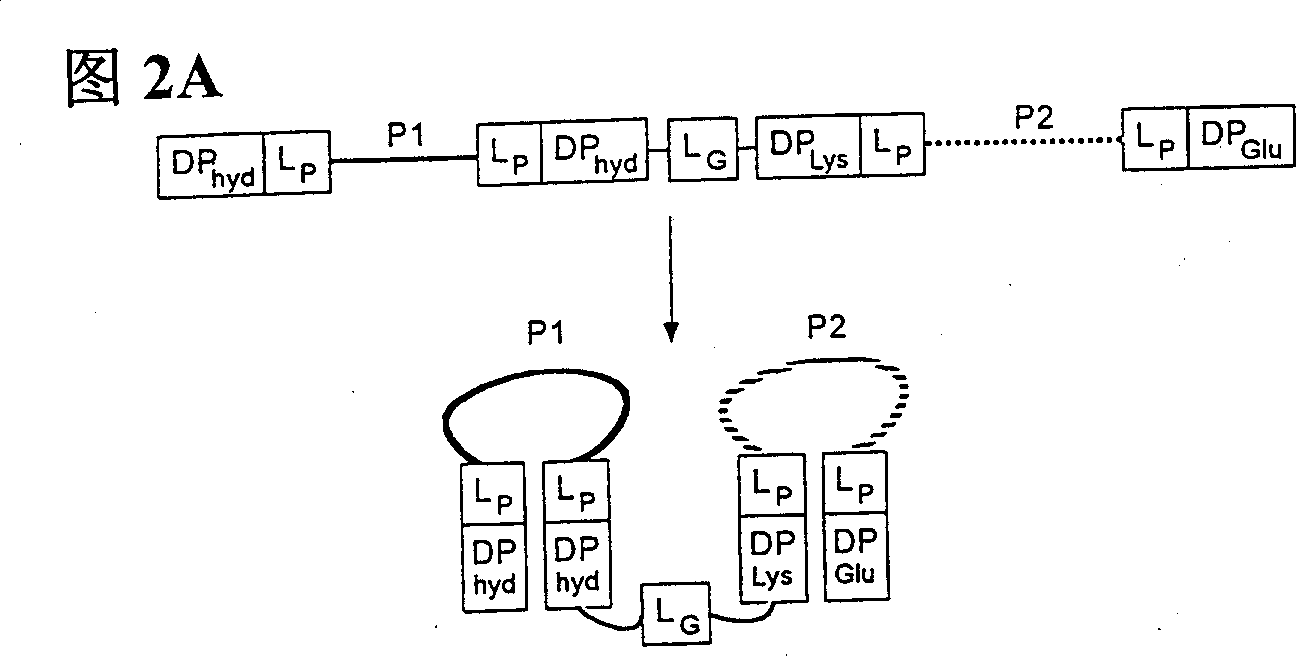
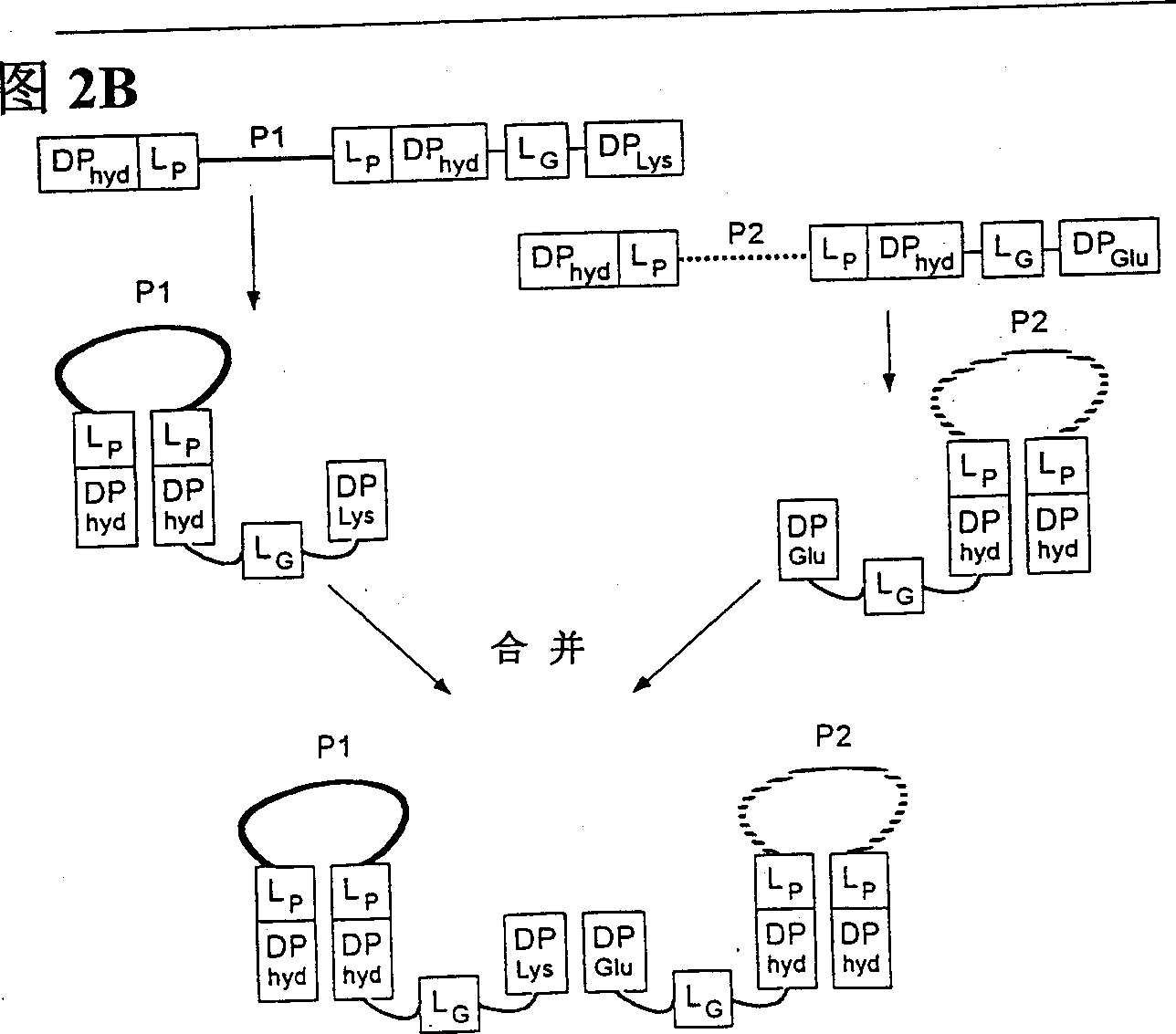
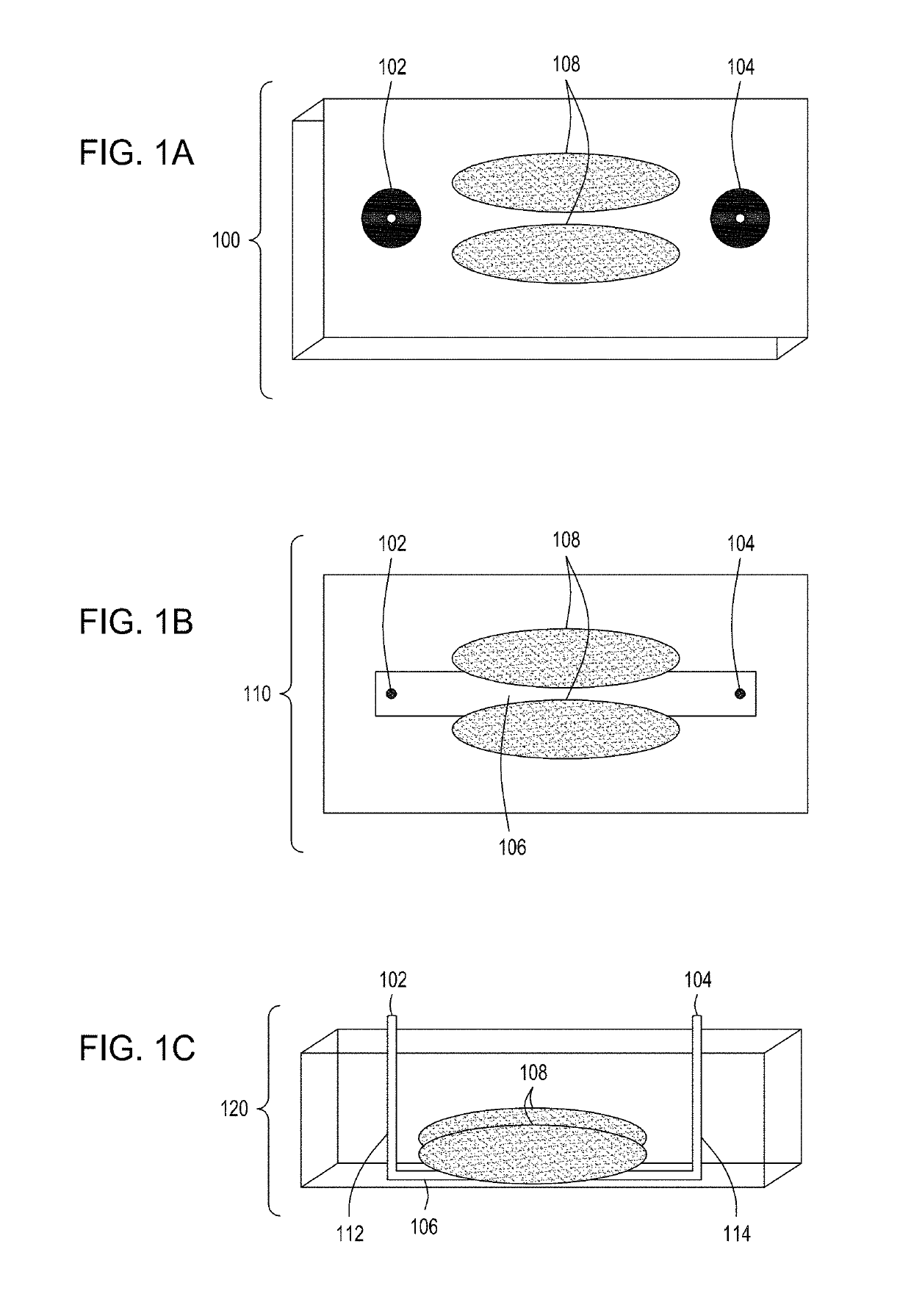
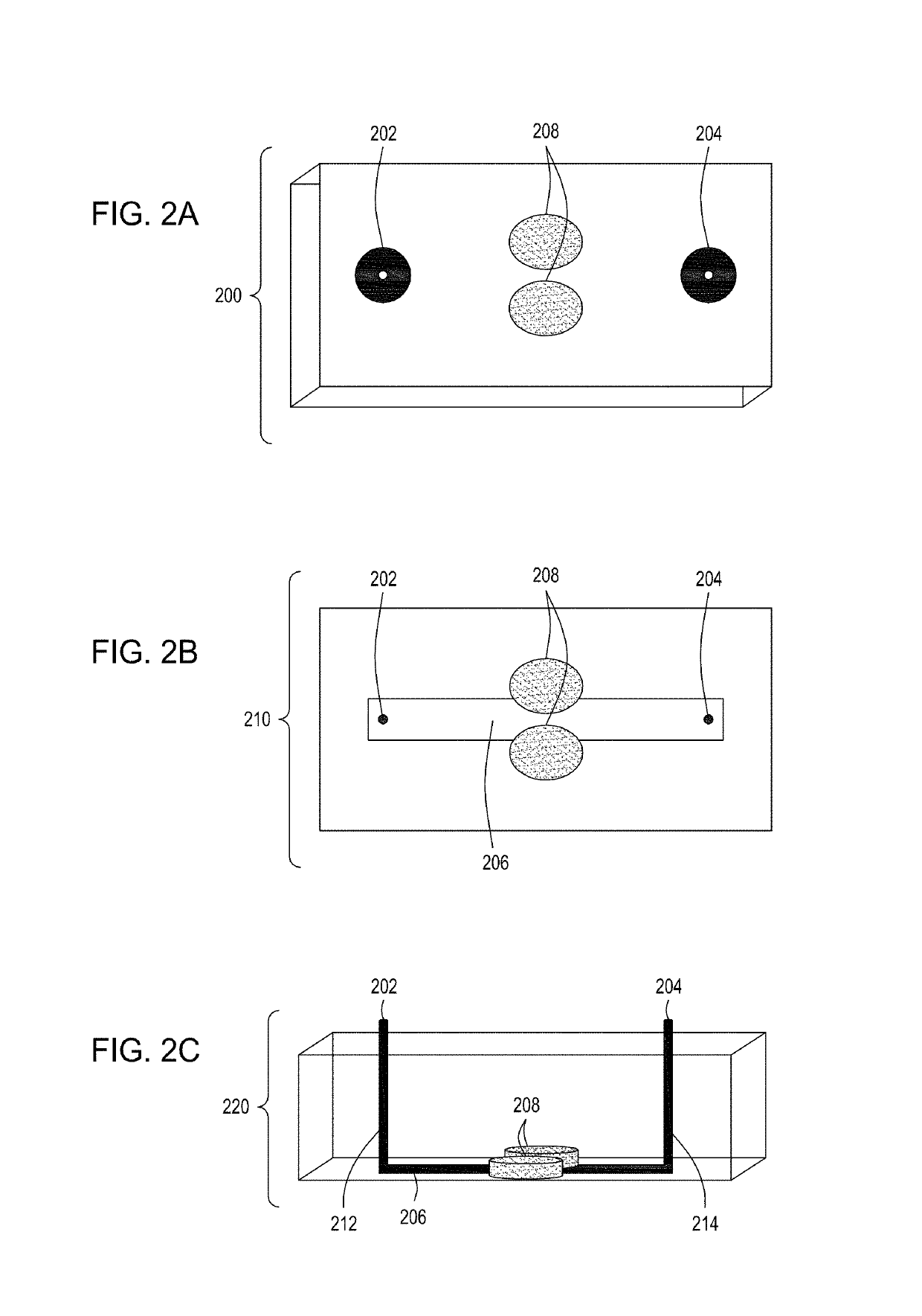
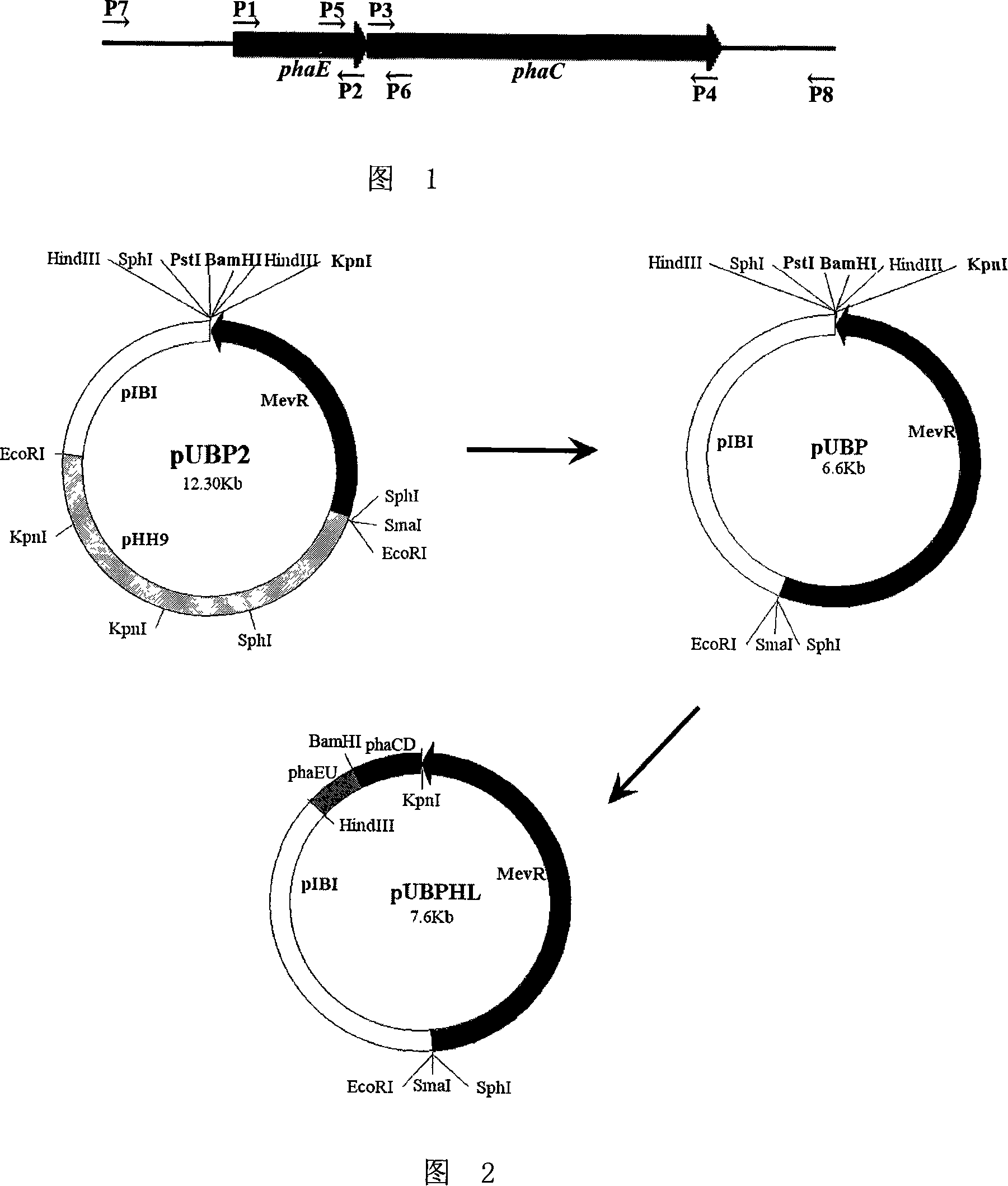
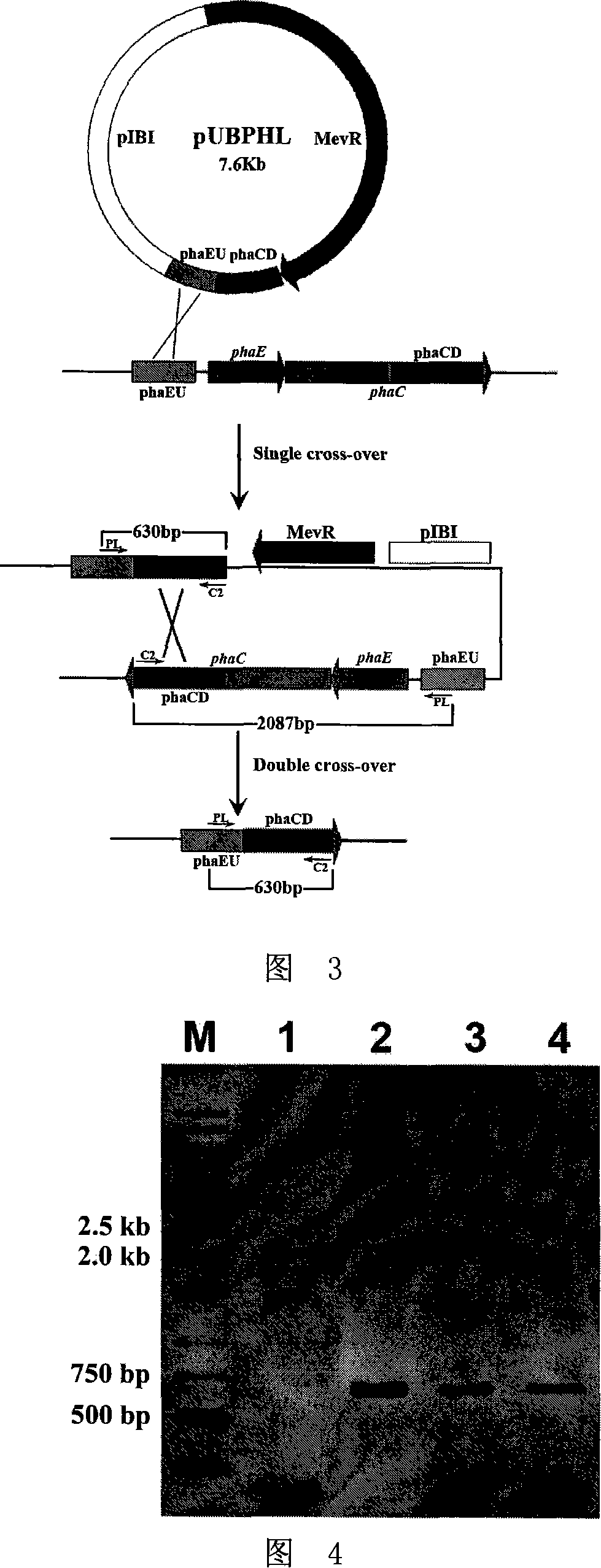
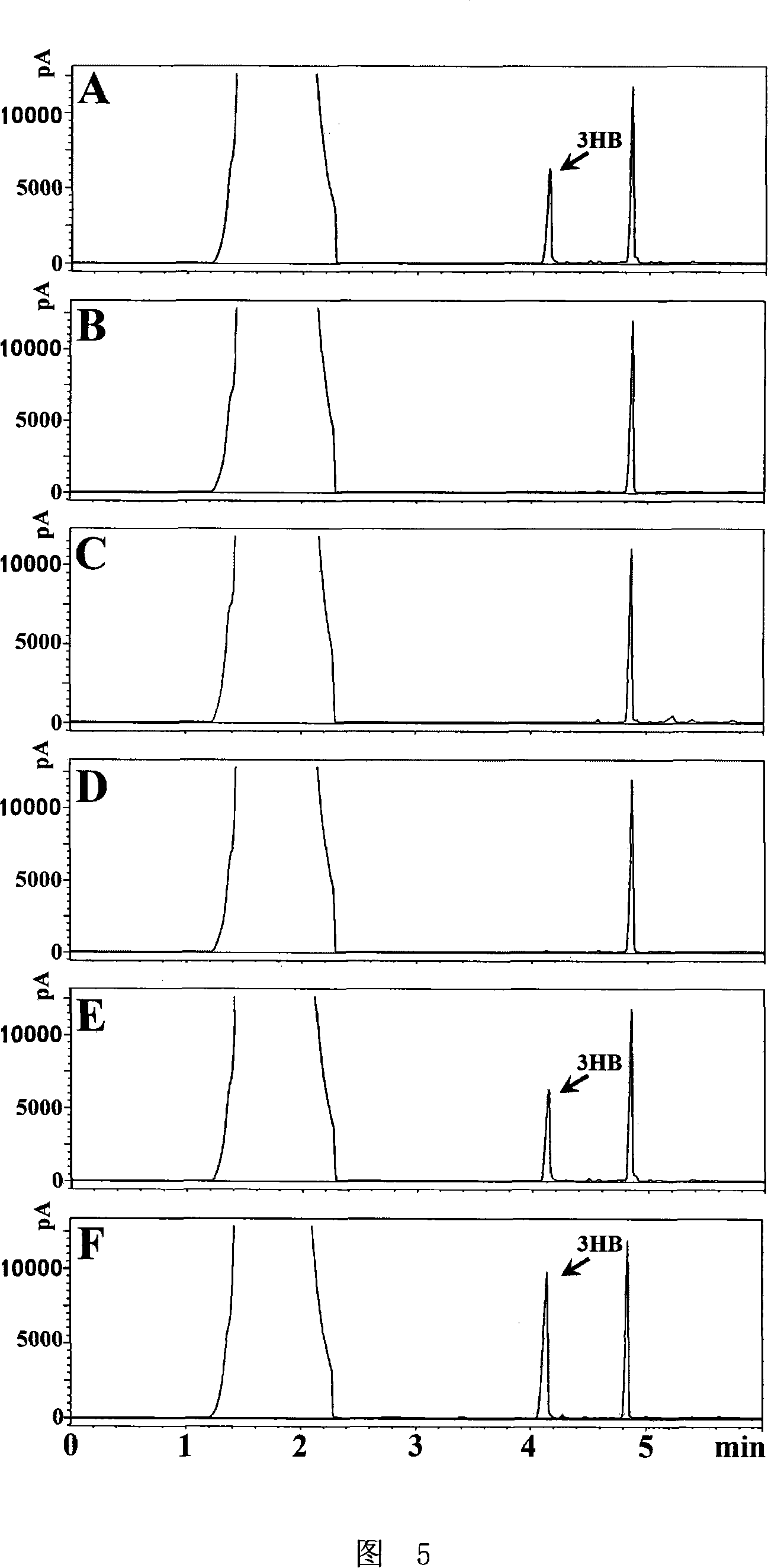
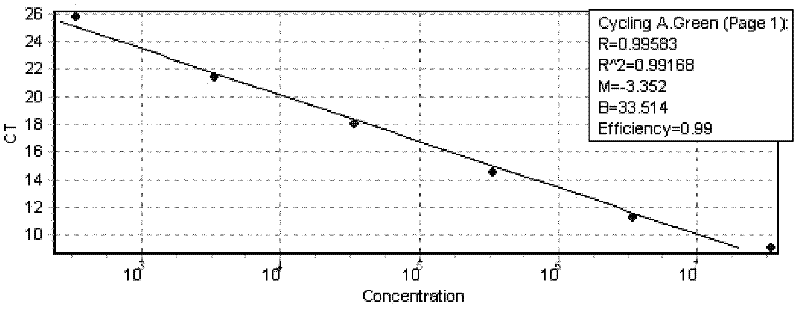
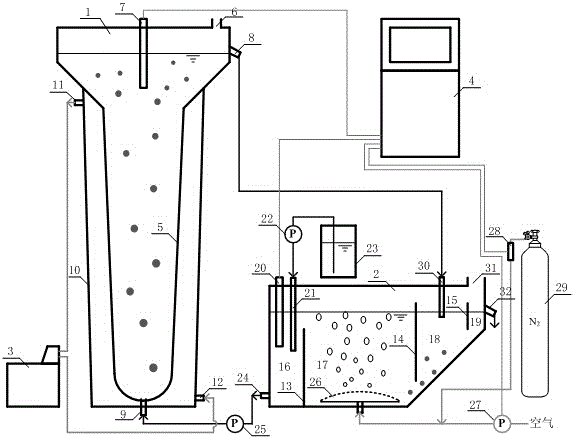
