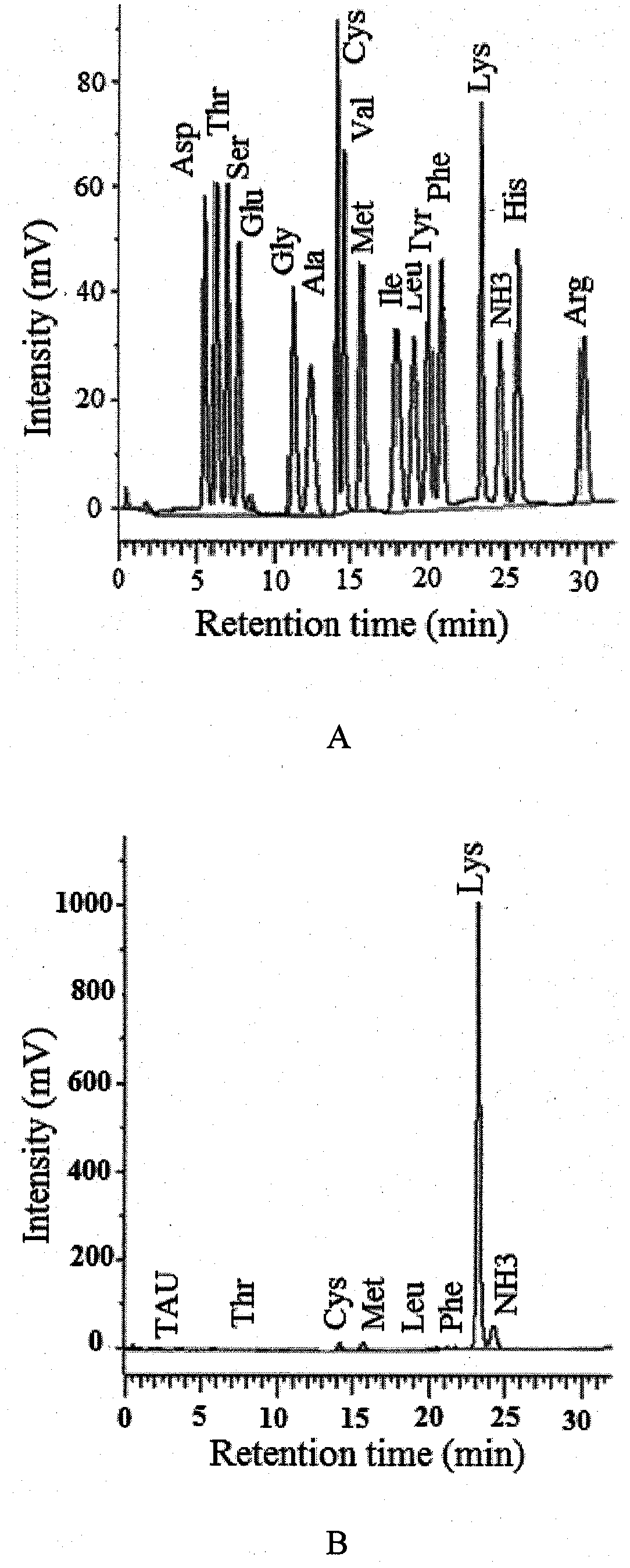
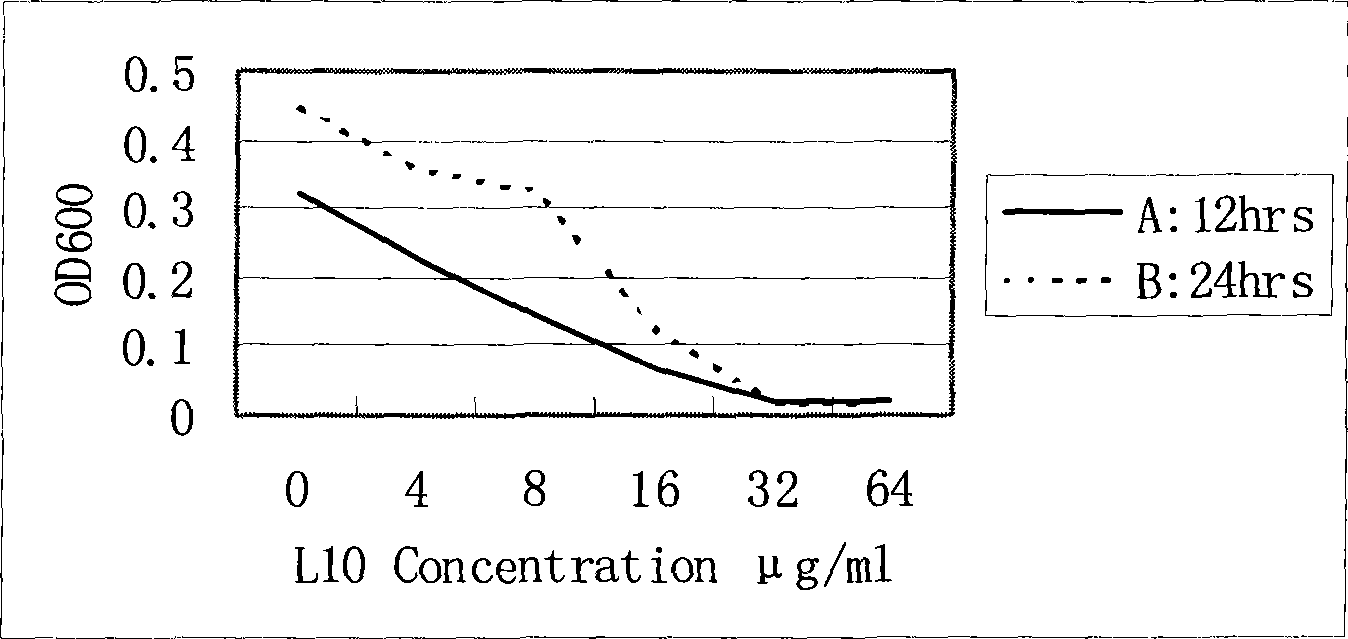
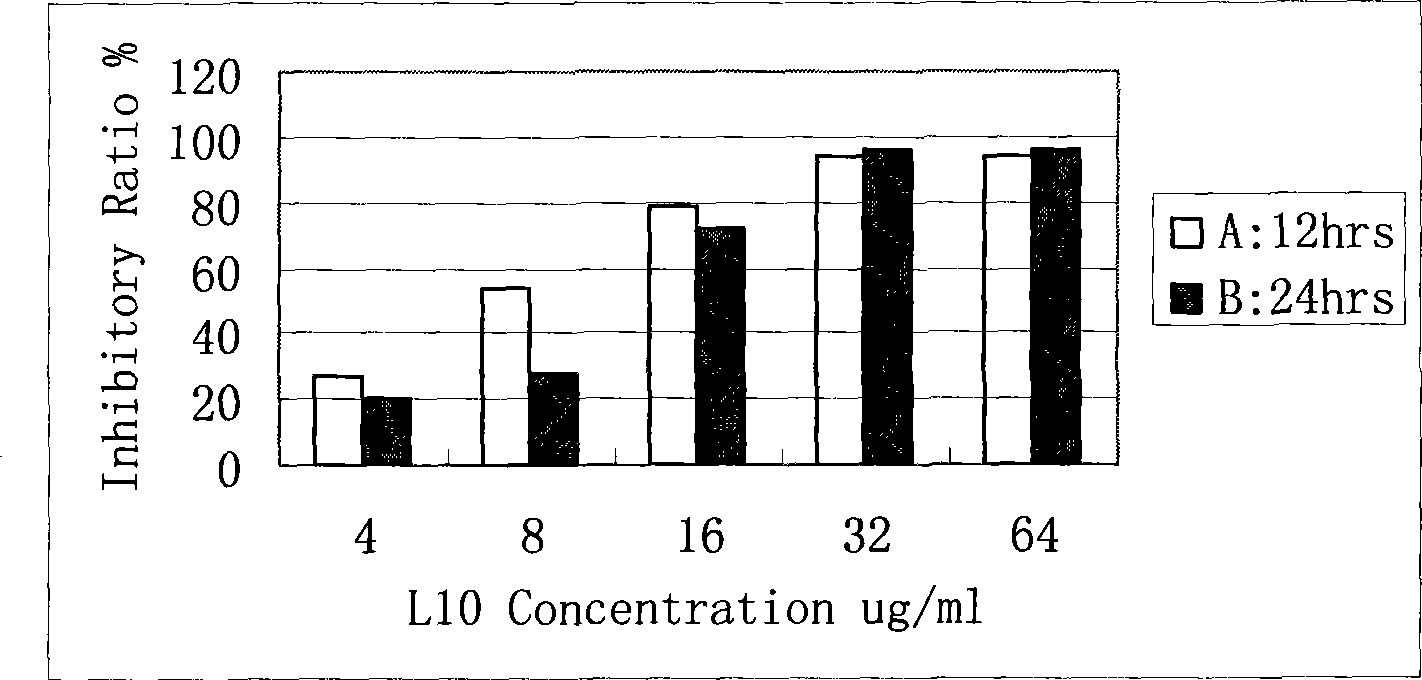
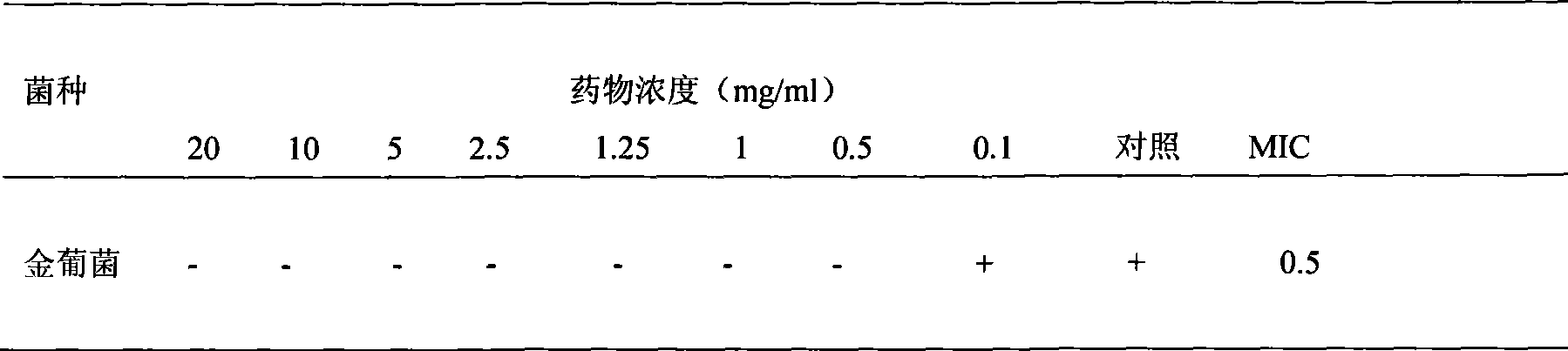
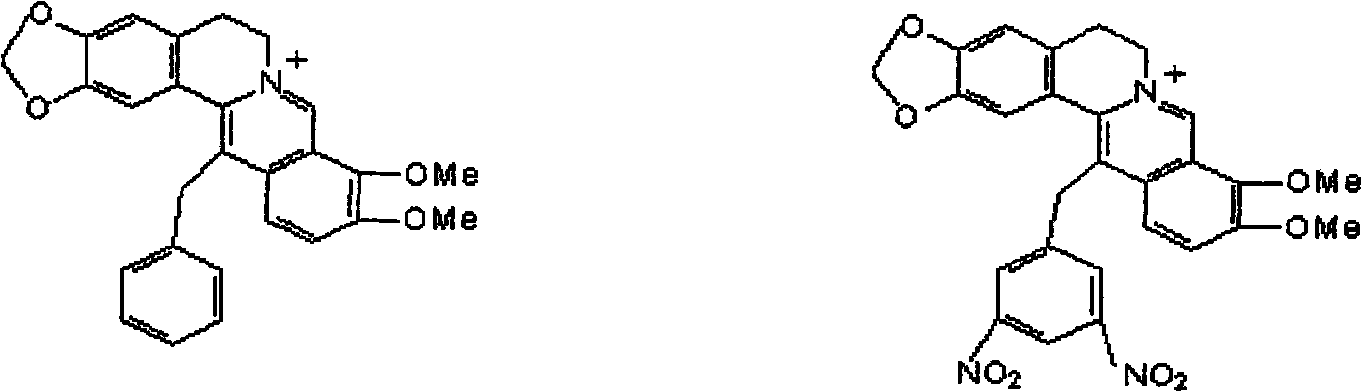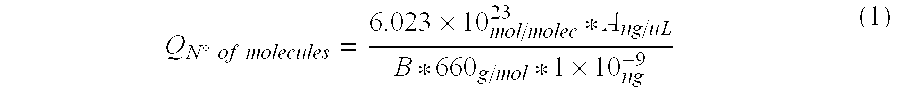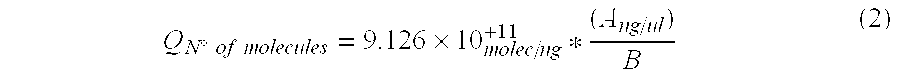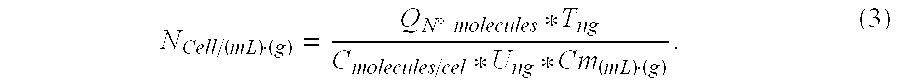Patents
Literature
420 results about "MICROBIAL CONCENTRATION" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
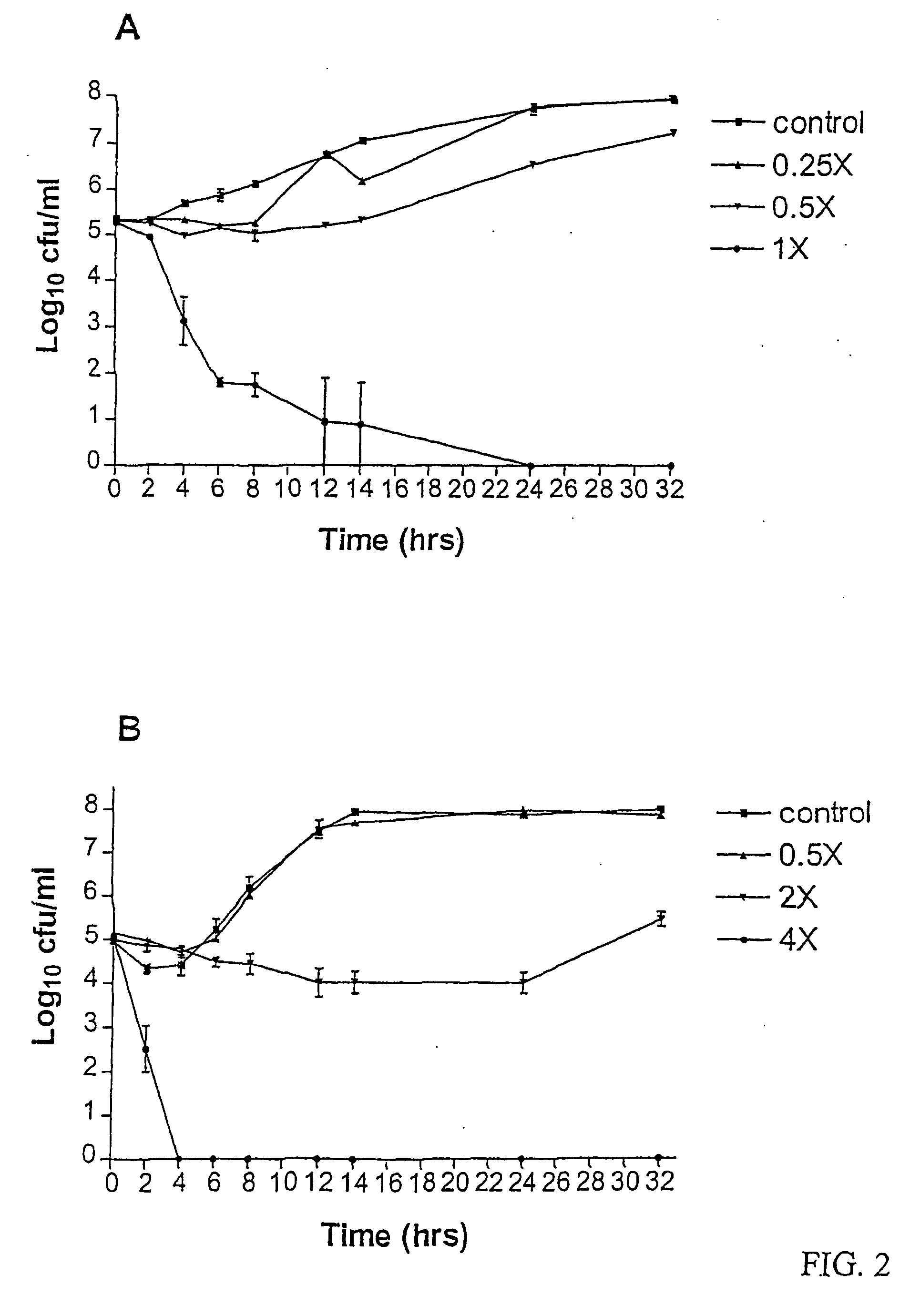
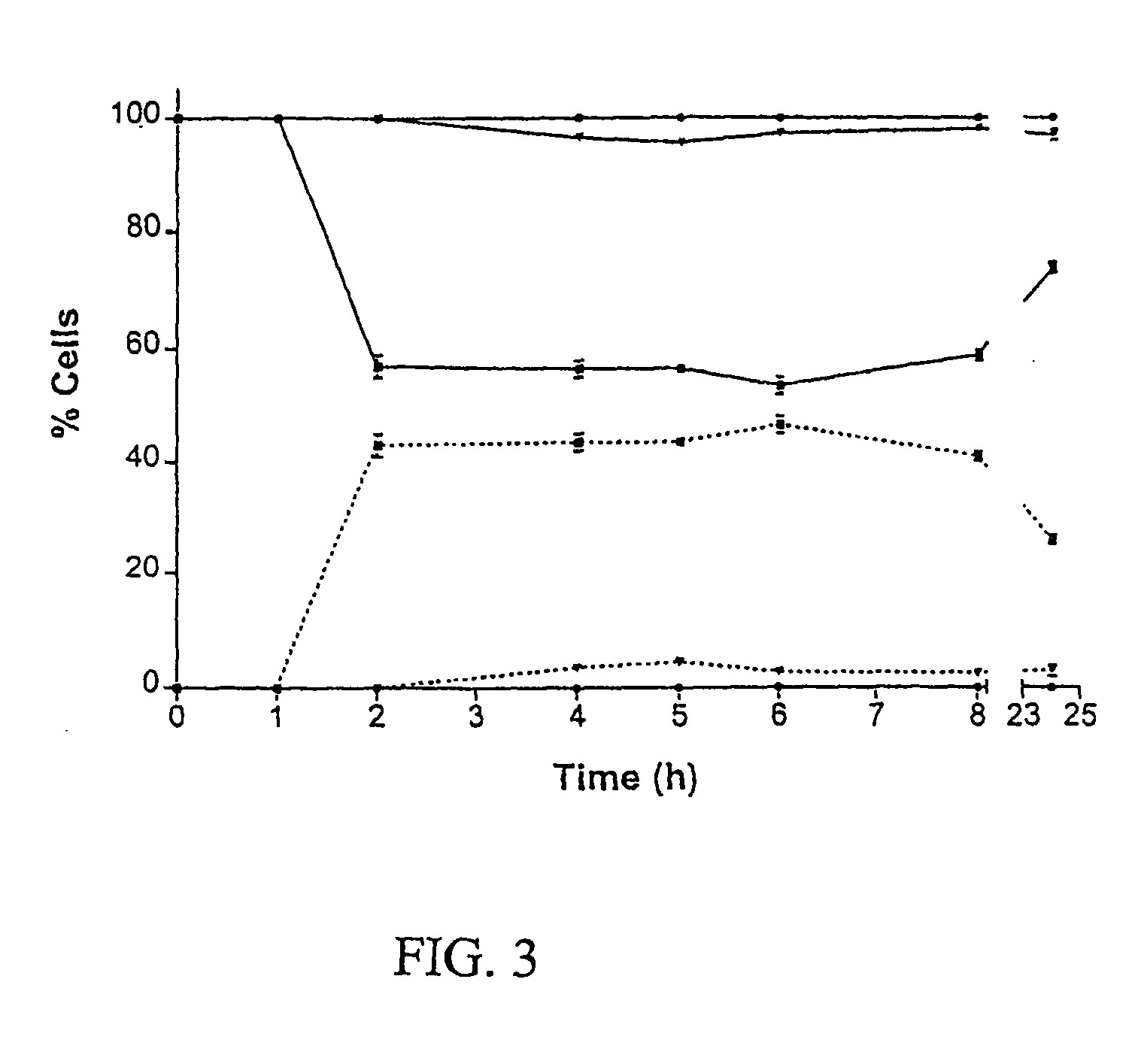
In [microbiology], the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is the lowest concentration of a chemical which prevents visible growth of a bacterium. This is in difference to the minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC), which is the concentration resulting in microbial death as defined by the inability to re-culture bacteria.
