Patents
Literature
31results about How to "Large isolation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
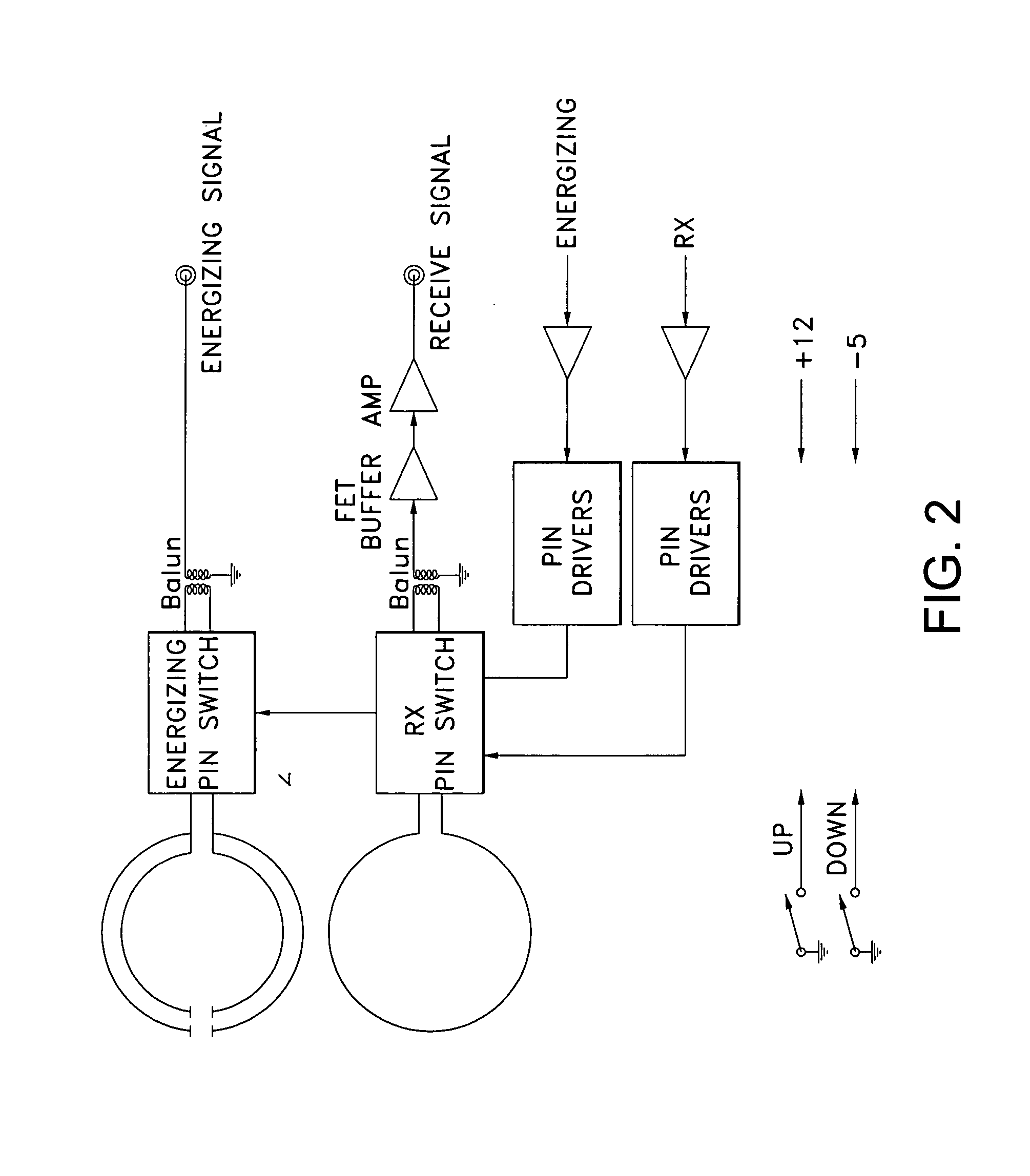
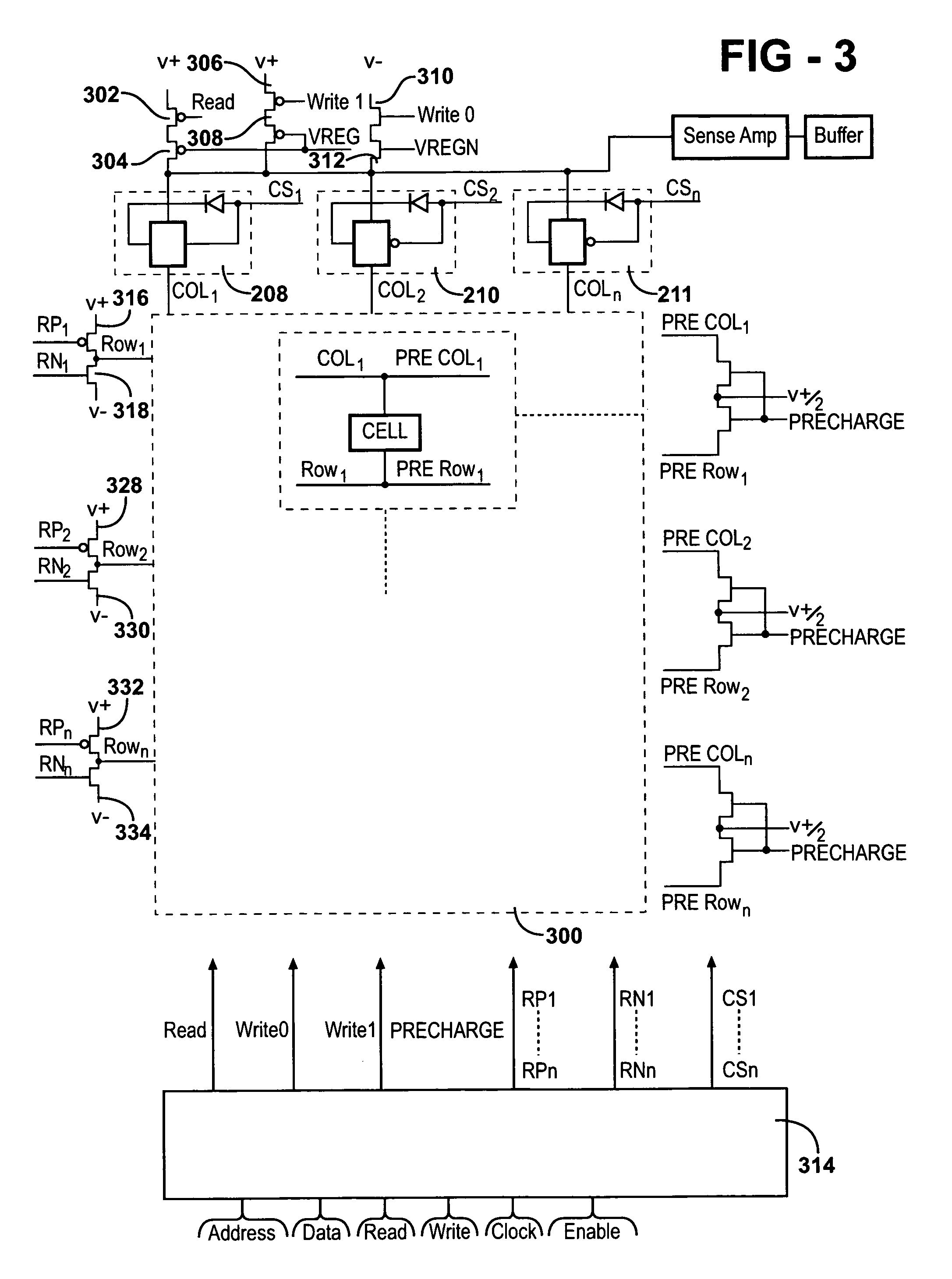
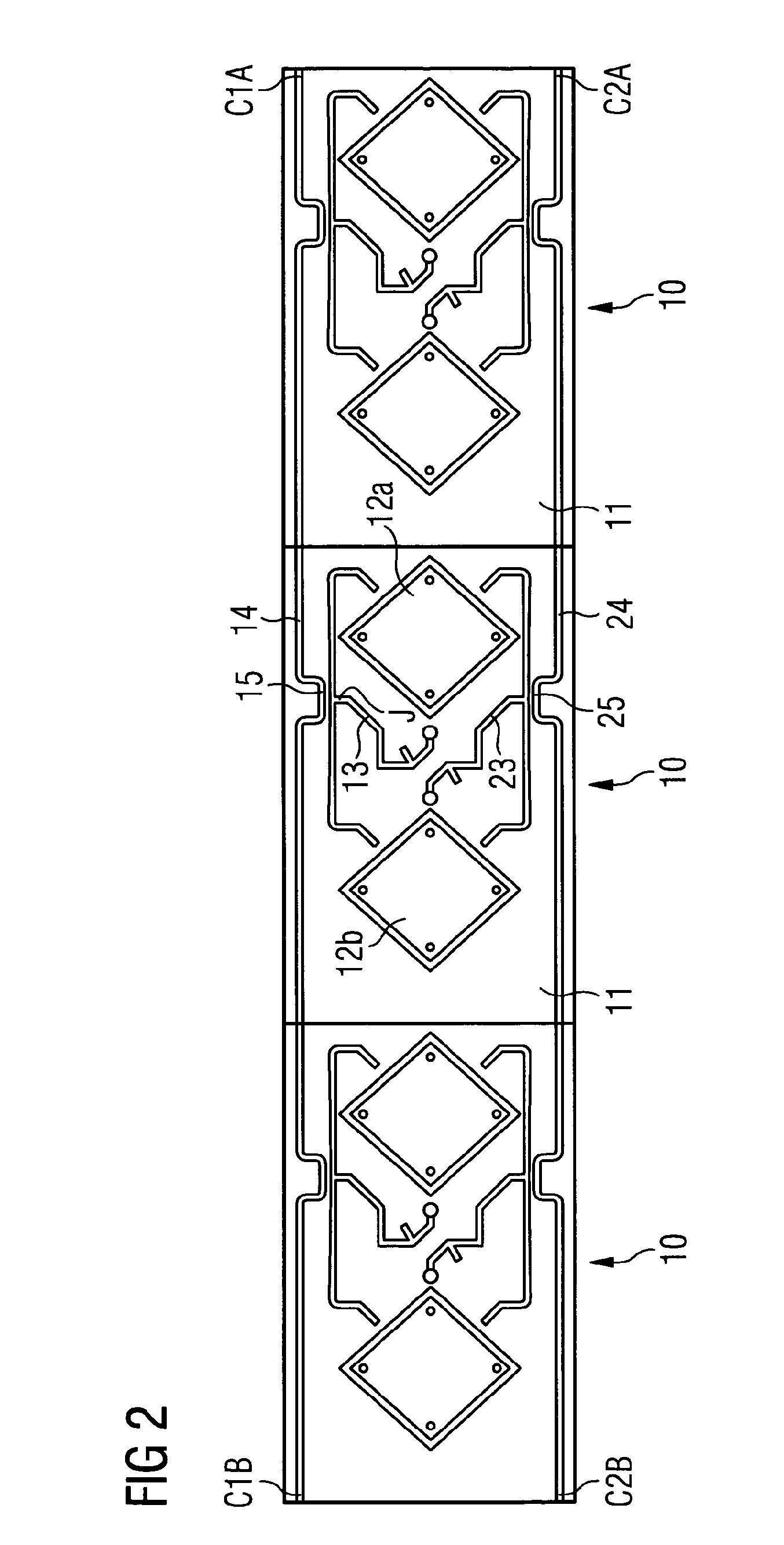
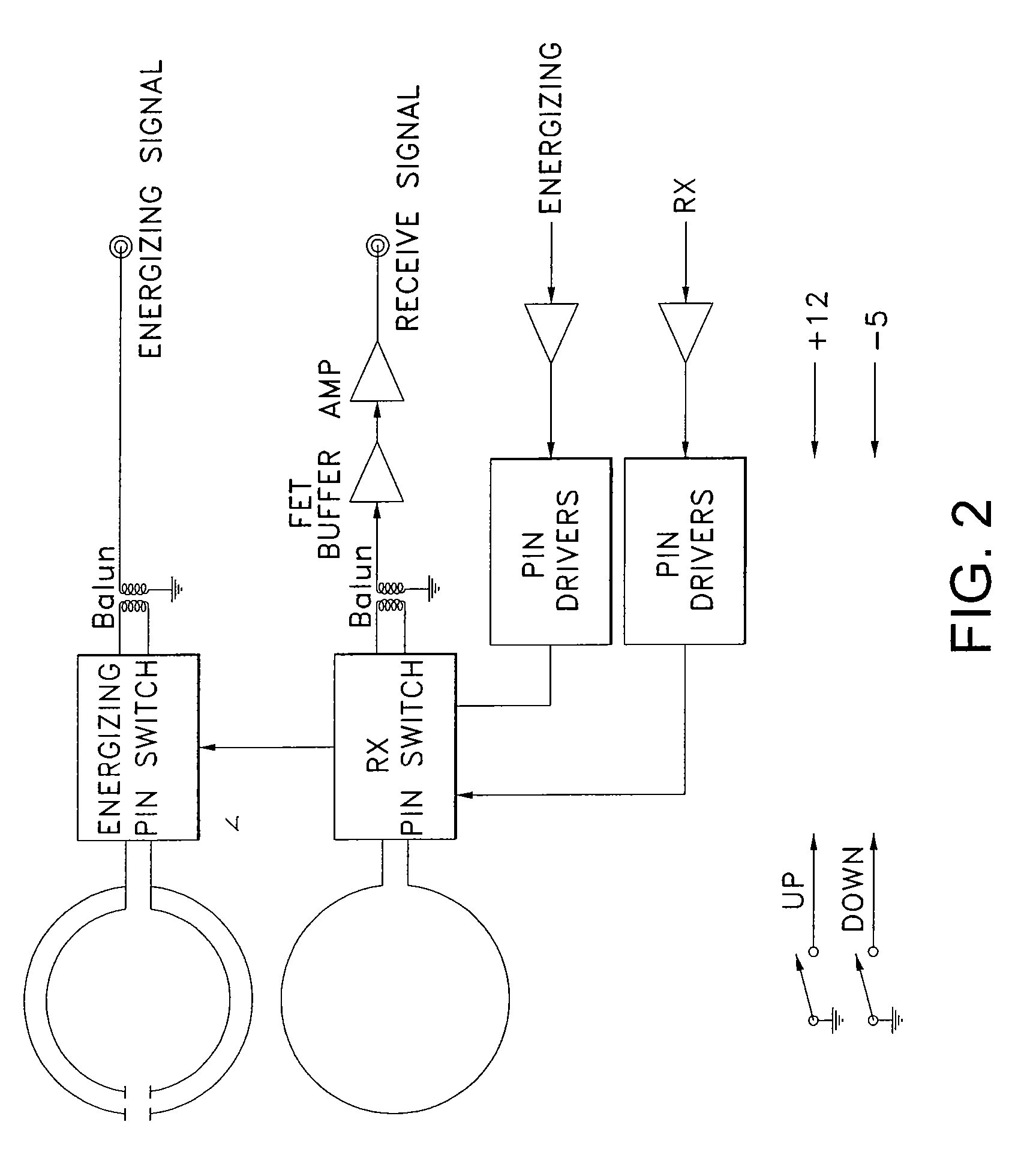
Coupling loop
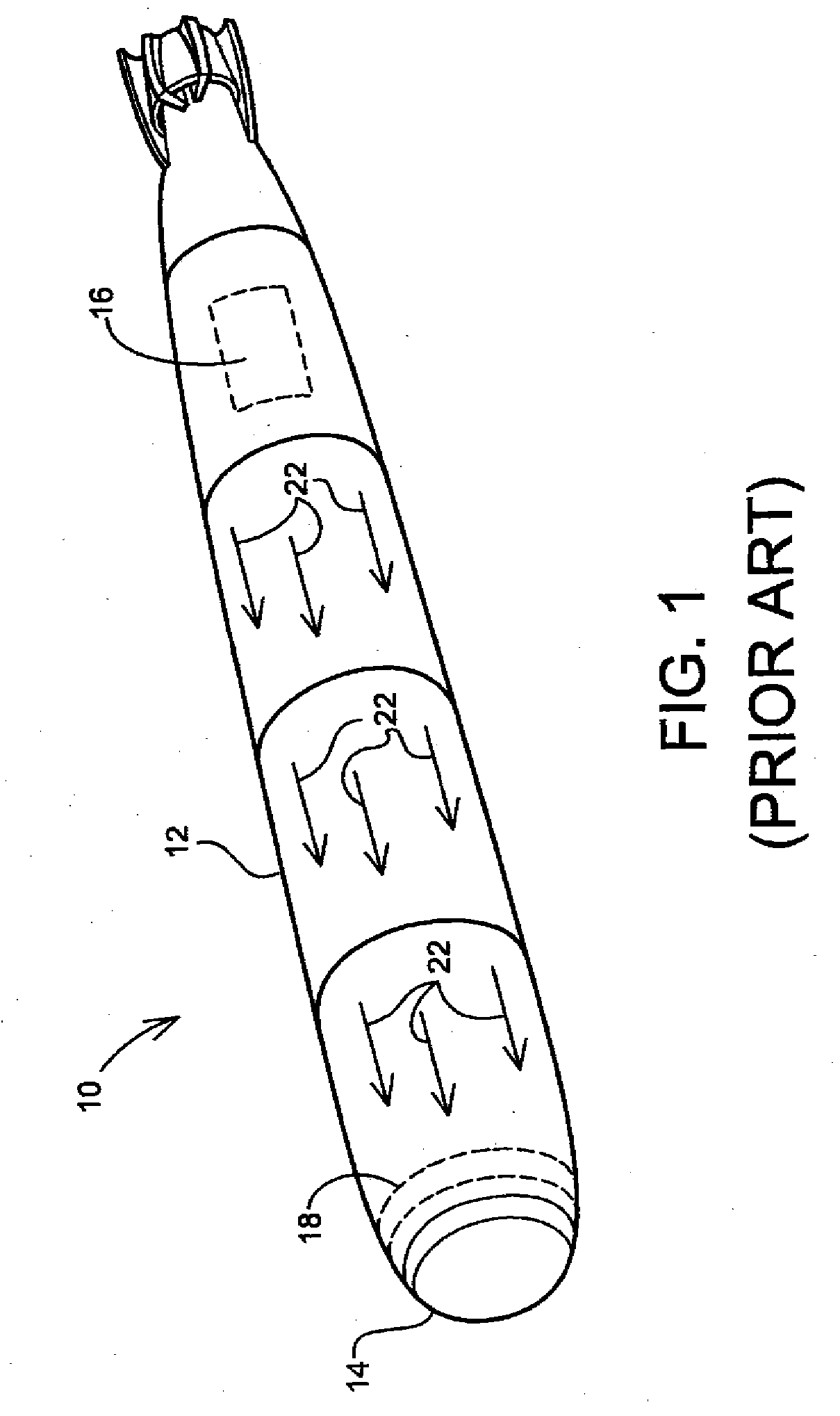
ActiveUS7432723B2Increase opportunitiesAvoid breakingCoaxial cables/analogue cablesNear-field transmissionCouplingFrequency matching
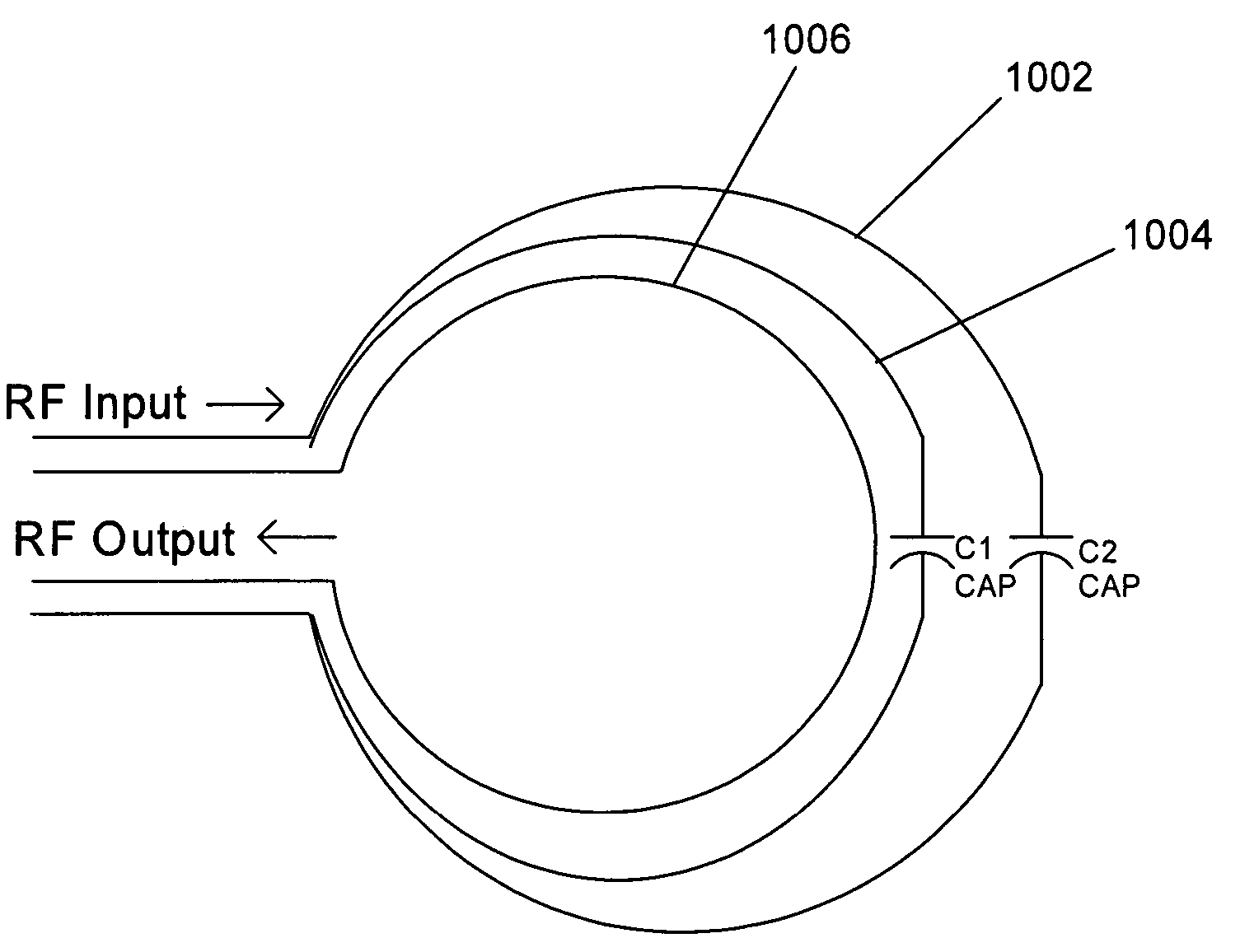
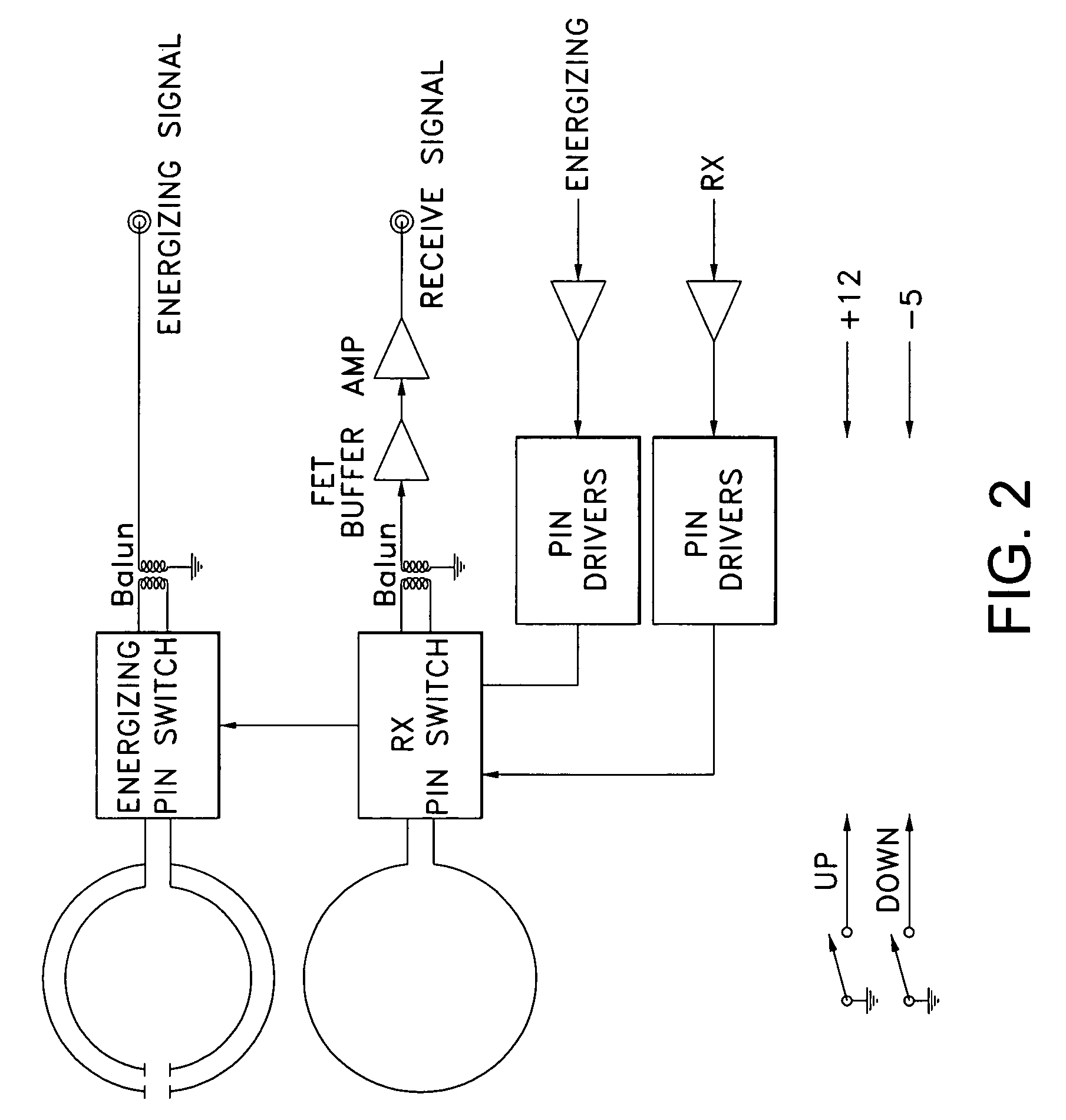
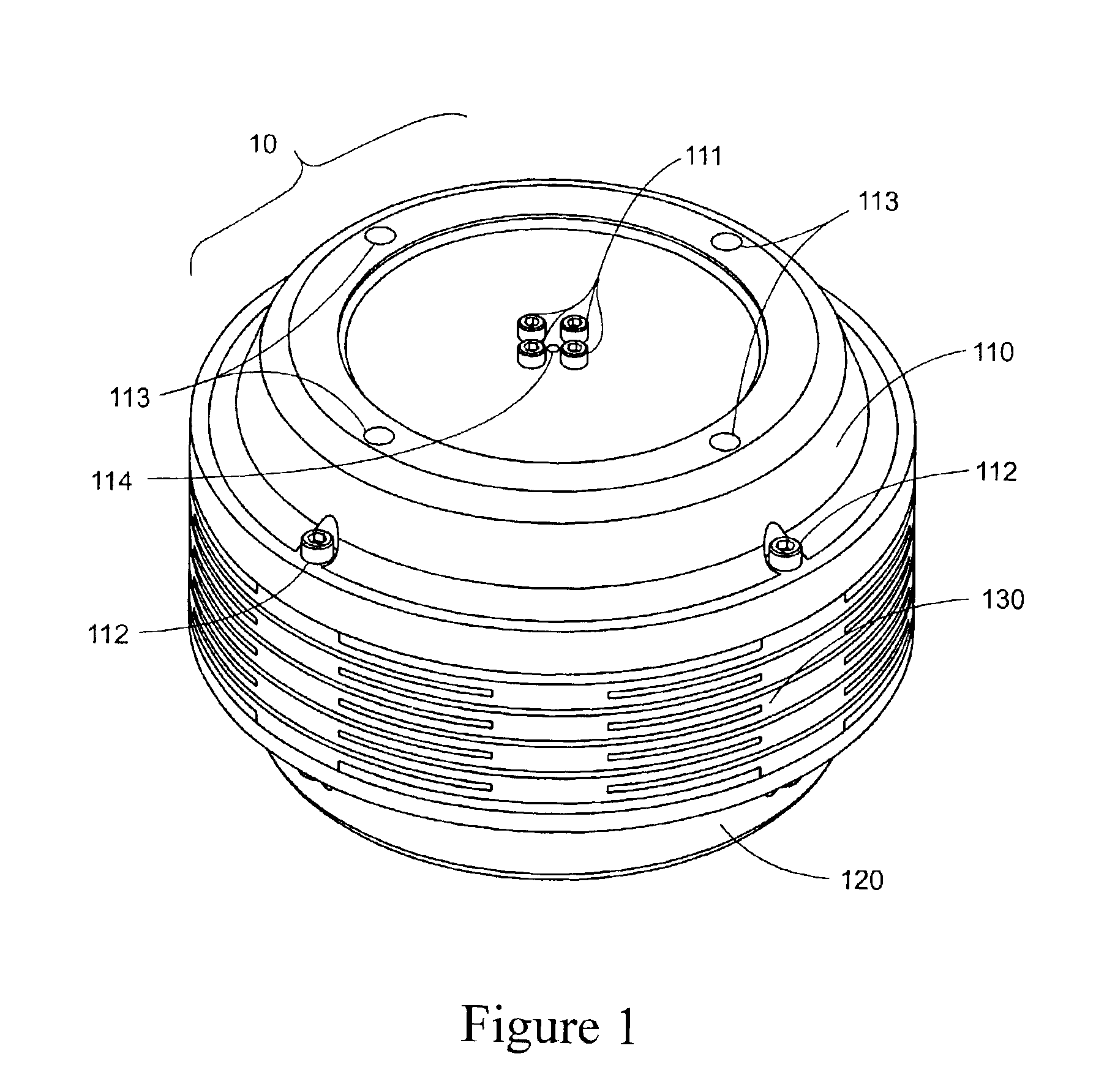
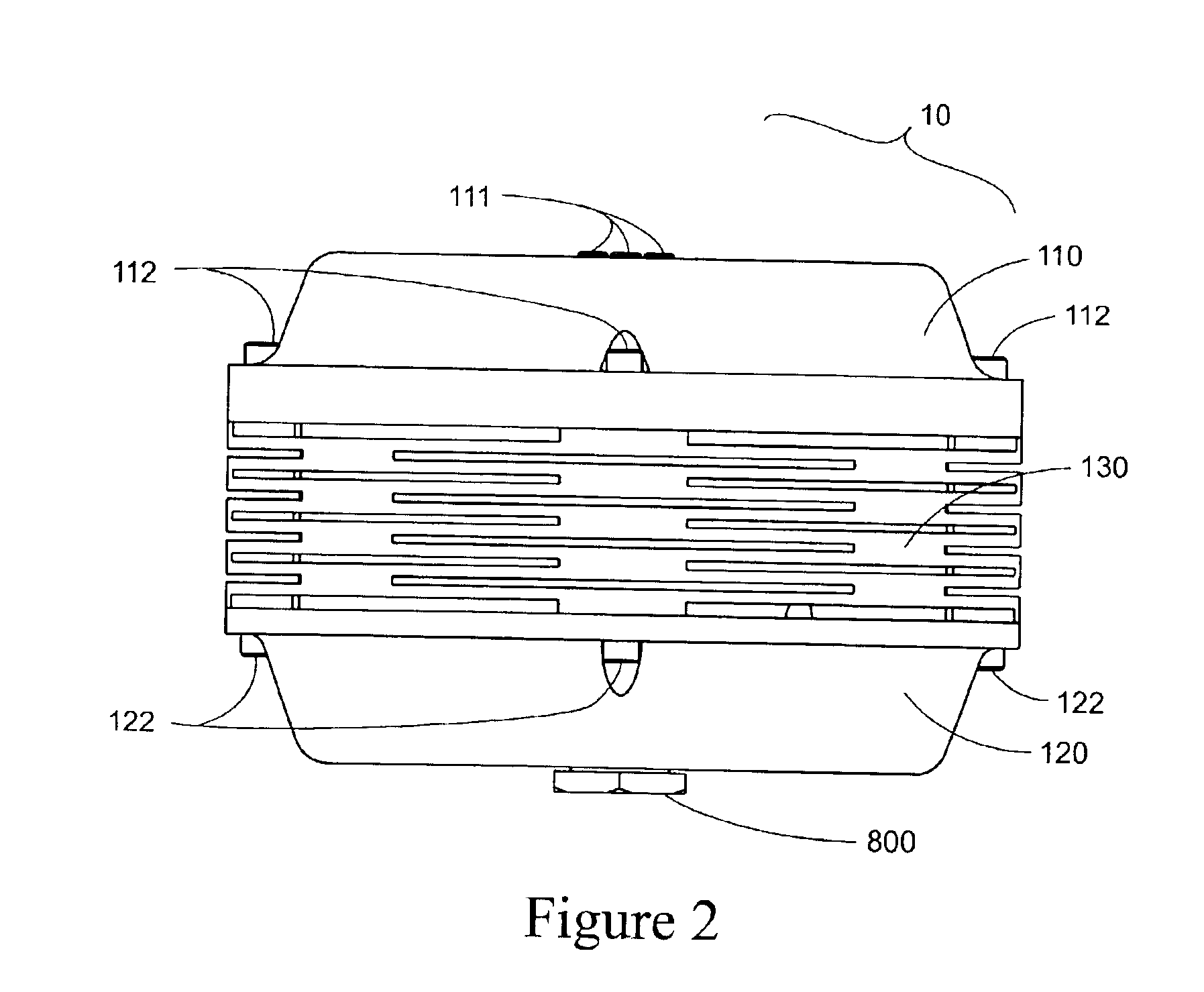
A coupling loop or antenna is provided that can be used with a system that determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. The coupling loop includes multiple loops. Preferably two tuned loops are used for transmitting the energizing signal to the sensor and an un-tuned loop is used for receiving the sensor signal from the sensor. Orientation features on the housing for the coupling loop and the sensor are provided to assist in positioning the coupling loop relative to the sensor to maximize the coupling between the sensor signal and the coupling loop.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
Electro-ferromagnetic, tunable electromagnetic band-gap, and bi-anisotropic composite media using wire configurations
InactiveUS20050146402A1High bandwidthSmall sizeRadiating elements structural formsResonatorsDielectricElectricity
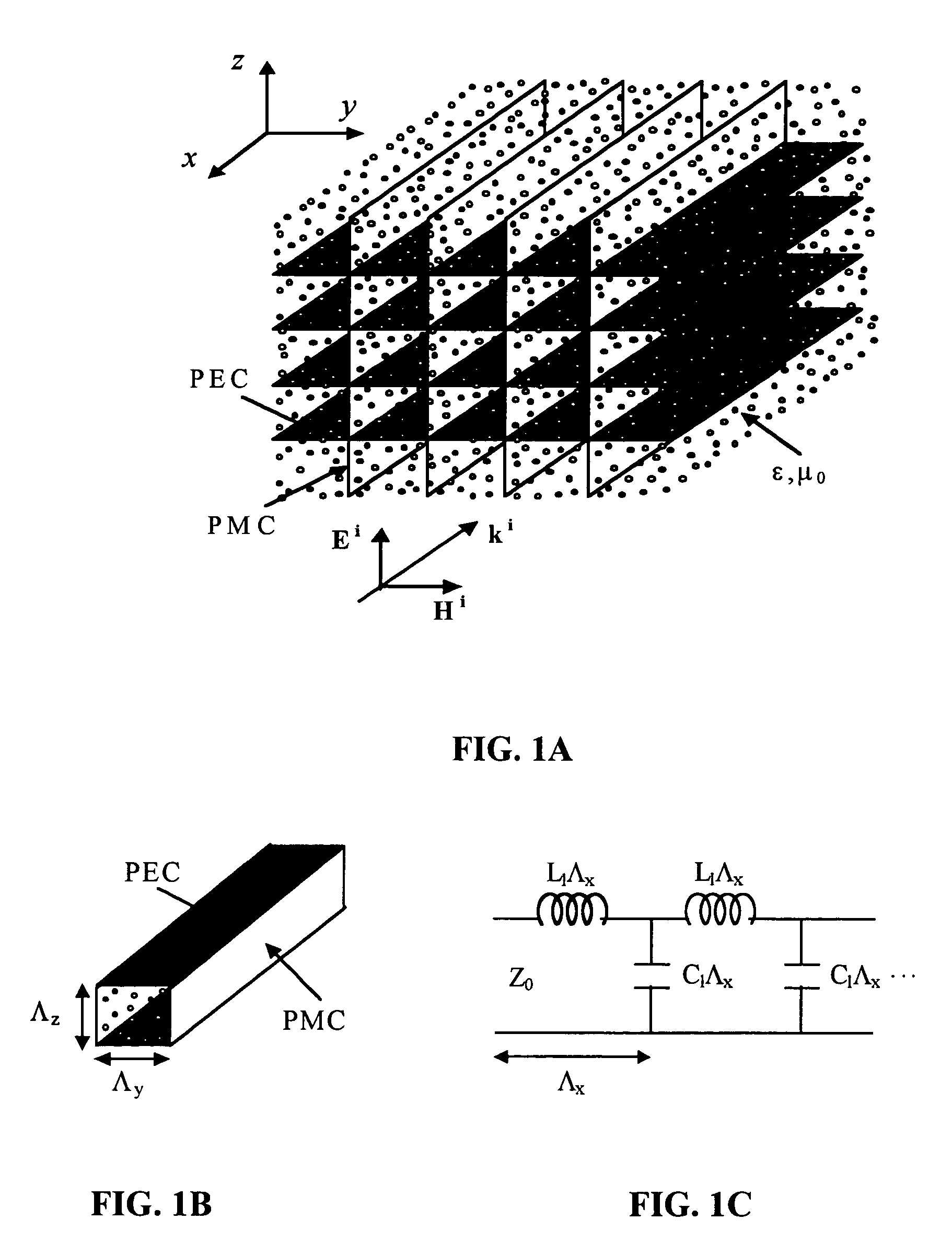
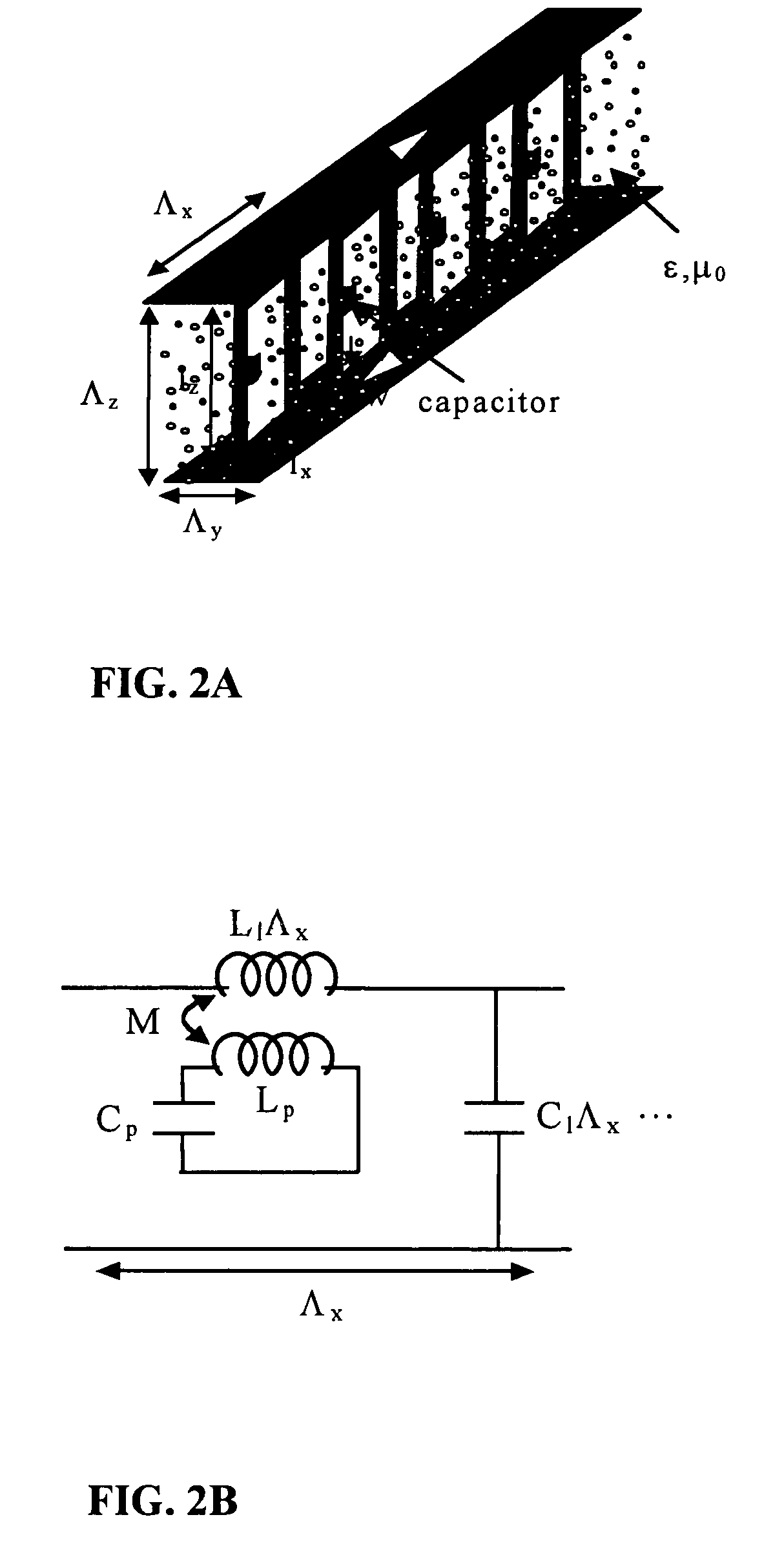
An artificial electro-ferromagnetic meta-material demonstrates the design of tunable band-gap and tunable bi-anisotropic materials. The medium is obtained using a composite mixture of dielectric, ferro-electric, and metallic materials arranged in a periodic fashion. By changing the intensity of an applied DC field the permeability of the artificial electro-ferromagnetic can be properly varied over a particular range of frequency. The structure shows excellent Electromagnetic Band-Gap (EBG) behavior with a band-gap frequency that can be tuned by changing the applied DC field intensity. The building block of the electro-ferromagnetic material is composed of miniaturized high Q resonant circuits embedded