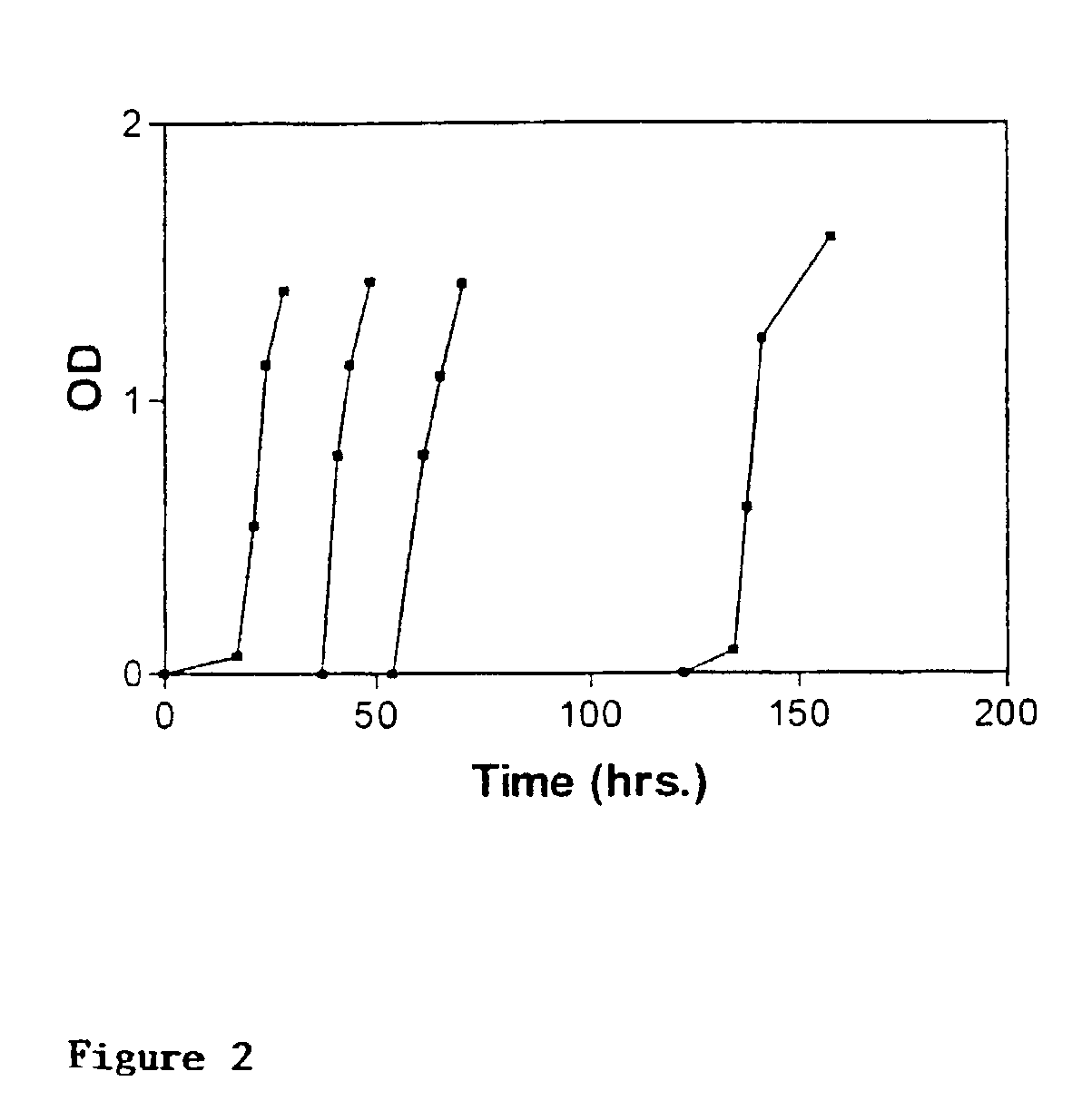
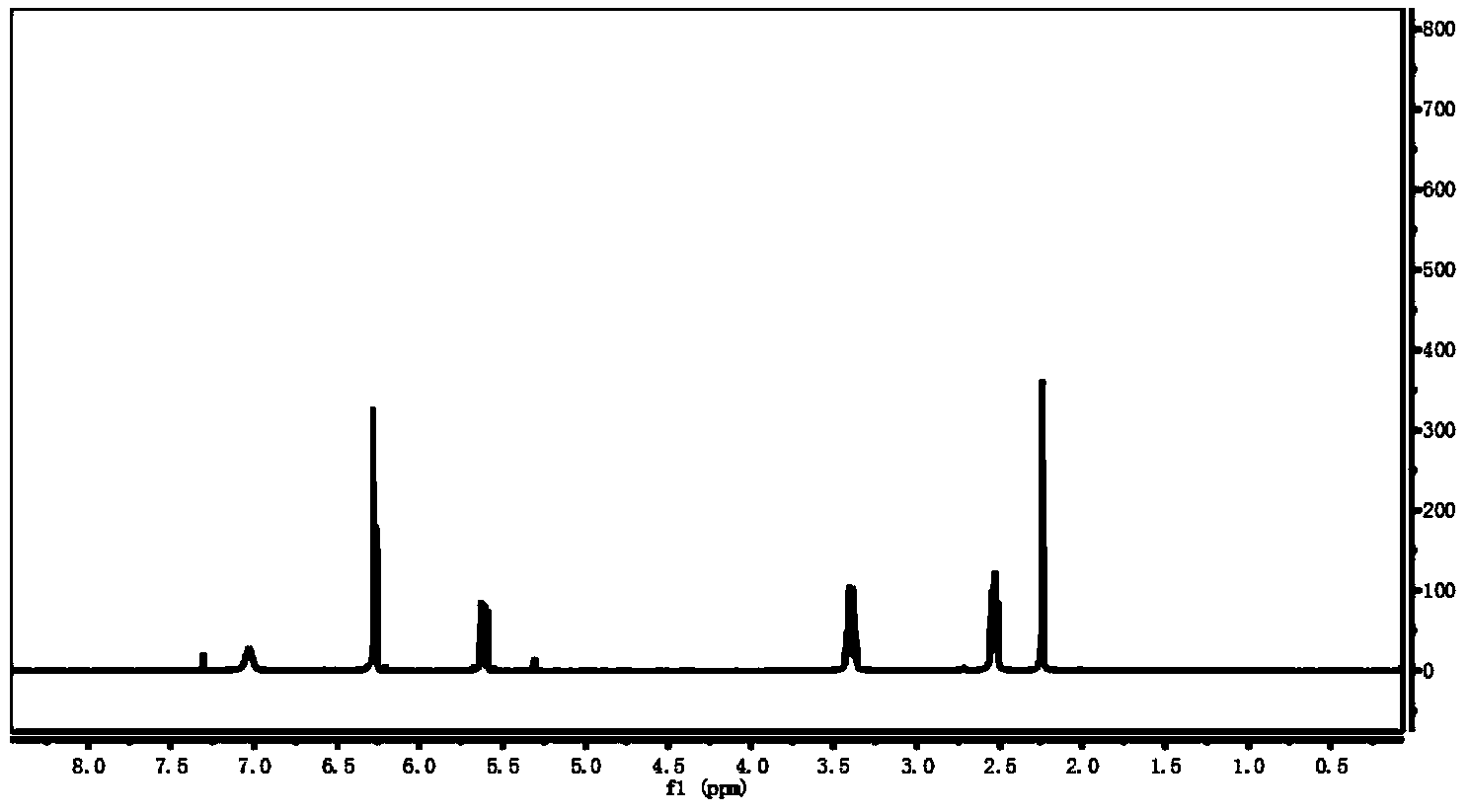
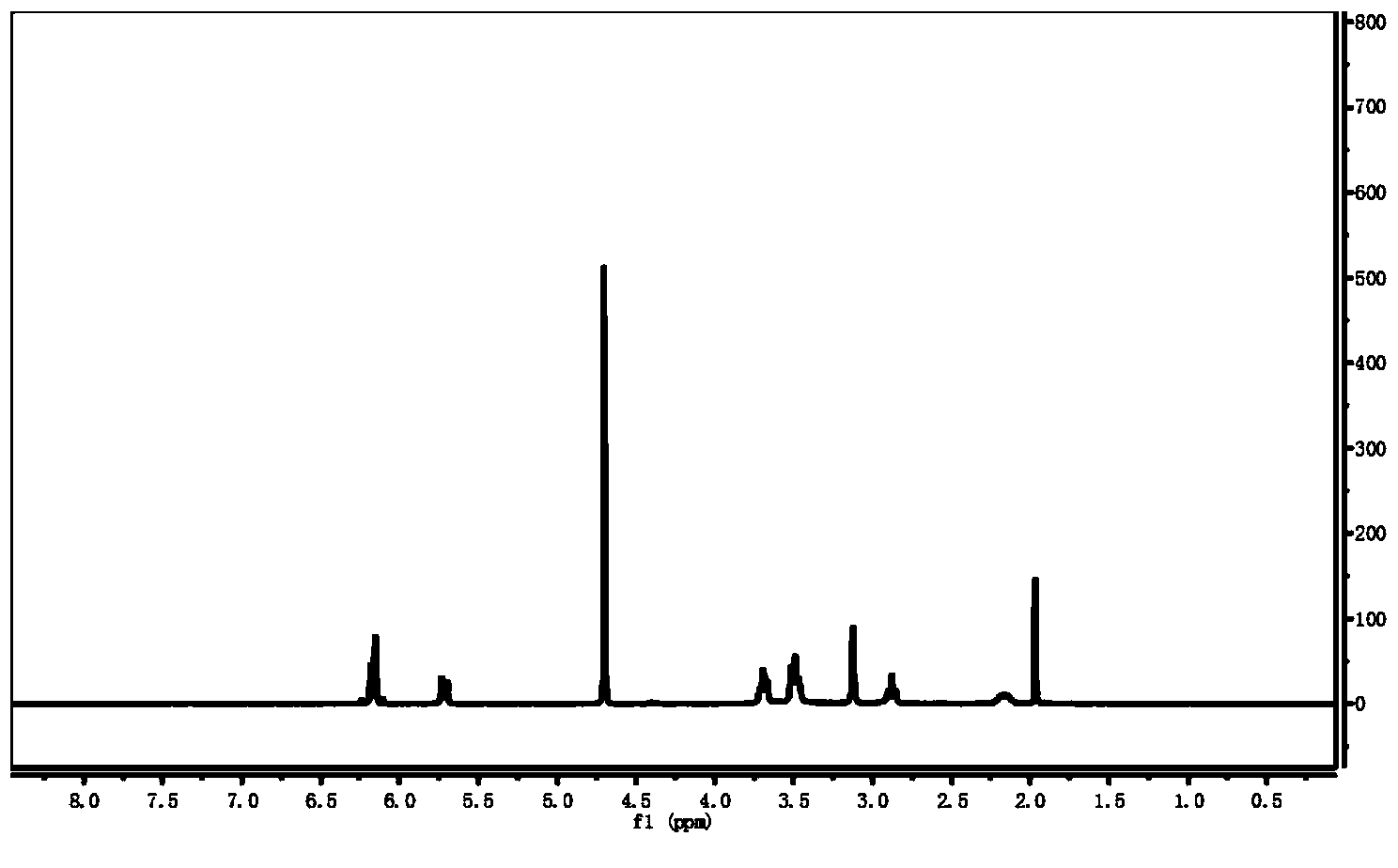
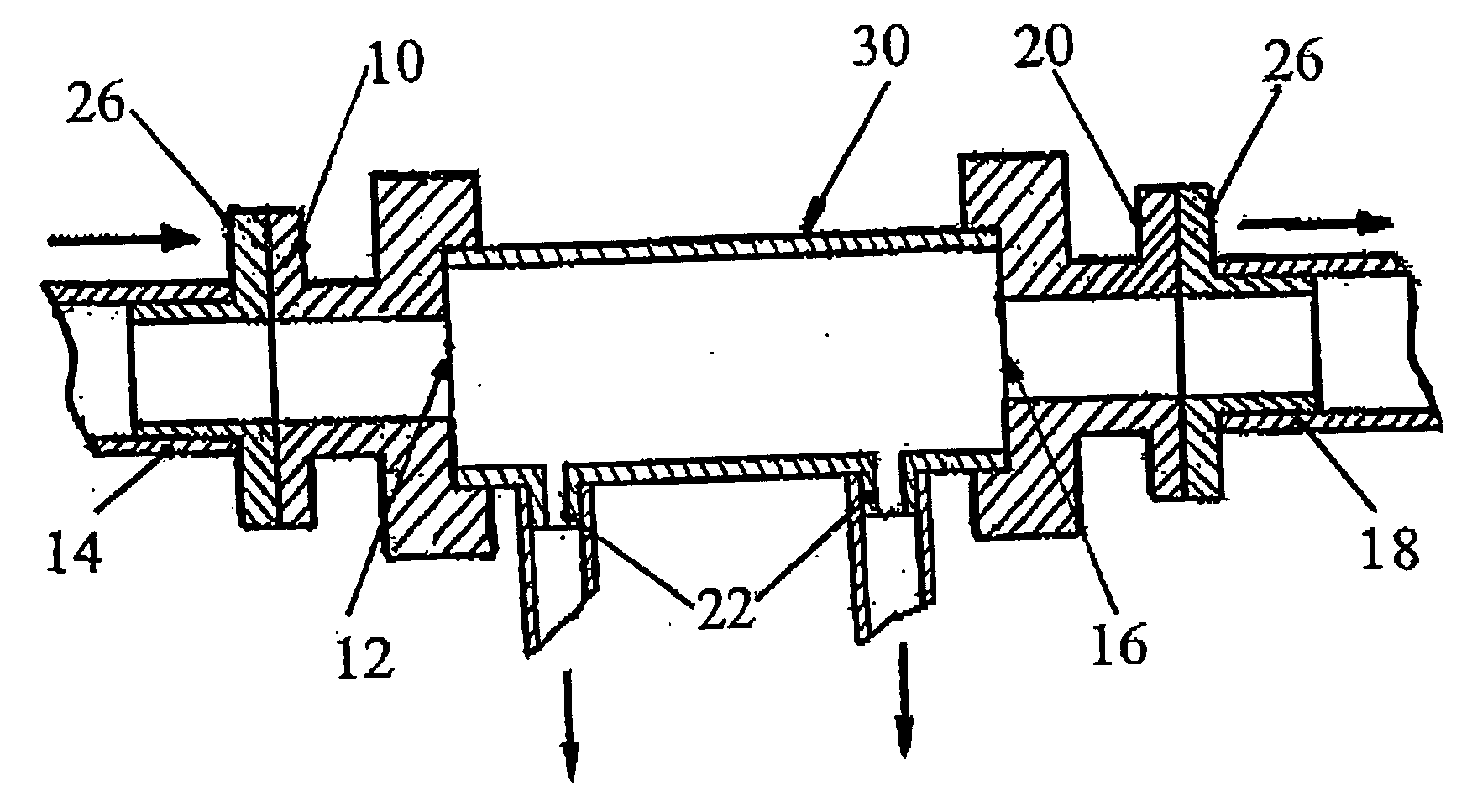
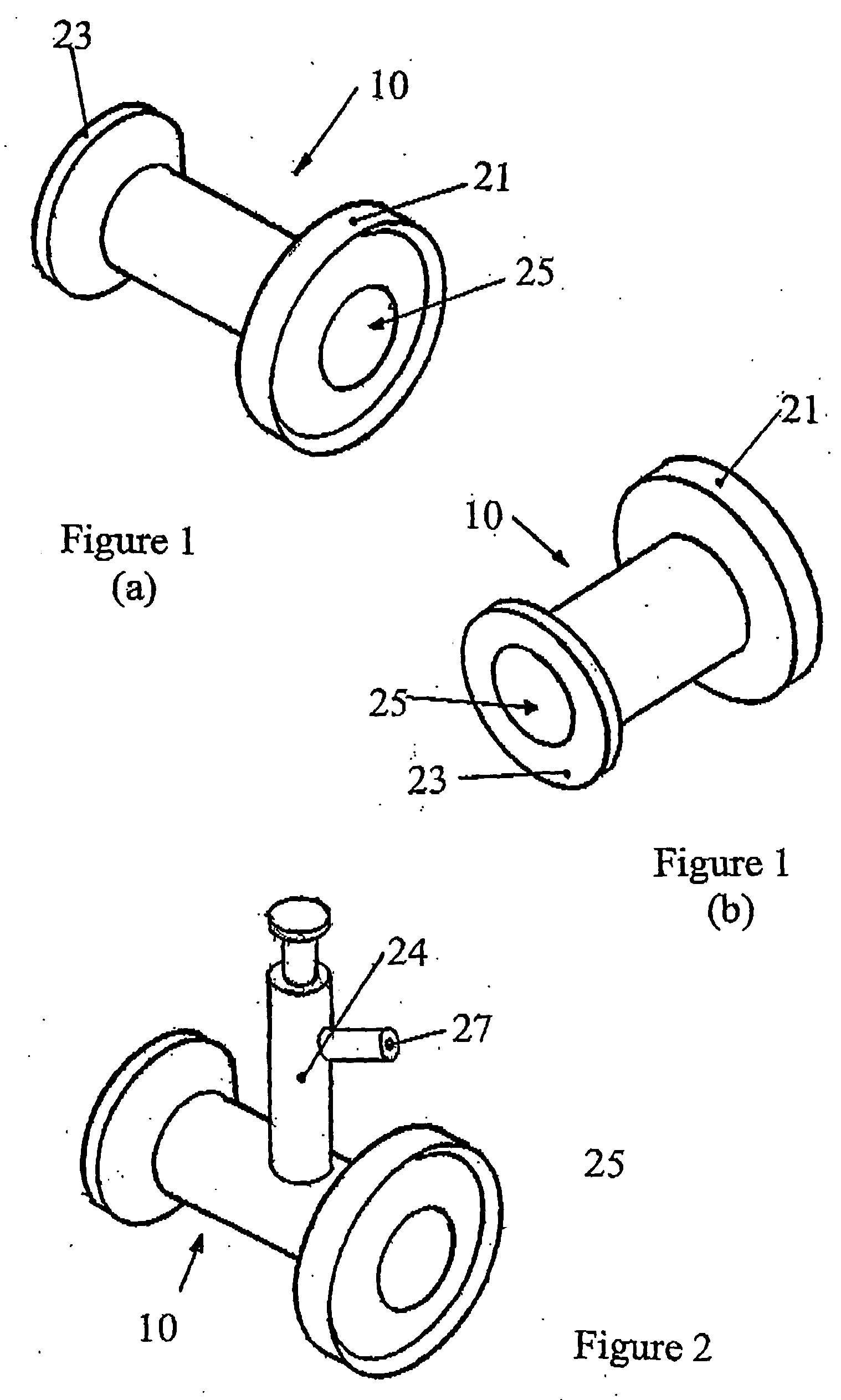
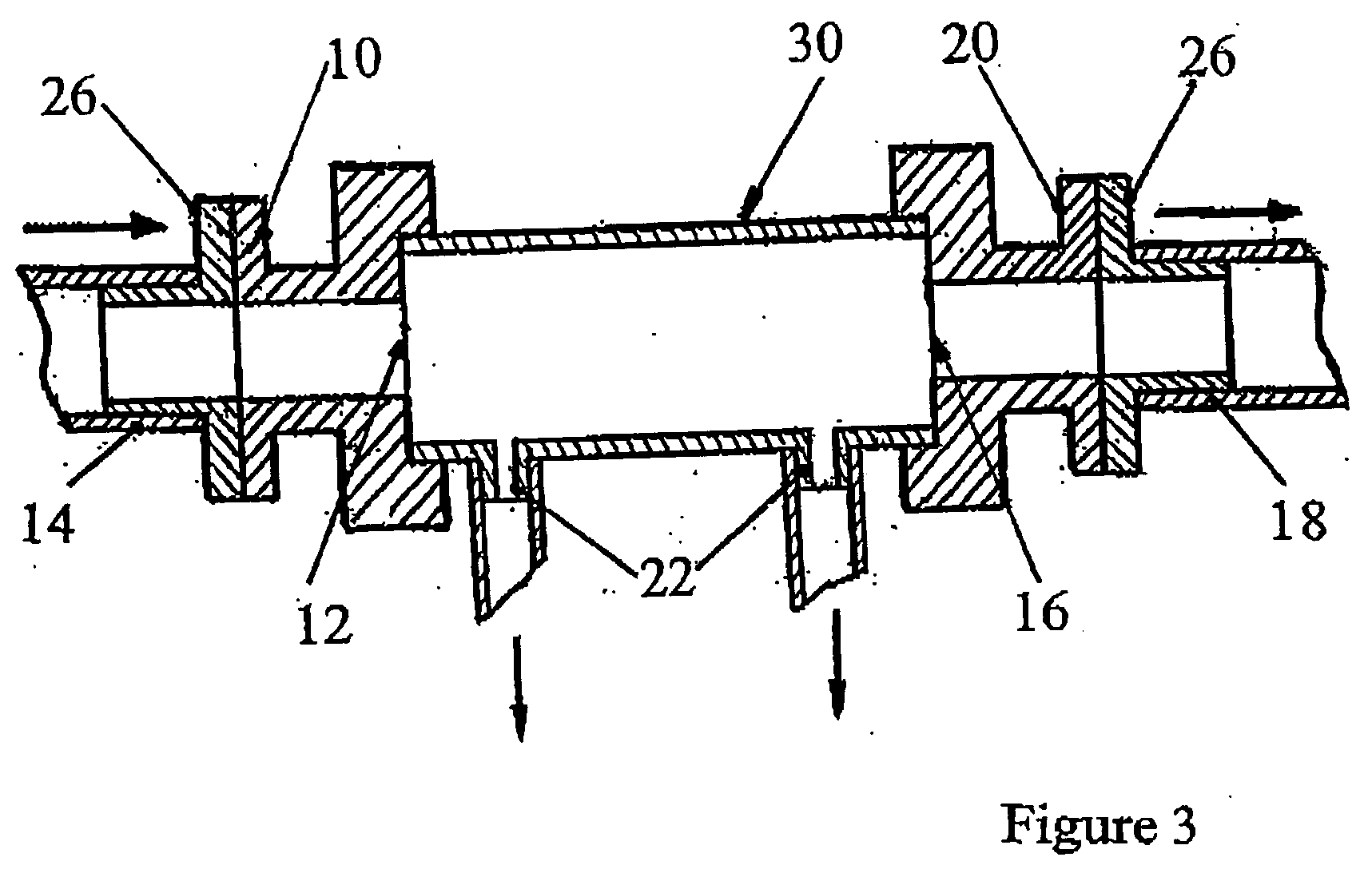
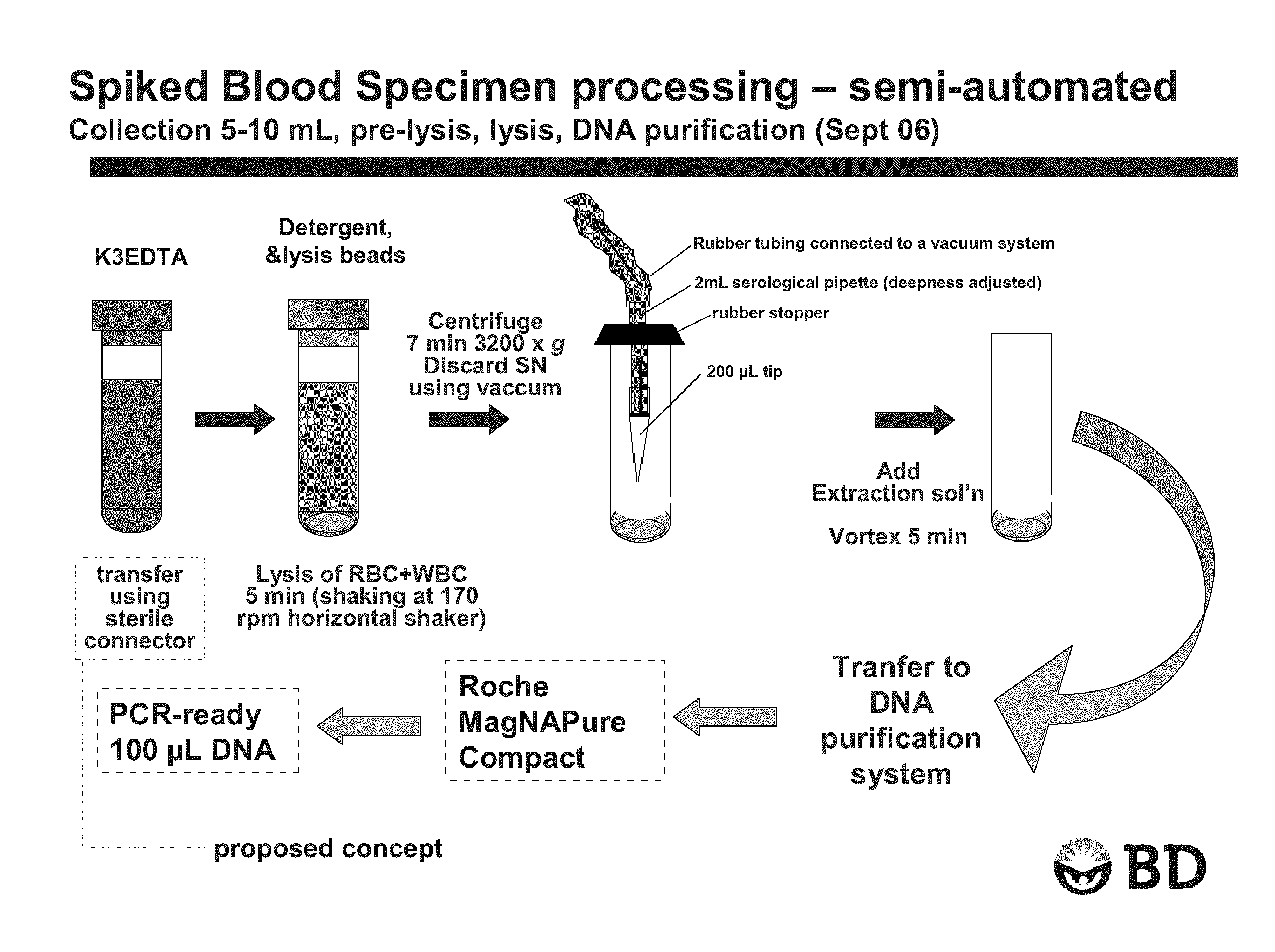
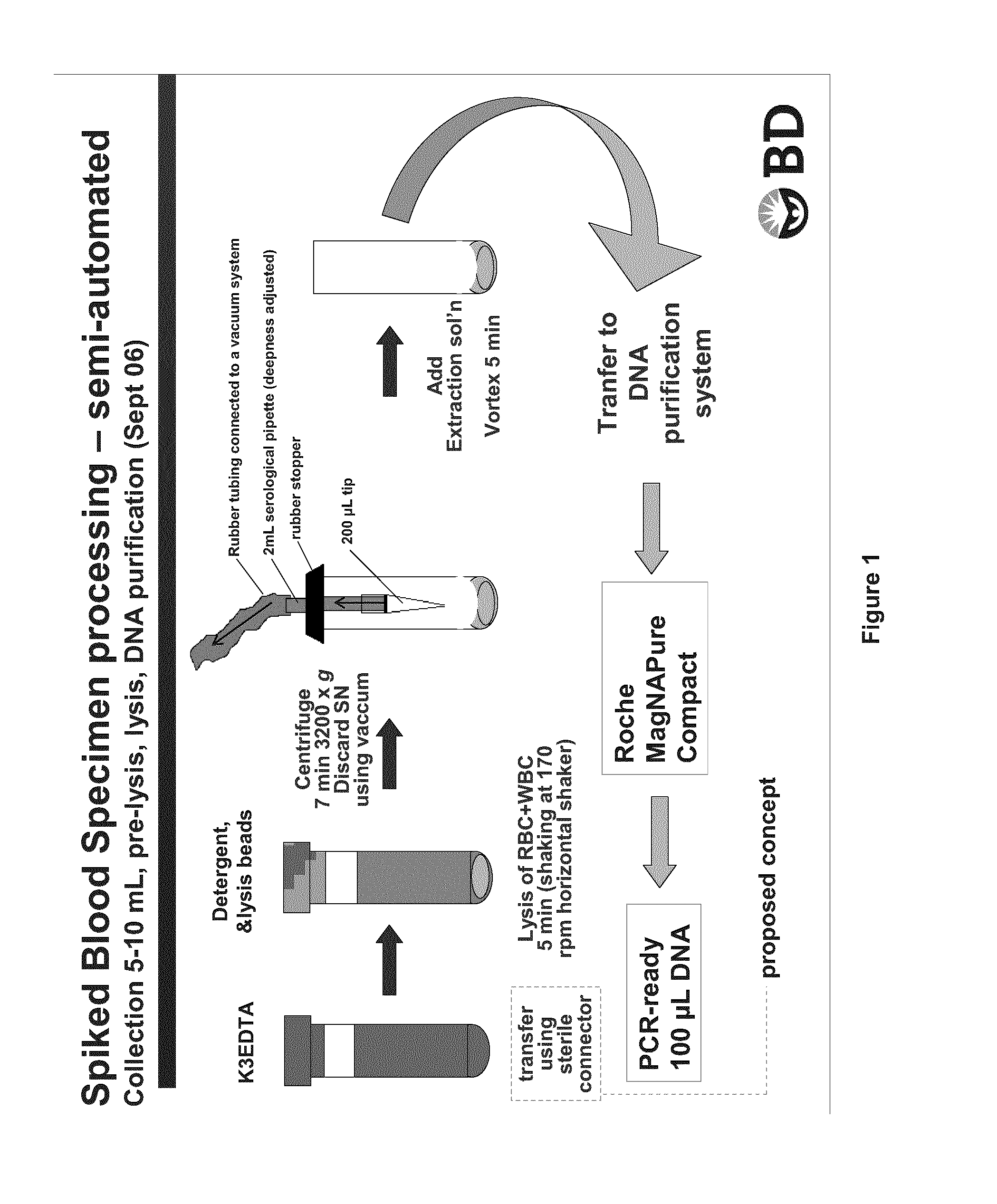
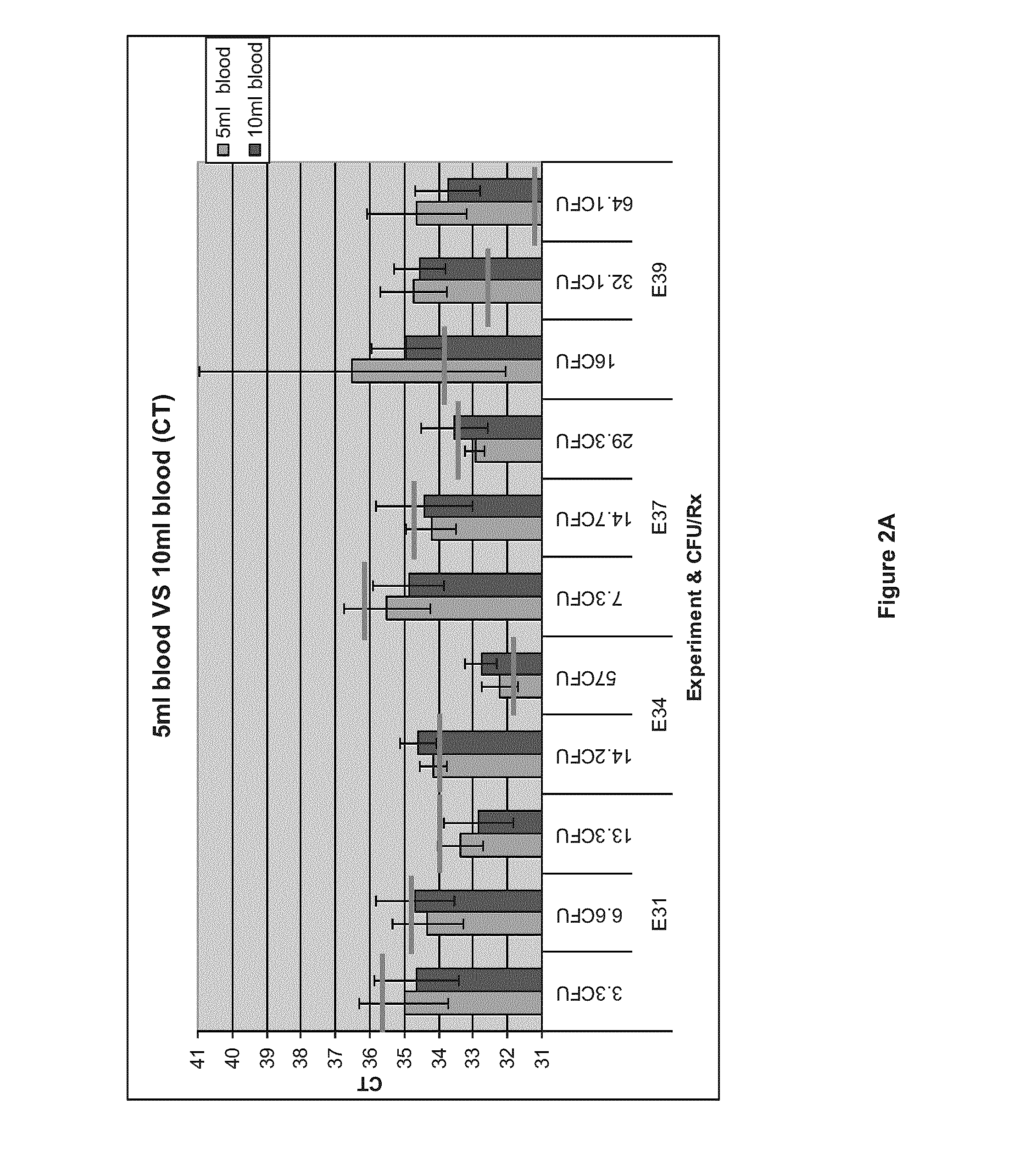
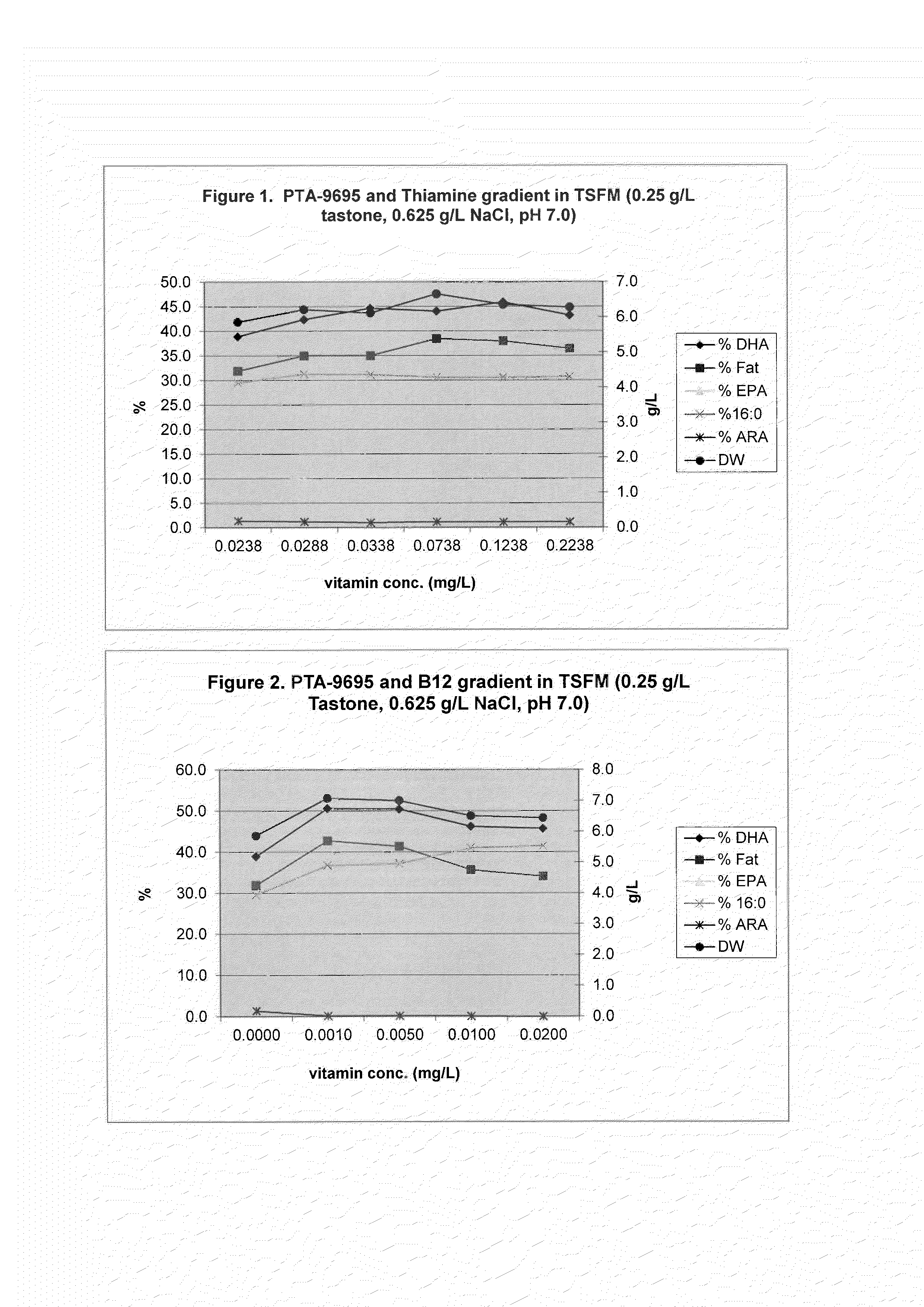
Patents
Literature
111 results about "Isolate - microorganism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for isolating and culturing unculturable microorganisms
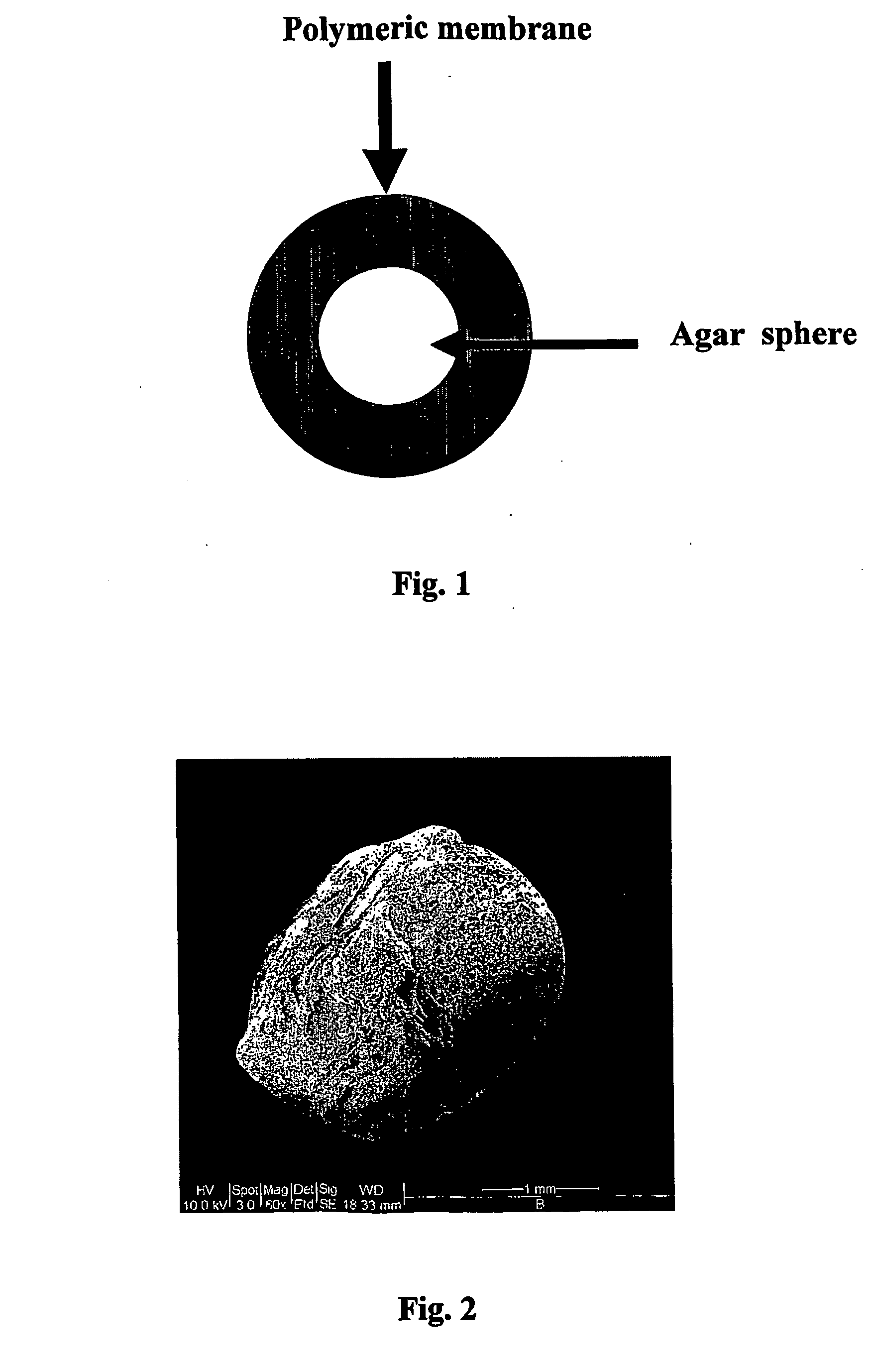
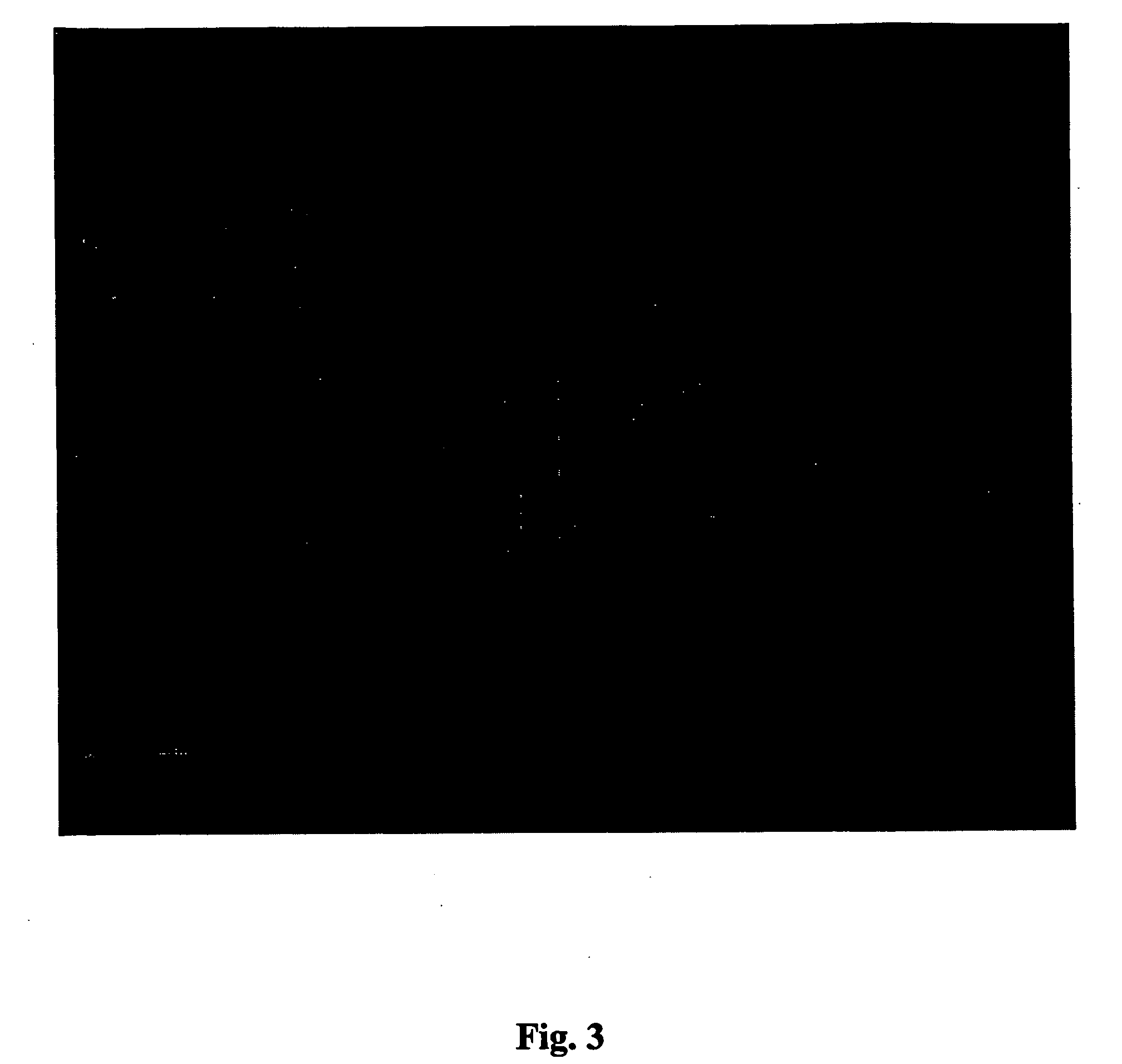
The invention provides a method for isolating and culturing a previously unculturable microorganism, which comprises: (i) collecting a sample from an environmental source; (ii) counting / estimating the number of microorganisms in the sample; (iii) diluting the sample in an appropriate medium; (iv) adding a gelating agent such as to entrap one or more microorganisms within a sphere of the gelating agent; (v) coating the spheres containing the entrapped microorganism(s) with a natural or synthetic polymer to form a polymeric membrane; (vi) incubating the coated spheres in the original environment for an appropriate time; (vii) cutting the spheres and scanning for microorganisms colonies; and (viii) isolating the microorganisms, and repeating steps (iii) to (vii) until a pure clone of said previously unculturable microorganism is obtained.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Storage and delivery of micro-organisms
InactiveUS20030165472A1Improve abilitiesEasy to storeBiocideAnimal watering devicesBiotechnologyOrganism
We describe a method of delivering a micro-organism to an animal, the method comprising providing a formulation comprising a micro-organism suspended in or on a matrix; providing a feed stream for the animal; detaching micro-organisms from the matrix; and entraining detached micro-organisms into the feed stream. An apparatus for delivering a micro-organism to an animal is also described.
Owner:UUTECH
Microbial concentration system
