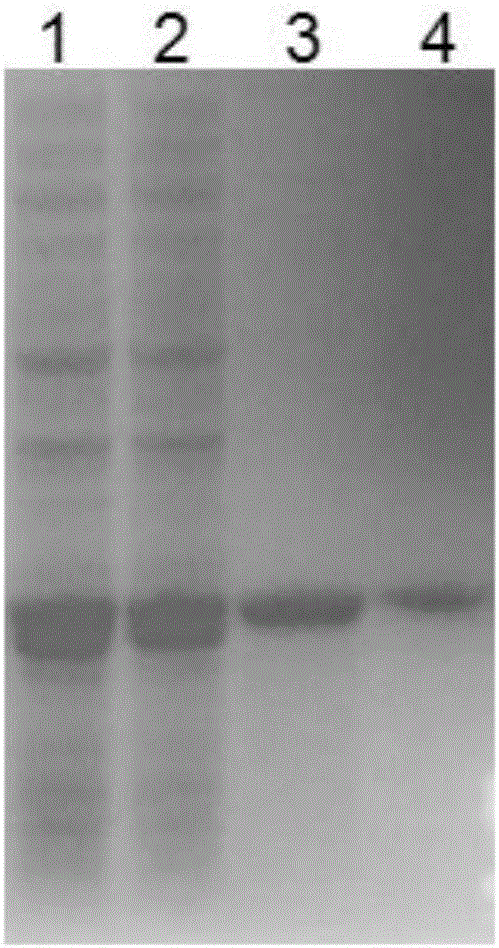
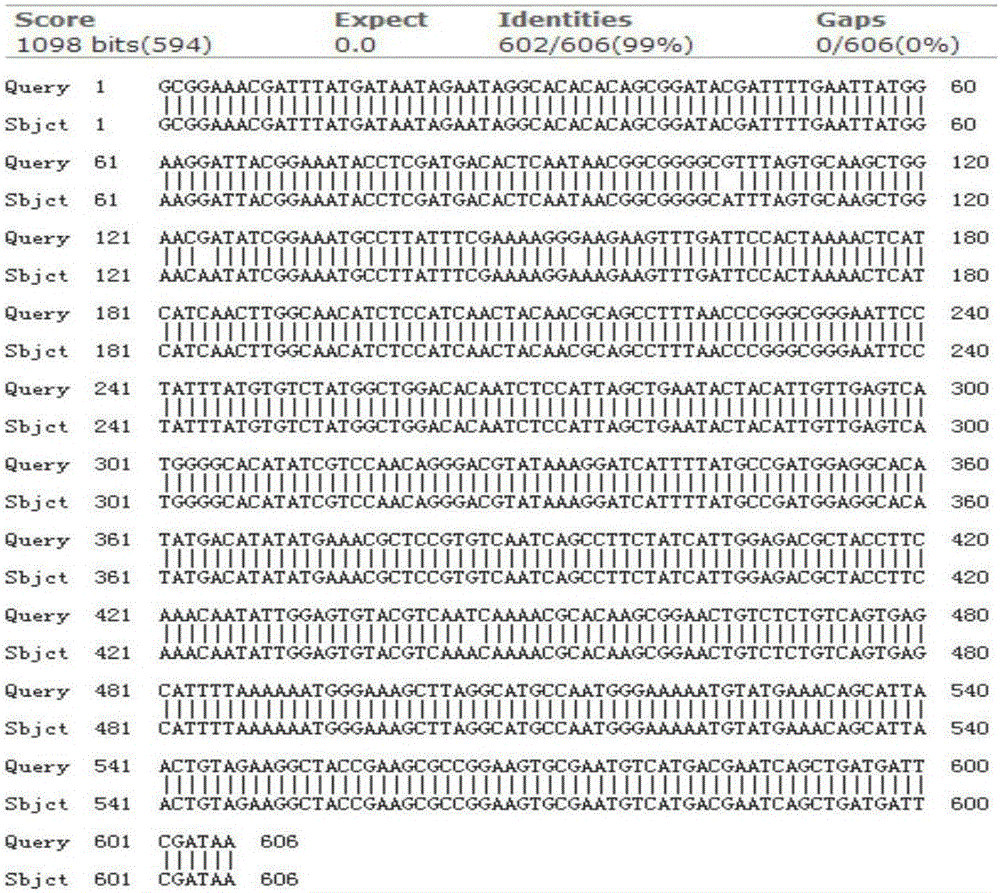
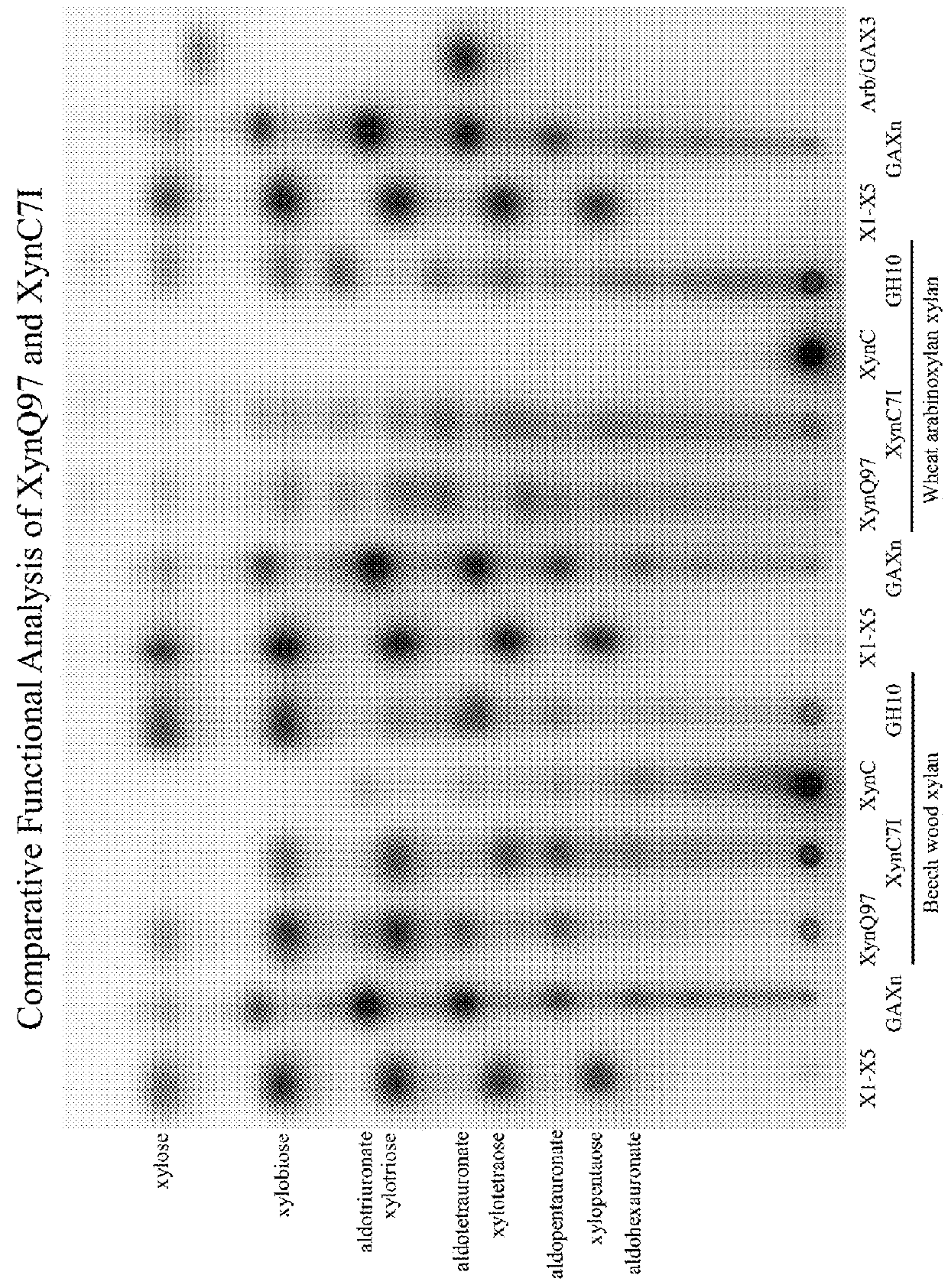
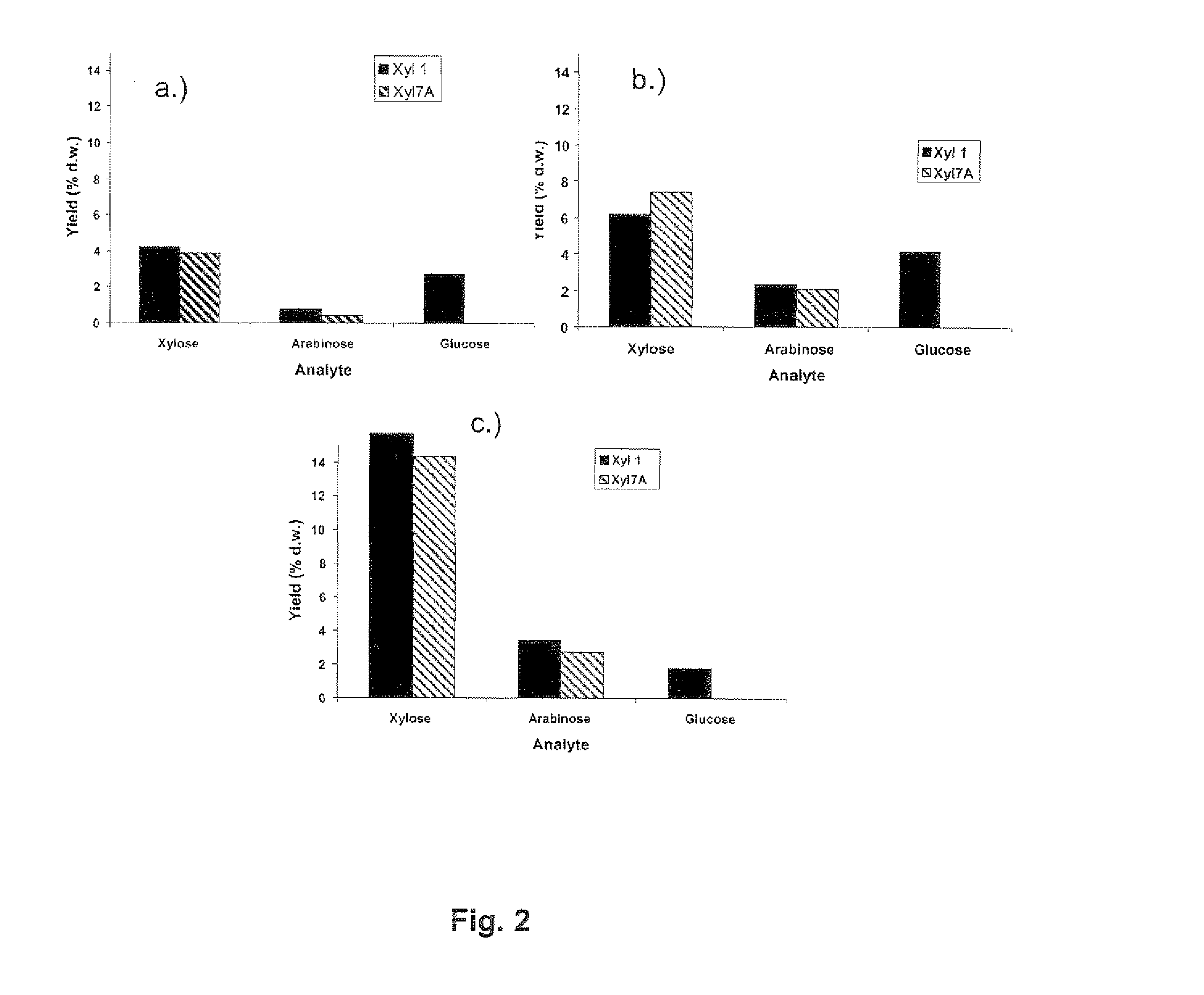
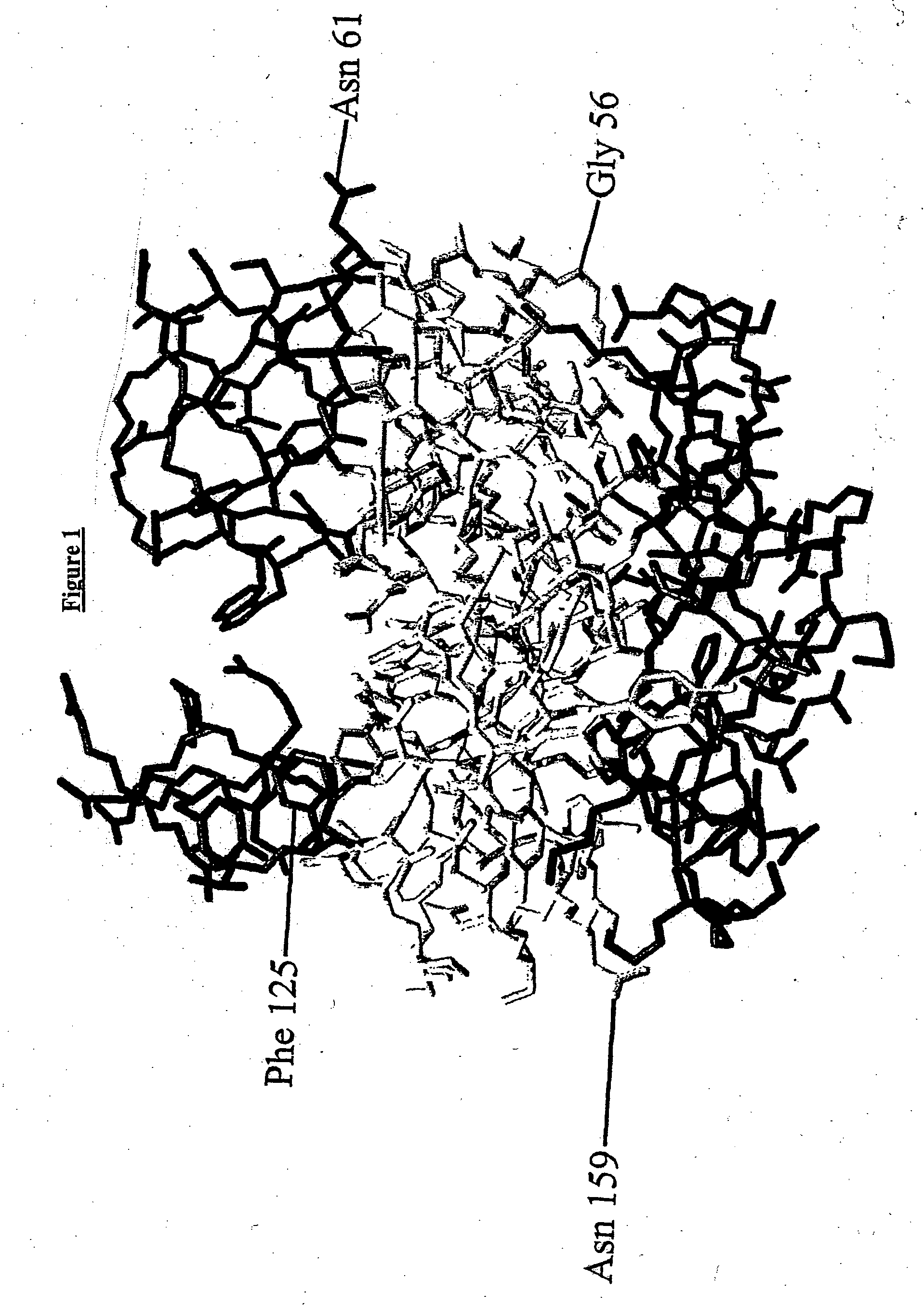
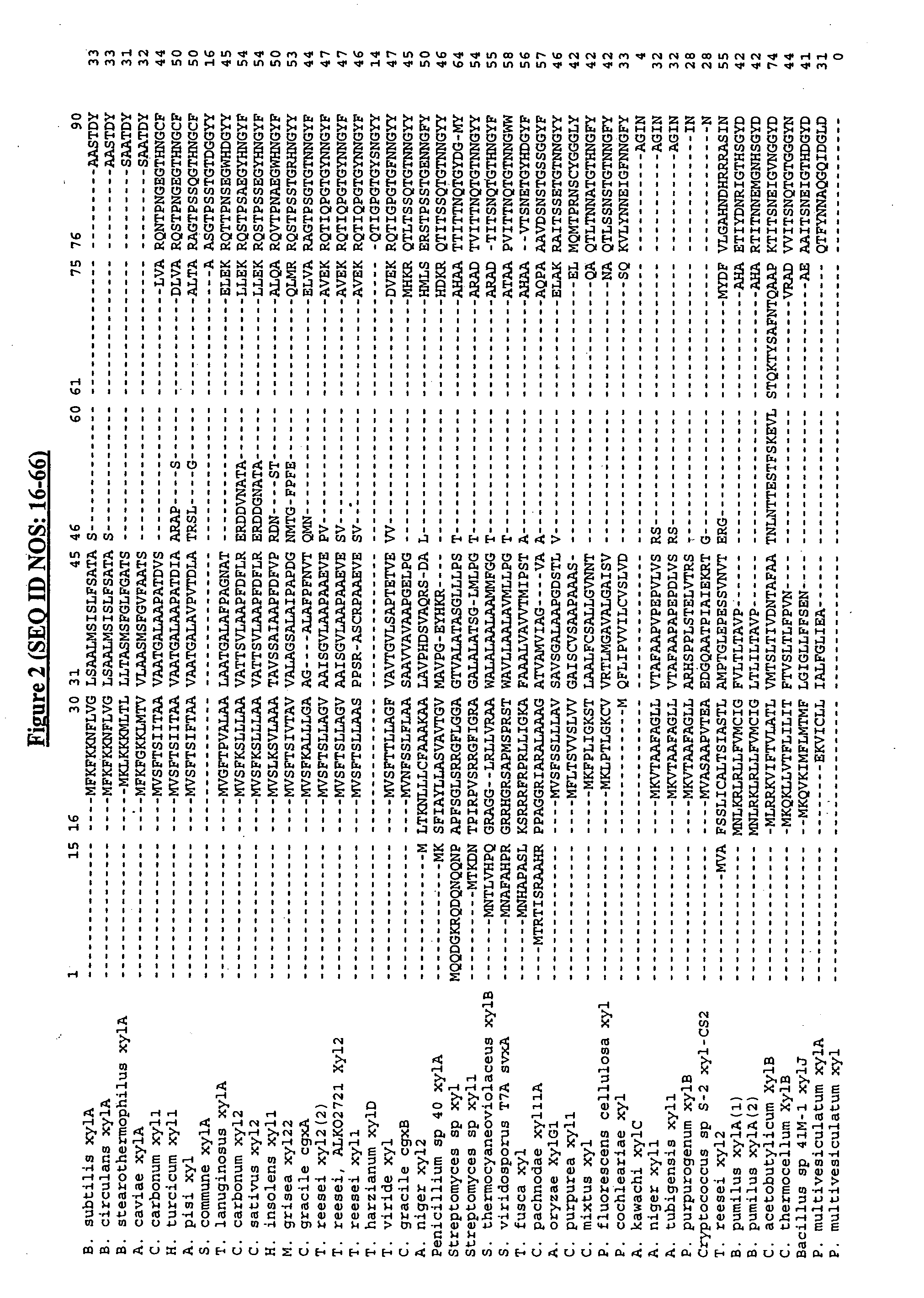
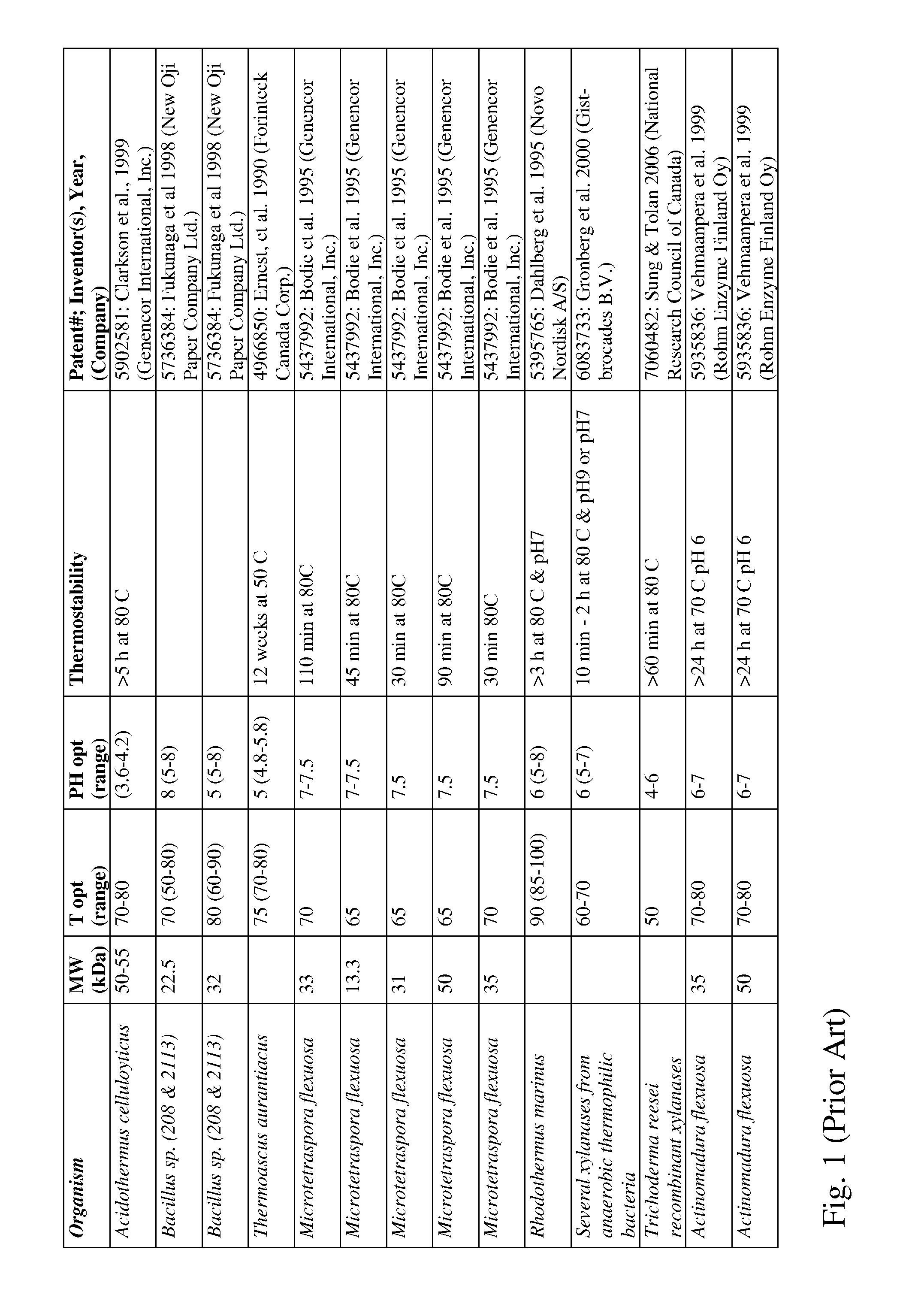
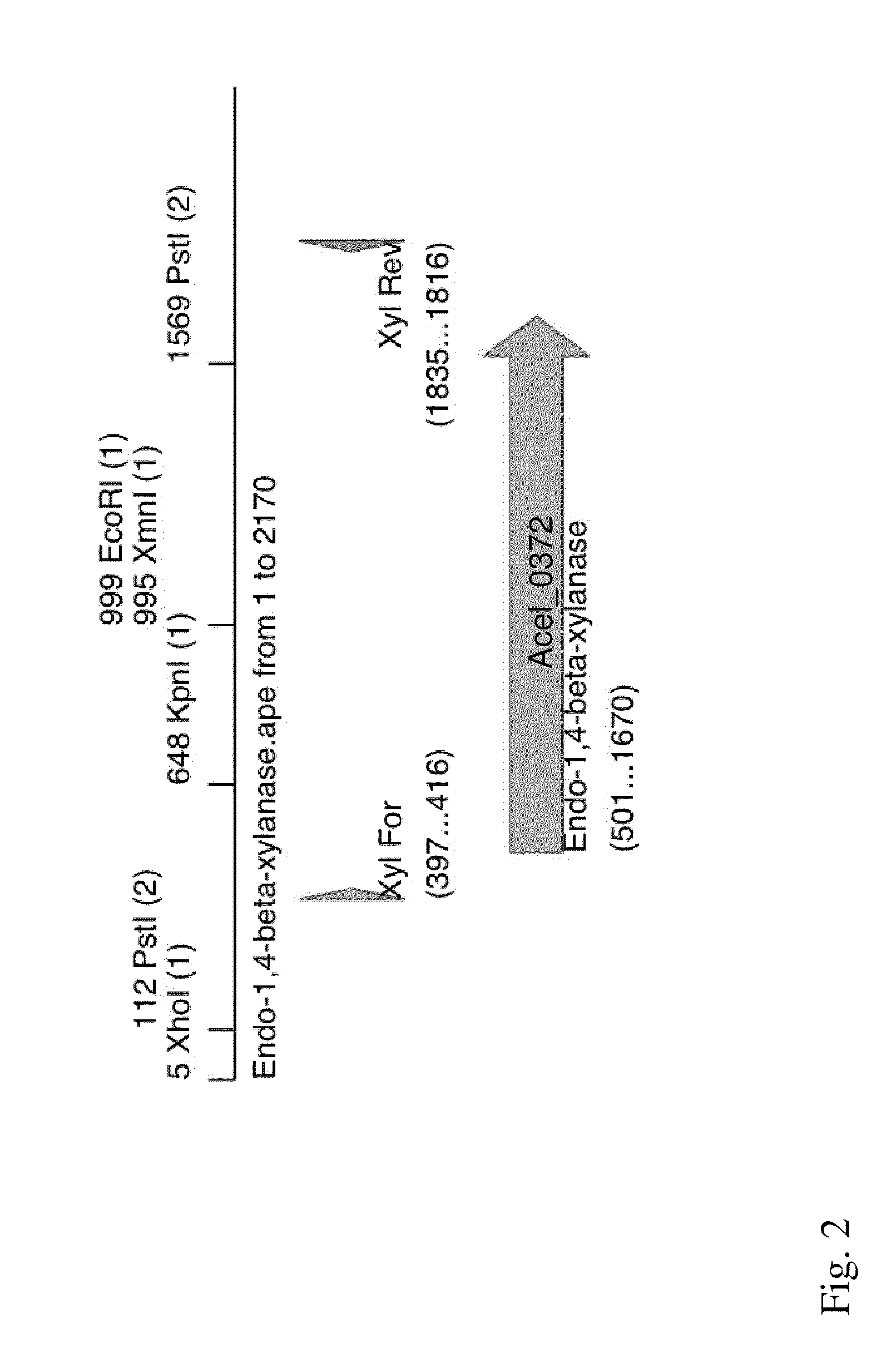
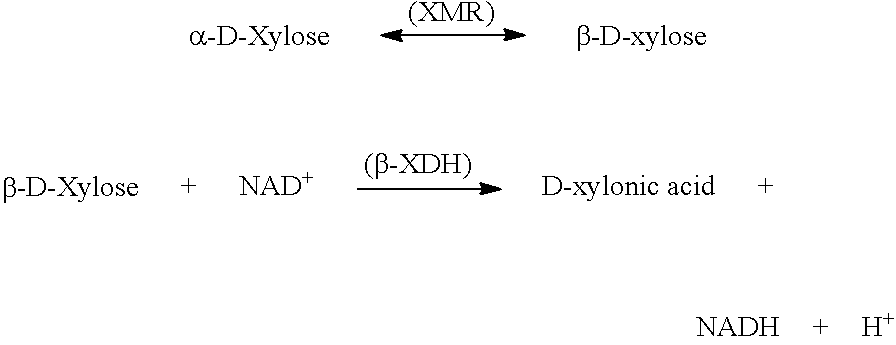Patents
Literature
90 results about "Exoxylanase activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A xylanase activity that acts on one of the ends of a xylan polymer which does not contain side chains. [GOC:jh2, ISBN:81-7736-269-0, PMID:16535010]
Glucanases, Nucleic Acids Encoding Them and Methods for Making and Using Them
InactiveUS20110117067A1Low viscosityImprove textureAntibacterial agentsFungiNucleotideExoxylanase activity
The invention relates to polypeptides having glucanase, e.g., endoglucanase, mannanase, xylanase activity or a combination of these activities, and polynucleotides encoding them. In one aspect, the glucanase activity is an endoglucanase activity (e.g., endo-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucano hydrolase activity) and comprises hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, cellulose derivatives (e.g., carboxy methyl cellulose and hydroxy ethyl cellulose) lichenin, beta-1,4 bonds in mixed beta-1,3 glucans, such as cereal beta-D-glucans or xyloglucans and other plant material containing cellulosic parts. In addition, methods of designing new enzymes and methods of use thereof are also provided. In alternative aspects, the new glucanases e.g., endoglucanases, mannanases, xylanases have increased activity and stability, including thermotolerance or thermostability, at increased or decreased pHs and temperatures.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Glycosyl hydrolase xylanases, compositions and methods of use for efficient hydrolysis and processing of xylan
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Glucanases, Nucleic Acids Encoding Them and Methods for Making and Using Them
