Patents
Literature
570results about "Unequal/adaptive error protection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
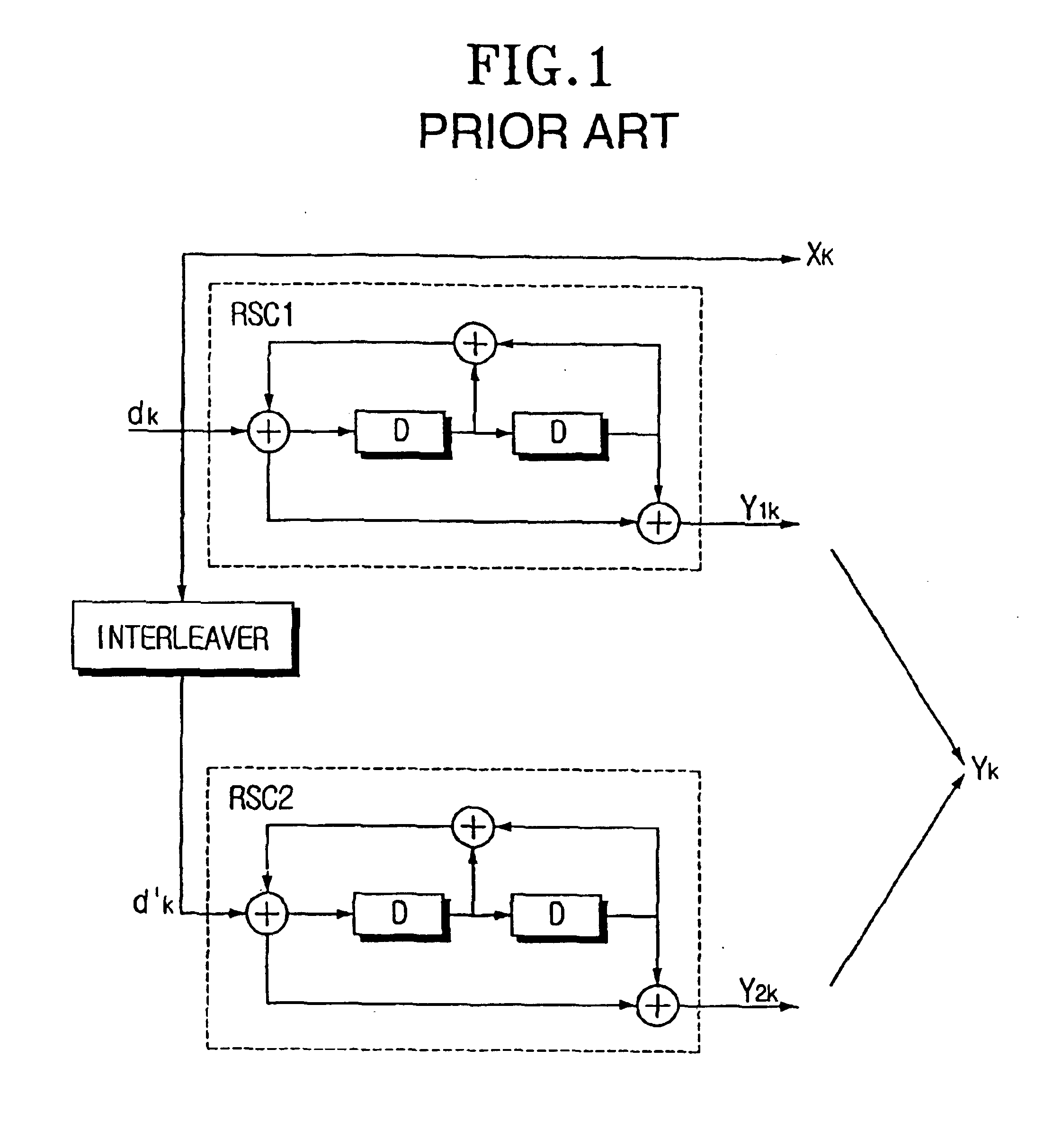
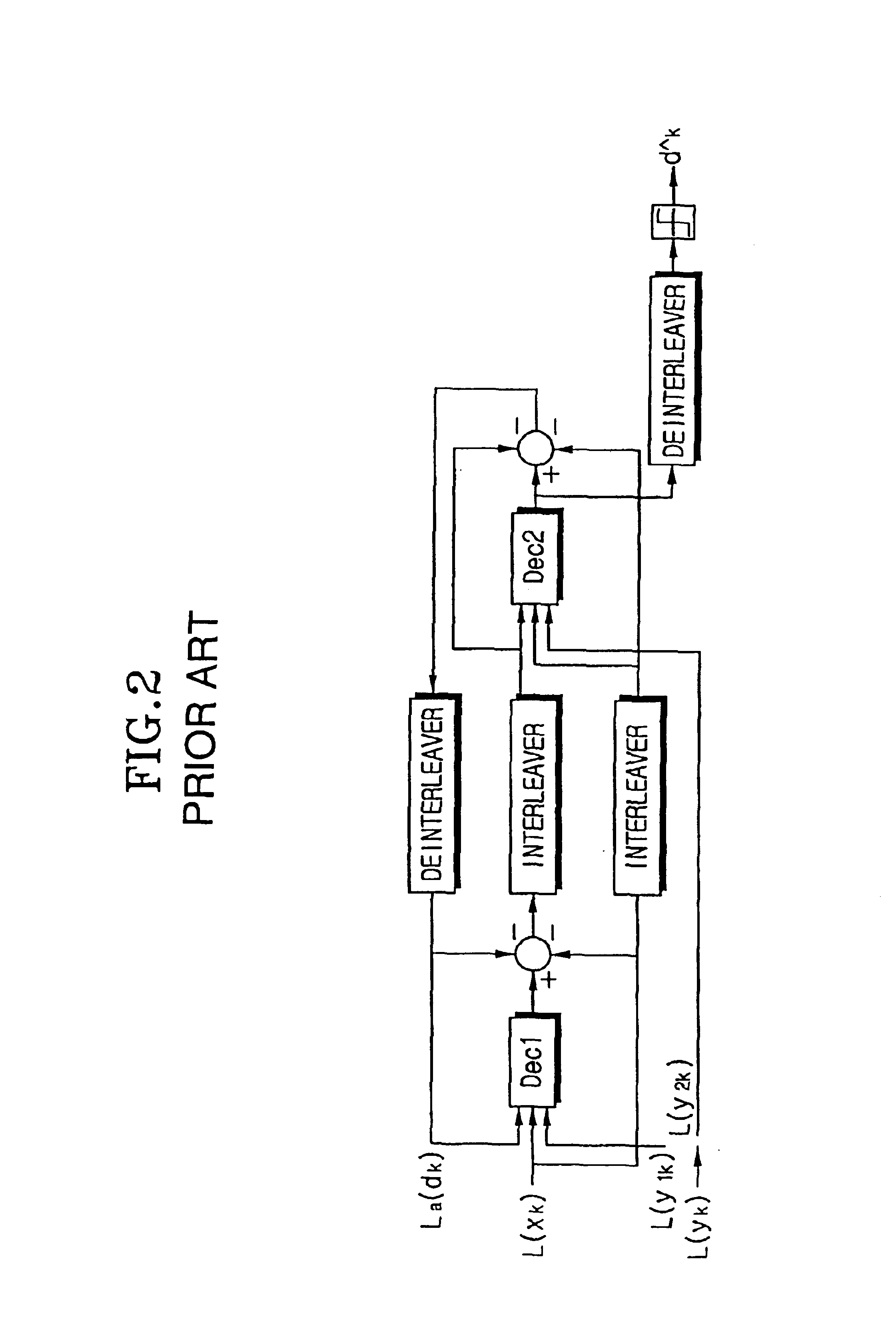
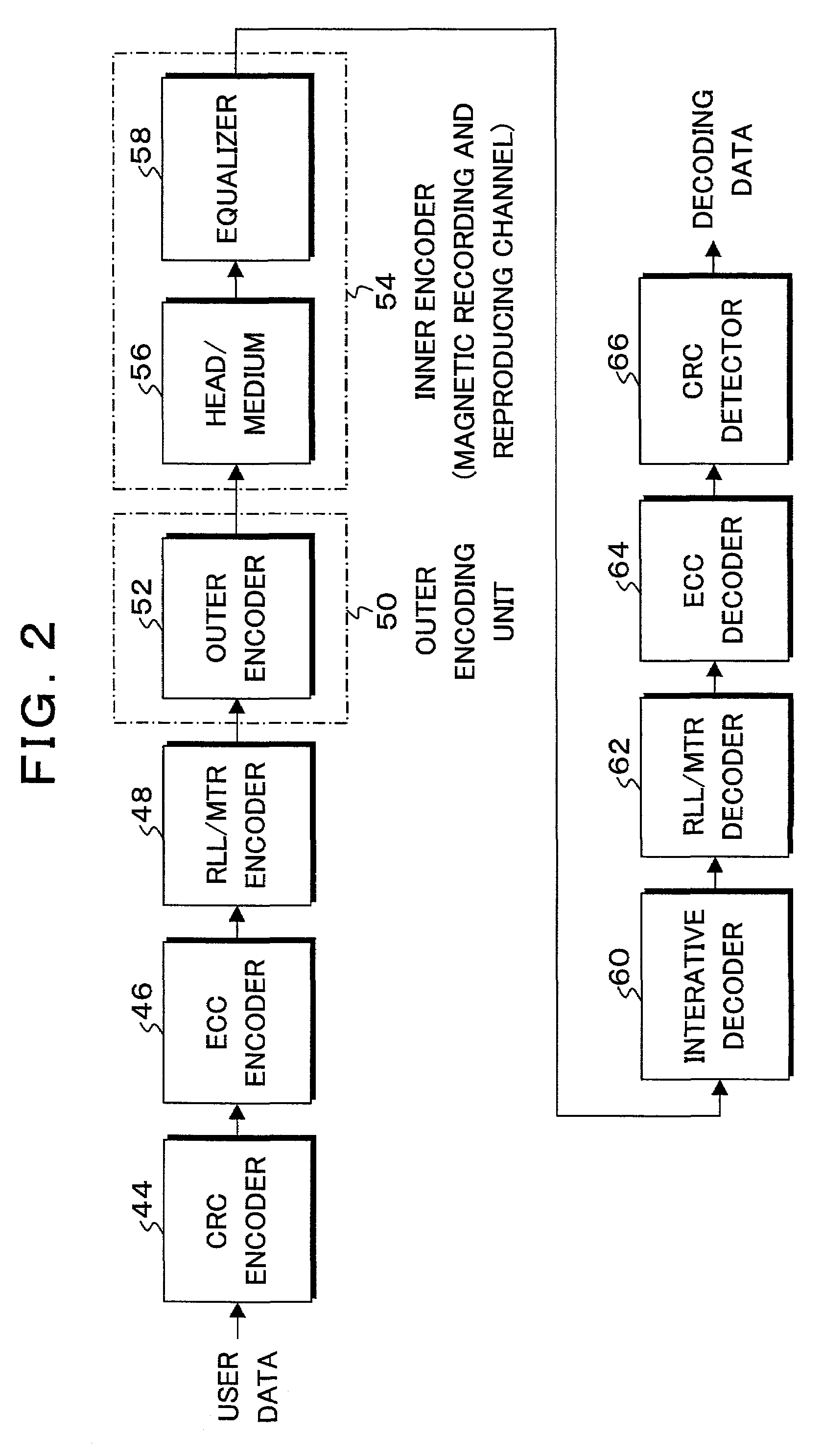
Method and coding means for error-correction utilizing concatenated parity and turbo codes
InactiveUS7093179B2Reduction in rateImprove overall utilizationError preventionError detection/correctionParallel computingTurbo coded
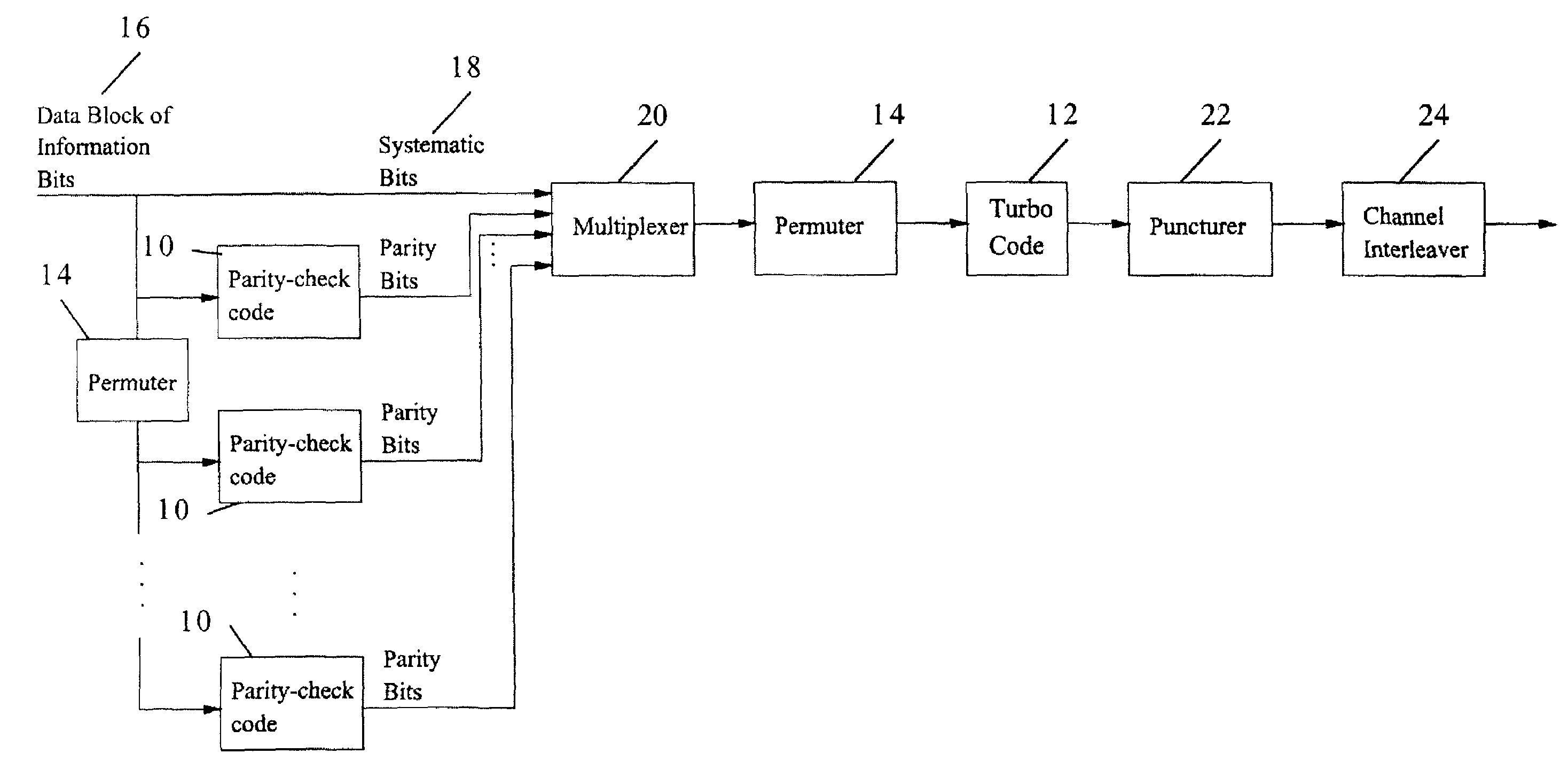
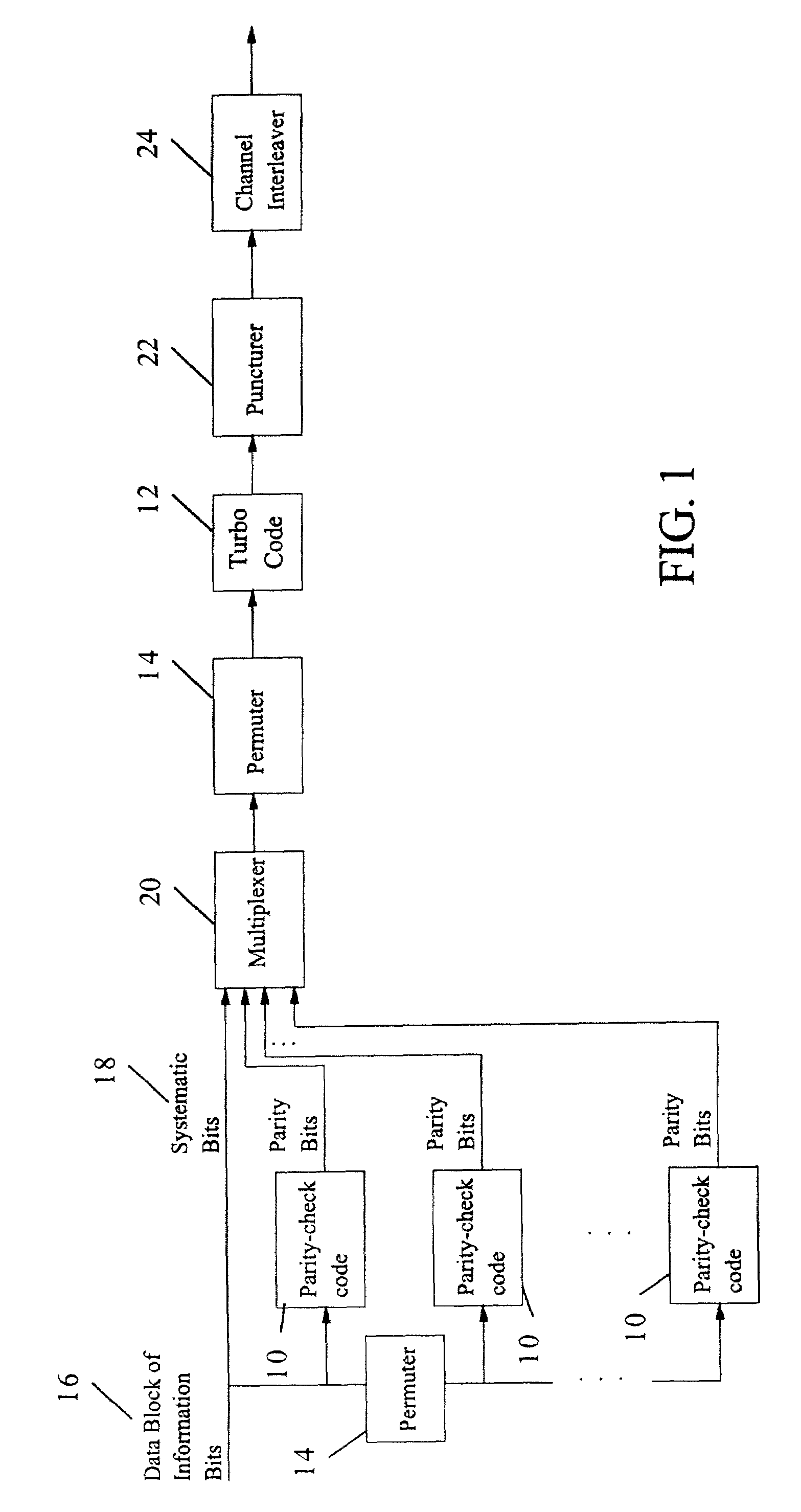
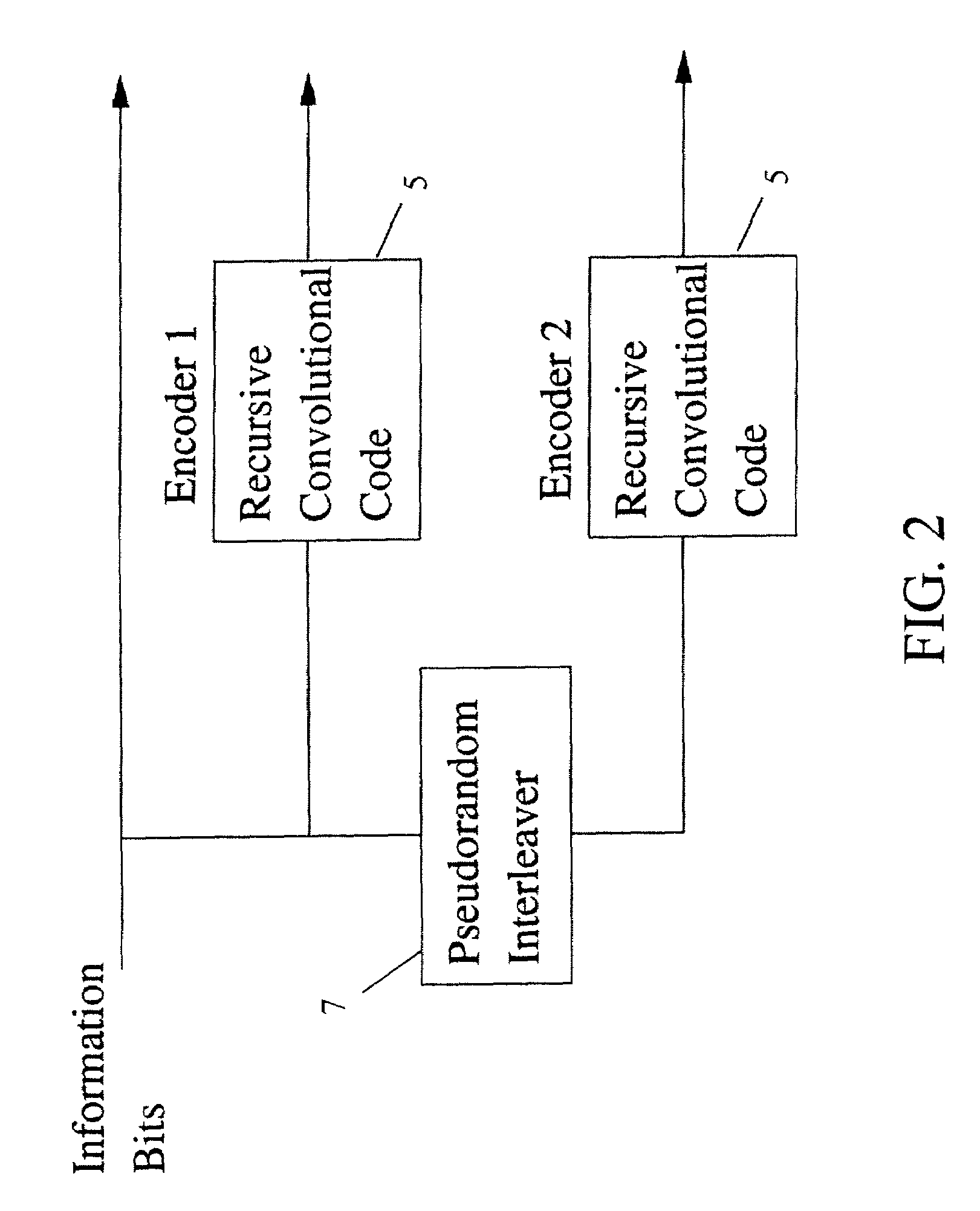
A method and apparatus for encoding and decoding data using an overall code comprising an outer parity-check and an inner parallel concatenated convolutional, or turbo code. The overall code provides error probabilities that are significantly lower than can be achieved by using turbo codes alone. The output of the inner code can be punctured to maintain the same turbo code rate as the turbo code encoding without the outer code. Multiple parity-check codes can be concatanated either serially or in parallel as outer codes. Decoding can be performed with iterative a posteriori probability (APP) decoders or with other decoders, depending on the requirements of the system. The parity-check code can be applied to a subset of the bits to achieve unequal error protection. Moreover, the techniques presented can be mapped to higher order modulation schemes to achieve improved power and bandwidth efficiency.
Owner:FLORIDA UNIV OF A FLORIDA +1
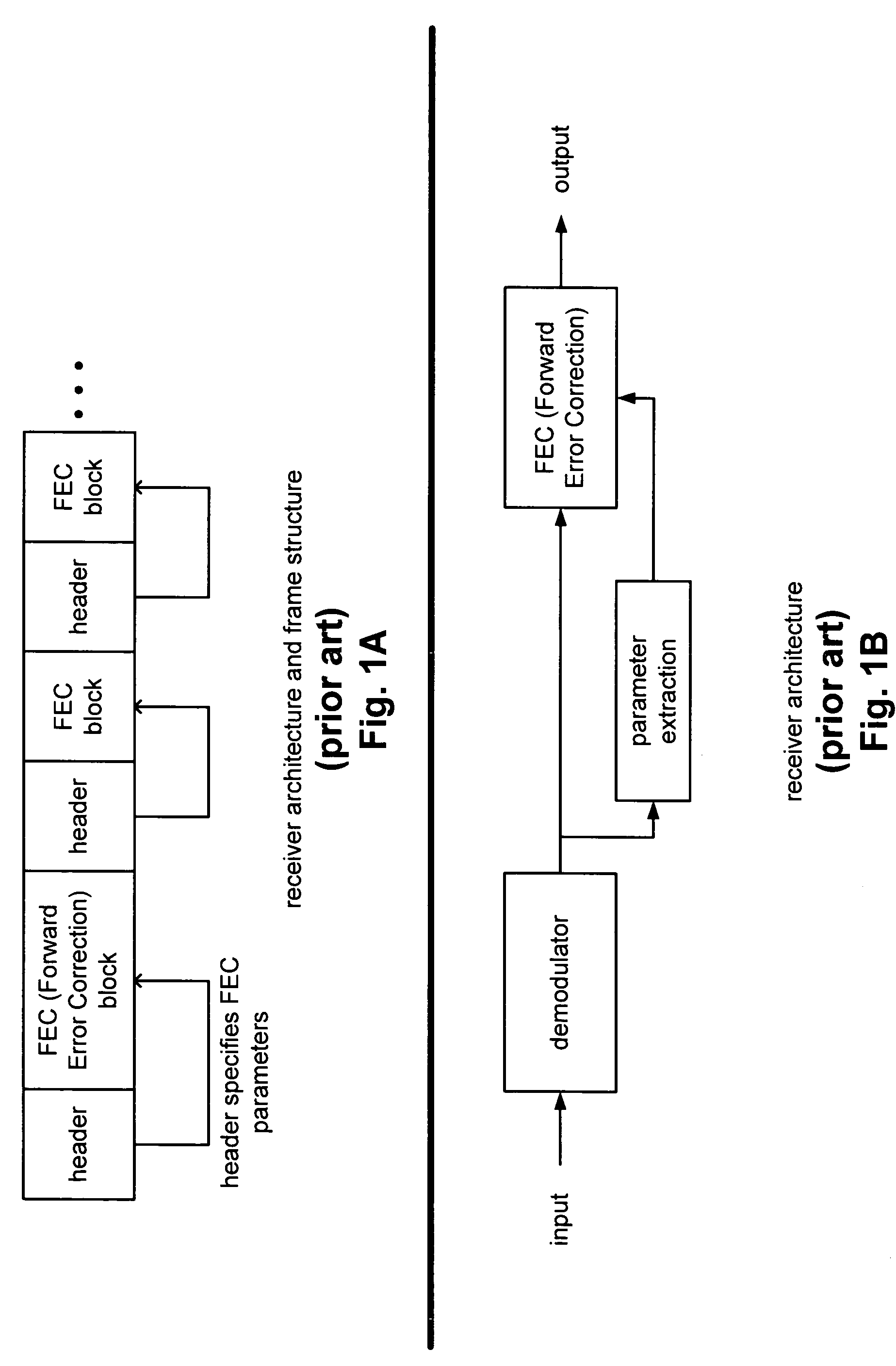
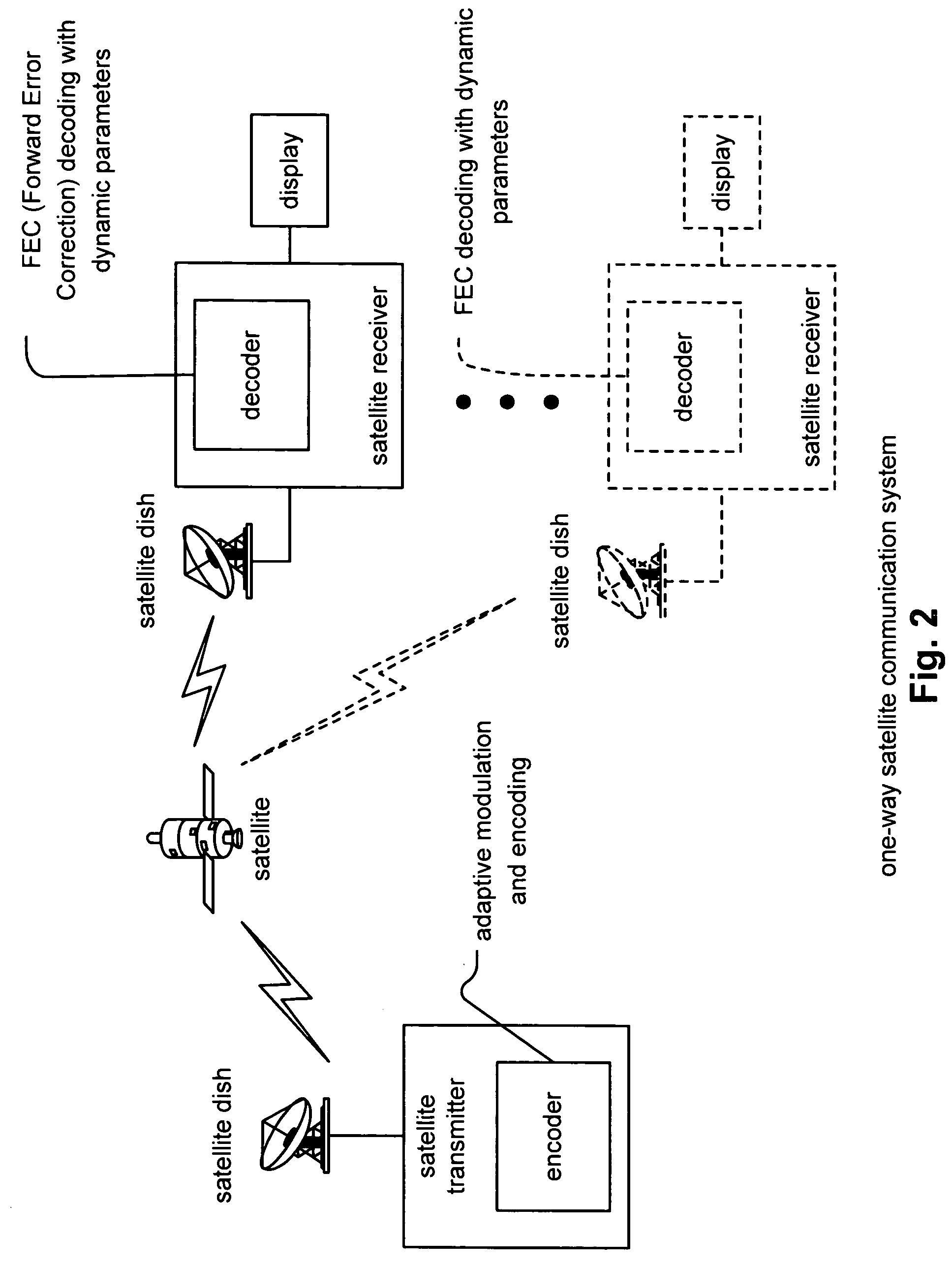
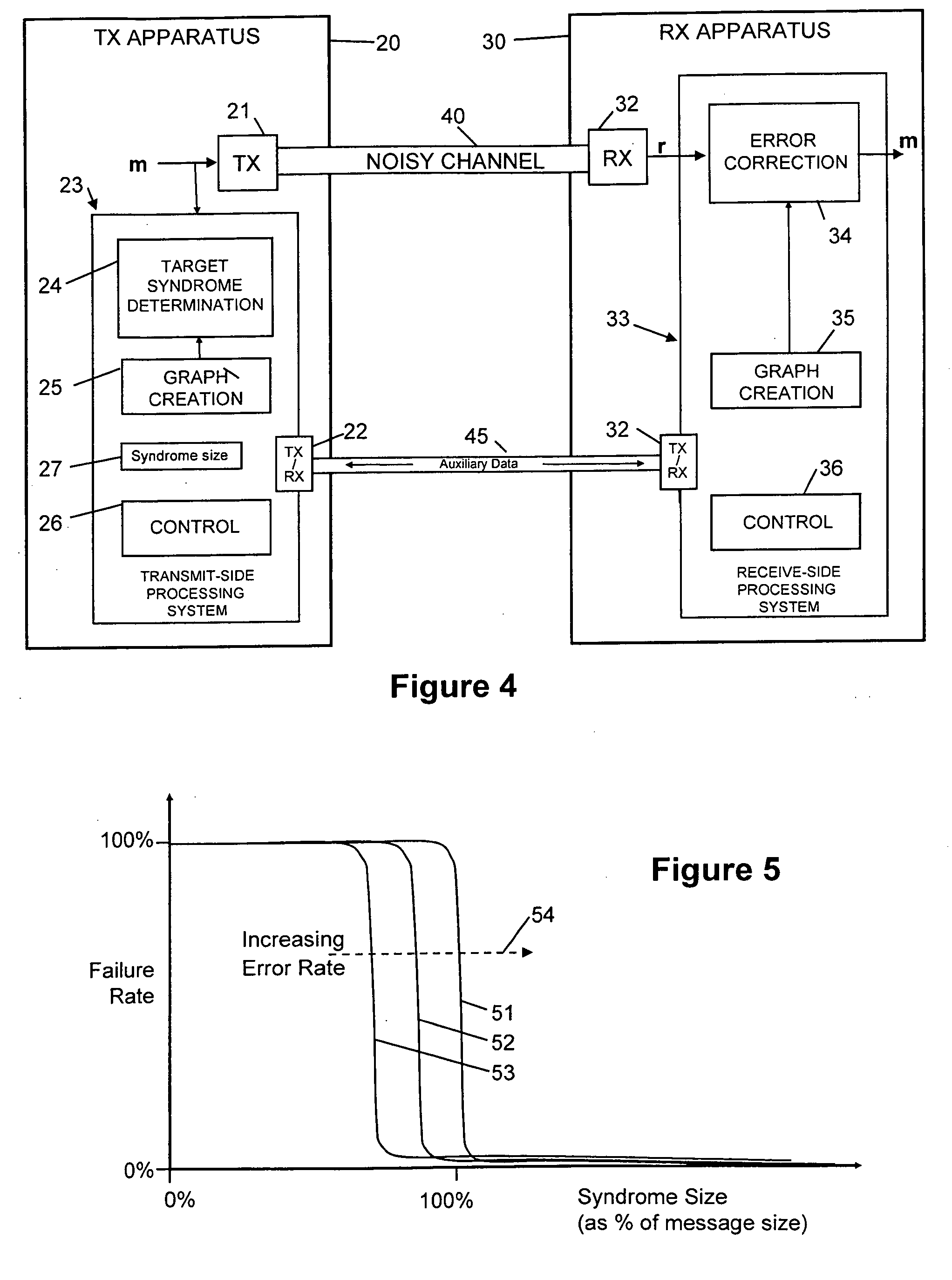
FEC (Forward Error Correction) decoder with dynamic parameters
InactiveUS7257764B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelReceiver specific arrangementsComputer hardwareCommunications system
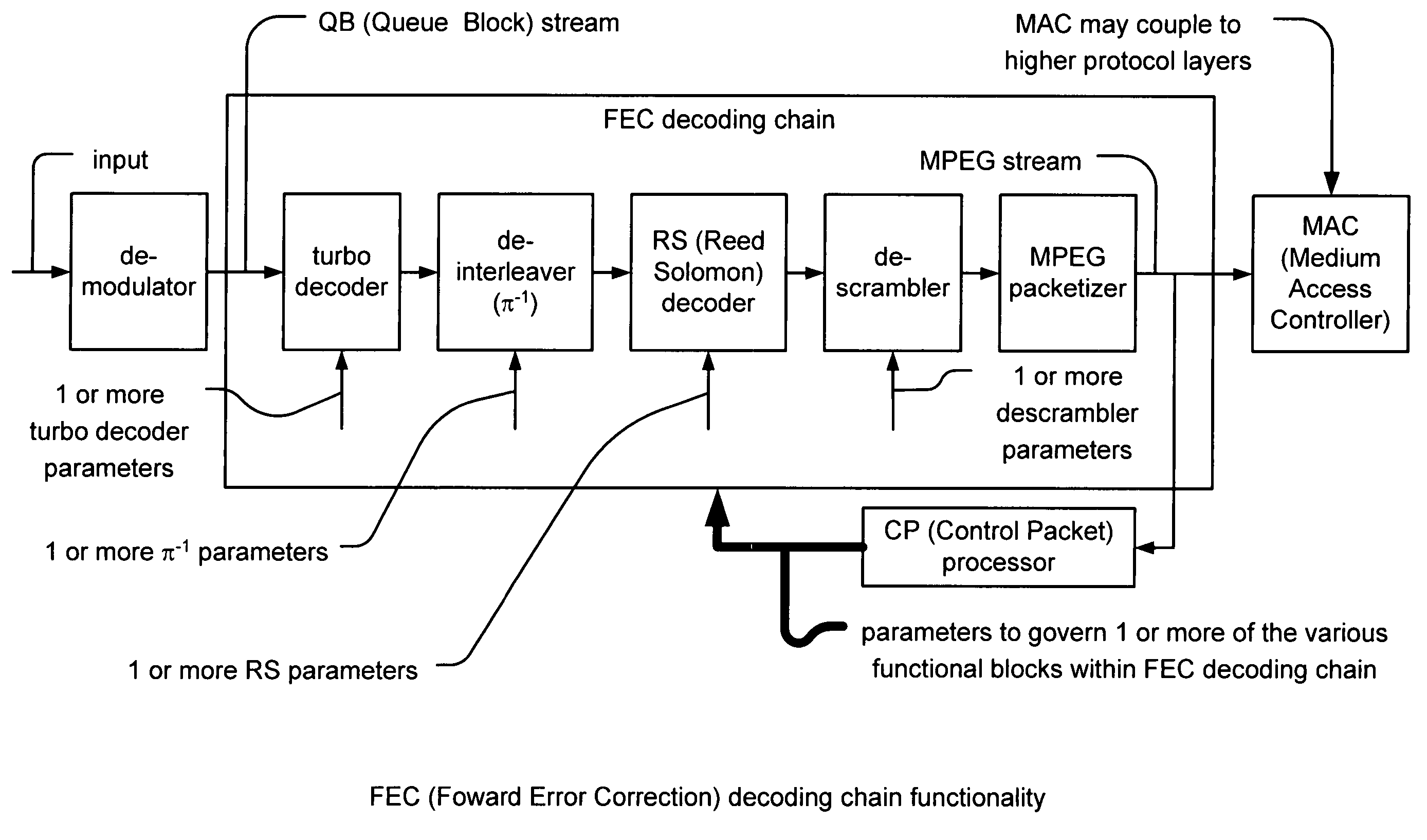
FEC (Forward Error Correction) decoder with dynamic parameters. A novel means by which FEC parameters may be encoded into, and subsequently extracted from, a signal stream to allow for adaptive changing of any 1 or more operational parameters that govern communications across a communication channel. FEC parameters are encoded directly into a data frame such that the data frame is treated identical to all other data frames within the signal stream. When the data frame actually includes FEC parameters, it is characterized as a CP (Control Packet) type. For example, when decoding an MPEG stream, an MPEG block that includes FEC parameters, that MPEG block is characterized as a CP MPEG block. The means by which FEC parameters are encoded and extracted from the signal stream allows for much easier adaptive modification of the manner by which signal are encoded, modulated, and processed within a communication system.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
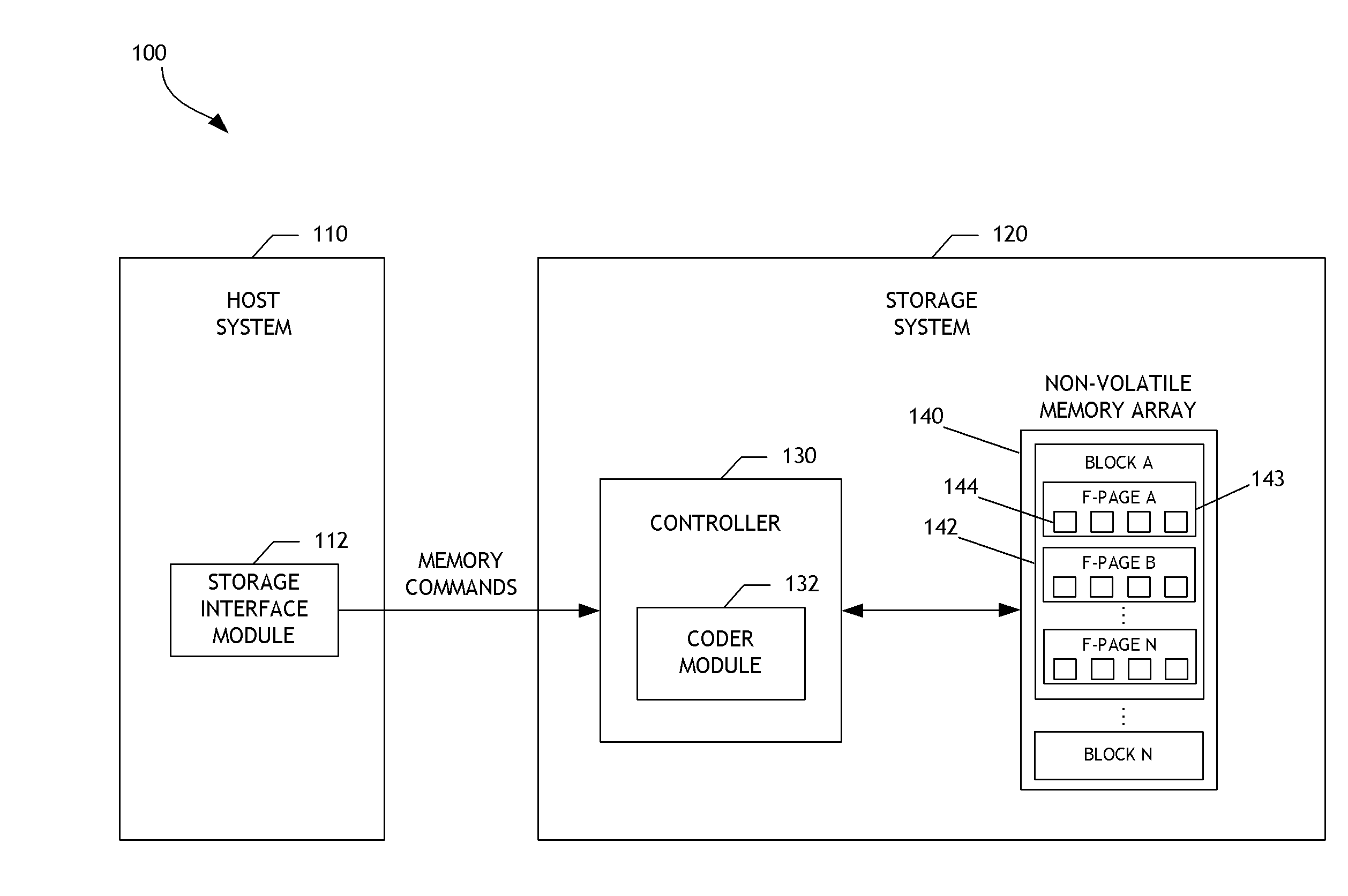
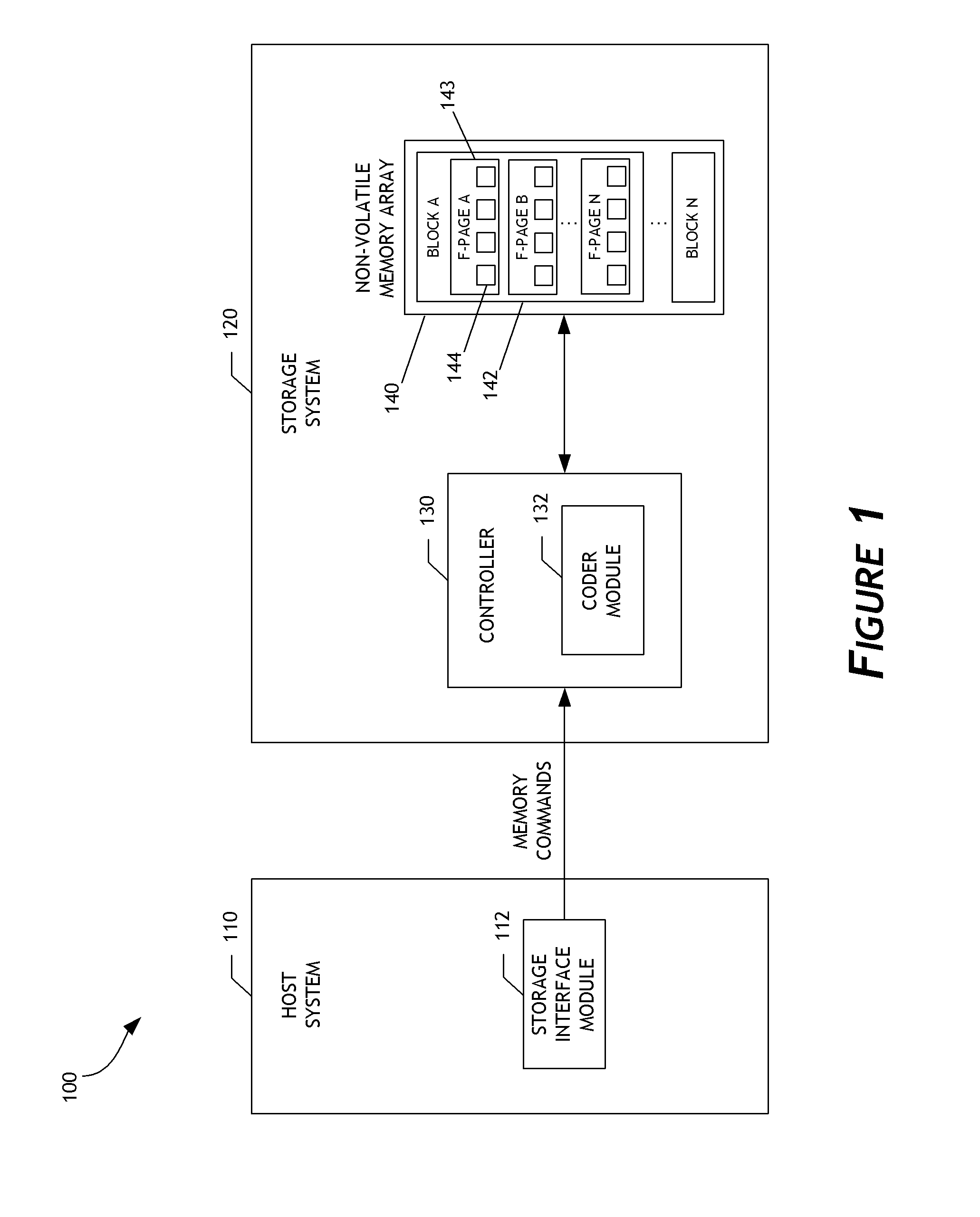
Adaptive error correction codes for data storage systems
ActiveUS20140115427A1Error detection/correctionUnequal/adaptive error protectionConcatenated error correction codeData encoding
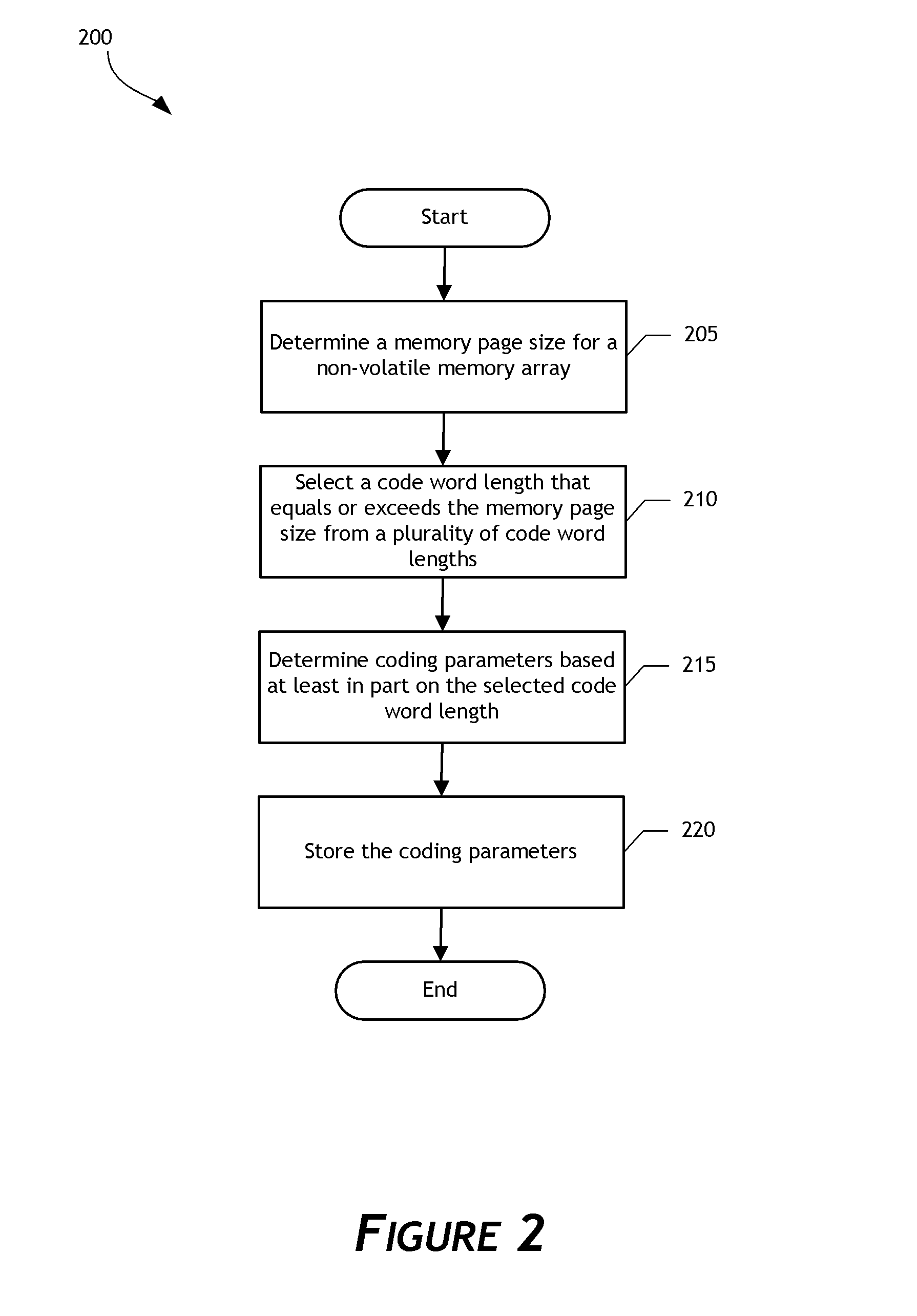
A data storage system configured to adaptively code data is disclosed. In one embodiment, a data storage system controller determines a common memory page size, such as an E-page size, for a non-volatile memory array. Based on the common memory page size, the controller selects a low-density parity-check (LDPC) code word length from a plurality of pre-defined LDPC code word lengths. The controller determines LDPC coding parameters for coding data written to or read from the memory array based on the selected LDPC code word length. By using the plurality of pre-defined LDPC code word lengths, the data storage system can support multiple non-volatile memory page formats, including memory page formats in which the common memory page size does not equal any LDPC code word length of the plurality of pre-defined LDPC code word lengths. Flexibility and efficiency of data coding can thereby be achieved.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Extended error correction codes
