Patents
Literature
109results about How to "Increased ethanol production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
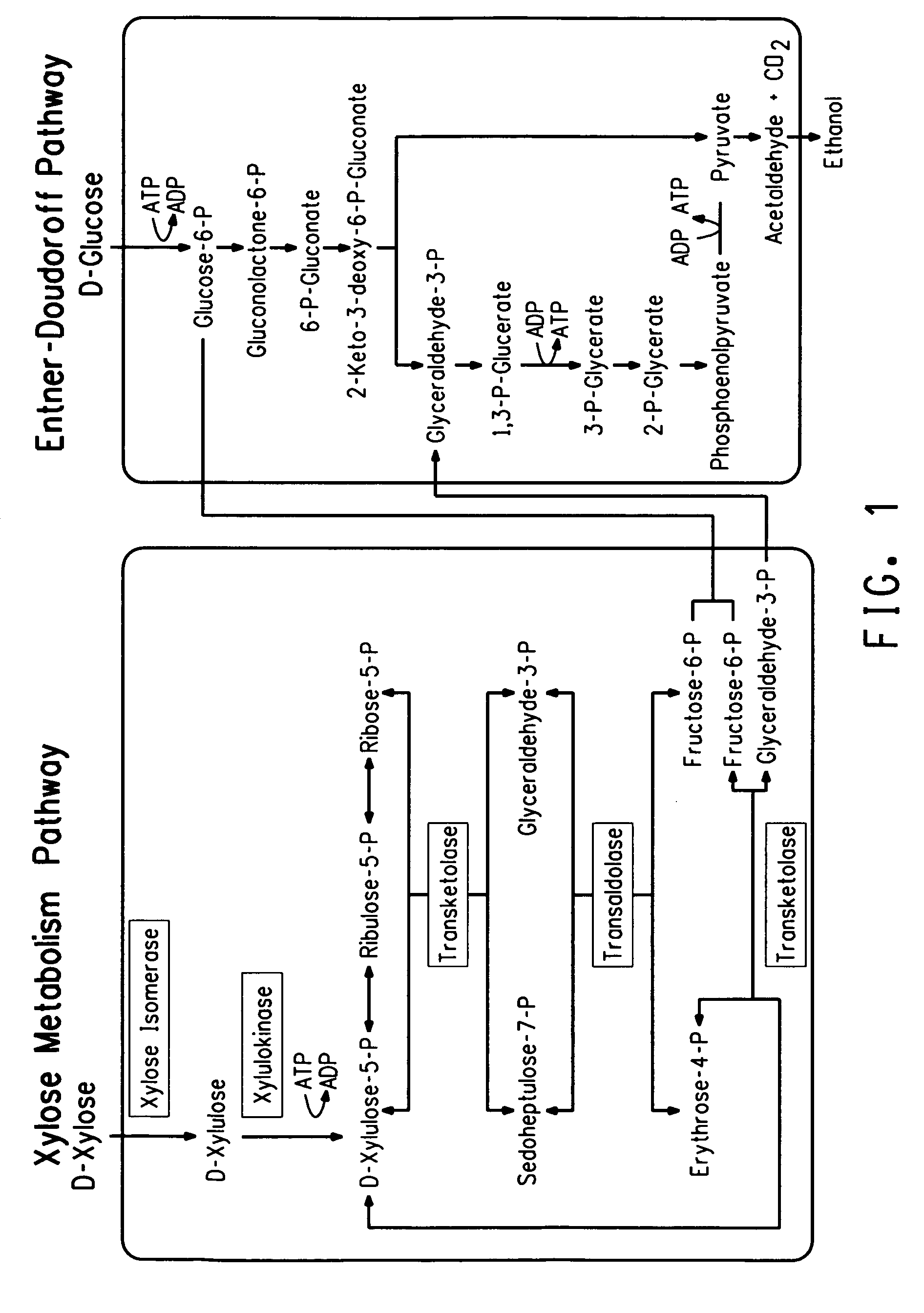
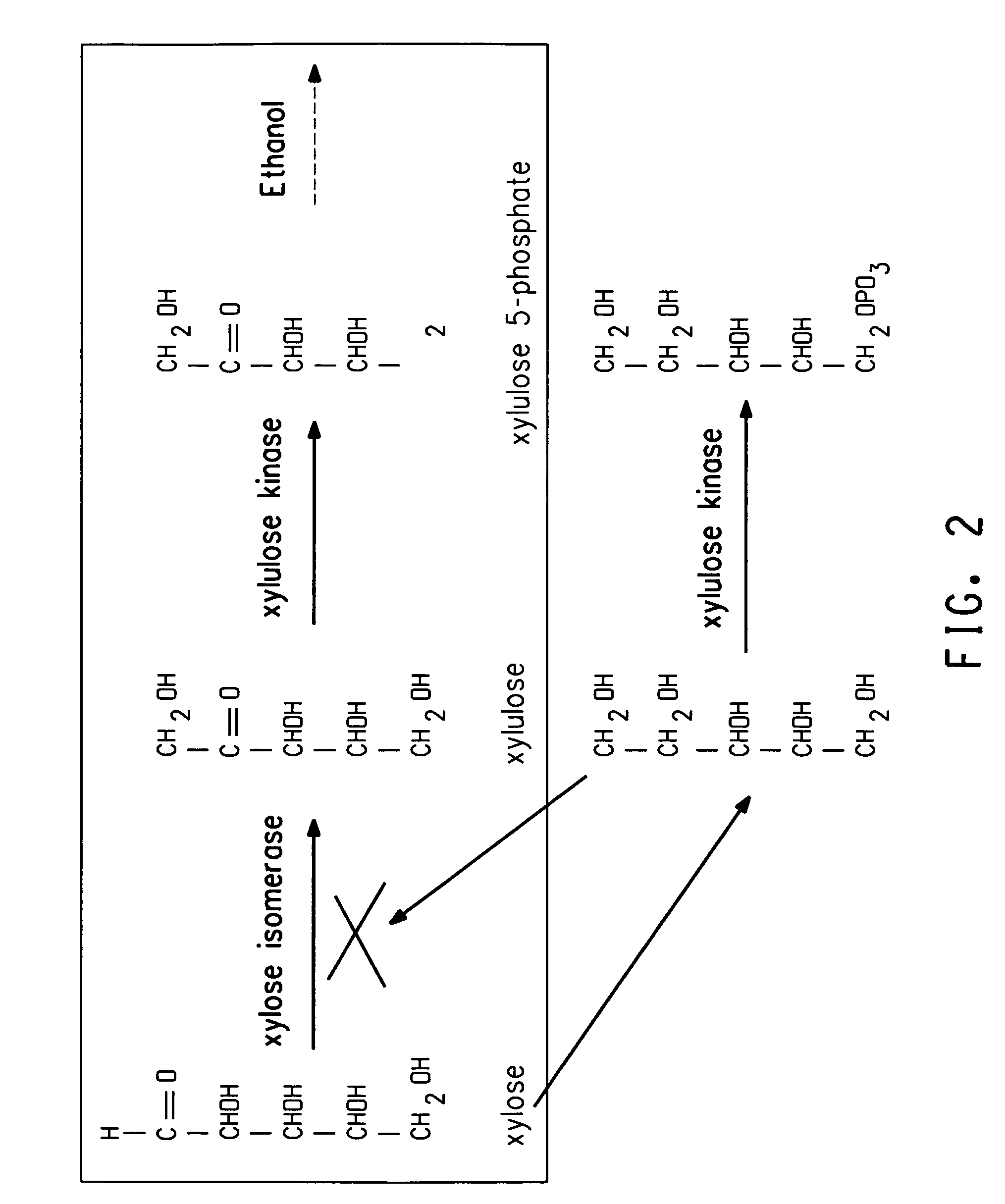
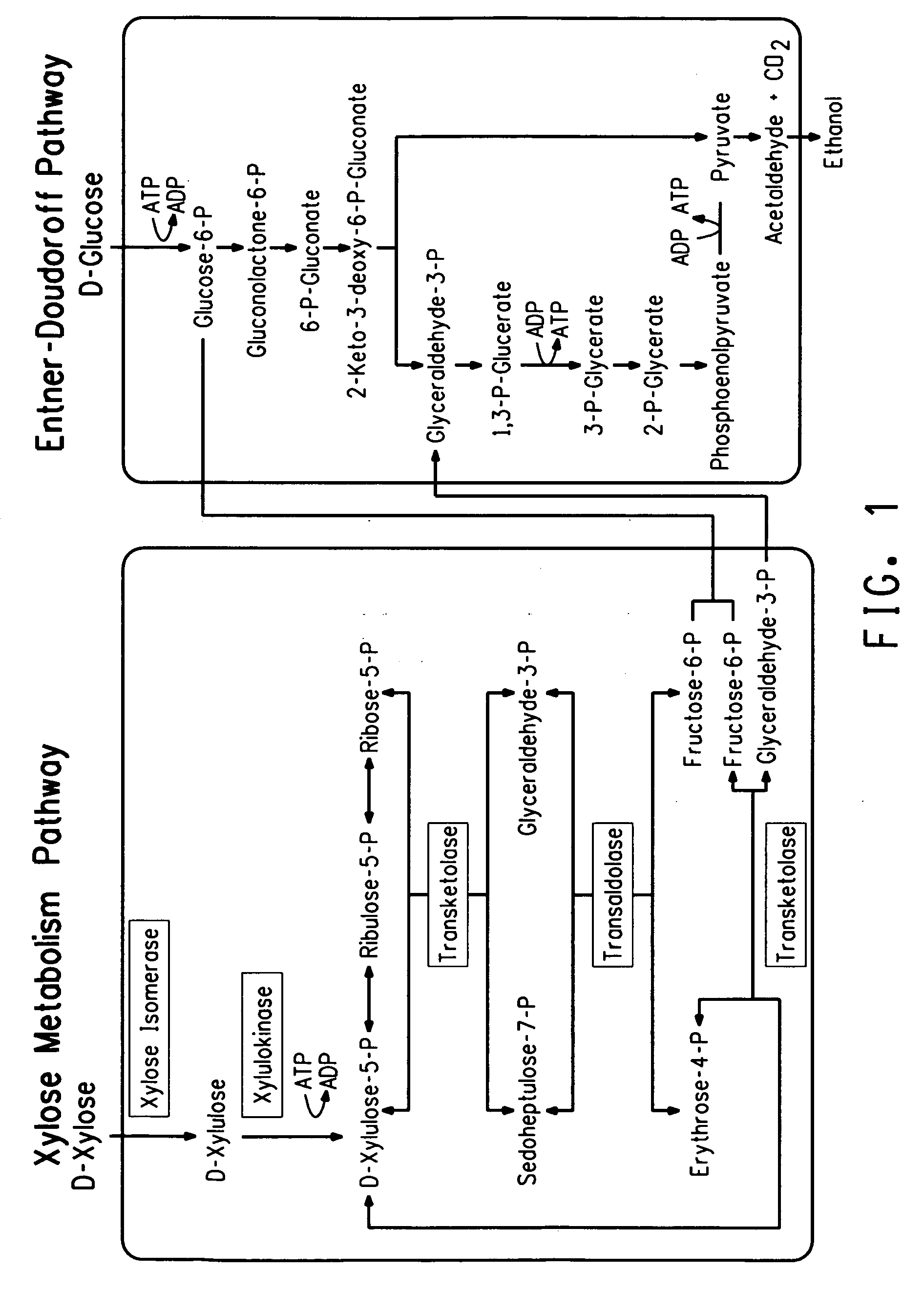
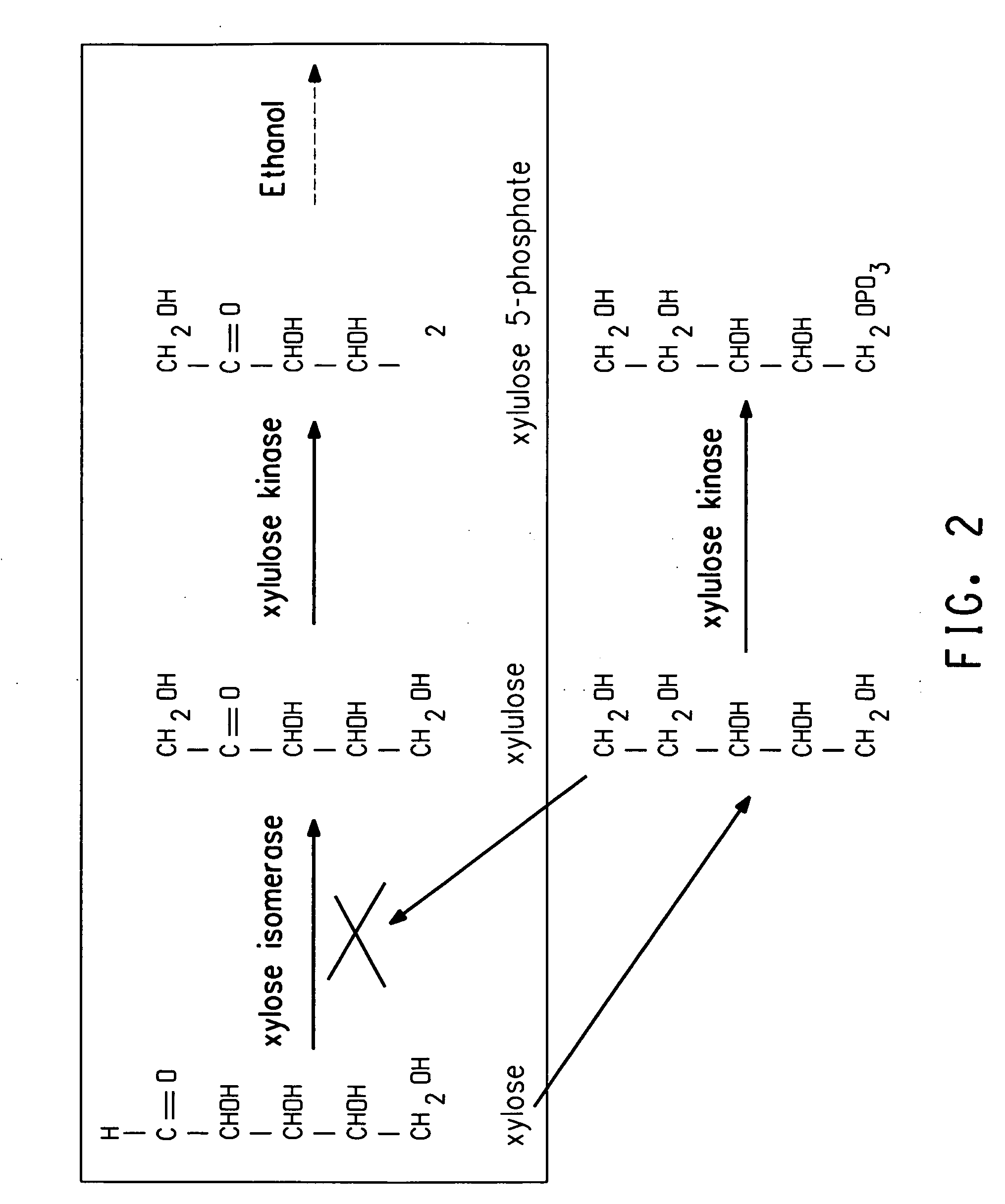
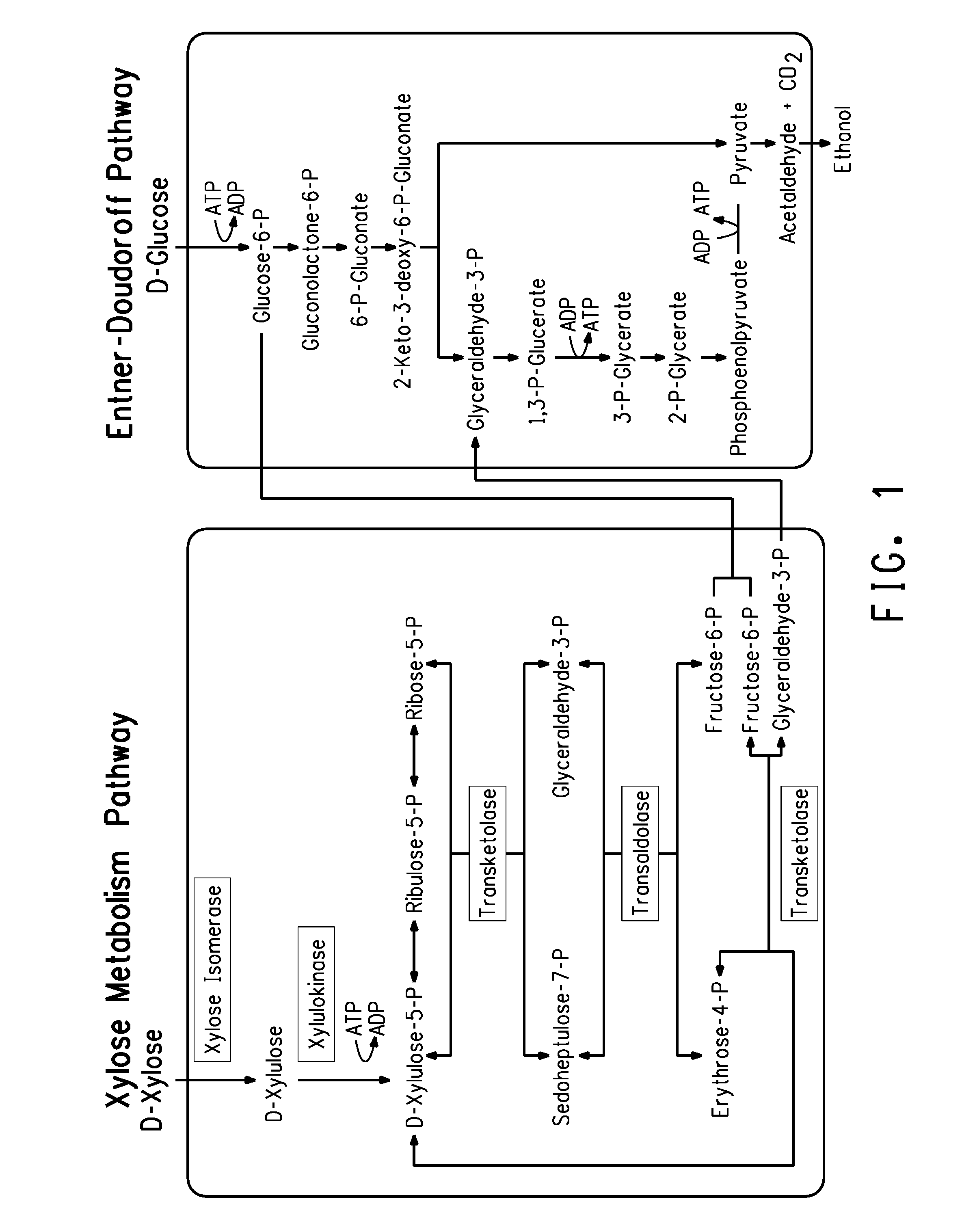
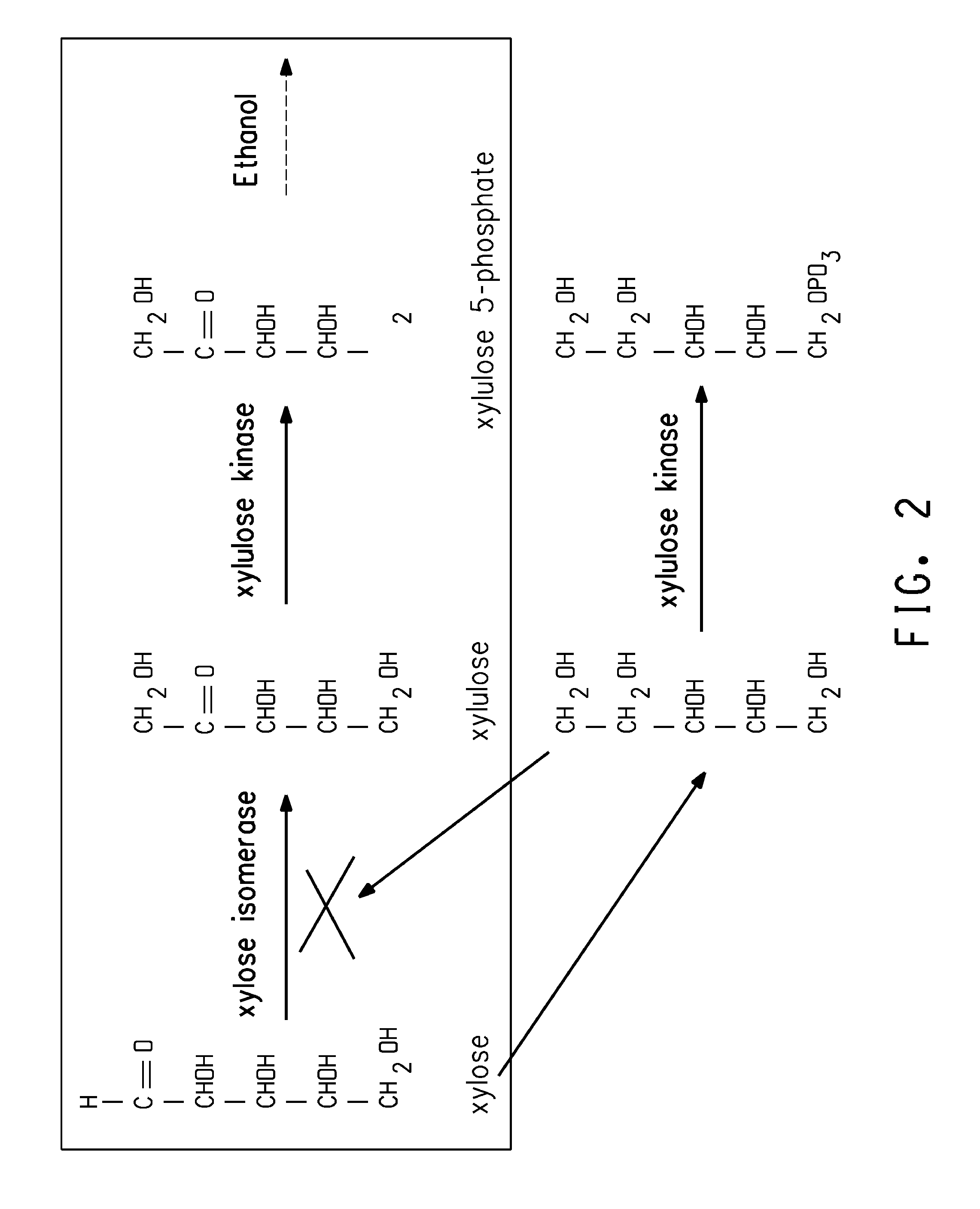
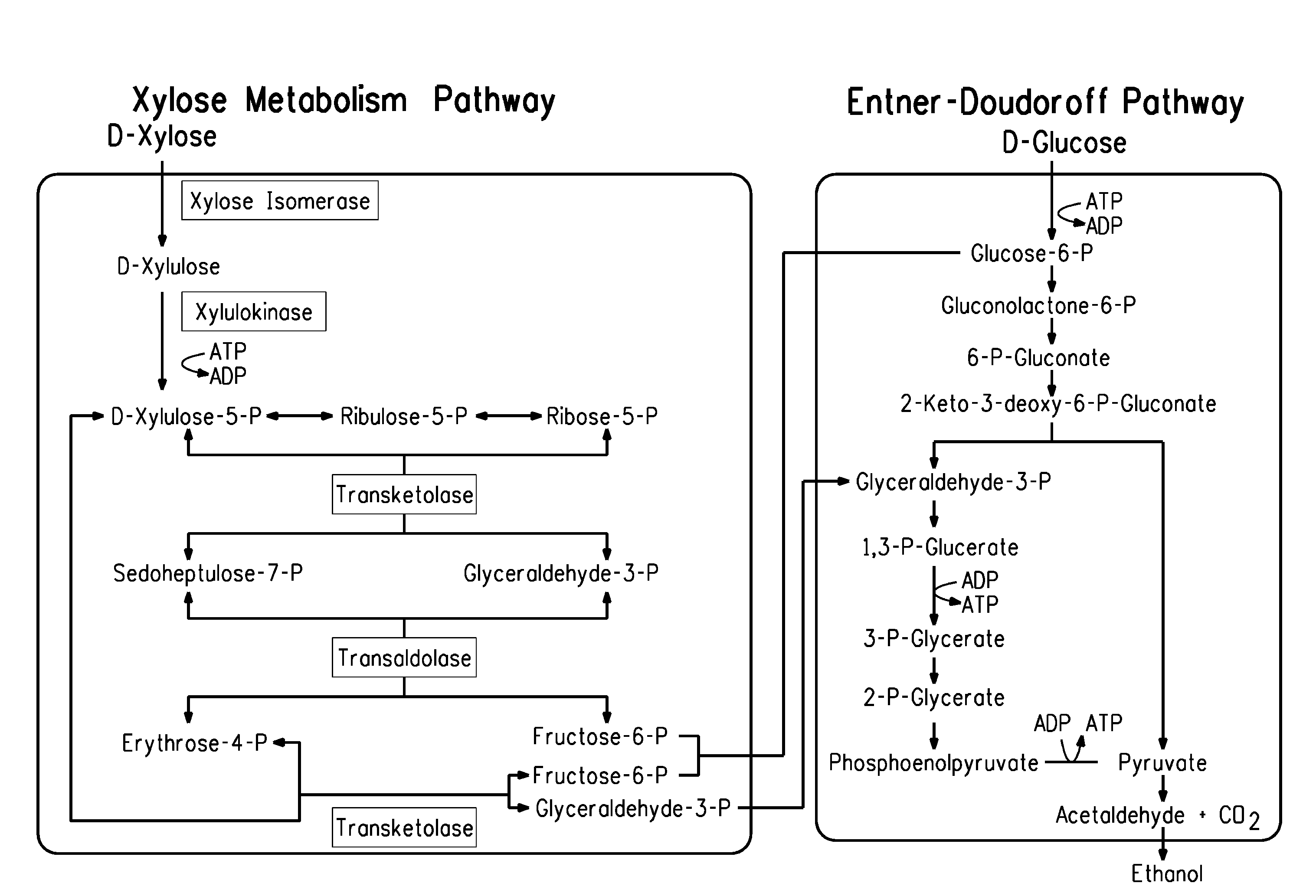
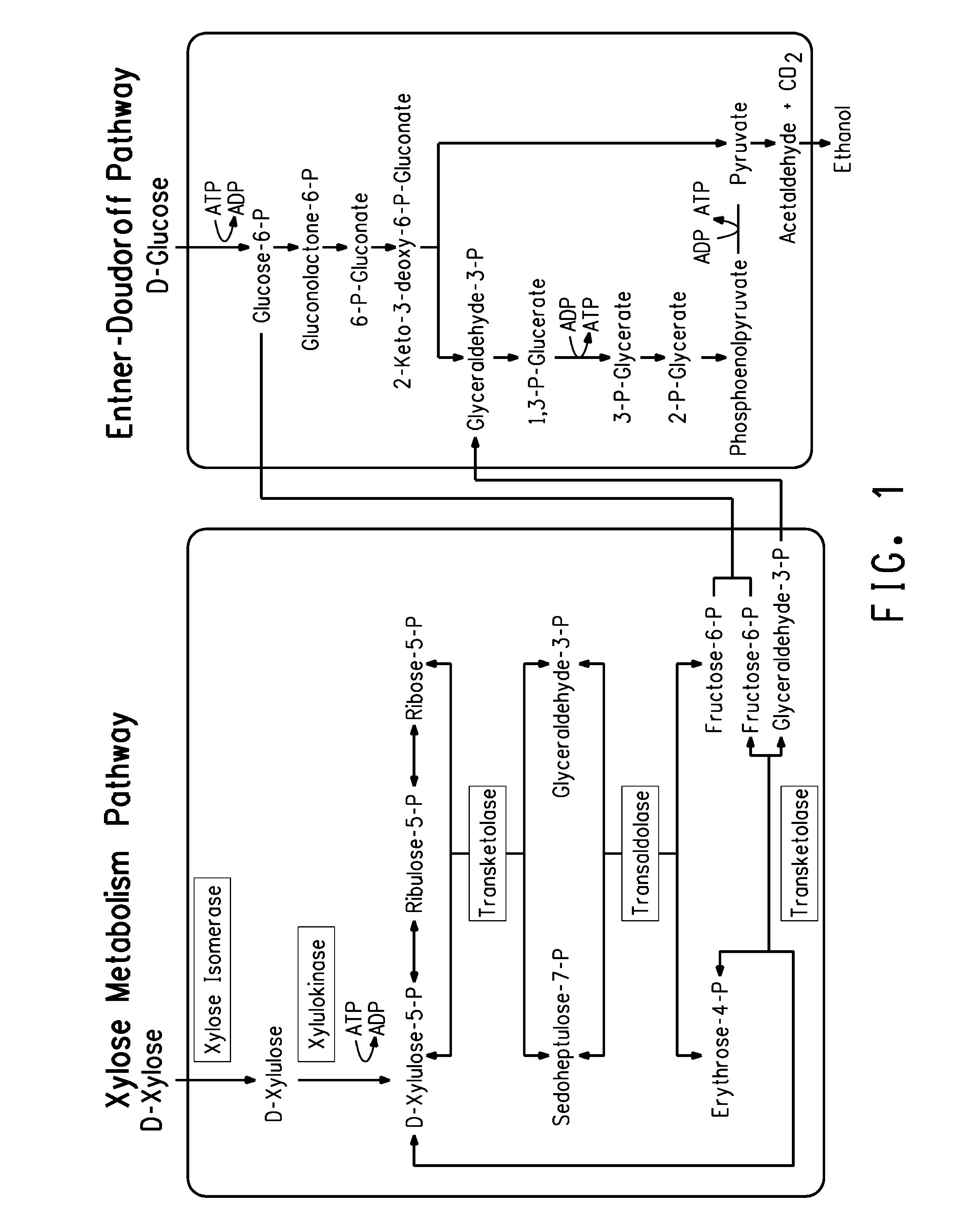
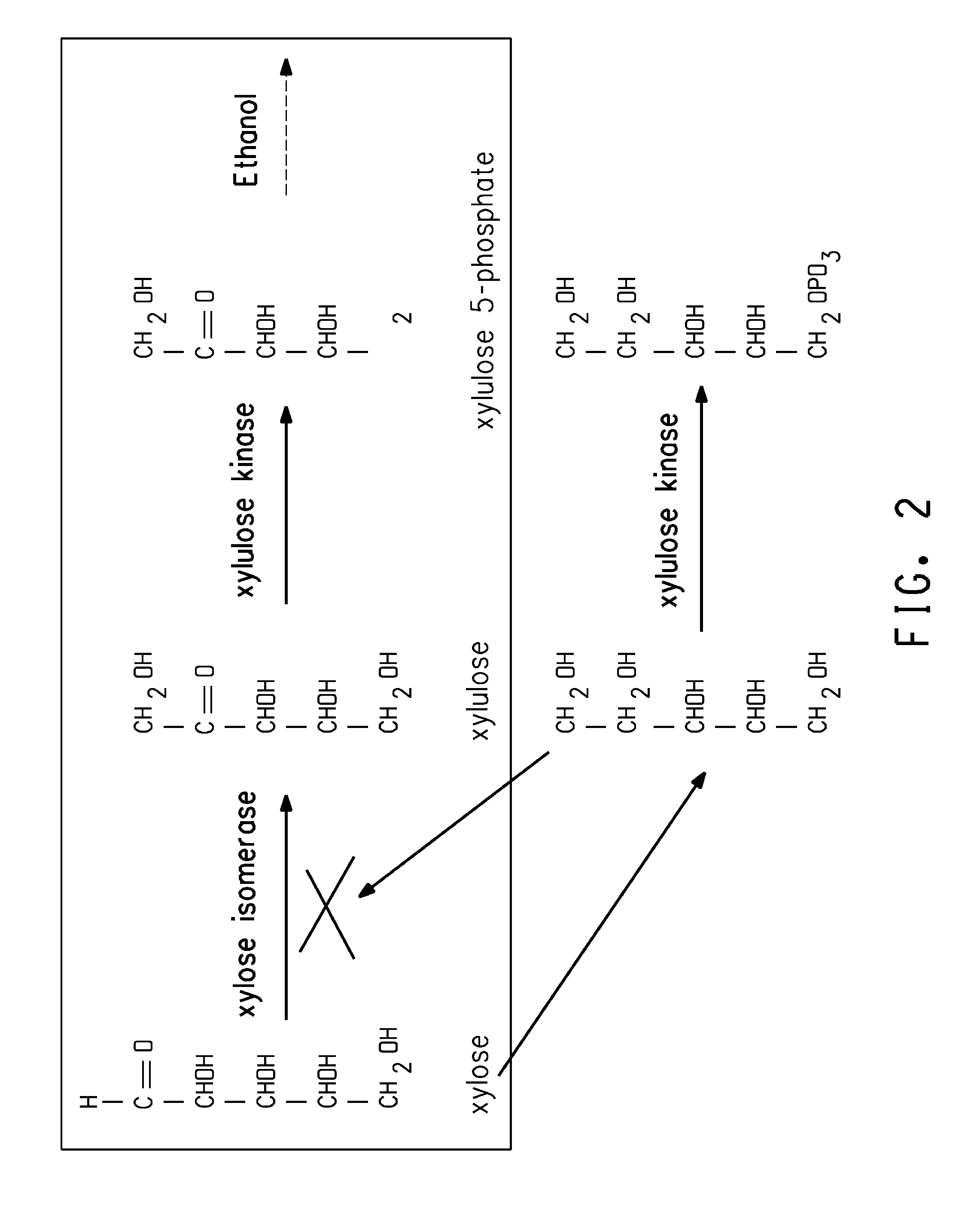
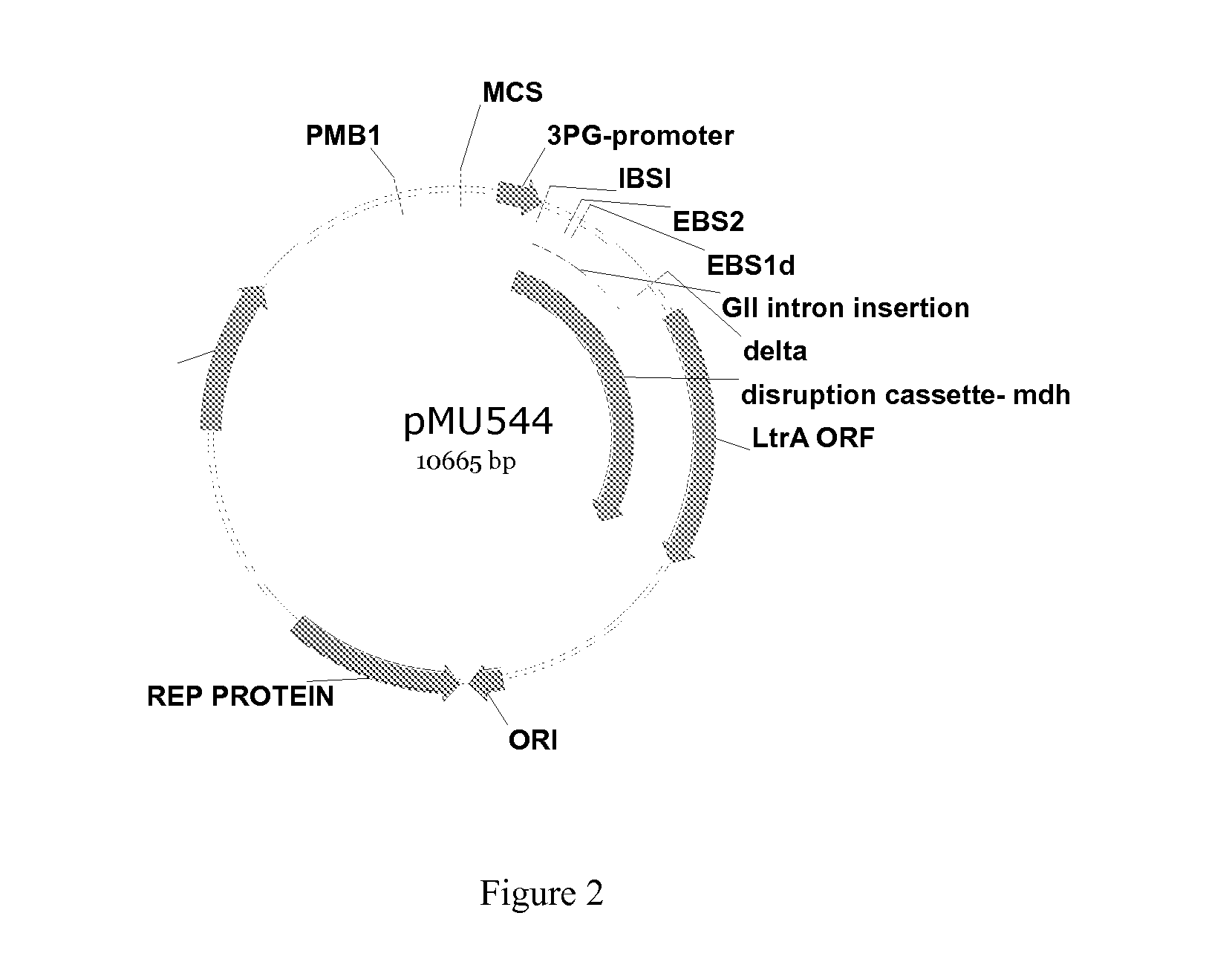
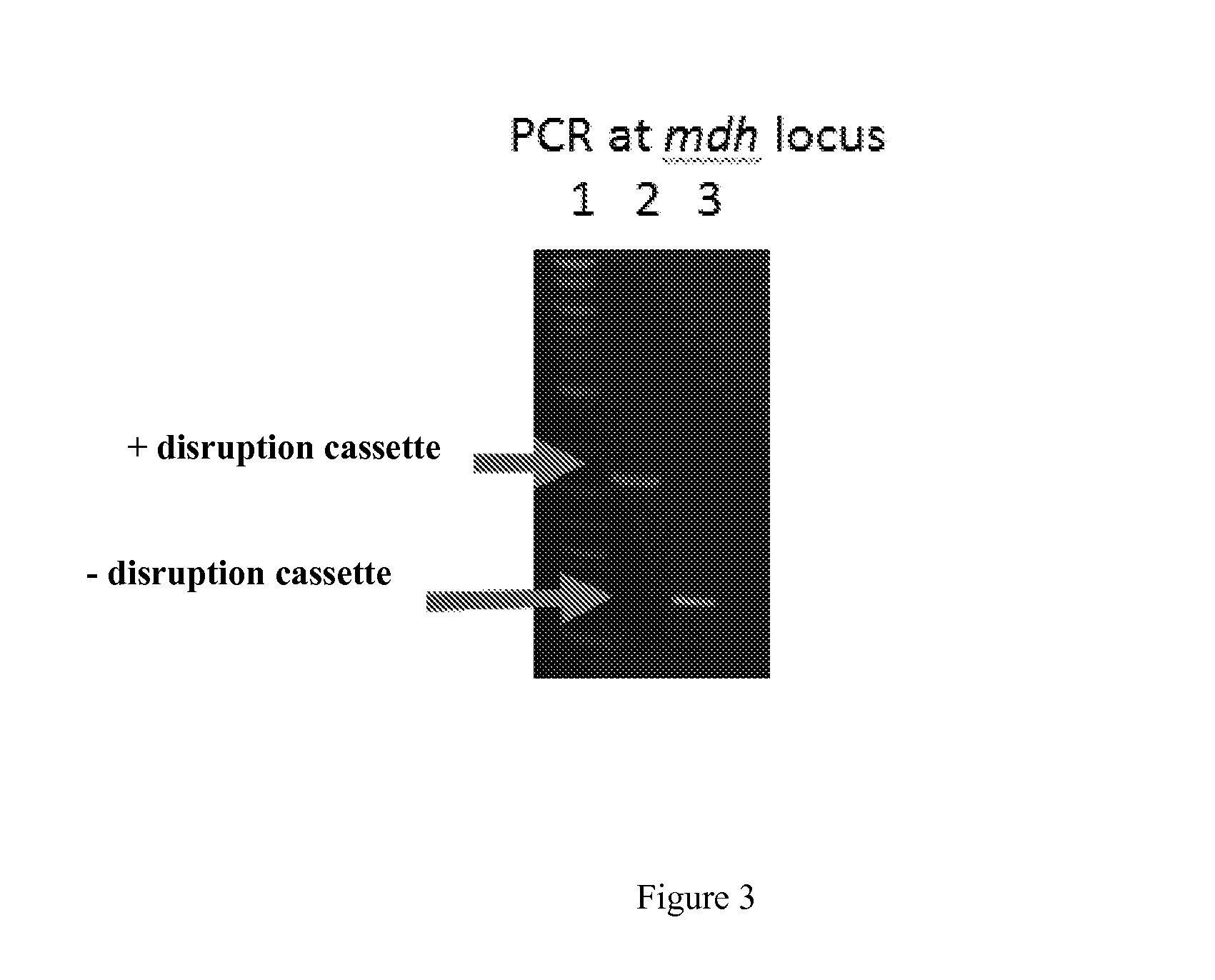
Xylitol synthesis mutant of xylose-utilizing zymomonas for ethanol production
InactiveUS7741119B2Reduce productionIncreased ethanol productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeFructoseOxidoreductase Gene
