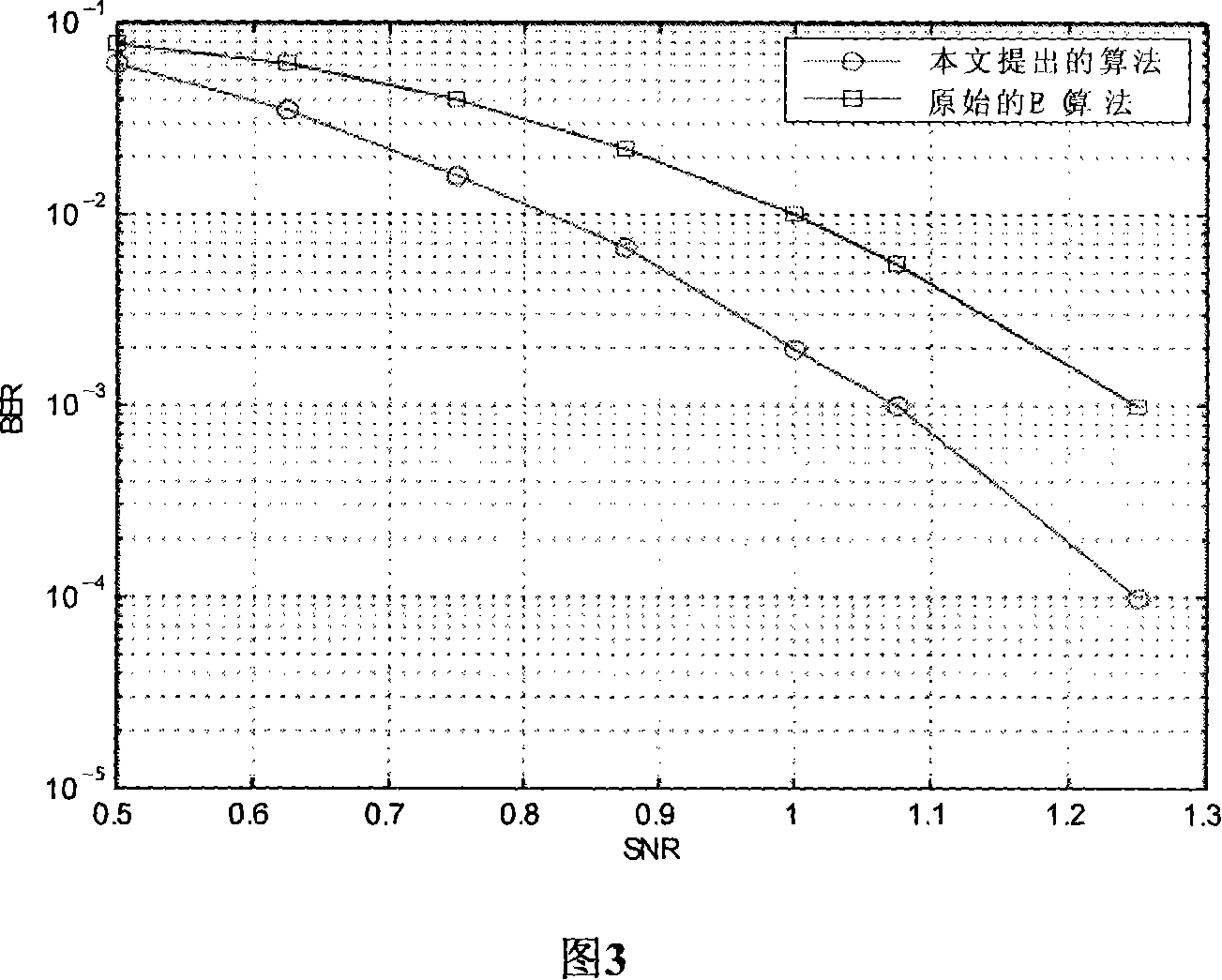
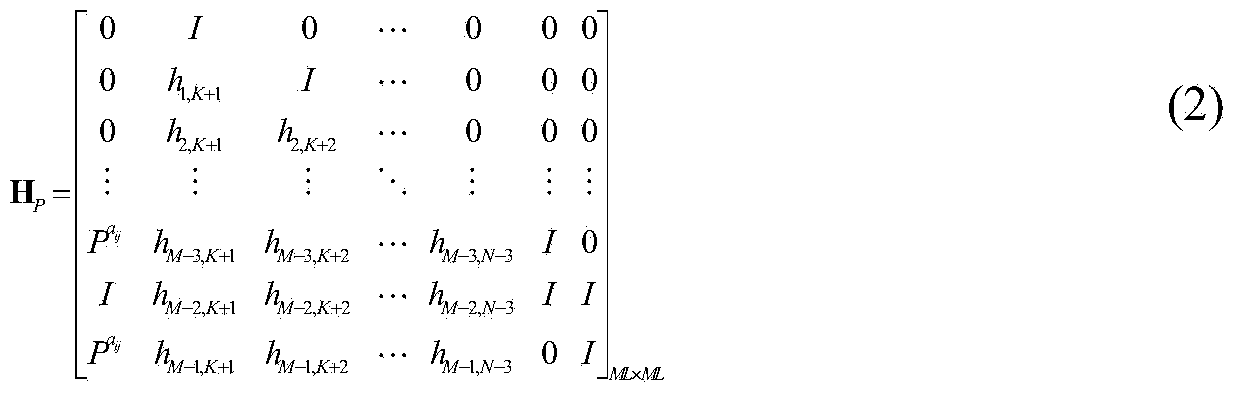Patents
Literature
192 results about "Cyclic code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
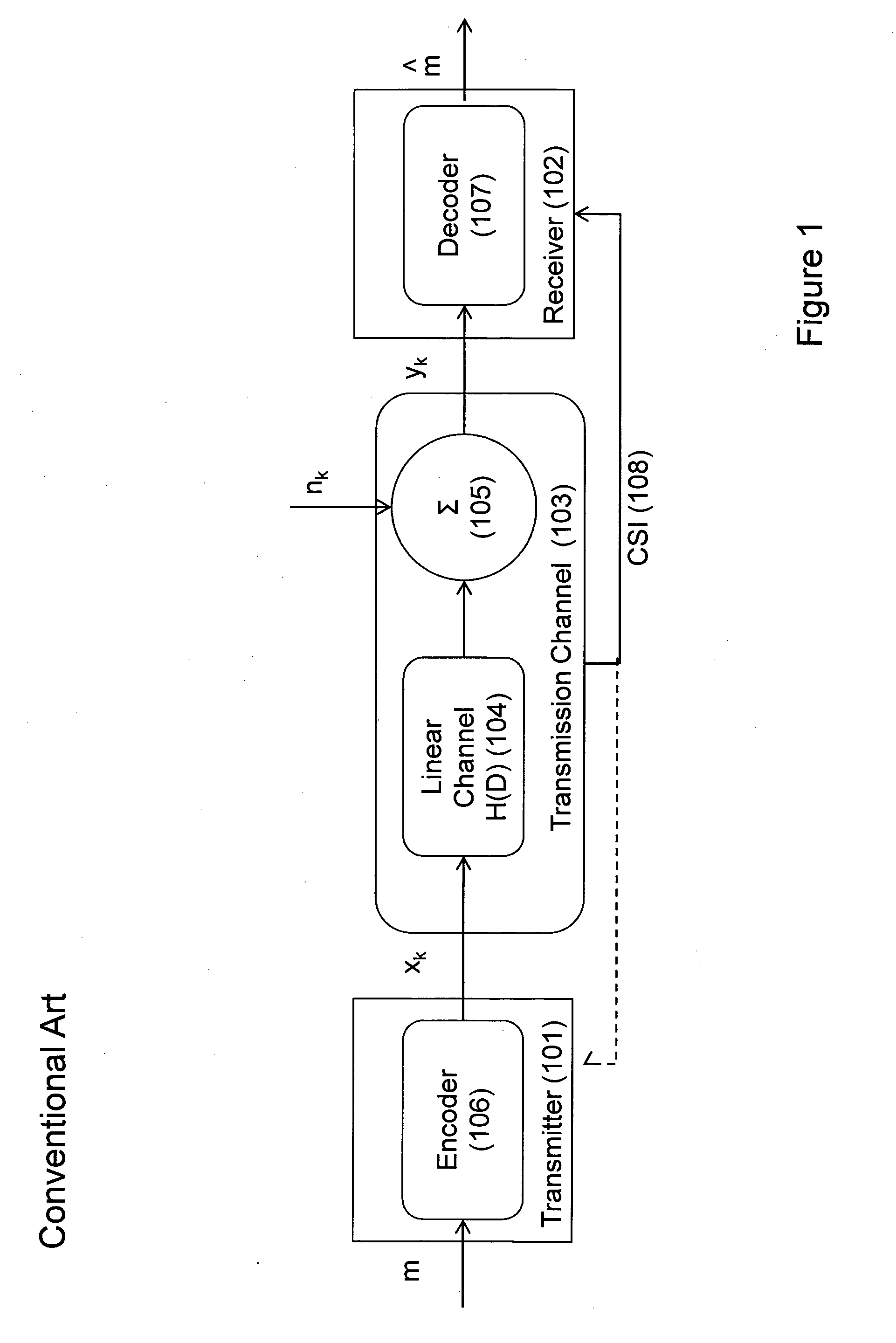
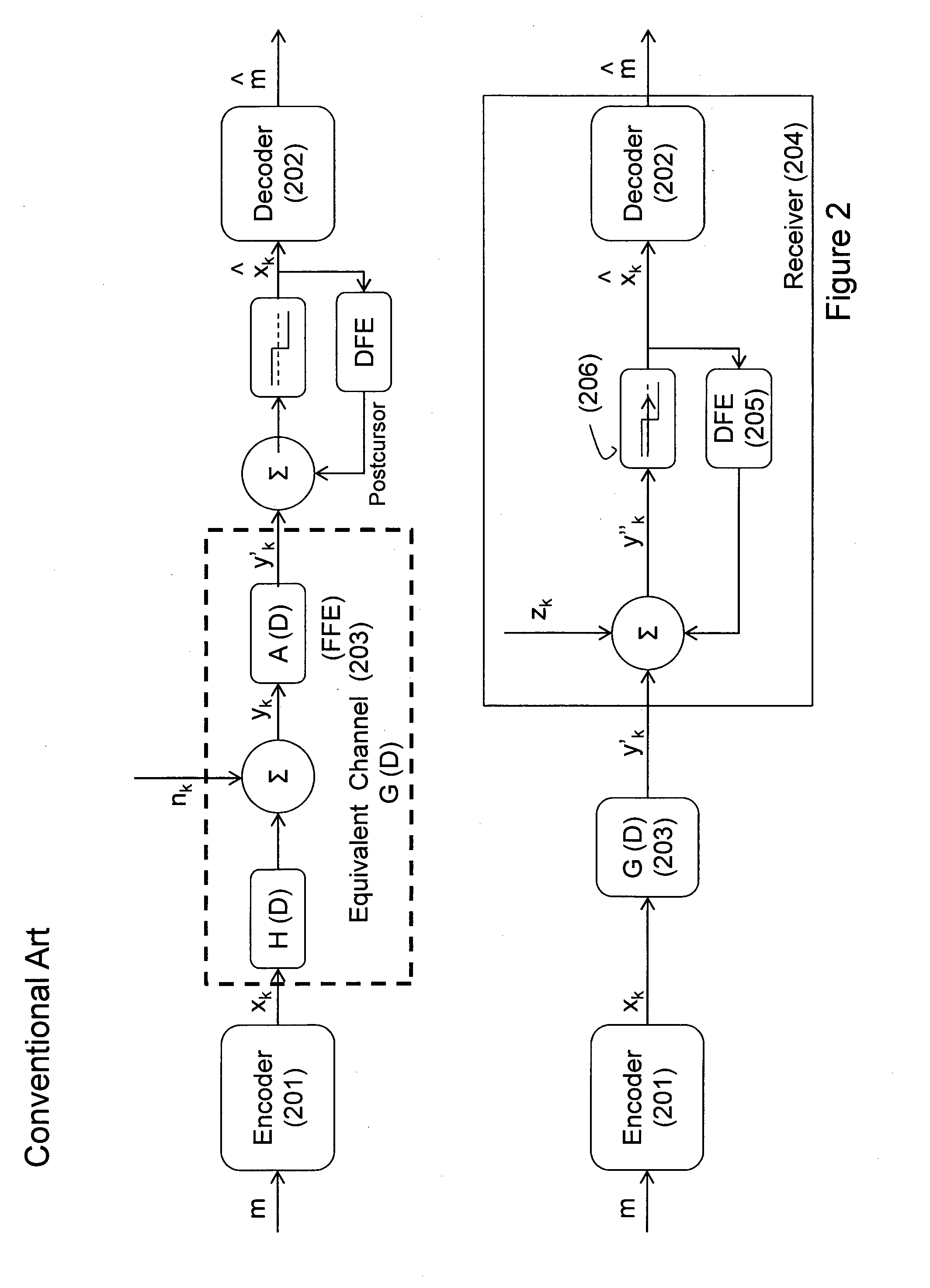
In coding theory, a cyclic code is a block code, where the circular shifts of each codeword gives another word that belongs to the code. They are error-correcting codes that have algebraic properties that are convenient for efficient error detection and correction.
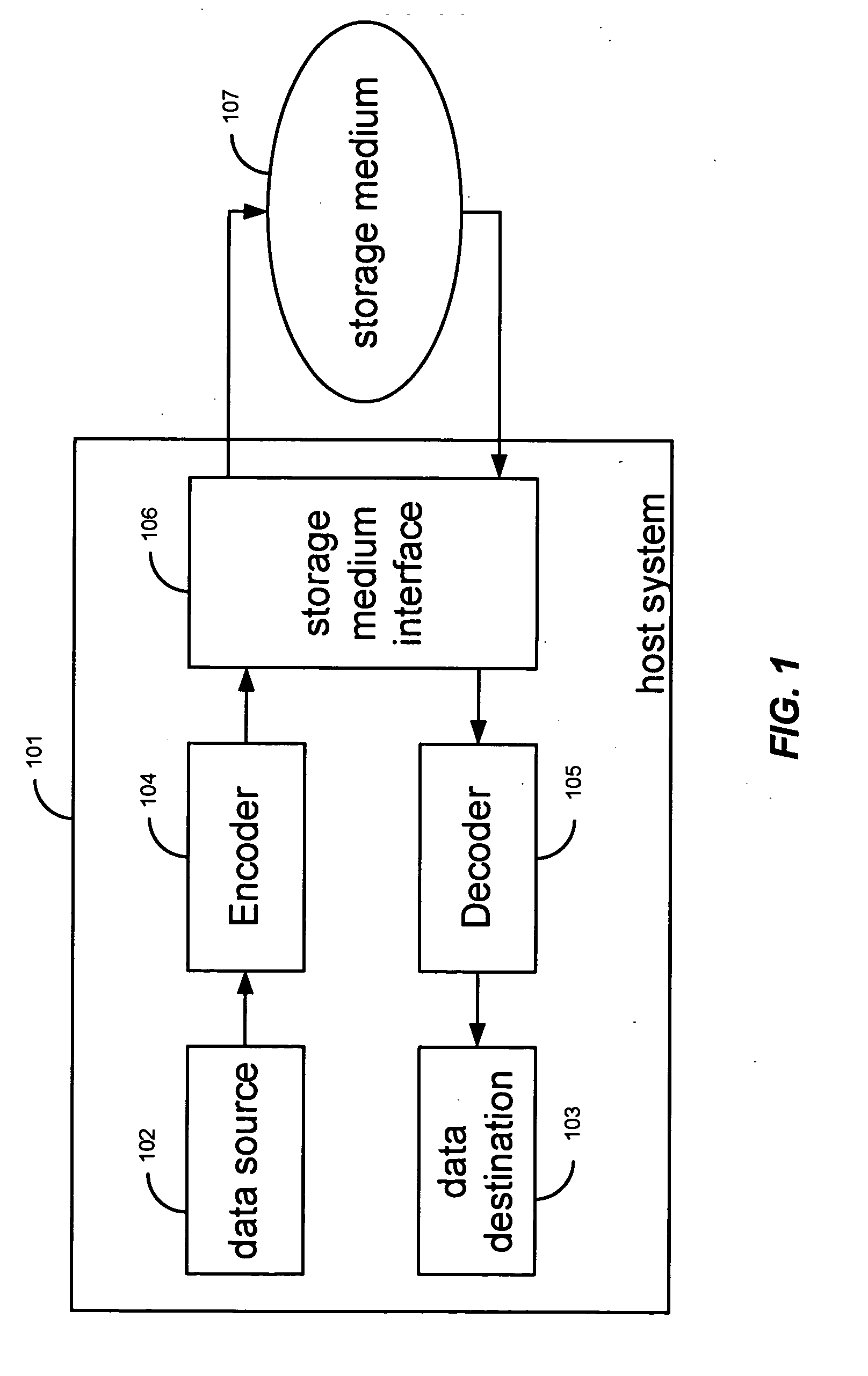
Fixed content distributed data storage using permutation ring encoding
InactiveUS7240236B2Highly available and reliable and persistent storageError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionCoding blockDatabase
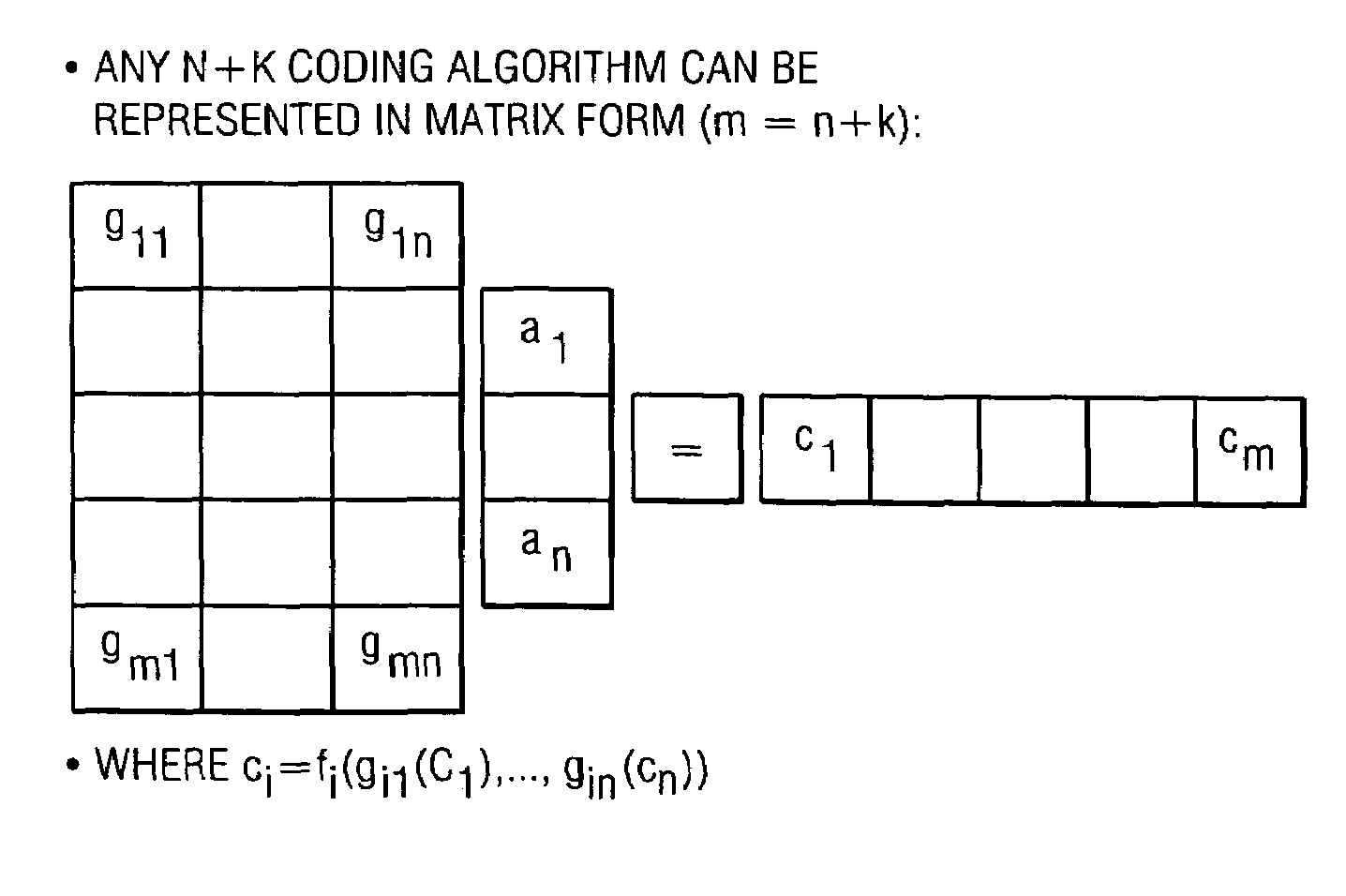
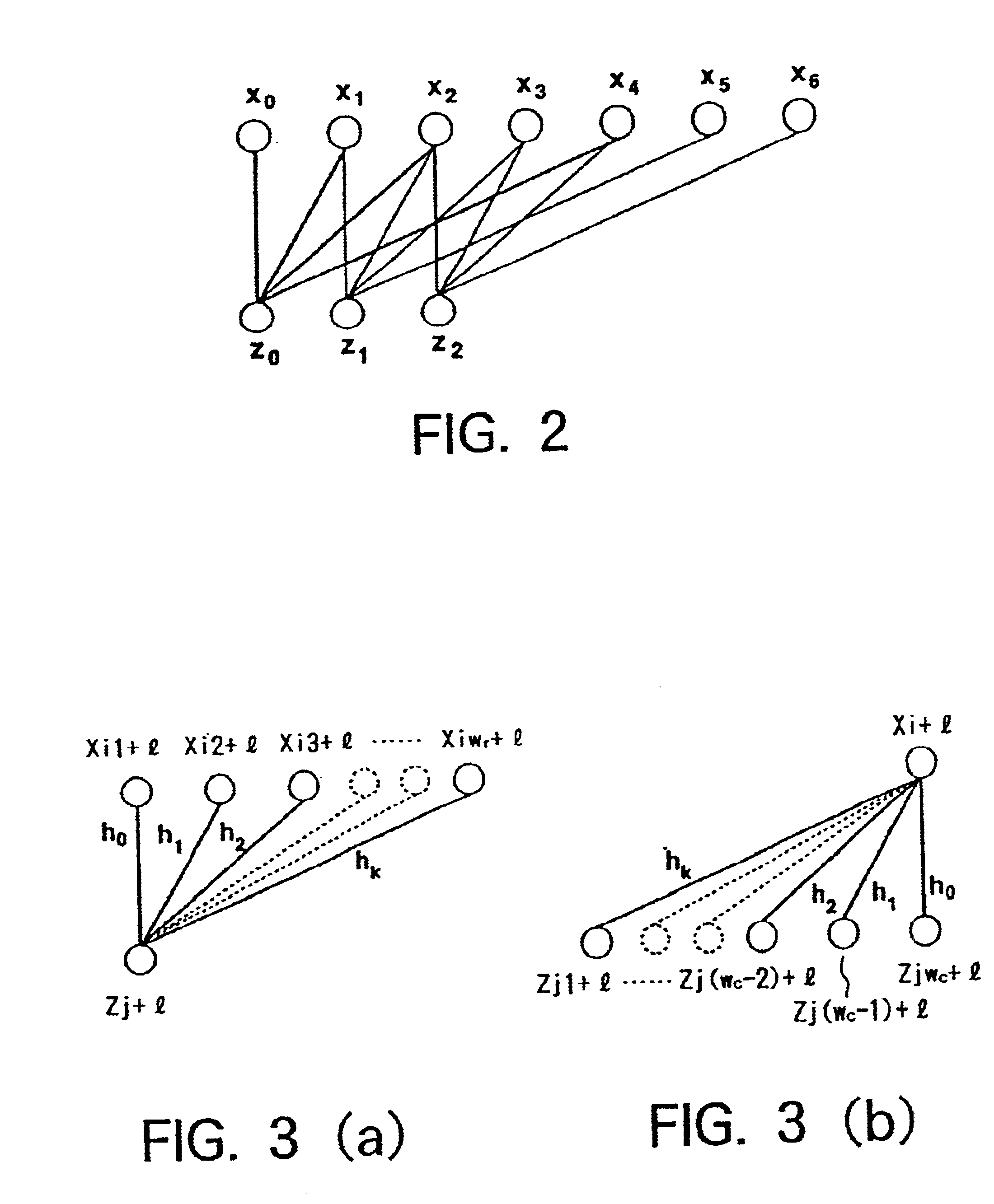
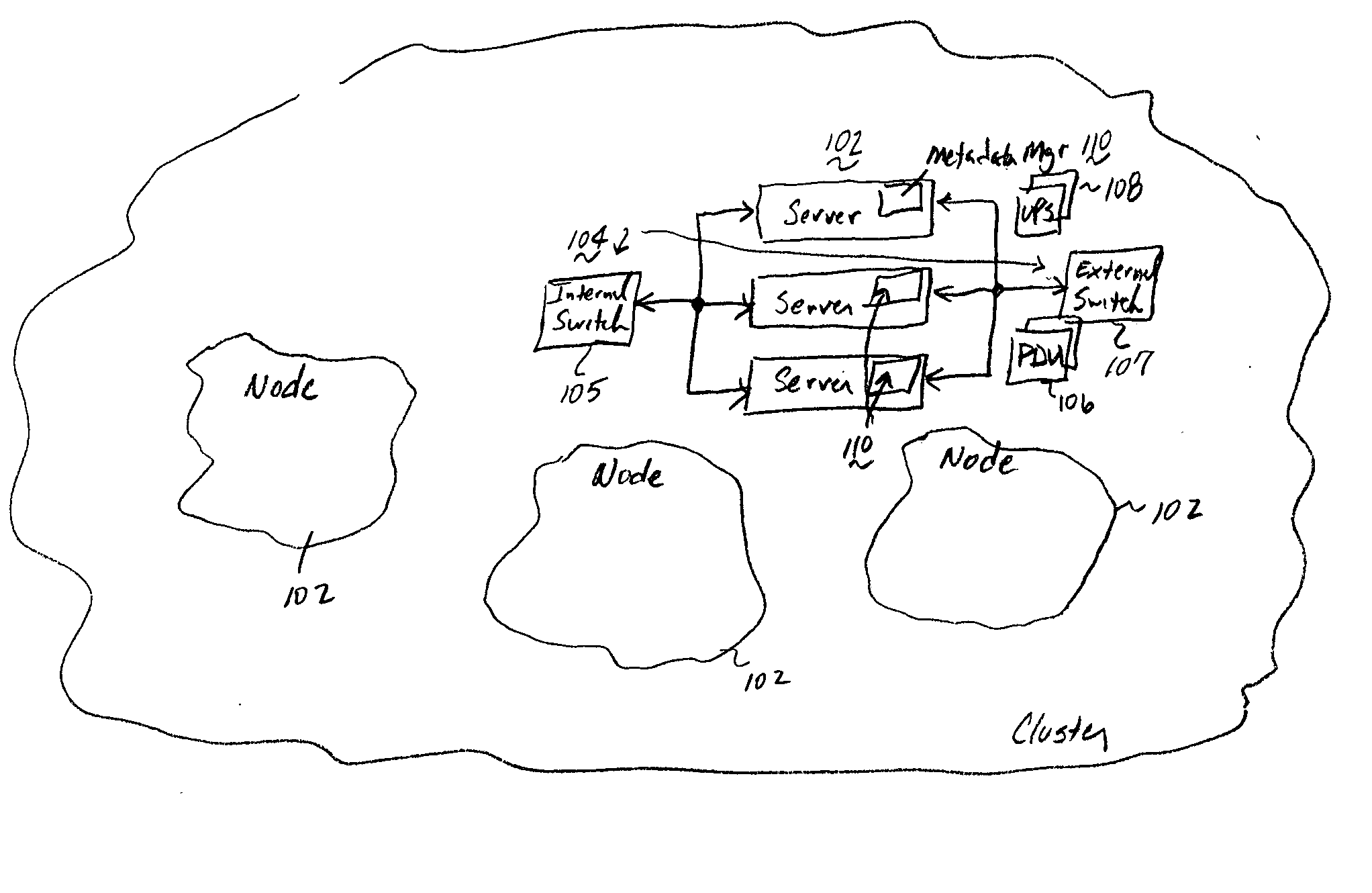
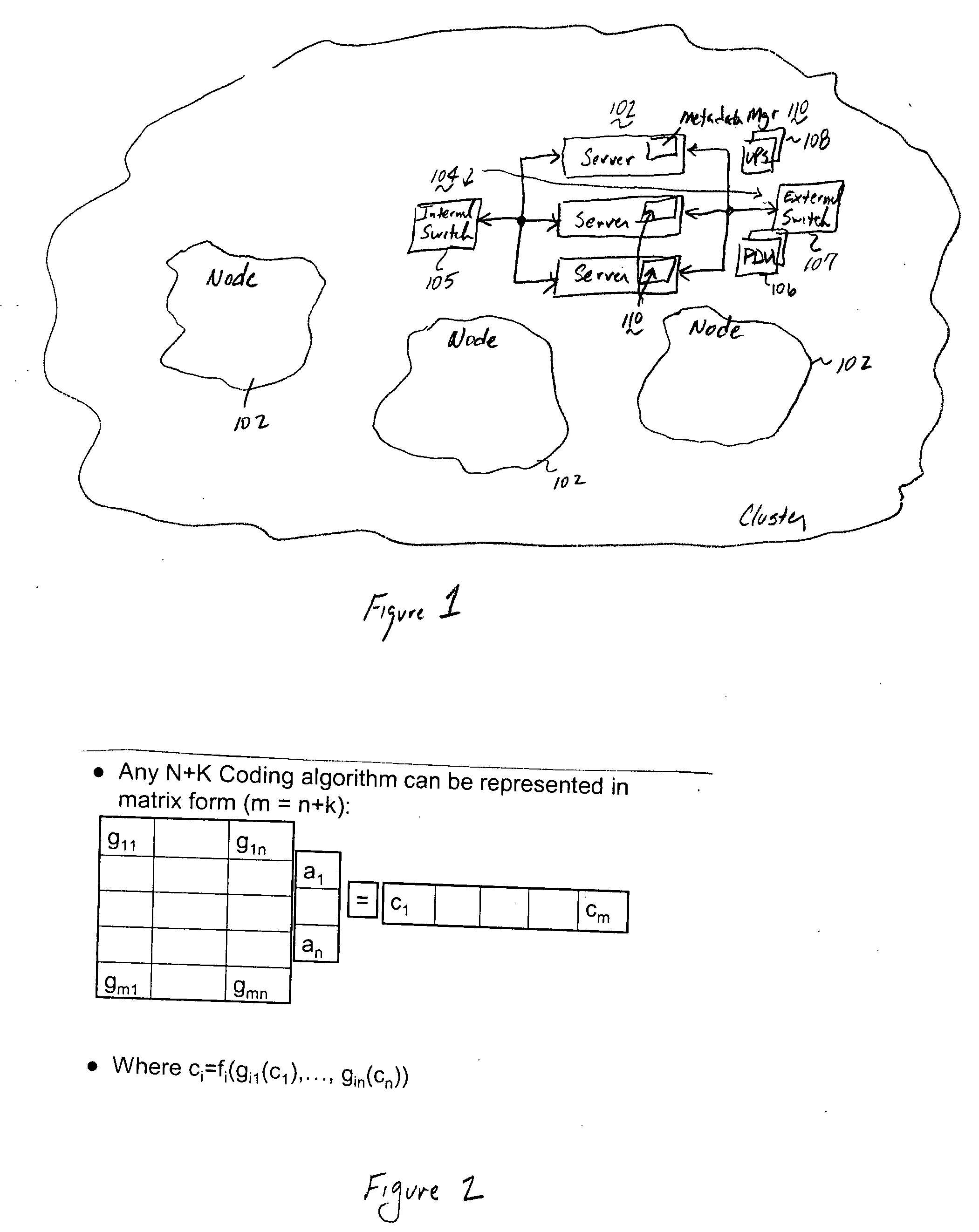
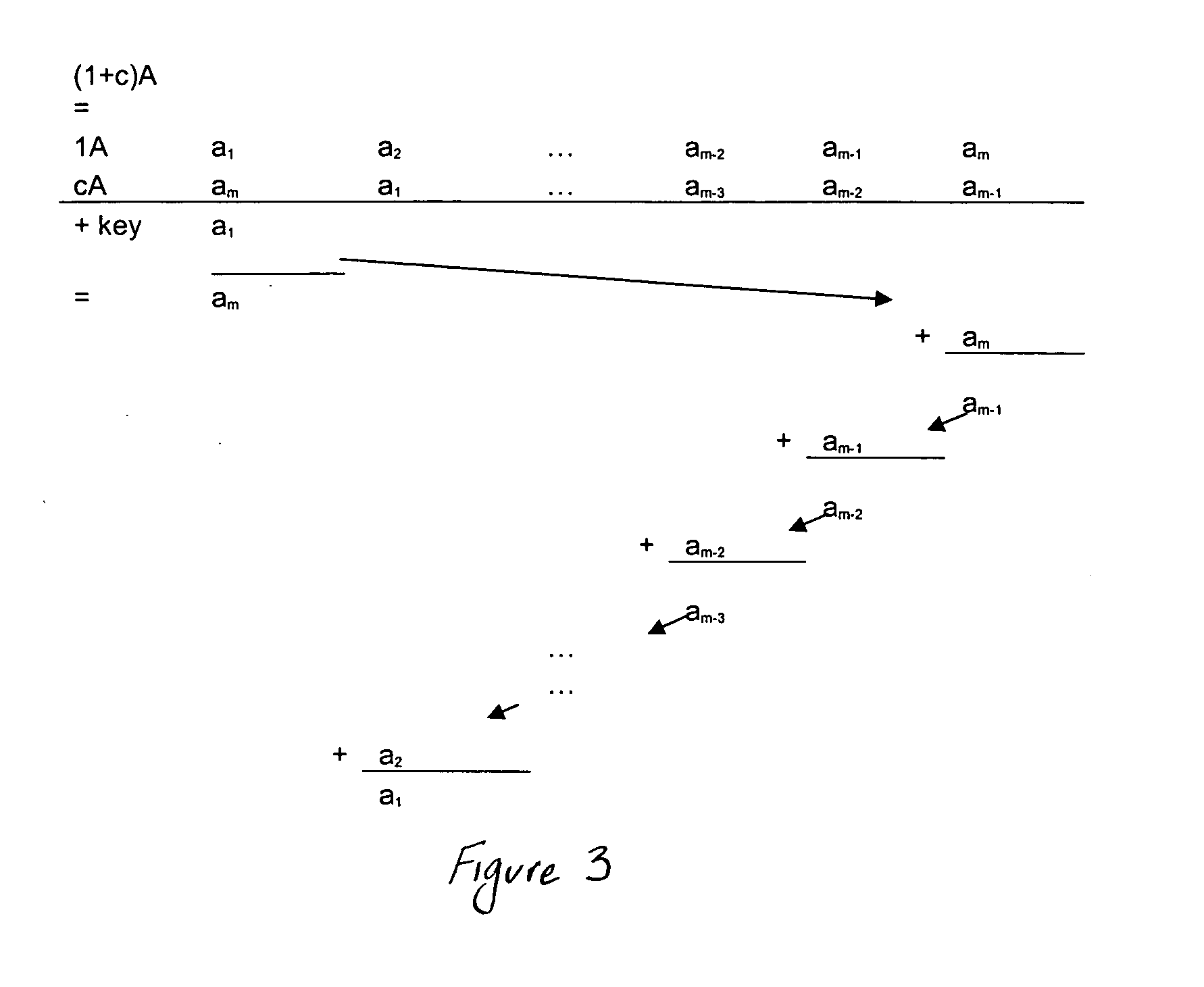
A file protection scheme for fixed content in a distributed data archive uses computations that leverage permutation operators of a cyclic code. In an illustrative embodiment, an N+K coding technique is described for use to protect data that is being distributed in a redundant array of independent nodes (RAIN). The data itself may be of any type, and it may also include system metadata. According to the invention, the data to be distributed is encoded by a dispersal operation that uses a group of permutation ring operators. In a preferred embodiment, the dispersal operation is carried out using a matrix of the form [IN<sub2>—< / sub2>C] where IN is an n×n identity sub-matrix and C is a k×n sub-matrix of code blocks. The identity sub-matrix is used to preserve the data blocks intact. The sub-matrix C preferably comprises a set of permutation ring operators that are used to generate the code blocks. The operators are preferably superpositions that are selected from a group ring of a permutation group with base ring Z2.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA CORP
Error correction by symbol reconstruction in binary and multi-valued cyclic codes
InactiveUS20080016431A1Rapidly detect and correct errorCode conversionCyclic codesAlgorithmSymbol of a differential operator
Methods, apparatus and systems for error correction of n-valued symbols in codewords of p n-valued symbols with n>2 and for n=2 and k information symbols have been disclosed. Coders and decoders using a Linear Feedback Shift Registers (LFSR) are applied to generate codewords and detect the presence of errors. An LFSR can be in Fibonacci or Galois configuration. Errors can be corrected by execution of an n-valued expression in a deterministic non-iterative way. Deterministic error correction methods based on known symbols in error are provided. Corrected codewords can be identified by comparison with received codewords in error. N-valued LFSR based pseudo-noise generators and methods to determine if an LFSR is appropriate for generating error correcting codes are also disclosed. Methods and apparatus applying error free assumed windows and error assumed windows are disclosed. Systems using the error correcting methods, including communication systems and data storage systems are also provided.