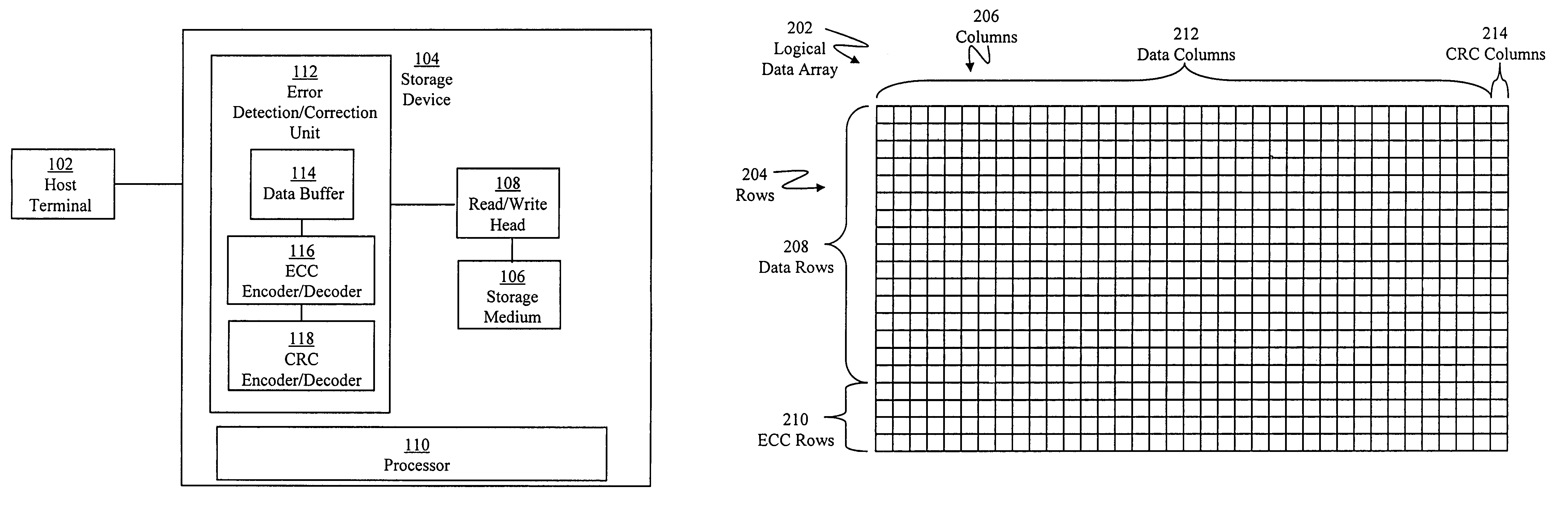
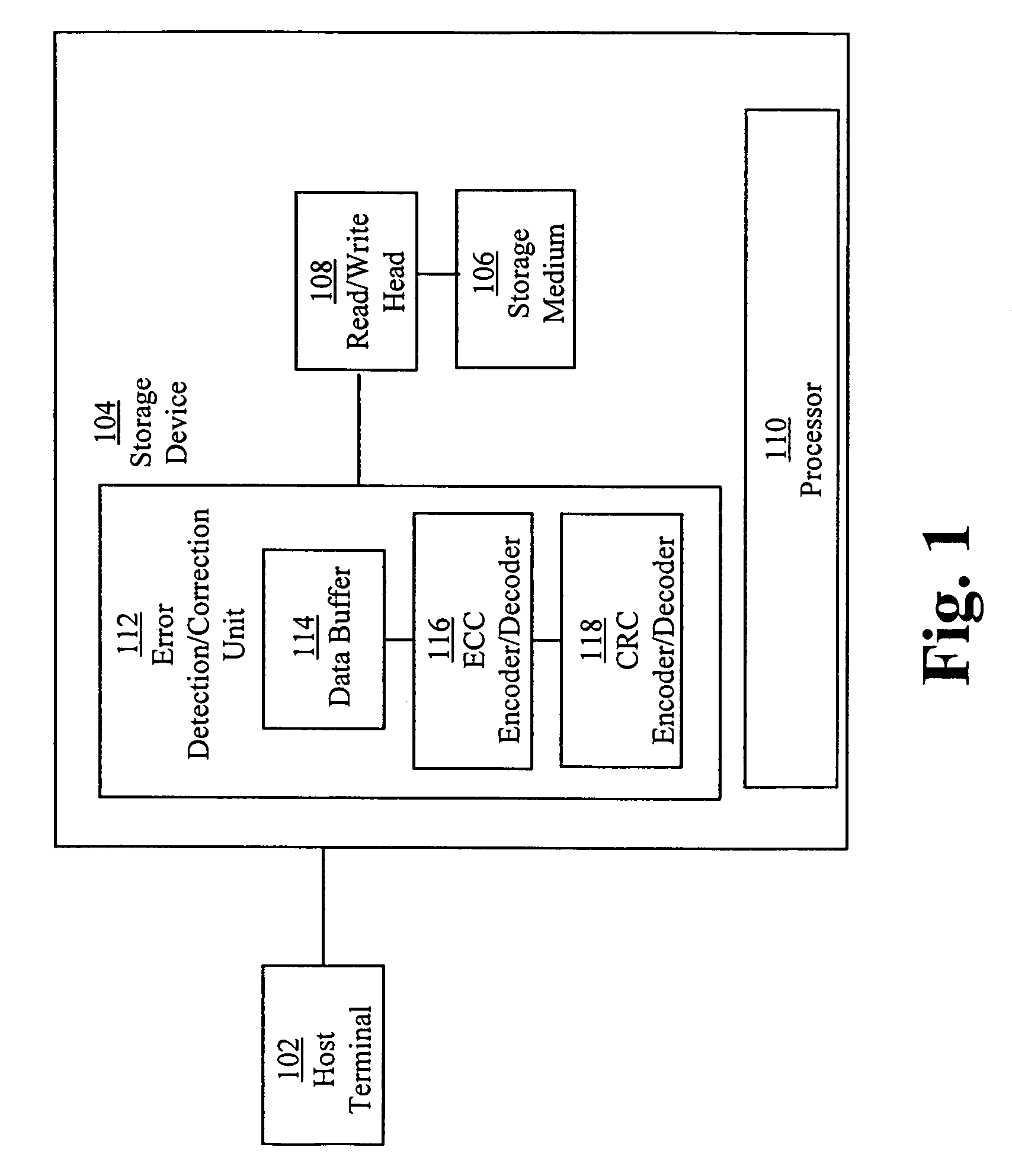
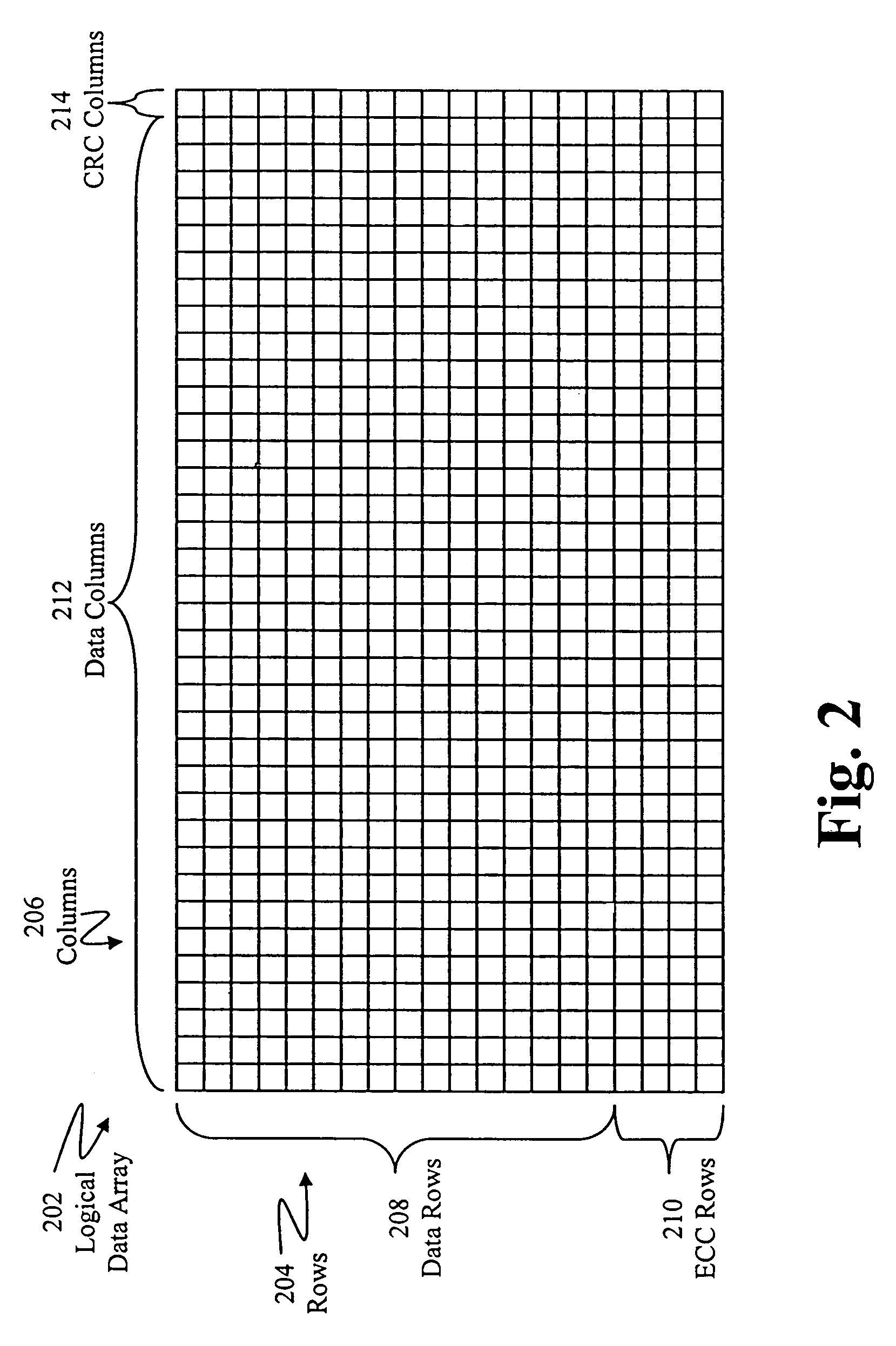
Errors in data retrieved from a storage medium are verified by retrieving a plurality of data blocks from the storage medium. A data set having data from multiple data blocks is selected, where the data set includes a plurality of rows corresponding to the data bocks and a row has data from a data block corresponding to the row. One or more error correction codes (ECCs) are retrieved from the storage medium, where the one or more ECCs correspond to the data set. A plurality of check sums are retrieved from the storage medium, where a check sum corresponds to a data block. Data blocks retrieved from the storage medium having errors are identified using the check sums corresponding to the data blocks. When the number of data blocks identified as having errors is greater than the number of ECCs for the data set, a first set of rows in the data set corresponding to the data blocks identified as having errors is selected, where the number of rows in the first set of rows is equal to the number of ECCs for the data set and less than the number of data blocks identified as having errors. Data for the first set of rows are generated using the ECCs for the data set, and the rows corresponding to the data blocks identified as having errors are verified based on the generated data for the first set of rows.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
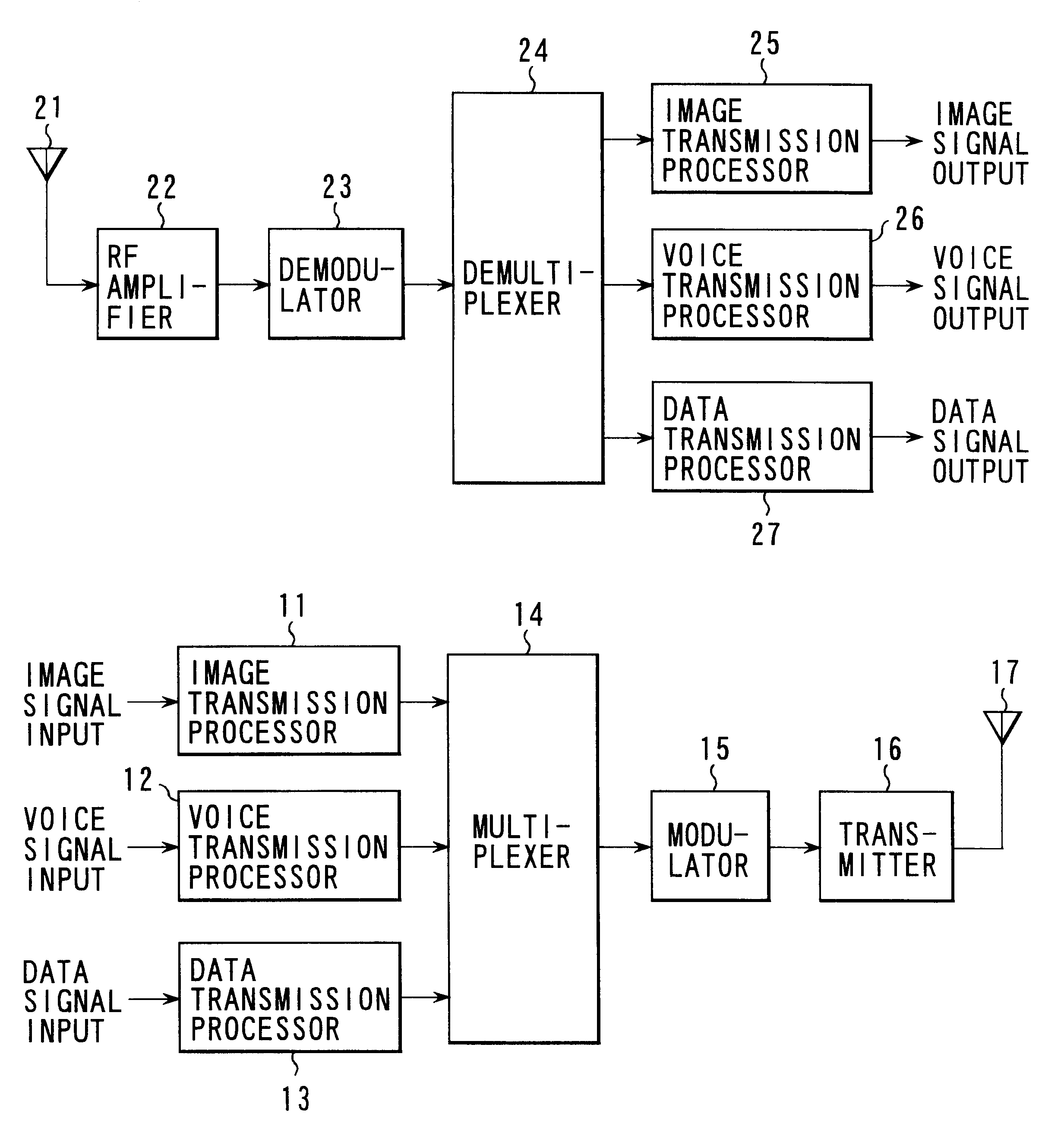
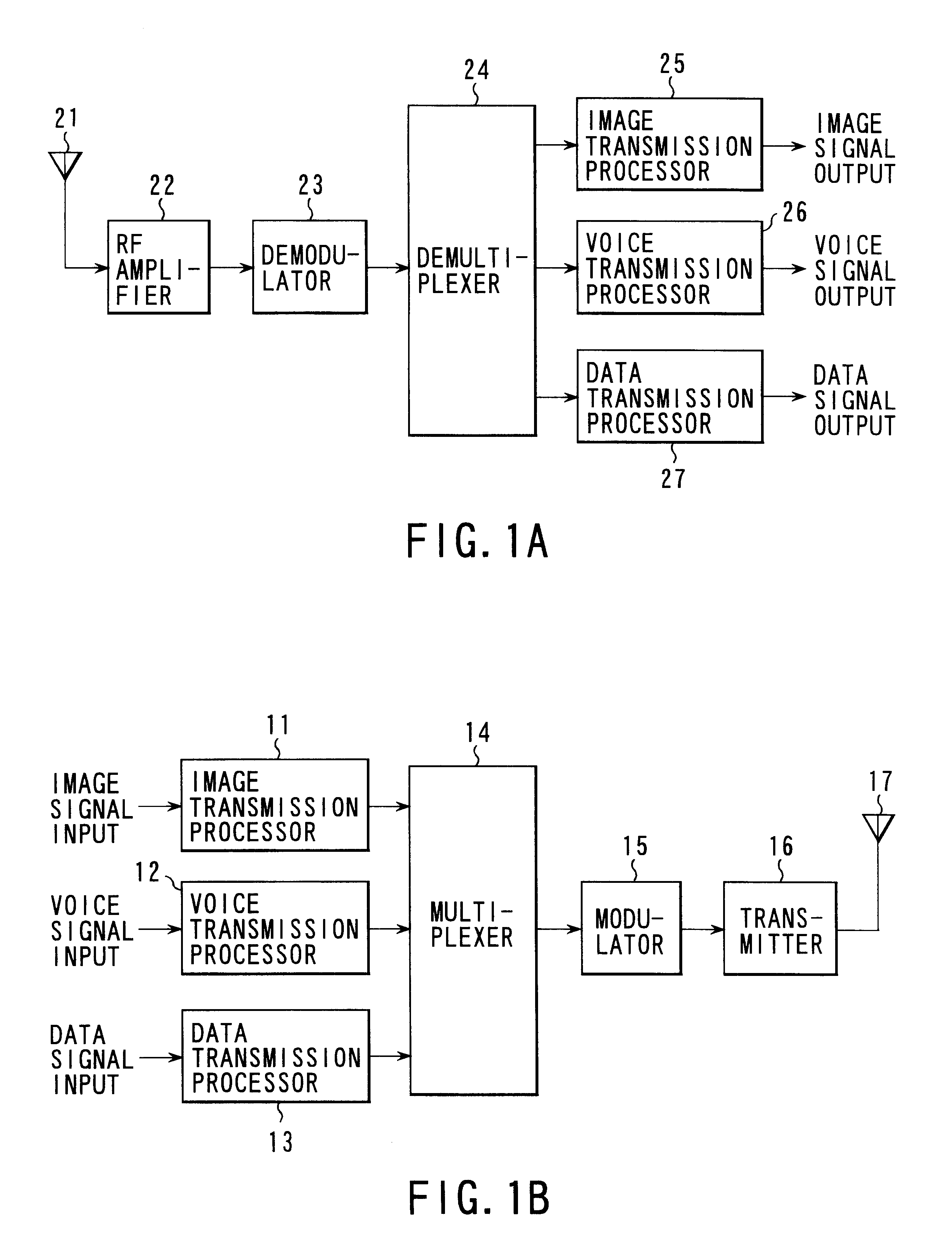
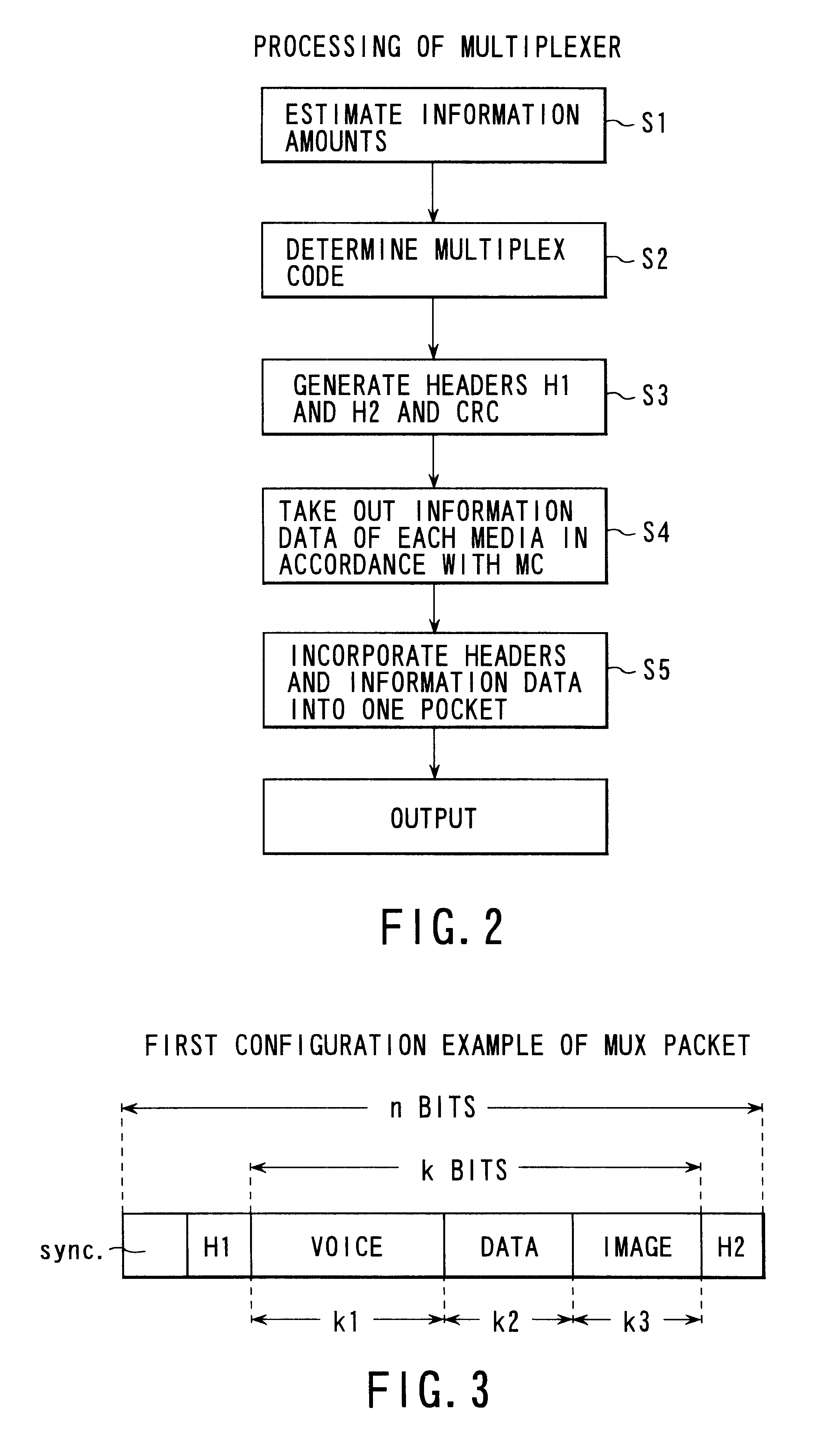
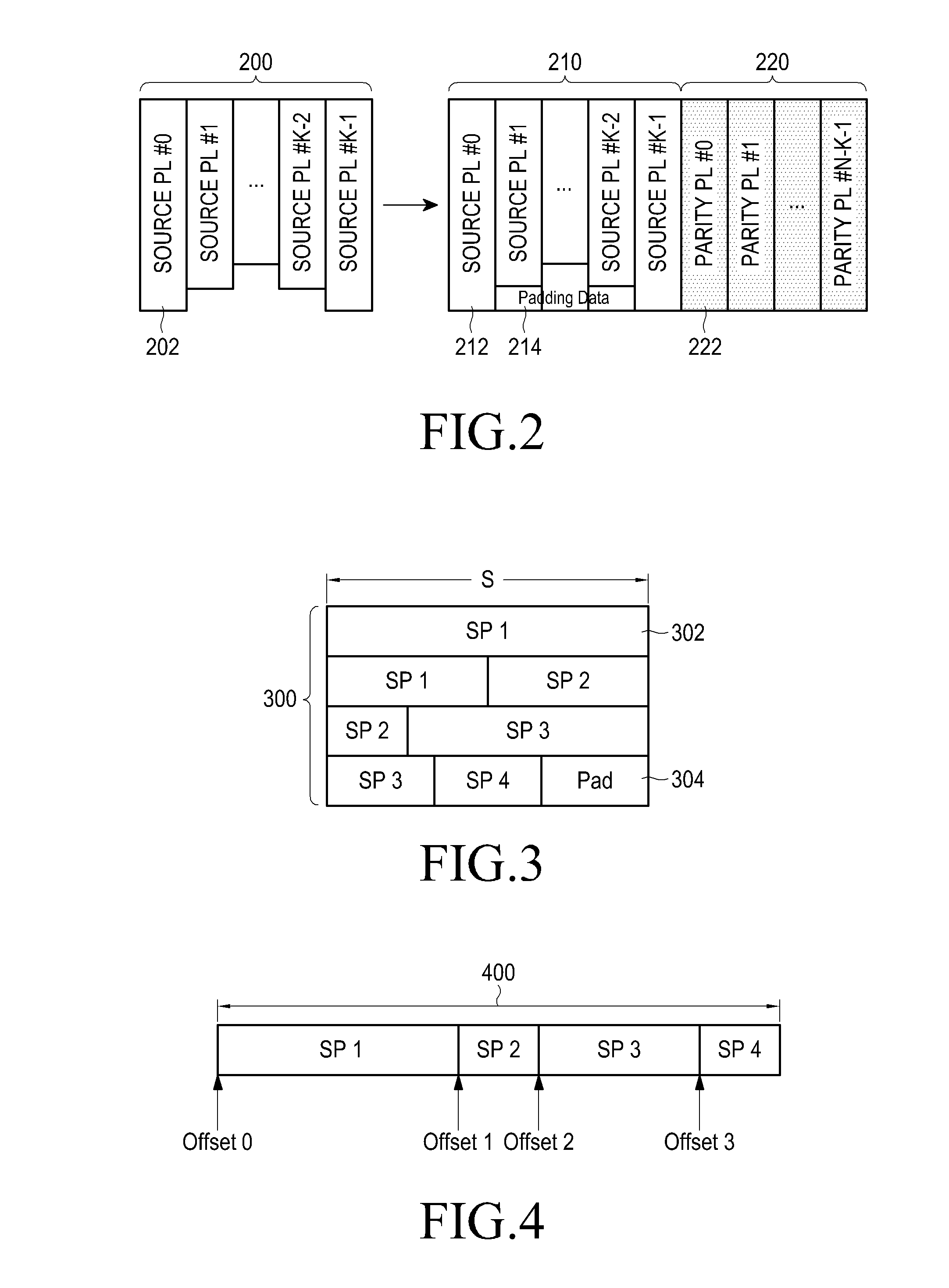
Information data multiplex transmission system, its multiplexer and demultiplexer and error correction encoder and decoder
InactiveUS6490243B1Reduce the probability of packet lossAccurate readingData representation error detection/correctionPulse modulation television signal transmissionMultiplexingMultiplexer
A multiplexing unit on the transmitting side estimates information amounts supplied from respective signal processing units, determines a multiplex code on the basis of respective information amounts, derives a parity of the first determined multiplex code to form a second multiplex code, adds a CRC to each of the multiplex codes to generate two headers H1 and H2, takes out information data of respective media according to the multiplex codes, incorporates the information data into a packet together with the two headers H1 and H2, and outputs the packet. If error correction of H1 is impossible on the receiving side, error correction decoding is conducted by using the header H2. If error correction of H2 is also impossible, error correction decoding is conducted collectively for H1 and H2.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Wireless communication system, wireless communication device, and wireless communication method
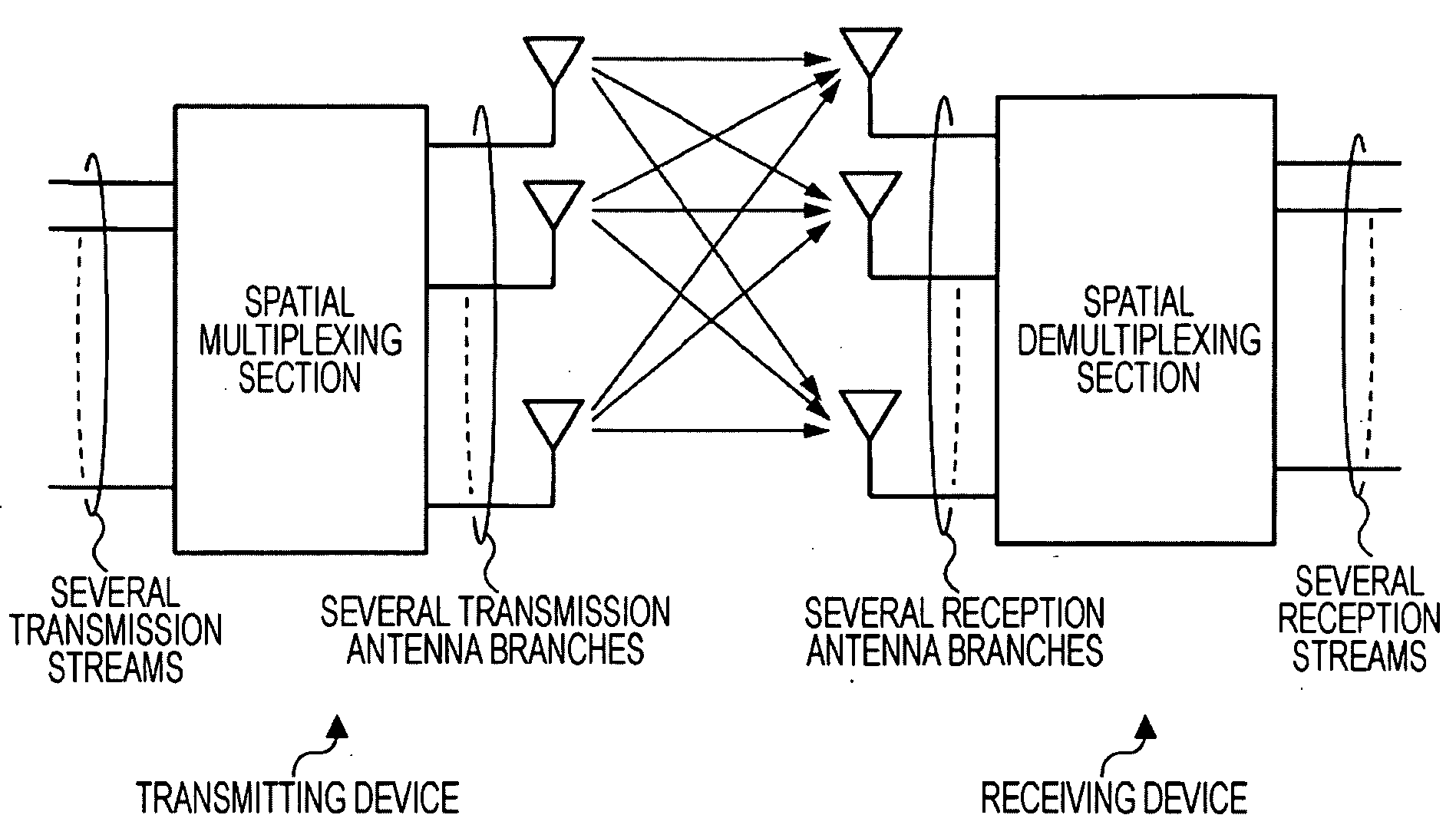
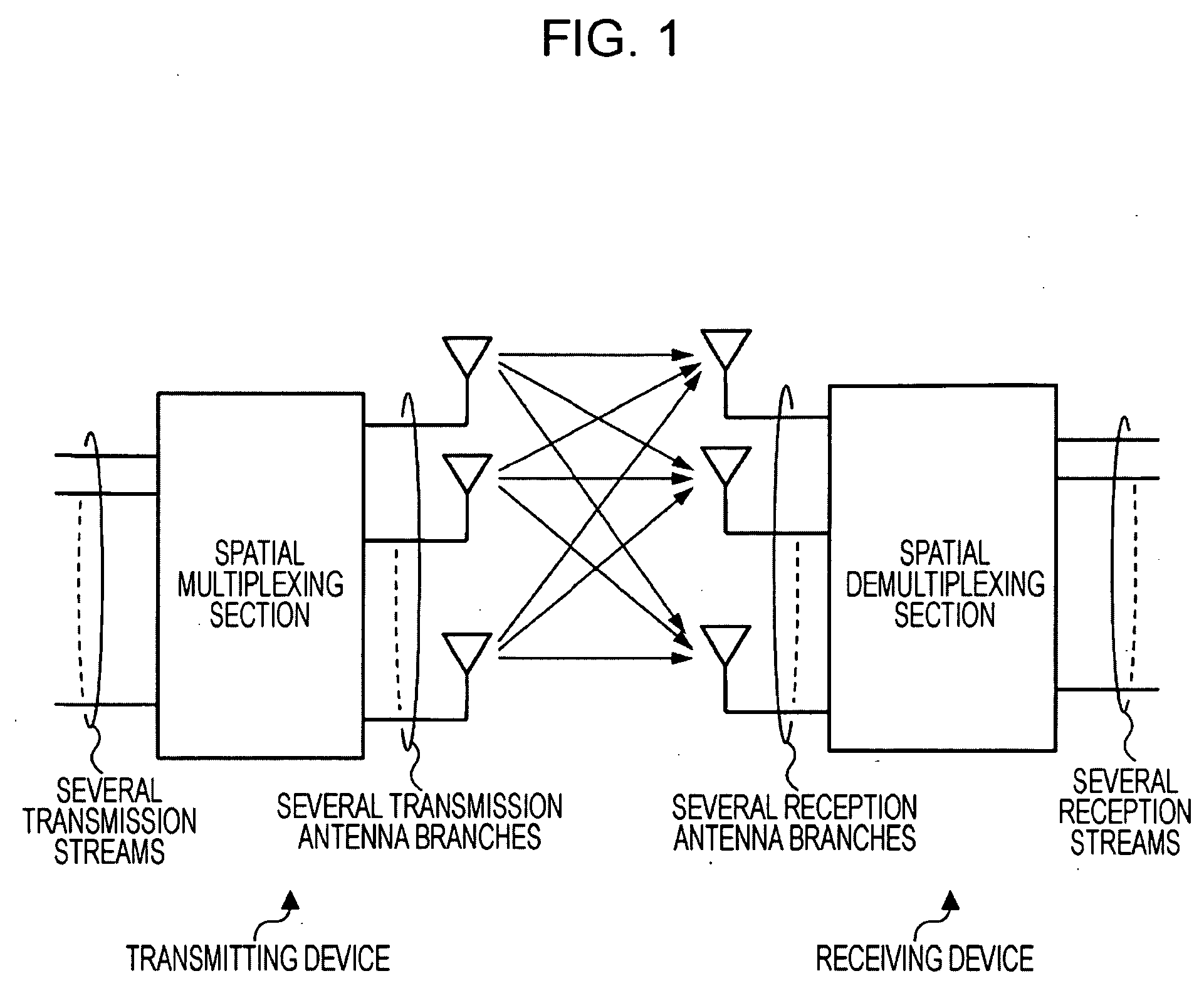
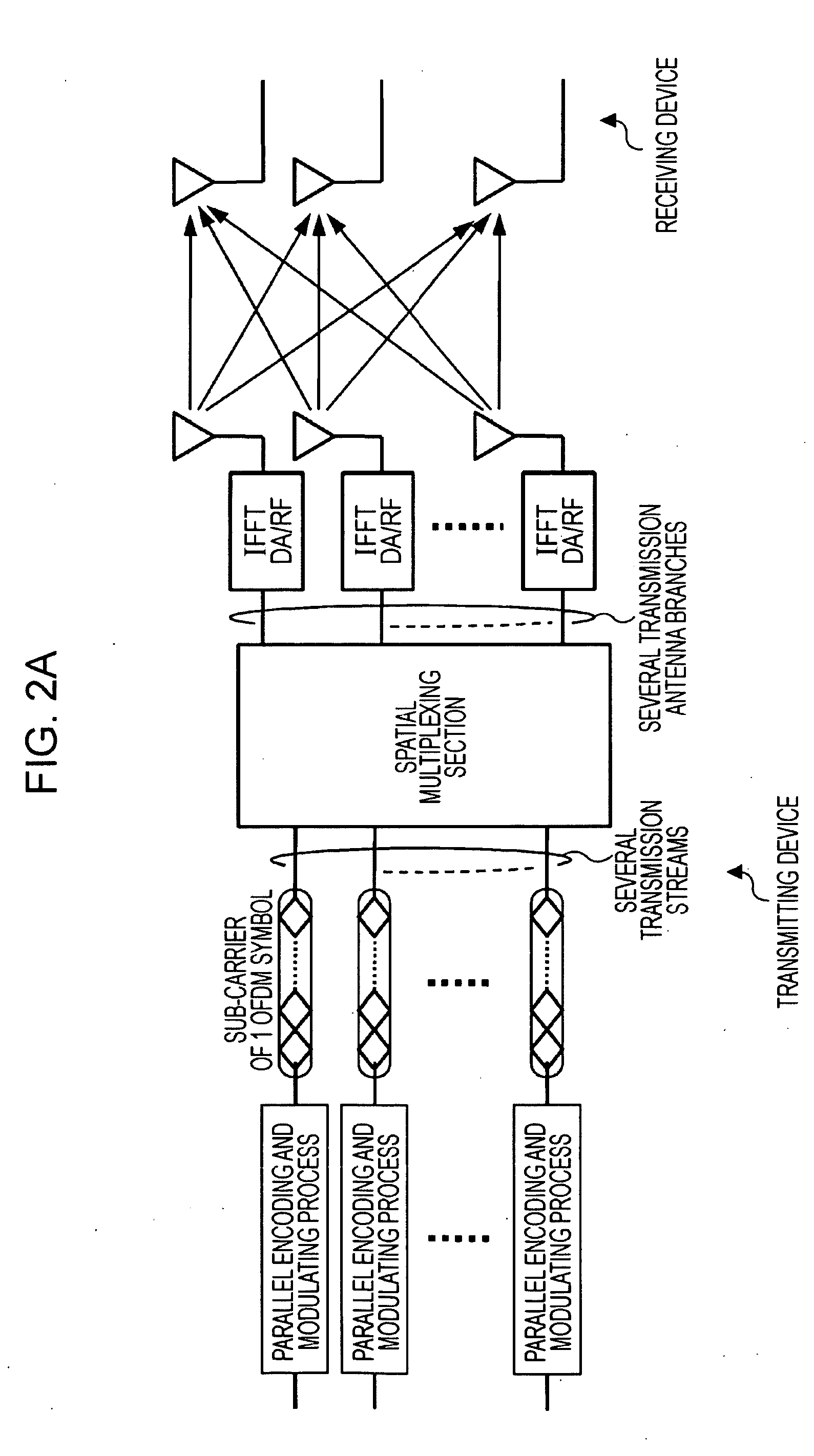
ActiveUS20090052578A1Improve transmission performanceConvenient wireless communicationSpatial transmit diversityModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemSpatial multiplexing