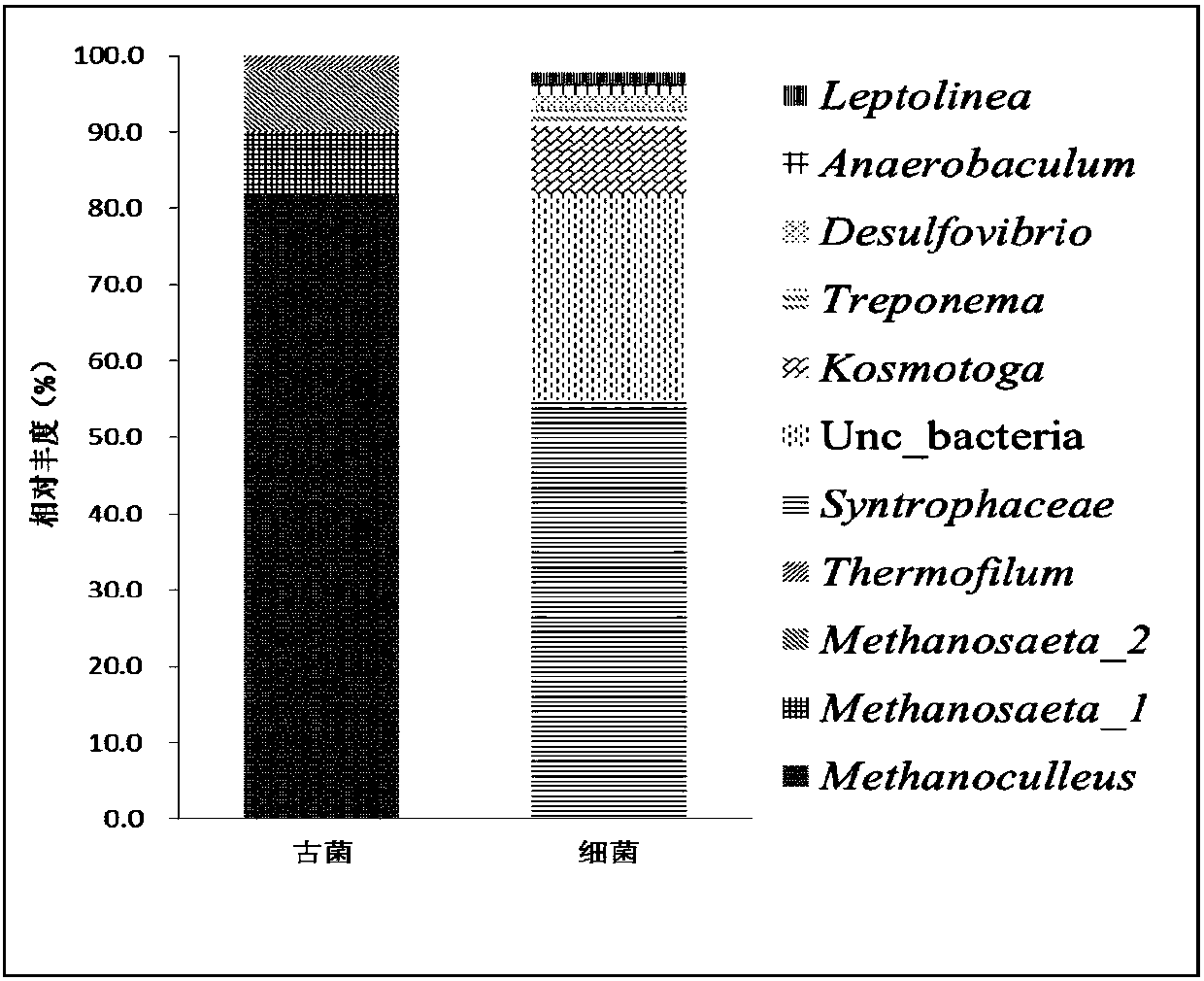
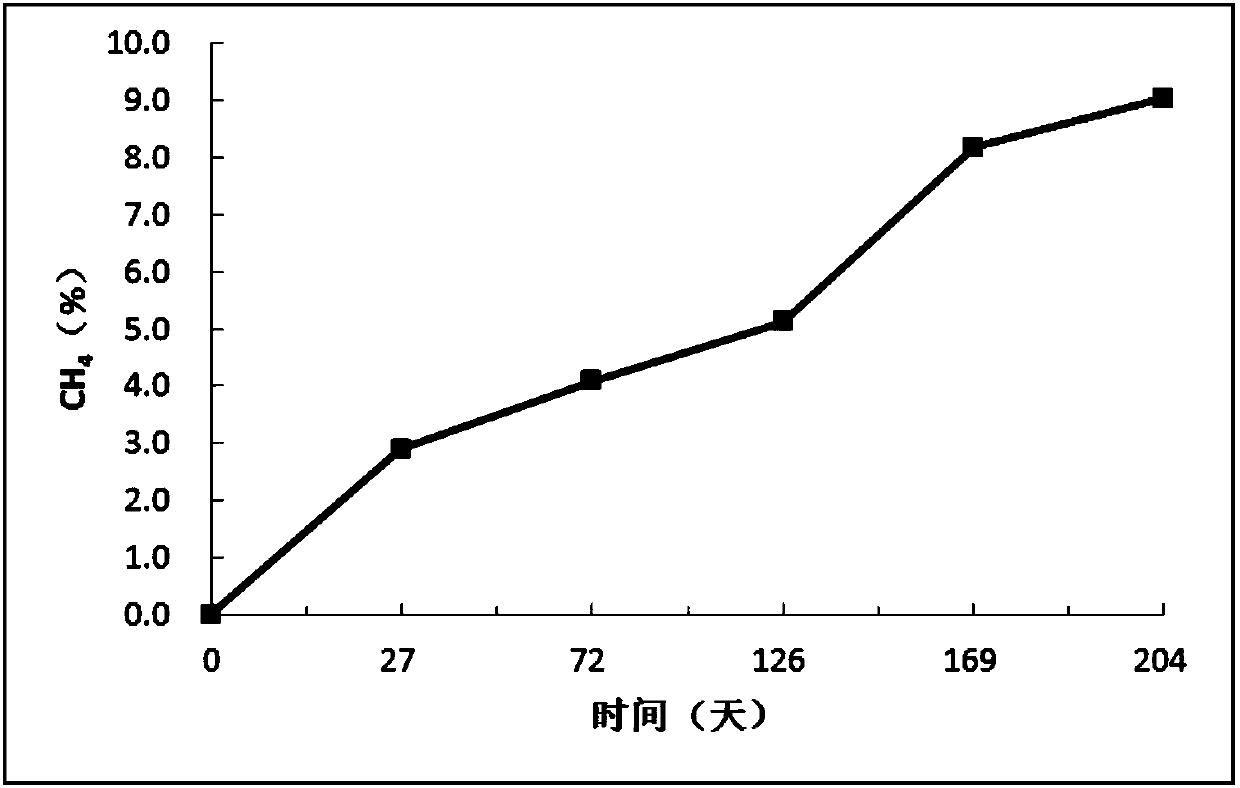
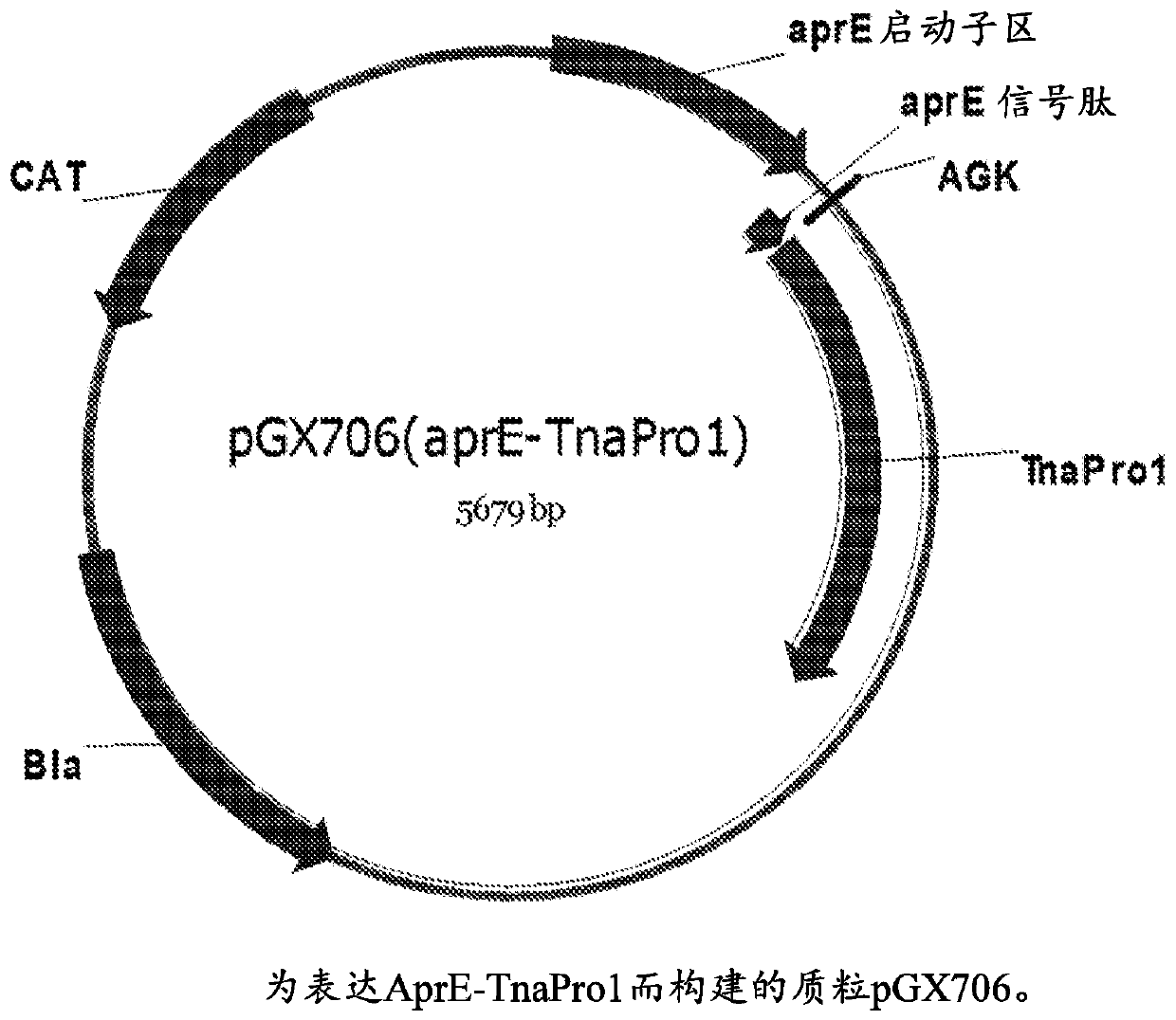
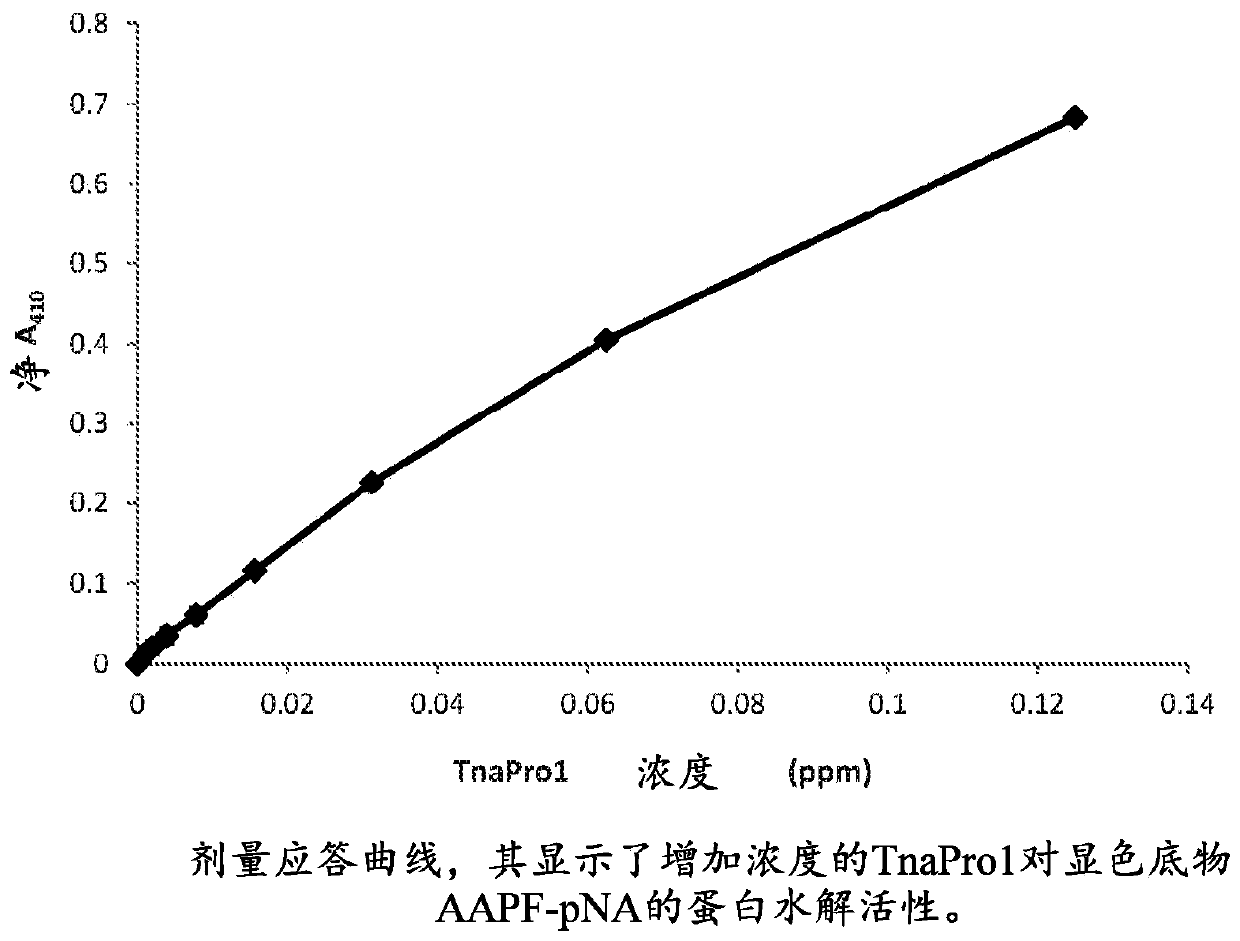
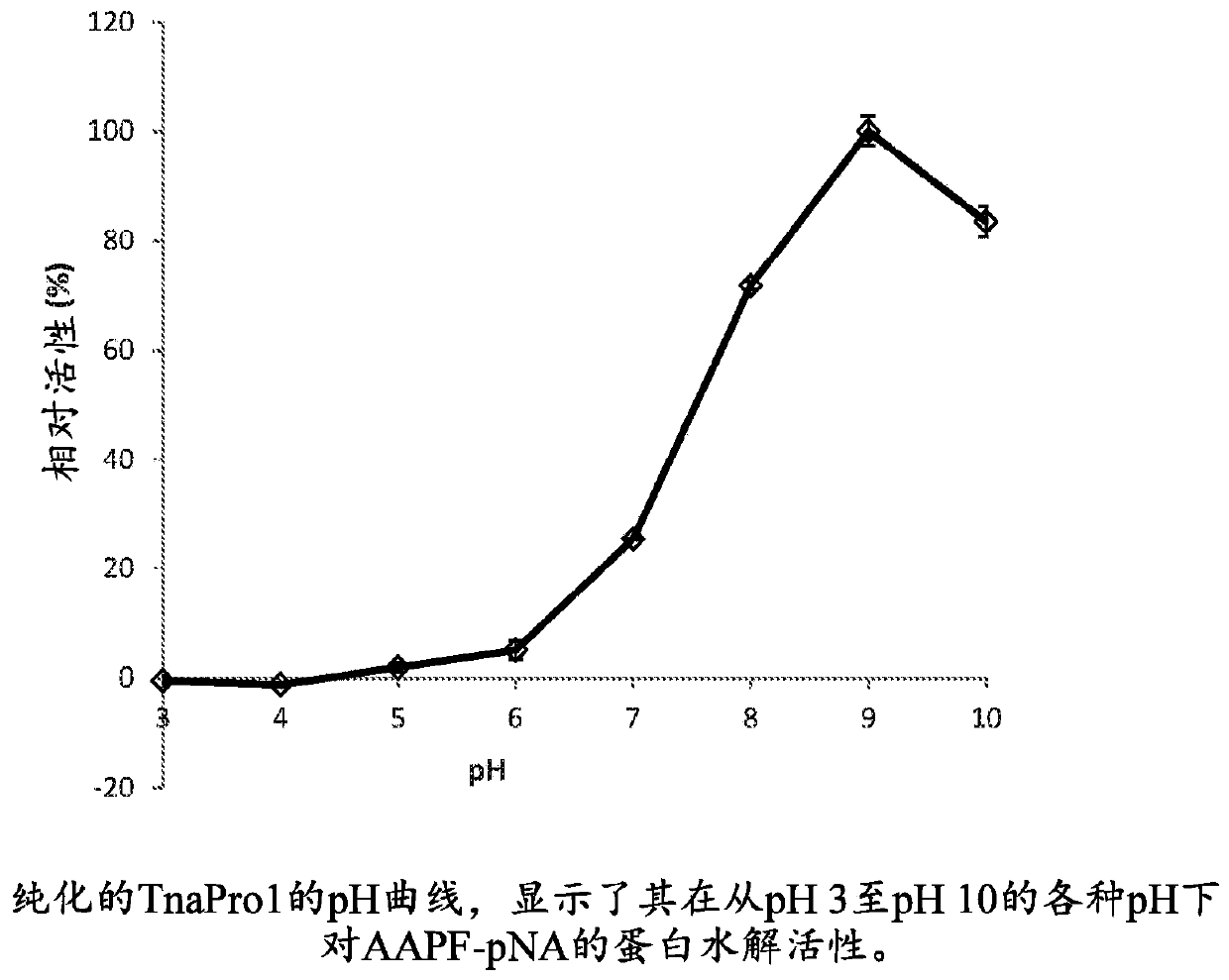
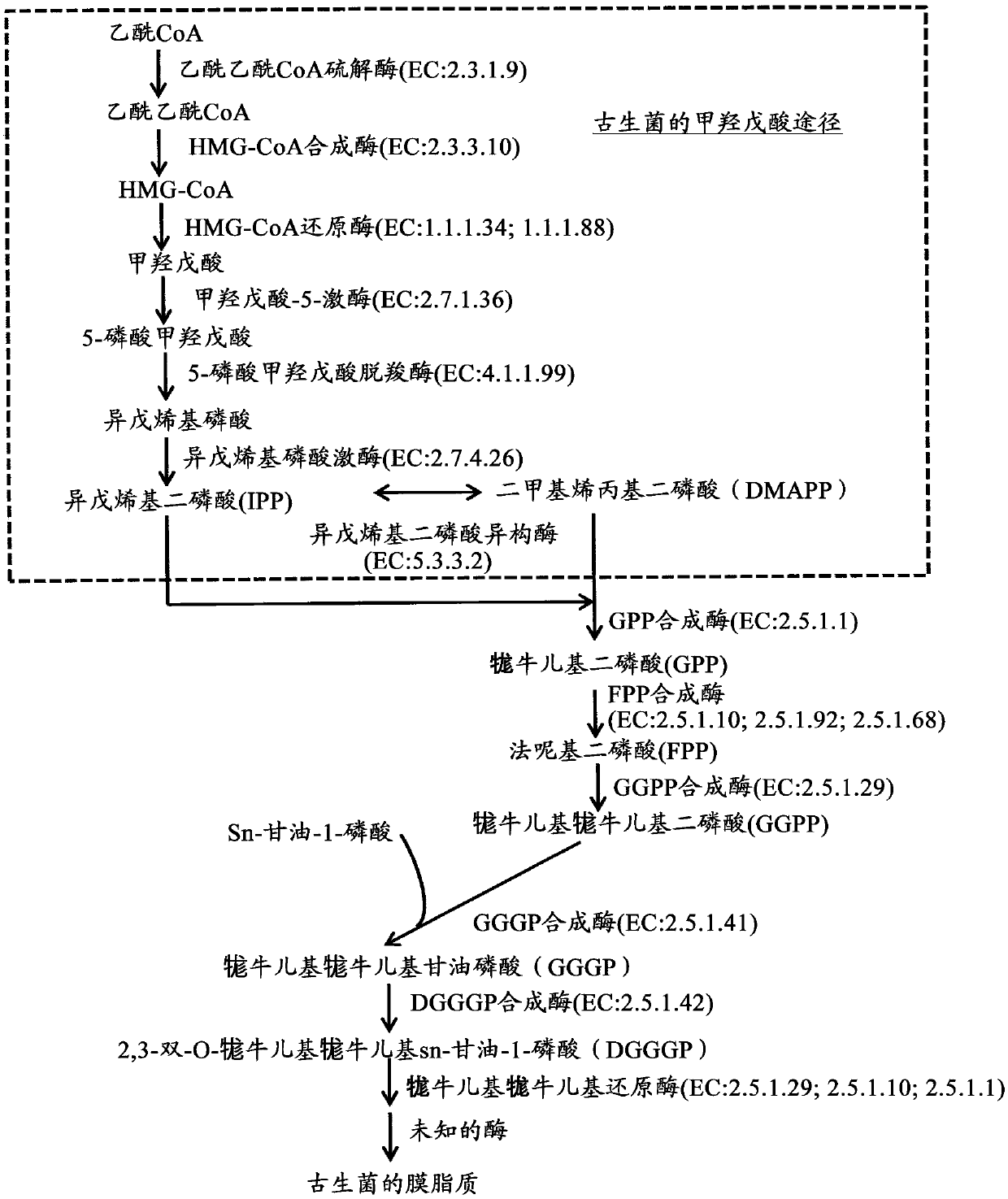
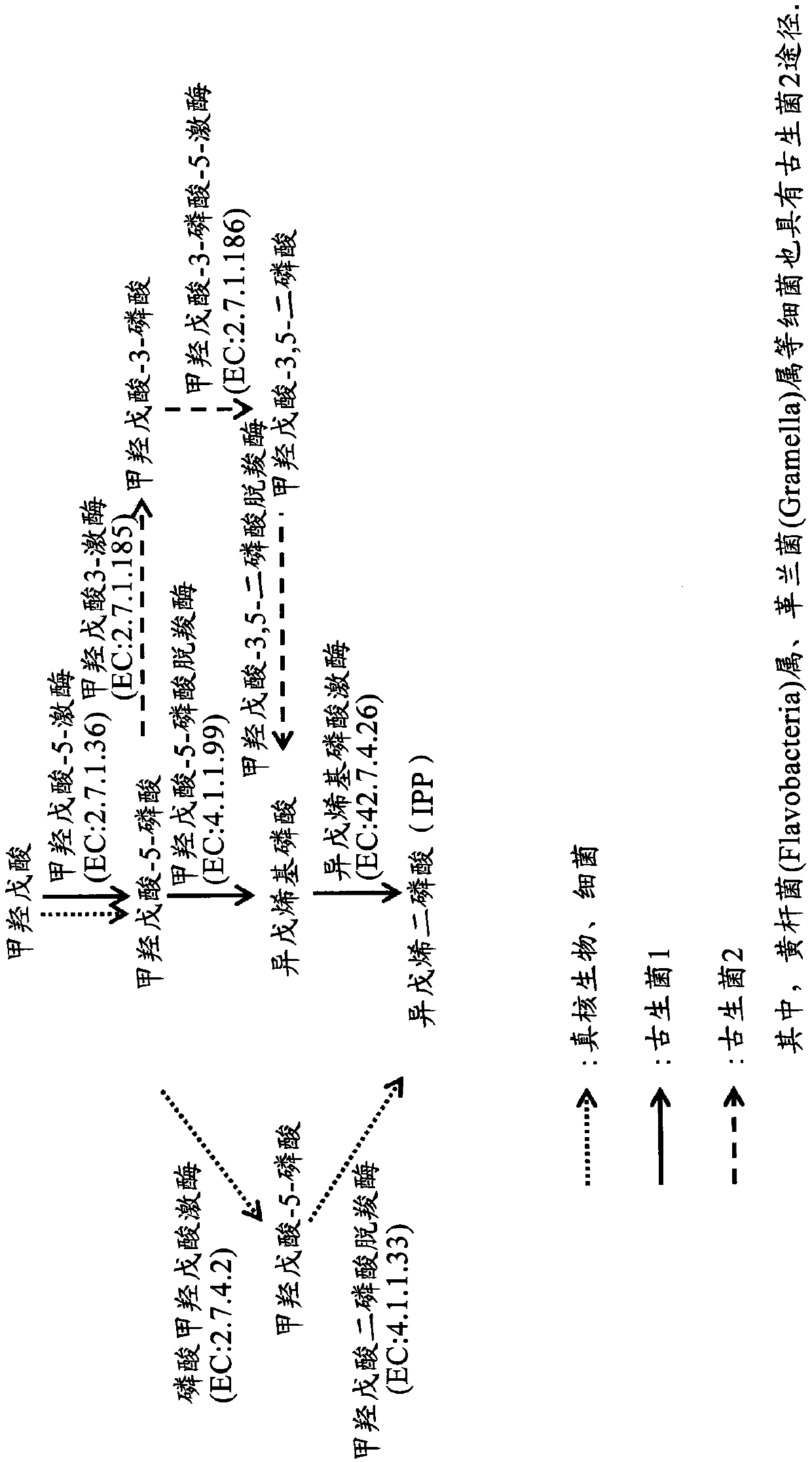
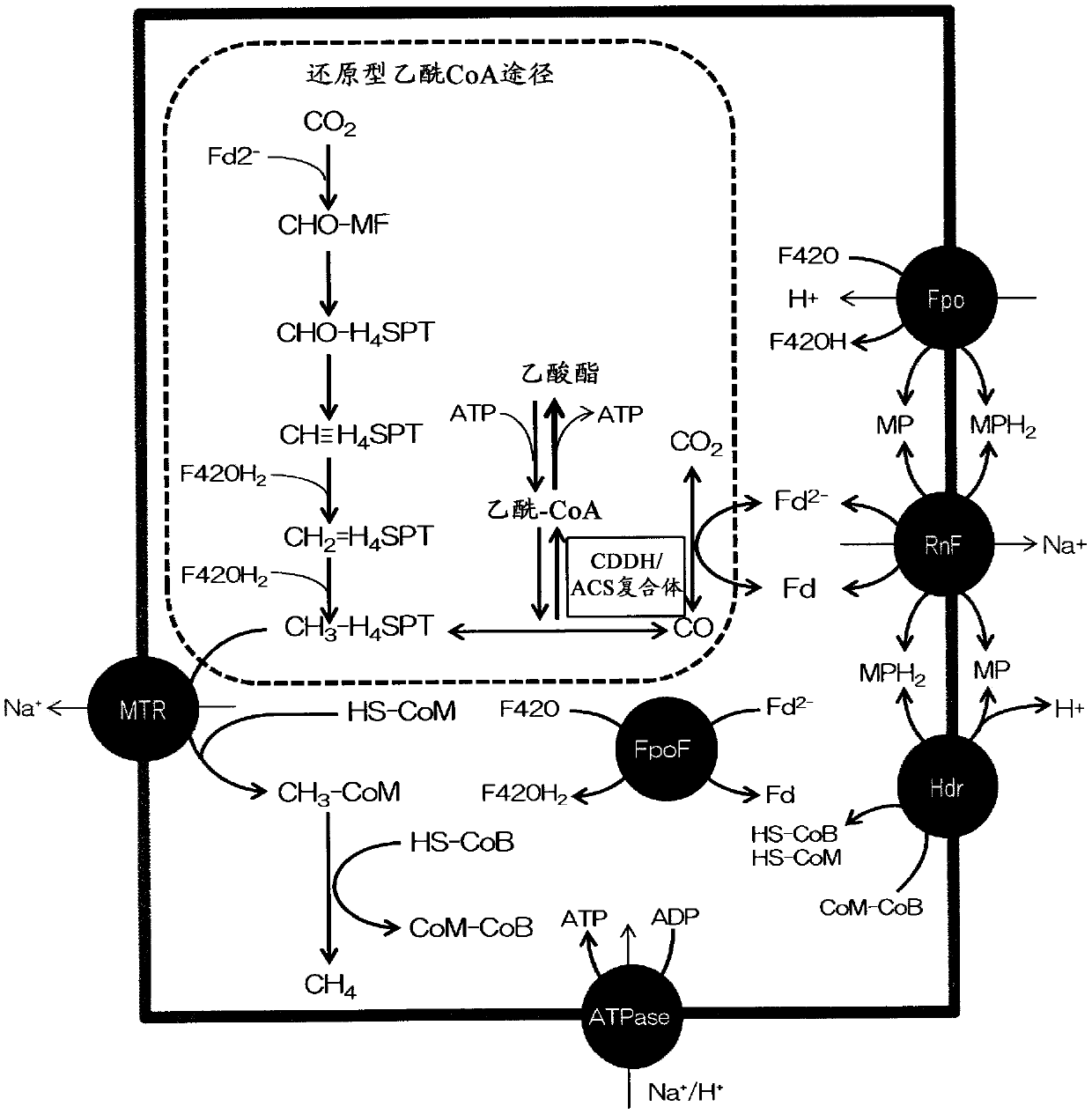
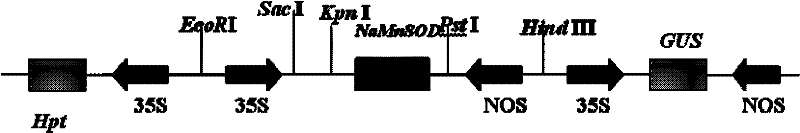Patents
Literature
109 results about "Archaea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Archaea (/ɑːrˈkiːə/ or /ɑːrˈkeɪə/ ar-KEE-ə or ar-KAY-ə) (singular archaeon) constitute a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms are prokaryotes, and have no cell nucleus. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this classification is outmoded.