Owner:TERNARYLOGIC
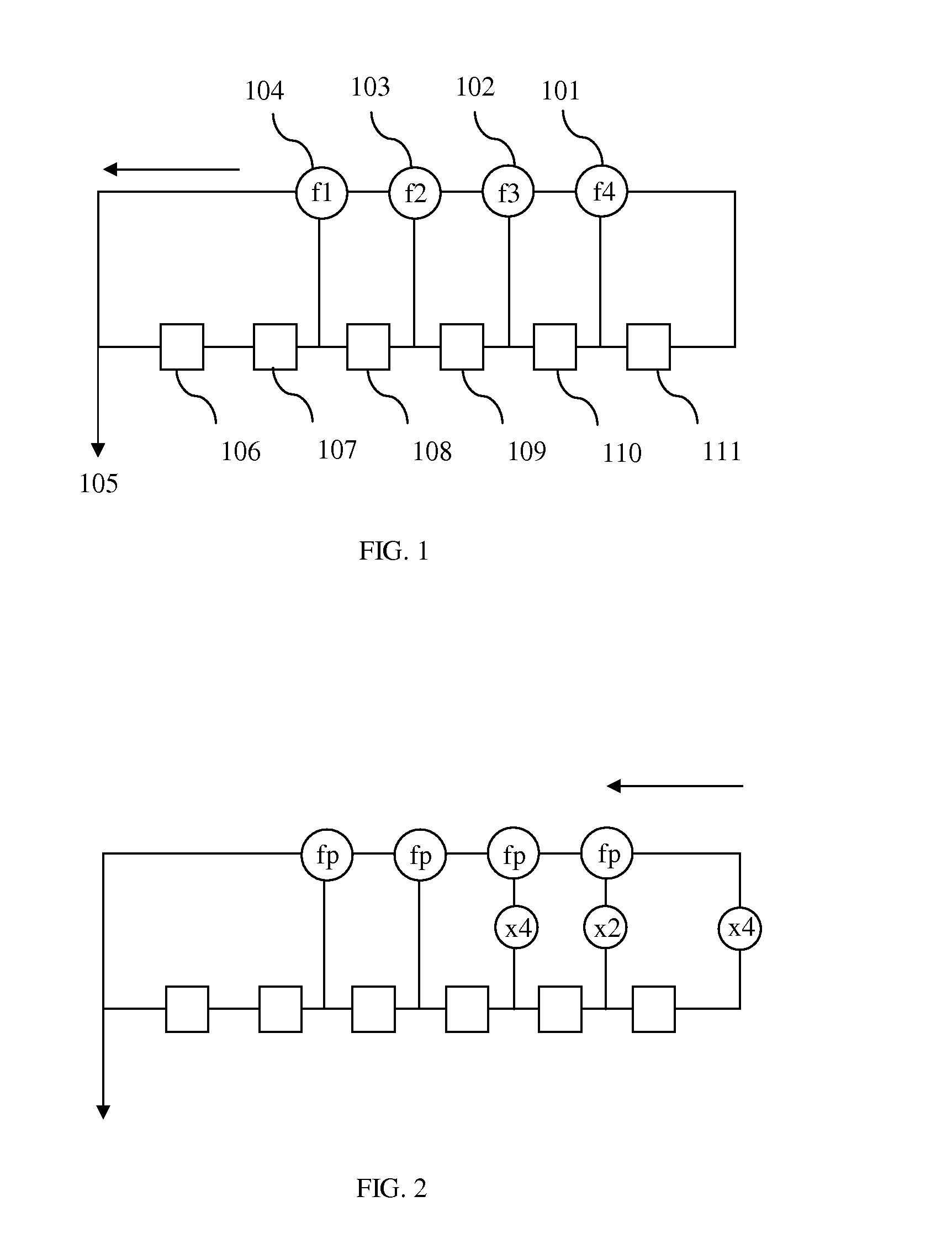
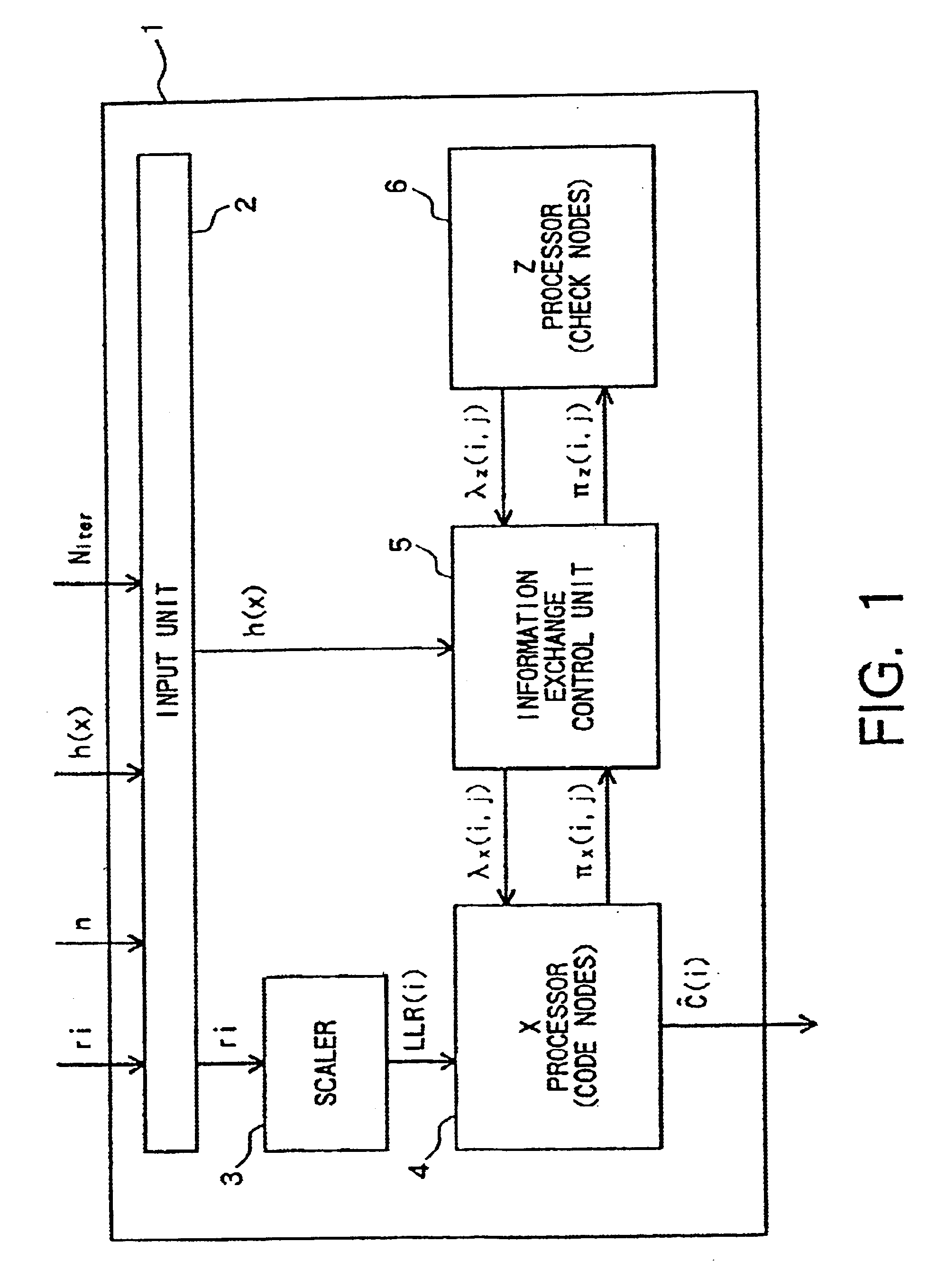
Decoder for iterative decoding of binary cyclic codes
InactiveUS6751770B2Promote resultsEasy to implementOther decoding techniquesCode conversionTanner graphReverse order
Owner:SONY CORP
Fixed content distributed data storage using permutation ring encoding
InactiveUS20050216813A1Highly available and reliable and persistent storageError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionCoding blockDistributed data store
A file protection scheme for fixed content in a distributed data archive uses computations that leverage permutation operators of a cyclic code. In an illustrative embodiment, an N+K coding technique is described for use to protect data that is being distributed in a redundant array of independent nodes (RAIN). The data itself may be of any type, and it may also include system metadata. According to the invention, the data to be distributed is encoded by a dispersal operation that uses a group of permutation ring operators. In a preferred embodiment, the dispersal operation is carried out using a matrix of the form [IN<sub2>—< / sub2>C] where IN is an n×n identity sub-matrix and C is a k×n sub-matrix of code blocks. The identity sub-matrix is used to preserve the data blocks intact. The sub-matrix C preferably comprises a set of permutation ring operators that are used to generate the code blocks. The operators are preferably superpositions that are selected from a group ring of a permutation group with base ring Z2.
Owner:HITACHI VANTARA CORP
Methods, systems, and computer program products for parallel correlation and applications thereof
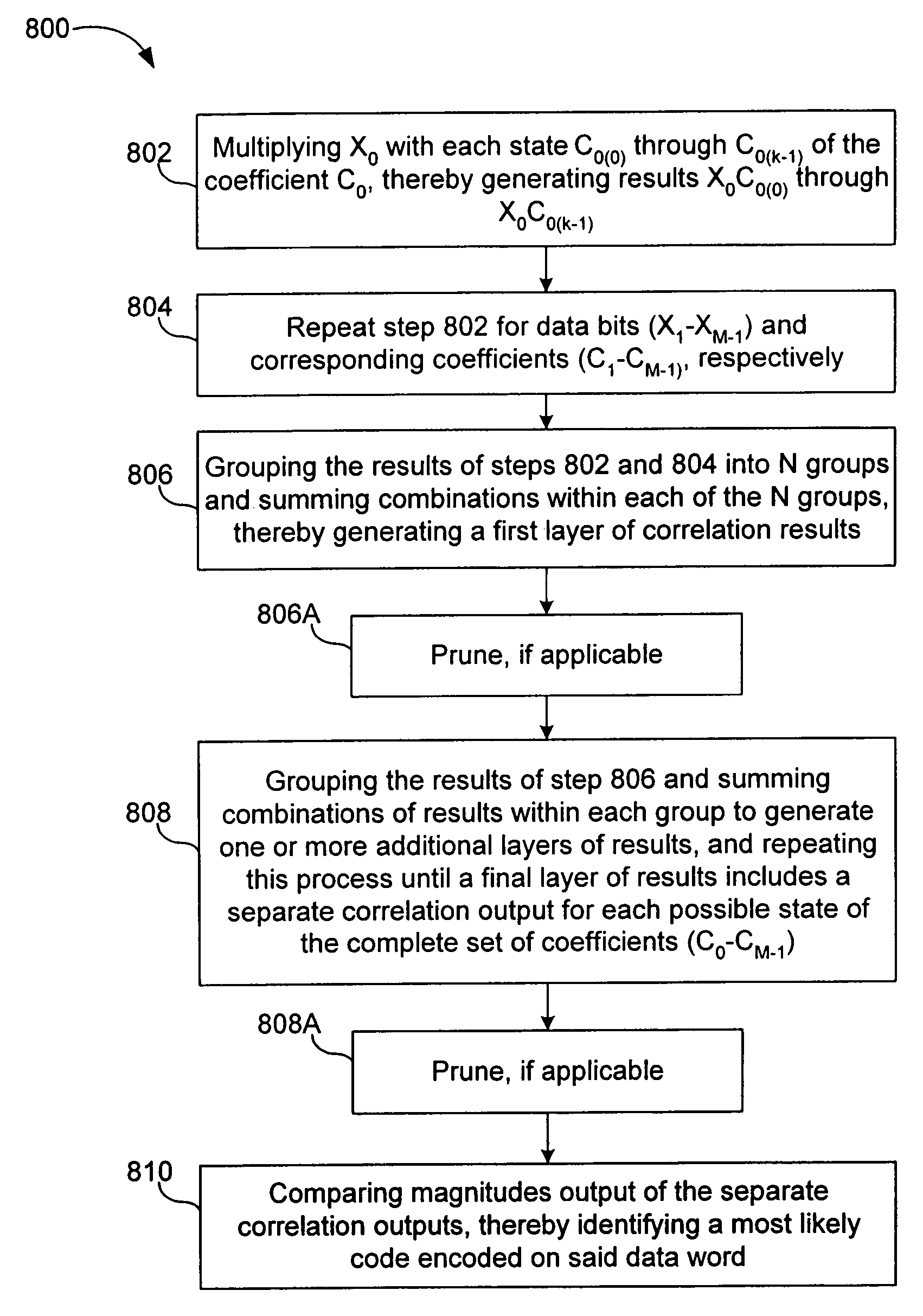
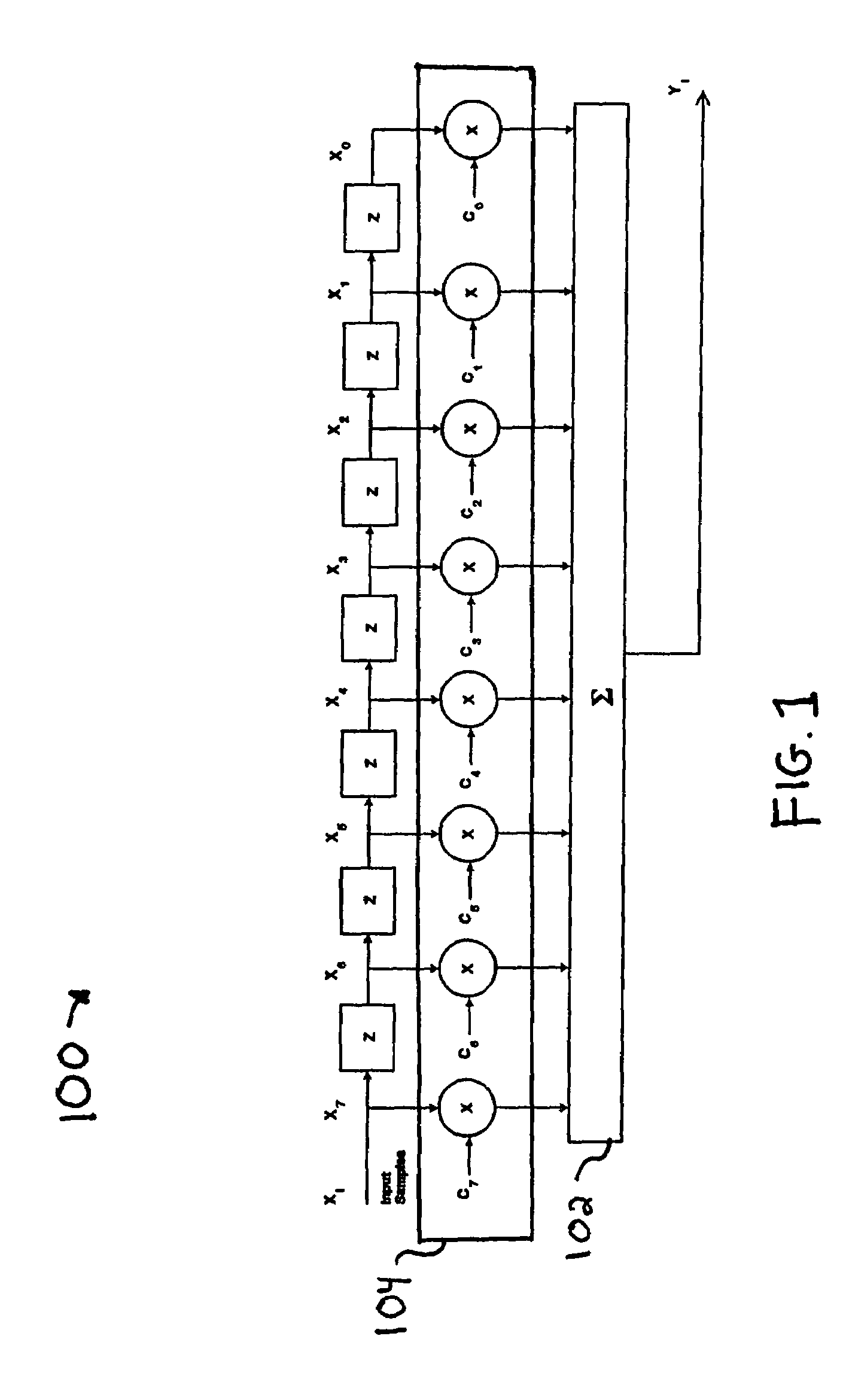
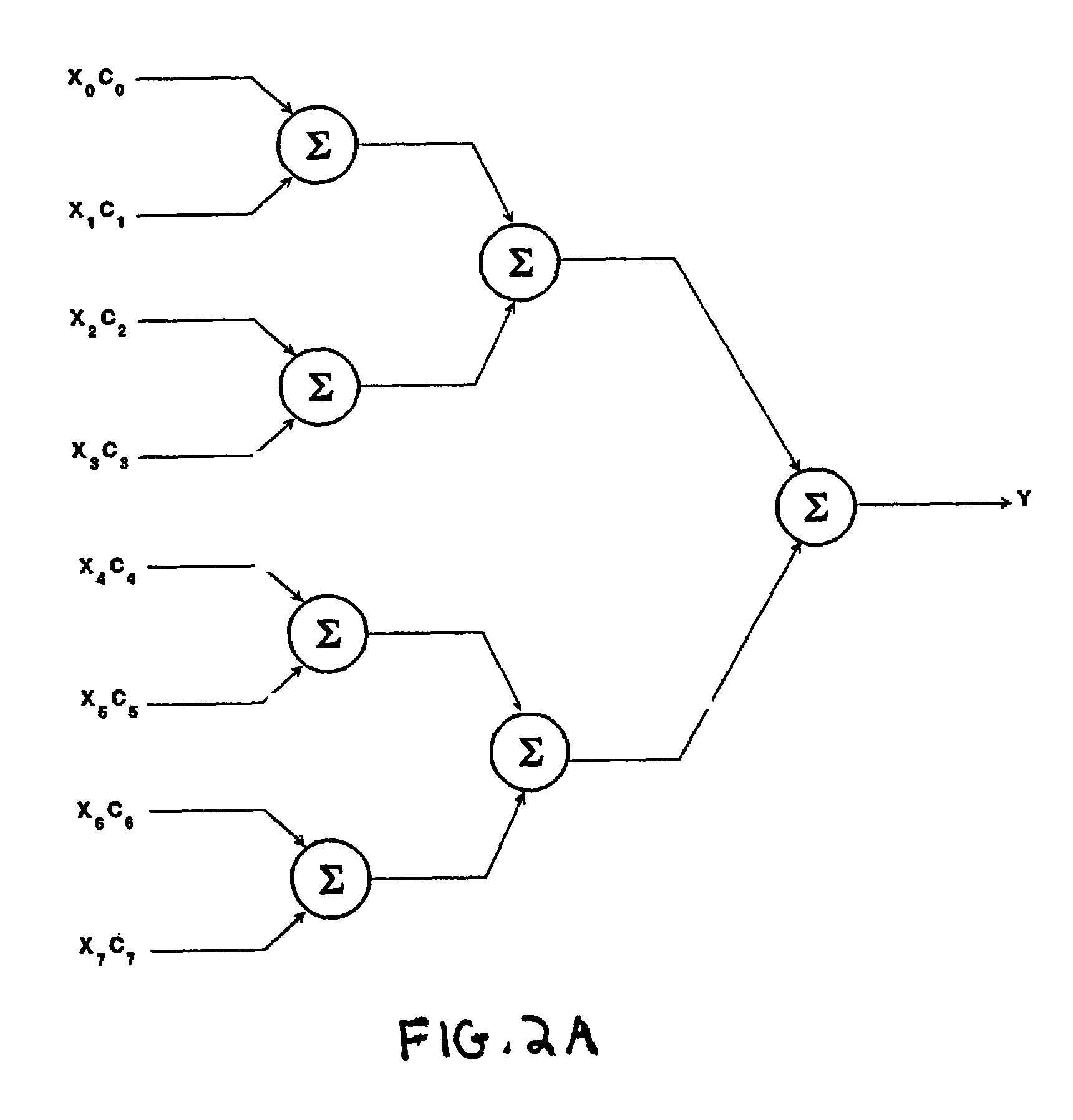
A fast correlator transform (FCT) algorithm and methods and systems for implementing same, correlate an encoded data word (X0-XM−1) with encoding coefficients (C0-CM−1), wherein each of (X0-XM−1) is represented by one or more bits and each said coefficient is represented by one or more bits, wherein each coefficient has k possible states, and wherein M is greater than 1. X0 is multiplied by each state (C0(0) through C0(k−1)) of the coefficient C0, thereby generating results X0C0(0) through X0C0(k−1). This is repeated for data bits (X1-XM−1) and corresponding coefficients (C1-CM−1), respectively. The results are grouped into N groups. Members of each of the N groups are added to one another, thereby generating a first layer of correlation results. The first layer of results is grouped and the members of each group are summed with one another to generate a second layer of results. This process is repeated until a final layer of results is generated. The final layer of results includes a separate correlation output for each possible state of the complete set of coefficients (C0-CM−1). The final layer of results is compared to identify a most likely code encoded on the data word. The summations can be optimized to exclude summations that would result in invalid combinations of the encoding coefficients (C0-CM−1). Substantially the same hardware can be utilized for processing in-phase and quadrature phase components of the data word (X0-XM−1). The coefficients (C0-CM−1) can represent real numbers and / or complex numbers. The coefficients (C0-CM−1) can be represented with a single bit or with multiple bits (e.g., magnitude). The coefficients (C0-CM−1) represent, for example, a cyclic code keying (“CCK”) code set substantially in accordance with IEEE 802.11 WLAN standard.
