Patents
Literature
266 results about "Code space" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In computing, Code space may refer to: In memory address space: code space, where machine code is stored. For a character encoding: code space (or codespace), the range of code points.
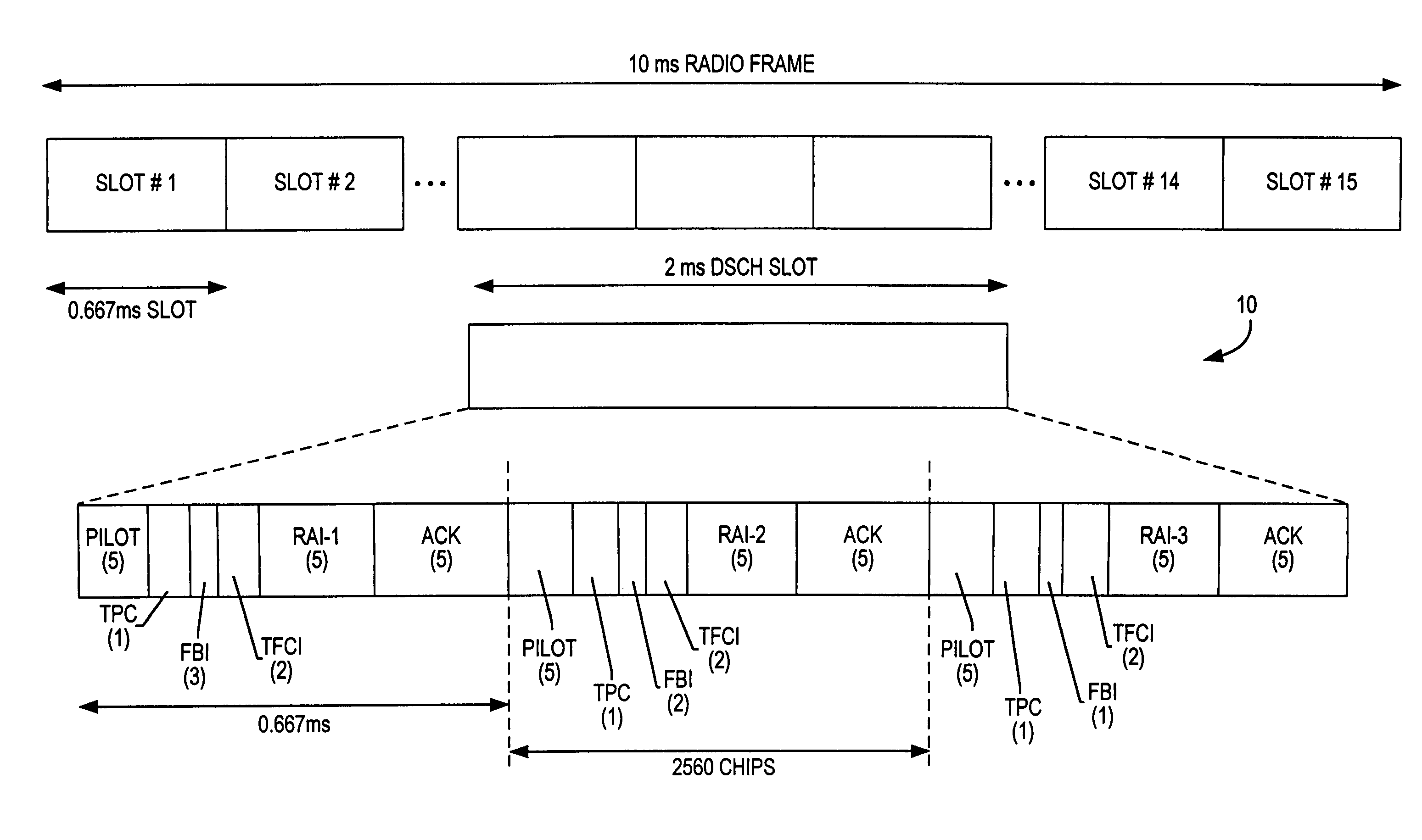
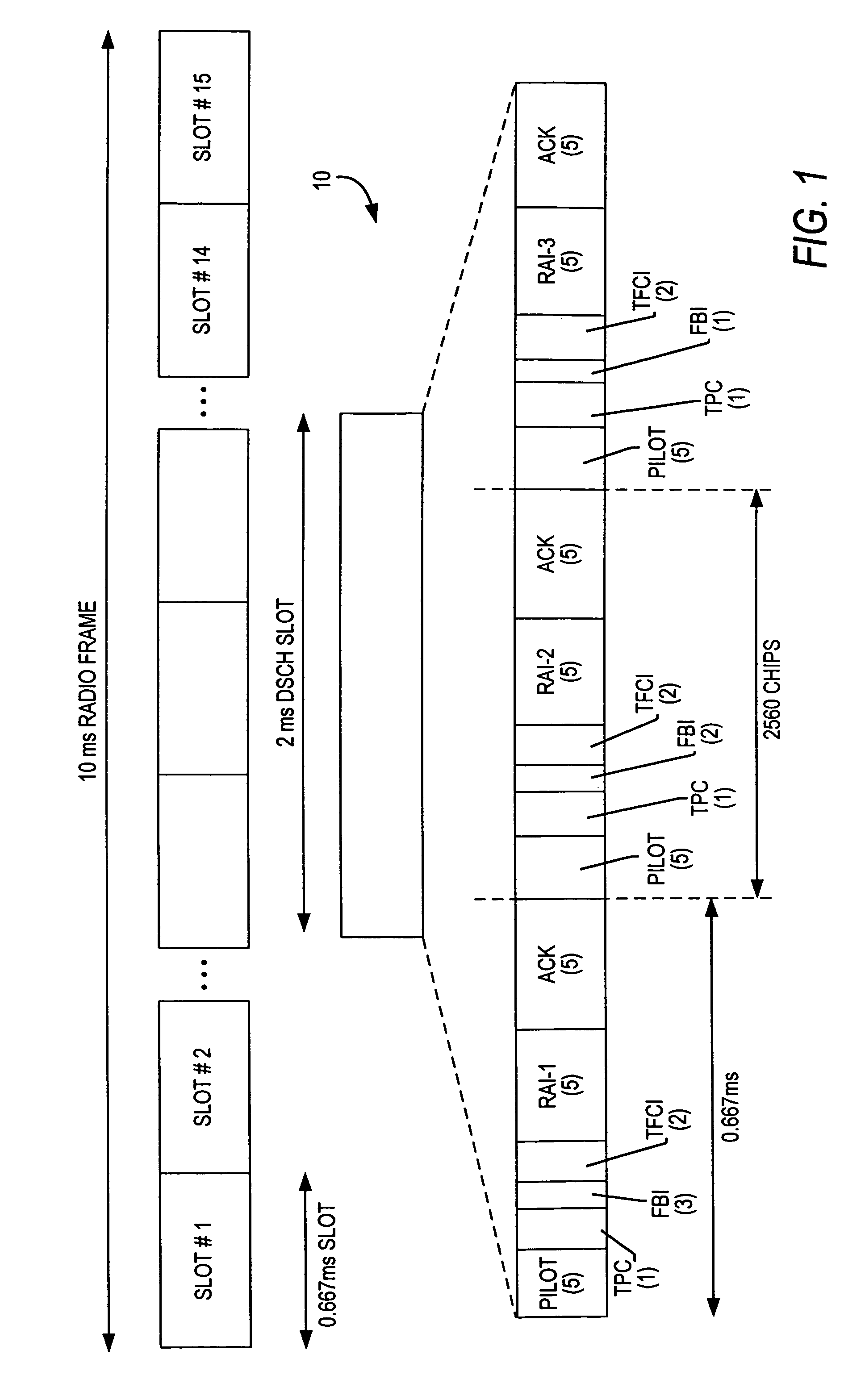
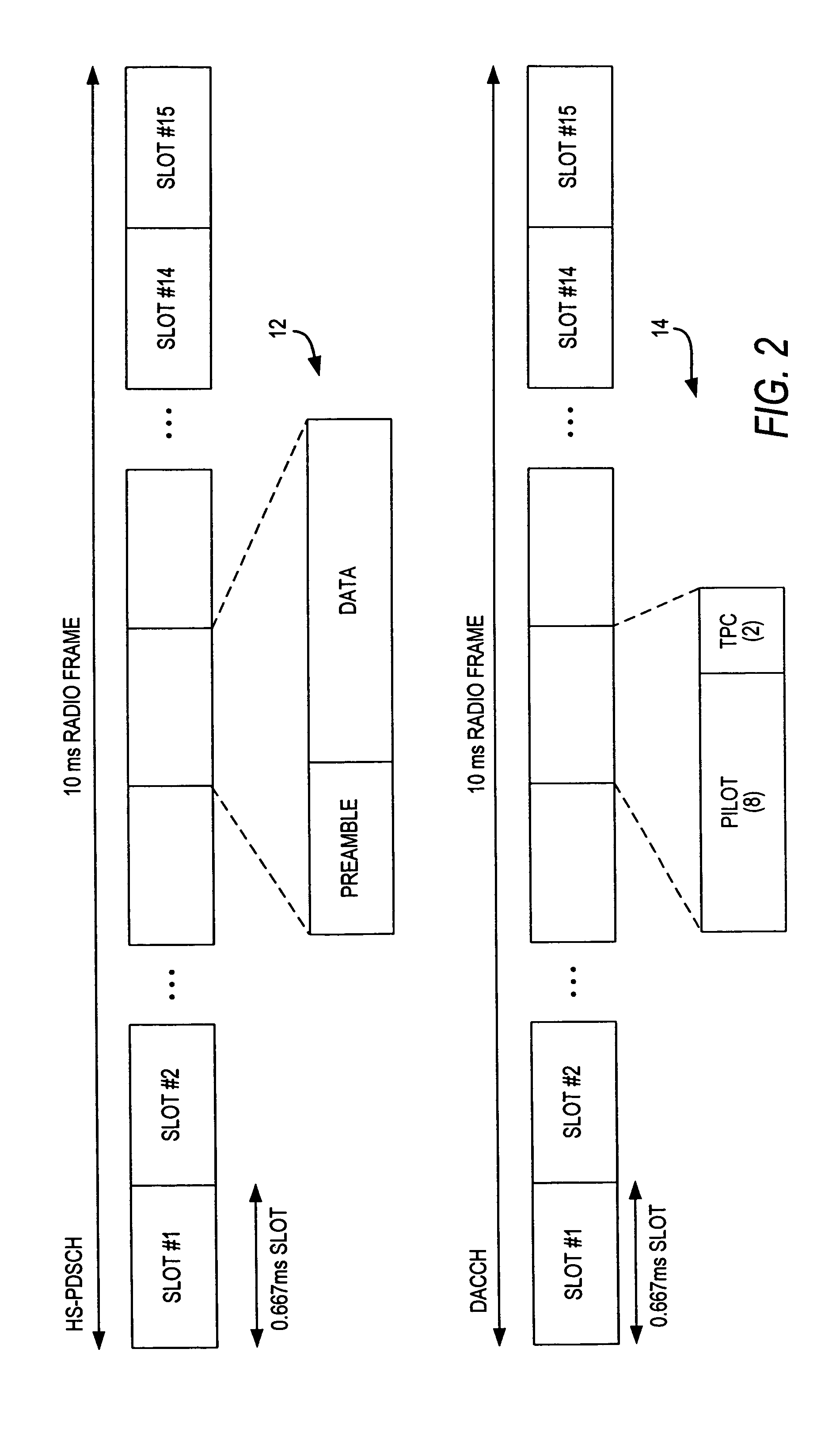
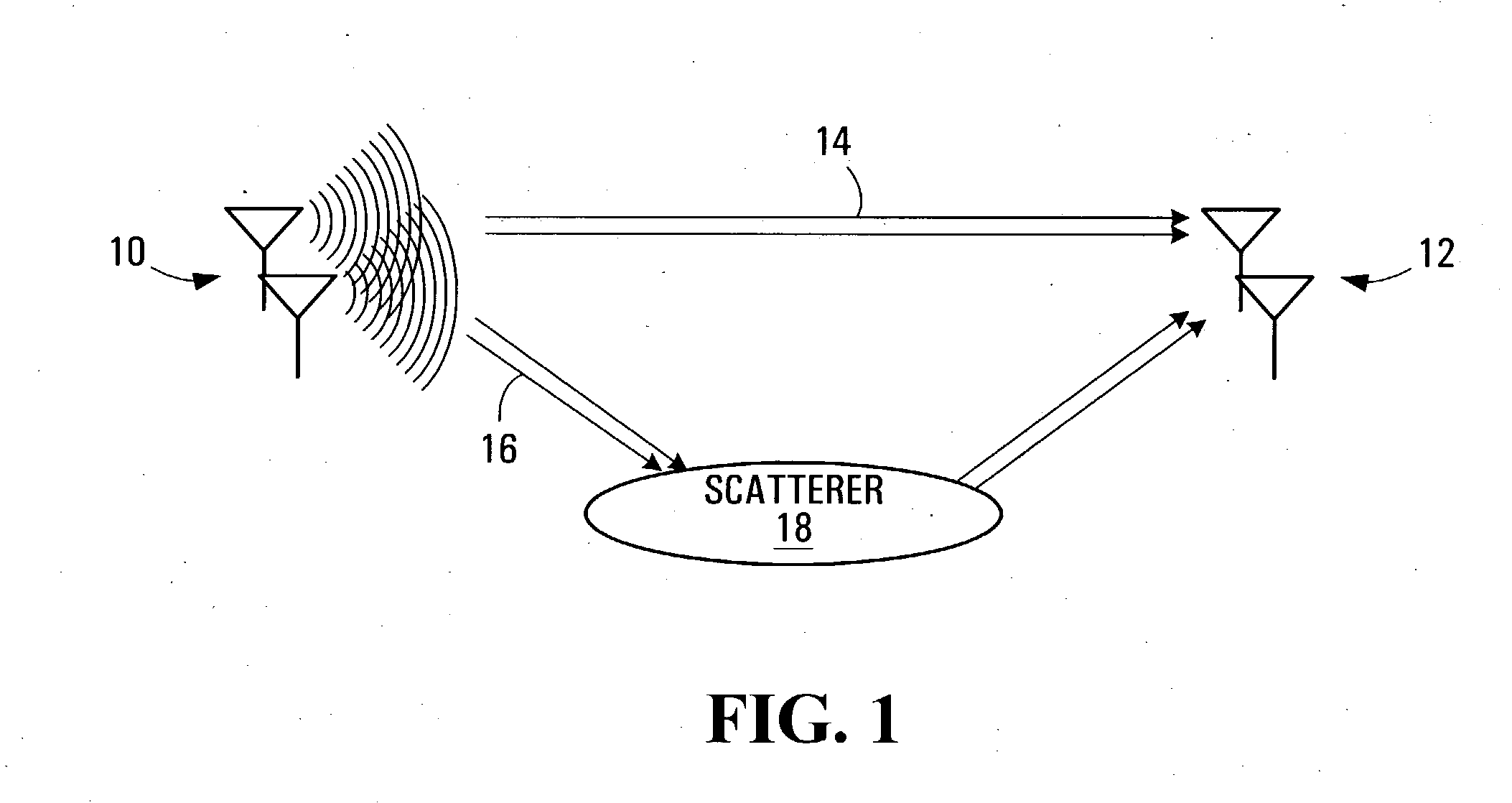
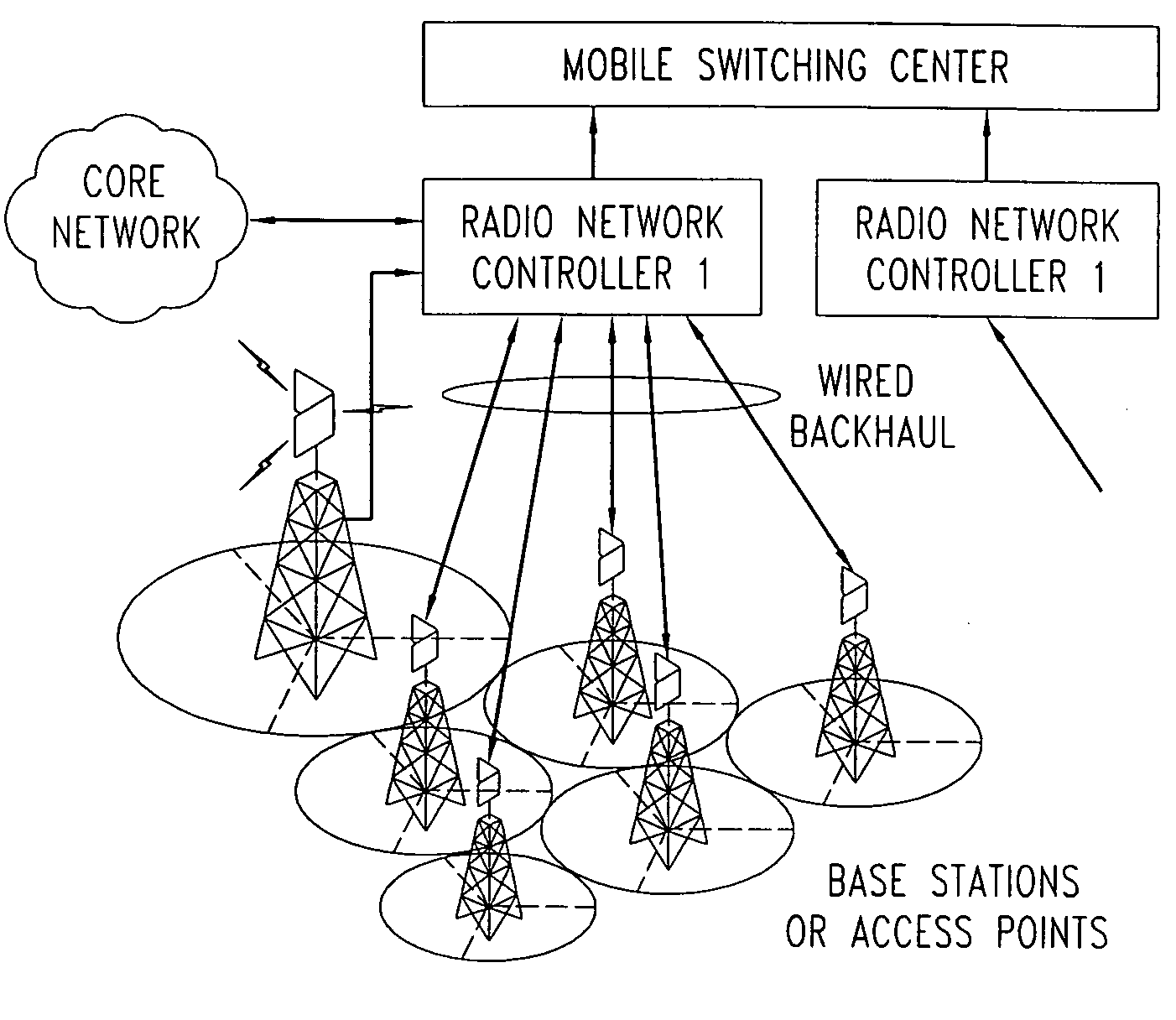
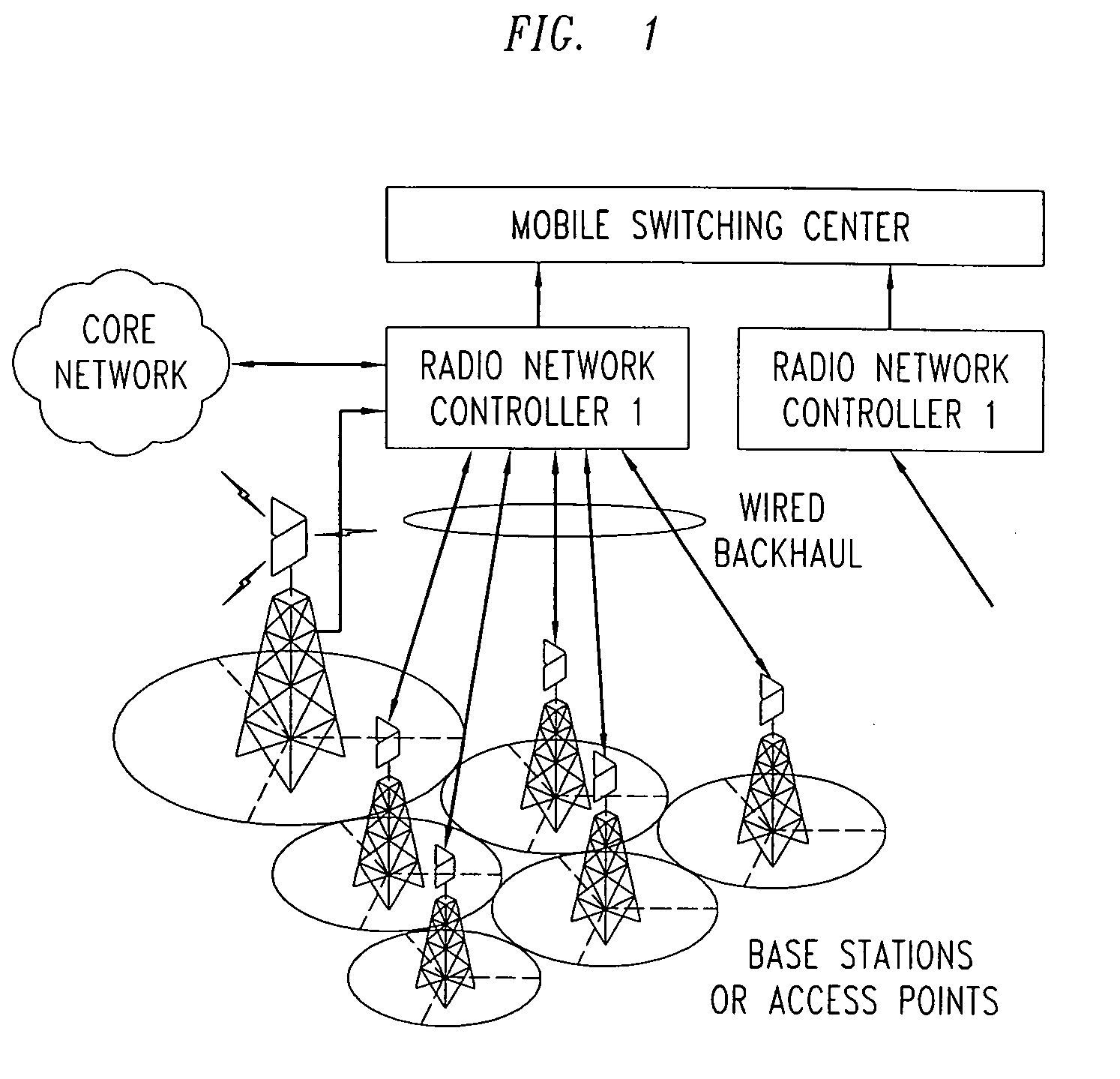
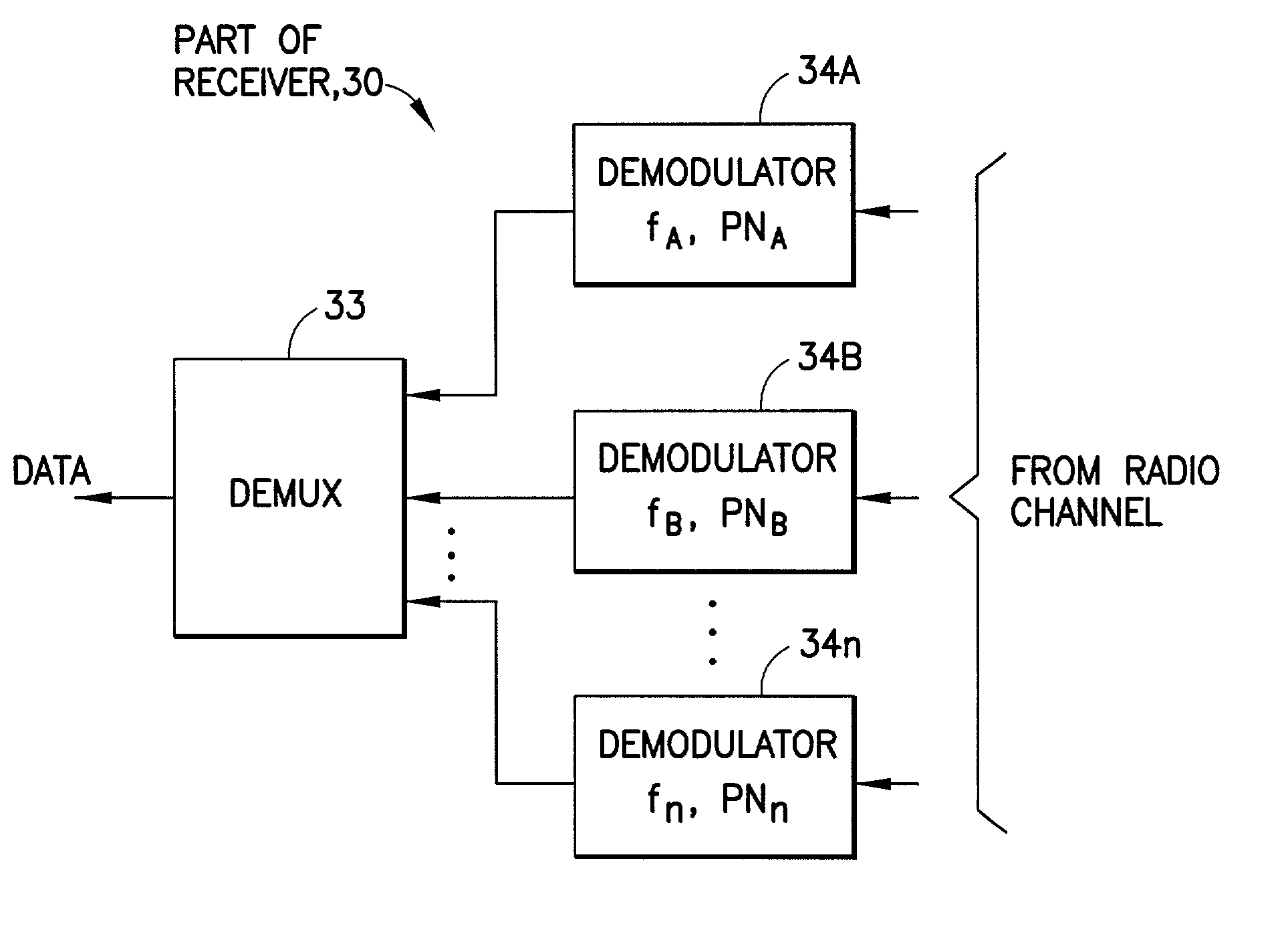
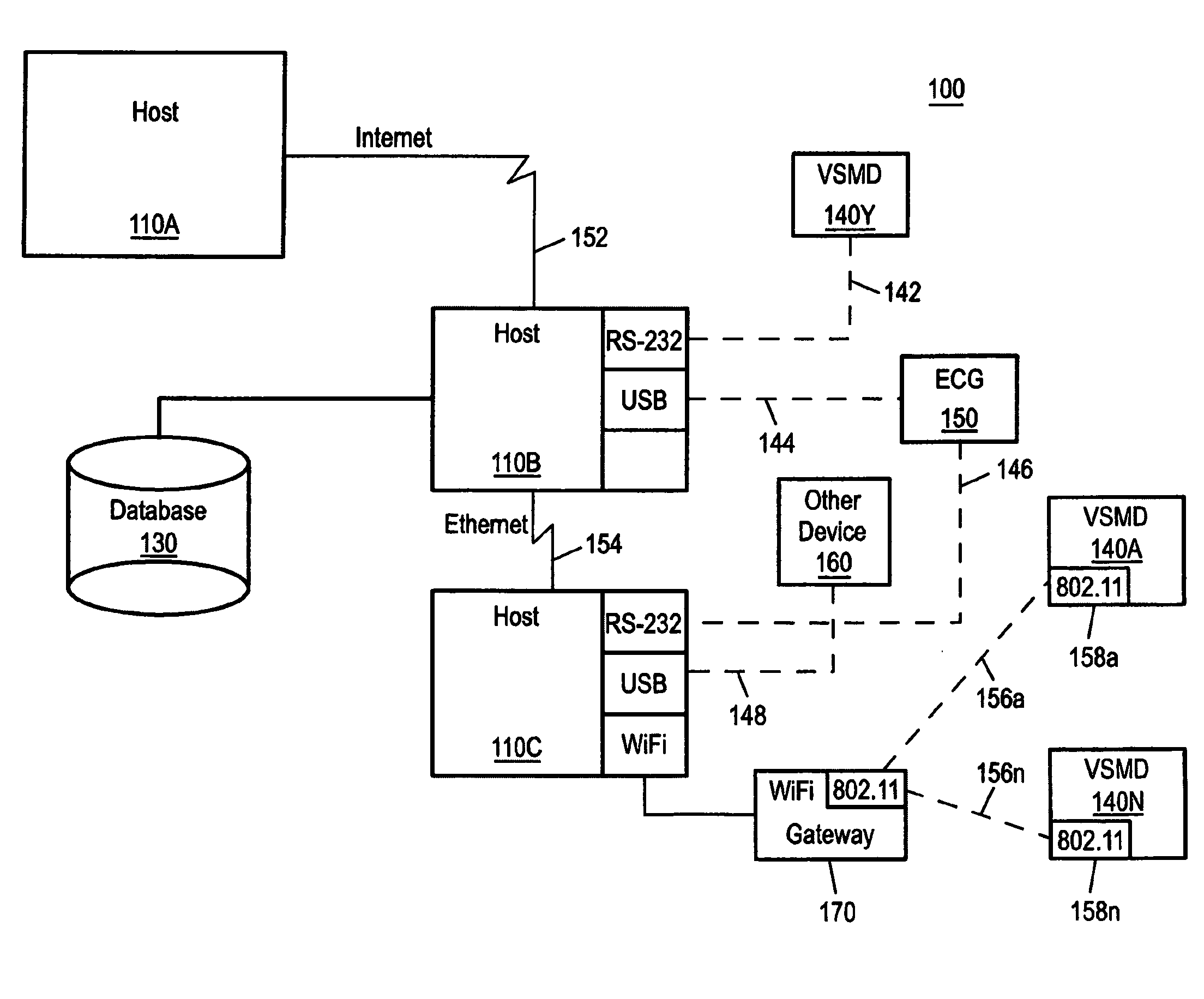
Downlink and uplink channel structures for downlink shared channel system
InactiveUS7006464B1Improve spectral efficiencyAdapt quicklyPower managementTransmission control/equalisingCode spaceTransmitted power
An uplink and downlink channel structure supports a shared downlink data channel. The new structure accommodates advanced physical and Medium Access Control (MAC) layer techniques, such as incremental redundancy (IR), fast adaptation to channel conditions, and multiple input multiple output (MIMO) antenna configuration. The proposed changes are intended to lead to a downlink structure that achieves higher spectral efficiency for the packet oriented services over then shared downlink channel. Additionally, the new structure uses the base station transmit power information and of the channelization (OVSF) code space more efficiently.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
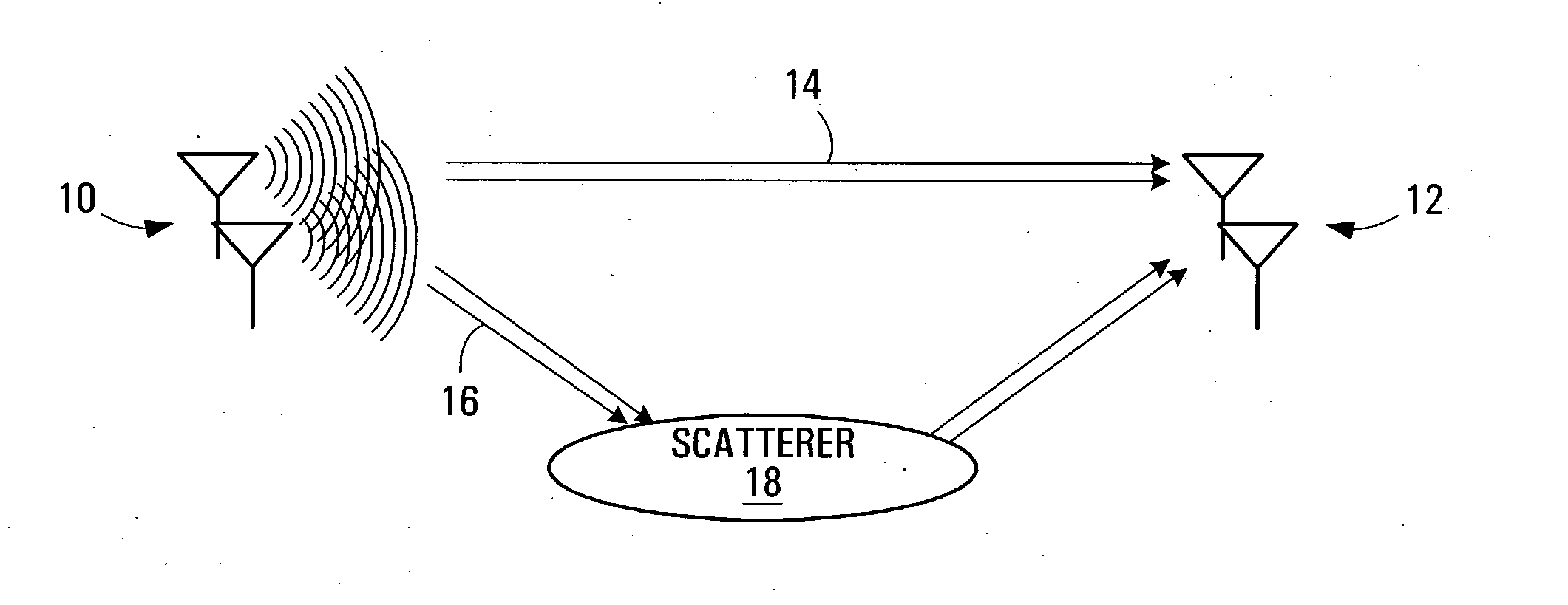
Virtual MIMO transmitters, receivers, systems and methods
A system for doing BLAST with fewer receive antennas or even only one receiving antenna is provided. A system implementation architecture is provided together with a detailed analysis on its principle and theory behind this engineering solution to reduce the MIMO technology cost by using fewer antennas whilst achieving high spectrum efficiency. Examples are provided on how to implement this idea in