Ultrasensitive sensor and rapid detection of analytes
The present invention relates to systems and methods for real time, rapid detection, identification, and enumeration of a wide variety of analytes, which include but are not limited to, cells (Eukarya, Eubacteria, Archaea), microorganisms, organelles, viruses, proteins (recombinant or natural proteins), nucleic acids, prionss, and any chemical, metabolites, or biological markers. The systems and methods, which include the laser / optic / electronic units, the analytic software, the assay methods and reagents, and the high throughput automation, are particularly adapted to detection, identification, and enumeration of pathogens and non-pathogens in contaminated foods, clinical samples, and environmental samples. Other microorganisms that can be detected with the present invention include clinical pathogens, protozoa and, viruses.
Owner:KIM LAB INC
Method for editing prokaryotic genomes using endogenic CRISPR-Cas (CRISPR-associated) system
ActiveCN105331627AReduce workloadWide range of application hostsBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionGenome editingWorkload
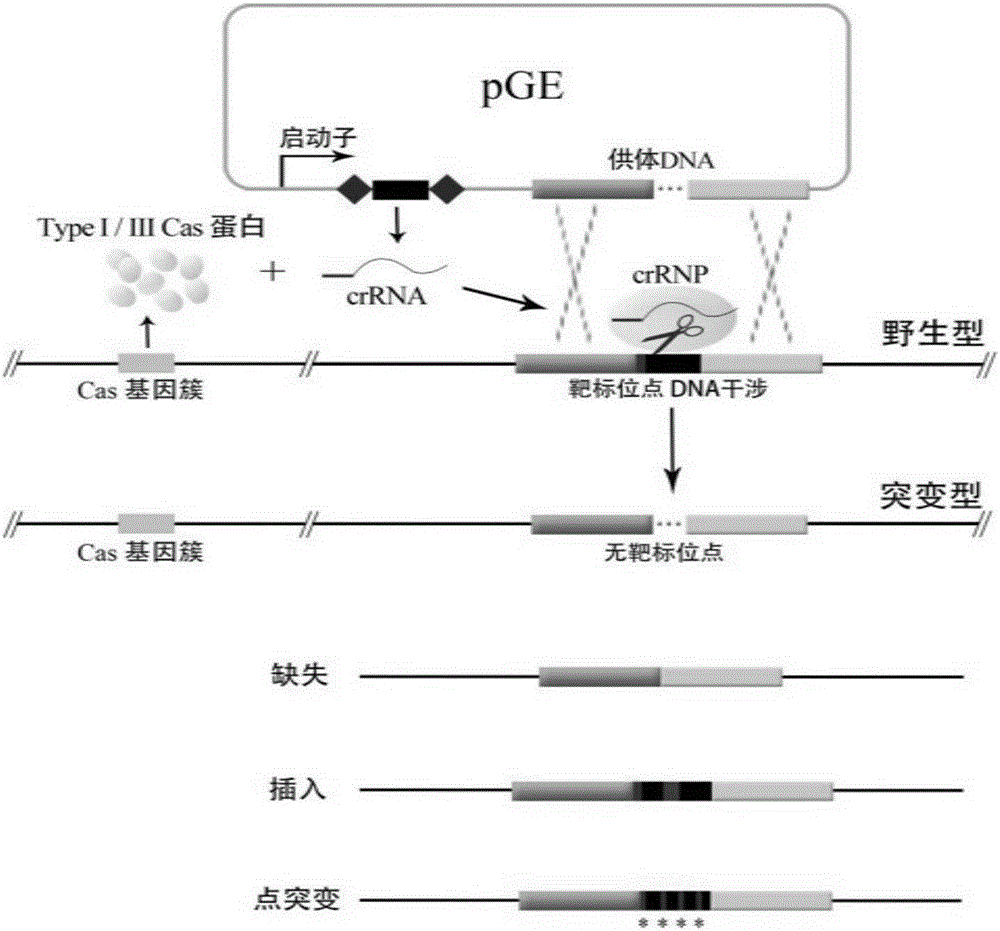
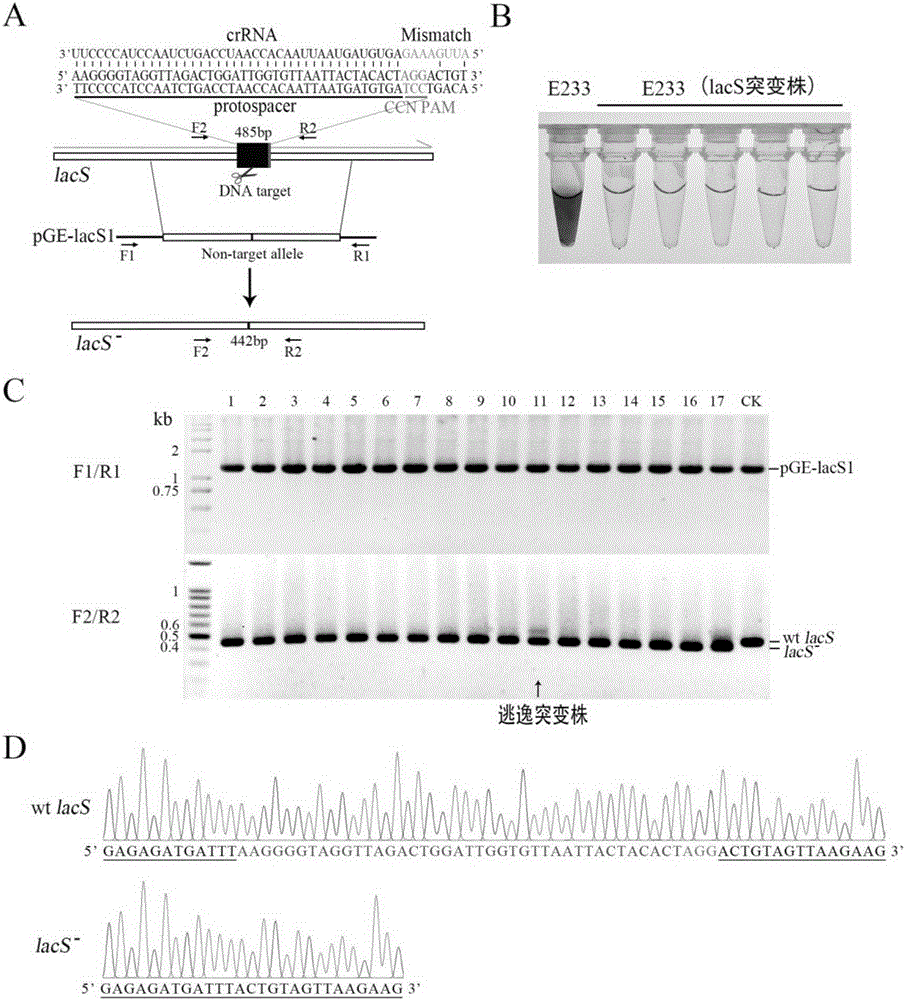
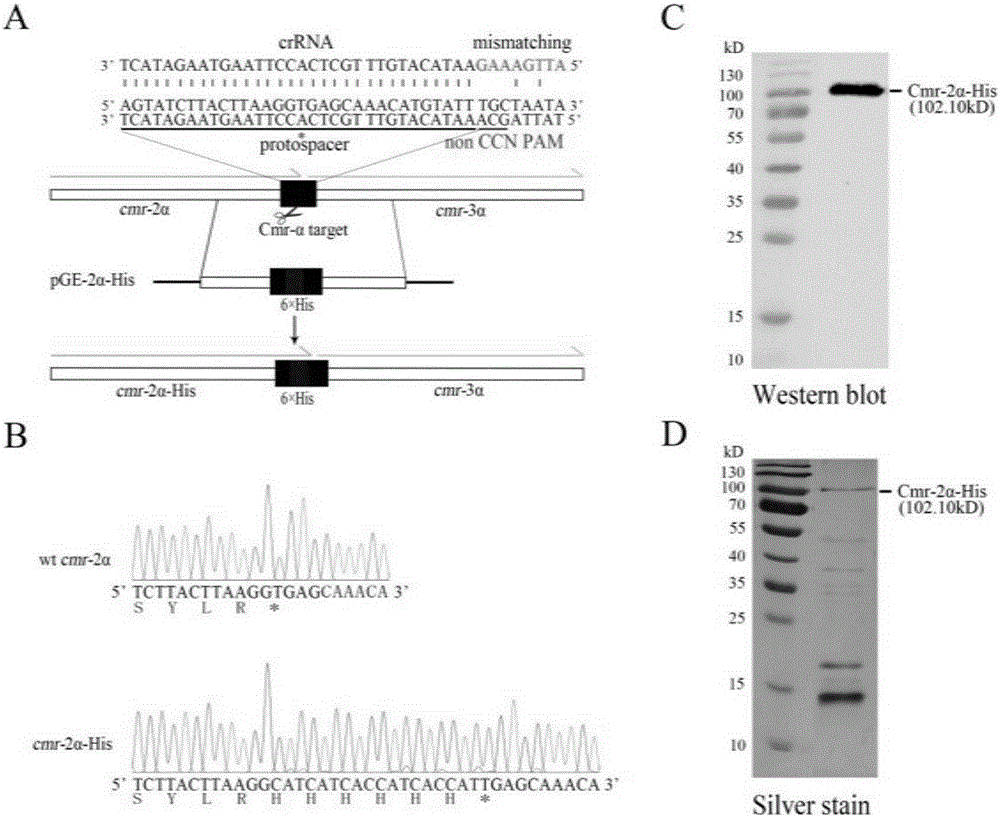
The invention relates to a method for editing prokaryotic genomes using an endogenic CRISPR-Cas (CRISPR-associated) system. An editor plasmid carrying both an artificial CRISPR cluster and a donor DNA is required to be established for the genome editing of a prokaryote containing the endogenic CRISPR-Cas system, after NDA interference is caused by the endogenic CRISPR-Cas to the genome, and the genome is edited through homologous recombination. The method has the advantages that a range of applicable hosts is wide, all bacteria and archaea containing the endogenic CRISPR-Cas being available for operation; the method is applicable to operations in various editing manners, such as deletion, insertion and point mutation; the editing efficiency is higher, screening positive rage is high, and the background is low; a flow is simple, a short period of time is required, and the workload of prokaryotic genome editing is greatly reduced.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Rna-guided nucleic acid modifying enzymes and methods of use thereof
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
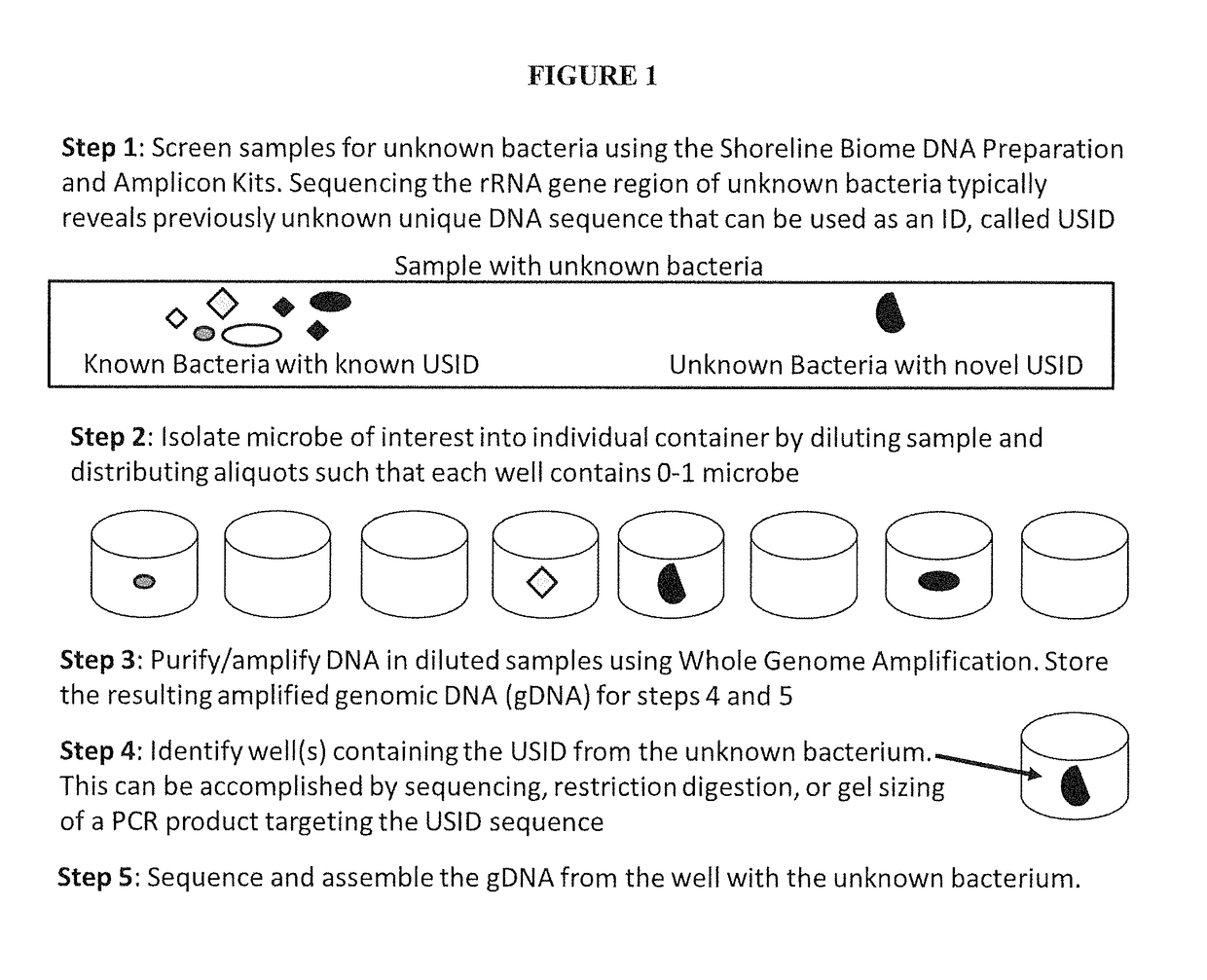
High Throughput Method for Identification and Sequencing of Unknown Microbial and Eukaryotic Genomes from Complex Mixtures
Disclosed are methods for screening biological samples for the presence unknown microbes, such as bacteria and archaea or unknown eukaryotes using rRNA gene sequences or other highly conserved genetic regions, across multiple biological samples using a unique sequence tag (barcode) corresponding to the sample. The screening process tracks the unknown microbe or eukaryote in a diluted sample where the DNA has been prepared using whole genome amplification. The whole genome of the unknown microbe or eukaryote is then sequenced and assembled.
Owner:SHORELINE BIOME LLC
Incorporation of modified nucleotides by archaeon DNA polymerases and related methods
InactiveUS20060199214A1Efficiently incorporateEffective mergerBacteriaSugar derivativesEnzymeDNA polymerase
The present invention is directed toward improving the efficiency of chain terminator incorporation by Family B archaeon DNA polymerases. Previously, the low efficiency of ddNTP, and more especially dye-labeled ddNTP, incorporation has limited the usefulness of this group of DNA polymerases in protocols requiring chain terminator incorporation.
