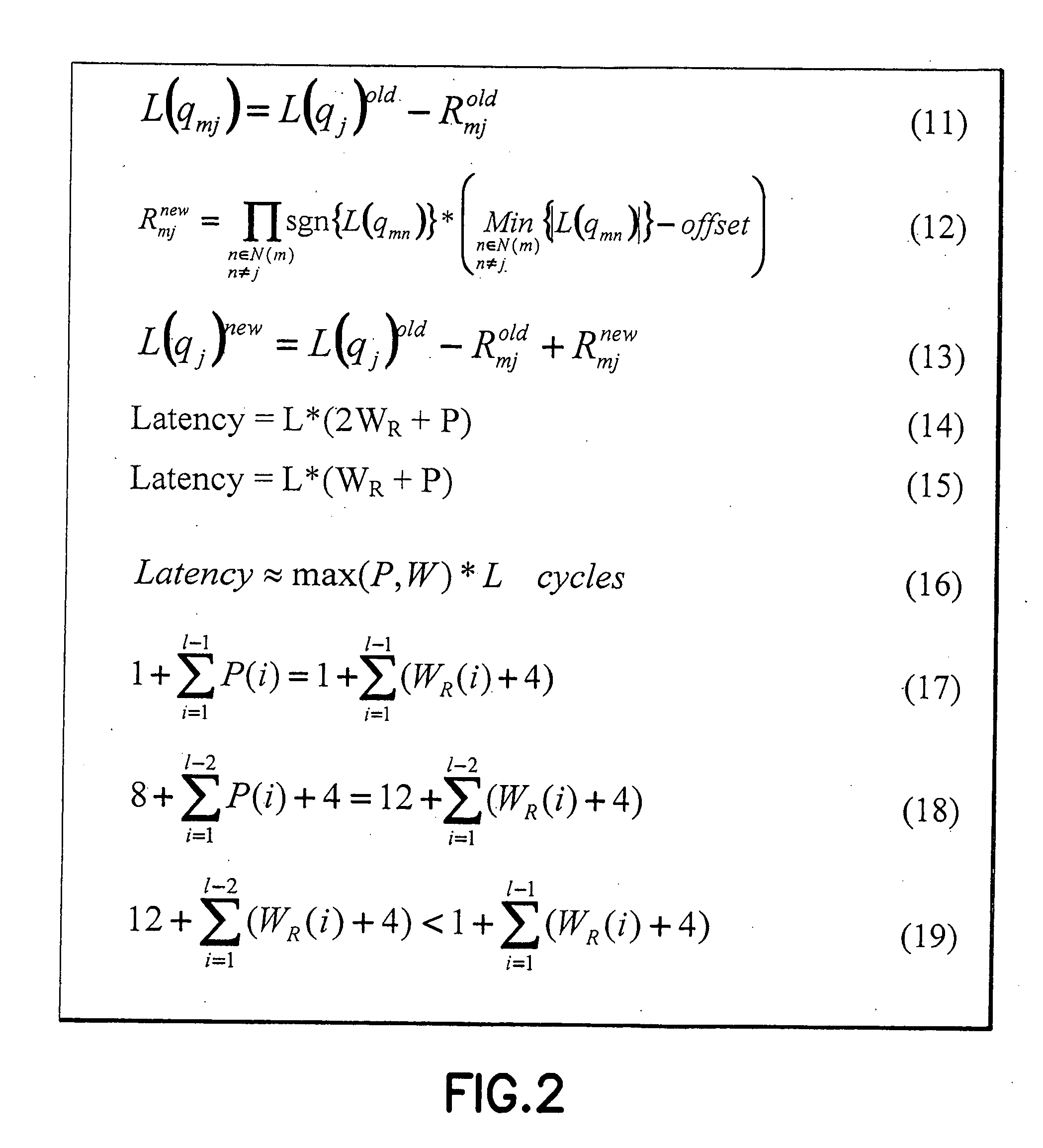Patents
Literature
342 results about "Belief propagation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
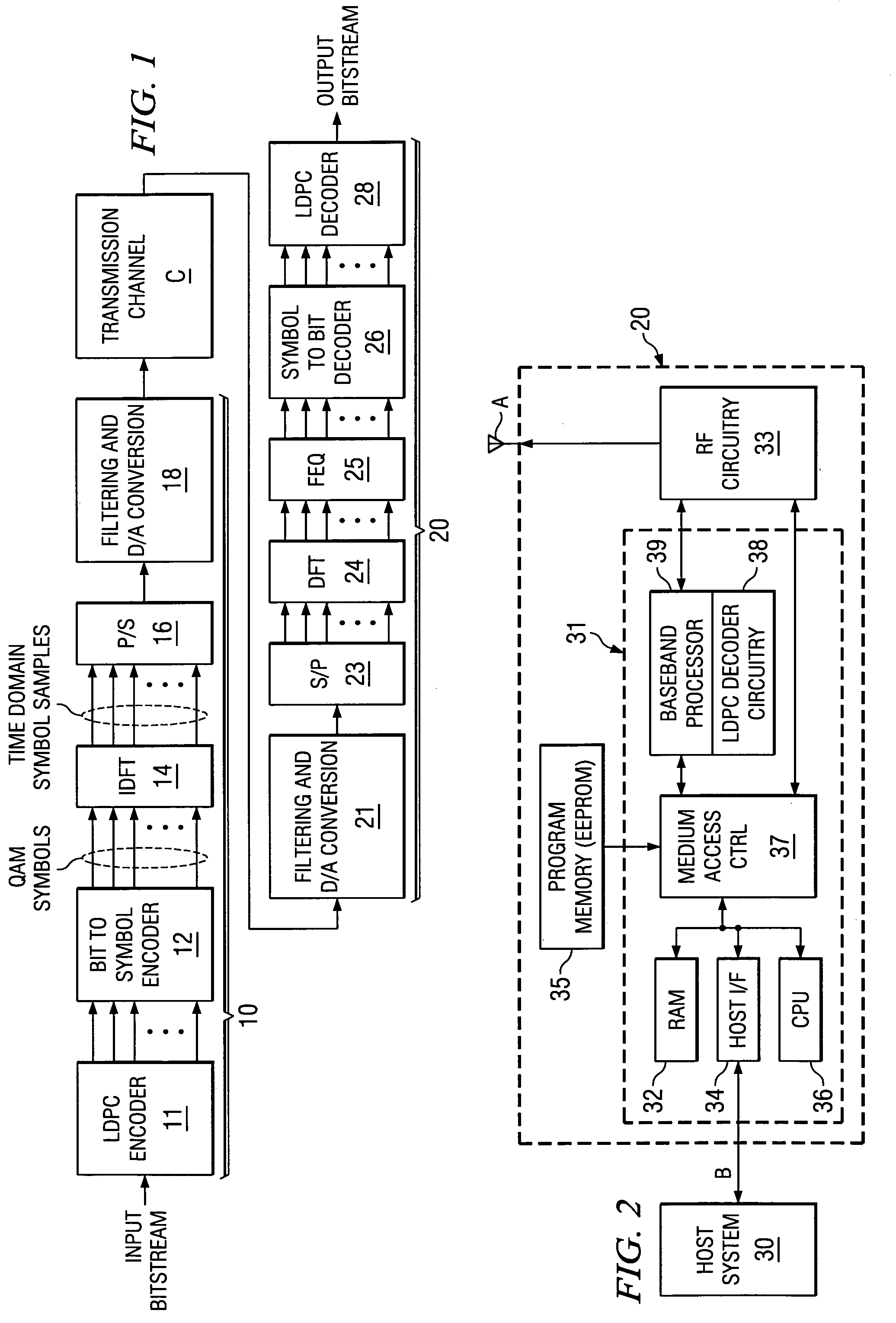
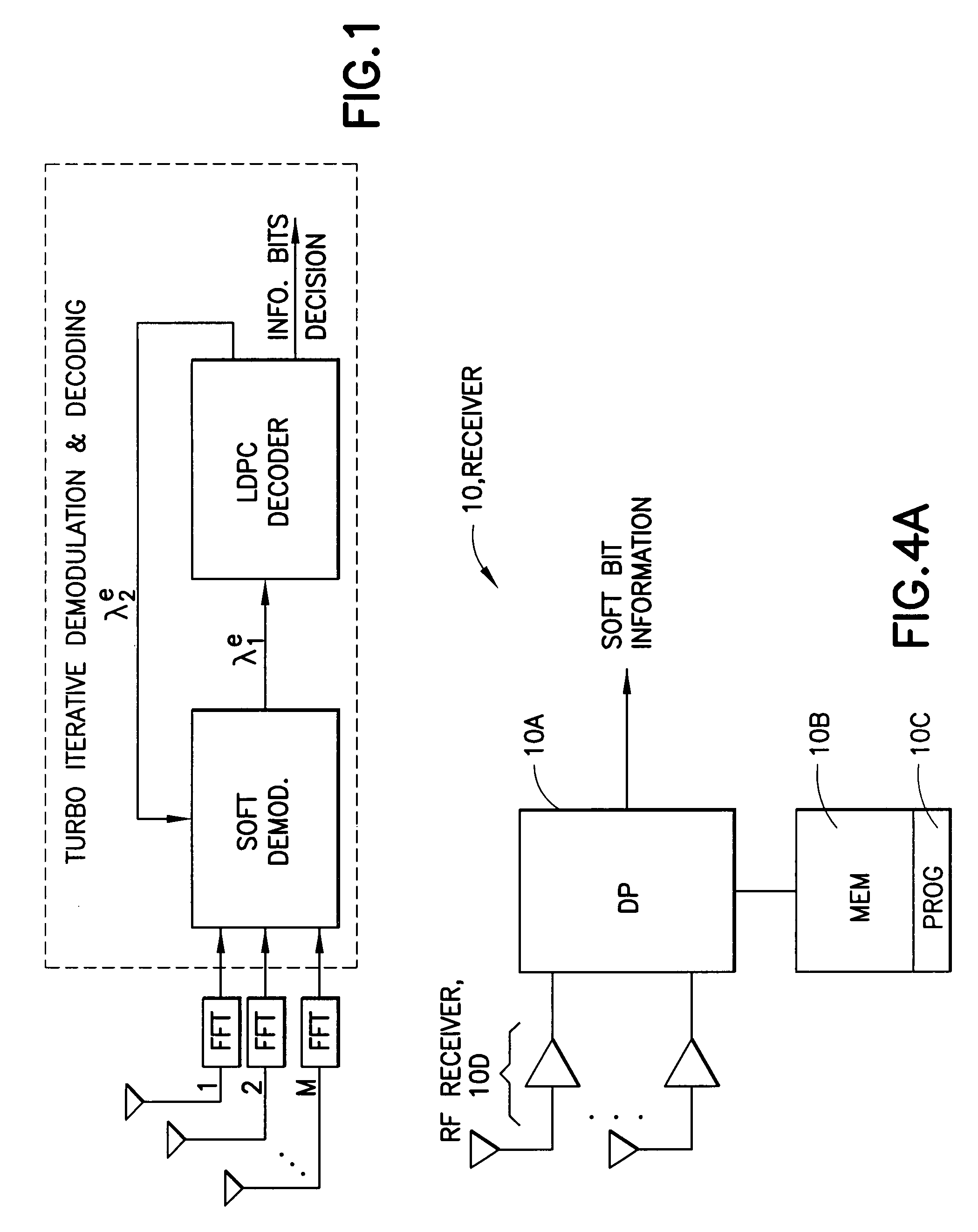
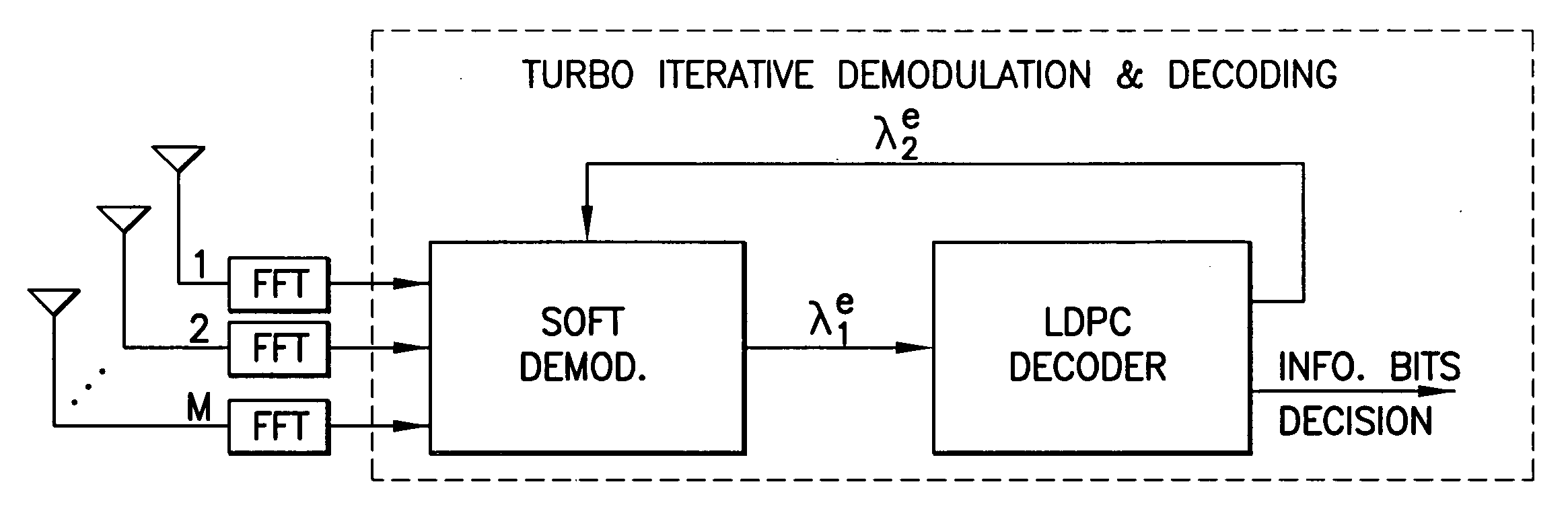
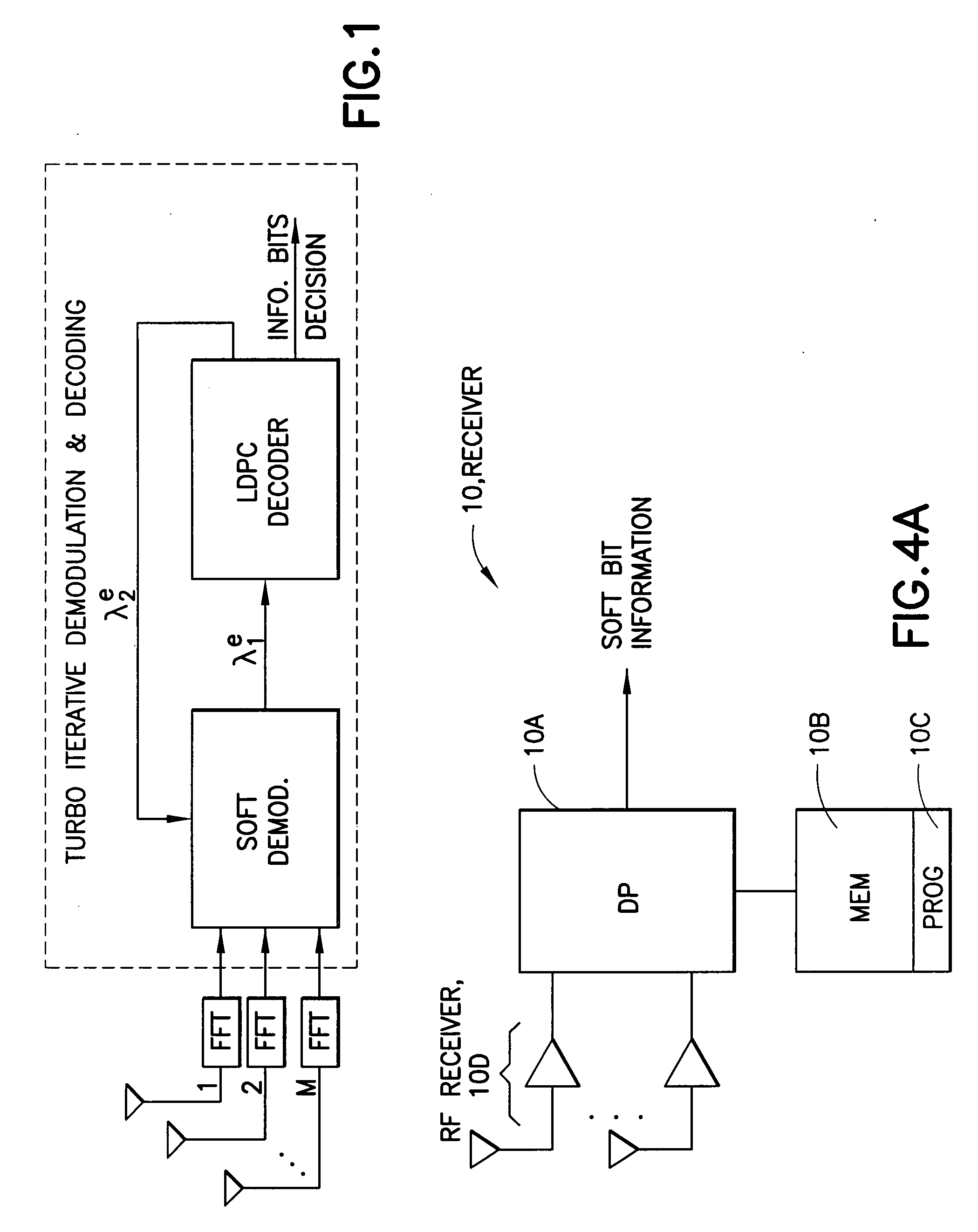
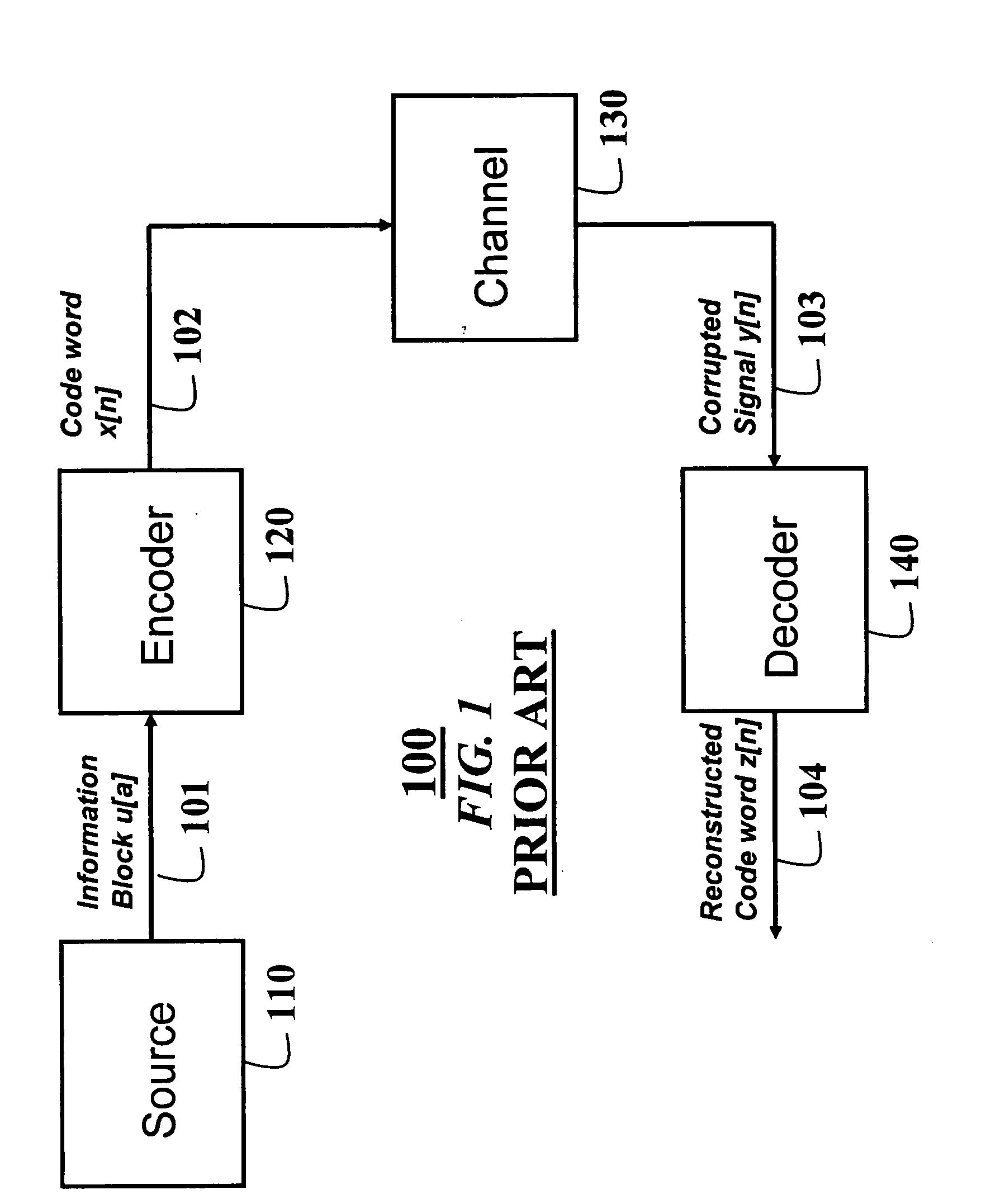
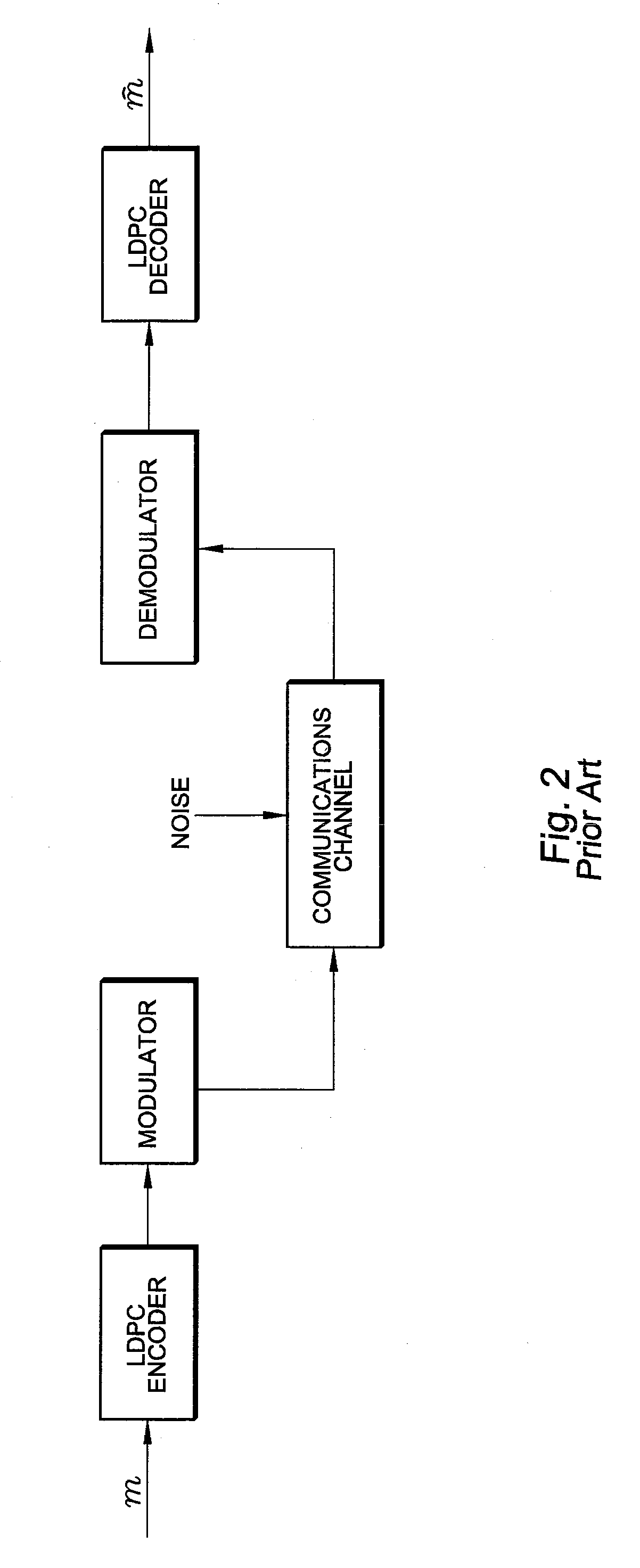
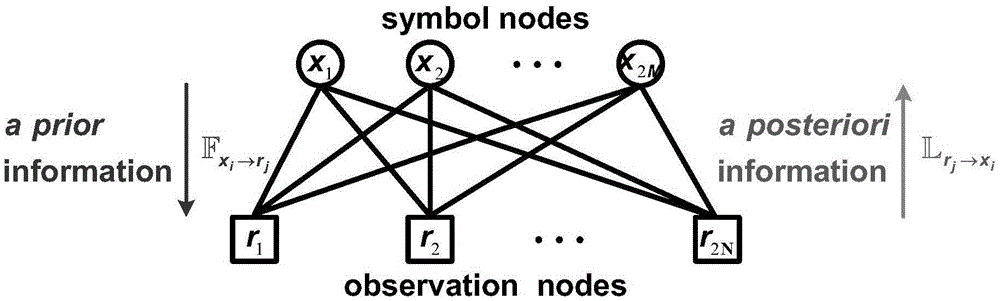
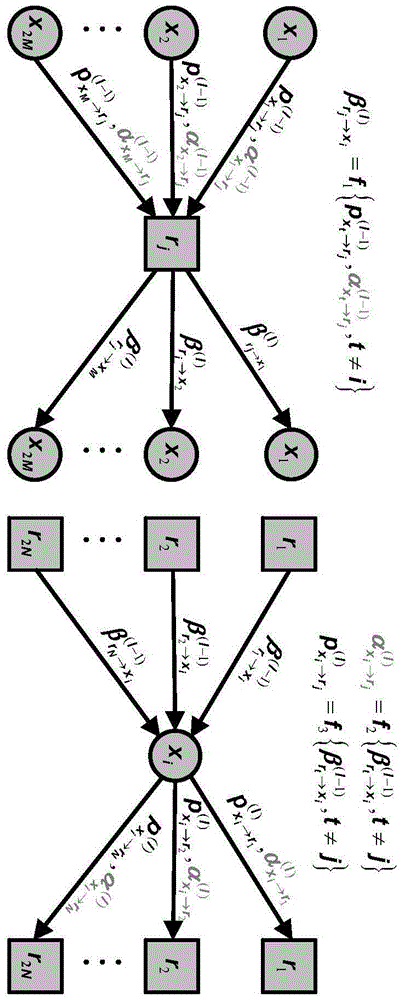
Belief propagation, also known as sum-product message passing, is a message-passing algorithm for performing inference on graphical models, such as Bayesian networks and Markov random fields. It calculates the marginal distribution for each unobserved node (or variable), conditional on any observed nodes (or variables). Belief propagation is commonly used in artificial intelligence and information theory and has demonstrated empirical success in numerous applications including low-density parity-check codes, turbo codes, free energy approximation, and satisfiability.