ActiveUS20140295523A1Low viscosityImprove textureAntibacterial agentsBiofuelsNucleotideExoxylanase activity
The invention relates to polypeptides having glucanase, e.g., endoglucanase, mannanase, xylanase activity or a combination of these activities, and polynucleotides encoding them. In one aspect, the glucanase activity is an endoglucanase activity (e.g., endo-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucano hydrolase activity) and comprises hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, cellulose derivatives (e.g., carboxy methyl cellulose and hydroxy ethyl cellulose) lichenin, beta-1,4 bonds in mixed beta-1,3 glucans, such as cereal beta-D-glucans or xyloglucans and other plant material containing cellulosic parts. In addition, methods of designing new enzymes and methods of use thereof are also provided. In alternative aspects, the new glucanases e.g., endoglucanases, mannanases, xylanases have increased activity and stability, including thermotolerance or thermostability, at increased or decreased pHs and temperatures.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
New method for xylanase secretory expression in escherichia coli
PendingCN109825488AReduce manufacturing costReduce purification timeHydrolasesFermentationEscherichia coliExoxylanase activity
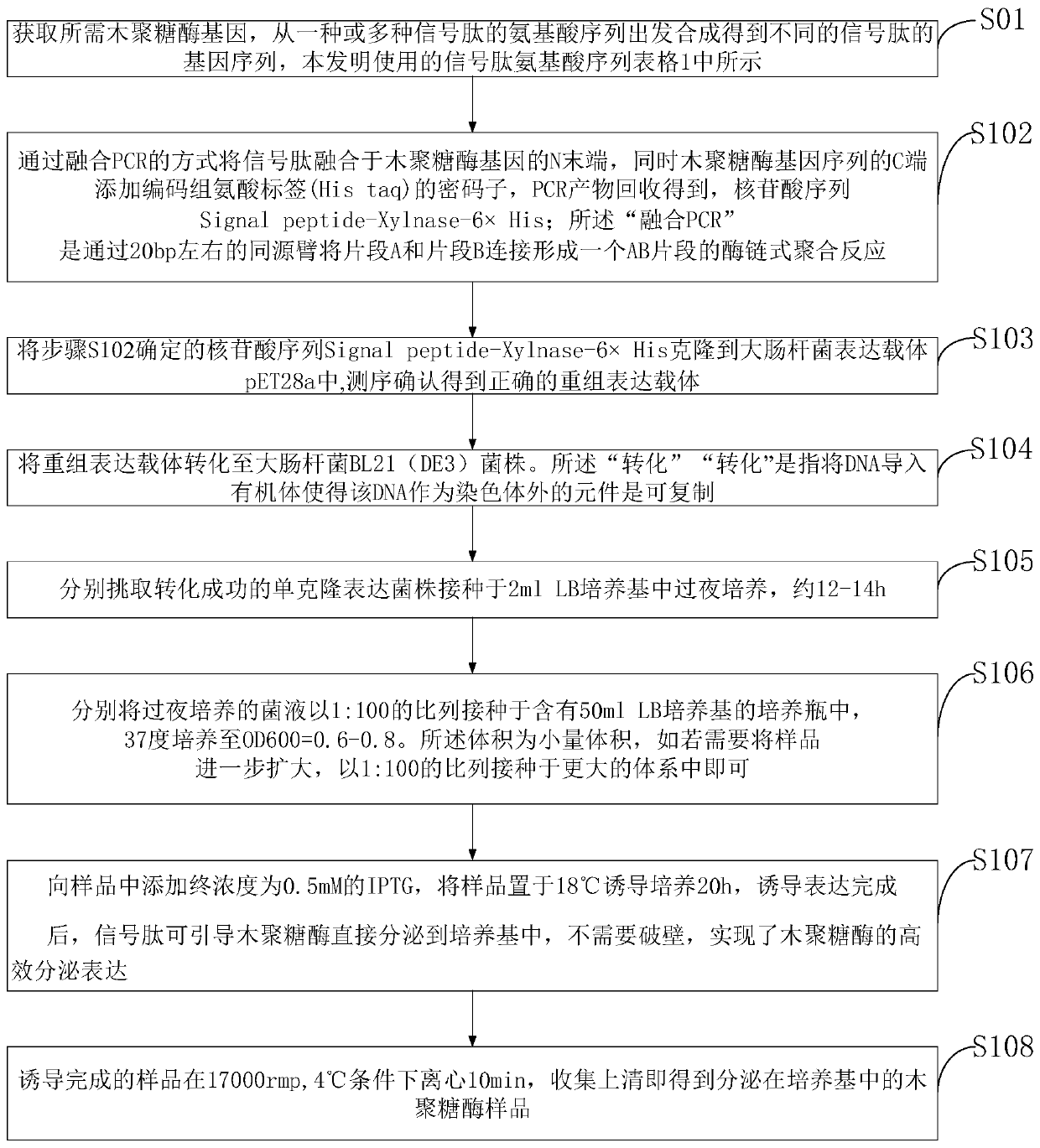
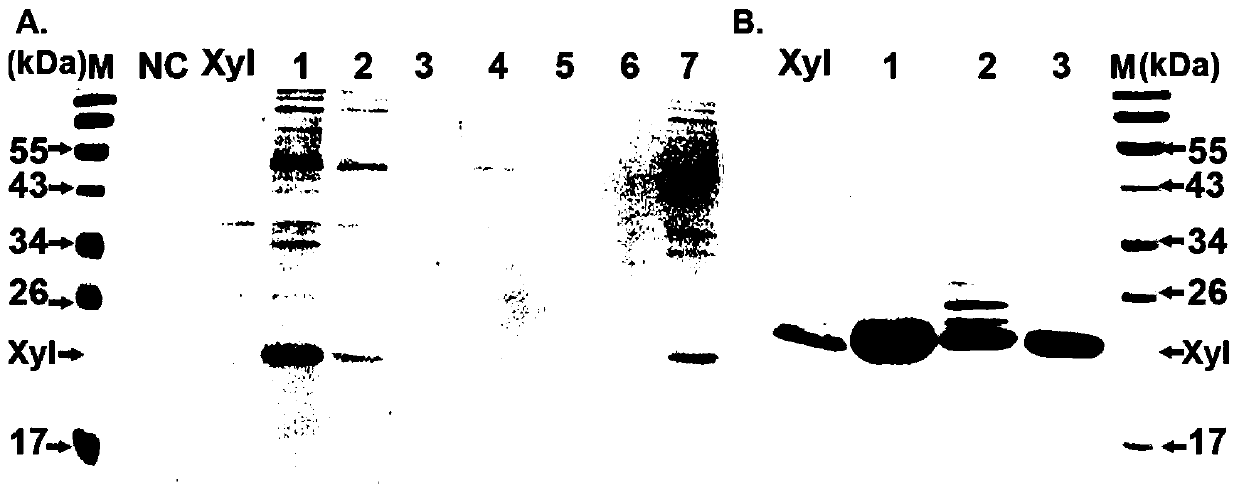
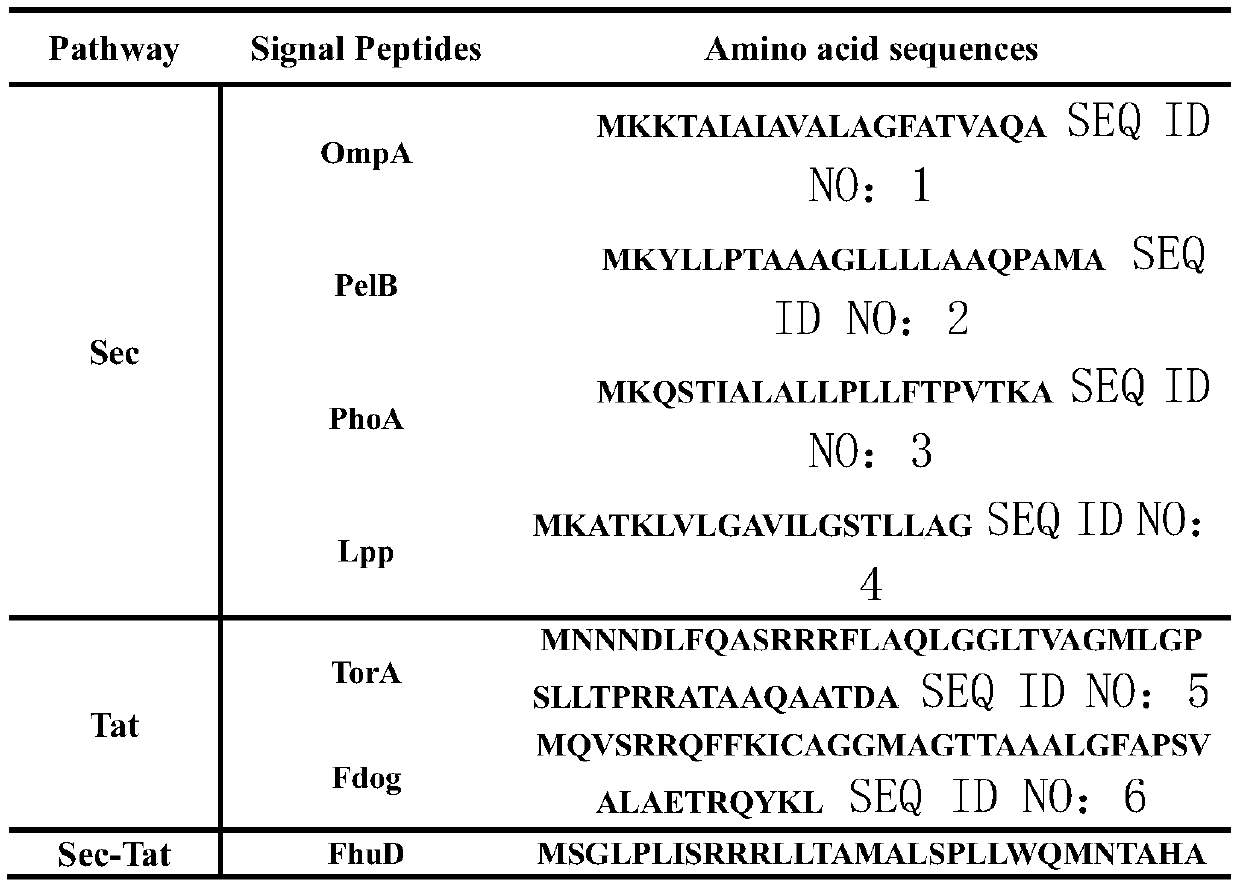
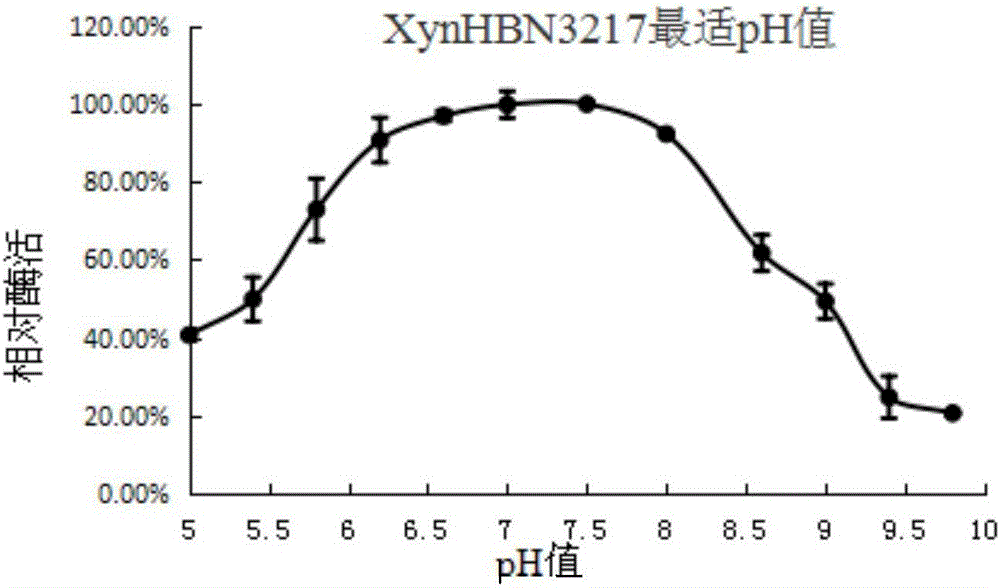
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and discloses a new method for xylanase secretory expression in escherichia coli. A signal peptide is fused to the N terminal of a xylanase gene, meanwhile, a codon of an encoding histidine tag is added to the C terminal of a xylanase gene sequence, and a target gene nucleotide sequence Signal peptide-Xylnase-6*His is obtained through PCR product recovery; in a target gene cloning and expression vector pET28a, a correct recombinant expression vector is obtained through sequencing; the recombinant