in a low-loss dielectric background. The resonant circuits are constructed from metallic loops terminated with a printed capacitor loaded with a ferro-electric material. Modifying the topology of the embedded-circuit, a bi-anisotropic material (tunable) is examined. The embedded-circuit meta-material is treated theoretically using a transmission line analogy of a medium supporting TEM waves.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
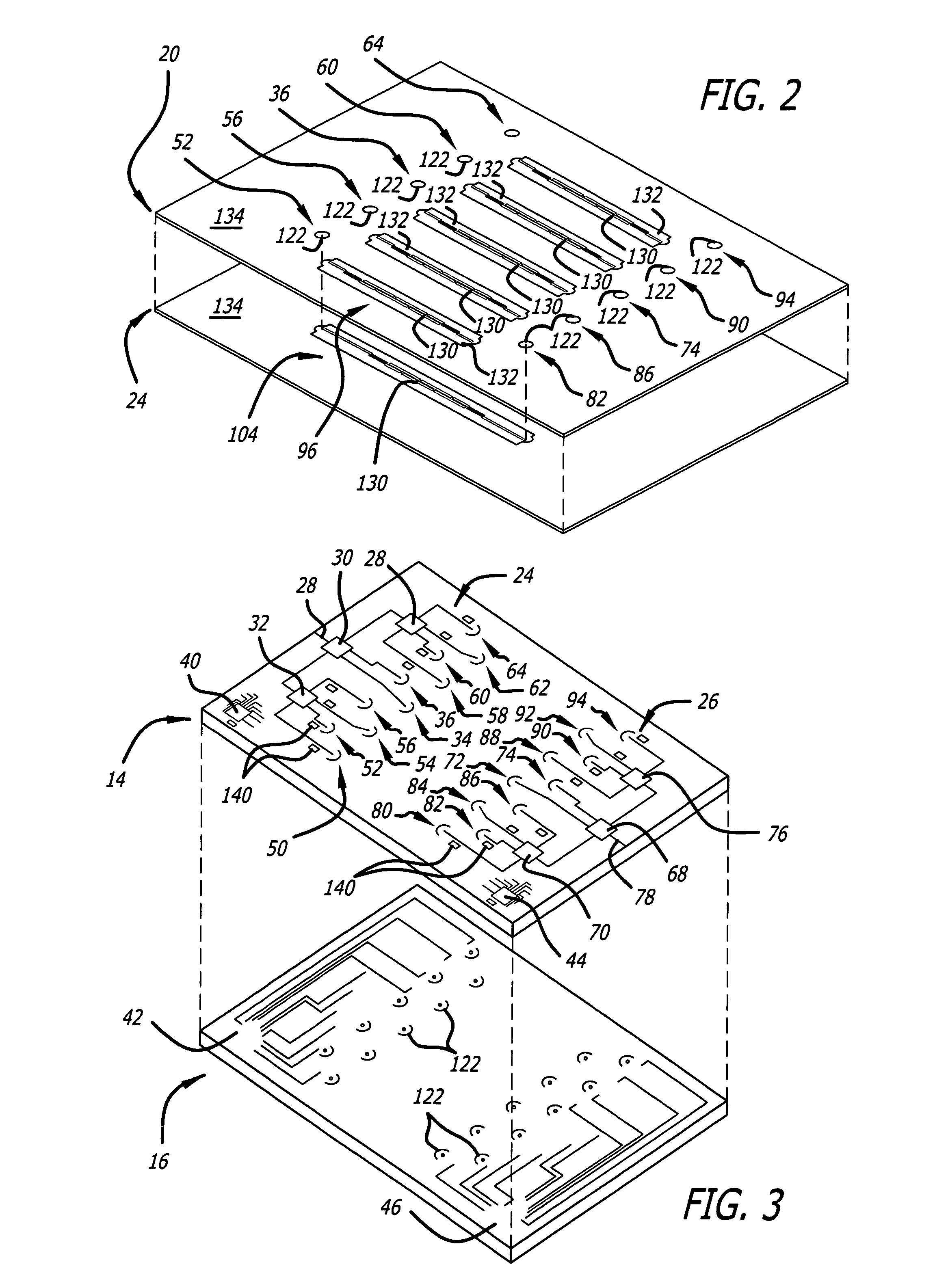
Coupling loop and method for positioning coupling loop
ActiveUS20060244465A1Avoid breakingIncrease opportunitiesCoaxial cables/analogue cablesNear-field transmissionCouplingFrequency matching
A coupling loop or antenna is provided that can be used with a system that determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. The coupling loop includes multiple loops. Preferably two tuned loops are used for transmitting the energizing signal to the sensor and an un-tuned loop is used for receiving the sensor signal from the sensor. Orientation features on the housing for the coupling loop and the sensor are provided to assist in positioning the coupling loop relative to the sensor to maximize the coupling between the sensor signal and the coupling loop.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
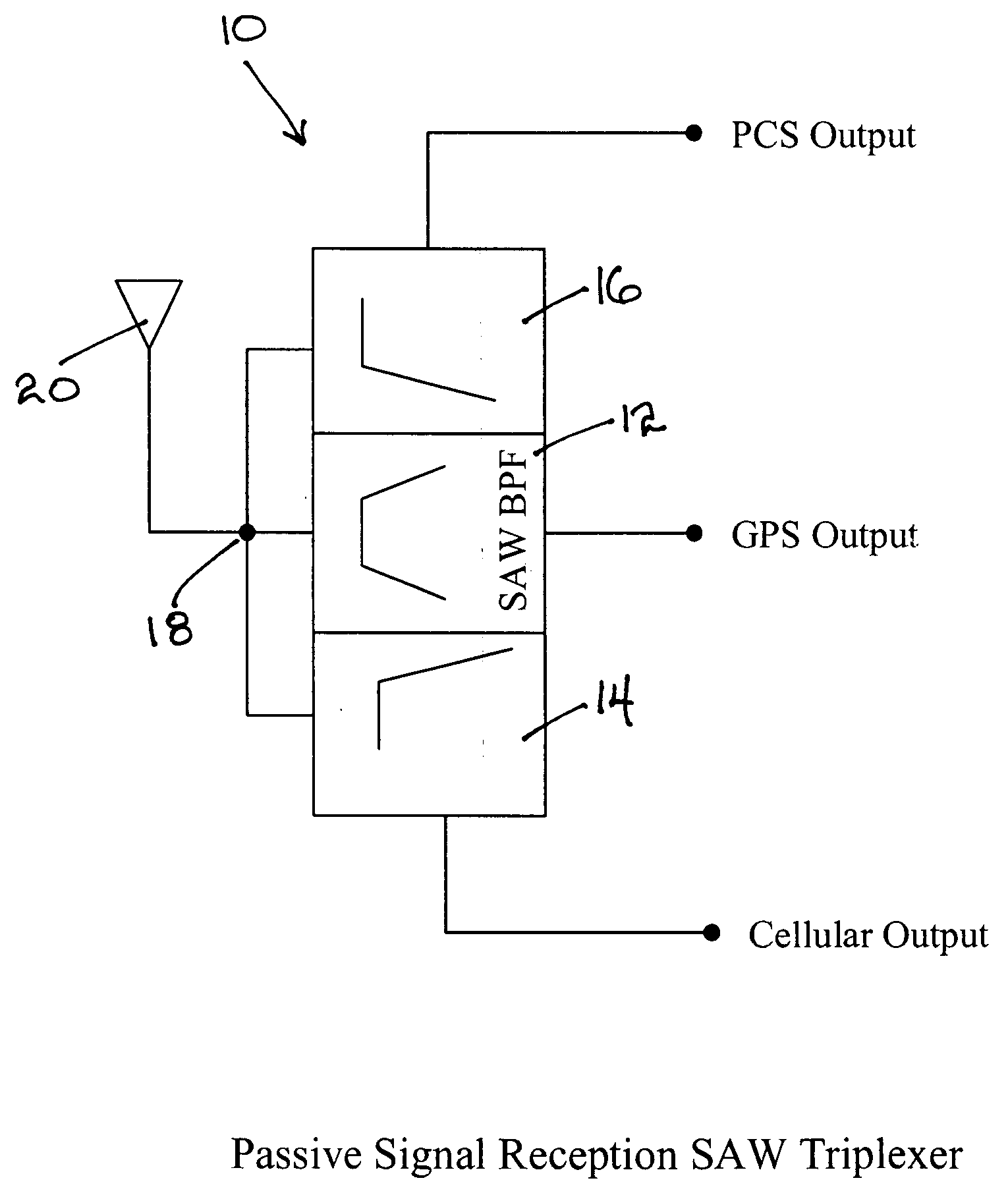
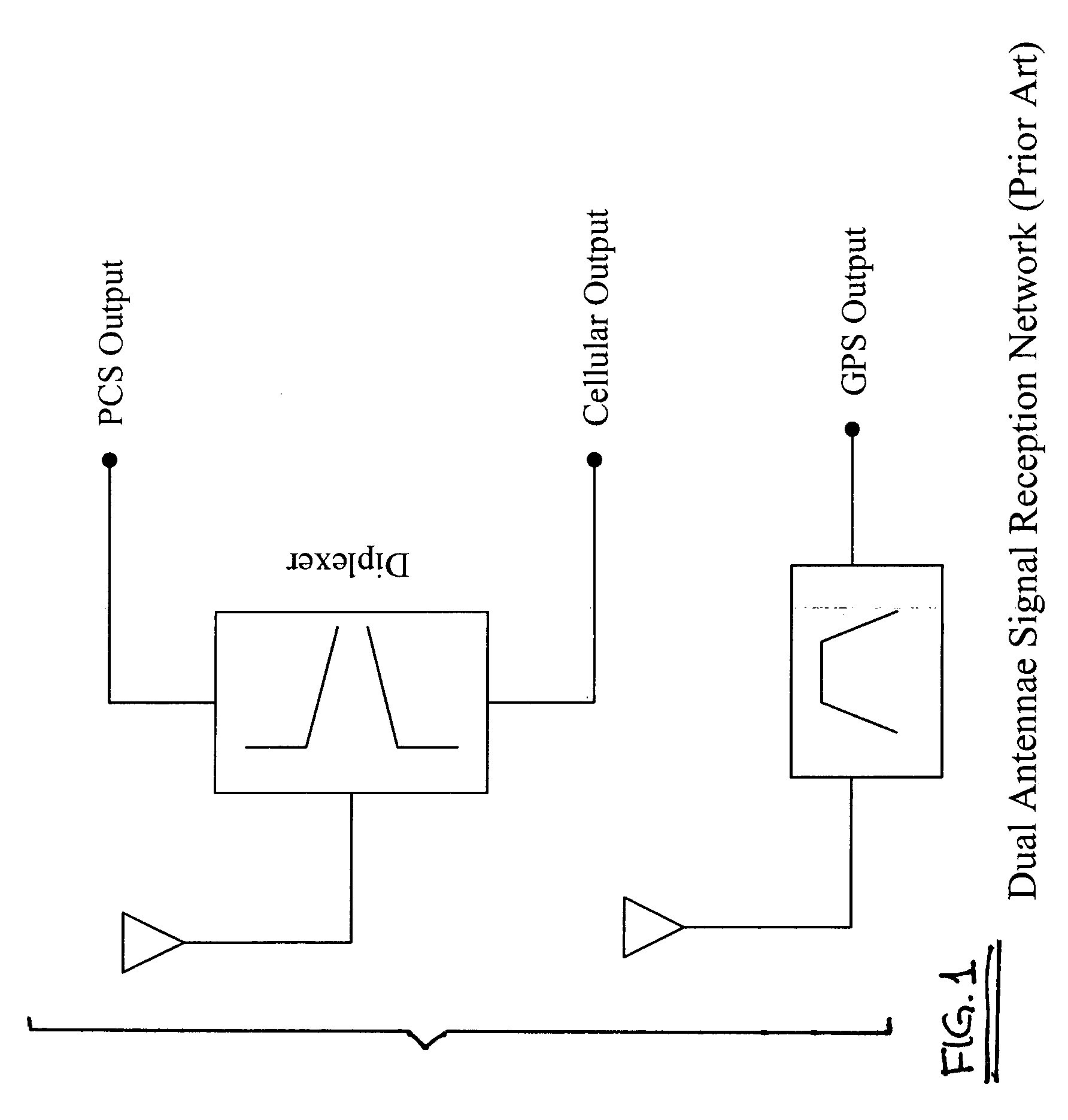
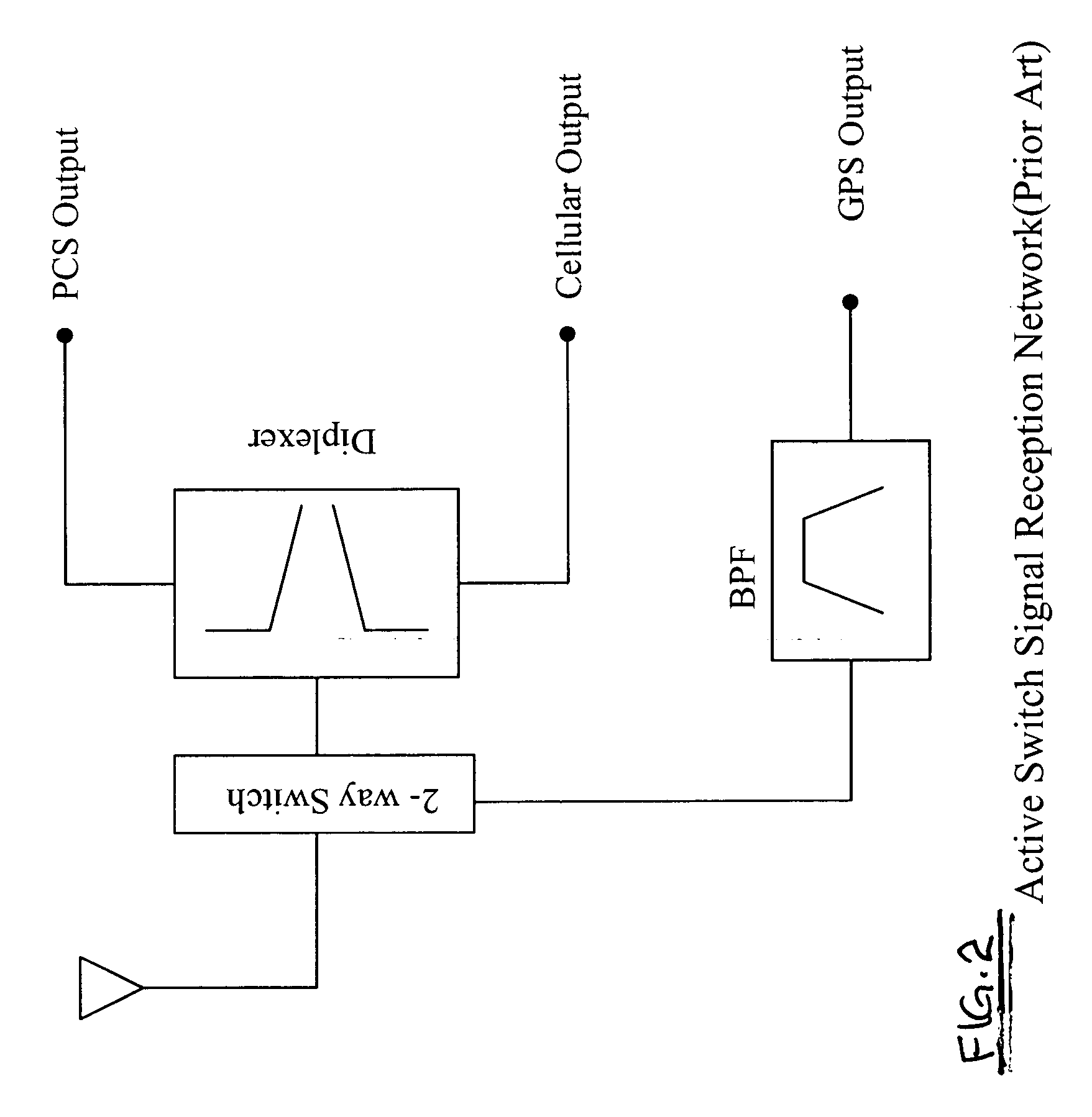
Triband passive signal receptor network
InactiveUS20060067254A1Low insertion lossLarge isolationImpedence networksRepeater circuitsBandpass filteringLow-pass filter
A surface acoustic wave (SAW) triplexer receives radio frequency signals in three bands and provides output signal components for PCS, GPS, and cellular signal processing ports. The triplexer includes low pass filter and a high pass network operating with an antenna terminal for reception and separation of an incoming signal in a low and high frequency bands, and a SAW filter connected to the input terminal for reception and separation of the incoming signal within a frequency band located between that of the low and the high bands. A low insertion loss bandpass filter is provided by the SAW filter having a transducer and reflectors fabricated on a piezoelectric substrate.