Channel-polarization-based encoder for staggered structure duplication code, and encoding and decoding methods thereof
InactiveCN102122966ASimple structureStrong error correction abilityCode conversionError correction/detection using interleaving techniquesTanner graphCoding block
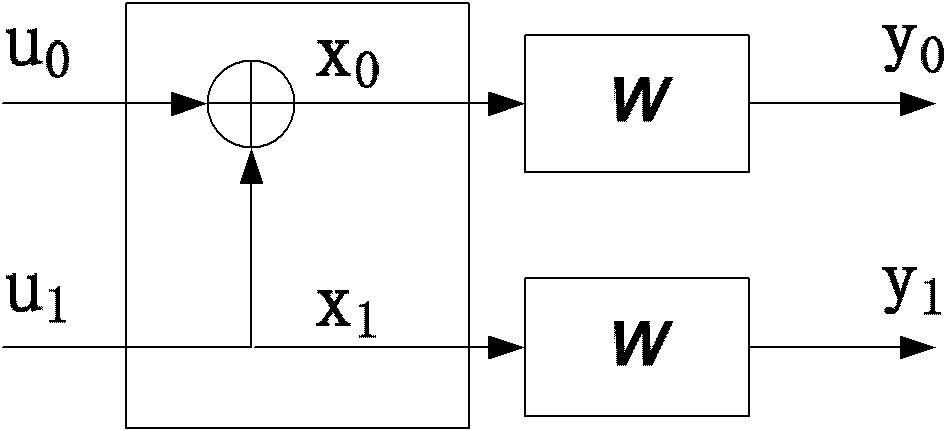
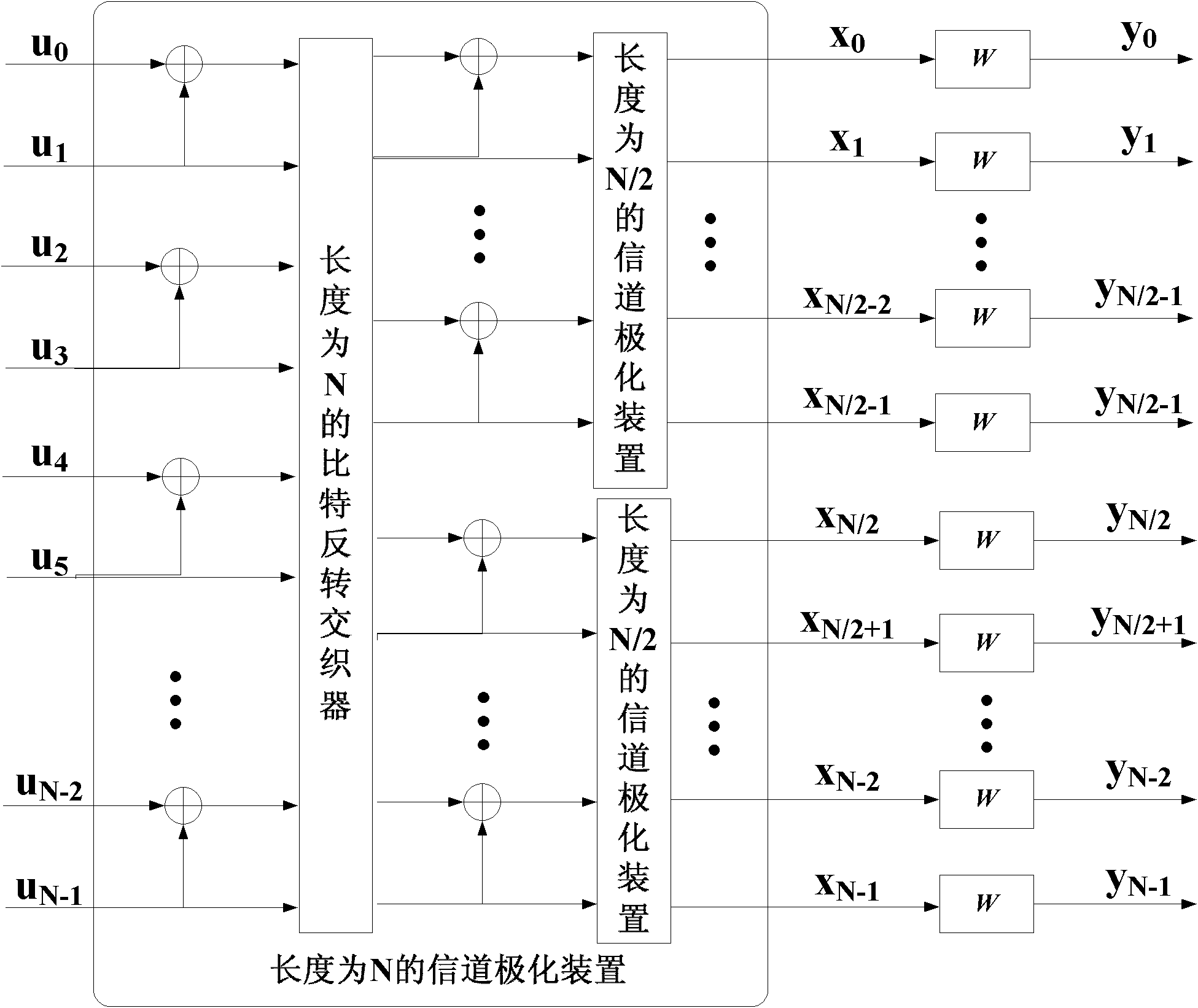
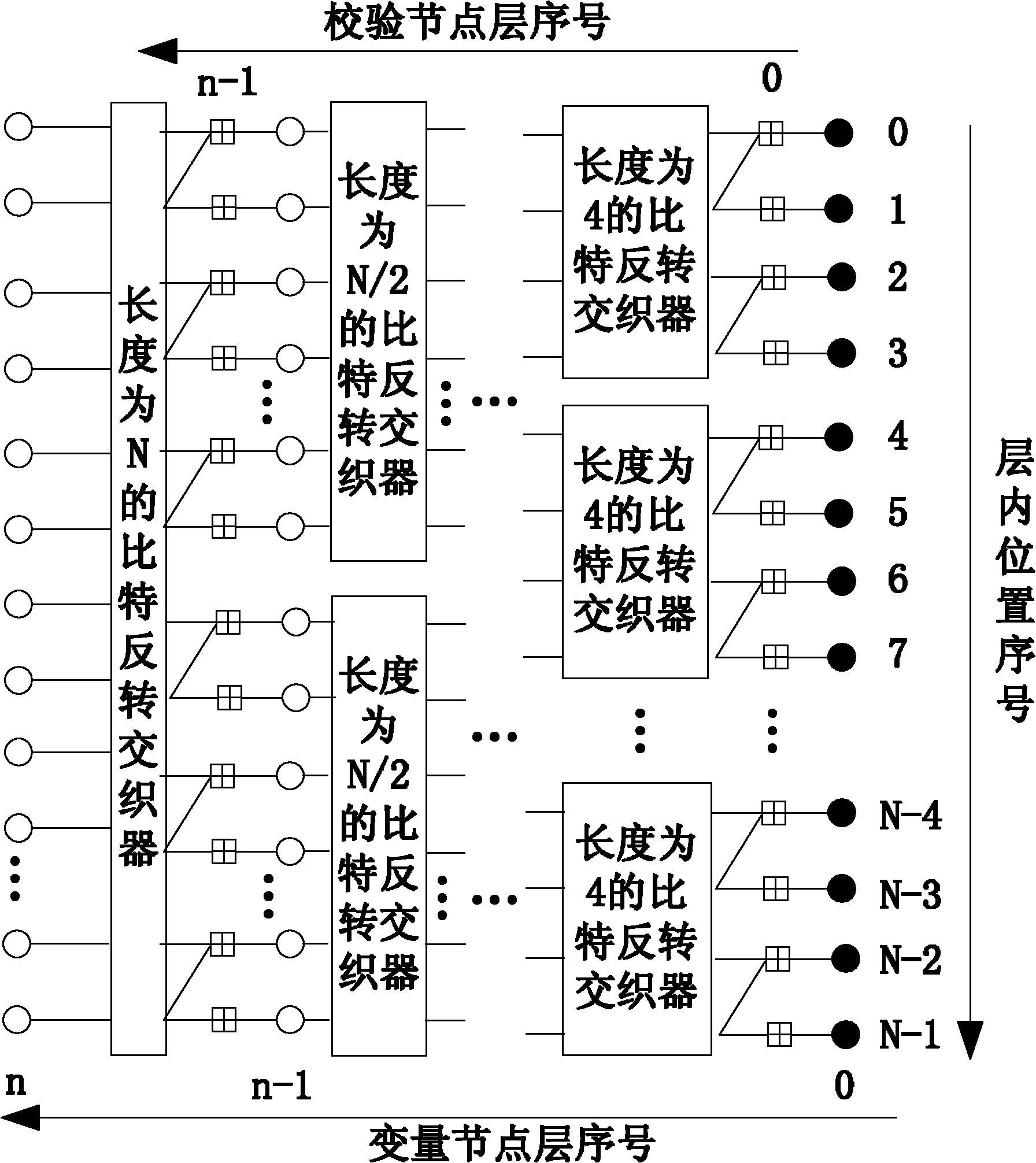
The invention discloses a channel-polarization-based encoder for a staggered structure duplication code, and an encoding method and decoding methods thereof. The encoder consists of a duplication bit buffer with a storage capacity of L bits, a bit position mapper with a length N and a channel polarization device with the length N which are connected in sequence. The encoding method based on the encoder comprises the following steps of: embedding duplicated encoding into a channel polarization process, and introducing a duplicated relationship between parts of the bits of code blocks transmitted in sequence during the channel polarization for encoding. In addition, the invention further provides two decoding methods, which comprise the following steps of: decoding by using a simple and rapid successive cancellation (SC) algorithm, and performing iterative decoding by using a Tanner-graph-based belief propagation algorithm with excellent performance. On the basis of the innovative structure encoder, the encoding and decoding methods provided by the invention are stronger in error correction capability under the condition of not increasing the decoding complexity, and the transmission performance is obviously improved. The encoding and decoding methods are particularly applicable to an actual communication engineering system and have a good popularization and application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Hardware-efficient low density parity check code for digital communications
ActiveUS7178080B2Efficient implementationEfficient constructionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMatrix groupParity-check matrix
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
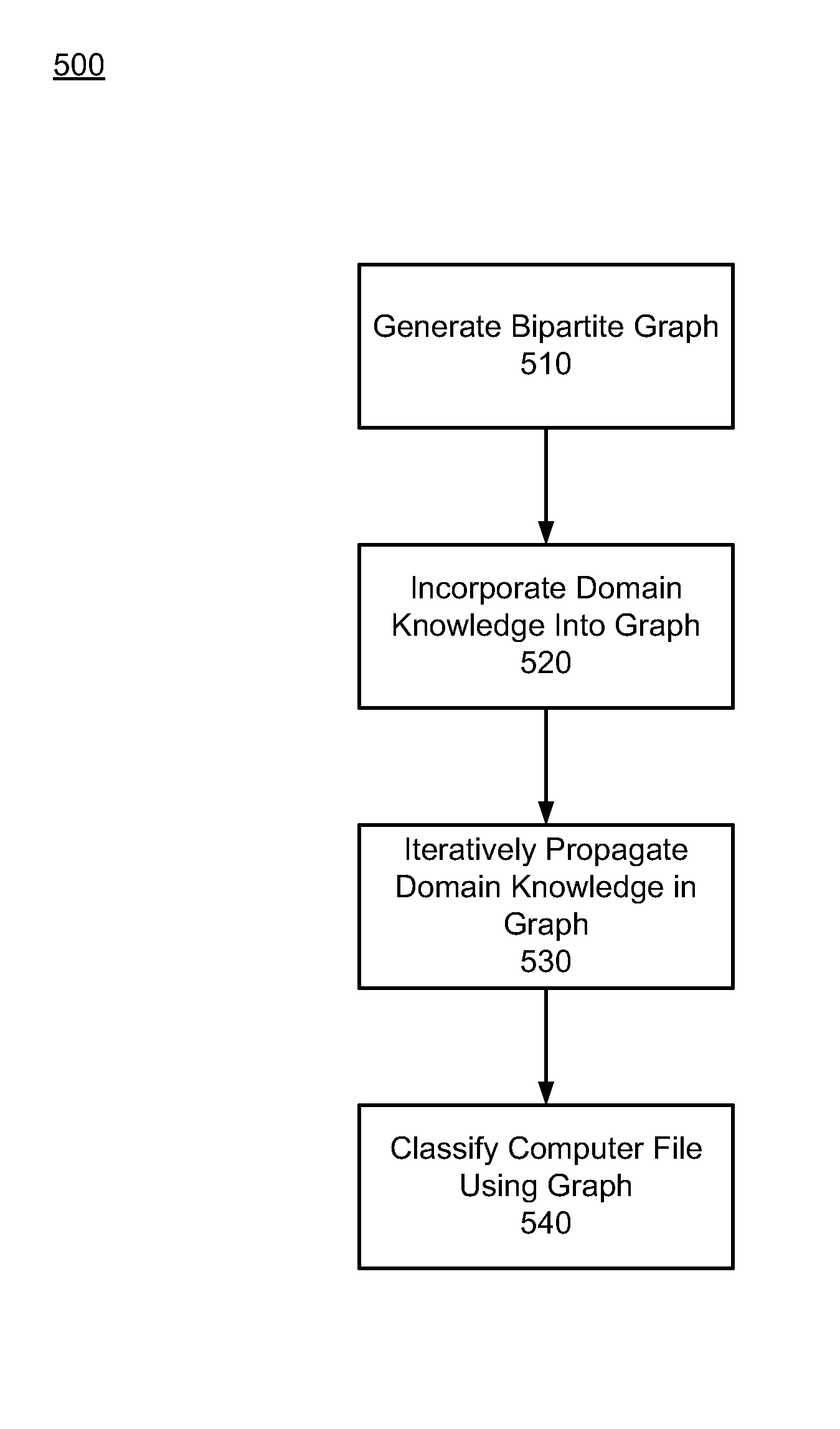
Inferring file and website reputations by belief propagation leveraging machine reputation
The probability of a computer file being malware is inferred by iteratively propagating domain knowledge among computer files, related clients, and / or related source domains. A graph is generated to include machine nodes representing clients, file nodes representing files residing on the clients, and optionally domain nodes representing source domains hosting the files. The graph also includes edges connecting the machine nodes with the related file nodes, and optionally edges connecting the domain nodes with the related file nodes. Priors and edge potentials are set for the nodes and the edges based on related domain knowledge. The domain knowledge is iteratively propagated and aggregated among the connected nodes through exchanging messages among the connected nodes. The iteration process ends when a stopping criterion is met. The classification and associated marginal probability for each file node are calculated based on the priors, the received messages, and the edge potentials associated with the edges through which the messages were received.
Owner:CA TECH INC
Regional depth edge detection and binocular stereo matching-based three-dimensional reconstruction method
ActiveCN101908230AStable matching costReduce mistakesImage analysis3D modellingObject pointReconstruction method