A strain of xylose-utilizing Zymomonas was engineered with a genetic modification to the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene resulting in reduced expression of GFOR enzyme activity. The engineered strain exhibits reduced production of xylitol, a detrimental by-product of xylose metabolism. It also consumes more xylose and produces more ethanol during mixed sugar fermentation under process-relevant conditions.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
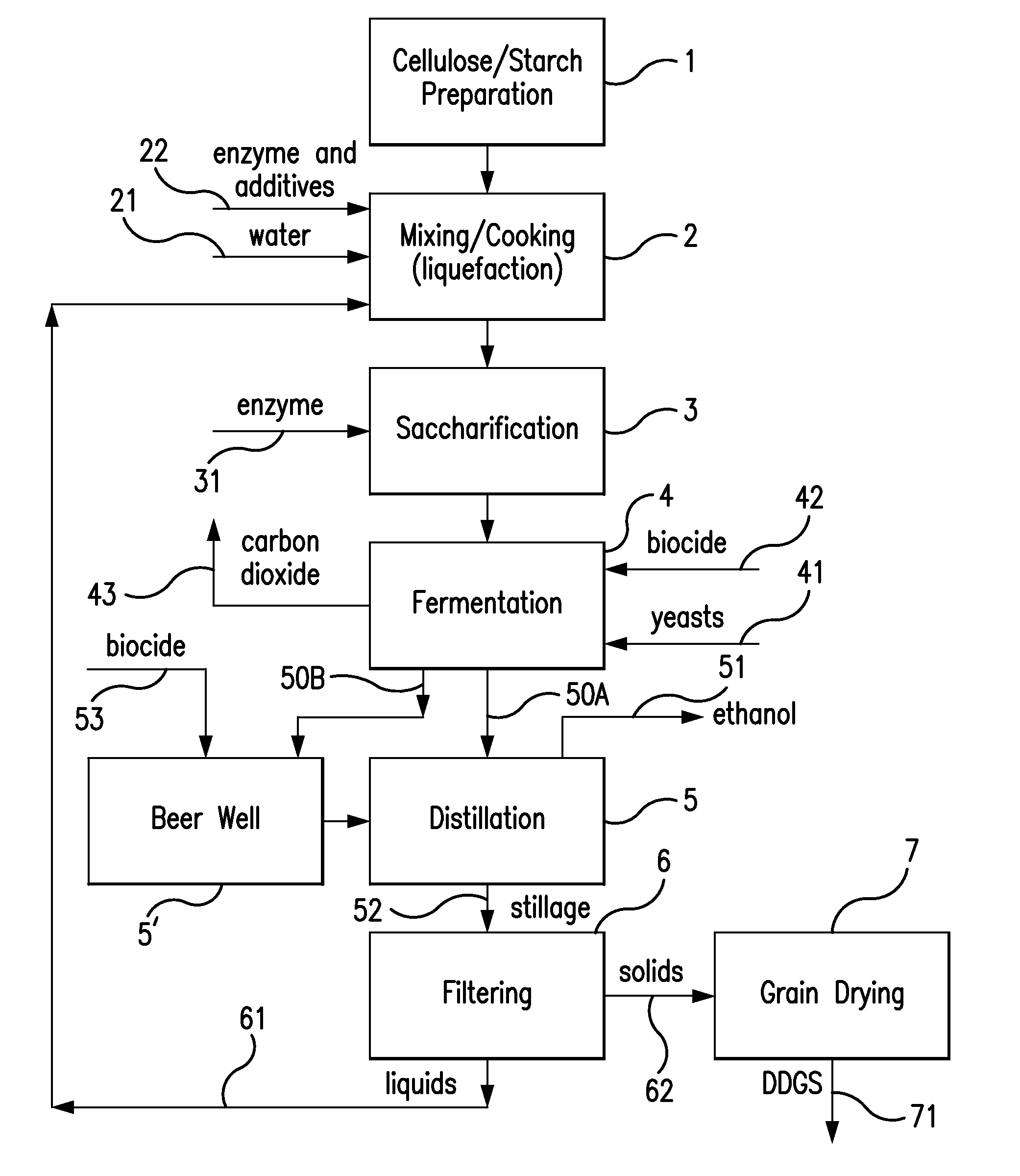
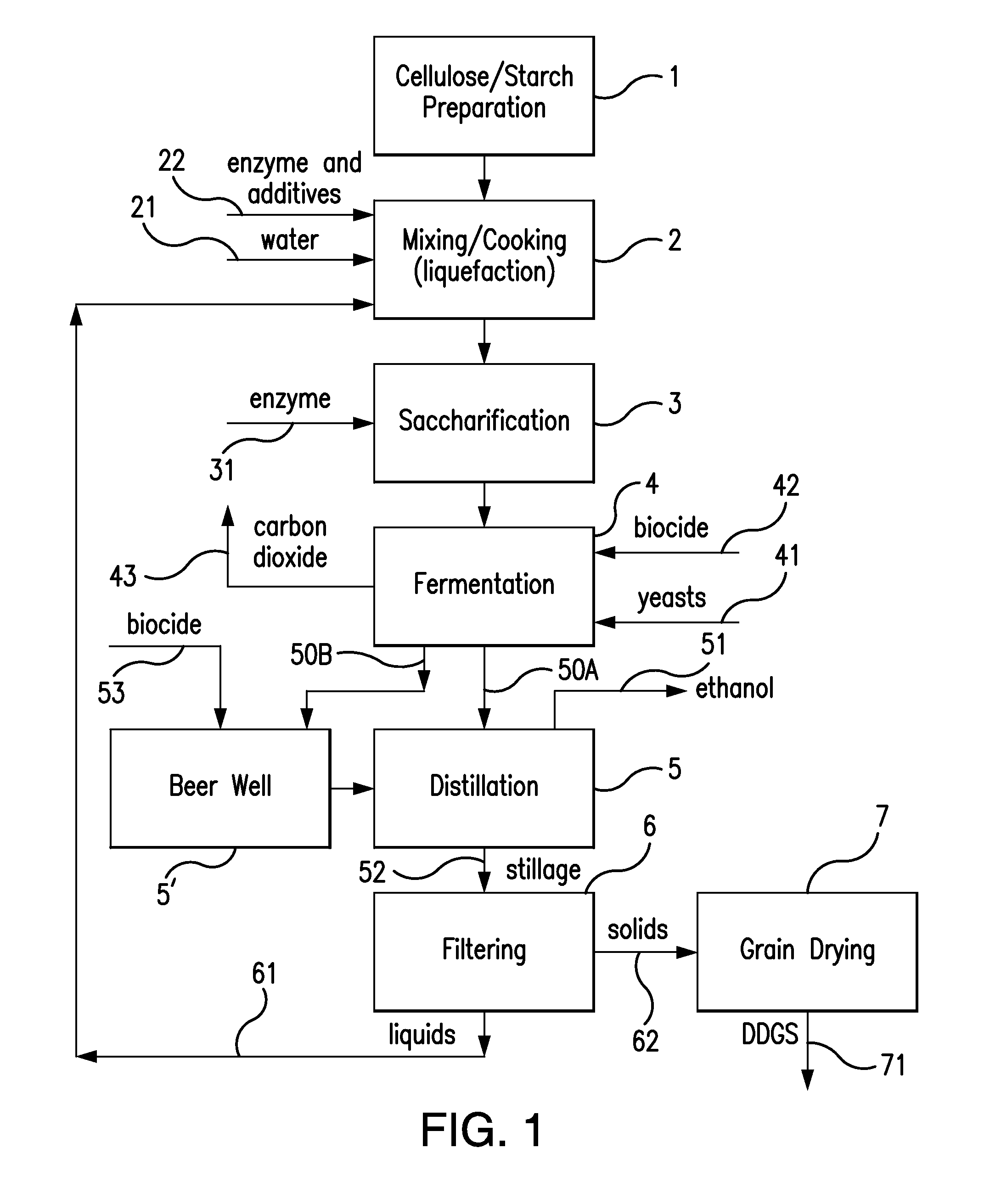
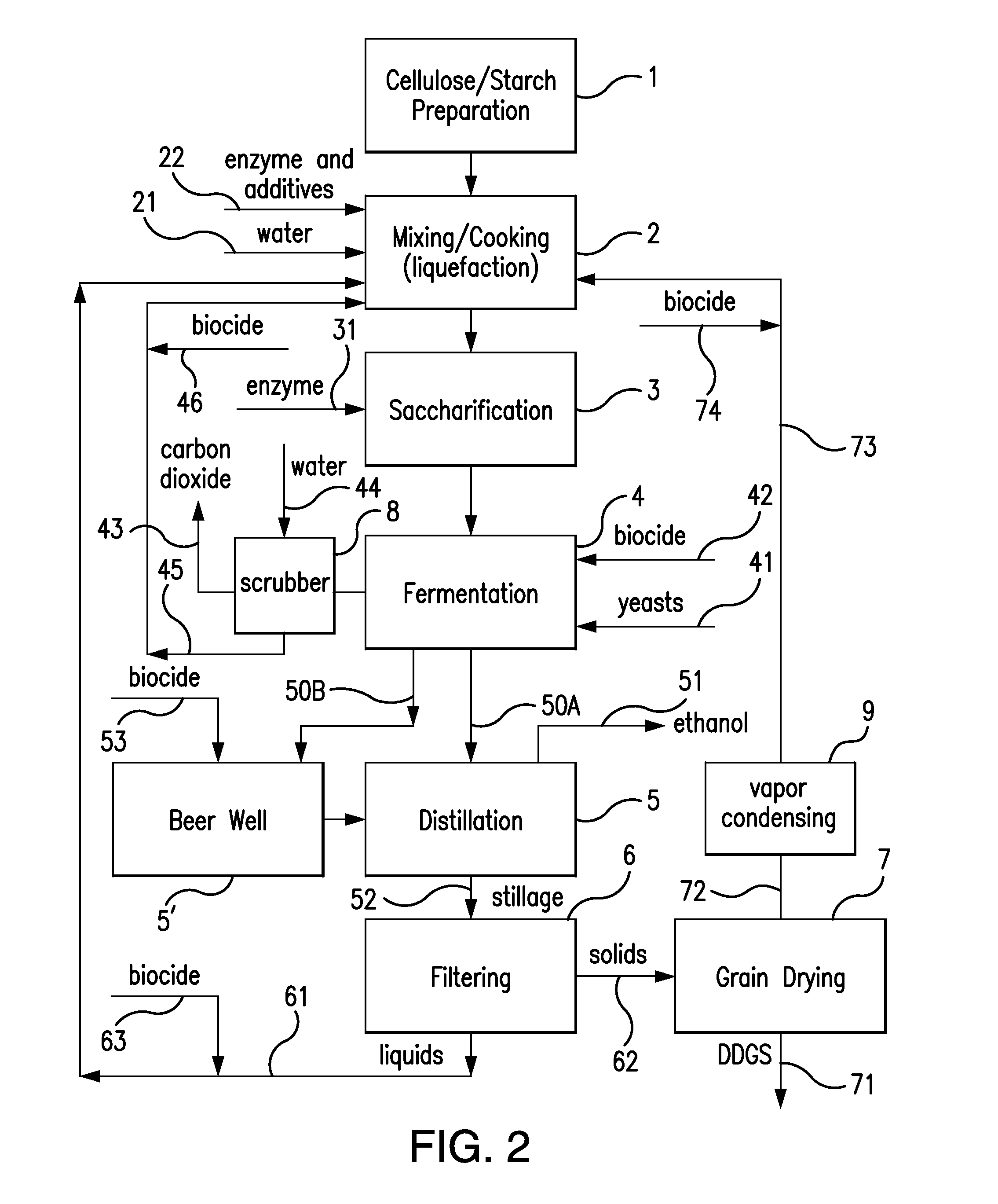
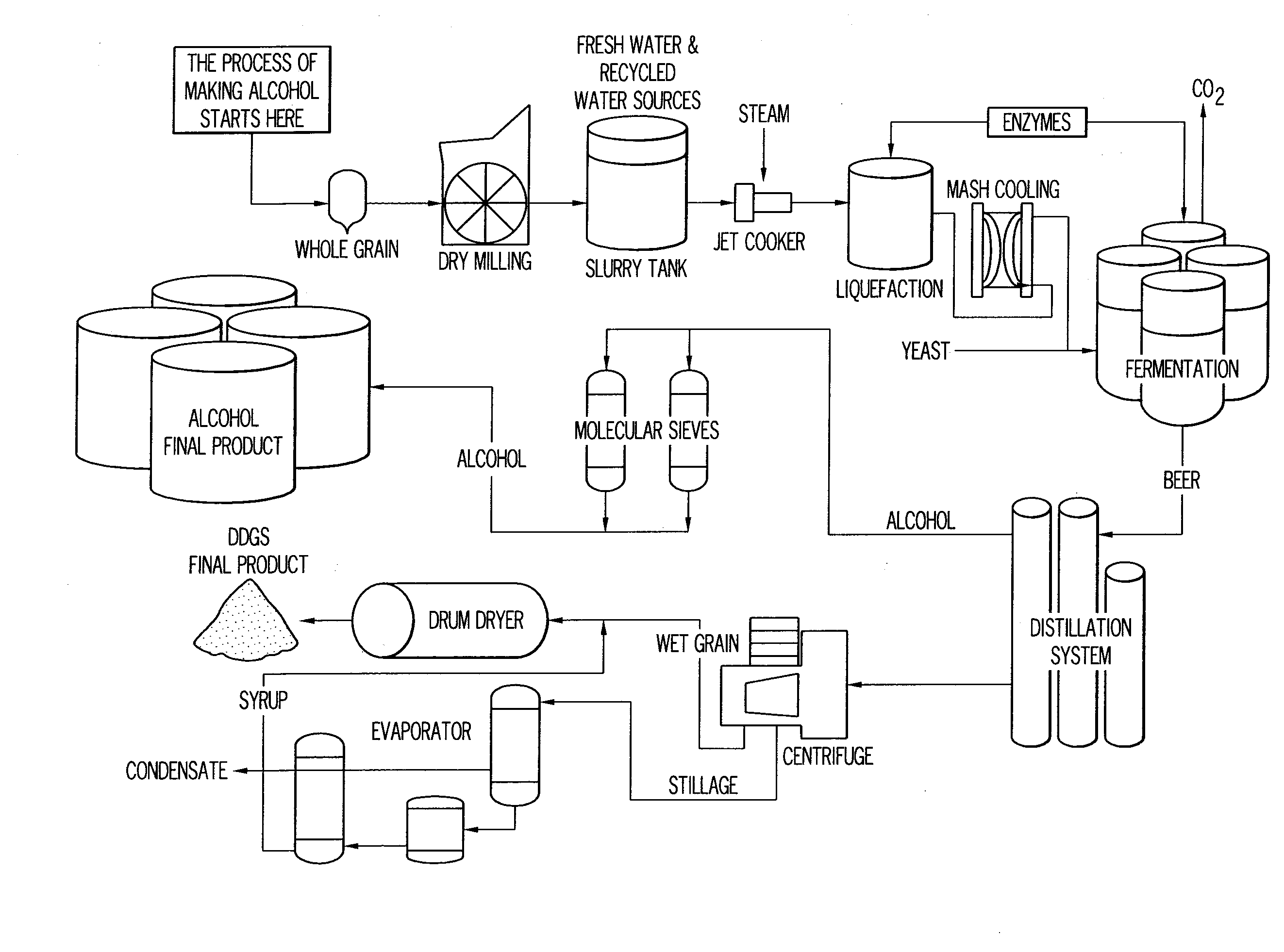