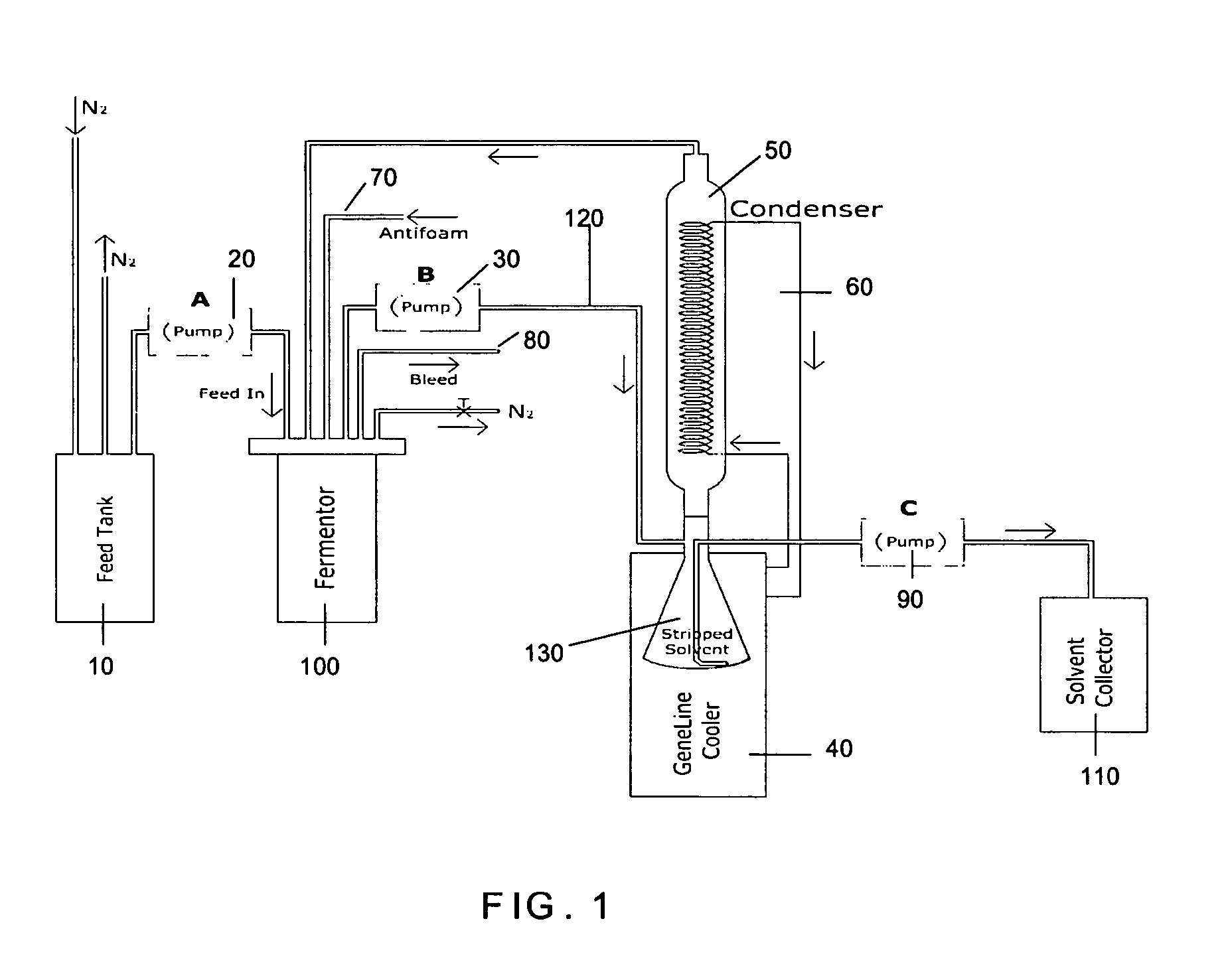
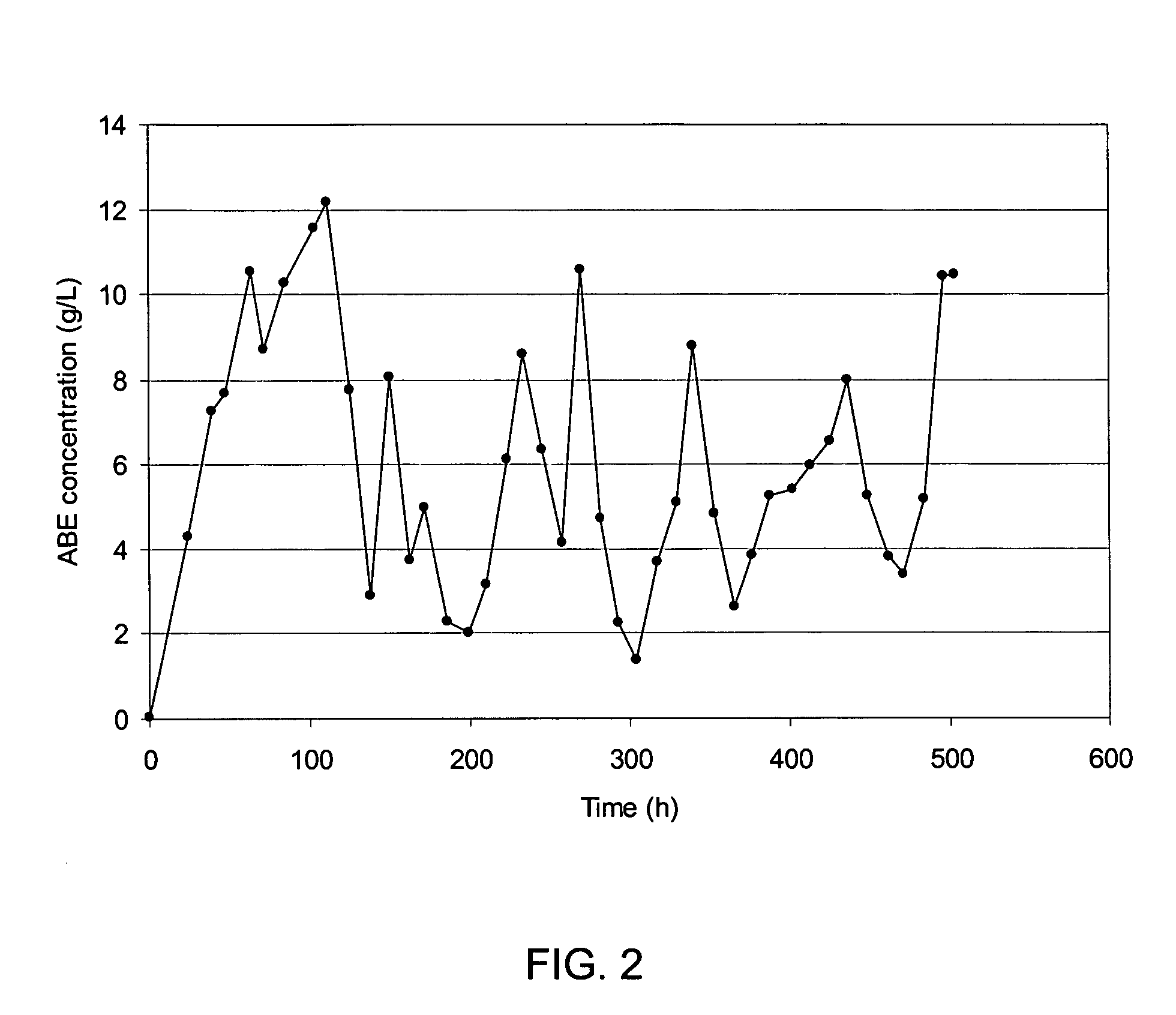
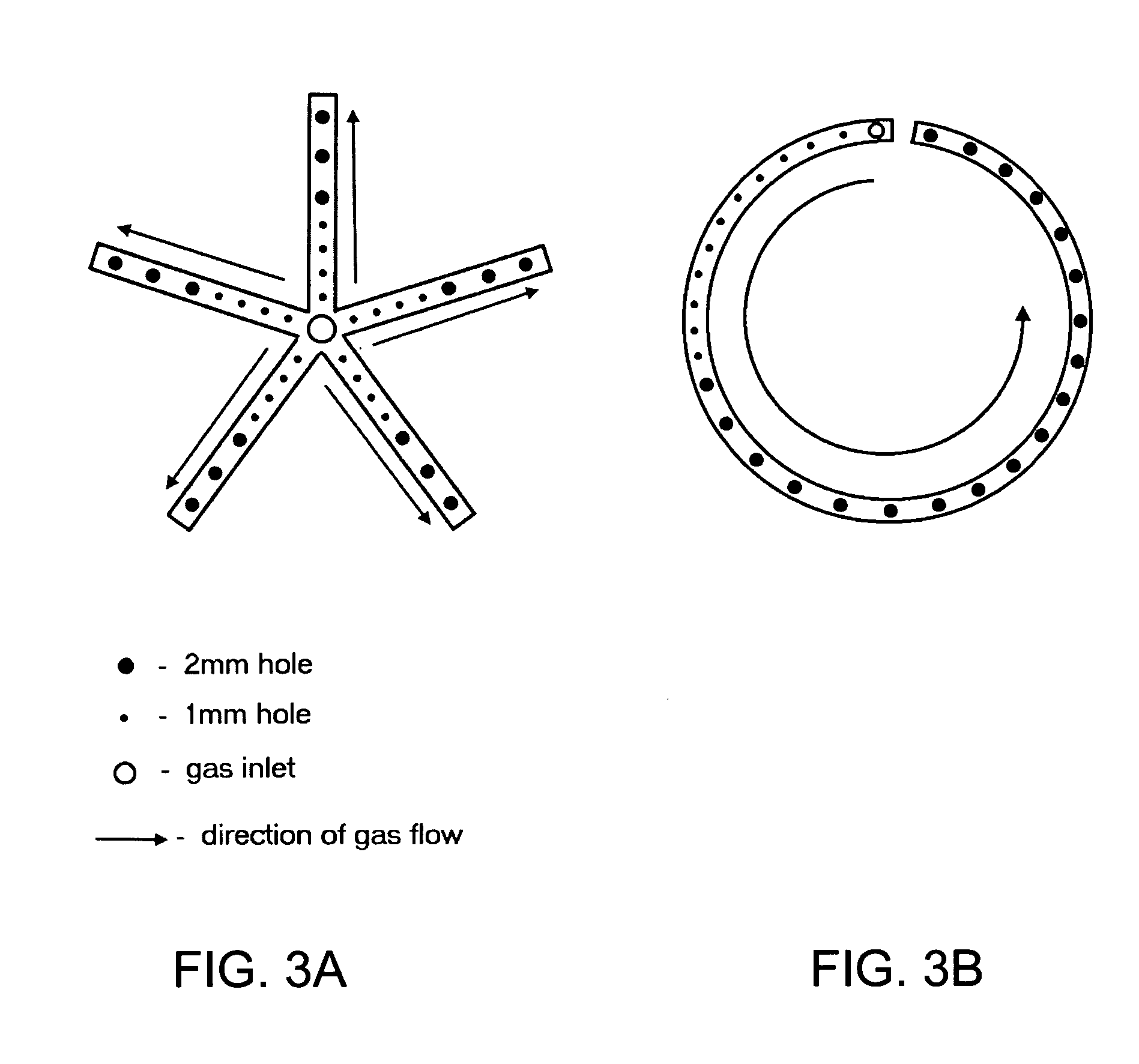
Process for continuous solvent production
InactiveUS20050089979A1High solventProducing strainBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicrobial inoculationSolvent
A continuous process for production of solvents, particularly acetone-butanol-ethanol (ABE) using fermentation of solventogenic microorganisms and gas stripping is provided. The solventogenic microorganisms are inoculated in a nutrient medium containing assimilable carbohydrates (substrate) and optional other additives. Control of the solventogenic microorganism concentration in the fermentor (cell concentration) and the assimilable carbohydrate concentration in the fermentor, along with removal of solvents formed results in a continuous process for production of solvents.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
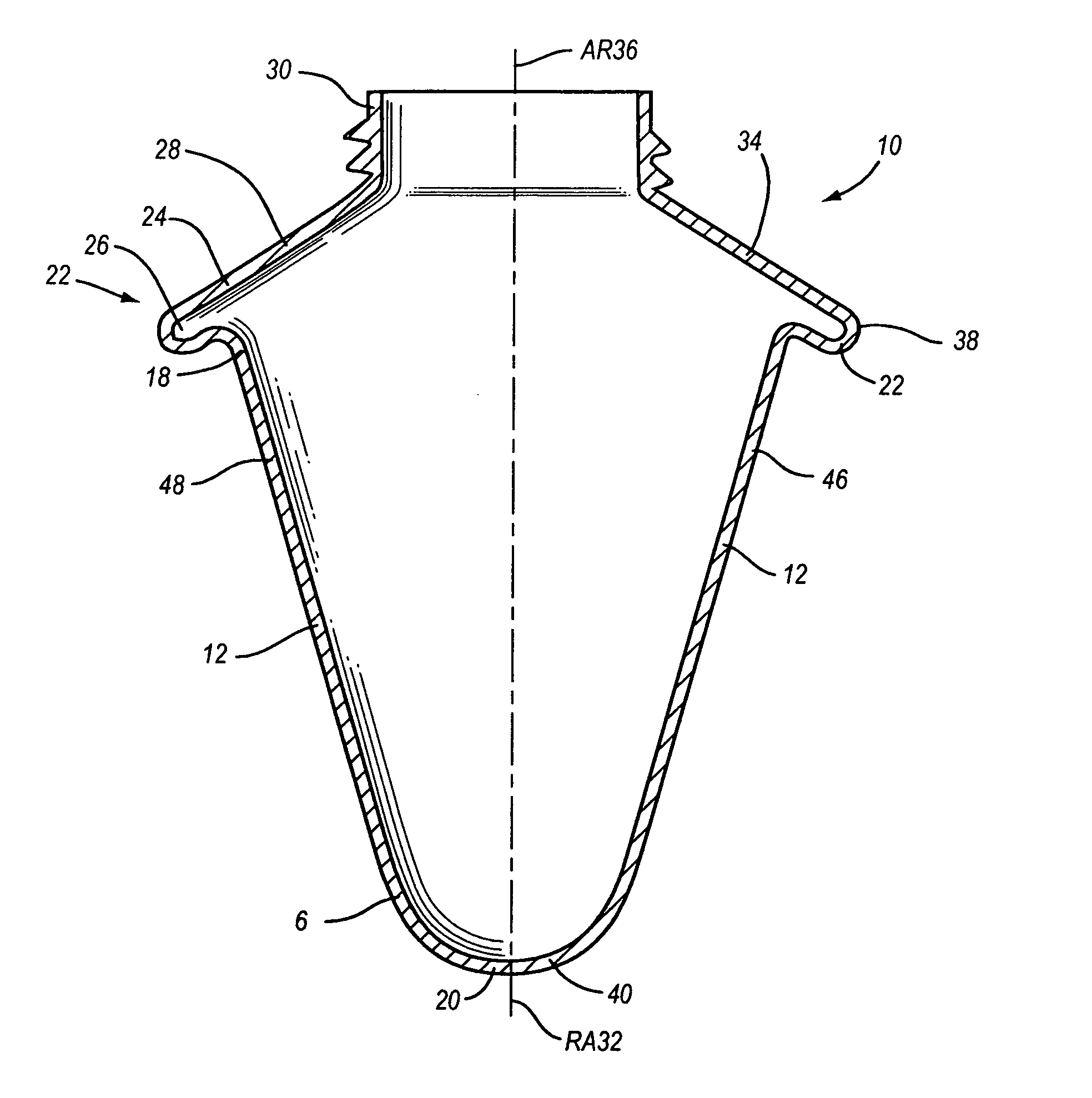
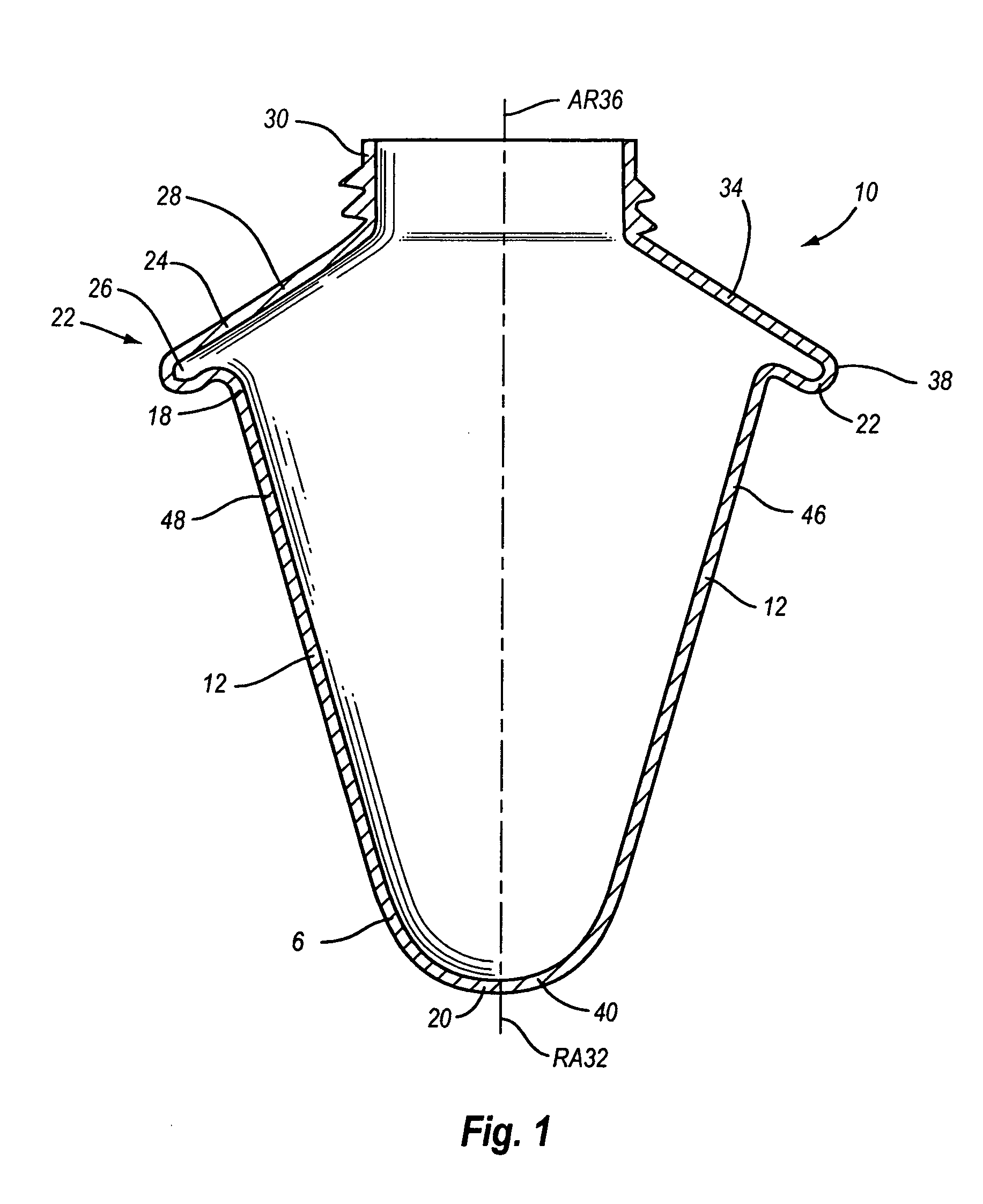
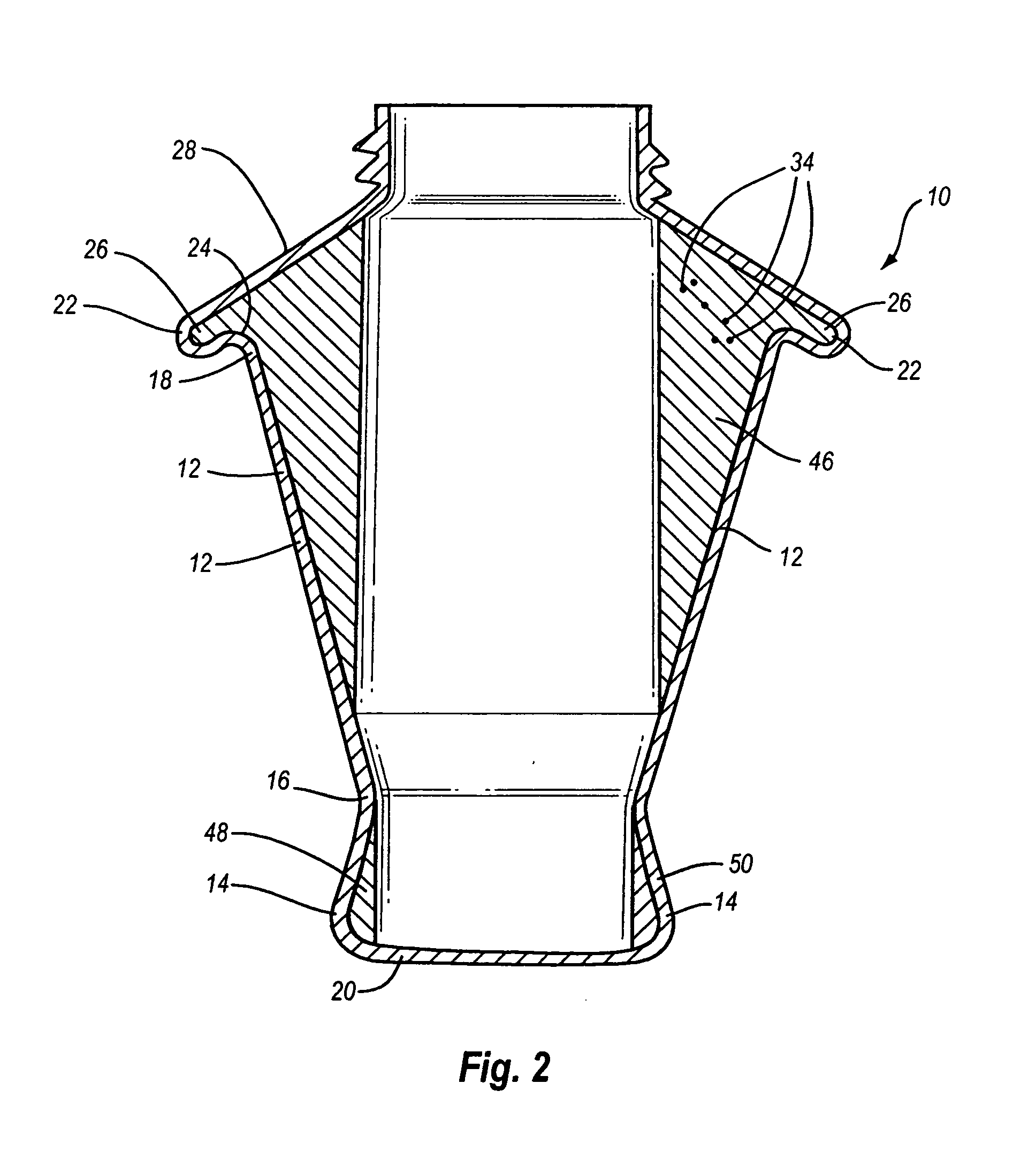
Microbial concentration system
InactiveUS20050054506A1Collection of sample efficientEfficient collectionWithdrawing sample devicesLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringIsolate - microorganism
A centrifuge separation chamber of particular use for separating microbes. The chamber has an upwardly flared conical shape, and a sample collecting groove at its widest point. Sample is collected in the sample groove as the chamber spins. When slowed to a stop, the supernatant sinks to the bottom of the chamber, leaving the sample in the sample groove where it can be easily accessed.