Owner:PARKER VISION INC
Low-density parity-check (LDPC) encoder
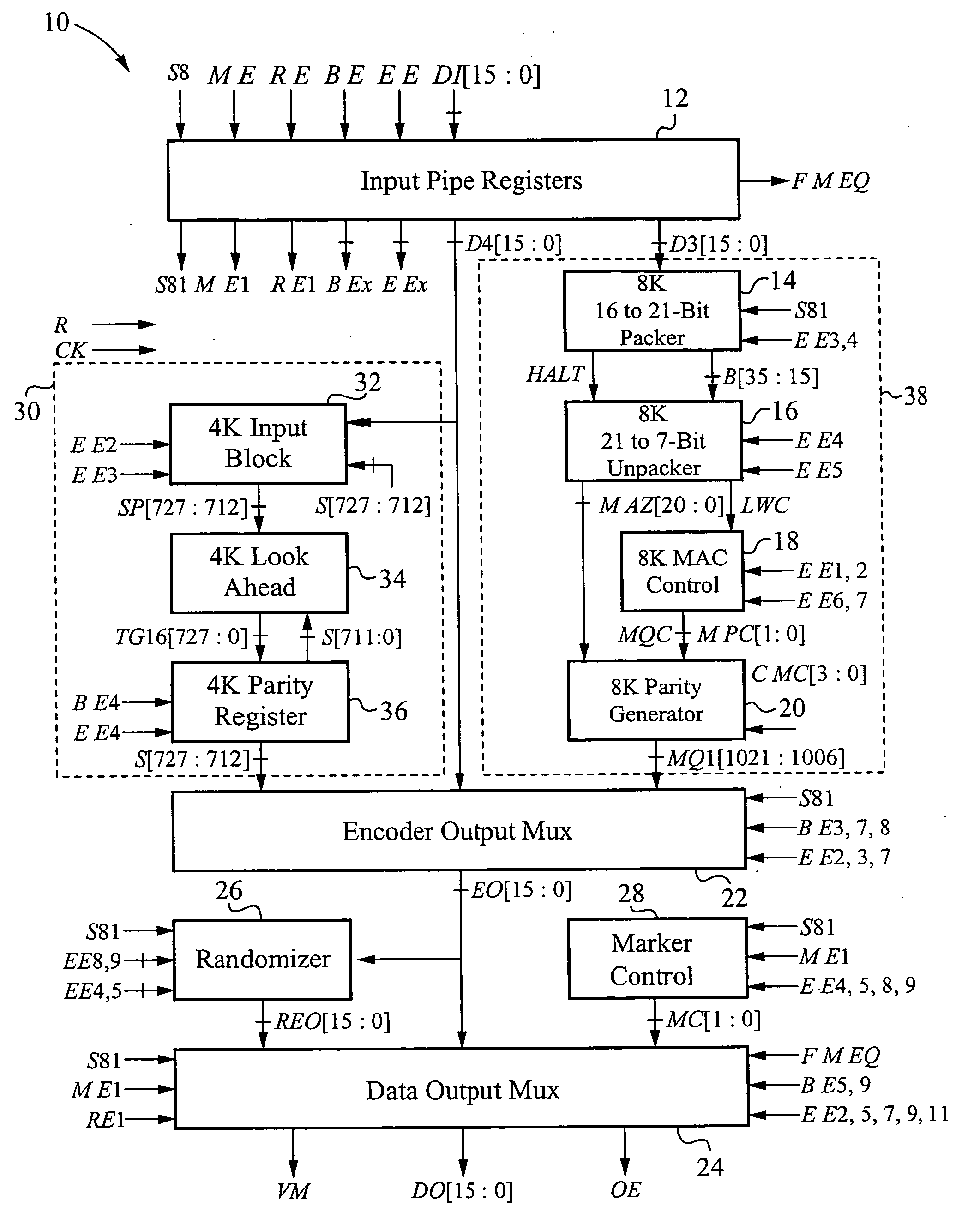
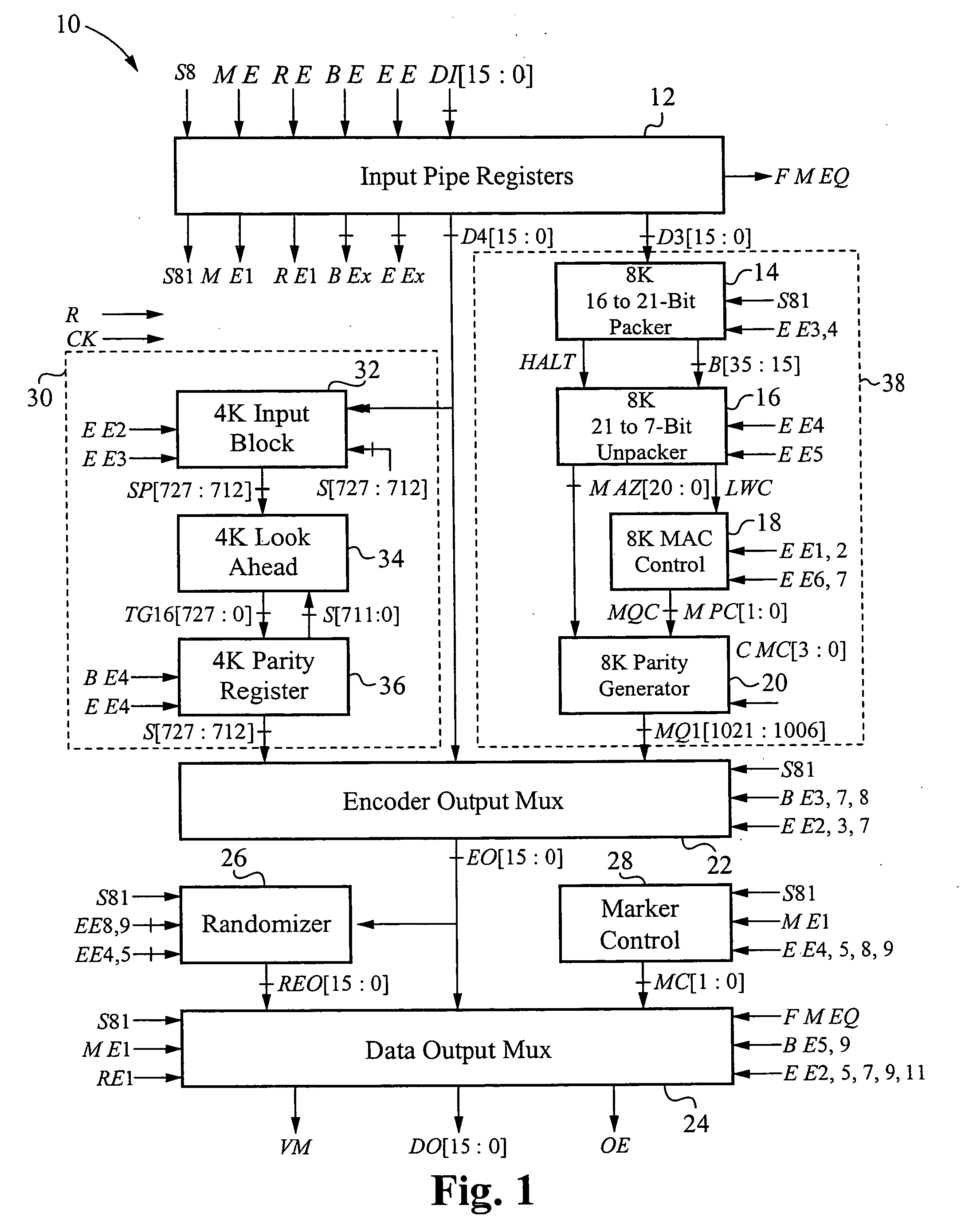
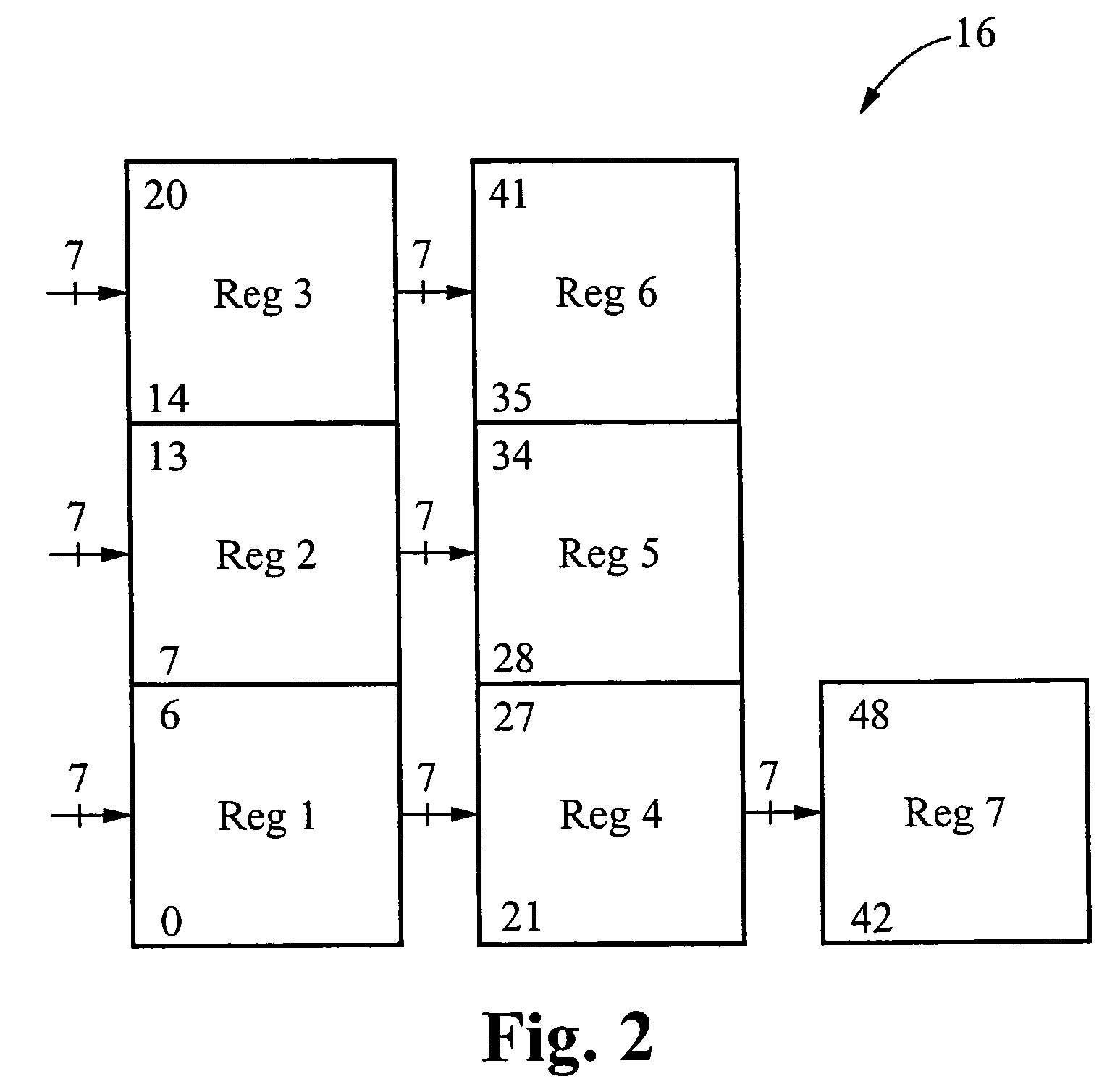
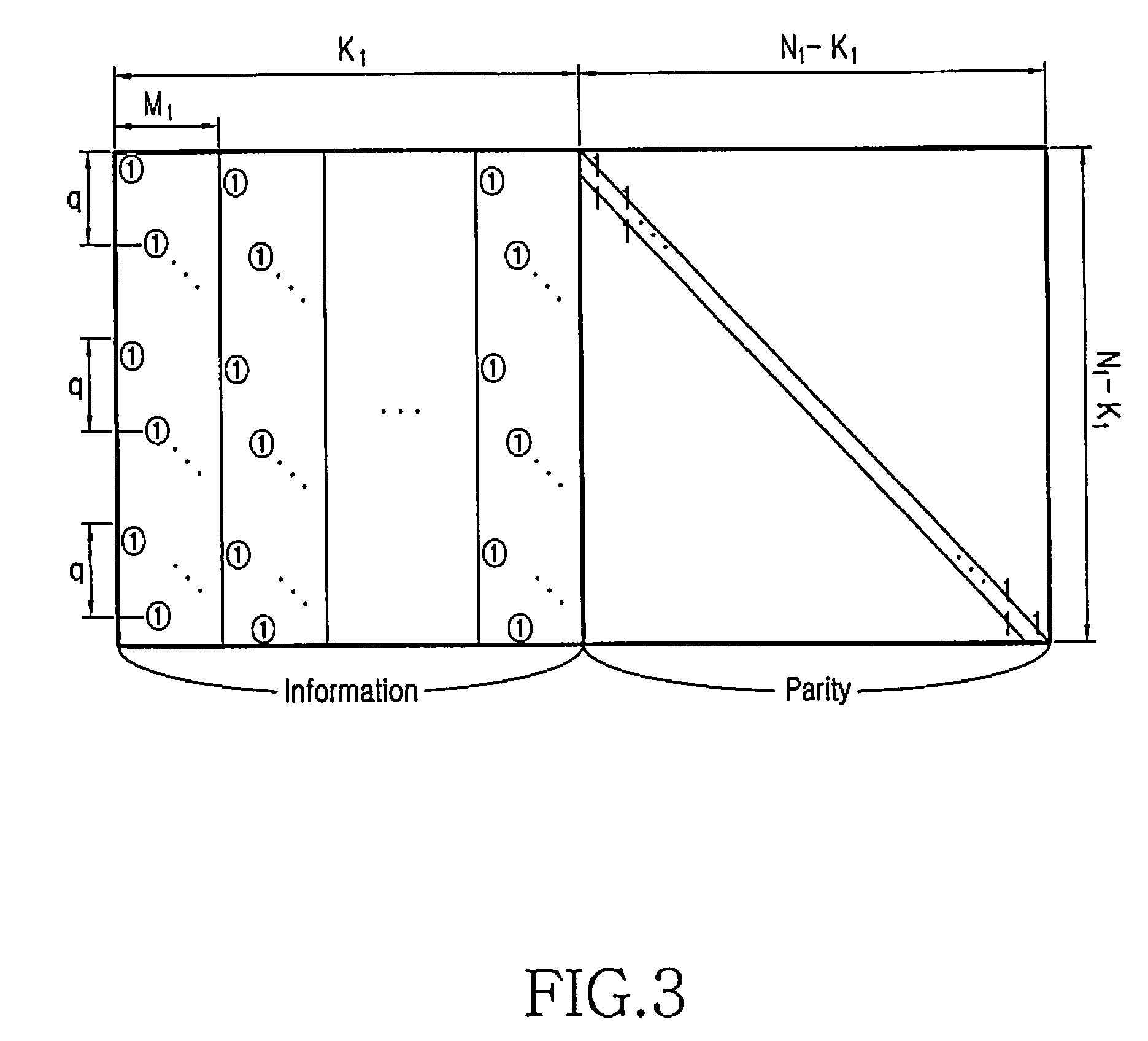
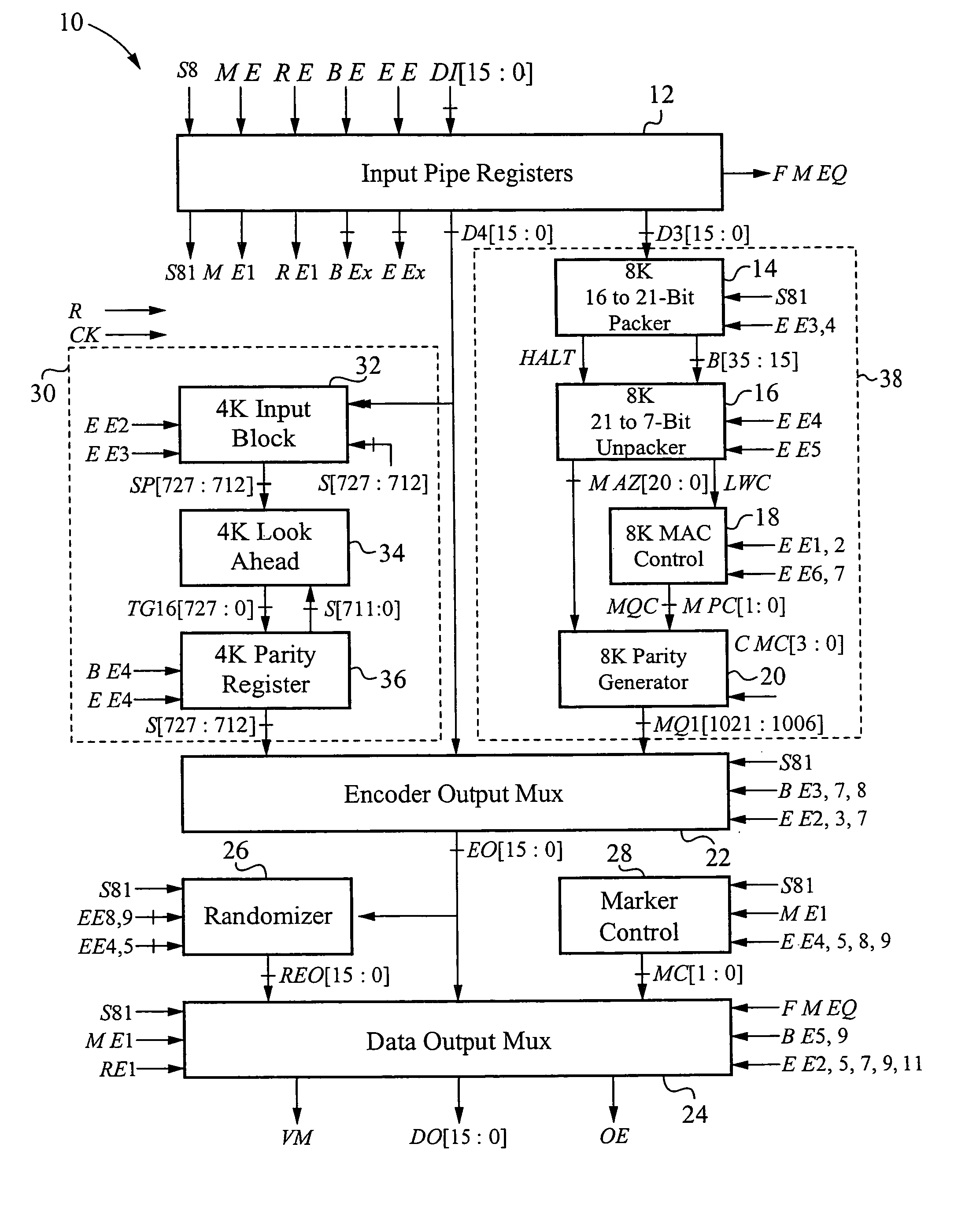
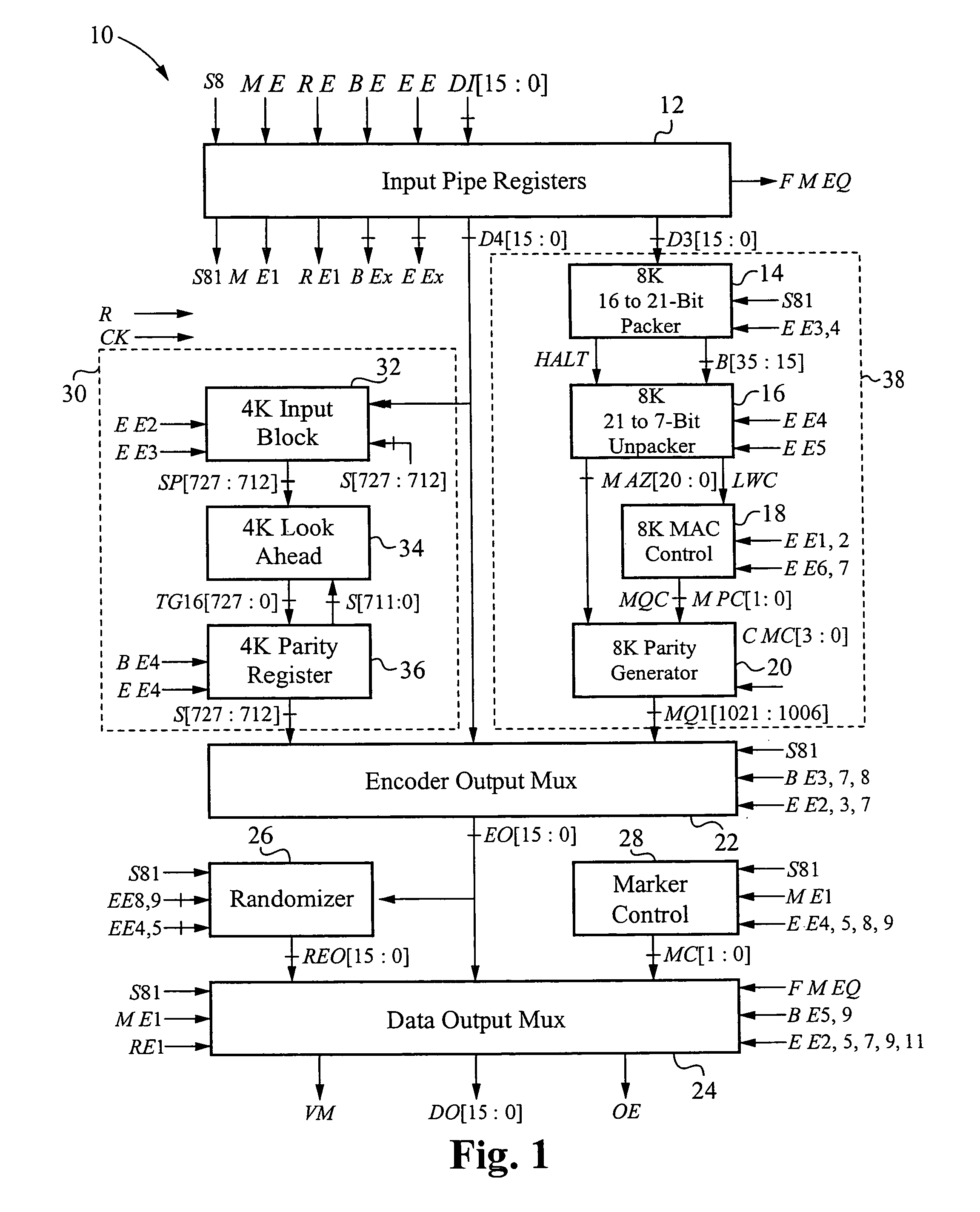
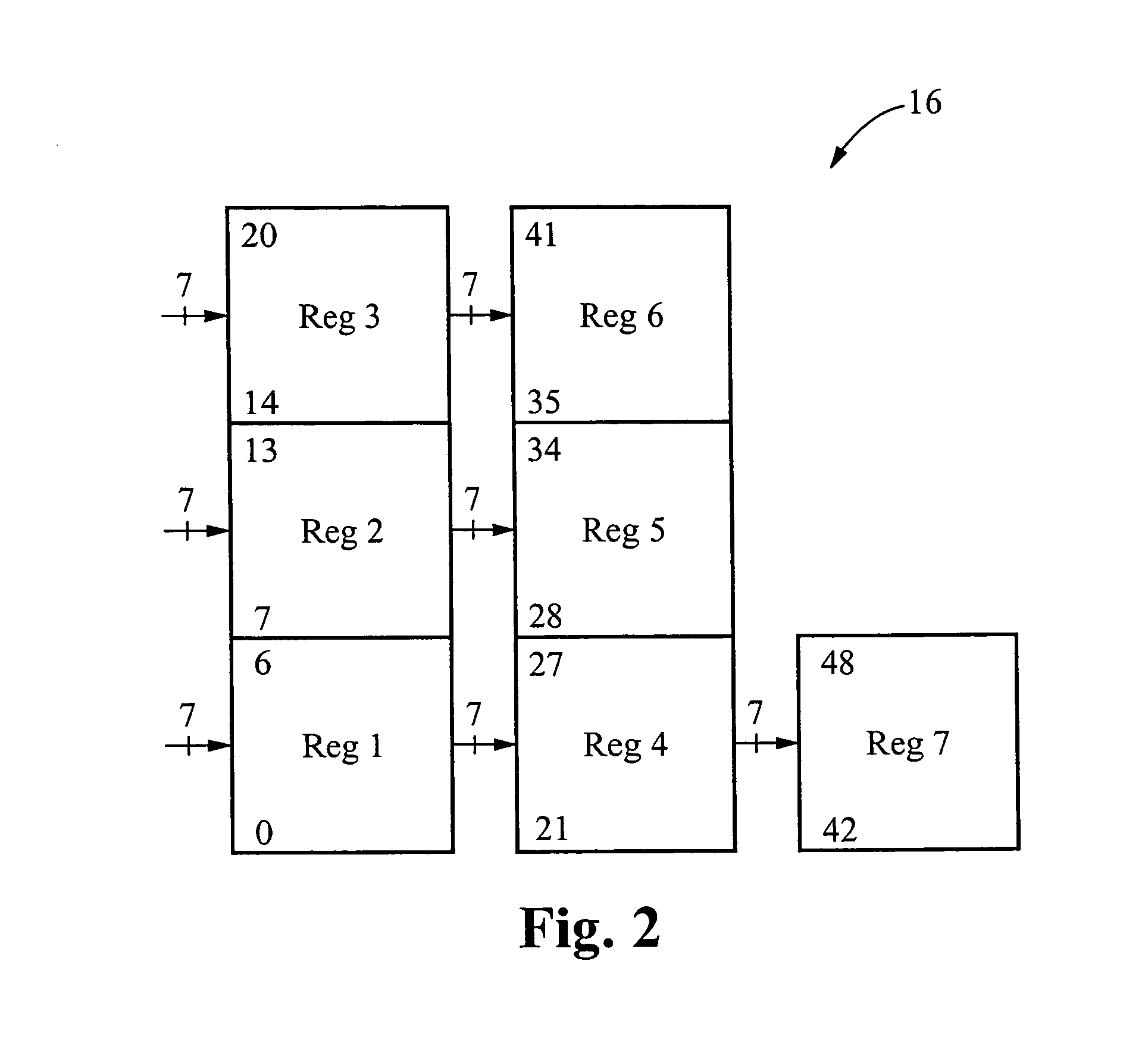
The encoder chip of the present invention uses LDPC codes to encode input message data at a transmitting end, thereby generating a series of codewords. The encoder chip implements two low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes. The first LDPC code is a (4088,3360) code (4K) which is shortened from a (4095,3367) cyclic code. The second LDPC code is a quasi-cyclic (8158,7136) code (8K). The message data and the generated codewords are transmitted to a receiving end where the received codewords are decoded and checked for errors. To generate the codewords, the encoder applies a generator matrix G to the input message data. The G matrix is generated by first defining an H matrix. An H matrix is initially defined as 16×2 array of right-circulant sub-matrices. The G matrix is formed by manipulating the H matrix according to a 4-step algorithm. A randomizer and a synchronization marker are also included within the encoder.
Owner:IDAHO RESARCH FOUNDATION INC
Method and apparatus for using fire decoder to correct burst errors in a real-time communications system
InactiveUS6754871B1Error preventionBurst error correctionProcessor registerReal time communication systems
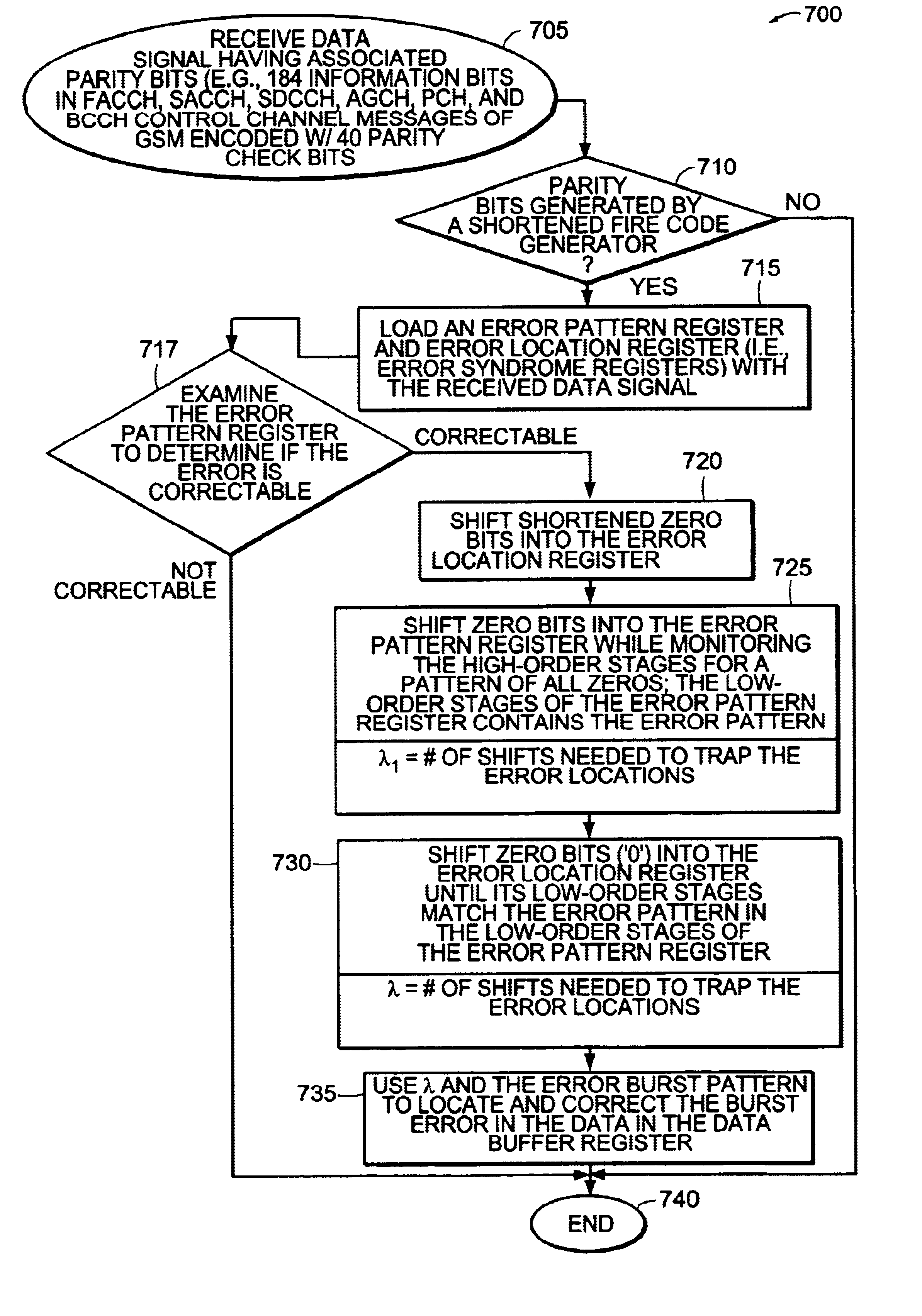
Error bursts are detected and corrected in a communication system using shortened cyclic codes, such as shortened Fire codes. Data is loaded into a first error syndrome register and a second error syndrome register. The data in the registers may be evaluated to determine if the data bits contain a correctable error. Shortened zero bits are shifted into the second error syndrome register. A number of zero bits are shifted into the first error syndrome register to trap an error burst pattern in the data. A determination is made as to the number of zero bits shifted into the second error syndrome register to trap the location of the error burst in the data. Using the number of zero bits shifted into the second error syndrome register and the error burst pattern, the error in the data is located and corrected.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
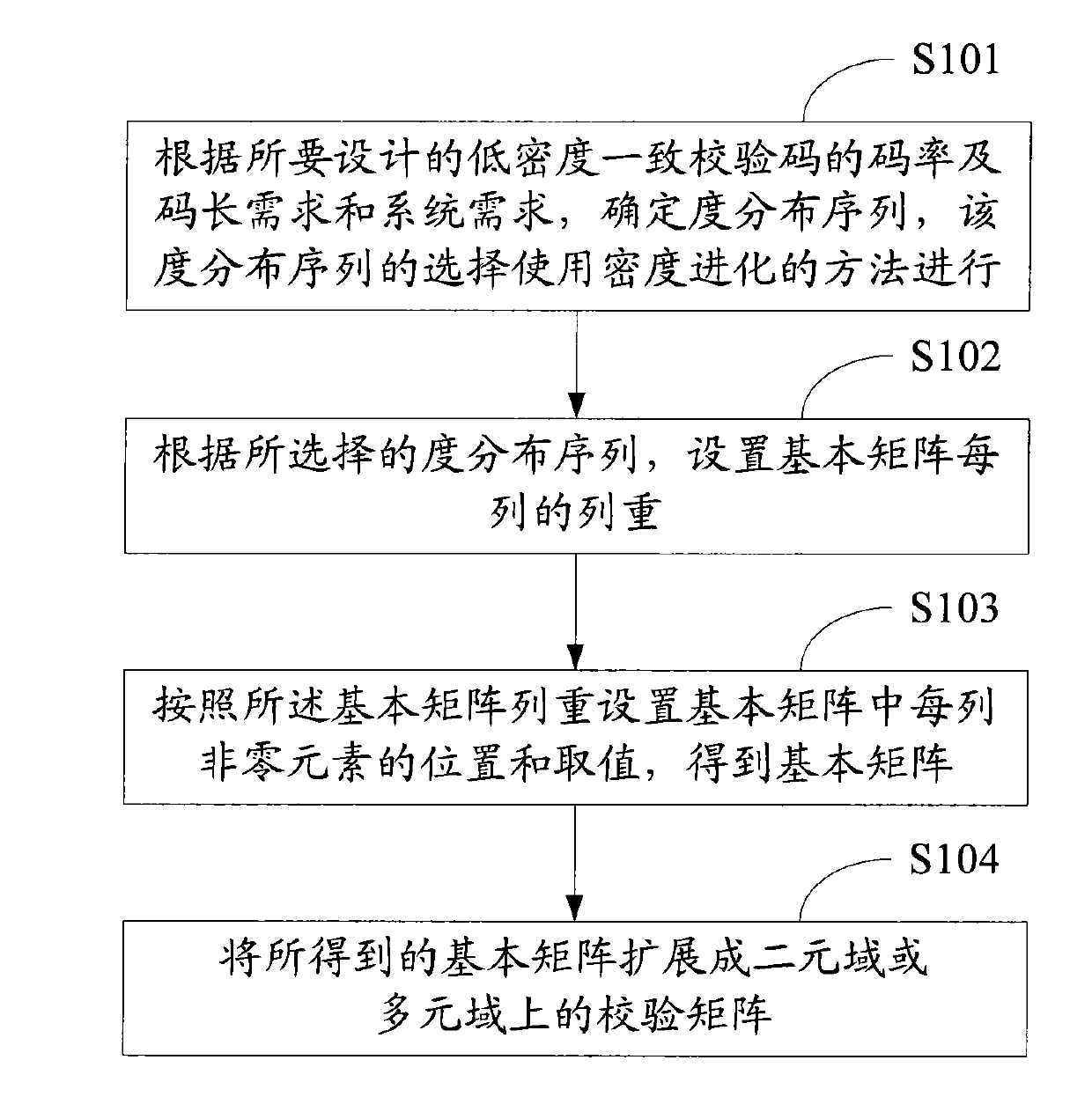
Method and device for generating and coding quasi-cyclic LDPC code
ActiveCN101662290AError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionAlgorithmSystem requirements
The invention relates to the technical filed of the error correction and coding of communication and information systems and discloses a method for generating a quasi-cyclic low density parity check code. The method comprises the following steps: according to the requirements on code rate and code length of the low density parity check code to be designed and system requirements, determining a degree distribution sequence which is selected by adopting a density evolution method; setting the column weight of each column of a basic matrix according to the selected degree distribution sequence; setting the positions and values of non-zero elements in each column in the basic matrix according to the column weights of the basic matrix to obtain the basic matrix; and expanding the obtained basic matrix into a check matrix. At the same time, the invention also discloses a method for coding the quasi-cyclic low density parity check code and provides corresponding devices. The methods and the devices provided by the embodiment of the invention enable finally obtained code words to effectively reduce influences of cycle overlapping.