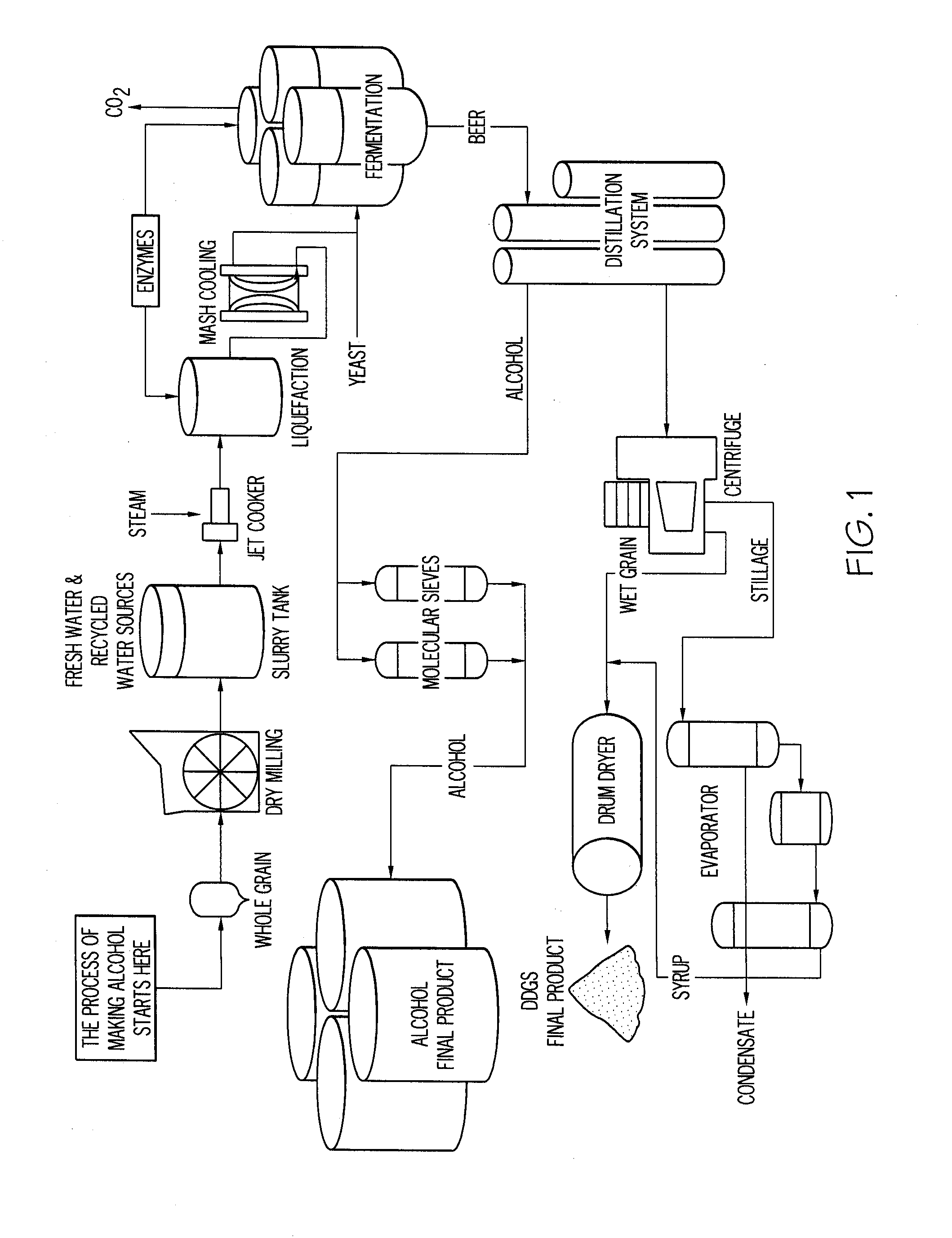
Ethanol plant process
InactiveUS20090166172A1Shorten process cycleIncrease ethanol productionOrganic compound preparationBeer fermentationEthanol fuelProcess engineering
The present invention conserves water by reducing the heat load placed on a cooling tower during the ethanol fuel production process. An air cooler is placed between the ethanol vapor condenser and the cooling tower thereby minimizing process temperature spikes before water enters the cooling tower. This, in turn, shortens the process cycle thereby increasing ethanol production. During certain climactic conditions, the cooling tower may be completely bypassed, thereby conserving more water and increasing ethanol production.