InactiveUS20050054506A1Collection of sample efficientEfficient collectionWithdrawing sample devicesLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringIsolate - microorganism
A centrifuge separation chamber of particular use for separating microbes. The chamber has an upwardly flared conical shape, and a sample collecting groove at its widest point. Sample is collected in the sample groove as the chamber spins. When slowed to a stop, the supernatant sinks to the bottom of the chamber, leaving the sample in the sample groove where it can be easily accessed.
Owner:BRADLEY BRUCE J
Systems and methods for the isolation and identification of microorganisms from hydrocarbon deposits
InactiveUS20060223160A1Easy extractionPromote recoveryBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroaerophileGenetic Materials
The present invention provides systems and methods to isolate microorganisms and optionally their genetic material. The isolation of microorganisms is conducted under anaerobic or other similar conditions to facilitate the preparation of microorganisms that are anaerobes, whether obligate or facultative, as well as microaerophiles. In an alternative format, the isolation of microorganisms is from a carbonaceous substrate which typically hinders or retards isolation therefrom.
Owner:LUCA TECH
Process to increase the bioleaching speed of ores or concentrates of sulfide metal species, by means of continuous inoculation with leaching solution that contains isolated microorganisms, with or without presence of native microorganisms
ActiveUS20080127779A1Decrease ore bioleaching timeImprove bioleaching conditionSolvent extractionGold compoundsTailings damPotassium
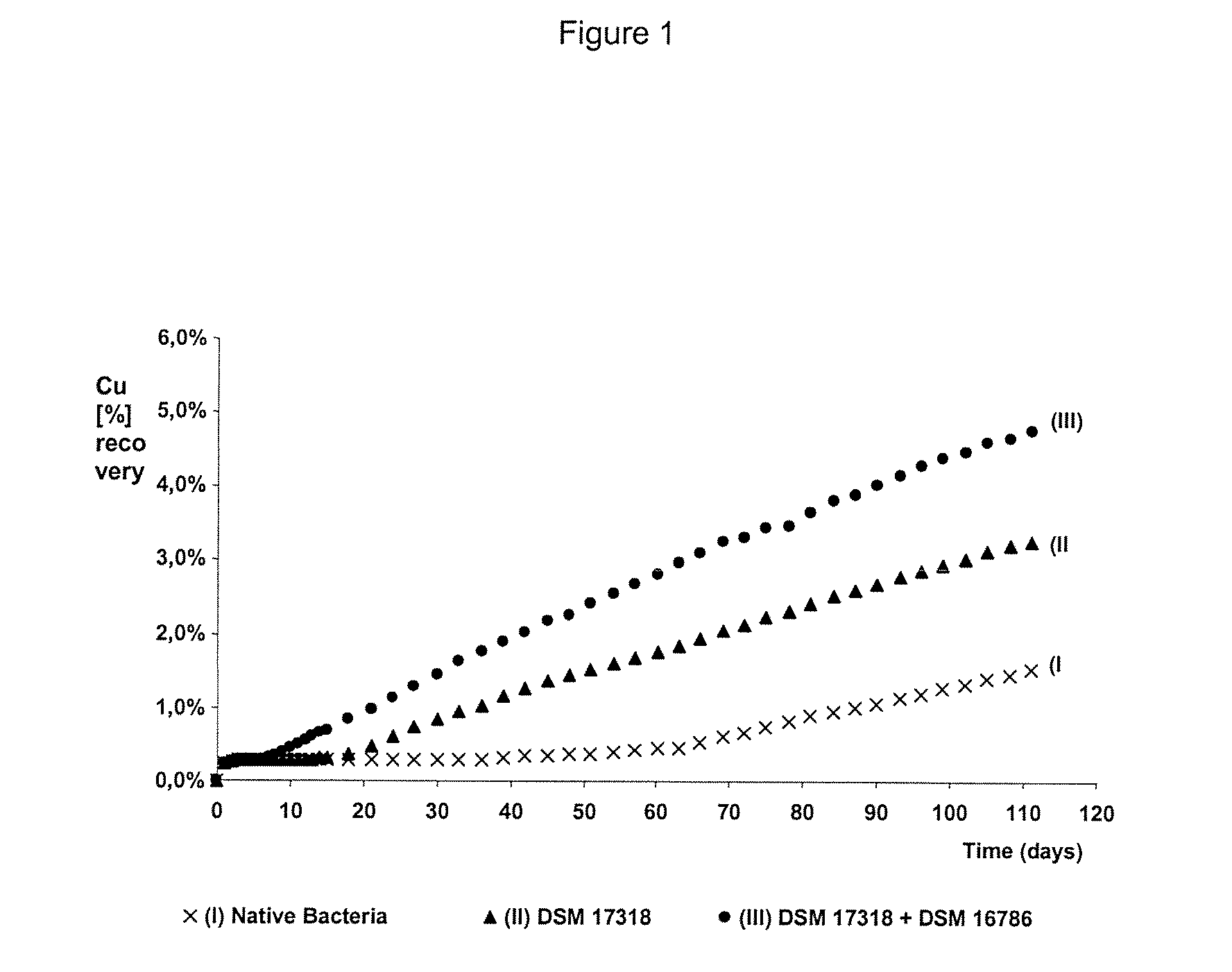
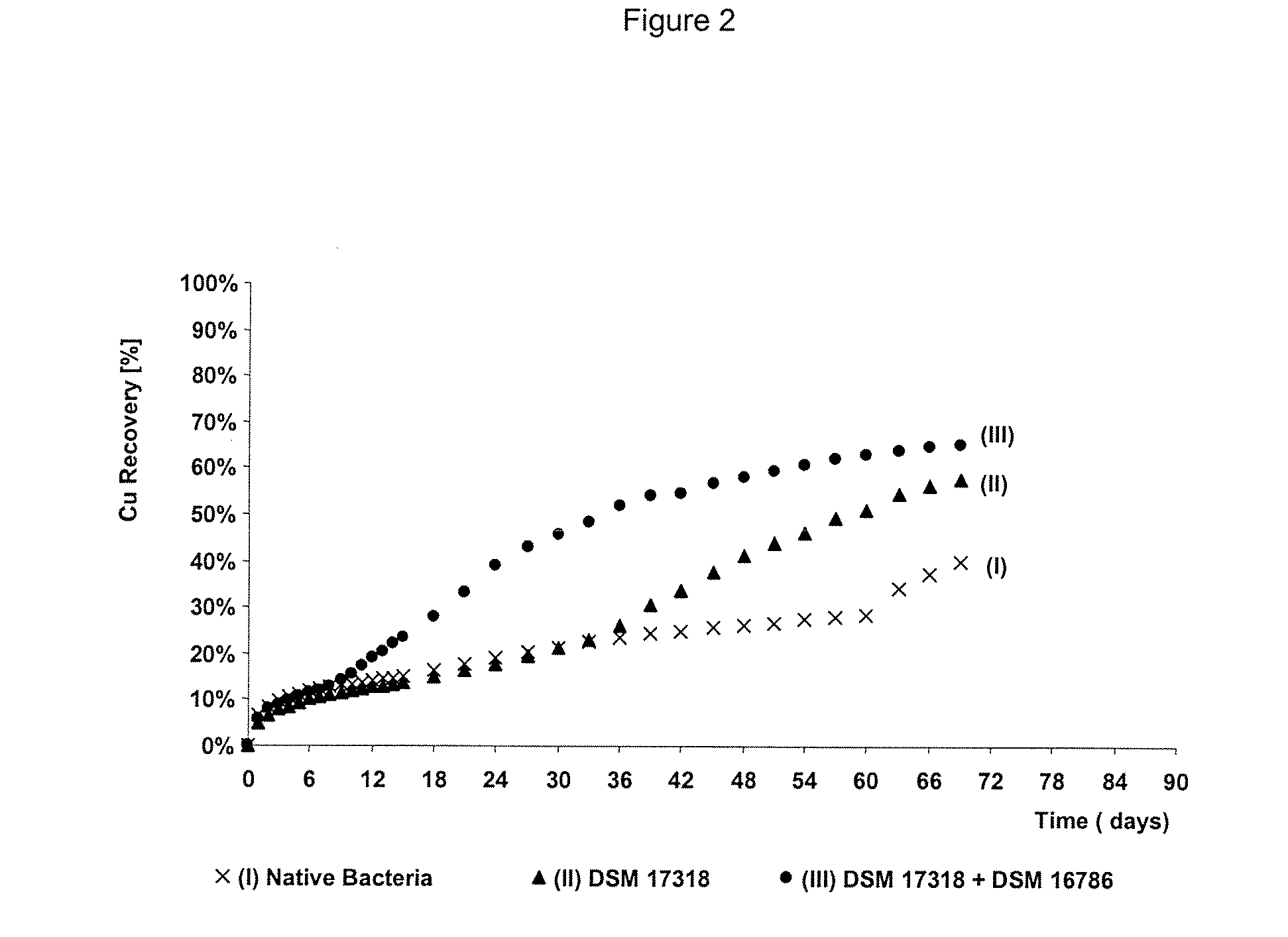
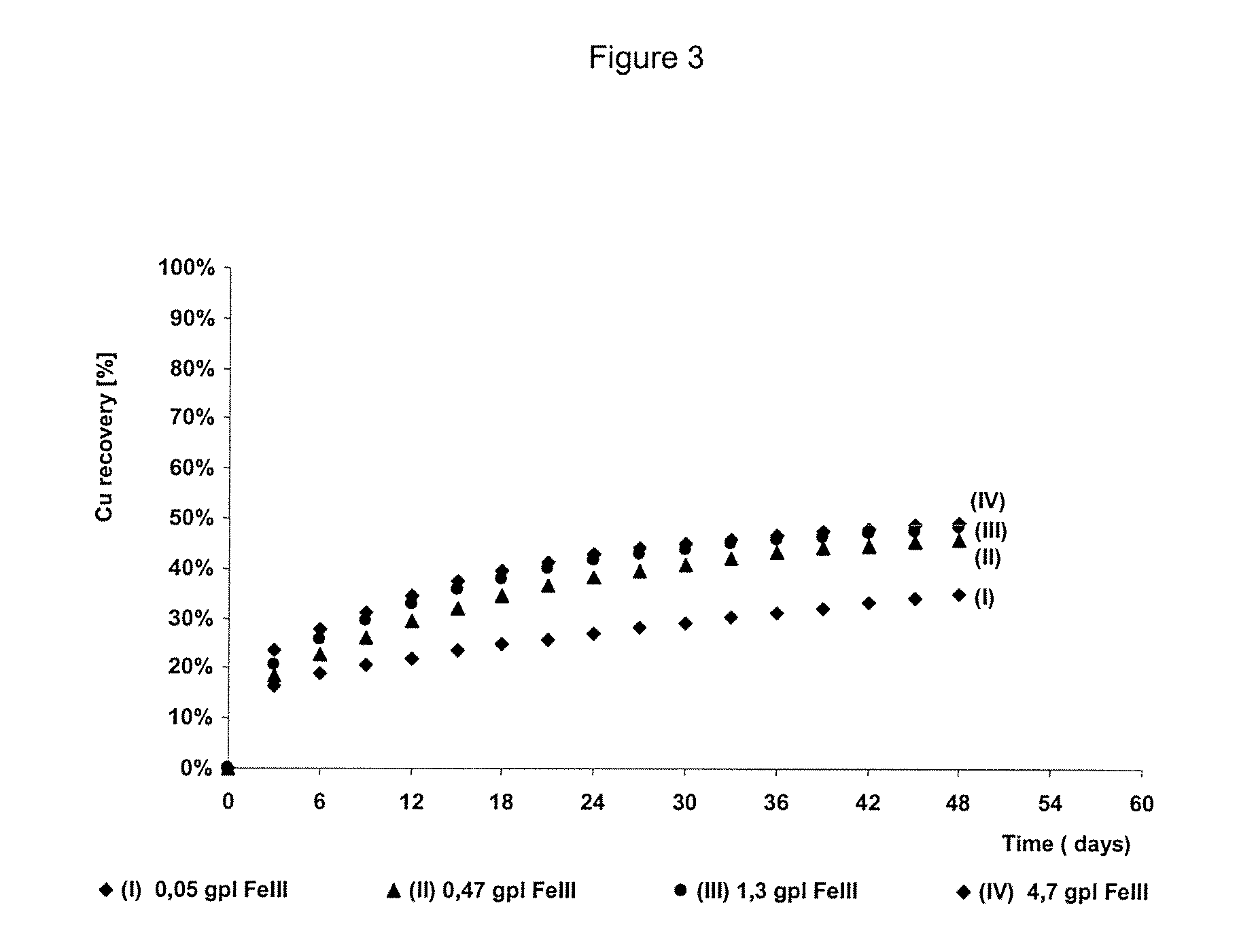
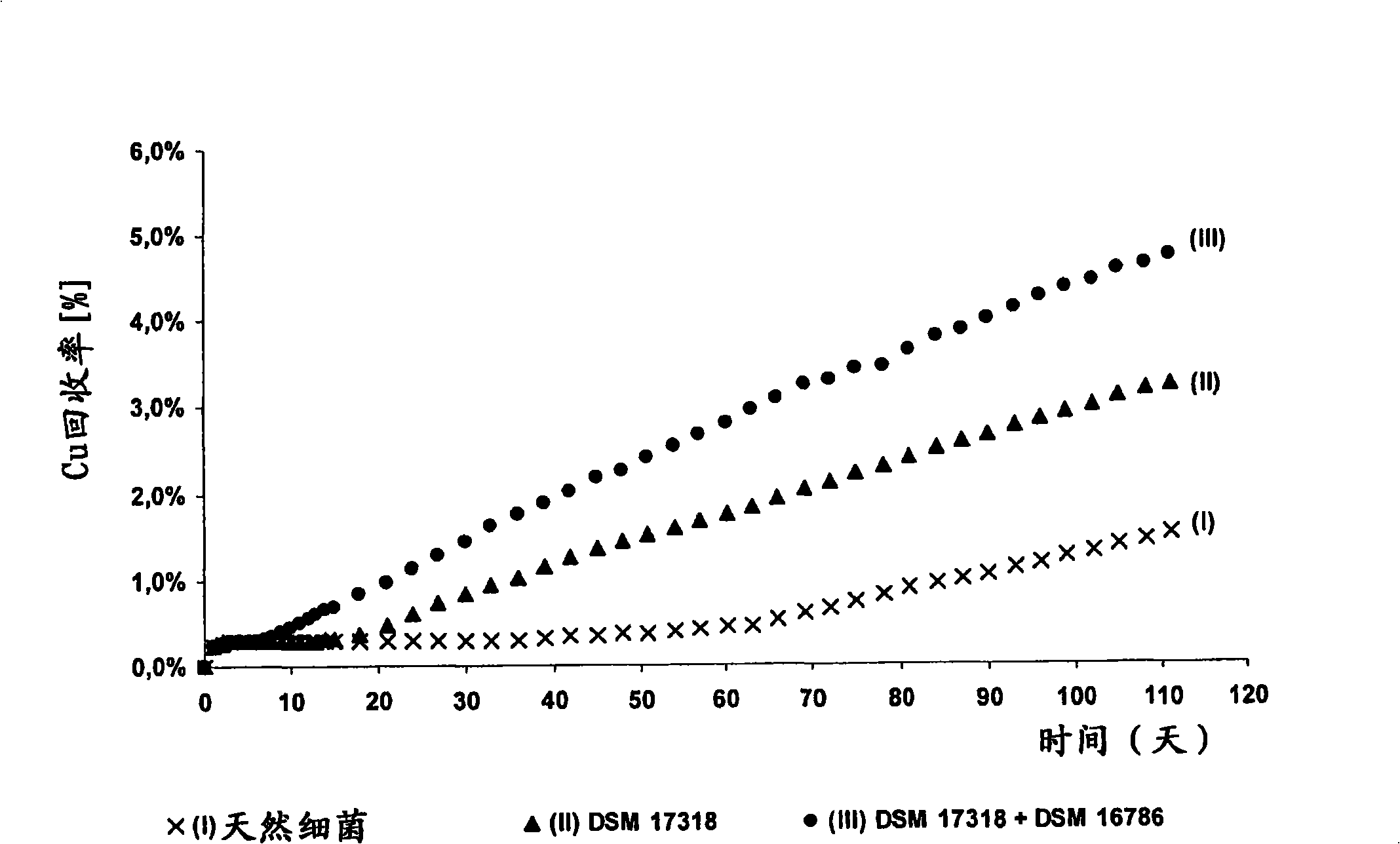
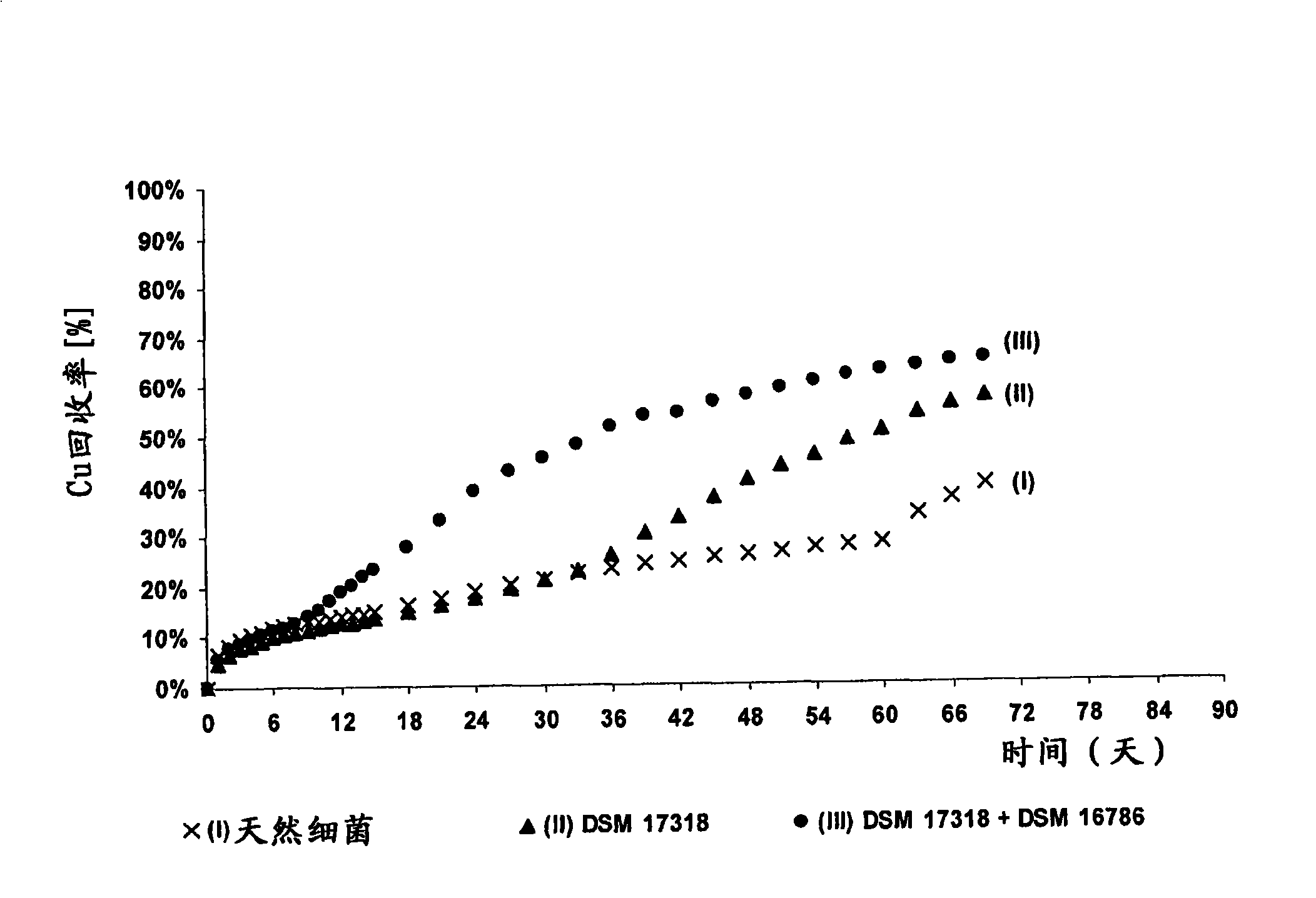
The invention publishes a process to increase the bioleaching speed of ores or concentrates of sulfide metal species in heaps, tailing dams, dumps, or other on-site operations. The process is characterized by the continuous inoculation of the ores or concentrates with isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans type, together with isolated microorganisms of the Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans type, with or without native microorganisms, in such a way that the total concentration of microorganisms in the continuous inoculation flow is of around 1×107 cells / ml to 5,6×107 cells / ml. In particular, the invention publishes the continuous inoculation of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318 together with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786 microorganisms, or with other native microorganisms at a concentration higher than 5×107 cells / ml. In addition to the inoculation of isolated bacteria, the invention includes the addition of oxidizing agents such as the ferric ion produced externally, together with nutrients in the shape of salts of ammonium, magnesium, iron, potassium, as well as air enriched continuously with carbon dioxide to promote bacterial action in the bioleaching process of ores or concentrates.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Process for isolating microorganisms from samples and system, apparatus and compositions therefor
InactiveUS20100144005A1Lessen and eliminate effectEasy to moveBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIsolate - microorganismParticle physics
A process for isolating microorganisms from samples, particularly Shigella spp. from food samples, and a system, apparatus and composition therefor are provided. Magnetic particles are used to capture microorganisms and a system having separate magnetically-based apparatuses for collecting, concentrating and retrieving is used to isolate the magnetic particles having bound microorganisms. The apparatus for concentrating magnetic particles utilizes a small magnet assisted by vibration to concentrate collected particles at a localized region on the bottom of a container. The process, system and apparatus of the present invention are simple and inexpensive providing improved magnetic particle recovery adaptable to large scales.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF HEALTH
Methods, kits and systems for processing samples
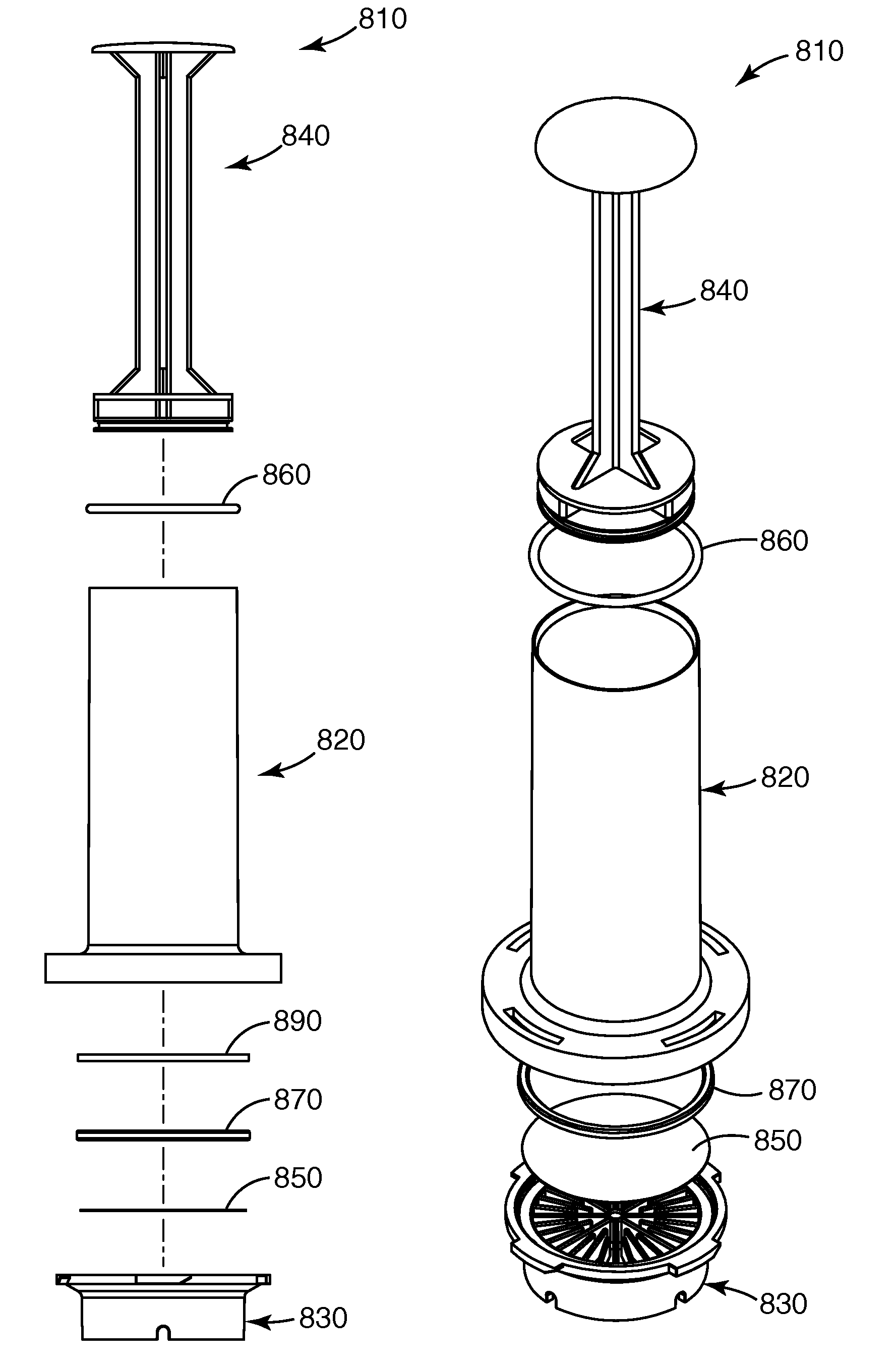
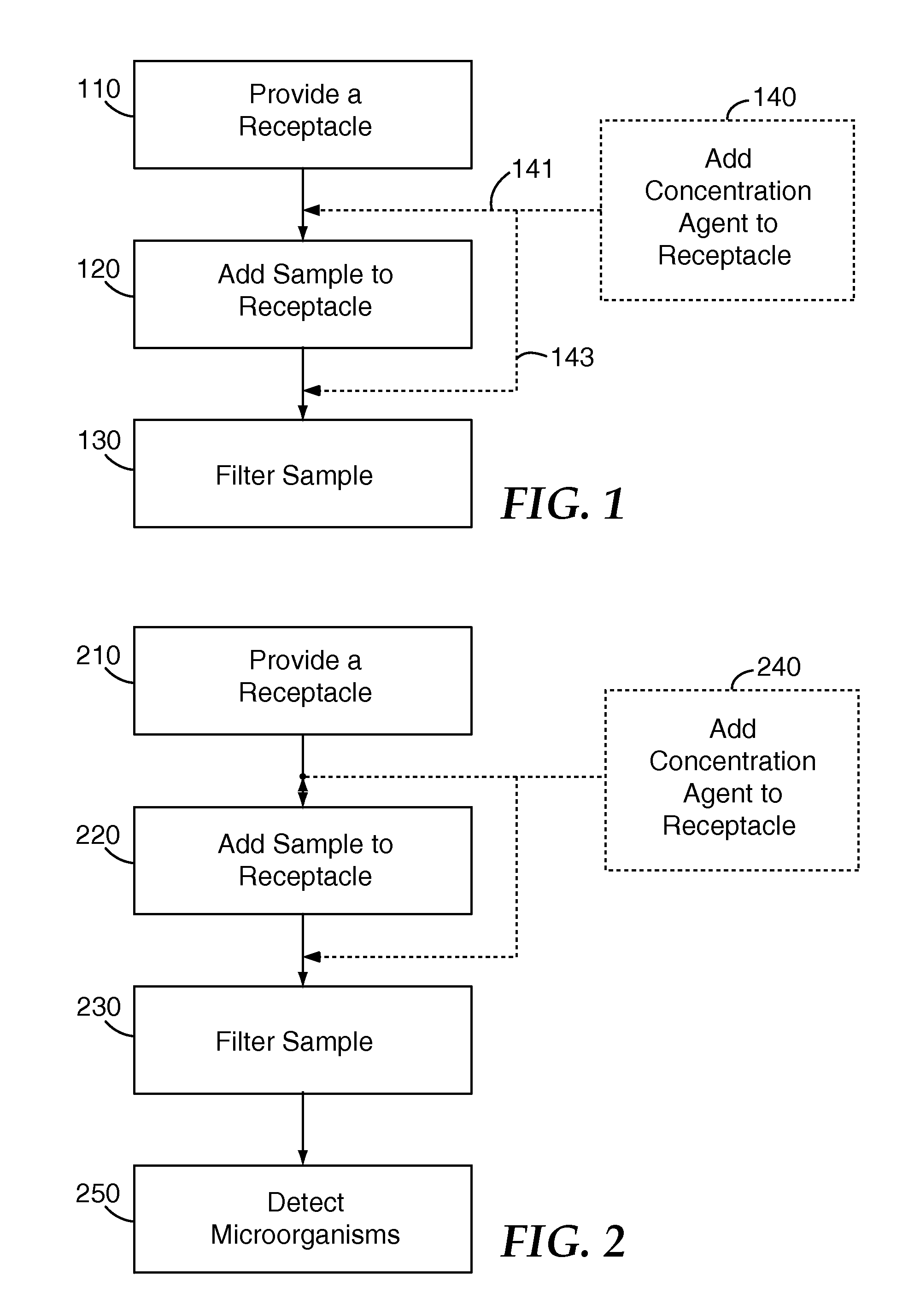
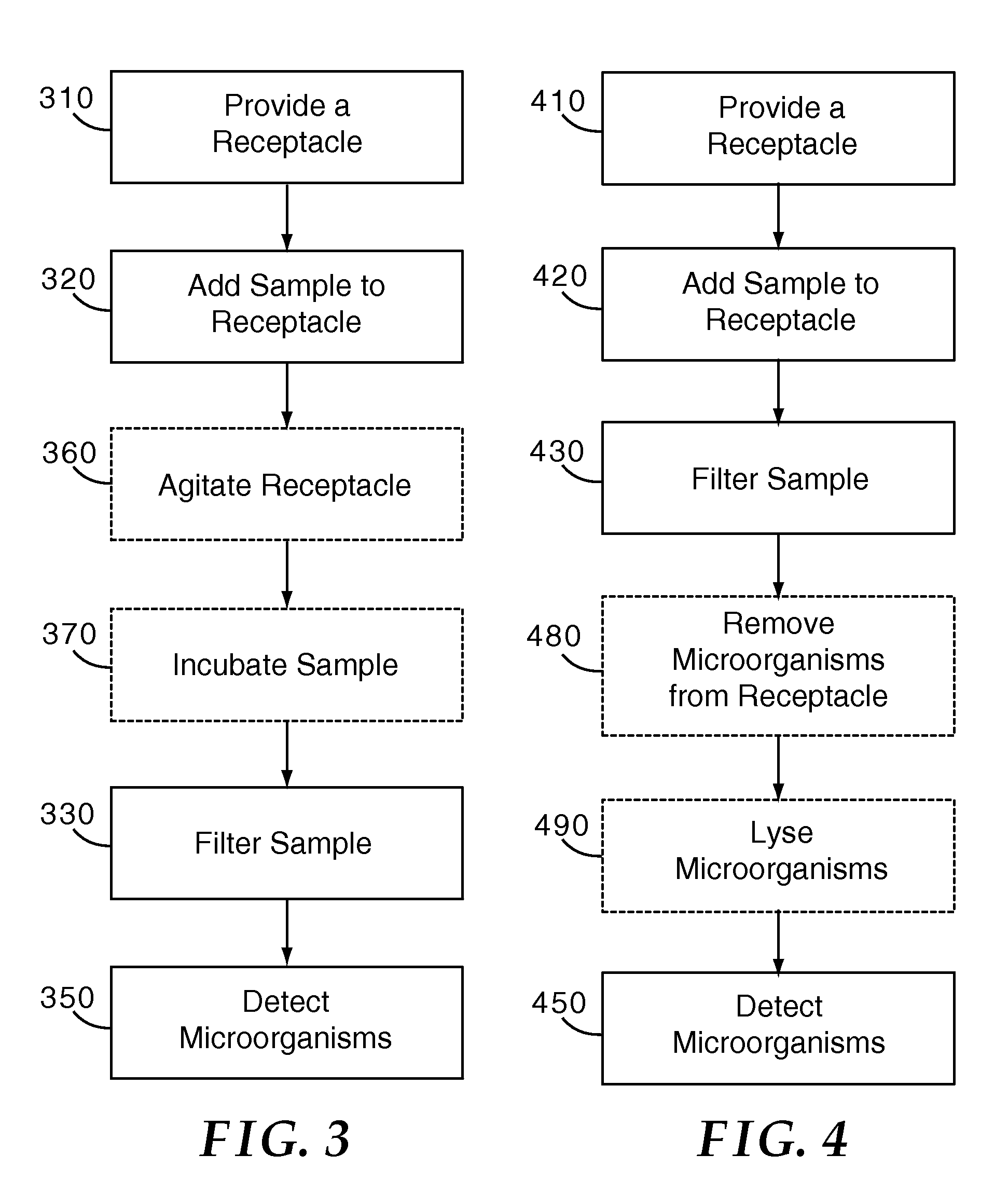