expression vector is convertedto a escherichia coli strain; IPTG is added into a sample, and induction culture is carried out on the sample; efficient secretory expression of xylanase is achieved. According to the method, xylanase can be directly secreted into a culture medium; compared with original escherichia coli intracellular expression or yeast secretory expression, the high activity of xylanase can be ensured, the operation is easier, more time is saved, and the cost is lower.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Xylanase mutant with improved specific enzymatic activity and coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106191083AIncreased specific enzyme activityReduce manufacturing costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionXylanNucleotide
The invention relates to a xylanase mutant with improved specific enzymatic activity and a coding gene and application thereof. The xylanase mutant a protein shown in (a), (b) or (c): (a), a protein composed of amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; a protein derived from (a) by subjecting the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO. 1 to substitution, deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues and which has xylanase activity; (c), a protein coded by subjecting the amino acid sequences of code (a) and the amino acid sequences of code (b) to molecular hybridization and which has xylanase active amino acid sequences. The xylanase mutant according to the invention has specific enzymatic activity increased by 2.8 times, is applicable to degrading xylan substrates, has a wide range of acting temperature and pH, and has the advantages such as good resistance to acids and bases.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Glucanases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention relates to polypeptides having glucanase, e.g., endoglucanase, mannanase, xylanase activity or a combination of these activities, and polynucleotides encoding them. In one aspect, the