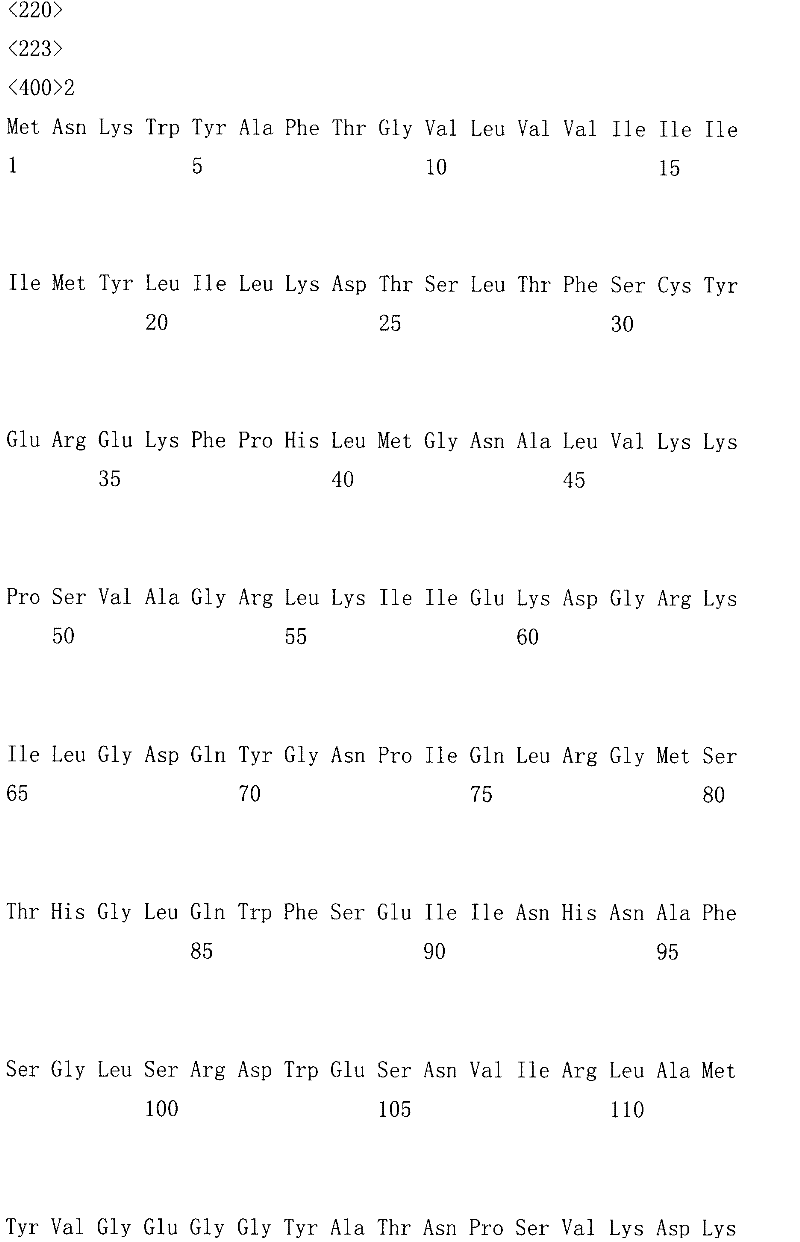Patents
Literature
48 results about "Endoglucanase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Endoglucanases and cellulase preparations containing the same
InactiveUS6921655B1High whitenessImprove freeness (drainage)Organic detergent compounding agentsBacteriaGlucanaseEndoglucanase activity
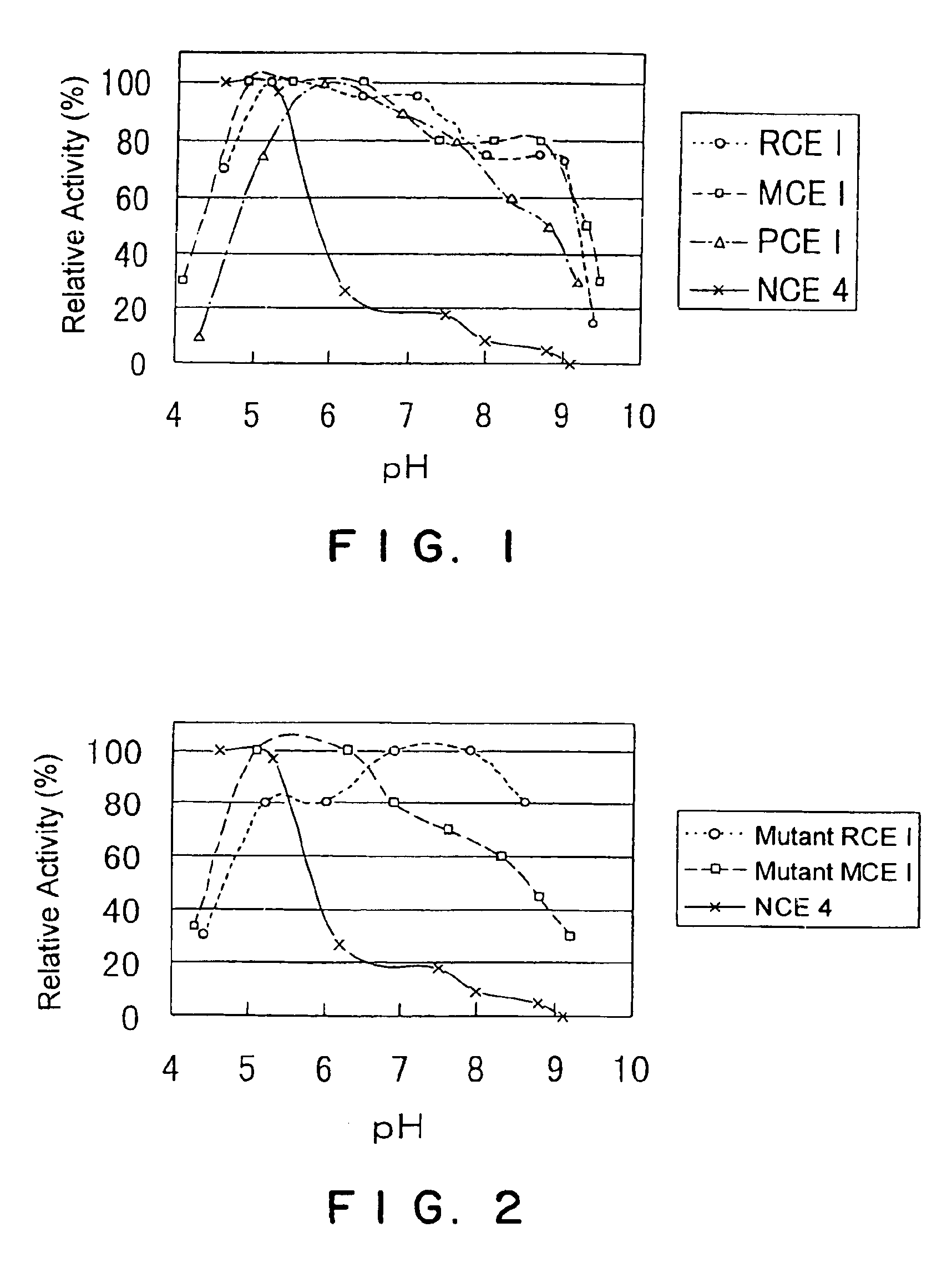
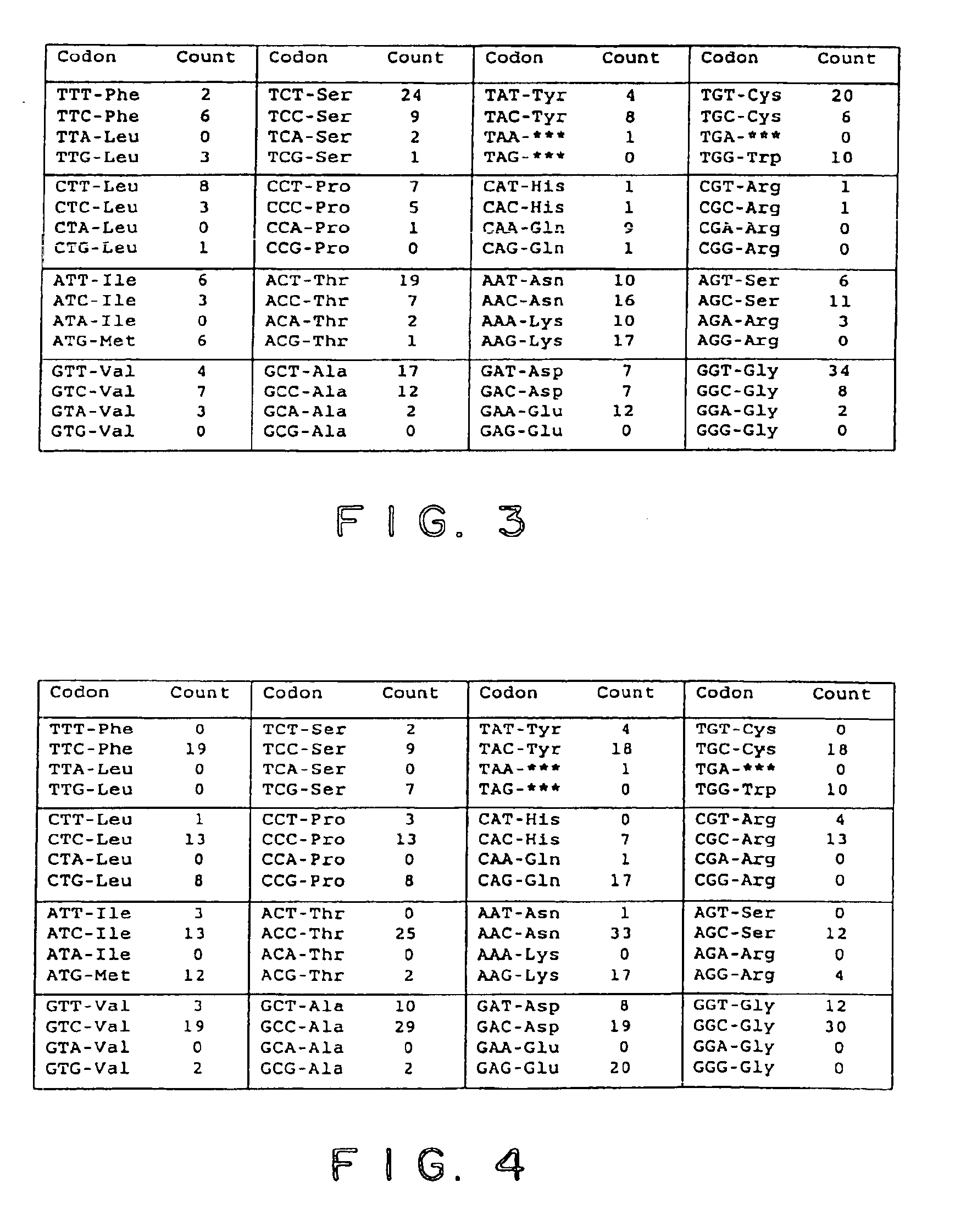
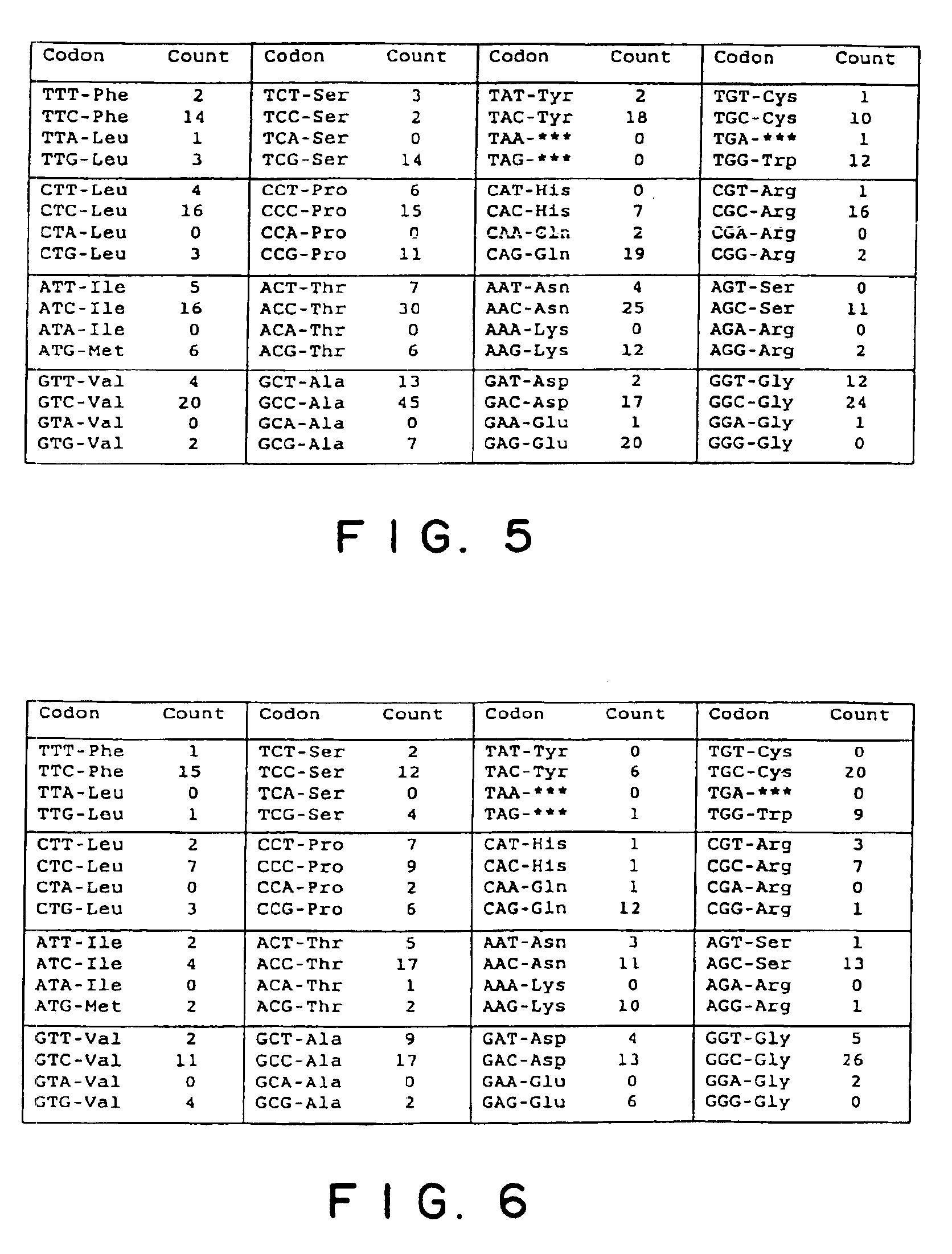
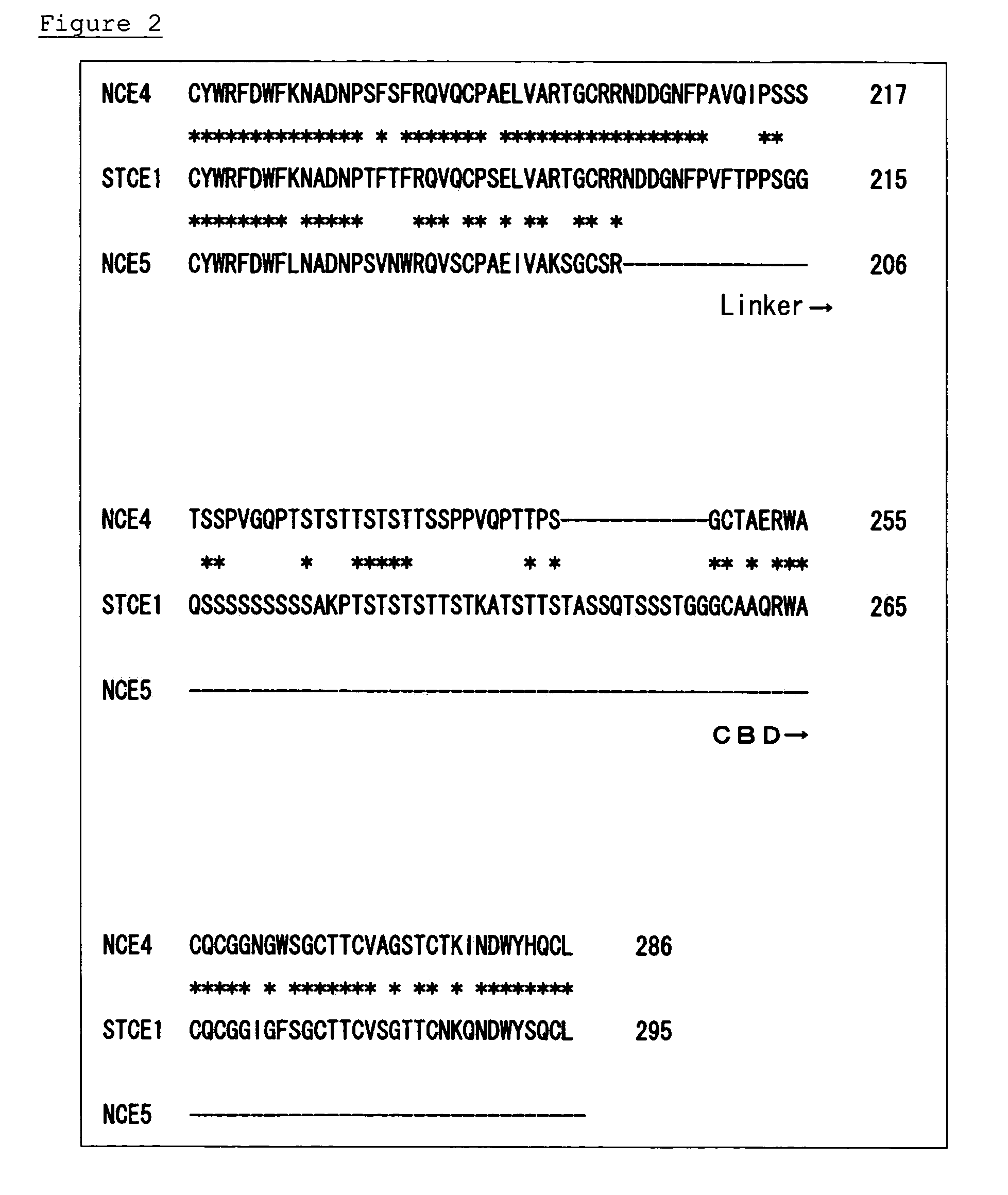
It is an object of the present invention to provide enzymes that have high endoglucanase activity and yet exhibit high activity even under alkaline conditions, and genes encoding the same. The enzyme according to the invention has the following properties: a) exhibiting endoglucanase activity; and b) capable of completely removing fuzz from regenerated cellulose fabrics at a concentration of 1 mg of the protein / L or below. The enzyme of the invention having endoglucanase activity is a protein comprising the amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 or 11; a modified protein thereof exhibiting endoglucanase activity; or a homologue of the protein or the modified protein.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA PHARMA CO LTD
Surfactant tolerant cellulase and method for modification thereof
ActiveUS8569033B2Efficient productionReduce presenceSugar derivativesMicroorganismsNucleotideL-Pyroglutamic Acid
A method for suppressing a reduction in an endoglucanase activity in the presence of a surfactant, characterized by modifying a protein having the endoglucanase activity in which the N-terminus is an amino acid other than pyroglutamic acid, to a protein having the N-terminus of pyroglutamic acid, is disclosed. Further, a modified protein having an endoglucanase activity wherein the N-terminal amino acid is converted into pyroglutamic acid by an amino acid modification, a polynucleotide encoding the protein, an expression vector comprising the polynucleotide, a host cell transformed with the expression vector, and a process for producing the protein by cultivating the host cell, are disclosed.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Glucanases, Nucleic Acids Encoding Them and Methods for Making and Using Them
InactiveUS20110117067A1Low viscosityImprove textureAntibacterial agentsFungiNucleotideExoxylanase activity
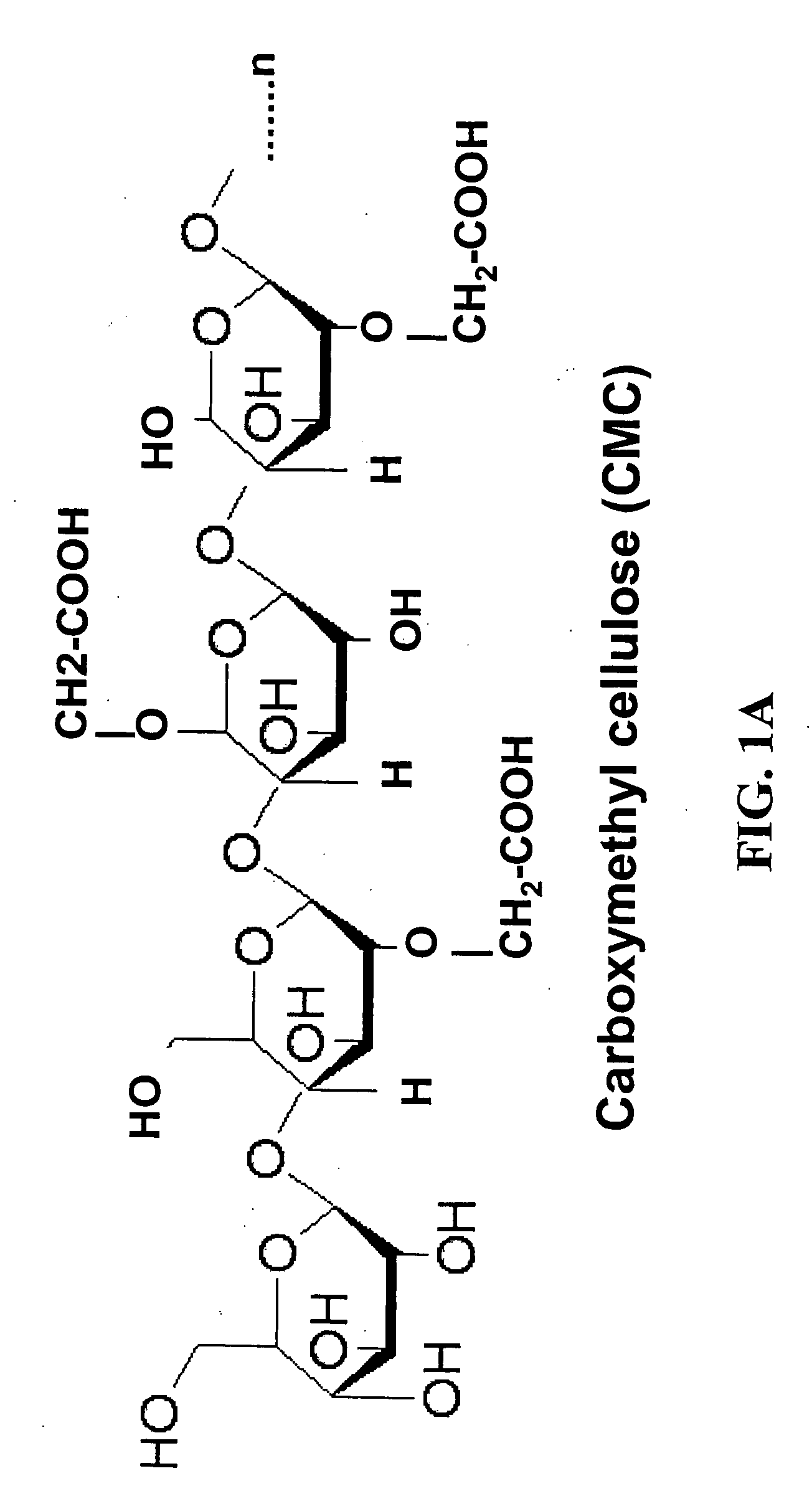
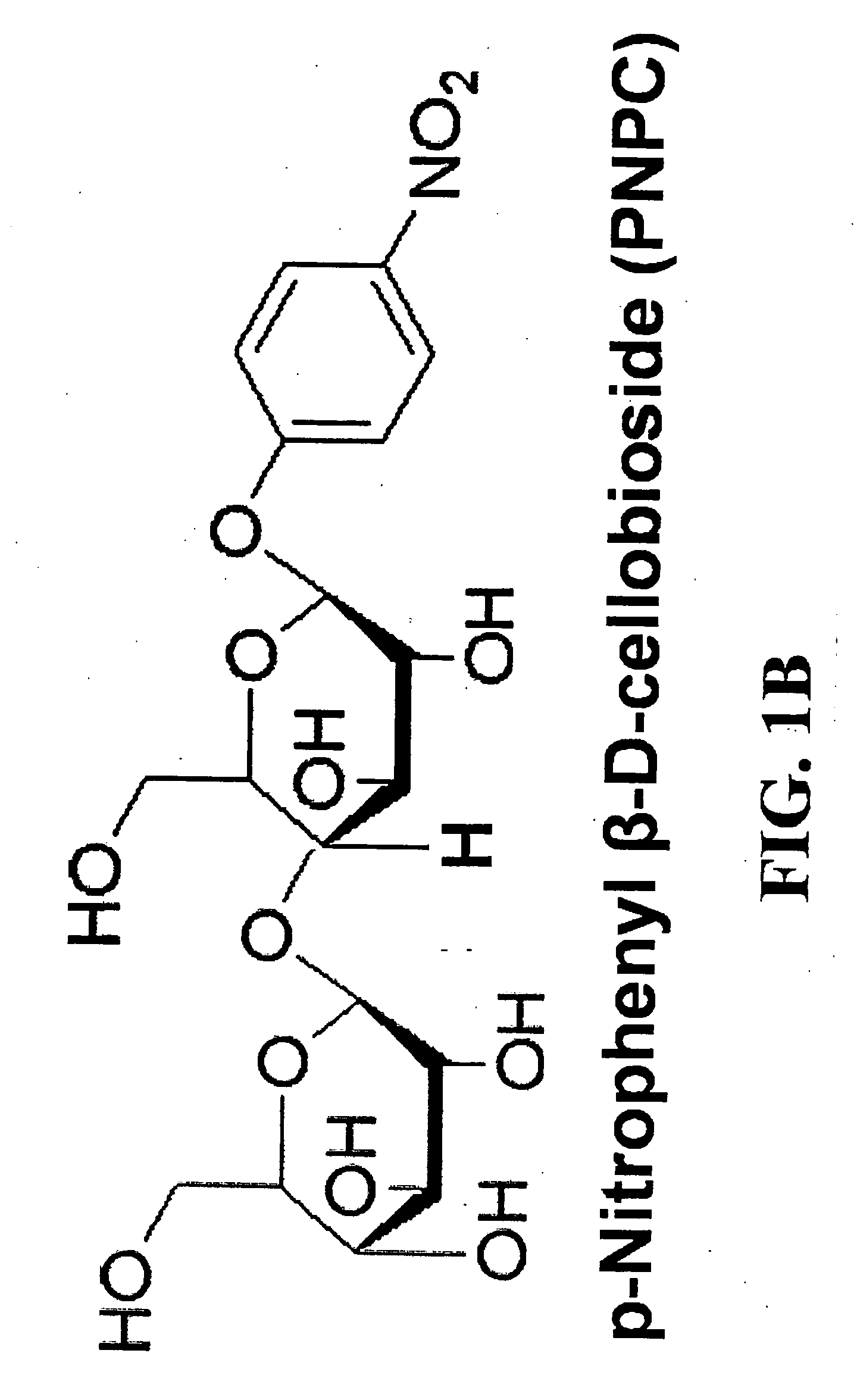
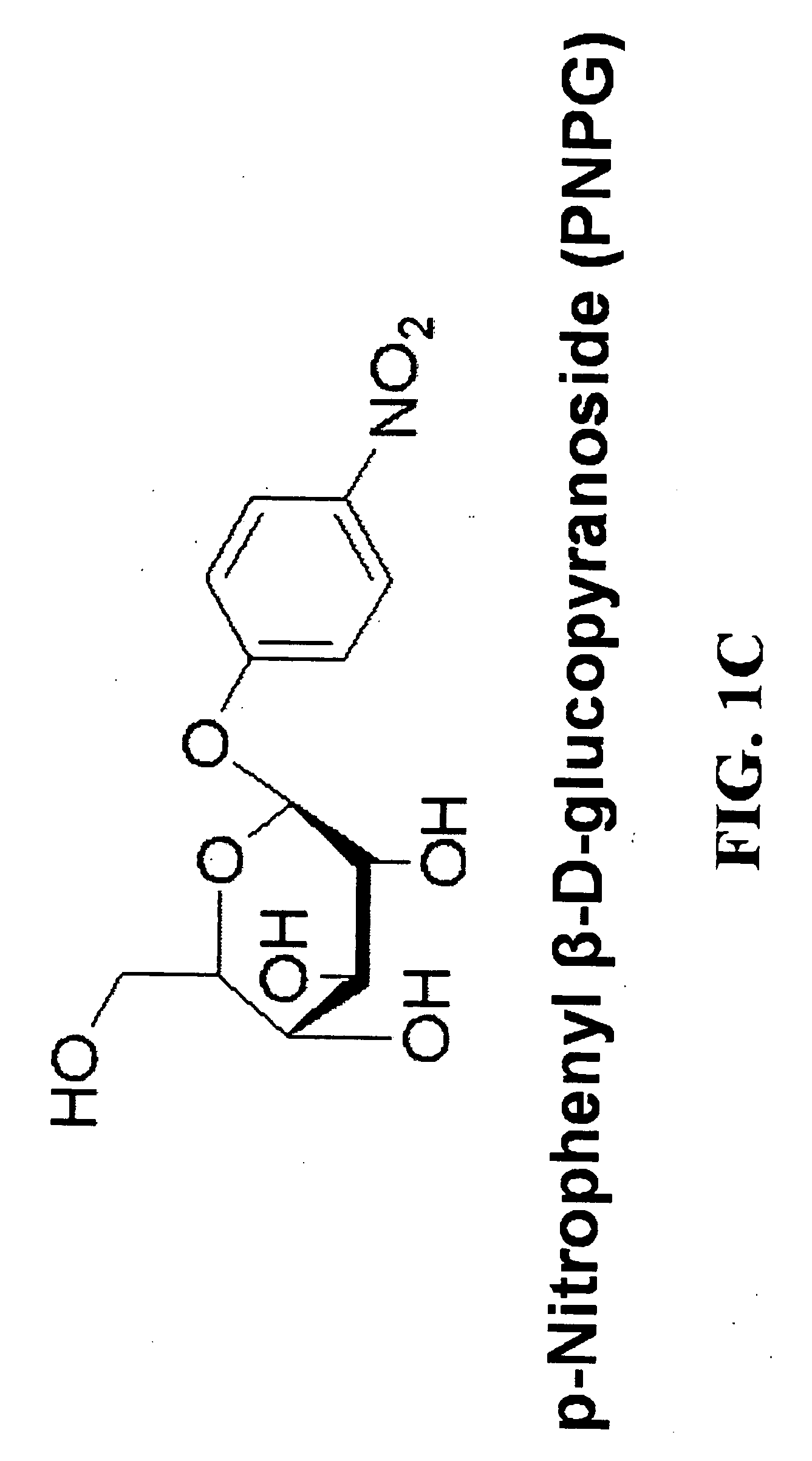
The invention relates to polypeptides having glucanase, e.g., endoglucanase, mannanase, xylanase activity or a combination of these activities, and polynucleotides encoding them. In one aspect, the glucanase activity is an endoglucanase activity (e.g., endo-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucano hydrolase activity) and comprises hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, cellulose derivatives (e.g., carboxy methyl cellulose and hydroxy ethyl cellulose) lichenin, beta-1,4 bonds in mixed beta-1,3 glucans, such as cereal beta-D-glucans or xyloglucans and other plant material containing cellulosic parts. In addition, methods of designing new enzymes and methods of use thereof are also provided. In alternative aspects, the new glucanases e.g., endoglucanases, mannanases, xylanases have increased activity and stability, including thermotolerance or thermostability, at increased or decreased pHs and temperatures.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Glucanases, Nucleic Acids Encoding Them and Methods for Making and Using Them
