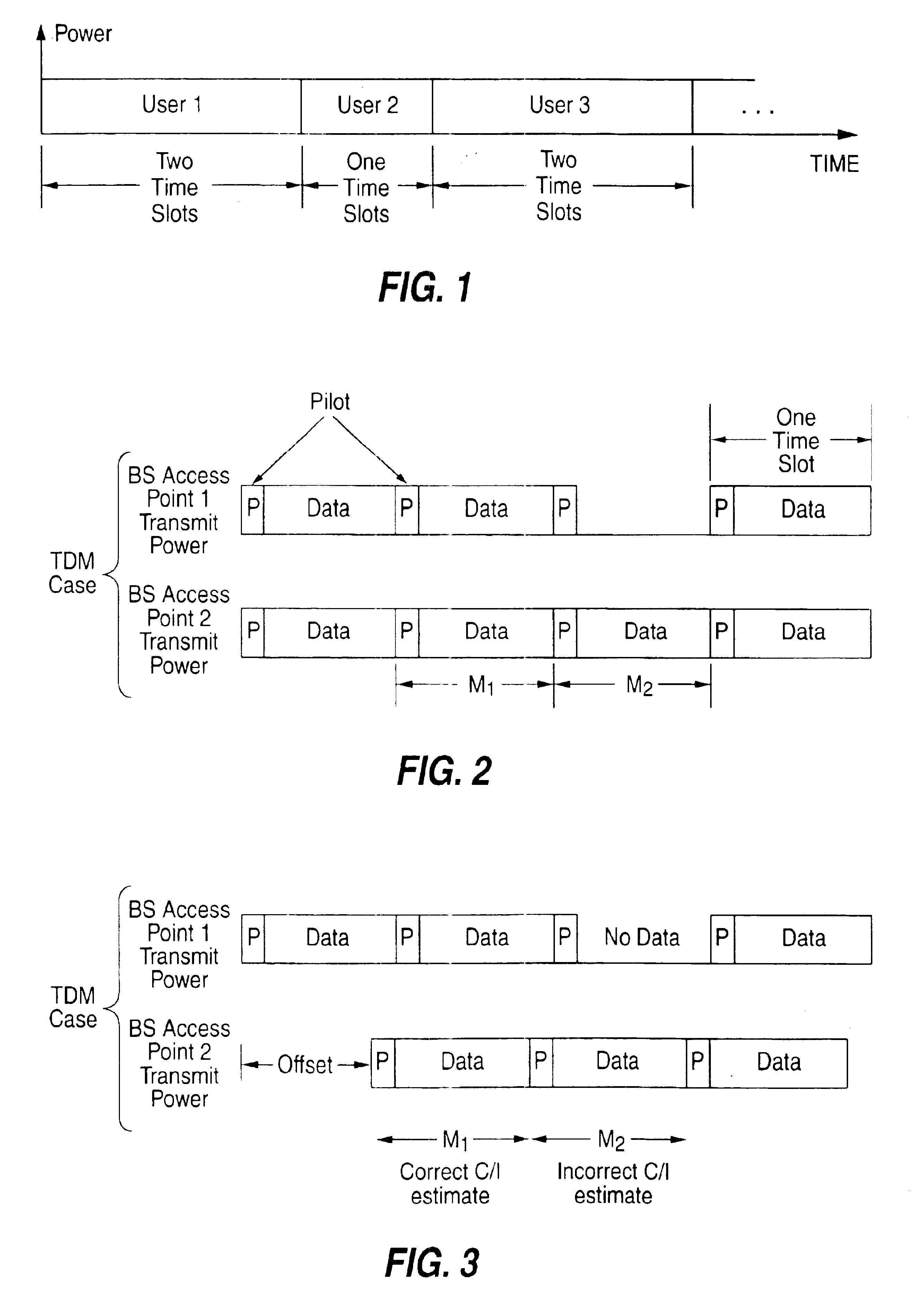
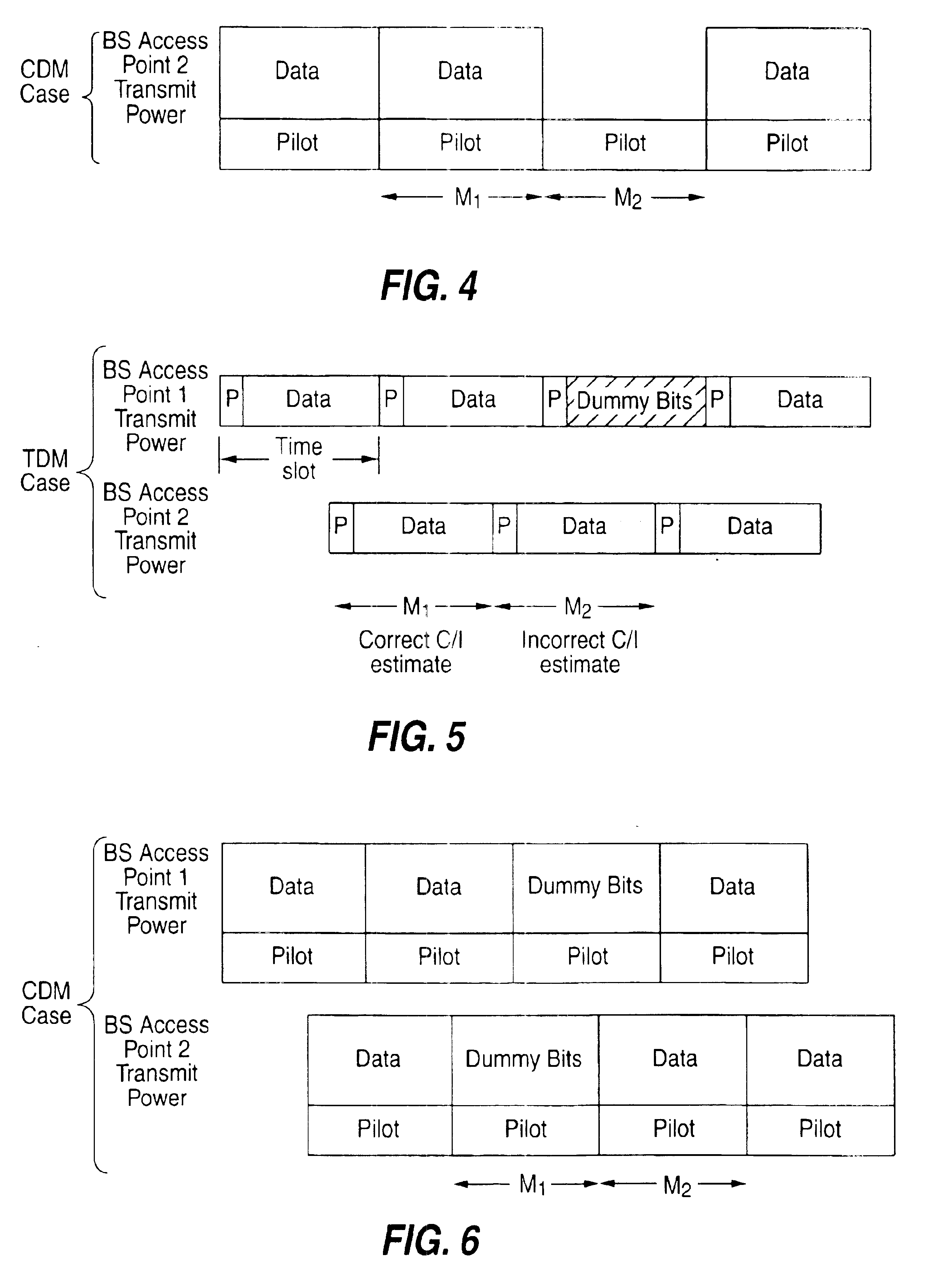
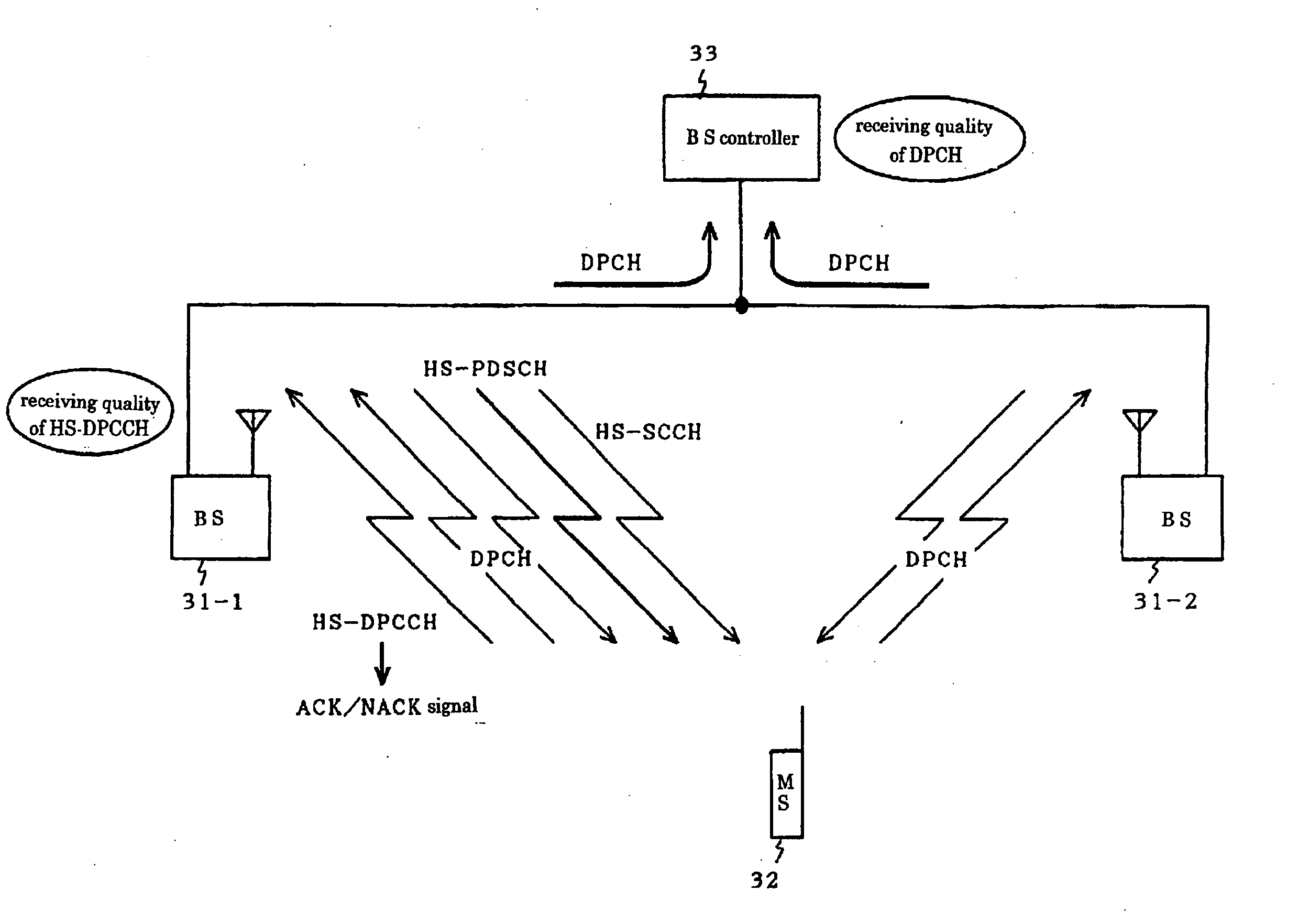
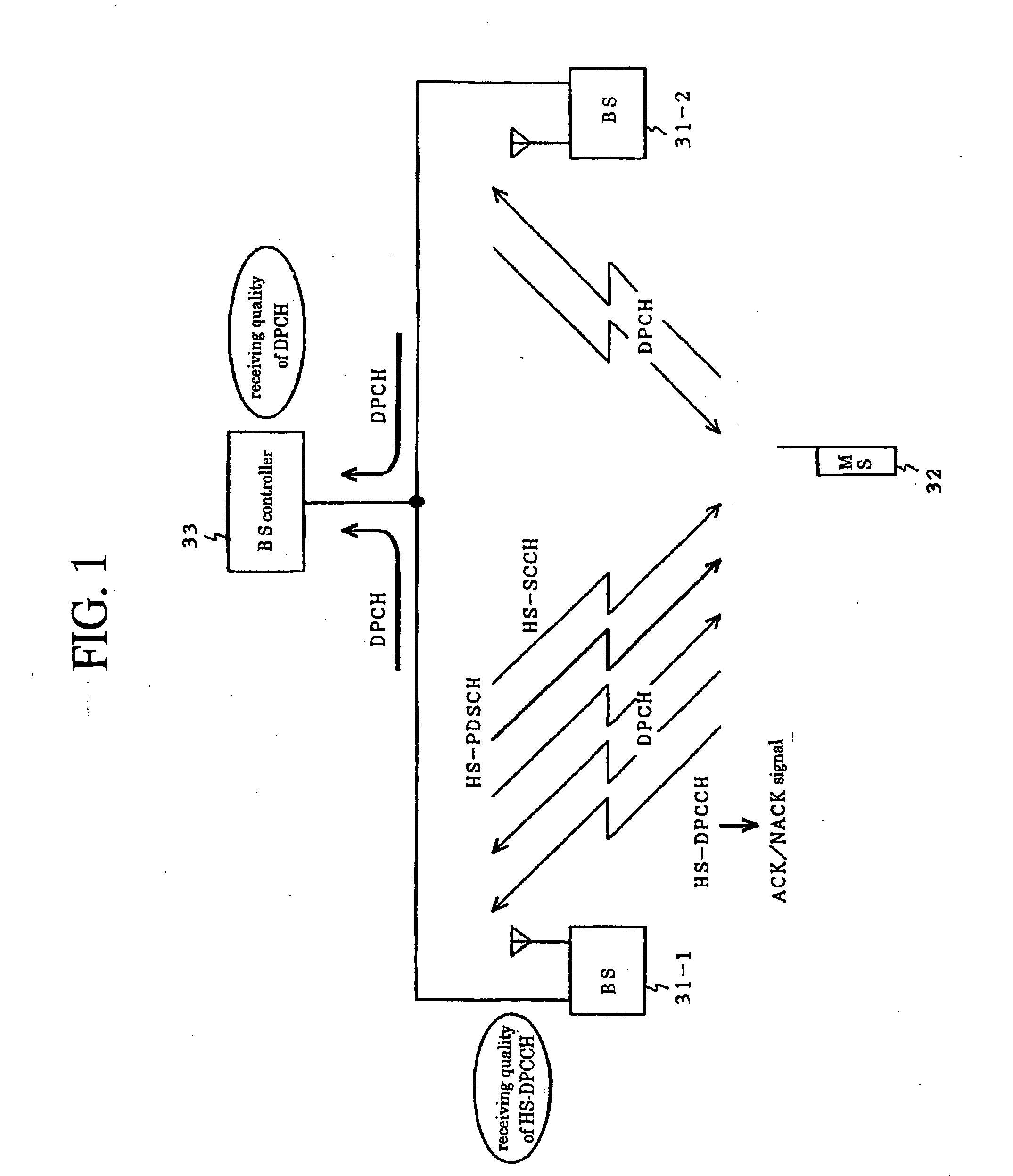
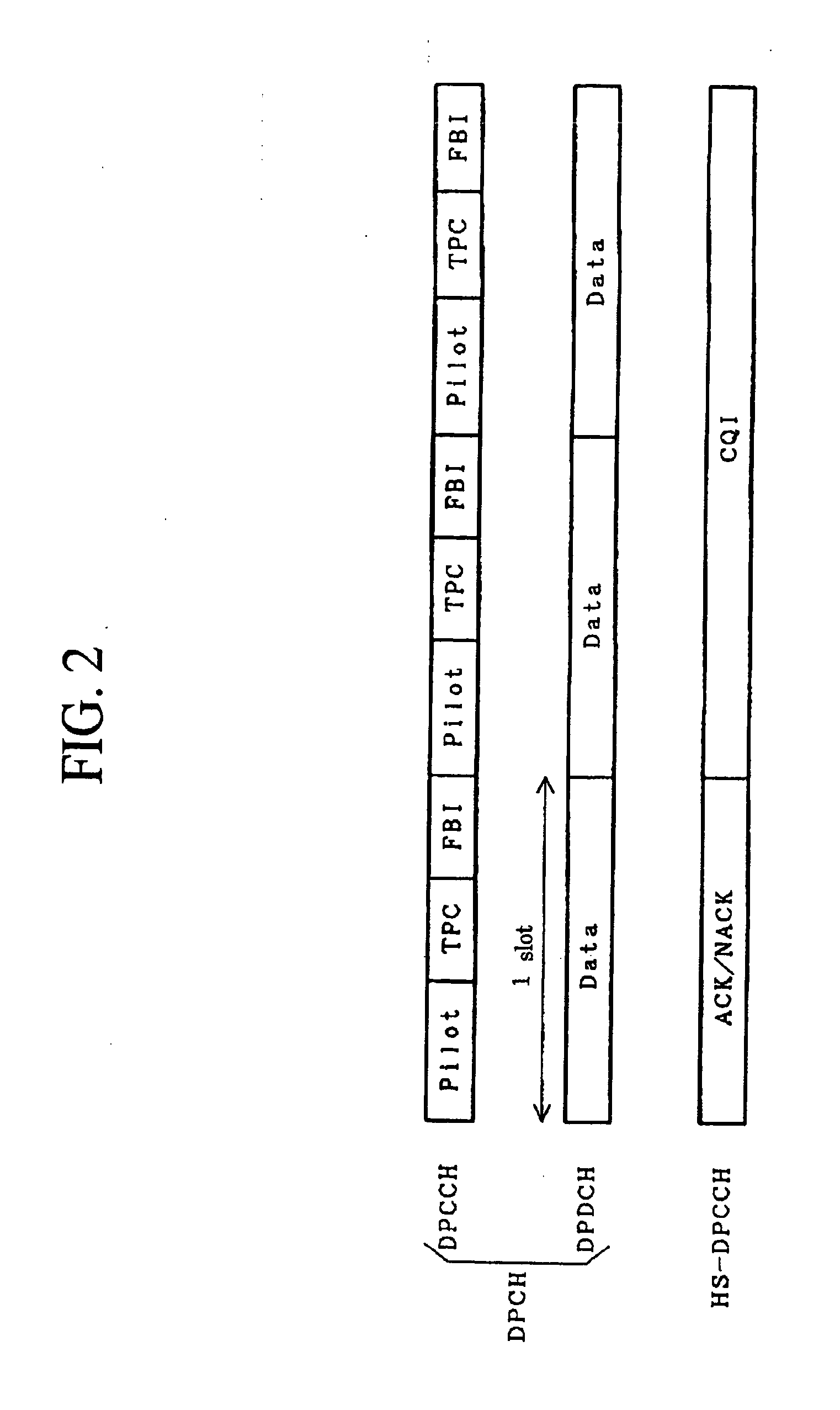
Patents
Literature
547 results about "Signal-to-interference ratio" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The signal-to-interference ratio (SIR or S/I), also known as the carrier-to-interference ratio (CIR or C/I), is the quotient between the average received modulated carrier power S or C and the average received co-channel interference power I, i.e. cross-talk, from other transmitters than the useful signal.
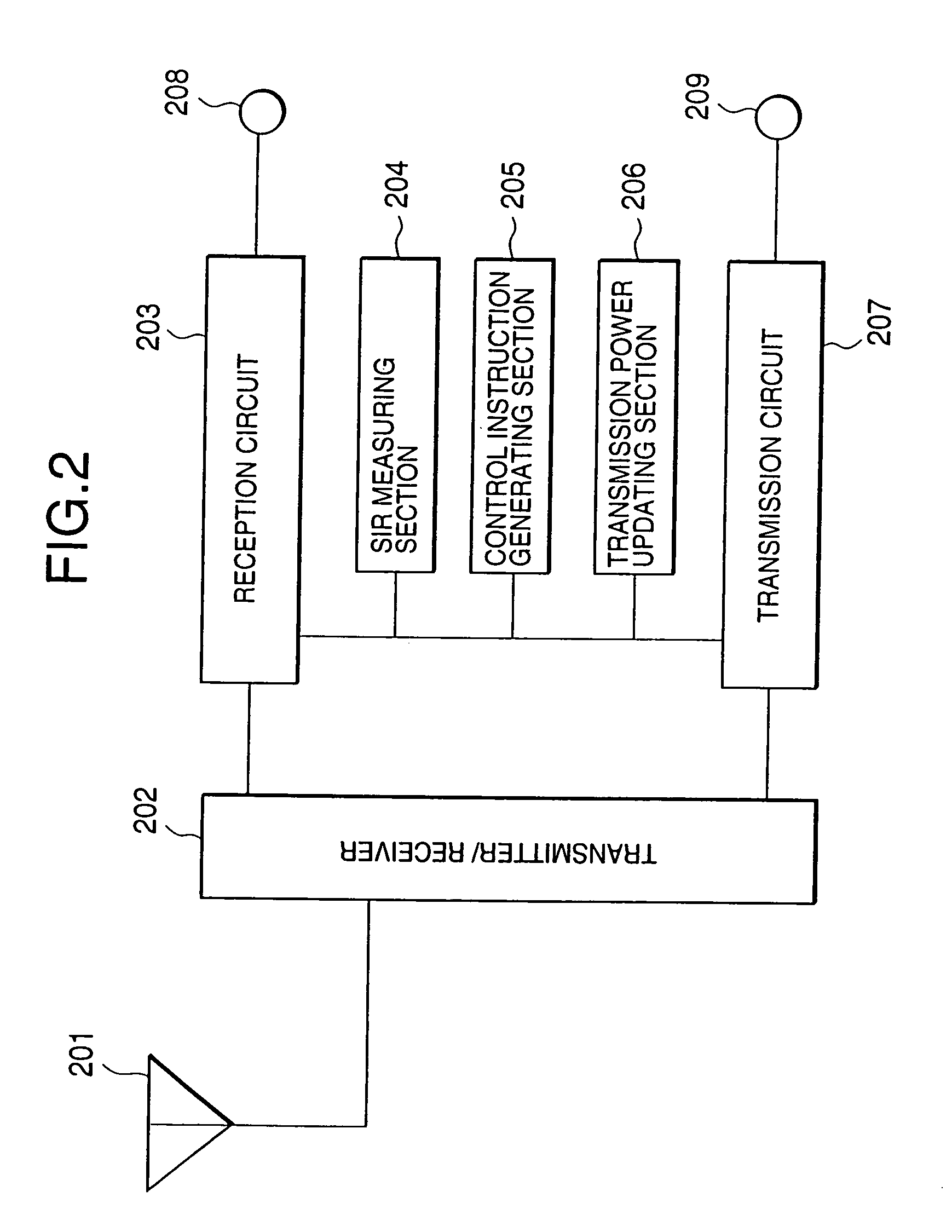
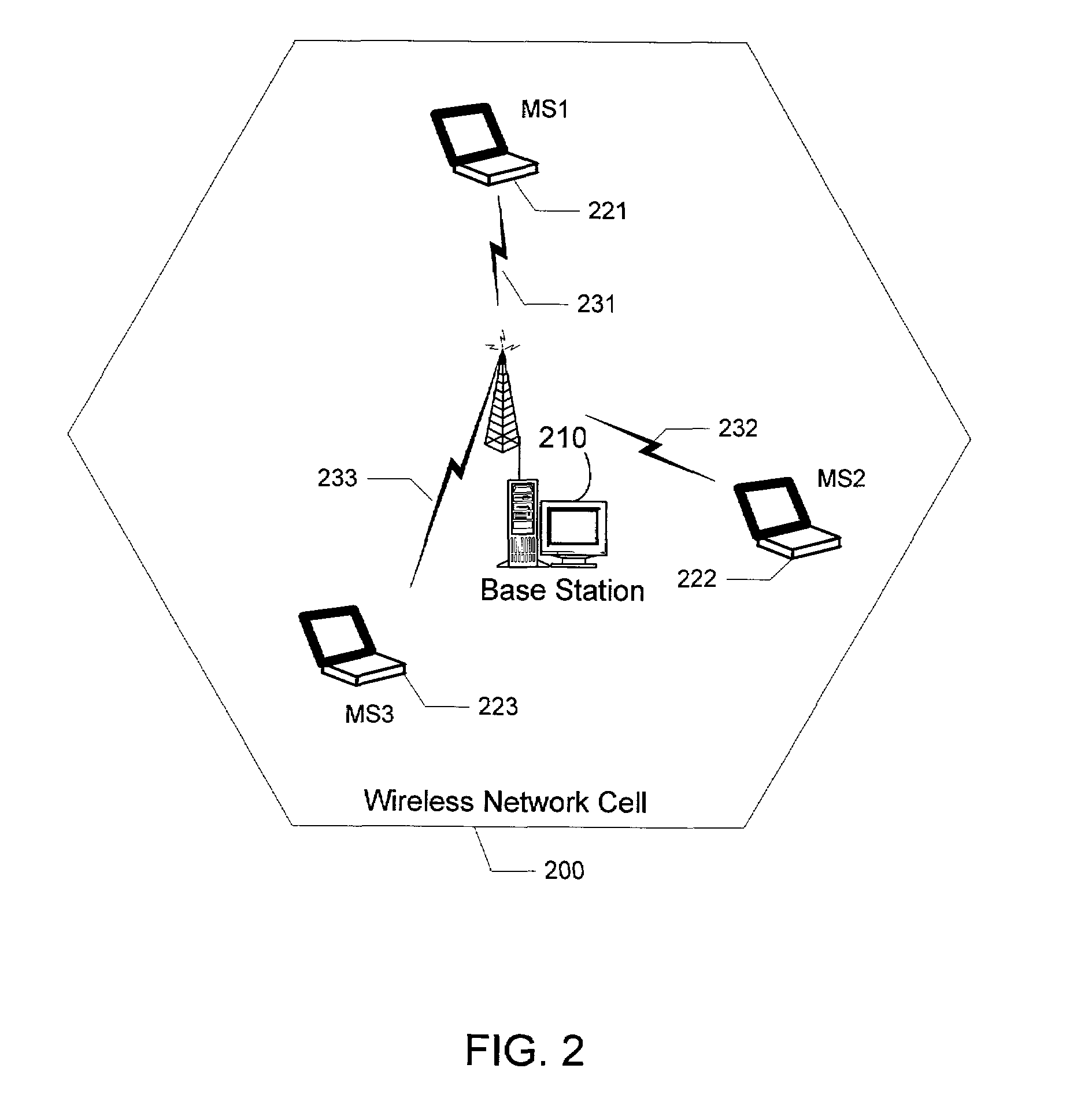
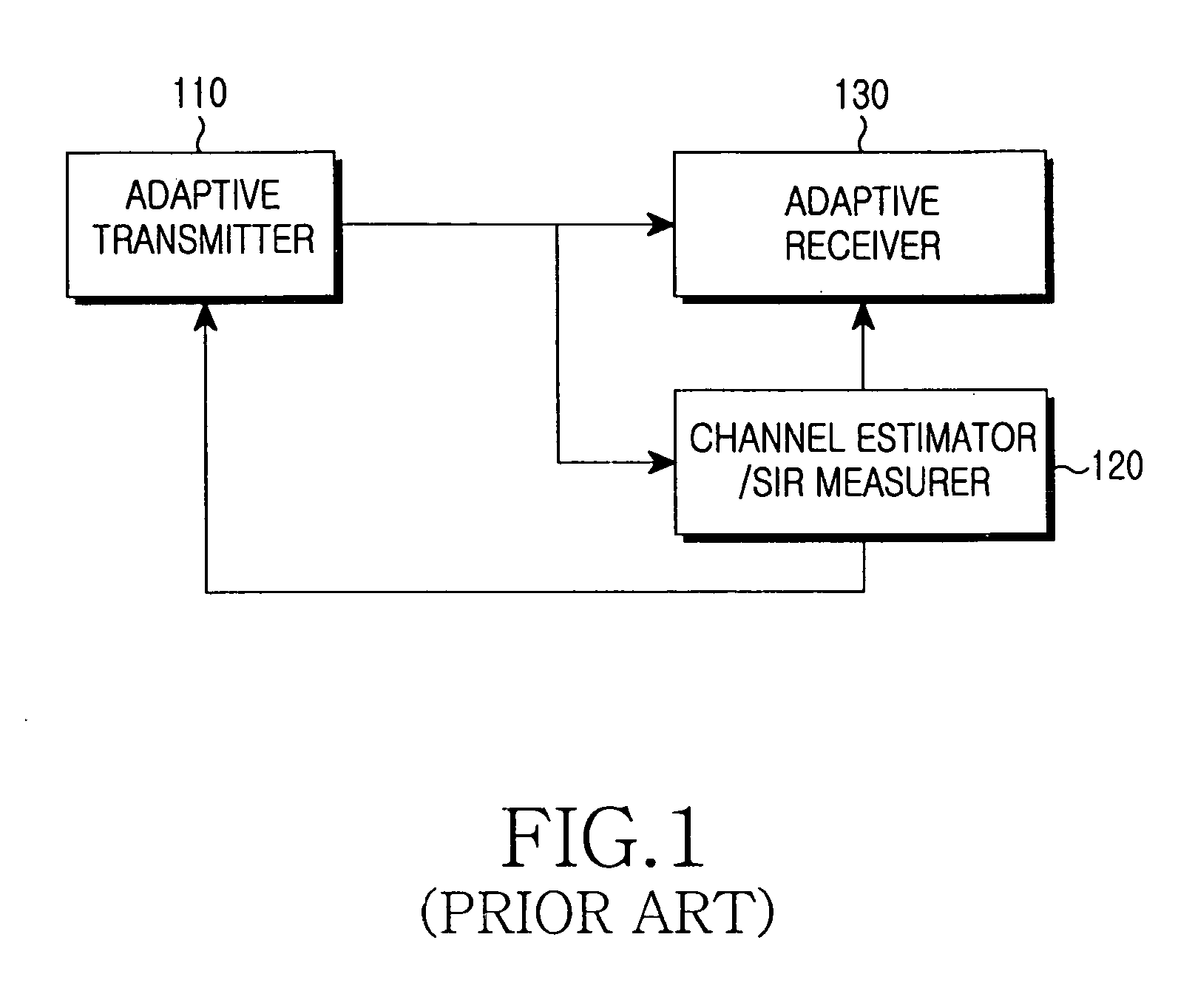
Radio communication apparatus, base station and system
InactiveUS20060013285A1Modulated-carrier systemsOrthogonal multiplexSignal to noise power ratioTransmitter
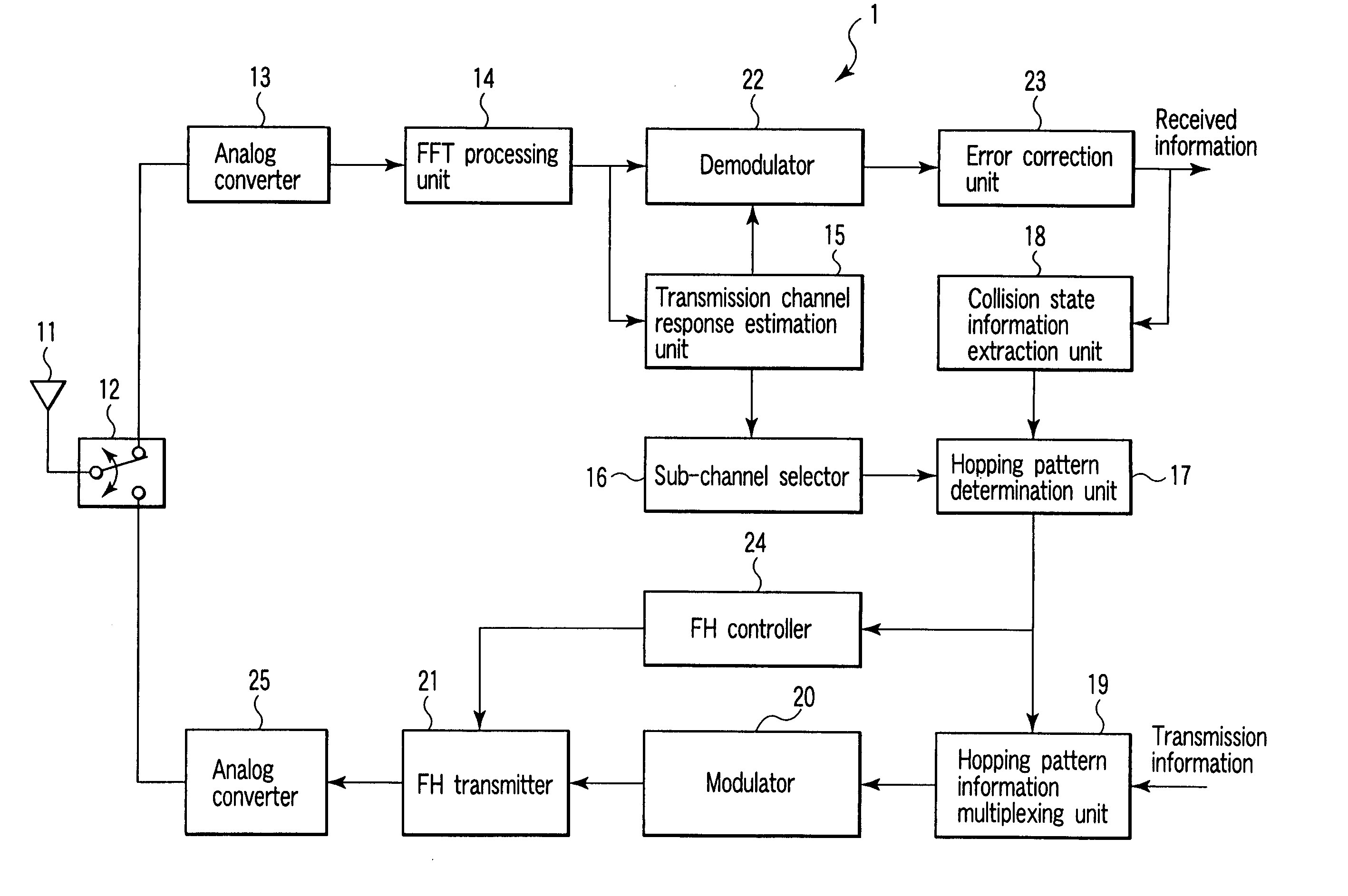
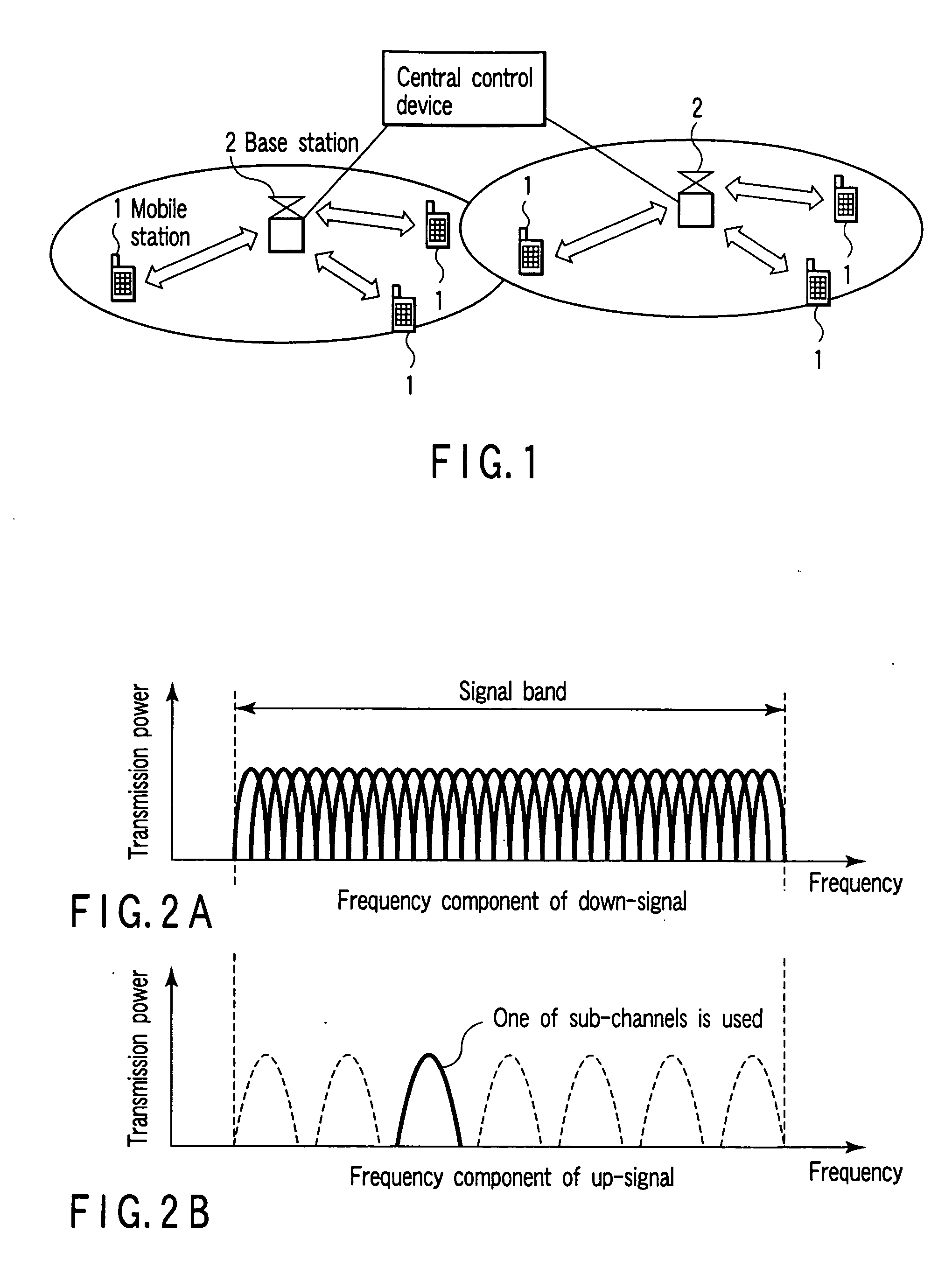
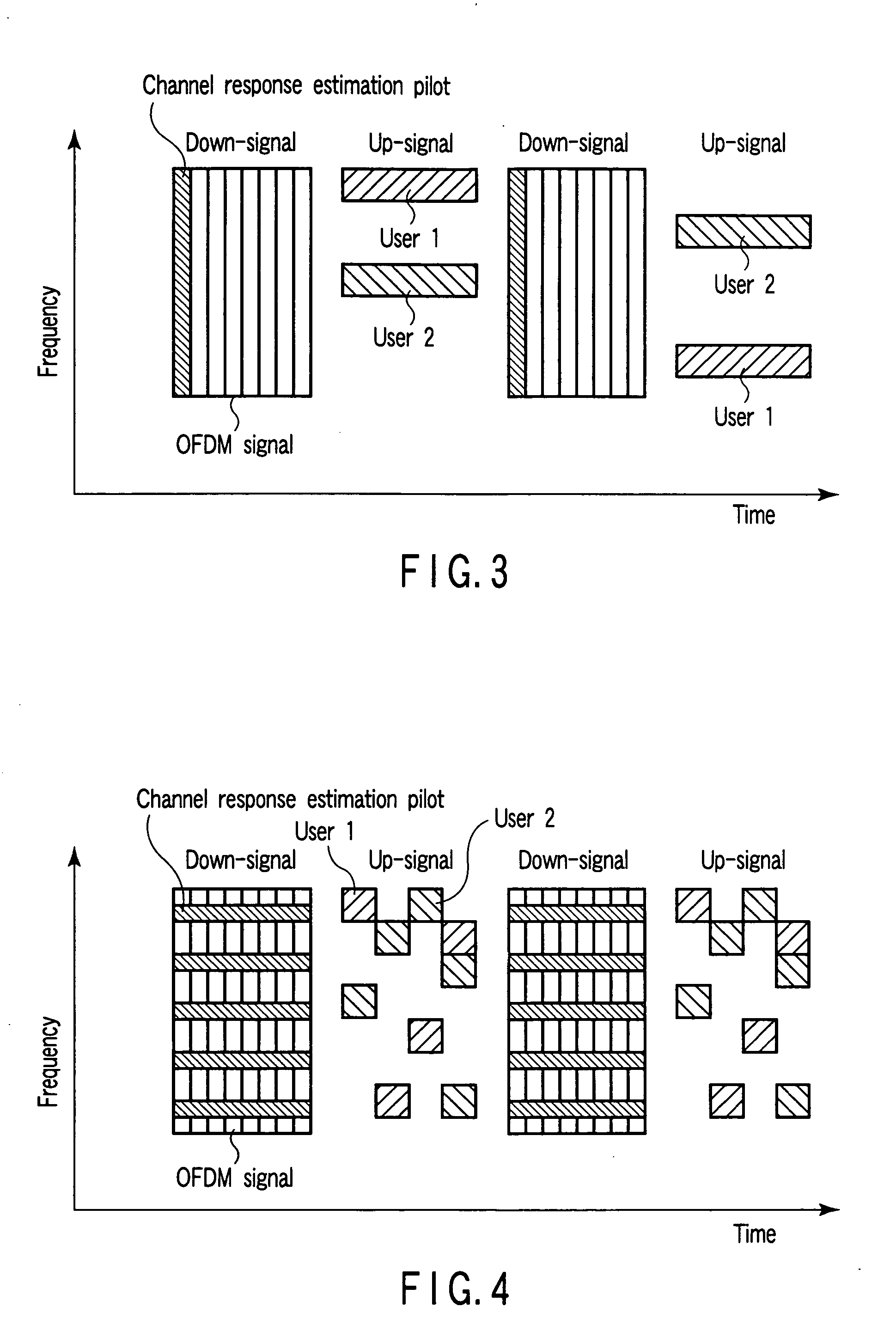
Radio communication apparatus for receiving OFDM signal from base station and transmitting FH signal to base station, using sub-channels, base station comparing hopping pattern information items indicating hopping patterns from radio communication apparatuses including radio communication apparatus, and generating collision information when hopping patterns include colliding hopping patterns, includes estimation unit configured to estimate channel response values of sub-channels based on OFDM signal, selector which selects, from sub-channels, several sub-channels which have higher channel response values than a value, each of channel response values being expressed by power level, signal-to-noise power ratio, or signal-to-interference ratio, determination unit configured to determine hopping pattern from selected sub-channels, transmitter which transmits, to base station, hopping pattern information item indicating determined hopping pattern, receiver which receives collision information from base station, and correction unit configured to correct hopping pattern based on collision information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
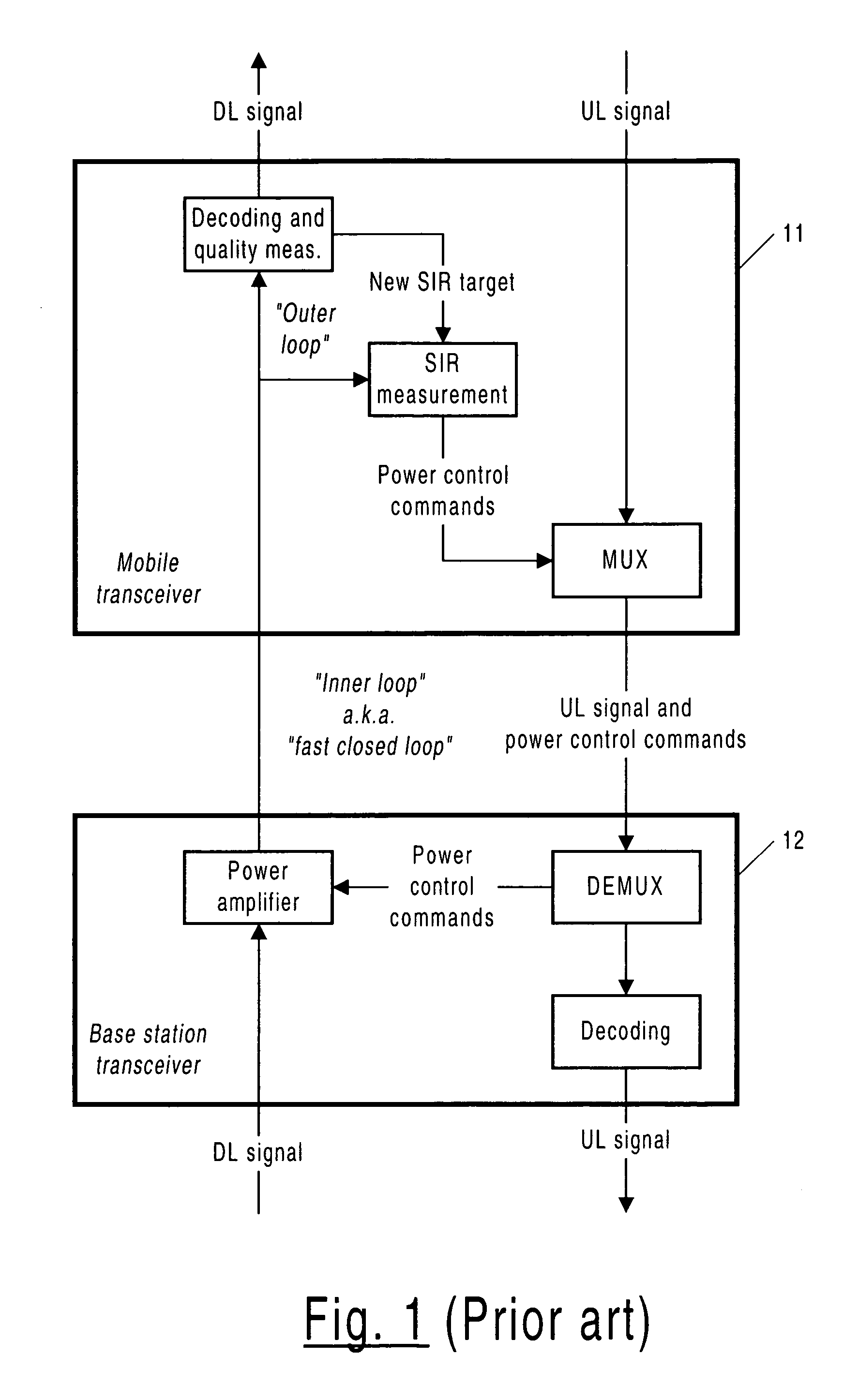
Power control in a radio data communication system adapted using transmission load
InactiveUS6912228B1Not affectReduce wastePower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemTransmitted power
The present invention employs a power control methodology that adapts to the transmission load associated with communications between a base station and a mobile terminal. In one example embodiment, the base station gradually adjusts the power data transmitted to the mobile terminal based on that associated transmission load. As a result, radio channel quality measurements influenced by that base station data transmission to the mobile terminal are not significantly affected by the transmit power adjustment. In other words, the rate at which the transmit power is changed is slower than the rate at which mobile stations measure channel quality. For example, mobile terminals may detect a signal-to-interference ratio every time slot and use that quality measurement for purposes of selecting a maximum transmission rate for the next time slot. The transmit power might be changed by an incremental amount once every ten time slots. By only gradually changing the base station transmit power, the accuracy of the mobile terminal channel quality estimates is not significantly affected. Moreover, if there is a relatively low transmission load, the base station does not waste resources or generate unnecessary interference by transmitting at maximum power.