Owner:BRADLEY BRUCE J
Sludge composting method
ActiveCN101781131AEasy to getShort fermentation timeBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationEcological environmentSludge compost
The invention provides a sludge composting method, and relates to a sludge treatment method which comprises the steps of preferable accessory selection, CK21 fungus spraying inoculation, heavy metal passivation and powder granulation, and then three-dimensional composite biological organic fertilizer with organic, inorganic and microbial active constituents is obtained. Mushroom compost and pig manure are used as accessories which are easily obtained and degraded, the stacker fermentation time is short, only one time of fermentation is needed, the C / N ratio can be effectively adjusted, and the water content of the sludge is reduced; and the efficient beneficial bio-fungus community CK21 is adopted. The microbial concentration is high, the secretion ability of the enzyme is strong, organic matters can be quickly decomposed so as to prevent the corruption of the organic matters, no odor exists, sludge is used for CK21 inoculation, fermentation starts fast, and the effect is good; and the product is inoculated with the CK21 fungus secondarily so as to further balance and activate nutrients, and the microbial natural reproduction is utilized to realize the is called flower dipping absorbing of the plants to nutrients. The invention has the advantages of optimizing the composting conditions, shortening the composting time, reducing energy consumption of turning, and reducing the damage of the heavy metal on the ecological environment.
Owner:厦门市政环境科技股份有限公司
Preparation method of floating embedding bacterium agents for in-situ remediation of oil polluted water
InactiveCN102888392AAvoid competition effectsImprove purification effectMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierPetroleum PollutionEnvironmental engineering
The invention relates to a preparation method of floating embedding bacterium agents for in-situ remediation of oil polluted water, specifically relating to a technology for fixing oil degradation bacteria by using expanded graphite, sodium alginate and calcium chloride, absorbing and degrading to purify the petroleum polluted water. The preparation method of the floating embedding bacterium agents comprises the following steps: adding petroleum degrading bacteria liquid into sodium alginate sol containing the expanded graphite, mixing uniformly, dropping into calcium chloride solution and cross-linking overnight at 4 degrees centigrade to obtain the floating embedding bacterium agents fixing hydrocarbon degradation bacteria. The floating embedding bacterium agents prepared by the preparation method has the advantages of high mechanical strength, good floatability and mass transfer performance and high degradation efficiency; the floating embedding bacterium agents can be directly put onto the surface of the petroleum polluted water; the embedding bacterium agents can float on an oil-water interface for long term so as to ensure effective contact between the bacterium agent and the petroleum; the embedding technology increases the concentration of microorganisms, prevents the bacteria influencing by the water using environment, effectively improves the degradation efficiency, recovers and recycles conveniently and has no secondary pollution risk.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
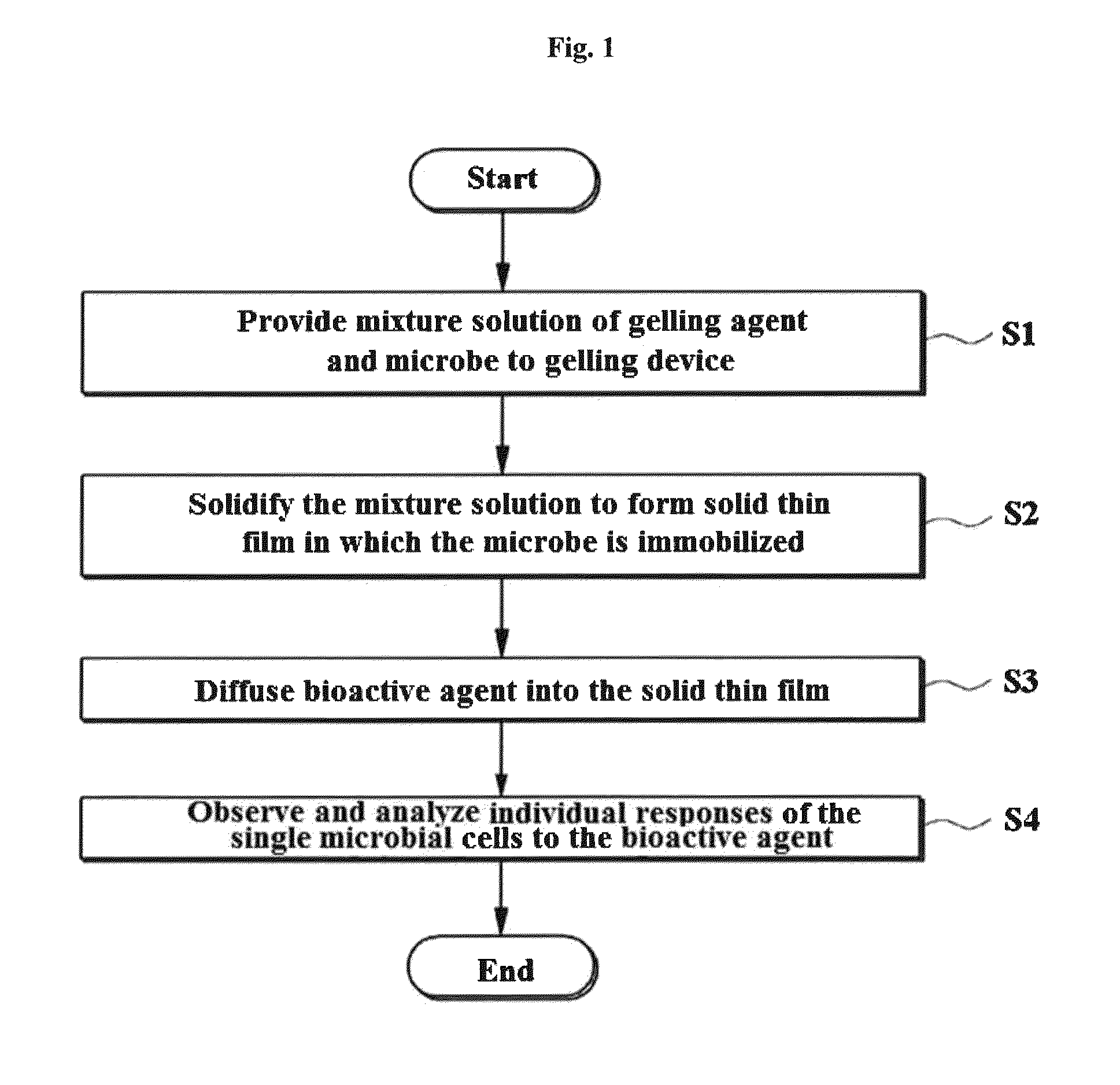
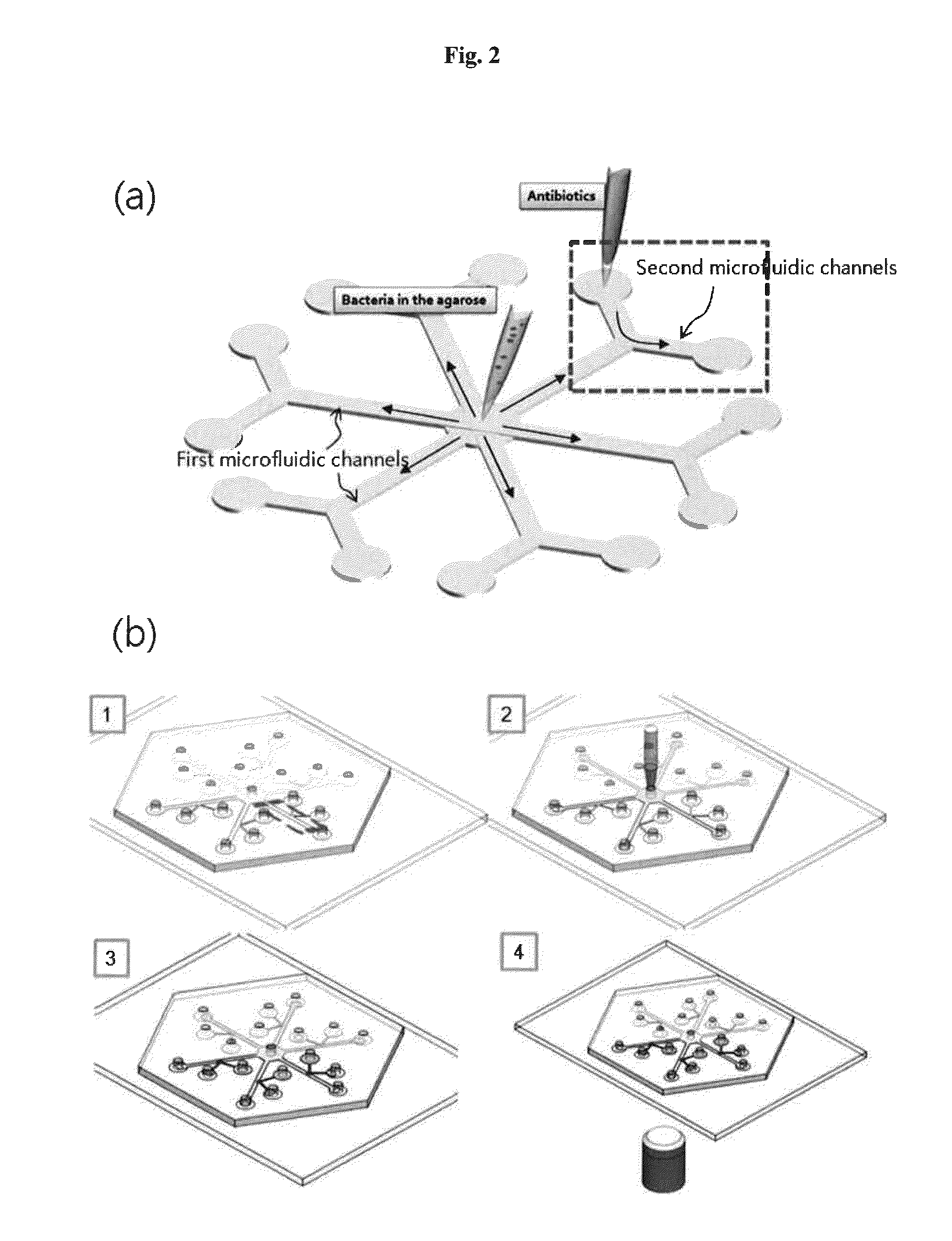
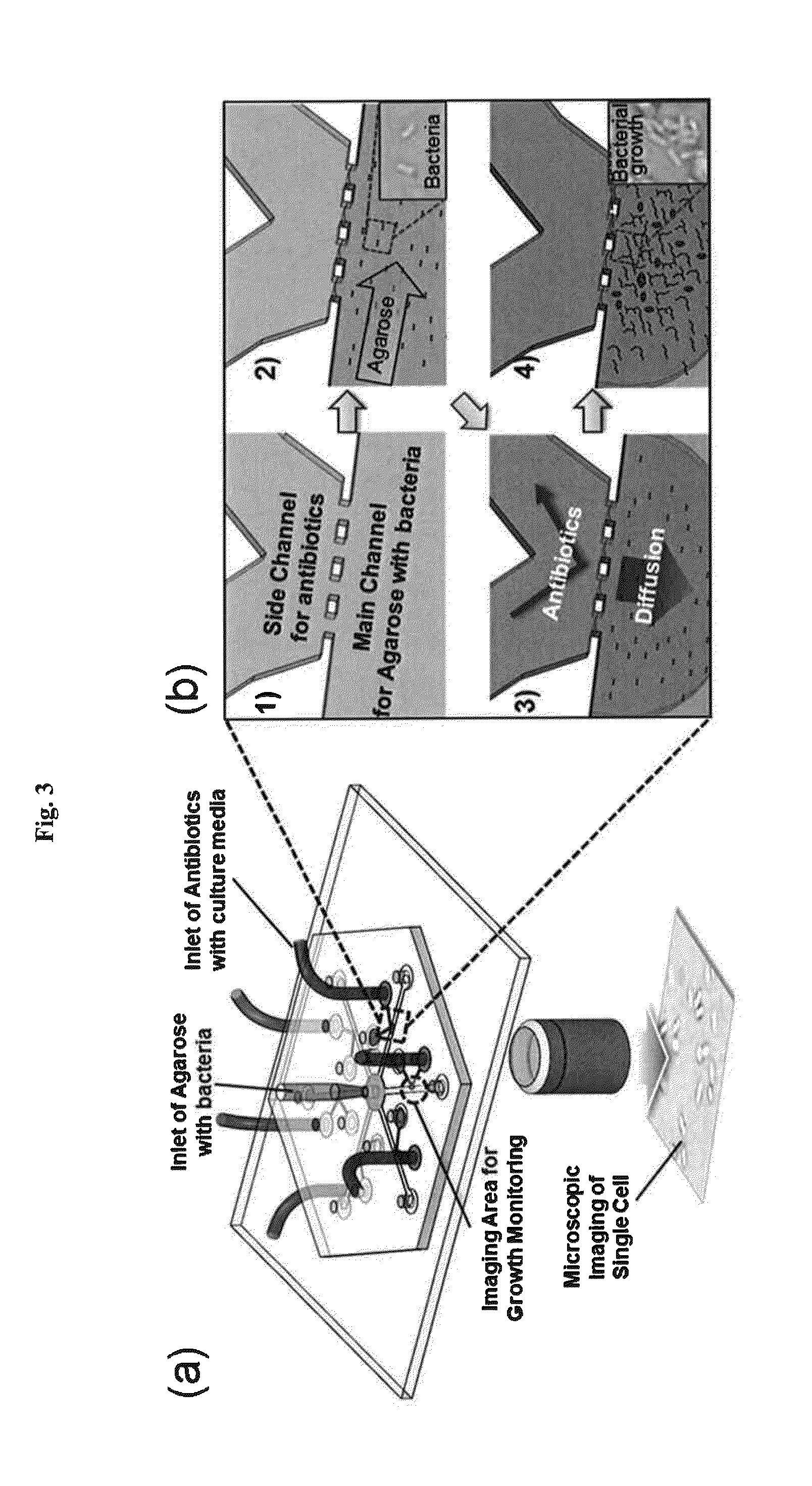
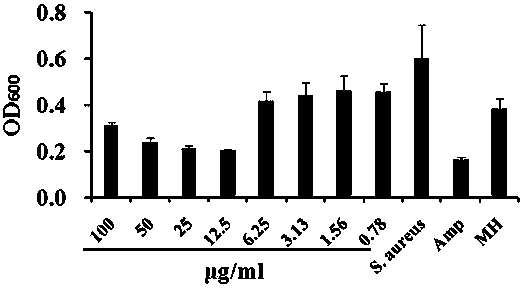
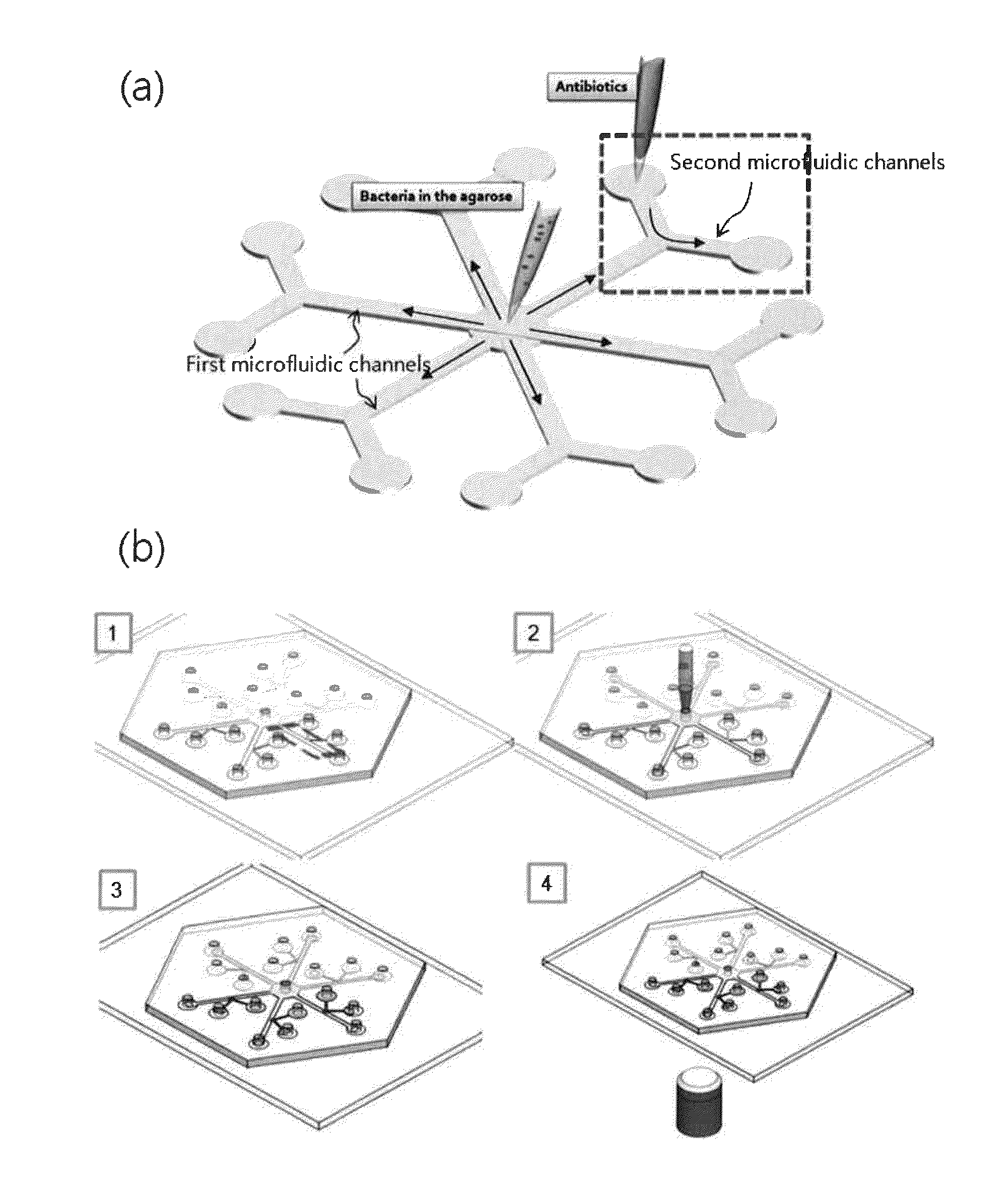
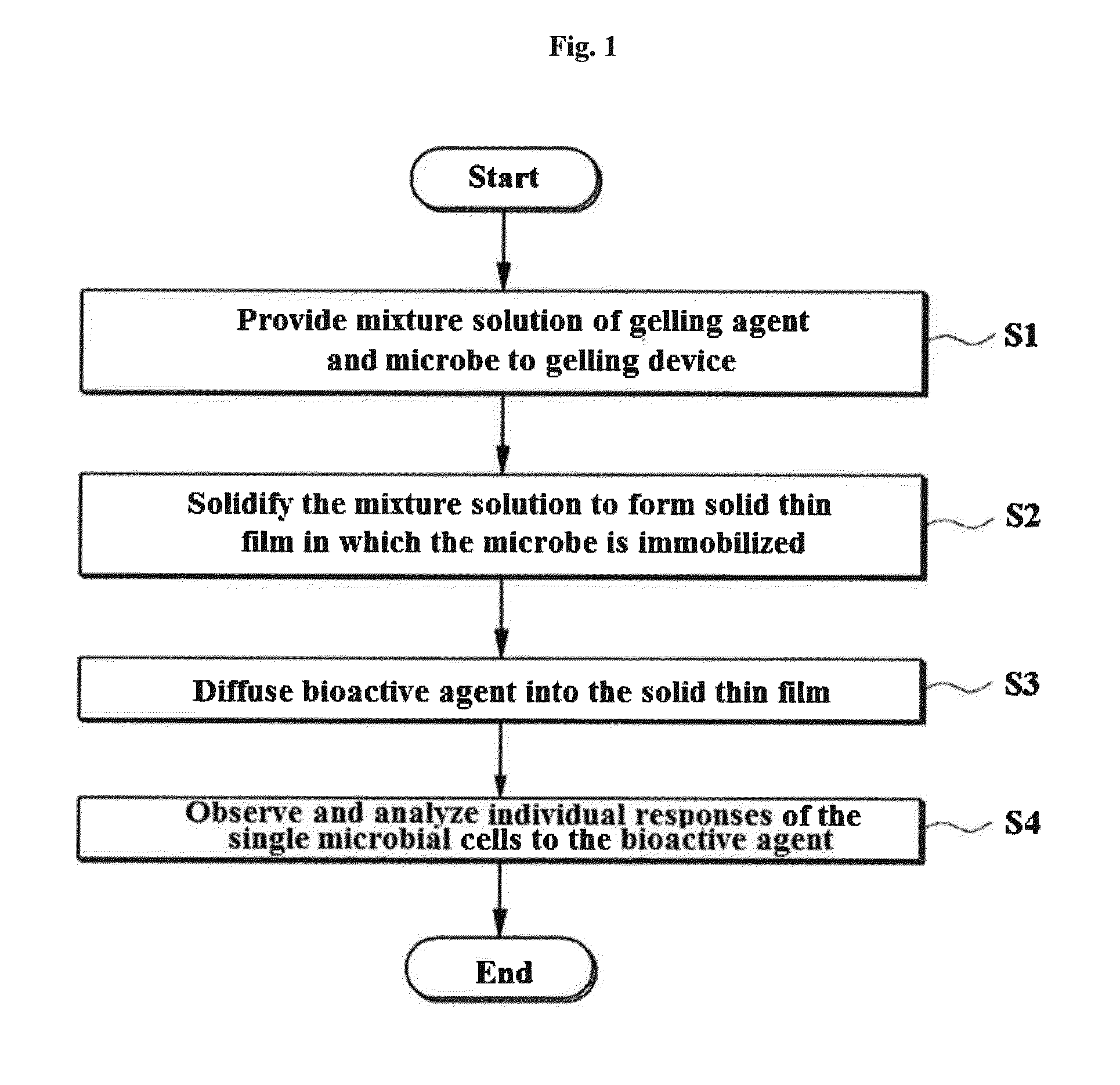
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing system based on bacterial immobilization using gelling agent, antibiotic diffusion and tracking of single bacterial cells
ActiveUS9133498B2Prevent burstBioreactor/fermenter combinationsImage analysisDiffusionMinimum inhibitory concentration
A testing method is disclosed. The testing method includes: providing a mixture solution of a gelling agent and a microbe to a gelling device; solidifying the mixture solution to form a solid thin film in which the microbe is immobilized; supplying a bioactive agent to the solid thin film and allowing the bioactive agent to diffuse into the solid thin film; and imaging the individual responses of the single microbial cells to the bioactive agent, and determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the bioactive agent based on the analysis of the images to obtain AST results.
