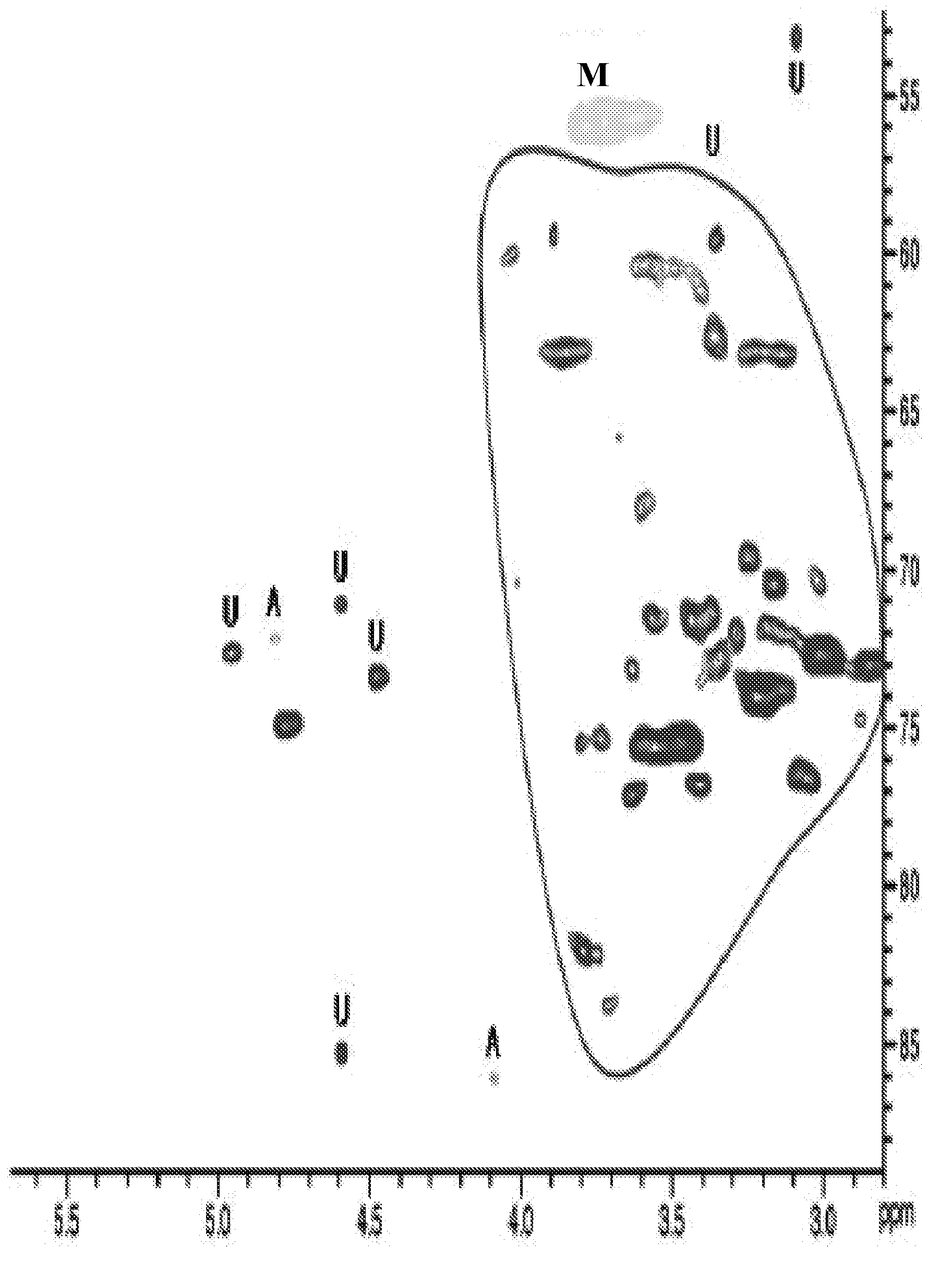
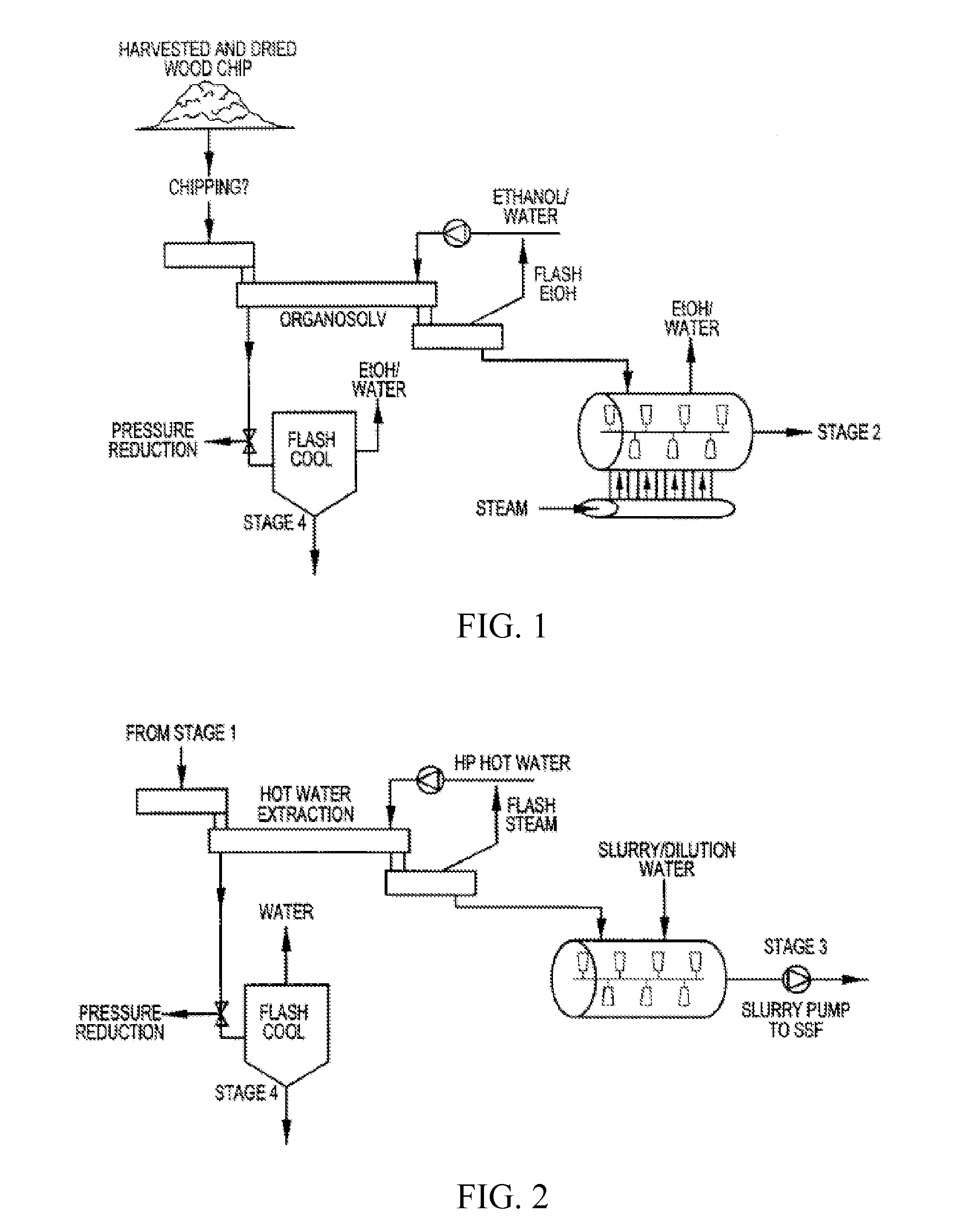
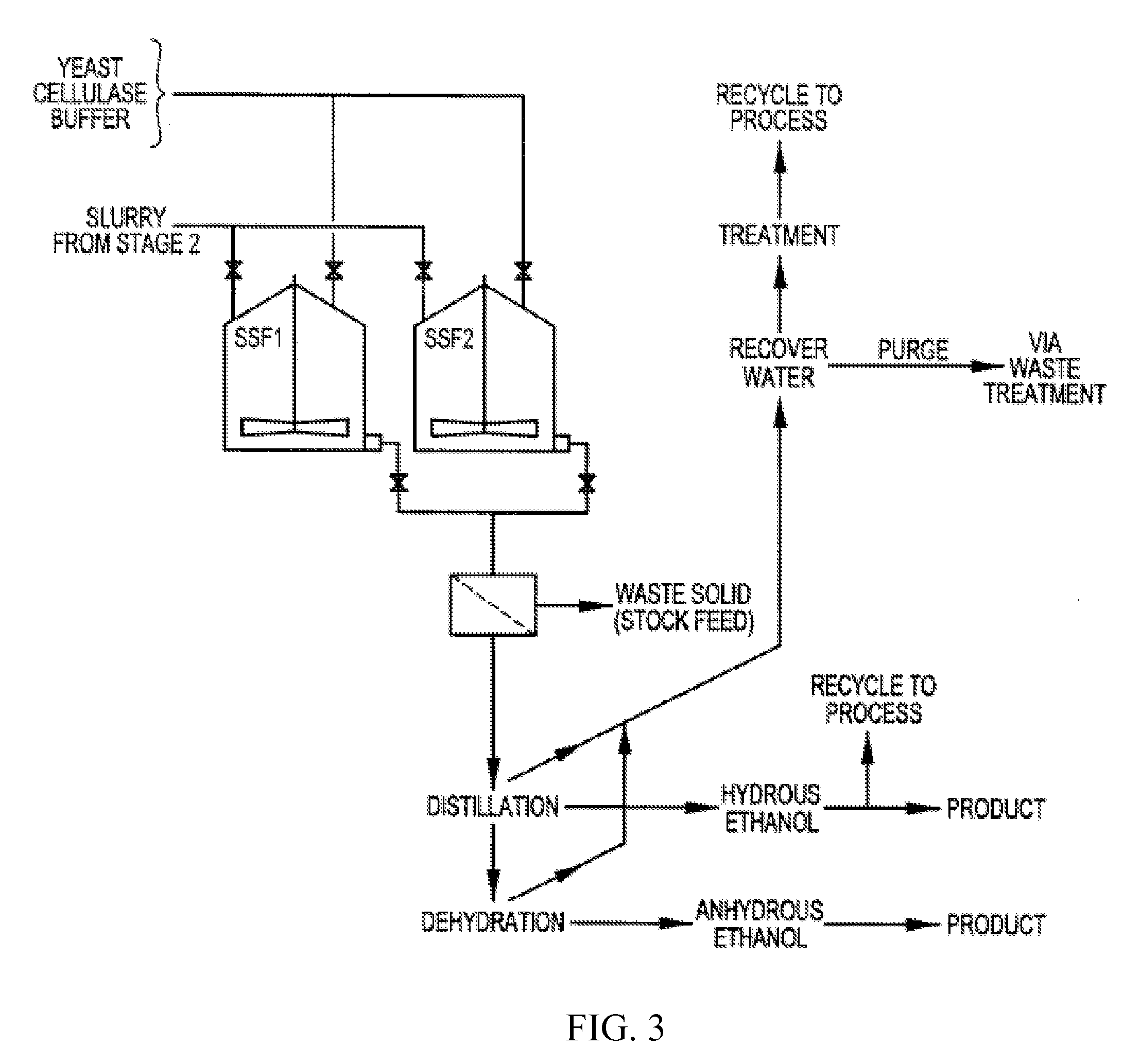
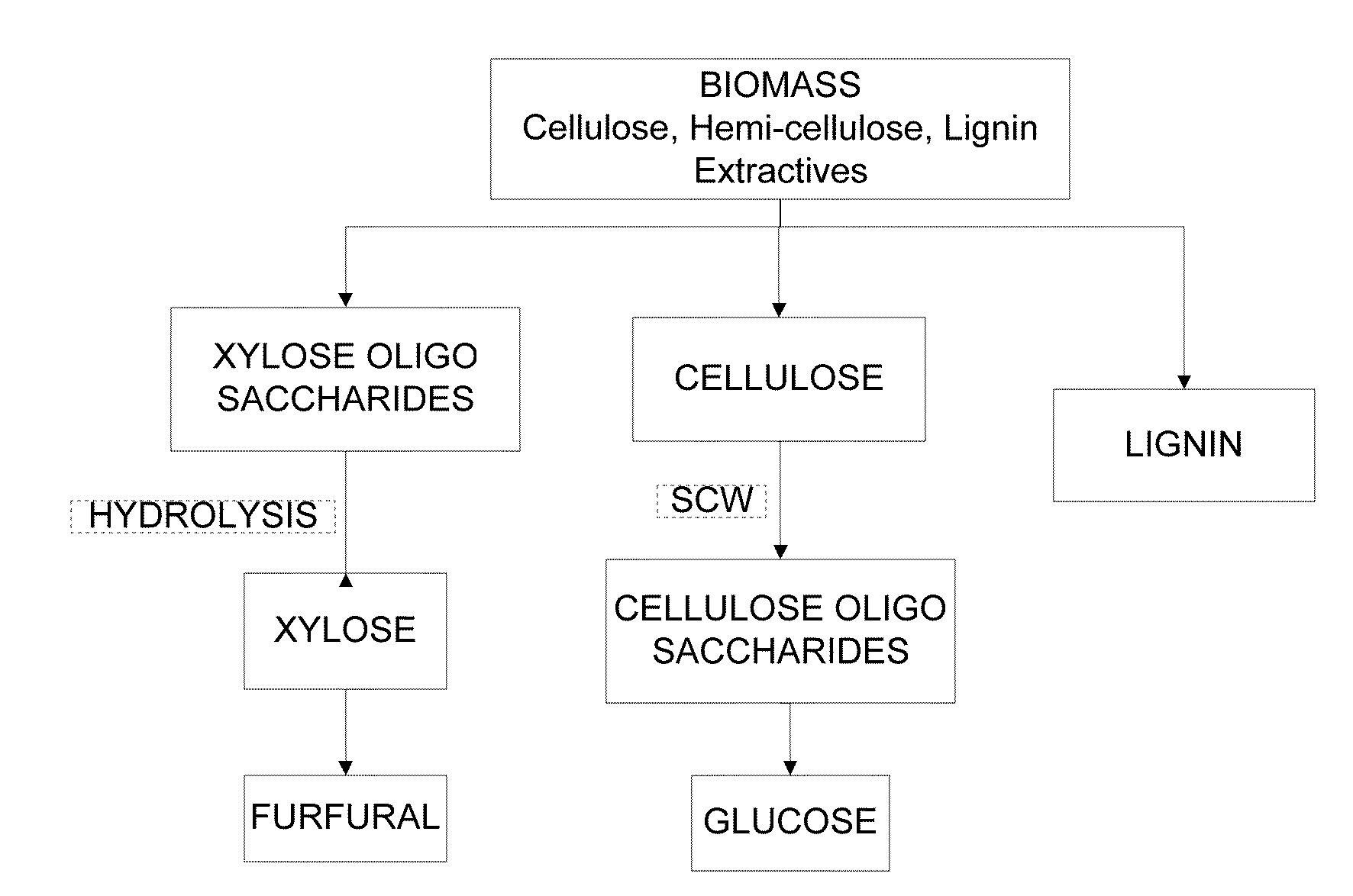
Patents
Literature
488results about "Xylose production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
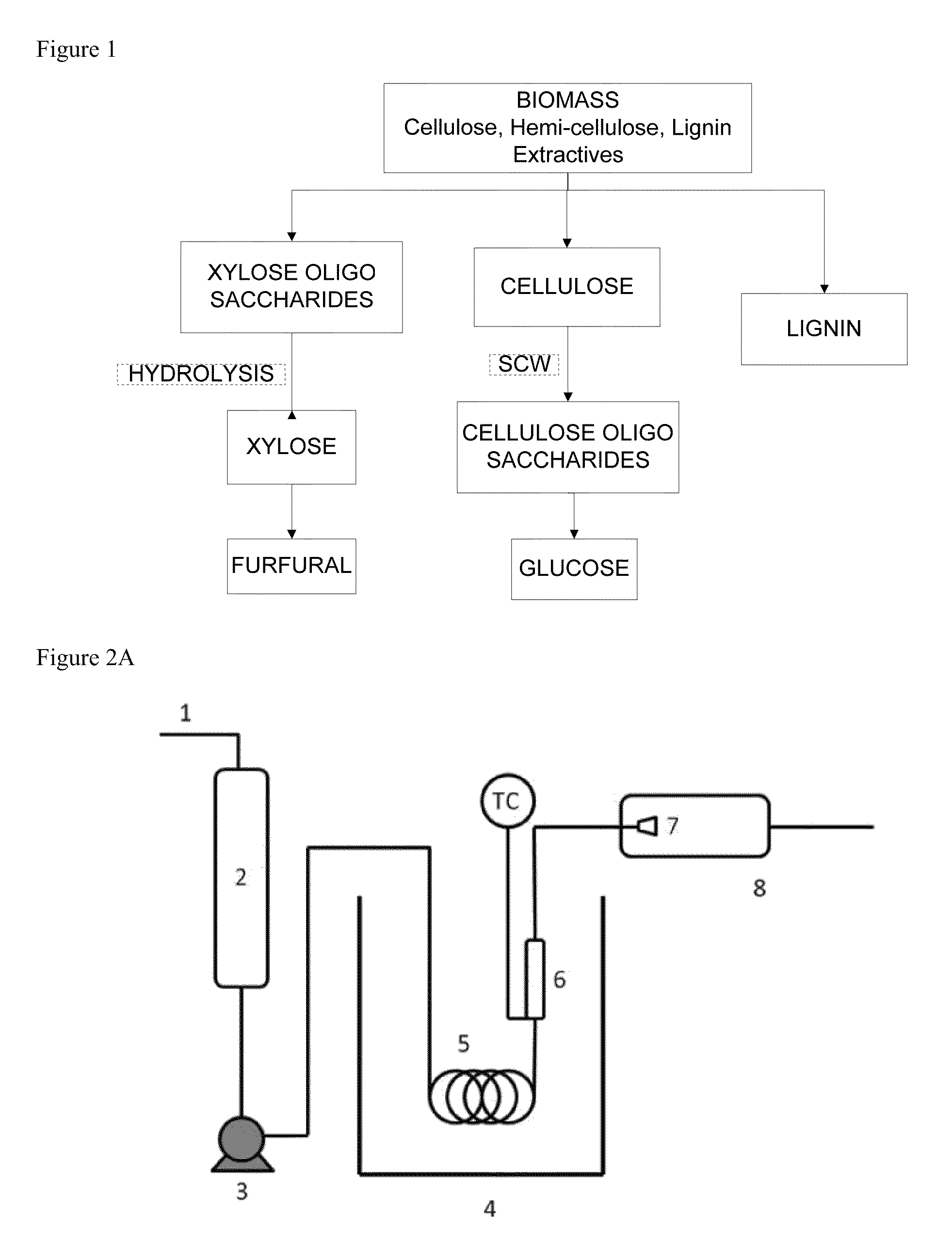
Lignin and other products isolated from plant material, methods for isolation and use, and compositions containing lignin and other plant-derived products
InactiveUS20090062516A1Good for healthImprove responseSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationFiberElastomer
Lignin polymers having distinctive properties, including a generally high molecular weight and generally homogeneous size distribution, as well as preservation of native reactive side groups, are isolated by solvent extraction of plant materials. Methods for isolation of lignin polymers, and for use of the isolated lignin polymers are disclosed. Compositions containing lignin isolated from plant materials, such as carbon fiber composites, resins, adhesive binders and coatings, polyurethane-based foams, rubbers and elastomers, plastics, films, paints, nutritional supplements, food and beverage additives are disclosed. Xylose and xylose derivatives, furfural, fermentable sugars, cellulose and hemi-cellulose products may be used directly or further processed. The lignin polymers and other plant-derived products disclosed herein may be produced in abundance at low cost, and may be used as substitutes for feedstocks originating from fossil fuel or petrochemical sources in the manufacture of various products.
Owner:VERTICHEM CORP
Nano-catalytic-solvo-thermal technology platform bio-refineries
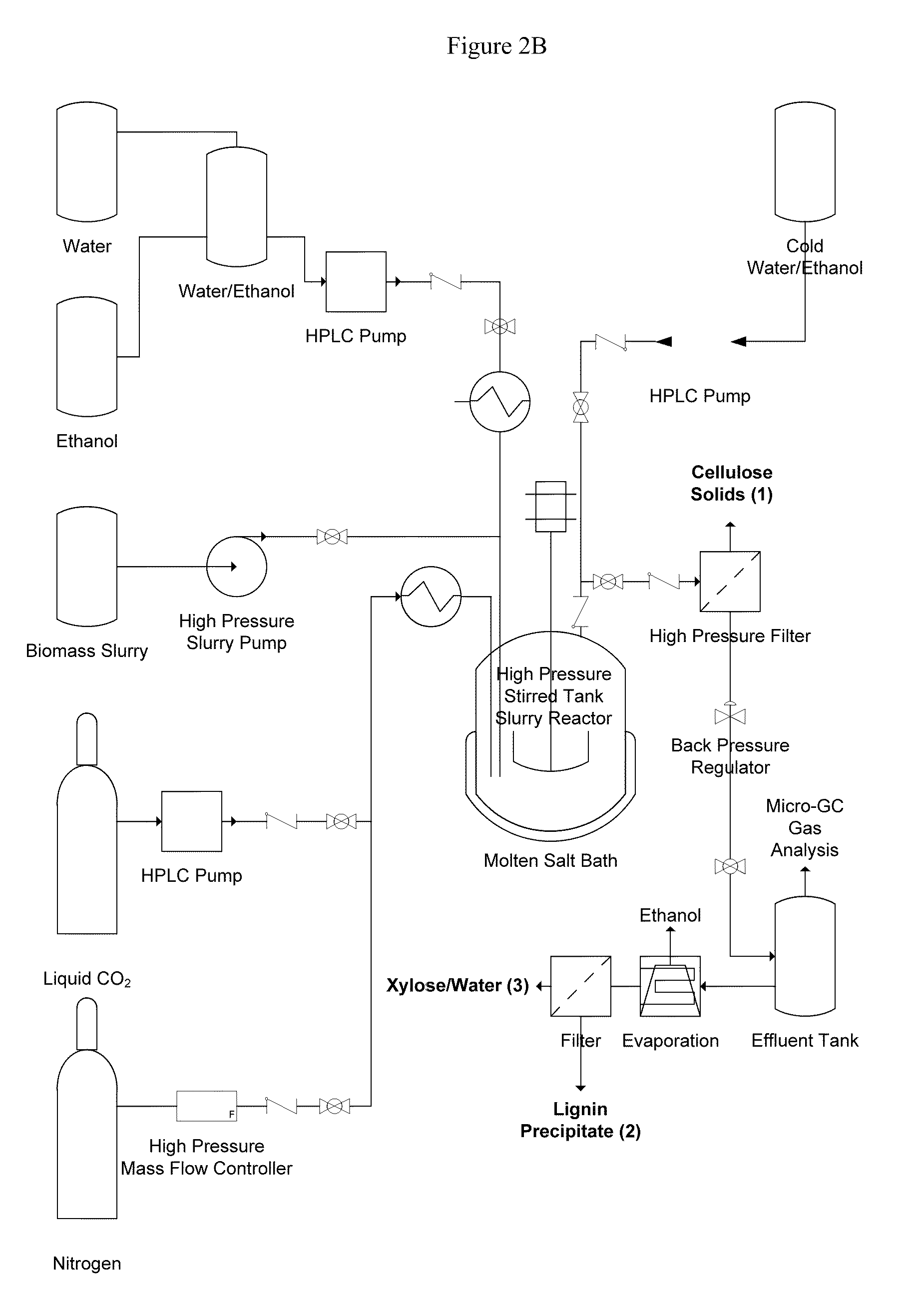
Methods of making glucose and / or furfural from biomass require one or more supercritical fluids that may be used to process biomass, cellulose from the biomass, and / or xylose from the biomass. Examples of supercritical fluids for use in processing biomass include ethanol, water, and carbon dioxide at a temperature and pressure above the critical points for ethanol and carbon dioxide but at a temperature and / or pressure below that of the critical point for water. A supercritical fluid containing carbon dioxide and water may be used to convert cellulose to glucose or convert xylose to furfural. The fluid has a temperature and pressure above the critical point of carbon dioxide, but at least one of the temperature and pressure is below the critical point for water.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
