Patents
Literature
131 results about "Incremental redundancy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
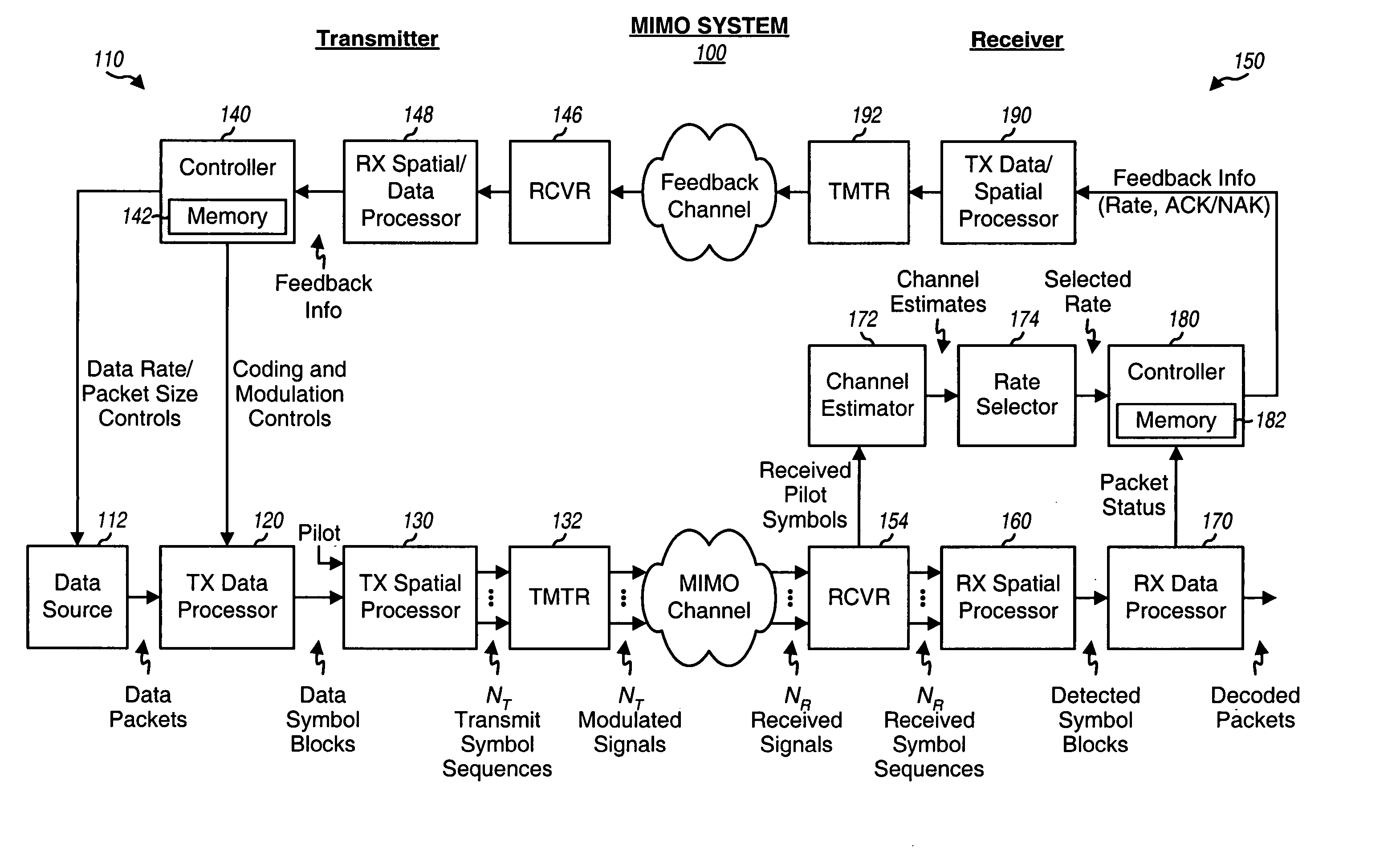
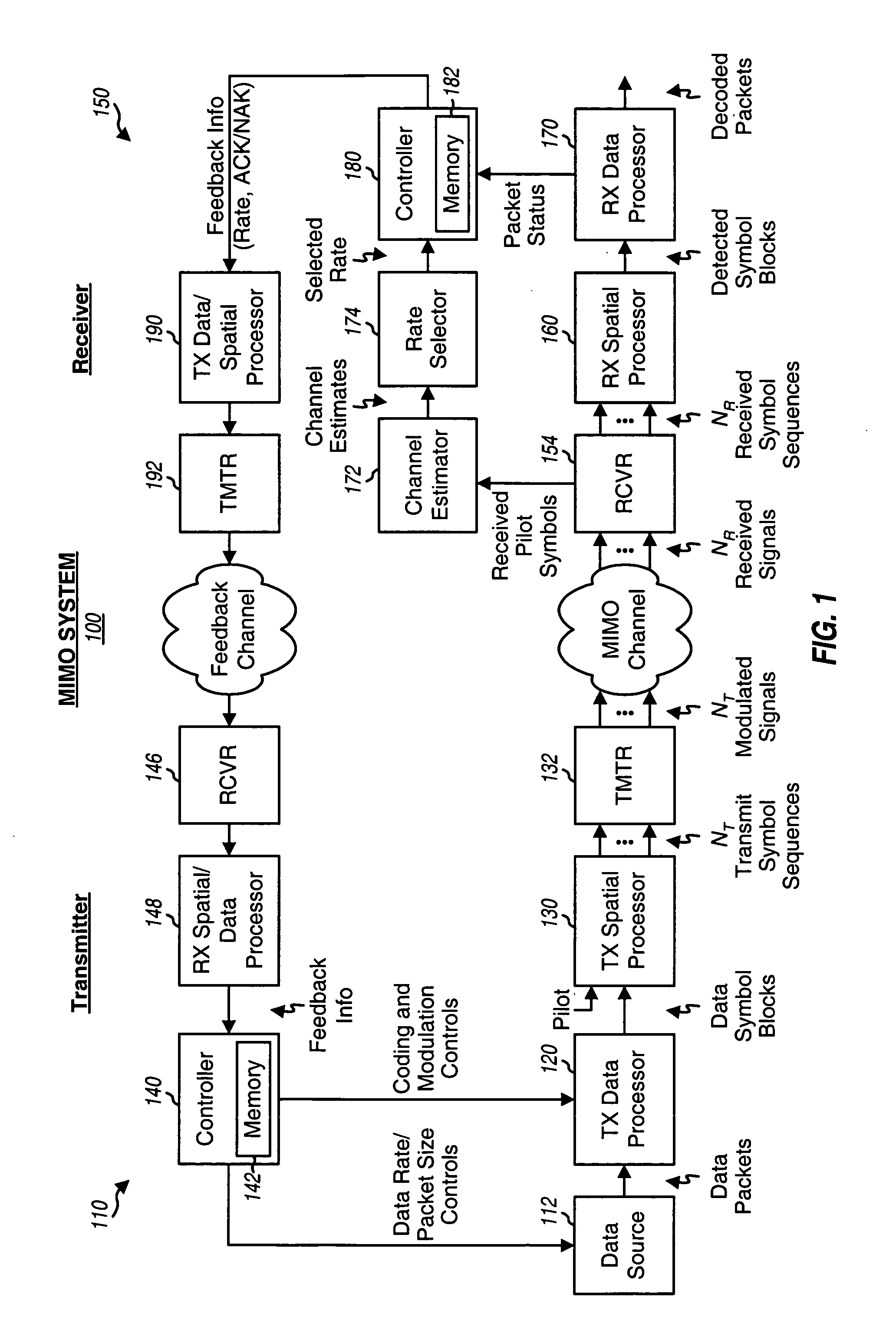
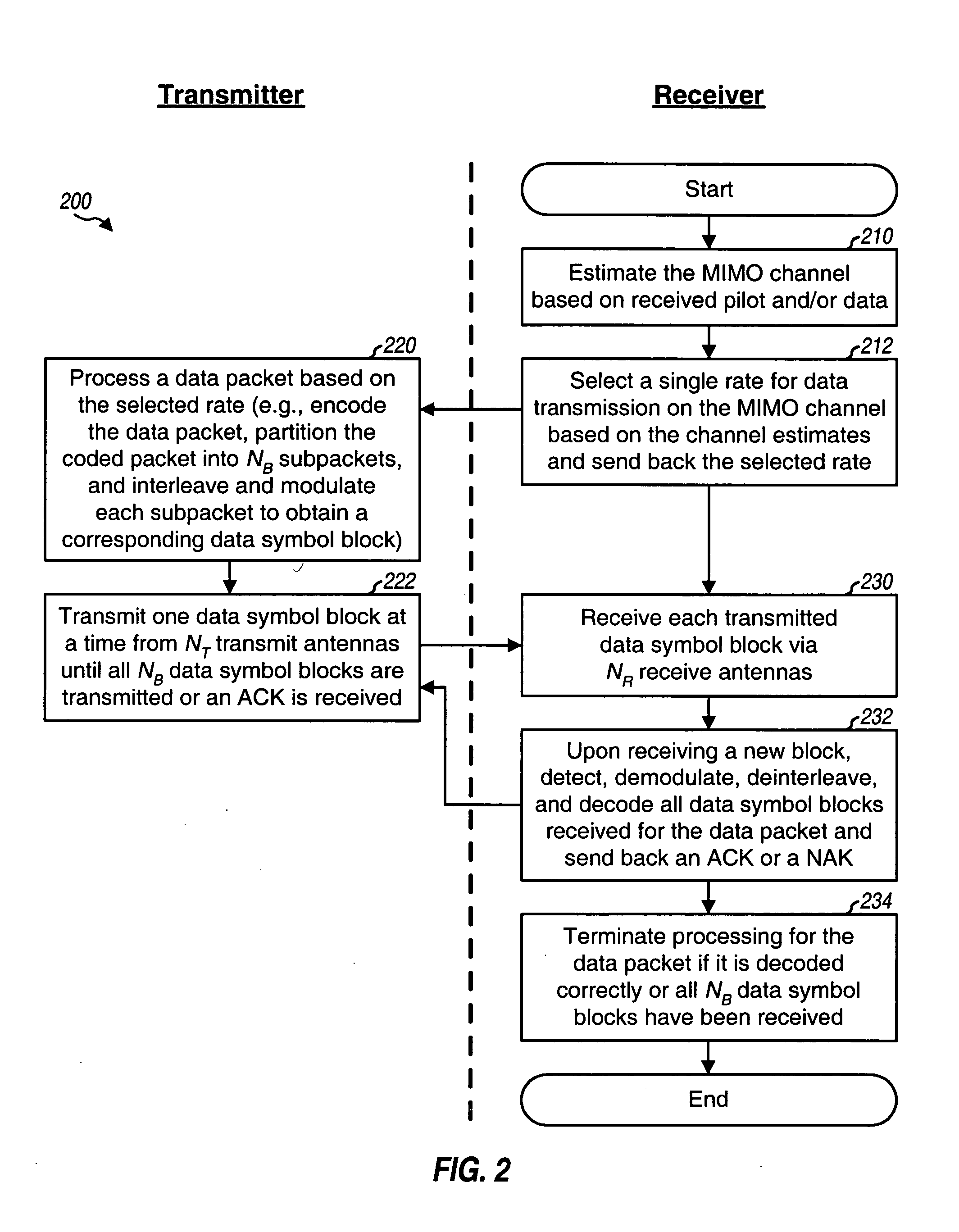
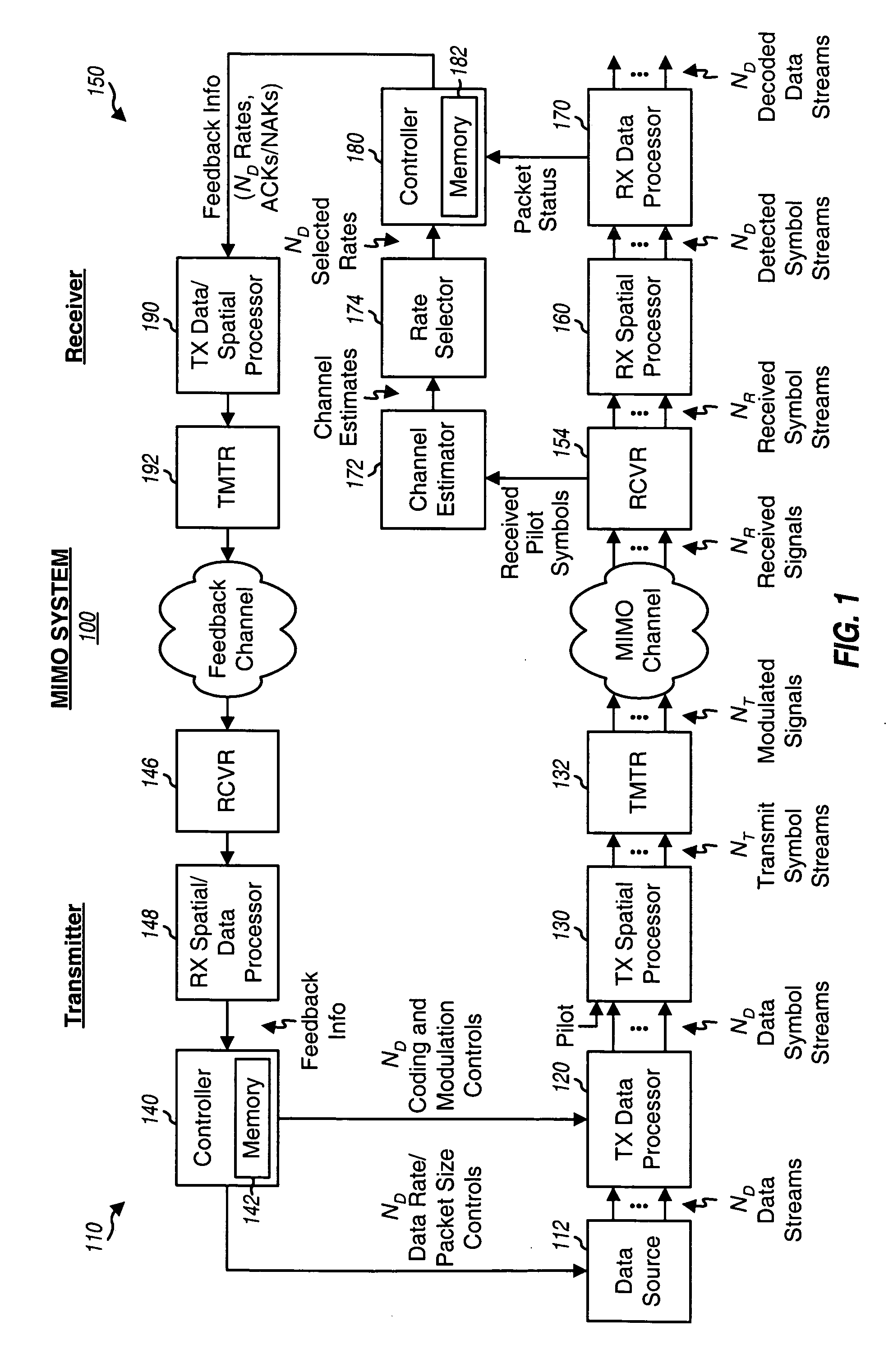
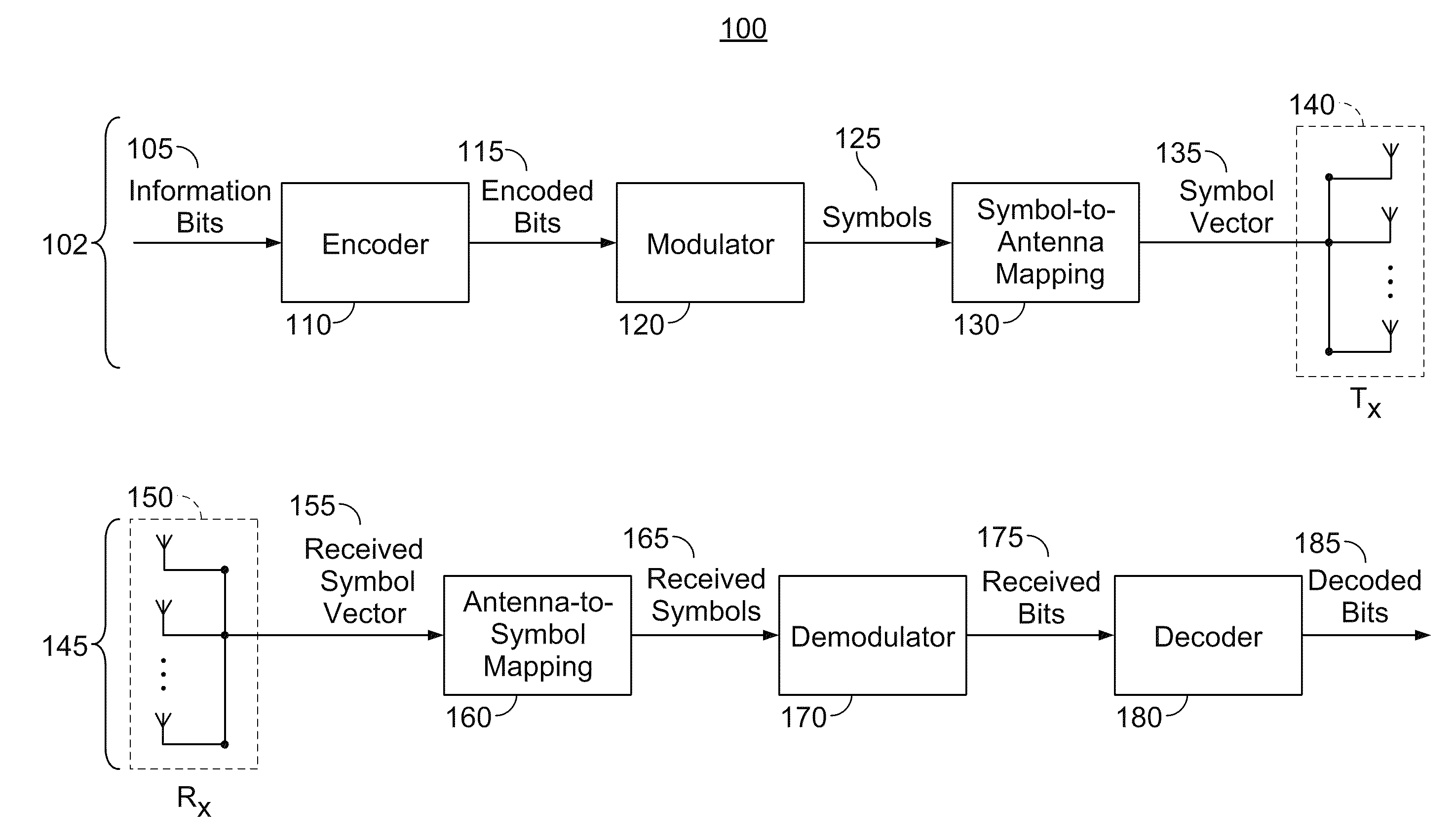
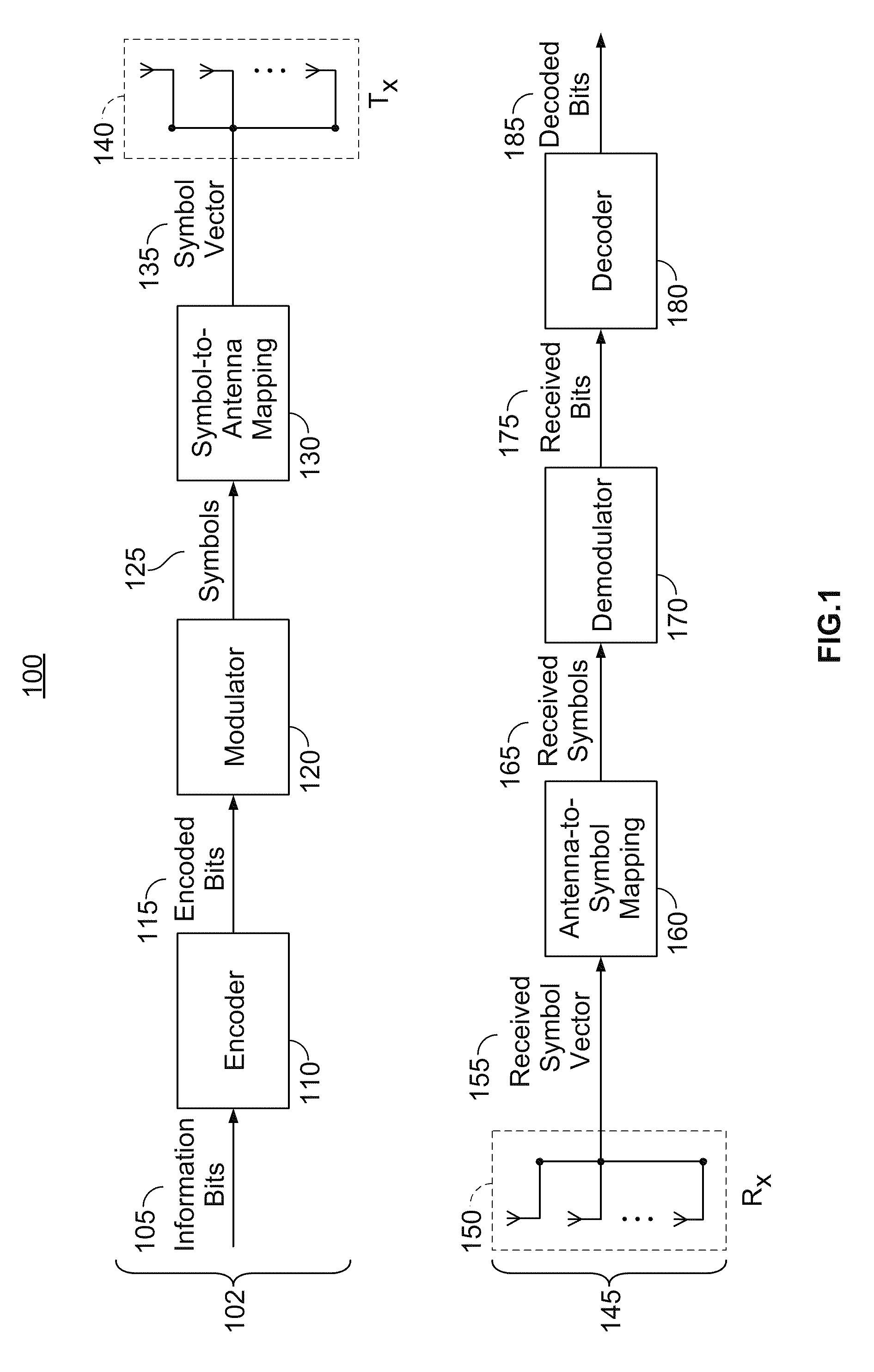
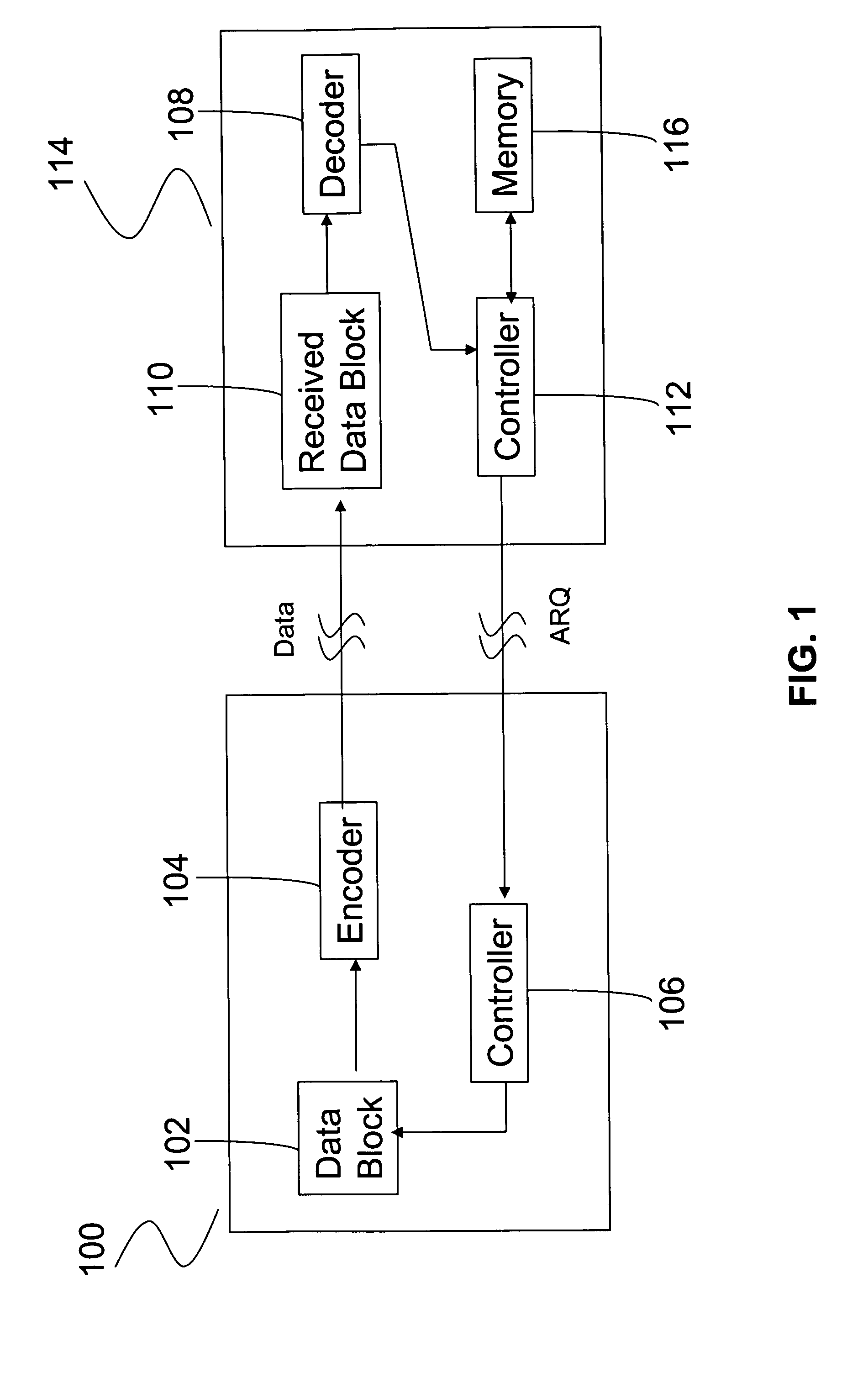
Incremental redundancy transmission in a MIMO communication system
ActiveUS20050052991A1Sufficient informationError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork packetComputer science
For an incremental redundancy (IR) transmission in a MIMO system, a transmitter processes (e.g., encodes, partitions, interleaves, and modulates) a data packet based on a selected rate to obtain multiple data symbol blocks. The transmitter transmits one data symbol block at a time until a receiver correctly recovers the data packet or all blocks are transmitted. Whenever a data symbol block is received from the transmitter, the receiver detects a received symbol block to obtain a detected symbol block, processes (e.g., demodulates, deinterleaves, re-assembles, and decodes) all detected symbol blocks obtained for the data packet, and provides a decoded packet. If the decoded packet is in error, then the receiver repeats the processing when another data symbol block is received for the data packet. The receiver may also perform iterative detection and decoding on the received symbol blocks for the data packet multiple times to obtain the decoded packet.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
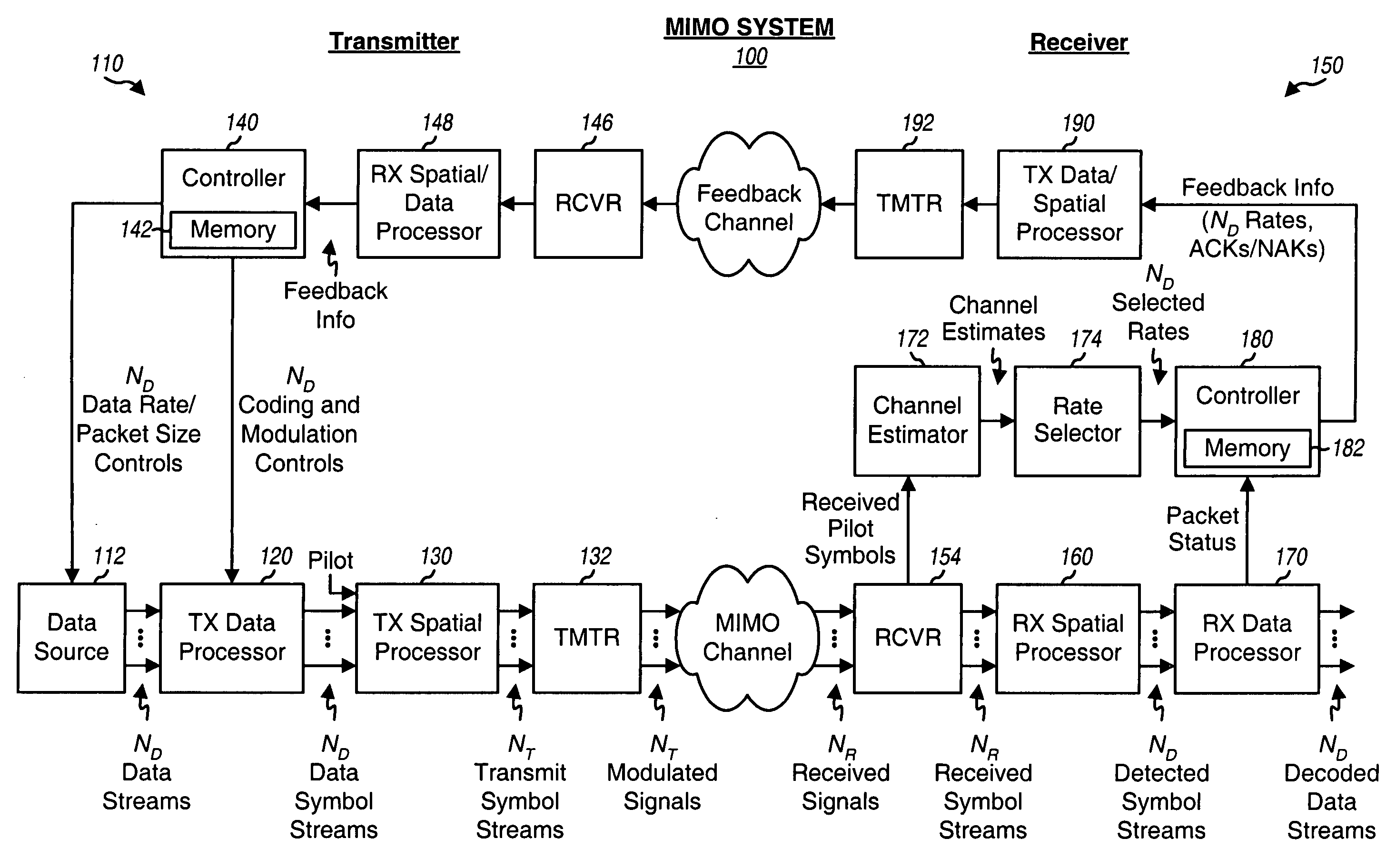
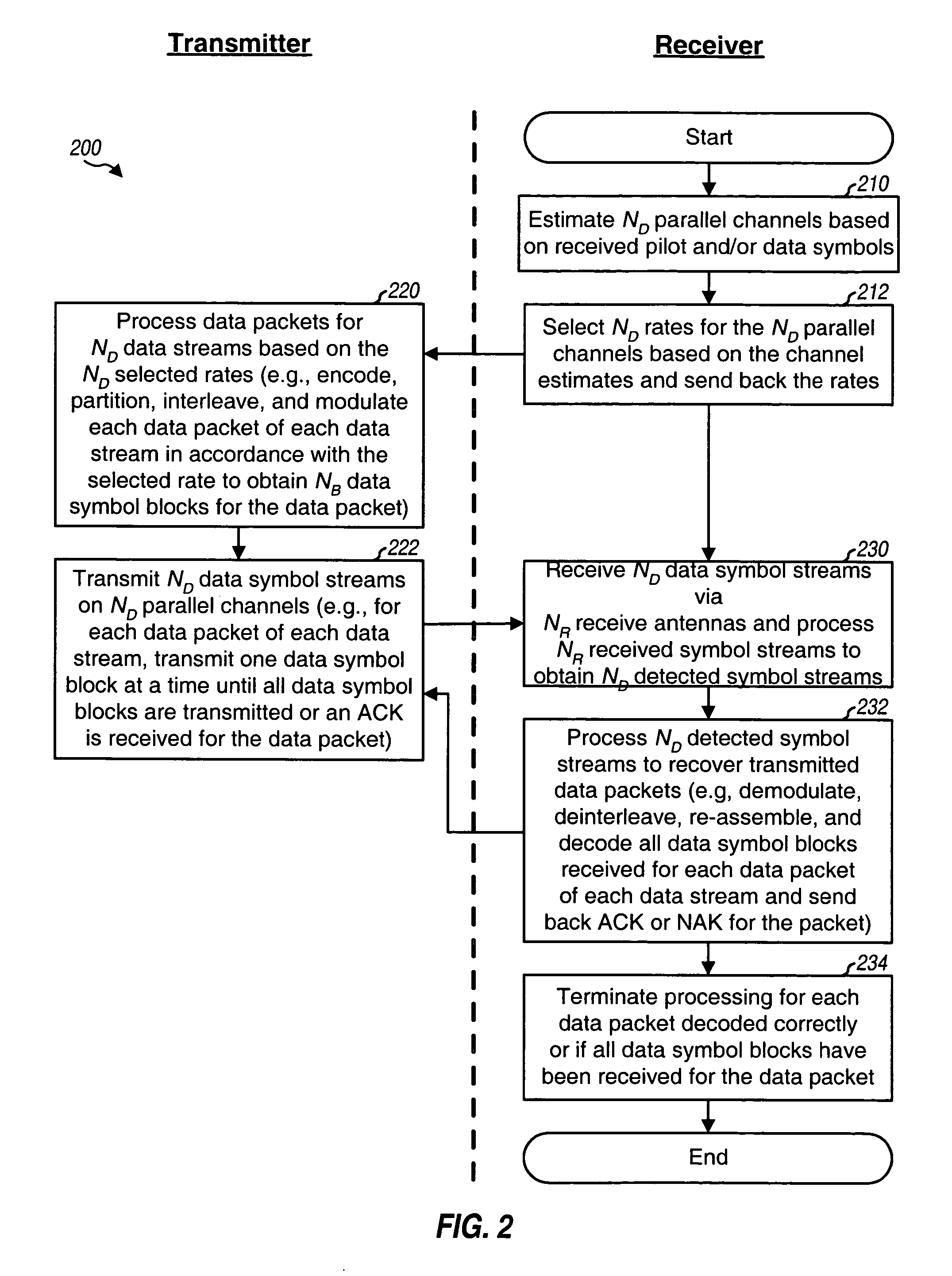
Incremental redundancy transmission for multiple parallel channels in a MIMO communication system
ActiveUS20050063378A1Increase chanceError prevention/detection by using return channelEnergy efficient ICTComputer scienceTransmitter
For incremental redundancy transmission on multiple parallel channels in a MIMO system, a transmitter processes (e.g., encodes, partitions, interleaves, and modulates) each data packet for each parallel channel based on a rate selected for the parallel channel and obtains multiple symbol blocks for the packet. For each data packet, the transmitter transmits one symbol block at a time on its parallel channel until a receiver recovers the packet or all blocks have been transmitted. The receiver performs detection and obtains symbol blocks transmitted on the parallel channels. The receiver recovers the data packets transmitted on the parallel channels independently or in a designated order. The receiver processes (e.g., demodulates, deinterleaves, re-assembles, and decodes) all symbol blocks obtained for each data packet and provides a decoded packet. The receiver may estimate and cancel interference due to recovered data packets so that data packets recovered later can achieve higher SINRs.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
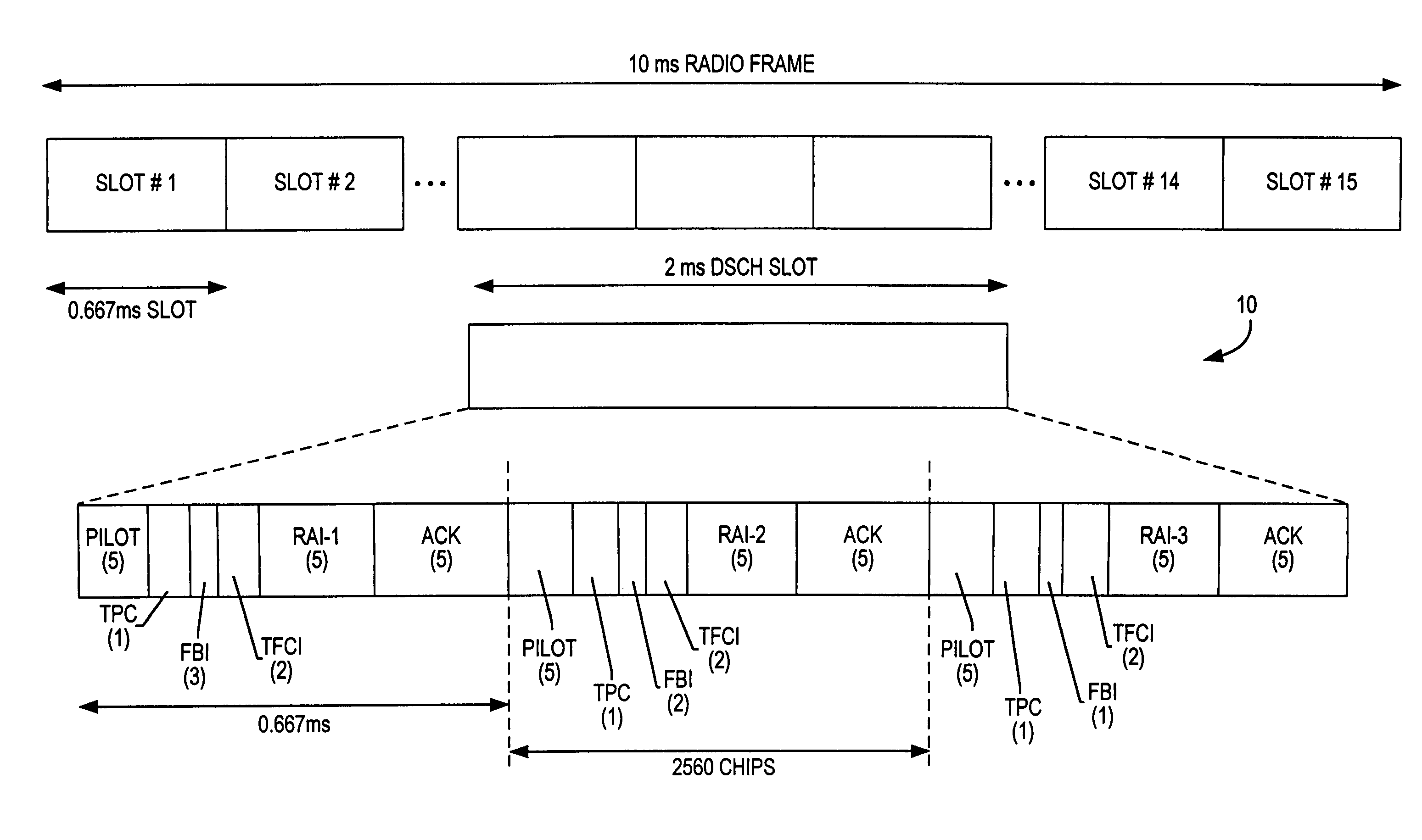
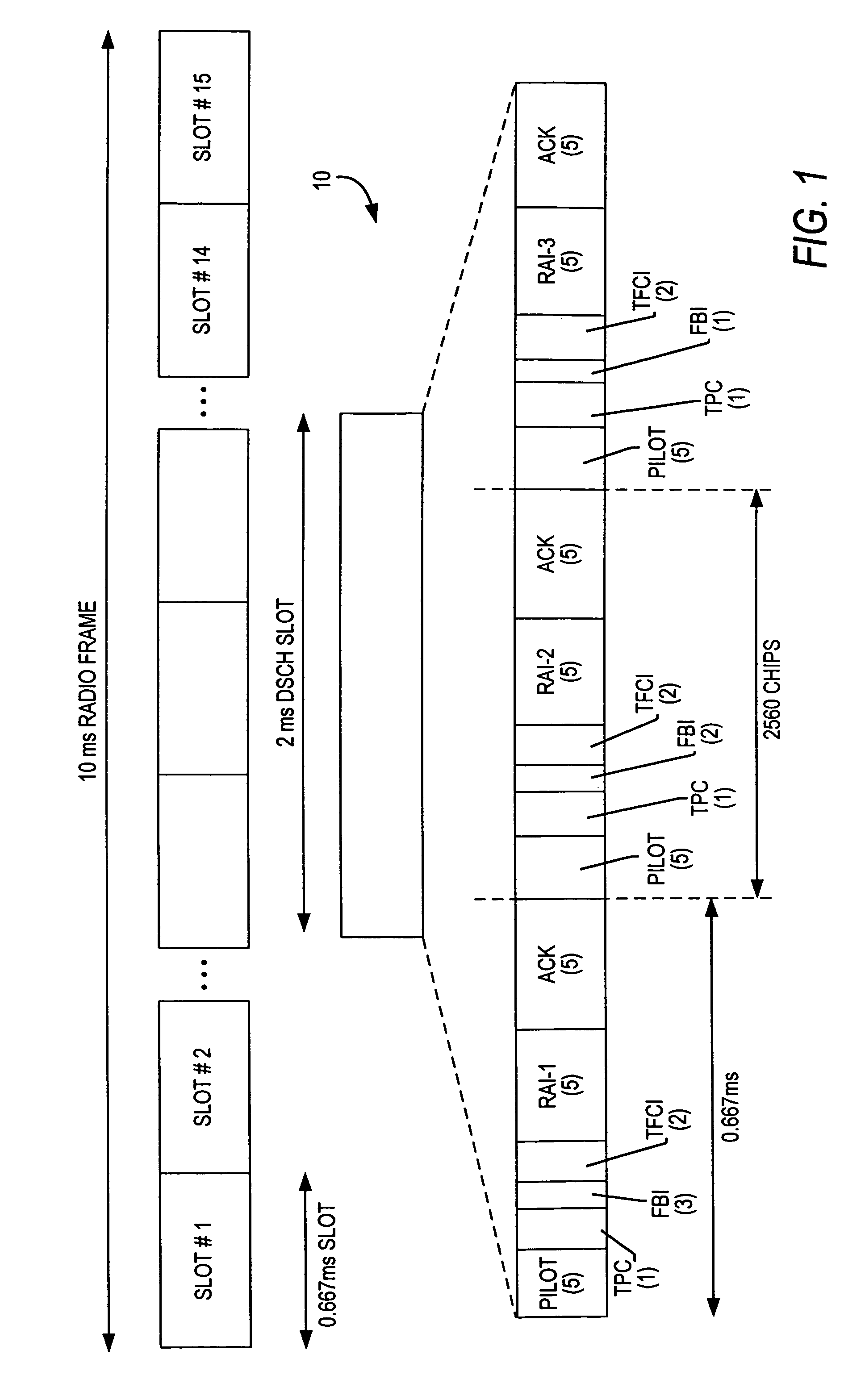
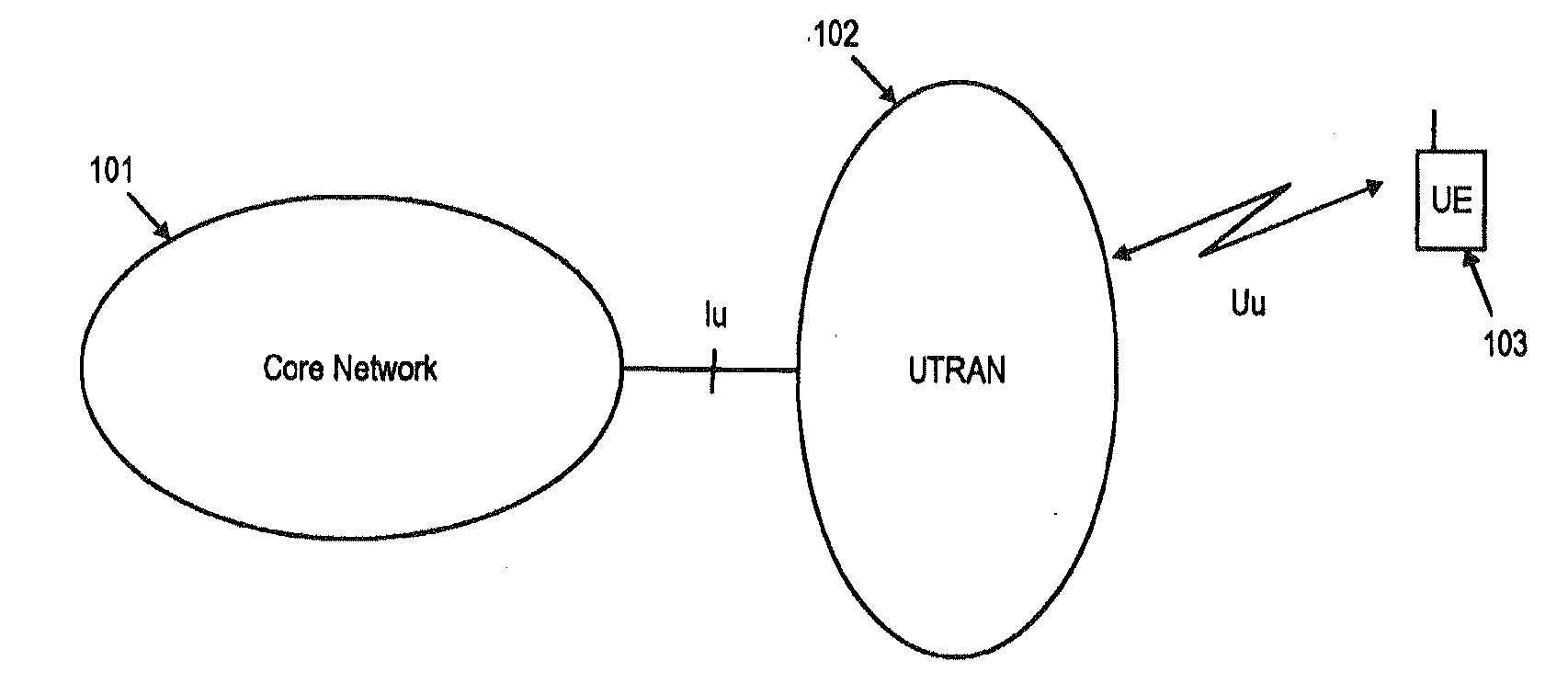
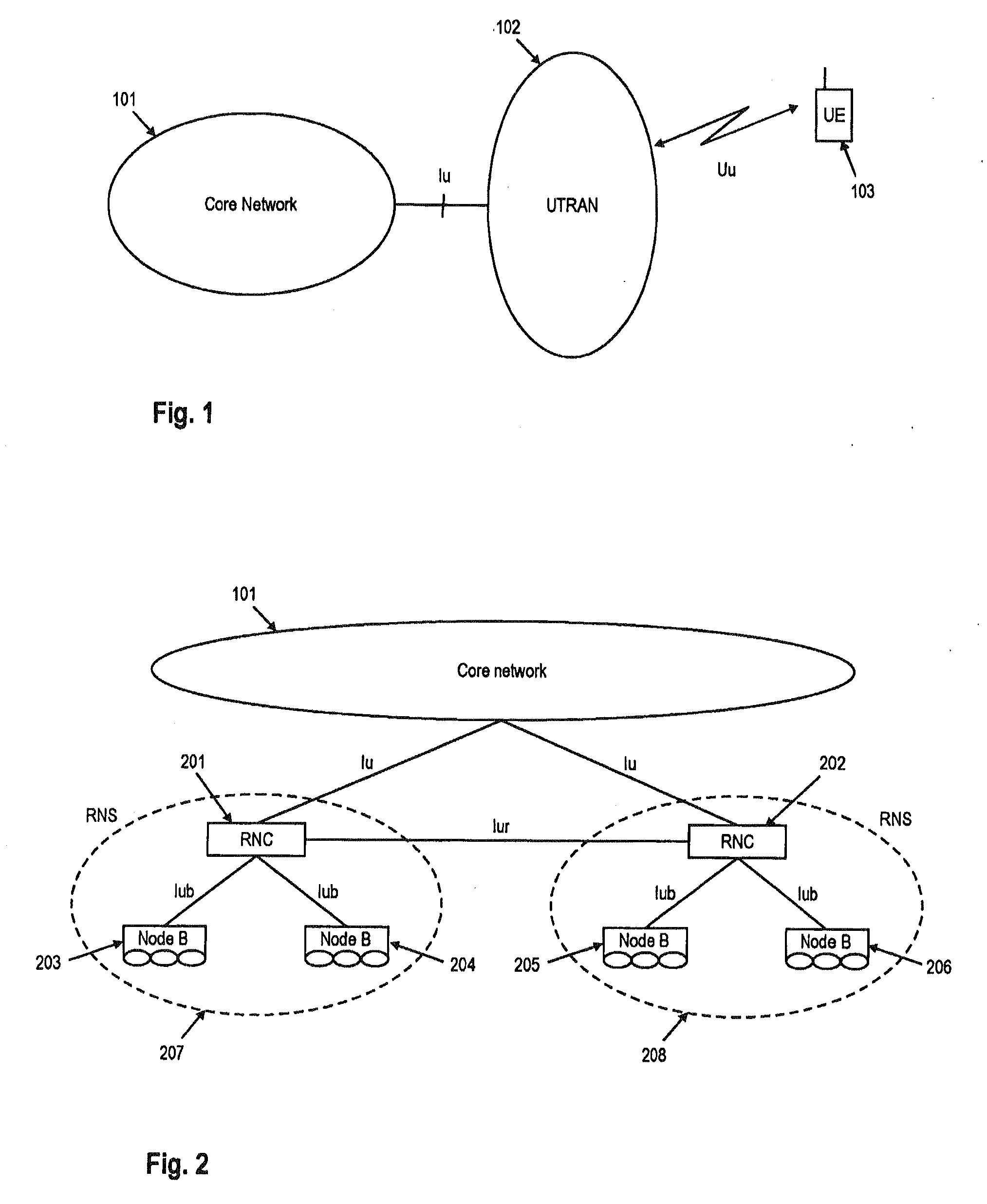
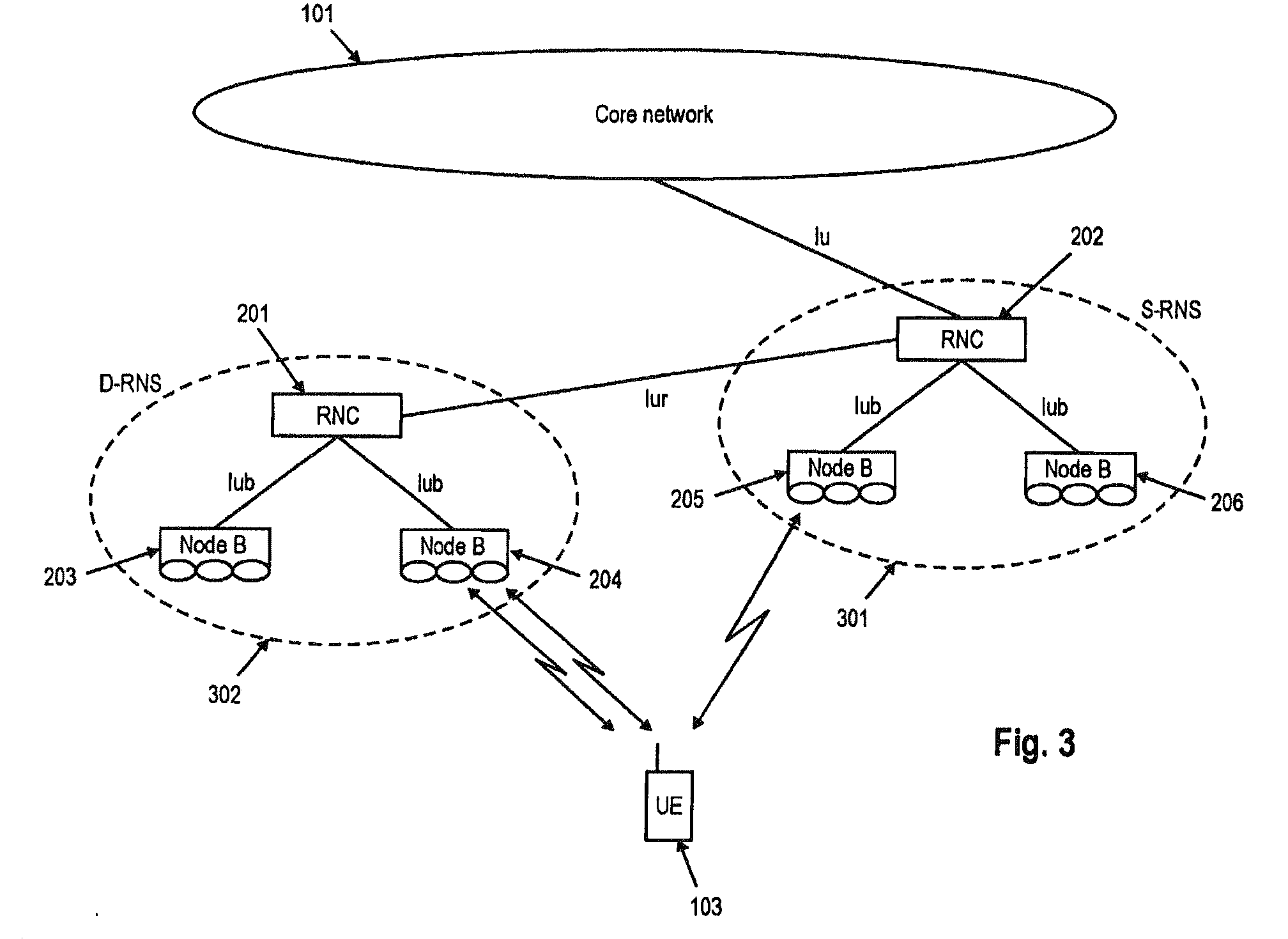
Downlink and uplink channel structures for downlink shared channel system
InactiveUS7006464B1Improve spectral efficiencyAdapt quicklyPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCode spaceTransmitted power