ActiveUS20140295523A1Low viscosityImprove textureAntibacterial agentsBiofuelsNucleotideExoxylanase activity
The invention relates to polypeptides having glucanase, e.g., endoglucanase, mannanase, xylanase activity or a combination of these activities, and polynucleotides encoding them. In one aspect, the glucanase activity is an endoglucanase activity (e.g., endo-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucano hydrolase activity) and comprises hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, cellulose derivatives (e.g., carboxy methyl cellulose and hydroxy ethyl cellulose) lichenin, beta-1,4 bonds in mixed beta-1,3 glucans, such as cereal beta-D-glucans or xyloglucans and other plant material containing cellulosic parts. In addition, methods of designing new enzymes and methods of use thereof are also provided. In alternative aspects, the new glucanases e.g., endoglucanases, mannanases, xylanases have increased activity and stability, including thermotolerance or thermostability, at increased or decreased pHs and temperatures.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
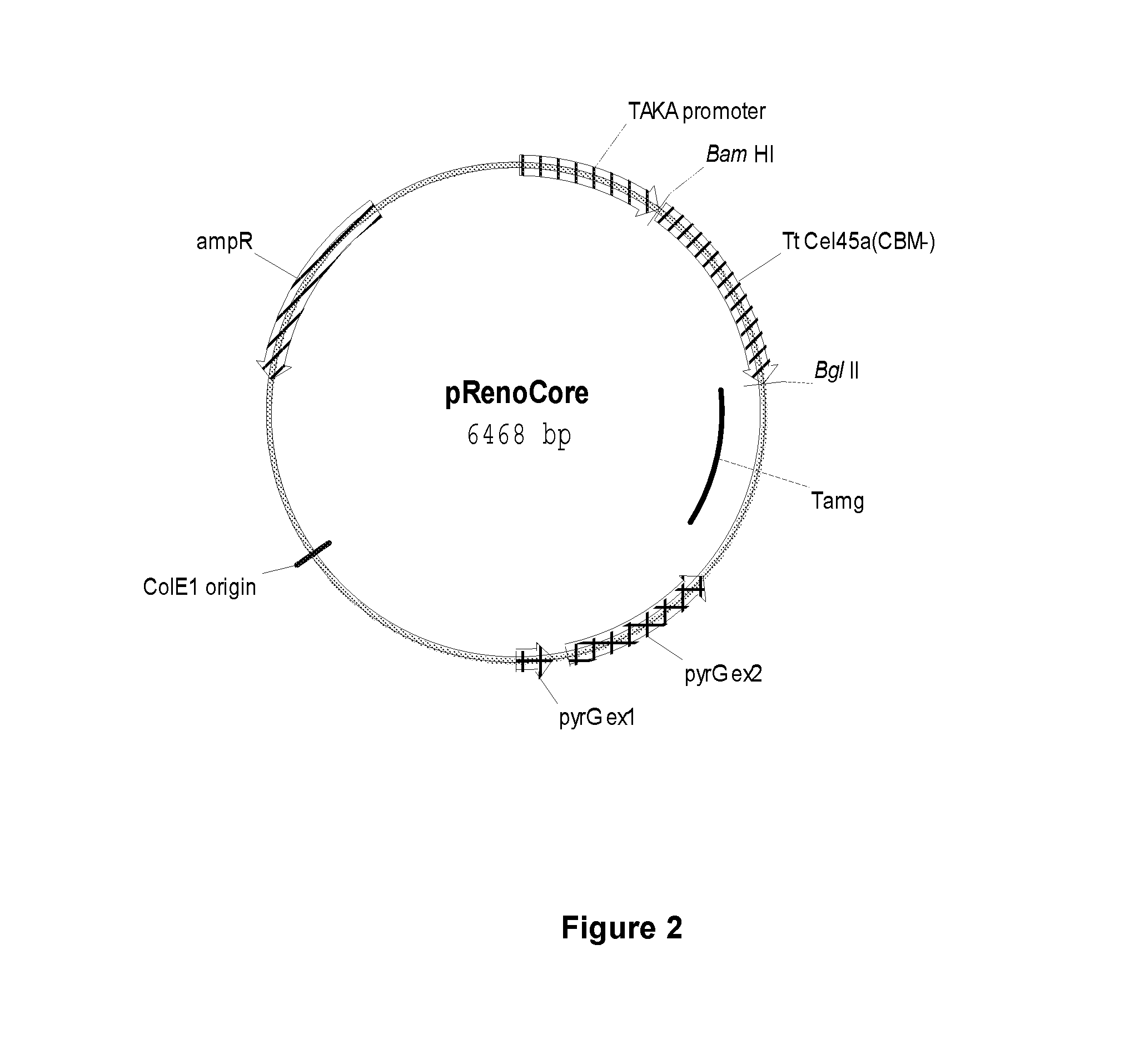
Compositions and methods for enhancing the degradation or conversion of cellulose-containing material
The present invention relates to methods for degrading or converting a cellulose-containing material, comprising: treating the cellulose-containing material with an effective amount of a cellulolytic enzyme composition comprising a polypeptide having cellulolytic enhancing activity, and one or more (several) components selected from the group consisting of a CEL7 polypeptide having endoglucanase activity, a CEL12 polypeptide having endoglucanase activity, a CEL45 polypeptide having endoglucanase activity, a CEL7 polypeptide having cellobiohydrolase activity with a cellulose binding domain, and a CEL7 polypeptide having cellobiohydrolase activity without a cellulose binding domain. The present invention also relates to such cellulolytic enzyme compositions.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Wood pulp treatment
InactiveUS20140209259A1Lower energy requirementsMaintain tensile strengthPulp properties modificationFibrous raw materialsGlycanMannanase activity
A process using a multicomponent enzyme preparation to treat screened once refined pulps and reduces the specific energy consumption and / or increasing production while maintaining or increasing handsheet physical properties. The enzyme preparation has a major endoglucanase activity, a significant mannanase activity and a relatively small cellobiohydrolase activity. This enzyme mixture is prepared from a genetically modified strain of Trichoderma reseii.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
