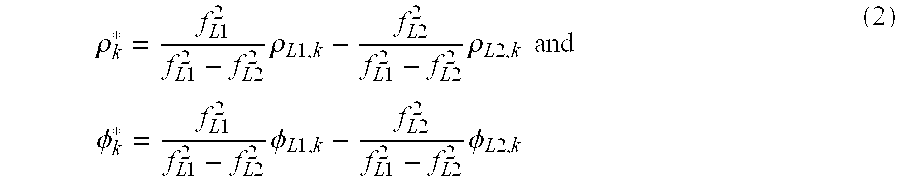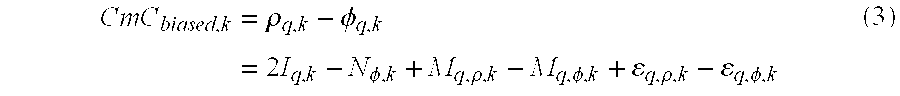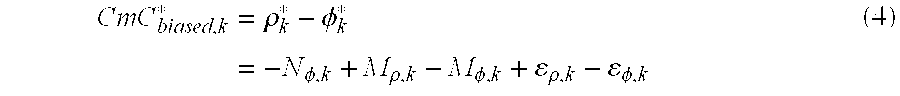Patents
Literature
52 results about "Error mitigation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
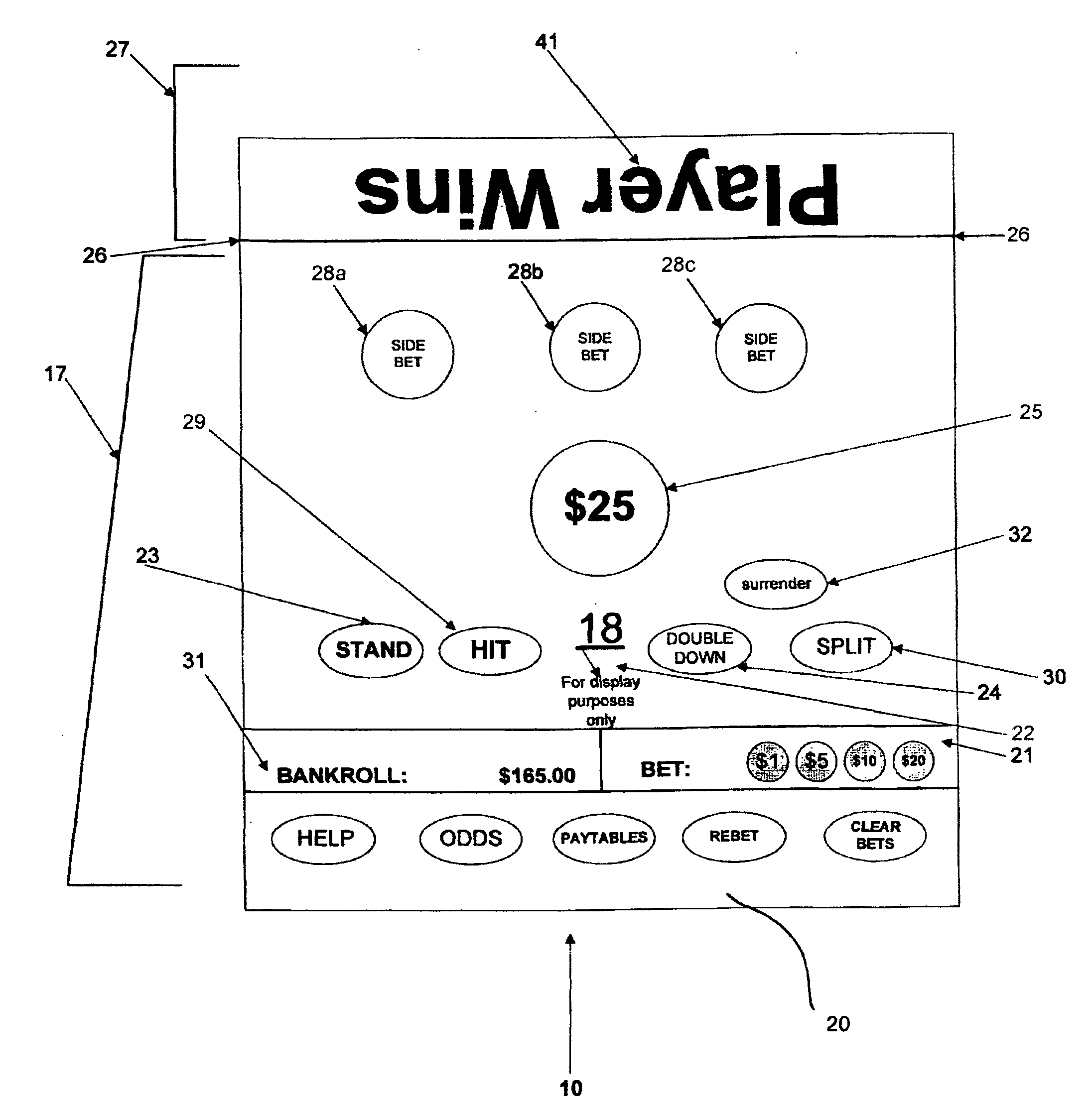
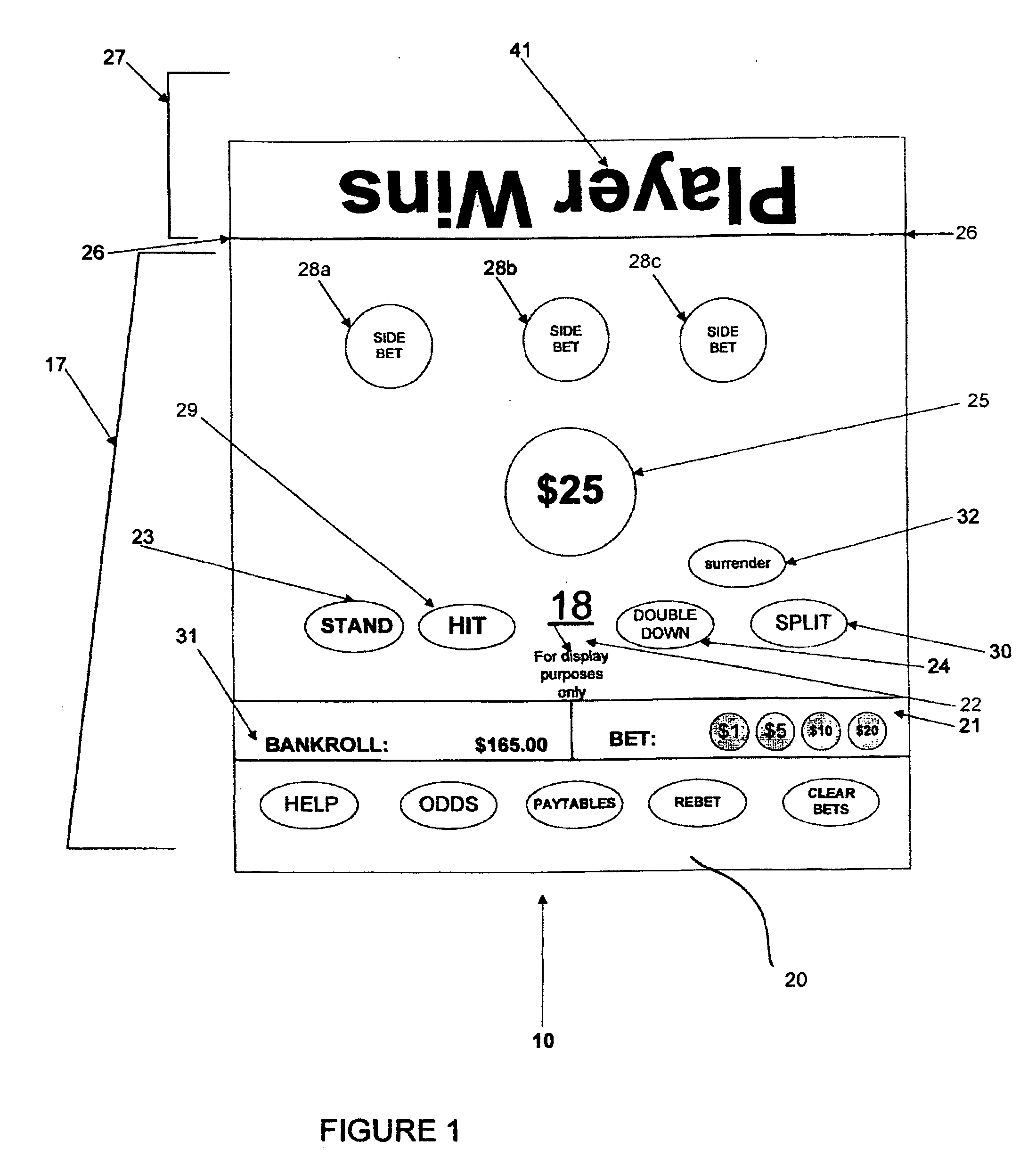
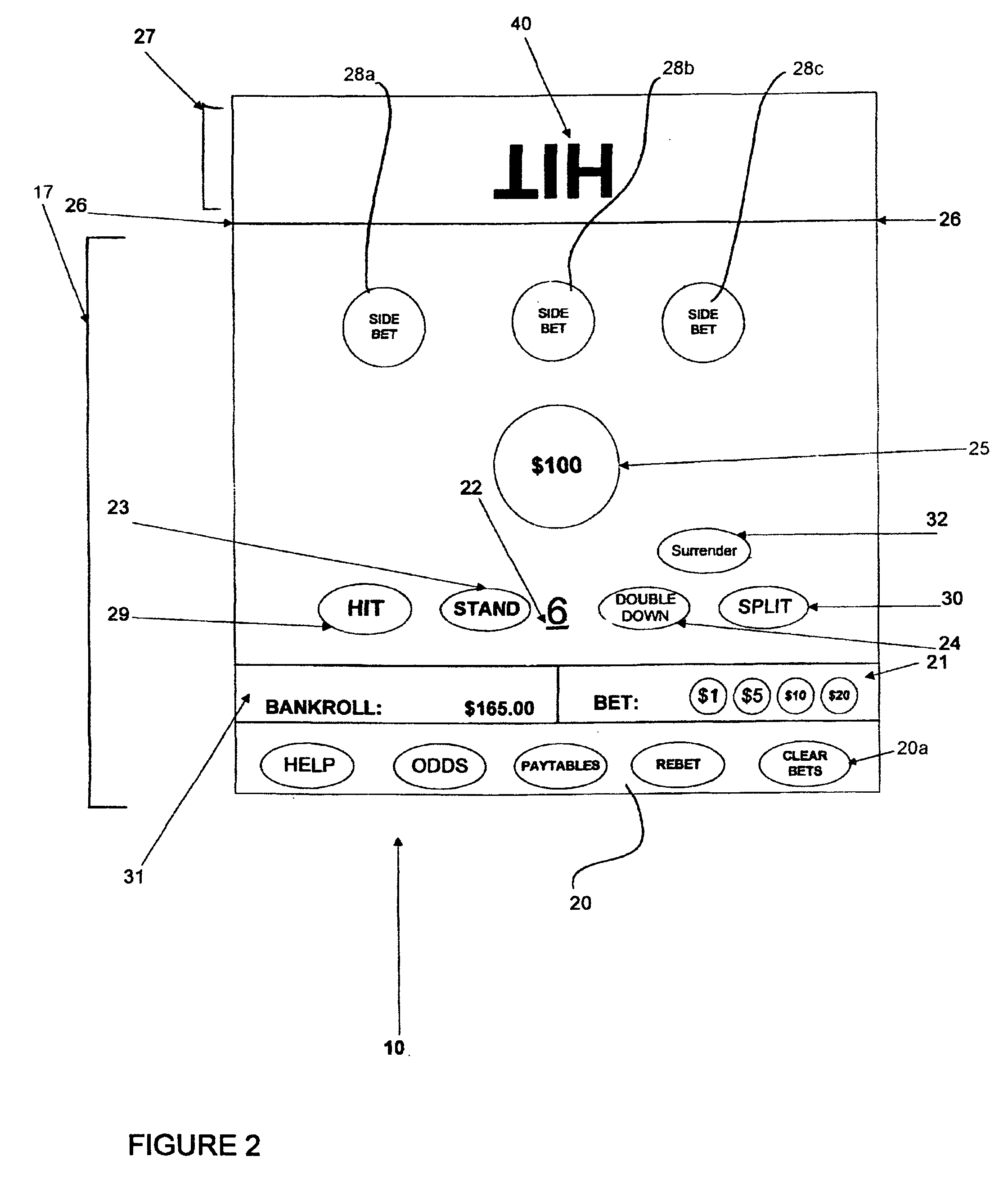
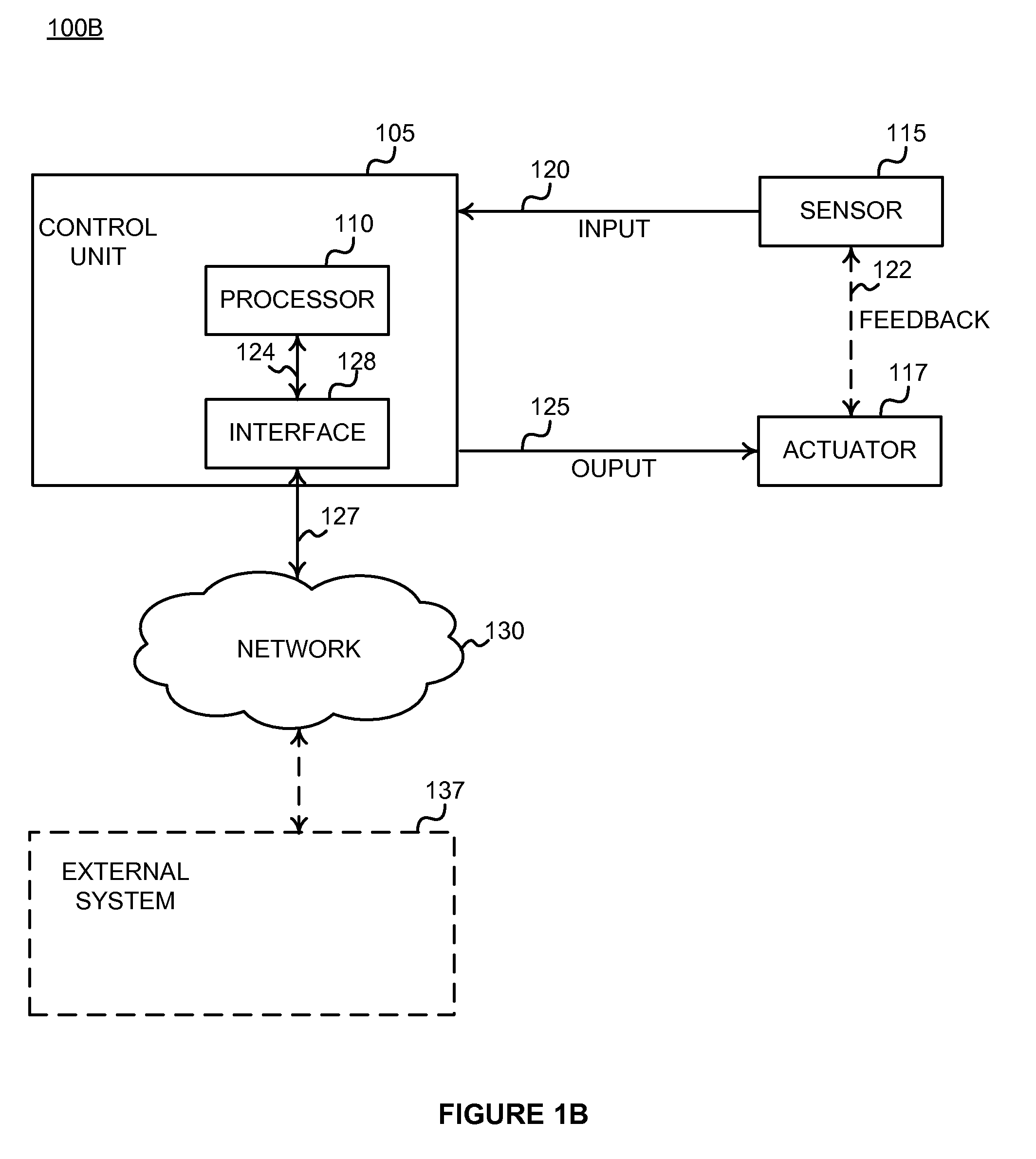
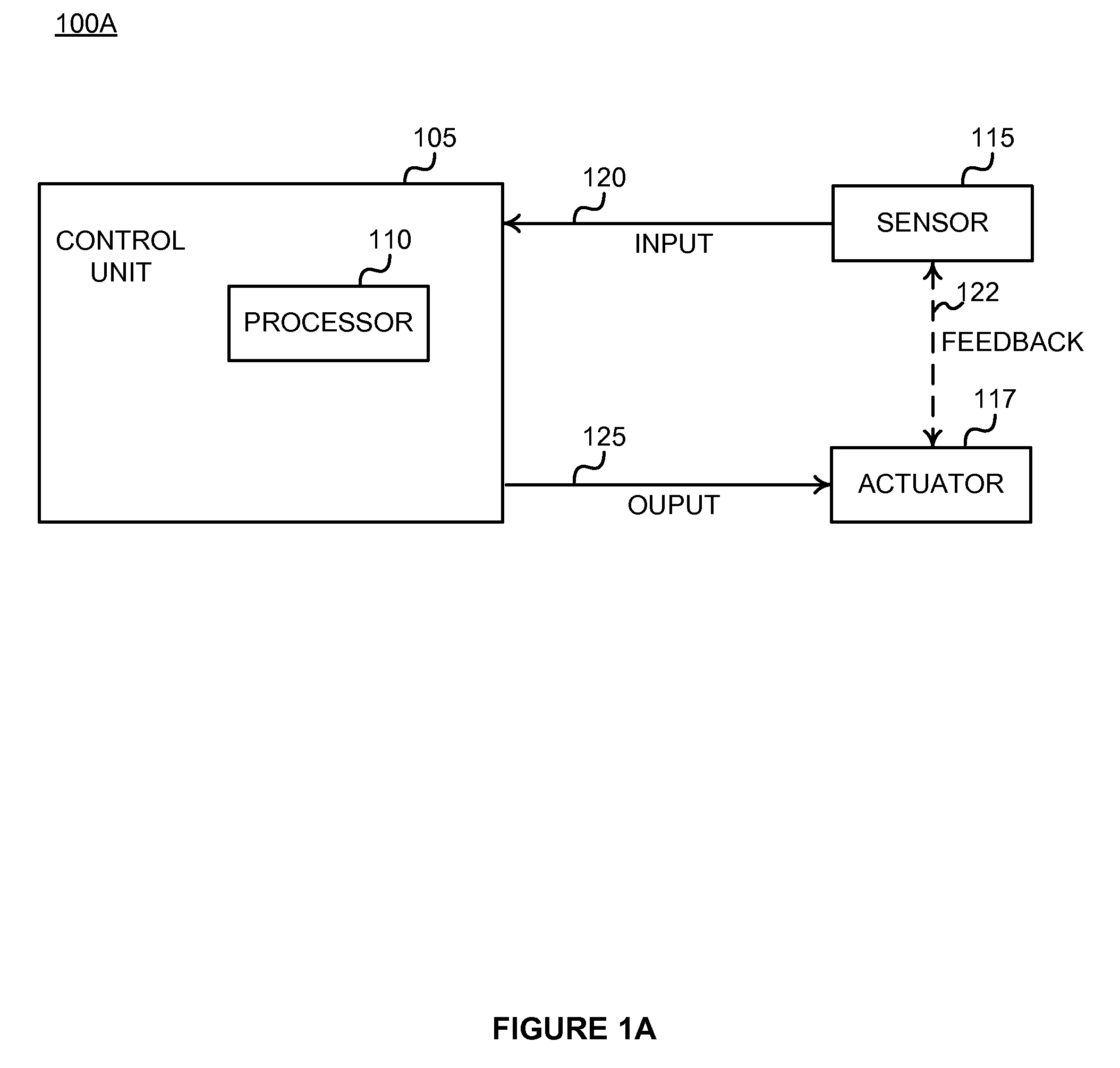
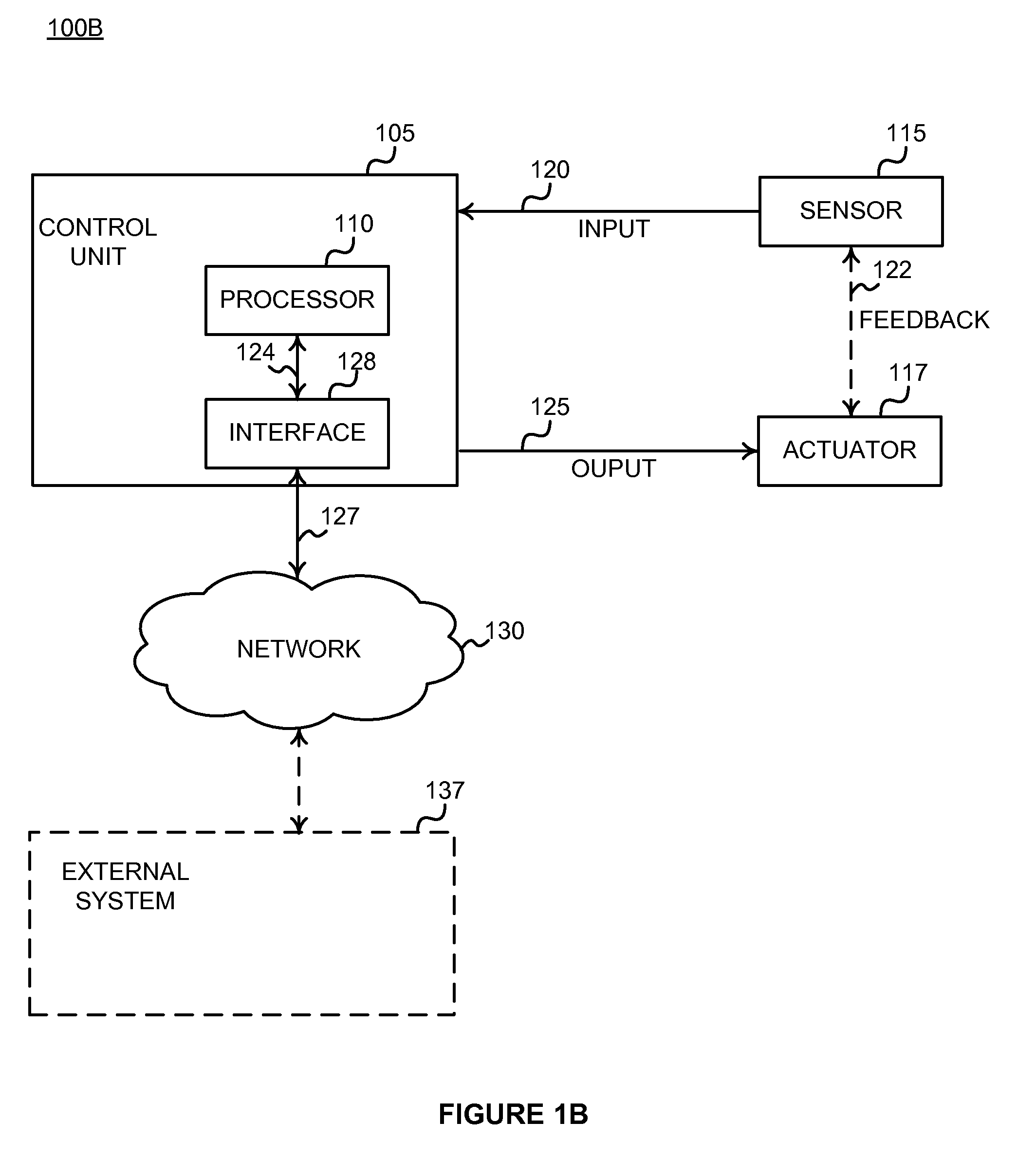
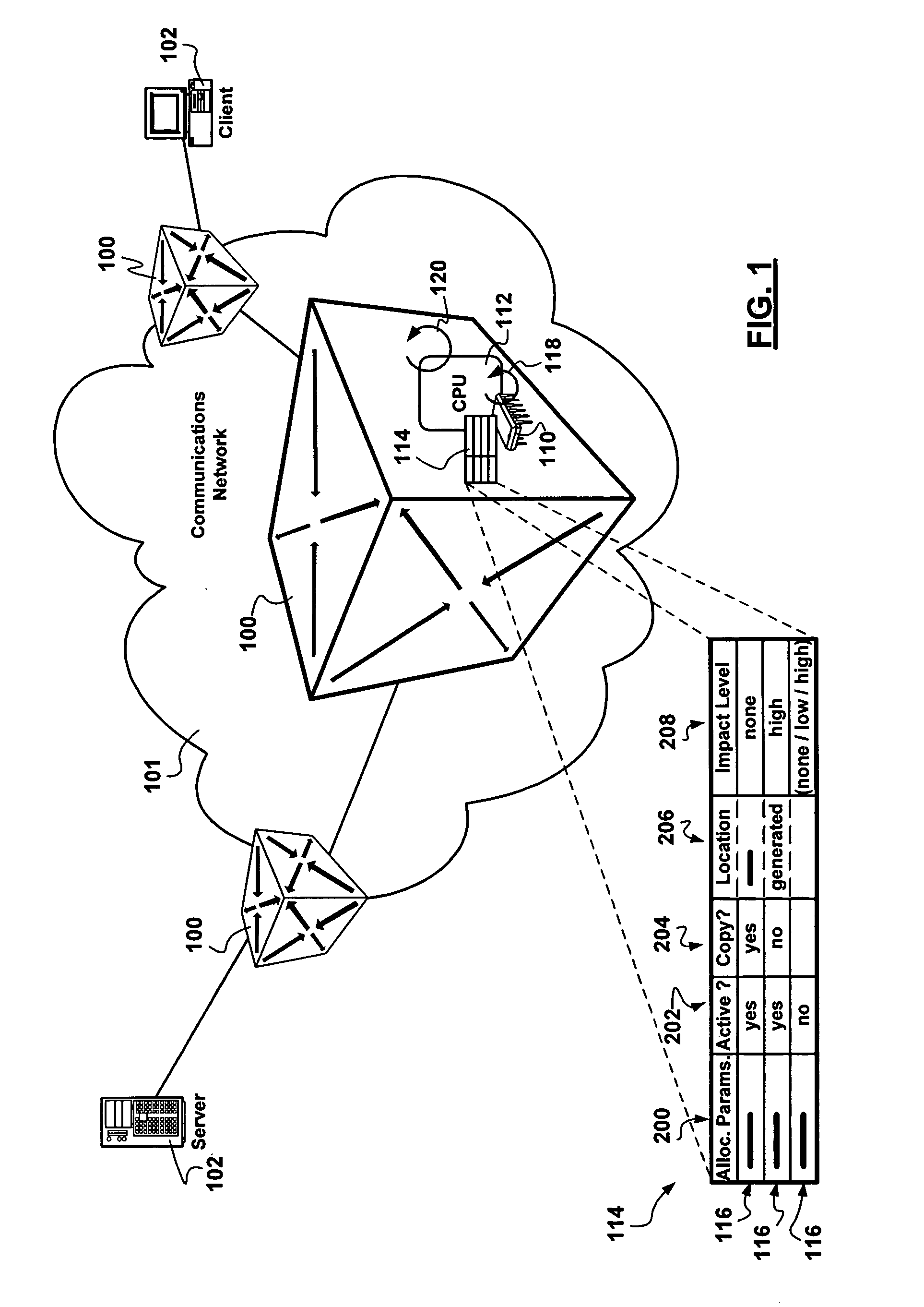
Method, apparatus and system for egregious error mitigation
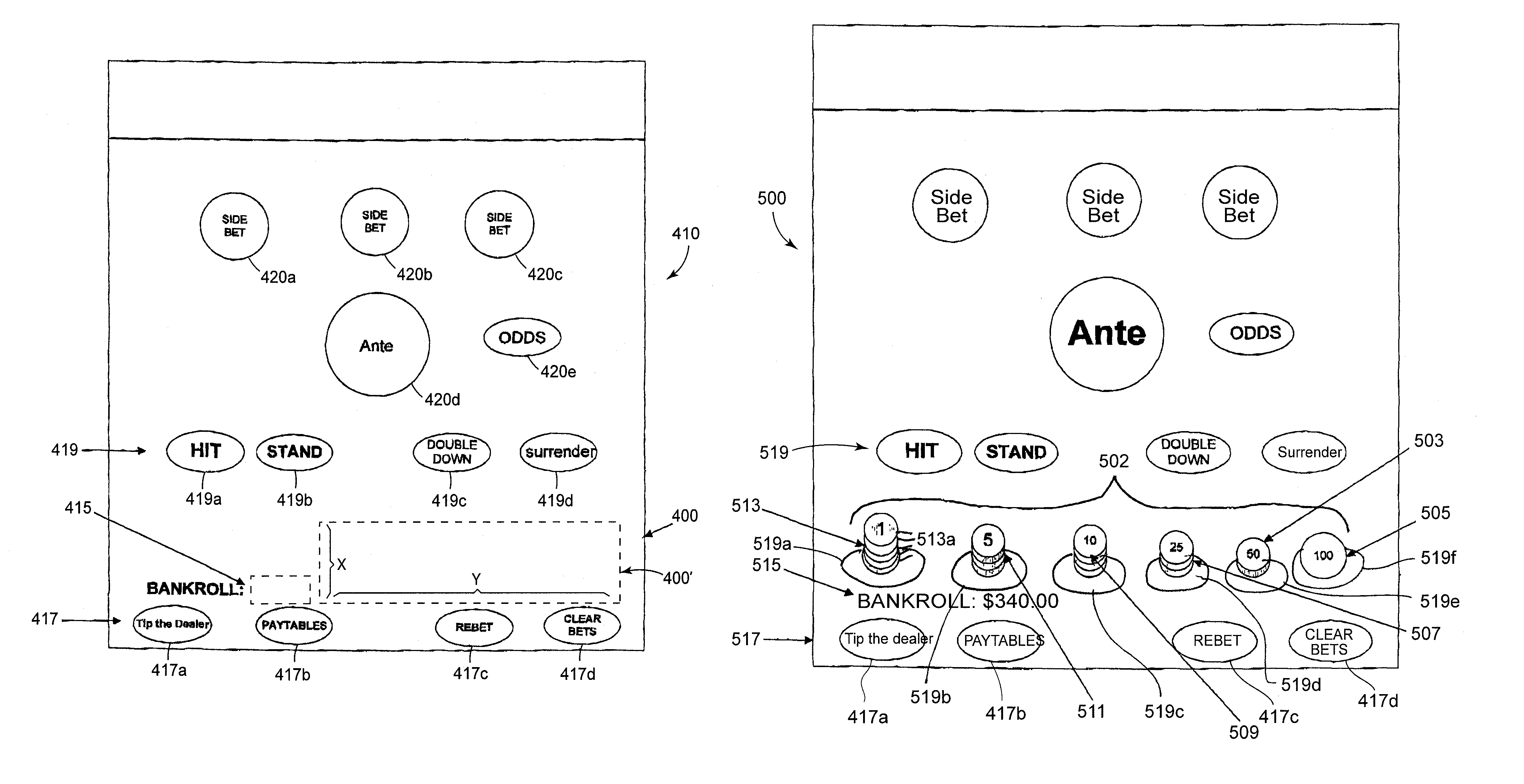
A playing card gaming system is disclosed that provides the player with an opportunity to withdraw a game play decision that is less advantageous to a player than at least one other play decision. The system includes a player interface that displays a prompt when a less advantageous decision is made. The display may include an area that provides the dealer with a visual indication that the player is being asked to confirm an election. A card delivery system with a playing card information reader provides card information to the system. A game processor determines if player elections are disadvantageous.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
Wireless Tracking System And Method With Multipath Error Mitigation
ActiveUS20080012767A1Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationError mitigationComputer science
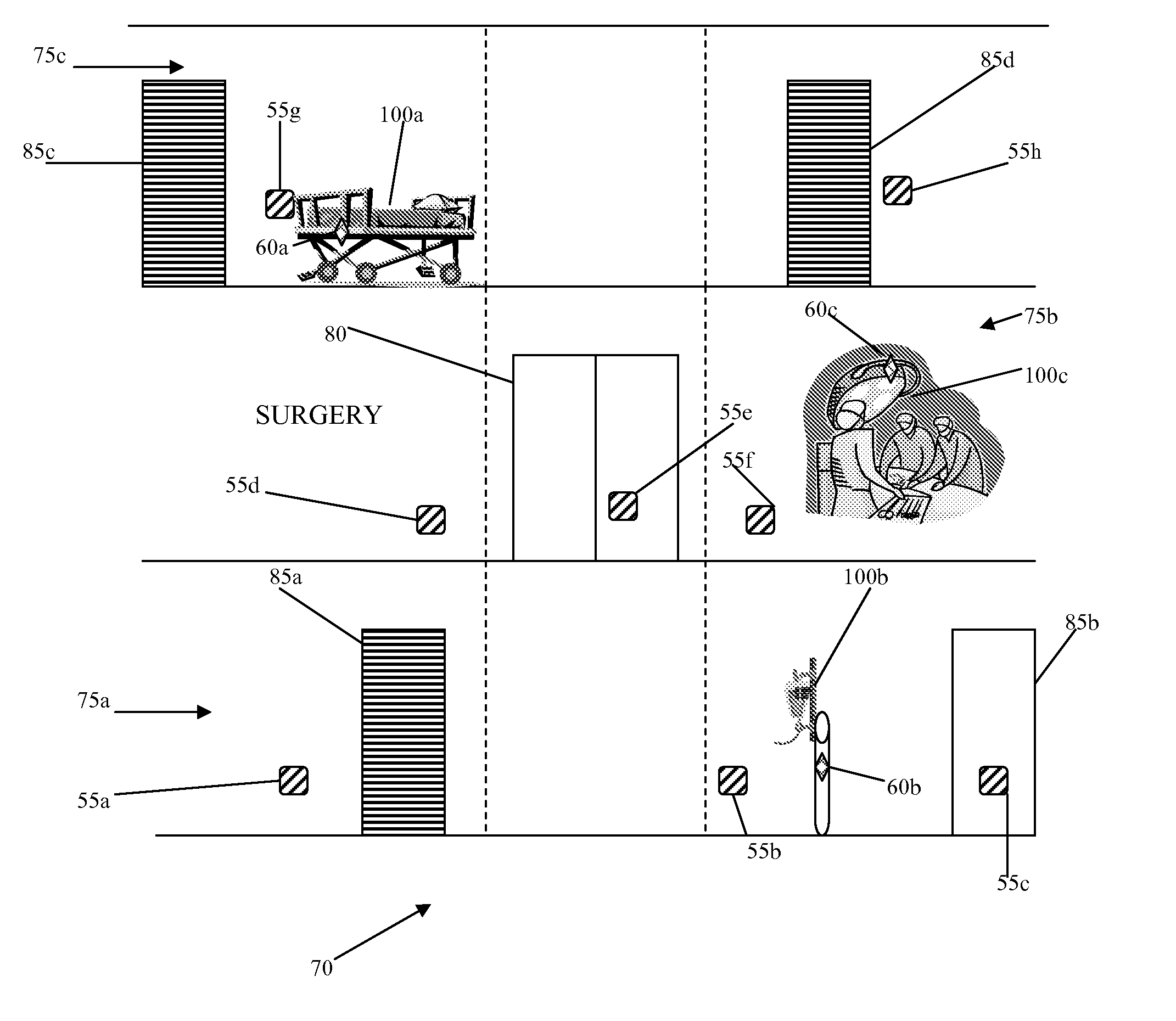
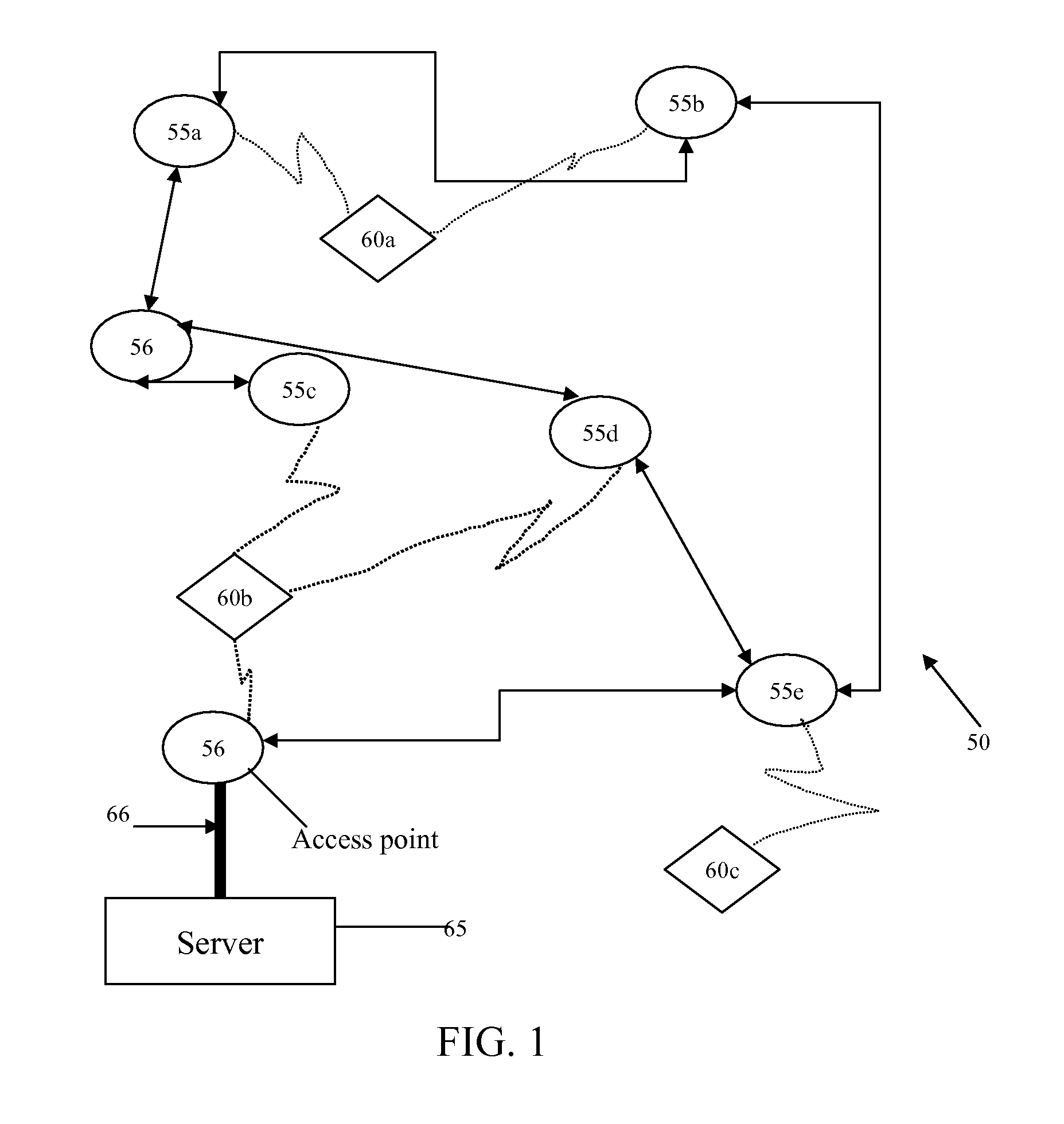
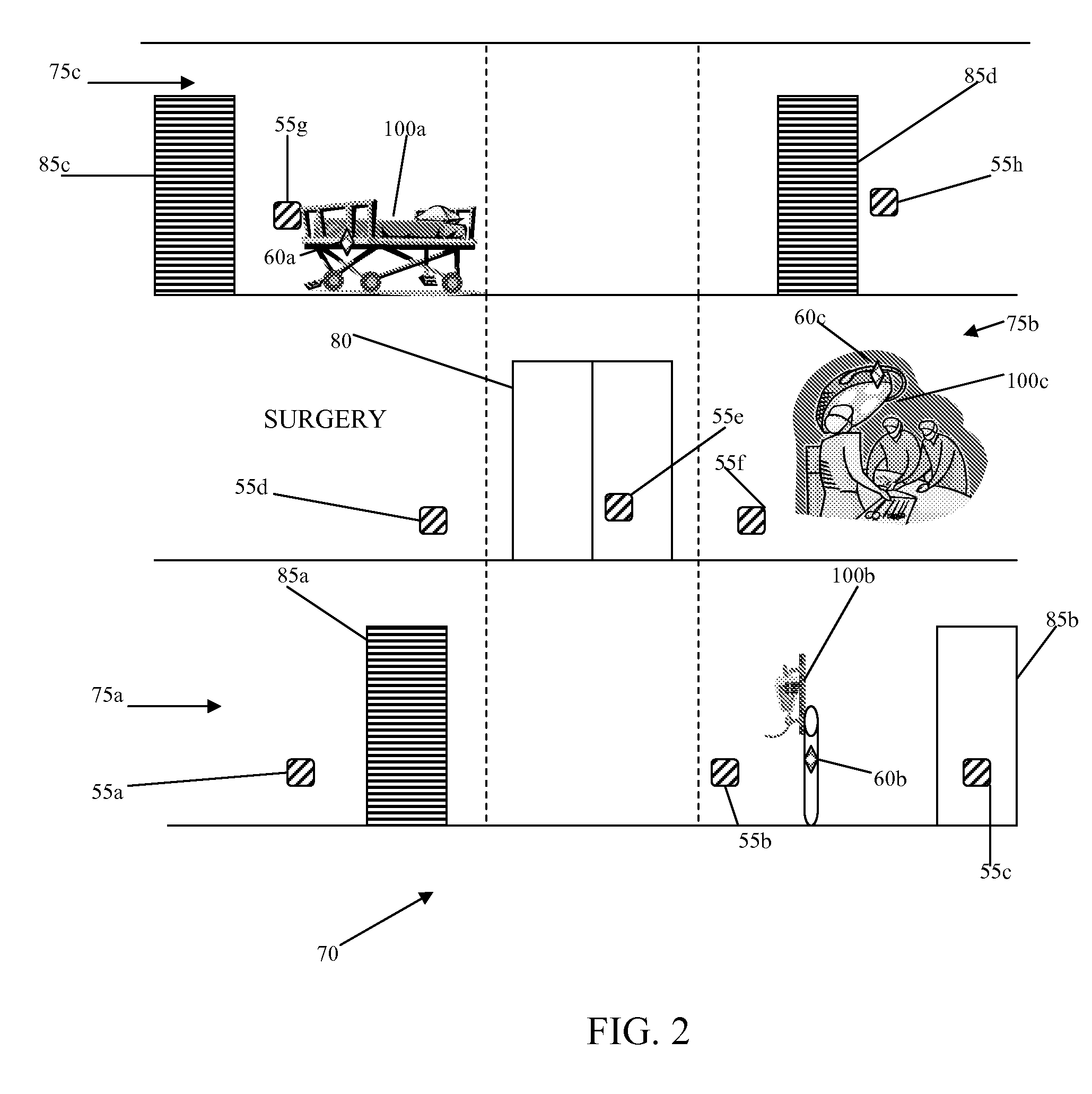
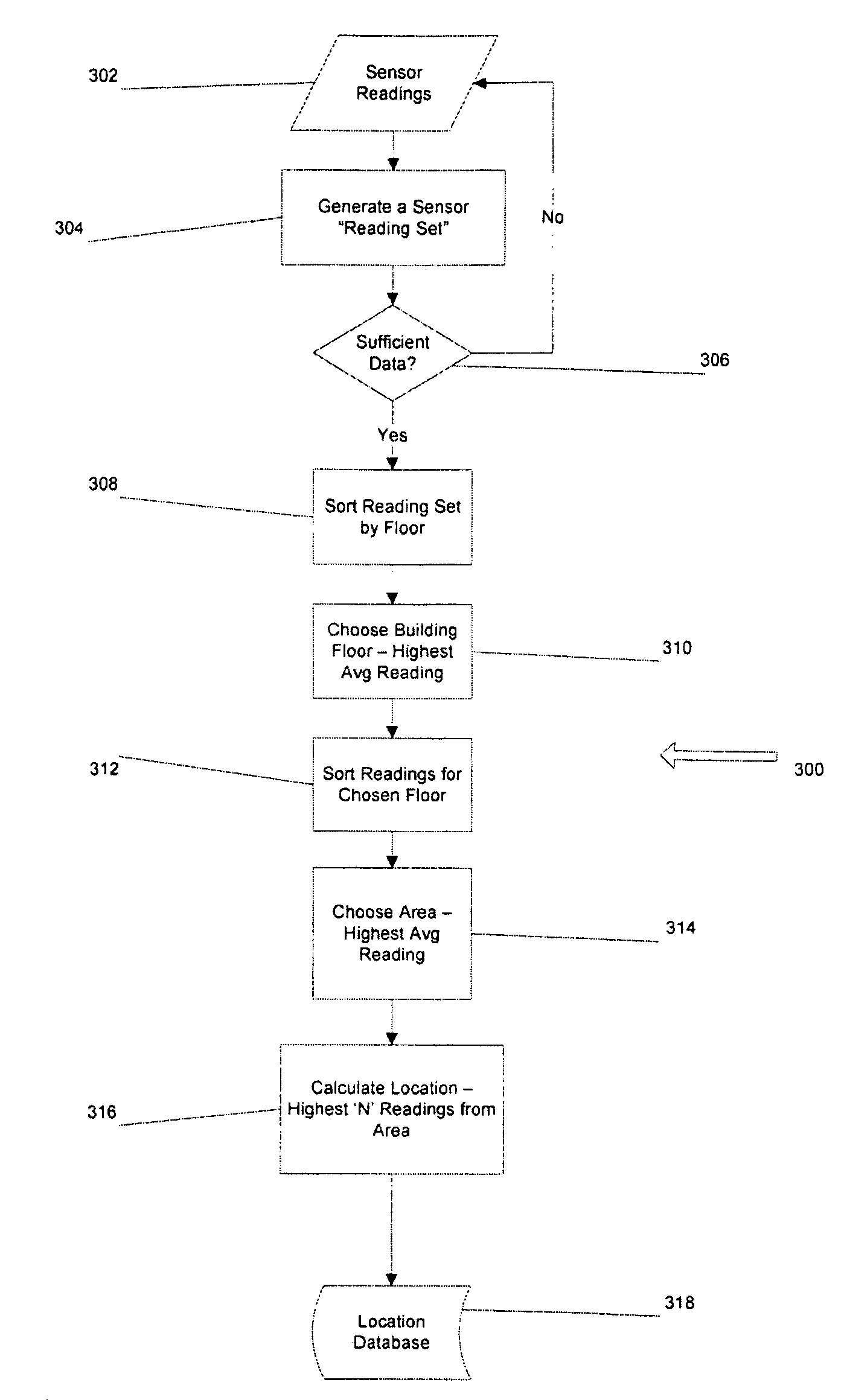
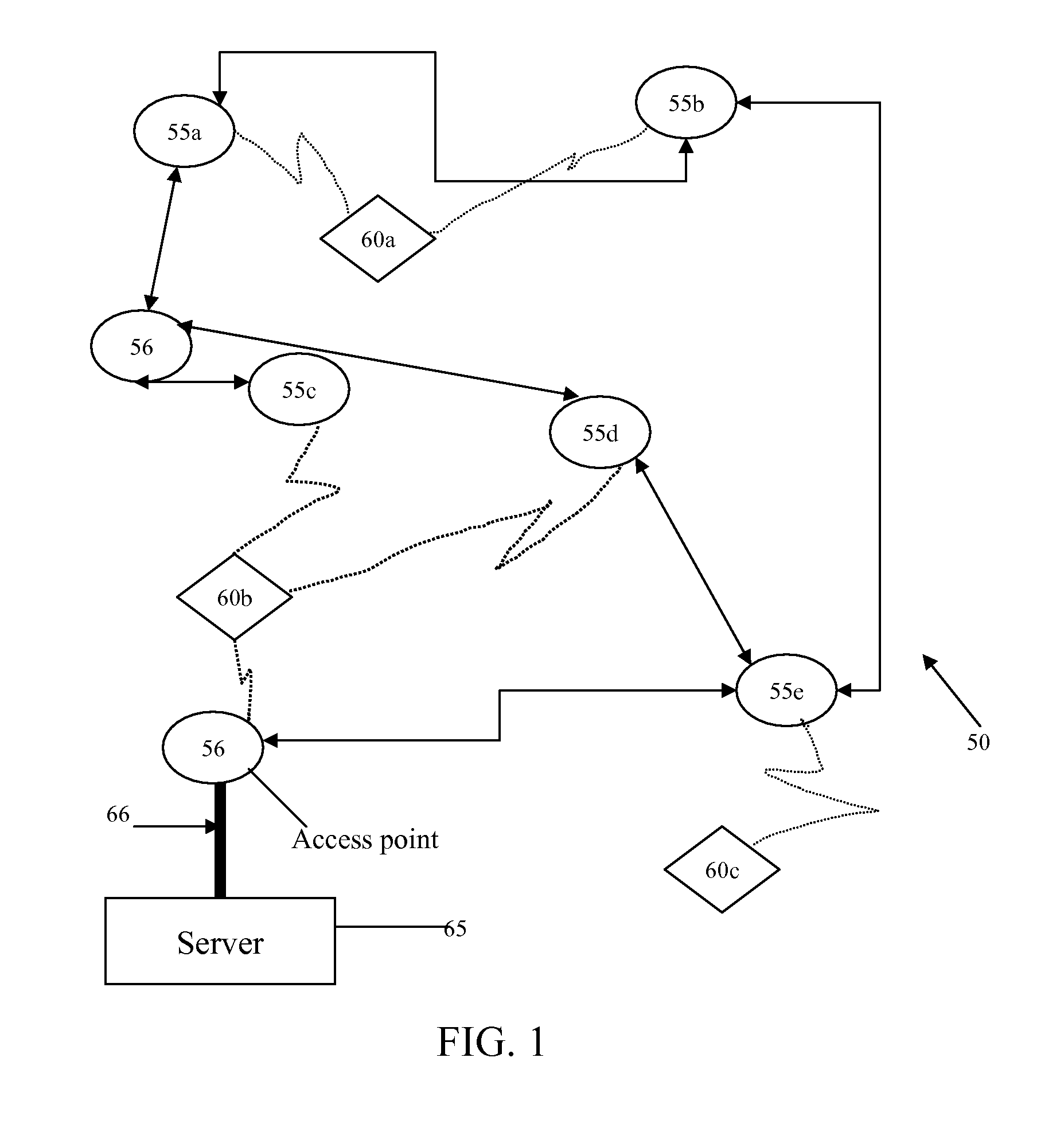
A system (50) and method (300) for providing multipath error mitigation for real-time wireless tracking of an object (100) is disclosed herein. A plurality of sensor readings are obtained from a tag (60) attached to an object (100) within an indoor facility (70). A plurality of reading sets are generated and sorted by zones. A zone with the highest average reading is preferably selected and the location of the object (100) is calculated based on the selected zone readings. In this manner, faulty position readings are eliminated from the location calculation thereby allowing for more accurate tracking of the object (100) within the indoor facility (70).
Owner:CENTRAK
Wireless tracking system and method with multipath error mitigation
ActiveUS7545326B2Direction finders using radio wavesPosition fixationError mitigationTracking system
