Patents
Literature
37results about How to "Performance degradation can be reduced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
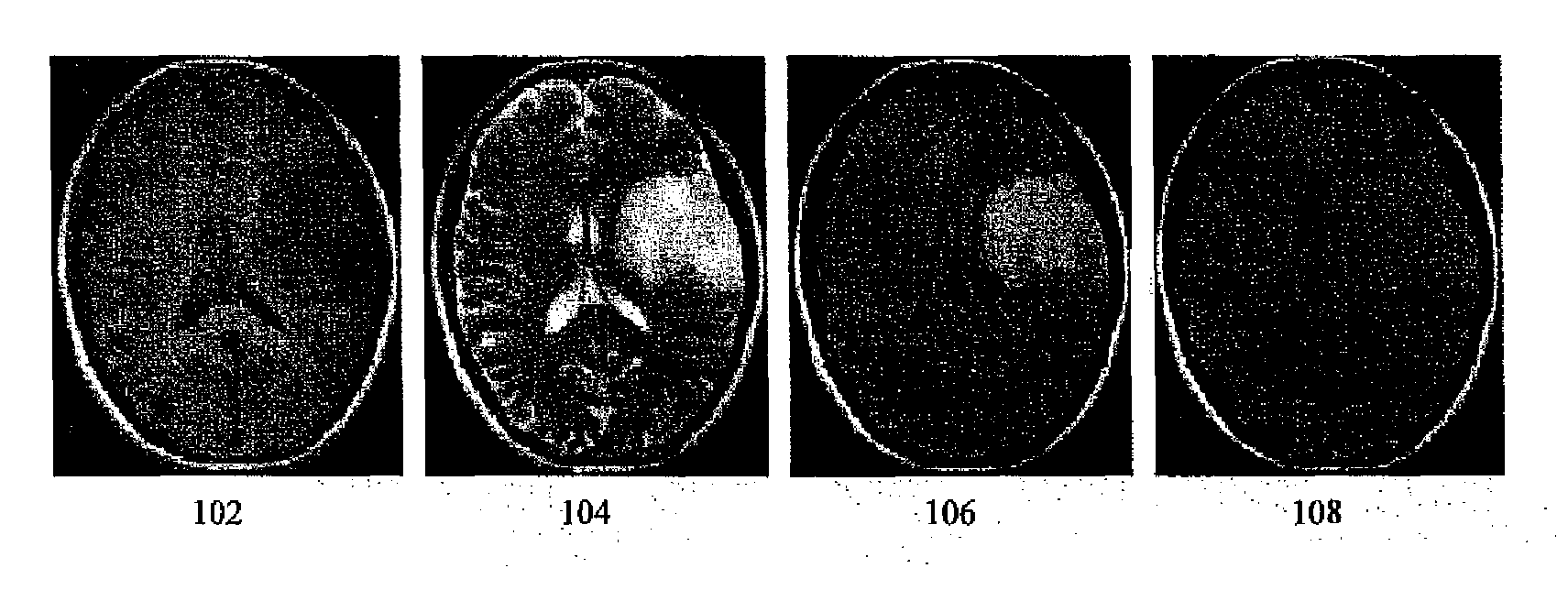
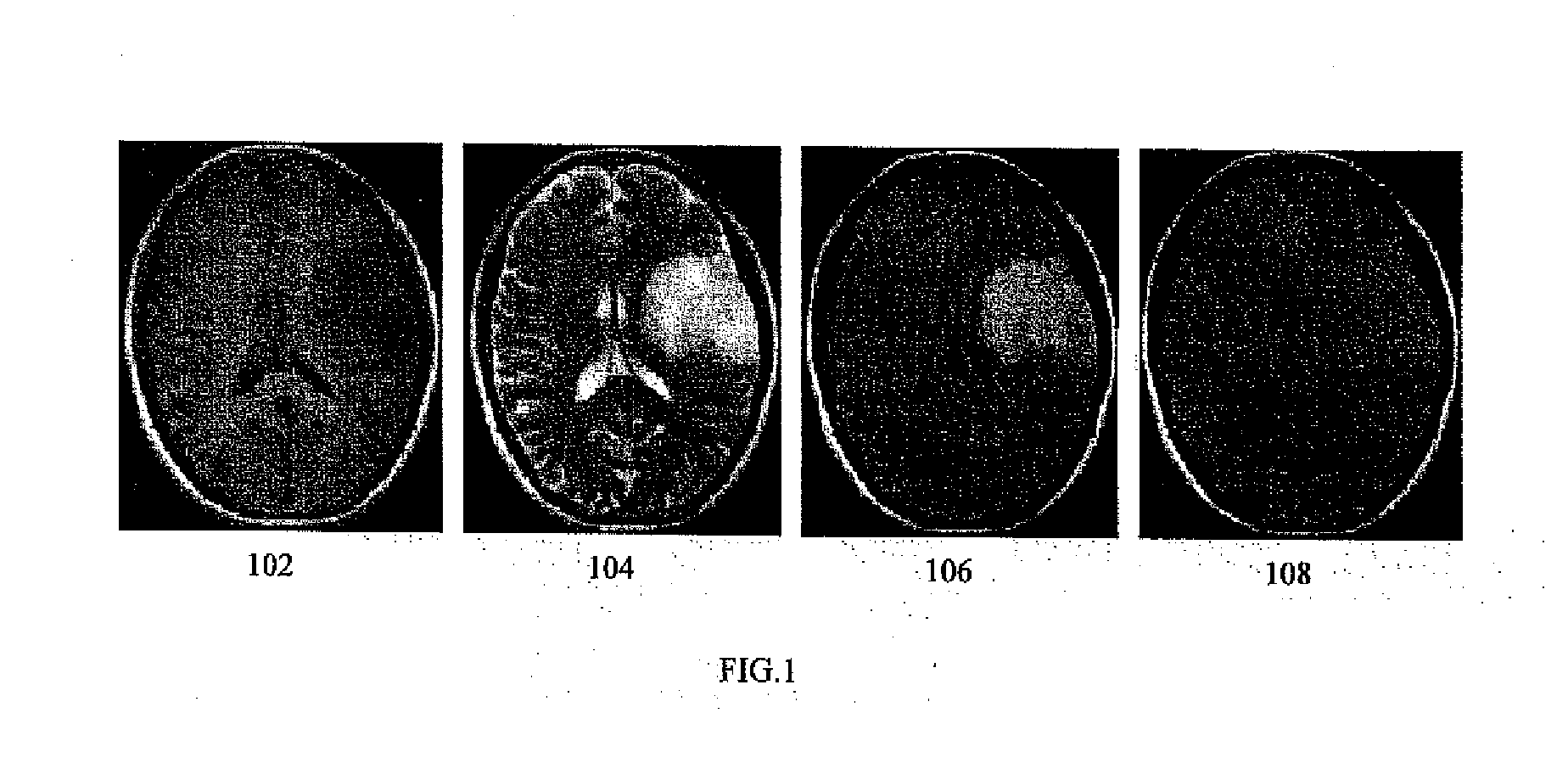
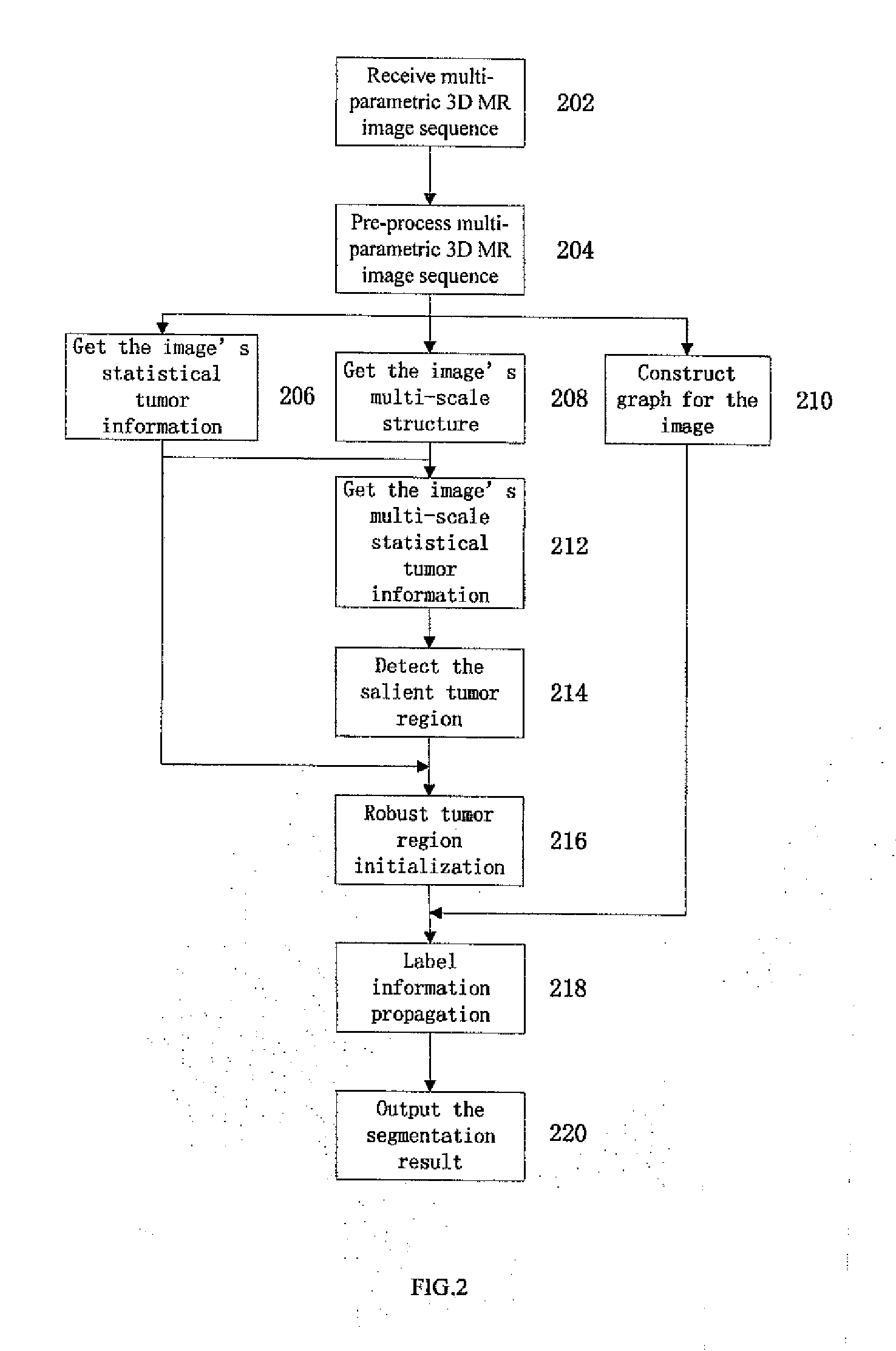
Method for brain tumor segmentation in multi-parametric image based on statistical information and multi-scale struture information
InactiveUS20130182931A1Accurate and reliable tumor segmentationPerformance degradation can be reducedImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionVoxel
A method for brain tumor segmentation in multi-parametric 3D magnetic resonance (MR) images, comprising: determining, for each voxel in the multi-parametric 3D MR image sequence, a probability that the voxel is part of brain tumor; extracting multi-scale structure information of the image; generating multi-scale tumor probability map based on initial tumor probability at voxel level and multi-scale structure information; determining salient tumor region based on multi-scale tumor probability map; obtaining robust initial tumor and non-tumor label based on tumor probability map at voxel level and salient tumor region; and generating a segmented brain tumor image using graph based label information propagation. The present invention is capable of achieving statistical reliable, spatially compact, and robust tumor label initialization, which is helpful to the accurate and reliable tumor segmentation. And the label information propagation framework could partially alleviate the performance degradation caused by image inconsistency between images to be segmented and training images.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
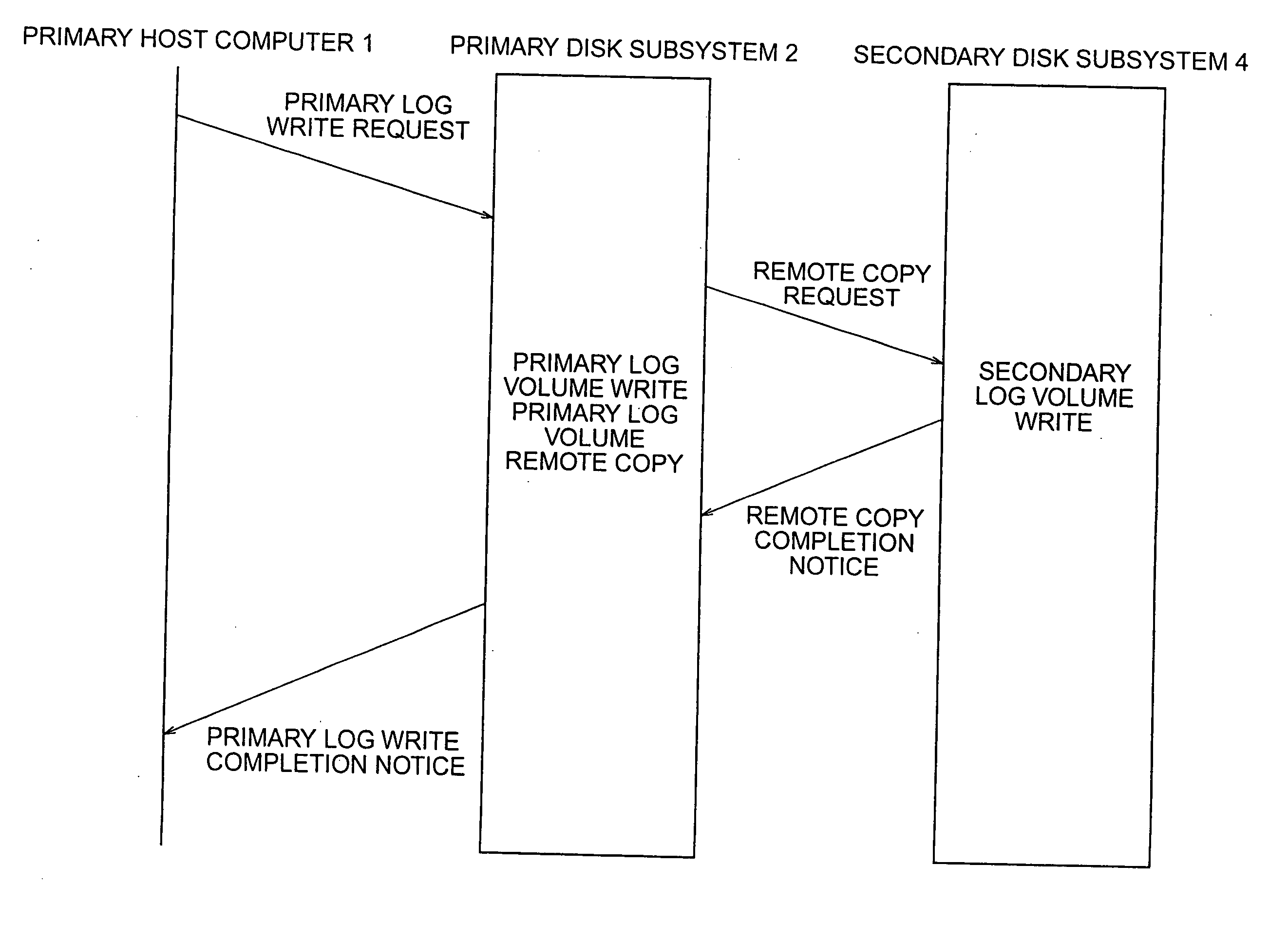
Disaster recovery processing method and apparatus and storage unit for the same
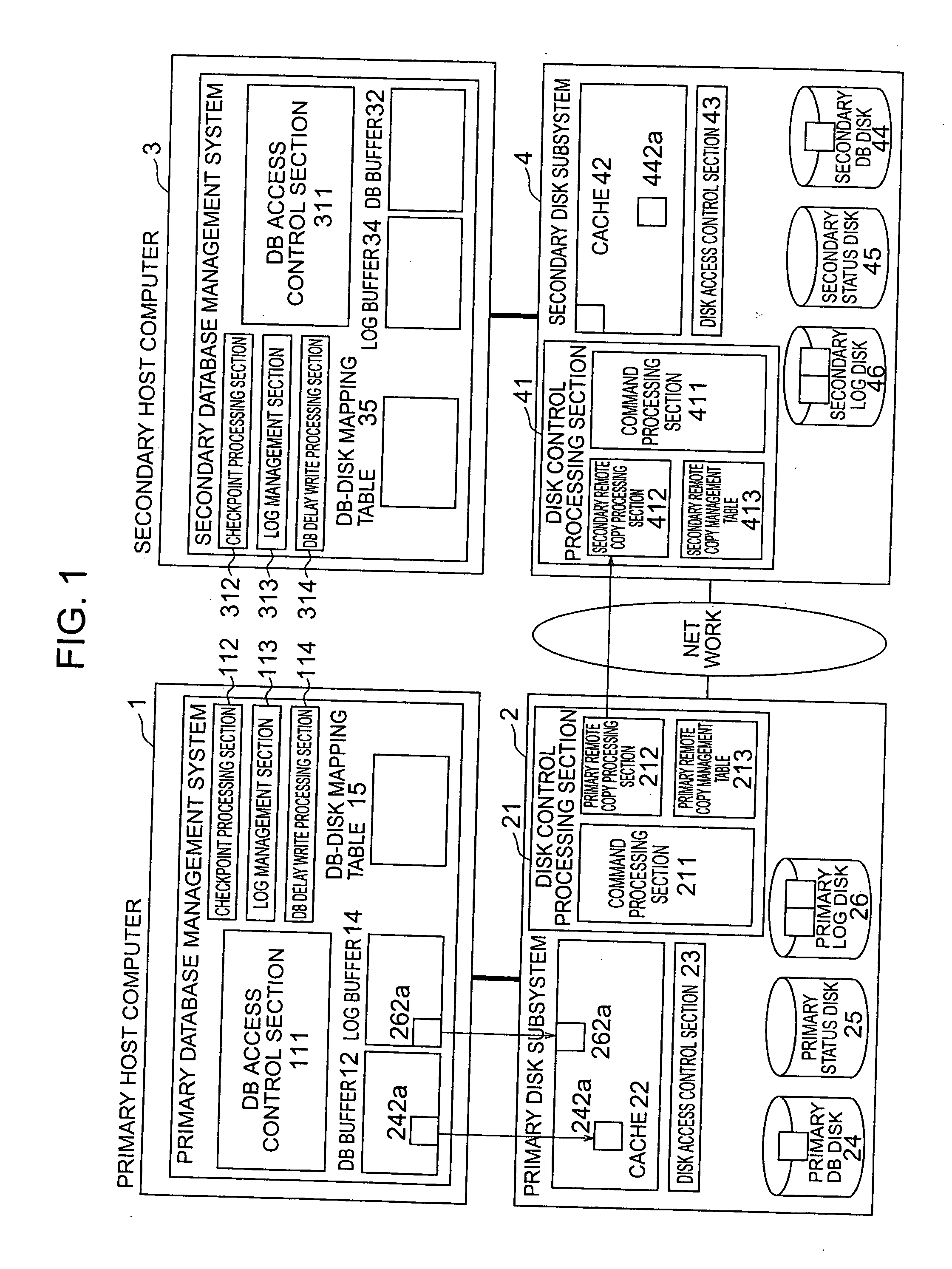
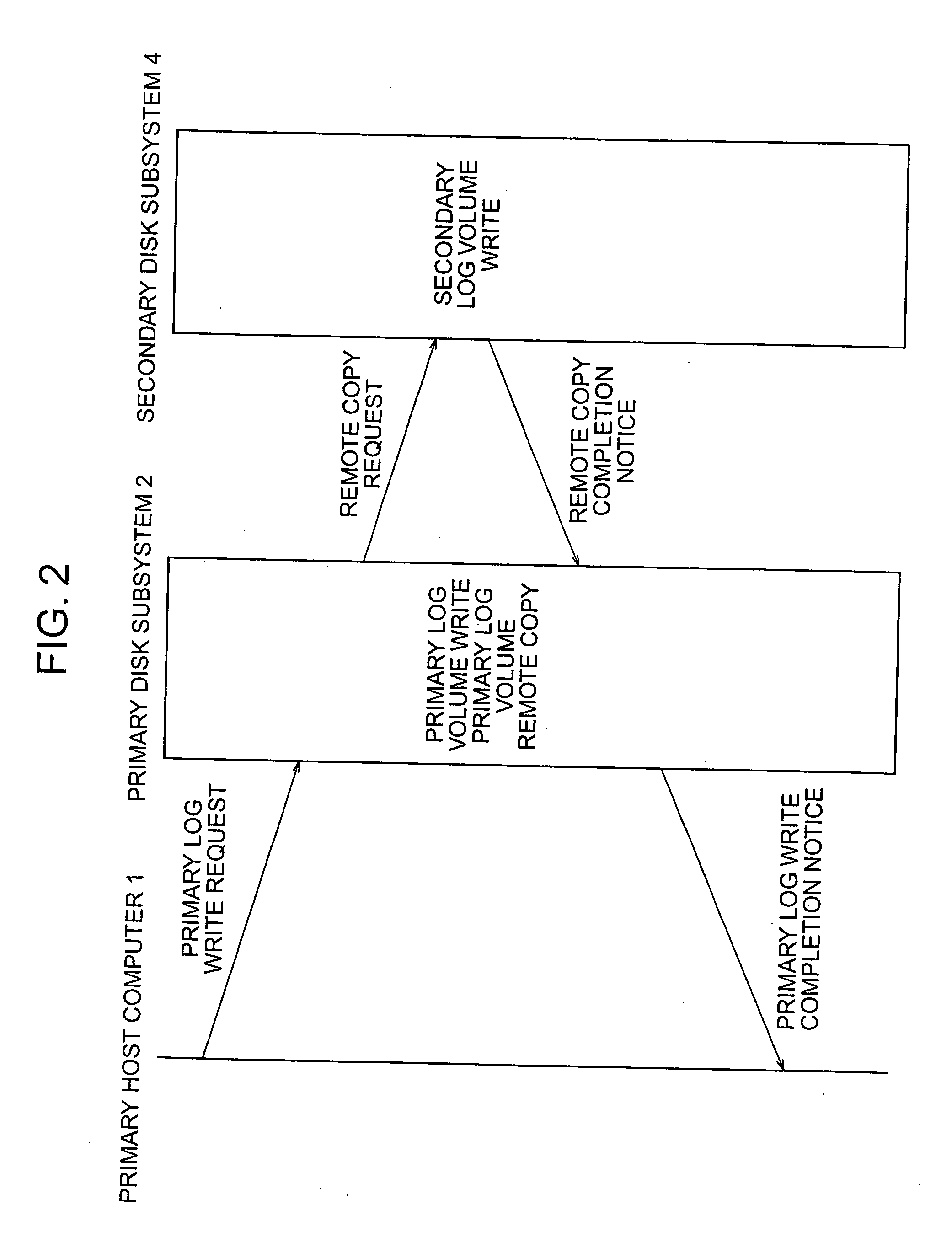
ActiveUS20060010180A1Improve the modification ratePerformance degradation can be reducedInput/output to record carriersData processing applicationsDatabaseStorage cell
A technique capable of constructing a disaster recovery system reduced in performance degradation of a primary system is provided. The technique includes a step of conducting synchronous writing of log information into a secondary storage subsystem in a secondary system when a write request received from a host computer is a write request of log information, a step of temporarily storing a write request and conducting asynchronous writing into the secondary storage subsystem when the received write request is a write request of database data or status information, a step of modifying log information, data in a database area, and status information in the secondary storage subsystem according to contents of a write request received from a primary storage subsystem, and a step of recovering the database area according to contents of log information in a location indicated by the status information.