Endoglucanase as well as encoding gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101225376AHigh carboxymethyl cellulase activityExtensive degradationFungiBacteriaCelluloseEndoglucanase activity
The invention discloses an endoglucanase and a coding gene of the endoglucanase and an application of the endoglucanase and the coding gene. The endoglucanase is one type of the protein with the following amino acid residue sequence: 1) SEQ ID No. : 2 in the sequence table; 2) the amino acid residue sequence of the SEQ ID No.: 2 in the sequence table forms a protein with the endoglucanase activity by the substitution and / or the deletion and / or the addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residues. The an endoglucanase and a coding gene of the endoglucanase has the advantages that: the endoglucanase has very high carboxymethyl cellulose enzyme activity (36780U / g), and the enzyme has a wide PH value range and a wide temperature range. The endoglucanase and the coding gene of the endoglucanase can be widely used in the degradation of cellulose.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Glucanases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention relates to polypeptides having glucanase, e.g., endoglucanase, mannanase, xylanase activity or a combination of these activities, and polynucleotides encoding them. In one aspect, the glucanase activity is an endoglucanase activity (e.g., endo-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucano hydrolase activity) and comprises hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, cellulose derivatives (e.g., carboxy methyl cellulose and hydroxy ethyl cellulose) lichenin, beta-1,4 bonds in mixed beta-1,3 glucans, such as cereal beta-D-glucans or xyloglucans and other plant material containing cellulosic parts. In addition, methods of designing new enzymes and methods of use thereof are also provided. In alternative aspects, the new glucanases e.g., endoglucanases, mannanases, xylanases have increased activity and stability at increased pH and temperature.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Method for reducing viscosity in saccharification process
InactiveUS20140134677A1Reduces viscosity of mixtureImprove saccharificationFermentationGlycosylasesEndoglucanase activityHydrolase
The present invention relates to compositions that can be used in hydrolyzing biomass such as compositions comprising a polypeptide having glycosyl hydrolase family 61 / endoglucanase activity, methods for hydrolyzing biomass material, and methods for reducing viscosity of biomass mixture using a composition comprising a polypeptide having glycosyl hydrolase family 61 / endoglucanase activity.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Endoglucanases
In one aspect, the invention provides a purified thermostable enzyme derived from the archael bacterium AEPII 1a. In one aspect, the enzyme has a molecular weight of about 60.9 kilodaltons and has a cellulase activity. The enzyme can be produced from native or recombinant host cells, and can be used to aid in the digestion of cellulose. The invention also provides polypeptides having endoglucanase activity having homology to SEQ ID NO:2.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Endoglucanases for Treatment of Cellulosic Material