An uplink and downlink channel structure supports a shared downlink data channel. The new structure accommodates advanced physical and Medium Access Control (MAC) layer techniques, such as incremental redundancy (IR), fast adaptation to channel conditions, and multiple input multiple output (MIMO) antenna configuration. The proposed changes are intended to lead to a downlink structure that achieves higher spectral efficiency for the packet oriented services over then shared downlink channel. Additionally, the new structure uses the base station transmit power information and of the channelization (OVSF) code space more efficiently.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
Transmitter and receiver for broadcasting data and providing incremental redundancy
ActiveUS20120272117A1Increase probabilityImprove robustnessError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionData streamBroadcast data
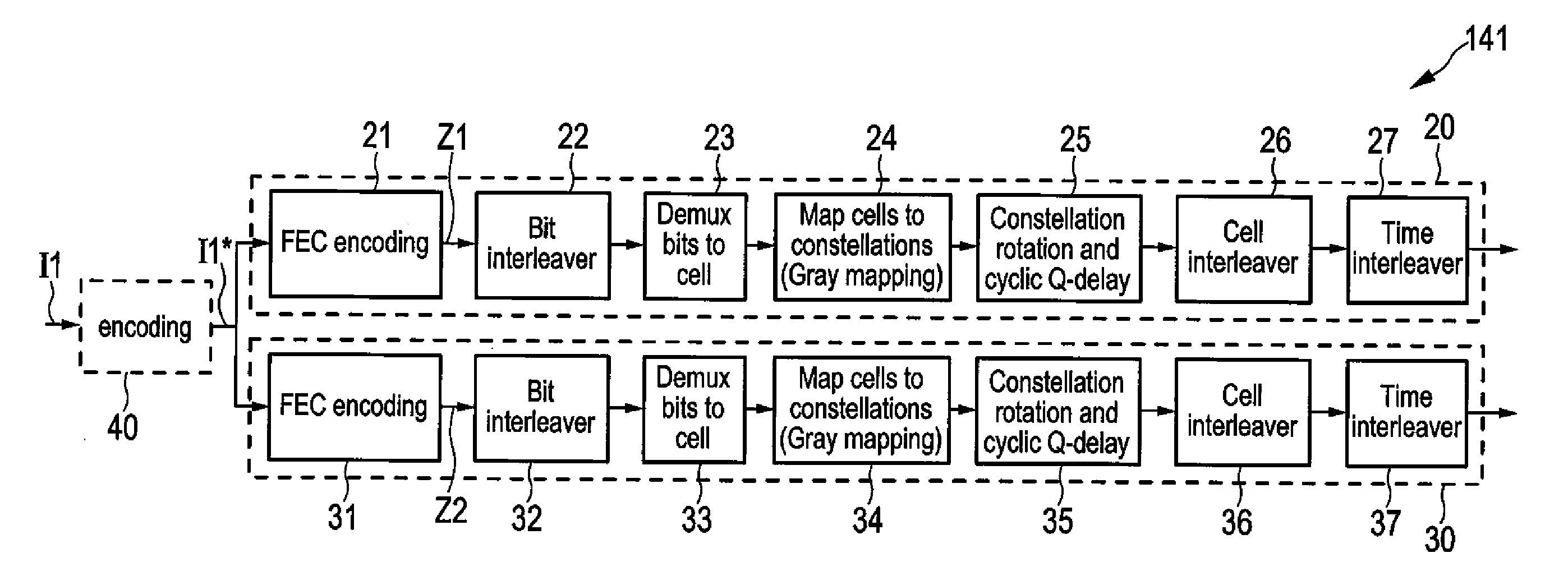
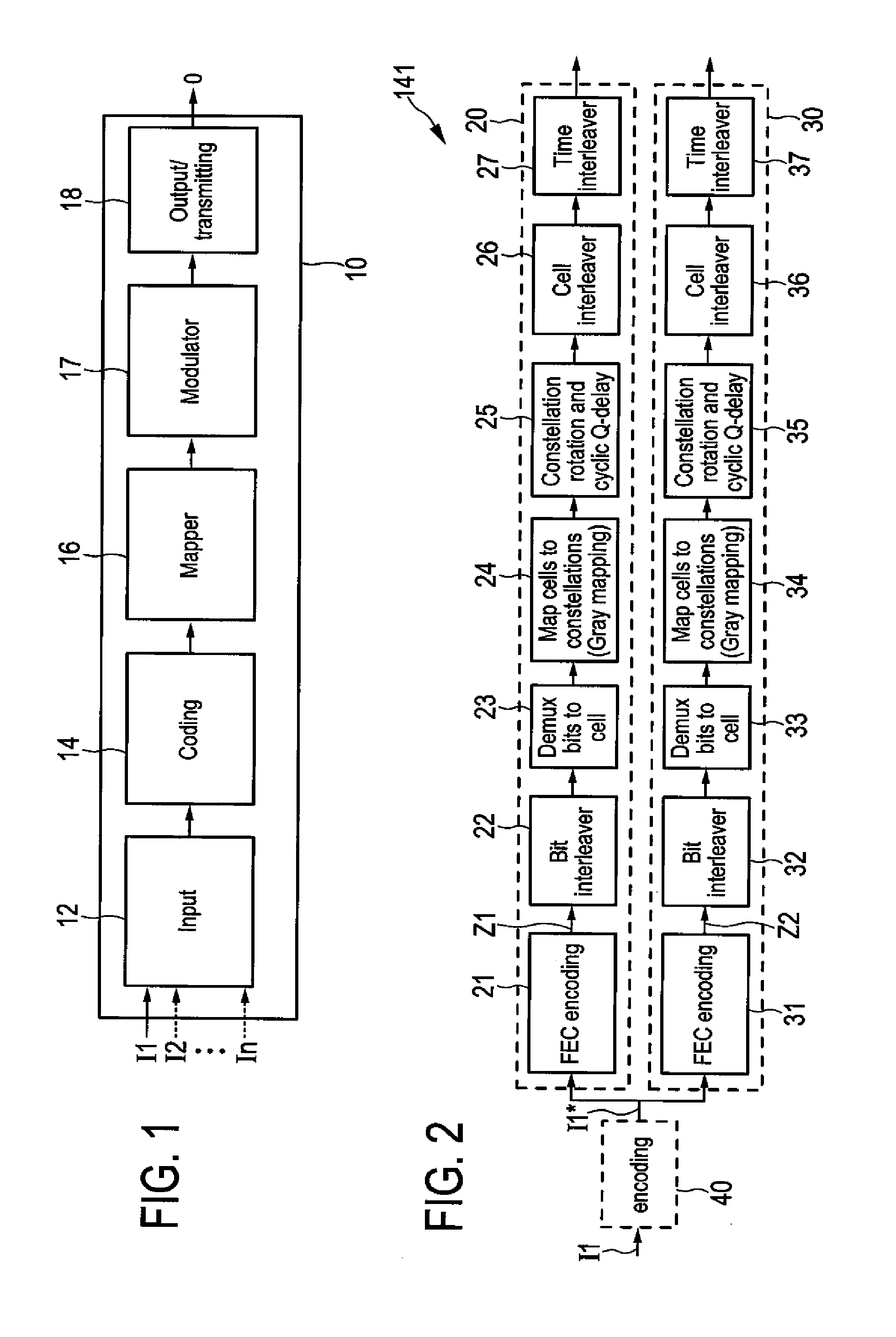
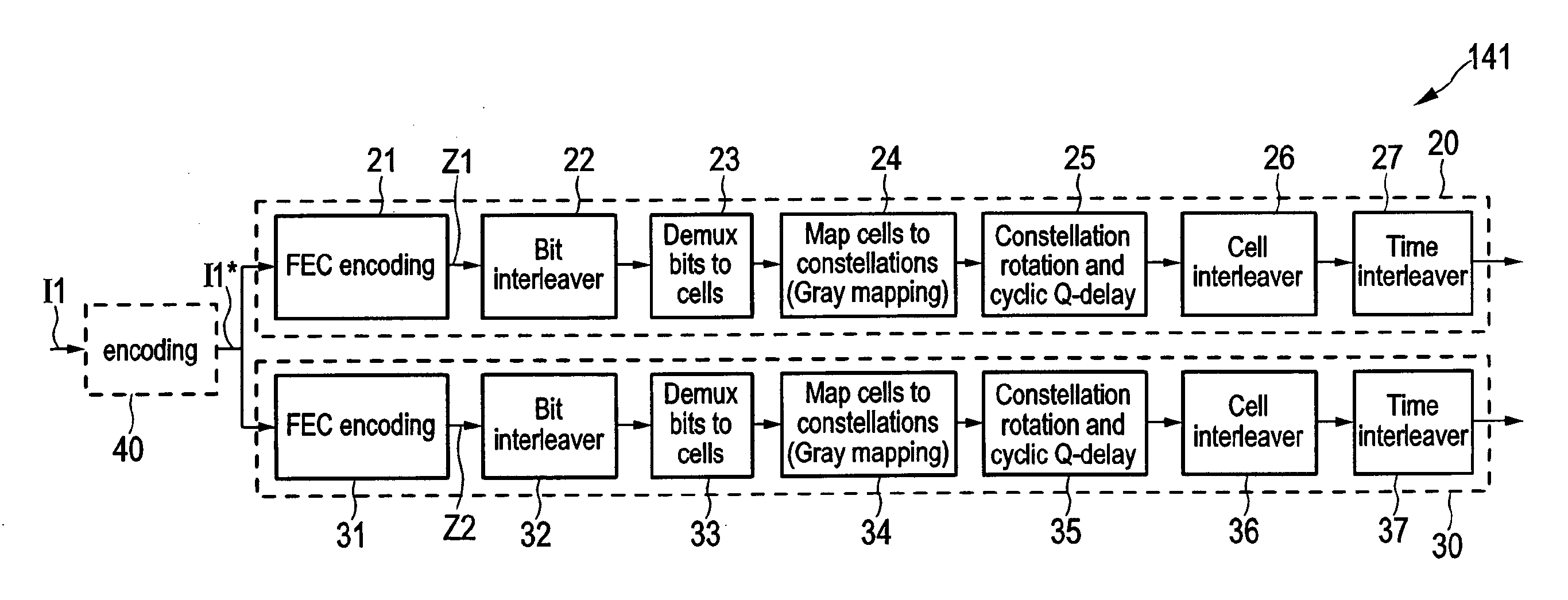
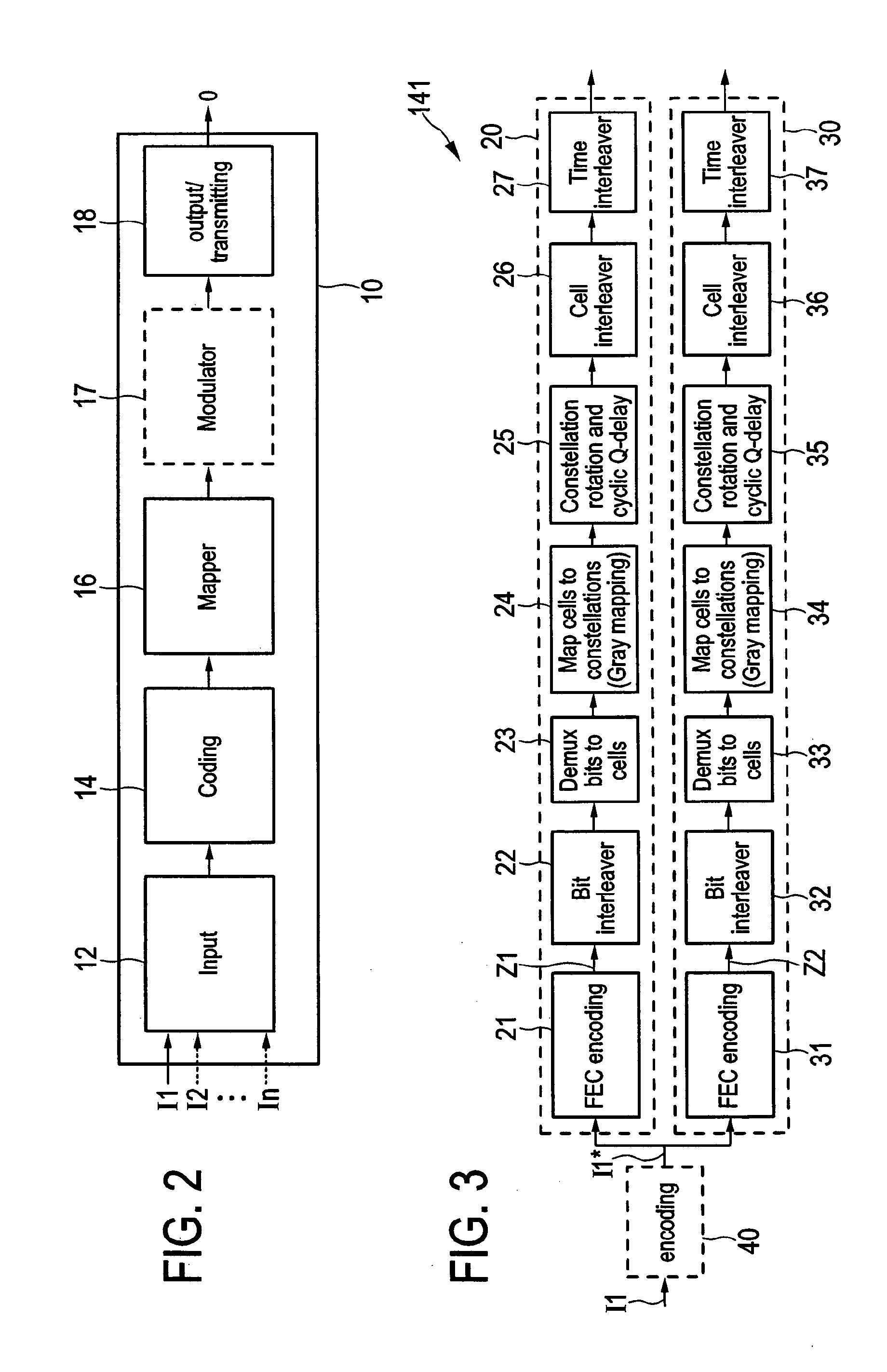
A transmitter for broadcasting data in a broadcasting system that improves the decoding quality, if needed, comprises a data input, and an encoder for error correction code encoding the input data words into codewords, a codeword comprising a basic codeword portion and an auxiliary codeword portion, wherein said encoder is adapted for generating said basic codeword portion from an input data word according to a first code and for generating said auxiliary codeword portion from an input data word according to a second code, said basic codeword portion being provided for regular decoding and said auxiliary codeword portion being provided as incremental redundancy if regular decoding of the codeword by use of the basic codeword portion is erroneous. Further, the transmitter comprises a data mapper for mapping the codewords onto frames of a transmitter output data stream, and a transmitter unit for transmitting said transmitter output data stream.
Owner:SATURN LICENSING LLC
Apparatus and method for transmitting/receiving a signal in a communication system using a low density parity check code
InactiveUS7954041B2Performance maximizationError prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionCommunications systemLow-density parity-check code
An apparatus and method are provided for transmitting a signal in a communication system using a low density parity check (LDPC) code. An LDPC codeword is generated by encoding an information word at a coding rate. A puncturing pattern is generated when a hybrid automatic repeat request (HARQ) scheme to be applied to the LDPC codeword is an incremental redundancy (IR) scheme. An additional pattern is generated when the HARQ scheme to be applied to the LDPC codeword is a partial chase combining (CC) scheme. A signal is transmitted by applying the puncturing pattern to the LDPC codeword at an associated coding rate when the HARQ scheme to be used is the IR scheme. A signal is transmitted by applying the additional pattern to the LDPC codeword at an associated coding rate when the HARQ scheme to be used is the partial CC scheme.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for control signalling enabling flexible link adaptation in a radiocommunication system
InactiveUS6865233B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelChannel coding adaptationControl signalOriginal data
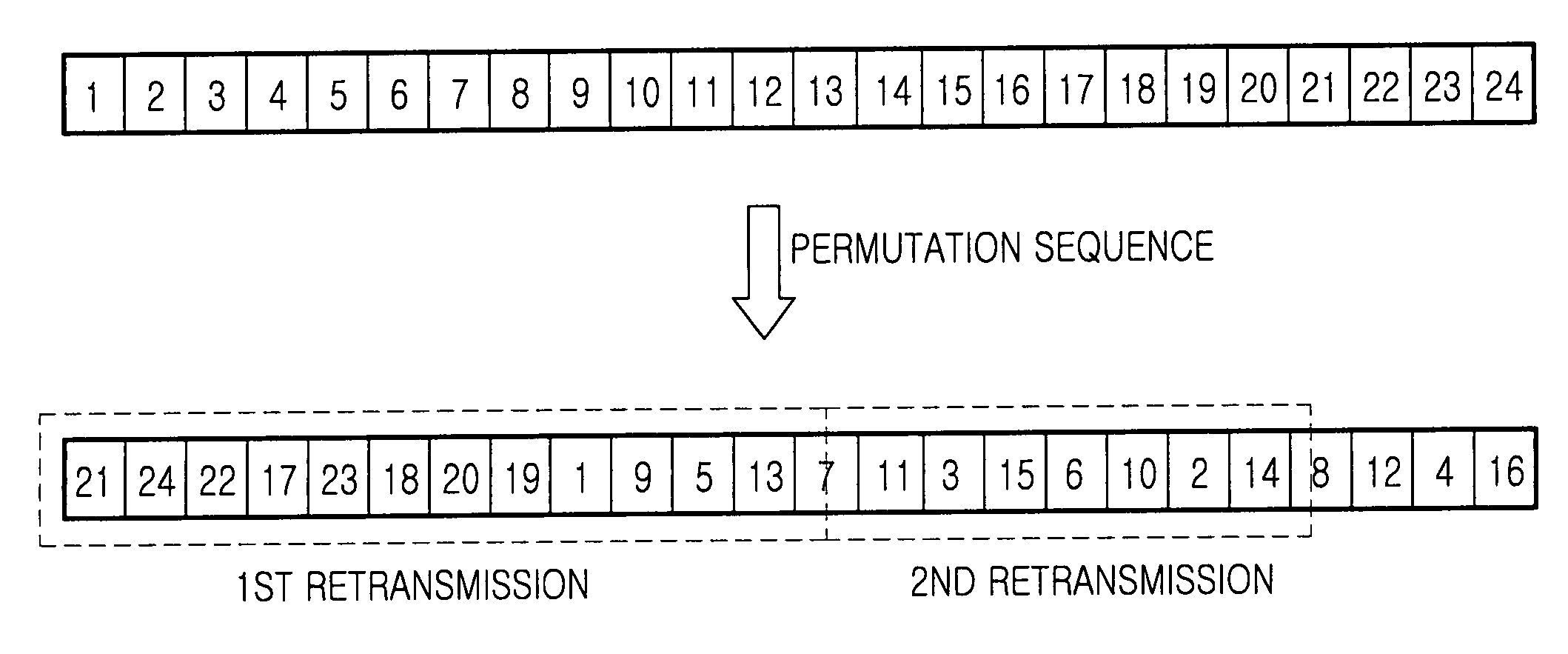
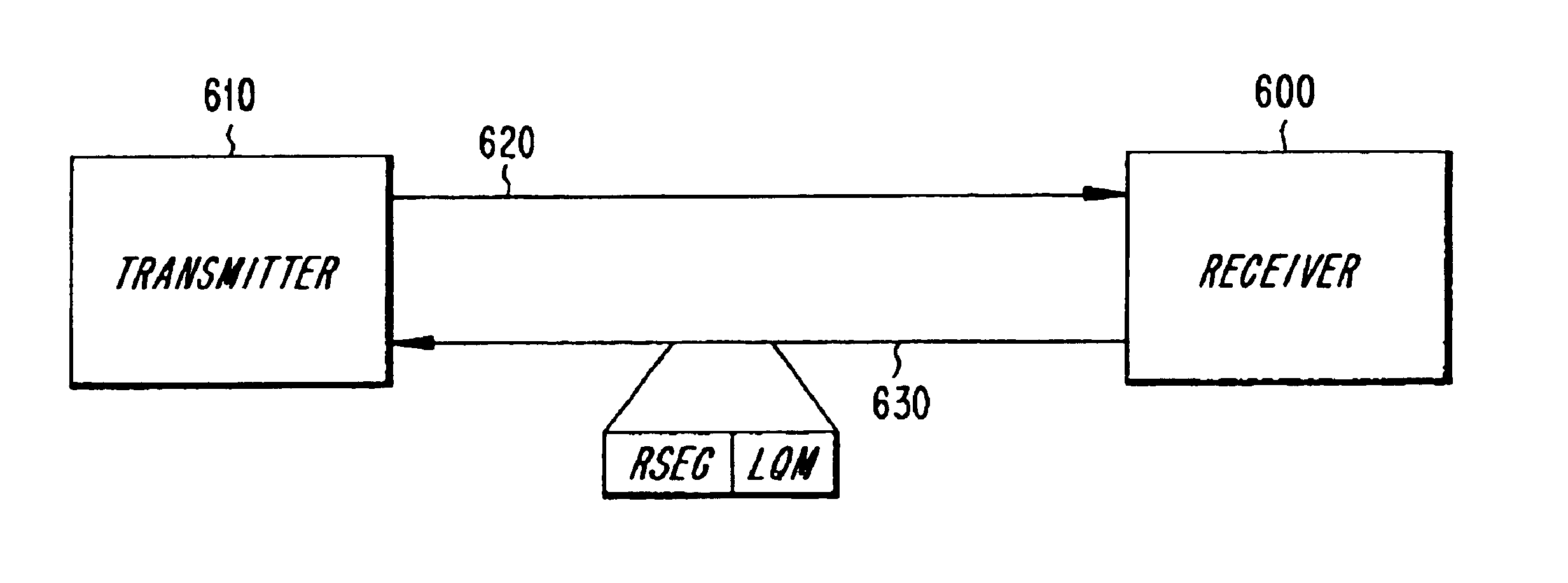