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Cellular system, mobile station, base station and transmission power control method as well as program to be executed for implementing the method
ActiveUS20050043051A1Quality is easy to controlQuality improvementPower managementTransmission control/equalisingInterference ratioTarget signal
In a cellular system, each mobile station concurrently linked to plural link base stations in soft handover state and receiving packet from the packet-transmitting base station controls a transmission power of an up-link dedicated physical channel based on a first transmission power control information included in down-link dedicated physical channels of the link base stations. In other state, the mobile station controls the transmission power based on a second transmission power control information included in a down-link dedicated physical channel of the packet-transmitting base station. This accelerates the power increase up to a target power level causing that the measured signal-to-interference-ratio at the packet-transmitting base station reaches a target signal-to-interference-ratio, thereby improving receiving quality of control signal from the mobile station at the packet-transmitting base station.
Owner:NEC CORP
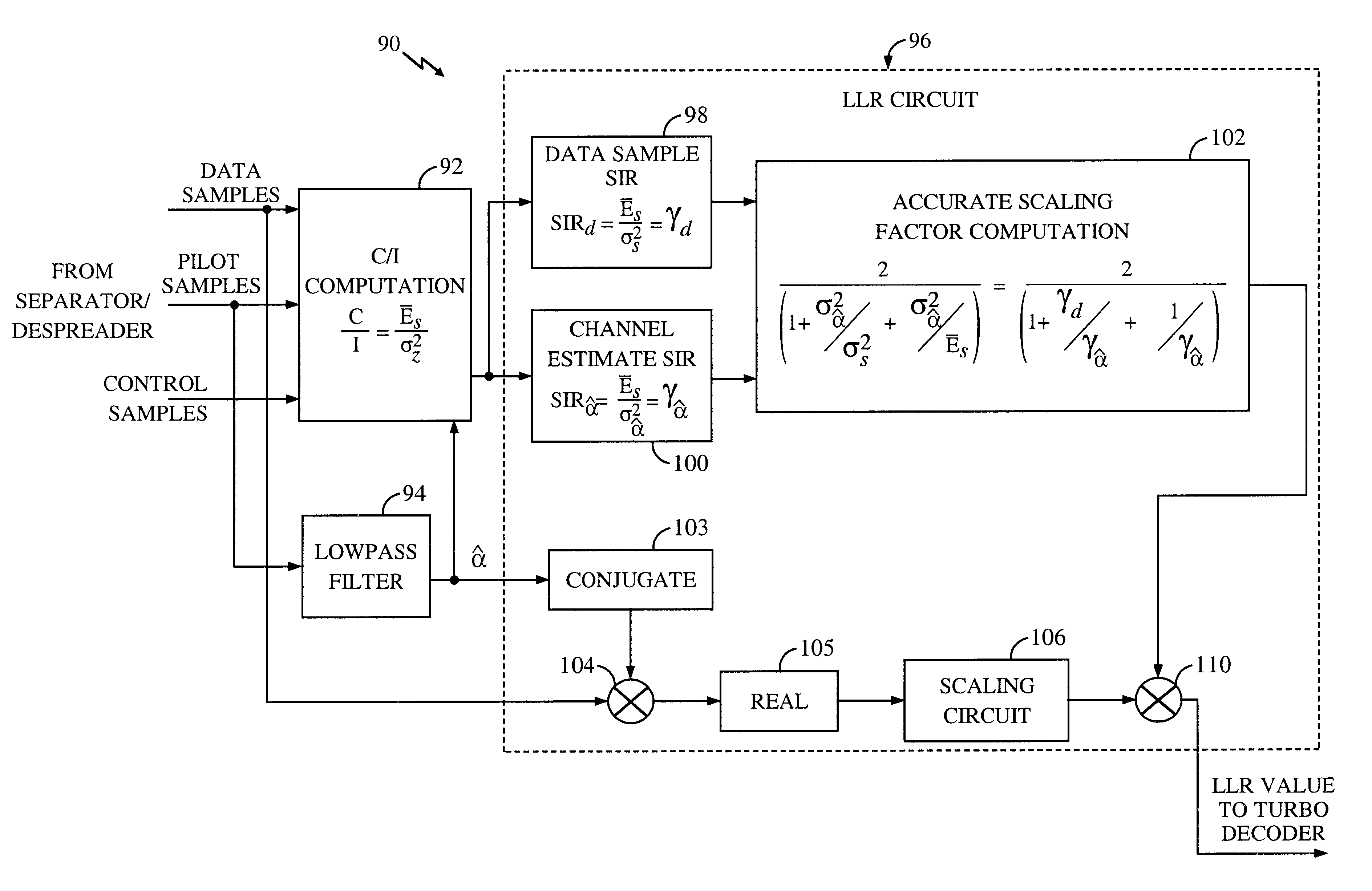
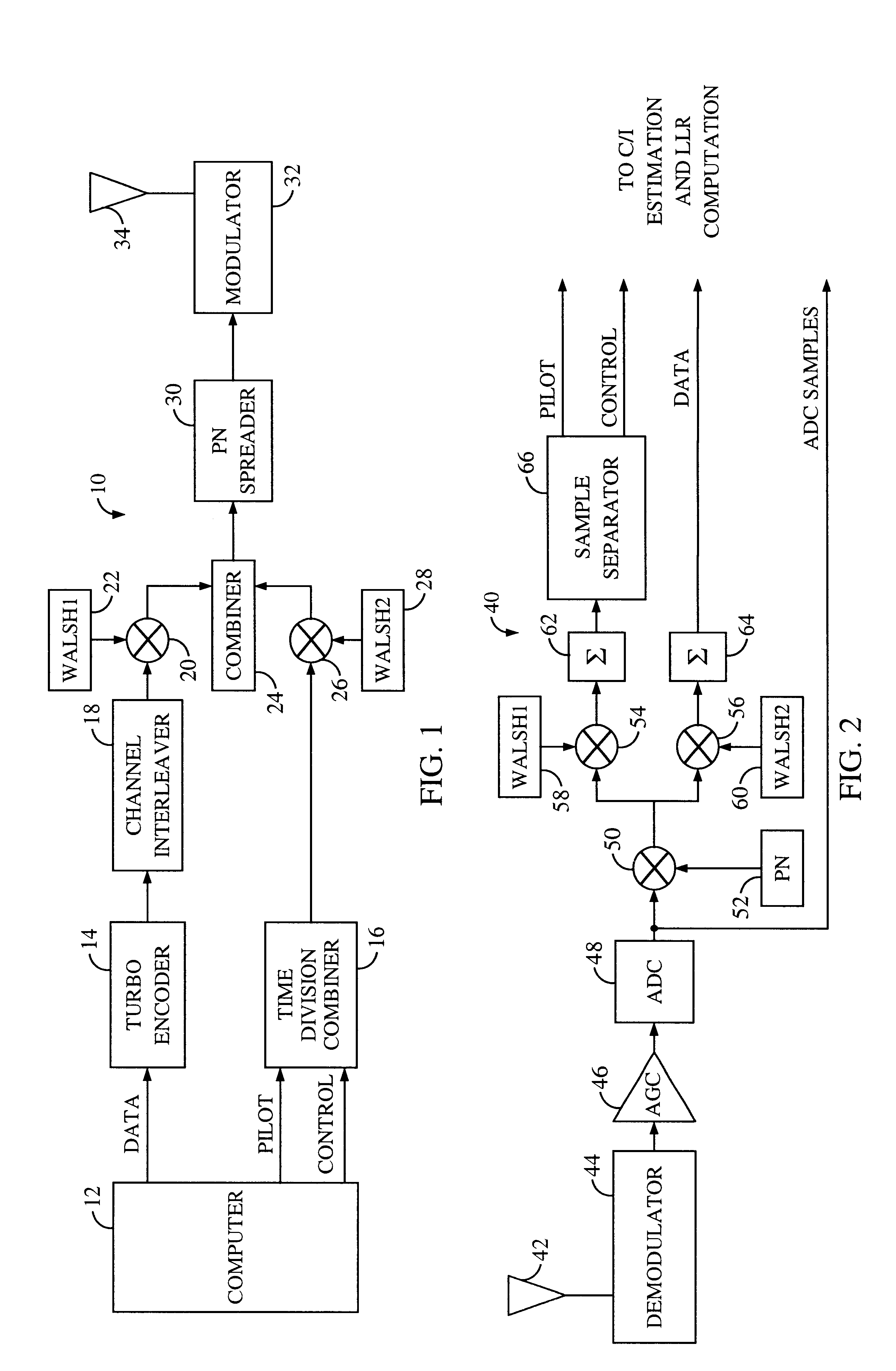
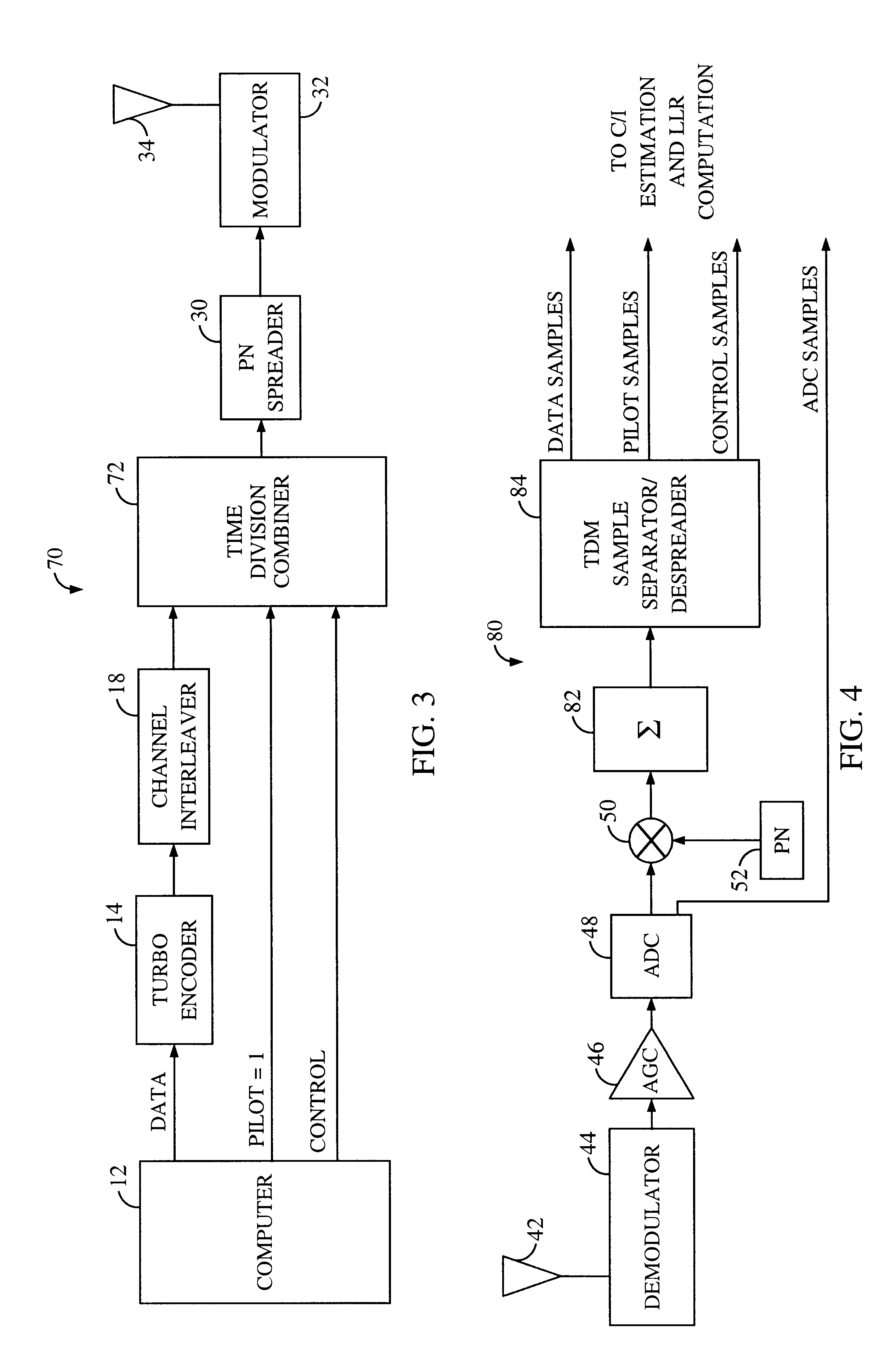
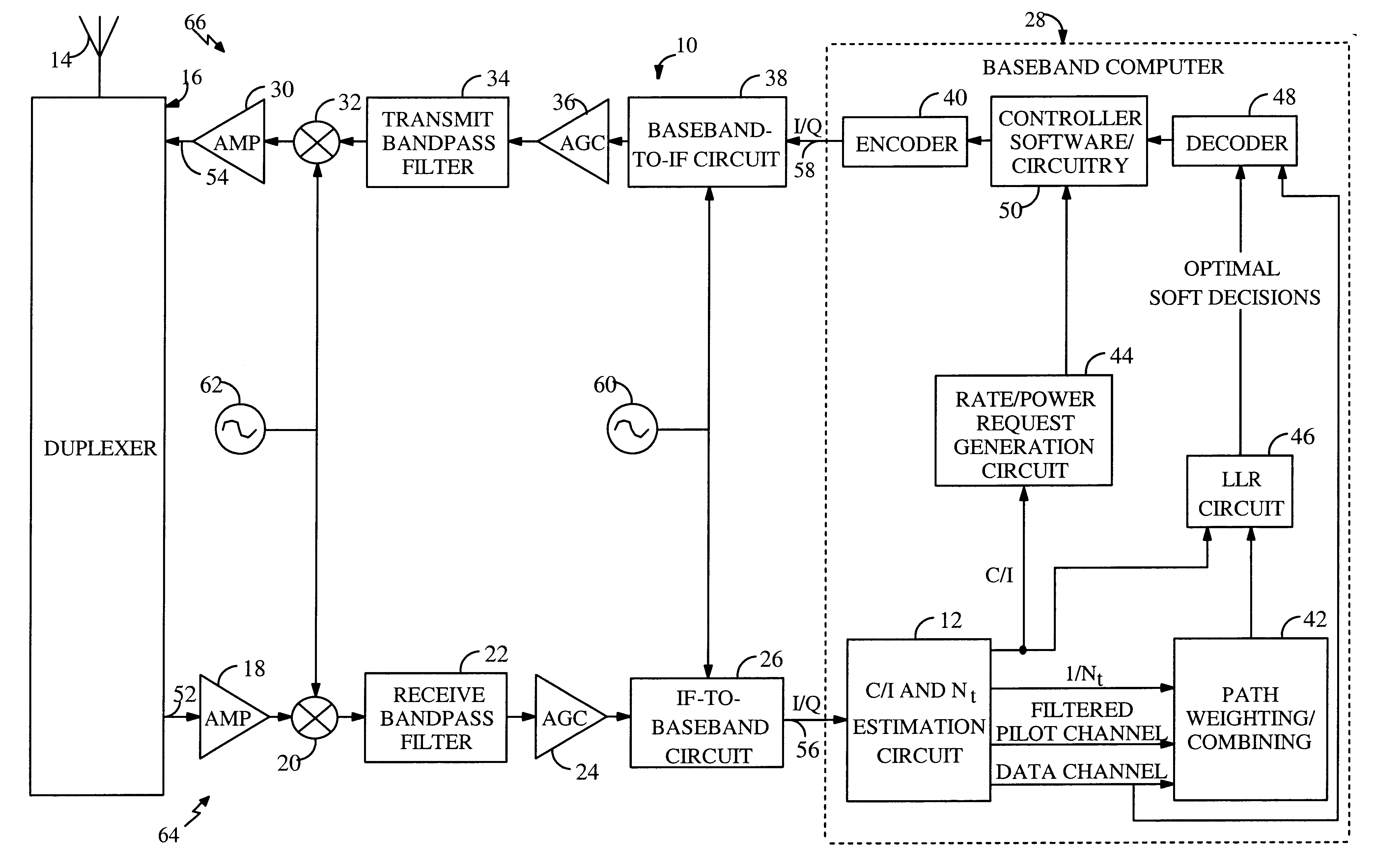
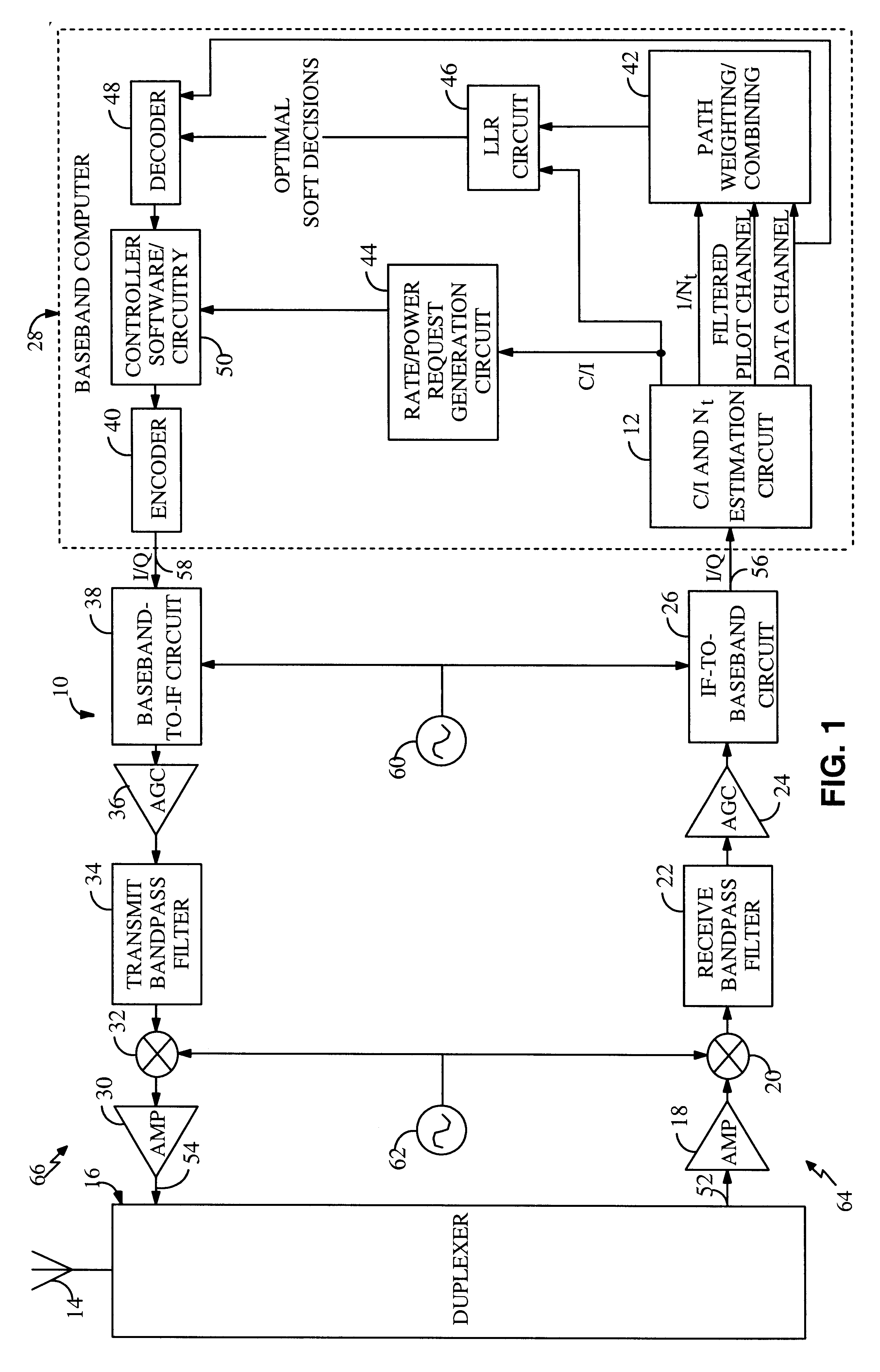
System and method for performing accurate demodulation of turbo-encoded signals via pilot assisted coherent demodulation
InactiveUS6377607B1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorError correction/detection using convolutional codesTransceiverInterference ratio
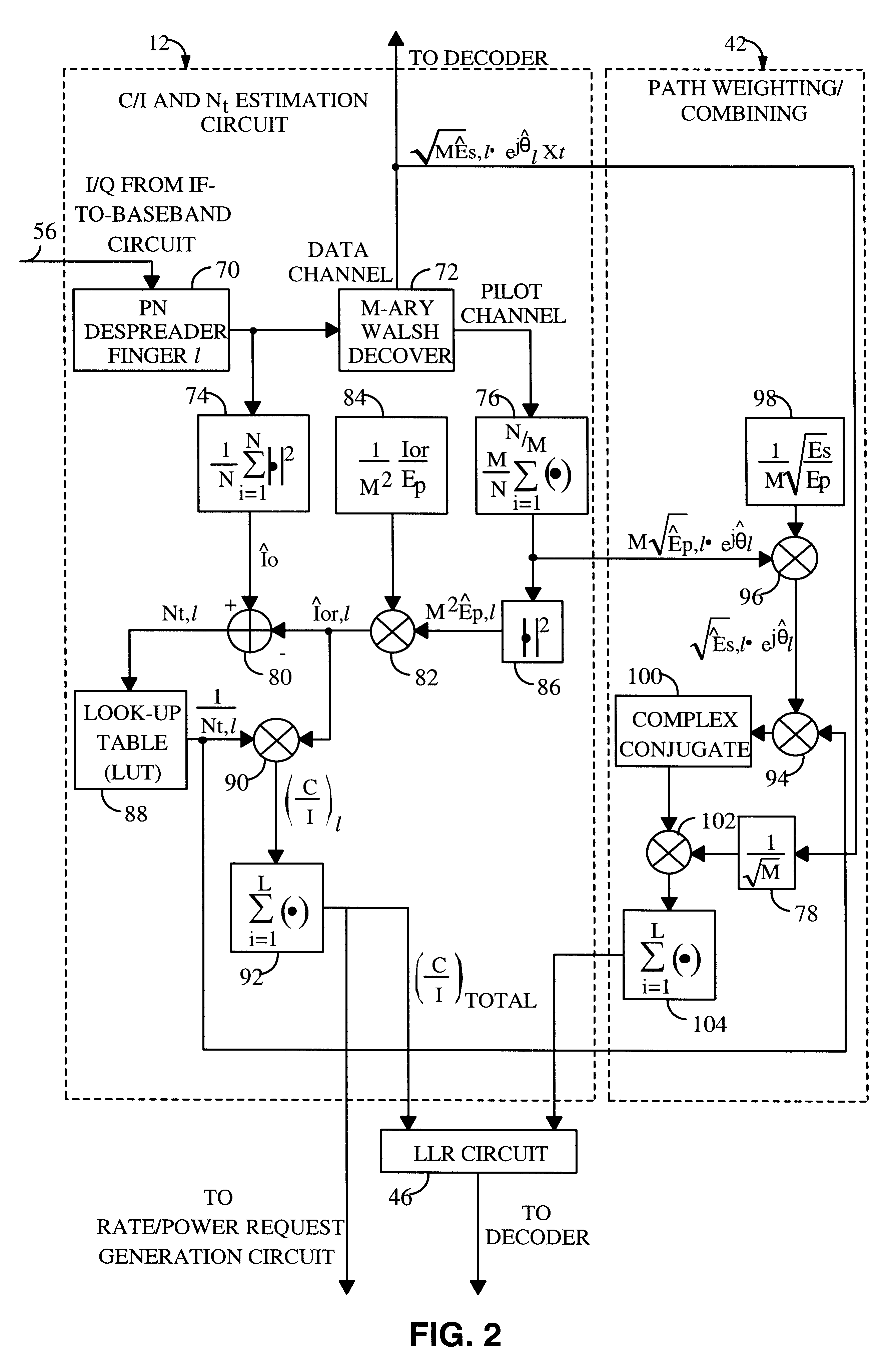
An efficient telecommunications receiver system for accurately decoding a received composite signal having a data signal component and a pilot signal component. The receiver system includes a first circuit for receiving the composite signal and extracting a pilot signal and a data signal from received composite signal. A second circuit calculates a log-likelihood ratio as a function of a channel estimate based on the pilot signal. A third circuit scales the log-likelihood ratio by a predetermined log-likelihood ratio scaling factor and provides an accurate log-likelihood value in response thereto. A fourth circuit decodes the received composite signal based on the accurate log-likelihood value and the data signal. In a specific embodiment, the pilot signal and the data signal comprise pilot samples and data samples, respectively. The third circuit includes a carrier signal-to-interference ratio circuit for computing a first signal-to-interference ratio and a second signal-to-interference ratio based partly on the pilot signal. The first signal-to-interference ratio is based on the data samples, and the second signal-to-interference ratio is based on the pilot samples. The