InactiveUS20140051128A1Reduction of enzyme loadIncrease flexibilityNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCelluloseFermentable sugar
The present invention relates to production of fermentable sugars from lignocellulosic material by enzymatic conversion. The fermentable sugars are useful e.g. in the production of bioethanol. Novel polypeptides having endoglucanase activity, polynucleotides encoding them and vectors and host cells containing the polynucleotides are disclosed. A method for treating cellulosic material with the novel endoglucanase as well as uses of the enzymes and enzyme preparations and a method of preparing them are described.
Owner:ROAL O Y (FI)
Method for treating textile with endoglucanase
InactiveCN103429736ASave energyNo weight lossBiochemical fibre treatmentDetergent compounding agentsEngineeringEndoglucanase activity
The present invention relates to the method for manufacturing textile, by treating textile with an isolated polypeptide having endoglucanase activity, especially in biostoning and bio- polishing process.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Carbohydrate based cellulase inhibitors as feeding stimulants in termites
InactiveUS20080107619A1Increase feed rateIncrease termite mortalityBiocideAnimal repellantsEndoglucanase activityDigestion
A method, composition and system for controlling termites wherein single carbohydrate-based compounds are used as both cellulase inhibitors and feeding stimulants. Di-saccharides, cellobioimidazole (CBI), fluoro-methyl cellobiose (FMCB), and mono-saccharides, fluoro-methyl glucose (FMG) and analogs thereof inhibit termite cellulose digestion, which leads to starvation or stimulates termite feeding to cause mortality. CBI, FMCB and FMG were tested against enzyme fractions that represented endogenous (foregut / salivary gland / midgut) and symbiotic (hindgut) termite cellulases in vitro and in vivo. Feeding stimulation by di-saccharides results in greater cellulase inhibitor intake throughout midrange concentrations (1 mM-10 mM), which is associated with significant termite mortality. In contrast, the monosaccharide inhibitor, FMG did not stimulate feeding, but did inhibit feeding at concentrations above 1 mM, causing mortality. With modification to create longer β-glycosidic chain lengths, the cellulase inhibitors identified herein can also be targeted to endoglucanase activity for increased efficacy and use as novel termite control compositions.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Laundry and cleaning compositions containing xyloglucanase enzymes
InactiveUS6489279B2Reduce the amount of solutionOrganic detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsEndoglucanase activityLaundry
Laundry or cleaning products comprising one or more enzymes exhibiting endoglucanase activity specific for xyloglucan, and methods for laundering fabrics and cleaning dishes and tableware with aqueous solutions containing an effective amount of one or more enzymes exhibiting endoglucanase activity specific for xyloglucan.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Method for reducing viscosity in saccharification process
