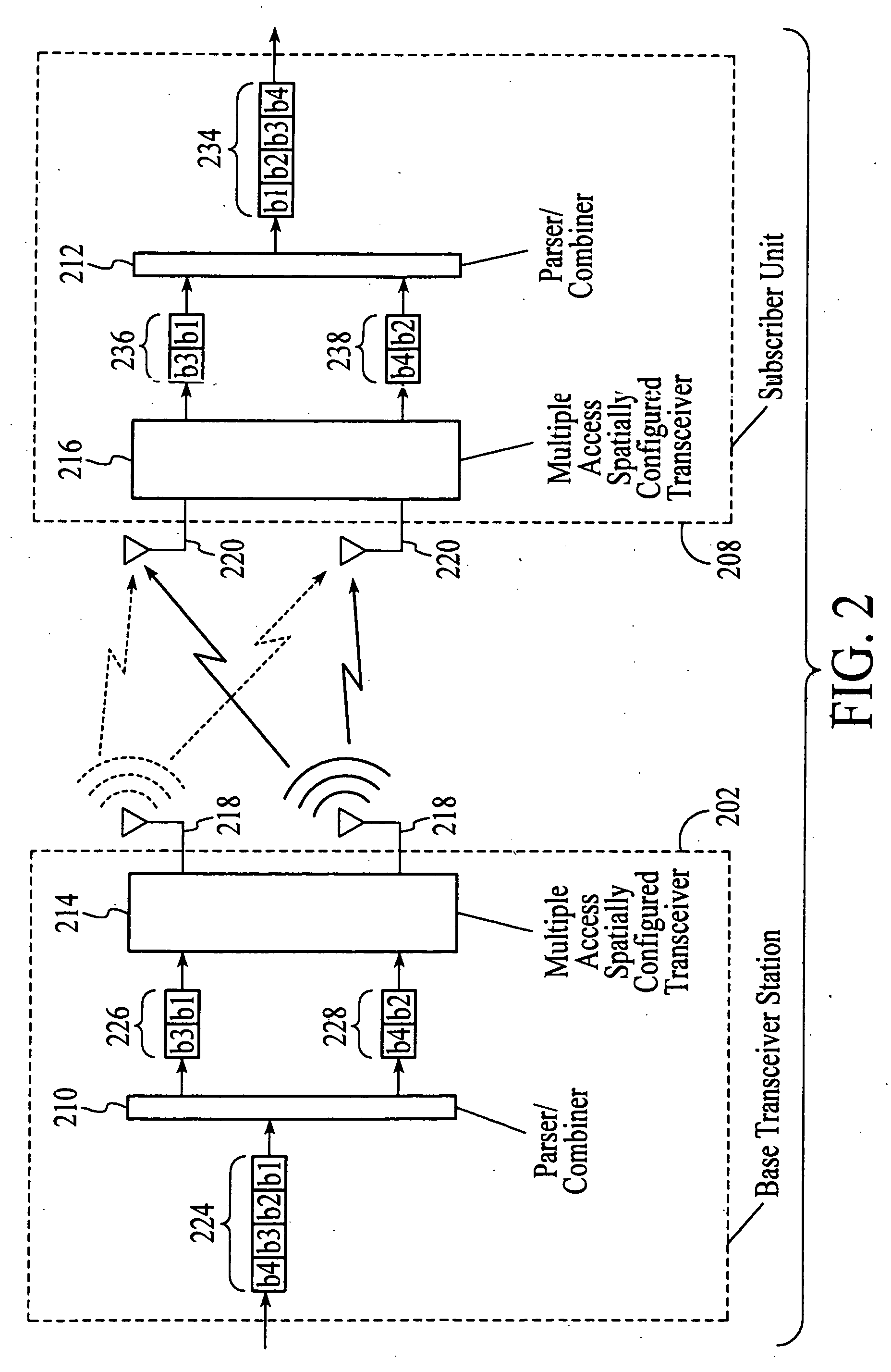
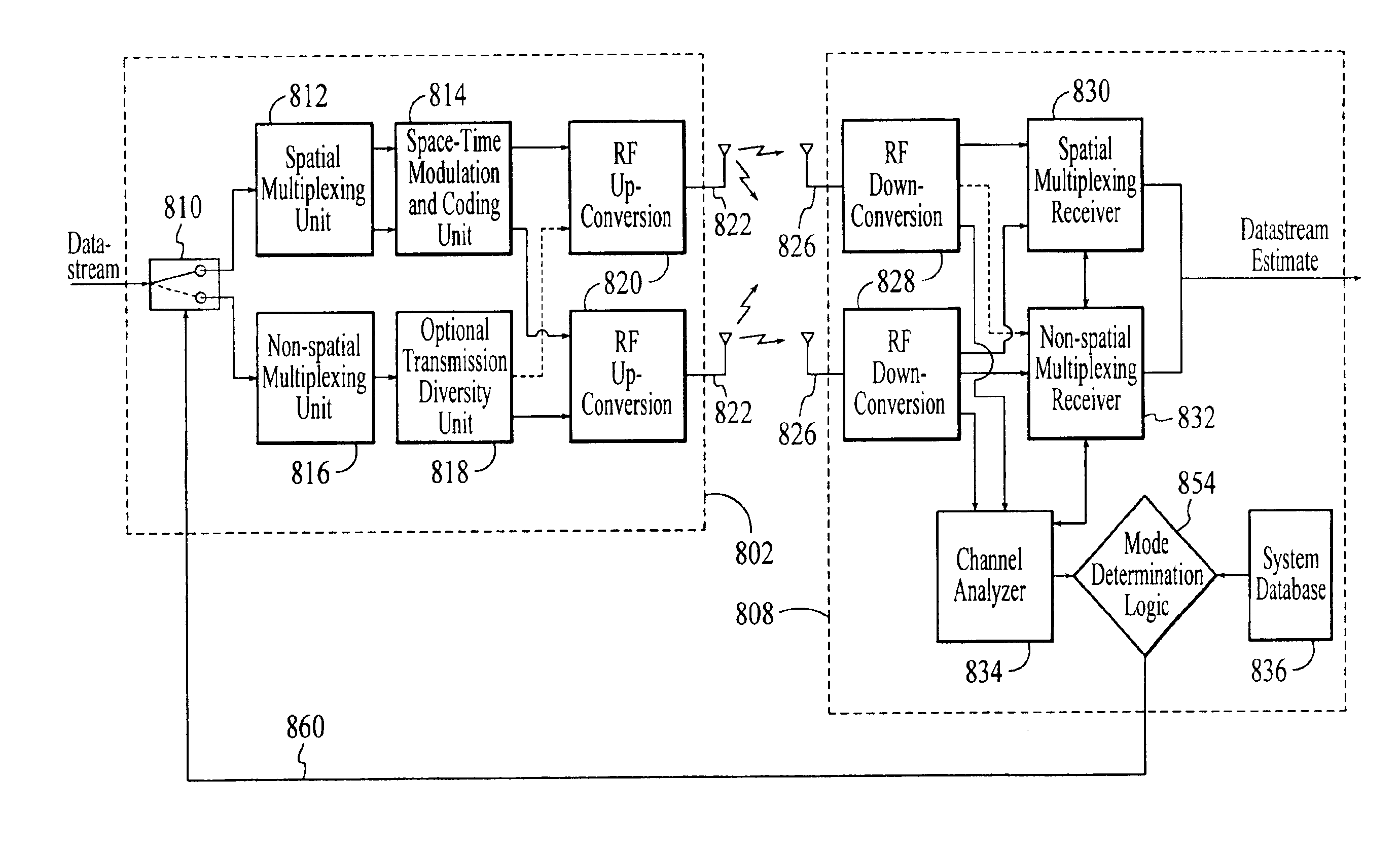
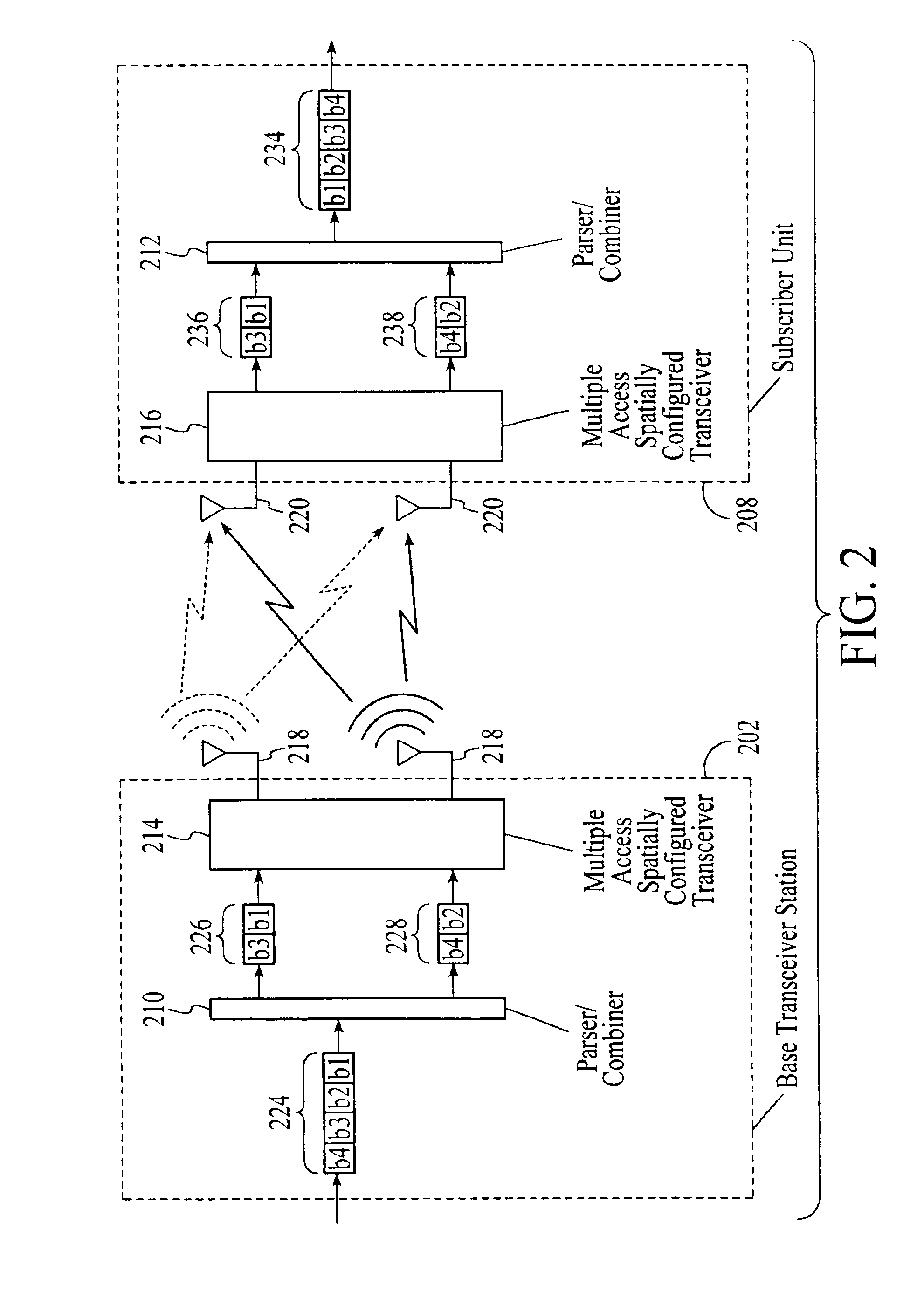
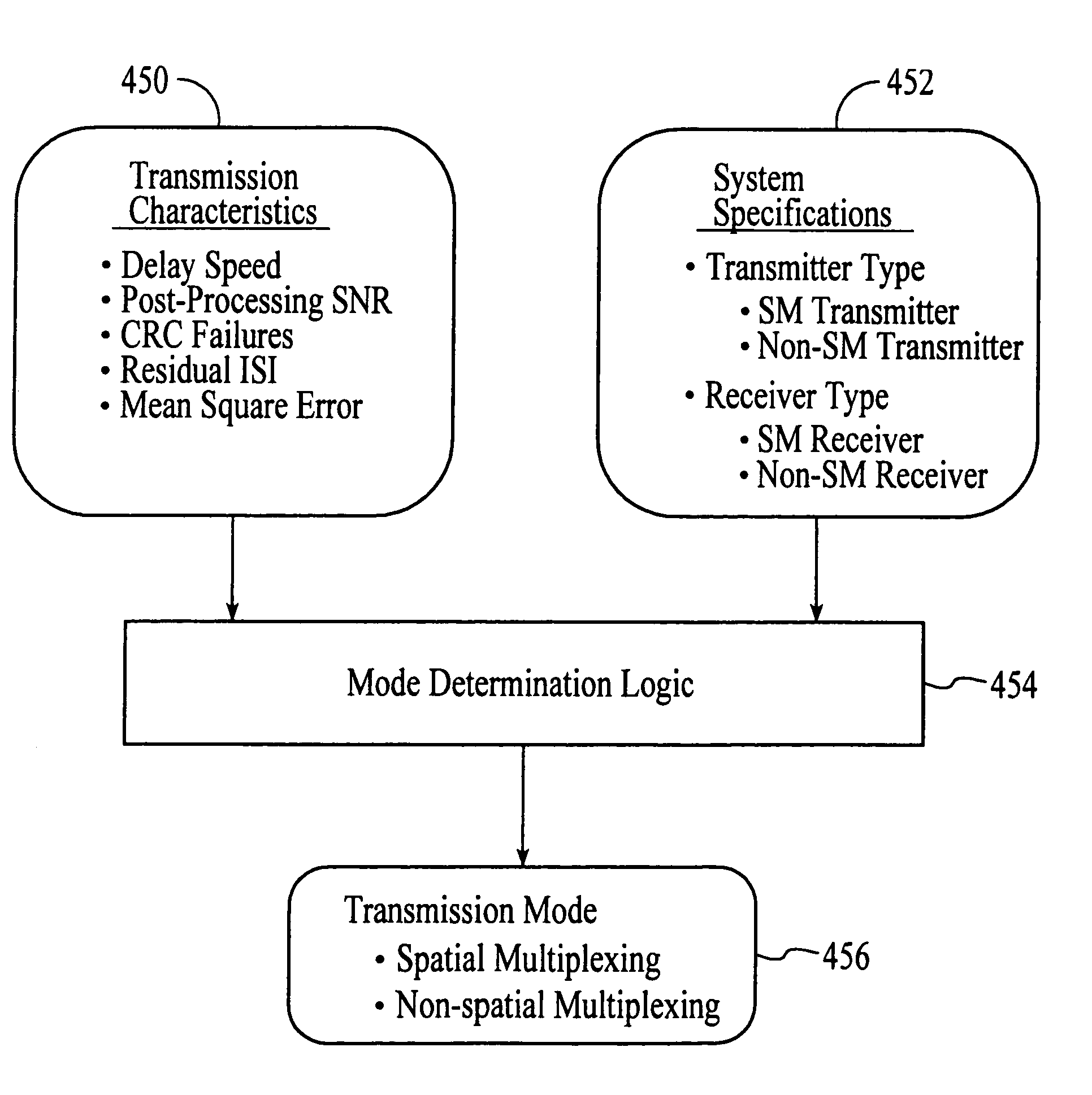
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS6937592B1Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionOperation modeMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
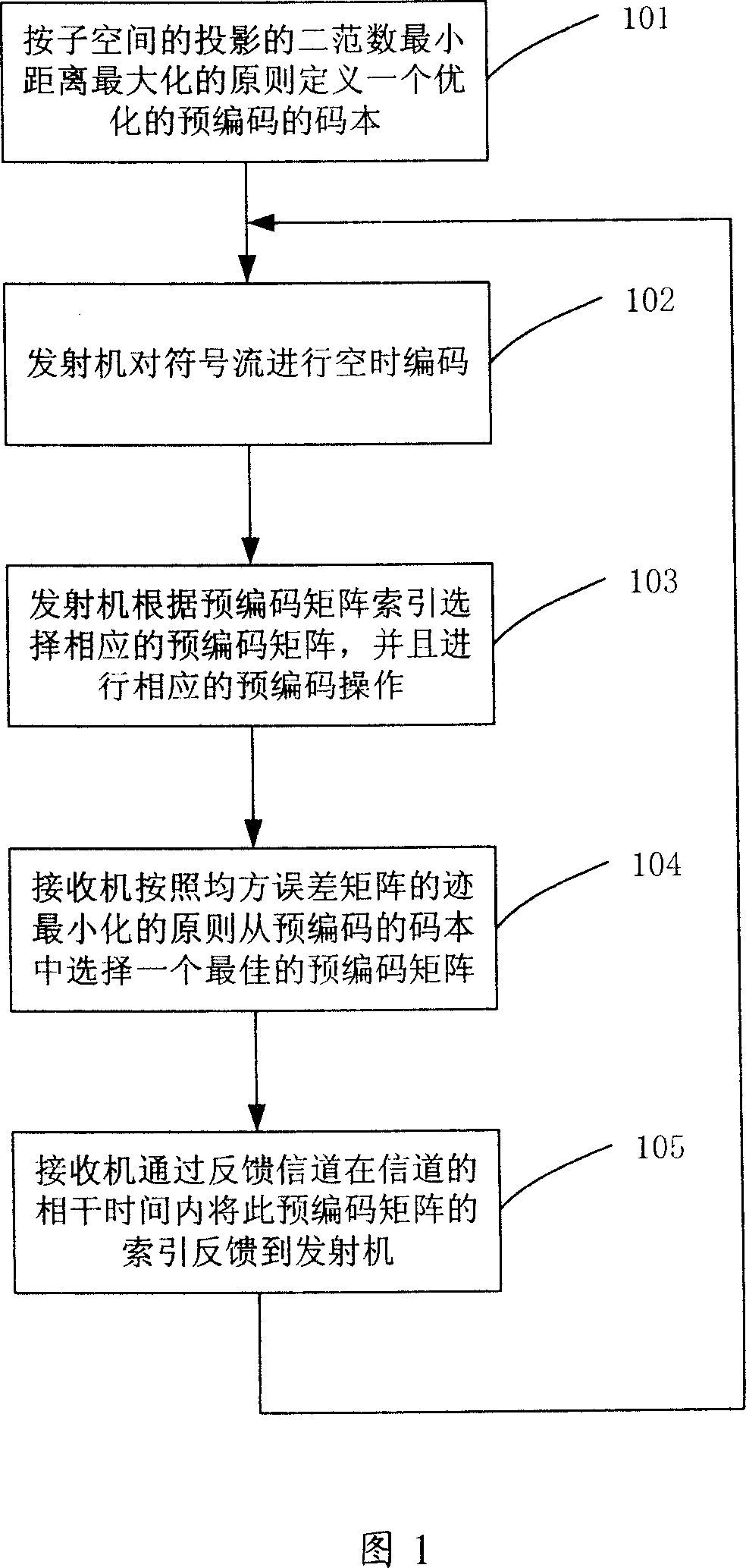
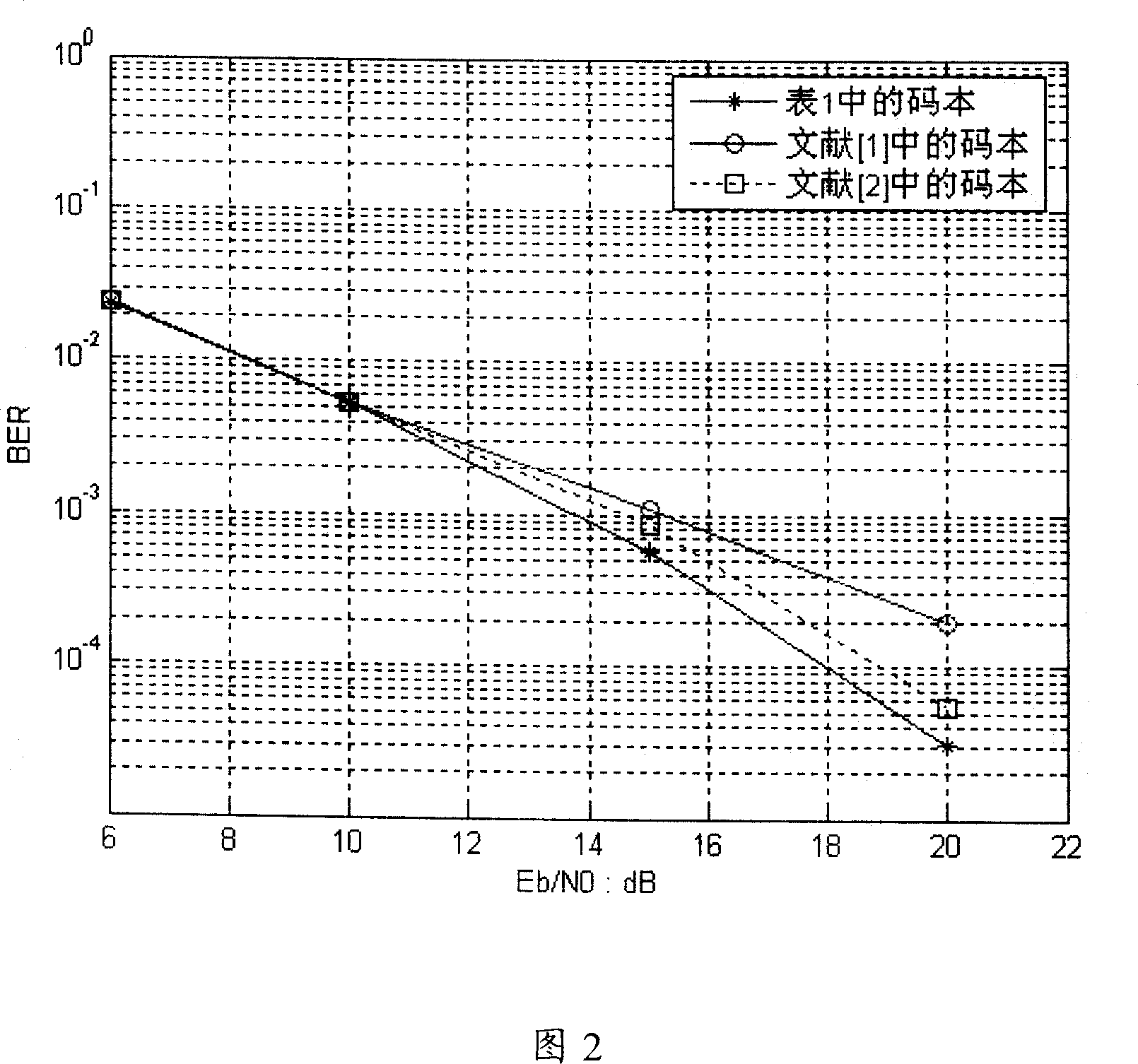
Multi-input multi-output space multiplexing precoding method of wireless communication system
InactiveCN101136718AImprove communication performanceSpatial transmit diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionMulti inputCoherence time
Using precoded space multiplexing of limited fed back, the method defines a group of set of precoded matrix (i.e. precoded codebook) known by transmitter and receiver. Using algorithm of channel estimation to obtain current state information of channel, the receiver selects an optimal precoded matrix from precoded codebooks according to minimized principles of trace of mean square error matrix as well as through a feedback channel, feeds index of the precoded matrix back to the transmitter within coherence time of channel. Based on the said index of the precoded matrix, the transmitter obtains the precoded matrix, and then carries out precoded operations on vectors of transmit signal based on the precoded matrix. Precoded codebook can be designed based on maximized principle of minimum distance between two norms of projections of subspaces. Using limited bit number fed back, the invention raises communication performance.