A system (50) and method (300) for providing multipath error mitigation for real-time wireless tracking of an object (100) is disclosed herein. A plurality of sensor readings are obtained from a tag (60) attached to an object (100) within an indoor facility (70). A plurality of reading sets are generated and sorted by zones. A zone with the highest average reading is preferably selected and the location of the object (100) is calculated based on the selected zone readings. In this manner, faulty position readings are eliminated from the location calculation thereby allowing for more accurate tracking of the object (100) within the indoor facility (70).
Owner:CENTRAK INC
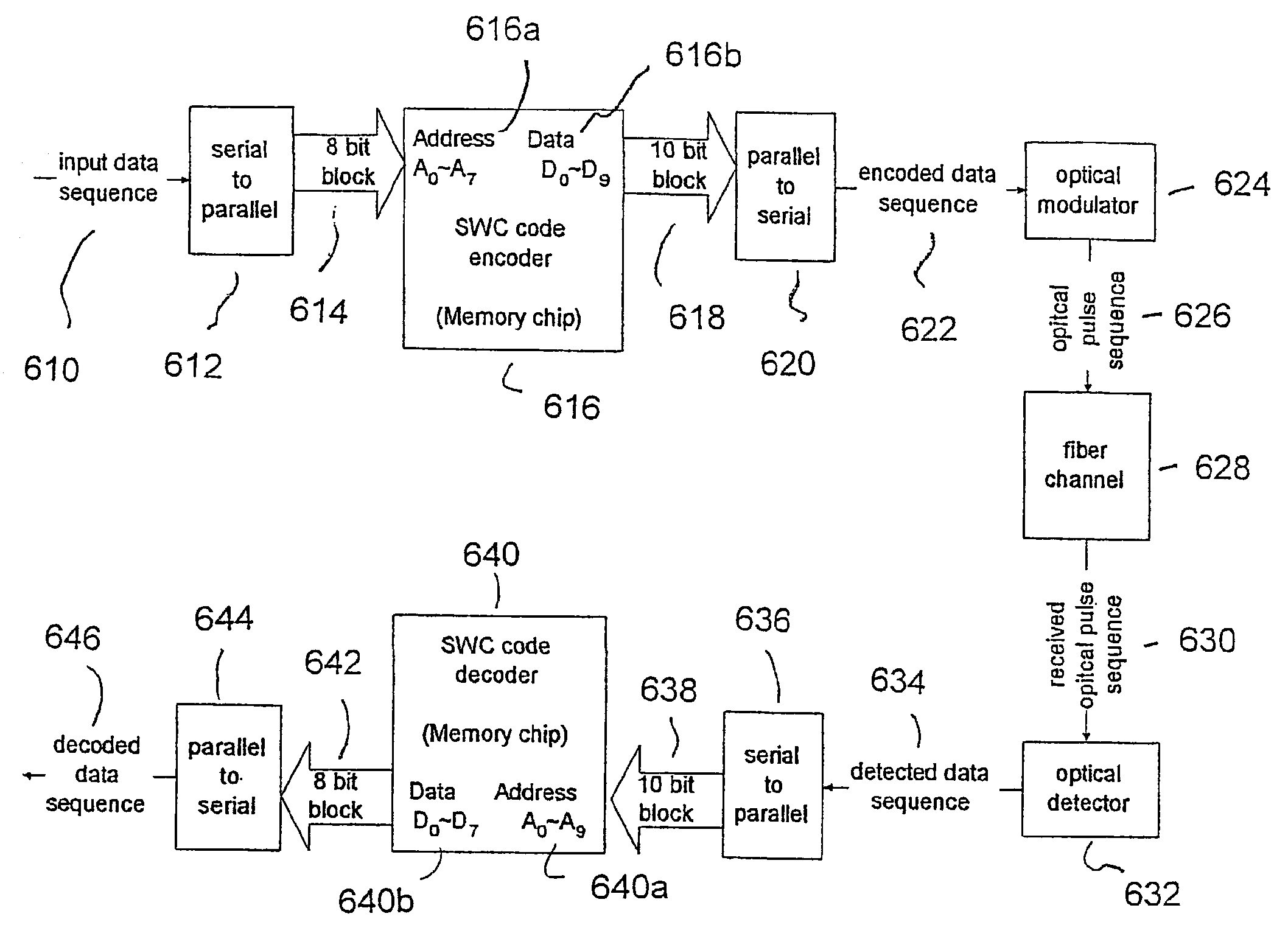
Error mitigation system using line coding for optical WDM communications
InactiveUS7016606B2Error detection/correctionWavelength-division multiplex systemsData streamEngineering
An apparatus and method of line coding to mitigate collision induced errors in Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) optical communications systems is disclosed. The apparatus and method prevents Soliton-Soliton-Collision induced errors by reducing a variance in a number of possible collisions between solitons in multiple channels in a WDM fiber optic communication system using a sliding window criterion. The sliding window criterion defines a set of parametric values based on physical properties of the transmission network, a transmission frequency and a defined data block size. N-bit codes are iteratively selected and sequentially assigned to segments of a mapping table indexed by all possible unique combinations of “1”s and “0”s in a block of data. Input data blocks are mapped to corresponding code words having a reduced number of transitions for transmission on the fiber optic network. Received code words are converted back to a data stream corresponding to the input data stream.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Mobile device indoor navigation
ActiveUS20150168538A1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesPosition fixationPositioning technologyMobile device
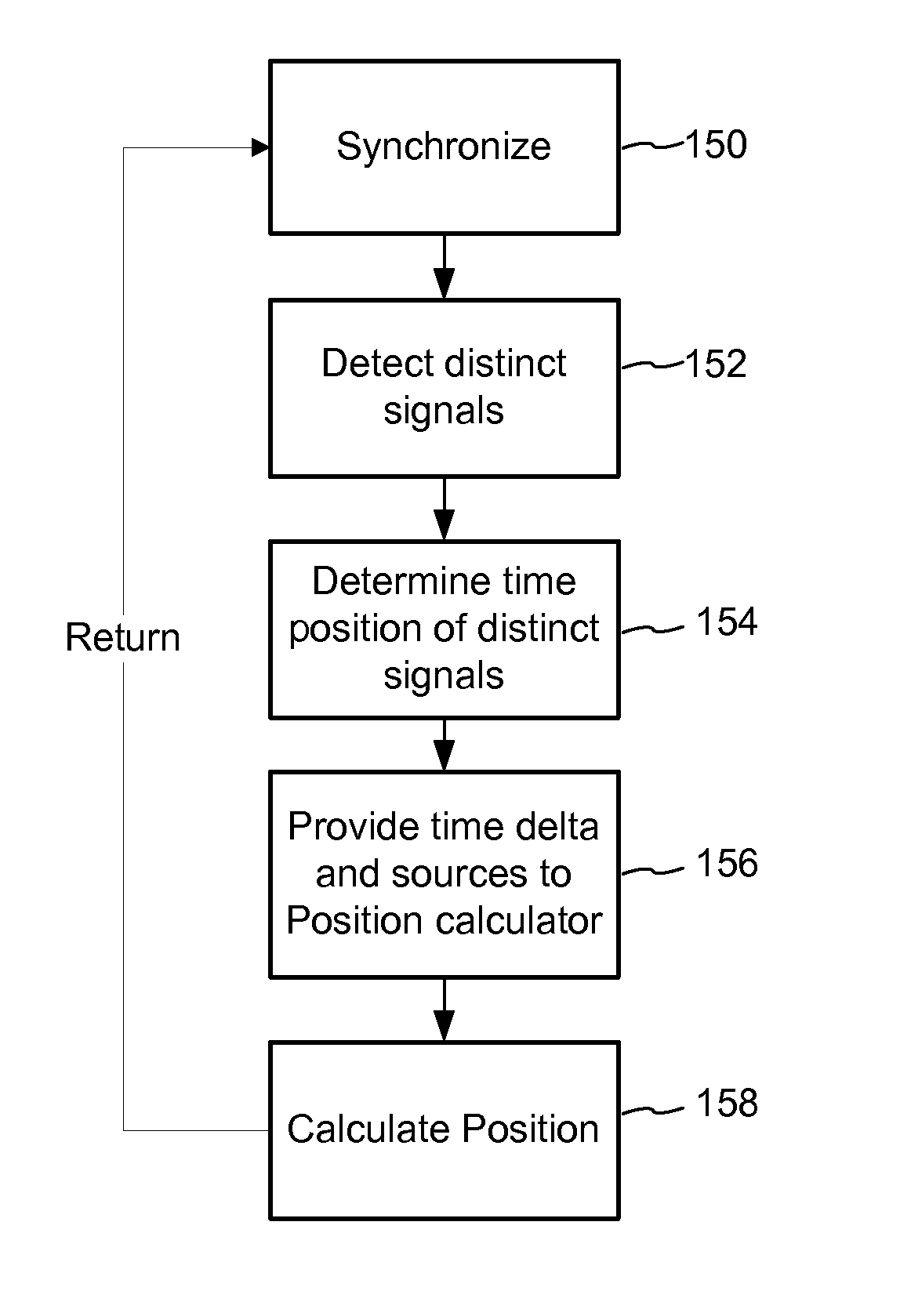
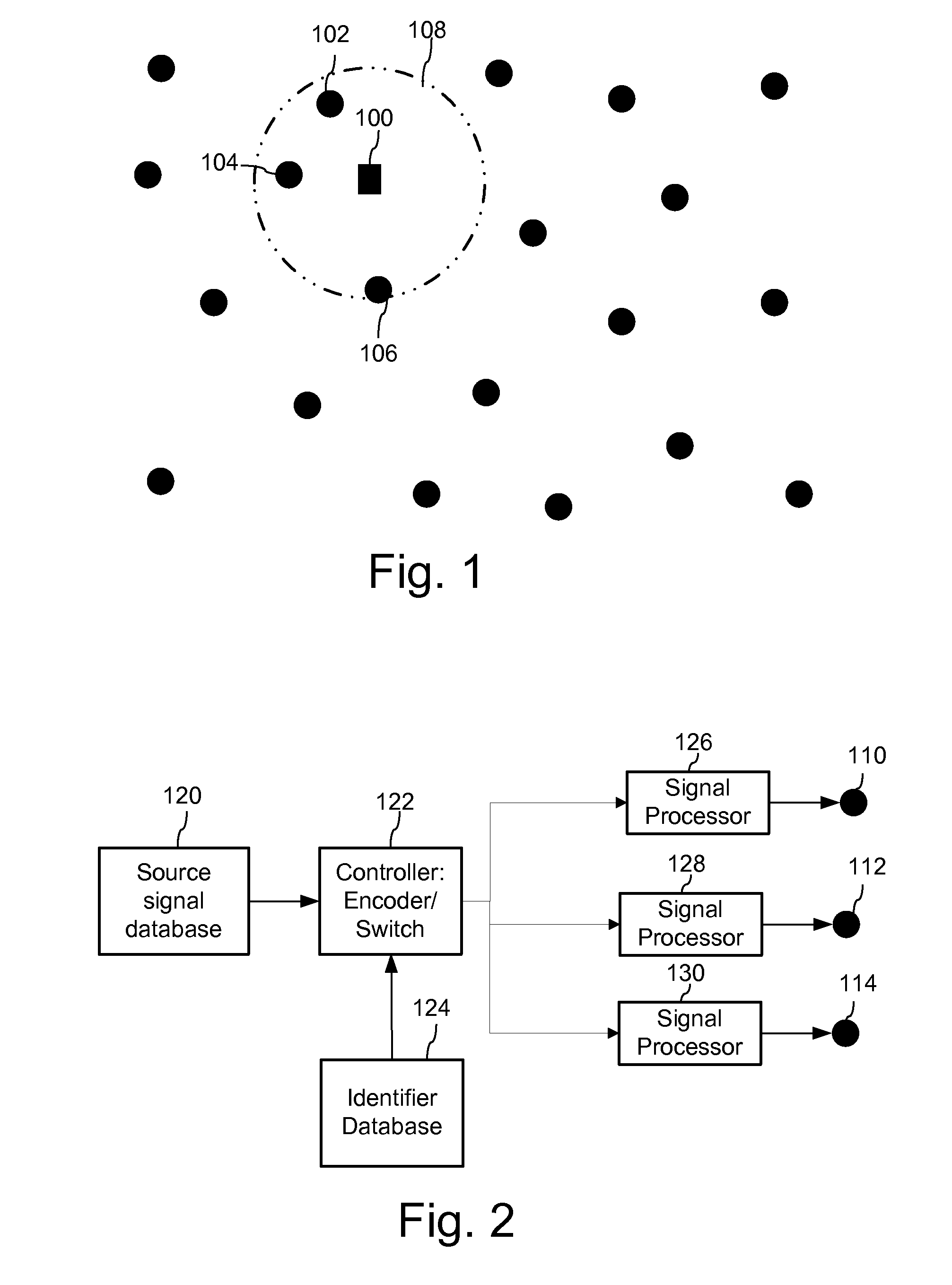
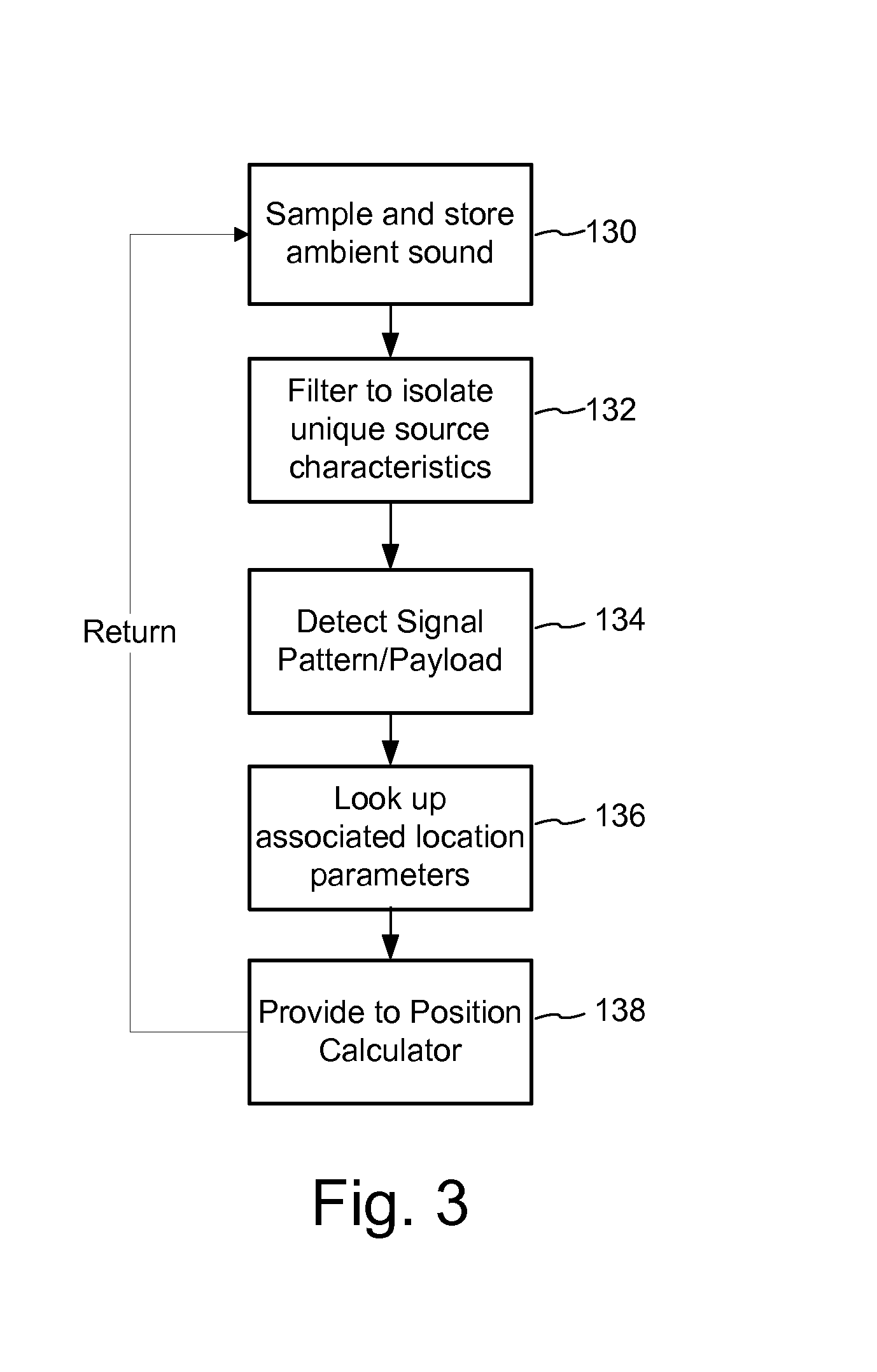
Mobile device positioning employs various forms of audio signal structures and detection methodologies. In one method, detection of an audio signal from a first source enables construction of a signal to facilitate detection of an audio signal from another source. Signals detected from these sources enable positioning of the mobile device receiving those signals. Another method forms audio signals transmitted from audio sources so that they have parts that add constructively and parts that differentiate the sources to enable positioning. Another audio signal based positioning method adaptively switches among positioning methods so that positioning remains operative as a mobile device moves toward and away from the sources. Another method tracks positioning history, evaluates it for errors and performs error mitigation to improve accuracy. Various other positioning technologies are detailed as well.