ActiveUS20170096651A1Low viscosityImprove saccharification and yieldFermentationGlycosylasesEnzyme familyEndoglucanase activity
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Endoglucanase as well as encoding gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101225377AHigh carboxymethyl cellulase activityExtensive degradationFungiBacteriaCelluloseEndoglucanase activity
The invention discloses an endoglucanase and a coding gene of the endoglucanase and an application of the endoglucanase and the coding gene. The endoglucanase is one type of the protein with the following amino acid residue sequence: 1) SEQ ID No.: 2 in the sequence table; 2) the amino acid residue sequence of the SEQ ID No.: 2 in the sequence table forms a protein with the endoglucanase activity by the substitution and / or the deletion and / or the addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residues. The endoglucanase and a coding gene of the endoglucanase has the advantages that: the endoglucanase has very high carboxymethyl cellulose enzyme activity (4029U / g), and the enzyme has a wide PH value range and a wide temperature range. The endoglucanase and the coding gene of the endoglucanase can be widely used in the degradation of cellulose.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Polypeptides Having Endoglucanase Activity and Polynucleotides Encoding Same
InactiveUS20140093919A1Convenient ligationPromote hydrolysisBacteriaFermentationEndoglucanase activityPolynucleotide
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having endoglucanase activity and polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Surfactant tolerant cellulase and method for modification thereof
ActiveUS20070099265A1Efficient productionReduce presenceFungiSugar derivativesNucleotideL-Pyroglutamic Acid
A method for suppressing a reduction in an endoglucanase activity in the presence of a surfactant, characterized by modifying a protein having the endoglucanase activity in which the N-terminus is an amino acid other than pyroglutamic acid, to a protein having the N-terminus of pyroglutamic acid, is disclosed. Further, a modified protein having an endoglucanase activity wherein the N-terminal amino acid is converted into pyroglutamic acid by an amino acid modification, a polynucleotide encoding the protein, an expression vector comprising the polynucleotide, a host cell transformed with the expression vector, and a process for producing the protein by cultivating the host cell, are disclosed.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA KAISHA LTD
Method for treating textile with endoglucanase
InactiveUS8802423B2Reduced pilling formationSave energyBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsDetergent compounding agentsEndoglucanase activityChemistry
The present invention relates to the method for manufacturing textile, by treating textile with an isolated polypeptide having endoglucanase activity, especially in biostoning and bio-polishing process.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Bacillus subtilis for inhibiting phomopsis and application thereof