Owner:QUANTA MATRIX
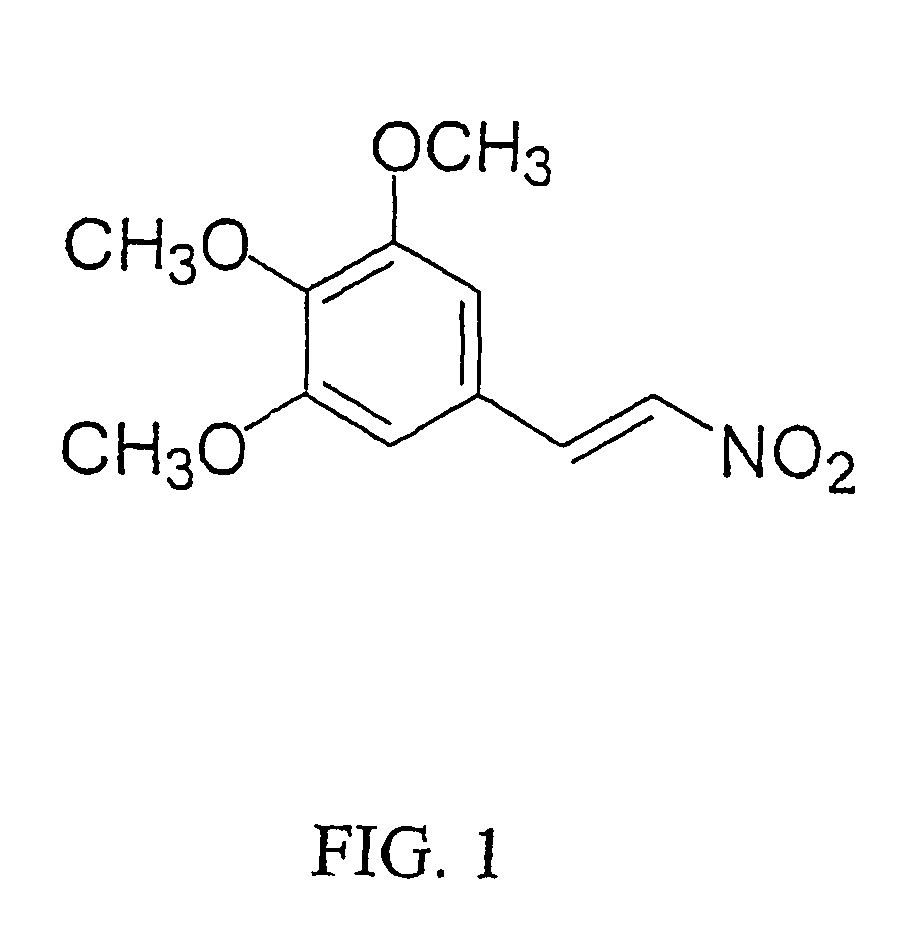
Antifungal phenylethylene
The antifungal and cancer cell growth inhibitory activities of 1-(3′,4′,5′-trimethoxyphenyl)-2-nitro-ethylene (TMPN) were examined. TMPN was fungicidal for the majority of 132 reference strains and clinical isolates tested, including those resistant to fluconazole, ketoconazole, amphotericin B or flucytosine. Minimum fungicidal concentration / minimum inhibitory concentration (MFC / MIC) ratios were ≦2 for 96% of Cryptococcus neoformans clinical isolates and 71% of Candida albicans clinical isolates. TMPN was fungicidal for a variety of other basidiomycetes, endomycetes and hyphomycetes, and its activity was unaffected by alterations in media pH. TMPN was slightly cytotoxic for murine and human cancer cell lines (GI50=1-4 μg / ml), and weakly inhibited mammalian tubulin polymerization (IC50=0.60 μg / ml). TMPN may also be used as a biochemical probe for tubulin and fungal dimorphism studies.
Owner:ARIZONA STATE UNIVERSITY
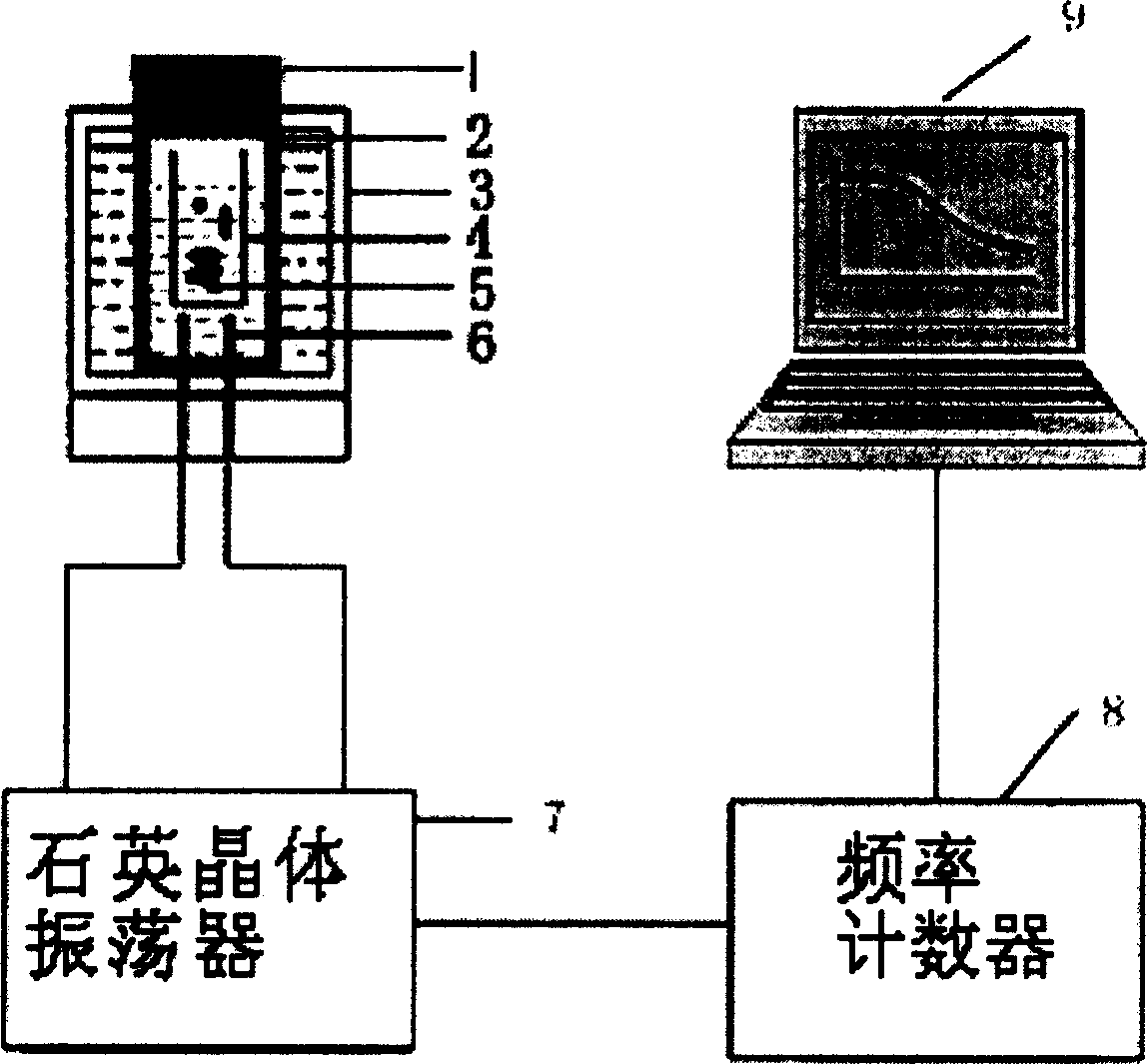
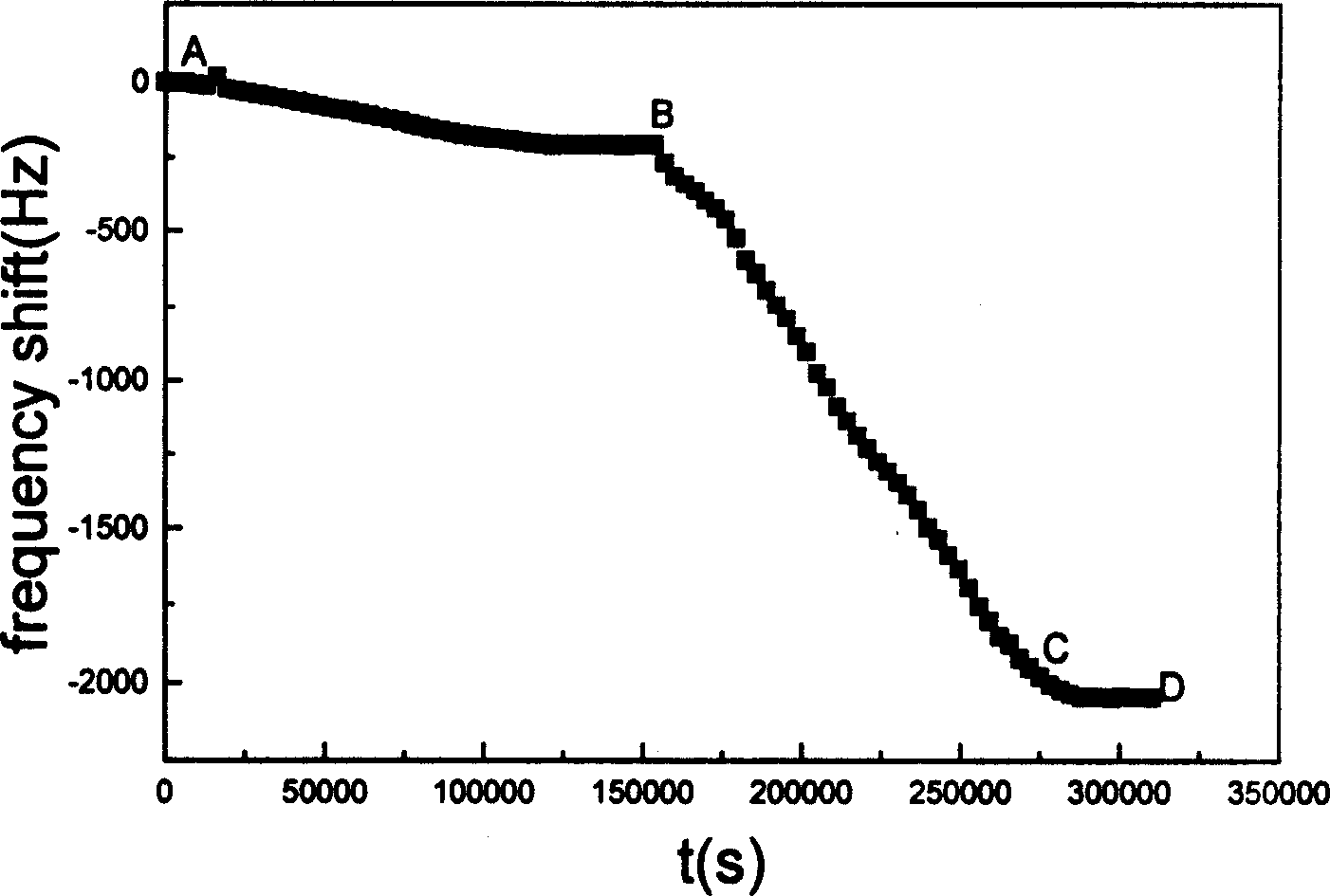
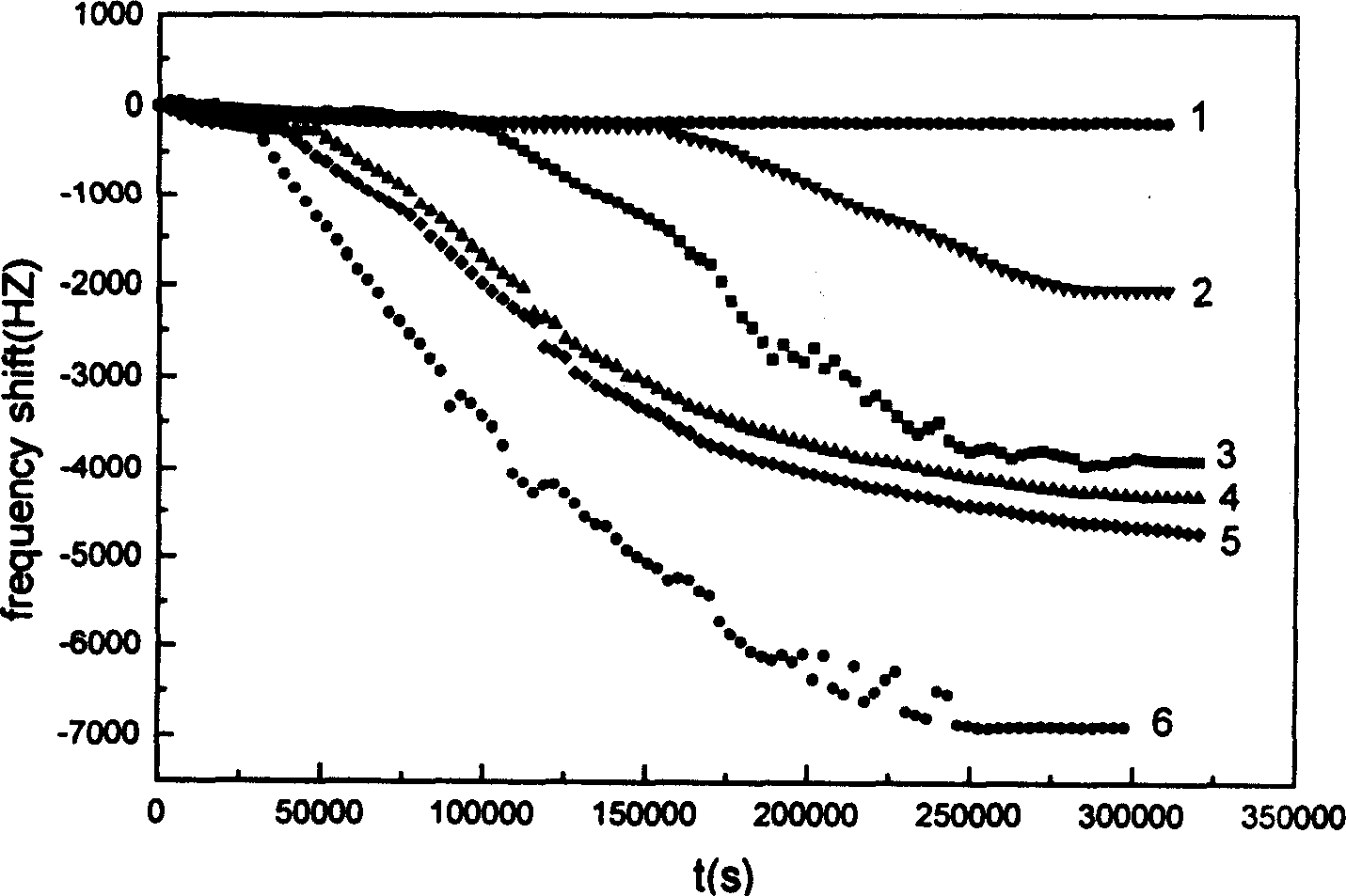
Method and apparatus for detecting microbe by piezoelectric quartz crystal sensor
InactiveCN1584579AOvercoming nutritional requirementsOvercome consistencyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCulture cellPiezoelectric quartz
A method and device for detecting microbe with piezoelectric quarts crystal transducer includes leading microbial metablin CO2 from culture cell to basic solution detection cell, measuring reaction variation with transducer and counting it out with frequency counter, obtaining linear relation between FDT and microbial concentration for carrying out microbial quantitative and qualitative detection by measuring response curve of microbe in different concentration.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Antibacterial small molecules and methods for their synthesis