glucanase activity is an endoglucanase activity (e.g., endo-1,4-beta-D-glucan 4-glucano hydrolase activity) and comprises hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-D-glycosidic linkages in cellulose, cellulose derivatives (e.g., carboxy methyl cellulose and hydroxy ethyl cellulose) lichenin, beta-1,4 bonds in mixed beta-1,3 glucans, such as cereal beta-D-glucans or xyloglucans and other plant material containing cellulosic parts. In addition, methods of designing new enzymes and methods of use thereof are also provided. In alternative aspects, the new glucanases e.g., endoglucanases, mannanases, xylanases have increased activity and stability at increased pH and temperature.
Owner:BP CORP NORTH AMERICA INC
Analyzing method for detecting activity of soil xylanase
InactiveCN101586145AReduce incubation timeShort training timeMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiltrationExoxylanase activity
The invention relates to an analyzing method for detecting activity of soil xylanase, which comprises the following steps: firstly, weighting n sieved air dry soil samples into n thick test tubes, adding acetic acid buffer solution into each test tube, oscillating by a vortex oscillator, getting soil suspension into 96 micropore plates under the oscillation condition, adding 4-MUB-7-Beta-D-xyloside substrate solution into n-1 holes, and adding water with equal quantity into the other one hole so as to be used as non-substrate contrast, adding substrate solution with equal quantity and water with equal quantity into the (n+1)th hole so as to be used as soli-free contrast, oscillating and culturing under constant temperature; secondly, adding NaOH into the micropore plates to terminate the reaction after the culture is finished; thirdly, performing the fluorimetric determination to resultant of reaction by a multifunctional microplate reader; and fourthly, calculating the activity of the xylanase. Compared with the traditional method, the invention shortens the culture time, omits the operation