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Method and system for leveraging spares in a data storage system including a plurality of disk drives
InactiveUS6845465B2Increase data efficiencyAccess time be reduceError preventionRedundant data error correctionMagnetic disksData storage system
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Automatic gain control apparatus and method in a wireless communication system
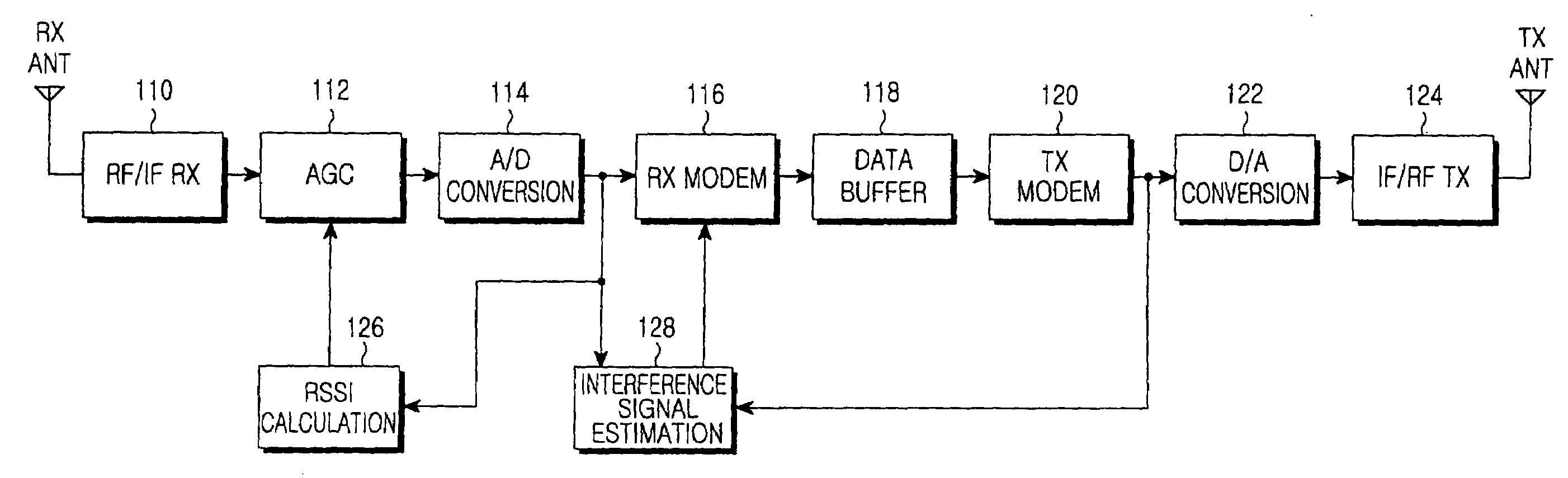
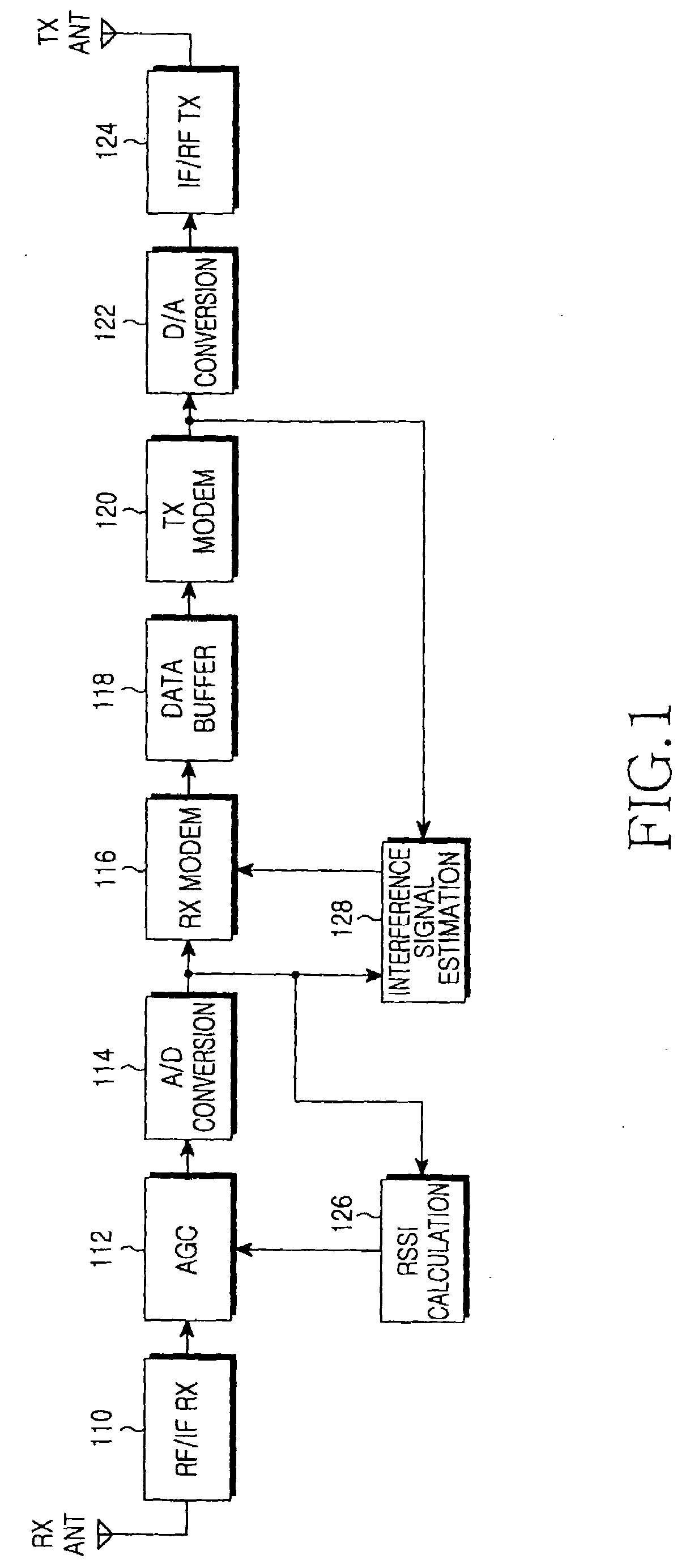
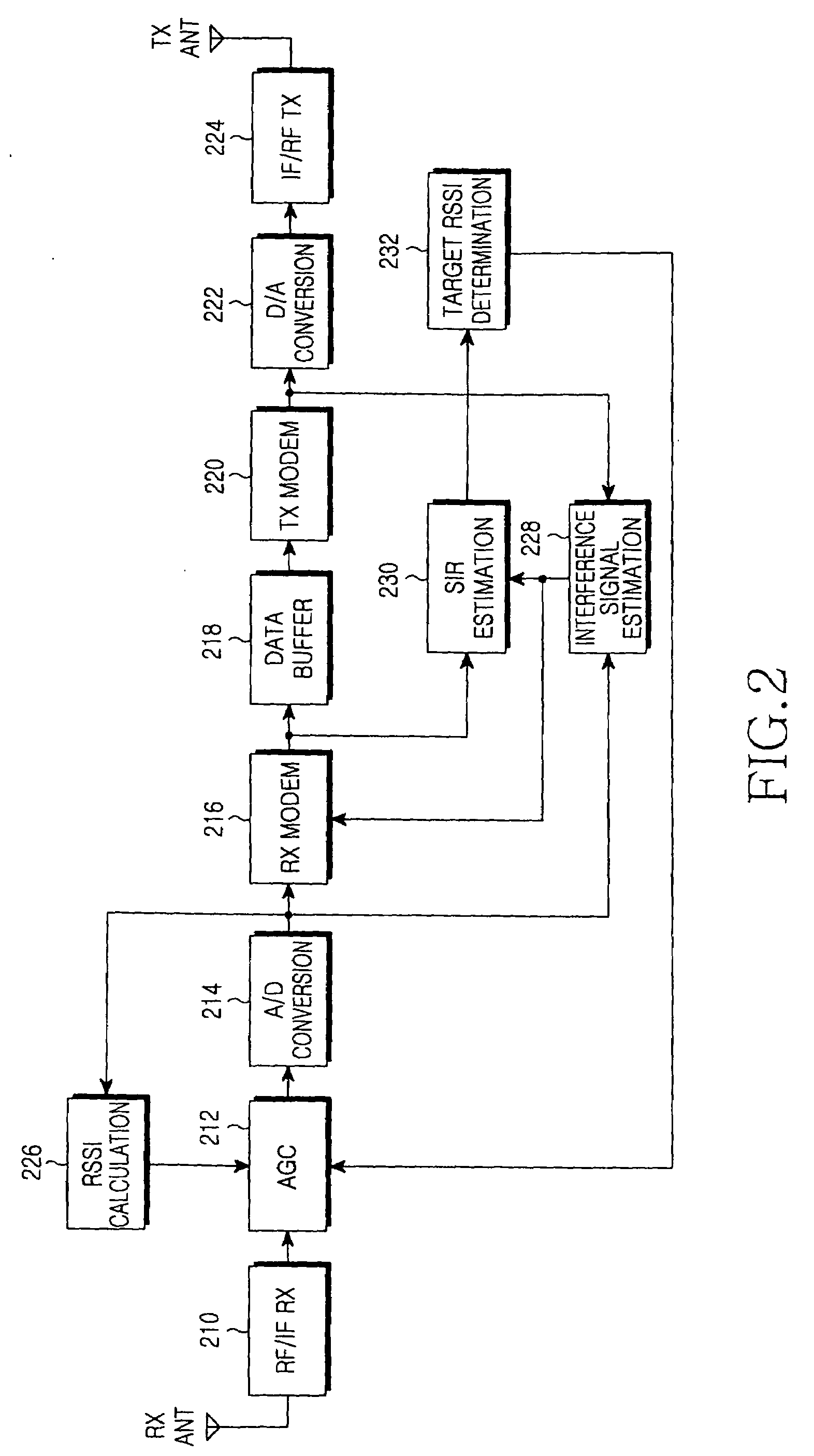
ActiveUS20090290516A1Performance degradation can be reducedEasy to quantifyGain controlRadio relay systemsFull duplex relaySignal-to-interference ratio
An apparatus and method for adaptively adjusting a target Received Signal Strength Indicator (RSSI) for Automatic Gain Control (AGC) in a full-duplex relay apparatus with an interference cancellation function. A Signal to Interference Ratio (SIR) estimation block estimates an SIR based on an interference signal estimated from a received signal and an interference-cancelled signal determined by cancelling the estimated interference signal from the received signal. A target RSSI determination block determines a target RSSI according to the estimated SIR. An AGC block adjusts a gain for the received signal based on the determined target RSSI.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
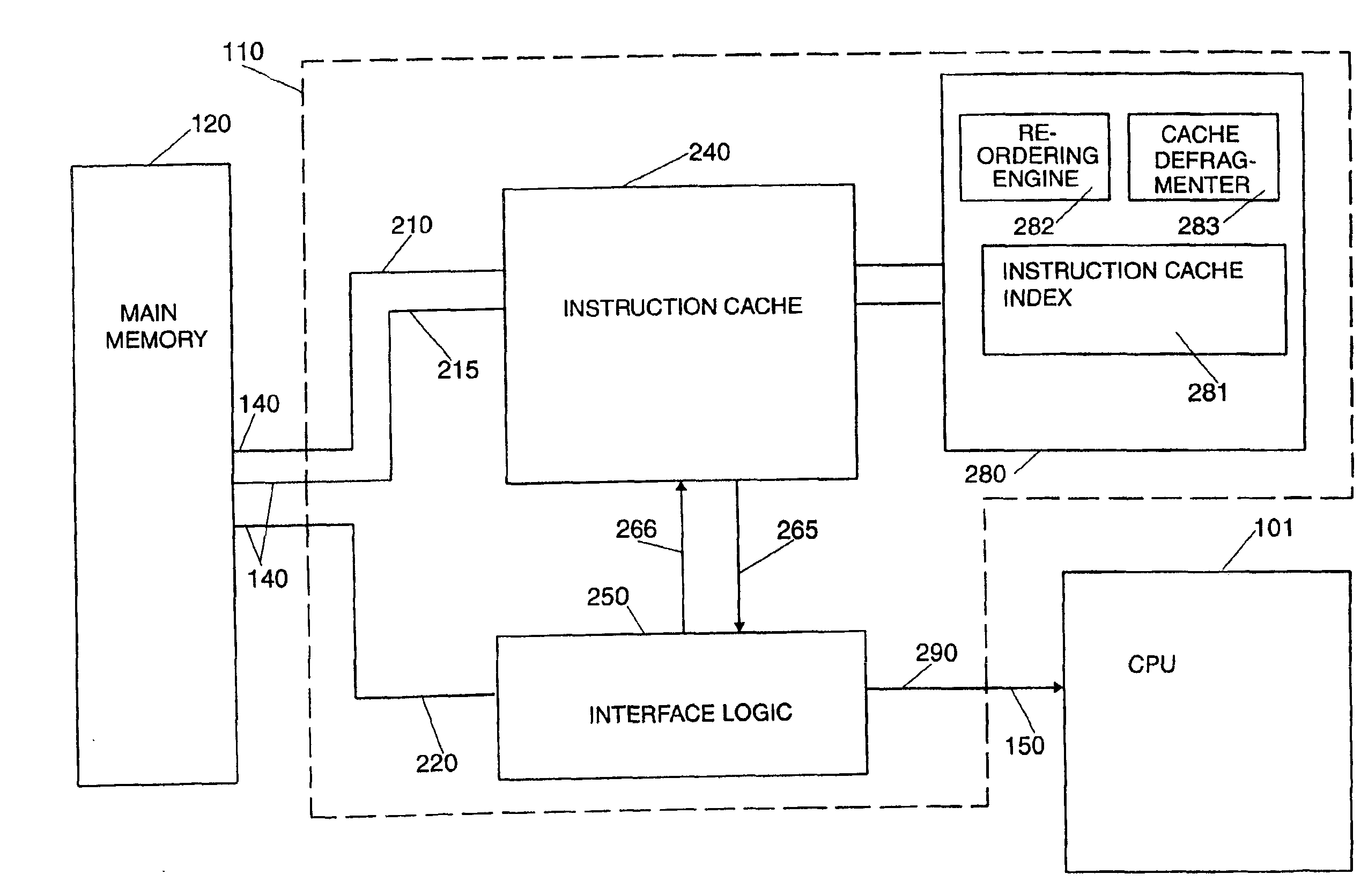
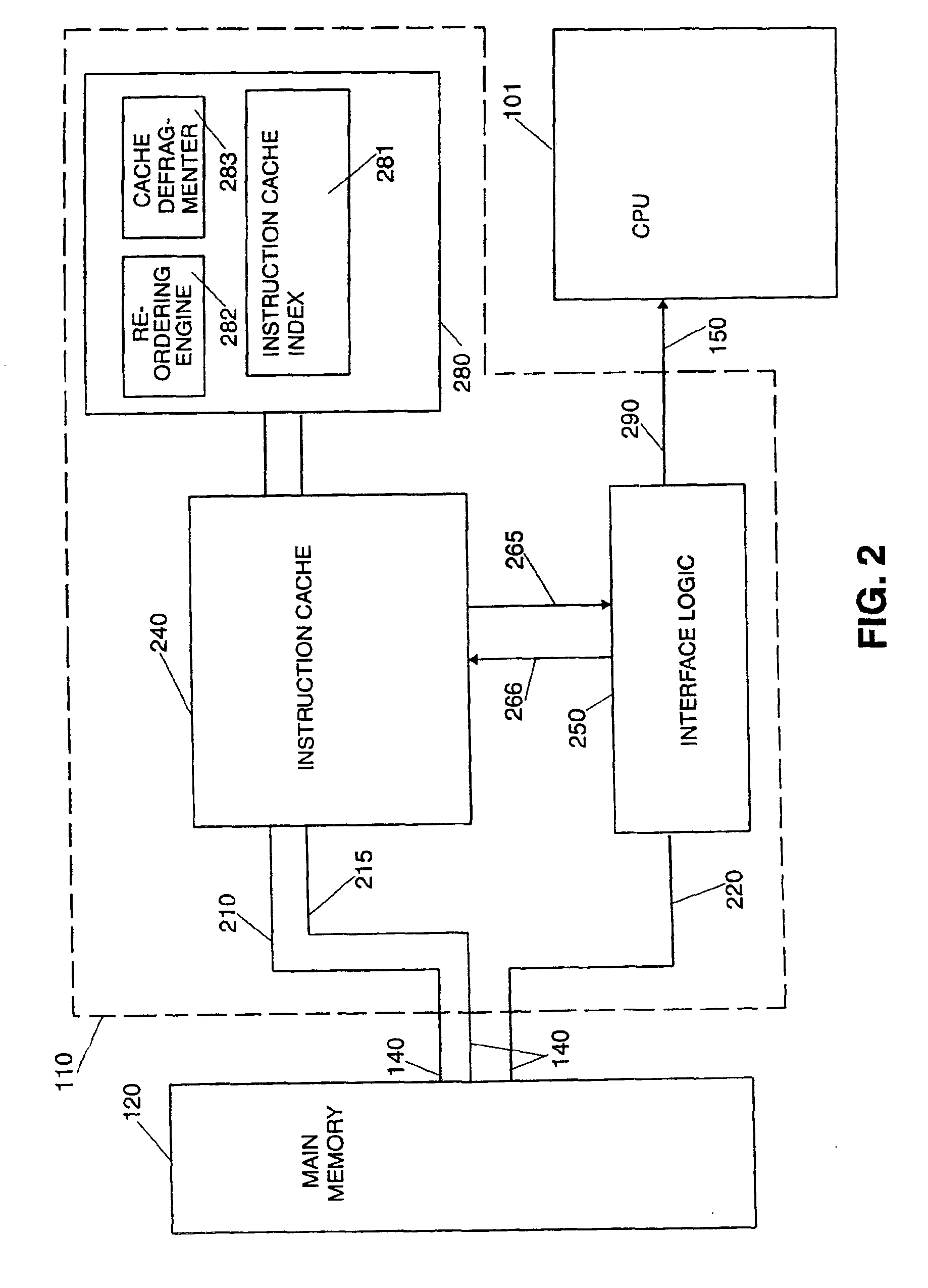
Scheme for reordering instructions via an instruction caching mechanism
InactiveUS6920530B2Reduce complexityImprove caching efficiencyProgram control using stored programsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationBasic blockStore instruction
A method and system for storing instructions retrieved from memory in a memory cache to provide said instructions to a processor. First a new instruction is received from the memory. The system then determines whether the new instruction is a start of a basic block of instructions. If the new instruction is the start of a basic block of instructions, the system determines whether the basic block of instructions is stored in the memory cache responsive. If the basic block of instructions is not stored in the memory cache, the system retrieves the basic block of instructions for the new instruction from the memory. The system then stores the basic block of instructions in a buffer. The system then predicts a next basic block of instructions needed by the processor from the basic block of instructions. The system determines whether the next block of instructions is stored in the cache memory and retrieves the next basic block of instructions from the memory if the next block of instructions is not stored in memory.