ActiveUS20090270423A1Good water solubilityEnhance and expand biological activityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSynthesis methodsMinimum inhibitory concentration
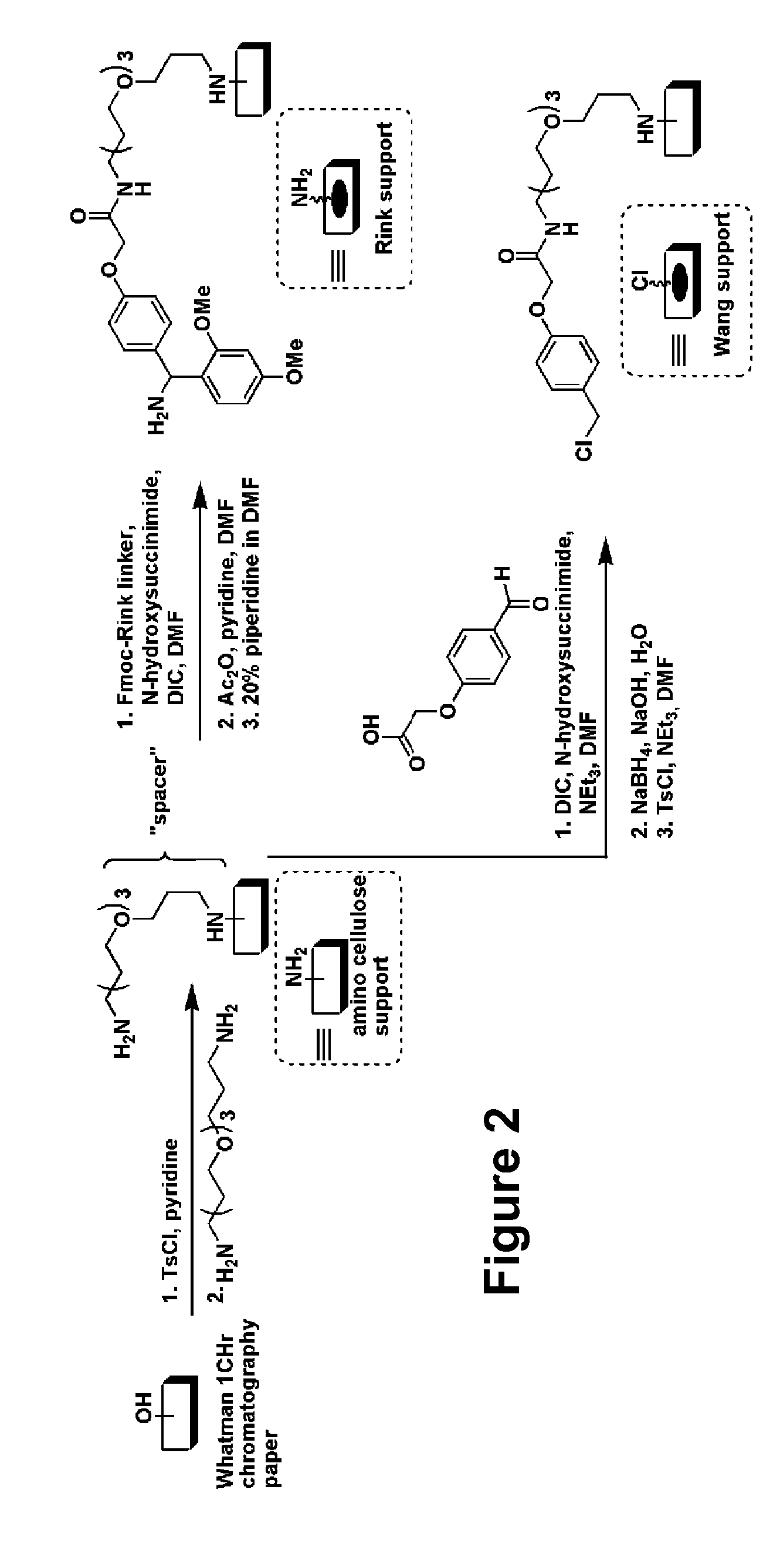
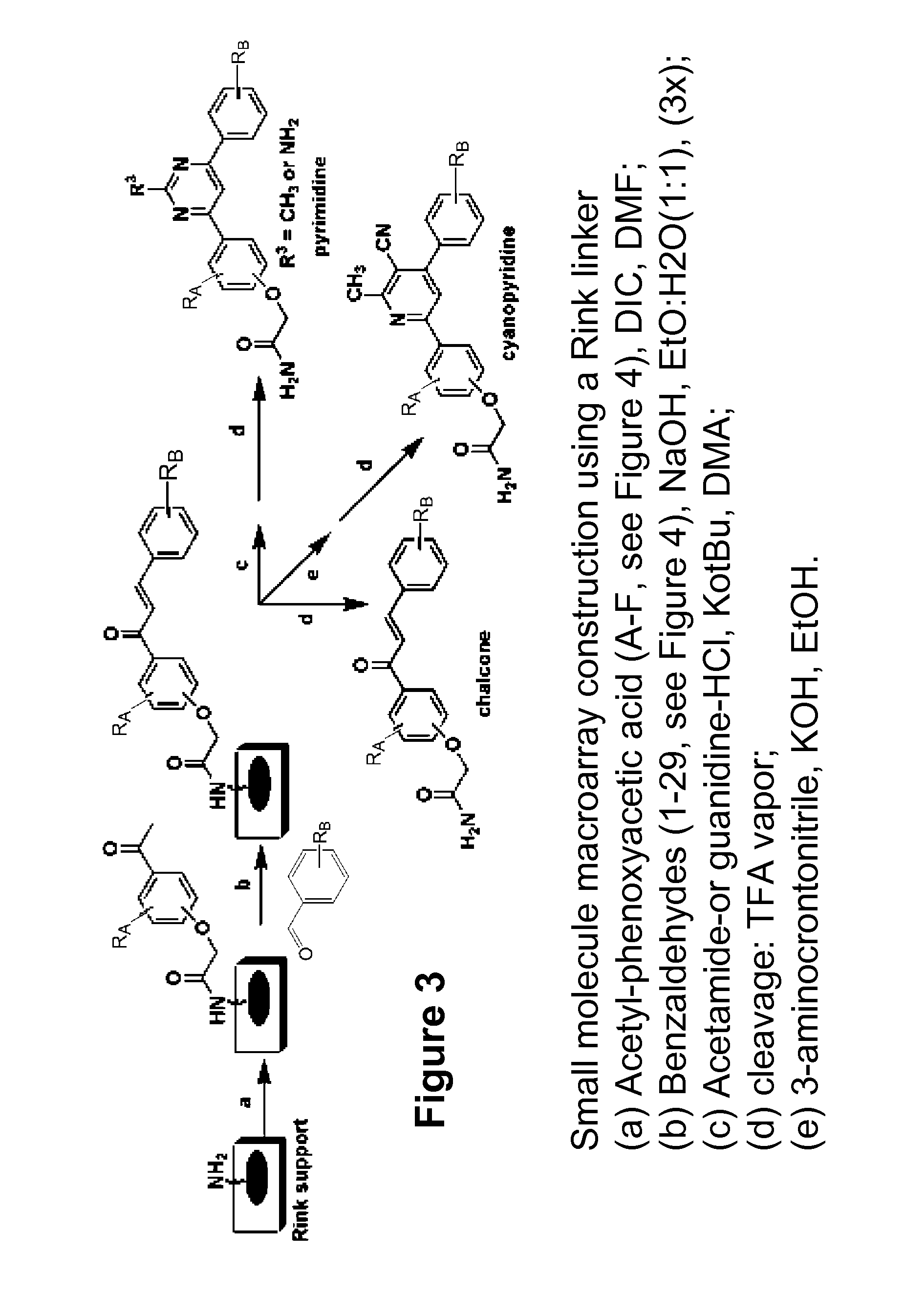
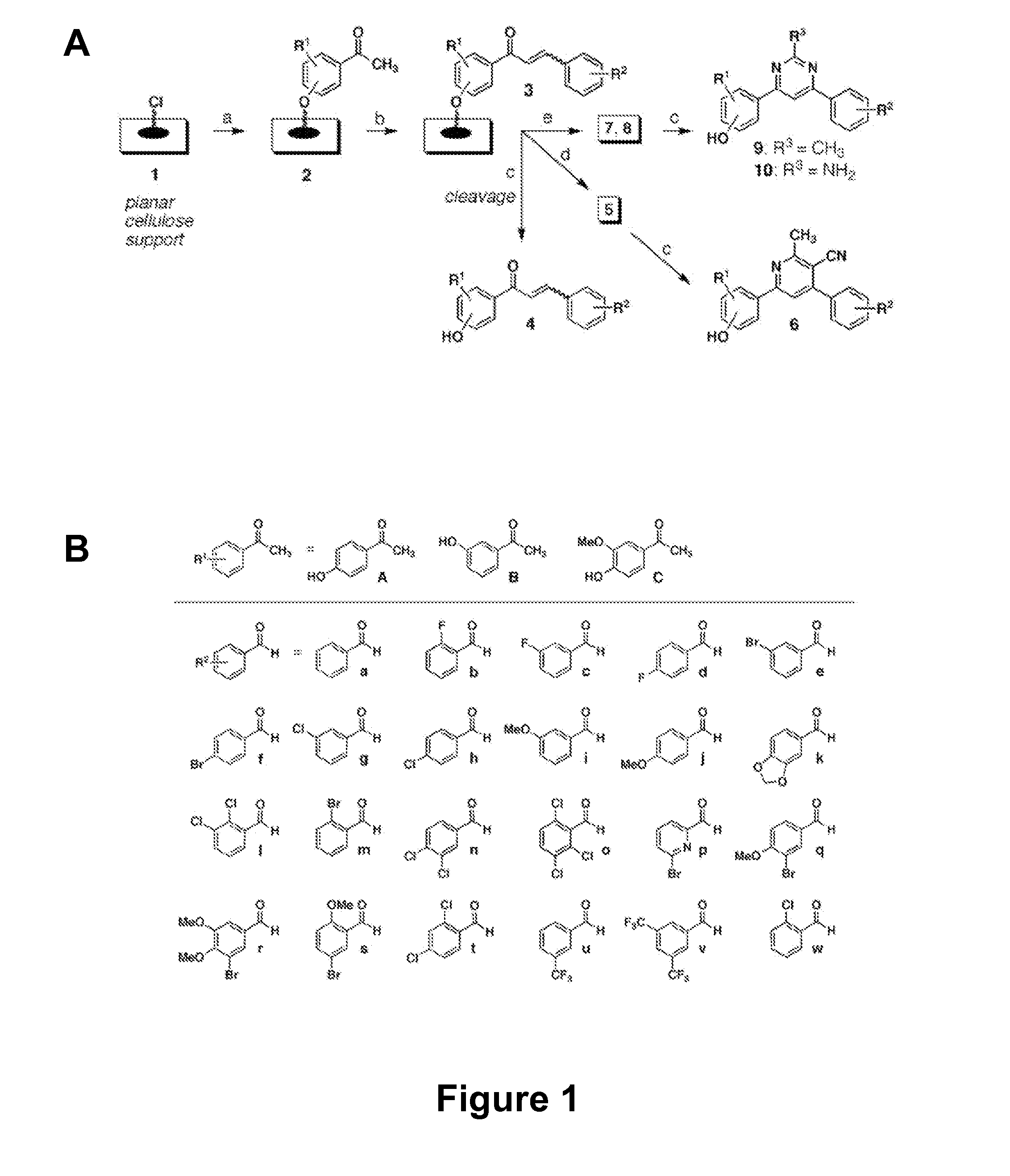
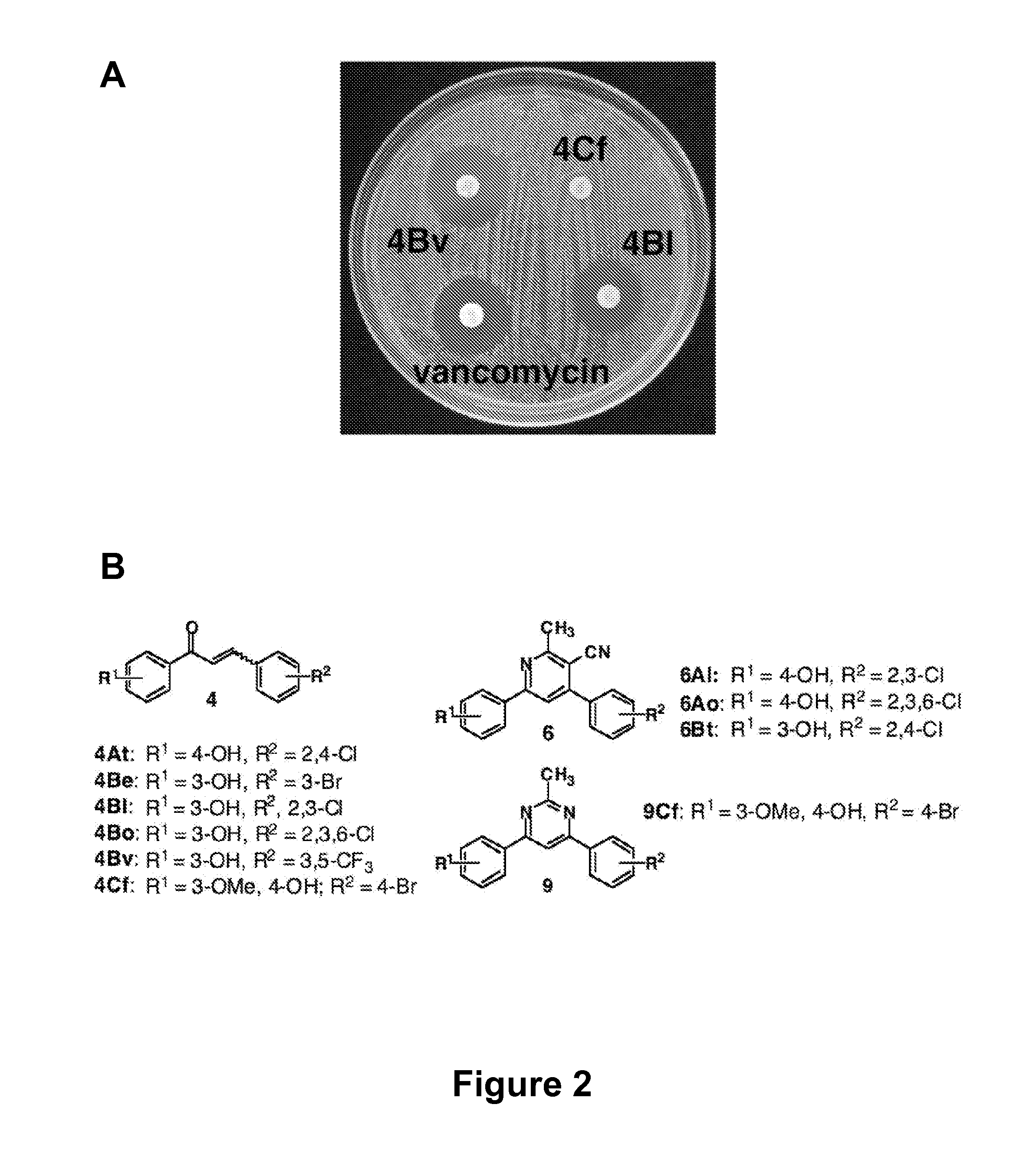
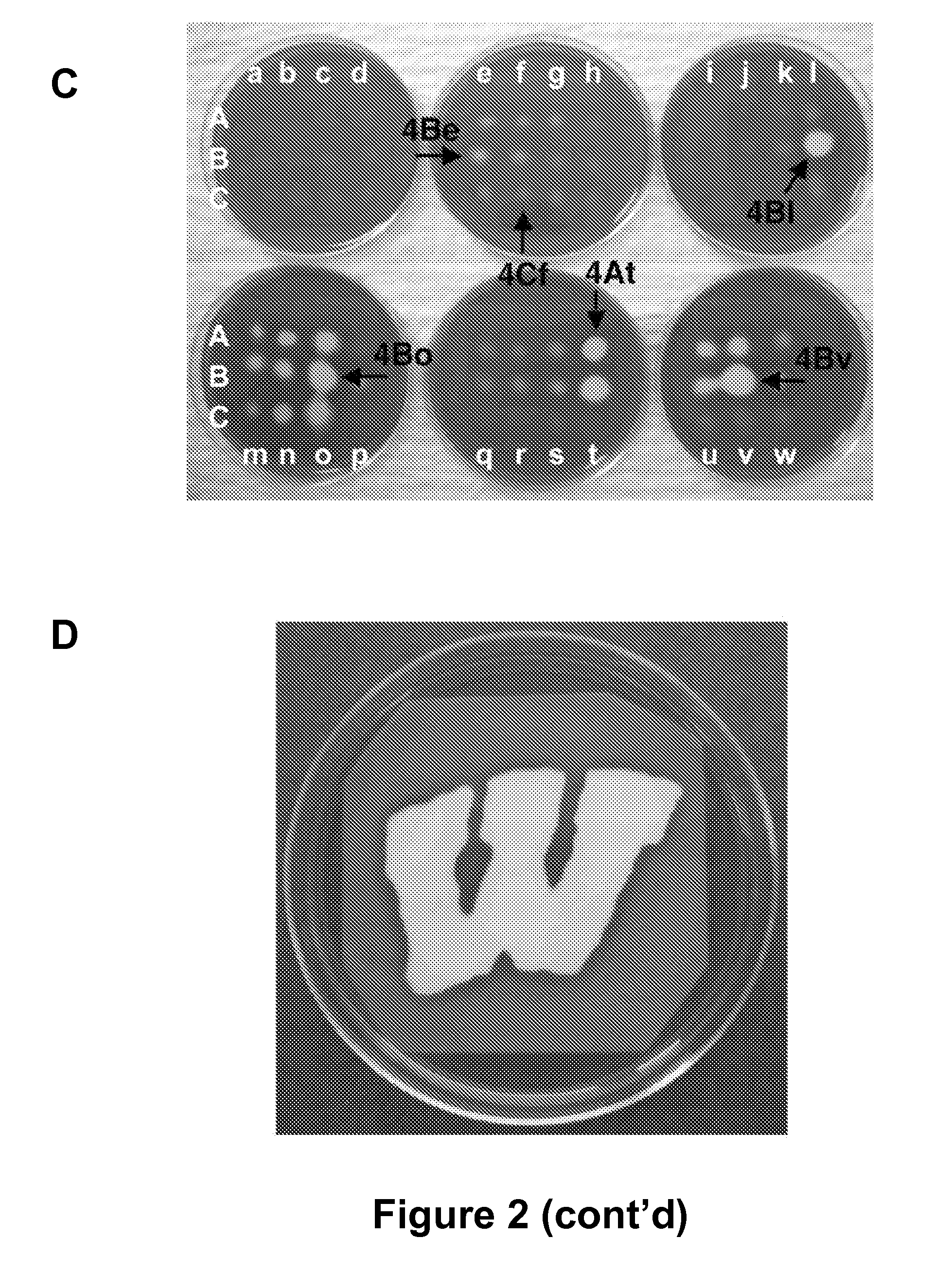
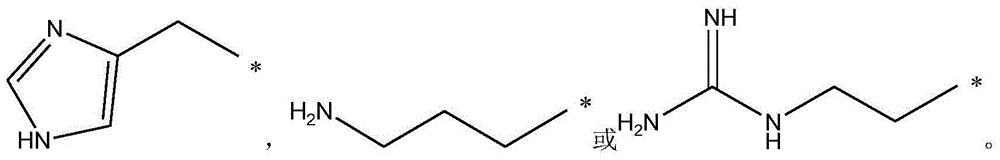
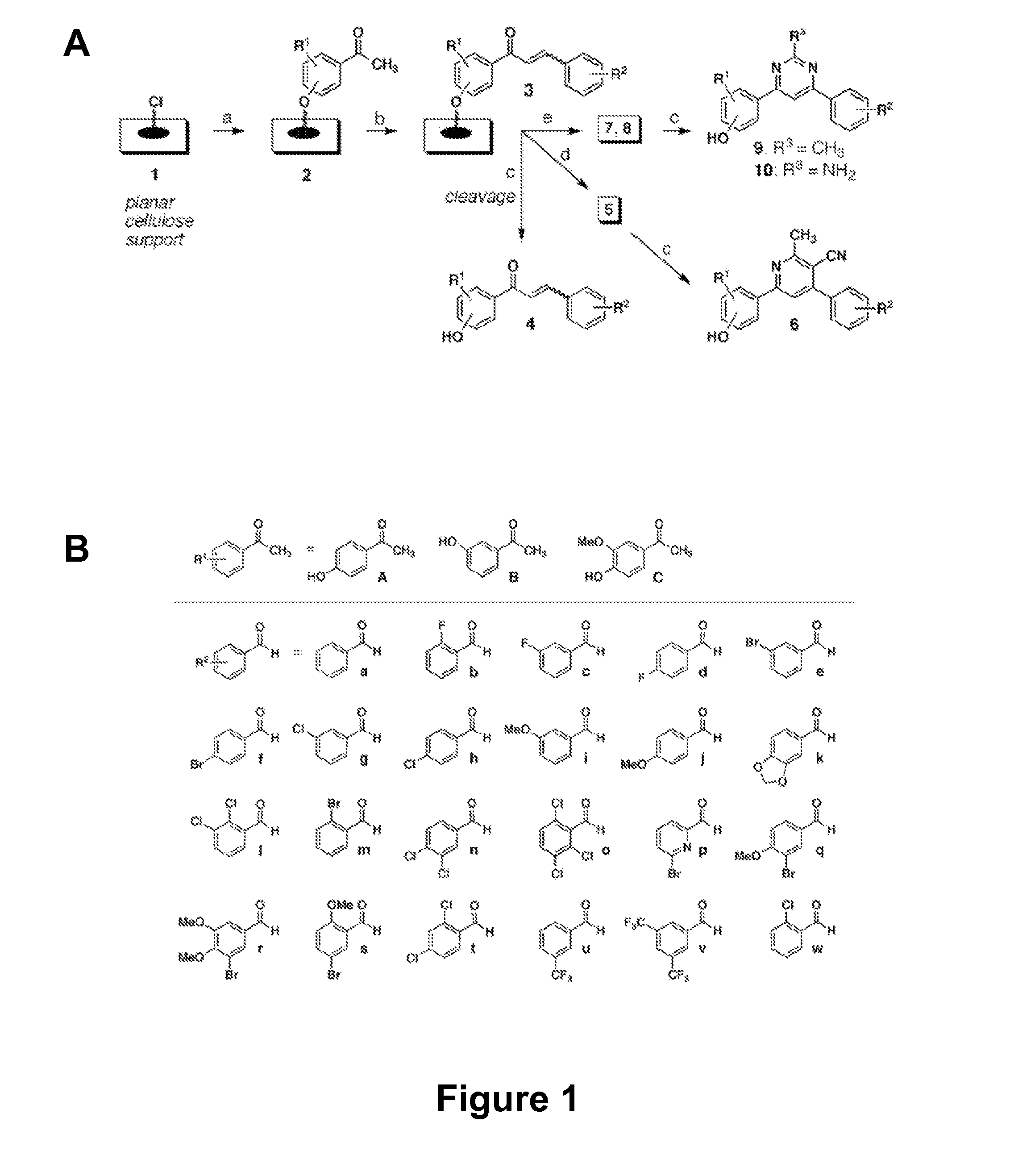
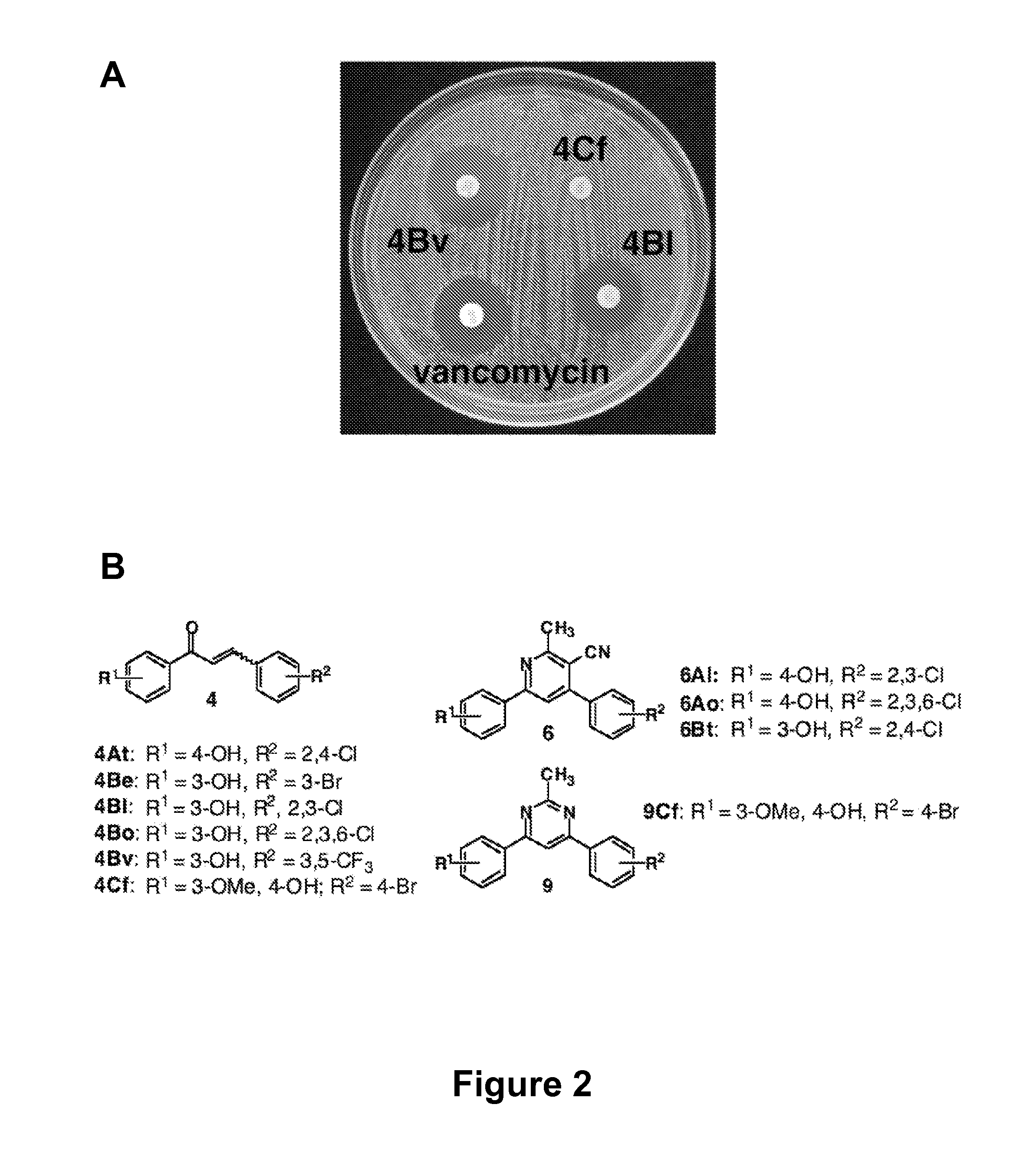
The present invention relates generally to compounds providing antibacterial therapeutic agents and preparations, and related methods of using and making antibacterial compounds. Antibacterial compounds of the present invention include chalcone, alkylpyrimidine, aminopyrimidine and cyanopyridine compounds and derivatives thereof exhibiting minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) similar to or less than conventional antibacterial compounds in wide use.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method and compositions for transdermal administration of antimicrobial medications
InactiveUS20060222692A1Avoid gastrointestinal side effectsReduce the possibilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideSerum concentrationMedicine
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for improved efficacy and delivery of time-dependent antimicrobial drug compositions to a patient. Transdermal dosage forms and methods for steady-state delivery of drug to produce and maintain a serum concentration of drug above the minimum inhibitory concentration or minimum microbicidal concentration are provided.