ActiveCN109929782APromote degradationStrong endoglucosidase activityAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsKiwi fruitStaphylococcus aureus
The invention provides a bacillus subtilis for inhibiting phomopsis which is bacillus subtilis T8 deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 5, 2018 with the preservation numberof CCTCC NO: M 2018860. The bacillus subtilis T8 has good cellulose degradation capability, can produce cellulase, and has strong endoglucanase activity, filter paper enzymatic activity, exonucleaseactivity and beta-glucosidase activity. The bacillus subtilis T8 can inhibit phomopsis, and an ethanol supernatant and a protein have inhibitory effects on the phomopsis. In addition, the bacillus subtilis T8 can inhibit the growth of escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus, candida albicans, shigella dysenteriae and enterobacter faecalis, and has a development and utilization value in inhibitinghuman pathogenic bacteria. The invention also provides application of the bacillus subtilis T8 in producing cellulase and preventing kiwi fruit soft rot.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY JIANGXI ACADEMY OF SCI
Endoglucanase as well as encoding gene and use thereof
InactiveCN101225378AHigh carboxymethyl cellulase activityExtensive degradationFungiBacteriaCelluloseEndoglucanase activity
The invention discloses an endoglucanase and a coding gene of the endoglucanase and an application of the endoglucanase and the coding gene. The endoglucanase is one type of the protein with the following amino acid residue sequence: 1) SEQ ID No.: 2 in the sequence table; 2) the amino acid residue sequence of the SEQ ID No.: 2 in the sequence table forms a protein with the endoglucanase activity by the substitution and / or the deletion and / or the addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residues. The endoglucanase and a coding gene of the endoglucanase has the advantages that: the endoglucanase has very high carboxymethyl cellulose enzyme activity (42229U / g), and the enzyme has a wide PH value range and a wide temperature range. The endoglucanase and the coding gene of the endoglucanase can be widely used in the degradation of cellulose.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
NOVEL beta-1,6-ENDOGLUCANASE PRODUCING GENTIOBIOSE OR GLUCOSE FROM beta-GLUCAN
The present invention relates to a novel beta-1,6-endoglucanase producing gentiobiose or glucose from beta-glucan, and more specifically, the present invention provides an effect of producing gentiobiose or glucose at high yield through beta-1,6-endoglucanase showing beta-1,6-endoglucanase activity on beta-glucan.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