a CDMA platform and in a OFDM platform. For the CDMA system, the code space is automatically doubled or tripled and therefore a significant system capacity increase is realized. For OFDM systems, the throughput is doubled similar as 2×2 blasting. The system complexity is minimum and full standards backward compatibility can be achieved.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
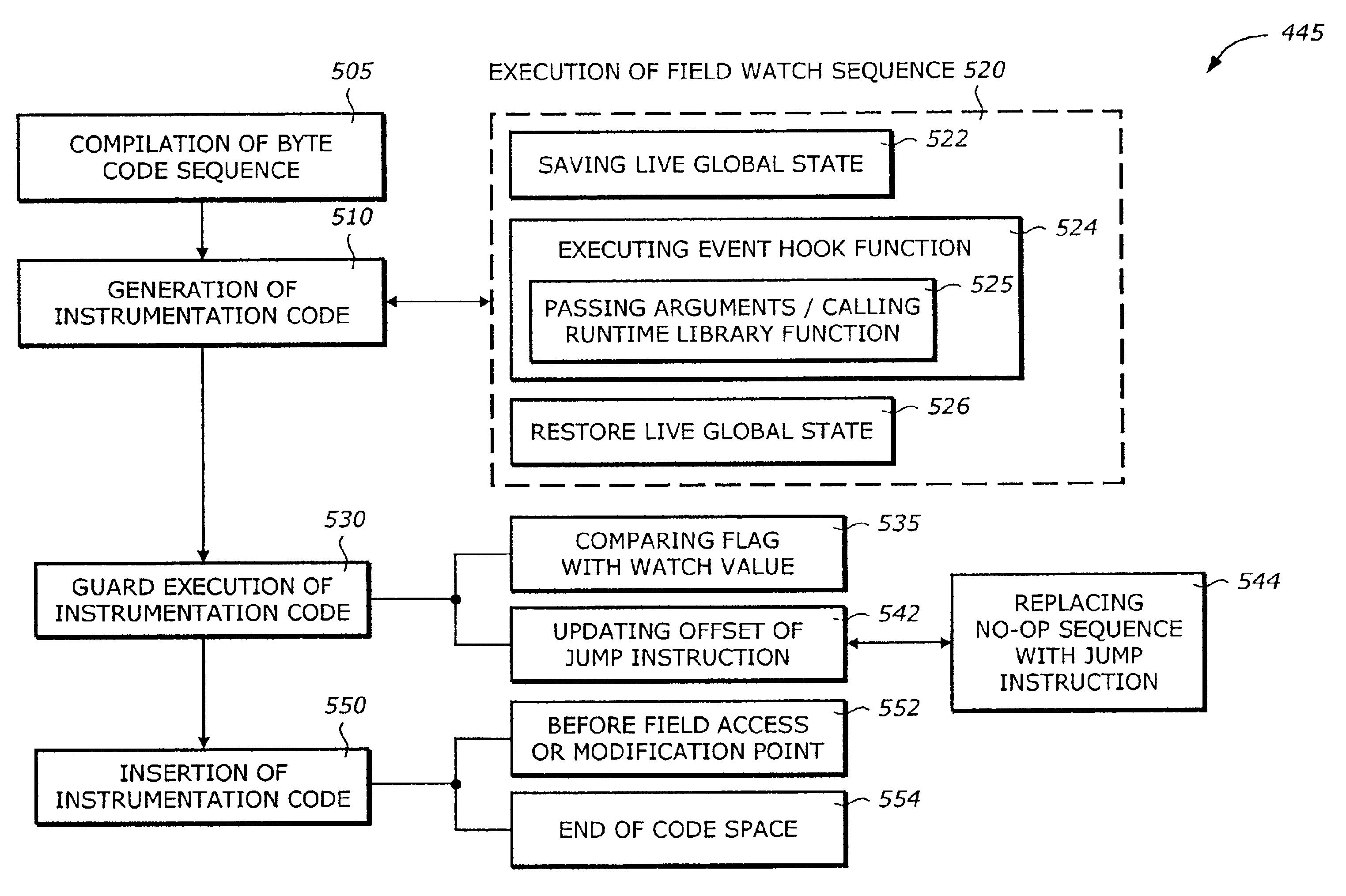
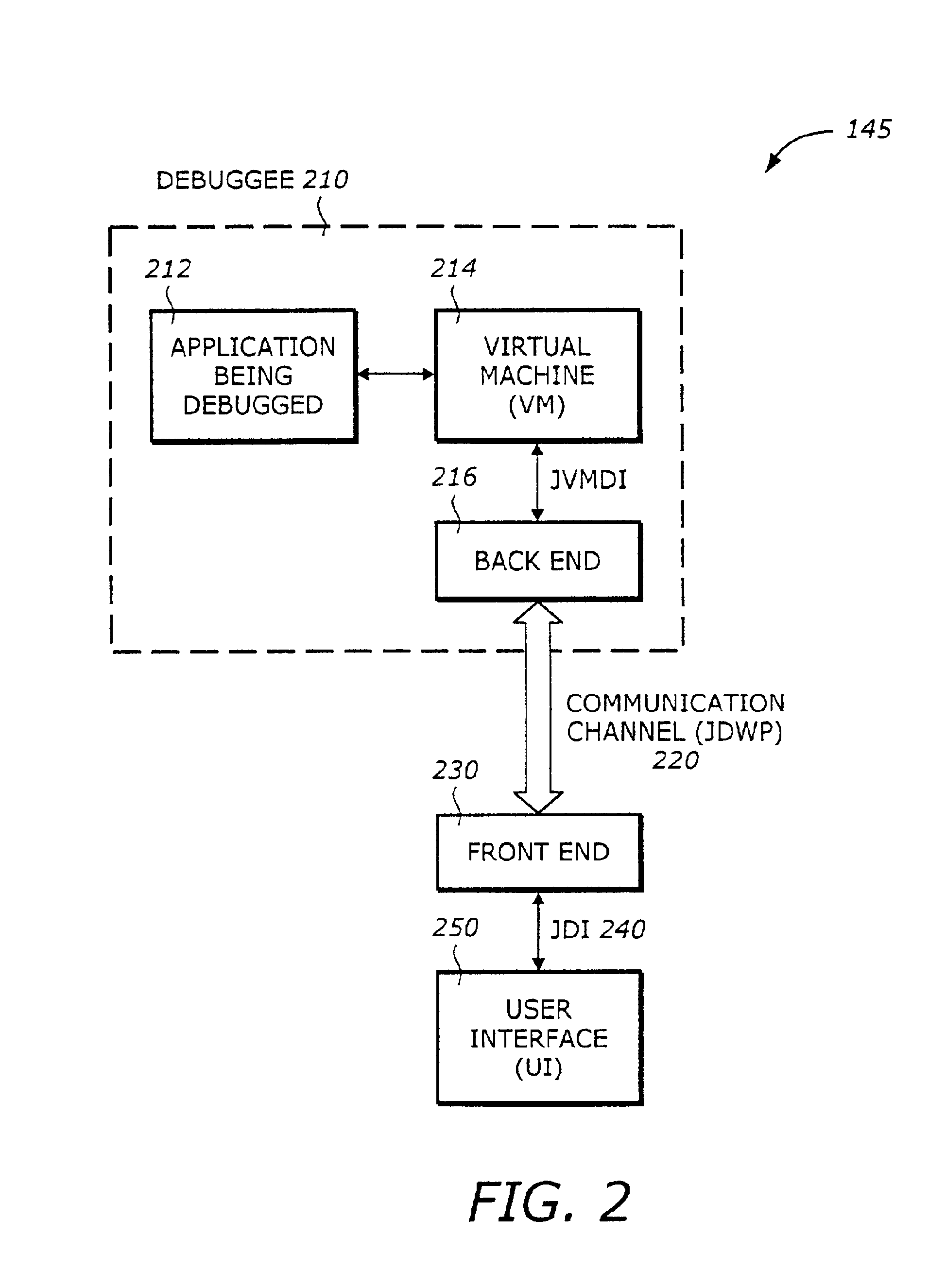
Static compilation of instrumentation code for debugging support
The present invention is a method and system to support debug. A function is compiled. The function includes a byte code sequence having a field byte code that accesses or modifies a field. The compiled function provides a native code and occupies a code space. An instrumentation code corresponding to a field match of a field is generated. The instrumentation code is inserted to the native code.
Owner:INTEL CORP
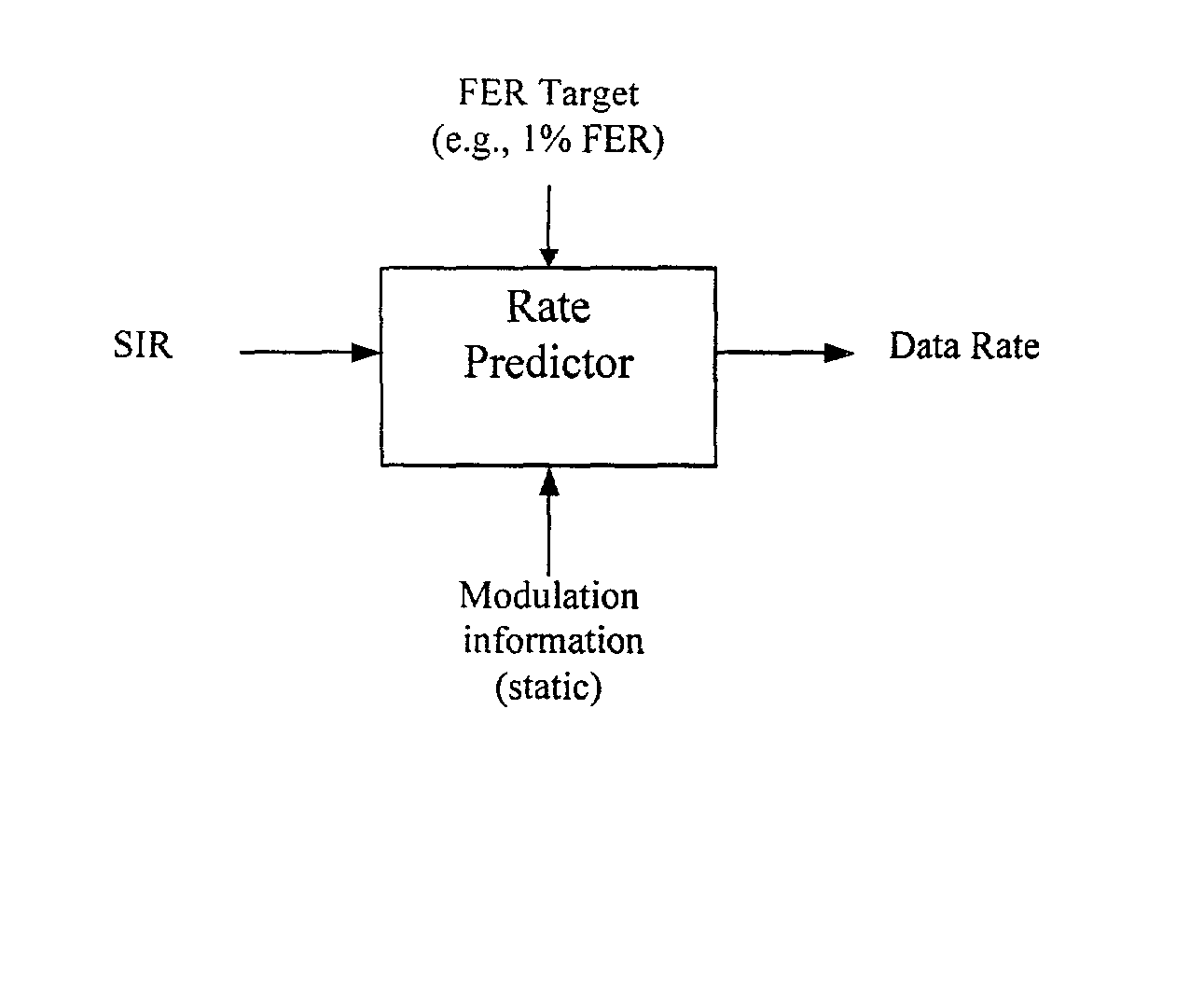
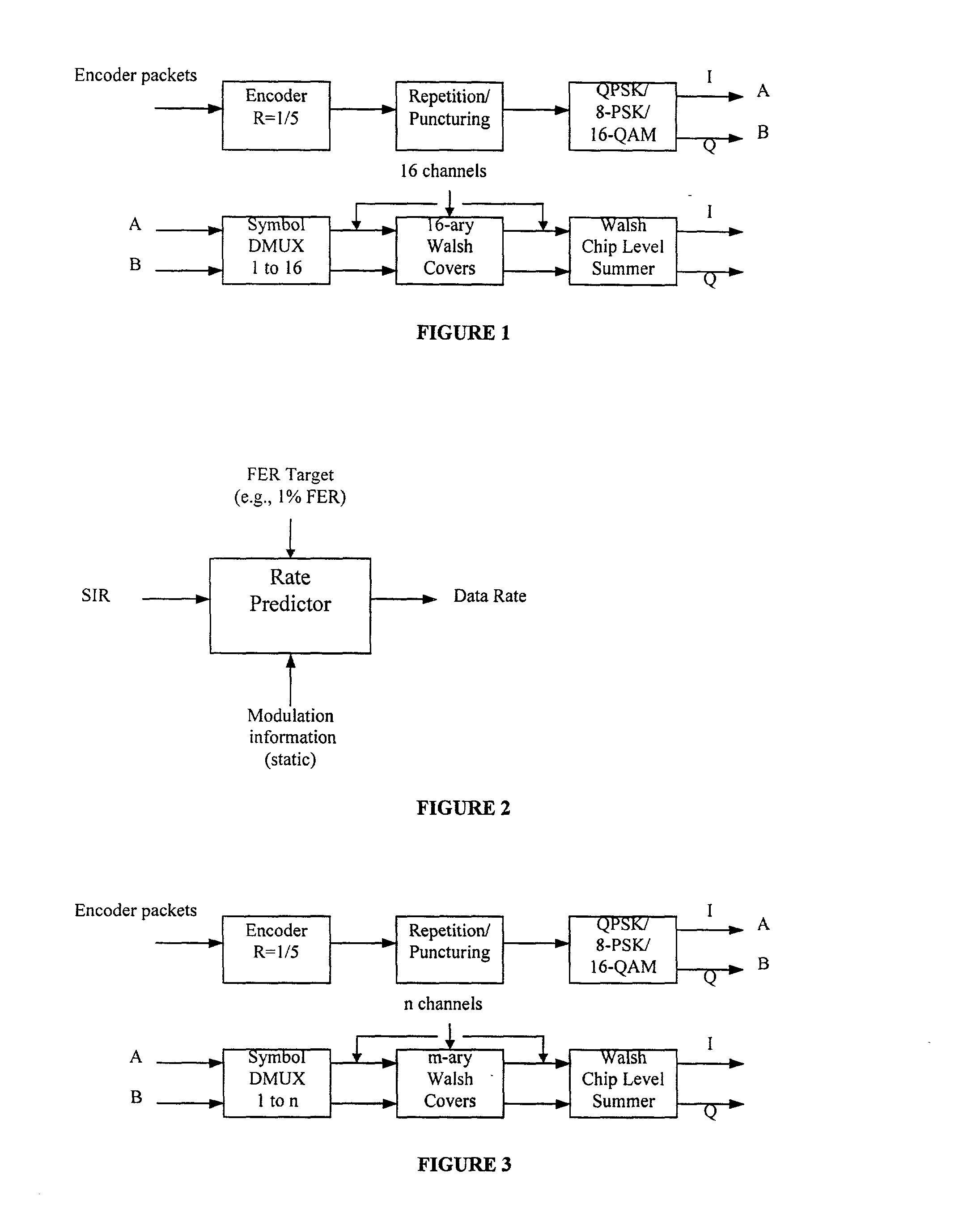
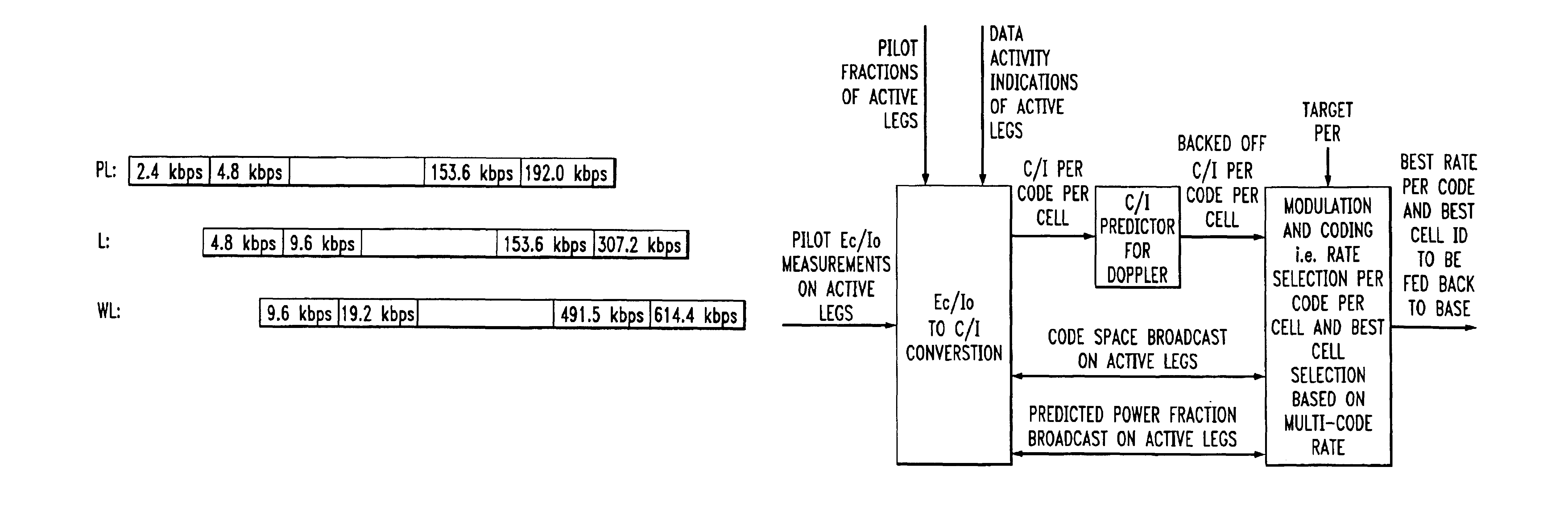
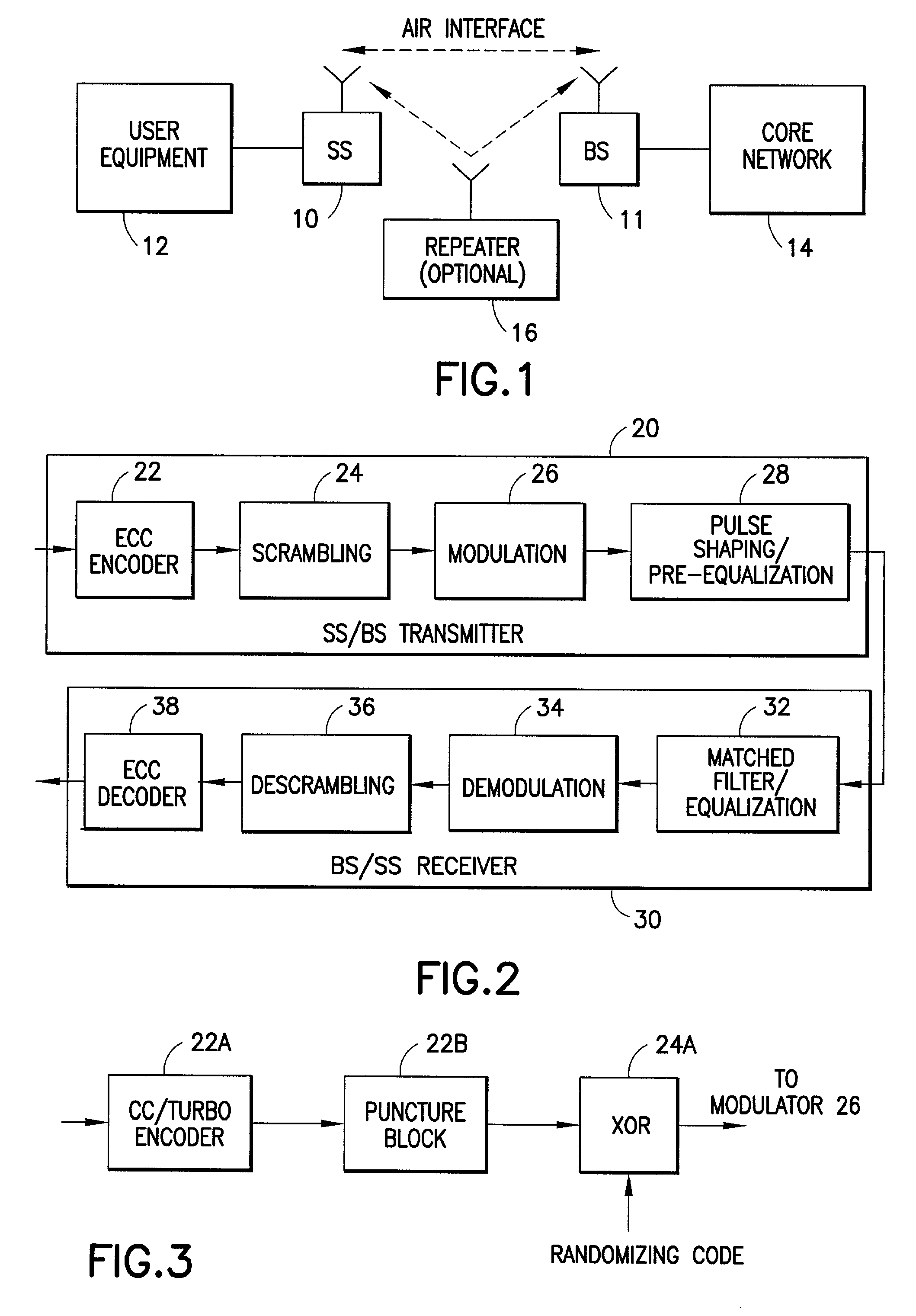
Method for data rate selection in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS20020110101A1Frequency-division multiplex detailsOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemCell selection
Data rate determination is provided in a system where the available power fraction and available Walsh codes in each active leg are dynamically changing over time. This method adapts the rate (modulation and coding) based on the combined resource (power & code space) levels seen at each cell. The method results in maximization of the rate supportable by each cell given their resource constrained situation while meeting the constraints of target packet or frame error rate and orthogonality. Furthermore, improved fast cell selection by the mobile results due to this approach that is based on knowledge of combined resource (power & code space) levels across the cells in the active set.