Method for producing ethanol and co-products from cellulosic biomass
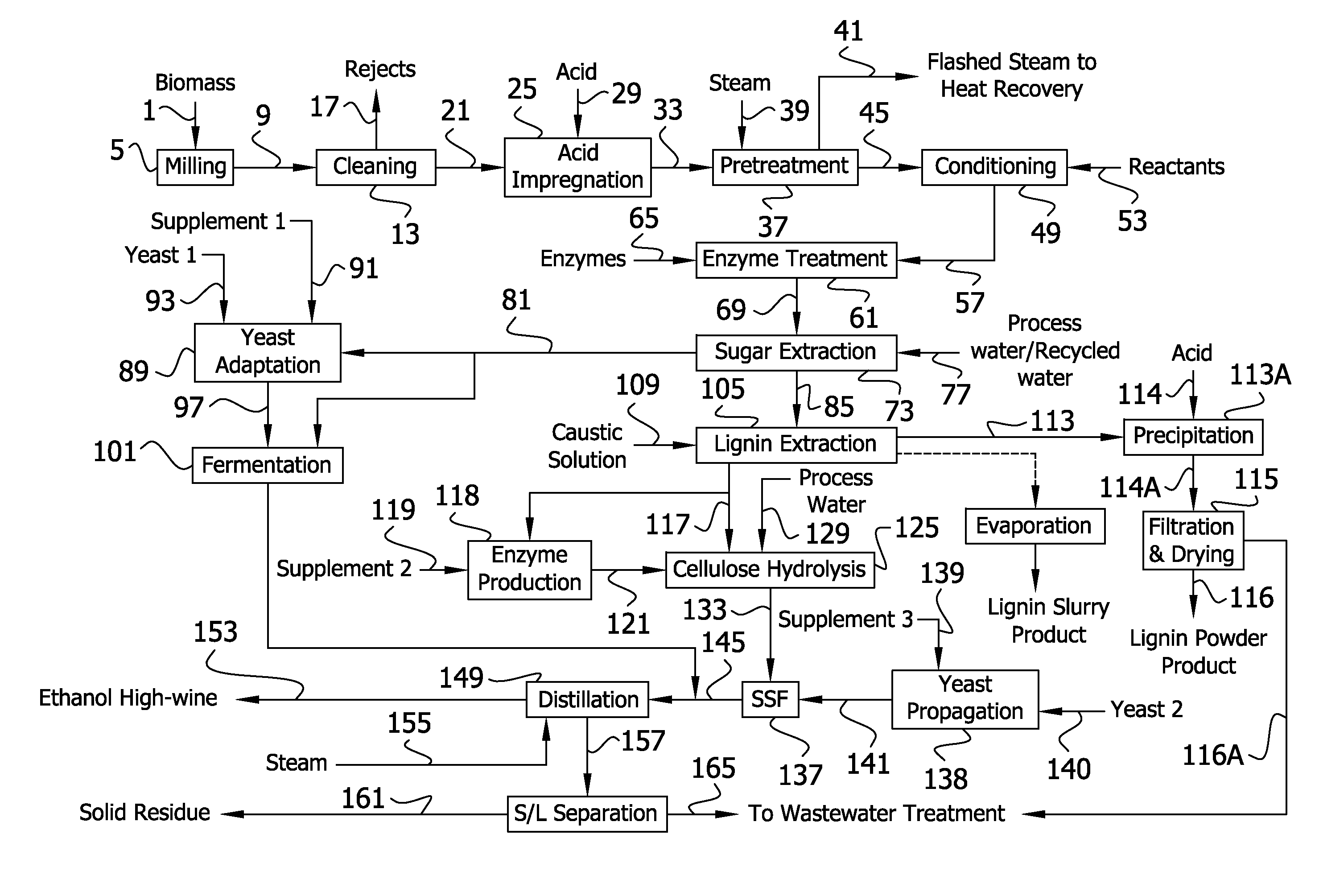
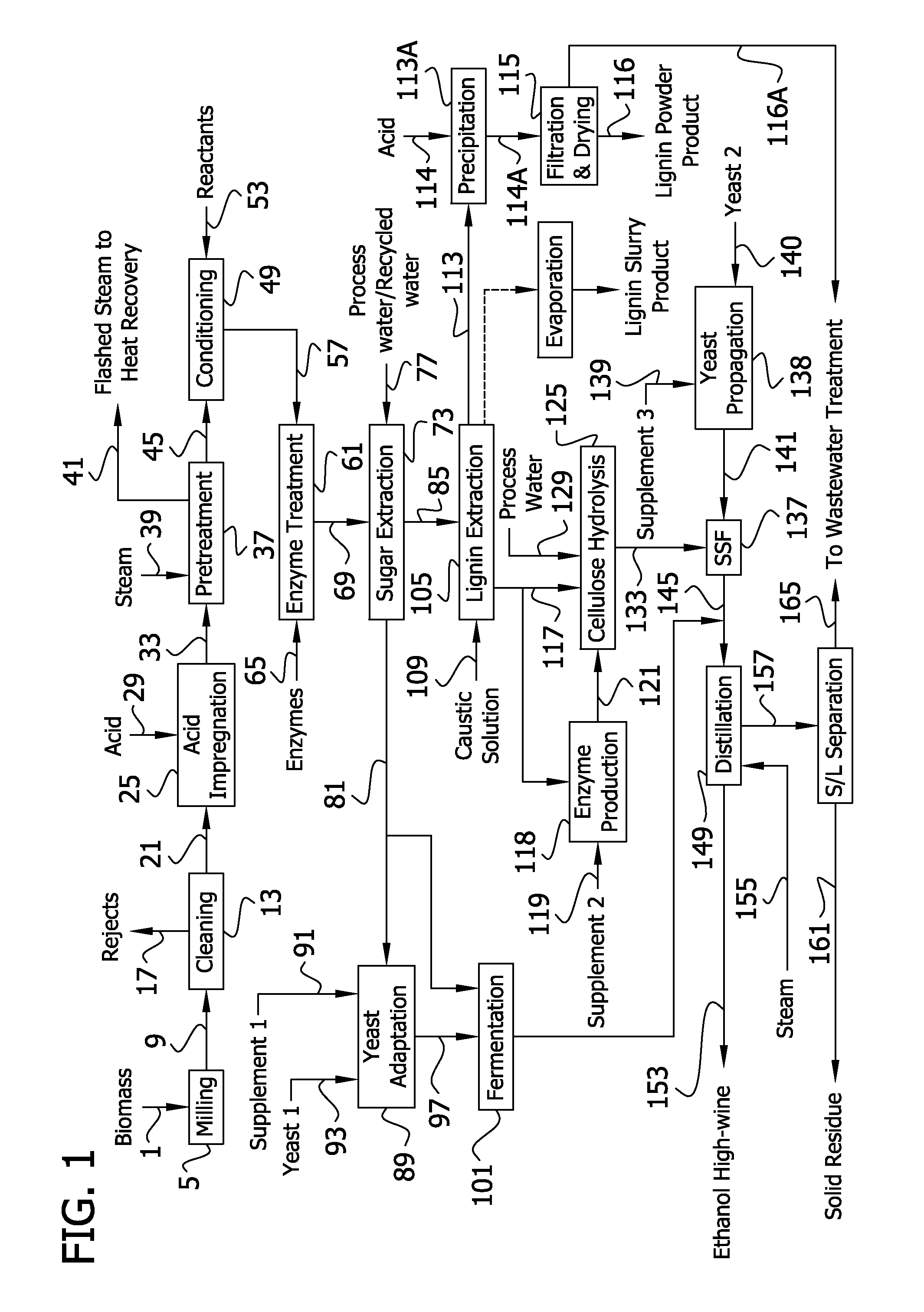
InactiveUS20120006320A1Increased ethanol productionImproved co-productsFuel supply regulationPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
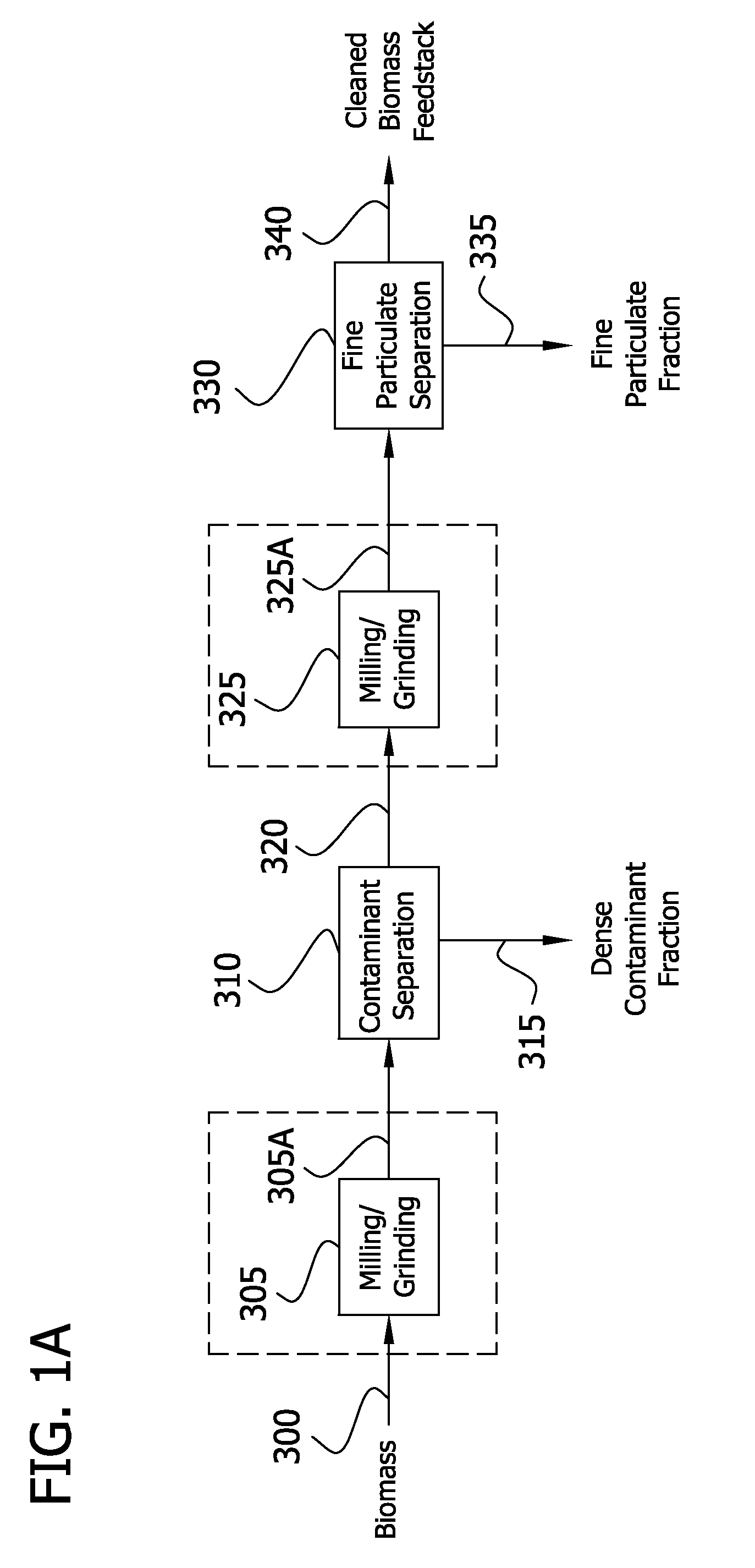
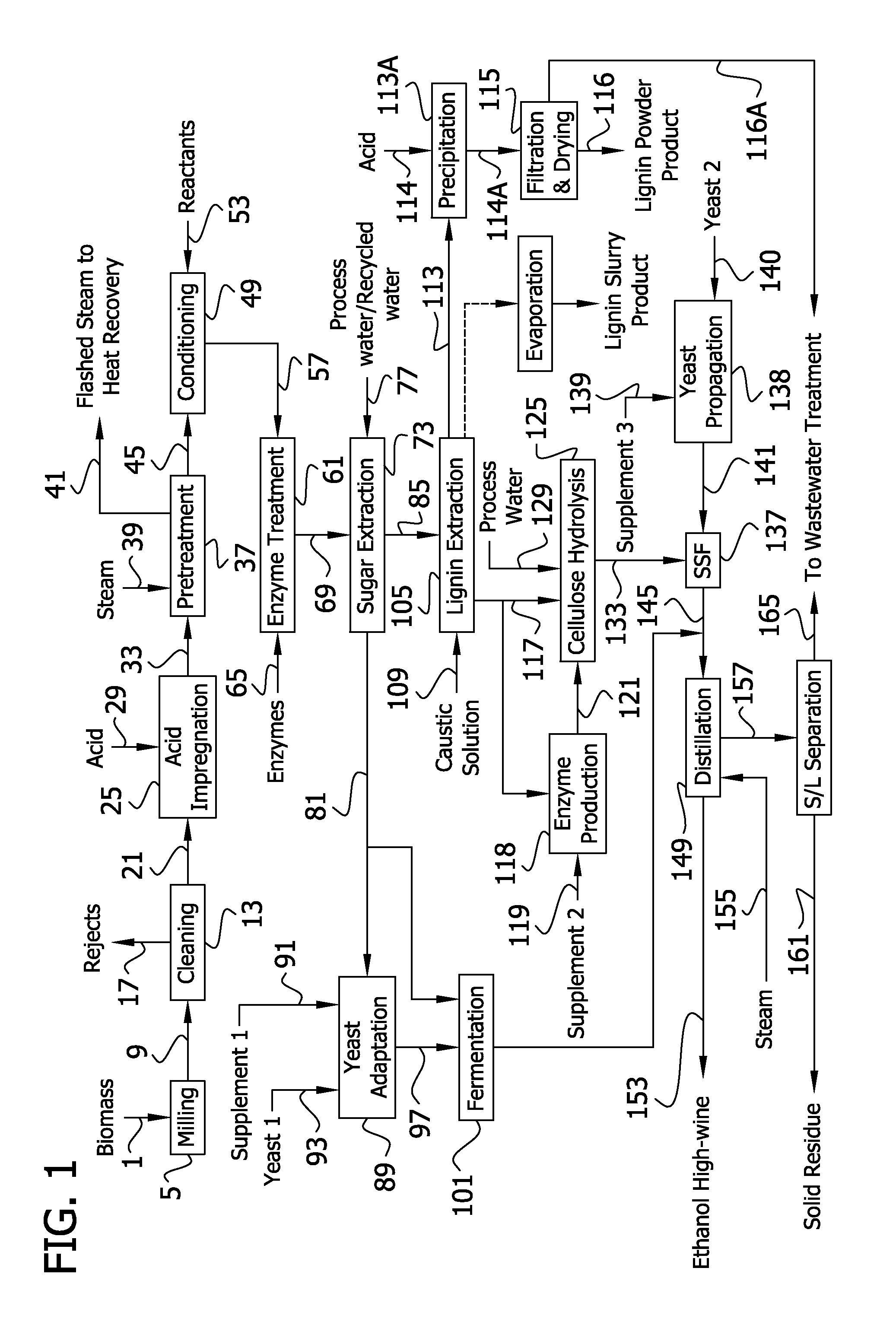
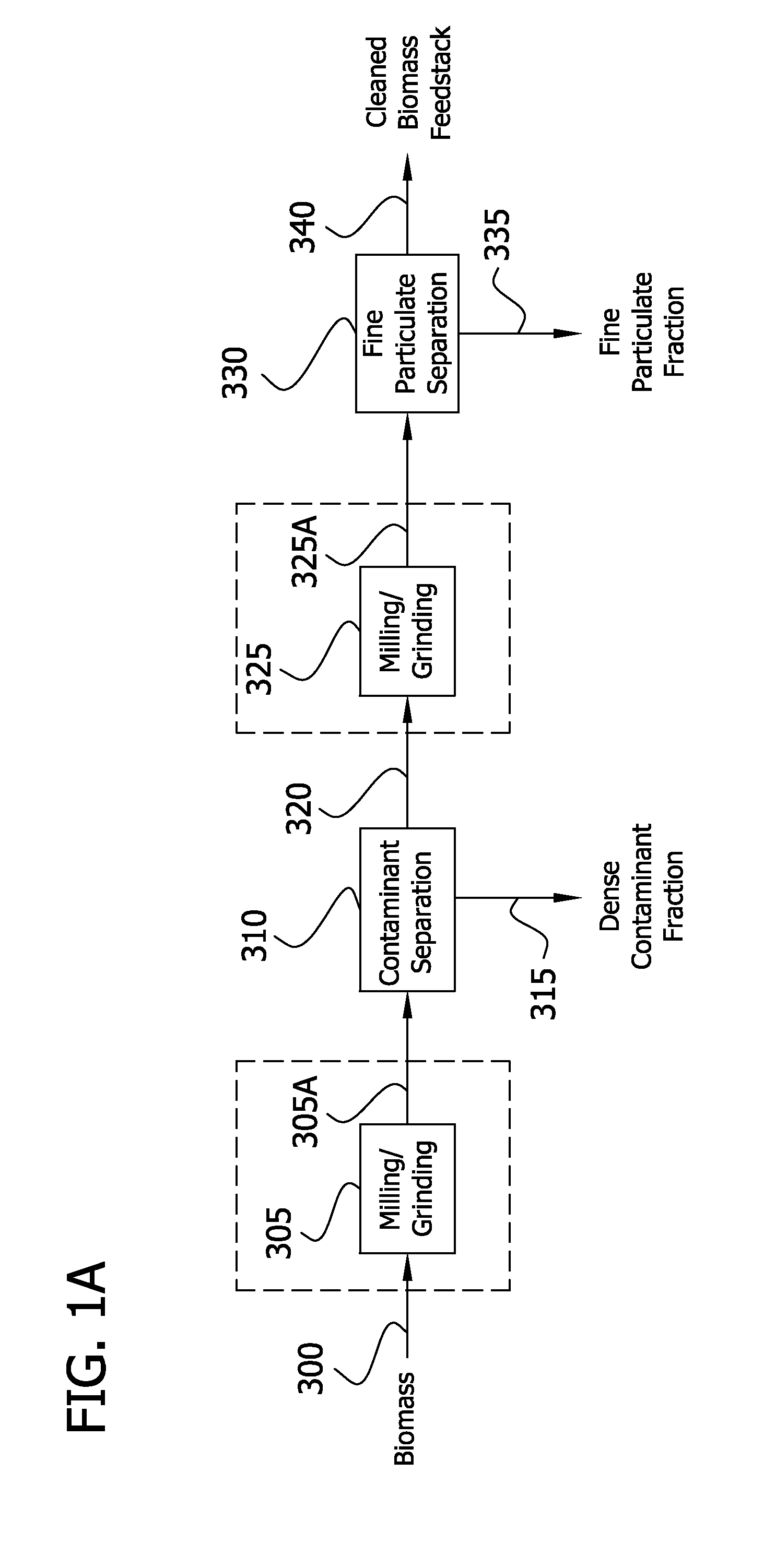
The present invention generally relates to processes for production of ethanol from cellulosic biomass. The present invention also relates to production of various co-products of preparation of ethanol from cellulosic biomass. The present invention further relates to improvements in one or more aspects of preparation of ethanol from cellulosic biomass including, for example, improved methods for cleaning biomass feedstocks, improved acid impregnation, and improved steam treatment, or “steam explosion.”
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGY NEW TECH
Process for the treatment of lignocellulosic biomass
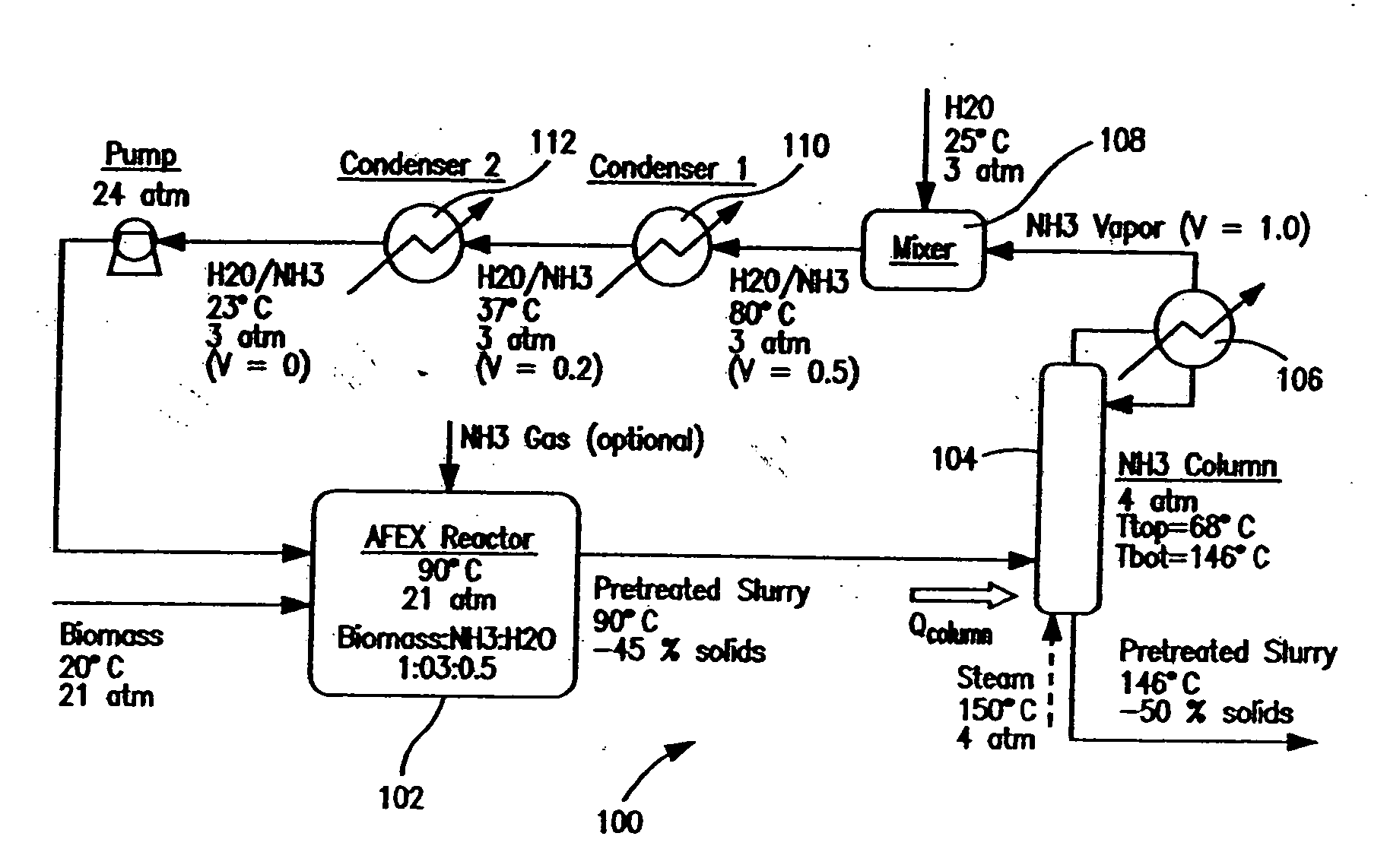
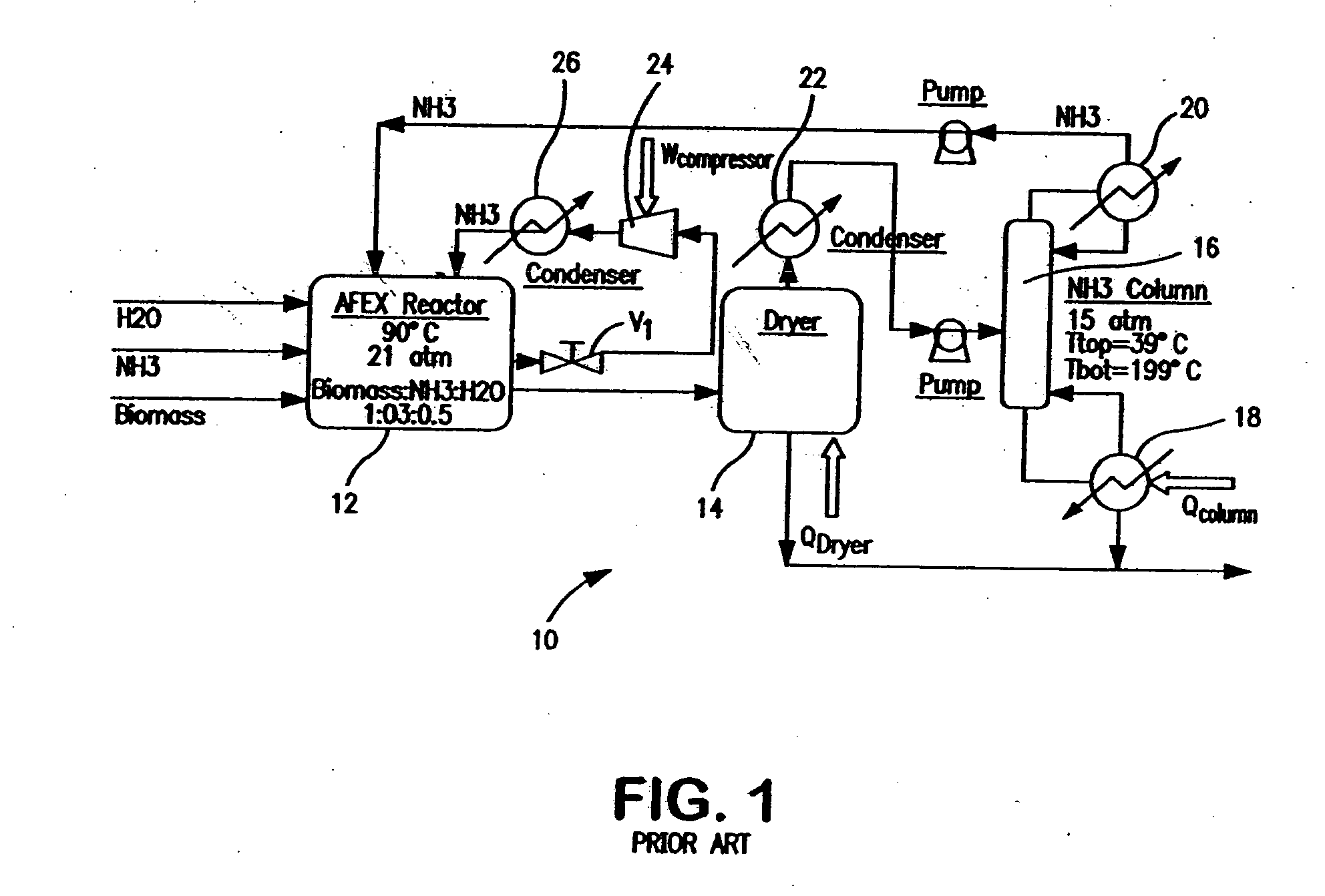
ActiveUS20080008783A1Lower the volumeIncreasing fractionBiofuelsAnimal feeding stuffCelluloseEnergy source
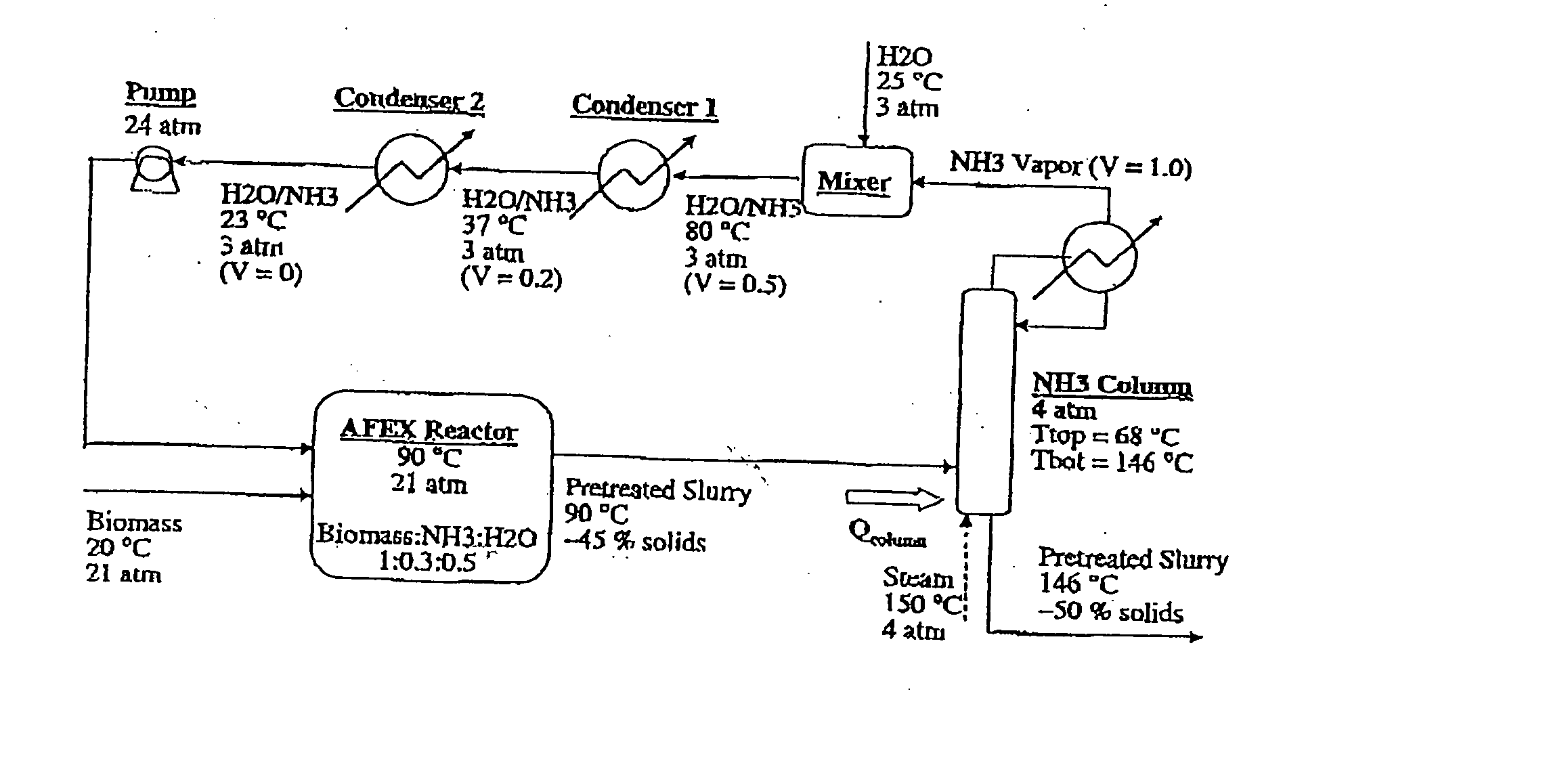
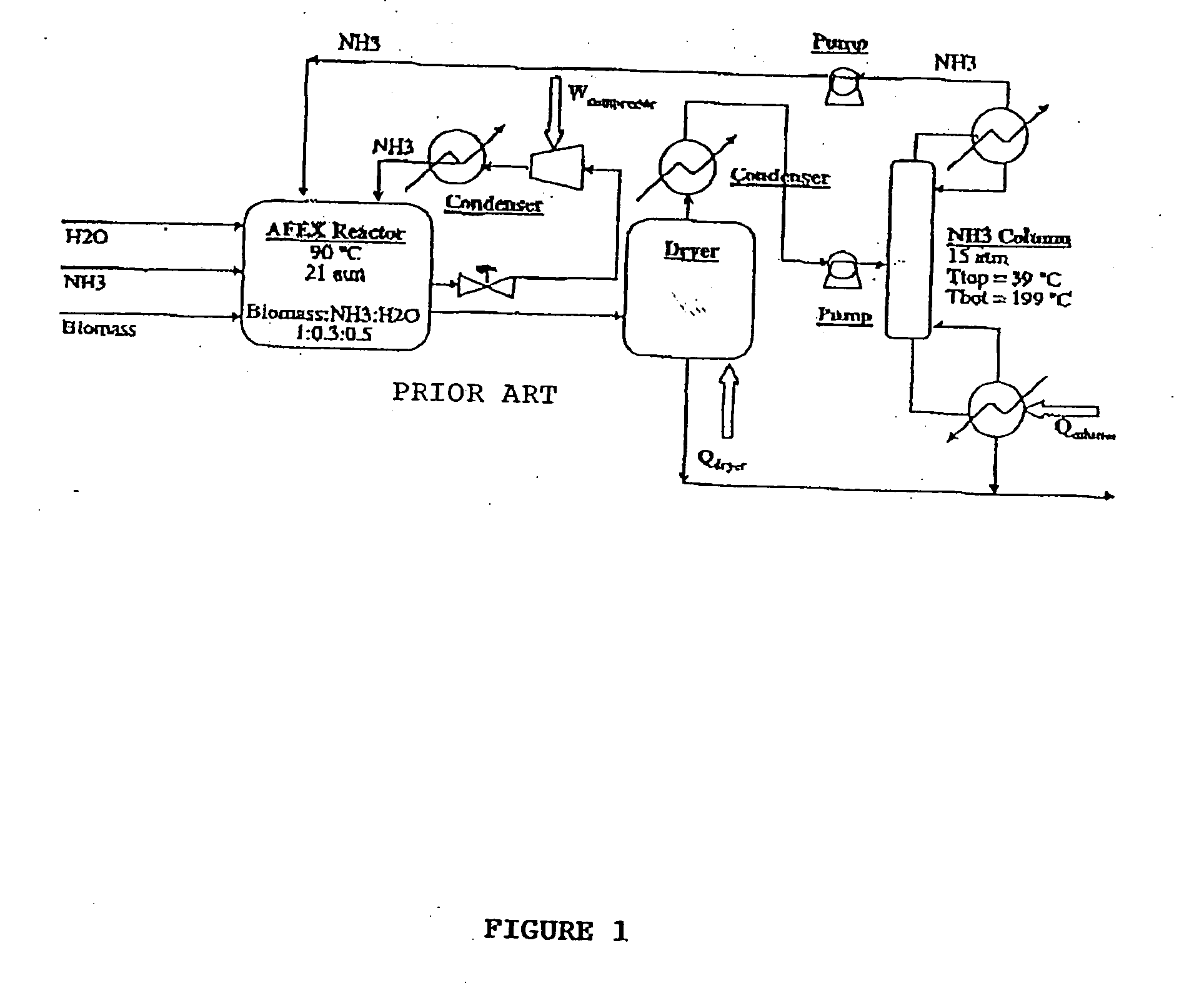
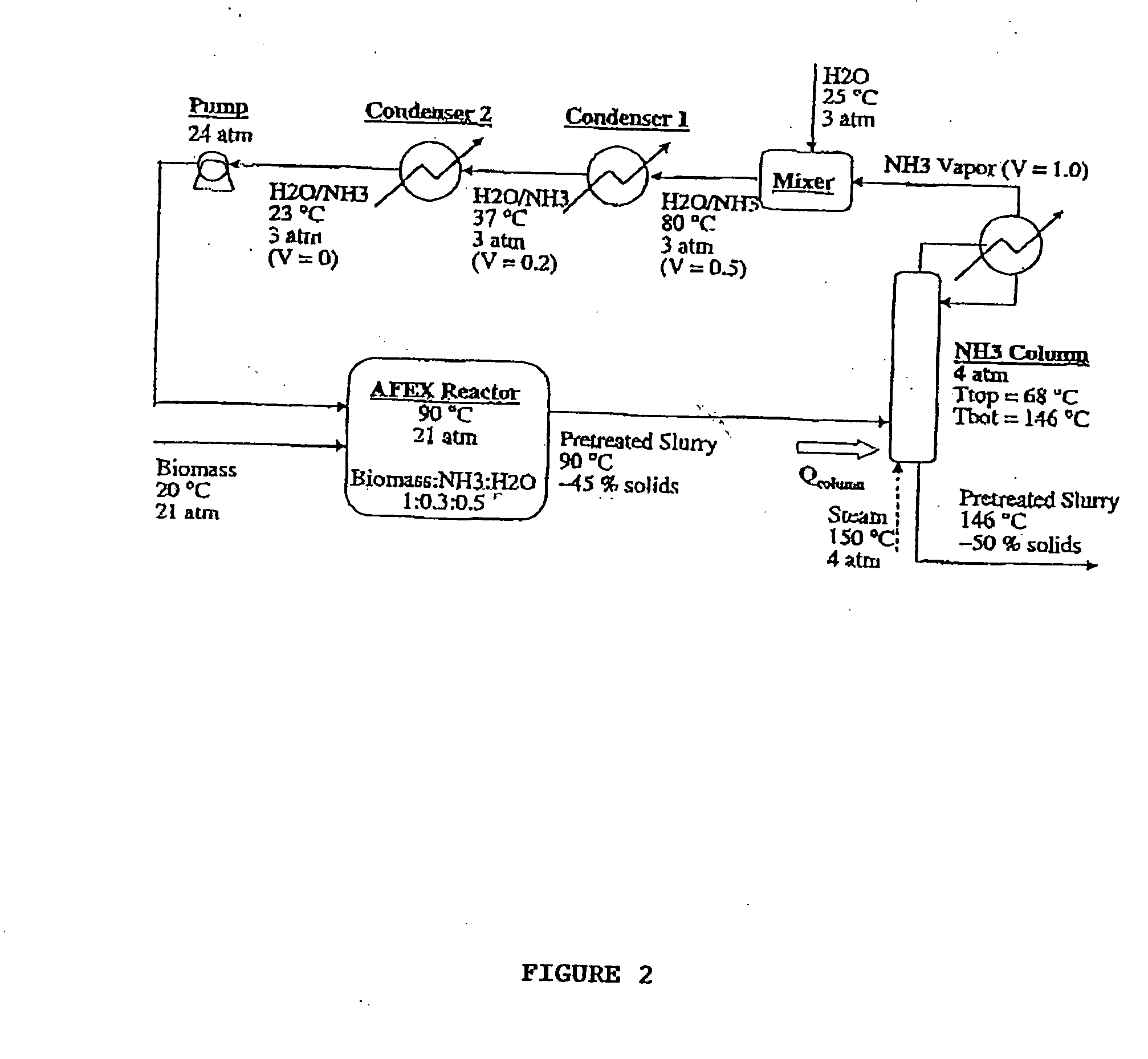
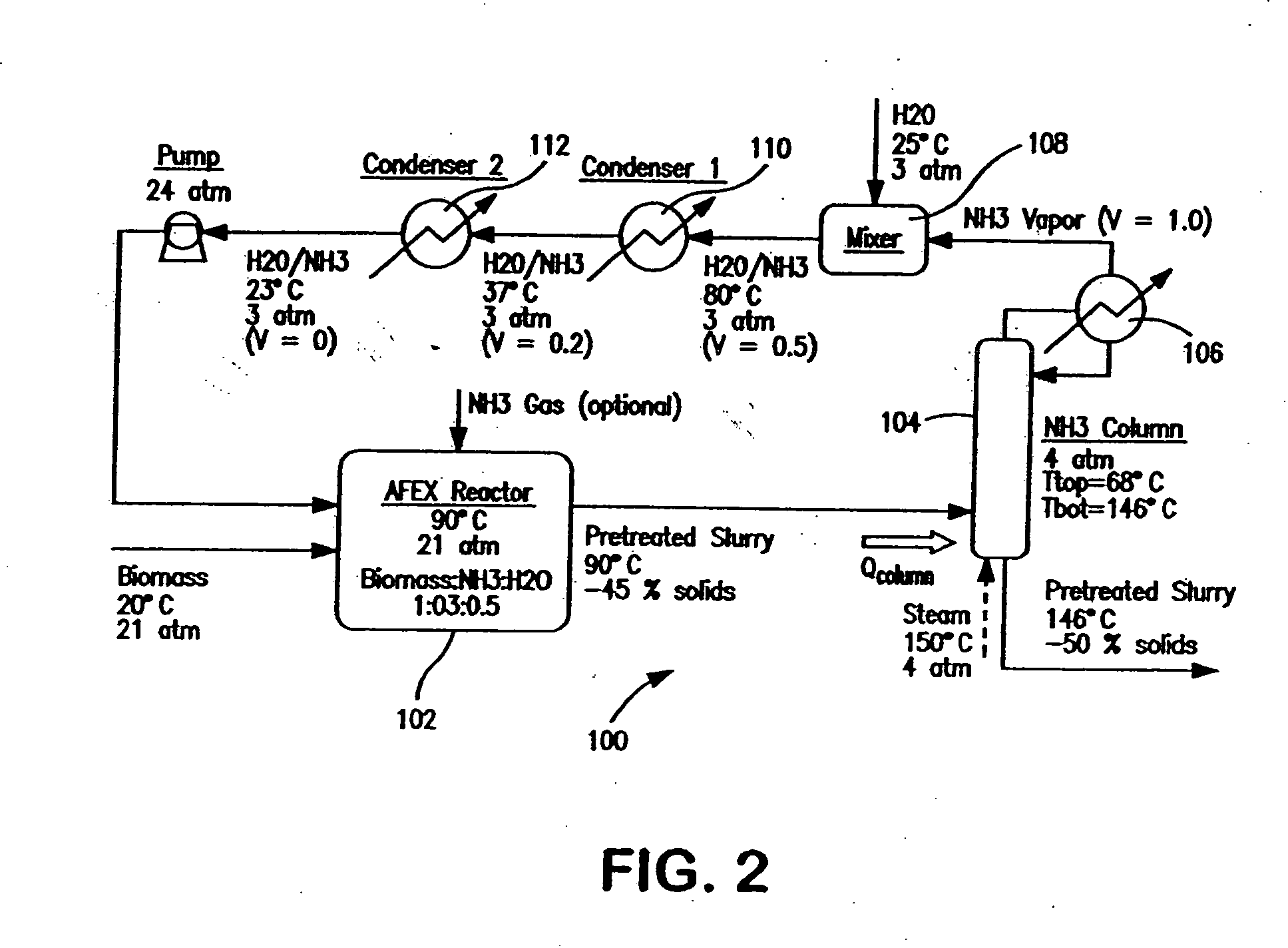
A process for the treatment of biomass to render structural carbohydrates more accessible and / or digestible using concentrated ammonium hydroxide with or without anhydrous ammonia addition, is described. The process preferably uses steam to strip ammonia from the biomass for recycling. The process yields of monosaccharides from the structural carbohydrates are good, particularly as measured by the enzymatic hydrolysis of the structural carbohydrates. The monosaccharides are used as animal feeds and energy sources for ethanol production.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