The invention discloses a regional depth edge detection and binocular stereo matching-based three-dimensional reconstruction method, which is implemented by the following steps: (1) shooting a calibration plate image with a mark point at two proper angles by using two black and white cameras; (2) keeping the shooting angles constant and shooting two images of a shooting target object at the same time by using the same camera; (3) performing the epipolar line rectification of the two images of the target objects according to the nominal data of the camera; (4) searching the neighbor regions of each pixel of the two rectified images for a closed region depth edge and building a supporting window; (5) in the built window, computing a normalized cross-correlation coefficient of supported pixels and acquiring the matching price of a central pixel; (6) acquiring a parallax by using a confidence transmission optimization method having an acceleration updating system; (7) estimating an accurate parallax by a subpixel; and (8) computing the three-dimensional coordinates of an actual object point according to the matching relationship between the nominal data of the camera and the pixel and consequently reconstructing the three-dimensional point cloud of the object and reducing the three-dimensional information of a target.
Owner:江苏省华强纺织有限公司 +1
Layered low density parity check decoding for digital communications
ActiveUS7139959B2Efficient implementationMost efficientError preventionError detection/correctionParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
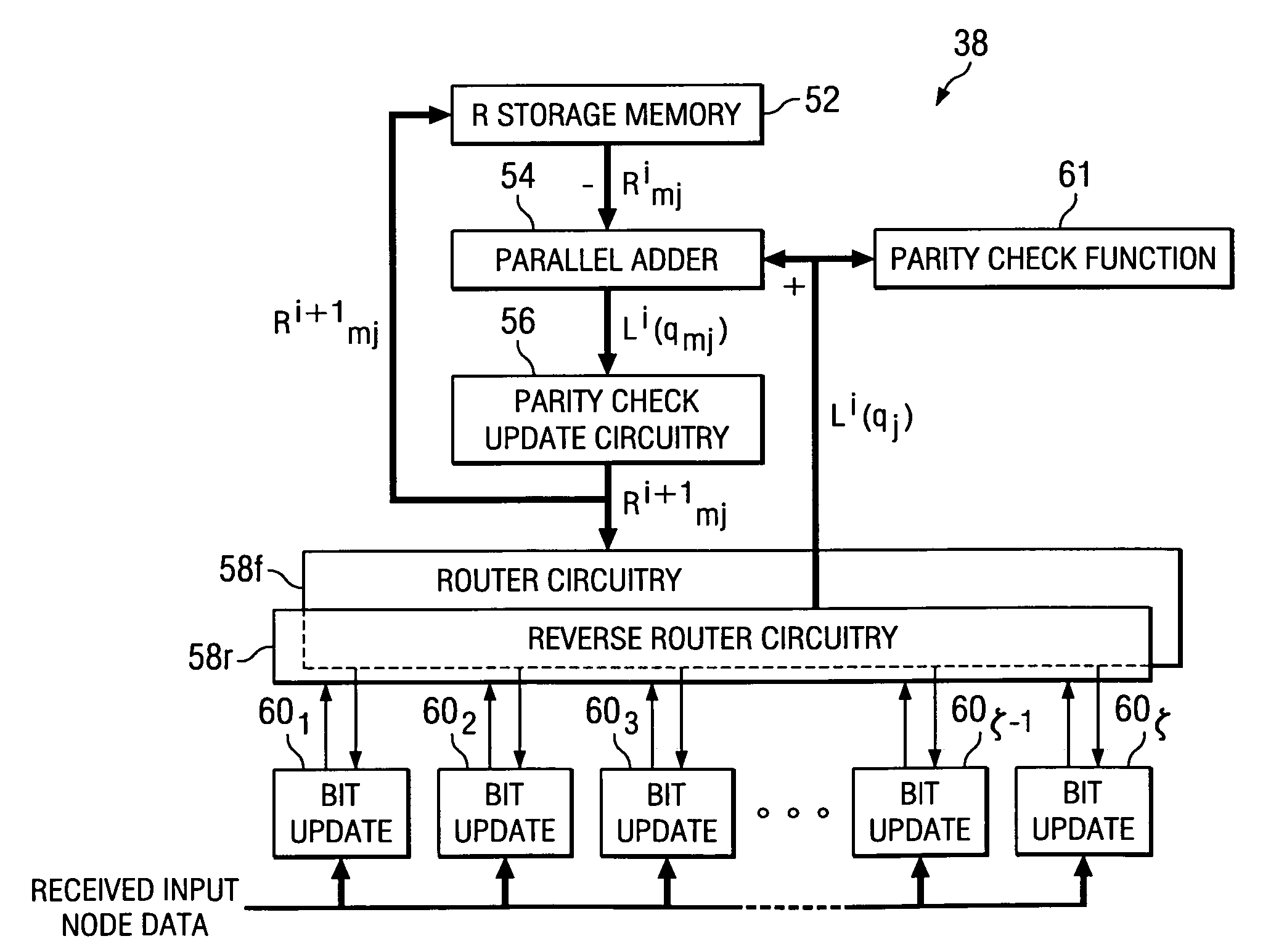
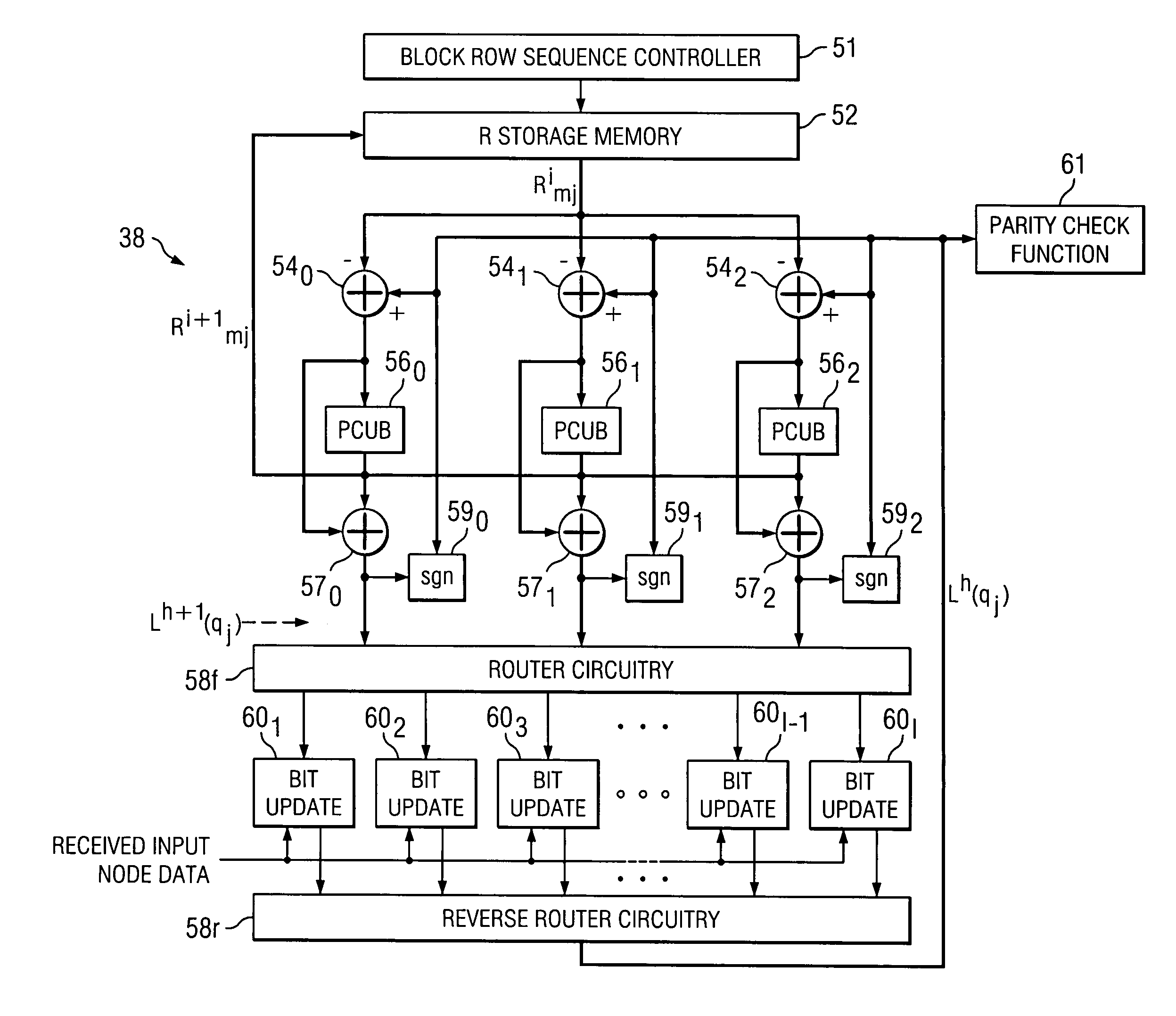
A low density parity check (LDPC) code that is particularly well adapted for hardware implementation of a belief propagation decoder circuit (38) is disclosed. The LDPC code is arranged as a parity check matrix (H) whose rows and columns represent check sums and input nodes, respectively. The parity check matrix is grouped into subsets of check sum rows, in which the column weight is a maximum of one. The decoder circuitry includes a parity check value estimate memory (52). Adders (54) generate extrinsic estimates, from immediately updated input node probability estimates, and the extrinsic estimates are applied to parity check update circuitry (56) for generating new parity check sum value estimates. These parity check sum value estimates are stored back into the memory (52), and after addition with the extrinsic estimates, are stored in a column sum memory (66) of a corresponding bit update circuit (60) as updated probability values for the input nodes.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
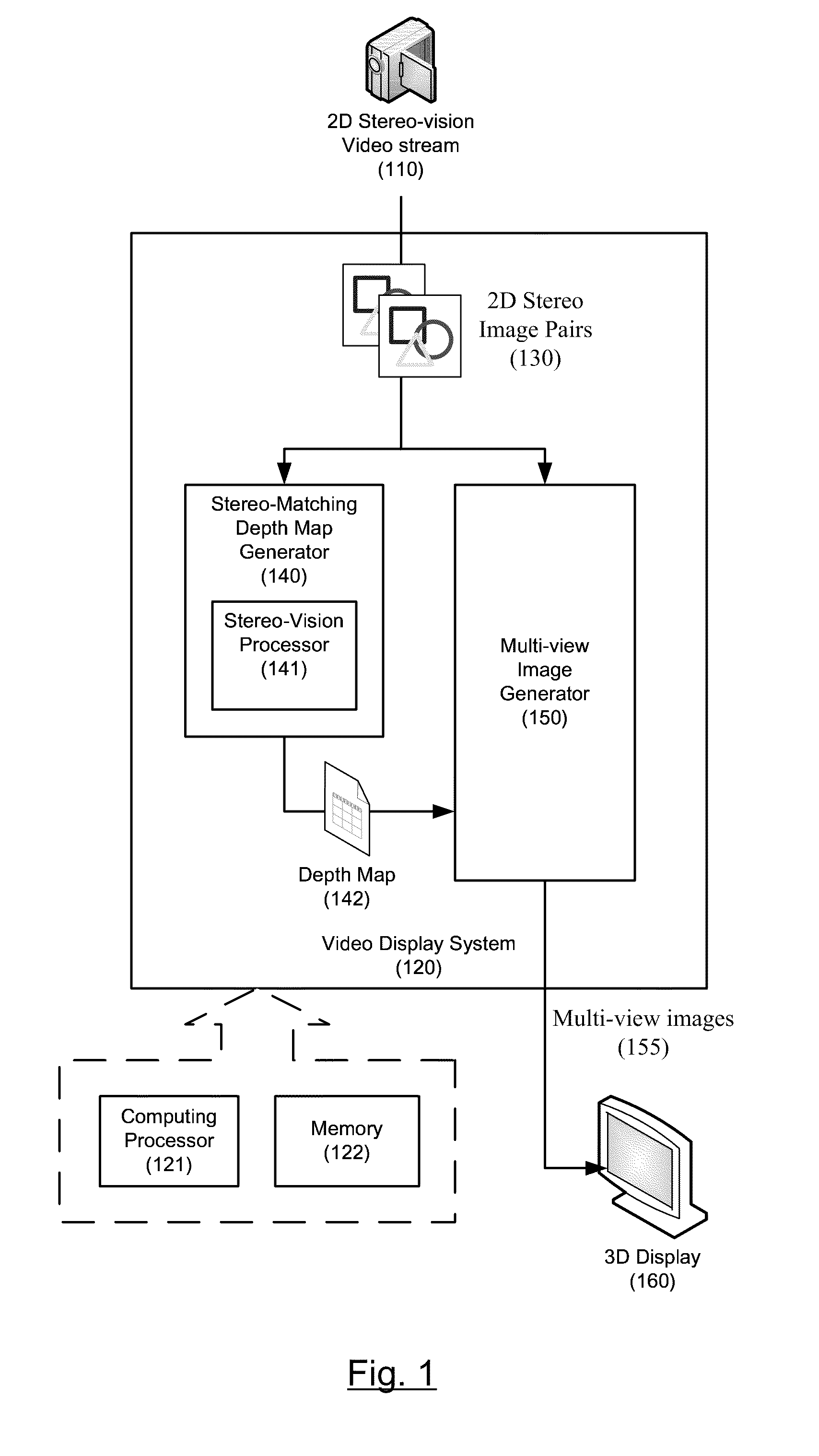
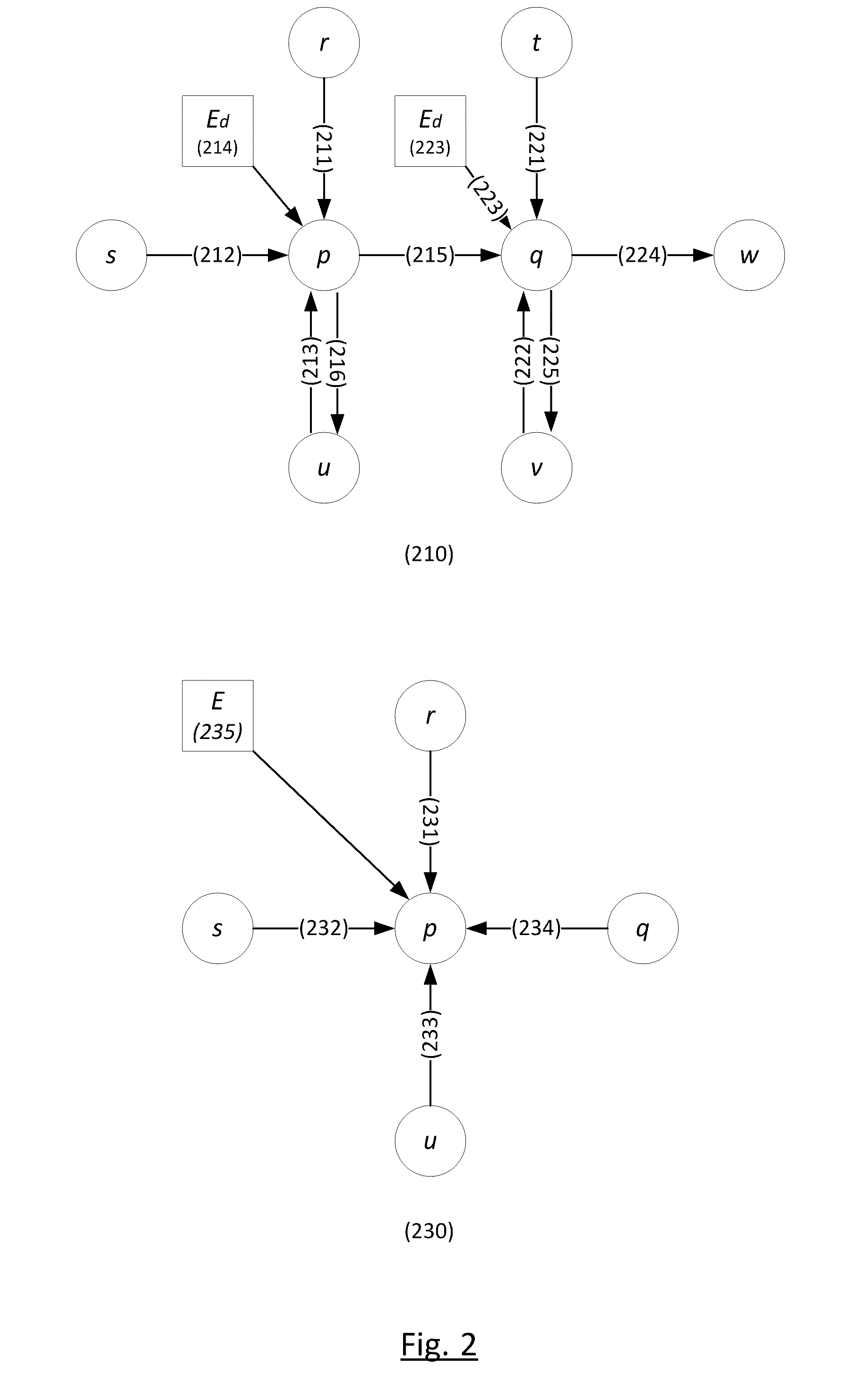
Stereo-Matching Processor Using Belief Propagation
In accordance with at least some embodiments of the present disclosure, a processor for performing stereo matching of a first image and a second image is described. The processor may include a first pipeline stage configured to generate data costs associated with a first tile selected from the first image, wherein the data costs is generated based on pixels in the first tile and corresponding pixels in the second image. The processor may include a second pipeline stage configured to generate disparity values associated with the first tile and an outbound message from the first tile to one of neighboring tiles in the first image, wherein the disparity values and the outbound message are generated based on the data costs and inbound messages from the neighboring tiles to the first tile. The processor may further include a third pipeline stage configured to store the disparity values and the outbound message in a memory, wherein the outbound message is used by the second pipeline stage as one of the inbound messages during processing of a second tile selected from the first image.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD +1
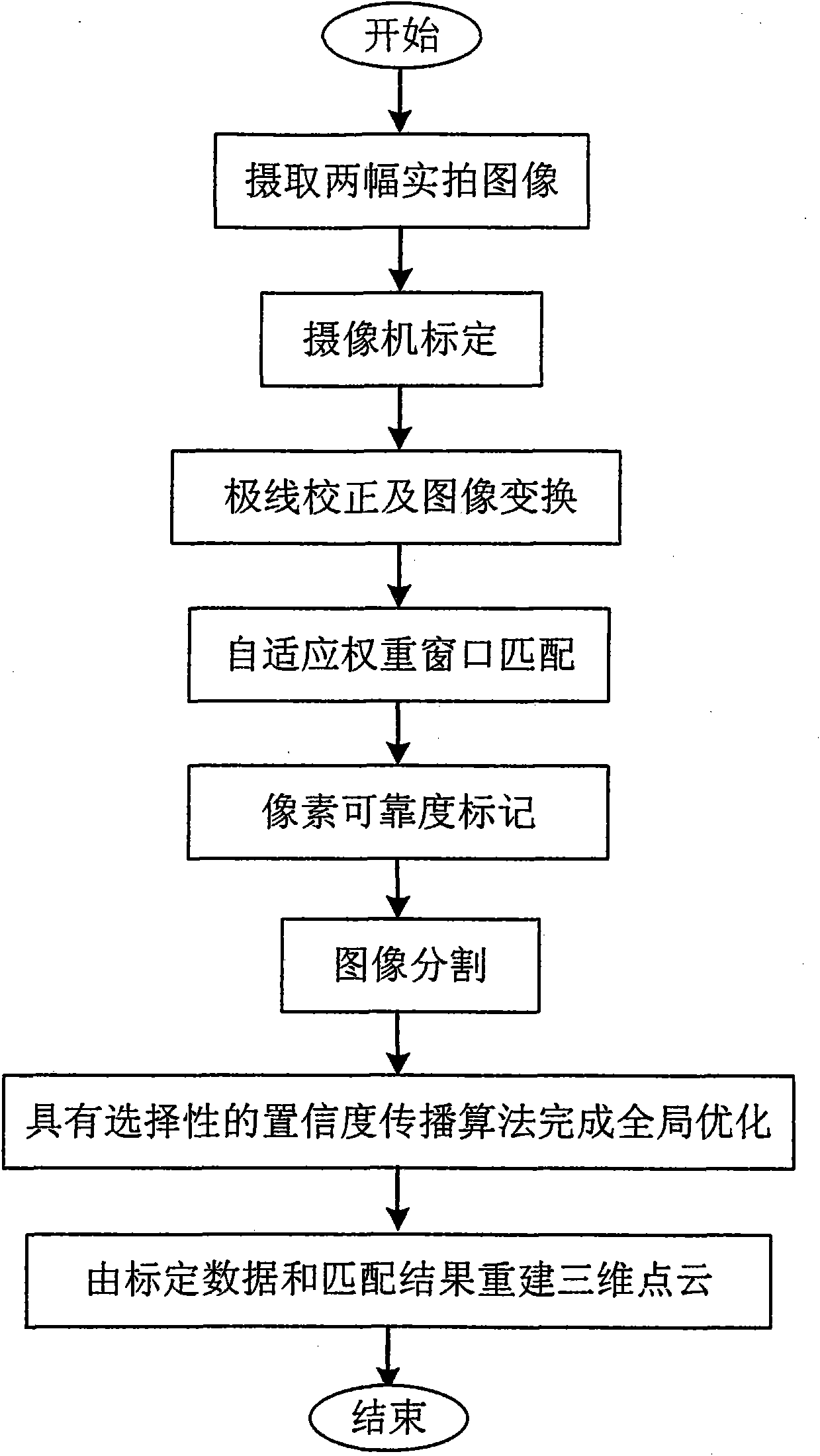
Color image three-dimensional reconstruction method based on three-dimensional matching
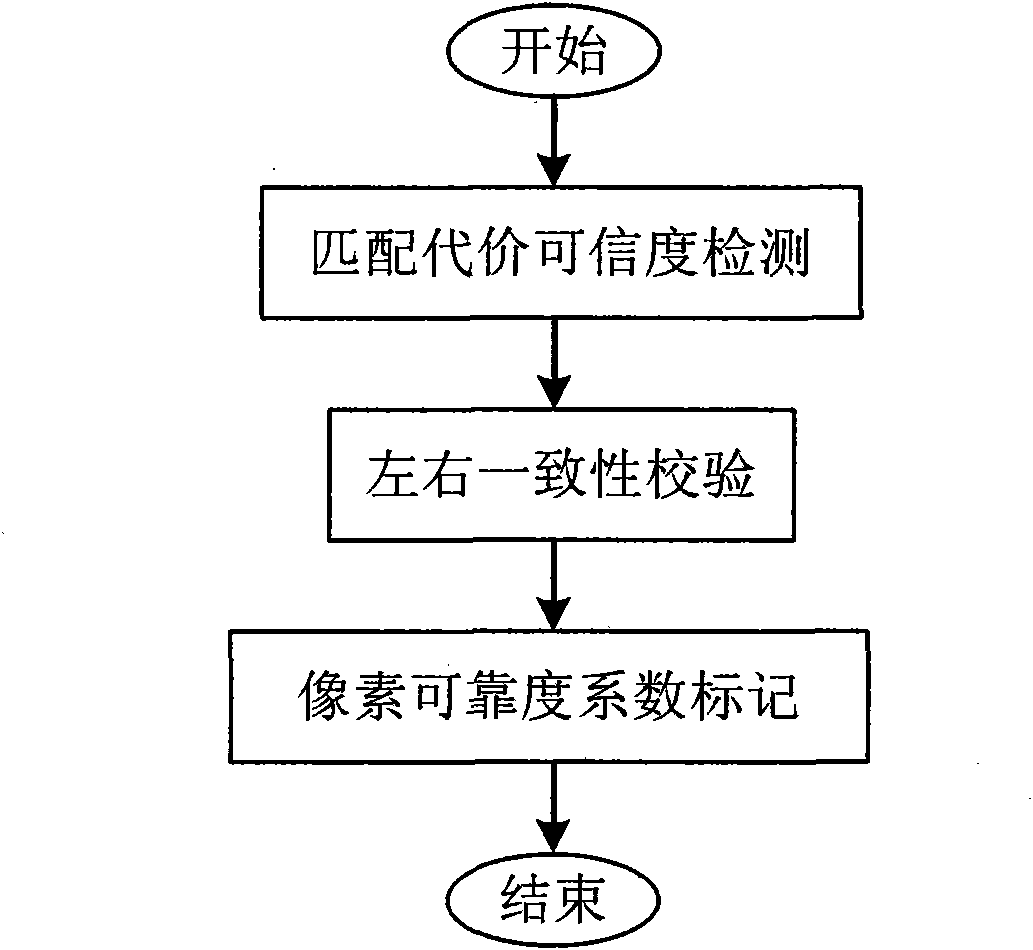
InactiveCN101976455AAvoid spreadingReduce computational complexityImage analysis3D modellingColor imageObject point