Owner:ZTE CORP
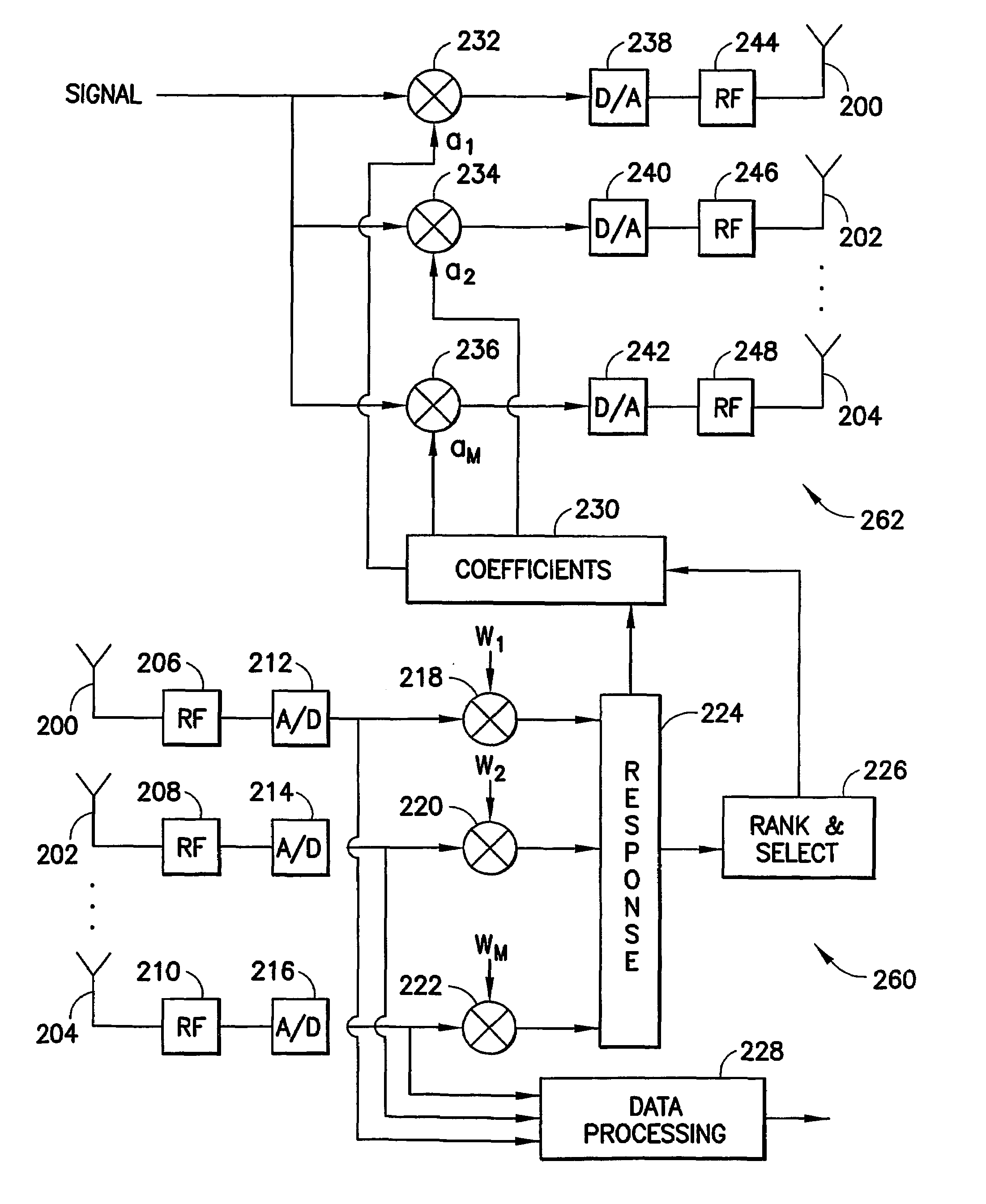
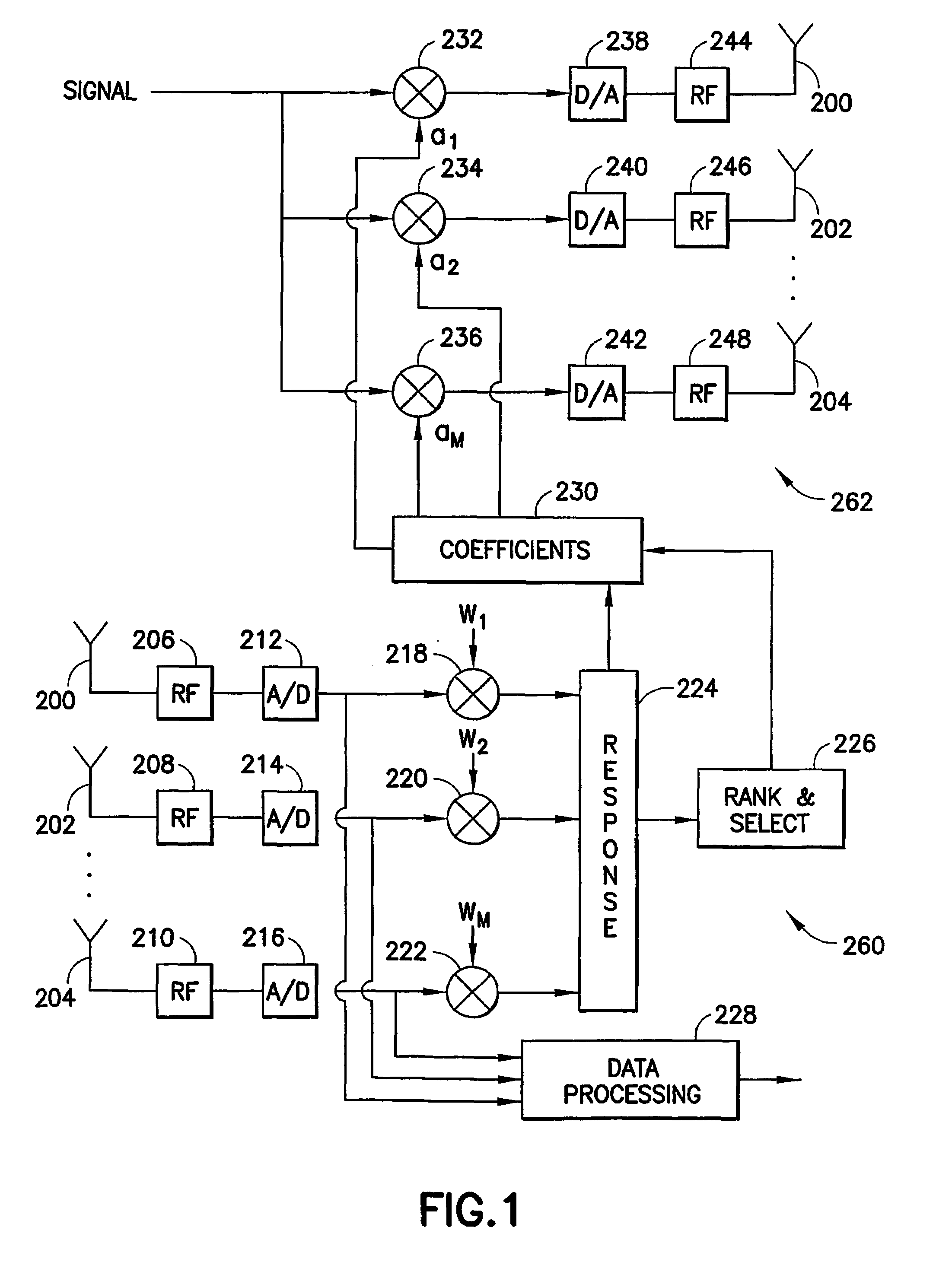
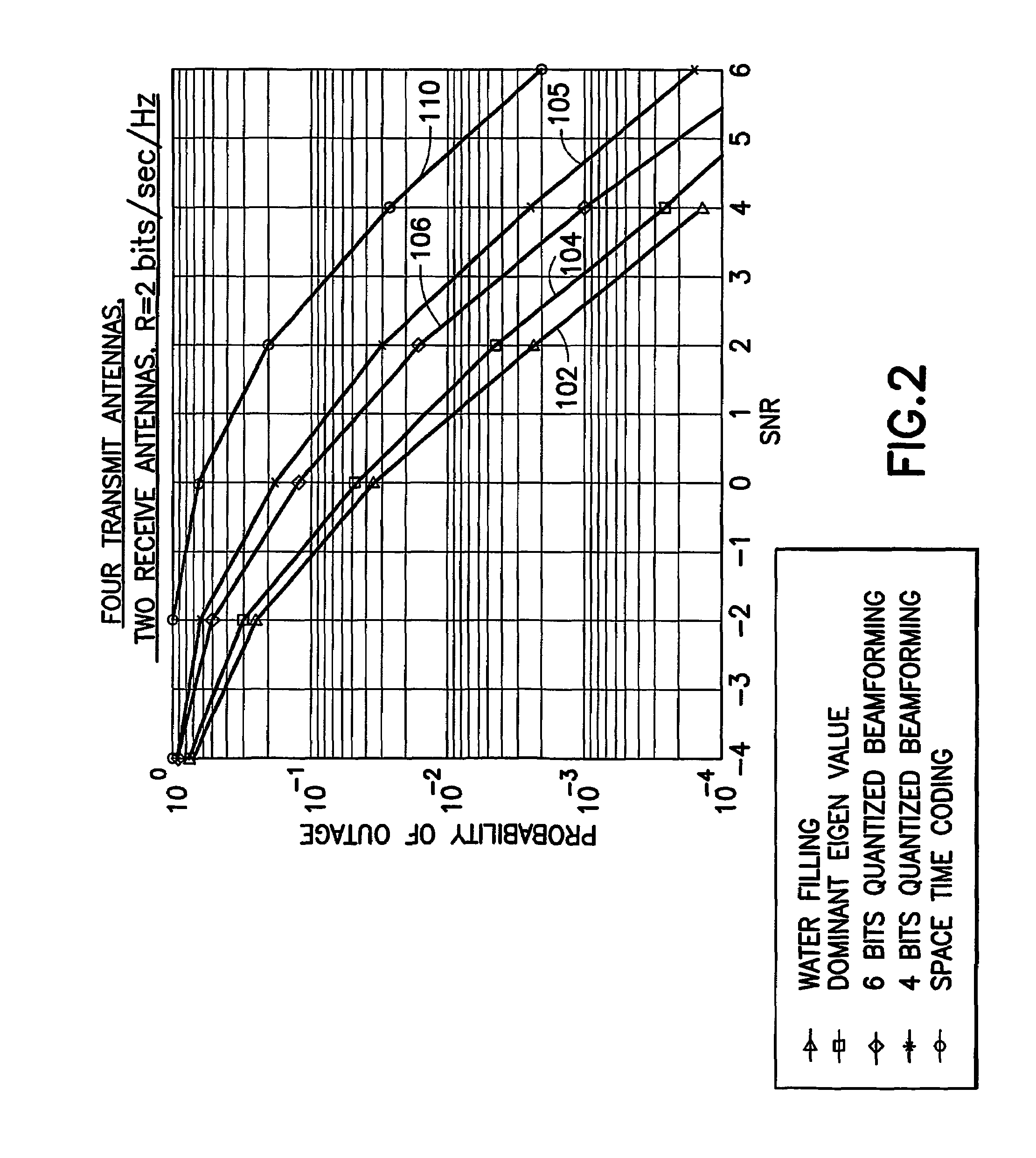
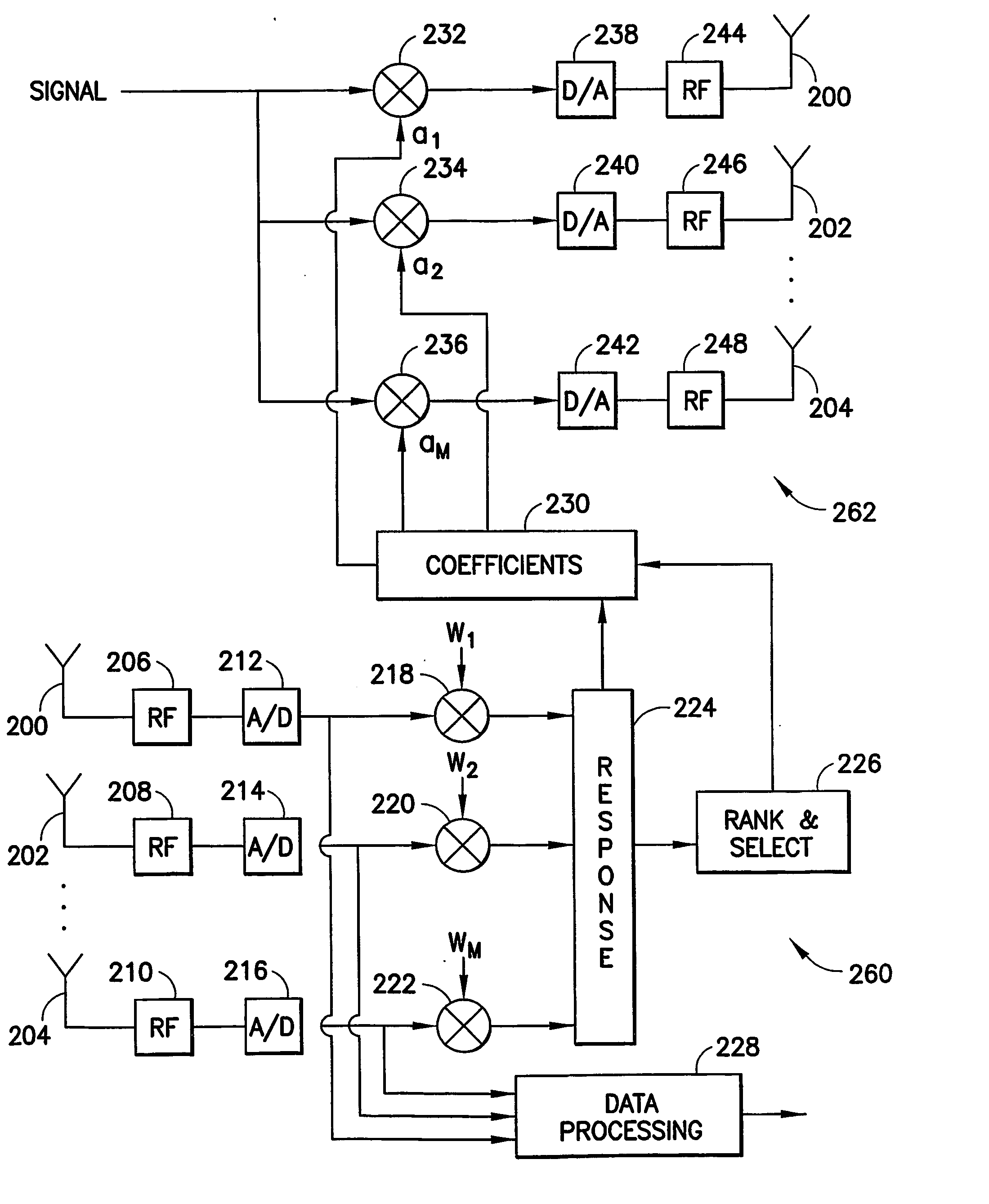
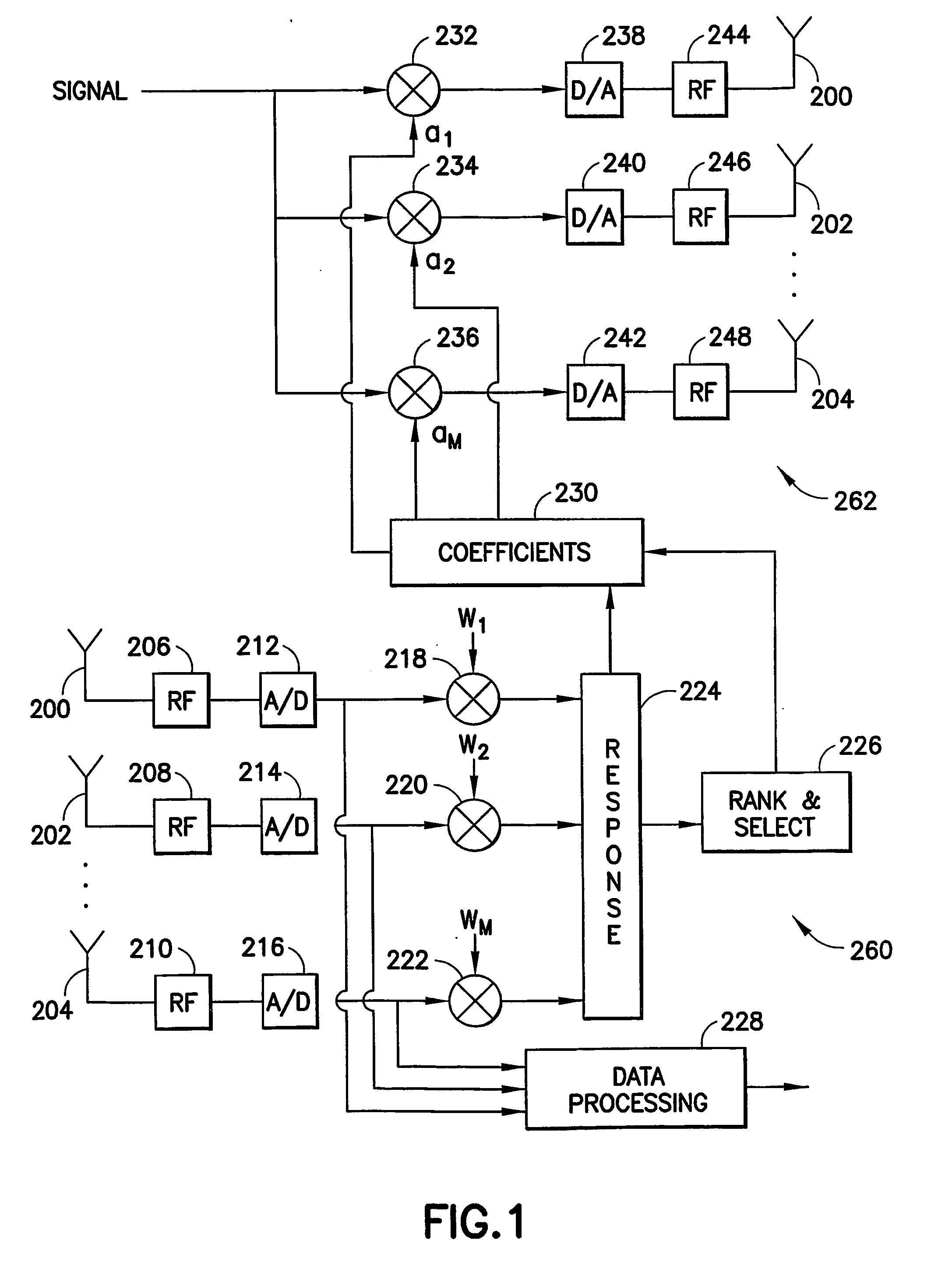
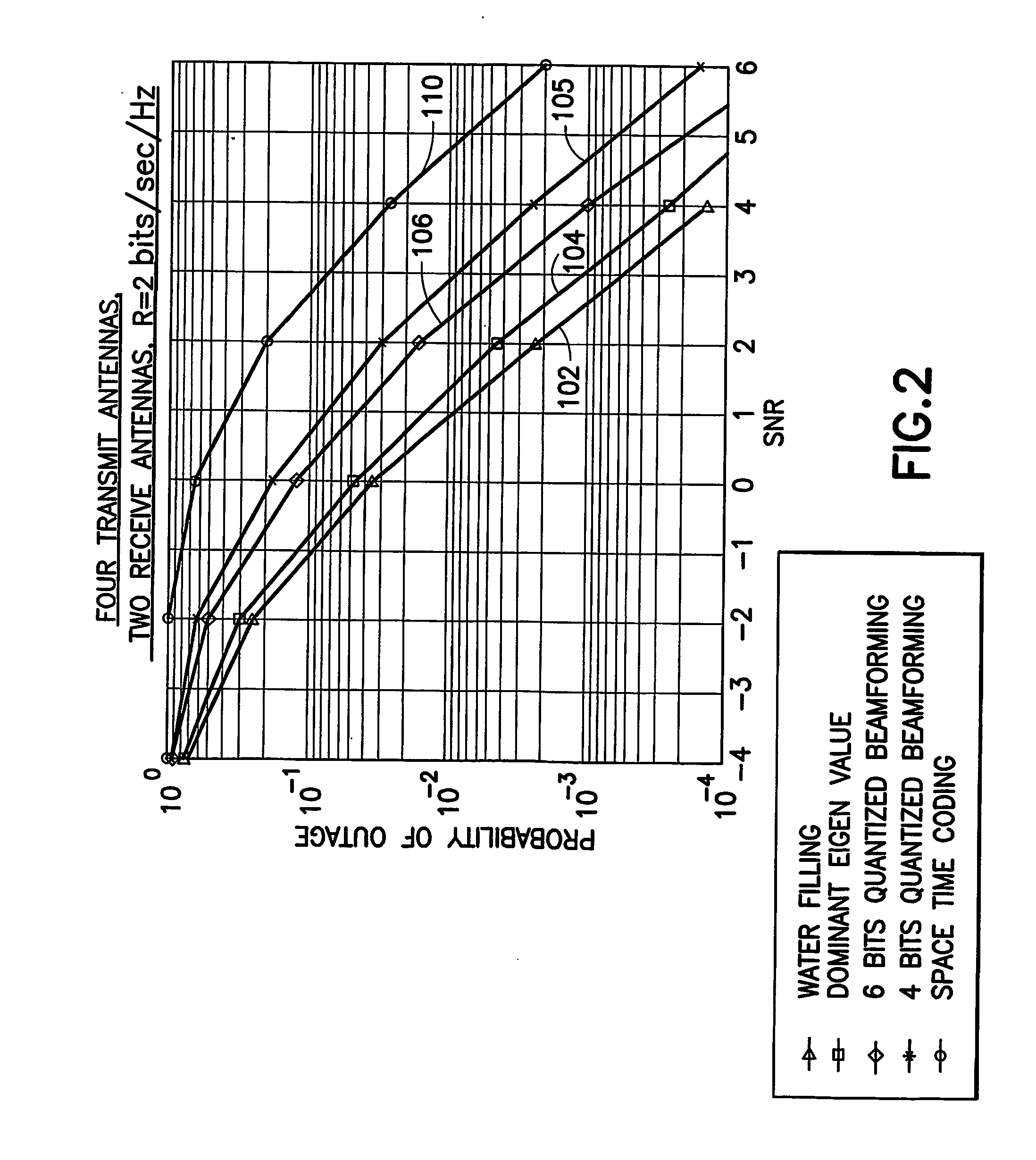
Low complexity beamformers for multiple transmit and receive antennas
InactiveUS7330701B2Power managementSpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationRound complexity
Beamforming systems having a few bits of channel state information fed back to the transmitter benefit from low complexity decoding structures and performances gains compared with systems that do not have channel state feedback. Both unit rank and higher rank systems are implemented. Substantial design effort may be avoided by following a method of using functions formulated for space-time systems with the change that the channel coherence time is equated to the number of transmit antennas and the number of antennas in the space-time formulation is fixed at one.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
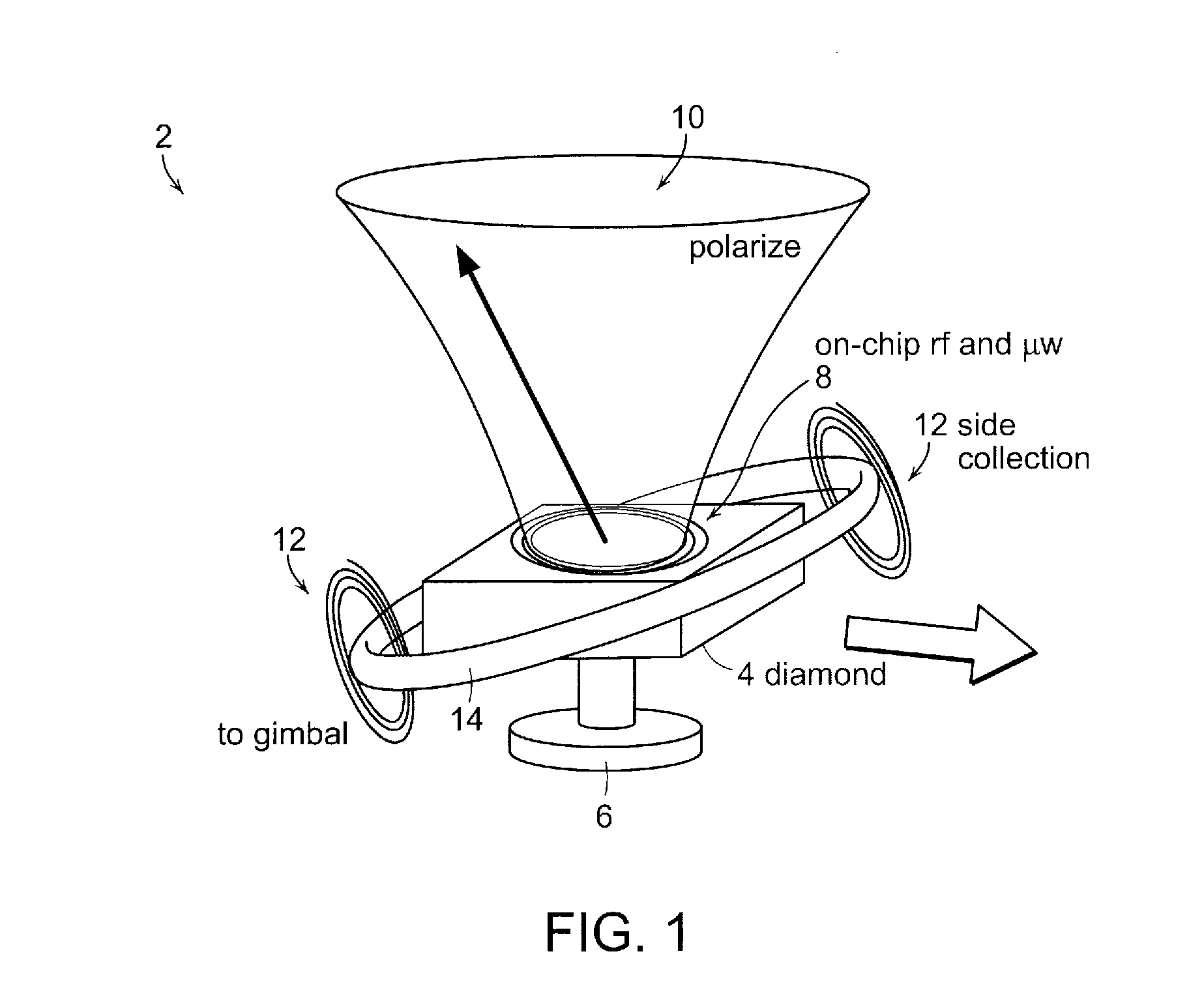
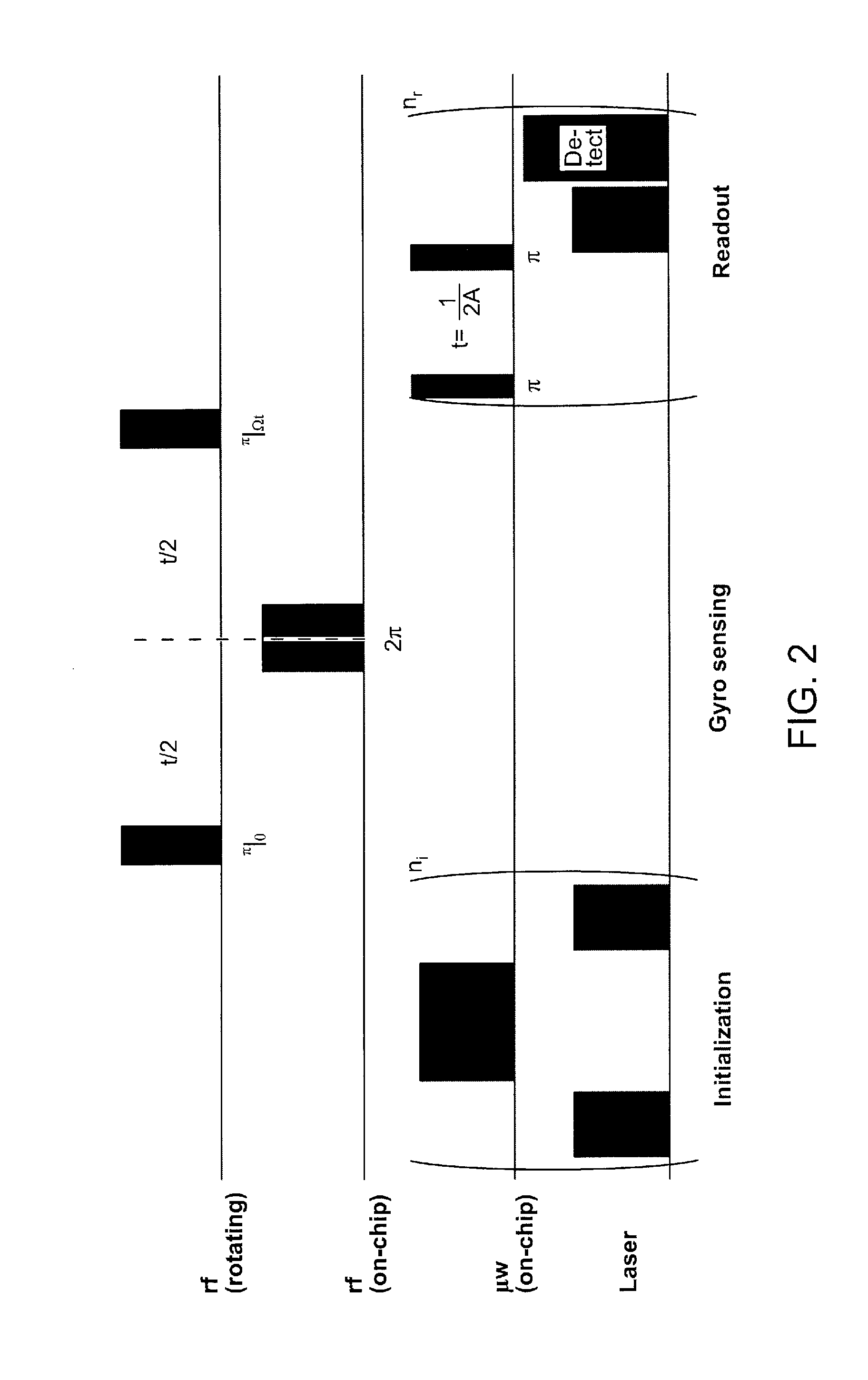
Stable three-axis nuclear spin gyroscope
ActiveUS20140327439A1Efficient optical polarization and measurement of electronic spinAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceTurn-sensitive devicesGyroscopeElectronic spin
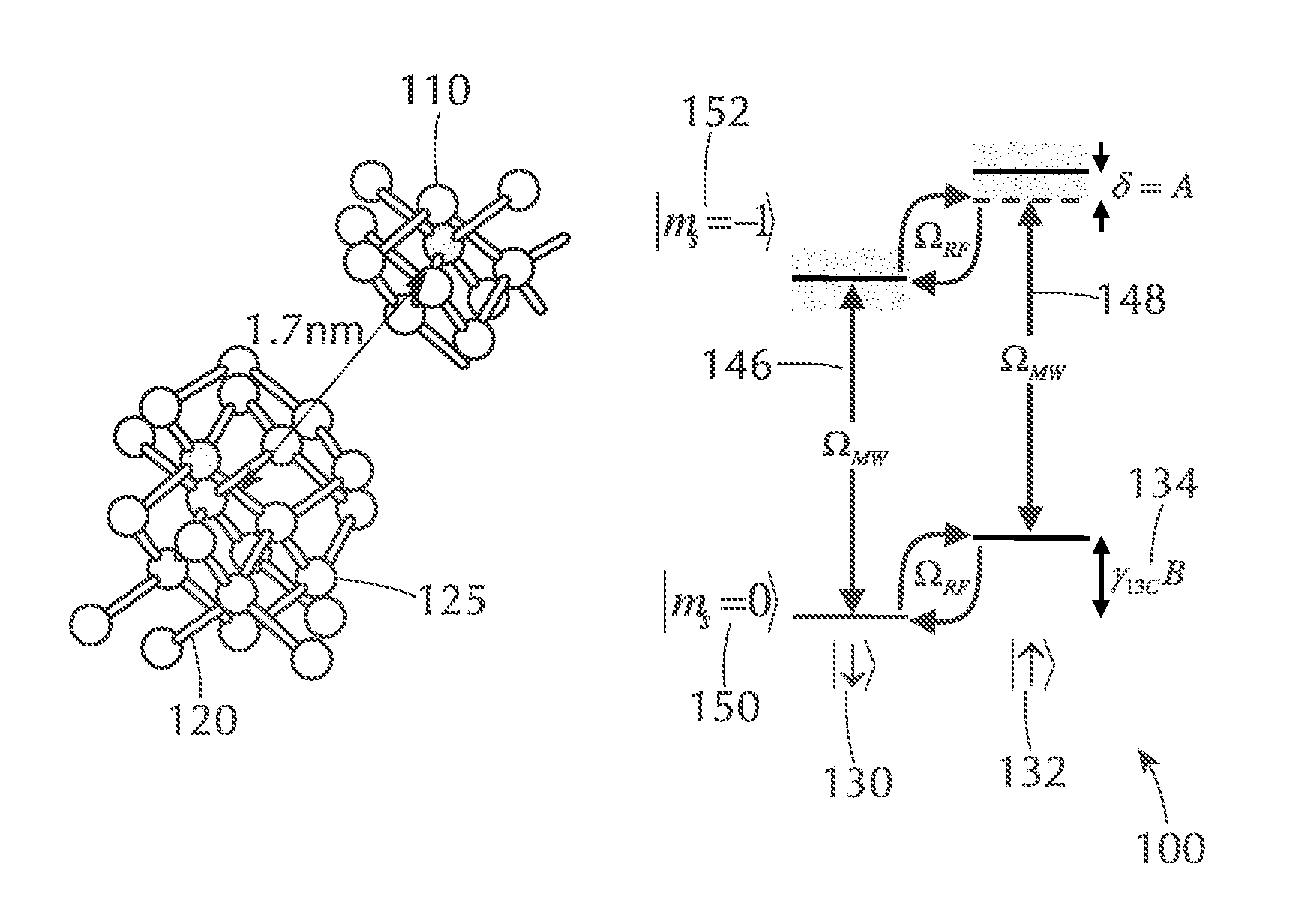
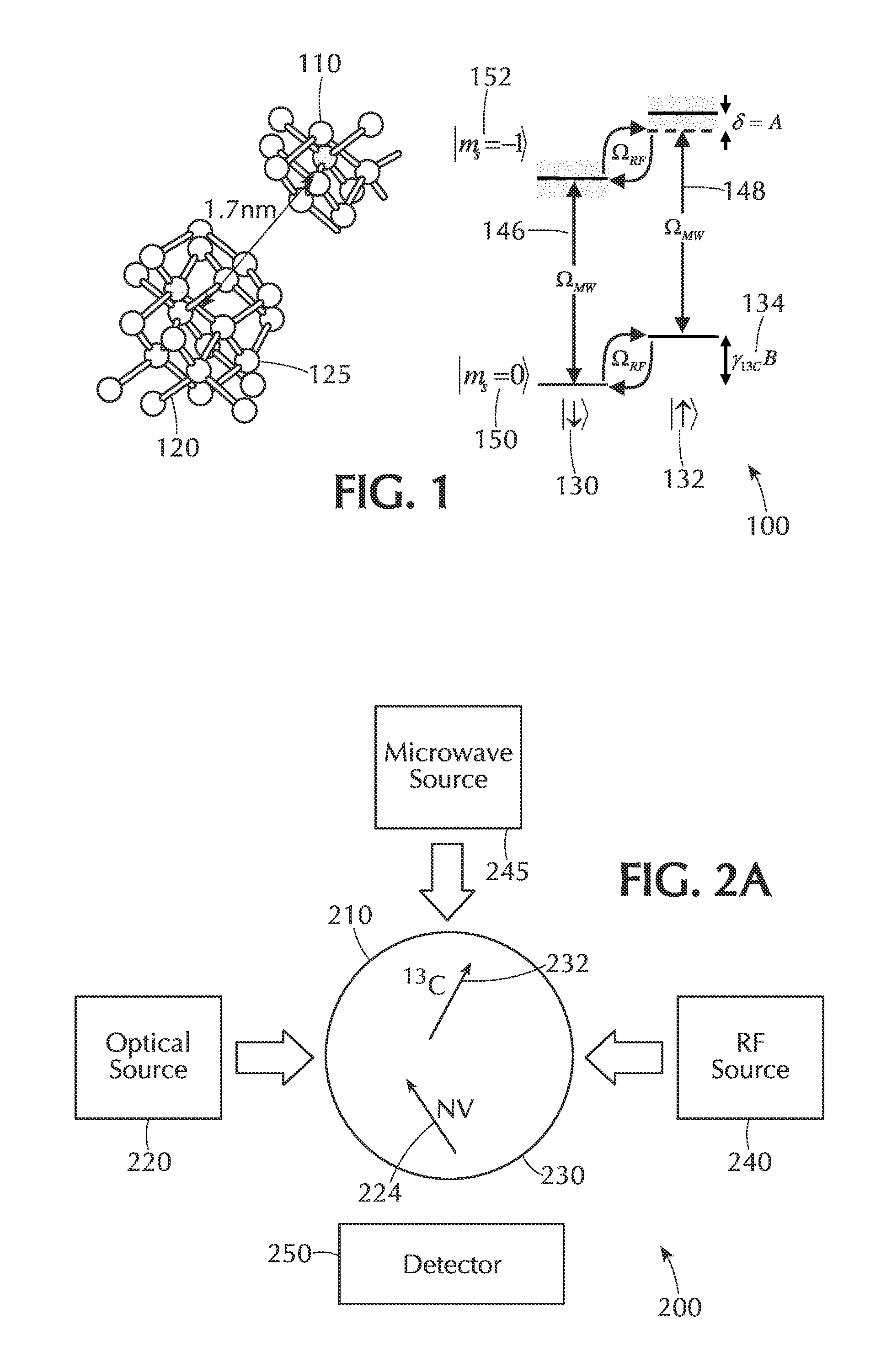
An n-NV-based gyroscope is provided that includes a diamond structure implanted with a plurality of NV centers, whose nuclear spins form a spin gyroscope. A number of radio-frequency (rf) coils and microwave (μw) co-planar waveguides are fabricated on the diamond structure to provide a sensitive and stable three-axis gyroscope in the solid state while achieving gyroscopic sensitivity by exploiting the coherence time of the 14N nuclear spin associated with the NV centers in the diamond structure combined with the efficient optical polarization and measurement of electronic spin.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Low complexity beamformers for multiple transmit and receive antennas
InactiveUS20060111148A1Power managementSpatial transmit diversityChannel state informationRound complexity
Beamforming systems having a few bits of channel state information fed back to the transmitter benefit from low complexity decoding structures and performances gains compared with systems that do not have channel state feedback. Both unit rank and higher rank systems are implemented. Substantial design effort may be avoided by following a method of using functions formulated for space-time systems with the change that the channel coherence time is equated to the number of transmit antennas and the number of antennas in the space-time formulation is fixed at one.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
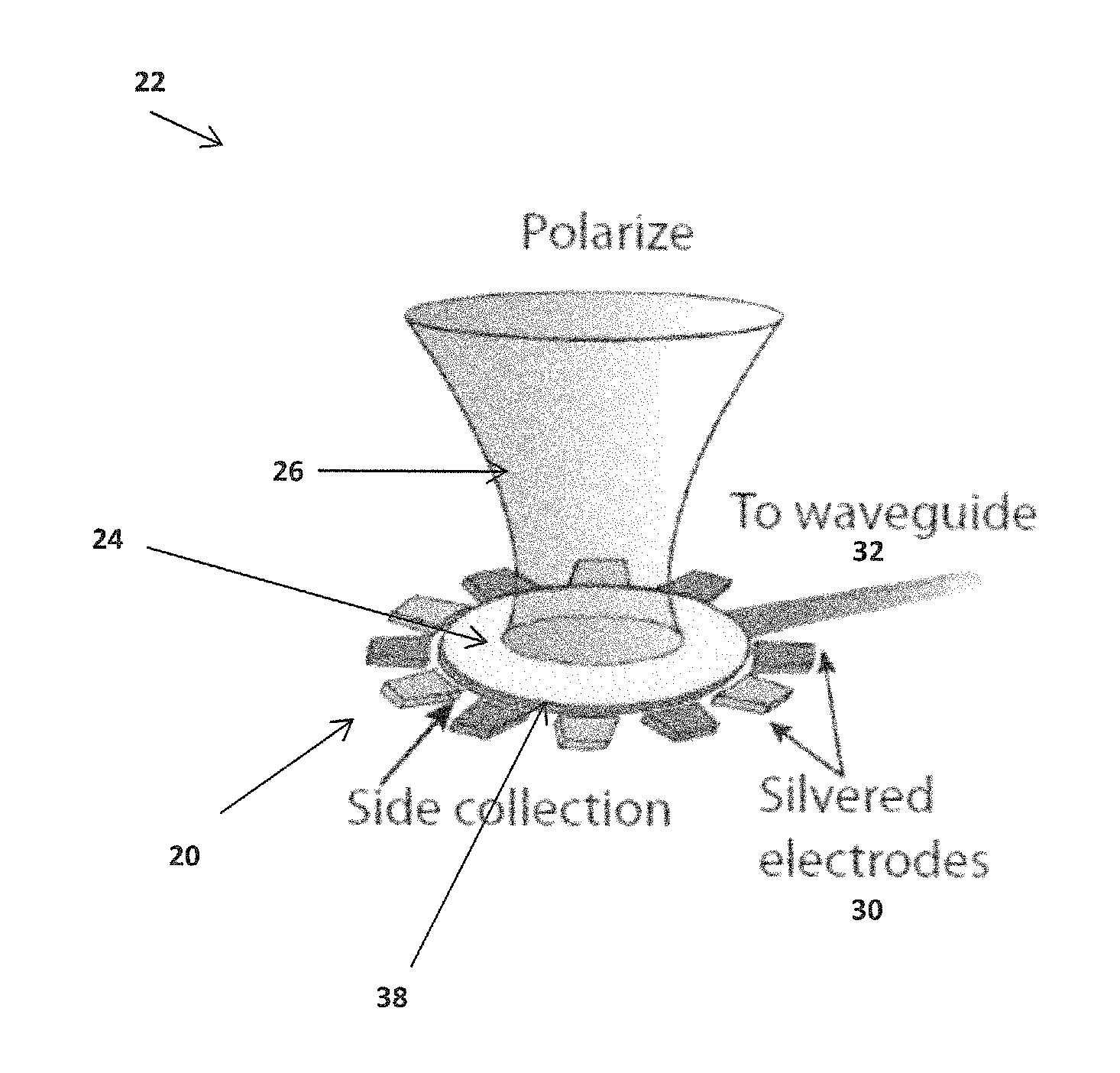
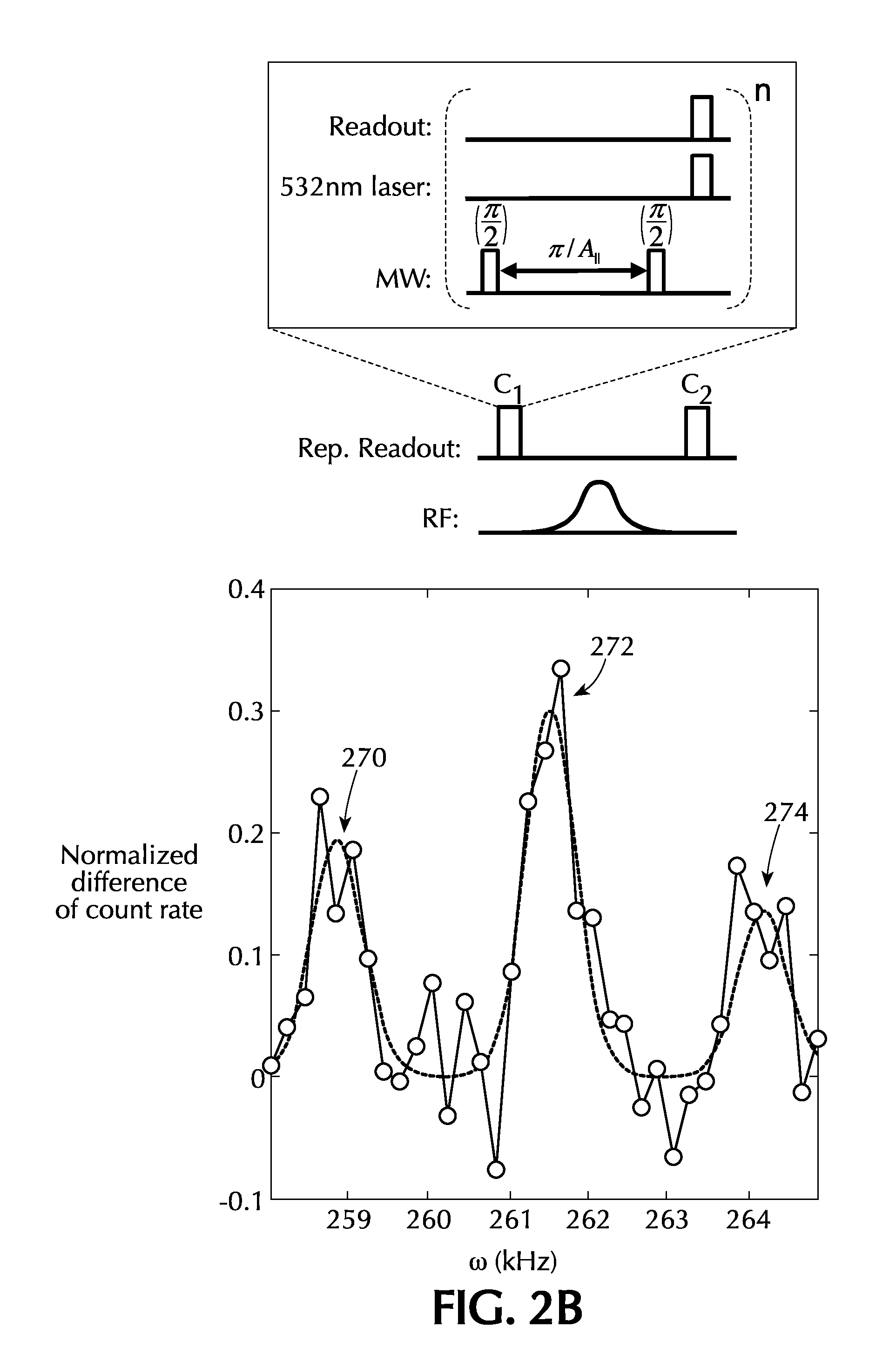
Solid-State Quantum Memory Based on a Nuclear Spin Coupled to an Electronic Spin
ActiveUS20150009746A1Effective decouplingHigh fidelity initializationQuantum computersNanoinformaticsOptical radiationElectronic spin