Owner:SAWTEK
Multiband antenna arrangement
InactiveUS7683839B2Low envelope correlationImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsNon-resonant antennasComputer moduleEngineering
Owner:RPX CORP
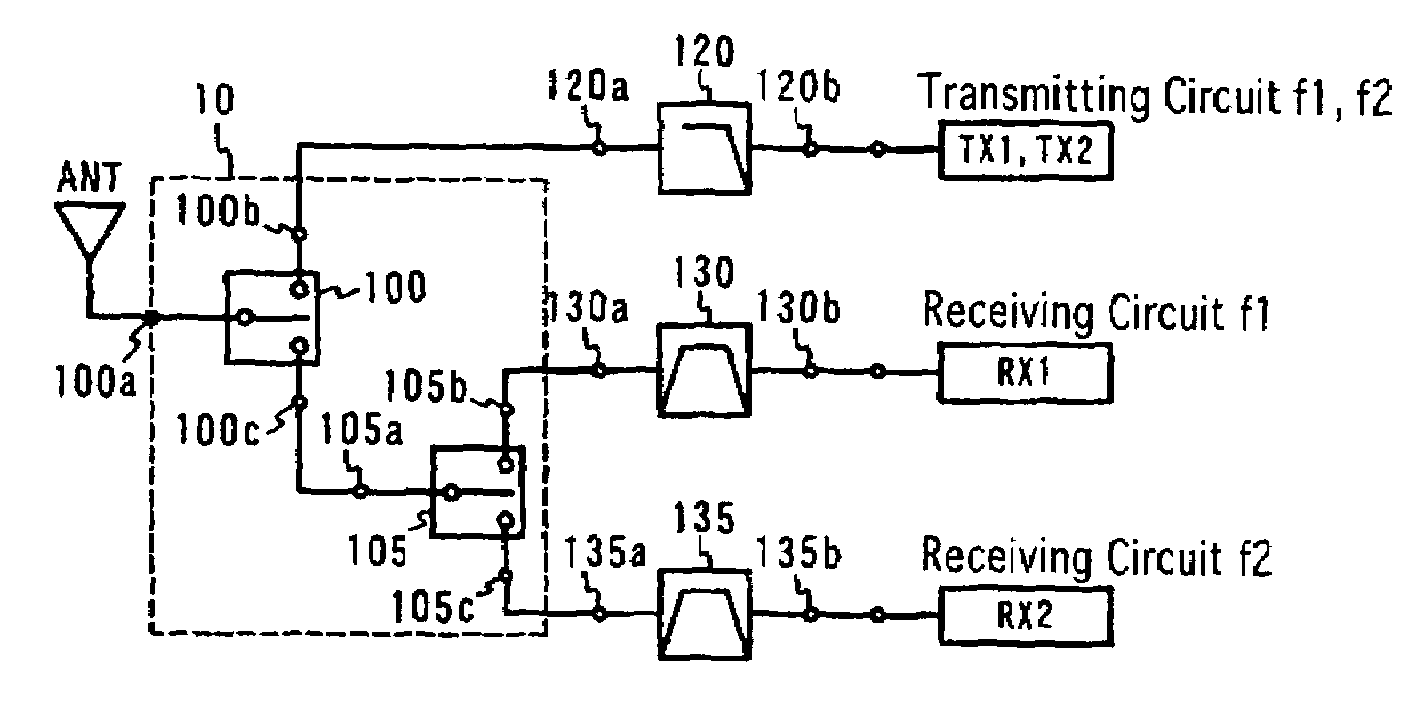
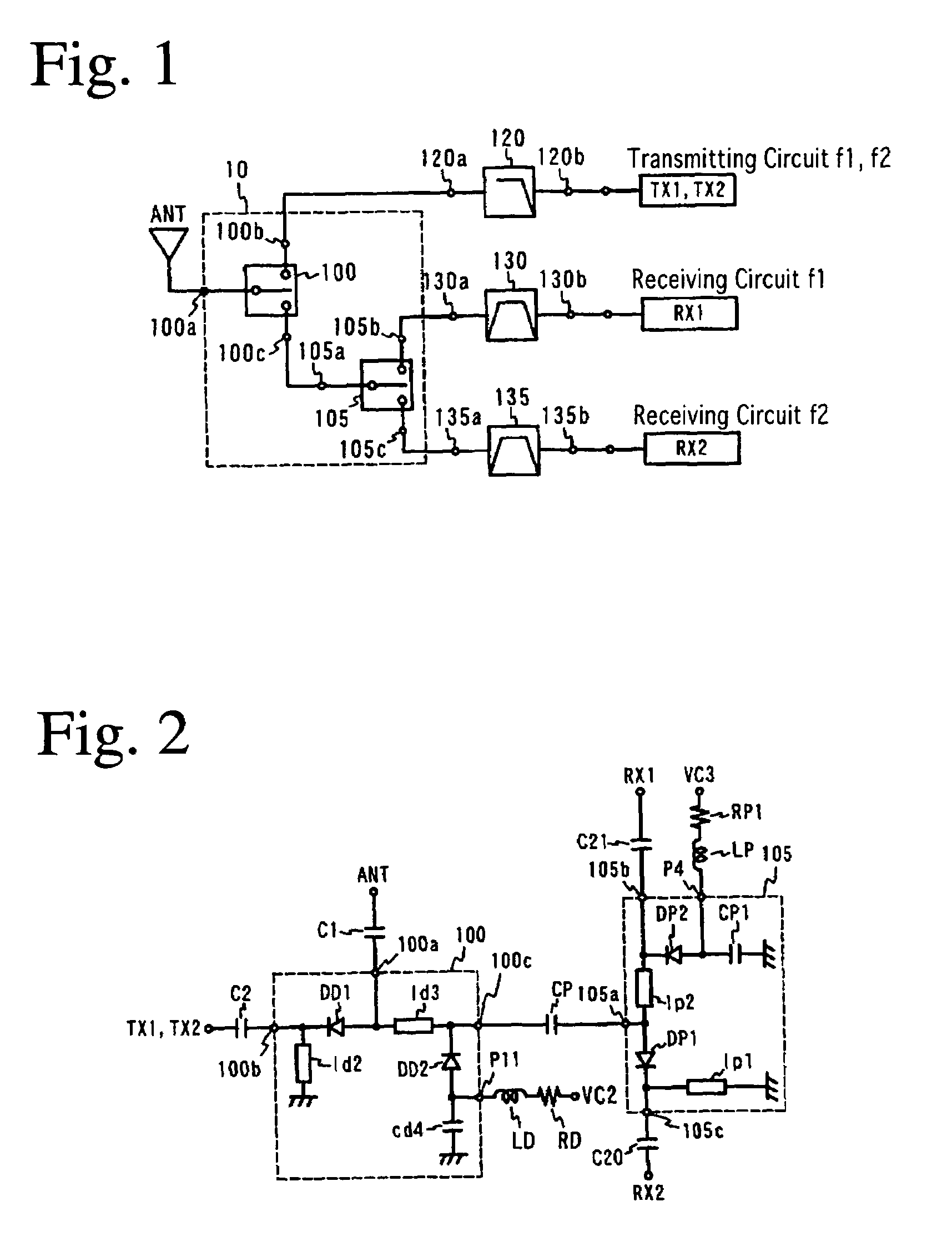
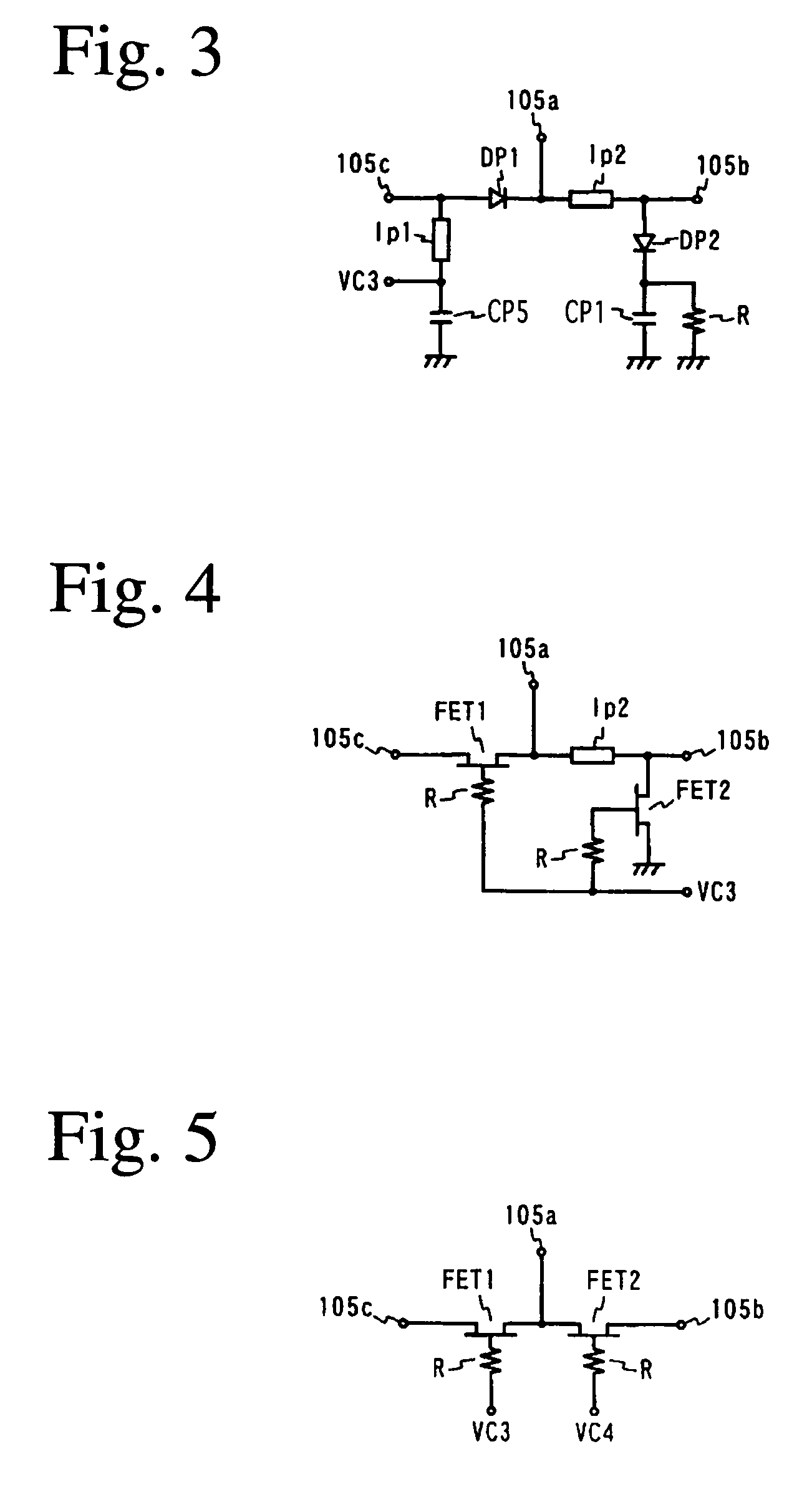
Switch circuit and composite high-frequency part
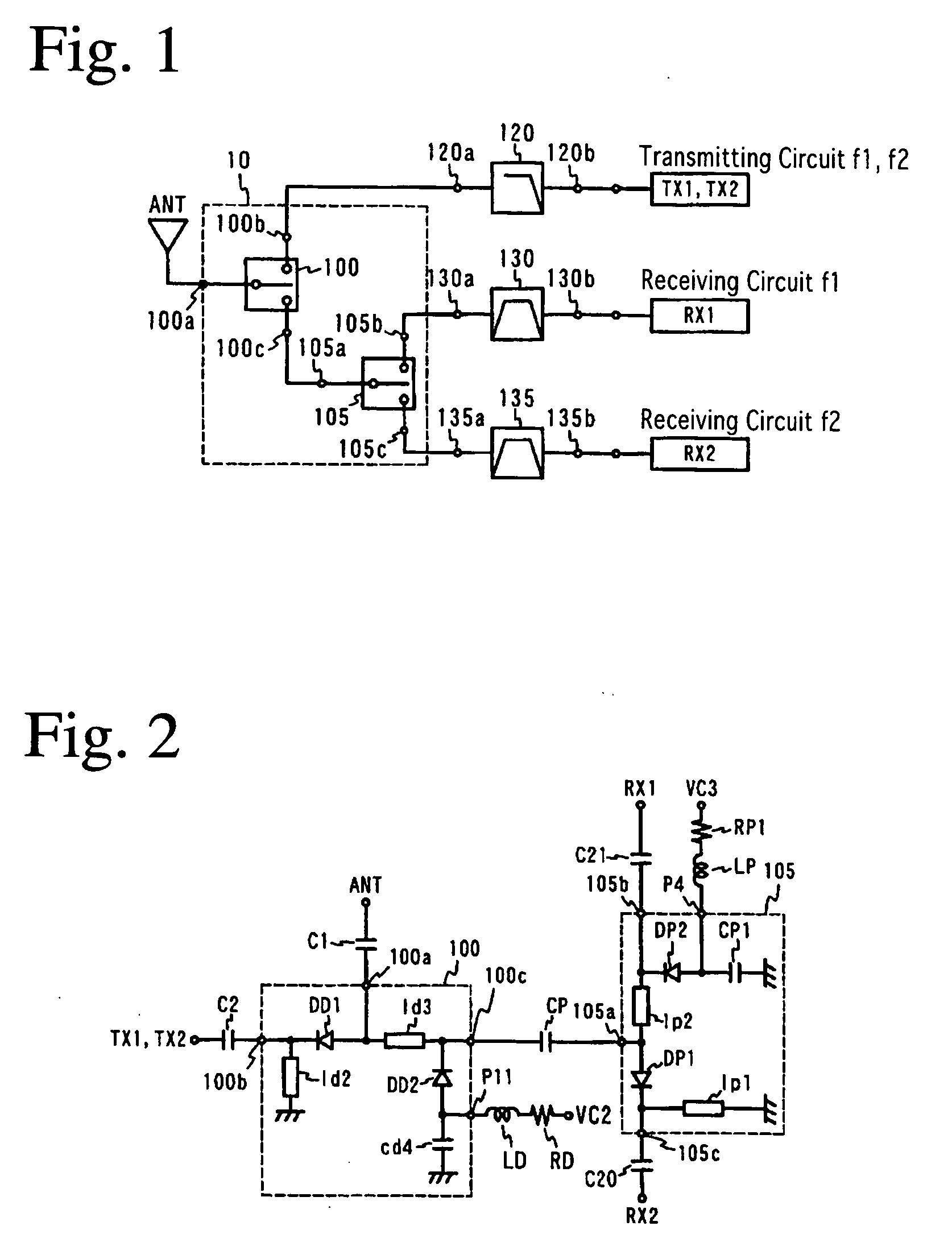
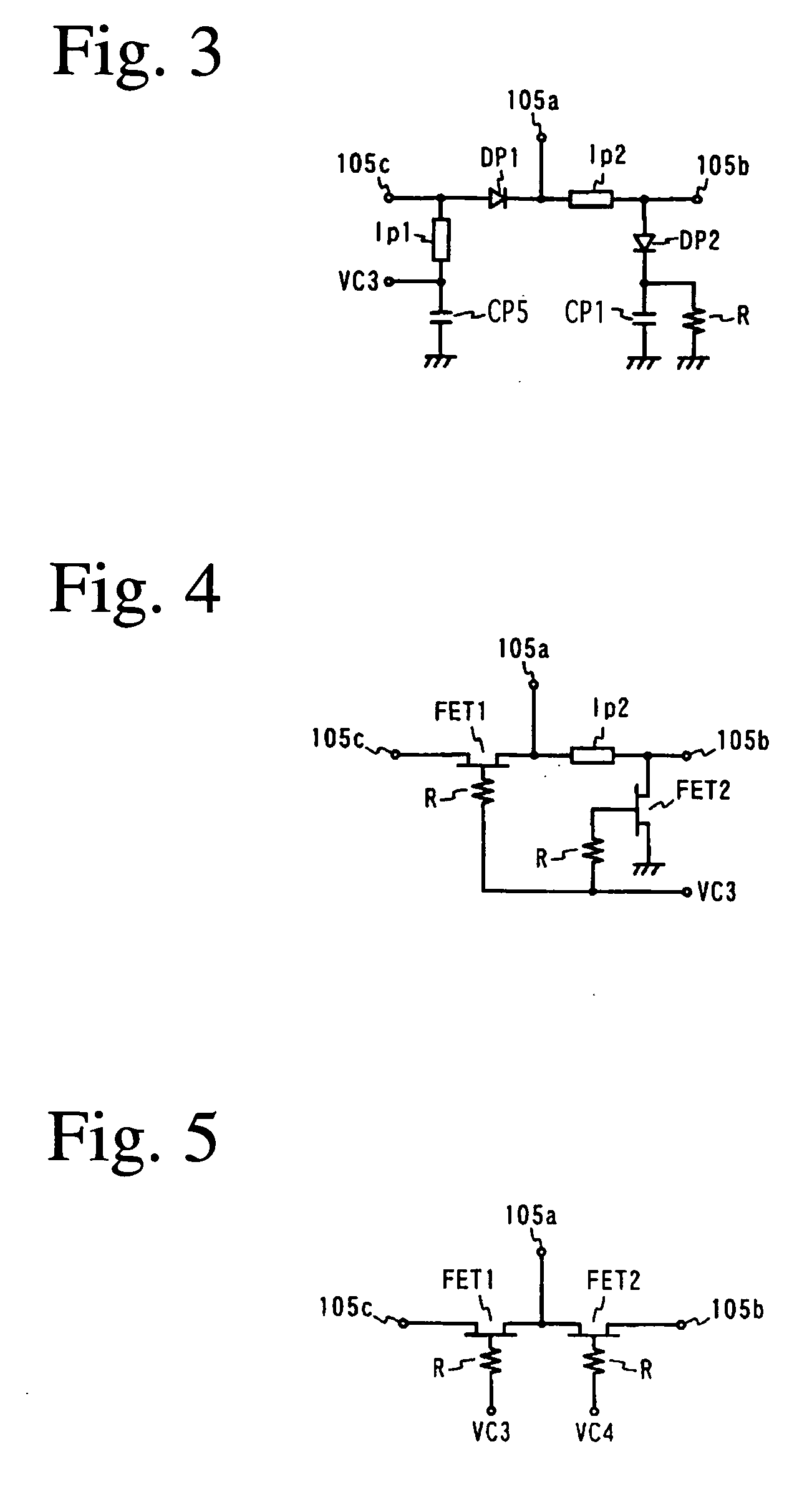
InactiveUS20050048927A1Small leakageLarge isolationTransmissionCoupling devicesCommunications systemFrequency band
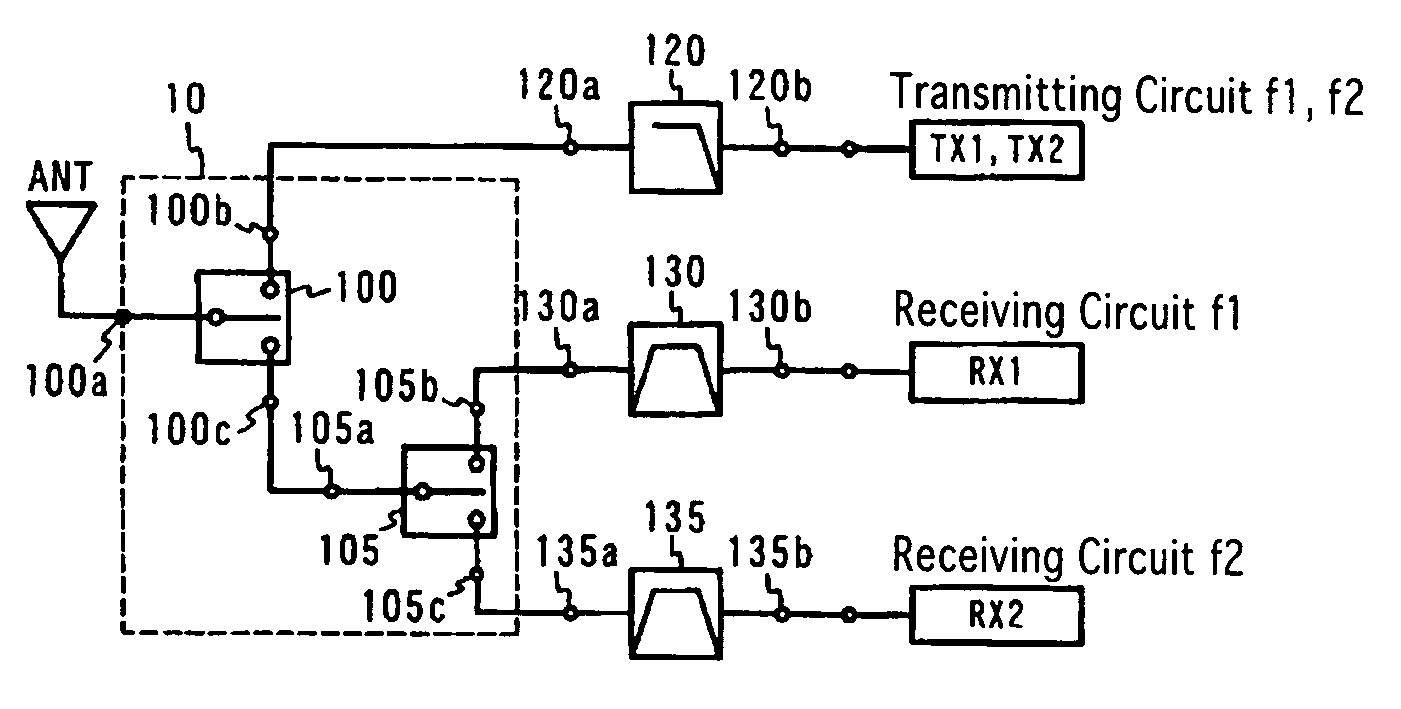
A switch circuit for selectively switching connection of an antenna side circuit with a reception circuit and a transmission circuit of two communication systems one of which has a reception frequency band partially overlapped with a transmission frequency of the other. The switch circuit includes (a) a first switch unit for switching connection of the antenna side circuit with the transmission circuit side of the first and tie second communication systems and the reception circuit side of the first and the second communication system and (b) a second switch unit connected between the first switch unit and the reception circuit of the first and the second communication system for switching connection of the antenna side circuit with the reception circuit of the first and the second communication system. (c) The transmission circuit side of the first and the second communication system of the first switch unit is connected to a transmission circuit shared by the first and the second communication system. (d) When the transmission circuit of the first and the second communication system is connected to the antenna side circuit, the second switch unit cuts off the connection between the reception circuit of the first communication system and the first switch unit.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Method and apparatus for accessing a bidirectional memory
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
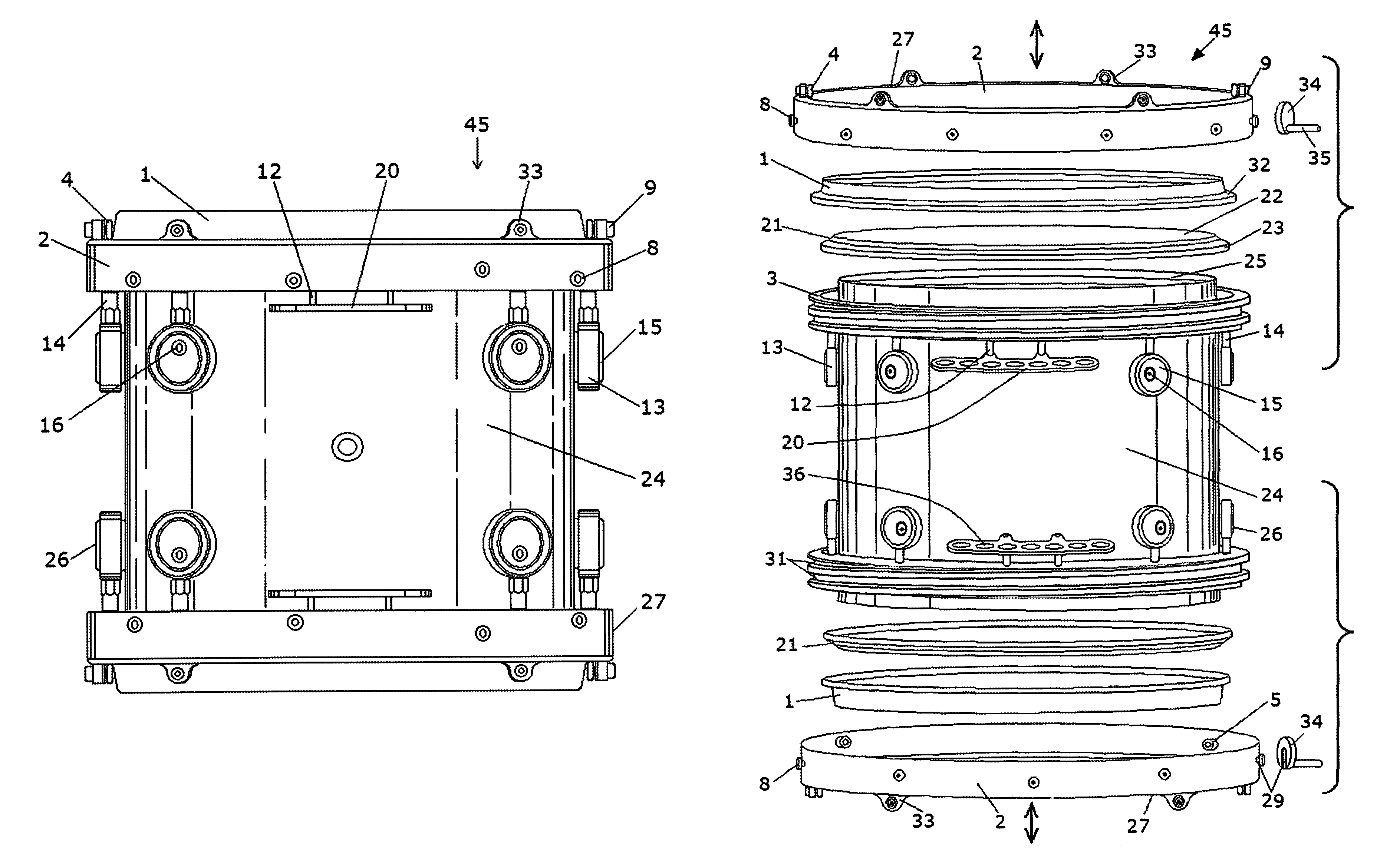
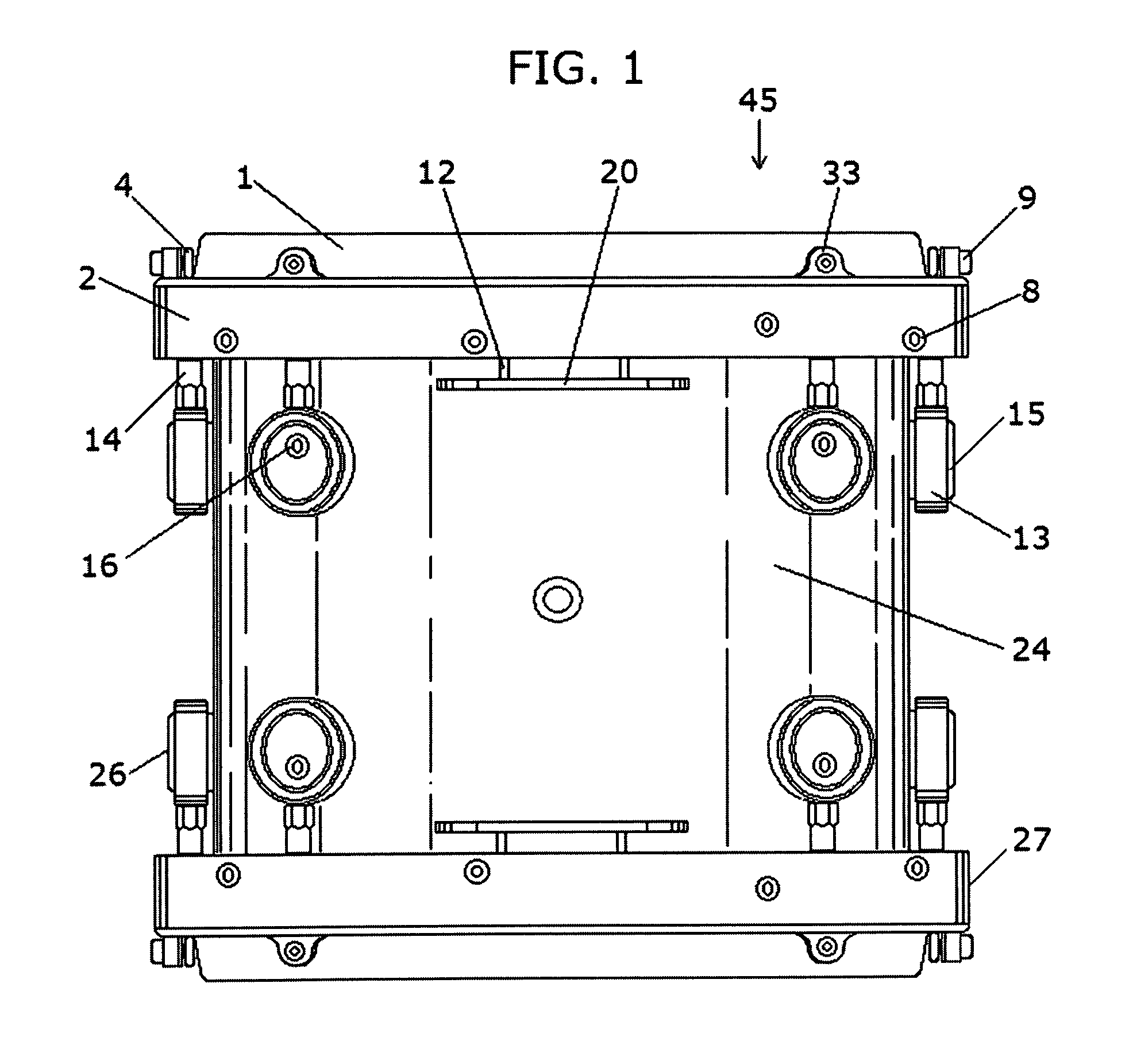
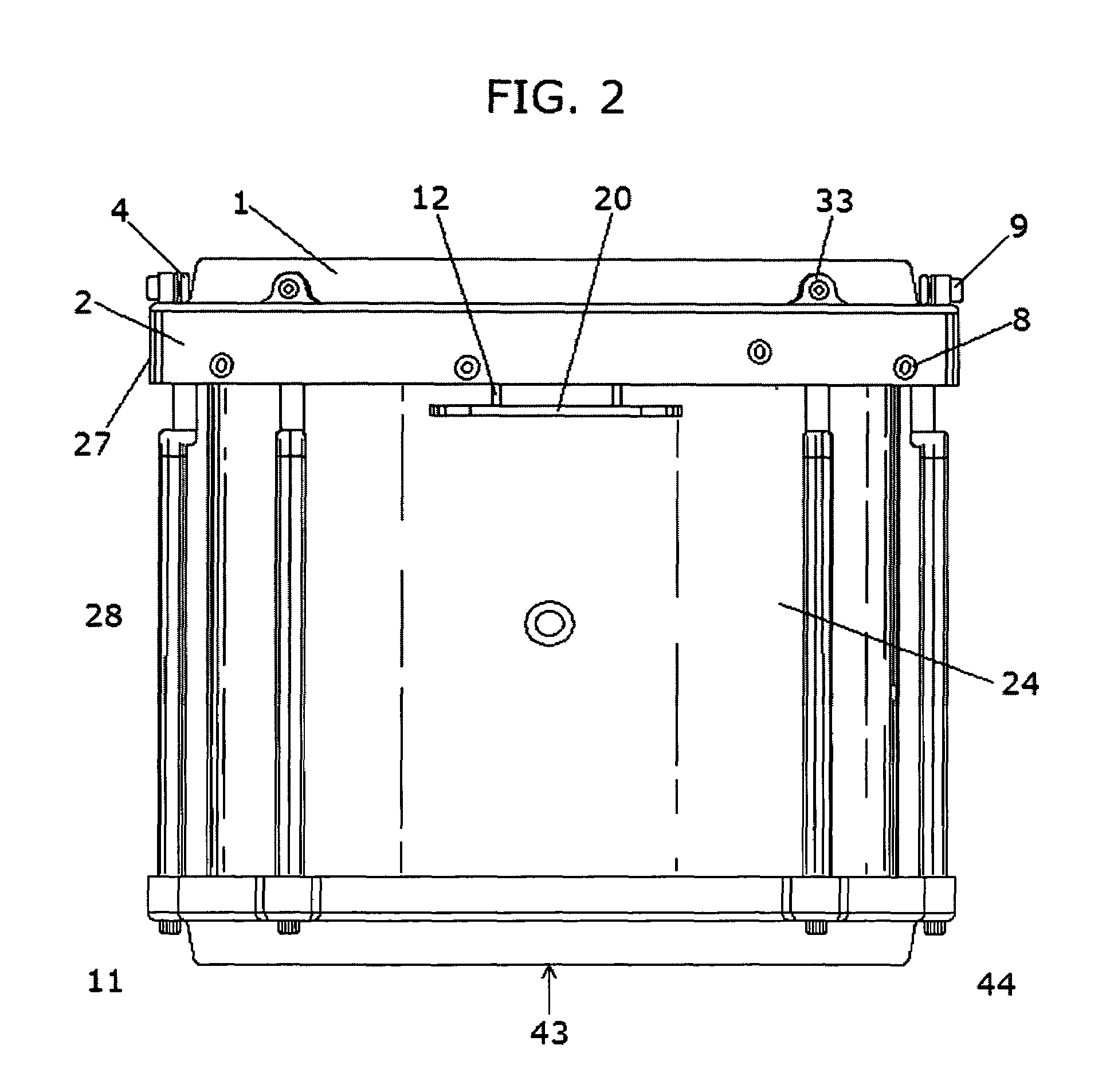
Rotation activated drum tuning system
ActiveUS7501567B1Increased mechanical advantageMinimized contact areaPercussion musical instrumentsBearing downEngineering
A drum tuning system which rotates clockwise or counterclockwise to adjust the tension of a drum head fitted over the open end of a drum body. It utilizes a rotating ring having numerous opposing equally spaced vertically projecting tabs along the top of the body's diameter, each with inward facing wheels that ride on the horizontal surface of a separate inner hoop bearing down on the drum head. The rotating actuator ring is fitted with multiple radial cleats projecting from its outside diameter for grasping it. A radius plate having horizontal holes extends from the drum body, and a tool engages the radial cleats on the rotating actuator ring to facilitate rotation. Multiple adjustable eccentric lugs are used to raise and lower the drum camming mechanism in relation to the open end of the drum body where attached. Horizontal projecting links support the drum attached to suspension mounting systems.