Owner:HONOR DEVICE CO LTD
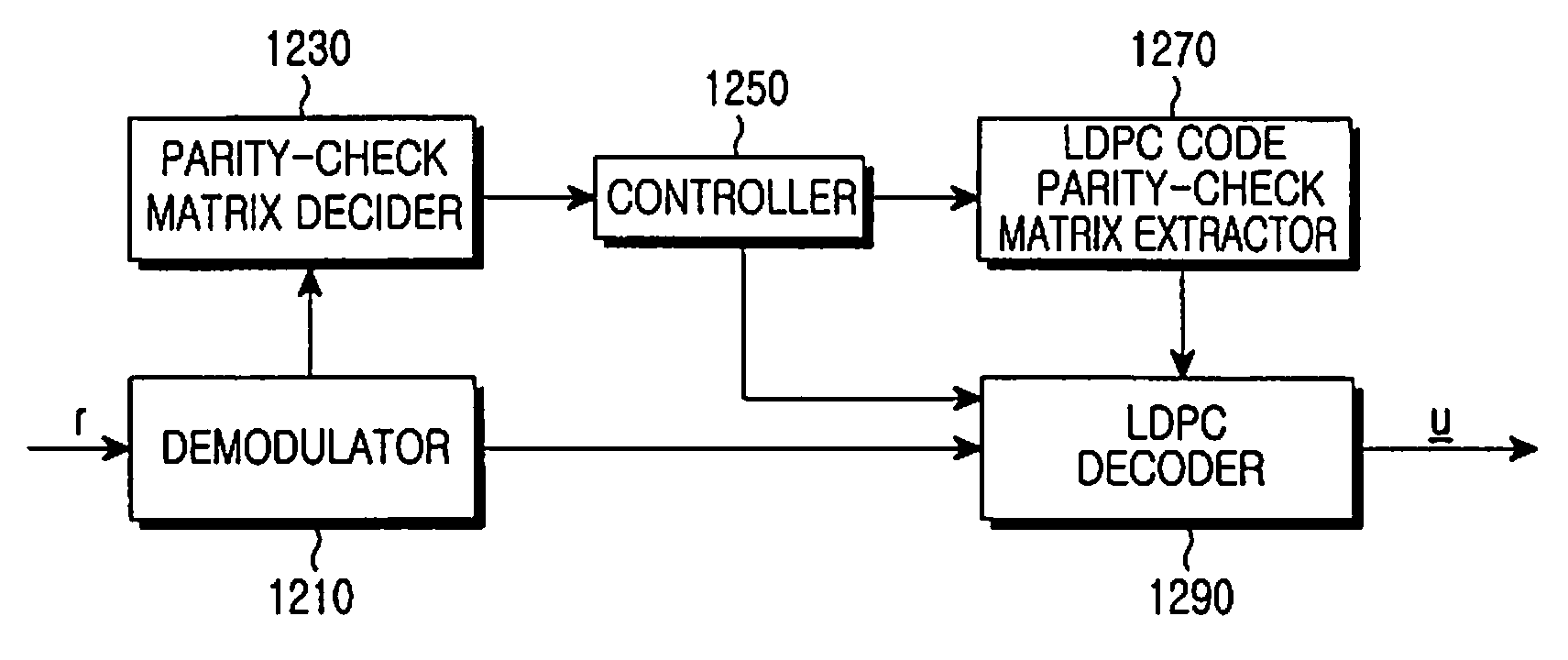
Apparatus and method for encoding and decoding channel in a communication system using low-density parity-check codes
ActiveUS20090210767A1Error correction/detection using multiple parity bitsCode conversionCommunications systemTheoretical computer science
An apparatus and method for generating a parity-check matrix of a Low-Density Parity-Check (LDPC) code are provided. Parameters for designing the LDPC code are determined, and a first parity-check matrix of a quasi-cyclic LDPC code is formed according to the determined parameters. A second parity-check matrix is created through the elimination of a predetermined portion of a parity part in the first parity-check matrix, and a third parity-check matrix is created by rearranging the second parity-check matrix.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Decoder for iterative decoding of binary cyclic codes
InactiveUS20020116677A1Promote resultsEasy to implementOther decoding techniquesCode conversionTanner graphReverse order
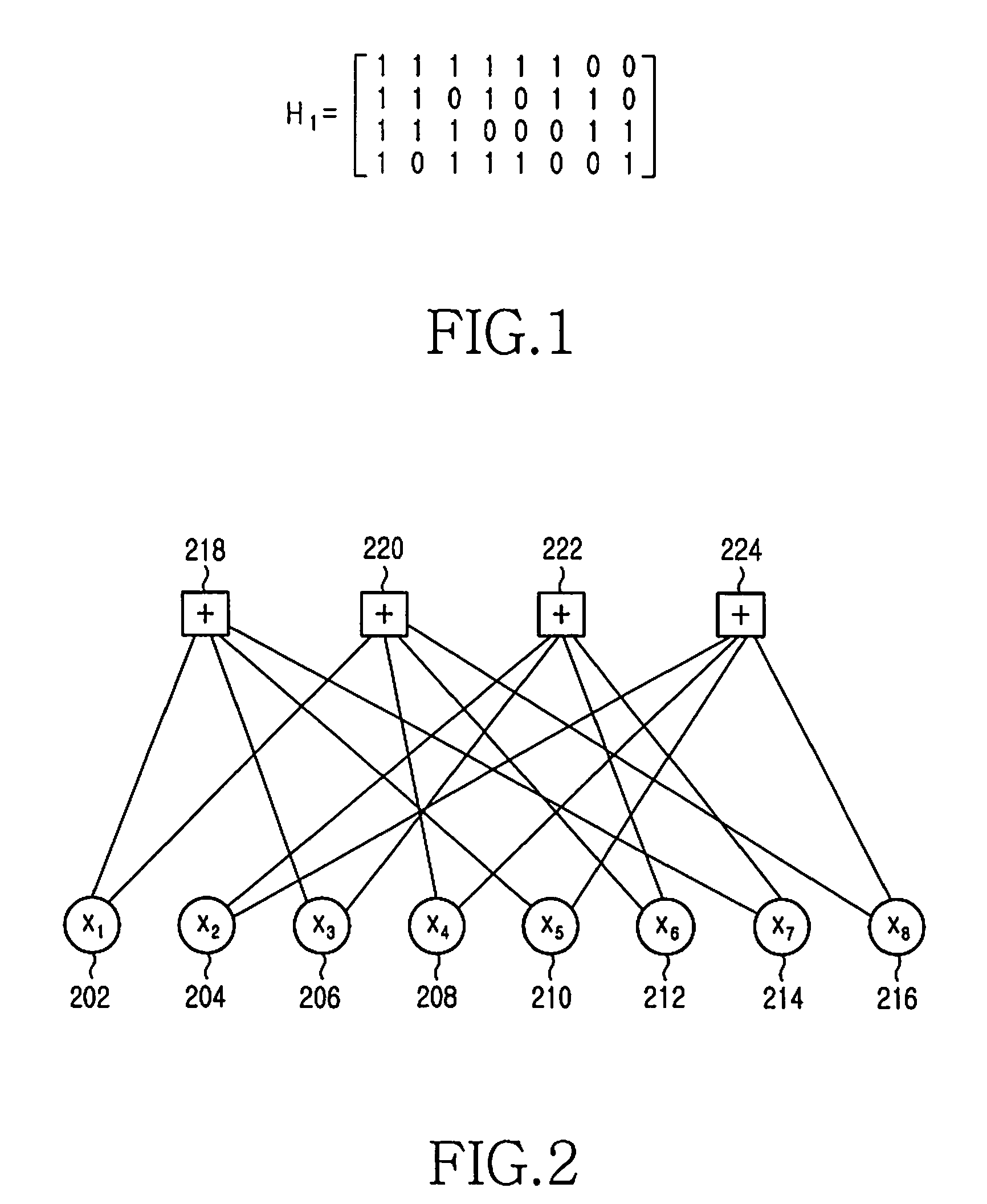
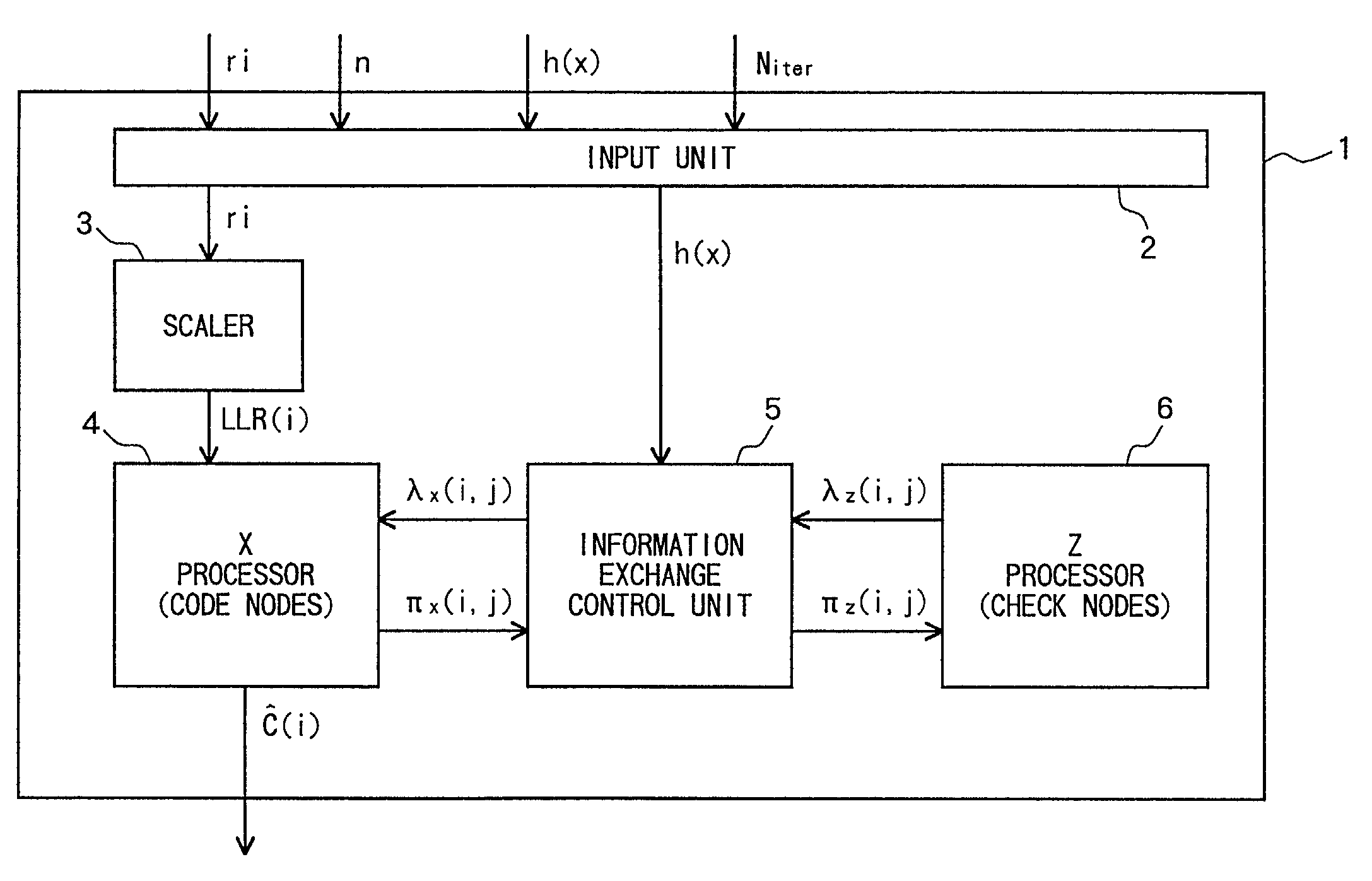
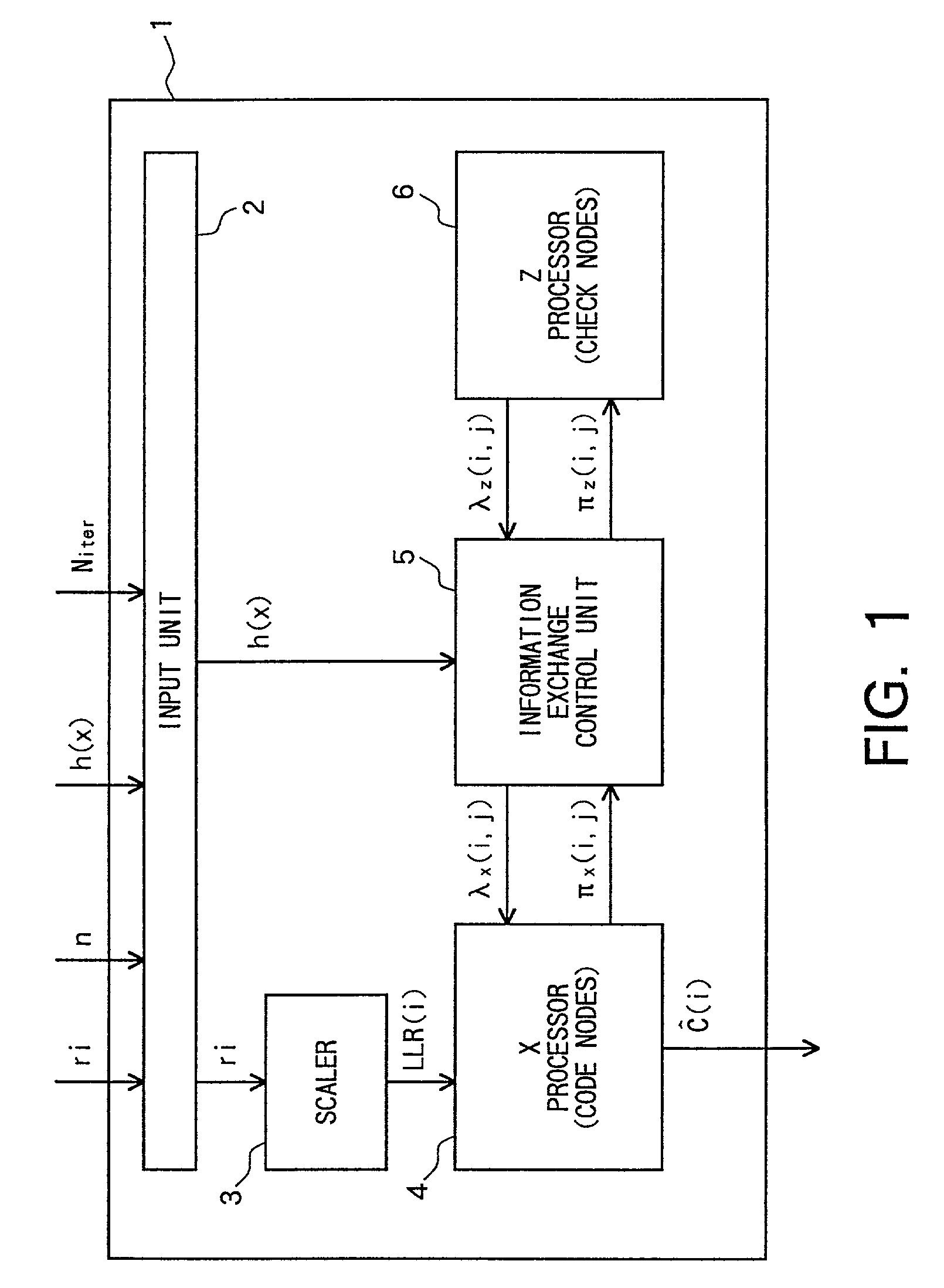
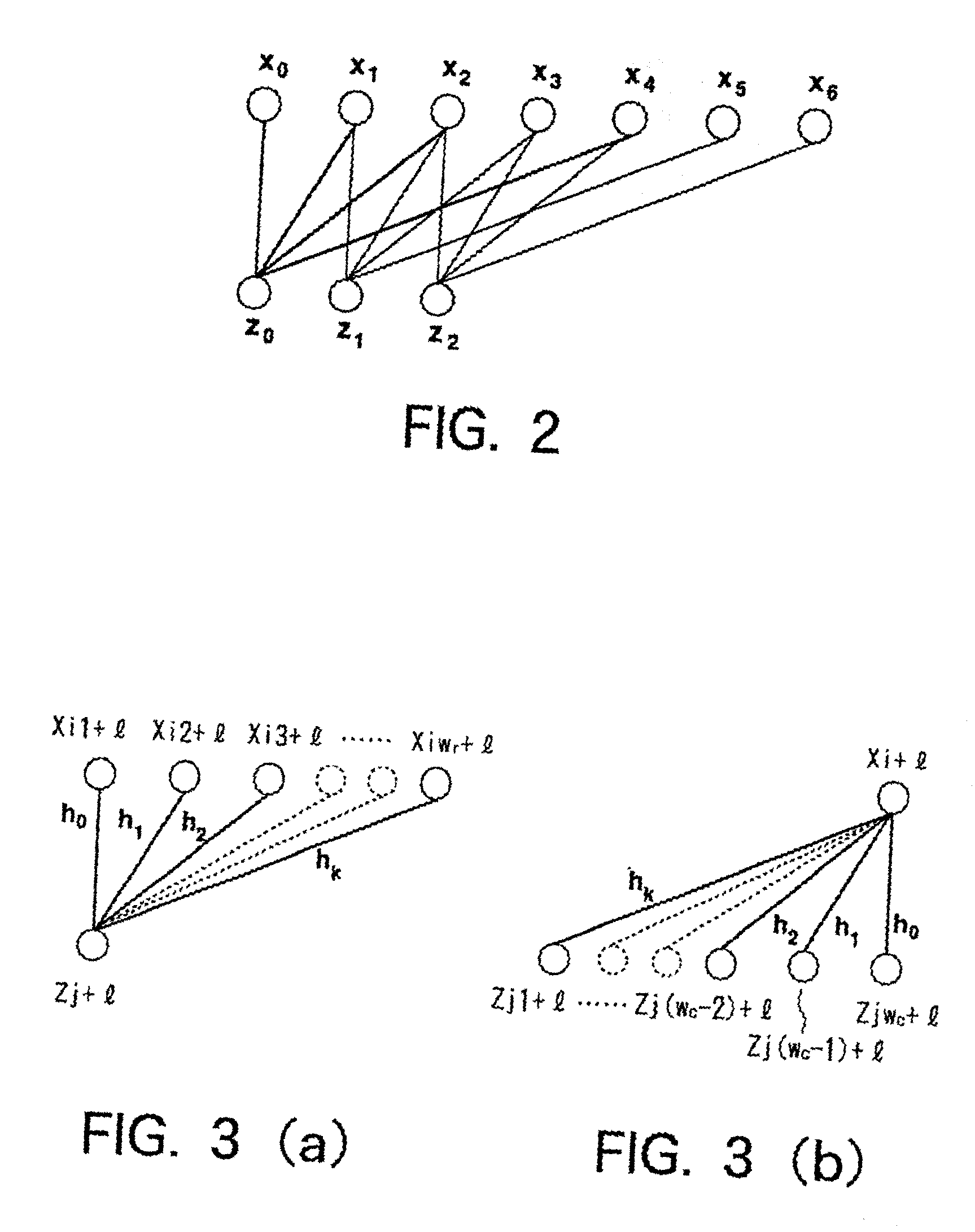
A decoder for performing soft decision iterative decoding of a cyclic code based on belief propagation, includes an information exchange control unit, an X processor, and a Z processor. The information exchange control unit takes pix-metrics that were calculated by the X processor for nonzero elements in each of n-cyclic shifts of the parity-check polynomial of the code, and distributes the pix-metrics to the Z processor as the piz-metrics for a corresponding check node. The information exchange control unit takes lambdz-metrics that were calculated by the Z processor for nonzero elements in each of n-cyclic shifts in a reverse order of the parity-check polynomial, and distributes them to the X processor as lambdx-metrics for the corresponding code node. The operation of the information exchange control unit can be represented by the Tanner graph associated with an extended parity-check matrix, which is produced by adding k rows to the parity-check matrix of the cyclic code, wherein the X processor functions as the code nodes and the Z processor functions as the check nodes.
Owner:SONY CORP
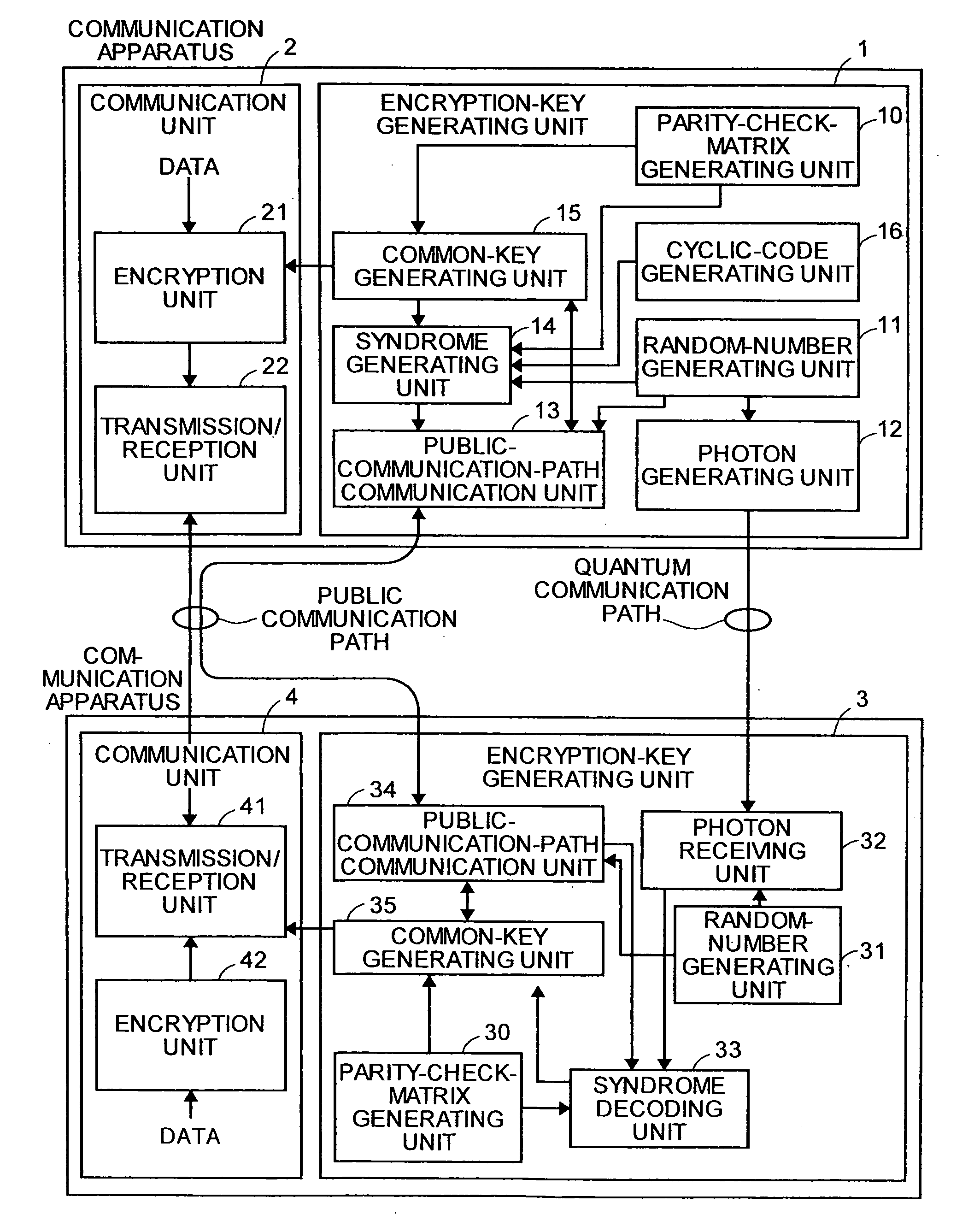
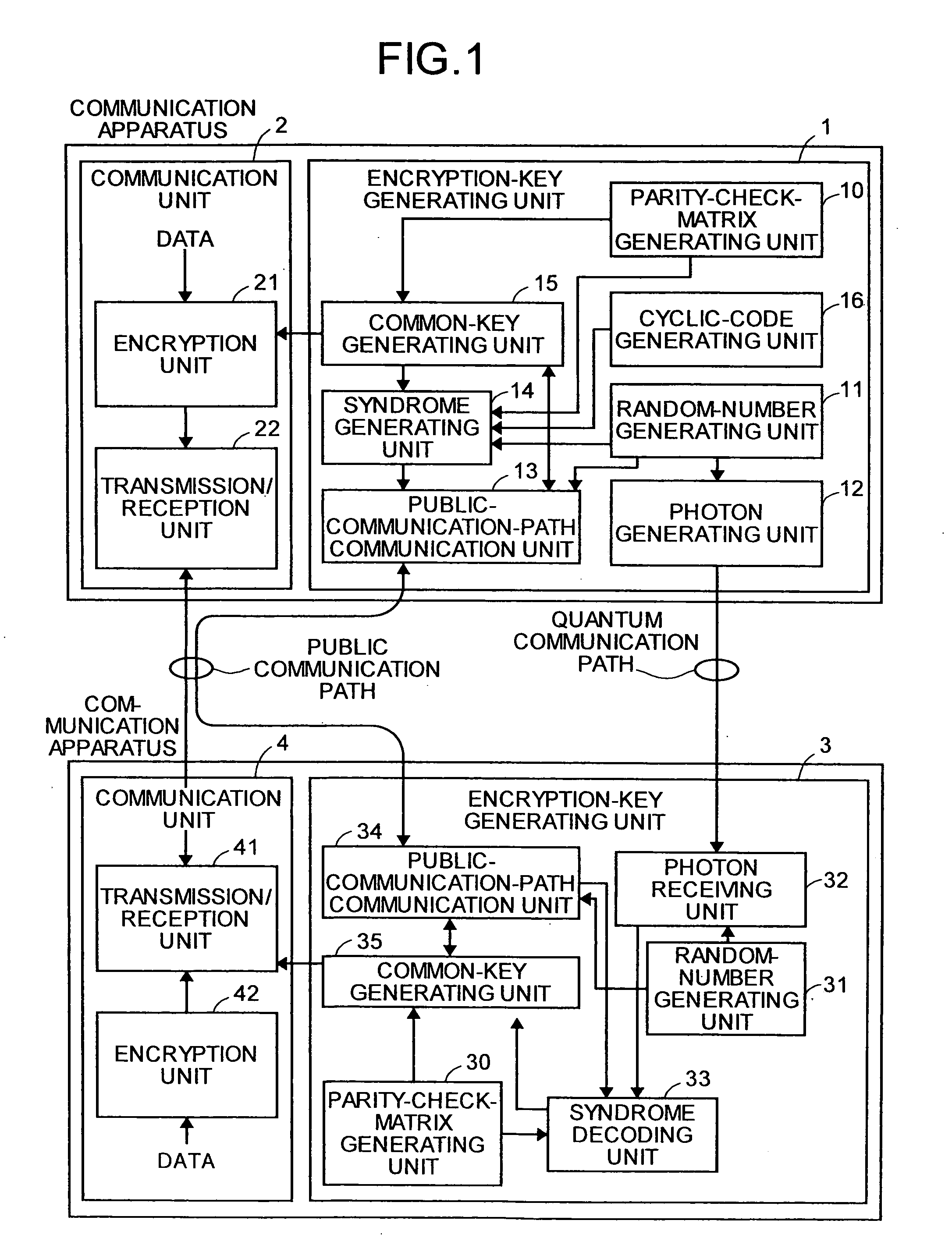
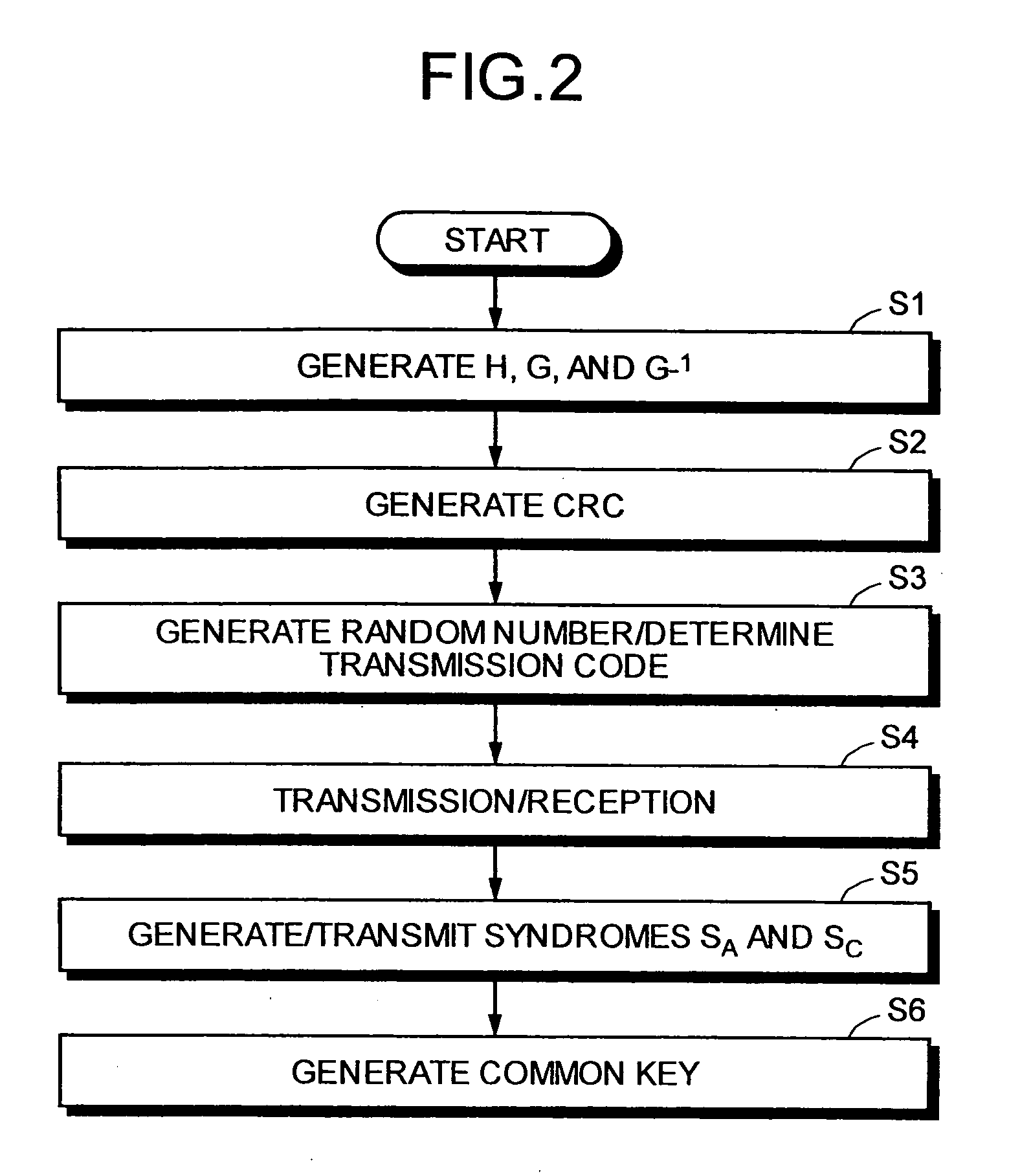
Quantum Key Distribution Method and Communication Apparatus
InactiveUS20080144833A1Stable characteristicsKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesComputer hardwareParity-check matrix
In a quantum key distributing method of the present invention, a communication apparatus on a reception side performs error correction using parity check matrixes for an LDPC code that have an extremely high error correction ability. In the quantum key distributing method of the present invention, a cyclic code syndrome generated by a communication apparatus on a transmission side and an estimated cyclic code syndrome generated based on an estimated word after error correction are compared to perform error detection for the estimated word.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
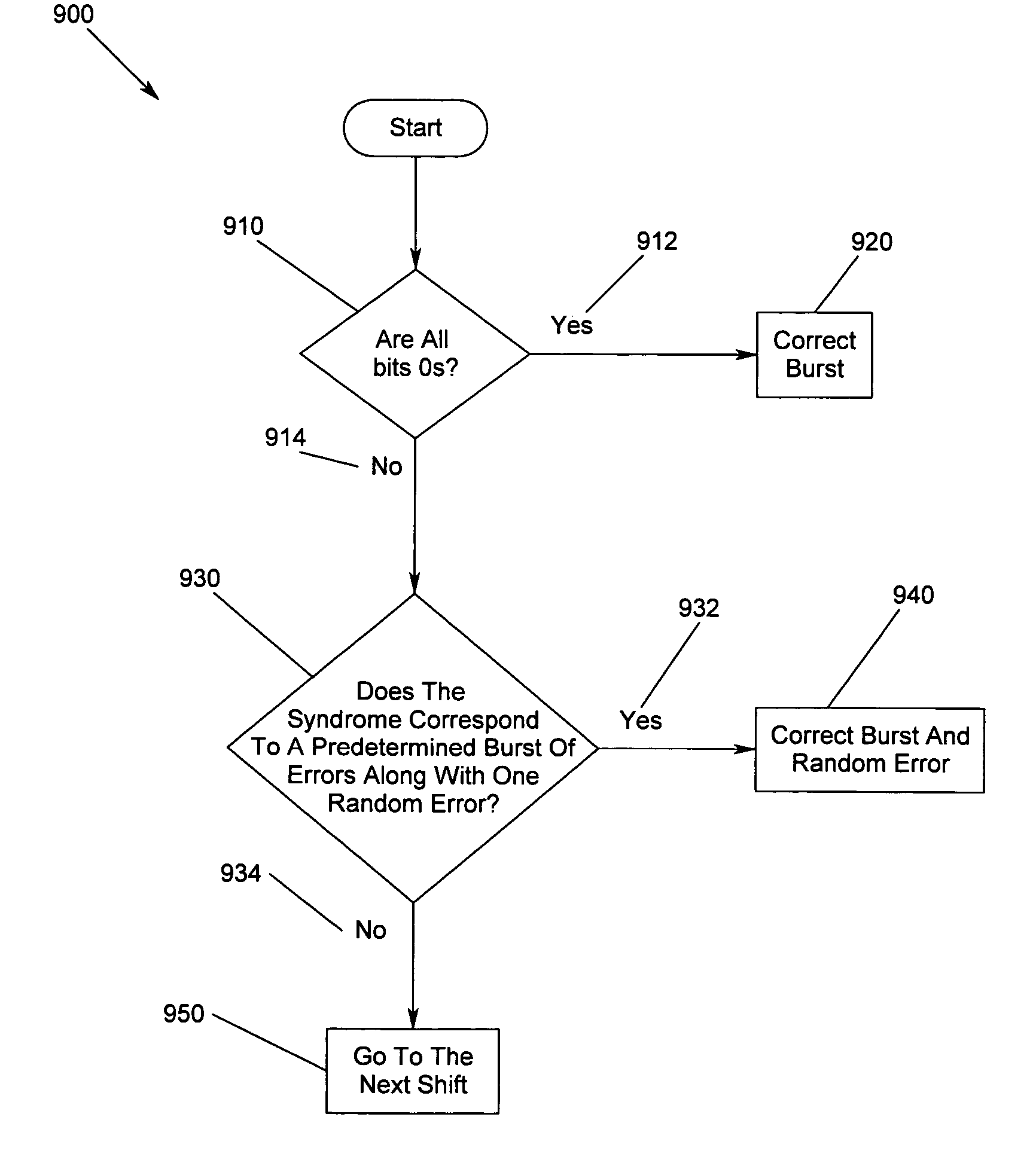
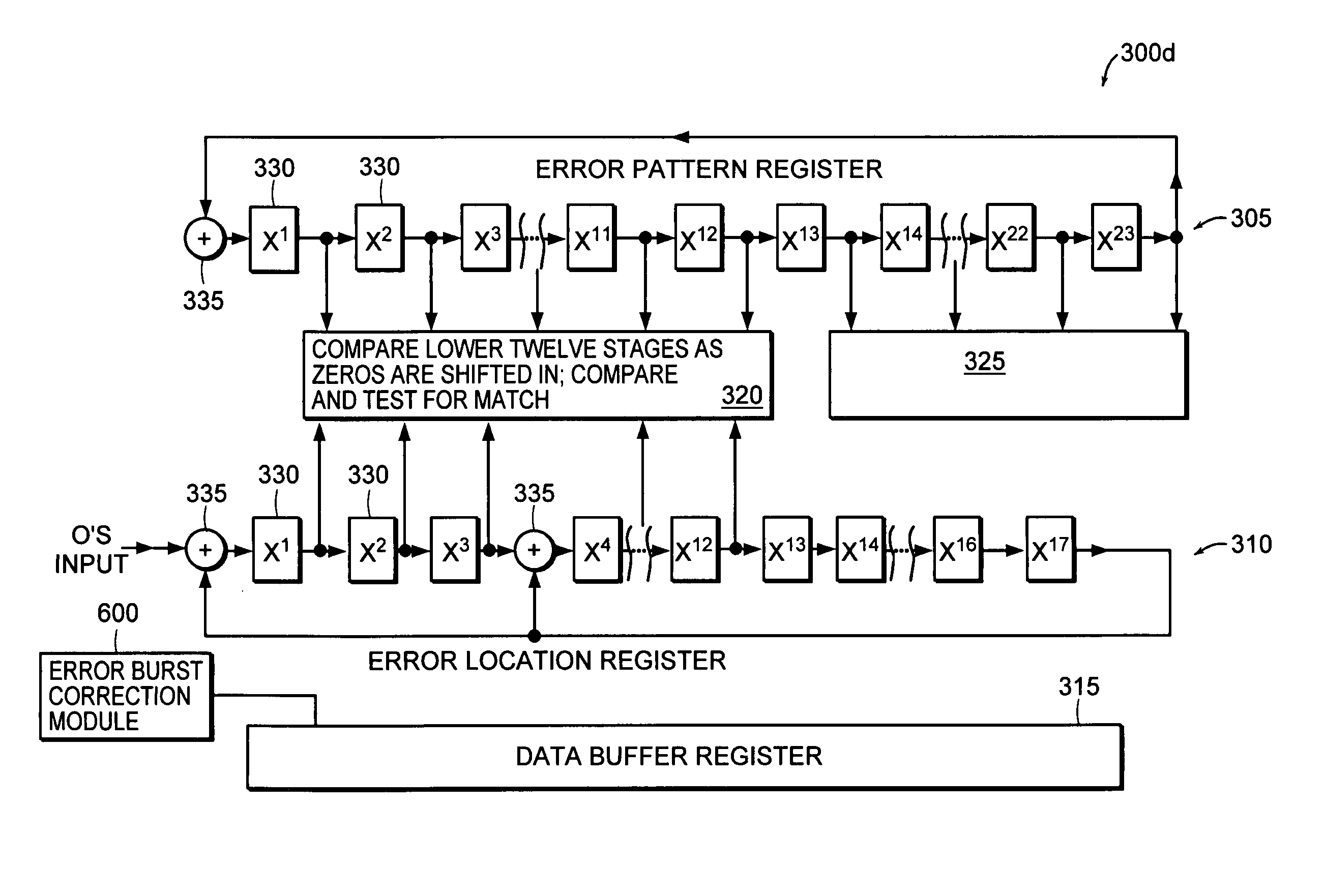
Method, apparatus and program storage device for correcting a burst of errors together with a random error using shortened cyclic codes
A method, apparatus and program storage device for correcting a burst of errors together with a random error using cyclic or shortened cyclic codes is disclosed. The present invention solves the above-described problems by providing a received word to a syndrome register defined by a polynomial of degree n-k, said polynomial generating a cyclic or shortened cyclic code, wherein n is the length and k is the number of information bits in the codeword. The syndrome gets modified each time the received (possibly noisy) word is shifted. The contents of the syndrome register are processed to identify a random error together with an error burst of the received word. Then correction of the random error and the burst is made and a corrected codeword is generated.