Owner:GEMPLU
System and method for debugging computer program based on execution history
ActiveUS8935673B1Easy to debugEasy to navigateMemory loss protectionNuclear monitoringCode spaceSystem of record
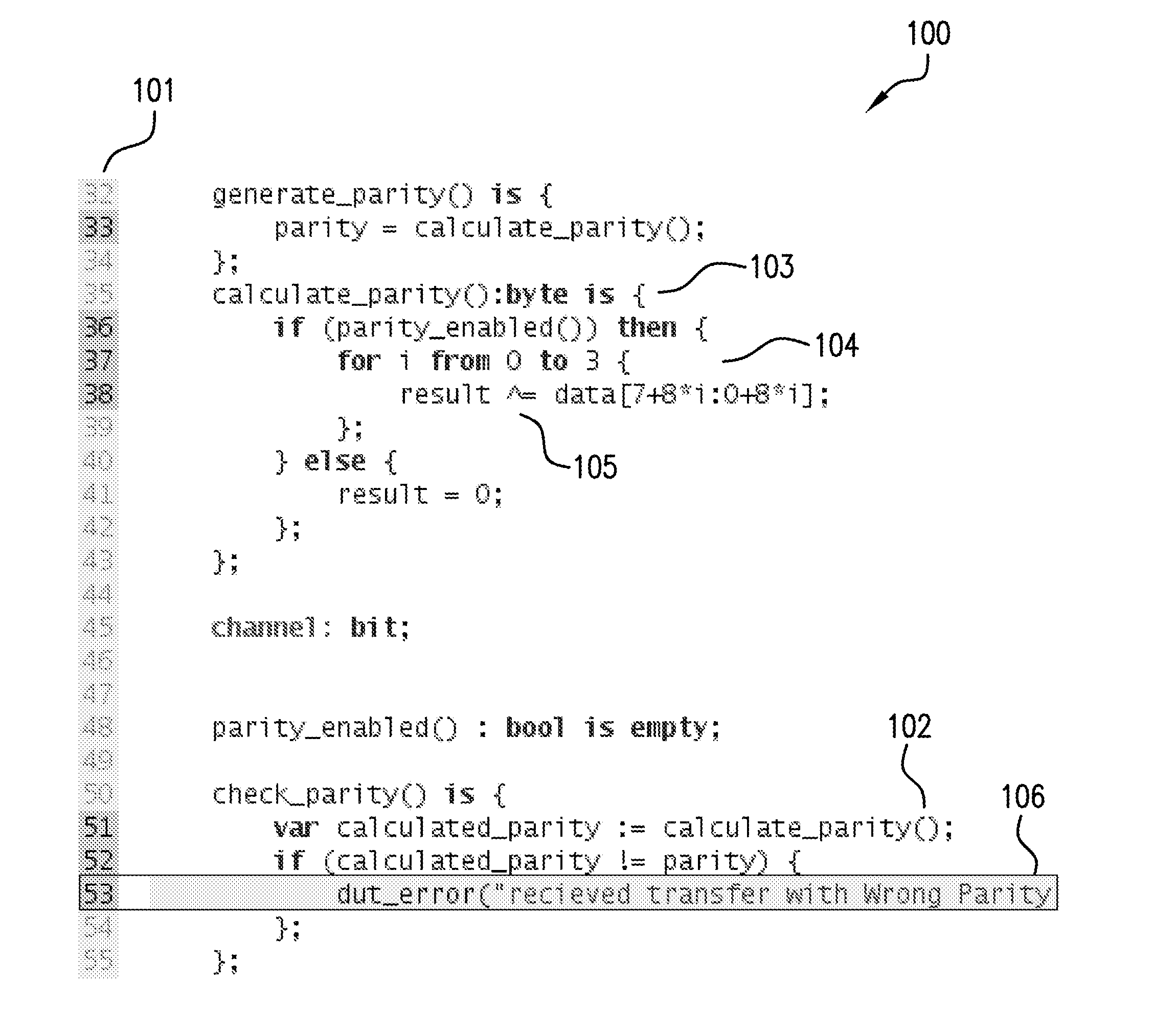
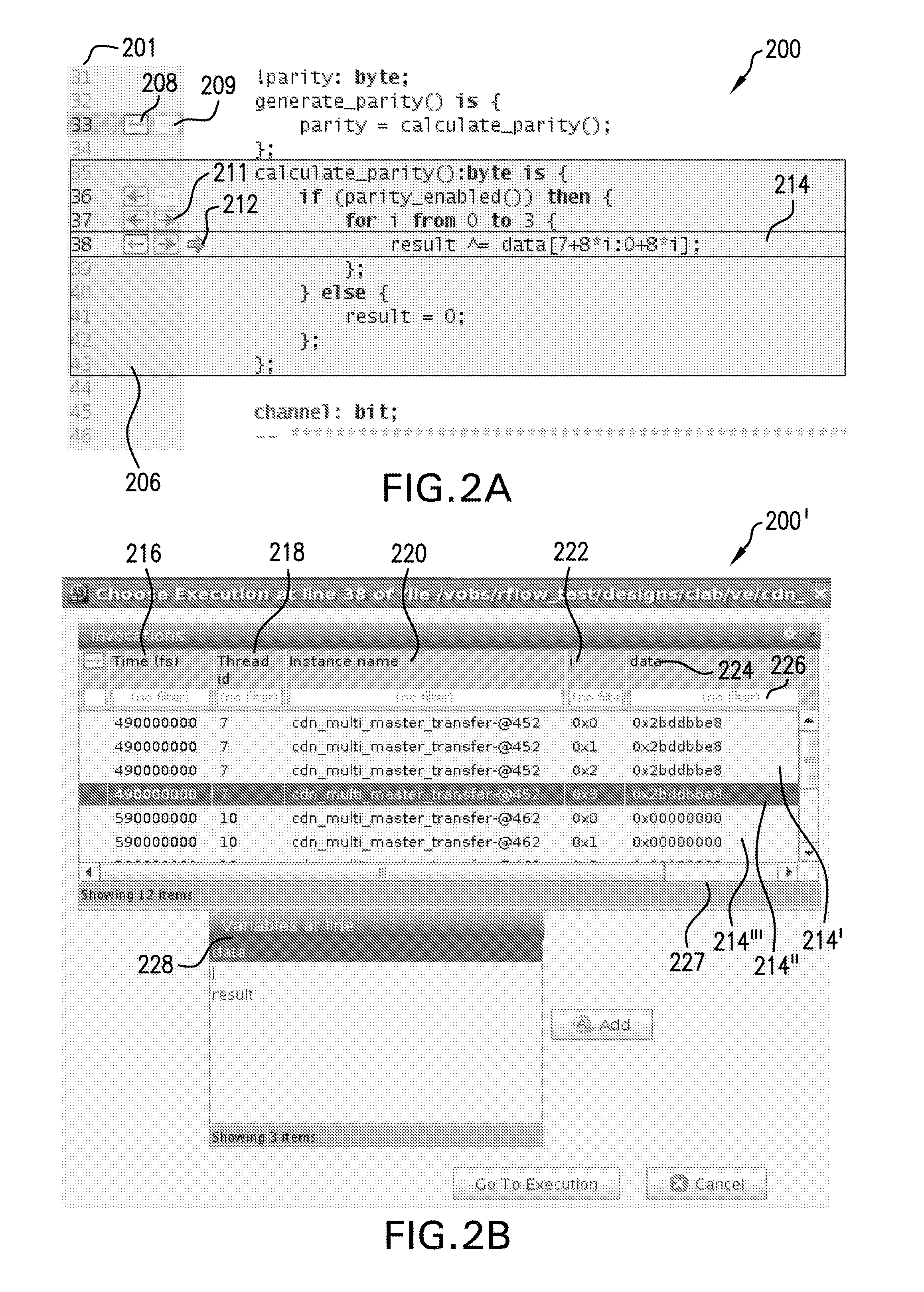
A system and method are provided for enhanced navigation along execution time and code space in a debugger to assist a user in remediating errors, streamlining, or reverse engineering a computer program and the source code thereof. Snapshots of system states are recorded, a causality tree of commands is constructed through execution of the program to be debugged, and an intelligent display of system states captured during runtime and indexed or cross-referenced by time are displayed to the user in an intelligent manner to aid the user with certain debugging tasks. Additionally, further features in assisting the user to locate a root cause of an error or unexpected value and remediate that cause are also provided.
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
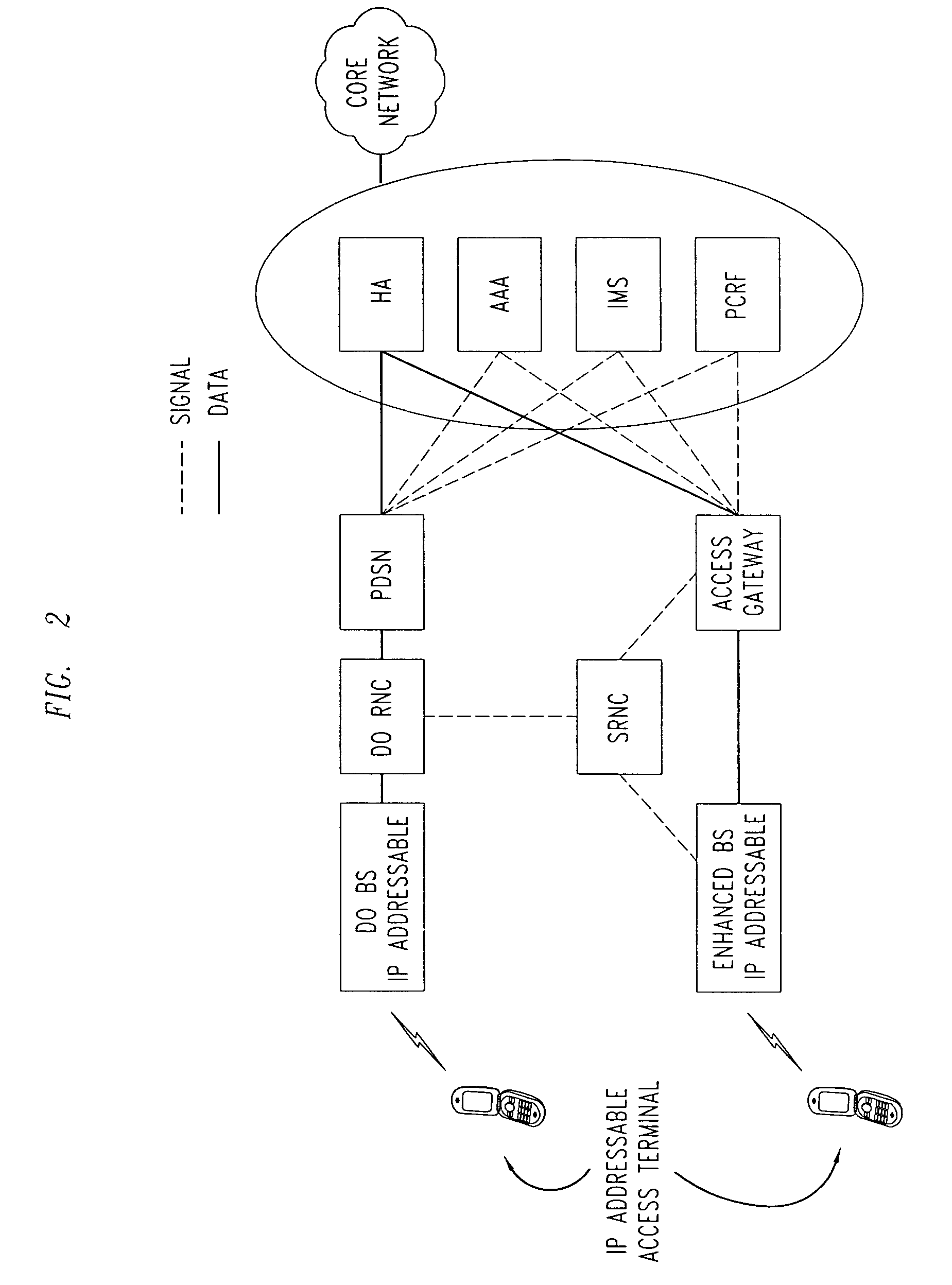
Method for routing via access terminals
ActiveUS20090252088A1Increase flexibilityEfficient resource allocationFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexCode spaceComputer science
An access-terminal routing methodology is provided that may be used to enable a wireless, meshed backhaul between base stations using existing wireless-access resources (time, bandwidth, code-space, power), protocols, and base station infrastructure. Accordingly, the invention provides a means to extend the coverage of existing networks by adding standalone base stations without wired or specialized wireless backhaul.
Owner:RPX CORP
Method for data rate selection in a wireless communication system
InactiveUS6930981B2Easy to useEfficiently using bandwidthFrequency-division multiplex detailsOrthogonal multiplexCommunications systemCell selection
Data rate determination is provided in a system where the available power fraction and available Walsh codes in each active leg are dynamically changing over time. This method adapts the rate (modulation and coding) based on the combined resource (power & code space) levels seen at each cell. The method results in maximization of the rate supportable by each cell given their resource constrained situation while meeting the constraints of target packet or frame error rate and orthogonality. Furthermore, improved fast cell selection by the mobile results due to this approach that is based on knowledge of combined resource (power & code space) levels across the cells in the active set.
Owner:GEMPLU
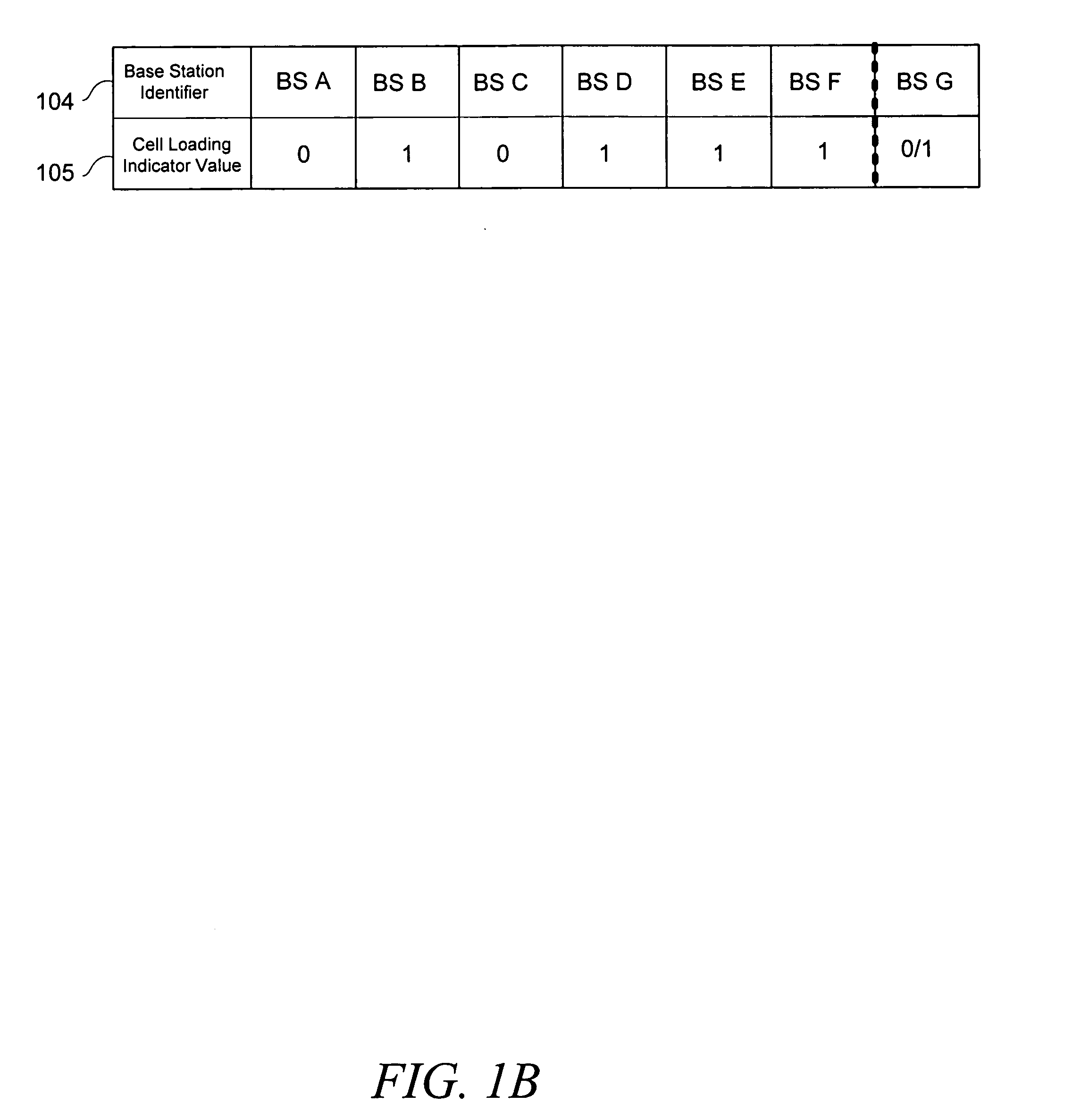
Mobile station connection management utilizing suitable parameter information
ActiveUS20050136937A1Active connectionAssess restrictionTime-division multiplexCode spaceConnection management
A method and apparatus managing a list of base stations (“BSs”) for which a mobile station (“MS”) can establish an optimal communications channel are disclosed. In accordance with the teachings disclosed herein, a MS acquires suitable parameter information (“information”) and bases a subsequent switching decision based upon such information. Suitable parameters comprise cell loading and / or service priority, and MS needs. Such information comprises, for example, a number of BS users, switching latency associated with a particular BS, applications available by a BS, available code space, and a number of MSs for which a particular BS can provide resources. A MS decision to switch from a first BS to a second BS is predicated upon the acquired information.
Owner:APPLE INC
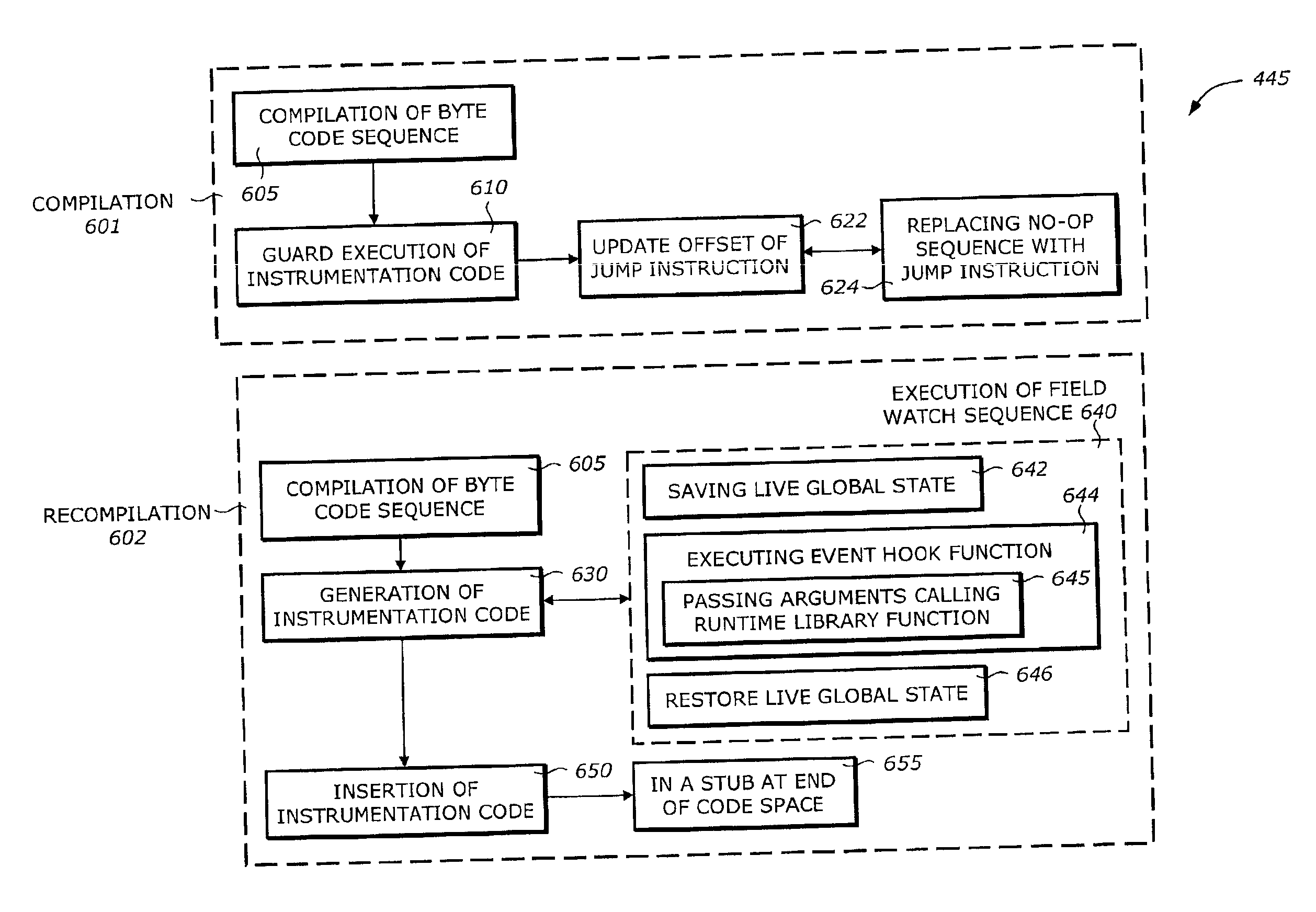
Debugging support using dynamic re-compilation
The present invention is a method and system to support debug. A function is re-compiled when a field watch for a field is activated. The function includes a byte code sequence having a field byte code that accesses or modifies the field. The re-compiled function provides a native code and occupies a code space. An instrumentation code corresponding to the field watch of the field is generated. The instrumentation code is inserted to the native code.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Communication method, method for forwarding data message during the communication process and communication node thereof
ActiveUS20120176932A1Data switching by path configurationWireless network protocolsCode spaceIdentity recognition
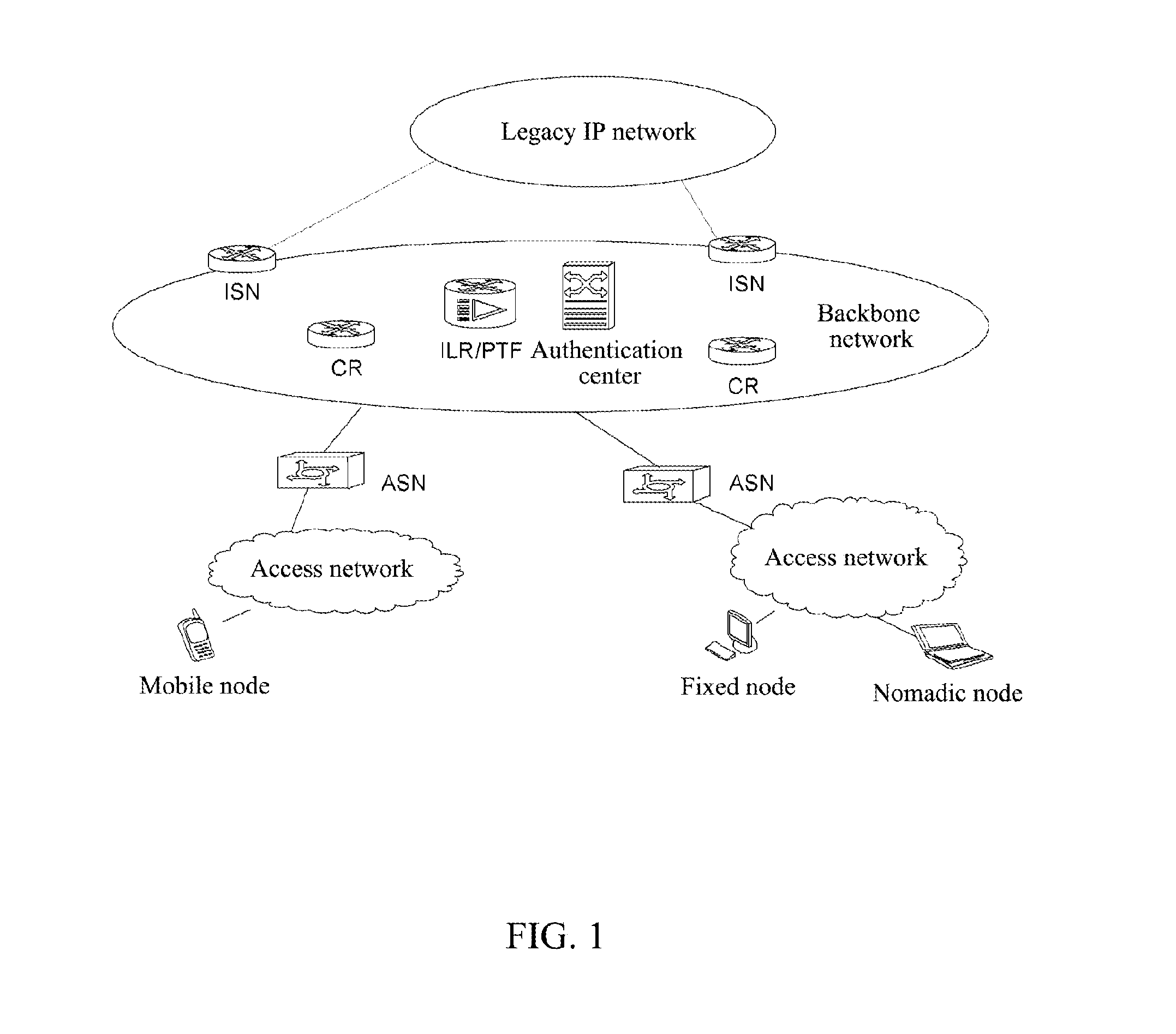
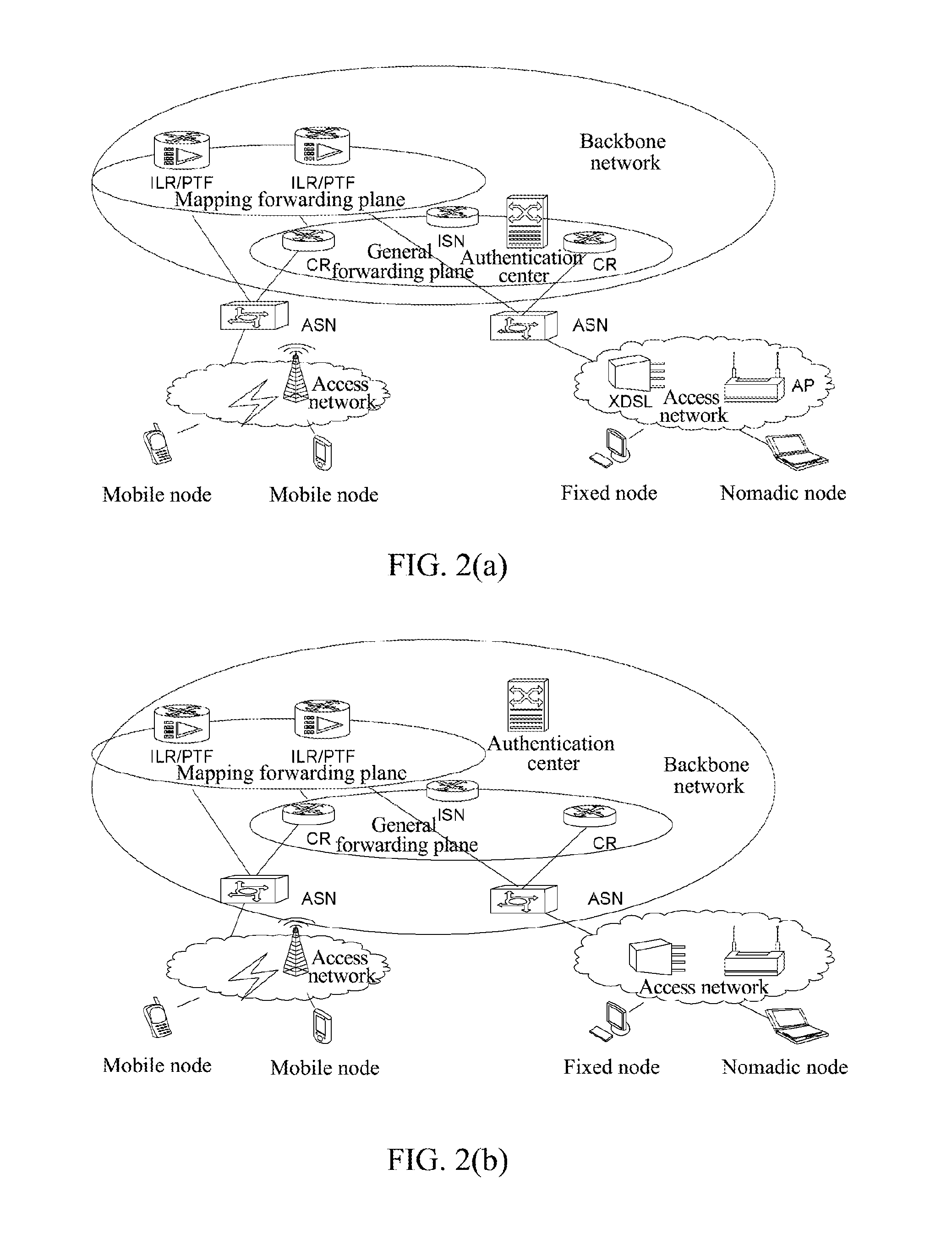
The present invention provides a communication method, and a method for forwarding a data message during the communication process and a communication node. Wherein, the configuration mode for identity recognition is clarified, and under the architecture based on access identifier and location separation in the network, a specific method for implementing identity recognition is provided, and the processing performed by each network element is regulated; the requirement for the number of the coding spaces is met, meanwhile the present invention realizes the intercommunication and interconnection with the legacy IP network, realizes the compatibility with the upper application programs of IPv4 / IPv6, and supports the various application programs of the IPv4 / IPv6 network to transplant smoothly to the architecture based on access identifier and location separation in the network.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Aiming indicia for a bar code and method of use
InactiveUS6843417B1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsCode space
Owner:RPX CORP +1
Method of and system for testing equipment during manufacturing
InactiveUS20040102187A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsAutomatic exchangesComputer hardwareCode space
A platform system for a mobile terminal for a wireless telecommunications system includes a mobile-terminal platform assembly. The mobile-terminal platform assembly includes a software services component having at least one functional software unit, a hardware component having at least one hardware unit associated with and controlled by the at least one functional software unit, and an interface component having at least one interface for providing access to the mobile-terminal platform assembly. The platform system also includes test application software loaded, installed, and run on the mobile-terminal platform assembly via the interface component. The test application software tests both software and hardware of the mobile terminal during both production testing and testing performed during a lifecycle of the mobile terminal. The test application software may be located in an unprotected code space of the mobile terminal in order to allow the test application software to be overwritten as needed to make space for other applications.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
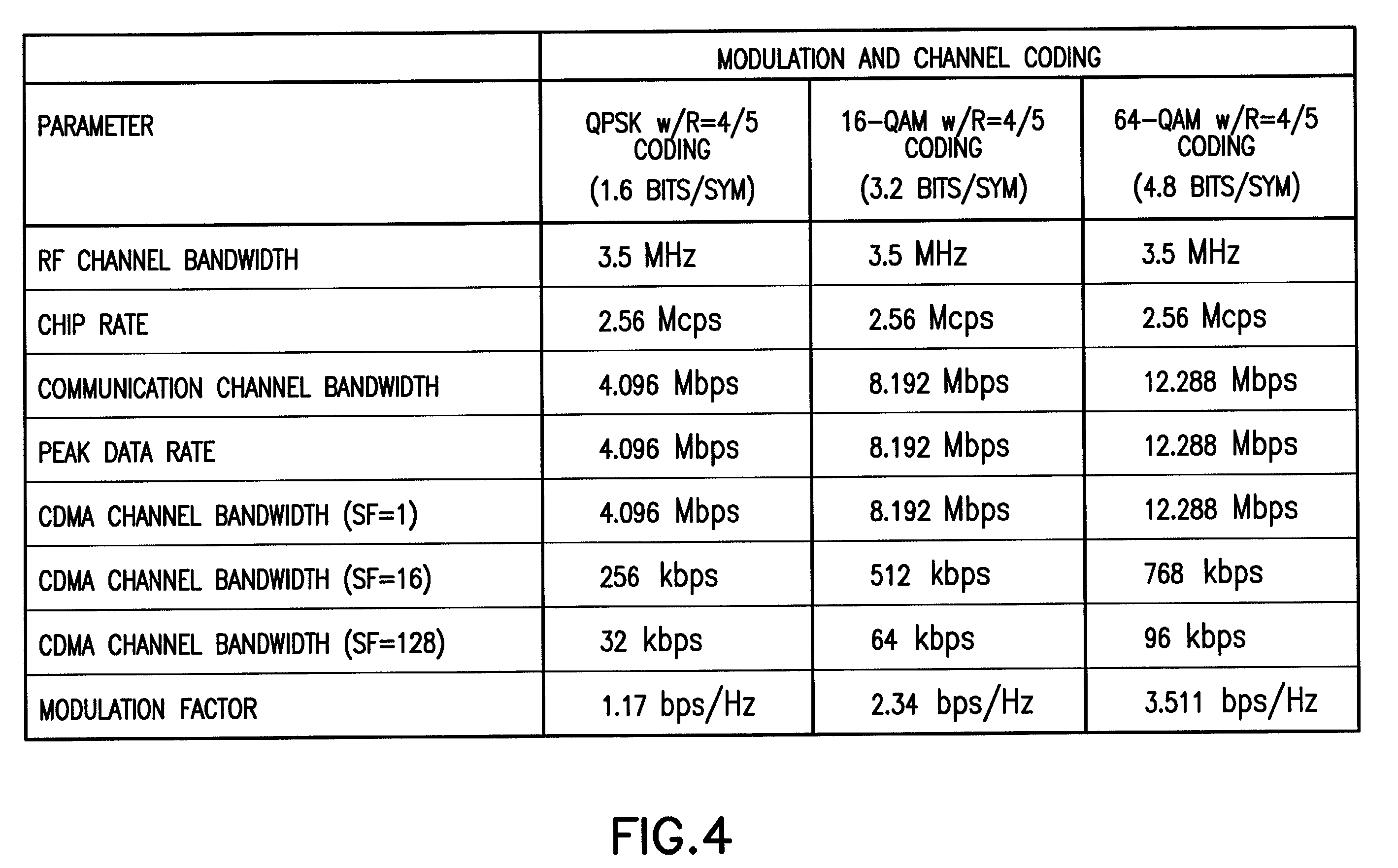
Two-dimensional channel bonding in a hybrid CDMA/FDMA fixed wireless access system to provide finely variable rate channels
InactiveUS7190683B2Improve concentration efficiencyRelatively large bandwidthModulated-carrier systemsTime-division multiplexCommunications systemCode space
A communications system employs the use of both synchronous CDMA and FDMA to provide a variable bandwidth waveform with multiple bonded transmitters and receivers that are agile in both frequency and PN code to permit a variable bandwidth and variable rate multiple access system. In a first aspect the teachings provide the use of both CDMA and FDMA together to enable an improved concentration efficiency by making a larger pool of bandwidth available to each user. In a second aspect these teachings enable channel bonding across both code space and frequency space, thus making the system capable of operating within a variable (not necessarily contiguous) bandwidth and at a finely variable rate.