Control signalling for systems employing link adaptation and incremental redundancy is described. A link adaptation / incremental redundancy message can be transmitted from a receiving entity to a transmitting entity to inform the transmitting entity of the receiving entity's incremental redundancy status or preference. Another message, which indicates whether resegmentation should be performed for retransmitted blocks can also be transmitted from a receiving entity to a transmitting entity. Both of these messages can be used by the transmitting entity to determine an appropriate modulation / coding scheme for subsequent transmissions of both original data blocks and retransmitted data blocks. The messages can be used together or independently in either link (uplink or downlink) between a base station and a mobile station in a radiocommunication system.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Method of link adaptation in enhanced cellular systems to discriminate between high and low variability
ActiveUS7289574B2Quick and easy changeReduce capacityError prevention/detection by using return channelEnergy efficient ICTDependabilityLink adaptation
To perform link adaptation at radio interfaces of an enhanced packet data cellular network the system behavior is simulated for different C / I conditions. Two sets of tables are obtained, each table including upgrade and downgrade thresholds expressed in terms of Block Error Rate (BLER). The tables are specialized for taking into account EGPRS type II hybrid ARQ, Incremental Redundancy (IR). Transmitted blocks are checked for FEC and results are sent to the network that continuously updates BLER. A reliability filter output is used to decide the weight between new and old measurements. IR efficiency is tested for each incoming block and an indicative variable IR_status is filtered. Each threshold of BLER to be used is obtained by linear interpolation between the tabulated threshold without IR and with perfect IR, both weighed with filtered IR_status. Filtered BLER is compared with interpolated thresholds for testing the incoming of a MCS switching condition.
Owner:RPX CORP +2
Systems and Methods for Use with Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing
ActiveUS20080187136A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelKey distribution for secure communicationResource managementDown link
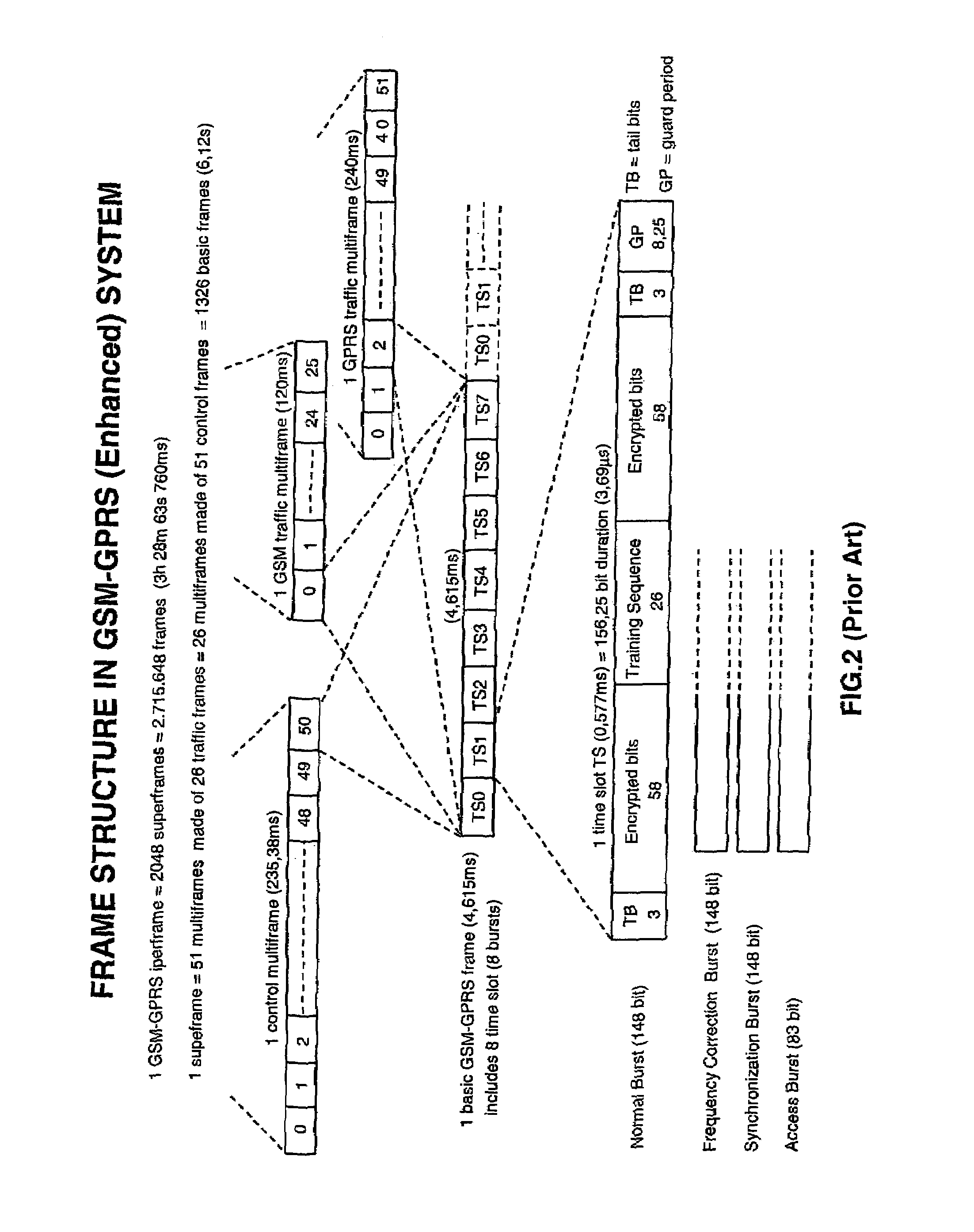
Systems and methods are provided for enabling H-ARQ communication between a base station and one or more wireless terminals. Methods for enabling incremental redundancy (IR) based H-ARQ, Chase based H-ARQ and Space-Time Code combining (STC) based H-ARQ between devices for down-link and up-link direction transmissions are provided in the form of an information element (IE) for use with a Normal MAP convention as currently accepted in the draft version standard of IEEE 802.16. In addition, embodiments of the invention provide a resource management scheme to protect a network from abuse of resources from a wireless terminal not registered with the network. Components of the down-link and up-link mapping components of a data frame transmitted from the base station to one or more wireless terminals included messages that are readable by all wireless terminals as well as some messages that are encrypted and only readable by wireless terminals that are authenticated as being registered with the network.