The invention relates to a color image three-dimensional reconstruction method based on three-dimensional matching, comprising the following steps of: (1) simultaneously and respectively taking an image from proper angles by using two color cameras; (2) respectively calibrating the internal parameter matrixes and the external parameter matrixes of the two cameras; (3) carrying out polar line correction and image transformation according to calibrated data; (4) working out matching cost for each pixel point in the two corrected images by applying a self-adaption weight window algorithm and acquiring an initial parallax image; (5) marking the reliability coefficient of the pixel initial matching result by adopting matching cost reliability detection and left and right consistency verification; (6) carrying out color segmentation on the images through a Mean-Shift algorithm; (7) carrying out global optimization by a selective confidence propagation algorithm on the basis of color segmentation and pixel reliability classification results to obtain a final parallax image; and (8) working out the three-dimensional coordinates of actual object points on the images according to the calibrated data and the matching relation, thereby reconstructing the three-dimensional point cloud of an object.
Owner:南通洁万家纺织有限公司 +1
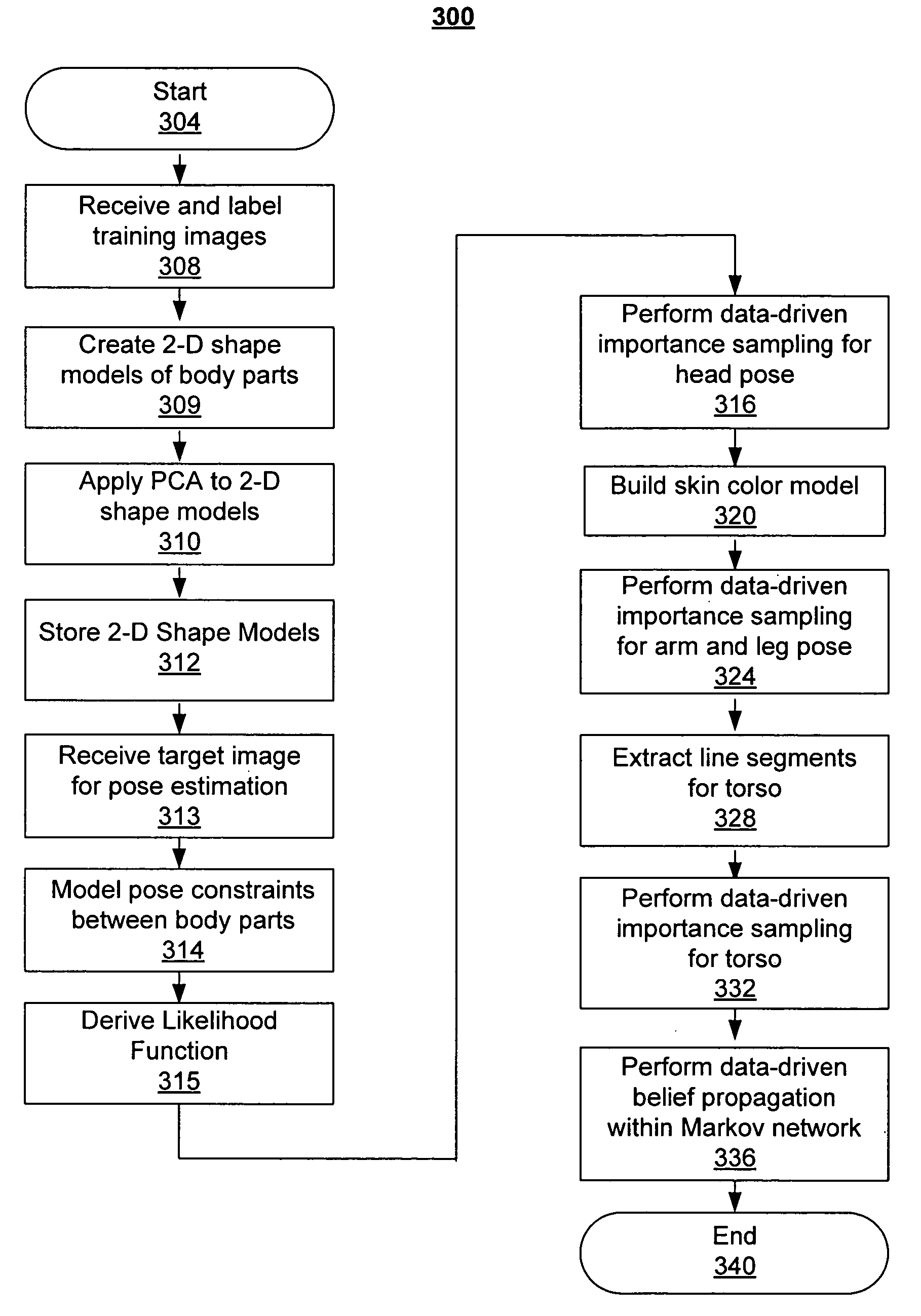
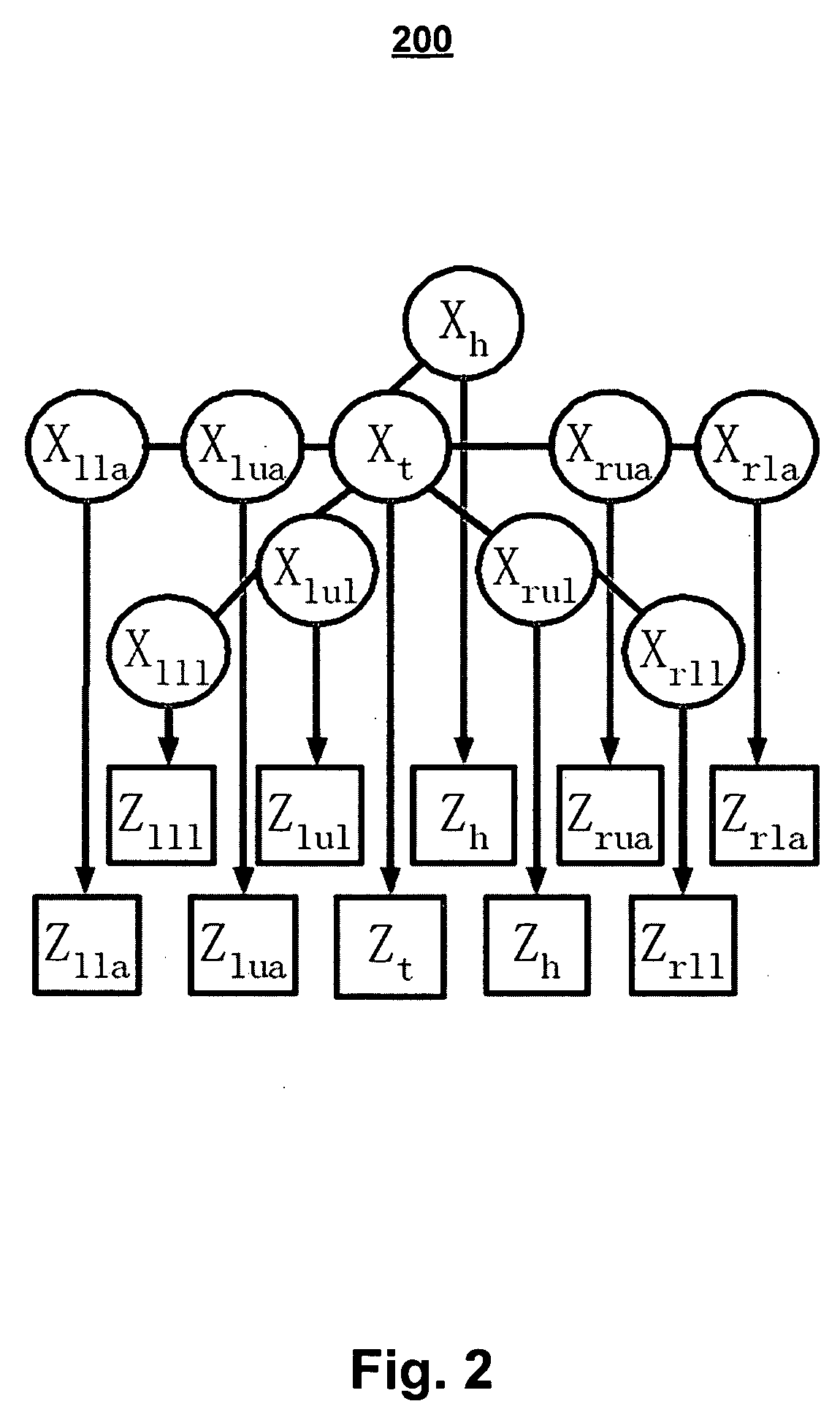
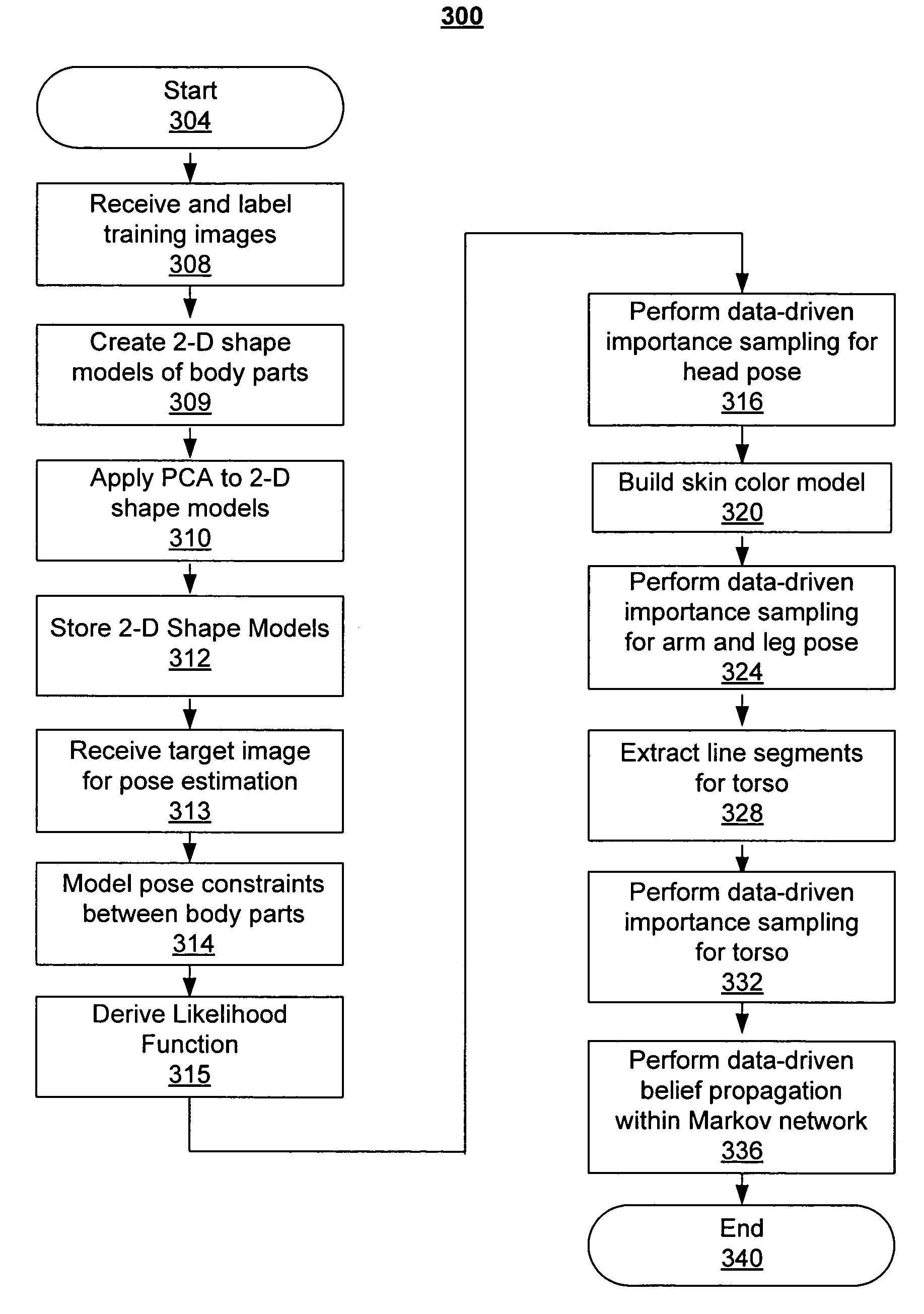
Human pose estimation with data driven belief propagation
A statistical formulation estimates two-dimensional human pose from single images. This is based on a Markov network and on inferring pose parameters from cues such as appearance, shape, edge, and color. A data-driven belief propagation Monte Carlo algorithm performs efficient Bayesian inferencing within a rigorous statistical framework. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in estimating human pose from single images.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Decoder for iterative decoding of binary cyclic codes
InactiveUS6751770B2Promote resultsEasy to implementOther decoding techniquesCode conversionTanner graphReverse order
Owner:SONY CORP
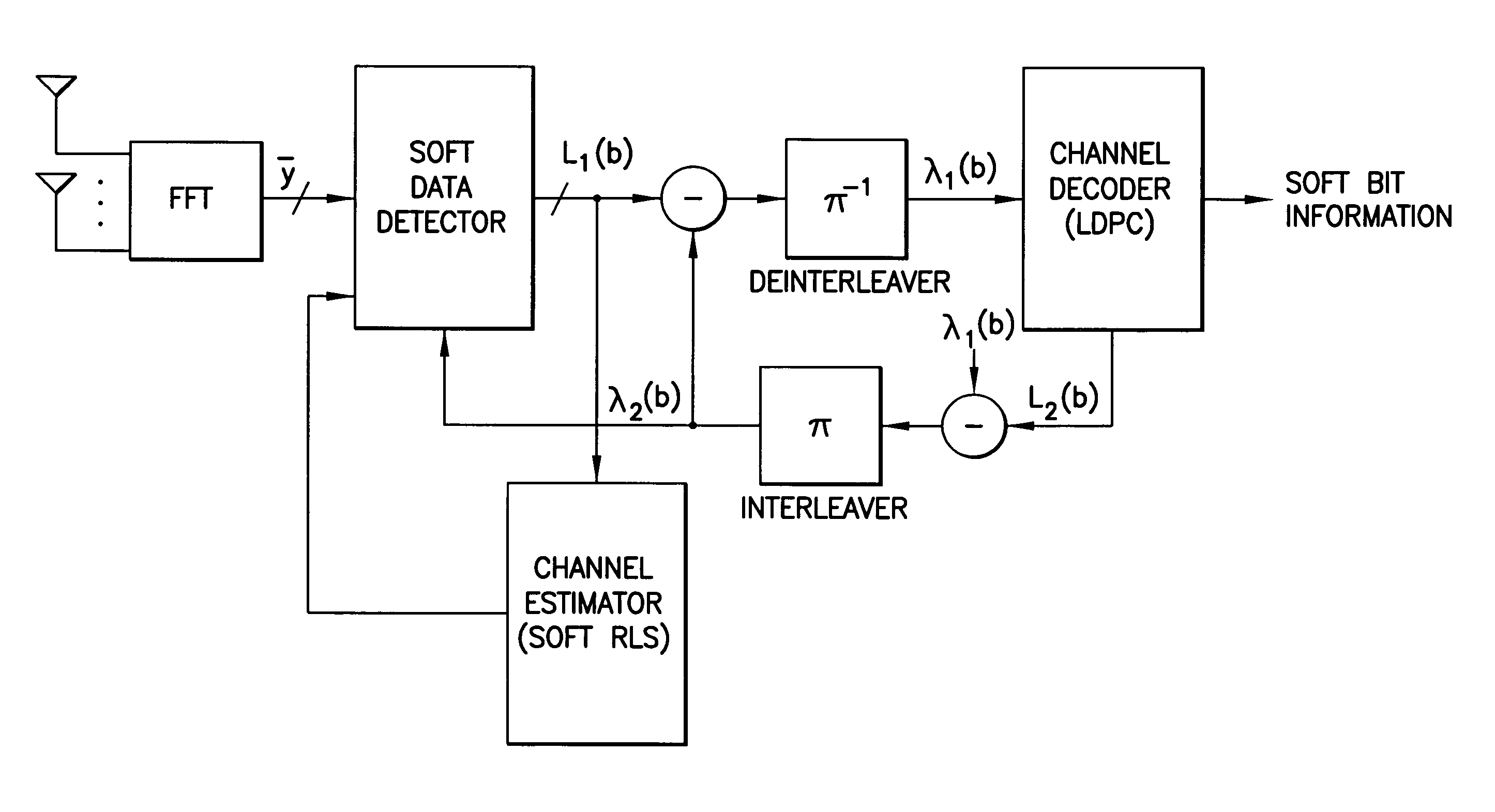
Method, apparatus and computer program product providing soft iterative recursive least squares (RLS) channel estimator
InactiveUS8060803B2Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionBelief propagationMIMO-OFDM
Disclosed is an apparatus having a detector for an iterative LDPC-coded MIMO-OFDM system, where the detector is configured to use a structured irregular LDPC code in conjunction with a belief propagation algorithm. Also disclosed is an apparatus having a detector for a structured irregular LDPC-coded MIMO-OFDM system, where the detector is configured to use an iterative Recursive Least Squares-based data detection and channel estimation technique. Corresponding methods and computer program products are also disclosed.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
LDPC decoder, corresponding method, system and computer program
ActiveUS20050138519A1Reduce storage requirementsReduce computational complexityError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceBelief propagation
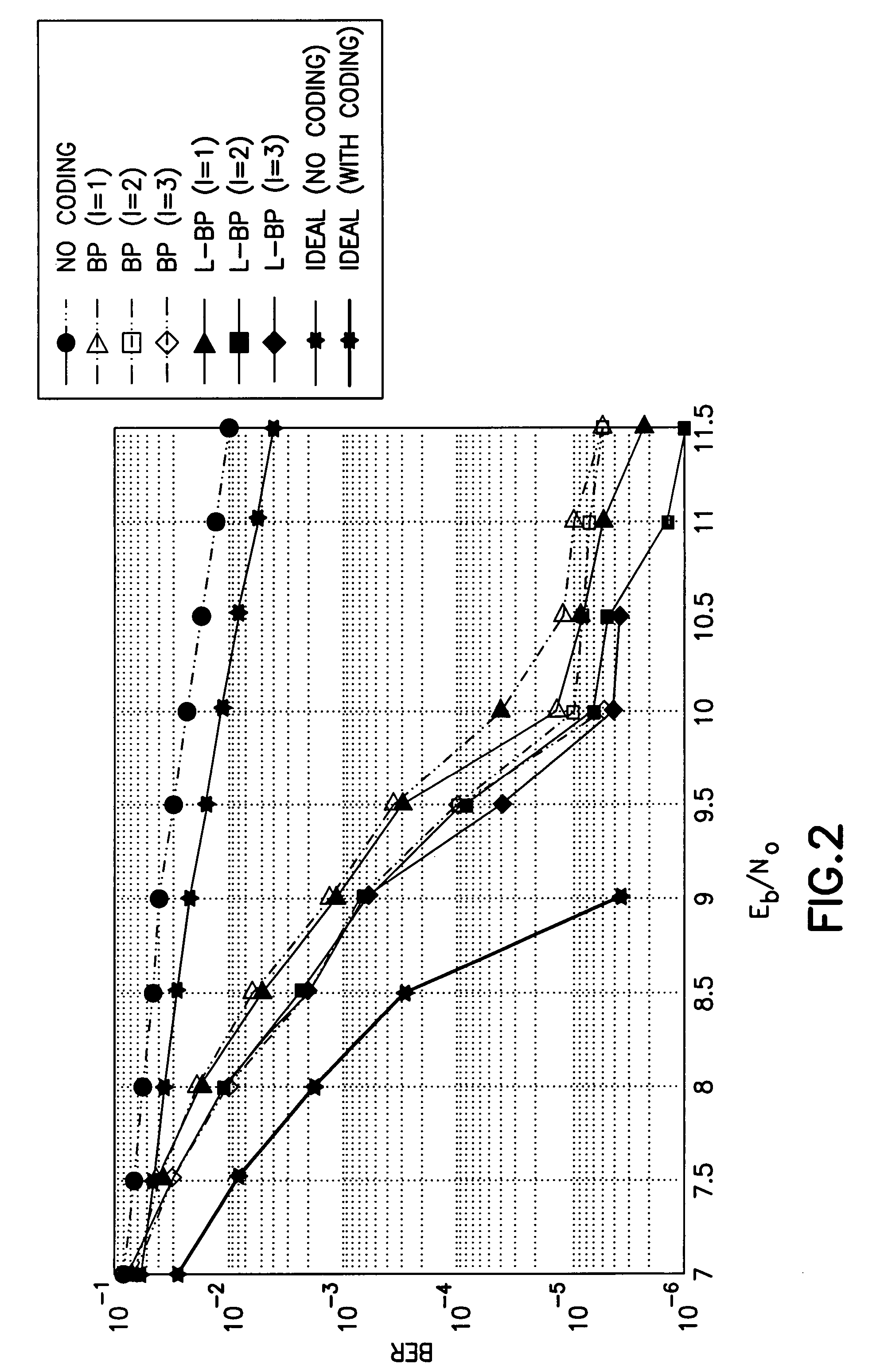
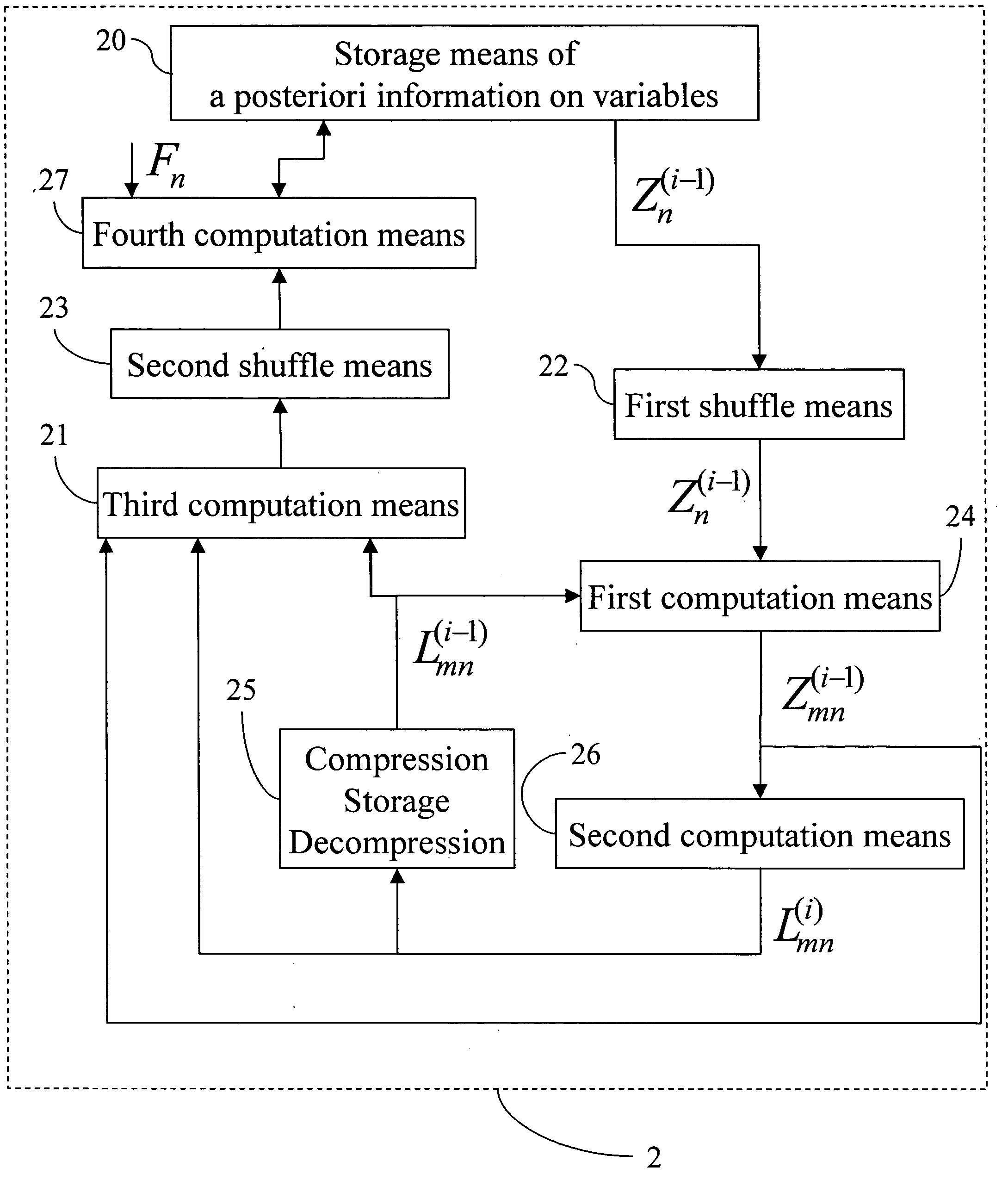
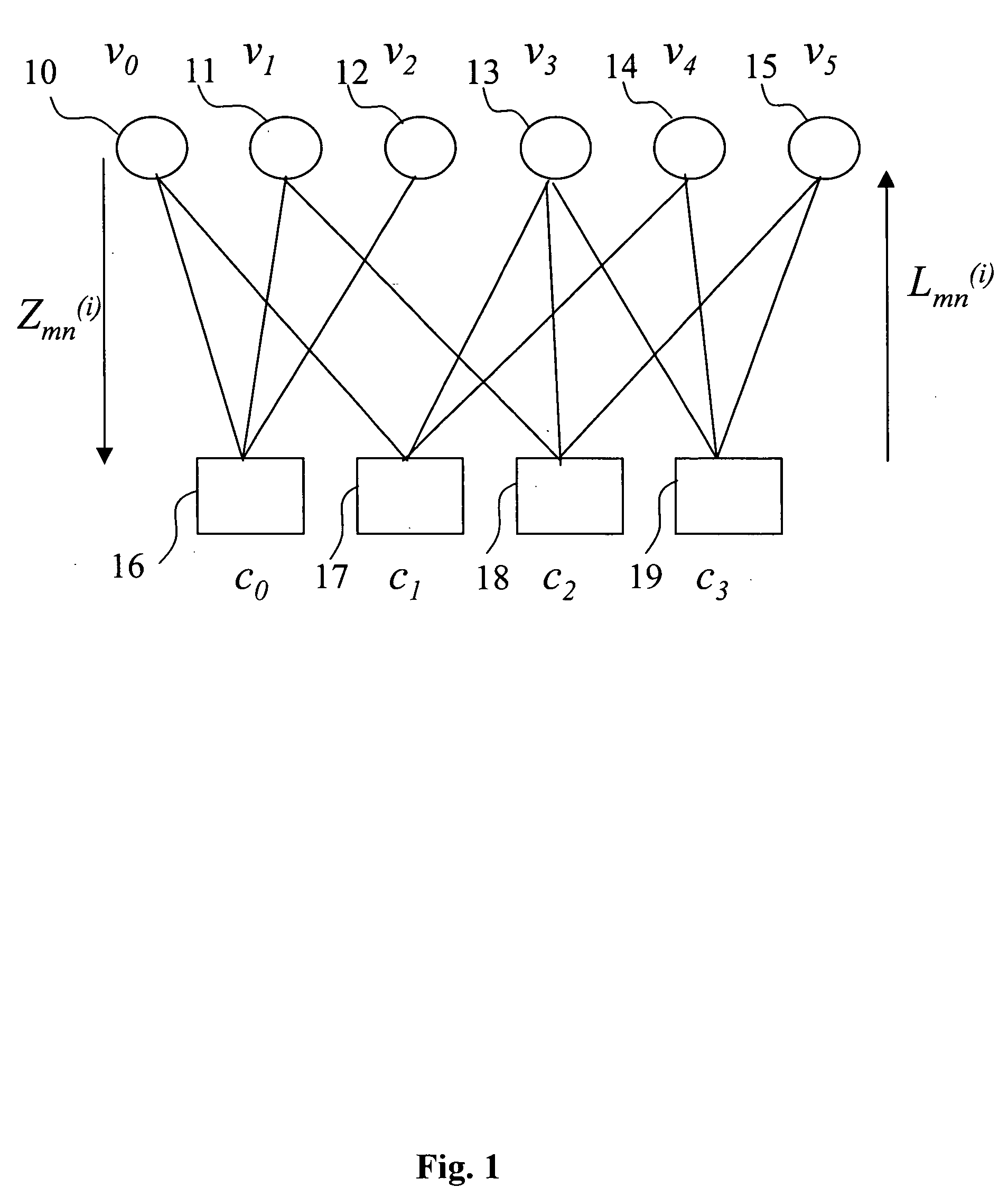
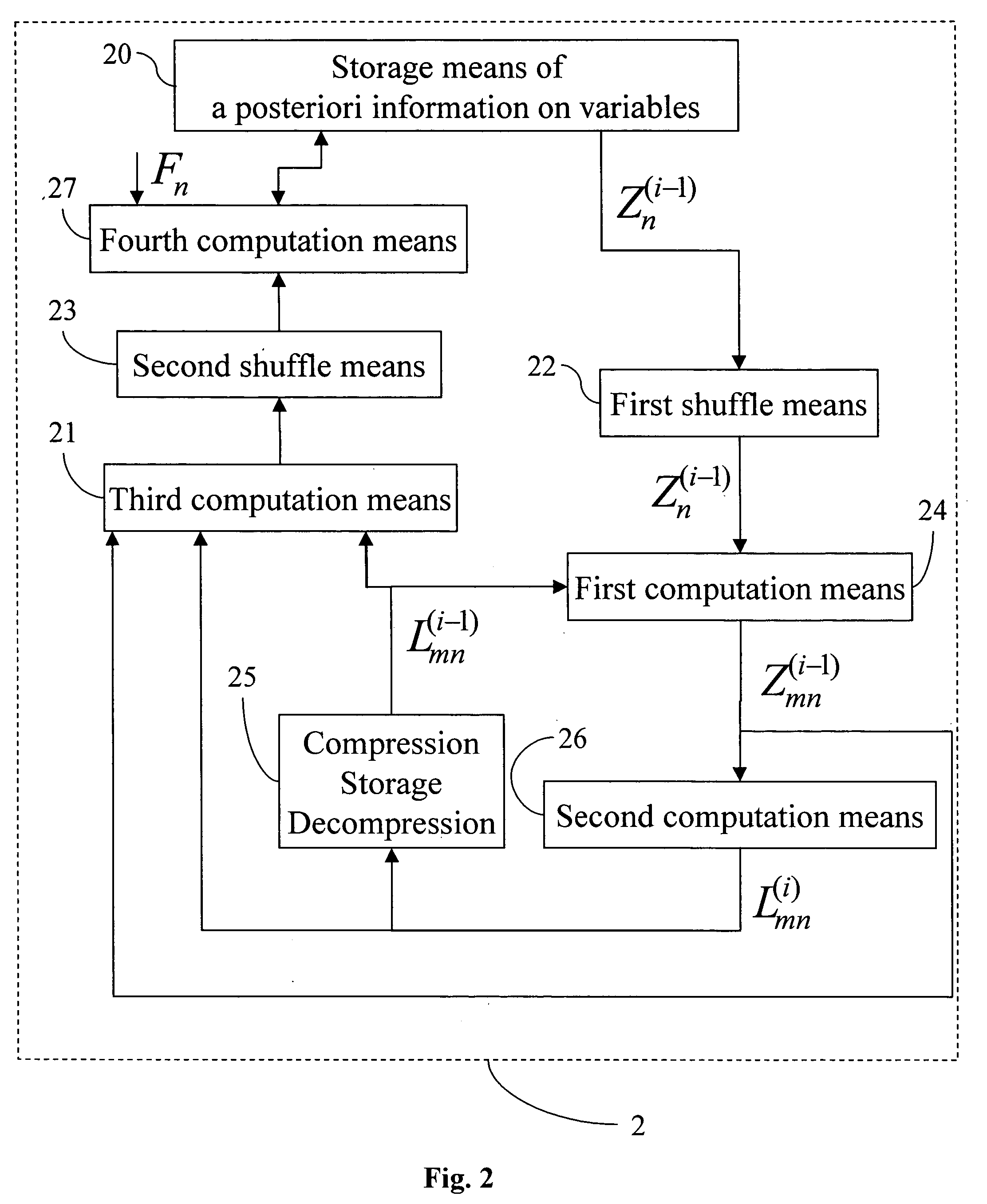
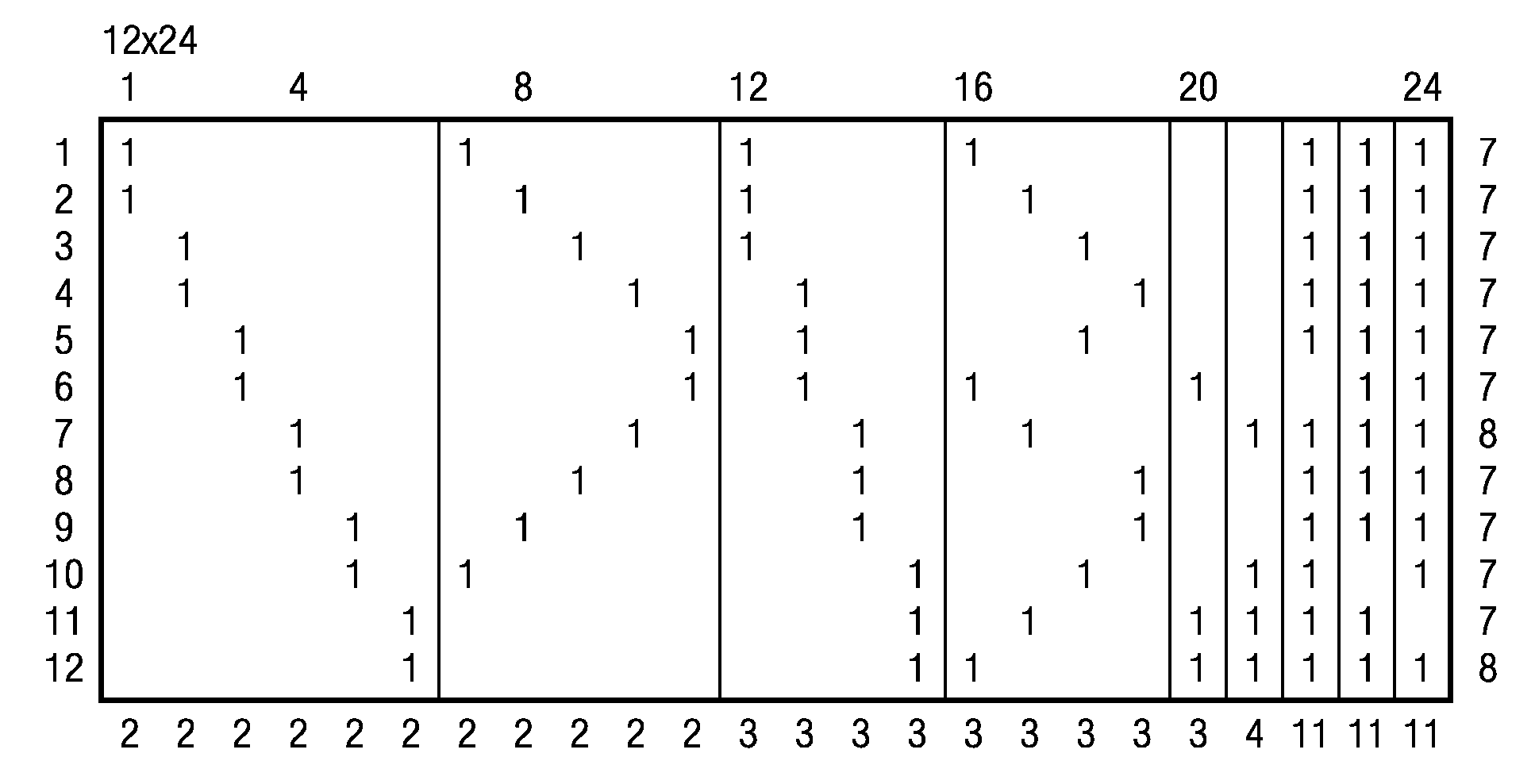
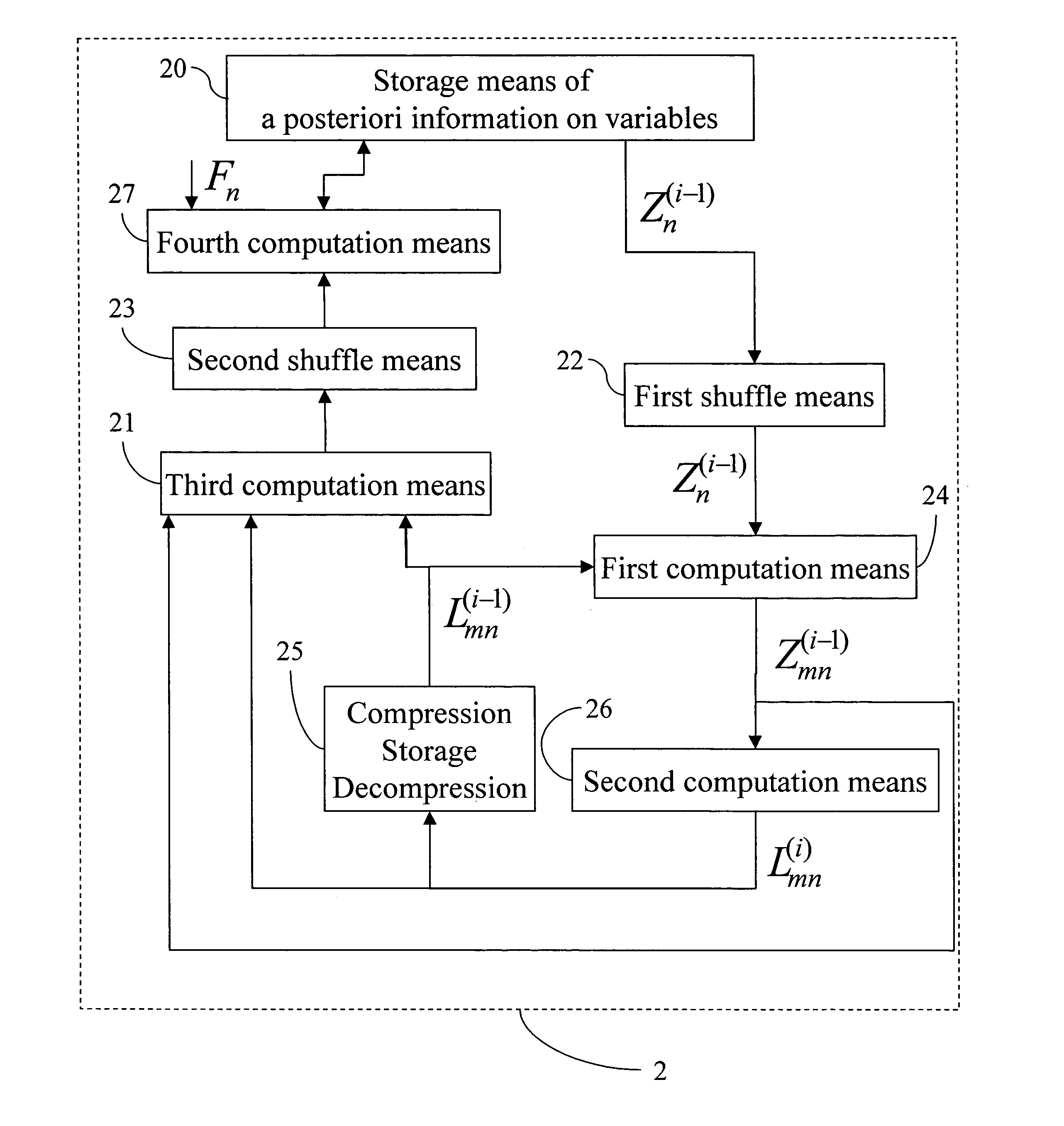
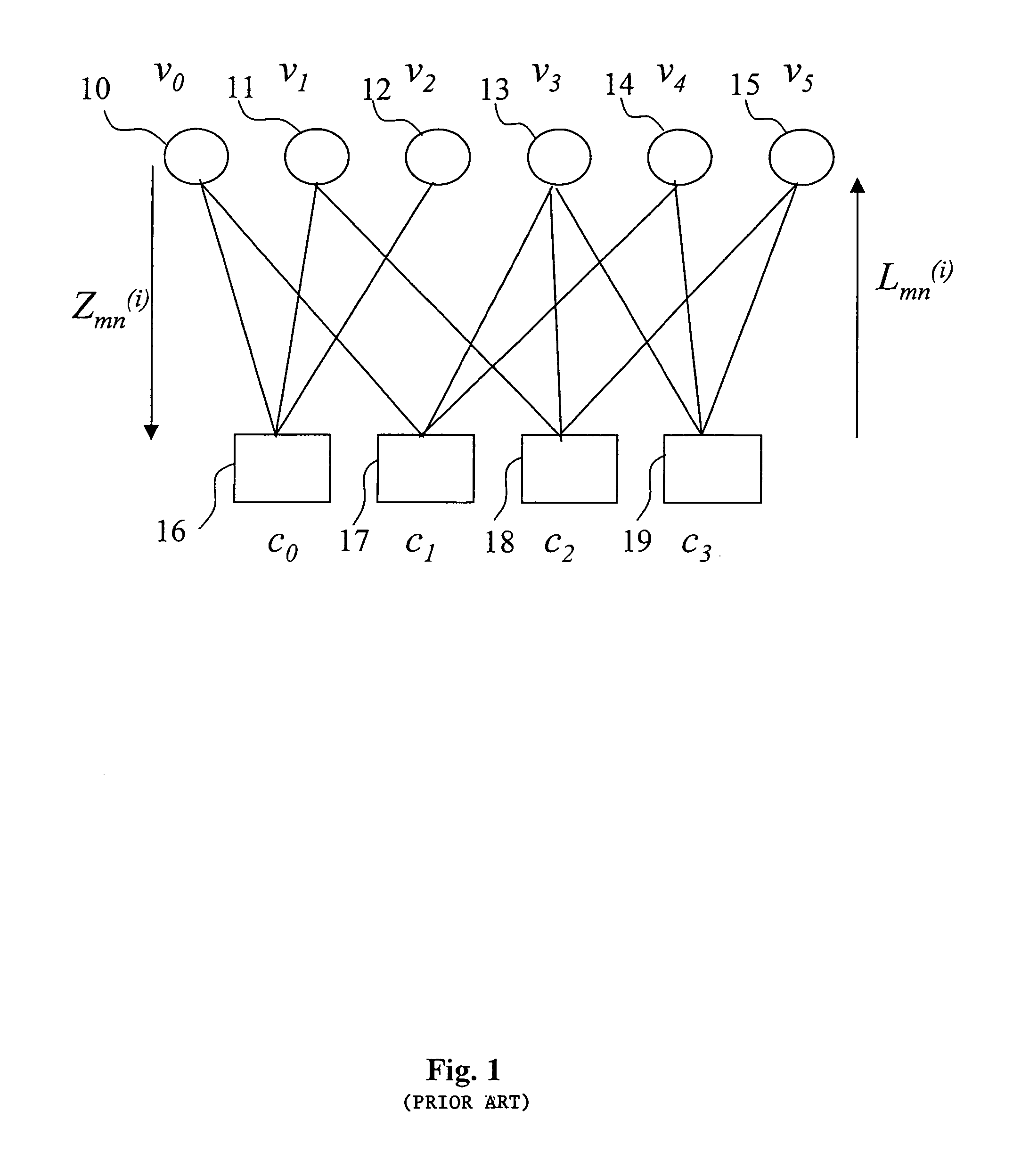
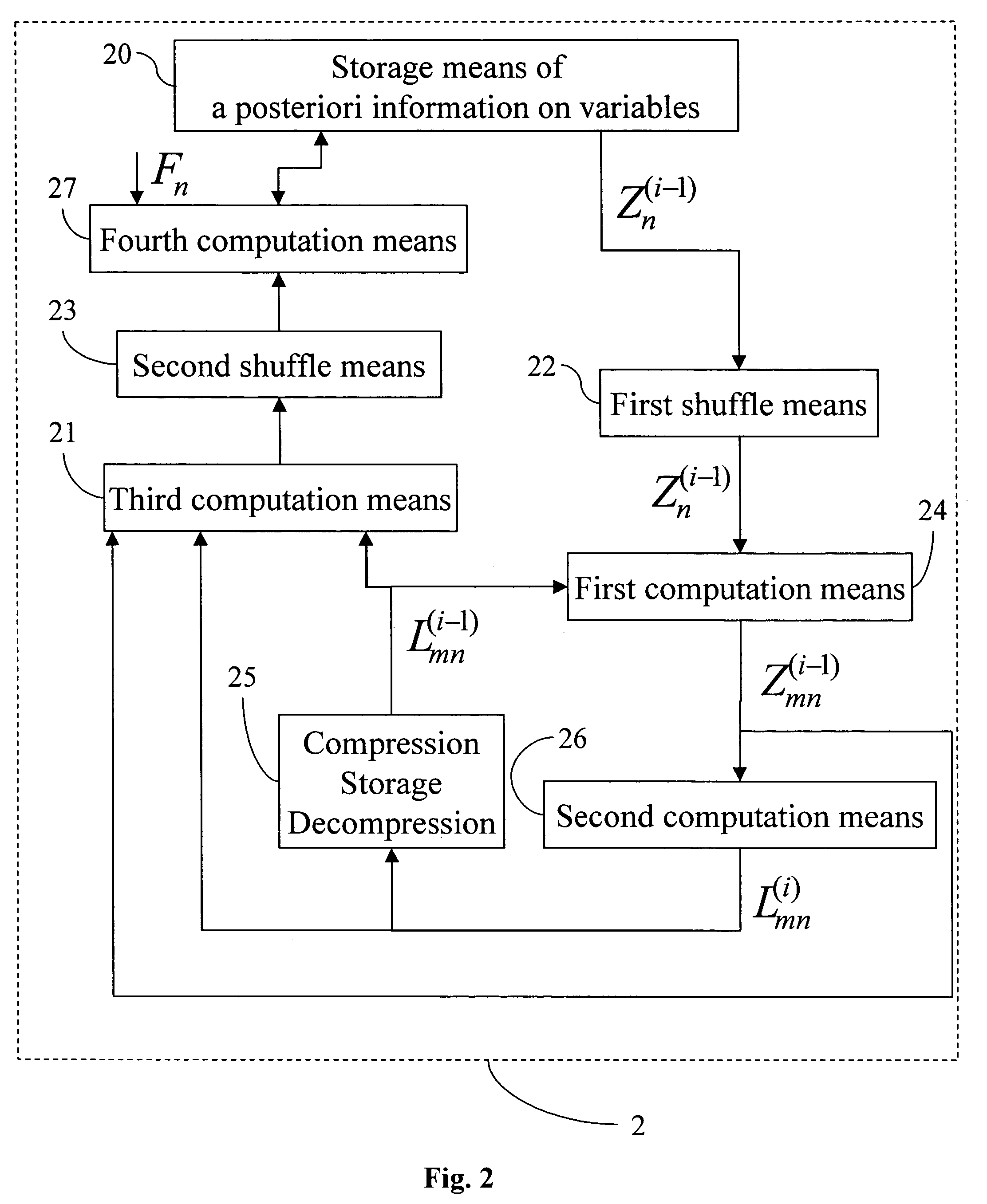
A decoder of LDPC codewords on GF(rq), using the iterative belief propagation algorithm comprises at least storing means to store a posteriori information on variables. Updating means updates the a posteriori information on variables, and computation means computes variables to constrain messages from a posteriori information on variables and variable to constraint messages from previous iteration. Computation means computes a constraint to variable messages from variable to constraint messages computed by the first computation means. Computation means updates the a posteriori information on variables. Shuffle means transfers the a posteriori information on variables to the first computation means, and shuffle means transfers information from the second computation means to the storing means. Compression-storage-decompression means constraint to variable messages. In one form, the invention concerns also corresponding method, computer program and system.