A system comprising a solid state lattice containing an electronic spin coupled to a nuclear spin; an optical excitation configuration which is arranged to generate first optical radiation to excite the electronic spin to emit output optical radiation without decoupling the electronic and nuclear spins; wherein the optical excitation configuration is further arranged to generate second optical radiation of higher power than the first optical radiation to decouple the electronic spin from the nuclear spin thereby increasing coherence time of the nuclear spin; a first pulse source configured to generate radio frequency (RF) excitation pulse sequences to manipulate the nuclear spin and to dynamically decouple the nuclear spin from one or more spin impurities in the solid state lattice so as to further increase the coherence time of the nuclear spin; a second pulse source configured to generate microwave excitation pulse sequences to manipulate the electronic spin causing a change in intensity of the output optical radiation correlated with the electronic spin and with the nuclear spin via the coupling between the electronic spin and the nuclear spin; and a detector configured to detect the output optical radiation correlated with the electronic spin and the nuclear spin so as to detect a nuclear spin state of the nuclear spin.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
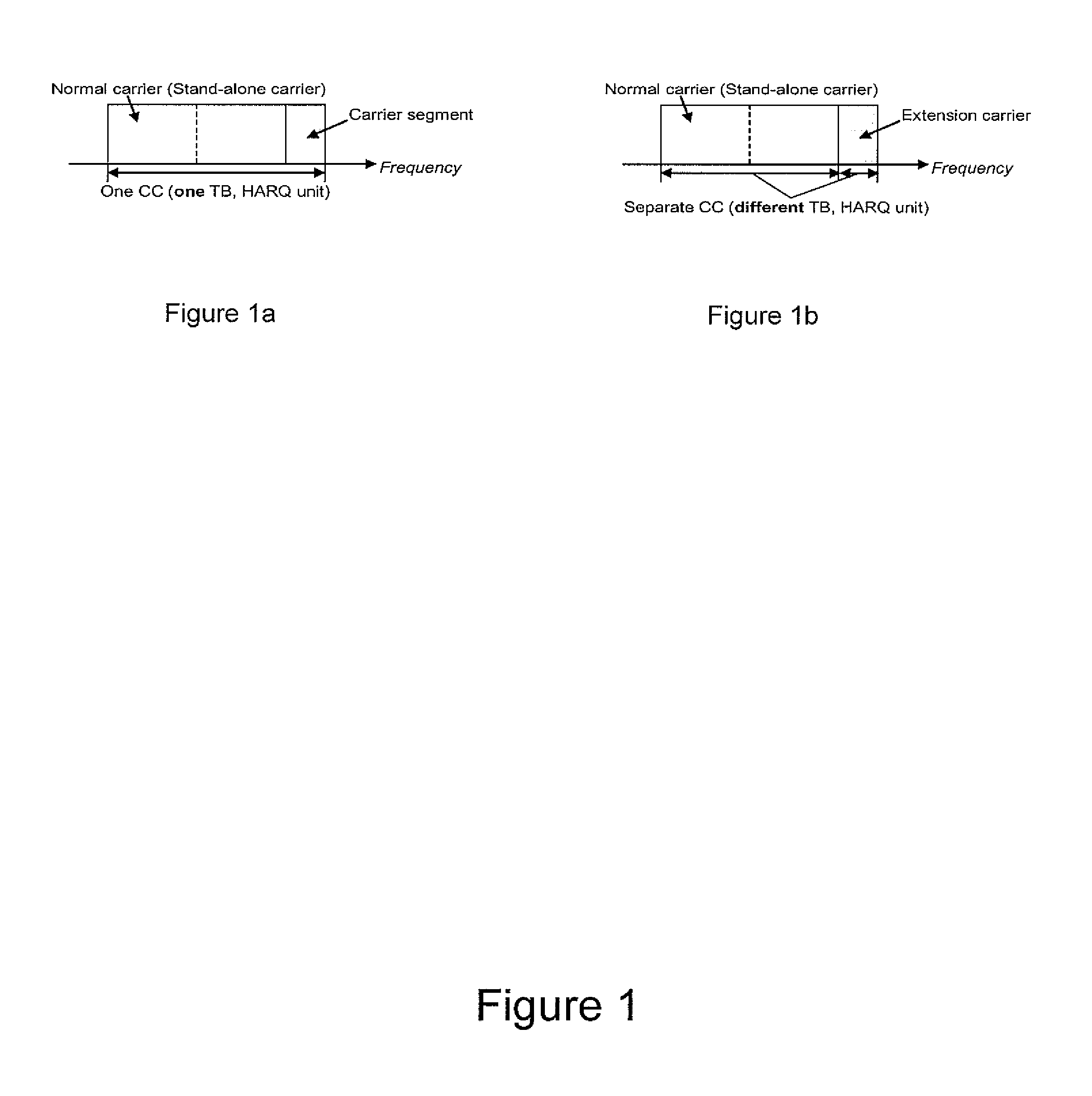
Method and Apparatus for Establishing a Time-Frequency Reference Signal Pattern Configuration in a Carrier Extension or Carrier Segment
InactiveUS20140219237A1Transmission path divisionPilot signal allocationCell specificResource element
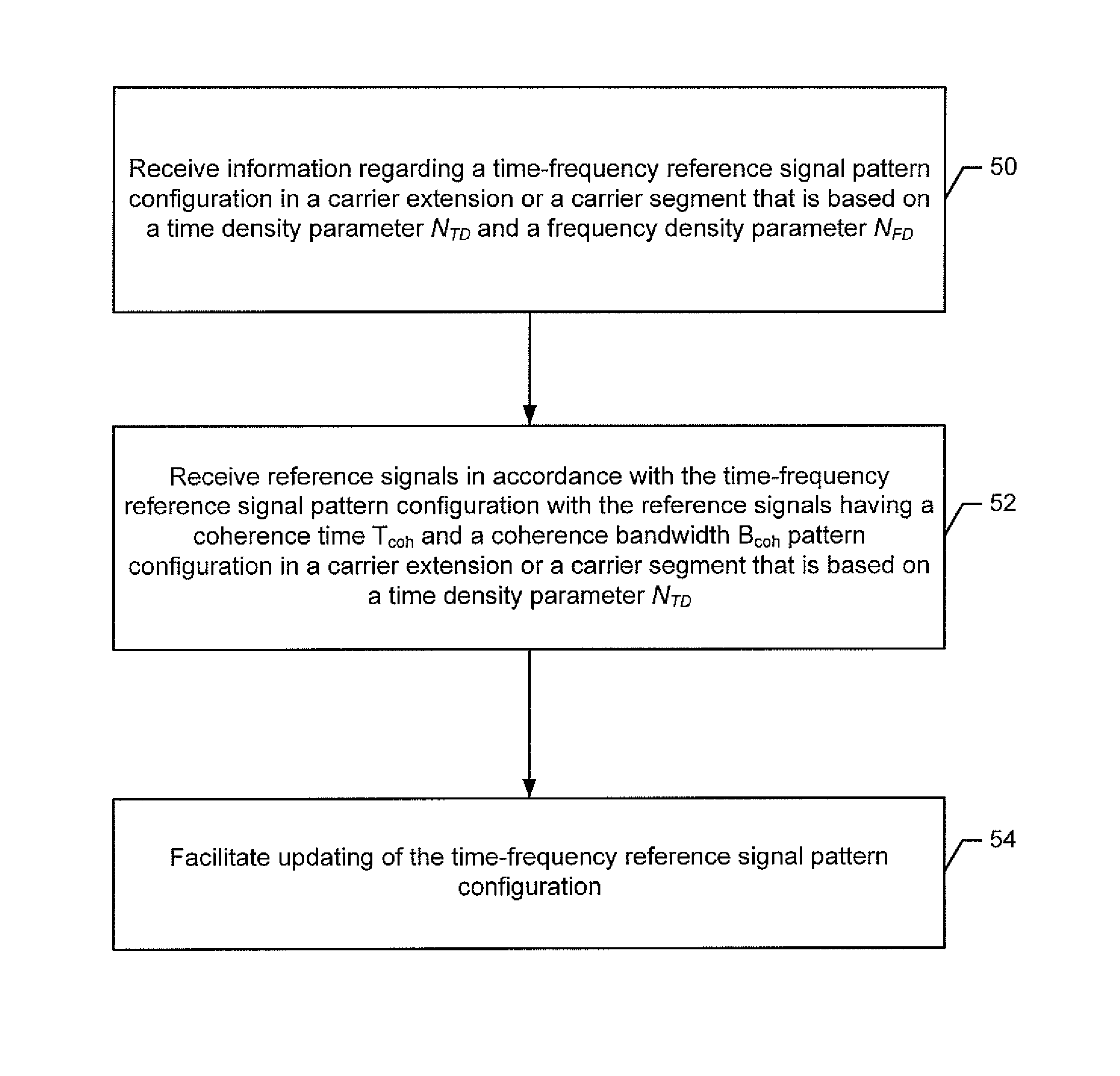
Methods, apparatus and computer program products are provided for establishing a time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration in a carrier extension or a carrier segment, such as for cell-specific reference signals (CRS) and / or demodulation reference signals (DM RS). One method includes receiving information regarding a time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration in a carrier extension or carrier segment. The time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration defines a subframe to include a reference signal based upon a time density parameter and defines a resource element to be utilized within the subframe based upon a frequency density parameter. This method also includes receiving reference signals pursuant to the time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration such that reference signals have a coherence time Tcoh with at least one subframe including a reference signal in the CE or CS per Tcoh and a coherence bandwidth Bcoh with at least one resource element containing a reference signal per Bcoh.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Channel adaptation using variable sounding signal rates
InactiveUS7280804B2Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission systemsCarrier signalCoherence time
Systems, devices and methods for updating link adaptations in multi-carrier modulated signals between an access point (AP) and a wireless local area network (WLAN) station (STA) include (are configured for) periodically transmitting a channel sounding signal from the AP. The STA receives each unsolicited channel sounding signal and evaluates the current channel conditions between the AP and STA. The AP adjusts a rate of transmission of the channel sounding signals in accordance with the channel coherence time so that the channel estimates performed by the STA will be valid within the time varying characteristics of the channel. Depending on the length of the coherence time for network environment, the channel sounding signals may be AP beacons, low overhead signal fragments with no payload, or a combination of both.