Glucanases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention relates to polypeptides having glucanase, e.g., endoglucanase, mannanase, xylanase activity or a combination of these activities, and polynucleotides encoding them. In one aspect, the glucanase activity is an endoglucanase activity (e.g., endo-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucano hydrolase activity) and comprises hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, cellulose derivatives (e.g., carboxy methyl cellulose and hydroxy ethyl cellulose) lichenin, beta-1,4 bonds in mixed beta-1,3 glucans, such as cereal beta-D-glucans or xyloglucans and other plant material containing cellulosic parts. In addition, methods of designing new enzymes and methods of use thereof are also provided. In alternative aspects, the new glucanases e.g., endoglucanases, mannanases, xylanases have increased activity and stability at increased pH and temperature.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
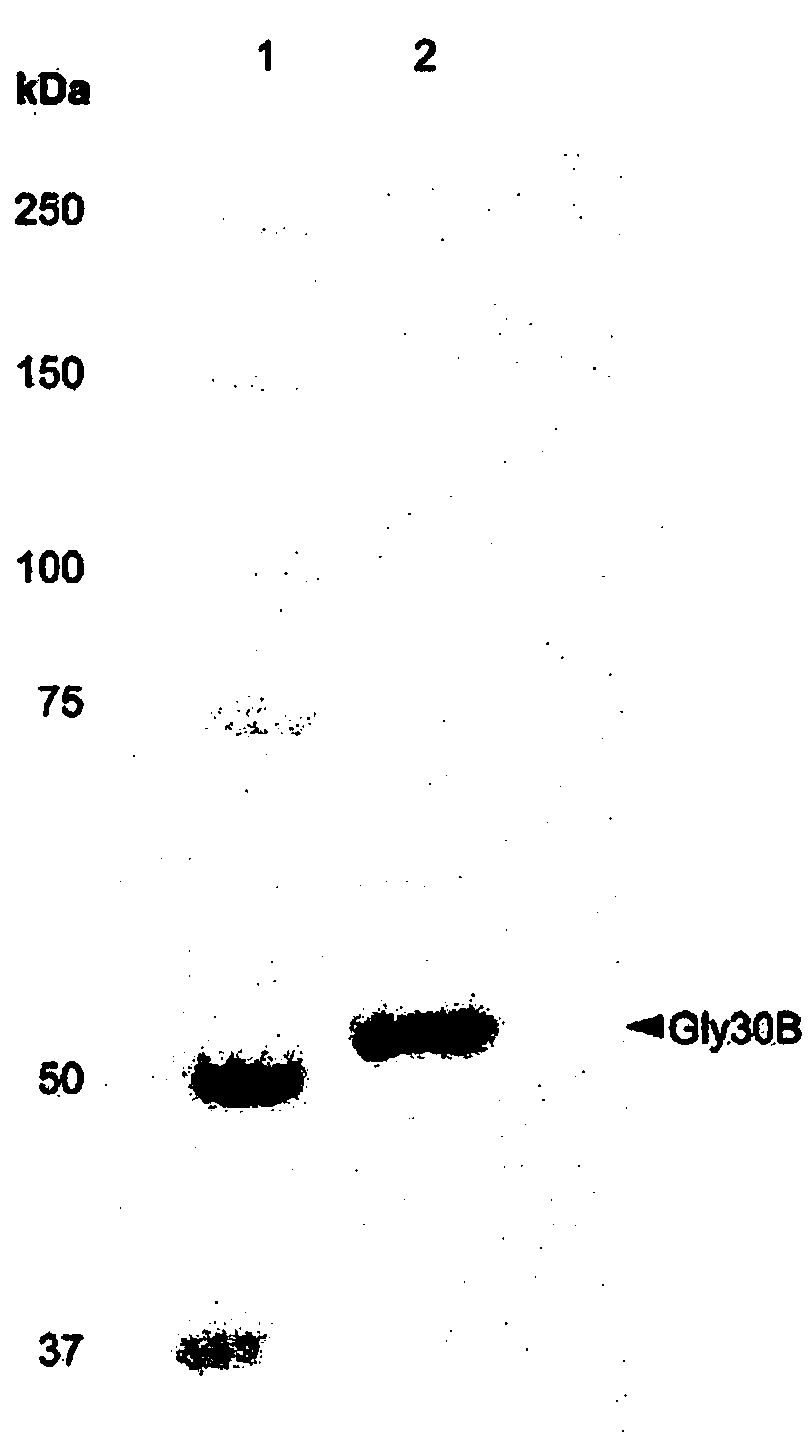
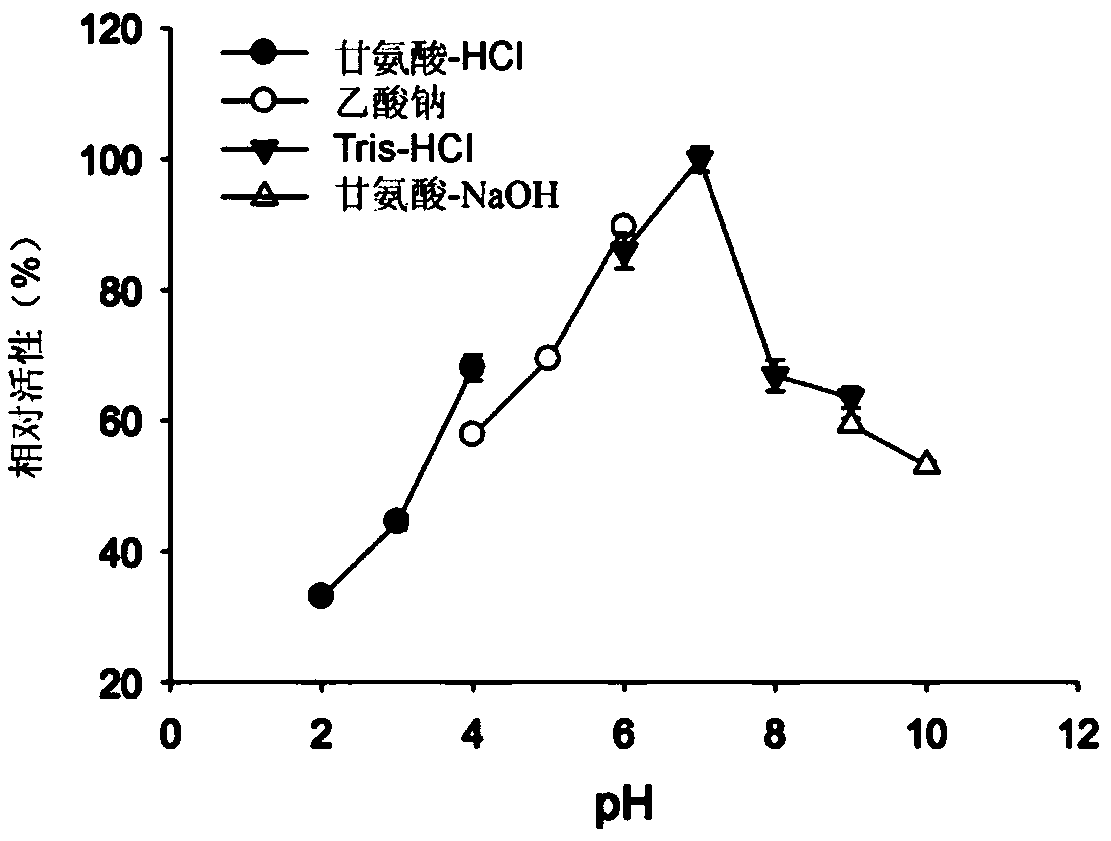
NOVEL [beta]-1,3-1,6-ENDOGLUCANASE PRODUCING, FROM [beta]-GLUCAN, OLIGOSACCHARIDES OR GLUCOSE
The present invention relates to a novel [beta]-1,3-1,6-endoglucanase producing, from [beta]-glucan, oligosaccharides or glucose. More specifically, the present invention provides an effect of producing oligosaccharides or glucose of various degrees of polymerization in high yields by using a [beta]-1,3-1,6-endoglucanase exhibiting [beta]-1,3-endoglucanase and [beta]-1,6-endoglucanase activity on[beta]-glucan and exhibiting transglycosylation activity on laminarioligosaccharide.
Owner:KOREA UNIV RES & BUSINESS FOUND
Polypeptides having endoglucanase activity and polynucleotides encoding same
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having endoglucanase activity and polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Mutant of endoglucanase, coding gene and application thereof
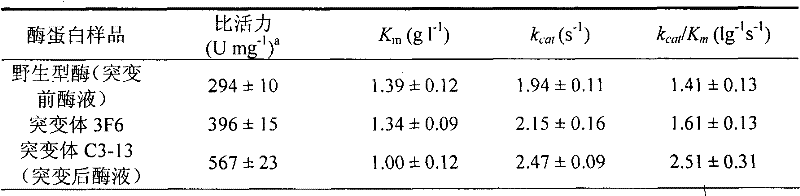
ActiveCN102443576AHigher than vitalityWide operating temperature rangeFungiBacteriaAgricultural scienceWild type
The invention discloses a mutant of endoglucanase, coding gene and application thereof. A protein provided by the invention is artificially synthesized and named as celA-mut(3F-6) or celA-mut(C3-13); the protein is a protein 1) or protein 2) as below: 1) a protein consisting of amino acid residue sequence in a sequence 2 in the sequence table; 2) a protein consisting of amino acid residue sequence in a sequence 4 in the sequence table; 3) a protein obtained by replacement and / or deletion and / or addition of one or a plurality of amino acid residues on the amino acid residue of the sequence2 or a sequence 4 in the sequence table, and with endoglucanase activity and derived from 1). Experiments of the invention have proved that the mutant of endoglucanase obtained by the invention has increased vitality compared with a wild type thereof and wide operational temperature range while maintaining an optimum reaction temperature (75 DEG C), therefore the mutant of endoglucanase has good industrial application prospect.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polypeptides Having Endoglucanase Activity and Polynucleotides Encoding Same
InactiveUS20140255998A1Convenient ligationPromote hydrolysisEnzymesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having endoglucanase activity and polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES INC