A wireless communication system includes a transmitting device and a receiving device each including a plurality of antennas. A plurality of streams are subjected to spatial multiplexing and are transmitted in a downlink in which packets are transmitted from the transmitting device to the receiving device. In the transmitting device, each of the plurality of transmission streams is divided into a plurality of bit-series groups having decoding characteristics to which priority levels are assigned, the bit-series groups are subjected to encoding processes and modulating processes in accordance with the priority levels and further subjected to weighting and synthesizing, and each of the plurality of transmission streams in which a plurality of bit series items are synthesized with one another is spatially multiplexed and transmitted.
Owner:PANTECH CORP
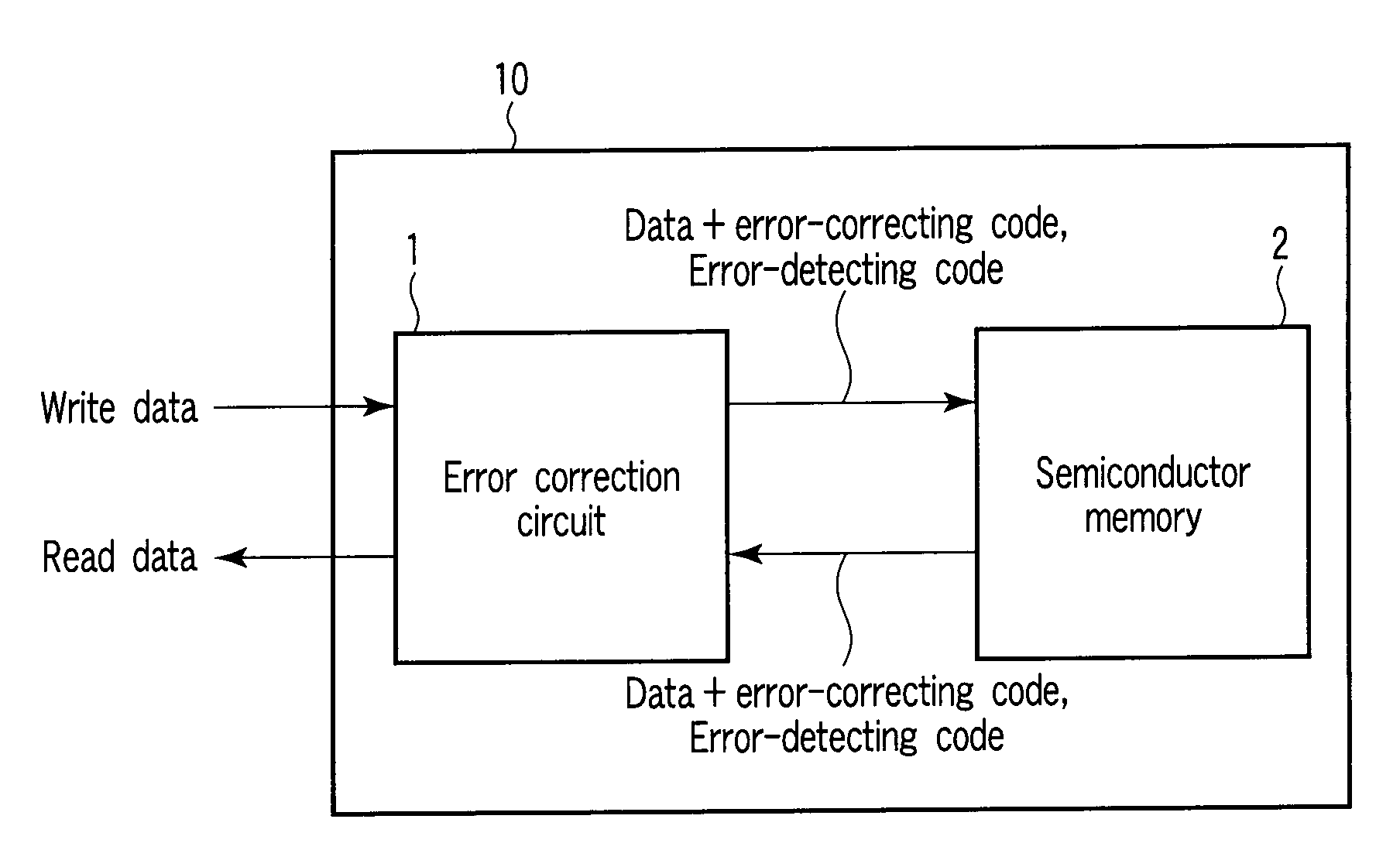
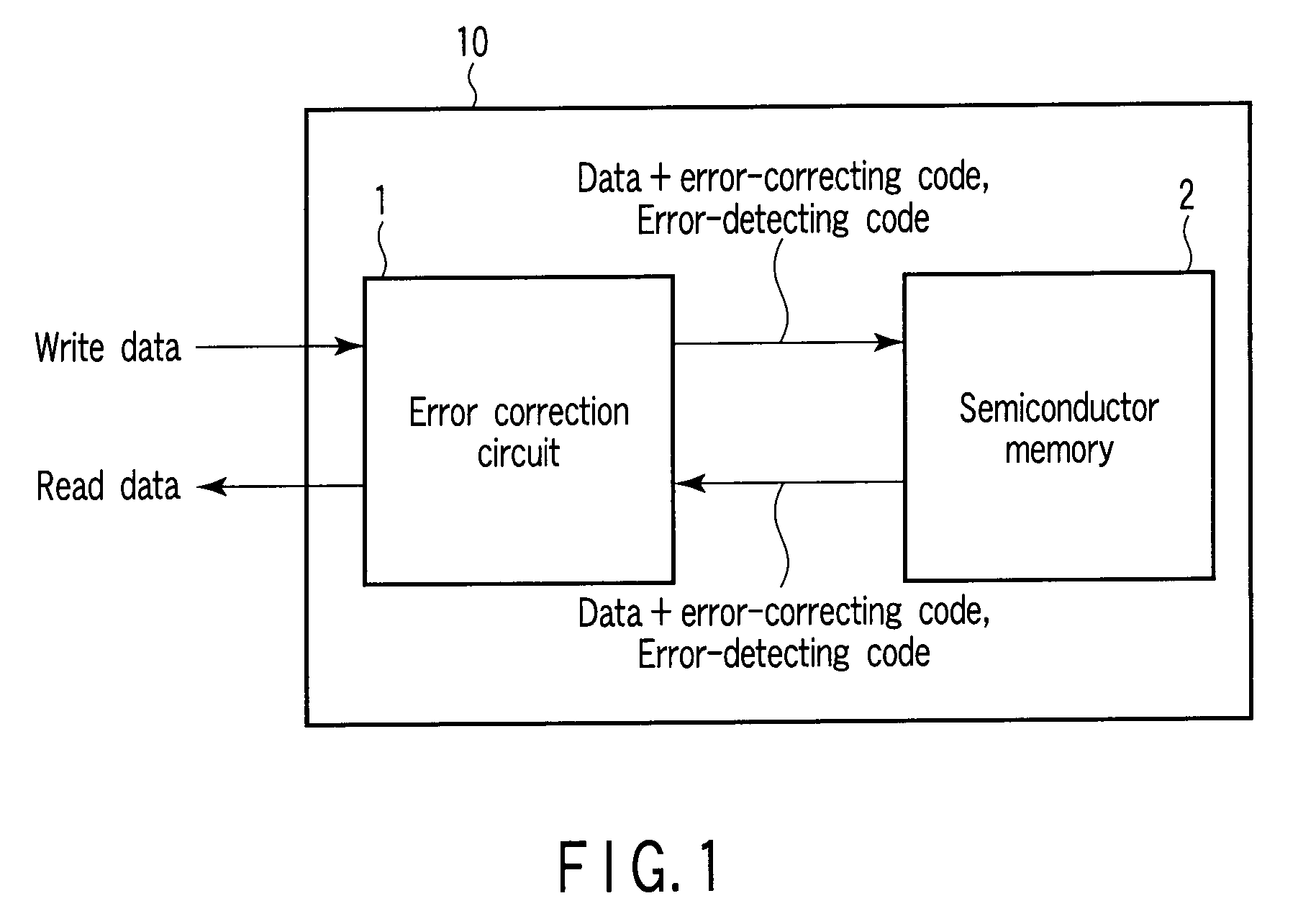
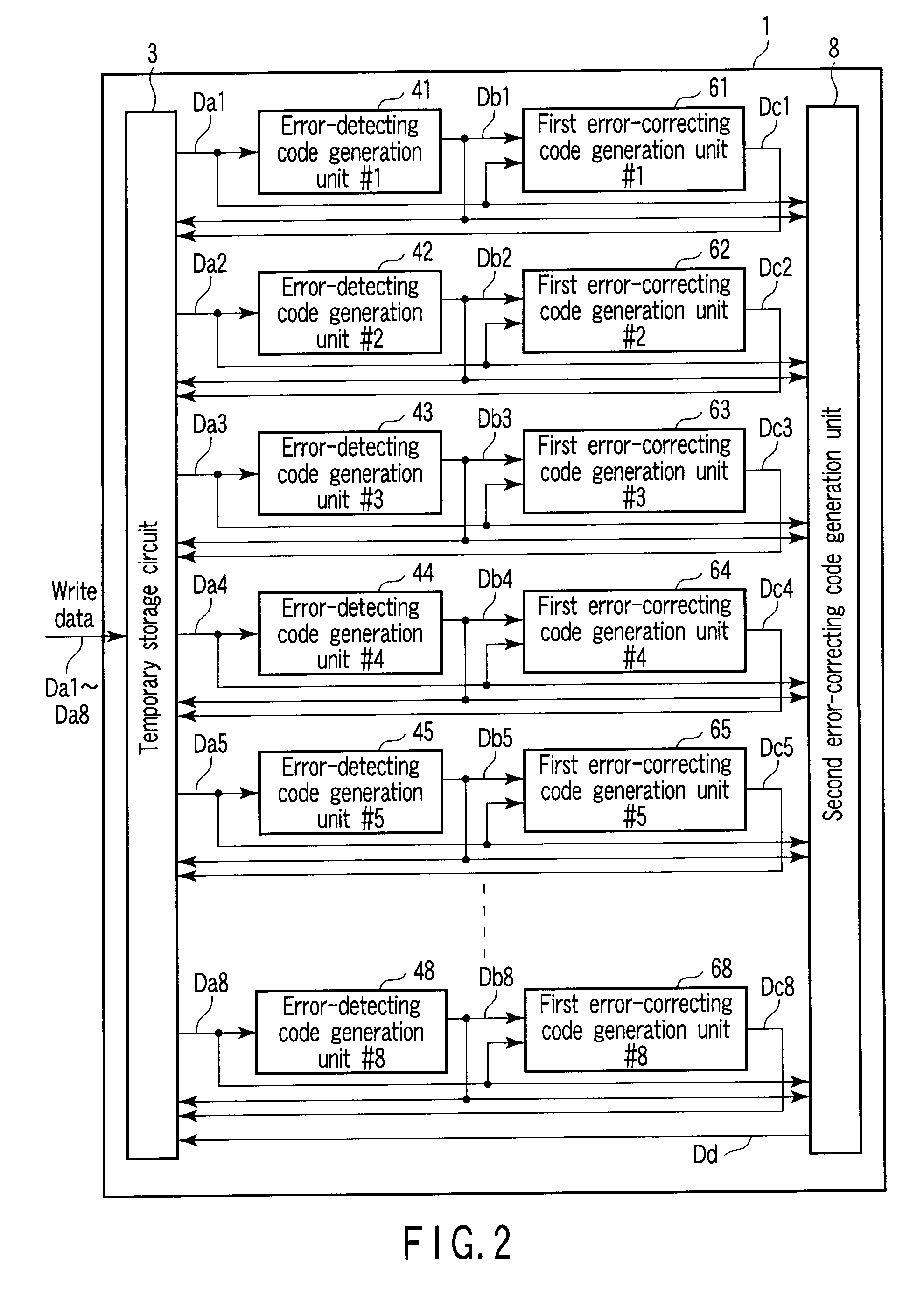
Semiconductor memory device and method of controlling the same
ActiveUS20090183052A1Detecting faulty computer hardwareCode conversionSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor memory device includes a plurality of detecting code generators configured to generate a plurality of detecting codes to detect errors in a plurality of data items, respectively, a plurality of first correcting code generators configured to generate a plurality of first correcting codes to correct errors in a plurality of first data blocks, respectively, each of the first data blocks containing one of the data items and a corresponding detecting code, a second correcting code generators configured to generate a second correcting code to correct errors in a second data block, the second data block containing the first data blocks, and a semiconductor memory configured to nonvolatilely store the second data block, the first correcting codes, and the second correcting code.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
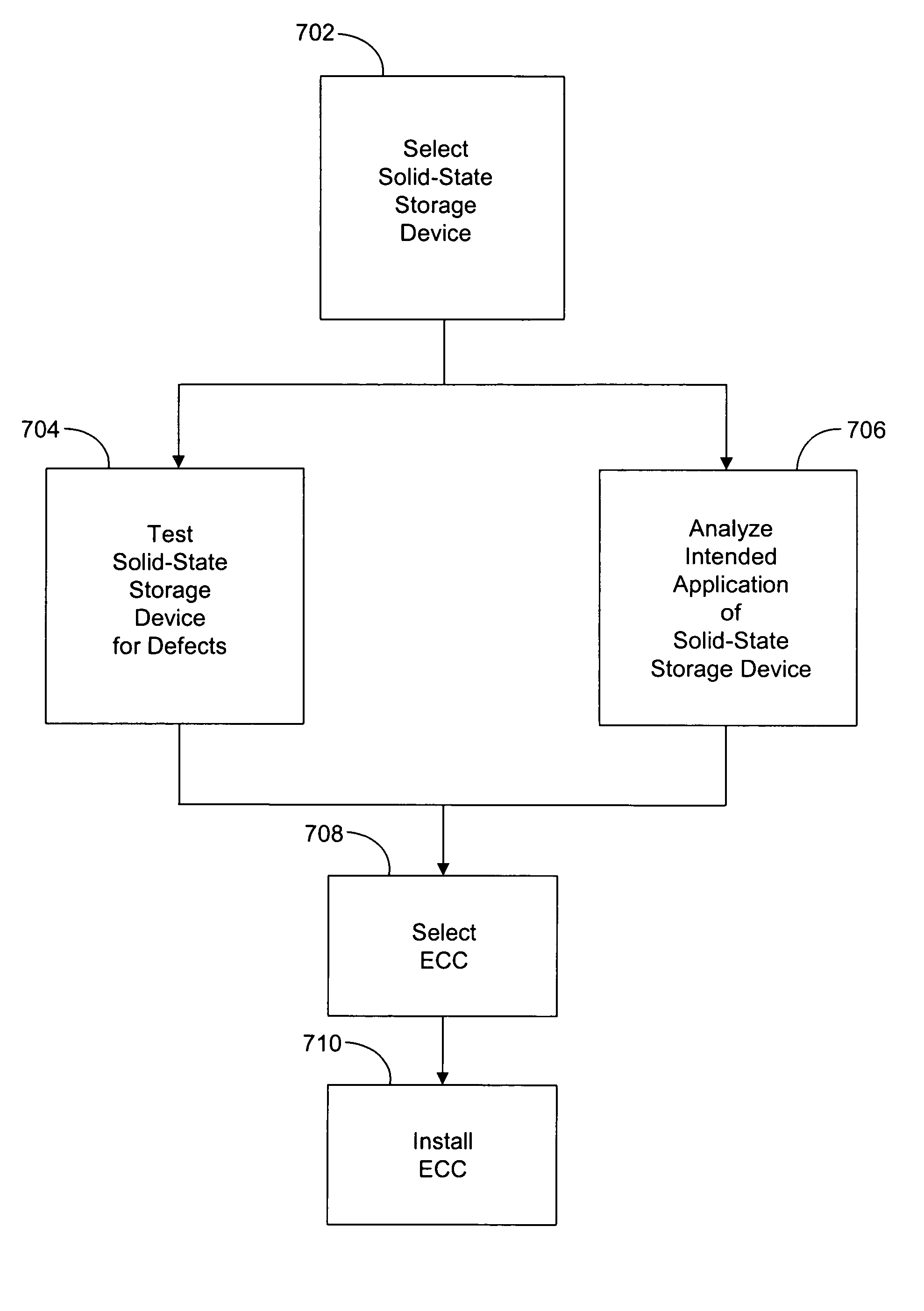
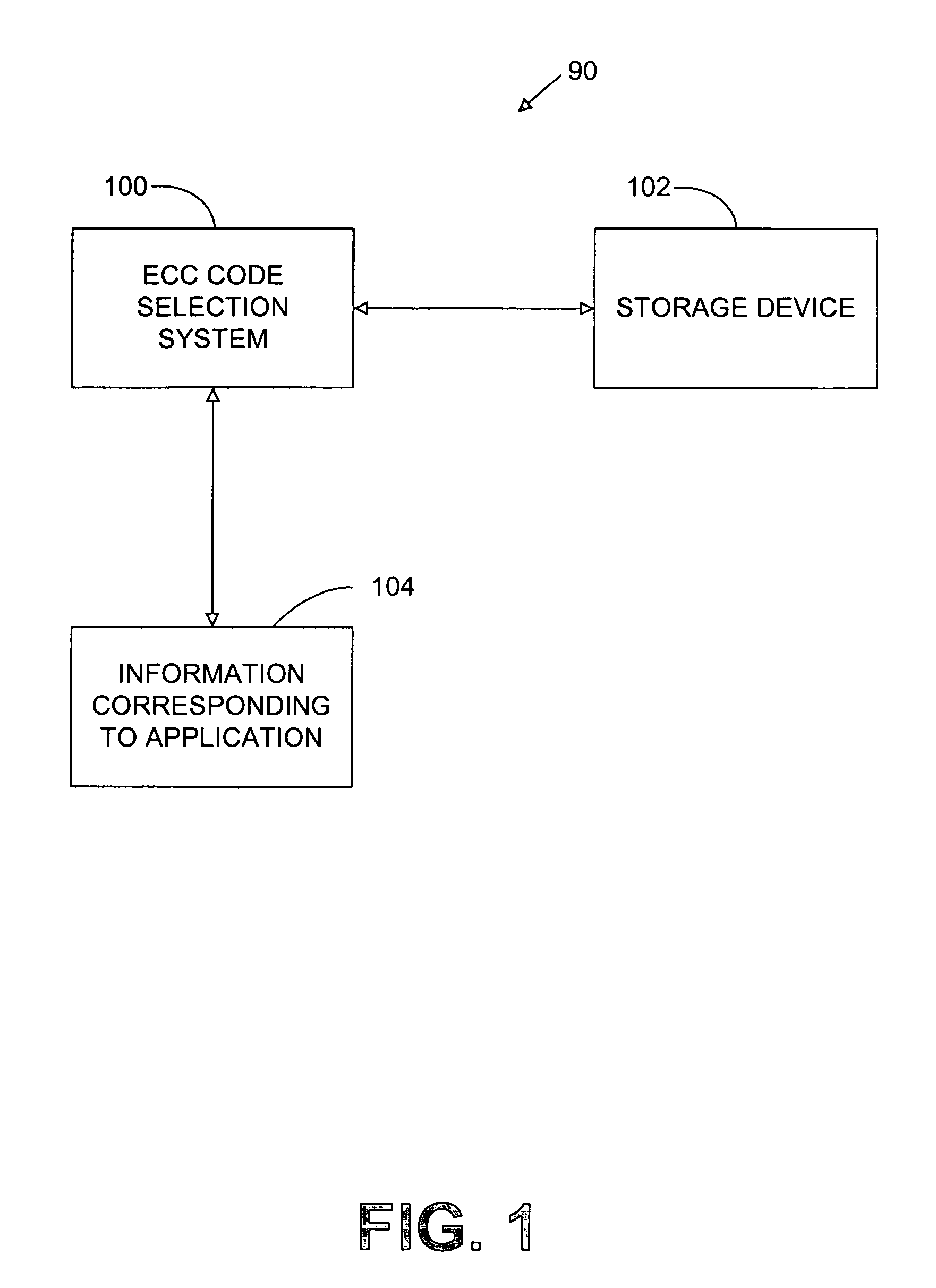
System and method for configuring a solid-state storage device with error correction coding
ActiveUS7210077B2Memory loss protectionUnequal/adaptive error protectionSolid-state storageSelection system
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Read error recovery utilizing ECC and read channel quality indicators
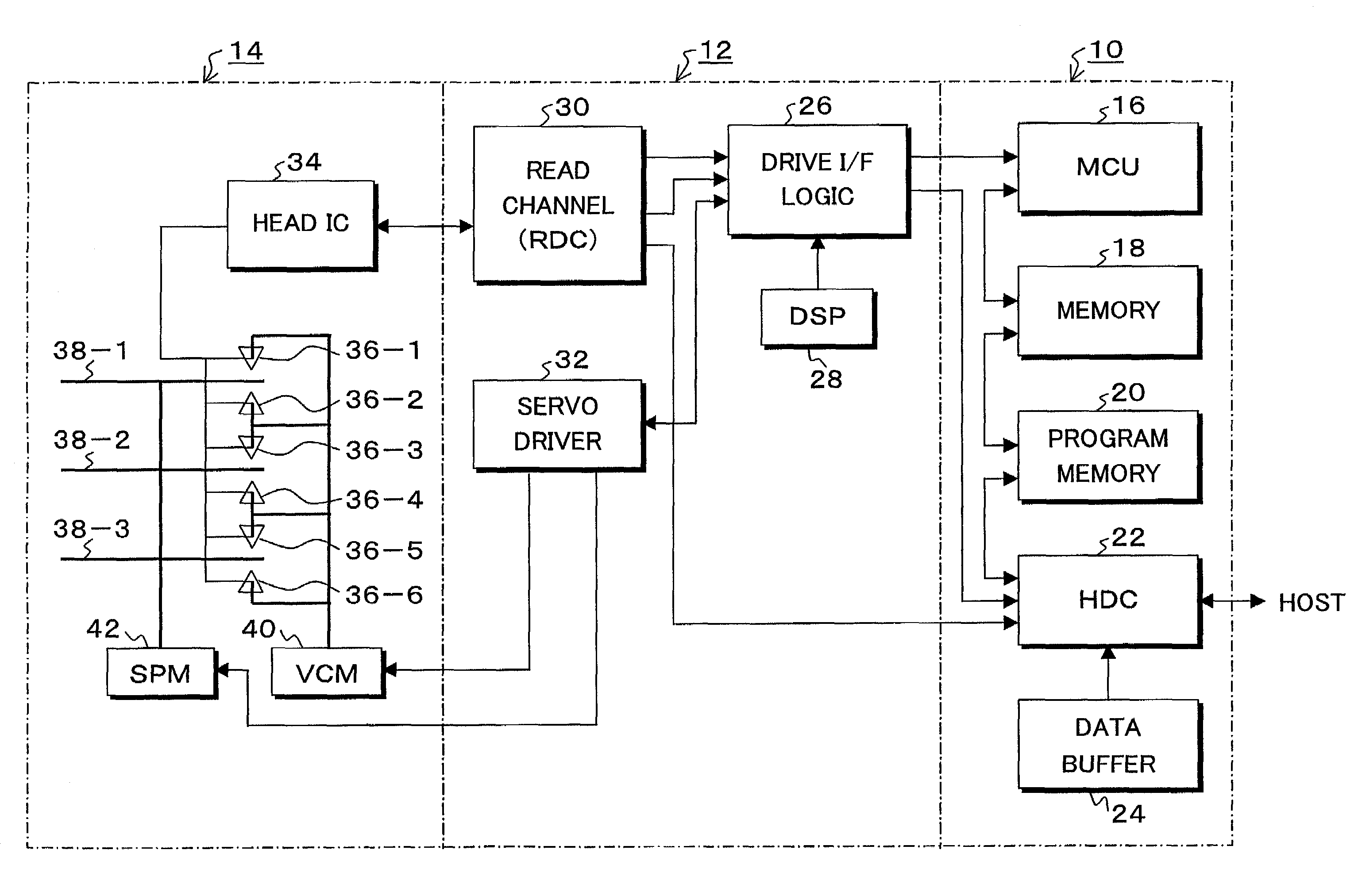
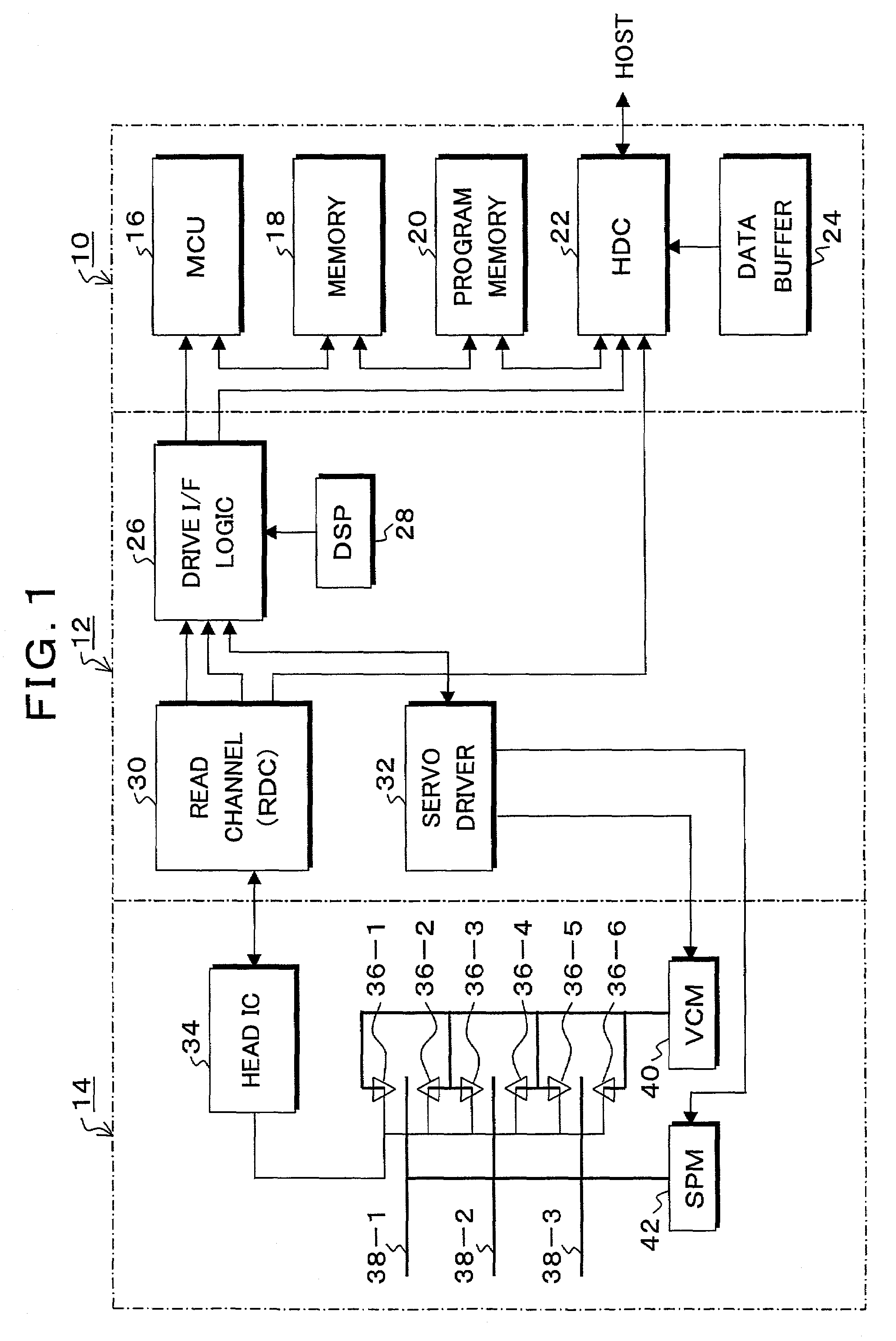
PCT No. PCT / US97 / 04906 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 21, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 21, 1997 PCT Filed Mar. 27, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 43835 PCT Pub. Date Nov. 20, 1997An apparatus and method for recovering from read errors detected by a read channel (70) in a sequence of data read from a disc (18) of a disc drive (10) by using read channel quality indicators to determine the appropriateness of using error correction in combination with other corrective actions utilized in the recovery process. Upon the detection of an uncorrected error in the retrieved data, the disc drive (10) enters a read error recovery routine wherein one or more corrective actions (102, 122) are applied in an effort to resolve the error. One of the channel quality indicators comprises a channel quality measurement (108, 128) determined as the sum of the square of the sampled data bit error values recovered during the read operation. When the channel quality measurement is at or below a threshold value indicative that the probability of passing undetected erroneous data is at an acceptable level (110, 130), error correction is applied to the data (112, 138); otherwise, error correction is disallowed (118, 140). Additional channel quality indicators comprise erasure pointers (132) which identify a particular set of symbols that are suspected of containing a read error. In such a case, the disc drive determines that the total number of symbols identified by the erasure pointers is below a predetermined erasure threshold before applying error correction (134, 136, 138), the erasure threshold selected to be within the correction capability of error correction circuitry 90.