first signal-to-noise ratio and the second signal-to-noise ratio provide input to a circuit for computing the predetermined log-likelihood ratio scaling factor that is included in the third circuit. In a more specific embodiment, the first circuit includes a despreader for despreading the received composite signal in accordance with a predetermined spreading function and providing a despread signal in response thereto. The spreading function is a pseudo noise sequence or a Walsh function. The first circuit further includes a decovering circuit that extracts the pilot signal and the data signal from the despread signal. In the illustrative embodiment, the accurate receiver system further includes a circuit for generating a rate and / or power control message and transmitting the rate and / or power control message to an external transceiver in communication with the efficient receiver system.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
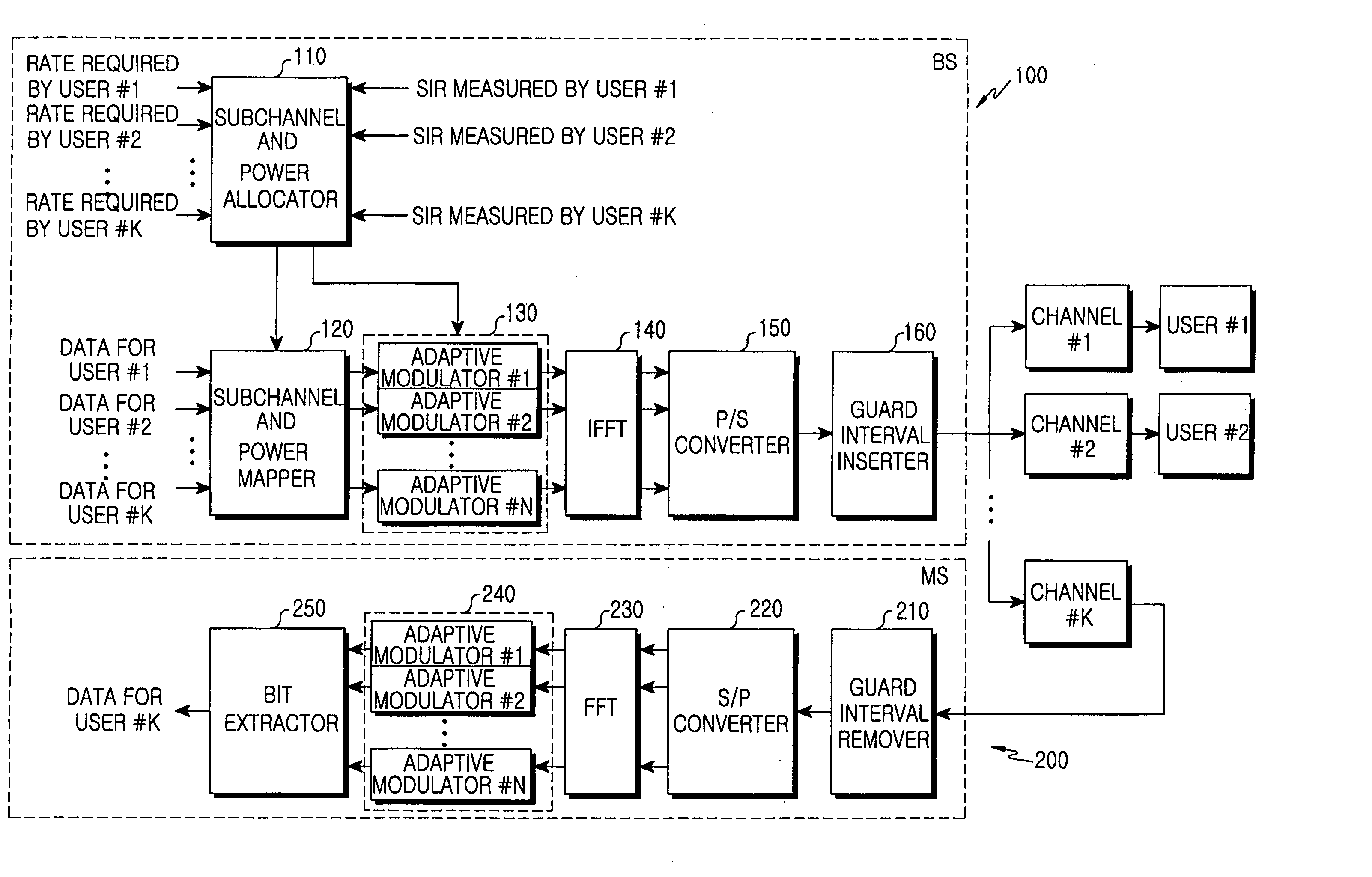
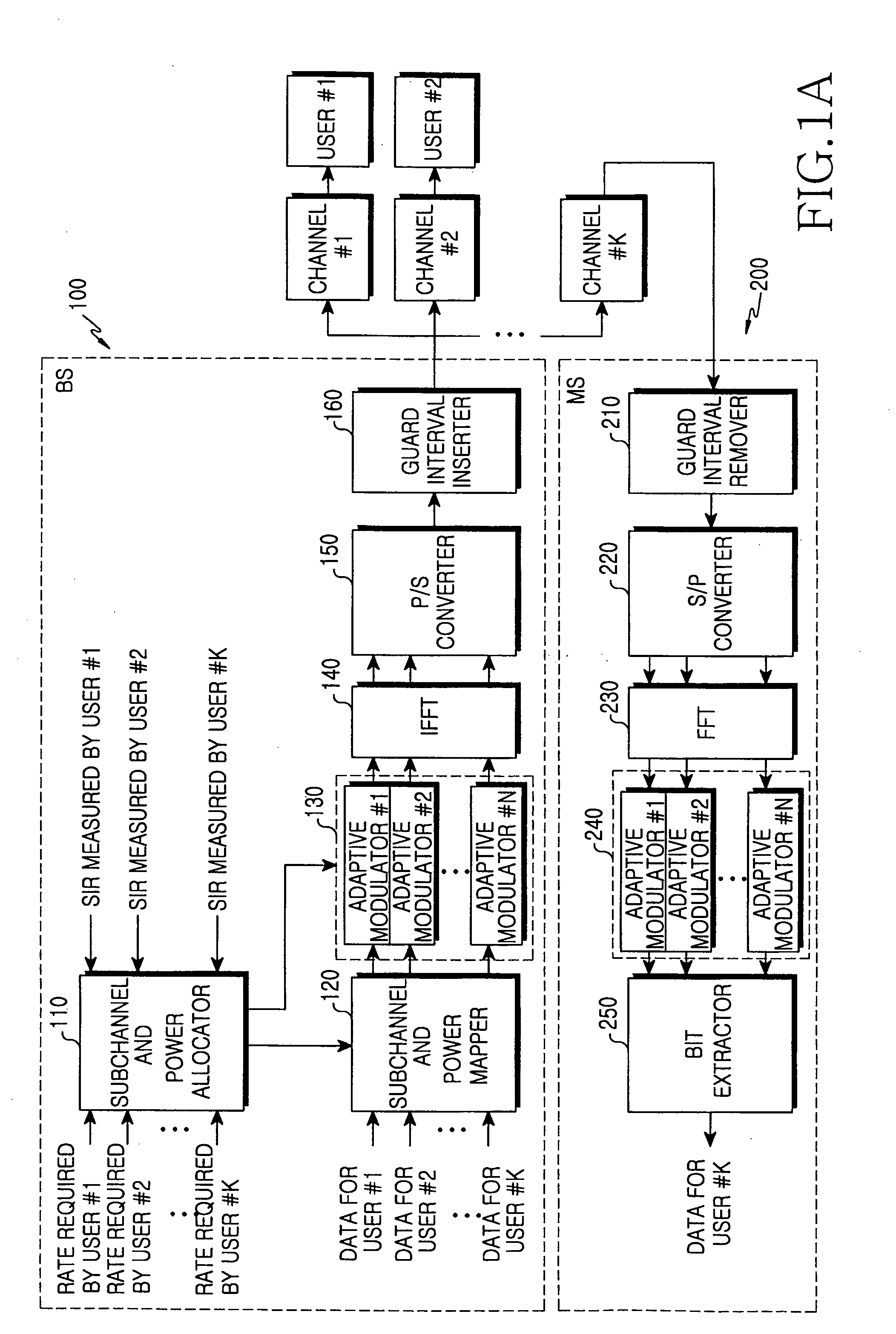
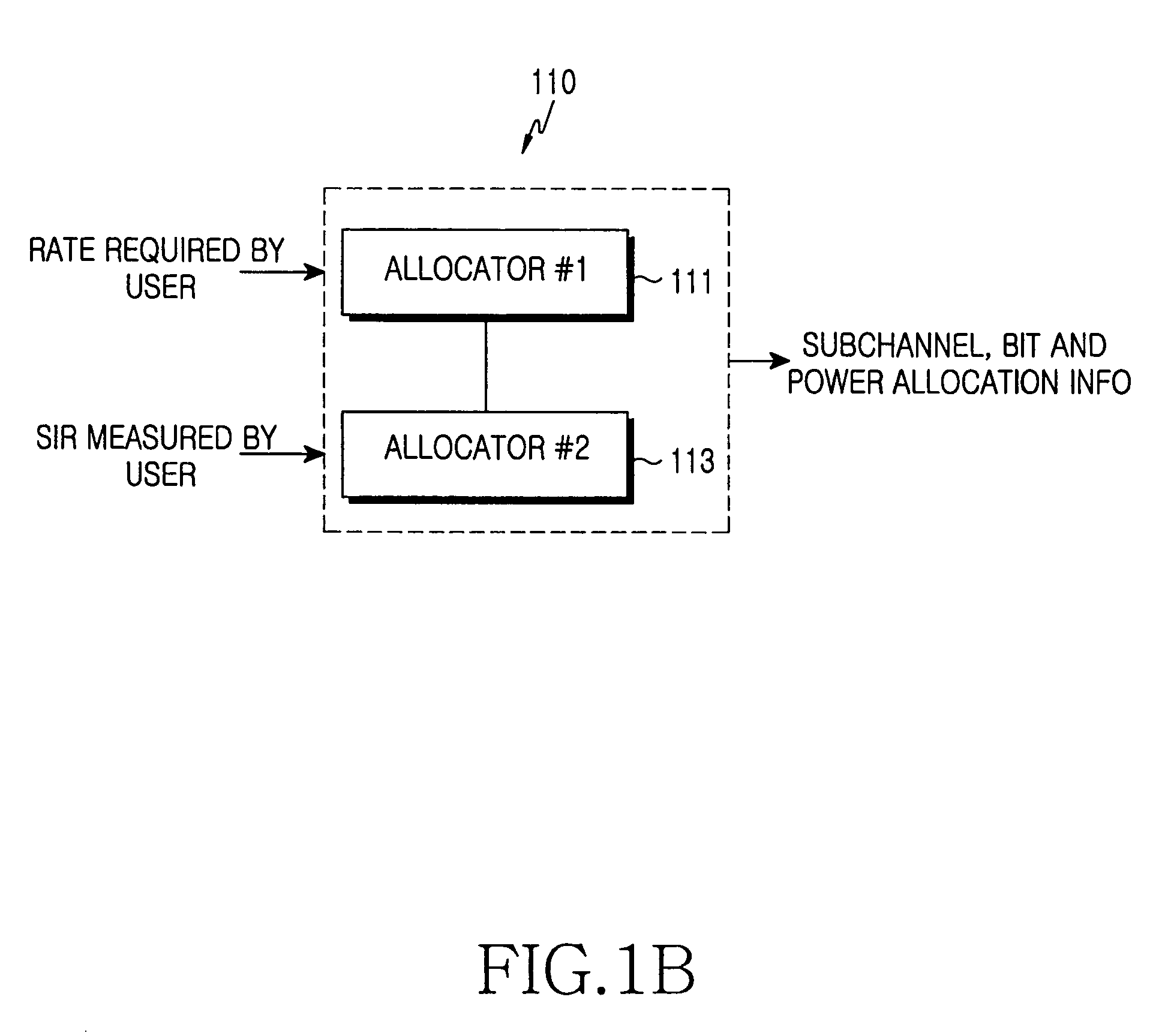
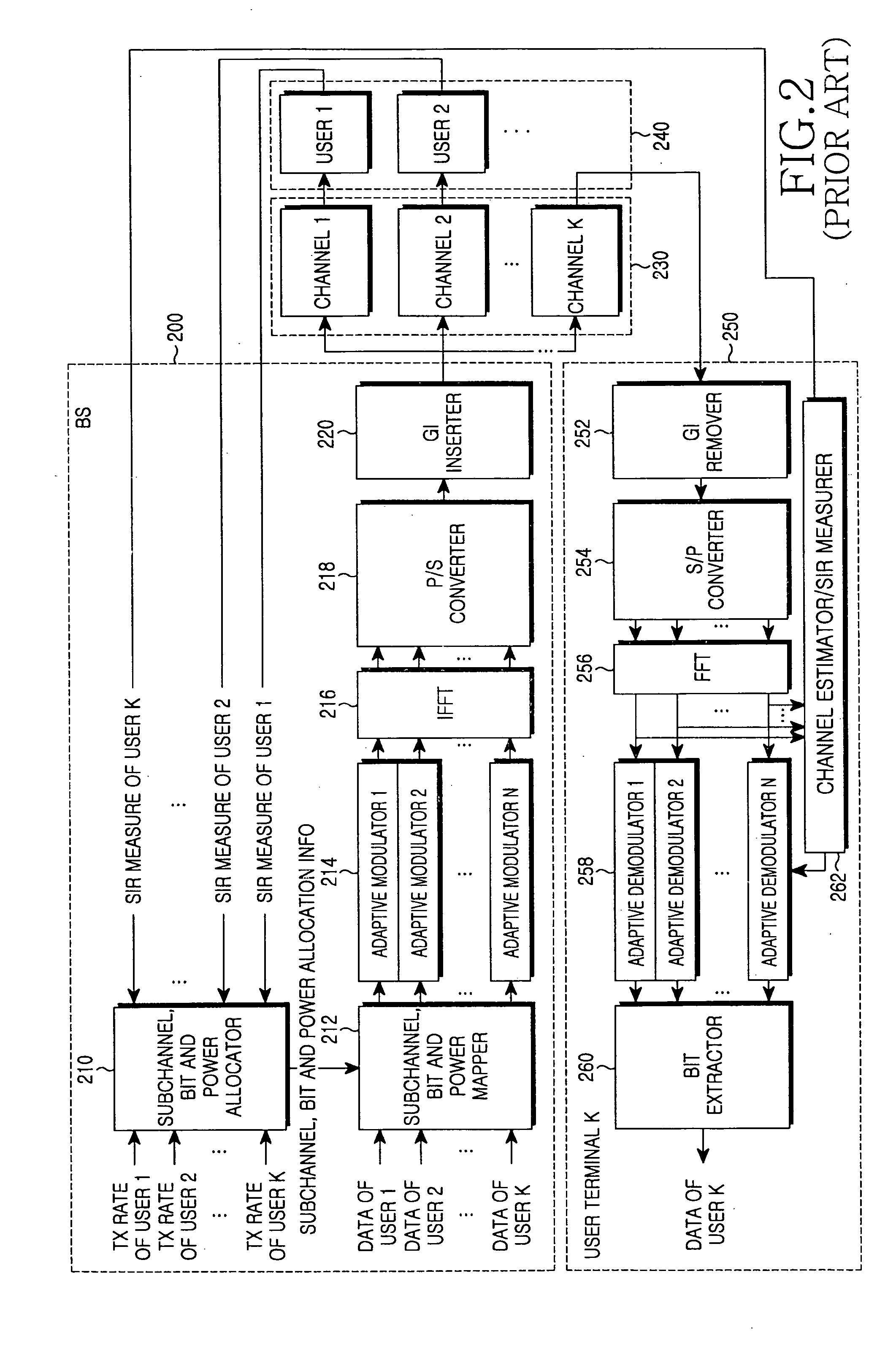
Apparatus and method for allocating subchannel and power in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access system
InactiveUS20060078059A1Improve transmission performanceSecret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsComputer scienceOrthogonal frequency-division multiple access
An apparatus and method for allocating transmission power of a subchannel for each individual user in an orthogonal frequency division multiple access (OFDMA) system. The apparatus and method comprises determining the number-of-transmission bits per symbol approximating an estimated signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) for each of subchannels when transmission power is uniformly allocated to the subchannels; and calculating a required SIR corresponding to the number-of-transmission bits per symbol, and allocating transmission power to each of the subchannels according to the required SIR.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
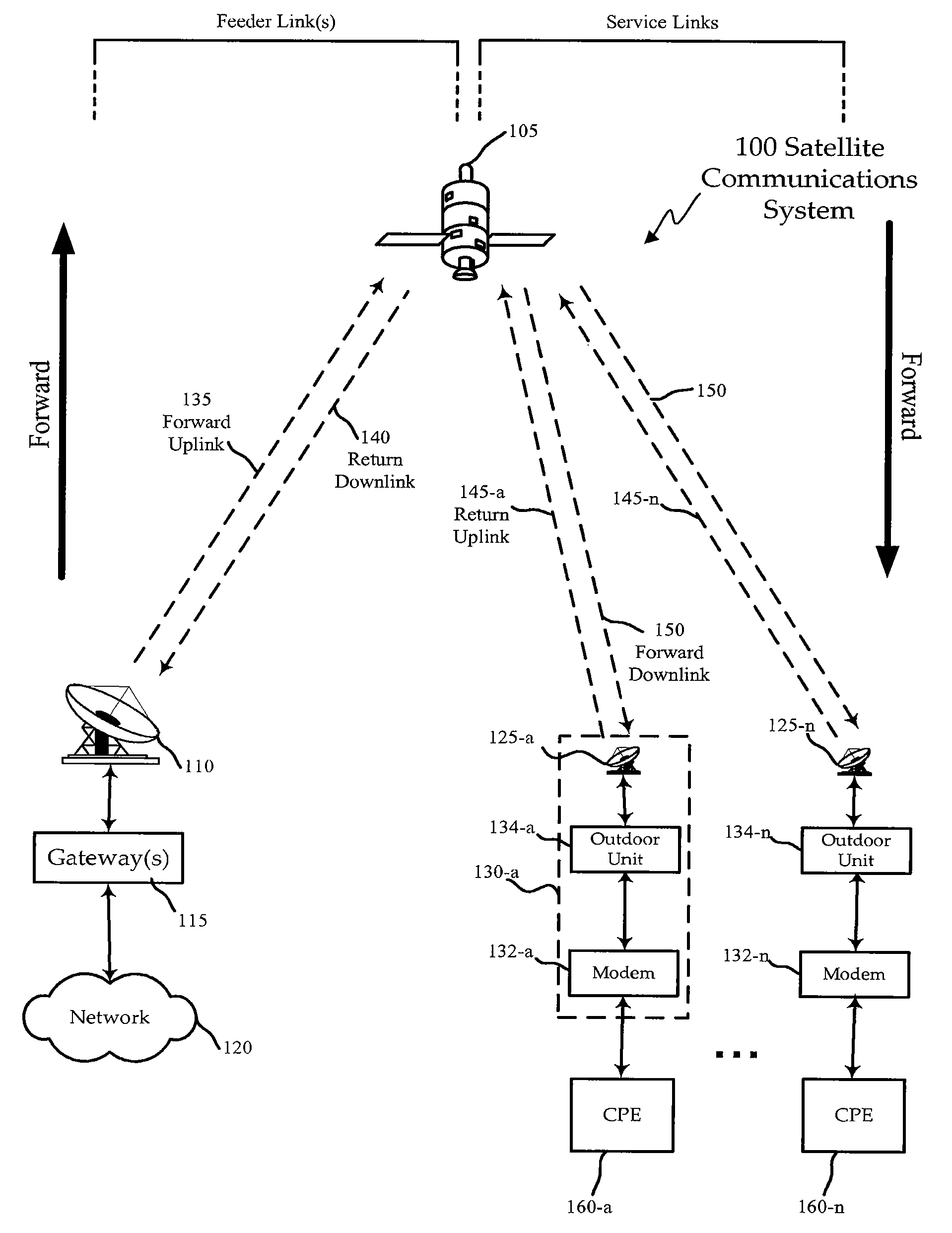
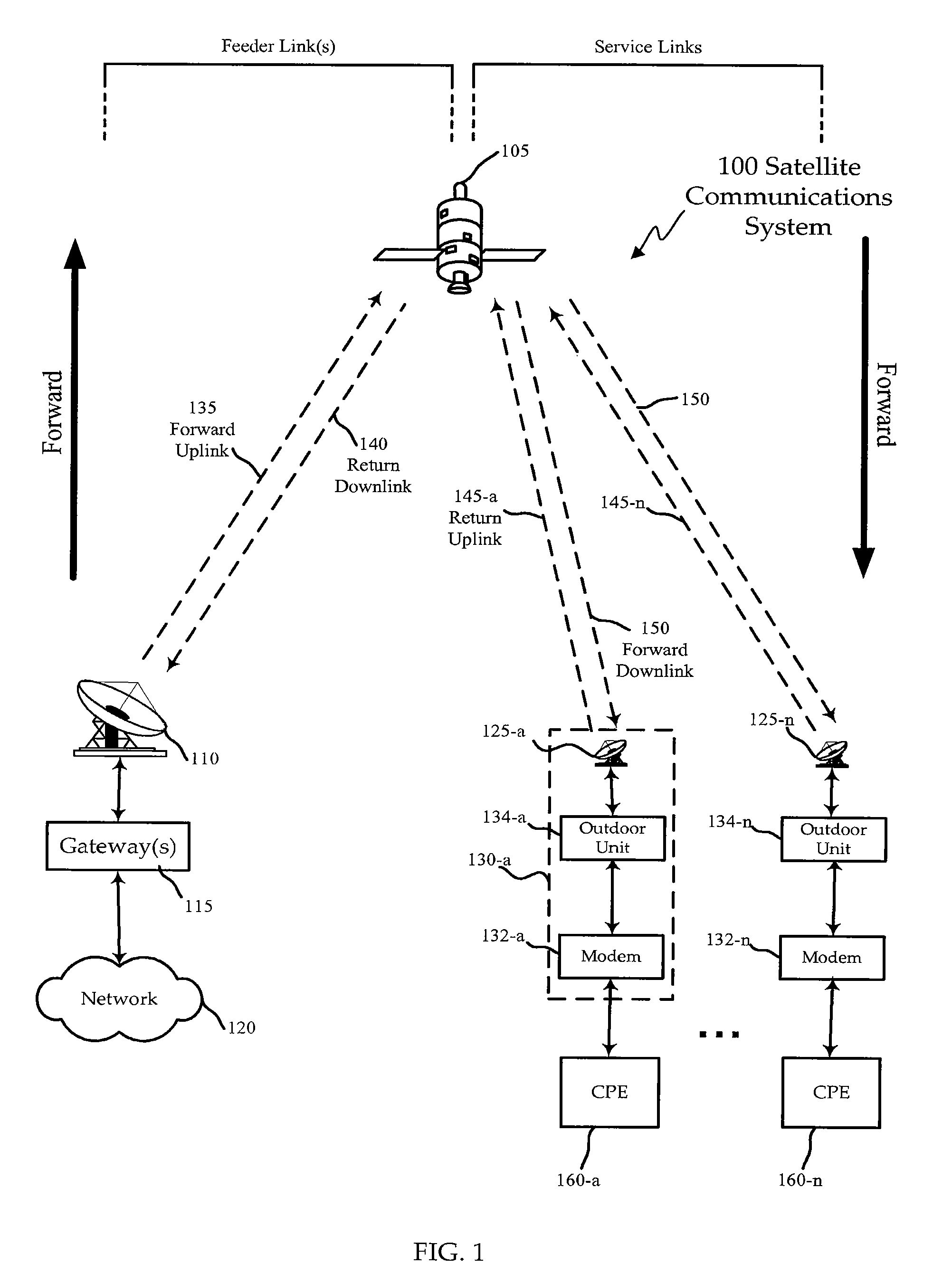
Capacity Maximization for a Unicast Spot Beam Satellite System
ActiveUS20090023384A1Maximizing average data-carrying capacityImprove data carrying capacityActive radio relay systemsTransmission monitoringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Light beam
Methods, systems, and apparatuses are presented for improved satellite communications. The satellite system may comprises at least one gateway, a satellite in orbit configured to communicate with the at least one gateway and provide a plurality of spot beams, and a plurality of subscriber terminals. The spot beams may include a first spot beam to illuminate a first region and a second spot beam to illuminate a second region adjacent to and overlapping with the first region. The first spot beam as sent to at least one subscriber terminal may be affected by (1) interference from other signal sources including the second spot beam at a signal-to-interference ratio C / I and (2) noise at a signal-to-noise ratio C / N. Reception of signals from the first spot beam by the at least one of the first plurality of subscriber terminals may be interference-dominated such that C / I is less than C / N.