Owner:SPINAZZOLA DAVID MICHAEL
Process for isolating microorganisms from samples and system, apparatus and compositions therefor
InactiveUS20100144005A1Lessen and eliminate effectEasy to moveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIsolate - microorganismParticle physics
A process for isolating microorganisms from samples, particularly Shigella spp. from food samples, and a system, apparatus and composition therefor are provided. Magnetic particles are used to capture microorganisms and a system having separate magnetically-based apparatuses for collecting, concentrating and retrieving is used to isolate the magnetic particles having bound microorganisms. The apparatus for concentrating magnetic particles utilizes a small magnet assisted by vibration to concentrate collected particles at a localized region on the bottom of a container. The process, system and apparatus of the present invention are simple and inexpensive providing improved magnetic particle recovery adaptable to large scales.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF HEALTH
Magnetorheological fluid vibration isolator
InactiveUS6896109B2Significantly vary effective stiffnessIncrease effective viscosityMachine framesNon-rotating vibration suppressionMotion dynamicsMagnetorheological fluid
The invention disclosed is a magnetorheological fluid device offering vibration isolation and broad modulation range damping in a high load carrying and compact form. A cylindrically shaped flexure structure has a bottom cap attached to one end and a top cap attached to the other end. A piston comprising a toroidal displacement body, a central shaft, and intermediate connecting plate, attaches to the top cap. A fluid chamber surrounding and generally conforming to the shape of the toroidal displacement body, is attached to the bottom cap. Two bellows attaching between the piston connecting plate and top and bottom portions of the fluid chamber complete an enclosed volume around the toroidal displacement body and allow frictionless motion of the toroidal displacement body relative to the fluid chamber. Electromagnetic coils placed within the inner and outer radius walls of the fluid chamber effect a magnetic field across the outer radius gap and inner radius gap between the toroidal displacement body and fluid chamber. Longitudinal deflection of the cylindrical flexure structure effects motion of the top cap relative to the bottom cap which in turn effects longitudinal motion of the toroidal displacement body within the fluid chamber. Magnetorheological fluid is forced from the top of the toroidal displacement body to the bottom, and vice-versa, across the inner radius and outer radius gaps between the fluid chamber and the inner radius of the toroidal displacement body. Static payload loads are supported with a high-strength, linear-elastic load path while base motion dynamic vibration loads are substantially isolated and damped without stiction effects.
Owner:MOOG INC
Antenna Arrangement
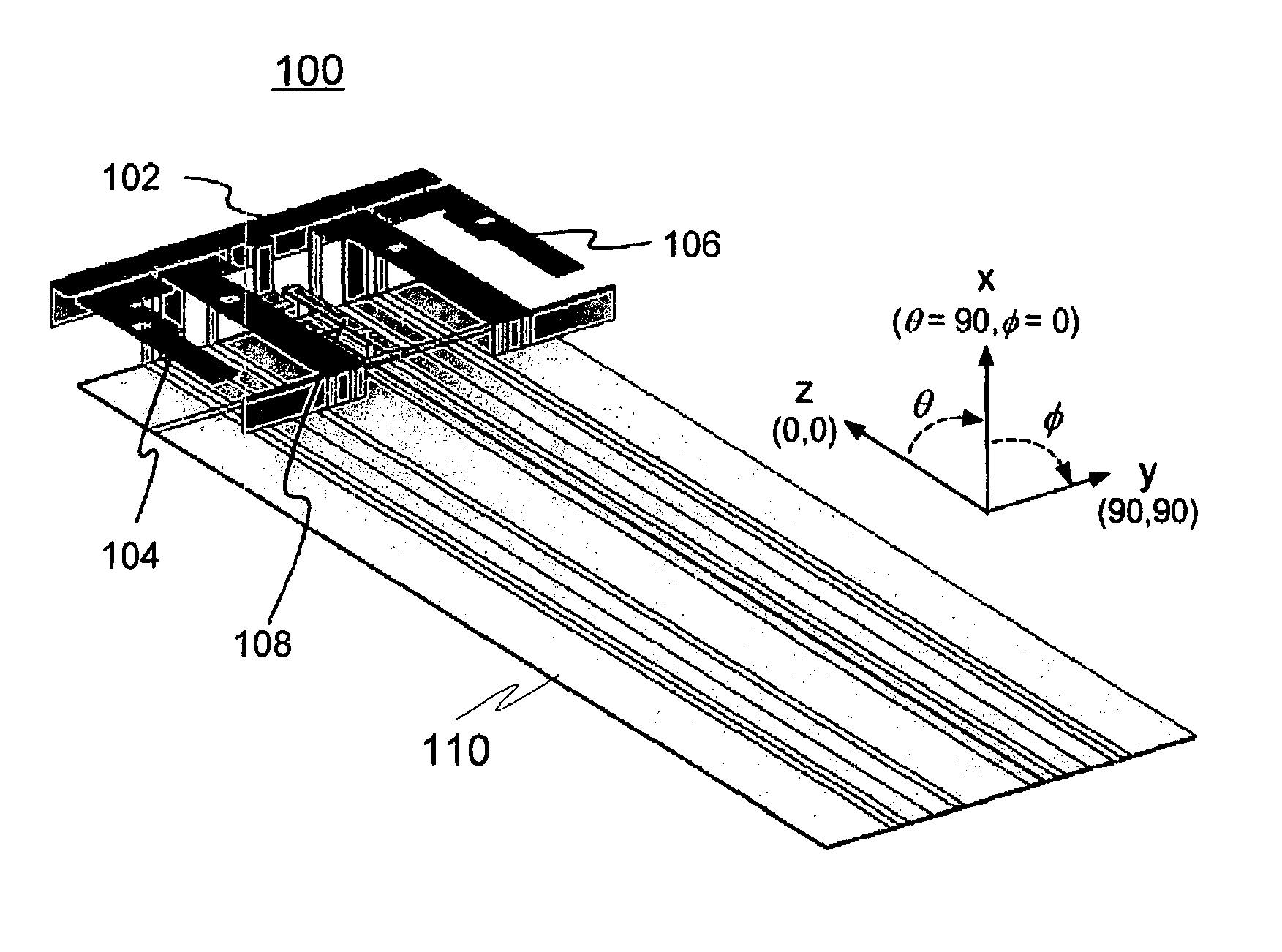
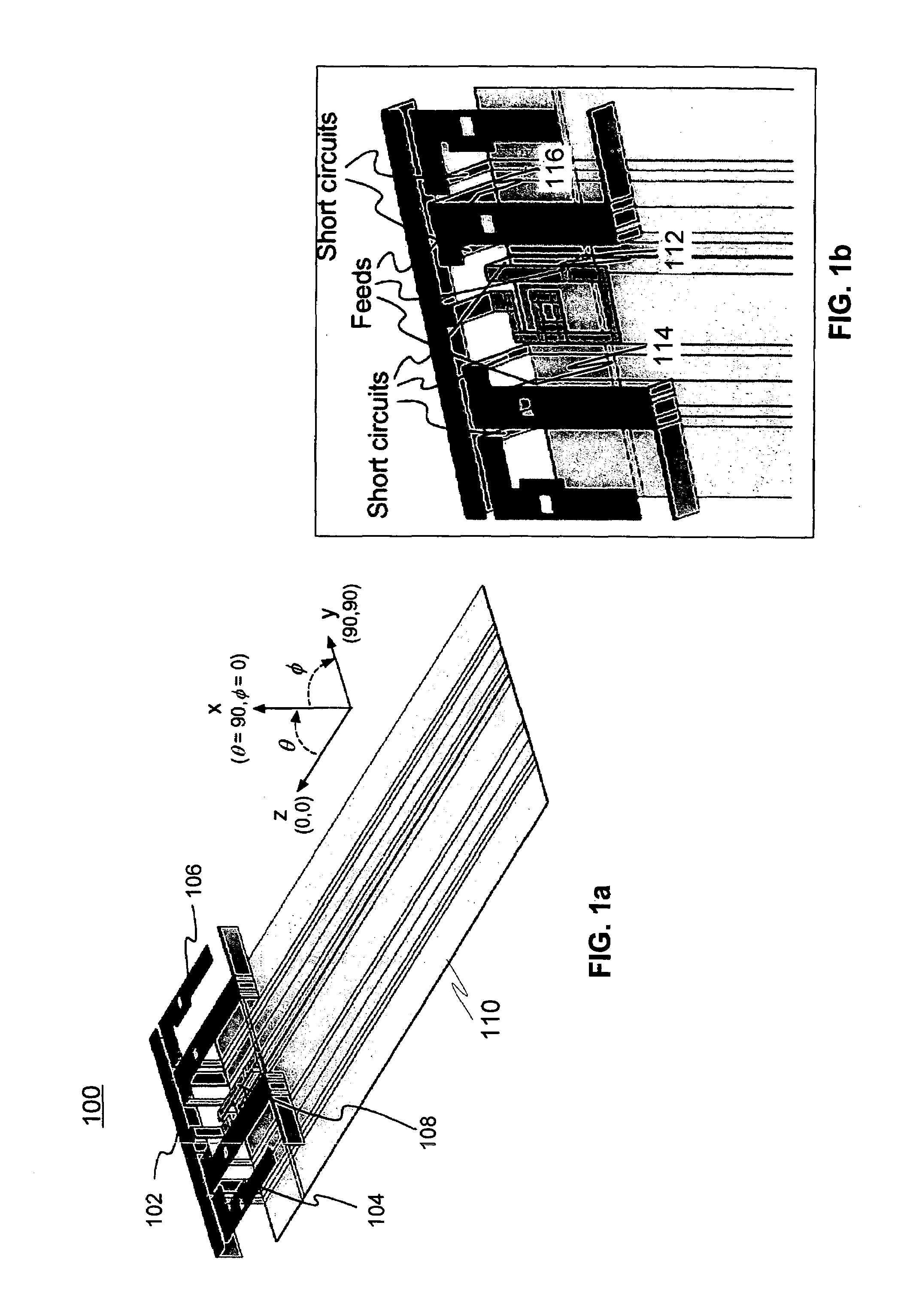
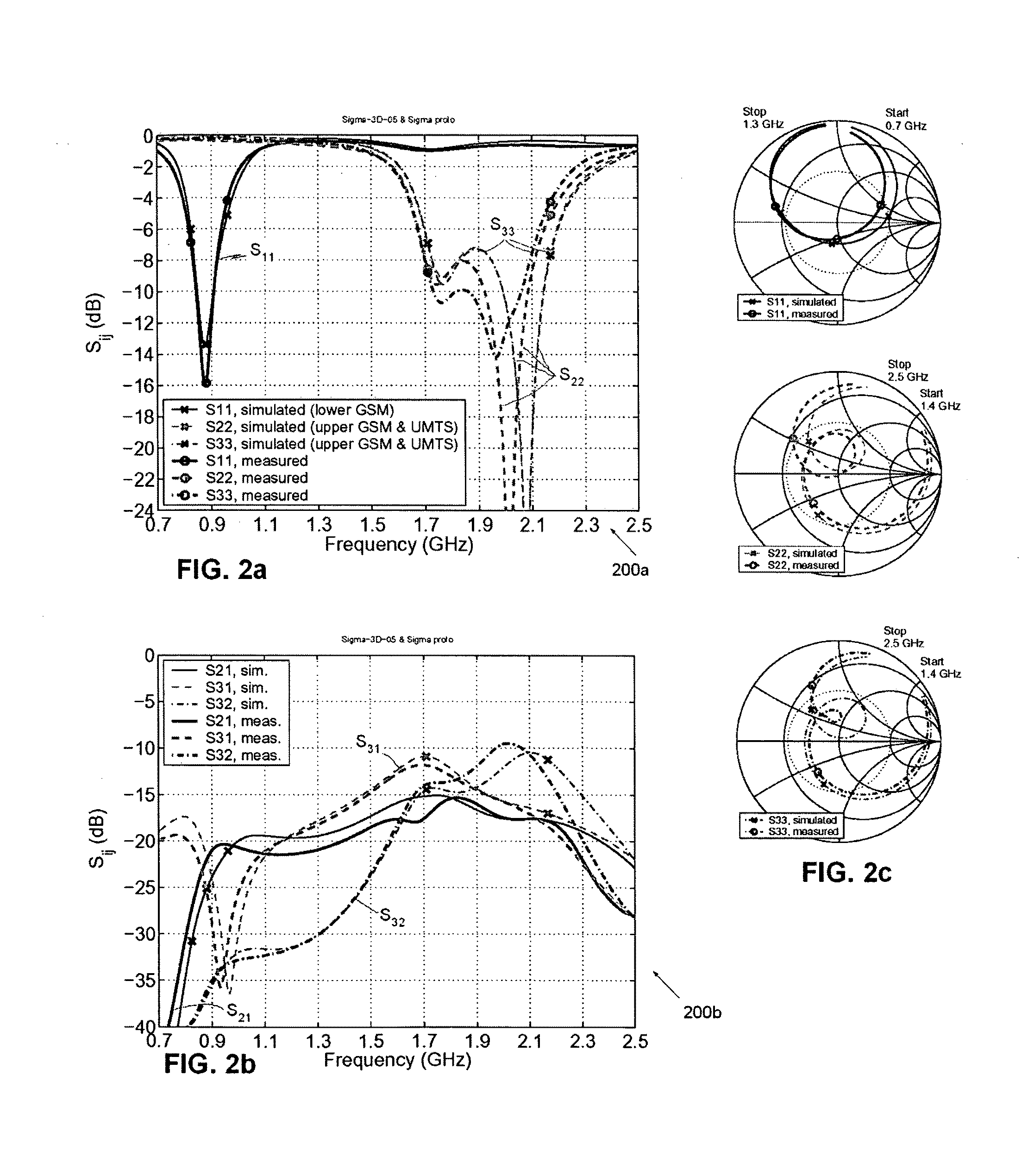
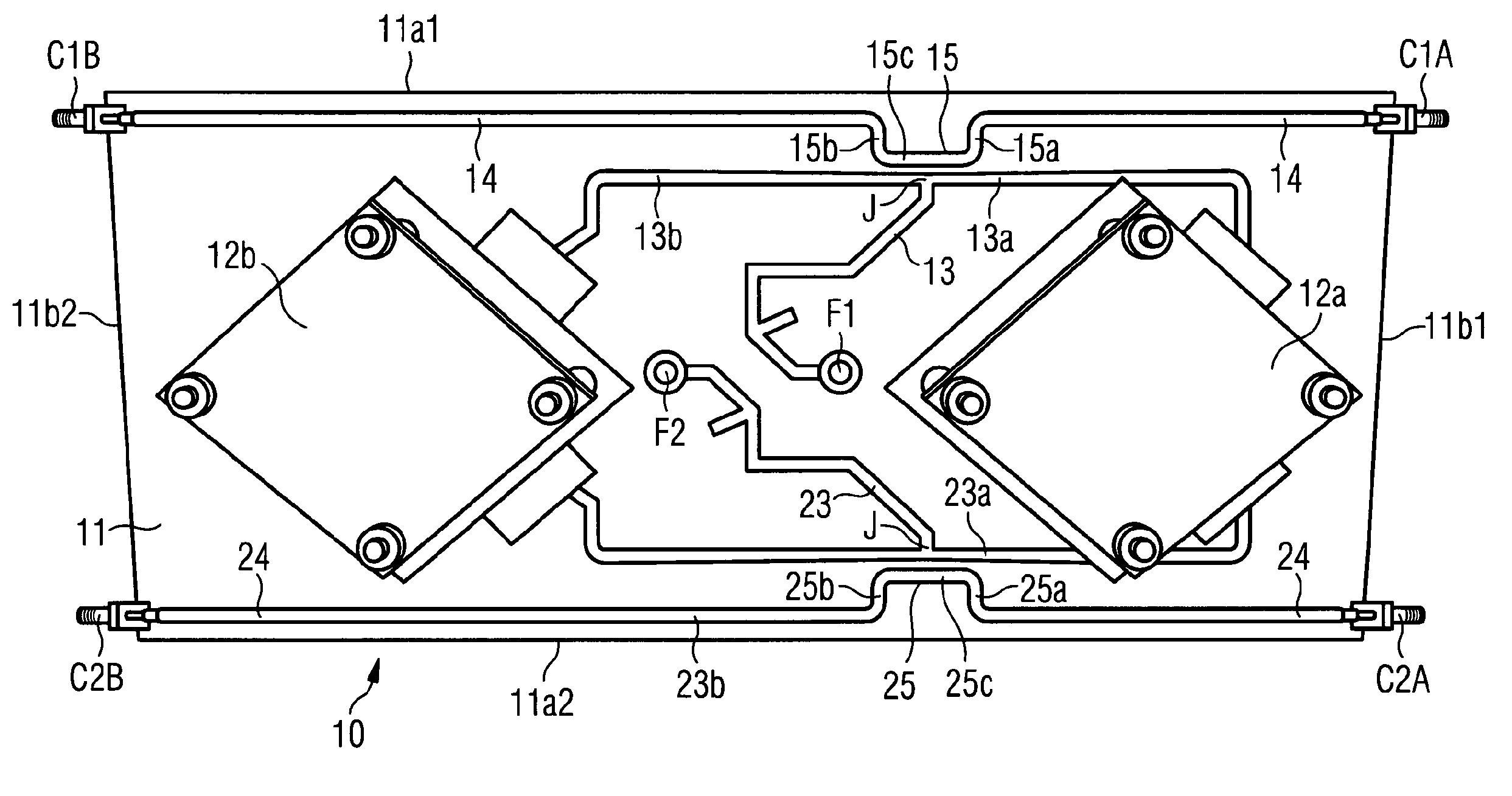
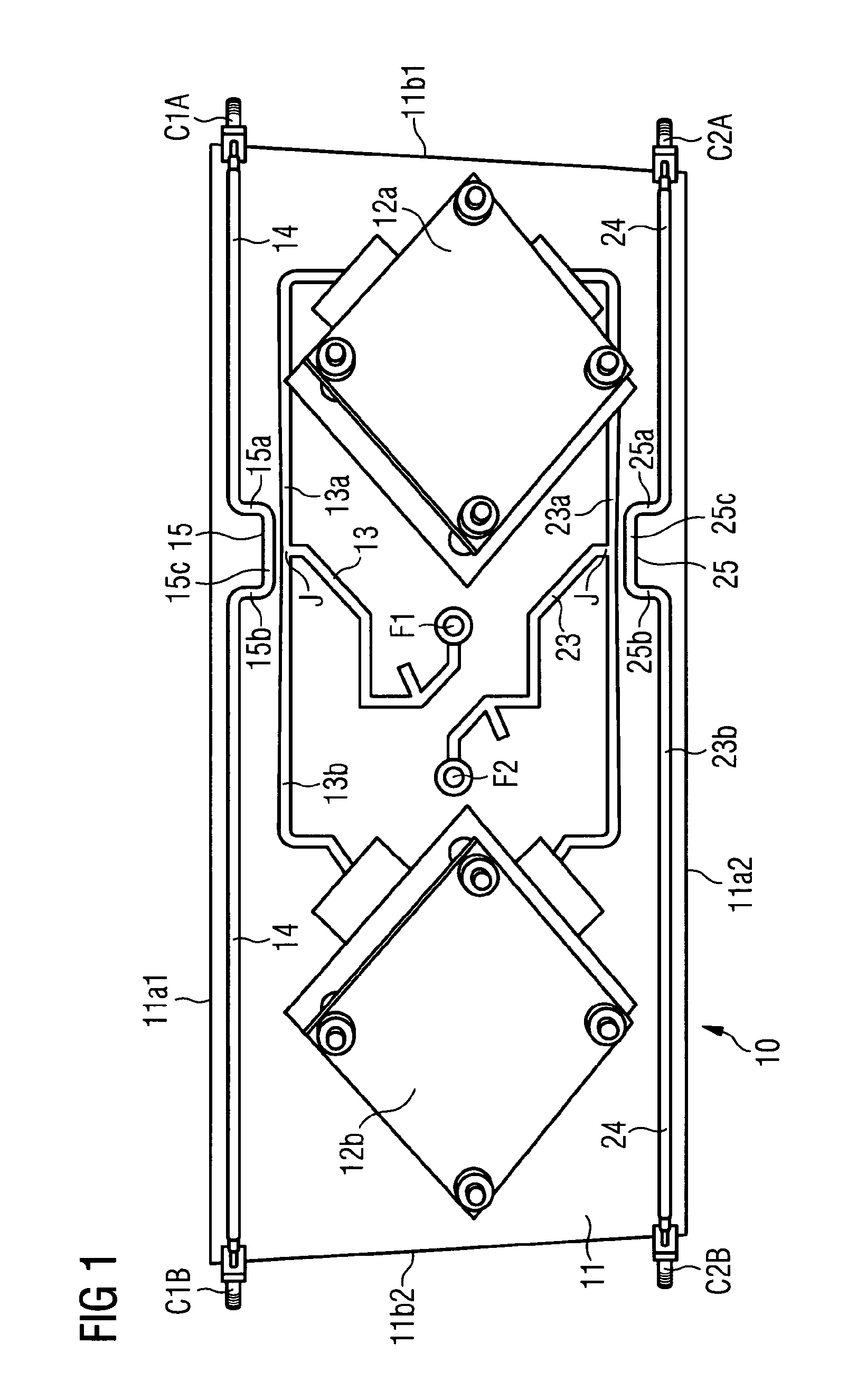
InactiveUS20130265203A1Large isolationMinimizing phase and amplitude shiftAntenna supports/mountingsIndividually energised antenna arraysFeed lineEngineering
An antenna arrangement is provided, which includes first and second antenna elements. A feeder line connects the first and second antenna elements for feeding a signal to and from the first and second antenna elements and the signal is inductively coupled between the feeder line and a calibration line so it can be fed to measurement equipment.