A method for isolating microorganisms from a sample, the sample including sample matrix and microorganisms, the method including the steps of providing a receptacle, the receptacle configured to allow filtering of the sample and to reversibly contain the sample and a concentration agent; adding the sample to the receptacle, wherein a microorganism-bound composition will be formed in the receptacle, the microorganism-bound composition including concentration agent-bound microorganisms and sample matrix; and filtering the microorganism-bound composition through a filter to collect the concentration agent-bound microorganisms on the filter, wherein the filter has an average pore size that is greater than the average size of the microorganisms. Kits and systems are also disclosed herein.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
High-throughput microbial culturing
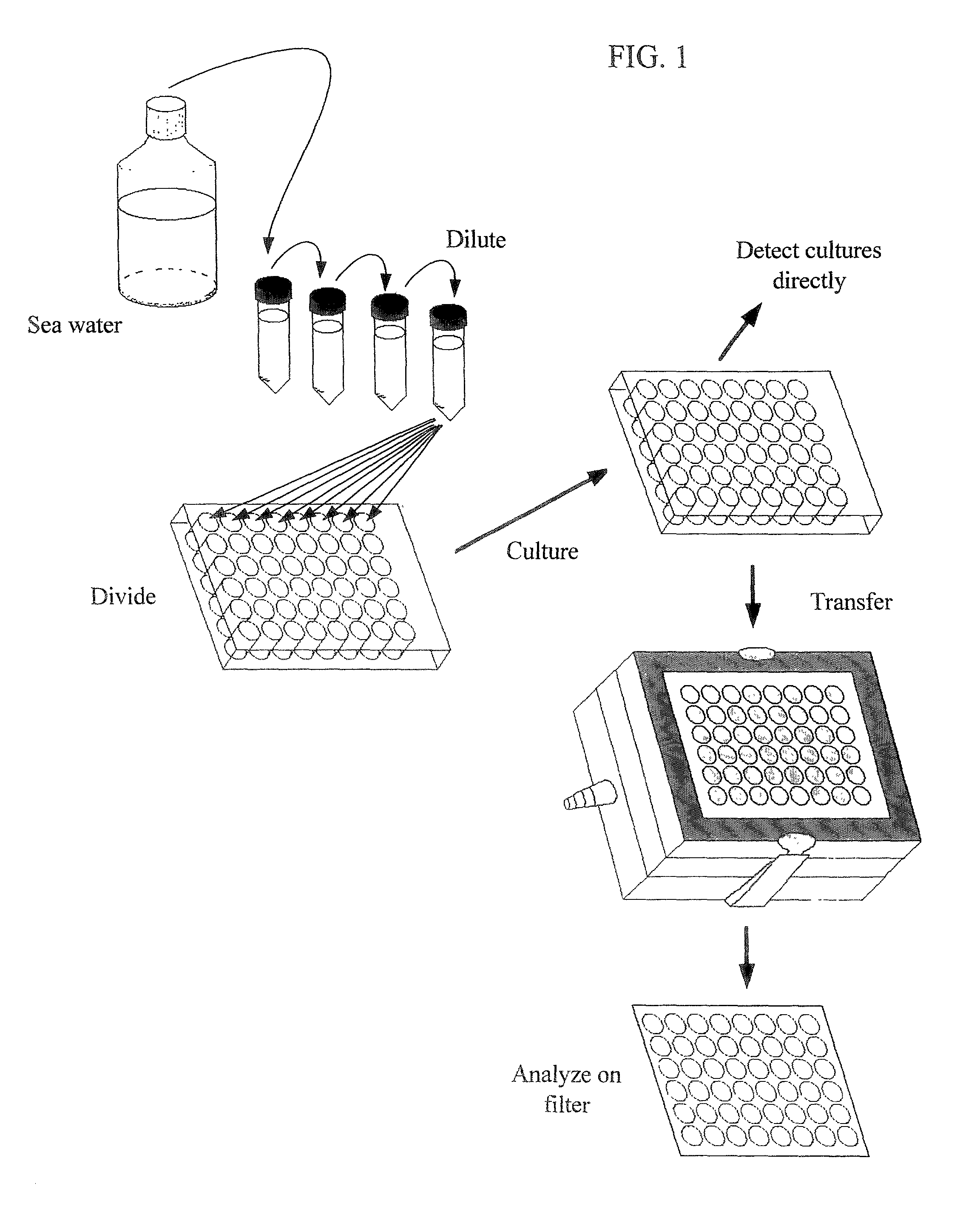
InactiveUS6951714B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrobiologyIsolate - microorganism
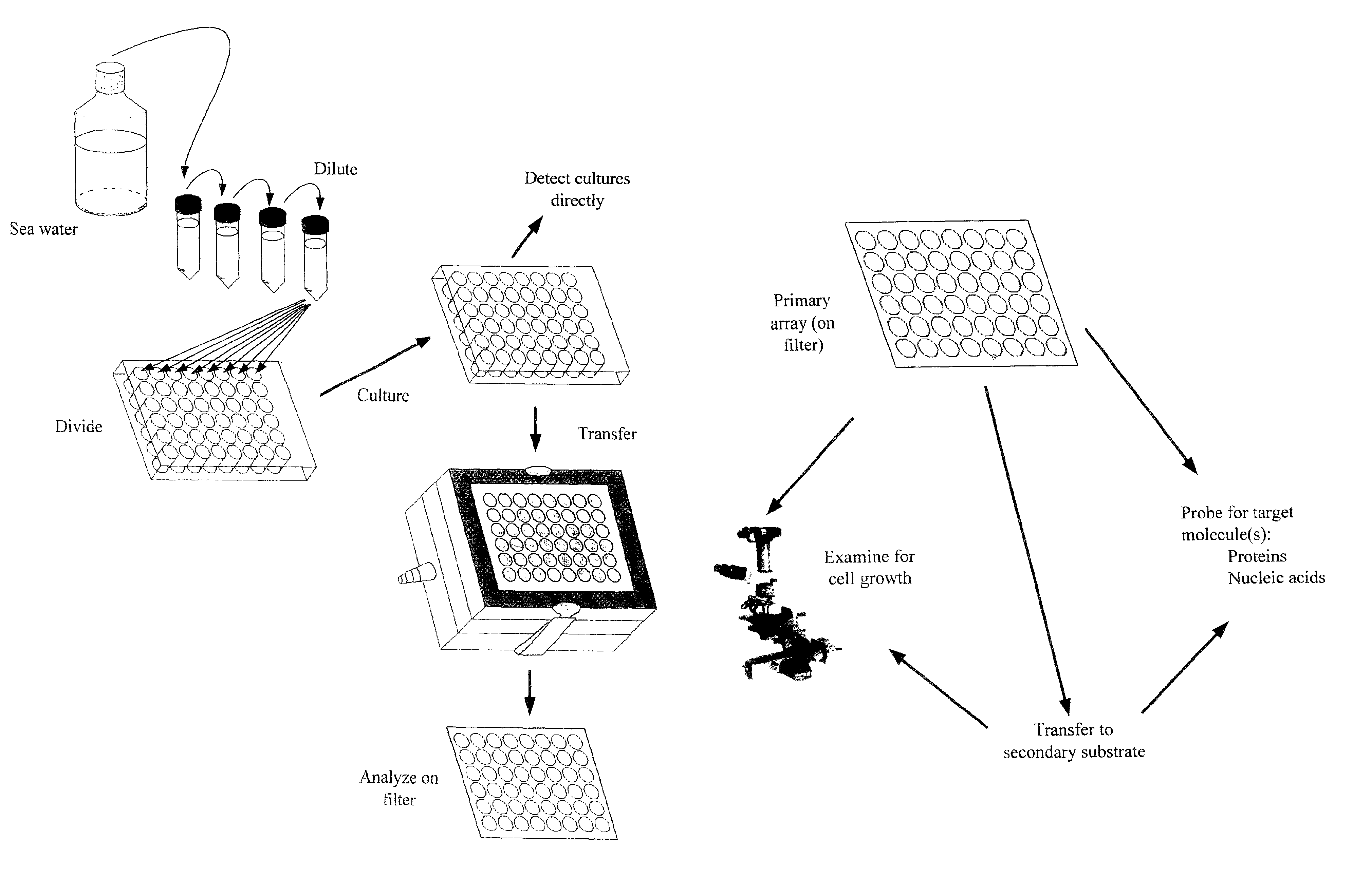
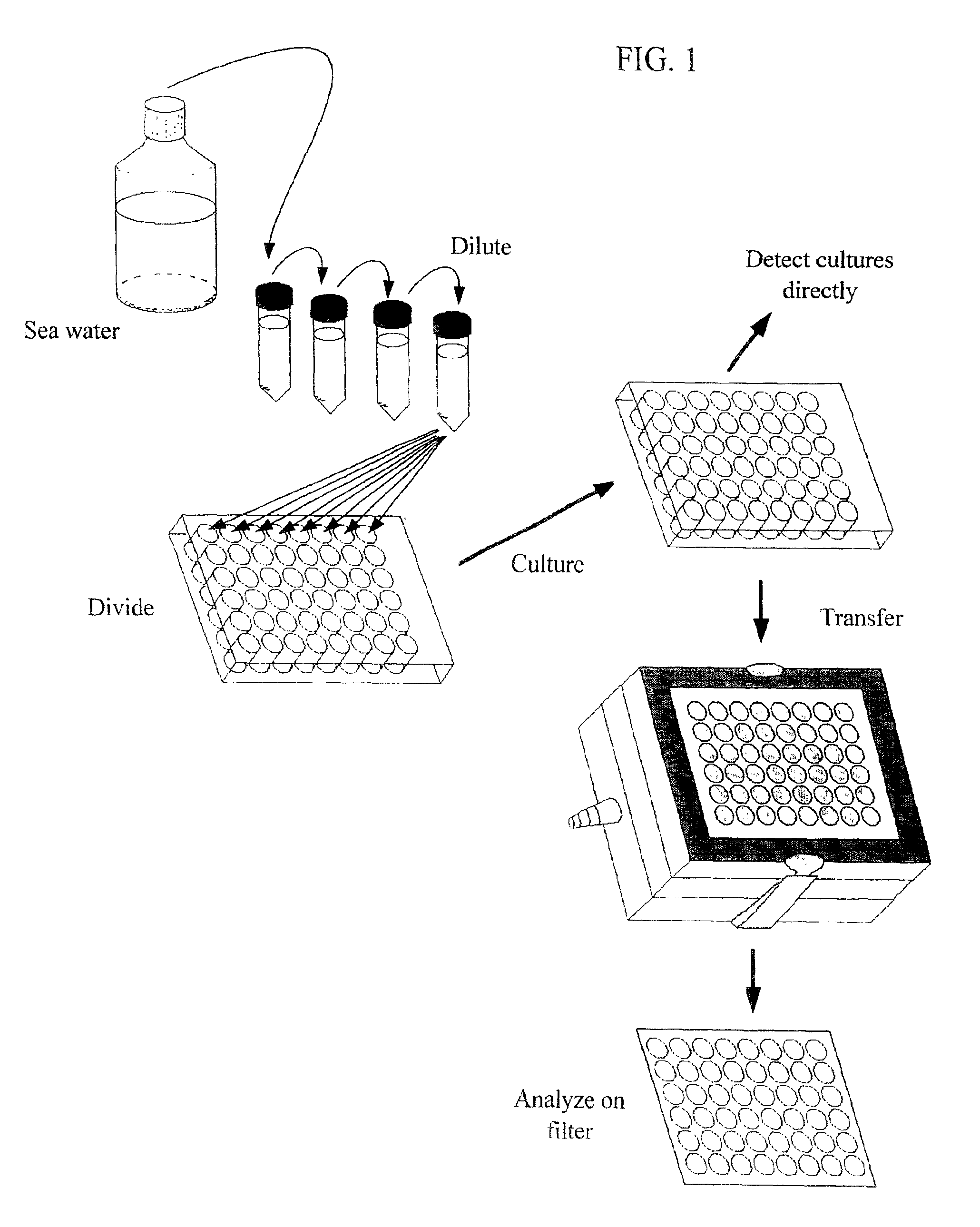
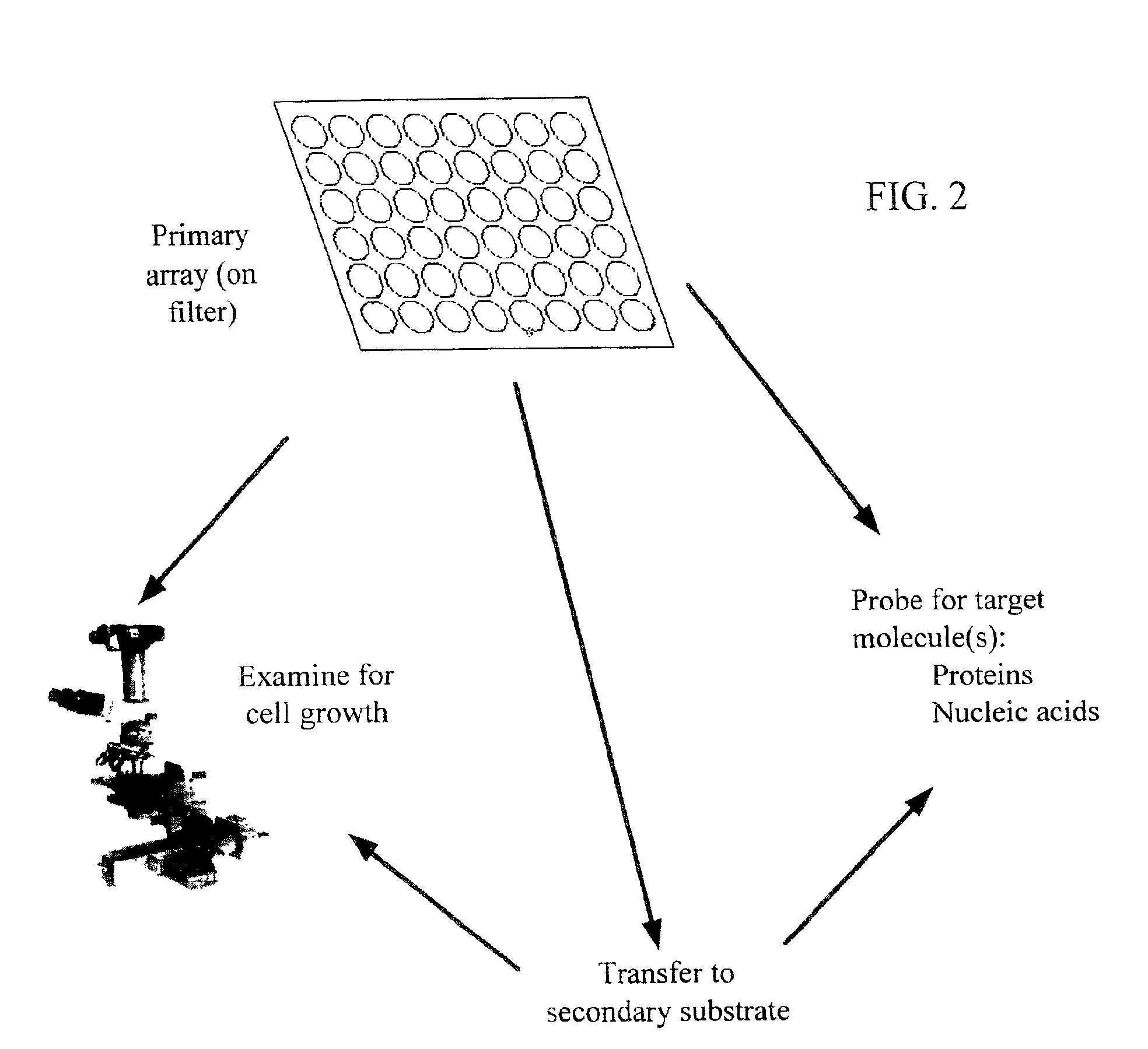
Methods for isolating microbial species, particularly previously uncultured species, from non-laboratory source environments (such as soil, freshwater, seawater, etc.) are disclosed. These methods can include the use of cultures in arrays, and cells deposited on solid surfaces in arrays for detection, and flow cytometry and / or cell sorting and / or dilution cultures.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
Reactor for the culture, biooxidation of solutions and/or large-scale propagation of isolated microorganisms and/or native microorganisms that are useful in ore leaching
InactiveUS20080102514A1Reducing average phasingIncrease concentrationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrobiologyIsolate - microorganism
The invention publishes a reactor and method for the culture, biooxidation of cations in solution and / or large-scale propagation of jointly isolated microorganisms, with or without native microorganisms that are useful in sulfide metal ore bioleaching. The invention particularly publishes a reactor for the large-scale culture and / or propagation of an association of Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318 isolated microorganisms jointly with Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786 with or without the presence of other microorganisms.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Agriculturally beneficial microbes, microbial compositions, and consortia