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
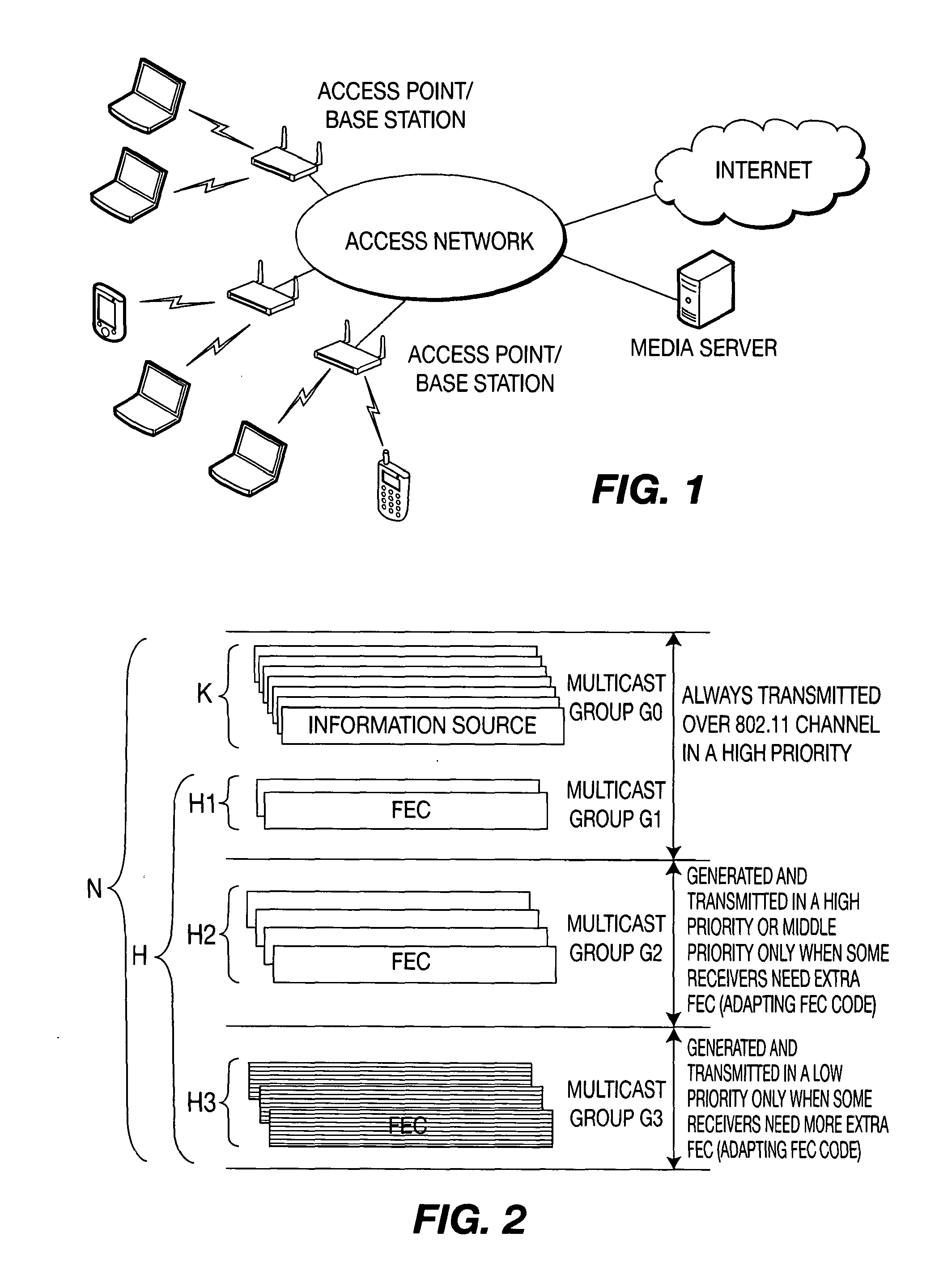
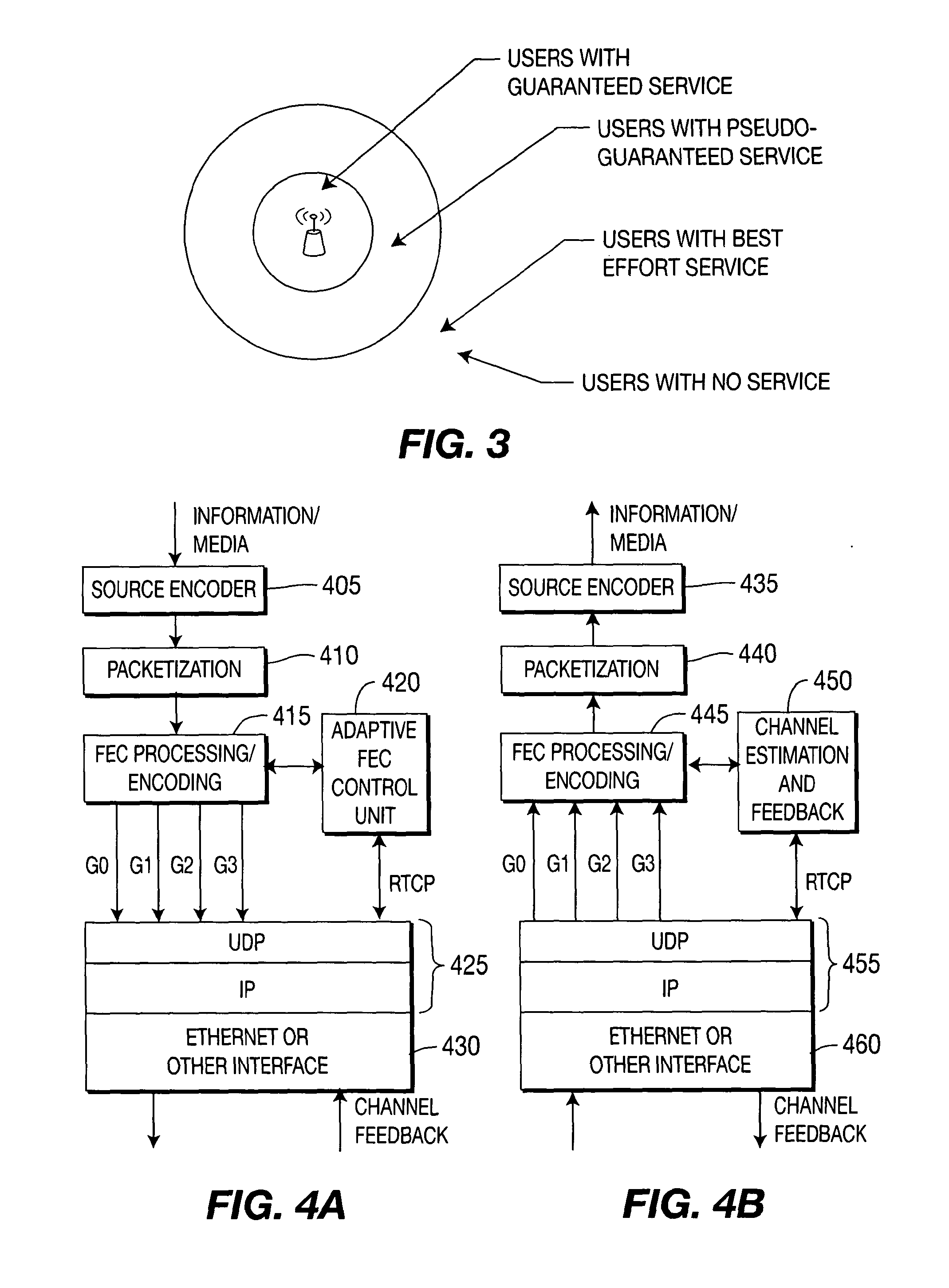
Method and system for adapting forward error correction in multicast over wireless networks
ActiveUS20120011413A1Efficient and reliable deliverySystem throughput is maximizedTransmission systemsUnequal/adaptive error protectionWireless mesh networkForward error correction
A method and apparatus are described including receiving channel condition feedback from a device over a wireless channel, determining response to the channel condition feedback if a forward error correction coding rate is sufficient for the device to recover lost data, adjusting the forward error correction coding rate responsive to the second determining act and generating forward error correction packets using the adjusted forward error correction coding rate from source data.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL CE PATENT HLDG
Encoding apparatus and encoding method in data communication system
ActiveUS20130097470A1Easy to operateImprove data transfer efficiencyError preventionCode conversionCommunications systemPayload
An encoding method and apparatus in a data communication system are provided. The method includes inputting a source block including a plurality of source payloads, converting the source block to an information block including a plurality of information payloads according to an Information Block Generation (IBG) mode selected from a plurality of IBG modes, transmitting a delivery block generated by adding a parity block generated by encoding the information block according to a selected encoding scheme to the source block to a receiver, and transmitting information indicating the selected IBG mode to the receiver.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
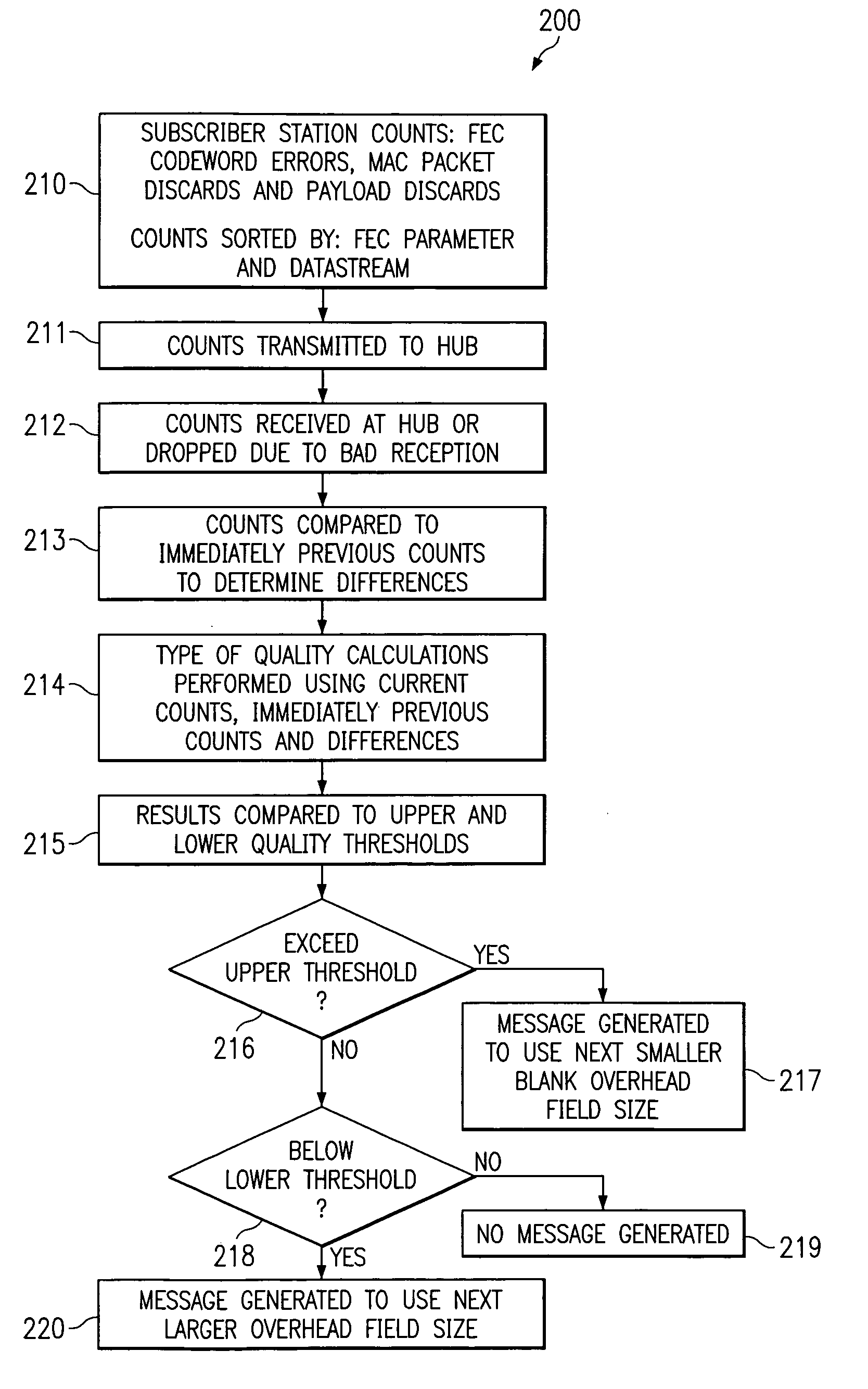
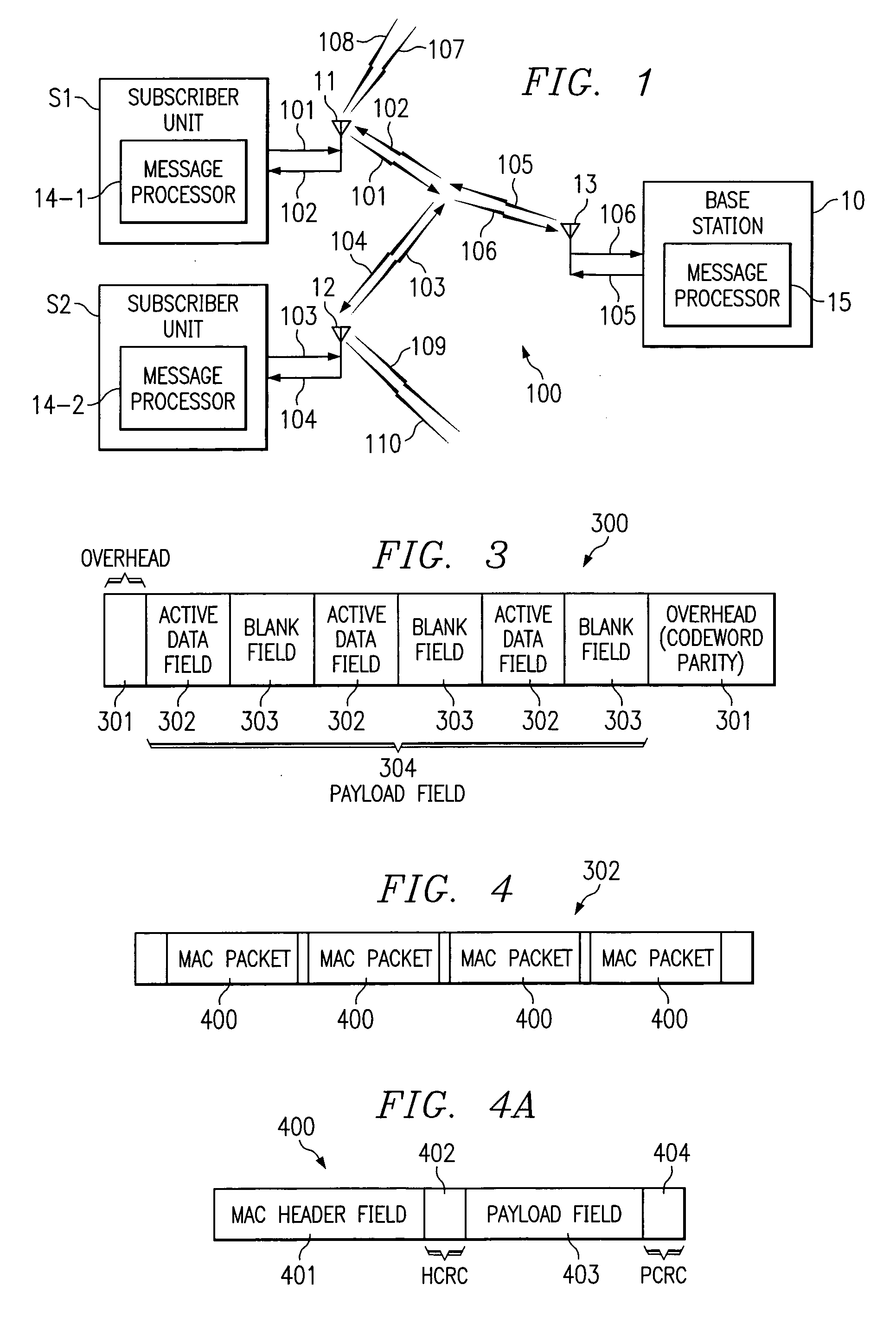
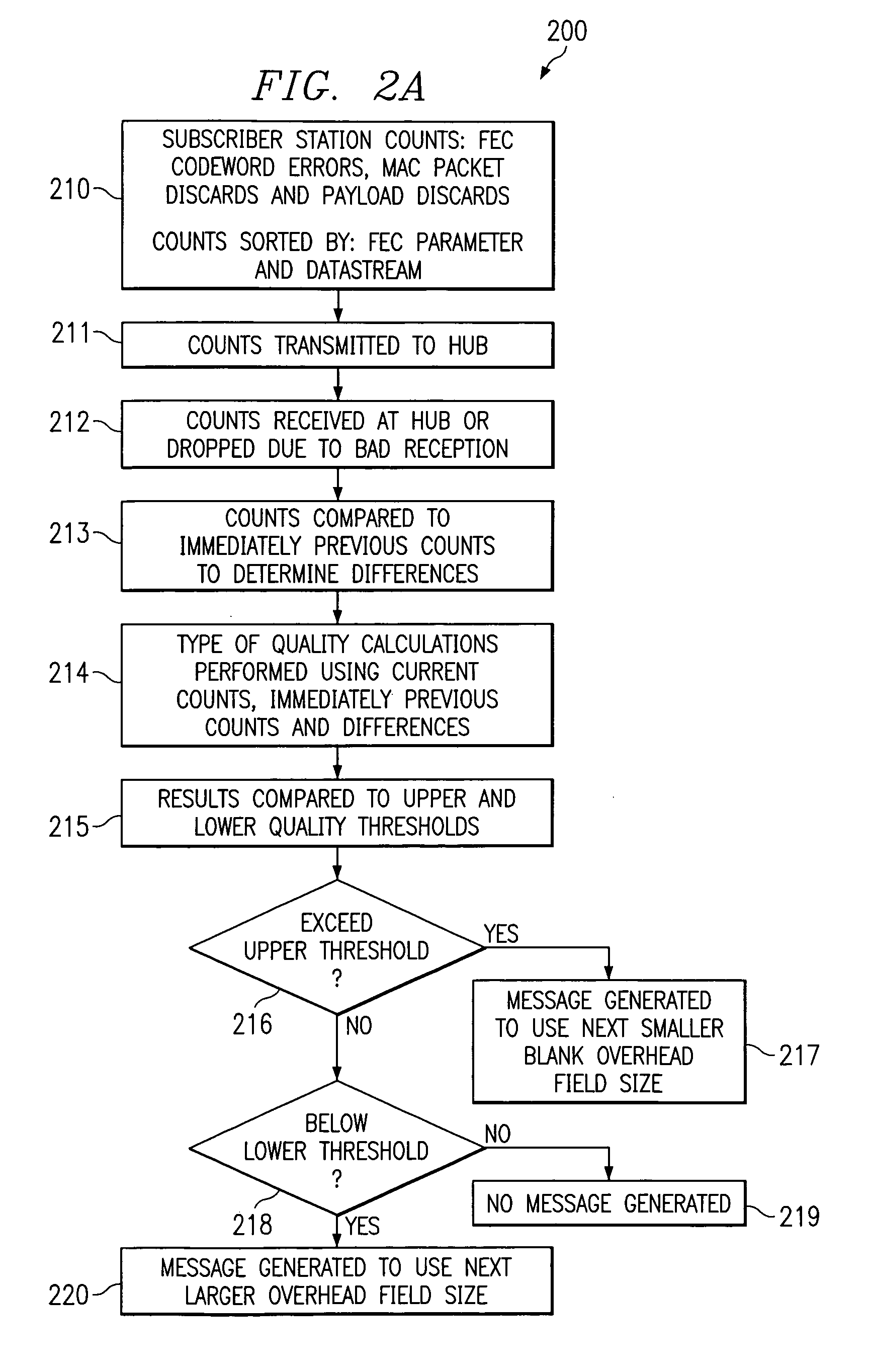
System and method for interference mitigation using adaptive forward error correction in a wireless RF data transmission system
InactiveUS6928603B1Improve availabilityIncrease capacityData representation error detection/correctionCode conversionData streamTransport system
An adaptive forward error correction system for mitigating interference and fading in RF data transmissions has a hub and subscriber stations transmitting and receiving forward error correction encoded data packets. The hub and subscriber stations count codewords and / or packets received with errors. The hub calculates a type of quality measure using the counts and compares this measure to quality thresholds. If an upper threshold is exceeded, the hub increases a size of transmitted active data fields and decreases a size of blank data fields. If a lower threshold is not met, the hub decreases a size of transmitted active data fields and increases a size of blank data fields. Similar changes by subscriber stations are directed by the hub. These changes are coordinated in headers associated with the packets or codewords, via a separate control channel or multi cast via a data stream used for transmitting the data packets.