Owner:HITACHI GLOBAL STORAGE TECH NETHERLANDS BV
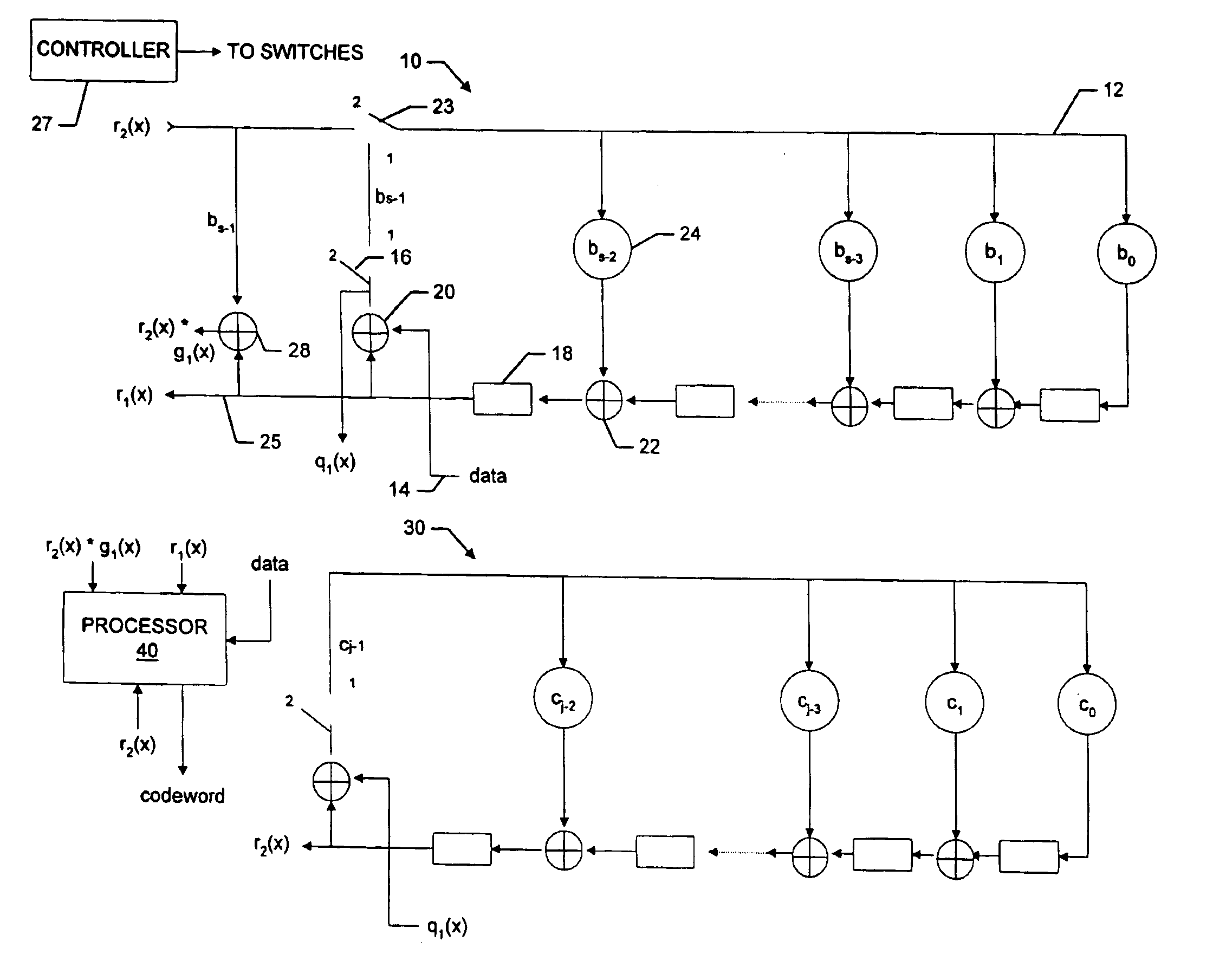
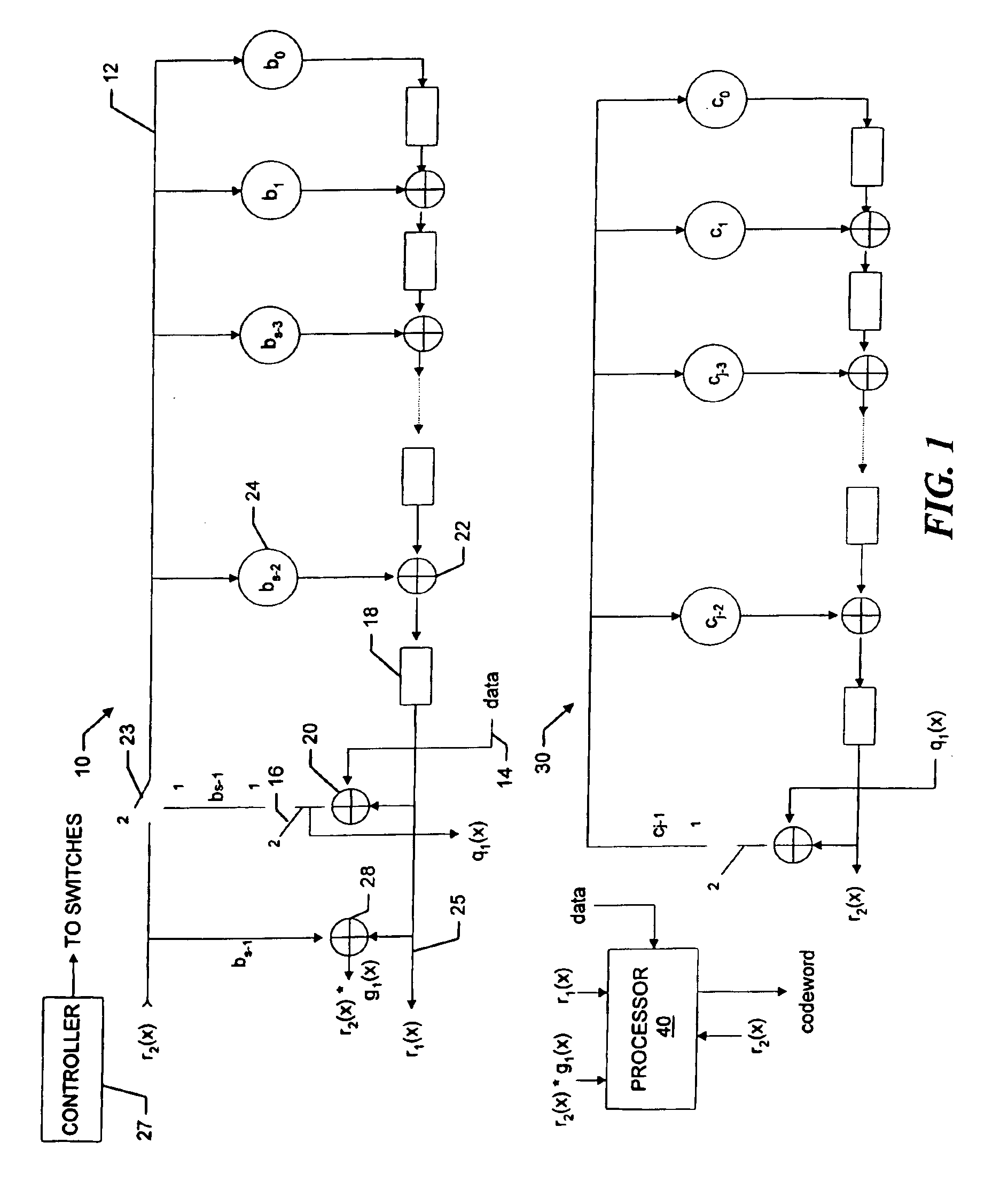
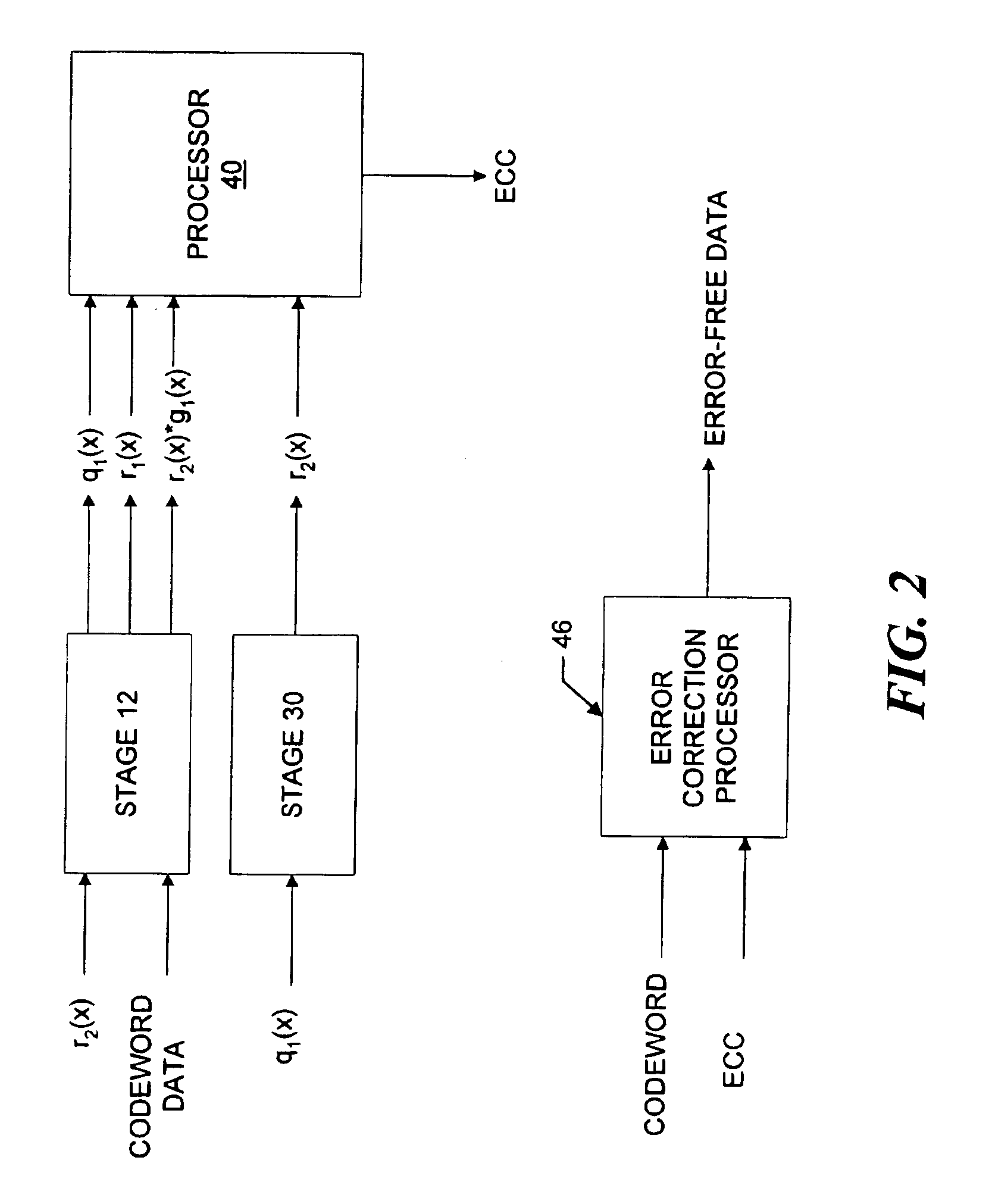
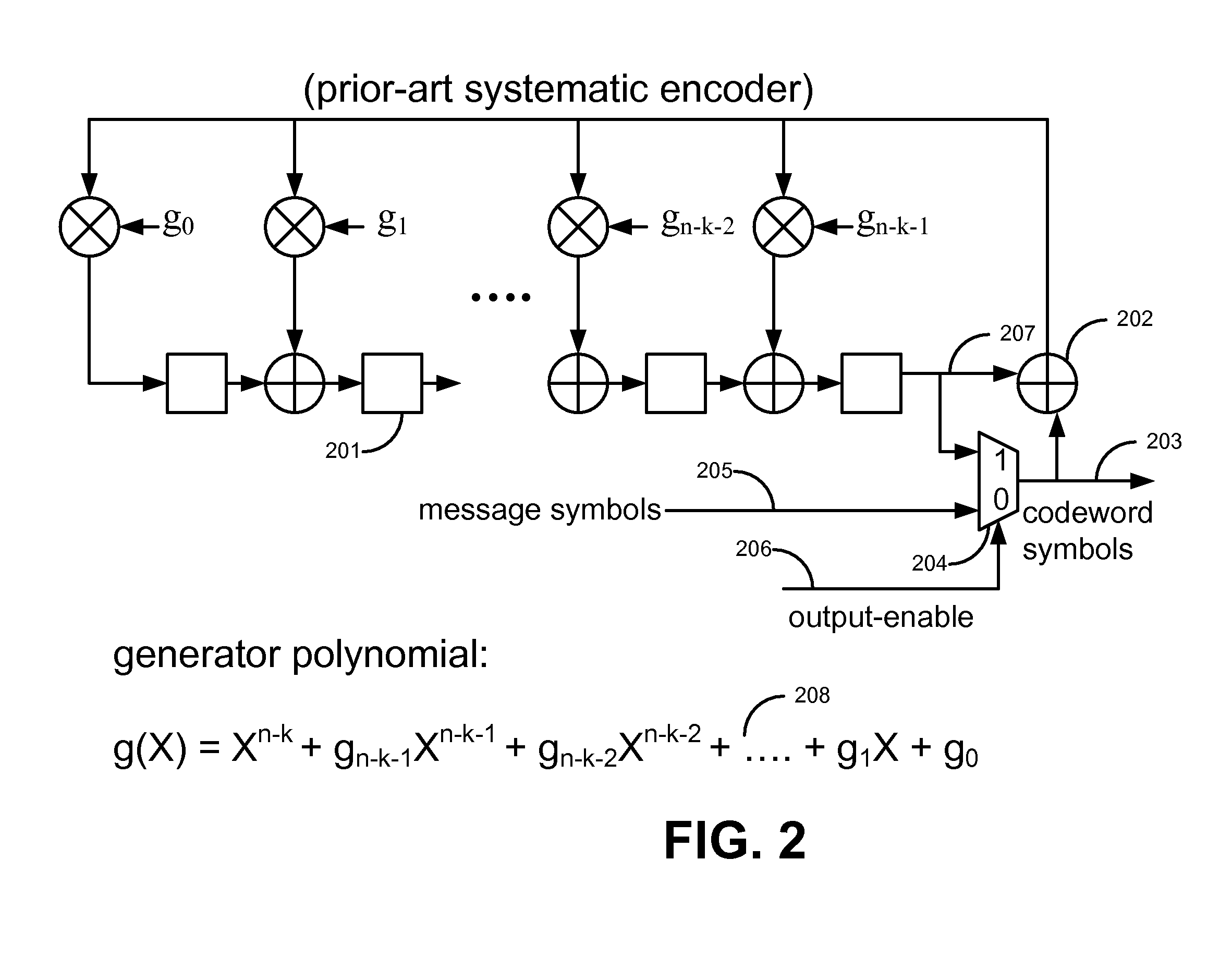
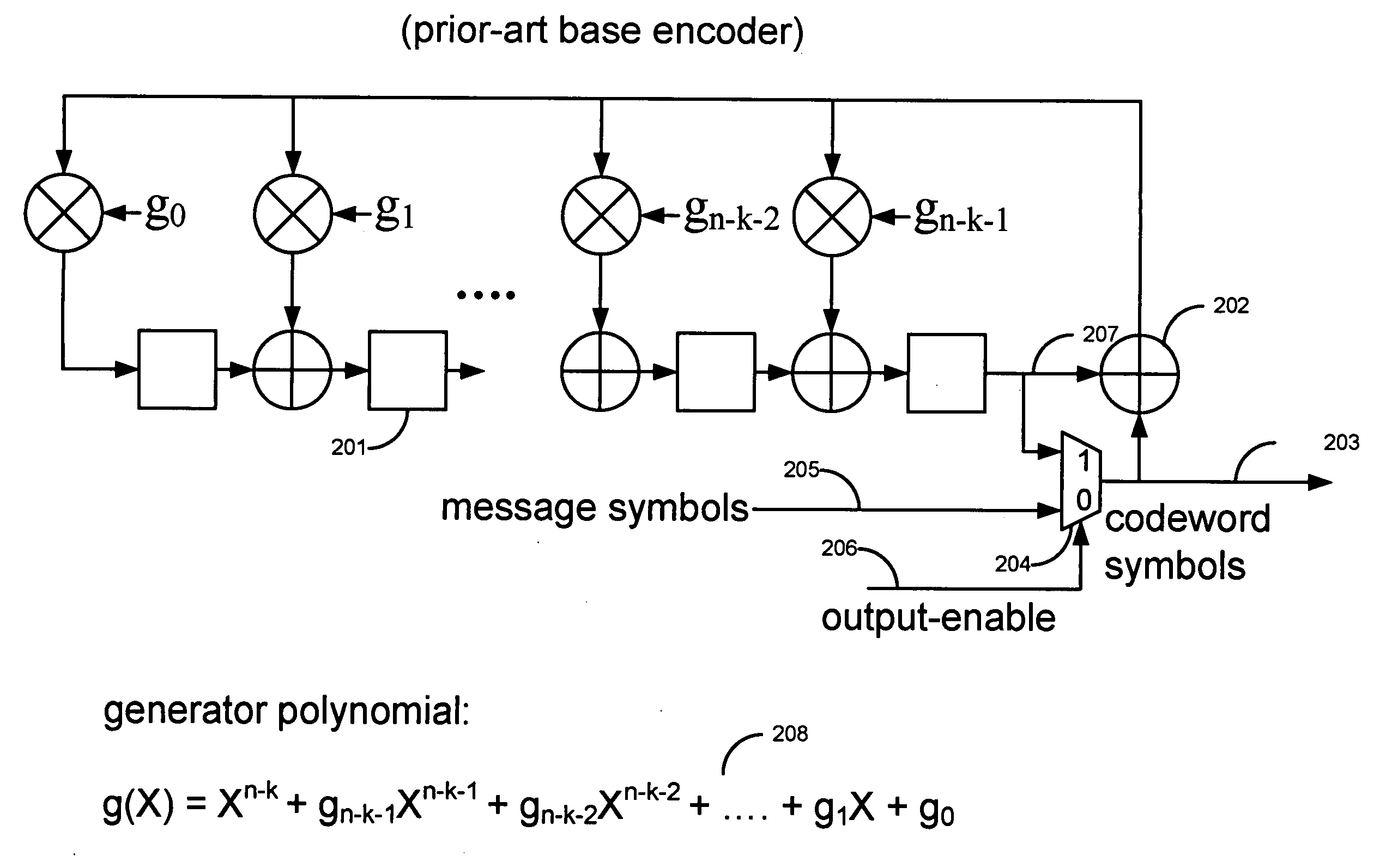
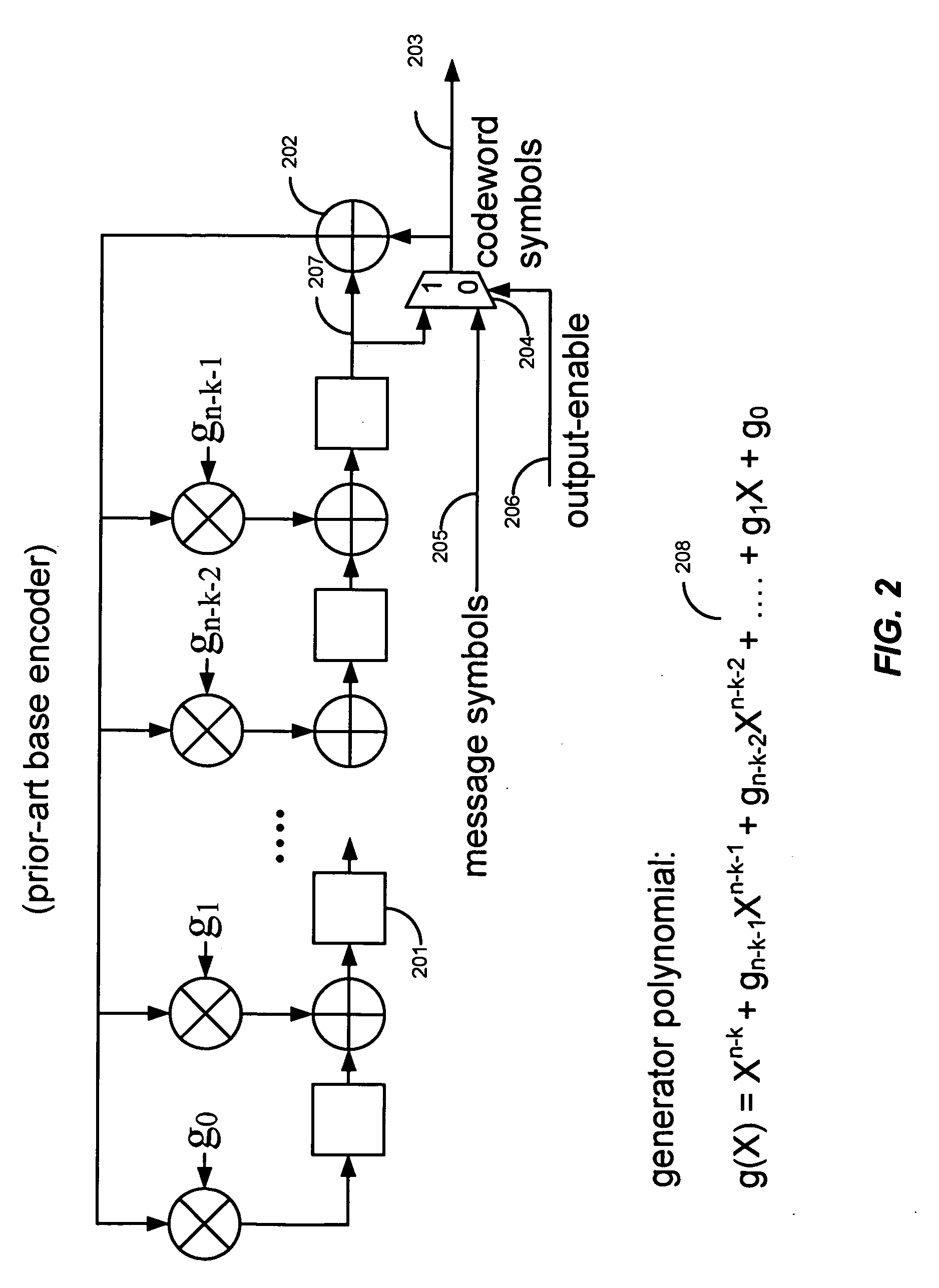
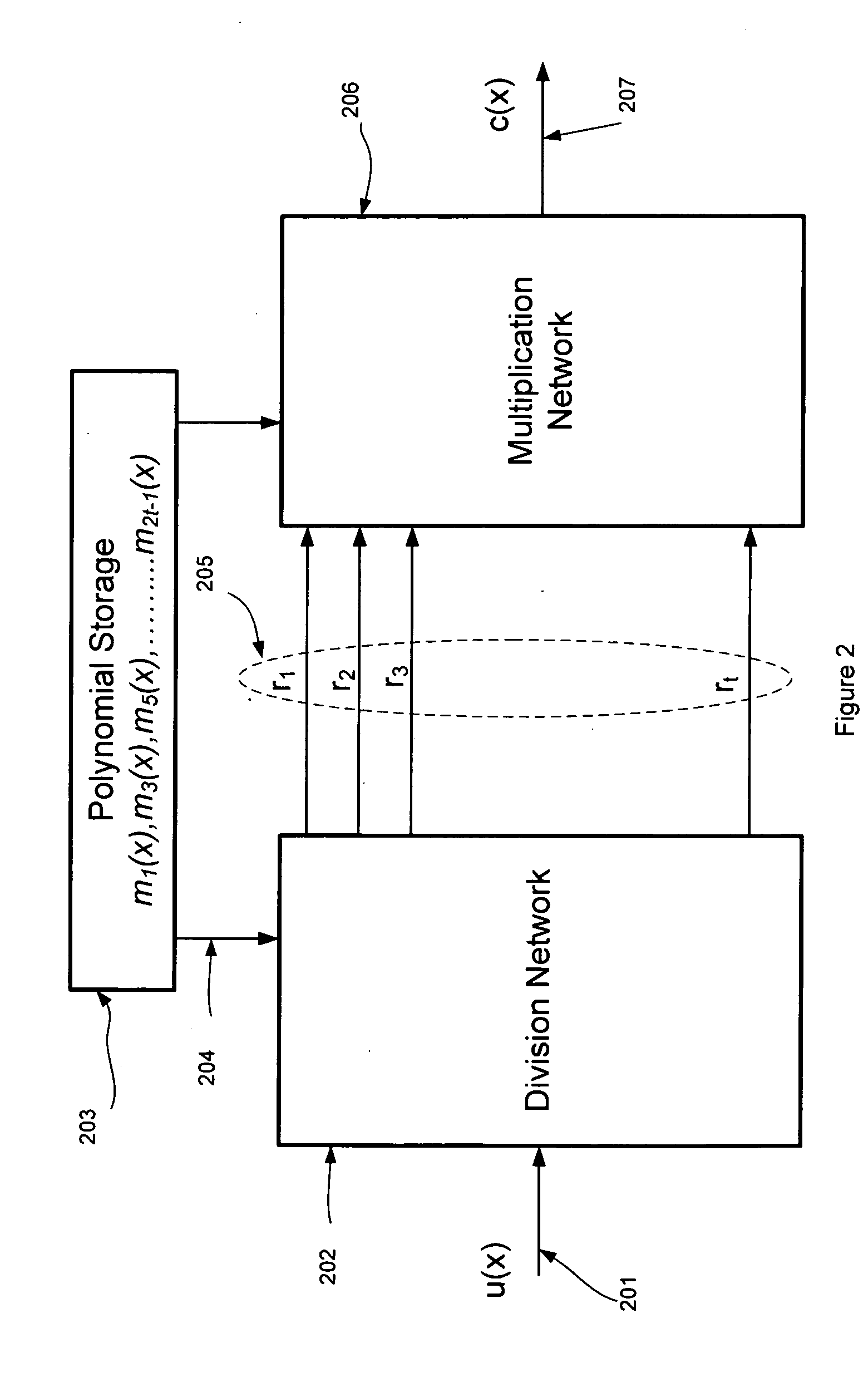
Variable redundancy cyclic code encoders
A multiple-stage encoder encodes the data in accordance with one, two, . . . , or f factors of an associated cyclic code generator polynomial g(x)=g1(x)*g2(x)* . . . *gf(x) to produce data code words that include a selected number of ECC symbols. The encoder encodes the data d(x) in a first stage using a first factor gm(x) of a selected polynomial ps(x) to produce d(x)*xs=q1(x)g1(x)+r1(x), where q1(x) is a quotient and r1(x) is a remainder and g1(x) has degree s. In a next stage the encoder encodes q1(x) using a next factor gm(x) of the selected polynomial to produce qm(x)=q1(x)gm(x)+rm(x) and so forth, until the remainders associated with all of the factors of the selected generator polynomial have been produced. The system then manipulates the remainders to produce a remainder rs(x) that is associated with the selected polynomial ps(x), and uses a cyclically shifted version of the remainder rs(x) as the code word ECC symbols. The same circuitry is used to both produce and manipulate the remainders, and may also be used for decoding the code words in accordance with the selected polynomials.