Owner:VIASAT INC
System and method for providing an accurate estimation of received signal interference for use in wireless communications systems
A system for providing an accurate interference value signal received over a channel and transmitted by an external transceiver. The system includes a first receiver section for receiving the signal, which has a desired signal component and an interference component. A signal extracting circuit extracts an estimate of the desired signal component from the received signal. A noise estimation circuit provides the accurate interference value based on the estimate of the desired signal component and the received signal. A look-up table transforms the accurate noise and / or interference value to a normalization factor. A carrier signal-to interference ratio circuit employs the normalization factor and the received signal to compute an accurate carrier signal-to-interference ratio estimate. Path-combining circuitry generates optimal path-combining weights based on the received signal and the normalization factor. In the illustrative embodiment, the system further includes a circuit for employing the accurate interference value to compute a carrier signal-to-interference ratio. An optimal path-combining circuit computes optimal path-combining weights for multiple signal paths comprising the signal using the accurate interference value and provides optimally combined signal paths in response thereto. A log-likelihood ratio circuit computes a log-likelihood value based on the carrier signal-to-interference ratio and the optimally combined signal paths. A decoder decodes the received signal using the log-likelihood value. An additional circuit generates a rate and / or power control message and transmits the rate and / or power control message to the external transceiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
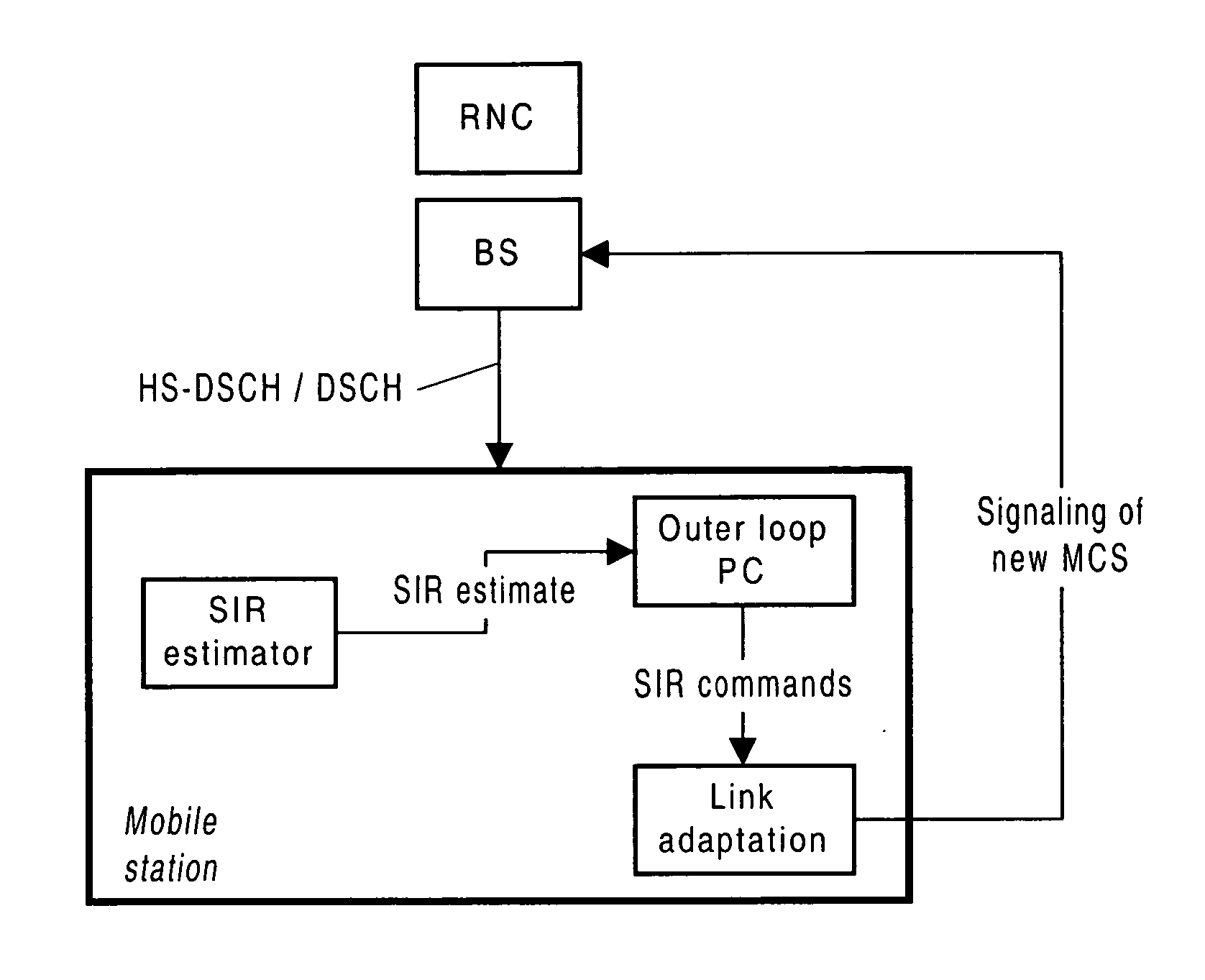
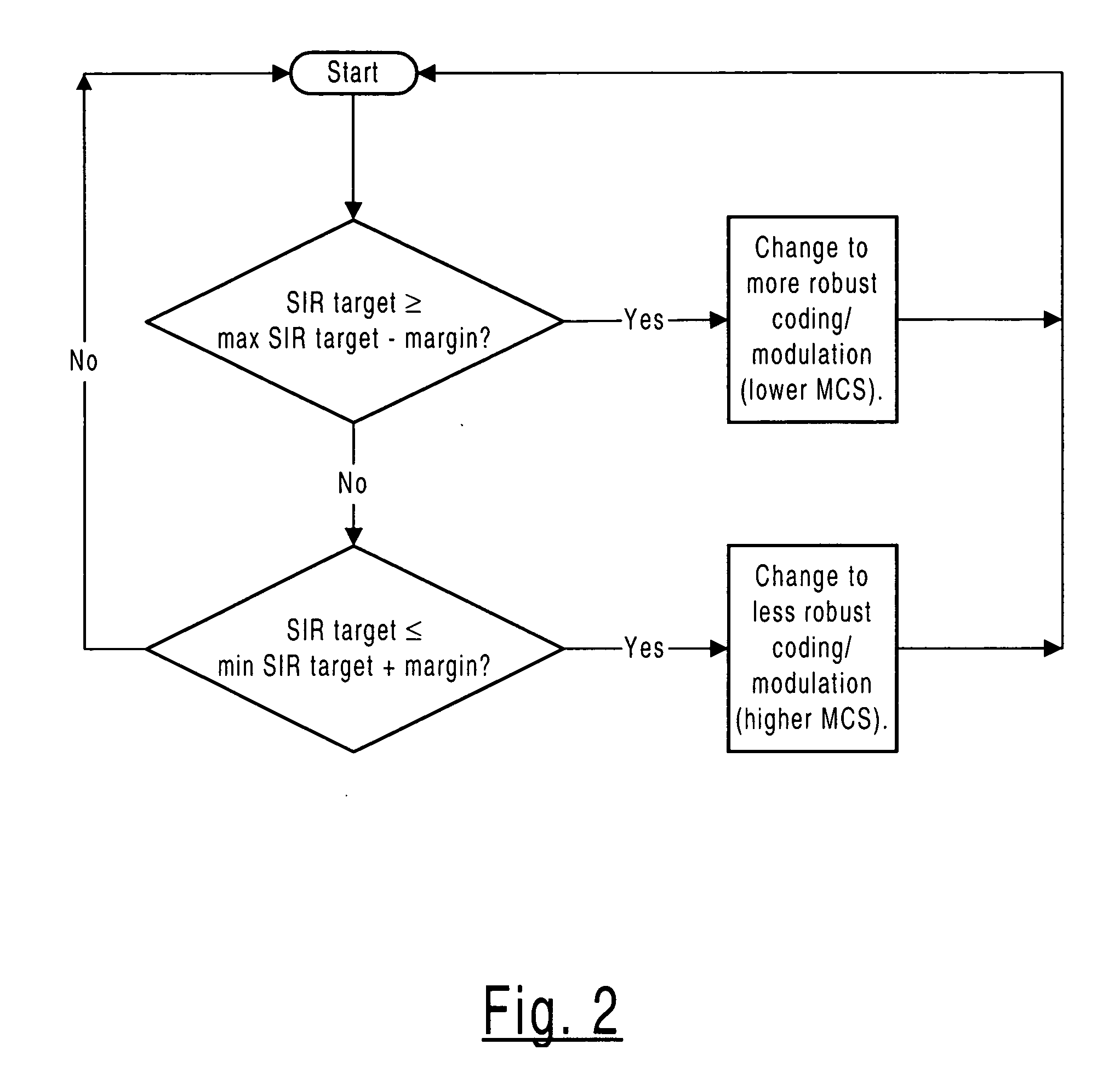
Method for determining whether to perform link adaptation in WCDMA communications
InactiveUS7027420B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorSignal qualityLink adaptation
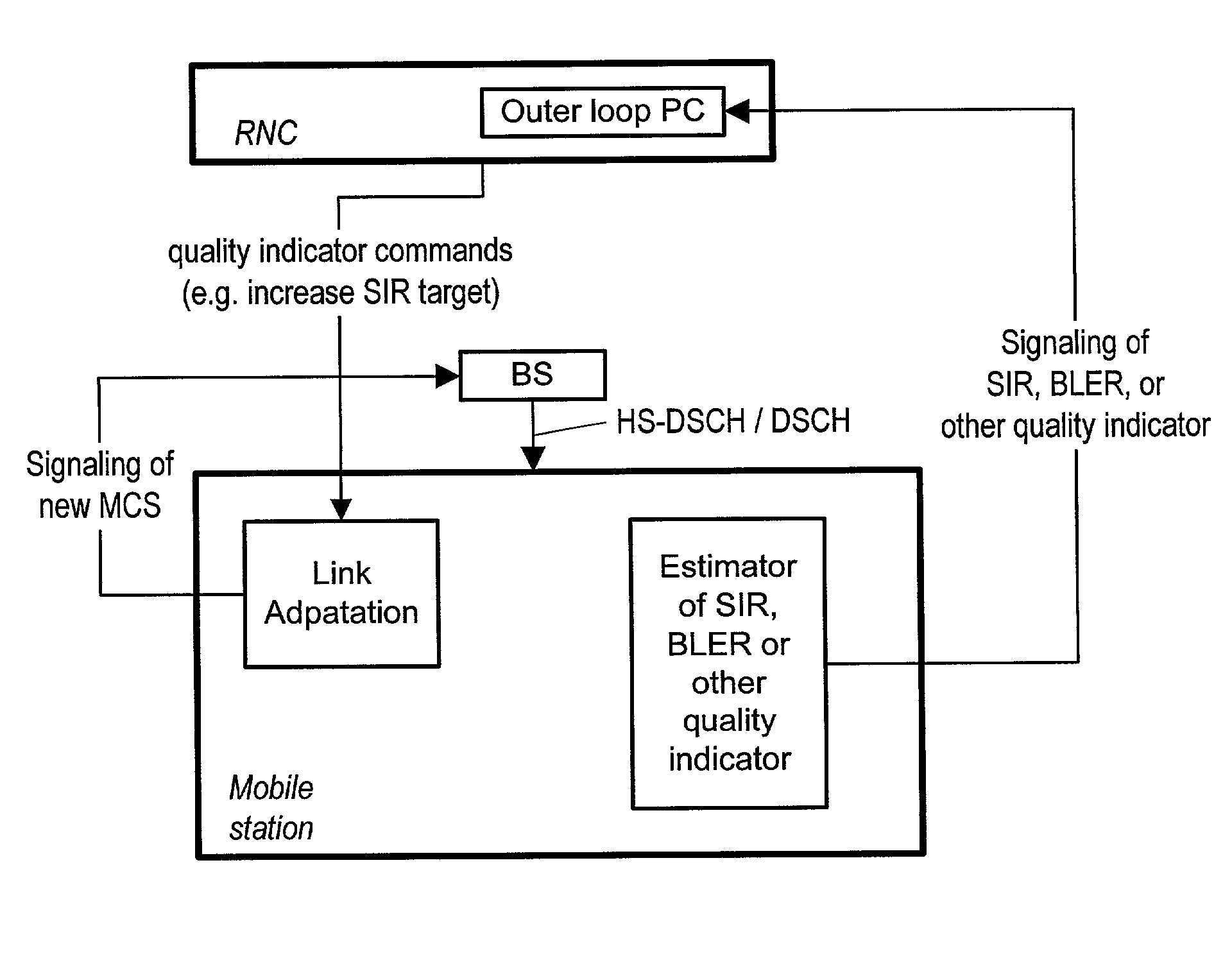
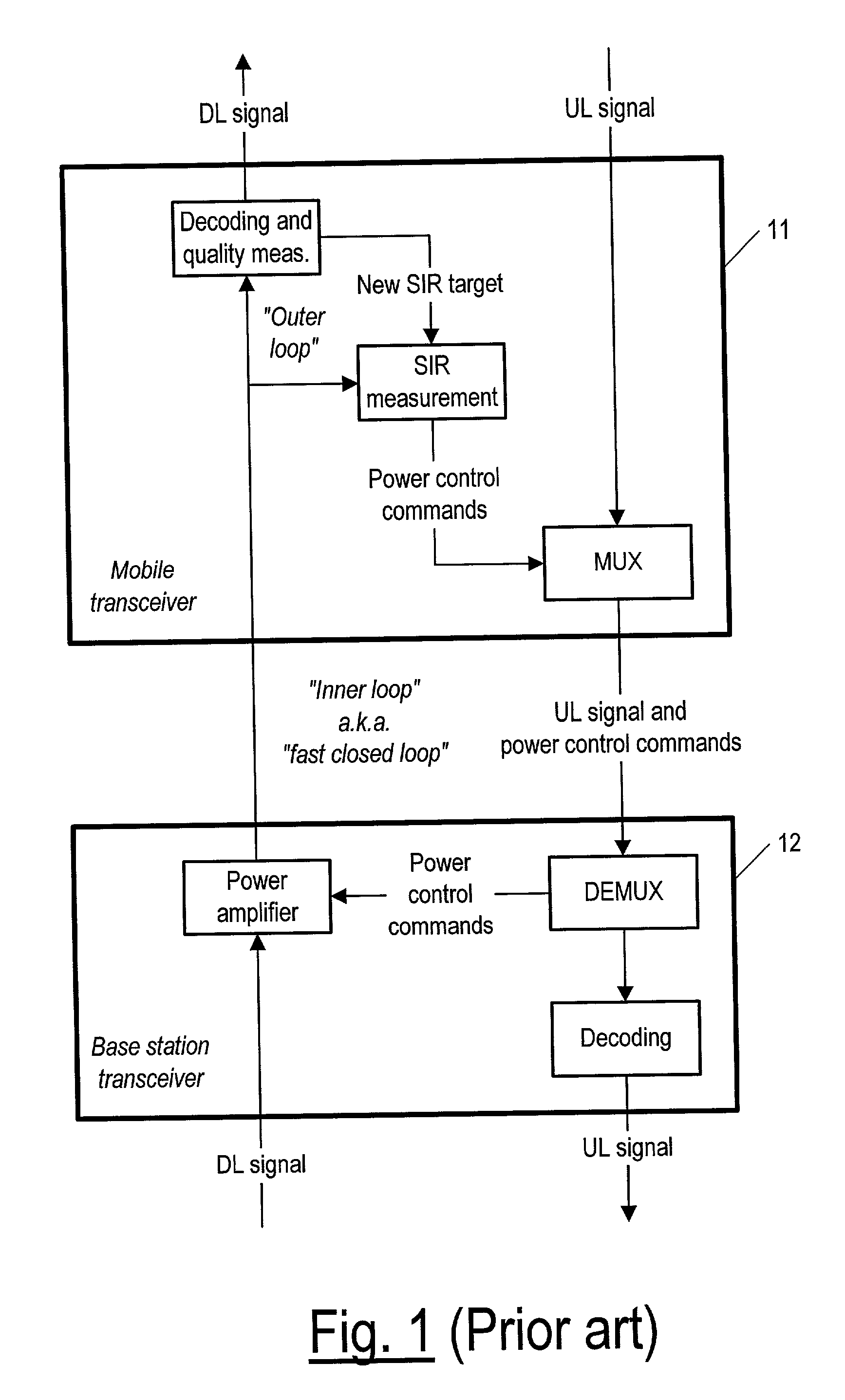
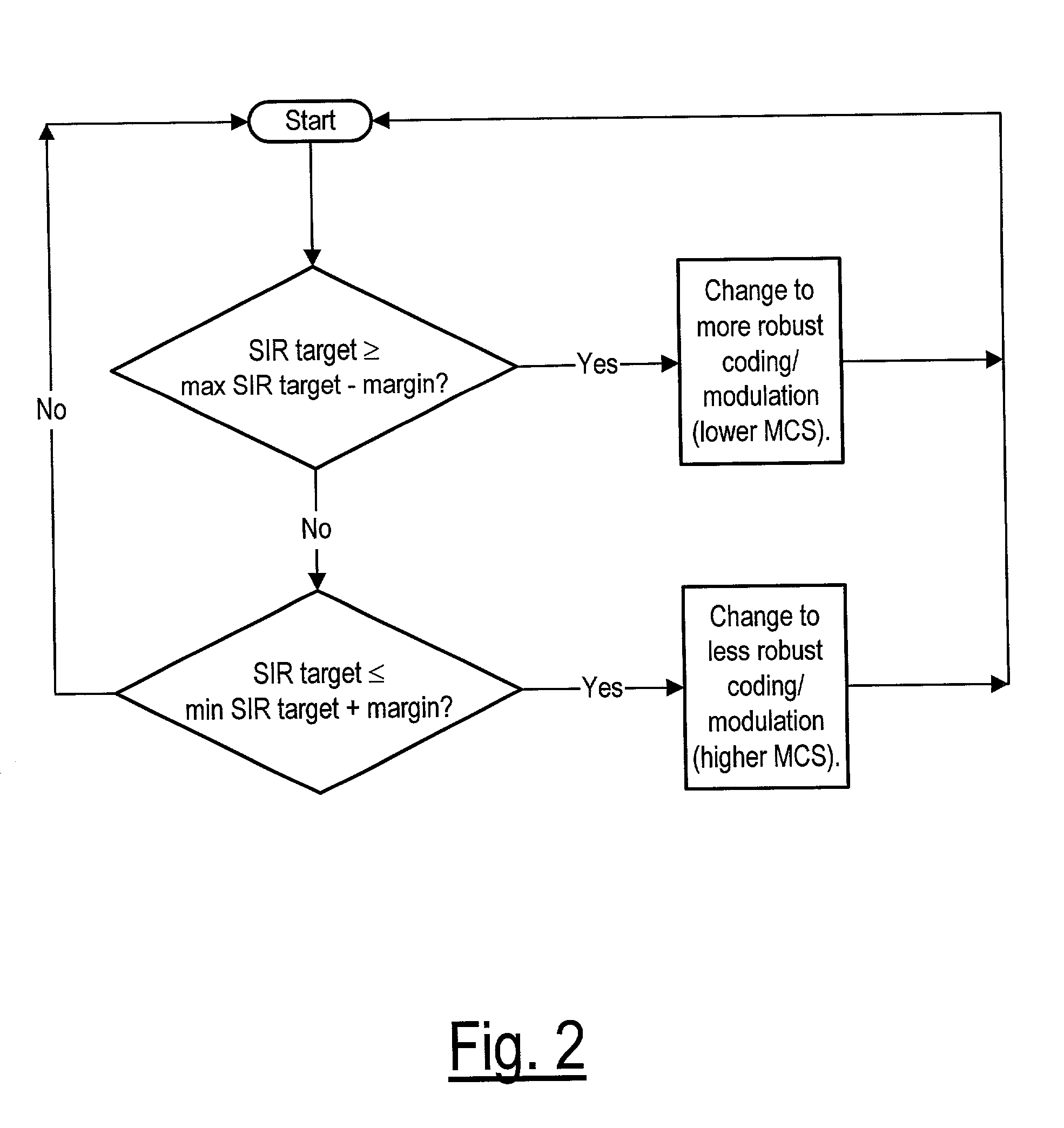
An apparatus and corresponding method for deciding whether to perform link adaptation for communication transmitted from a first communication device to a second communication device, where the second communication device examines a signal received from the first communication device and provides a first indication of the quality of the signal. The method includes the steps of: recording at least one first indication of the quality of the signal as received by the second communication device; providing a second indication of the quality of the signal based on the at least one first indication of the quality of the signal; and deciding to perform link adaptation based on the second indication of the quality of the signal. The first indication of the quality of the signal is for example a signal to interference ratio (SIR) estimate. Often, the second indication of the quality of the signal is a changed SIR target value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Dynamic sub-carrier assignment in OFDM systems
InactiveUS20060126493A1Improve communication efficiencyHigh signal to interferenceModulated-carrier systemsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemCarrier signal
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Impairment correlation estimation in a spread spectrum system
ActiveUS20050215218A1Suppress noiseSuppress interferenceRadio transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputer scienceMulti path
A method and apparatus derives an impairment correlation matrix to process signals received at a wireless receiver over multiple paths of a multi-path channel. The receiver includes first and second impairment correlation estimators for estimating first and second impairment correlation matrices based on despread symbols received over multiple paths of a multi-path channel. The receiver then derives the impairment correlation matrix based on the estimated first and second impairment correlation matrices. The receiver may combine traffic despread values to suppress interference using weighting factors calculated based on the derived impairment correlation matrix. Further, the receiver may estimate a signal-to-interference ratio based on the derived impairment correlation matrix.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Transmission power control method and transmission power control apparatus in mobile communication system
InactiveUS6963753B1Keep the quality constantConstantPower managementSite diversityControl objectiveMobile station
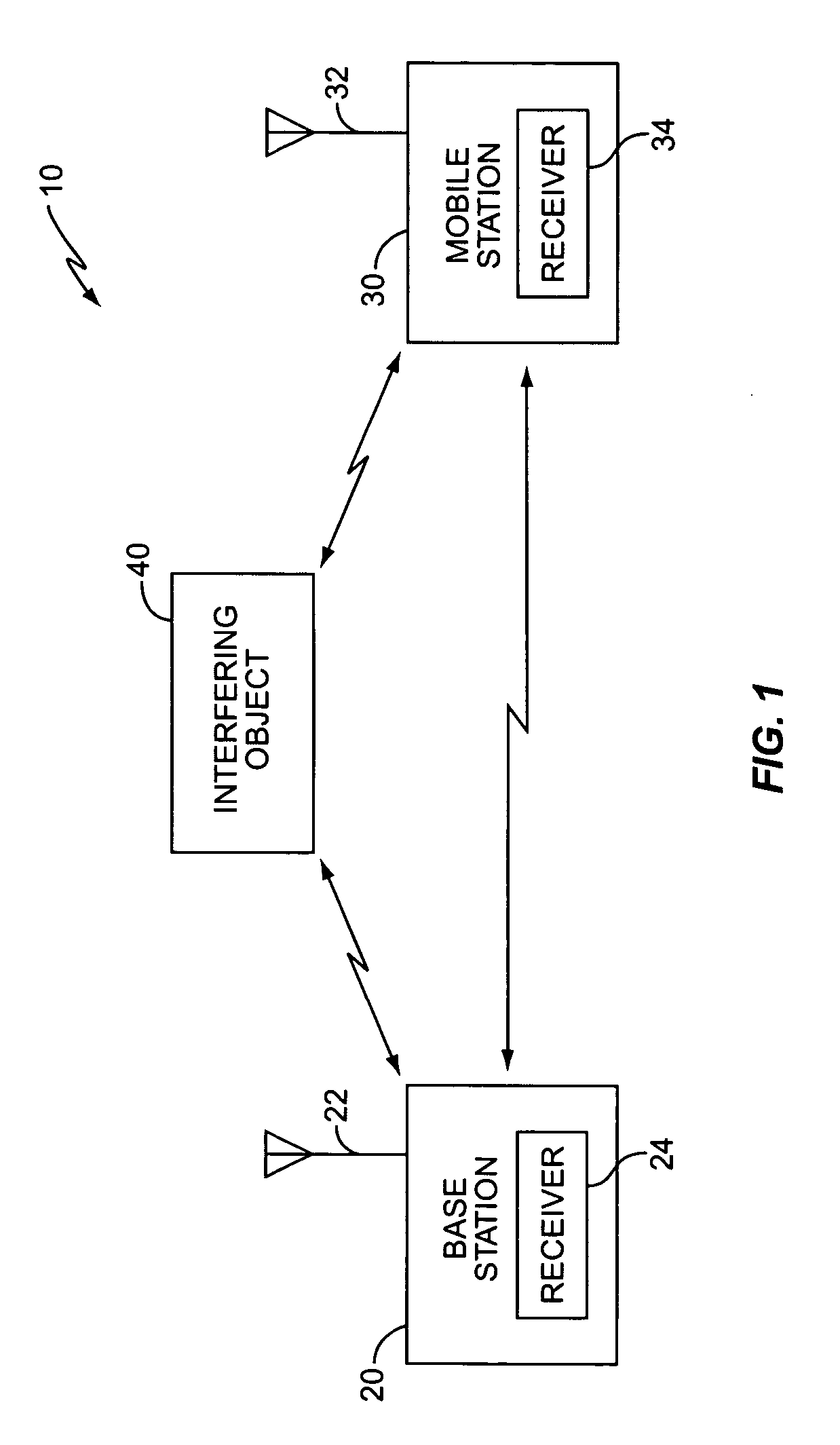
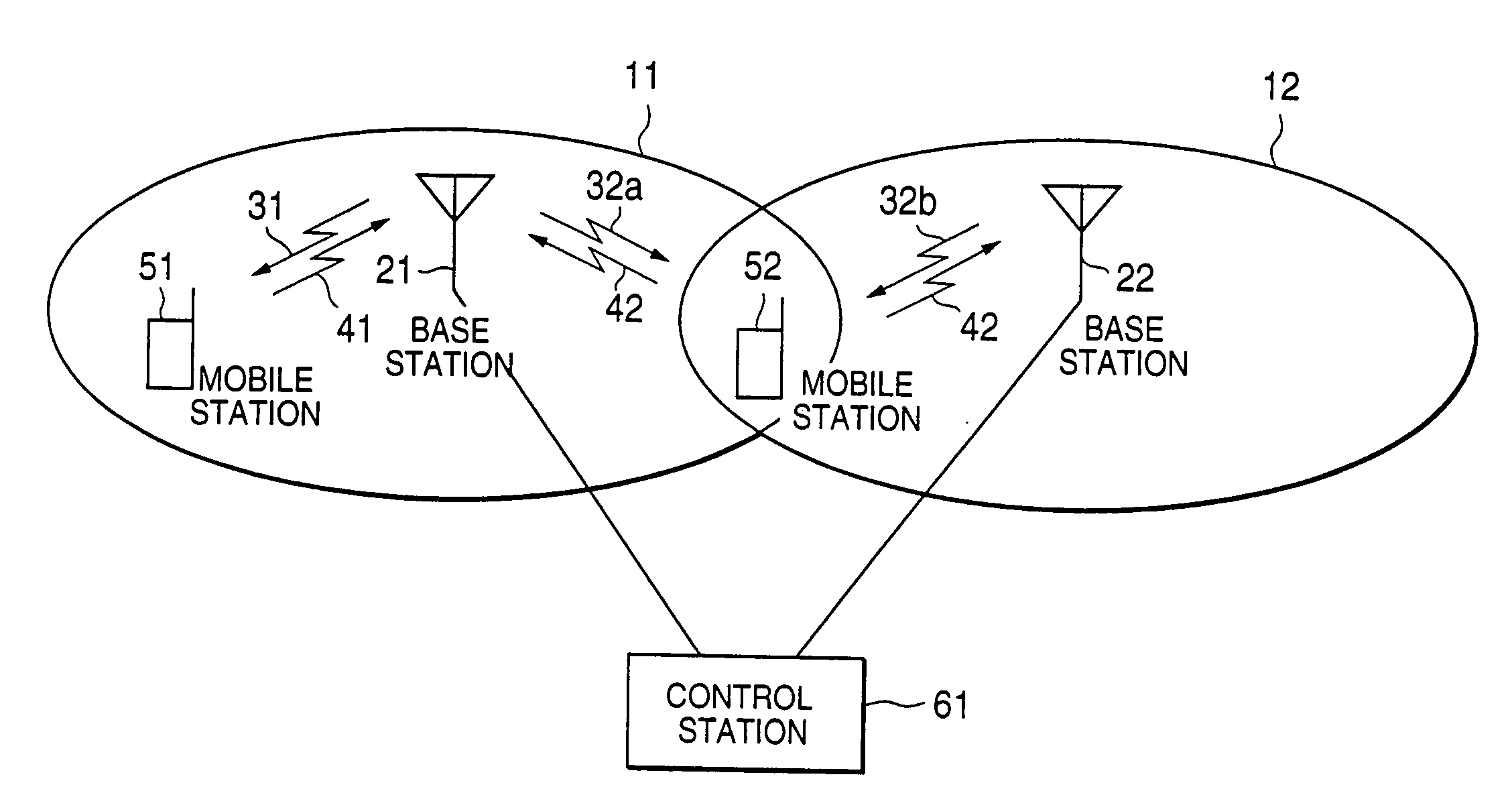
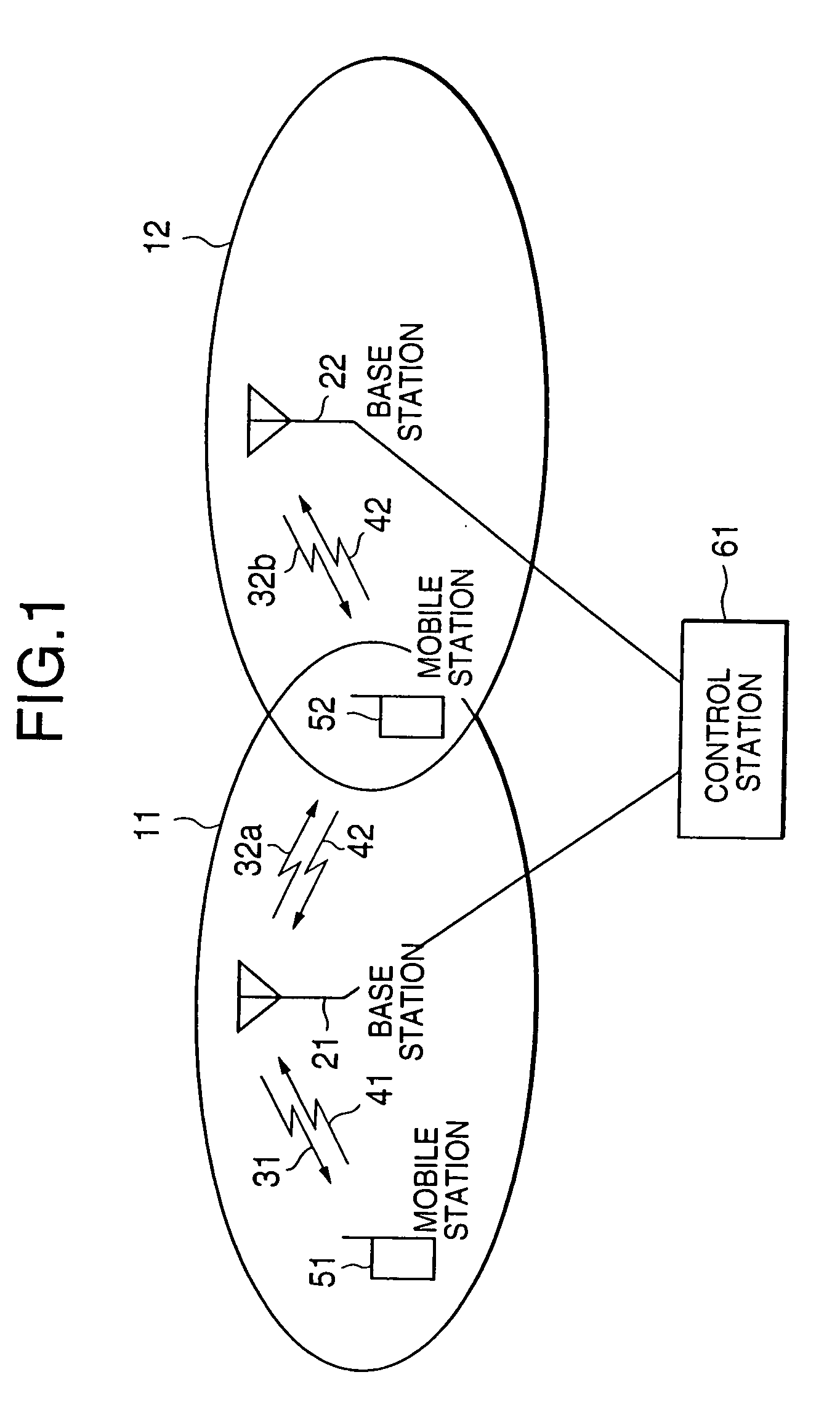
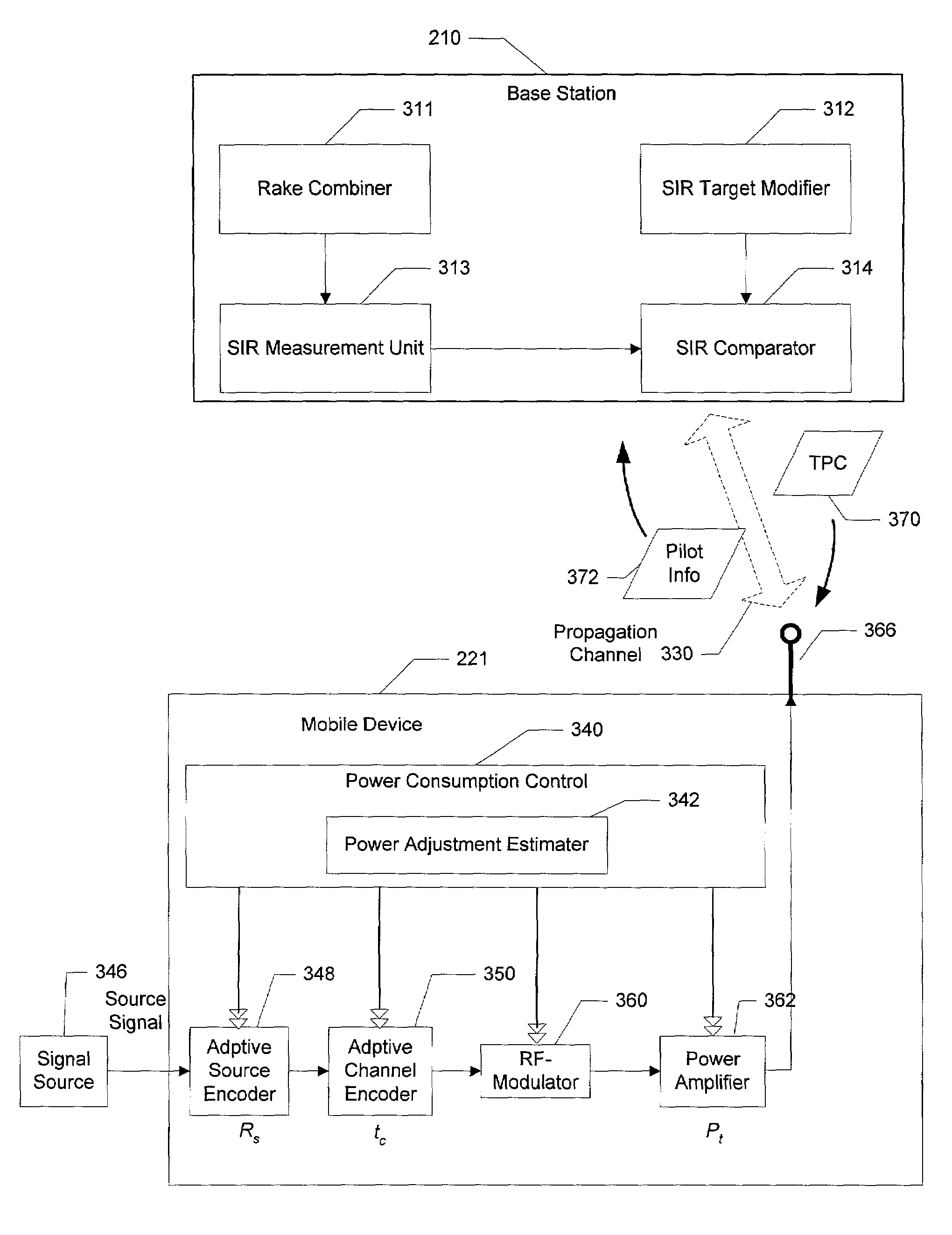
This invention relates to a transmission power control method and transmission power control apparatus in a mobile communication system. The reception quality of a signal (31, 32a, 32b, 41, or 42) transmitted from another mobile station (51 or 52) or base station (21 or 22) is compared with a predetermined control target value such as a signal-to-interference ratio. The comparison result is used for transmission power control on a remote station. If a frame error is detected in a transmitted signal, the control target value is increased by SIRinc. If no frame error is detected, the control target value is decreased by SIRdec. As SIRdec, the product of a target value of a frame error rate and SIRinc is set. With this operation, when a propagation environment such as multibus or moving speed changes, the control target value for transmission power control is changed within a short period of time, and channel quality is maintained constant, thus realizing desired channel quality.