Owner:RPX CORP
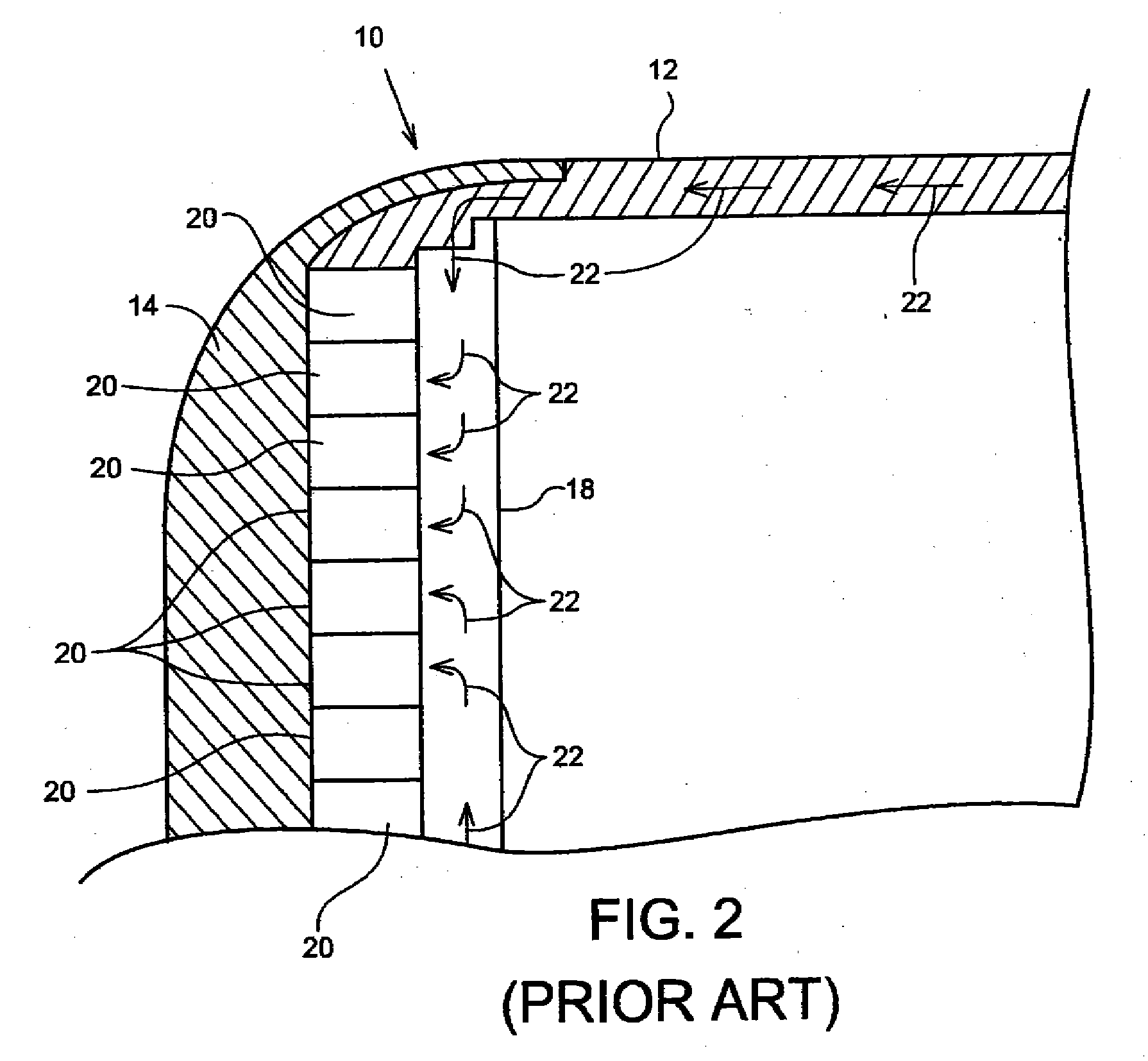
Cable Assembly for a Coupling Loop
InactiveUS20070181331A1Increase opportunitiesAvoid breakingCoaxial cables/analogue cablesNear-field transmissionCoaxial cableCoupling
A coupling loop or antenna is provided that can be used with a system that determines the resonant frequency of a sensor by adjusting the phase and frequency of an energizing signal until the frequency of the energizing signal matches the resonant frequency of the sensor. A cable attached to the coupling loop provides maximum isolation between the energizing signal and the sensor signal by maximizing the distance between the coaxial cables that carry the signals and maintaining the relative positions of the coaxial cables throughout the cable assembly.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG II S A R L SJM LUX II
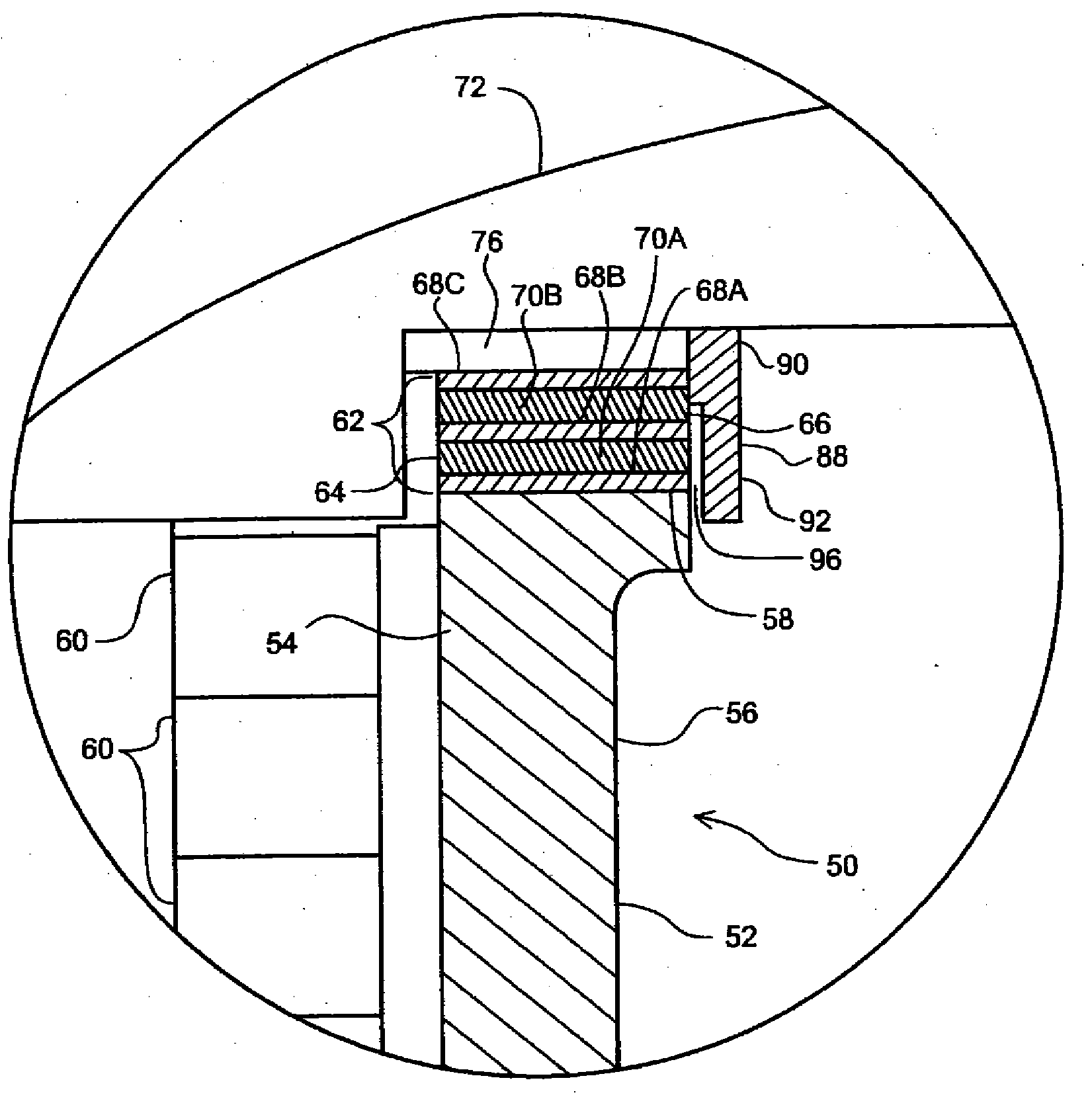
Air gap for tungsten/aluminum plug applications
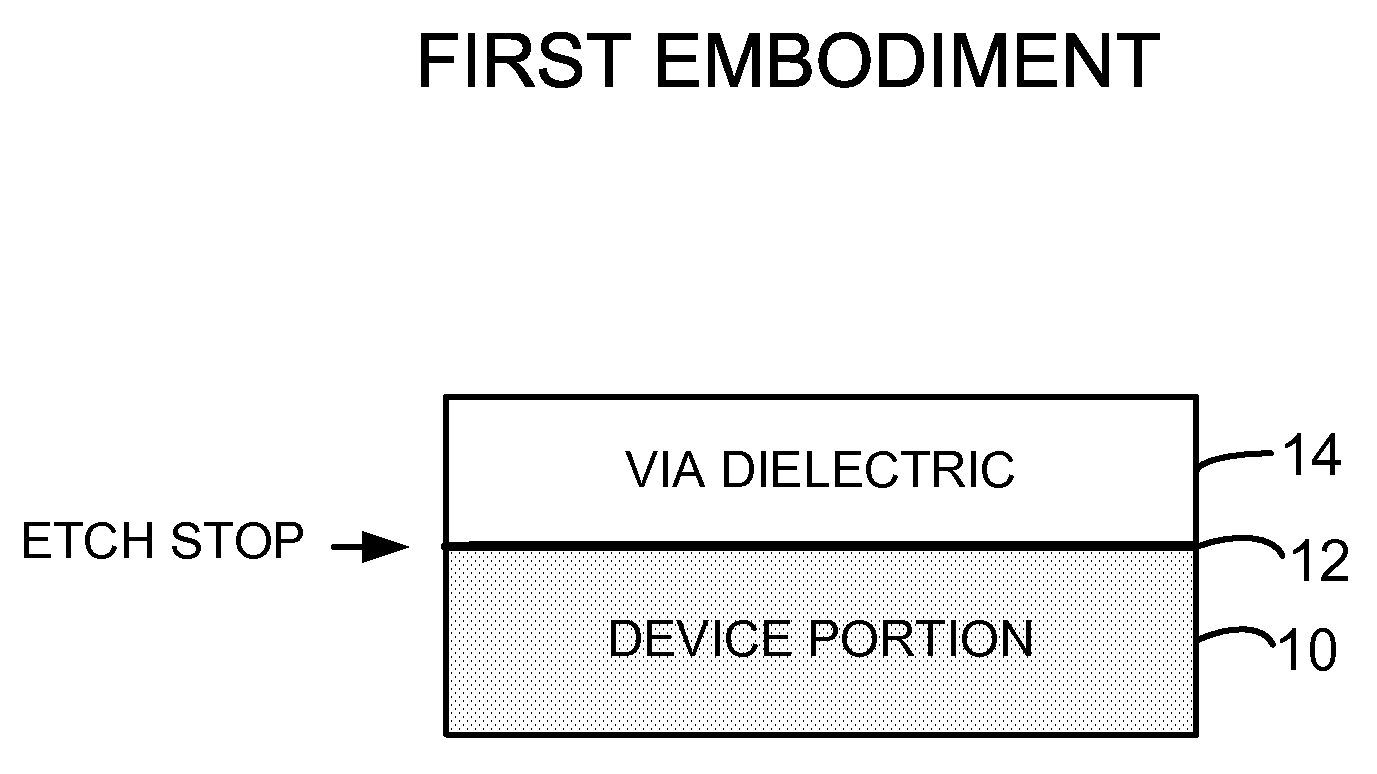
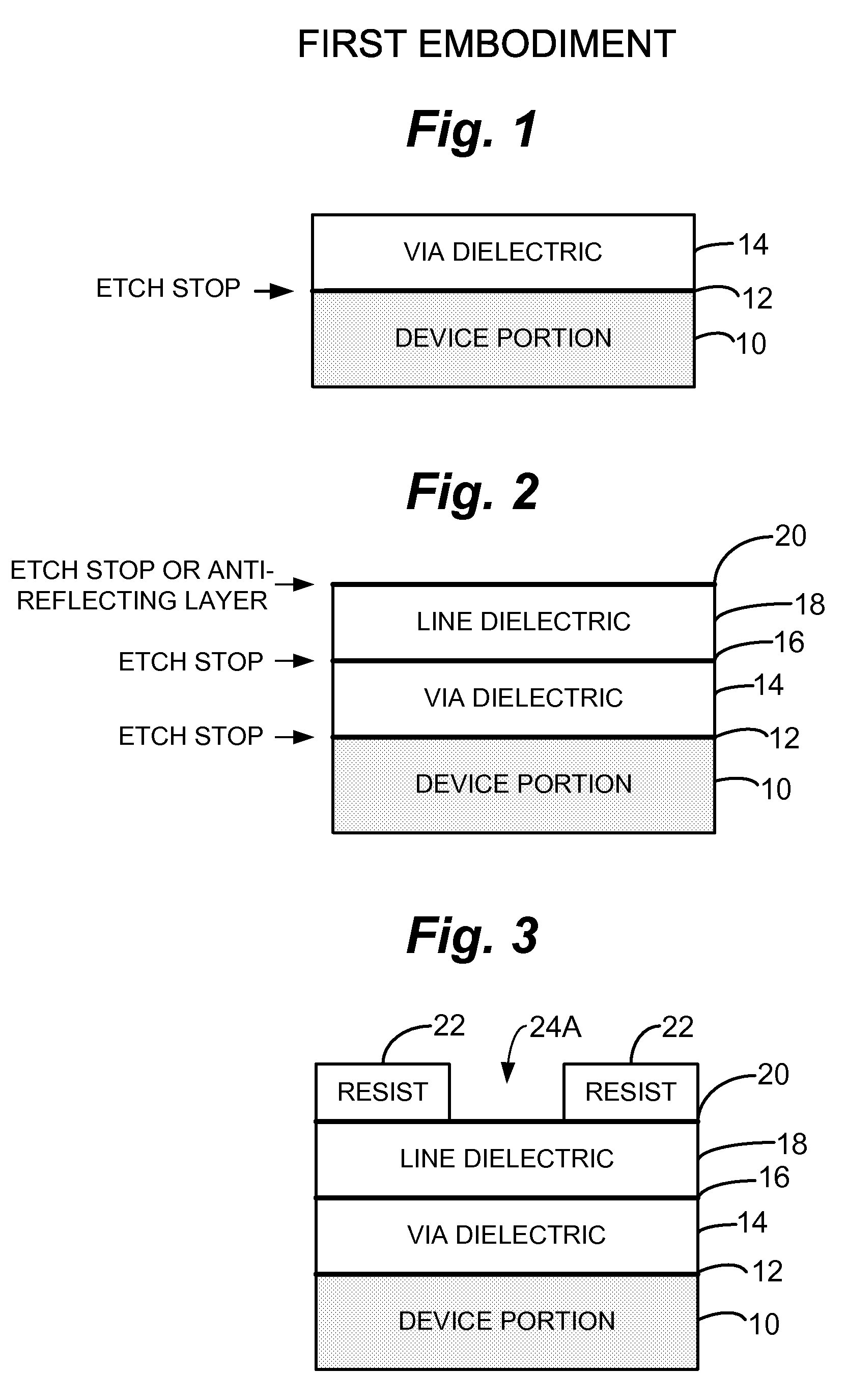
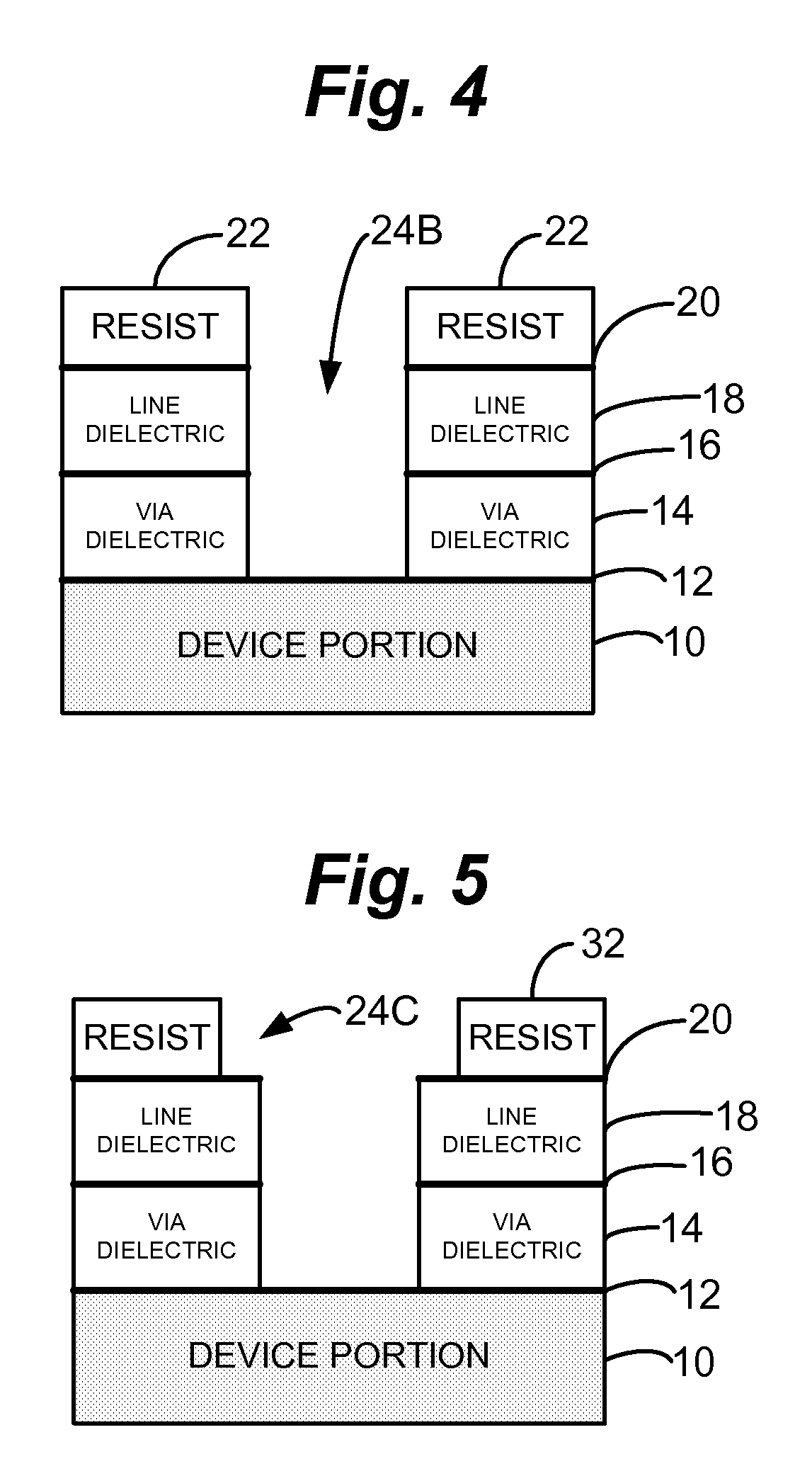
InactiveUS20070076339A1Large isolationEasy to manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentCapacitanceCombined use
An air gap structure substantially reduces undesired capacitance between adjacent interconnects, metal lines or other features in an integrated circuit device. The air gap extends above, and may also additionally extend below, the interconnects desired to be isolated thus minimizing fringing fields between the lines. The integrated air gap structure can be utilized in conjunction with a tungsten plug process. Also, multiple levels of the integrated air gap structure can be fabricated to accommodate multiple metal levels while always ensuring that physical dielectric layer support is provided to the device structure underlying the interconnects.
Owner:LUR WATER +3
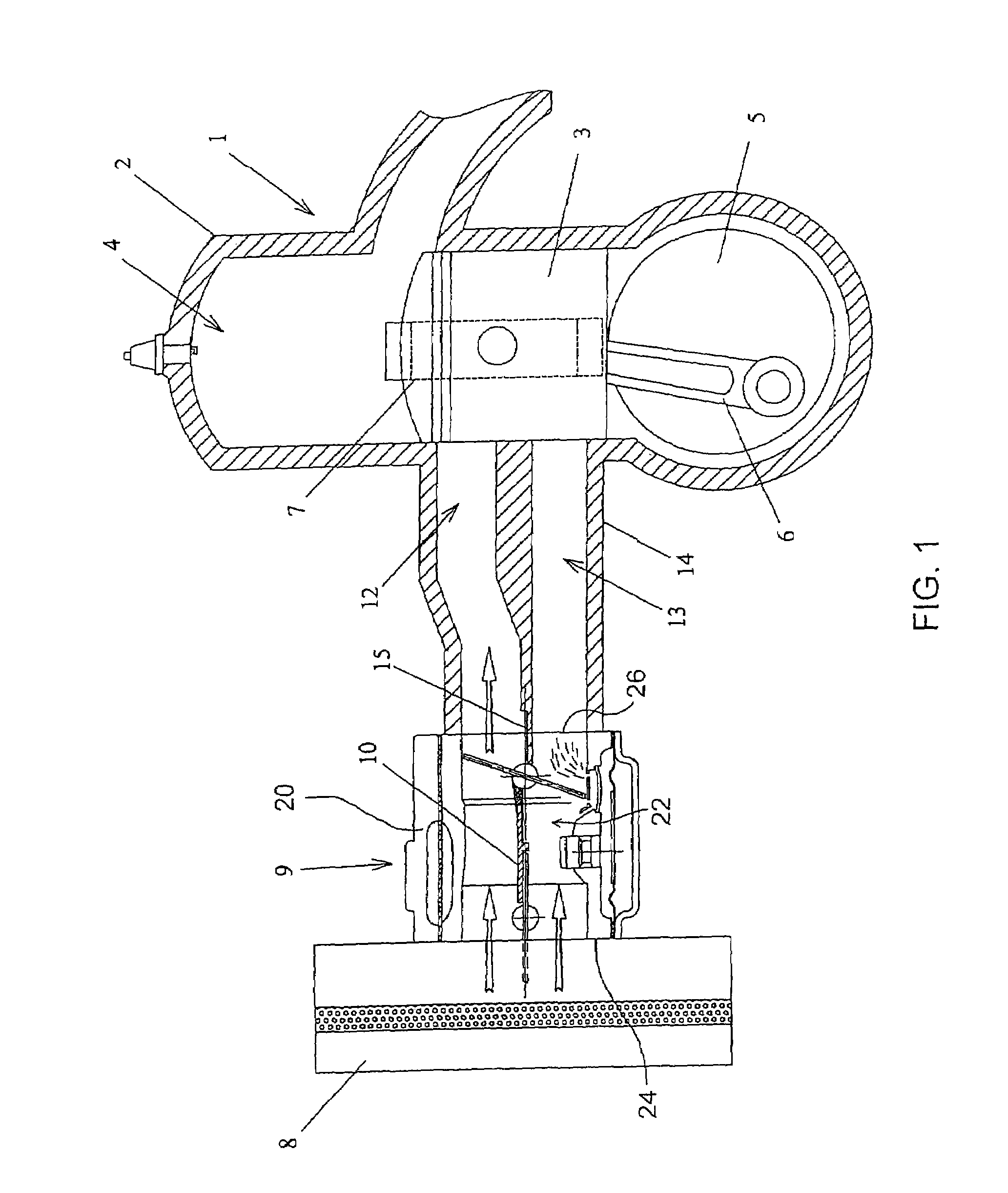
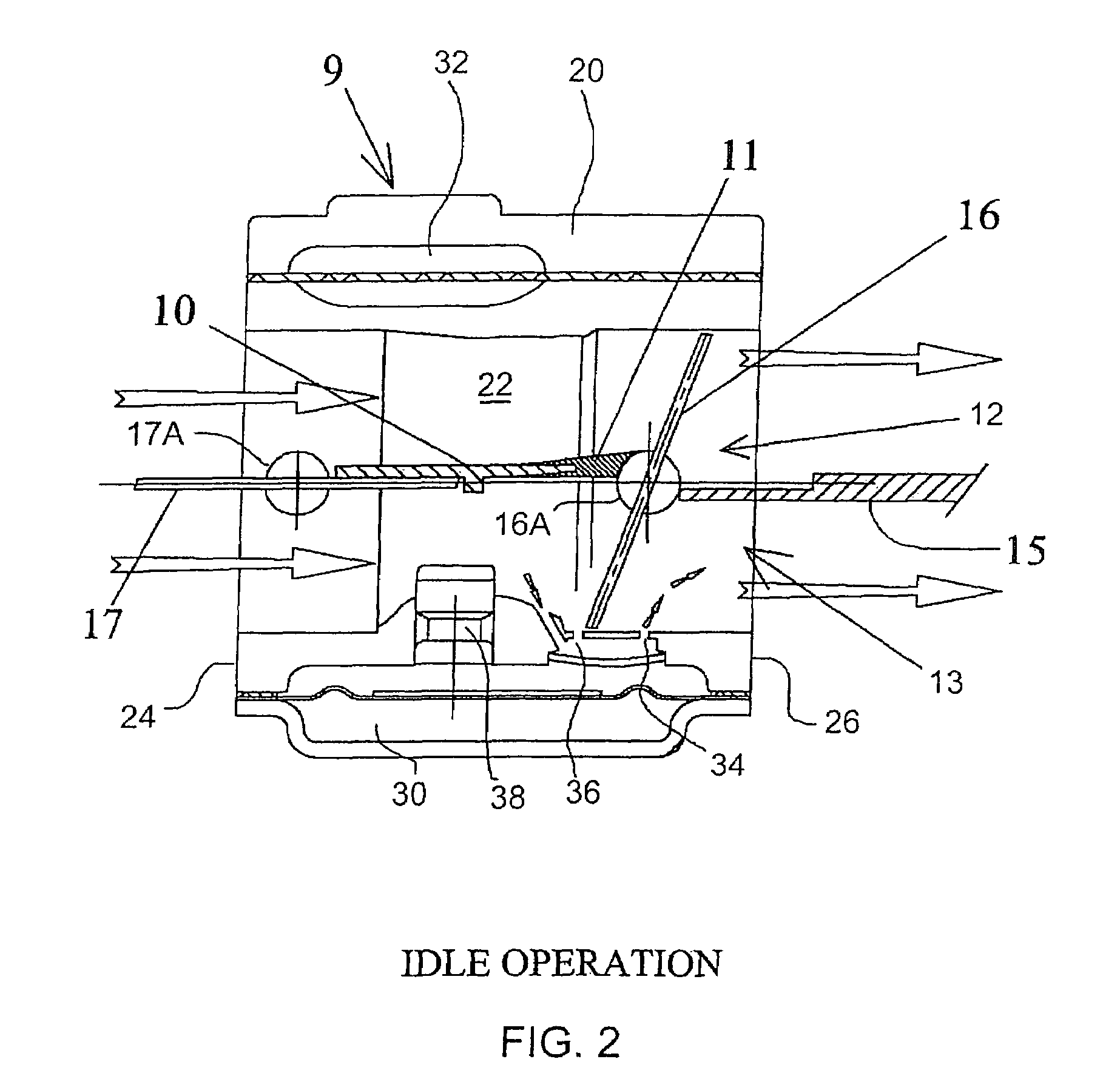
Carburetor
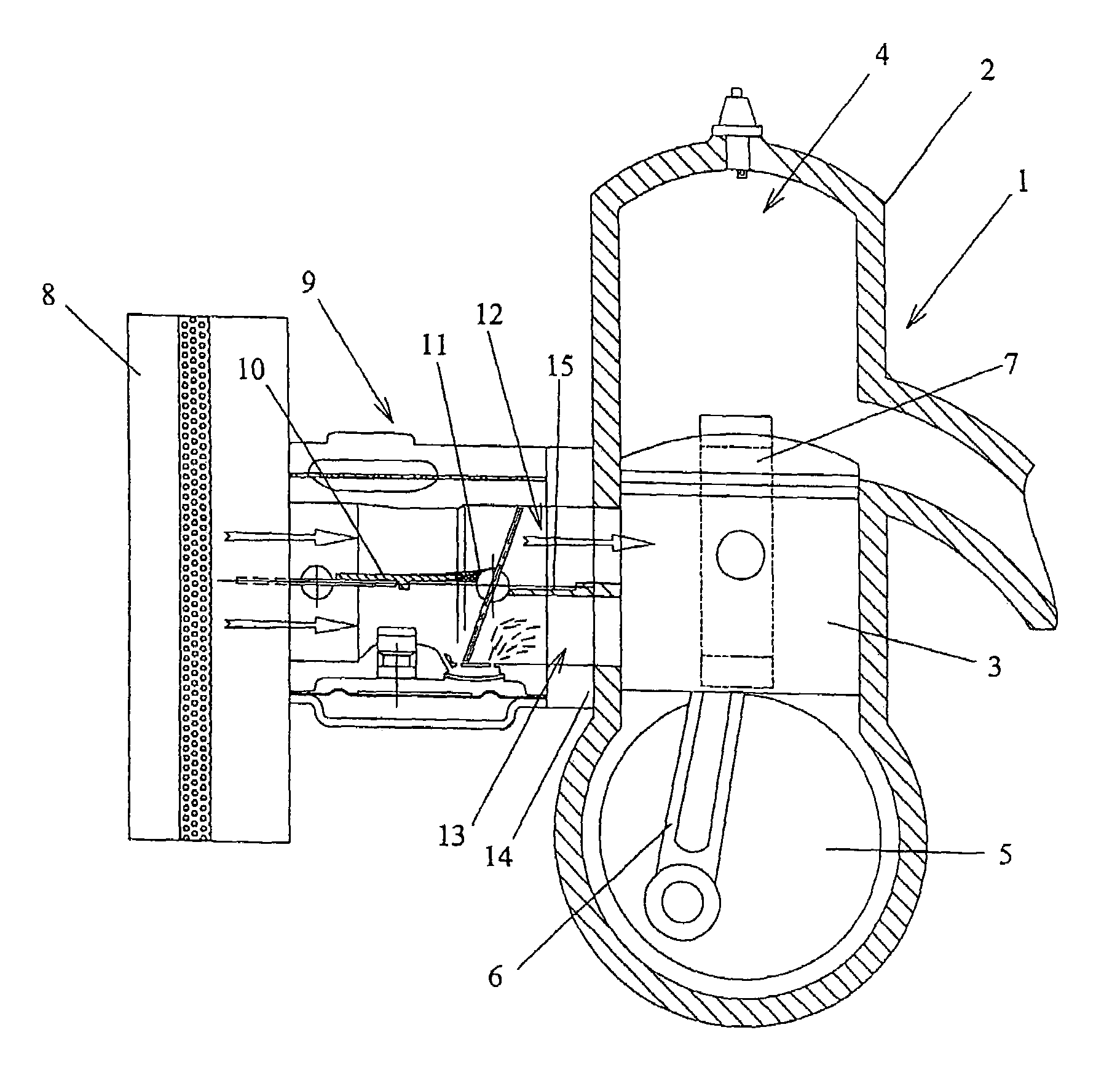
ActiveUS7694943B2Reduce in quantityEfficient separationInternal combustion piston enginesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringCarburetor
A carburetor for feeding separate lean and rich channels of an engine intake duct includes a body having a mixing passage with an air intake side and an engine outlet side. A throttle shutter is rotatable about an axis transverse the mixing passage, and a partition is located within the mixing passage upstream of the throttle shutter. The downstream edge of the partition is adjacent the throttle shutter axis whereby in use of the carburetor the partition defines an extension of the lean and rich channels upstream of the throttle shutter, the partition thus providing substantial isolation between the lean and rich channels for all rotational positions of the throttle shutter. In a preferred embodiment a choke shutter is located upstream of the throttle shutter and is rotatable about a further axis transverse the mixing passage, the upstream edge of the partition being adjacent to the axis of the choke shutter.