Owner:NETGEAR INC
Preventing programming errors from occurring when programming flash memory cells
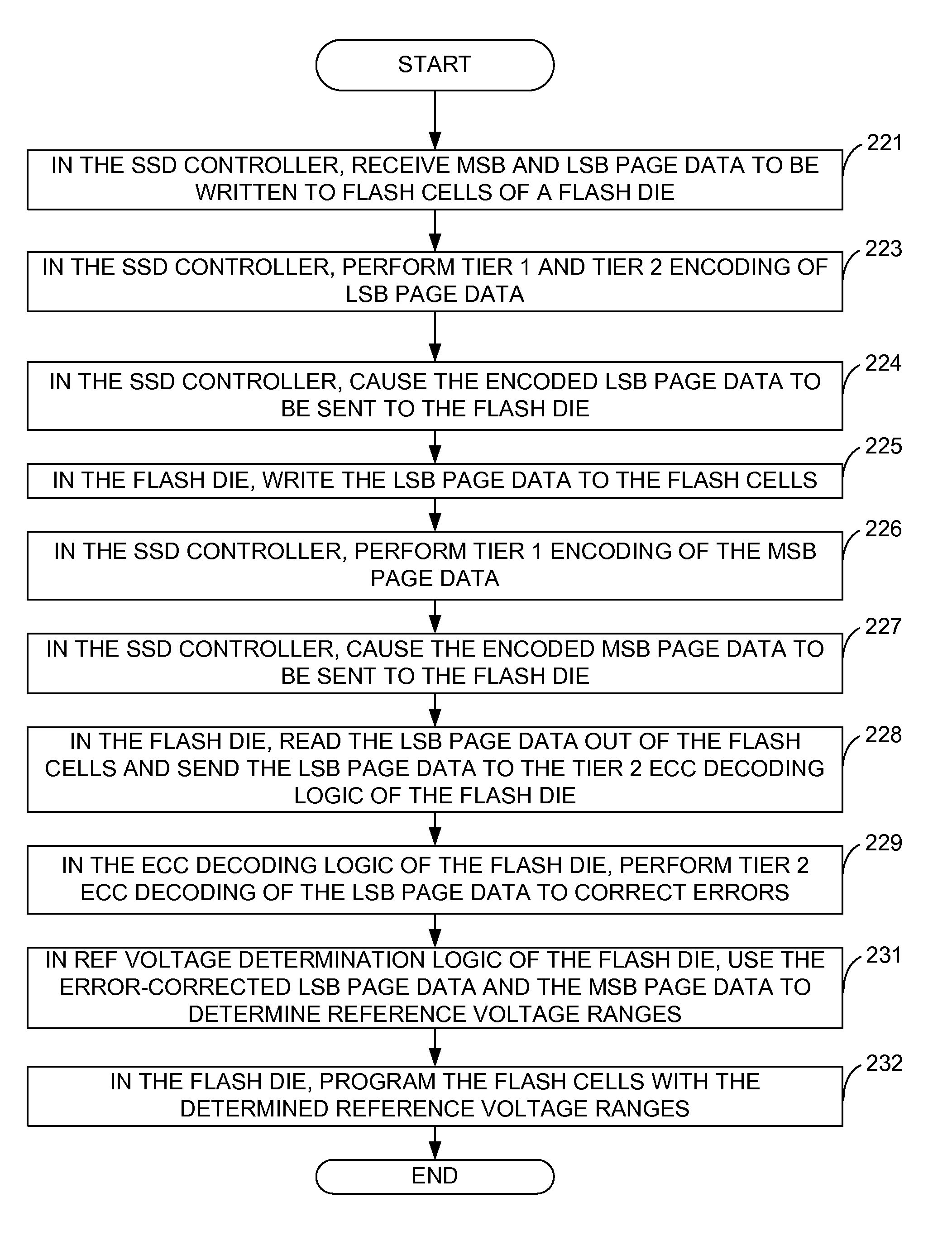
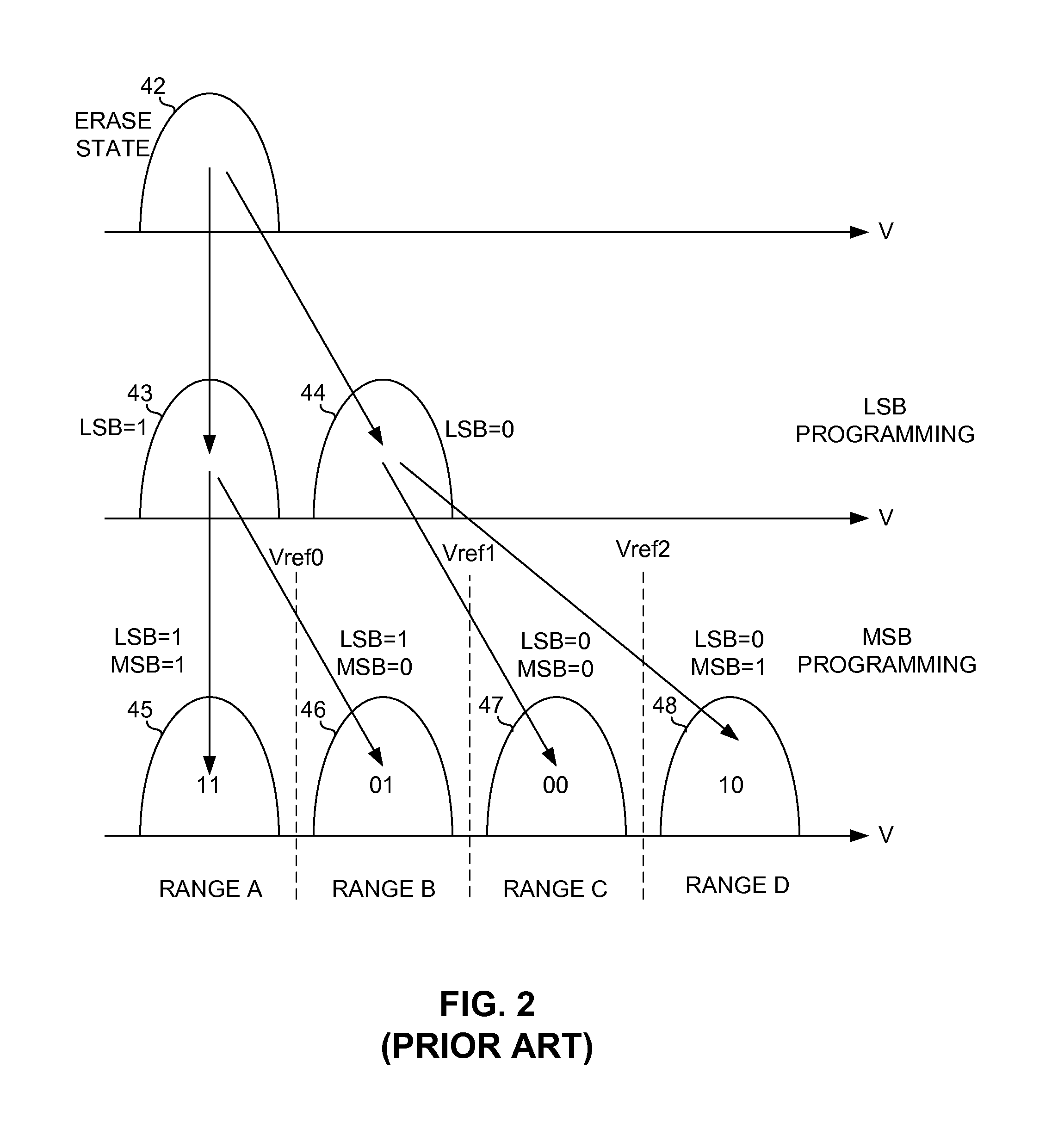
ActiveUS9417960B2Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsRead-only memoriesVoltage referenceVoltage range
Mis-programming of MSB data in flash memory is prevented by using ECC decoding logic on the flash die that error corrects the LSB values prior to the LSB values being used in conjunction with the MSB values to determine the proper reference voltage ranges. Error correcting the LSB page data prior to using it in combination with the MSB page data to determine the reference voltage ranges ensures that the reference voltage ranges will be properly determined and programmed into the flash cells.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for varying lengths of low density party check codewords
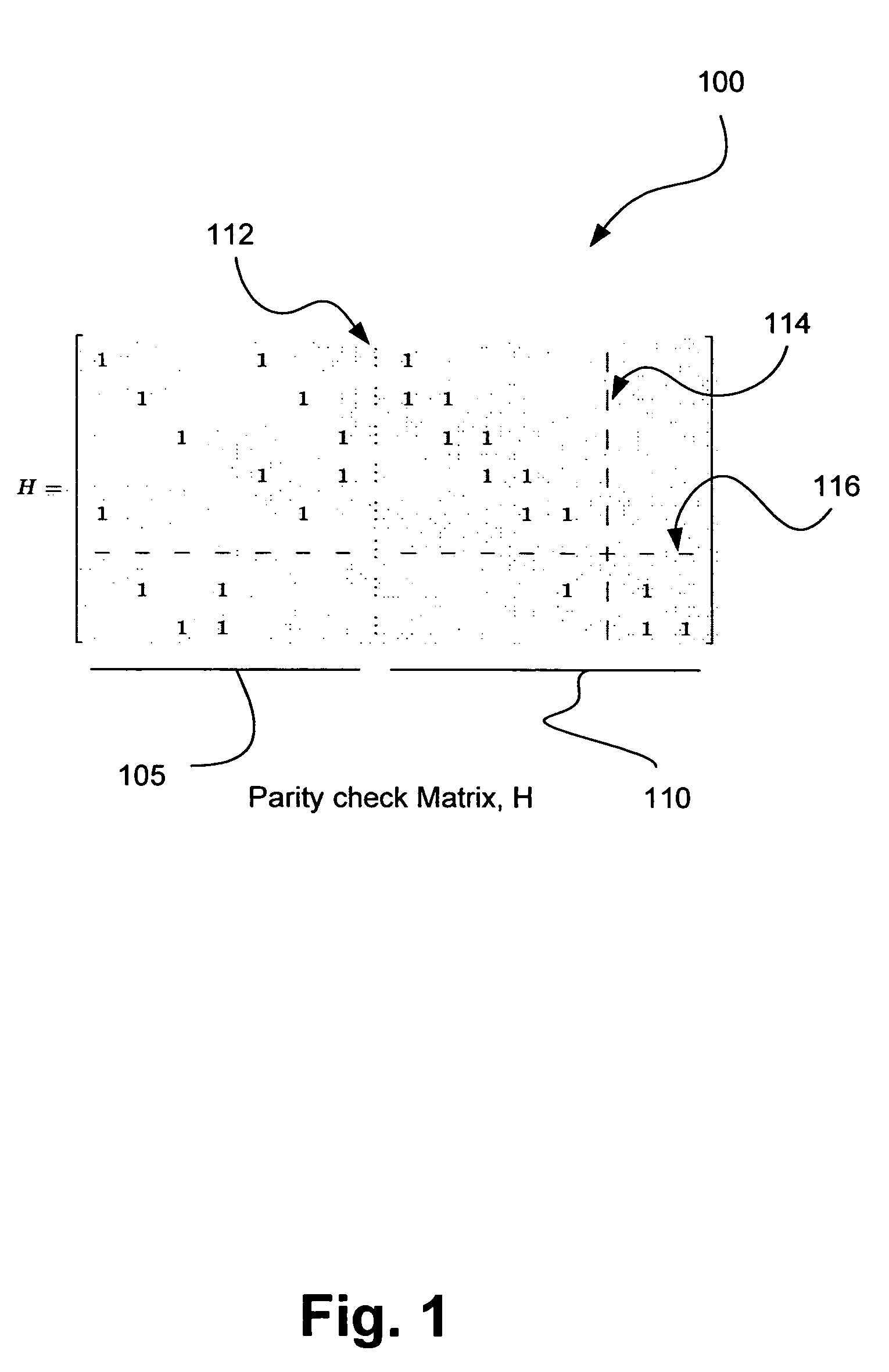
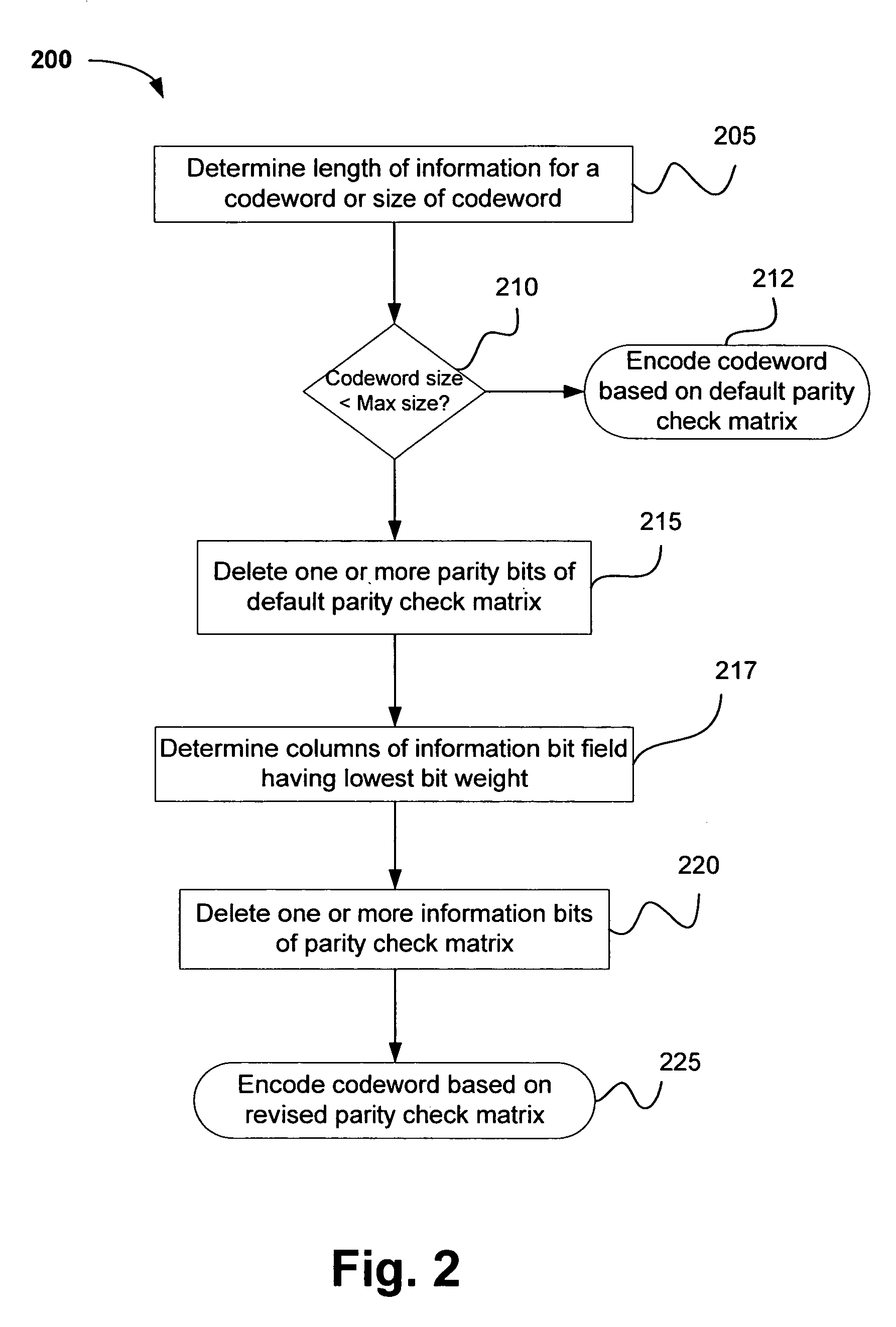
ActiveUS7263651B2Error preventionNetwork traffic/resource managementParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
A method and apparatus for encoding / decoding information using low density parity check (LDPC) codewords of varying lengths. In one implementation, an encoder / decoder uses a parity check matrix having a size that corresponds to a length of information for each codeword. In one example, the size of the parity check matrix may be retrieved from multiple stored matrices having different sizes. In other examples, a mother code matrix may be dynamically adjusted by puncturing parity bits and / or deleting information bits. Other inventive embodiments and adaptations are also disclosed.
Owner:APPLE INC
Methods and devices for coding or decoding an audio signal or bit stream
InactiveUS6975254B1Increase probabilityConvenient amountBroadcast with distributionSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumGrating
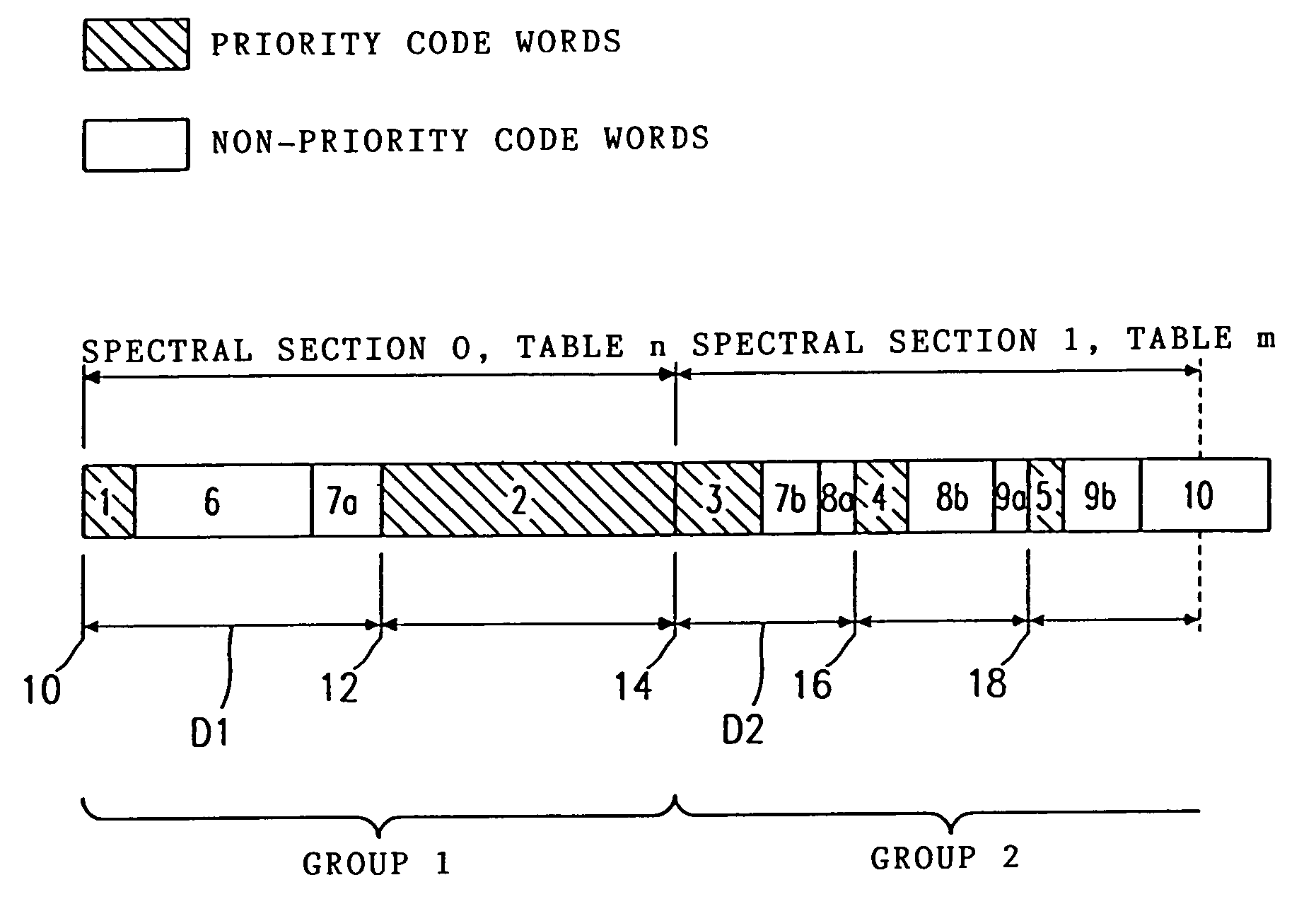
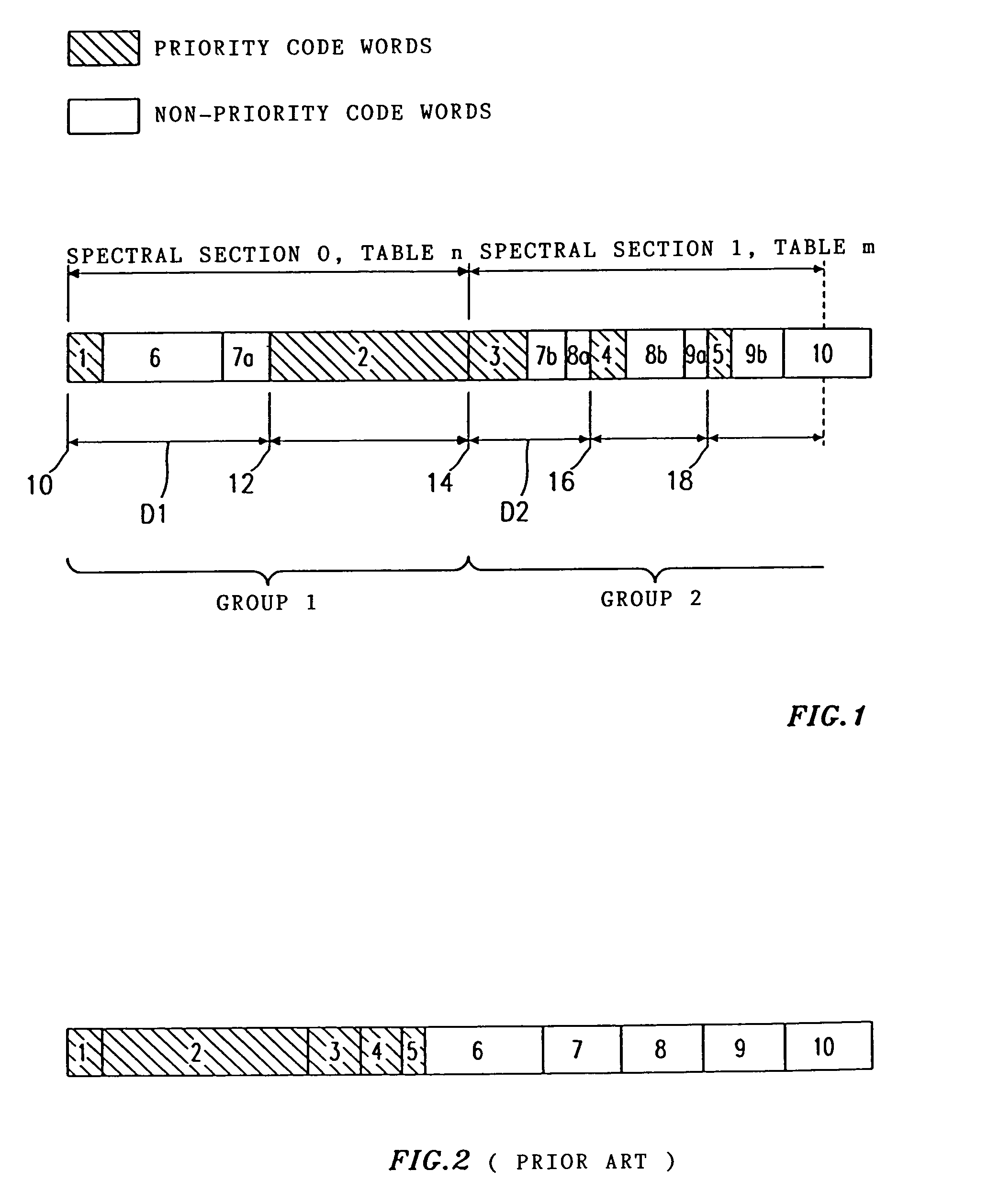
In a method for coding an audio signal to obtain a coded bit stream, discrete-time samples of the audio signal are transformed into the frequency domain to obtain spectral values. The spectral values are coded with a code table having a limited number of code words of different lengths to obtain spectral values coded by code words, the length of a code word assigned to a spectral value being that much shorter the higher the probability of occurrence of the spectral value is. A raster is then specified for the coded bit stream, the raster having equidistant raster points and the distance between the raster points depending on the code table(s) used. In order to obtain error-tolerant Huffman coding, priority code words, which represent particular spectral values which are psychoacoustically more important than other spectral values, are so arranged in the raster that the start of each priority code word coincides with a raster point.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
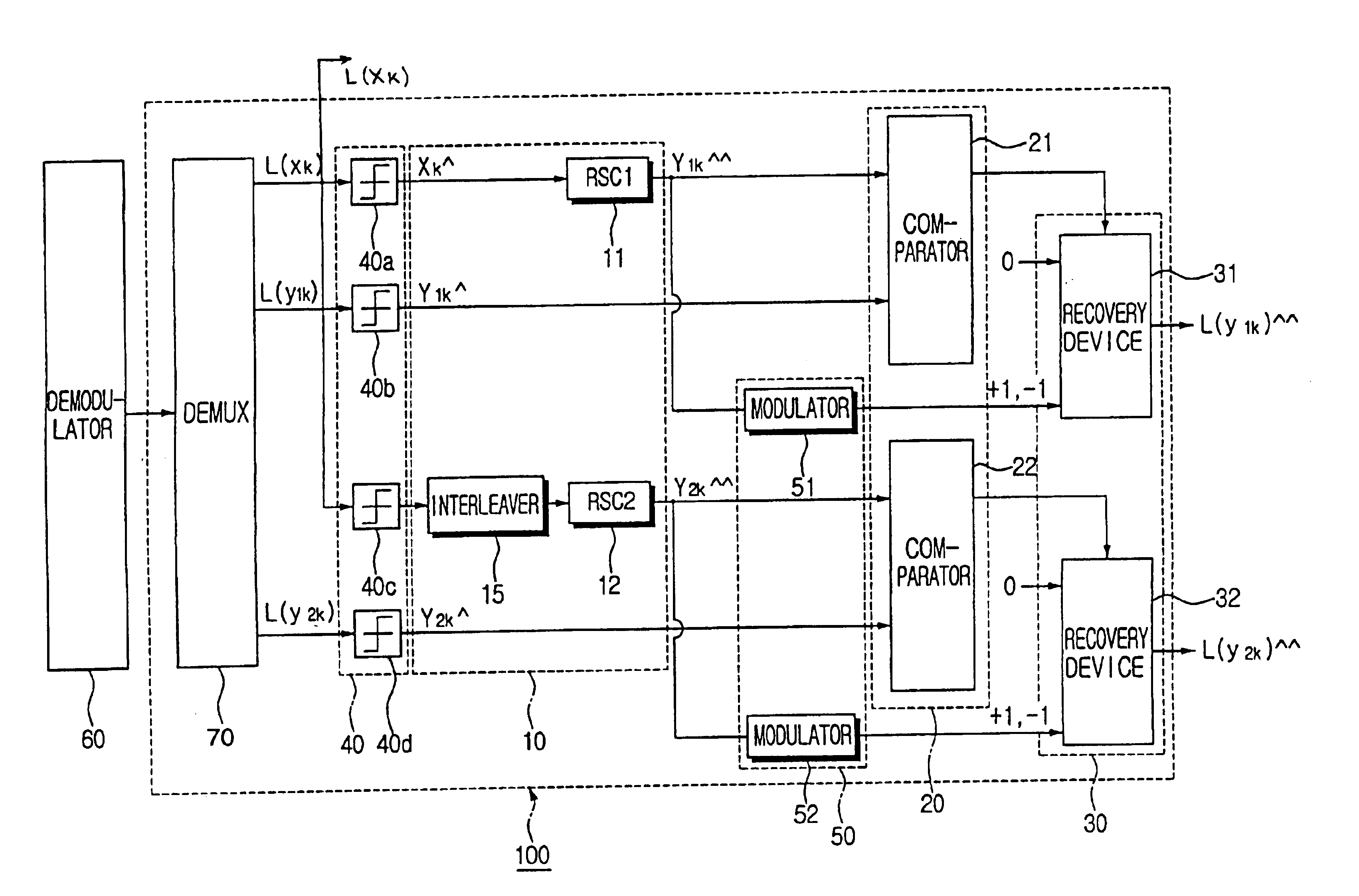
Pre-decoder for a turbo decoder, for recovering punctured parity symbols, and a method for recovering a turbo code
InactiveUS6910170B2Improve decoding performanceReduce the number of iterationsError correction/detection using convolutional codesOther decoding techniquesTurbo encoderTurbo coded
A pre-decoder applied to a turbo decoder for decoding a punctured turbo code. The turbo code consists of a data bit stream and a plurality of parity bit streams, parts of which are punctured. The pre-decoder has an arithmetic unit for calculating estimated parity bit streams by carrying out, with respect to the data bit stream, the same algorithm used by a turbo encoder to produce the parity bit streams, a comparison unit for comparing the plurality of parity bit streams with the estimated parity bit streams, and a recovery unit for substituting estimated parity symbols for corresponding punctured parts of the parity symbol streams when related non-punctured bits of the parity bit streams are identical with corresponding estimated non-punctured parity bits. The punctured parity symbols are recovered by the pre-decoder completely, or at least partially, and provided to the turbo decoder. Accordingly, the decoding performance of the turbo decoder is enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
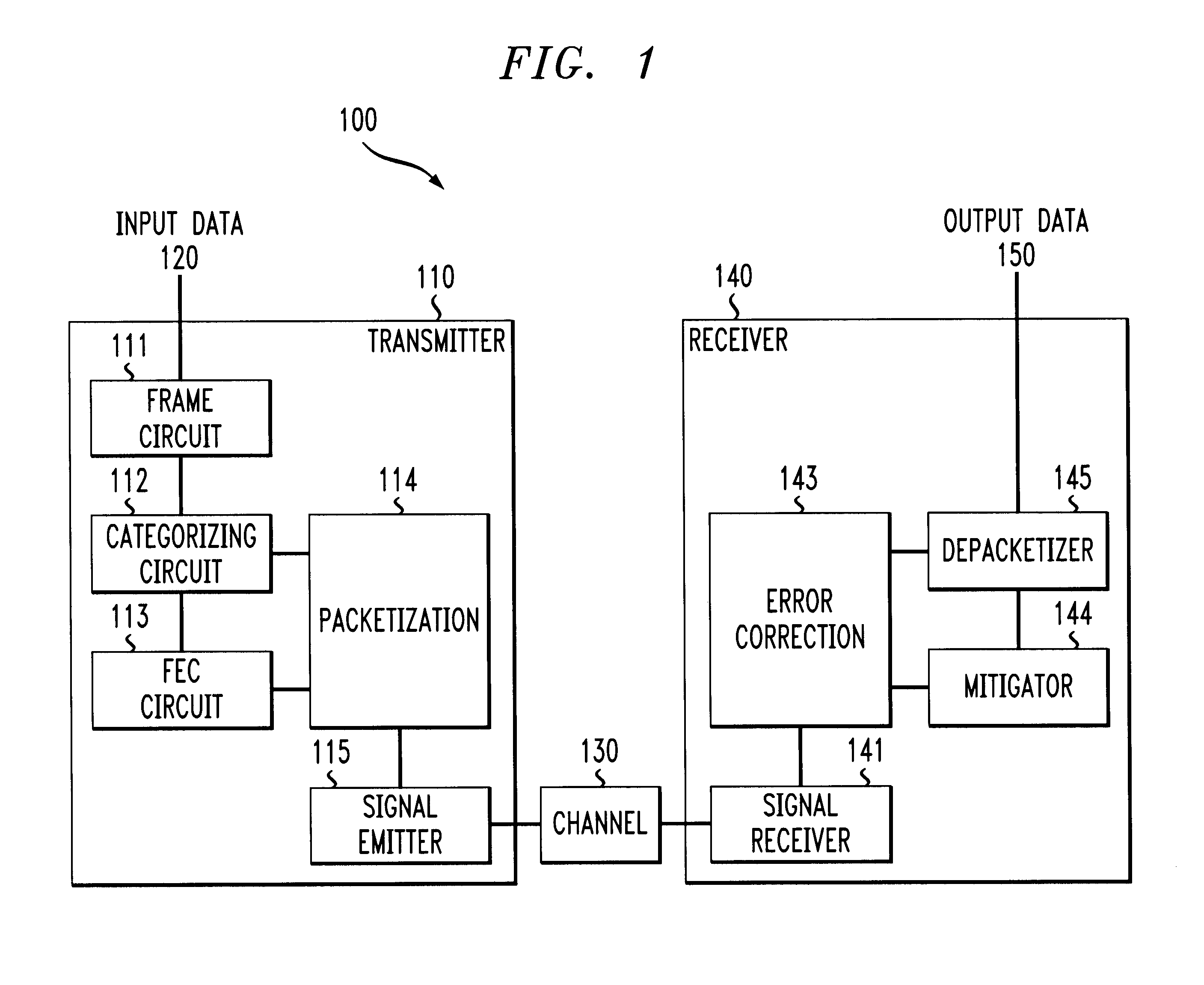
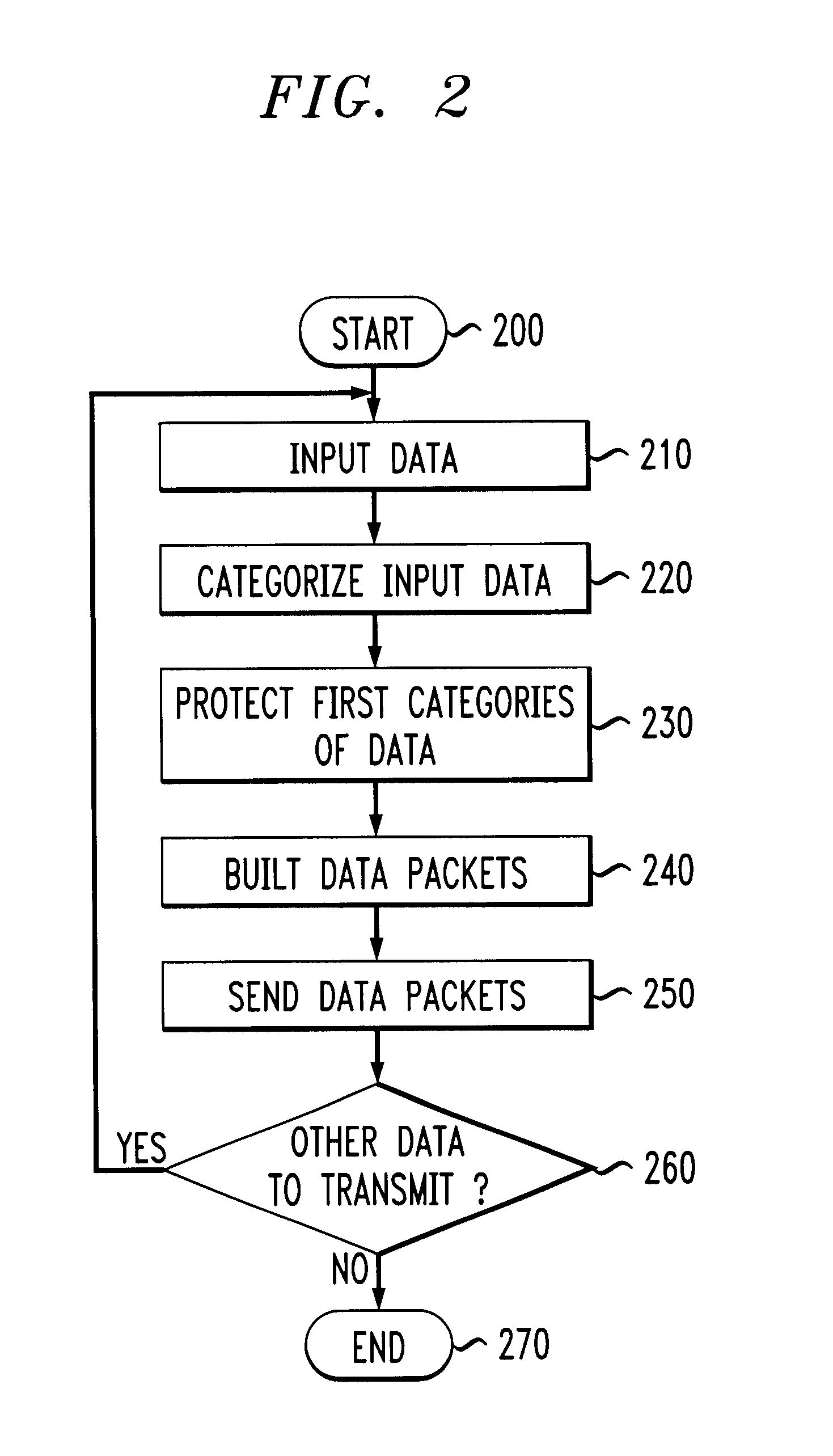
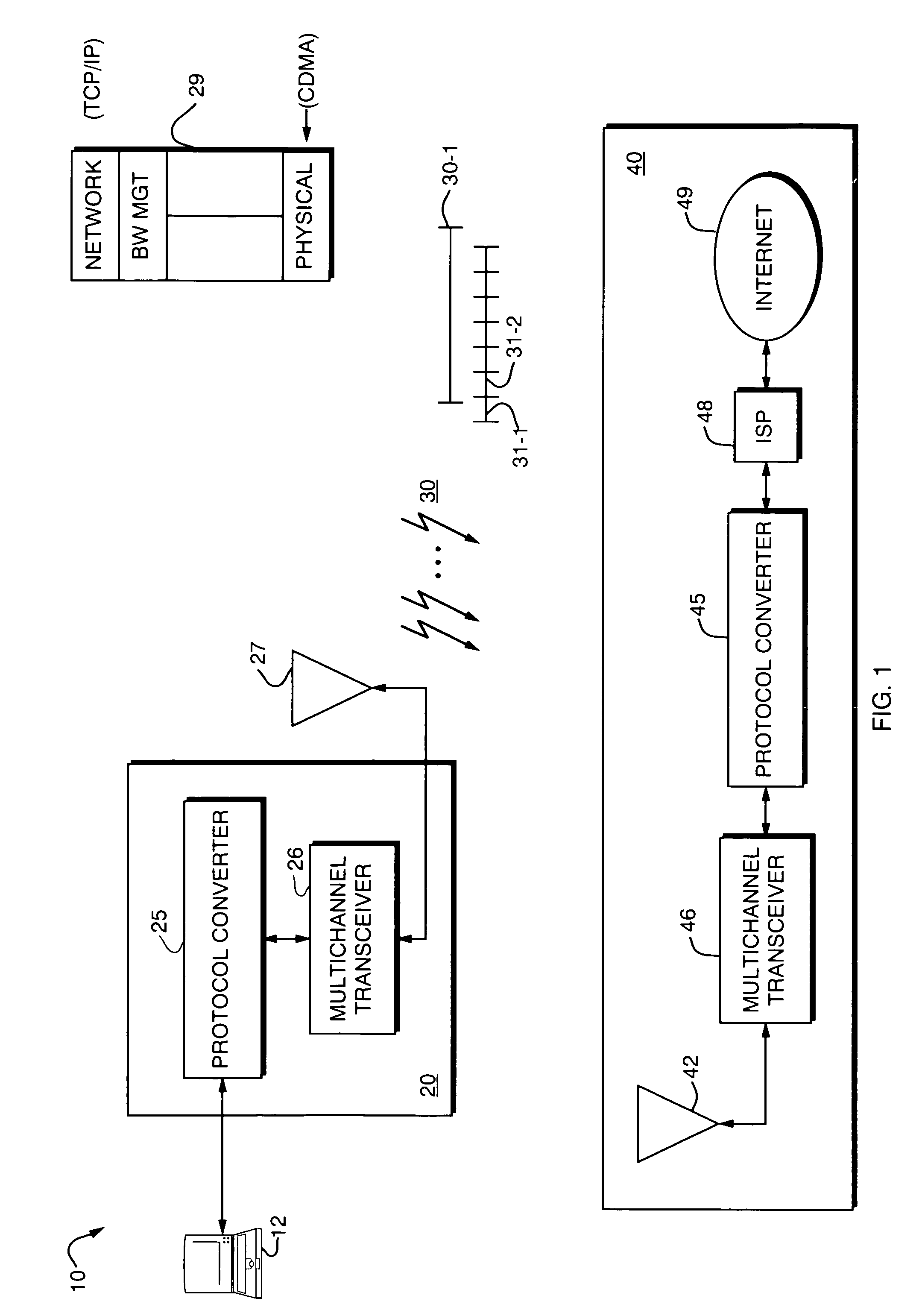
System and methods for transmitting data
InactiveUS6850559B1Increase demandError prevention/detection by using return channelModulated-carrier systemsForward error correctionComputer science