Owner:DIGIMARC CORP
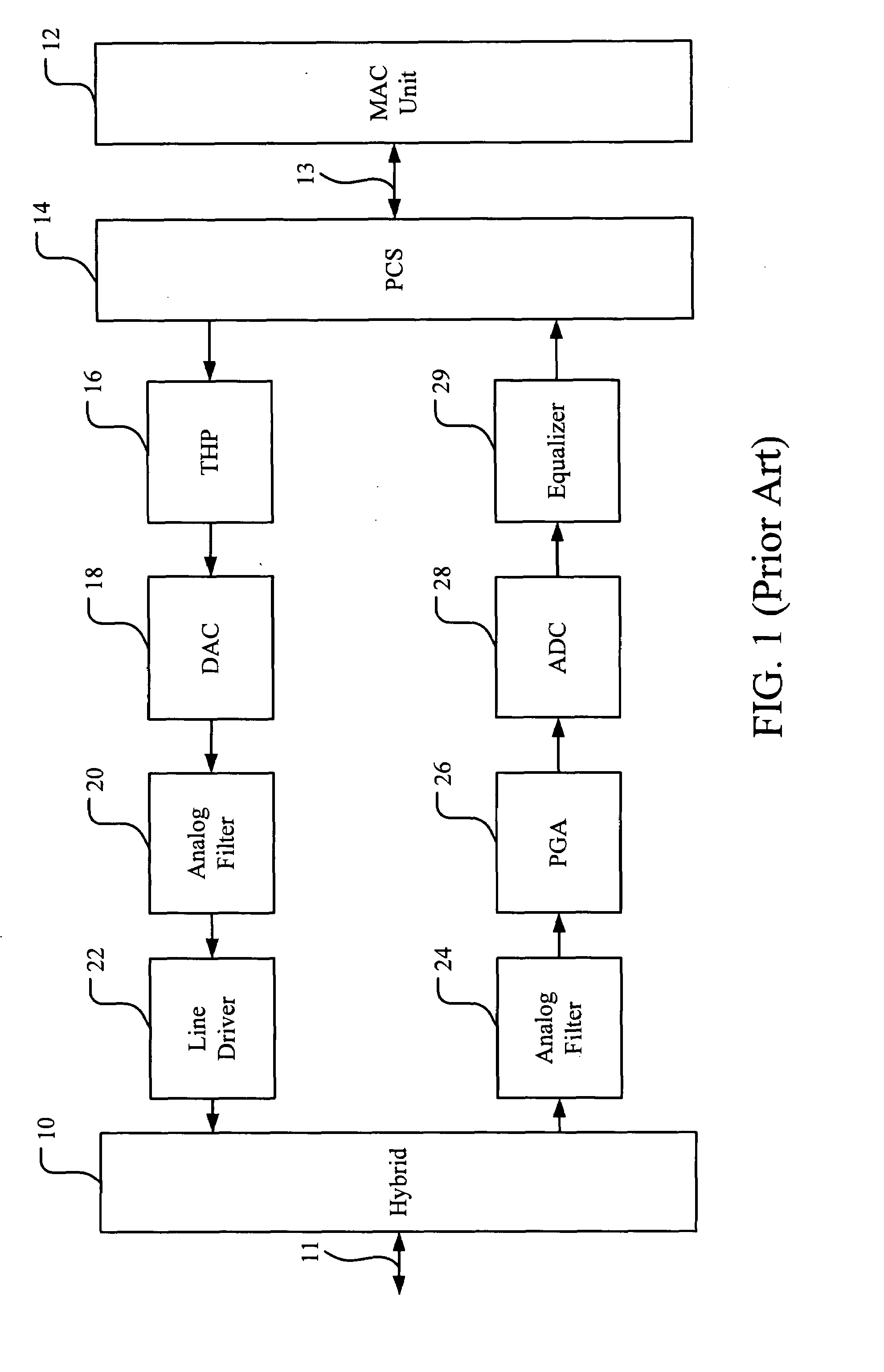
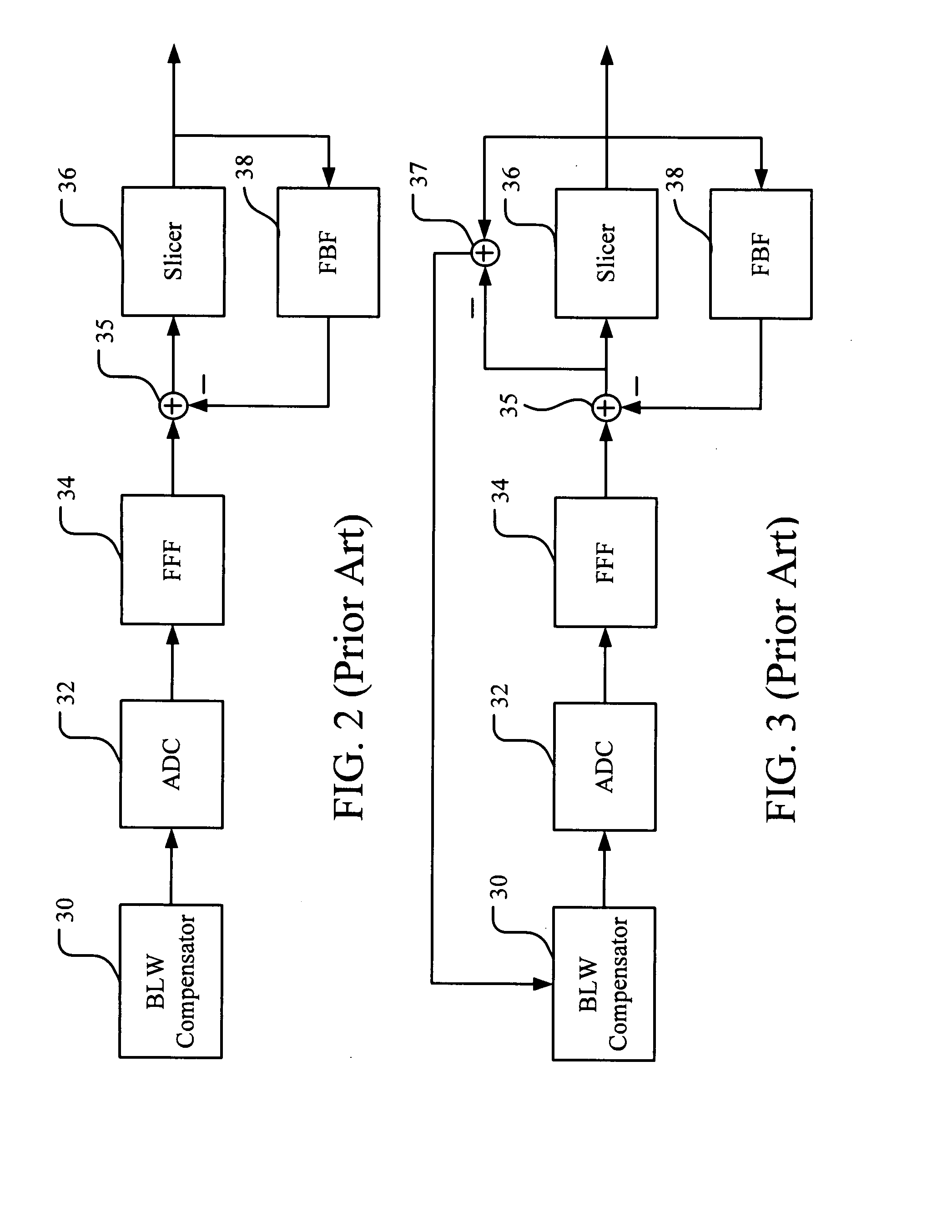
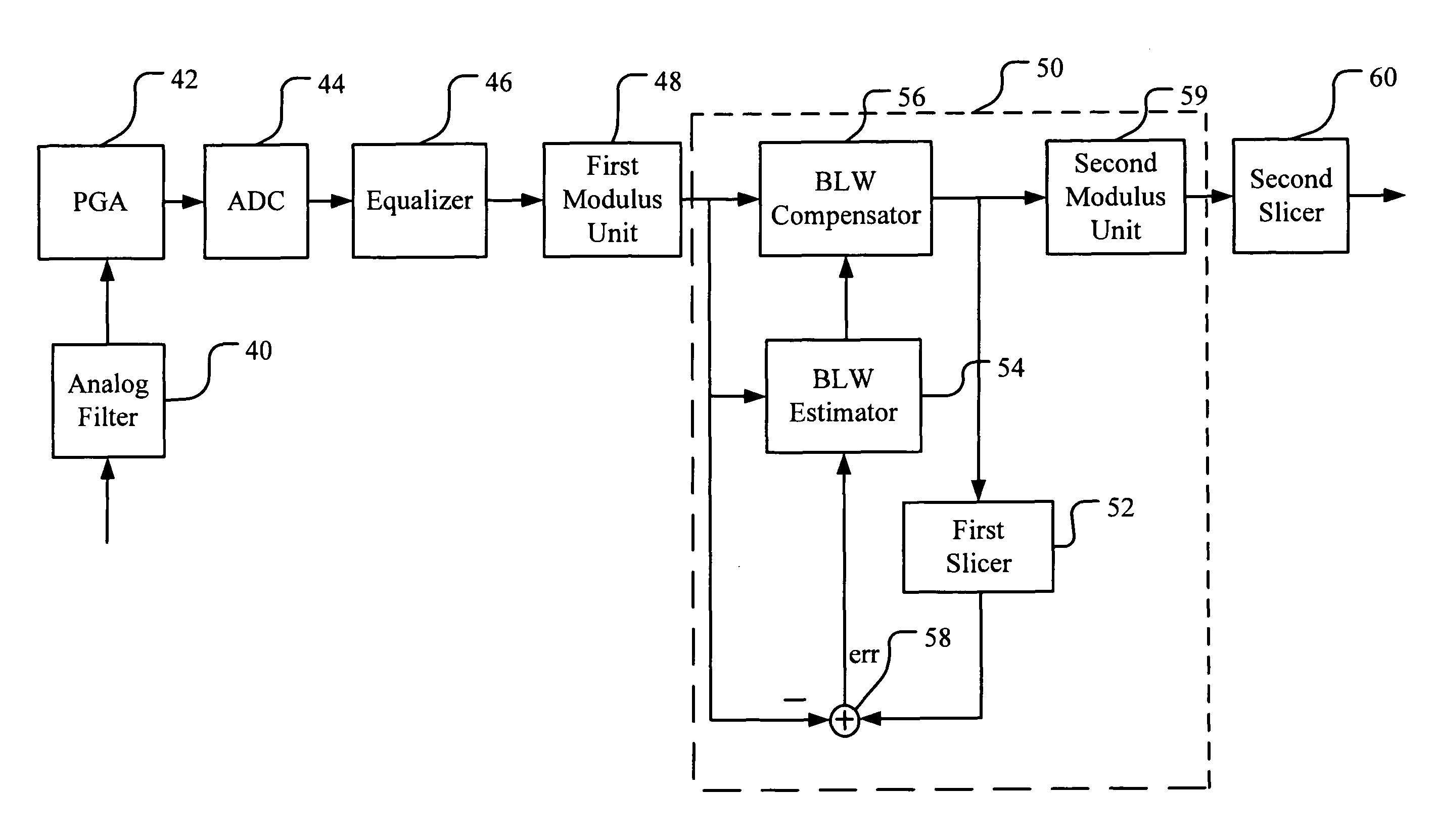
Method and apparatus for baseline wander compensation in Ethernet application
ActiveUS20080212715A1Reduce impactInaccurate estimationError preventionDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCommunications systemError mitigation
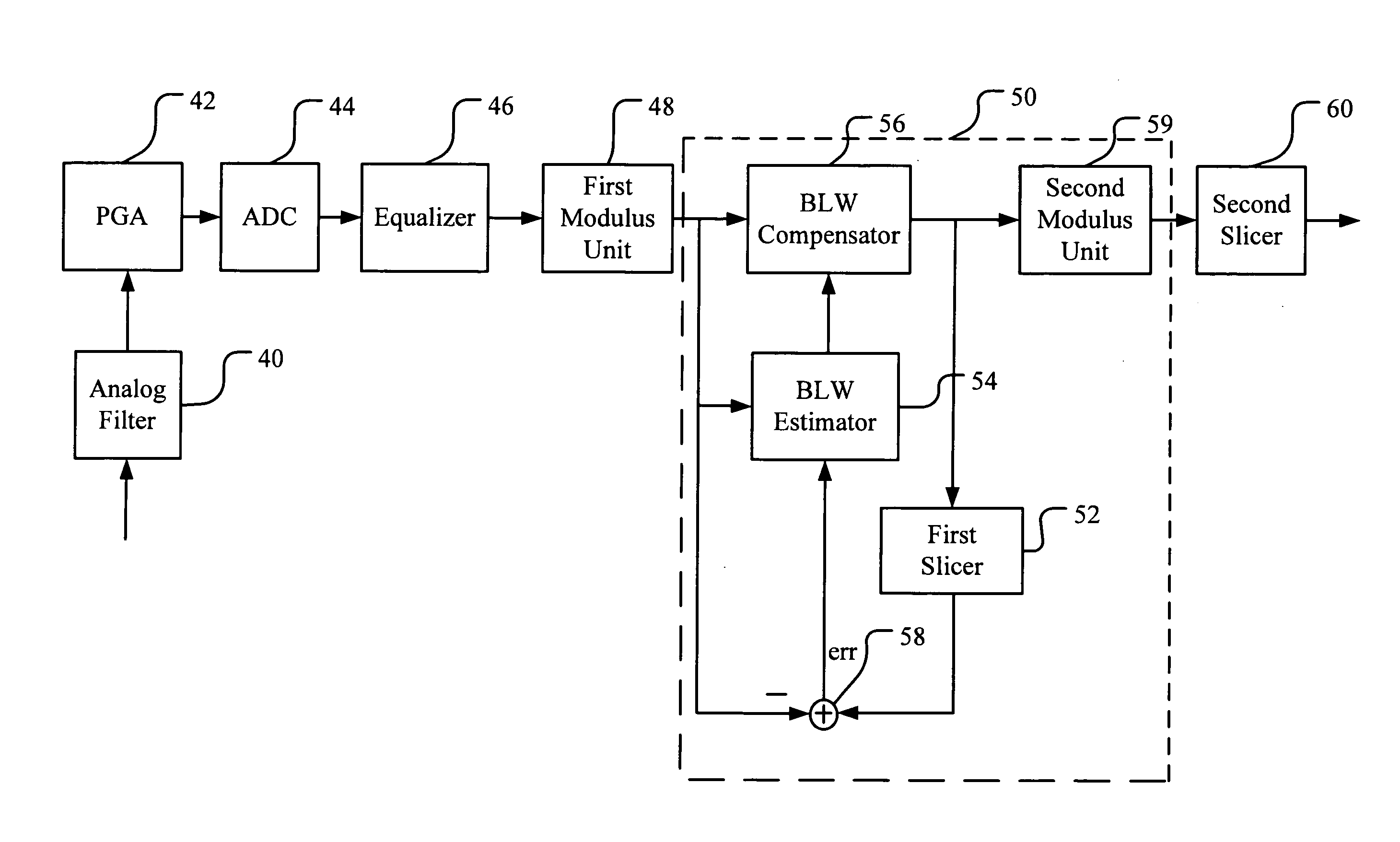
An embodiment of the proposed invention is primarily applied to compensate the BLW in communication systems using THPs in their transmitters, especially suitable for the 10GBase-T Ethernet application. The present apparatus includes an additional decision device (slicer) used to generate DC offset information (error signal) and an extra modulus unit after our BLW compensator to reconvert compensated symbols to correct 16-PAM signals. In addition, the estimated error signals in our method are generated from the difference between the input of the BLW compensator and the output of the decision device. These error signals are then weighted to alleviate the impact of erroneous DC offset information on the performance of the BLW compensator. Therefore, a more direct and accurate DC offset information can be derived to improve the inaccurate BLW estimation in previous works.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
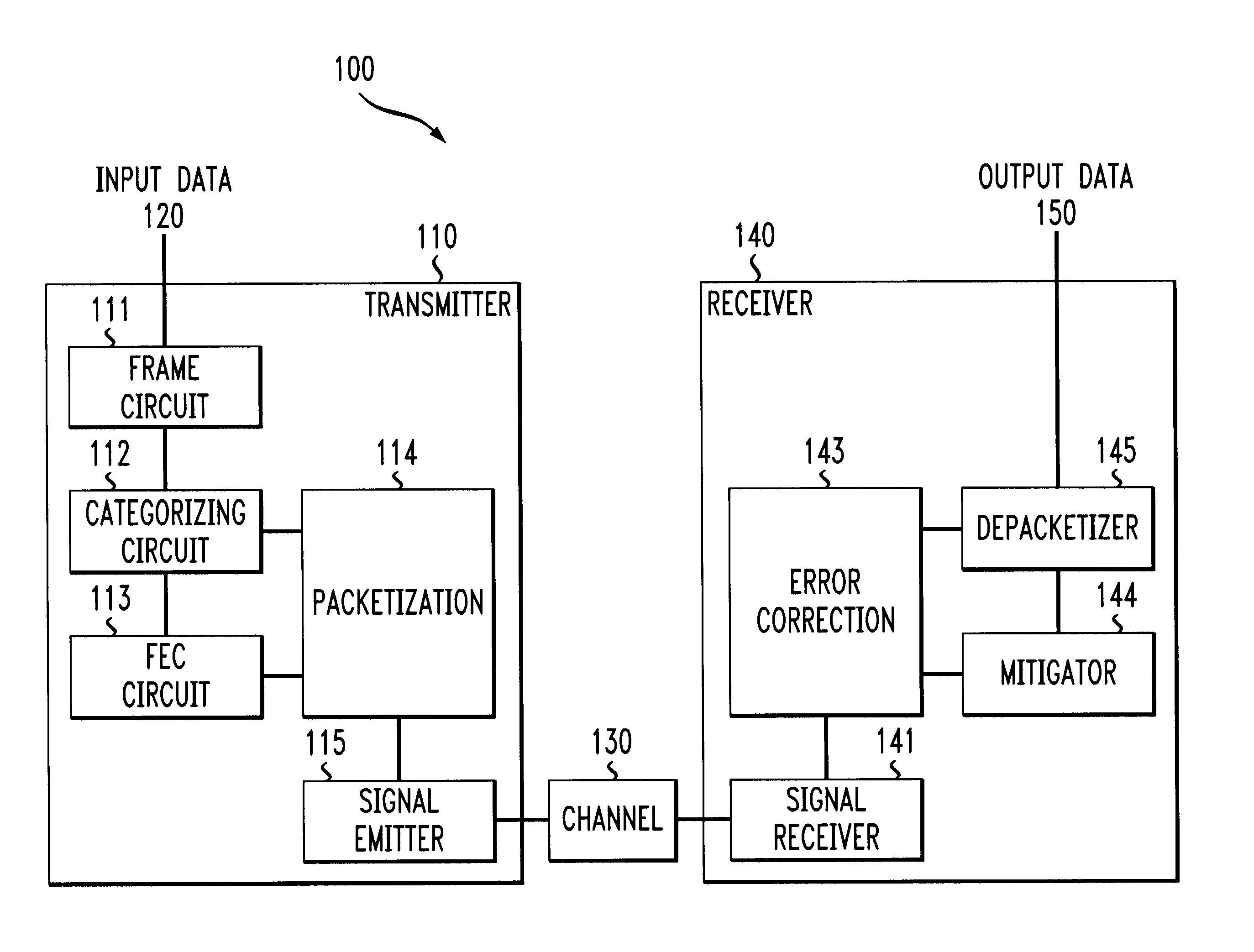
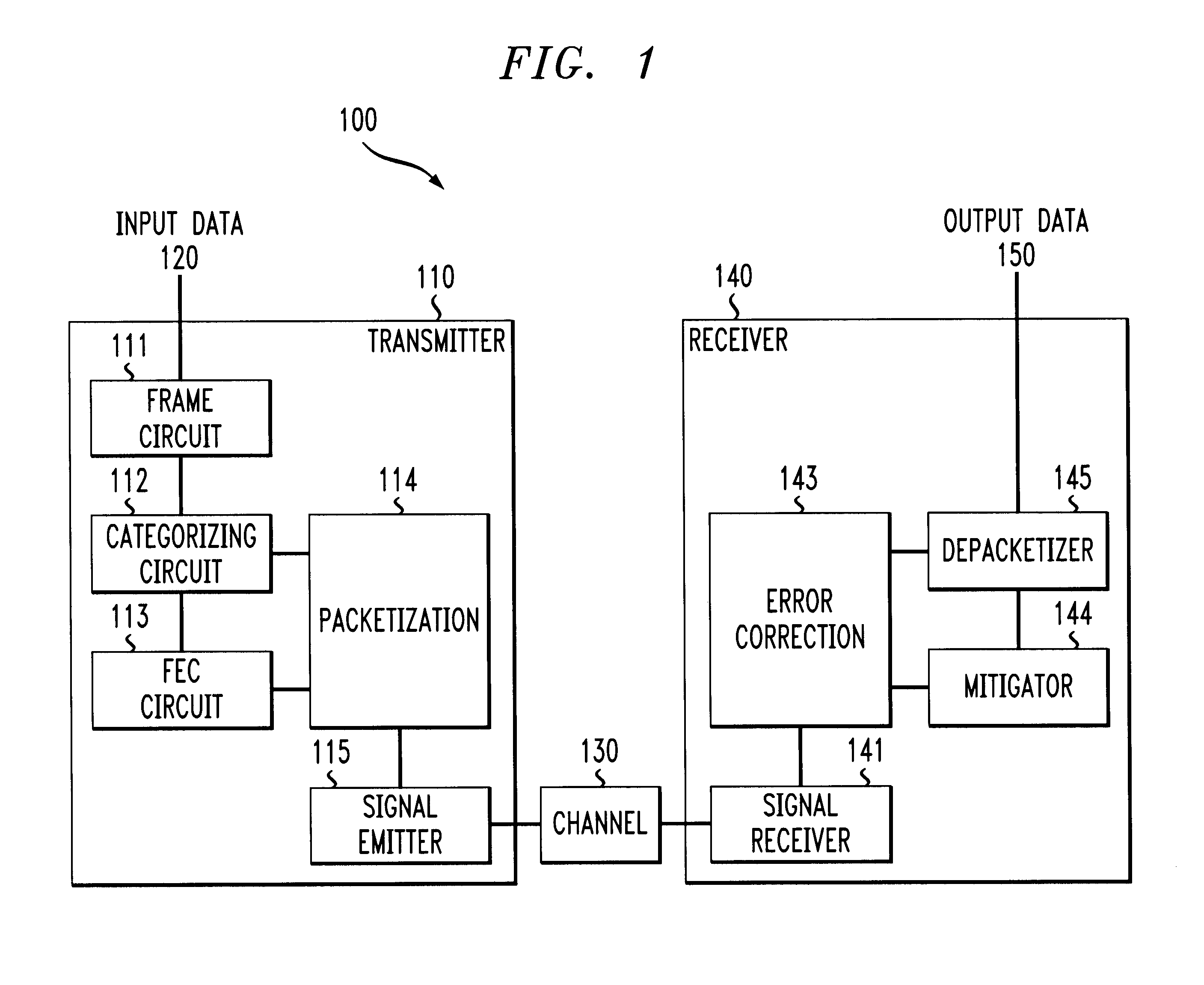
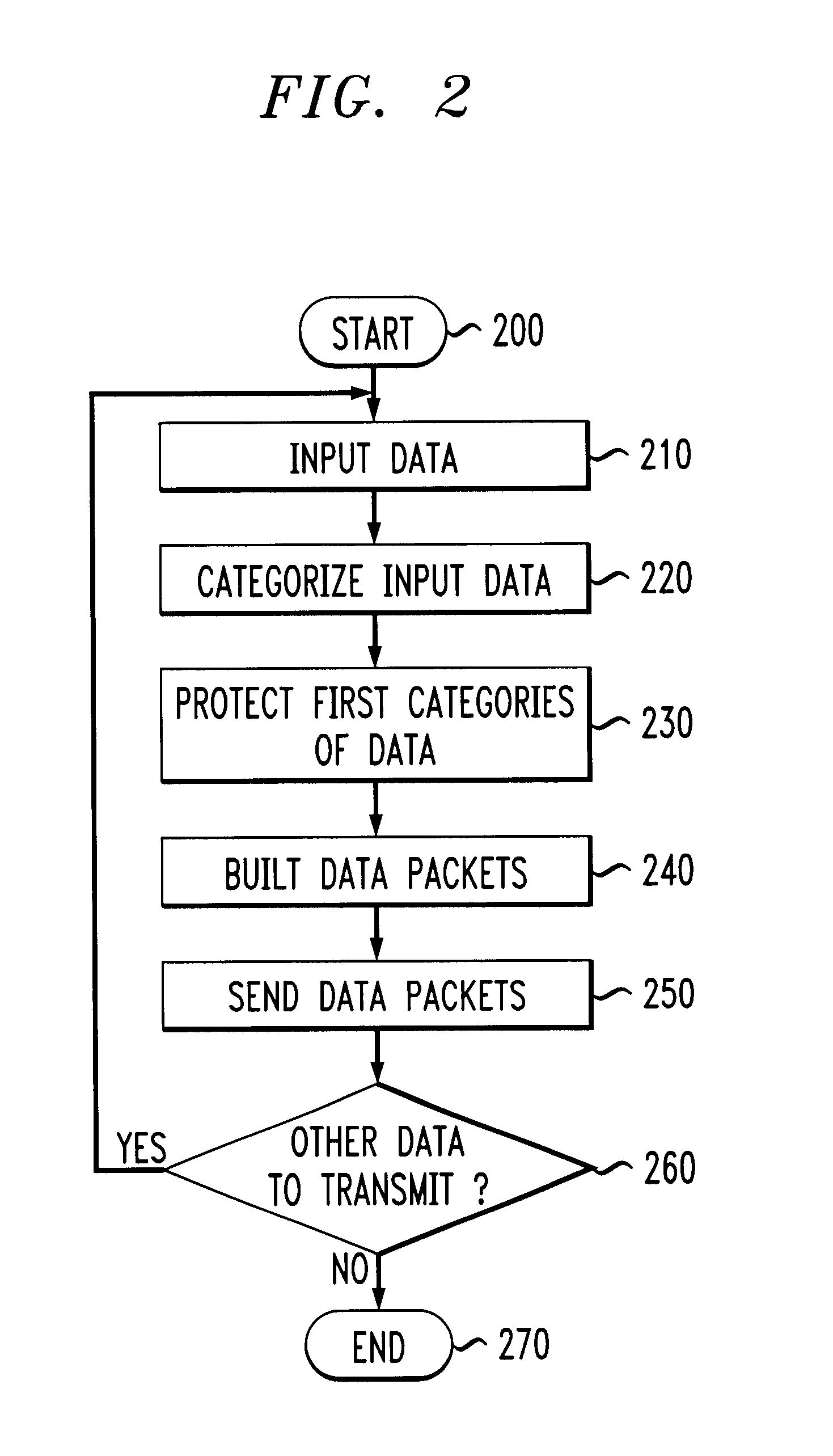
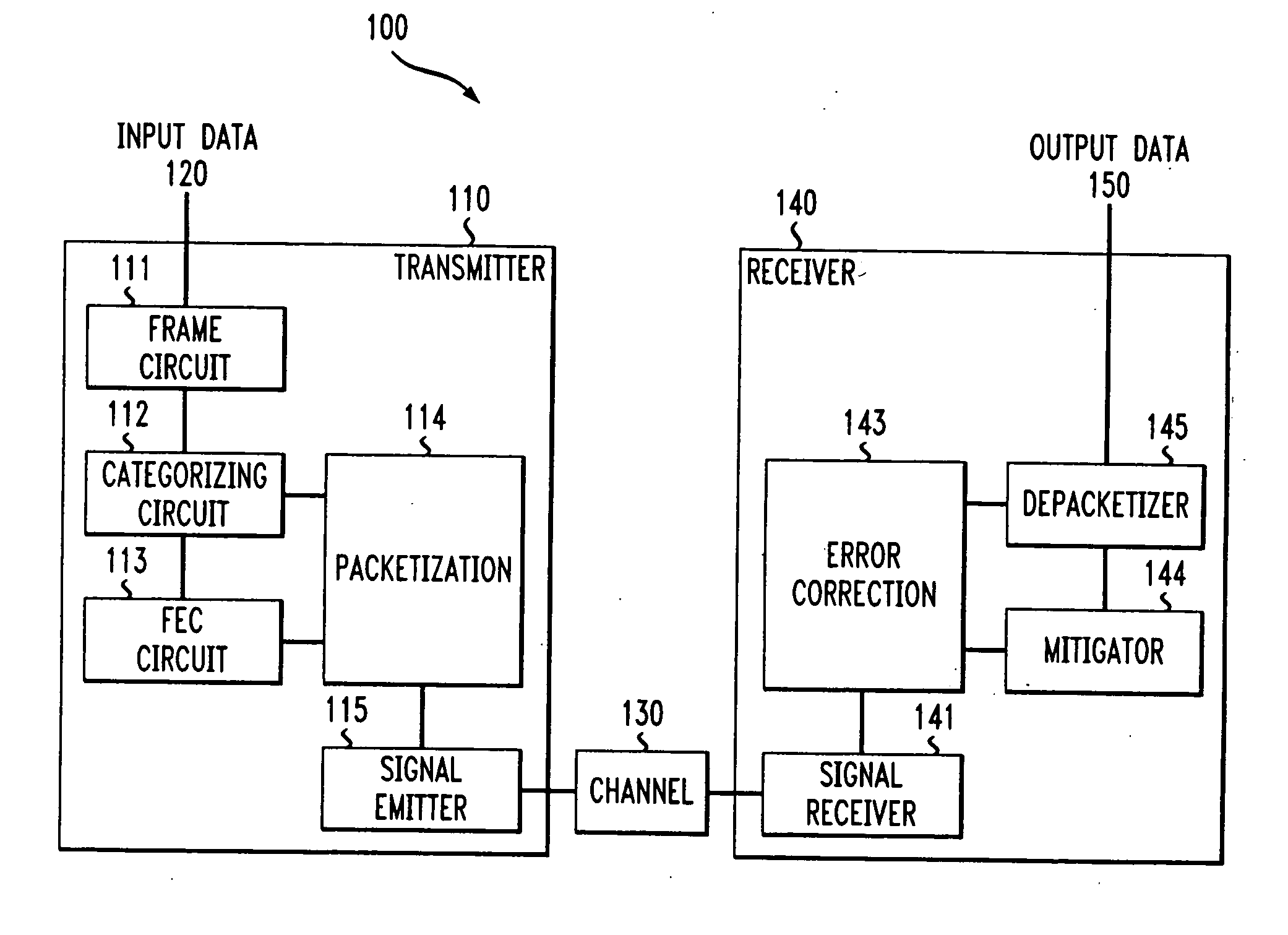
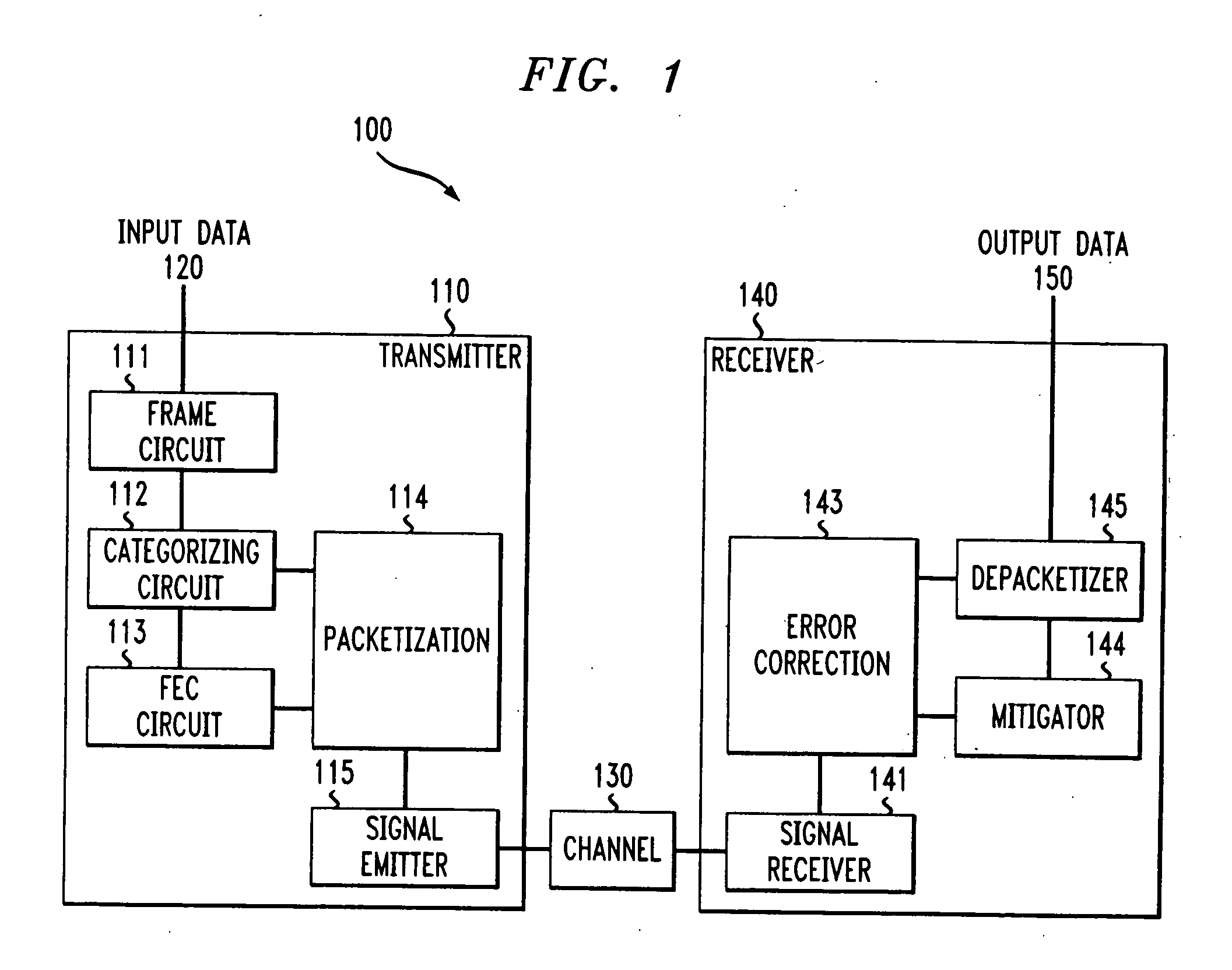
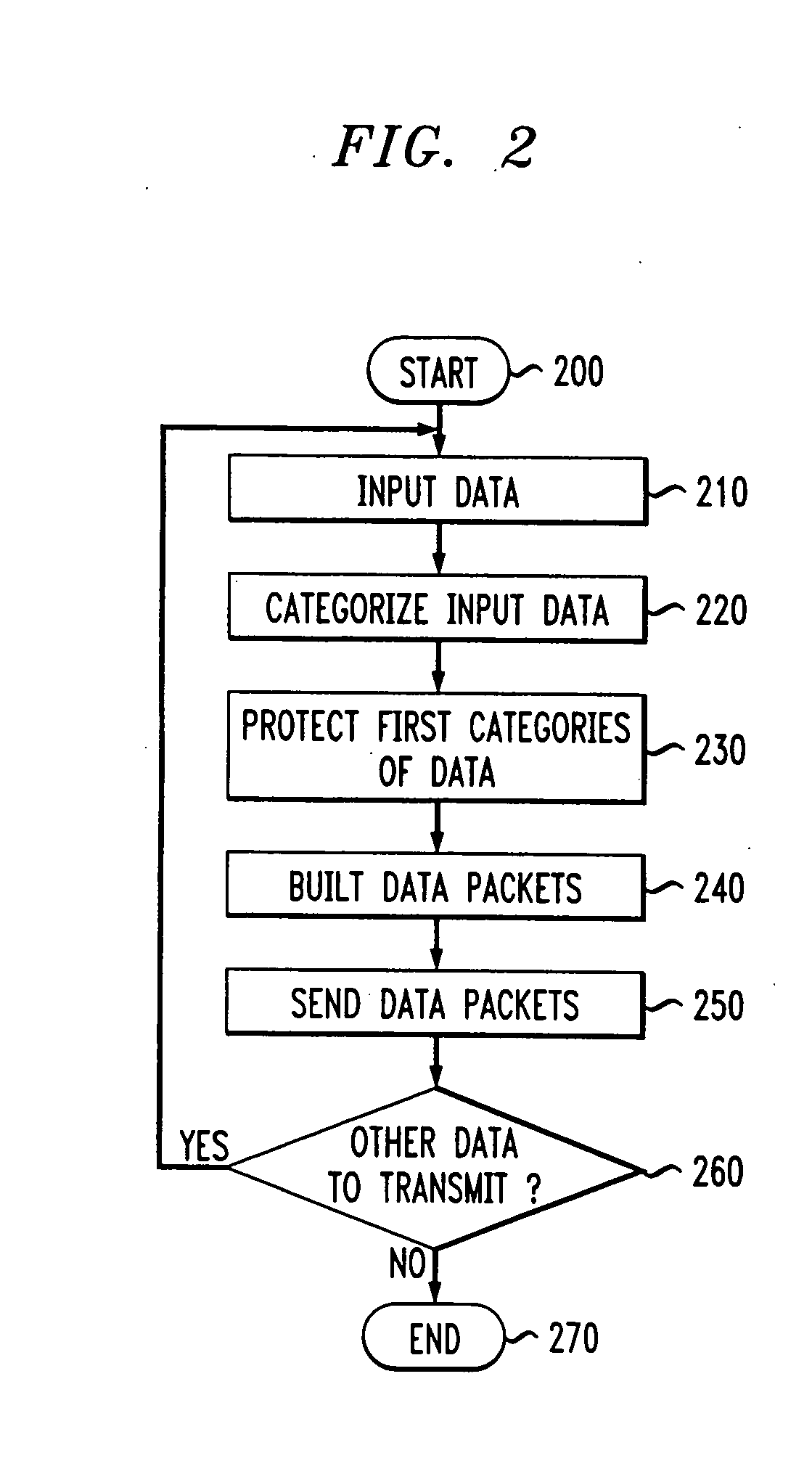
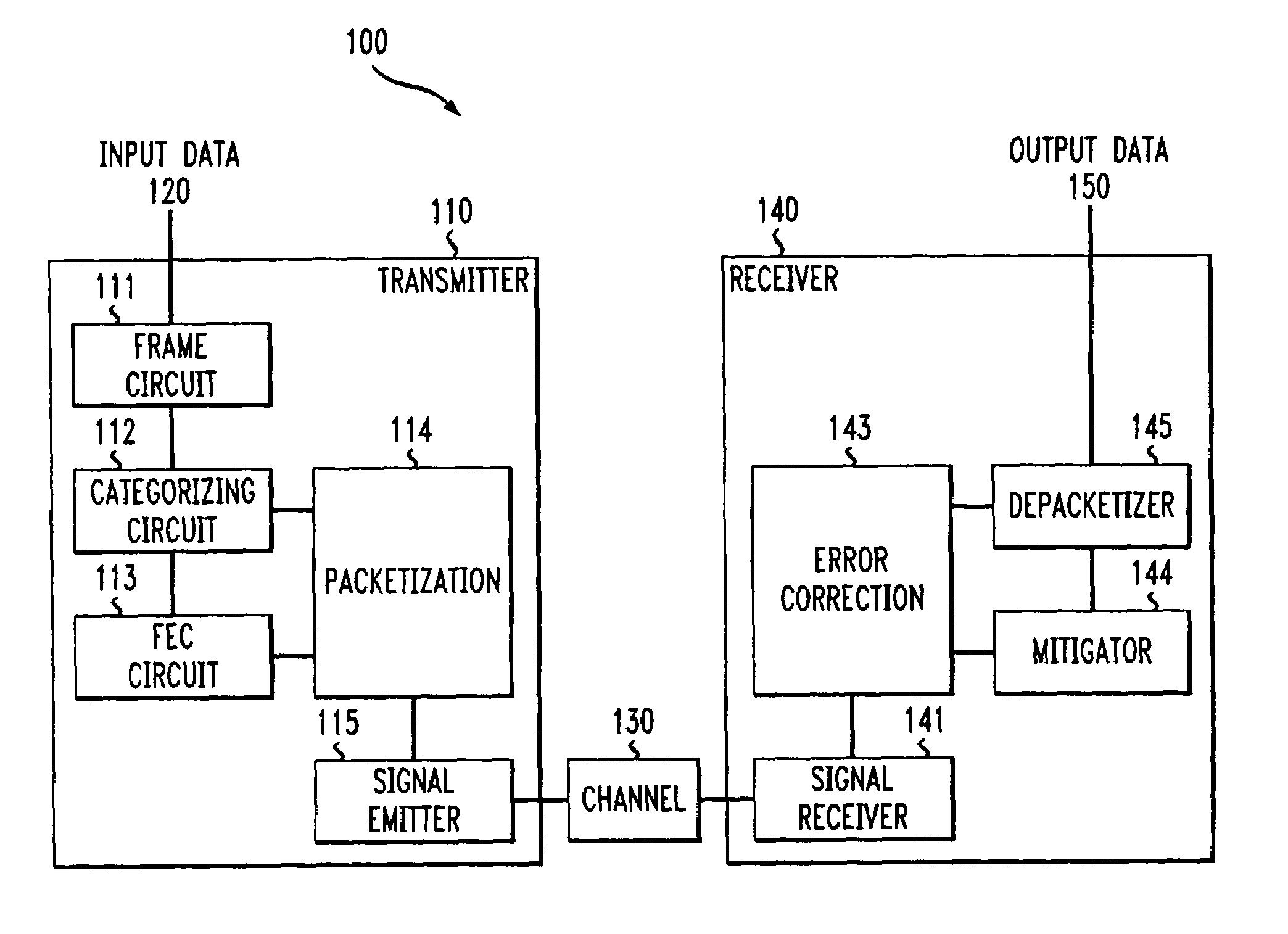
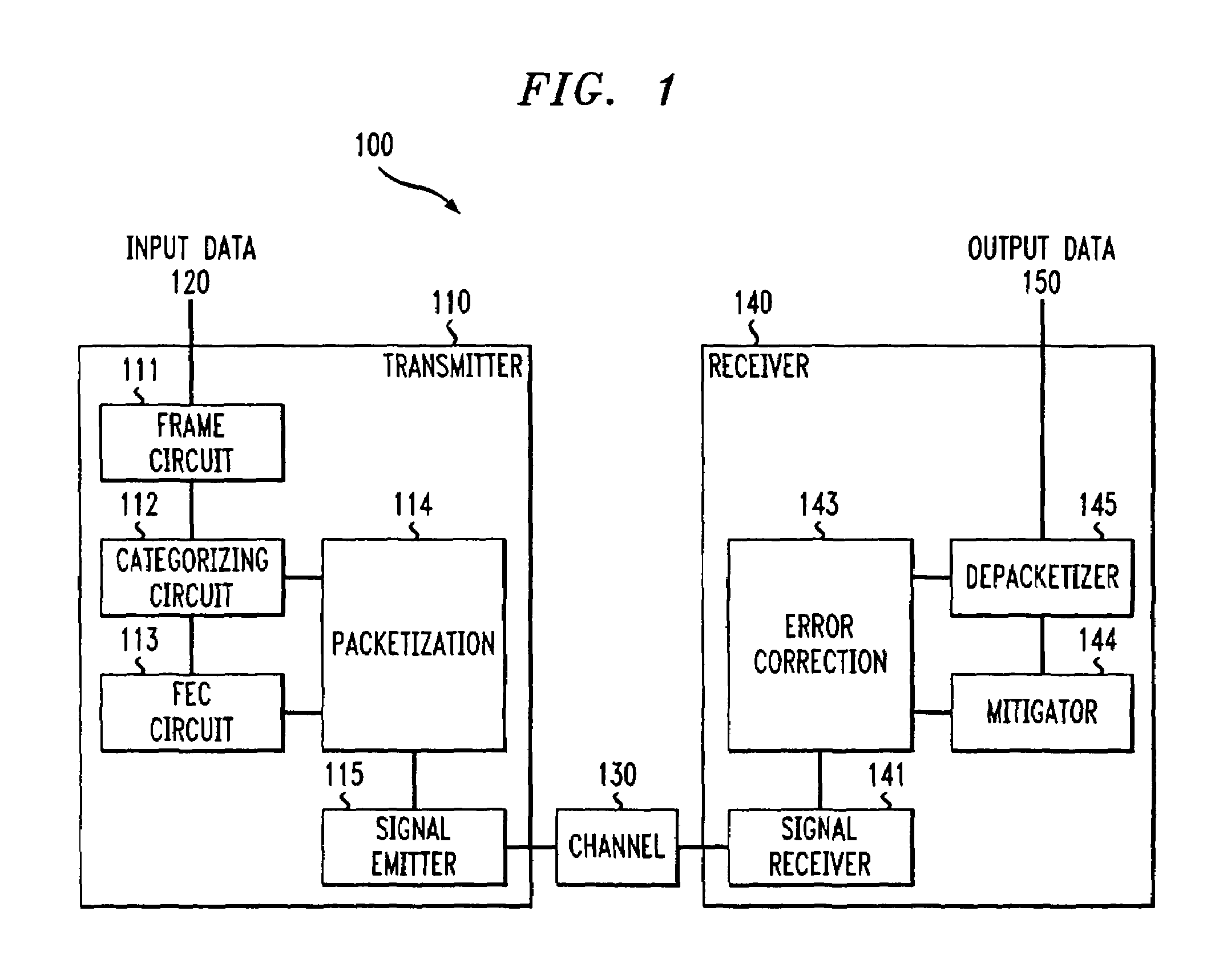
System and methods for transmitting data
InactiveUS6850559B1Increase demandError prevention/detection by using return channelModulated-carrier systemsForward error correctionComputer science
A system and method for transmitting data over a channel, in which the data are categorized in at least two different categories. For example, the data are categorized according to the effect on perceived degradation on the data when error mitigation is performed on the data. Corrupted data of the first category are replaced using a first replacement method, such as retransmission and forward error correction. The corrupted data of the second category are replaced using a second replacement method different from the first replacement method, e.g., error mitigation or interpolation.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