Owner:INTEL CORP
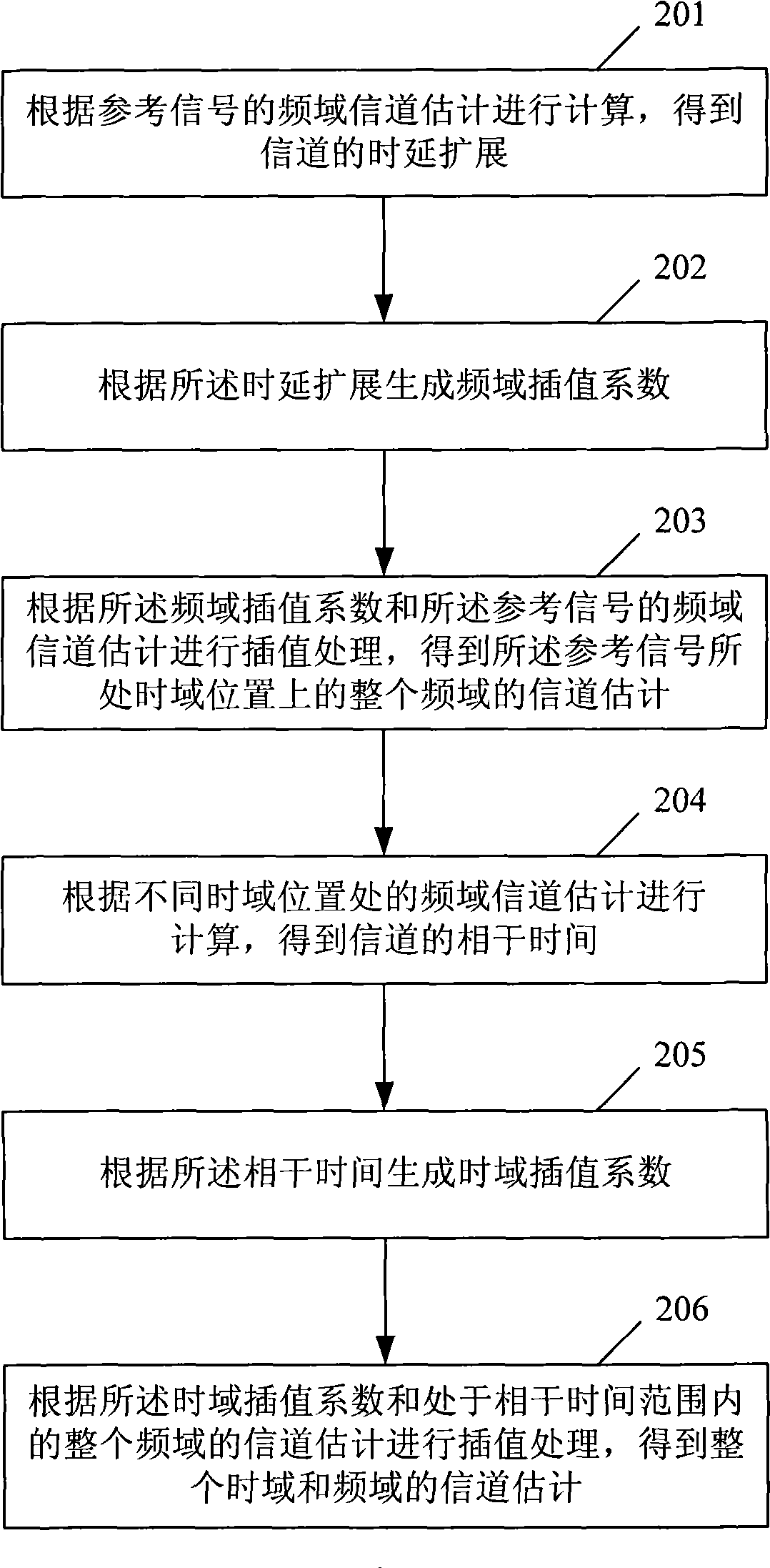
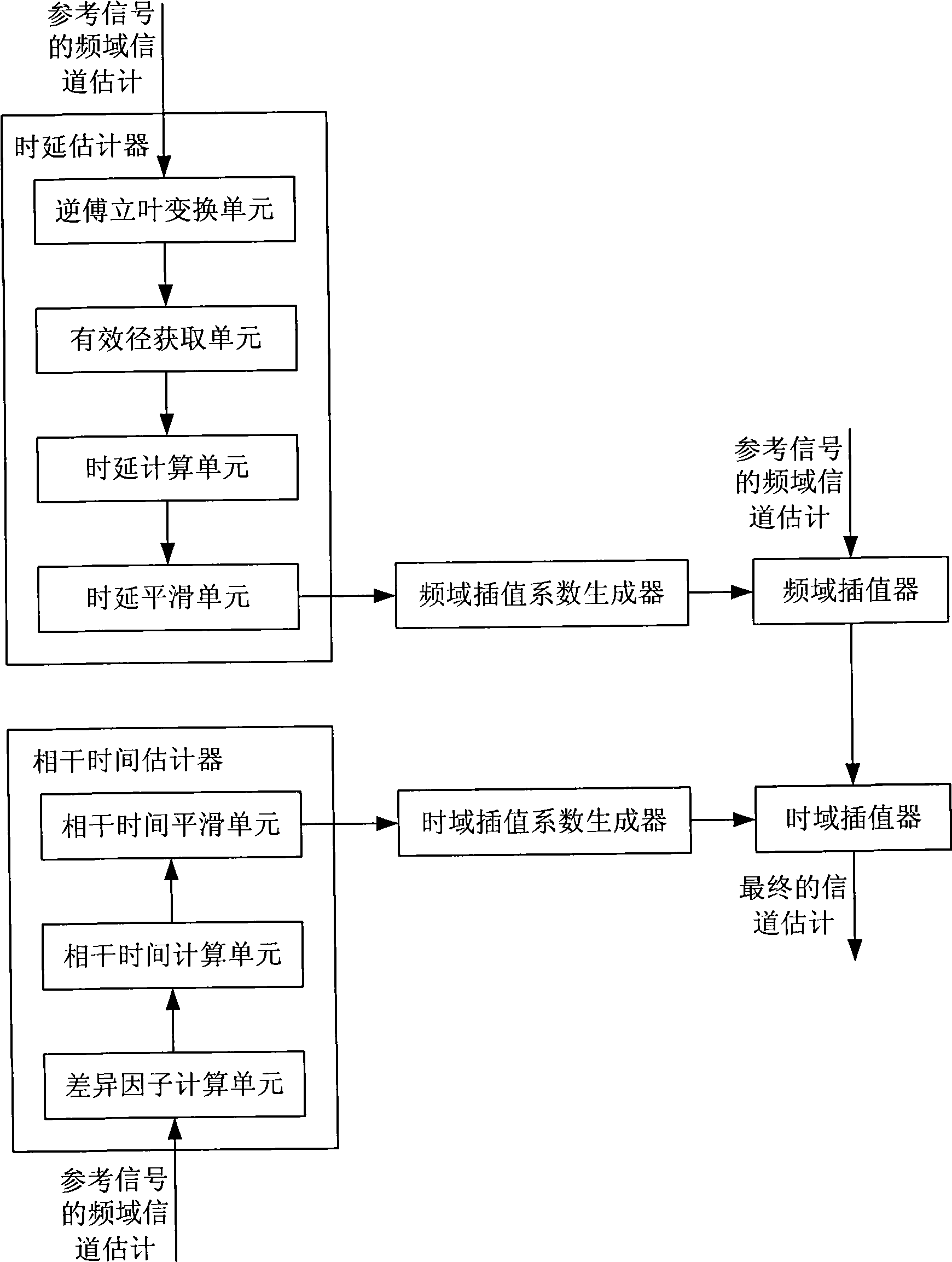
Channel estimation method for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing system and device thereof
The invention provides a channel estimation method for Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing system and a device thereof. The channel estimation method comprises the following steps: A. calculating according to the frequency domain channel estimation of a reference signal to obtain the delay spread of the channel; B. generating a frequency domain interpolation coefficient according to the delay spread; C. carrying out interpolation according to the frequency domain interpolation coefficient and the frequency domain channel estimation of the reference signal to obtain the channel estimation of the whole frequency of the position where the reference signal is located; D. calculating according to the frequency domain channel estimation at different time domain positions to obtain the coherence time of the channel; E. generating a time domain interpolation coefficient according to the coherence time; and F. carrying out interpolation according to the time domain interpolation coefficient and the channel estimation of the whole frequency located with the range of the coherence time to obtain the whole channel estimation of the time domain and the frequency domain. In light of the invention, the channel estimation result can self-adaptively change with the change of the channel.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SEMICON BEIJING
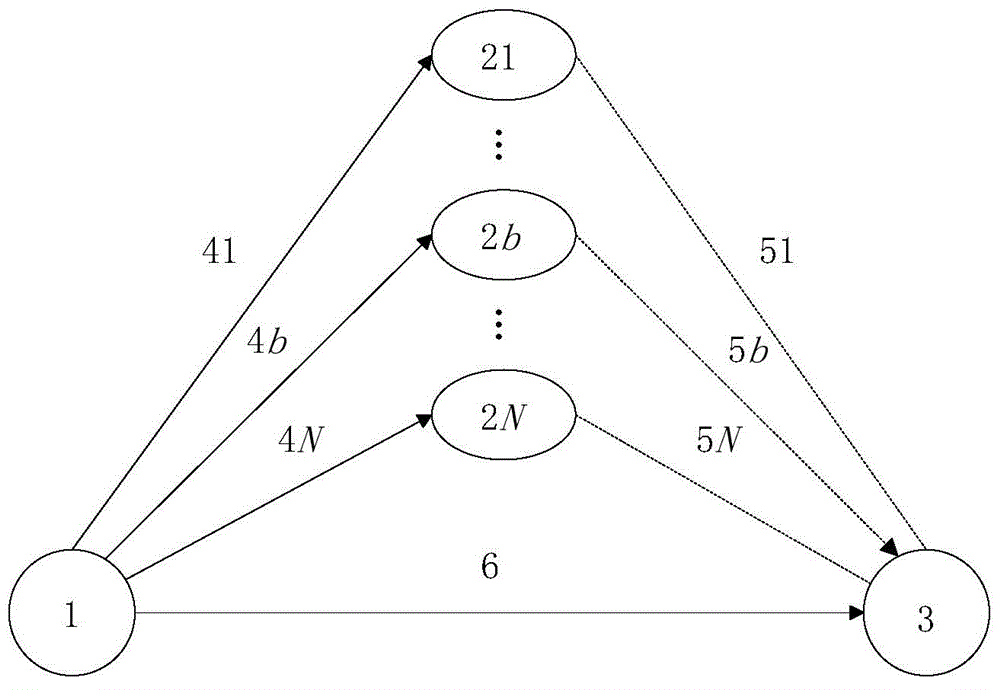
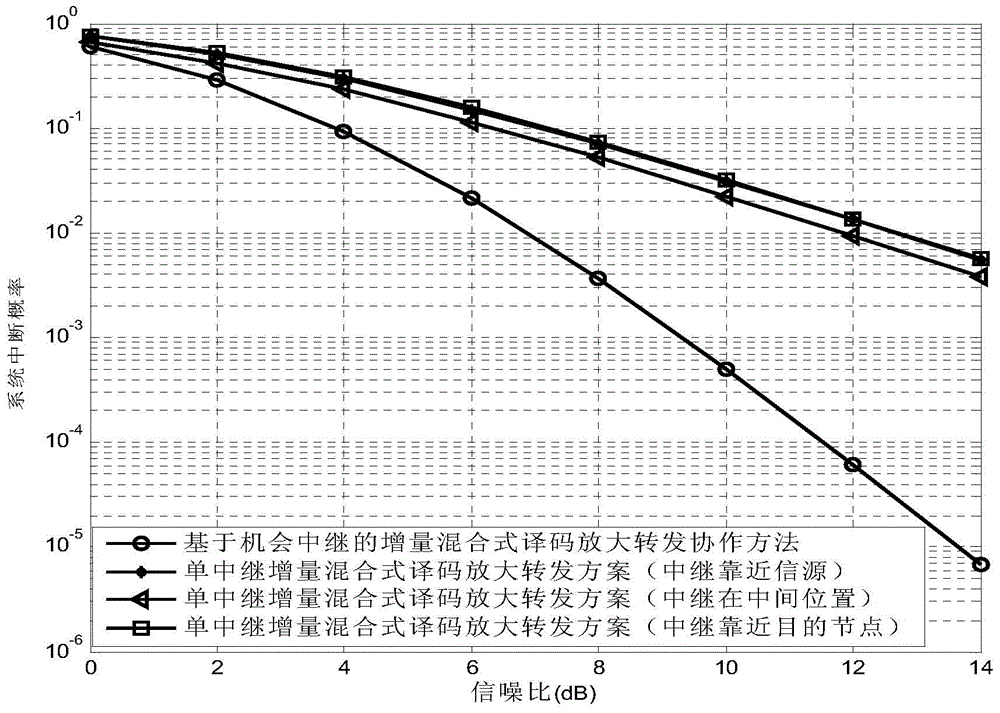
Increment mixing decoding amplification forwarding cooperation method based on opportunistic relaying
ActiveCN103561447AImprove robustnessImprove performanceRadio relay systemsHigh level techniquesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Coherence time
The invention provides an increment mixing decoding amplification forwarding cooperation method based on opportunistic relaying and belongs to the technical field of wireless digital transmission. A system comprises an information source node, a destination node and N relay nodes. Each node is provided with an antenna. The system works in a half-duplex transmission mode. The communication process of the system includes the first step of selecting the relay nodes with optimal communication channel conditions to participate in cooperation from the N relay nodes according to the opportunistic relaying criteria within each coherence time period of a communication channel, and the second step of selecting a corresponding cooperative transmission method, namely, direct transmission, decode-and-forward transmission and amplification forwarding transmission, through comparison between the threshold valve of an instant signal-to-noise ratio of links and a corresponding set signal-to-noise ratio of the links. According to the increment mixing decoding amplification forwarding cooperation method based on opportunistic relaying, relays and cooperation schemes can be flexibly selected according to the conditions of the communication channel and the relay nodes. Consequently, the performance of a cooperative relay system is improved, and the transmission power and the bit error rate required by the system are reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
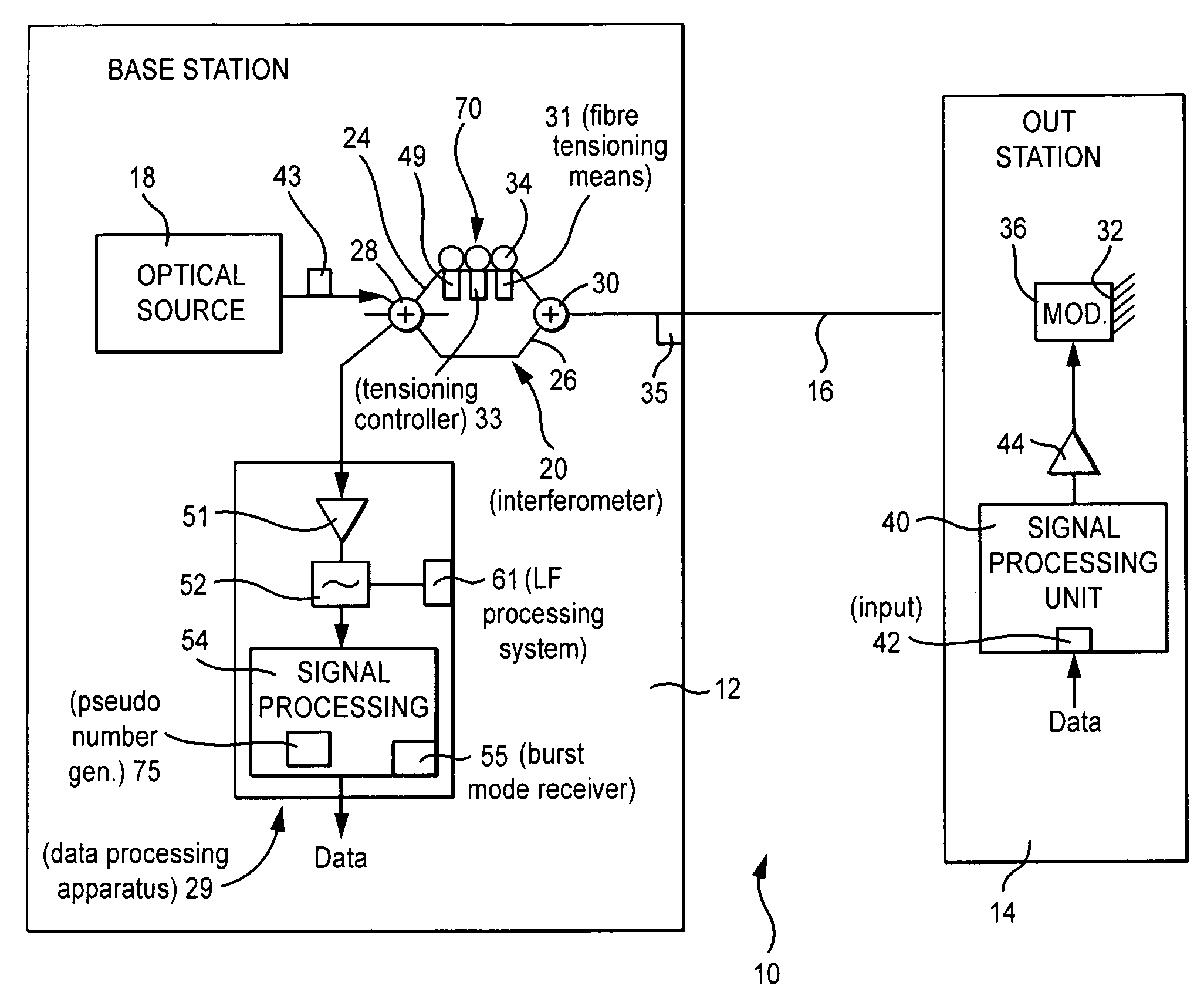
Secure optical communication
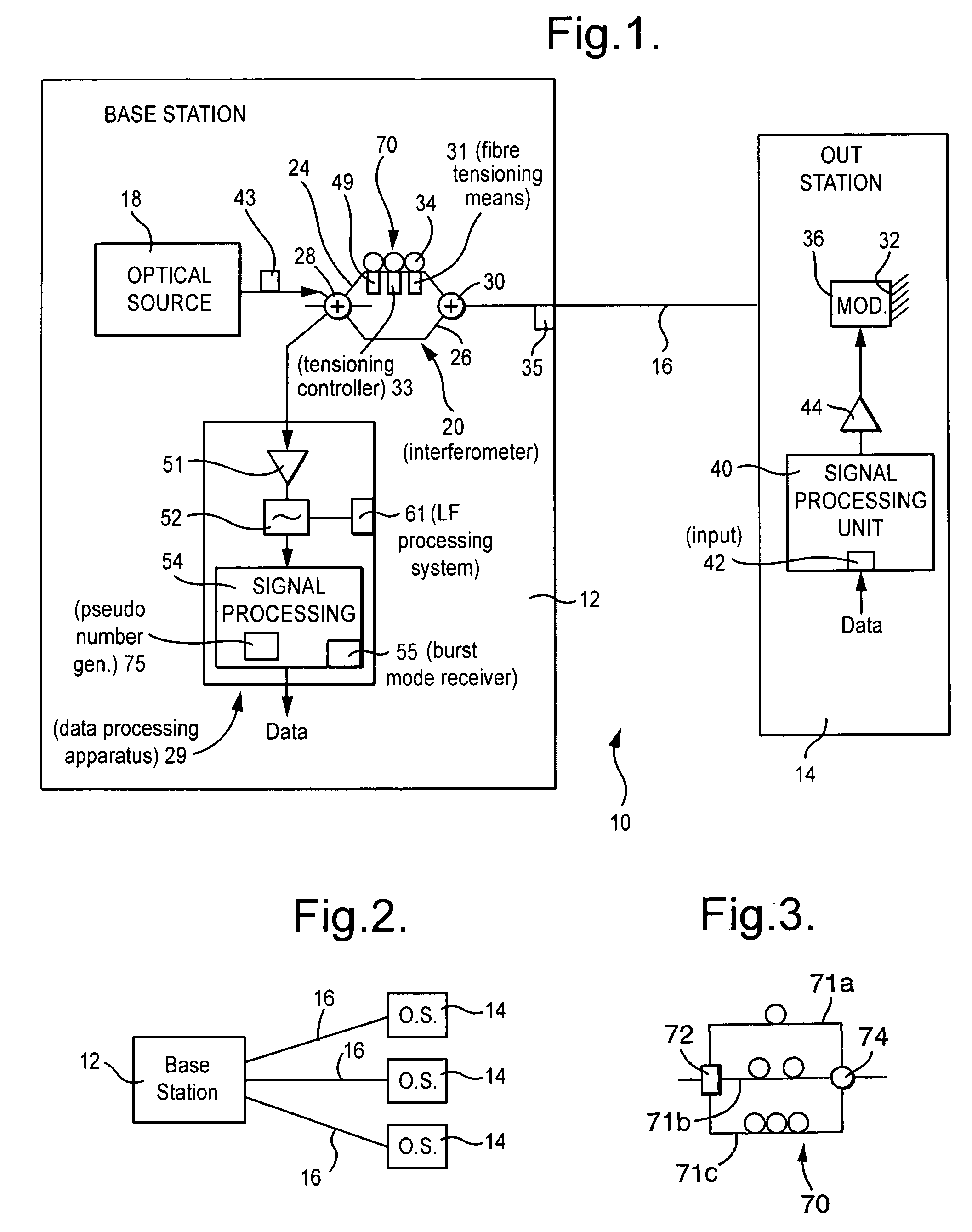
ActiveUS7796896B2Reduce riskExtended durationSecret communicationUsing optical meansCoherence timePhase modulation
A secure optical communication scheme uses differential delay D in an unbalanced Mach-Zehender interferometer to provide two copies of the optical source signal at a remote phase modulator separated in time by D. As D is much bigger than the coherence time source, the two copies of the signal are effectively uncorrelated. Both signals are phase-modulated by the remote sender's data and returned to the unbalanced interferometer. The phase modulator will be converted into amplitude modulation by the action of the interferometer.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
Multi-user massive MIMO channel estimation method based on Bayesian method
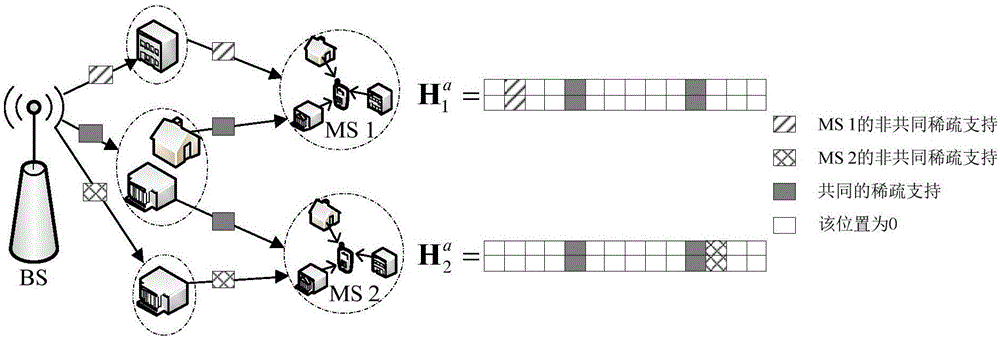
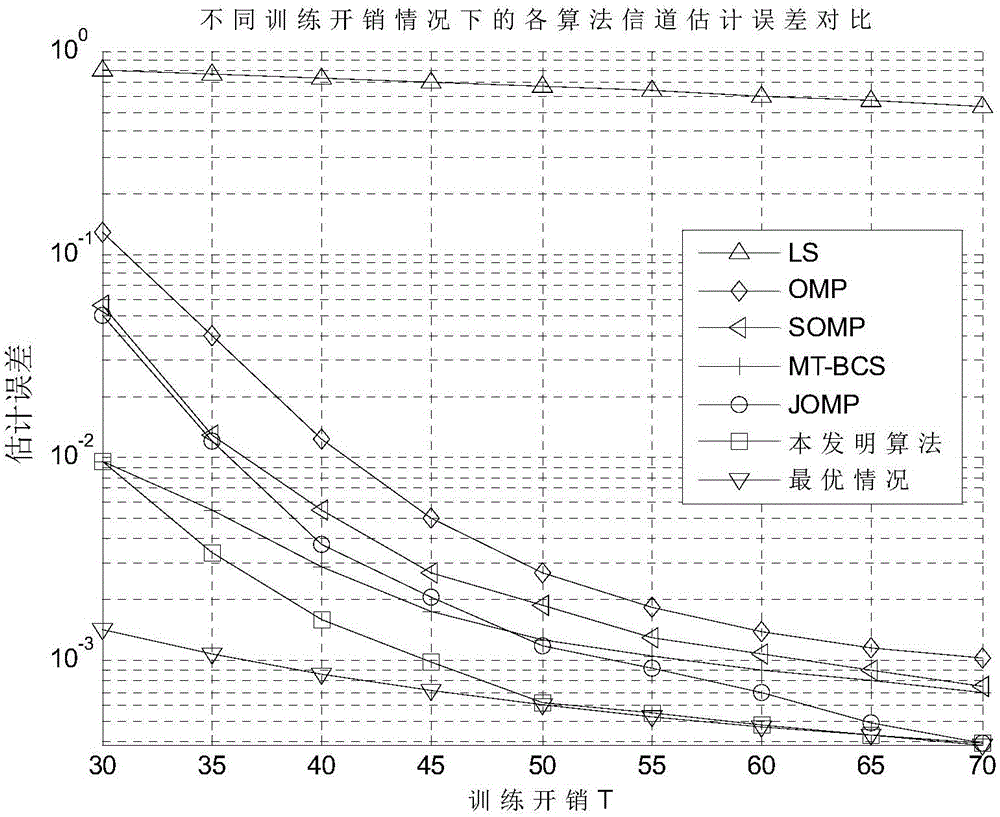
InactiveCN105119853AReduce overheadShorten the timeBaseband system detailsEstimation methodsCoherence time
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication, and specifically relates to a channel estimation method for a multi-user massive MIMO (MU-Massive MIMO) system in the frequency division duplex (FDD) mode. In the multi-user massive MIMO system, according to the method, the combined sparsity of the channel is employed, a sparse signal reconstruction algorithm based on the Bayesian method is introduced to perform channel estimation, the expense of channel estimation is greatly reduced, the channel estimation time is far less than the channel coherence time, the expense of channel estimation is reduced to 20% of the expense by employing a conventional channel estimation method, the channel estimation time is far less than the channel coherence time, and the realization of the massive MIMO channel estimation is possible in reality.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