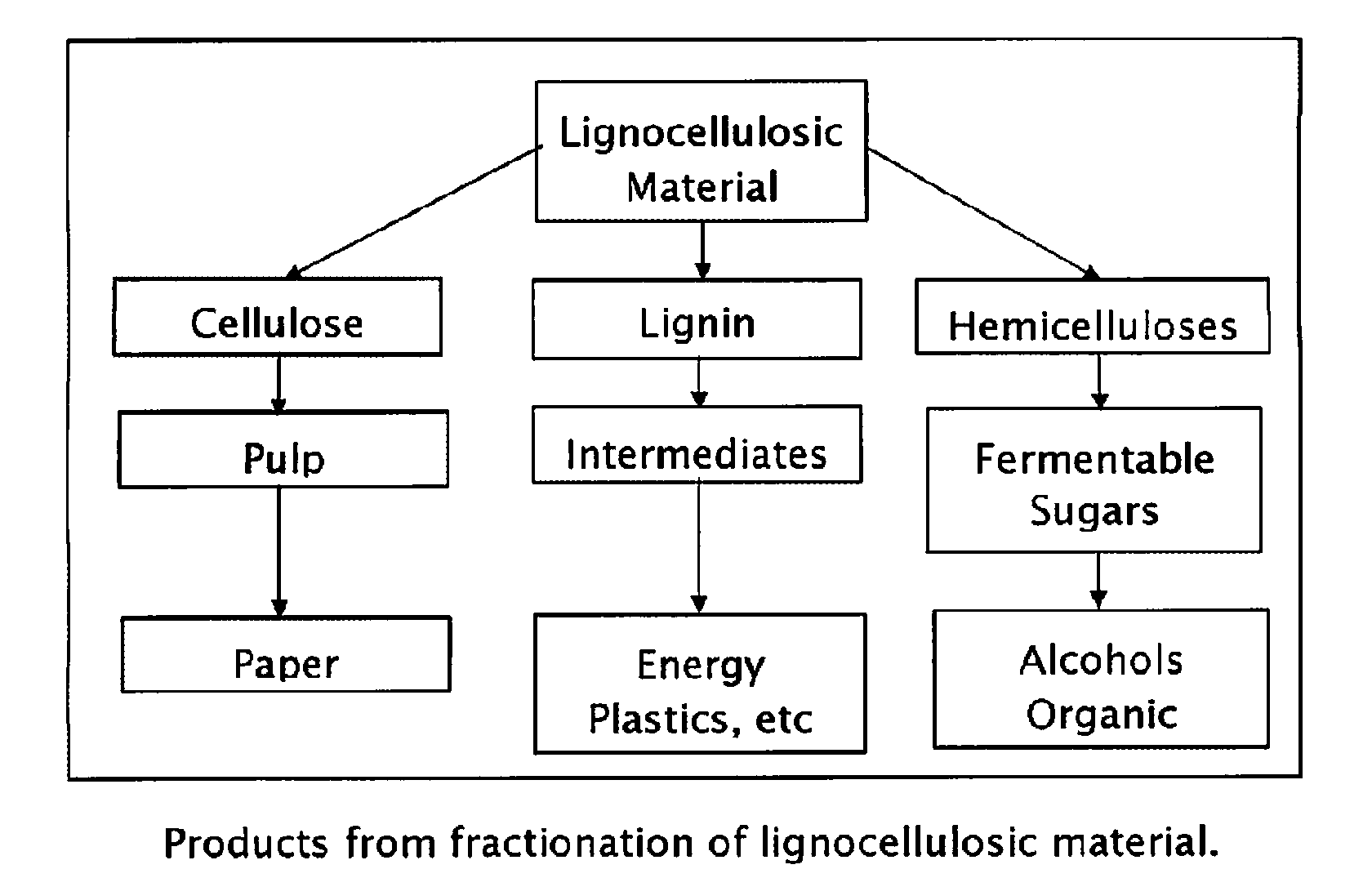
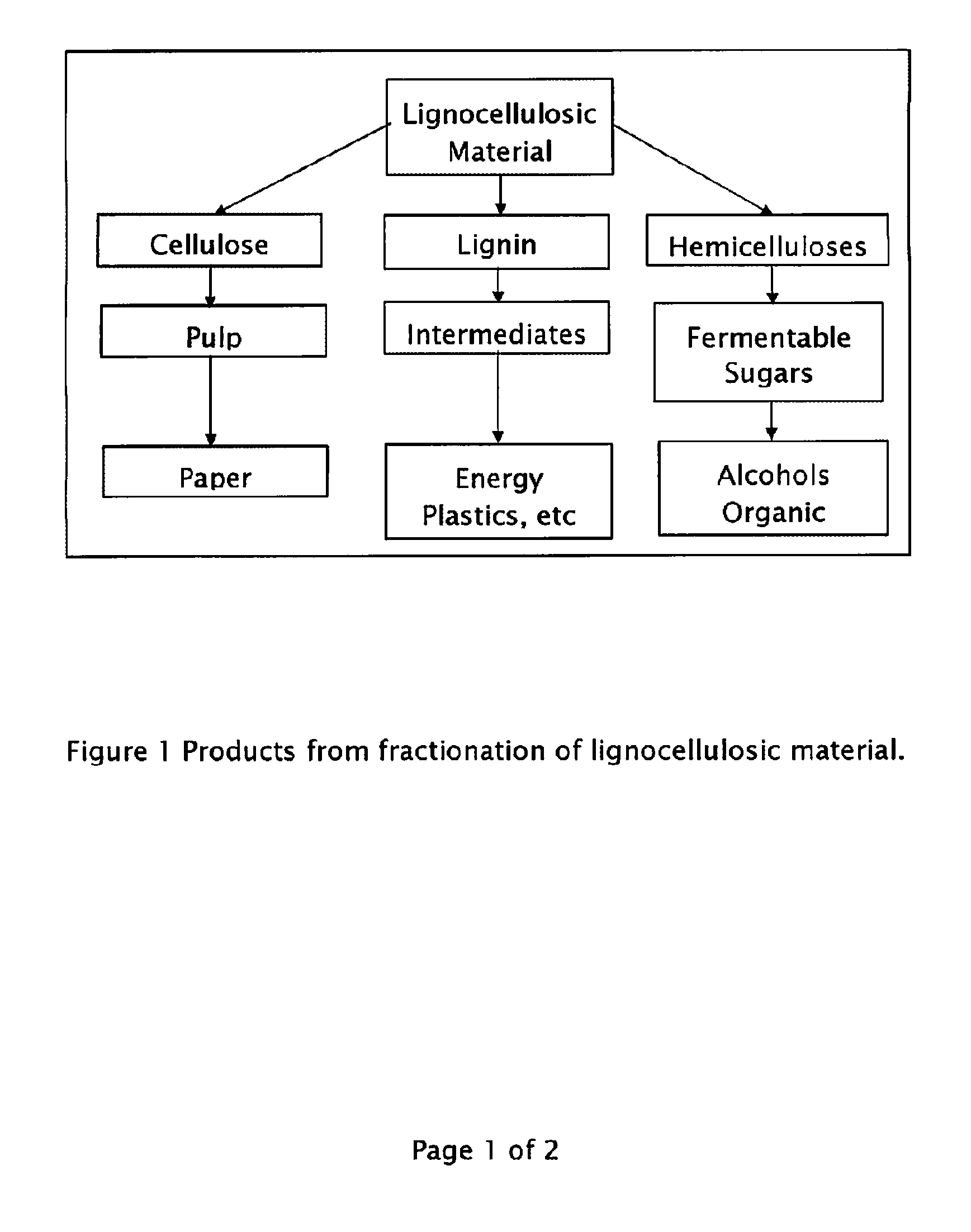
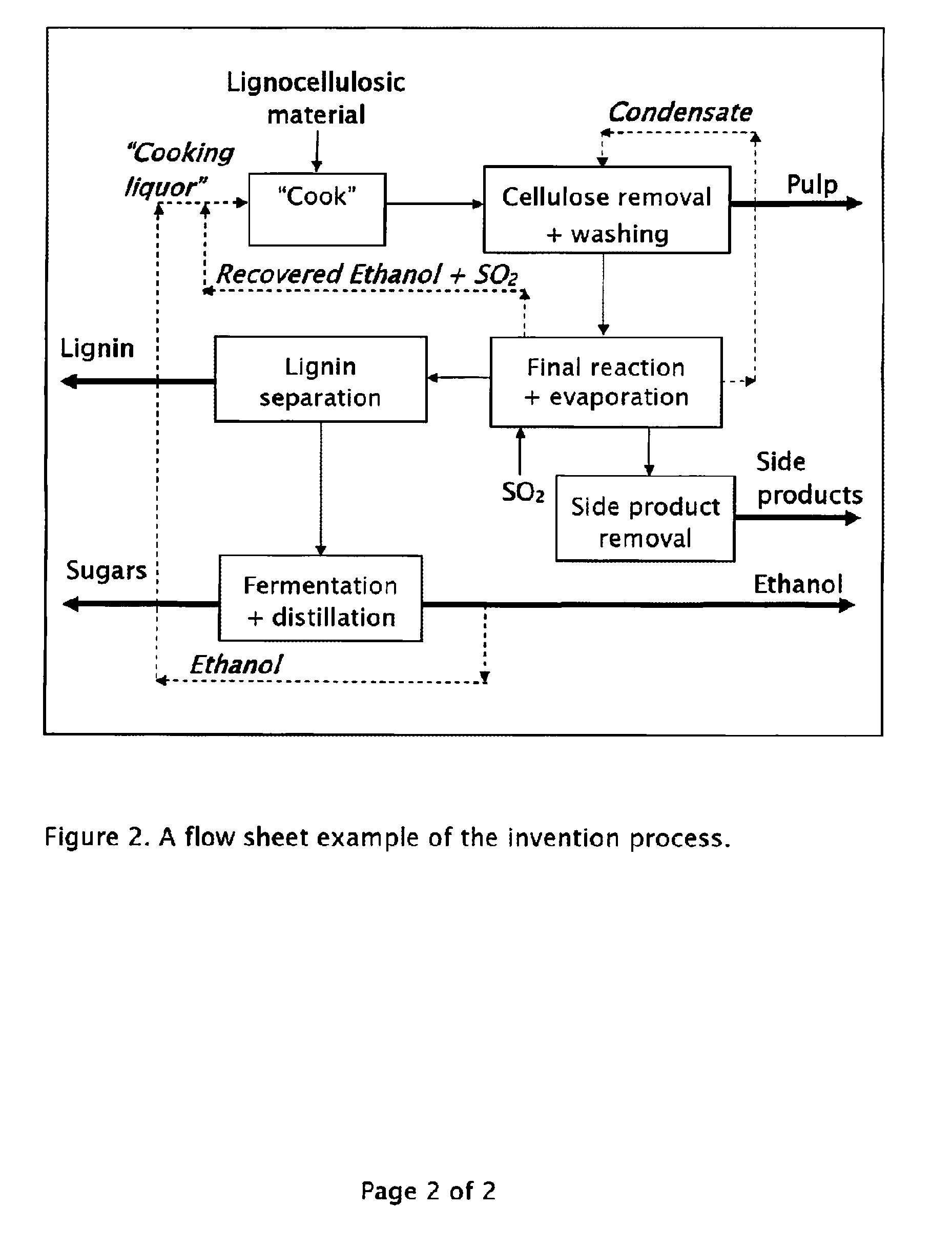
Method for the production of fermentable sugars and cellulose from lignocellulosic material
ActiveUS8030039B1High yieldIncreased ethanol yieldFats/resins/pitch/waxes removal in pulpPulping with organic compoundsOrganic acidAlcohol
A method for the production of fermentable sugars and high viscosity cellulose from lignocellulosic material in a batch or continuous process is provided. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated in a fashion that cellulose is removed as pulp, cooking chemicals can be reused, lignin is separated for the production of process energy, and hemicelluloses are converted into fermentable sugars, while fermentation inhibitors are removed. High yield production of alcohols or organic acids can be obtained from this method using the final reaction step.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
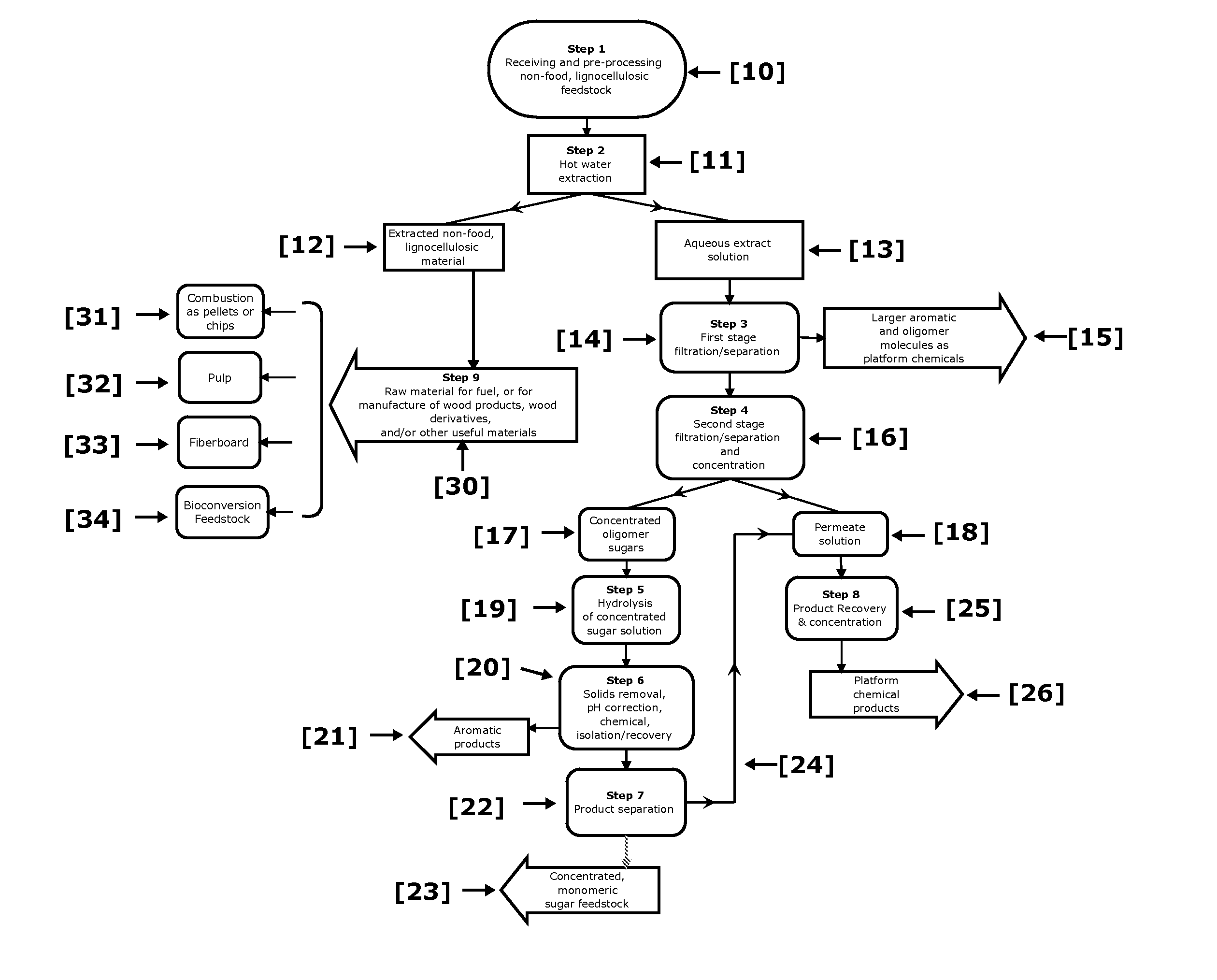
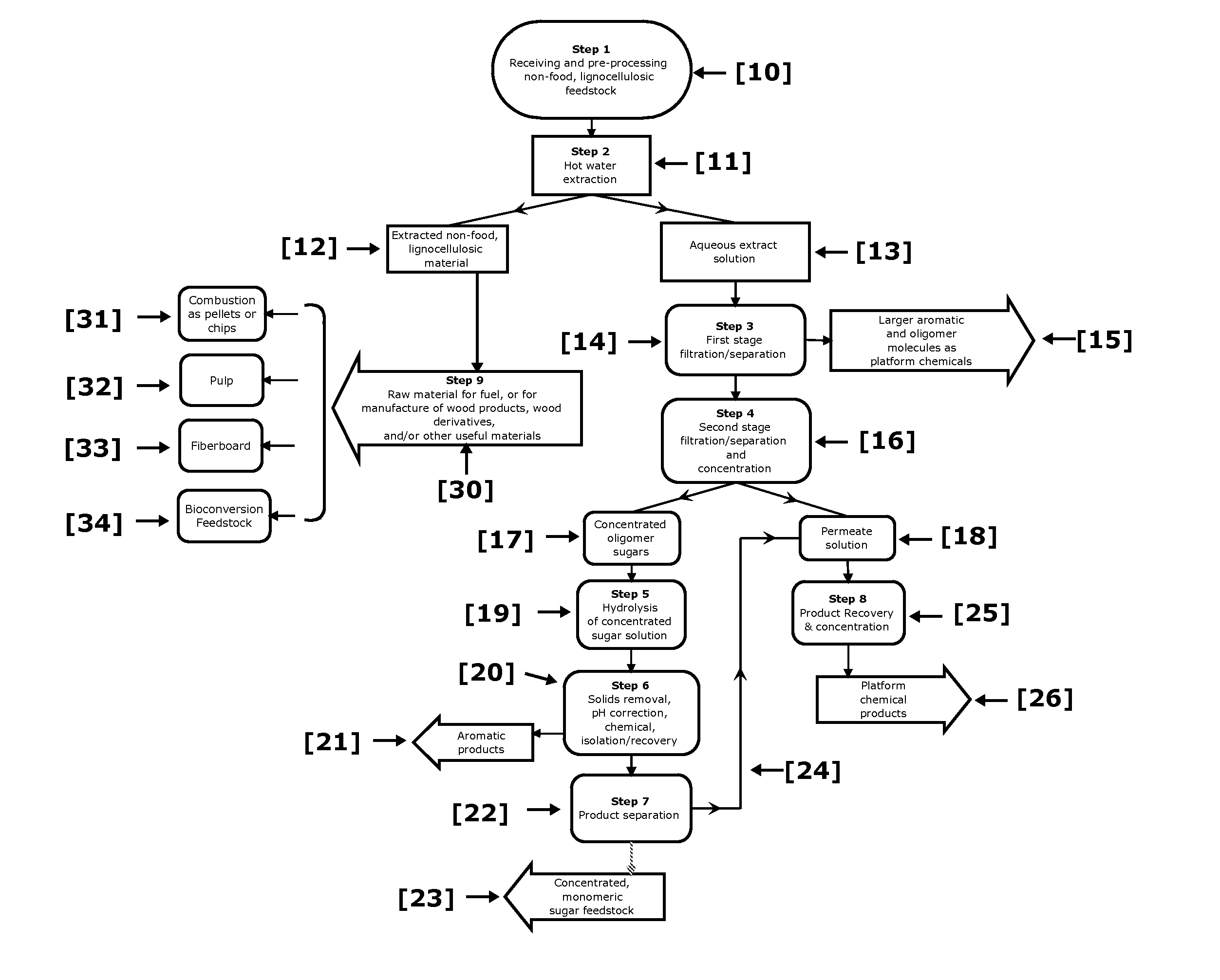
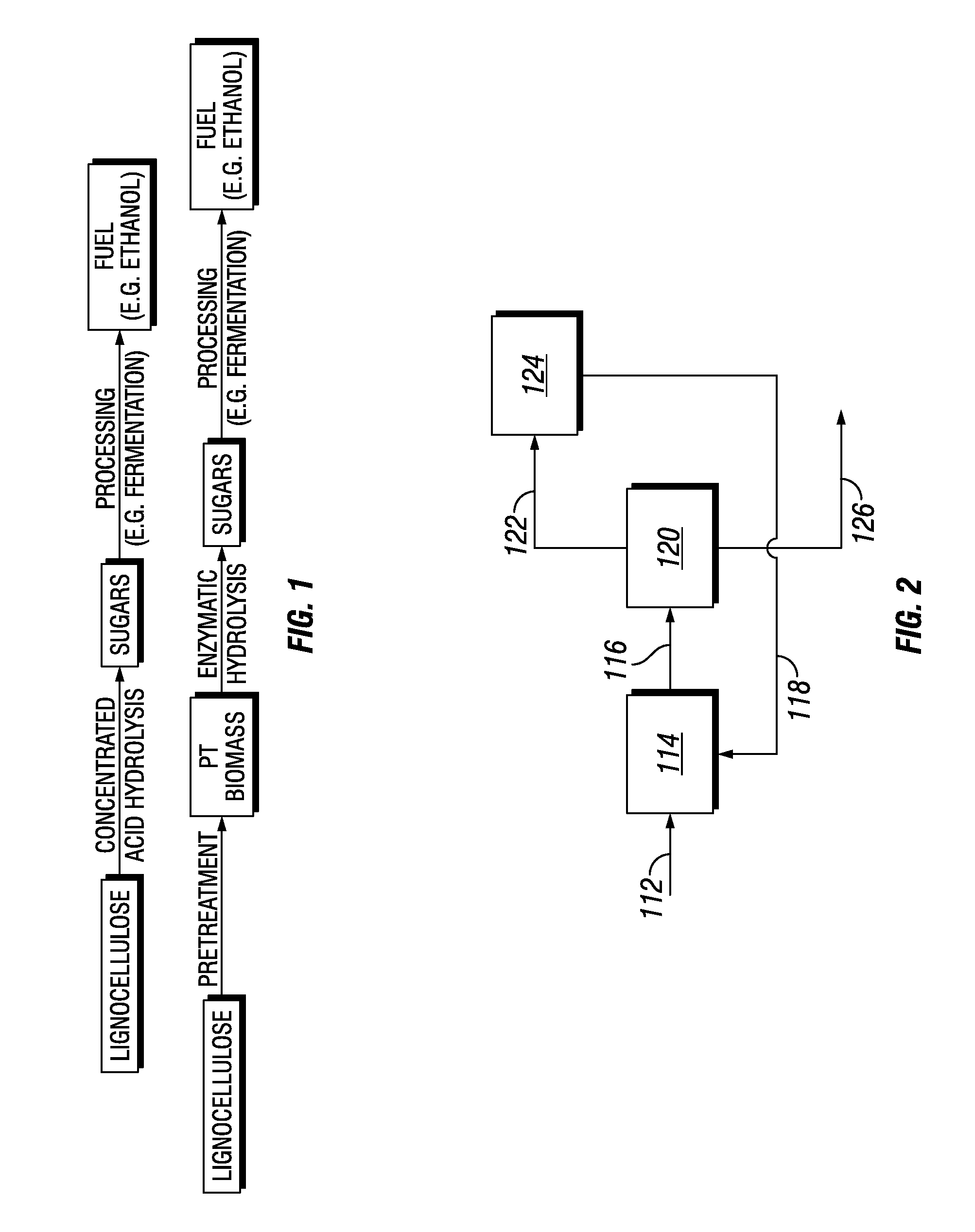
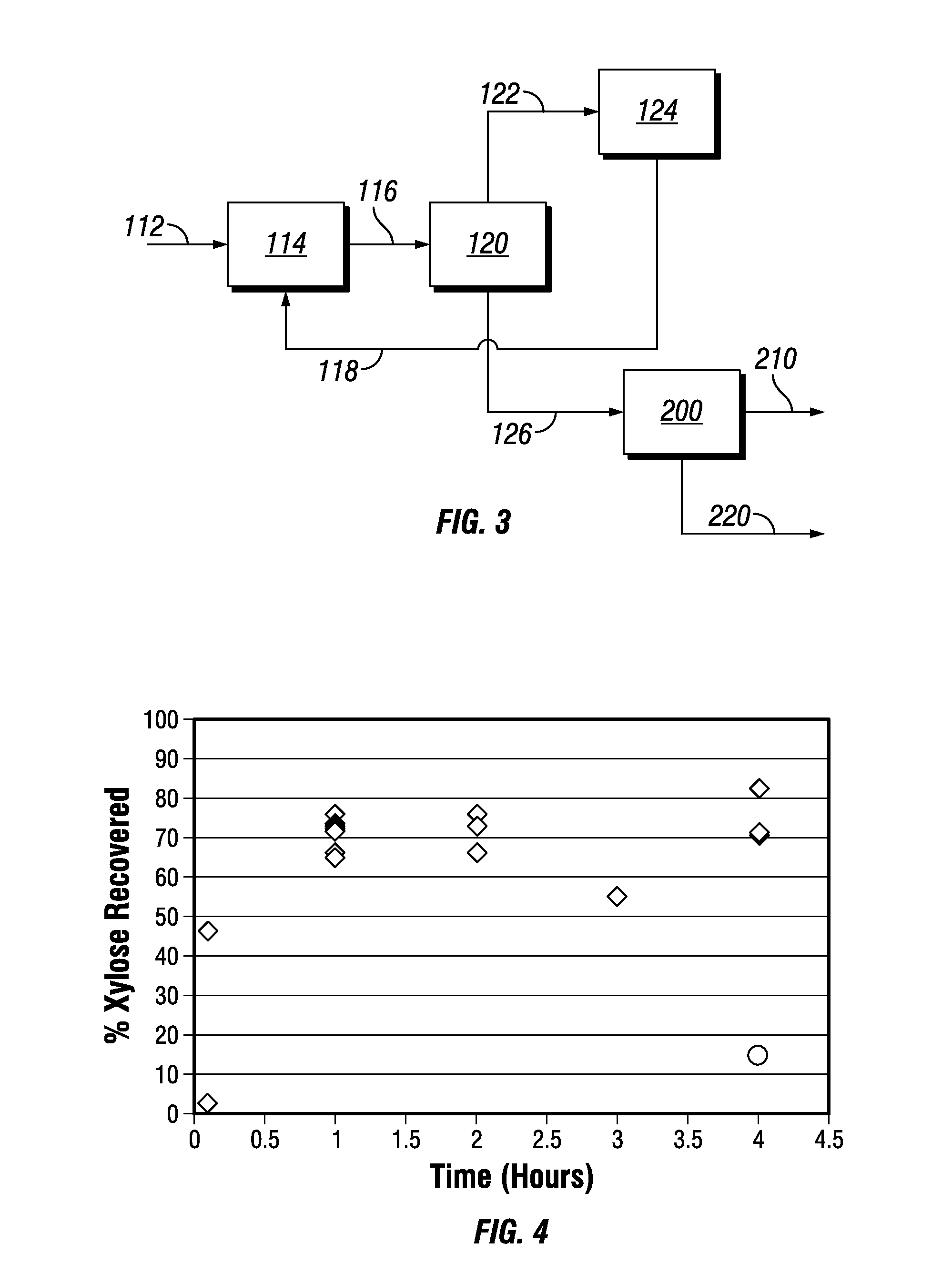
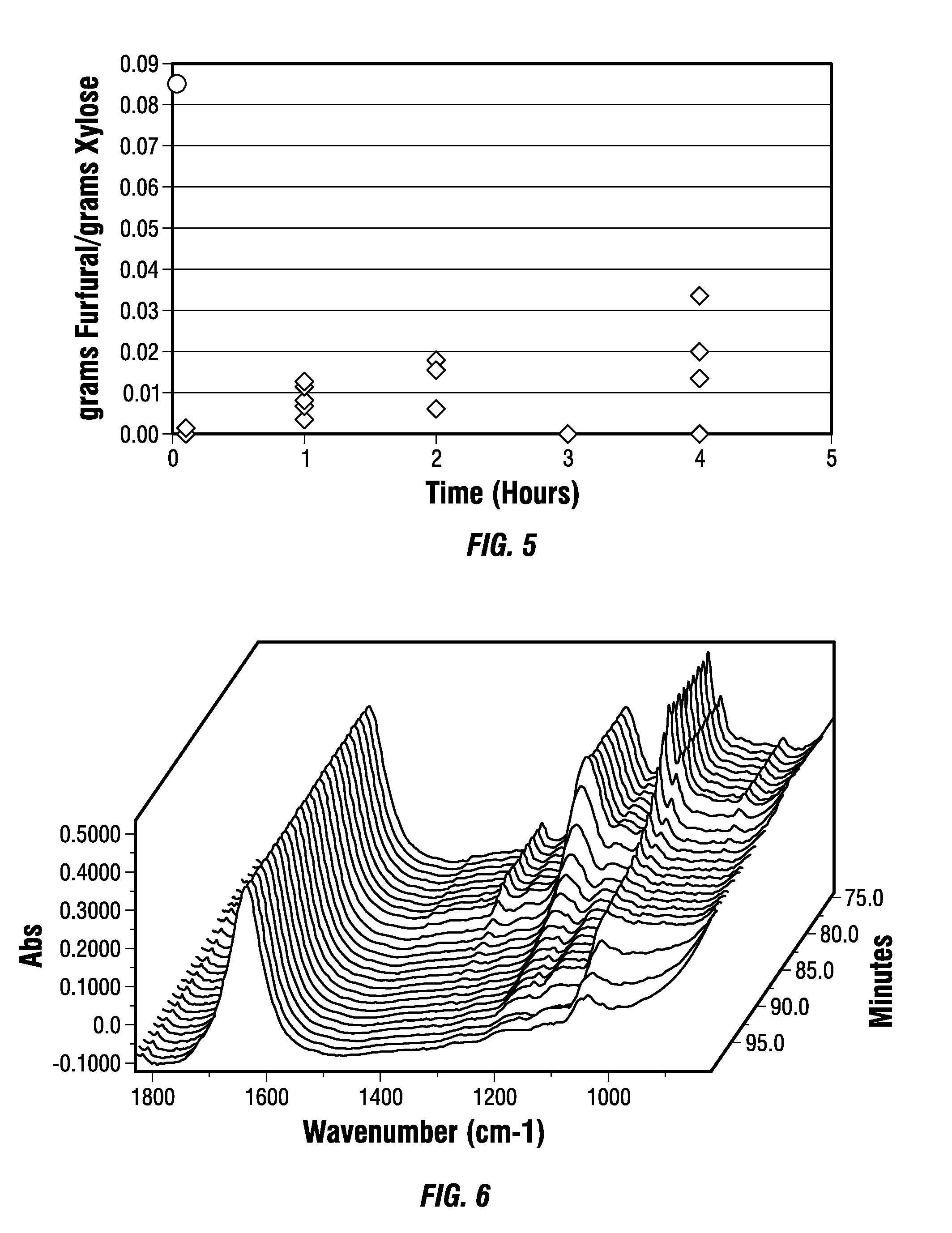
Biorefinery Process for Extraction, Separation, and Recovery of Fermentable Saccharides, other Useful Compounds, and Yield of Improved Lignocellulosic Material from Plant Biomass
ActiveUS20110129886A1Increase diversityIncrease probabilityCellulosic pulp after-treatmentBiofuelsFurfuralAqueous extract
Non-food plant biomass is subjected to hot-water extraction in a pressurized vessel at an elevated temperature up to about 250° C. and at a pH below about 7.0, to yield an aqueous extract containing hemicellulosic components, other wood-derived compounds, and a lignocellulosic residue. The separated aqueous extract or liquor is purified and concentrated through a multi-step process producing fermentable sugars. At each stage, inhibitory chemicals such as acetic acid, lignin, and furfural are separated and eventually recovered as commercial chemicals. The lignocellulosic residue may be further processed, as a material with enhanced resistance to sorption of water, for manufacture of improved pulp and paper, construction materials, pellet fuel, and / or other useful products.