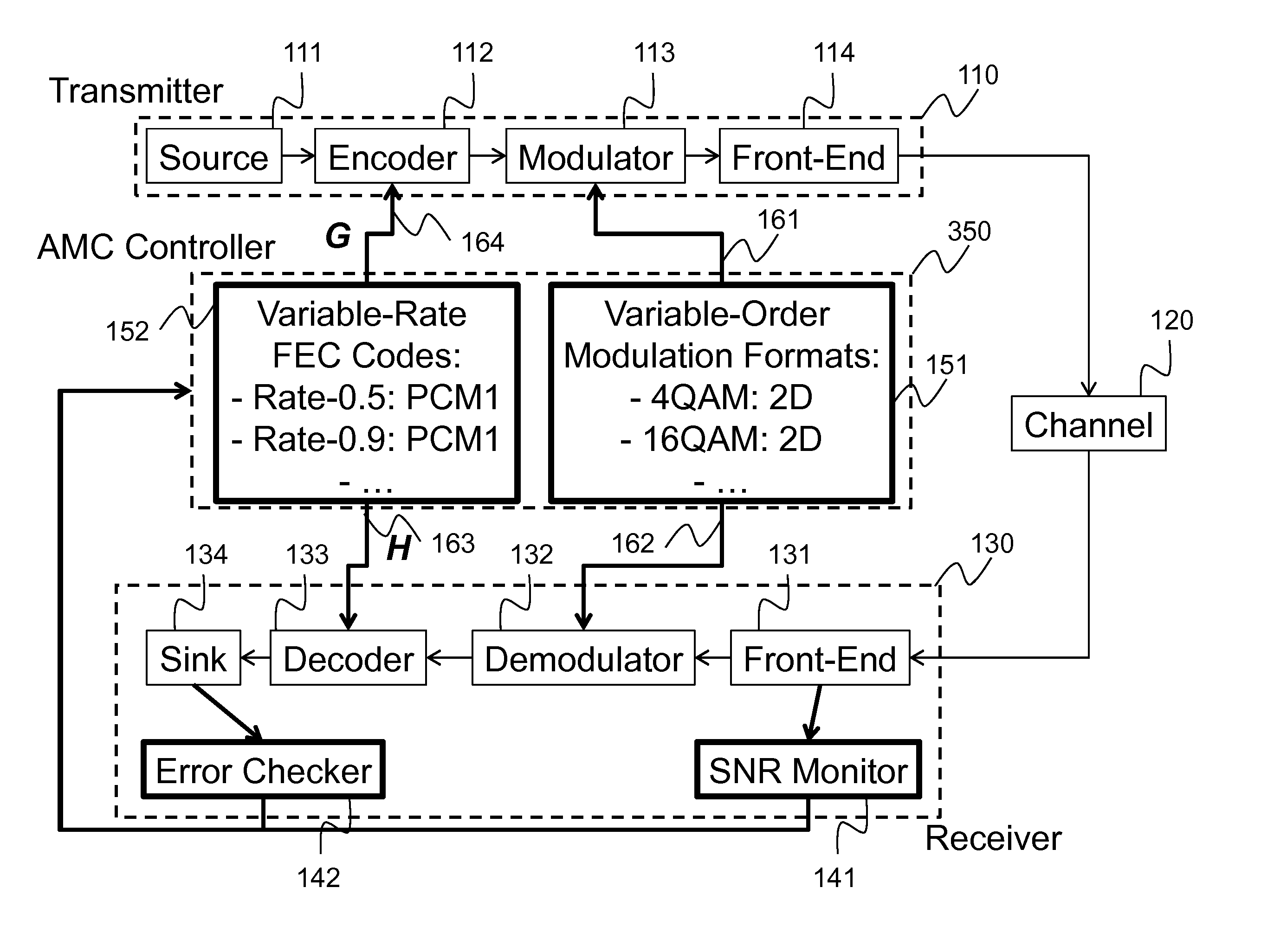
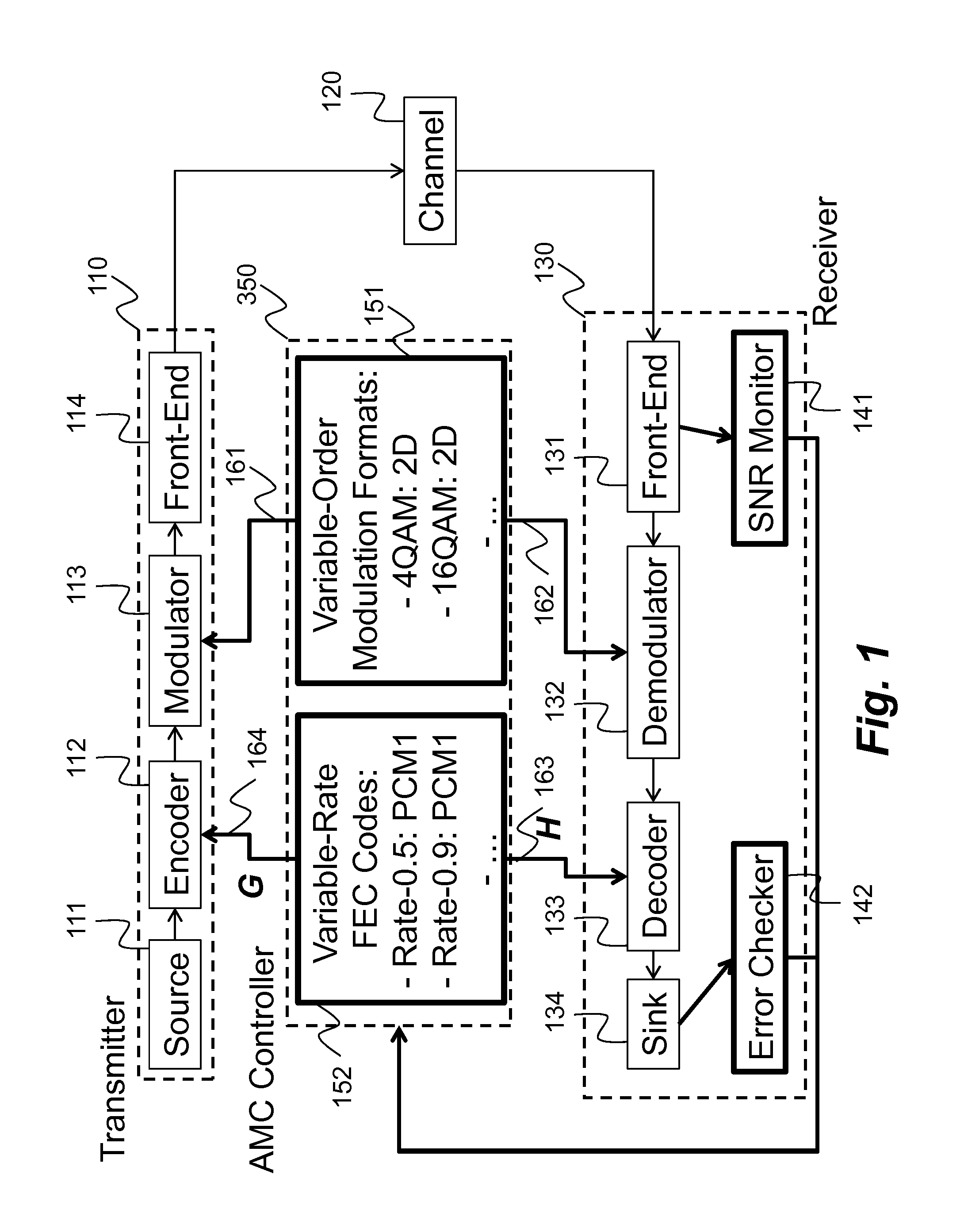
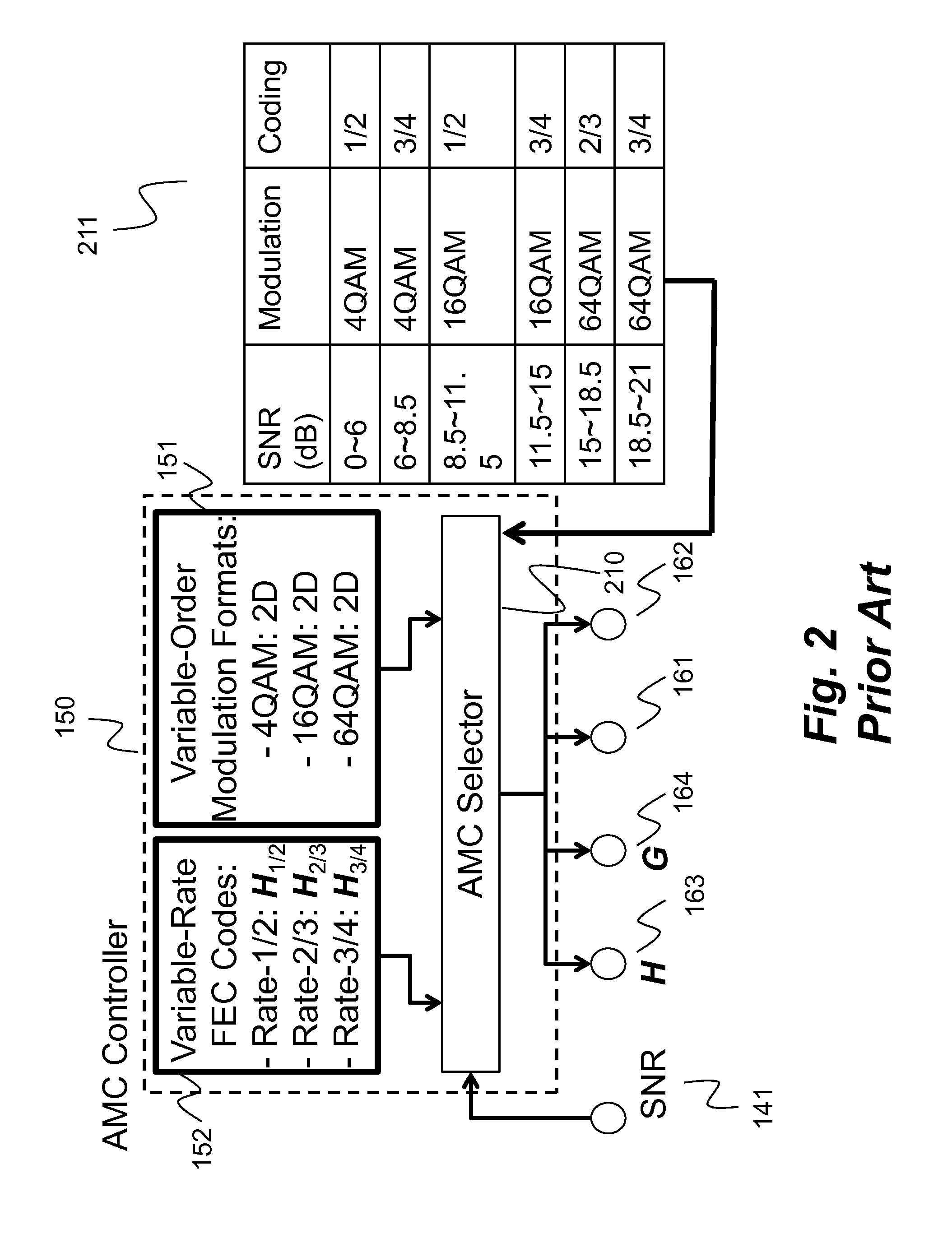
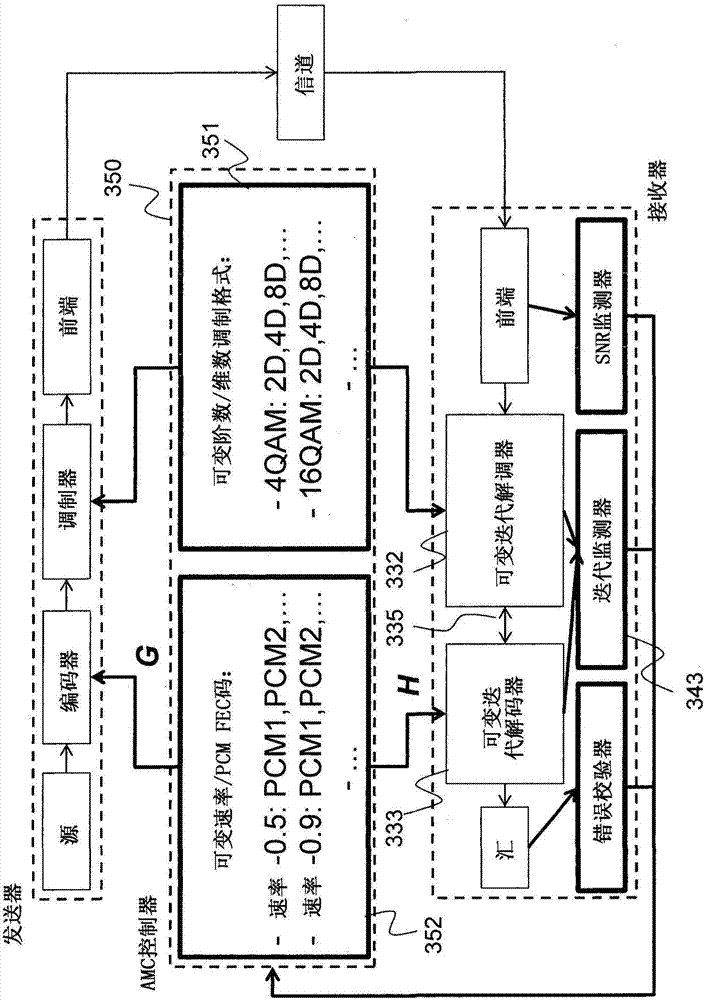
Method and System for Reliable Data Communications with Adaptive Multi-Dimensional Modulations for Variable-Iteration Decoding
ActiveUS20160233979A1Improve performanceSimple processError correction/detection using block single space codingOther decoding techniquesBelief propagationError mitigation
In an advanced adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) scheme, the code rate and the parity-check matrix (PCM) for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes are adapted according to modulation formats and variable-iteration receivers. The degree distribution for the PCM adaptation is designed by heuristic optimization to minimize the required SNR via an extrinsic information transfer (EXIT) trajectory analysis for finite-iteration decoding. The method uses dynamic window decoding by generating spatially coupled PCM for quasi-cyclic LDPC convolutional coding. The method also provides a way to jointly optimize labeling and decoding complexity for high-order and high-dimensional modulations. The problem to use a large number of different LDPC codes for various modulation formats and variable-iteration decoding is also dealt with by linearly dependent PCM adaptation across iteration count to keep using a common generator matrix. This PCM adaptation can improve a convergence speed of belief propagation decoding and mitigate an error floor issue.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
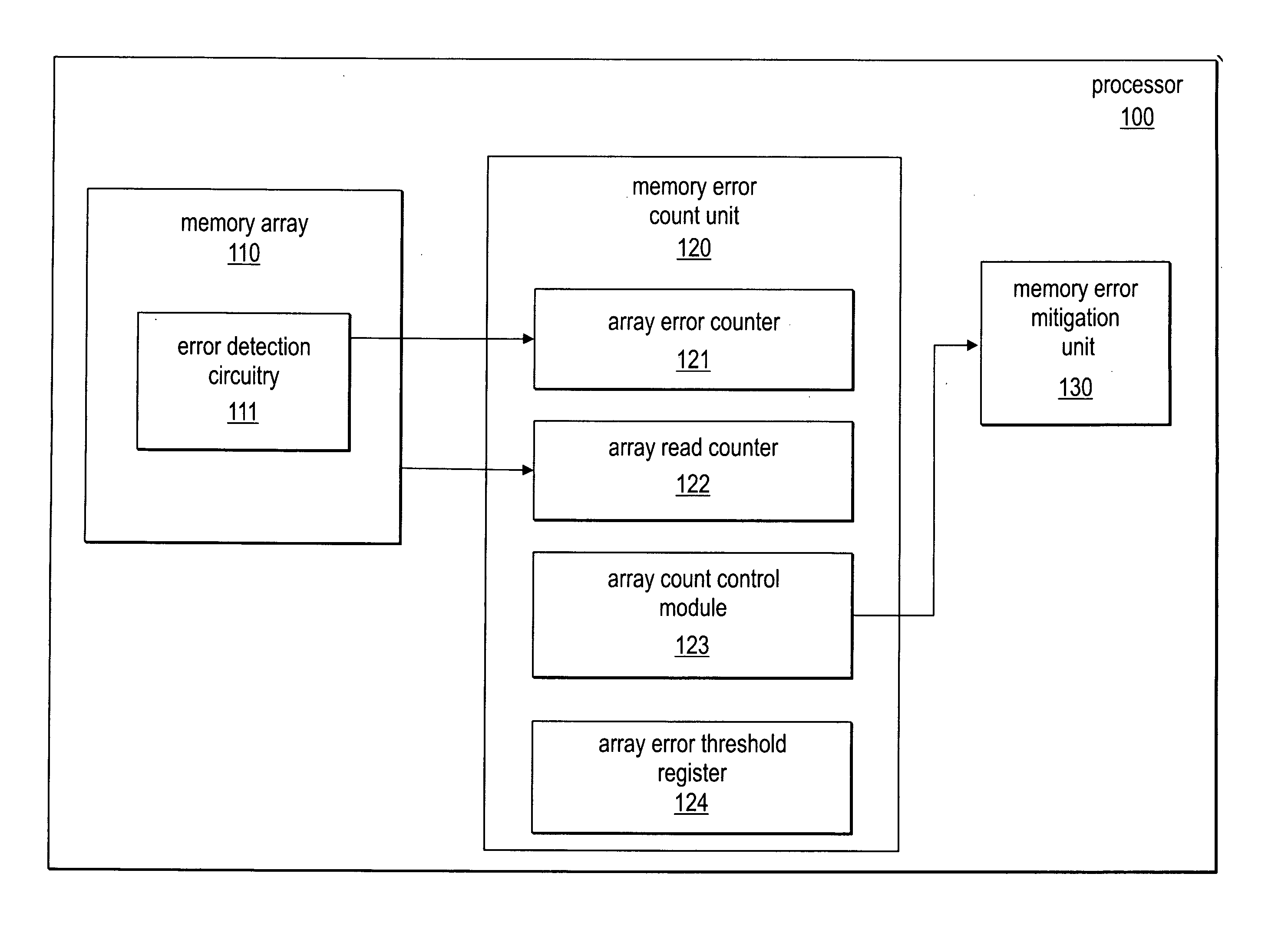
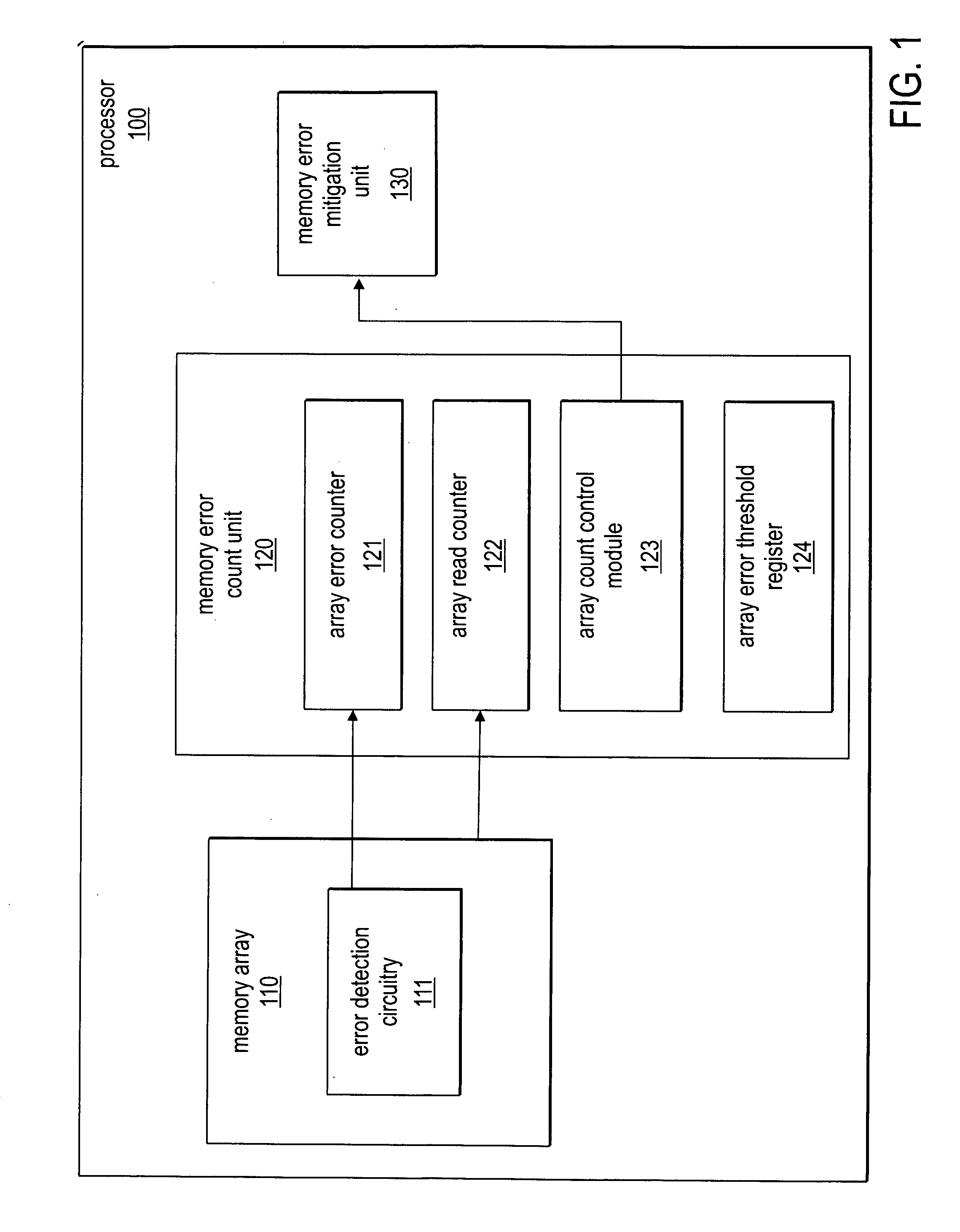
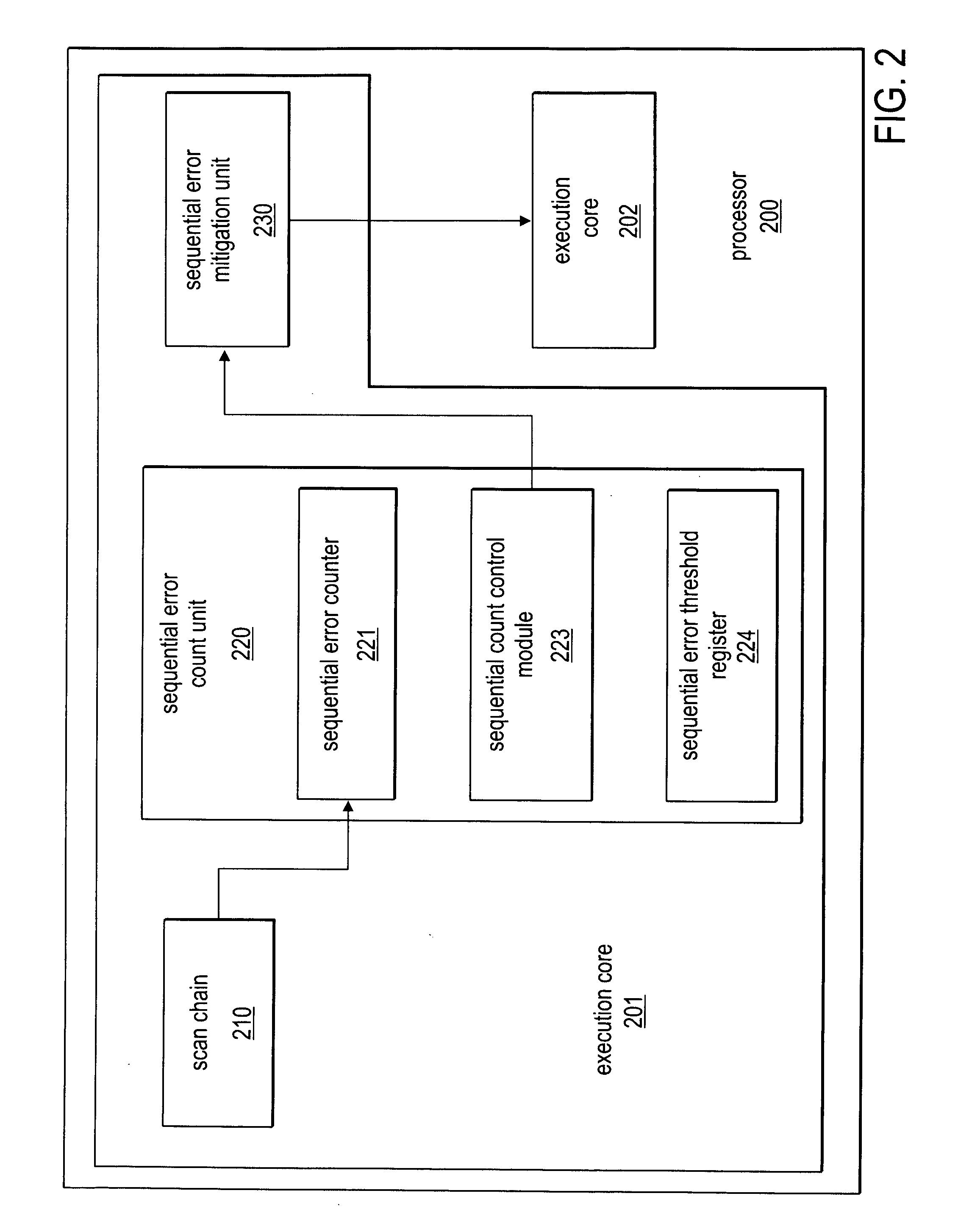
Selective activation of error mitigation based on bit level error count
InactiveUS20070011513A1Non-redundant fault processingStatic storageComputer hardwareBiological activation
Embodiments of apparatuses and methods for selective activation of error mitigation based on bit level error counts are disclosed. In one embodiment, an apparatus includes a plurality of state elements, an error counter, and activation logic. The error counter is to count the number of bit level errors in the state elements. The activation logic is to increase error mitigation if the number of bit level errors exceeds a threshold value.