Owner:NEC CORP
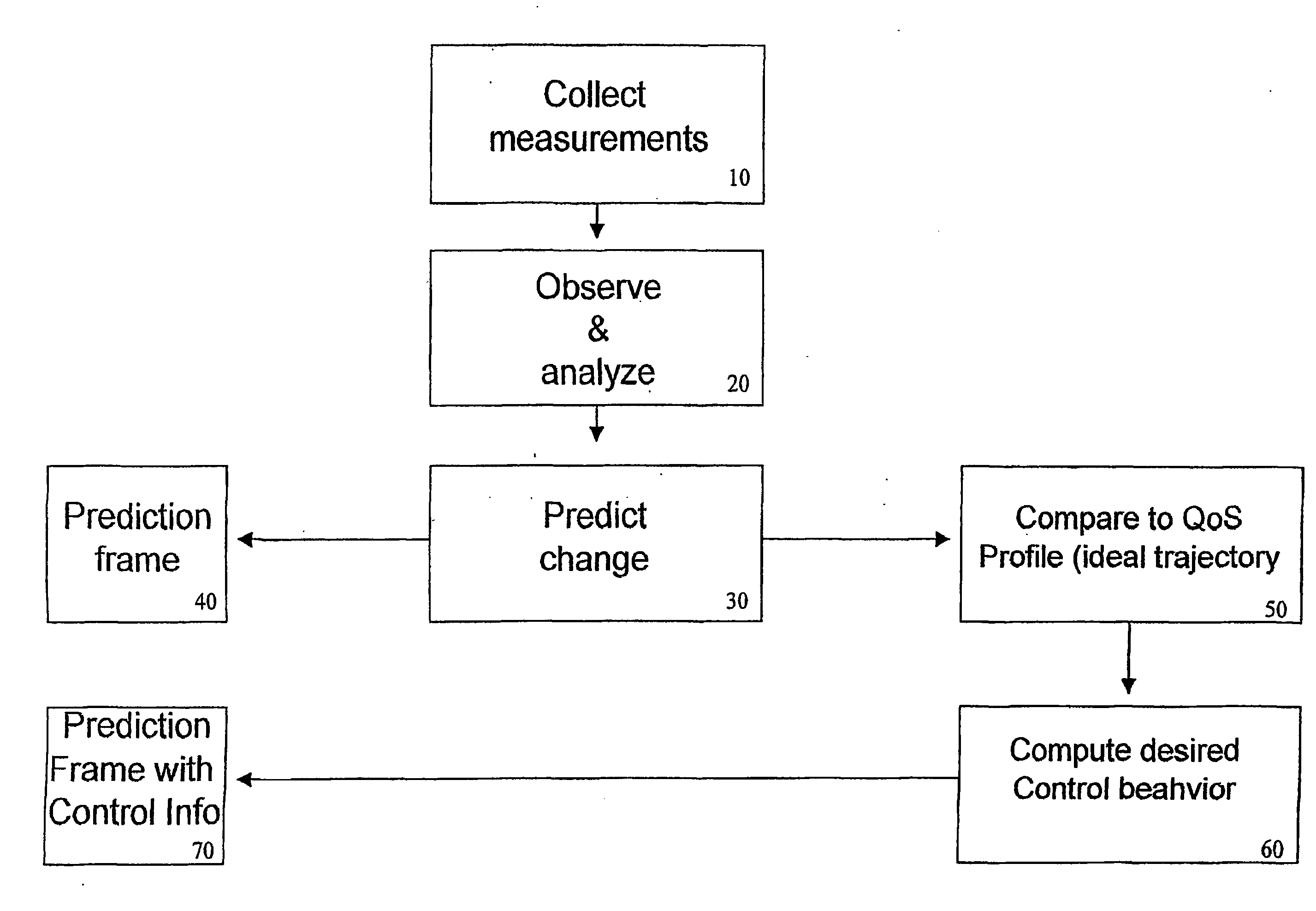
Quality of service state predictor for and advanced mobile devices
InactiveUS20040185786A1Fair distributionQuality improvementTransmission monitoringQos quality of serviceRadio access network
A mobile device and method for predictive computing of variable mobile link parameters per session and state in a future time interval within Radio Access Networks (RAN). The system narrows its prediction errors as time progresses. An ideal control value is also estimated, so that mobile QoS applications can determine their intervention point while coexisting with link layer resource management mechanisms. The system is provided with certain measurement elements from the RAN. With the information contained in these elements, the system estimates the Received Signal Strength (RSSI), Received Wideband Power (RSCP), Signal Interference Ratio (SIR), Bit Error Rate (BER), the transmission delay per frame (delay), the variation between delay measurements throughout a certain number of measurement time frames and the mean bit throughput rate (Chip Rate) for a future time interval. The system also calculates the optimal power control (gain) for a defined value target of a given link parameter. The estimates are passed on to other Systems for further processing.
Owner:FG MICROTEC
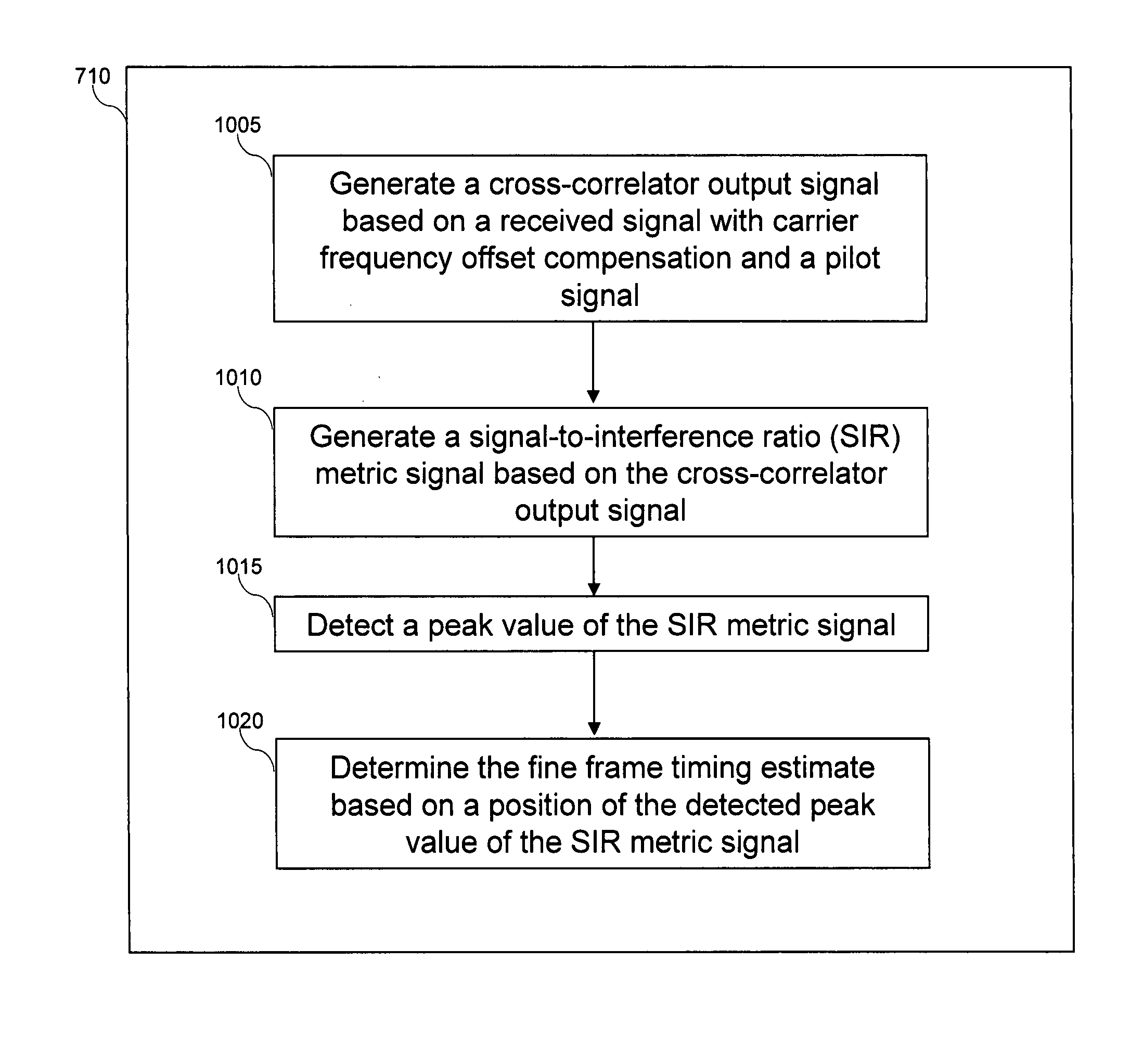
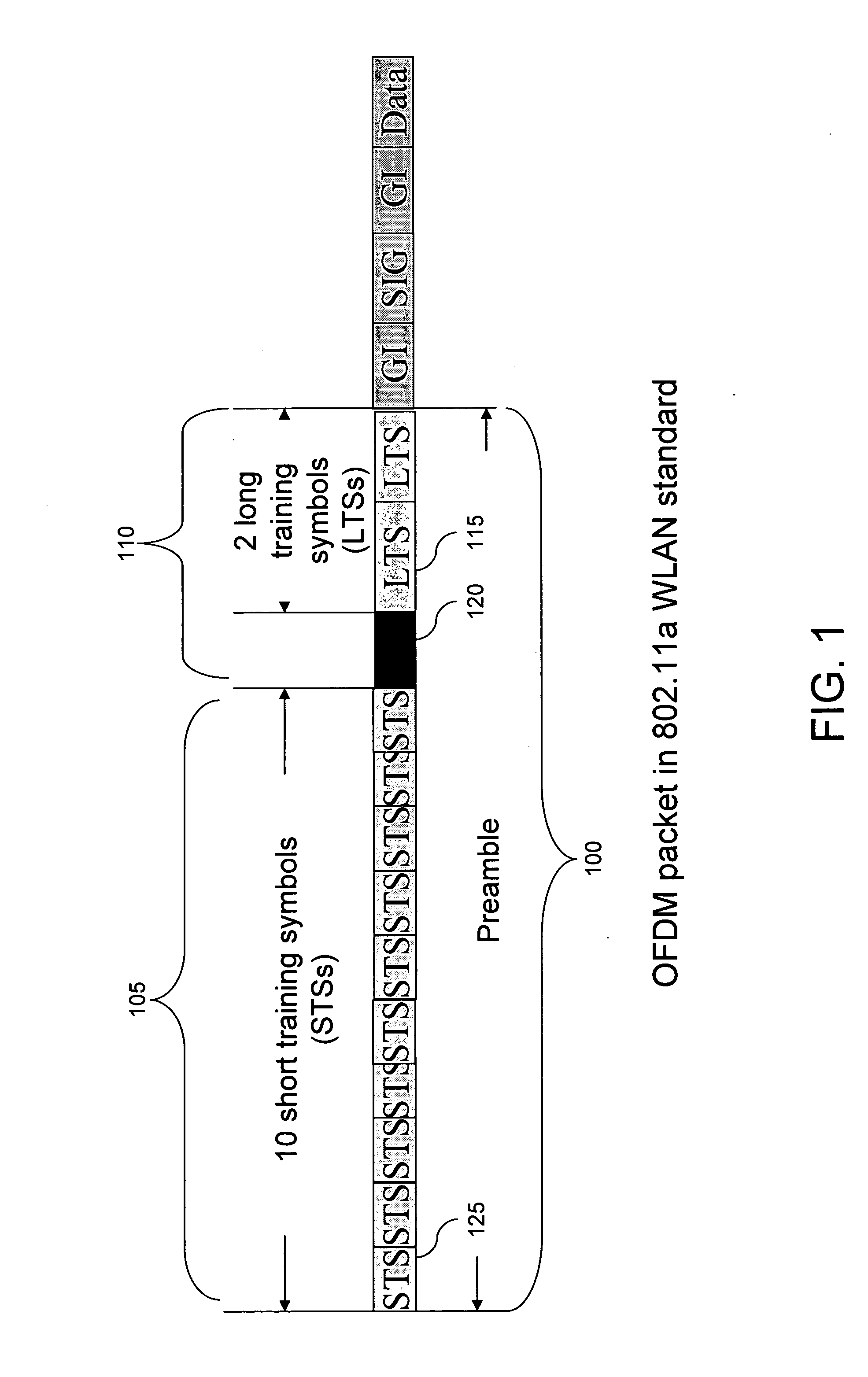
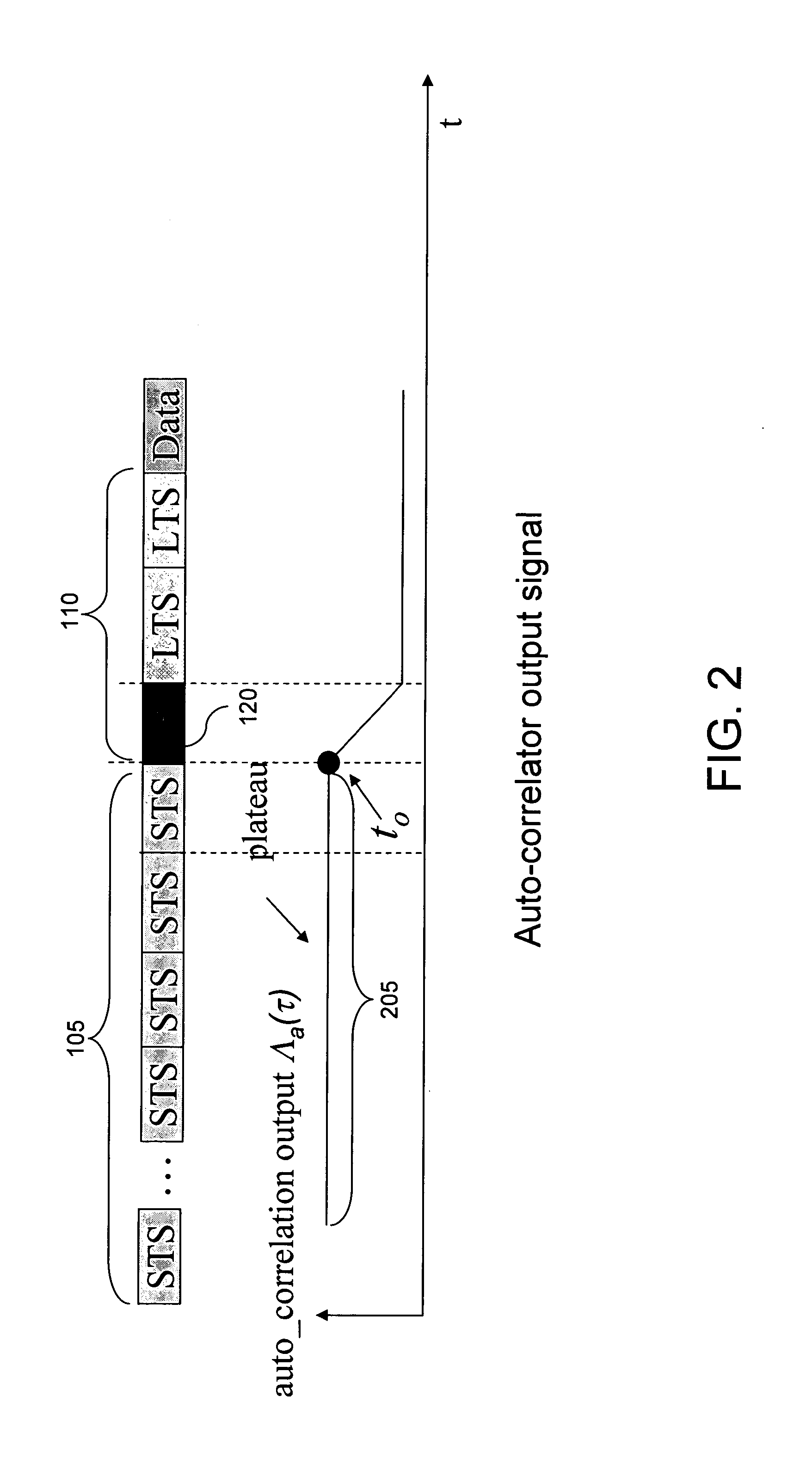
Frame timing synchronization for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM)
InactiveUS20070217524A1Secret communicationMulti-frequency code systemsCyclic delay diversityDifferentiator
A frame timing synchronization technique for orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) systems is presented. First, a coarse synchronization technique generates a coarse frame timing estimate. The coarse synchronization technique applies a sliding window differentiator to the output of a conventional auto-correlator to mitigate the plateau effect associated with conventional auto-correlation techniques. Second, a fine synchronization technique generates a fine frame timing estimate. The fine synchronization technique uses the coarse frame timing estimate to reduce the number of cross-correlation calculations. Additionally, the fine synchronization technique acquires a fine frame timing estimate based on a signal-to-interference ratio (SIR) metric, which is more robust to multi-paths and pseudo multi-paths caused by cyclic delay diversity (CDD) schemes than conventional cross-correlation synchronization techniques. A fine-tuning technique generates a desired frame timing estimate by searching a first signal path in a searching window around the fine frame timing estimate to further refine frame timing synchronization.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
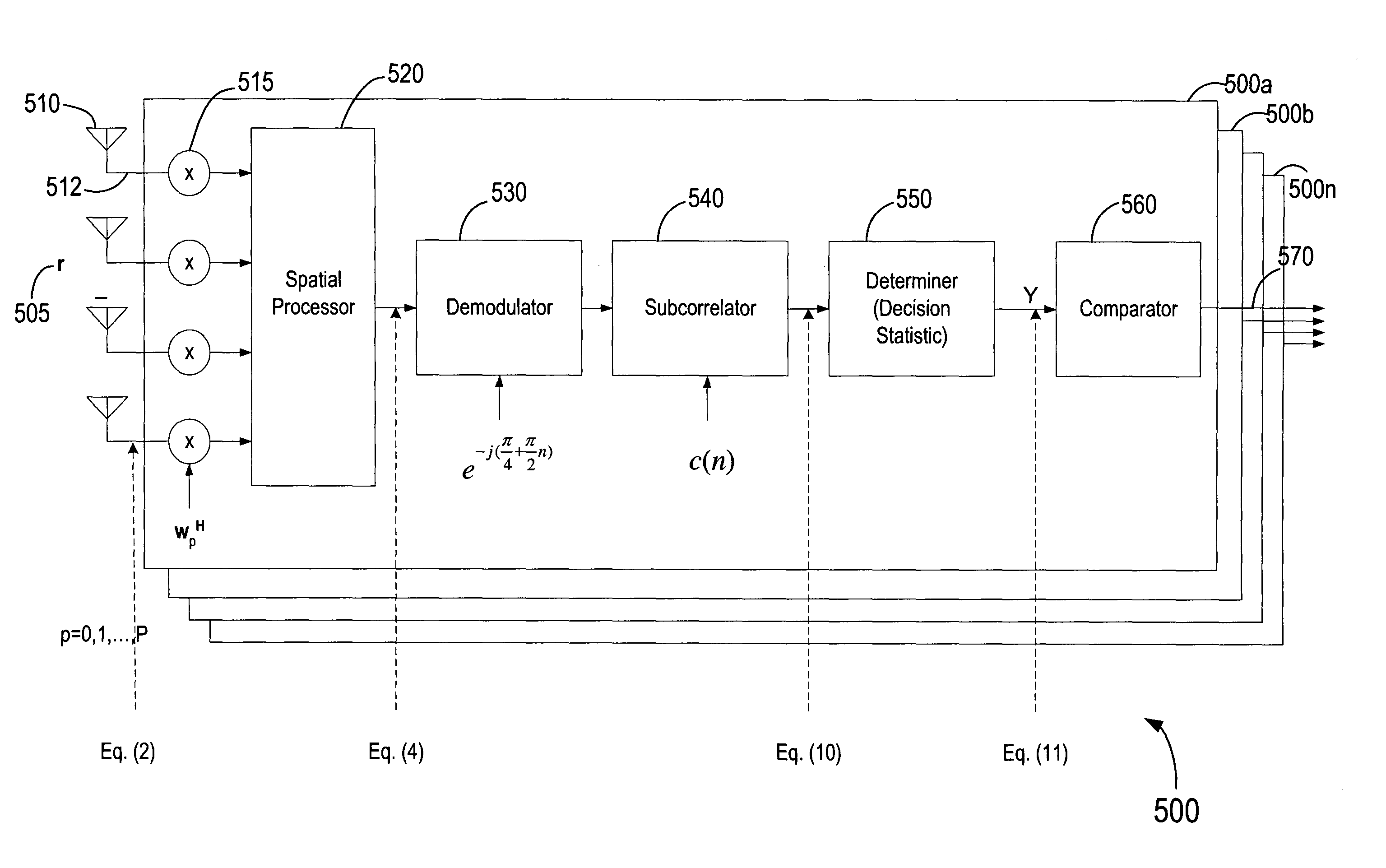
Method and arrangement for detecting a random access channel preamble using multiple antenna reception in a communication system
InactiveUS20050047530A1Power managementSpatial transmit diversityCommunications systemRandom-access channel
In a method and arrangement for detecting a random access channel preamble in a received uplink signal, the uplink signal is received at one or more receive antennas and contains data related to a random access channel preamble. The received uplink signal is subjected to spatial processing and temporal processing in order to detect the random access channel preamble. A best cell portion for communicating with a user may also be determined based on the detected preamble. The best cell portion represents a portion of a cell where a received uplink signal from a user has a highest signal to interference ratio. The detected random access channel preamble is indicative of the best cell portion for communicating with the user.
Owner:WSOU INVESTMENTS LLC +1
System and method for reducing power consumption for wireless communications by mobile devices
InactiveUS7096034B2Maximize system capacityReduce transmit powerPower managementEnergy efficient ICTSignal qualitySystem capacity
A power control scheme for a wireless network communication system that includes a base station and multiple wireless mobile device dynamically adjusts transmission power of a mobile device in conjunction with adjusting its bit allocation in source coding and channel coding to minimize its total power consumption while maximizing the system capacity in terms of the total effective transmission rates received by the base station. The base station sets a target signal quality value for each mobile station, and the target values are determined by the base station such that the total effective data rate from all the mobile devices is maximized under constraints of the total received power and the error protection level requirements for the mobile devices. The base station periodically measures a signal quality value, such as a signal-to-interference ratio (SIR), from transmissions received by the base from each mobile device, compares it with the measured signal quality value for that mobile device, and sends a control signal instructing the mobile device to increase or decrease its transmission power based on the result of the comparison. When the mobile device receives the control signal, it determines an amount of adjustment to its transmission power by performing a minimum calculation under constraints on the total data distortion and the maximum transmission rate to adjust the parameters for source coding, channel coding, and transmission under the constraints to result in a redistribution of power between the components that provides the minimized total power consumption.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for determining whether to peform link adaptation in WCDMA communications
InactiveUS20060256732A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorSignal qualityLink adaptation
An apparatus and corresponding method for deciding whether to perform link adaptation for communication transmitted from a first communication device to a second communication device, where the second communication device examines a signal received from the first communication device and provides a first indication of the quality of the signal. The method includes the steps of: recording at least one first indication of the quality of the signal as received by the second communication device; providing a second indication of the quality of the signal based on the at least one first indication of the quality of the signal; and deciding to perform link adaptation based on the second indication of the quality of the signal. The first indication of the quality of the signal is for example a signal to interference ratio (SIR) estimate. Often, the second indication of the quality of the signal is a changed SIR target value.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
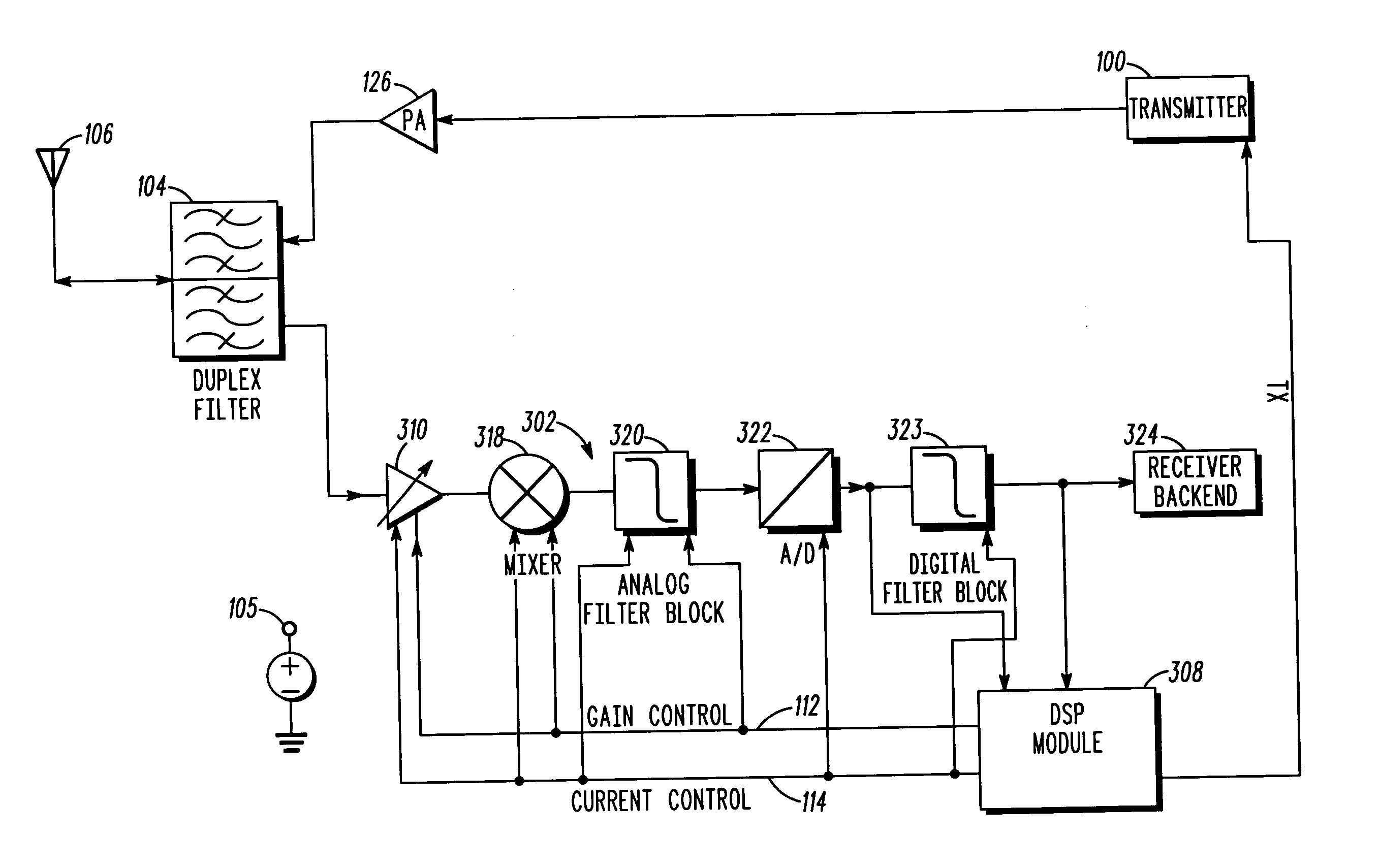
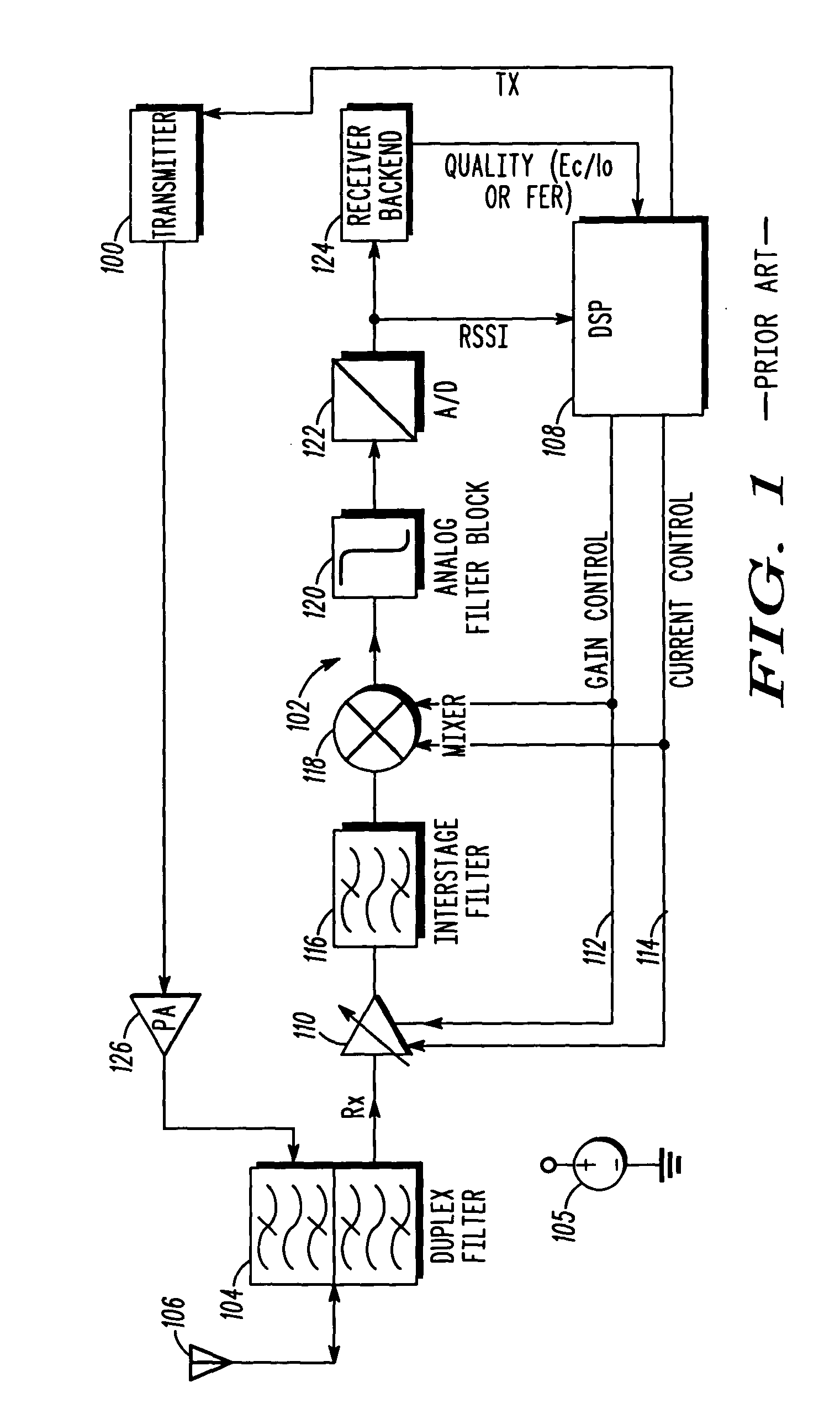
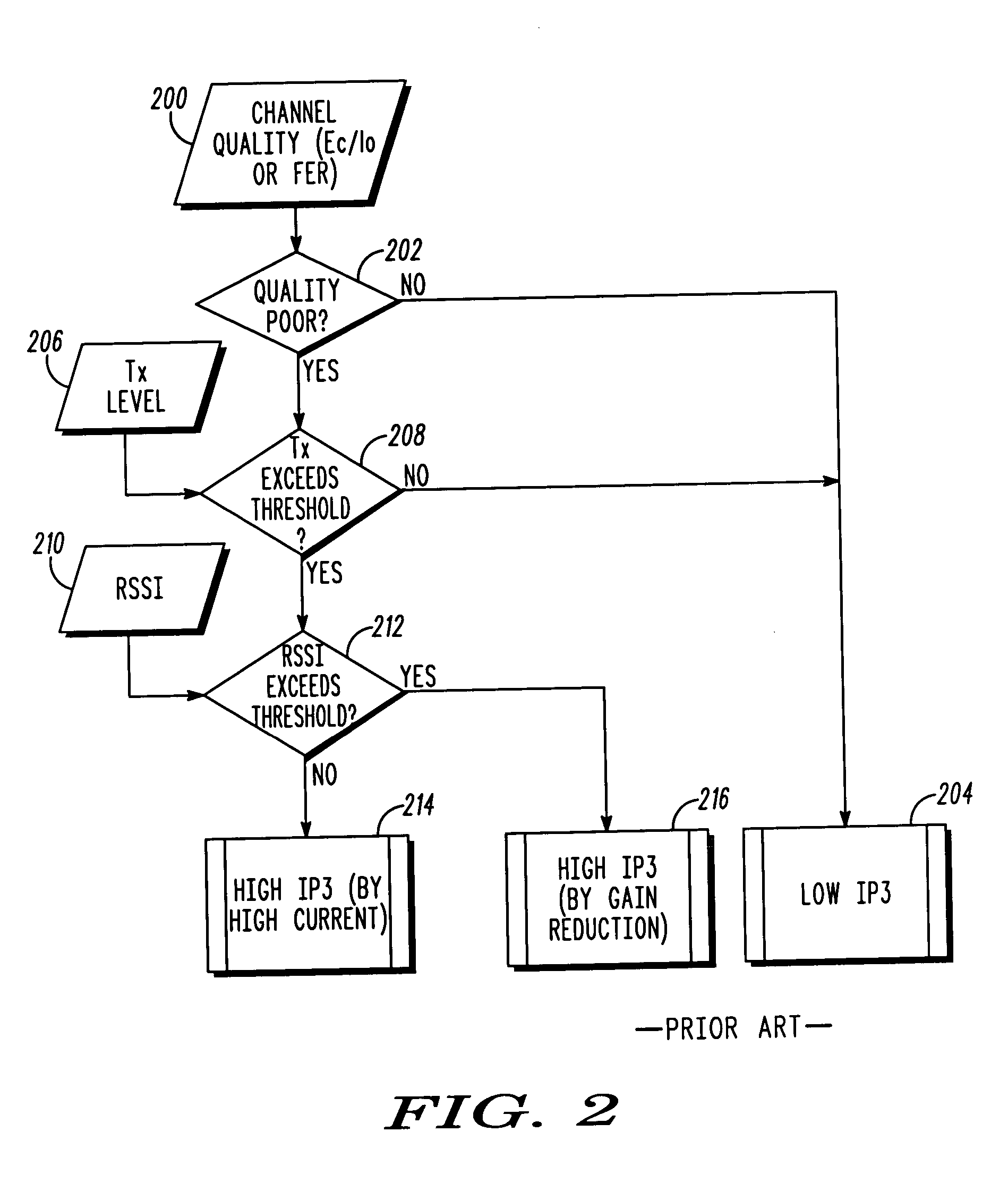
Current reduction by dynamic receiver adjustment in a communication device