Owner:JACK WILLIAM +3
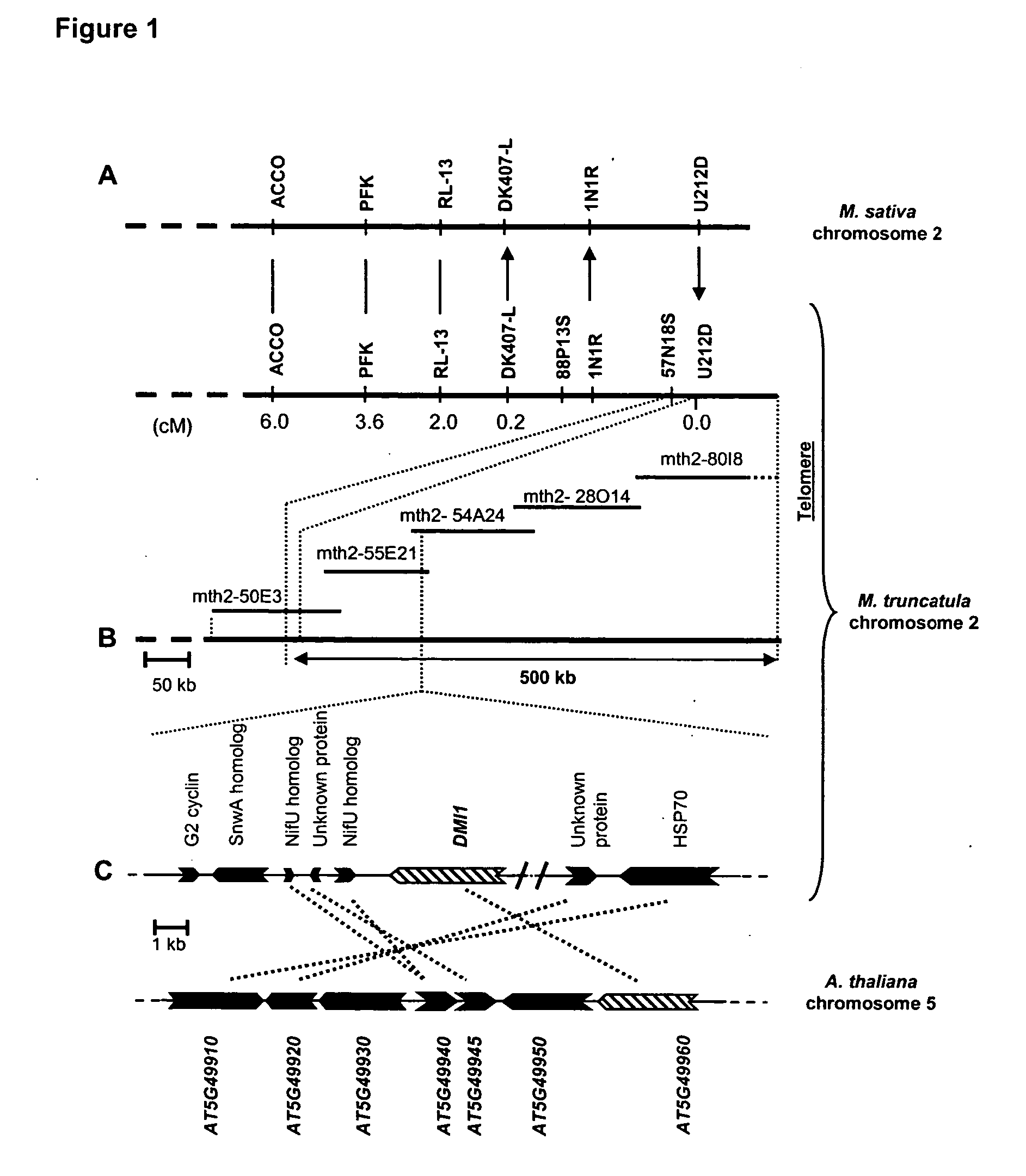
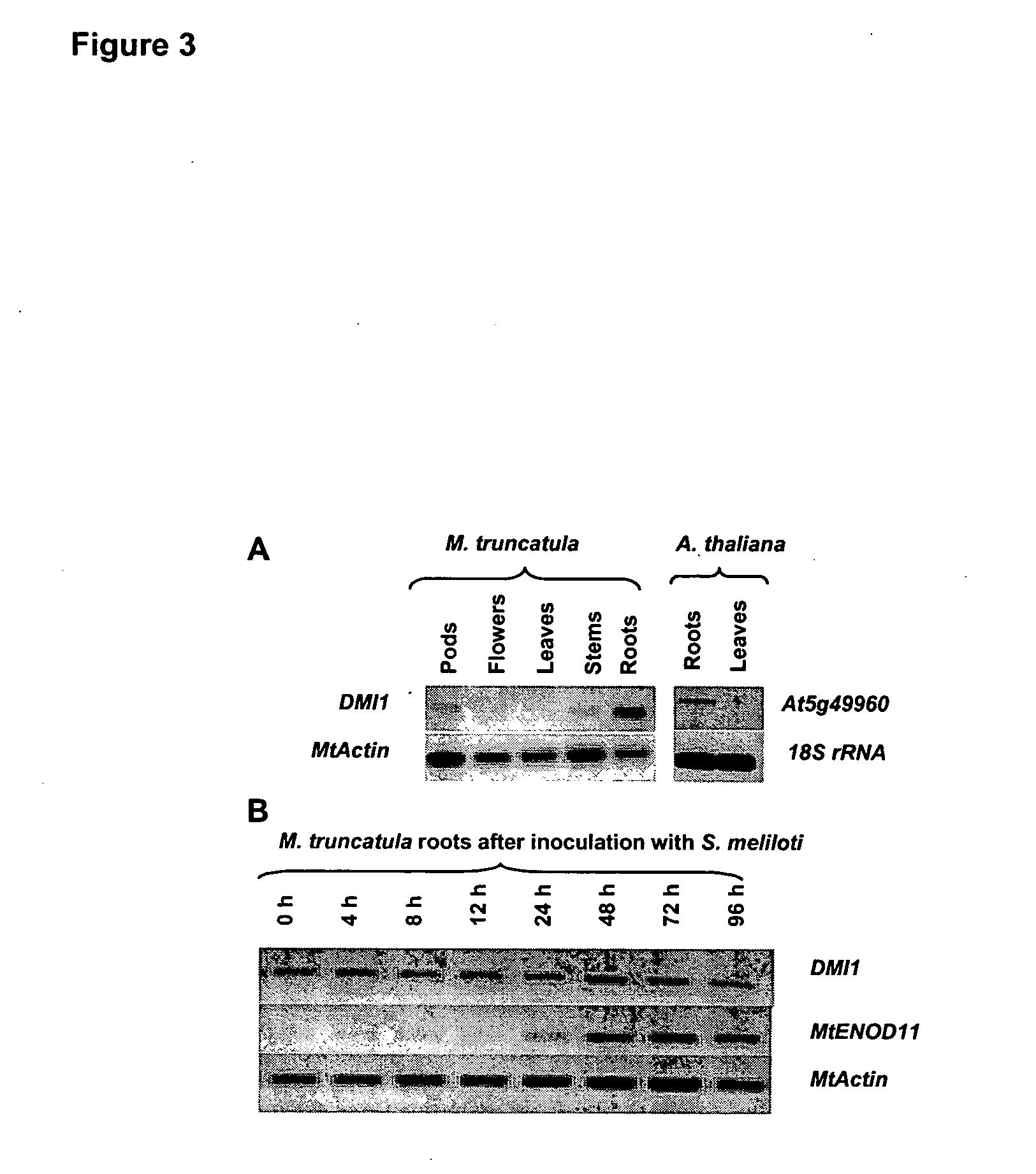
The DMI1 gene encodes a protein that is required for the early steps of bacterial and fungal symbioses
InactiveUS20050081262A1Enhanced nitrogenEnhanced phosphorous acquisitionBryophytesSugar derivativesBacteroidesPlant nodule
Mycorrhizal and rhizobial associations represent the two most important symbiotic relationships between higher plants and microorganisms, providing access to otherwise limiting supplies of phosphate and nitrogen, respectively. Although many higher plants are able to establish a symbiotic relationship with arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi, legumes are unusual among plants because they also form associations with nitrogen fixing soil bacteria called rhizobia. This symbiosis requires the production of bacterial signals, “Nod factors” that trigger several key developmental responses in the host plant (Dénarié et al., 1996). The DMI1 gene of the model legume M. truncatula plays a major role both in the early steps of Nod factor signaling and in the establishment of mycorrhizal symbiosis. Dmi1 mutants do not exhibit many of the early responses to Nod factors and are incapable of forming nitrogen fixing root nodules. Here we describe the cloning and preliminary characterization of DMI1. The DMI1 gene encodes a novel protein with low global similarity to ligand-gated cation channels of archaea. The protein is highly conserved in angiosperms and ancestral to land plants. Interestingly a putative A. thaliana DMI1 orthologous gene is expressed in roots. As A. thaliana is unable to establish a mycorrhizal symbiosis, this finding suggests that DMI1 may also exhibit a function that is independent of symbiotic interactions.
Owner:INSTITUT NATIONAL DE LA RECHERCHE AGRONOMIQUE +1
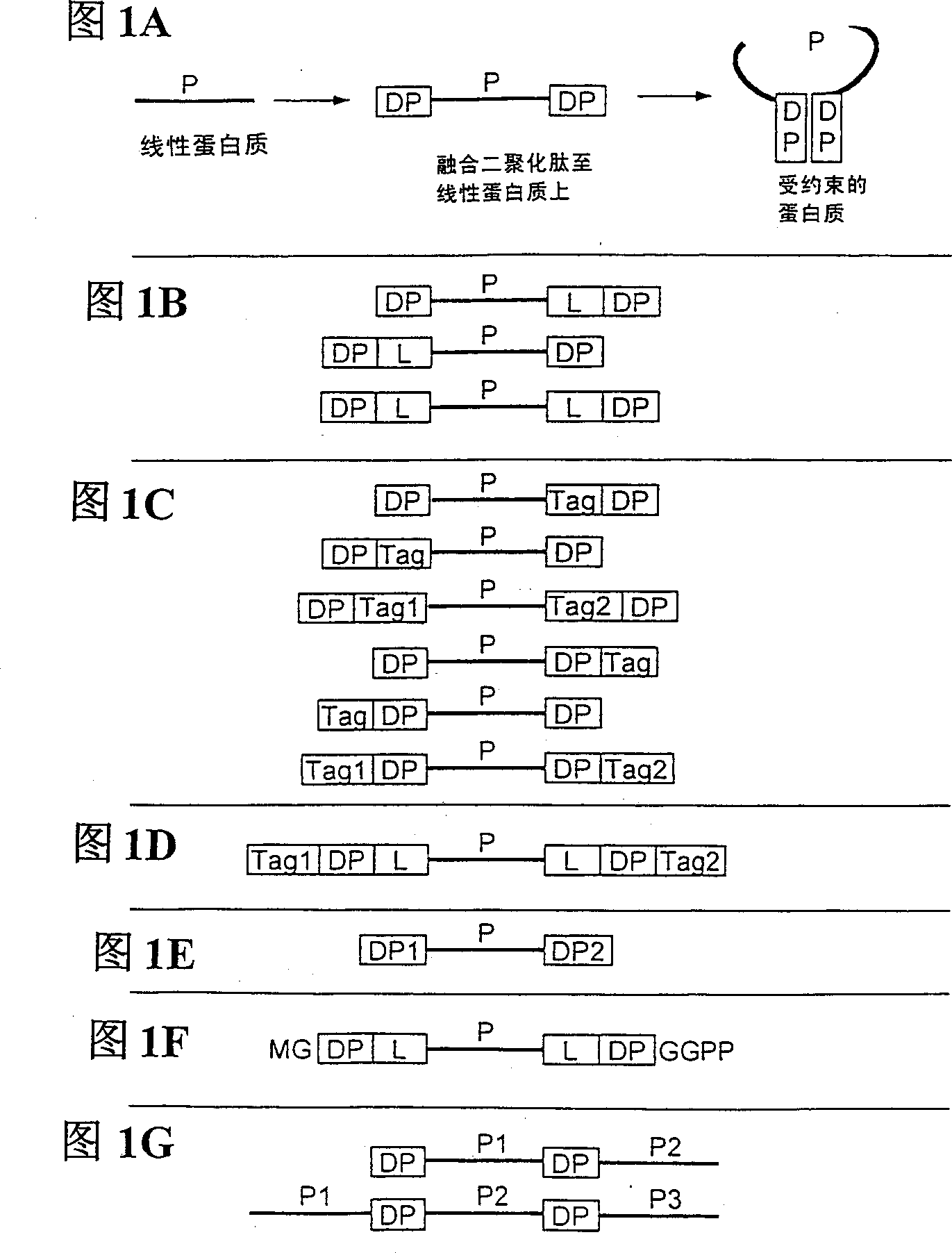
Peptides causing formation of compact structure
The present invention relates to compositions and methods comprising peptides with high mutual affinity that, when attached to a protein, assist the protein to fold into a compact structure. By virtue of its stability and binding, this scaffold extends the activity of any contained protein sequence in the presence of cellular and other proteases. This compact structure may have other included functional sequences, which are superior to linear and less constrained peptides for library screening, building structure-biased peptide libraries, and targeting specific intracellular and extracellular compartments. The compositions of the present invention can be displayed on viral, archaeal, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell surfaces for library screening, drug screening and display. The methods of the present invention are useful for in vivo screening of intracellular effector proteins that modulate signaling pathways, and for identification of interacting proteins in vitro. Therefore, the present invention can be used as a scaffold for gene therapy, for the isolation of new therapeutic drugs, and has potential utilization value for use as a therapeutic agent in physiological fluids.
Owner:RIGEL PHARMA
Modification of cells by introduction of exogenous material
ActiveUS20190100774A1Reduce widthOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionYeastPlant cell
Owner:INSCRIPTA INC
Glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant and preparation method thereof and application
InactiveCN105462949AGood thermal stabilityHigh application valueFermentationGenetic engineeringGlutamate decarboxylaseMutant
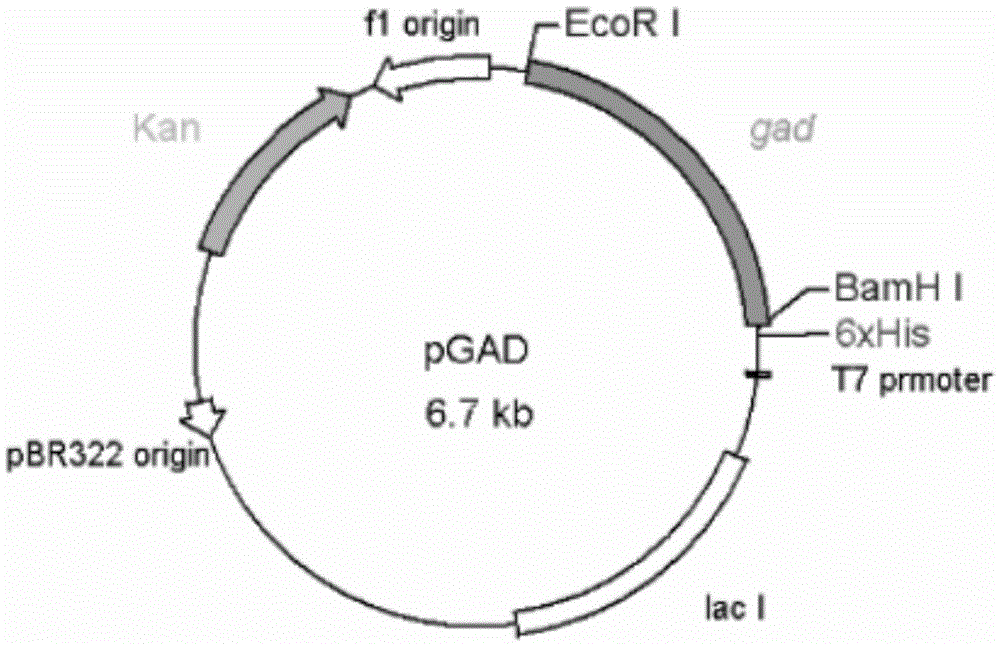
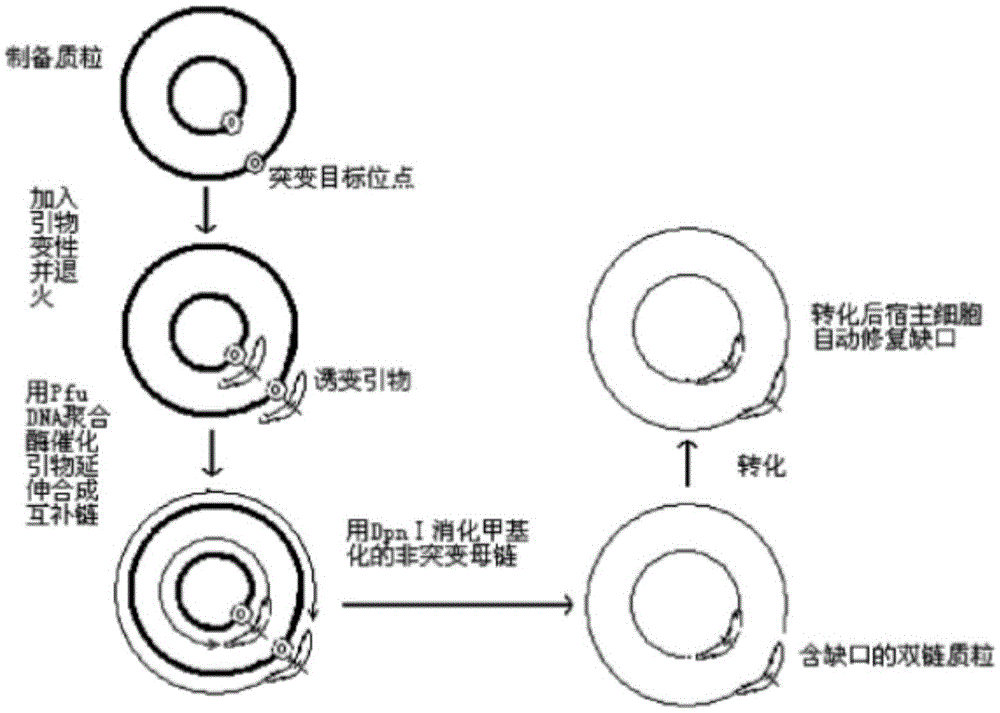
The invention discloses a glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant and a preparation method thereof and application. An amino acid sequence of the mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No. 2, and a nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The invention further discloses an expression unit containing genes for encoding the glutamic acid decarboxylase mutant, a recombinant plasmid and a transformant. According to information of comparison with a thermococcus kodakarensis glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) amino acid sequence, a method of site-directed mutagenesis is adopted to introduce proline residue at an amino acid locus corresponding to lactobacillus brevis GAD, and the thermal stability of the GAD is improved through rational design. The mutant has better thermal stability in the process of catalyzing L-glutamic acid or sodium salts thereof to generate gamma-aminobutyric acid and is favorable for industrial production of gamma amino acid butyric acid (GABA).