procedures of filtration, and the like, and simplifies the operation steps; meanwhile, the determination data of fluorescent materials in the micropore plate can be obtained within 15s through the multifunctional microplate reader, huge samples are allowed to be simultaneously determined; and moreover, the invention has high accuracy and easy operation, stable and reliable result and good reproduction quality.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polypeptides having xylanase activity and polynucleotides encoding same
ActiveUS20050210548A1Improve digestibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementExoxylanase activityXylanase
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having xylanase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods for producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVO NORDISKBIOTECH INC
Catalytically inactive proteins and method for recovery of enzymes from plant-derived materials
An inactive xylanase molecule for the recovery of xylanase activity in plant-derived material containing active xylanase enzyme(s) and xylanase inhibitors. The inactive xylanase molecule of binds to xylanase inhibitors in the plant-derived material, thereby allowing accurate measurement of xylanase enzyme activity of the enzyme contained in the plant-derived material. The invention further includes amino acid molecules depicted by SEQ ID NOS. 4 through 112, wherein the catalytically active sites of each of the amino acids have been modified resulting in inactive xylanase molecules. A method of production of the inactive xylanase molecules includes expression of the inactive xylanase molecule in microbial or eukaryal (e.g., yeast including Pichia pastoris) host cell an expression cassette comprising a promoter operably linked to a nucleic acid molecule encoding the inactive xylanase molecule and using the expressed molecule in an assay to recover the xylanase enzyme activity in plant-derived material, for example, in plant-derived material such as animal feed.