Owner:BARCAROLE
Compact multilayer circuit
ActiveUS20070063789A1Improve isolationReduce overall form factorMultiple-port networksWaveguidesSignal routingHandling system
A compact multilayer signal processing system. In the illustrative embodiment, the system is adapted for use with microwave signals. The system includes a first mechanism for receiving an input signal and selectively routing the input signal onto a first signal path. A second mechanism routes the input signal along the first signal path vertically through one or more layers to a first circuit component. The first circuit component outputs an adjusted signal in response to receipt of the input signal. A third mechanism directs the adjusted signal to the output of the system. In a specific embodiment, the one or more layers include one or more groundplane layers. In this embodiment, the first mechanism includes an input switching network in communication with a controller. The switching network is positioned on a switching layer and communicates with one or more controllers to facilitate selectively switching the input signal onto one of plural input signal paths. The second mechanism further includes a first input waveguide that extends from the input switching network vertically through at least one groundplane layer and to an input end of the first circuit component. The third mechanism includes a first output waveguide extending from an output end of the first circuit component, vertically through at least one groundplane layer to an output switching network disposed on the switching layer. In the specific embodiment, the circuit layer includes plural circuit components that are coupled to respective input waveguides and output waveguides that extend vertically through the first groundplane layer to the input switching network and the output switching network, respectively.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Switch circuit and composite high-frequency part
InactiveUS7167687B2Small leakageLarge isolationTransmissionCoupling devicesCommunications systemEngineering
A switch circuit for selectively switching connection of an antenna side circuit with a reception circuit and a transmission circuit of two communication systems one of which has a reception frequency band partially overlapped with a transmission frequency of the other. The switch circuit includes (a) a first switch unit for switching connection of the antenna side circuit with the transmission circuit side of the first and tie second communication systems and the reception circuit side of the first and the second communication system and (b) a second switch unit connected between the first switch unit and the reception circuit of the first and the second communication system for switching connection of the antenna side circuit with the reception circuit of the first and the second communication system. (c) The transmission circuit side of the first and the second communication system of the first switch unit is connected to a transmission circuit shared by the first and the second communication system. (d) When the transmission circuit of the first and the second communication system is connected to the antenna side circuit, the second switch unit cuts off the connection between the reception circuit of the first communication system and the first switch unit.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
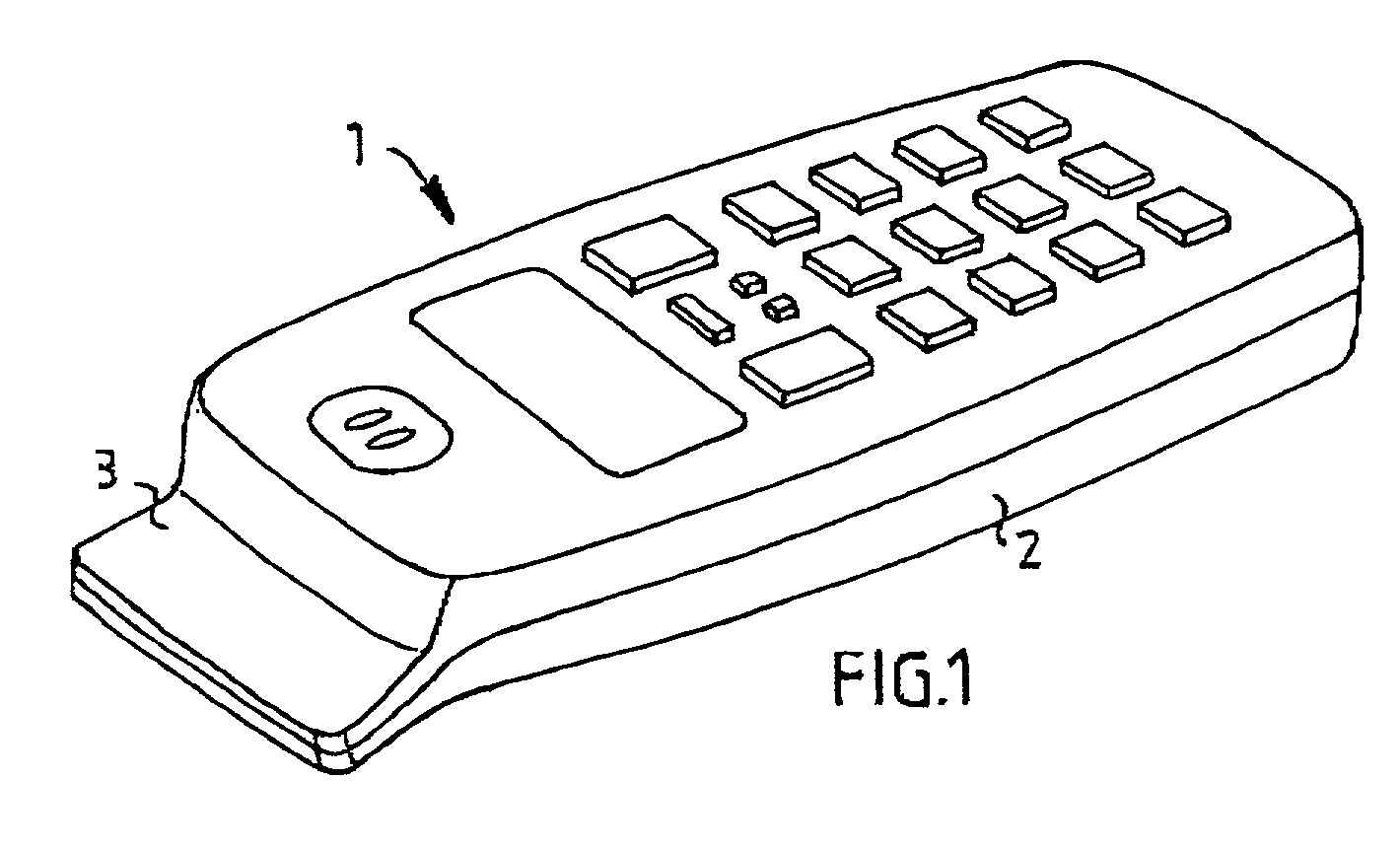
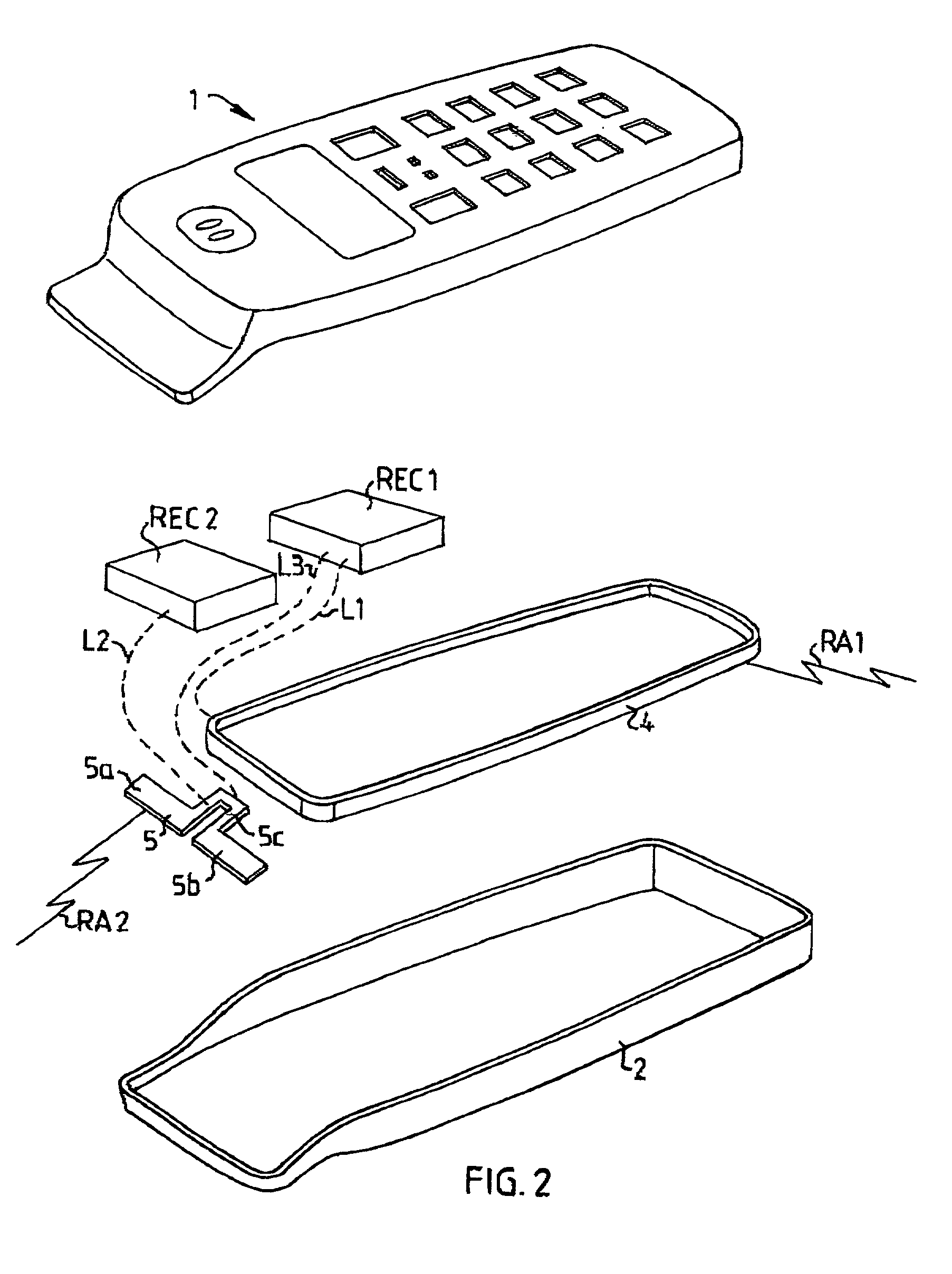
Device for mobile terminal
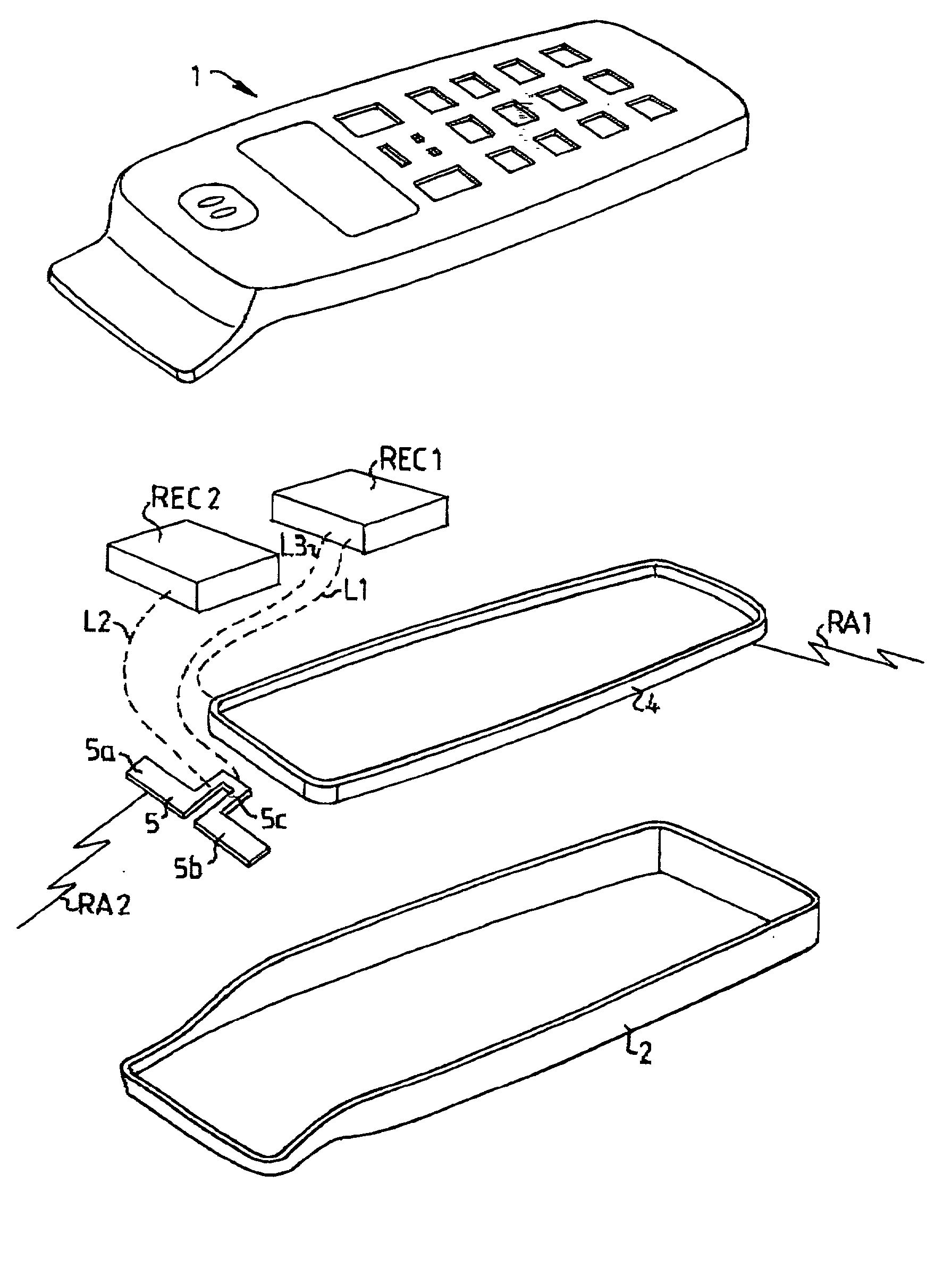
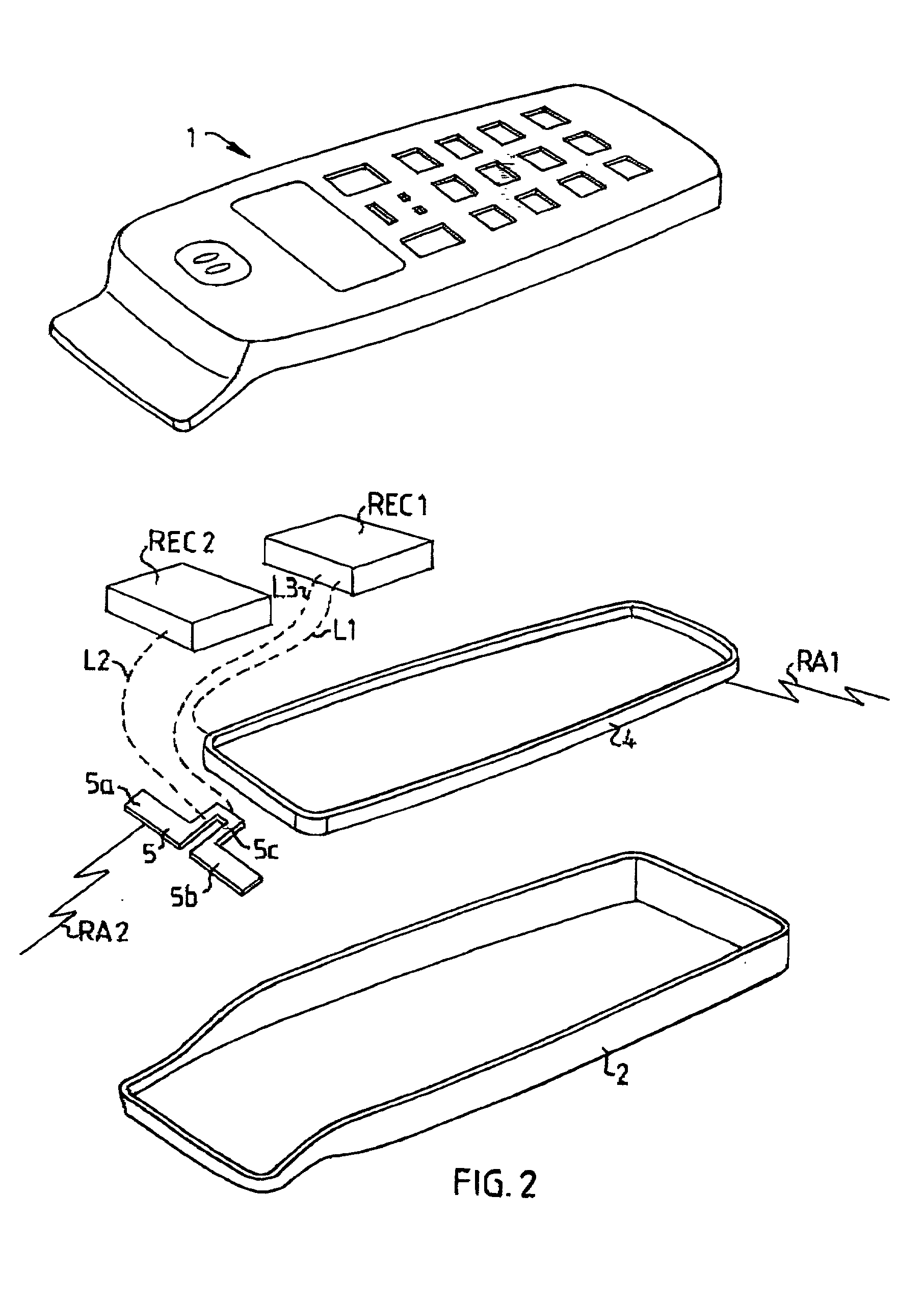
InactiveUS20020068601A1Large isolationSave valuable spaceAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentTerminal equipmentDipole antenna
The invention relates to a mobile terminal antenna system for a first radio application (RA1) and a second radio application (RA2) the system comprising first radio electronic circuits (REC1) for the first radio application (RA1), and second radio electronic circuits (REC2) for the second radio application (RA2). The system also comprises an end-fed antenna (4) for the first radio application (RA1), the end-fed antenna (4) having an extended shape and being connected to the first radio electronic circuits (REC1). The system comprises a dipole antenna (5) for the second radio application (RA2), the dipole antenna (5) being located near one end of the end-fed antenna (4) and connected to the second radio electronic circuits (REC2). The first radio electronic circuits (REC1) are connected to the dipole antenna (5), whereby the end-fed antenna (4) is adapted to be fed, during transmission, against the dipole antenna (5) by the first radio electronic circuits (REC1), whereby the dipole antenna (5) is adapted to serve as a counterpoise for the end-fed antenna (4).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Array Plate Apparatus Having Tunable Isolation Characteristics
InactiveUS20090000860A1Improve isolationFacilitate significant isolationMarine torpedoesCommunication jammingHull structureEnergy absorption
An apparatus having an array plate and an isolation section joined to the perimetrical edge of the plate. The isolation section has a plurality of isolation layers and a plurality of intermediate layers alternately arranged wherein an intermediate layer is positioned between consecutive isolation layers. An innermost isolation layer is joined to the perimetrical edge of the array plate and an outermost isolation layer is adapted to be joined to a hull structure of an underwater vehicle. Each isolation layer is made from energy absorbing material and each intermediate layer is made from generally rigid material. The isolation section substantially reduces vehicle self-noise from traveling to the array plate. Interchangeable depth stop members having various geometries are used to adjust the stiffness of the isolation section so as to maximize the isolation characteristics of the isolation section at particular water depths at which the underwater vehicle operates.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Embedded symmetric multiple axis antenna system with isolation among the multiple axes
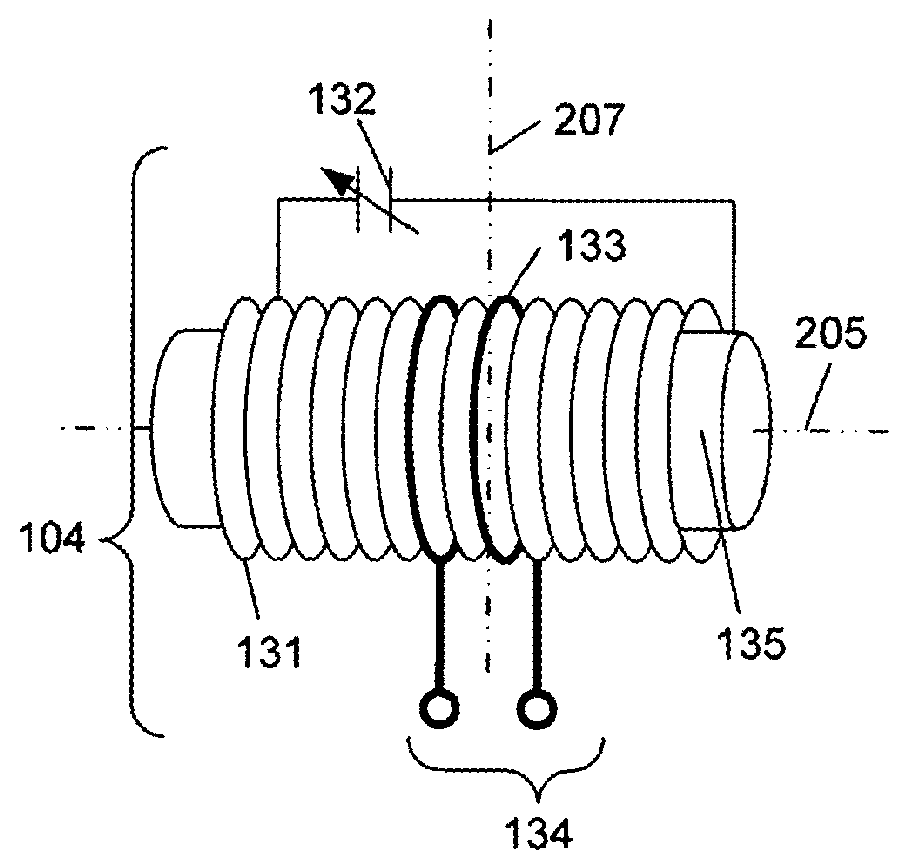
ActiveUS9997845B2Minimize couplingLarge isolationLoop antennas with ferromagnetic coreAntenna adaptation in movable bodiesCouplingAntenna element
The present disclosure pertains to a rotationally triply symmetric three axis magnetic antenna system having substantial isolation among the three axes, including a three axis skew orthogonal magnetic antenna system and device utilizing the antenna system. The antenna system comprising three substantially identical magnetic antenna elements disposed symmetrically about a reference point such that the magnetic axes from the three antenna elements are orthogonal to one another in direction and do not intersect one another. The three antenna elements are positioned in a substantial cross coupling null from one another to minimize cross coupling. The arrangement yields packaging efficiency for compact electronic devices. A 1, 1, diameter embodiment is disclosed. A location system utilizing the antenna system is disclosed. Methods for producing the antenna are disclosed. A moldable triple coil holder for the antenna system is described.
Owner:GAN CORP
Semiconductor switches and switching circuits for microwave
InactiveUS20060197106A1Large isolationReduce resistanceTransistorWaveguidesHigh isolationSemiconductor
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a small-sized switch attaining high isolation of not less than 80 dB, maintaining low insertion loss also in high frequencies not less than 60 GHz. A semiconductor switch according to the present invention utilizes FETs a gate electrode, a source electrode, and a drain electrode of each of which are formed on a semiconductor. The source electrode and the drain electrode are connected with the earth as well as are disposed in parallel to each other, and the gate electrode is formed between the source electrode and the drain electrode, and both the ends of the gate electrode are connected to the first input-output terminal 1 and the second input-output terminal.
Owner:MIZUTANI HIROSHI
Lens apparatus and image pickup apparatus including the same
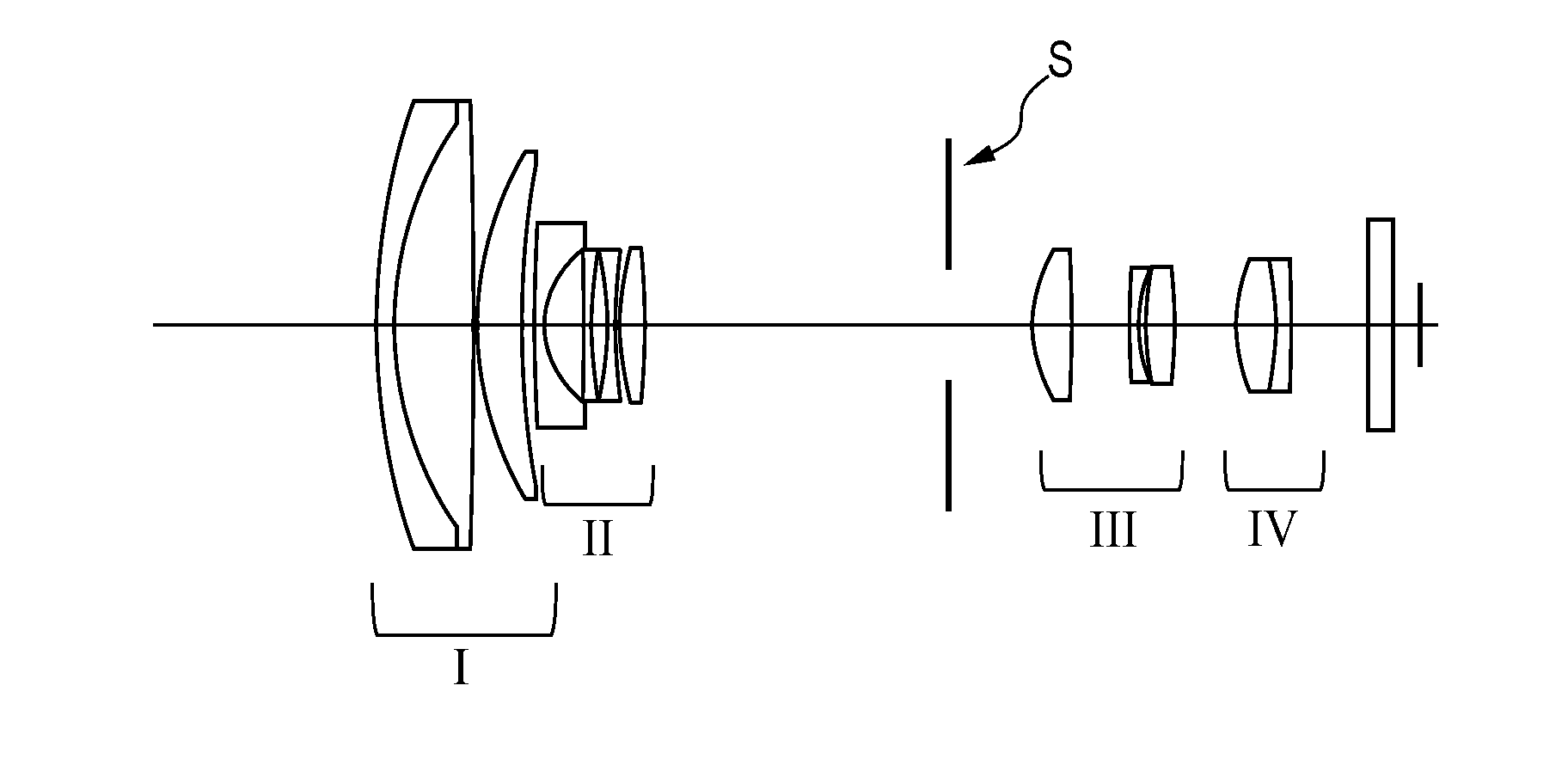
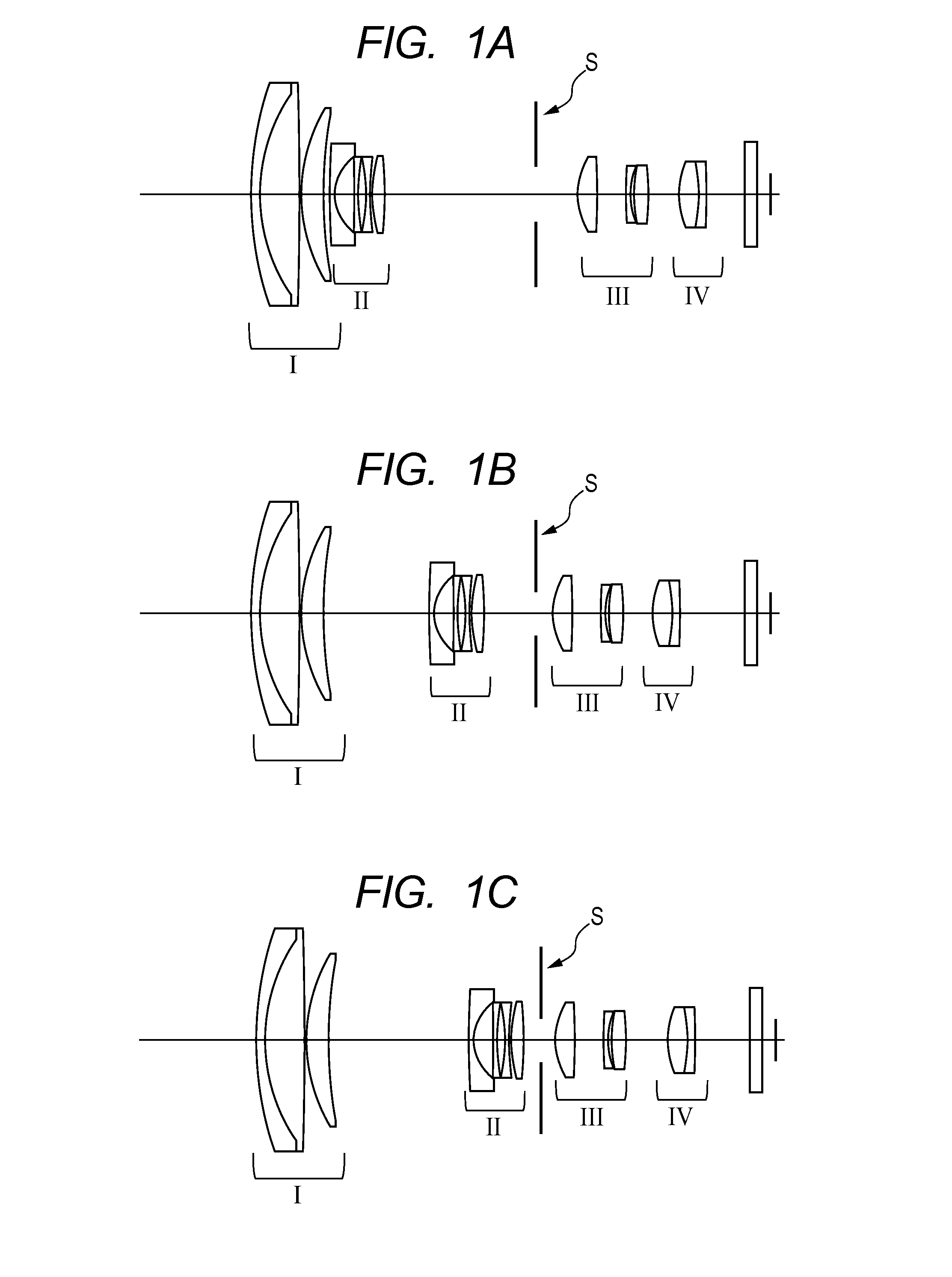
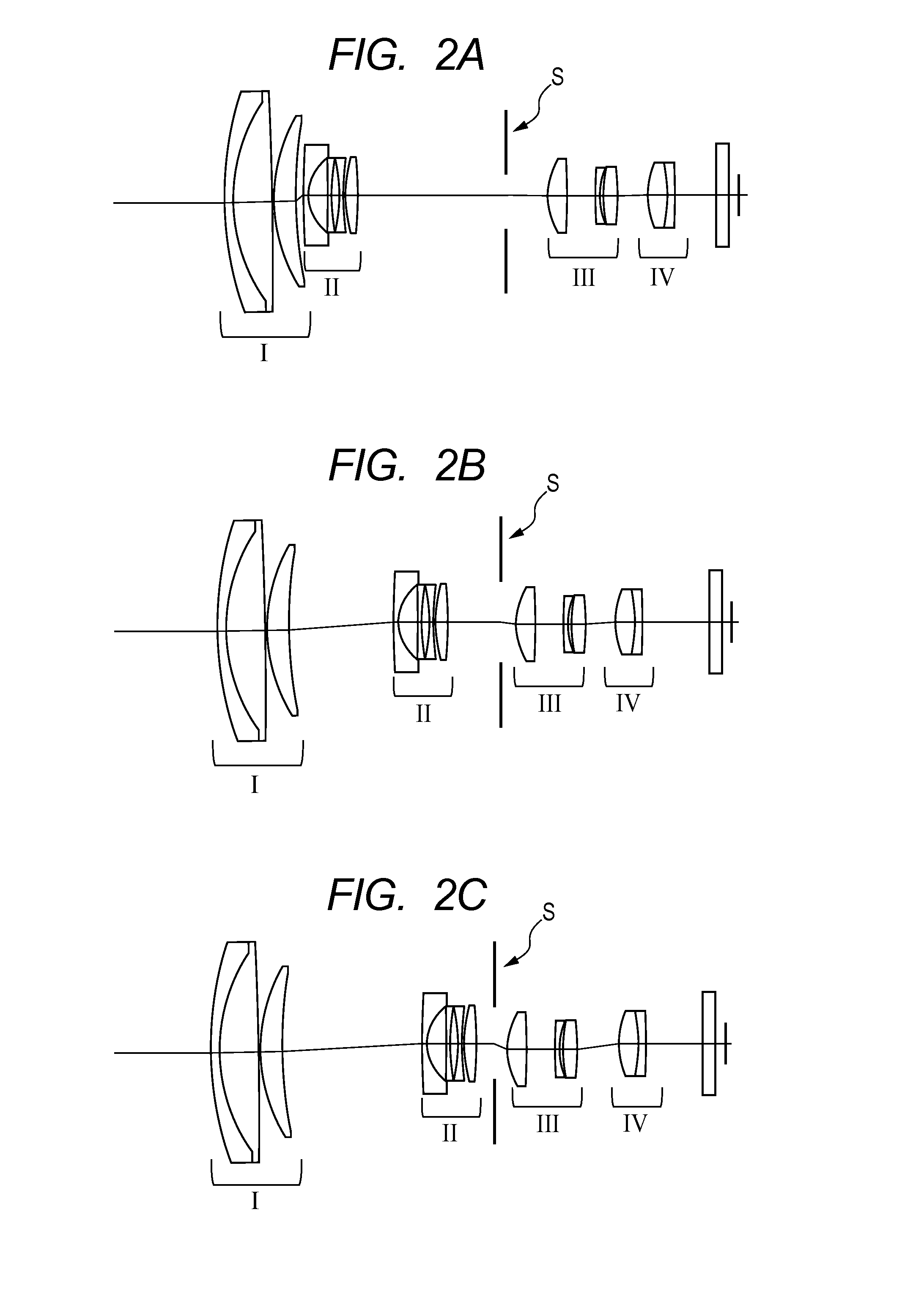
InactiveUS20140184839A1Raise the ratioLarge isolationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCamera lensOptical axis
A lens apparatus includes an optical system including multiple lens units, the optical system including: a first lens unit which is disposed closest to an object side in the optical system and is rotatable about a point in a vicinity of an optical axis of the optical system; and at least one lens unit which is movable in a direction including a component in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis. The following conditional expression is satisfied: 1.0<ft / |f1|<2.2, where ft represents a focal length of the optical system at a telephoto end, and f1 represents a focal length of the first lens unit. At least one of rotation of the first lens unit or movement of the at least one lens unit in the direction including the component in the direction perpendicular to the optical axis changes an image formation position in the direction perpendicular to the optical axis.