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Method for treating high-salt wastewater by using halophilic microorganisms
InactiveCN105084558AExpand the upper limit of salt tolerance concentrationShorten the debugging cycleTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSludgeMicrobial agent
The invention provides a method for treating high-salt wastewater by using halophilic microorganisms. The halophilic microorganisms can adapt to a high-salt environment to perform normal growth metabolism, and comprise haloduric and halophilic bacteria, yeasts, archaea and microfauna. The method for treating the high-salt wastewater by using the halophilic microorganisms comprises the following steps: adding a halophilic microbial flora into a biochemical system; performing mixed culture on the halophilic microbial flora in an influent salt concentration range of 1-25% to improve the pollution degradation capability of the halophilic microbial flora and obtain a halophilic microbial aggregate with good mud-water separation performance and precipitation performance, such as active sludge and a biomembrane; and stabilizing the process parameters and influent water quality of the biochemical system to ensure that the biochemical effluent reaches a standard or meets design requirements. By adopting the method provided by the invention, the high-salt wastewater with the influent salt concentration of 1-25% of the biochemical system can be subjected to biochemical treatment, and the halophilic microbial agent only needs to be added once, so that the investment and operation costs can be reduced.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
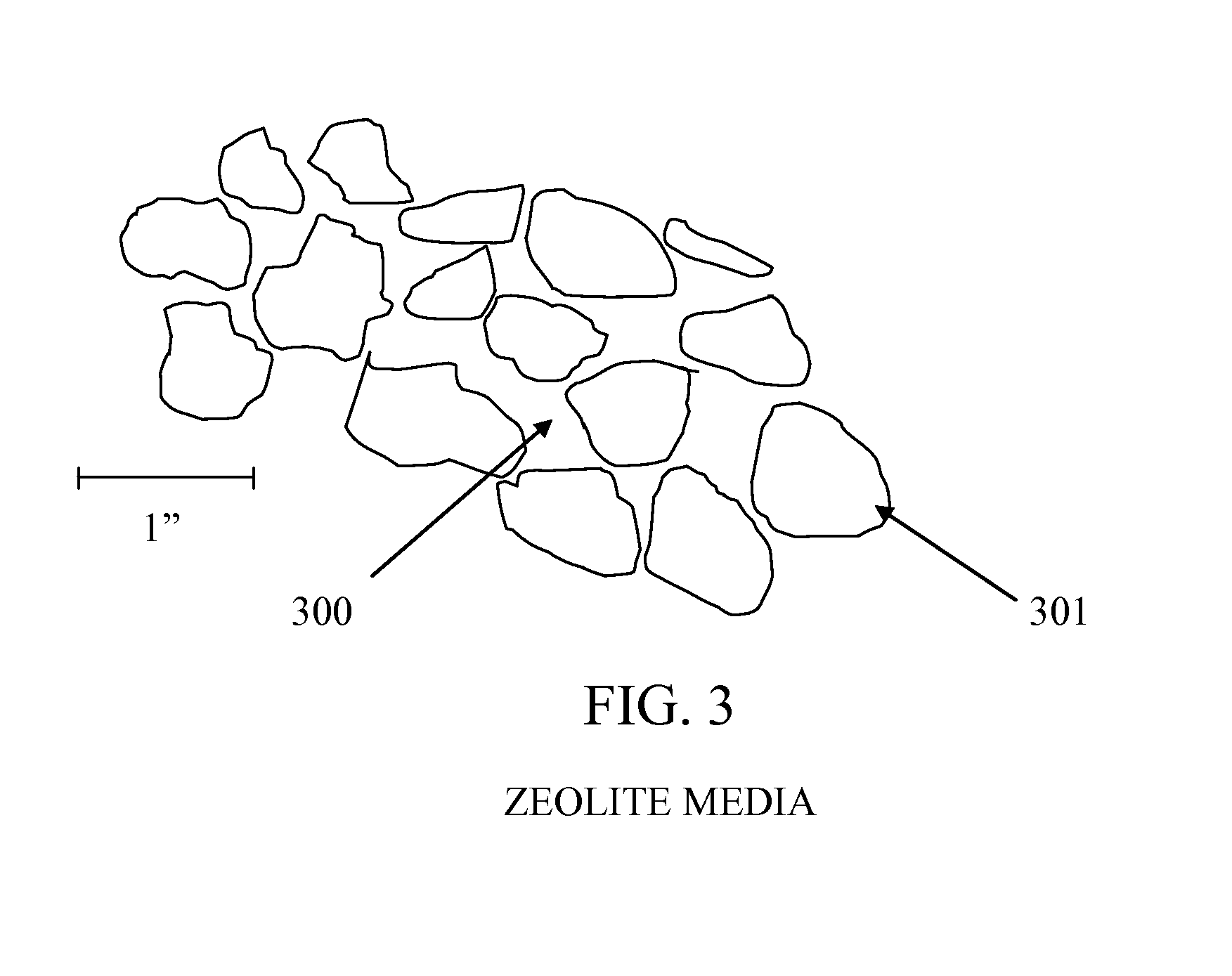
Self-Regenerating Zeolite Reactor for Sustainable Ammonium Removal
InactiveUS20150151996A1Reduce energy consumptionMaintenance requirement is minimalIon-exchanger regenerationWater contaminantsCation-exchange capacityIon exchange
A method of using micro-organisms to continuously and sustainably regenerate zeolite cation exchange capacity (CEC) for removing nitrogen (ammonium, nitrite, and nitrate) from wastewater. The zeolite immobilizes the ammonium ions, and the micro-organisms ingest the ammonium from the surface of the zeolite thereby freeing the cation exchange sites to trap more ammonium. The zeolite is continuously regenerated by the microbes, sustainably maintaining available ion exchange capacity for removing ammonium, and does not need to be shut down for regeneration or replacement. The microbial complex contains nitrifiers, anammox, denitrifiers, archaea, and others. All the micro-organisms co-exist in the same reactor promoting symbiotic interactions, thereby increasing treatment efficiency. The end product is di-nitrogen gas which dissipates into the atmosphere. The system does not require aeration, operates by gravity flow, and has very low energy requirements. Maintenance is minimal, and the system can significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions (nitrous oxide).Notes: This document uses the terms ammonia and ammonium interchangeably, just as the compounds themselves are interchangeable (NH3+H+NH4+). In aquatic systems ammonia (NH3) is predominantly found in the ionic form as ammonium (NH4).
Owner:COLLISON ROBERT SPENCER
Composite microbial agent, preparation method thereof and salty sewage treatment method
InactiveCN103740617AEasy to handleWide range of conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentSewage
The invention discloses a composite microbial agent, a preparation method thereof and a salty sewage treatment method. The composite microbial agent comprises halophilic archaea, halophilic bacteria and halotolerant bacteria. The preparation method comprises the following steps of performing liquid culturing on each component under different salinities respectively, and mixing bacterium solutions to obtain the composite microbial agent when each bacterium solution contains a certain amount of bacteria. The composite microbial agent can be added into salty sewage to treat the salty sewage. Different strains in the composite microbial agent are in different growth states under different salty conditions, and advantages in the growth of the strains within high, medium and low major salty ranges are achieved, so that the microbial agent can be used for treating organic sewage with different salinities, and is wide in application range.
Owner:徐州煤炭工业环保设备工程公司
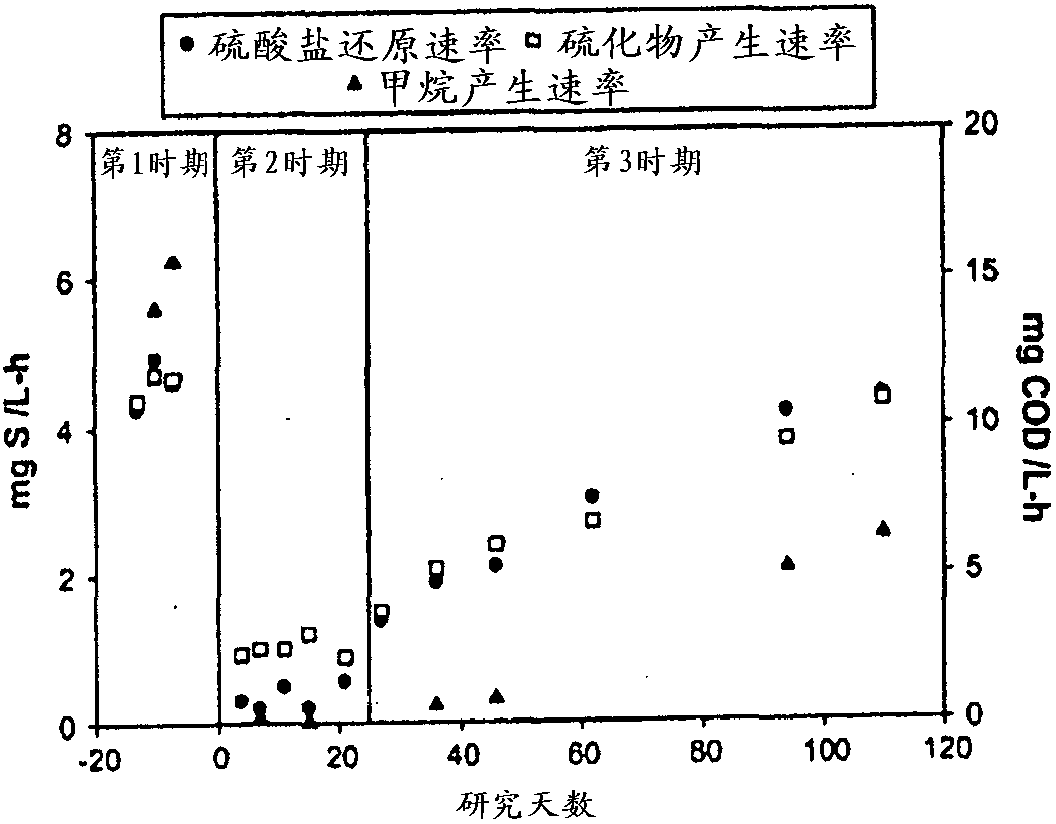
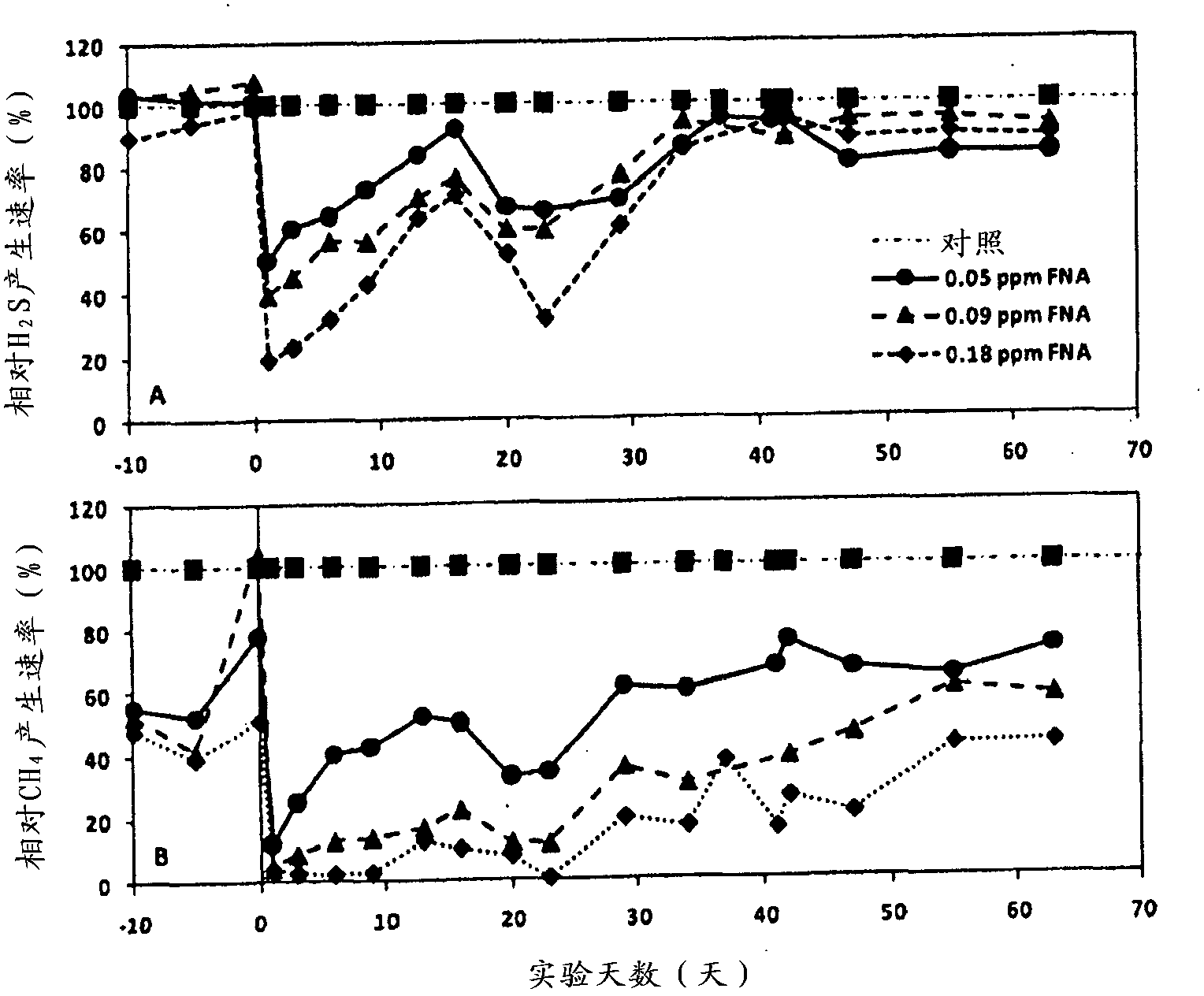
Control of bacterial activity, such as in sewers and wastewater treatment systems
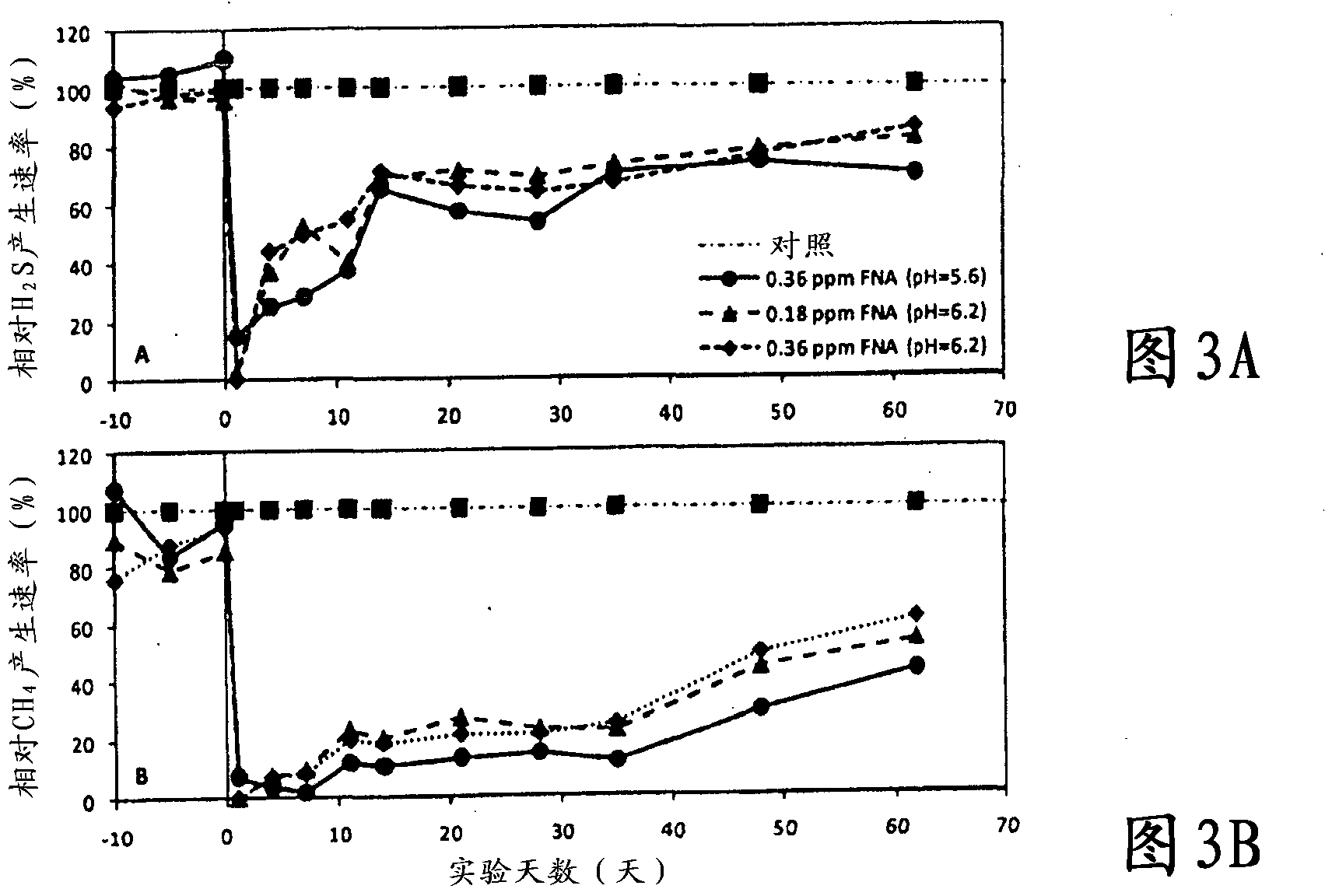
A method for controlling the activity of sulfate reducing bacteria or methanogenic archaea (or both) in environments containing such organisms comprises treating the environment with free nitrous acid (HNO2) or with a solution containing nitrite (NO2 -) having a pH of less than 7 or by adding nitrite to the environment and having a pH of less than 7 in the environment. The method can also disrupt biofilms.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
Endoglucanases
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified thermostable enzyme derived from the archael bacterium AEPII 1a. In one aspect, the enzyme has a molecular weight of about 60.9 kilodaltons and has a cellulase activity. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells, and can be used to aid in the digestion of cellulose. The invention also provides polypeptides having endoglucanase activity having homology to SEQ ID NO:2.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Enrichment culture method of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in sewage treatment system
The invention provides an enrichment culture method of ammonia-oxidizing archaea in a sewage treatment system. The enrichment culture method comprises the following steps: A, preparing an enrichment culture medium of an ammonia-oxidizing bacteria flora; B, carrying out enrichment culture onto an ammonia-oxidizing bacteria flora, wherein a biological membrane or active sludge containing the ammonia-oxidizing archaea is inoculated in the enrichment culture medium; C, preparing an enrichment culture medium of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea, wherein antibiotics are added into the enrichment culture medium of the ammonia-oxidizing bacteria flora; and D, carrying out enrichment culture on the ammonia-oxidizing archaea, wherein a filter is used for filtering an enrichment culture solution and then transferring into the enrichment culture medium of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea in the step C to obtain the enrichment culture solution of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea with a higher purity. Possibility is provided for researching physiological and biochemical characteristics of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea by the enrichment culture solution of the ammonia-oxidizing archaea with the higher purity; the ammonia-oxidizing archaea has stronger tolerance; if the ammonia-oxidizing archaea is introduced to an ammonia-oxidizing enhancing technology, important practical significance is provided for improving biological denitrification capacity of the sewage treatment.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Extremely halophilic archaea polyhydroxy fatty acid ester synthases and encoding gene and application
InactiveCN101139575AHigh PHA synthase activityIncreased PHA synthase activityBacteriaEnzymesEnzyme GenePHA synthase
The invention discloses an extremely halophilic archaea polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme and the code gene and application of the enzyme. The polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme comprises PhaEHh subunit and PhaCHh subunit; the PhaEHh subunit has amino acid residue sequence in sequence 1 in the sequence table or amino acid residue sequence got by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residue for the amino acid residue sequence in sequence 1 in the sequence table; the PhaCHh subunit has amino acid residue sequence in sequence 2 in the sequence table or amino acid residue sequence got by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residue for the amino acid residue sequence in sequence 2 in the sequence table. The polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme is of very high PHA enzyme activity; introducing the polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme gene phaECHh into a host bacterial strain will make possible high-efficient expression of PHA enzyme, and can improve the activity of the extremely halophilic archaea polyhydroxyalkanoates enzyme and PHA output.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for quantifying ammonia oxidizing archaea in lacustrine deposit
InactiveCN102230009ARapid research methodSimple research methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceNitrogen cycleLacustrine deposits
A method for quantifying ammonia oxidizing archaea in lacustrine deposit. The method comprises the following steps of (1) extracting DNA, and (2) constructing an ammonia oxidizing archaea plasmid standard substance and analyzing a sample, wherein the copy number of Ammonia oxidizing archaea in an unknown sample is obtained through processes of a detection of a Ct value of the unknown sample and a contrast of an amplification standard curve and the Ct value after the amplification standard curve is obtained. In the invention, ammonia oxidizing archaea in lacustrine deposit is detected quantificationally through a real-time fluorescent quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) technology. The method is a rapid, simple and accurate method for researching a nitrogen cycle mechanism of lacustrine deposit.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method for producing propionic acid by mixed bacteria system fermentation
ActiveCN106244661ADoes not affect activityIncreased PorphyromonadaceaeMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelHigh concentrationPropanoic acid
The invention relates to the technical field of microbes, and discloses a method for producing propionic acid by mixed bacteria system fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out sequencing batch anaerobic fermentation on a fermentation system composed of Methanogenic archaea / propionic-acid-producing bacteria-containing anaerobic sludge and an anaerobic fermentation culture medium, wherein in the fermentation process, the ammonium ion concentration in the fermentation system is enhanced to 1-2 g / L and kept constant, and methane is collected; and after the fermentation finishes, collecting the fermentation liquid, extracting the propionic acid, and adding the residual flora-containing solid into the anaerobic fermentation culture medium for the next fermentation round. The ammonium ion concentration is regulated to control the flora distribution of the Methanogenic archaea / propionic-acid-producing bacteria-containing anaerobic sludge, so that the fermentation environment is beneficial to the proliferation of the propionic-acid-producing bacteria; and the method can obtain a large amount of methane in the process of producing high-concentration high-purity propionic acid, has the advantages of unrestricted material sources and lower input-output ratio, and is beneficial to industrialized implementation.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Preparation method of straw feed
InactiveCN105961839AHigh nutritional valueReduce incinerationBacteriaFood processingIntracellular substanceFodder
The invention relates to a straw feed and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of culturing extremely halophilic archaea-halogranum amylolyticum TNN58; after the culturing of thalli is completed, performing cell pyrolysis by a water pyrolysis method. After centrifugal treatment, solids mainly comprise biological degradable plastics PHBV and part of intracellular substances, and precipitates can be used for PHBV extraction; supernatant contains a large quantity of nutrient substances, so that when the supernatant is added to straw, the content of nutrient substances such as protein in the straw can be effectively increased, and the nutrient value of the straw can be increased.