A system and method for transmitting data over a channel, in which the data are categorized in at least two different categories. For example, the data are categorized according to the effect on perceived degradation on the data when error mitigation is performed on the data. Corrupted data of the first category are replaced using a first replacement method, such as retransmission and forward error correction. The corrupted data of the second category are replaced using a second replacement method different from the first replacement method, e.g., error mitigation or interpolation.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
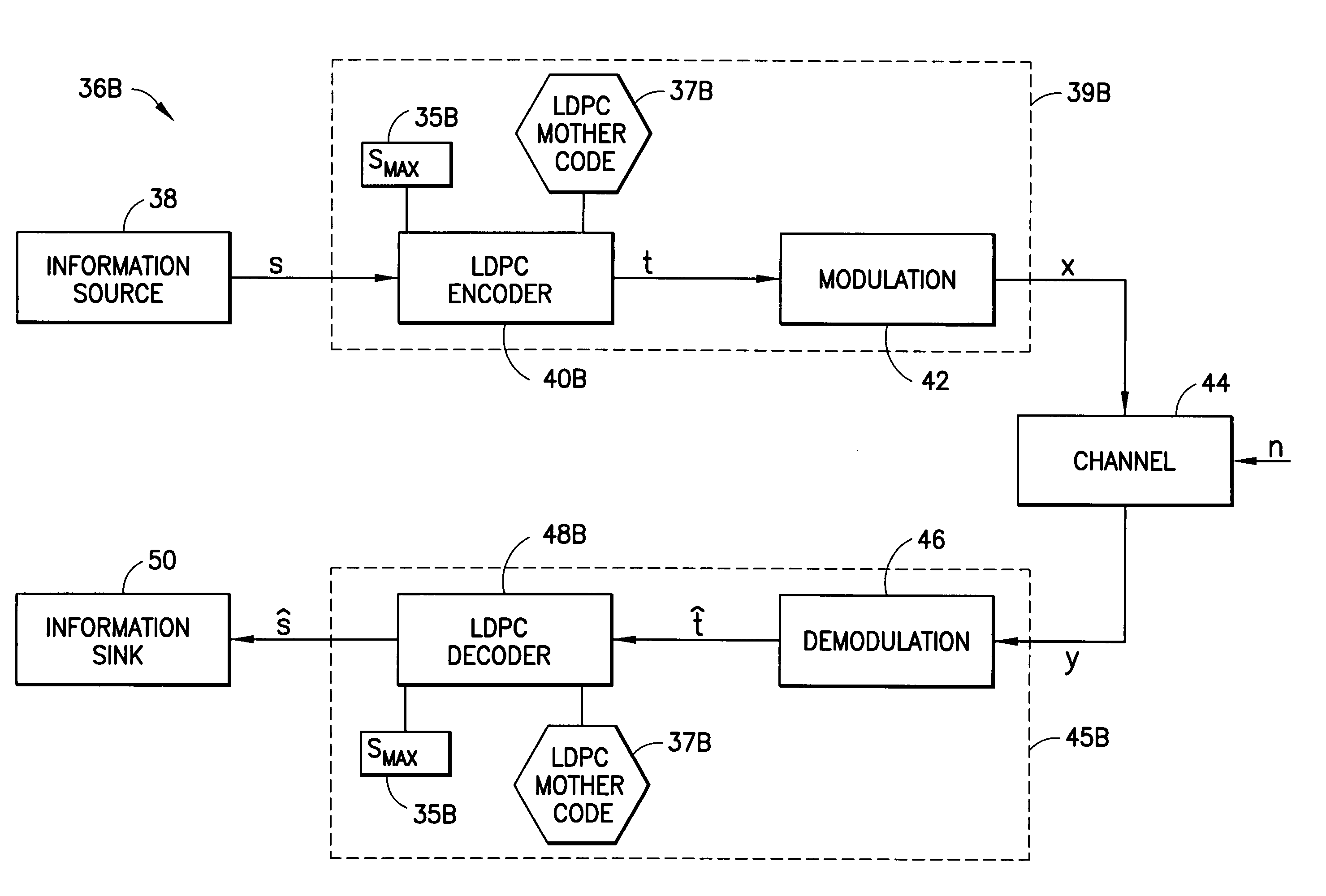
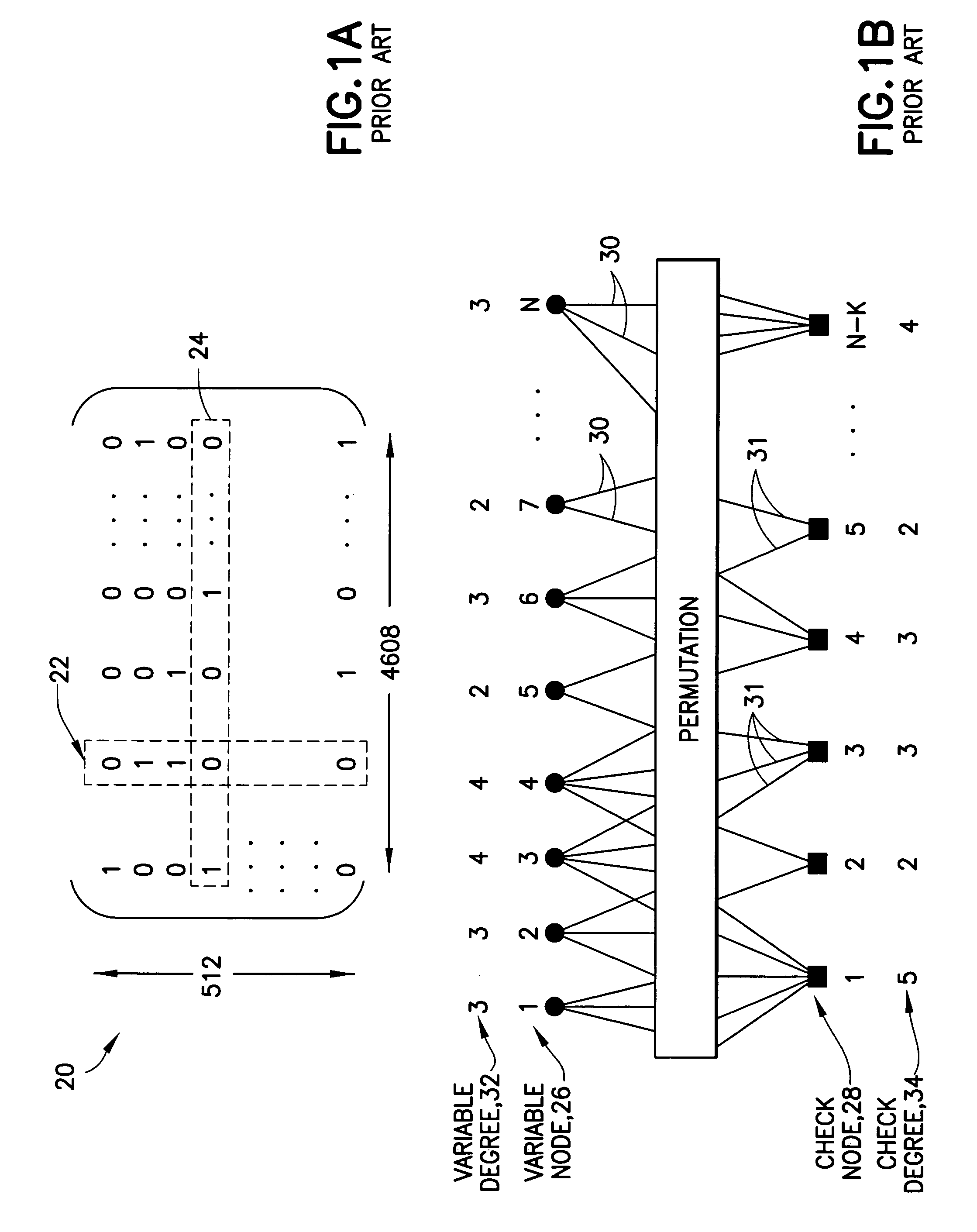
Low-density parity-check codes for multiple code rates
InactiveUS7222284B2Lower requirementReduce memory requirementsDigital variable displayError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeParallel computing
Puncture sequences S1, S2, etc. for code rates R1, R2, etc. less than a maximum code rate Rmax are defined subsets of a maximum rate puncture sequence Smax that corresponds to the maximum code rate Rmax. Each puncture sequence Si for a code rate Ri is related to the puncture sequence Si−1, of the previous code rate Ri−1, and preferably S1⊂S2⊂ . . . ⊂Smax−1⊂Smax. The puncture sequences are groups of one or more memory elements, each of which is a variable degree, a variable node location, a check degree, or a check node location. A method for deriving such a puncture sequence for variable code rates is also disclosed.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Techniques for enhanced reliability of data transfer with dynamic scaling
ActiveUS7856583B1Easy to useReduce bandwidth usageTransmission systemsCode conversionData transmissionComputer science
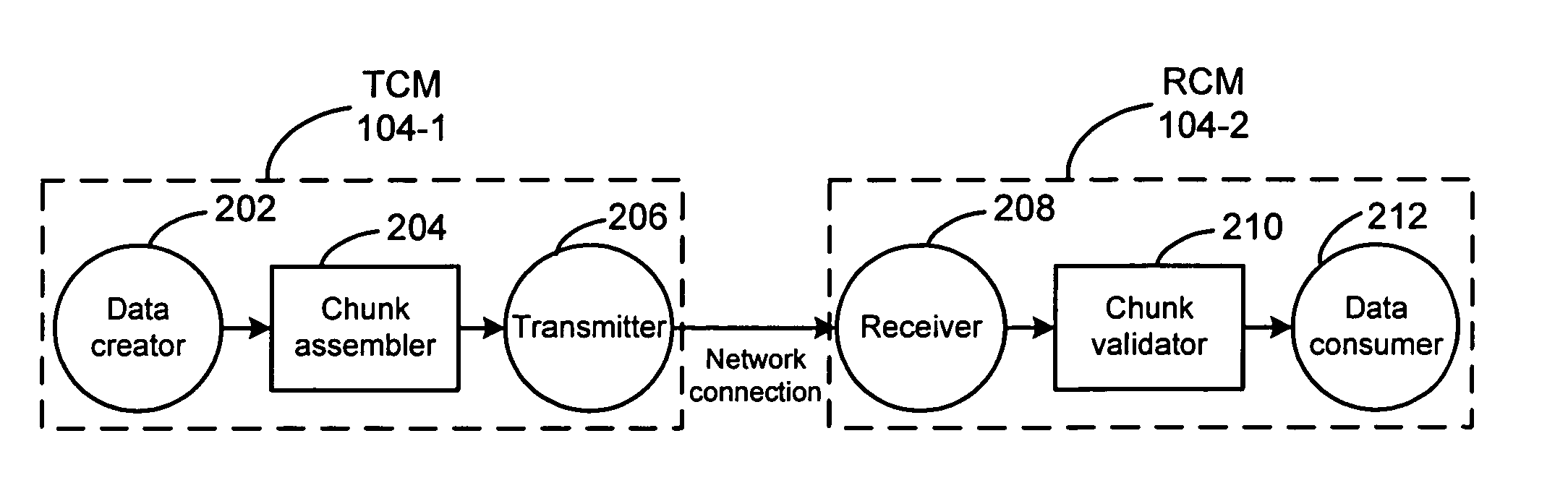
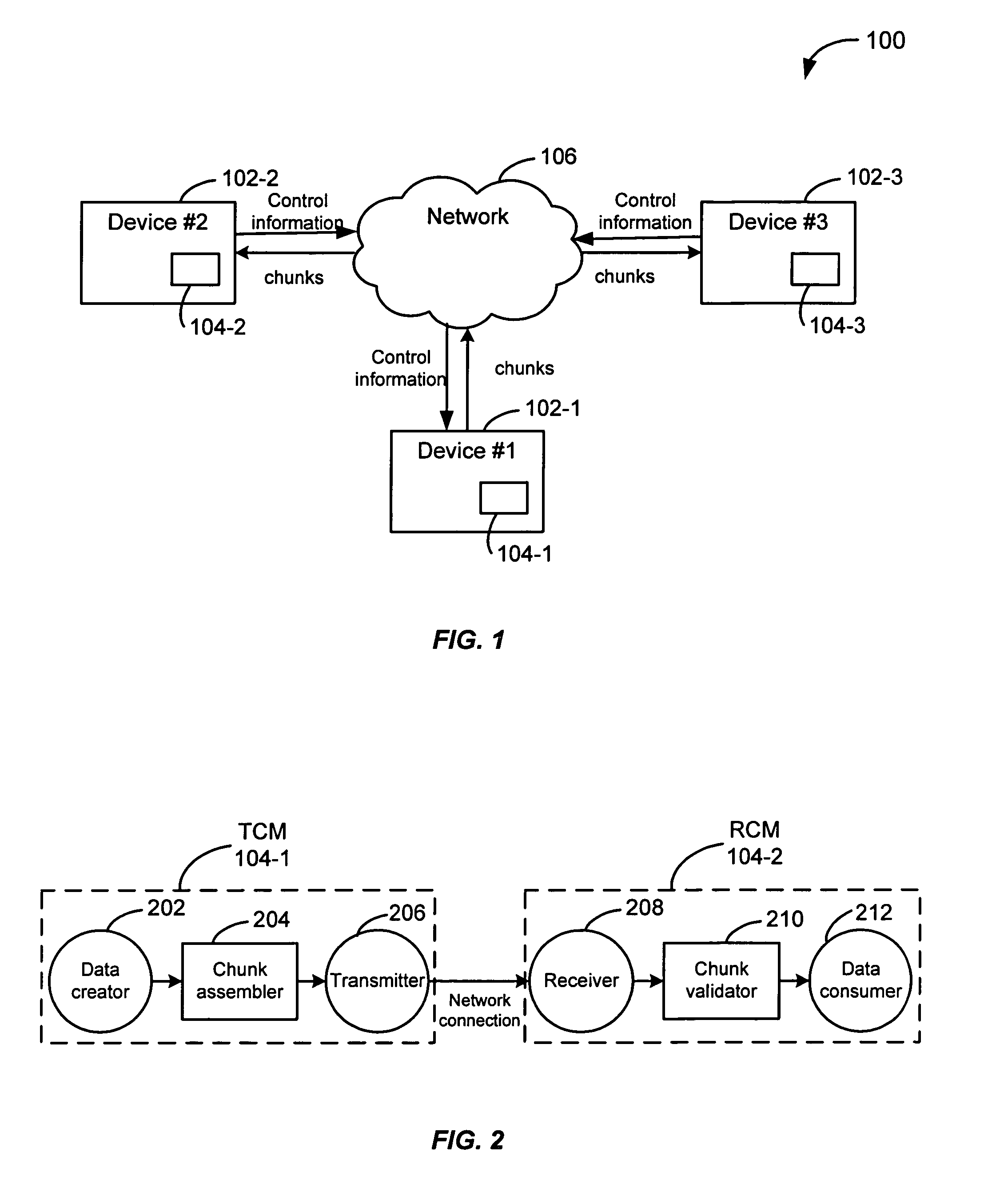
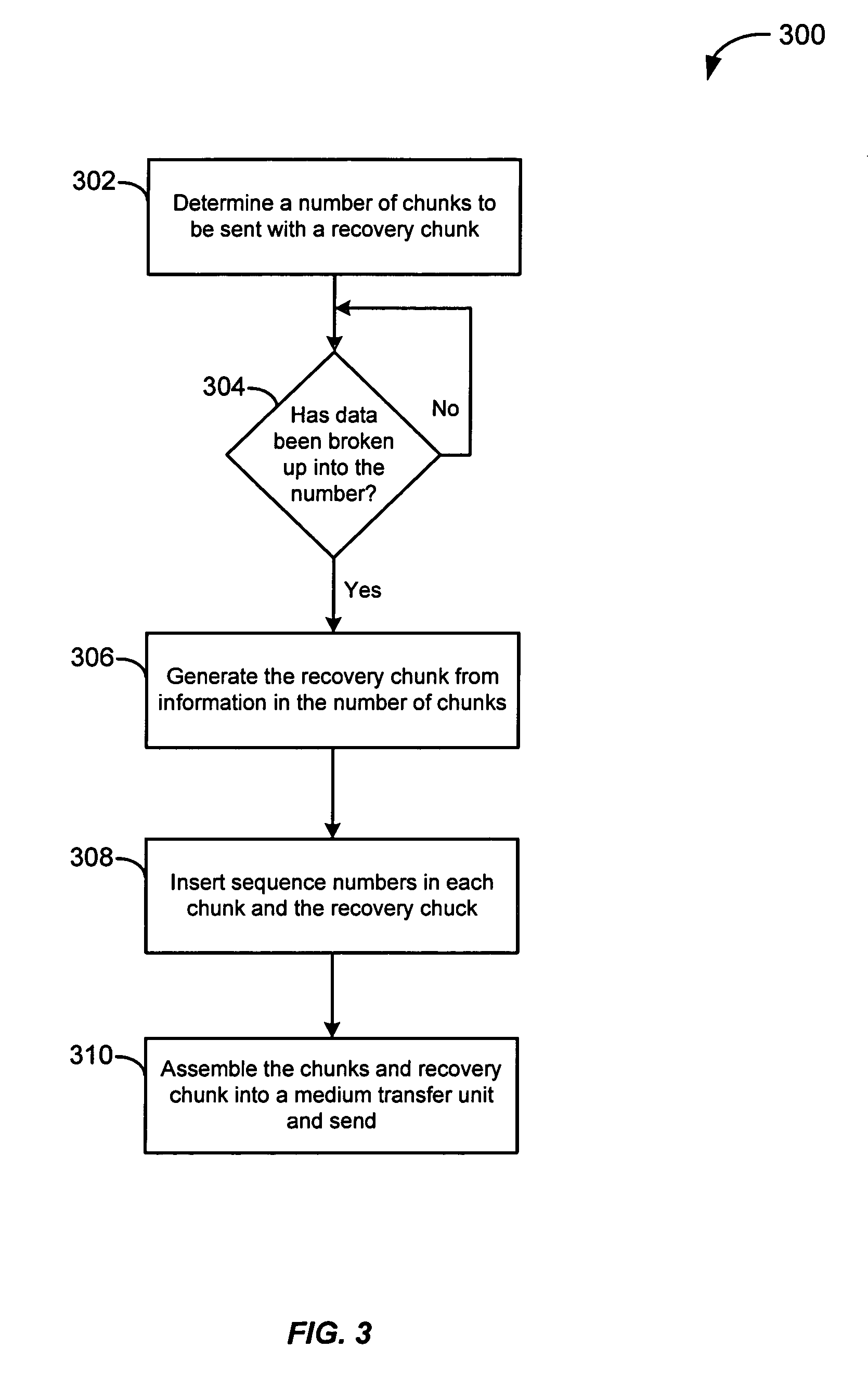
A recovery chunk is generated based on information found in each chunk in a group of chunks. For example, the group of chunks includes three chunks of which information in the three chunks is used to generate a recovery chunk. The recovery chunk is then used to recover a single lost chunk in the group of chunks. The three chunks and the recovery chunk are sent to a receiver over a network. If one of the three chunks is lost, the recovery chunk is used to generate the lost chunk. The recovery chunk is used to recover a single lost chunk, however, the recovery chunk is not used to recover more than one lost chunk in the group. The number of chunks is also dynamically adjusted based on chunk loss at a receiver. This adjustment is based on the bandwidth used and reliability desired.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
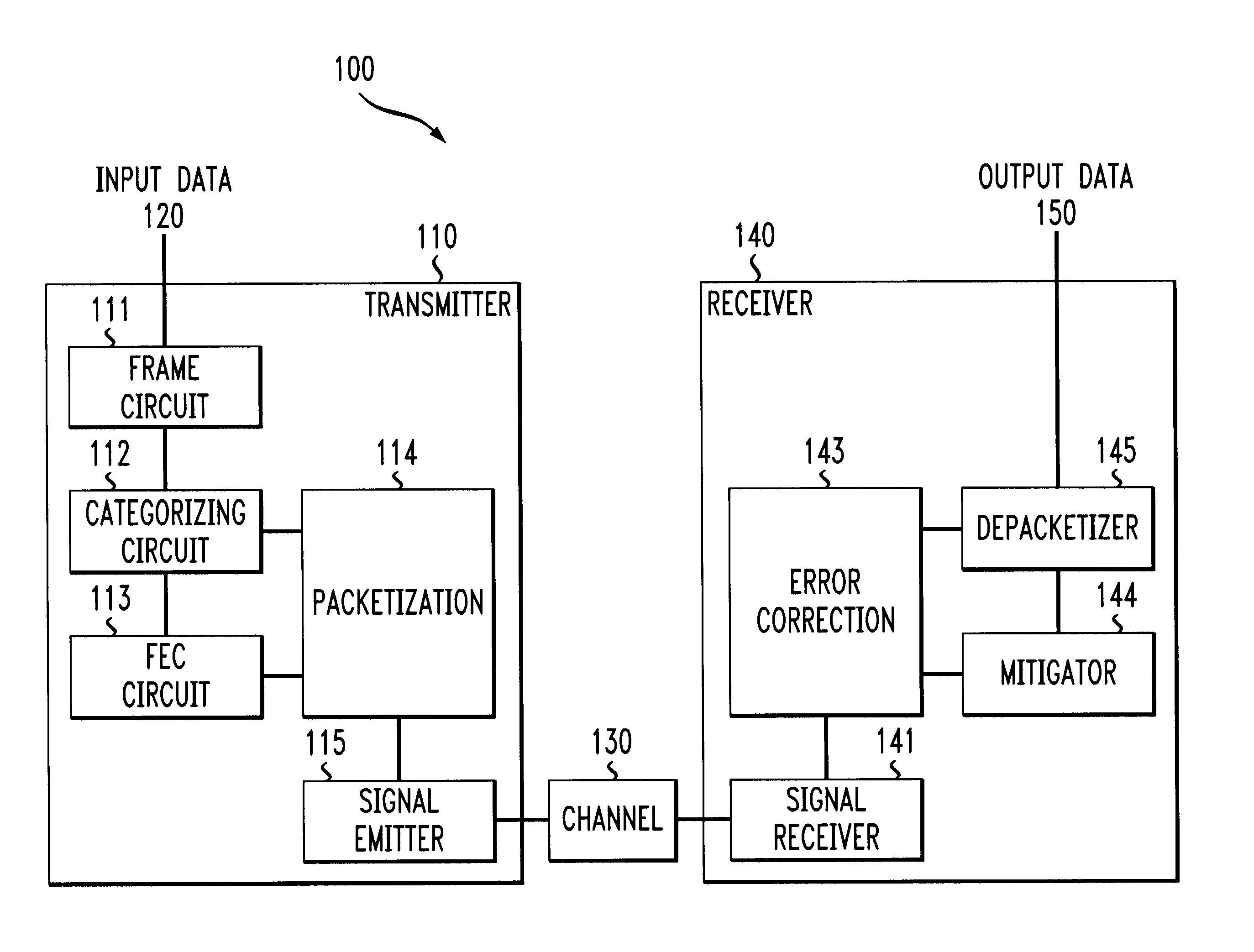
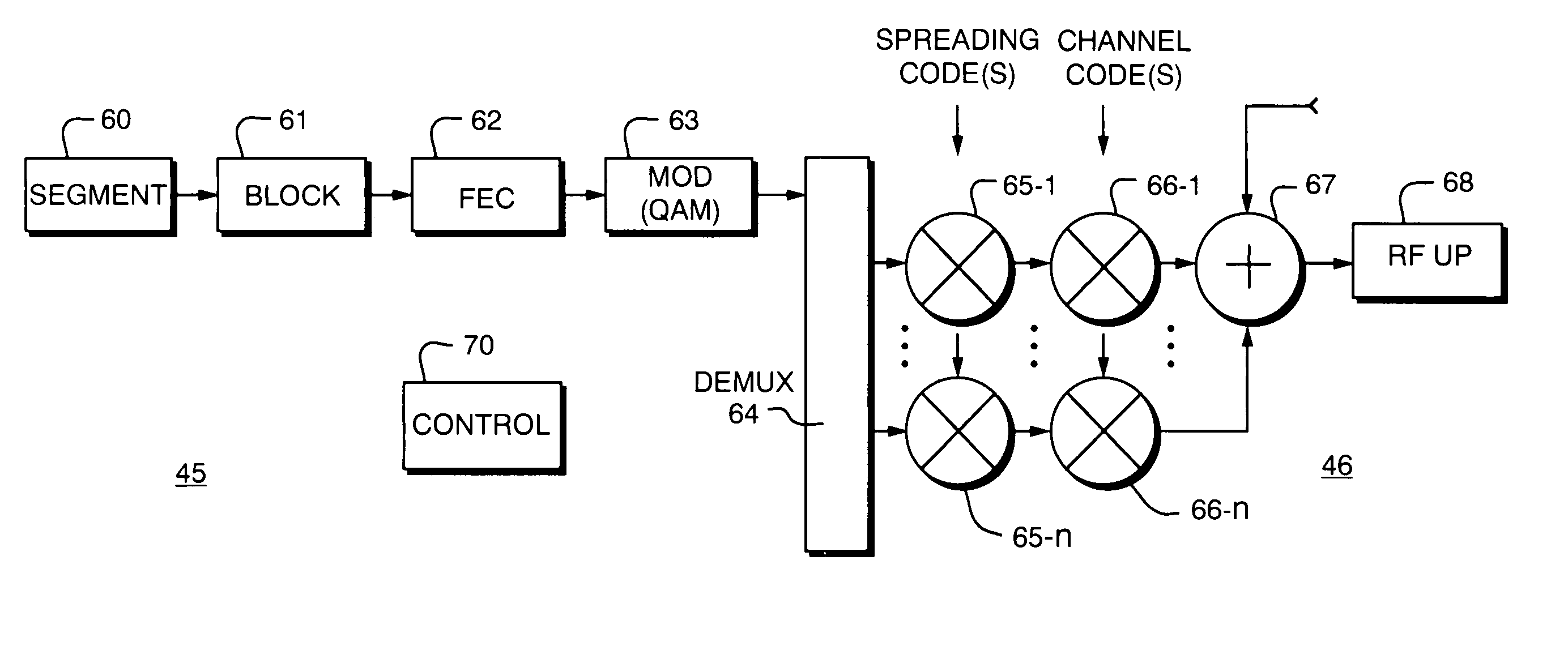
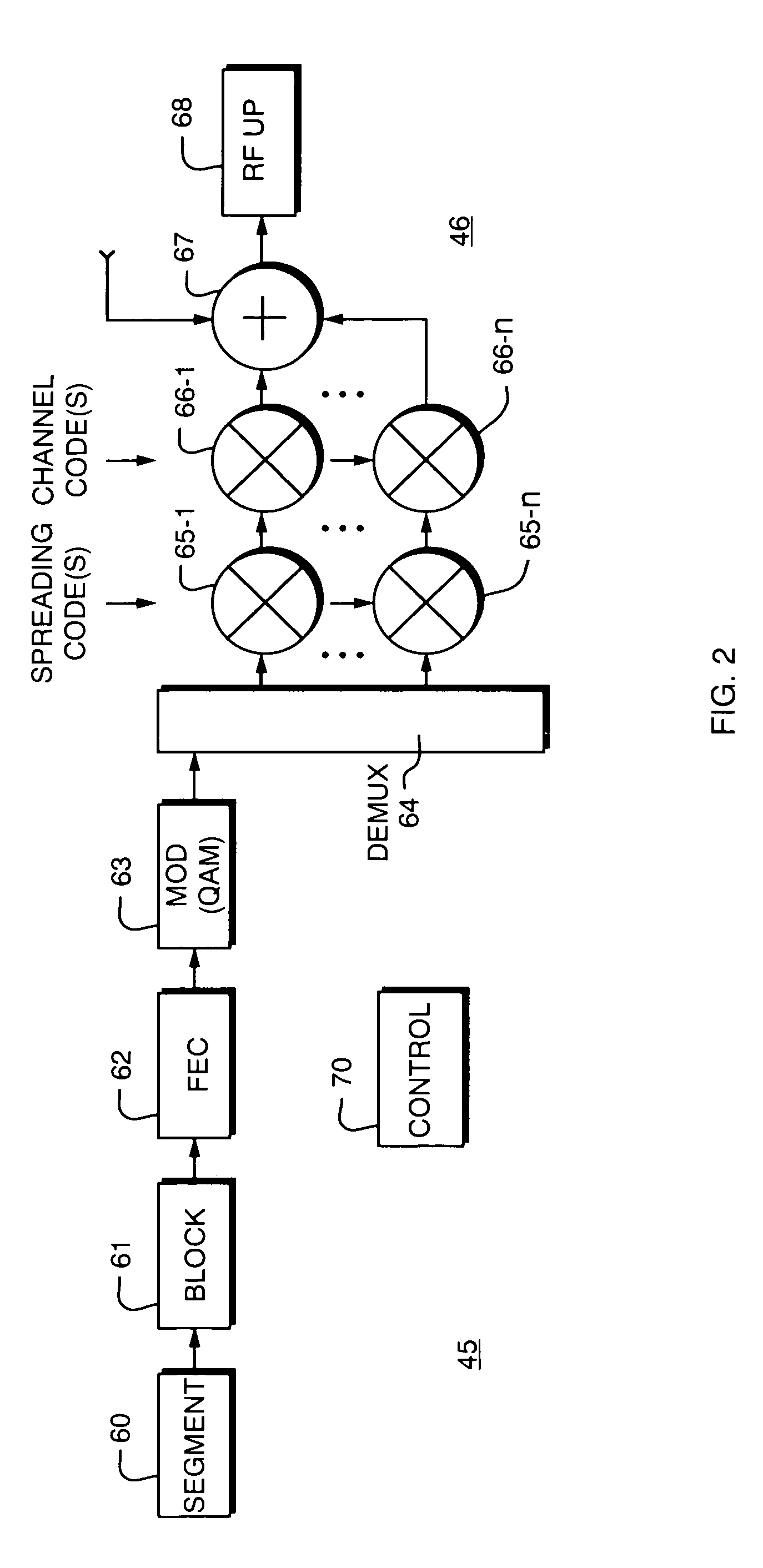
System and method for forward error correction
ActiveUS7076724B2Data representation error detection/correctionError preventionData streamForward error correction
A system and method are provided for transferring a packet across a data link. The packet may include a stream of data symbols which is delimited by one or more framing symbols. Corruptions of the framing symbol which result in valid data symbols may be mapped to invalid symbols. If it is desired to transfer one of the valid data symbols that has been mapped to an invalid symbol, the data symbol may be replaced with an unused symbol. At the receiving end, these unused symbols are replaced with the corresponding valid data symbols. The data stream of the packet may be encoded with forward error correction information to detect and correct errors in the data stream.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
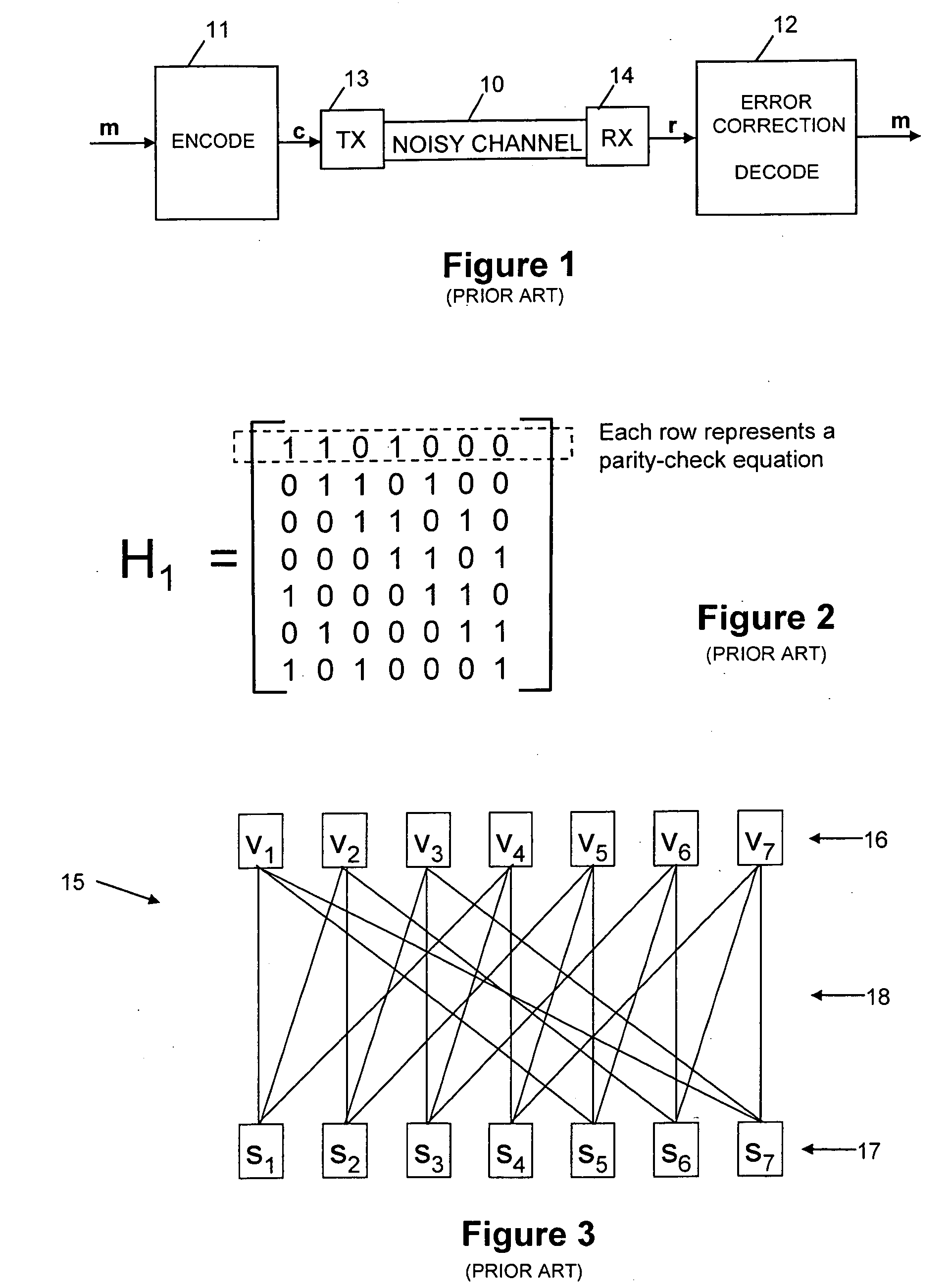
Error detection method and apparatus
To identify errored bits in a binary data set, an ordered plurality of modulo-2 summations of respective selections of the data-set bits are compared with a target syndrome. The selections of data-set bits are defined by the connection of sum nodes to variable nodes in a logical network of nodes and edges where each variable node is associated with a respective data-set bit and each sum node corresponds to a respective modulo-2 summation. Any sum node for which the corresponding summation of selected data-set bits is found to be inconsistent with the target syndrome is identified as errored. Predetermined patterns of errored sum nodes are then looked for to identify one or more associated errored data-set bits. The identified errored data-set bits can then be flipped to correct them
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Transmission apparatus and method, reception apparatus and method, storage medium, and program
InactiveUS20050160346A1Guaranteed normal transmissionRedundant dataError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionStreaming dataPacket generator