Owner:APPLE INC
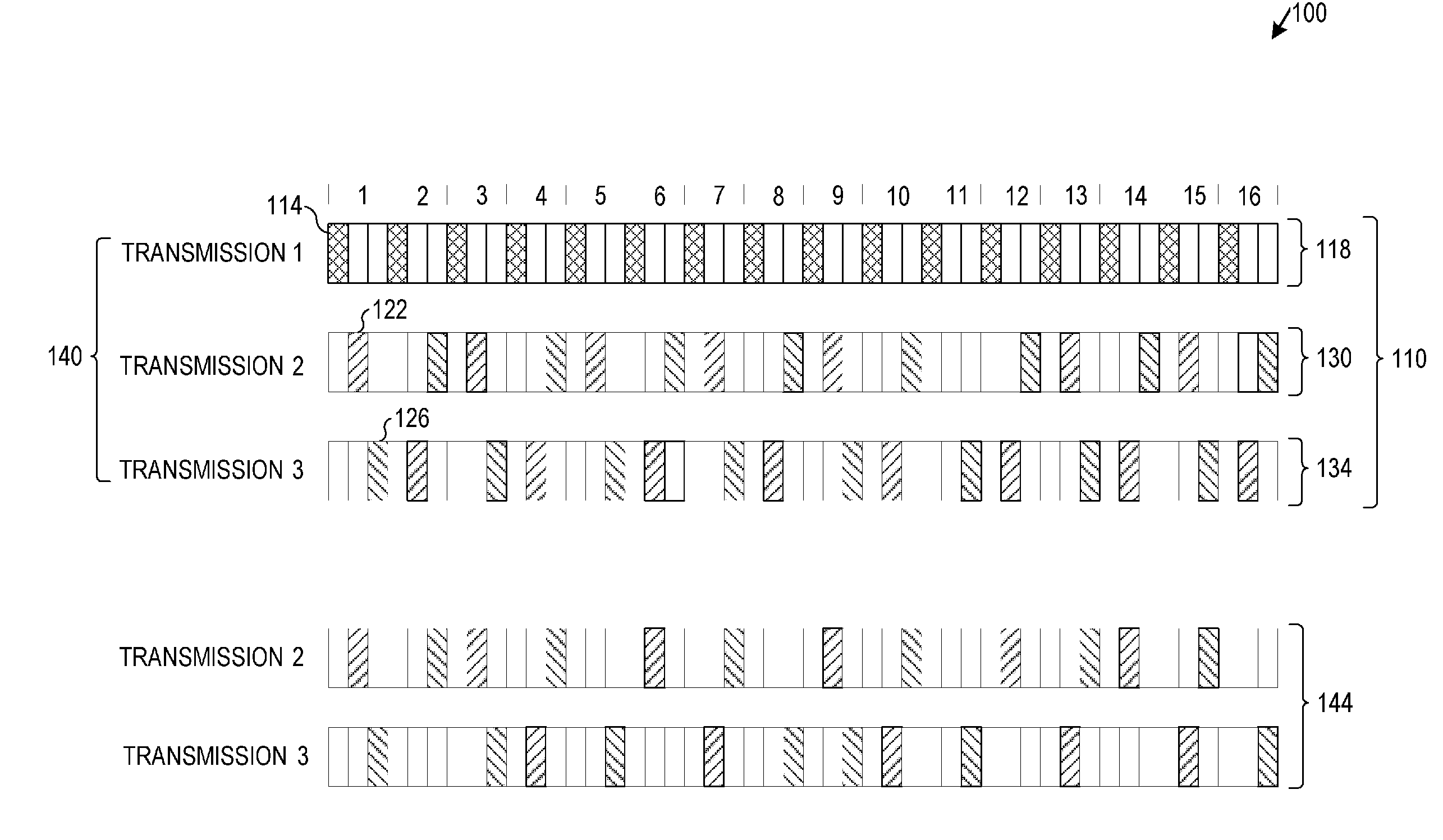
Adaptive hybrid retransmission method for wireless communications
ActiveUS7564827B2Exact matchFine granularityError prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsMultiplexingCommunications system
An adaptive incremental redundancy (i.e., Hybrid ARQ) method is described for retransmitting information in a communication channel of a wireless communication system. More specifically, code multiplexing is used within fixed length frames in order to change the number of codes, modulation, and coding on retransmissions to provide the desired redundancy for successful decoding. The operation of adaptive Hybrid ARQ in the code domain also provides finer granularity in which to efficiently transmitting redundancy. In one illustrative embodiment, a method for retransmitting information in a communication channel having a plurality of fixed length frames each divided into a plurality of time slots of equal duration includes the step of code multiplexing a retransmission of a previous transmission within one of the fixed length frames using one or more of a plurality of codes. The number of codes used for the retransmission is variable based on the condition of the communication channel.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC
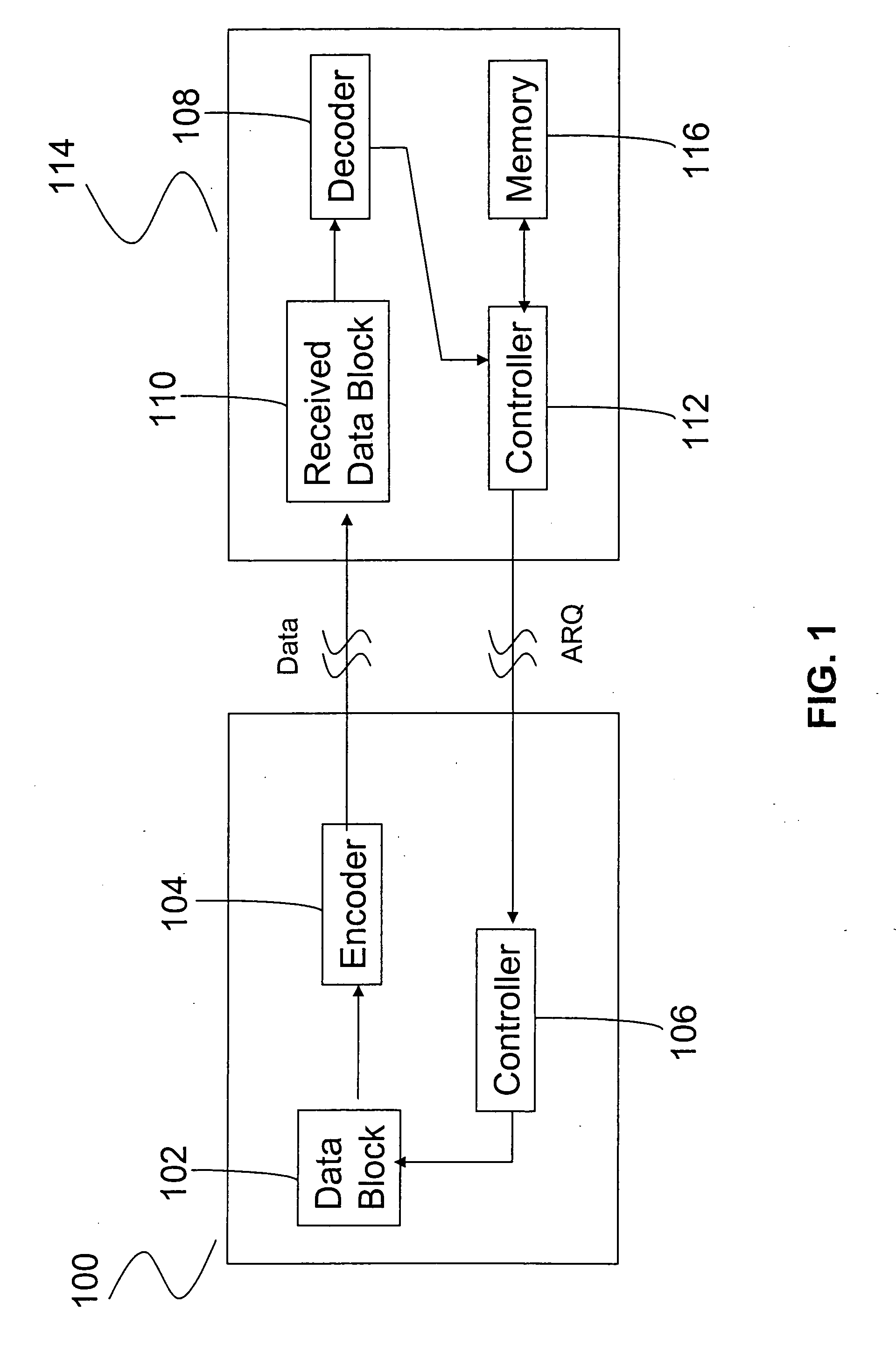
Method and apparatus for asynchronous incremental redundancy reception in a communication system
ActiveUS7206280B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsAsynchronous communicationCommunications system
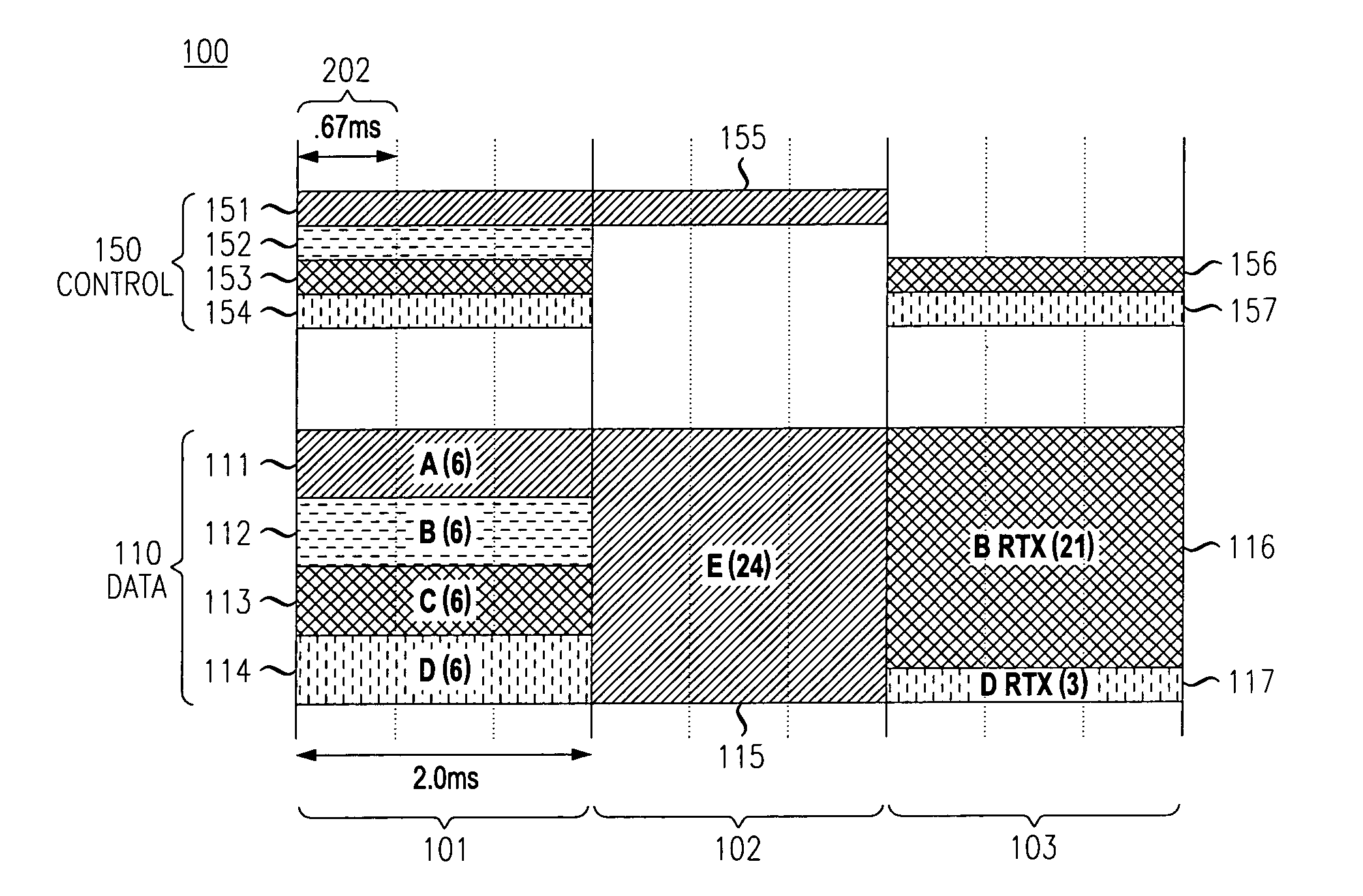
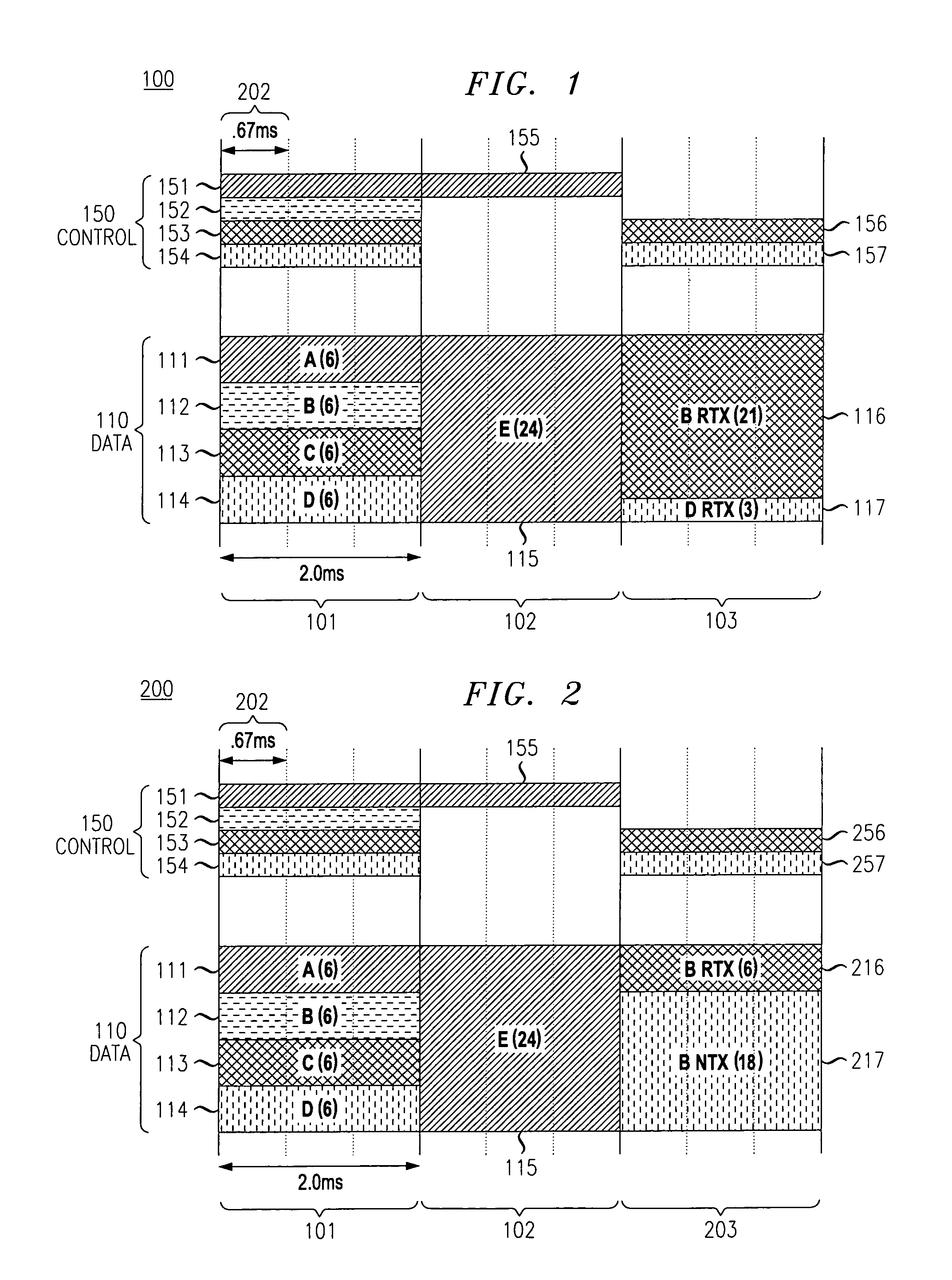
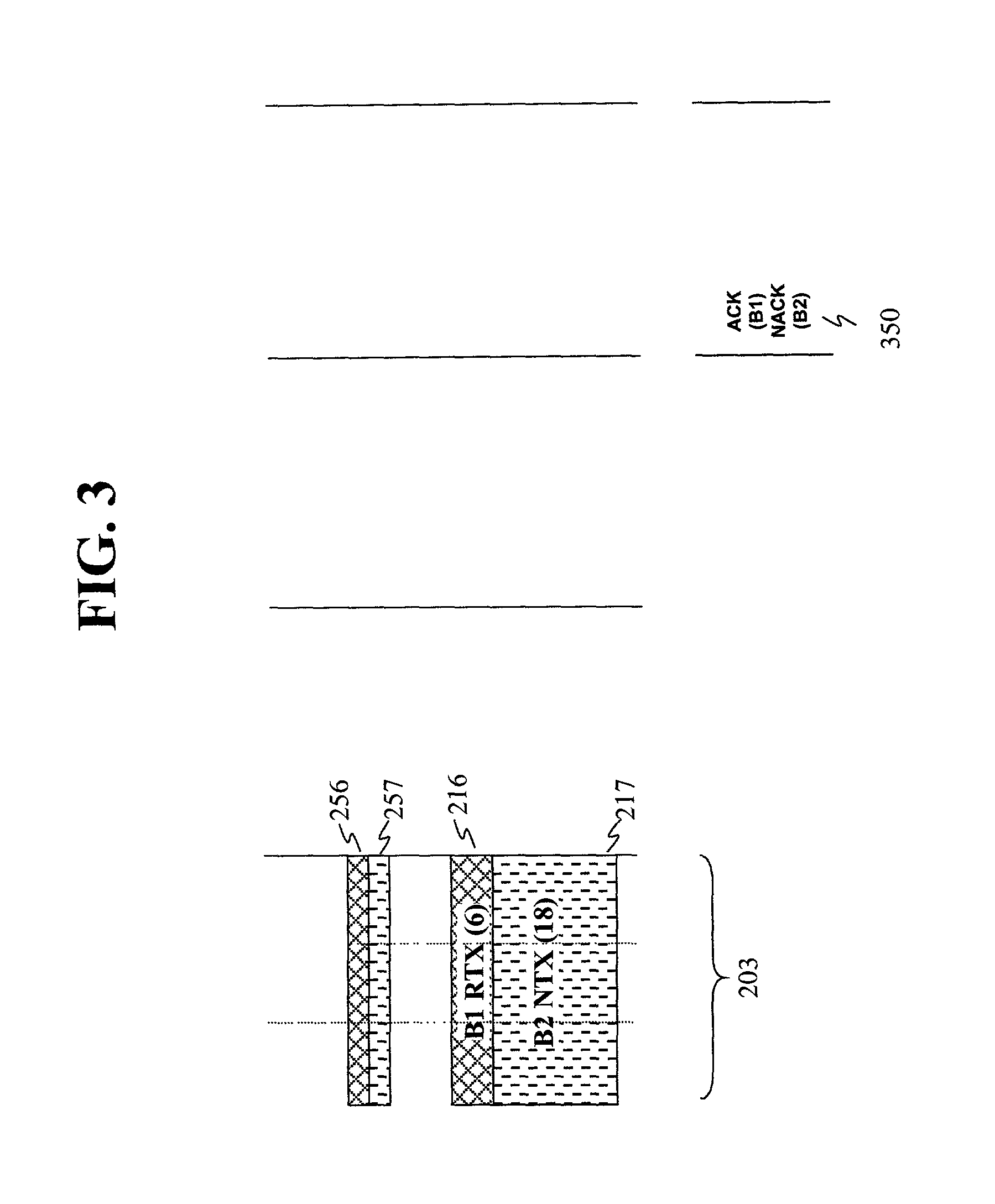
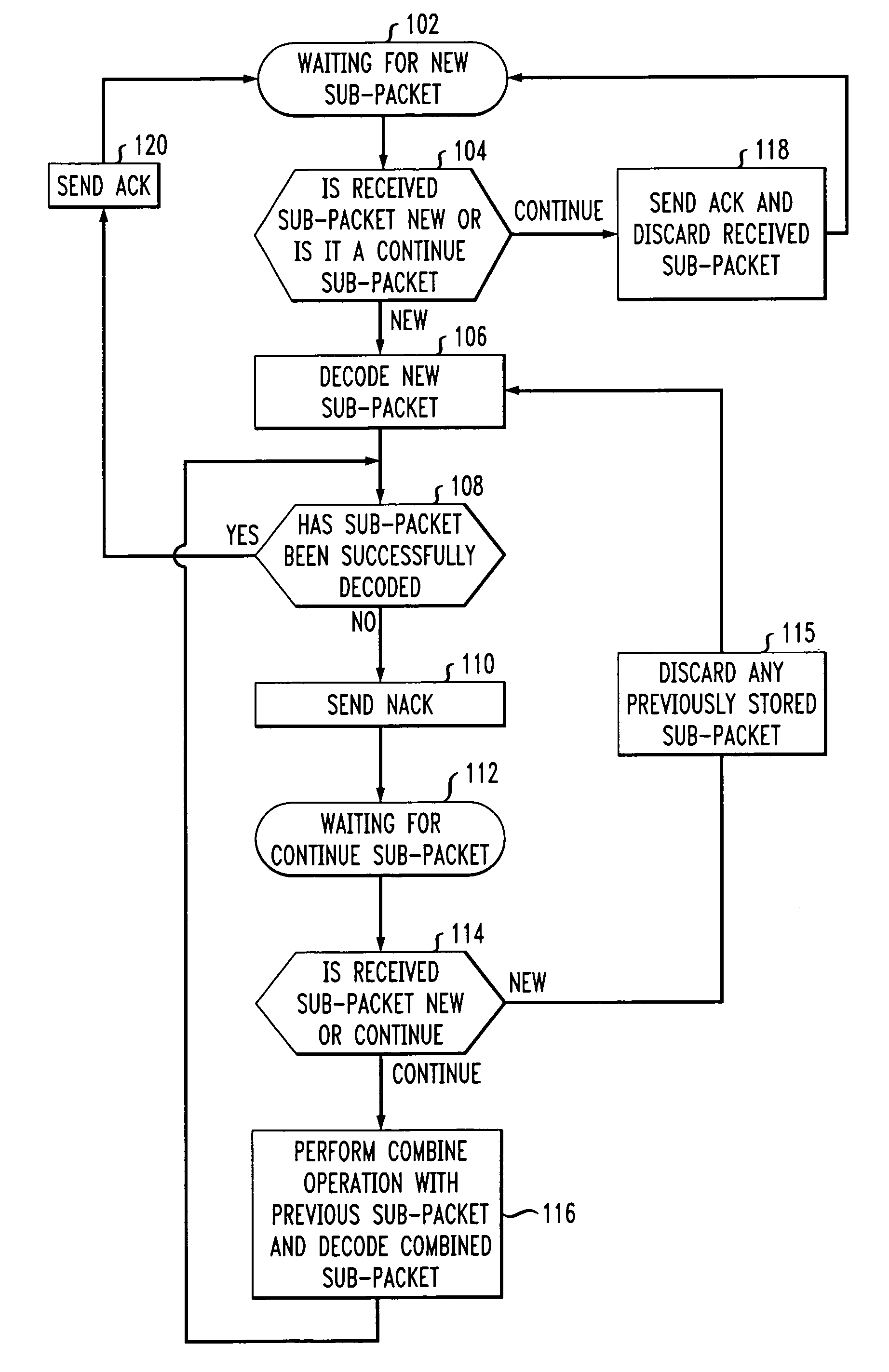
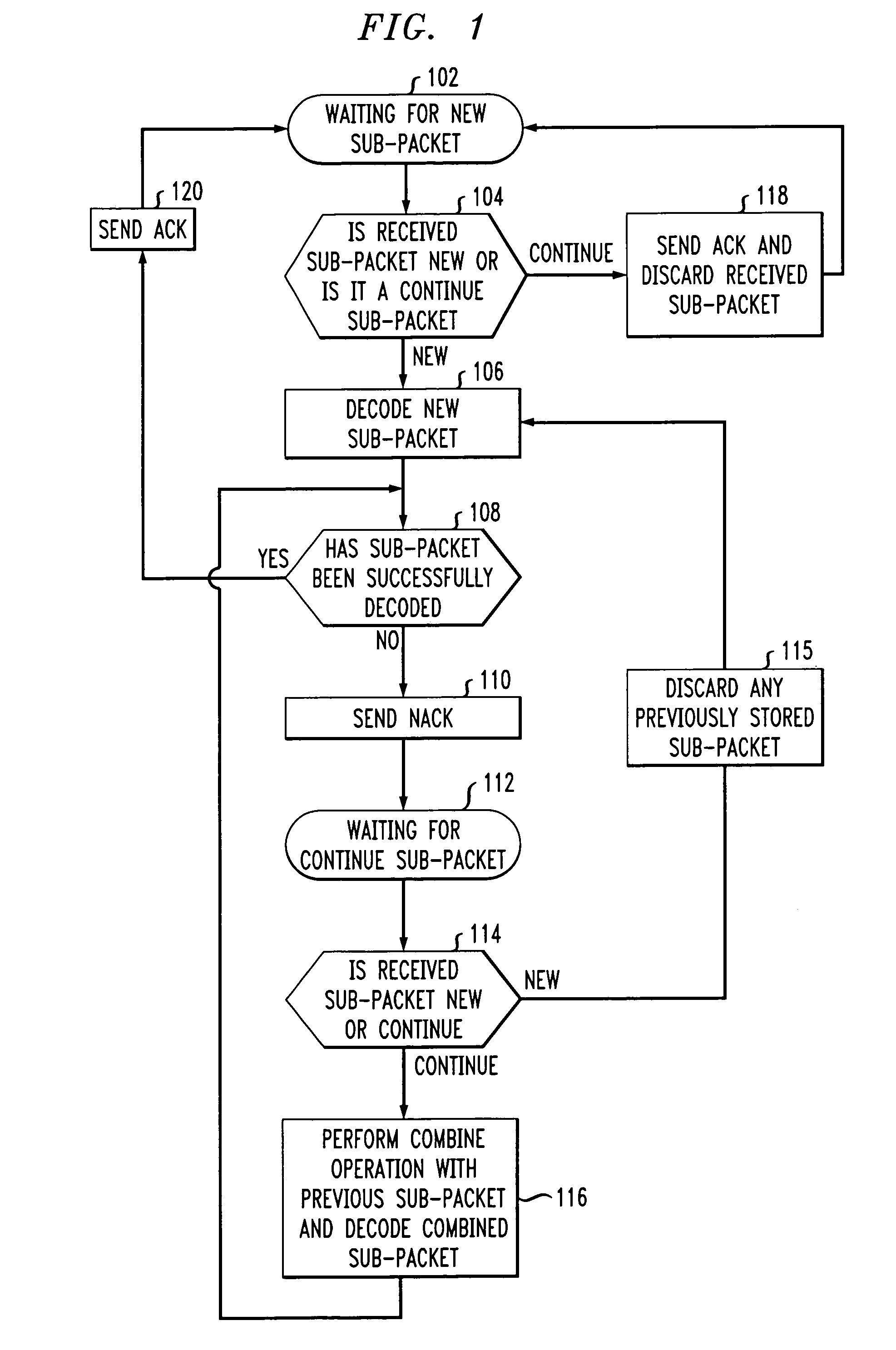
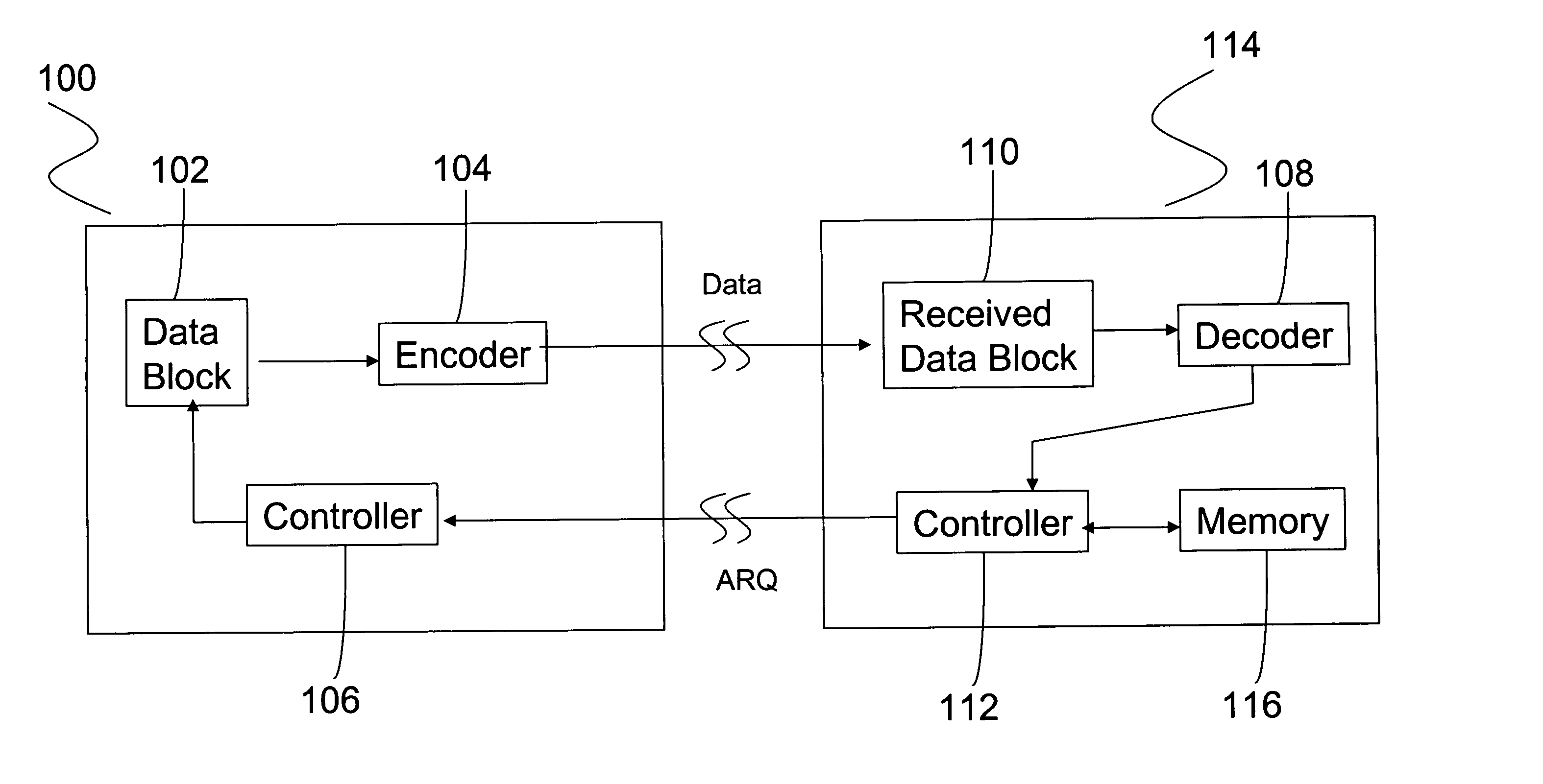
An ARQ method using Incremental Redundancy that can be used in either synchronous or asynchronous communication systems. Information received by receiving equipment contains a one-bit NEW / CONTINUE flag indicating whether the received information is the beginning of new information or the continuation (or retransmission) of previously transmitted information. An ACK message is transmitted by the receiving equipment when such equipment receives information containing a NEW flag and successfully decodes such information. The receiving equipment also transmits an ACK message when it receives information containing a CONTINUE flag while it was waiting for NEW information. Thus, the method of the present invention allows for relatively quick recovery from misinterpretations of ACK / NACK messages and accommodates subscribers having different transmission requirements.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
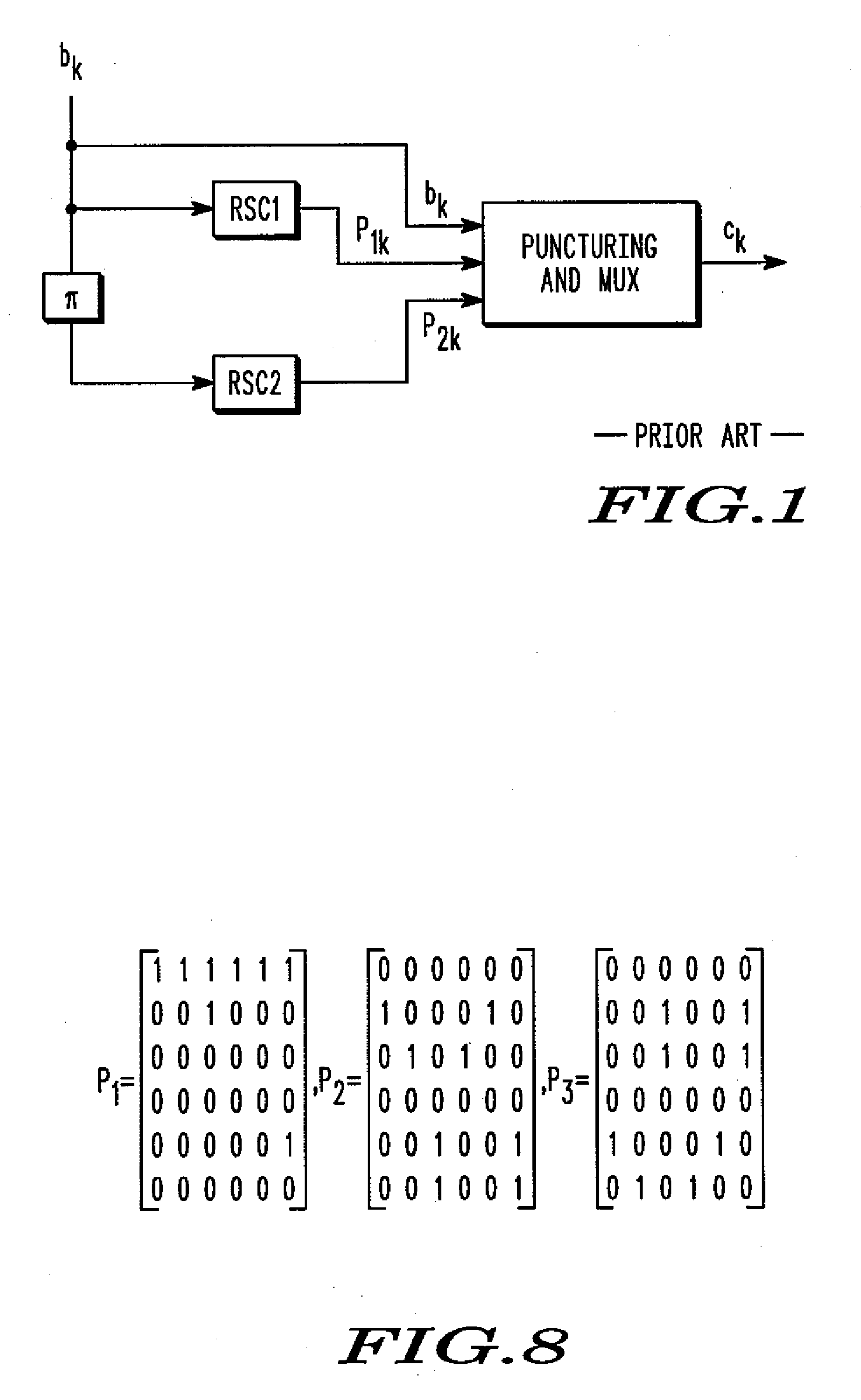
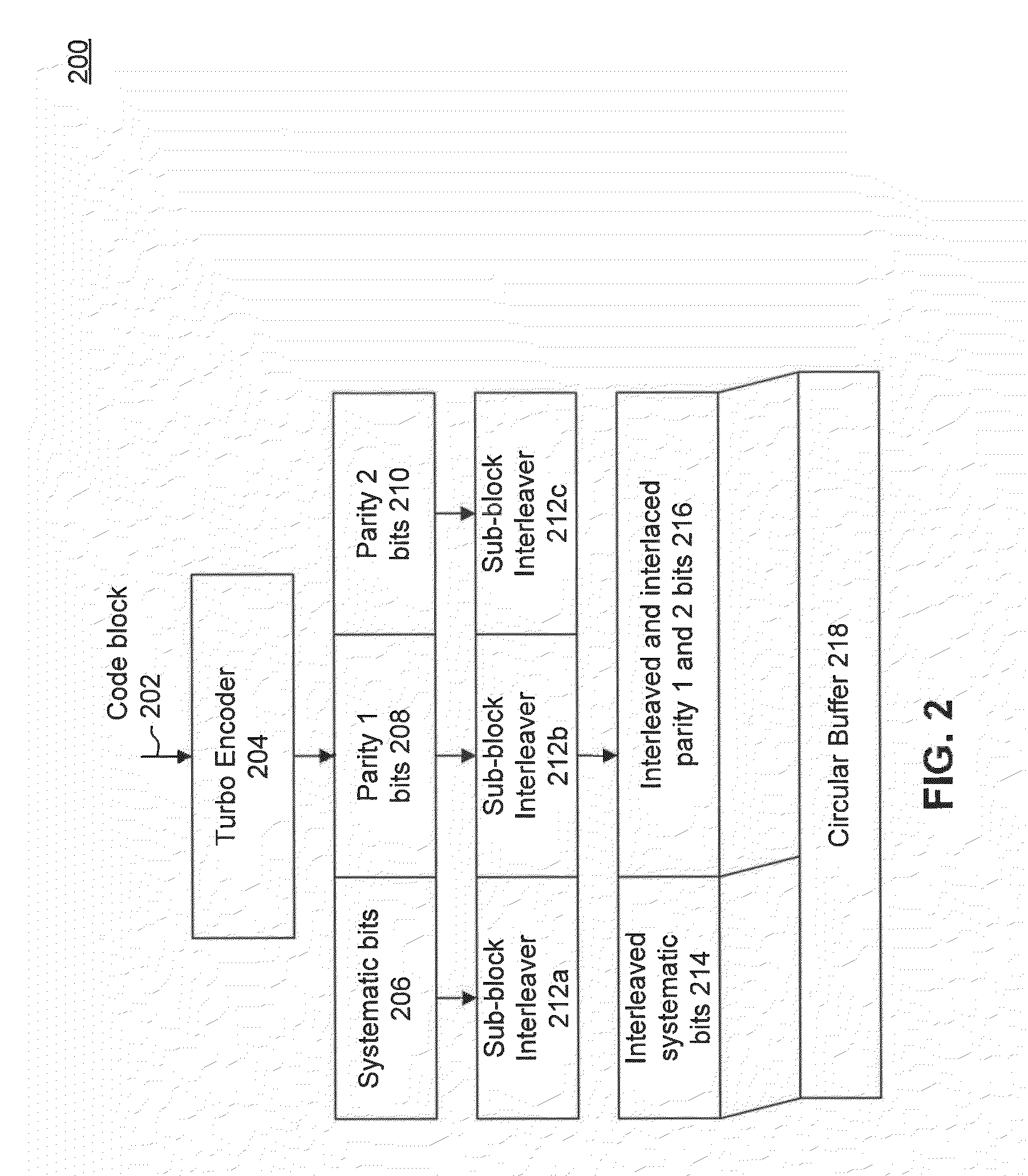
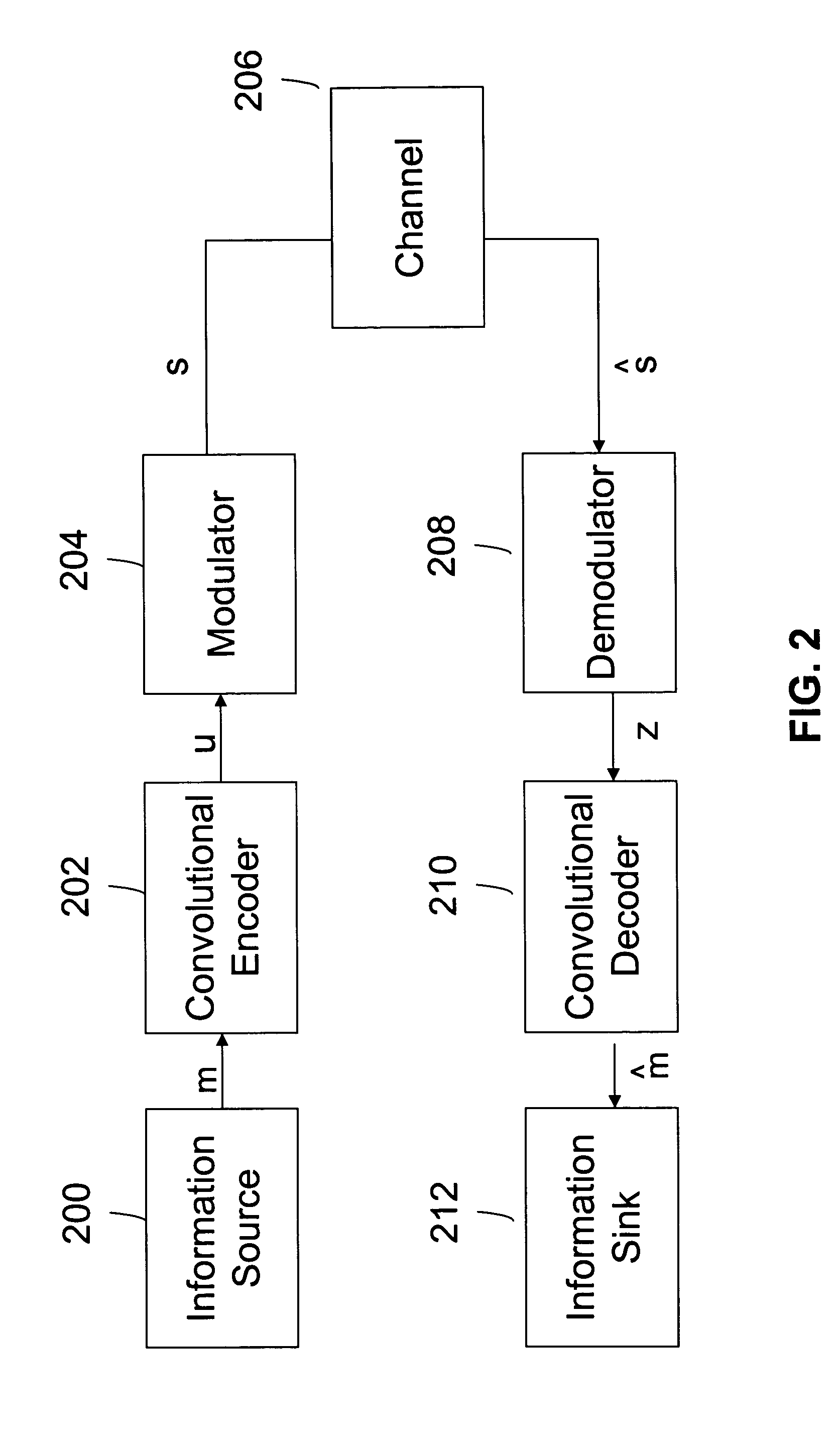
Turbo code based incremental redundancy
InactiveUS7000173B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using convolutional codesData streamComputer science
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
Harq Protocol Optimization for Packet Data Transmission
InactiveUS20080298387A1Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementControl signalPacket data transmission
The invention relates to a HARQ method using incremental redundancy and providing synchronous retransmissions. Further, the invention relates to a receiving entity and a transmitting entity employing the HARQ method and to a mobile communication system. To optimize conventional HARQ retransmission protocols, the invention introduces a ternary feedback which allows requesting a self-decodable version of a data packet under certain conditions. Further, the ternary feedback is provided in a backward compatible manner using a combination of conventional HARQ feedback signaling and scheduling related control signaling.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