Owner:APPLIED BIOREFINERY SCI
Treating biomass to produce materials useful for biofuels
Fermentable sugar useful for the production of biofuels can be produced from biomass by contacting the biomass with a solution containing at least one α-hydroxysulfonic acid. The α-hydroxysulfonic acid can be easily removed from the product and recycled.
Owner:SHELL USA INC
Biomass hydrolysis
ActiveUS20110065159A1Facilitate enhanced yield of glucoseImprove glucose yieldSugar derivativesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCelluloseHydrolysate
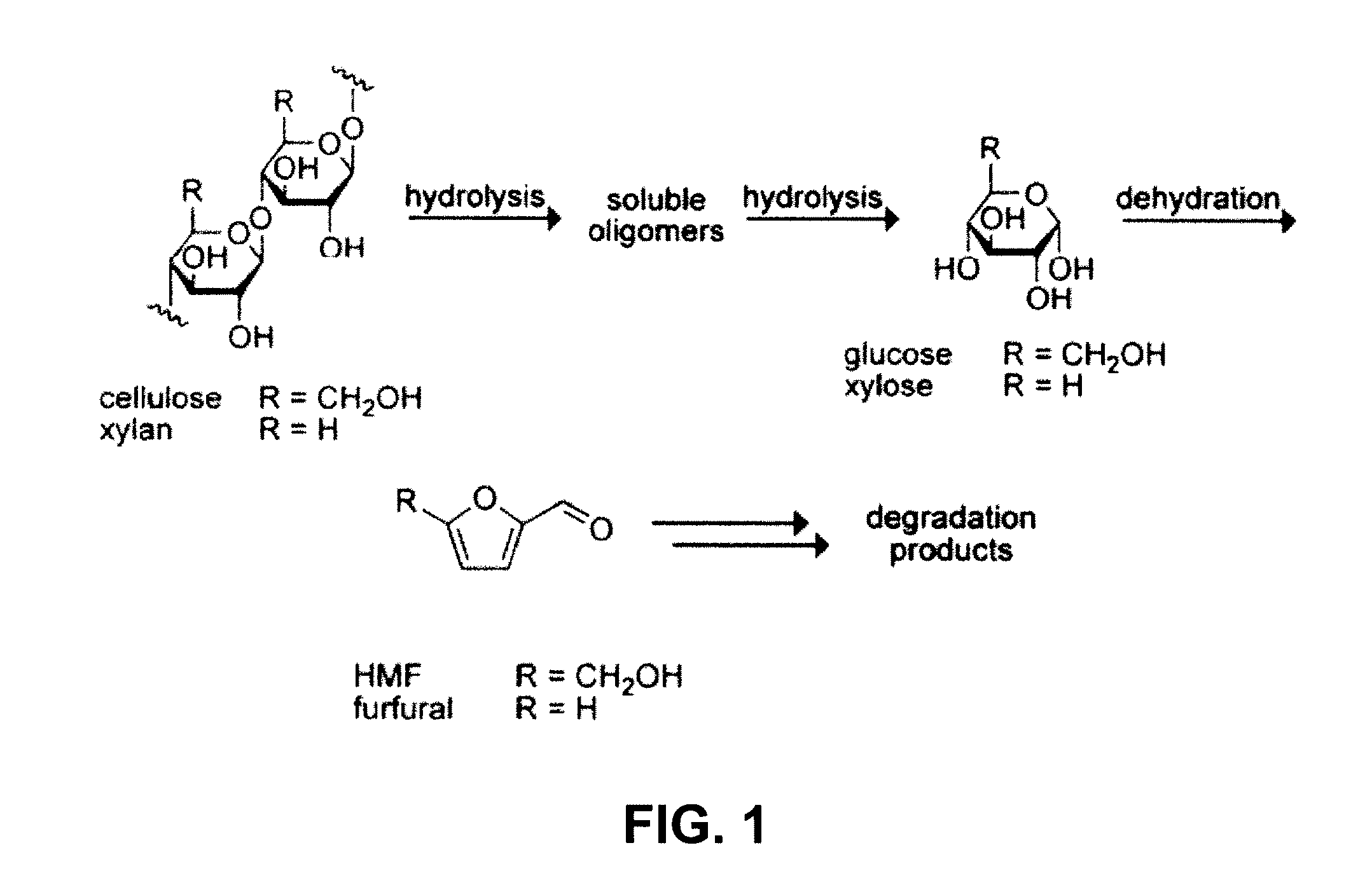
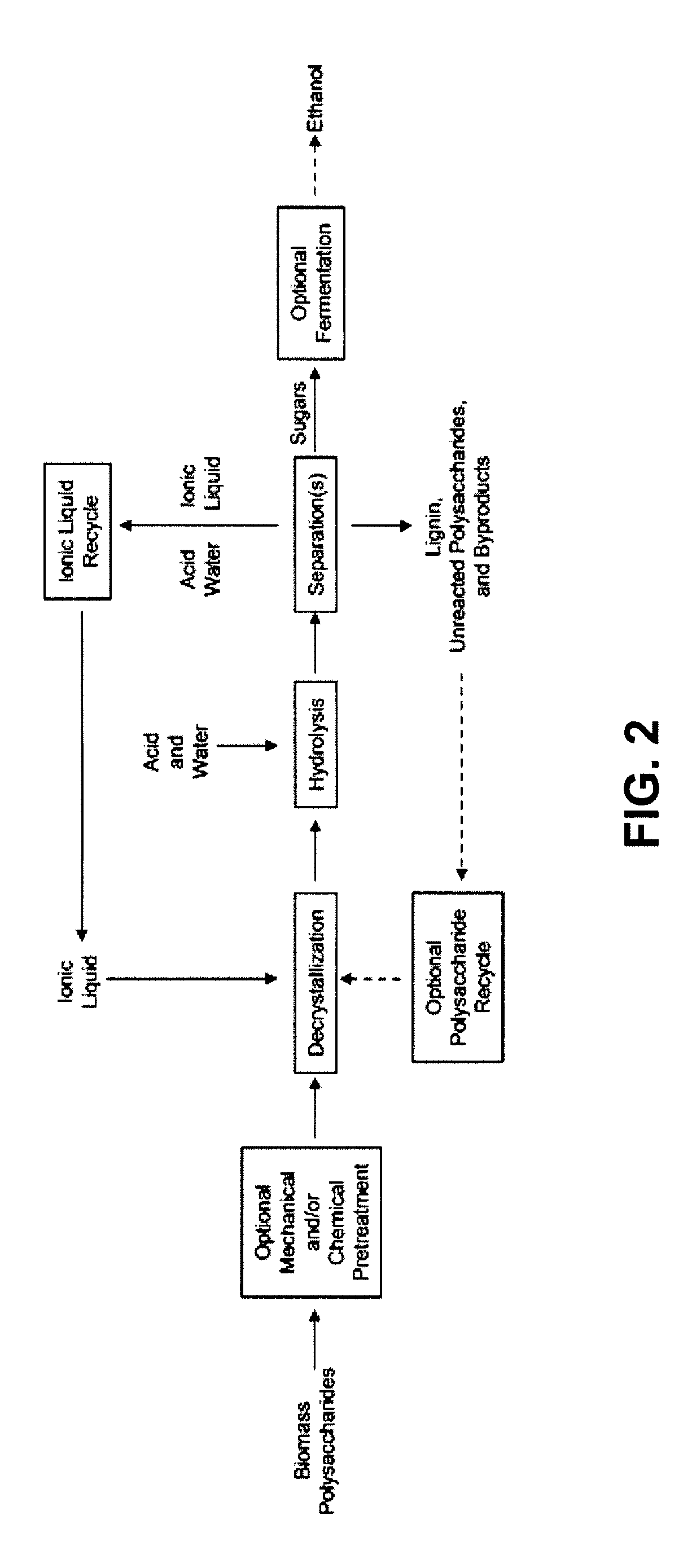
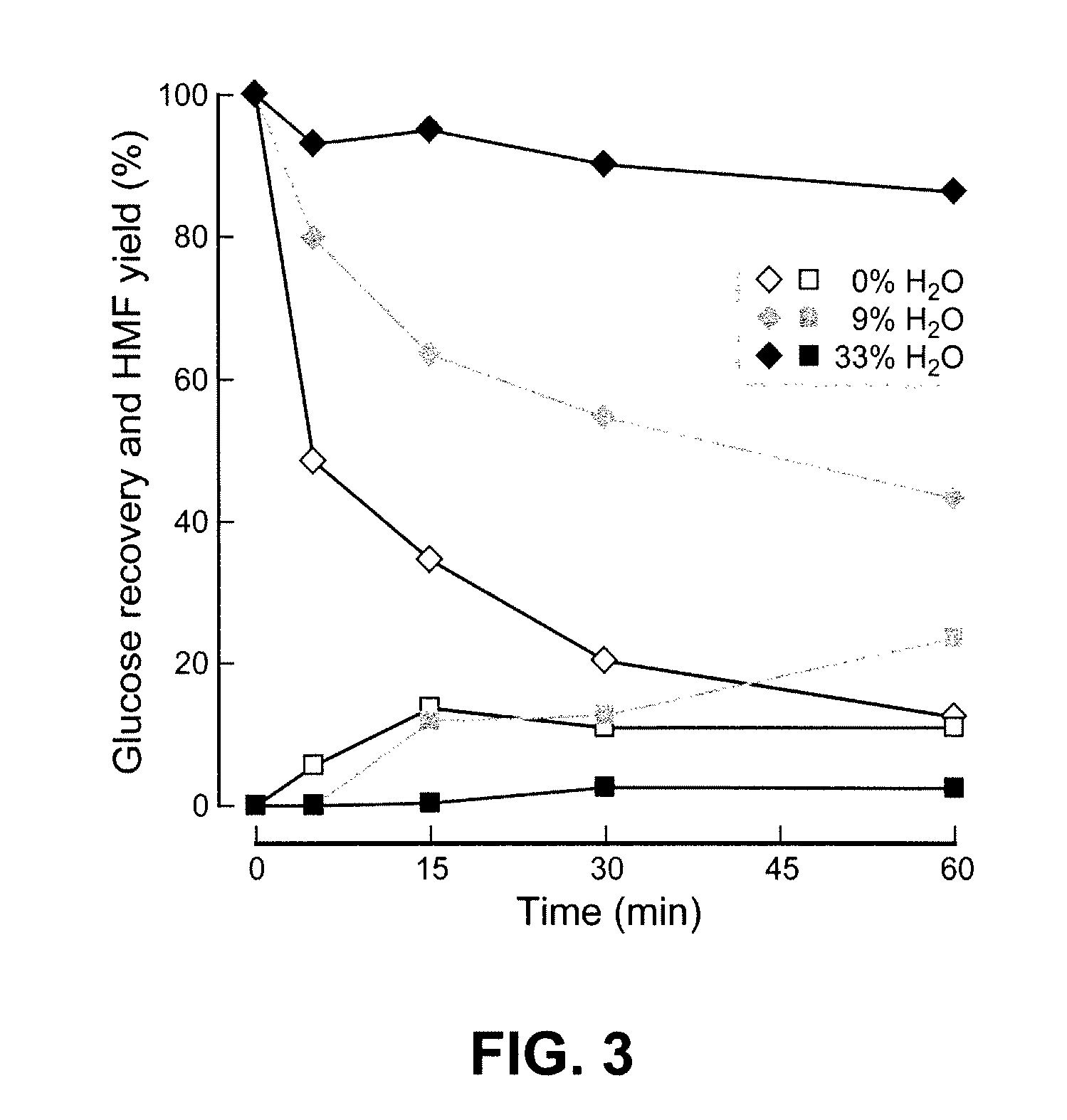
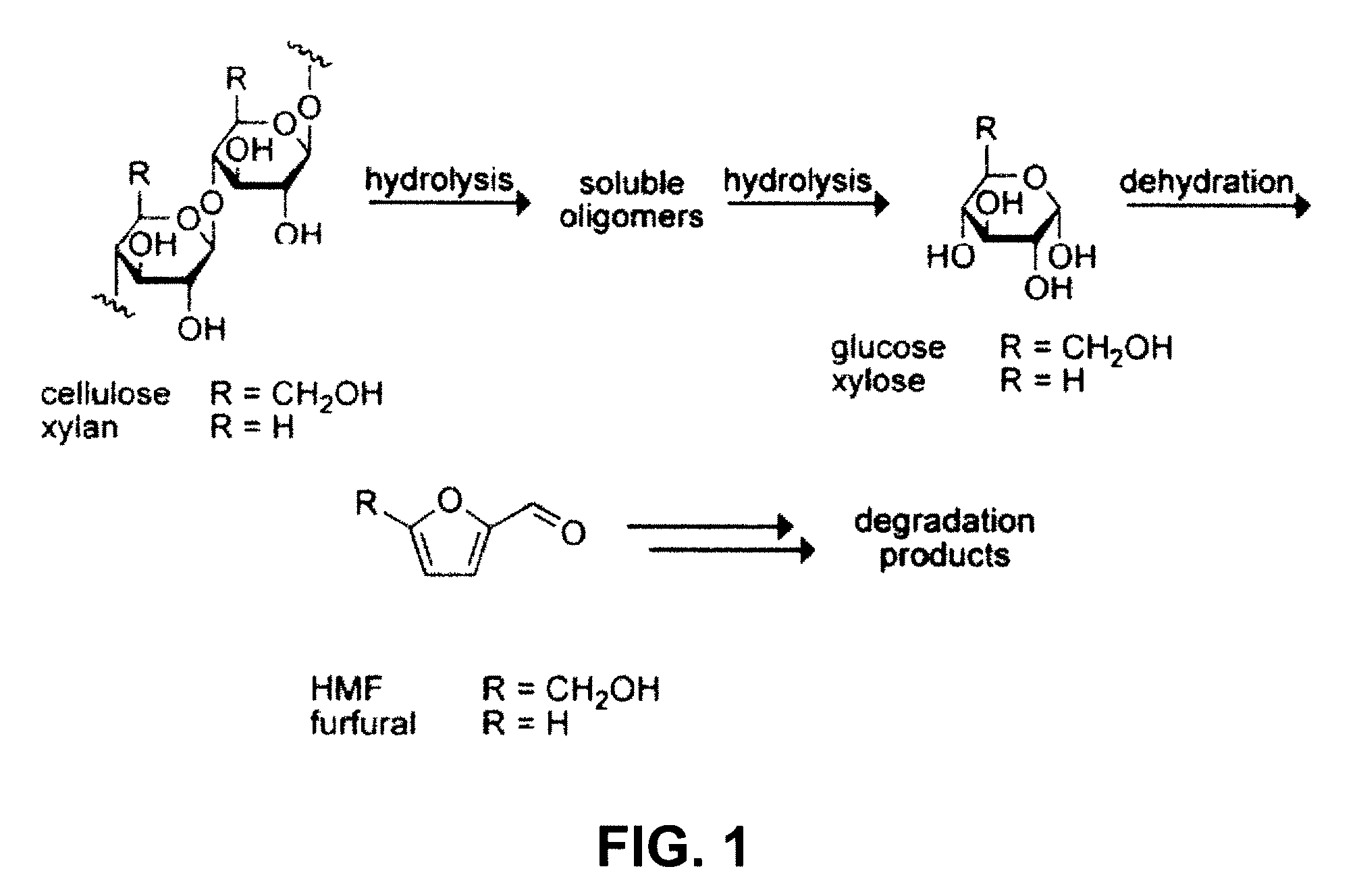
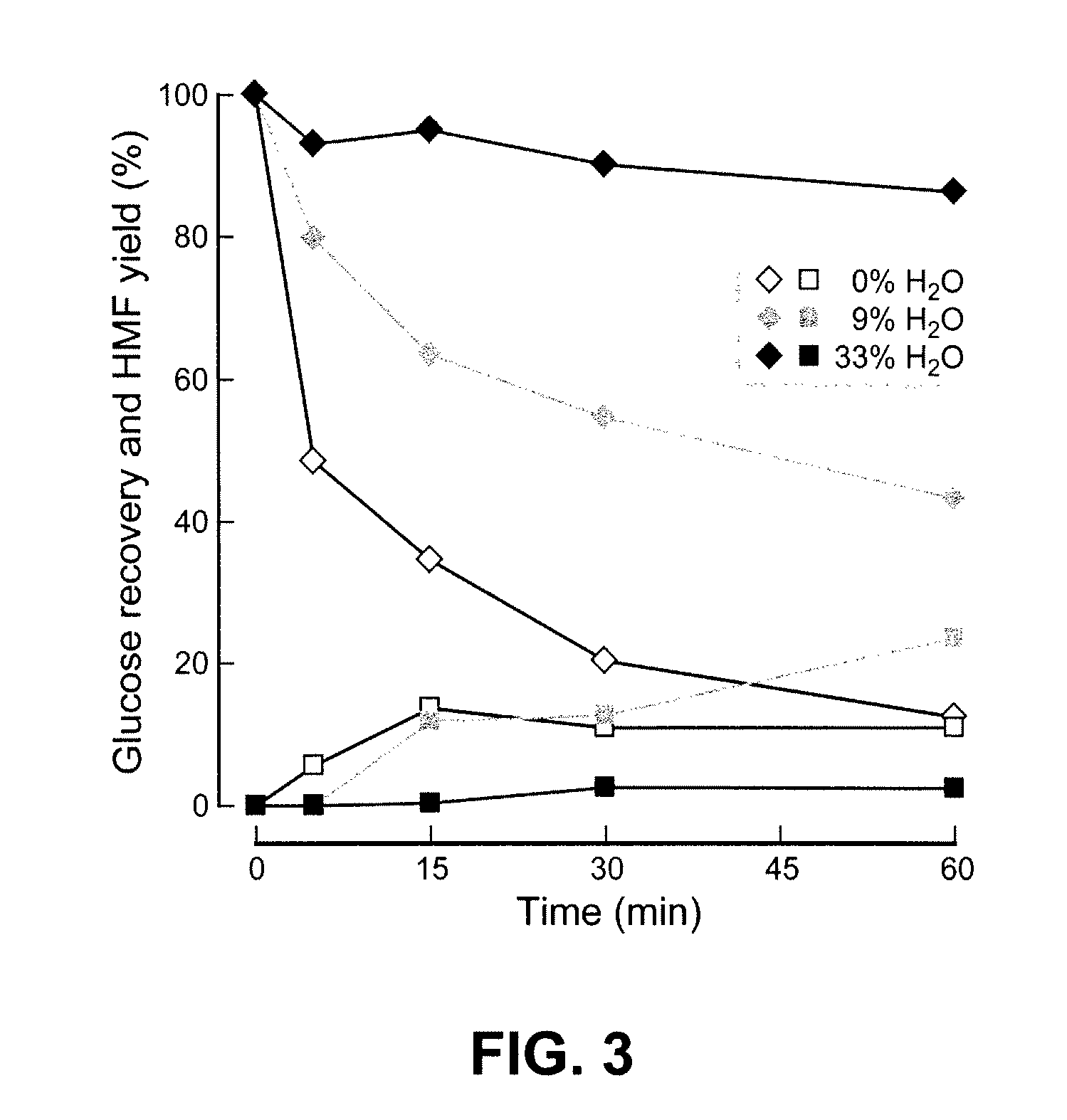
High-yielding method for chemical hydrolysis of lignocellulose into monosaccharides. The process of the invention can additionally be applied to cellulose, xylan and related biomass polysaccharides, such as galactan, mannan, or arabinan. The method is employed for hydrolysis of a biomass polysaccharide substrate. The process is carried out in an ionic liquid in which cellulose is soluble in the presence of catalytic acid at a temperature sufficiently high to initiate hydrolysis. Water is added to the reaction mixture after initiation of hydrolysis at a rate controlled to avoid precipitation yet avoid undesired sugar dehydration products such ad HMF. Hydrolysis product is useful as feedstock for fermentations including fermentation processes for ethanol, butanol and other fuels.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for producing ethanol and co-products from cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20110262984A1Increased ethanol productionImproved co-productsPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsBiofuelsCelluloseCo product
The present invention generally relates to processes for production of ethanol from cellulosic biomass. The present invention also relates to production of various co-products of preparation of ethanol from cellulosic biomass. The present invention further relates to improvements in one or more aspects of preparation of ethanol from cellulosic biomass including, for example, improved methods for cleaning biomass feedstocks, improved acid impregnation, and improved steam treatment, or “steam explosion.”