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Polypeptides having Xylanase Activity and Polynucleotides Encoding Same
ActiveUS20170202242A1Convenient ligationImprove feeding efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifAccessory food factorsBiotechnologyExoxylanase activity
The present invention relates to polypeptides having xylanase activity and polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides. The invention also relates to compositions comprising the polypeptides of the invention and the use of the polypeptides of the invention to release xylose and in animal feed.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Neutral high temperature xylanase as well as coding genes and application thereof
ActiveCN107129976AHigh activityHas a degradative effectFermentationGlycosylasesIndustrial fermentationGlucanase
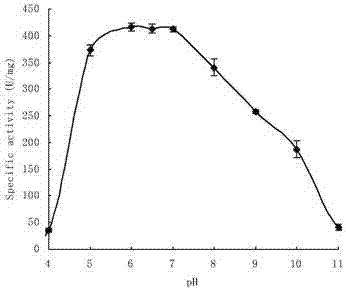
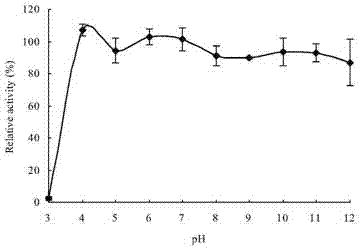
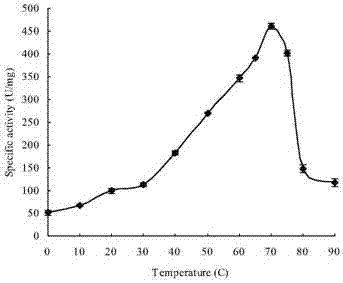
The invention provides a neutral high temperature xylanase CtXyn10A as well as genes and application thereof. The neutral high temperature xylanase CtXyn10A has proteins of amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID No. 3 and / or SEQ ID No. 5 in a sequence table; and / or is characterized in that amino acid residue sequences shown in SEQ ID No. 3 and / or SEQ ID No. 5 in the sequence table are replaced and / or deleted and / or added by one or several amino acid residues, and have proteins with xylanase activity and derived from the proteins with the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID No. 3 and / or SEQ ID No. 5 in the sequence table. The xylanase CtXyn10A has an optimum pH of 6.0 to 7.0 and an optimum temperature of 70 DEG C, keeps enzyme activity of 20% or above at 90 DEG C and pH 9.0, and specific activity is 461 U / mg; the xylanase CtXyn10A has the activity of xylanase, glucanase and cellulase, is easy to produce by industrial fermentation, and can be widely used in food, paper, energy industry and the like as a novel broad-spectrum enzyme preparation.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for Producing Blasting Fermentation-Treated Bagasse
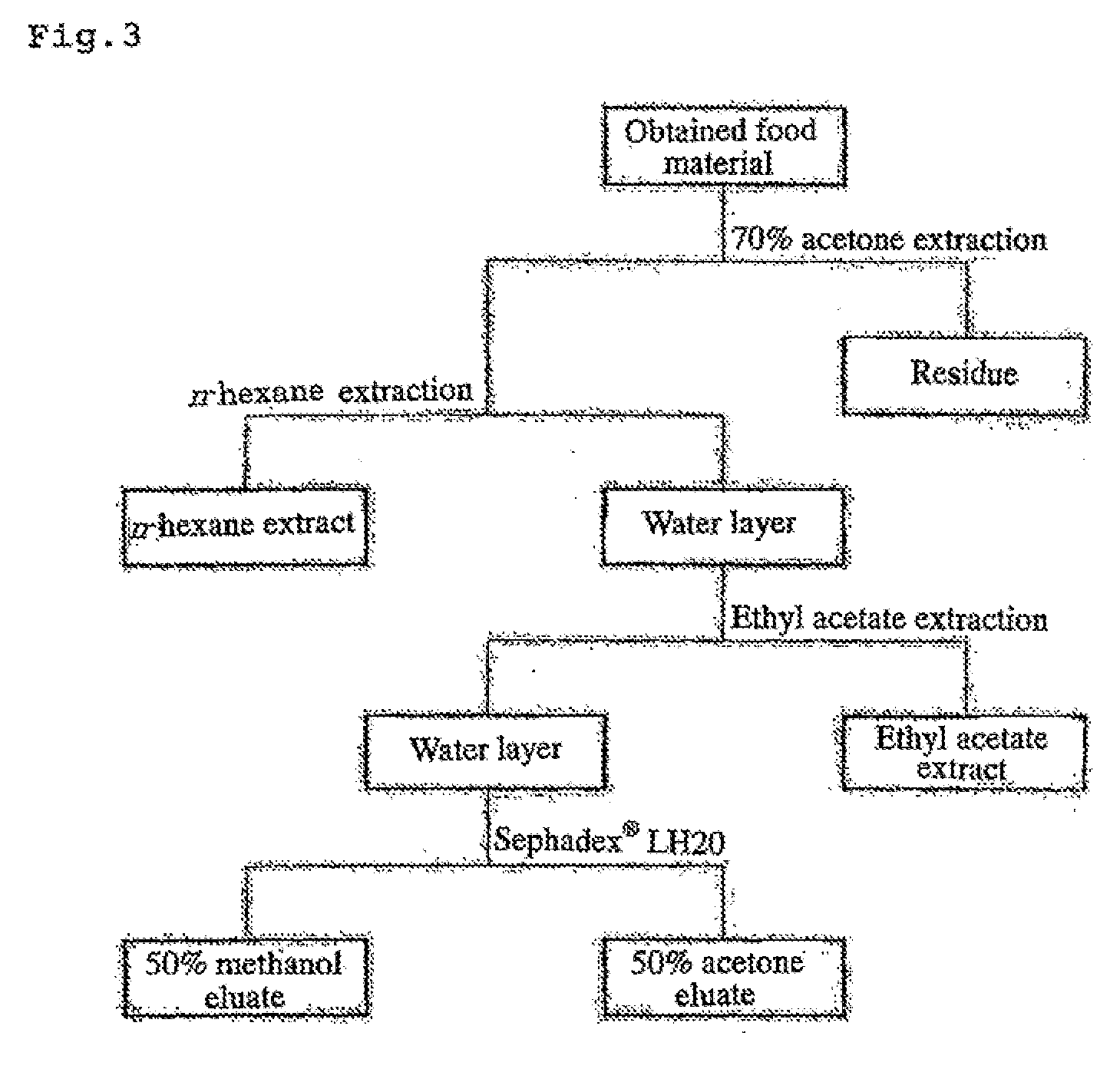
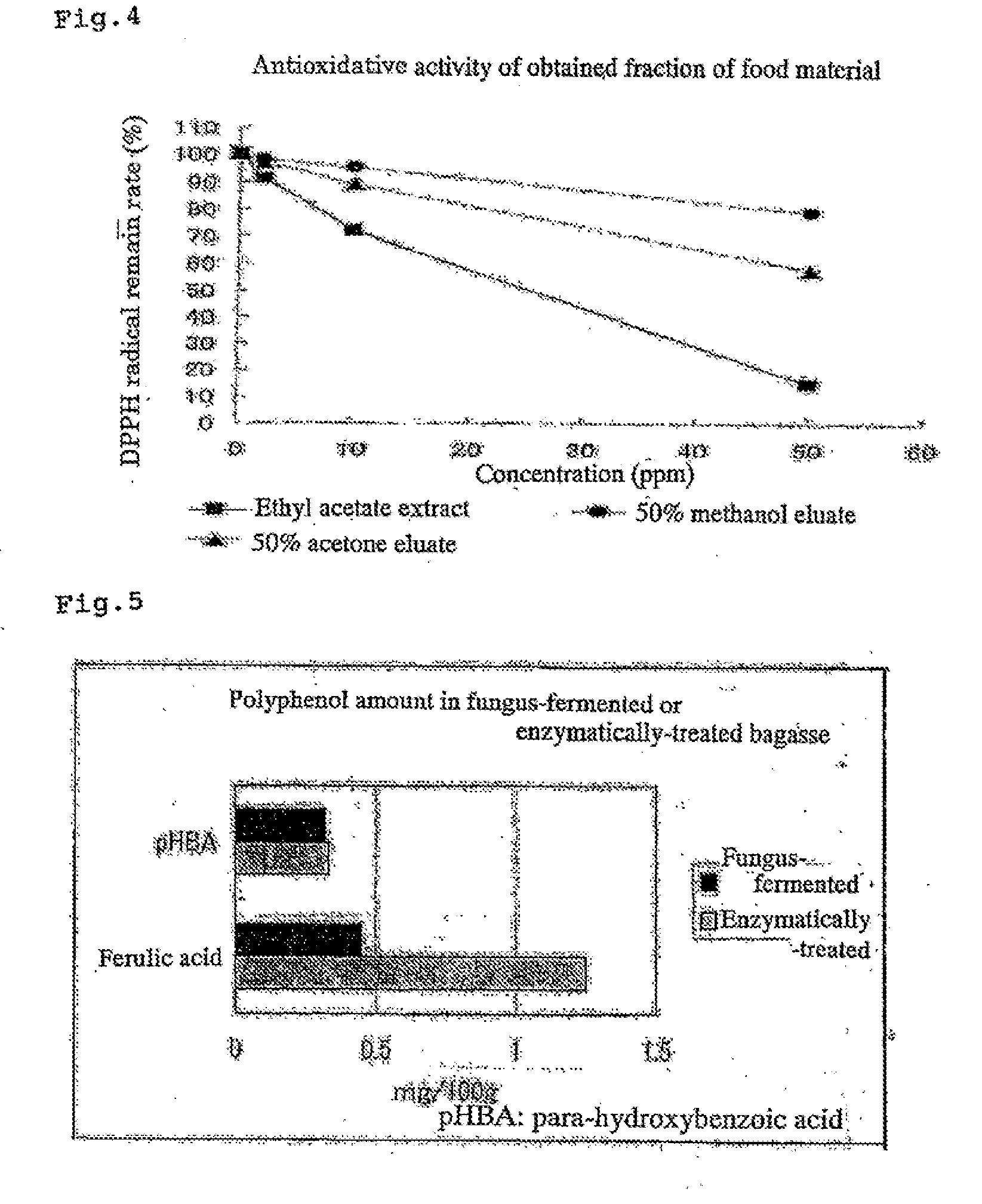
InactiveUS20080248161A1Simple processLow costMetabolism disorderTea extractionExoxylanase activityFood material
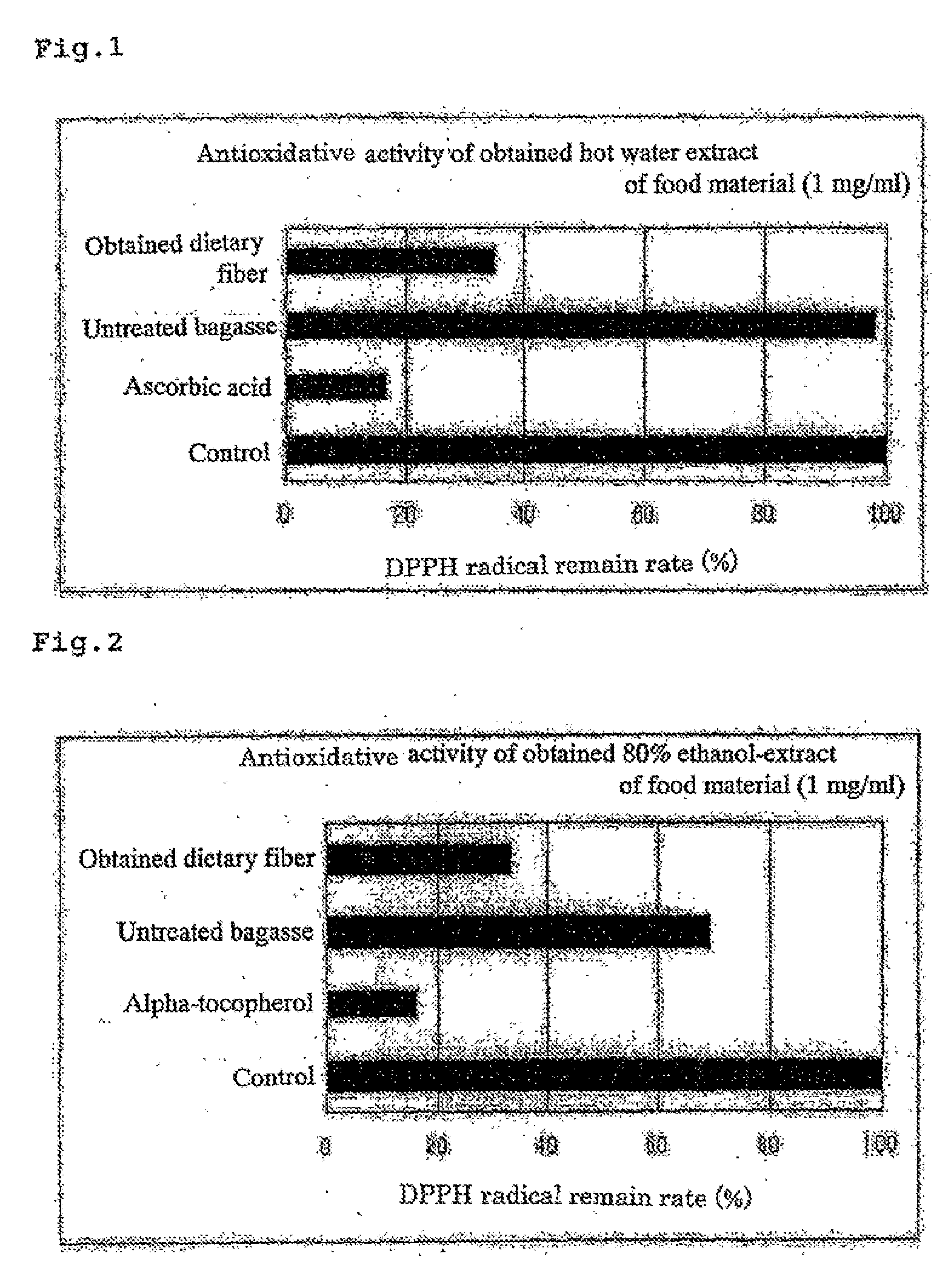