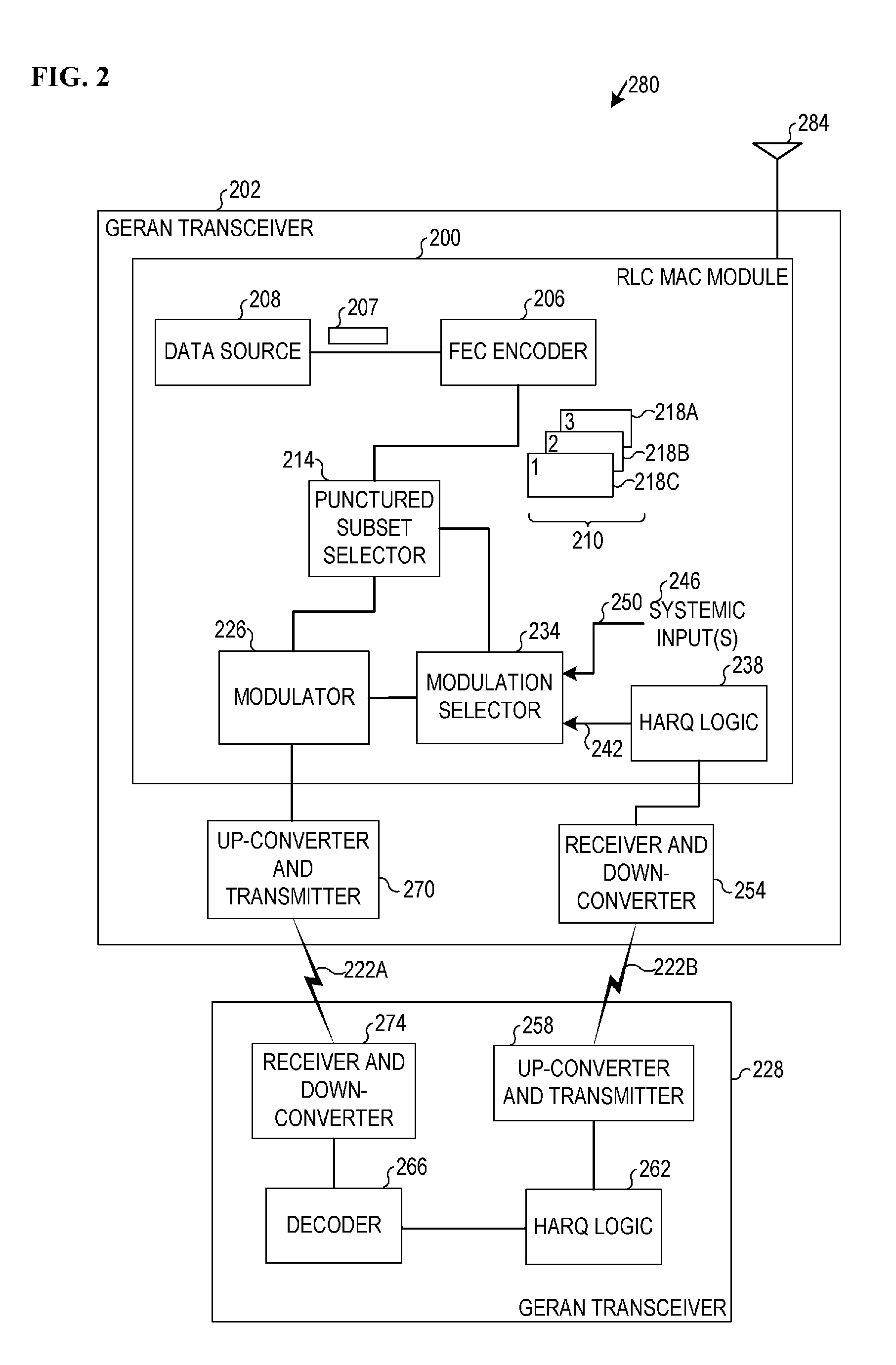
Incremental redundancy using high-order modulation and coding schemes
ActiveUS20080002565A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionRadio Link ControlMedia access control
Embodiments of a radio link control media access control module and associated methods may be described herein. Other embodiments may be described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
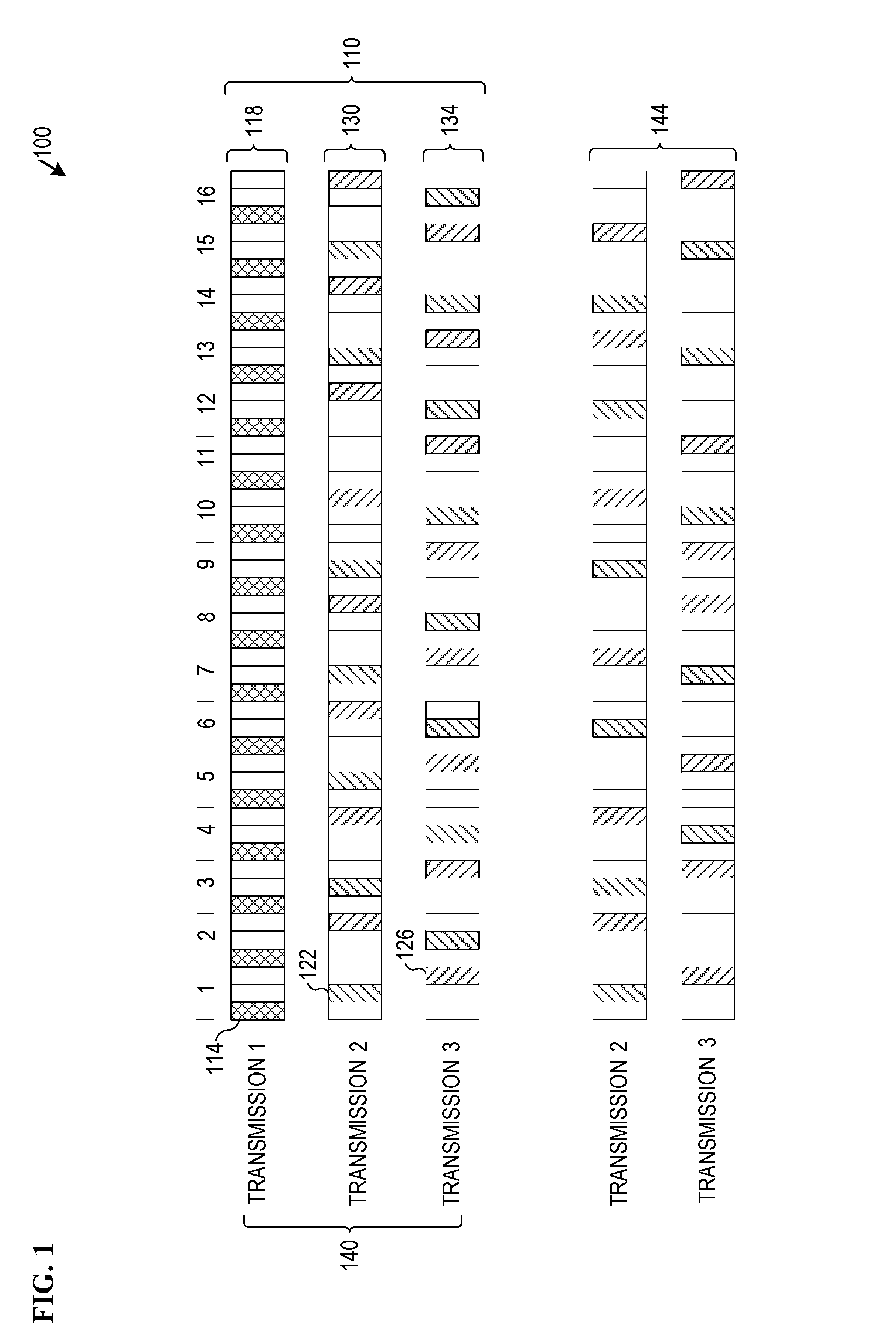
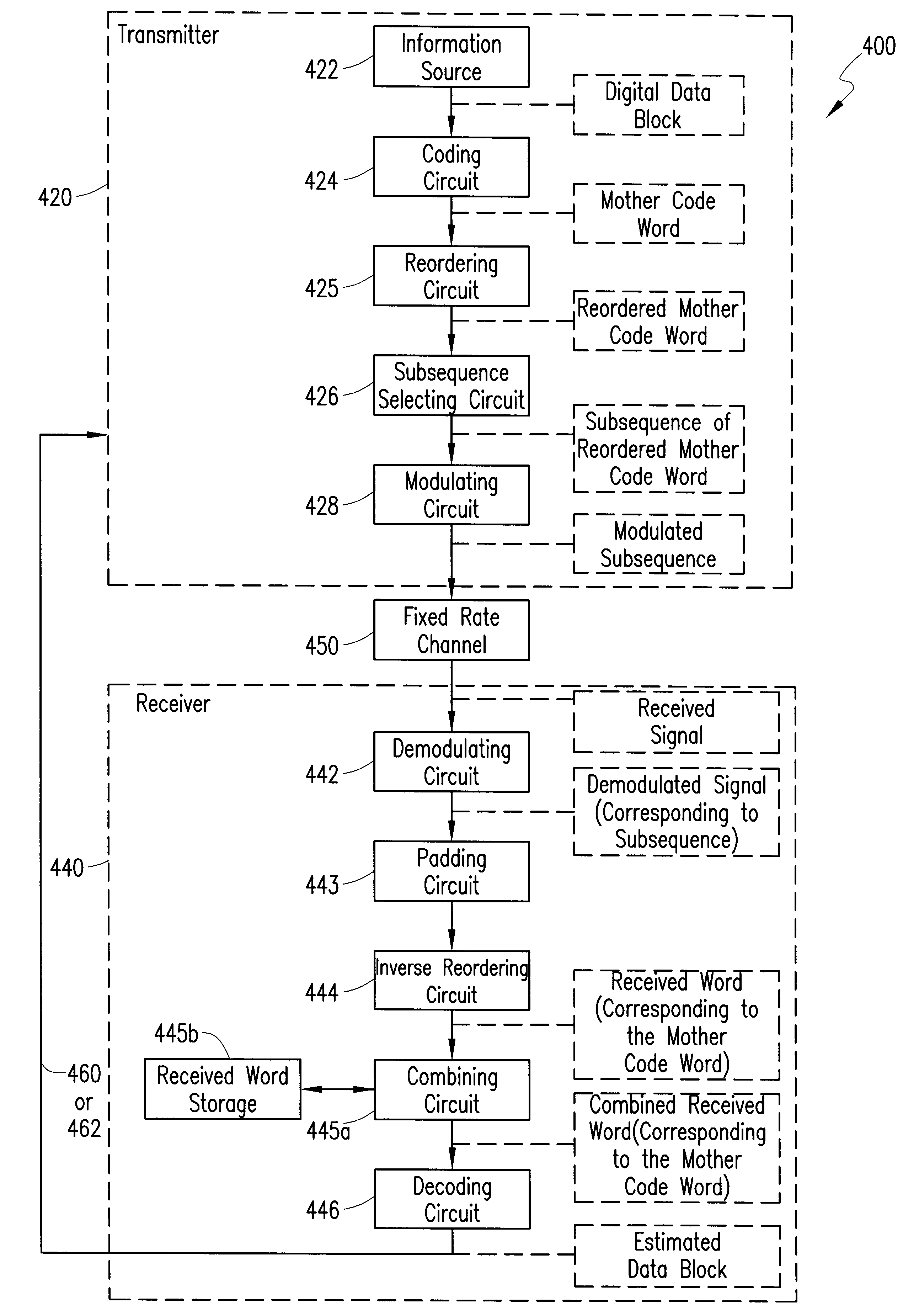
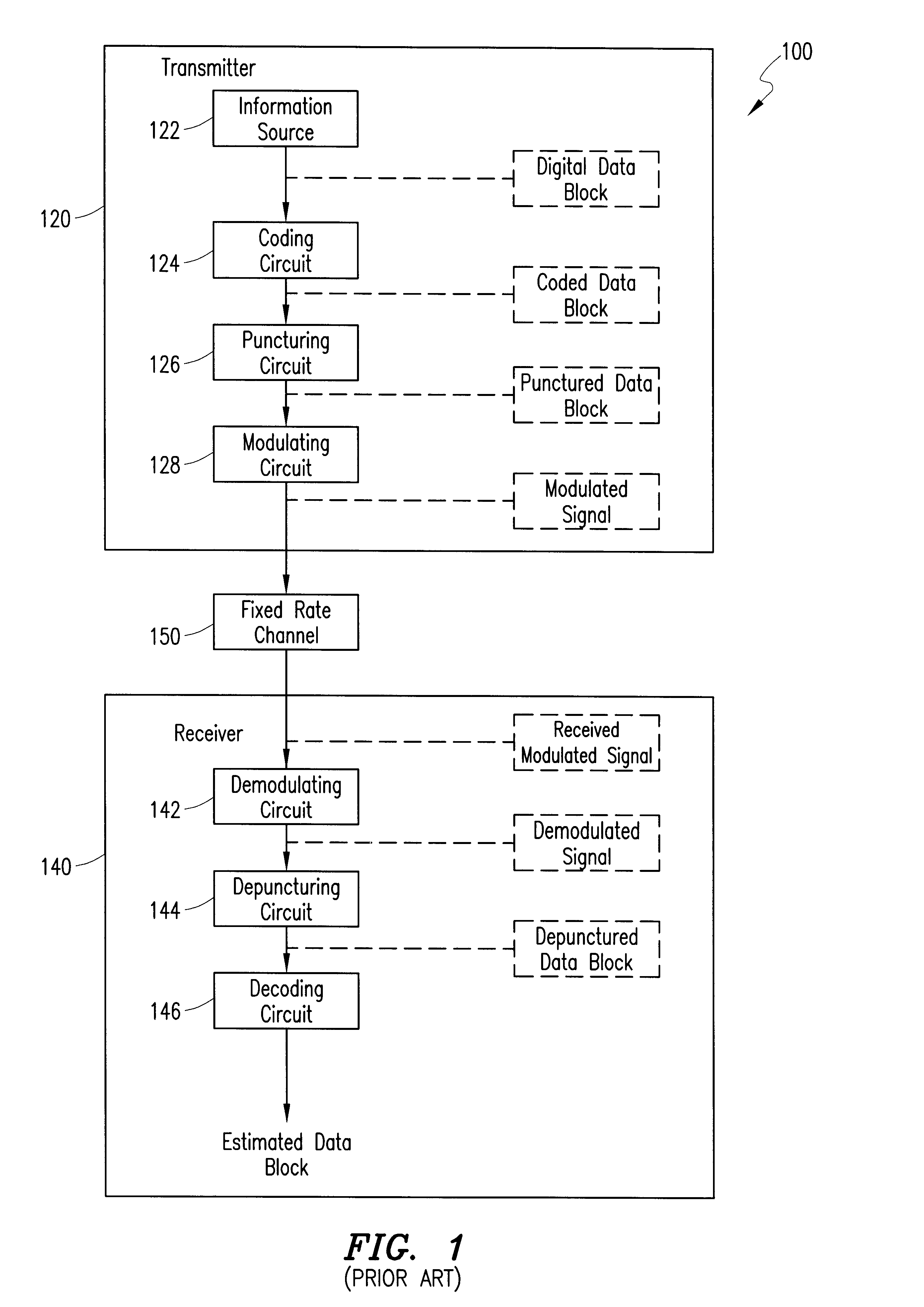
Telecommunications system and method for supporting an incremental redundancy error handling scheme using available gross rate channels
InactiveUS6604216B1Error prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionDigital dataCommunications system
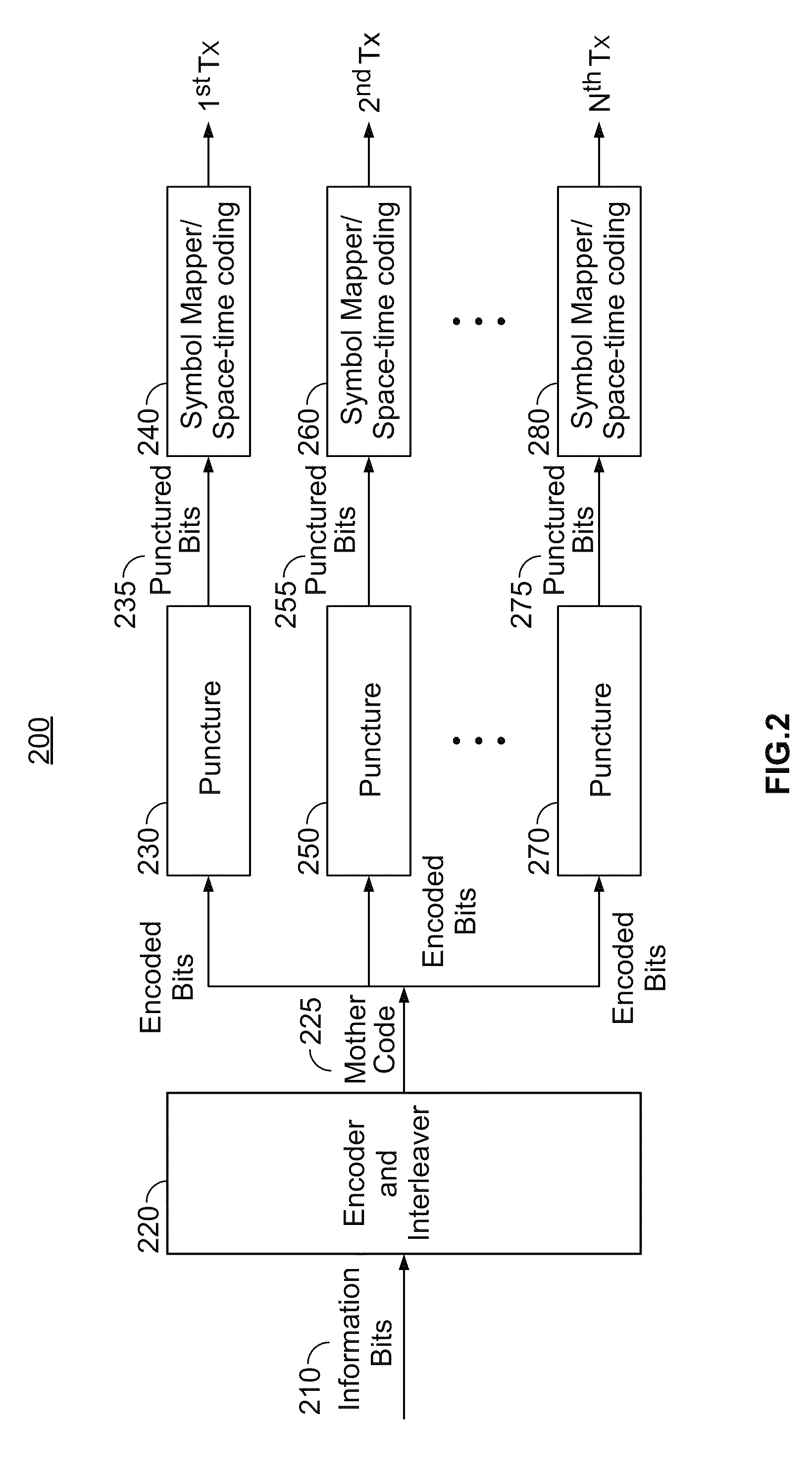
A wireless communications system, transmitter, receiver and method are provided that are capable of supporting incremental redundancy error handling schemes using available gross rate channels. More specifically, the transmitter includes a coding circuit for coding a digital data block and generating a mother code word, and a reordering circuit for reordering the mother code word and generating a reordered mother code word. The transmitter also includes a modulating circuit for modulating at least one subsequence each of which has a desired number of bits taken from the reordered mother code word to fill the available bandwidth of at least one available gross rate channel. The transmitter continues to forward the modulated subsequences to the receiver until the receiver successfully decodes the digital data block.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
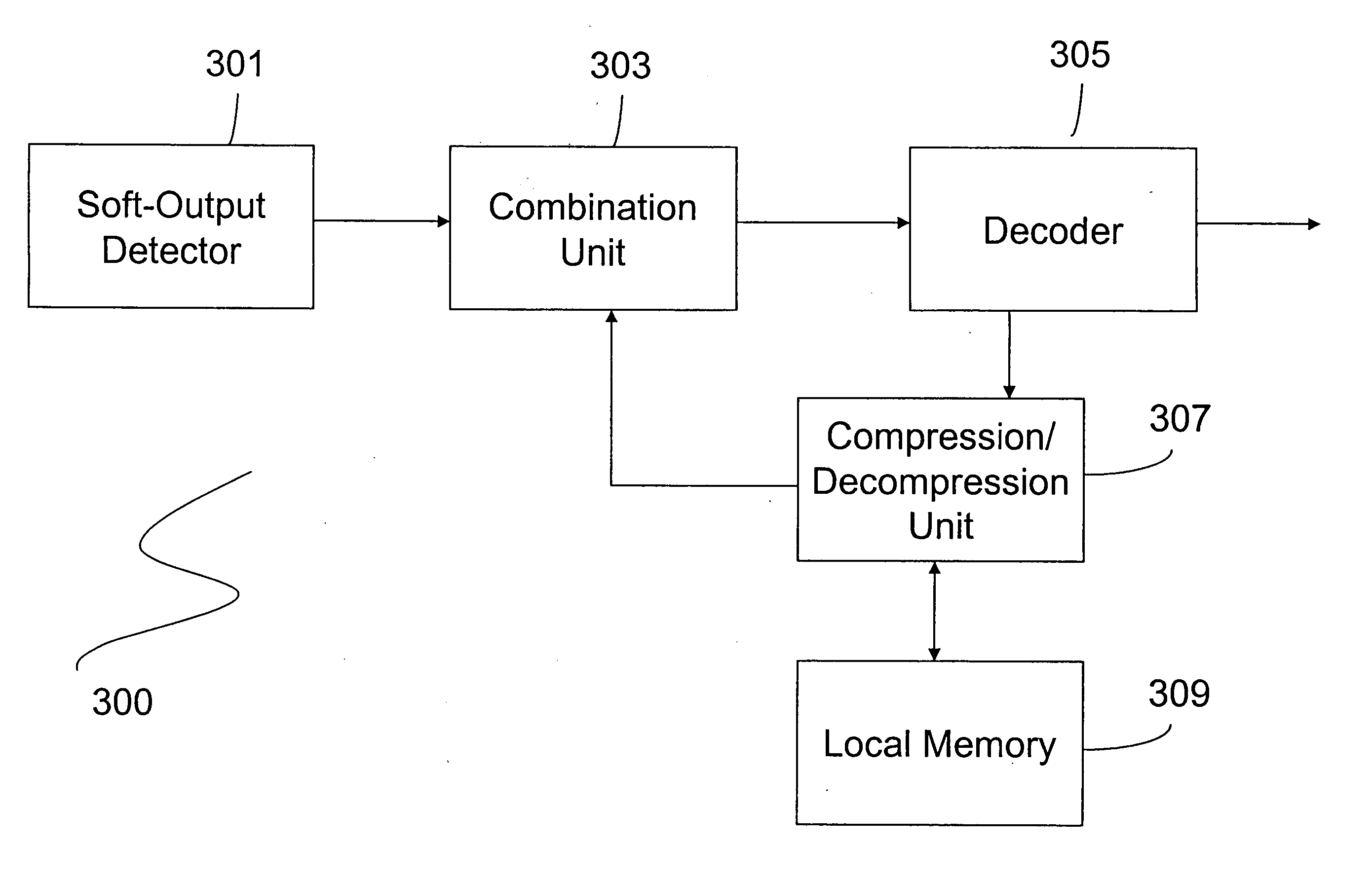
Data compression with incremental redundancy
InactiveUS20050138530A1Efficient storageError prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesData transmissionComputer science
In a packet-based data transmission including incremental redundancy (IR) protocols, the memory consumption of the IR protocol is reduced by compressing and storing failed data units in their punctured format. The failed data units are compressed using low complexity compression / decompression algorithms. The compression algorithm includes two parts: calculating and storing a scale factor for each transmission burst that estimates the soft values in the burst, and storing each soft values' sign in local memory instead of the complete soft value. If the currently received data unit is a retransmission, its compressed versions in the punctured format stored in the IR memory are decompressed, de-punctured and combined with the currently received data unit. The combined data unit is then decoded. The decompression restores an estimated soft-value by multiplying the sign value stored in the IR memory with its corresponding scale factor obtained from a mapping table.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Receiver and receiving method for receiving data in a broadcast system using incremental redundancy received through a unicast system
ActiveUS20120254684A1Increase probabilityImprove robustnessError correction/detection using concatenated codesError correction/detection using LDPC codesComputer hardwareData stream