Owner:TURBOCONCEPT SARL +1
Hardware-Efficient Low Density Parity Check Code for Digital Communications
InactiveUS20070011568A1Efficient implementationEfficient constructionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionMatrix groupMemory bank
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
LDPC decoder, corresponding method, system and computer program
ActiveUS7174495B2Storage requirements is greatly reducedError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsTheoretical computer scienceBelief propagation
A decoder of LDPC codewords using the iterative belief propagation algorithm stores a posteriori information on variables. An updating device updates the a posteriori information on variables, and a first computation device computes variables to constrain messages from a posteriori information on variables and variable to constraint messages from previous iteration. A second computation device computes a constraint to variable messages from variable to constraint messages computed by the first computation device. A further computation device updates the a posteriori information on variables. A shuffle device transfers the a posteriori information on variables to the first computation device, and a further shuffle device transfers information from the second computation device to the storing device. The decoder further includes a device for compression-storage-decompression of the constraint to variable messages. The disclosure also relates to a corresponding method, computer program and system.
Owner:TURBOCONCEPT SARL +1
Finite element methods and systems
ActiveUS20150120261A1Address limitationsComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationMulticore architectureCpu architecture
The computational efficiency of Finite Element Methods (FEM) on parallel architectures is typically severely limited by sparse iterative solvers. Standard iterative solvers are based on sequential steps of global algebraic operations, which limit their parallel efficiency, and prior art techniques exploit sophisticated programming techniques tailored to specific CPU architectures to improve performance. The inventors present a FEM Multigrid Gaussian Belief Propagation (FMGaBP) technique that eliminates global algebraic operations and sparse data-structures based upon reformulating the variational FEM into a probabilistic inference problem based upon graphical models. Further, the inventors present new formulations for FMGaBP, which further enhance its computation and communication complexities where the parallel features of FMGaBP are leveraged to multicore architectures.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
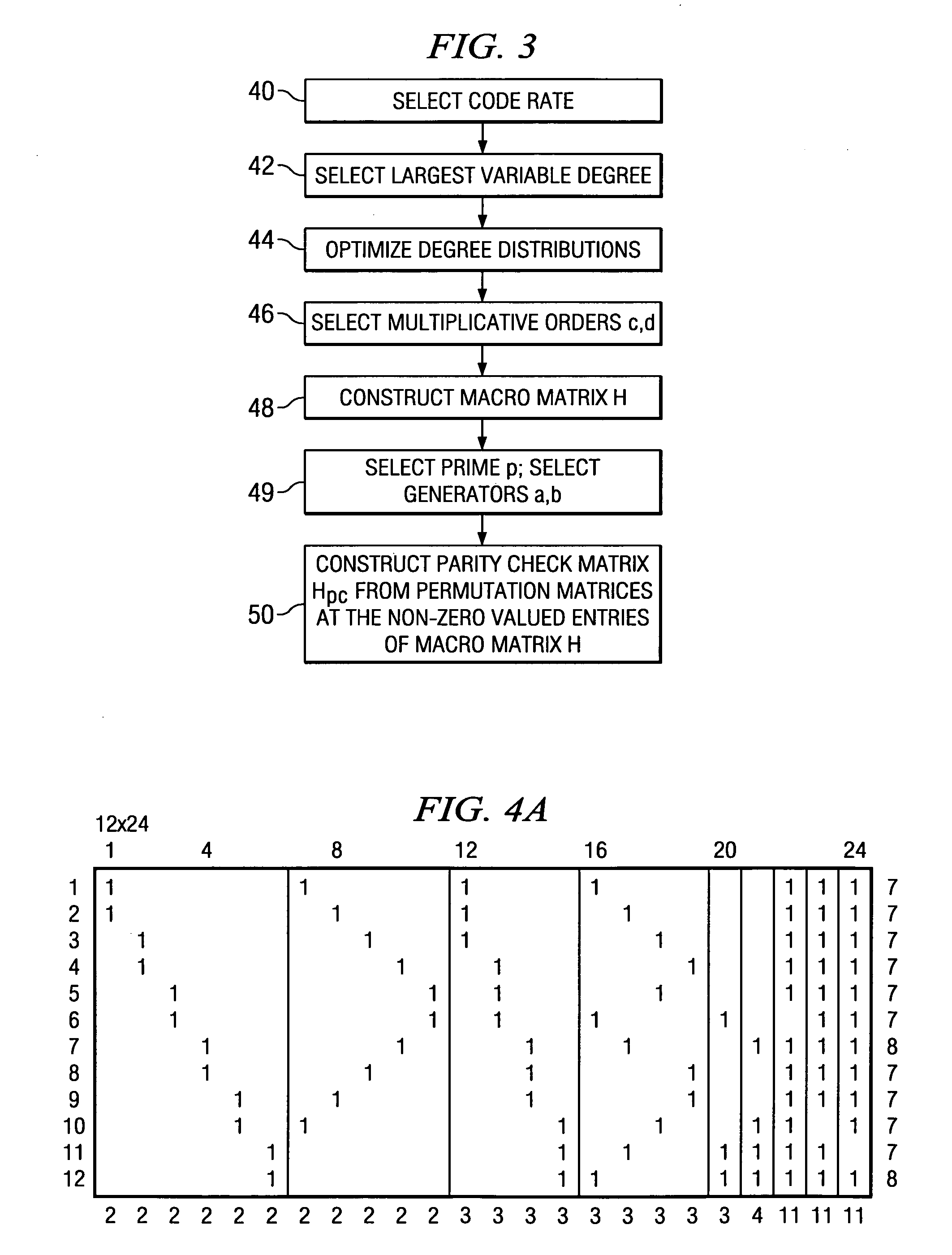
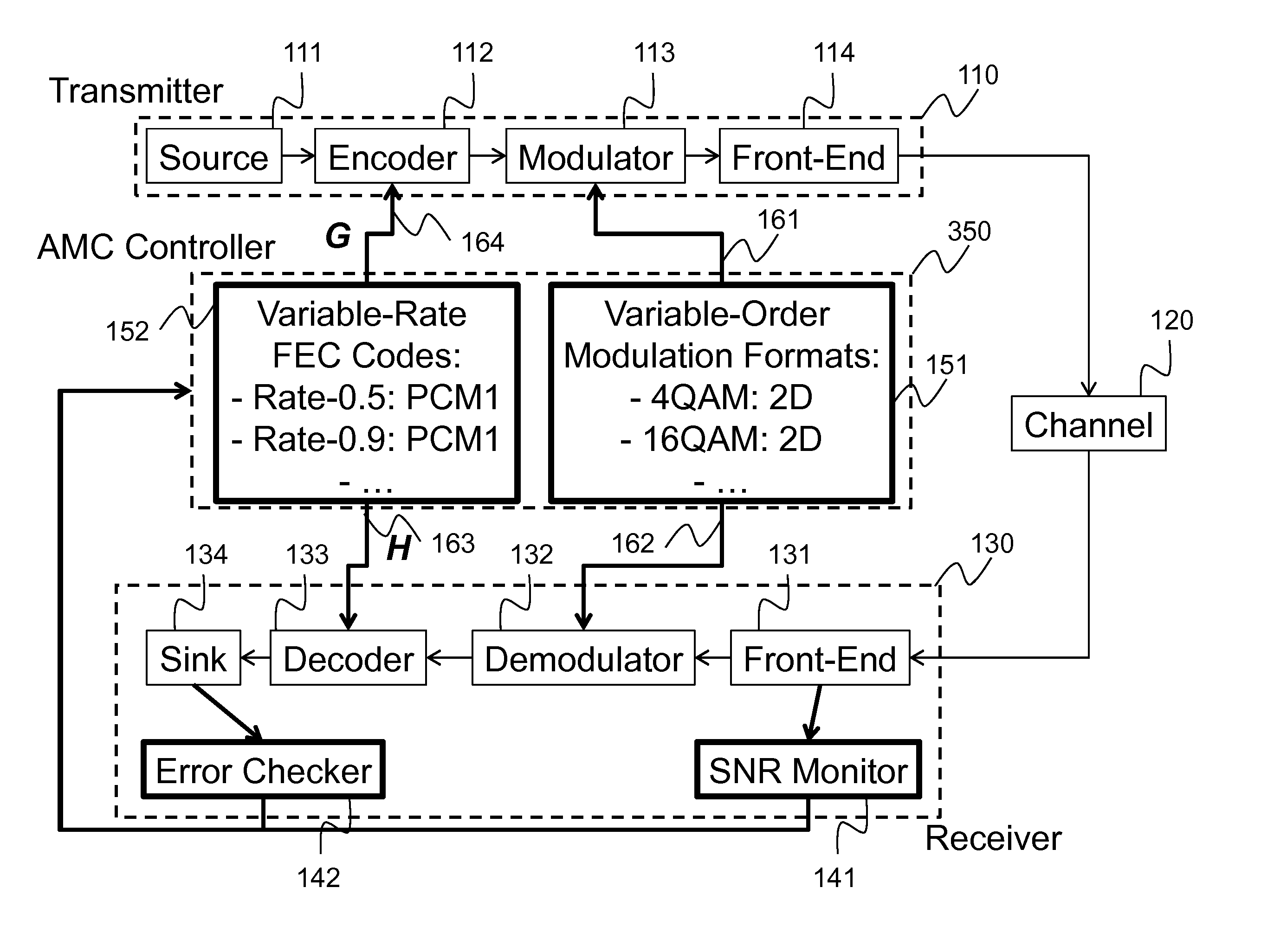
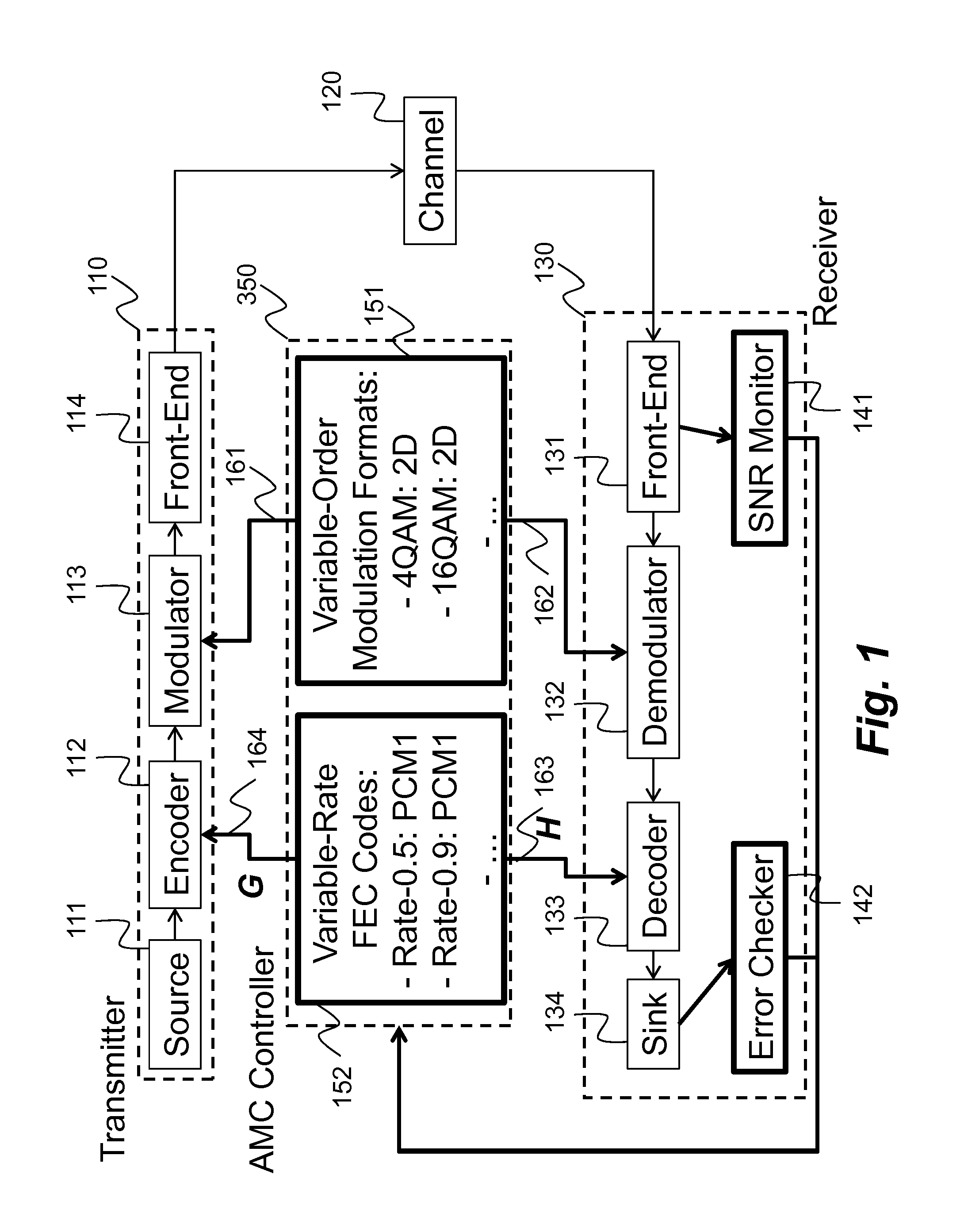
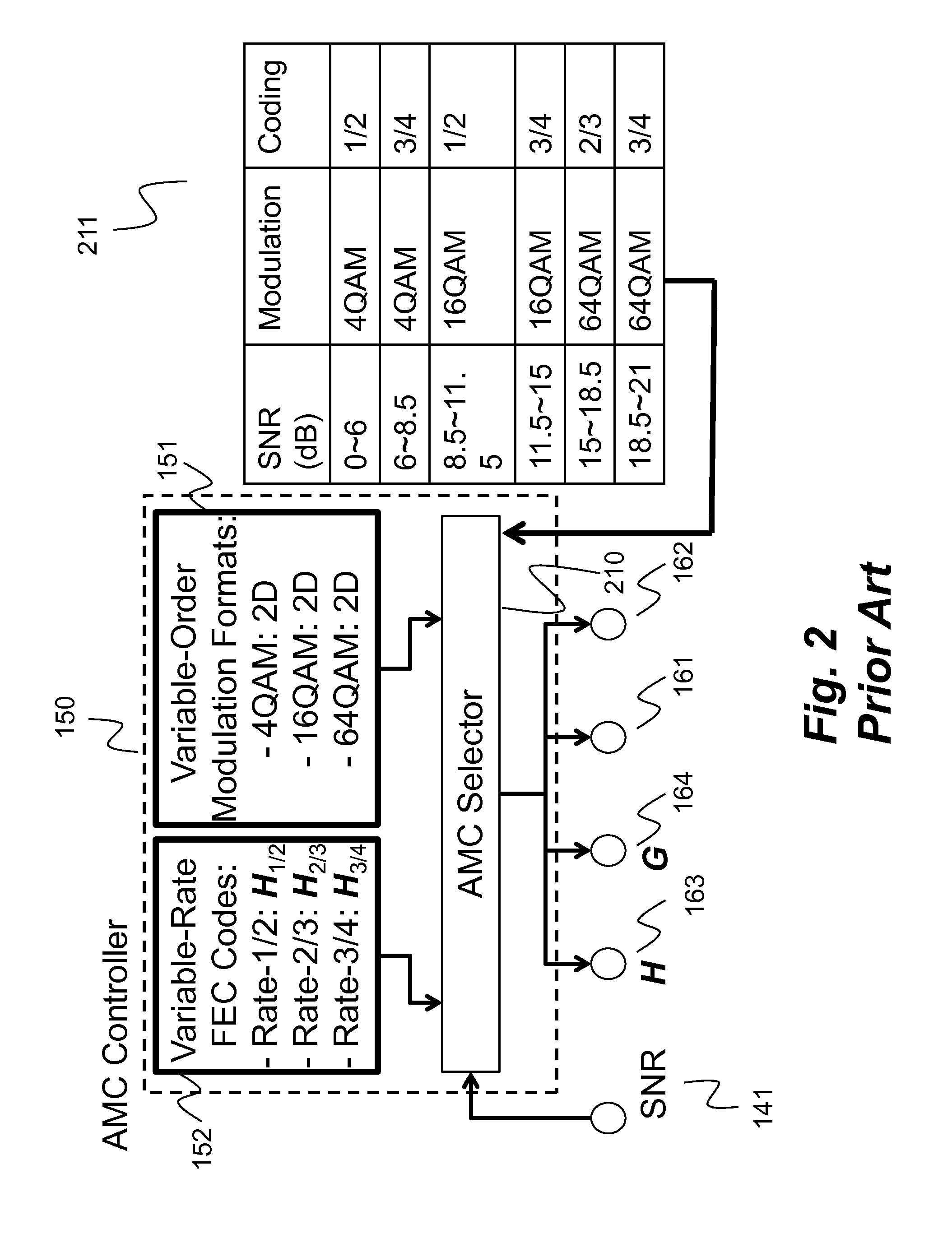
Method and System for Reliable Data Communications with Adaptive Multi-Dimensional Modulations for Variable-Iteration Decoding
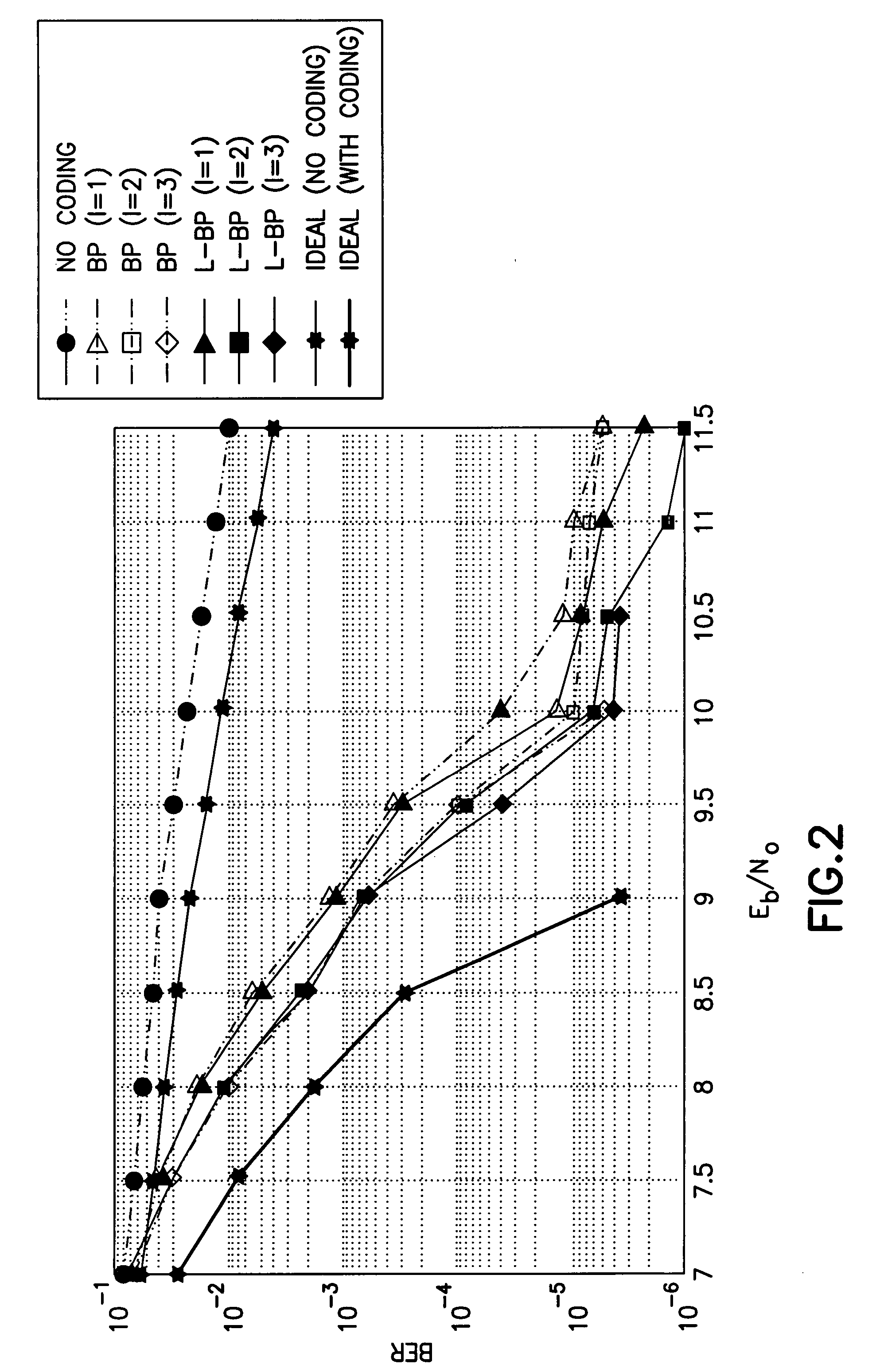
ActiveUS20160233979A1Improve performanceSimple processError correction/detection using block single space codingOther decoding techniquesBelief propagationError mitigation
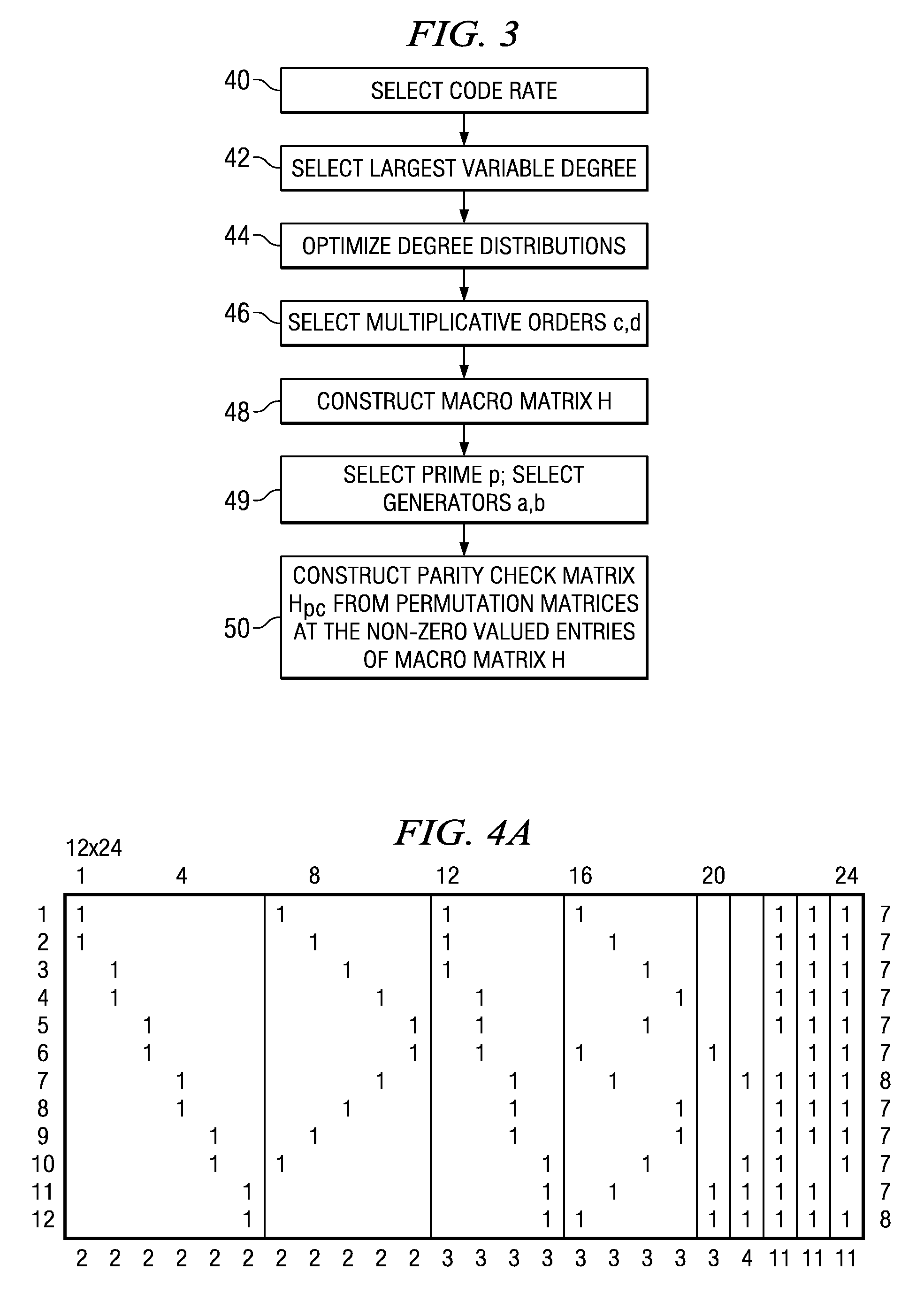
In an advanced adaptive modulation and coding (AMC) scheme, the code rate and the parity-check matrix (PCM) for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes are adapted according to modulation formats and variable-iteration receivers. The degree distribution for the PCM adaptation is designed by heuristic optimization to minimize the required SNR via an extrinsic information transfer (EXIT) trajectory analysis for finite-iteration decoding. The method uses dynamic window decoding by generating spatially coupled PCM for quasi-cyclic LDPC convolutional coding. The method also provides a way to jointly optimize labeling and decoding complexity for high-order and high-dimensional modulations. The problem to use a large number of different LDPC codes for various modulation formats and variable-iteration decoding is also dealt with by linearly dependent PCM adaptation across iteration count to keep using a common generator matrix. This PCM adaptation can improve a convergence speed of belief propagation decoding and mitigate an error floor issue.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method, apparatus and computer program product providing soft iterative recursive least squares (RLS) channel estimator
ActiveUS20070283220A1Data representation error detection/correctionCode conversionBelief propagationLeast squares
Disclosed is an apparatus having a detector for an iterative LDPC-coded MIMO-OFDM system, where the detector is configured to use a structured irregular LDPC code in conjunction with a belief propagation algorithm. Also disclosed is an apparatus having a detector for a structured irregular LDPC-coded MIMO-OFDM system, where the detector is configured to use an iterative Recursive Least Squares-based data detection and channel estimation technique. Corresponding methods and computer program products are also disclosed.