A method for reducing current drain in a communication device includes a first step of detecting interference including intermodulation and crossmodulation products. A next step includes determining a frequency offset of the interference with reference to the operating receiver band. A next step includes measuring a power level of the interference. A next step includes calculating a receiver linearity required to achieve a desired signal-to-interference ratio. A next step includes adjusting the receiver linearity in order to achieve the desired signal-to-interference ratio. Optionally, the receiver dynamic range can be adjusted to suit the reduced signal swing due to the reduced linearity.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
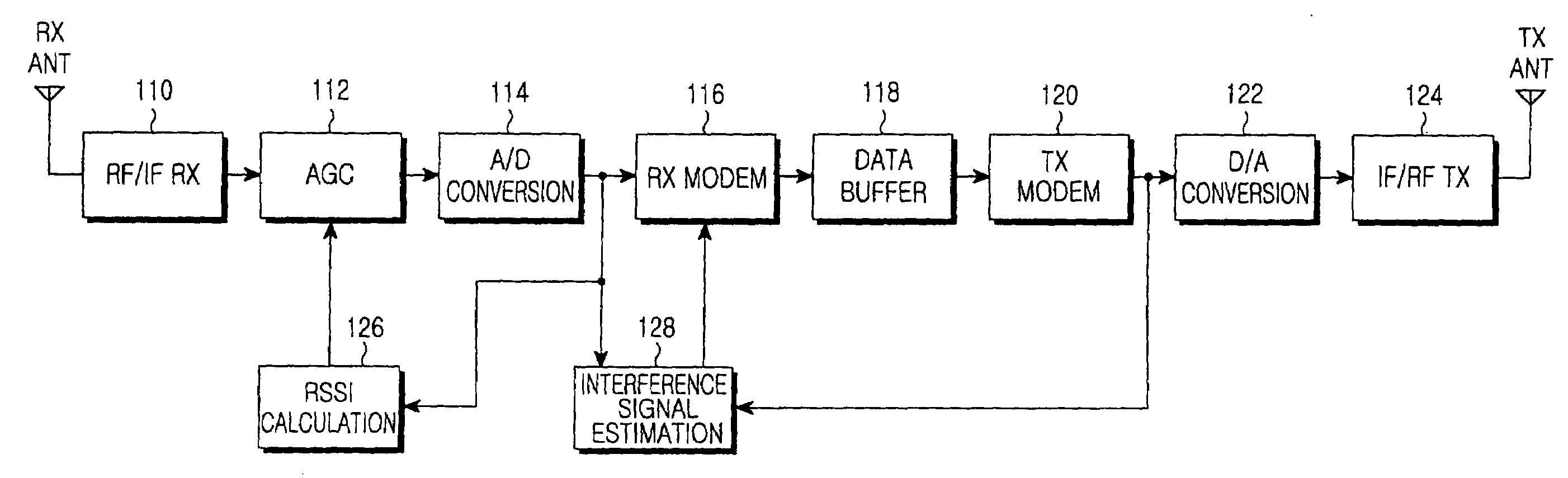
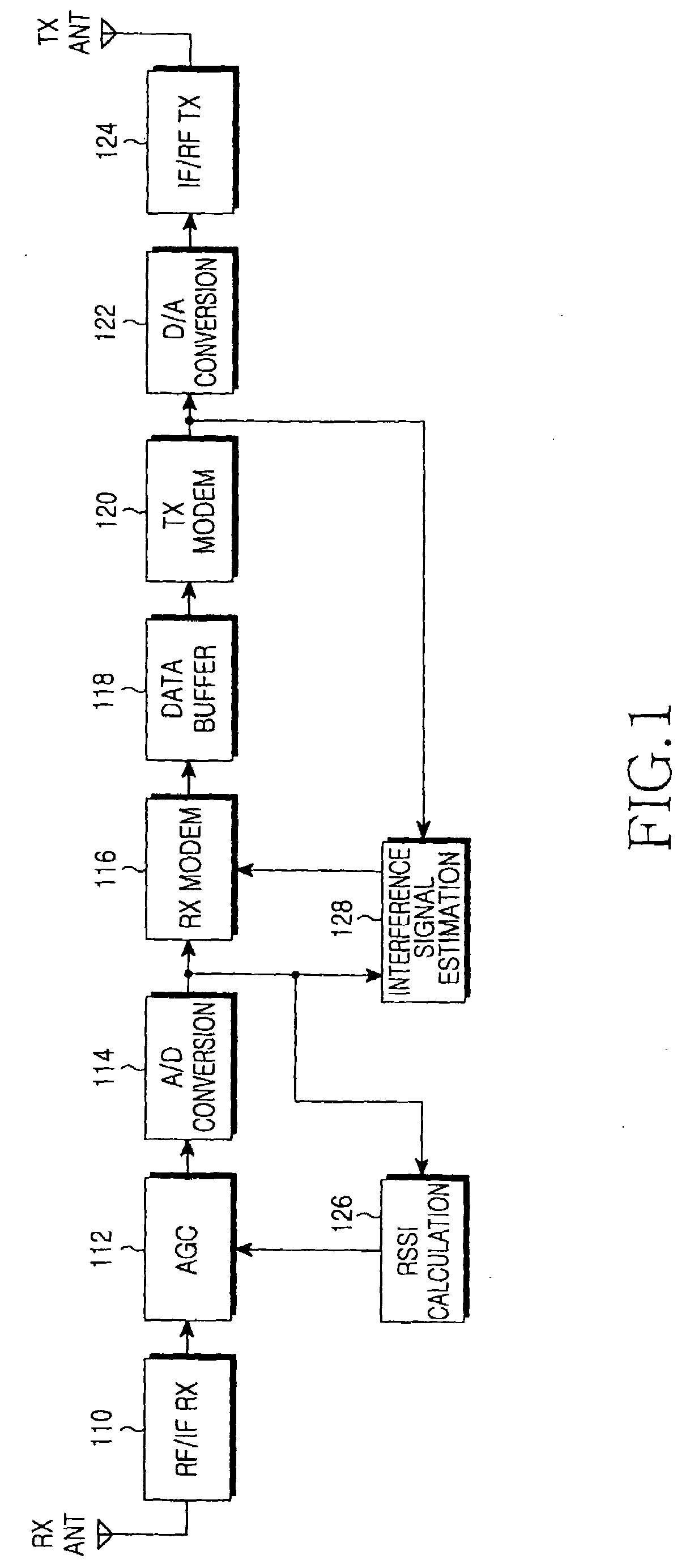
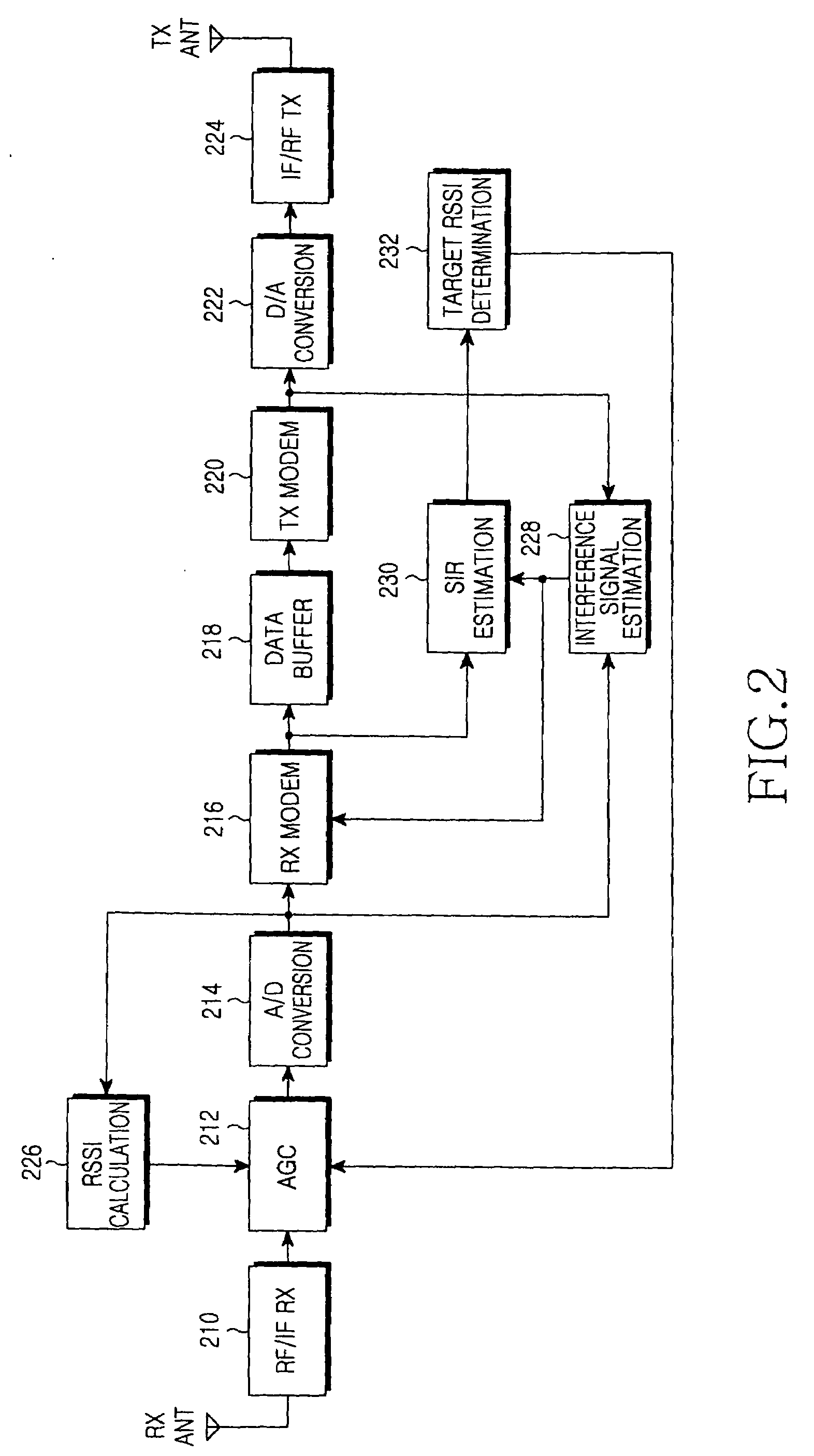
Automatic gain control apparatus and method in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20090290516A1Performance degradation can be reducedEasy to quantifyGain controlRadio relay systemsFull duplex relaySignal-to-interference ratio
An apparatus and method for adaptively adjusting a target Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) for Automatic Gain Control (AGC) in a full-duplex relay apparatus with an interference cancellation function. A Signal to Interference Ratio (SIR) estimation block estimates an SIR based on an interference signal estimated from a received signal and an interference-cancelled signal determined by cancelling the estimated interference signal from the received signal. A target RSSI determination block determines a target RSSI according to the estimated SIR. An AGC block adjusts a gain for the received signal based on the determined target RSSI.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
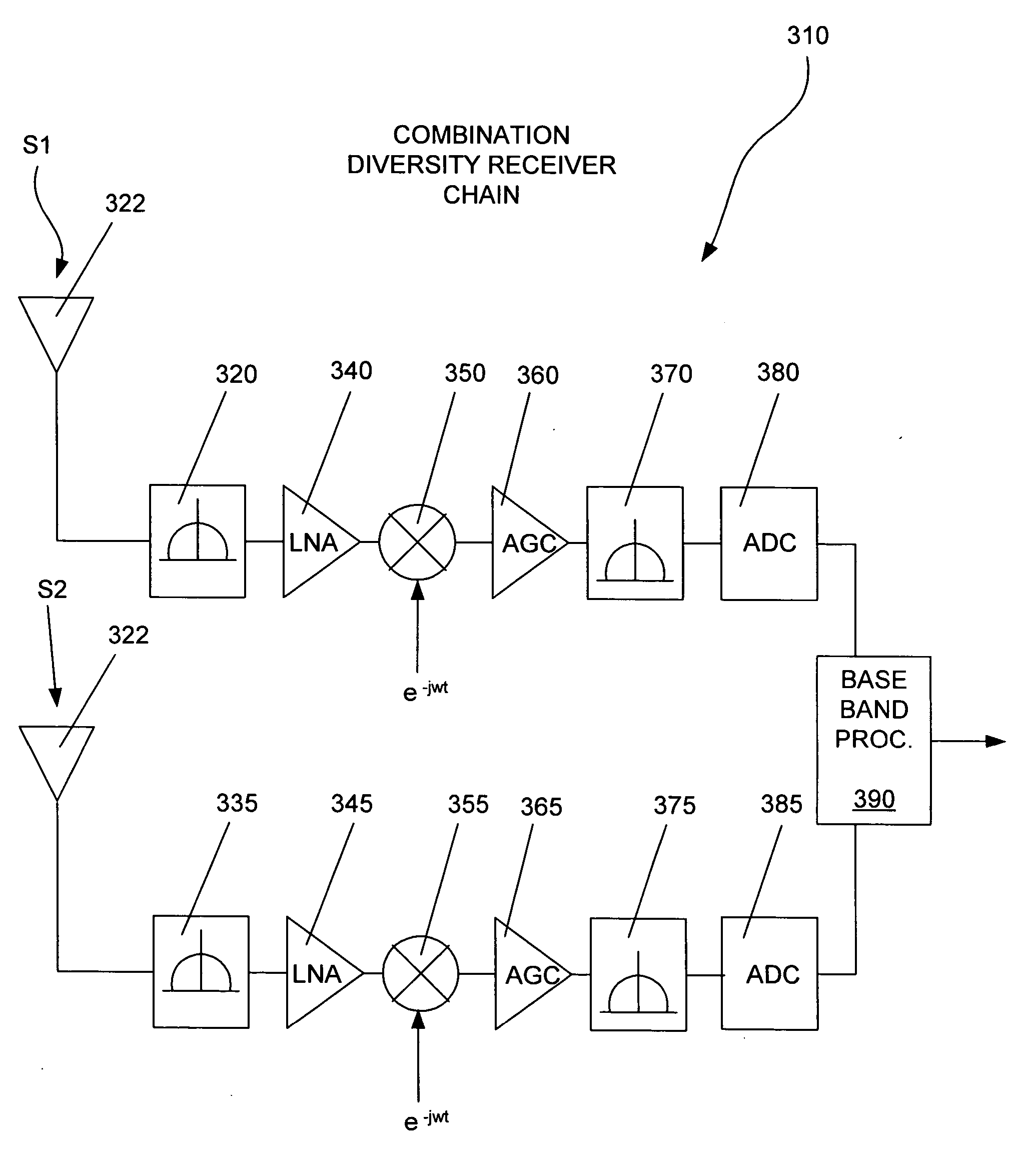
Phase combining diversity
ActiveUS20060073802A1Diversity/multi-antenna systemsInput/output processes for data processingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Phase relationship
Embodiments of methods of receiving transmitted signals are disclosed. The methods include a first antenna receiving a second signal, a second antenna receiving a second signal, adjusting a phase relationship between the first signal and the second signal, combining the phase adjusted first signal and second signal, and processing the phase adjusted first signal and second signal to determine the phase adjustment for optimizing at least one of signal to noise ratio and signal to interference ratio of the combined signals.
Owner:NOVANTA INC
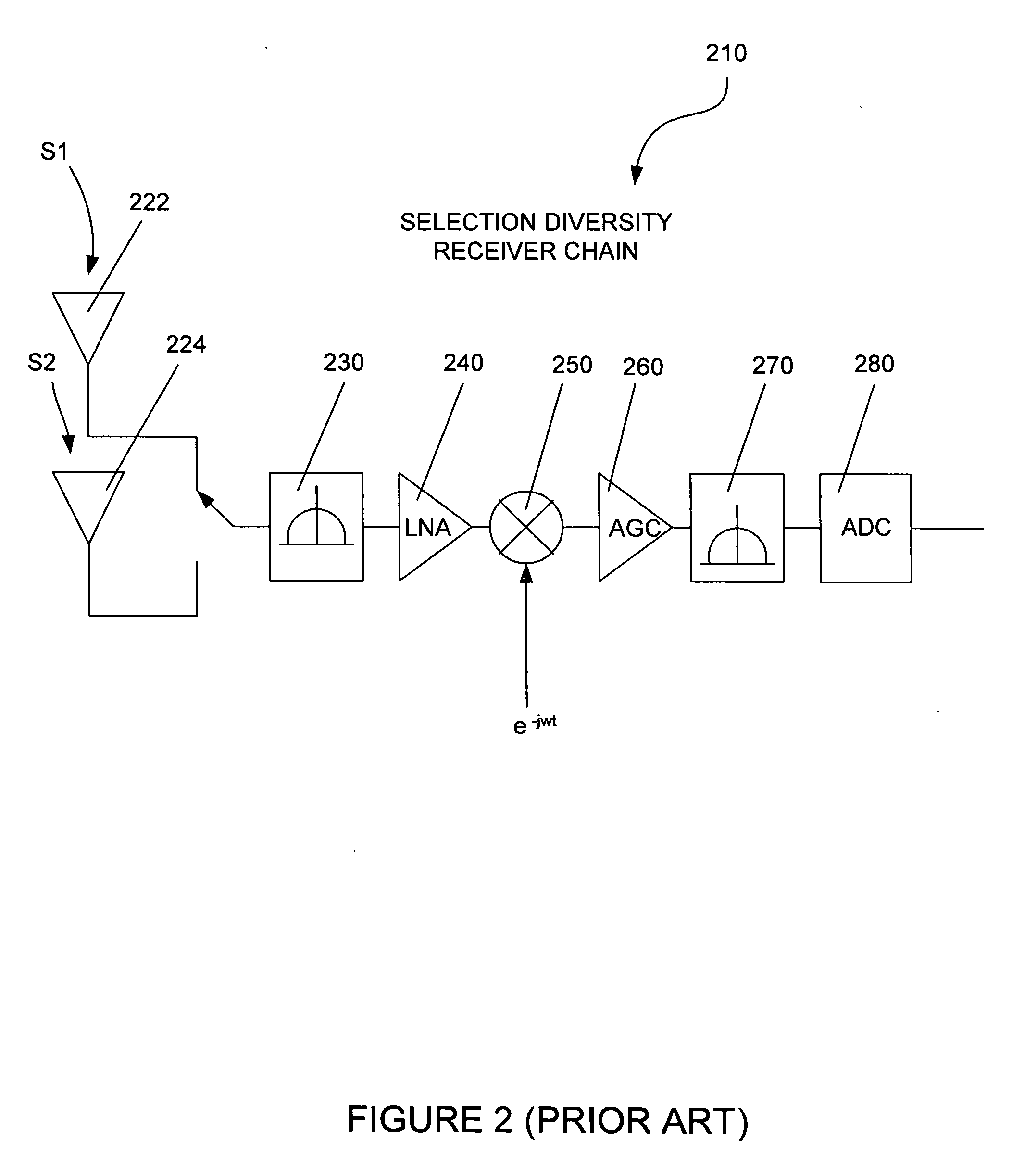
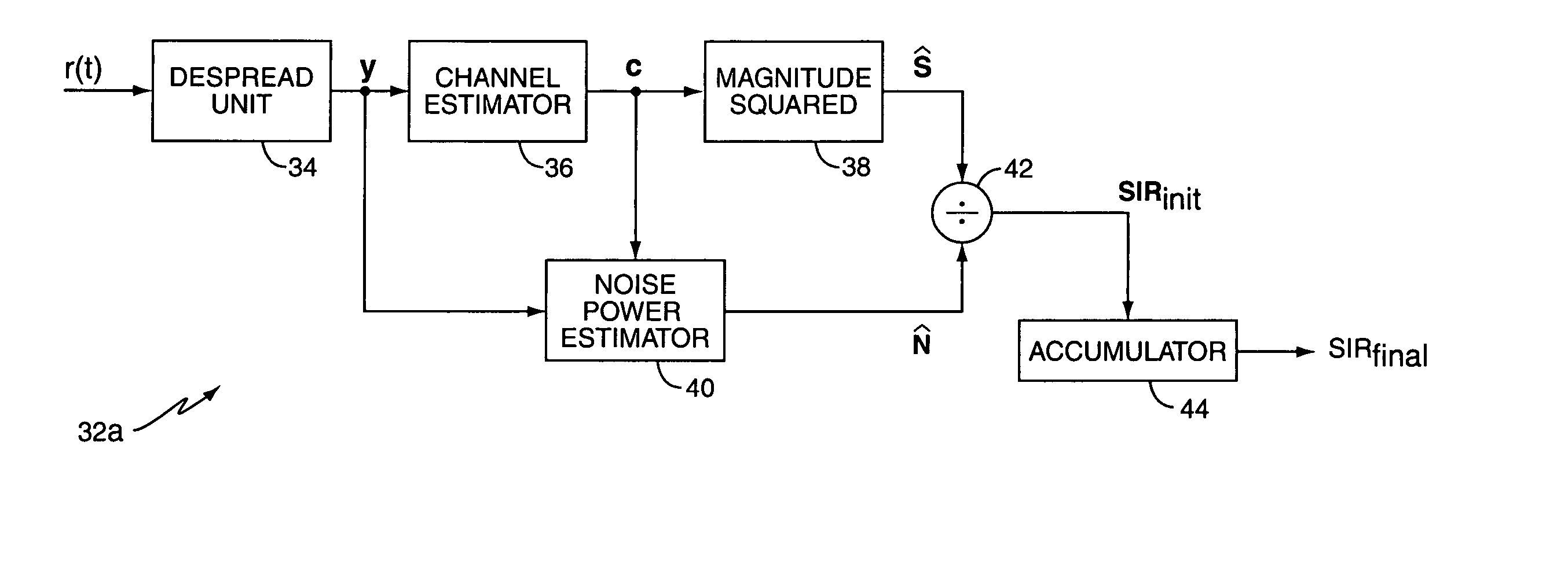
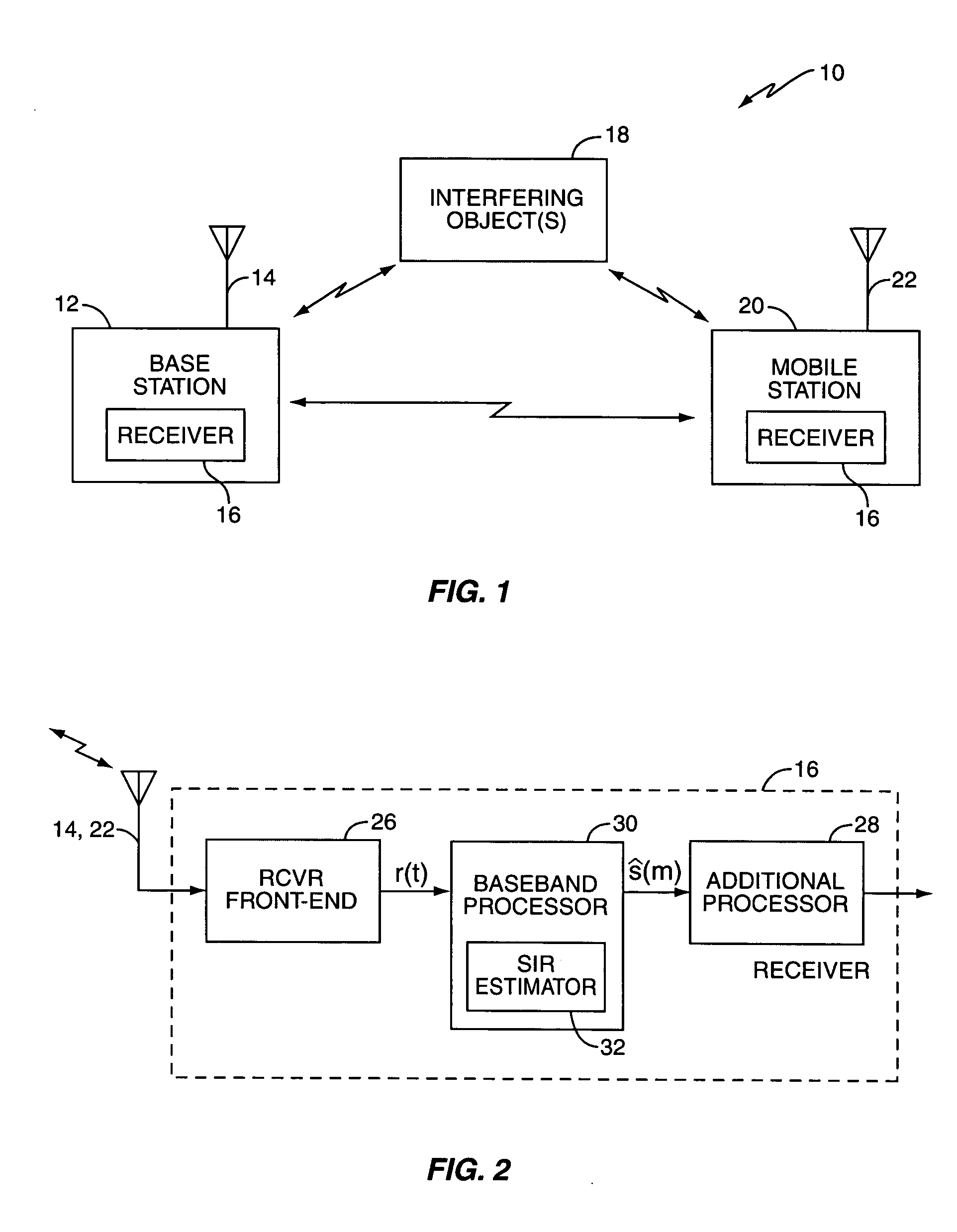
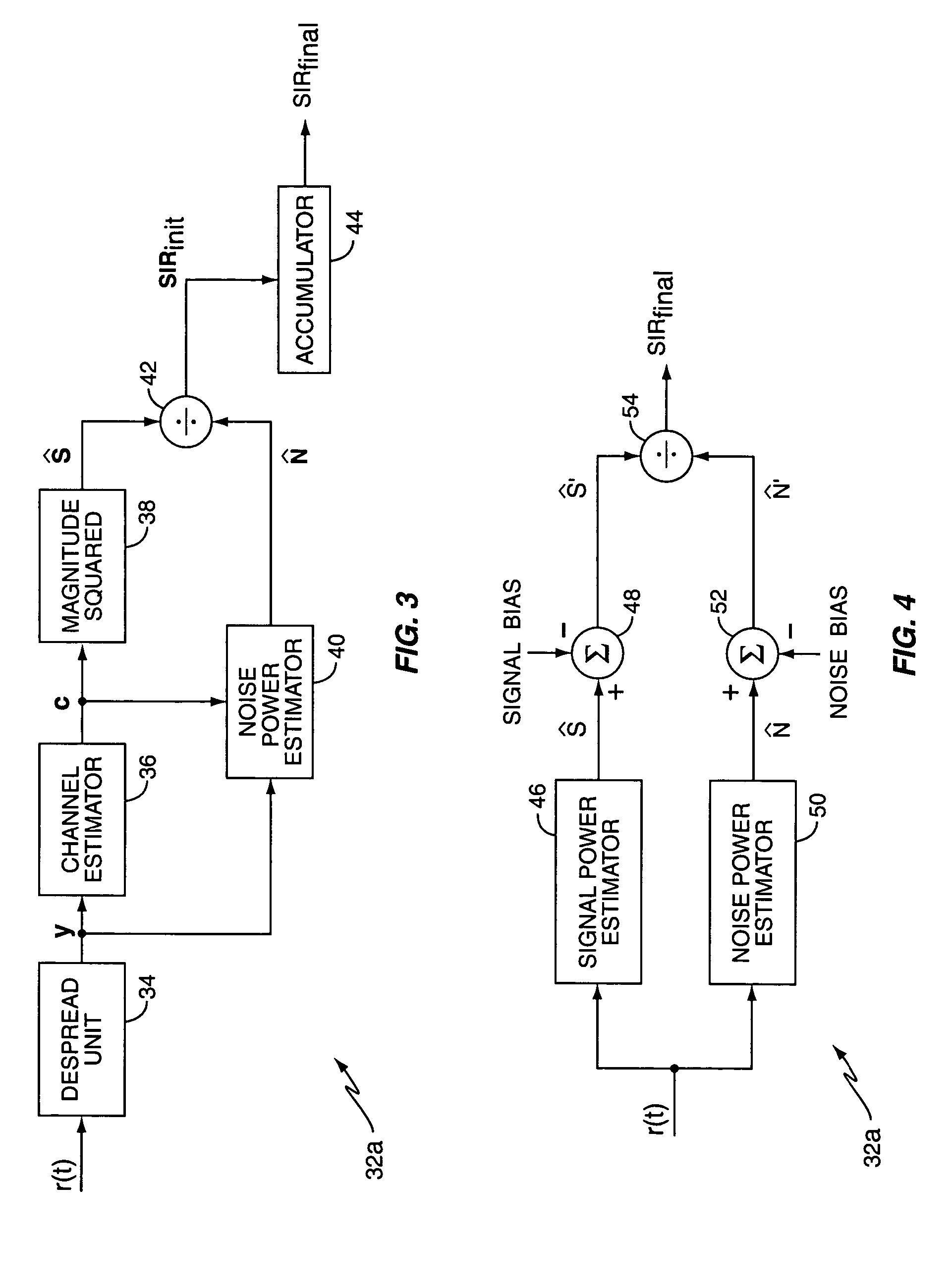
SIR estimation in a wireless receiver
ActiveUS20050281358A1Error detection/prevention using signal quality detectorLine-faulsts/interference reductionComputer scienceMulti path
A method and apparatus for removing bias from an initial signal-to-interference ratio (SIR). In an exemplary embodiment, an initial SIR calculator in an SIR processor calculates the initial SIR based on the signal received by the wireless receiver, while an average SIR calculator in the SIR processor generates an average SIR. Using the average SIR, a bias remover removes the bias from the initial SIR. Further, according to an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, the bias remover generates a scaling factor based on the average SIR and an offset parameter, where the offset parameter is derived from at least one of a count of the despread values processed by the wireless receiver and a count of the paths of a multi-path channel processed by the wireless receiver. In this embodiment, the bias remover comprises a multiplier that multiplies the initial SIR by the scaling factor to remove the bias from the initial SIR.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
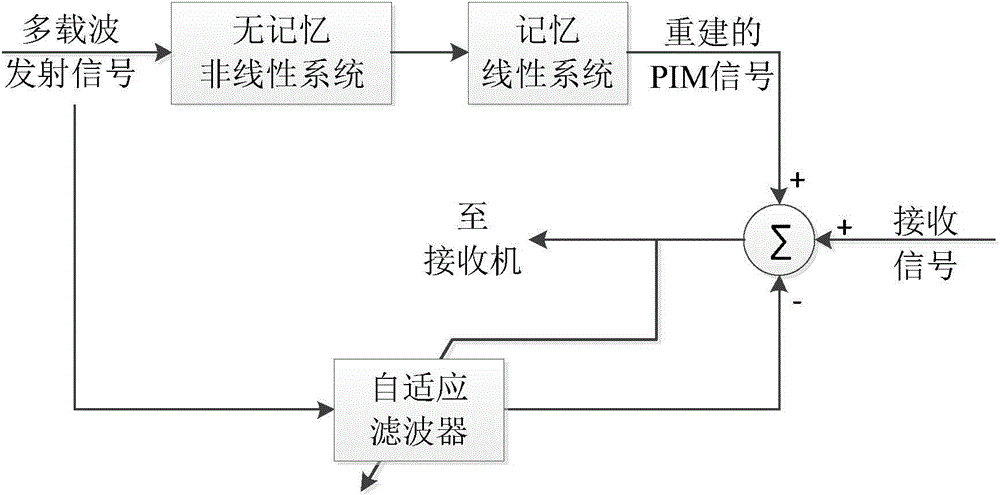
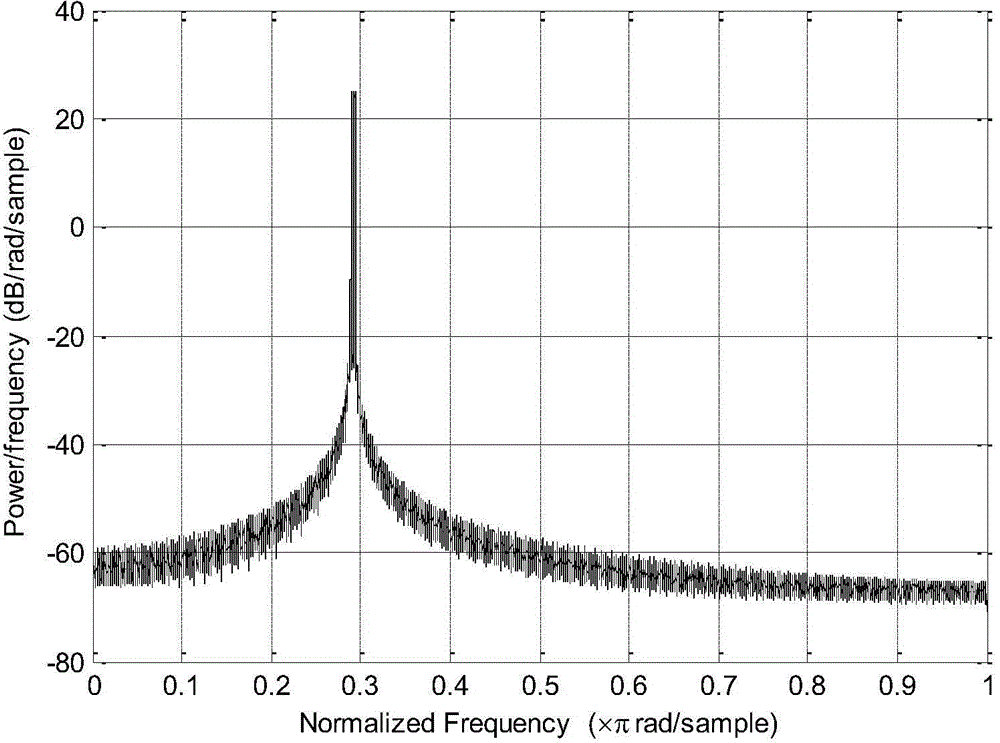
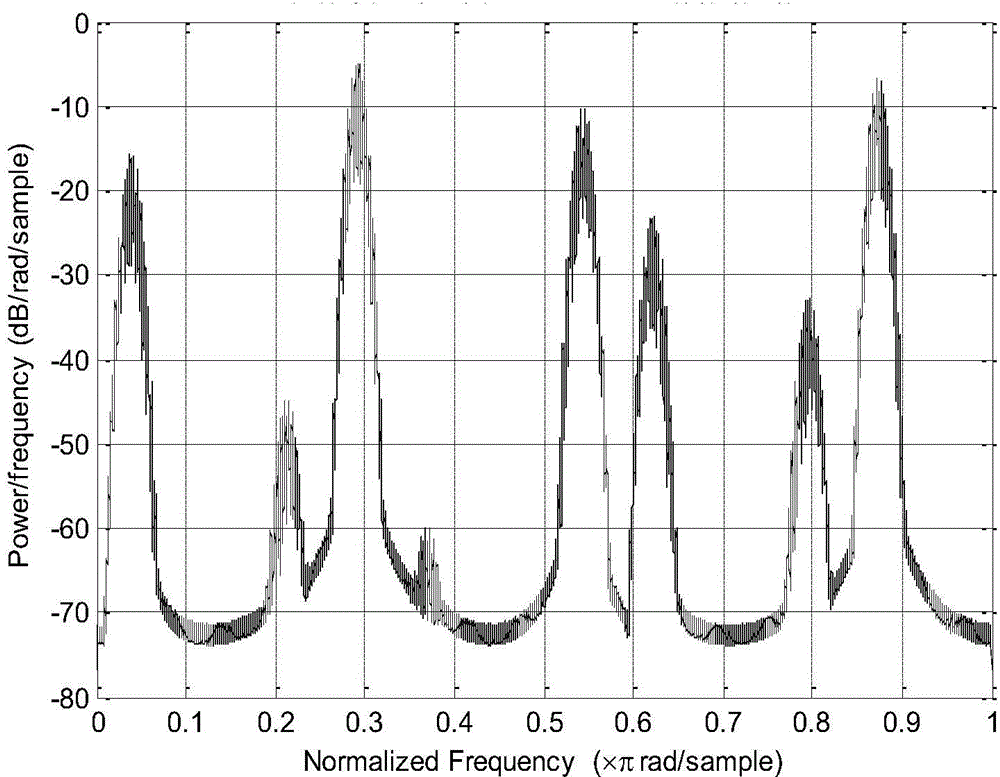
Method for suppressing passive intermodulation interference based on adaptive filtering
InactiveCN103986482AEasy to implementSimple methodTransmissionAdaptive filtering algorithmDigital signal processing
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communication signal processing and the technical field of full-duplex communication systems and relates to a method for suppressing passive intermodulation interface in a full-duplex communication system, in particular to a technology for suppressing passive intermodulation interface based on adaptive filtering. A simplified model of a passive nonlinear device is established and used for conducting interference suppression according to a digital signal processing method. The self-adaptive filtering algorithm is adopted as the estimation algorithm which is effect and enables hardware implementation to be achieved easily, so that compensation for passive intermodulation interface on intermediate frequency signals is achieved. A simulation result shows that passive intermodulation interface can be effectively suppressed and certain signal-to-ratio gain is achieved. The method is simple, computation complexity is low, resource cost is low, hardware implementation is easily achieved, the method is stable in performance, the system is strong in adaptability, the real-time performance is good, the method can be used for effectively suppressing passive intermodulation interference, and the higher signal to interference ratio gain is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Wireless transceivers, methods, and computer program products for restricting transmission power based on signal-to-interference ratios
InactiveUS20050075122A1Efficient communicationReduce transmit powerPower managementTransmission control/equalisingWireless transceiverTransceiver
A method for controlling transmission power from a wireless transceiver. Signal to interference ratios (SIRs) are estimated for a signal that is received from another wireless device. An out-of-sync condition between the wireless transceiver and the other wireless device is identified based on the SIRs. Change of the transmission power from the wireless transceiver is restricted based on the SIRs and when an out-of-sync condition has not been identified.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Systems and methods for making channel assignments to reduce interference and increase capacity of wireless networks
InactiveUS7257376B2Increase capacityReduce distractionsTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationSystem capacityMobile station
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Phase combining diversity
ActiveUS7324794B2Diversity/multi-antenna systemsInput/output processes for data processingSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Engineering
Embodiments of methods of receiving transmitted signals are disclosed. The methods include a first antenna receiving a second signal, a second antenna receiving a second signal, adjusting a phase relationship between the first signal and the second signal, combining the phase adjusted first signal and second signal, and processing the phase adjusted first signal and second signal to determine the phase adjustment for optimizing at least one of signal to noise ratio and signal to interference ratio of the combined signals.