Owner:FAIRFIELD CLINICAL TRIALS
Preparation method of dual bacteriostatic cinnamyl aldehyde microcapsule
ActiveCN102885379ASolve the problem of excessive volatilizationMask the pungent spicy smellMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsEscherichia coliIrritation
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dual bacteriostatic cinnamyl aldehyde microcapsule, which comprises the following steps of: dissolving chitosan in glacial acetic acid to prepare chitosan solution; adding cellulose and performing enzymolysis reaction to obtain modified chitosan solution; dissolving Arabic gum in water to prepare Arabic gum solution; adding cinnamyl aldehyde, and emulsifying and dispersing at high speed to obtain emulsion; dropwise adding the modified chitosan solution into the emulsion, performing coagulation reaction, adding geniposide, and solidifying; and leaching, drying, and thus obtaining the dual bacteriostatic cinnamyl aldehyde microcapsule. The preparation method has the advantages that cinnamyl aldehyde bacteriostatic component loss is reduced, irritation and spicy of cinnamyl are covered, and cinnamyl aldehyde is slowly released in high-temperature and high-humidity environments; the modified chitosan and cinnamyl aldehyde simultaneously have dual bacteria-resistant effects, and can generate a good bacteria-resistant effect when added into a minced fish product; bacteria-resistant concentration is low, the lowest bacteria-resistant concentration of Escherichia coli can reach 0.10 percent, and the lowest bacteria-resistant concentration of staphylococcus aureus can reach 0.15 percent.
Owner:BOHAI UNIV
Antibacterial agents and related screening methods using small molecule macroarrays
ActiveUS20080009528A1Common methodFacilitates effectiveAntibacterial agentsBiocideHalogenMinimum inhibitory concentration
The present invention relates generally to compounds providing antibacterial therapeutic agents and preparations, and related methods of using and making antibacterial compounds. Antibacterial compounds of the present invention include chalcone, alkylpyrimidine, aminopyrimidine and cyanopyridine compounds and derivatives thereof exhibiting minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) similar to or less than conventional antibacterial compounds in wide use. For example, the present invention provides chalcone and cyanopyridine compounds, and derivatives thereof, exhibiting high antibacterial activities having multiple electron withdrawing group substituents, such as halogens and fluorinated alky groups, and optionally having hydroxyl and / or alkoxyl groups substituents.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Application of perylene tetracarboxylic dianhydride amidation compound in anti-staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN110156781AEasy to makeGood water solubilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic chemistryBacteroidesStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention provides an application of a perylene tetracarboxylic dianhydride amidation compound in anti-staphylococcus aureus. The compound is simple to prepare, a perylene tetracarboxylic dianhydride compound and N,N-dimethylethylenediamine are used as raw materials, multiple steps are carried out, the compound can inhibit the growth of staphylococcus aureus, and the bacteriostasis circle of the compound is up to about 10 mm measured by the K-B method. The compound is subjected to 2-fold gradient dilution, and the measured minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against staphylococcus aureus is up to 6.25 mg / mL. The growth curve inhibition test shows that when a growth curve of the bacteria in the non-drug treatment group enters the logarithmic phase, a growth curve of the bacteria in the compound treatment group is still in the lag phase, and indicates that the compound can inhibit the division of staphylococcus aureus. The discovered compound in the future can be used for the control of staphylococcus aureus infection, can also be applied in the preparation of antibacterial biomaterials, and has certain application value.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
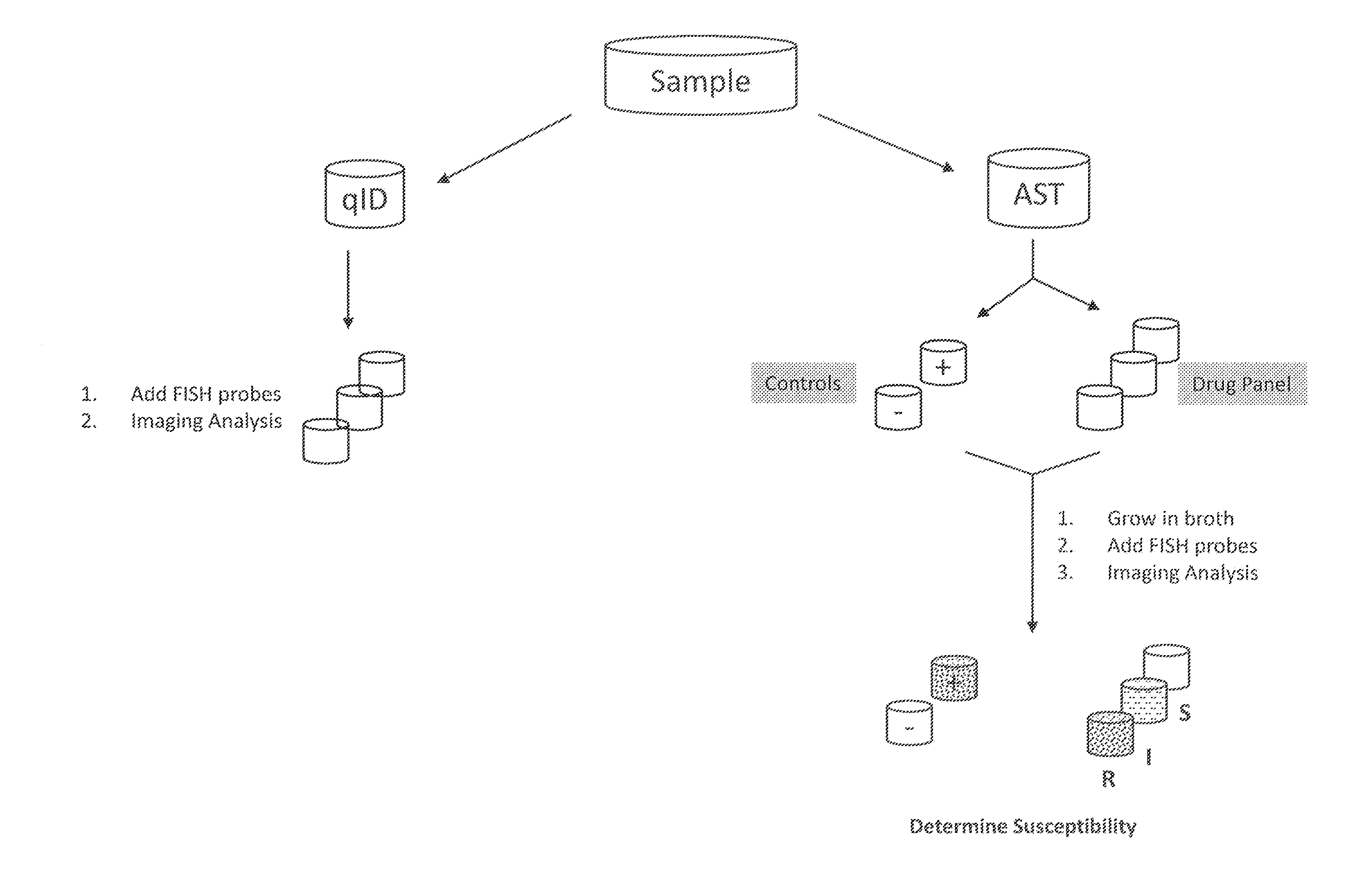
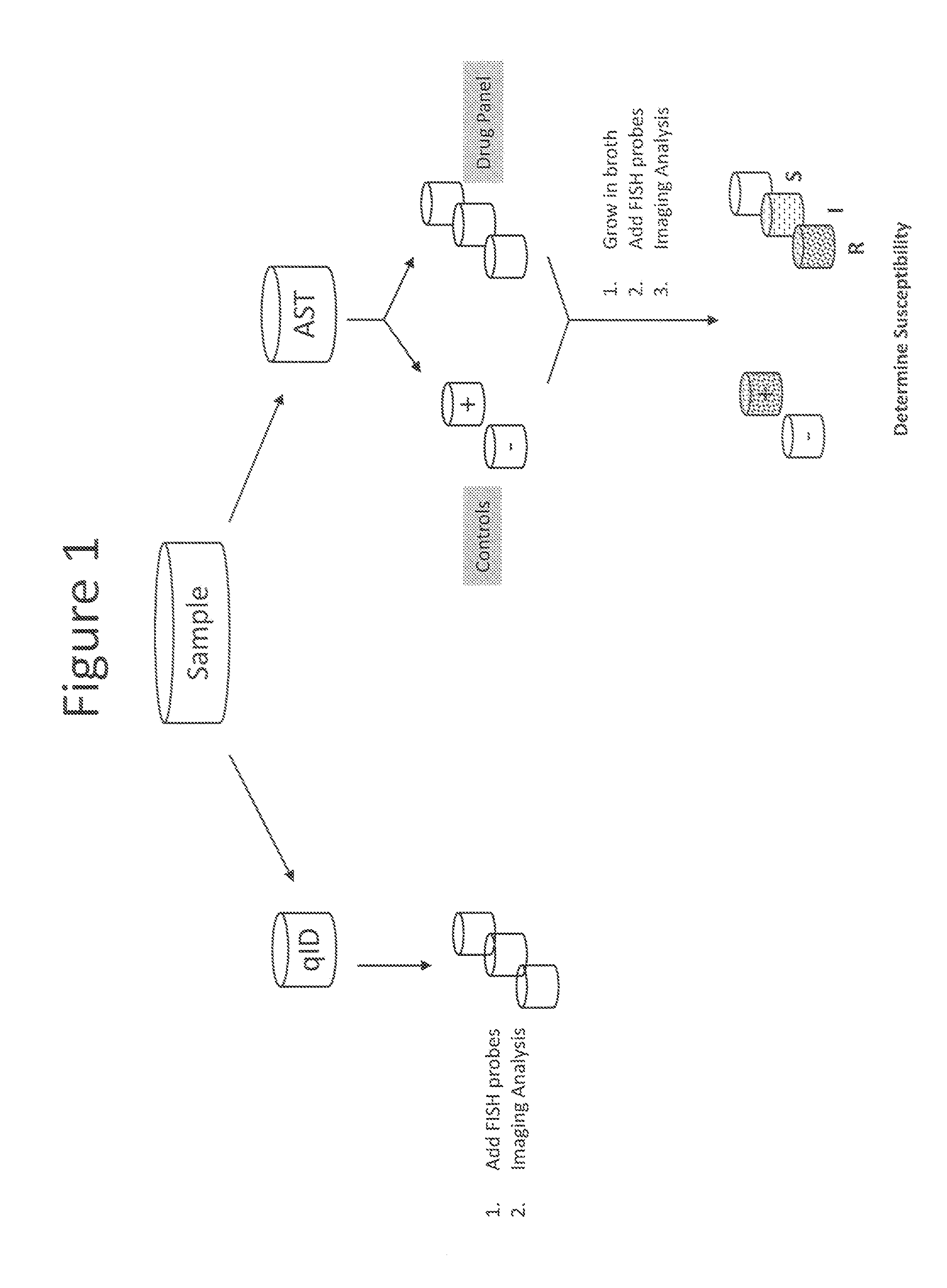
Antibiotice Susceptibility Profiling Methods
InactiveUS20110269130A1Low costReduce the necessary timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMinimum inhibitory concentrationRapid identification
The invention provides methods for the rapid determination of the antibiotic susceptibility of a microorganism, such as, an infectious microorganism in a biological sample, using fluorescence in situ hybridization (“FISH”). Methods of the invention may be applied to the rapid identification, typing, antibiotic susceptibility determination, and / or antibiotic minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination for any infectious microorganism, such as a Gram positive bacteria, a Gram negative bacteria, or a yeast.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Process for preparing bacteriostatic peptide by discarded tobacco leaf protein
InactiveCN1827773AHigh extraction rateImprove securityFermentationProtein foodstuffs working-upFood additiveBioactive peptide
The method comprises the following steps: using base solubilization and acid precipitaton method to extract protein from tobacco leaf to prepare tobacco leaf protein plasm; using composite proteinase to decompose the tobacco leaf protein plasm to prepare tobacco leaf protein enzymolysis liquid; using ultrafilter membrane to fractional separate the tobacco leaf protein enzymolysis liquid to get tobacco leaf protein bacteriostatic peptide mixed liquid; cooling drying or spray drying; getting the tobacco leaf protein bacteriostatic peptide compound which can suppress the growth of Gram-negative bacterium. The lowest bacteriostatic concentration is 0.05%. The invention uses the base solubilization and acid precipitaton method to improve the extraction rate of tobacco leaf protein, uses the biology enzymolysis to control the degradation speed of protein, and uses the ultrafilter membrane to separate enzymolysis liquid to get biology active peptide to simplify the operation technology and improve the effective concentration of biology active peptide.
Owner:GUANGDONG BRANCH OF CHINA TOBACCO GENERAL +1
Use of hop acids in fuel ethanol production
InactiveUS20060263484A1Accurate doseEffective controlMilk preparationBeer fermentationBacteroidesMinimum inhibitory concentration
Six hop acids are common to hops and beer: alpha acid, beta acids, isoalpha acids, rho-isoalpha acids, tetrahydro-isoalpha acids, and hexahydro-isoalpha acids. The six hop acids were tested to determine which were the most effective in inhibiting the growth of bacteria common to fuel ethanol production. The bacteria used in the tests were Lactobacillus brevis and Lactobacillus fermentum. The minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) of the hop acids were determined using MRS-broth. Molasses mash and wheat mashes were used as the growth media for the fermentations. In all cases the hop acids controlled the growth of these two lactobacillus bacteria with tetrahydroisoalpha acid, hexahydroisoalpha acid, and isoalpha acid killing the most bacteria at the lowest MIC. Treating yeast propagators, steep tanks, and fermenters with a minimum inhibitory concentration of hop acids will stop bacteria growth, increase ethanol yields and avoid the need for antibiotics.
Owner:JOHN I HAAS
D-type non-natural amino acid containing antimicrobial peptide analog, synthesis therefor and application of D-type non-natural amino acid containing antimicrobial peptide analog
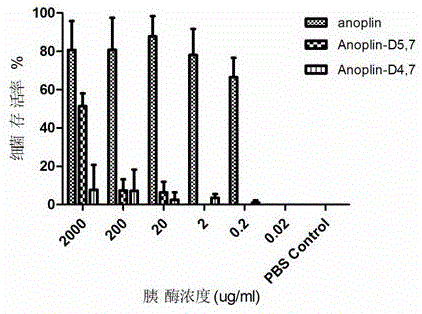
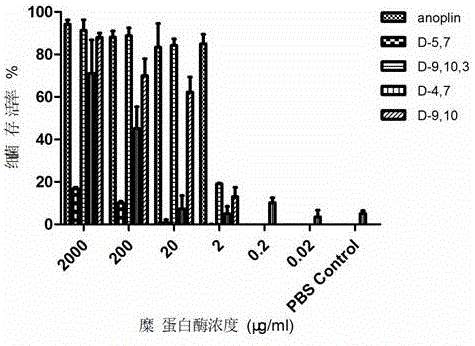
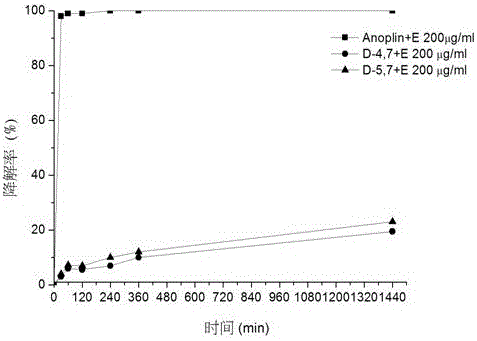
ActiveCN106632600AInhibition formationInhibition formation rateAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsAntimicrobial peptidesAntibacterial activity
The invention discloses a D-type amino acid containing antimicrobial peptide analog. The D-type amino acid containing antimicrobial peptide analog is obtained through separately introducing D-type amino acids to a hydrophilic surface and a hydrophobic surface of a natural antimicrobial peptide Anoplin and modifying the hydrophilic surface and the hydrophobic surface. Shown by determination on minimal inhibitory concentration to common standard bacteria, biomembrane formation inhibiting tests and enzymolysis stability tests, synthesized hydrophilic-surface D-type peptide analogs all reserve the antimicrobial activity of the original stock peptide and meanwhile represent relatively high bacterial biomembrane formation inhibiting capability. The chymotrypsin tolerance is enhanced by 10 times compared with that of the stock peptide Anoplin. Although the antimicrobial activity of synthesized hydrophobic-surface D-type substituted analogs is lowered to some extent compared with that of the stock peptide, the stability of the synthesized hydrophobic-surface D-type substituted analogs is improved remarkably; and compared with the stock peptide, the trypsin tolerance is improved by 10<4> to 10<5> times, and the chymotrypsin tolerance is improved by 10<2> times. Therefore, the synthesized D-type amino acid containing analog has a very good application prospect in the aspect of preparation of long-acting clinical antibacterials.
Owner:倪京满
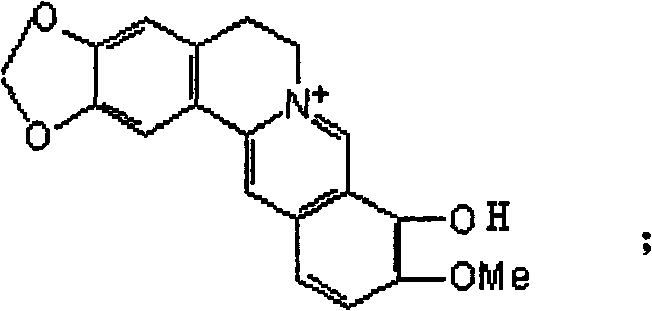
Synthetic method of berberine 13-bit derivant and berberrubine 13-bit derivant
InactiveCN101665491AEffective against Gram-positive bacteriaAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsBerberineAntimicrobial drug
The invention provides a synthetic method of a berberine 13-bit derivant and a berberrubine 13-bit derivant. The synthetic method is used to prepare derivants as follows: 13-benzyl berberine, 13-(2',4'-binitro) benzyl berberine, 13-benzyl berberrubine and 13-(2', 4'-binitro) benzyl berberrubine, which show excellent inhibiting effect on gram-positive bacterium, wherein the value of minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the berberine is 64mug / ml, the value of MIC of the berberrubine is larger then 128mug / ml, the values of MIC of the 13-benzyl berberine, the 13-(2',4'-binitro) benzyl berberine, the 13-benzyl berberrubine and the 13-(2',4'-binitro) benzyl berberrubine are respectively 32mug / ml, 16mug / ml, 32mug / ml and 8mug / ml. The synthetized derivants, the antimicrobial activity of whichis better than matrixes, can be used as raw materials of antimicrobial drugs.