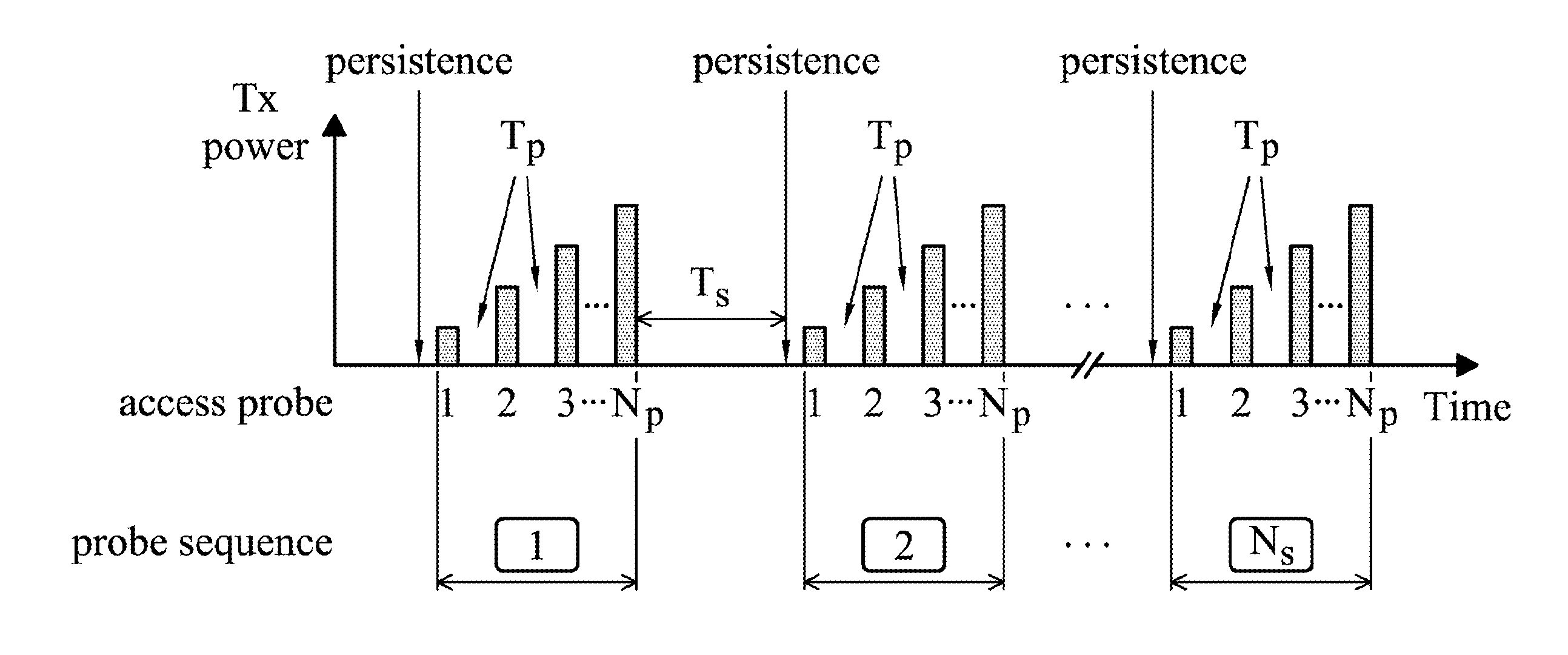
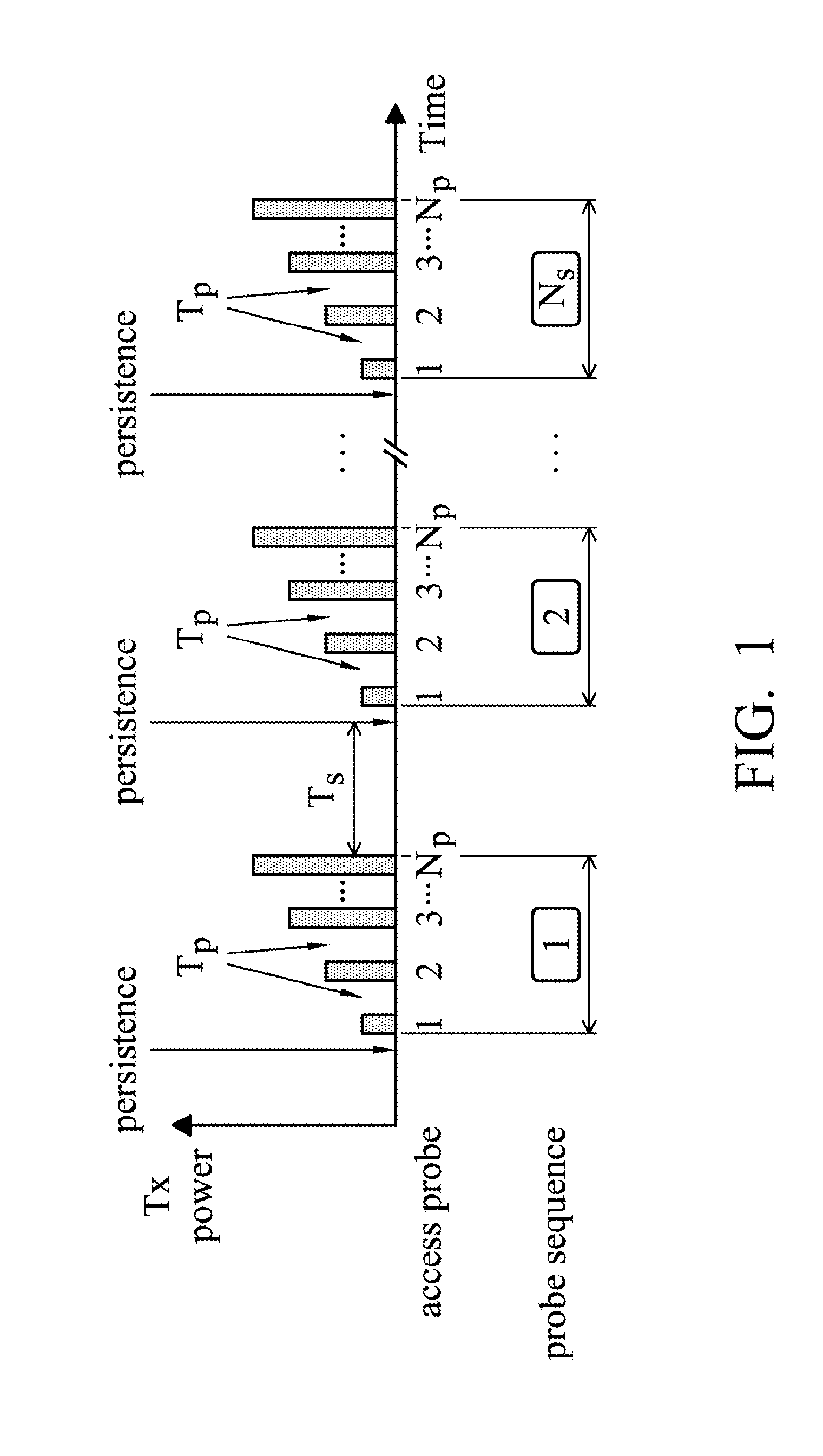
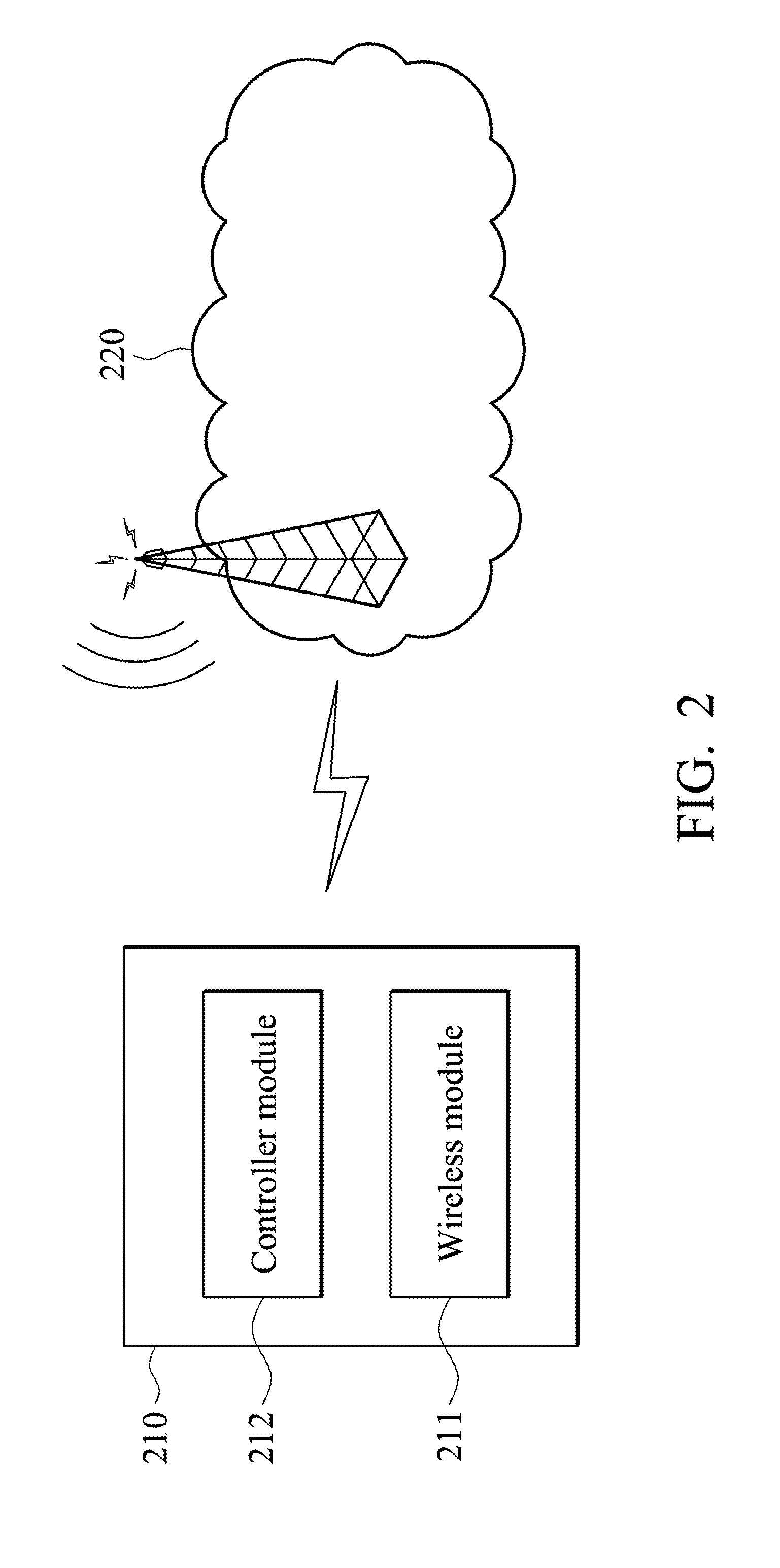
Apparatus, System, and Method for Access Procedure Enhancements
InactiveUS20110051697A1Power managementNetwork traffic/resource managementWireless transmissionTelecommunications
A mobile communication device for access procedure enhancement is provided. In the mobile communication device, a wireless module performs wireless transmissions and receptions to and from a service network. Also, a controller module transmits an access probe to the service network via the wireless module, and retransmits the access probe in response to not receiving an acknowledgement of the access probe from the service network via the wireless module in a waiting period of time. The waiting period of time is determined according to a coherence-time related offset. The controller module further repeats the retransmission of the access probe until the acknowledgement of the access probe is received from the service network via the wireless module
Owner:INTEL CORP
Wiring method of superconducting quantum bit system for surface coding scheme and wiring board
ActiveCN105957832AAvoid the problem of decoherence time dropSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCoherence timeQuantum system
The invention provides a wiring method of a superconducting quantum bit system for a surface coding scheme and a wiring board, and belongs to the field of a quantum system. The wiring board comprises a quantum chip substrate, a plurality of insulating layers, a wiring layer and a plurality of grounding layers, wherein the quantum chip substrate is provided with a plurality of quantum bits and a plurality of couplers, and the insulating layers are arranged at the lower surface of the quantum chip substrate in a covering manner; the wiring layer is arranged in the insulating layers of the plurality of insulating layers, and the wiring layer is connected with the quantum bits and / or the couplers; and the plurality of grounding layers are correspondingly arranged at the upper surfaces and the lower surfaces of the plurality of insulating layers. According to the wiring method provided by the invention of the superconducting quantum bit system for the surface coding scheme and the wiring board, a problem that the quantum bit de-coherence time is reduced because key devices such as the quantum bits are covered with an insulating film is avoided through the wiring board provided with the quantum chip substrate, the insulating layers and the grounding layers.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Non-orthogonal multiple access method based on large-scale MIMO
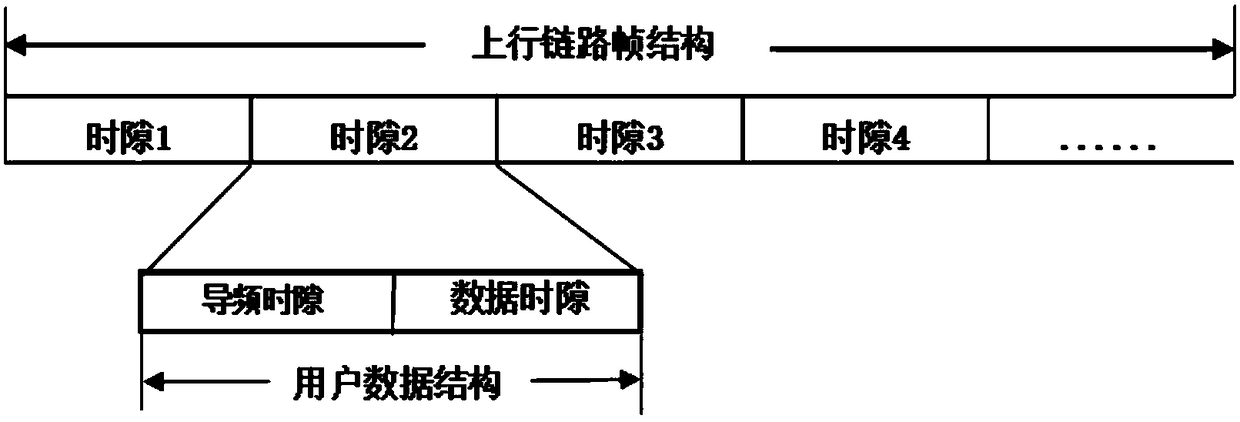
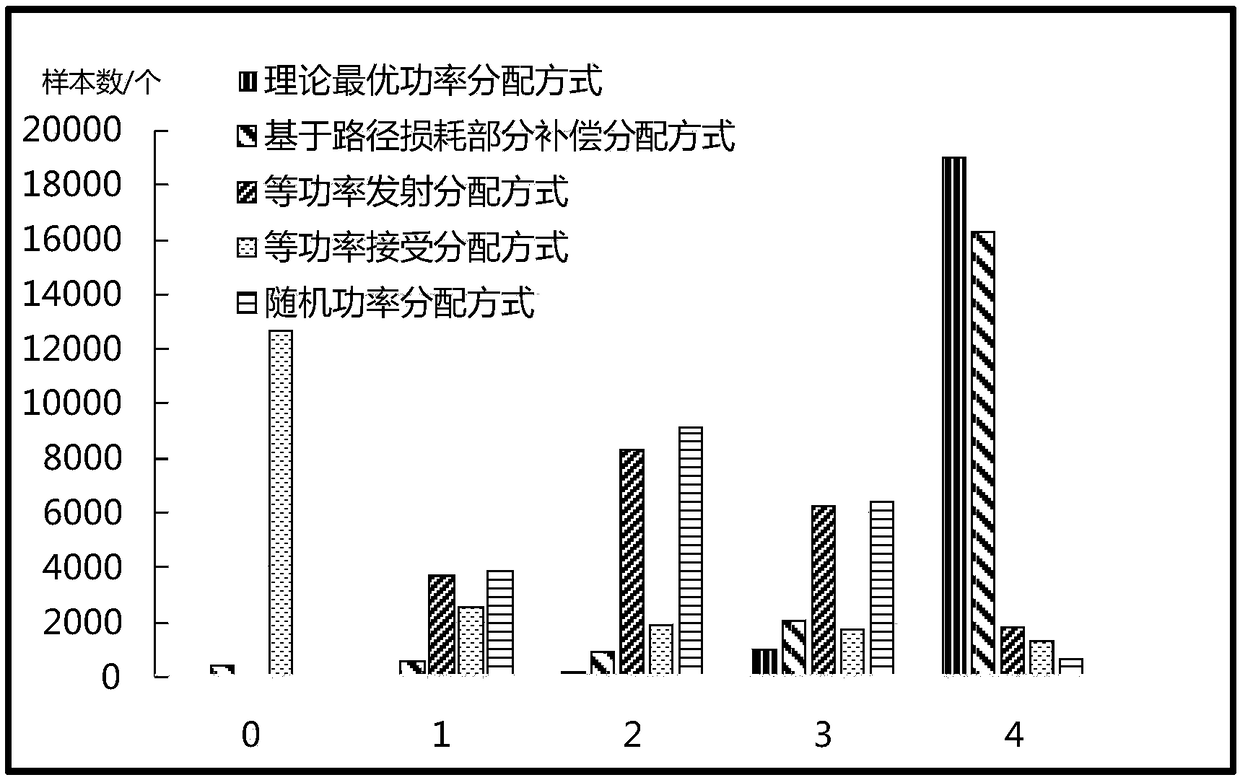
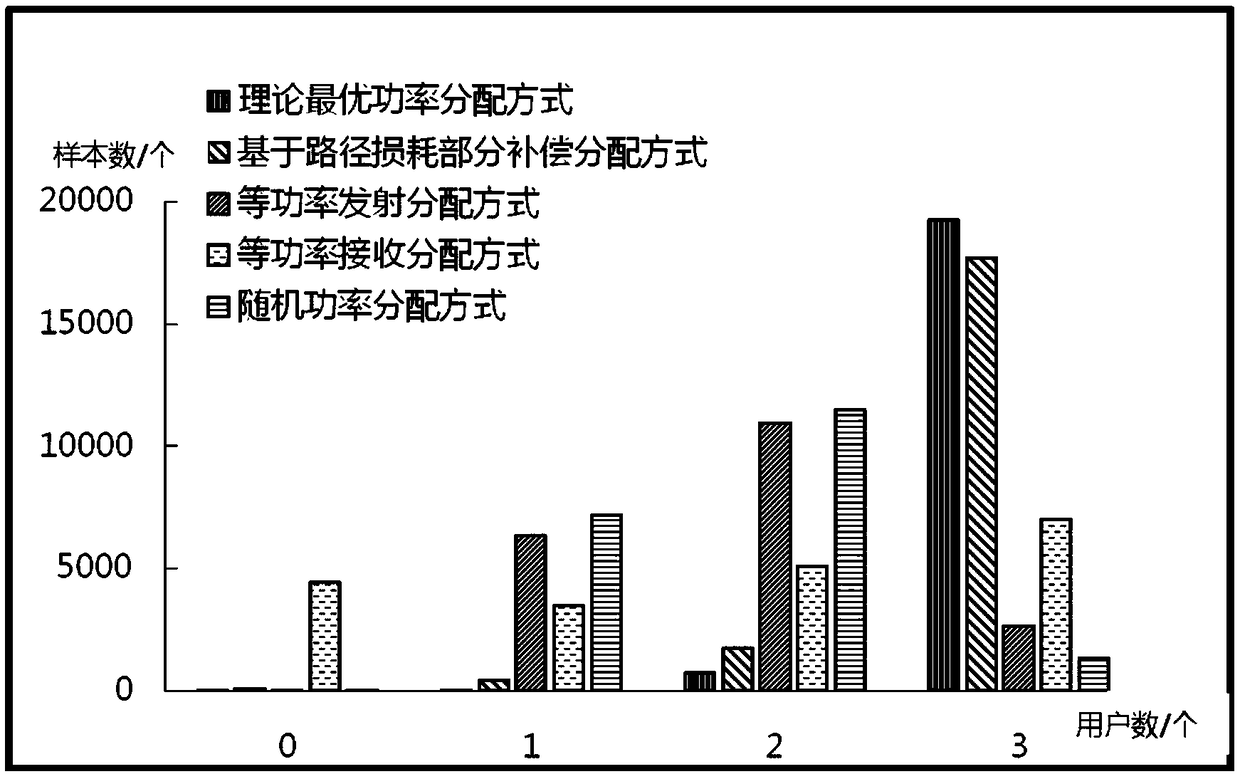
ActiveCN108650006AHigh overload rateMore received powerRadio transmissionChannel estimationInterference eliminationAccess method
The invention relates to a non-orthogonal multiple access method based on large-scale MIMO. The method comprises the following steps of step 1, determining an optimal demodulation sequence; step 2, determining received power of a user; step 3, determining optimal emission power of the user; step 4, determining a data frame structure, wherein different users accessing the same base station follow the same uplink frame structure for synchronous transmission, and the time slot length used by the user does not exceed the coherence time of a wireless channel; step 5, adopting a pilot selection way,wherein a way of obtaining a pilot frequency by the user is that each user randomly selects the pilot frequency used by the user from a given pilot frequency set independently; and step 6, making a plurality of user terminals send signals to the base station at the optimal transmitting power based on the step 4 and the step 5, and after the base station receives the signals, only estimating a multi-user composite channel at an antenna end by means of the channel hardening capability of the large-scale MIMO, and utilizing a serial interference elimination technology to finally complete the recovery of all user signals.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
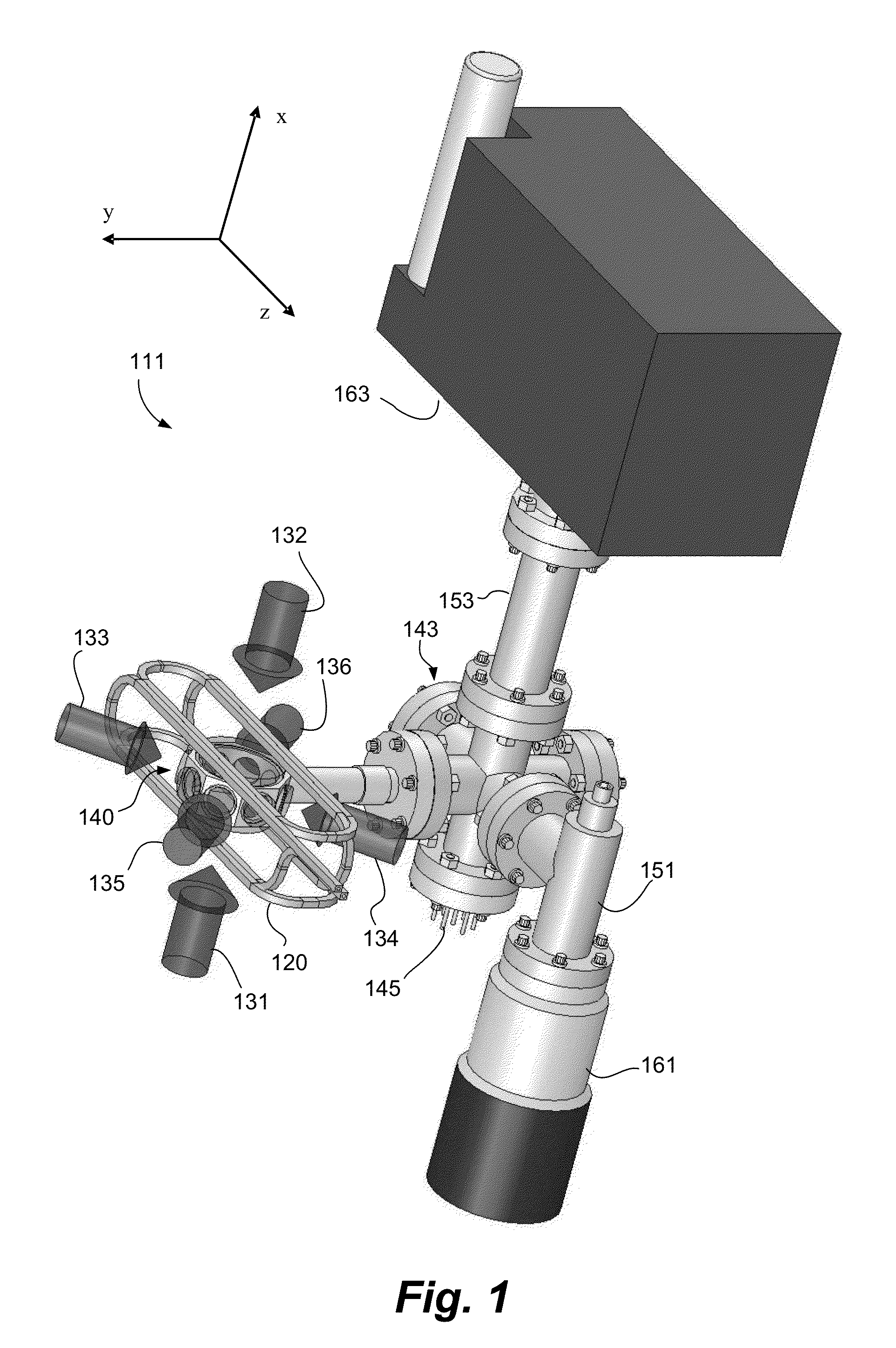
Two-dimensional magneto-optical trap for neutral atoms
ActiveCN102969038ANeutron particle radiation pressure manipulationOptical elementsMagneto-optical trapLong axis