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
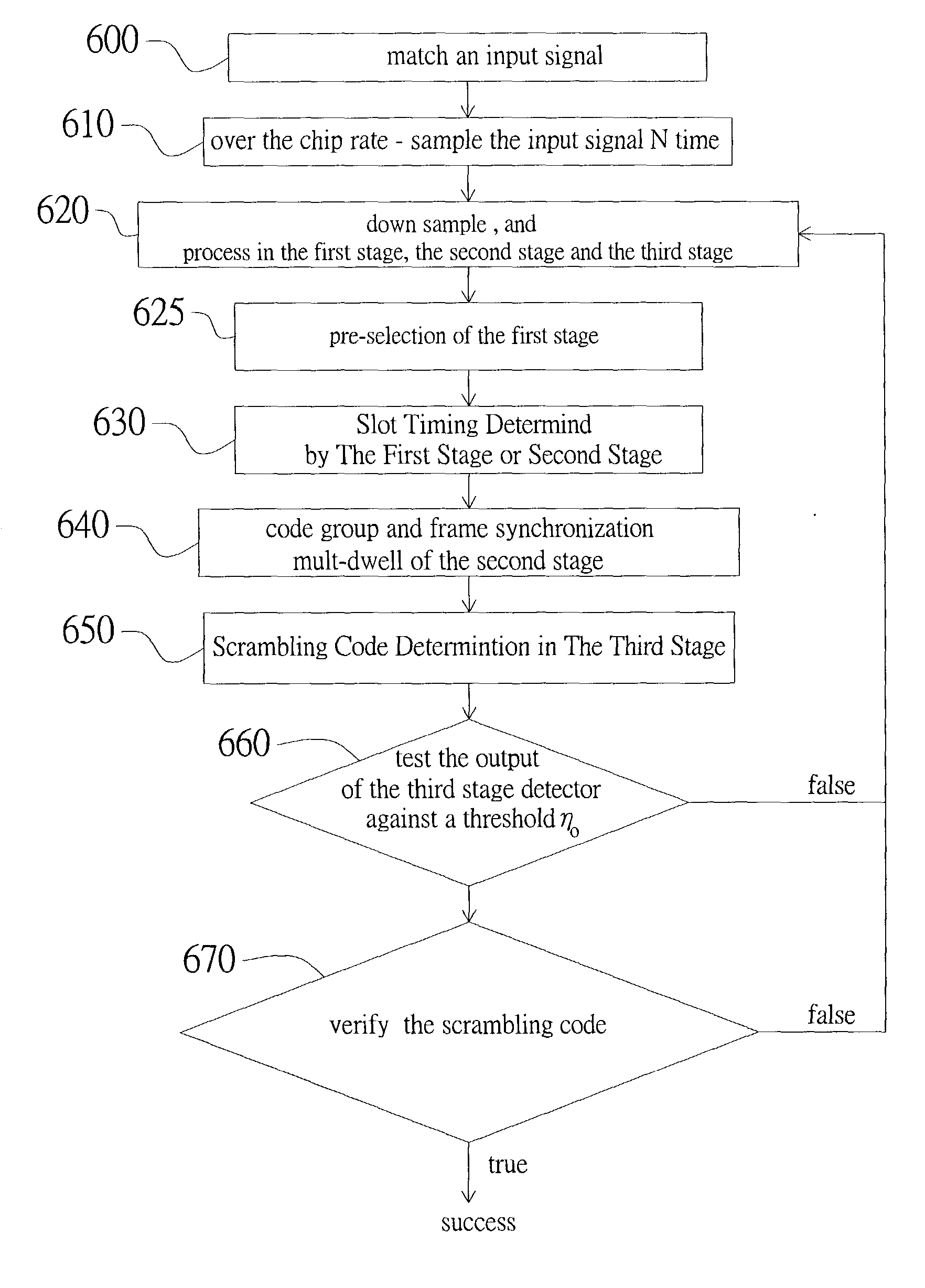
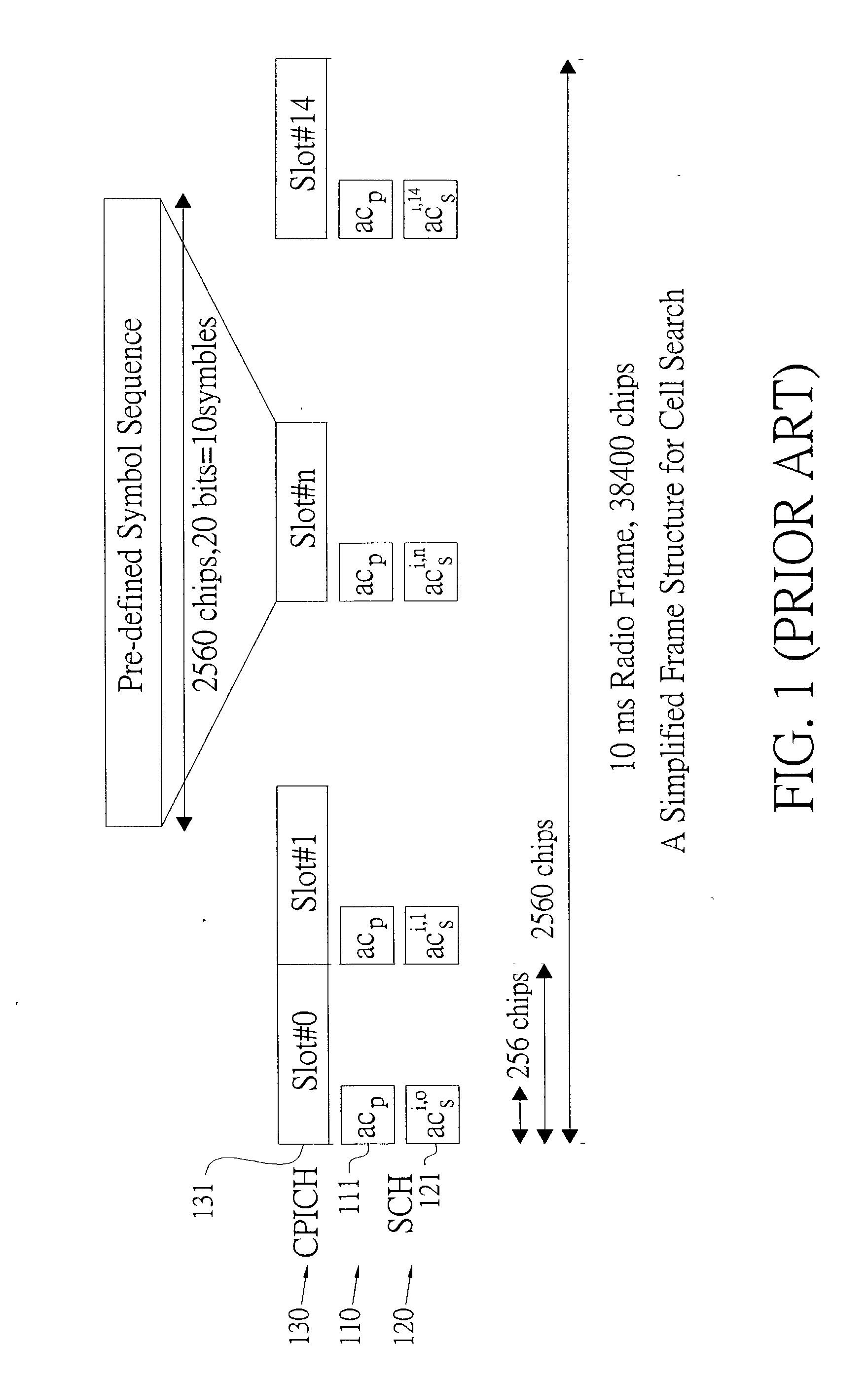
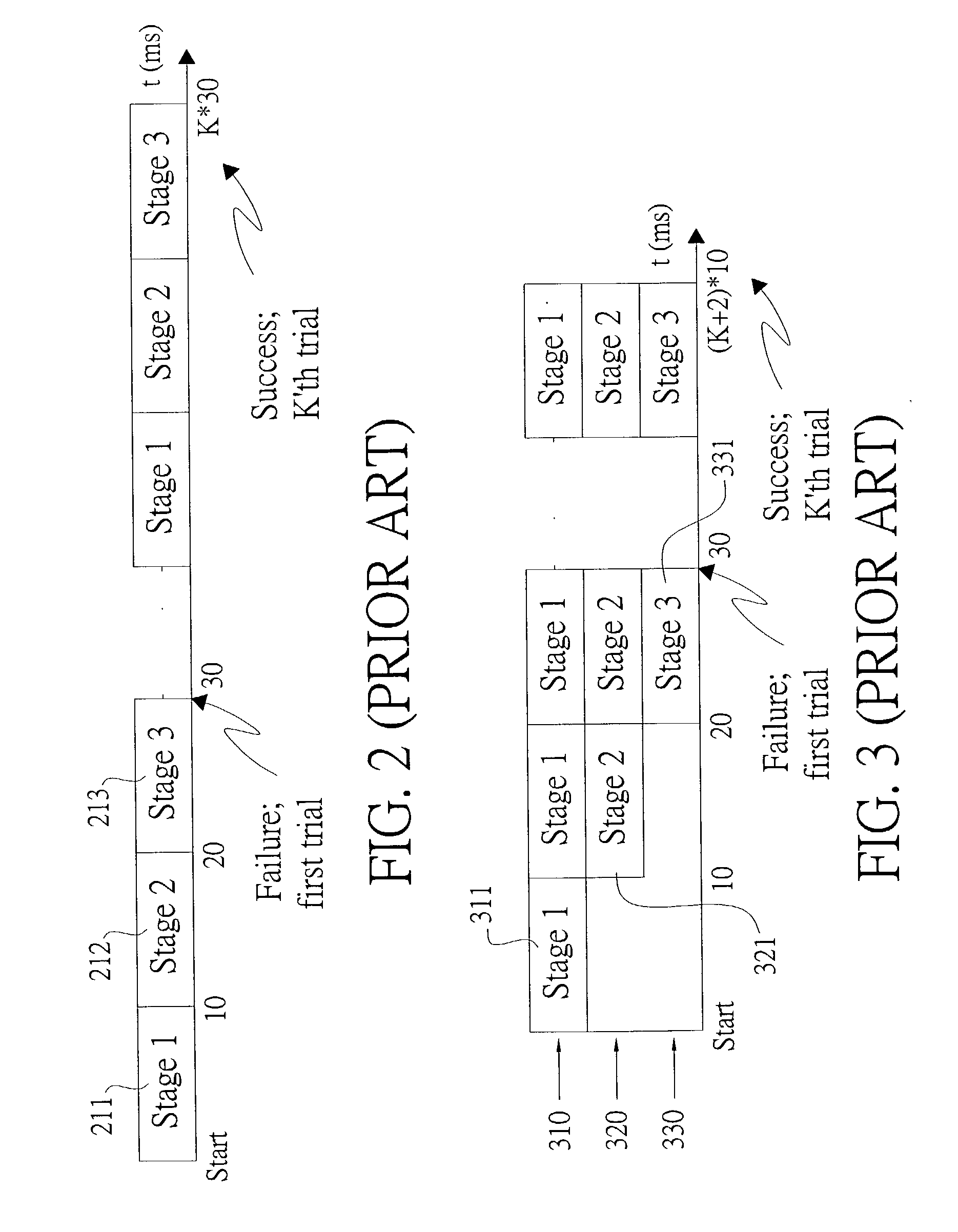
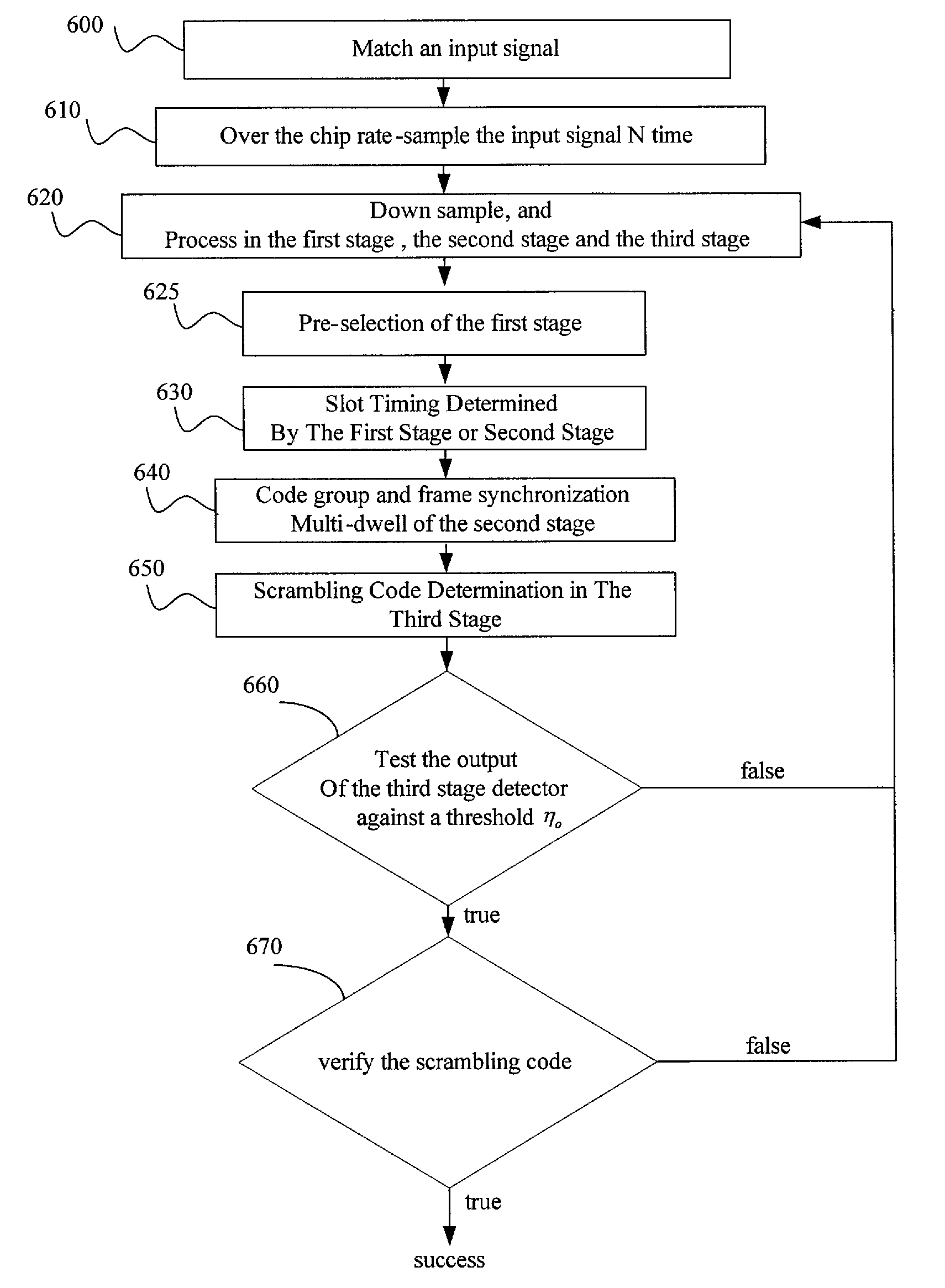
Method for cell search under effect of high clock offset
InactiveUS20030193922A1Performance degradation can be reducedHigh clock offsetTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionThree stageClock offset
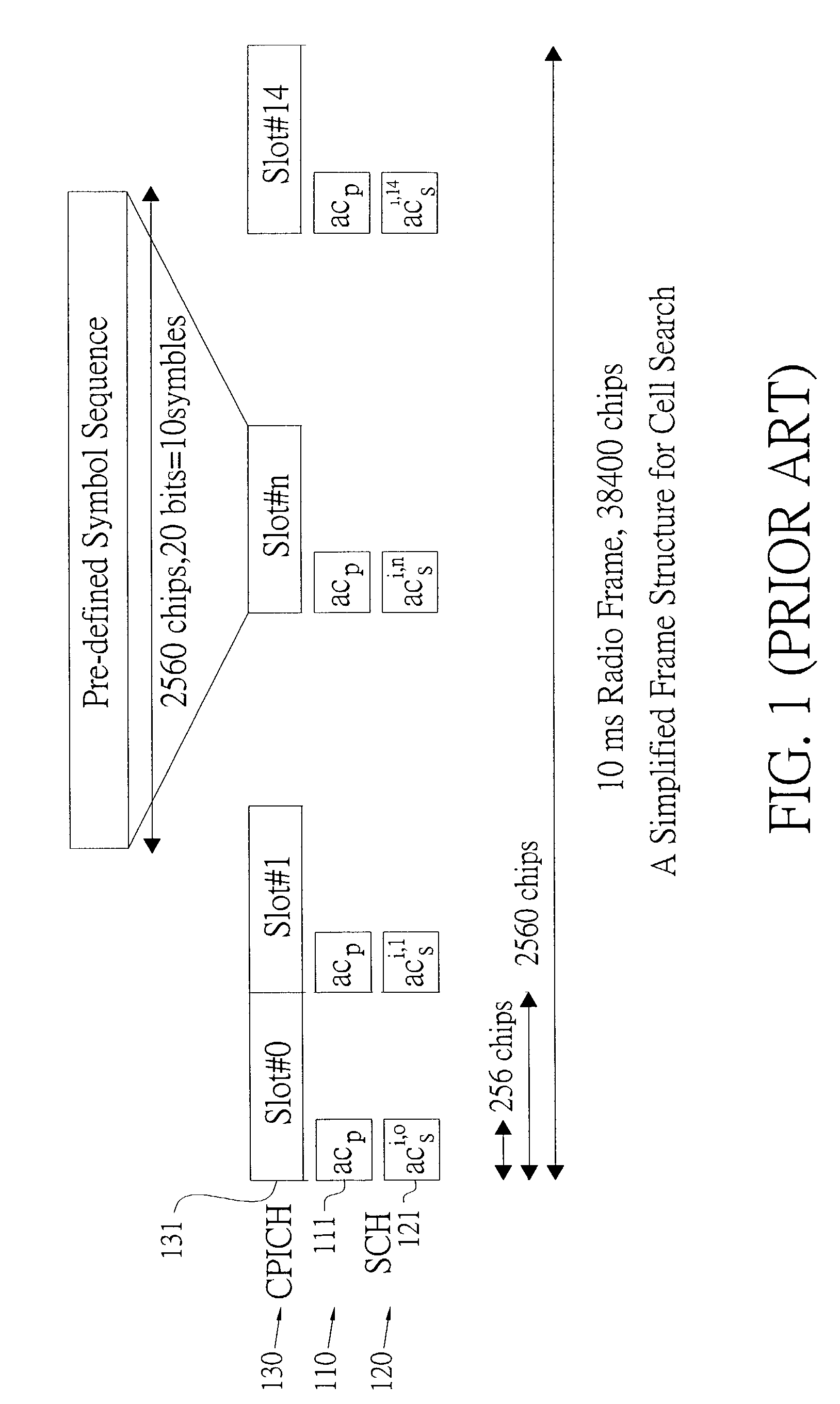
The present invention discloses a cell search method for a CDMA system, using a three-stage cell search. The method comprises matching an incoming signal from the base station, wherein the frequency of the incoming signal having an uncertain range; over-sampling the incoming signal N times against a chip rate and outputting the N over-samples; down-sampling the incoming signal and outputting N over-samples to a first stage, a second stage and a third stage. The first stage further comprises selecting a first group of slot boundaries as a first group of candidates after pre-selection, and the first group of candidates transmitting to a deciding selection stage of the first stage and the second stage to be continuously processed. The cell search method of the present invention can be used to reduce the effect of clock offset on the performance of cell search and to accomplish fast cell search.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
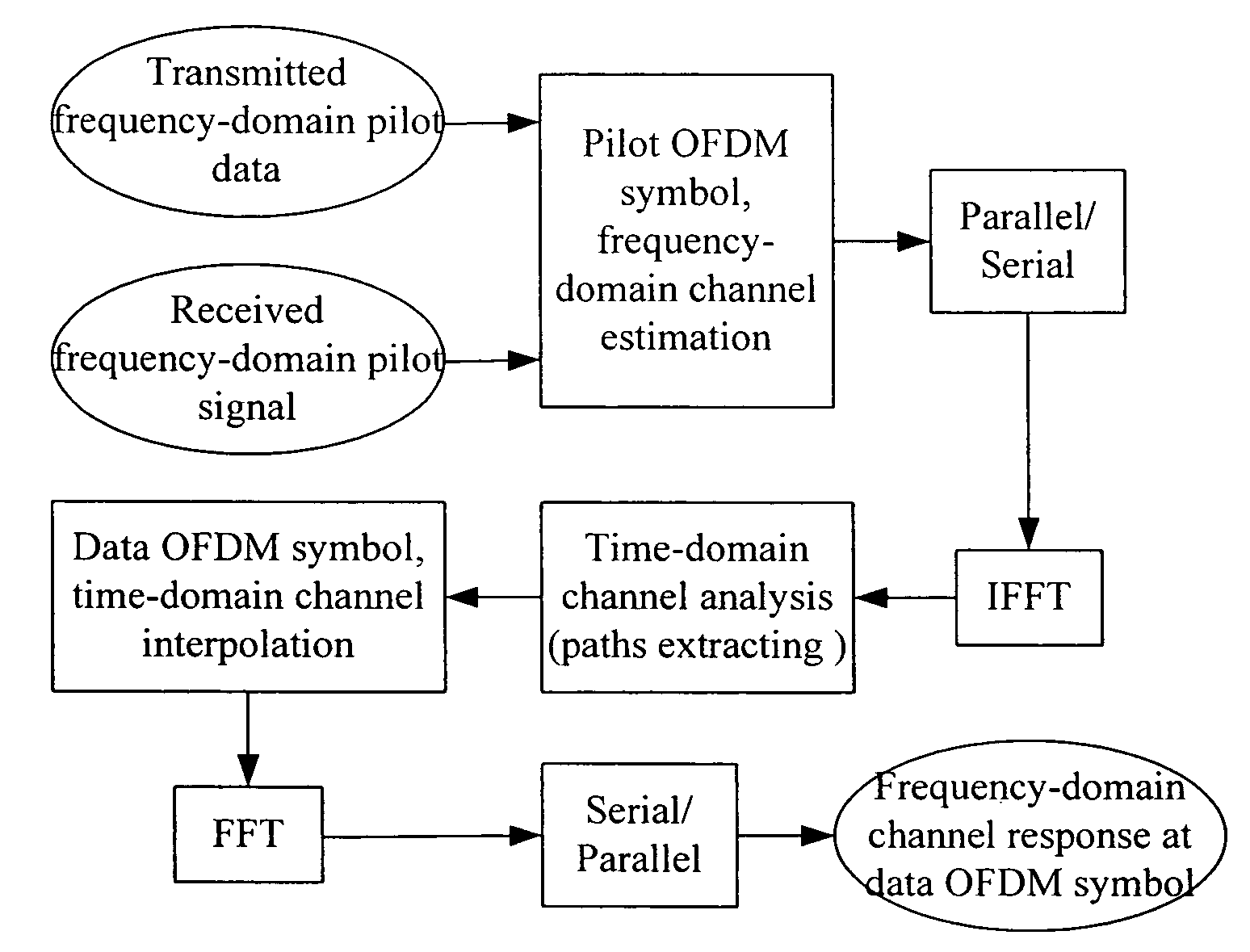
Method for channel estimation in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system and device thereof
ActiveUS7688907B2Performance degradation can be reducedImprove performanceError preventionTransmission path divisionCommunications systemEngineering
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Secondary lithium batteries having novel anodes
ActiveUS8828608B2Improve abilitiesPerformance degradation can be reducedMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureSulfurNitrogen
A secondary lithium battery having an anode comprising graphene nanosheets doped with a doping element selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, boron, sulfur, phosphorous and combinations thereof. The secondary lithium battery and the anode provide capacity and other performance without degradation during long term charge and discharge cycling.