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGY NEW TECH
Process of producing xylose and dissolving pulp
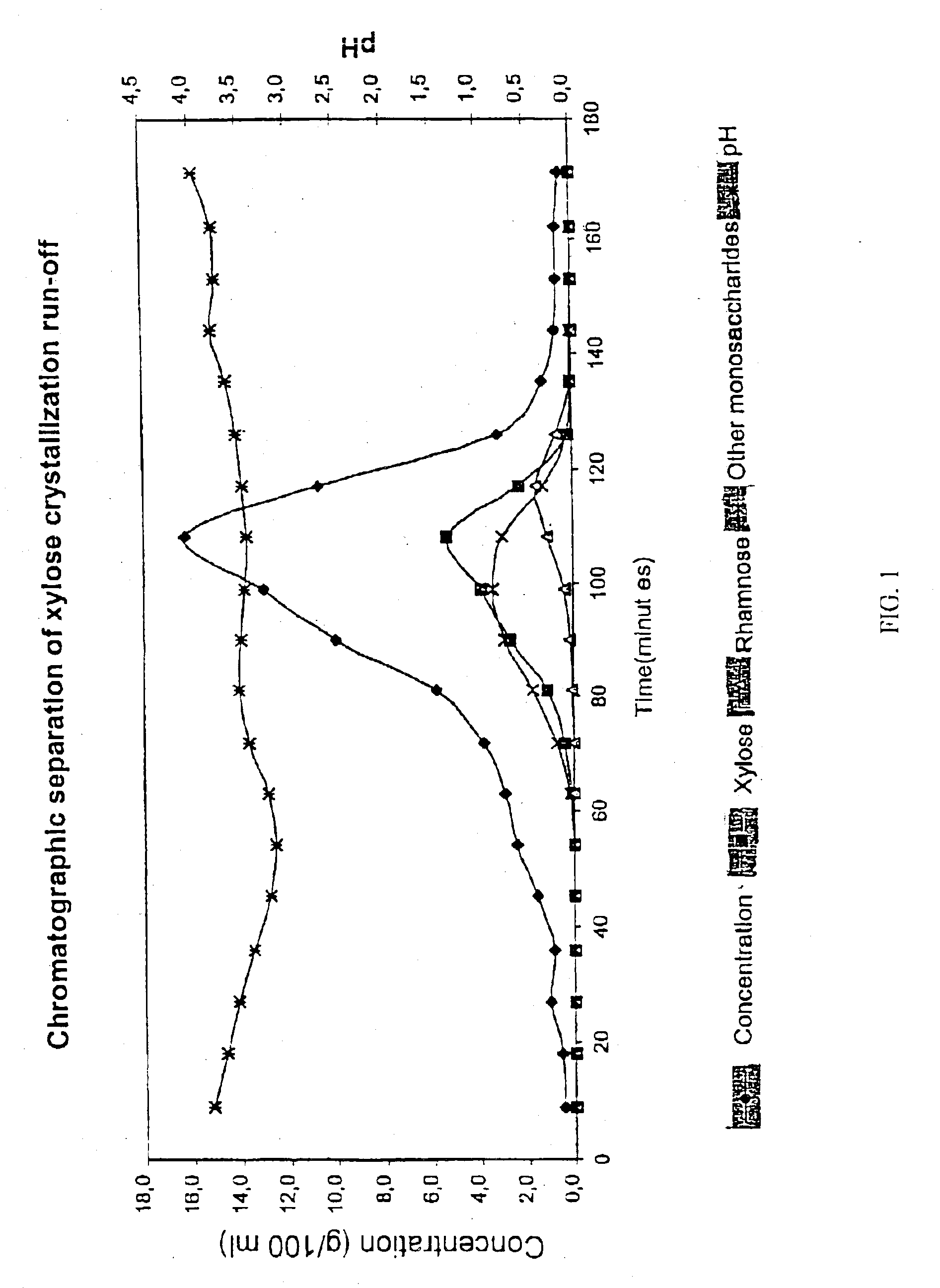
ActiveUS20110192560A1High yieldReduce the amount requiredPretreatment with water/steamWashing/displacing pulp-treating liquorsChromatographic separationXylan
The present invention relates to a process for the production of xylose and dissolving pulp from xylan-containing biomass, such as hardwood. The invention is based on prehydrolysis of the xylan-containing biomass with SO2 in specified conditions, followed by chromatographic fractionation, nanofiltration or precipitation crystallization of the xylose-containing prehydrolyzate to obtain a xylose product having a xylose content of at least 55% on DS. The dissolving pulp obtained from the process can be used for example for the production of viscose.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
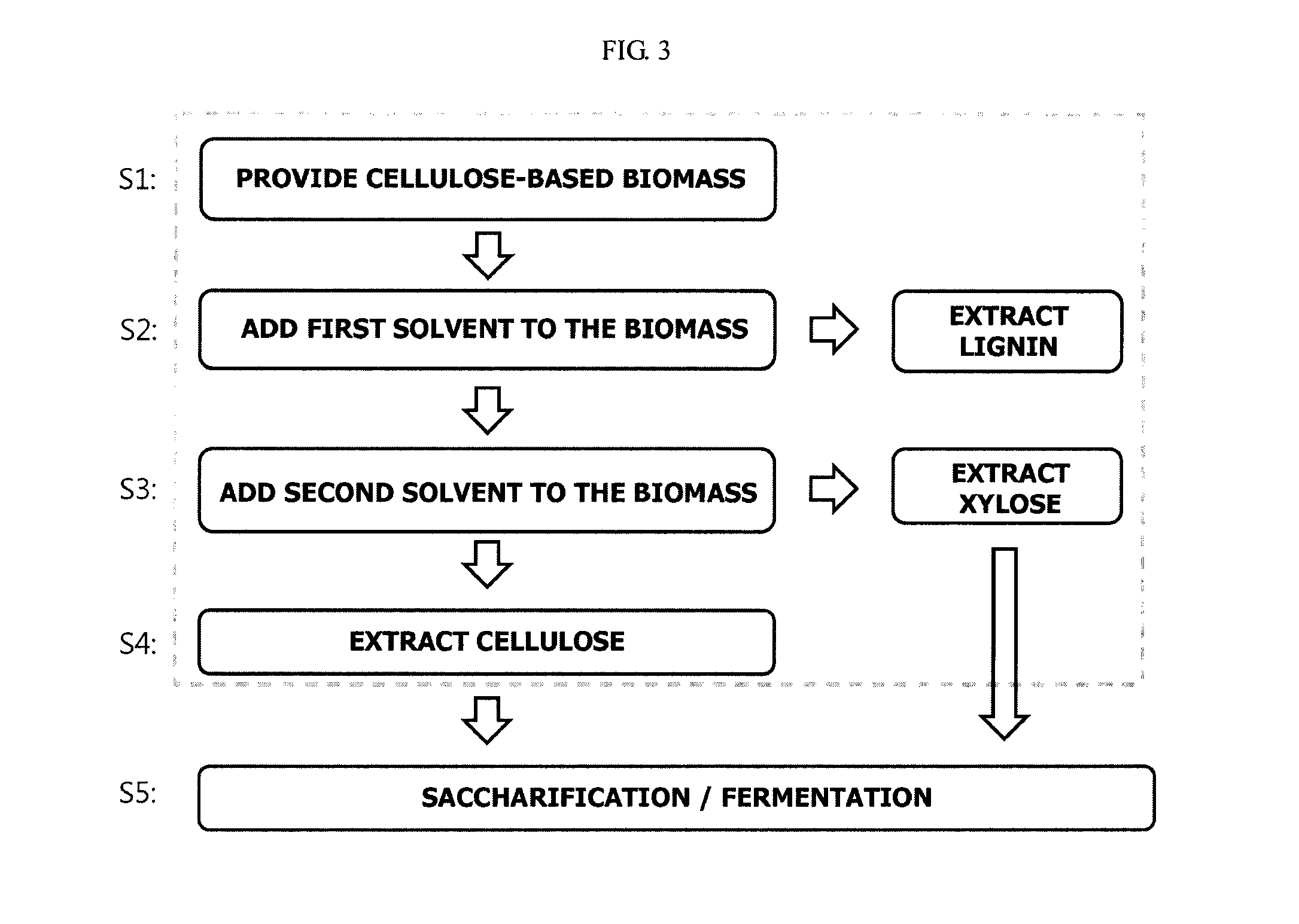
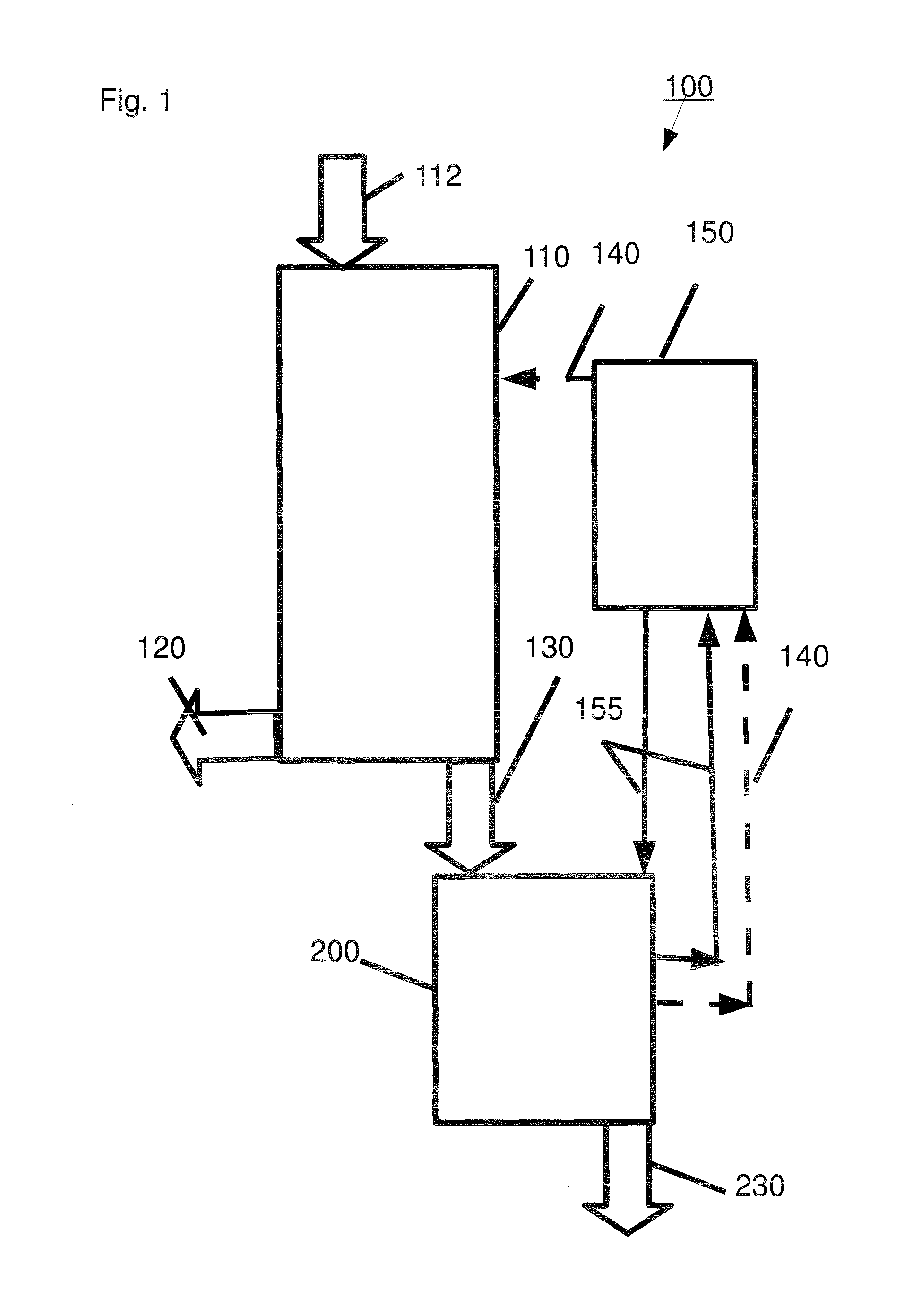
Method and apparatus for fractionating lignocellulose-based biomass
ActiveUS20100203605A1Improve processing efficiencyEnhanced interactionPressurized chemical processBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseLignin degradation
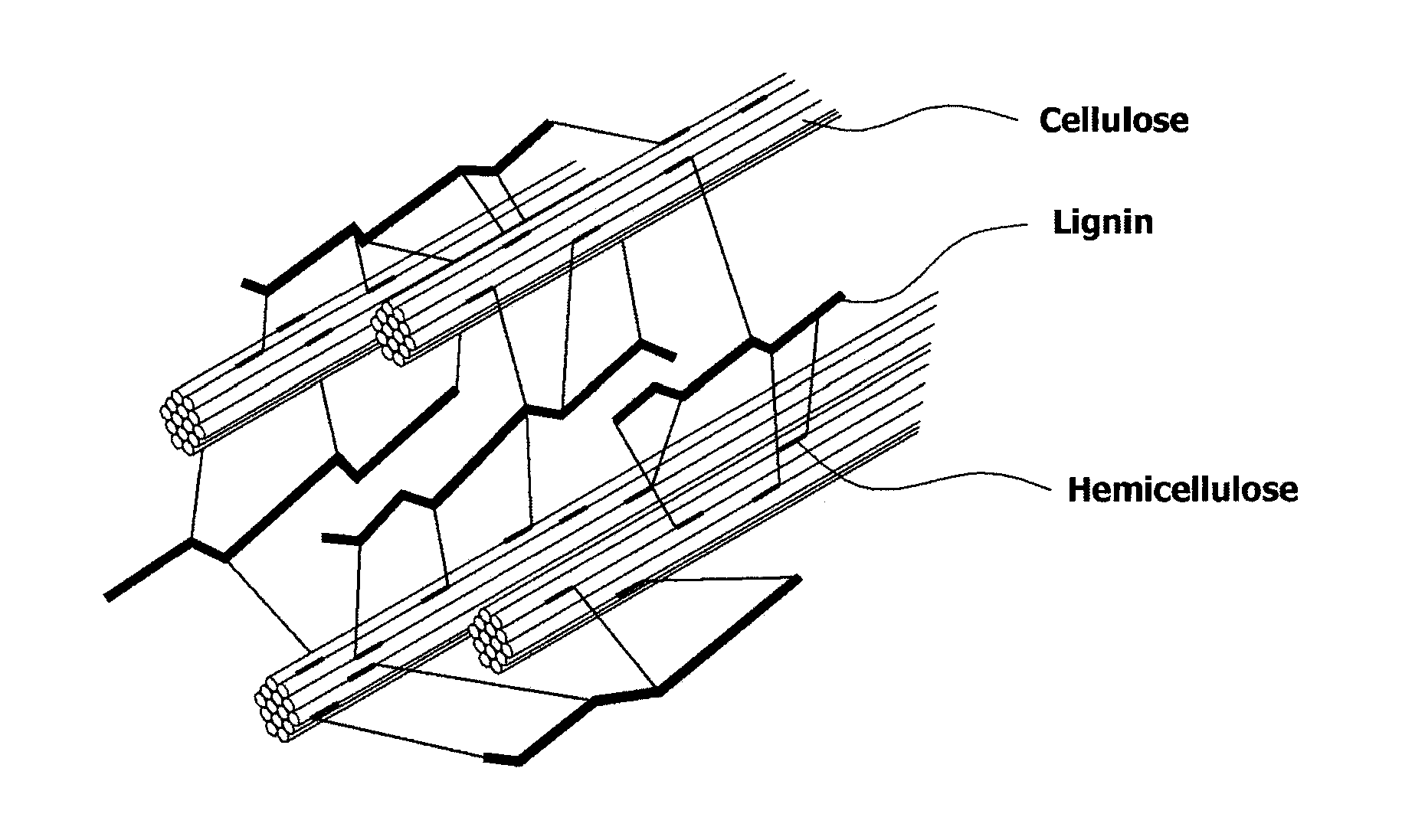
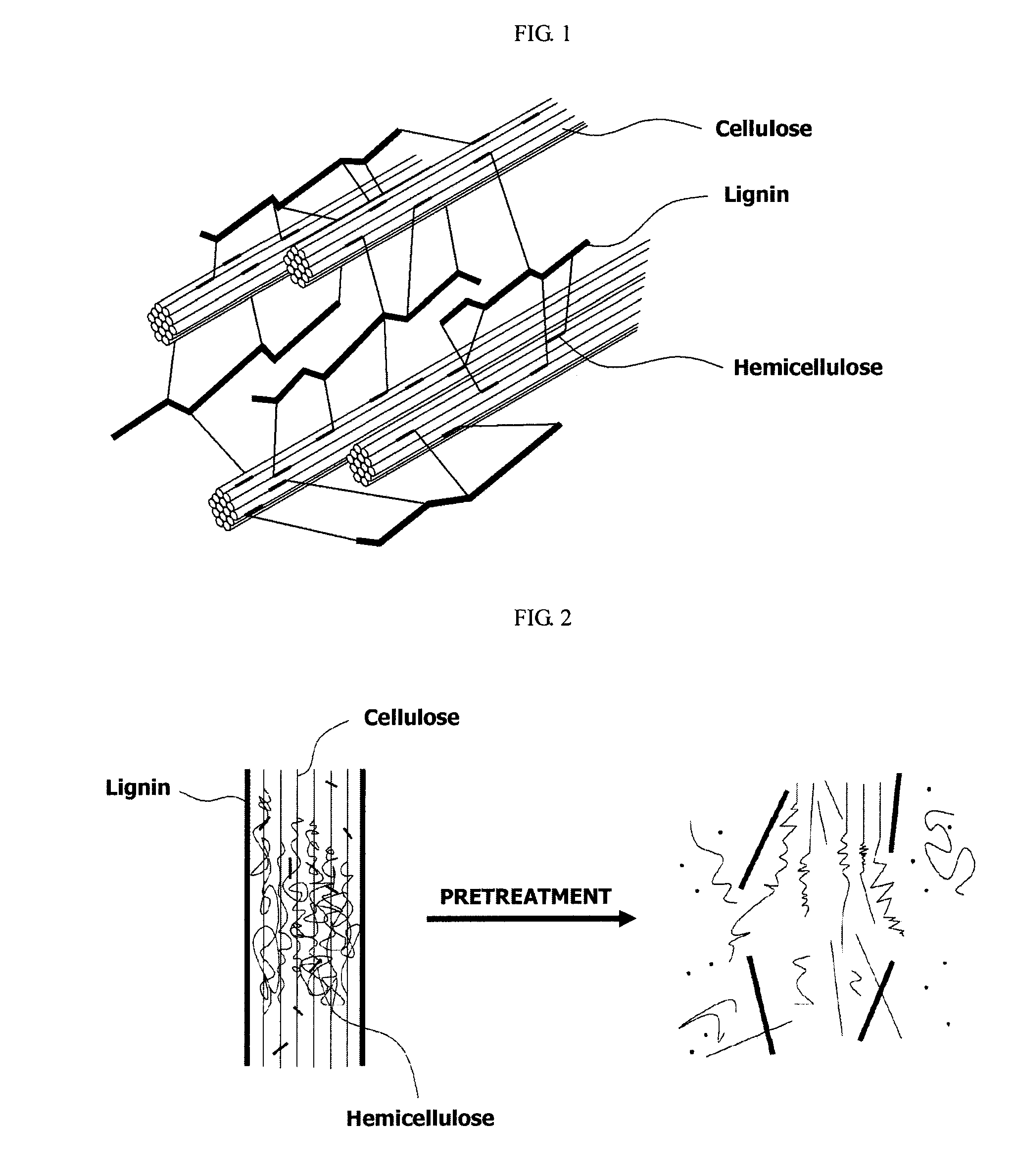
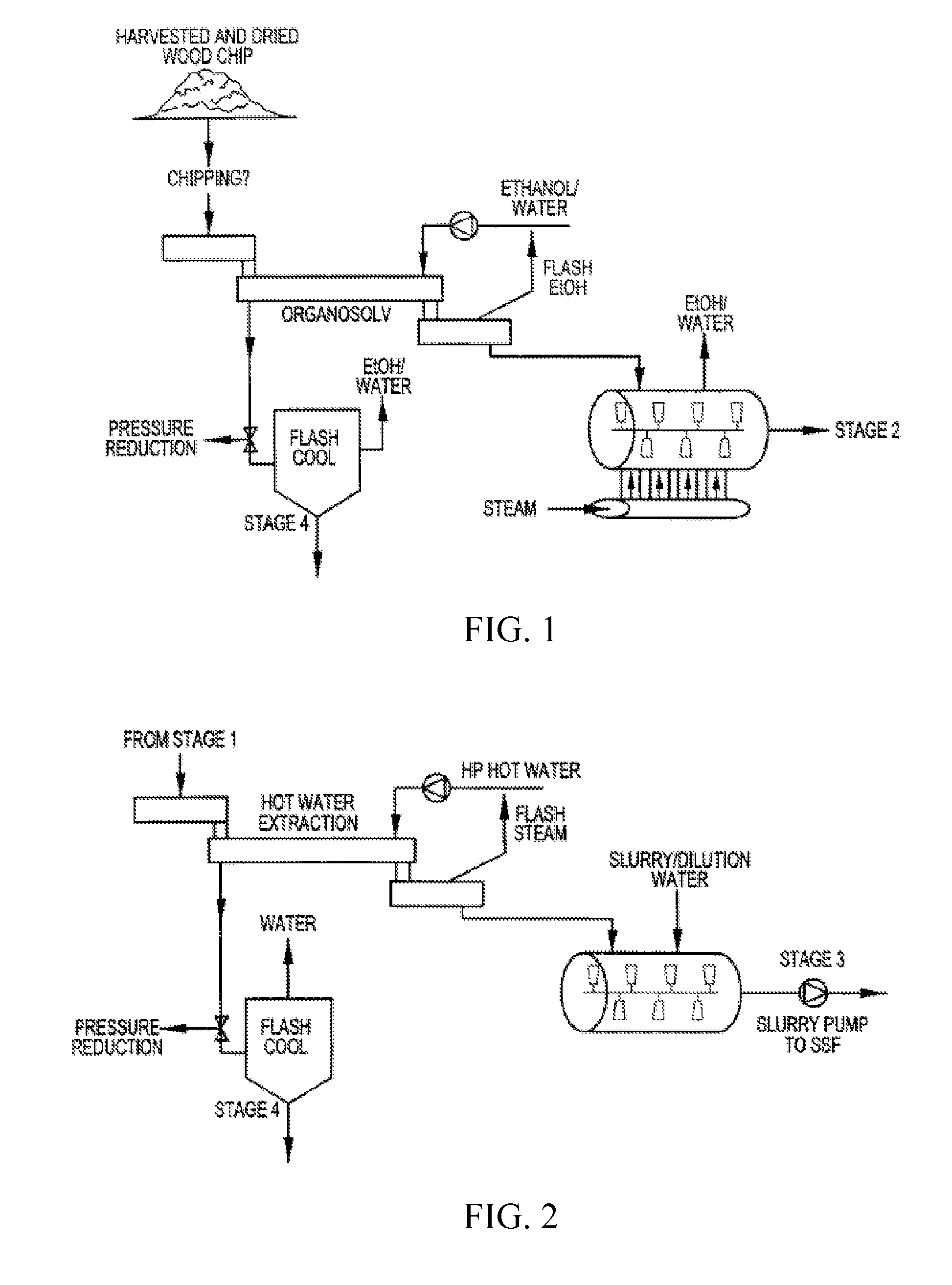
A method and apparatus for fractionating a lignocellulose-based biomass are provided. The method includes providing a lignocellulose-based biomass, extracting lignin from the biomass by adding a first solvent capable of dissolving the lignin, extracting xylose by adding a second solvent capable of dissolving hemicellulose to the biomass treated with the first solvent, and extracting the cellulose remaining in the biomass. In this method, a continuous process can be performed instead of a low efficiency batch-type process and components of the biomass can be obtained at high yield.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Biomass hydrolysis
ActiveUS8722878B2Reduce formationHigh yieldSugar derivativesOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCelluloseXylan
High-yielding method for chemical hydrolysis of lignocellulose into monosaccharides. The process of the invention can additionally be applied to cellulose, xylan and related biomass polysaccharides, such as galactan, mannan, or arabinan. The method is employed for hydrolysis of a biomass polysaccharide substrate. The process is carried out in an ionic liquid in which cellulose is soluble in the presence of catalytic acid at a temperature sufficiently high to initiate hydrolysis. Water is added to the reaction mixture after initiation of hydrolysis at a rate controlled to avoid precipitation yet avoid undesired sugar dehydration products such ad HMF. Hydrolysis product is useful as feedstock for fermentations including fermentation processes for ethanol, butanol and other fuels.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for separating xylose from lignocelluloses rich in xylan, in particular wood
InactiveUS20050065336A1Many solutionsHigh cellulose yieldSugar derivativesXylose productionXylanPre treatment
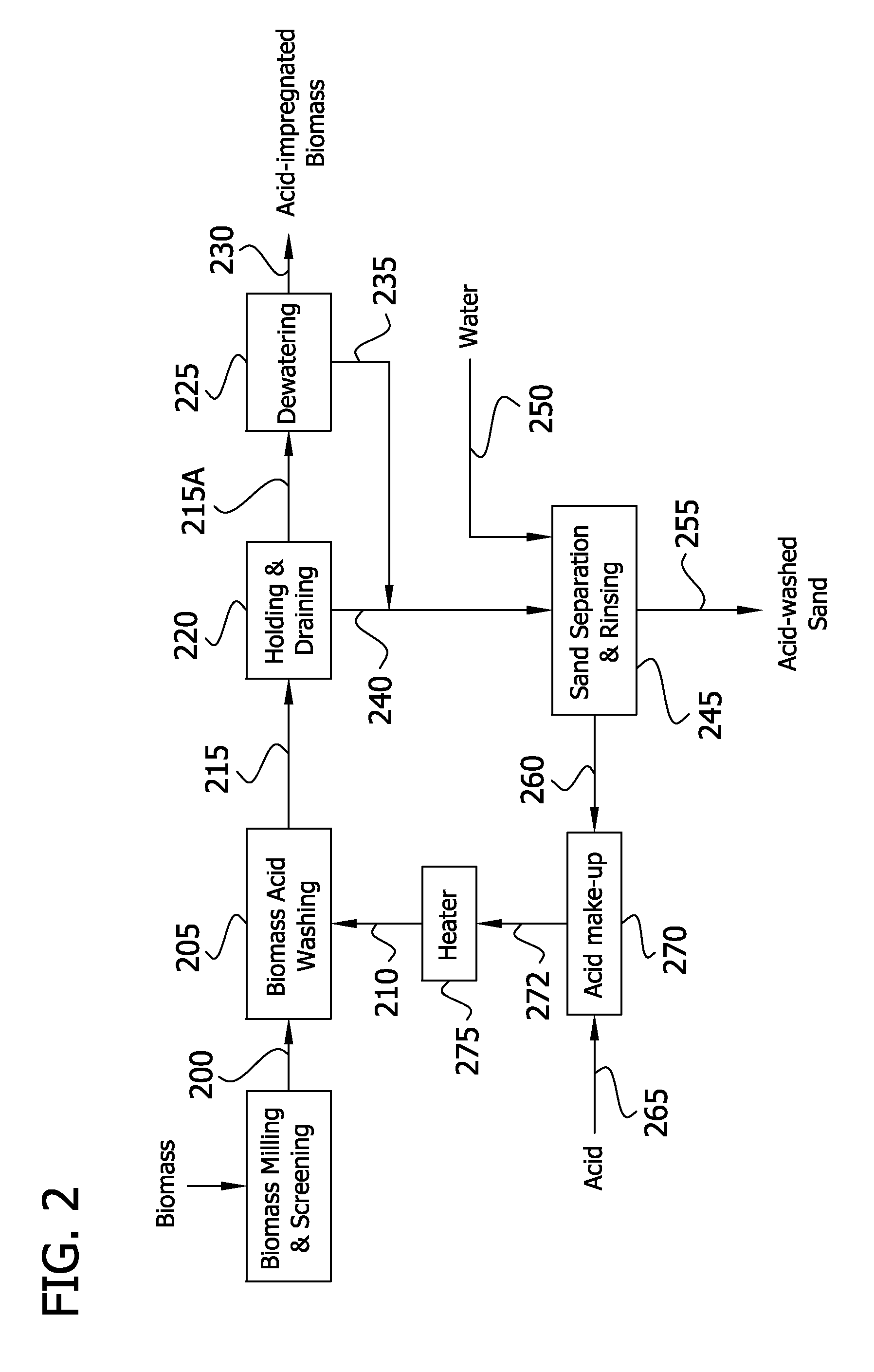
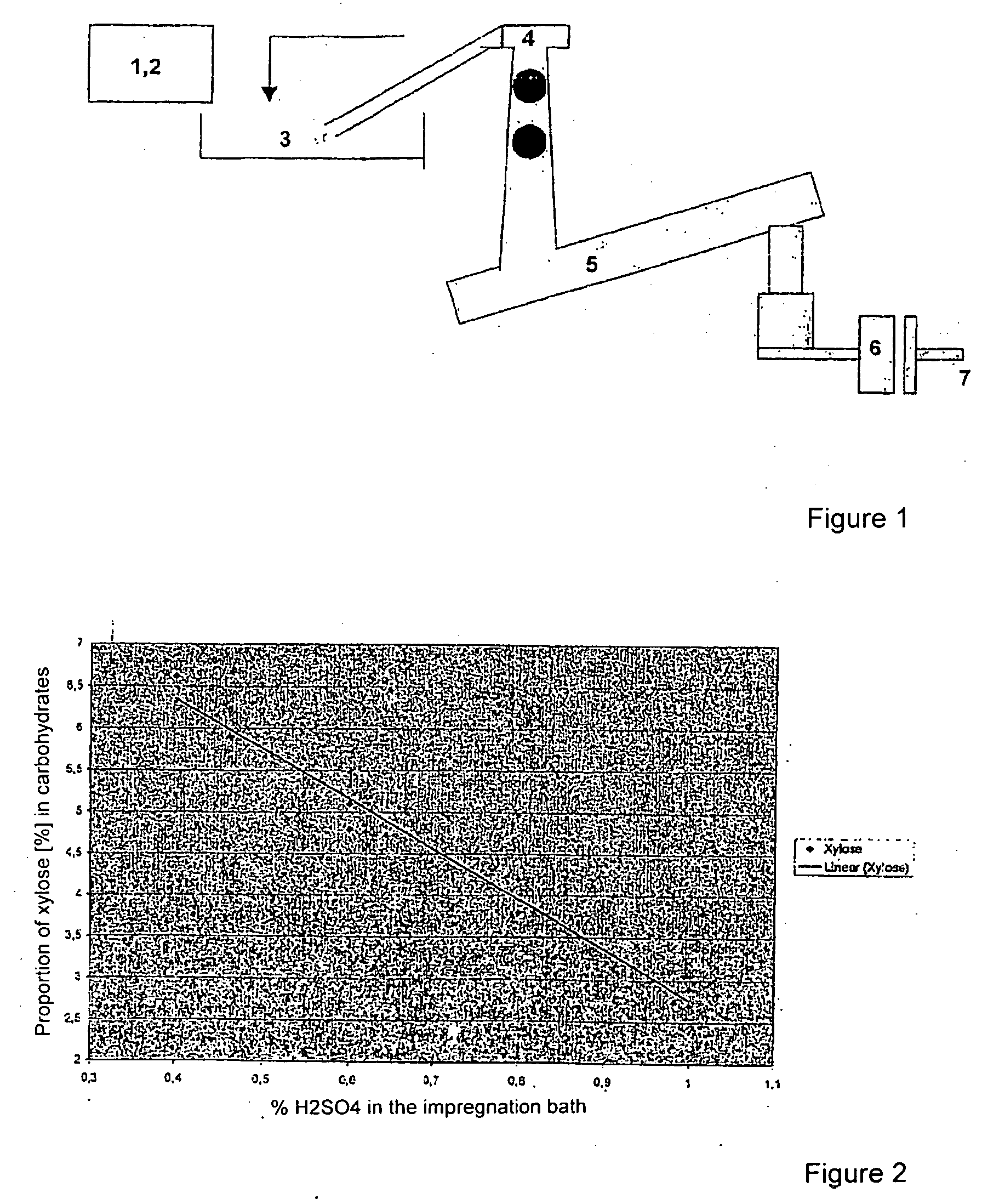
The invention is directed to a method for separating xylose from lignocelluloses rich in xylan, particularly wood, and for obtaining pulp, characterized by the following steps: (1) pretreating wood chips through mechanical destruction of the original structure; (2) impregnating the obtained wood mass with diluted mineral acid; (3) carrying out prehydrolysis of the obtained wood mass modified by the process under the influence of steam at an elevated temperature to hydrolyze the obtained hemicelluloses; and (4) removing the hemicelluloses from the residual pulp by washing, filtering and / or centrifuging while obtaining an aqueous solution rich in xylose. The combination of method steps according to the invention makes it possible to achieve high α-cellulose contents with very low proportions of xylose, that is, highly pure chemical pulp qualities, while at the same time enabling a virtually quantitative separation of the valuable xylose.
Owner:RHODIA ACETOW AG
Method for recovering products
InactiveUS6987183B2Ion-exchanger regenerationSugar crystallisationChromatographic separationArabinose
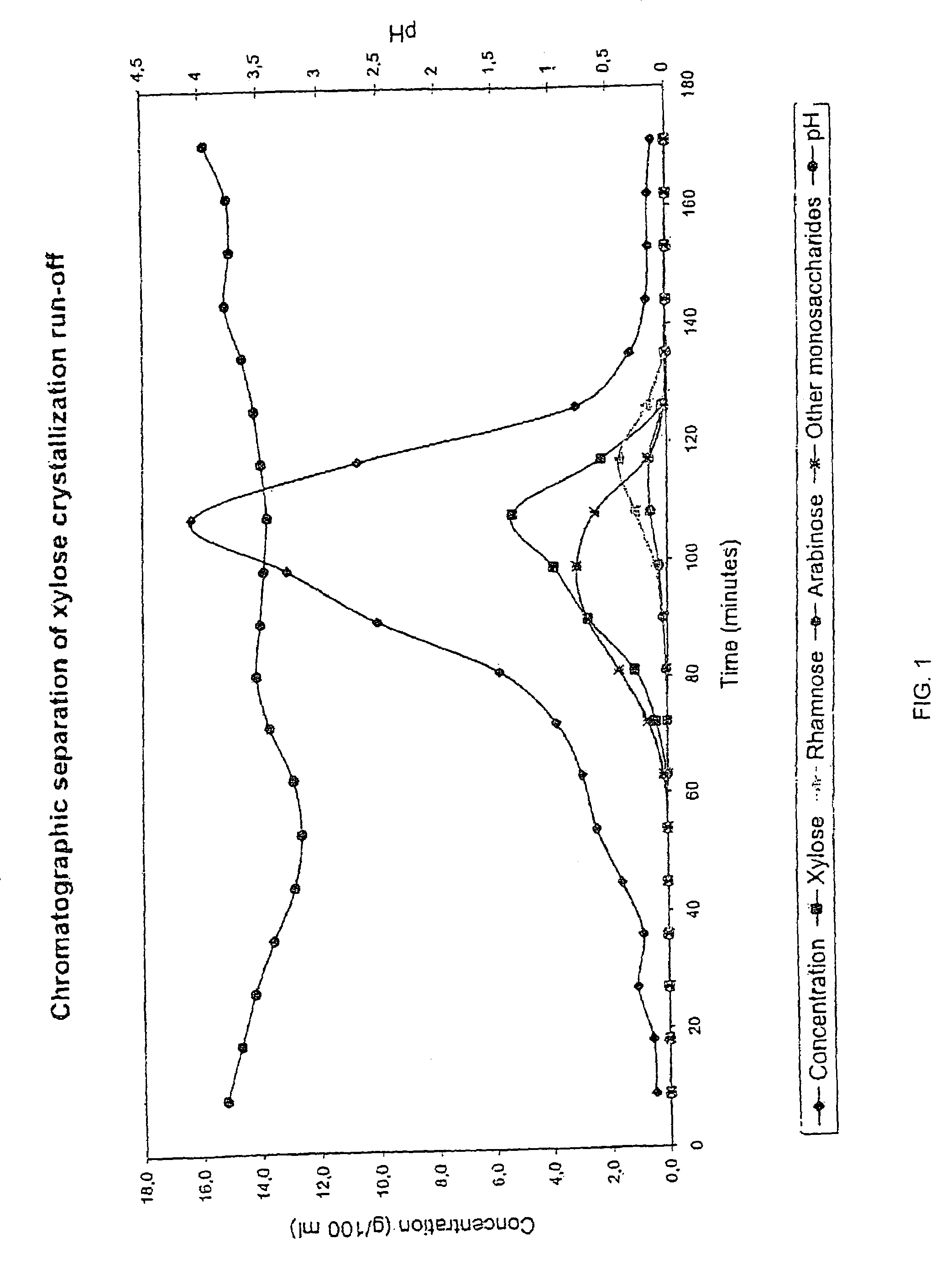
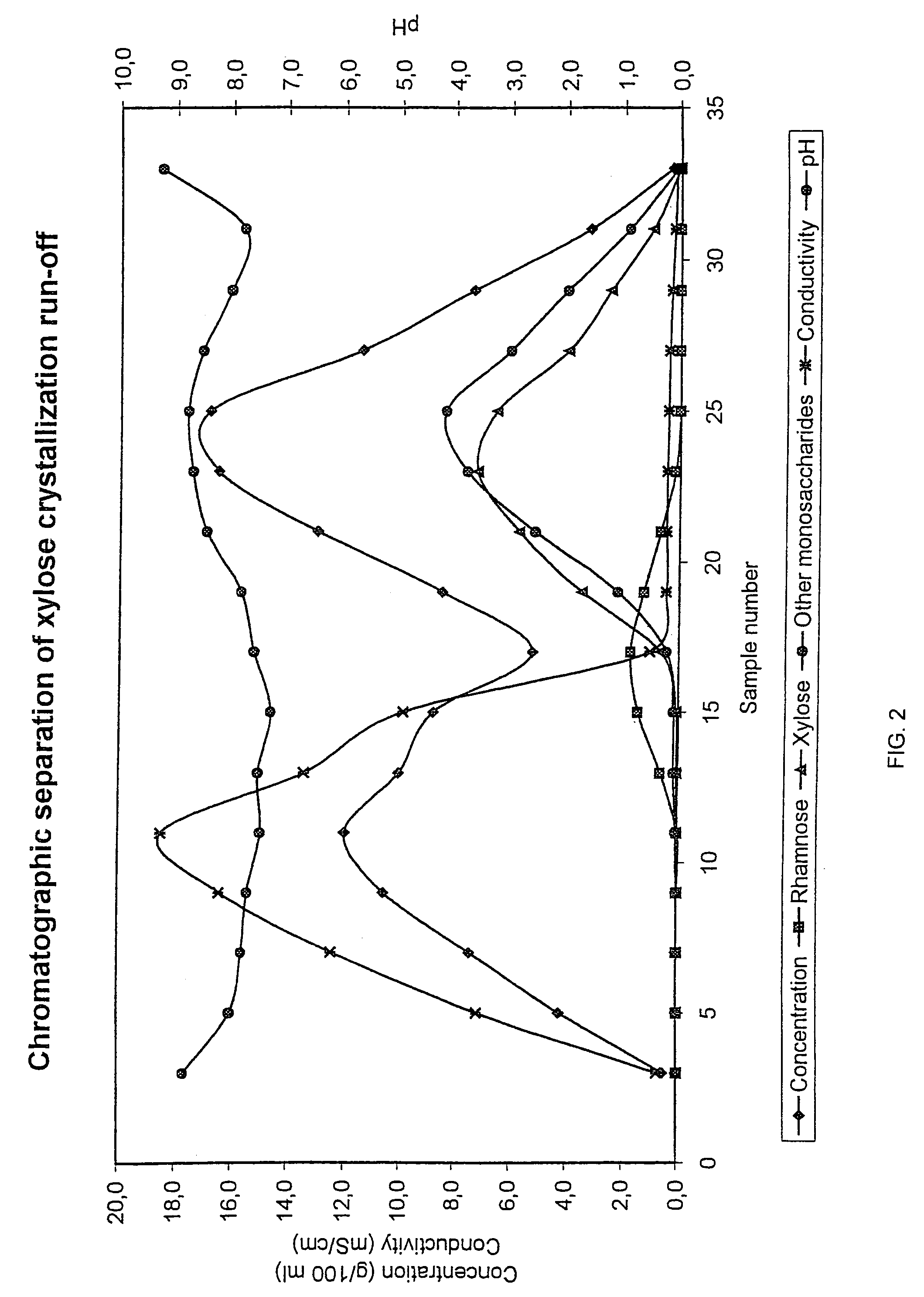
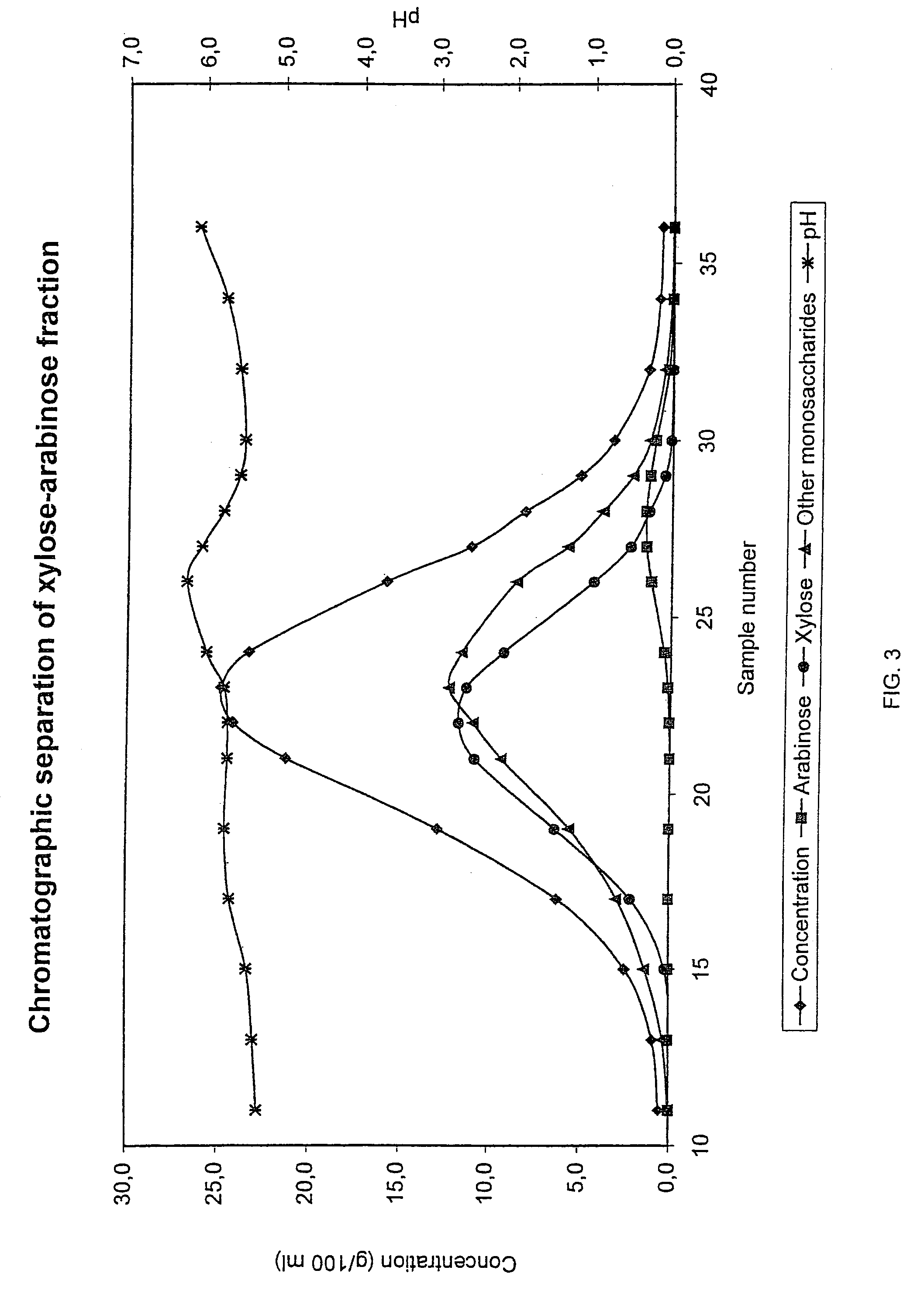
The present invention is directed to a method comprising a multistep process for recovering one or more monosaccharides from a solution containing at least two monosaccharides selected from the group consisting of rhamnose, arabinose, xylose and mixtures thereof by using chromatographic separation comprising at least one step, where a weak acid cation exchange resin is used for the chromatographic separation.