A two-dimensional (2D) magneto-optical trap (MOT) for alkali neutral atoms establishes a zero magnetic field along the longitudinal symmetry axis. Two of three pairs of trapping laser beams do not follow the symmetry axes of the quadruple magnetic field and are aligned with a large non-zero degree angles to the longitudinal axis. In a dark-line 2D MOT configuration, there are two orthogonal repumping beams. In each repumping beam, an opaque line is imaged to the longitudinal axis, and the overlap of these two line images creates a dark line volume in the longitudinal axis where there is no repumping light. The zero magnetic field along the longitudinal axis allows the cold atoms maintain a long ground-state coherence time without switching off the MOT magnetic field, which makes it possible to operate the MOT at a high repetition rate and a high duty cycle.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Adaptive pilot design for mobile system
A method, and device implementing the method, for adaptively allocating pilot signals in a wireless communication system. The method includes receiving channel data, including channel length (L) data, inter-carrier interference power (PICI) data, coherence time (CT) data, and a number of subcarriers (N). The method further includes selecting, when L is greater than a first channel length threshold (LTH1), a first number of pilot signals between a minimum value of L and a maximum number of pilot signals NP,MAX, wherein the first number of pilot signals NP are equally spaced in time according to the CT data, and equally spaced in frequency. Further, the method includes selecting, when L is less than LTH1 and PICI is less than a power threshold (PTH), a second number of pilot signals such that the second number of pilot signals is between the minimum value of L and NP,MAX, wherein the second number of pilot signals are equally spaced in time according to the CT data, and equally spaced in frequency. Finally, the method includes selecting, when L is less than LTH1 and PICI is greater than PTH, a third number of pilot signals such that the third number of pilot signals is equal to n times L (nL), wherein n is an integer, the third number of pilot signals being equally spaced in time according to the CT data, and allocated according to a cluster(n) clustered pilot scheme with a cluster size equal to n, the n-sized clusters being clustered in frequency.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Method and apparatus for establishing a time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration in a carrier extension or carrier segment
InactiveCN103703833ANetwork traffic/resource managementTransmission path divisionCell specificResource element
Methods, apparatus and computer program products are provided for establishing a time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration in a carrier extension or a carrier segment, such as for cell-specific reference signals (CRS) and / or demodulation reference signals (DM RS). One method includes receiving information regarding a time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration in a carrier extension or carrier segment. The time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration defines a subframe to include a reference signal based upon a time density parameter and defines a resource element to be utilized within the subframe based upon a frequency density parameter. This method also includes receiving reference signals pursuant to the time-frequency reference signal pattern configuration such that reference signals have a coherence time Tcoh with at least one subframe including a reference signal in the CE or CS per Tcoh and a coherence bandwidth Bcoh with at least one resource element containing a reference signal per Bcoh.
Owner:BROADCOM CORP
Optimal training sequence and channel estimation method and system for superimposed training based OFDM systems
InactiveUS20110007829A1Reduce the impactReliable least squares based channelMultiple-port networksElectric signal transmission systemsDelay spreadTime domain
The present invention relates to a method for minimizing means square estimation error (MSEE) and bit error rate during channel estimation and equalization between a transmitter and a receiver of an orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems. The method comprises transmitting from said transmitter to said receiver a training sequence for channel estimation being superimposed onto data at specific pilot to data power ratio (PDPR), receiving the OFDM signals along with the training sequence as an input, cross-correlating said received signal to a specific lag determined by the rms delay spread of the channel, with a specific known training sequence stored in a register, and which is also the sequence that is added to the data at the transmitter in the time domain having a prescribed pilot to data power ratio. The cross-correlated data being processed over a length of samples which can be extended to exploit the coherence time of the channel and processed along with the stored values of the inverse of autocorrelation values of superimposed training (ST) sequence so as to obtain a reliable least squares based channel estimate in a way the PDPR is limited or otherwise. The invention also relates to a system comprising means for computing a time domain least squares (LS) based channel estimate at the receiver.
Owner:INDIAN INST OF TECH
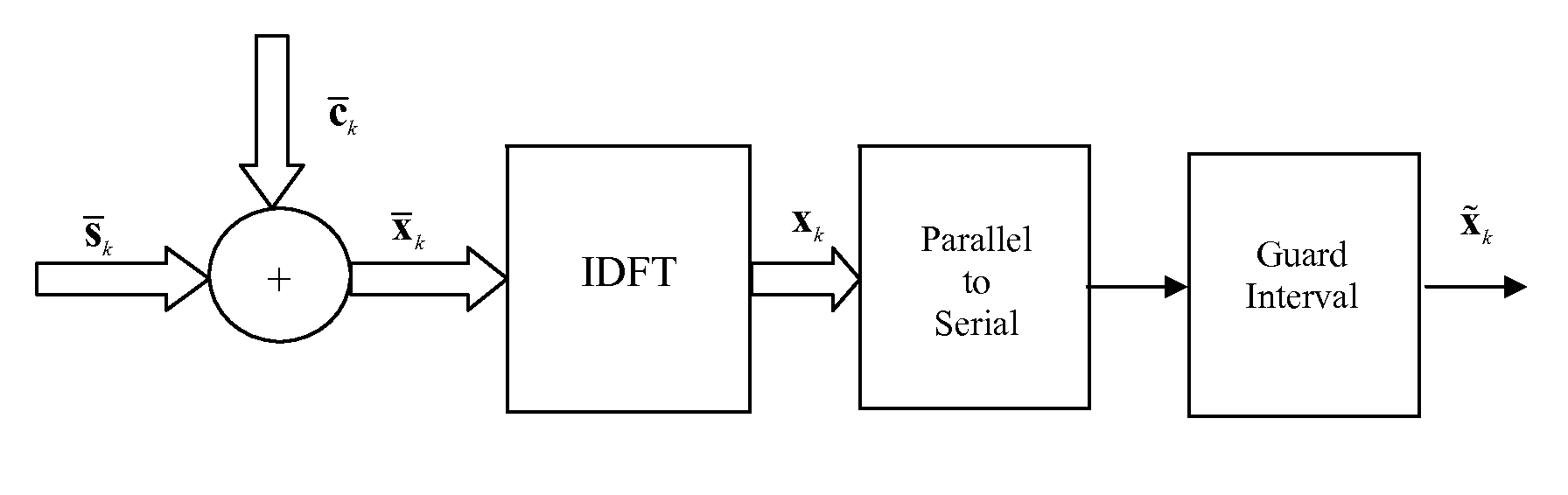
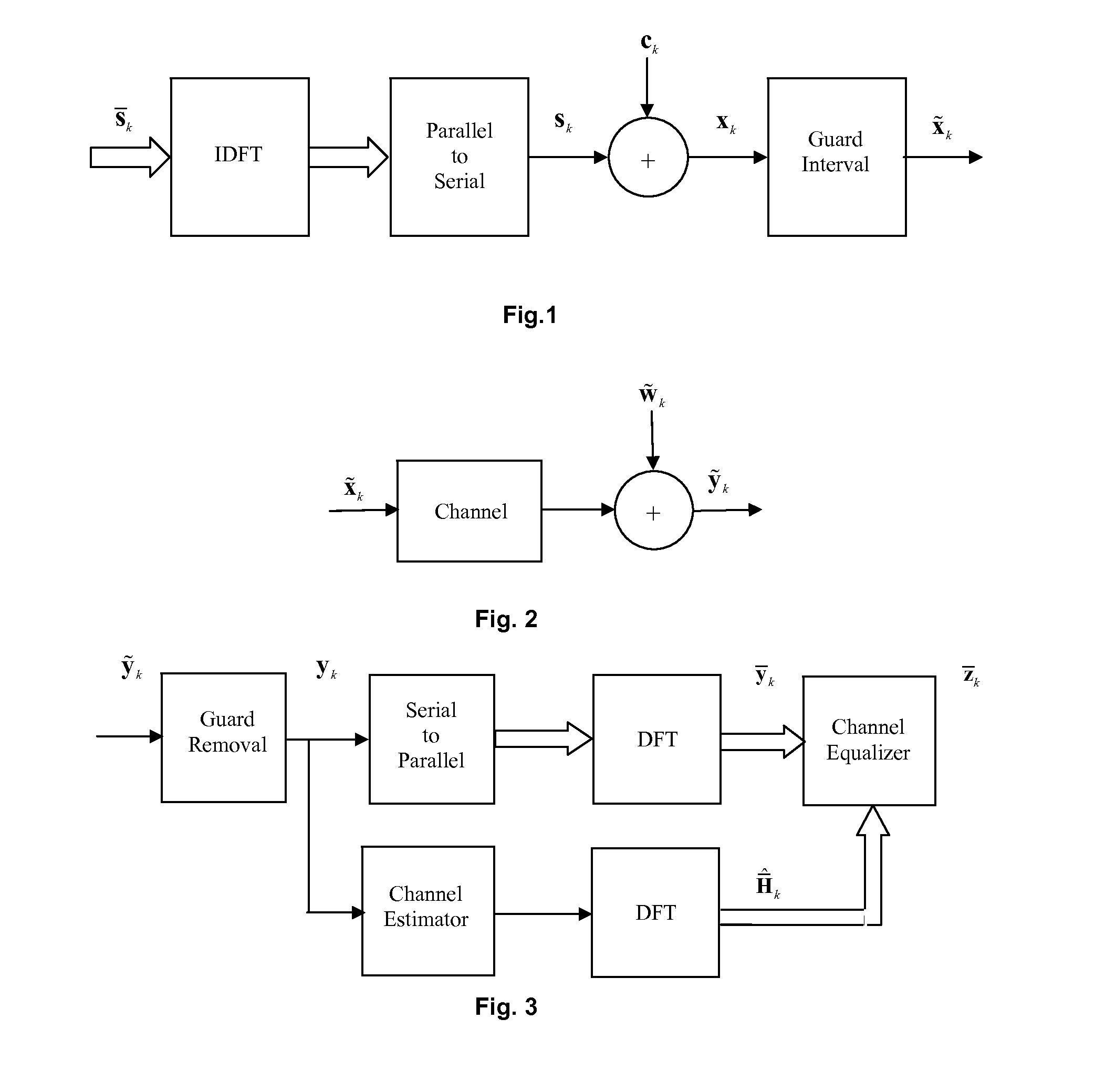
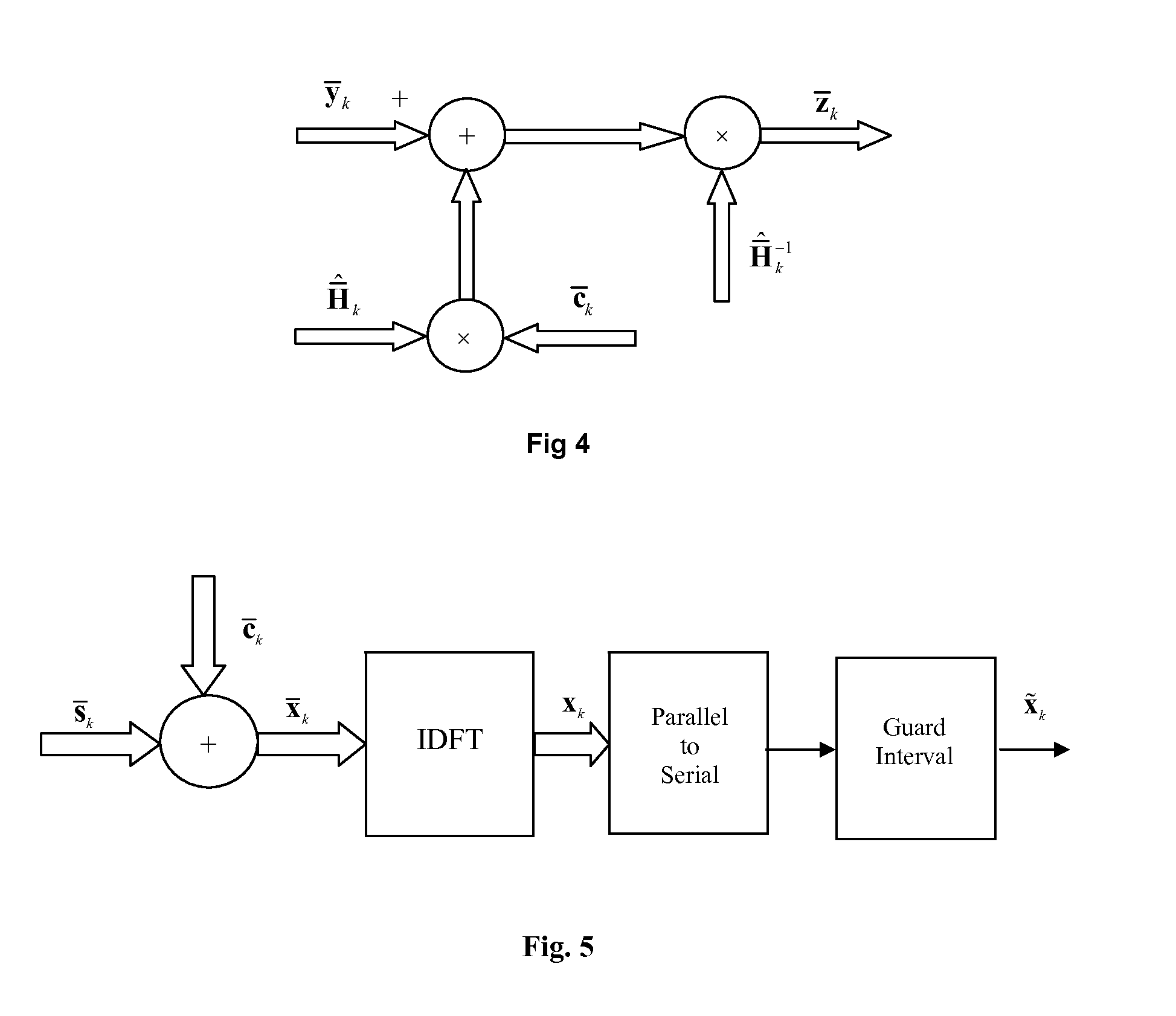