Owner:NANOSIENERGY INC
Method for channel estimation in orthogonal frequency division multiplexing system and device thereof
ActiveUS20070183519A1Improve performanceEnhances channel environment adaptabilityError preventionTransmission path divisionCommunications systemData transmission
A method for channel estimation in an Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (OFDM) system, including: a transmitter determining a distribution density of pilot OFDM symbols according to the maximum Doppler frequency shift supported by the system, and transmitting pilot OFDM symbols and data OFDM symbols based on the distribution density of the pilot OFDM symbols; a receiver estimating frequency-domain channel information of the data OFDM symbols according to the received pilot OFDM symbols. The invention solves the problem of a large performance loss at a high-delay channel and a system with rapidly varying channel. The invention offers a better performance of channel estimation while the channel environment is varying rapidly, enhances the performance of a high-delay channel, makes a data communication system more suitable to a changing environment and makes better performance to the practical channel estimation, so that the data transmission efficiency of the system is increased.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Rotor and rotary electric machine using the same
ActiveUS20140021820A1Performance degradation can be reducedReduce intensityMagnetic circuit rotating partsSynchronous machines with stationary armatures and rotating magnetsElectric machineMagnetic reluctance
Owner:DAIKIN IND LTD
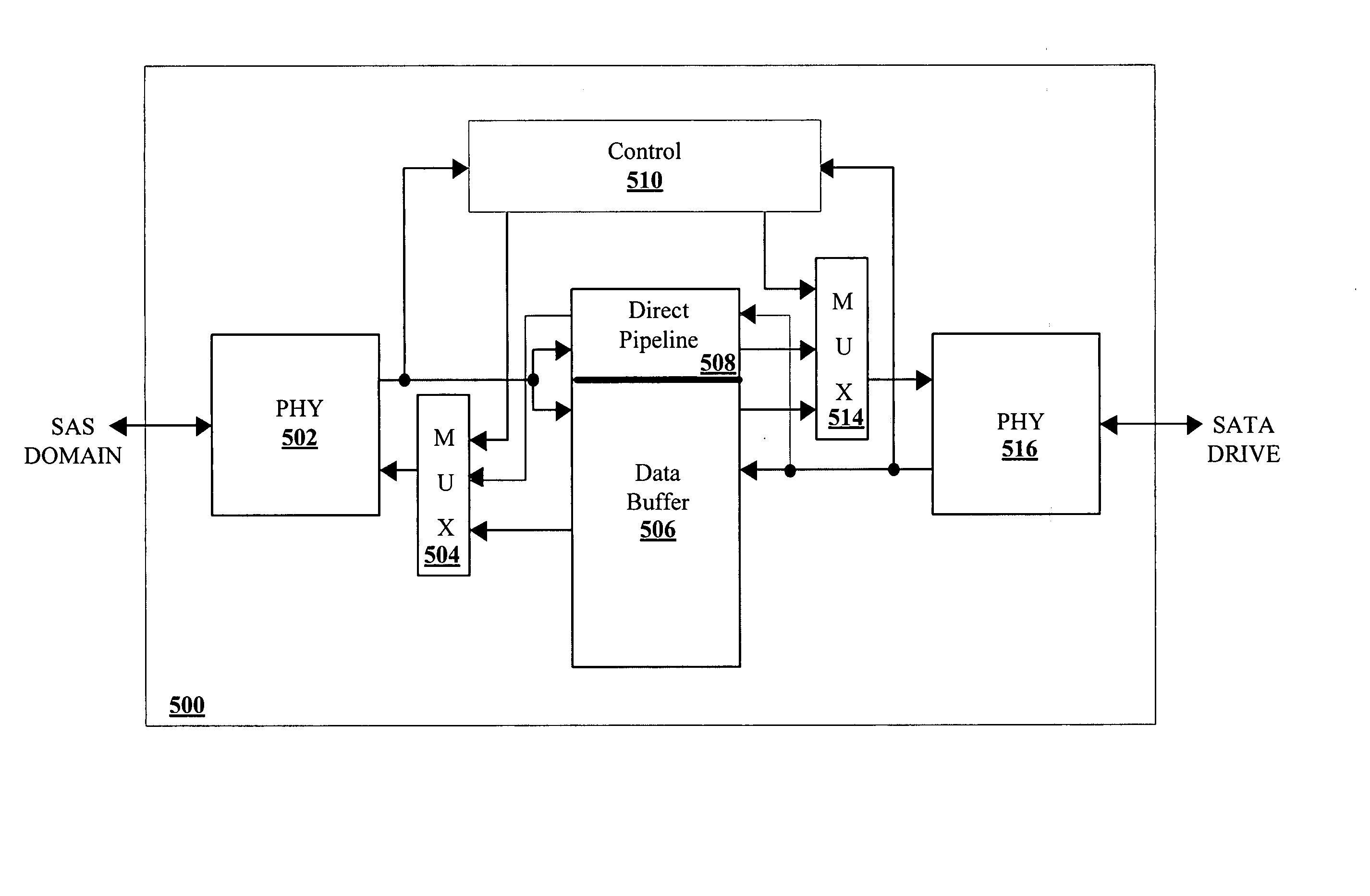
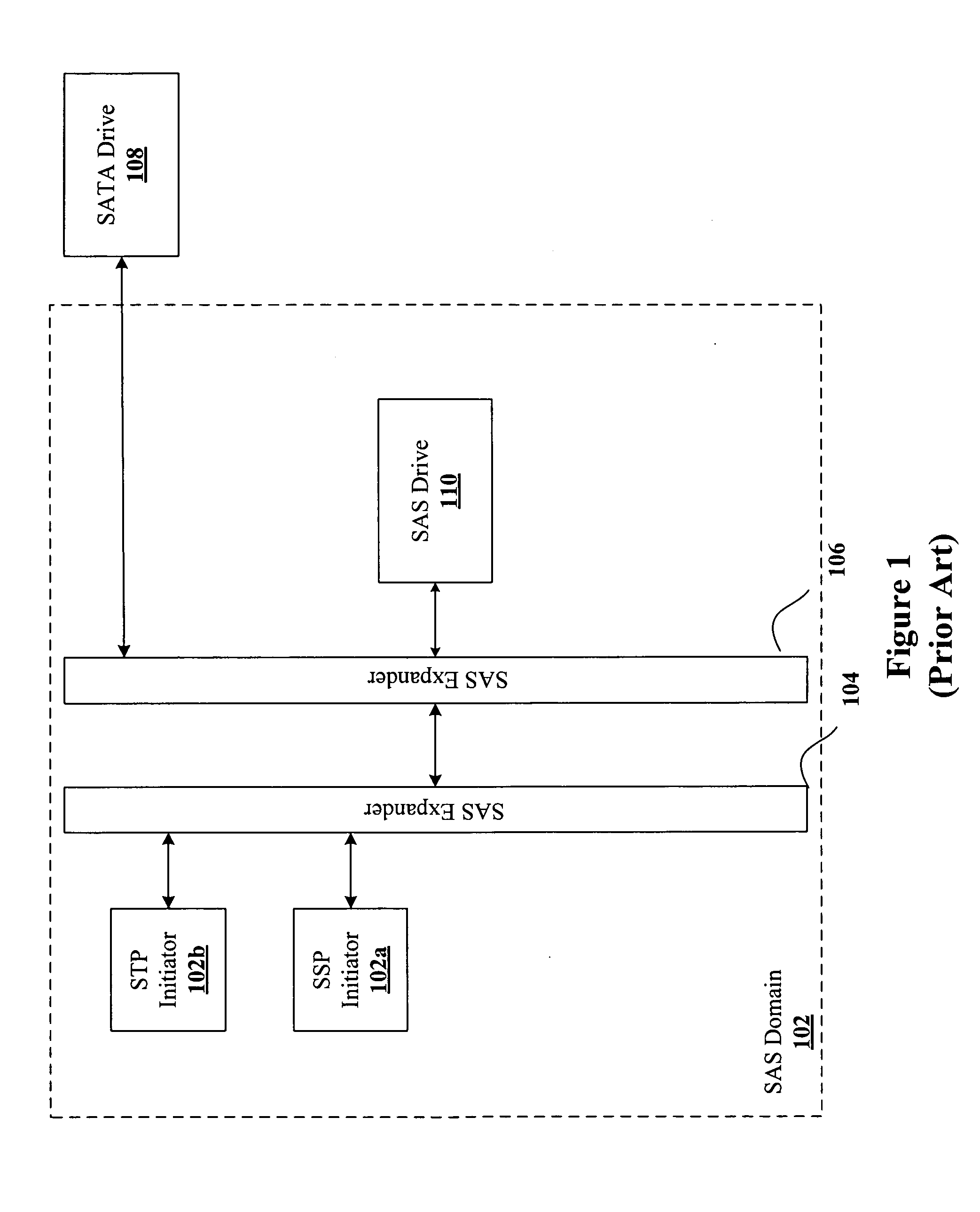
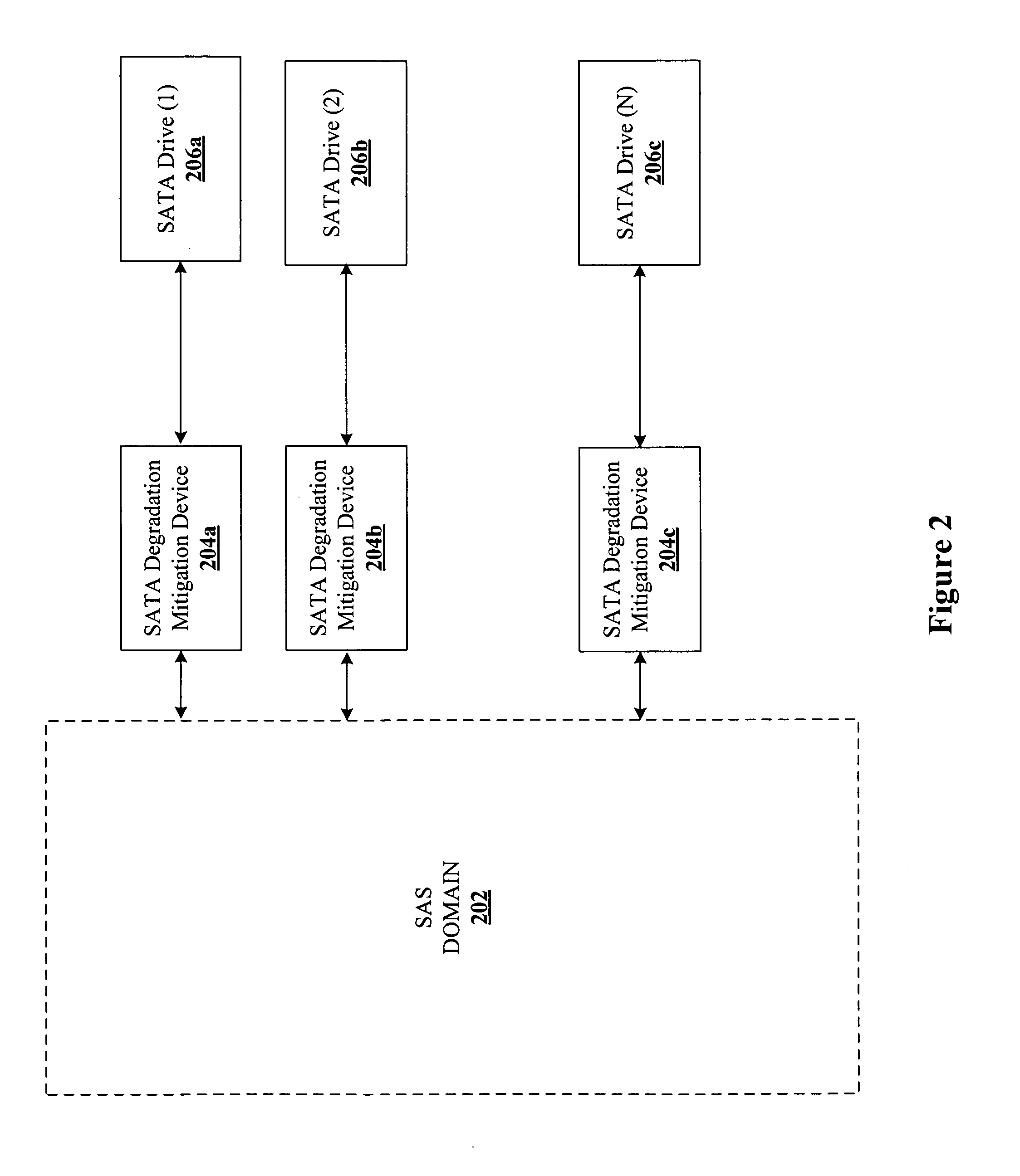
Mitigating performance degradation caused by a SATA drive attached to a SAS domain
InactiveUS20070136521A1Performance degradation can be reducedReduce congestionMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingHigh rateOverall efficiency
The present invention provides a device and method for mitigating performance degradation caused by SATA drives attached to a SAS domain. In one of the embodiments of the present invention, a SATA degradation mitigation device (“SDMD”) is installed between a SAS domain and one or more SATA drives. The SDMD effectively reduces congestion on intermediate links by buffering SATA data and transmitting the data at a rate which is higher than the rate at which the SATA data is received from a drive. Conversely, write data from the SAS domain may be buffered at the SDMD at a higher rate and subsequently sent to the SATA drive at a lower rate. This SATA data buffering and subsequent increase in data rate improves the overall efficiency of a SAS domain storage system by reducing data congestion arising out of low-performance SATA drives clogging the intermediate links.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
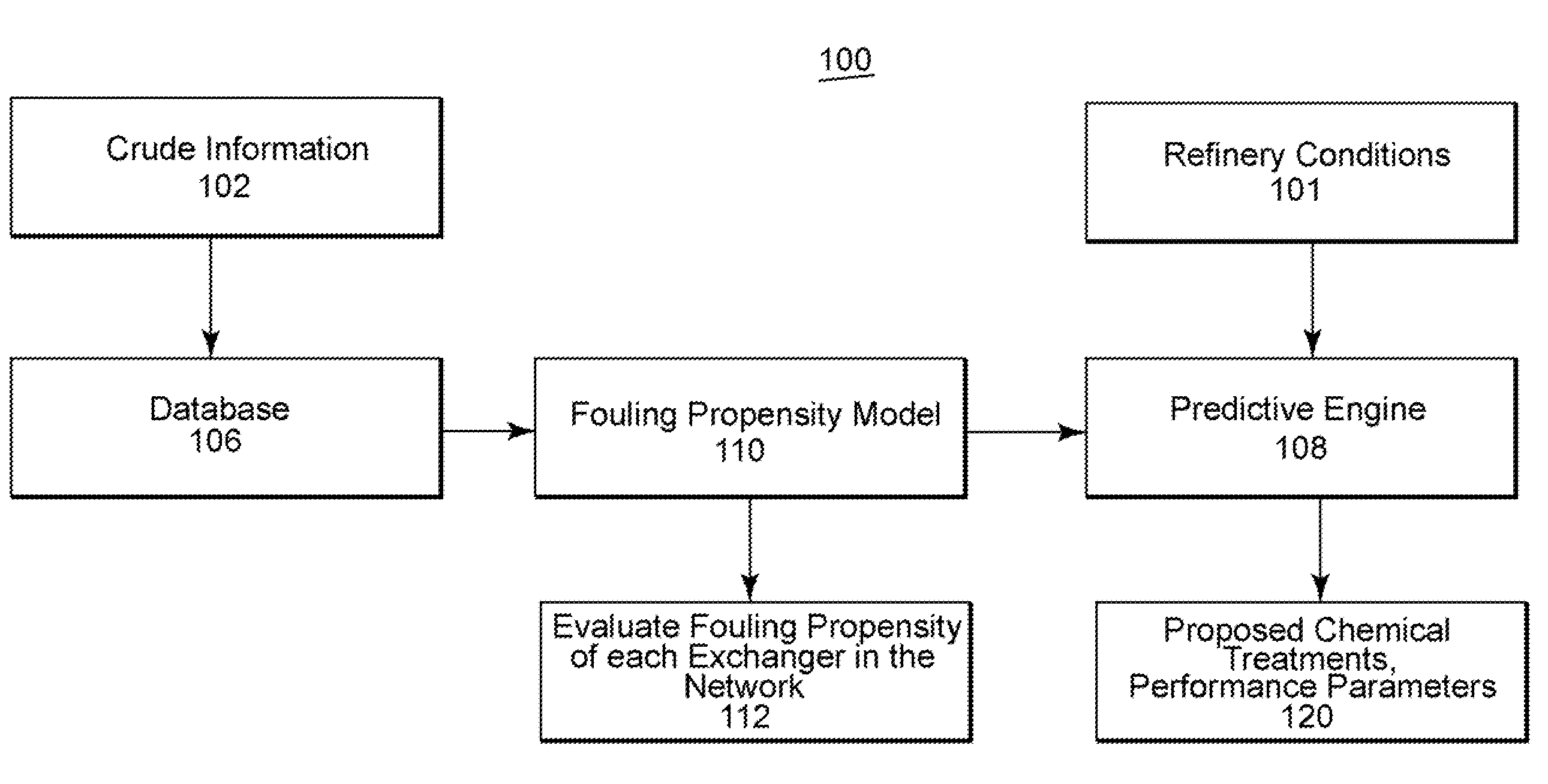
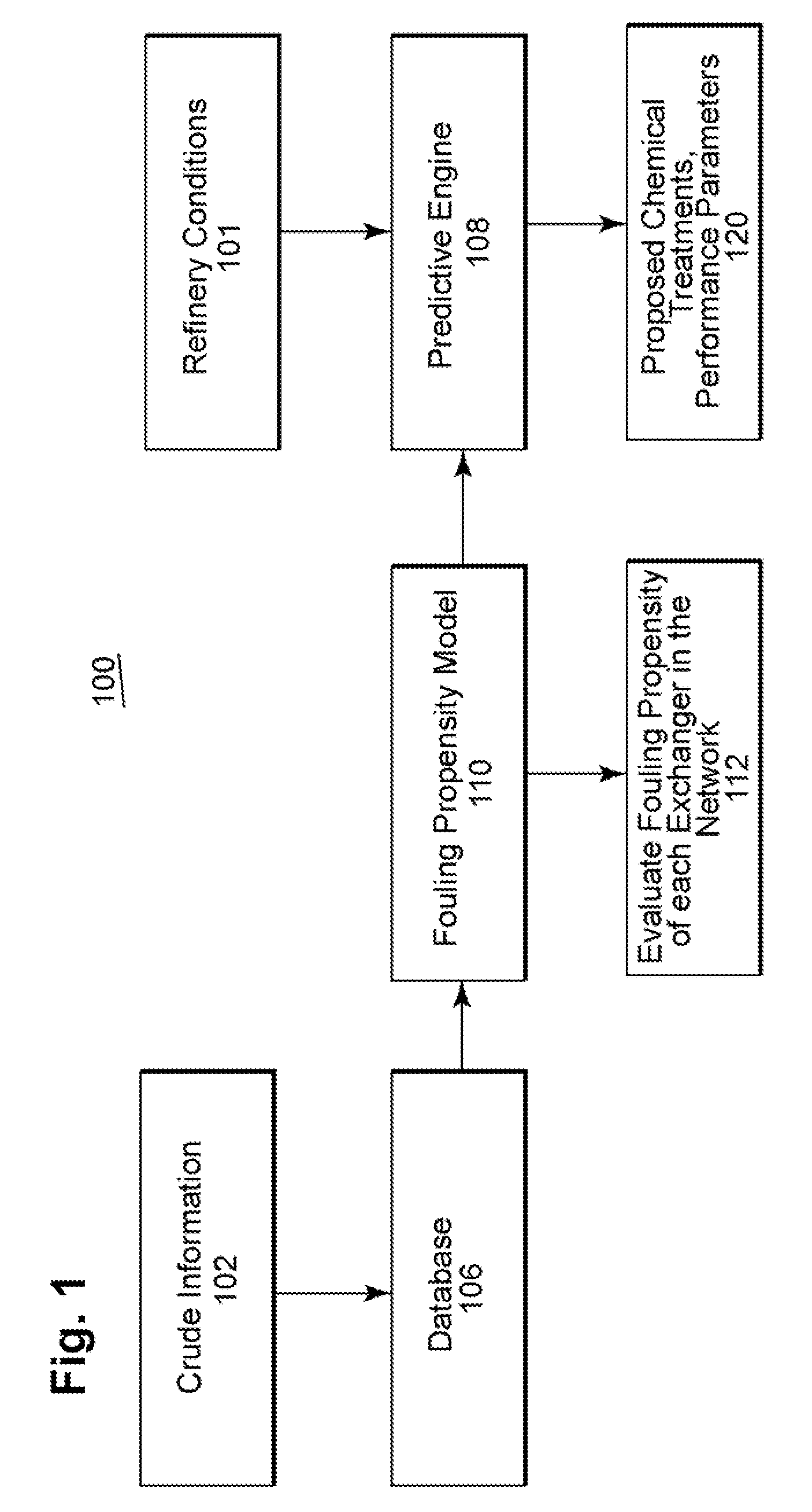
Method and system for assessing the performance of crude oils
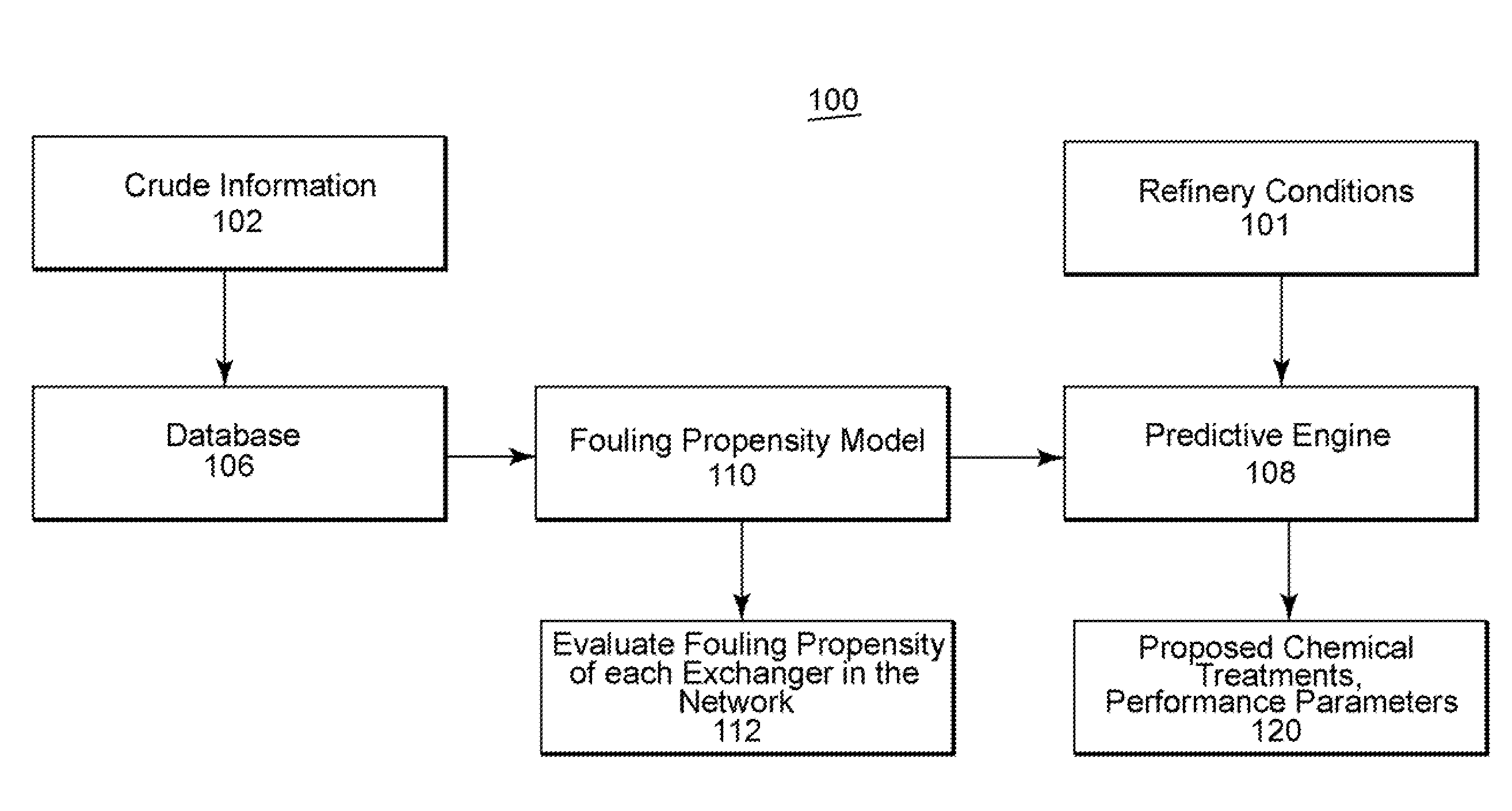
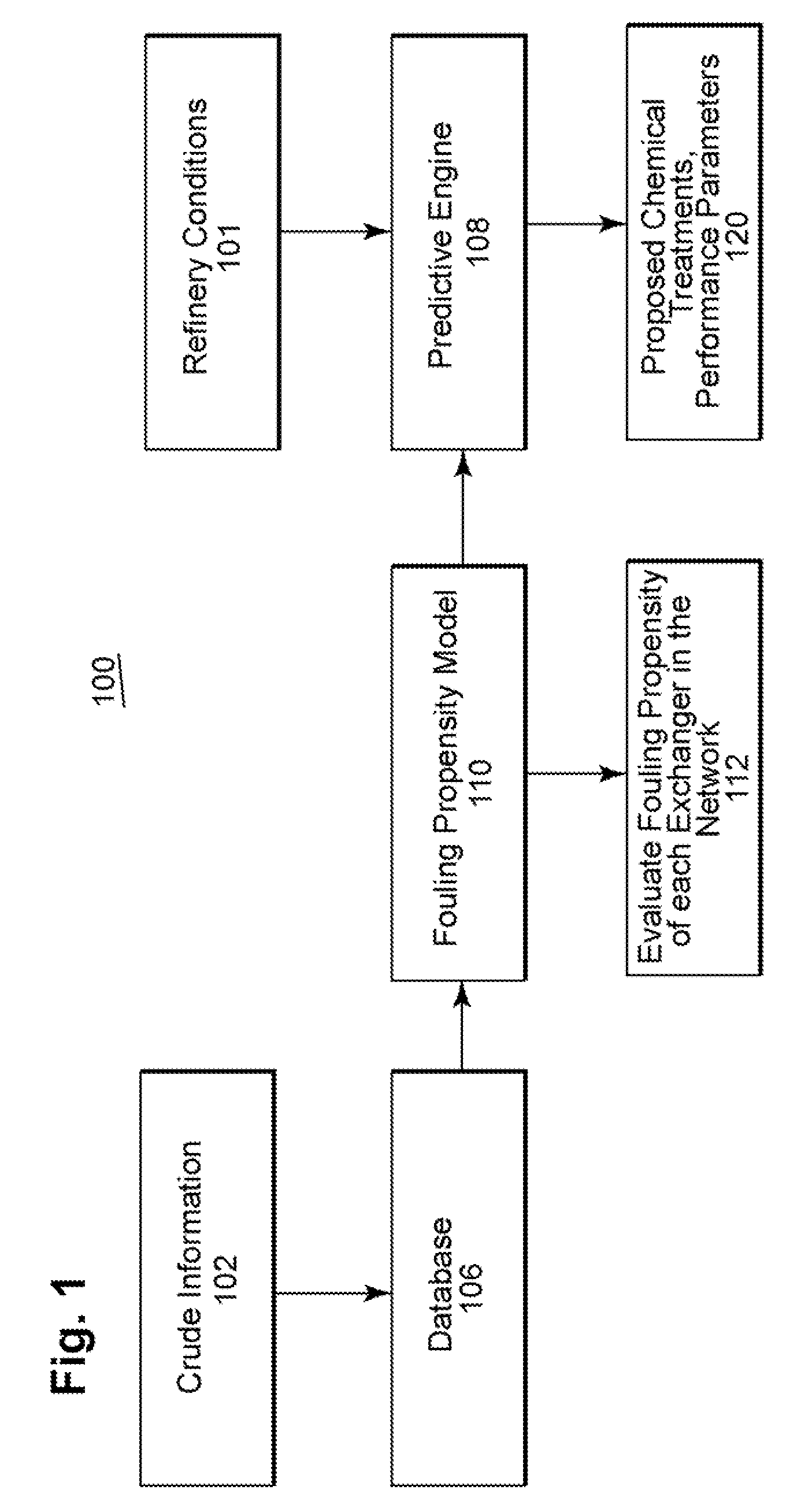
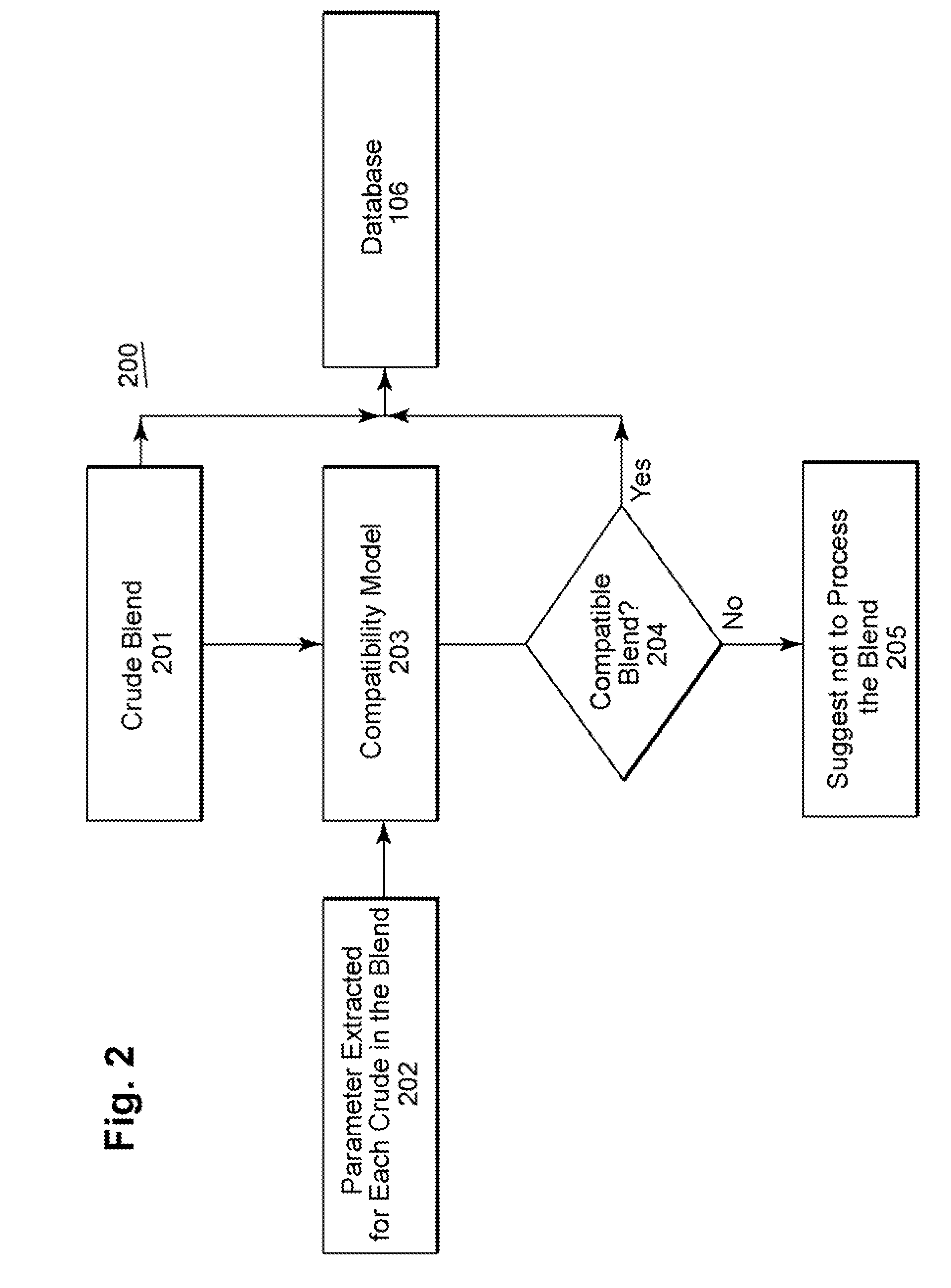
ActiveUS20080147365A1Performance degradationImprove performanceDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringQualitative propertyModel parameters
A methodology and system is disclosed which addresses outstanding needs of refiners to process cheaper crudes or blends of crudes. This method and system comprises a number of steps, including characterizing the impact of various constituents in the crude which result in fouling of heat exchangers; estimating model parameters; monitoring and predicting qualitative and quantitative performance; and determining optimal dosage of chemical treatments.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Method for cell search under effect of high clock offset
InactiveUS7173958B2Performance degradation can be reducedFast cell searchTime-division multiplexRadio transmissionThree stageCell search
The present invention discloses a cell search method for a CDMA system, using a three-stage cell search. The method comprises matching an incoming signal from the base station, wherein the frequency of the incoming signal having an uncertain range; over-sampling the incoming signal N times against a chip rate and outputting the N over-samples; down-sampling the incoming signal and outputting N over-samples to a first stage, a second stage and a third stage. The first stage further comprises selecting a first group of slot boundaries as a first group of candidates after pre-selection, and the first group of candidates transmitting to a deciding selection stage of the first stage and the second stage to be continuously processed. The cell search method of the present invention can be used to reduce the effect of clock offset on the performance of cell search and to accomplish fast cell search.