Owner:INTEL CORP
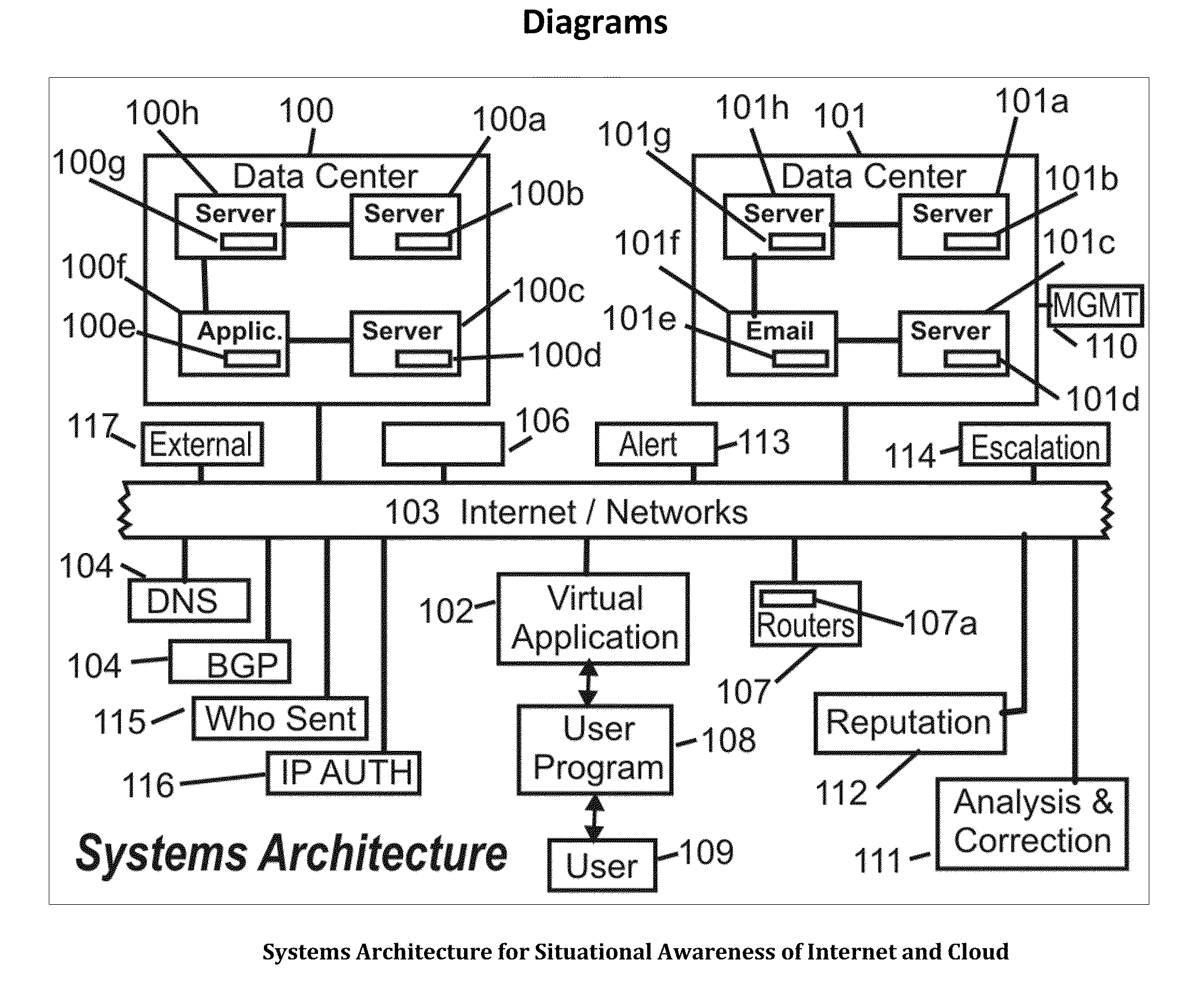
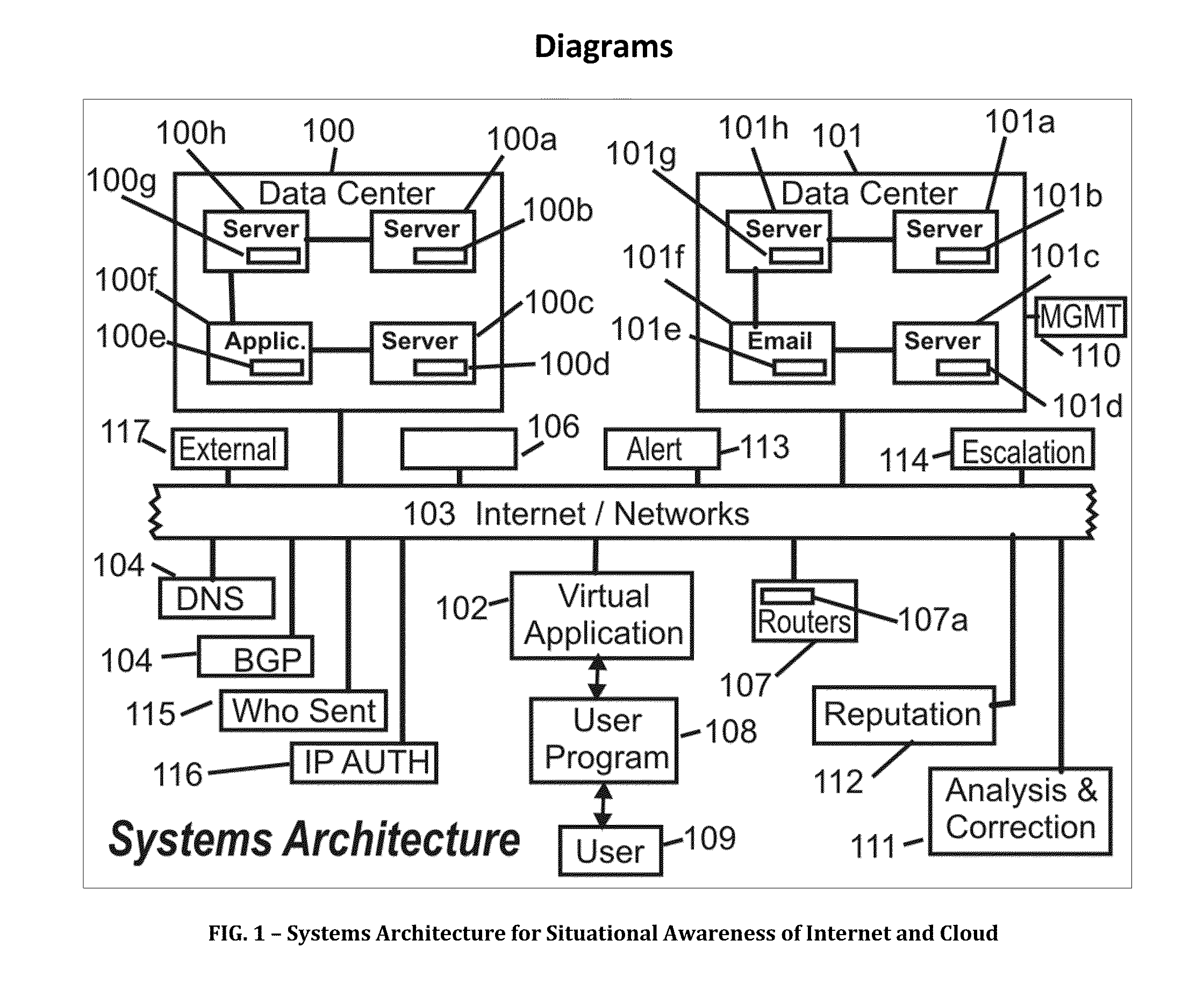
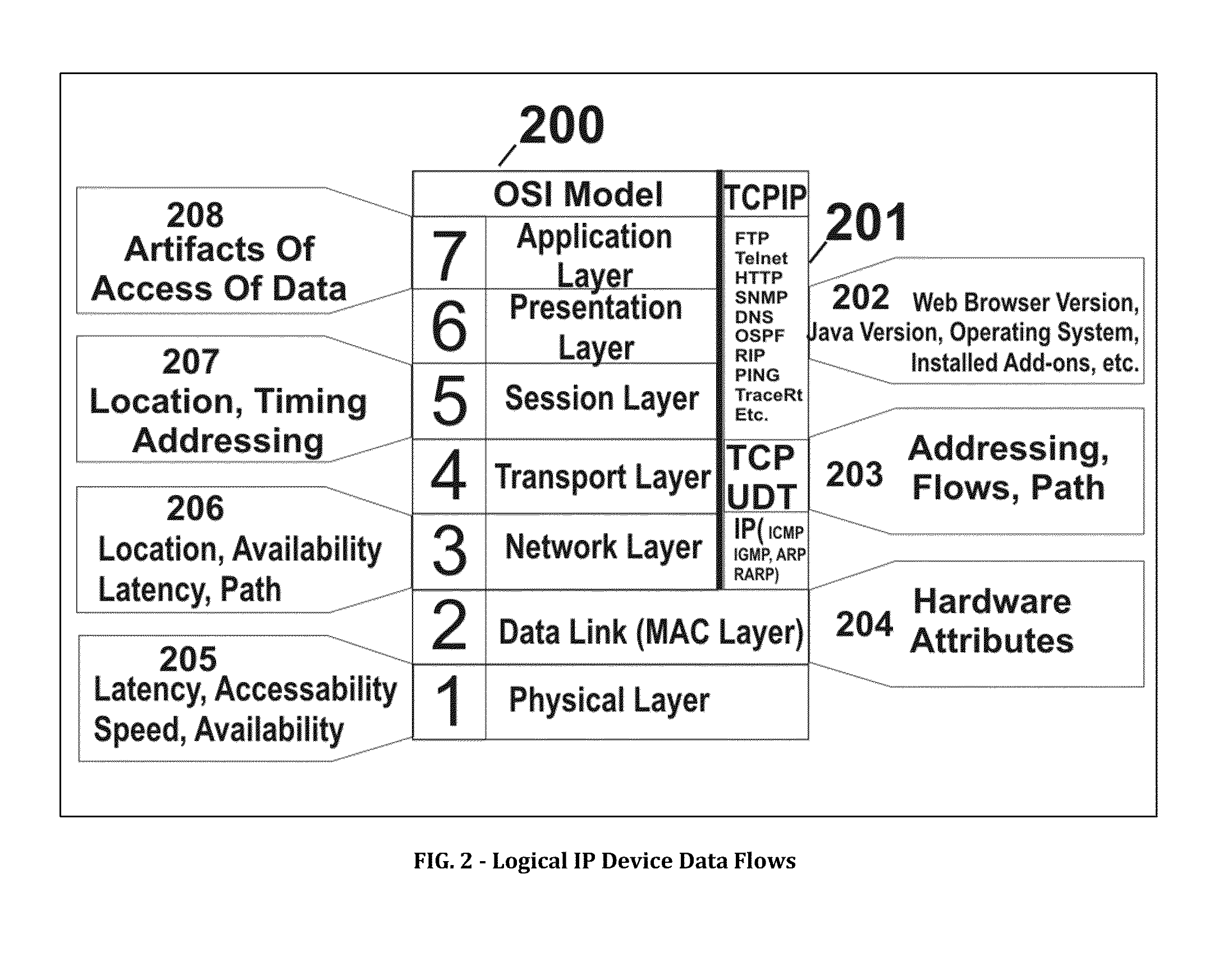
Systems, methods and devices for providing situational awareness, mitigation, risk analysis of assets, applications and infrastructure in the internet and cloud
InactiveUS20120011590A1Memory loss protectionError detection/correctionAnalysis dataApplication software
The present invention determines a situational awareness for alerting, mitigating error, distortion or failures, and managing the Internet (or equally component intranets), connected networks and cloud infrastructure. Specifically, this invention focuses on determining who originates messages, from what system, and the path taken, thereby analyzing the reputation of all the nodes and links through which data passes.It can provide a mechanism determine the ongoing veracity of the “purported” device, and maintain a reputation database of devices, data, applications and networks for analysis of how the Internet is being used or potentially subverted—effectively creating a score indicating component and total system integrity. It can calculate a correlation of risk analysis of all adjacent data describing the universe of the Internet. This invention will be particularly useful for helping detect and mitigate compromises to data, networks, systems and other assets within the Internet and Cloud.
Owner:DONOVAN JOHN JOSEPH
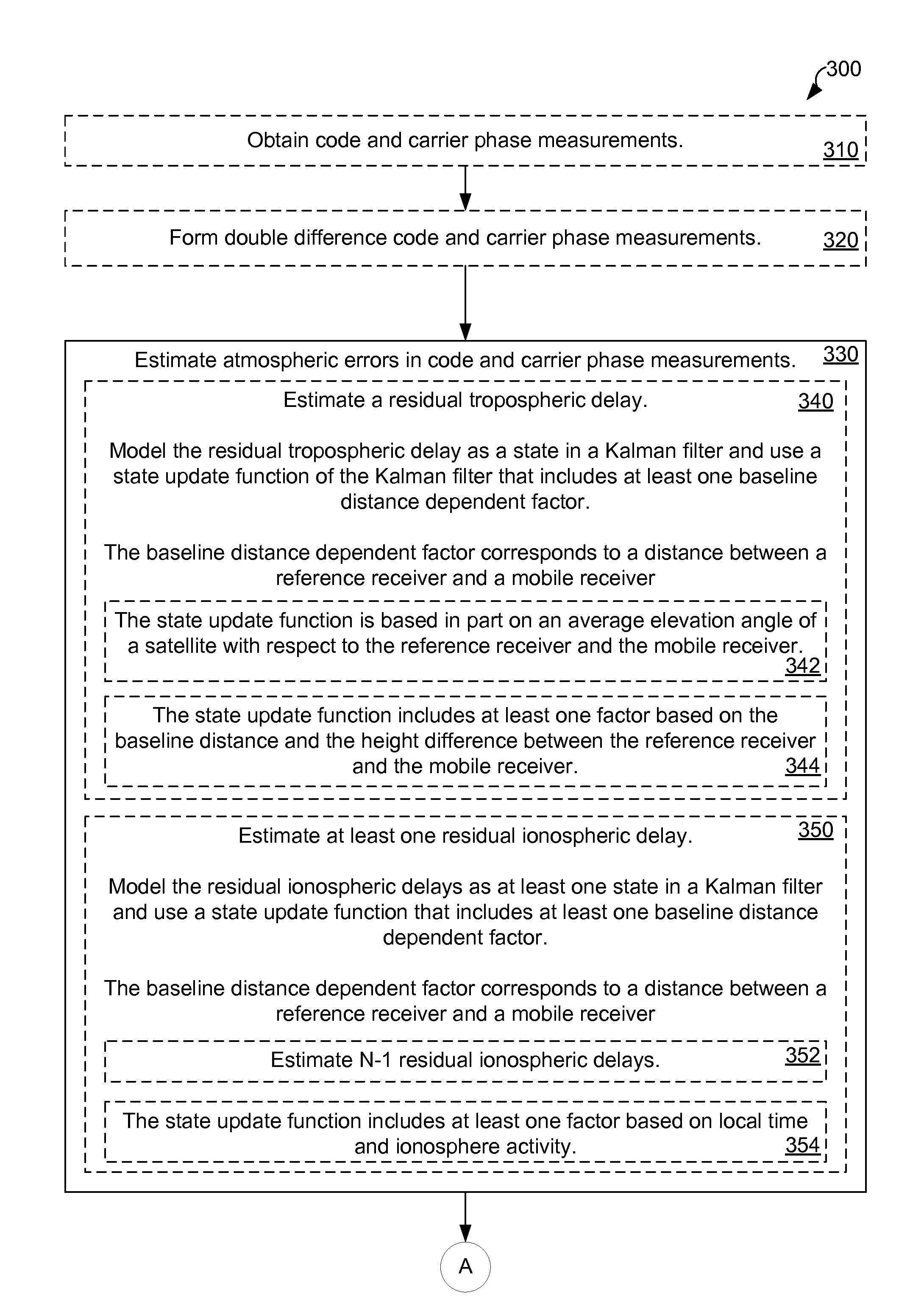
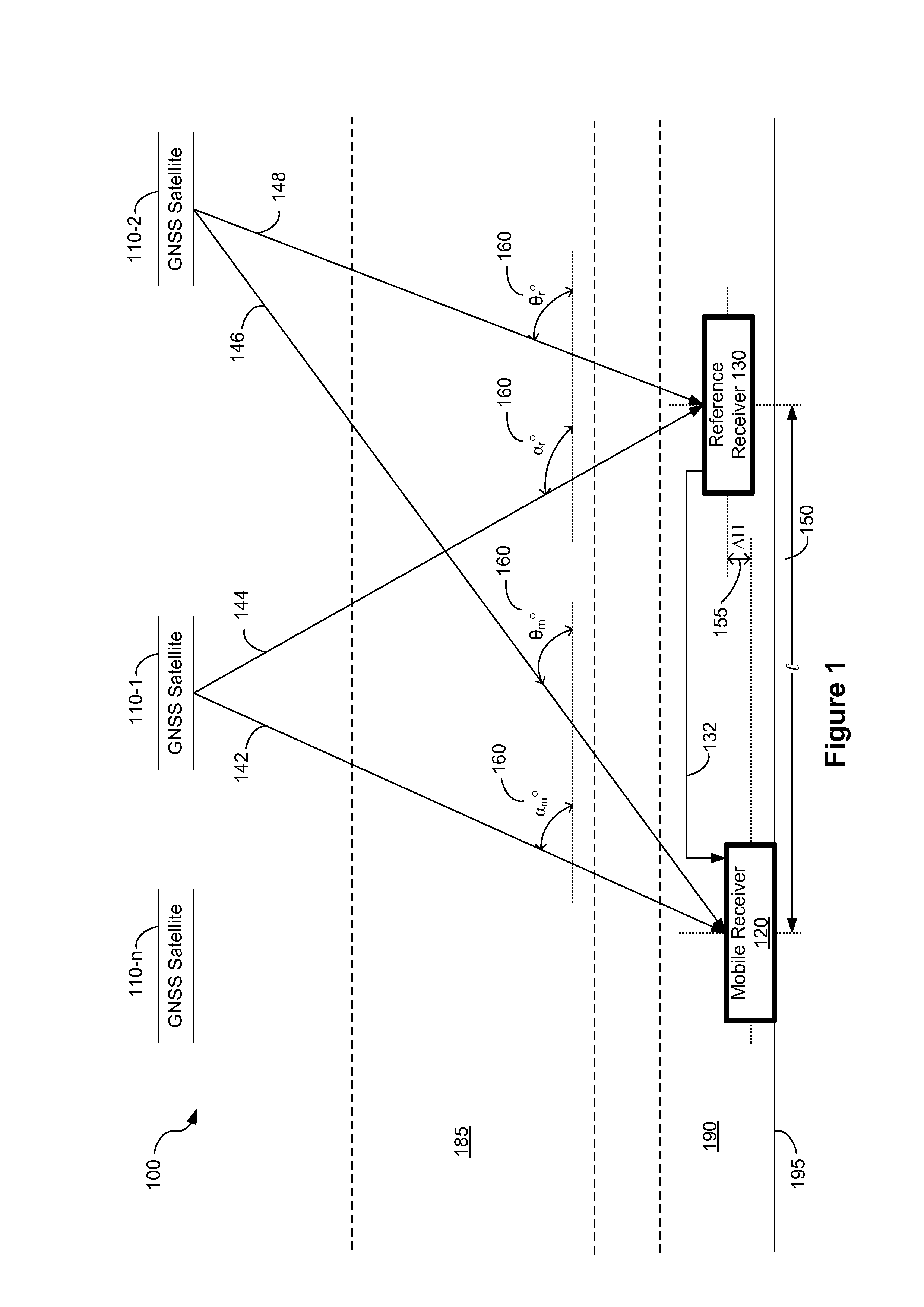
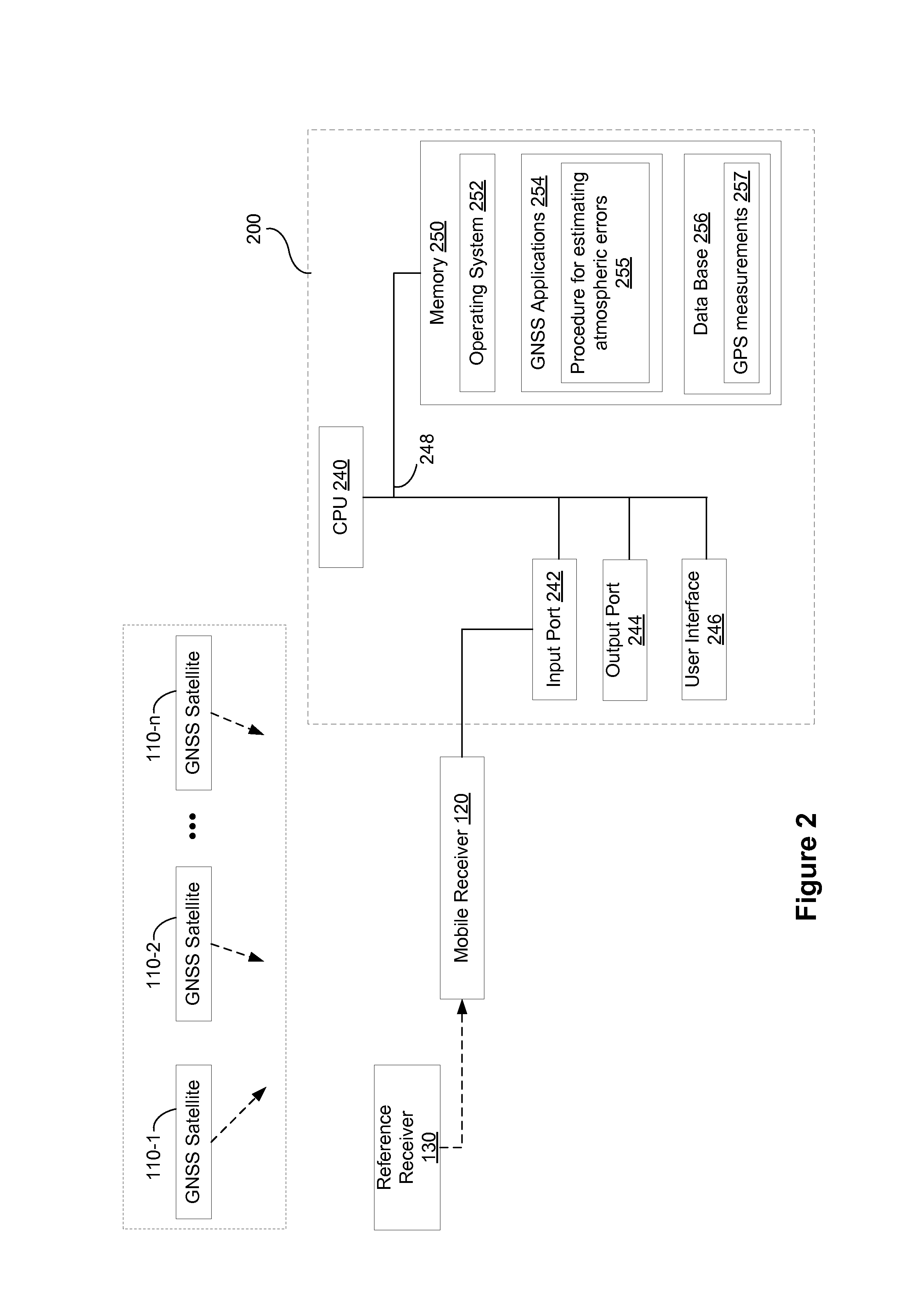
Distance dependent error mitigation in real-time kinematic (RTK) positioning
ActiveUS8242953B2Distance can be inaccuratePosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingKaiman filterDynamic noise
A method for mitigating atmospheric errors in code and carrier phase measurements based on signals received from a plurality of satellites in a global navigation satellite system is disclosed. A residual tropospheric delay and a plurality of residual ionospheric delays are modeled as states in a Kalman filter. The state update functions of the Kalman filter include at least one baseline distance dependant factor, wherein the baseline distance is the distance between a reference receiver and a mobile receiver. A plurality of ambiguity values are modeled as states in the Kalman filter. The state update function of the Kalman filter for the ambiguity states includes a dynamic noise factor. An estimated position of mobile receiver is updated in accordance with the residual tropospheric delay, the plurality of residual ionospheric delays and / or the plurality of ambiguity values.
Owner:DEERE & CO
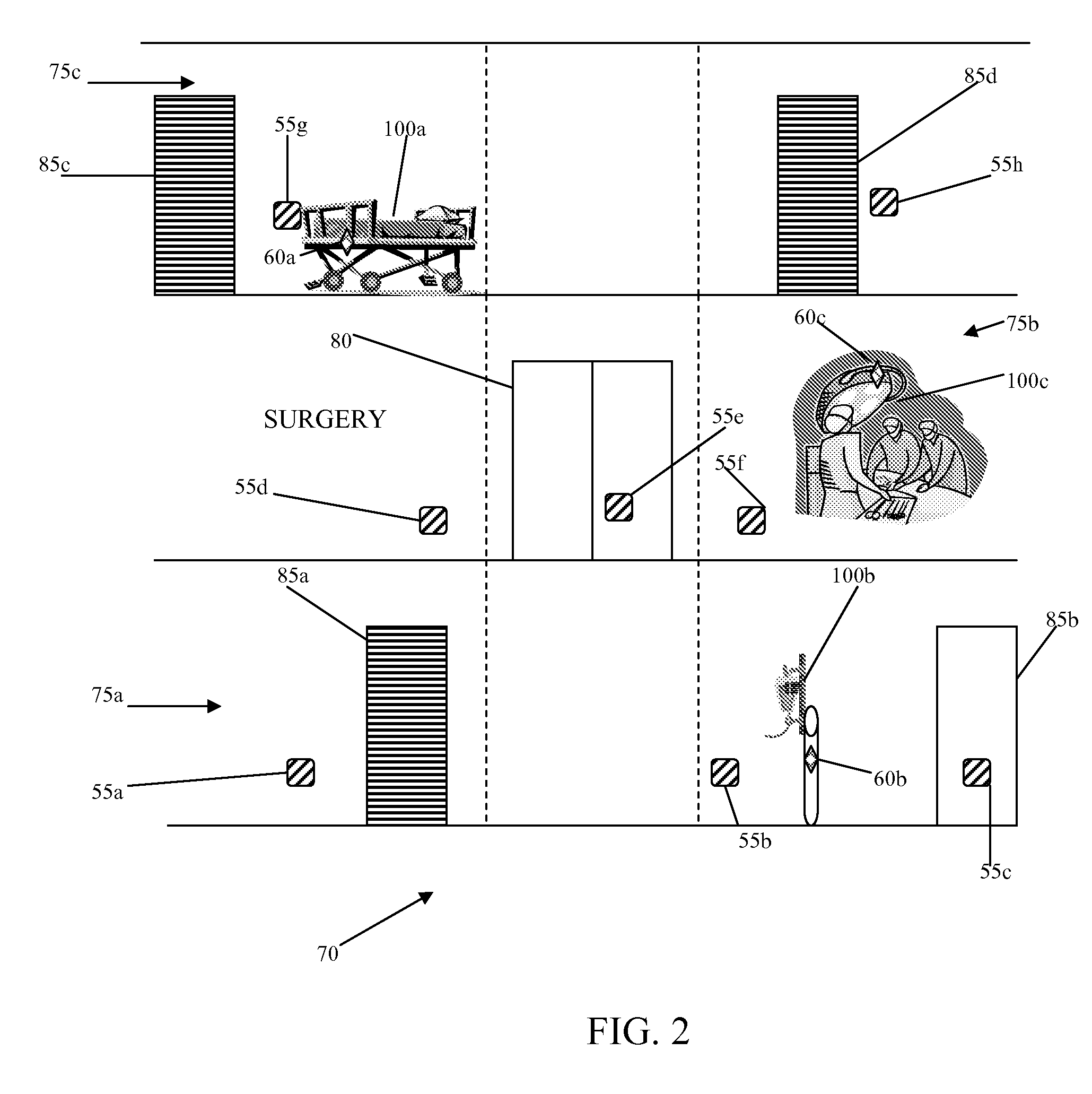
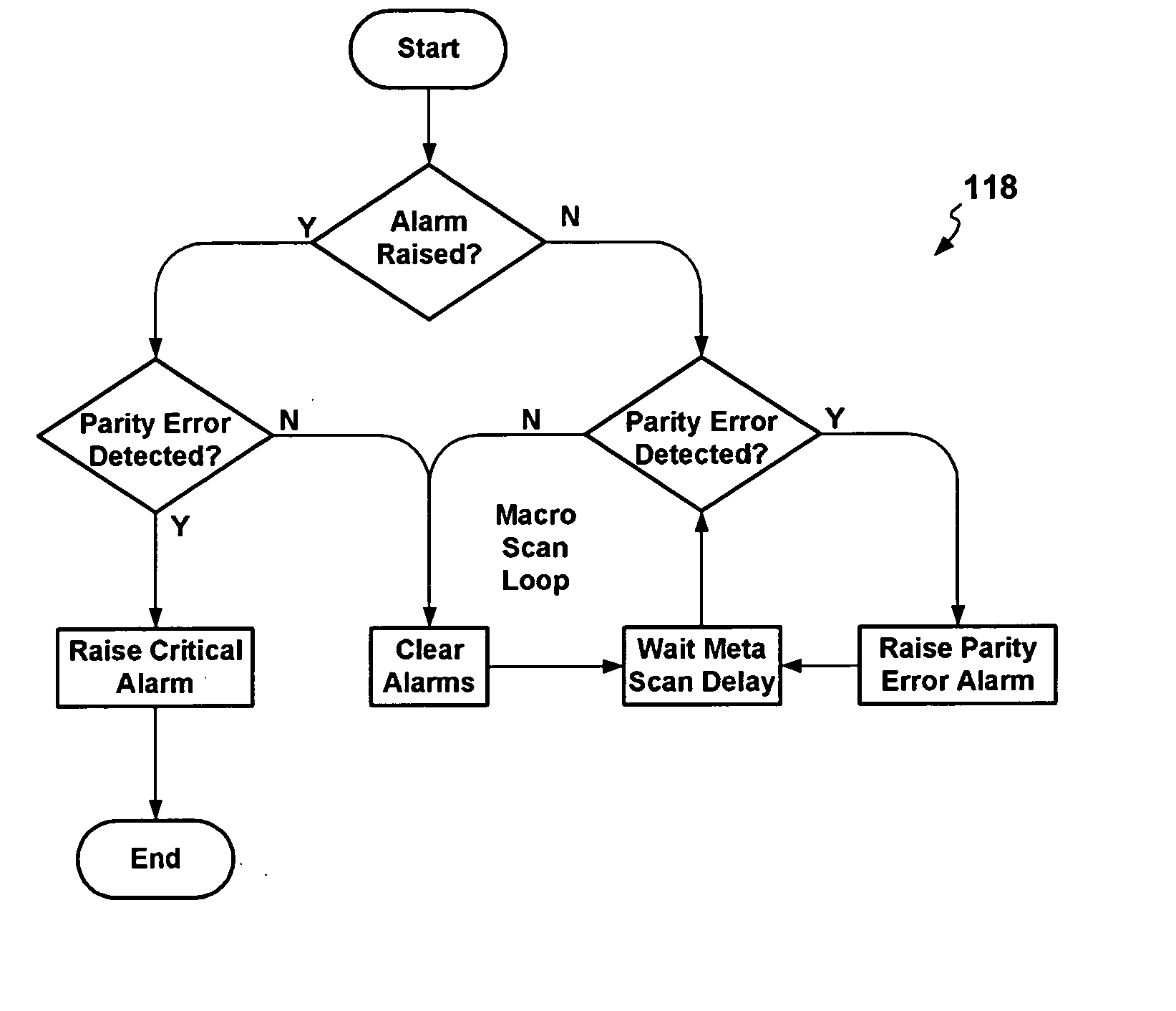
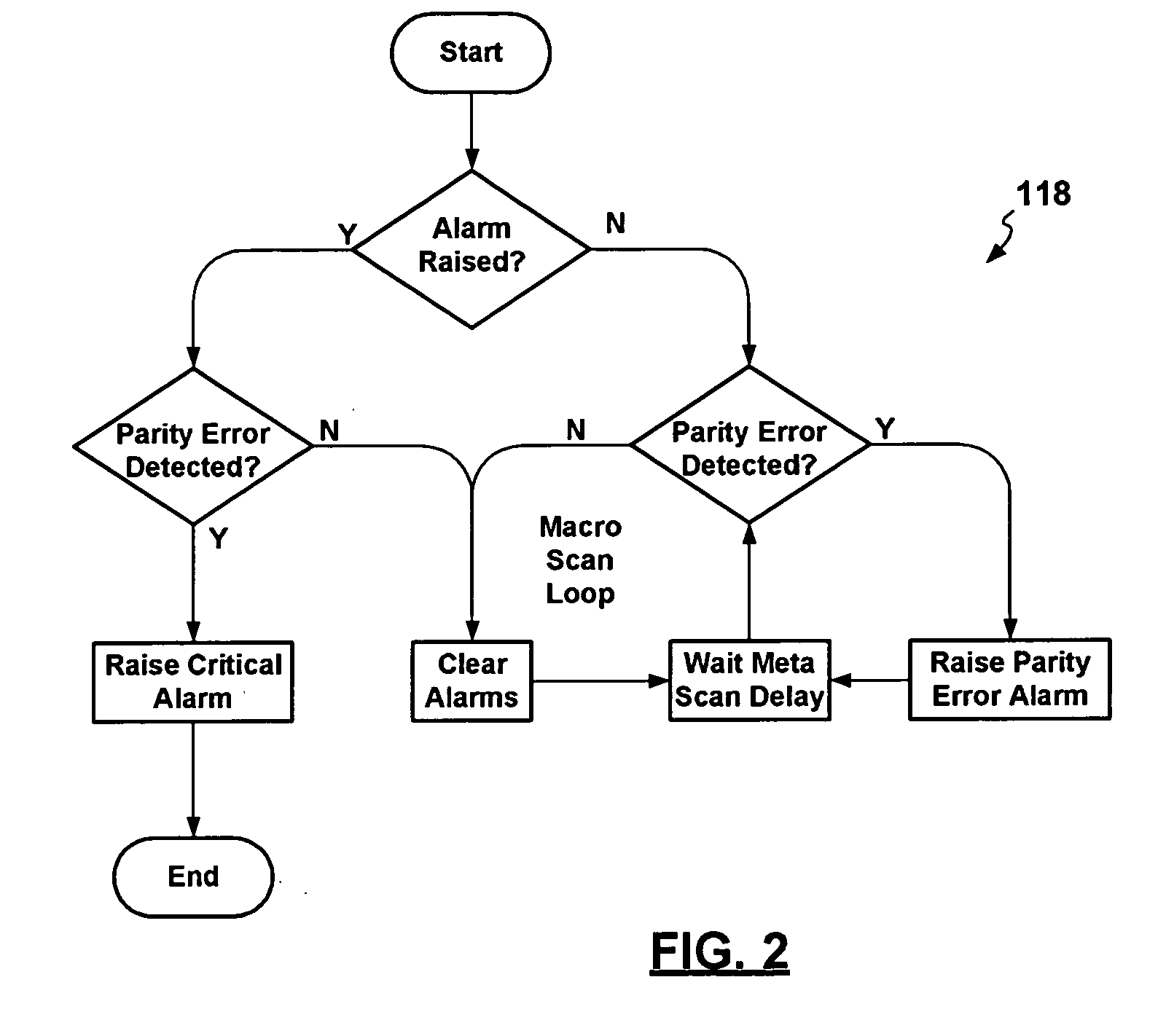
Egregious error mitigation system
ActiveUS20100113120A1Card gamesApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingLeader electionDisplay device
A playing card gaming system is disclosed that provides the player with an opportunity to withdraw a game play decision that is less advantageous to a player than at least one other play decision. The system includes a player interface that displays a prompt when a less advantageous decision is made. The display may include an area that provides the dealer with a visual indication that the player is being asked to confirm an election. A card delivery system with a playing card information reader provides card information to the system. A game processor determines if player elections are disadvantageous.
Owner:BALLY GAMING INC
Method and apparatus for baseline wander compensation in Ethernet application
ActiveUS8107573B2Reduce impactInaccurate estimationError preventionDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionCommunications systemError mitigation
An embodiment of the proposed invention is primarily applied to compensate the BLW in communication systems using THPs in their transmitters, especially suitable for the 10GBase-T Ethernet application. The present apparatus includes an additional decision device (slicer) used to generate DC offset information (error signal) and an extra modulus unit after our BLW compensator to reconvert compensated symbols to correct 16-PAM signals. In addition, the estimated error signals in our method are generated from the difference between the input of the BLW compensator and the output of the decision device. These error signals are then weighted to alleviate the impact of erroneous DC offset information on the performance of the BLW compensator. Therefore, a more direct and accurate DC offset information can be derived to improve the inaccurate BLW estimation in previous works.
Owner:REALTEK SEMICON CORP
Reat-time WaveSmooth(TM) error mitigation for Global Navigation Satellite Systems
InactiveUS20050212696A1Efficient removalCancel noisePosition fixationBeacon systemsIonosphereCarrier signal
WaveSmooth™ is a technique to mitigate inherent measurement error for GNSS signals. The WaveSmooth™ technique can be applied for single-frequency or multi-frequency GNSS users. For single-frequency GNSS users, WaveSmooth™ enables smoothing of GNSS measurements, in real-time using wavelets without introducing significant ionosphere divergence. For multi-frequency GNSS users, the WaveSmooth™ technique effectively mitigates multipath error in a real-time fashion. The WaveSmooth™ techniques utilizes wavelet aided methods and operate on the GNSS Code minus Carrier (CmC) signal to mitigate inherent GNSS measurement errors in a real-time fashion to improve the performance of these GNSSs. The WaveSmooth™ error mitigated pseudorange measurement can be used, along with the original carrier phase measurement for a high performance user solution.