Owner:CONVERSANT WIRELESS LICENSING LTD
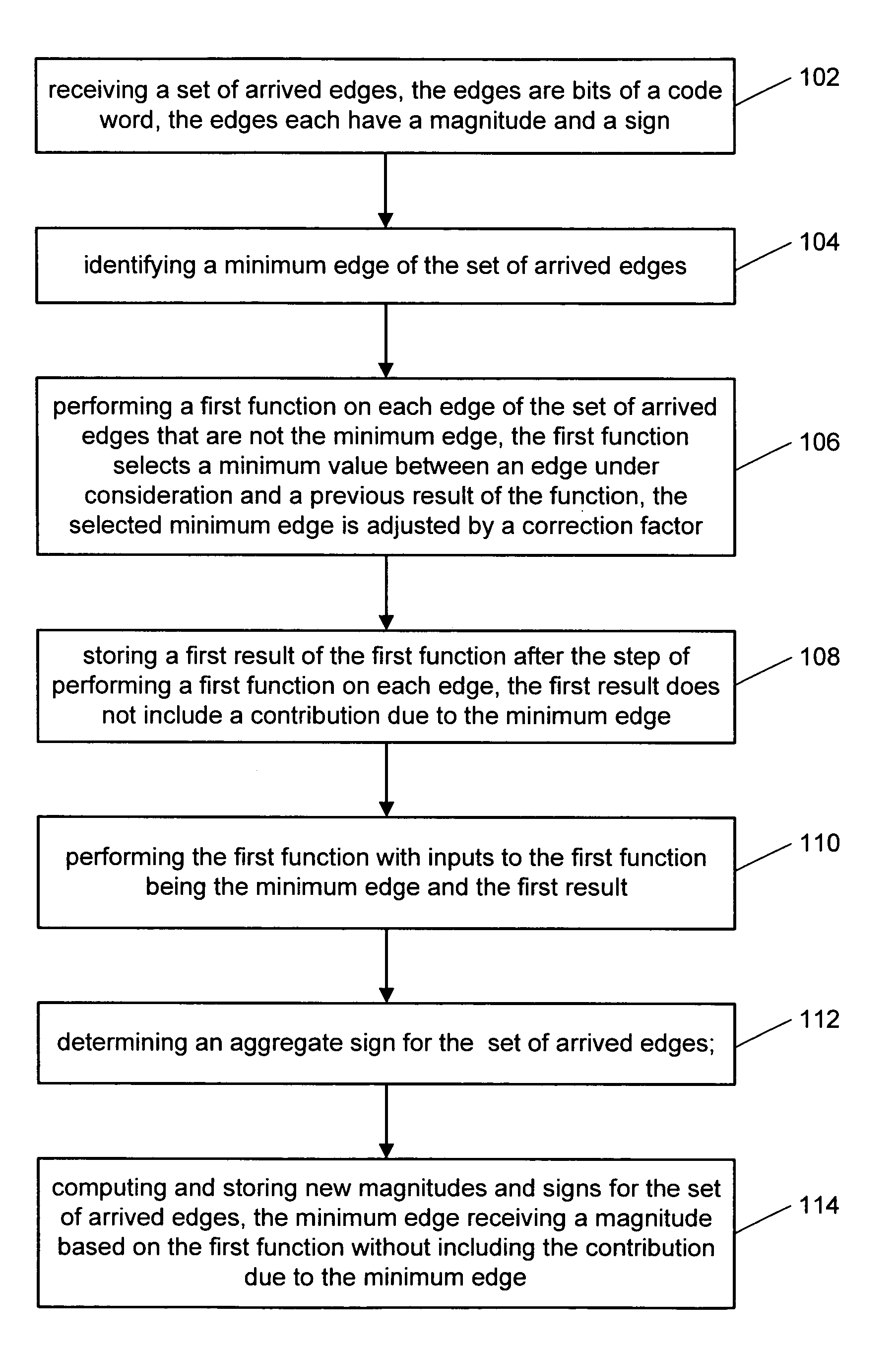
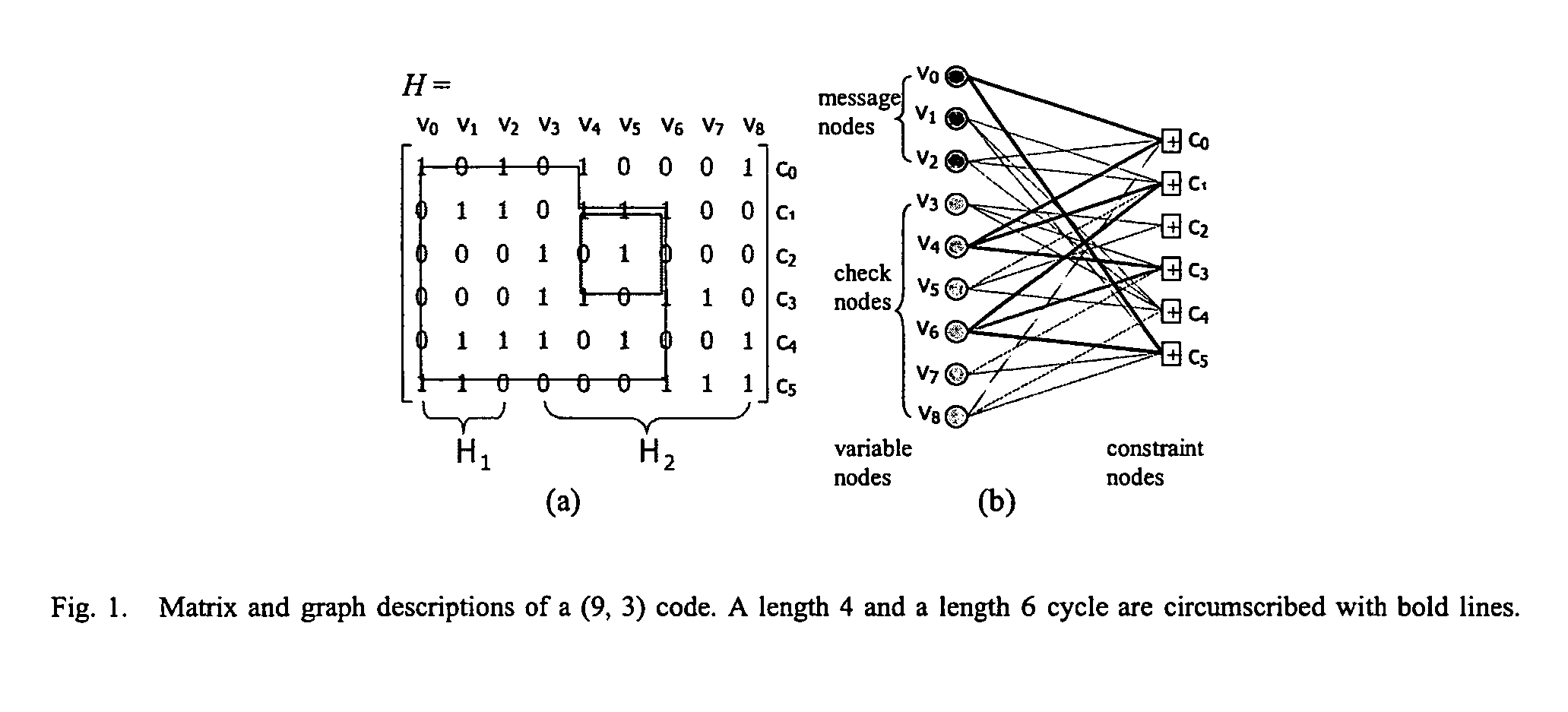
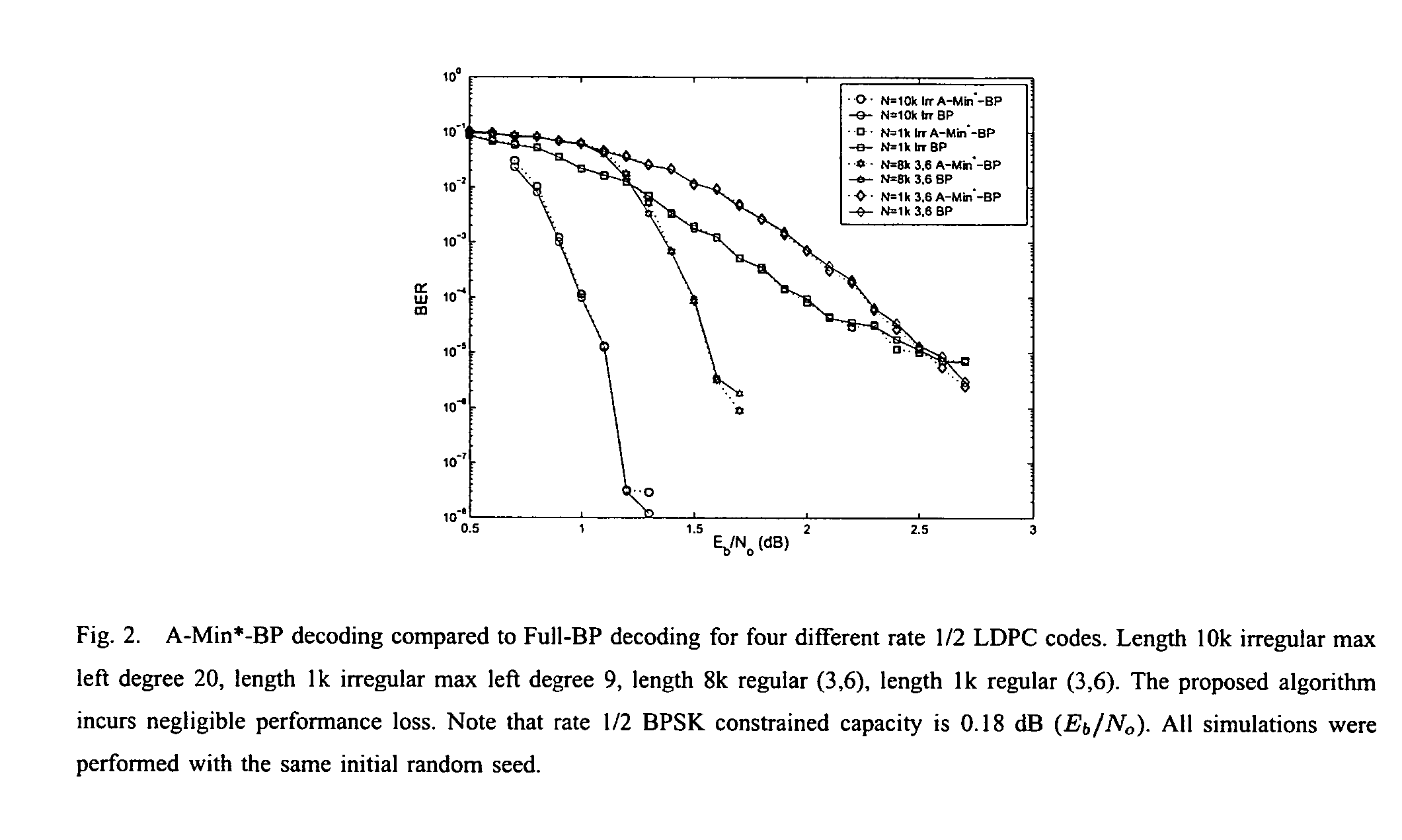
Decoding low density parity codes
InactiveUS7340671B2Little or no performance lossReduce complexityError detection/correctionError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsLow-density parity-check codeTheoretical computer science
The present invention includes a technique for updating messages that originate at the constraint nodes of bi-partite graphs in Low Density Parity Check codes. The technique computes only two outgoing magnitudes at each constraint node and exhibits no measurable performance loss as compared to exact belief propagation which computes a unique magnitude for each departing edge from a given constraint node. The technique eliminates the need for memory based table look-up in the constraint node processing and has been implemented, in one embodiment, using only shift, add, and comparison operations.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Human pose estimation with data driven belief propagation
A statistical formulation estimates two-dimensional human pose from single images. This is based on a Markov network and on inferring pose parameters from cues such as appearance, shape, edge, and color. A data-driven belief propagation Monte Carlo algorithm performs efficient Bayesian inferencing within a rigorous statistical framework. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the method in estimating human pose from single images.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Method, computer program product, apparatus and device providing scalable structured high throughput LDPC decoding
The invention relates to low density parity check decoding. A method for decoding an encoded data block is described. Decoding is performed in a pipelined manner using a layered belief propagation technique and scalable resources, which are configurable to accommodate at least two codeword lengths and at least two code rates. A computer program product, apparatus and device are also described.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Binocular vision positioning and three-dimensional mapping method for indoor mobile robot
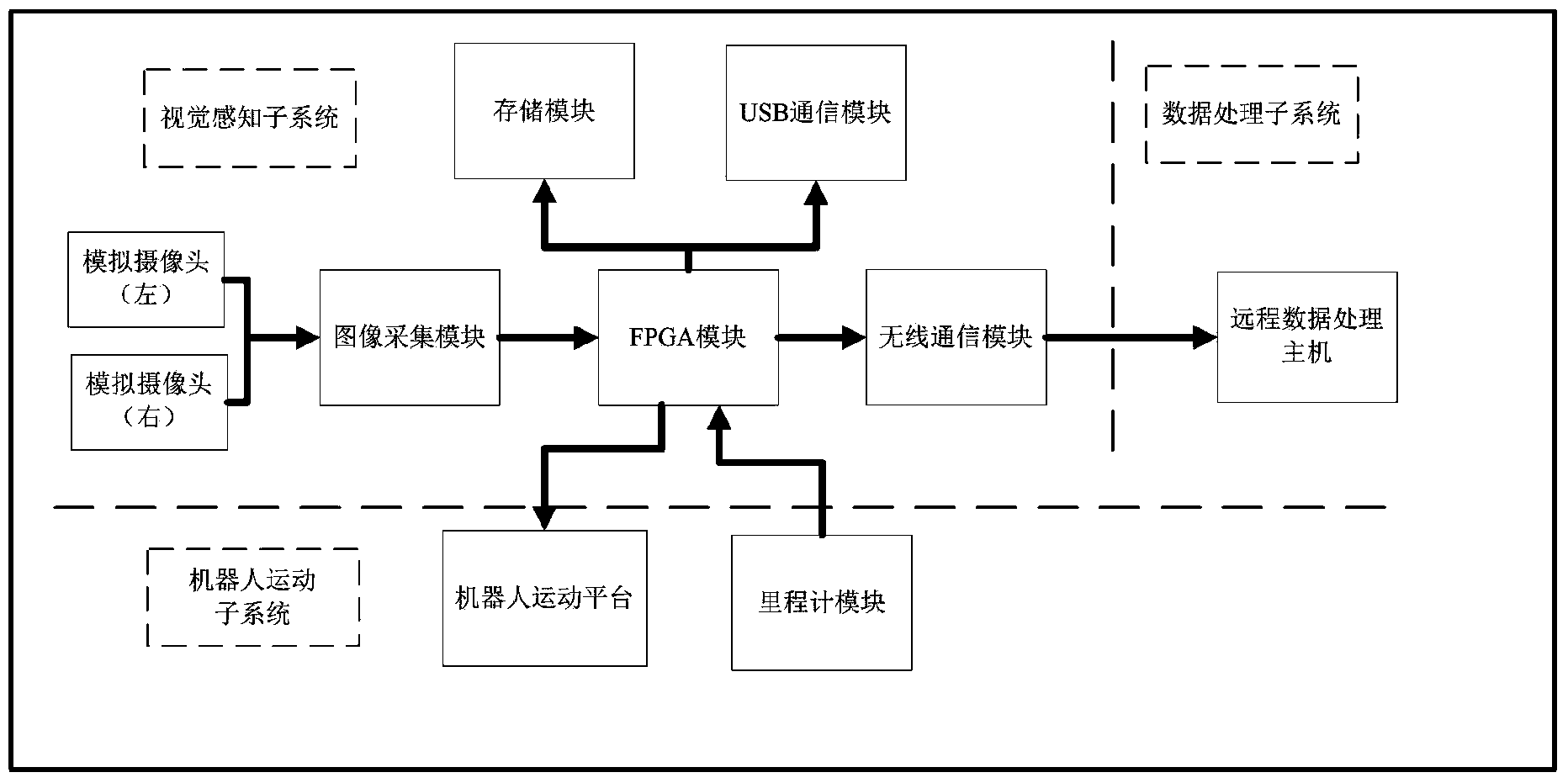
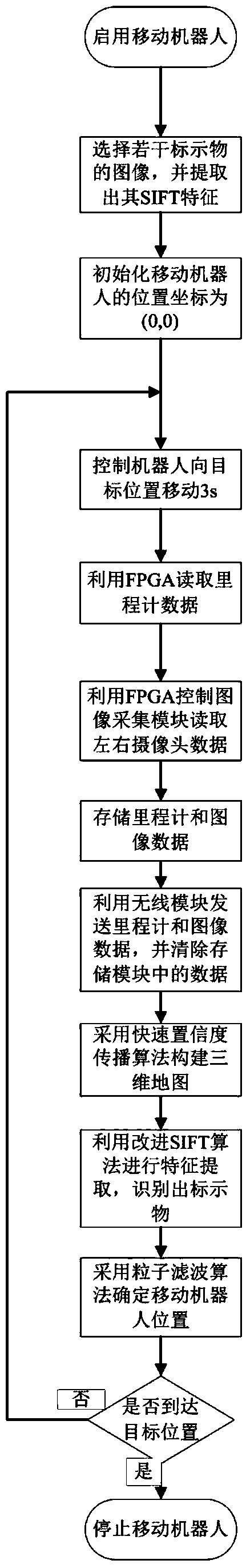
InactiveCN103926927AStrong ability to express the environmentSolve the shortcomings of high complexity and poor real-time performancePosition/course control in two dimensions3D modellingOdometerVisual positioning
The invention discloses a binocular vision positioning and three-dimensional mapping method for an indoor mobile robot. A binocular vision positioning and three-dimensional mapping system for the indoor mobile robot is mainly composed of a two-wheeled mobile robot platform, an odometer module, an analog camera, an FPGA core module, an image acquisition module, a wireless communication module, a storage module, a USB module and a remote data processing host computer. The FPGA core module controls the image acquisition module to collect information of a left image and a right image and sends the information of the left image and the right image to the remote data processing host computer. Distance information between images and the robot is obtained on the remote data processing host computer according to the information of the left image and the right image in a fast belief propagation algorithm, a three-dimensional environmental map is established in the remote data processing host computer, recognition of a specific marker is realized in an improved SIFT algorithm, and then the position of the mobile robot is determined through information integration in a particle filter algorithm. The binocular vision positioning and three-dimensional mapping system is compact in structure and capable of having access to an intelligent space system so that the indoor mobile robot can detect the environment in real time and provide more and accurate services according to the corresponding position information at the same time.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
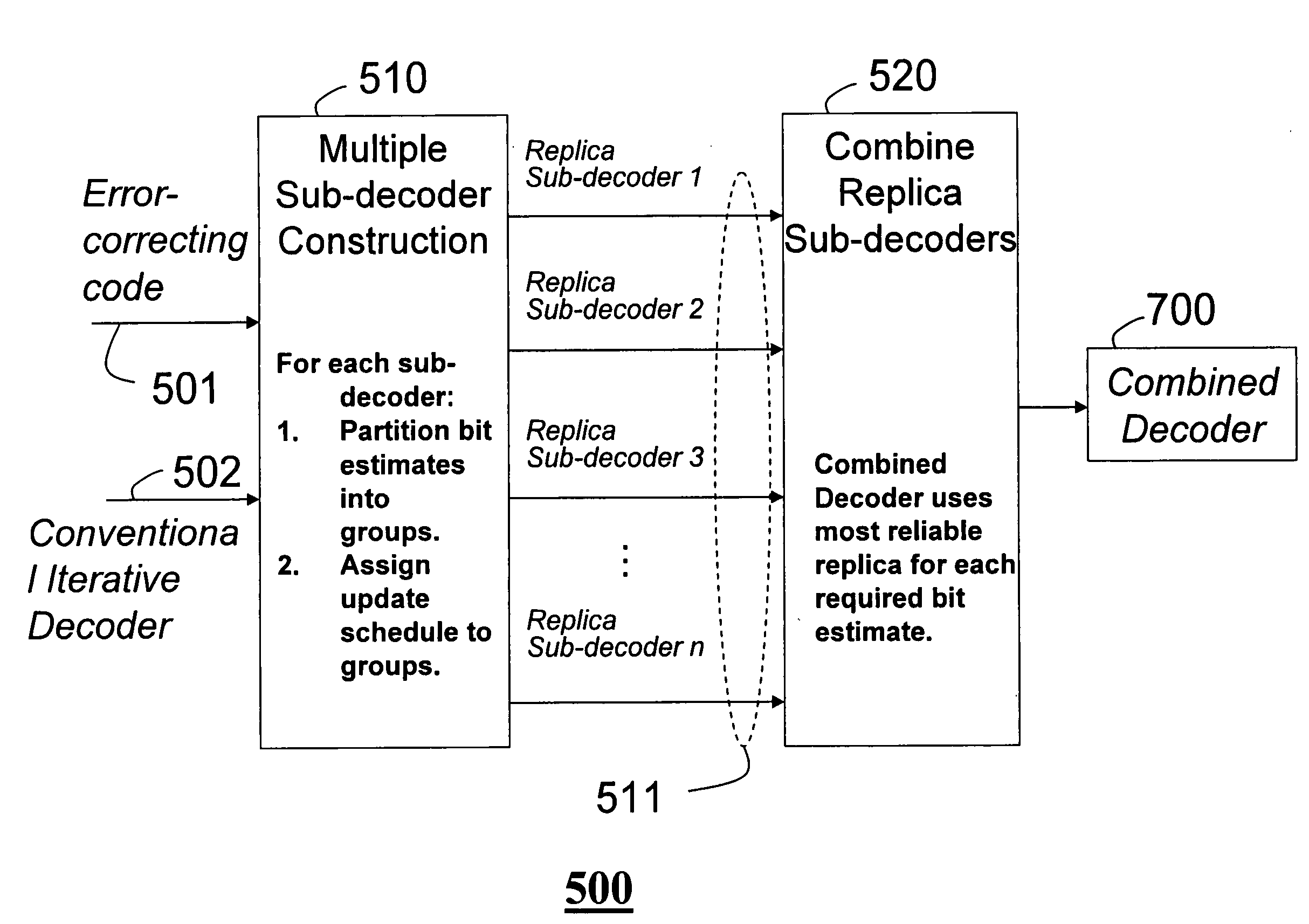
Method and system for replica group-shuffled iterative decoding of quasi-cyclic low-density parity check codes
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
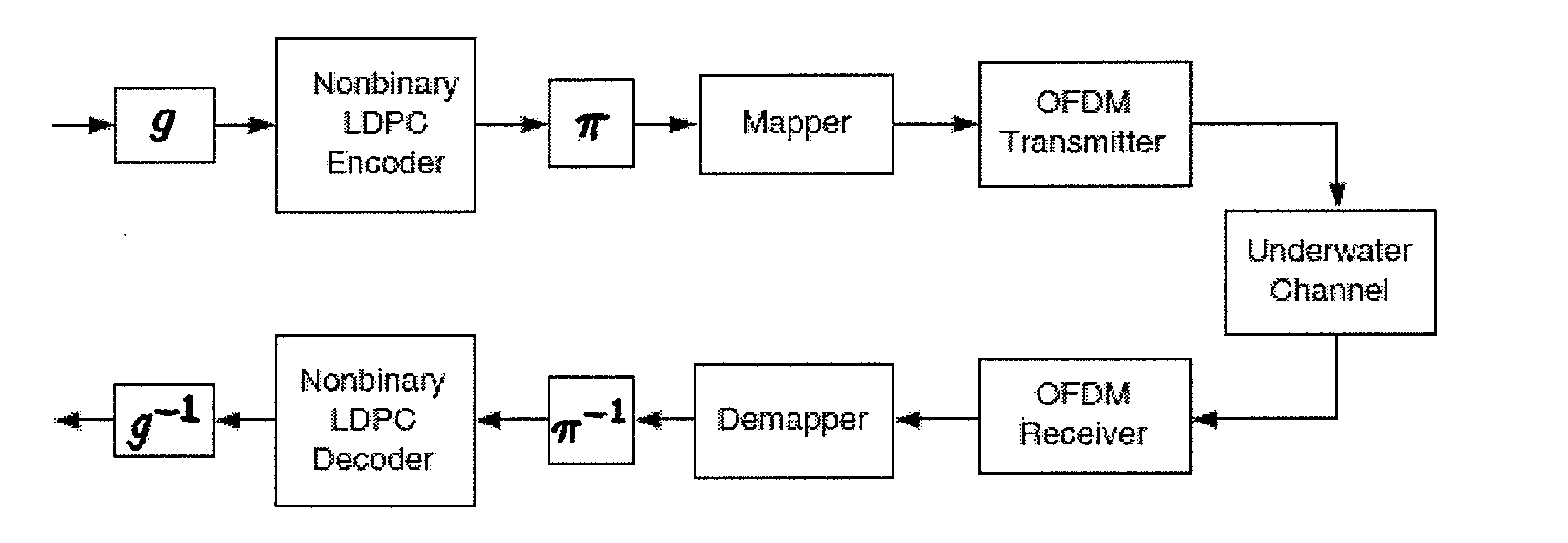
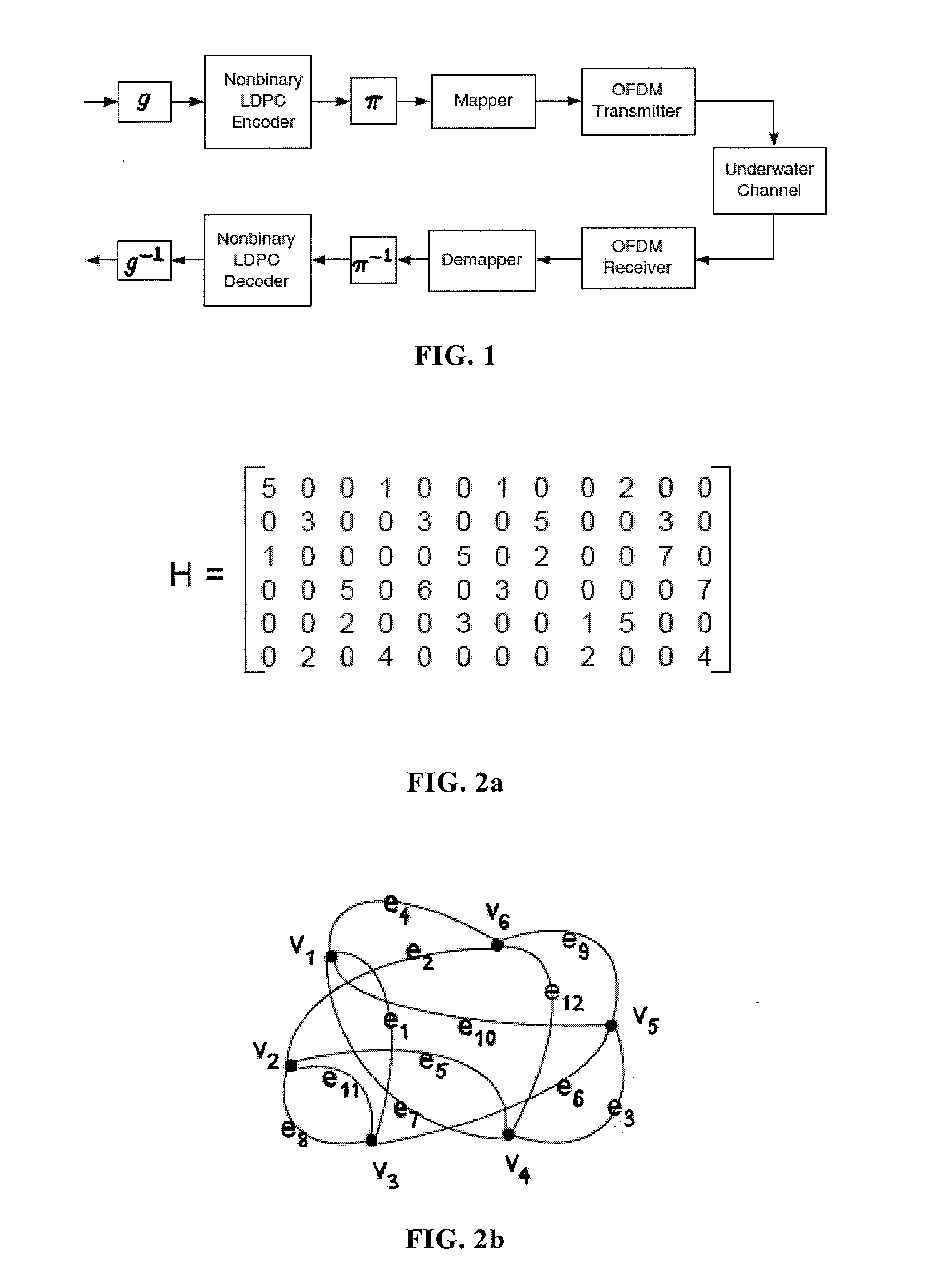
Apparatus, Systems and Methods Including Nonbinary Low Density Parity Check Coding For Enhanced Multicarrier Underwater Acoustic Communications
ActiveUS20110029845A1Improve throughputConsiderable resource reductionSonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic transmissionError correction/detection using LDPC codesTheoretical computer sciencePeak value
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Shuffled LDPC decoding
InactiveUS20100251059A1Low costSimple structureCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesParity-check matrixTheoretical computer science
An LDPC decoder iteratively decodes an LDPC code represented by a parity check matrix H consisting of a plurality of circulants based on a Log-Likelihood Ratio Belief-Propagation algorithm. First computation means (1010) compute for a next iteration symbol messages λκm from a representation of a corresponding symbol value stored in a first memory 1005 and from check node messages Λmn from a previous iteration. A shuffler (1030) changes a sequence of the symbol message received from the first computation means (1010) in dependence on a position of the non-zero elements in a corresponding sub-matrix. Second computation N means (DP-O, DP-I, DP-D-I) compute the check node messages in dependence on symbol messages received from the barrel shifter and store a representation of the computed check node message in a second memory (1015). Third computation means (1020) update the representation of the symbol values in the first memory in dependence on output of the first and second computing means. The principle of “staggered” or “shuffled” LDPC decoding is used. One embodiment is designed for multi-diagonal circulants.