Owner:ACCTON TECHNOLOGY CORPORATION
Method and terminal for distributed access
InactiveUS20150009917A1Performance degradation be reduceFacilitate communicationWireless commuication servicesDistributed computingResource location
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Dynamic interface management for interference mitigation
InactiveUS20160364363A1Mitigate interferenceMitigates performance impactElectrical apparatus interference reductionArchitecture with single central processing unitIntegrated circuitEngineering
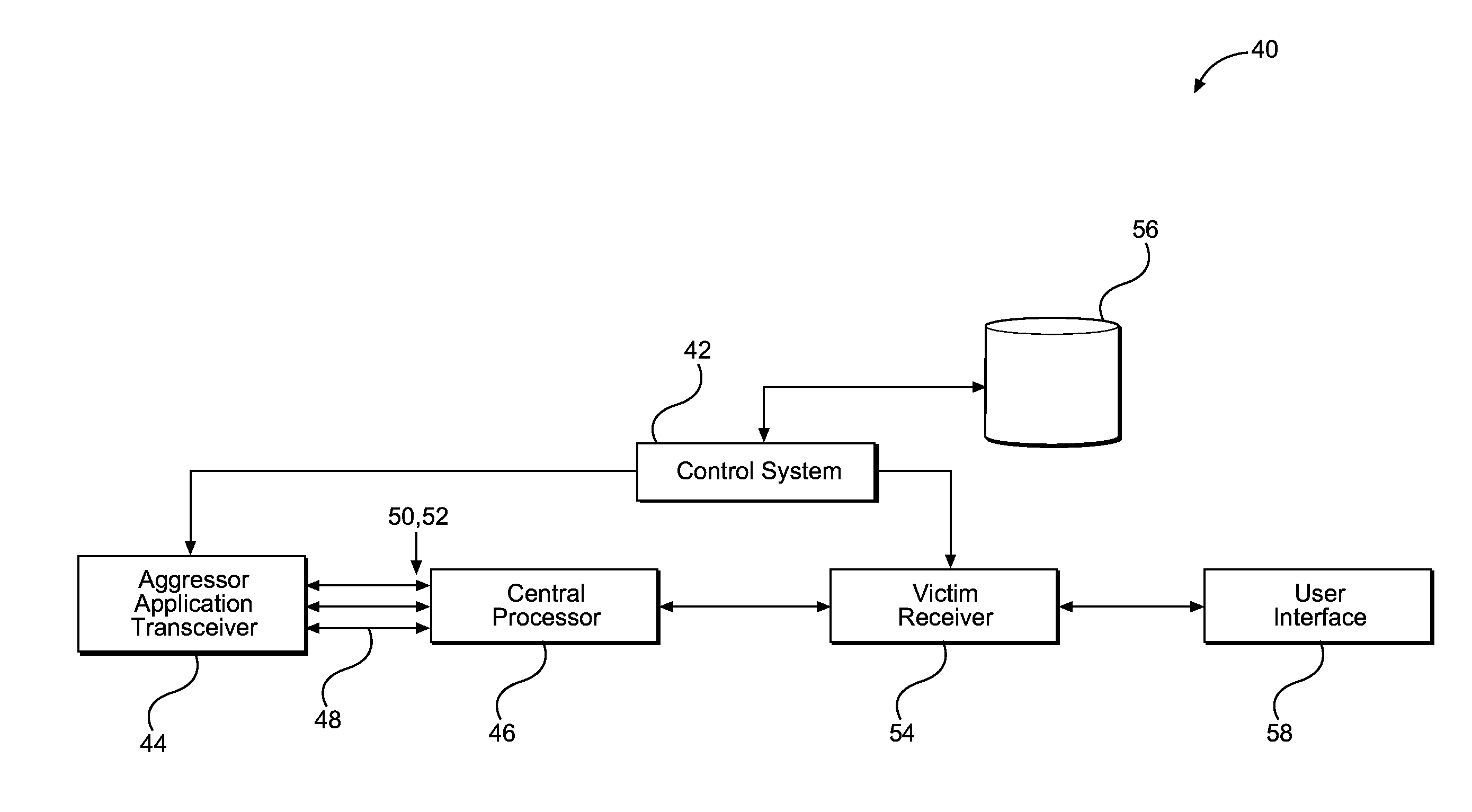
Dynamic interface management for interference mitigation is disclosed. In one aspect, an integrated circuit (IC) is provided that employs a control system configured to mitigate interference caused by an aggressor communications bus. The control system is configured to receive information related to interference conditions and adjust a data / clock mode of an interface corresponding to the aggressor communications bus. In this manner, the interface is configured to couple to the aggressor communications bus. The interface is configured to transmit signals to and receive signals from the aggressor communications bus. The control system is configured to use the information related to the interference conditions to set the data / clock mode of the interface to mitigate the interference experienced by a victim receiver, whether the victim receiver is wired or wireless. Thus, the control system provides designers with an additional tool that may reduce performance degradation of the victim receiver attributable to the interference.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method and system for assessing the performance of crude oils
ActiveUS7813894B2Low cleanlinessPerformance degradation can be reducedDigital computer detailsNuclear monitoringChemical treatmentModel parameters
A methodology and system is disclosed which addresses outstanding needs of refiners to process cheaper crudes or blends of crudes. This method and system comprises a number of steps, including characterizing the impact of various constituents in the crude which result in fouling of heat exchangers; estimating model parameters; monitoring and predicting qualitative and quantitative performance; and determining optimal dosage of chemical treatments.
Owner:BL TECH INC
Dynamic interface management for interference mitigation
InactiveUS20160364359A1Reduced performance impactReduce electromagnetic interferenceDigital computer detailsElectrical apparatus interference reductionControl systemElectromagnetic interference
Dynamic interface management for interference mitigation is disclosed. In one aspect, an integrated circuit (IC) is provided that employs a control system configured to mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by an aggressor communications bus. The control system is configured to receive information related to EMI conditions and adjust a data / clock mode of an interface corresponding to the aggressor communications bus. In this manner, the interface is configured to couple to the aggressor communications bus. The interface is configured to transmit signals to and receive signals from the aggressor communications bus. The control system is configured to use the information related to the EMI conditions to set the data / clock mode of the interface to mitigate the EMI experienced by a victim receiver. Thus, the control system provides designers with an additional tool that may reduce performance degradation of the victim receiver attributable to EMI.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
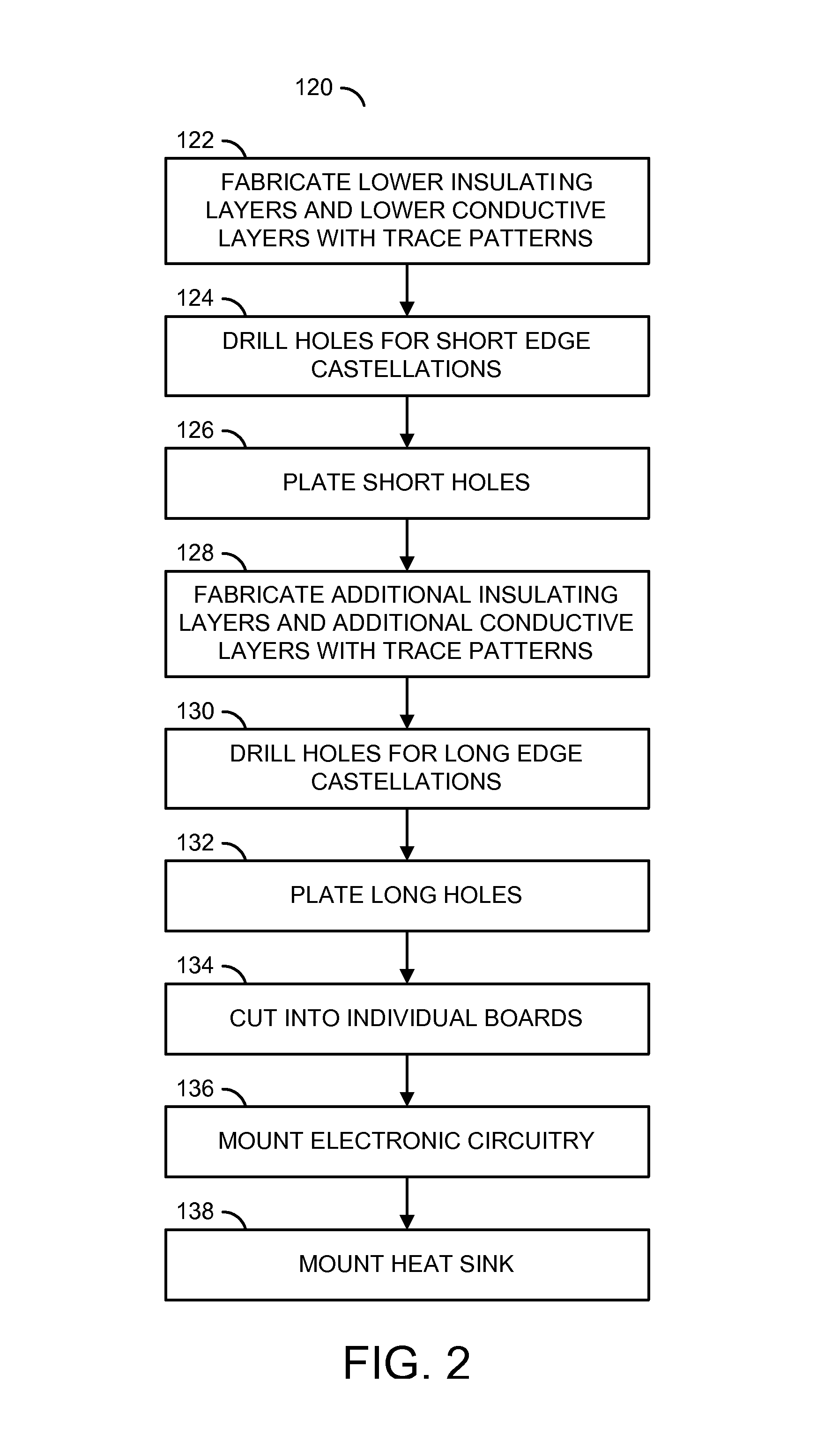
Blind via edge castellation
InactiveUS9538636B1Performance degradation can be reducedLess layersSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh frequency circuit adaptationsEngineeringElectroplating
An apparatus having a plurality of insulating layers, a plurality of conductive layers and a plating is disclosed. The conductive layers may be separated by the insulating layers. A first pattern in a first of the conductive layers generally extends to an edge castellation. A second pattern in a second of the conductive layers may also extends to the edge castellation. The plating may be disposed in the edge castellation and connect the first pattern to the second pattern. The plating in the castellation may extend at most between a subset of the conductive layers.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
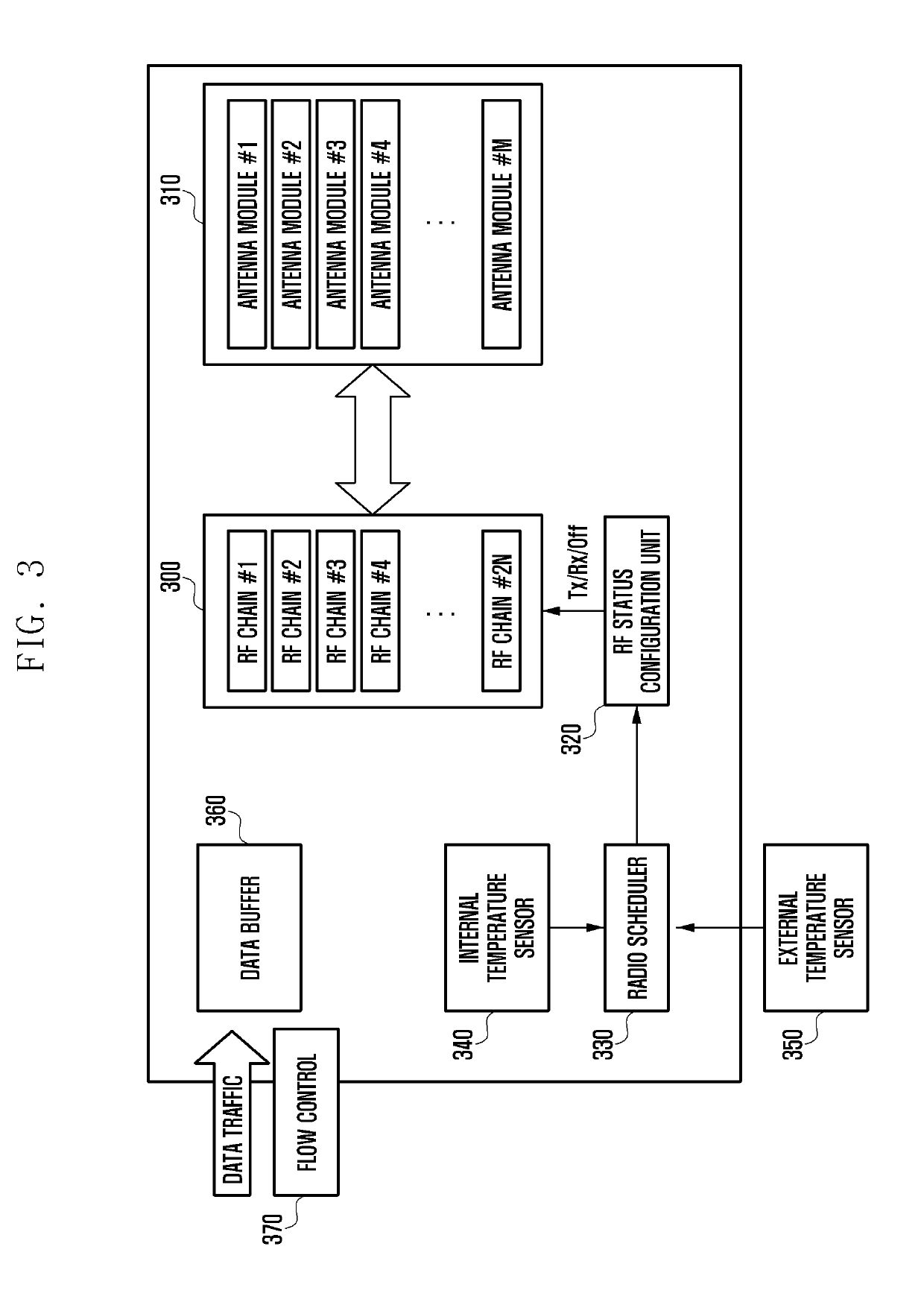
Apparatus having multiple RF chains coupled to multiple antennas and operating method thereof in wireless communication system
ActiveUS20190123787A1Reduce device sizeReduce performance degradationPower managementNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemData rate