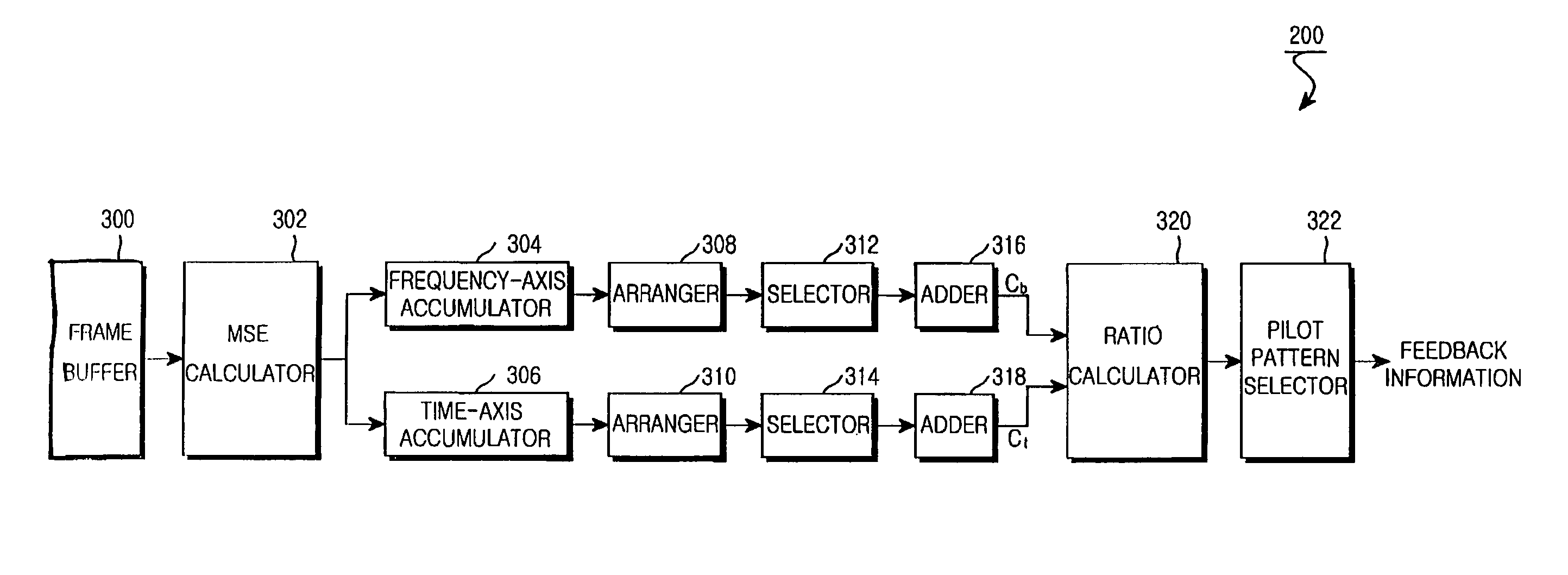
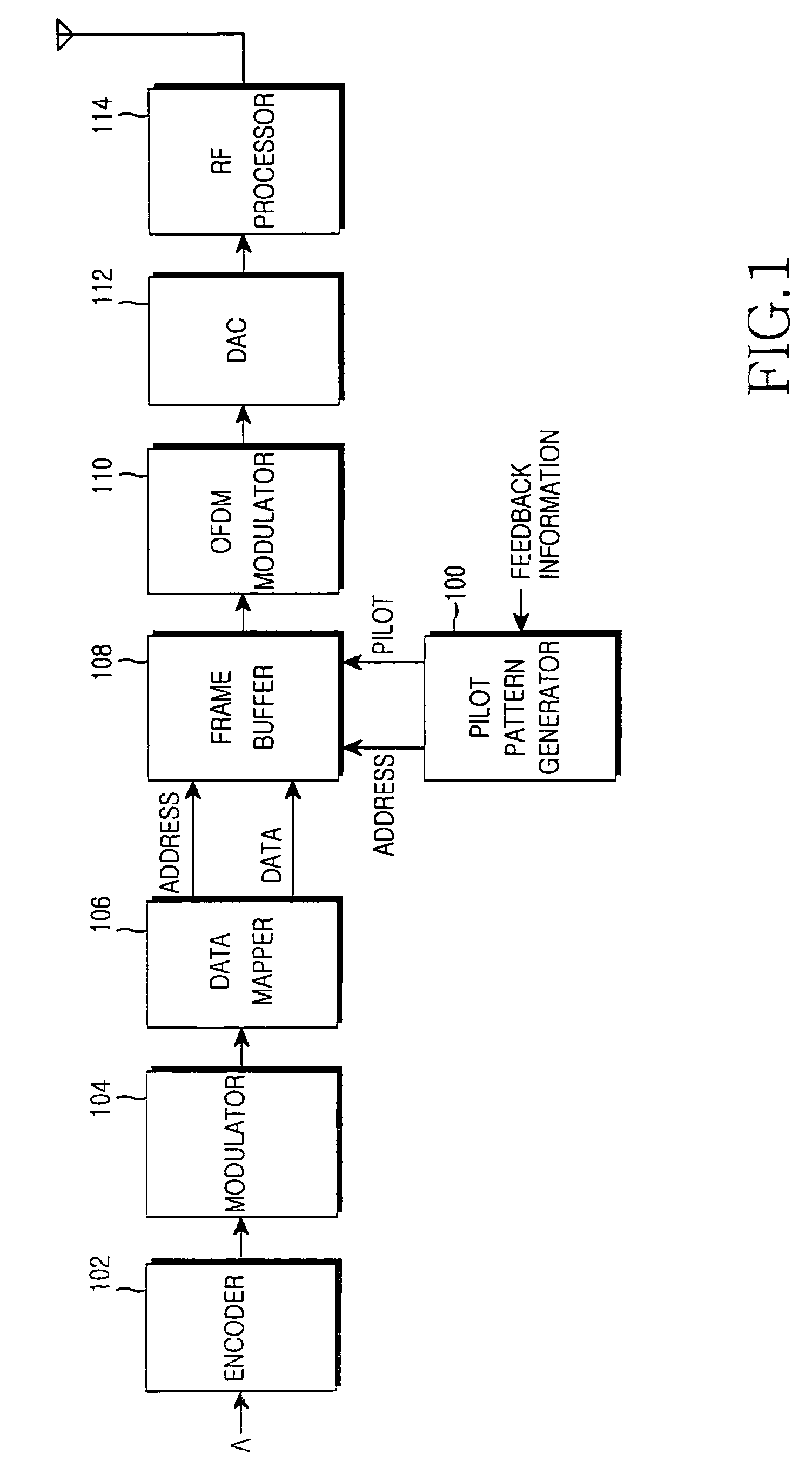
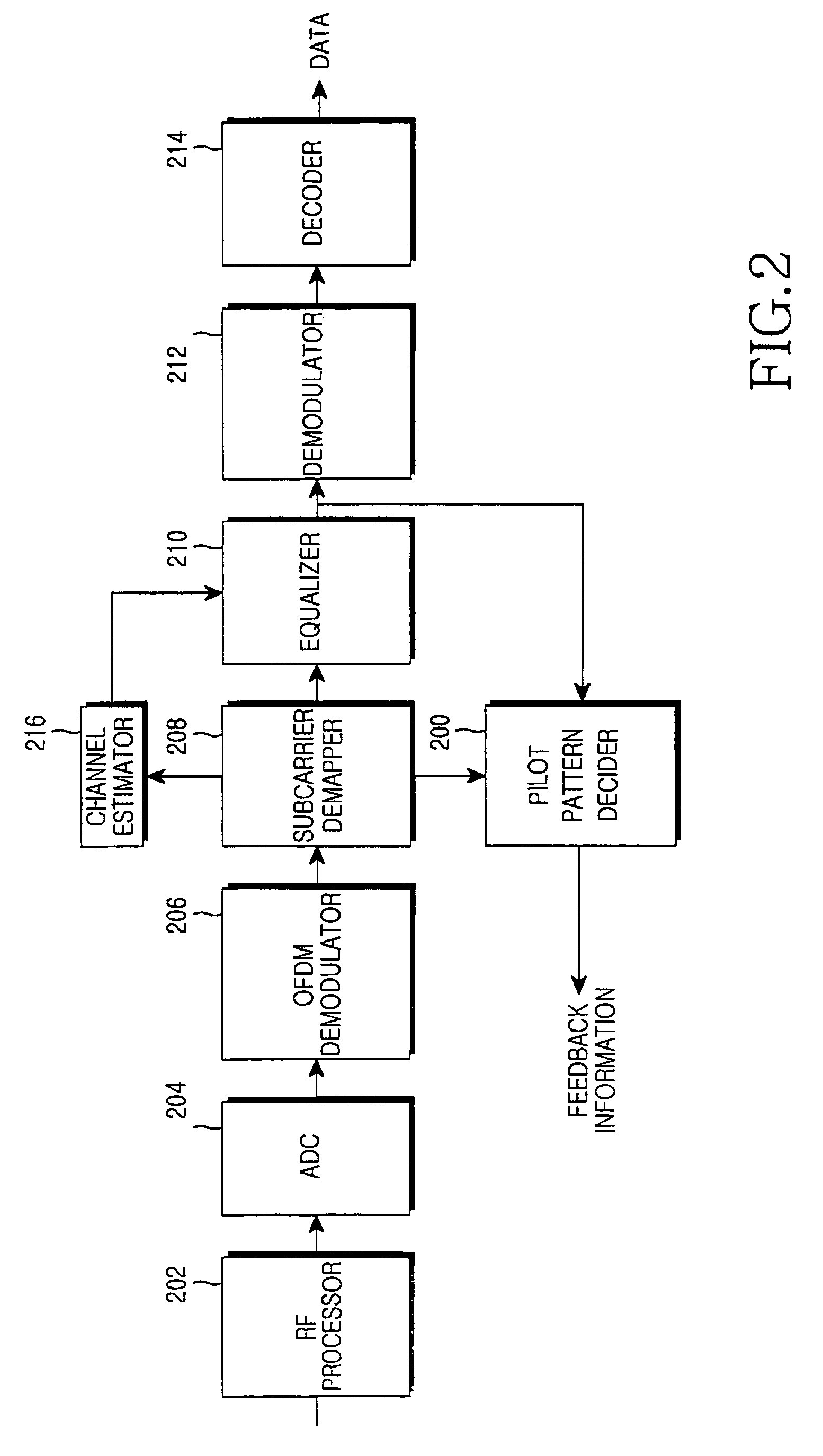
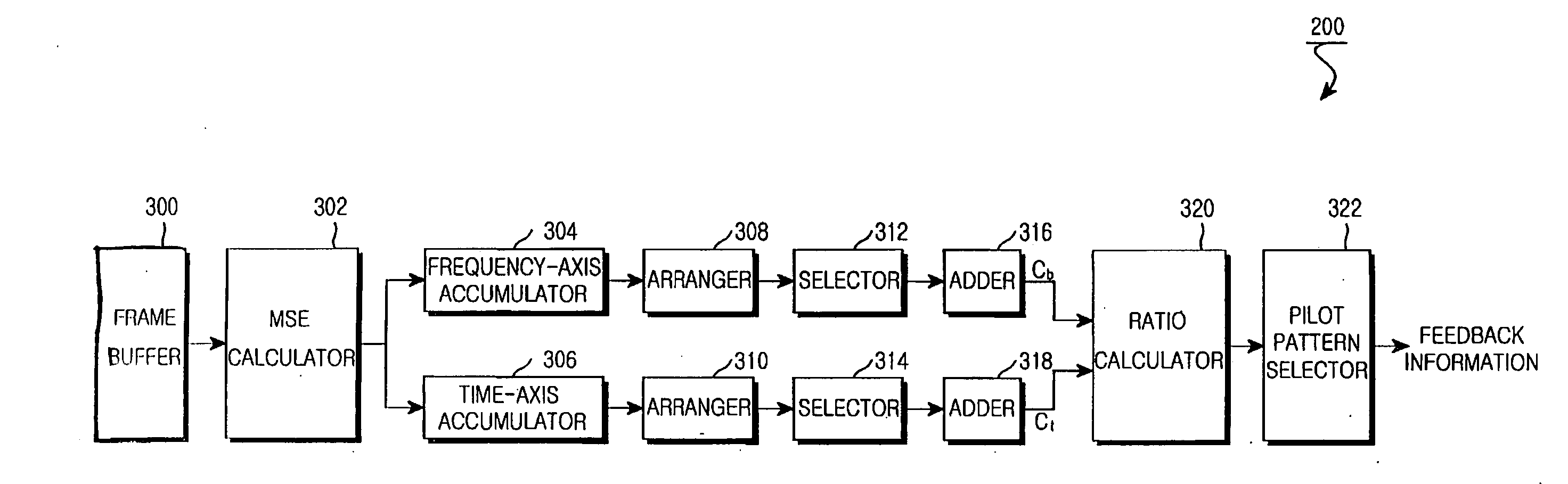
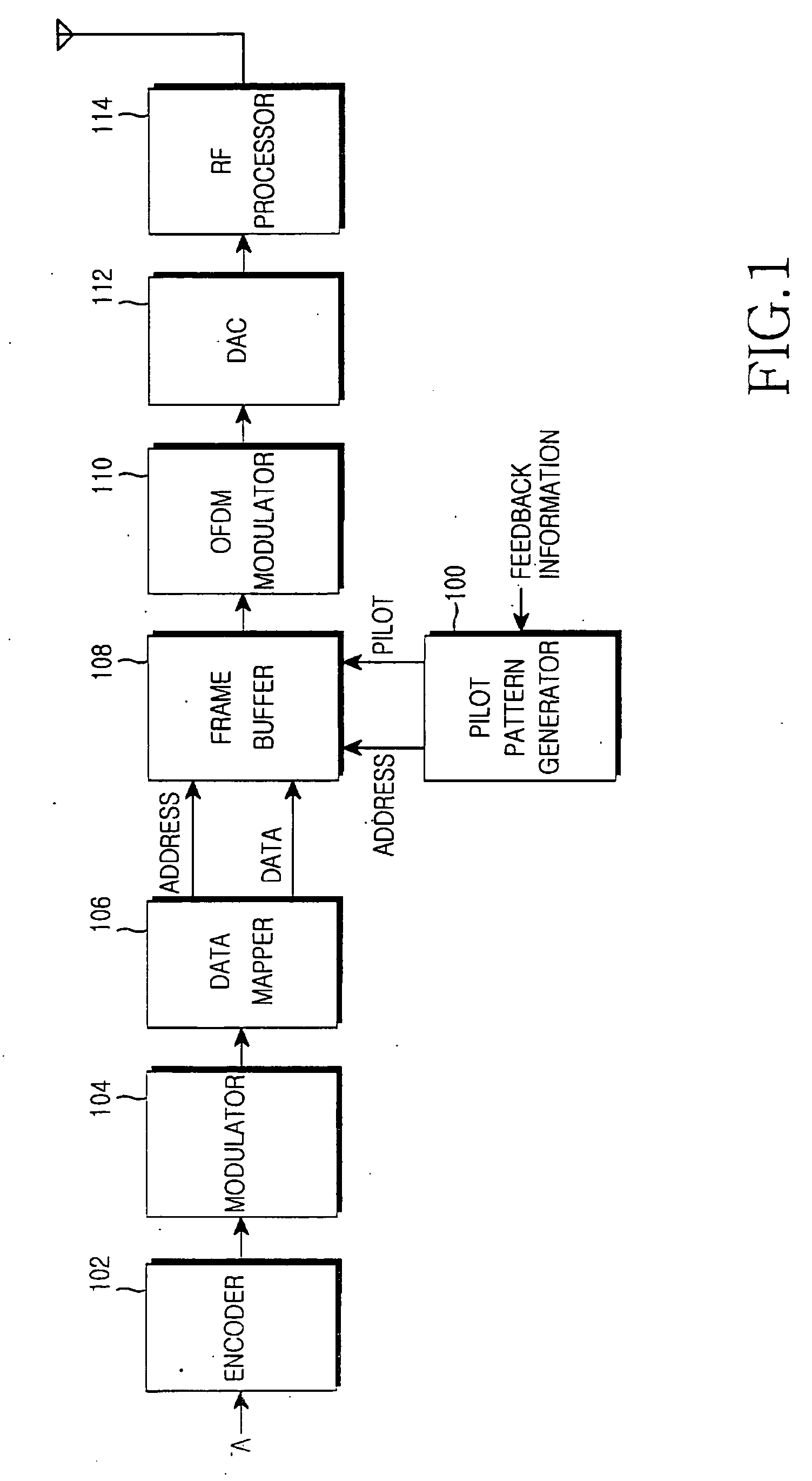
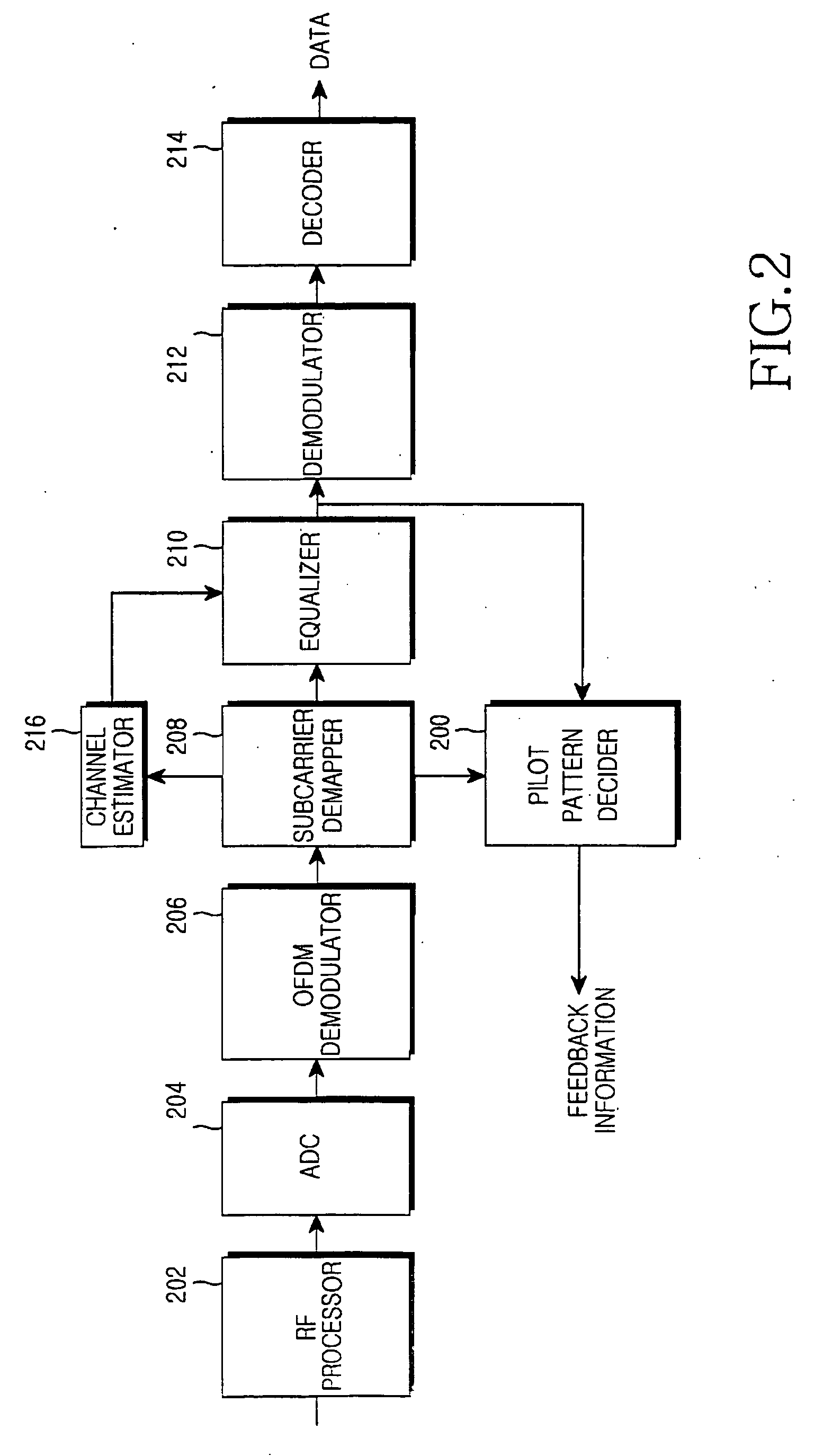
Apparatus and method for determining pilot pattern in a broadband wireless access communication system
InactiveUS7792201B2Minimizes channel estimation errorLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFast Fourier transformCommunications system
An apparatus and method for determining a pilot pattern in a Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) communication system are provided. In the pilot pattern determining method, an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) demodulator generates frequency-domain data by fast-Fourier-transform (FFT)-processing a received signal. A pilot pattern decider calculates a coherence bandwidth and a coherence time using subcarrier values received from the OFDM demodulator, and selects one of a plurality of pilot patterns according to the ratio of the coherence bandwidth to the coherence time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
DWDM channel detection system
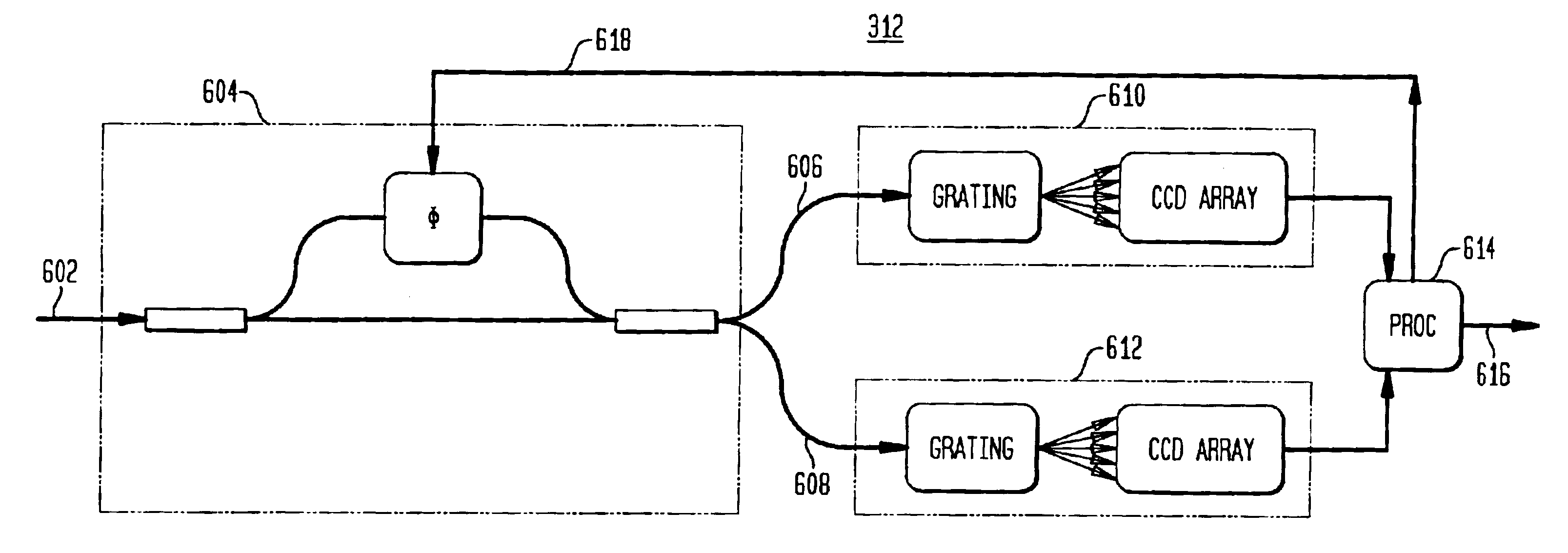
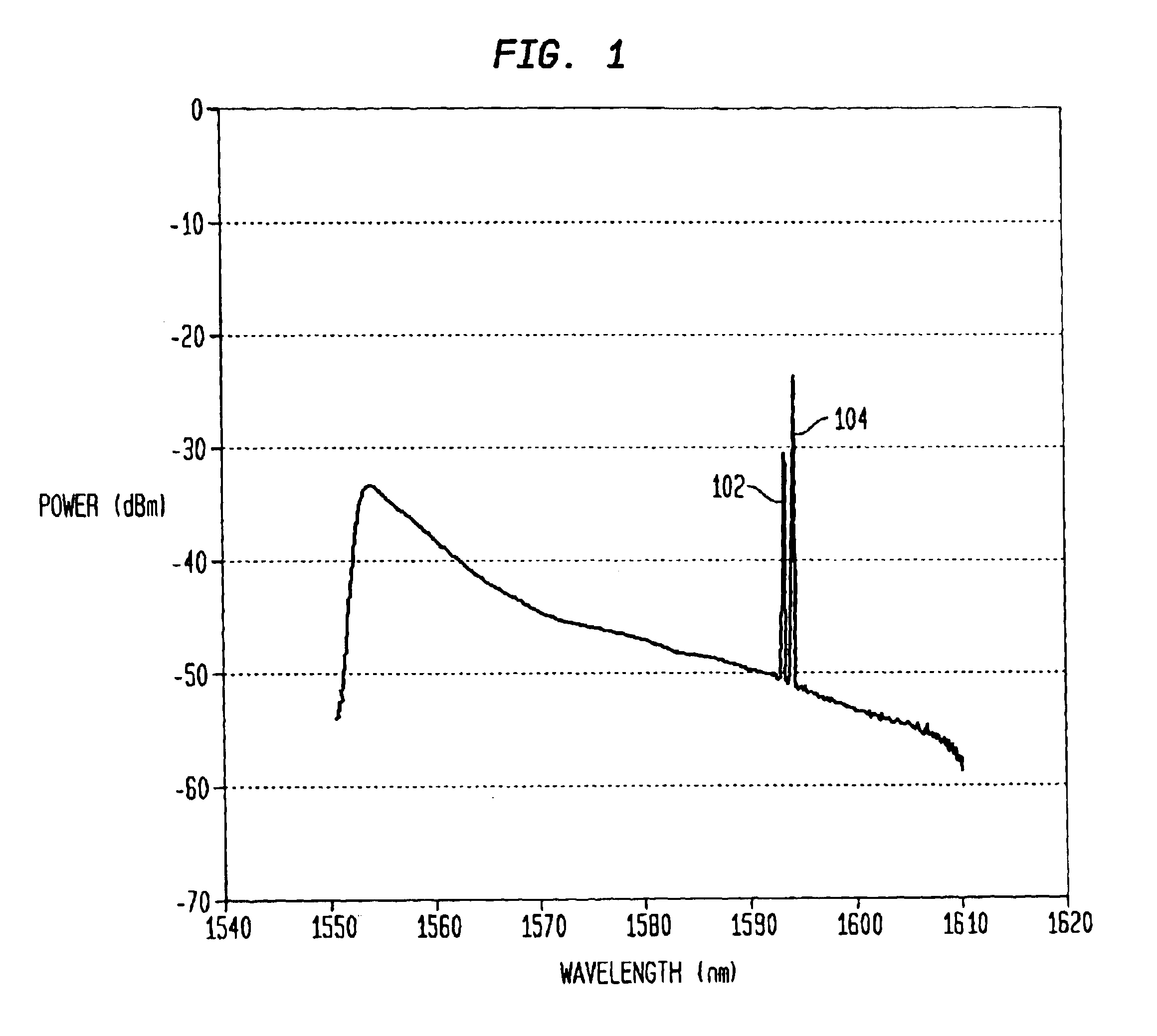
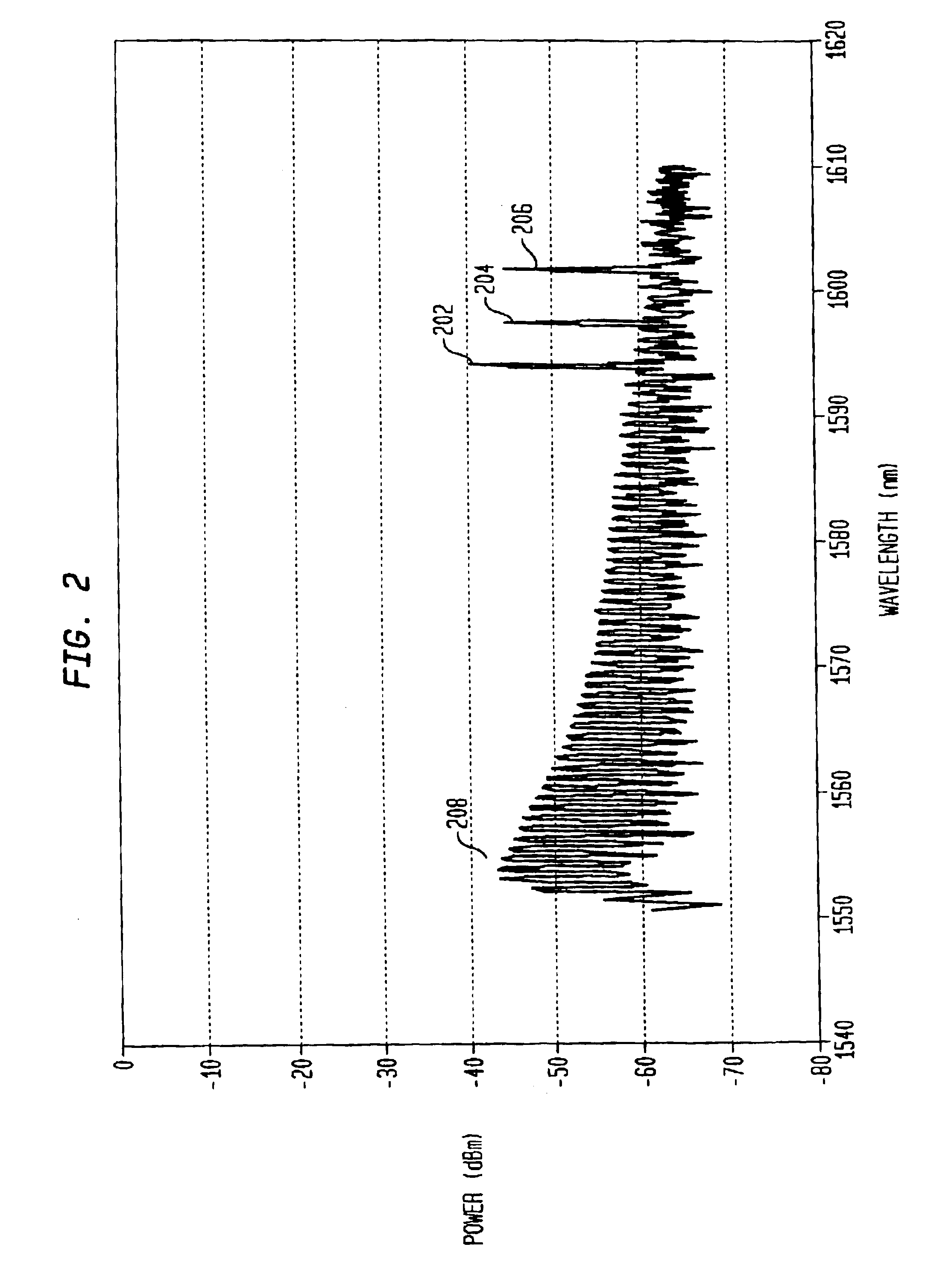
ActiveUS6911645B2Control delayRadiation pyrometryWavelength-division multiplex systemsSpectrum analyzerCoherence time
A channel detection system includes an interferometer coupled to a spectrum analyzer to differentiate additive spontaneous emission (ASE) noise from optical channels in a dense wave-division multiplex (DWDM) signal. It is assumed that channels, if present, are centered at frequencies corresponding to a standardized channel grid. The relative delay of the interferometer is chosen to be greater than the coherence time of the ASE noise but less than the coherence time of the channels with the interferometer's free spectral range set to an integer divisor of the channel-to-channel frequency spacing of the grid such that active channels experience a high degree of interference. The phase delay of the interferometer is then adjusted to maximize the interference at each grid-aligned frequency. The spectrum-analyzed outputs are compared (e.g., subtracted from one another and then thresholded) to determine the channels present in the DWDM signal.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC
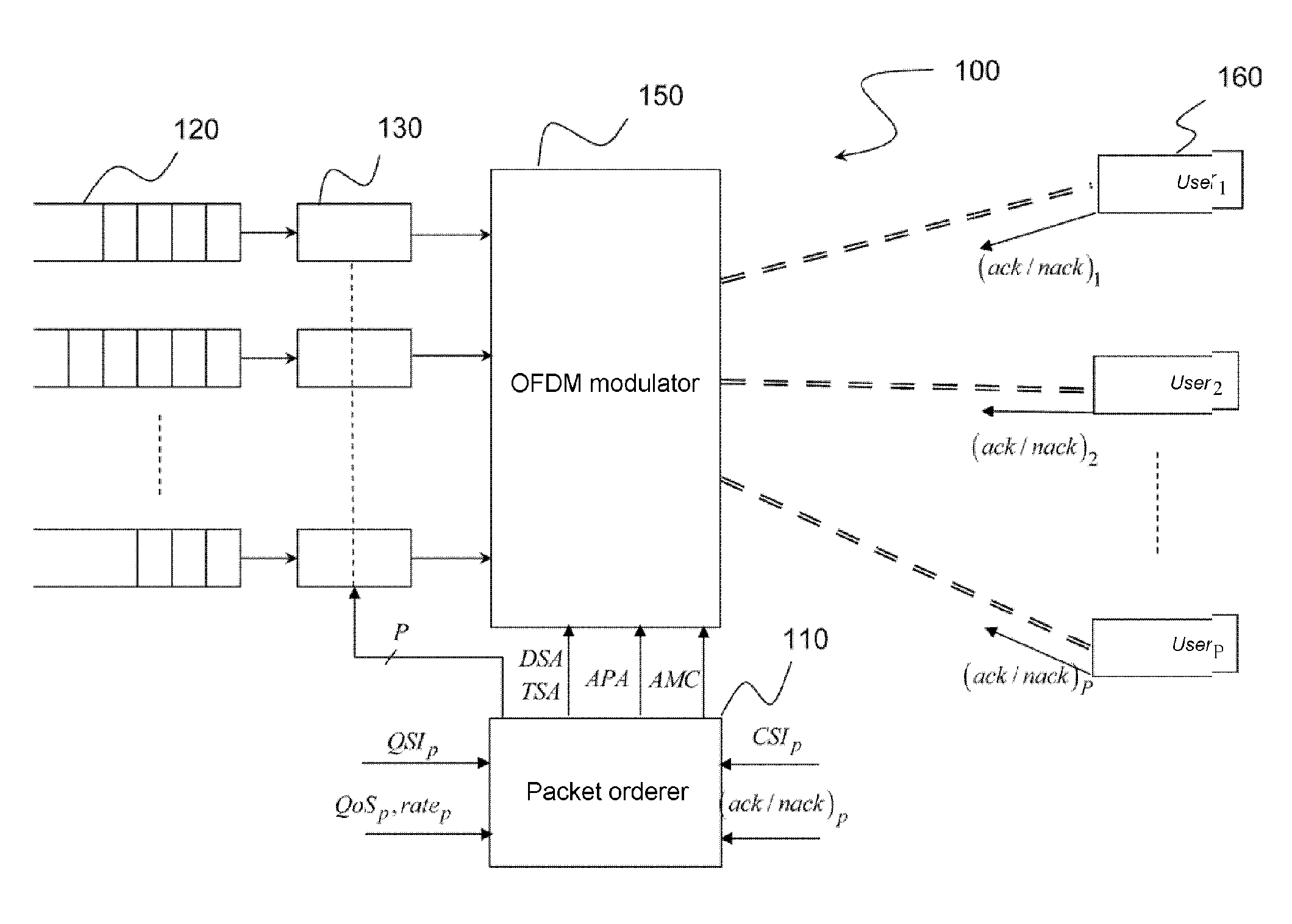
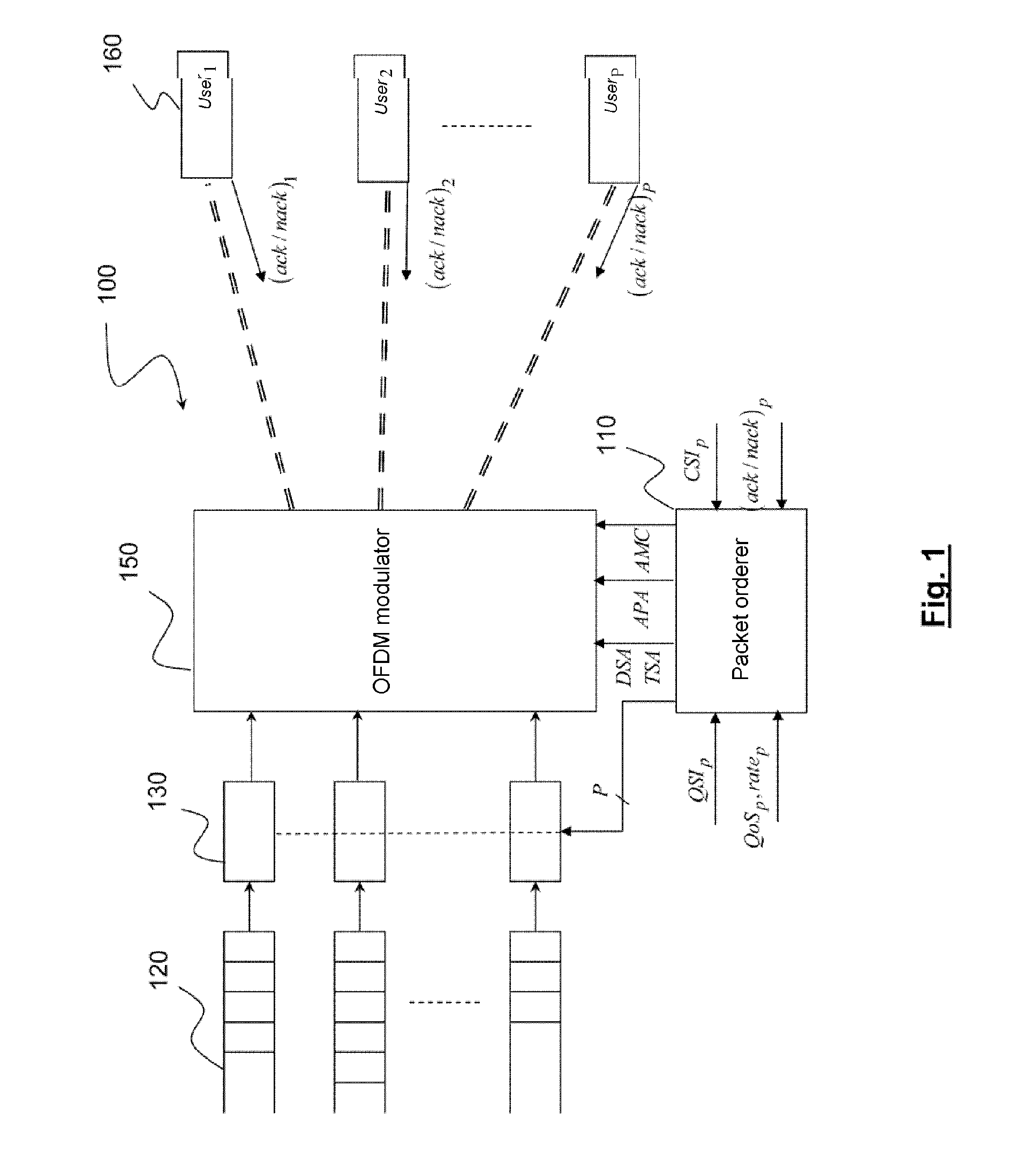
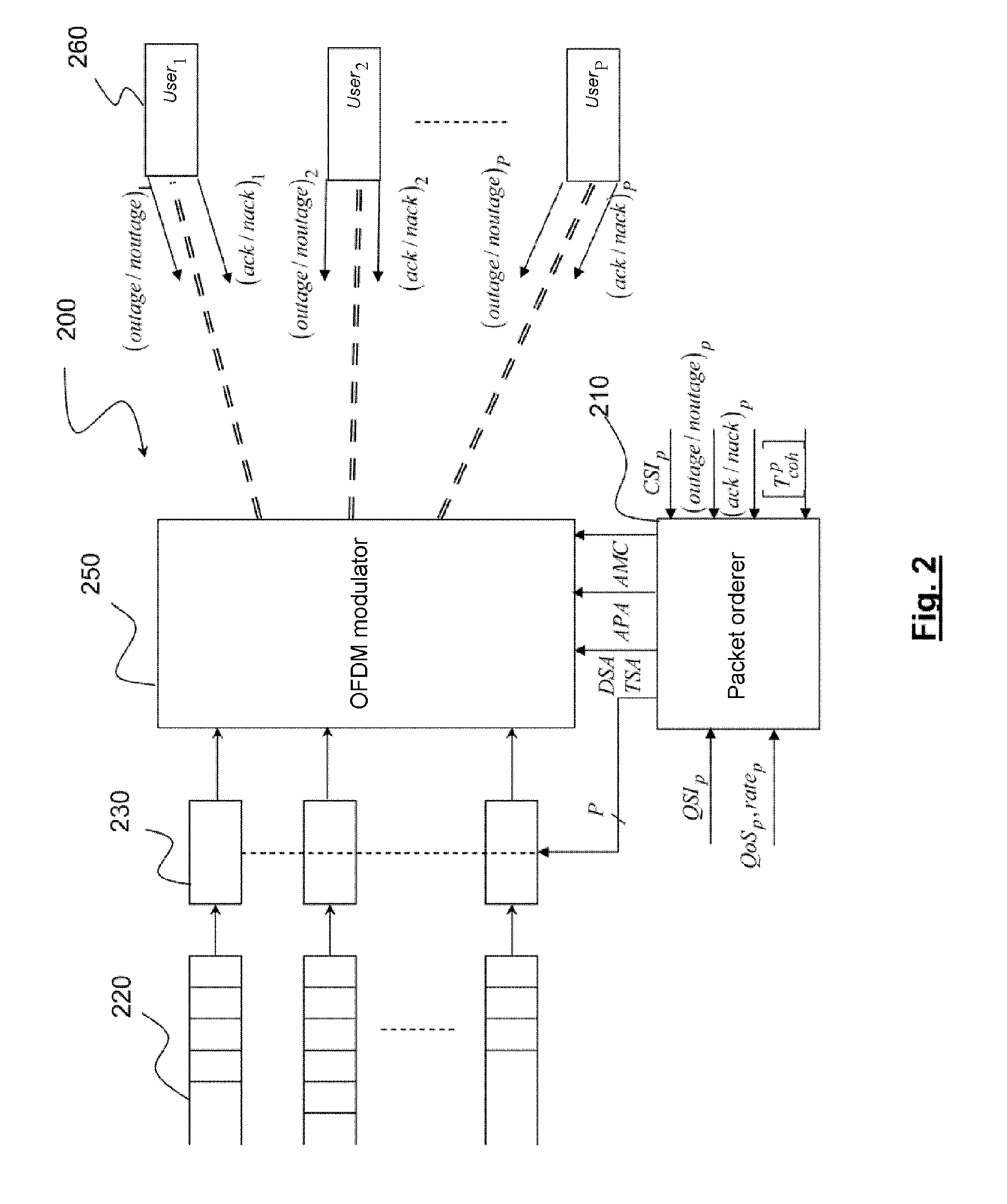
Multi-access telecommunications system with adapted strategy for packet retransmission
ActiveUS20110044314A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsCarrier signalTransmission channel
A wireless OFDMA telecommunications system comprising a transmitter adapted to transmit, by means of an OFDM modulator, a plurality of data packets destined for receivers of a plurality of users, via the same plurality of transmission channels, the transmission channel of a user being associated with a group of sub-carriers of the OFDM multiplex and a set of OFDM symbol times of a transmission interval, each receiver being adapted to signal to the transmitter the loss of a packet transmitted over the transmission channel of the corresponding user, said transmitter further comprising a packet scheduler adapted to control retransmission of each packet lost by means of said modulator. Each receiver comprises detection means of an outage situation of the transmission channel of the corresponding user and signals this to said transmitter by means of an outage information (OUTAGE / NOUTAGE). In the event of outage, said scheduler prohibits any retransmission of a packet lost over said channel during a predetermined time (Tout) greater than or equal to the coherence time of said channel.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Wireless sensor network node collaboration method based on feedback channel
InactiveCN101364857AExtend your lifeReduce transmit powerEnergy efficient ICTSpatial transmit diversityWork periodChannel state information
A wireless sensor network node cooperation method based on a feedback channel is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: (1) transmitting a training sequence to a receiving cluster by a sensor network transmitting cluster; (2) transmitting a channel fading coefficient to a relay node after the receiving cluster receives an information; (3) determining transmission nodes that should participate in the cooperation by the relay node according to the channel fading coefficient; (4) selecting a transmission node to transmit a data information, and setting other nodes in the sleep state; and (5) re-transmitting a training sequence by the transmitting cluster to form a new work period after the coherence time comes. The wireless sensor network node cooperation method has the advantages that the nodes with better channel state can participate in cooperation to transmit information by using the feedback channel to feedback the state information of the channels, thereby finally reducing the transmission power and saving transmission energy.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Wireless communications system that supports multiple modes of operation