Owner:BEIJING UNION UNIVERSITY
Anaerobic biodegradation method for azo dye gold orange II and treatment method for wastewater
ActiveCN108928917AAchieve degradationFacilitate mass adoptionWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsMicroorganismGold Orange
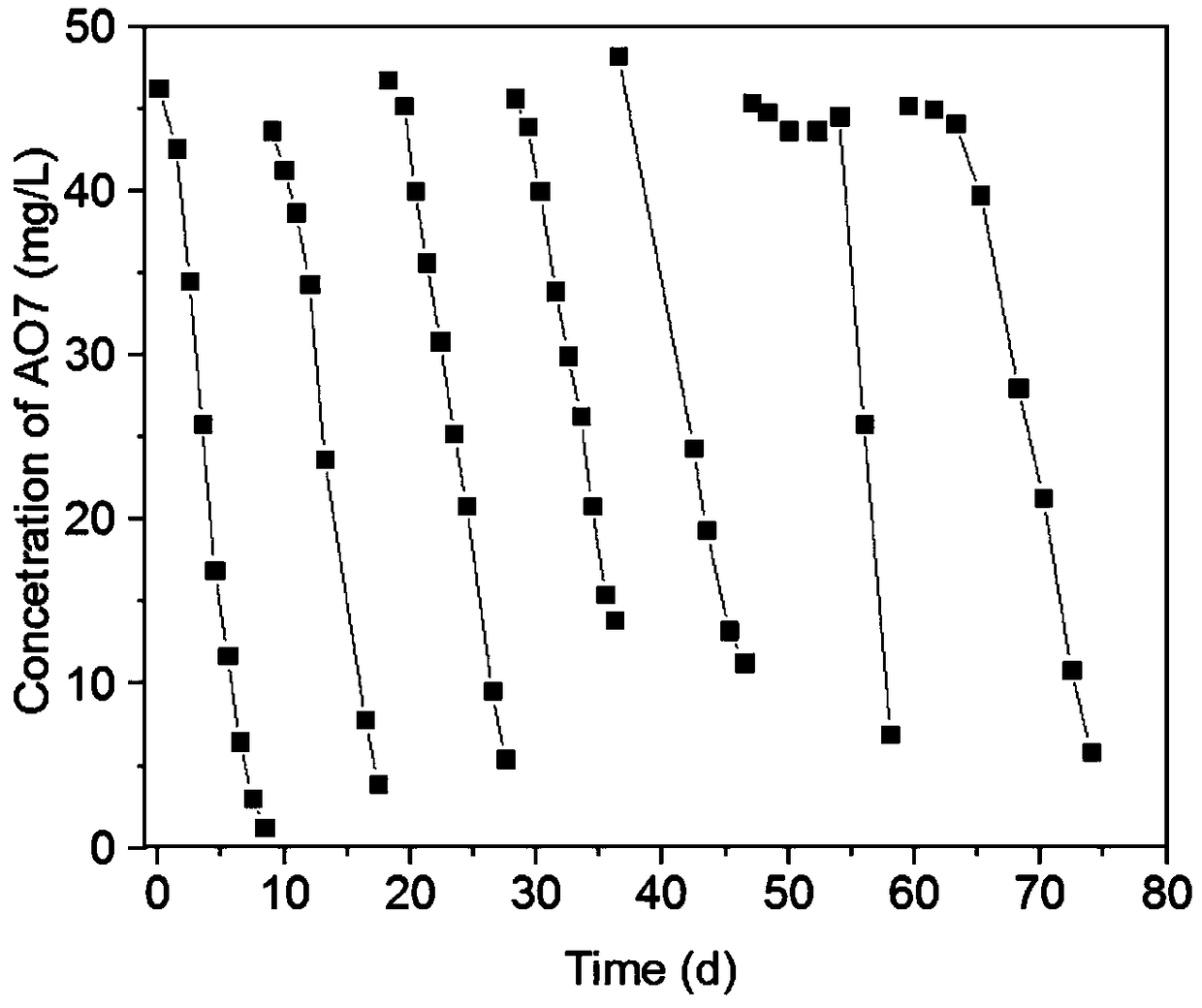
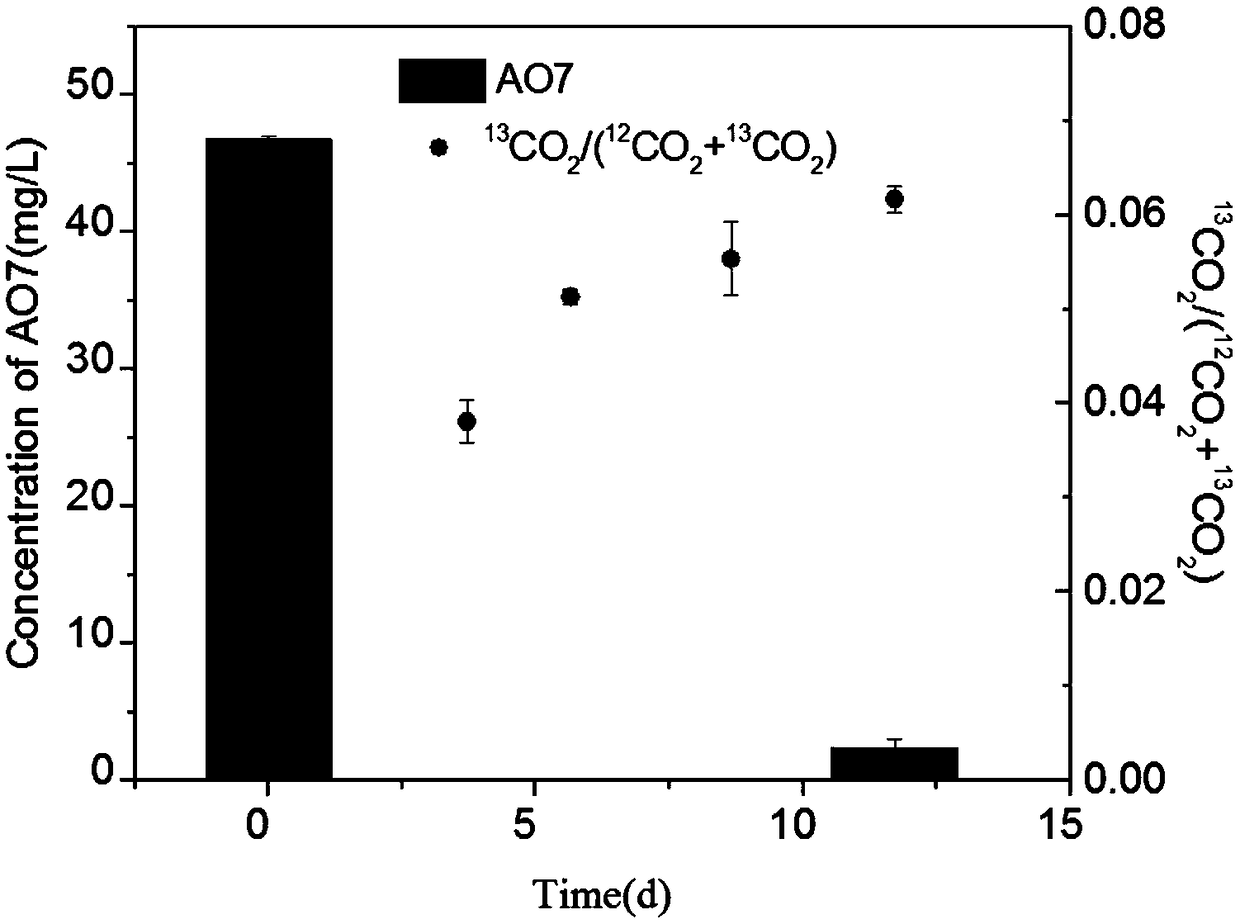
The invention provides an anaerobic biodegradation method for the azo dye gold orange II. According to the anaerobic biodegradation method, a sequencing batch mode is employed; methane is used as an electron donor; azo dye gold orange II is used as an electron acceptor; and denitrification anaerobic methane oxidation (DAMO) archaea is adopted for anaerobic biodegradation of the azo dye gold orangeII. When the DAMO archaea oxidizes methane into carbon dioxide, generated electrons are transfered to the azo dye gold orange II so as to reduce the azo dye gold orange II into p-aminobenzenesulfonicacid and 1-amino-2-naphthol, and thus, the anaerobic microbial degradation of the azo dye by the DAMO archaea is realized. The anaerobic biodegradation method of the invention has great advantages ineconomical performance and environmental protection; and the DAMO archaea widely exists in nature, which is beneficial for large-scale application of the DAMO archaea in anaerobic microbial treatmentof azo dyes and even other organic substances.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
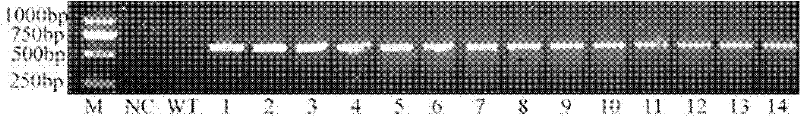
Application of extremely halophilic archaea NaSOD gene in improving rice salt tolerance
InactiveCN102399816AHigh ROS scavenging abilityImprove salt toleranceFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHalotoleranceGenetically modified rice
The invention discloses an application of an extremely halophilic archaea (Natrinema altunense sp.) NaSOD gene in improving rice salt tolerance. The base sequence of the extremely halophilic archaea NaSOD is shown by SEQ ID NO.3. The over-expression NaSOD genetically modified rice has the advantages of higher ROS scavenging capability and capability of reducing membrane lipid peroxidation caused by salt treatment so that higher photosynthetic rate can be guaranteed. According to the invention, the extremely halophilic archaea NaSOD gene is transferred into the rice so that the salt tolerance of the rice can be obviously improved.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV +2
Marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea enrichment device capable of automatically controlling dissolved oxygen
ActiveCN104556410APromote growthIncrease abundanceBiological water/sewage treatmentWater bathsEngineering
The invention discloses a marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea enrichment device capable of automatically controlling dissolved oxygen. The enrichment device comprises a reactor, a water feeder, a low-temperature water-bath kettle and a control cabinet, wherein a main body of the reactor is a funnel-shaped tank body, a reactor pressure balance opening and a reactor DO probe are arranged at the upper end of the funnel-shaped tank body, a reactor water inlet is formed in the lower end of the funnel-shaped tank body, and a temperature-controllable jacket is arranged outside the funnel-shaped tank body; the water feeder is divided into four parts, namely, a water-distribution zone, an aeration zone, a sedimentation zone and a water drainage zone, the water-distribution zone is provided with a water feeder DO probe, a feeding pipe and a water feeder water outlet, the aeration zone is provided with an aerating disc, the sedimentation zone is provided with a water feeder water inlet pipe and the water drainage zone is provided with a water feeder gas outlet and a water feeder water drainage opening. The enrichment device can provide low-temperature, low-dissolved-oxygen, low-shearing-force and high-salinity environment required for the growth of marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea; by virtue of the dissolved oxygen probe, an air pump and a nitrogen steel cylinder, the dissolved oxygen in the reactor influent water is controlled at a relatively low level so that the effective enrichment of marine ammonia-oxidizing archaea is achieved and the high-purity enriched culture product is obtained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for promoting anaerobic degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon in oil reservoir to produce methane
PendingCN107686849APromote degradationStimulate growth metabolismWaste based fuelFluid removalHydrogenMethanogenesis
The invention provides a method for promoting the anaerobic degradation of petroleum hydrocarbon in an oil reservoir to produce methane. The method comprises the following steps of (1), detecting andanalyzing the structure of a microbiologic population in the oil reservoir, so as to judge whether the oil reservoir contains a syntrophic hydrocarbon-degrading methanogenesis strain or not; (2), whenthe syntrophic hydrocarbon-degrading methanogenesis strain is contained in the oil reservoir, adding an additive A into the oil reservoir, and then shutting a well, wherein the additive is hydrogen nutritional methanogenesis archaea or mixed flora containing the hydrogen nutritional methanogenesis archaea; when the methanogenesis syntrophic hydrocarbon-degrading strain is not contained in the oilreservoir, adding an additive B into the oil reservoir, and then shutting the well, wherein the additive B is mixed bacteria containing the hydrogen nutritional methanogenesis archaea and syntrophichydrocarbon-degrading bacteria.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
DNA Marker for detecting coal geology microbe archaea species, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107130030AUniform brightnessSpecies-specificMicrobiological testing/measurementVector-based foreign material introductionMicroorganismElectrophoresis