Owner:CASEY LEONARD RAY
Process for the production of animal feed and ethanol and novel animal feed
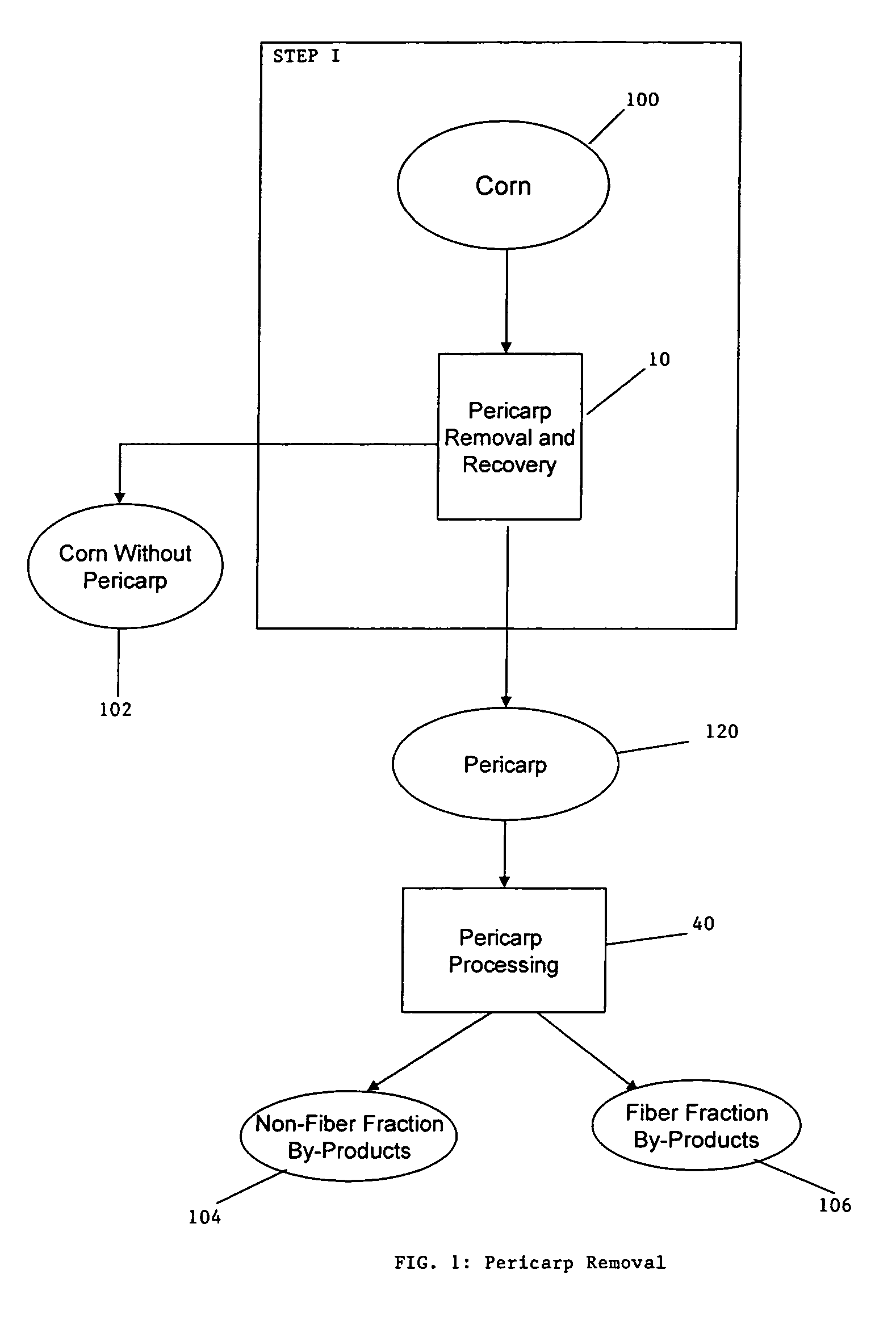
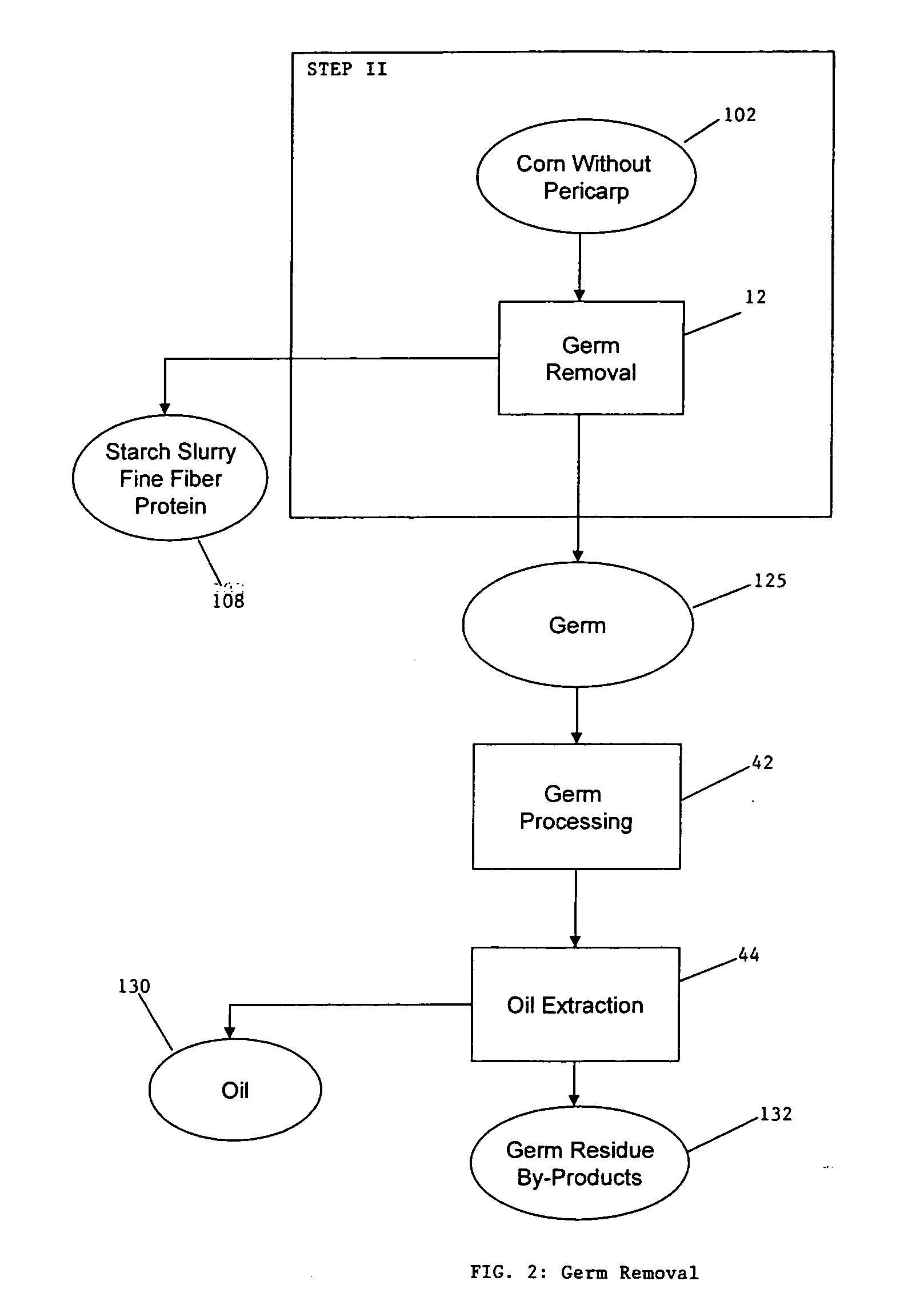
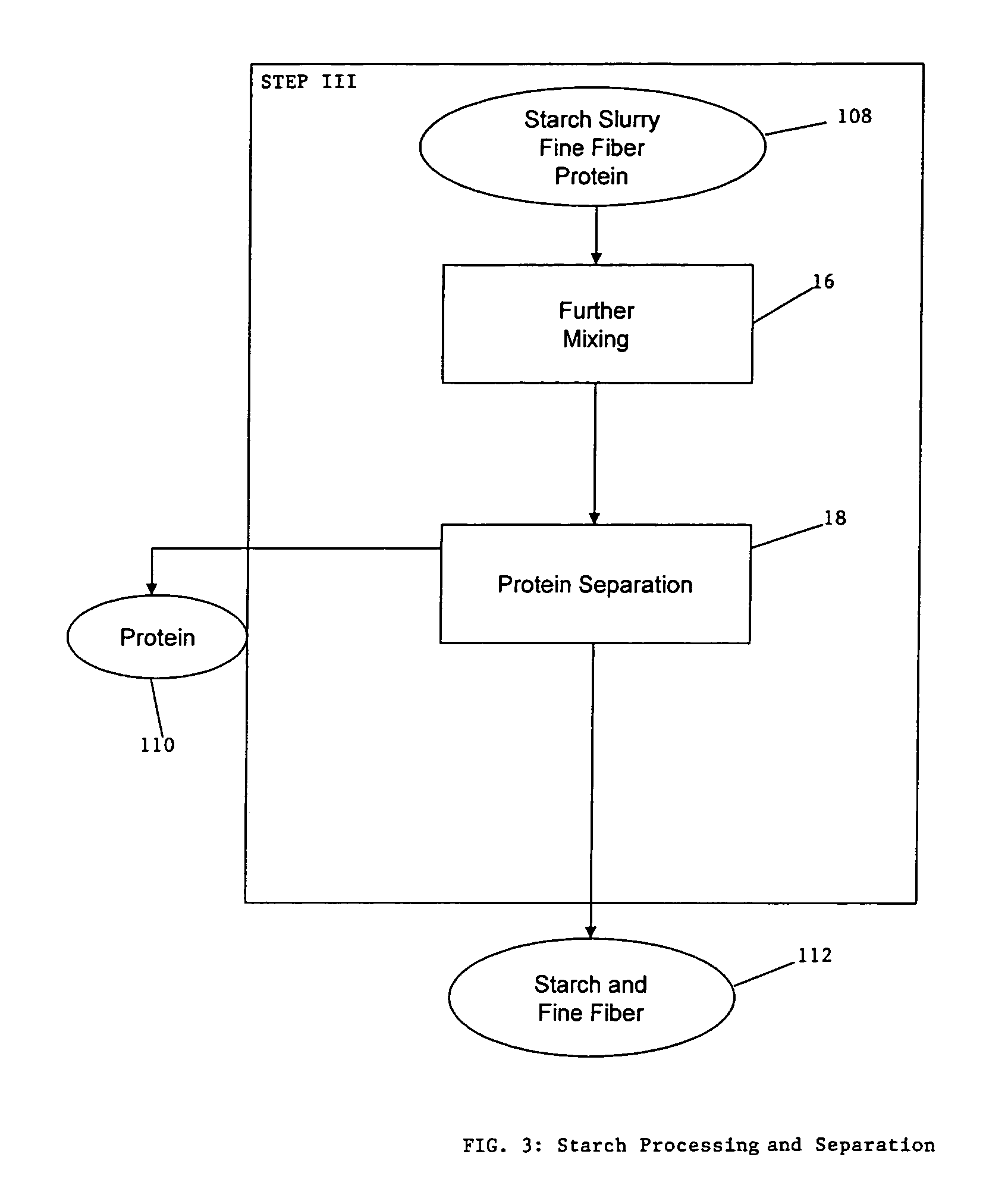
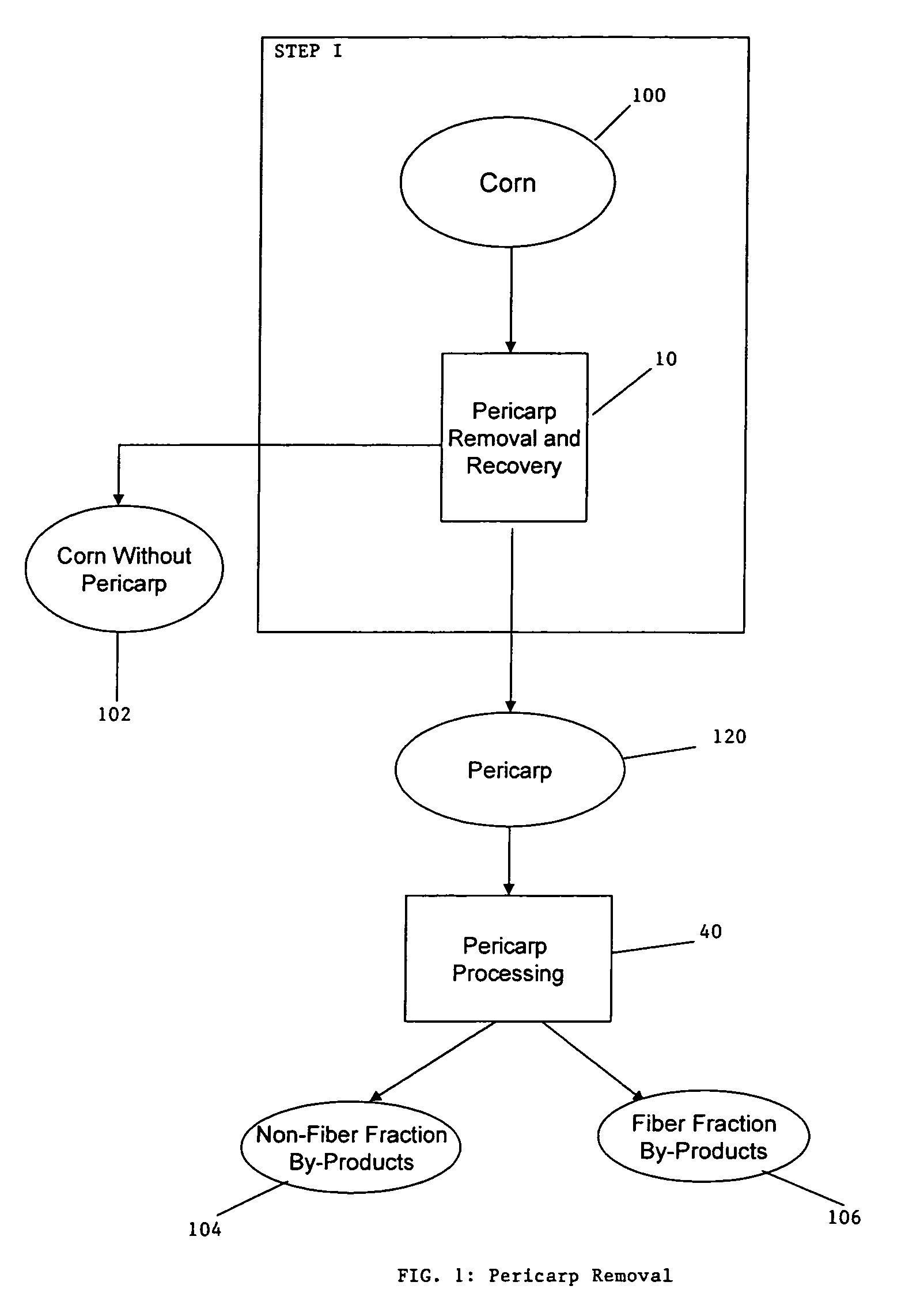
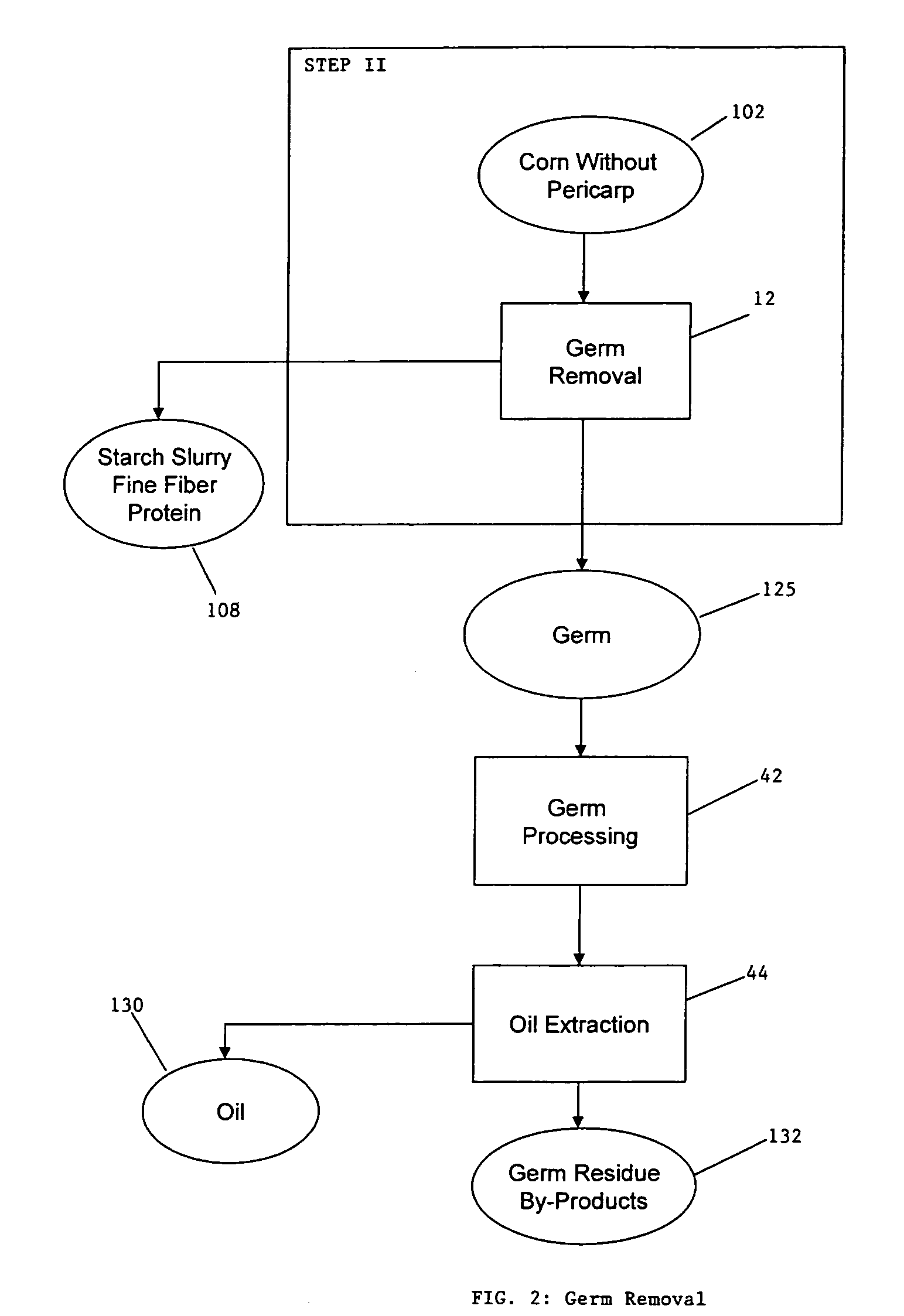
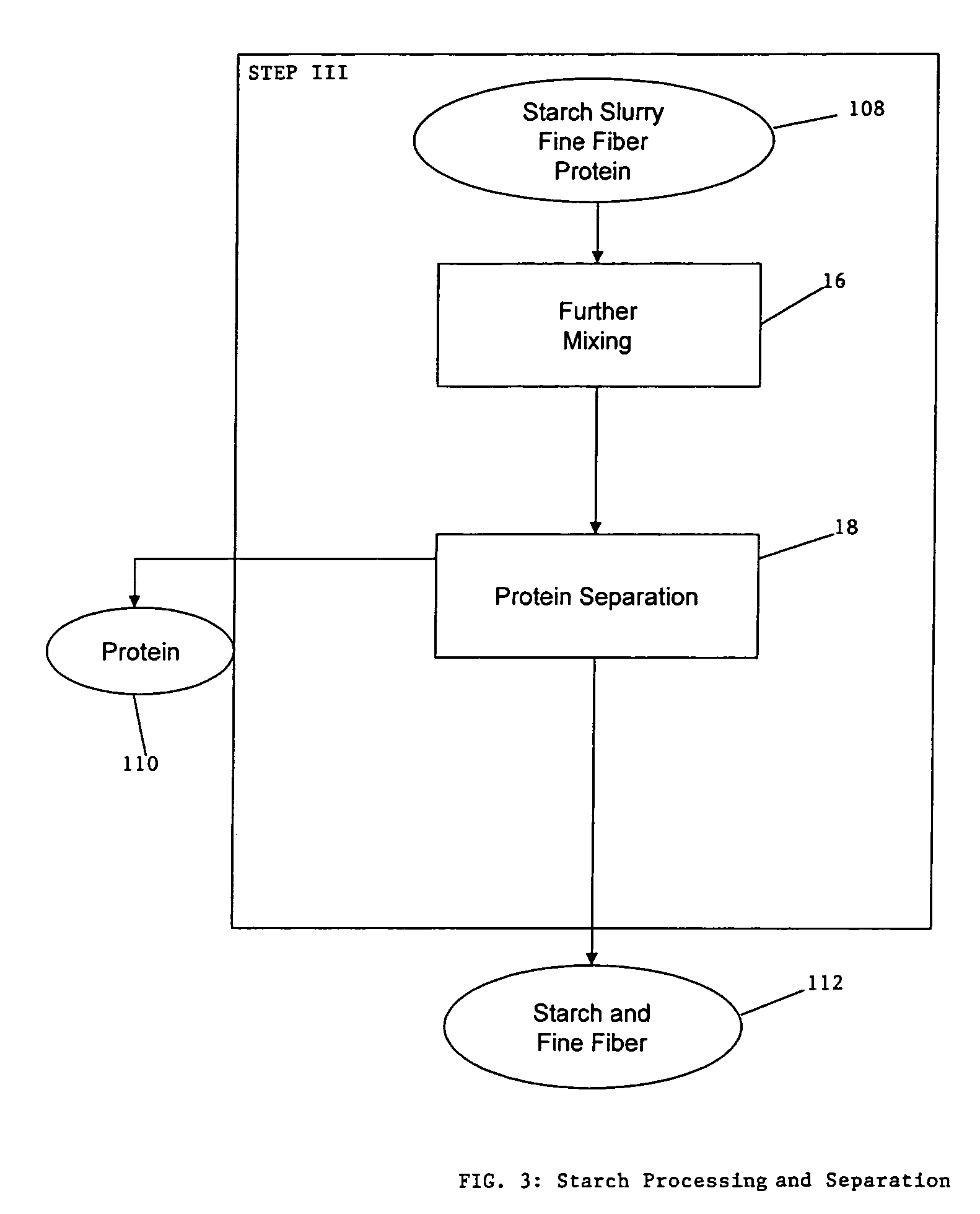
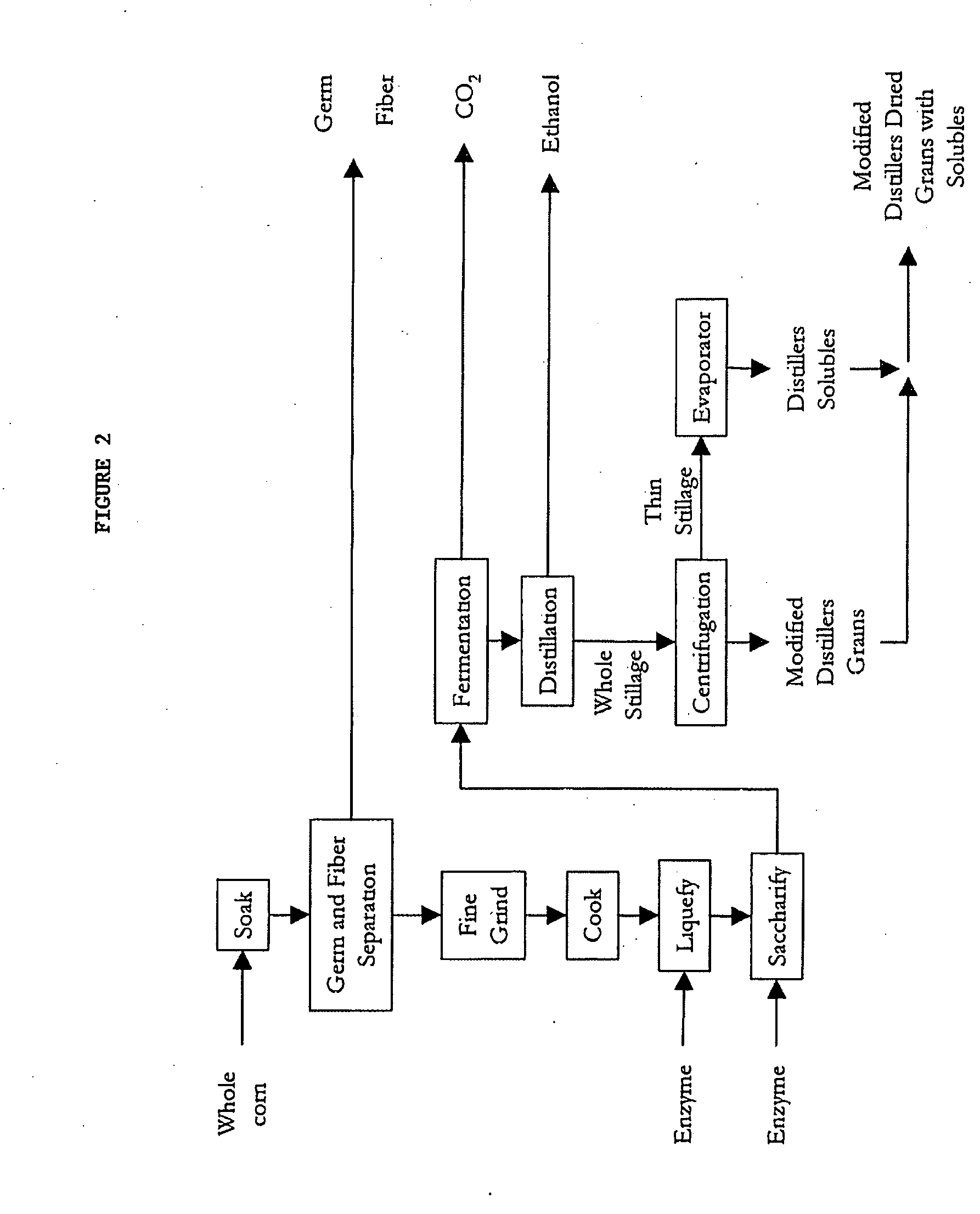
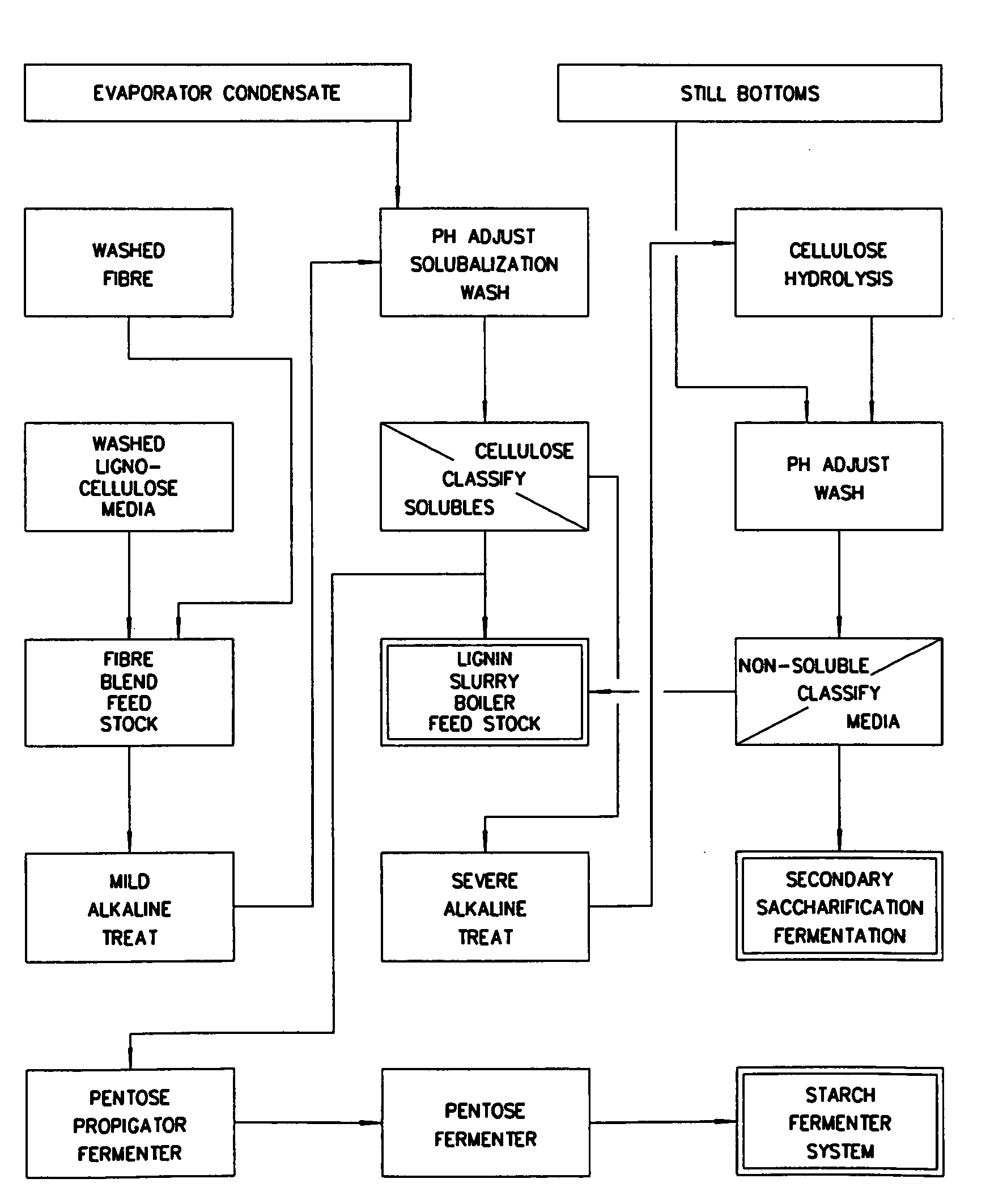
ActiveUS20060251764A1Enhance digestibilityDecrease in crystallinityGrain huskingBiocideChemistryBiomass
A method for the production of ethanol and a modified animal feed is provided. The method replaces the starch in known corn-based animal feed with biomass fiber treated to make it more digestible by animals. The process includes wherein the pericarp and germ are removed from the corn kernel and processed for by-products. The starch and protein are also removed and separated. The starch is then fermented