Owner:L 3 COMM CORP
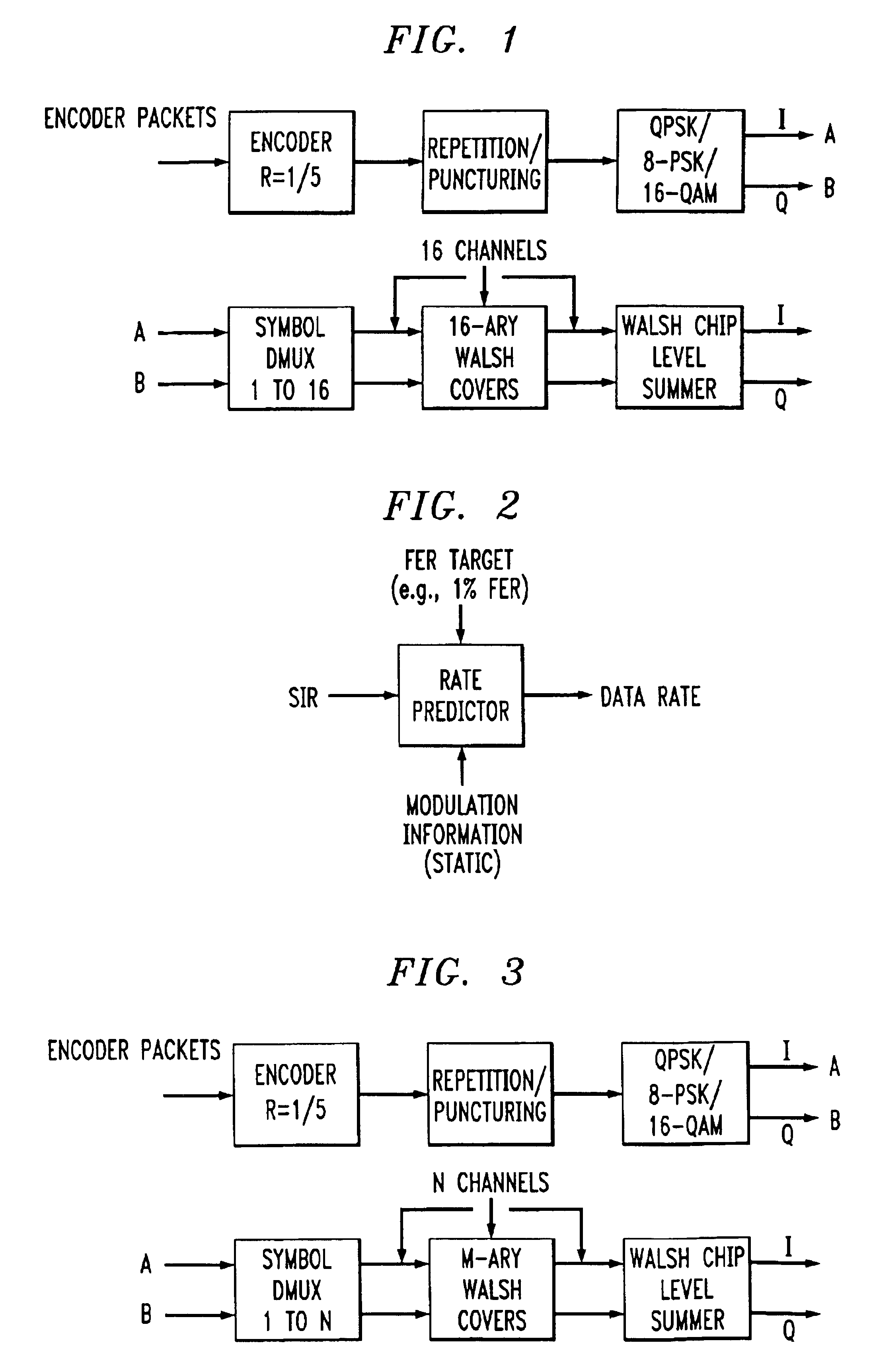
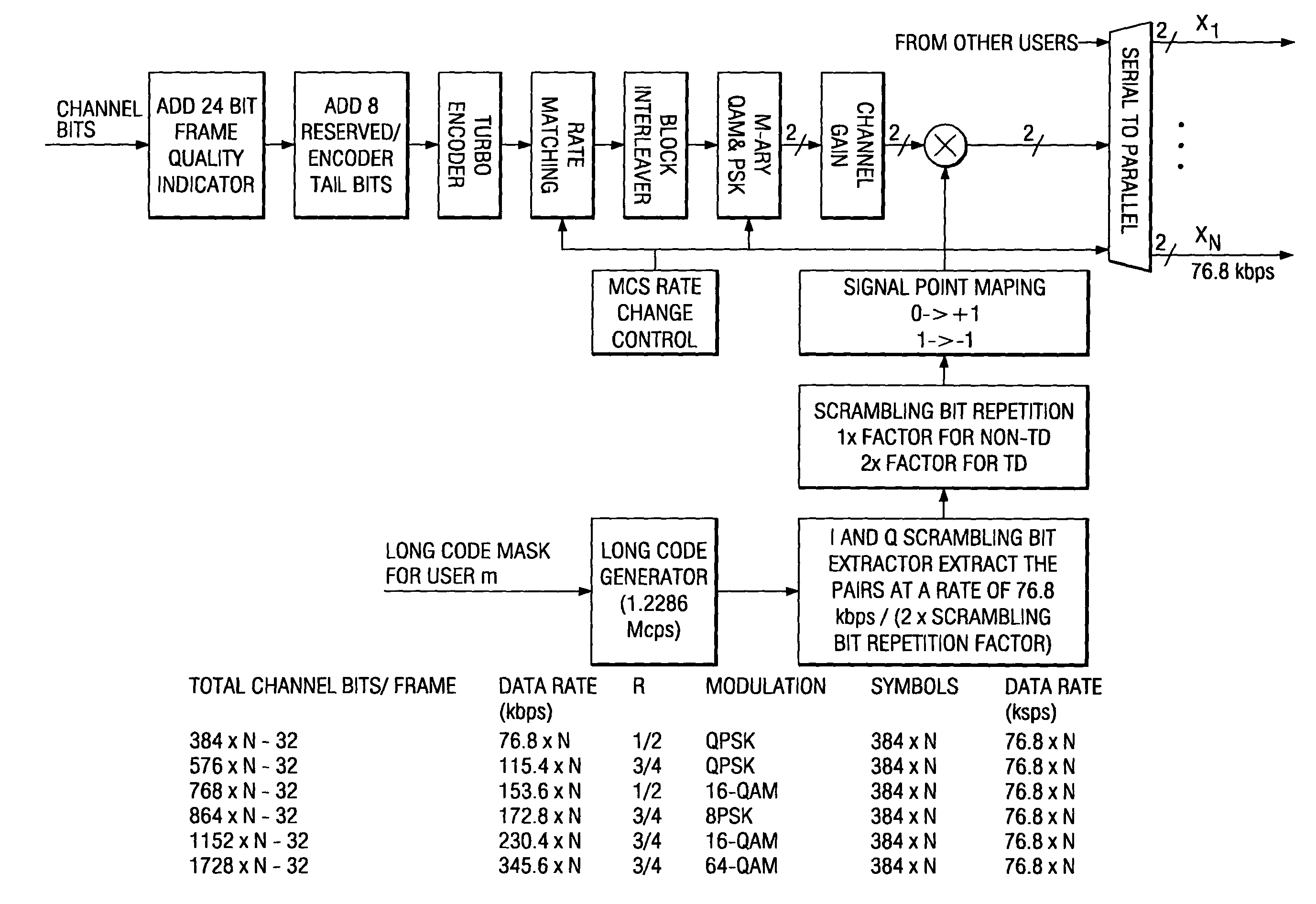
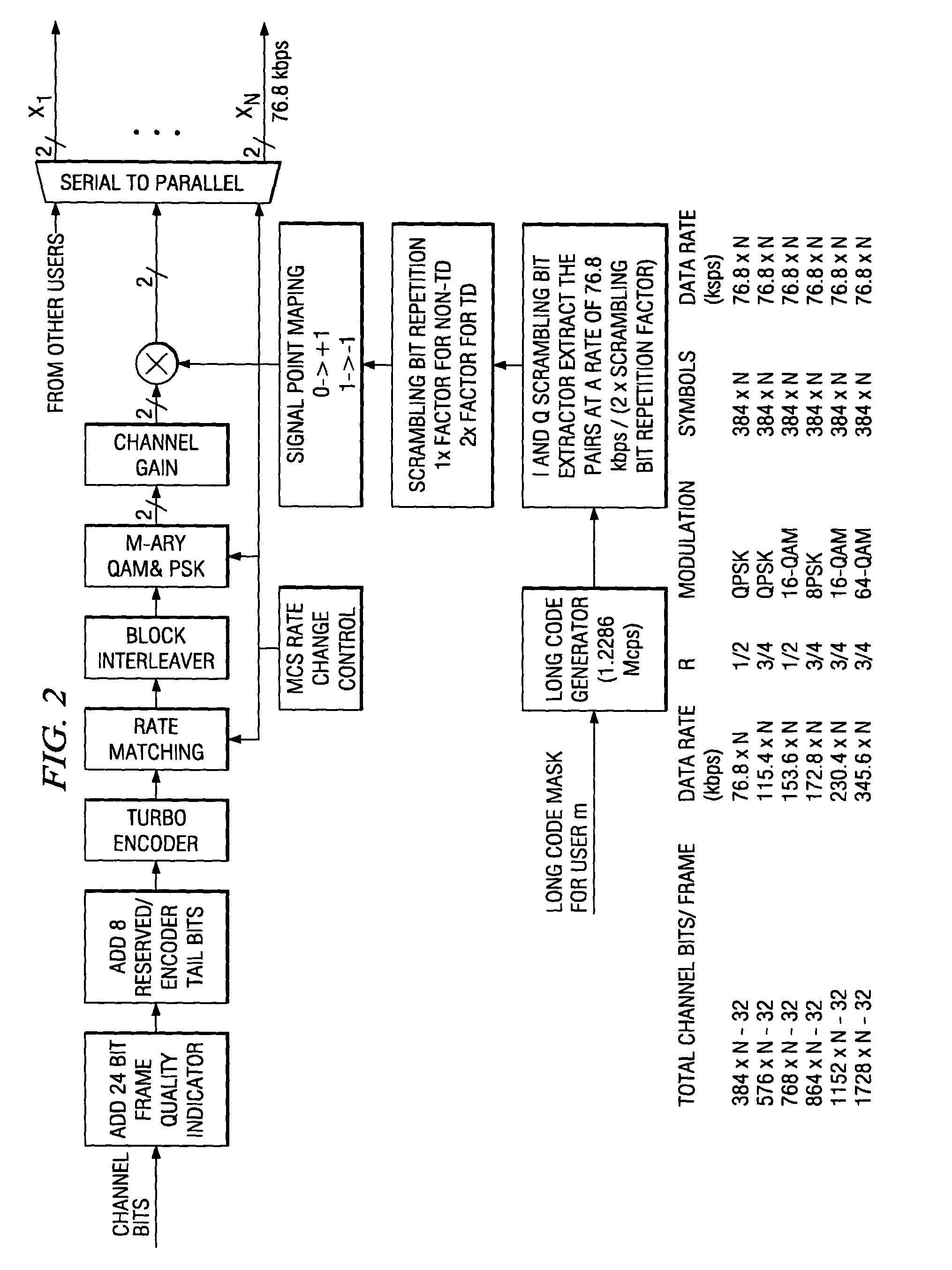
Method of rate matching for link adaptation and code space management
InactiveUS20050050427A1Reduce constraintsUnequal/adaptive error protectionCode conversionComputer hardwareRound complexity
A method of symbol combining and incremental redundancy for link adaptation and code space management was proposed. In order to reduce constraints on the Walsh codes allocation, MCS level change, as well as frame duration change for the initial transmission and re-transmissions, a “rate matching” stage is proposed between the Turbo encoder and block interleaver on the transmitter. In the initial transmission, the Turbo encoded symbols are interleaved with or without any puncturing or repeating (i.e. puncture / repeat factor is set to 1). The coded symbols are also stored in the memory for possible retransmissions. In the re-transmission, the transmitter first determines the number of Walsh codes available for this user and MCS level and frame duration according to the C / I feedback values from MS. The stored coded symbols are then punctured or repeated according to “rate matching factors”. On the receiver side, “rate matching factors” can be derived from the number of code channels, MCS level and frame duration of current re-transmissions and initial transmission. Then, de-puncturing / de-repeating is performed before coded symbol combining. A similar rate matching based IR / symbol combining scheme can be used to design different IR using different rate matching algorithms. It has low implementation complexity and is easily made backward compatible.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
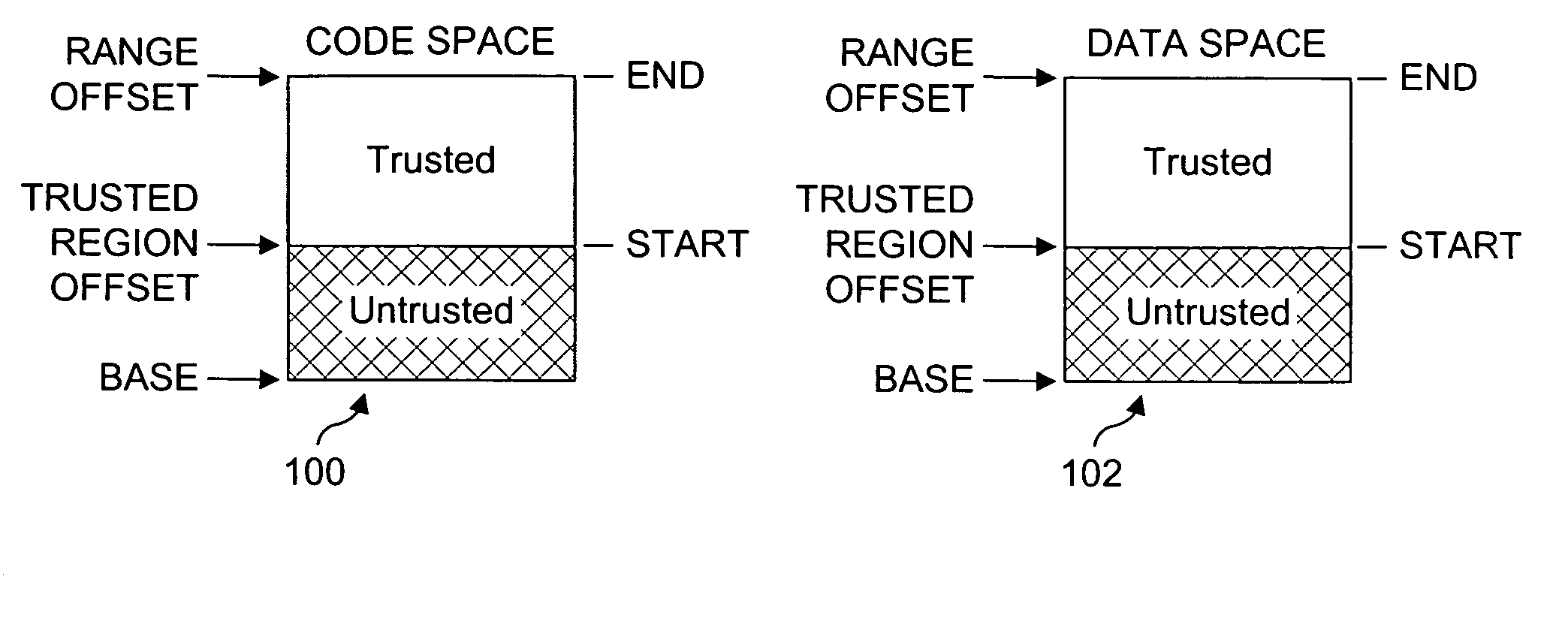
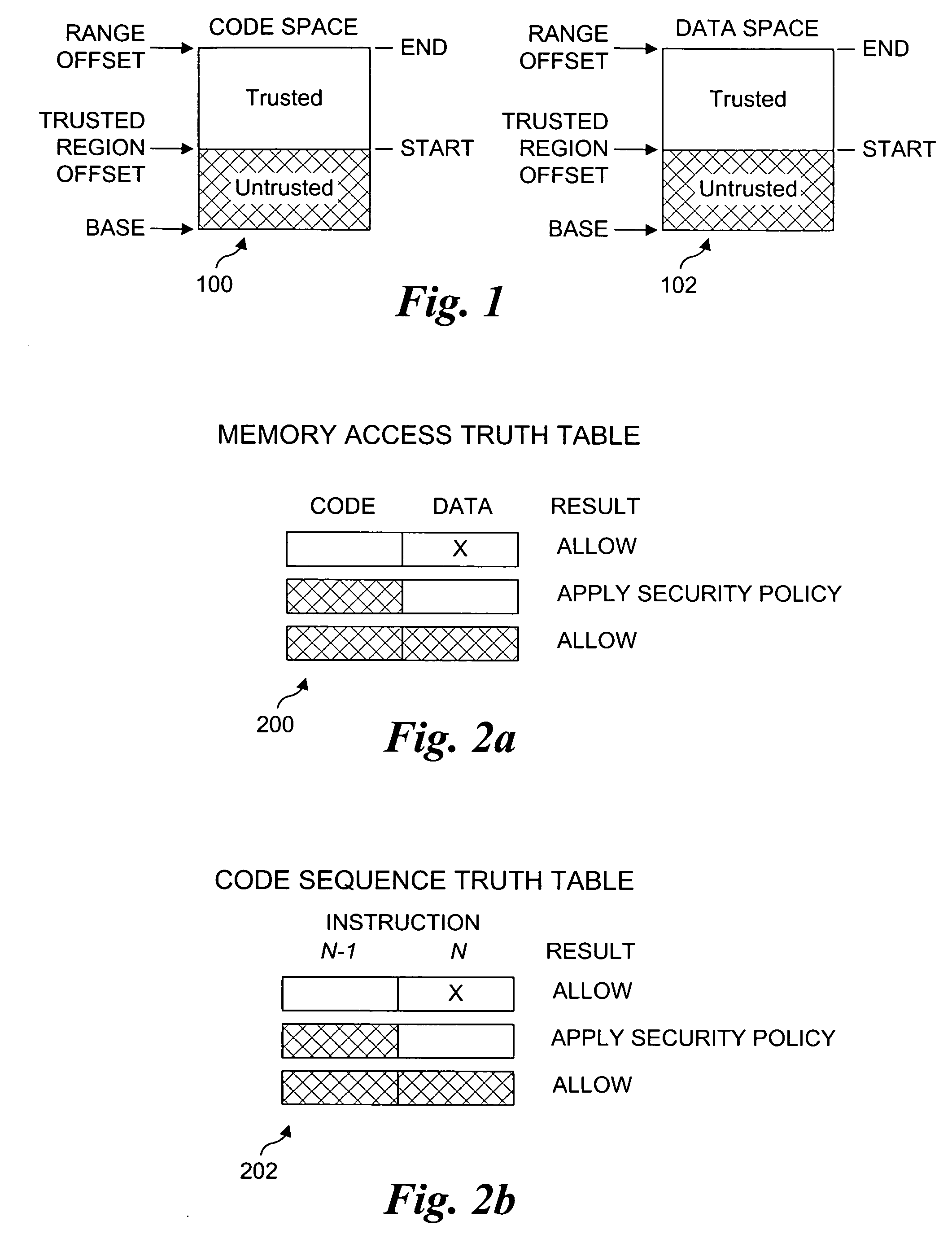
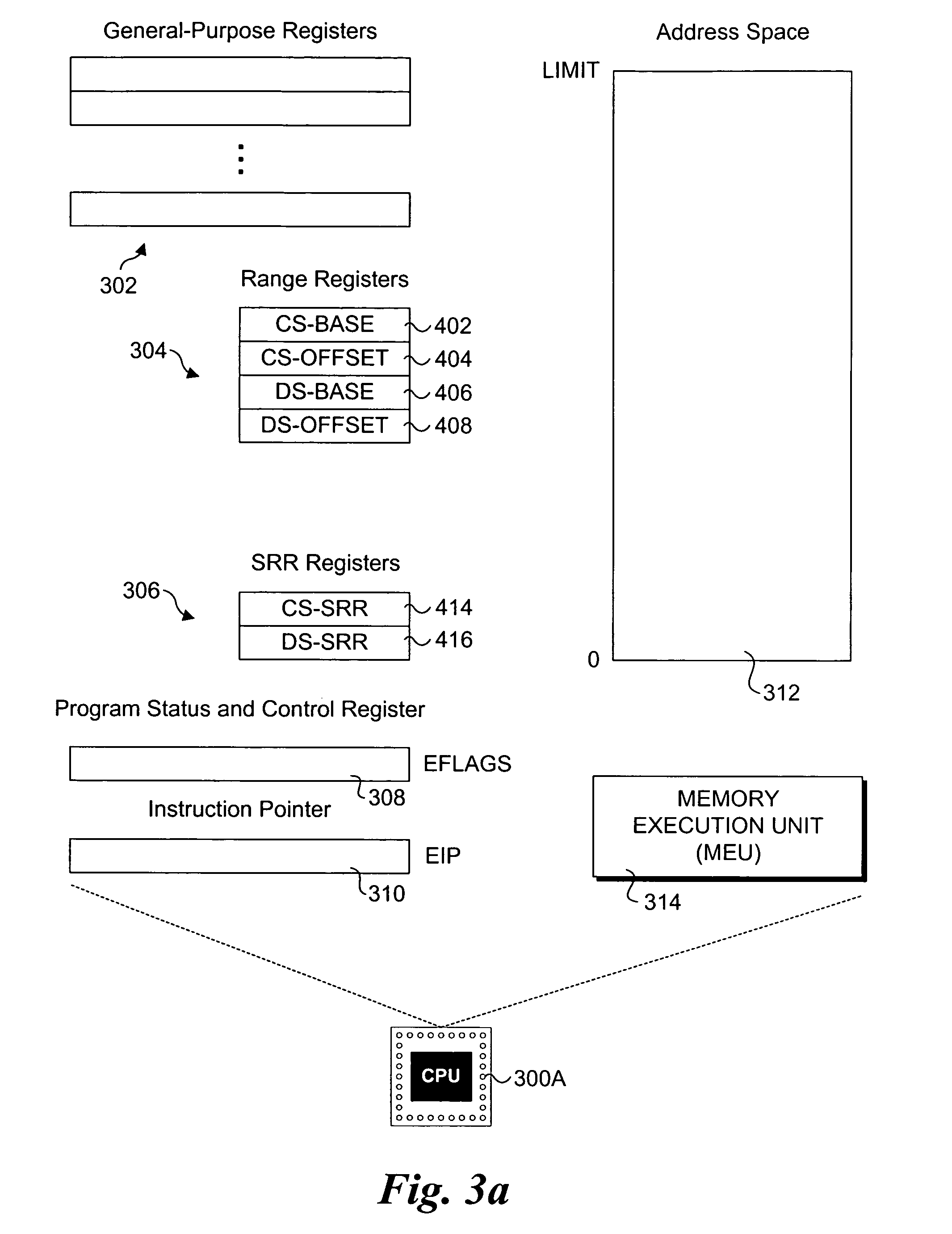
Processor extensions and software verification to support type-safe language environments running with untrusted code
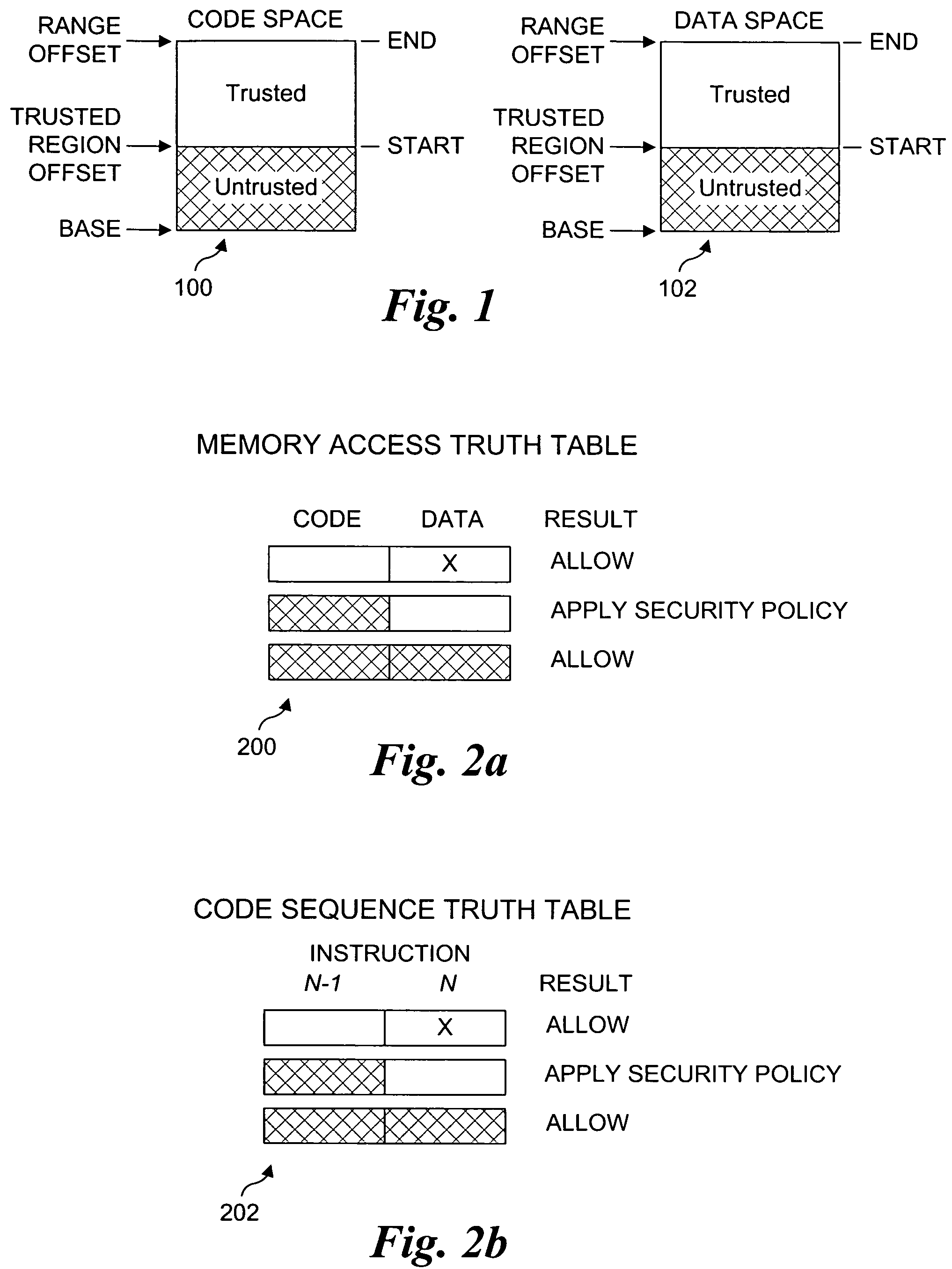
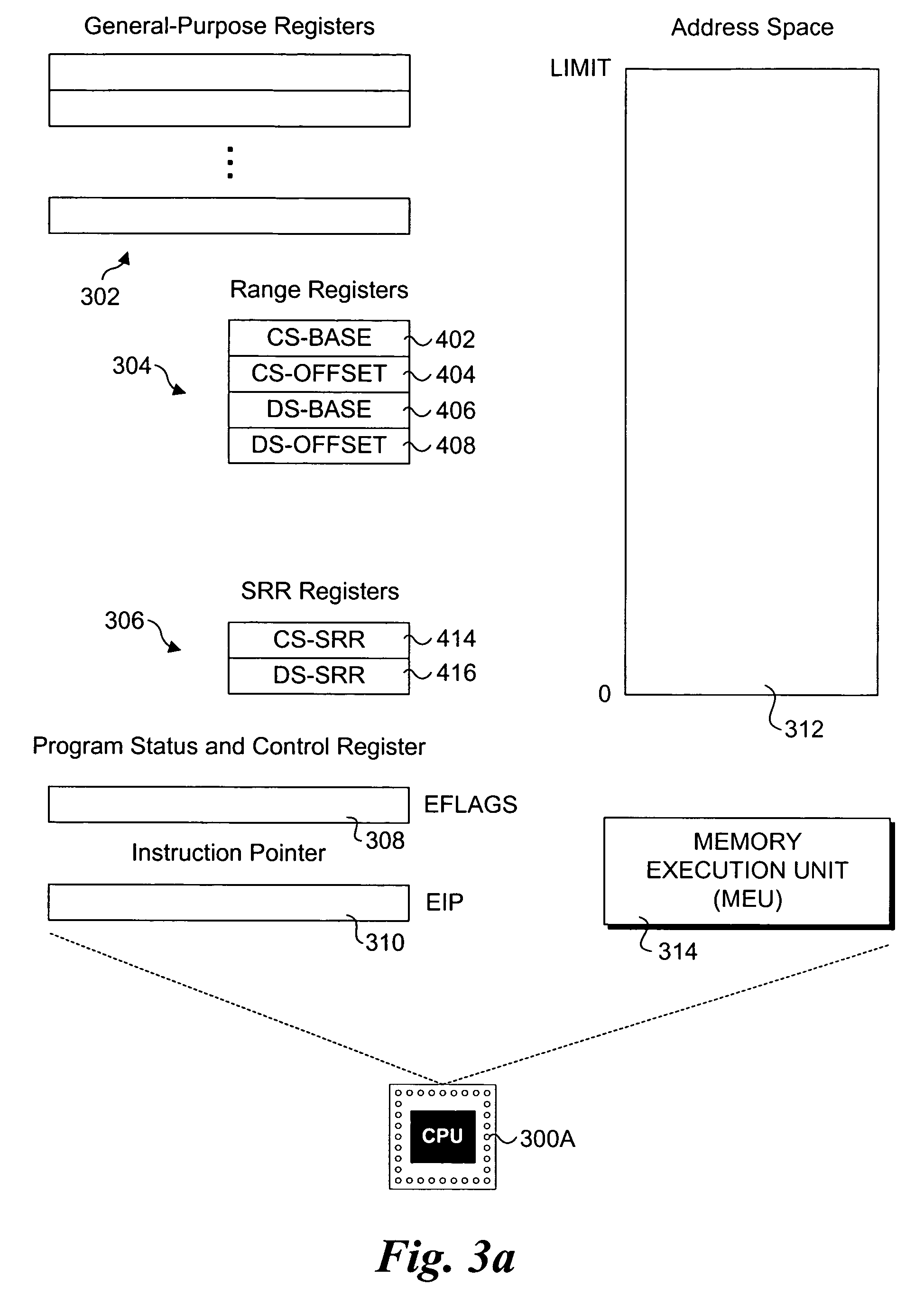
Processor extensions and software verification to support type-safe language environments running with untrusted code. Code and data spaces are partitioned into trusted and untrusted regions. Type-safe code is loaded into the trusted region of the code space, while non-type-safe code is loaded into the untrusted region of the code space. The trusted region of the data space is allocated to the type-safe code. The untrusted region of the data space is allocated to the non-type-safe code. Hardware-based truth tables are employed for defining allowable and disallowable code sequences and memory access operations. For code sequences, allowable operations are based on the location (i.e., region) of a code sequence including a current instruction and a prior instruction. For memory access, the location of the requesting instruction and data requested are considered. Disallowed code sequence or memory access operations cause the processor to generate a safe access protection trap. In response to the safe access protection trap, a software-based dynamic verifier applies a security policy to determine whether to allow the operation to proceed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Two-dimension code coding and decoding method and device based on local color verification
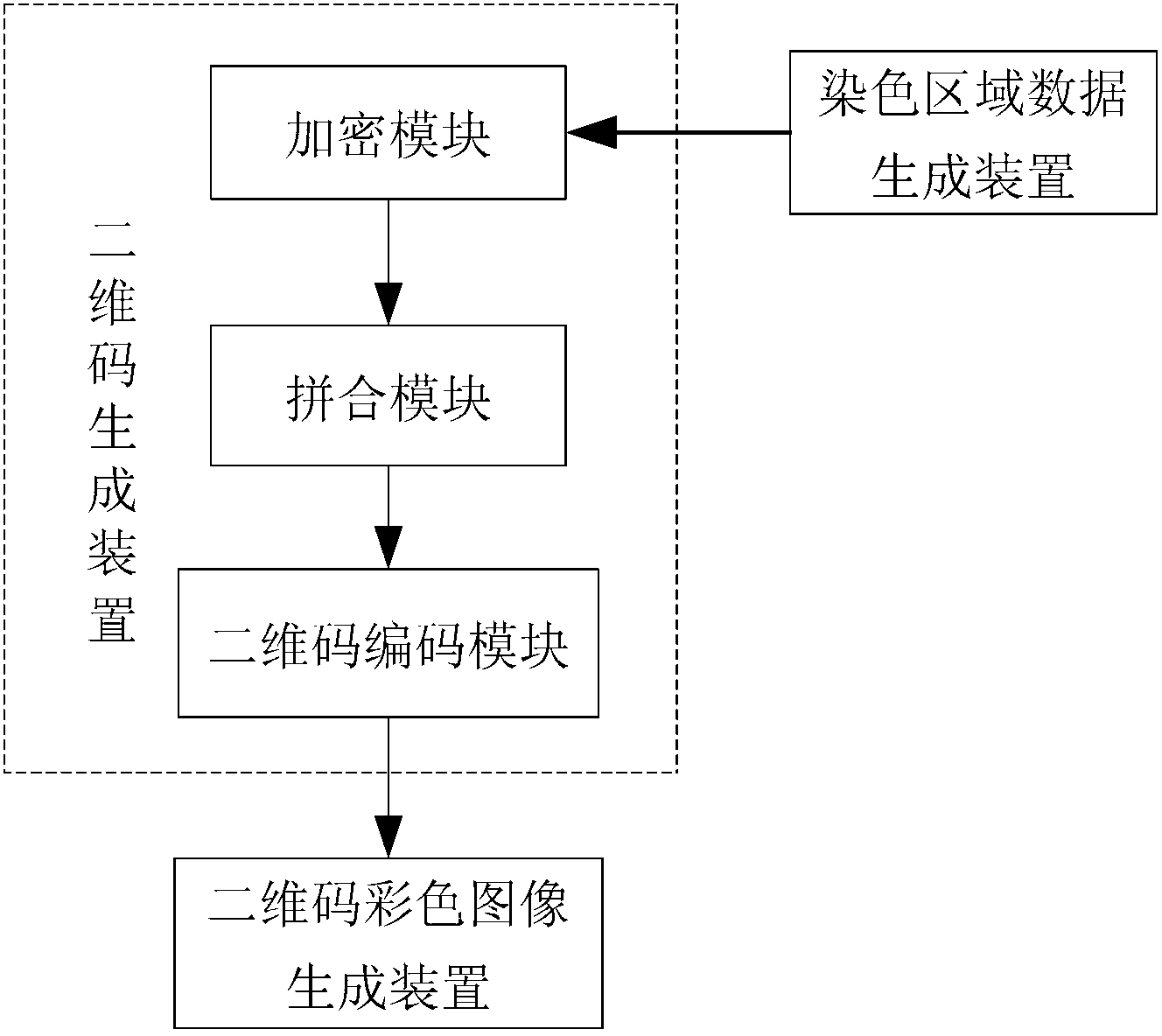
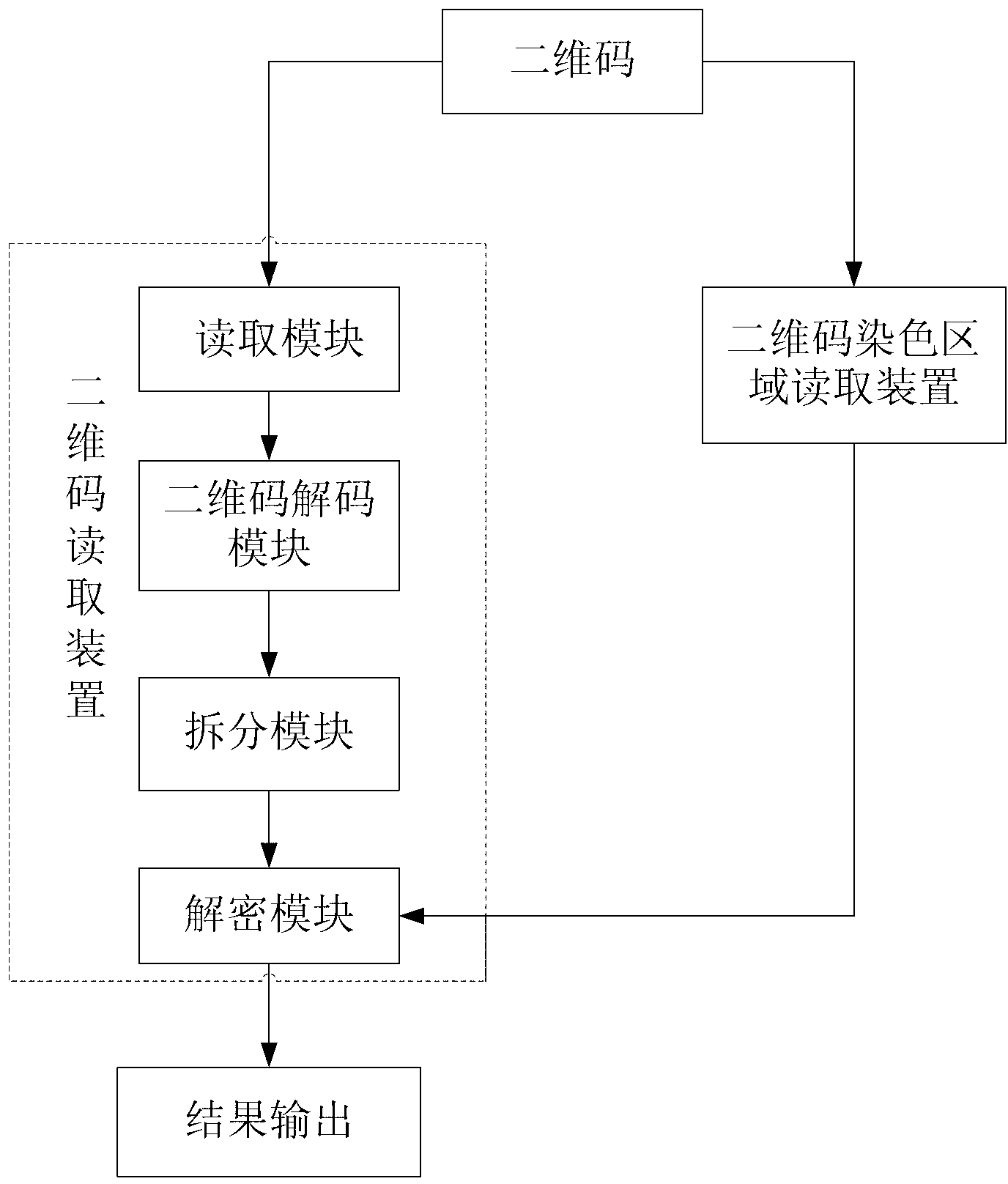
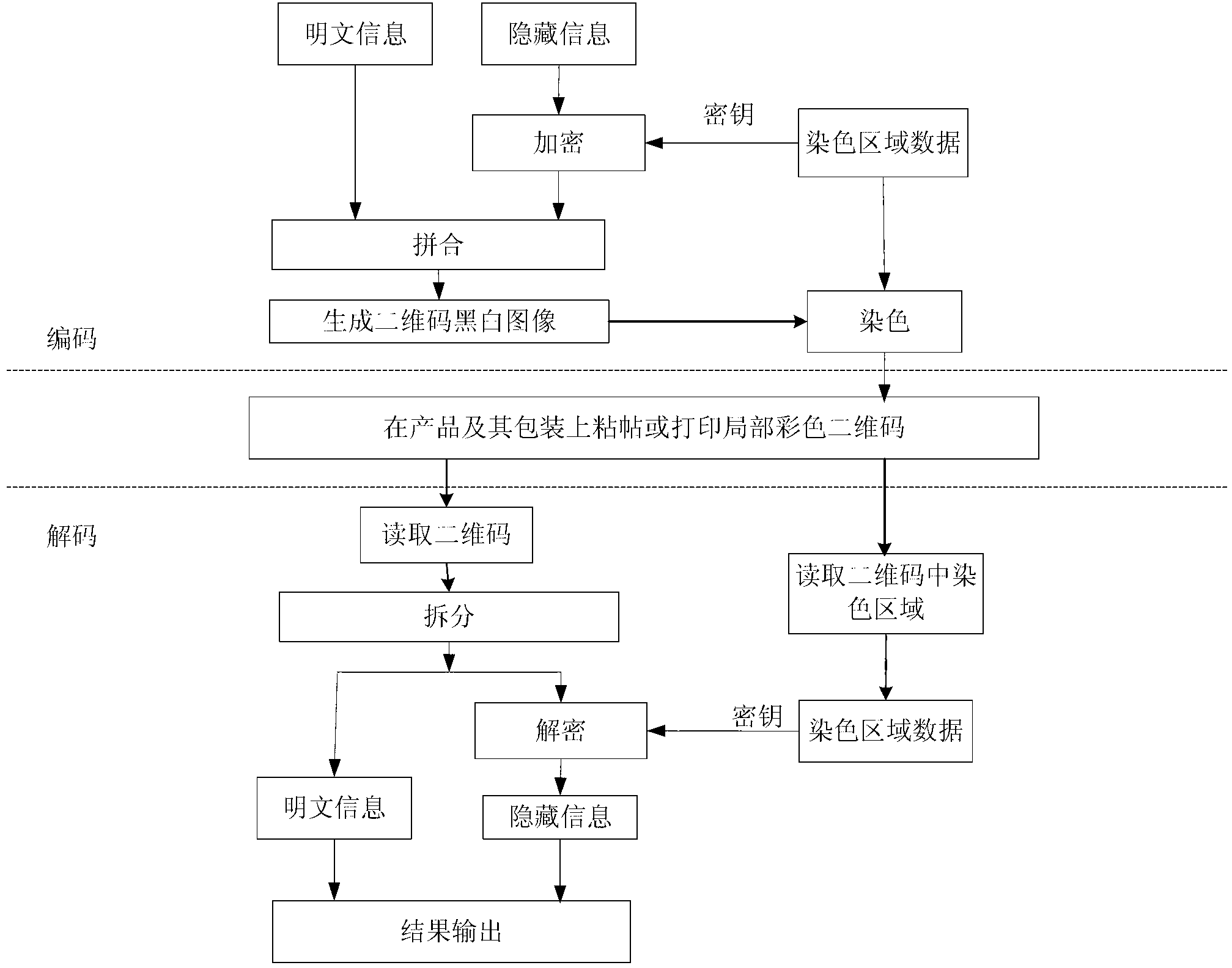
ActiveCN102916804ARealize monitoringRealize regulationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesRecord carriers used with machinesPattern recognitionCode space
The invention discloses a two-dimension code coding and decoding method and devices based on local color verification. The coding method comprises the following steps of: generating coloring region data randomly according to a predefined coloring region coding and decoding table, and taking the generated coloring region data as a secret key to perform encryption so as to obtain two-dimension code generation information; generating two-dimension code black-and-white images by a two-dimension code generation algorithm; and finally coloring the generated two-dimension code black-and-white images according to the coloring region data to obtain local colored two-dimension code images. The decoding method comprises the following steps of: reading the coloring region data on the two-dimension code images, and using a standard two-dimension code decoding algorithm to decode; and performing decryption on the decoded information by taking the coloring region data as the secret key via a decipherment algorithm to obtain original information of the two-dimension cod images. By using the invention based on original black and white colors, the coloring region information is increased, coding space of two-dimension codes can be expanded, and counterfeited difficulty is increased.