ActiveUS20180020671A1Improve crop performanceClosing worldwide yield gapBiocideBacteriaPlant traitsCrop species
Owner:BIOCONSORTIA
Methods and kits for isolating microorganisms from culture
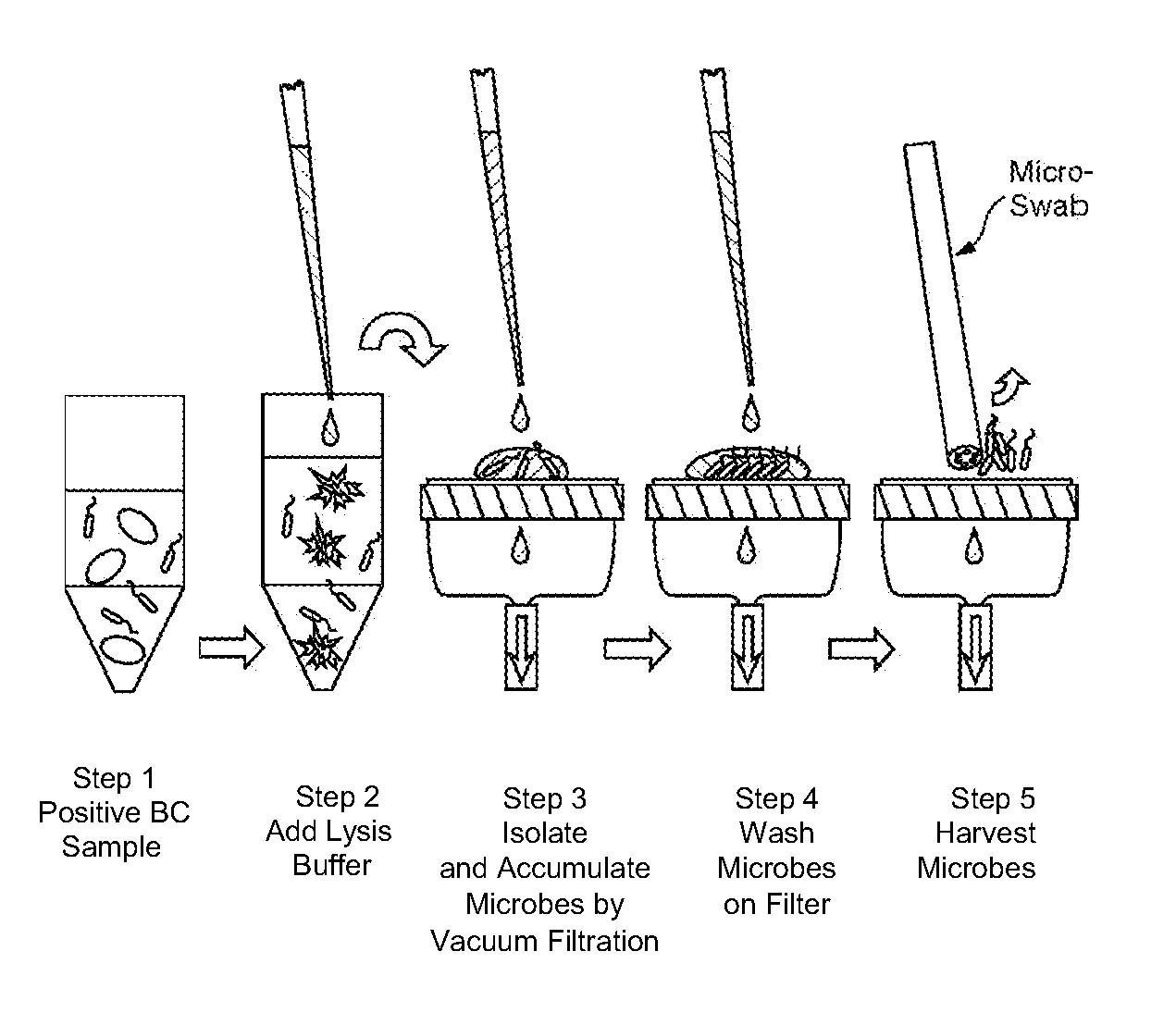
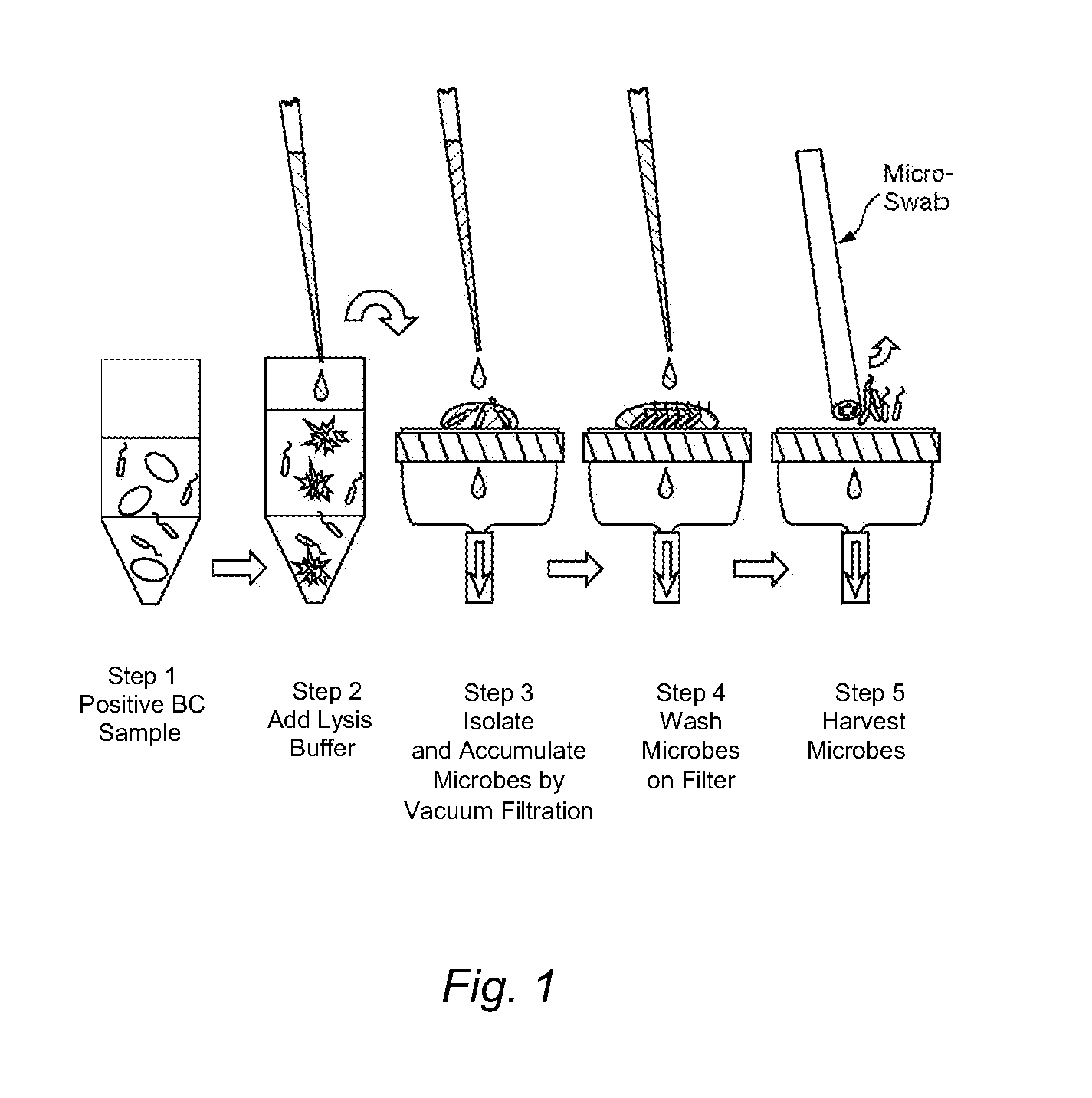
ActiveUS20130045532A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest sampleFiltration
The present invention is directed to methods and kits for separating, accumulating, characterizing and / or identifying microorganisms known to be present or that may be present in a test sample. The method of the invention comprises optional lysing non-microorganism cells and / or particulates that may be present in a test sample, followed by a subsequent filtration step for isolation and / or accumulation of microorganisms. The kit of the present invention may comprise at least one filter membrane or an integrated filtration and sample transfer device for isolation and / or accumulation of microorganisms.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX INC
High-throughput microbial culturing
Methods for isolating microbial species, particularly previously uncultured species, from non-laboratory source environments (such as soil, freshwater, seawater, etc.) are disclosed. These methods can include the use of cultures in arrays, and cells deposited on solid surfaces in arrays for detection, and flow cytometry and / or cell sorting and / or dilution cultures.
Owner:THE STATE OF OREGON ACTING BY & THROUGH THE OREGON STATE BOARD OF HIGHER EDUCATION ON BEHALF OF OREGON STATE UNIV
Probiotic compositions and methods
Owner:MANKOVITZ ROY
Eicosapentaenoic acid-producing microorganisms, fatty acid compositions, and methods of making and uses thereof
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Agriculturally beneficial microbes, microbial compositions, and consortia