The present invention is to provide a method for producing a material which contains xylo-oligosaccharides being rich in xylobiose and xylotriose, an antioxidant active substance and a dietary fiber, and which is useful as a food material and a health supplement, by a simple process, with efficiency, and at a low cost. The method comprises the steps of: subjecting a hemicellulose-containing plant resource such as bagasse to a steam treatment followed by an explosion treatment (2.5 Mpa, 70 seconds); mixing wheat bran into this steamed and exploded material; adjusting water content of this mixture to about 50%; subsequently, preparing koji with the use of a koji fungus having a high xylanase activity obtained by conducting single spore isolation from Aspergillus sojae (NFRI1147); adding water to the koji thus obtained; mixing the steamed and exploded material into a koji dispersion wherein koji is dispersed in water; adjusting water content of this mixture to about 50%; and subsequently, fermenting the mixture. After conducting the fermentation, a treatment to terminate the fermentation is conducted and the resultant is dried and then finely ground. As the steamed and exploded material to be mixed into the koji dispersion, 8- to 10-fold amount of the steamed and exploded material used for the koji preparation, is used.
Owner:RYUKYU BIO RESOURCE DEV +2
Industrial process of producing xylanase with Aspergillus usamii
InactiveCN101067129AImplement solid-state fermentation industrial productionProduction methods are environmentally friendlyFungiMicroorganism based processesInorganic saltsExoxylanase activity
The industrial process of producing xylanase with Aspergillus usamii belongs to the field of enzyme engineering technology. In the industrial process of producing xylanase, bagasse, corn cob, bran and other crop leftovers are used as the fermenting base material, and proper amount of inorganic salt, surfactant, water, etc are added for solid fermentation in a 30M3 solid fermenting tank with Aspergillus usamii E001 strain. The mature fermented material is stoved with hot blast at 45-50 deg.c to obtain xylanase product possessing xylanase activity of 7783-9616 IU / g. The present invention provides also the recipe of fermenting culture medium and the fermenting conditions.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glycosyl hydrolase xylanases, compositions and methods of use for efficient hydrolysis and processing of xylan
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Polypeptides with xylanase activity
InactiveUS20120021092A1Increase bleachingHigh activityMilk preparationSugar derivativesExoxylanase activityXylanase
Polypeptides with xylanase activity modified to increase bran solubilisation and / or xylanase activity. The modification comprises modification of one or more amino acids in position 113, 122 or 175 in combination with one or more further amino acid modifications in position 11, 12, 13, 34, 54, 77, 81, 82, 104, 110, 113, 118, 122, 141, 154, 159, 162, 164, 166, 175 or 179, wherein the positions are determined as the position corresponding to the position of Bacillus subtilis xylanase (SEQ ID NO 1).