The present disclosure relates to a 5G or pre-5G communication system for supporting a data rate higher than that of 4G communication systems such as LTE systems. A method for controlling a device having a plurality of radio frequency (RF) chains coupled to a plurality of antennas in a wireless communication system according to an embodiment of the present invention includes comparing a measured temperature of the device with a temperature threshold, controlling status of at least one of the RF chains according to a comparison result between the measured temperature and the temperature threshold, and transmitting a radio signal using at least one of the antennas that is connected to the at least one RF chain.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adjusting application parameters for interference mitigation
ActiveUS20160087732A1Performance degradation can be reducedReduce electromagnetic interferenceReceivers monitoringElectrical apparatus interference reductionControl systemElectromagnetic interference
Aspects of adjusting application parameters for interference mitigation are disclosed. In one aspect, a computing device is provided that employs a control system configured to detect and mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated within the computing device. More specifically, the control system is configured to detect possible EMI conditions and adjust parameters within the computing device to mitigate such EMI. In this manner, the computing device includes an aggressor application and a victim receiver. The control system is configured to analyze performance tradeoffs based on an acceptable performance level of the aggressor application and the performance degradation experienced by the victim receiver. Based on such analysis, the control system is configured to adjust parameters associated with the aggressor application to mitigate the EMI. Thus, the control system provides designers with an additional tool that may reduce the performance degradation of the victim receiver attributable to the EMI.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
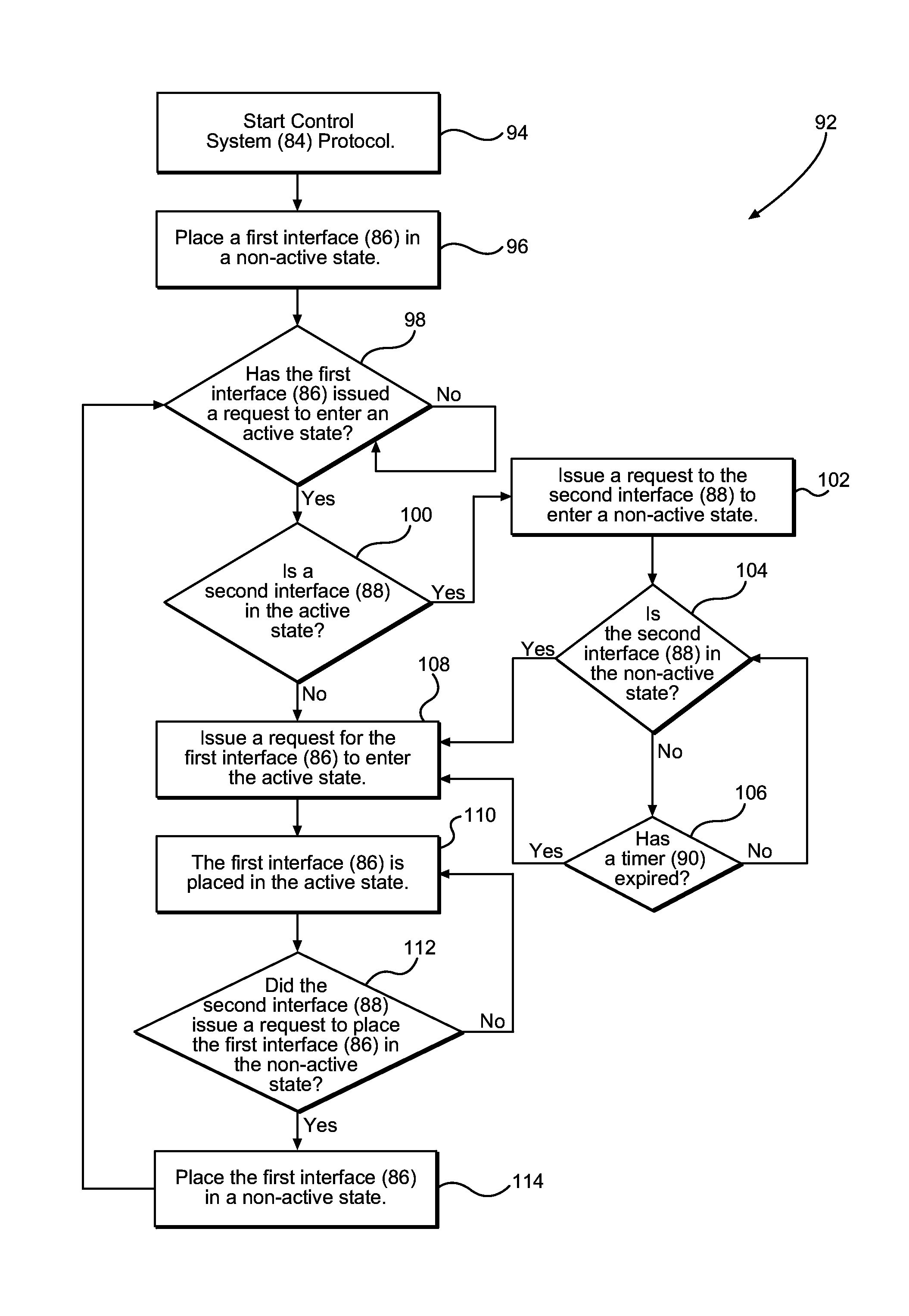
Priority arbitration for interference mitigation
ActiveUS20160088554A1Reduce electromagnetic interferencePerformance degradation can be reducedPower managementTransmission systemsControl systemElectromagnetic interference
Aspects of priority arbitration for interference mitigation are disclosed. In one aspect, a computing device is provided that employs a control system configured to arbitrate the activity of multiple interfaces. This arbitration mitigates potential electromagnetic interference (EMI) that may degrade the performance of the computing device. Upon a first interface requesting to become active, the control system is configured to determine if a second interface is currently active. If so, the control system is configured to arbitrate the activity of the first interface and the second interface to mitigate the potential EMI generated if the interfaces are concurrently active. The computing device includes an aggressor controller and a victim receiver, each corresponding to a particular interface. The control system is configured to arbitrate such activity so that the aggressor controller and corresponding cable do not generate EMI during a time period that would degrade the performance of the victim receiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Dynamic lane management for interference mitigation
InactiveUS20160179741A1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceLow experience requirementDigital computer detailsElectrical apparatus interference reductionDynamic channelControl system
Dynamic lane management for interference mitigation is disclosed. In one aspect, an integrated circuit (IC) is provided that employs a control system configured to mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by an aggressor communications bus. The control system is configured to receive information related to EMI conditions and adjust which lanes of the aggressor communications bus are employed for signal transmission. The IC includes an interface configured to couple to the aggressor communications bus. The interface is configured to transmit signals to and receive signals from the aggressor communications bus. The control system is configured to use the information related to the EMI conditions to assign signals to be transmitted via particular lanes of the aggressor communications bus to mitigate the EMI experienced by a victim receiver. The control system provides designers with an additional tool that may reduce the performance degradation of the victim receiver attributable to EMI.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
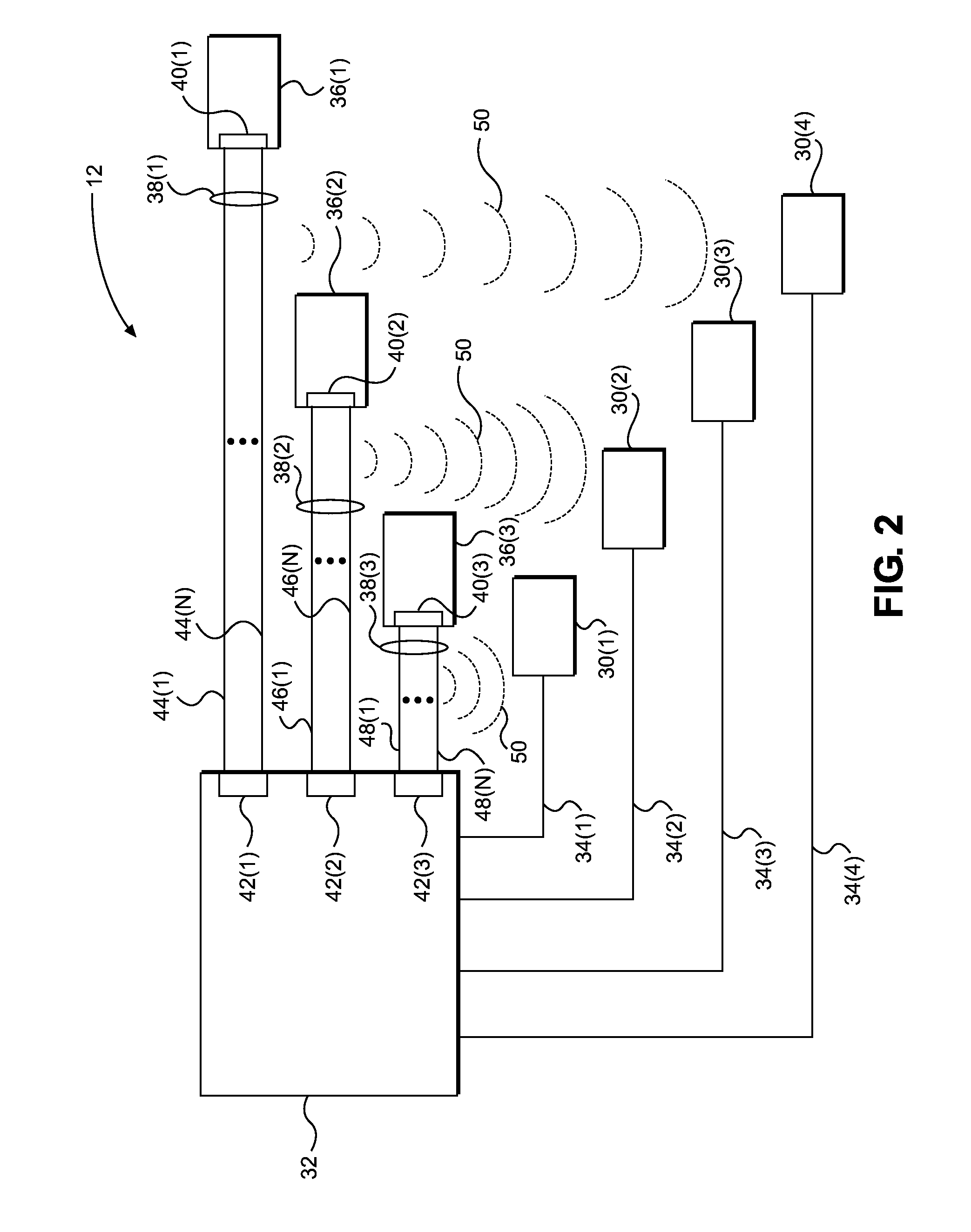
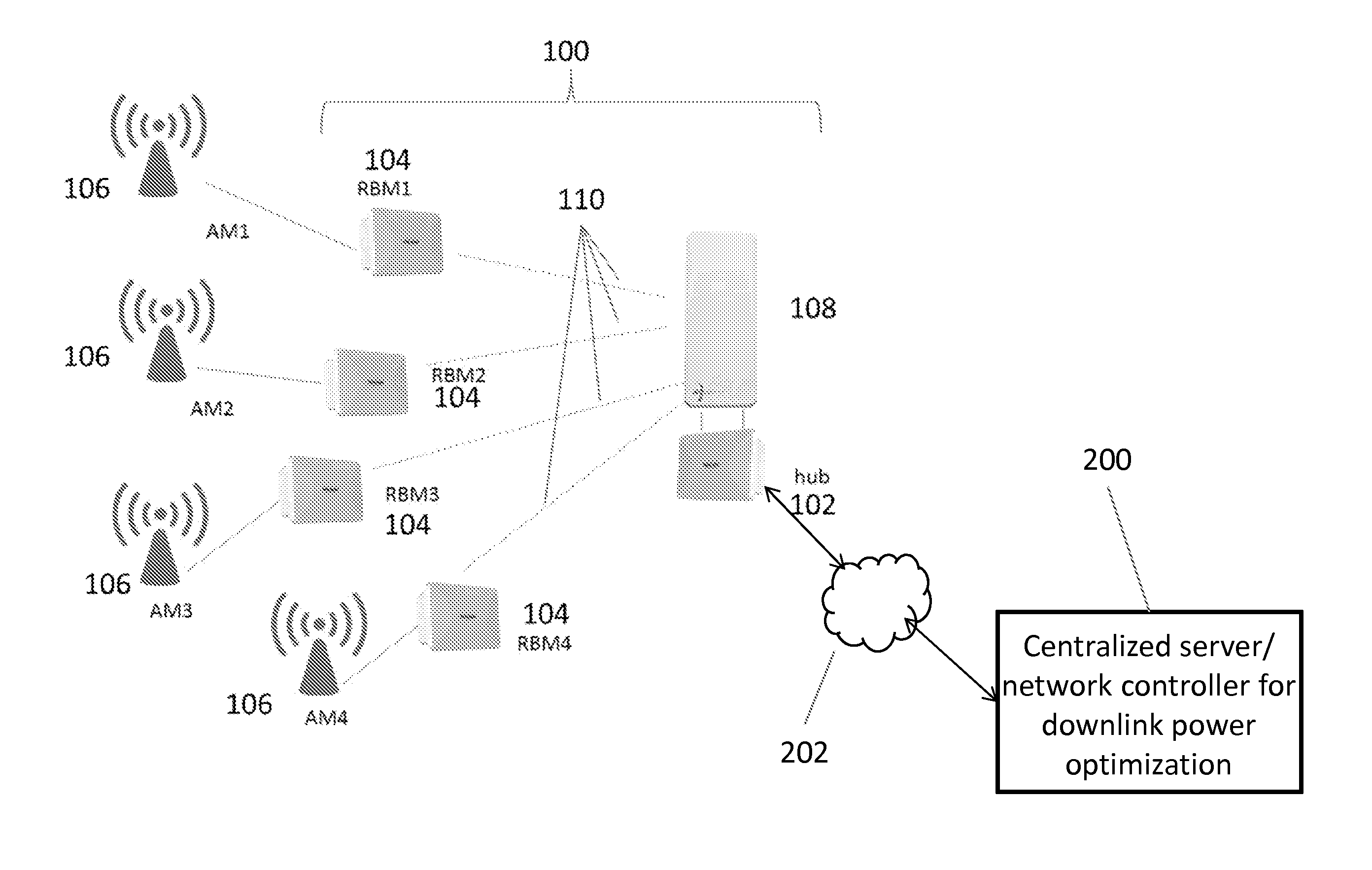
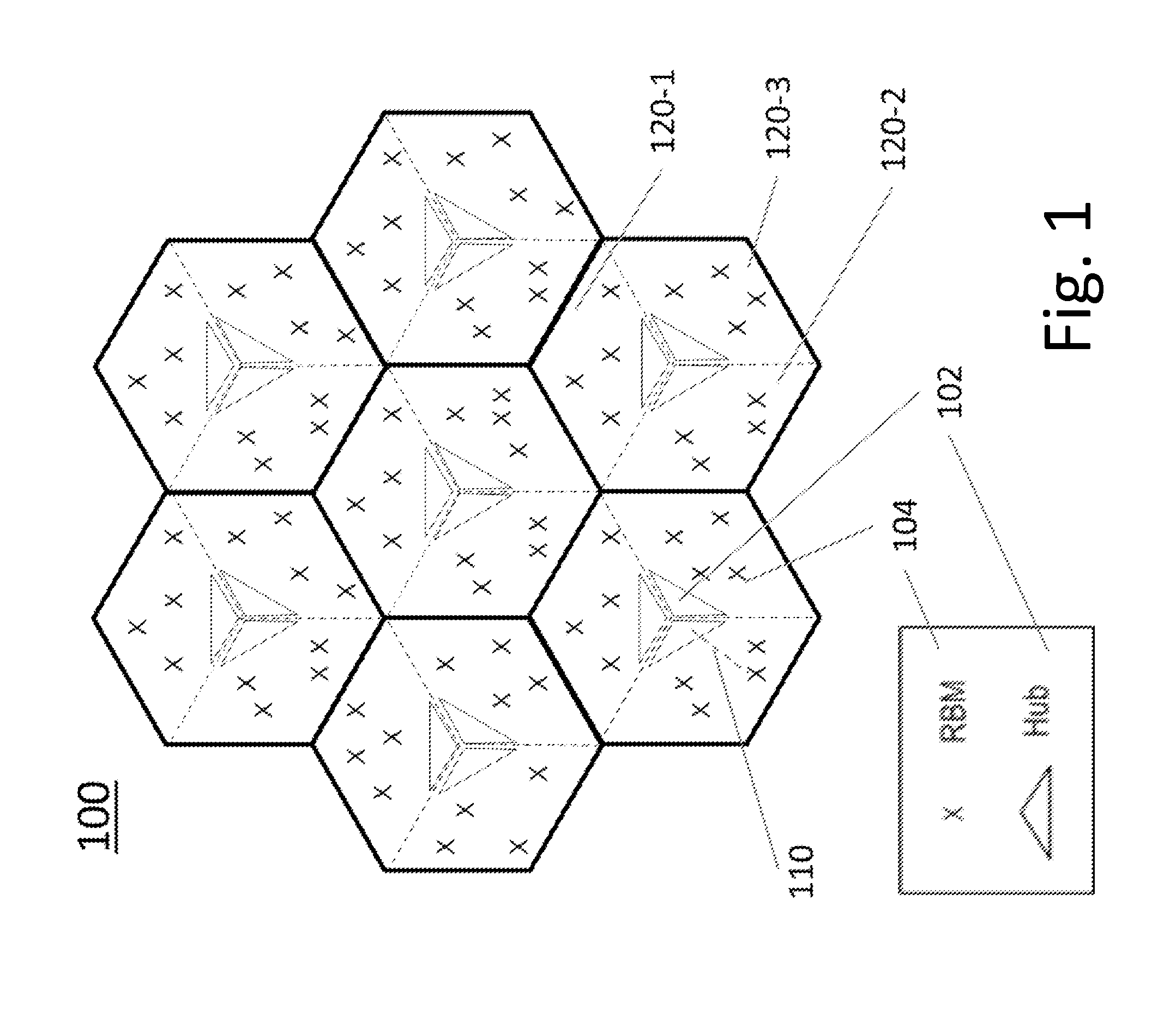
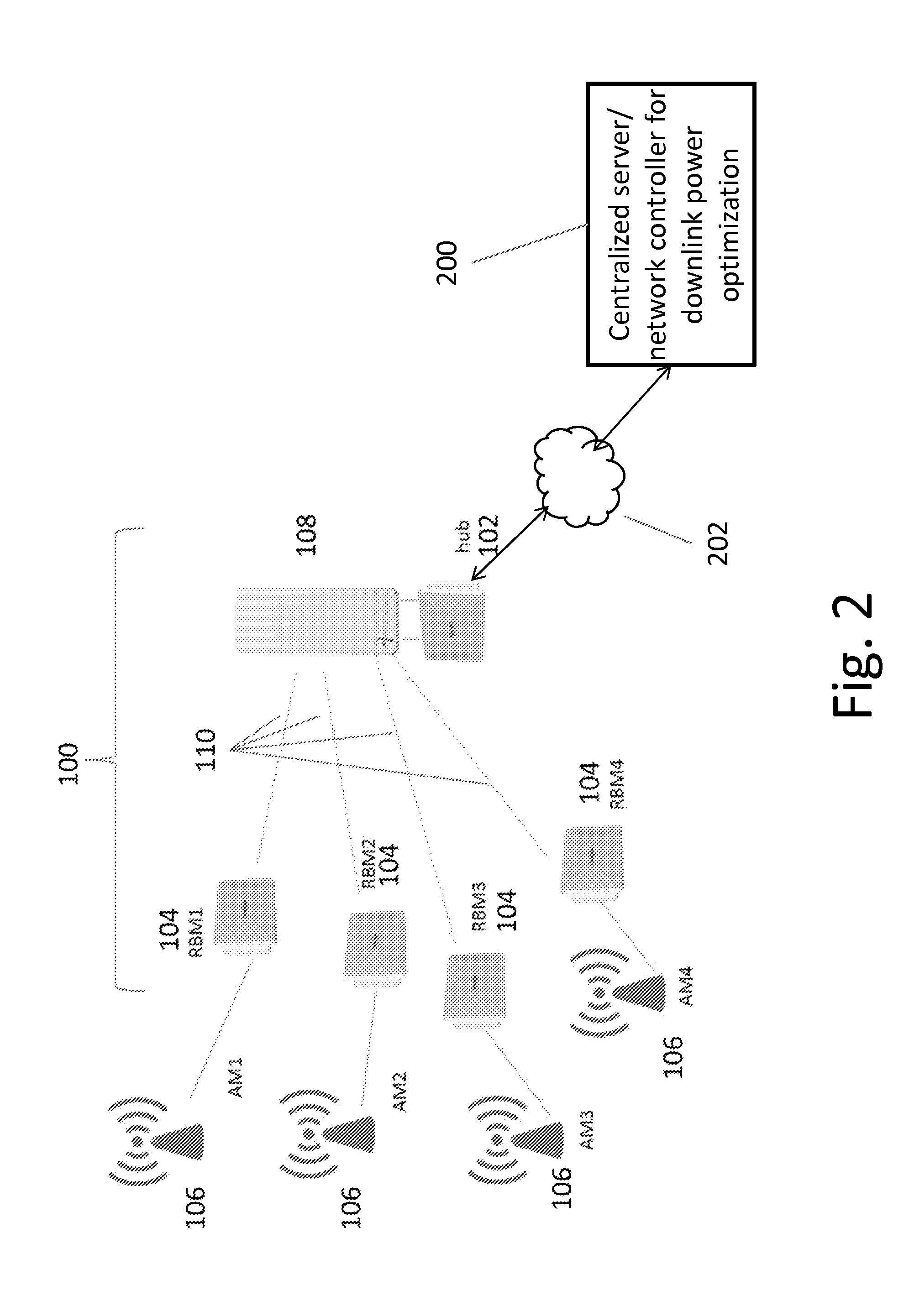
System and method for downlink power optimization in a partitioned wireless backhaul network with out-of-neighborhood utility evaluation
ActiveUS20150057004A1Mitigate disadvantage of knownMitigate of methodPower managementNetwork planningTransmitted powerCurve fitting