InactiveUS7586873B2Network traffic/resource managementAssess restrictionOperation modeMultiple modes
A wireless communications adapts its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to transmission-specific variables. An embodiment of a wireless communications system for transmitting information between a base transceiver station and a subscriber unit includes mode determination logic. The mode determination logic is in communication with the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit. The mode determination logic determines, in response to a received signal, if a subscriber datastream should be transmitted between the base transceiver station and the subscriber unit utilizing spatial multiplexing or non-spatial multiplexing. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic has an input for receiving a measure of a transmission characteristic related to the received signal. In an embodiment, the mode determination logic includes logic for comparing the measured transmission characteristic to a transmission characteristic threshold and for selecting one of spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing in response to the comparison of the measured transmission characteristic to the transmission characteristic threshold. In an embodiment, the transmission characteristic includes at least one of delay spread, post-processing signal-to-noise ratio, cyclical redundancy check (CRC) failure, residual inter-symbol interference, mean square error, coherence time, and path loss. By adapting the mode of operation in response to transmission-specific variables, the use of spatial multiplexing can be discontinued in unfavorable conditions. Additionally, because the wireless communications system can adapt its mode of operation between spatial multiplexing and non-spatial multiplexing, the communications system is compatible with both subscriber units that support spatial multiplexing and subscriber units that do not support spatial multiplexing.
Owner:APPLE INC
Apparatus and method for determining pilot pattern in a broadband wireless access communication system
InactiveUS20070153931A1Minimizes channel estimation errorLine-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsFast Fourier transformCommunications system
An apparatus and method for determining a pilot pattern in a Broadband Wireless Access (BWA) communication system are provided. In the pilot pattern determining method, an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) demodulator generates frequency-domain data by fast-Fourier-transform (FFT)-processing a received signal. A pilot pattern decider calculates a coherence bandwidth and a coherence time using subcarrier values received from the OFDM demodulator, and selects one of a plurality of pilot patterns according to the ratio of the coherence bandwidth to the coherence time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Scheduling of data packets over an air interface of a cellular communication system
ActiveUS20100202418A1Optimize schedulingImprove balanceTelephonic communicationTime-division multiplexAir interfaceCellular communication systems
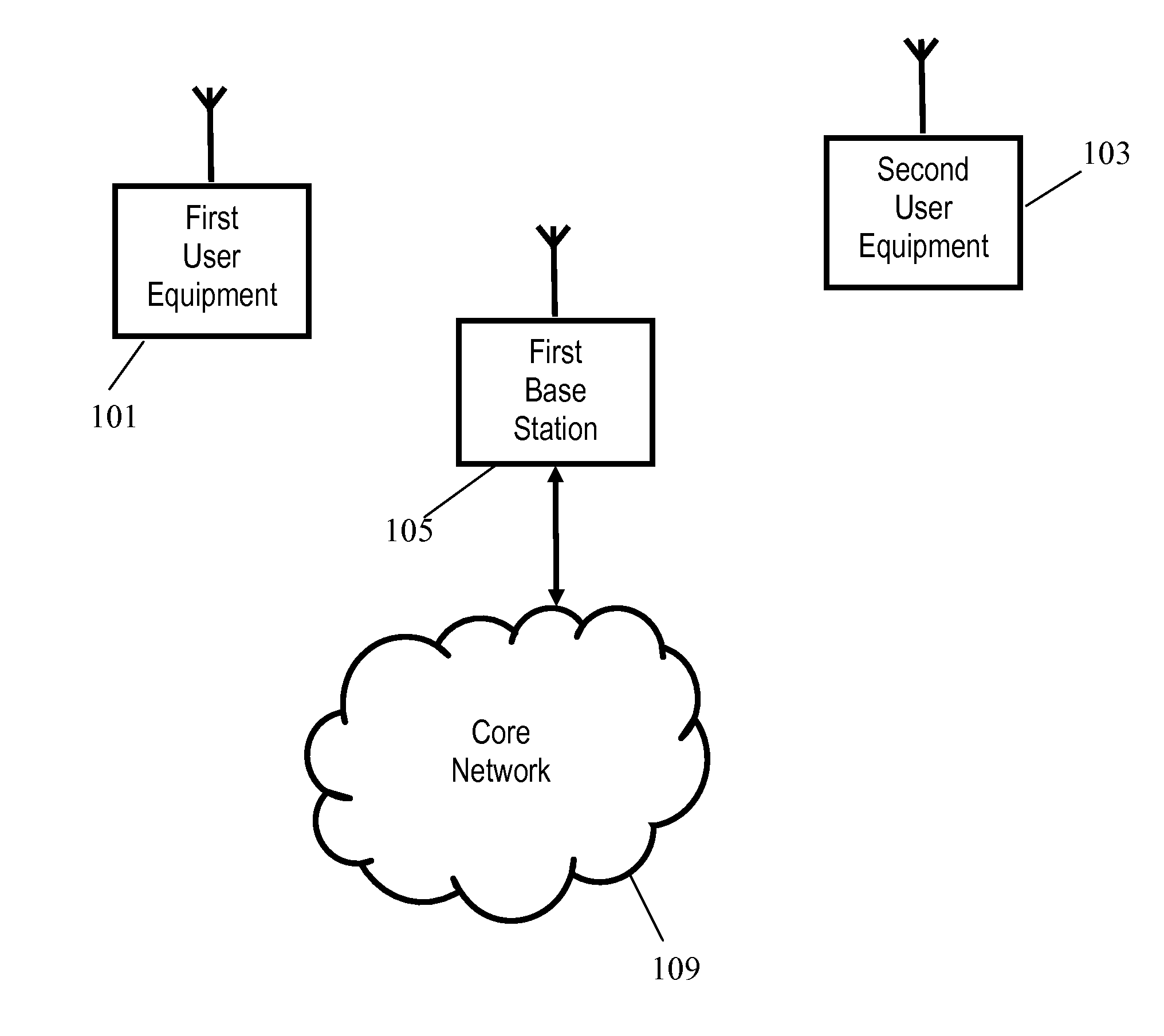
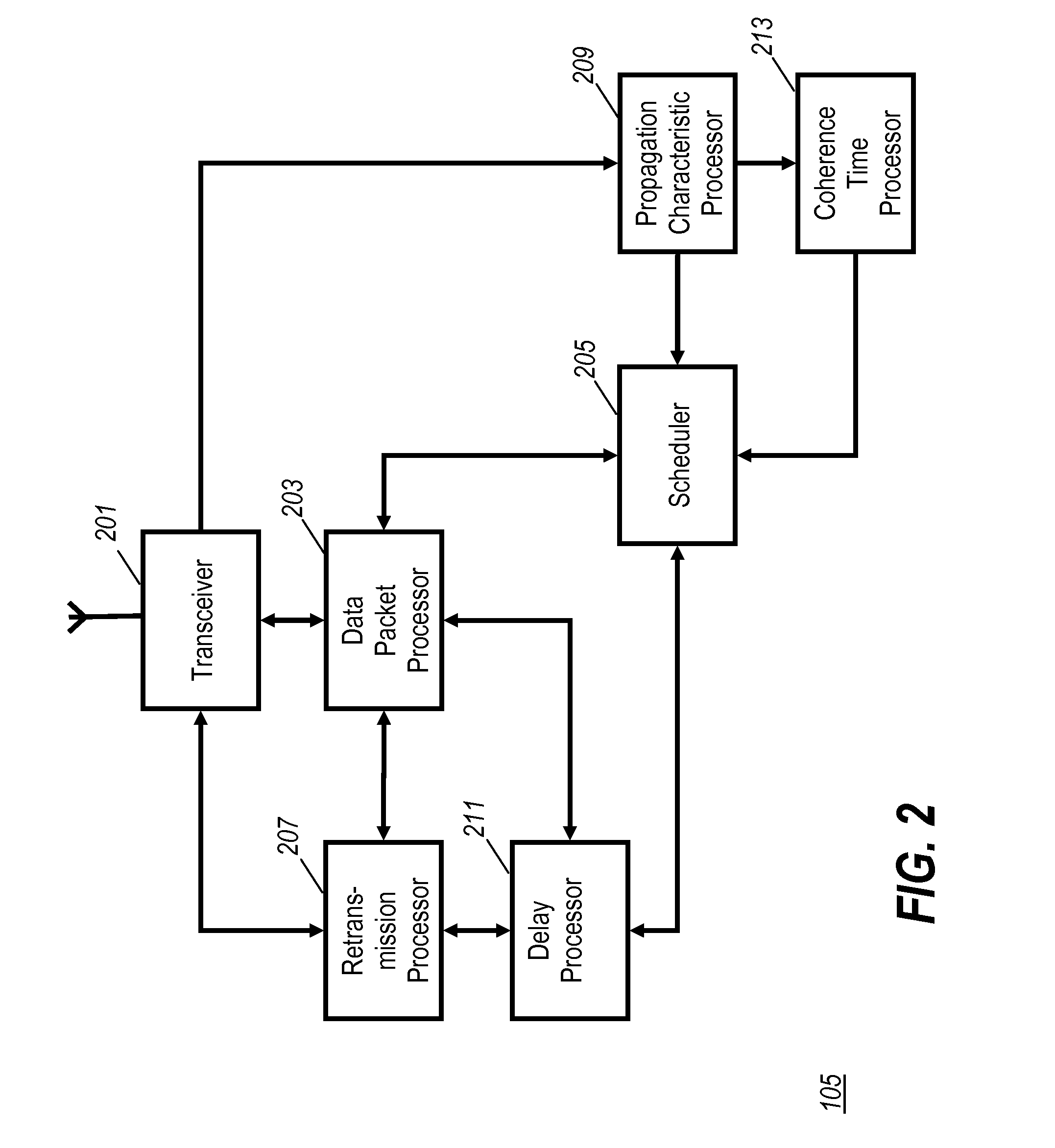
A scheduler (105) for scheduling data packets over an air interface of a cellular communication system comprises a coherence time processor (213) which determines a coherence time for a user equipment (101, 103). A scheduling unit (205) then schedules at least a first data packet for the user equipment (101, 103) in response to the coherence time. In some embodiments, the system may use a retransmission scheme and a scheduling which depends on a time varying propagation characteristic. In such embodiments, an available delay may be allocated to retransmissions or propagation dependent scheduling dependent on the coherence time. The scheduler may e.g. be implemented in a base station.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Two-dimensional magneto-optical trap for neutral atoms
A two-dimensional (2D) magneto-optical trap (MOT) for alkali neutral atoms establishes a zero magnetic field along the longitudinal symmetry axis. Two of three pairs of trapping laser beams do not follow the symmetry axes of the quadruple magnetic field and are aligned with a large non-zero degree angles to the longitudinal axis. In a dark-line 2D MOT configuration, there are two orthogonal repumping beams. In each repumping beam, an opaque line is imaged to the longitudinal axis, and the overlap of these two line images creates a dark line volume in the longitudinal axis where there is no repumping light. The zero magnetic field along the longitudinal axis allows the cold atoms maintain a long ground-state coherence time without switching off the MOT magnetic field, which makes it possible to operate the MOT at a high repetition rate and a high duty cycle.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com