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Processor extensions and software verification to support type-safe language environments running with untrusted code
Processor extensions and software verification to support type-safe language environments running with untrusted code. Code and data spaces are partitioned into trusted and untrusted regions. Type-safe code is loaded into the trusted region of the code space, while non-type-safe code is loaded into the untrusted region of the code space. The trusted region of the data space is allocated to the type-safe code. The untrusted region of the data space is allocated to the non-type-safe code. Hardware-based truth tables are employed for defining allowable and disallowable code sequences and memory access operations. For code sequences, allowable operations are based on the location (i.e., region) of a code sequence including a current instruction and a prior instruction. For memory access, the location of the requesting instruction and data requested are considered. Disallowed code sequence or memory access operations cause the processor to generate a safe access protection trap. In response to the safe access protection trap, a software-based dynamic verifier applies a security policy to determine whether to allow the operation to proceed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
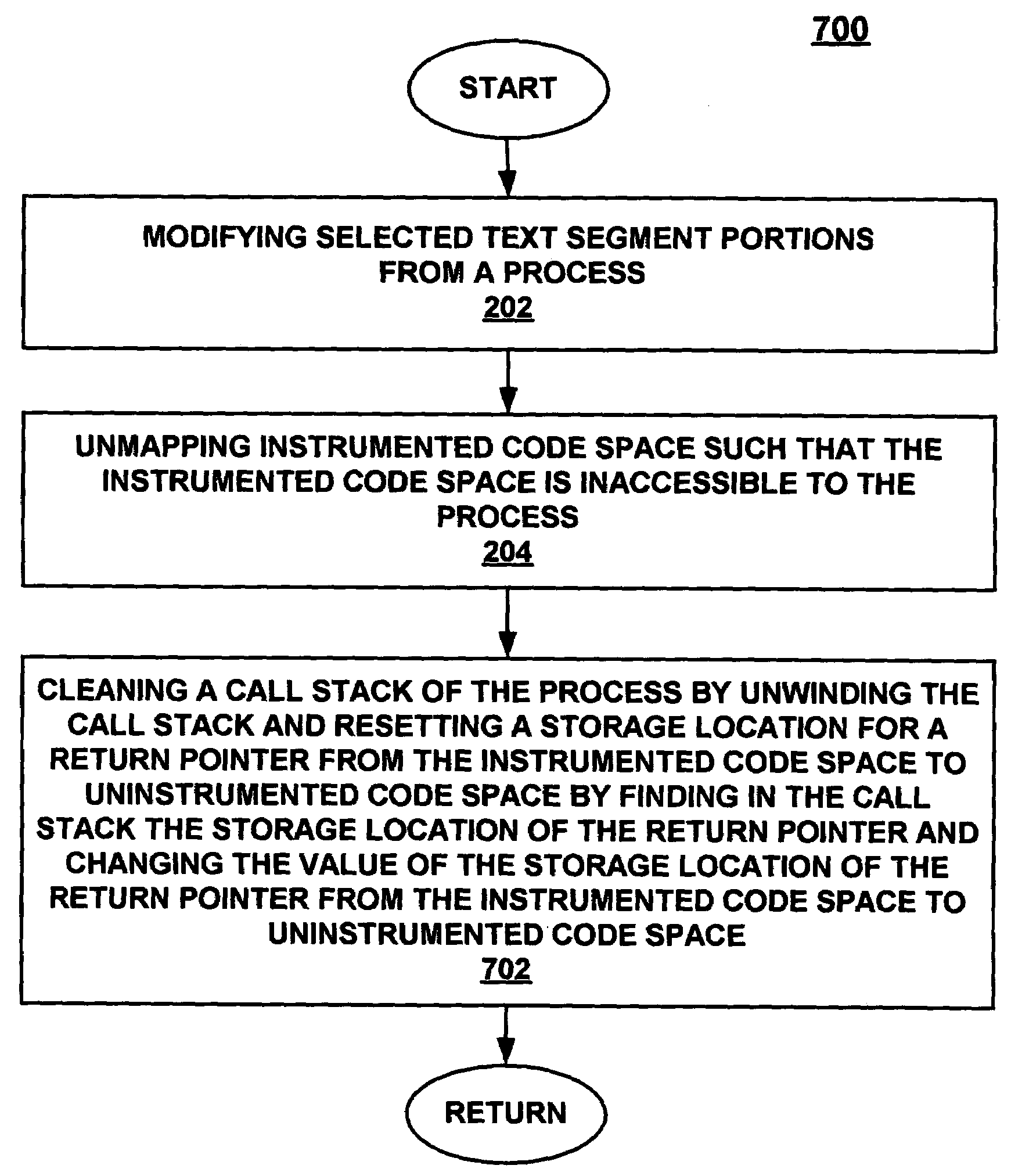
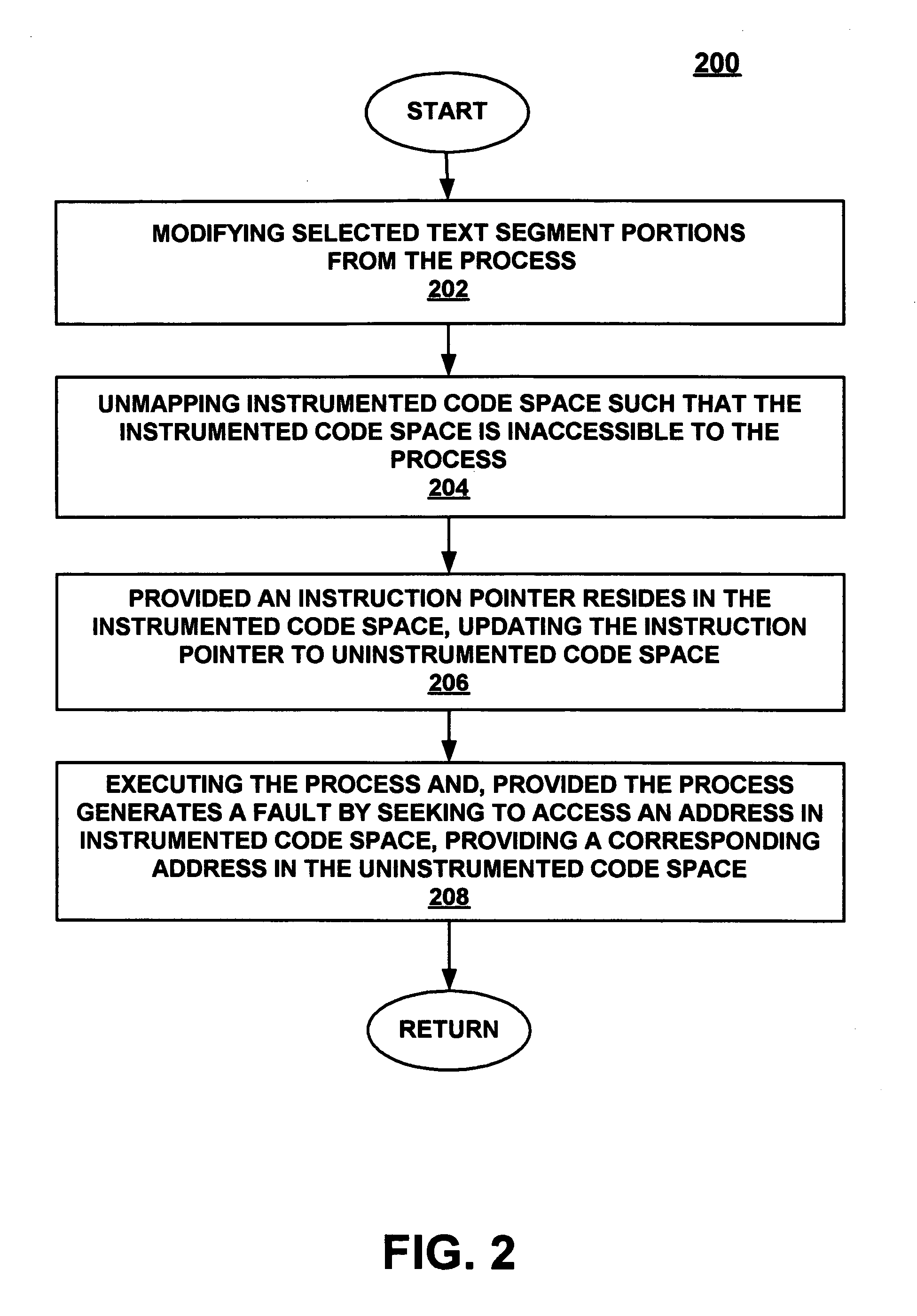
Uninstrumenting in-line code instrumentation via stack unwinding and cleanup
A method and system for reverting a process in an in-line instrumented state to an uninstrumented state. In one embodiment, the present invention modifies selected text segment portions from the process to be uninstrumented. The present embodiment then unmaps instrumented code space such that the instrumented code space is inaccessible to the process. In this embodiment, the present invention also cleans a call stack of the process by unwinding the call stack and resetting the storage locations for return pointers from the instrumented code space to uninstrumented code space.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
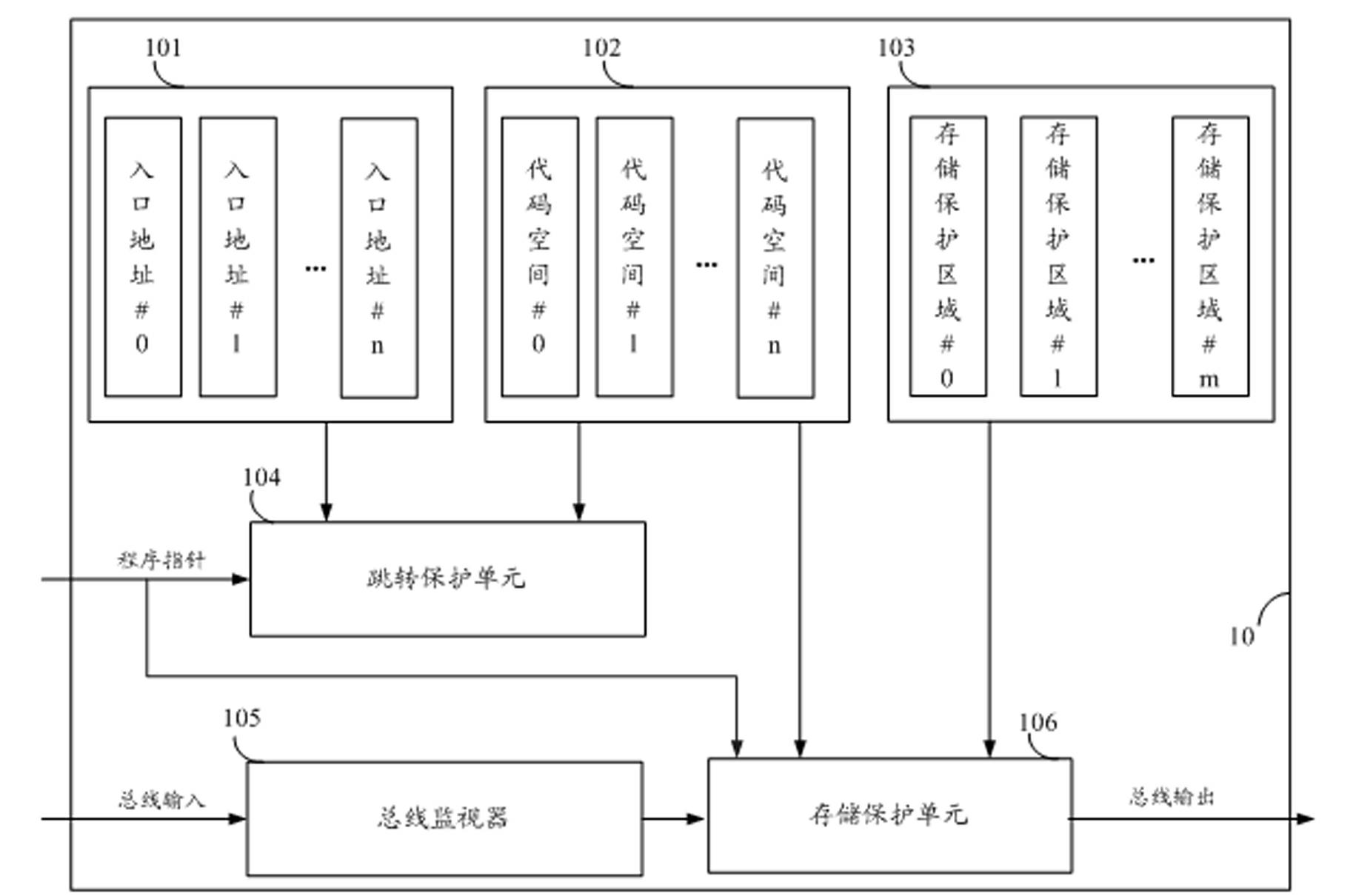
Storage protecting controller and method for improving safety of SOC (system on chip)
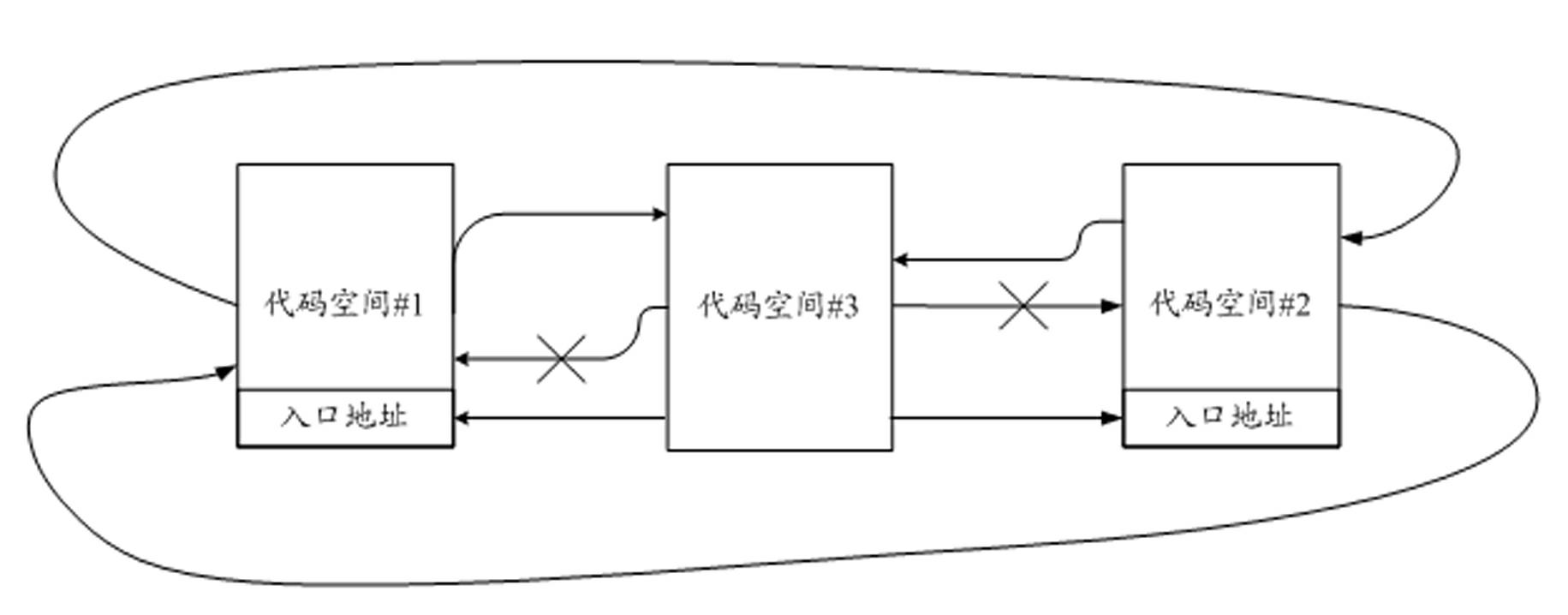
ActiveCN102592083AImprove resistance to attackImprove securityUnauthorized memory use protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionCode spaceSpace partitioning
The invention discloses a storage protecting controller and a method for improving safety of an SOC (system on chip). The method includes the steps: dividing a program code space of a processor into a plurality of code spaces, and setting an entry address corresponding to each code space; dividing a storage space into a plurality of storage protecting areas, individually setting access authority attributes of the processor to the storage protecting areas when each code space executes program codes; judging whether a program pointer of the processor skips or not and whether skip is abnormal or not, and generating skip abnormal indication if the skip is abnormal; and monitoring whether access of a current bus to the storage space is abnormal or not, and stopping access of the bus if access of the current bus to the storage space is abnormal, so that the program pointer of the processor is prevented from skipping from one code space to another code space to execute a program, and abnormal access to the storage protecting areas is prevented. The storage protecting controller can effectively improve program code running safety, and can be widely applied to SOC chips of various types.