Owner:BARTONE CHRIS GREGORY +1
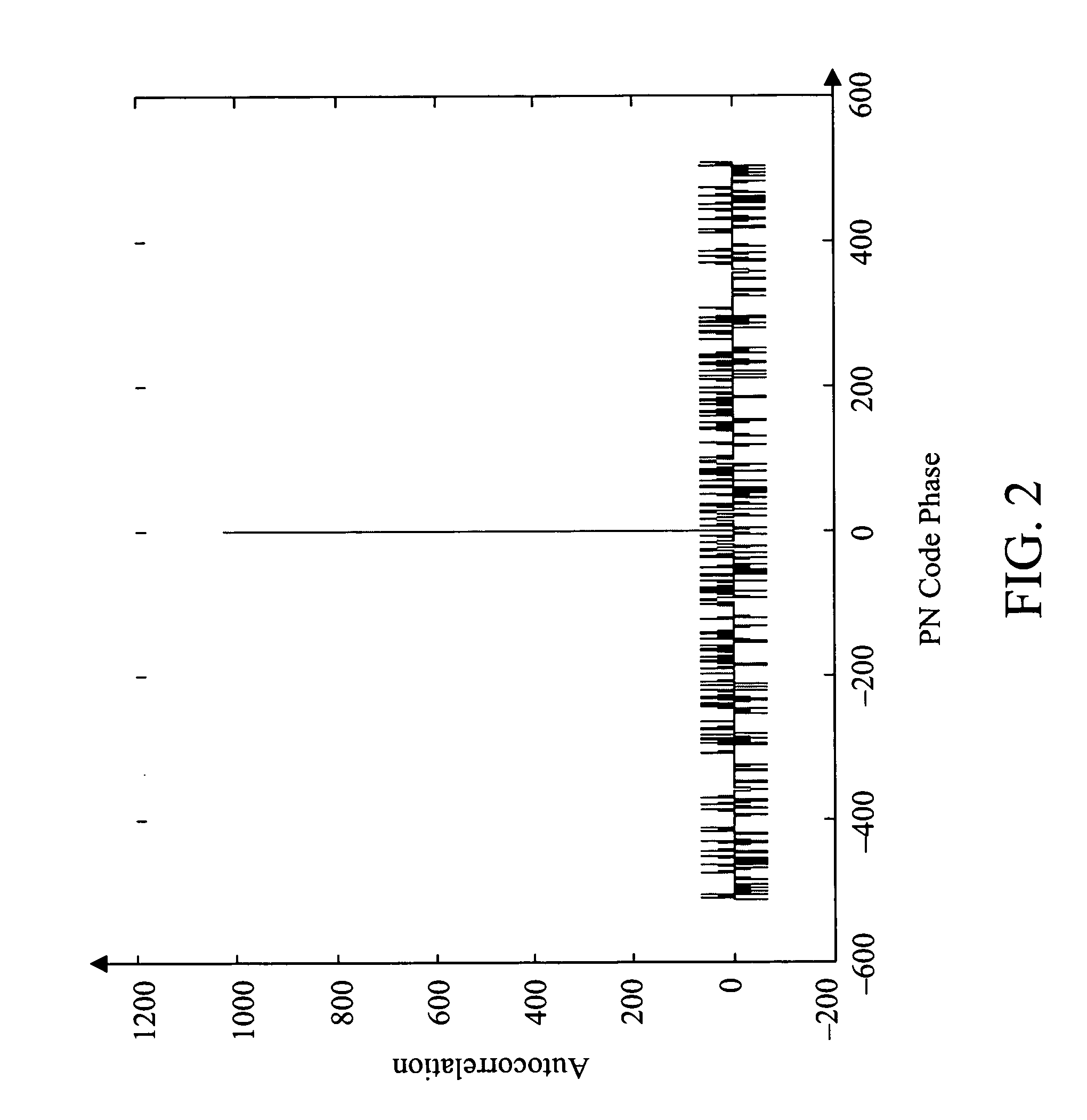
False reacquisition mitigation in high sensitivity navigational satellite signal receivers
InactiveUS20070109189A1Detect and mitigate false reacquisitionEasy to identifyPosition fixationSatellite radio beaconingSide lobeError mitigation
The techniques to detect and mitigate the false reacquisition in a global satellite navigation receiver are disclosed. The false reacquisition due to frequency side-lobes and code autocorrelation secondary lobes are considered for mitigation. A set of two threshold values is used to detect correct reacquisition and reject false reacquisition. While the reacquisition of the signal is straight forward when the correlation is clear with the power above the first threshold, it is not so clear when the power is between two thresholds. So a further search for the maximum power among the retained dwells results in correct reacquisition. The search range depends upon the signal blockage interval and receiver dynamics. The feedback from navigational solution may be used to determine the search range both in frequency and code phase. In the case of frequency side-lobes, which occur only at specified frequency components, these frequencies are tested for maximum power response. The code side-lobes have similar characteristics and can be distinguished by the actual peak.
Owner:CSR TECH HLDG
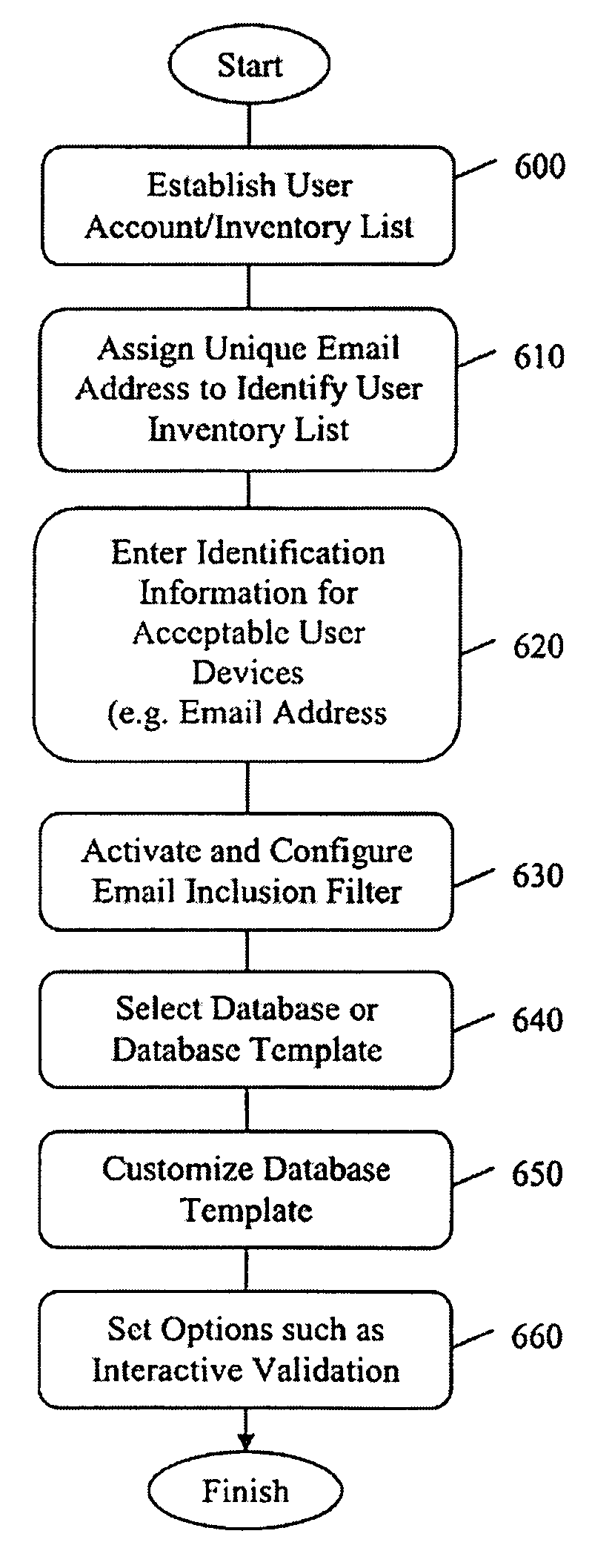
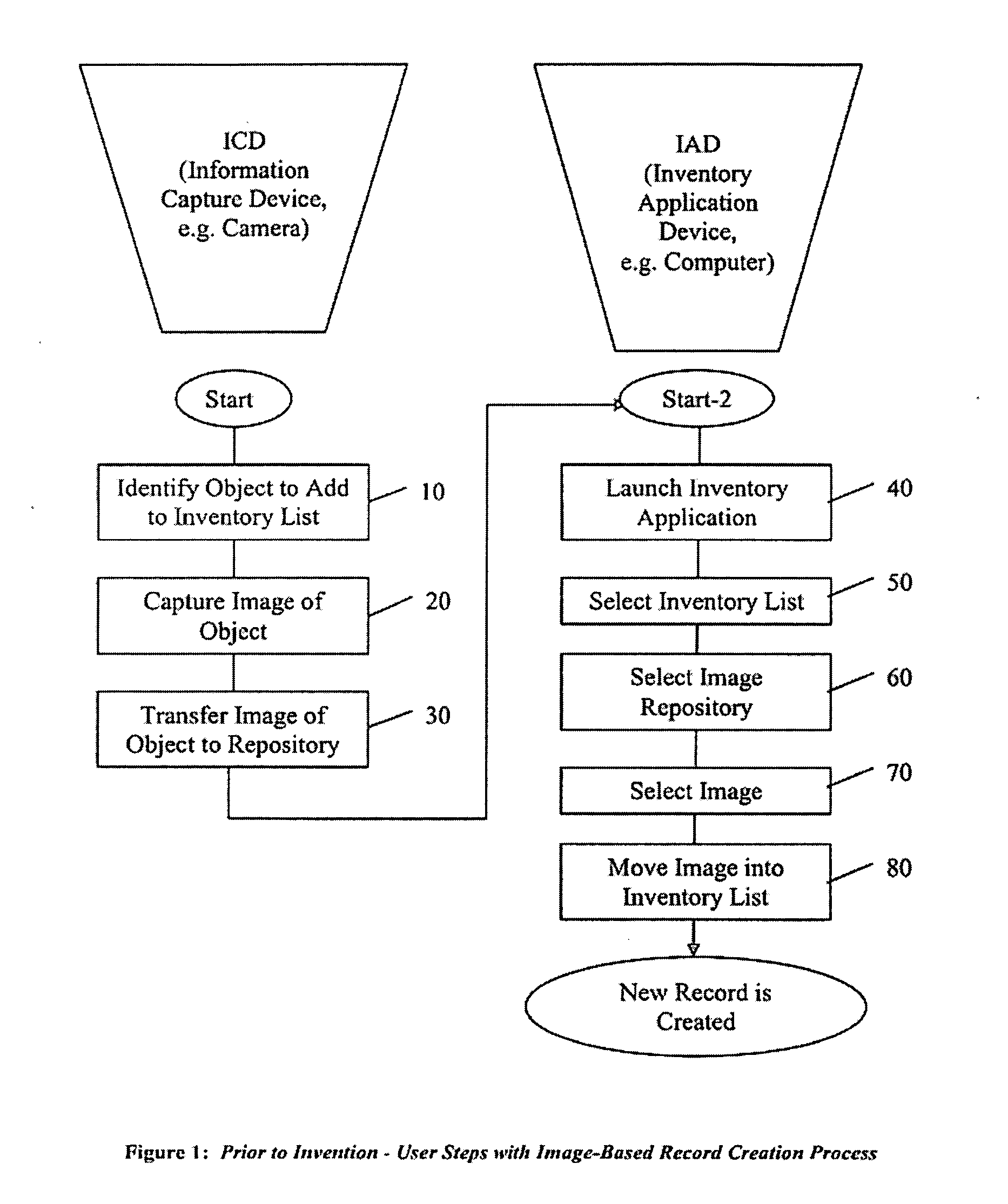
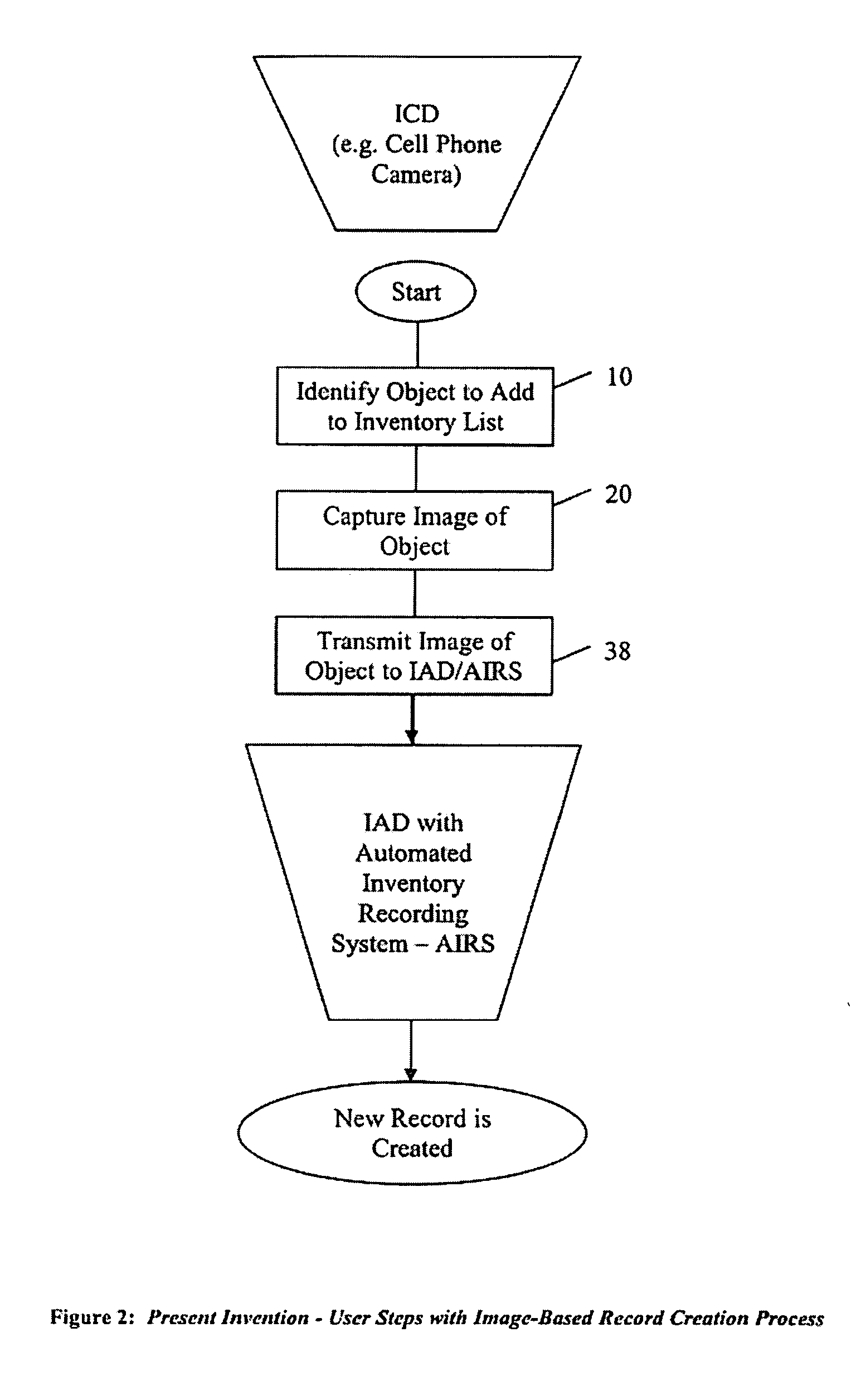
Method and Apparatus for Automated Record Creation Using Information Objects, Such as Images, Transmitted Over a Communications Network to Inventory Databases and Other Data-Collection Programs
InactiveUS20090138560A1Reduce the number of stepsSimplify speed up creationMultiple digital computer combinationsOther databases retrievalEmail addressInformation object
A method, process and apparatus for automating software record creation are disclosed. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, although not limited thereto, the present invention uses a unique email address as a proxy for and to correspond to a specific database table that in turn is associated with a specific user. In the context of an inventory system and this preferred embodiment the present invention enables an information object, such as a photograph, to be captured remotely and transmitted over a communications network to a proxy email address where it is automatically processed into an inventory record on the desired inventory list without the user needing to have any further interaction with the inventory system than the transmission of the object. Additionally, in this preferred embodiment that utilizes email as the transportation method, inclusion filtering is employed to restrict data submission thereby preventing or greatly mitigating false record entries.
Owner:JAMES JOSEPH STAHL JR
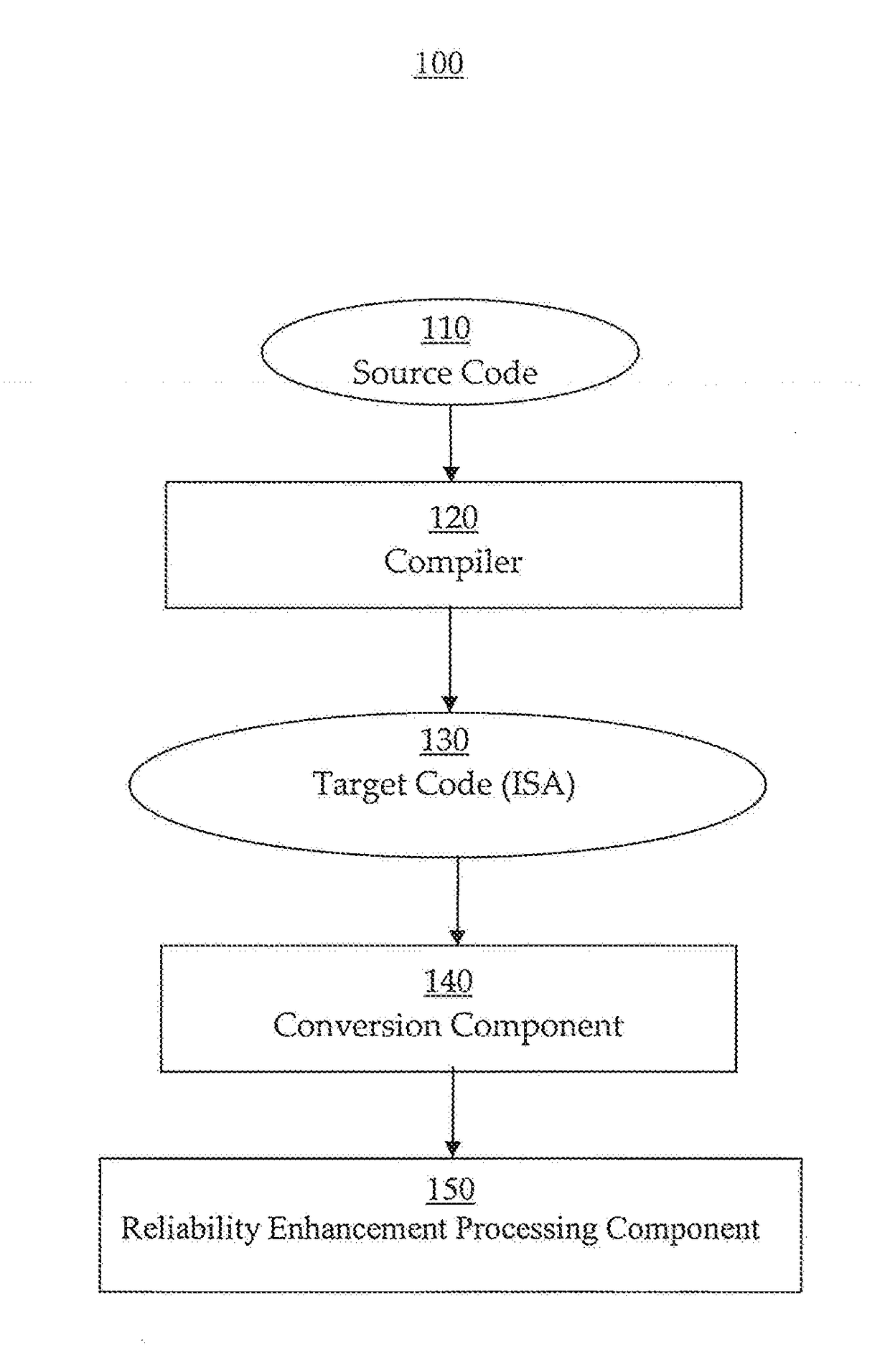
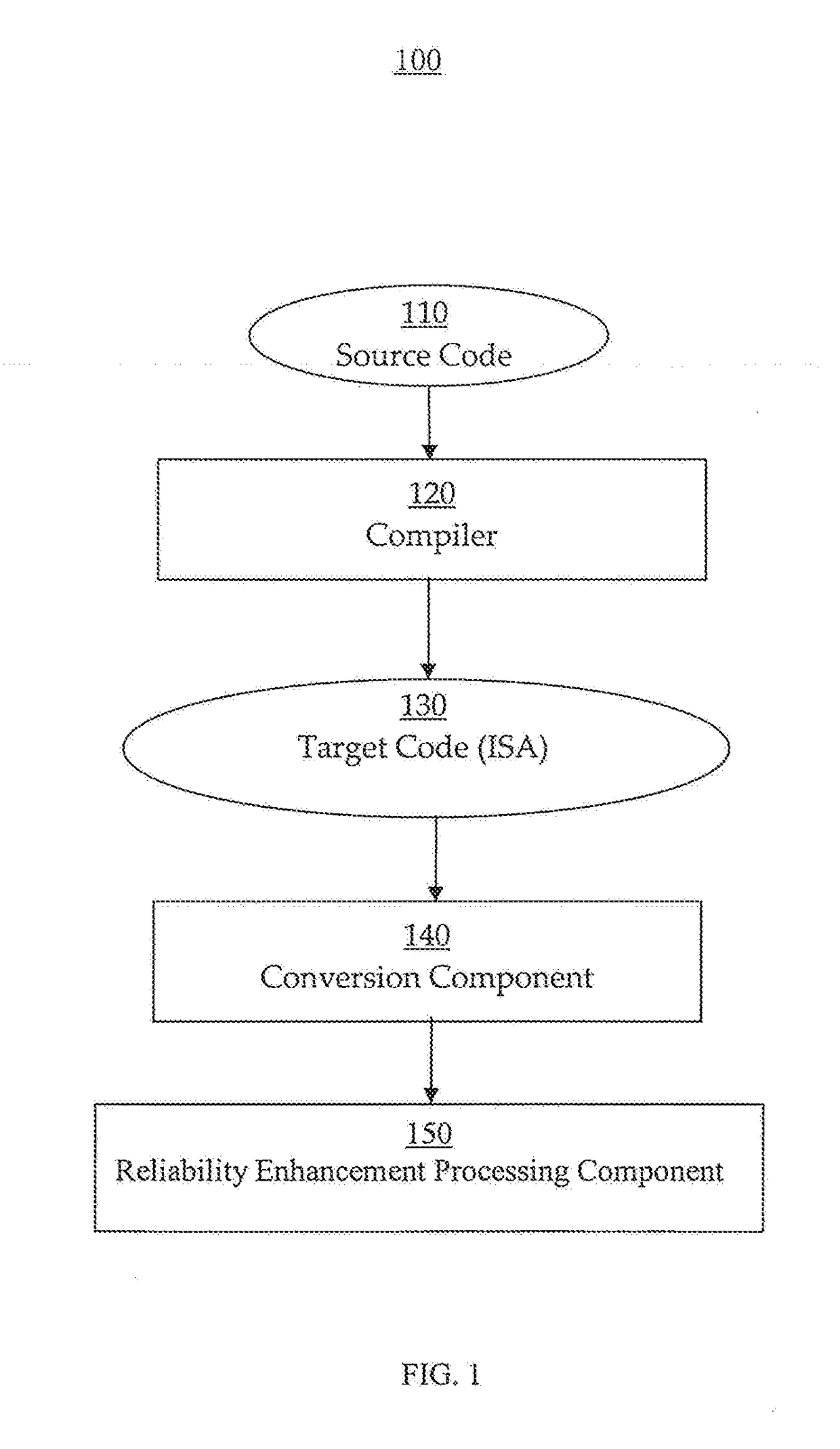
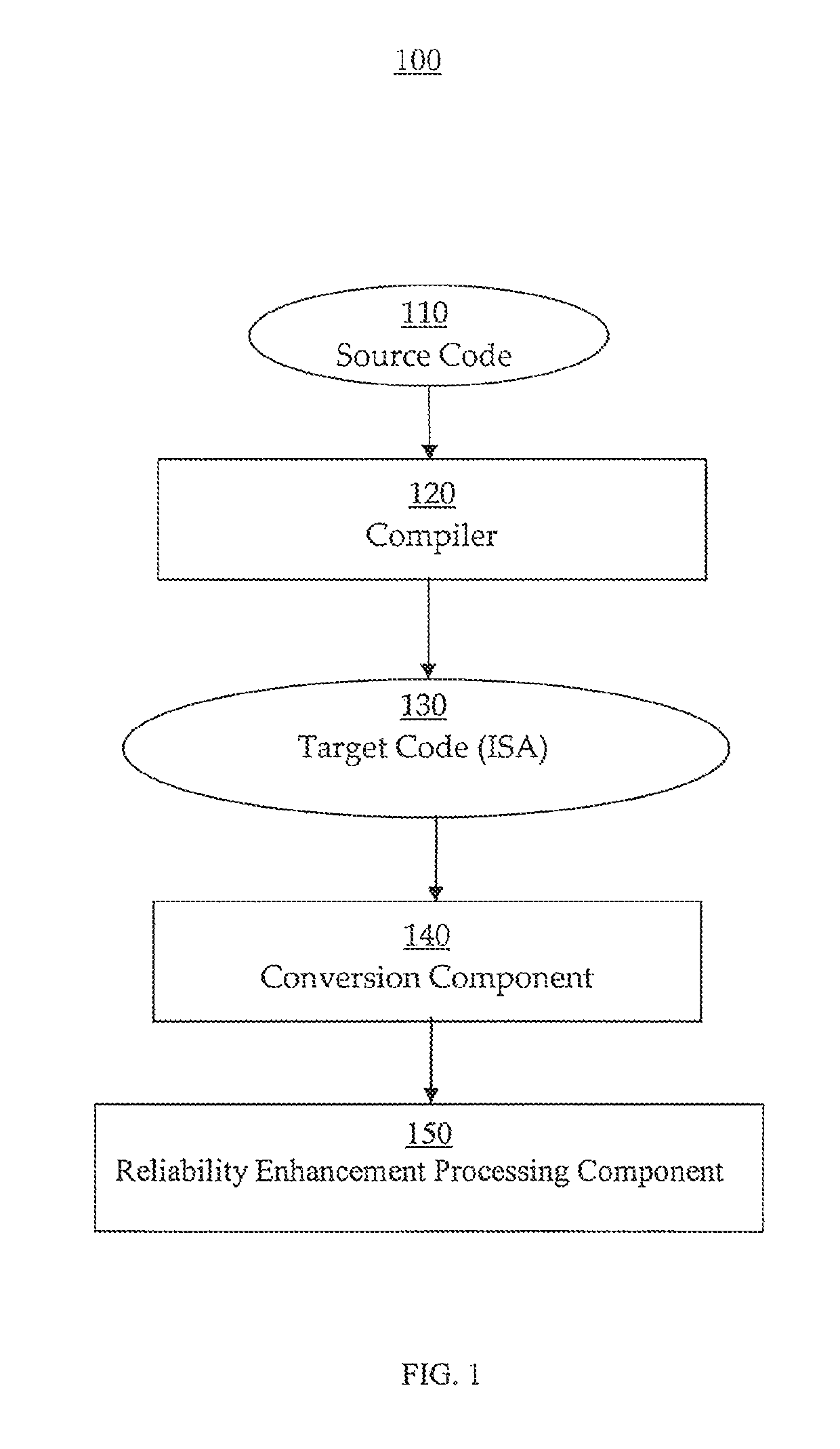
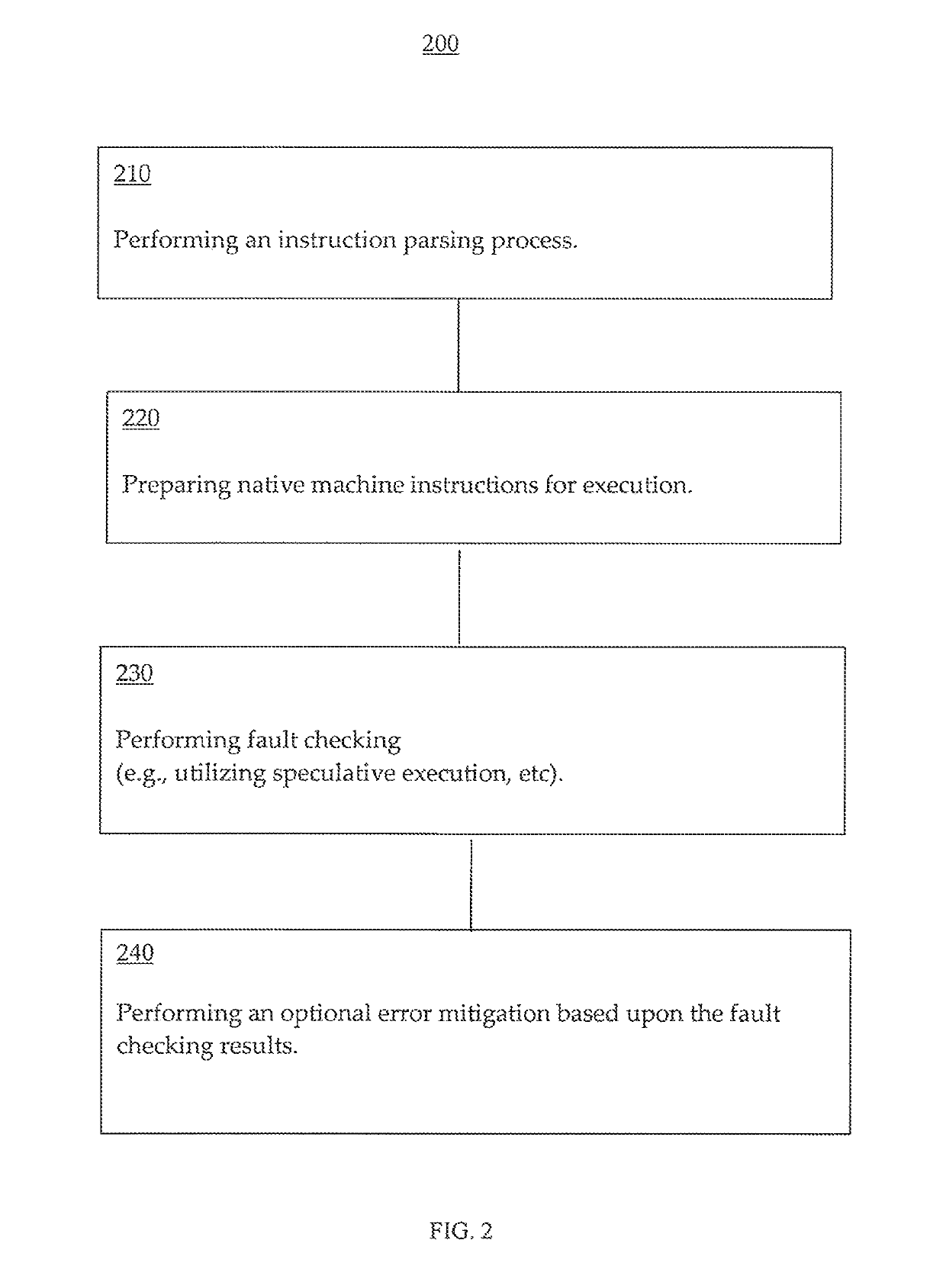
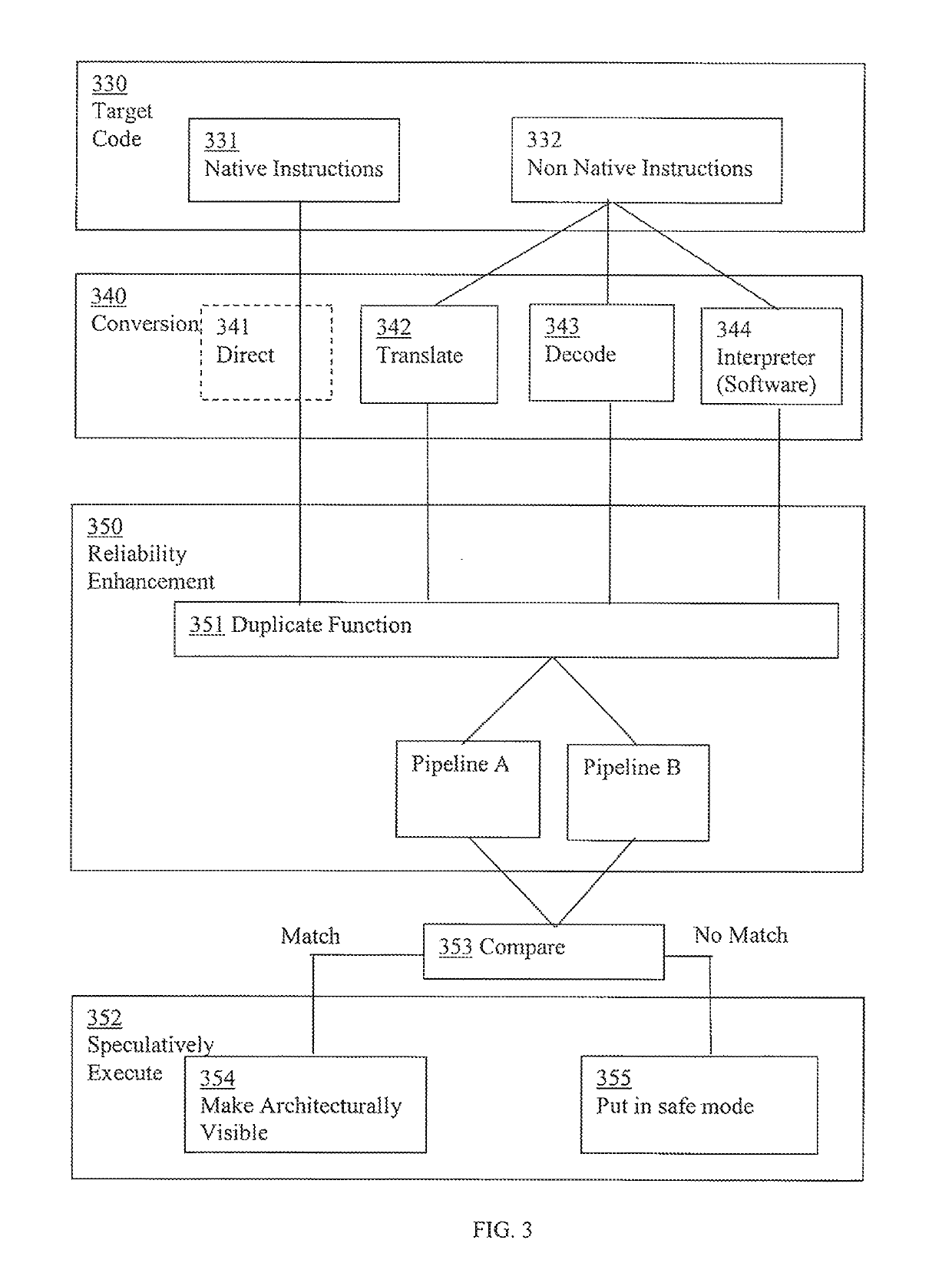
Reliability enhancement systems and methods
ActiveUS20180121273A1Improve reliabilitySoftware testing/debuggingConcurrent instruction executionProgram instructionDependability
Systems and methods for enhancing reliability are presented. In one embodiment, a system comprises a processor configured to execute program instructions and contemporaneously perform reliability enhancement operations (e.g., fault checking, error mitigation, etc.) incident to executing the program instructions. The fault checking can include: identifying functionality of a particular portion of the program instructions; speculatively executing multiple sets of operations contemporaneously; and comparing execution results from the multiple sets of operations. The multiple sets of operations are functional duplicates of the particular portion of the program instructions. If the execution results have a matching value, then the value can be made architecturally visible. If the execution results do not have a matching value, the system can be put in a safe mode. An error mitigation operation can be performed can include a corrective procedure. The corrective procedure can include rollback to a known valid state.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
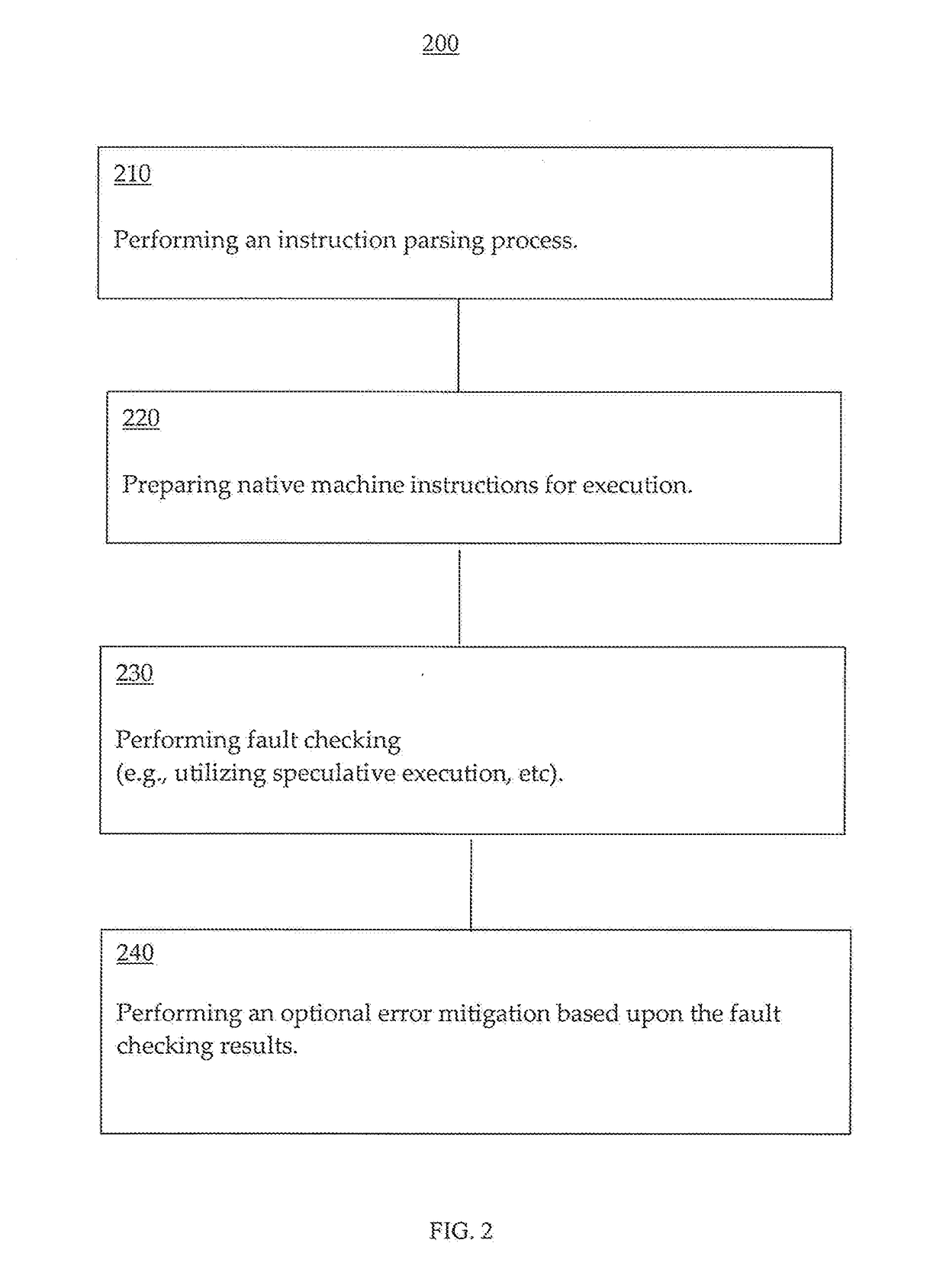
Reliability enhancement utilizing speculative execution systems and methods
ActiveUS10289469B2Concurrent instruction executionSoftware testing/debuggingSpeculative executionProgram instruction
Systems and methods for enhancing reliability are presented. In one embodiment, a system comprises a processor configured to execute program instructions and contemporaneously perform reliability enhancement operations (e.g., fault checking, error mitigation, etc.) incident to executing the program instructions. The fault checking can include: identifying functionality of a particular portion of the program instructions; speculatively executing multiple sets of operations contemporaneously; and comparing execution results from the multiple sets of operations. The multiple sets of operations are functional duplicates of the particular portion of the program instructions. If the execution results have a matching value, then the value can be made architecturally visible. If the execution results do not have a matching value, the system can be put in a safe mode. An error mitigation operation can be performed can include a corrective procedure. The corrective procedure can include rollback to a known valid state.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
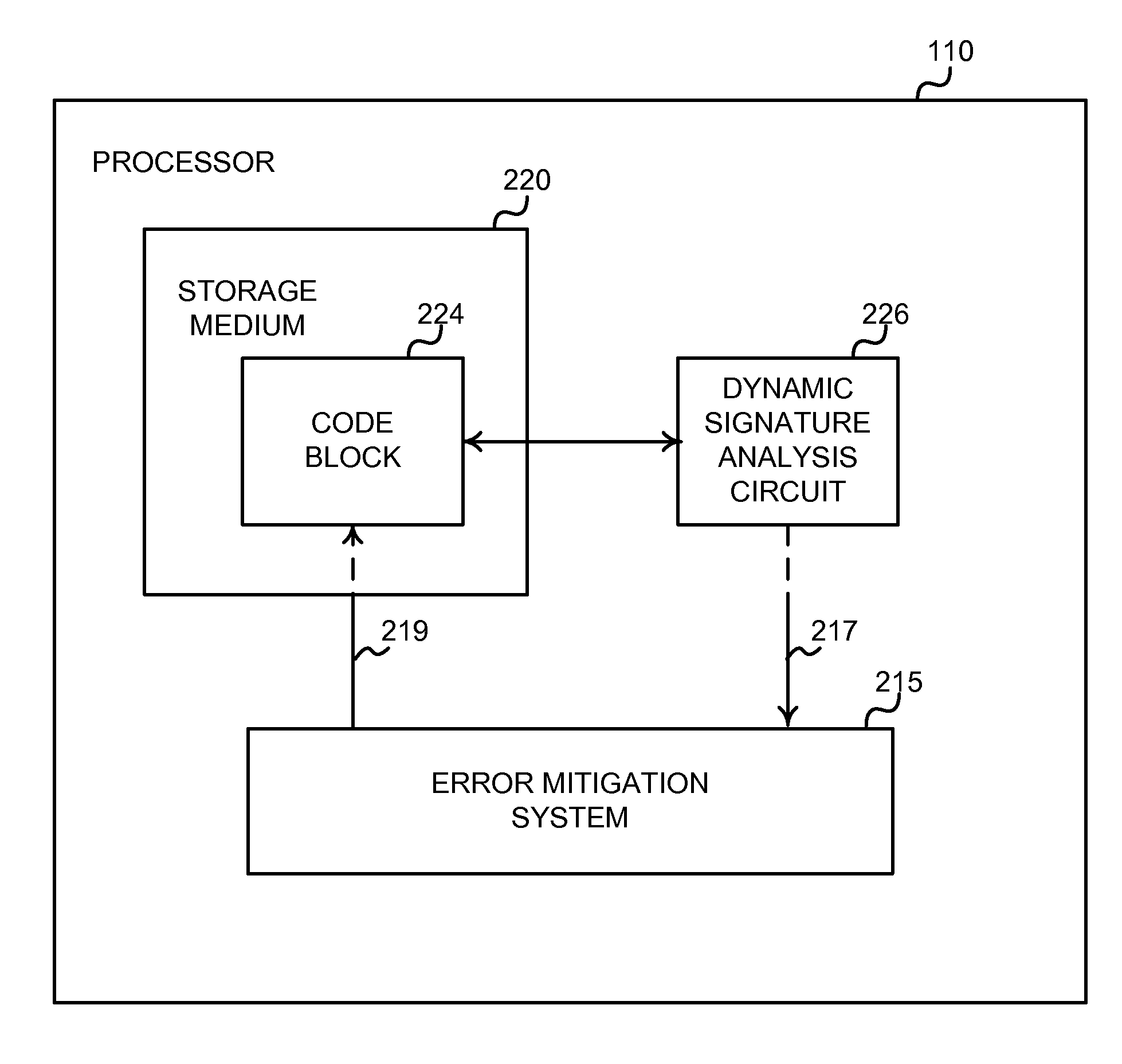
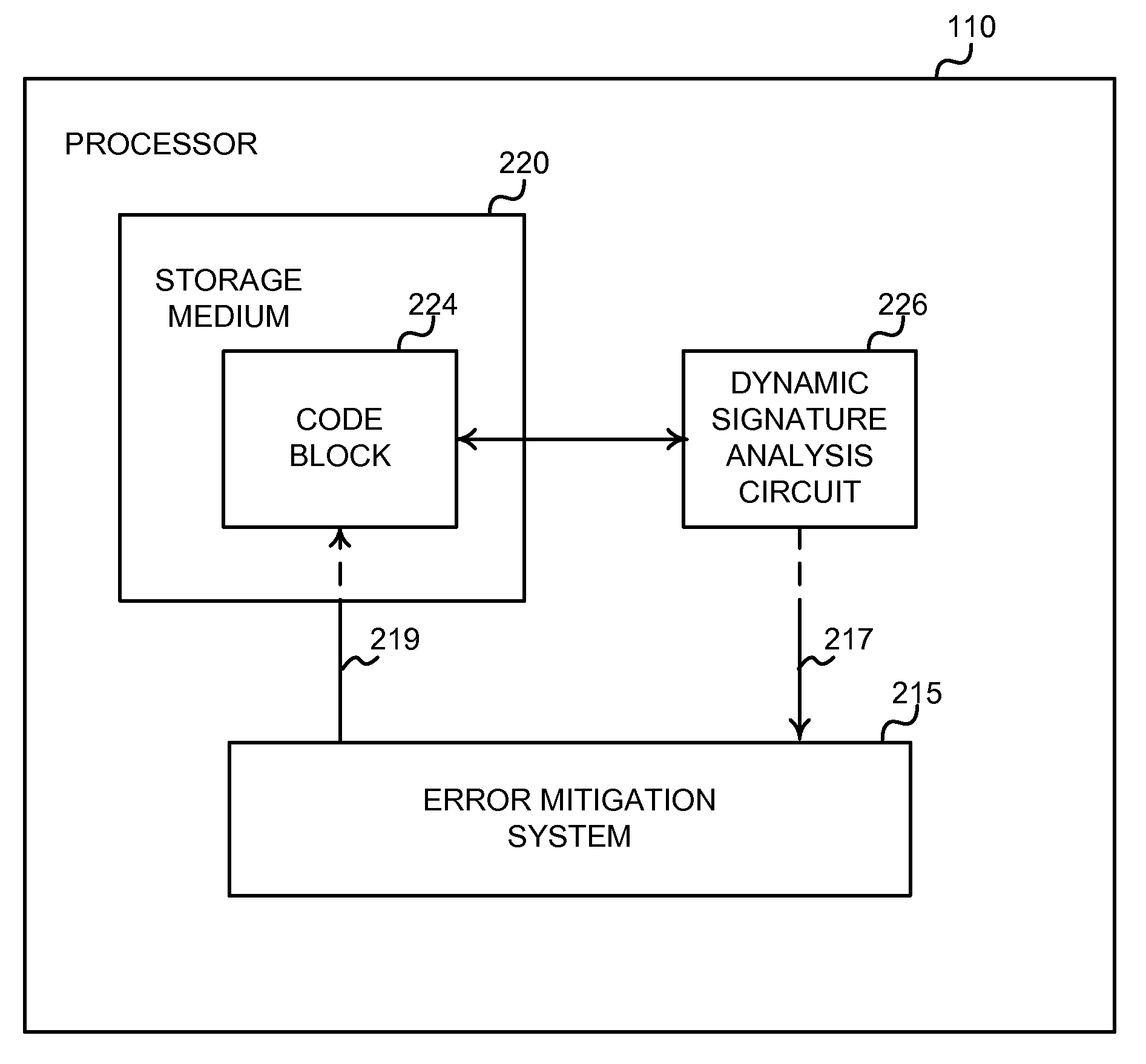
Architecture for a self-healing computer system