Owner:NOVANTA INC
Apparatus and method of radio access management for a radio communication system
ActiveUS20070010270A1Improve accuracyImprove performancePower managementTransmission control/equalisingCommunications systemInterference (communication)
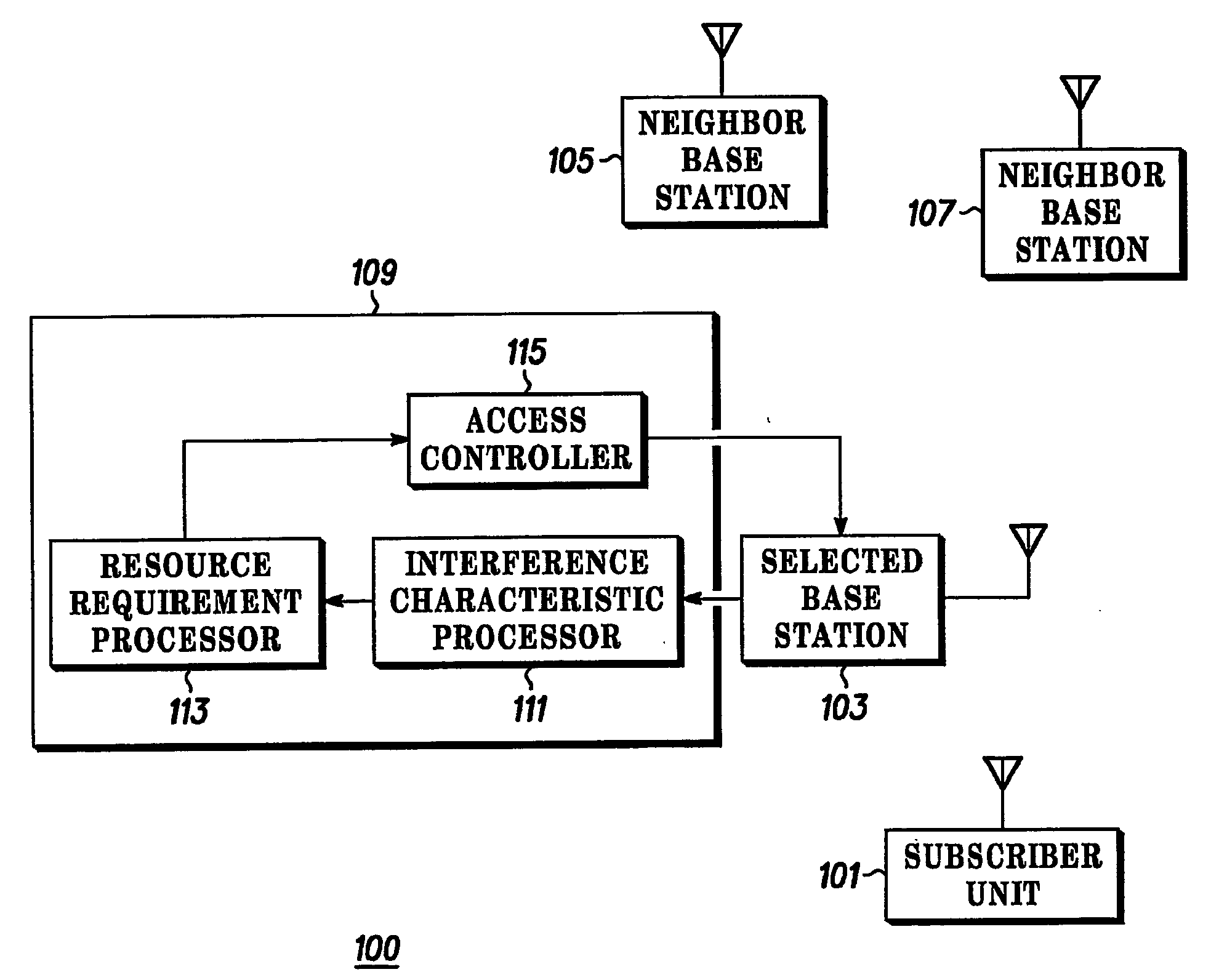
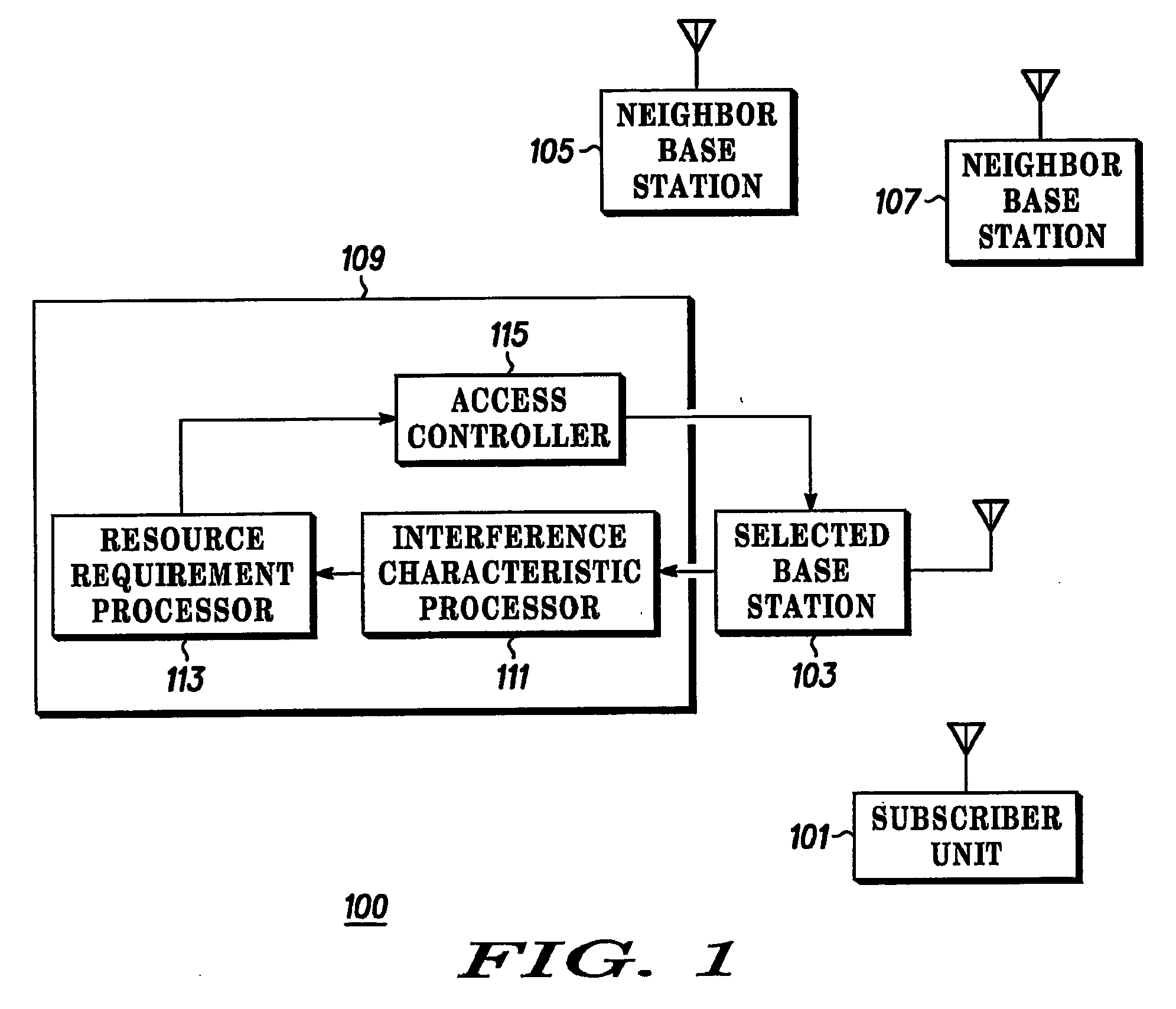
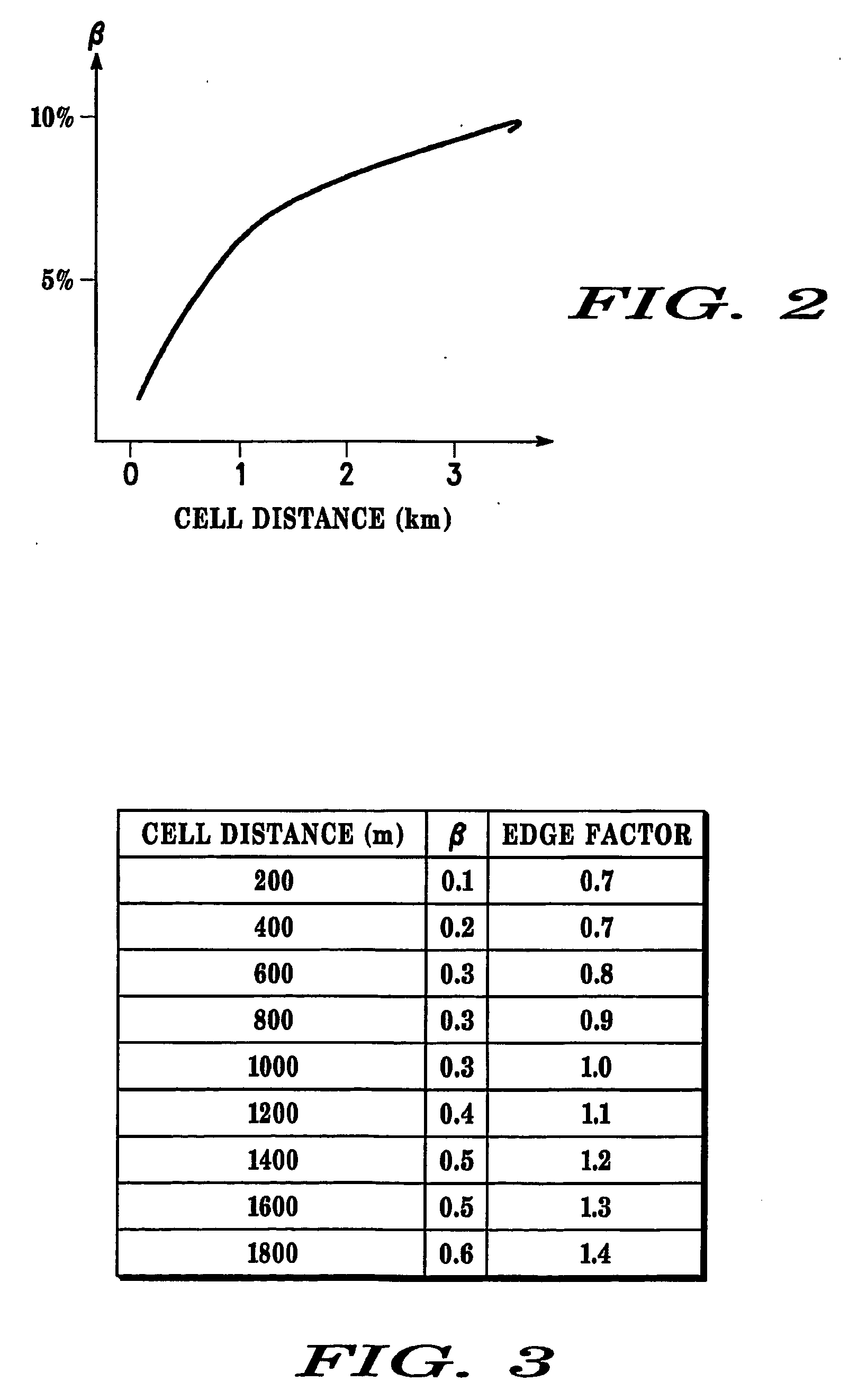
The invention relates to access management in a radio communication system. A subscriber unit (101) transmits an access message to a base station (103). A Radio Access Controller (RNC) (109) receives information of the access request. The RNC (109) comprises an interference characteristic processor (111) which determines an interference characteristic associated with the subscriber unit (101). The interference characteristic may include an inter-cell interference factor and an intra-cell orthogonality factor determined as a function of the distance between the base station and the subscriber unit and / or based on subscriber unit measurements of pilot signals from the selected base station (103) and neighbouring base stations (105, 107). The interference characteristic processor (111) is coupled to a resource requirement processor (113) which determines a resource requirement for achieving a desired signal to interference ratio for the requested service in response to the interference characteristic. The RNC (109) further comprises an access controller (115) which accepts or rejects the request in response to the determined resource requirement.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Method and Apparatus in a Telecommunication System
ActiveUS20080268864A1Improve accuracyAvoid congestionNetwork traffic/resource managementSubstation equipmentRadio networksTelecommunications
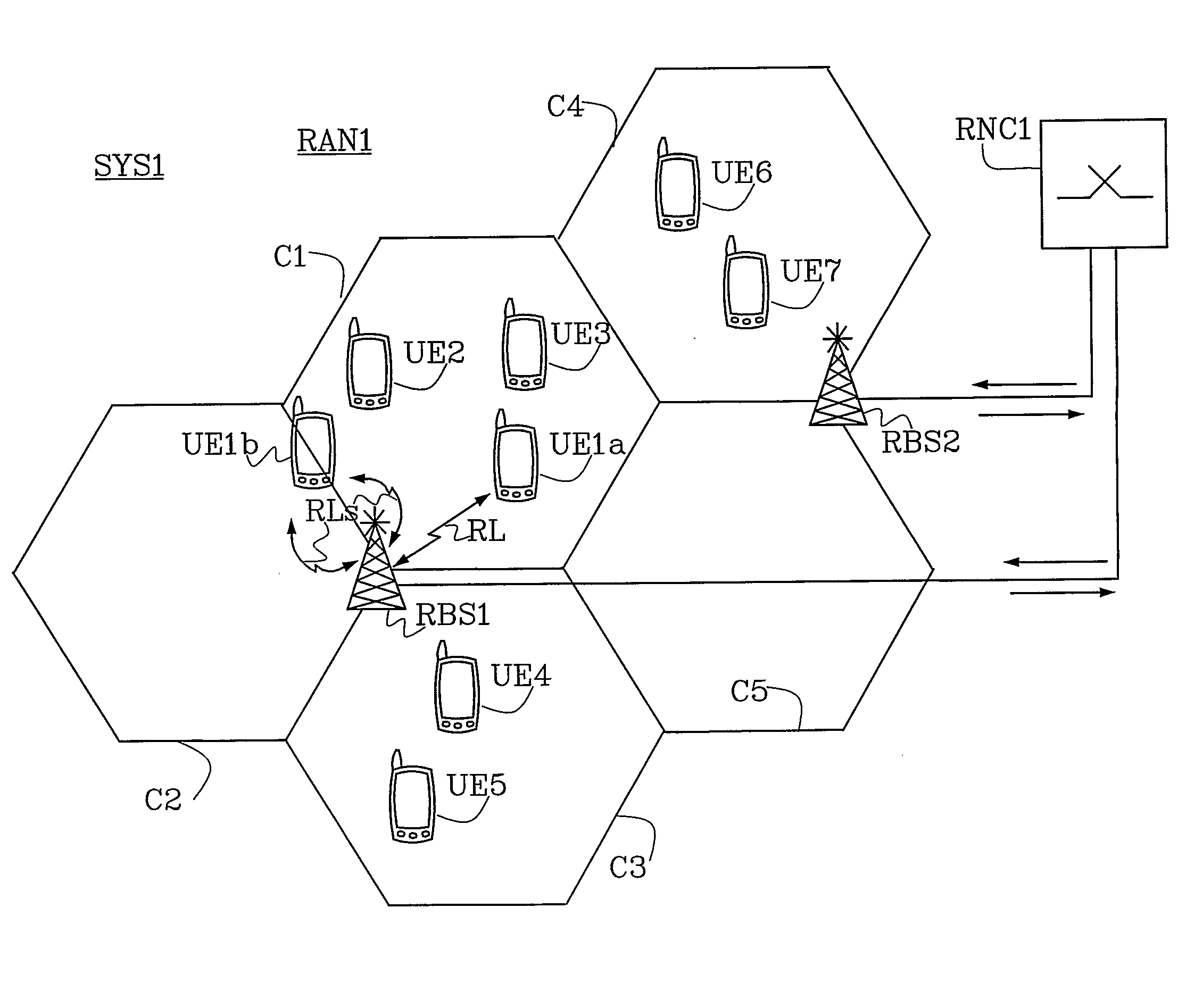
The present invention relates in general to the radio communications field and, in particular, to a method and apparatus for detecting congestion in a spread spectrum Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) cellular communication system. By measuring the number of Signal-to-Interference Ratio Error reports being received at the Radio Network Controller a potential congestion can be detected in the cell when the number of reports being received is above a threshold. Further can a differentiation be made between a potential or a serious congestion and different actions be performed dependant on if a potential or a serious congestion is detected.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method for selecting wireless access point and wireless access point
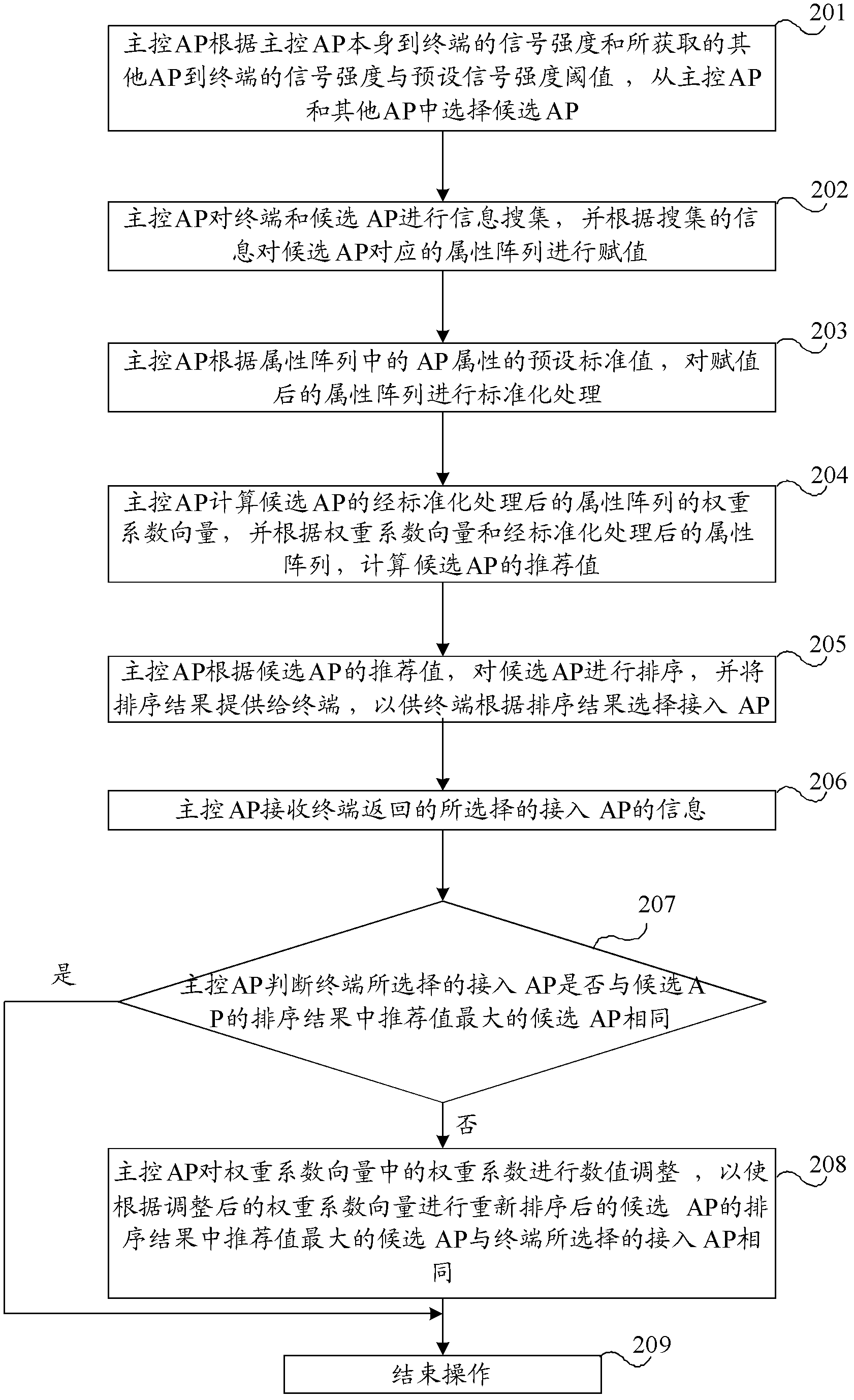
InactiveCN102547910ASolve problems that prevent normal business operationsAssess restrictionWeight coefficientComputer science
The invention provides a method for selecting a wireless access point and the wireless access point. The method comprises the following steps that: a master control access point (AP) selects candidate APs according to a terminal access signal intensity threshold value and a preset threshold value of the master control AP and other APs; the master control AP acquires information of a terminal and the candidate APs, and performs assignment on an attribute array according to the acquired information, wherein the attribute array comprises signal intensity between the candidate APs and the terminal, the access capabilities of the candidate APs, a channel utilization rate and a signal-to-interference ratio; the master control AP calculates the weight coefficient vector of the attribute array, and calculates recommended values of the candidate APs according to the weight coefficient vector and the attribute array; and the master control AP sequences the candidate APs according to the recommended values of the candidate APs and provides a sequencing result for the terminal, so that the terminal can select an AP according to the sequencing result. By the technical scheme, the AP is selected on the basis of a plurality of attributes, so that the terminal can successfully access a network and participate in normal services according to the selected AP.