A receiver includes: a broadcast receiver receiving a receiver input data stream segmented into frames, wherein basic codeword portions of codewords are mapped onto the frames, a codeword including at least a basic codeword portion generated from an input data word according to a first code; a data demapper demapping the basic codeword portions; a decoder error correction code decoding the codewords into output data words of at least one output data stream in a regular decoding using the basic codeword portion in a codeword; a check unit checking if the regular decoding of a codeword is erroneous; a unicast request unit requesting, if the regular decoding of a codeword is erroneous, an auxiliary codeword portion of the erroneously decoded codeword for incremental redundancy in an additional decoding; a unicast receiver unit receiving an auxiliary codeword portion of the erroneously decoded codeword.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method, device and system for transmitting data
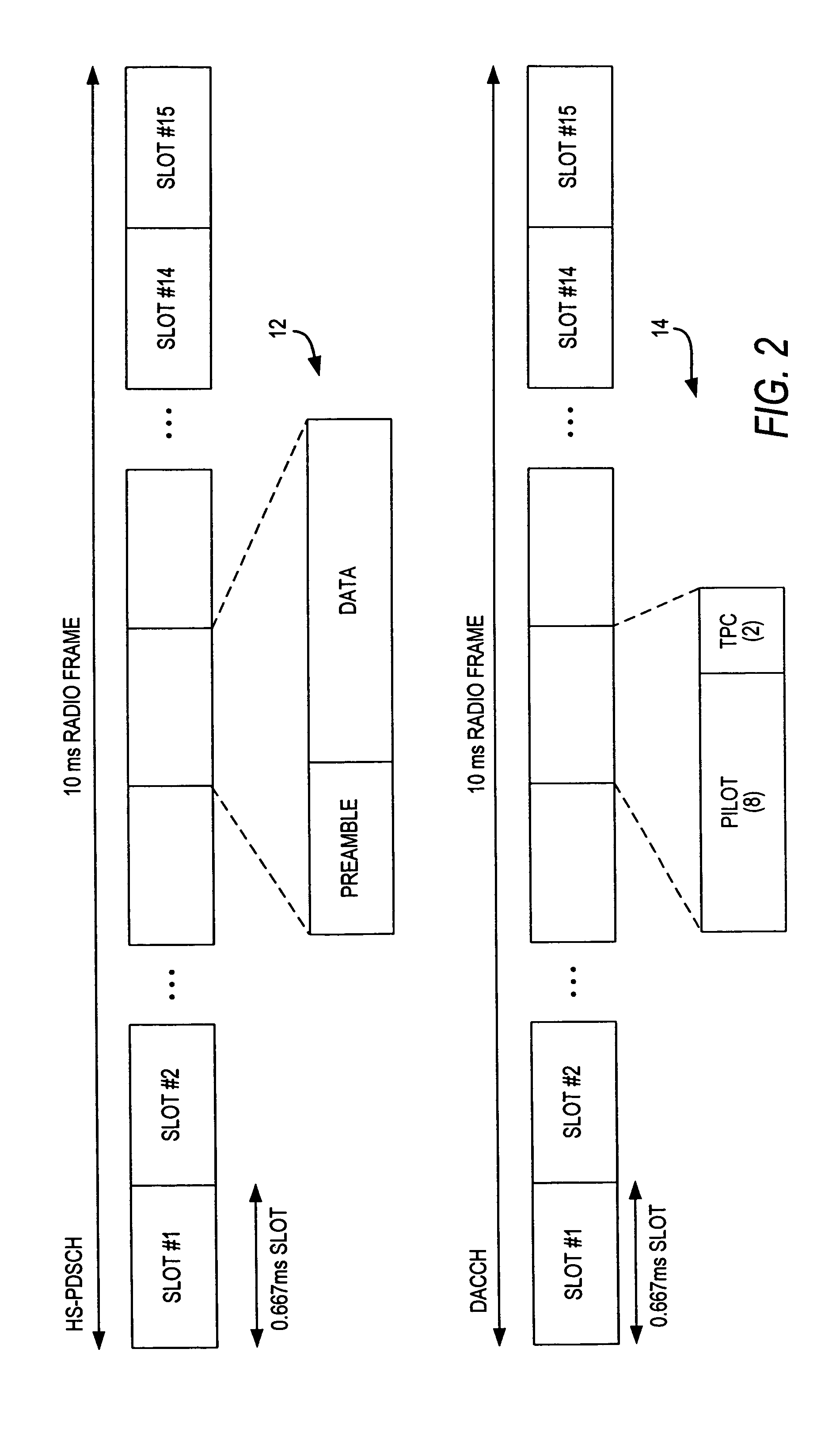
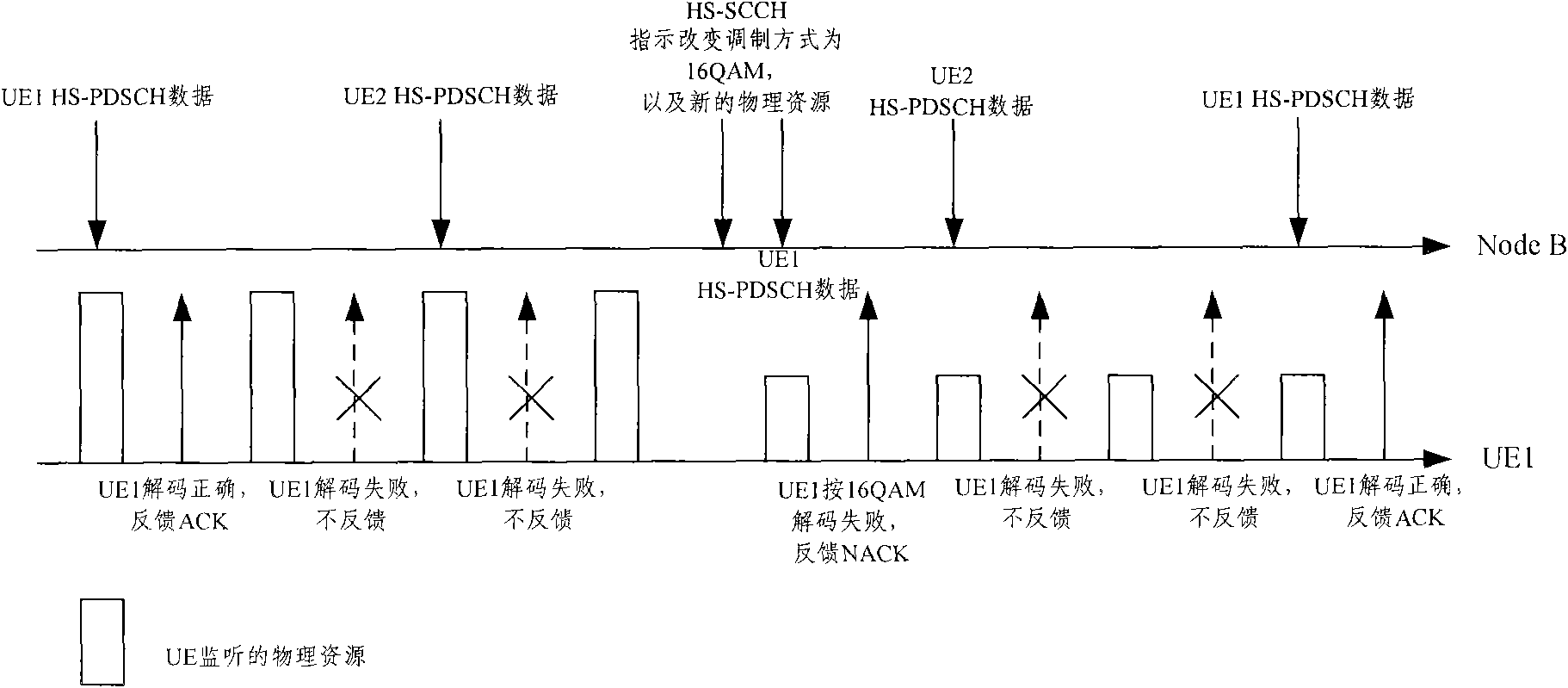
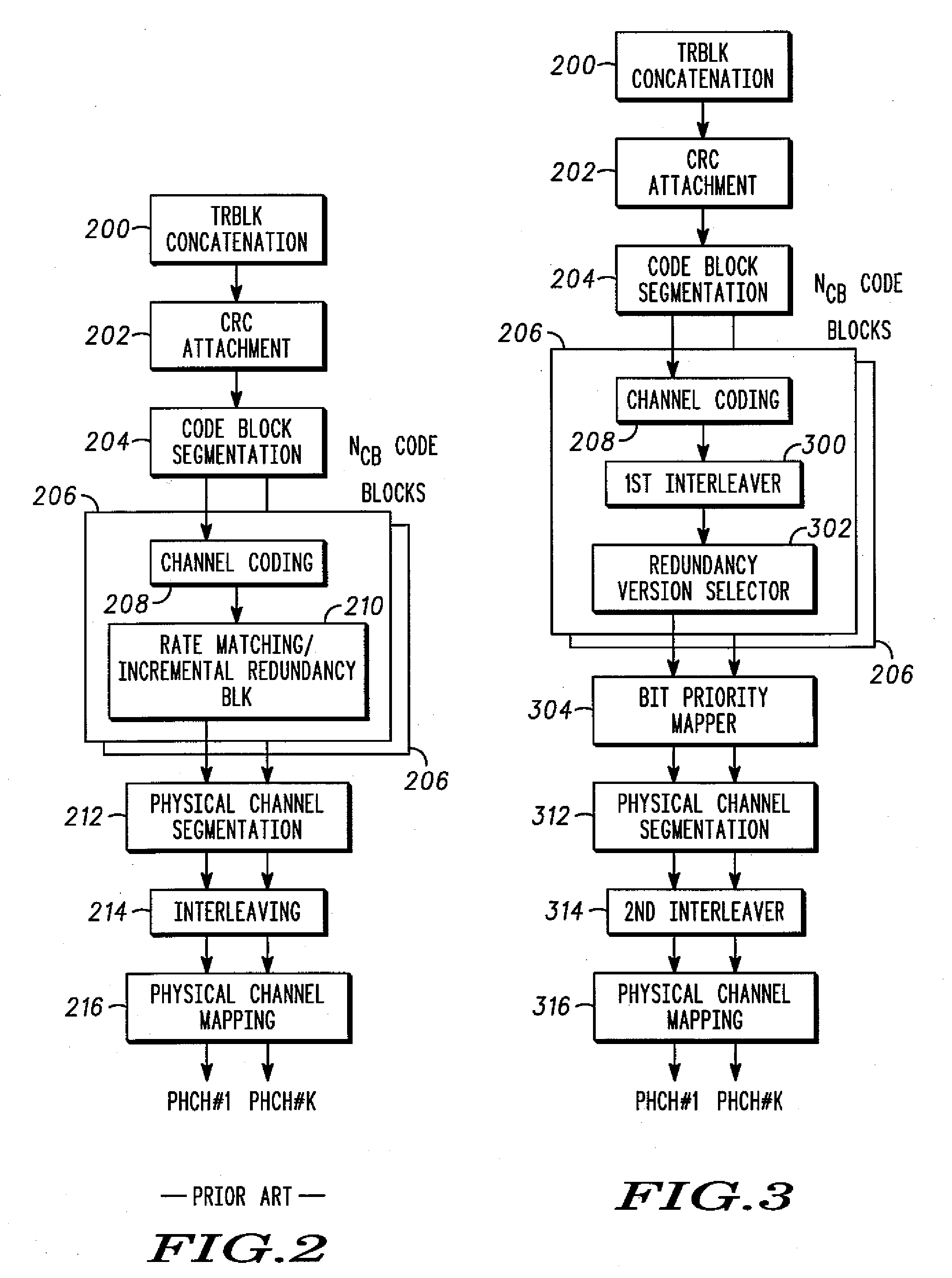
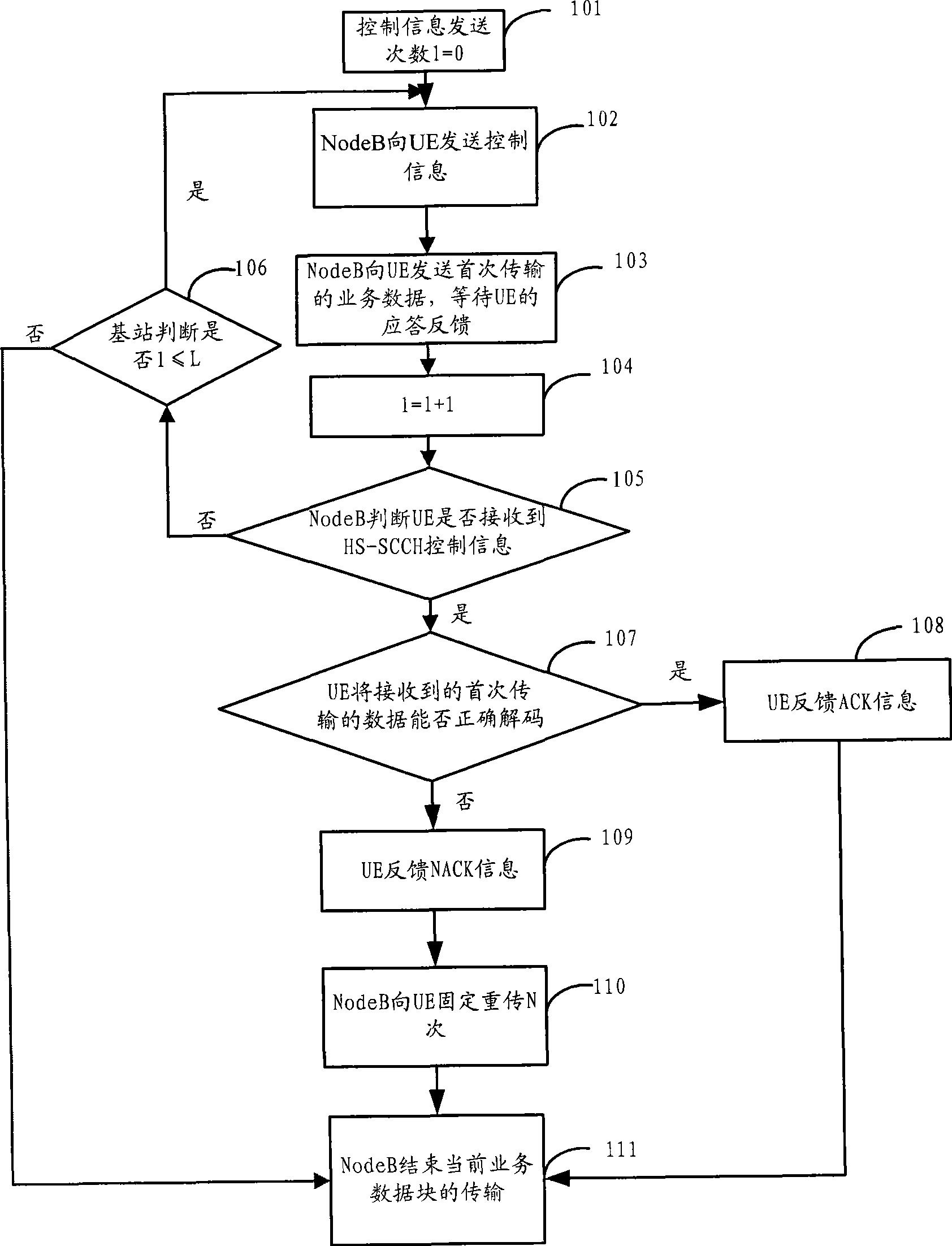
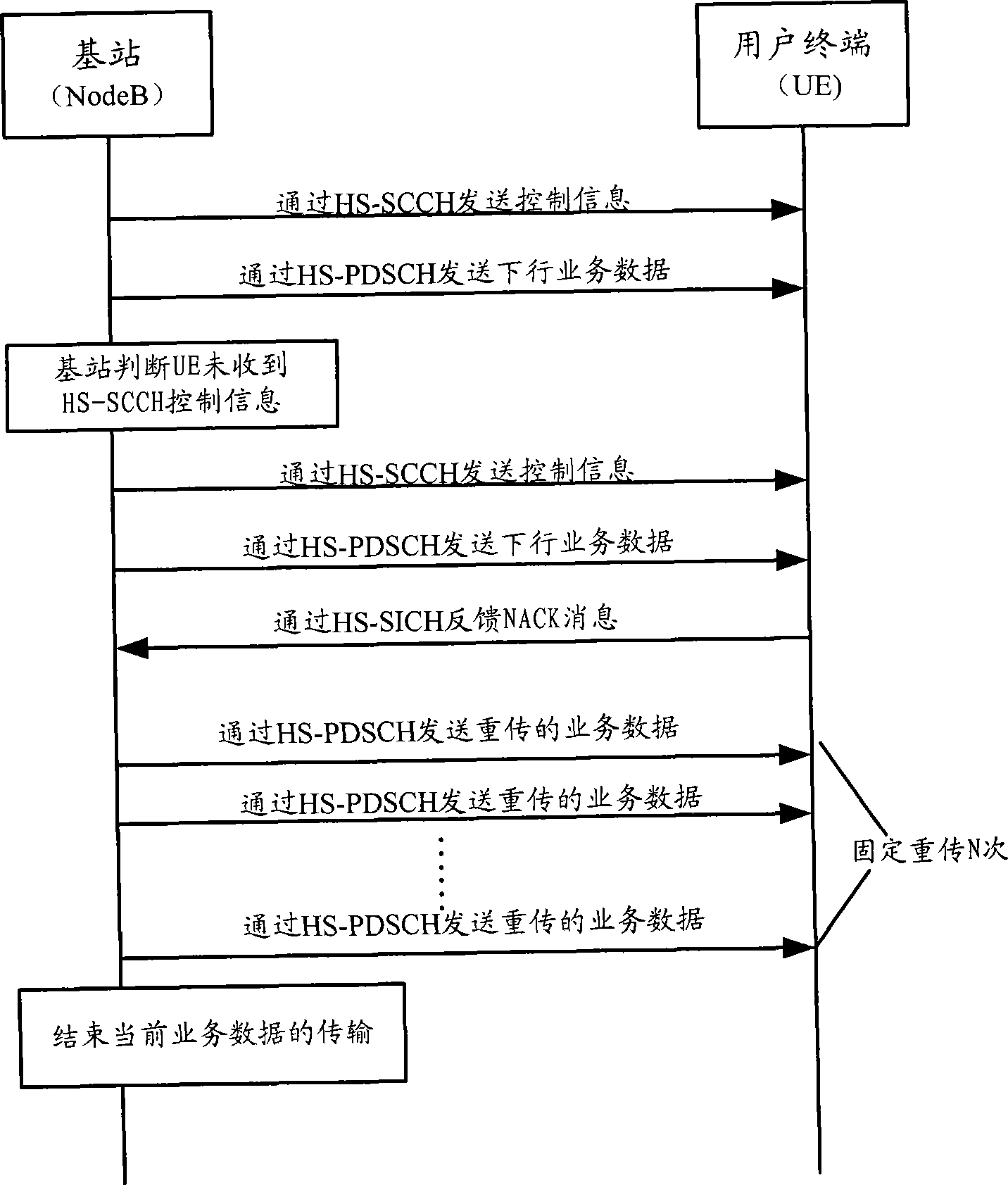
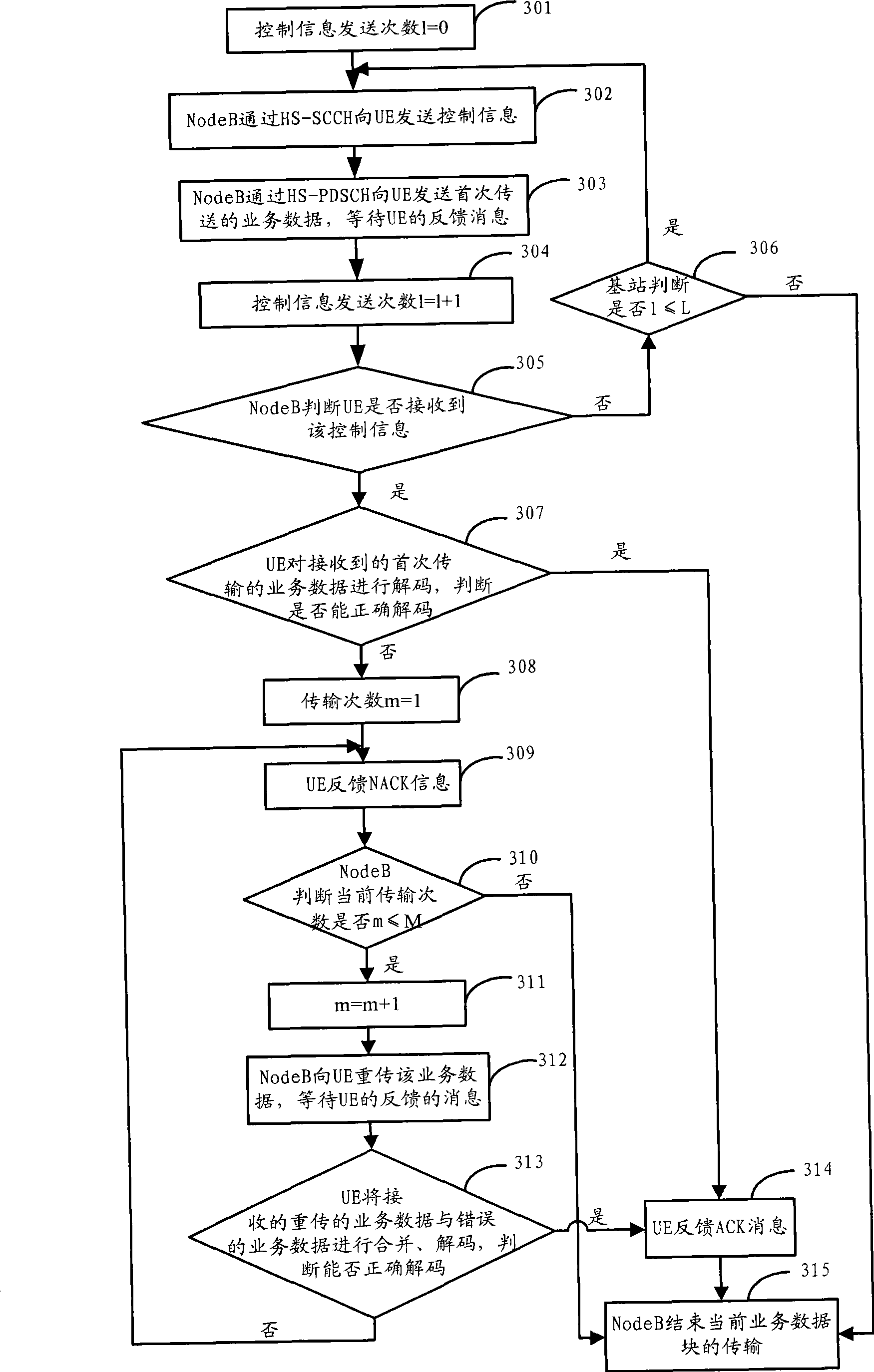
ActiveCN101631007AFlexibleImprove performanceError prevention/detection by using return channelResource informationControl channel
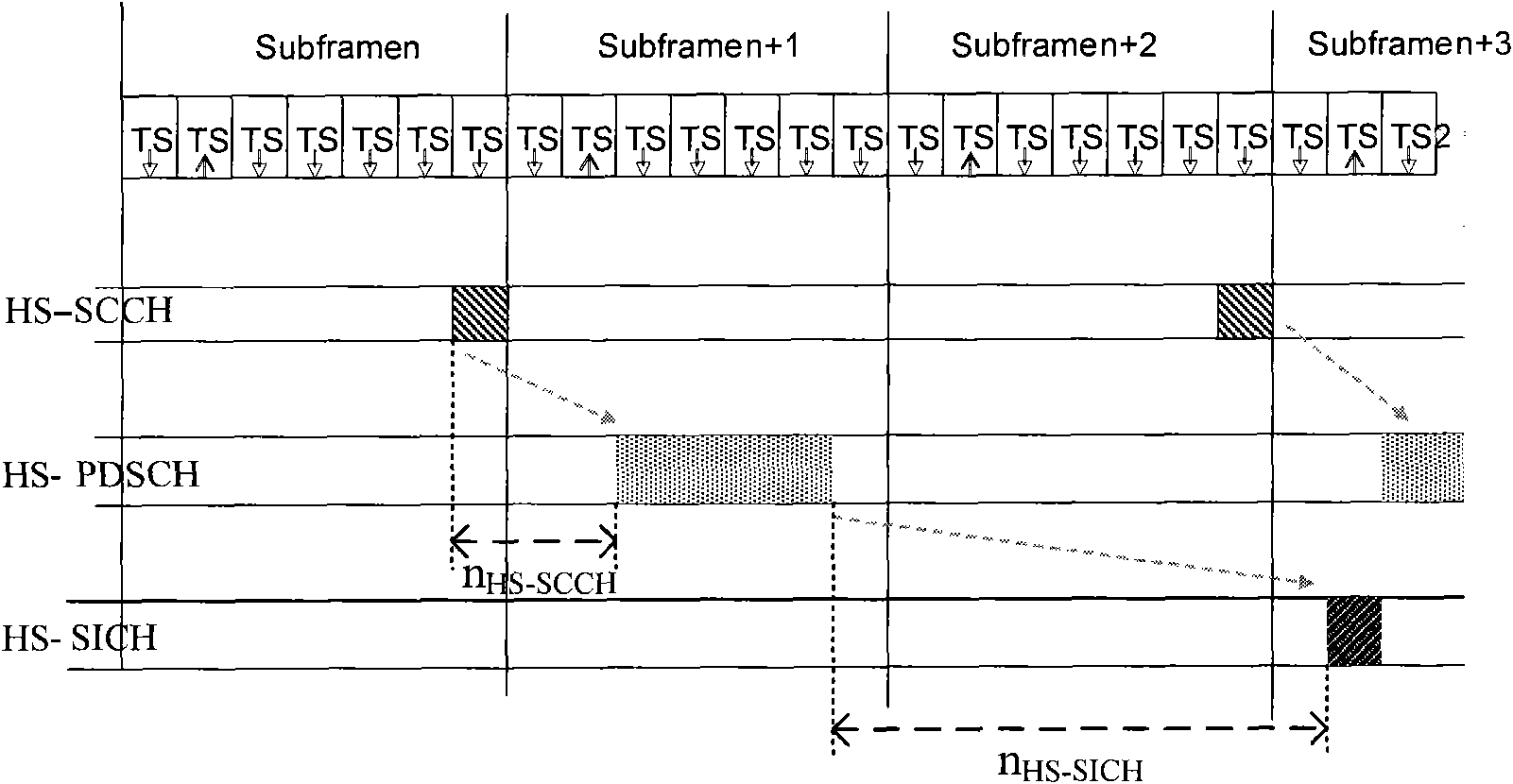
The invention discloses a data transmission method. The method comprises the following steps that: when a base station Node B sends control information to terminal UE through a high-speed sharing control channel HS-SCCH, the HS-SCCH carries physical resource information of a high-speed physical downlink sharing channel HS-PDSCH needed to be monitored by the UE, a UE identification ID, a PTR pointer and transmission frequency, and also carries a modulation mode instruction, a transmission block size, an HS-SCCH circulation serial number HCSN, an incremental redundancy version number, a high-speed sharing information channel HS-SICH instruction, a feedback mode, a monitoring time instruction, and one or more kinds of control information in resource adjusting time. The invention also discloses a data transmission device and a system. The method, the device and the system can flexibly change the control information of data transmission.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
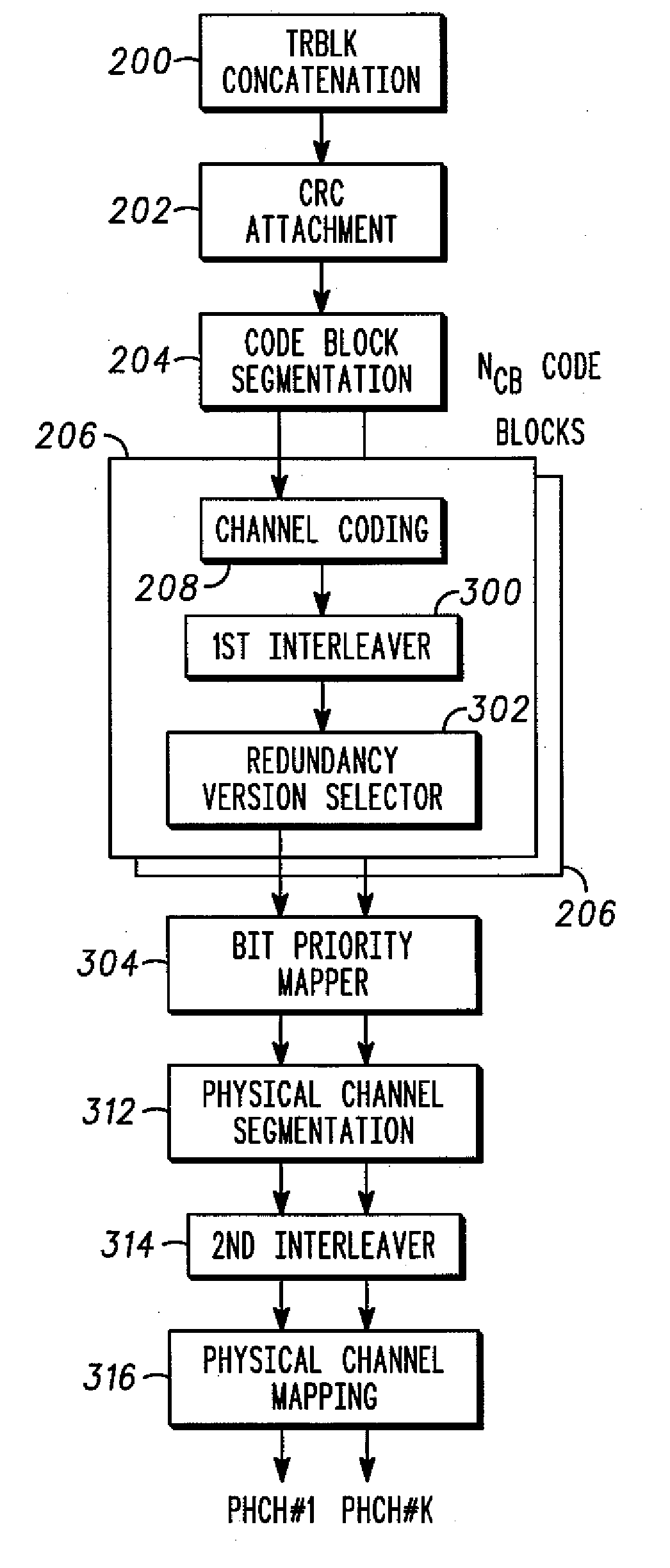
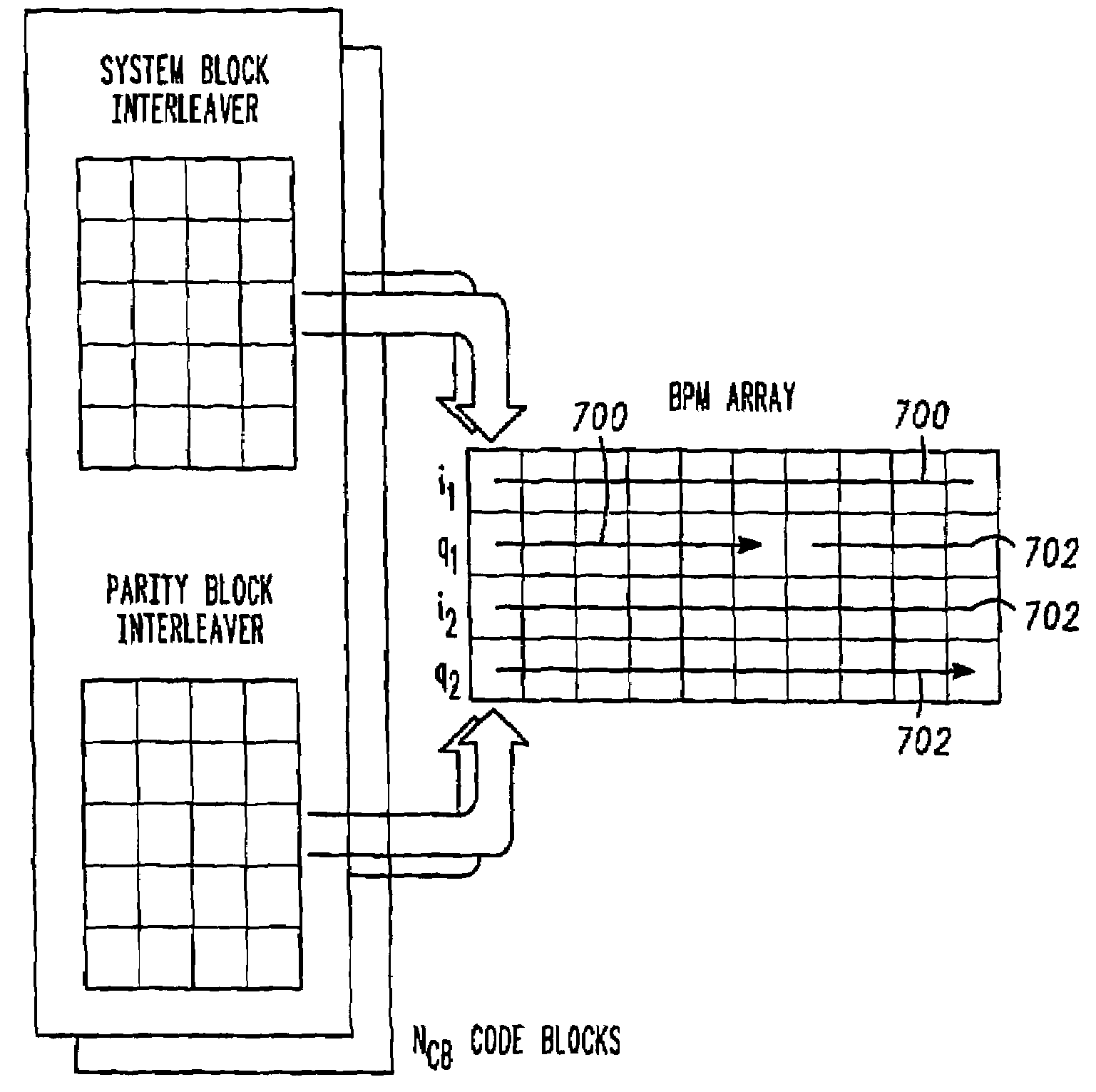
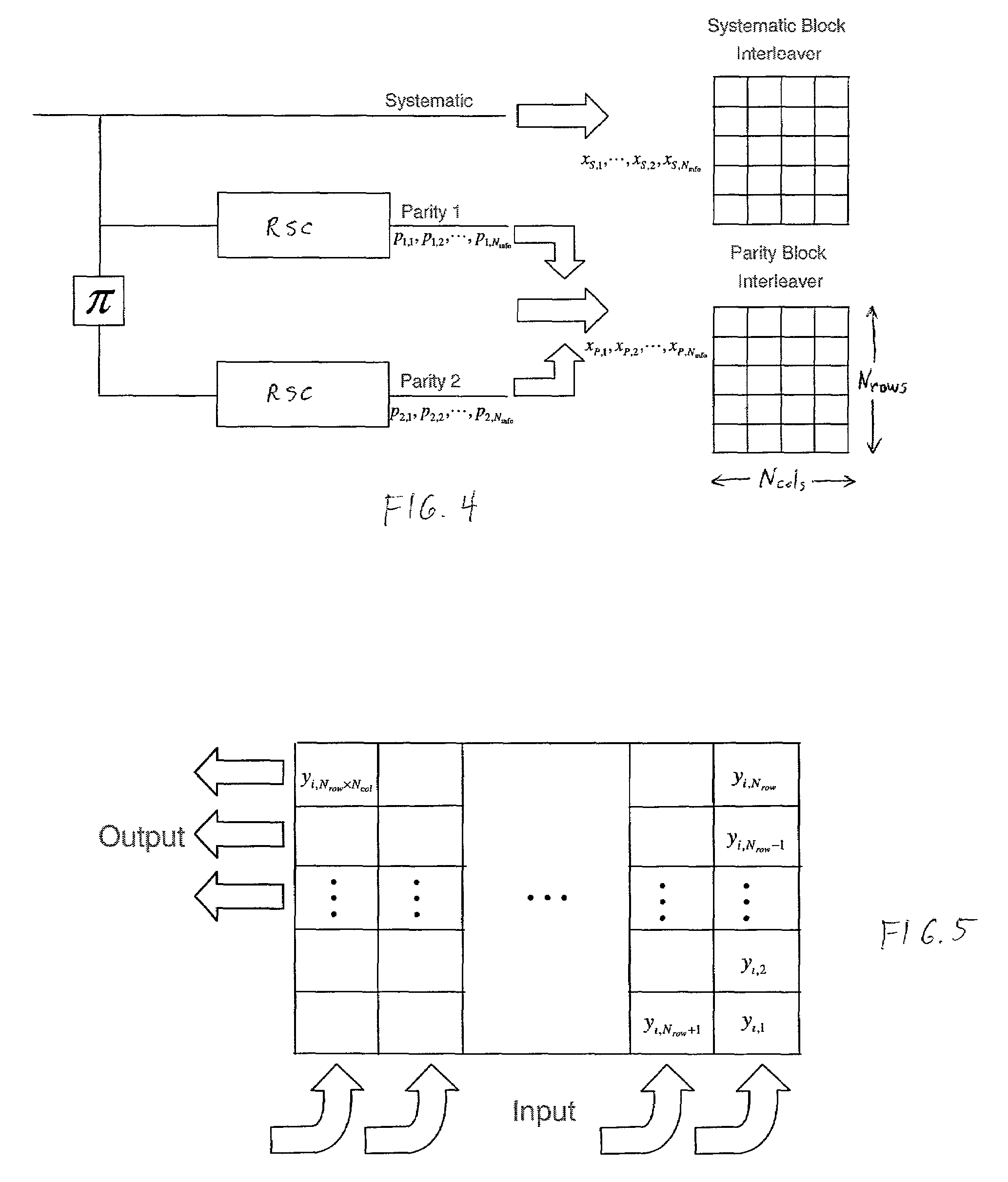
Block puncturing for turbo code based incremental redundancy
InactiveUS20070061690A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/correctionData streamTheoretical computer science
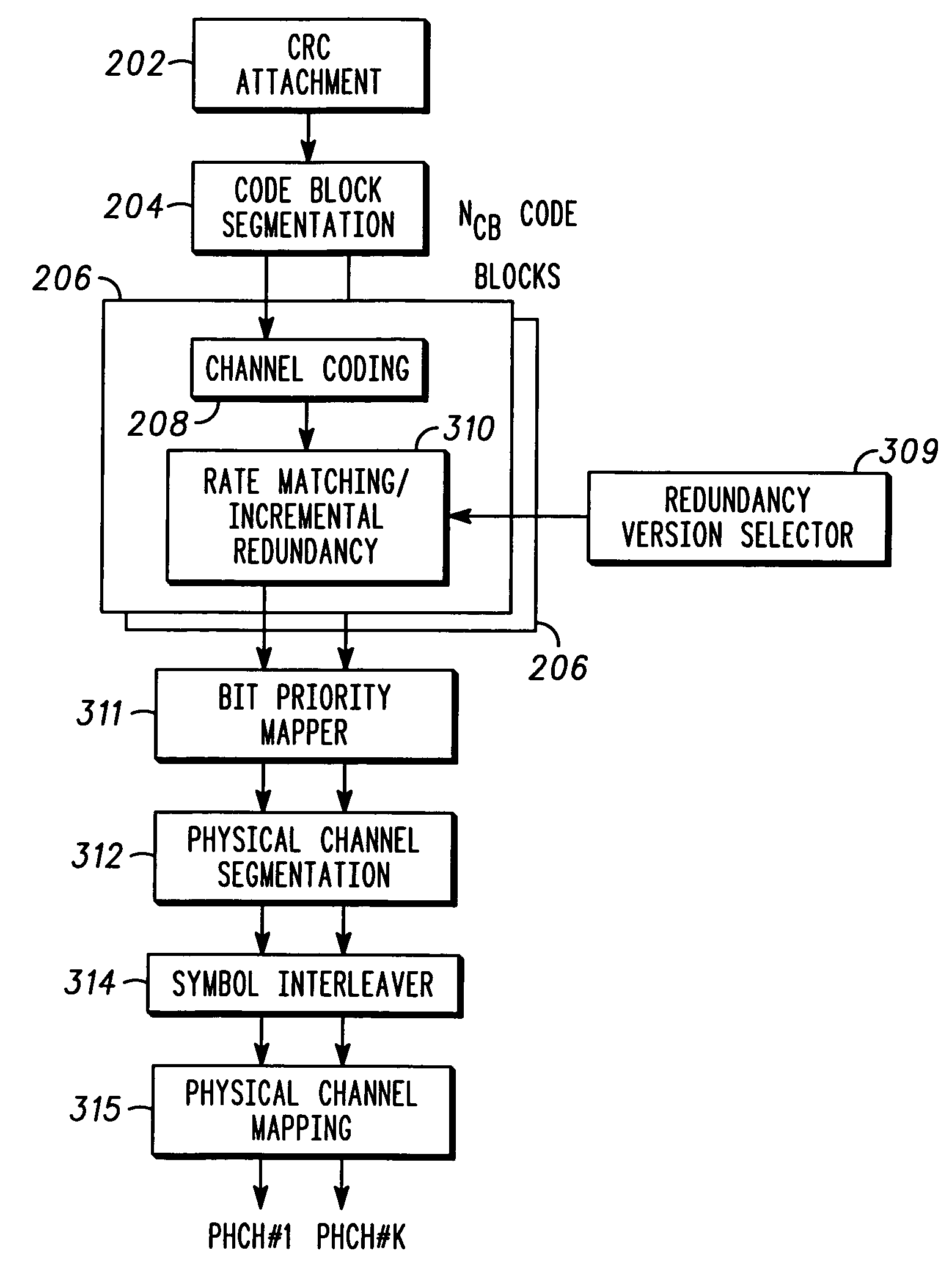
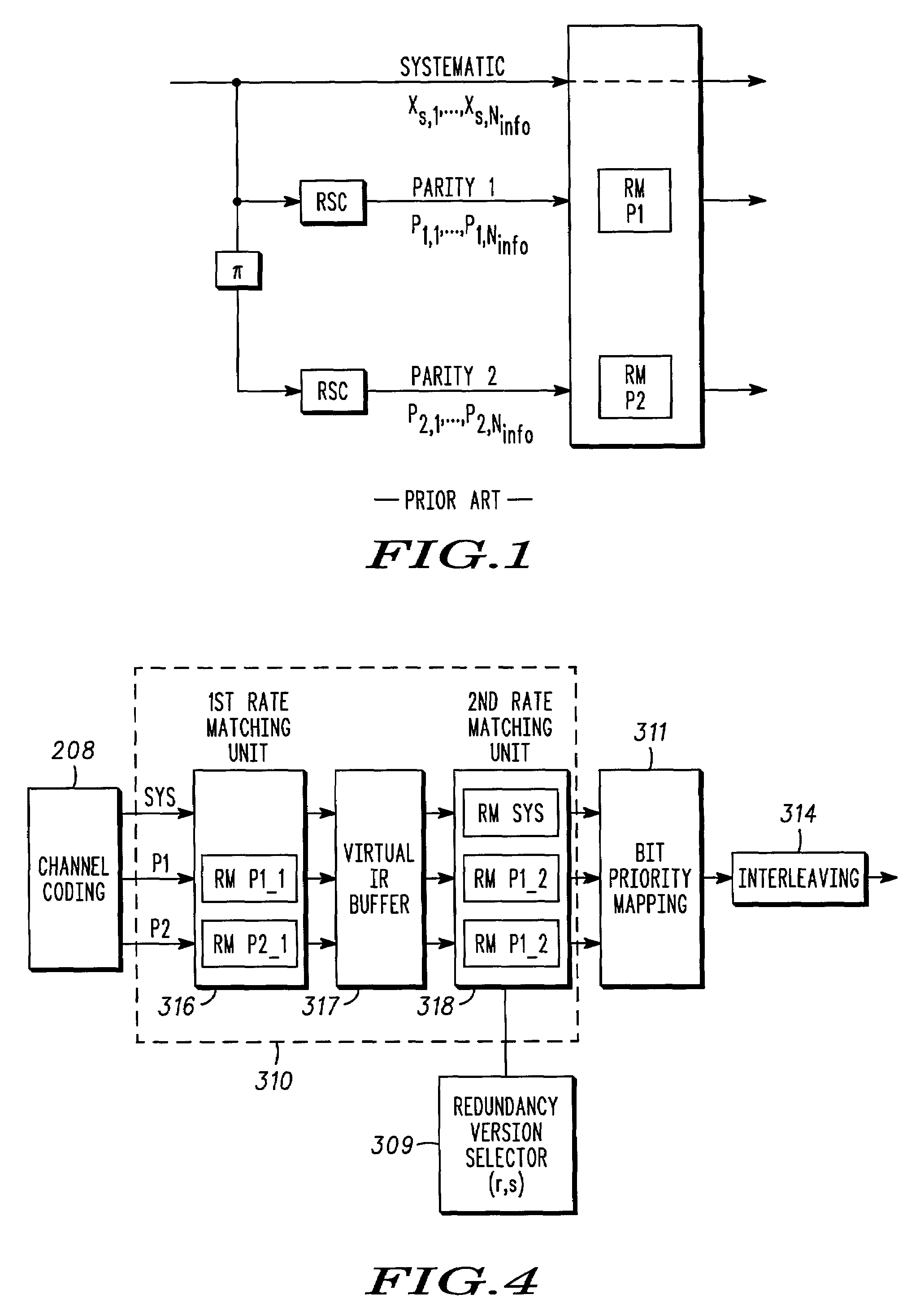
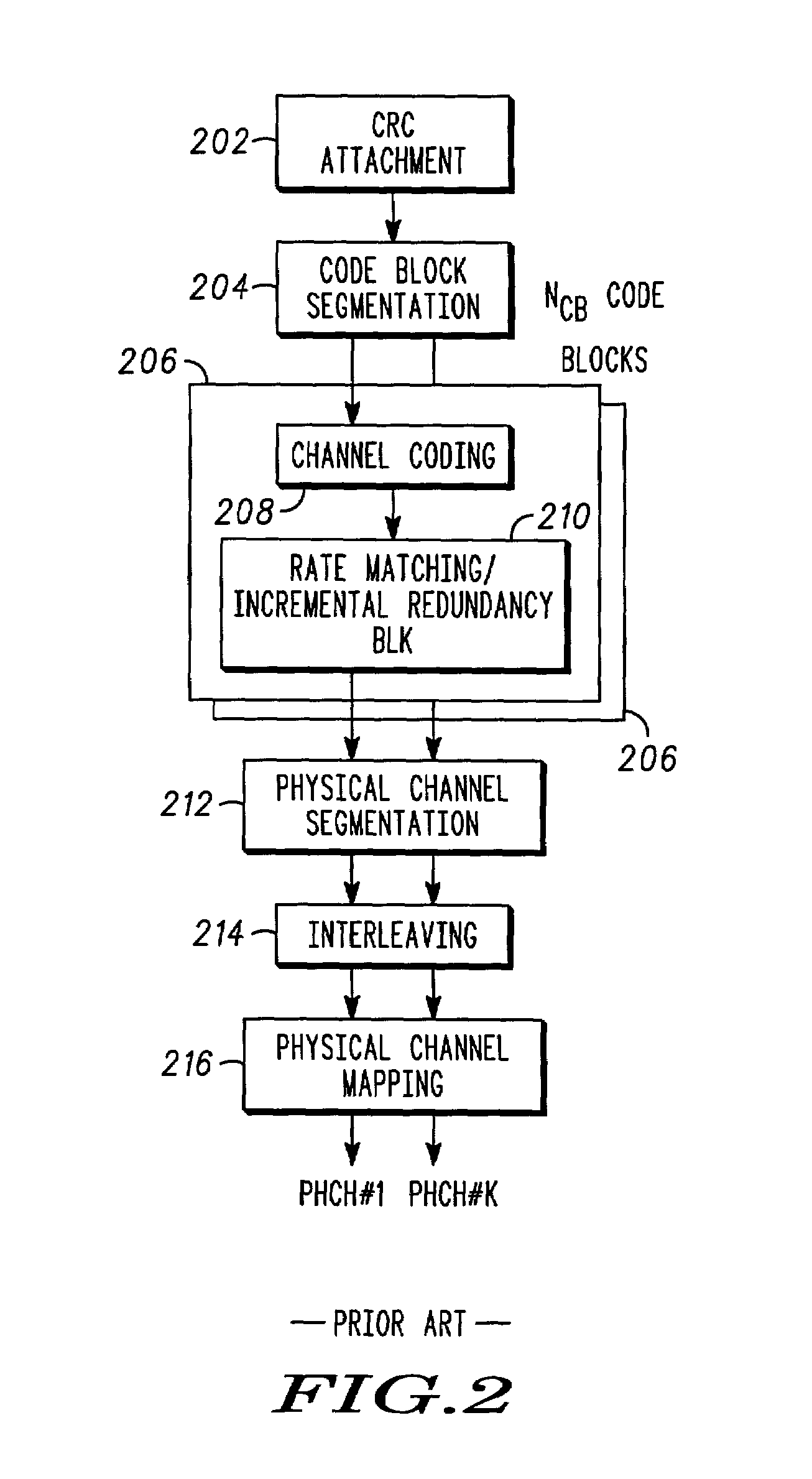
A method of block puncturing for turbo code based incremental redundancy includes a first step (1200) of coding an input data stream into systematic bits and parity bits. A next step (1202) includes loading the systematic bits and parity bits into respective systematic and parity block interleavers in a column-wise manner. A next step (1204) includes selecting a predefined redundancy. A next step (1206) includes outputting bits from the block interleavers in a row-wise manner in accordance with the selected predefined redundancy.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Method, apparatus and system for service data transmission in HSDPA
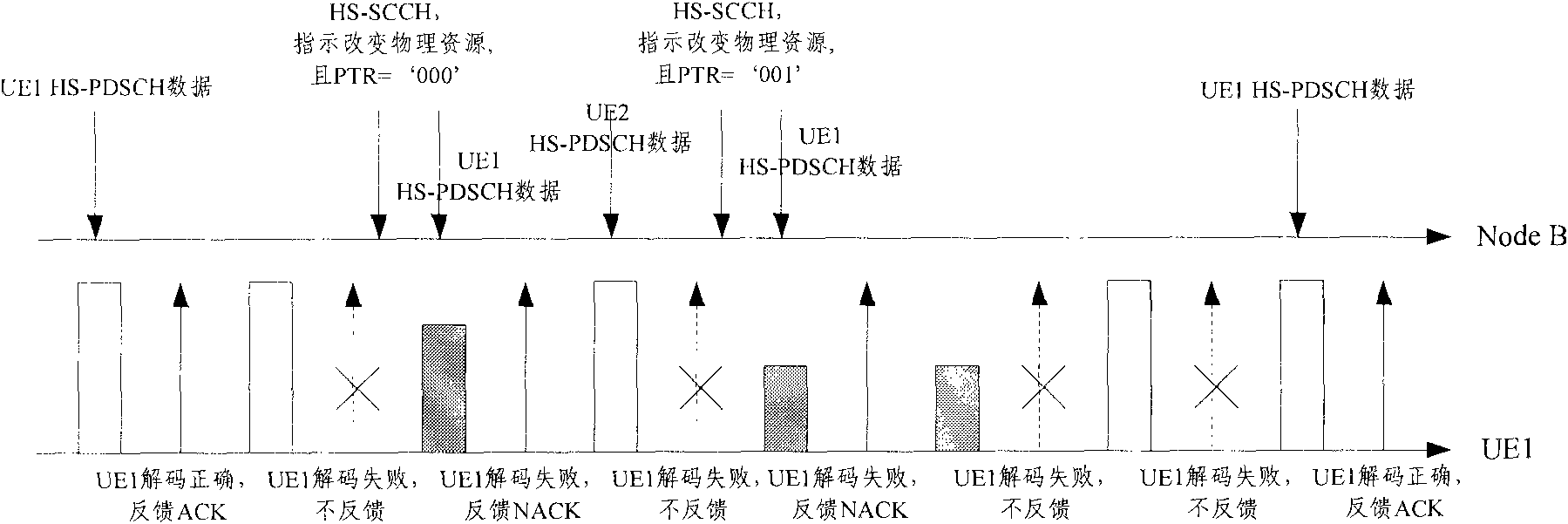
InactiveCN101399651AReduce overheadReduce the amount of informationError prevention/detection by using return channelPhase-modulated carrier systemsTransfer procedureNetwork packet