The invention relates to a special specie DNA Marker for detecting coal geology microbe archaea in the denaturing gel gradient electrophoresis (DGGE) molecule detection of coal geology environment microbe florae, and belongs to the field of molecular microbial ecology. The DNA Marker for detecting coal geology microbe archaea species is composed of a DNA fragment a with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.1, a DNA fragment b with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.2, a DNA fragment c with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.3, a DNA fragment d with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.4, a DNA fragment e with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.5, a DNA fragment f with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.6, a DNA fragment g with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.7, and a DNA fragment h with the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ. ID. NO.8.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Preparation method for archaea thermophilic esterase and (S)-ketoprofen
InactiveCN103194467AHigh purityHigh resolution activityHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses a preparation method for archaea thermophilic esterase and (S)-ketoprofen. The method comprises preparation of a strain, a plasmid, enzymes and a culture medium, PCR amplification and construction of recombinant plasmid, and inducible expression of a gene and purification of protein. Specifically, the method comprises the following steps: (1) designing a pair of primers, carrying out amplification with a whole genome sequence of Thermotogamaritima as a template, carrying out enzyme digestion with endonuclease, connecting the primers to pET15b which has undergone enzyme digestion by same endonuclease, transforming ligation productsinto escherichia coli DH5 alpha, carrying out screening to obtain a recombinant plasmid and carrying out double digestion and sequencing confirmation; and (2) carrying out inducible expression of the gene and purification of the protein so as to obtain the archaea thermophilic esterase. According to the invention, through usage of a genetic engineering method, the gene of the esterase is cloned and expressed in escherichia coli, the protein of the esterase is prepared, and the protein has a high purity (more than 95%). The optimal reaction temperature and the reaction pH value of the esterase are 70 DEG C and 5.0 to 5.5, respectively; the esterase has good acid resistance and can maintain about 50% of its activity when treated for 60 min in a reaction system where the temperature is 70 DEG C and the pH value is 4.5.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Methods of using archaeal serine protease
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Recombinant cells and method for producing isoprene or terpene
InactiveCN109689857AEfficient productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesLycopersenePhytoene synthesis
Owner:SEKISUI CHEM CO LTD
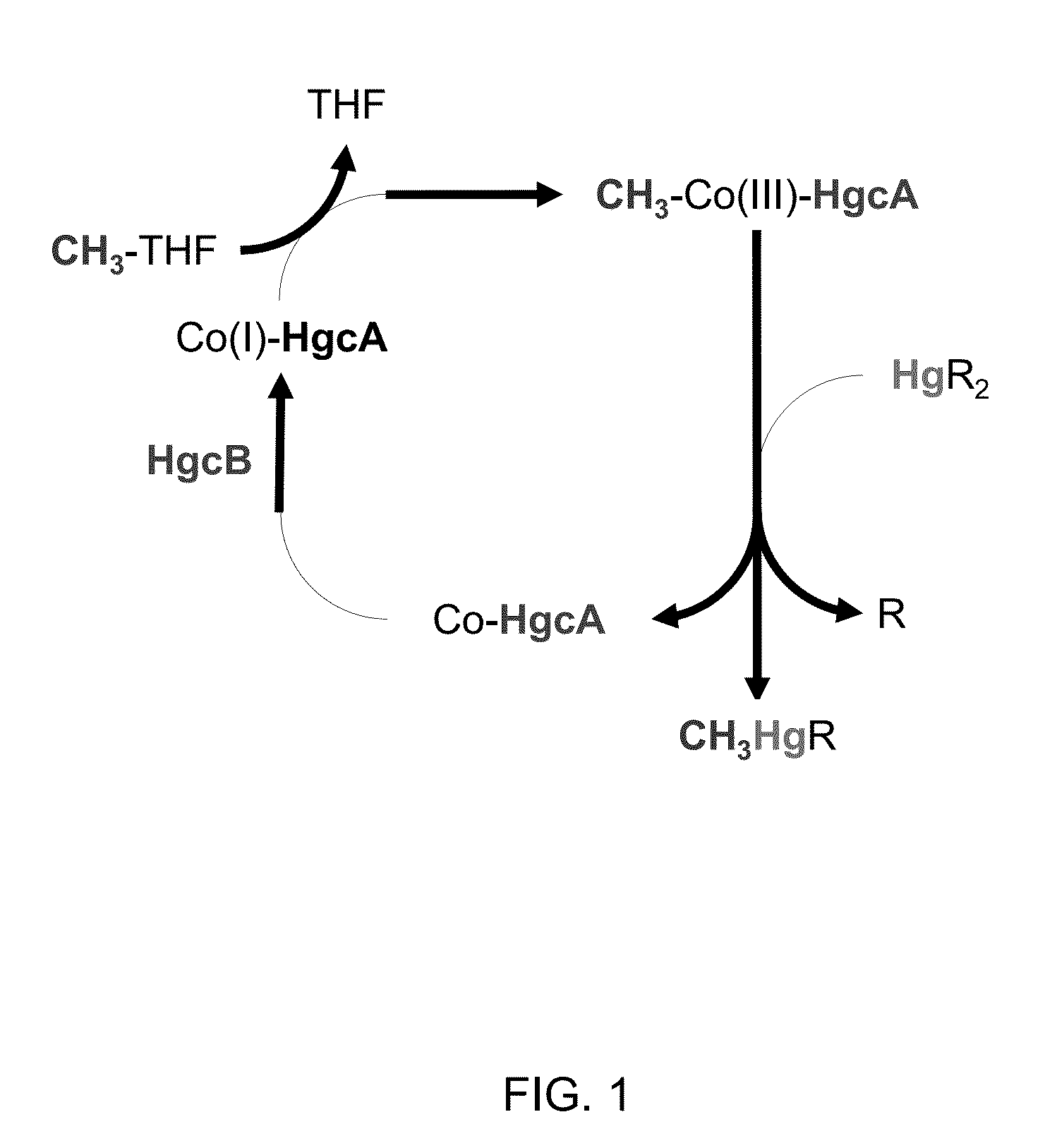
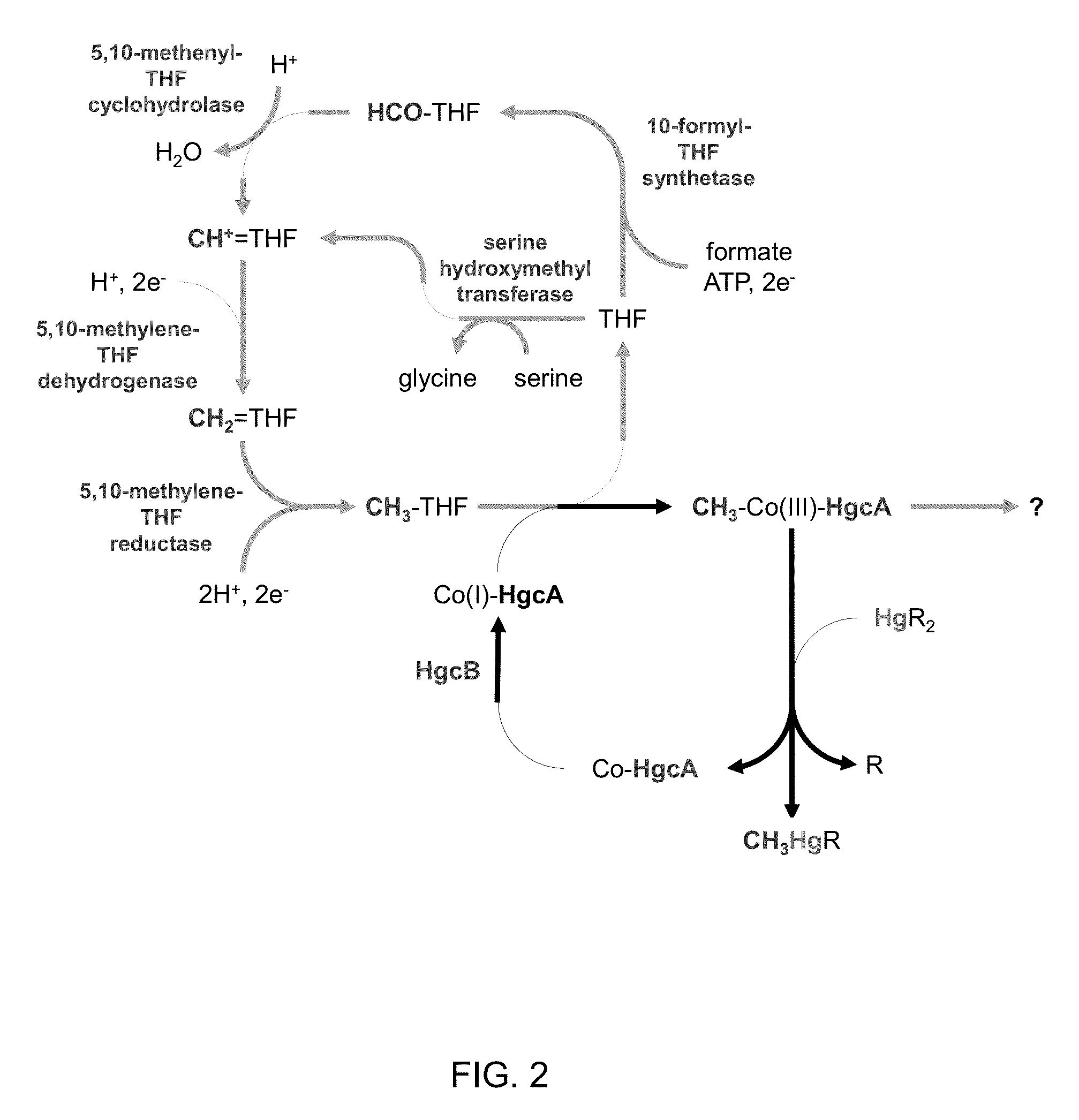
Mercury methylation genes in bacteria and archaea
Two genes required for this mercury methylation have been identified in bacteria and archaea. These genes are the hgcA gene and hgcB, a corrinoid protein that facilitates methyl group transfer to Hg, and a corrinoid protein-associated ferredoxin with two [4Fe-4S] binding motifs involved in generating cob(I)almin, respectively. The invention provides nucleic acid probes and primers for detecting methylmercury and or for assessing mercury methylation potential in environmental, clinical and other samples. The invention also provides antibodies against these proteins, antibodies against these proteins, methods of using the antibodies and methods of biocatalysis.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Method for diagnosing parkinson's disease through bacterial metagenome analysis
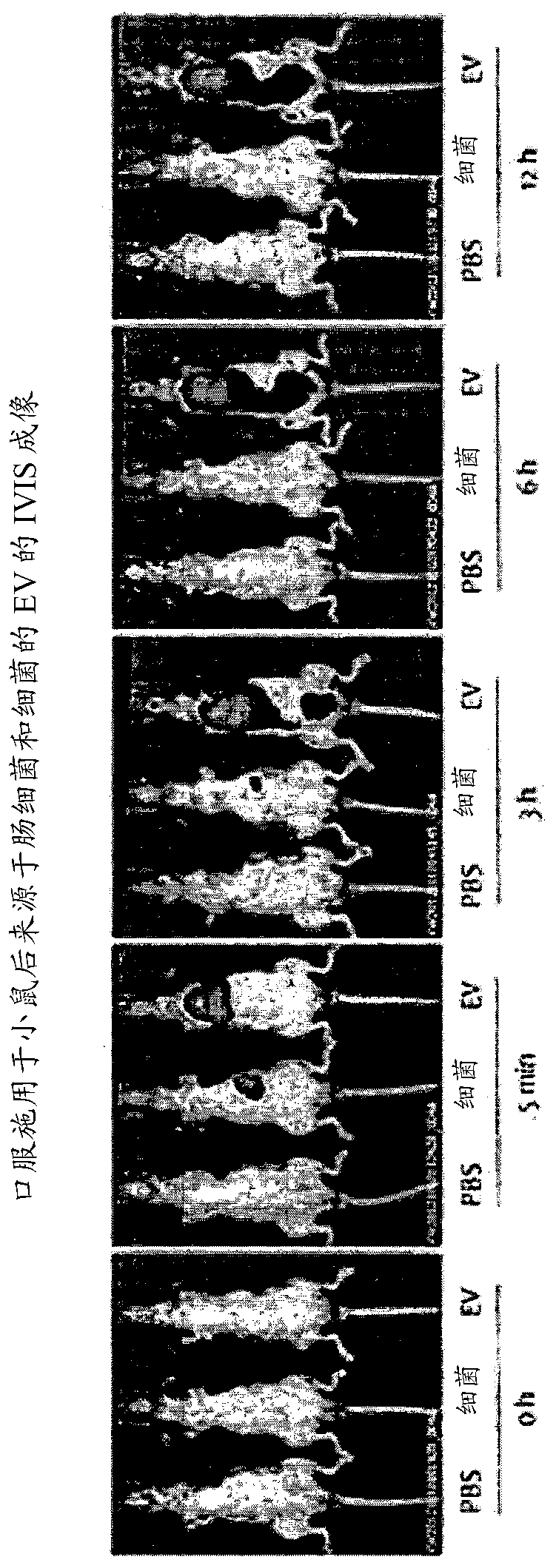
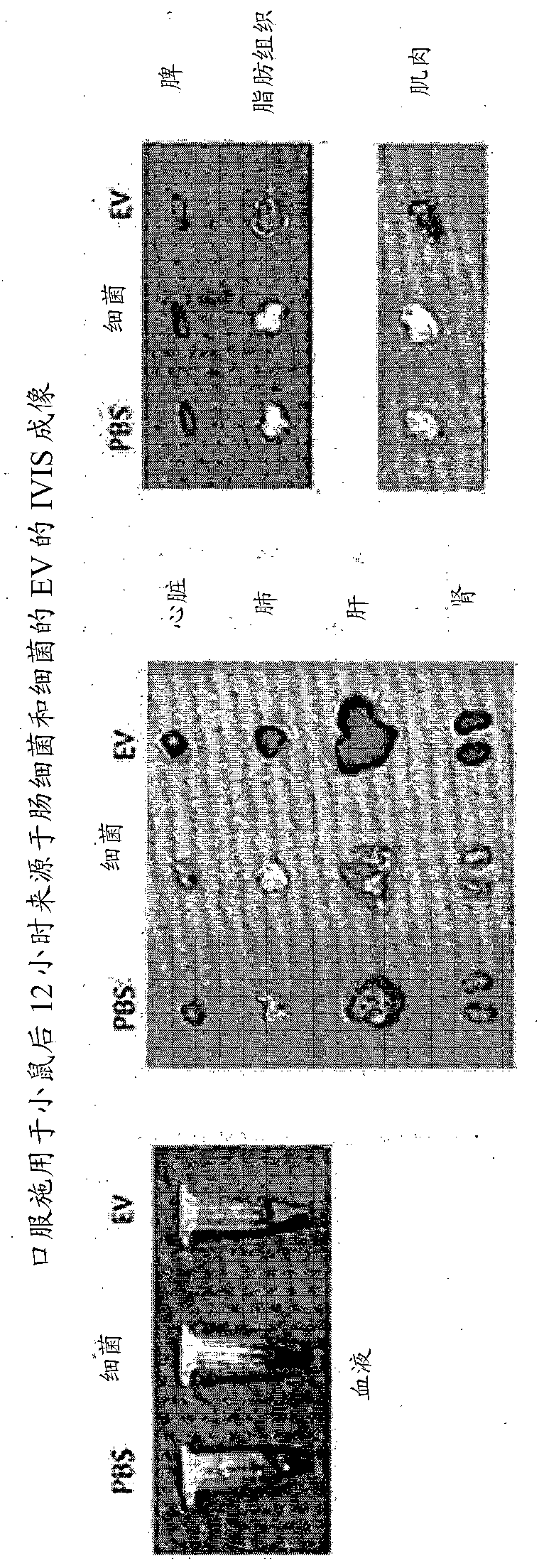
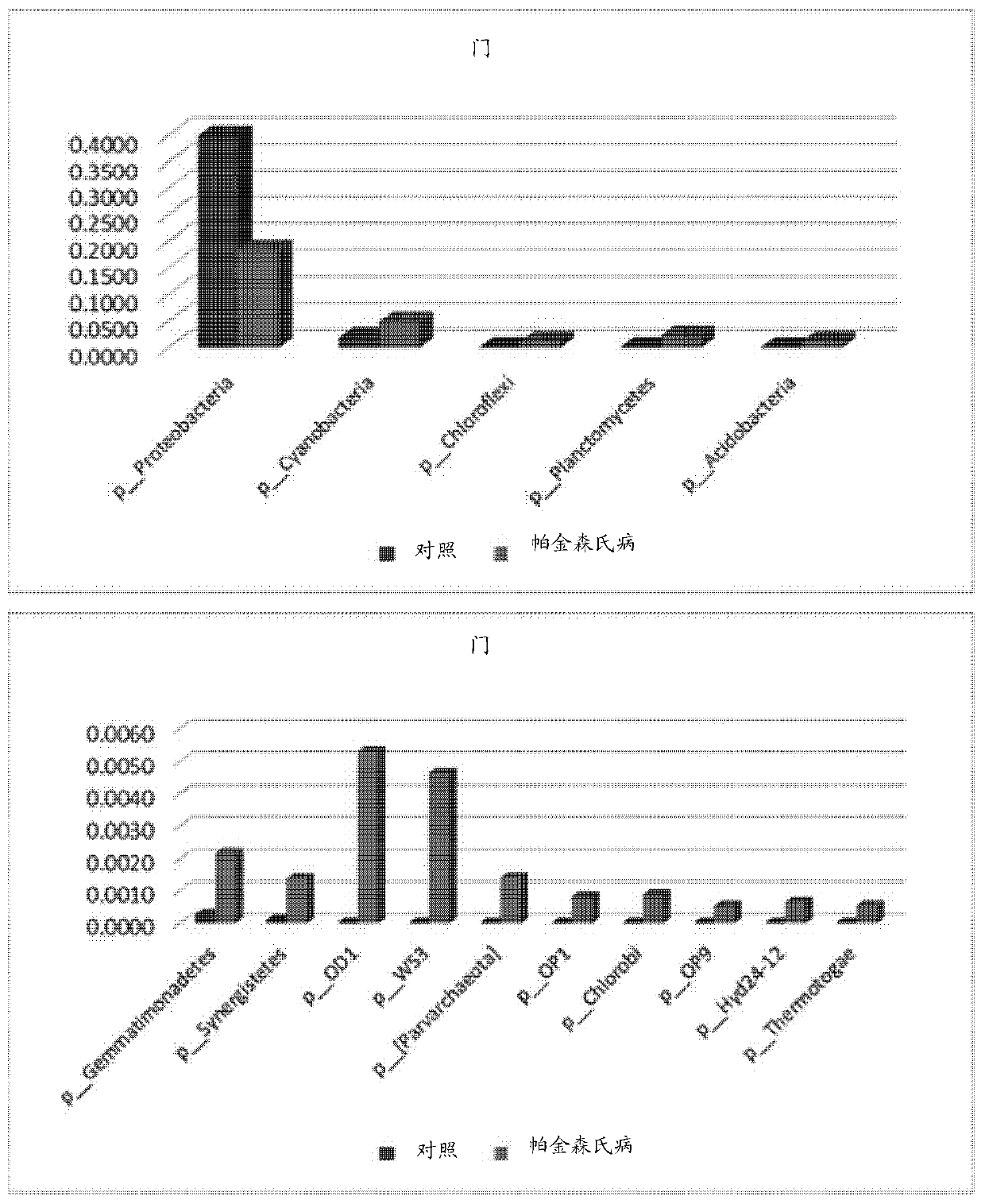
PendingCN110546280AAchieve early diagnosisSlow onsetMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseExtracellular vesicle
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing Parkinson's disease through bacterial metagenome analysis and, more specifically, to a method for performing bacterial metagenome analysis by using a sample derived from a subject so as to analyze increases and decreases in the amount of extracellular vesicles derived from specific bacteria, thereby diagnosing Parkinson's disease. The extracellular vesicles secreted from microbes, such as bacteria and archaea, present in the environment are absorbed into the body so as to be distributed to the brain, thereby directly influencing inflammatory responses and brain functions, and since early diagnosis of Parkinson's disease, which is characterized by inflammation, before symptoms occur is difficult, effective treatment has been difficult. Through the bacteria-derived extracellular vesicle metagenome analysis using a human-derived sample, according to the present invention, the risk of onset of Parkinson's disease can be predicted inadvance such that Parkinson's disease risk groups are diagnosed and predicted in an early stage, thereby enabling the time of onset of the disease to be delayed or the onset of the disease to be prevented through appropriate management, and early diagnosis is enabled even after the onset of the disease, thereby enabling the incidence of Parkinson's disease to be lowered and therapeutic effects tobe increased.
Owner:MD HEALTHCARE INC
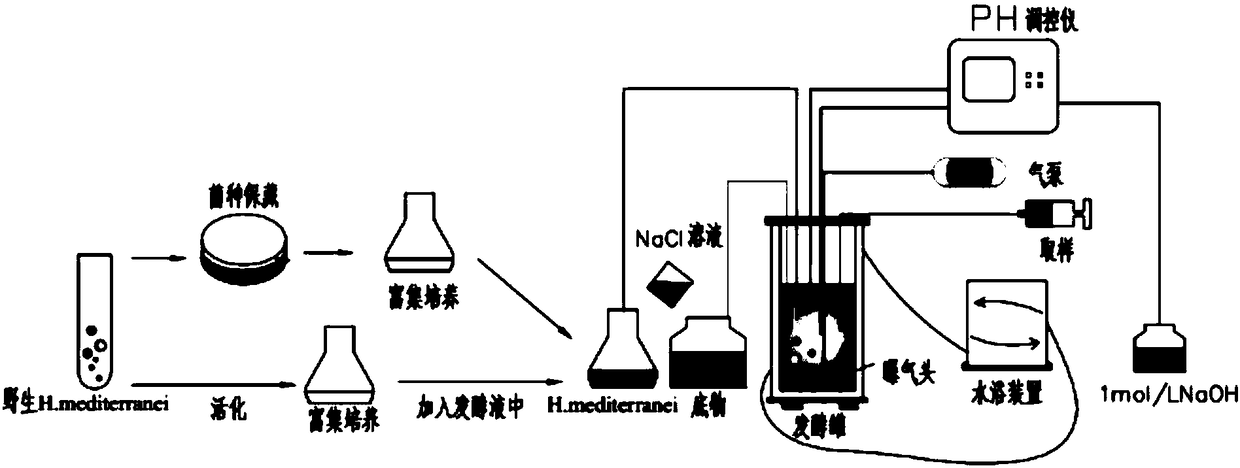
Method for increasing PHA yield by inhibiting halophilic archaea EPS yield
InactiveCN108103114AGrowth inhibitionSimplify the sterilization processMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismFermentation broth
The invention discloses a method for increasing PHA yield by inhibiting halophilic archaea EPS yield, and belongs to the field of producing polymer by microbial fermentation. According to the technical method, adjusting on concentration of NaCl in fermentation liquor can be used for inhibiting synthesis of EPS, so that propensity synthesis of PHA is promoted. When NaCl concentration in fermentation liquor is controlled to be 200g / l-250g / l, the yield of EPS can be inhibited, so that synthesis amount of PHA is remarkably improved. The technical method for synthesizing PHA by adjusting Haloferaxmediterranei propensity is simple to implement, and is easy for engineering operation.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com