Owner:SHENZHEN STATE MICRO TECH CO LTD
Dynamic medical object information base
ActiveUS20080140770A1Multiple digital computer combinationsHospital data managementInformation repositoryCode space
A dynamic medical object information base (DMOIB) is used with a communication protocol. A medical object information base (MOIB) may generally define rules of creation and modification of data defined for use in medical products. A dynamic version of the MOIB adapts to changing data classifications. DMOIB is preferably compatible with non-dynamic MOIB systems. DMOIB preferably reduces code space and simplifies management of software projects. DMOIB may allow for an entirely dynamic system using a discovery / negotiation process for determining full features of a device. DMOIB may also allow for generation of a dynamic interface to handle data from devices.
Owner:WELCH ALLYN INC
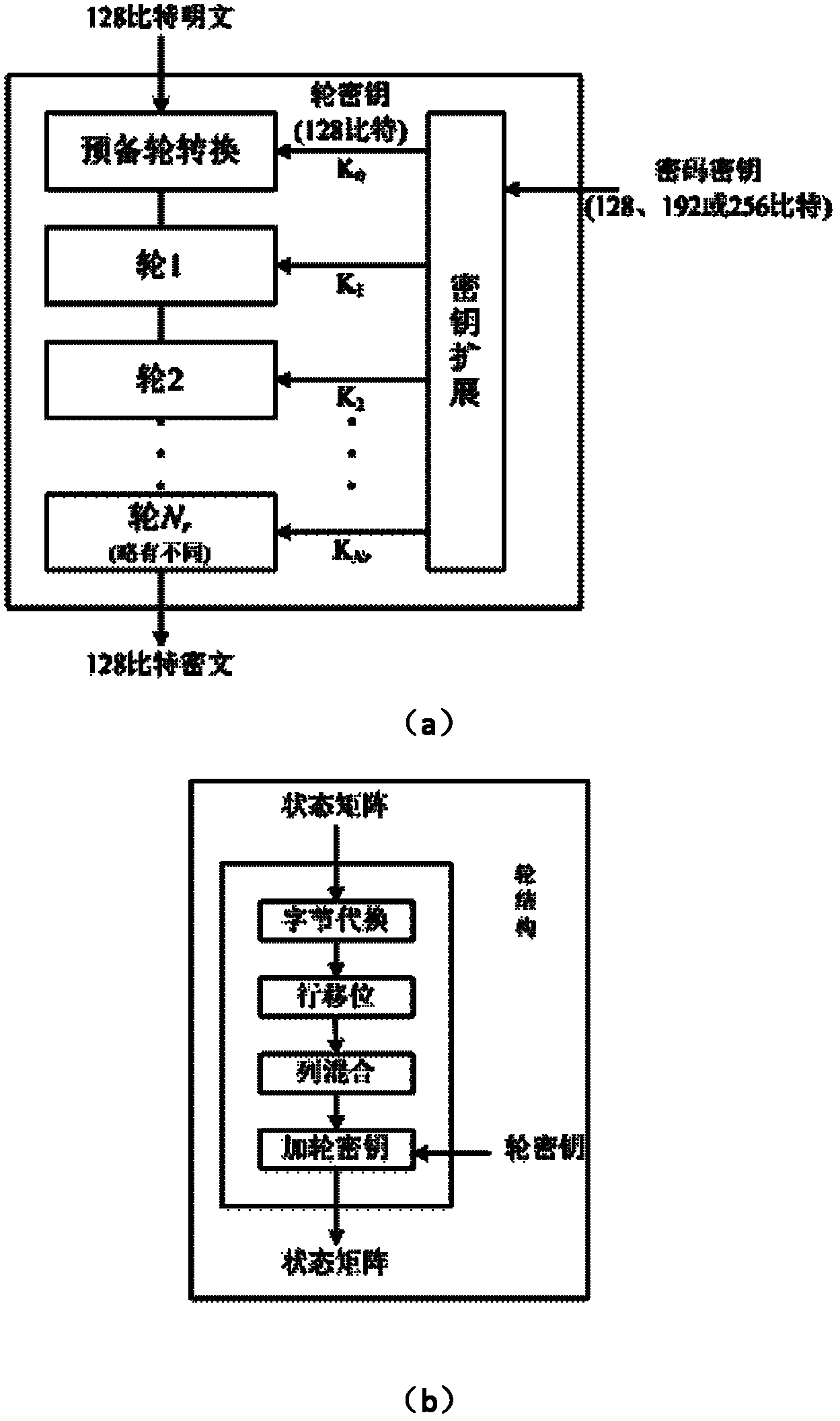
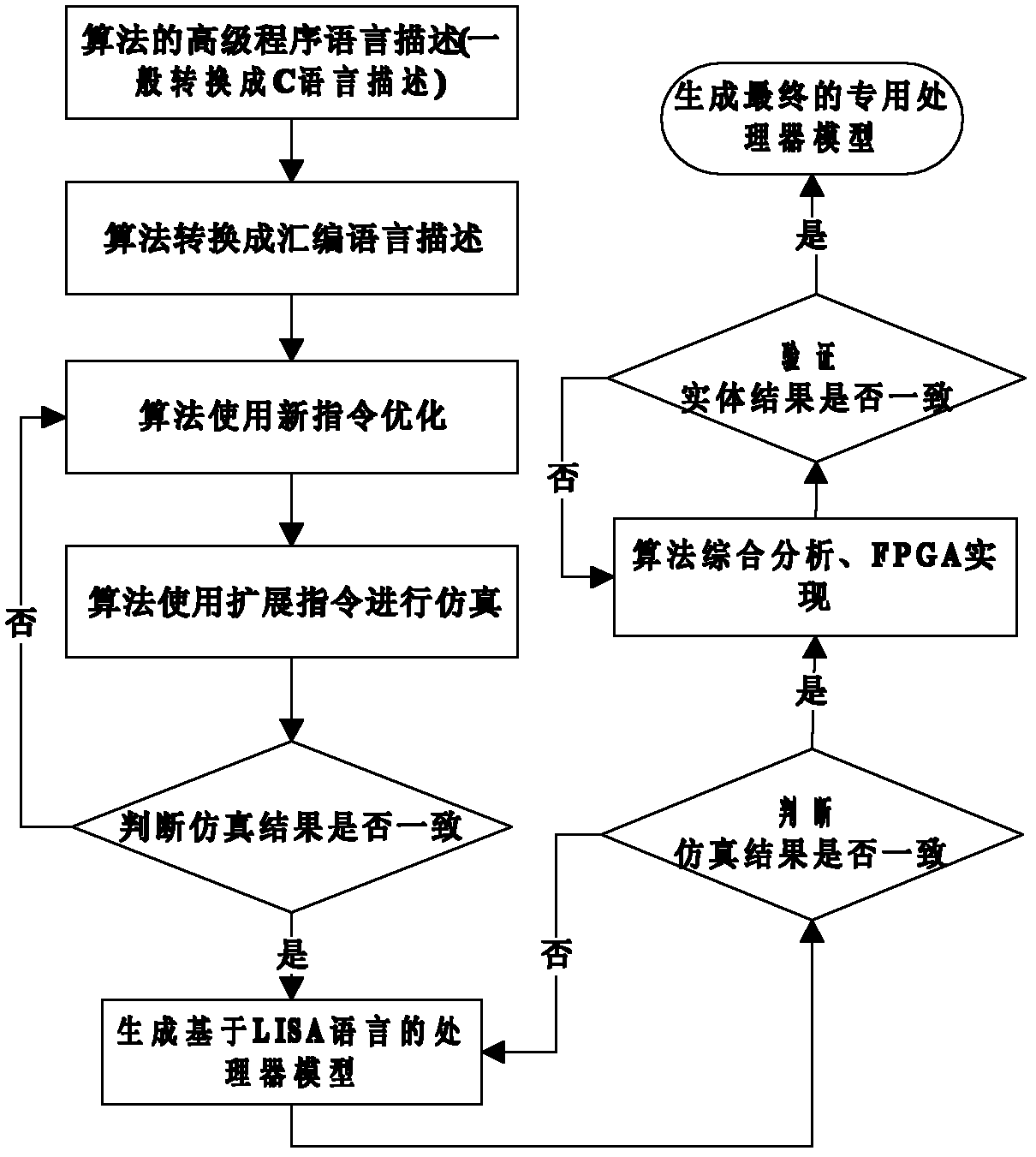
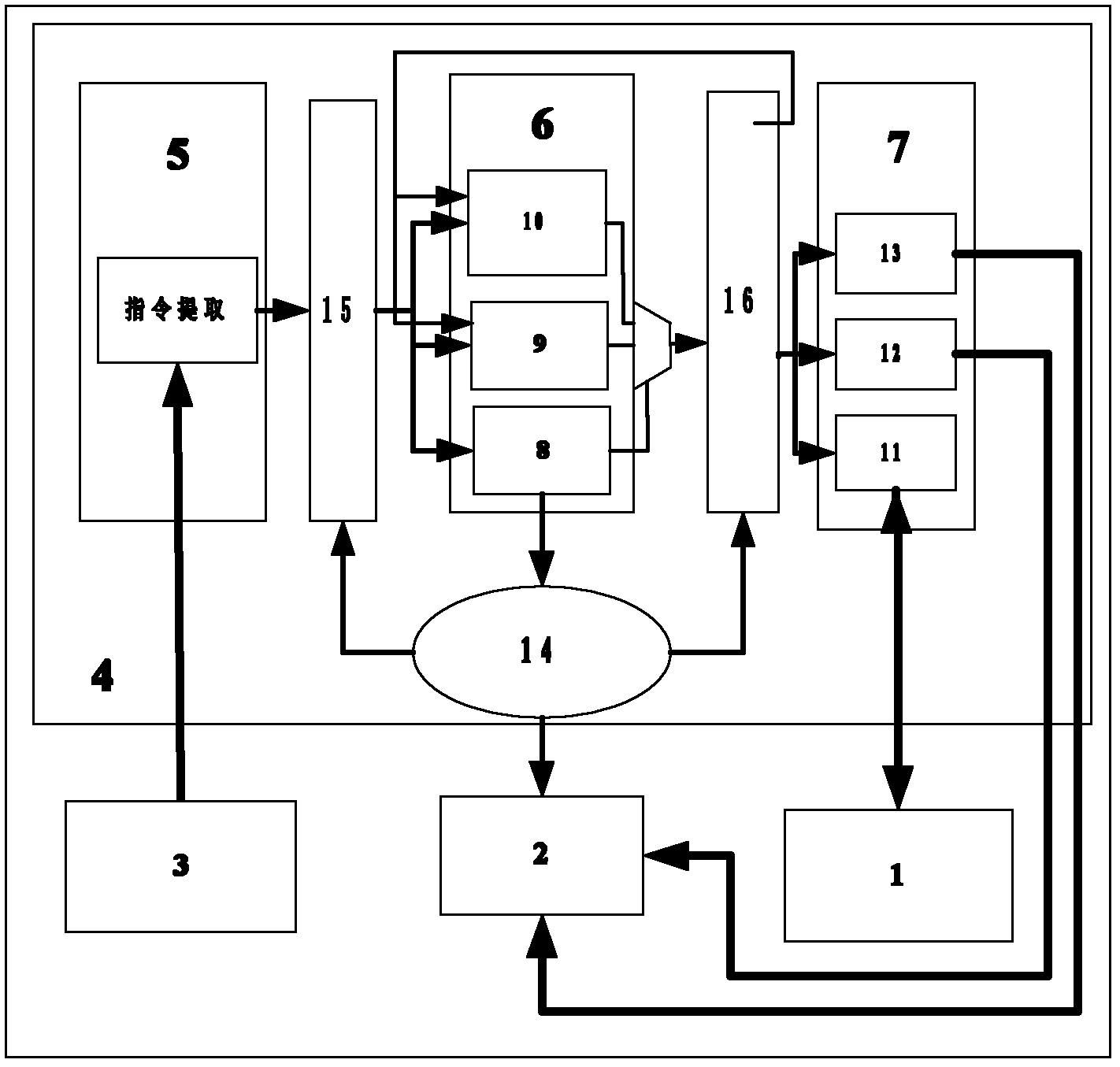
Instruction optimization method and processor for AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) symmetric encryption algorithm
InactiveCN102221990AImprove execution efficiencySave storage spaceMachine execution arrangementsCode spaceAssembly line
The invention discloses an instruction optimization method and an instruction processor for AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) symmetric encryption algorithm, wherein the instruction processor mainly comprises four parts of: a data memory, a code memory, a register file and an assembly line, wherein the assembly line comprises an addressing unit, a decoding unit, an execution unit and an assembly line controller. With the instruction optimization method, in the aspect of execution efficiency is reduced by 57.3x% relative to an ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) processor in a way that the clock periodicity required for AES_ASIP performing AES encryption algorithm is counted through periodic emulation, so that the execution efficiency of the algorithm is greatly improved; and in the aspect of code space, the instruction code occupies 783 bytes of memory space on the ARM processor, while the instruction code on the AES_ASIP just occupies 416 bytes of memory space, so that 46.6x% of code memory space is saved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
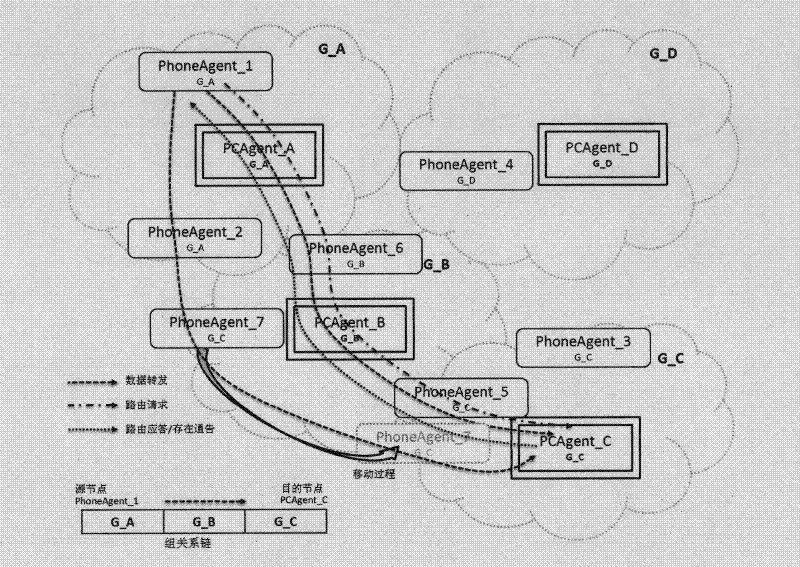
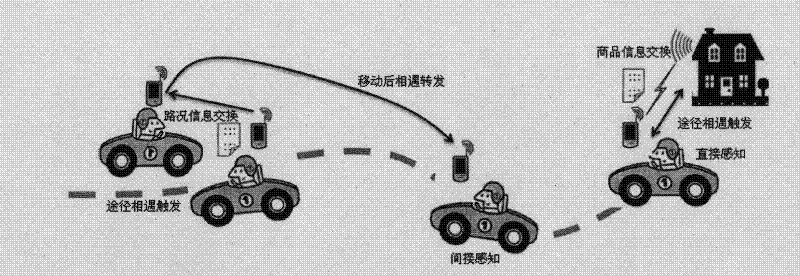
Site sensing communication method of ad hoc wireless network
InactiveCN102413536AImprove communication reliabilityNetwork topologiesWireless mesh networkCode space
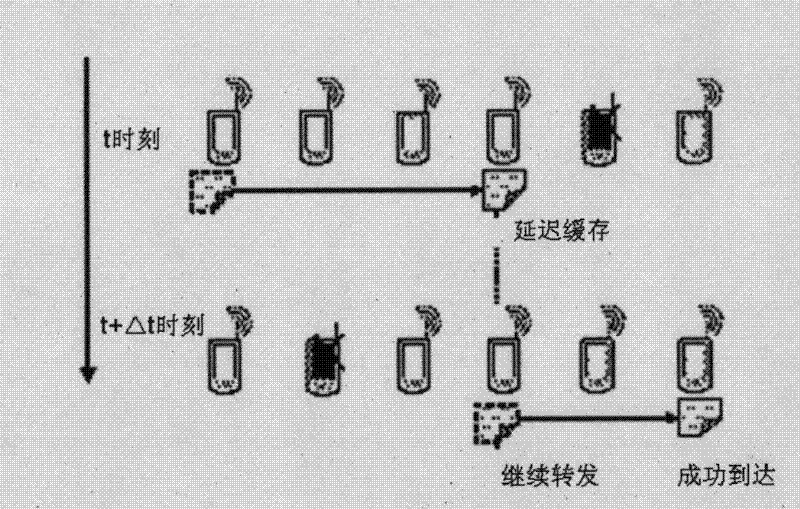
The invention discloses a site sensing communication method of an ad hoc wireless network, which comprises the following steps that: 1) all mobile and fixed entities in the communication process are equipped with wireless terminals and set as an ad hoc mode, and directly communicate in a point-to-point peer mode without needing a base station or center to transfer; 2) when the entity terminals encounter, the identity is recognized through neighbor discovery, and if the restriction stipulated by the route is met, mutual communication is triggered; otherwise, the entity terminals can delay the transfer and cache the held information until the restriction is met or time is up to discard the information; and 3) a node of each entity terminal can issue the public information thereof or the place thereof; and when the entity terminals encounter, data information interaction is performed according to the communication process so as to realize mutual sensing and recognition of the entities on the site. The method disclosed by the invention has a small code space, a high information transfer submission rate and high expandability and invulnerability, realizes point-to-point direct sensing communication, can obtain the site information around the actual environment of each terminal, and can be applied to the induction of traffic information.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Wireless network equipment upgrading program and communication data encryption method
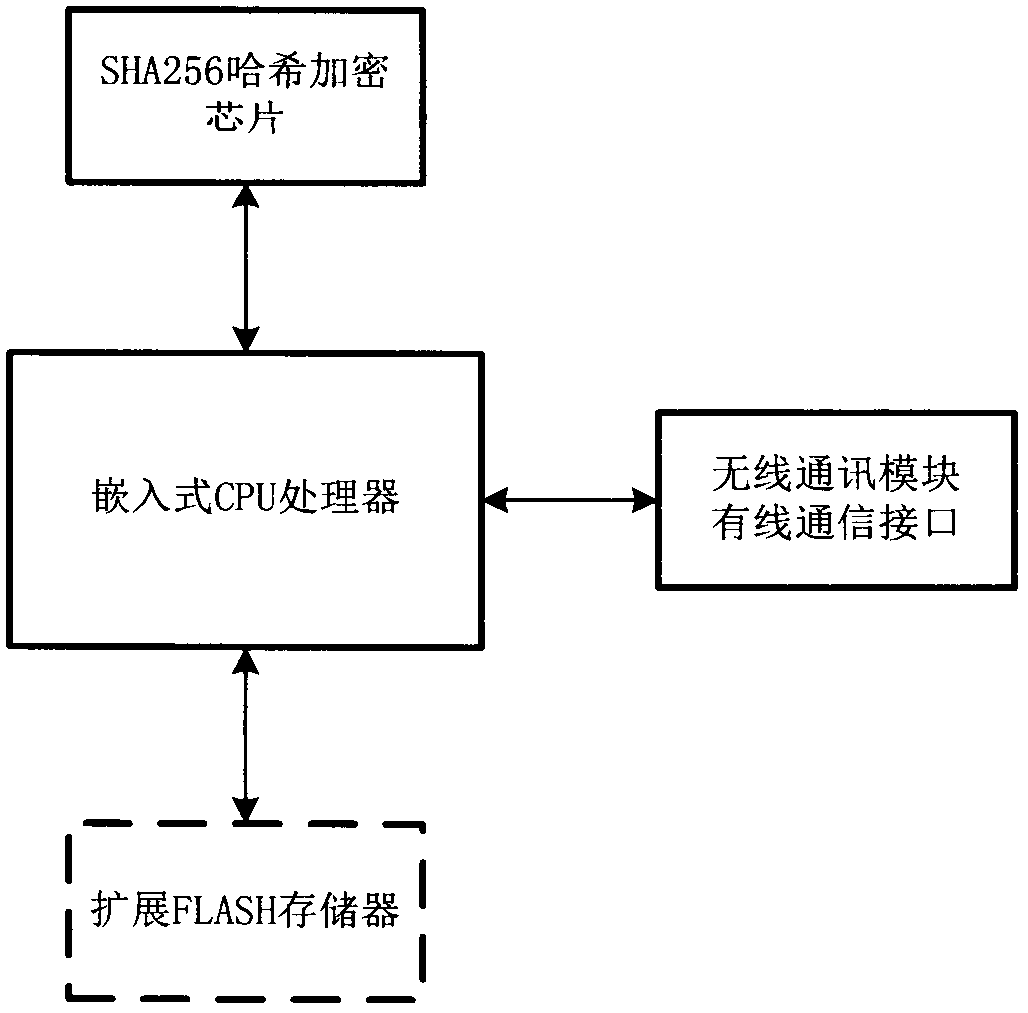
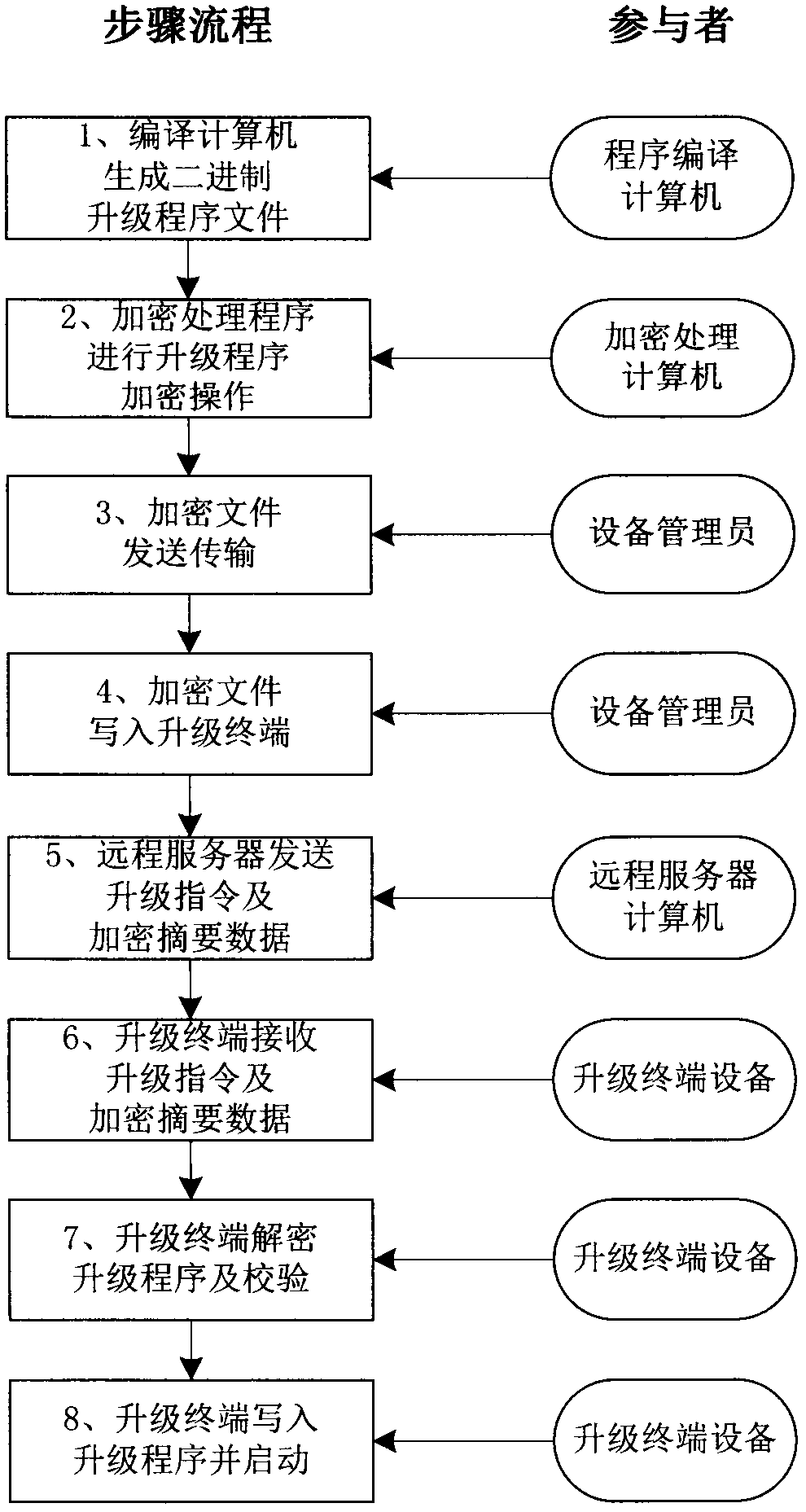
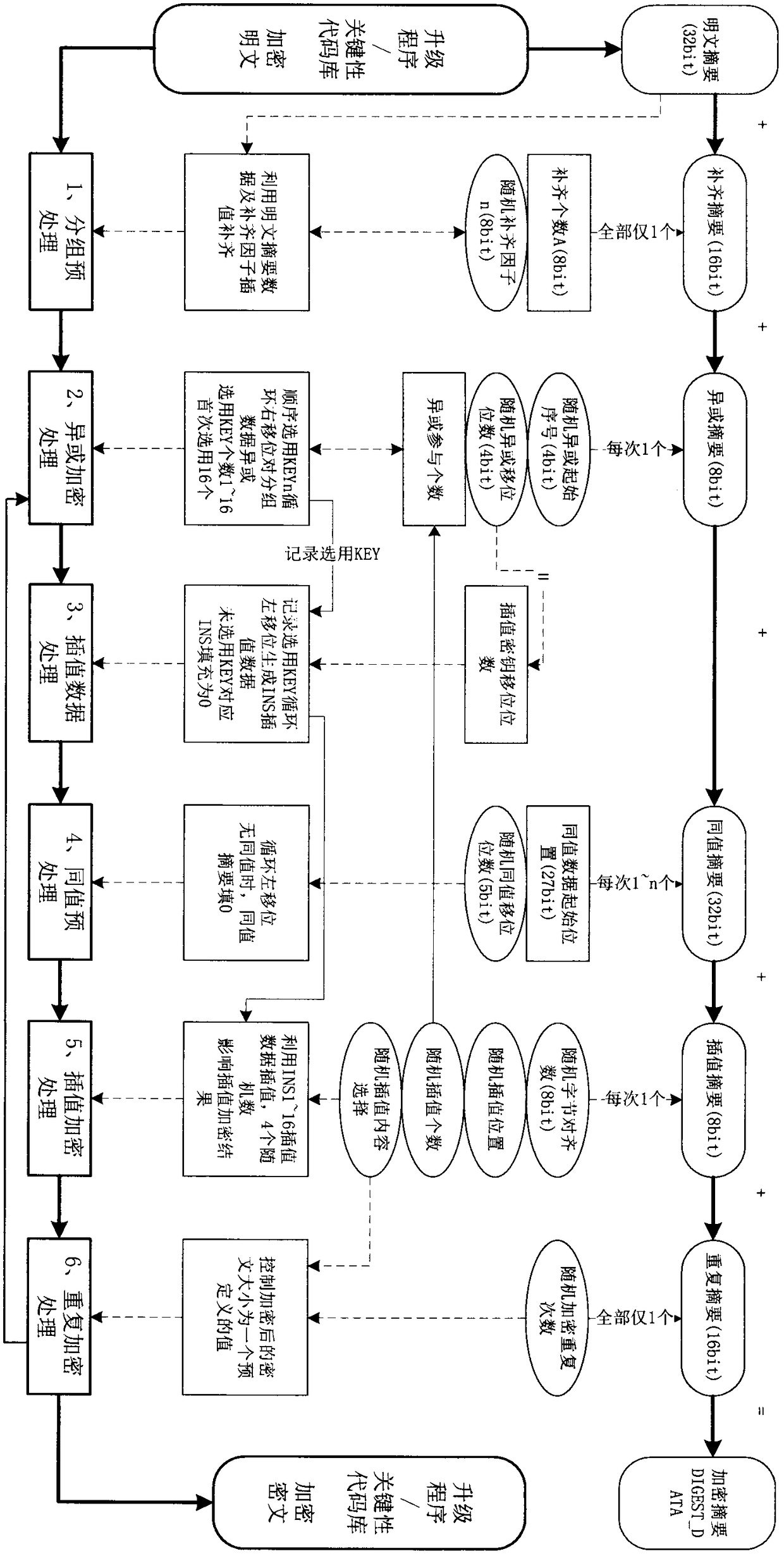
ActiveCN109429222AEnsure safetyGuaranteed confidentialityKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareCode space
The invention discloses a wireless network equipment upgrading program and communication data encryption method. Through simple grouping, XOR, shifting, interpolation processing and an SHA256 hash algorithm, encryption of an embedded upgrading program is realized; and high-reliability encryption of data blocks of the upgrading program is realized by using a cryptographic digest algorithm. When thegrouping, the XOR, the shifting and the interpolation processing are carried out in a program data encryption process each time, numerous random numbers are used; the random numbers and other key data form a cryptographic digest; a ciphertext of the upgrading program can be decrypted only through the cryptographic digest; and encrypted ciphertexts and cryptographic digests generated by encryptingthe same data in different encryption processing devices at different moments are different. According to the method, relatively few code spaces of a CPU of wireless network equipment are occupied; the requirement on the operation speed of the CPU is relatively low; the encryption of the upgrading program and the communication data can be realized by adopting the cheap CPU; and the security of equipment communication and the integrity of the data are ensured.