and distilled to ethanol and stillage. The bioavailable modified animal feed comprises the pericarp and germ removed from corn kernels and optionally by-products of the pericarp and germ processing, and lignocellulosic materials. The modified animal feed may optionally include energy materials such as animal and vegetable fats, vegetable soapstocks, or glycerin, and combinations thereof.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
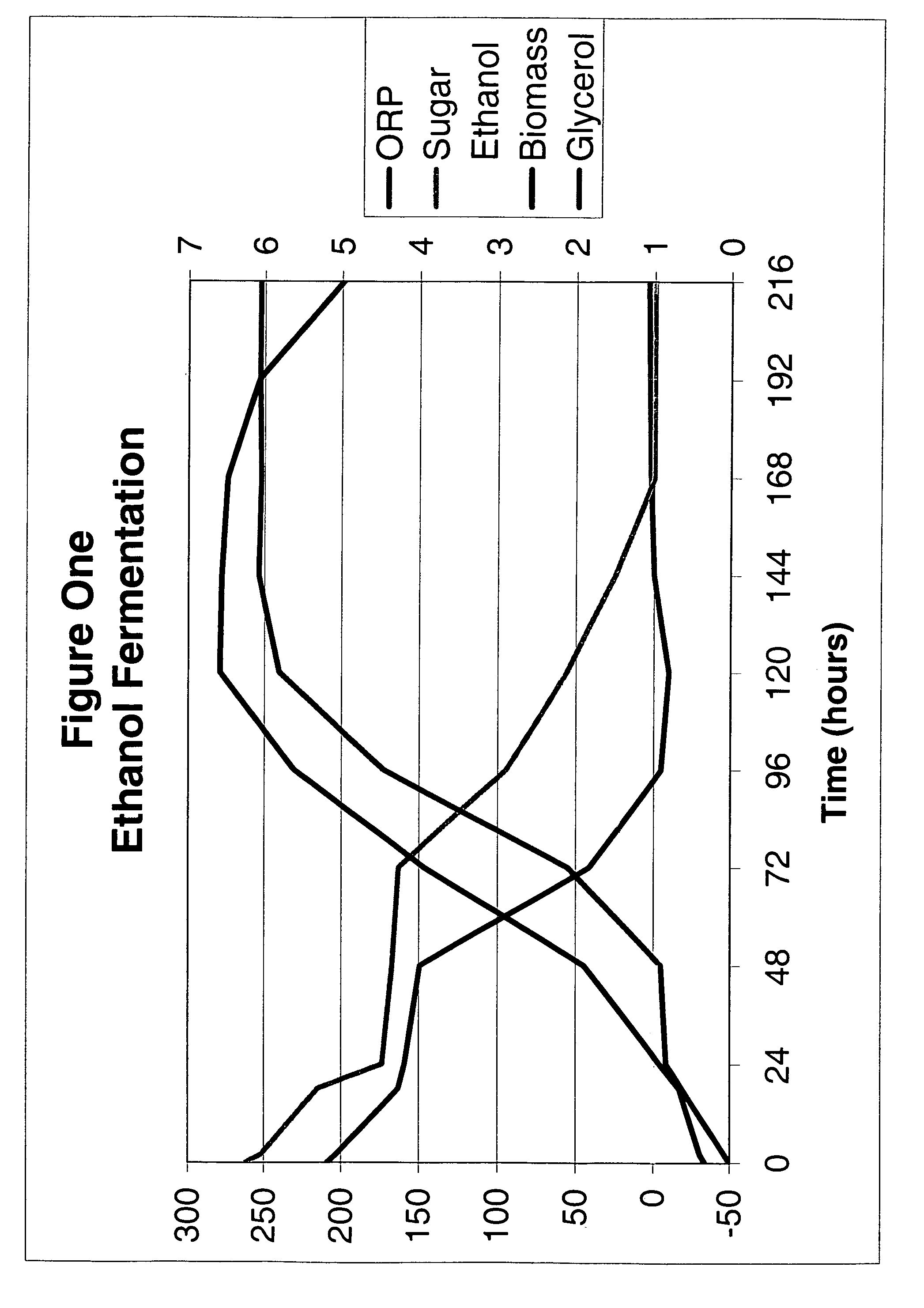
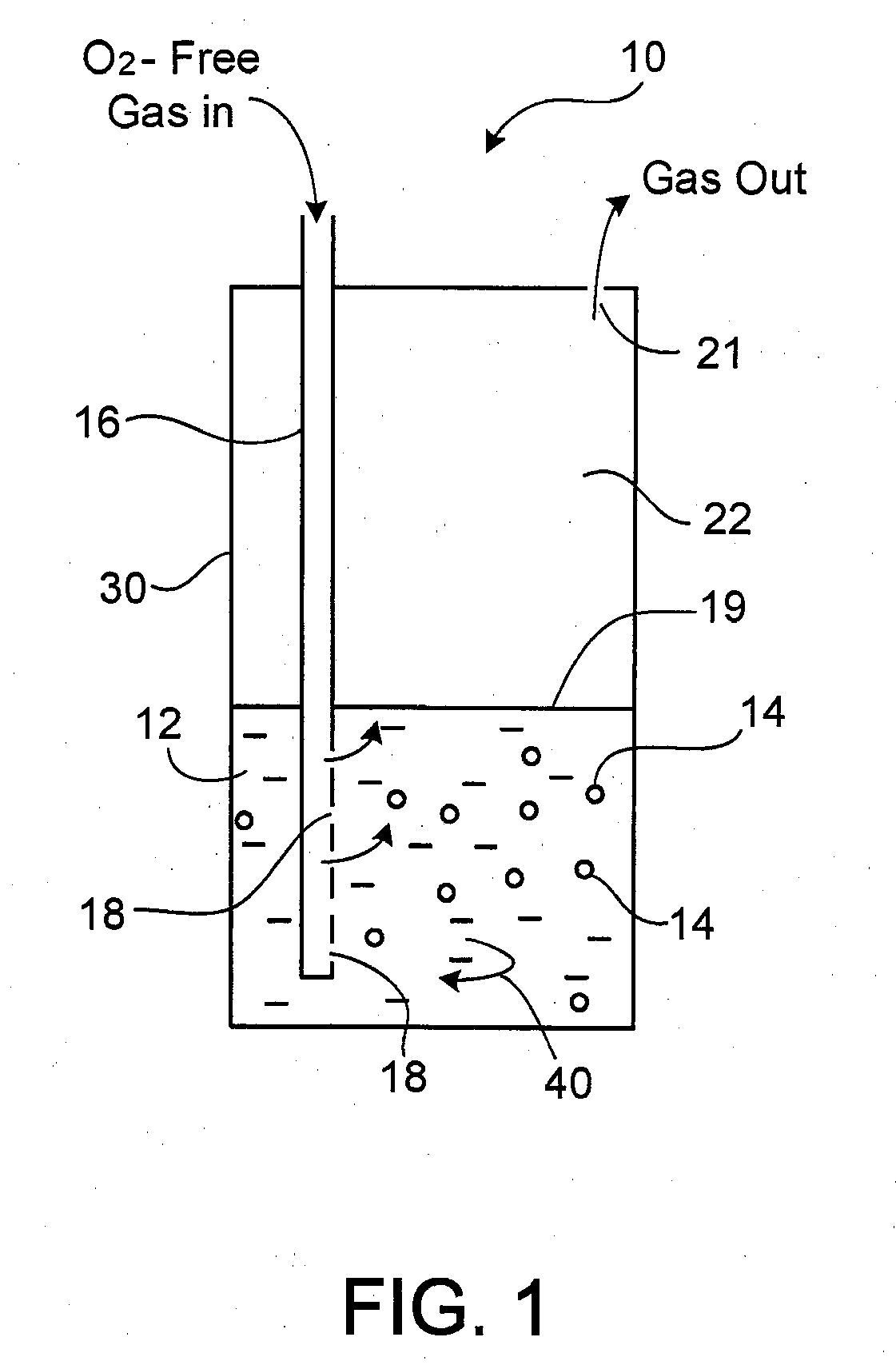
Ethanol fermentation using oxidation reduction potential
InactiveUS7078201B2Increased ethanol productionReduce formationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiofuelsOxidation-Reduction AgentRedox
A process to improve ethanol yield, decrease fermentation time and reduce byproduct formation by monitoring and controlling oxidation reduction potential (redox) of the fermentor is disclosed.