The self-healing system comprises a self-healing processor and an error mitigation system. The self-healing processor includes a code block associated with the operation of a portion of digital logic. The self-healing processor also includes a dynamic signature analysis circuit. The processor executes the code block. The dynamic signature analysis circuit creates a dynamic signature representing the operation of the portion of digital logic associated with the code block. The error mitigation system receives the dynamic signature from the dynamic signature analysis circuit. The error mitigation system compares the dynamic signature to a static signature to determine if the signatures match. If the signatures do not match, then the digital logic associated with the code block has an error. The error mitigation system retries execution of the code block. The error mitigation system stores log information describing the above events.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Architecture for a self-healing computer system
ActiveUS20100281134A1Avoid mistakesMultiple digital computer combinationsNon-redundant fault processingSelf-healingComputer hardware
The self-healing system comprises a self-healing processor and an error mitigation system. The self-healing processor includes a code block associated with the operation of a portion of digital logic. The self-healing processor also includes a dynamic signature analysis circuit. The processor executes the code block. The dynamic signature analysis circuit creates a dynamic signature representing the operation of the portion of digital logic associated with the code block. The error mitigation system receives the dynamic signature from the dynamic signature analysis circuit. The error mitigation system compares the dynamic signature to a static signature to determine if the signatures match. If the signatures do not match, then the digital logic associated with the code block has an error. The error mitigation system retries execution of the code block. The error mitigation system stores log information describing the above events.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
System and methods for transmitting data
InactiveUS20050010850A1Increase demandError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionForward error correctionReplacement method
A system and method for transmitting data over a channel, in which the data are categorized in at least two different categories. For example, the data are categorized according to the effect on perceived degradation on the data when error mitigation is performed on the data. Corrupted data of the first category are replaced using a first replacement method, such as retransmission and forward error correction. The corrupted data of the second category are replaced using a second replacement method different from the first replacement method, e.g., error mitigation or interpolation.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
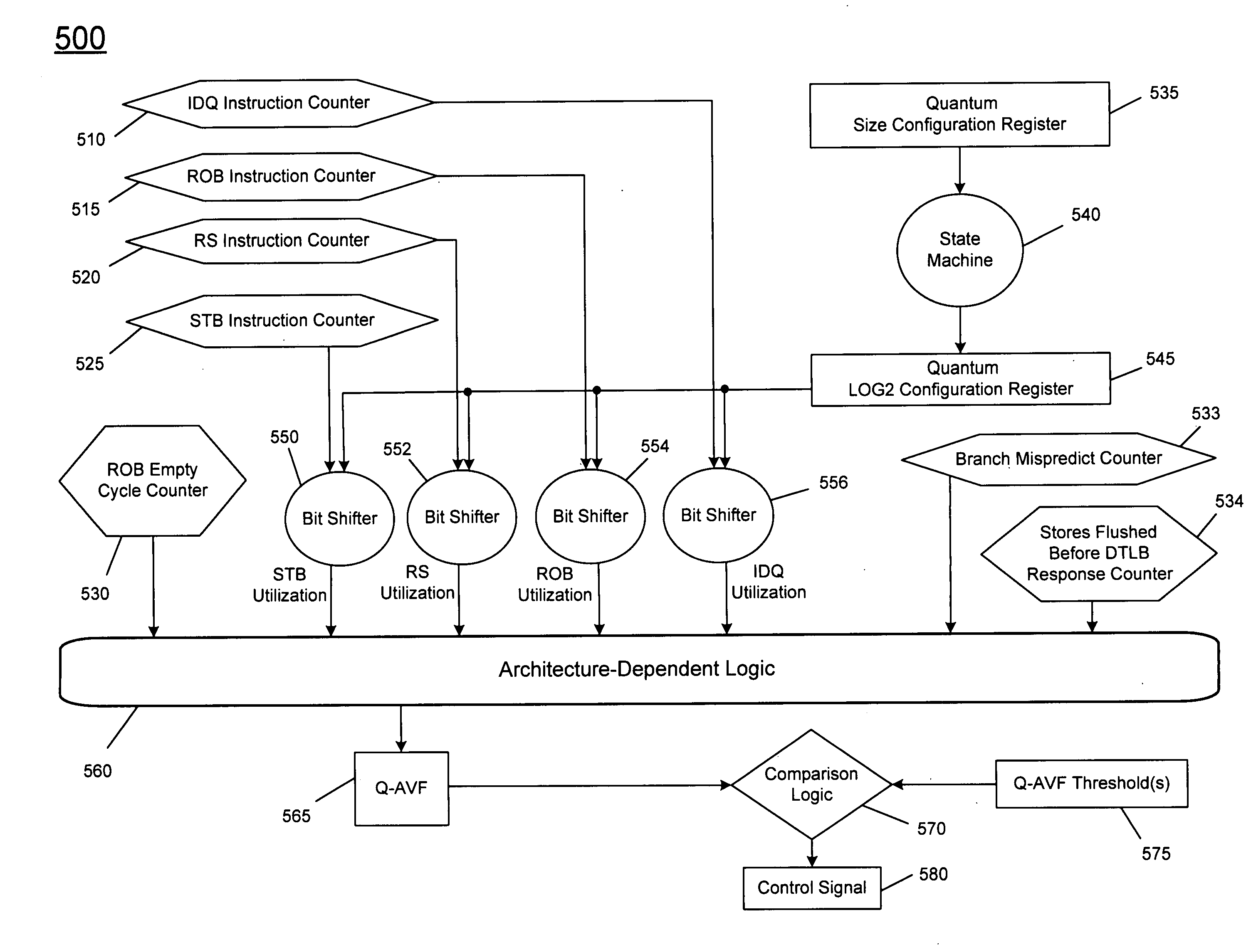
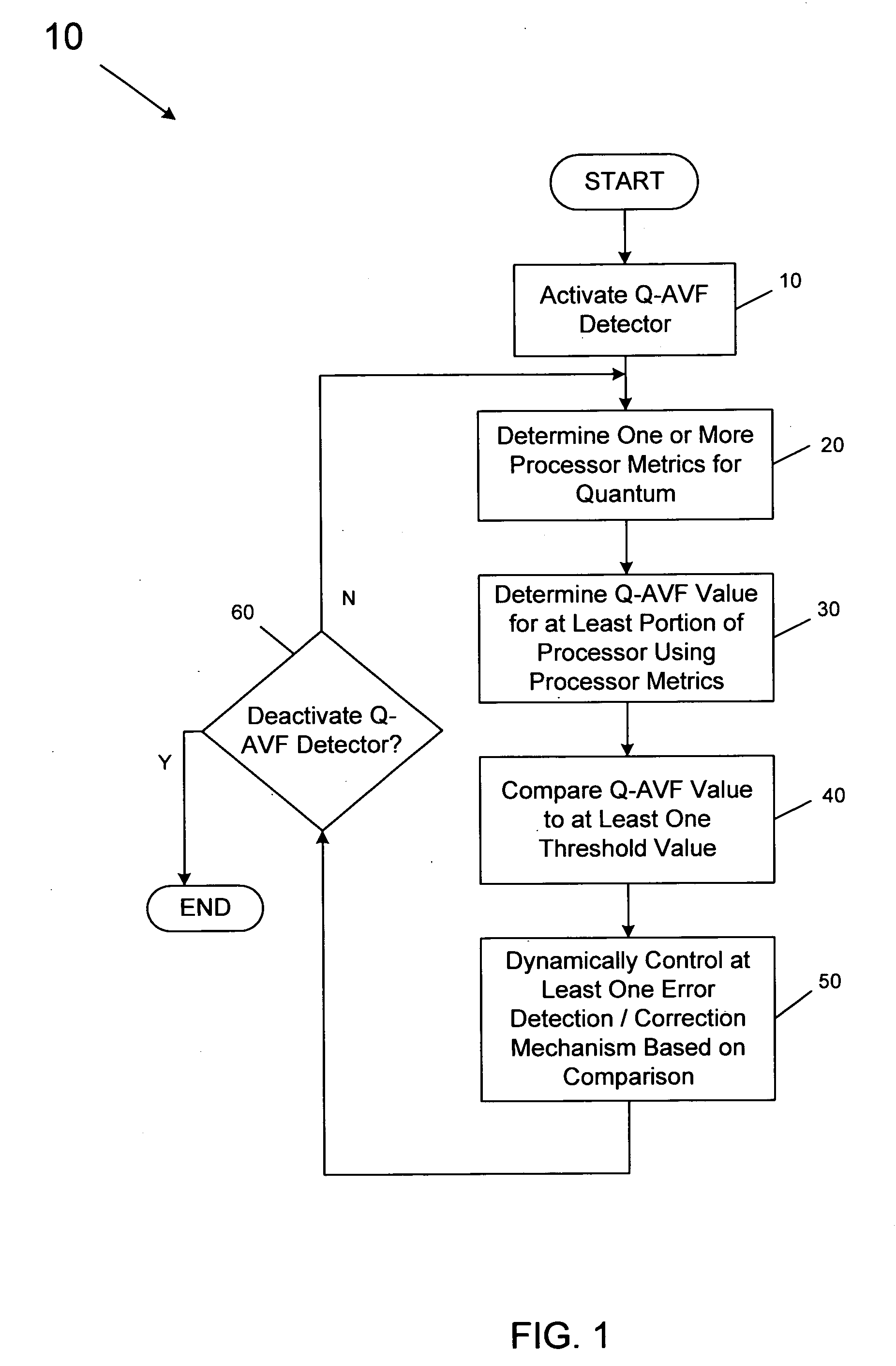
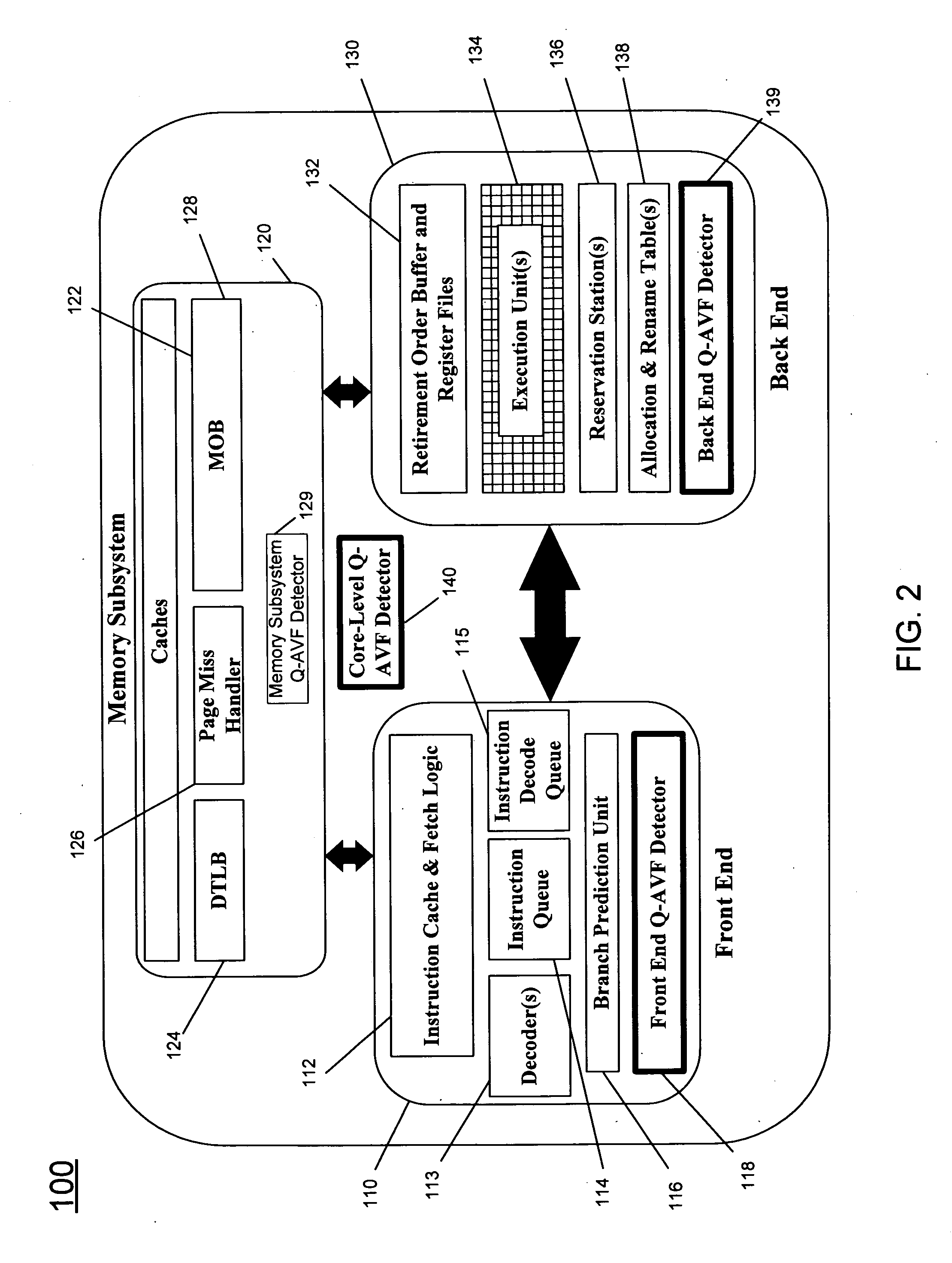
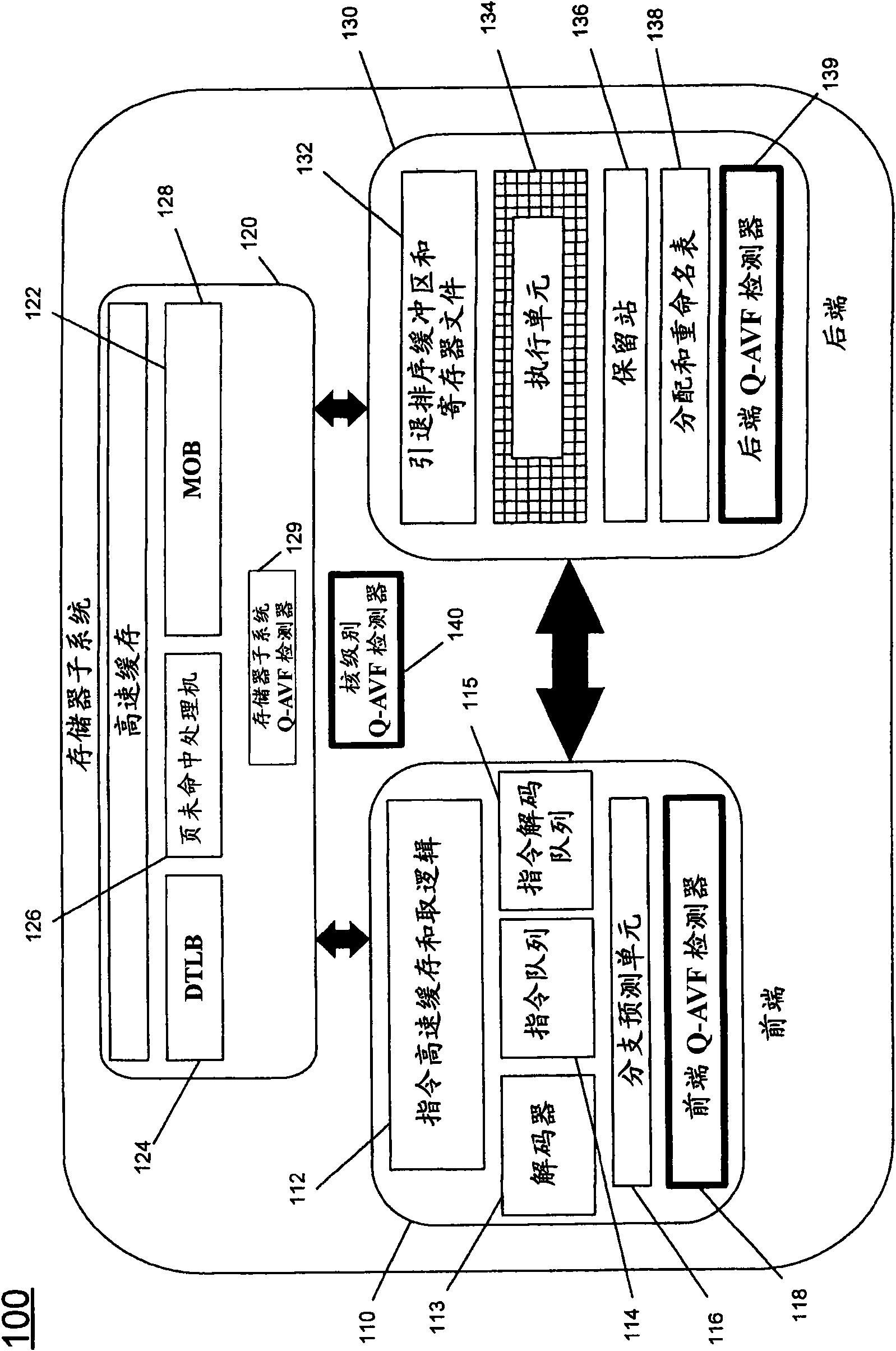
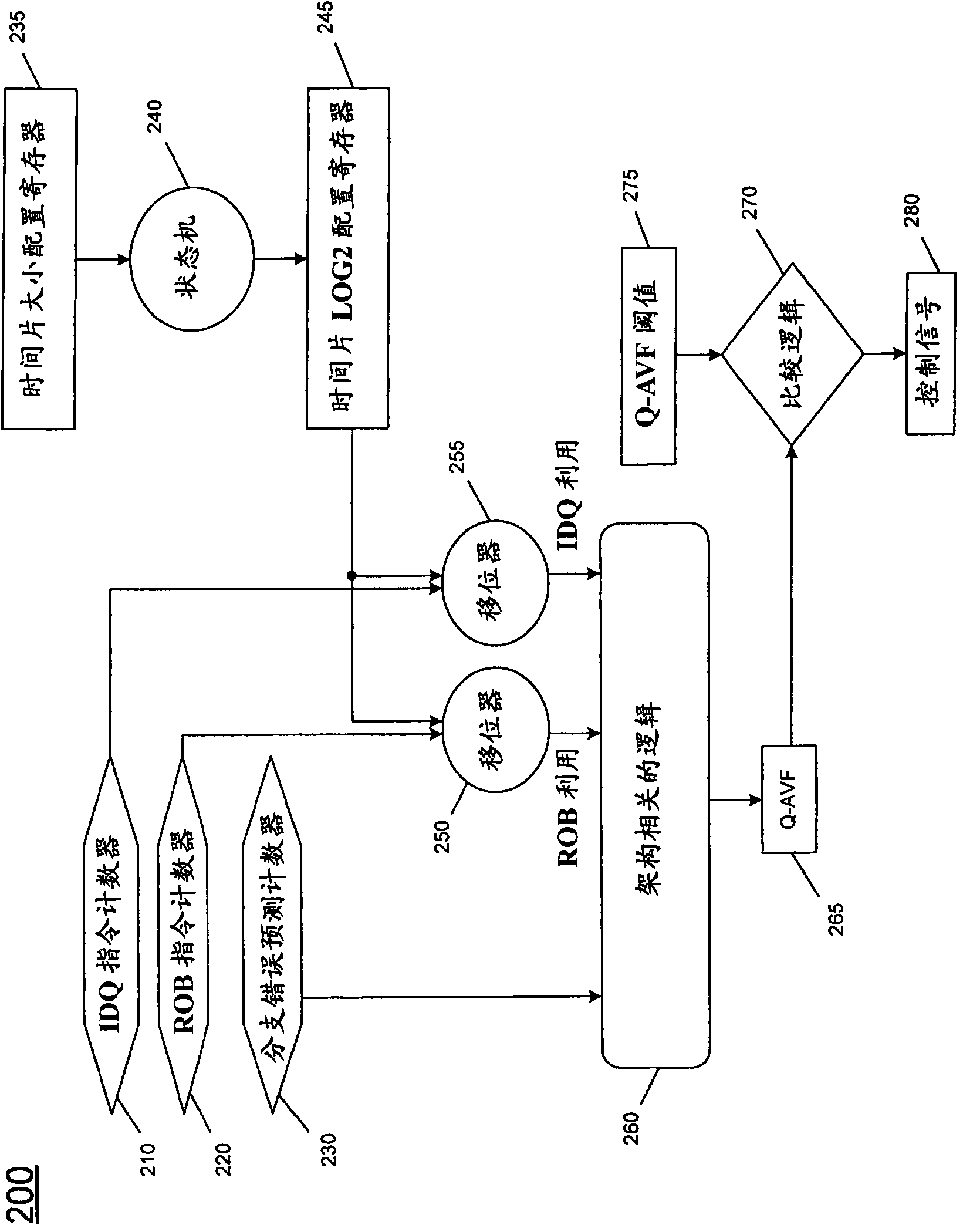
Detecting architectural vulnerability of processor resources
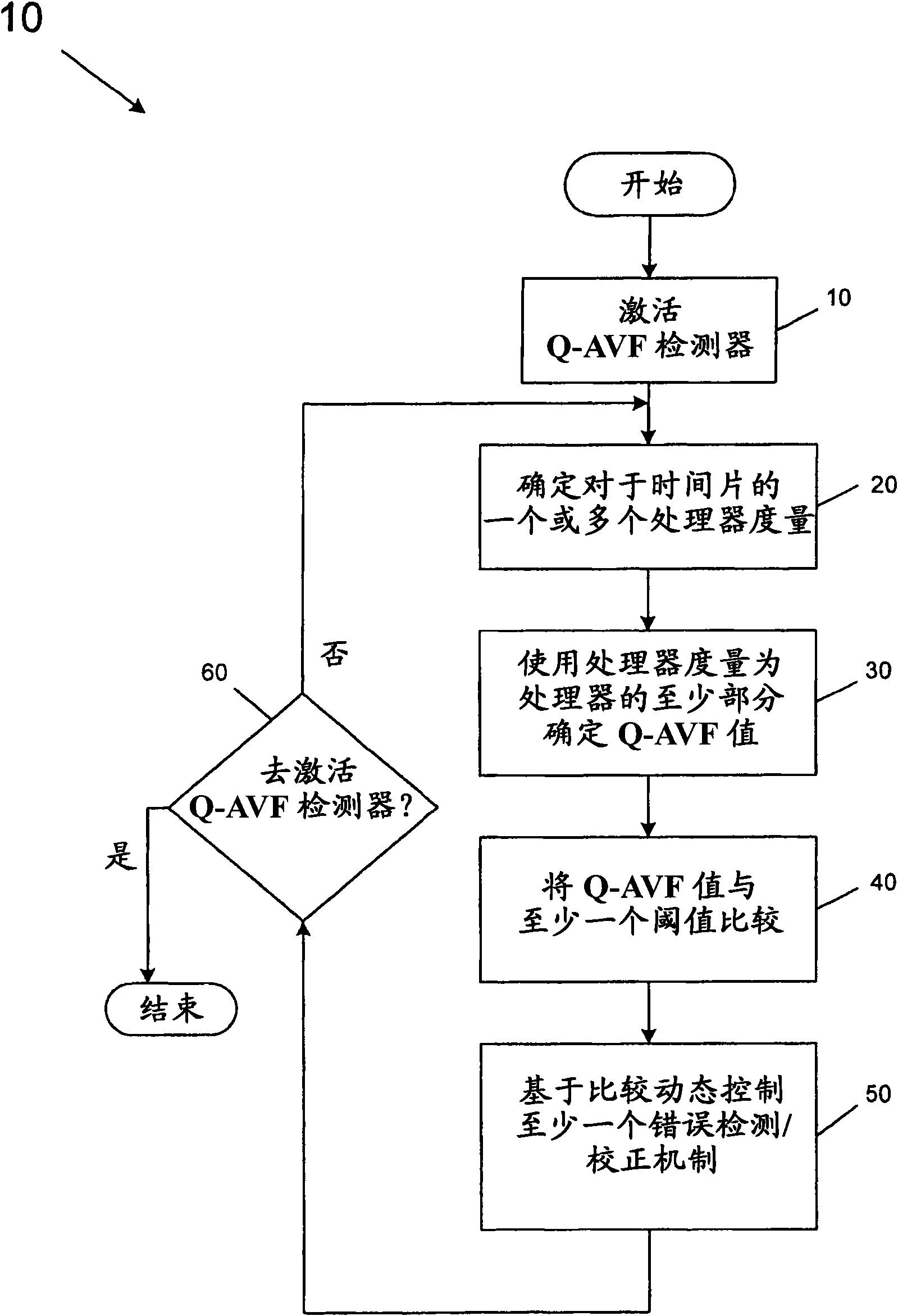
In one embodiment, a quantum detector is provided to detect a vulnerability measure for a processor based on a processor metrics each associated with operation of a processor structure during a quantum, along with a controller to control an error mitigation unit based on the vulnerability measure. Other embodiments are described and claimed.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
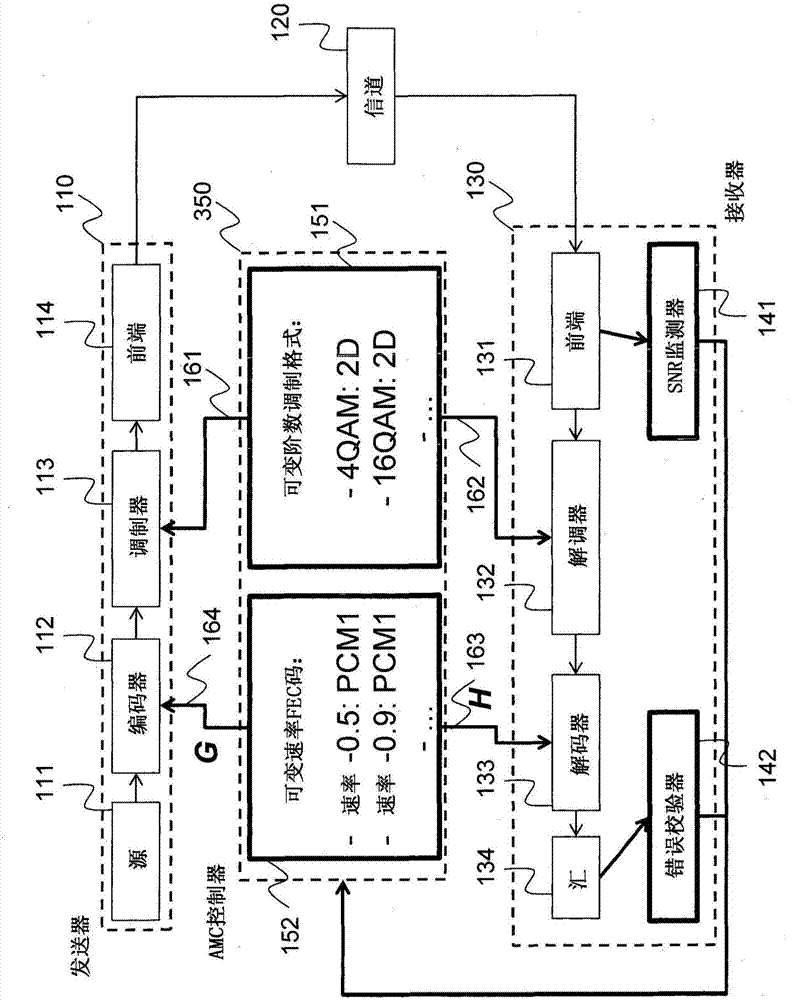
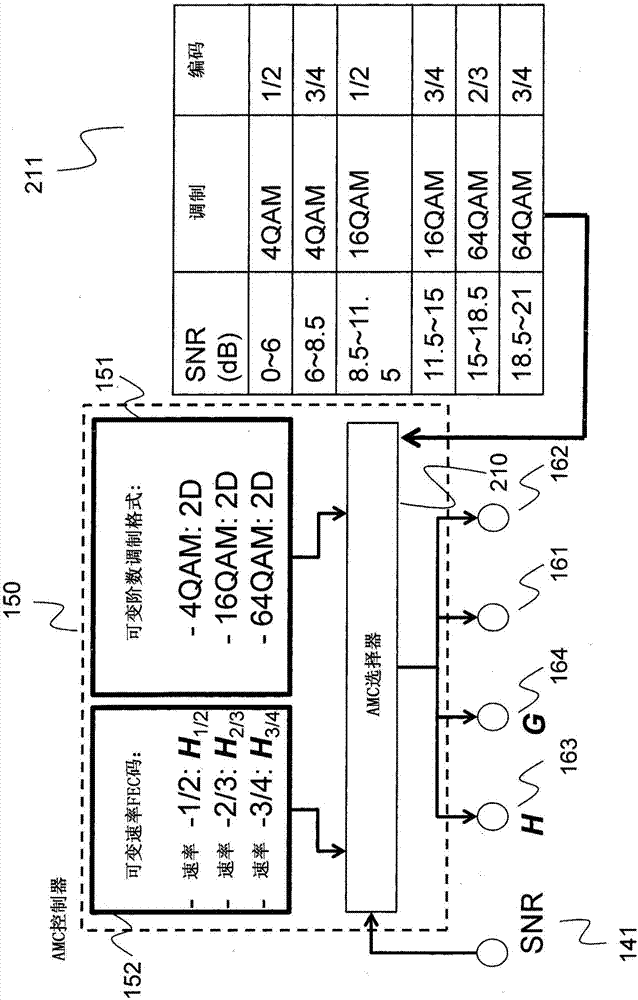
Method for adaptive modulation and coding, AMC, and AMC controller
ActiveCN107251439AMinimize power consumptionError correction/detection using block single space codingError correction/detection using LDPC codesHigh dimensionalBelief propagation
In an advanced adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) scheme, the code rate and the parity-check matrix (PCM) for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes are adapted according to modulation formats and variable-iteration receivers. The degree distribution for the PCM adaptation is designed by heuristic optimization to minimize the required SNR via an extrinsic information transfer (EXIT) trajectory analysis for finite-iteration decoding. The method uses dynamic window decoding by generating spatially coupled PCM for quasi-cyclic LDPC convolutional coding. The method also provides a way to jointly optimize labeling and decoding complexity for high-order and high-dimensional modulations. The problem to use a large number of different LDPC codes for various modulation formats and variable-iteration decoding is also dealt with by linearly dependent PCM adaptation across iteration count to keep using a common generator matrix. This PCM adaptation can improve a convergence speed of belief propagation decoding and mitigate an error floor issue.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Background mitigation reads in a non-volatile memory system
ActiveUS20190391746A1Accurately reflectRemissionInput/output to record carriersDisjoint-setError mitigation
A controller of a non-volatile memory manages each of multiple disjoint sets of physical pages as a respective page group. The controller mitigates errors by repetitively performing background mitigation reads of each of the plurality of blocks including, in order, performing a background mitigation read of a first physical page in a first page group in a first block; prior to again performing a background mitigation read in the first block, performing a background mitigation read of a first physical page in a first page group in each other of the plurality of blocks; performing a background mitigation read of a first physical page in a second page group in the first block; and prior to again performing a background mitigation read in the first block, performing a background mitigation read of a first physical page in a second page group in each other of the plurality of blocks.