Owner:叶毅嵘
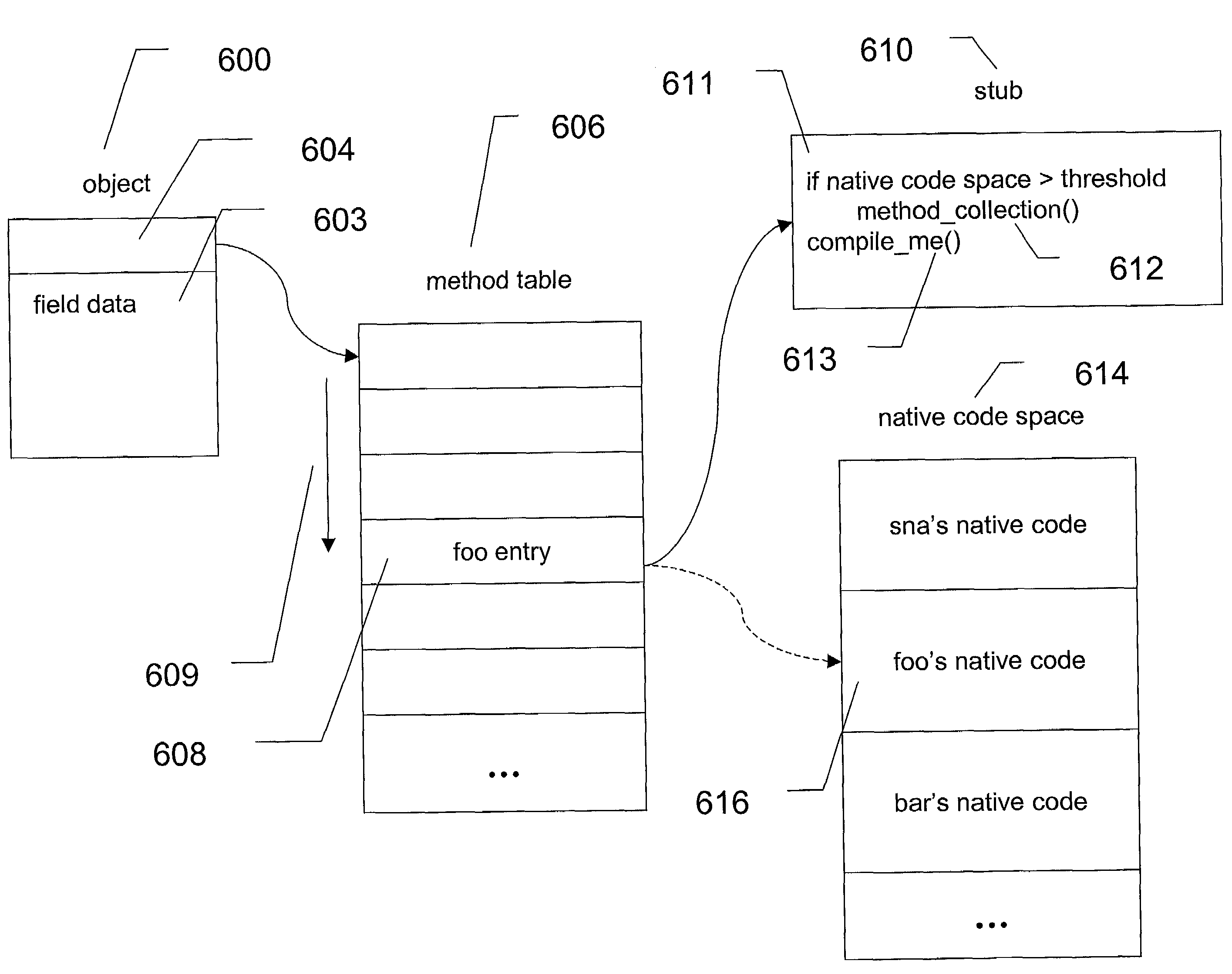
Method and system of controlling dynamically compiled native code size
Space occupied by native code associated with a first method and stored within a native code space is reclaimed by determining whether the native code space exceeds a threshold in response to the invocation of a second method. Once the determination is made, byte code is compiled into native code associated with the second method and the native code associated with the first method may be reclaimed. In one embodiment, this reclamation occurs in response to a determination that the threshold has been exceeded and that the first method is inactive. In another embodiment, reclamation occurs in response to a determination that the threshold has been exceeded and that the first method is cold.
Owner:BEIJING XIAOMI MOBILE SOFTWARE CO LTD
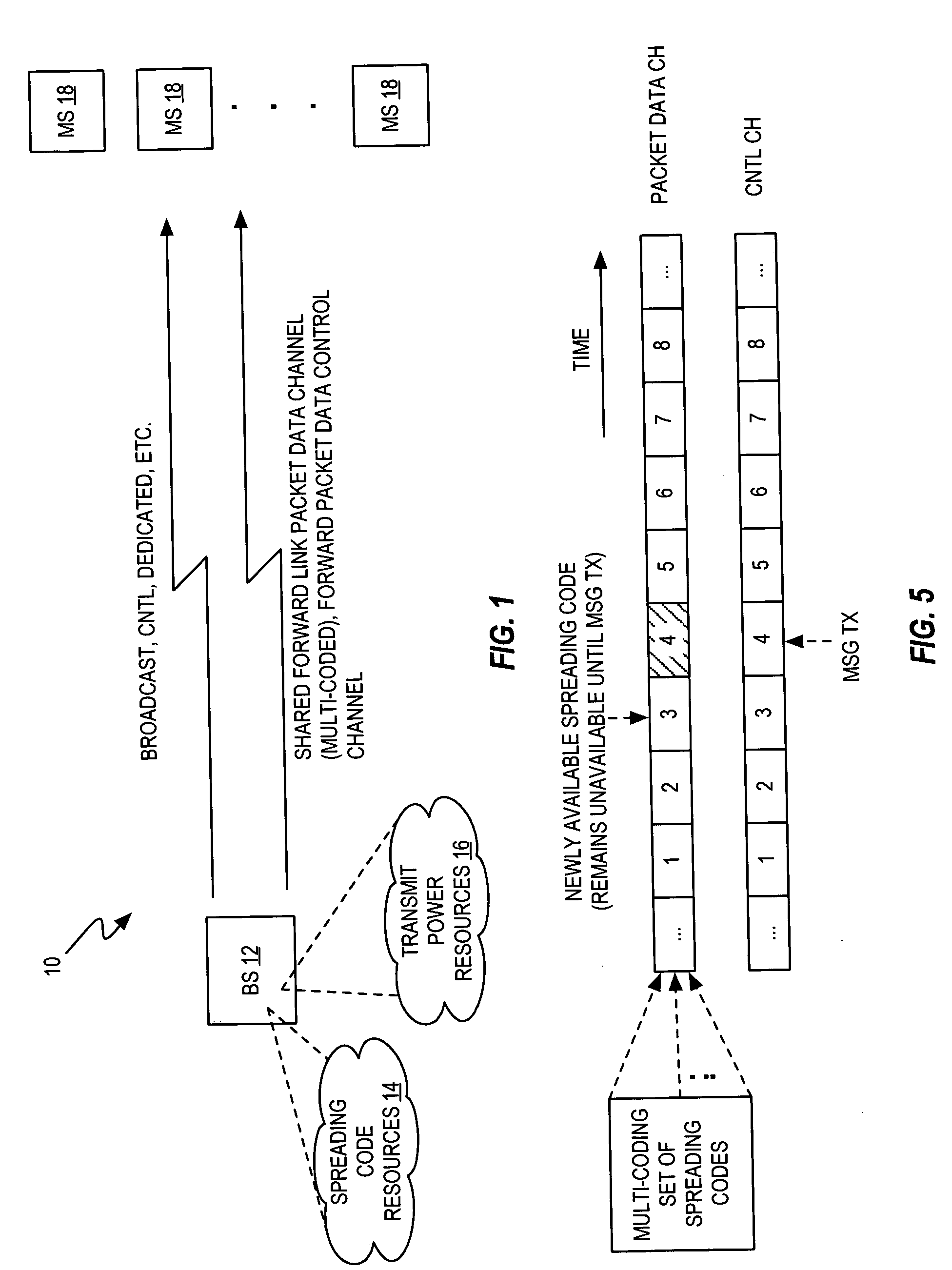
Optimal frequency of walsh mask broadcast for forward high-speed packet data channels
InactiveUS20050195759A1Increase net gainImprove data throughputRadio transmission for post communicationOrthogonal multiplexCode spaceMobile station
A base station in a wireless communication network multi-codes a shared packet data channel using a continually changing set of spreading codes, and dynamically updates the transmission frequency of messages identifying the spreading codes to be used for that multi-coding based on tracking the net gain in data throughput for the shared channel that is obtained by transmitting such messages. In a 1xEV-DV network context, for example, a Walsh code in the defined Walsh code space that is not contiguous with the Walsh codes currently allocated to multi-coding the 1xEV-DV Forward Packet Data Channel (F-PDCH) generally remains unavailable for such use until an updated Walsh Mask Broadcast (WMB) message is transmitted to the mobile stations being served on the F-PDCH. The base station thus is configured to determine the frequency at which to send such messages and thereby make the unavailable codes available for multi-coding use.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
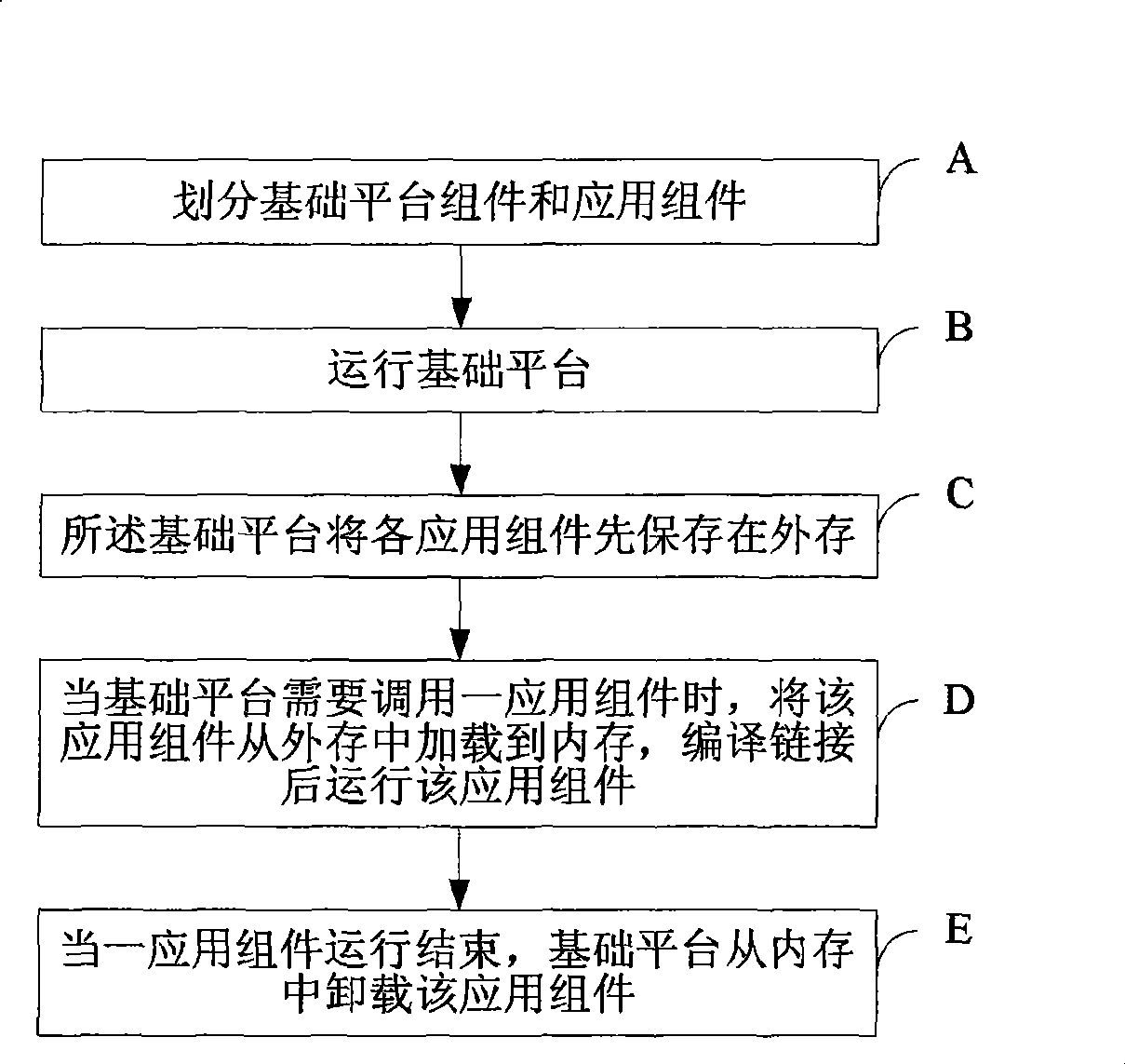
Method and apparatus for implementing dynamic loading in embedded real-time operating system
The invention discloses a method and device for implementing dynamic loading in an embedded type real-time operating system, the method comprises: dividing an application module into a basic platform component and a plurality of application components; operating the basic platform comprising a basic platform component, a database schema defining language DDL component and a real-time operating system RTOS; firstly storing the application components in an external memory by the basic platform; loading the application components from the external memory into the internal memory when the basic platform need call one application component, and operating the application component after translating and editing links; uninstalling the application component from the internal memory by the basic platform, when the application component operation is closed. The invention can save code memory space, reduce product cost and complete more functions on the same code space.
Owner:JIANGSU DAHAI INTELLIGENT SYST
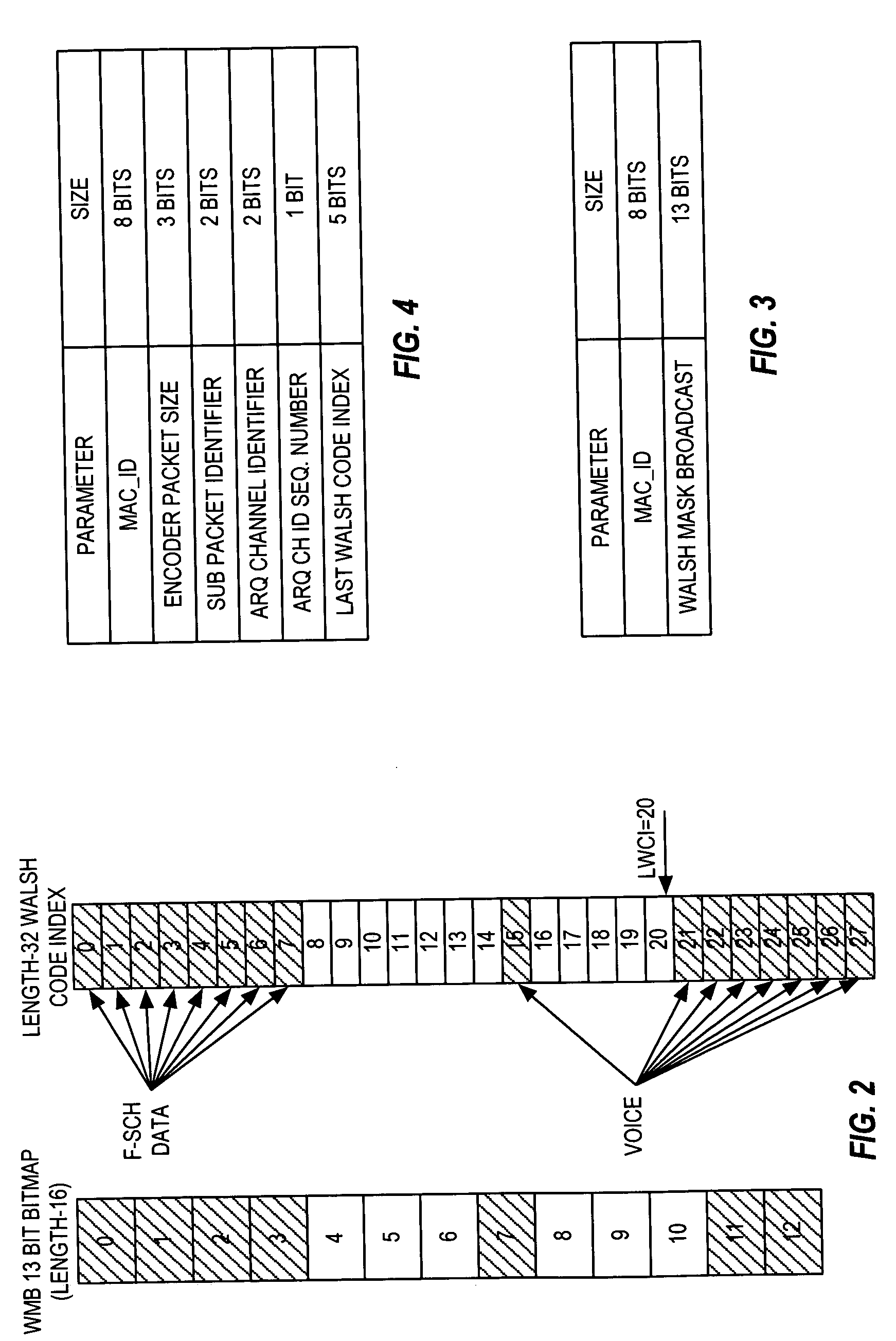
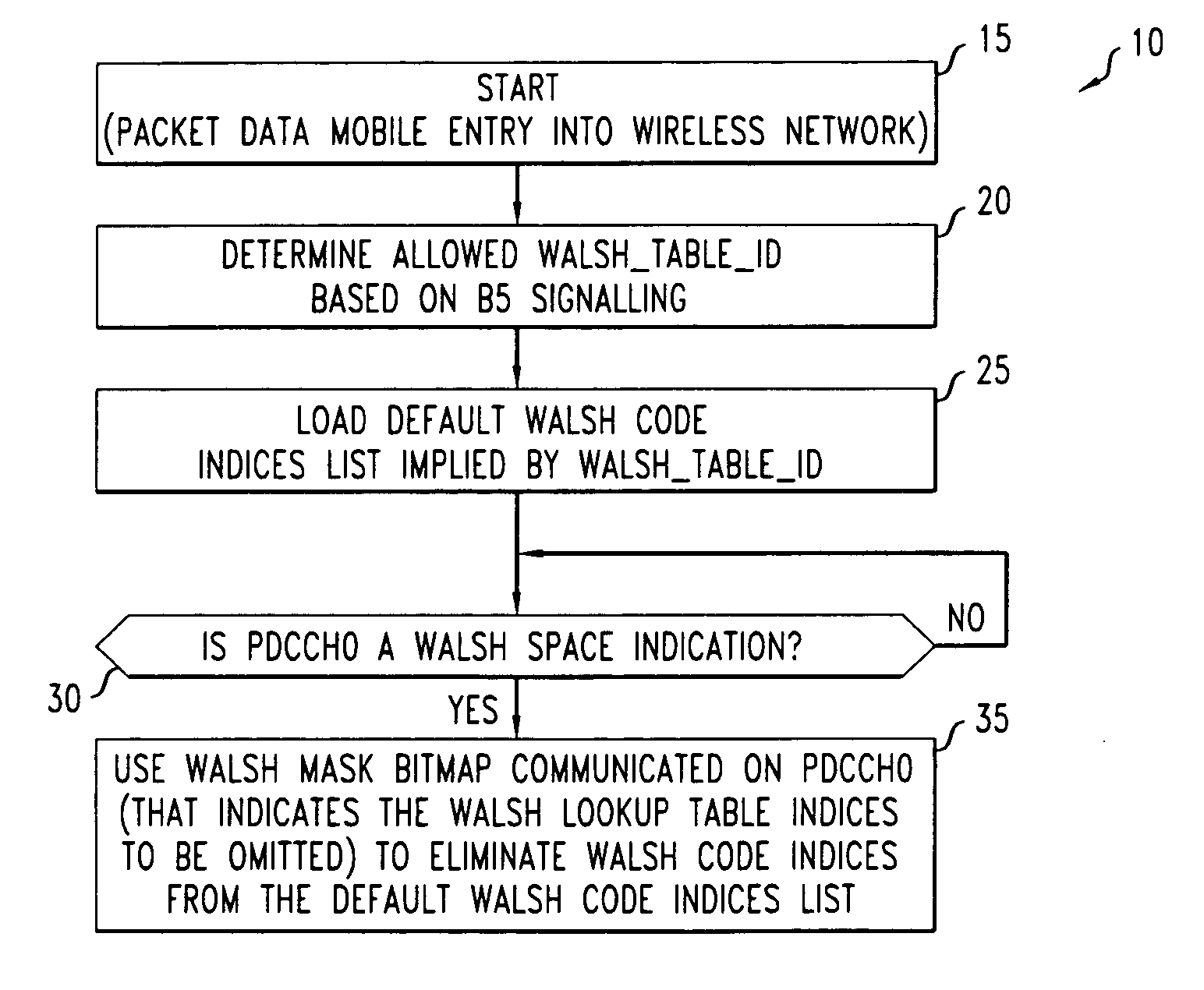
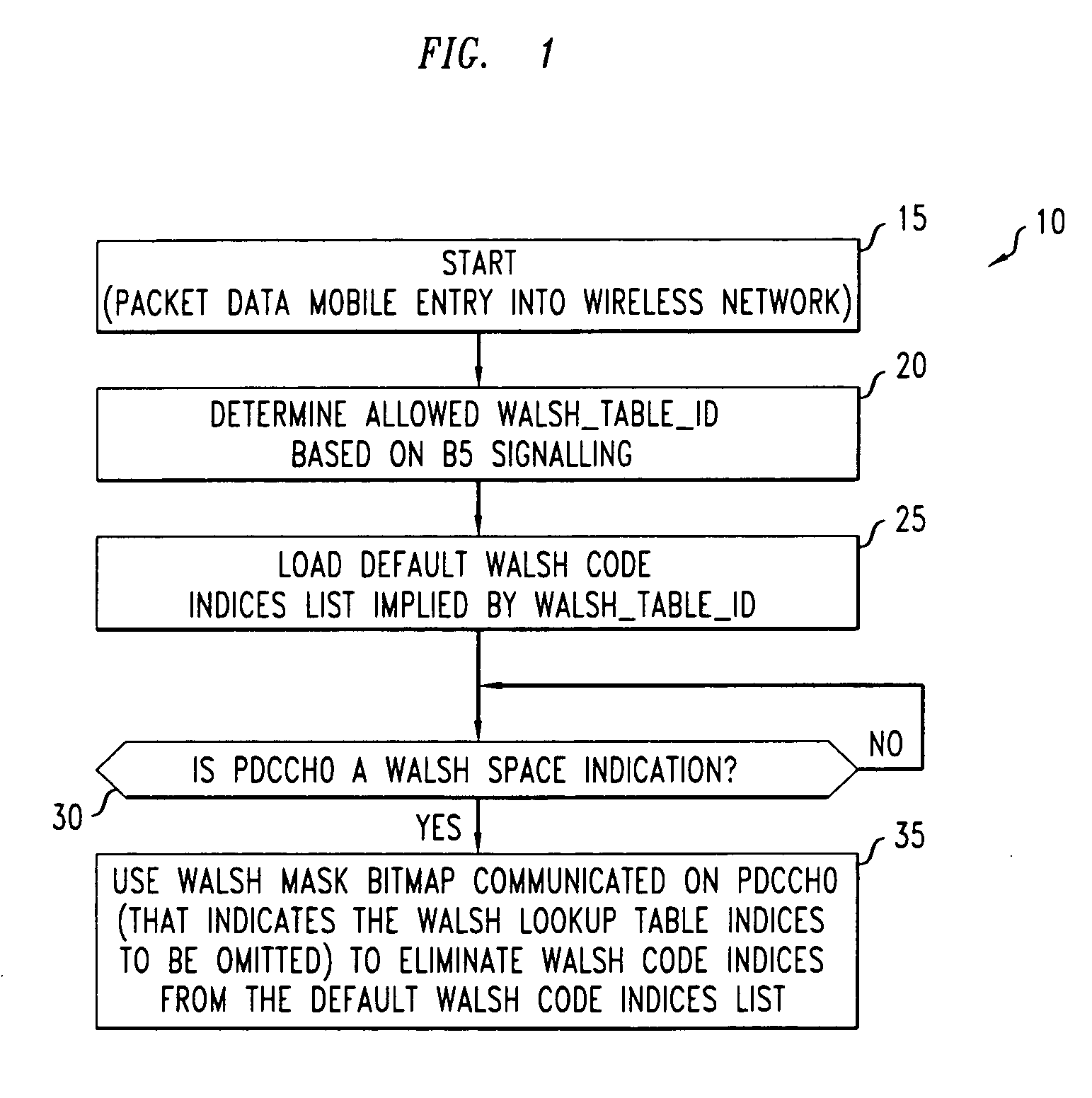
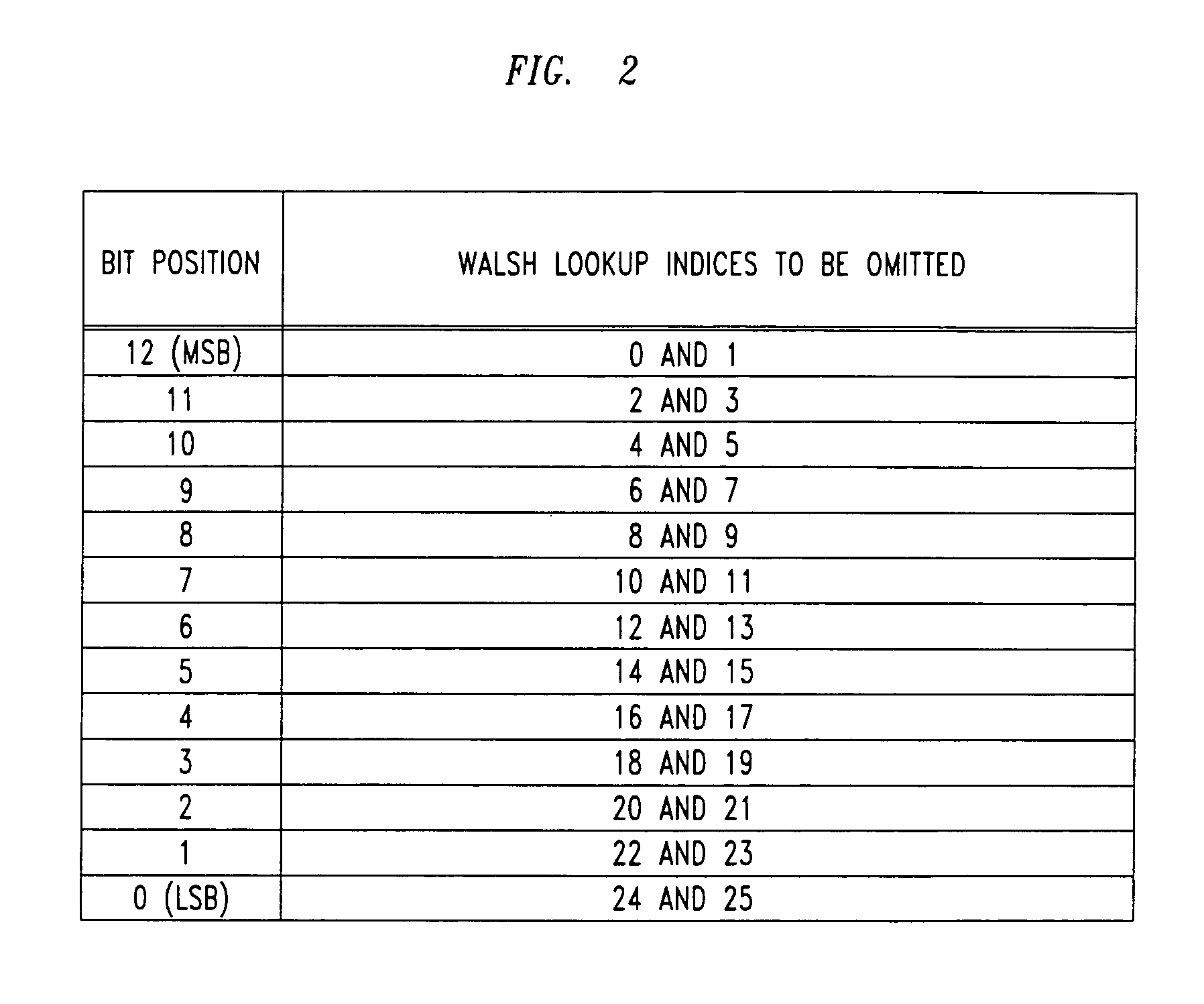
Method for identifying walsh code space
A method of identifying the available Walsh code space. The method includes at least one wireless unit receiving a Walsh code-based signal. The Walsh code-based signal may be transmitted by a base station, for example. The Walsh code-based signal may be realized by 13 bits, for example, corresponding to indices in a look-up table within the mobile unit that should not be employed. Thereafter, the wireless unit may determine the remaining Walsh code space. This determination step may include ascertaining which indices in the look-up table are relevant, and thusly, removing irrelevant indices. Subsequently, the step of determining the remaining Walsh code space may include examining the Walsh Table ID signal received from the base station to identify the remaining Walsh codes space.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