Owner:BURMASTER BRIAN M
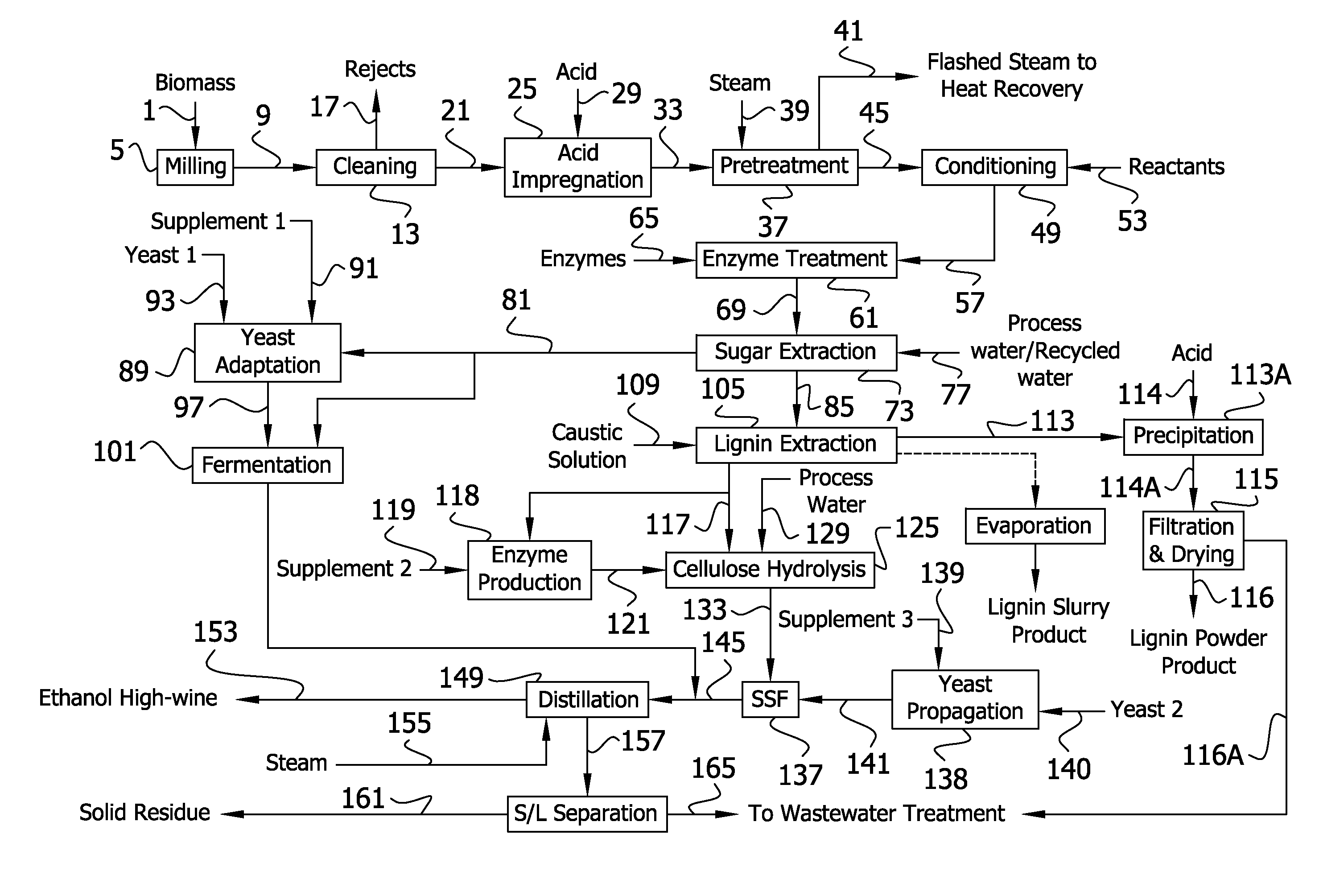
Method for producing ethanol and co-products from cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20120006320A1Increased ethanol productionImproved co-productsFuel supply regulationPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsCelluloseLignocellulosic biomass
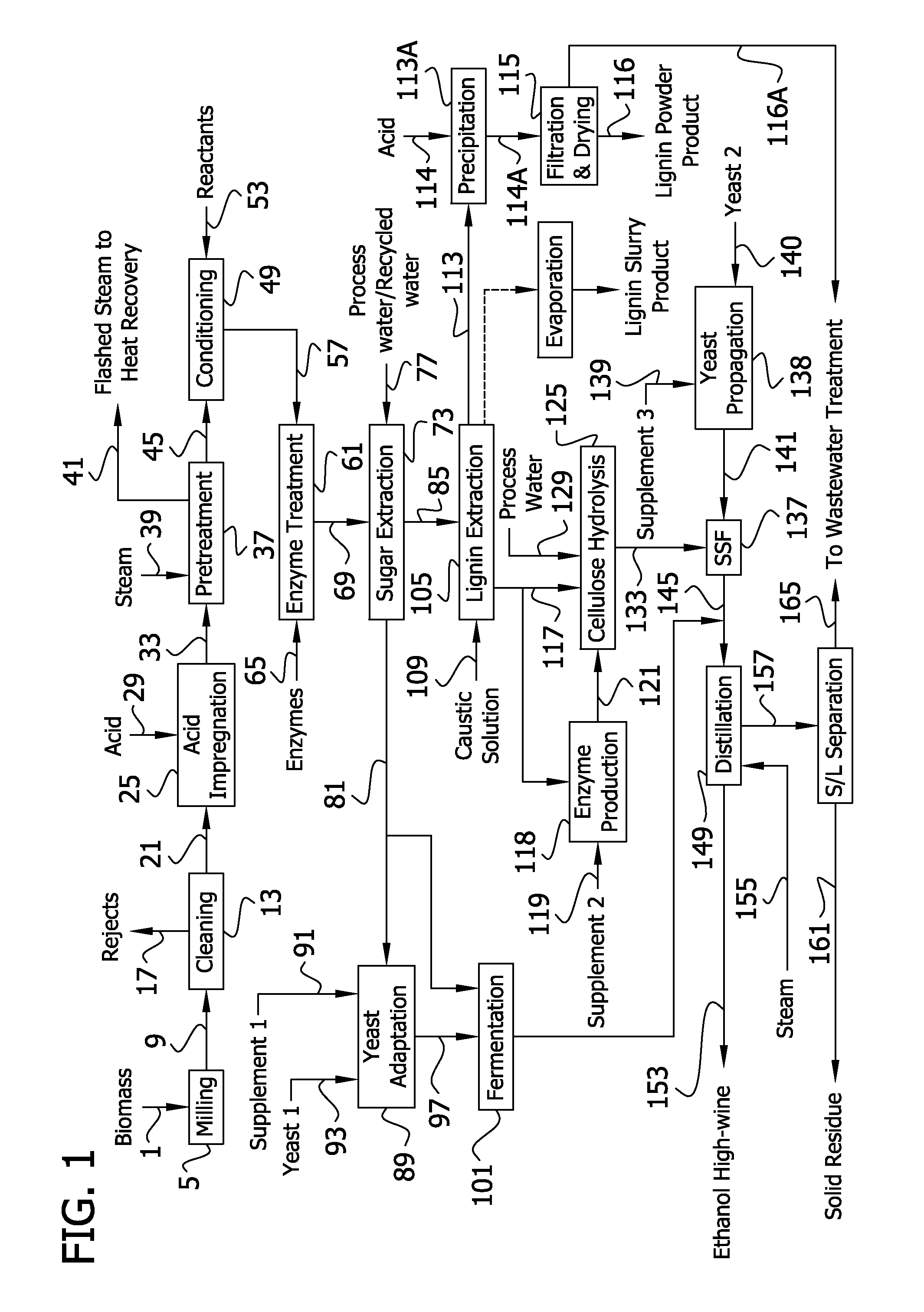
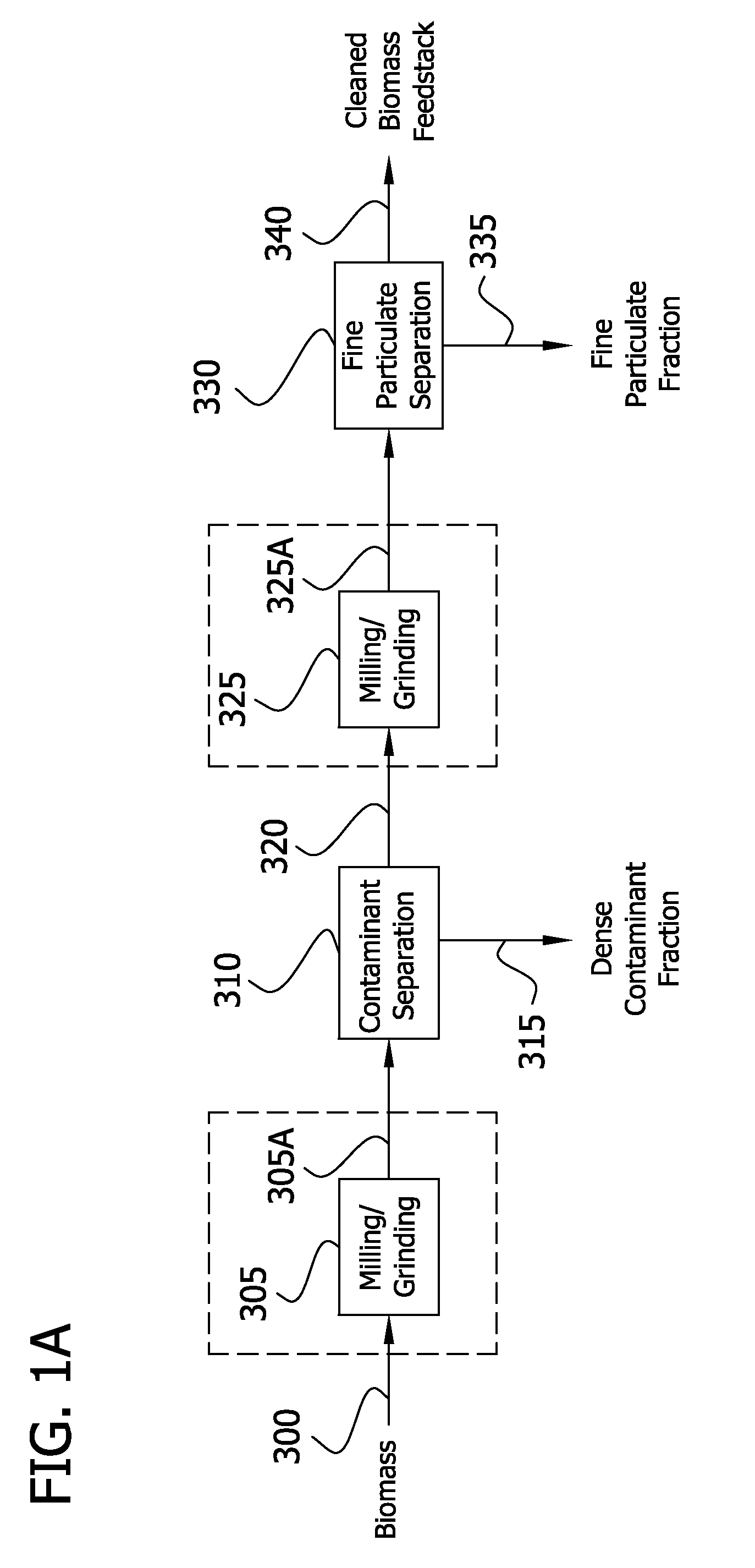
The present invention generally relates to processes for production of ethanol from cellulosic biomass. The present invention also relates to production of various co-products of preparation of ethanol from cellulosic biomass. The present invention further relates to improvements in one or more aspects of preparation of ethanol from cellulosic biomass including, for example, improved methods for cleaning biomass feedstocks, improved acid impregnation, and improved steam treatment, or “steam explosion.”
Owner:ABENGOA BIOENERGY NEW TECH
Designer Organisms for photosynthetic production of ethanol from carbon dioxide and water
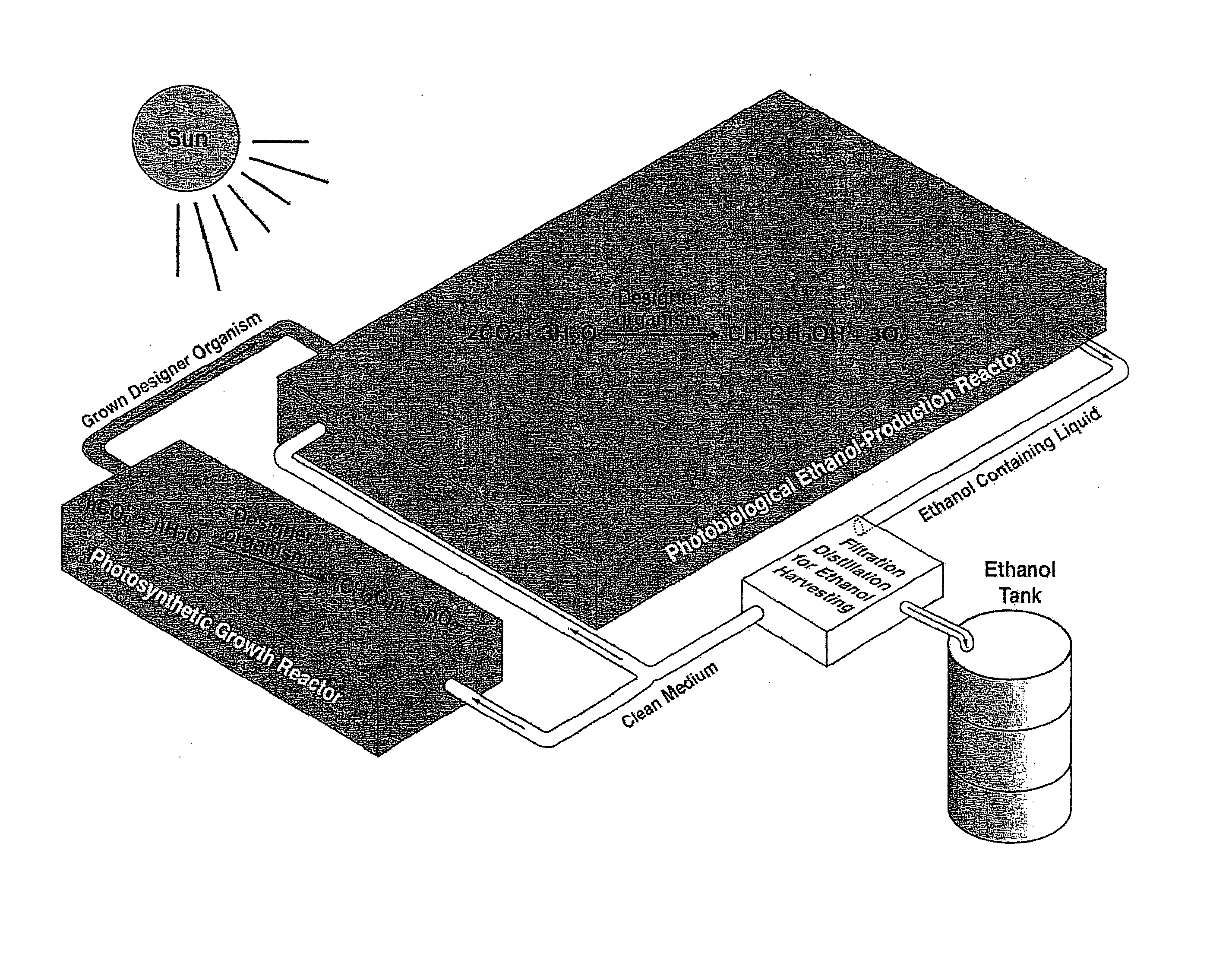
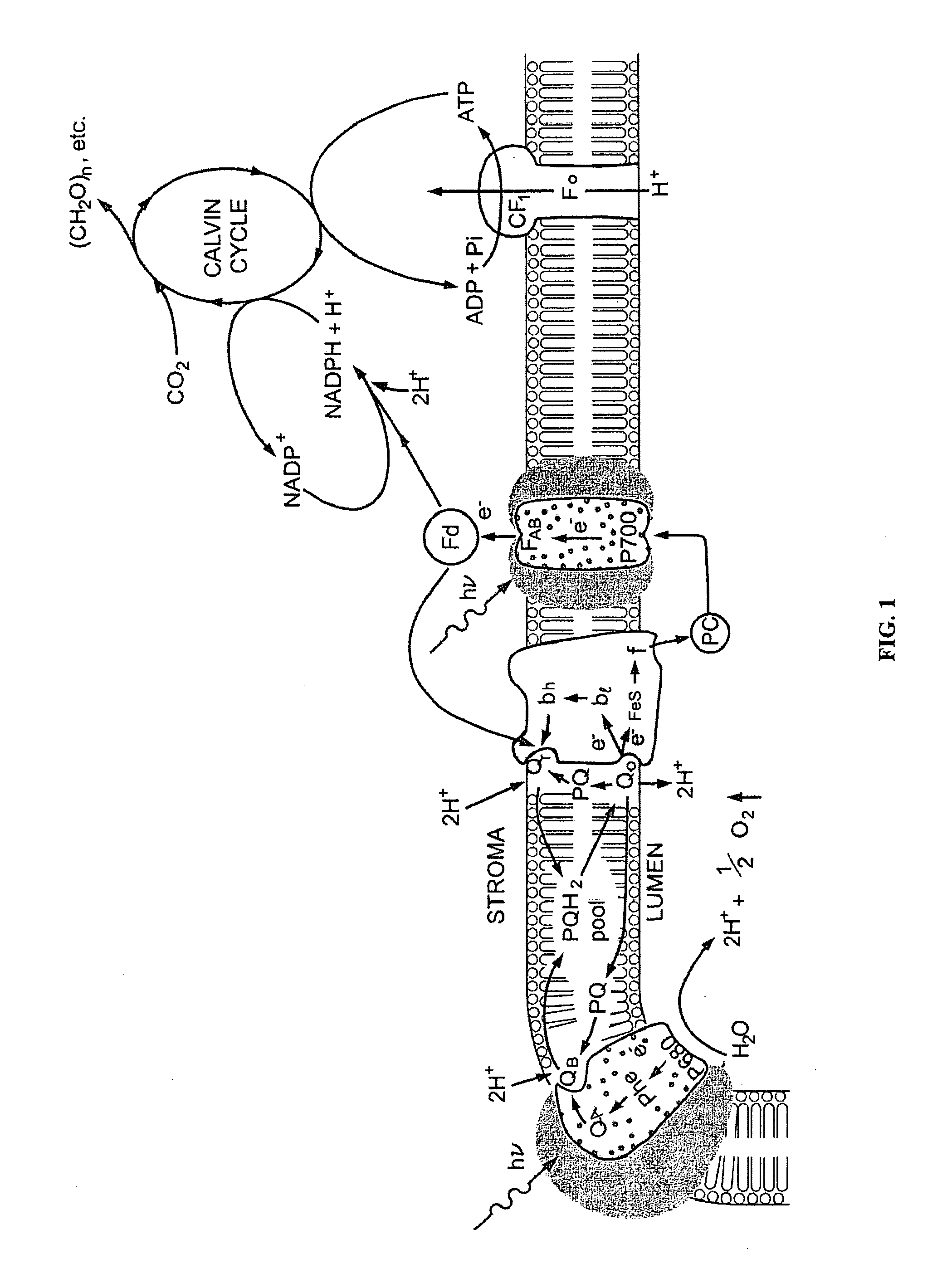
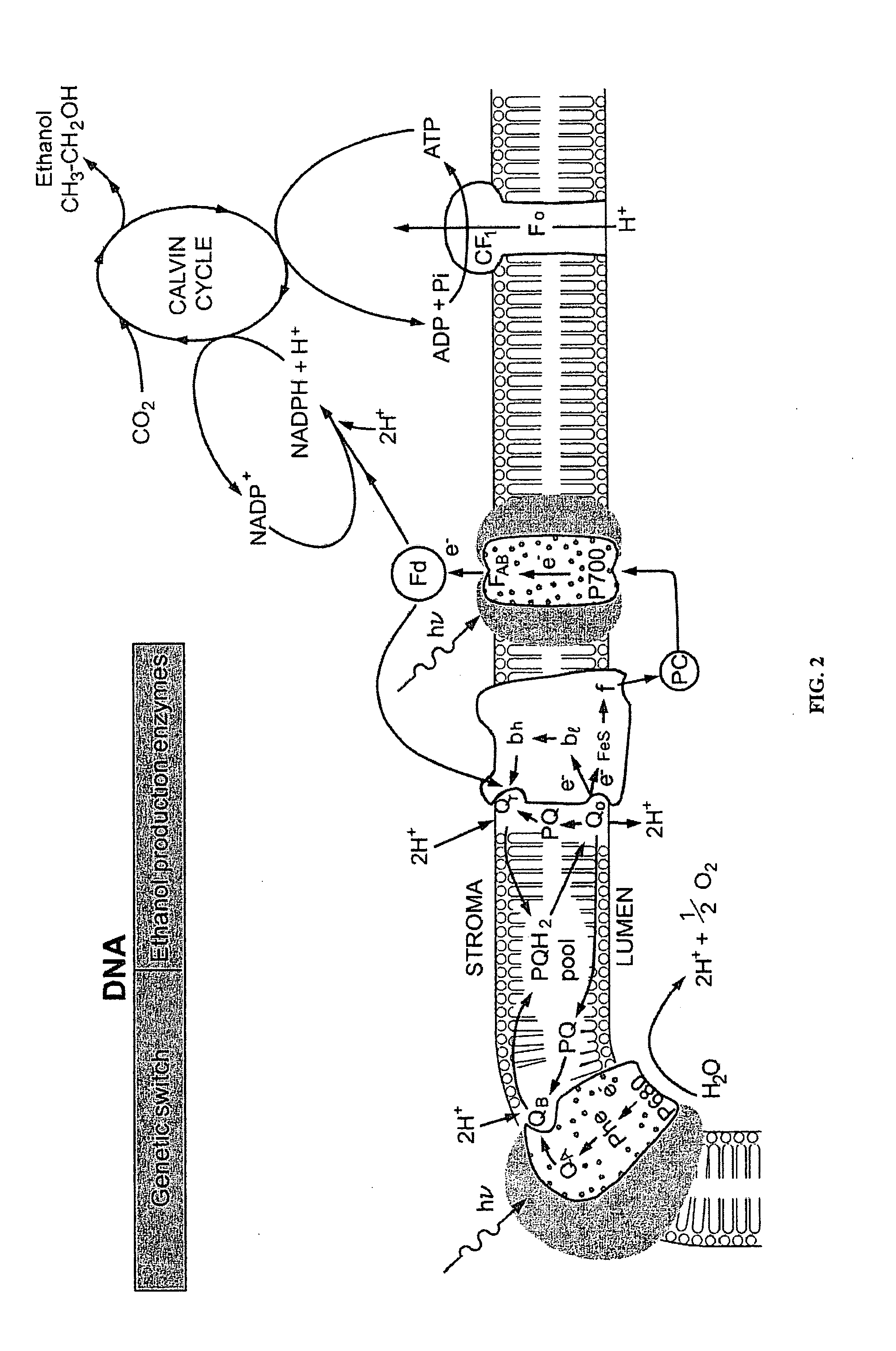
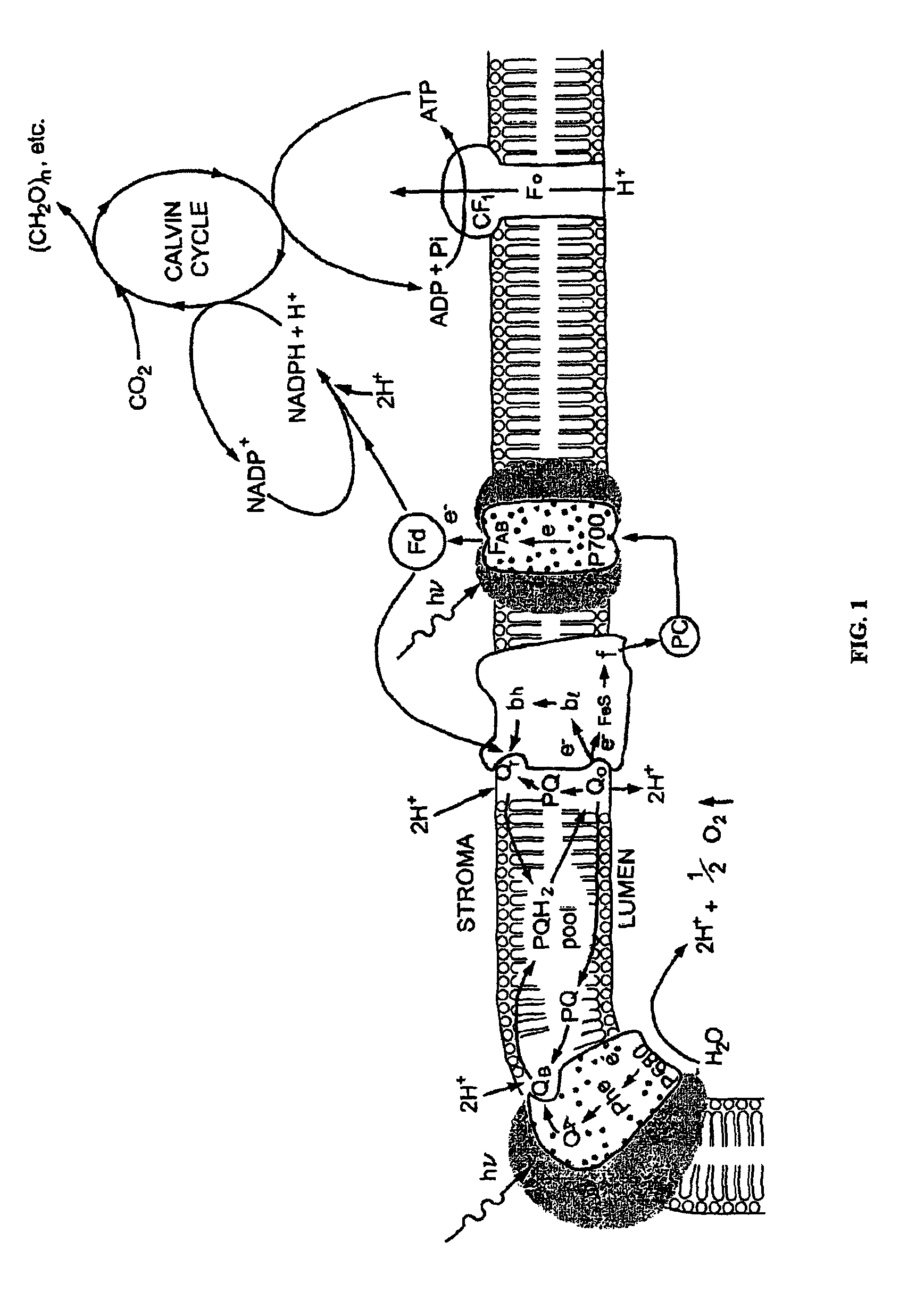
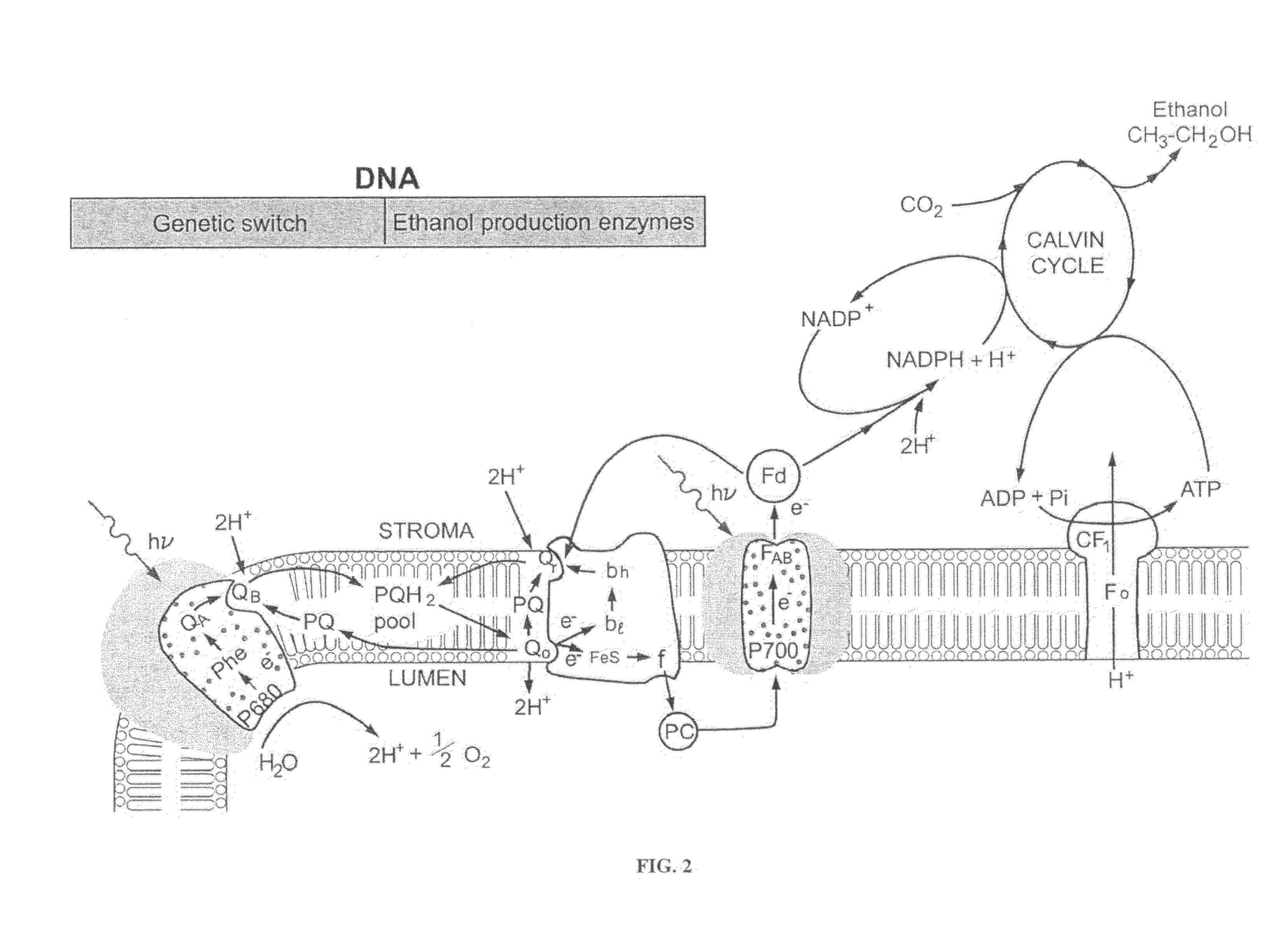
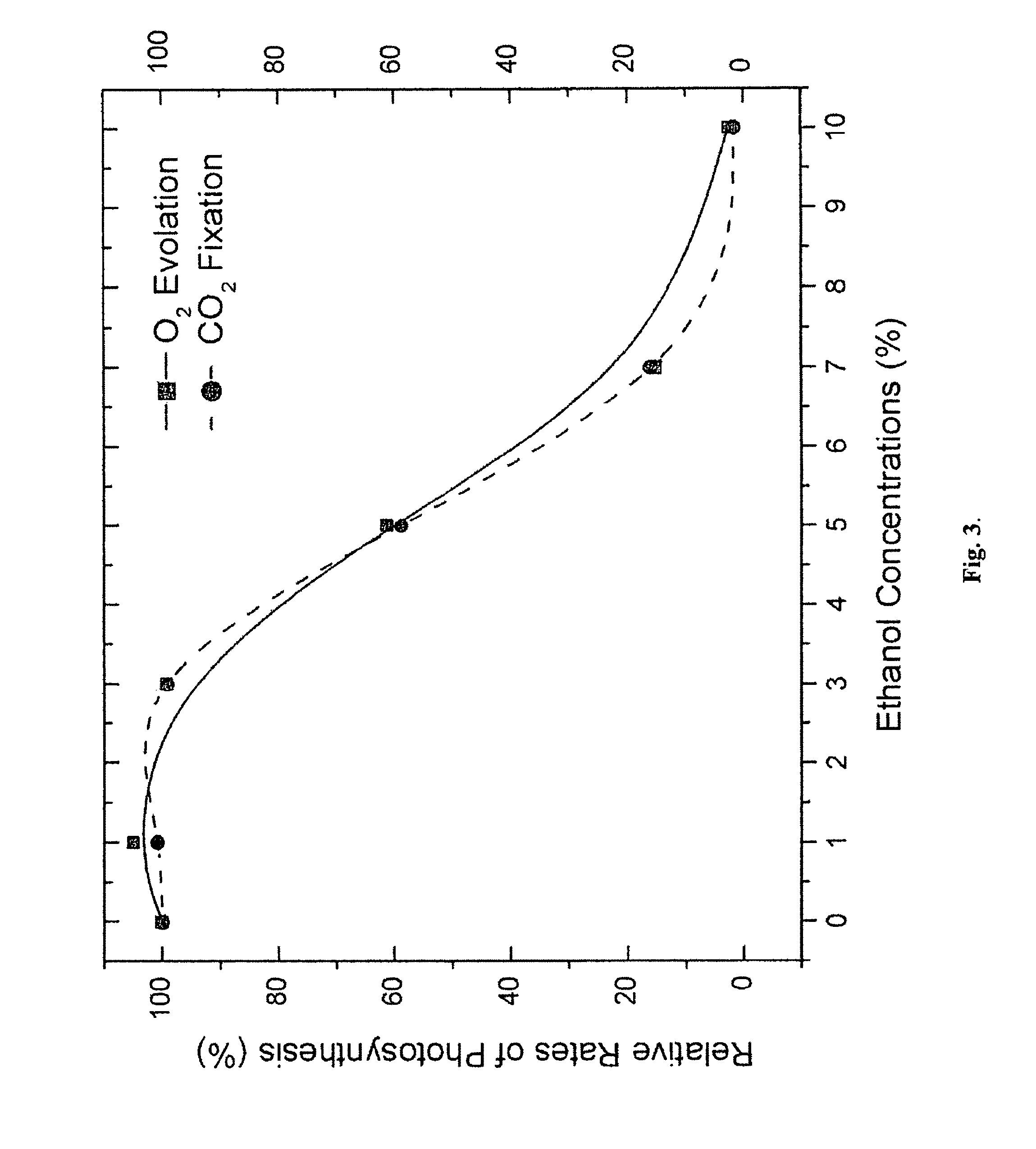