The invention discloses a method for transmitting service data in HSDPA, a device and a system thereof. UE time slot track is notified to distribute information by high-level signaling, by adopting synchronous mode of hybrid automatic repeat request, permanently adopting incremental redundancy versions of QPSK modulation and predefinition used during different transmission times. A base station only transmits control information including cyclical sequence number of a high-speed shared control channel, size index of transmission blocks and user identifications to UE on a physical control channel in the first transmission of data. Regarding small data packet service, such as transmission of VoIP service, information content of the control information is reduced, and transmission times of the control information during transmitting process can be greatly reduced, therefore, network load is reduced, and transmission efficiency of data of the small data packet service in HSDPA is improved.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
High performance, flexible, and compact low-density parity-check (LDPC) code
ActiveUS20170359148A1Low costIncrease data rateError prevention/detection by using return channelError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsAutomatic repeat requestGranularity
Certain aspects of the present disclosure generally relate to techniques for puncturing of structured low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes. Certain aspects of the present disclosure generally relate to methods and apparatus for a high-performance, flexible, and compact LDPC code. Certain aspects can enable LDPC code designs to support large ranges of rates, blocklengths, and granularity, while being capable of fine incremental redundancy hybrid automatic repeat request (IR-HARQ) extension while maintaining good floor performance, a high-level of parallelism to deliver high throughout performance, and a low description complexity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Method of link adaptation in enhanced cellular systems to discriminate between high and low variability
InactiveCN1505880AIncrease variabilityAddress variabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelEnergy efficient ICTPeak valueLink adaptation
Method to perform link adaptation at the radio interfaces of an enhanced packet data cellular network handling several Modulation and Coding Schemes (MCS) for maximizing data throughput. In a preliminary off-line step the system behaviour, in terms of net throughput of the various available MCSs, is simulated for different C / l conditions. From the simulation two sets of tables are obtained, each table including upgrade and downgrade thresholds expressed in terms of Block Error Rate (BLER). Thresholds correspond to switching points from an MCs to the two available MCSs having the immediate less or more protection. The two sets of tables are referred to higher or lower diversity RF environments and are further specialized for taking into account EGPRS type II hybrid ARQ, namely Incremental Redundancy (IR). During transmission the transmitted blocks are checked for FEC and the results are sent to the network. The network continuously updates BLER using exponential smoothing. In order to achieve the correct time response, in spite of that RLC blocks can be received or not, a reliability filter is provided whose output is used to decide the weight between the new and old measurements to make the BLER filter impulse response exponentially decreasing with time. The IR efficiency is tested for each incoming block and an indicative variable IR status is filtered using the same approach used for BLER. Each actual threshold of BLER to be used in link adaptation is obtained by a linear interpolation between the tabulated threshold without IR and with perfect IR, both weighed with filtered IR status. Filtered BLER is then compared with said interpolated thresholds for testing the incoming of a MCS switching condition. Power control pursues the goal of maintaining constant QoS peak throughput per time slot(Fig 16).