Owner:ST ERICSSON SA
Decoder for iterative decoding of binary cyclic codes
InactiveUS20020116677A1Promote resultsEasy to implementOther decoding techniquesCode conversionTanner graphReverse order
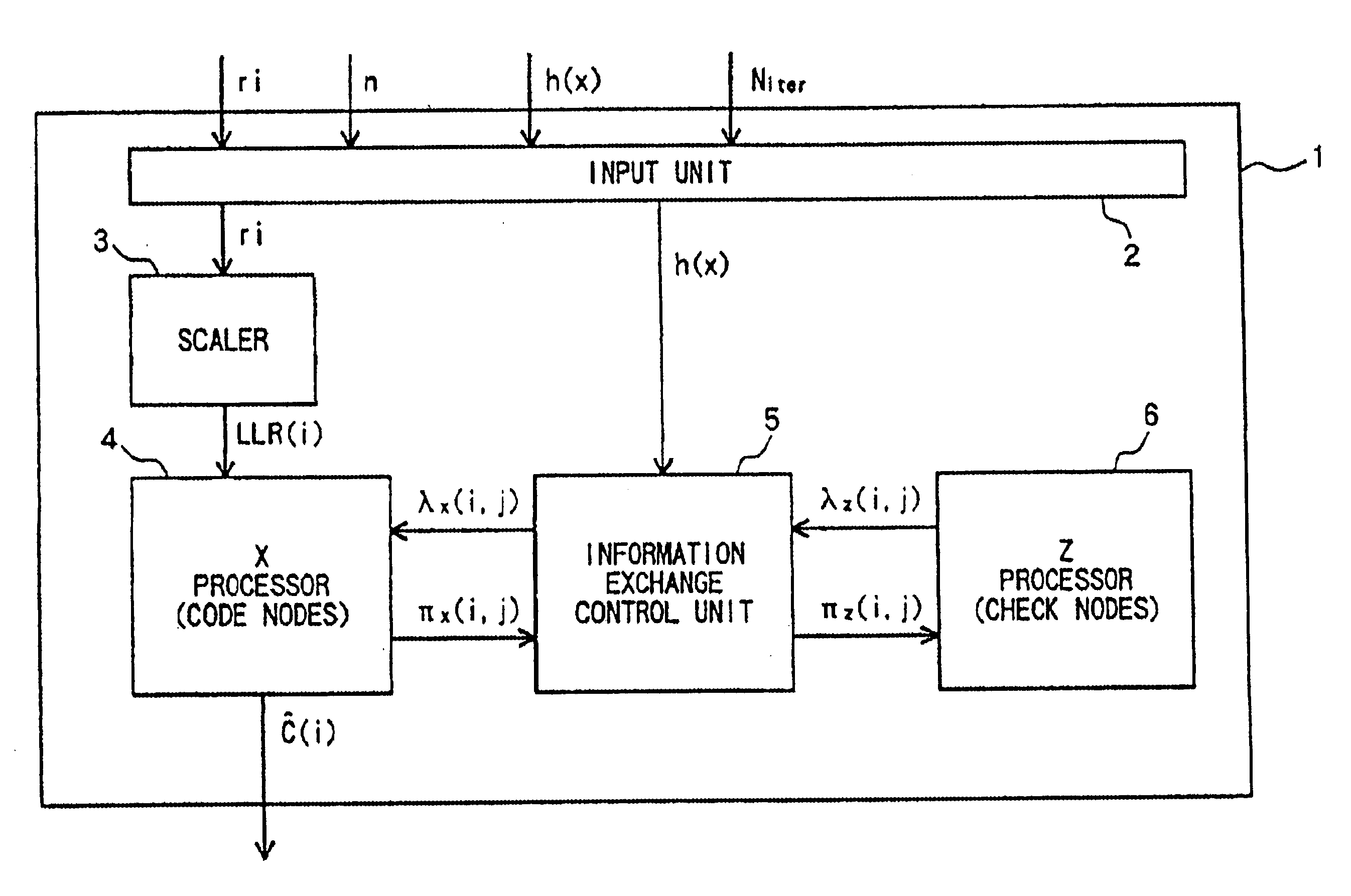
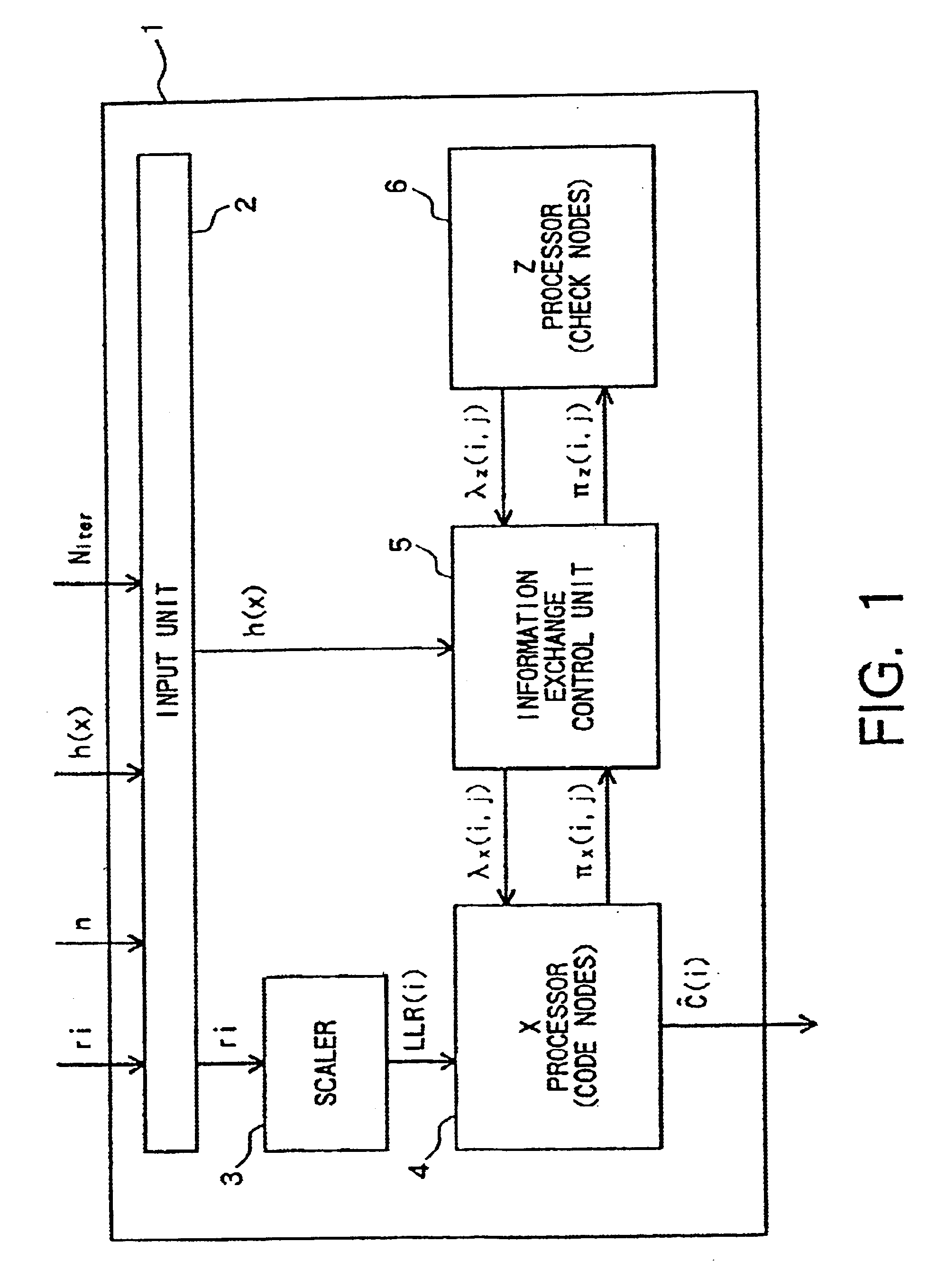
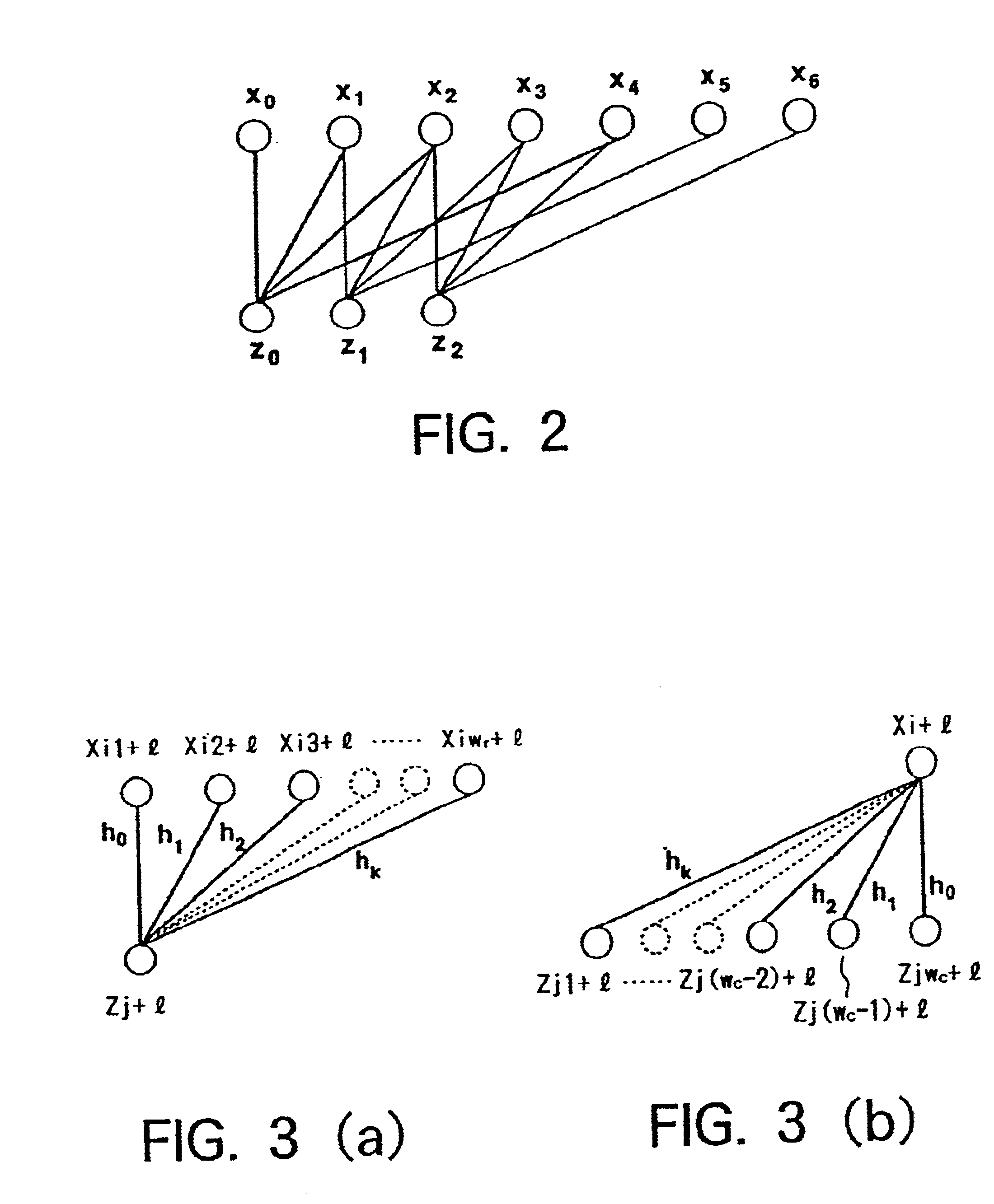
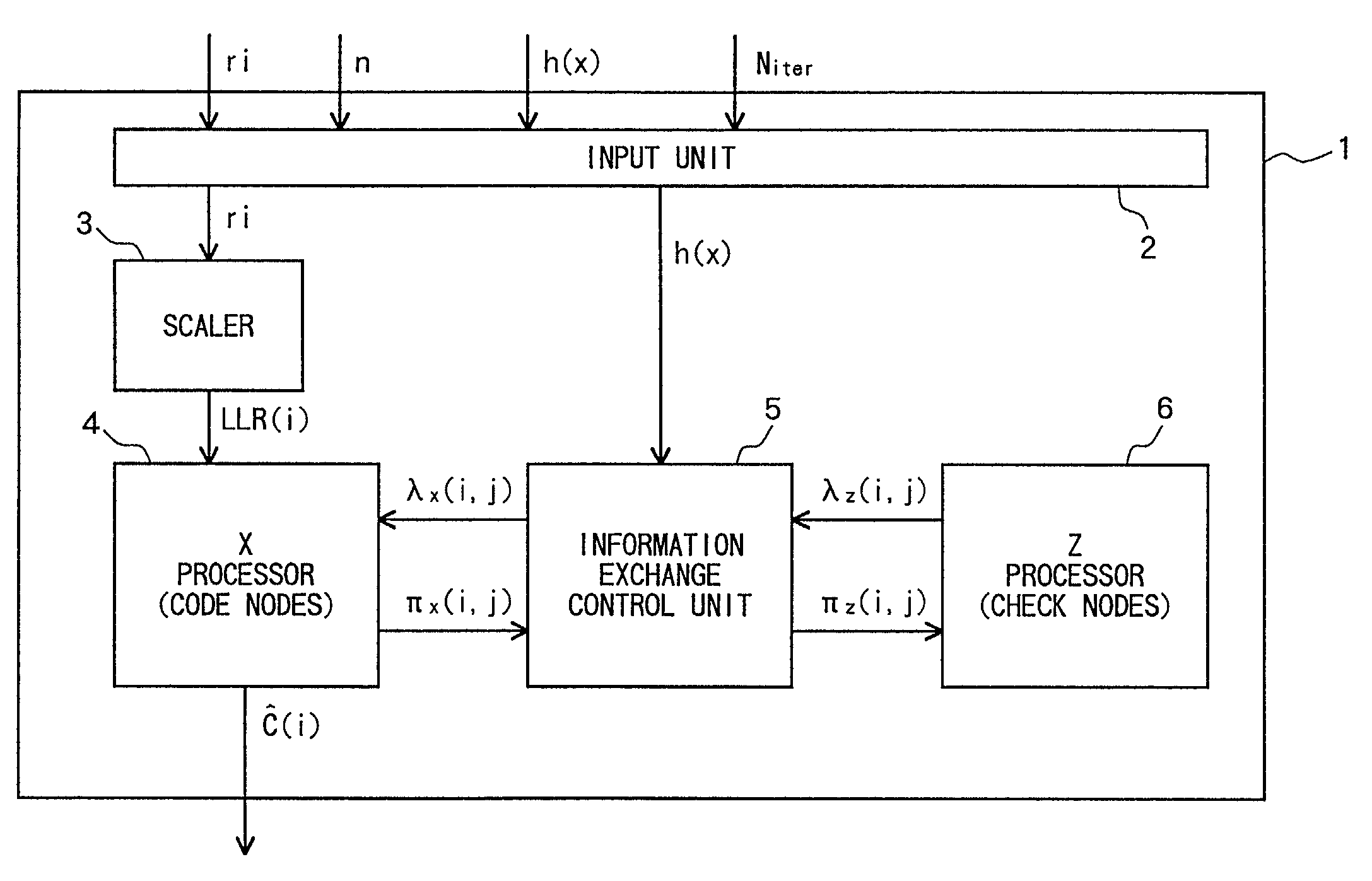
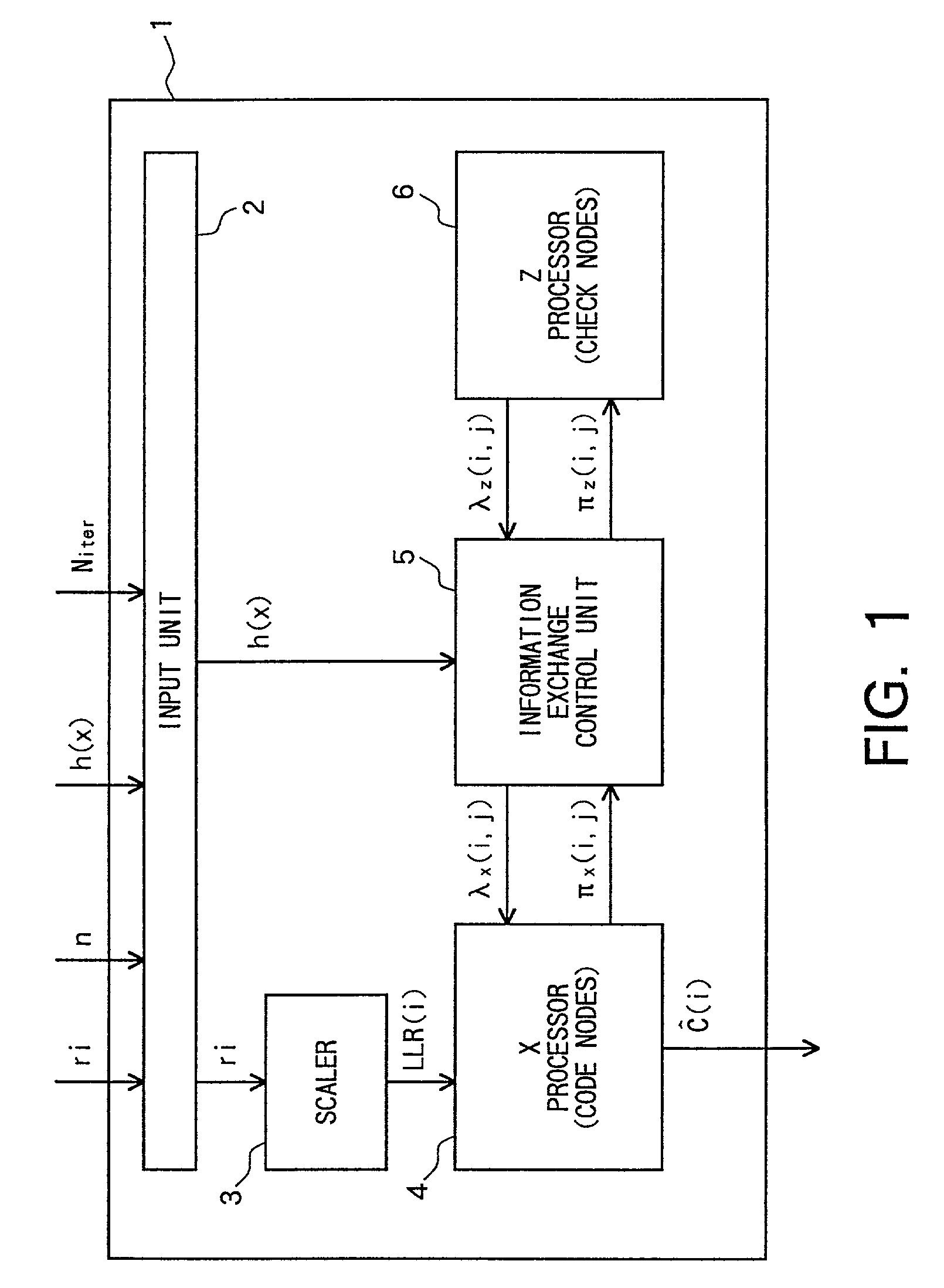
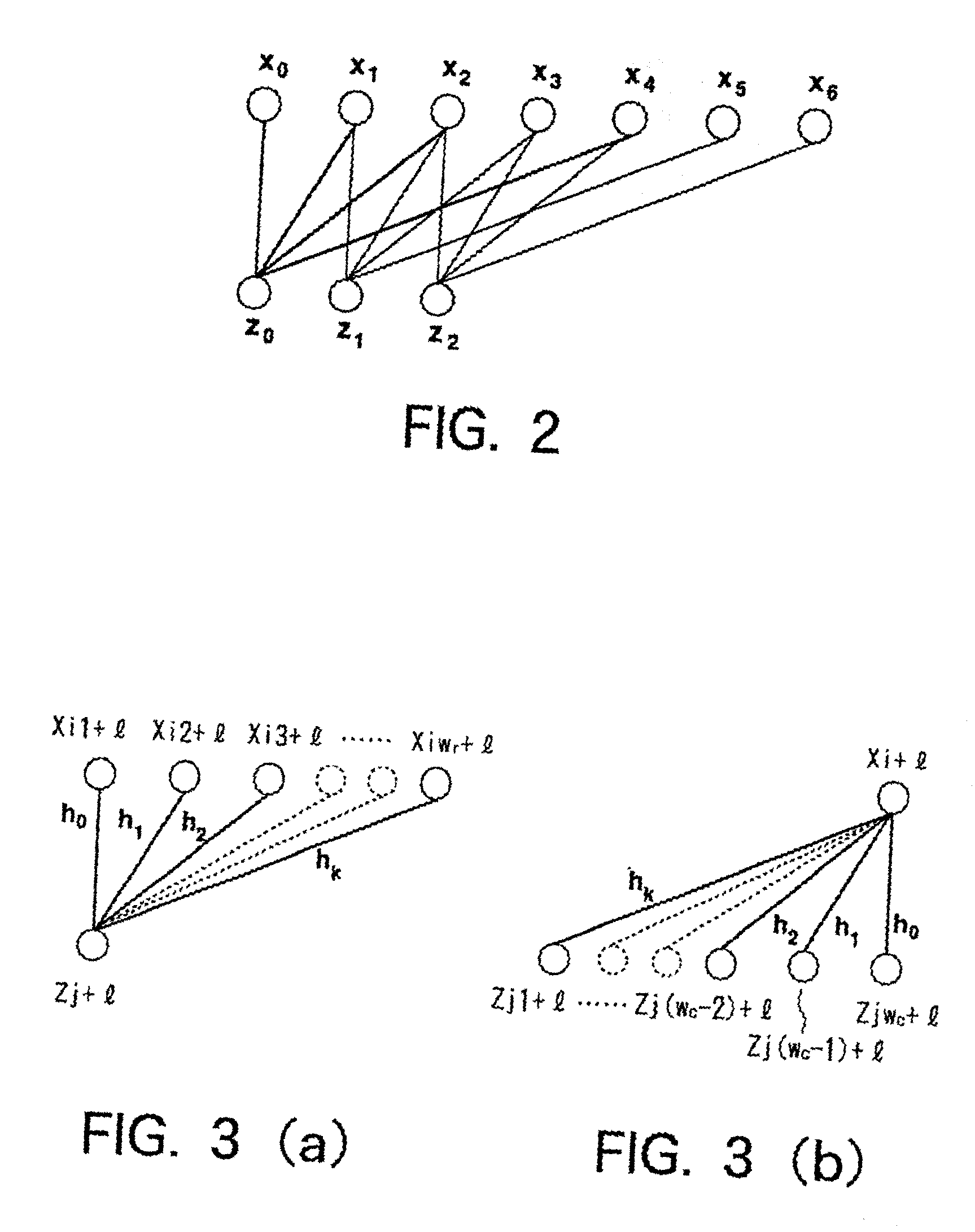
A decoder for performing soft decision iterative decoding of a cyclic code based on belief propagation, includes an information exchange control unit, an X processor, and a Z processor. The information exchange control unit takes pix-metrics that were calculated by the X processor for nonzero elements in each of n-cyclic shifts of the parity-check polynomial of the code, and distributes the pix-metrics to the Z processor as the piz-metrics for a corresponding check node. The information exchange control unit takes lambdz-metrics that were calculated by the Z processor for nonzero elements in each of n-cyclic shifts in a reverse order of the parity-check polynomial, and distributes them to the X processor as lambdx-metrics for the corresponding code node. The operation of the information exchange control unit can be represented by the Tanner graph associated with an extended parity-check matrix, which is produced by adding k rows to the parity-check matrix of the cyclic code, wherein the X processor functions as the code nodes and the Z processor functions as the check nodes.
Owner:SONY CORP
Candidate pruning for patch transforms
ActiveUS8340463B1Minimize artifactImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionProgram instruction
Systems and methods for performing image editing operations may divide an input image into overlapping patches and assign those patches to locations in a reconstructed output image such that visual artifacts are minimized. The methods may use belief propagation to compute a joint probability for the assignment of active patch labels to output image nodes. The computation may include an exclusivity term, steering the solution such that each patch is preferably only used once in the output image. The methods may include a pre-computation of a pruned list of candidate patches for placing next to each patch in the output image, dependent on local evidence (e.g., color, intensity, or user-driven placement) for each patch. The pre-computation may include determining groupings of patches, each forming a highly compatible loop of neighboring patches for a given candidate patch. The methods may be implemented as program instructions executable by a CPU and / or GPU.