The present invention provides a revolutionary photosynthetic ethanol production technology based on designer transgenic plants, algae, or plant cells. The designer plants, designer algae, and designer plant cells are created such that the endogenous photosynthesis regulation mechanism is tamed, and the reducing power (NADPH) and energy (ATP) acquired from the photosynthetic water splitting and proton gradient-coupled electron transport process are used for immediate synthesis of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) directly from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The ethanol production methods of the present invention completely eliminate the problem of recalcitrant lignocellulosics by bypassing the bottleneck problem of the biomass technology. The photosynthetic ethanol-production technology of the present invention is expected to have a much higher solar-to-ethanol energy-conversion efficiency than the current technology and could also help protect the Earth's environment from the dangerous accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Processes for making ethanol
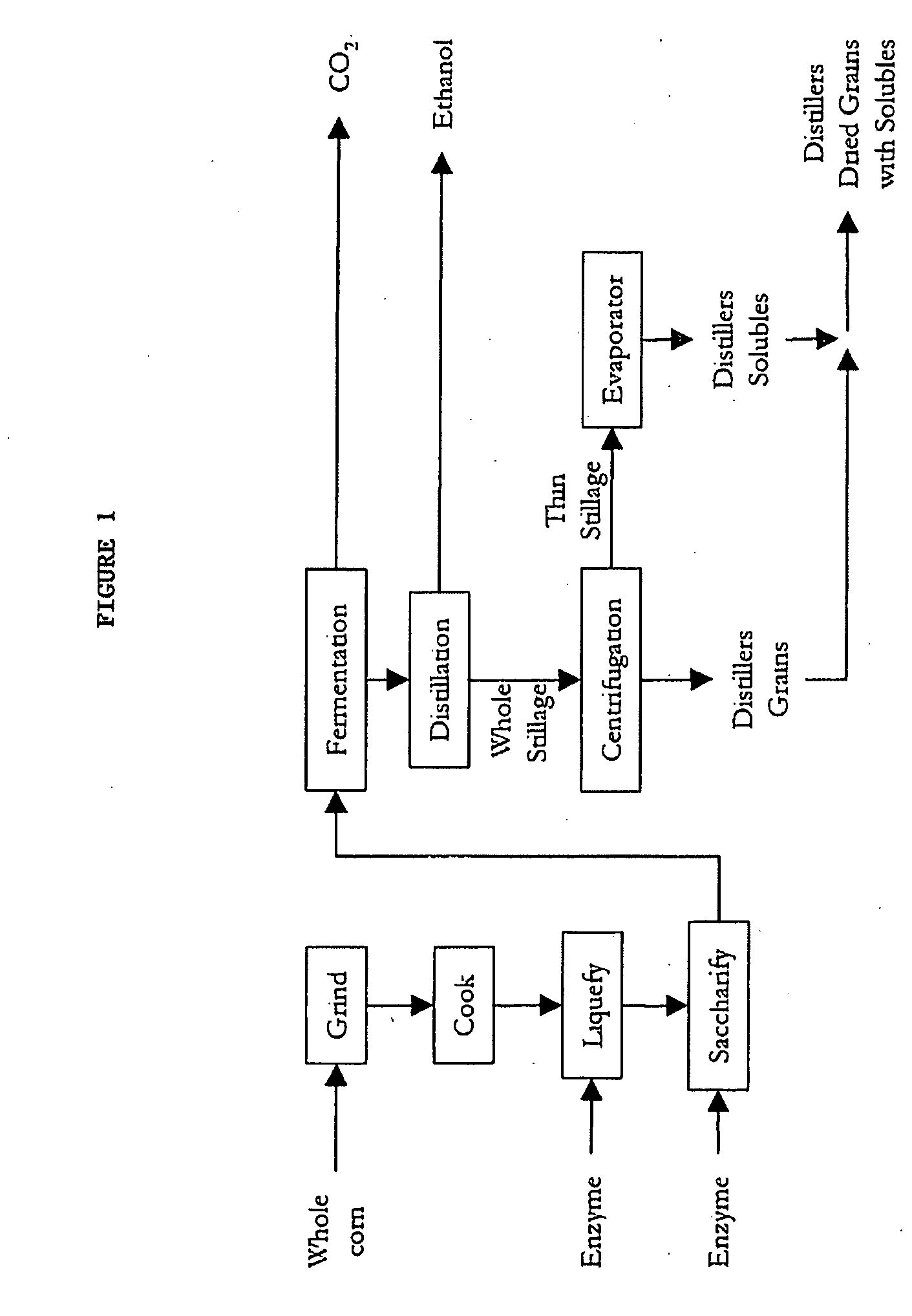
The present invention provides improved processes for recovering components of distillers' grain, such as, the components of distillers' dried grain (DDG), for use in various applications, including in the production of ethanol.