Owner:SIEMENS INFORMATION & COMM NEWTWORKS INC
Block puncturing for turbo code based incremental redundancy
InactiveUS7260770B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionData streamTheoretical computer science
A method of block puncturing for turbo code based incremental redundancy includes a first step (1200) of coding an input data stream into systematic bits and parity bits. A next step (1202) includes loading the systematic bits and parity bits into respective systematic and parity block interleavers in a column-wise manner. A next step (1204) includes selecting a predefined redundancy. A next step (1206) includes outputting bits from the block interleavers in a row-wise manner in accordance with the selected predefined redundancy.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
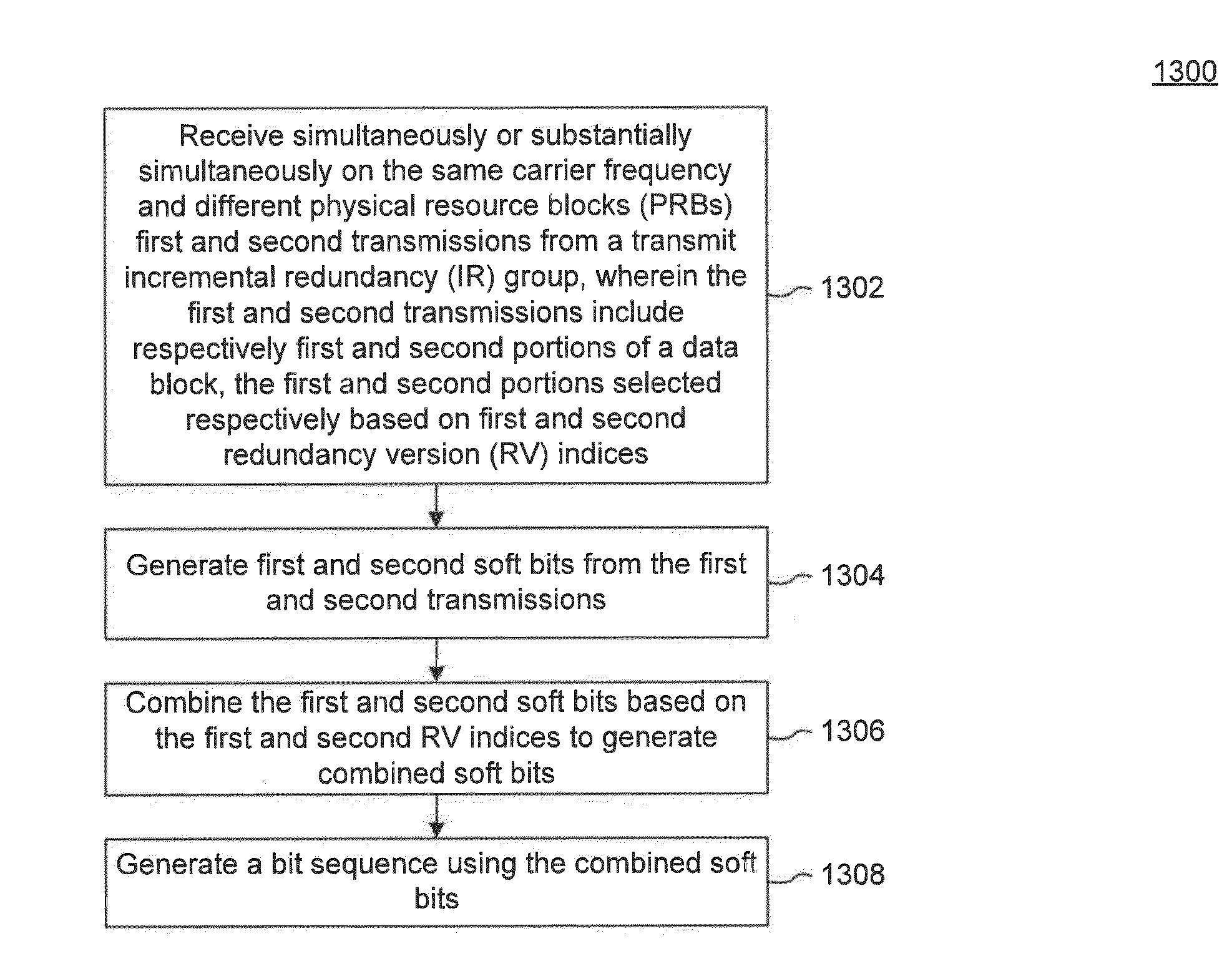
Multi-Cell Incremental Redundancy
Embodiments enable cooperative transmissions from a group of cells (can include the serving cell and one or more neighboring cells) to a user equipment (UE). The cooperative transmissions emulate Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (HARQ) transmissions to the UE. Specifically, when the UE is experiencing high interference, the UE's serving cell can create a transmit incremental redundancy (IR) group for the UE, which is used to transmit information in a HARQ-like fashion to the UE. Because interference is reduced, the UE can decode the information at a lower coding rate and higher coding gain.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Symbol vector-level combining transmitter for incremental redundancy HARQ with MIMO
ActiveUS20090279633A1Improve application performanceFew interruption in serviceSite diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionLog likelihoodComputer science
Owner:NXP USA INC
Data compression with incremental redundancy
InactiveUS20050044473A1Efficient storageError prevention/detection by using return channelData representation error detection/correctionData transmissionComputer science
In a packet-based data transmission including incremental redundancy (IR) protocols, the memory consumption of the IR protocol is reduced by compressing and storing failed data units in their punctured format. The failed data units are compressed using low complexity compression / decompression algorithms. The compression algorithm includes two parts: calculating and storing a scale factor for each transmission burst that estimates the soft values in the burst, and storing each soft values' sign in local memory instead of the complete soft value. If the currently received data unit is a retransmission, its compressed versions in the punctured format stored in the IR memory are decompressed, de-punctured and combined with the currently received data unit. The combined data unit is then decoded. The decompression restores an estimated soft-value by multiplying the sign value stored in the IR memory with its corresponding scale factor obtained from a mapping table.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Harq protocol optimization for packet data transmission
InactiveCN101053194AError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementCommunications systemControl signal
The invention relates to a HARQ method using incremental redundancy and providing synchronous retransmissions. Further, the invention relates to a receiving entity and a transmitting entity employing the HARQ method and to a mobile communication system. To optimize conventional HARQ retransmission protocols, the invention introduces a ternary feedback which allows requesting a self-decodable version of a data packet under certain conditions. Further, the ternary feedback is provided in a backward compatible manner using a combination of conventional HARQ feedback signaling and scheduling related control signaling.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Signaling cell combining capabilities
InactiveUS20070104167A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsWireless commuication servicesData packRadio networks
The specification and drawings present a new method, system, apparatus and software product for providing combining capability information of a Node B (supporting a cell to which a user equipment is set-up) to radio network controllers as related to HSUPA (High Speed Uplink Packet Access). The Node B can support among others, e.g., incremental redundancy (IR) combining and / or Chase combining. Furthermore, the combining capability information of the node B can be, e.g., for combining data received on an uplink enhanced dedicated channel (E-DCH).
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Method and apparatus for link error prediction in a communication system
InactiveUS20050182994A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method is provided to accurately predict the probability of successfully recovering frames of (coded) information received over a wireless link, without having to decode the frame. This method, which consists of three steps, requires only limited information about the received signals and the forward error correction code and retransmission scheme being used. First, the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of each of the received signals is measured, where the average SNR is determined for multiple segments that together constitute the frame. Next, an algorithm is employed that takes these SNR values as inputs and determines the so-called effective SNR. The algorithm translates the measured SNR values using an appropriate convex metric, and subsequently combines the resulting values, thereby factoring in the effects of fading, multi-path, and other signal degradations. In the third stage, the effective SNR is used to determine the frame error rate by using a look-up table of a single reference curve that specifies the frame error rate of the actual error control code over an additive white Gaussian noise channel. This suffices to accurately predict the performance of a wide range of mobile communication channels. This method can be applied to a variety of retransmission strategies, including hybrid automatic-repeat request (ARQ) and incremental redundancy (IR) and combinations of these two strategies.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Method for puncturing a low density parity check code
InactiveUS20070202889A1Performance degradation can be minimizedPerformance of was minimizedError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceParity-check matrix
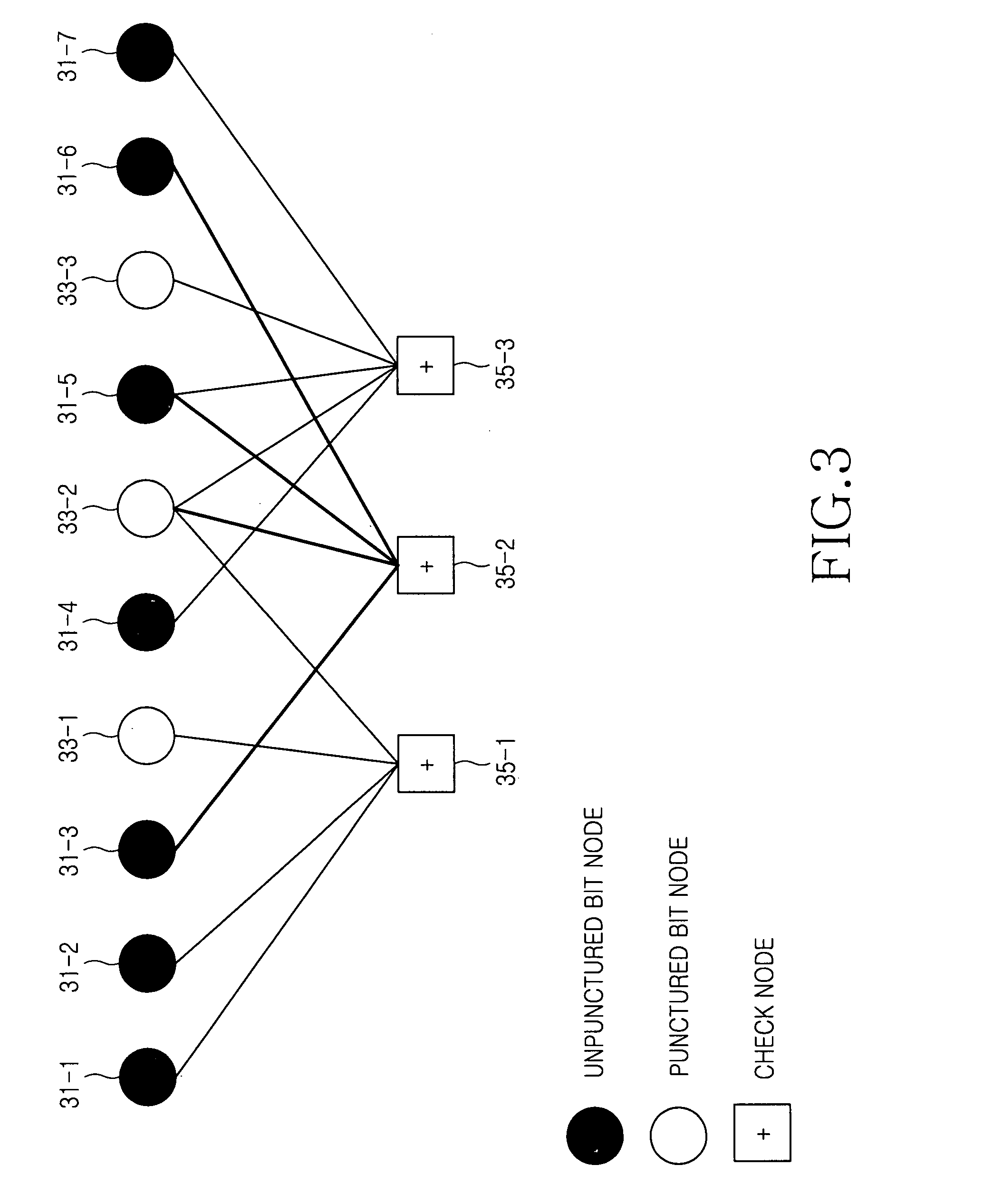
Provided is a method for puncturing a Low Density Parity Check (LDPC) code that is expressed in a factor graph configured by a bit node and a check node connected to an edge and is decoded by a parity check matrix with an information region and a parity region. A mother code with a code rate is generated. Bit nodes configuring the parity region are grouped in a block unit. A transmission code rate and the number of bits to be punctured in the mother code according to the transmission code rate are set. A puncturing process in either the block unit or a bit unit or both is performed according to the transmission code rate. All codes with required code rates can be obtained. The LDPC code puncturing method can be flexibly applied to Hybrid Automatic Repeat Request (H-ARQ) and Incremental Redundancy (IR) systems.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for rate matching to support incremental redundancy with flexible layer one
ActiveUS6996114B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsRadio access networkComputer science
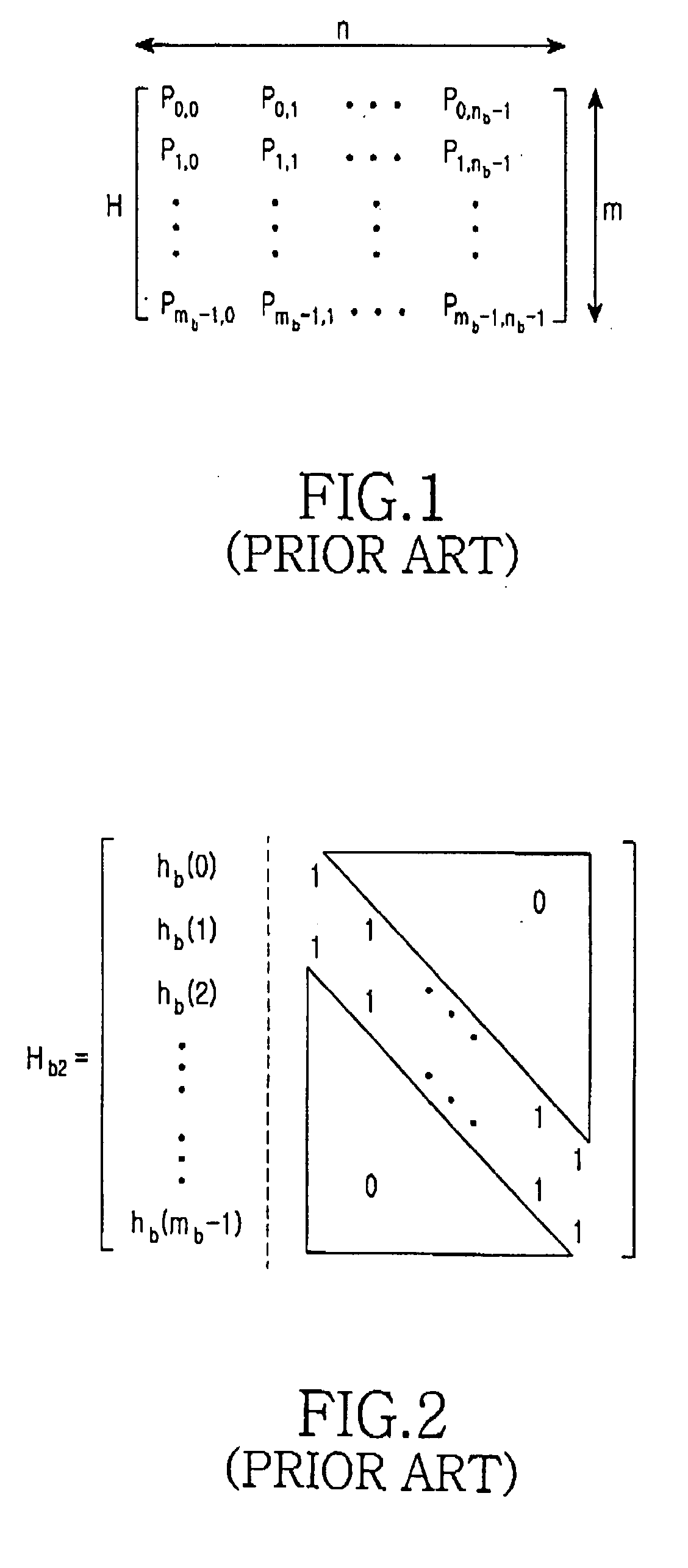
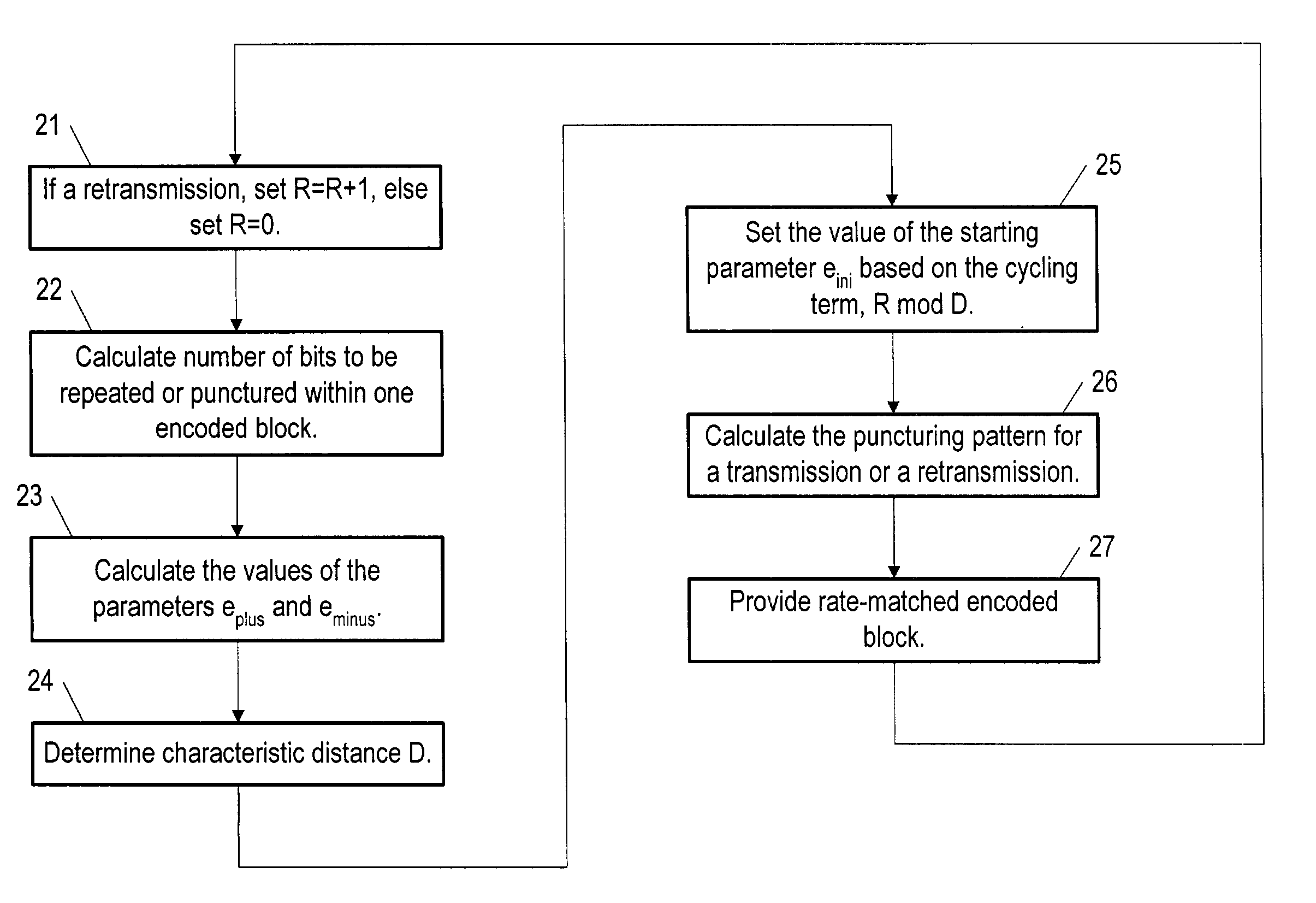
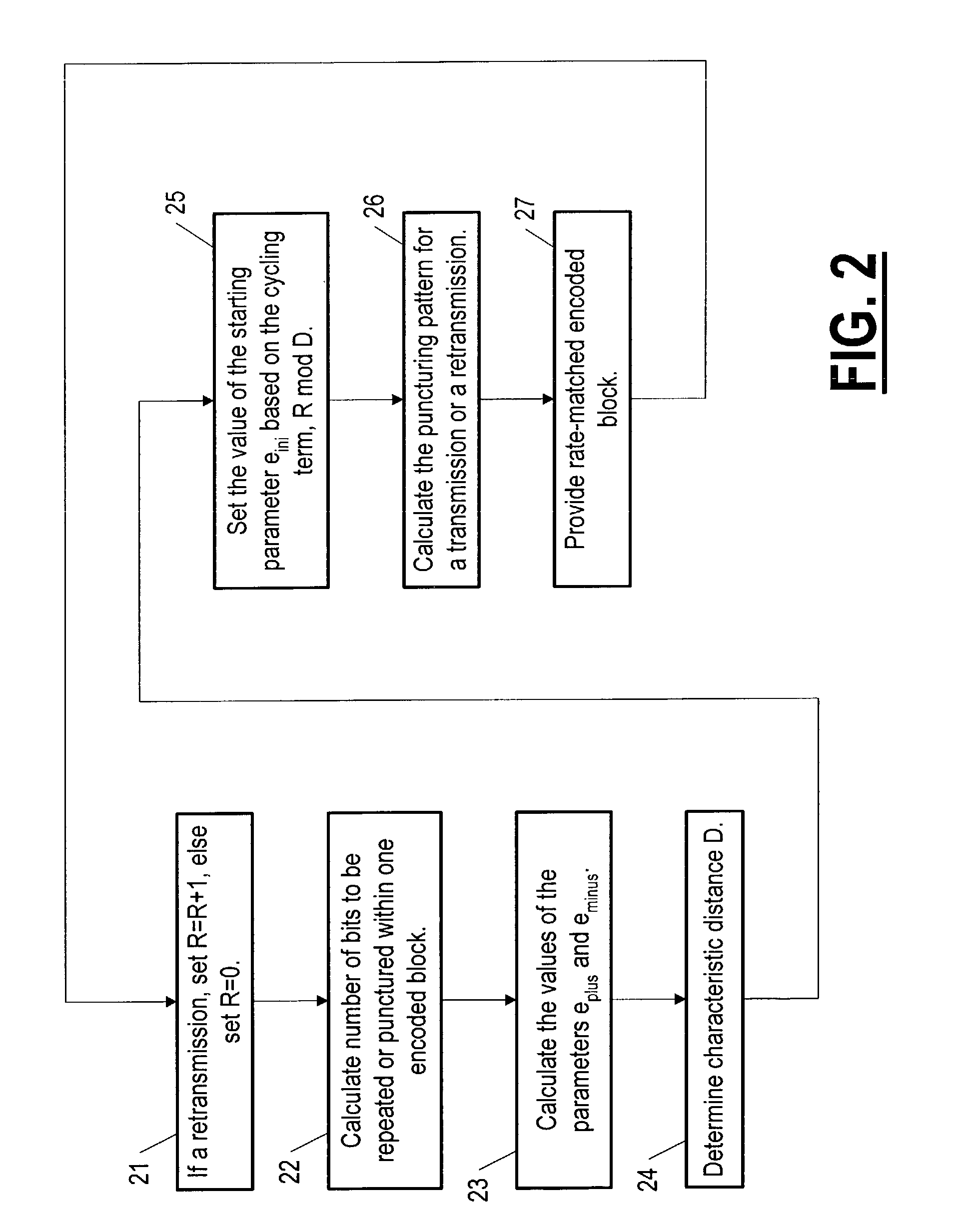
A method for rate matching in equipment used as part of, or in communication with, a radio access network implementing FLO (Flexible Layer One) so as to provide retransmission with incremental redundancy, the method using a rate-matching algorithm based on determining a starting parameter eini, the method characterized by: a step (21) of providing a retransmission parameter R controlled by the RLC protocol layer and having typically a value of one for a first retransmission and a next higher value for each subsequent transmission; a step (24) of determining a characteristic distance D related to the average distance between either punctured bits or between transmitted bits, depending on the value of the average distance between punctured bits; and a step (25) of determining a new value of eini based on a cycling term having a value depending on R but modulated by D so as to never exceed D−1.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com