Owner:MAXTOR
Method and apparatus for using fire decoder to correct burst errors in a real-time communications system
InactiveUS7231579B1Delay minimizationError preventionBurst error correctionCommunications systemAlgorithm
Error bursts are detected and corrected in a communication system using shortened cyclic codes, such as shortened Fire codes. Data is loaded into a first error syndrome register and a second error syndrome register. The data in the registers may be evaluated to determine if the data bits contain a correctable error. Shortened zero bits are shifted into the second error syndrome register. A number of zero bits are shifted into the first error syndrome register to trap an error burst pattern in the data. A determination is made as to the number of zero bits shifted into the second error syndrome register to trap the location of the error burst in the data. Using the number of zero bits shifted into the second error syndrome register and the error burst pattern, the error in the data is located and corrected.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
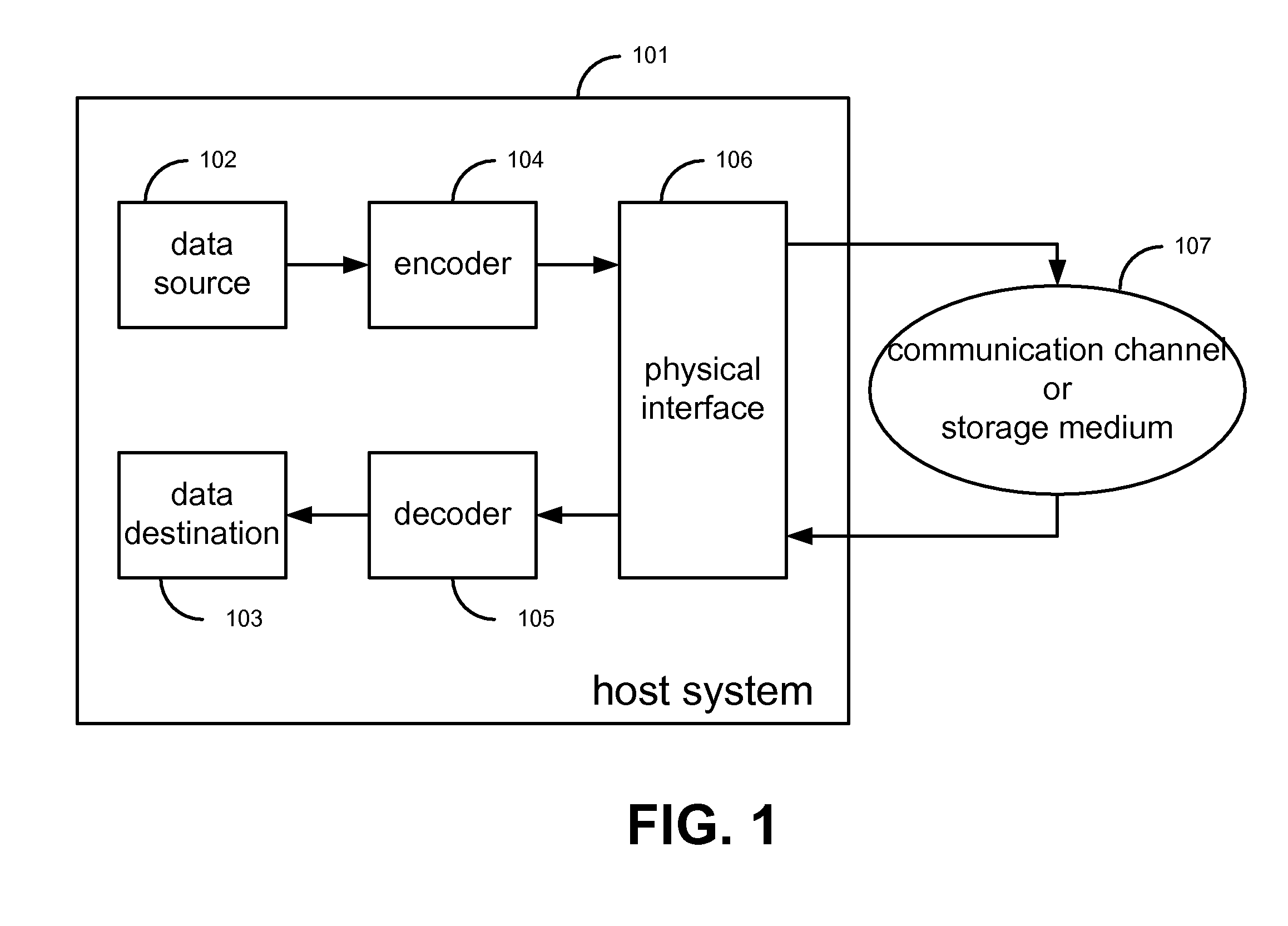
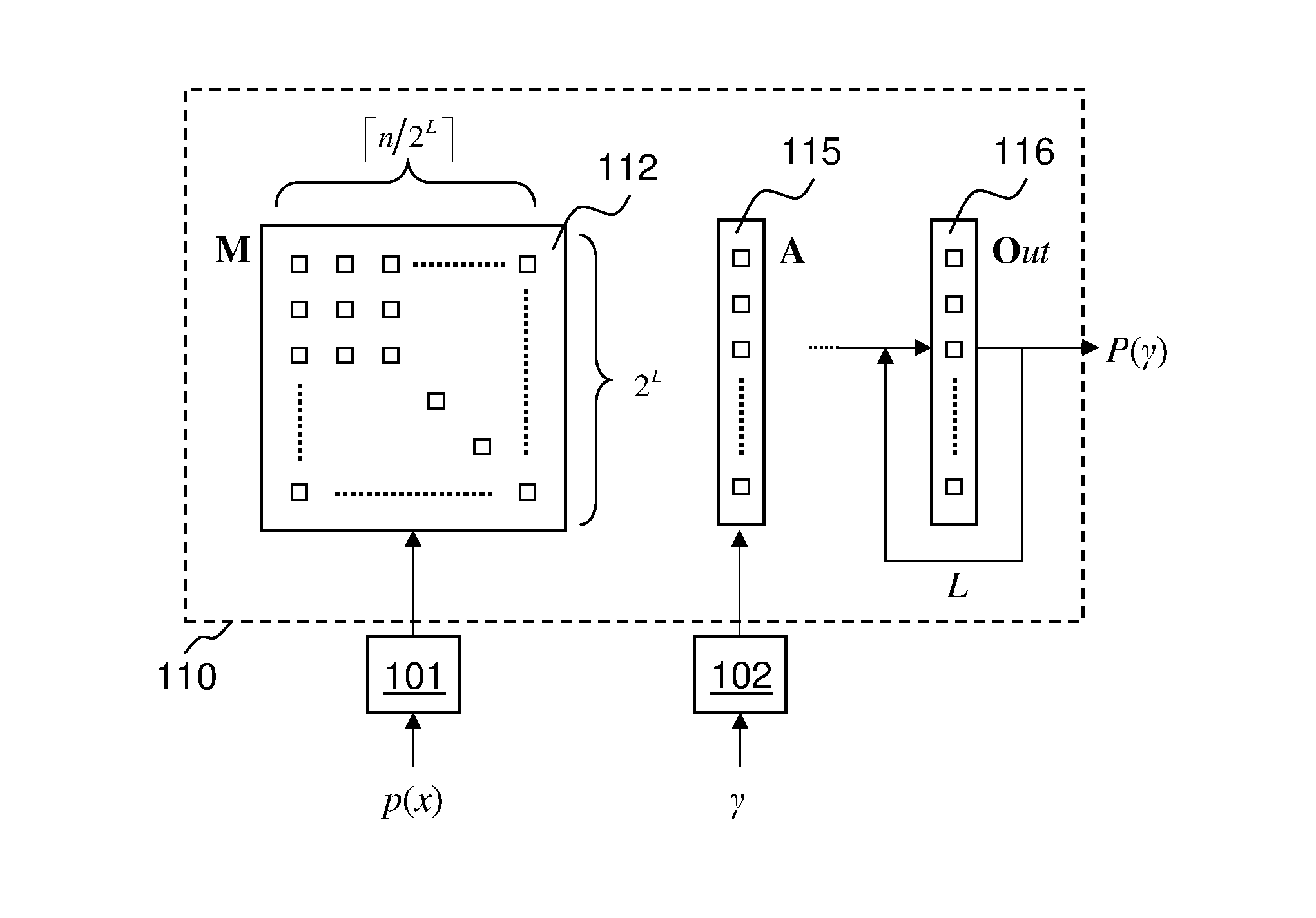
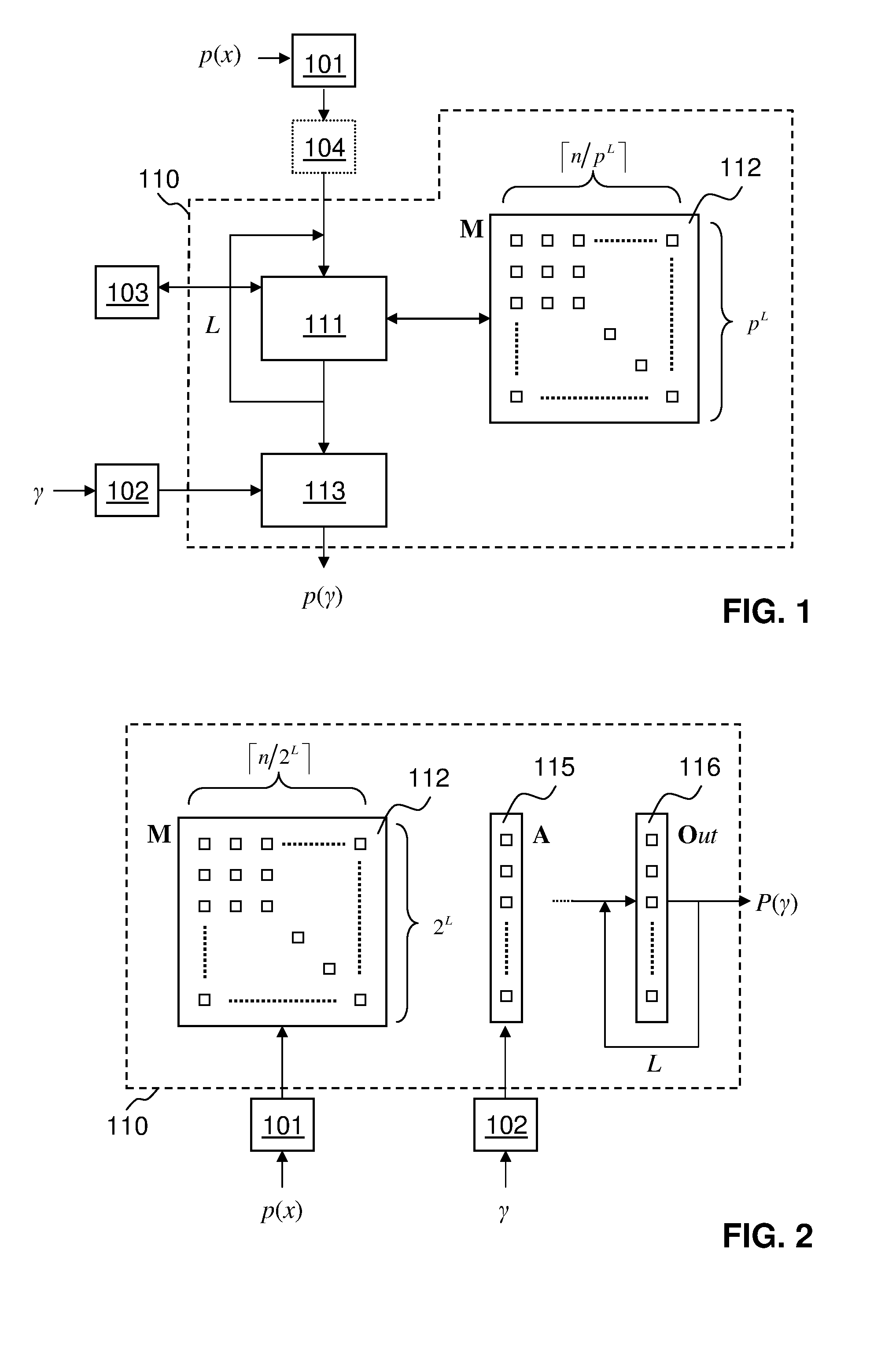
Methods and apparatus for encoding and decoding cyclic codes by processing multiple symbols per cycle
Provided are an encoder and a syndrome computer for cyclic codes which process M codeword symbols per cycle where M is greater than or equal to one, whereby the encoder and syndrome computer optionally further provide the configurability of a different M value for each cycle and / or the configurability of a different cyclic code for each codeword. Further provided is a hybrid device which provides the configurability of two modes of operation, whereby in one mode, the hybrid device functions as the encoder as provided above and, in the other mode, the hybrid device functions as the syndrome computer as provided above, with the majority of the components of the hybrid device being shared between the encoding function and the syndrome computing function.
Owner:LEE JOSEPH SCHWEIRAY
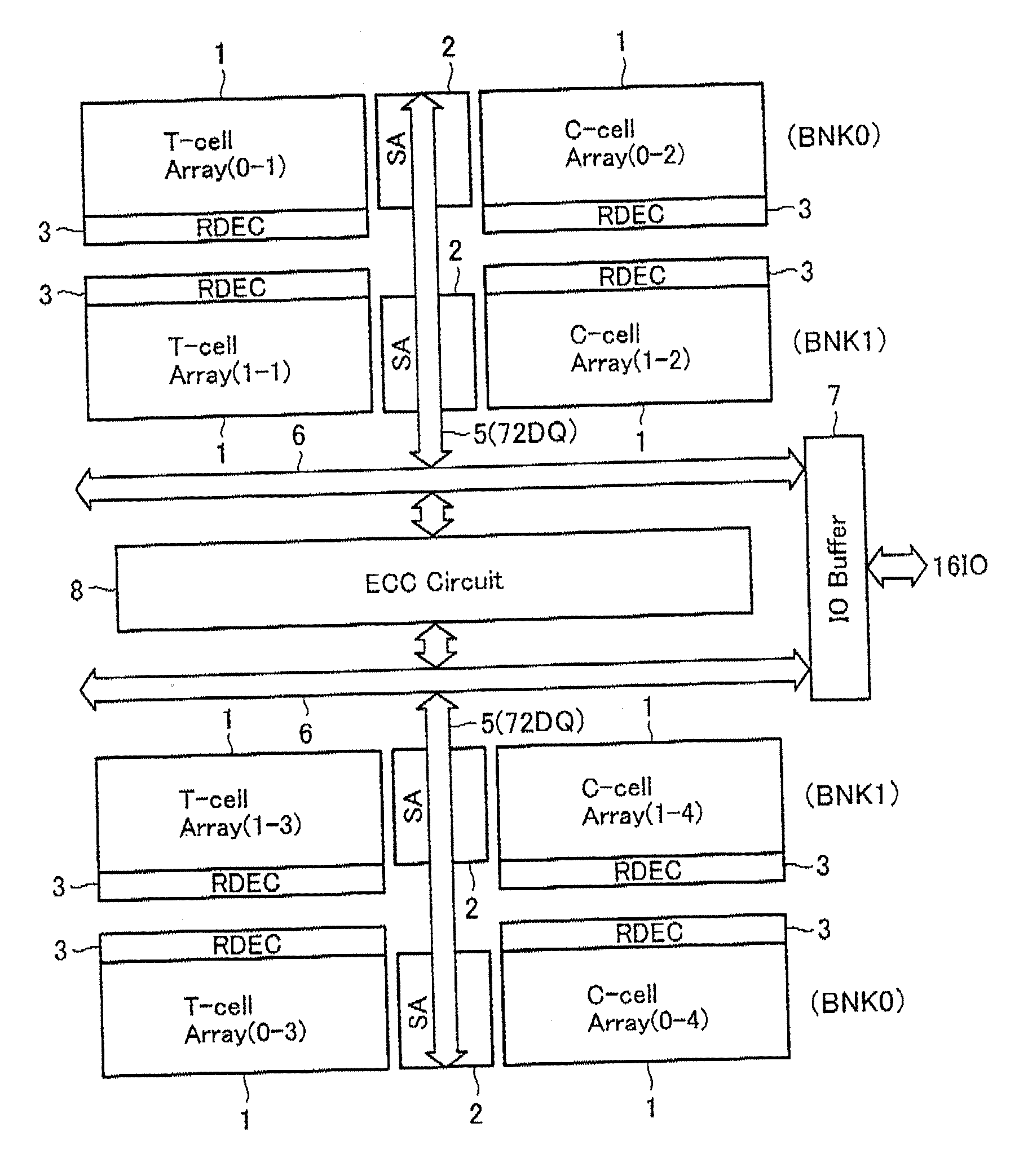
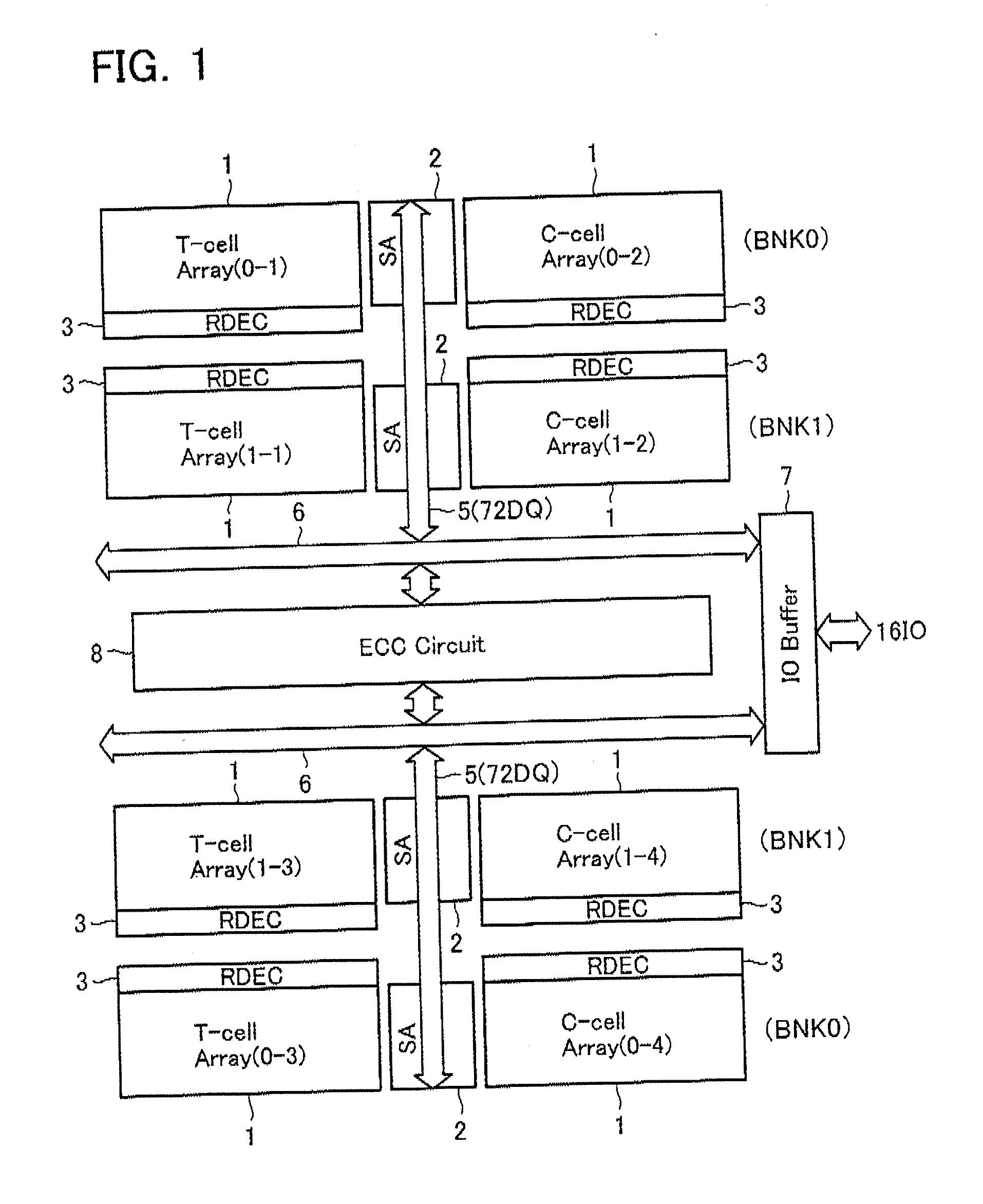
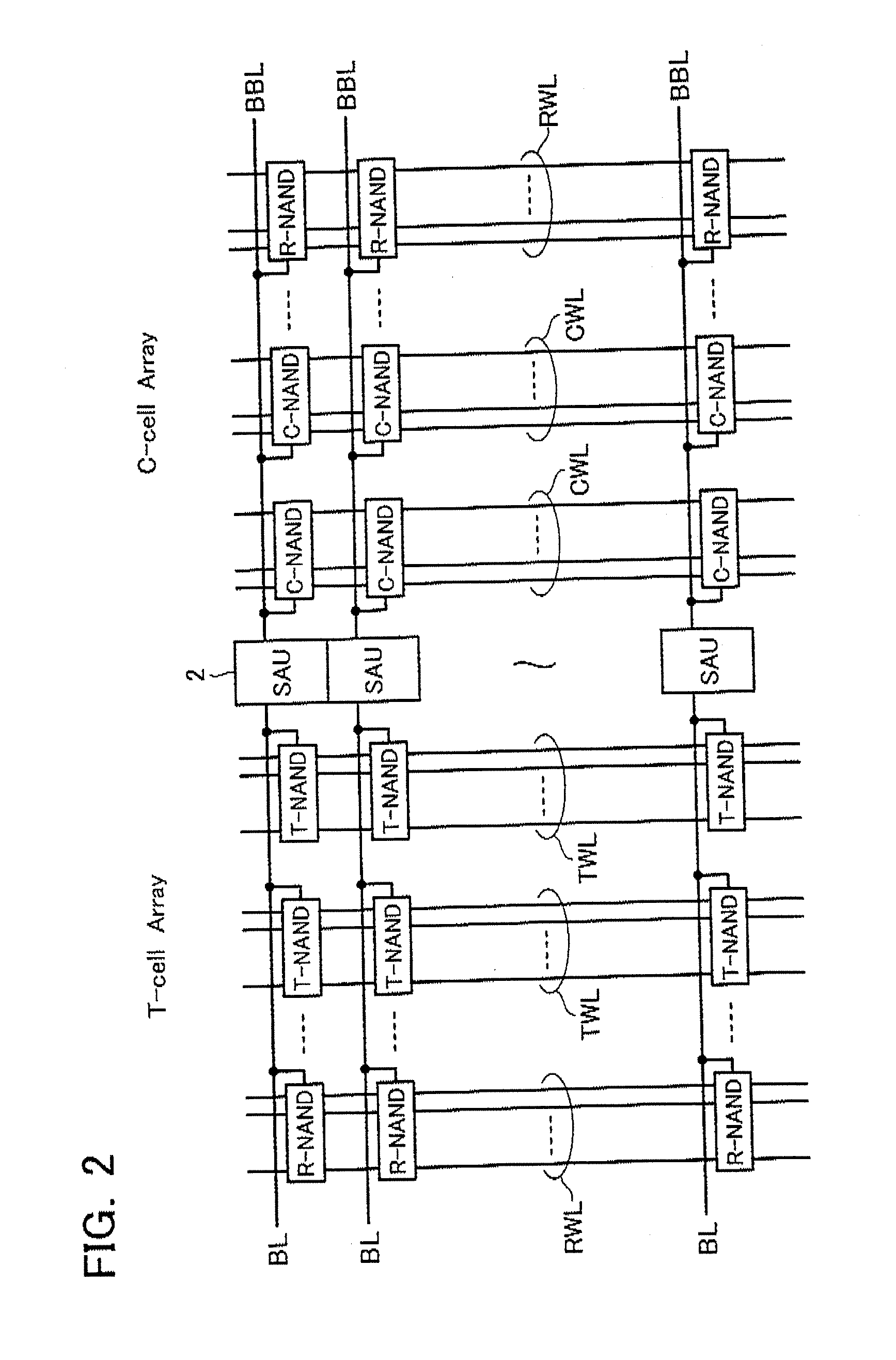
Semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20070198902A1Small scaleDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusBit numberingSemiconductor
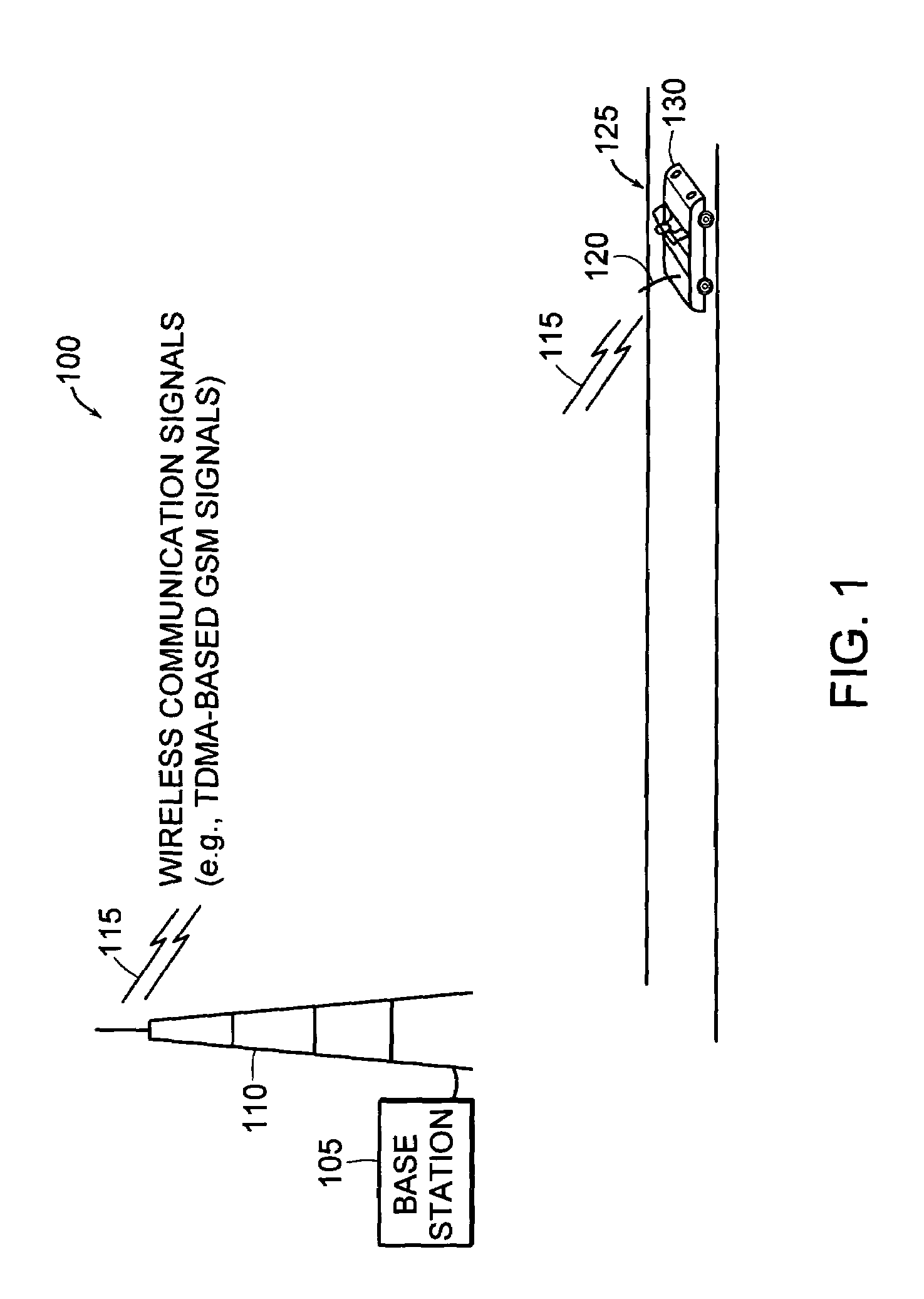
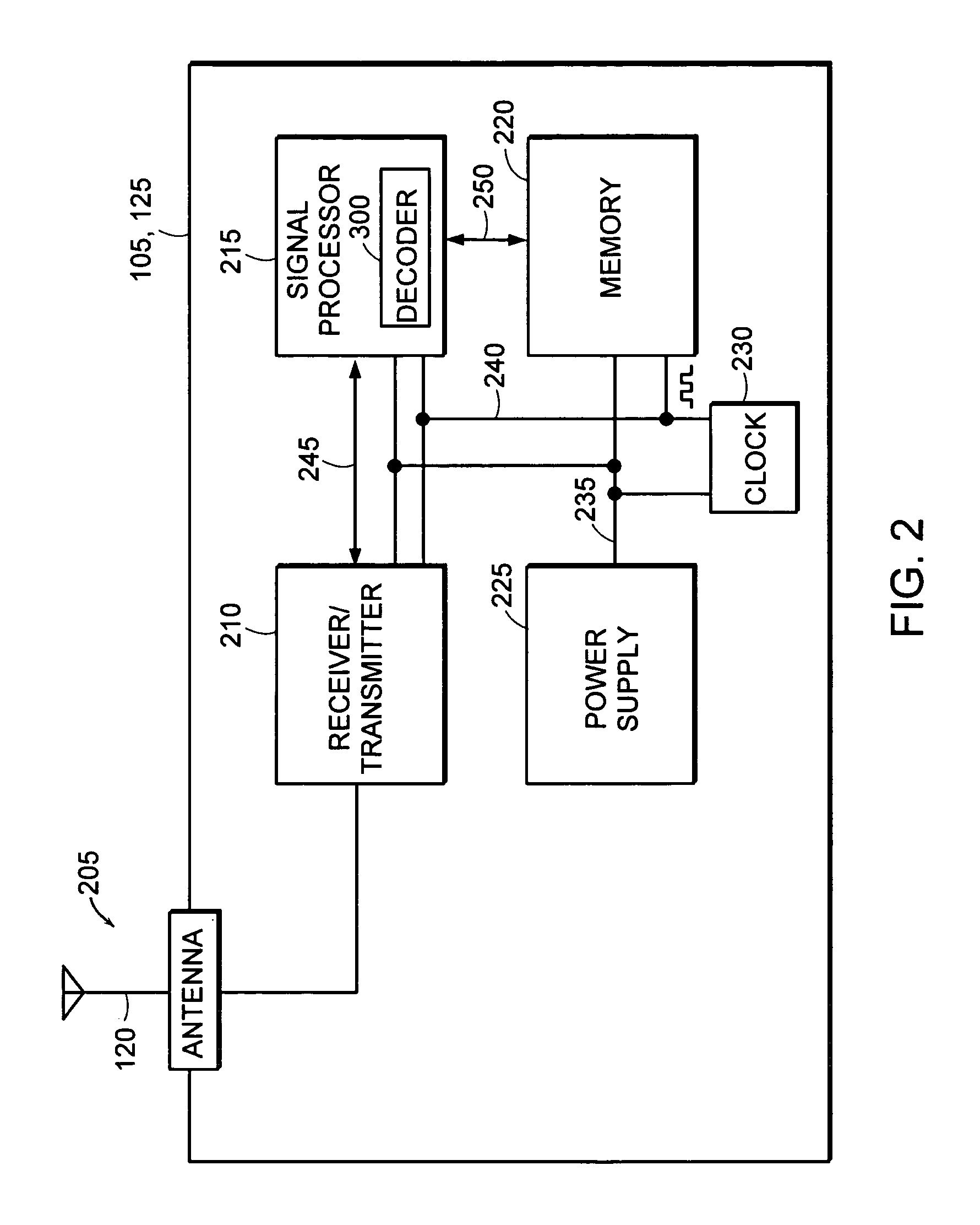
A semiconductor memory device has a built-in error detection and correction system, wherein the error detection and correction system is formed to have a cyclic code, with which multiple error bits are correctable, and wherein the cyclic code is configured in such a manner that a certain number of degrees are selected as information bits from the entire degree of an information polynomial having degree numbers corresponding to an error-correctable maximal bit number, the certain number being a number of data bits which are simultaneously error-correctable in the memory device.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Differential encoding space-time-frequency modulation method
InactiveCN101699808ASmall time-varyingThe influence of frequency variability is smallMulti-frequency code systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionDifferential modulationTransmitter antenna
The invention discloses a differential encoding space-time-frequency modulation method, and belongs to the technical field of wireless communication. The method comprises that: a mobile terminal of a communication system performs space-time encoding on an information bit sequence required to be transmitted to generate a unitary matrix code word sequence; the unitary matrix code word sequence is subjected to differential modulation to generate a matrix sequence to be transmitted; symbols in the matrix sequence to be transmitted are respectively mapped to a space domain, a time domain and a frequency domain so as to acquire a group of space-time-frequency three-dimensional signals; a plurality of groups of transmission signals are acquired through OFDM modulation, and each group of transmission signals is transmitted through a transmitter antenna; and the OFDM modulation and differential demodulation are directly carried out a receiving end, and required information is acquired. Through differential space-time-frequency block code mapping or differential space-time-frequency cyclic code mapping, the encoding and the differential modulation are respectively carried out at different dimensionalities, so that a requirement of a channel on relevance of the time domain and the frequency domain is reduced, and a requirement of reliable signal transmission in high-speed mobile environment in a wideband communication system can be met.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Transmission system with isi channel and method of operating thereof