Owner:ADOBE INC
Low complexity finite precision decoders and apparatus for LDPC codes
ActiveUS20110087946A1Improving message-passing processLow failure rateCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesNODALRound complexity
In this invention, a new class of finite precision multilevel decoders for low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes is presented. These decoders are much lower in complexity compared to the standard belief propagation (BP) decoder. Messages utilized by these decoders are quantized to certain levels based on the number of bits allowed for representation in hardware. A message update function specifically defined as part of the invention, is used to determine the outgoing message at the variable node, and the simple min operation along with modulo 2 sum of signs is used at the check node. A general methodology is provided to obtain the multilevel decoders, which is based on reducing failures due to trapping sets and improving the guaranteed error-correction capability of a code. Hence these decoders improve the iterative decoding process on finite length graphs and have the potential to outperform the standard floating-point BP decoder in the error floor region. The description and apparatus of 3-bit decoders for column-weight three LDPC codes is also presented.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL +2
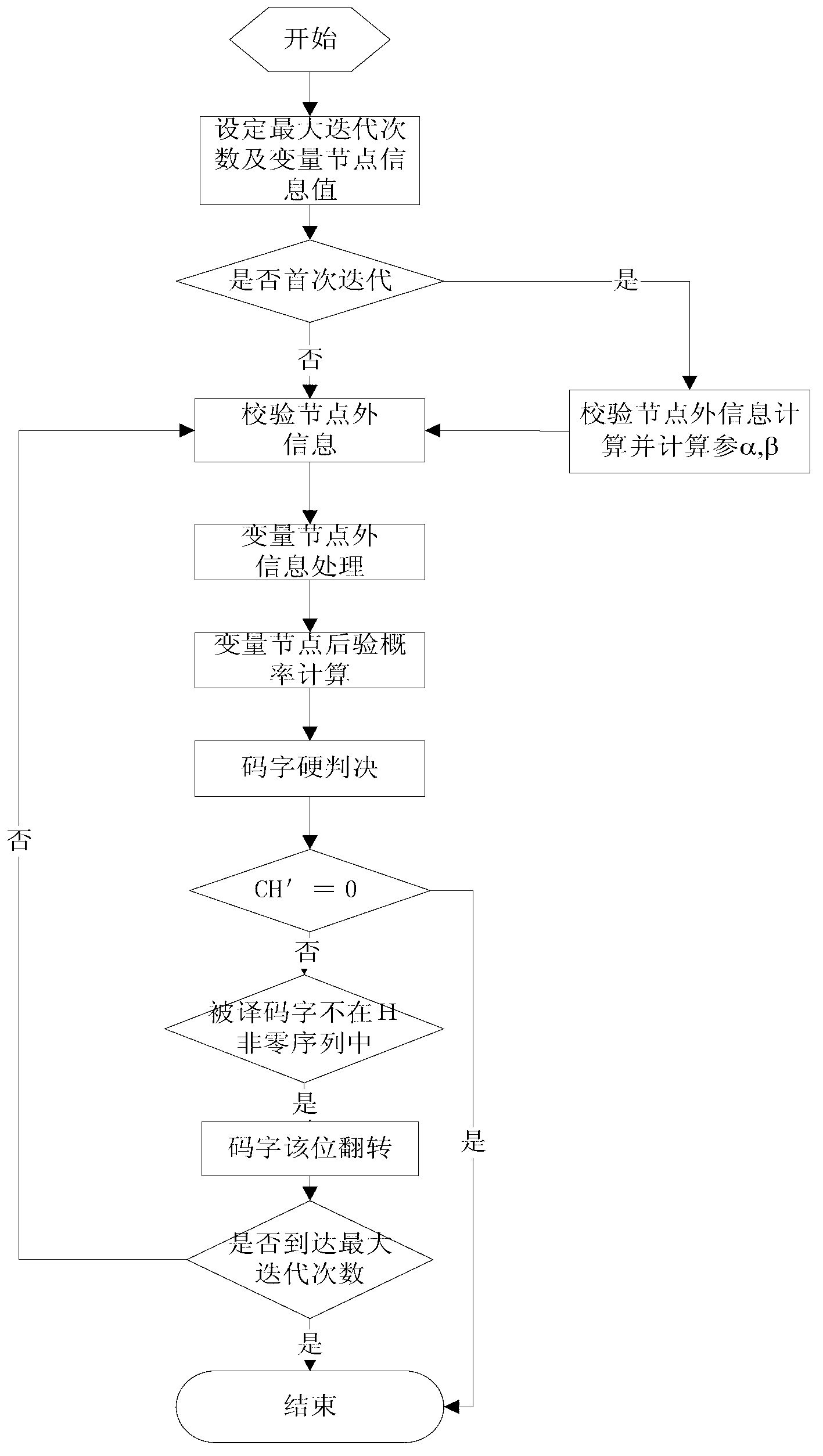
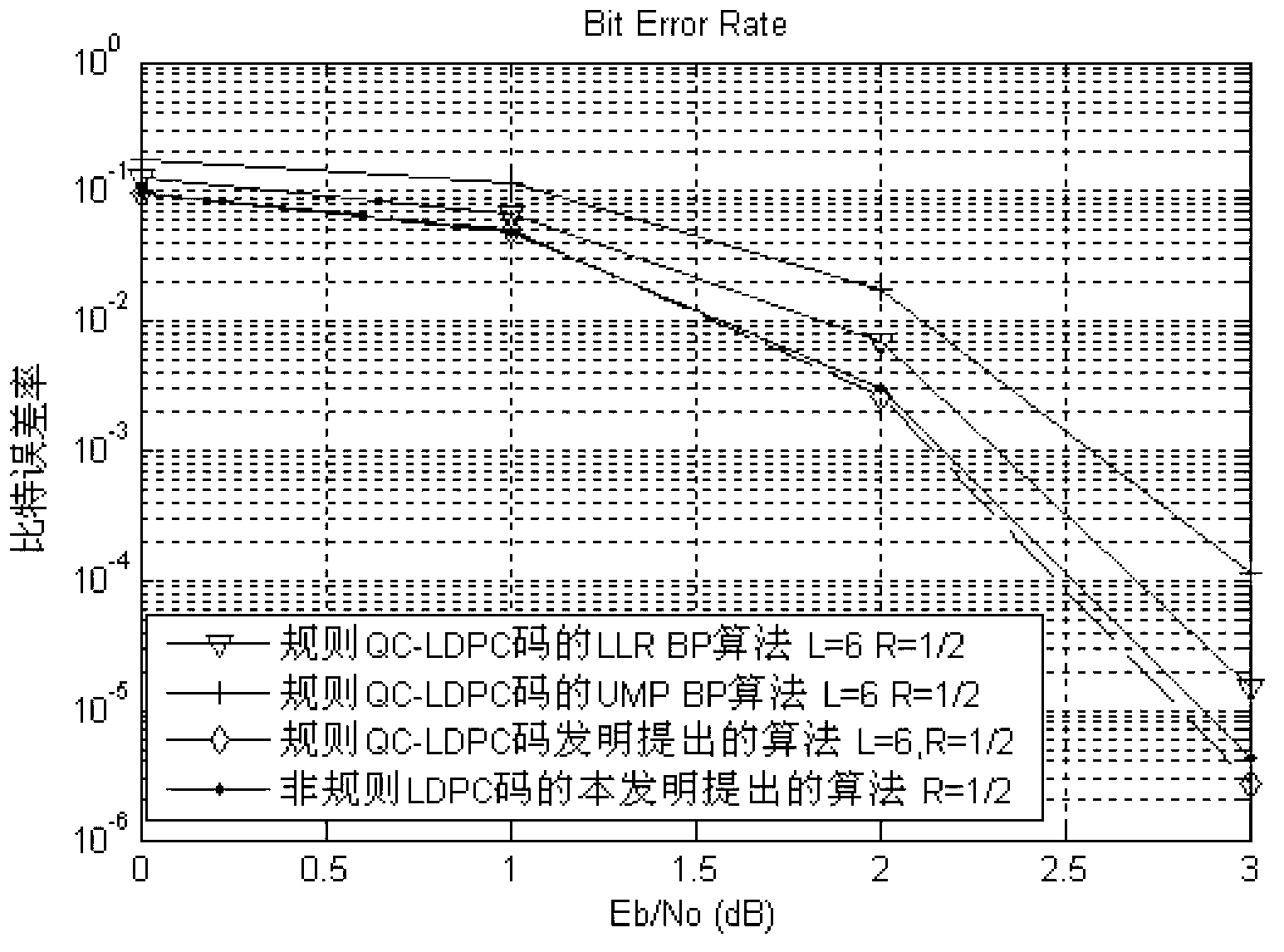
Quasi-cyclic low density odd-even check code belief propagation decoding method based on oscillation
InactiveCN103259545ASmall fluctuationImprove decoding performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Round complexity
The invention discloses a quasi-cyclic low density odd-even check code belief propagation decoding method based on oscillation. In the initial iteration, a mean value is used for obtaining normalizing factors alpha and beta, under different signal-to-noise ratios, an extrinsic information value of a check node is dynamically corrected to reduce fluctuation of the extrinsic information value of the check node, the quasi-cyclic low density odd-even check code belief propagation decoding method unites a bit flip method in hard decision decoding to reduce occurrences of the oscillation, decoding performance of transmission data can be improved, and decoding complexity can be reduced. Decoding methods of soft decision and hard decision are combined to obtain big decoding gains. Balancing states of complexity and decoding efficiency of a decoder are achieved due to the facts that combination of low density odd-even check code hard decision decoding and low density odd-even check code soft decision decoding and excellent coding gains of a soft decision belief propagation algorithm are utilized, and a hard decision decoding method is fully applied to reduce influences of accumulated error code words.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
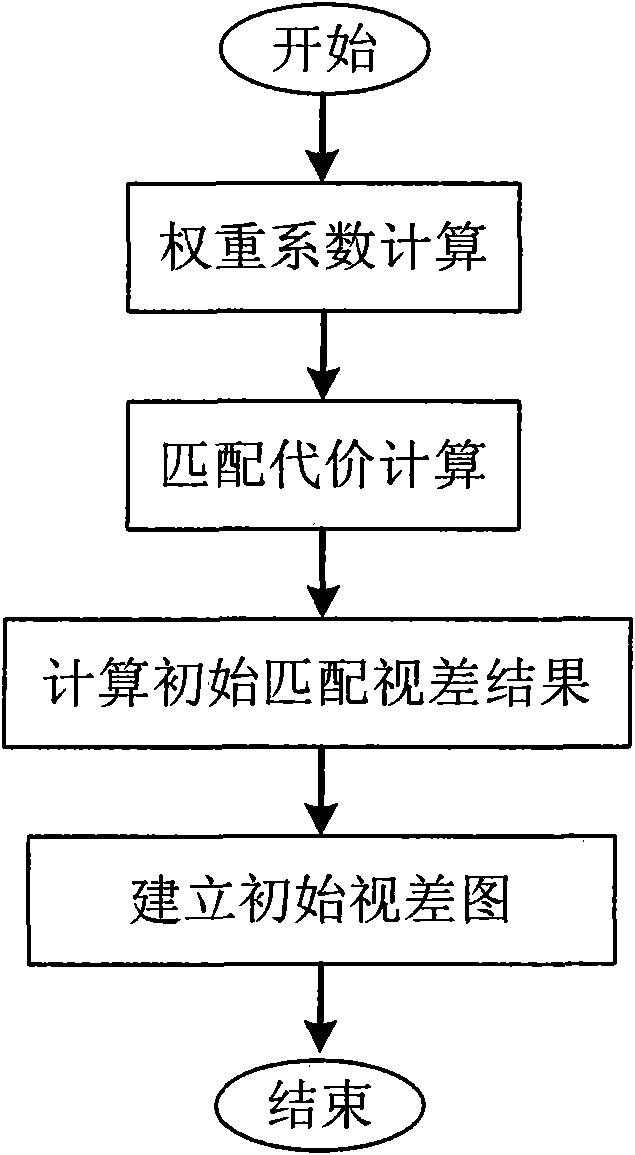
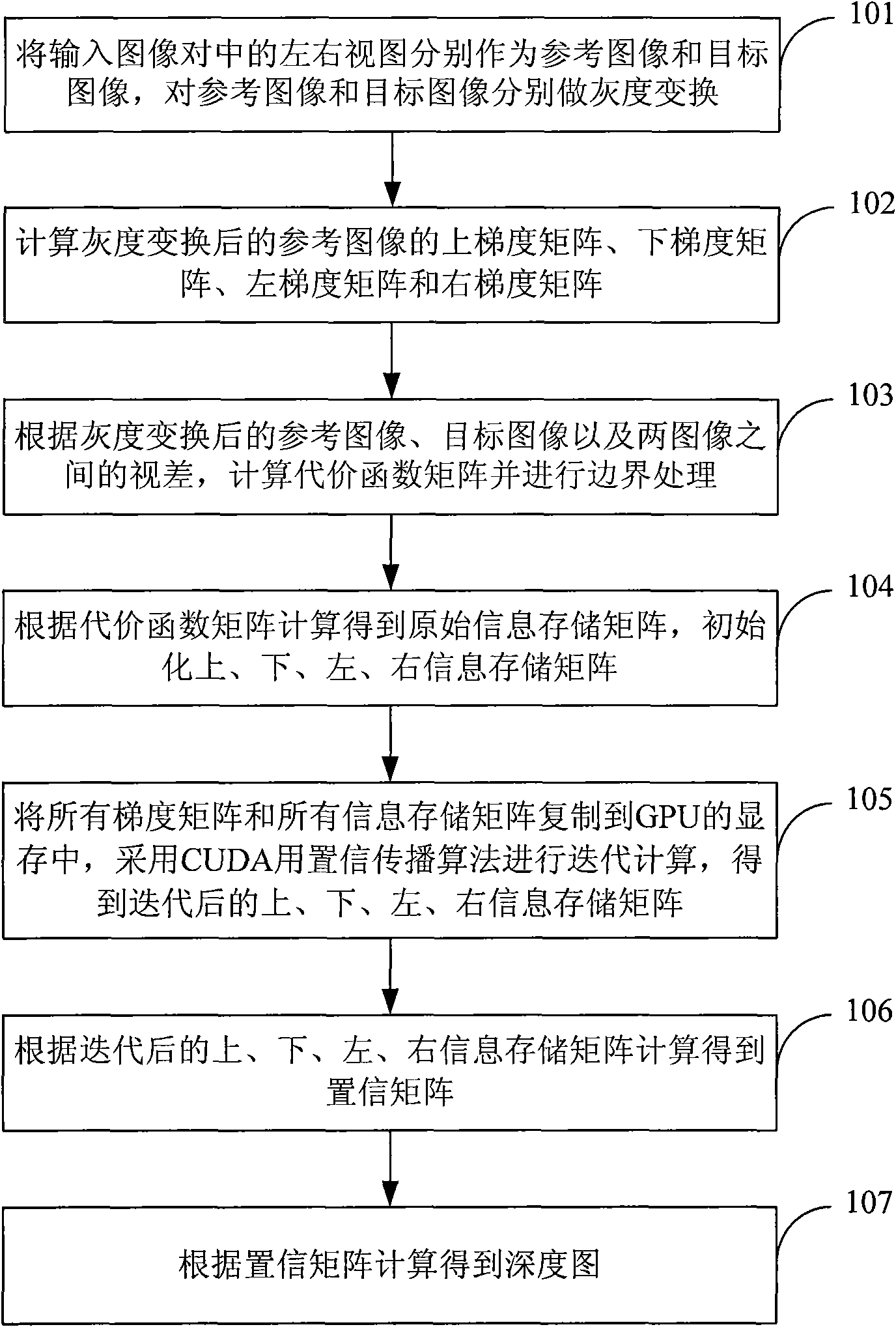
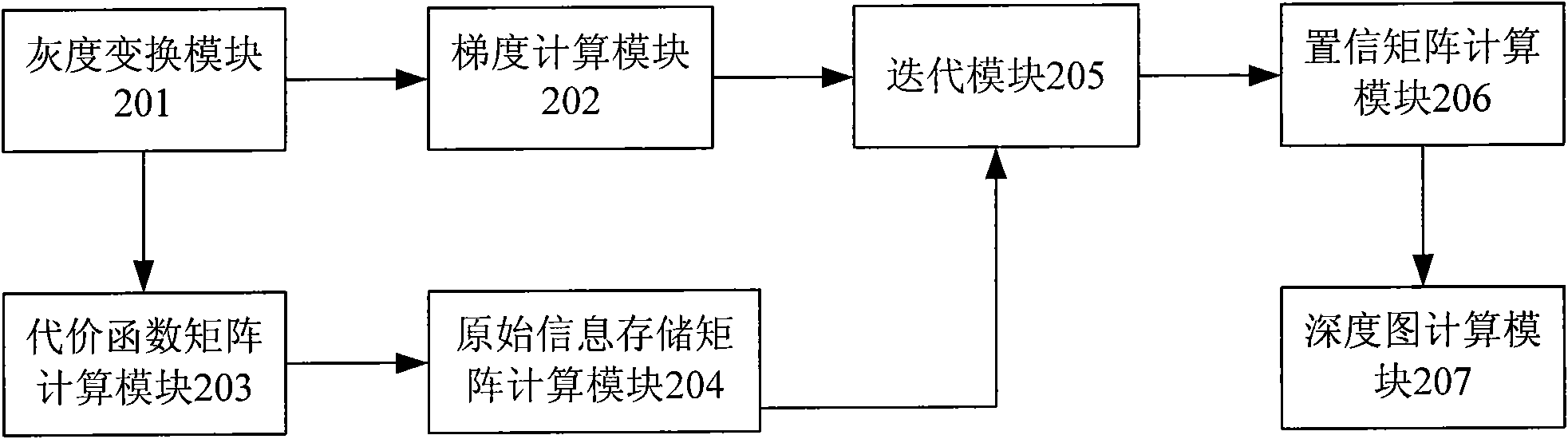
Method and device for generating depth map
ActiveCN101605270AResolution is slowQuality improvementImage analysisSteroscopic systemsParallaxReference image
The invention discloses a method and a device for generating a depth map, which belongs to the technical field of computer vision. The method comprises the following steps: performing gray-scale transformation by using a left view and a right view of an input image pair as a reference image and a target image respectively; computing upper, lower, left and right gradient matrixes of the reference image after the gray-scale transformation; computing a cost function matrix according to parallax, and processing borders; computing an original information storage matrix, and initializing upper, lower, left and right information storage matrixes; performing iterative calculation in a GPU memory by using a CUDA belief propagation algorithm to acquire upper, lower, left and right information storage matrixes after iteration, and computing a belief matrix according to the result of the iteration; and computing the depth map according to the belief matrix. The device comprises a gray-scale transformation module, a gradient computation module, a cost function matrix computation module, an original information storage matrix computation module, an iteration module, a belief matrix computation module and a depth map computation module. The method and the device improve computing efficiency of the depth map and realize high-quality and fast generation of the depth map.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for large-scale MIMO system
InactiveCN105656538AImprove performancePrevent inversionSpatial transmit diversityNODALPrior information
The invention discloses a low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for a large-scale MIMO system. A corresponding factor graph is built by utilizing an equivalent real number field model, and complex number field operation is translated into real number field operation, thereby implementing BP-based iteration detection; wherein the factor graph is used for representing a dependency relation between a receiving signal and a transmitting signal, the transmitting signal is utilized as a signal node, and the receiving signal is utilized as an observation node; each signal node updates prior information according to posterior information obtained from the observation node, and then transmits the updated prior information to all observation nodes connected with the signal node; each observation node calculates updates posterior information according to prior information obtained from the signal node, and then transmits the updated posterior information to a signal node connected with the observation node. According to the low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm for the large-scale MIMO system, a symbol-based large-scale MIMO detection algorithm is implemented; high-dimensional matrix inversion is avoided, and the low-complexity belief propagation detection algorithm can be greatly suitable for application scenarios of the large-scale MIMO.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
LDPC code linear programming decoding method based on minimum polyhedral model
ActiveCN105959015AReduce bit error rateImprove decoding speedError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionInformation transmissionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
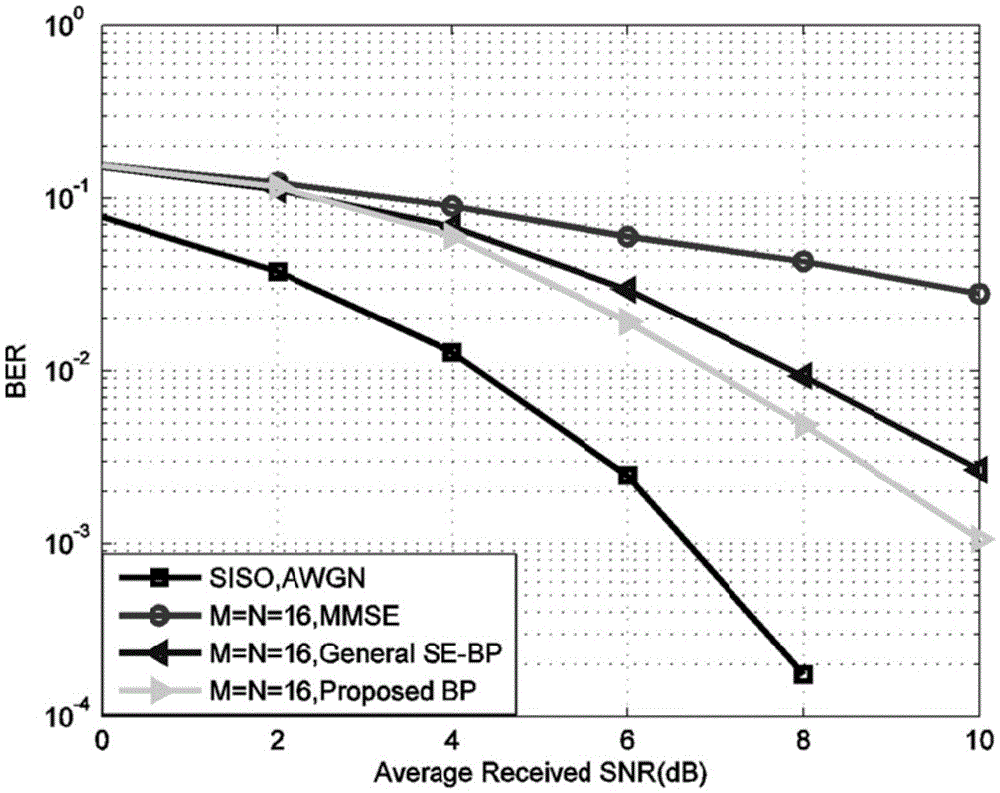
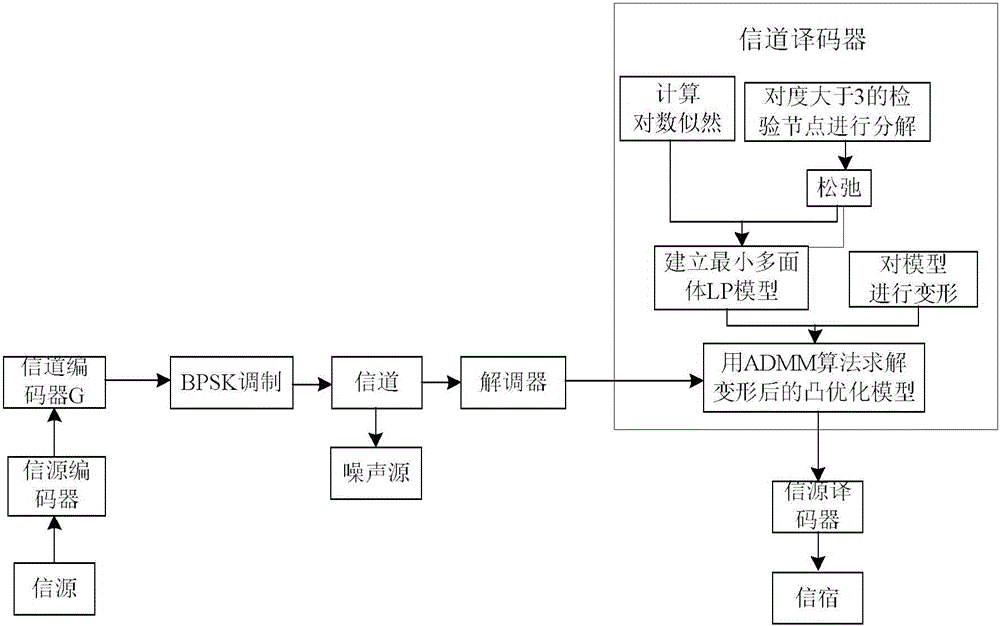
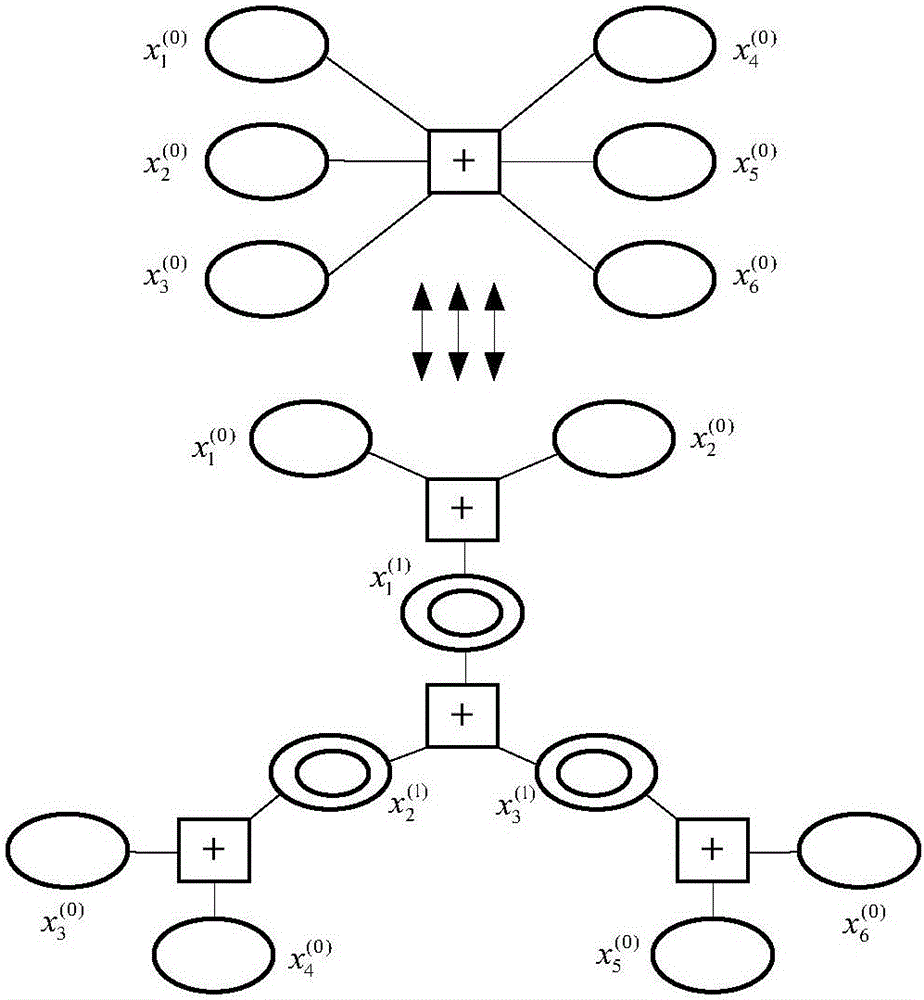
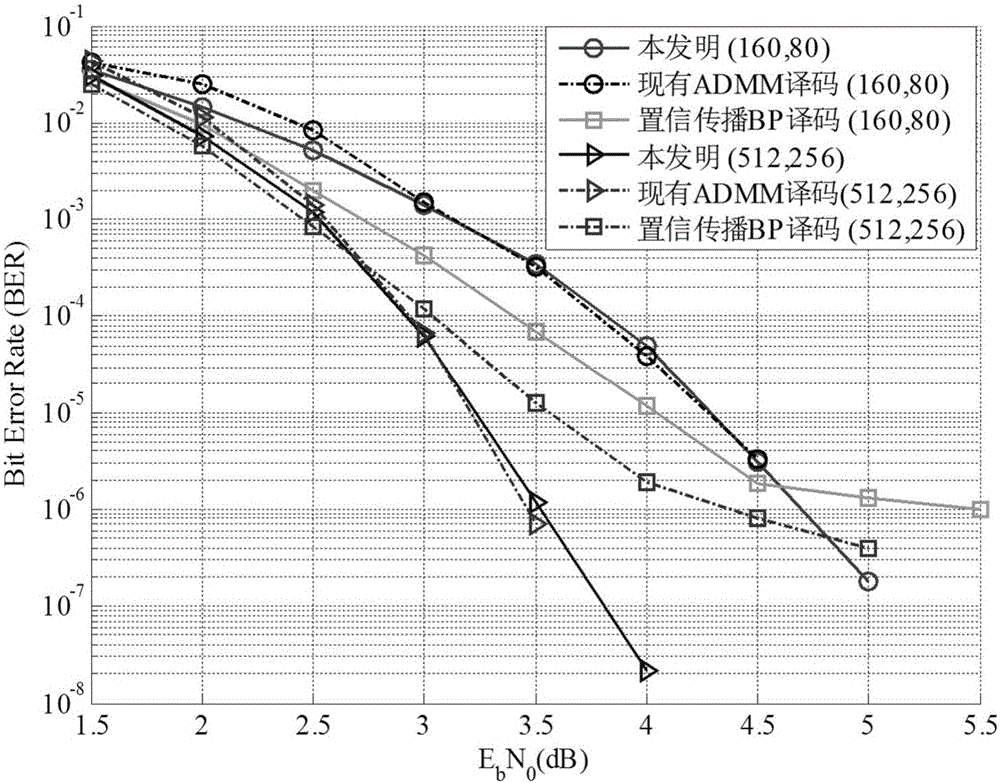
The invention discloses a LDPC code linear programming decoding method based on a minimum polyhedral model and mainly solves low decoding speed in conventional LDPC code linear programming decoding and an erroneous platform in information transmission decoding. The method comprises steps of: slacking the maximum likelihood decoding of a LDPC code into a linear programming LP model based on a minimum polyhedron by using a verification node decomposition method; establishing an augmented Lagrange function by using the sparsity and the orthogonality of a matrix in the LP model based on the minimum polyhedron, and carrying out iteration by using an alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM) to solve decoded codes. Compared with a LP decoding method based on the ADMM, the LDPC code linear programming decoding method is increased in decoding speed while not decreasing LP decoding performance, and does not generate an erroneous platform in a high signal-to-noise ratio compared with a belief propagation (BP) decoding method. The LDPC code linear programming decoding method can be used in the technical field of communication to increase the efficiency of a communication system decoding module.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com