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Polypeptides with xylanase activity
InactiveUS8623629B2High activityReduce the amount requiredMilk preparationSugar derivativesExoxylanase activityXylanase
Polypeptides with xylanase activity modified to increase bran solubilization and / or xylanase activity. The modification comprises modification of one or more amino acids in position 113, 122 or 175 in combination with one or more further amino acid modifications in position 11, 12, 13, 34, 54, 77, 81, 82, 104, 110, 113, 118, 122, 141, 154, 159, 162, 164, 166, 175 or 179, wherein the positions are determined as the position corresponding to the position of Bacillus subtilis xylanase (SEQ ID NO 1).
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Difunctional enzyme with endoglucanase/xylanase and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological engineering, in particular to a difunctional enzyme RuCelA with endoglucanase / xylanase and a preparation method and application thereof. The RuCelA sources from uncultured microorganism of rumen of Chinese yaks, and has a certain activity on phosphocellulose and filter. The RuCelA not only can hydrolyze polysaccharide but also can hydrolyze trisaccharide to obtain monosaccharide; meanwhile, the RuCelA has synergistic effect with xylanase to synergetically degrade xylan; and the RuCelA can be utilized to realize mono enzymatic degradation on preprocessed lignocellulose. The difunctional enzyme RuCelA of the invention can be widely applied to cellulose degradation, comprising cellulose biotransformation, chemical industry, spinning, food, bioenergy, feed ingredients, pharmaceutical Industry and other aspects.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Multi-enzyme product comprising glucoumylolytic, proteolytic and xylanolytic activities and process for preparing the same
Enzyme preparation (I) produced by fermenting wheat bran with an Aspergillus niger strain has glucoamylase, protease and xylanase activities of at least 100 U / g (dry basis), provided that the glucoamylase activity is at least 750 U / g and / or the xylanase activity is at least 300 U / g. An Independent claim is also included for the production of (I) by: (1) moistening and pasteurizing or sterilizing wheat bran; (2) inoculating an at least 10 cm thick layer of the bran with Aspergillus niger; and (3) fermenting the bran in an aerated and periodically agitated reactor at 28 - 38 degrees C for 1 - 3 days while maintaining the moisture content of the bran at 50 - 60 wt.%.
Owner:GIE AGRO IND
Thermostable xylanase for the selective hydrolysis of pentose-containing polysaccharides
ActiveUS20130109062A1Improve heat resistanceSugar derivativesHydrolasesNucleotideExoxylanase activity
The present invention relates to polypeptides having xylanase activity and nucleic acid sequences encoding such polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the nucleic acid constructs as well as methods for producing and using the polypeptides. One specific application of the xylanase is the selective hydrolysis of pentose sugar components of hemicellulose-containing plant biomass. The nucleotide sequence may be used for the production of the xylanase or optimized mutants thereof.
Owner:CLARIANT PROD DEUT GMBH
Methods of Producing GH8 Xylanase Variants
ActiveUS20120288585A1Increase volumeIncrease the cutting widthFungiDough treatmentBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having xylanase activity and isolated polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Technique for preparing (FOs) feruloyl oligosaccharides by adopting two-period-type combined regulation fermentation technology
InactiveCN102876757AImprove food safetyImprove resource utilizationMicroorganism based processesEnzymesFiberPullulan
The invention relates to a technique for preparing (FOs) feruloyl oligosaccharides by adopting a two-period-type combined regulation fermentation technology, belonging to the technical field of deep processing of agricultural and sideline products. The technique is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing a fermentation medium by adopting wheat bran as a main material, and regulating the initial pH and the initial temperature of fermentation liquor and then inoculating agrocybe aegevita and / or aureobasidium pullulans; and during the fermentation process, regulating the pH and the temperature of the fermentation liquor again, hydrolyzing wheat bran fibers by utilizing xylanase produced by microbes, so as to prepare the FOs. With the adoption of the technique, the reduction of the steps for preparing the FOs by adopting an enzymic method is facilitated; and the technique has the advantages of simple preparation process, low preparation cost and short preparation period, and can be used for improving the utilization ratio of wheat bran resources. Due to the adoption of the two-period-type combined regulation technology, the activity of the xylanase is ensured to be at the optimum level, so that the purpose of high yield of FOs is achieved. The technique is suitable for preparation of health-food-level FOs, and the yield of the FOs can reach 1123nmol / L.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Li's Trichoderma strains and use thereof
The present invention discloses a kind of Li's trichloderma strain and its application. Said strain is grown on the PDA solid culture medium, its formed colony is light-green byssoid, its edge is white and regular, its growth speed is rapid, its hypha is white, has septum, hyphal wall is smooth and its diameter is 2.0-5.0 micrometer. Its conidiophore is generated from short lateral branch of hypha, and opposite on the lateral branch. Said conidiophore is pitcher-shaped, vertical, colorless, its spore is green, and is ball-shaped, its diameter is 20-100 micrometers. Said invention possesses the following advantages: 1. convenient culture, its growth speed is rapid; 2. can simultaneously produce two feed enzyme preparations, beta-glucanase and xylanase with high activity.
Owner:HANGZHOU TIANKAI BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Enzyme
InactiveUS20050271769A1Reduce sensitivityReduce the amount requiredDough treatmentSugar derivativesXylanase inhibitorExoxylanase activity
The present invention relates to a variant xylanase polypeptide, or fragment thereof having xylanse activity, comprising one or more amino acid modifications such that the polypeptide or fragment thereof has an altered sensitivity to a xylanase inhibitor as compared with parent enzyme.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Methods for Improving By-Products from Fermentation Processes Using Xylanase
InactiveUS20160333332A1Increase capacityIncrease volumeFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteBiofuelsGlycanExoxylanase activity
Provided are GH10 xylanases or a fragment thereof including modified xlyanase enzymes, all having xylanase activity, wherein the enzyme or fragment thereof provides increased oil recovery from a grain-based material compared with a control or parent GH10 xylanase enzyme, the parent GH10 xylanase having been modified at at least one or more of the following positions 7, 25, 33, 64, 79, 89, 217 and 298, wherein the numbering is based on the amino acid numbering of FveXyn4 (SEQ ID No. 1). Methods of using the GH10 xylanases, for example, for improved oil recovery are also provided.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Acidothermus celluloyticus xylanase
A thermophilic endo-beta-1,4-xylanase derived from Acidothermus cellulolyticus is disclosed. The xylanase exhibits xylanase activity at an optimal temperature of 90° C. and an optimal pH range of about 4.5-6.0. The isolated xylanase is useful in the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic material.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Polypeptides Having Xylanase Activity and Polynucleotides Encoding Same
InactiveUS20190194635A1Convenient ligationImprove feeding efficiencyAccessory food factorsFermentationXylanNucleotide
The present invention relates to polypeptides having xylanase activity and polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides. The invention also relates to compositions comprising the polypeptides of the invention and the use of the polypeptides of the invention to solubilise xylan and in animal feed.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Polypeptides with xylanase activity
ActiveUS8951751B2Increase enzyme activityHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementExoxylanase activityXylanase
Polypeptides with xylanase activity modified to increase bran solubilization and / or xylanase activity. The modification comprises at least an amino acid modification i position 110 and may have further modifications of one or more amino acids in position 11, 12, 13, 34, 54, 77, 81, 99, 104, 113, 114, 118, 122, 141, 154, 159, 162, 164, 166 or 175 wherein the positions are determined as the position corresponding the position of Bacillus subtilis xylanase (SEQ ID NO 1) The polypeptides have at least 88% identity with SEQ ID NO 1 or 75% identity to a sequence selected from SEQ ID NO 2-22.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Compositions comprising polypeptides having xylanase activity and polypeptides having arabinofuranosidase activity
ActiveUS10711259B2Convenient ligationImprove feeding efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifBiofuelsExoxylanase activityPolynucleotide
Compositions comprising polypeptides having xylanase activity and polypeptides having arabinofuranosidase activity for use in e.g. animal feed. Polypeptides having arabinofuranosidase activity, polypeptides having xylanase activity and polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. Nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptide.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Method for producing oenological tannins and enzymatic composition
InactiveUS20030054056A1Improve impact on tasteBiocideTea extractionAmylosucrase activityExoxylanase activity
The invention concerns an enzymatic method for making oenological tannins starting with lumps of wood and an enzymatic method for transforming tannins into tannins for wine-making purposes. The inventive method comprises a step which consists in contacting the lumps of wood or tannins with an aqueous solution comprising a composition containing enzymes of the cellulase class. The invention also concerns an enzymatic composition mainly consisting of enzyme of the cellulase class for making oenological tannins, comprising an endocellulase activity, a xylanase activity a beta-mannanase and / or alpha-amylase activity.
Owner:ETAB ROBERT STIERNON
Polypeptides with xylanase activity,
ActiveUS20110312058A1Increase enzyme activityHigh activityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesExoxylanase activityXylanase
Polypeptides with xylanase activity modified to increase bran solubilisation and / or xylanase activity. The modification comprises at least an amino acid modification i position 110 and may have further modifications of one or more amino acids in position 11, 12, 13, 34, 54, 77, 81, 99, 104, 113, 114, 118, 122, 141, 154, 159, 162, 164, 166 or 175 wherein the positions are determined as the position corresponding the position of Bacillus subtilis xylanase (SEQ ID NO 1) The polypeptides have at least 88% identity with SEQ ID NO 1 or 75% identity to a sequence selected from SEQ ID NO 2-22.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com