Owner:DANISCO SWEETENERS
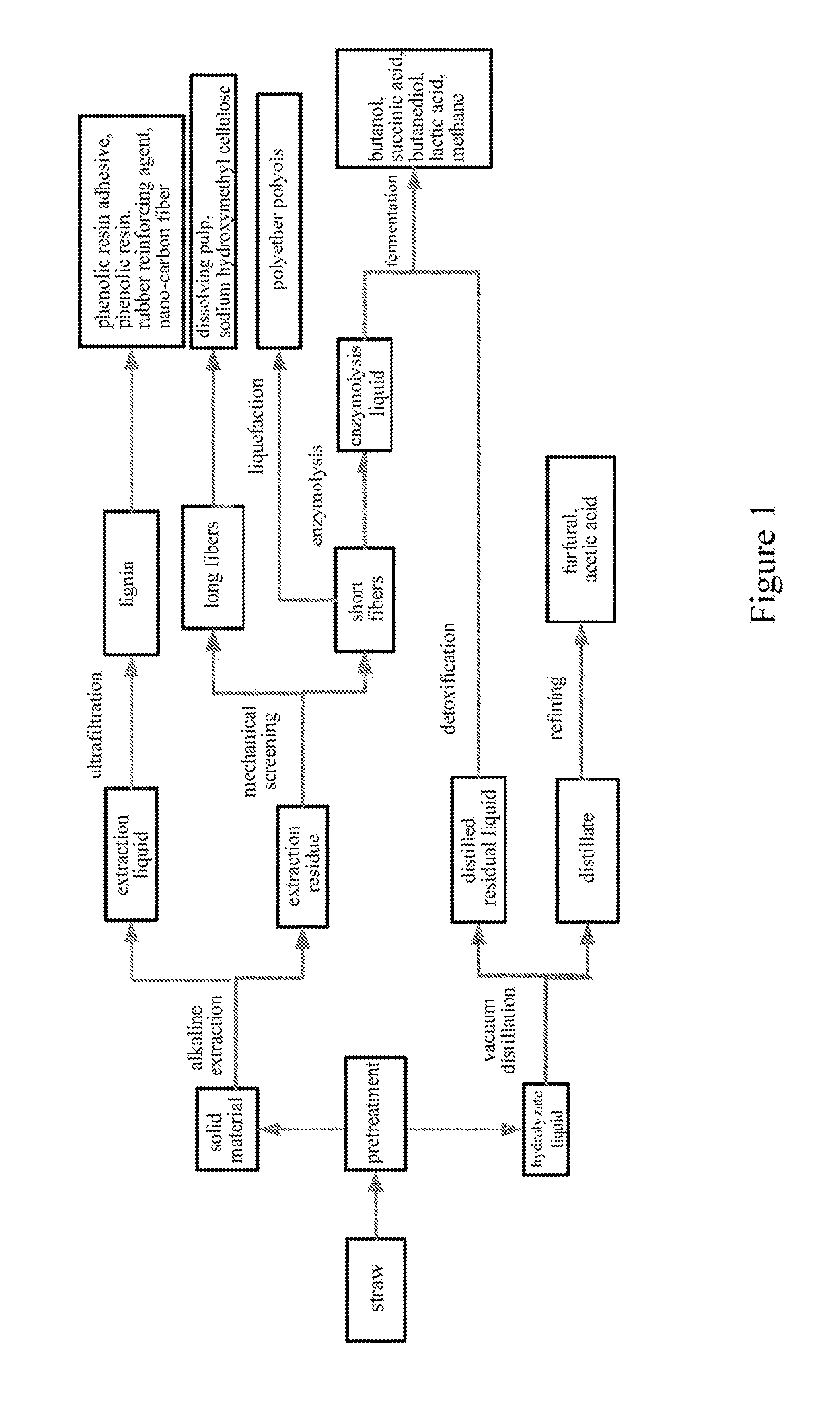
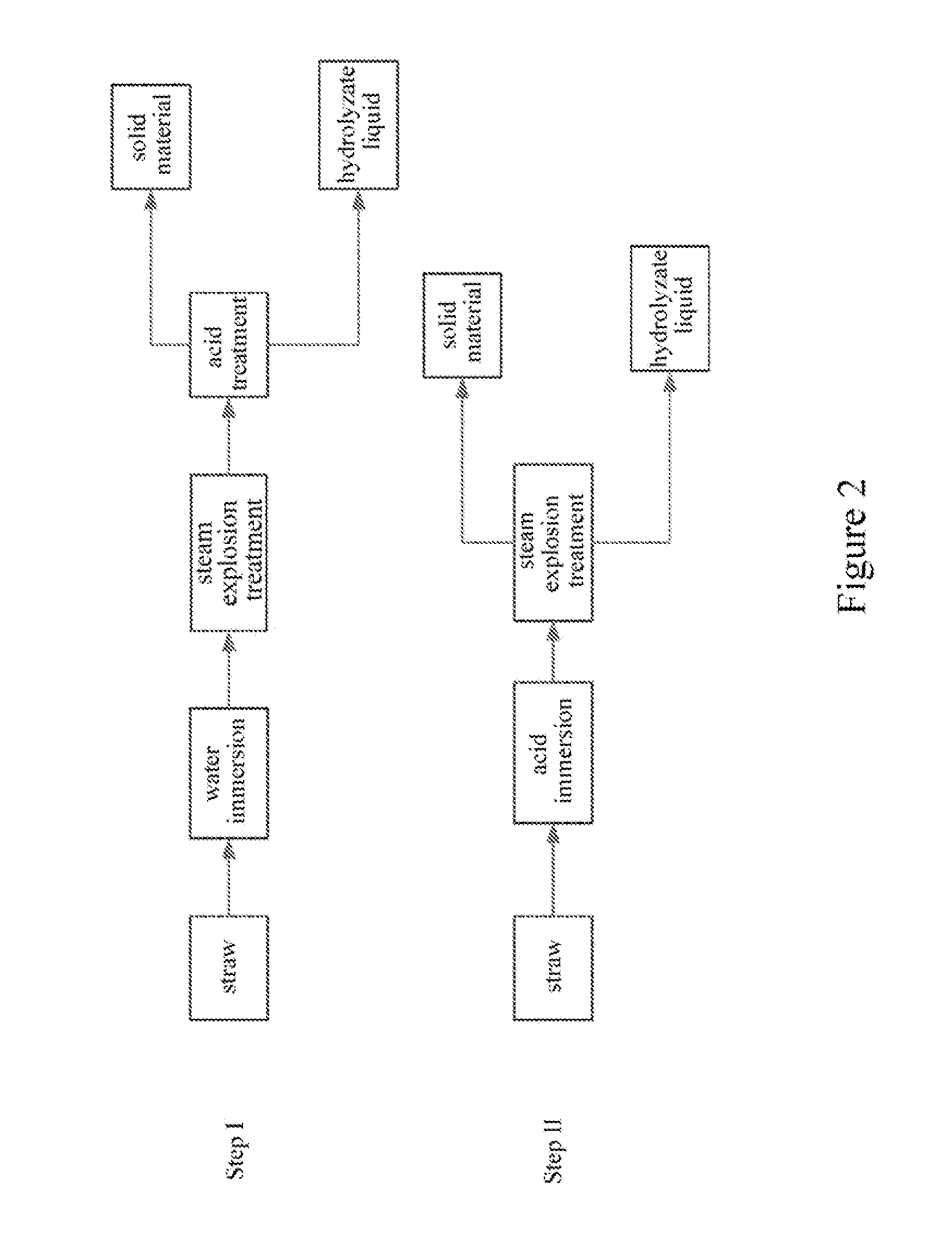
Process for producing bio-based product from straw hemicellulose and fully utilizing the components thereof
ActiveUS20130252293A1Low costHigh value utilizationPretreatment with water/steamBacteriaHigh concentrationSuccinic acid
Provided is a process for producing biomass-based product from straw hemicellulose and utilizing the components thereof thoroughly. Steam-explosion and acid-hydrolysis are combined in the pre-treatment of straw in the process, thus a higher concentration of a sugar liquid can be obtained, and furfural and acetic acid can be recovered. The hemicellulose obtained by the pre-treatment can be used directly as ferment materials for producing butanol, succinic acid, butylene glycol, lactic acid, hydrogen and firedamp, which reduces the cost of these biomass-based products. The cellulose and lignin obtained by extracting the straw with an alkaline solution can produce products, such as sodium hydroxymethyl cellulose etc. In the process, all components in the straw can be utilized thoroughly and waste and pollutant will not be produced.
Owner:HAINAN SUPER HEALTHY GRAIN CO
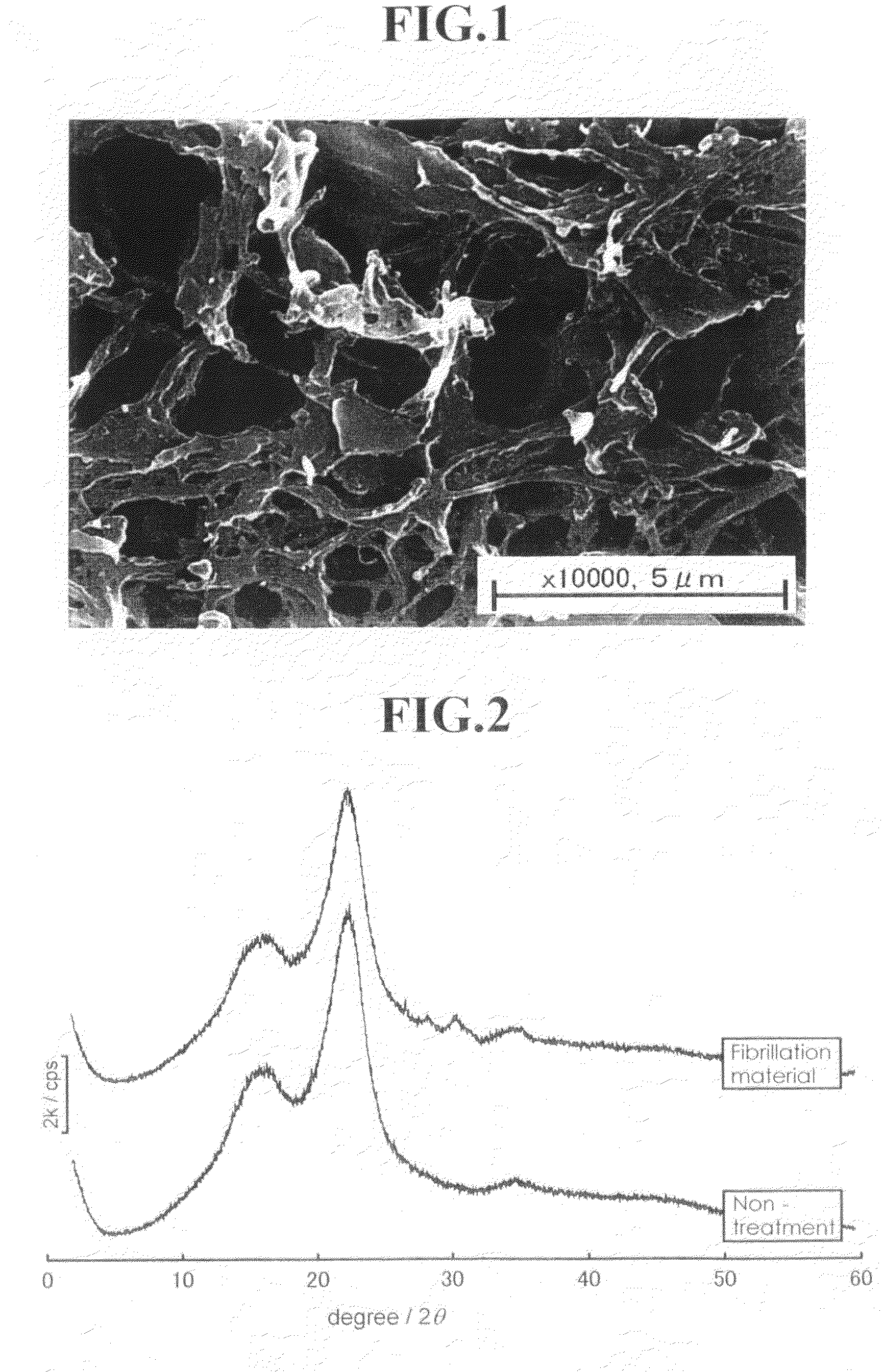
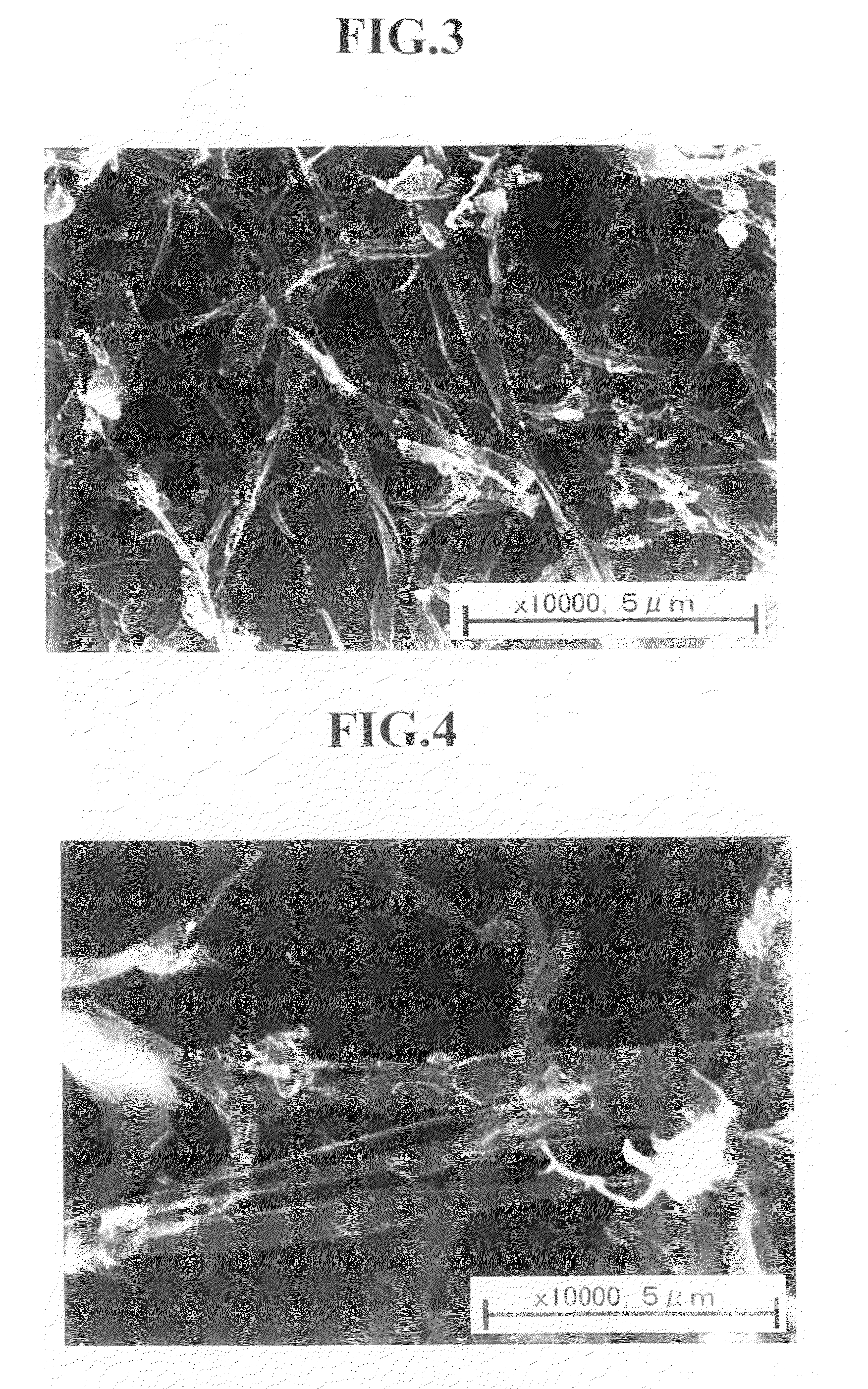
Fine fibrous cellulosic material and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20100151527A1Increase ratingsIncrease productionCellulosic pulp after-treatmentLayered productsPolymer scienceHemicellulose
[Problem] To provide a fine fibrous cellulosic material capable of producing a saccharide in a high yield by hydrolysis; to provide a process for producing the fine fibrous cellulosic material from a cellulosic material; and to provide a process for producing the saccharide using the fine fibrous cellulosic material.[Means for Solving Problems] The present invention is the fine fibrous cellulosic material containing cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, which the fine fibrous cellulosic material has a width of 1 μm or less and a length of 5,000 μm or less and is used for glycation reaction by hydrolysis.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Separation process
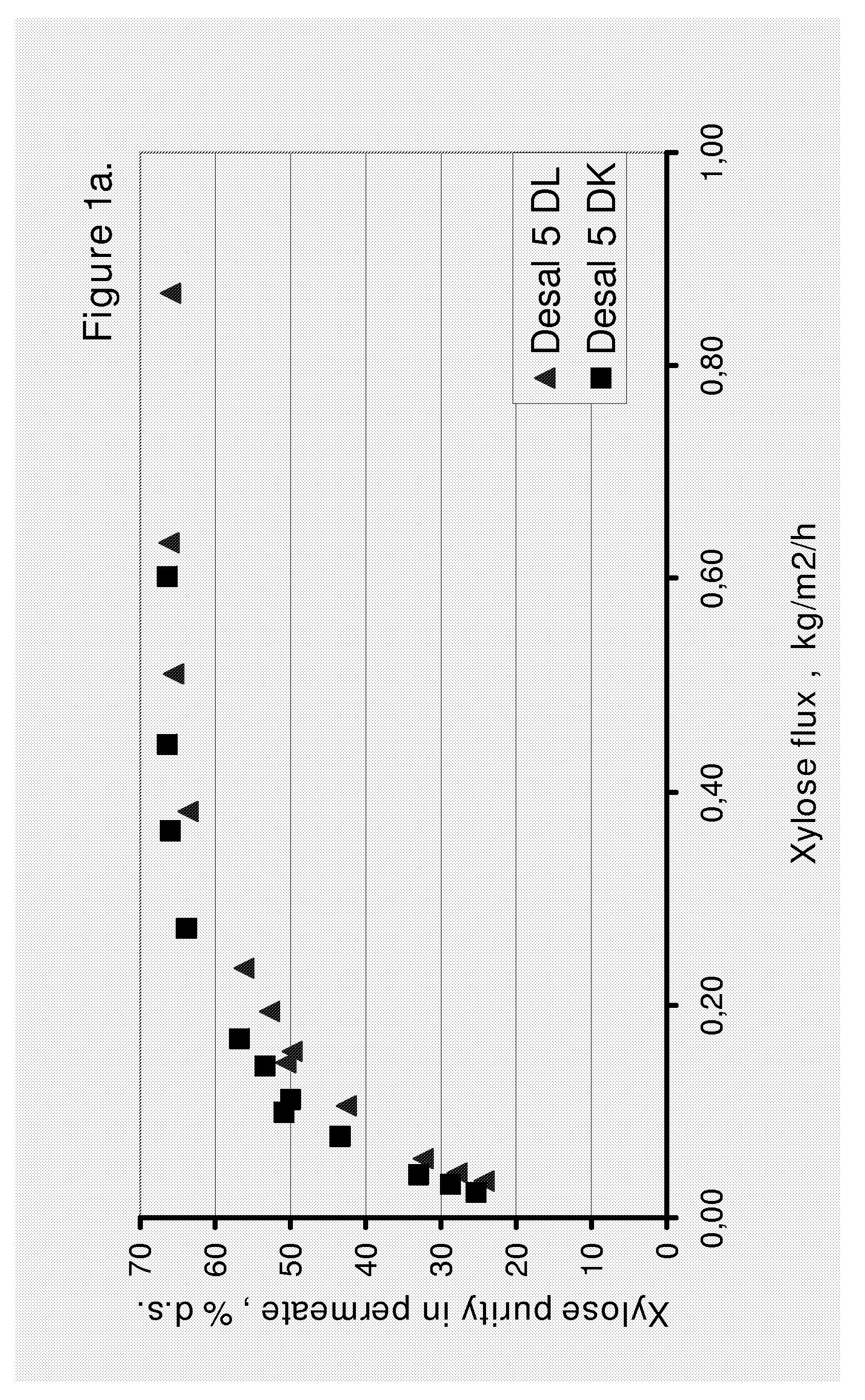
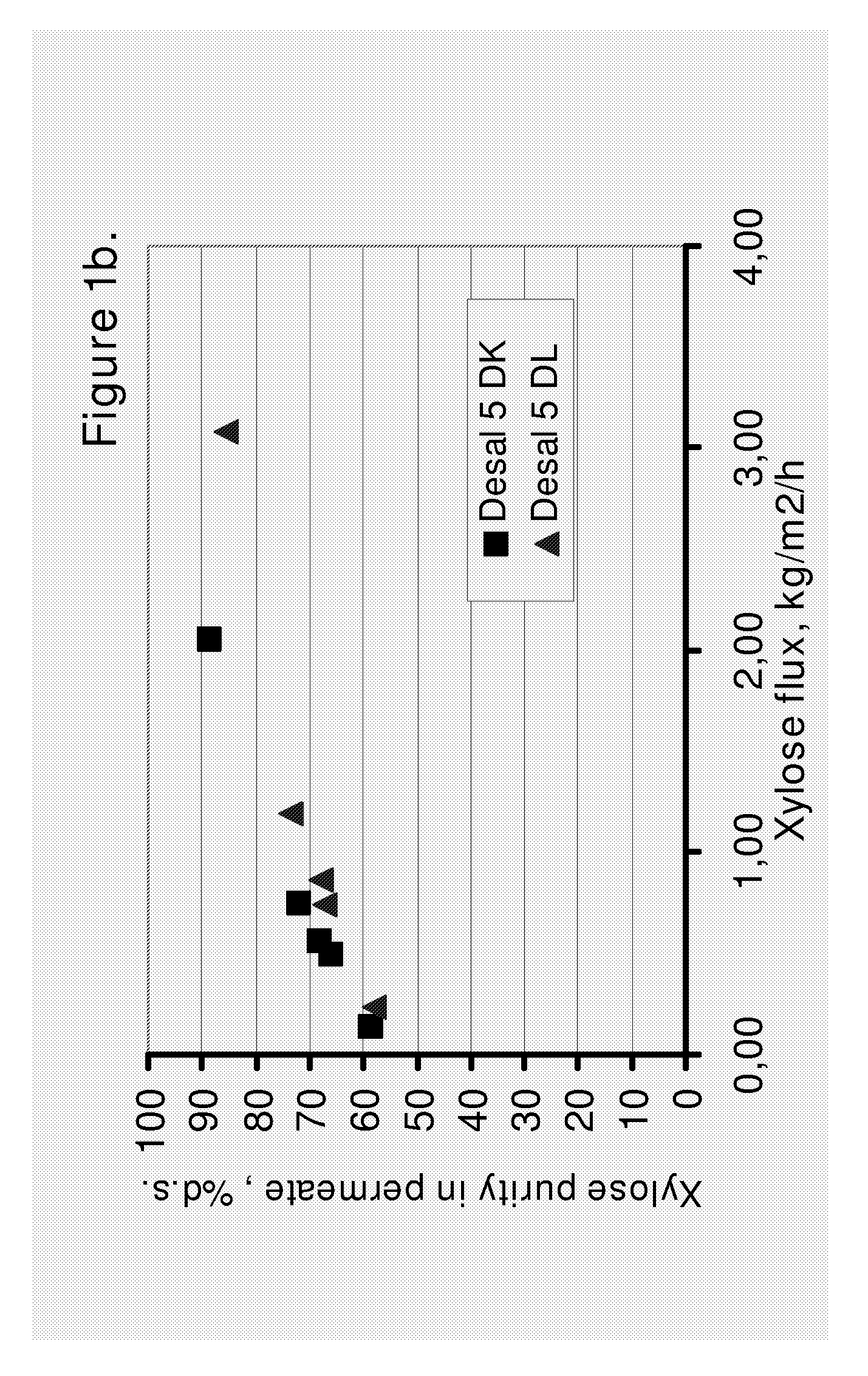
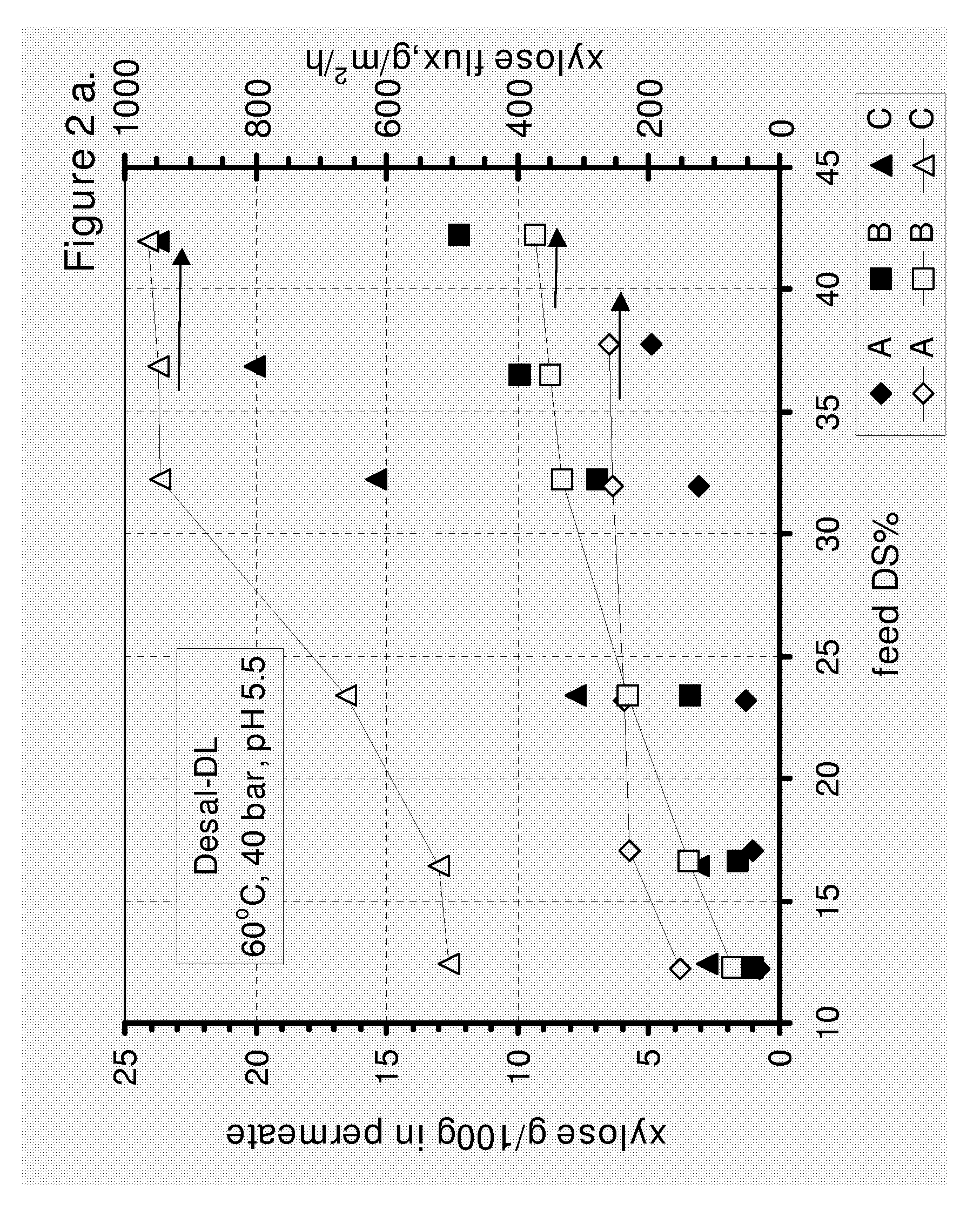
ActiveUS20090173339A1Improve performanceFavorable enrichment factor of xyloseMembranesPurification using adsorption agentsHydrolysateNanofiltration
The invention relates to an improved nanofiltration process of recovering xylose from a solution of a plant-based biomass hydrolysate. The process of the present invention is based on the regulation of the xylose flux in the nanofiltration process.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