The disclosure relates to isolated microorganisms-including novel strains of the microorganisms-microbial consortia, and agricultural compositions comprising the same. Furthermore, the disclosure teaches methods of utilizing the described microorganisms, microbial consortia, and agricultural compositions comprising the same, in methods for imparting beneficial properties to target plant species. In particular aspects, the disclosure provides methods of increasing desirable plant traits in agronomically important crop species.
Owner:生物联盟有限公司
Detection and characterization of microorganisms
InactiveUS6911312B2Quick distinctionRapid discovery of new infectious agentsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFluorescenceRapid identification
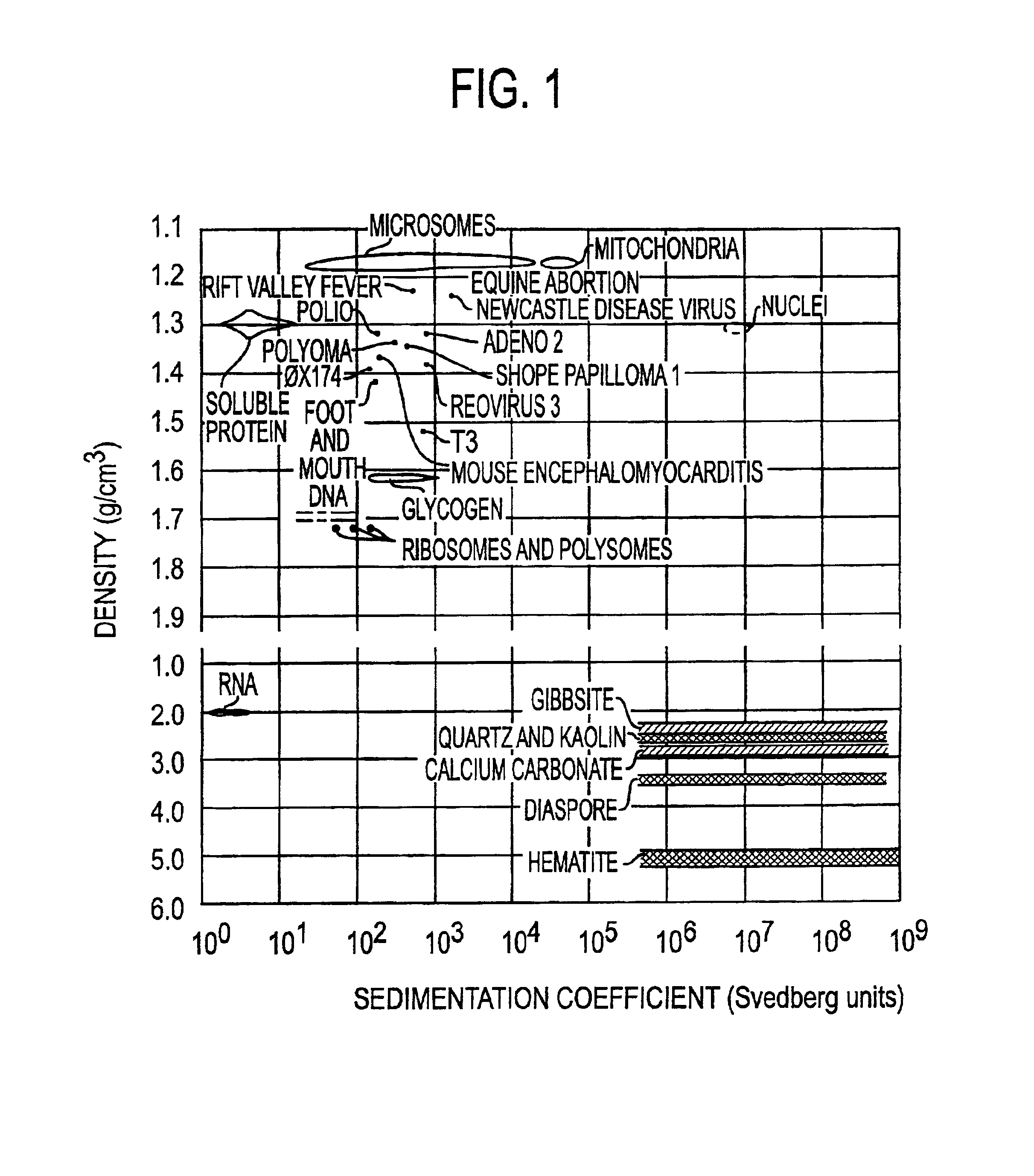
A method for separating microorganisms, especially infectious agents, from a mixture by two dimensional centrifugation on the basis of sedimentation rate and isopycnic banding density, for sedimenting such microorganisms through zones of immobilized reagents to which they are resistant, for detecting banded particles by light scatter or fluorescence using nucleic acid specific dyes, and for recovering the banded particles in very small volumes for characterization by mass spectrometry of viral protein subunits and intact viral particles, and by fluorescence flow cytometric determination of both nucleic acid mass and the masses of fragments produced by restriction enzymes. The method is based on the discovery that individual microorganisms, such as bacterial and viral species, are each physically relatively homogeneous, and are distinguishable in their biophysical properties from other biological particles, and from non-biological particles found in nature. The method is useful for distinguishing infections, for identifying known microorganisms, and for discovering and characterizing new microorganisms. The method provides very rapid identification of microorganisms, and hence allows a rational choice of therapy for identified infectious agents. A particularly useful application is in clinical trials of new antibiotics and antivirals, where it is essential to identify at the outset individuals infected with the targeted infectious agent.