Zygomycetes-derived endoglucanase enzyme lacking cellulose-binding domain
InactiveUS7445922B2Reduce probabilityFeel goodFungiOrganic detergent compounding agentsCelluloseDeinking
This invention relates to a protein that is a Zygomycetes-derived endoglucanase lacking the cellulose-binding domain and exhibits endoglucanase activity, and a method for using the same. This invention can enhance effects of an endoglucanase enzyme on fabric treatment such as reduction of fuzzing, improvement in feel and appearance, color clarification, partial color change, and softening of cellulose-containing fabrics and on performance improvement in the deinking of waste paper and drainage of paper pulp.
Owner:MEIJI SEIKA PHARMA CO LTD
Polypeptides Having Endoglucanase Activity and Polynucleotides Encoding Same
InactiveUS20140227739A1Convenient ligationPromote hydrolysisAnimal cellsBacteriaBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having endoglucanase activity and polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Novel protein having endoglucanase activity, DNA of the protein, and use of the same
Disclosed are: a novel protein having an endoglucanase activity, which is found in a basidiomycete (into which edible mushrooms are classified) and is user-friendly from a safety standpoint and the like; novel DNA encoding the protein; a vector carrying the DNA; a transformant harboring the vector; a method for producing a protein having an endoglucanase activity by using the transformant; a method for producing a sugar by using at least one member selected from a protein having an endoglucanase activity and a basidiomycete; a method for producing ethanol by using a sugar produced by the aforementioned method; a food, a feed and a detergent each comprising a protein having an endoglucanase activity; and a method for treating a cellulose-containing woven fabric by using a protein having an endoglucanase activity. The protein is characterized by being derived from a basidiomycete, having a molecular weight of 18 kDa as determined by SDS-PAGE, and having an endoglucanase activity.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com









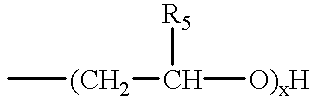
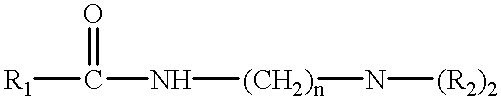





![NOVEL [beta]-1,3-1,6-ENDOGLUCANASE PRODUCING, FROM [beta]-GLUCAN, OLIGOSACCHARIDES OR GLUCOSE NOVEL [beta]-1,3-1,6-ENDOGLUCANASE PRODUCING, FROM [beta]-GLUCAN, OLIGOSACCHARIDES OR GLUCOSE](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/66ba3a54-27a1-403b-adf3-d46b3b54af84/HDA0001843918350000011.png)
![NOVEL [beta]-1,3-1,6-ENDOGLUCANASE PRODUCING, FROM [beta]-GLUCAN, OLIGOSACCHARIDES OR GLUCOSE NOVEL [beta]-1,3-1,6-ENDOGLUCANASE PRODUCING, FROM [beta]-GLUCAN, OLIGOSACCHARIDES OR GLUCOSE](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/66ba3a54-27a1-403b-adf3-d46b3b54af84/HDA0001843918350000021.png)
![NOVEL [beta]-1,3-1,6-ENDOGLUCANASE PRODUCING, FROM [beta]-GLUCAN, OLIGOSACCHARIDES OR GLUCOSE NOVEL [beta]-1,3-1,6-ENDOGLUCANASE PRODUCING, FROM [beta]-GLUCAN, OLIGOSACCHARIDES OR GLUCOSE](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/66ba3a54-27a1-403b-adf3-d46b3b54af84/HDA0001843918350000022.png)