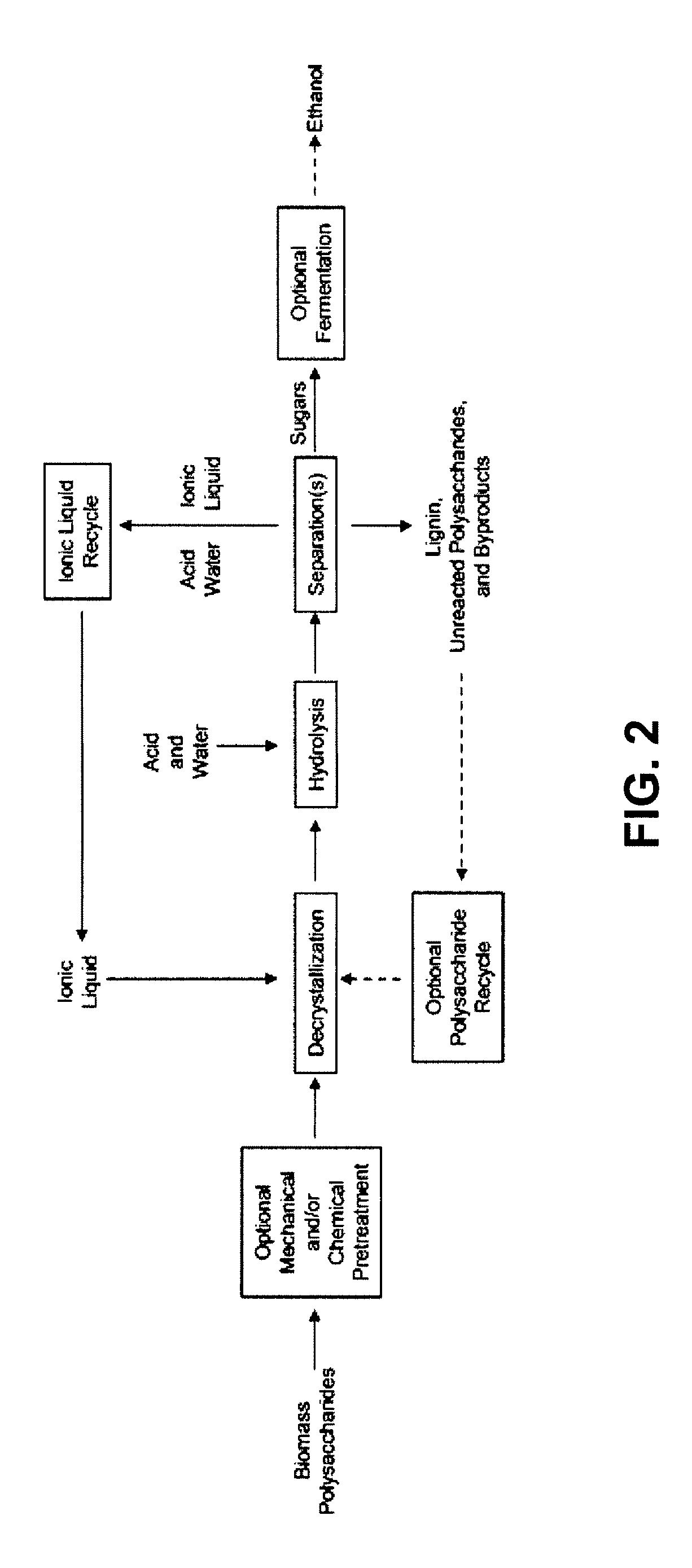
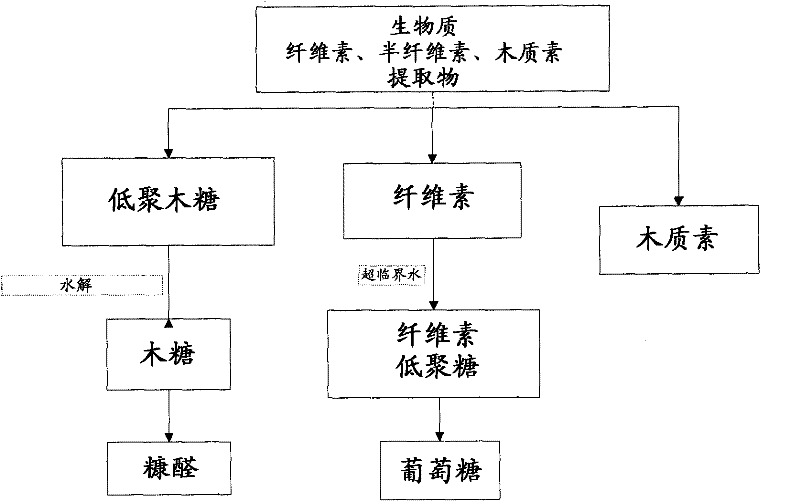
Novel method of acid hydrolysis of biomass and the recovery of sugars thereof by solvent extraction
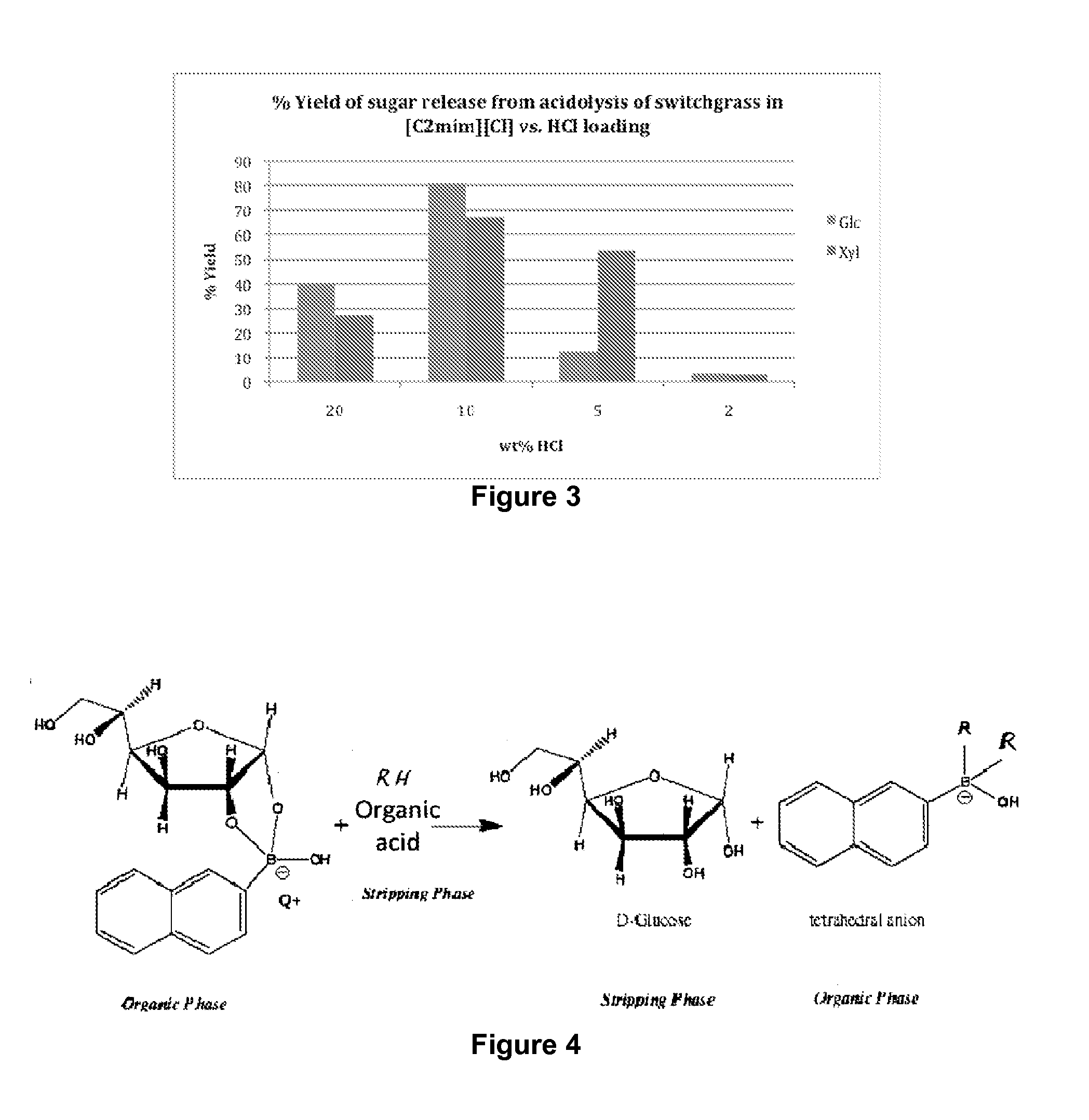
InactiveUS20120301948A1Minimize formationSugar derivativesOther chemical processesOrganic acidAcid hydrolysis
The present invention provides for a method of hydrolyzing a cellulose, hemicellulose, or ligno-cellulose comprising: (a) contacting (i) an ionic liquid (IL) or ionic liquid-aqueous (ILA) phase comprising cellulose, hemicellulose, or ligno-cellulose, or a mixture thereof, and (ii) an acid, such that the cellulose, hemicellulose, or ligno-cellulose is hydrolyzed into sugar, and (b) optionally adding water to the IL or ILA phase wherein the proportion of water in the IL or ILA phase does not exceed about 60% by weight. The present invention also provides for a method of recovering a sugar comprising contacting an IL or ILA phase and an organic phase comprising an organic acid.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Method of extraction of furfural and glucose from biomass using one or more supercritical fluids
Methods of making glucose and / or furfural from biomass require one or more supercritical fluids that may be used to process biomass, cellulose from the biomass, and / or xylose from the biomass. Examples of supercritical fluids for use in processing biomass include ethanol, water, and carbon dioxide at a temperature and pressure above the critical points for ethanol and carbon dioxide but at a temperature and / or pressure below that of the critical point for water. A supercritical fluid containing carbon dioxide and water may be used to convert cellulose to glucose or convert xylose to furfural. The fluid has a temperature and pressure above the critical point of carbon dioxide, but at least one of the temperature and pressure is below the critical point for water.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
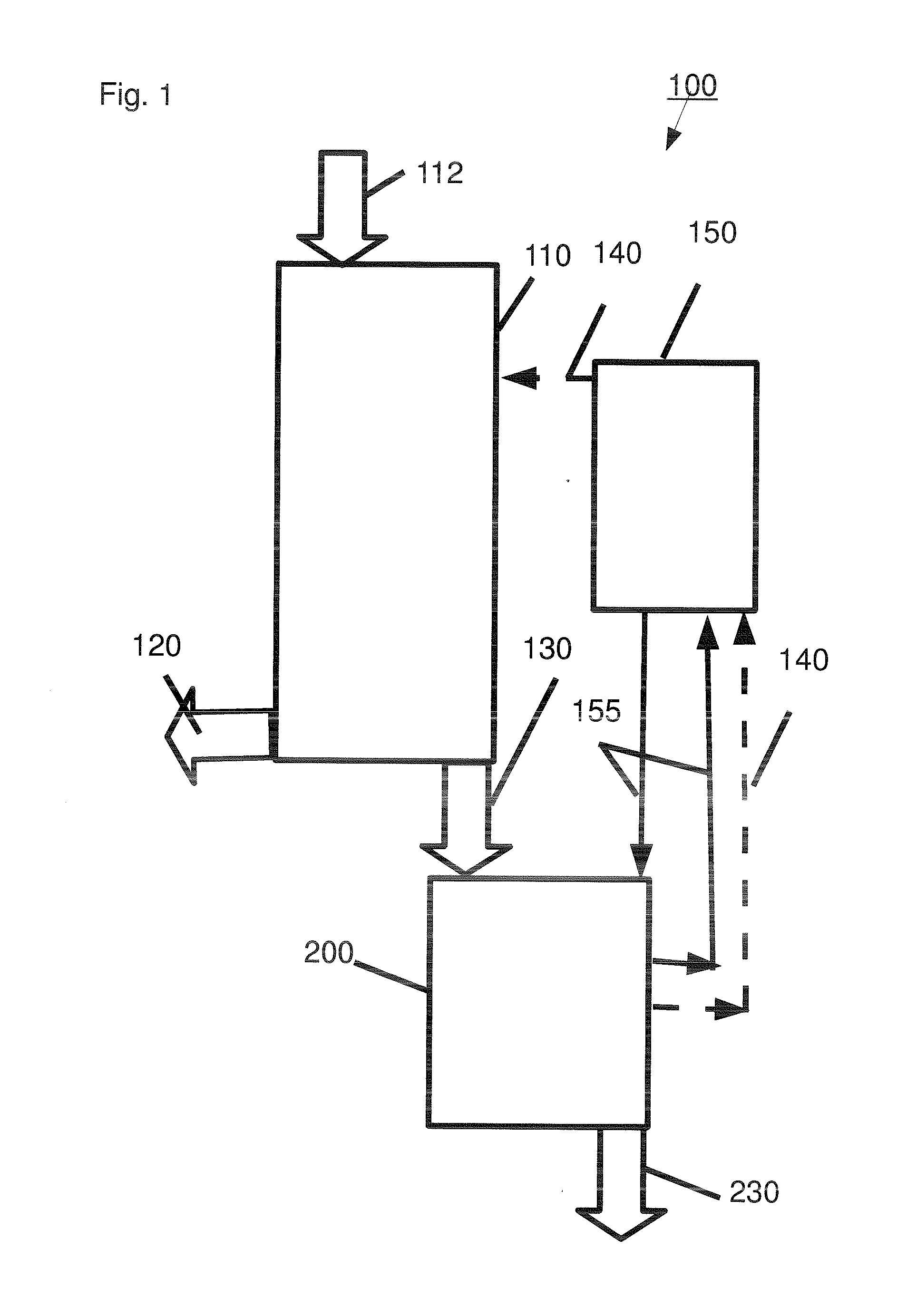
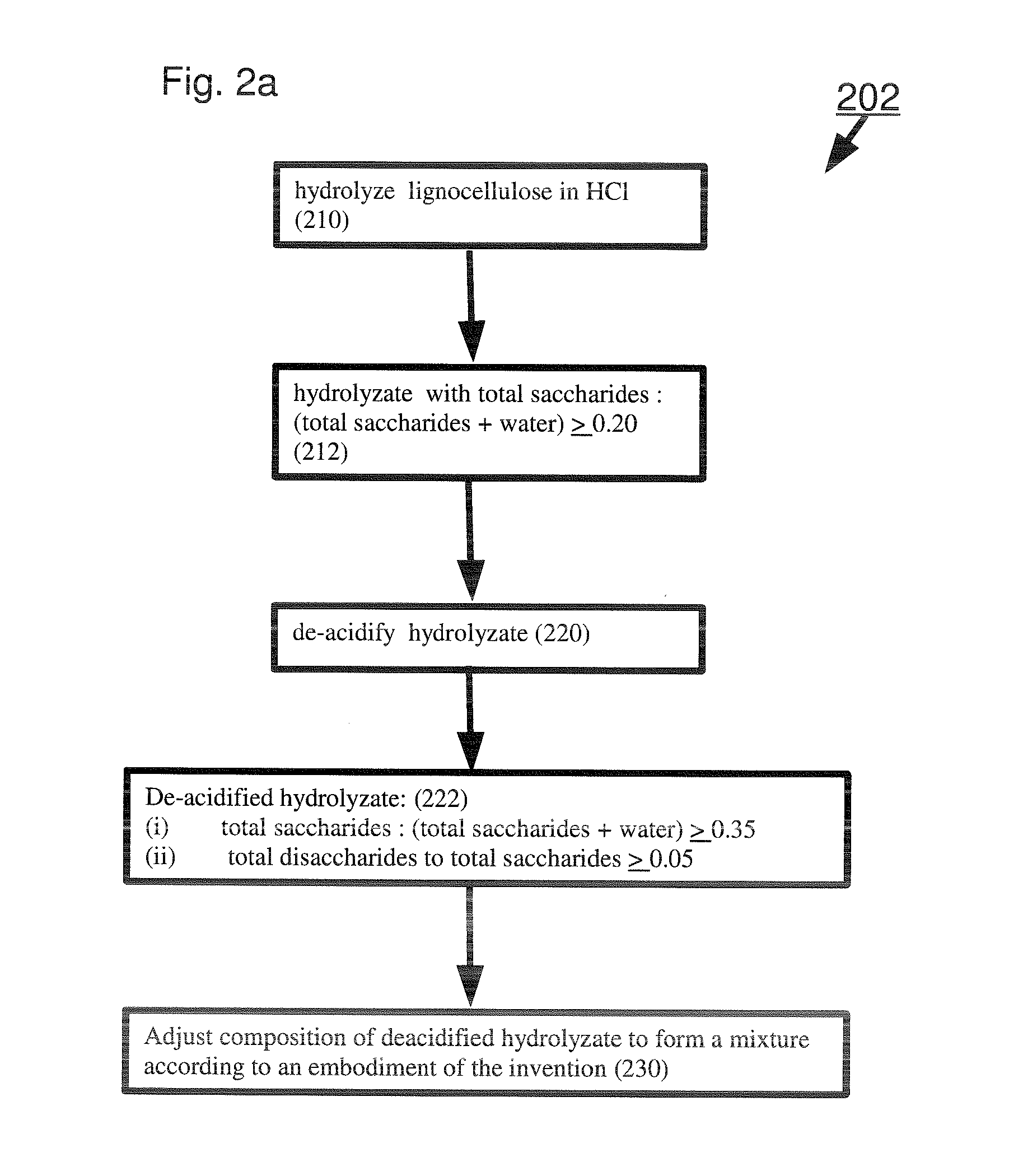
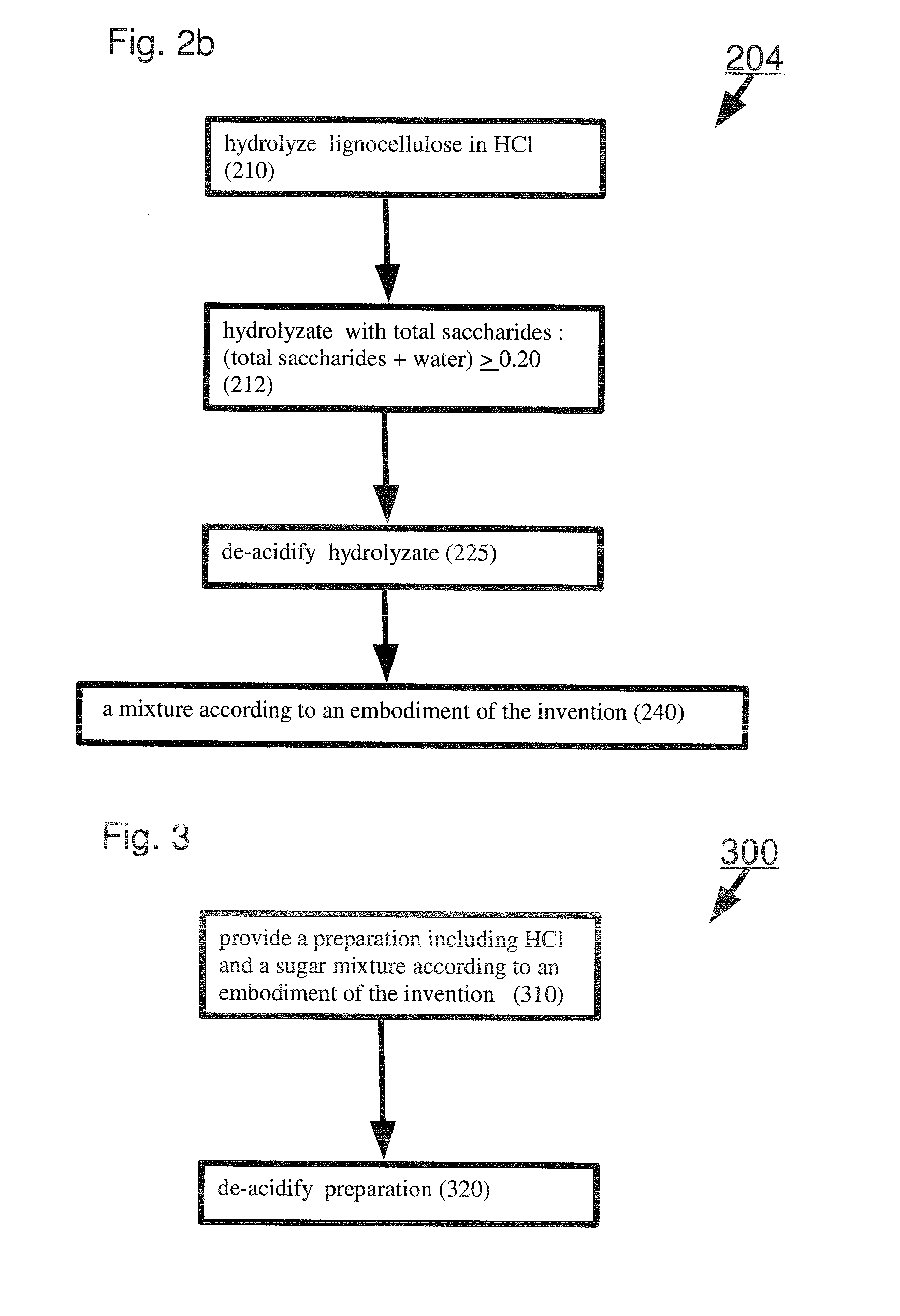
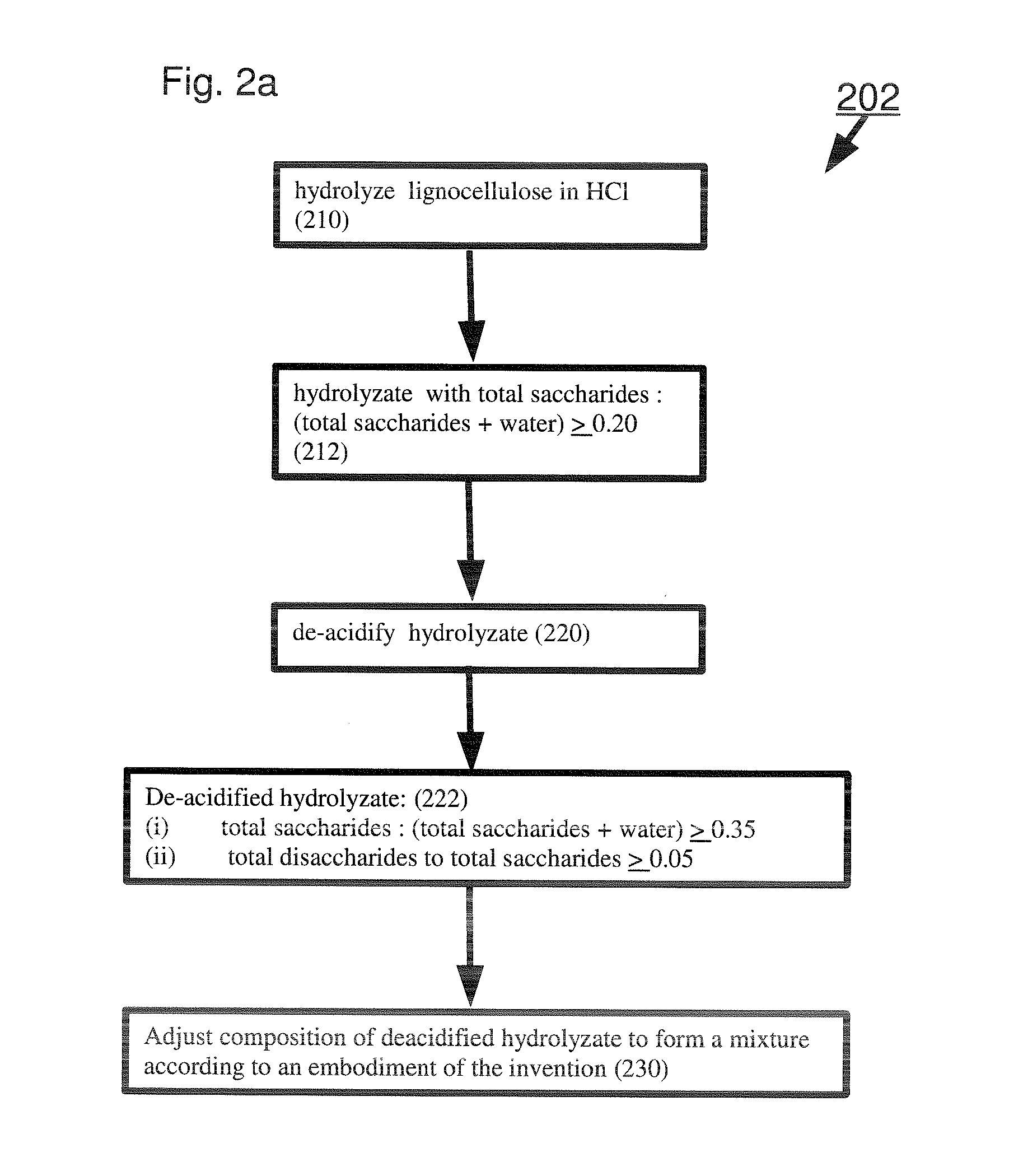
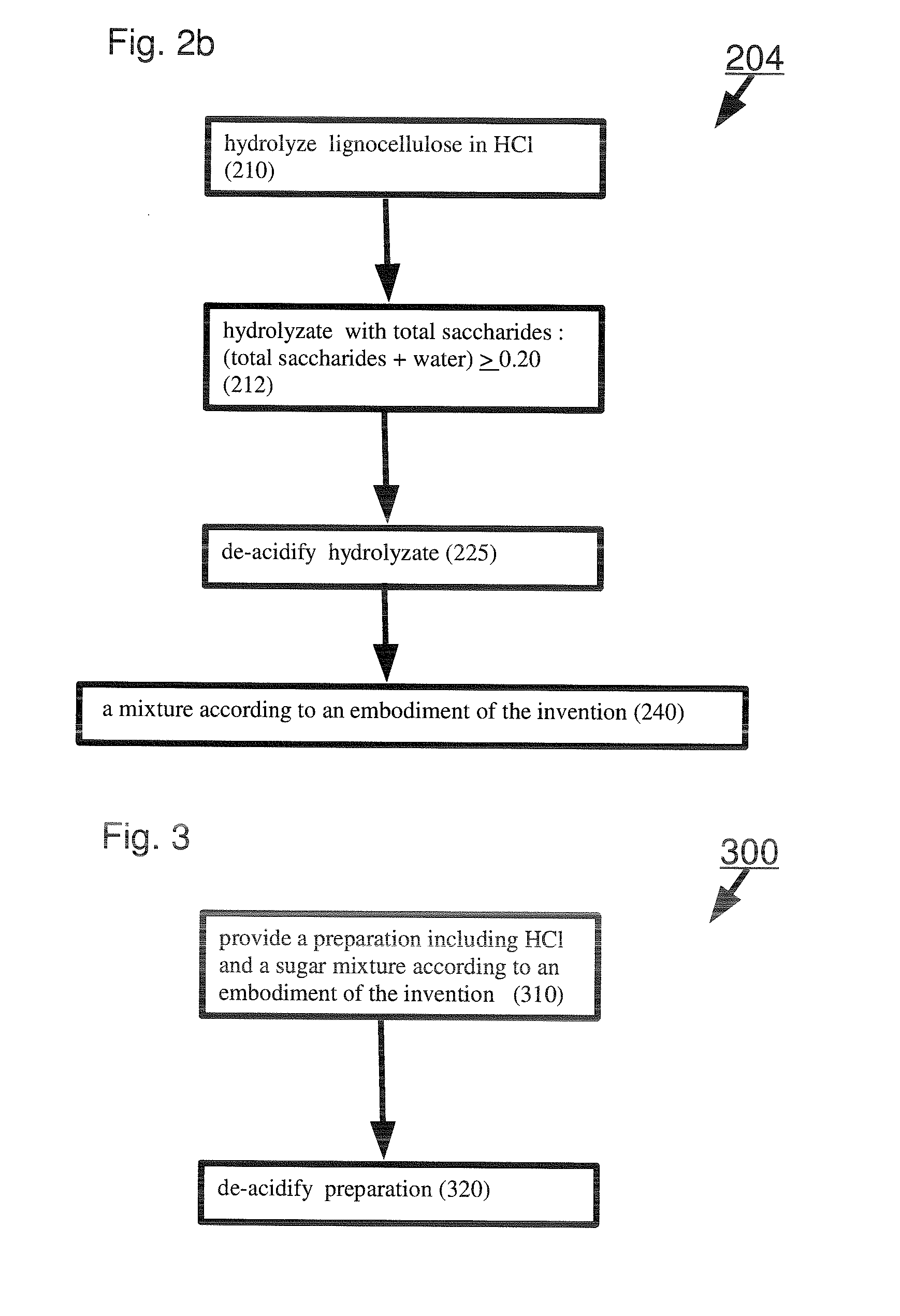
Sugar mixtures and methods for production and use thereof
A sugar mixture comprising: monosaccharides; oligosaccharides in a ratio ≧0.06 to total saccharides; disaccharides in a ratio to total saccharides ≧0.05; pentose in a ratio to total saccharides ≧0.05; at least one alpha-bonded di-glucose; and at least one beta-bonded di-glucose. Also disclosed are methods to make and / or use such mixtures.