InactiveUS20120300828A1Reduce outputBlocking phenomenonMultiple-port networksError preventionComputer hardwareTransfer system
There is provided a transmission system and method of operating thereof. The method comprises: dividing a data sequence to be transmitted into a plurality of data blocks; encoding one or more data blocks with one or more linear systematic cyclic codes thus giving rise to encoded data blocks; transmitting said encoded data blocks over an ISI transmission channel; upon receiving, applying a linear integer-forcing (IF) equalization to the received data blocks; processing the output of the IF equalization thereby detecting for each encoded data block a valid codeword with maximal likelihood of decoding; and reconstructing the data blocks using the respective detected valid codewords.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
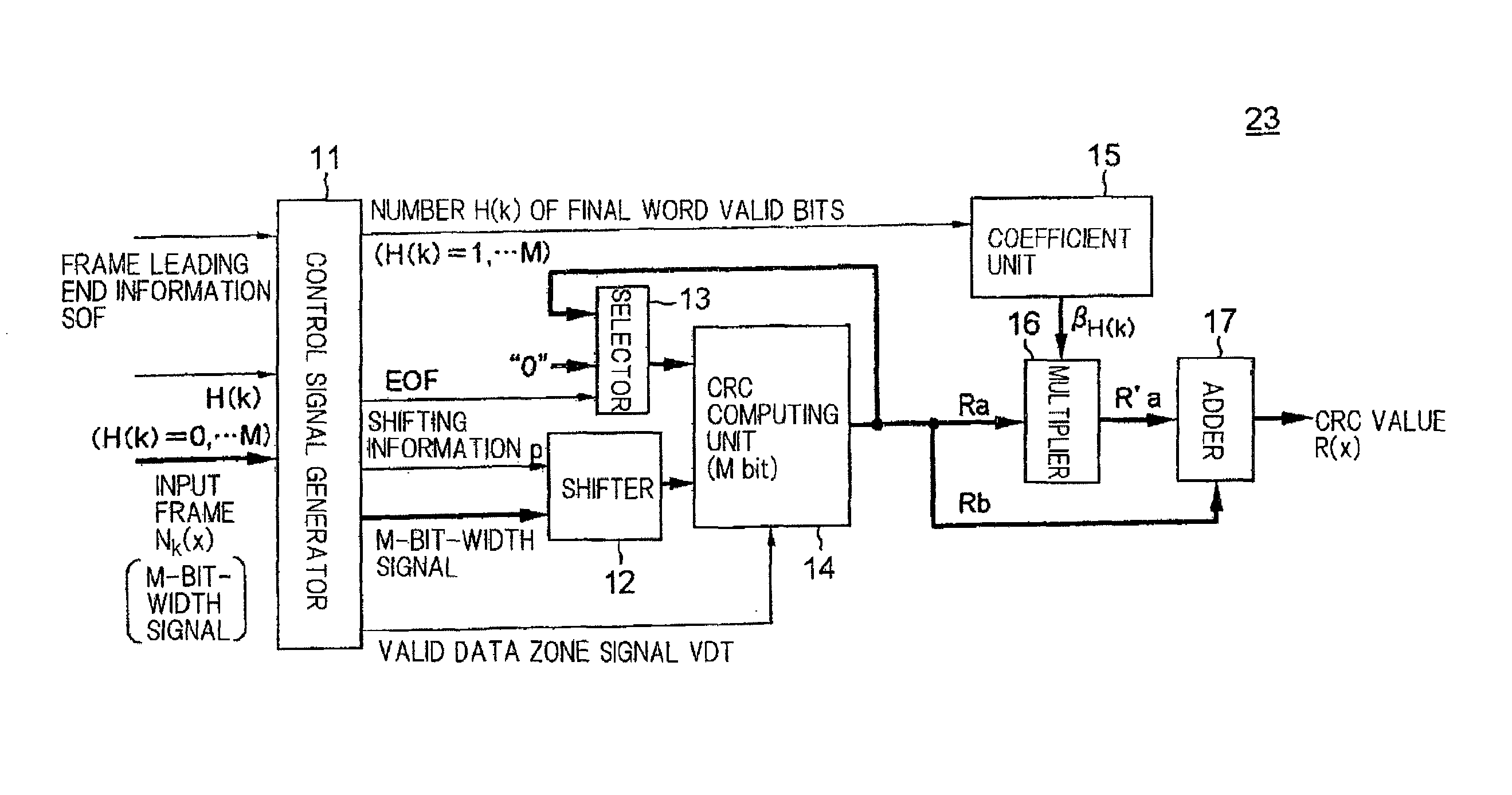
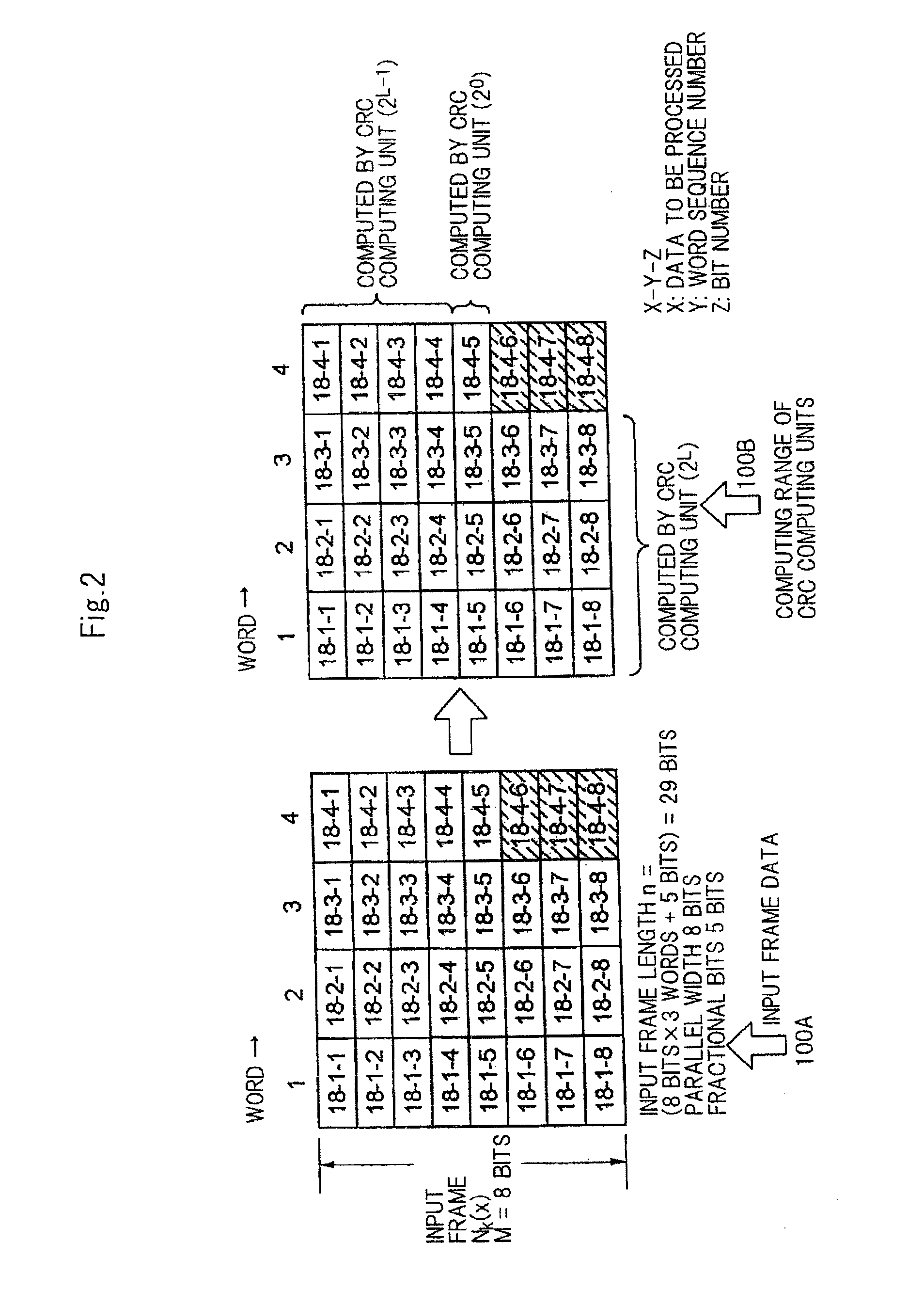
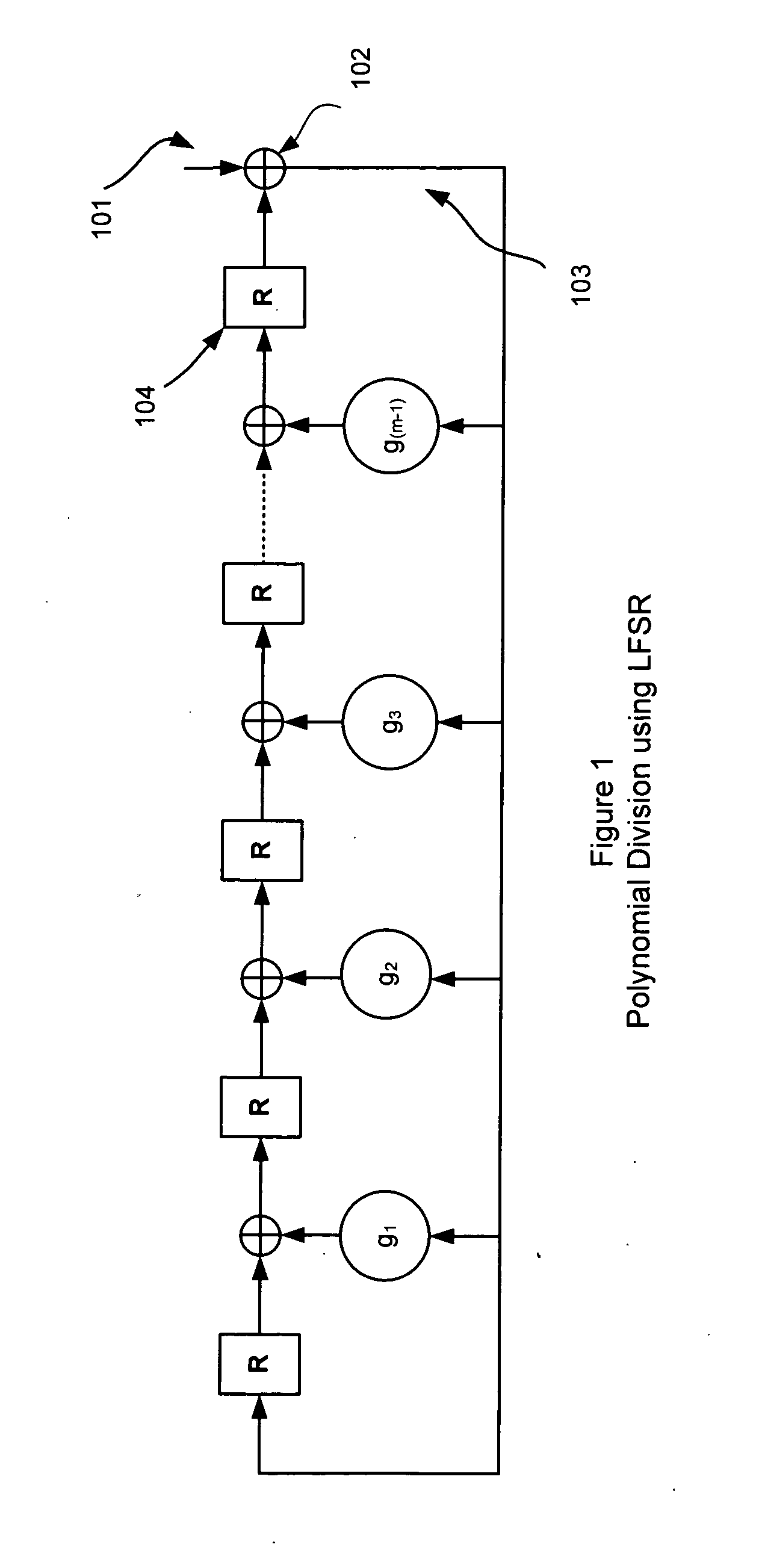
Cyclic code processing circuit, network interface card, and cyclic code processing method
ActiveUS20100070839A1Easy to processCircuit scale becomes largeError preventionCode conversionParallel processingNetwork interface
Processor 23 calculates a first remainder, which is a remainder produced when an integral multiple data block is divided by a generator poly-nomial, by processing bits represented by the number of parallel bits in parallel. The integral multiple data block comprises bits positioned closer to the leading end of the input data than a final word which is a word at the tail end of the input data, in the case where a plurality of bits making up the input data are successively divided from the leading end with respect to each word which comprises the bits represented by the number of parallel bits. Processor 23 calculates a second remainder, which is a remainder produced when a final word valid data block made up of bits of the input data other than the integral multiple data block is divided by the generator polynomial. Processor 23 calculates an input data remainder, which is a remainder produced when the input data are divided by the generator polynomial, based on the first remainder and the second remainder.
Owner:NEC CORP
Phase-modulated continuous wave radar system (with prbs codes)
InactiveUS20180095163A1Large isolationEasy to useRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterference resistanceRadar systems
A phase modulated continuous wave radar system comprising a radar control system utilizing a Pseudo Random Bit Sequence (PRBS) as a long modulation code with simultaneous autocorrelation and cross-correlation interference resistance. the transmitter is co-sited with the receiver, the receiver can be given prior knowledge of the specific transmitted code that it is correlating to. This prior knowledge, which is not accessible in general to bi-static systems such as GPS and cell phone technology, allows for increased randomization of cyclic code structures in monostatic radar systems.
Owner:LOVBERG JOHN +1
Error correction encoding apparatus, decoding apparatus, encoding method, decoding method, and programs thereof
ActiveUS20120089884A1Good effectSuppress power consumptionCode conversionError correction/detection using block codesComputer moduleLow density
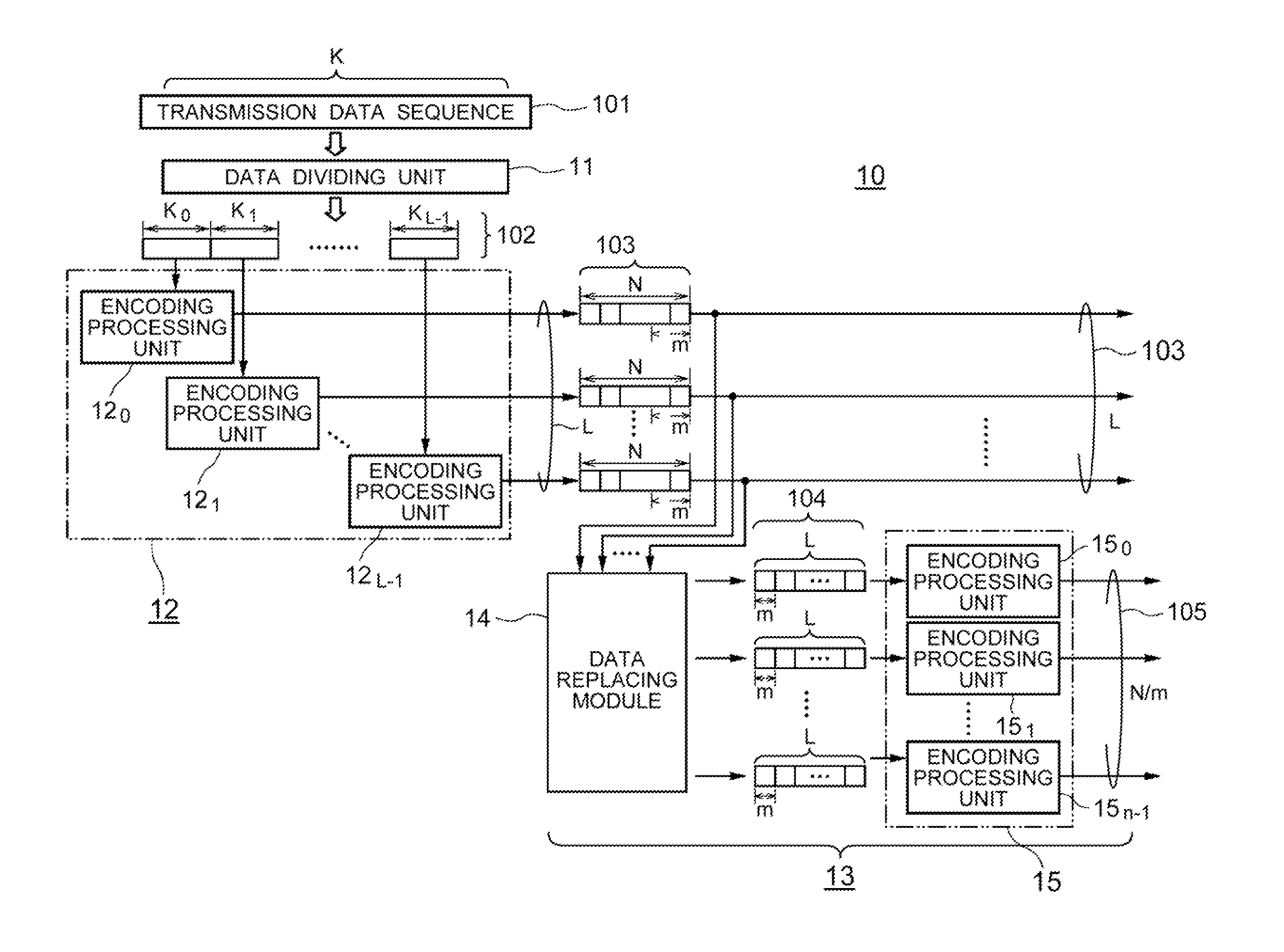
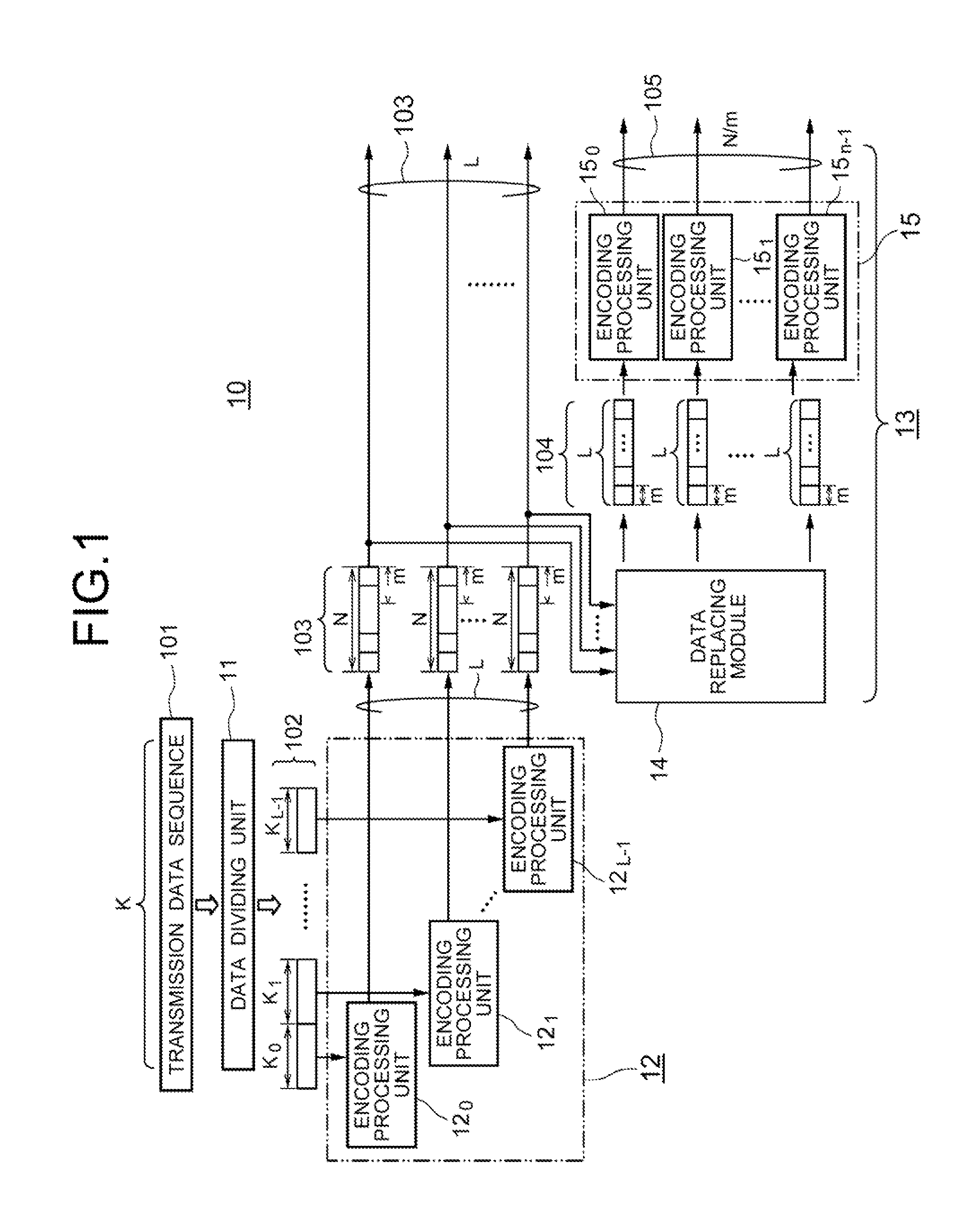
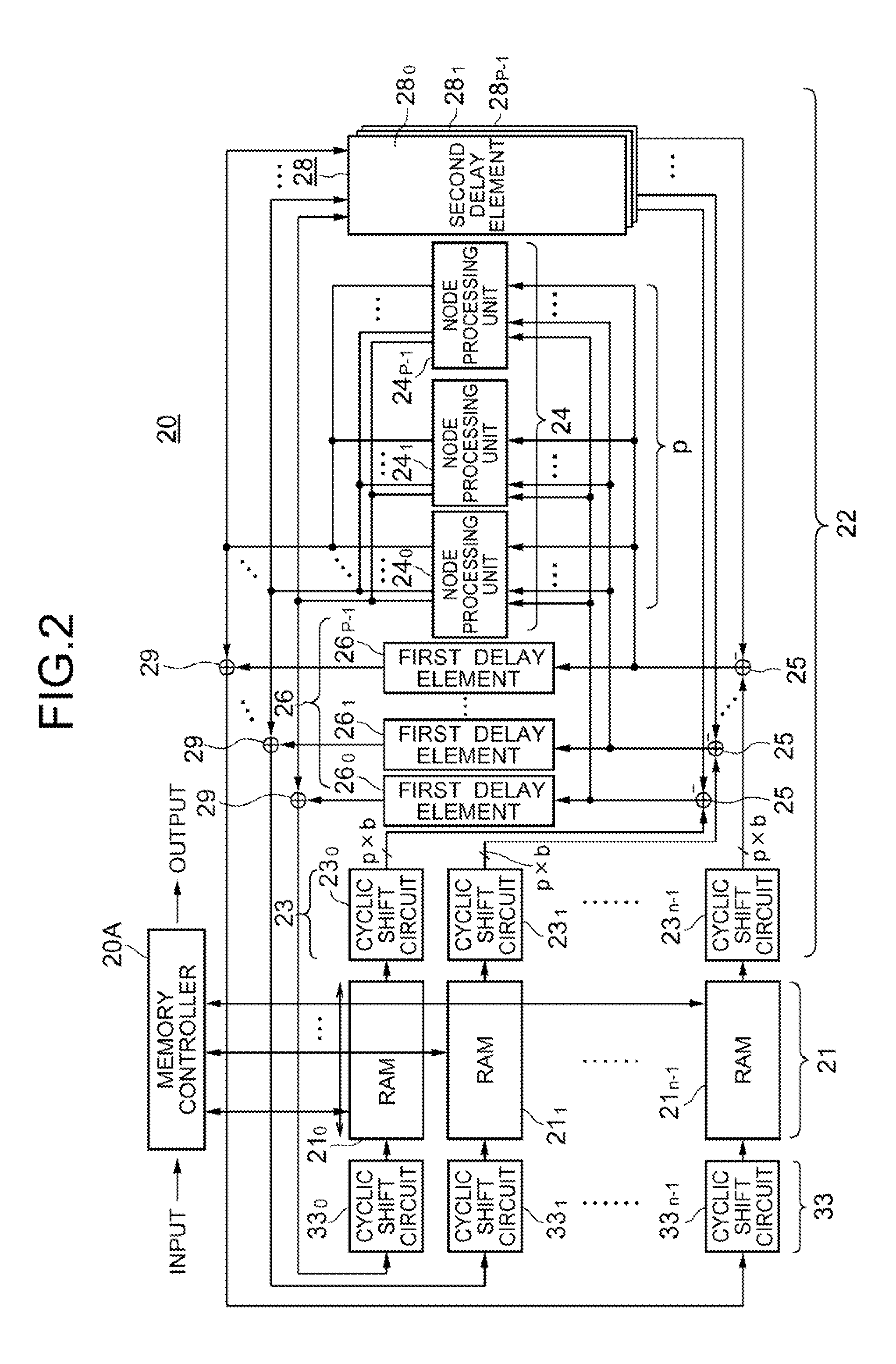
Provided is an encoding apparatus wherein a transmission data sequence is divided into L short sequences, each of which is then encoded by use of an m-stage pseudo-cyclic low-density parity check encoding system. Each of the L encoded sequences is further divided into shorter sequences, the number of which is identical to the number m of the stages of the pseudo-cyclic codes and each of which has a length m. The shorter sequences are rearranged in order by a replacing module, thereafter encoded, by use of the m-stage pseudo-cyclic low-density parity check encoding system, and outputted. Accordingly, a decoding apparatus with a simple structure where node processing circuits (e.g., minimum-value calculating circuits), the number of which is p that is a submultiple of the number m of the foregoing stages, are provided, can be employed to efficiently decode the codes having a large frame length and a large encoding gain.