Owner:CHANGCHUN UNIV OF TECH
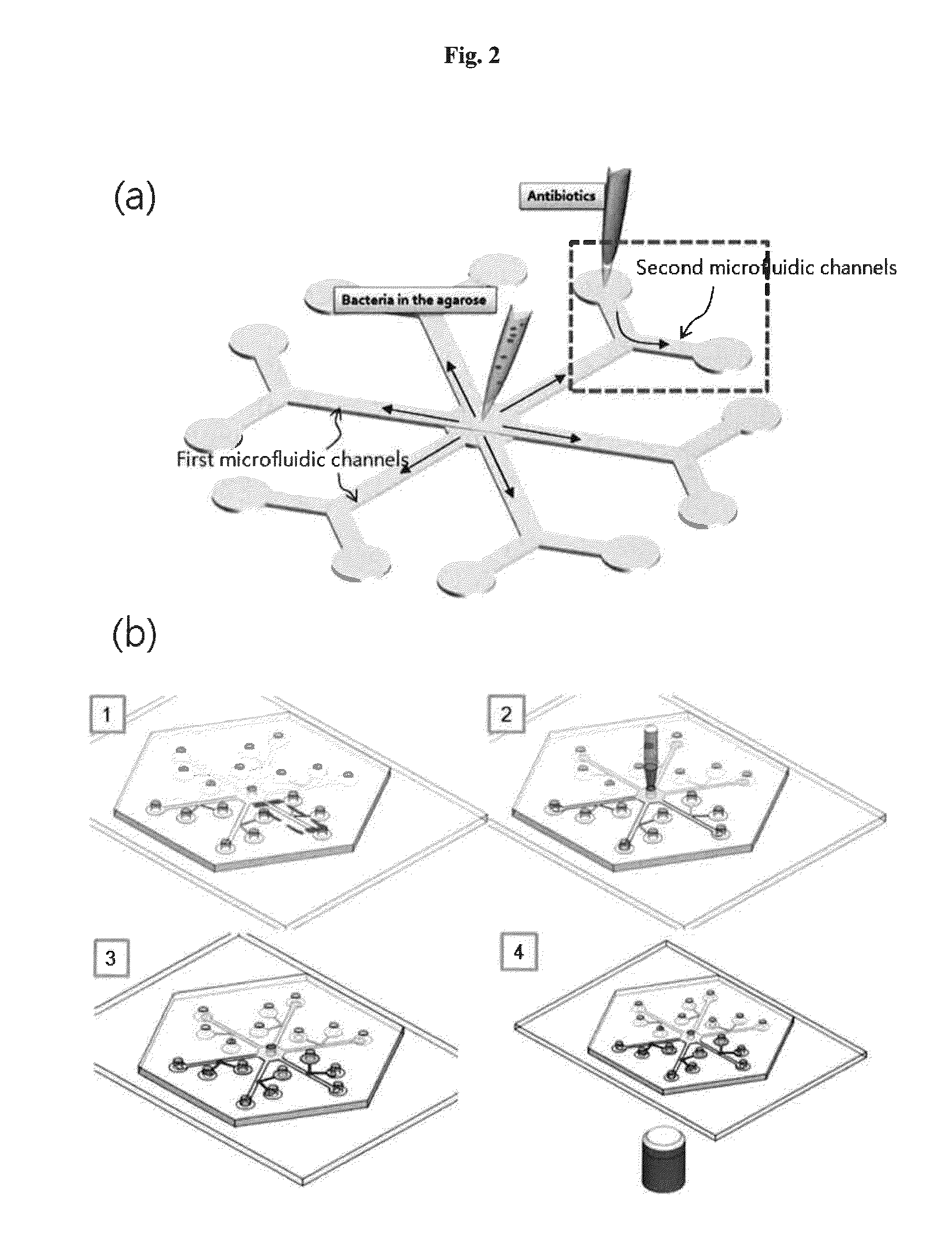
Rapid antibiotic susceptibility testing system based on bacterial immobilization using gelling agent, antibiotic diffusion and tracking of single bacterial cells
ActiveUS20130196364A1Prevent burstBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMinimum inhibitory concentrationDrug biological activity
A testing method is disclosed. The testing method includes: providing a mixture solution of a gelling agent and a microbe to a gelling device; solidifying the mixture solution to form a solid thin film in which the microbe is immobilized; supplying a bioactive agent to the solid thin film and allowing the bioactive agent to diffuse into the solid thin film; and imaging the individual responses of the single microbial cells to the bioactive agent, and determining the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the bioactive agent based on the analysis of the images to obtain AST results.
Owner:QUANTA MATRIX
Method for rapidly screening and evaluating antibiotic bioactivator
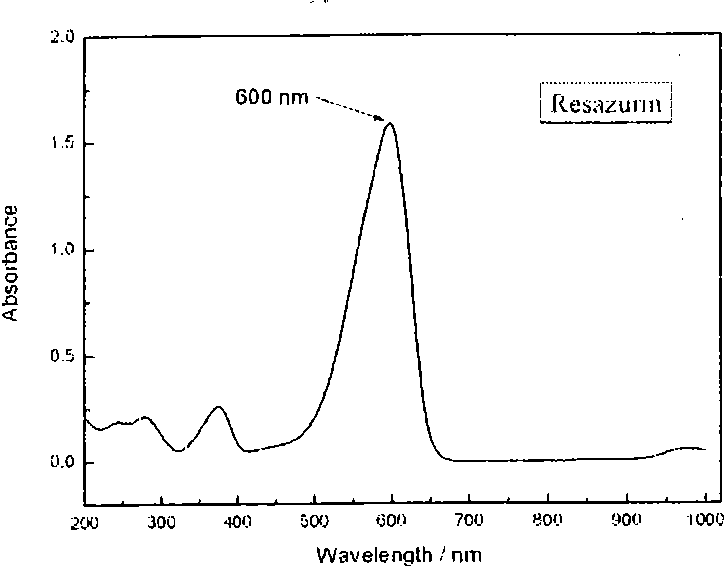
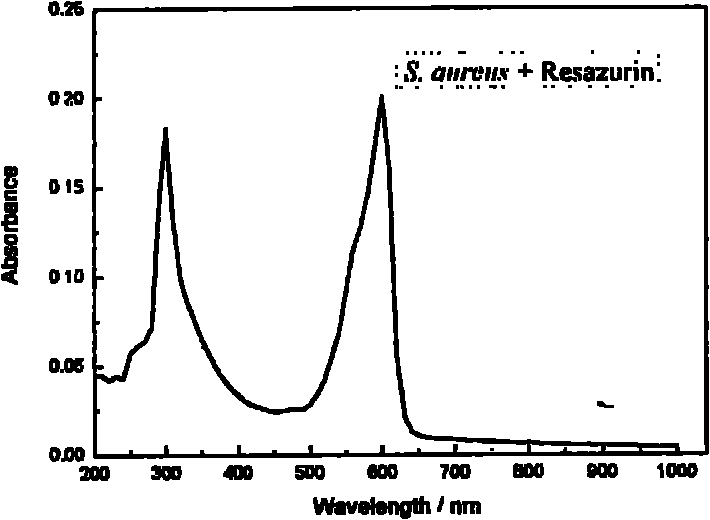
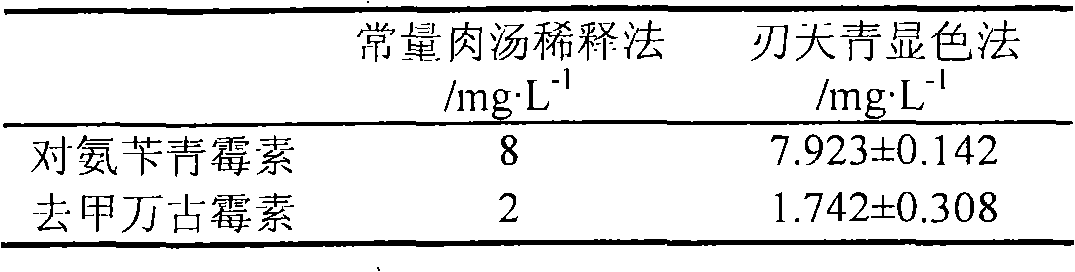
InactiveCN102199653AImprove efficiencyReduce usageMicrobiological testing/measurementResazurinMICROBIAL CONCENTRATION
The invention discloses a method for rapidly screening and evaluating an antibiotic bioactivator, in particular a test method for screening the antibiotic bioactivator by combining an accelerated solvent extraction apparatus and a microplate resazurin assay. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a bioactivator by the accelerated solvent extraction apparatus; adding the bioactivator and known antibiotic into a microplate according to concentration gradient, and adding experimental bacterial suspension into various holes; placing the microplate under suitable conditions, incubating, adding resazurin solution, and mixing uniformly; determining light absorption values of the holes of the microplate at 600nm by using a microplate reader; evaluating a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) value of the bioactivator to be screened according to light absorption values in known antibiotic holes and light absorption values in bioactivator holes at different concentrations; and further evaluating the antibiotic activity of the bioactivator. The method is rapid, simple and convenient, and the antibiotic activity of the bioactivator can be objectively and accurately evaluated, so that the high-throughput screening of the antibiotic bioactivator becomes possible.
Owner:HAINAN UNIVERSITY
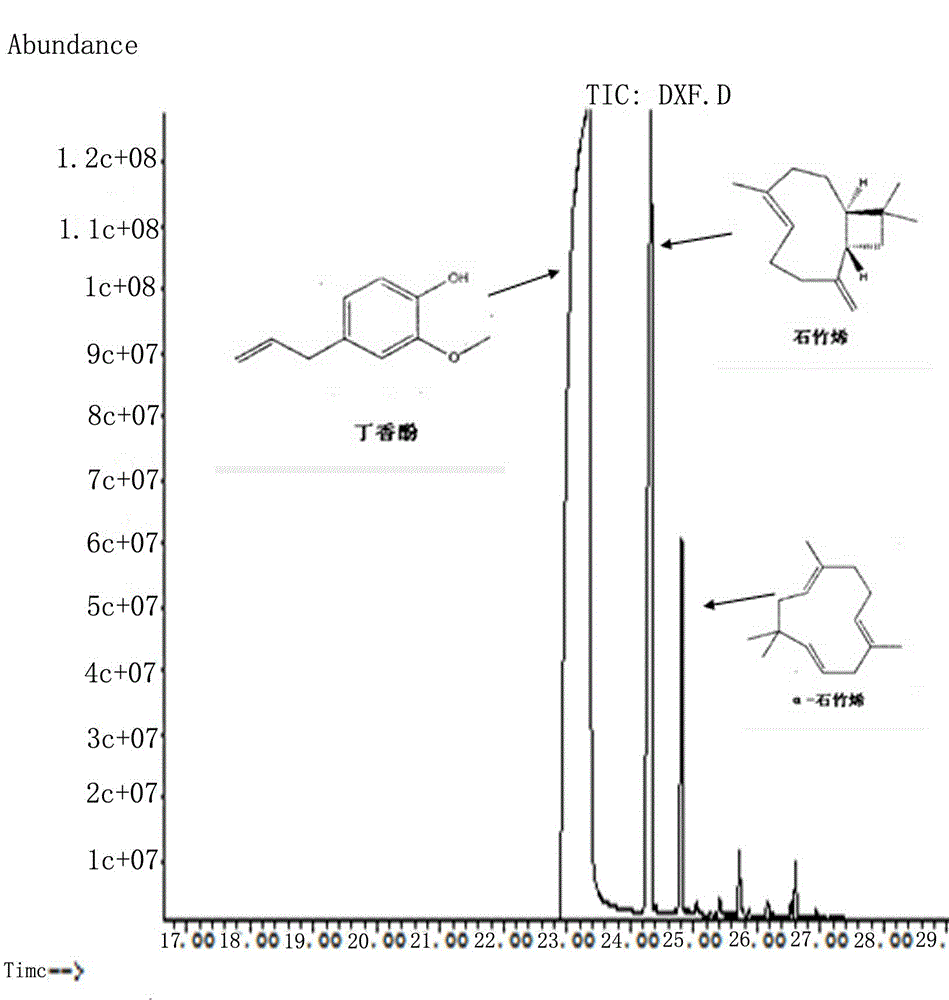
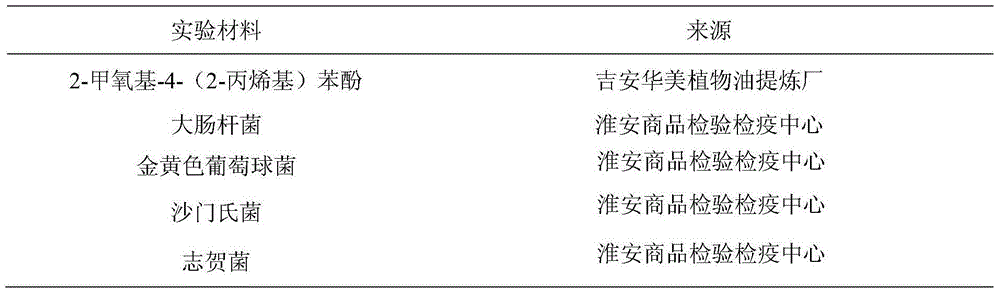
Application of eugenol in food-borne pathogenic bacterium in-vitro inhibition
The invention relates to application of eugenol and in particular relates to application of eugenol in food-borne pathogenic bacterium in-vitro inhibition, culture mediums of food-borne pathogenic bacterium are TSA culture mediums or TSB culture mediums with pH values being 5.0, 6.0 and 7.0; the diameter of an inhibition zone is measured for judging antibacterial activity of eugenol; and a multiple dilution method is adopted for carrying out minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) determination on various bacteria. The application of eugenol in the food-borne pathogenic bacterium in vitro inhibition has the advantages that escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, salmonella and shigella are taken as research objects, MIC of 2-methoxy-4-(2-propenyl) phenol on common pathogens in food is researched, influence of pH on antibacterial effect of 2-methoxyl-4-(2-propenyl) phenol is studied, and application value of 2-methoxy-4-(2-propenyl) phenol in food antisepsis aspect is researched; and application range of 2-methoxy-4-(2-propenyl) phenol can be beneficially expanded.
Owner:JIANGSU TIANSHENG PHARMA
Devices and Methods for the Selection of Agents with Efficacy Against Biofilm
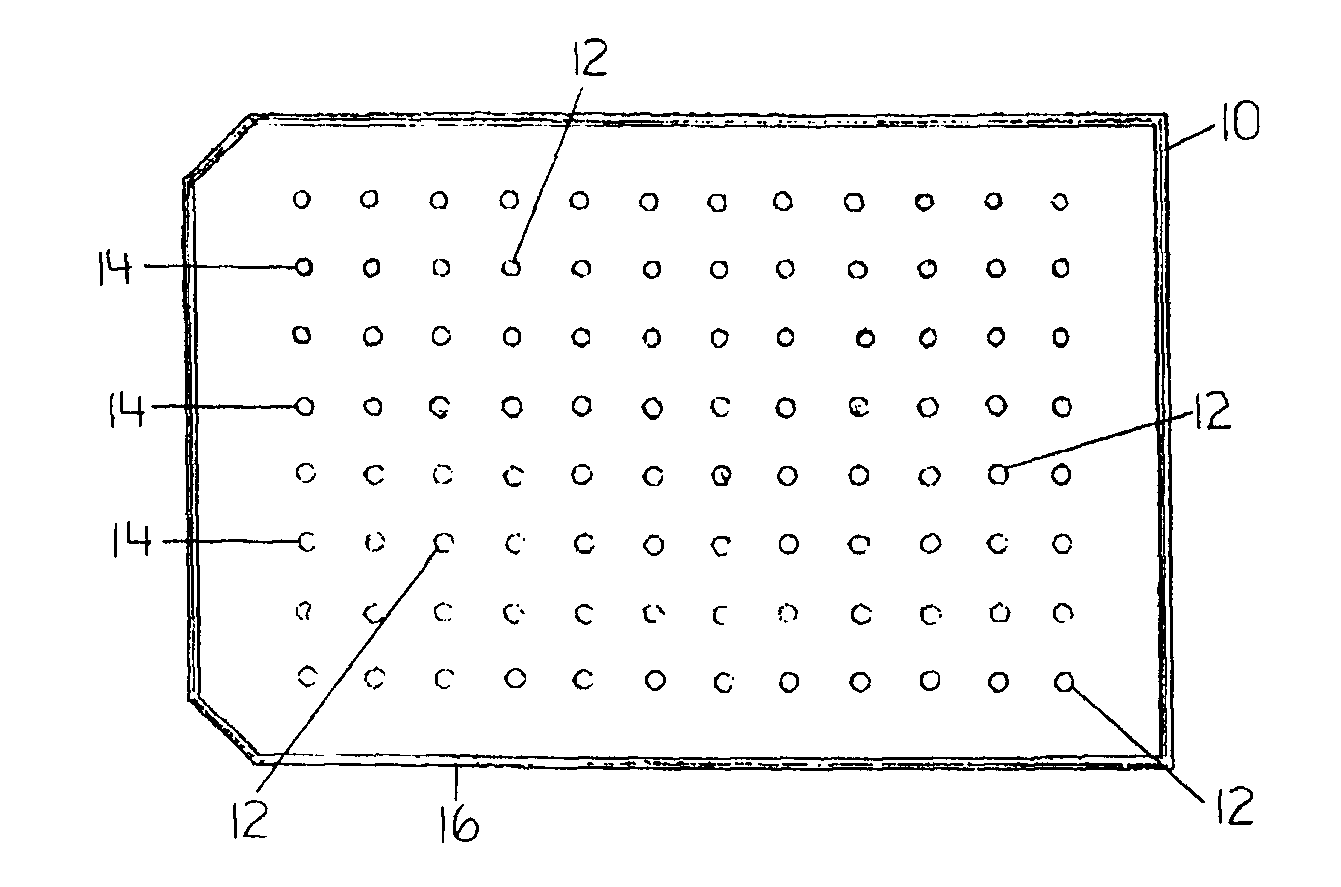
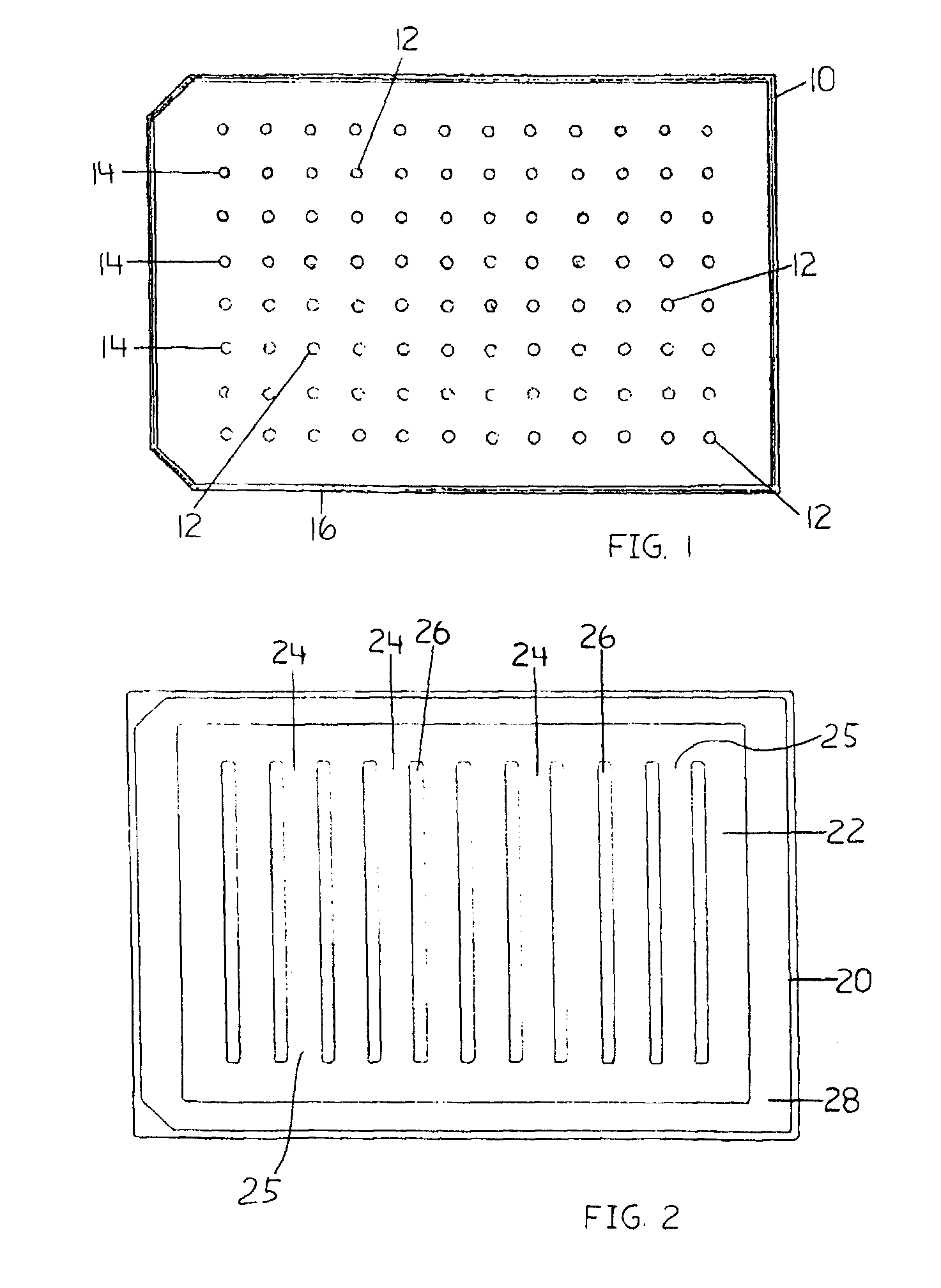
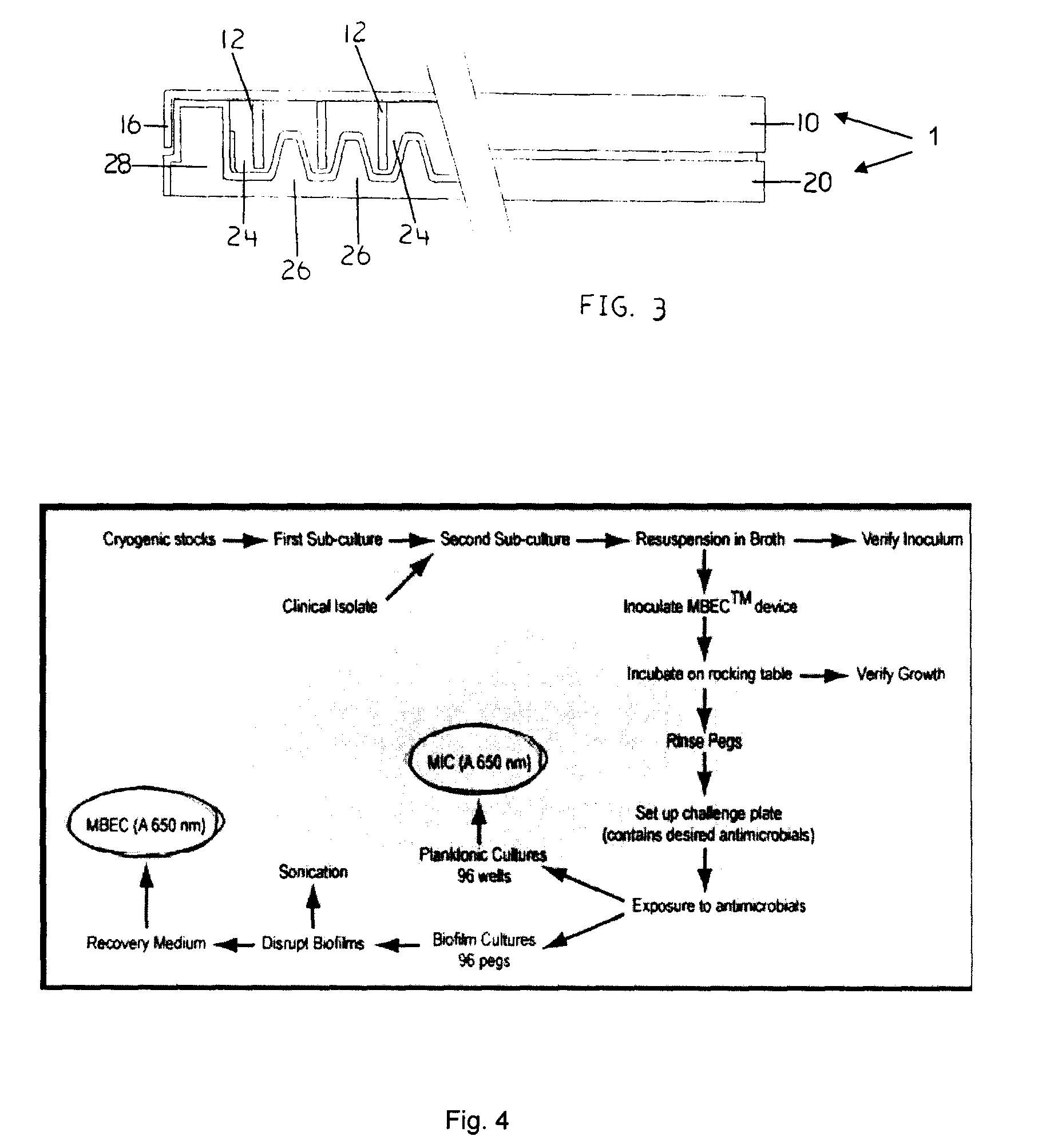
InactiveUS20080318268A1Efficient and cost-effectiveBroaden applicationBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibiotic sensitivityMinimum inhibitory concentration
This invention is a diagnostic plate that can be used to select antibiotic combinations with efficacy against microorganisms growing as a biofilm. The plate allows growth of biofilm on a plurality of projections, and the subsequent simultaneous challenge of biofilms on all projections of the plate to independent concentrations and combinations of anti-biofilm agents. Resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics is higher when they grow as a biofilm, as compared to when they grow in a planktonic state which is usually used to determine their level of antibiotic sensitivity. Growth of microorganisms that slough off the biofilm in the anti-biofilm agent challenge determines the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) which relates to sensitivity of the microorganisms in a planktonic state. Growth of any surviving microorganisms from the biofilm in a subsequent recovery step determines the Minimal Biofilm Eradication Concentration (MBEC) which relates to the sensitivity of the microorganisms growing as a biofilm. Enumeration of the surviving microorganisms in the recovery step determines the Minimum Biocidal Concentration (MBC).