Owner:VIRIDA
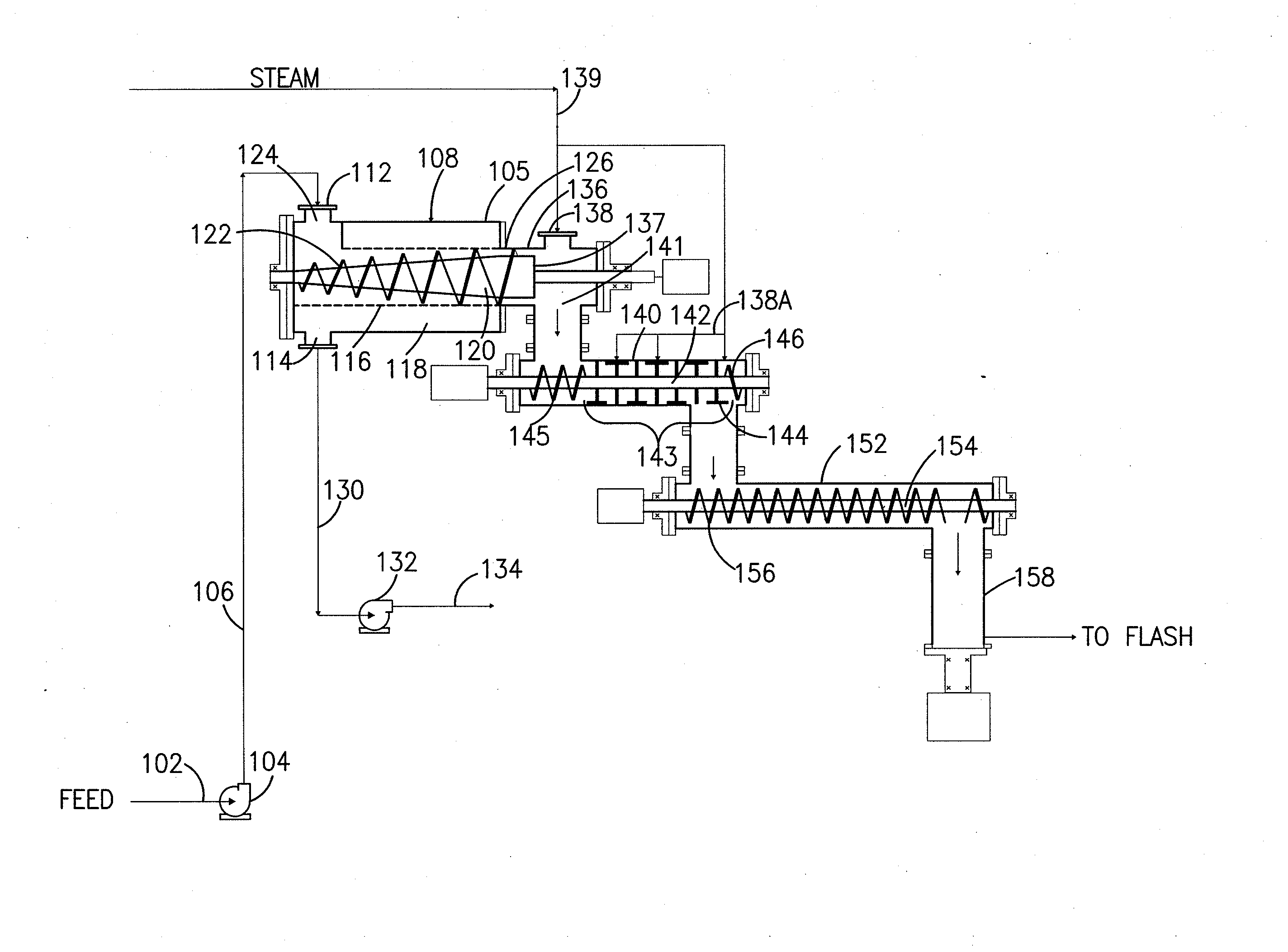
Method for heating a feedstock
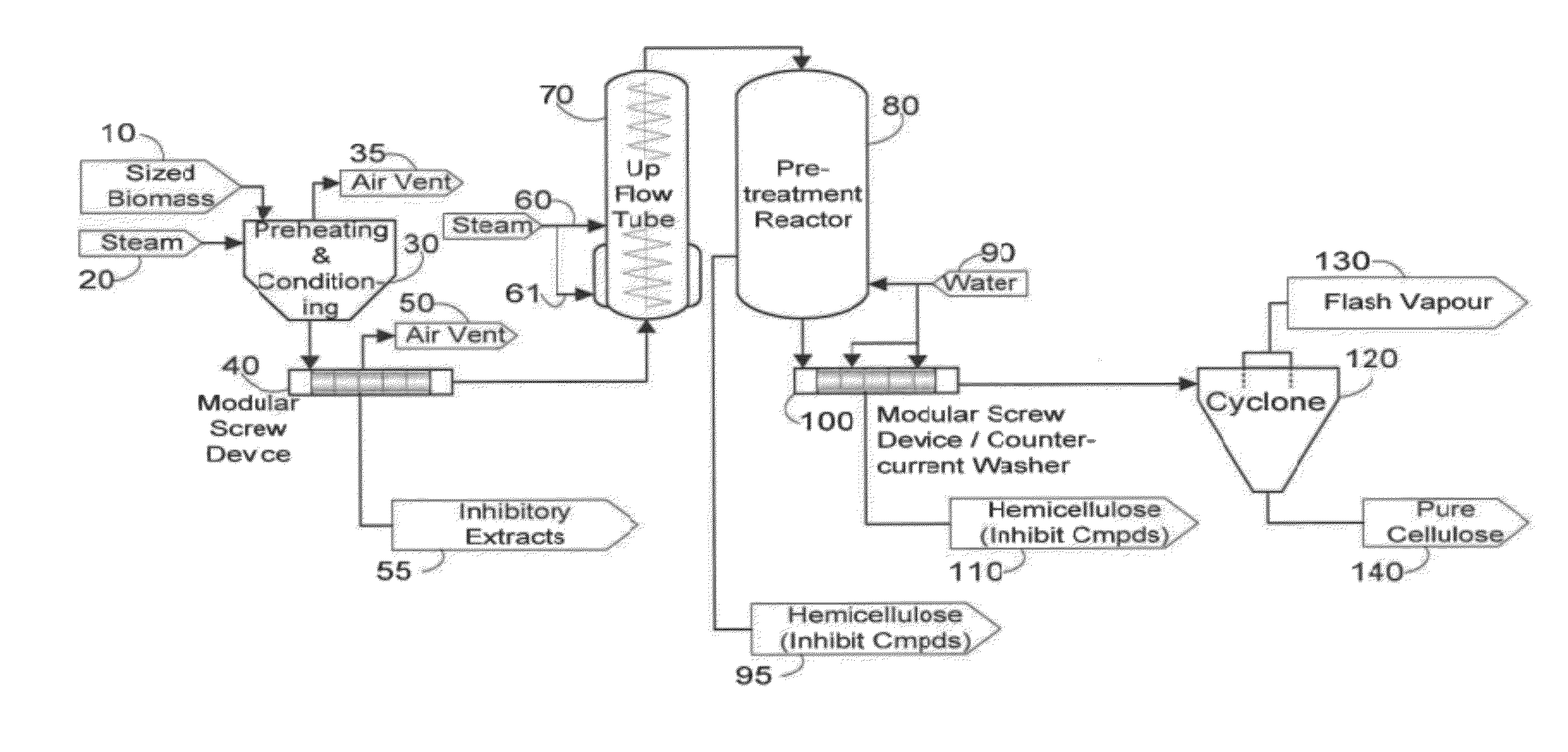
InactiveUS20130071903A1Large specific surface areaHigh yieldPretreatment with water/steamOther chemical processesCelluloseProcess engineering
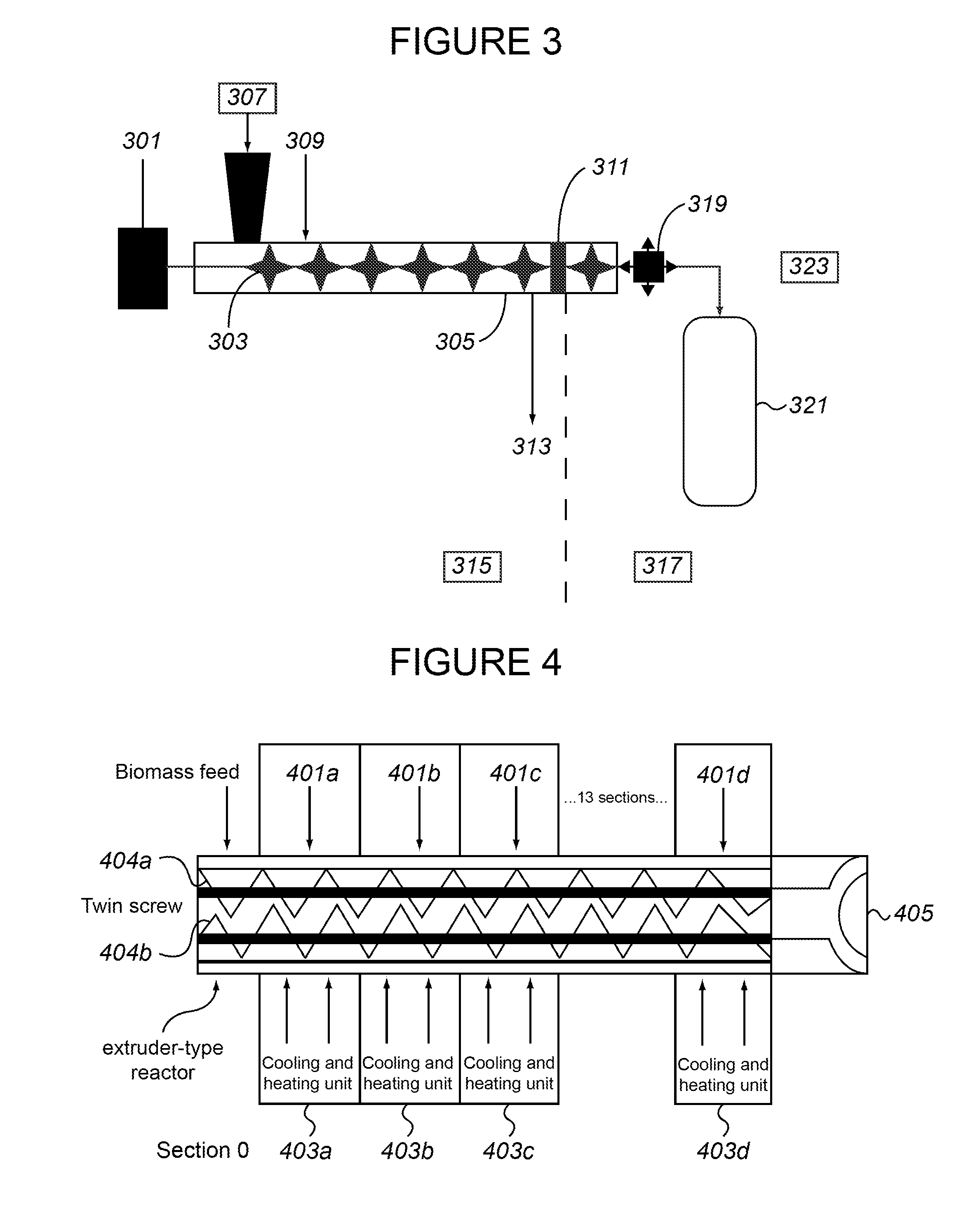
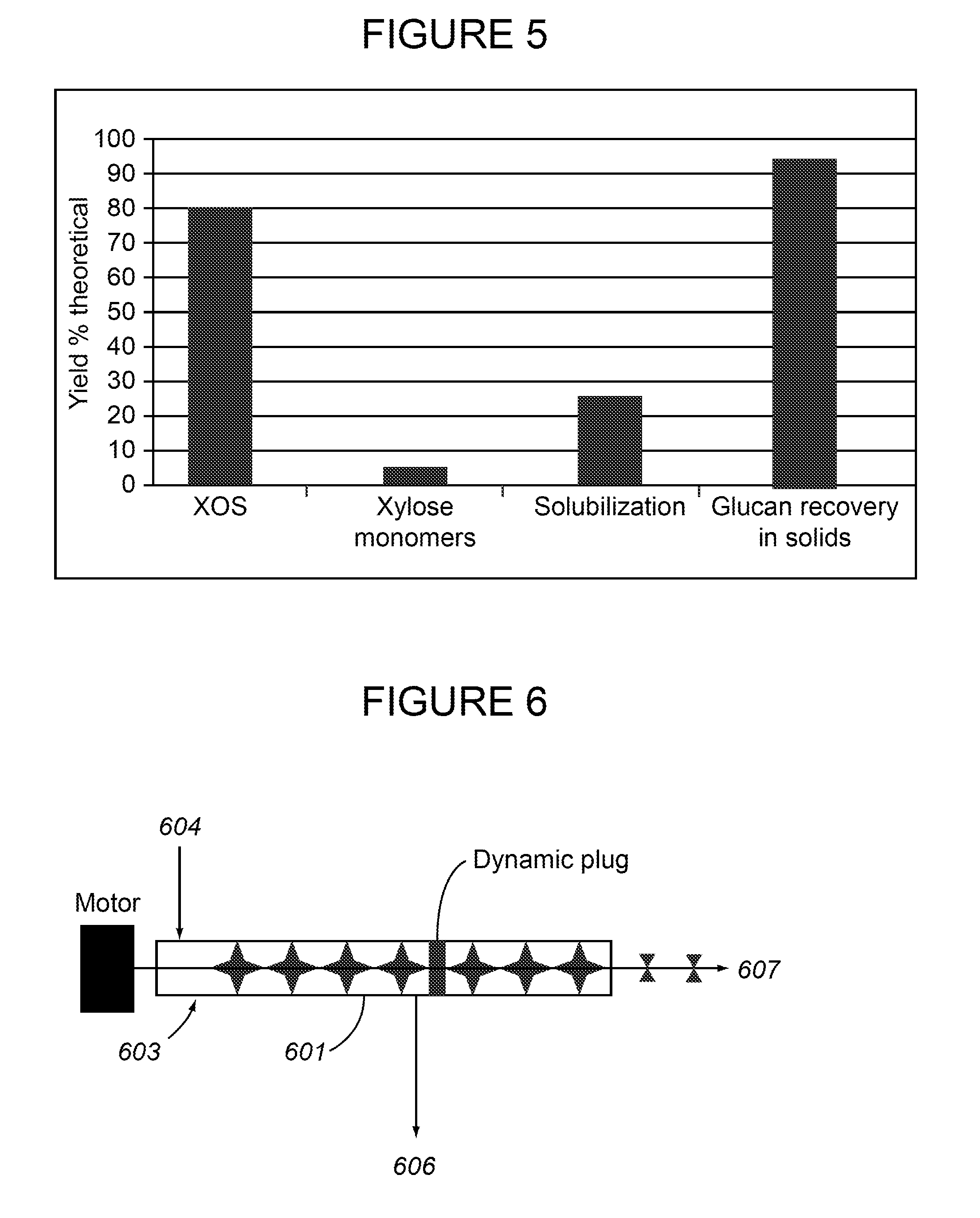
The present invention provides a method for producing a pretreated or hydrolyzed lignocellulosic feedstock. The method comprises feeding a lignocellulosic feedstock to a plug formation device and forming a feedstock plug therein. The plug or segments thereof are fed into an elongate chamber that comprises steam addition means for direct steam addition and a rotating shaft mounted co-axially within the chamber having one or more disintegrating elements mounted on it. Disintegrated feedstock particles are produced in the elongate chamber by the disintegrating elements. The disintegrated feedstock particles are heated by contact with the steam introduced through the steam addition means. The disintegrated feedstock particles are then treated in a reactor to produce the pretreated or hydrolyzed lignocellulosic feedstock. Further provided is a feedstock composition comprising disintegrated feedstock particles. Also provided are methods for reducing erosion on equipment by maintaining the discharge consistency from the plug formation device below 35 wt %.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
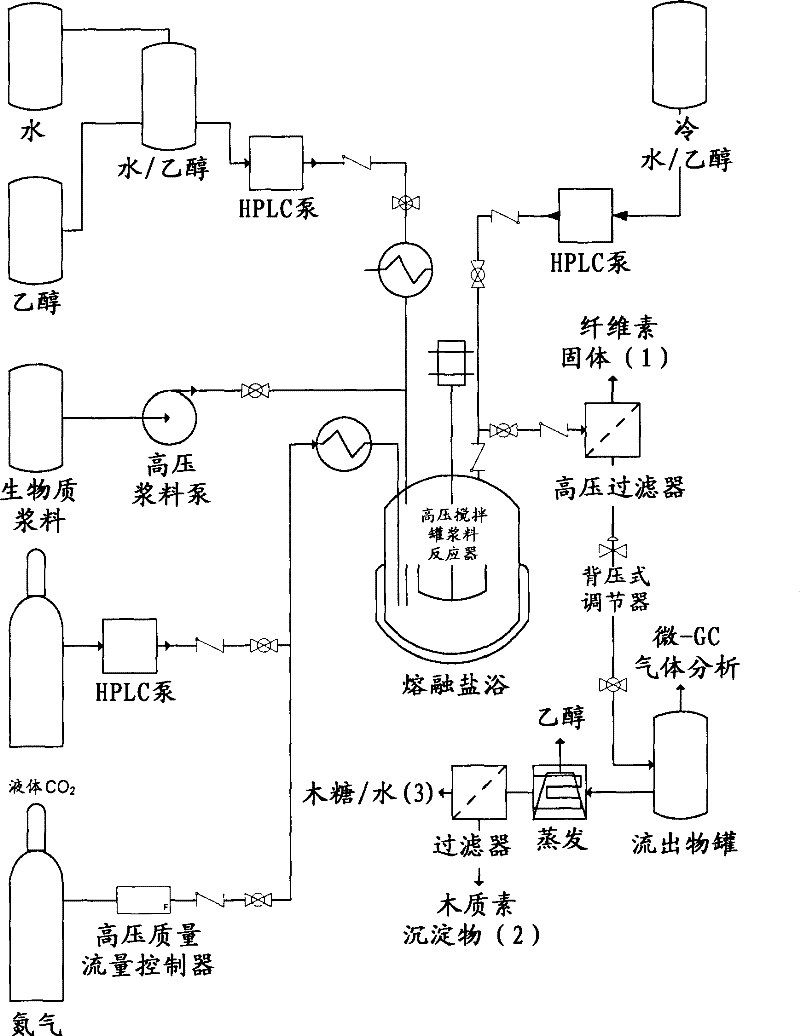
Production of fermentable sugars and lignin from biomass using supercritical fluids
Methods are disclosed for the continuous treatment of biomass comprising a pretreatment step, wherein said biomass is contacted with a first supercritical, near-critical, or sub-critical fluid to form a solid matrix and a first liquid fraction; and a hydrolysis step, wherein said solid matrix formed in said pretreatment step is contacted with a second supercritical or near-supercritical fluid to produce a second liquid fraction and a insoluble lignin-containing fraction. Also disclosed are apparatuses for the continuous conversion of biomass comprising a pretreatment reactor and a hydrolysis reactor associated with said pretreatment reactor.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
Lignin and other products isolated from plant material, methods for isolation and use, and compositions containing lignin and other plant-derived products
InactiveUS20130012610A1Great potentialTotal calories lowSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationFiberElastomer
Lignin polymers having distinctive properties, including a generally high molecular weight and generally homogeneous size distribution, as well as preservation of native reactive side groups, are isolated by solvent extraction of plant materials. Methods for isolation of lignin polymers, and for use of the isolated lignin polymers are disclosed. Compositions containing lignin isolated from plant materials, such as carbon fiber composites, resins, adhesive binders and coatings, polyurethane-based foams, rubbers and elastomers, plastics, films, paints, nutritional supplements, food and beverage additives are disclosed. Xylose and xylose derivatives, furfural, fermentable sugars, cellulose and hemi-cellulose products may be used directly or further processed. The lignin polymers and other plant-derived products disclosed herein may be produced in abundance at low cost, and may be used as substitutes for feedstocks originating from fossil fuel or petrochemical sources in the manufacture of various products.
Owner:VERTICHEM CORP
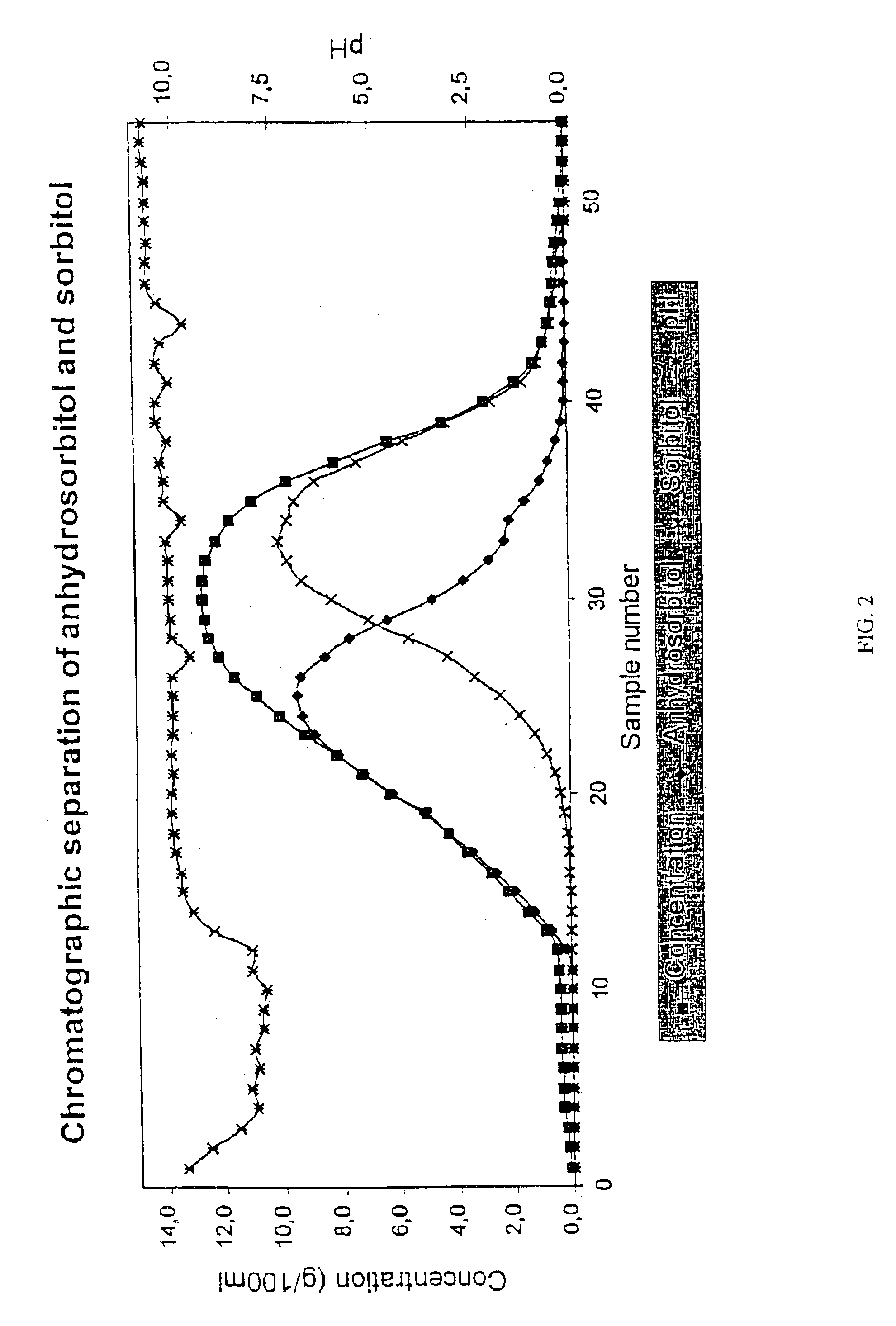
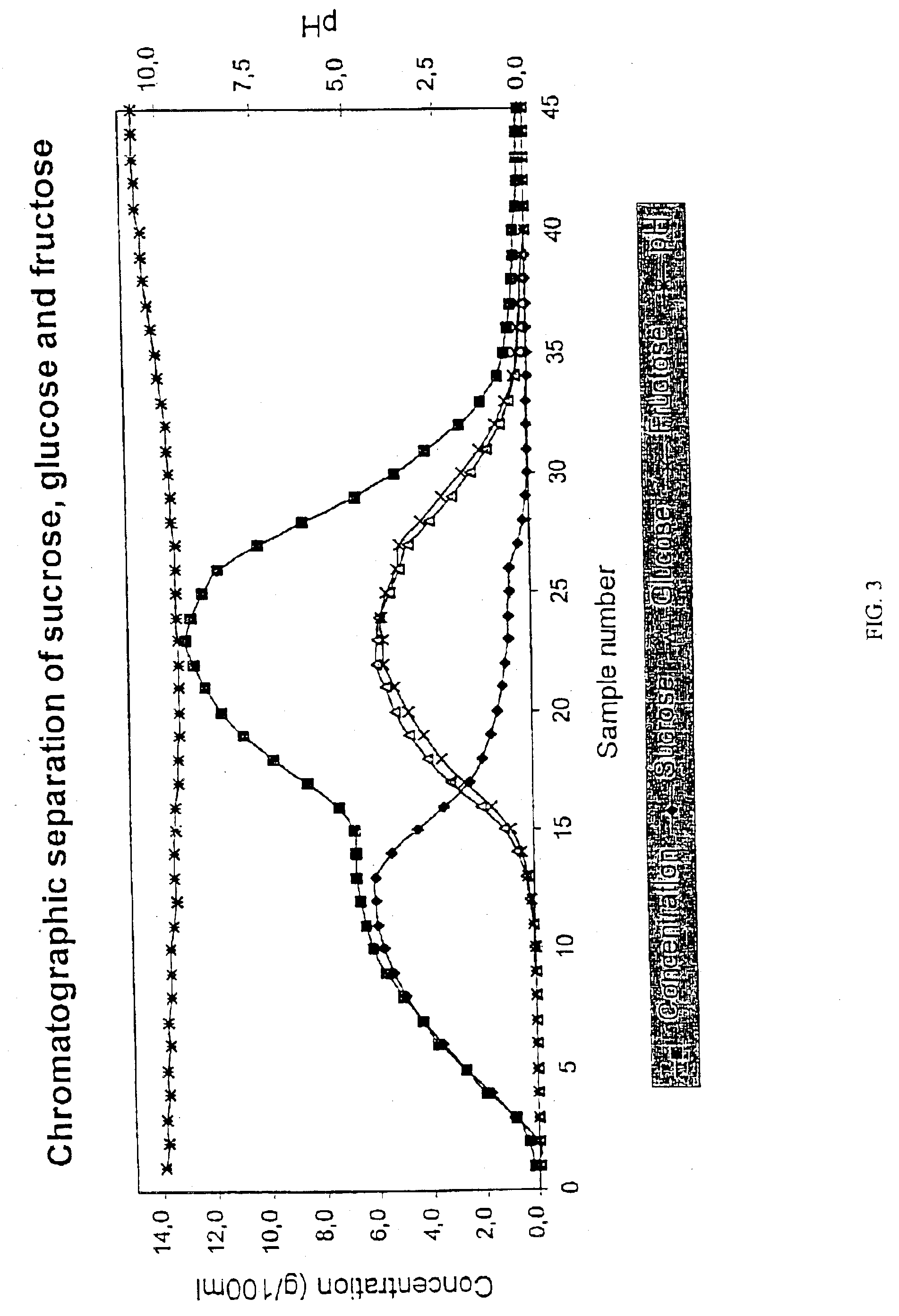
Use of a weakly acid cation exchange resin for chromatographic separation of carbohydrates
InactiveUS6924371B2High yieldEasy to separateChromatographic cation exchangersCation exchanger materialsChromatographic separationAlcohol sugars
The invention relates to the use of a weakly acid cation exchange resin for chromatographic separation of carbohydrates. In the invention the hydrophilic / hydrophobic interaction of carbohydrates, sugars and sugar alcohols with the weakly acid cation exchange resin is utilized. The weakly acid cation exchange resin is used for separation of hydrophobic saccharides, such as deoxy, methyl and anhydrosugars and anhydrosugaralcohols from more hydrophilic saccharides.
Owner:DANISCO SWEETENERS
Sugar mixtures and methods for production and use thereof
A sugar mixture comprising: monosaccharides; oligosaccharides in a ratio ≧0.06 to total saccharides; disaccharides in a ratio to total saccharides ≧0.05; pentose in a ratio to total saccharides ≧0.05; at least one alpha-bonded di-glucose; and at least one beta-bonded di-glucose. Also disclosed are methods to make and / or use such mixtures.
Owner:VIRIDA
Process for the Treatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass
A process for the treatment of biomass to render structural carbohydrates more accessible and / or digestible using concentrated ammonium hydroxide with or without anhydrous ammonia addition, is described. The process preferably uses steam to strip ammonia from the biomass for recycling. The process yields of monosaccharides from the structural carbohydrates are good, particularly as measured by the enzymatic hydrolysis of the structural carbohydrates. The monosaccharides are used as animal feeds and energy sources for ethanol production.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for producing sugar liquid
ActiveCN102639722AHigh yieldImprove fermentation production efficiencySemi-permeable membranesBacteriaCelluloseReverse osmosis
Provided is a method for producing a sugar liquid using a cellulose-containing biomass as the starting material. Sugar liquid having a very low fermentation-inhibiting substance content is produced by a method comprising (1) a step in which a cellulose-containing biomass is hydrolyzed to produce an aqueous sugar solution and (2) a step in which the resulting aqueous sugar solution is filtered through a nanofiltration membrane and / or reverse osmosis membrane, the pure sugar liquid is recovered from the unpermeated side, and the fermentation-inhibiting matter is removed from the permeated side.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Bagasse fractionation for cellulosic ethanol and chemical production
InactiveUS20120111514A1Reduce contentHigh lignin contentPretreatment with water/steamPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsEnzymatic hydrolysisFractionation
A process is defined for the continuous steam pretreatment and fractionation of bagasse to produce a concentrated cellulose solid stream that is sensitive to enzymatic hydrolysis. Valuable chemicals are recovered by fractionating the liquid and vapor stream composed of hydrolysis and degradation products of the hemicellulose. Cellulosic derived glucose is produced for fermentation to biofuels. A hemicellulose concentrate is recovered that can be converted to value added products including ethanol.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Methods for converting lignocellulosic materials to useful products
Owner:SYNGENTA PARTICIPATIONS AG
Production of Fermentable Sugars and Lignin from Biomass Using Supercritical Fluids
ActiveUS20120291774A1Improve the level ofBiofuelsPulp by-products recoveryFermentable sugarSupercritical fluid
Methods are disclosed for the continuous treatment of biomass comprising a pretreatment step, wherein said biomass is contacted with a first supercritical, near-critical, or sub-critical fluid to form a solid matrix and a first liquid fraction; and a hydrolysis step, wherein said solid matrix formed in said pretreatment step is contacted with a second supercritical or near-supercritical fluid to produce a second liquid fraction and a insoluble lignin-containing fraction. Also disclosed are apparatuses for the continuous conversion of biomass comprising a pretreatment reactor and a hydrolysis reactor associated with said pretreatment reactor.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com