Owner:NEC CORP
Method for configuring algorithm complex low quasi-cyclic LDPC codes
InactiveCN101072035AThe construction method is flexible, fast and efficientReduce complexityError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Computation complexity
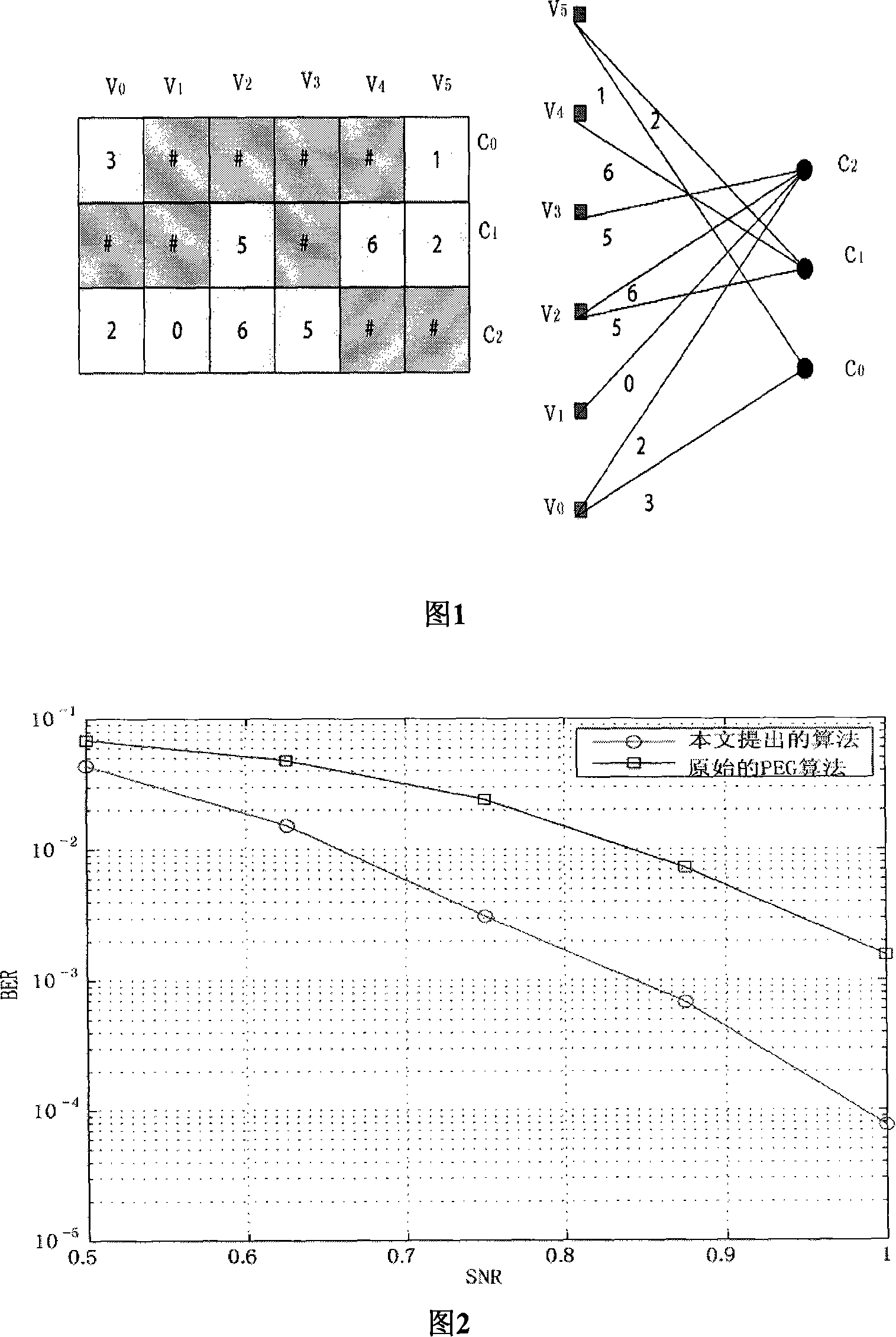
The method includes to steps: (1) constructing exponent matrix of parity check matrix of QC-LDPC codes; (2) using exponent expansion to convert the exponent matrix to parity check matrix H of QC-LDPC codes. When iterative decoding, code error rate of the constructed QC-LDPC codes is lower than the rate of traditional PEG algorithm obviously (specially, in condition of high SNR), and algorithm complexity is mach lower than algorithm complexity of traditional algorithm so that the constructing speed is much fast than speed of traditional method. Moreover, when constructing QC-LDPC codes, the disclosed method can control each parameter for generating code flexibly.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Low-density parity-check (LDPC) encoder
The encoder chip of the present invention uses LDPC codes to encode input message data at a transmitting end, thereby generating a series of codewords. The encoder chip implements two low-density parity-check (LDPC) codes. The first LDPC code is a (4088,3360) code (4K) which is shortened from a (4095,3367) cyclic code. The second LDPC code is a quasi-cyclic (8158,7136) code (8K). The message data and the generated codewords are transmitted to a receiving end where the received codewords are decoded and checked for errors. To generate the codewords, the encoder applies a generator matrix G to the input message data. The G matrix is generated by first defining an H matrix. An H matrix is initially defined as 16×2 array of right-circulant sub-matrices. The G matrix is formed by manipulating the H matrix according to a 4-step algorithm. A randomizer and a synchronization marker are also included within the encoder.
Owner:IDAHO RESARCH FOUNDATION INC
Low complexity quasi-cyclic LDPC code designing method based on mask operation
InactiveCN103825622AImprove performanceError correction/detection using multiple parity bitsFinite element methodTheoretical computer science
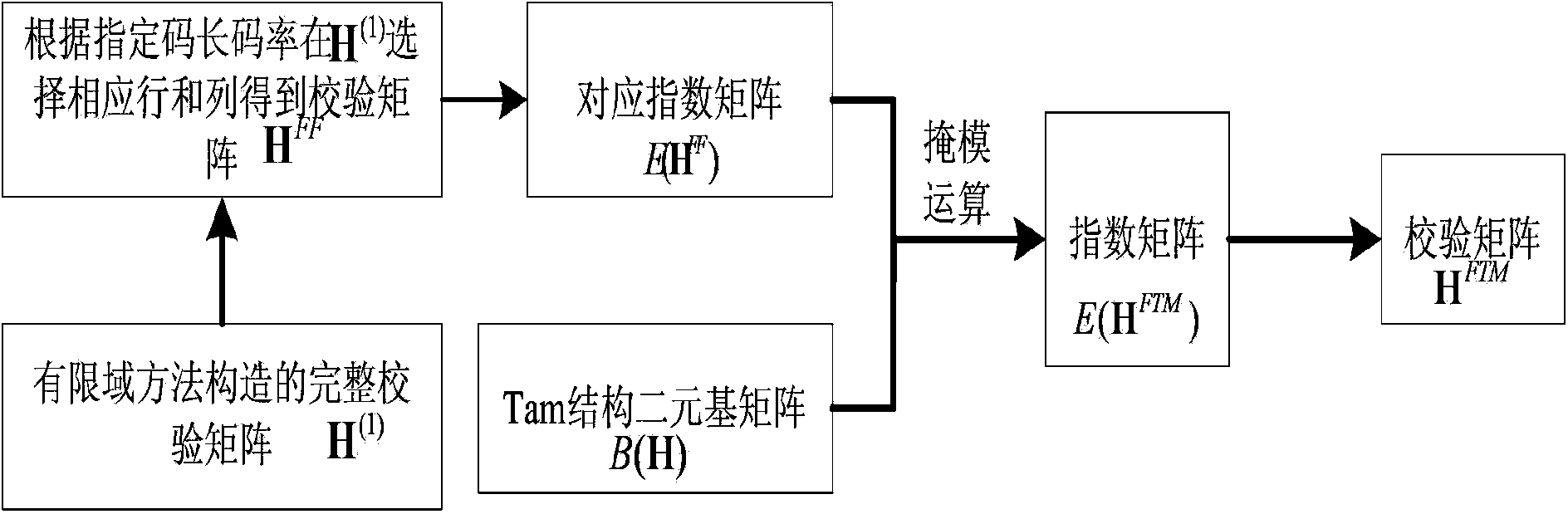
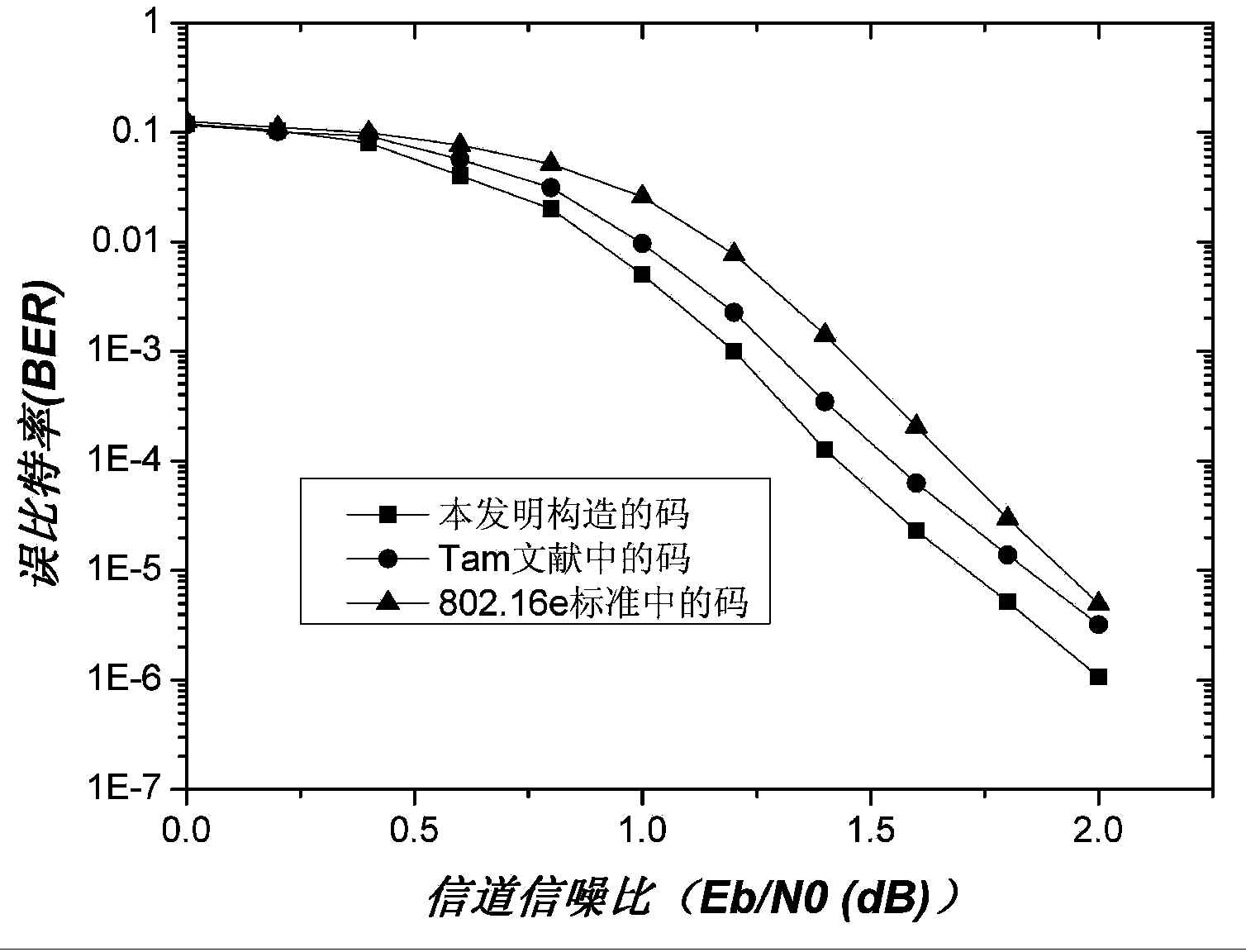
The invention discloses a low complexity quasi-cyclic LDPC code designing method based on mask operation. According to the low complexity quasi-cyclic LDPC code designing method based on the mask operation, a finite field method and a Tam structure are combined, quasi-cyclic LDPC codes constructed through the method retains the excellent properties of quasi-cyclic LDPC codes constructed through the infinite field method, a check matrix of the quasi-cyclic LDPC codes constructed through the method further has the Tam structure capable of carrying out simple recursion coding, and the quasi-cyclic LDPC codes constructed through the method are suitable for hardware implementation and have significant application potential in mobile communication and wireless sensor networks of a future new generation. Furthermore, the performance of the BER (bit error rates) of the quasi-cyclic LDPC codes constructed through the method is better than that of quasi-cyclic LDPC codes given by Tam and quasi-cyclic LDPC codes in IEEE802.16e under equal conditions.
Owner:YANCHENG TEACHERS UNIV
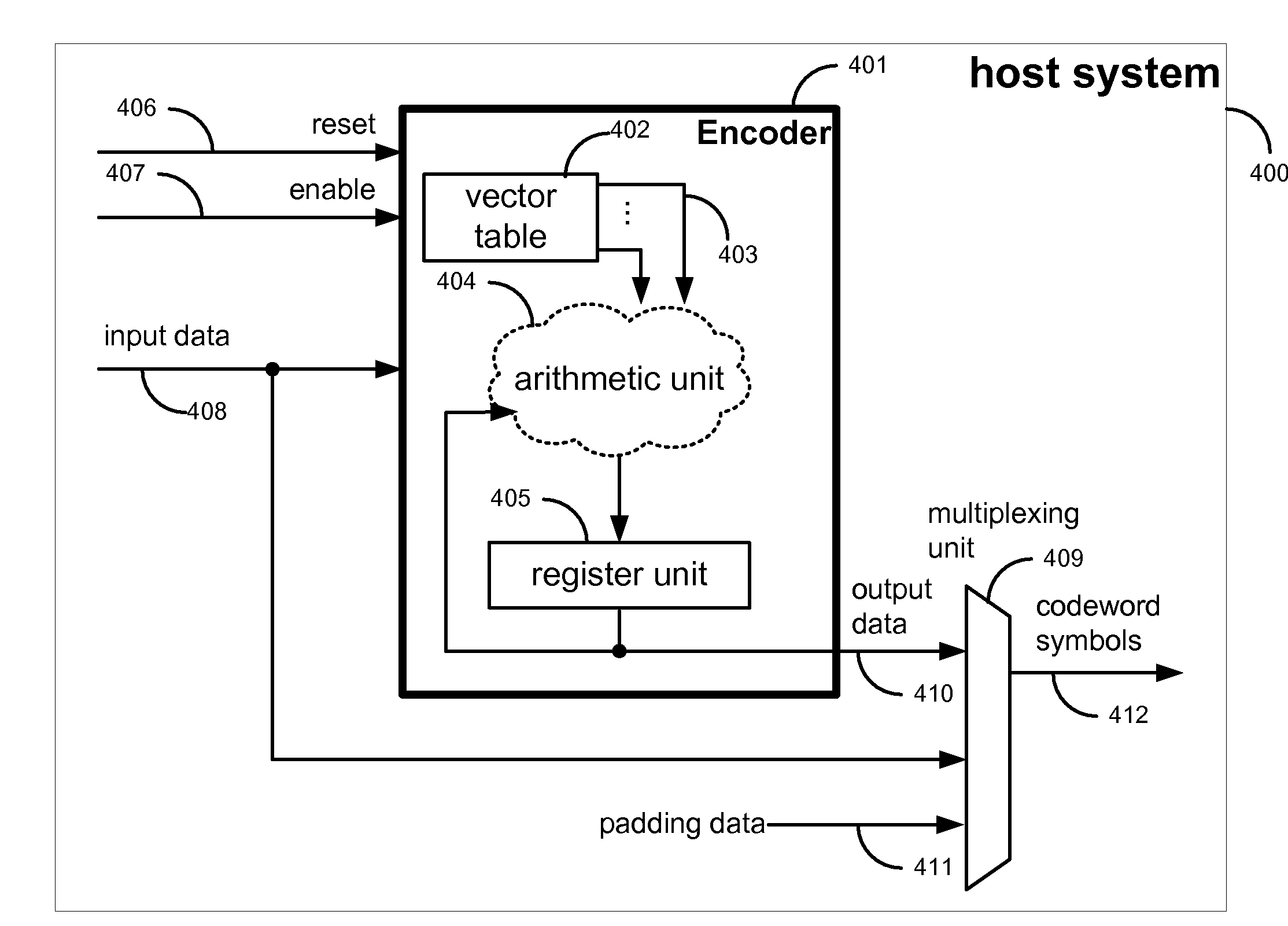
Encoder of cyclic codes for partially written codewords in flash memory
Provided is a systematic encoder of cyclic codes for partially written codewords in flash memories wherein all bits of an erased but unwritten area have a default value such as one. In the case where the host writes data to one or a plurality of discontinuous fragments in an area reserved for storing the message section of a codeword in the flash memory, the encoder computes the parity of the codeword by using only the data written to the flash memory as input and by asserting that all bits in the gaps between the written fragments have the default erased value, such that after both the data and the parity are written to the flash memory, the area reserved for storing the codeword would contain a valid codeword. On read back, the host reads the entire codeword area from the flash memory without having to distinguish between the written and unwritten fragments.
Owner:LEE JOSEPH SCHWEIRAY
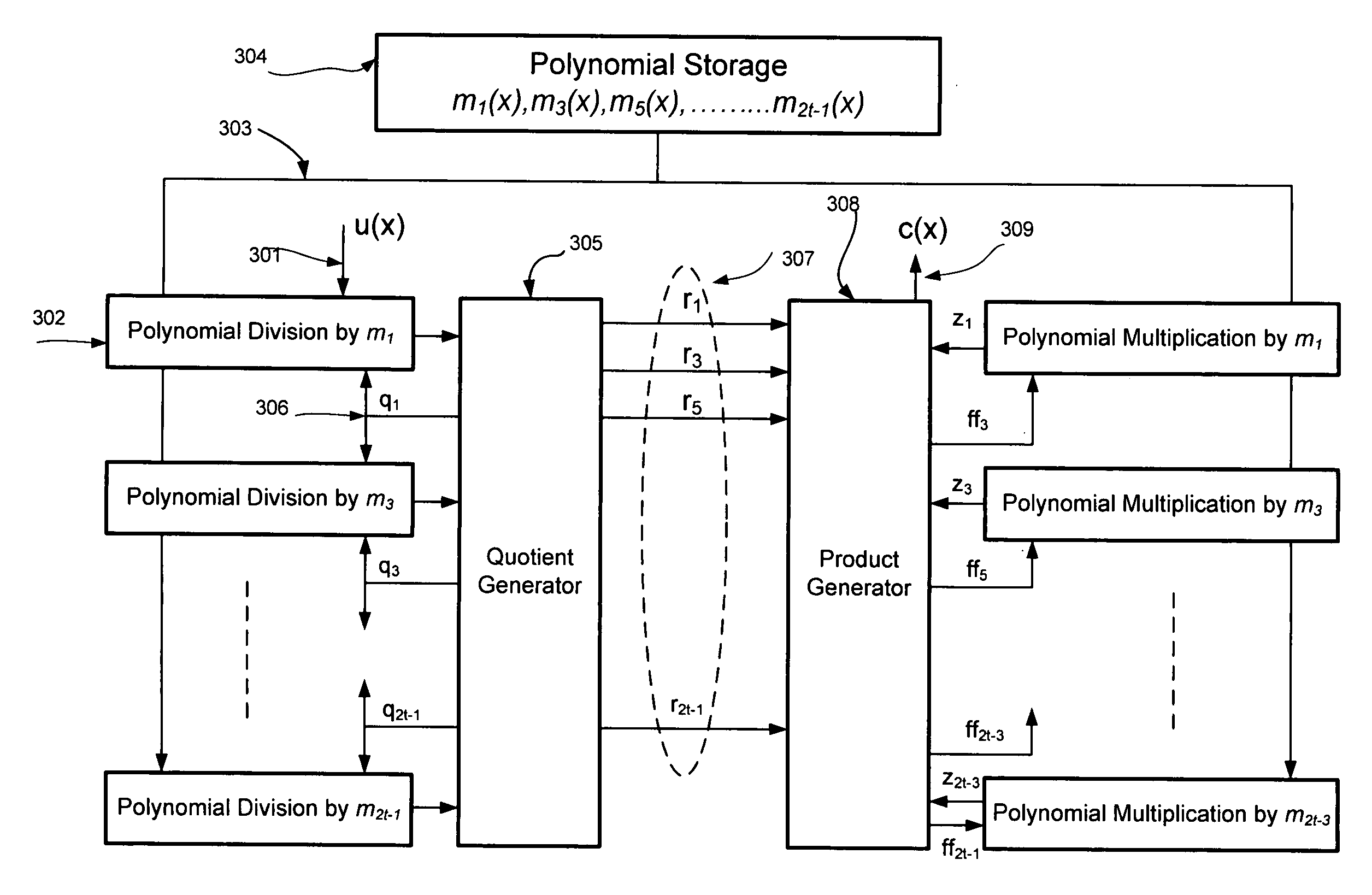
High-speed and agile encoder for variable strength long BCH codes
InactiveUS20110185265A1No additional costMinimal costCode conversionCyclic codesTheoretical computer scienceTrade offs
Agile BCH encoders are useful when the noise characteristics of the channel change which demands that the strength of the error correcting BCH code to be a variable. An agile encoder for encoding a linear cyclic code such as a BCH code, is a code that switches code strength (depth) relatively quickly in unit increments. The generator polynomial for the BCH code is provided in the factored form. The number of factored polynomials (minimal polynomials) chosen by the system determines the strength of the BCH code. The strength can vary from a weak code to a strong code in unit increments without a penalty on storage requirements for storing the factored polynomials. The BCH codeword is formed by a dividing network and a combining network. Special method is described that provides a trade off mechanism between latency and throughput while simultaneously optimizing the delay in the critical path which is in the forward path. Speed enhancements at minimal polynomial level are also provided by retiming, loop unfolding, loop unrolling, and special mathematical transformations. The presented invention can be implemented as an apparatus using software or hardware or in integrated circuit form.
Owner:CHERUKURI RAGHUNATH
Set of irregular LDPC codes with random structure and low encoding complexity
ActiveUS20070067694A1Easy to controlImprove performanceError detection/correctionCode conversionTheoretical computer scienceDistribution system
A set of irregular LDPC codes having a pseudo-random structure and low encoding complexity. A block-cyclic LDPC code has an irregular row or an irregular column weight and includes a parity check matrix and an encoding matrix each of which has a pseudo-random structure. This allows the code to have the irregular row weight or irregular column weight together with an overall randomness to the code structure. Blocks within the code can be shortened, adjacent blocks of code can be overlapped, and adjacent columns within a block can be arbitrarily permuted so to change the weighting of rows and columns. The LDPC codes are particularly useful in two-way communications system for an electrical distribution system (1) to restore data lost or corrupted during its transmission.
Owner:ACLARA TECH LLC
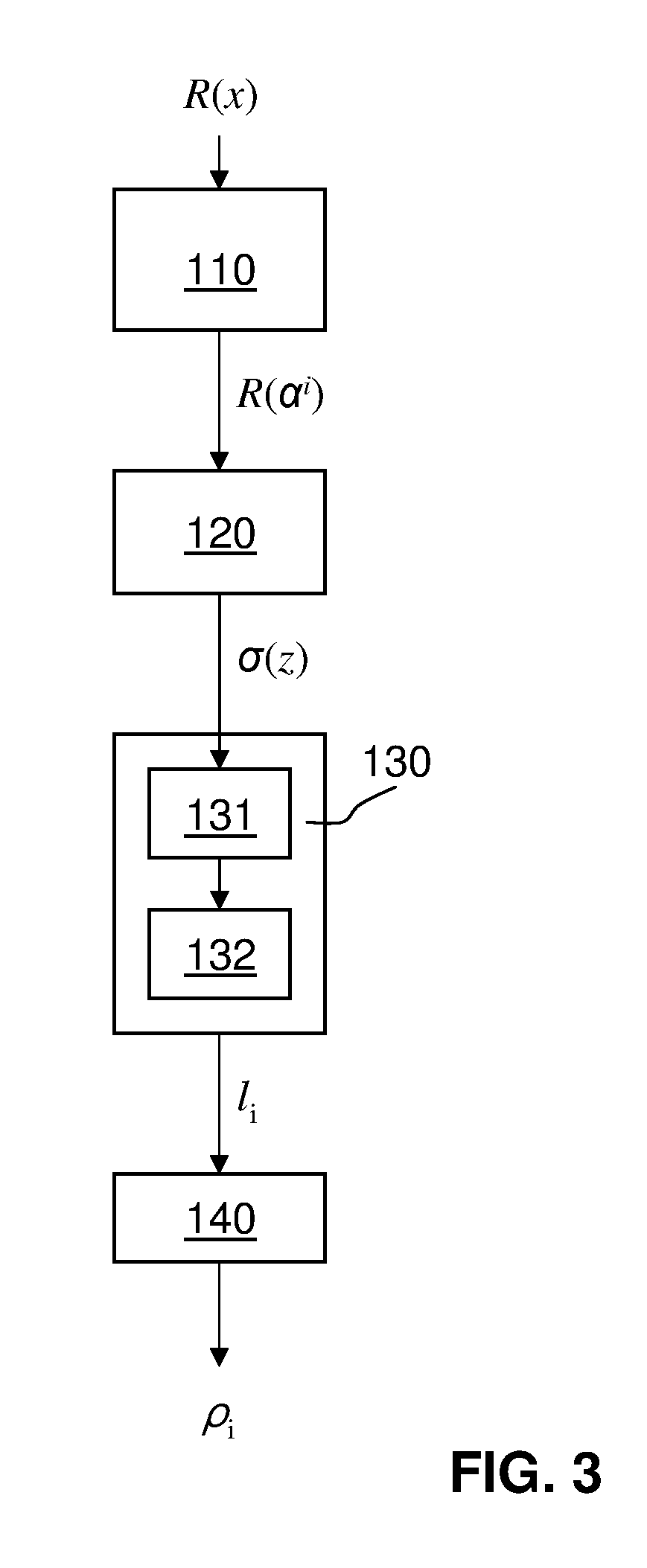
Evaluation of polynomials over finite fields and decoding of cyclic codes
InactiveUS20130326315A1Effective evaluationData efficientDigital data processing detailsCode conversionCantor–Zassenhaus algorithmDecomposition
An apparatus and method are disclosed for evaluating an input polynomial (p(x)) in a (possibly trivial) extension of the finite field of its coefficients, which are useful in applications such as syndrome evaluation in the decoding of cyclic codes. The apparatus comprises a decomposition / evaluation module (110) configured to iteratively decompose the input polynomial into sums of powers of the variable x, multiplied by powers of transformed polynomials, wherein each transformed polynomial has a reduced degree as compared to the input polynomial, and to evaluate the decomposed input polynomial. In another aspect, an apparatus and method of identifying errors in a data string based in a cyclic code are disclosed, which employ the Cantor-Zassenhaus algorithm for finding the roots of the error-locator polynomial, and which employ Shank's algorithm for computing the error locations from these roots.
Owner:UNIV ZURICH
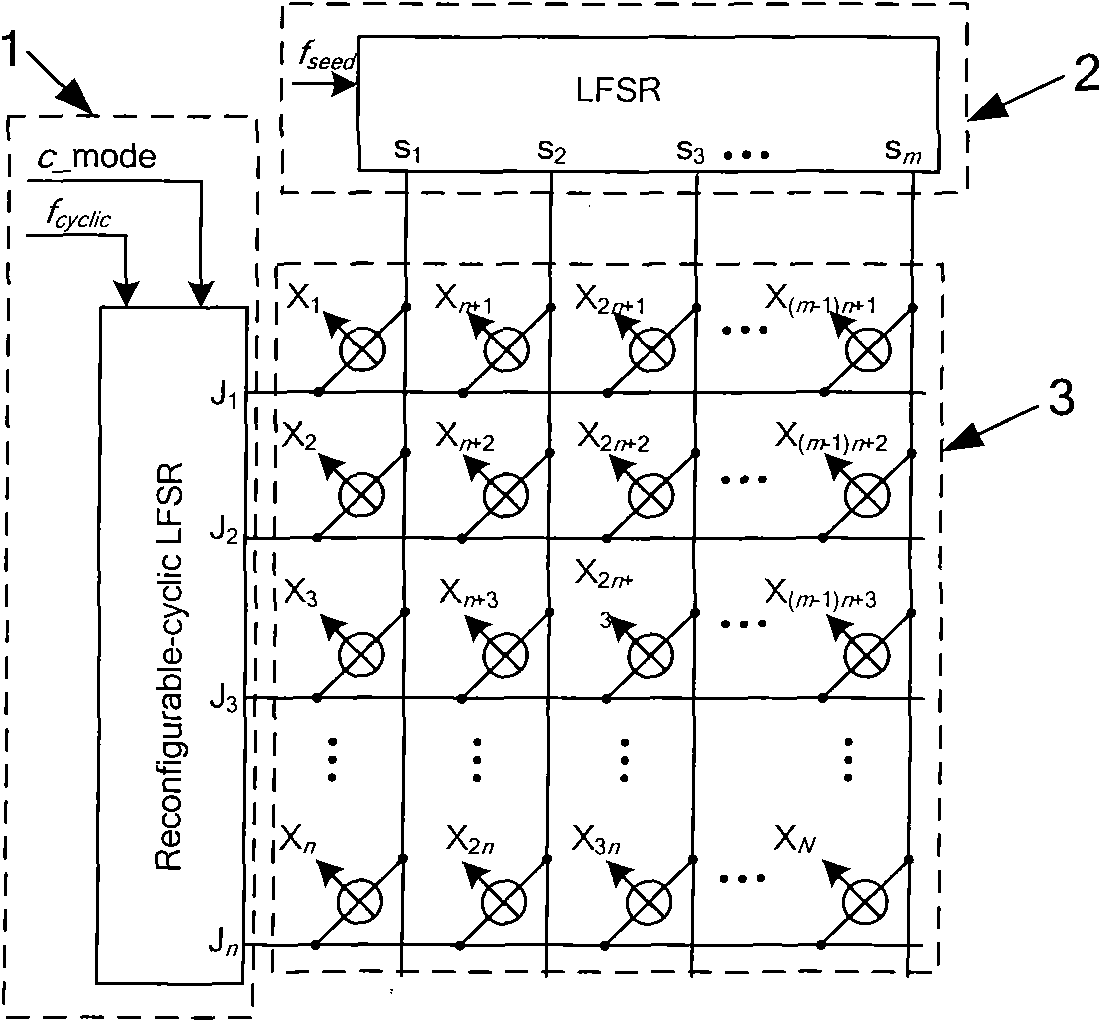
Test graphic generator of integrated circuit and test method thereof
InactiveCN101776730AReduce overheadReduce the number of test pattern transitionsElectrical testingFault coverageTest power
The invention relates to the field of an integrated circuit test, and discloses a test graphic generator of an integrated circuit and a test method thereof. The test graphic generator comprises a reconfigurable linear feedback shift register of cyclic code with single bit change, a liner feedback shift register based on a primitive polynomial and a two-dimensional exclusive or gate array; compared with the traditional test graphic generator, the test graphic generator has less hardware overhead, few quantity of repeated test graphics, short test time, uniform distribution of generated test graphics, and can obtain higher fault coverage rate; and the generated single jump test sequence reduces the conversion times of a tested circuit input end, thus greatly reducing the test power consumption of the tested integrated circuit.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
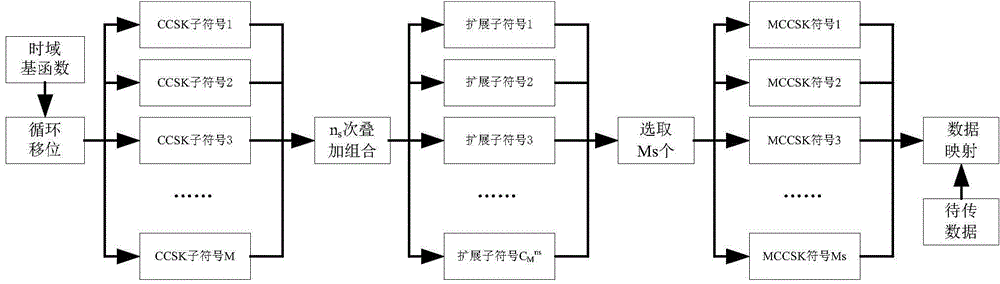
Multistage cyclic code shift keying modulation and demodulation method based on transform domain communication
InactiveCN104468451AIncrease diversityLarge amount of informationMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainCyclic code shift keying
The invention relates to a multistage cyclic code shift keying modulation and demodulation method based on transform domain communication, and belongs to the field of wireless digital communication. The method comprises the steps that a transmitting end generates a normalized frequency-domain basis function, carries out inverse Fourier transform on the normalized frequency-domain basis function to generate a time-domain basis function, generates MCCSK sub-symbols according to the time-domain basis function, and transmits the sub-symbols after carrying out data modulation through the sub-symbols; a receiving end generates a time-domain basis function corresponding to the transmitting end, and carries out MCCSK data demodulation according to the time-domain basis function to obtain demodulated data. According to the method, the diversity of modulation symbols is improved through the combinatorial number method, the symbols generated by cyclic code shift of the basis function are superposed and combined to generate more expanded symbols, symbols with the large minimum average symbol space are selected to be combined and used for modulation, the data are demodulated at the demodulation end in a multistage demodulation mode, and therefore the quantity of information carried by a unit waveform is increased, and the bit error rate loss is effectively controlled.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com