Owner:CHINA UNITED NETWORK COMM GRP CO LTD
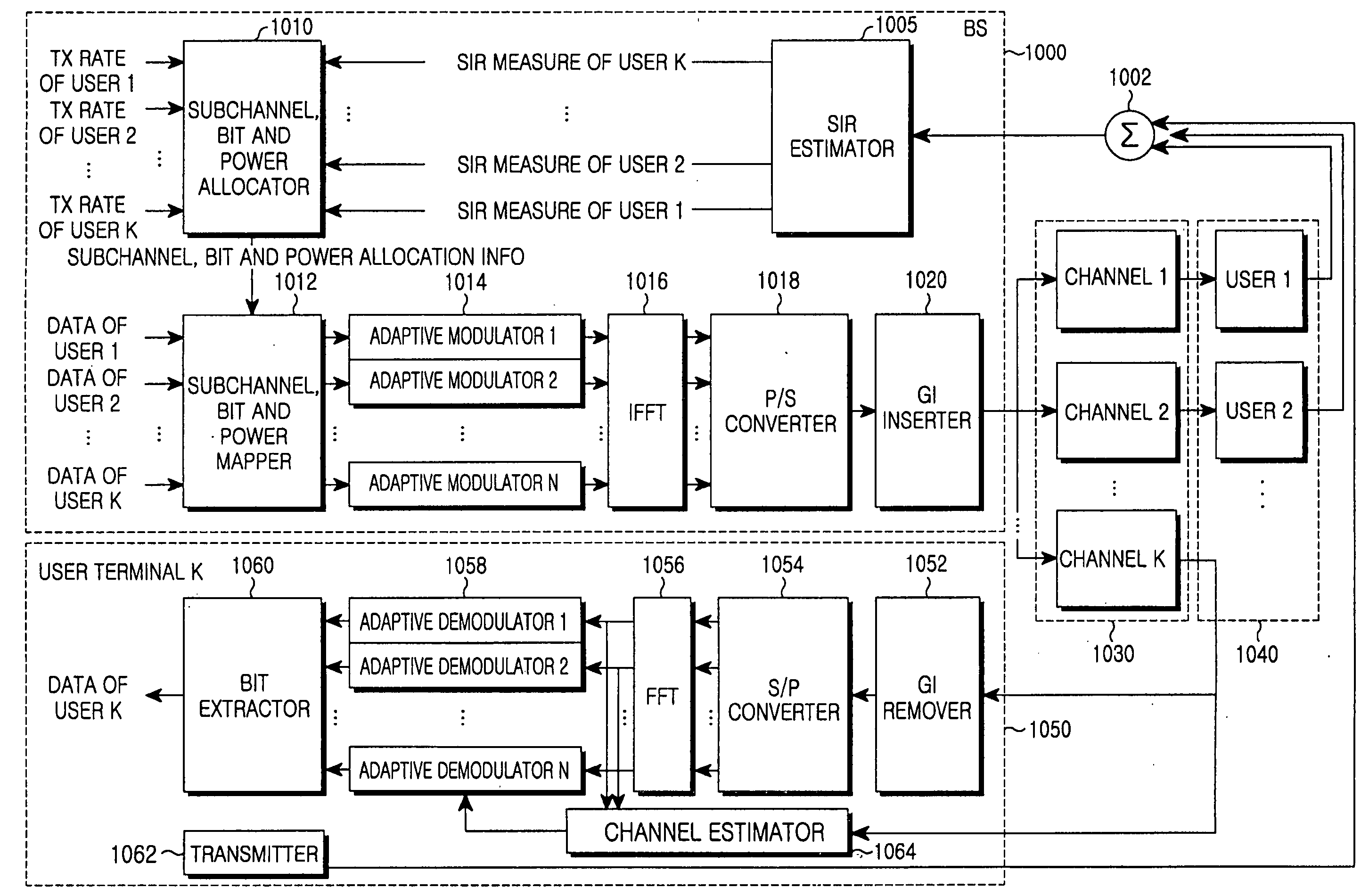
Apparatus and method for estimating a signal power to interference power ratio in a wireless communication system
ActiveUS20060045195A1Improve downlink performanceError preventionModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemEngineering
A transmission and reception apparatus and method for use in a wireless communication system, and an apparatus and method for adaptively transmit and receive a signal according to channel state in a wireless communication system. An apparatus for adaptively performing transmission according to a state of a channel transmitted from a transmitter to at least one receiver includes a signal to interference ratio estimator for estimating a signal to interference ratio of the channel using a signal transmitted from the at least one receiver; and an adaptive transmitter for transmitting data to the at least one receiver on a basis of the estimated signal to interference ratio.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Time division multiplexing method and system
InactiveUS20110141918A1Improve spectral efficiencyIncrease channel capacityError preventionTransmission systemsTime domainFrequency spectrum
The present invention provides the method and system of a Time Division Multiplexing which makes use of a number of symbols in the time domain transmitting data sequence in parallel. The method includes: the transmitting terminal forms the transmission signals which are overlapped by a number of symbols in the time domain, and the receiving terminal does data sequence detection in the time domain for the received signals according to the one-to-one relationship between the transmission data sequence and the time waveform of the transmission data sequence. In addition, the present invention also provides a kind of Time Division Multiplexing system based on the above method of the Time Division Multiplexing. The present invention makes actively use of these overlapping to produce the coding constraint relation, thus the spectral efficiency of the system is improved by a large margin. In random time-varying channel, with reasonable arrangement, the transmission reliability of the system can also be improved at the same time, and at the same threshold, Signal Interference Ratio and its spectral efficiency are far higher than those of the high-dimension modulation and other technologies. At the same spectrum efficiency, the number of the total levels of its systems and the needed threshold Signal Interference Ratio are also reduced significantly than those of the high-dimension modulation and other technologies.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
Dynamic sub-carrier assignment in OFDM systems
InactiveUS7031753B2Improve communication efficiencyImprove transfer rateModulated-carrier systemsSubstation equipmentCommunications systemCarrier signal
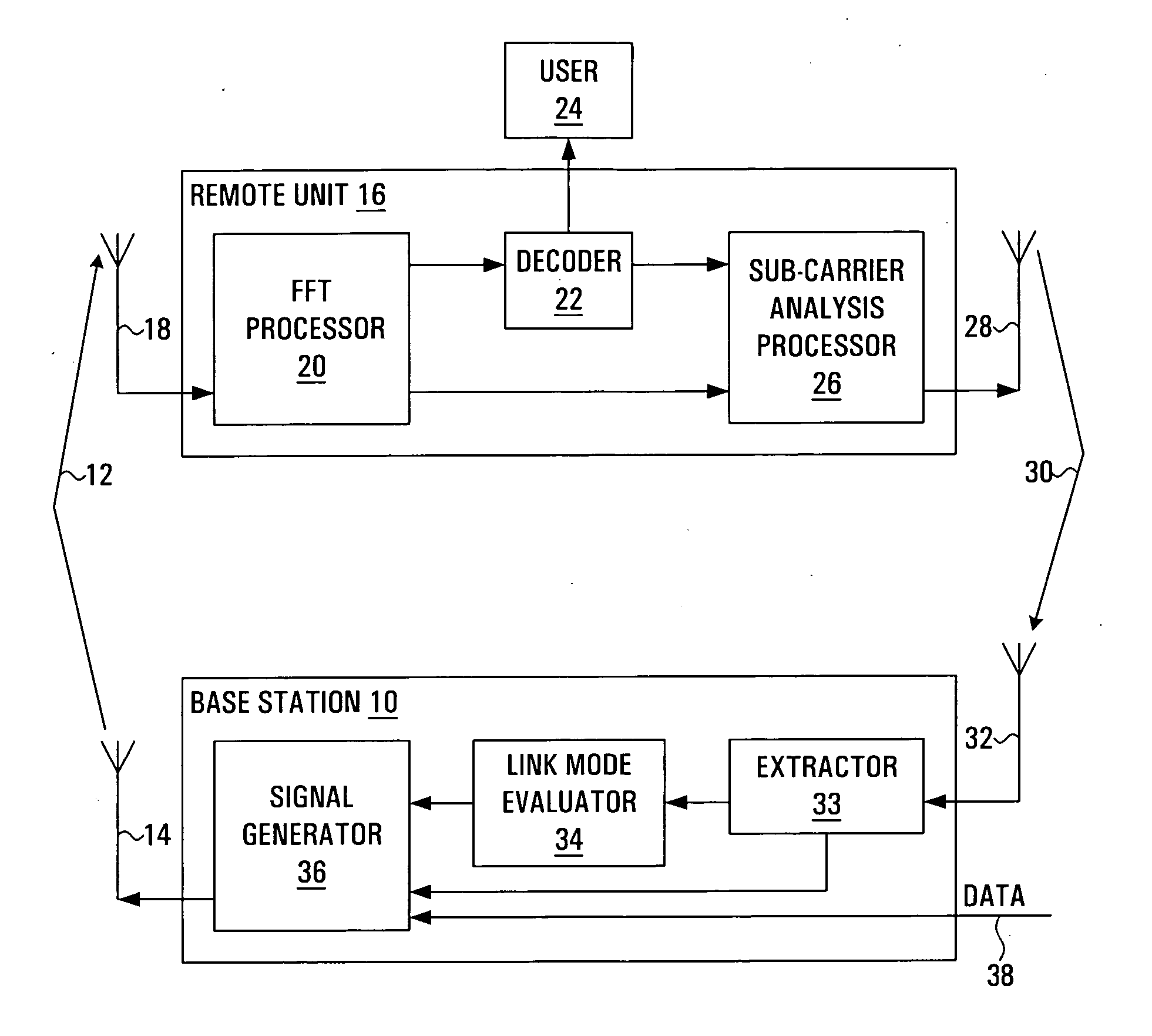
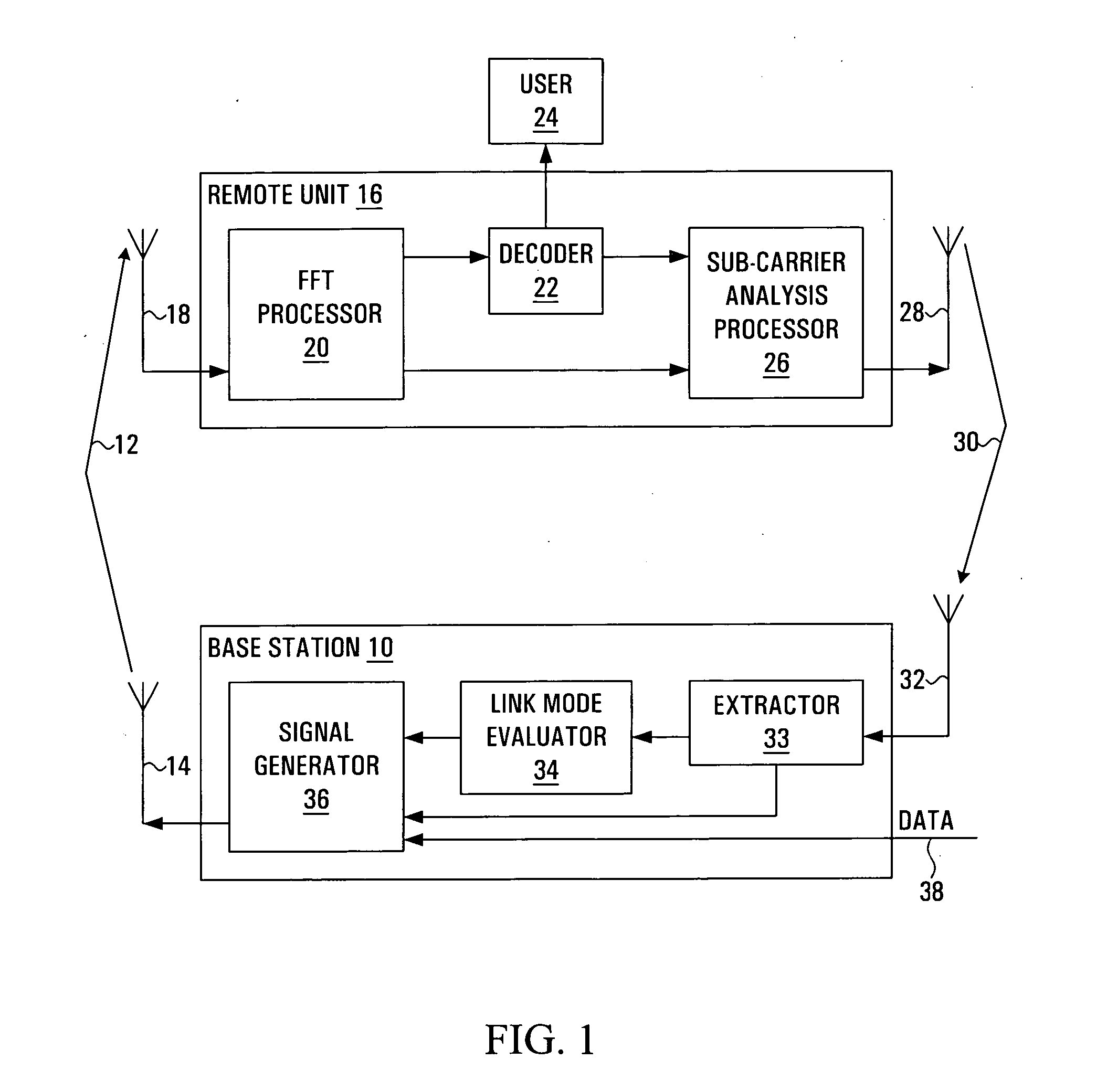
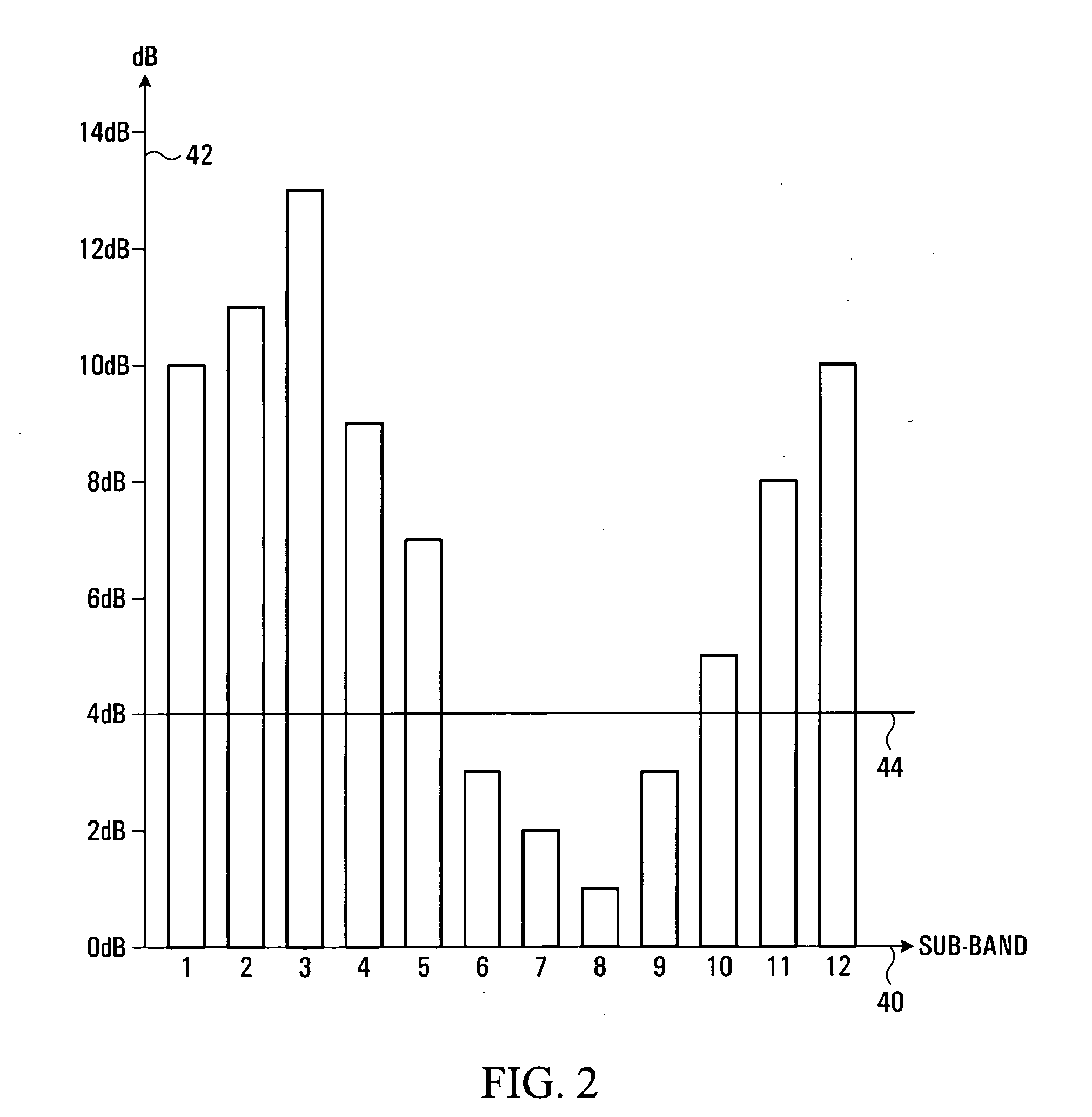
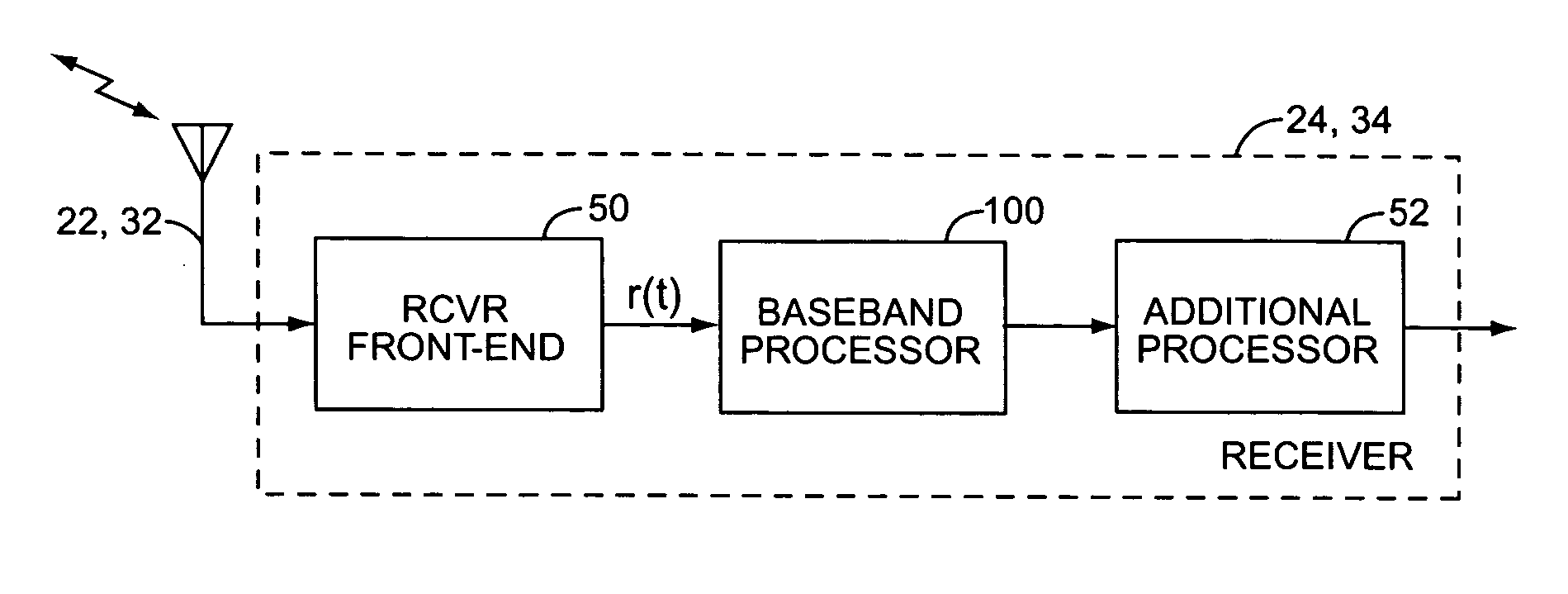
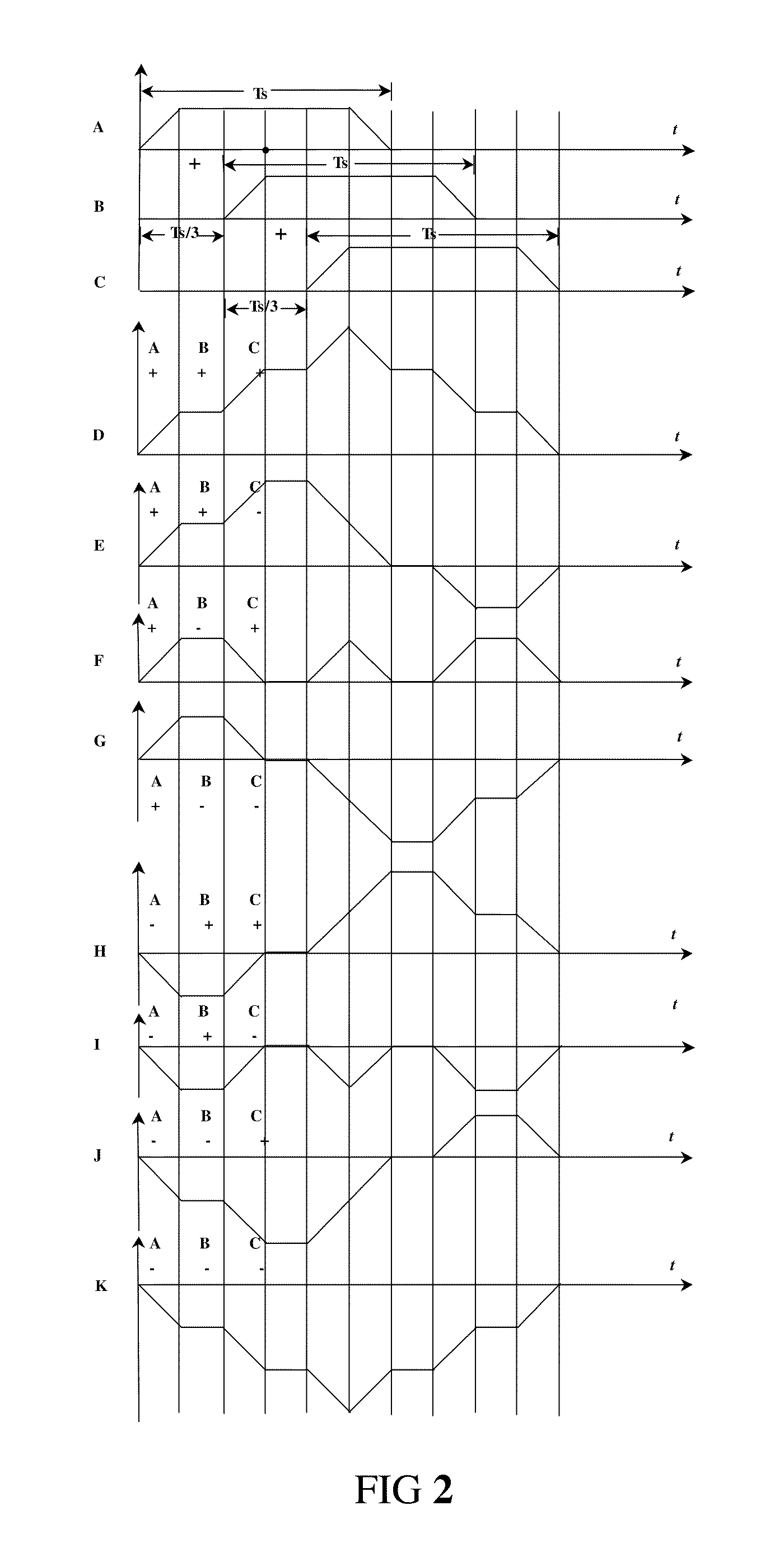
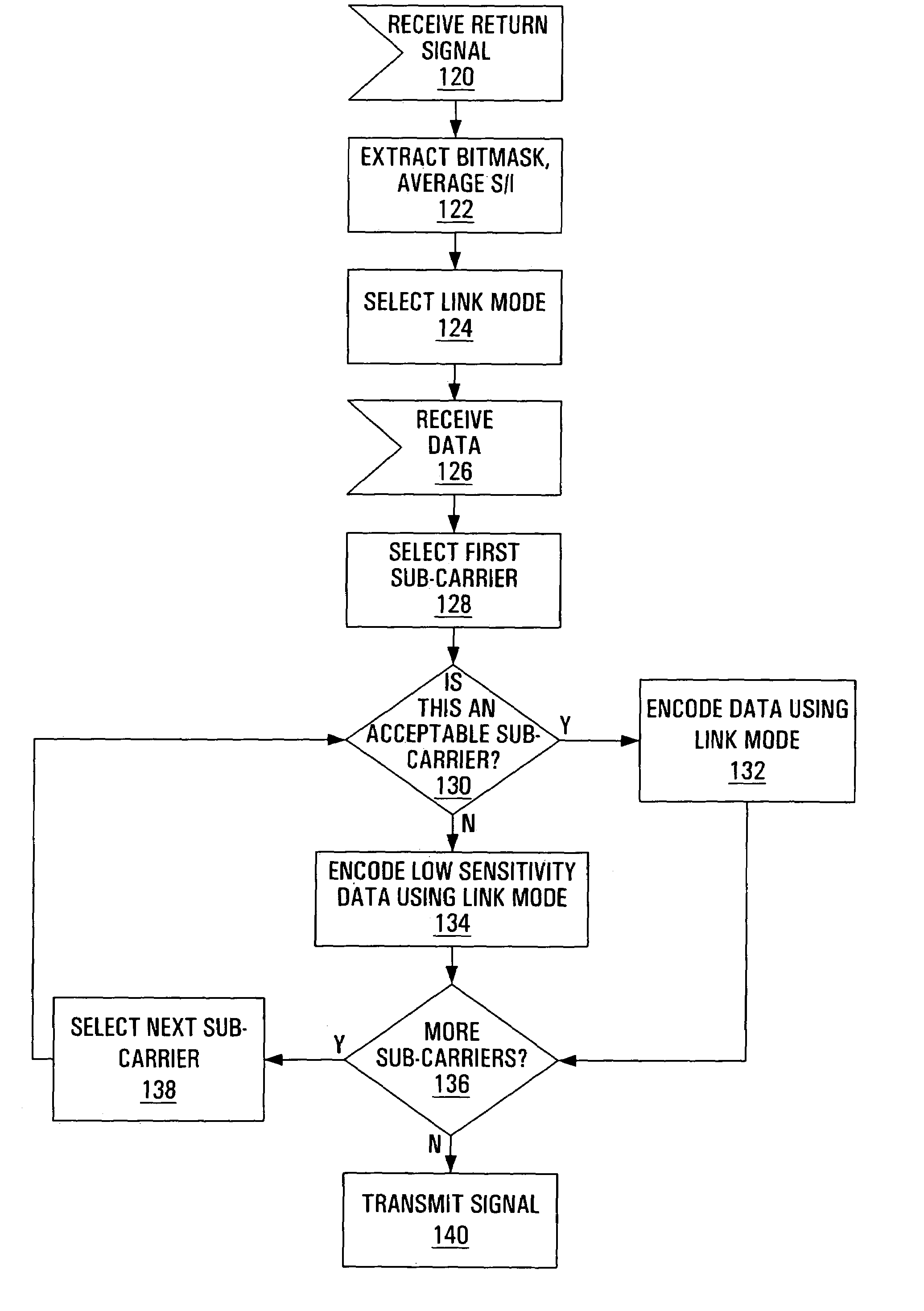
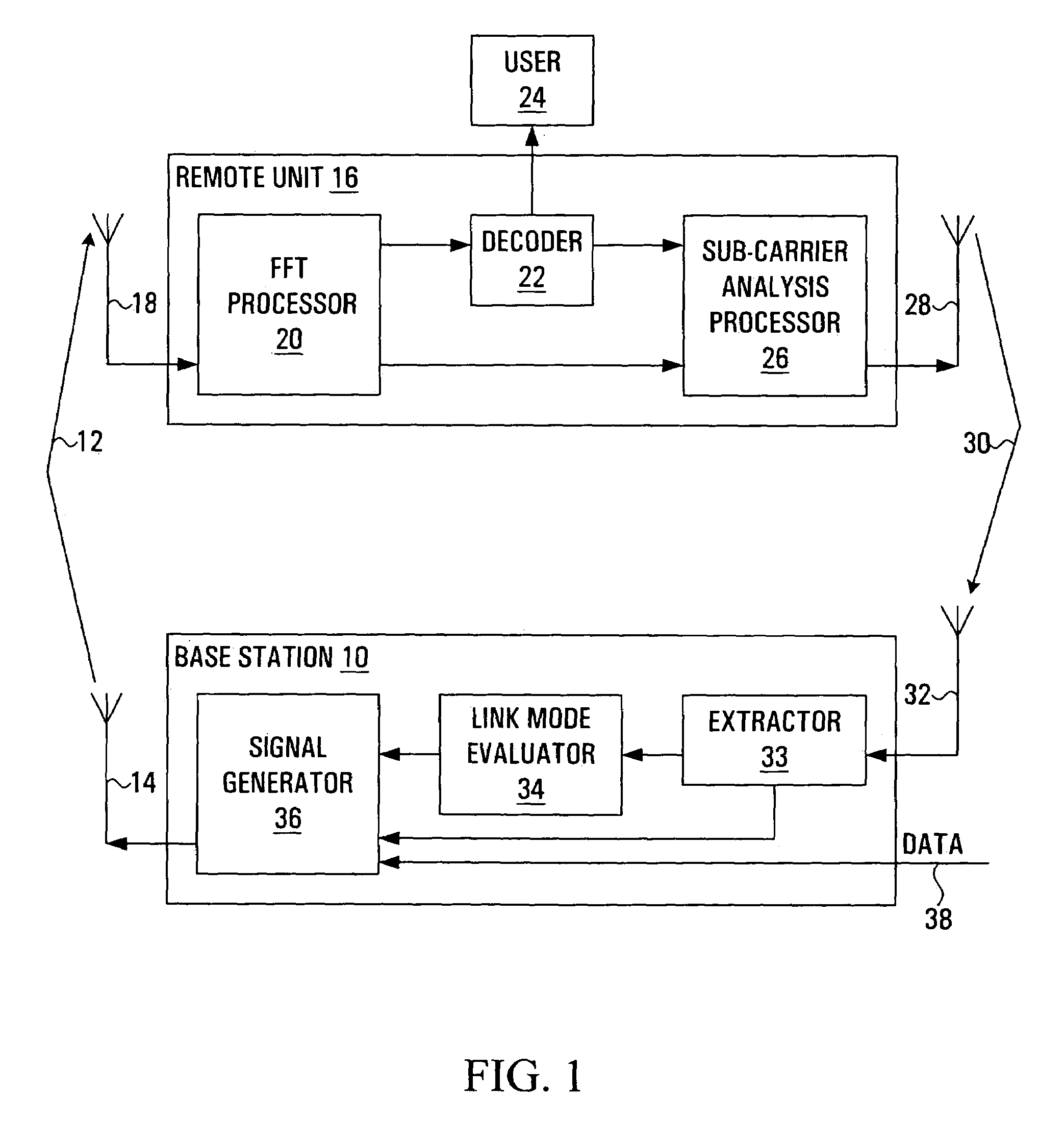
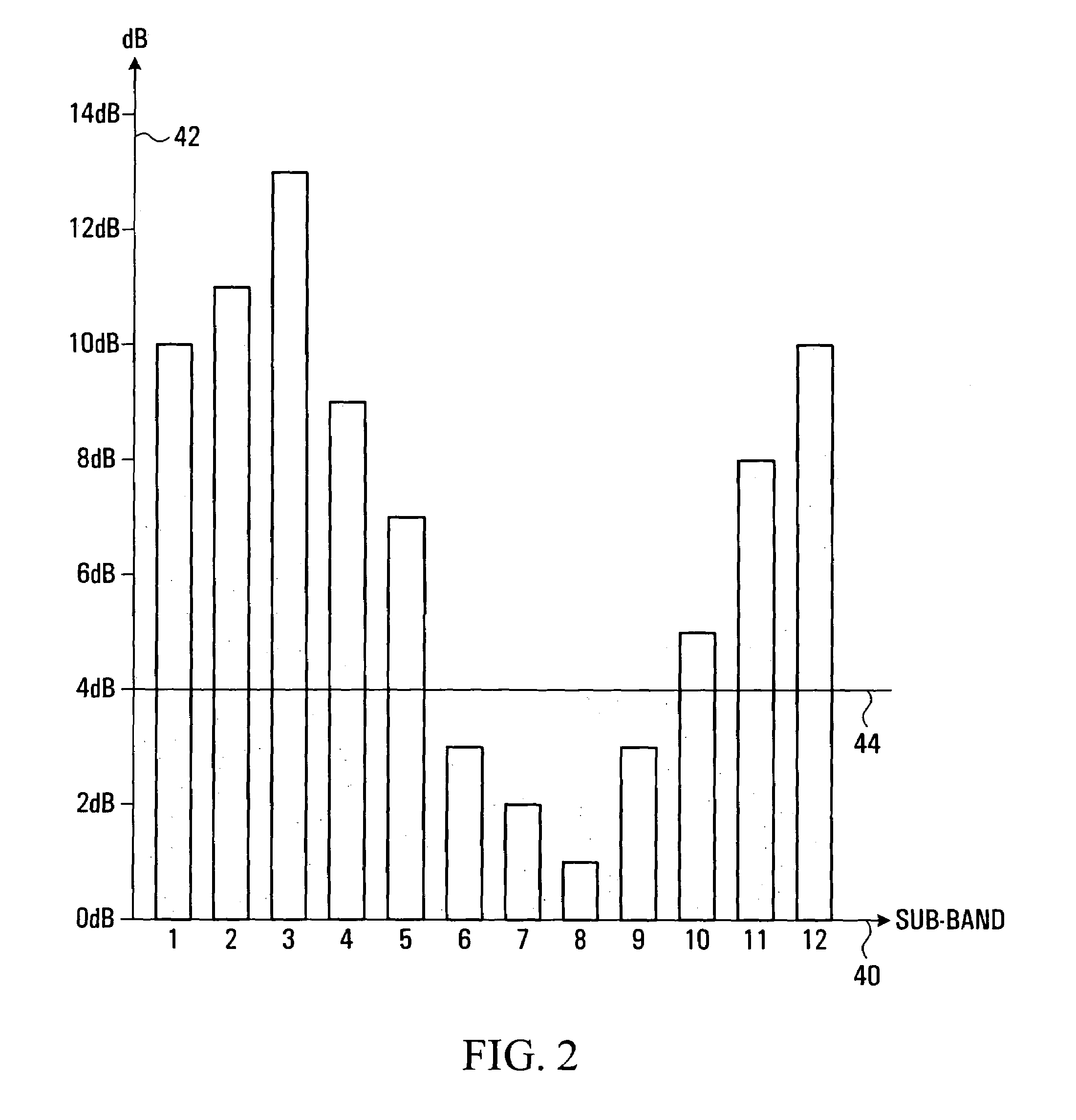
A method and apparatus are provided for selecting and signalling the identity of sub-carriers to be used for transmission of data in a radio communication system, and for using other sub-carriers. A remote unit determines which sub-carriers are acceptable for use in data transmission by comparing the signal to interference ratio of each sub-carrier with a threshold. A sequence of numbers is generated using one set of values to identify acceptable sub-carriers and another set of values to identify unacceptable sub-carriers. The sequence of numbers is transmitted to a base station. The average signal to interference ratio of sub-carriers whose signal to interference ratio was above the threshold can also be transmitted to the base station, thereby allowing the base station to determine an optimum set of transmission parameters for use only in the acceptable sub-carriers. Alternatively, the remote unit can determine the optimum set of transmission parameters itself for transmission to the base station. As yet another alternative, the remote unit can determine an optimum Link Mode for each acceptable sub-carrier, and use a reference to the Link Modes as the set of values identifying acceptable sub-carriers. The base station transmits data over the acceptable sub-carriers at the optimum Link Mode or Link Modes. The base station may use some of the unacceptable sub-carriers for transmission of low sensitivity data at the optimum Link Mode, and may use some of the unacceptable sub-carriers for transmission of data at a lower Link Mode. The transmission power of any unused unacceptable sub-carriers can be diverted to other sub-carriers.
Owner:BLACKBERRY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com