Owner:OLSON MERLE E +1
Beta-lactamase inhibitor
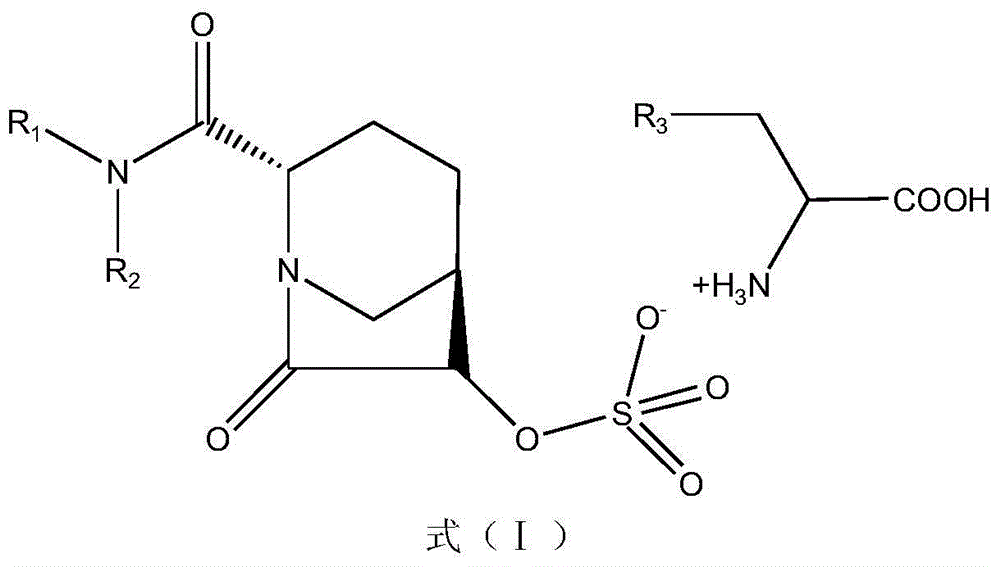
InactiveCN105801579AExtended half-lifeLower minimum inhibitory concentrationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHalf-lifeAvibactam sodium
The invention discloses a beta-lactamase inhibitor. The beta-lactamase inhibitor can inhibit A-type beta-lactamases (such as SHV, TEM and CTX), C-type beta-lactamase (mainly comprising an AmpC enzyme) and D-type beta-lactamase (such as OXA), has good inhibition effects and can reduce the lowest ceftazidime bacteriostasis concentration through combination with ceftazidime. Compared with tazobactam, the beta-lactamase inhibitor has a longer half life. A part of the beta-lactamase inhibitor has a half life longer than that of avibactam sodium. The beta-lactamase inhibitor provides more possibility for antibiotic development.
Owner:卢来春
Cyanopyridine antibacterial agents
ActiveUS7737164B2Common methodFacilitates effectiveAntibacterial agentsBiocideHalogenMinimum inhibitory concentration
The present invention relates generally to compounds providing antibacterial therapeutic agents and preparations, and related methods of using and making antibacterial compounds. Antibacterial compounds of the present invention include chalcone, alkylpyrimidine, aminopyrimidine and cyanopyridine compounds and derivatives thereof exhibiting minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) similar to or less than conventional antibacterial compounds in wide use. For example, the present invention provides chalcone and cyanopyridine compounds, and derivatives thereof, exhibiting high antibacterial activities having multiple electron withdrawing group substituents, such as halogens and fluorinated alky groups, and optionally having hydroxyl and / or alkoxyl groups substituents.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Antibacterial small molecules and methods for their synthesis
ActiveUS8367680B2Good water solubilityIncrease diversityAntibacterial agentsBiocideMinimum inhibitory concentrationSynthesis methods
The present invention relates generally to compounds providing antibacterial therapeutic agents and preparations, and related methods of using and making antibacterial compounds. Antibacterial compounds of the present invention include chalcone, alkylpyrimidine, aminopyrimidine and cyanopyridine compounds and derivatives thereof exhibiting minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) similar to or less than conventional antibacterial compounds in wide use.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
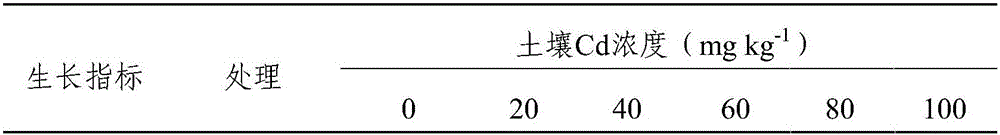
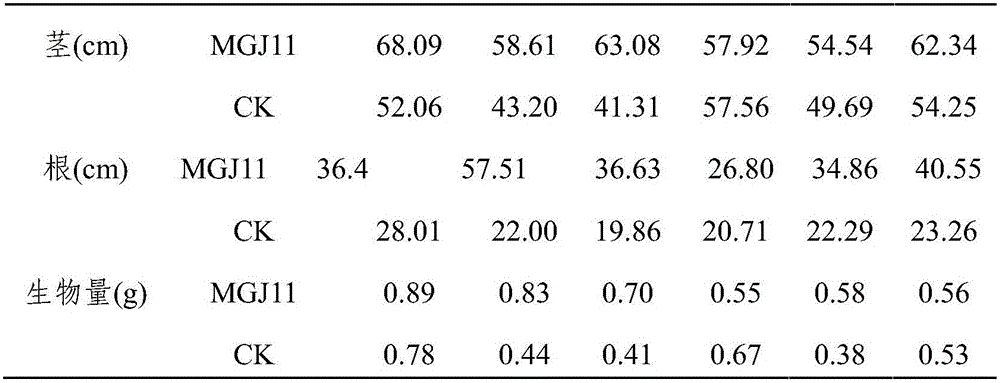
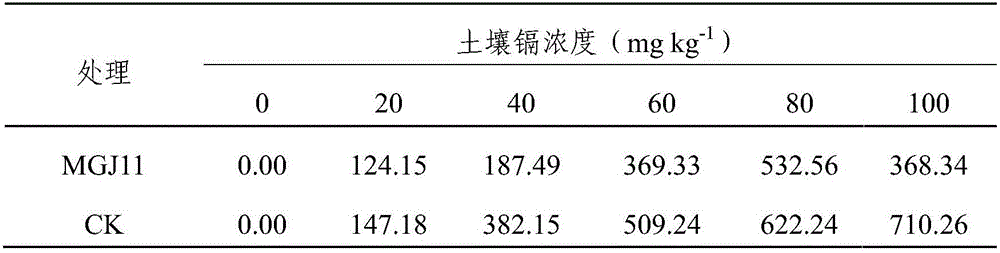
Ochrobacterum sp. MGJ11, and method of immobilizing heavy metal cadmium in soil therewith
ActiveCN105670955AReduced enrichmentPromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsMicroorganismSoil heavy metals
The invention relates to the technical field of microorganism and environment treatment, and particularly discloses an ochrobacterum sp. MGJ11, which is deposited with the CGMCC at Sep 16th, 2015 and is assigned the accession number CGMCC No.11385. The invention also discloses a method of immobilizing heavy metal cadmium in soil with the ochrobacterum sp. MGJ11, wherein the method particularly includes the steps of applying the ochrobacterum sp. MGJ11 to rhizosphere of plants, or mixing powder of the ochrobacterum sp. MGJ11 with seeds and planting the seeds, wherein the concentration of the inoculated microorganism is not less than 10<9> bacterial cells in every plant.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Drugs
ActiveCN102288586AMIC value is accurateLow costFluorescence/phosphorescenceMinimum inhibitory concentrationConcentration gradient
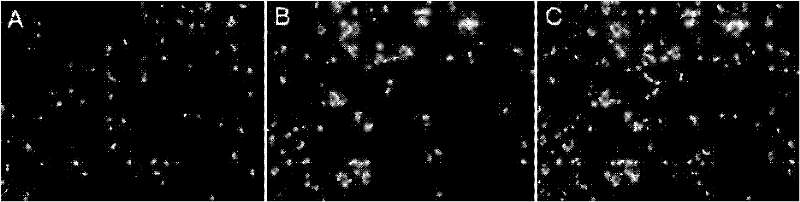
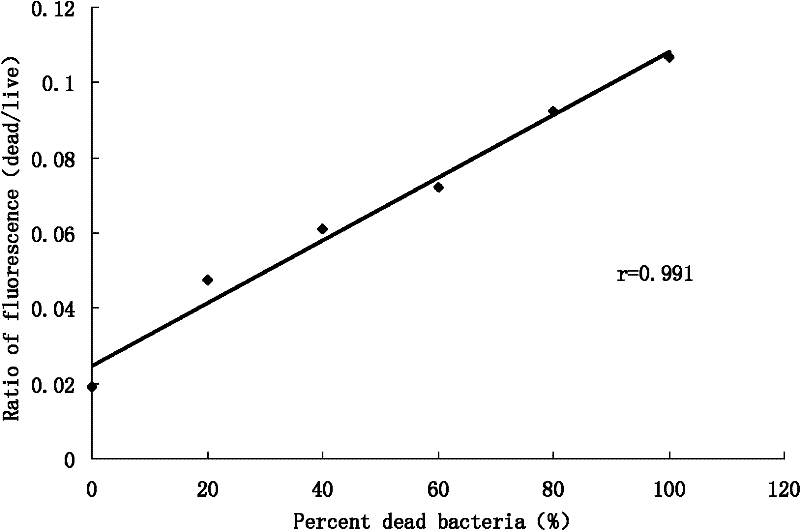
The invention discloses a method capable of rapidly, simply, conveniently and quantitatively detecting minimal inhibitory concentration, and the method comprises the following steps of: in accordance with the standard of CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute) (Version 2010), adding a fresh enterococcus suspension of a certain concentration into a sterile 96-well plate containing concentration gradient antibacterials for co-incubation; upon the ending of the 4-hour incubation, adding a fixed amount of fluorescent dyes SYTOX Green and DAPI (4,6-diamino-2-phenyl indole) to all the wells, protecting the wells from light for 15 minutes at room temperature, reading the fluorescent intensity of the two dyes in the wells by use of a fluorescent microplate reader respectively; after relevant background fluorescence is deducted, drawing a corresponding curve between bacterial fluorescence intensity ratio (Pdead / livel) and concentration of drug (CDrug), and determining the minimal concentration of drug corresponding to the moment the Pdead / livel is no longer fluctuated as the MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) of the antibiotic to the bacterium. The detection method provided by the invention has the characteristics of being simple, convenient, rapid and objective and being capable of performing mathematic statistics and analysis directly on detected data, becomes a new detection method for determining the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibacterials, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
Preparation method of cellulose-based antibacterial material dialdehyde cellulose-lysine
The invention relates to a novel cellulose-based antibacterial material, which is mainly produced via the steps of: controlling reaction temperature, time, pH value and oxidization ratio of dialdehydecellulose in order to perform a reaction to the dialdehyde cellulose and lysine, and when the reaction is finished, performing centrifugal separation and drying and grinding the product. The antibacterial material has excellent antibacterial activity, and can reach 30 mg / ml in minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) against Gram negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, and 7.5 mg / ml in MIC against Gram positive bacteria, such as staphylococcus aureus, with penicillin as a positive control and an LB liquid culture medium as a negative control; under special conditions, the antibacterial material can completely growth of bacteria. The antibacterial material has simple process and is free of toxic and side effect. The raw material, cellulose, has abundant sources and is environment friendly. The invention supplies a new idea for researching and developing novel antibacterial materials.
Owner:江苏灵源沂岸科技股份有限公司
Application of natural compound ursolic acid on antibiosis
InactiveCN101543499AHigh activityWidely distributed in natureAntibacterial agentsBiocideStaphylococcus cohniiAntibiotic tested
The invention relates to application of natural compound ursolic acid on antibiosis, in particular to application of the combination of the natural compound ursolic acid and penicillin on resisting drug resistant staphylococcus aureus. The compound ursolic acid is widely distributed in nature, so that the material source is wide. Aiming at the serious problem of the drug resistance of the staphylococcus aureus at present, the in vitro and in vivo antibiotic tests are carried out for the ursolic acid. Particularly the in vitro synergic test proves that the ursolic acid has better antibacterial activity on the drug resistant staphylococcus aureus under the combination action of the ursolic acid and the penicillin, and the lowest bacteriostatic concentration is 1.13 mu g / disc; moreover, the in vivo test also shows that the ursolic acid has better activity under the synergic action.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Method for quickly detecting drug resistance of bacteria
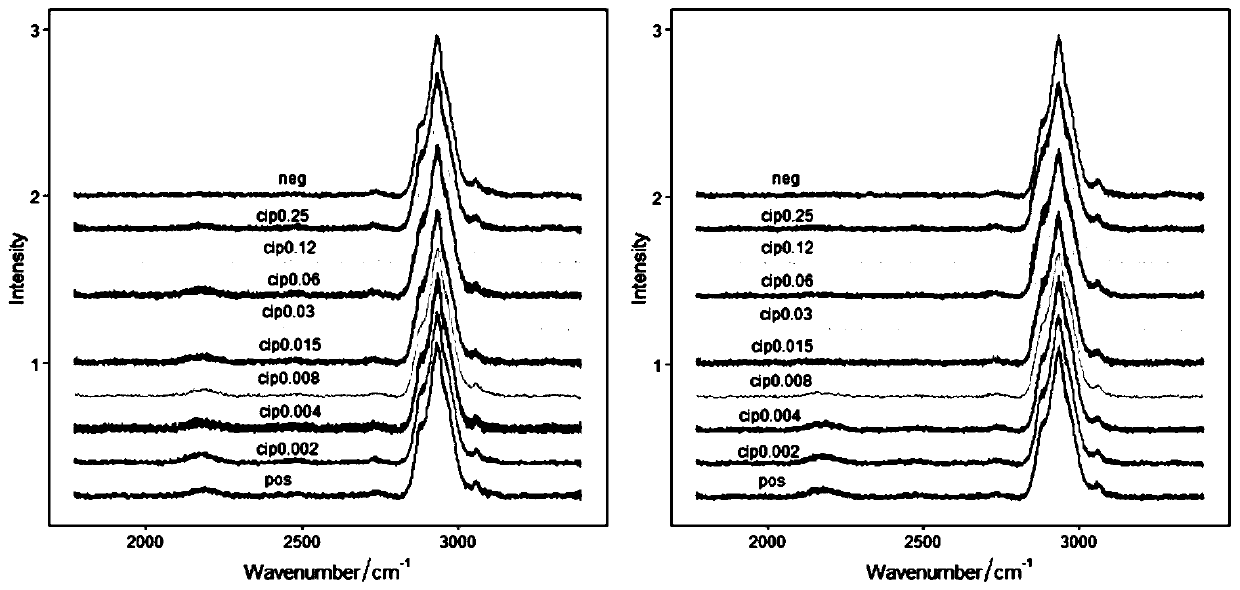
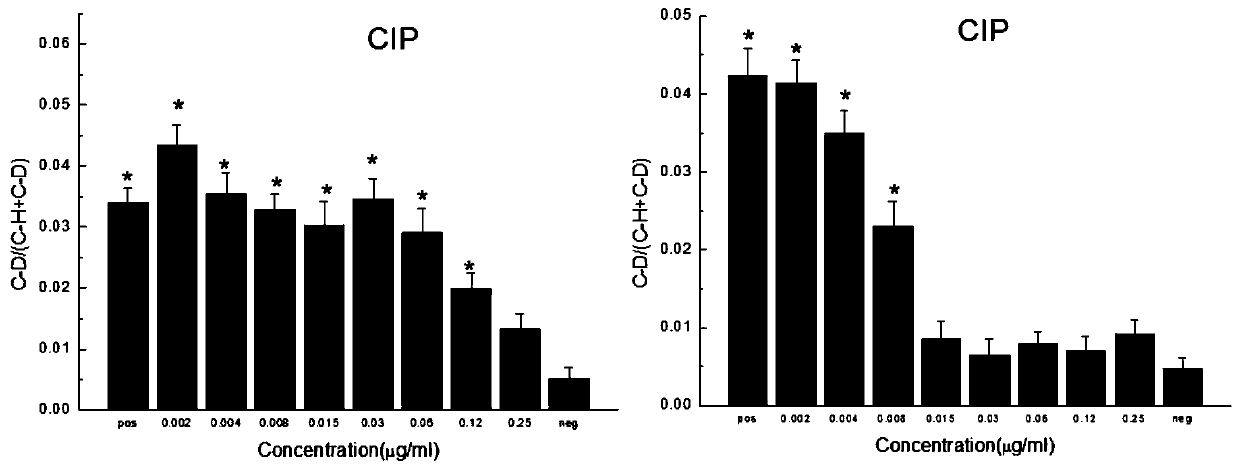
PendingCN110643675AStrong metabolic activityExactly give the sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRaman scatteringMinimum inhibitory concentrationDrug resistance
The invention relates to a method for quickly detecting drug resistance of bacteria. The method comprises the following steps: experimental groups of antibiotics with different concentrations, a positive control group and a negative control group are set, wherein the experimental groups of the antibiotics with the different concentrations refer to experimental groups of adding the antibiotics withthe different concentrations into culture mediums and adding heavy water in subsequent steps, the positive control group refers to the experimental group of adding antibiotics with a concentration of0 into a culture medium and adding heavy water in subsequent steps, and the negative control group refers to the experimental group of adding antibiotics with a concentration of 0 intp a culture medium without adding heavy water in subsequent steps, after incubation is performed, centrifugal washing is performed, samples are subjected to Raman detection, values of C-D / (C-D + C-H) are calculated respectively according to the obtained Raman spectra, a turning point of value decrease of C-D / (C-D + C-H) of the experimental groups of the antibiotics with different concentrations relative to the control groups is taken as a minimum inhibitory concentration of the antibiotics on the bacteria, and the minimum inhibitory concentration is compared with a breakpoint given in a CLSI susceptibility test standard to determine the bacterial sensitivity, intermediation or drug resistance. The method introduces a breakpoint comparison to more accurately give the sensitivity of the bacteria to the antibiotics.
Owner:上海氘峰医疗科技有限公司
Method for the identification and quantification of microorganisms useful in biomining processes
InactiveUS20110136125A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAcidithiobacillus thiooxidansMathematical formula
The present invention discloses a method to identify and quantify environmental microorganisms useful in biomining processes. These microorganisms are basically 10, belonging to Bacteria: Acidiphilium sp., Leptospirillum sp., Sulfobacillus sp., Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans and Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans; and Archaea: Acidianus sp., Ferroplasma sp., Metallosphaera sp., Sulfolobus sp. and Thermoplasma sp.The method comprises performing a PCR with specific primers designed in our laboratories for different taxons SEQ ID No. 4 to SEQ ID No.: 407. With qPCR results and other data obtained from the analyzed sample, the microorganism concentration of each analyzed taxon present in the sample is calculated using a mathematical formula.
Owner:BIOSIGMA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com