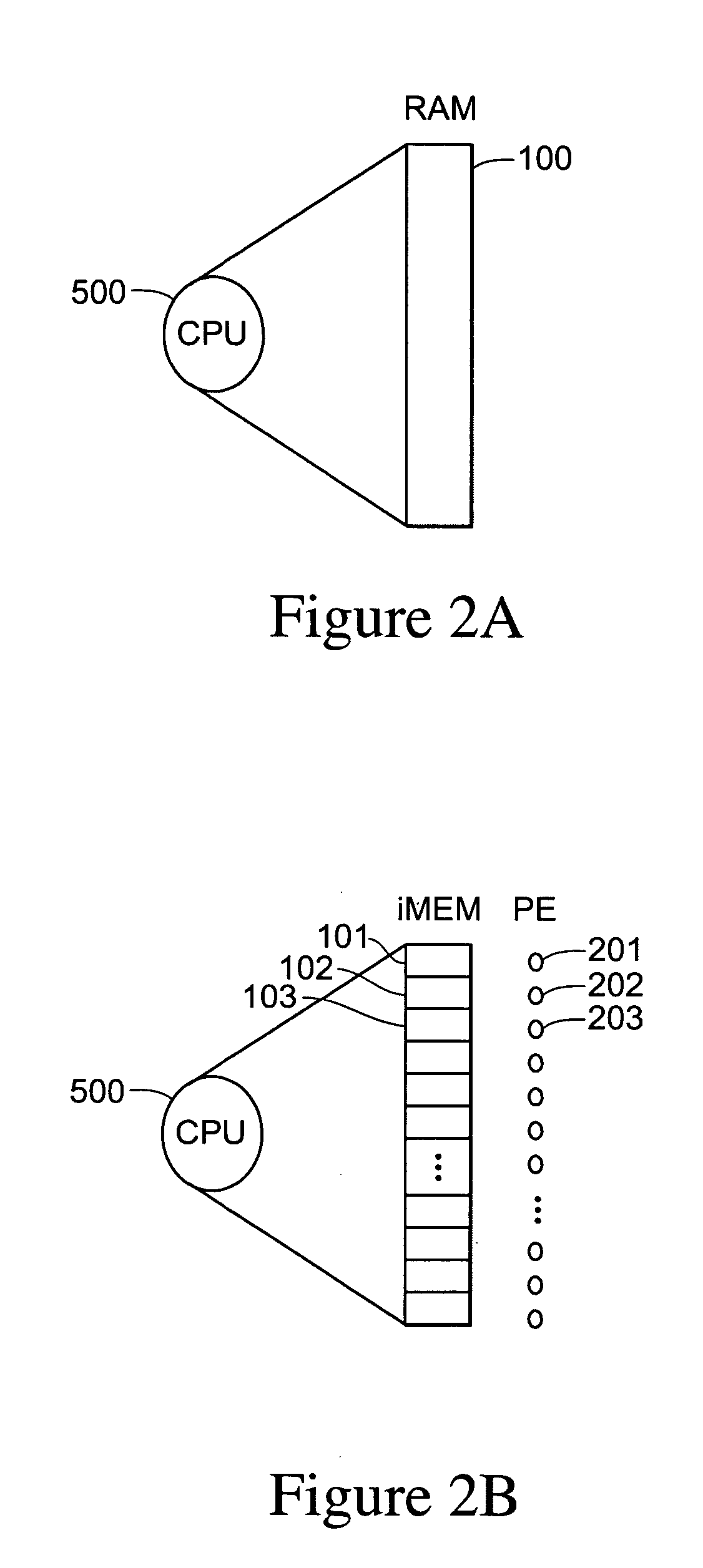
iMEM ASCII architecture for executing system operators and processing data operators
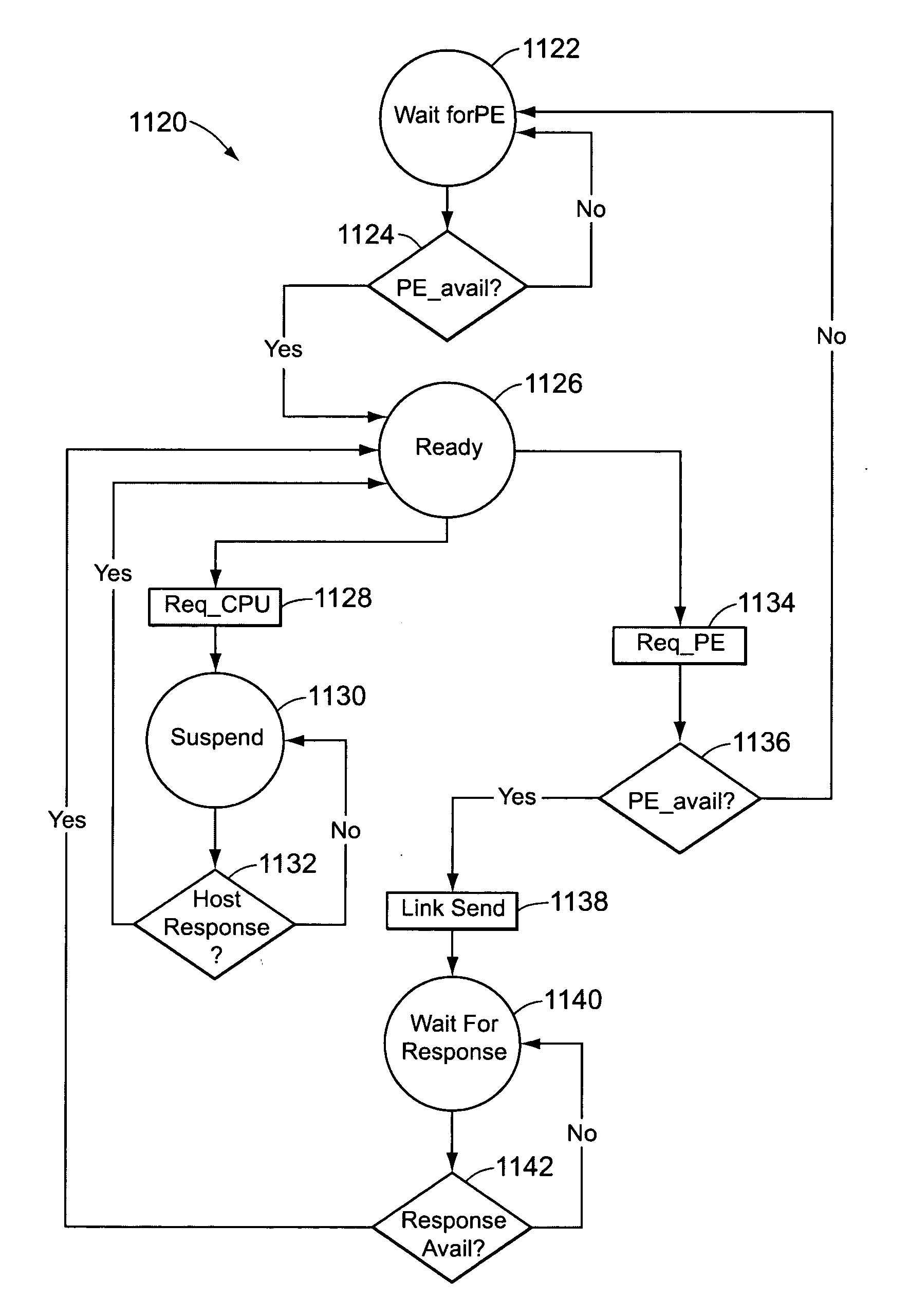
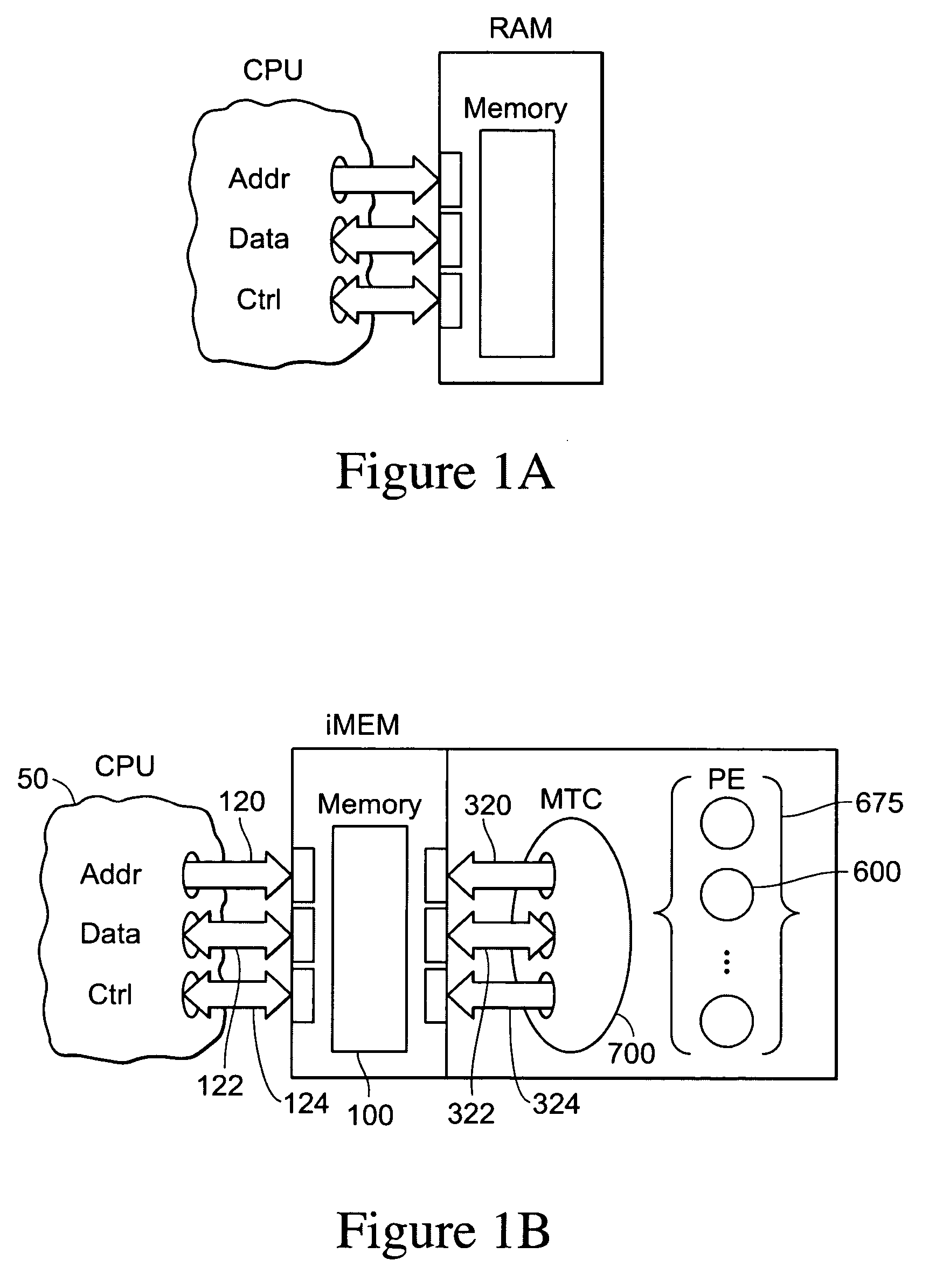
InactiveUS20050223384A1Extraordinary capabilityEconomic benefitProgram initiation/switchingSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationCode spaceLogical operations
A computing system that includes a number of processing elements, a memory and a multi-task controller is disclosed. The computing system operates on ASCII instructions which includes a set of ASCII operators. The operators include both ASCII data operators and ASCII system operators. The system operators include characters for specifying a request to obtain resources, to perform a task switch, to perform a task suspension, to execute a branch, to transfer results of an operation into a task data register, to transfer data into a processing element, to record the current location of instruction execution in the task code space, to treat a sequence of symbols as a group, and to perform an output function. Data operators include characters for specifying a request to perform arithmetic and logical operations on data.
Owner:KLINGMAN REVOCABLE TRUST
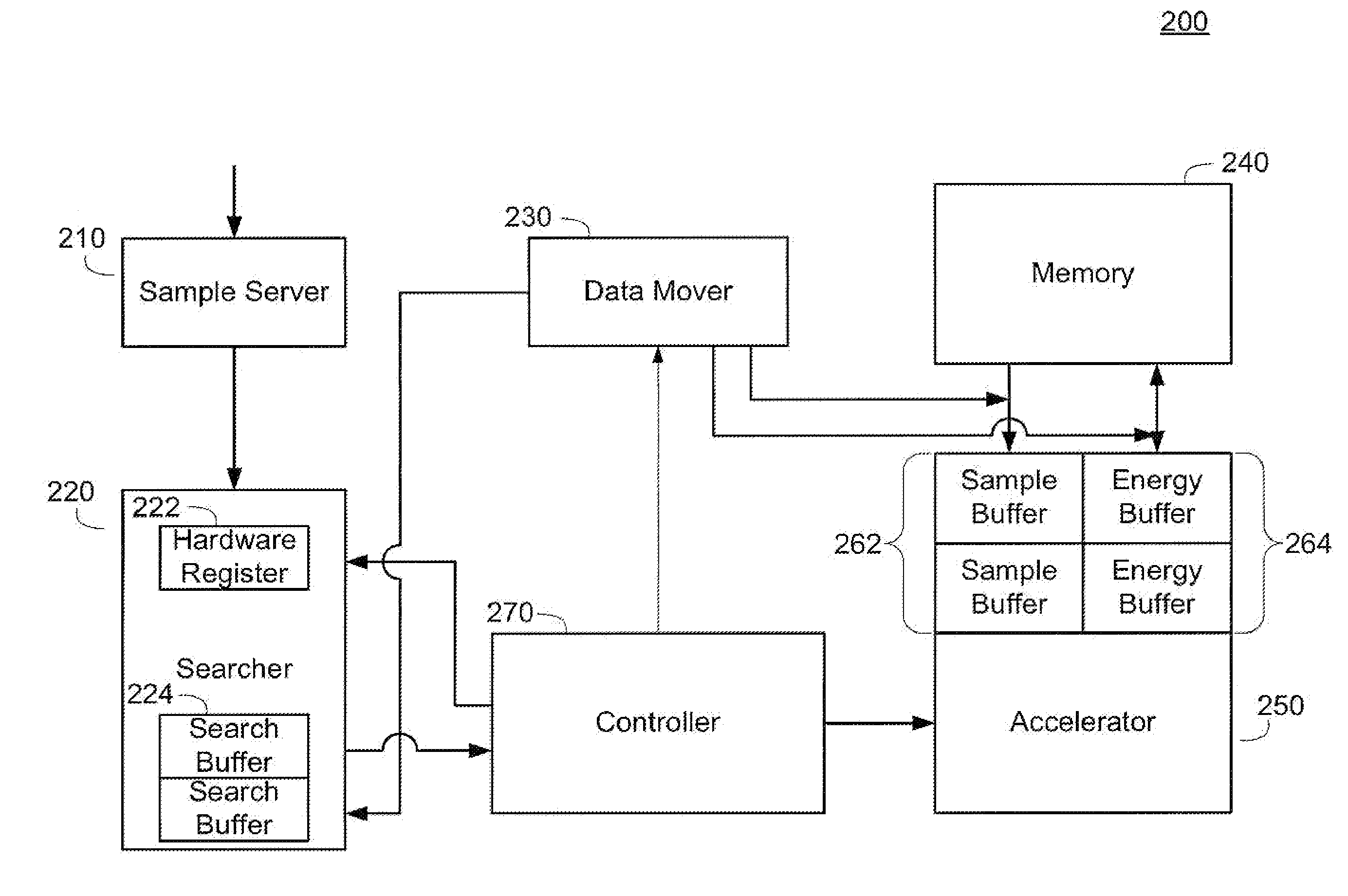
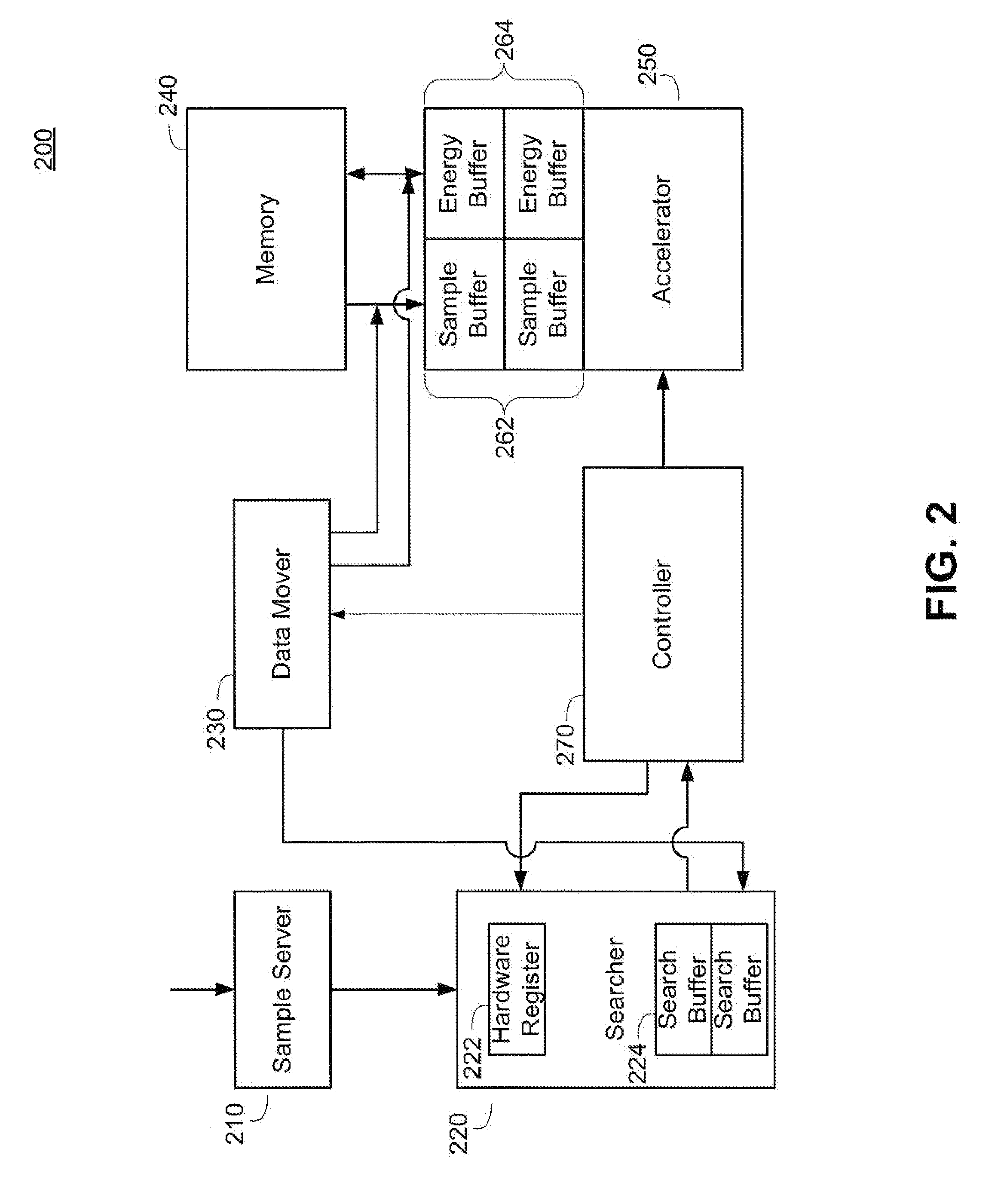
Method And Apparatus For Code Space Search In A Receiver
Apparatus and methods of implementing code space search of received signals are described herein. A code space search is implemented as a searcher that perform a subtask that is dynamically reconfigurable at each boundary of an initial integration time. Each particular subtask sets forth a programmable configuration of coherent integration hypothesis that are performed during the initial integration time. The searcher stores the results of the coherent integration hypothesis in a first portion of memory. A search accelerator operates on the initial integration results. The search accelerator can perform coherent integration of various frequency bins of different timing hypothesis, can generate energy values of the coherent integration results, and can generate a non-coherent energy summation. The energy values of the coherent integrations and non-coherent energy summations are stored in a second portion of memory. The ability to reconfigure the subtasks and accelerator operation provides flexibility in search space dimensions.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Biometric fingerprint authentication method based on quantum fuzzy commitment
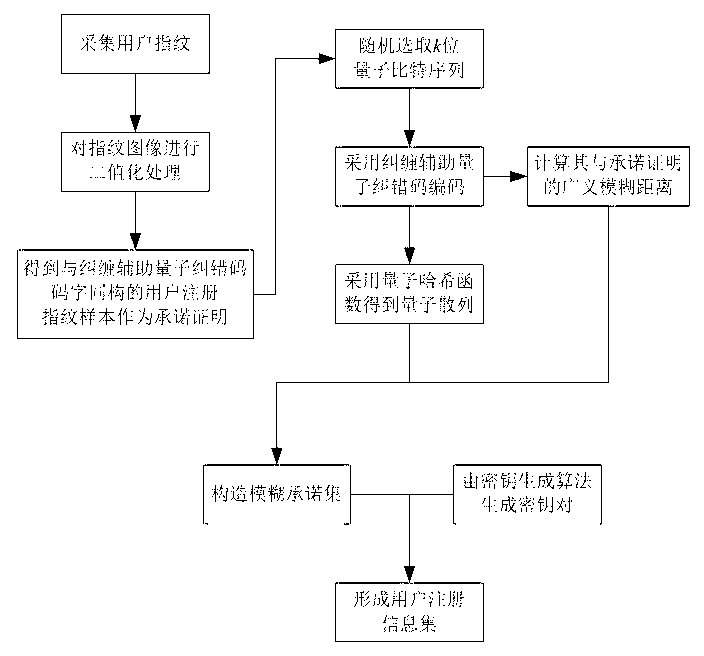
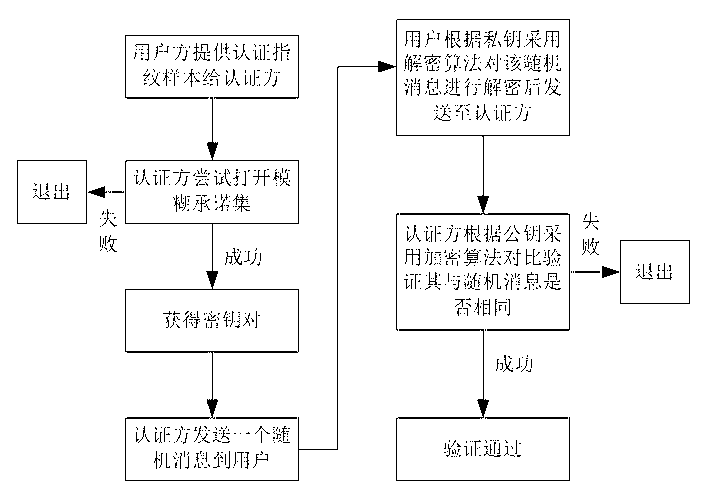
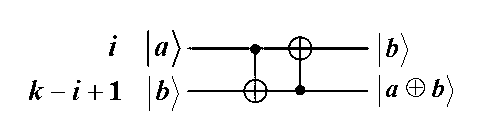
InactiveCN102750529AStrengthen privacy and security protectionObvious superiorityCharacter and pattern recognitionStorage securityBiometric data
The invention discloses a biometric fingerprint authentication method based on a quantum fuzzy commitment, which comprises a registration phase and an authentication phase. The registration phase comprises the following steps of: firstly, constructing a fuzzy commitment set to produce code words required for the commitment phase by using a quantum error correcting code space without self-dual constraint, and applying a noise addition transformation used for fuzzy proving to the code word; and then, constructing a quantum hash algorithm, and mixing, diffusing and encrypting a random quantum sequence so as to realize the security of using one key at one time in the sense of information theory. The authentication phase comprises the following step of opening the fuzzy commitment set by using a quantum fuzzy commitment to obtain random information for decrypting keys Messa. A new quantum fuzzy commitment system is constructed by combing the quantum hash algorithm on the basis of entangling assistant quantum error correcting codes. Compared with other similar fingerprint authentication methods, the biometric fingerprint authentication method based on a quantum fuzzy commitment has prominent advantages in the aspects of storage security and authentication security of biometric data, and the quantum biometric performance and the security of biological template information storage and transmission can be increased.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com