A system and method for downlink power optimization in a partitioned wireless backhaul network with out-of-neighborhood utility evaluation is disclosed. The method comprises performing initial downlink power optimization for each neighborhood independently, considering only in-neighborhood utilities, by obtaining the transmit powers of all hubs and a utility performance of all served remote backhaul modules (RBMs) in the neighborhood. Power optimization data for each neighborhood are then reported to a central processing unit for storage. Thereafter, for each neighborhood, an out-of-neighborhood utility evaluation is performed by the centralized processing unit, based on reported power optimization data from other neighborhoods, for example, by obtaining delta out-of-neighborhood sum utilities for each hub as a function of hub transmit power, by curve fitting of reported data. Power optimization for each neighborhood is then performed by optimizing both in-neighborhood sum utilities and out-of-neighborhood sum utilities, and hub transmit powers are updated accordingly.
Owner:BLINQ NETWORKS
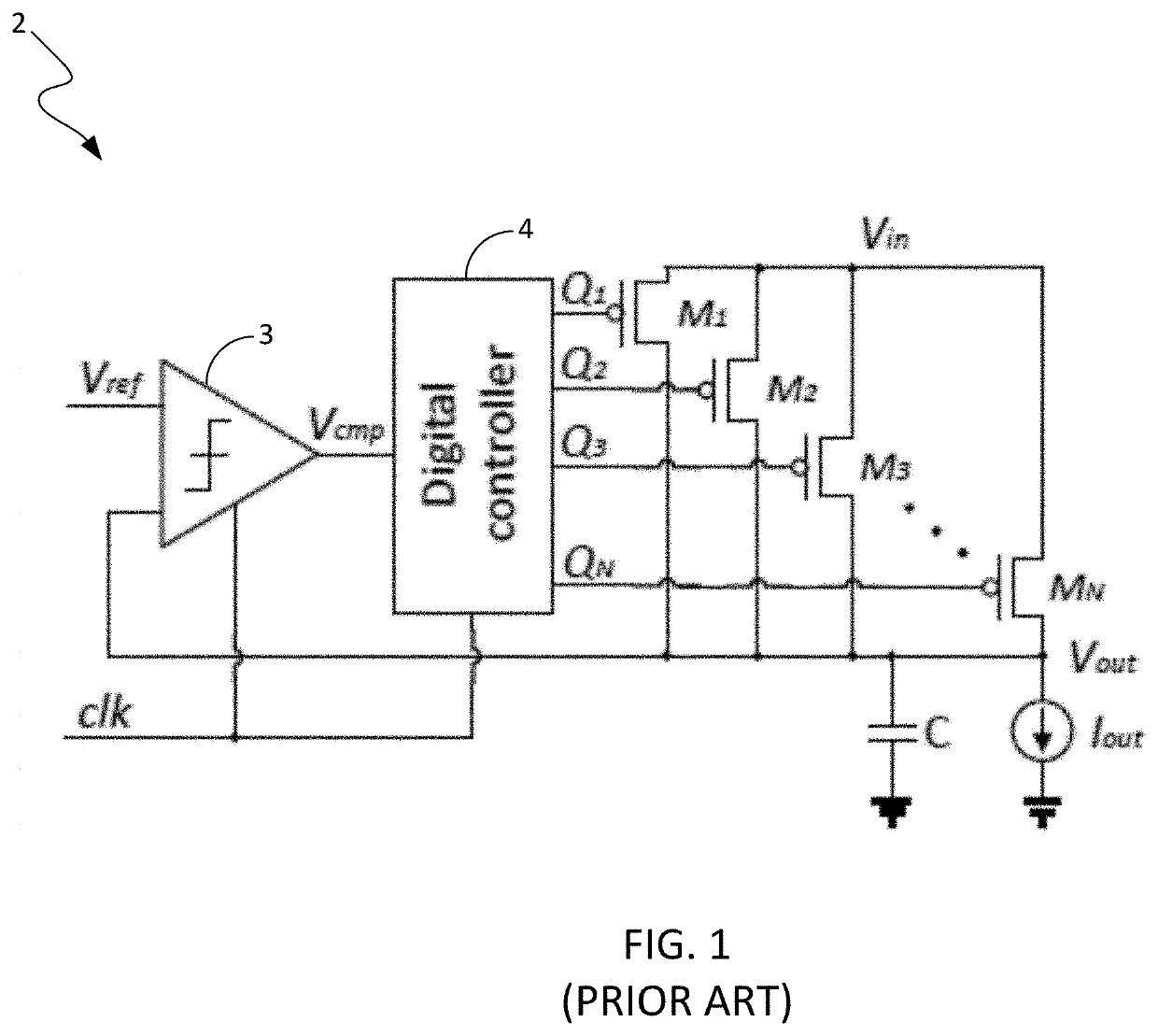
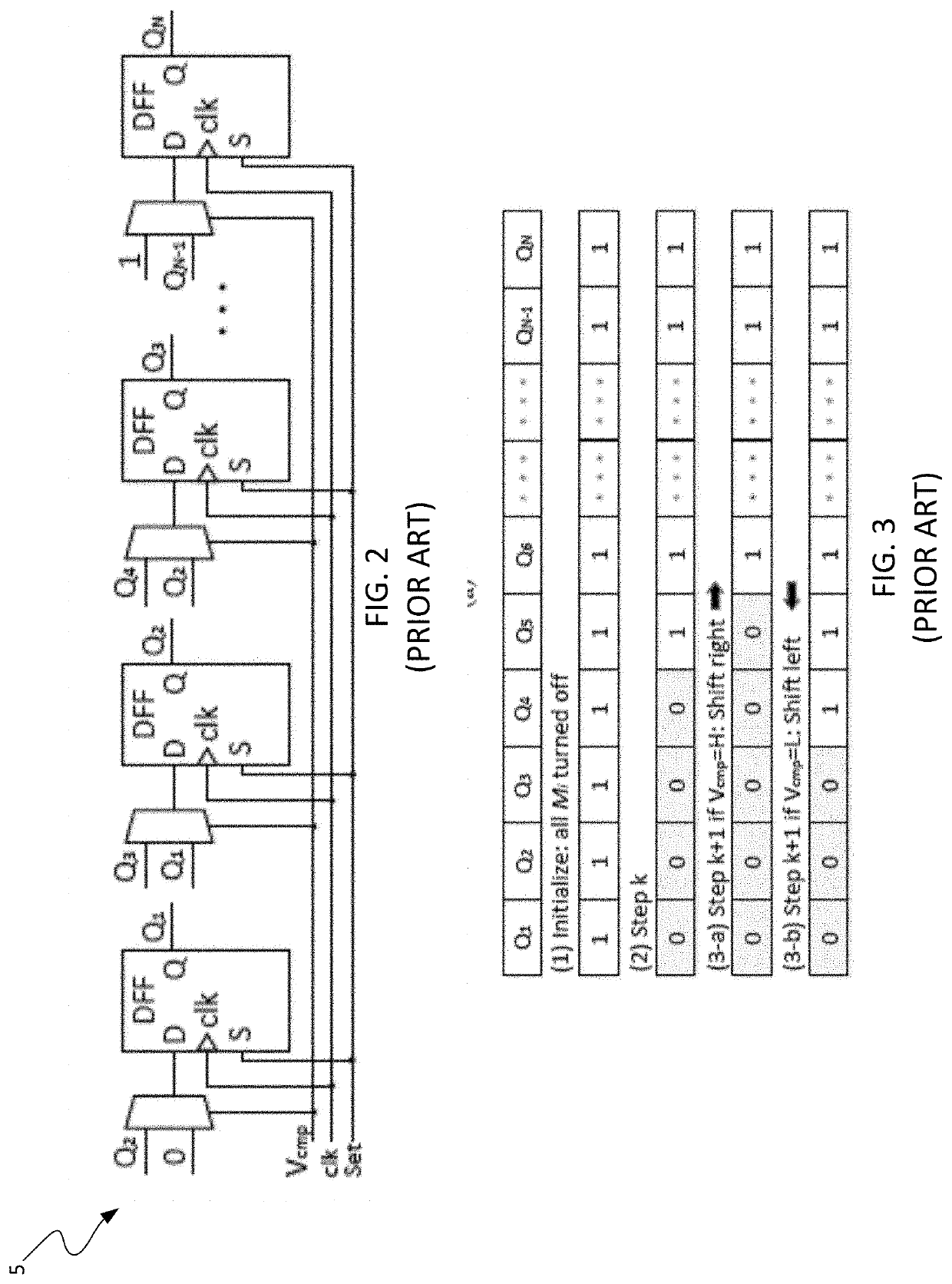
Method and apparatus for mitigating performance degradation in digital low-dropout voltage regulators (DLDOs) caused by limit cycle oscillation (LCO) and other factors
ActiveUS11099591B1Performance degradationPerformance degradation can be reducedElectric variable regulationHemt circuitsLimit cycle oscillation
A DLDO has a configuration that mitigates performance degradation associated with limit cycle oscillation (LCO). The DLDO comprises a clocked comparator, an array of power transistors, a digital controller and a clock pulsewidth reduction circuit. The digital controller comprises control logic configured to generate control signals that cause the power transistors to be turned ON or OFF in accordance with a preselected activation / deactivation control scheme. The clock pulsewidth reduction circuit receives an input clock signal having a first pulsewidth and generates the DLDO clock signal having the preselected pulsewidth that is narrower that the first pulsewidth, which is then delivered to the clock terminals of the clocked comparator and the digital controller. The narrower pulsewidth of the DLDO clock reduces the LCO mode to mitigate performance degradation caused by LCO.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA +1
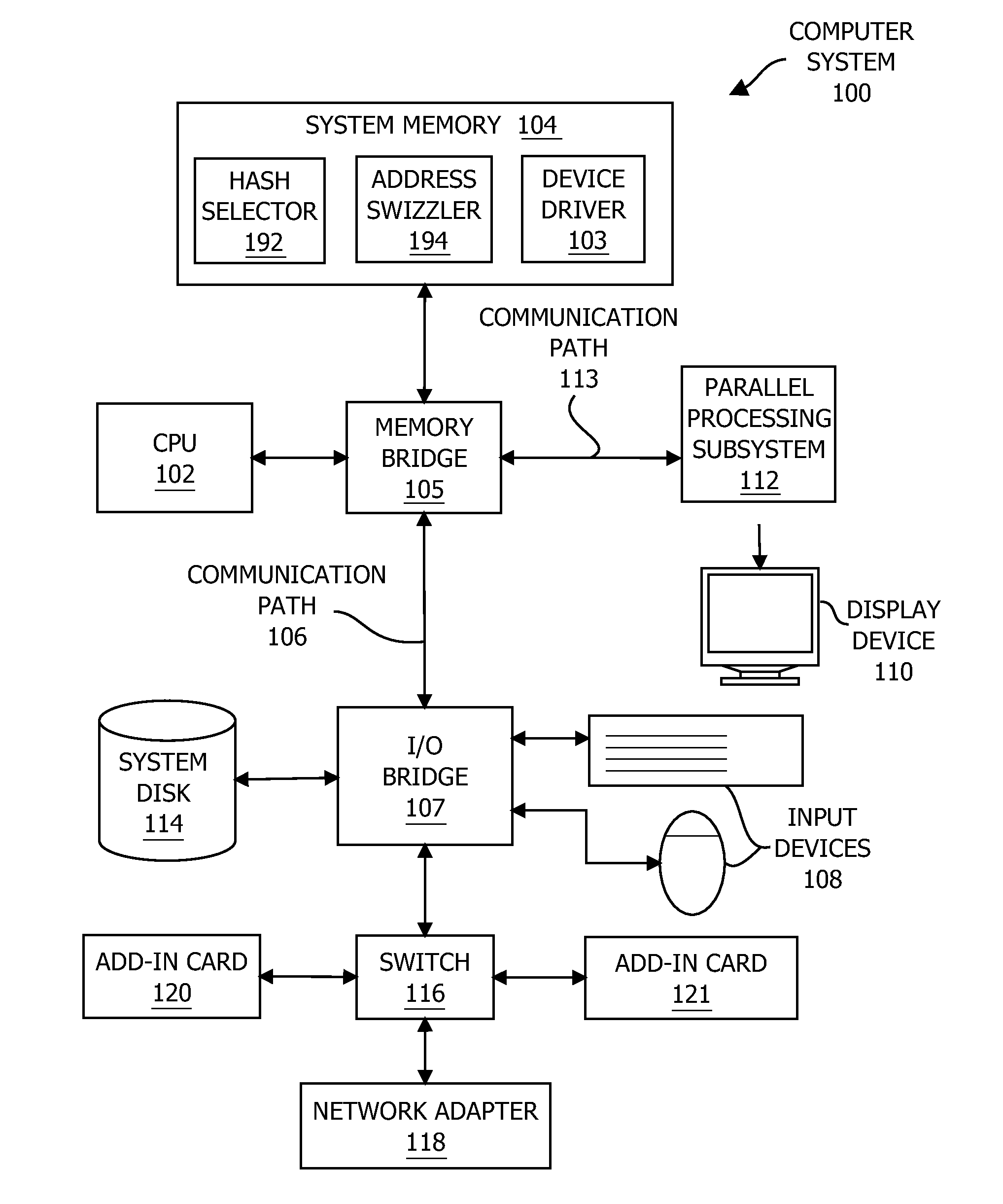
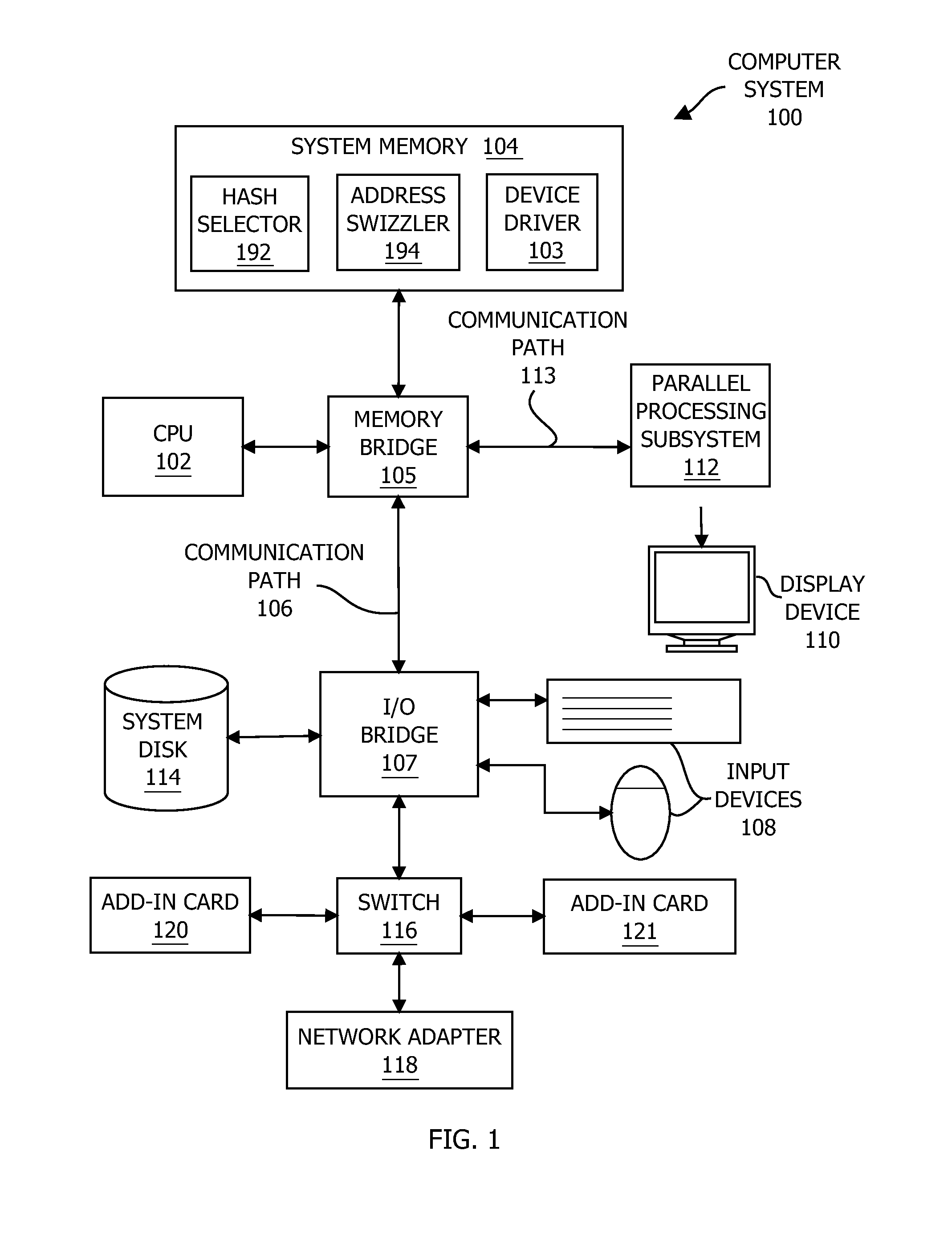
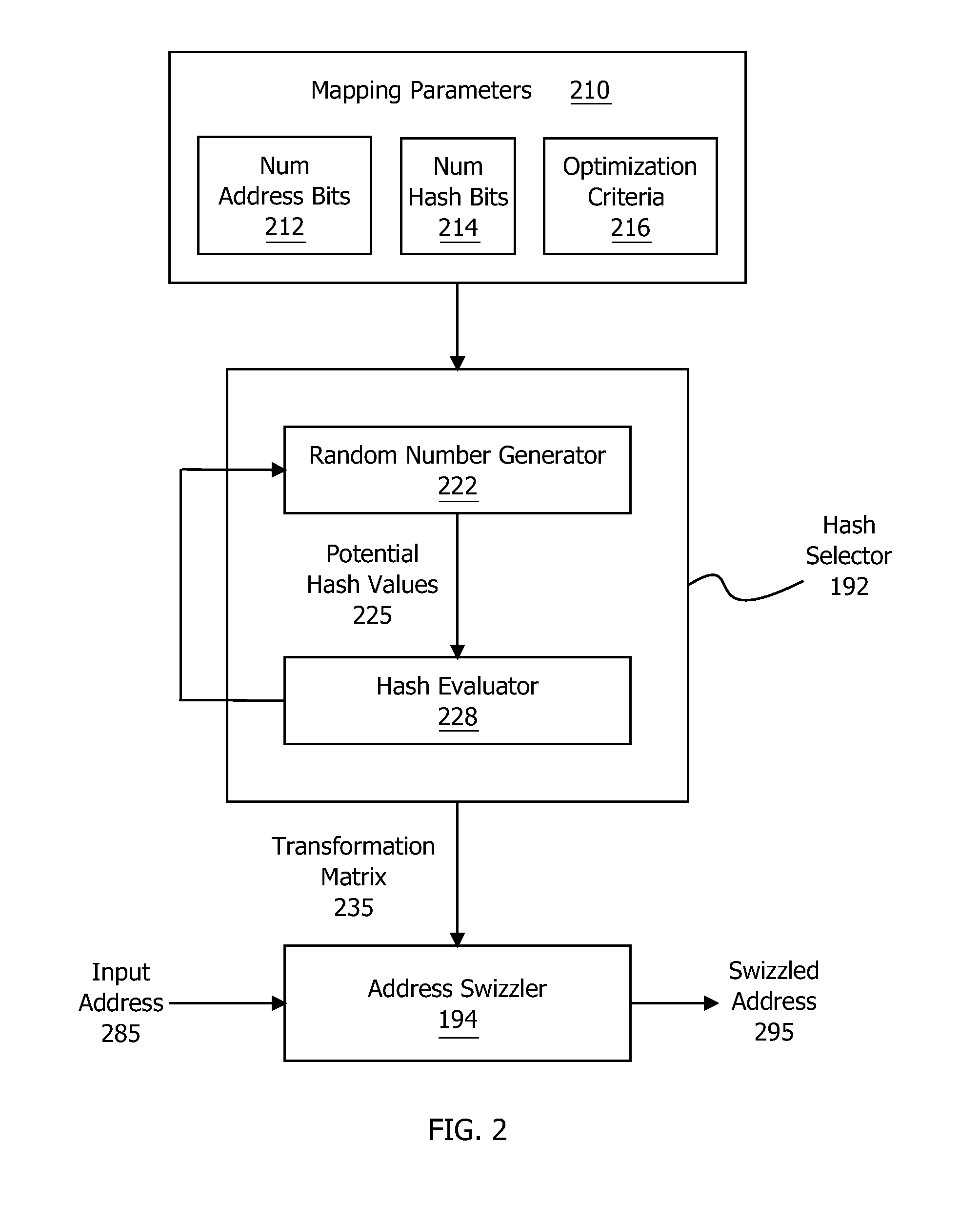
Selecting hash values based on matrix rank
ActiveUS20160062910A1Improve performancePerformance degradation can be reducedMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransformation matrixAlgorithm
One embodiment of the present invention includes a hash selector that facilitates performing effective hashing operations. In operation, the hash selector creates a transformation matrix that reflects specific optimization criteria. For each hash value, the hash selector generates a potential hash value and then computes the rank of a submatrix included in the transformation matrix. Based on this rank in conjunction with the optimization criteria, the hash selector either re-generates the potential hash value or accepts the potential hash value. Advantageously, the optimization criteria may be tailored to create desired correlations between input patterns and the results of performing hashing operations based on the transformation matrix. Notably, the hash selector may be configured to efficiently and reliably incrementally generate a transformation matrix that, when applied to certain strides of memory addresses, produces a more uniform distribution of accesses across caches lines than previous approaches to memory addressing.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
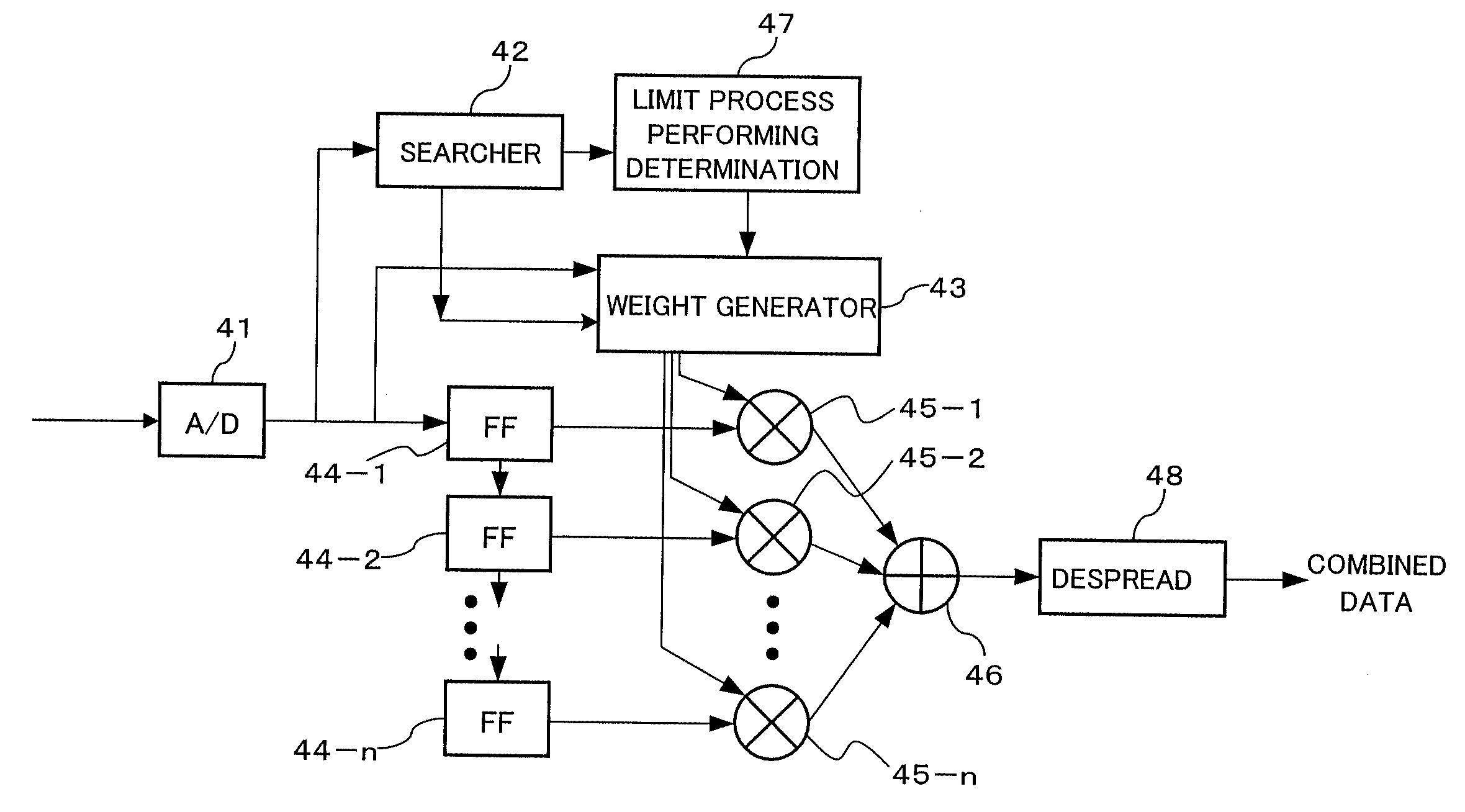
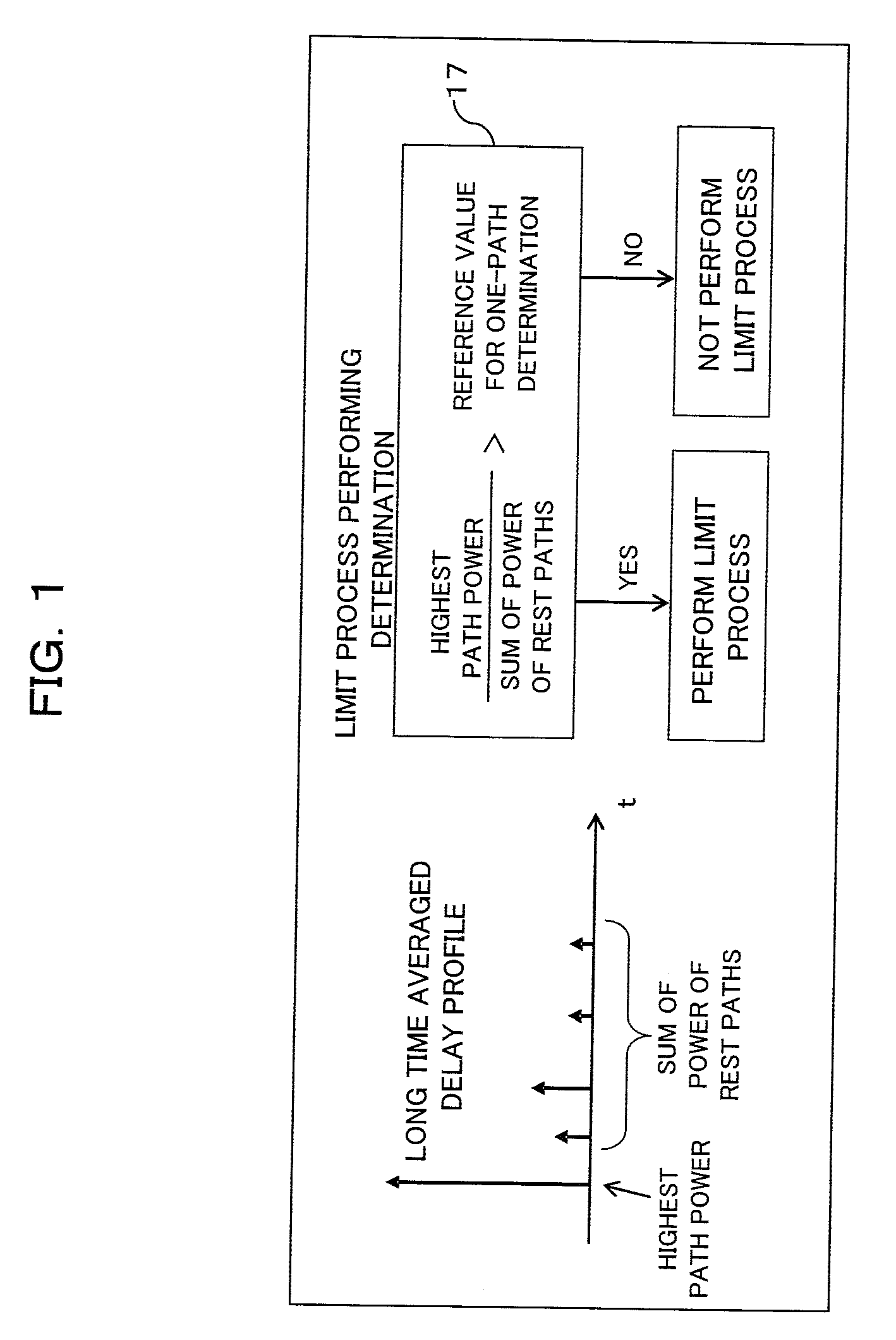
Receiver and Reception Processing Method
InactiveUS20090010313A1Improve performancePerformance degradation can be reducedMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsEngineeringMulti path
A receiver including: a delay profile generating unit to generate a delay profile from a received signal; combining unit operable to combine multiple received signals with different timings; a determining unit to determine whether or not the propagation environment of the received signals is multi-path, based on the delay profile; and a control unit operable to exclude any signal with timing whose power is equal to or lower than a predetermined threshold in the delay profile from the combining, upon the determination not being multi-path.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Fast inter-base station ring (FIBR): new millimeter wave cellular network architectures and processes
ActiveUS20210136656A1Reduce HO latencyReduce blockingError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementControl signalRing network