Owner:CANON KK
Window assemblies
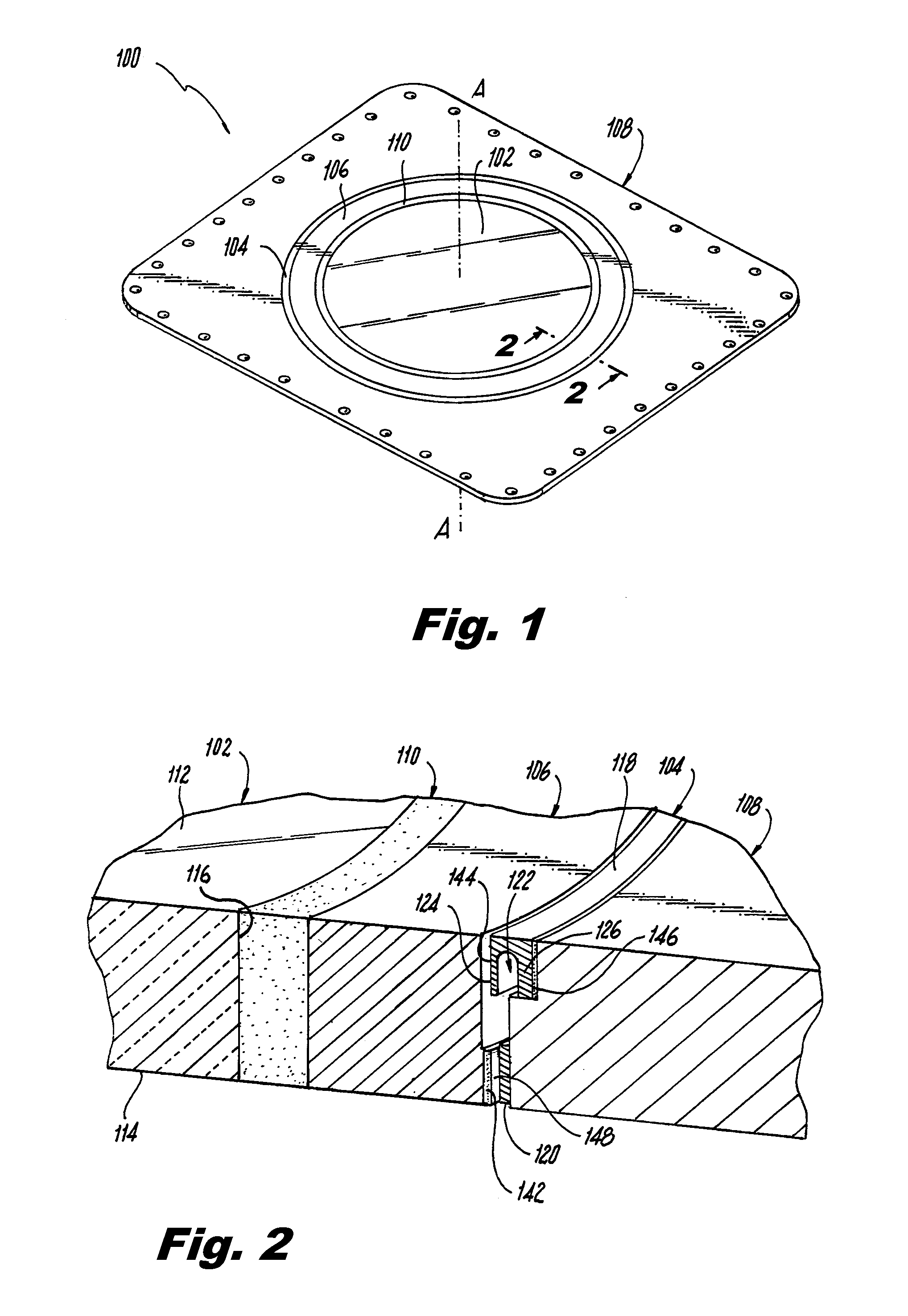
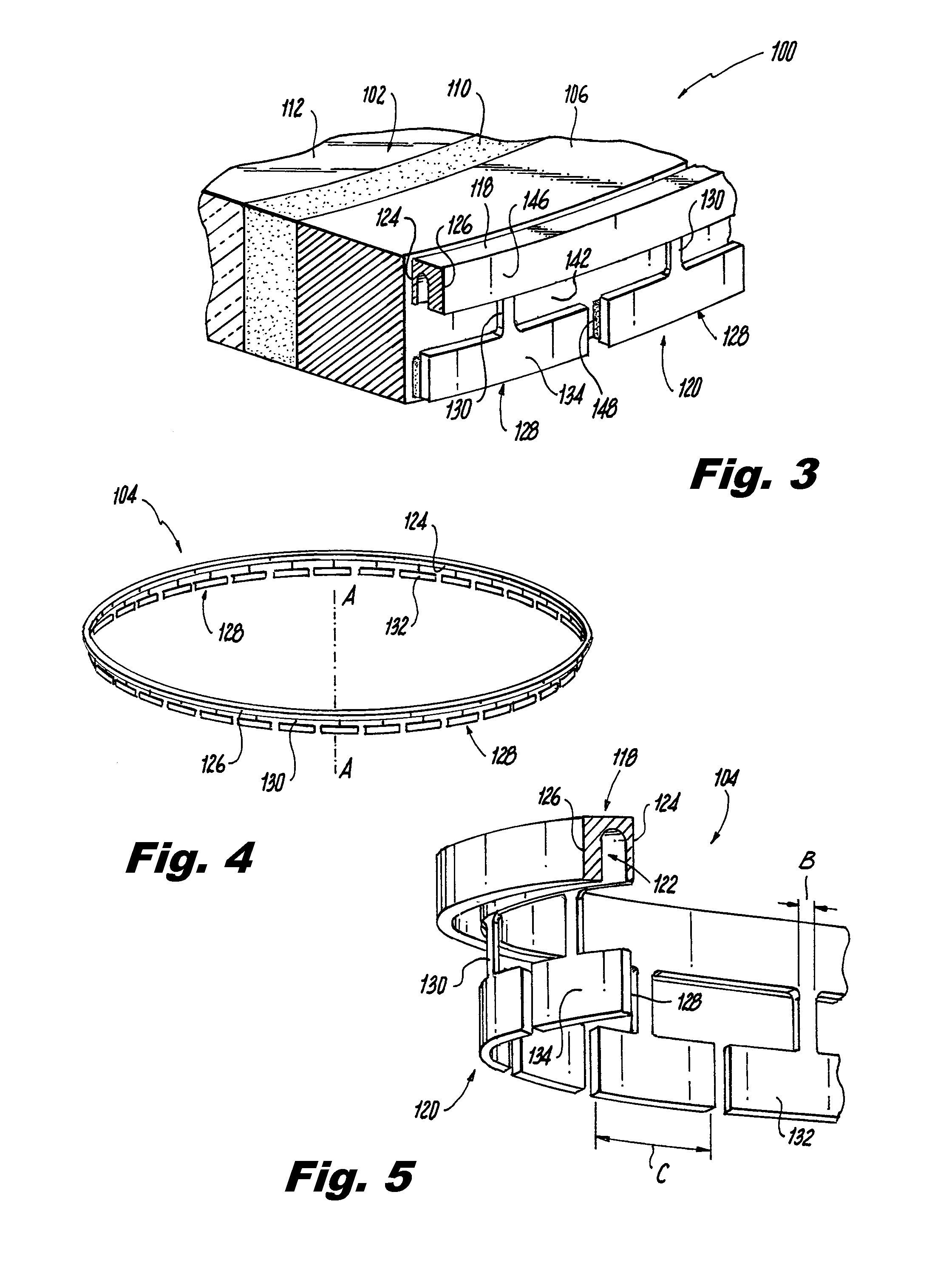
A flexure ring for a window assembly includes a continuous annular portion and a segmented portion. The continuous annular portion defines a ring axis. The segmented portion defines a plurality of circumferential segments. The continuous annular portion is connected to each circumferential segment by a respective neck. Each neck extends from the continuous annular portion to a respective one of the circumferential segments. The continuous annular portion, the segmented portion and the necks are configured to circumscribe a window pane.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
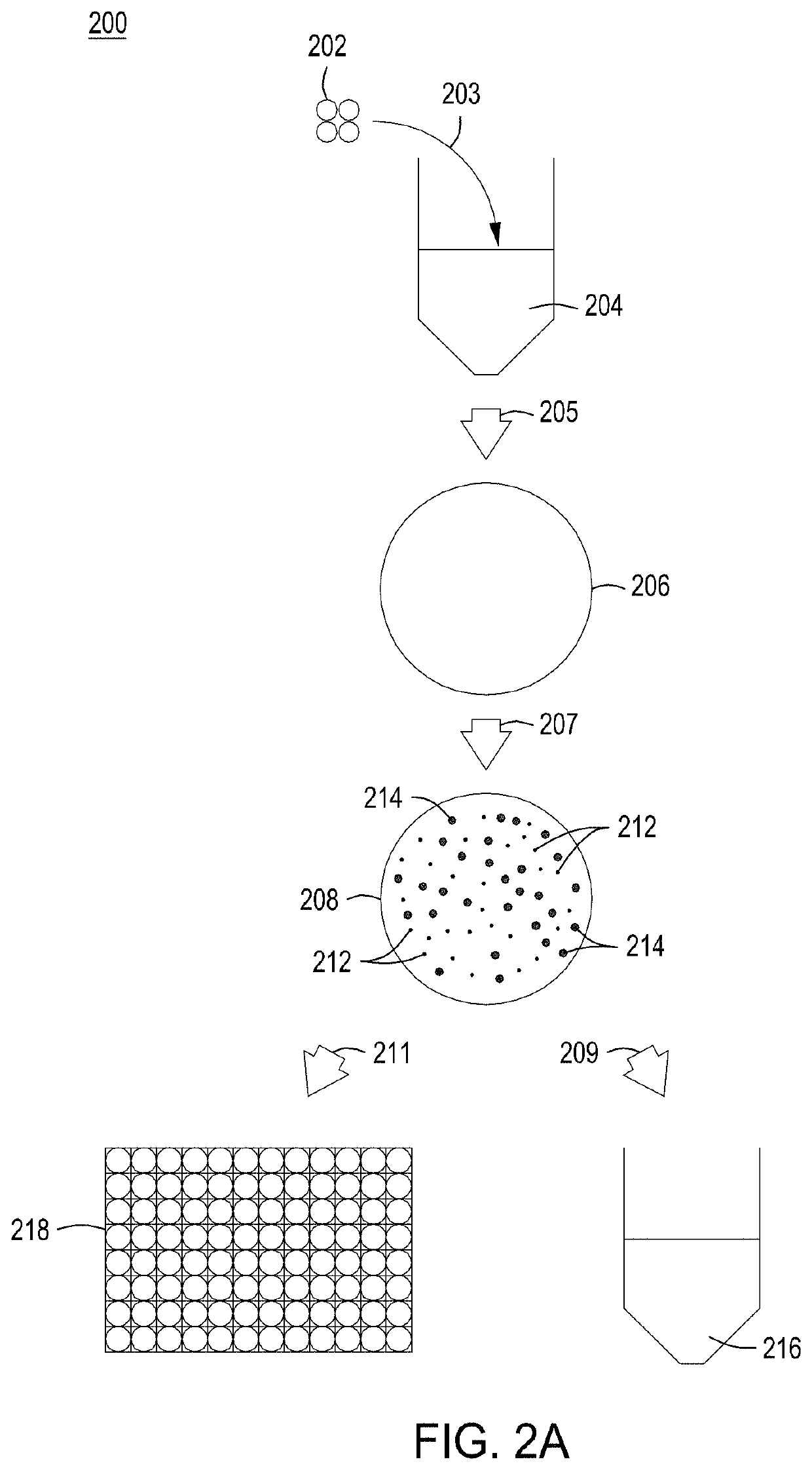
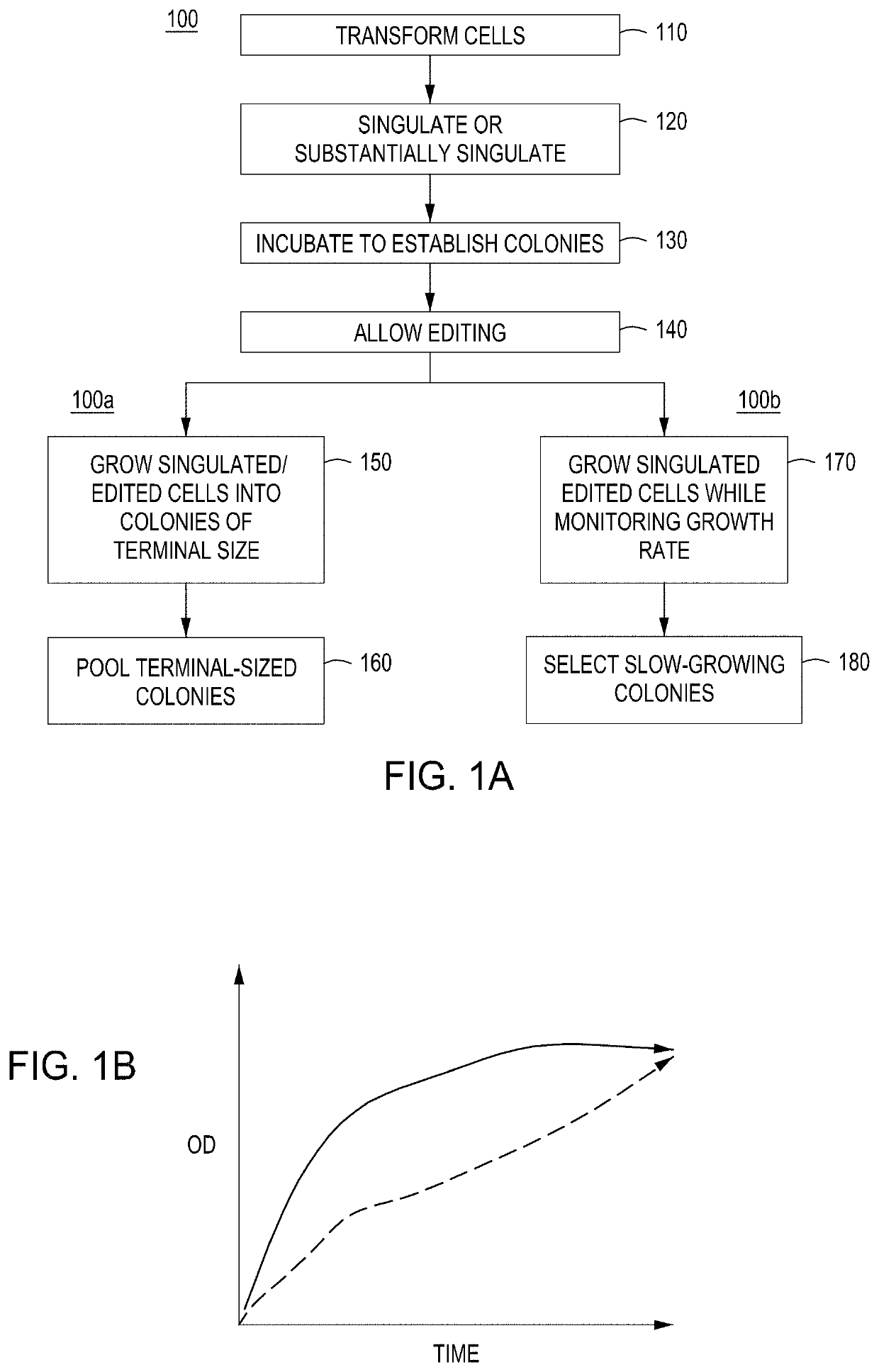
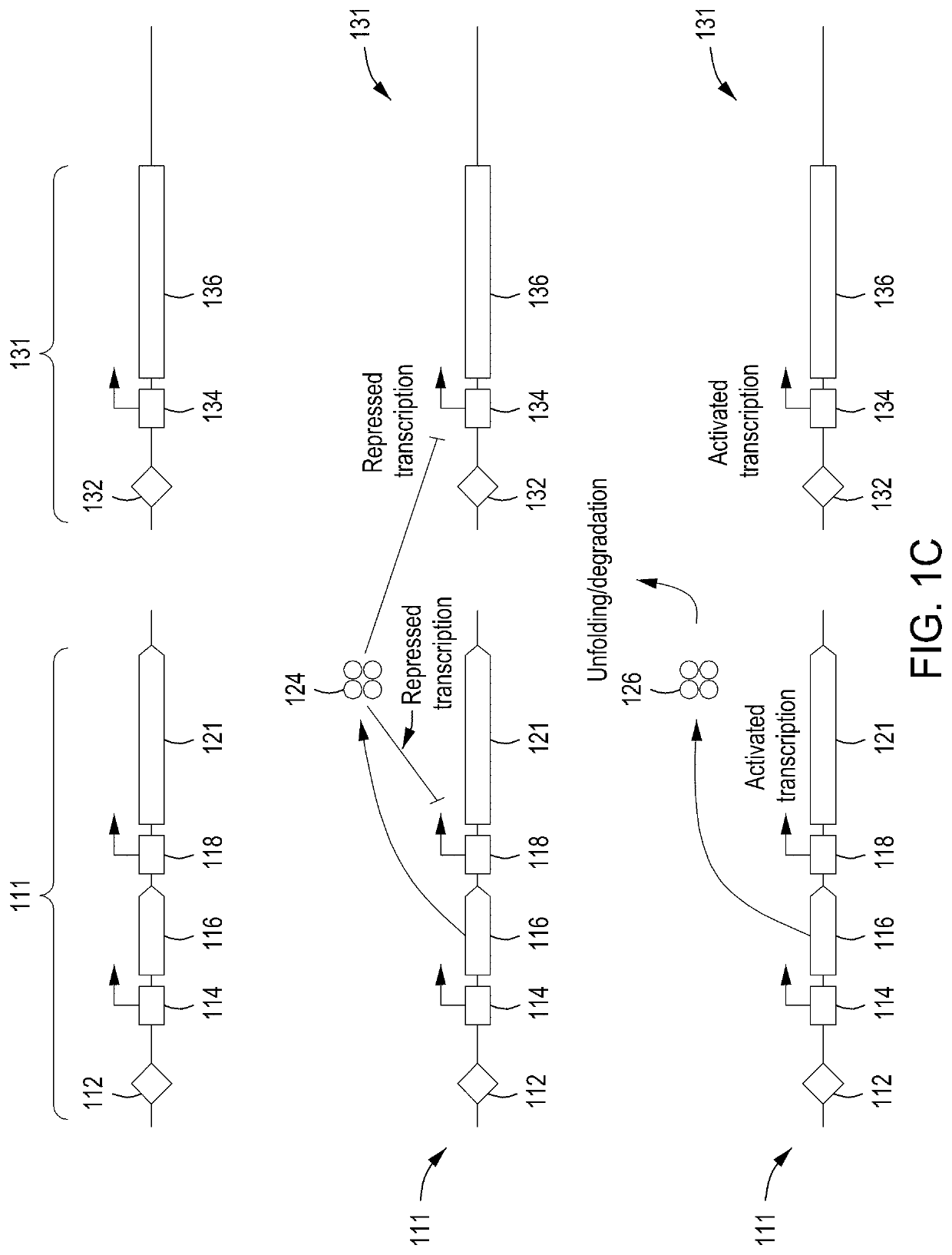
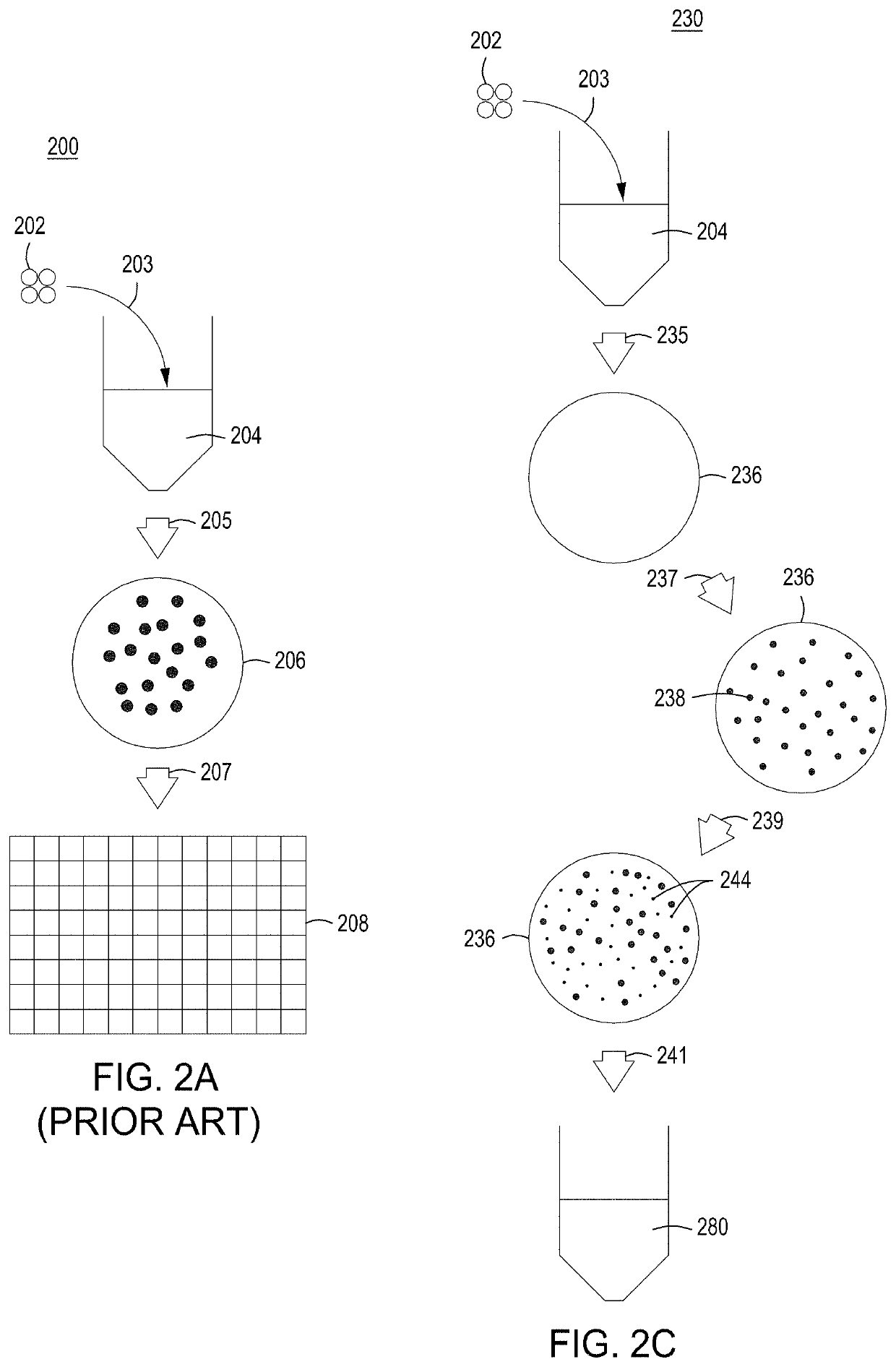
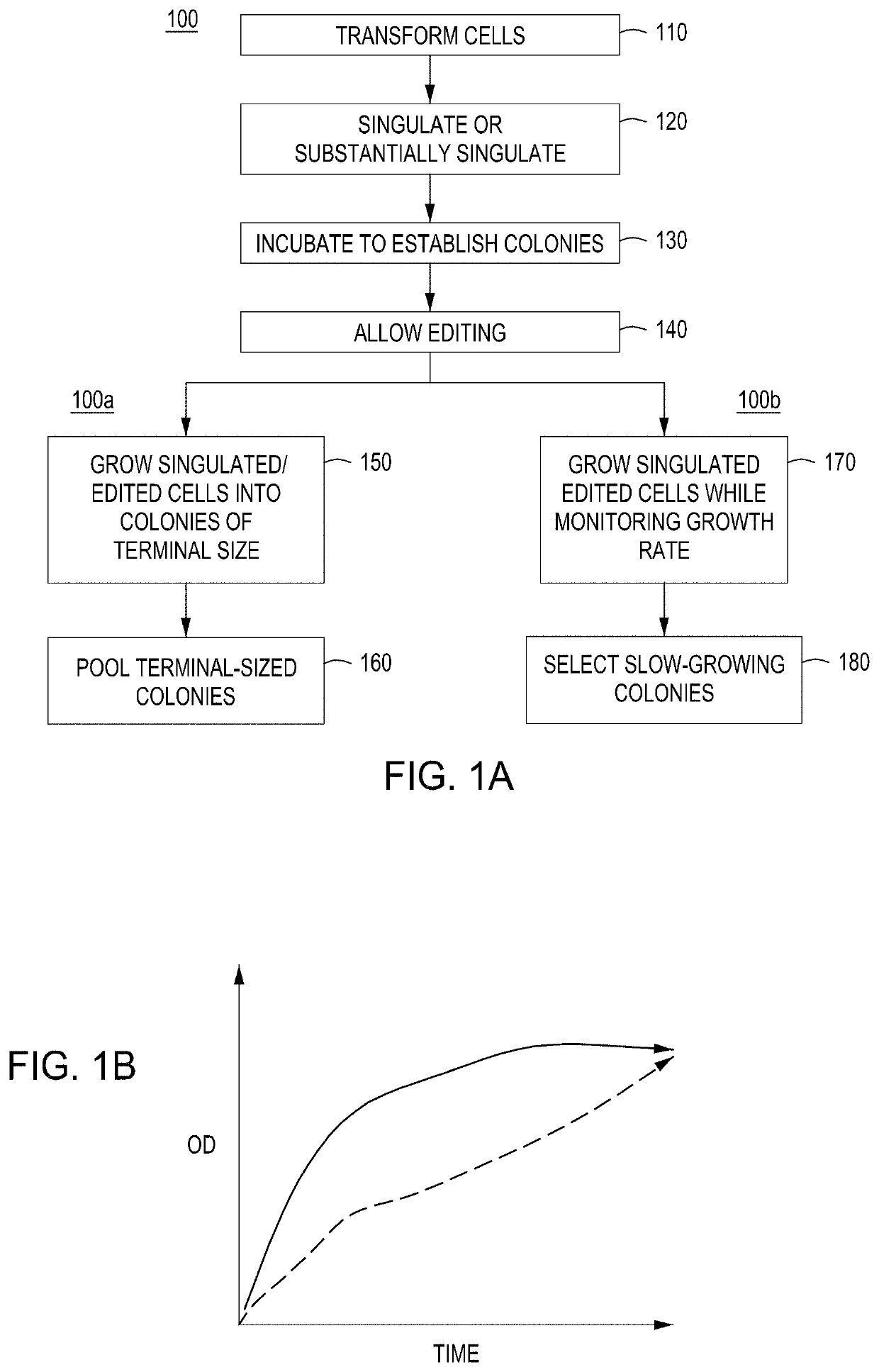
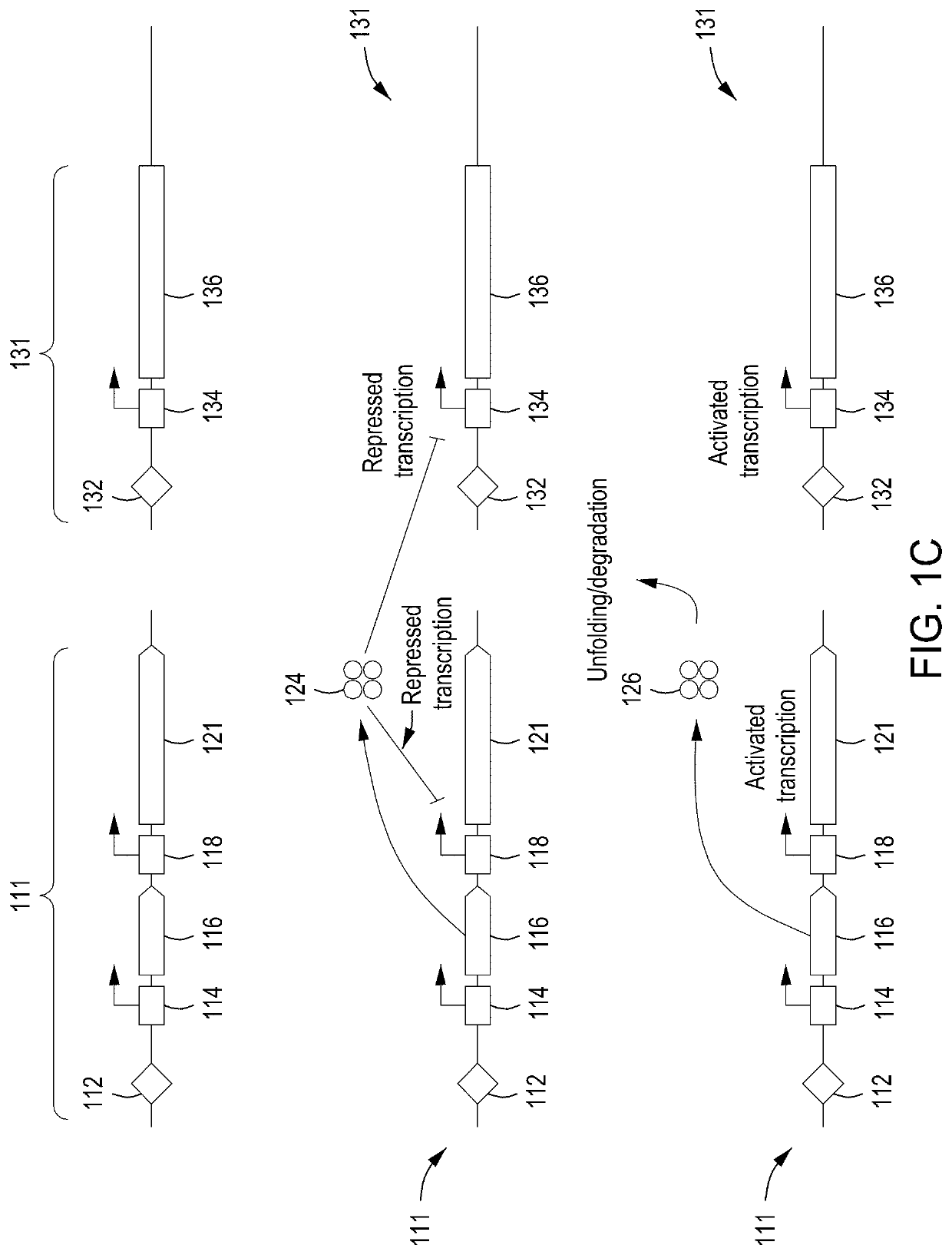
Detection of nuclease edited sequences in automated modules and instruments
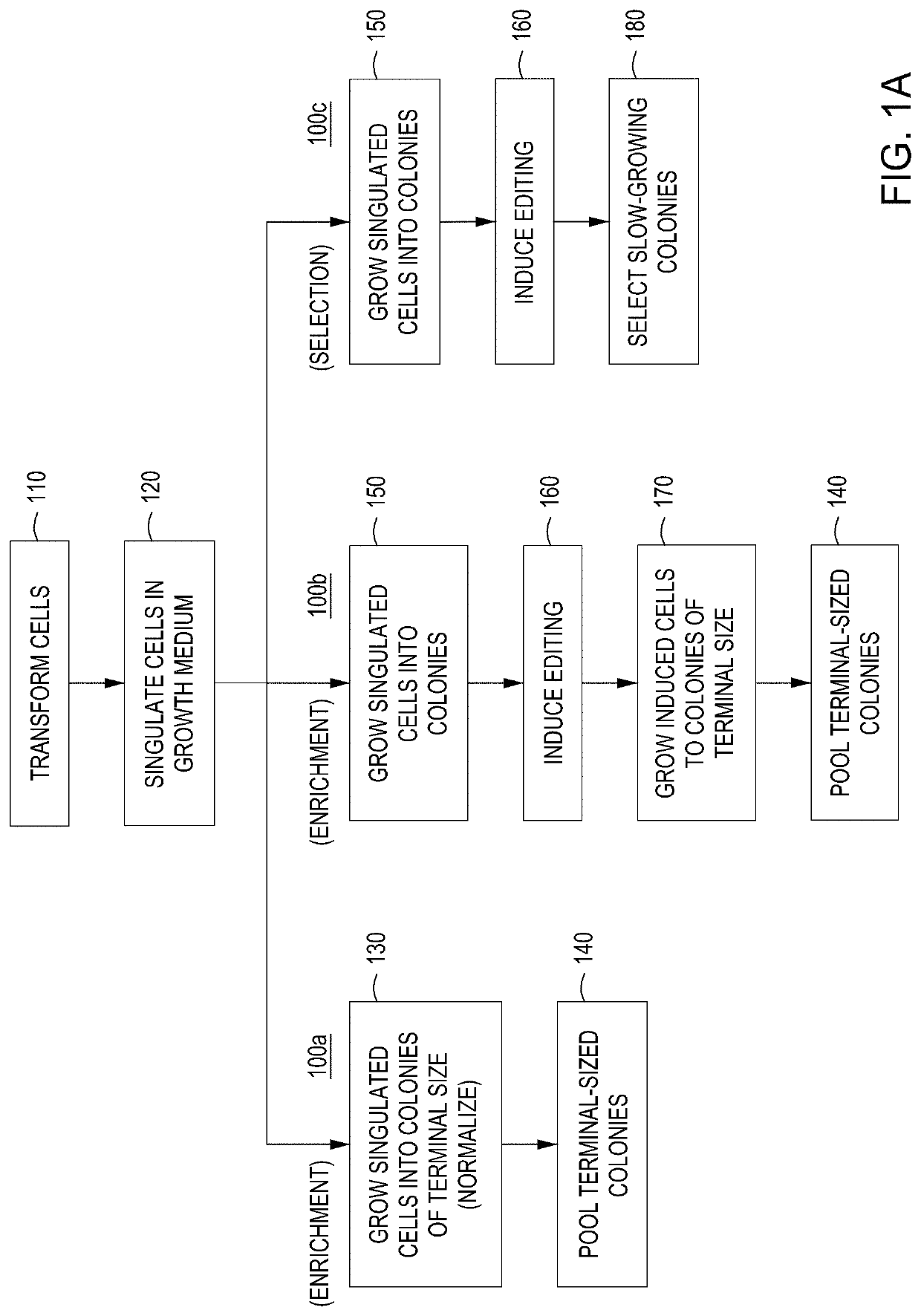
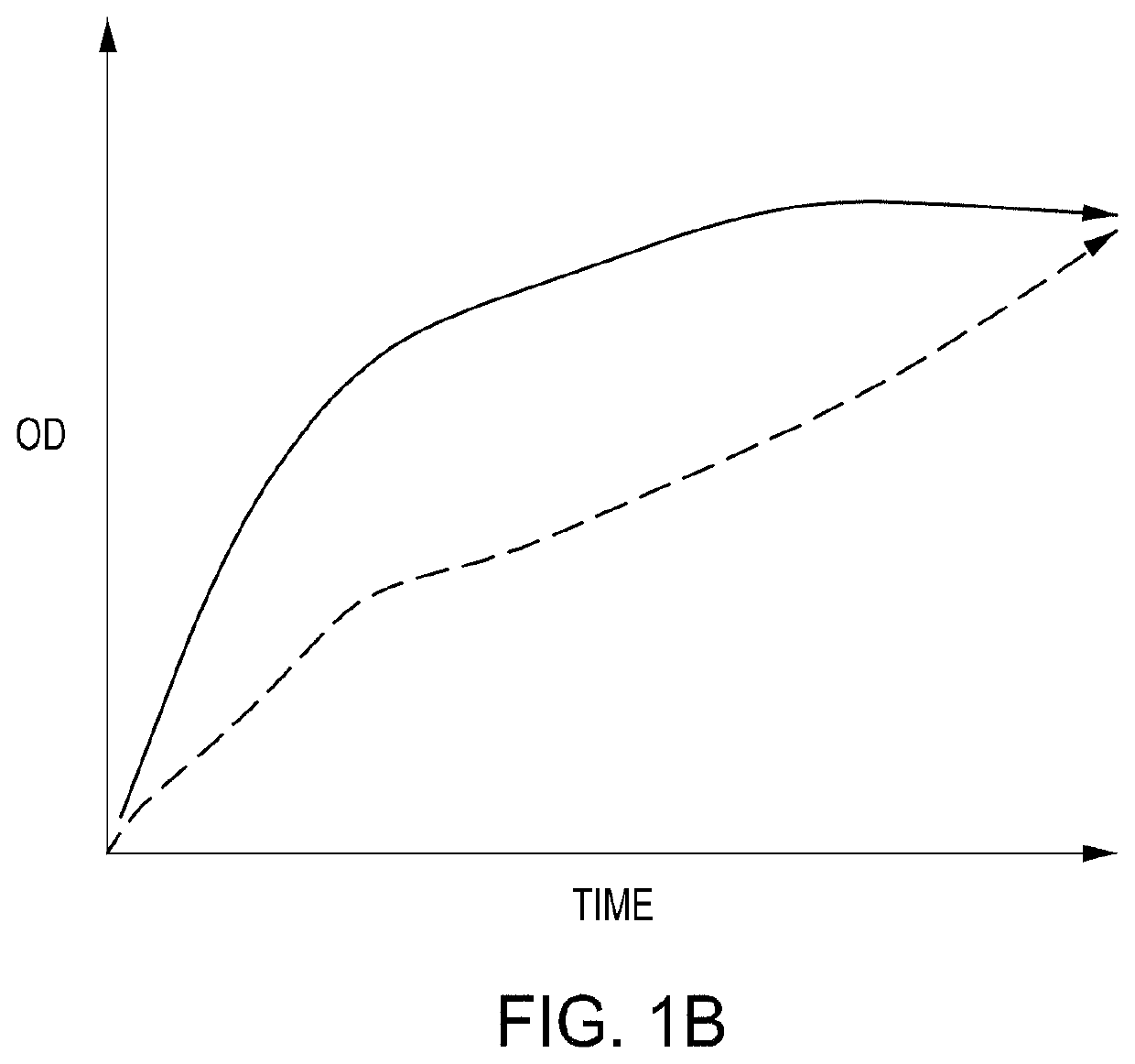
ActiveUS11142740B2Improve editing efficiencyEfficient editingStable introduction of DNALaboratory glasswaresGenome editingNuclease
Owner:INSCRIPTA INC
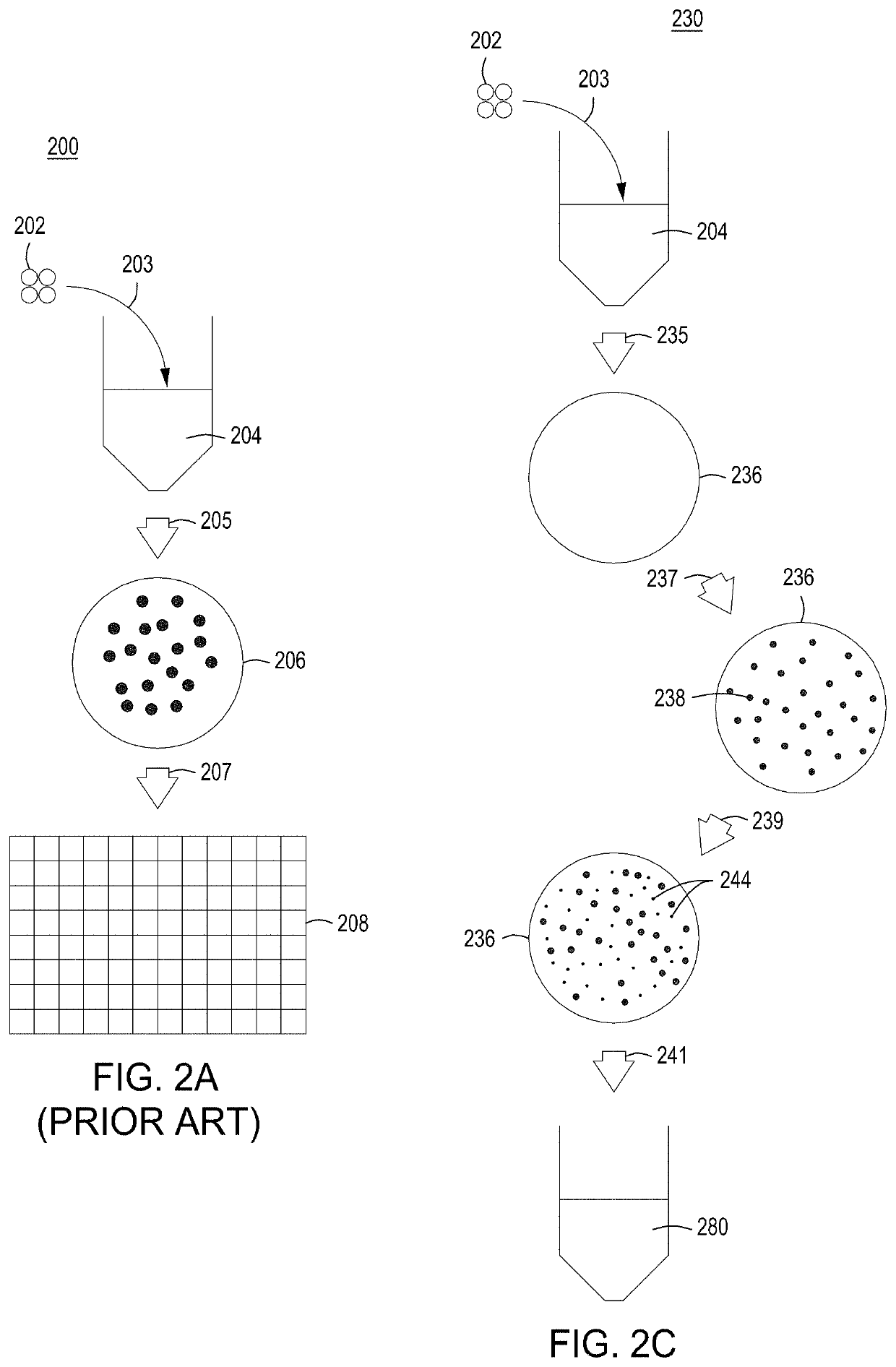
Instruments, modules, and methods for improved detection of edited sequences in live cells
ActiveUS10752874B2Facilitate “ cherry picking ”Raise the biasBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsGenome editingNuclease
The present disclosure provides instruments, modules and methods for improved detection of edited cells following nucleic acid-guided nuclease genome editing. The disclosure provides improved automated instruments that perform methods—including high throughput methods—for screening cells that have been subjected to editing and identifying cells that have been properly edited.