Owner:IBM CORP
Autonomous method and apparatus for mitigating soft-errors in integrated circuit memory storage devices at run-time
InactiveUS20070011575A1Reduce soft errorsImprove the level ofError detection/correctionStatic storageTerm memoryComputer science
Apparatus and methods for autonomously identifying and mitigating soft-errors affecting integrated circuit memory storage devices are provided. A soft-error mitigation process is invoked upon finding that an integrated circuit memory device is affected by a parity error. In a staged approach, unused memory regions of the integrated circuit memory device are reinitialized; if a redundant deployment prevails, the subsystem corresponding to the affected integrated circuit memory device is reset; memory regions having copies of contents thereof stored at remote locations are rewritten with obtained copies of the contents; and memory regions storing contents which are generated at run-time are reinitialized. Directed parity error scans are employed at each stage. If the parity error persists, one of the apparatus, and the subsystem corresponding to the affected silicon memory device is reset during a maintenance window. Advantages are derived from a run-time soft-error mitigation process which increases availability, and reduces maintenance overheads and the need for hardware replacement.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
System and methods for transmitting data
InactiveUS7042933B2Increase demandError prevention/detection by using return channelCode conversionForward error correctionComputer science
Owner:AT&T CORP
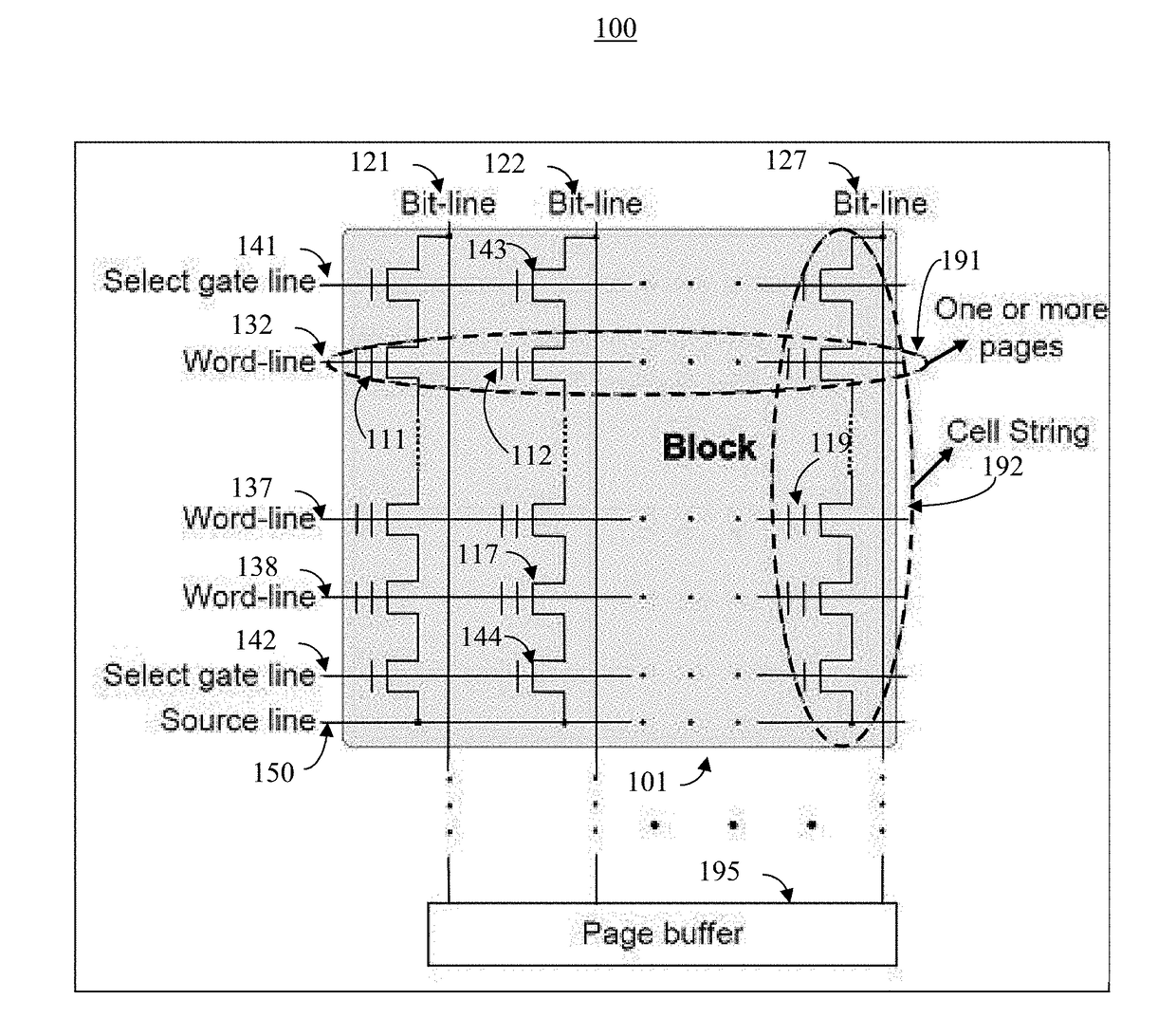
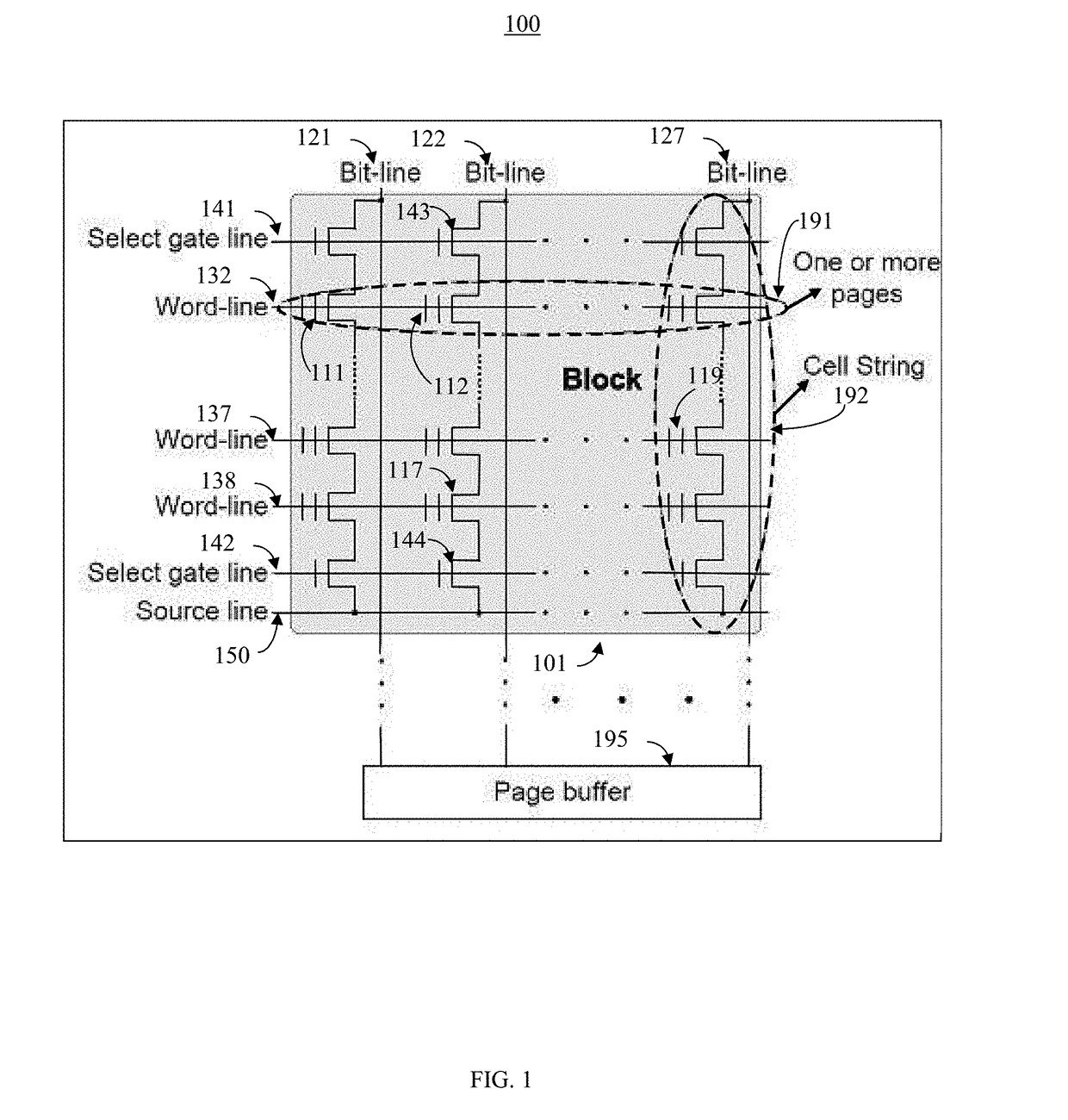
NAND flash storage error mitigation systems and methods
InactiveUS20170185328A1Improve efficiencyFacilitates effectiveMemory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersBit lineComputer architecture
The present invention facilitates efficient and effective information storage device operations. In one embodiment, a storage device comprises: a plurality of storage cells configured to store information; a plurality of word lines coupled to the plurality of storage cells; and a plurality of bit lines coupled to the plurality of storage cells, wherein the plurality of bit lines are configured to enable writing of the plurality of storage cells and the plurality of word lines are configured to enable reading of the storage cells. The information is configured in a plurality of information first type portions (e.g., codewords) which respectively include a plurality of second type portions (e.g., data chunks), and the information is stored by the plurality of storage cells in a distribution that ensures two second type portions from a respective first type portion are not stored in storage cells adjacent to one another.
Owner:ALIBABA GRP HLDG LTD
Decision Feedback Type Equalizer
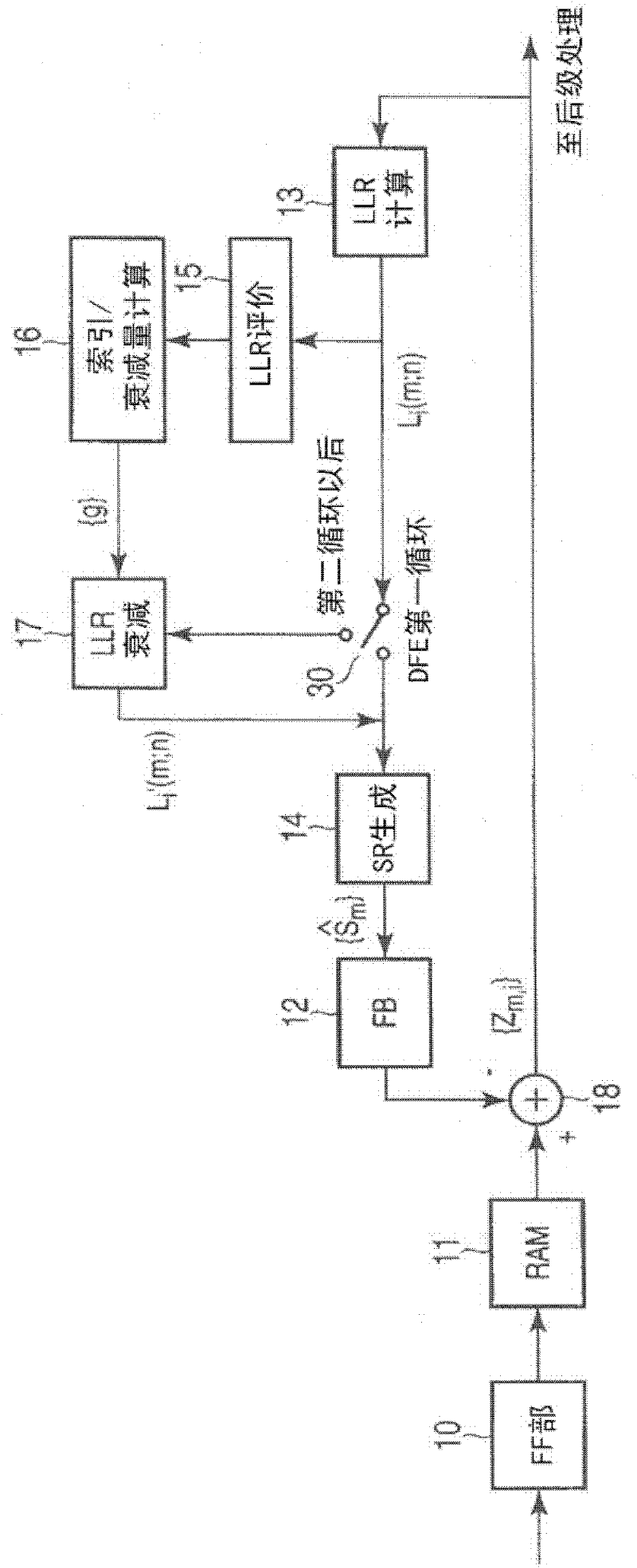
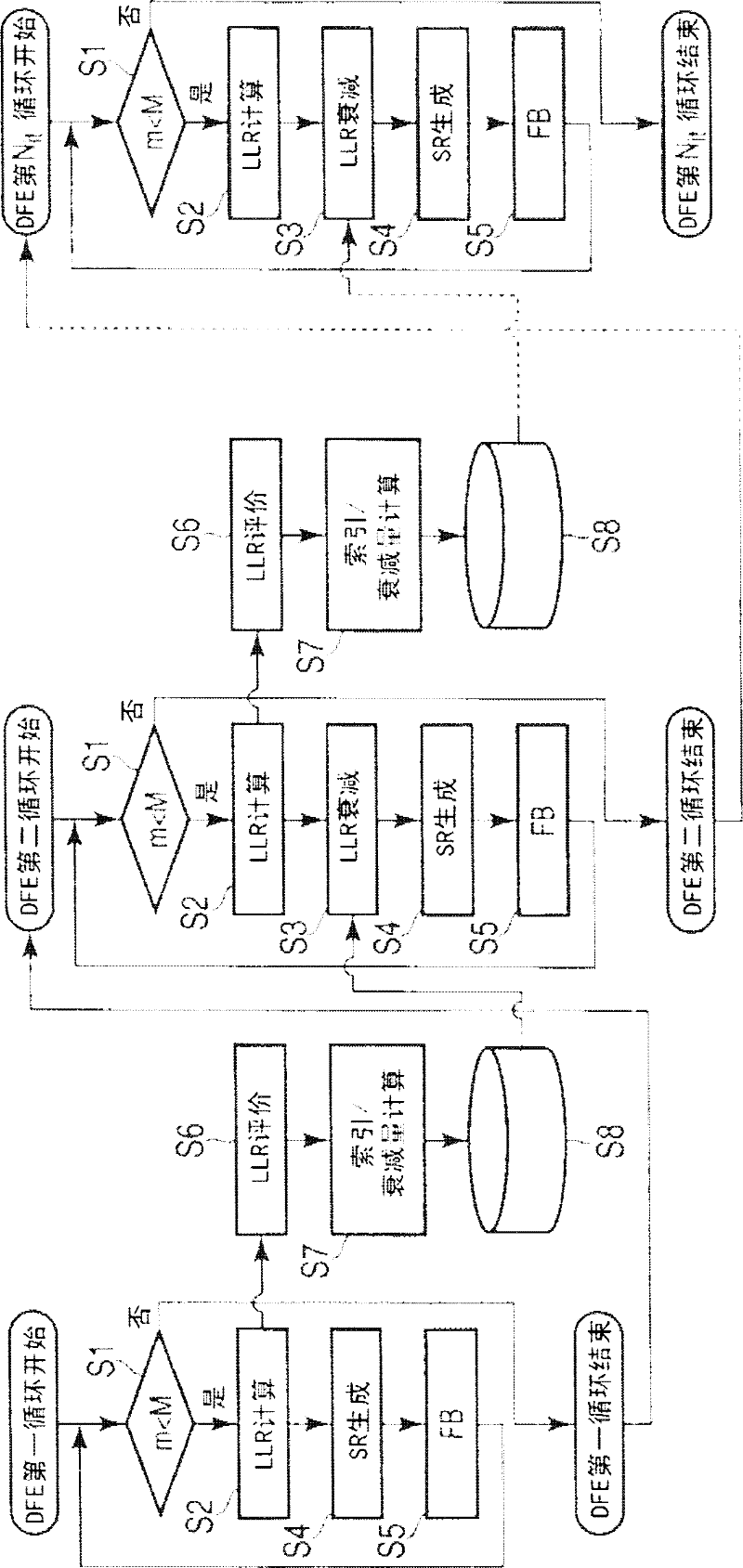
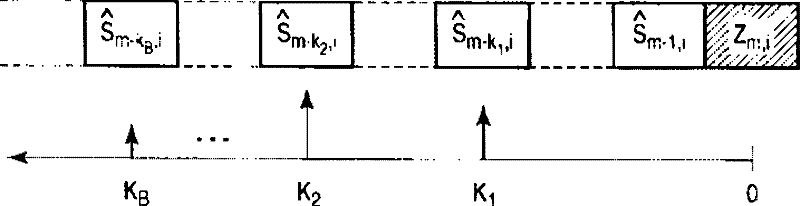
InactiveCN102404260AReduce error propagationTransmitter/receiver shaping networksUltrasound attenuationLog likelihood
The invention relates to a decision feedback type equalizer, capable of better reducing error dissemination. The decision feedback type equalizer comprises a storage device, a logarithm likelihood ratio calculating part, a logarithm likelihood ratio evaluation part, a decrement calculating part, and a logarithm likelihood ratio attenuation part, wherein the storage device is used for keeping input signals that make the decision responding to multiple signs to be repeatedly operated; the logarithm likelihood ratio calculating part is used for calculating the logarithm likelihood ratio according to the signals obtained by deducting the output of the feedback filter from the input signals kept in the storage device; the logarithm likelihood ratio evaluation part, according to the absolute value of the logarithm likelihood ratio, carries out confirmation over the signals transmitting the bit that is evaluated with low reliability; the decrement calculating part calculates and keeps the logarithm likelihood ratio attenuation amount corresponding to the whole or part of bits of the signals affected by the feedback filter; and the logarithm likelihood ratio attenuation part makes the logarithm likelihood ratio carry out attenuation according to the logarithm likelihood ratio attenuation amount calculated in the previous decision feedback cycle.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Storage apparatus and control apparatus thereof
InactiveUS20080082859A1Defective regionIncrease data storageModification of read/write signalsError detection/correctionComputer hardwareError mitigation
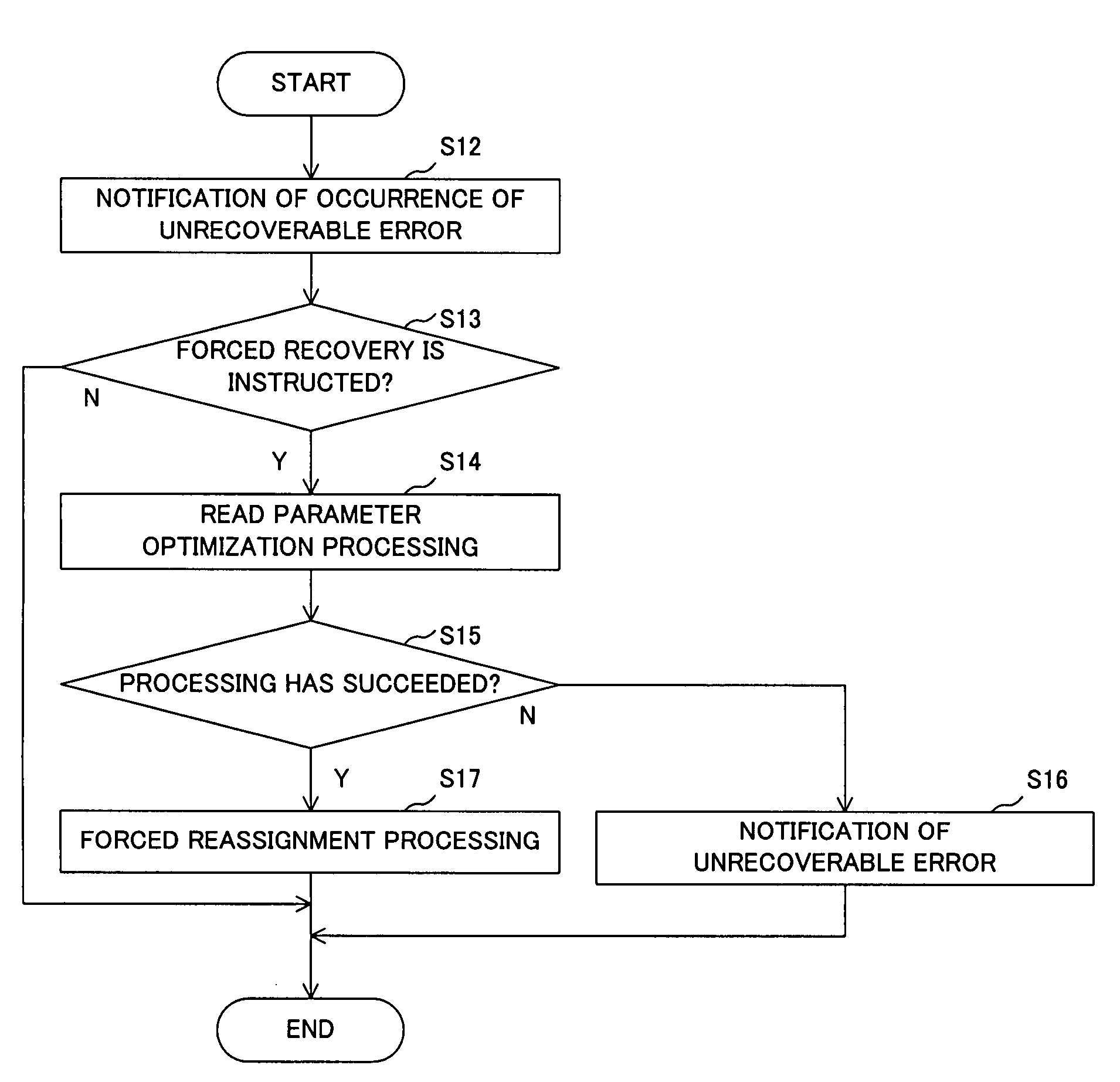
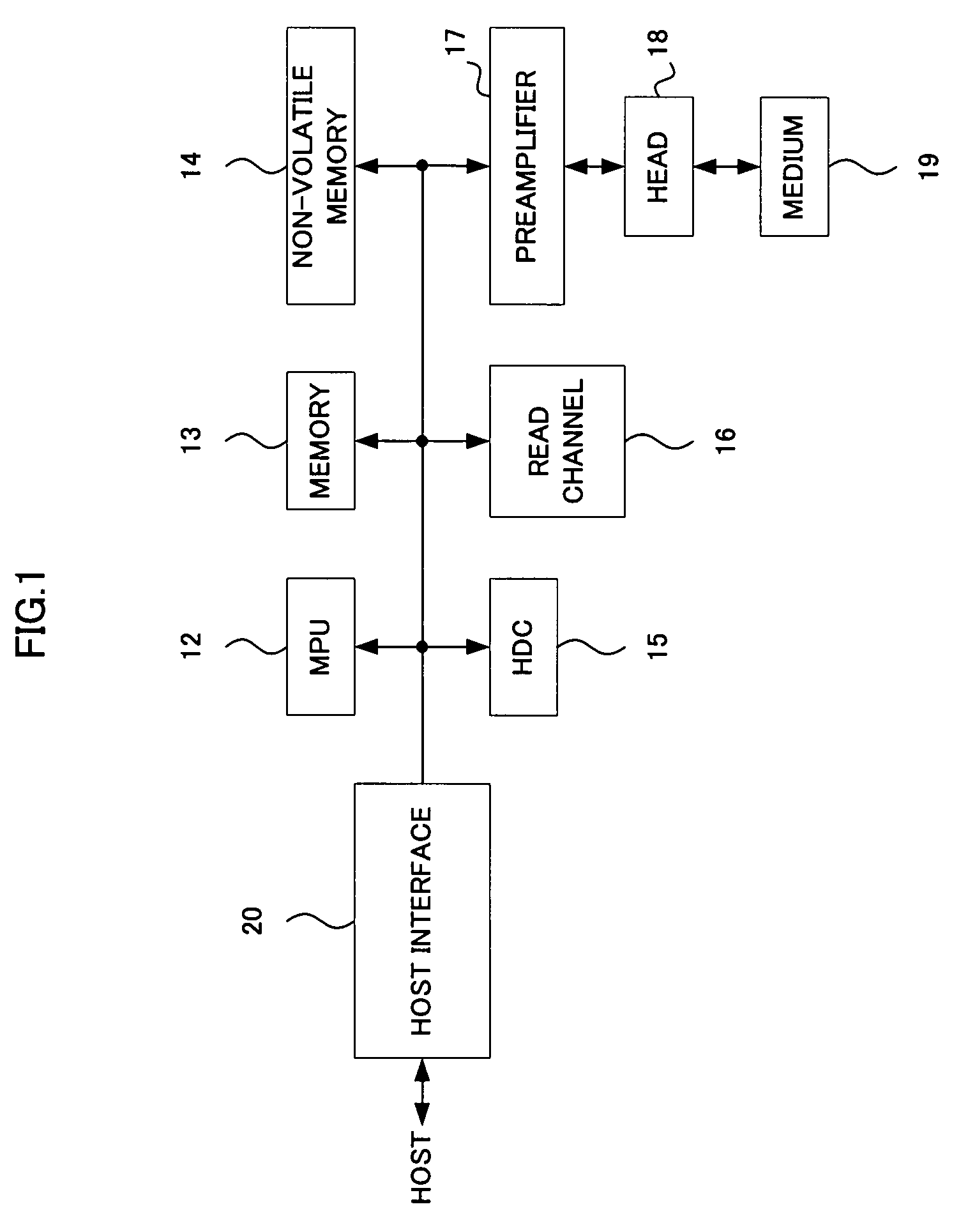
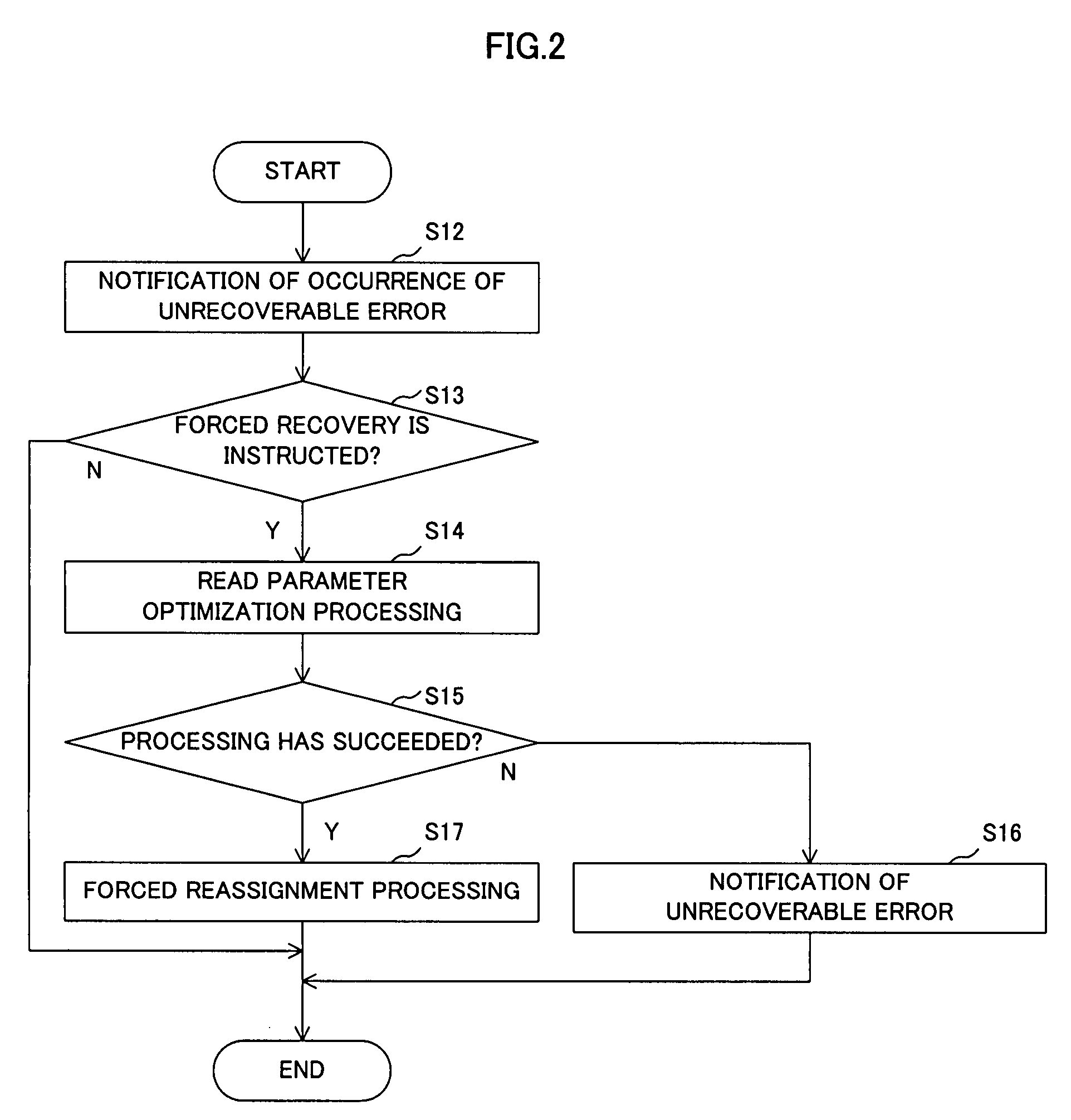
There is provided a storage apparatus capable of relieving an error region and a control apparatus thereof.A storage apparatus connectable to a host includes a host interface section 20 that notifies the host that data cannot be read out in the case where there is an error sector from which data cannot be read out by a read retry operation and acquires an instruction from the host; an MPU 12 that performs adjustment of a read parameter which is a parameter for data reading when the host interface section 20 acquires the error sector recovery instruction from the host; and a read channel 16 that uses a parameter that has been adjusted by the MPU 12 to read out data from the error sector.
Owner:TOSHIBA STORAGE DEVICE CORP
Detecting architectural vulnerability of processor resources
InactiveCN101566958ASoftware testing/debuggingEnergy efficient computingError mitigationQuantum detector
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com