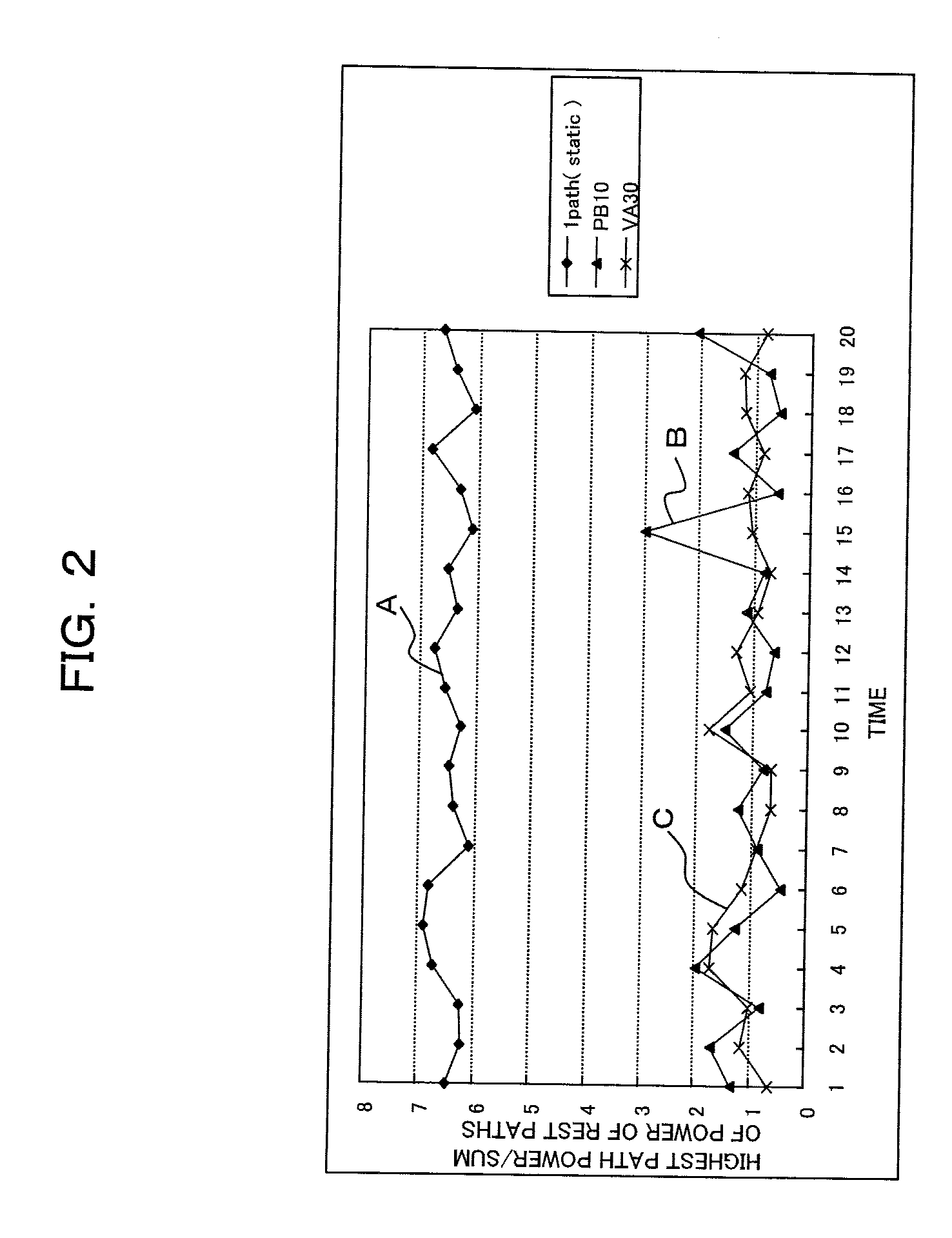
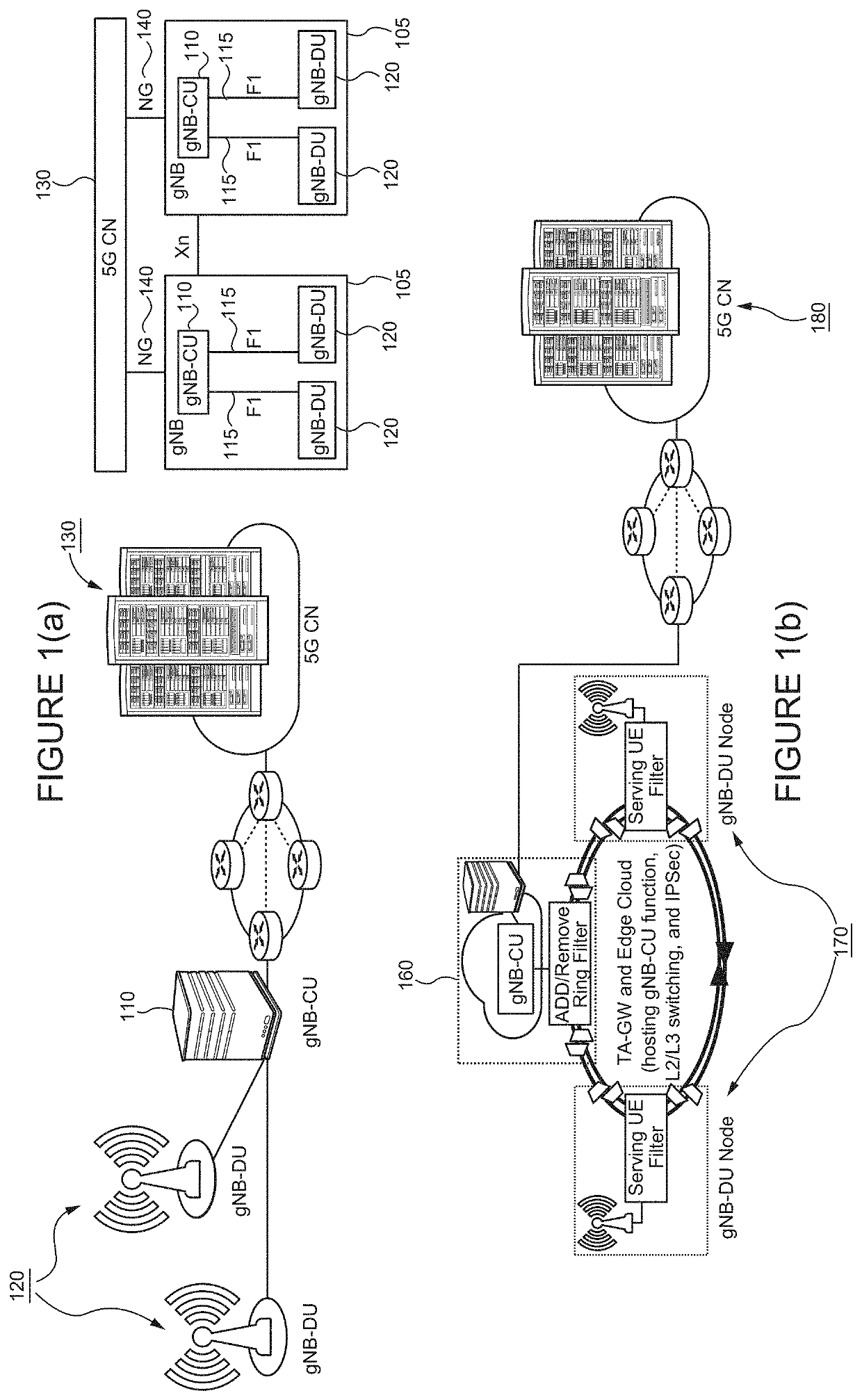
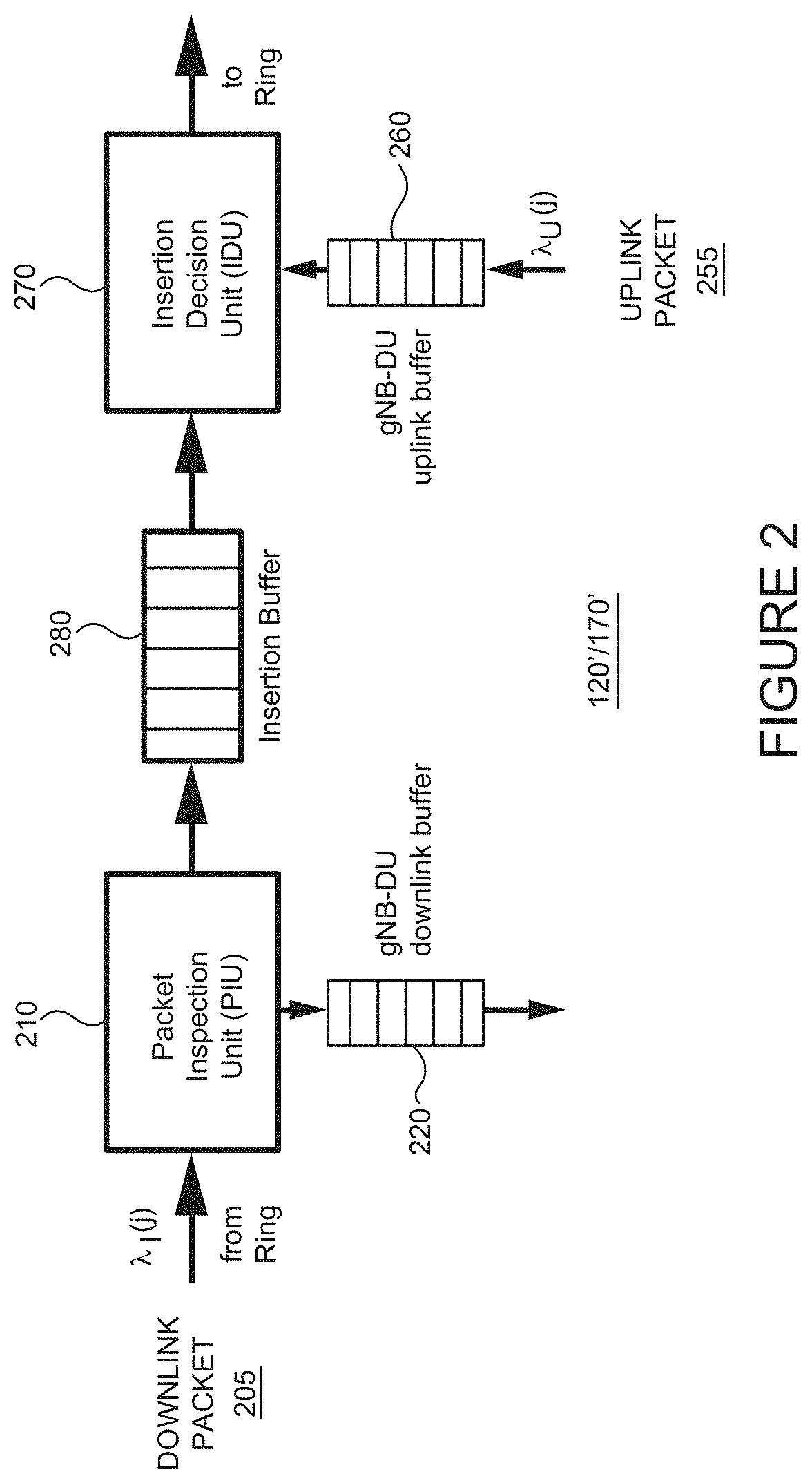
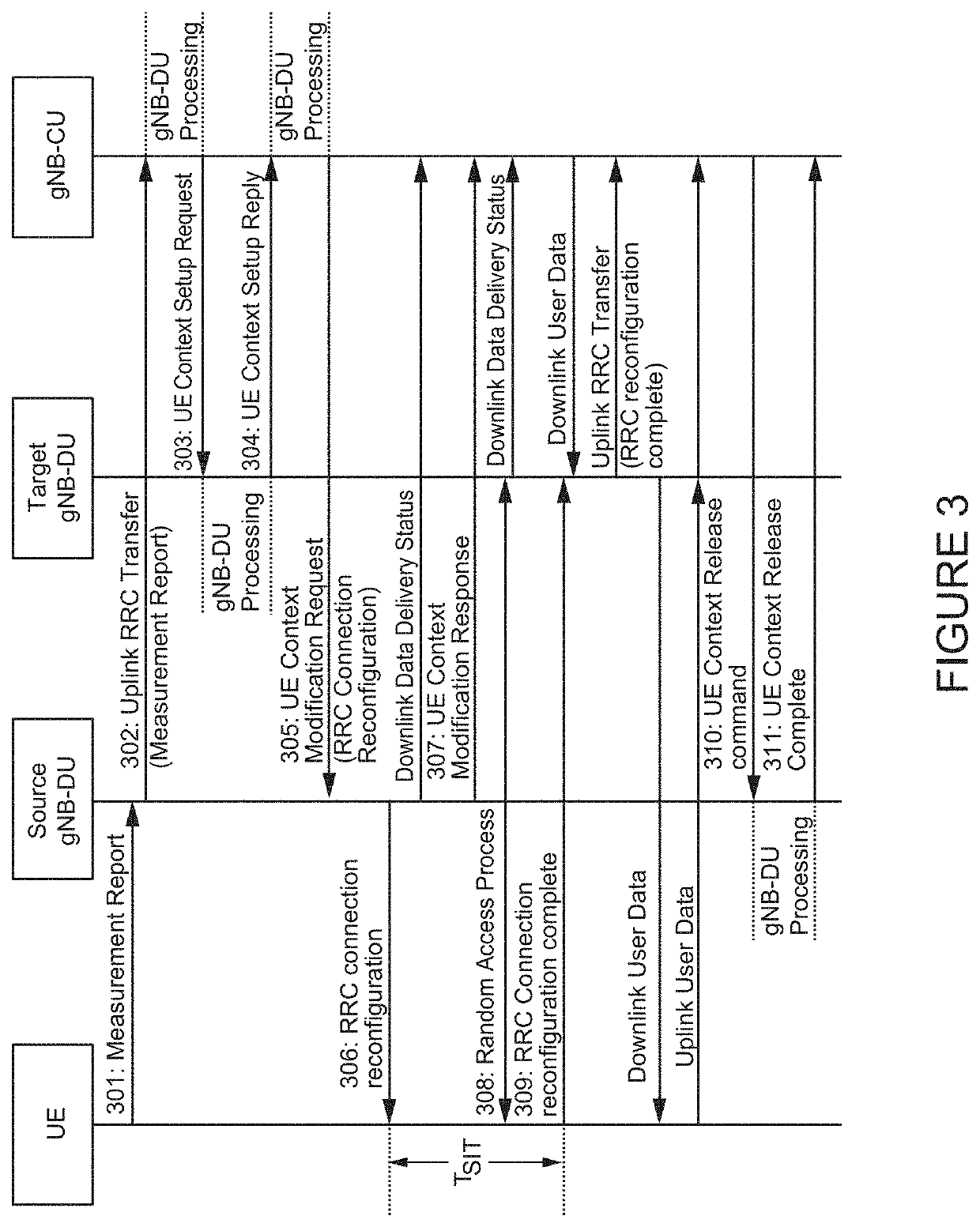
Fifth Generation (5G) Millimeter Wave (mmWave) cellular networks are expected to serve a large set of throughput intensive, ultra-reliable, and ultra-low latency applications. To meet these stringent requirements, while minimizing the network cost, the 3rd Generation Partnership Project has proposed a new transport architecture, where certain functional blocks can be placed closer to the network edge. In this architecture, however, blockages and shadowing in 5G mmWave cellular networks may lead to frequent handovers (HOs) causing significant performance degradation. To meet the ultra-reliable and low-latency requirements of applications and services in an environment with frequent HOs, a Fast Inter-Base Station Ring (FIBR) architecture is described, in which base stations that are in close proximity are grouped together, interconnected by a bidirectional counter-rotating buffer insertion ring network. FIBR enables high-speed control signaling and fast-switching among BSs during HOs, while allowing the user equipment to maintain a high degree of connectivity. The FIBR architecture efficiently handles frequent HO events in mm Wave and / or Terahertz cellular systems, and more effectively satisfies the QoS requirements of 5G applications.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Priority arbitration for interference mitigation
ActiveUS9510281B2Performance degradation can be reducedReduce electromagnetic interferencePower managementWireless commuication servicesTime segmentControl system
Aspects of priority arbitration for interference mitigation are disclosed. In one aspect, a computing device is provided that employs a control system configured to arbitrate the activity of multiple interfaces. This arbitration mitigates potential electromagnetic interference (EMI) that may degrade the performance of the computing device. Upon a first interface requesting to become active, the control system is configured to determine if a second interface is currently active. If so, the control system is configured to arbitrate the activity of the first interface and the second interface to mitigate the potential EMI generated if the interfaces are concurrently active. The computing device includes an aggressor controller and a victim receiver, each corresponding to a particular interface. The control system is configured to arbitrate such activity so that the aggressor controller and corresponding cable do not generate EMI during a time period that would degrade the performance of the victim receiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Adjusting application parameters for interference mitigation
ActiveUS9294202B1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceLow experience requirementReceivers monitoringElectrical apparatus interference reductionControl systemElectromagnetic interference
Aspects of adjusting application parameters for interference mitigation are disclosed. In one aspect, a computing device is provided that employs a control system configured to detect and mitigate electromagnetic interference (EMI) generated within the computing device. More specifically, the control system is configured to detect possible EMI conditions and adjust parameters within the computing device to mitigate such EMI. In this manner, the computing device includes an aggressor application and a victim receiver. The control system is configured to analyze performance tradeoffs based on an acceptable performance level of the aggressor application and the performance degradation experienced by the victim receiver. Based on such analysis, the control system is configured to adjust parameters associated with the aggressor application to mitigate the EMI. Thus, the control system provides designers with an additional tool that may reduce the performance degradation of the victim receiver attributable to the EMI.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
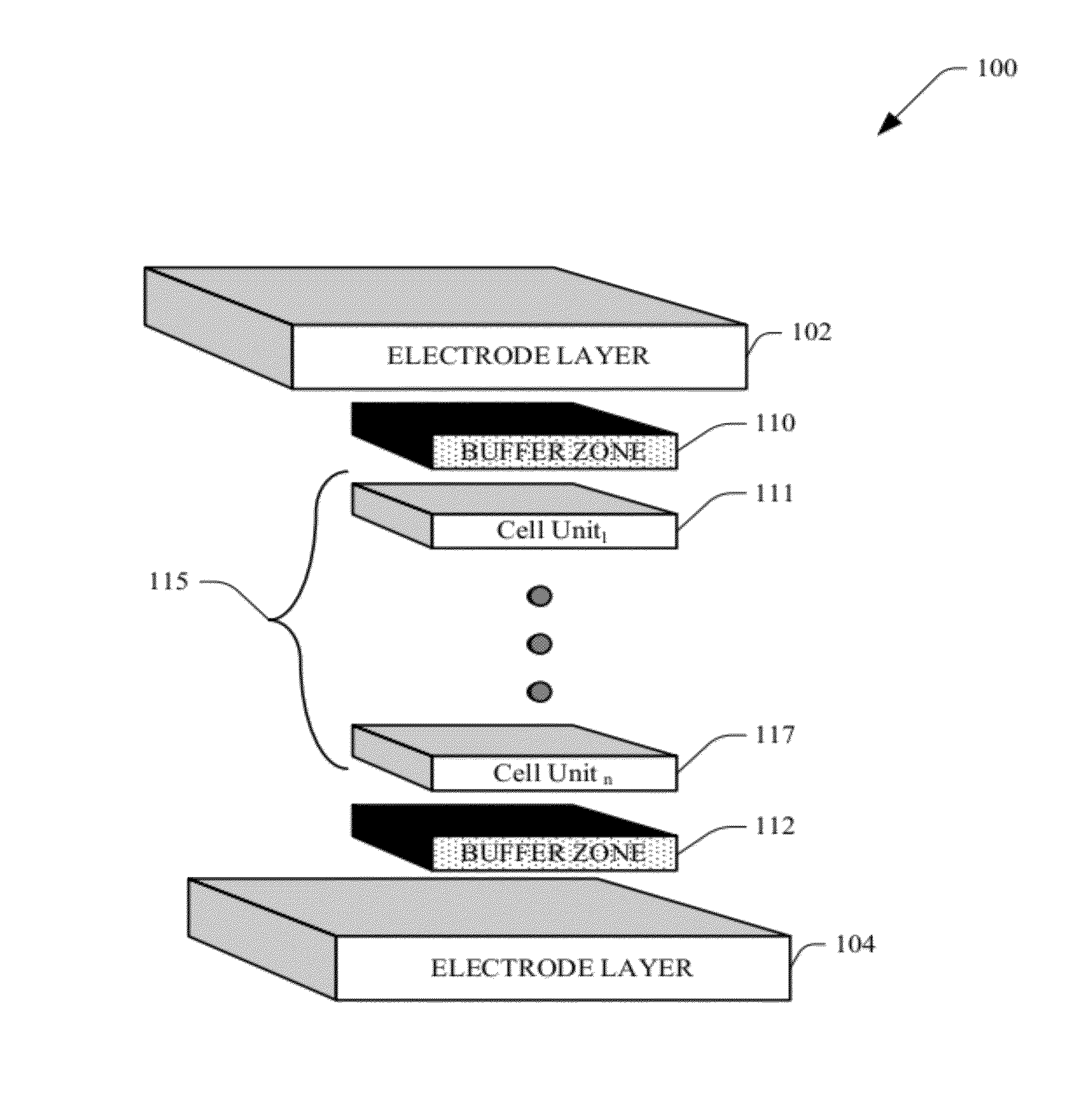
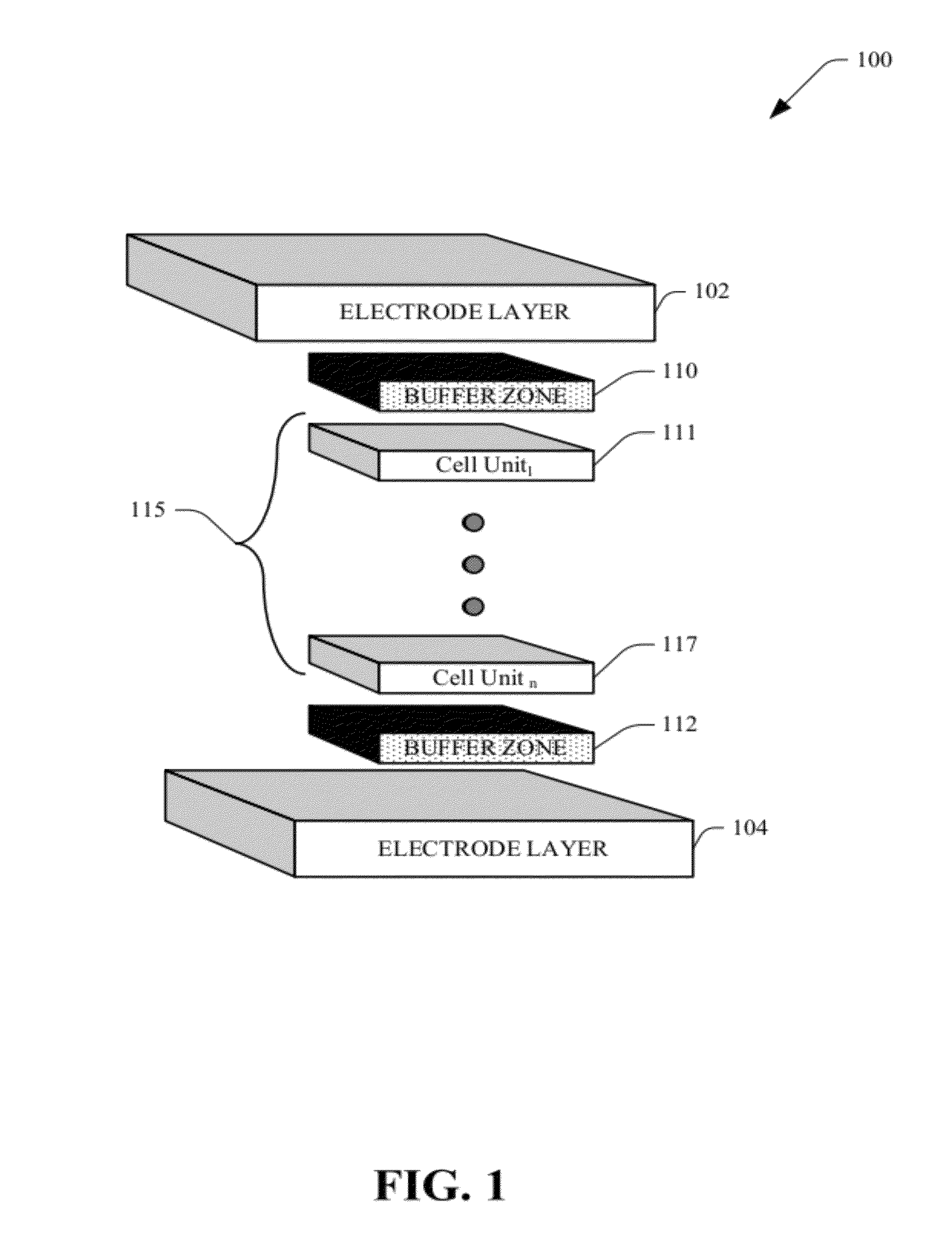
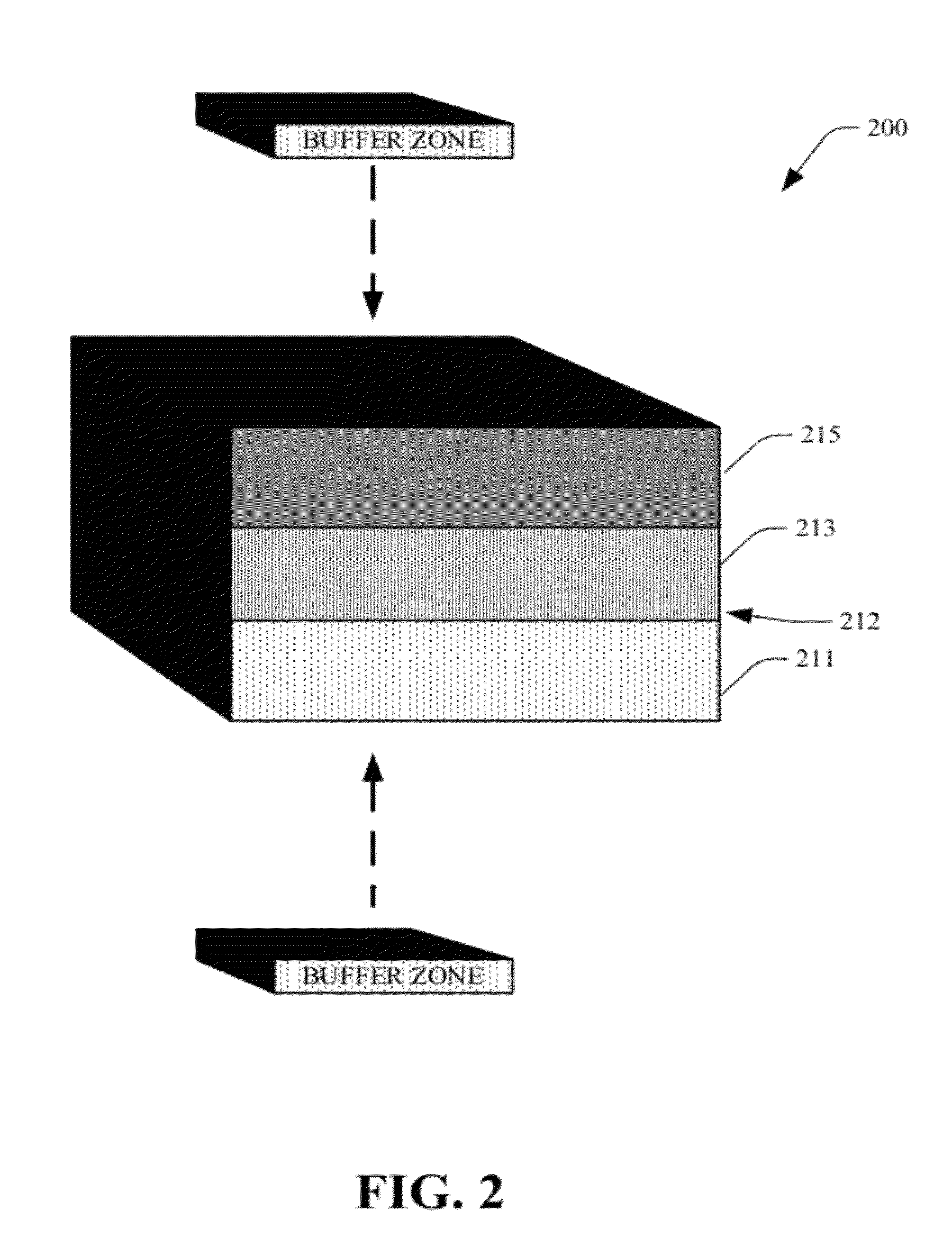
Photovoltaic cell with buffer zone
InactiveUS20120090677A1Easy to moveReduce riskPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesActive layerInduced stress
Systems and methods that provide a barrier for protection of active layers associated with a vertical multi junction (VMJ) photovoltaic cell. Buffer zone(s) in form of an inactive layer(s) arrangement safe guard the active layers against induced stress or strain resulting from external forces / thermal factors (e.g., welding). The buffer zone can be in form of a rim on a surface of an end layer of a cell unit, to act as a protective boundary for such active layer, and to further partially frame the VMJ cell for ease of handling and transportation.
Owner:MH GOPOWER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com