Owner:INSCRIPTA INC
Instruments, modules, and methods for improved detection of edited sequences in live cells
ActiveUS20200078738A1Facilitate “ cherry picking ”Raise the biasMembranesUltrafiltrationGenome editingNuclease
The present disclosure provides instruments, modules and methods for improved detection of edited cells following nucleic acid-guided nuclease genome editing. The disclosure provides improved automated instruments that perform methods—including high throughput methods—for screening cells that have been subjected to editing and identifying cells that have been properly edited.
Owner:INSCRIPTA INC
Device for mobile terminal
InactiveUS6968203B2Designing can be facilitatedEffective and more cost-effectiveAntenna supports/mountingsSubstation equipmentTerminal equipmentEngineering
The invention relates to a mobile terminal antenna system for a first radio application (RA1) and a second radio application (RA2) the system comprising first radio electronic circuits (REC1) for the first radio application (RA1), and second radio electronic circuits (REC2) for the second radio application (RA2). The system also comprises an end-fed antenna (4) for the first radio application (RA1), the end-fed antenna (4) having an extended shape and being connected to the first radio electronic circuits (REC1). The system comprises a dipole antenna (5) for the second radio application (RA2), the dipole antenna (5) being located near one end of the end-fed antenna (4) and connected to the second radio electronic circuits (REC2). The first radio electronic circuits (REC1) are connected to the dipole antenna (5), whereby the end-fed antenna (4) is adapted to be fed, during transmission, against the dipole antenna (5) by the first radio electronic circuits (REC1), whereby the dipole antenna (5) is adapted to serve as a counterpoise for the end-fed antenna (4).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Array plate apparatus having tunable isolation characteristics
InactiveUS7623409B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce the noise floorMarine torpedoesThermometers using physical/chemical changesHull structureInter layer
An apparatus having an array plate and an isolation section joined to the perimetrical edge of the plate. The isolation section has a plurality of isolation layers and a plurality of intermediate layers alternately arranged wherein an intermediate layer is positioned between consecutive isolation layers. An innermost isolation layer is joined to the perimetrical edge of the array plate and an outermost isolation layer is adapted to be joined to a hull structure of an underwater vehicle. Each isolation layer is made from energy absorbing material and each intermediate layer is made from generally rigid material. The isolation section substantially reduces vehicle self-noise from traveling to the array plate. Interchangeable depth stop members having various geometries are used to adjust the stiffness of the isolation section so as to maximize the isolation characteristics of the isolation section at particular water depths at which the underwater vehicle operates.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Lens apparatus and image pickup apparatus including the same
InactiveUS9628714B2Raise the ratioLarge isolationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsOptical axisConditional expression
A lens apparatus includes an optical system including multiple lens units, the optical system including: a first lens unit which is disposed closest to an object side in the optical system and is rotatable about a point in a vicinity of an optical axis of the optical system; and at least one lens unit which is movable in a direction including a component in a direction perpendicular to the optical axis. The following conditional expression is satisfied: 1.0<ft / |f1|<2.2, where ft represents a focal length of the optical system at a telephoto end, and f1 represents a focal length of the first lens unit. At least one of rotation of the first lens unit or movement of the at least one lens unit in the direction including the component in the direction perpendicular to the optical axis changes an image formation position in the direction perpendicular to the optical axis.
Owner:CANON KK
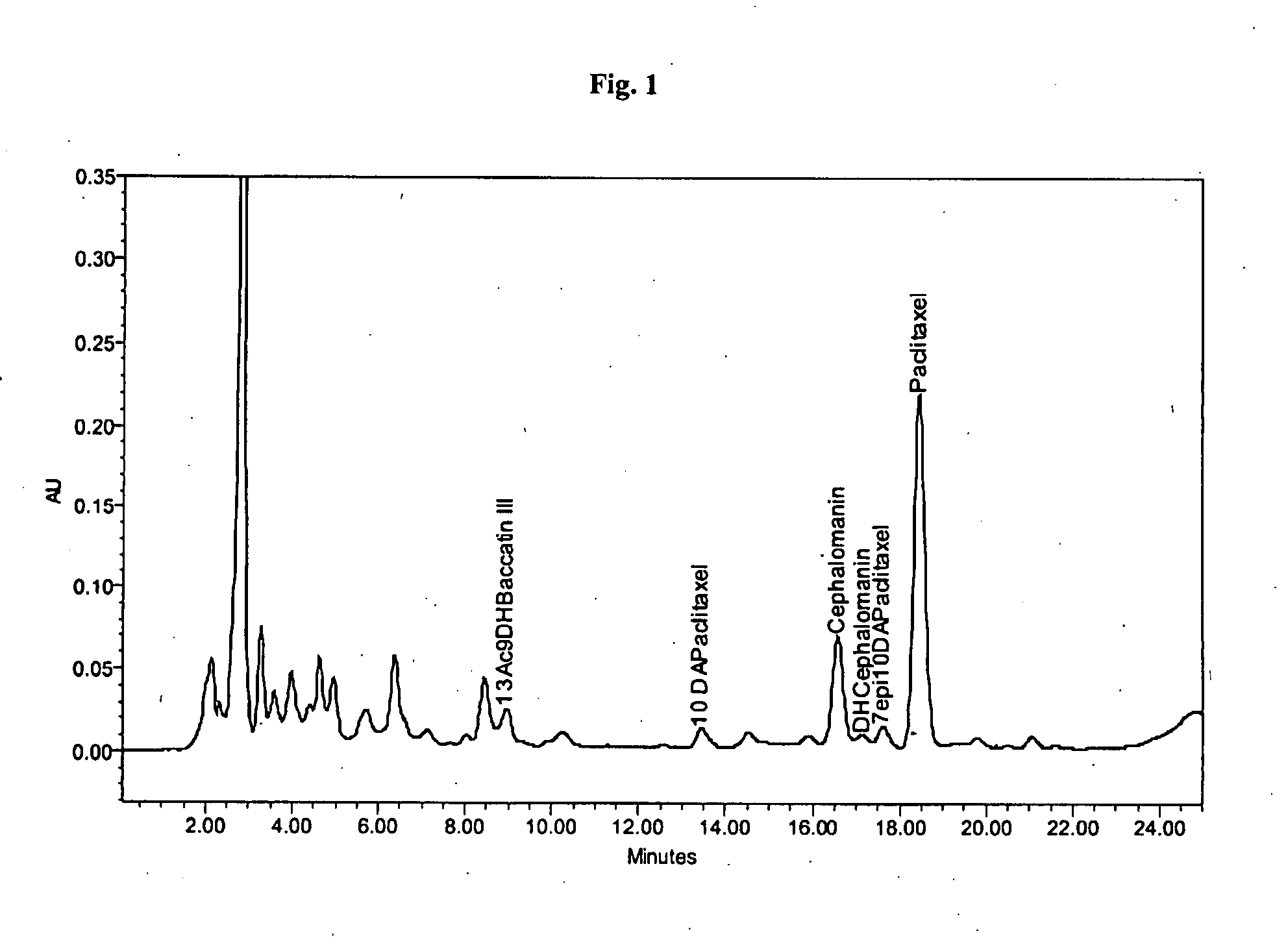
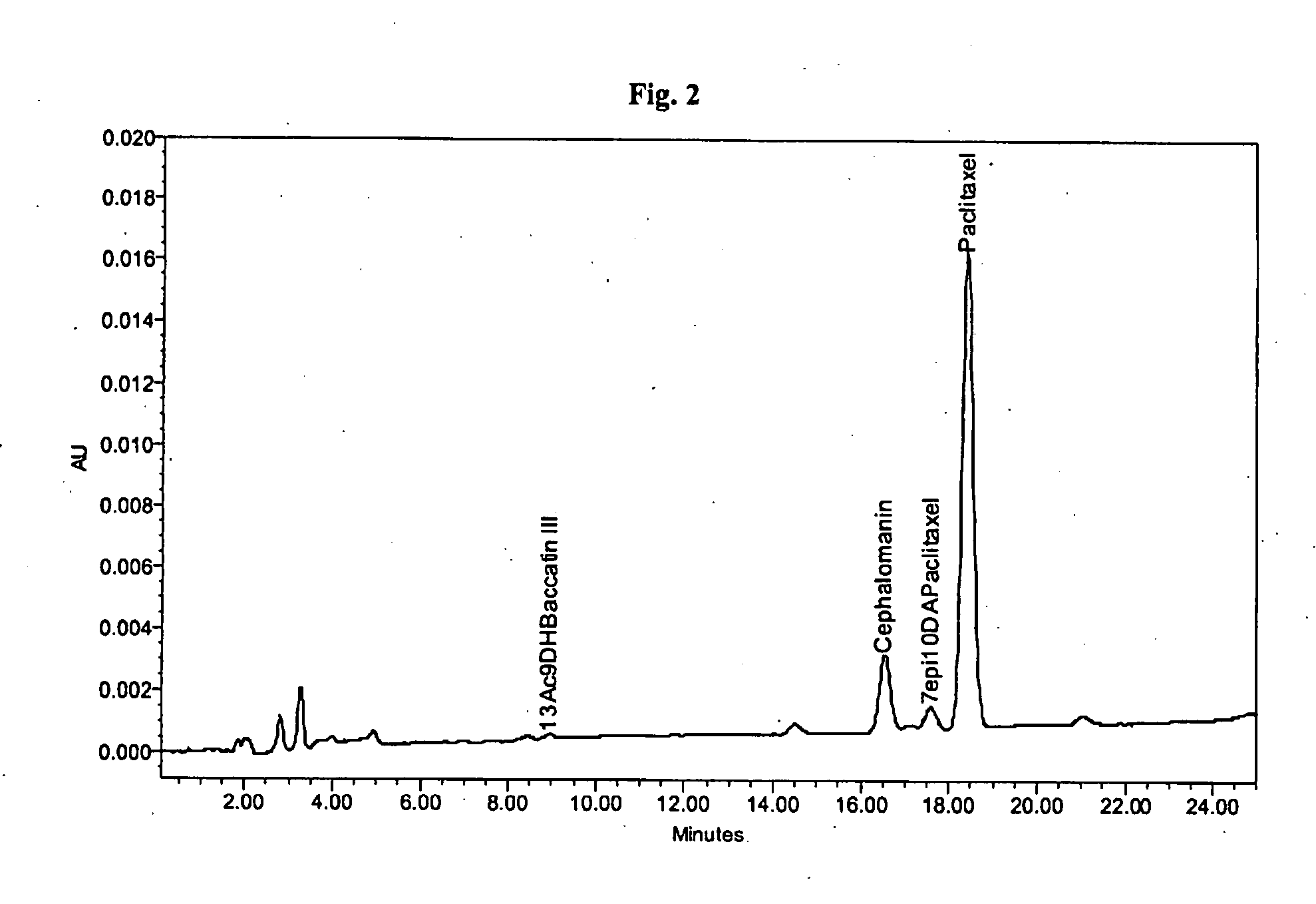
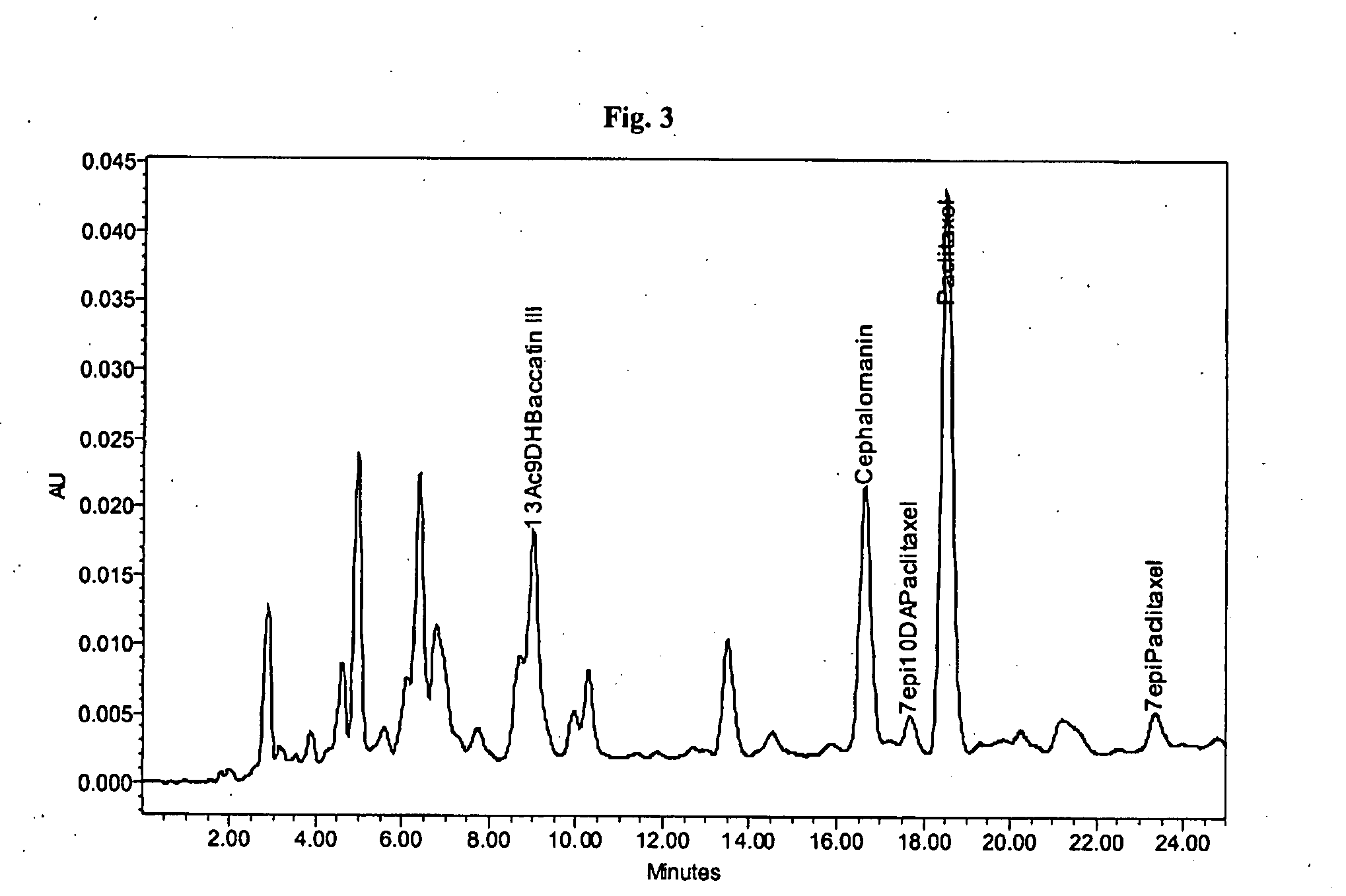
Process for the isolation of paclitaxel
InactiveUS20090216031A1Simple and inexpensive and efficient methodLarge isolationOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsMethyl isobutyl ketonePolyamide
Paclitaxel is isolated by a process including normal phase chromatography using a polyamide stationary phase and a mixture containing a dialkyl ketone and a less polar solvent as a mobile phase. Suitable dialkyl ketones include acetone or methyl isobutyl ketone. Suitable less polar co-solvents include a (C5-C8) aliphatic hydrocarbon, a (C6-C8) aromatic hydrocarbon, a (C1-C4) dialkyl ether or their mixtures.
Owner:IVAX PHARMA
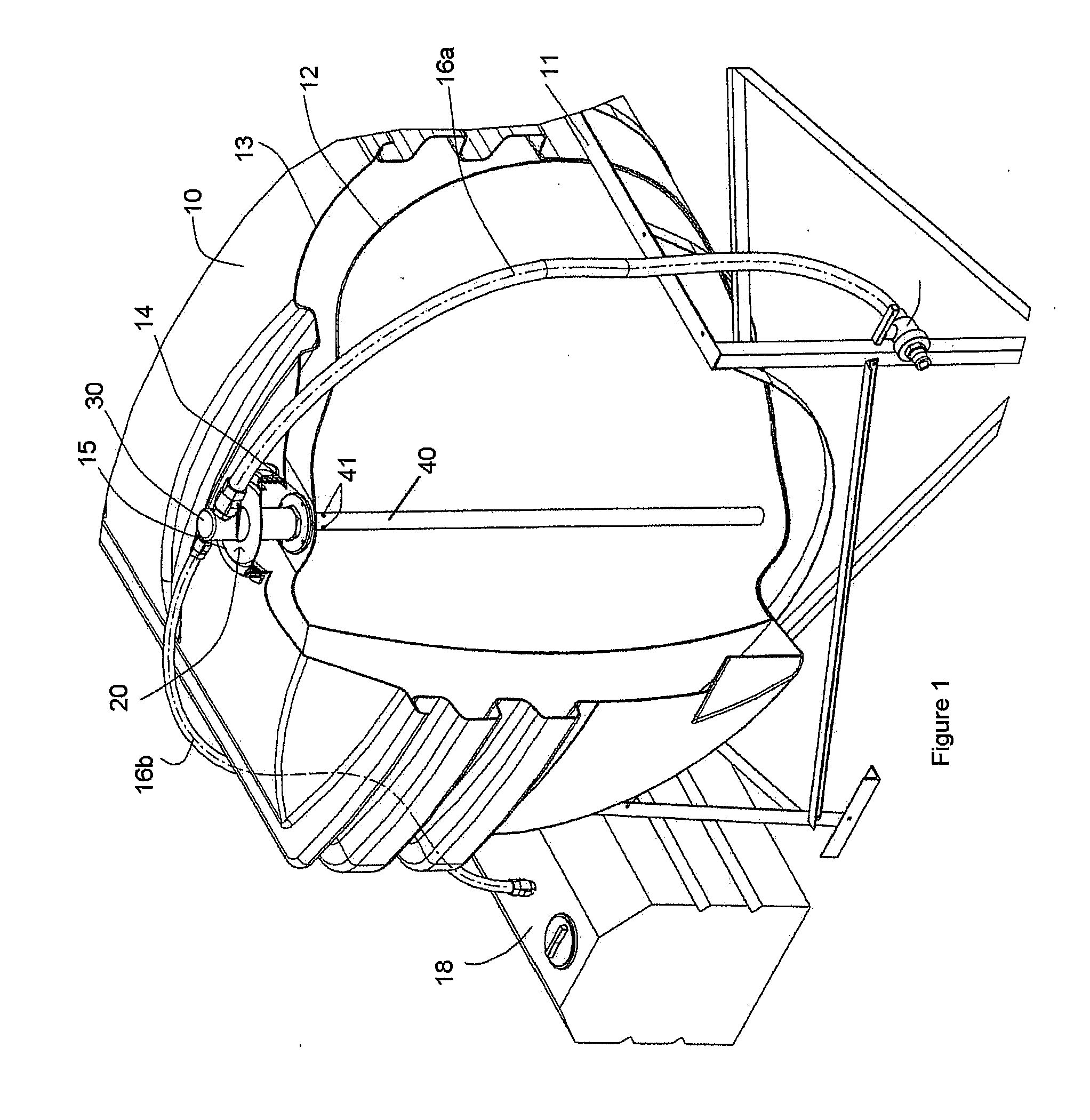
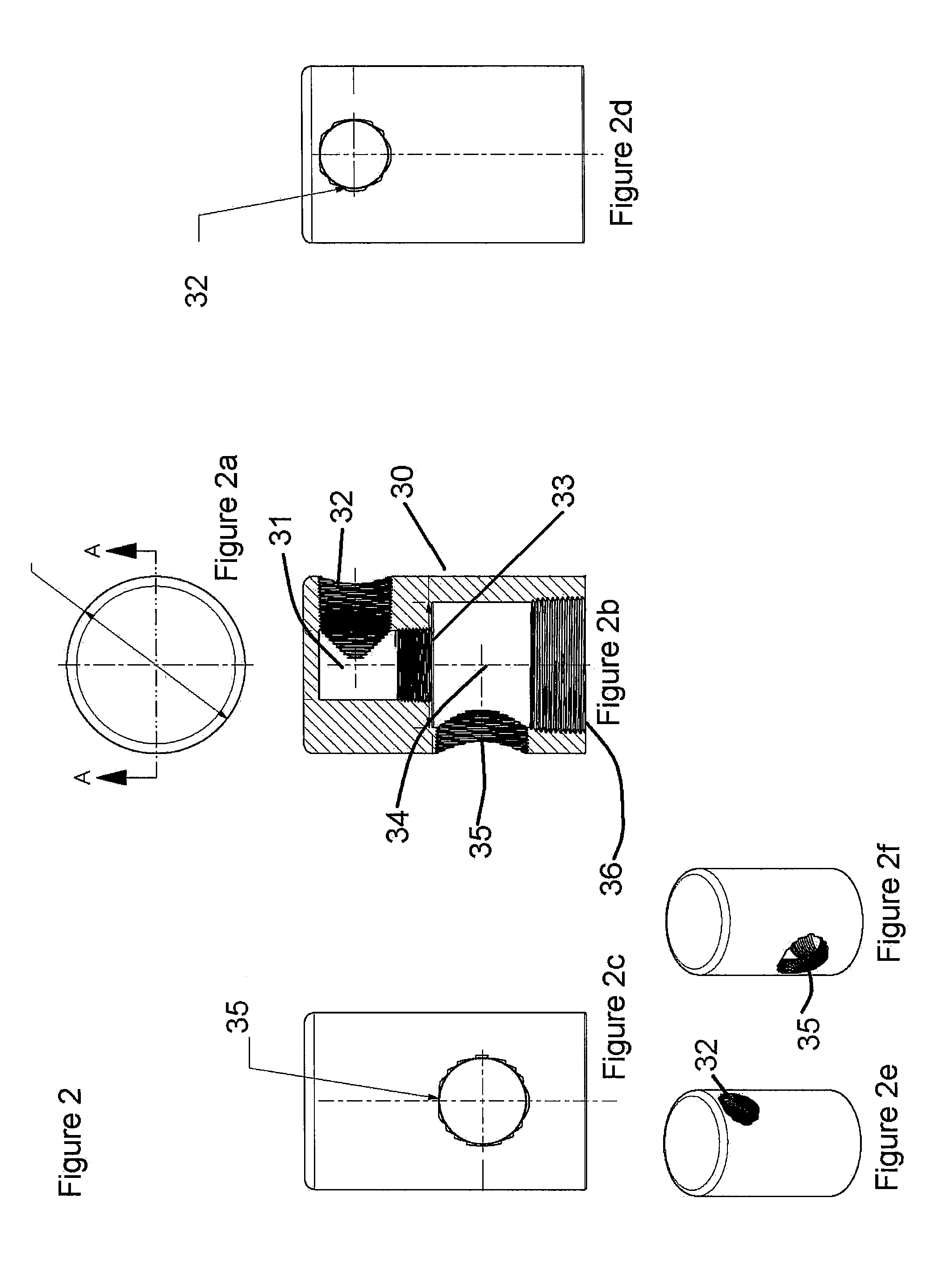
Fill fitting for a fluid storage tank
InactiveUS20100282362A1Avoid pollutionLarge isolationLighting and heating apparatusLarge containersEngineeringStinger
A fitting is provided for attachment to an outlet of a fluid storage tank. The fitting divides the opening into two fluid pathways for independent use in filling and venting of the tank. The fitting prevents spillage and improves site safety at the tank location. The fitting comprises a manifold for attachment to the tank opening, and the manifold is divided into two internal pathways from the tank opening to the exterior environment. A stinger tube is attachable to one of the pathways and extends into the tank to deliver fluid. The stinger includes a siphon break for use in standardizing tank fill levels and in emptying fluid from the manifold to avoid site spillage of tank contents.
Owner:MARMIT PLASTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com