A congestion / non-congestion determining unit determines whether or not a communications network is in a congestion state. An FEC (forward error correction) packet generator generates error correction packets containing error correction data for correcting error of streaming data contained in transmission packets. When the determination result changes from a non-congestion state to a congestion state, an FEC transmission controller controls the error-correction-packet generation so as to change the number of error correction packets. The present invention is applicable to a remote TV conference system.
Owner:SONY CORP
Adaptive hybrid ARQ algorithms
ActiveUS7155655B2Error prevention/detection by using return channelTransmission systemsReal-time computingComputer science
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Transmission apparatus, transmission control program, and transmission method
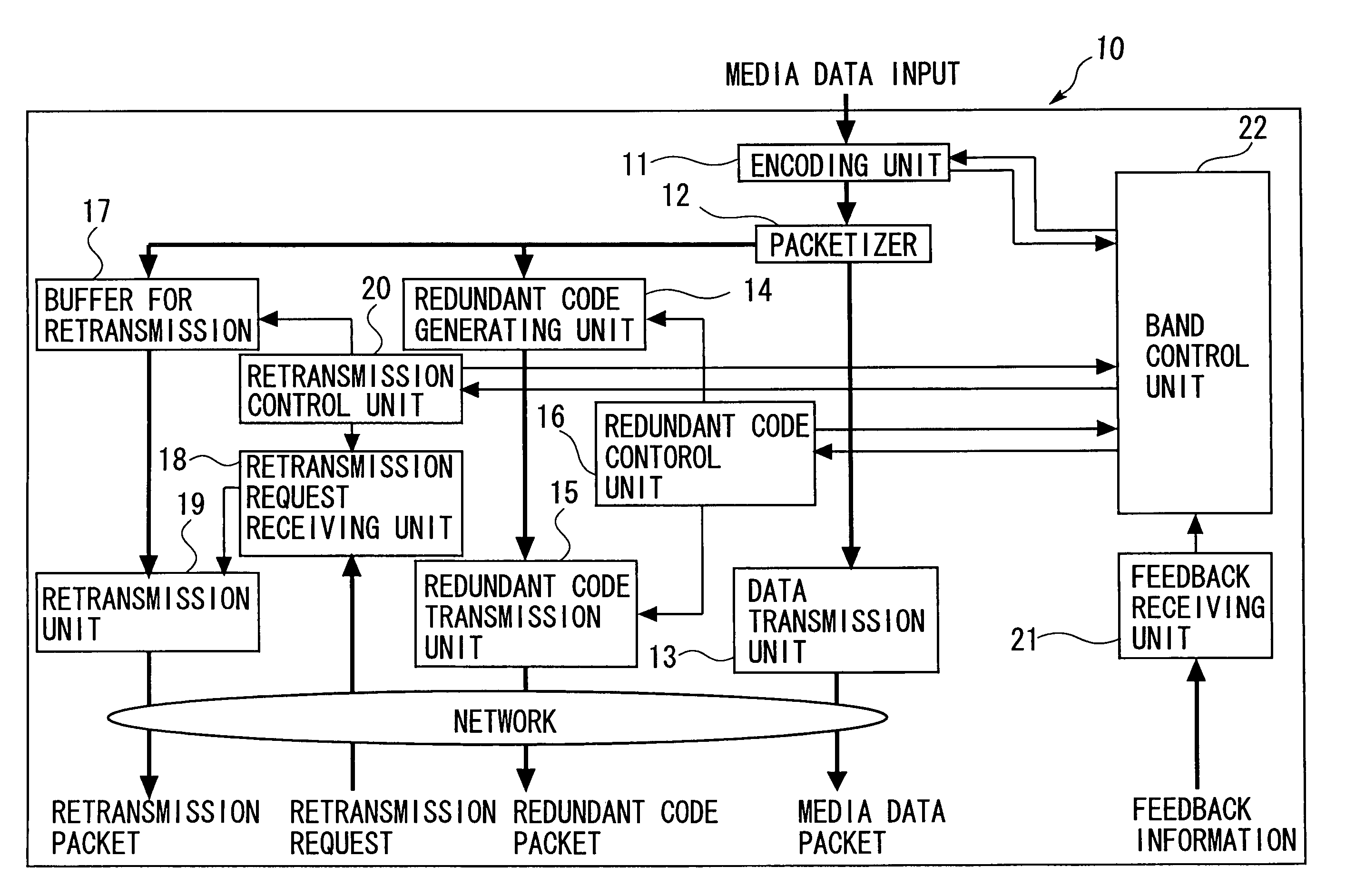
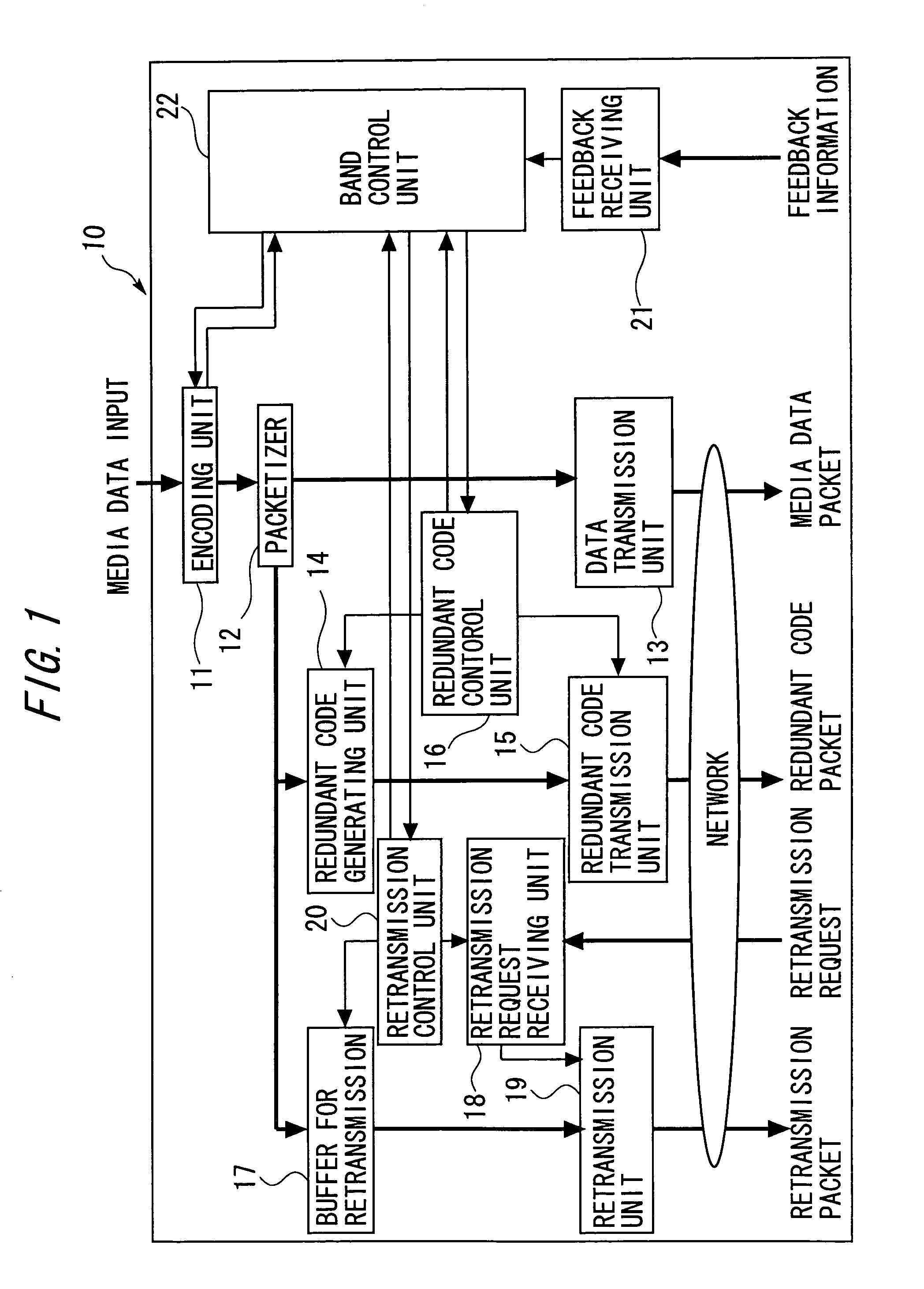
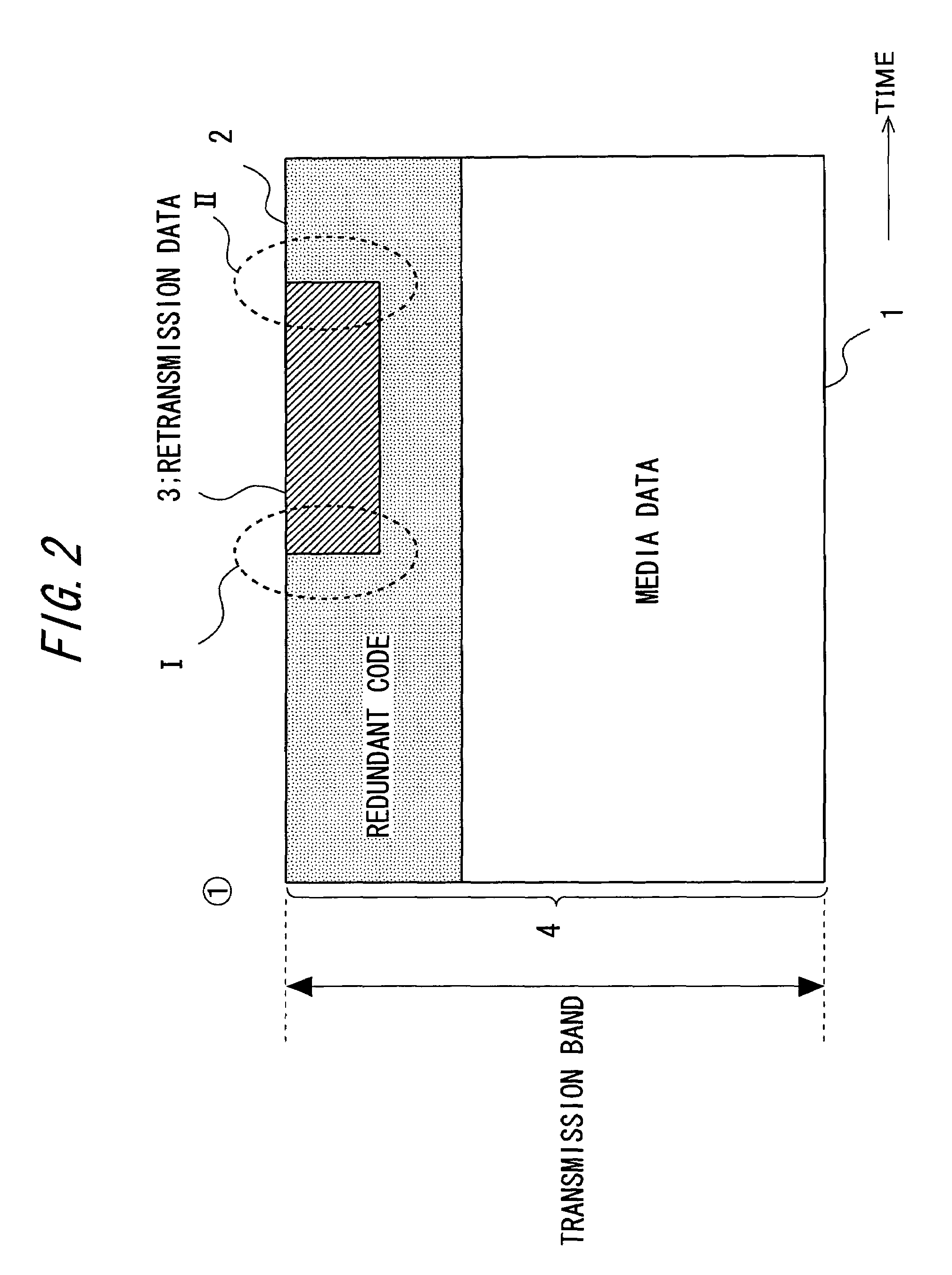
ActiveUS7376880B2Effective compensationControlling transmission line congestionError prevention/detection by using return channelOther decoding techniquesCommunication unitRedundant code
A transmission apparatus includes a communication unit for performing transmission and reception of encoded data packets with other terminals, a redundant code generating unit for generating a redundant code packet for restoring data lost due to the loss of a data packet, a redundant code control unit for controlling the band used by the redundant code packet, a buffer for accumulating retransmission packets that can be retransmitted when corresponding data are lost, a retrieval unit for retrieving a corresponding retransmission packet from the buffer for retransmission upon receiving a retransmission request for the data packet, a retransmission control unit for controlling the band used for retransmission, and a band control unit for controlling the bandwidth of a redundant code based on the band used for retransmission and the band currently used for the redundant code.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for configuring content in a broadcast system
ActiveUS20120240174A1Efficient reproductionUnequal/adaptive error protectionTwo-way working systemsComputer scienceBroadcast system
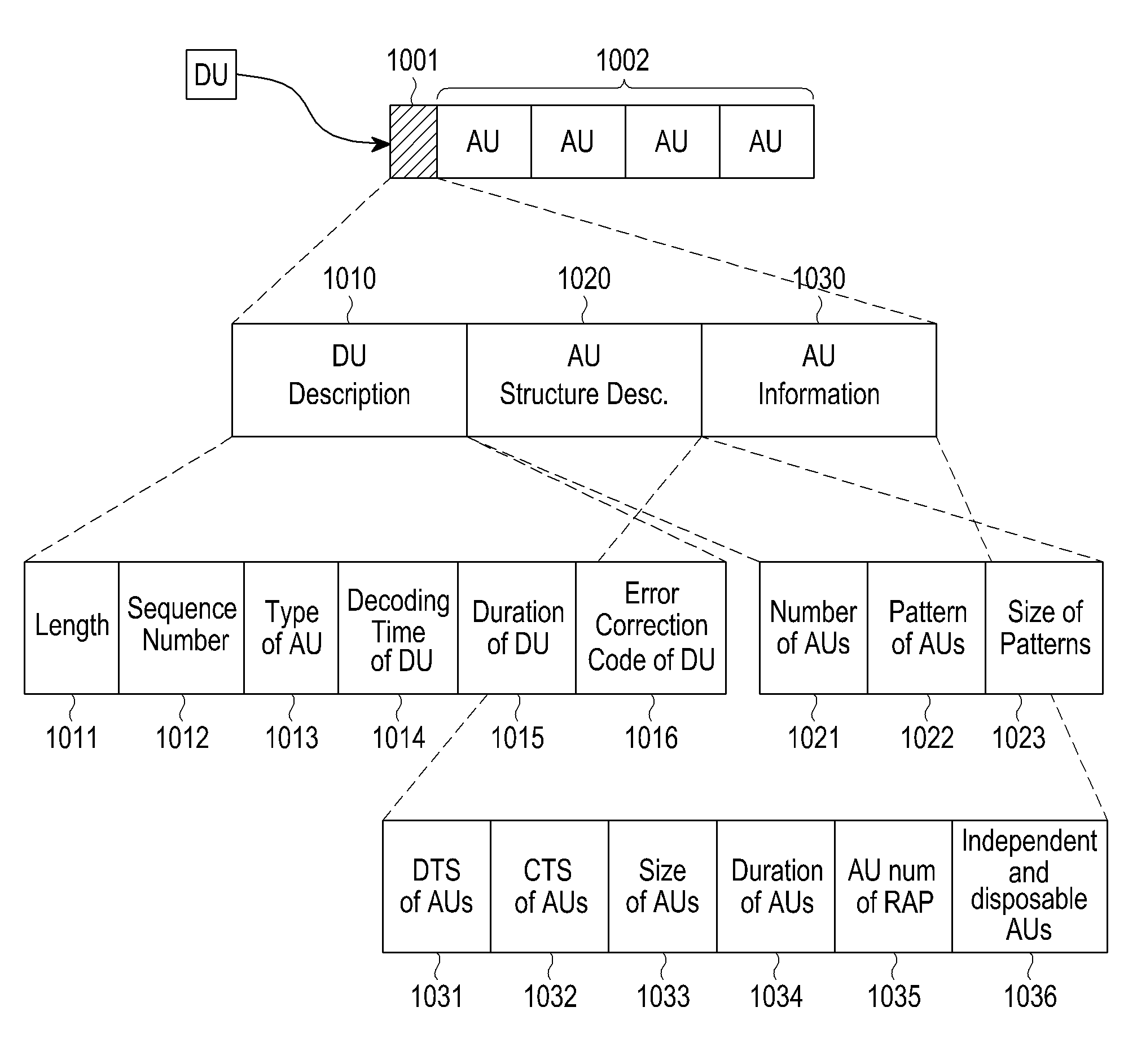
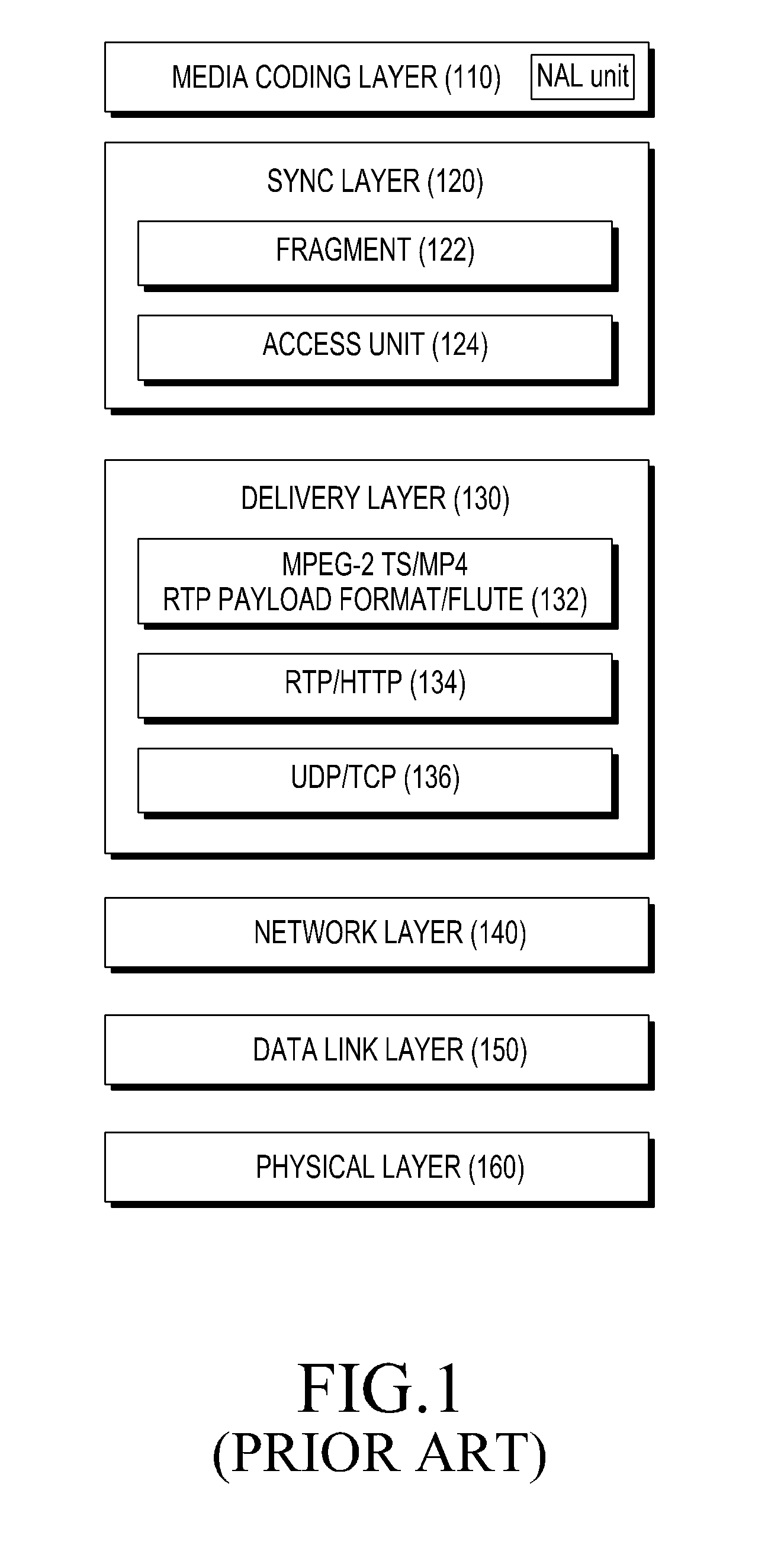
A method and an apparatus are provided for configuring content in a broadcast system. The method includes encapsulating a plurality of Access Units (AUs) transmitted from a higher layer to generate a Data Unit (DU); rearranging the AUs within the DU; and inserting a header into the DU to transfer the DU to a lower layer. The header includes DU description information and AU structure description information indicating a structure of the plurality of AUs.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Uniform and ununiform modulated constellation mapping based nonisoprotective mixed automatic retransmission inquiry method
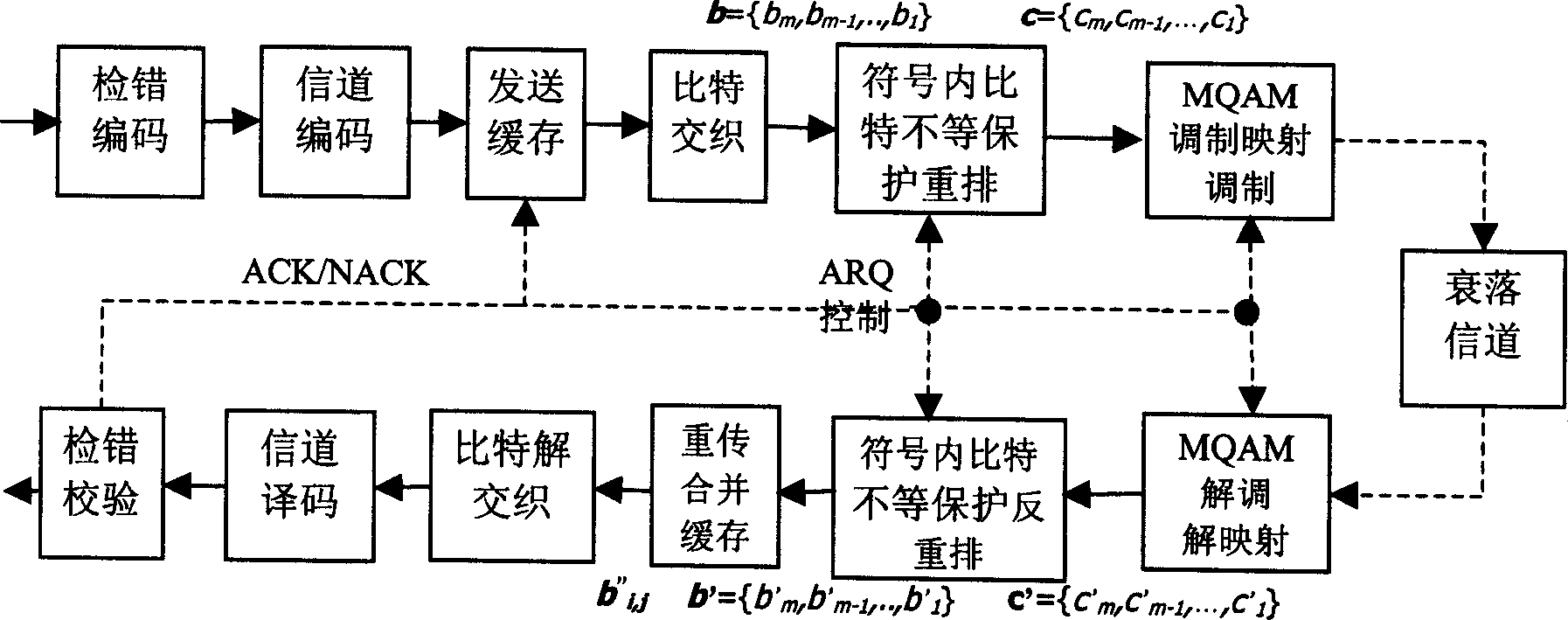
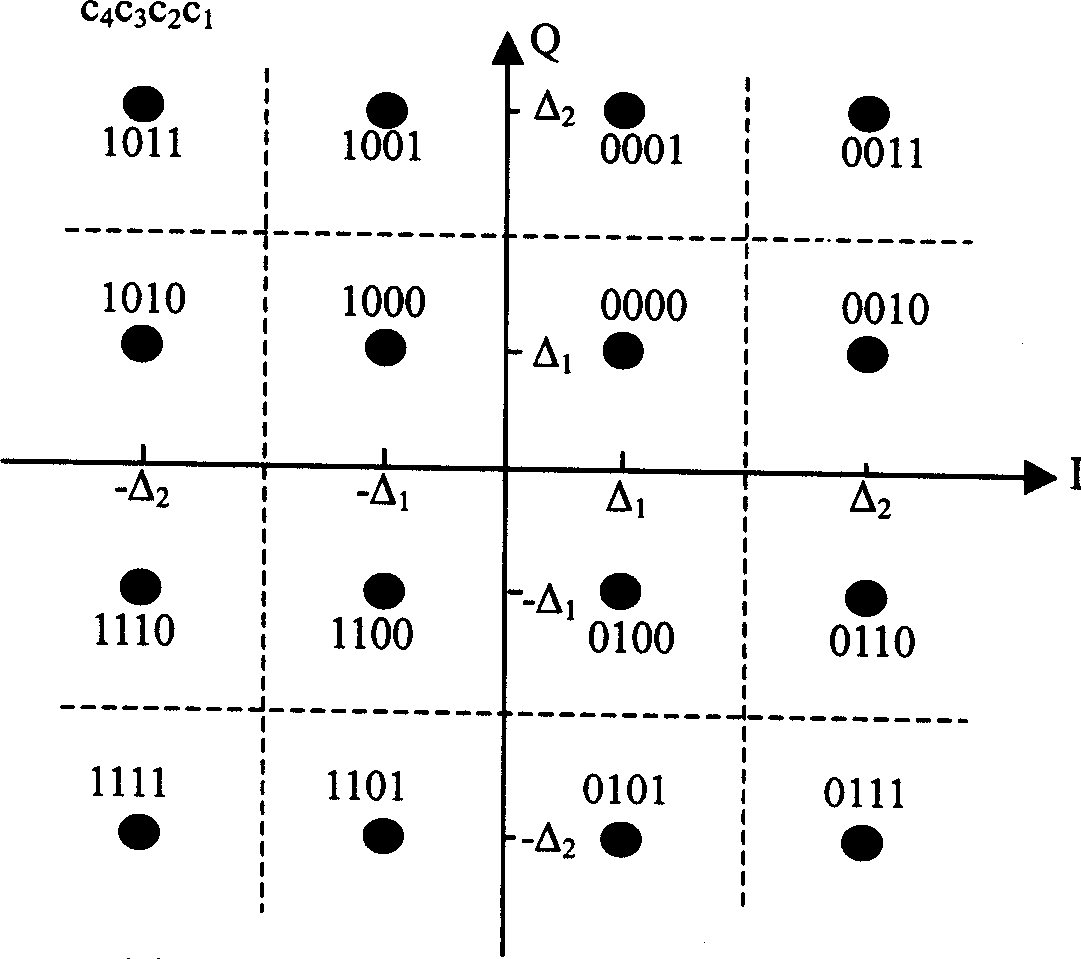
InactiveCN1490972AHigh error protectionImprove performanceUnequal/adaptive error protectionMultiple carrier systemsCommunications systemSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A unequal protection hybrid automatic retransfer request method based on equality and un-equality constellation diagram mapping, it is used in MQAM communication system with which the stage numbers is M and M=2, the modulation mapping of sending end and the resolving mapping of receiving end adopt constellation diagrams that have same distribution, in the first transmission and anterior m / 2-1 time retransmission, adopts equality constellation diagram, at the m / 2 time and the latter retransmission adopts un-equality constellation diagram, provides higher error protection for two most significant bit in the modification symbol; the bits un-equality protection in the modification symbol of sending end reset; uses m / 2 reset and opposite reset rules, at different retransmission time adopts circularly in turn, achieves alternative protecting the bits in modulation symbol; the bits in modulation symbol of receiving end reset oppositely. Reset oppositely the bits according to the reset rules of sending end, recover it into bits sequence soft value before sending end bits resetting. It promotes the signals S / N of combining soft value after demodulating and resolving mapping at receiving end, reduces efficiently grouping retransmission time, makes the output of system maximum.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and an arrangement relating to mobile radio systems with the possibility of switching channel coding schemes
InactiveUS6937582B1Improve data transfer rateImprove transmission qualityModulated-carrier systemsUnequal/adaptive error protectionMobile radioWireless connectivity
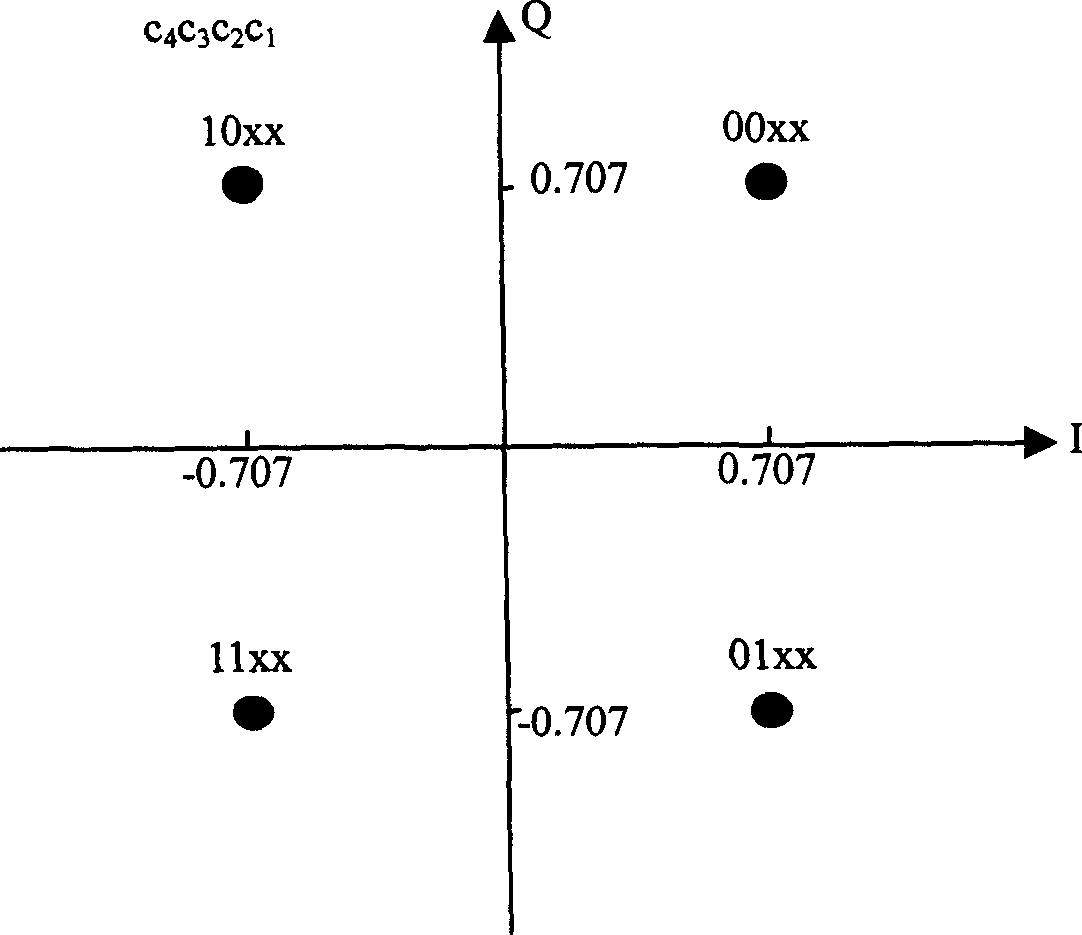
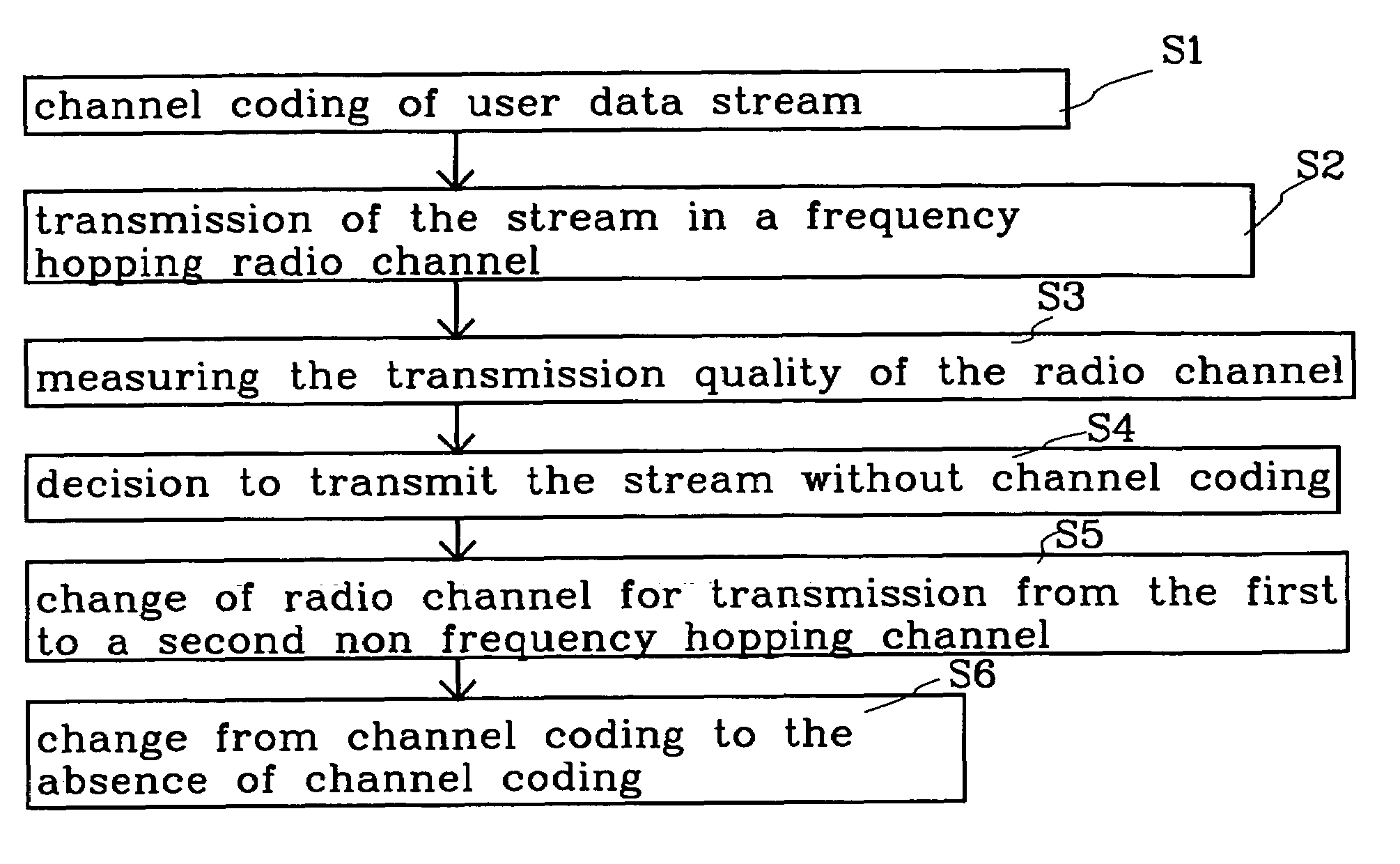
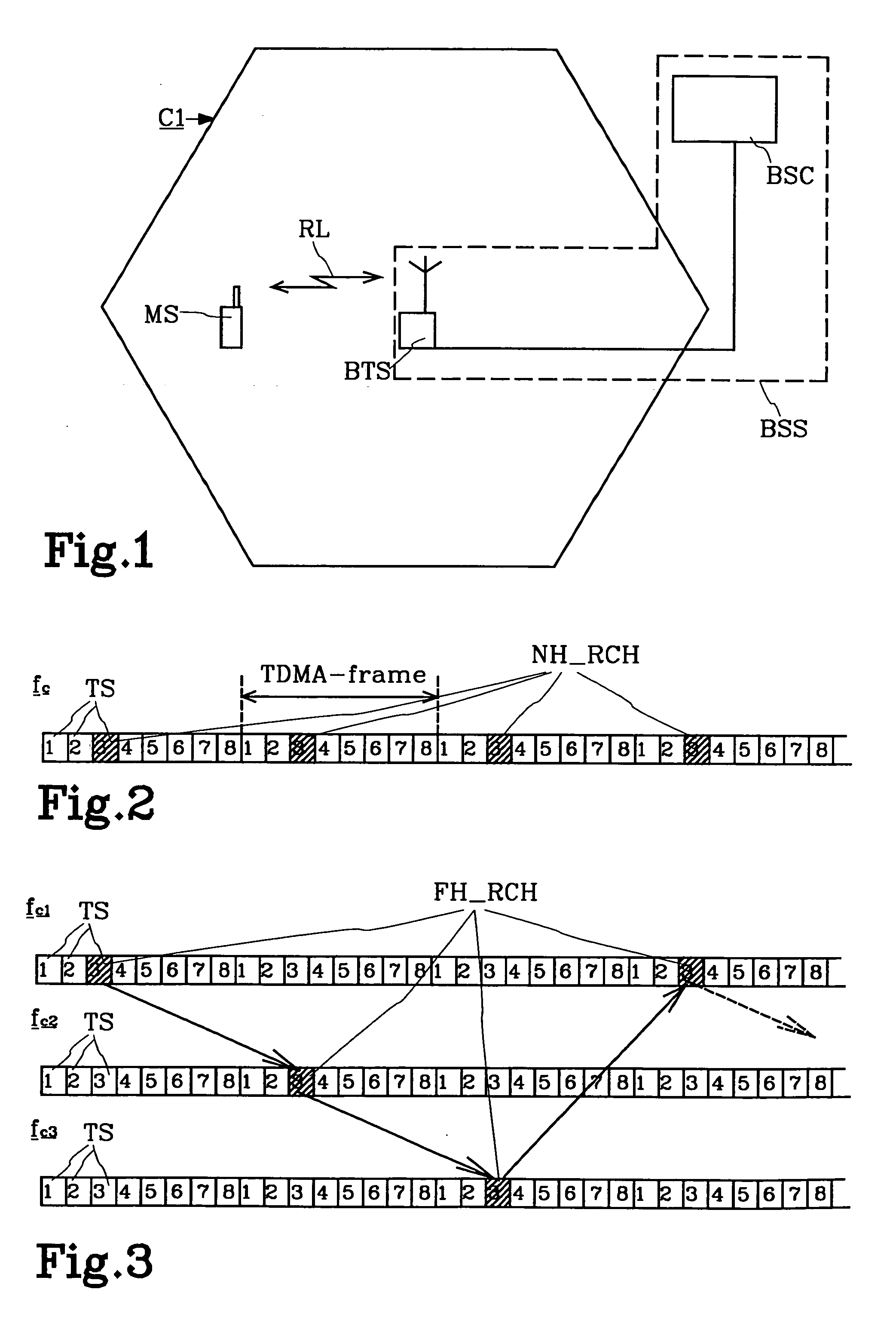
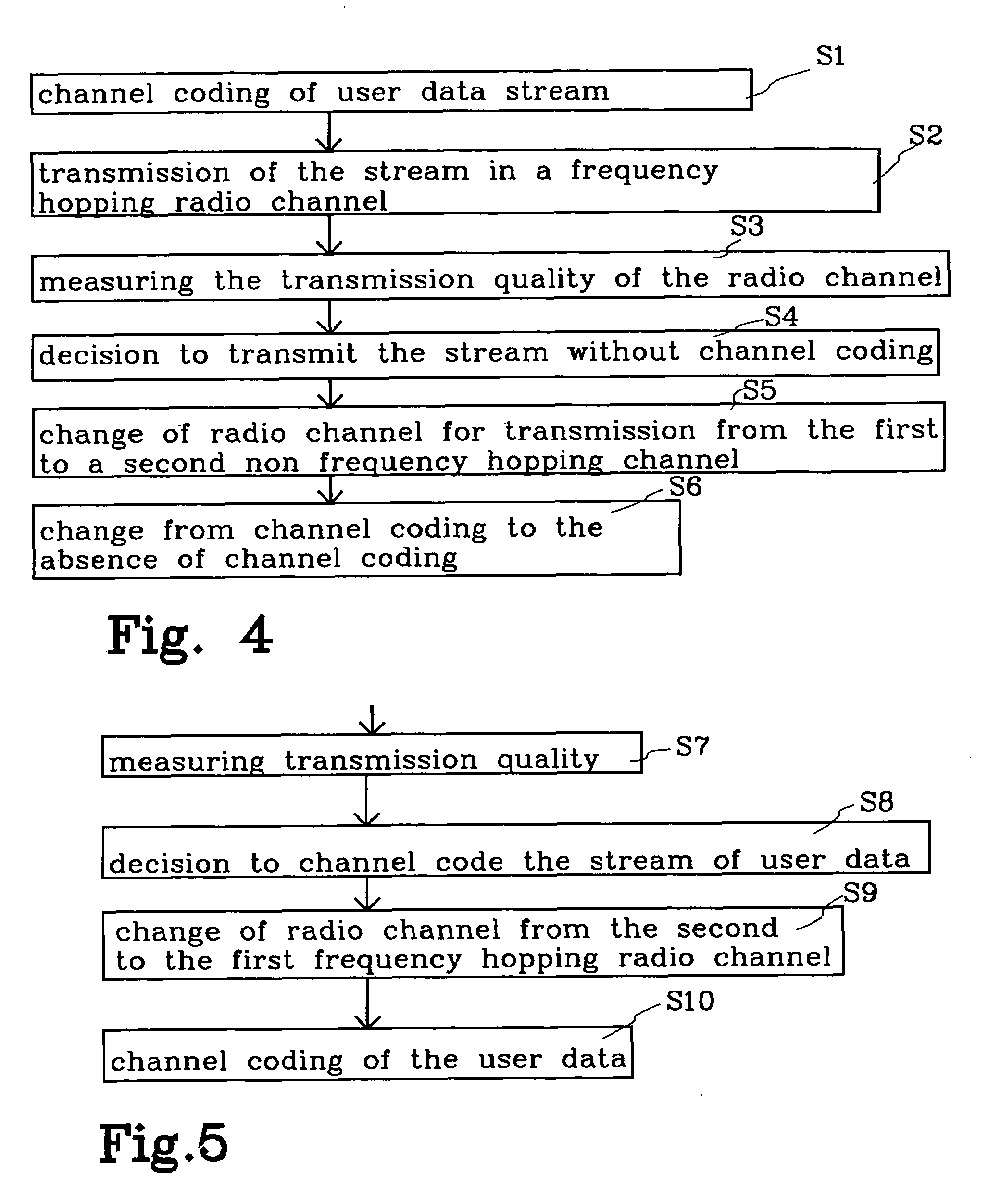