Owner:LARGE SCALE PROTEOMICS
Method and Apparatus for Automatically Isolating Microbial Species
InactiveUS20080318310A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringBiochemistry
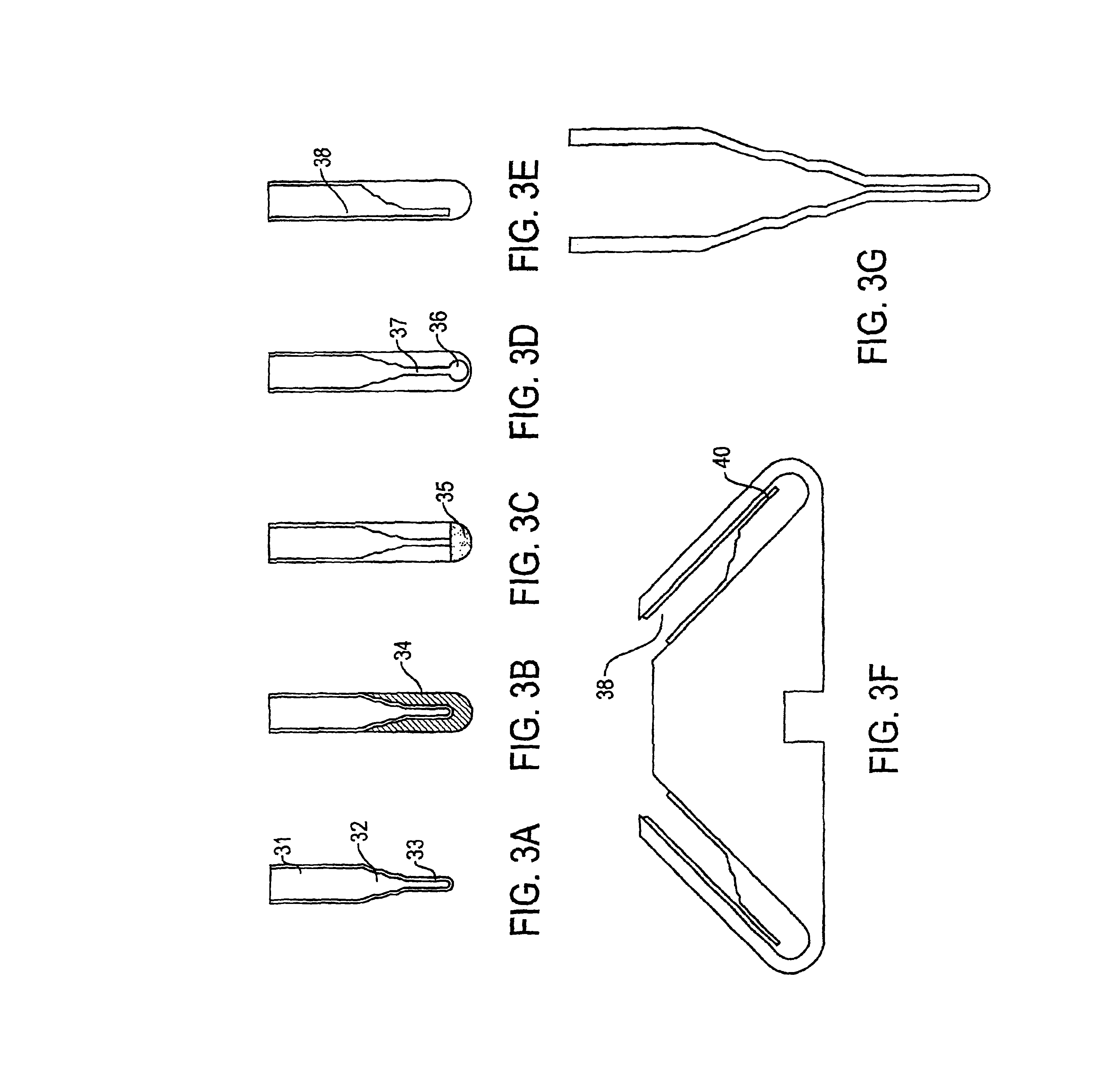
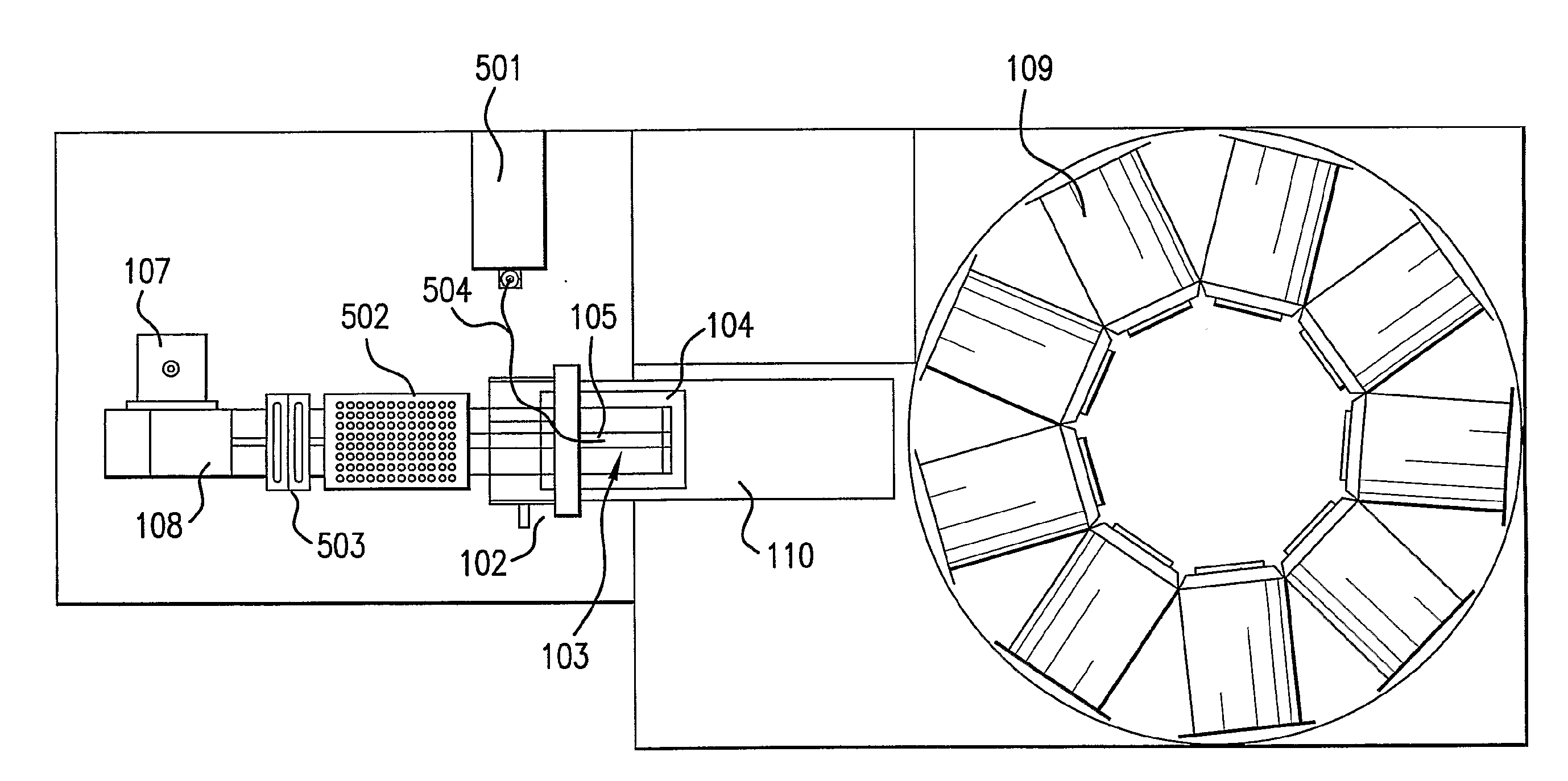
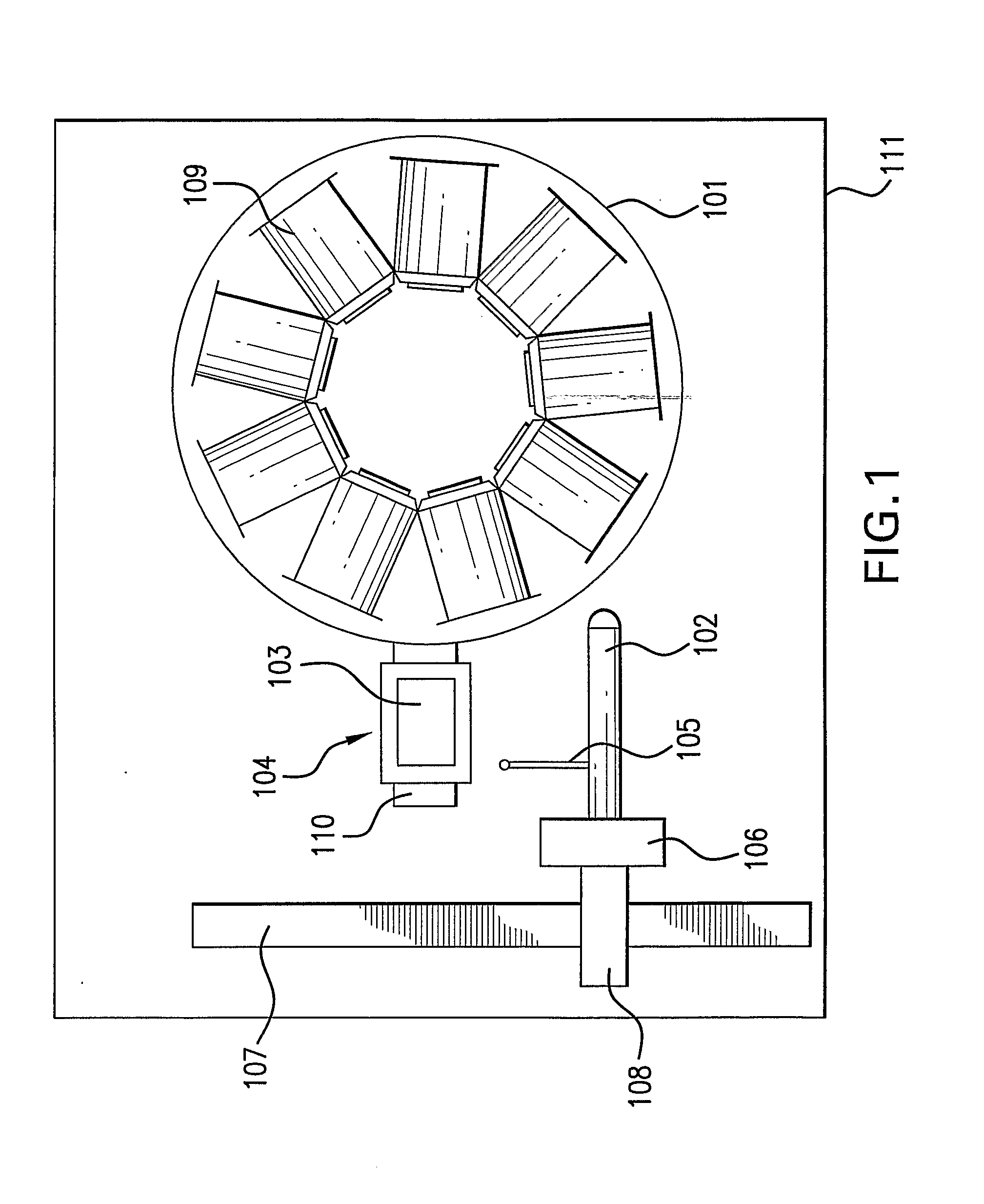
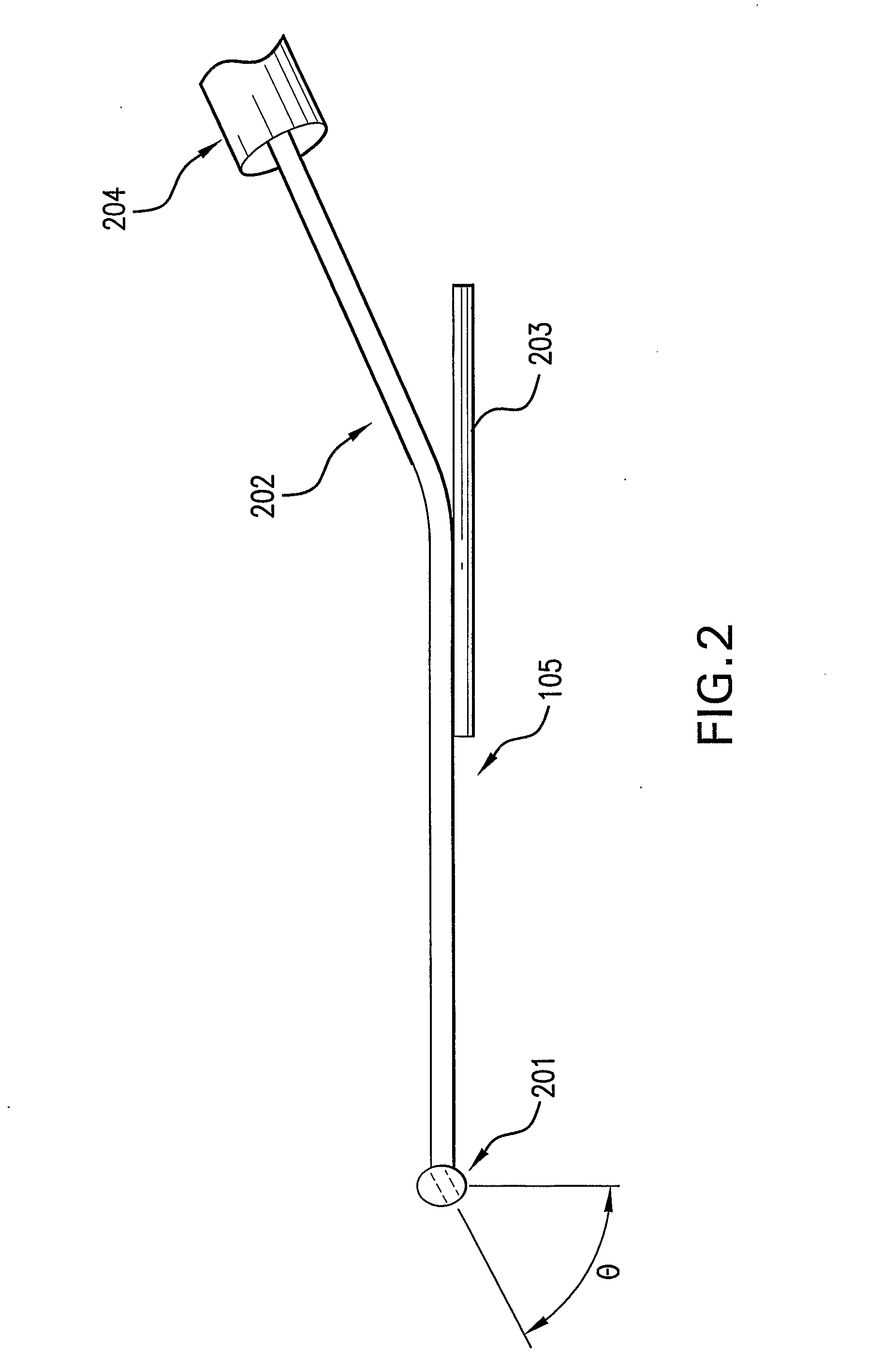
This invention relates to an apparatus for streaking a sample on a media-coated (agar) plate in a predefined pattern utilizing a plate carousel system to house and retrieve a plate to a fixed location, a streaking mechanism having a floating stylus having a tip capable of gliding over the agar surface and depositing a sample onto the surface of the agar, a sample dispensing system and an optional wash station.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Process for Treating Wastewater
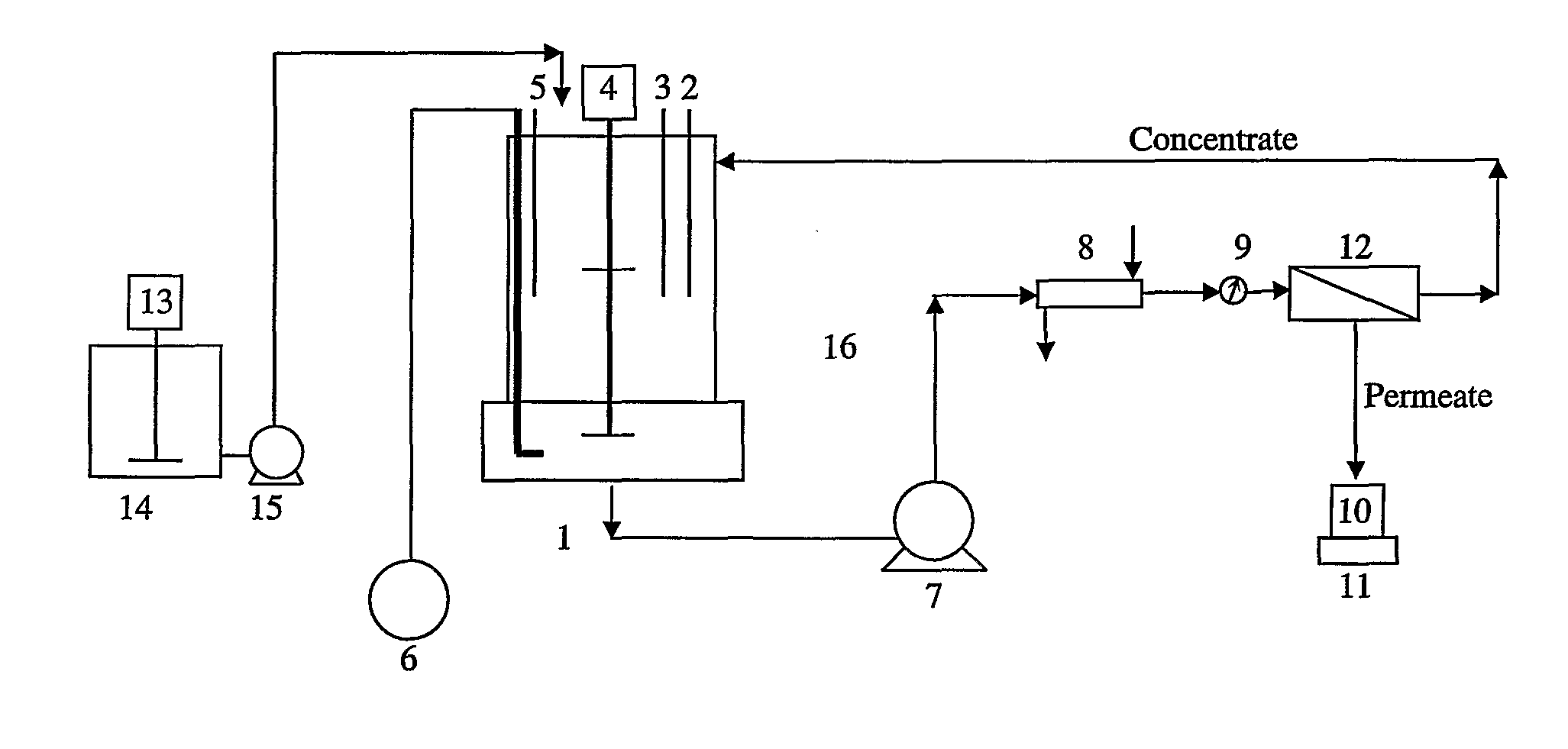
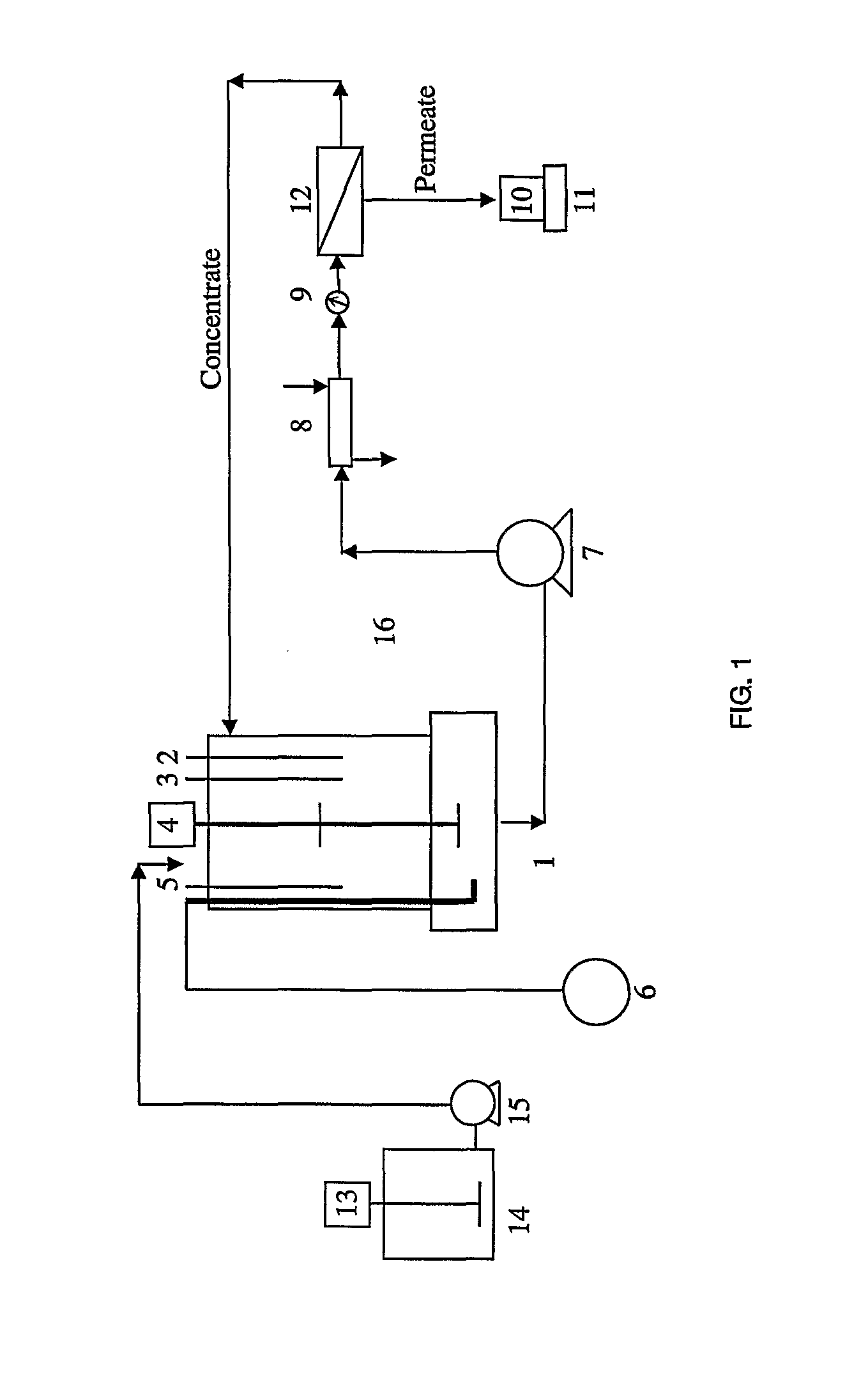
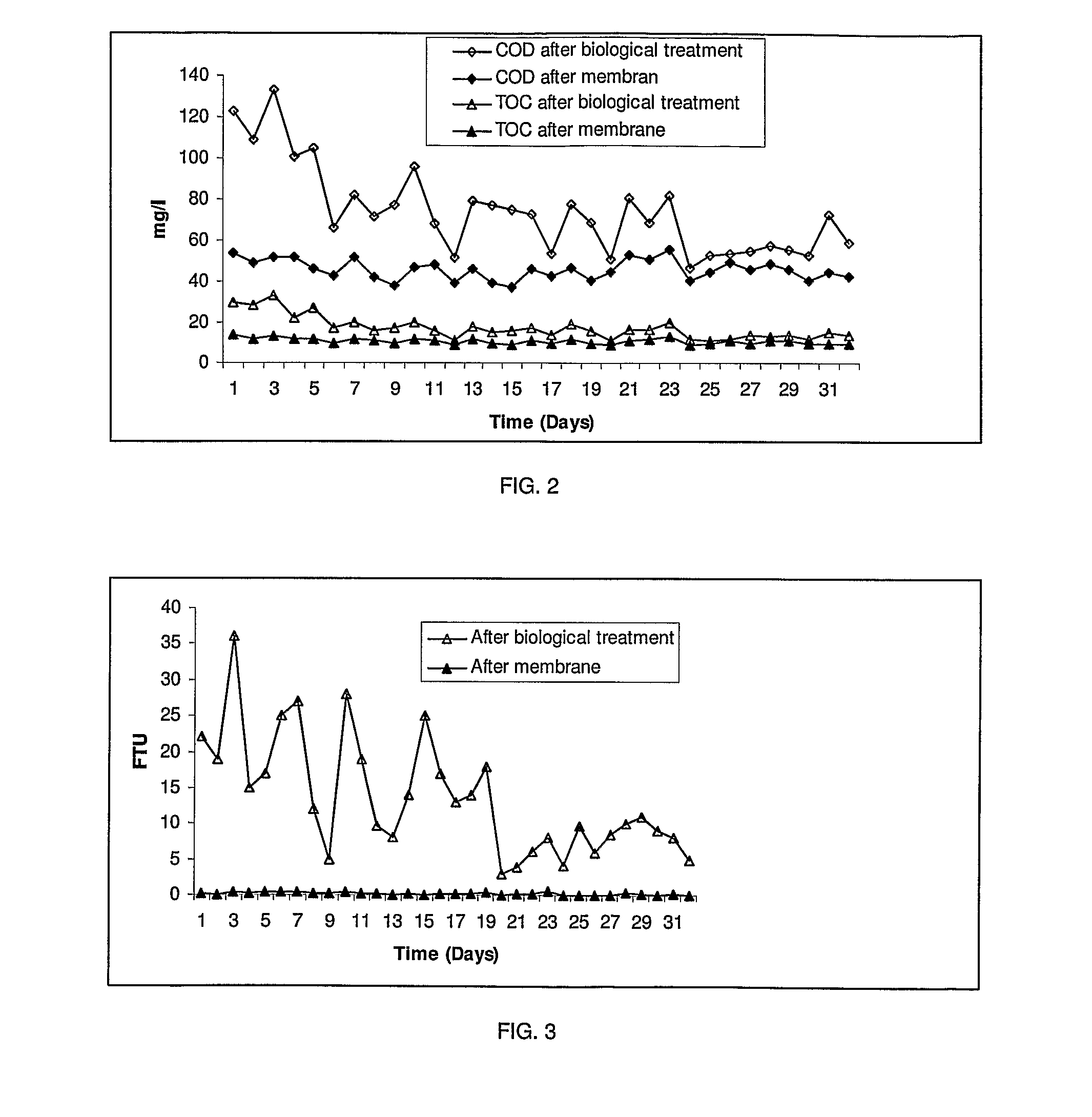
InactiveUS20110180475A1Waste water treatment from quariesTreatment using aerobic processesWastewaterIsolate - microorganism
The present invention relates to a process for treating wastewater. The process includes the steps of (a) mixing different constituents of said wastewater inside a container, (b) withdrawing said wastewater from container, (c) feeding said wastewater to a bioreactor, (d) contacting said wastewater with an isolated microorganism or an isolated microorganism consortium, (e) aerating a suspension of said wastewater with said isolated microorganism or said isolated microorganism consortium, (f) withdrawing said suspension of said wastewater with said isolated microorganism or said isolated microorganism consortium from said bioreactor, (g) filtering receiving flow from step (f) to separate a concentrate stream from a permeate stream, (h) returning said concentrate stream to said bioreactor and (i) removing permeate stream.
Owner:UNIVERSITI PUTRA MALAYSIA
Storage and delivery of micro-organisms
InactiveUS20070286844A1Easy to storeImprove abilitiesBiocideBacteria material medical ingredientsBiotechnologyIsolate - microorganism
A method of delivering a micro-organism to an animal, the method comprising providing a formulation comprising a micro-organism suspended in or on a matrix; providing a fee stream for the animal; detaching micro-organisms from the matrix; and entraining detached micro-organisms into the feed stream. An apparatus for delivering a micro-organism to an animal is also described.
Owner:UUTECH
Concentration and enrichment of microbial cells and microbial nucleic acids from bodily fluids
ActiveUS8481265B2Improve concentrationEfficient extractionSugar derivativesBacteriaMicrobial fuel cellMicrobiology
The present invention relates to a method for isolating microorganisms and / or microorganisms nucleic acids from a bodily fluid that may comprise or may be suspected to comprise microorganisms and / or host cells and / or host cells debris. Microorganisms nucleic acids may further be isolated by lysing the isolated microorganisms. The present invention also relates to a method for detecting microorganisms in a bodily fluid. The present invention further relates to a saponin formulation and its use.
Owner:UNIV LAVAL
Method and device for eliminating microbial aerosol in indoor air by using corona discharge
InactiveCN103331209AEasy to cleanEasy to operate and maintainDeodrantsElectric supply techniquesElectricityCorona discharge
The invention discloses a method and a device for eliminating microbial aerosol in indoor air by using corona discharge. The method, on one hand, inactivates microorganism at room temperature by using low-temperature plasma motivated by corona discharge, on the other hand, separates microbial aerosol in the air by utilizing the high-voltage electric field acting force, which induces the corona to discharge, and the microbial aerosol is deposited on the earth electrode of the discharging corona by the acting force. According to the deposition of microbial aerosol, the corona discharge module is fetched out at intervals to have a cleaning. After being cleaned, the corona discharge module is put back into the processing system to eliminate microbial aerosol. The two processes are operated alternatively, thus longtime efficient operation of processing system is realized. The method and the device for eliminating microbial aerosol in indoor air by using corona discharge have the advantages of efficiency, energy saving and no secondary pollution.
Owner:北京御住环境科技有限公司
Zwitterion-containing water-soluble cross-linking agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103880714ASynthetic conditions are mildEasy to implementBacteriaOrganic compound preparationCell AggregationsProtein molecules
The invention discloses a zwitterion-containing water-soluble cross-linking agent as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the compound is a formula I. The compound has good water solubility and anti-nonspecific adsorption feature, so that the compound can be used as a cross-linking agent to prepare the polymer with high cross-linking degree, the obtained polymer has excellent biological pollution resistant feature, and can be widely applied to the fields such as biomedicine and materials. The water-soluble cross-linking agent is capable of reducing the protein aggregation speed, so that the protein molecule can be more easily presented in crystal form, and therefore the water-soluble cross-linking agent can be used for synthesizing the biomaterial for promoting protein crystallization. Furthermore, the cross-linking agent molecule comprises two-NH-C=O groups capable of generating hydrogen bond interaction with the carbohydrate (-OH) abound on the surface of microorganism; therefore, the cross-linking agent molecule can be used as an additive to prepare a molecular imprinting film material so as to selectively separate the microorganism (structural formula).
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Methods, compositions, and kits for the concentration and detection of microorganisms
InactiveUS20050123954A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingMicrobiologyIsolate - microorganism
The present invention includes methods, kits and compositions useful for the detection of microorganisms. These agents and methods are primarily directed to a method of detecting the presence of a microorganism in a sample, involving concentrating or isolating the microorganism through the use of a binding agent, and subsequently performing nucleic acid amplification of a microorganism polynucleotide.
Owner:BIOCONTROL SYST
Viral concentration process
InactiveUS20050064585A1Maximum working pressureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberHollow fibre
An apparatus for isolating a microorganism from a liquid, the apparatus comprising: a first endcap engageable with an inlet end of a hollow fibre filter, the first endcap including a first passage having an inlet engageable with a liquid input conduit; and an outlet into the filter; and a second endcap engageable with an outlet end of the hollow fibre filter, the second endcap including a second passage having an outlet engageable with a liquid return conduit, and an inlet from the filter; the first passage and the second passage being independently sized such that in conjunction with a flow restriction means which restricts a flow of the liquid through the second passage, a predetermined exit liquid flow rate from at least one permeate outlet of the filter is achieved; the microorganism is captured within the hollow fibre filter; and the maximum working pressure of the hollow fibre filter is not exceeded.
Owner:SYDNEY WATER CORP
Enrichment & isolation of microbial cells & microbial nucleic acids from a biological sample
ActiveUS20140335522A1Suitable for processingAvoiding multiple fold dilutionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism lysisMicrobial fuel cellLysis
A method for enrichment and isolation of microbial cells and microbial nucleic acids from a biological sample is described. The method comprises (i) adding to an initial volume of biological sample a differential cell lysis solution to obtain a final concentration of 0.1 to 1% of SDS in the sample; (ii) mixing the solution obtained in step (i) for a period of time sufficient to lyse the host cells present in the biological sample, while preserving the integrity of cells; and (iii) separating the microbial cells from the lysed host cells components. Differential cell lysis solutions and kits for practicing the method of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:GENEOHM SCI CANADA
Eicosapentaenoic acid-producing microorganisms, fatty acid compositions, and methods of making and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130172590A1Improve concentrationOrganic chemistryProtozoaMicrobial oilEicosapentaenoic acid
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Cell isolation method
InactiveCN1395620AUniversal binding ability is beneficialAdvantages FlexibilityBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrobiologyIsolate - microorganism
Owner:挪威诊断联合股份有限公司
Food compositions and methods
Compositions are provided according to the present invention which include microorganisms and / or products of microorganismal metabolism. Humans and other animals have difficulty gaining nutritional benefit from many highly abundant plant materials, such as cellulose. A traditional means of gaining the benefit of these nutrients has been through the cultivation of animals capable of utilizing such materials, subsequently consuming their meat and milk products. However, raising such animals is time consuming and expensive. Compositions and methods according to the present invention allow circumvention of the use of these cultivated animals for meat and milk. Microorganisms are isolated from an animal which is a traditional source of food for a second type of animal, such as humans or pets, in order to produce compositions of the invention. Such compositions provide nutritional benefit to the consumer.
Owner:MANKOVITZ ROY J
Method for separation and purification of large-fragment DNA from soil
InactiveCN103103180AEasy to operateOperation steps are adjustableDNA preparationMicrobe DNABiological studies
The invention belongs to the fields of soil microorganisms, biochemistry and molecular biology and relates to a method for separation and purification of a large-fragment DNA from soil. The method is used for indirect separation and purification of a large-fragment DNA having molecular weight more than 30kb from various types of soil, wherein the large-fragment DNA is used for construction of a metagenomic library, or is used for separation of soil microbial gene clusters. The method solves the problem that separation of microbial cells from soil and preparation of large-fragment soil DNA having high purity and satisfying various biological study demands are realized difficultly by the existing indirect method, and is an efficient method for extraction of soil microorganism DNA having a large fragment and high purity.
Owner:XINJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving biological leaching speed of metallic sulphide ore or concentrate by using leaching liquid containing separated microorganism to inoculate continuously
ActiveCN101260465AHigh recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementThiobacillus ferrooxidansTailings dam
The invention discloses a method for increasing biological lixiviating speed of metal sulphate ore or ore concentrate in waste pile, tailing dam, scrap yard or other on-line processing. The method is charactered in that an acidophilic thiobacillus thiooxidans type isolated microbe and an acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans type isolated microbe process inoculability continuously to ore or ore concentrate in the event that nature microbe is not exist, and microbe total concentration in continuous inoculability flow reaches about 1*10<7> cells / ml to 5.6*10<7> cells / ml. Especially, the invention discloses continuous inoculability microbe as follows: acidophilic thiobacillus thiooxidans Licanantay DSM 17318, and acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans Wenelen DSM 16786, or other nature microbe above 5*10<7> cells / ml concentration. The invention also includes adding oxide (for example, high-iron ion generated on outside), and adding nutriment in forms of ammonium salt, magnesium salt, ferric salt and kali salt, in addition, injecting air containing CO2 continuously for improving bacilli action in biological lixiviating process of ore or ore concentrate.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com