The present invention relates to a mobile radio system in which channel coding on the radio link is changed during an ongoing connection. The invention can be related in particular to the packet data services GPRS and EDGE. According to the invention, a change of radio channel is made from a frequency hopping channel to a non frequency hopping radio channel in connection with changing the channel coding during an ongoing radio connection, wherein channel coding of user data that has earlier been channel coded is terminated when transmitted by radio. Channel changes are effected within a cell.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Information recording and reproducing apparatus and method and signal decoding circuit having improved noise processing characteristics
InactiveUS7031090B2Effective applicationImprove decoding performanceModification of read/write signalsOther decoding techniquesMaximum a posteriori estimationComputer science
In a Maximum A posteriori Probability decoding (MAP decoding), a correlation and a deviation of noises for past and future states which depend on input signal patterns in past N bits and future Q bits are calculated by training by a noise correlation arithmetic operating unit 84 and they are stored. Upon reproduction, in a white noise arithmetic operating unit 91, white noise values for the past and future states in which colored noises are converted into white noises are obtained by using the stored correlation and deviation of the noises. In an input signal arithmetic operating unit 92, an input signal (channel information) Λc(yk|Smk) of the MAP decoding is calculated from the white noise values and the deviation for the past and future states. A likelihood in the MAP decoding is obtained from the input signal.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
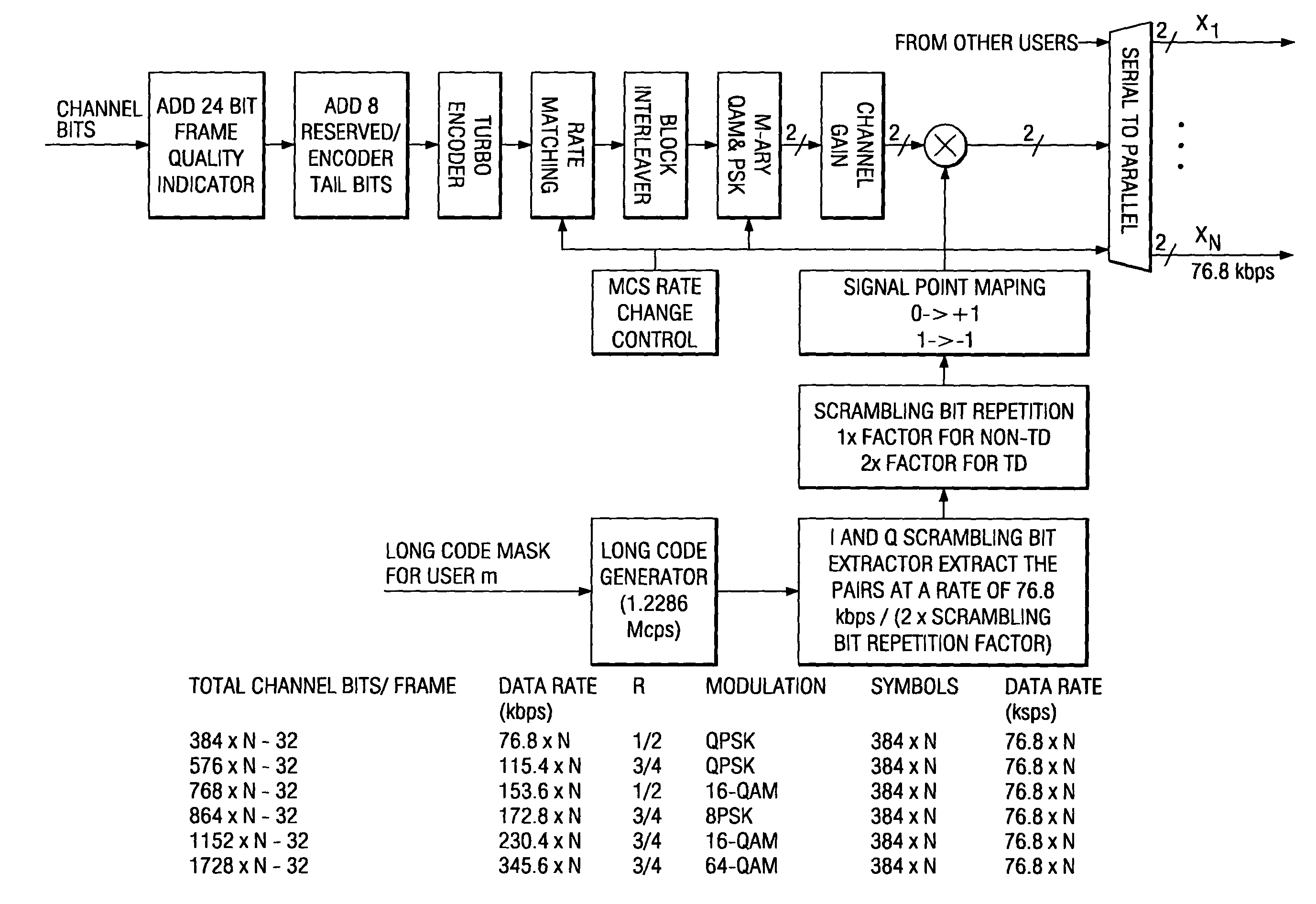
Method of rate matching for link adaptation and code space management
InactiveUS20050050427A1Reduce constraintsUnequal/adaptive error protectionCode conversionComputer hardwareRound complexity
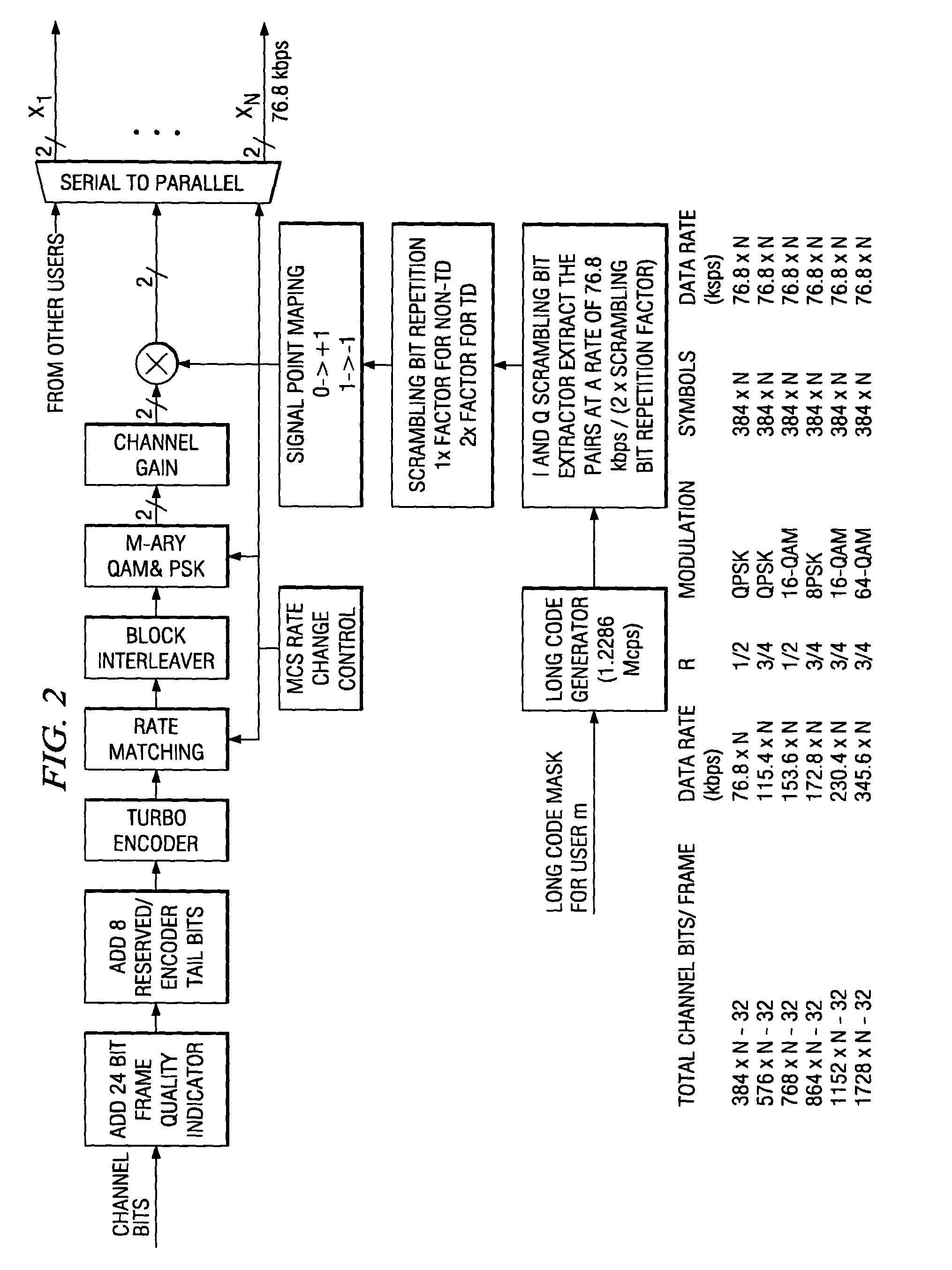
A method of symbol combining and incremental redundancy for link adaptation and code space management was proposed. In order to reduce constraints on the Walsh codes allocation, MCS level change, as well as frame duration change for the initial transmission and re-transmissions, a “rate matching” stage is proposed between the Turbo encoder and block interleaver on the transmitter. In the initial transmission, the Turbo encoded symbols are interleaved with or without any puncturing or repeating (i.e. puncture / repeat factor is set to 1). The coded symbols are also stored in the memory for possible retransmissions. In the re-transmission, the transmitter first determines the number of Walsh codes available for this user and MCS level and frame duration according to the C / I feedback values from MS. The stored coded symbols are then punctured or repeated according to “rate matching factors”. On the receiver side, “rate matching factors” can be derived from the number of code channels, MCS level and frame duration of current re-transmissions and initial transmission. Then, de-puncturing / de-repeating is performed before coded symbol combining. A similar rate matching based IR / symbol combining scheme can be used to design different IR using different rate matching algorithms. It has low implementation complexity and is easily made backward compatible.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Maximizing data rate by adjusting codes and code rates in CDMA system
InactiveUS6973140B2Eliminate needEasy to useError prevention/detection by using return channelChannel dividing arrangementsData rateForward error correction
The present invention provides for making code rate adjustments and modulation type adjustments in a pseudonoise (PN) encoded CDMA system. Coding rate adjustments may be made by changing the number of information bits per symbol, or Forward Error Code (FEC) coding rate. A forward error correction (FEC) block size is maintained at a constant amount. Therefore, as the number of information bits per symbol are increased, an integer multiple of bits per epoch is always maintained. The scheme permits for a greater flexibility and selection of effective data rates providing information bit rates ranging from, for example, approximately 50 kilobits per second to over 5 mega bits per second (Mbps) in one preferred embodiment.
Owner:APPLE INC
Popular searches
Error correction/detection by combining multiple code structures Error correction/detection using interleaving techniques Error detection only Radio transmission Channel coding adaptation Signalling characterisation Forward error control use Transmission rate adaptation Error correction/detection using linear codes Static storage
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com