Owner:NOVOZYMES NORTH AMERICA INC +1
Process for the production of animal feed and ethanol and novel animal feed
A method for the production of ethanol and a modified animal feed is provided. The method replaces the starch in known corn-based animal feed with biomass fiber treated to make it more digestible by animals. The process includes wherein the pericarp and germ are removed from the corn kernel and processed for by-products. The starch and protein are also removed and separated. The starch is then fermented and distilled to ethanol and stillage. The bioavailable modified animal feed comprises the pericarp and germ removed from corn kernels and optionally by-products of the pericarp and germ processing, and lignocellulosic materials. The modified animal feed may optionally include energy materials such as animal and vegetable fats, vegetable soapstocks, or glycerin, and combinations thereof.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Xylitol synthesis mutant of xylose-utilizing zymomonas for ethanol production
InactiveUS20080286870A1Reduce productionIncreased ethanol productionBacteriaUnicellular algaeSugarGlucose-fructose oxidoreductase
A strain of xylose-utilizing Zymomonas was engineered with a genetic modification to the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene resulting in reduced expression of GFOR enzyme activity. The engineered strain exhibits reduced production of xylitol, a detrimental by-product of xylose metabolism. It also consumes more xylose and produces more ethanol during mixed sugar fermentation under process-relevant conditions.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
Ethanol production using xylitol synthesis mutant of xylose-utilizing zymomonas
InactiveUS7741084B2Reduce productionIncreased ethanol productionBacteriaBiofuelsFructoseMicrobiology
Production of ethanol using a strain of xylose-utilizing Zymomonas with a genetic modification of the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene was found to be improved due to greatly reduced production of xylitol, a detrimental by-product of xylose metabolism synthesized during fermentation.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
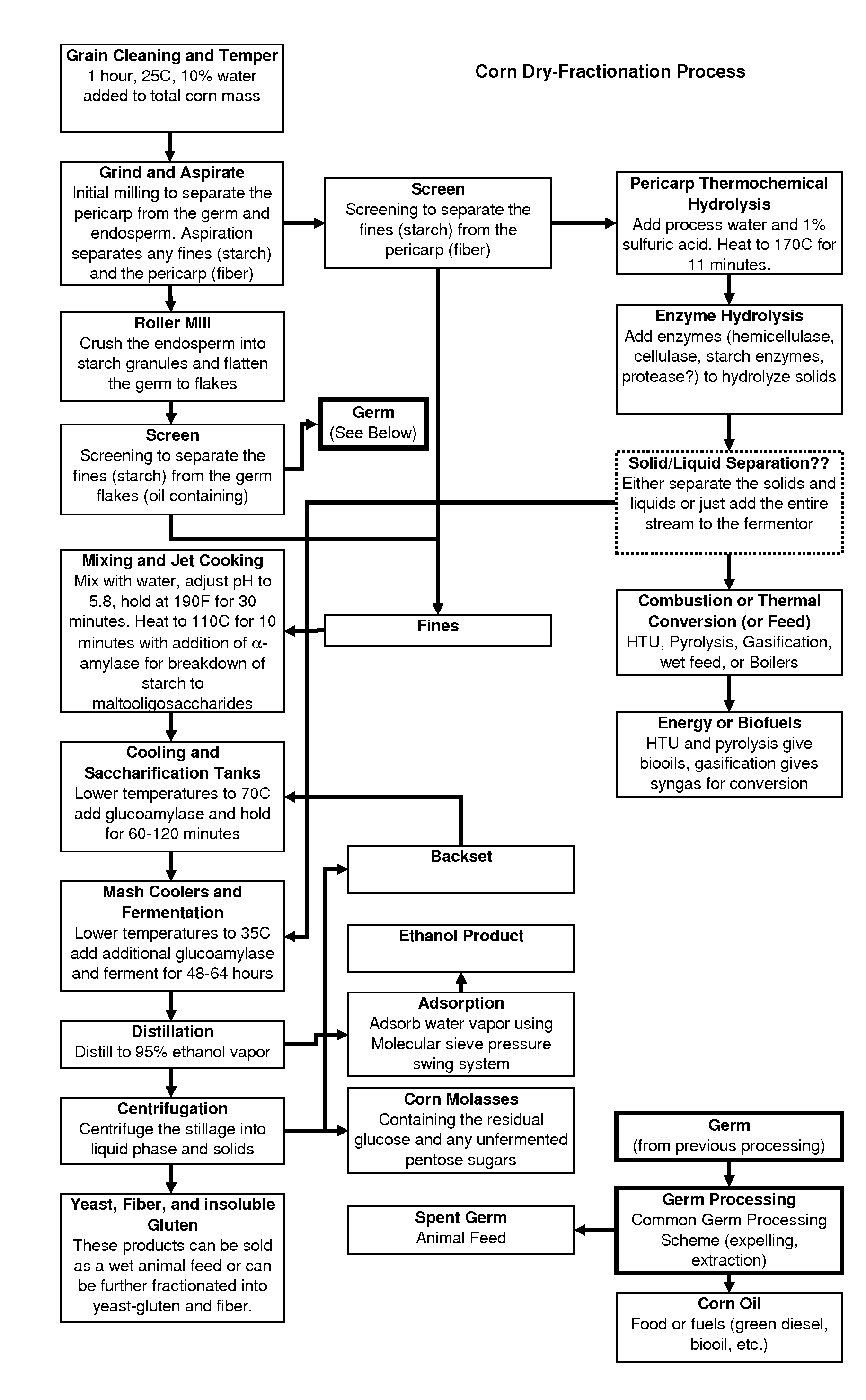
Dry fractionation of corn
InactiveUS20090029432A1High value streamIncreased ethanol productionBiofuelsFermentationFractionationHydrolysis
Novel grain processing methods and the products obtained therefrom are disclosed. Methods may include separation of pericarp fractions, hydrolysis of the pericarp fractions one or more time, and fractionation of the hydrolyzed pericarp fractions. Hydrolyzed pericarp fractions have applications including fermentation media, livestock feed, and fuel feedstocks.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Apparatus and method for producing fuel ethanol from biomass
InactiveUS20080020437A1Improve performanceEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismVegetable oil
Cellulosic biomass at the growing site is pulverized and hydrolyzed in collectors which transfer the comminuted biomass into pretreatment units. In the pretreatment units enzymes and / or other agents are added to the pretreatment units to disassociate the lignin from the cellulose and hemicellulose, and to further decompose the biomass to simple sugars. The sugar solution is transferred to a fermentation unit and fermenting microorganisms are added to produce ethanol. Preferably vegetable oil or other ethanol-miscible liquid is added to provide a medium to extract the ethanol from the solution for transfer to a device where heating or distillation removes the ethanol which is collected for use as a liquid fuel. All of the units are preferably mounted for easy deployment to various locations in the vicinity of the numerous growing sites which produce the biomass.
Owner:SAVARESE JOHN J
Method of Synthesizing Higher-Molecular Alcohol
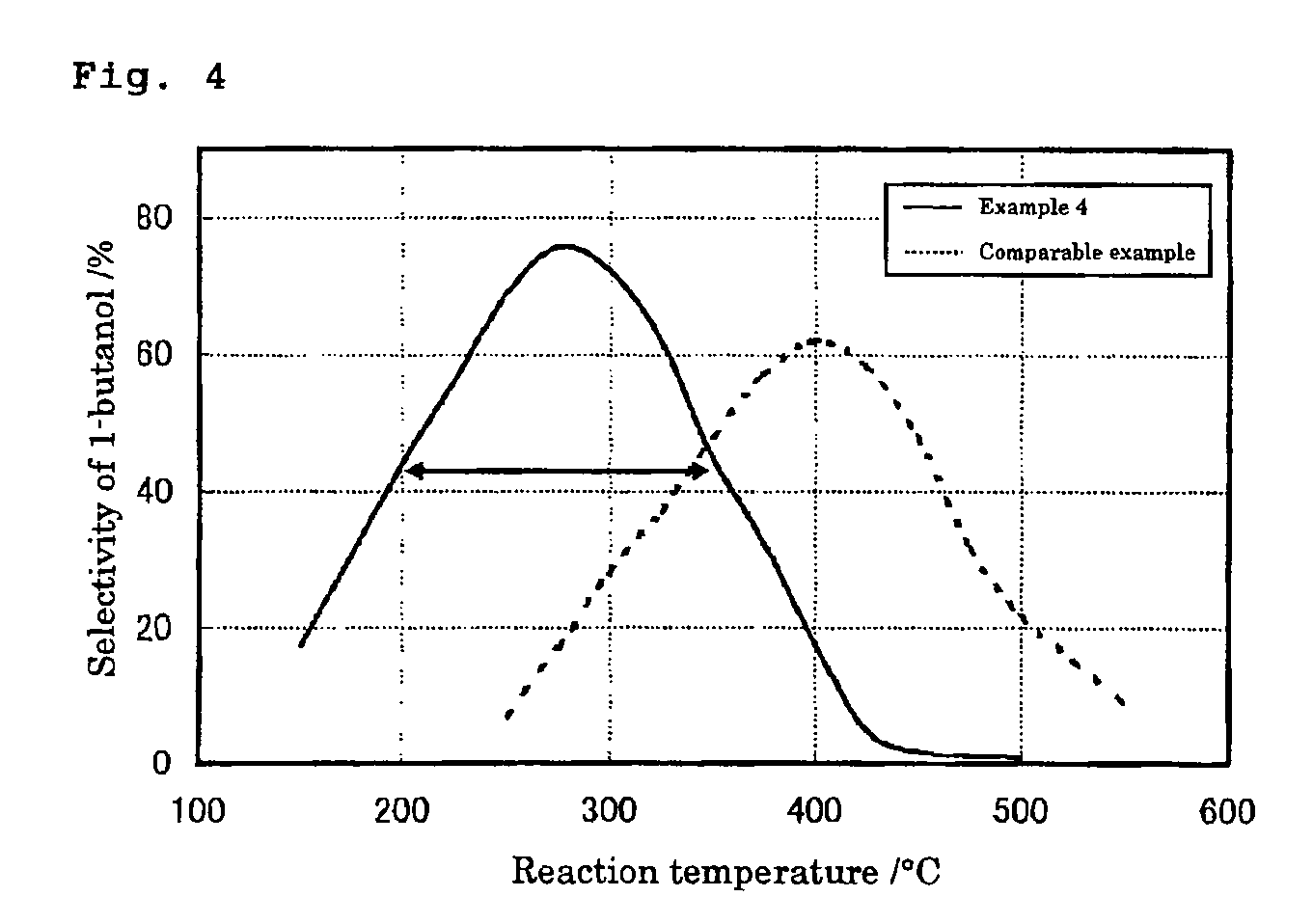
ActiveUS20070255079A1Efficient collectionIncreased ethanol productionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationOctanolSynthetic Polymeric Macromolecules
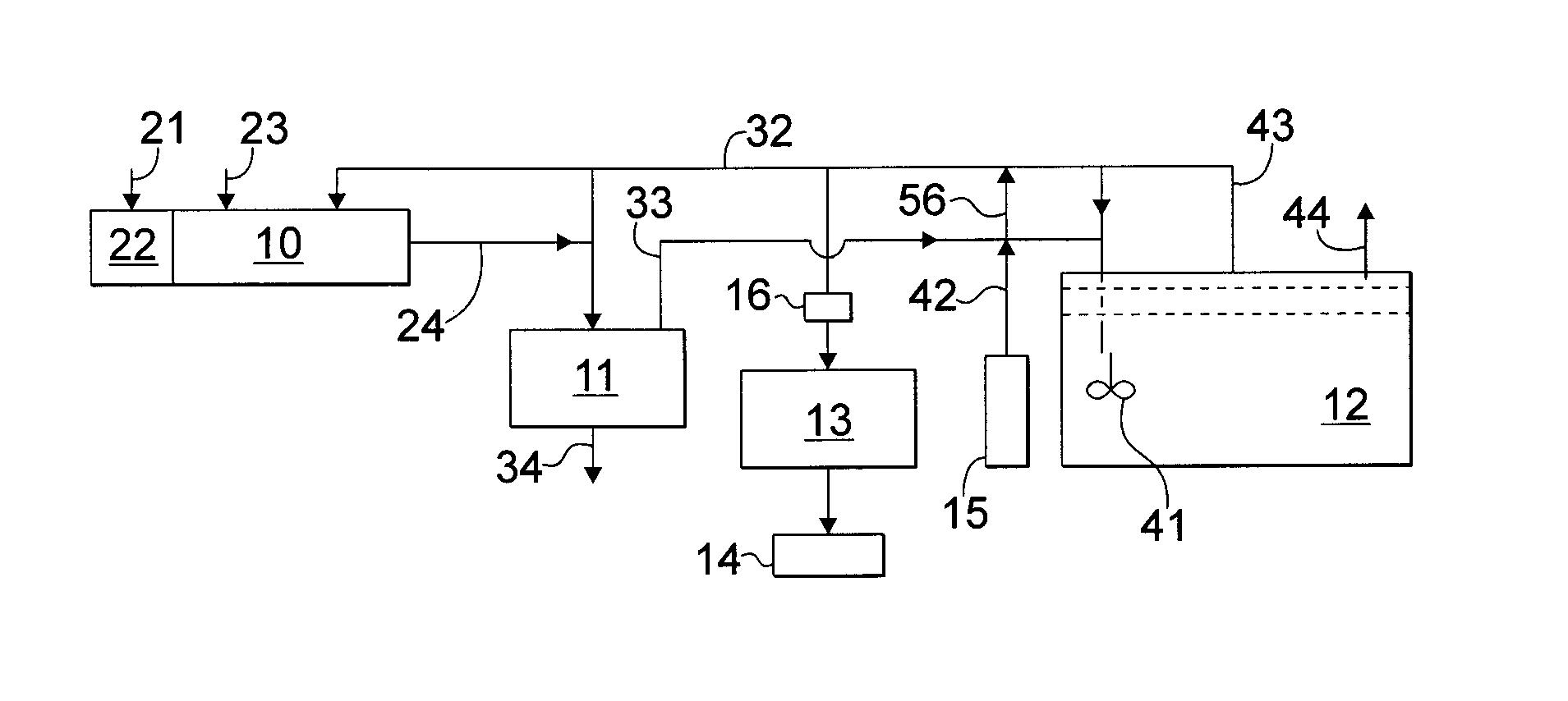
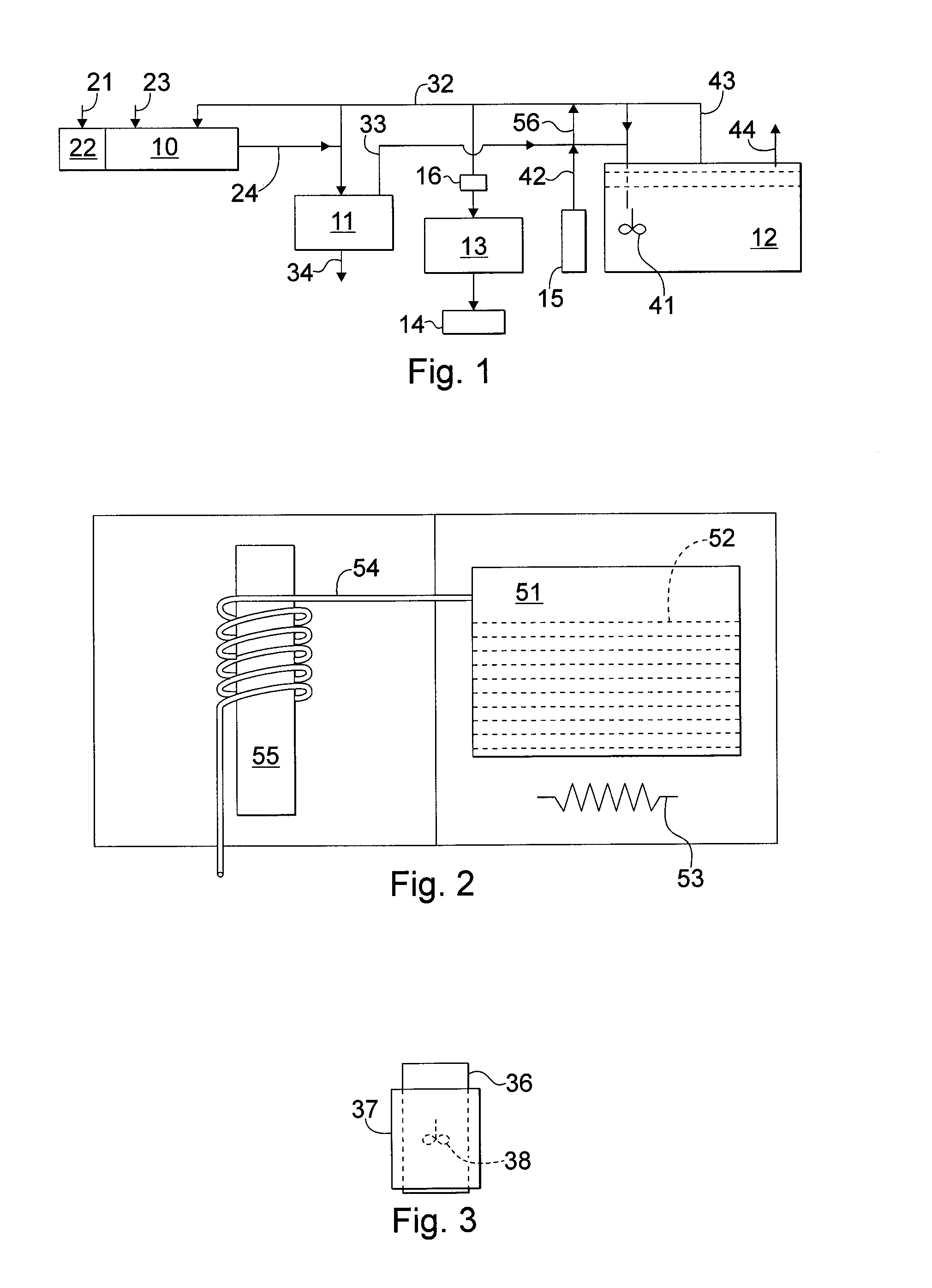
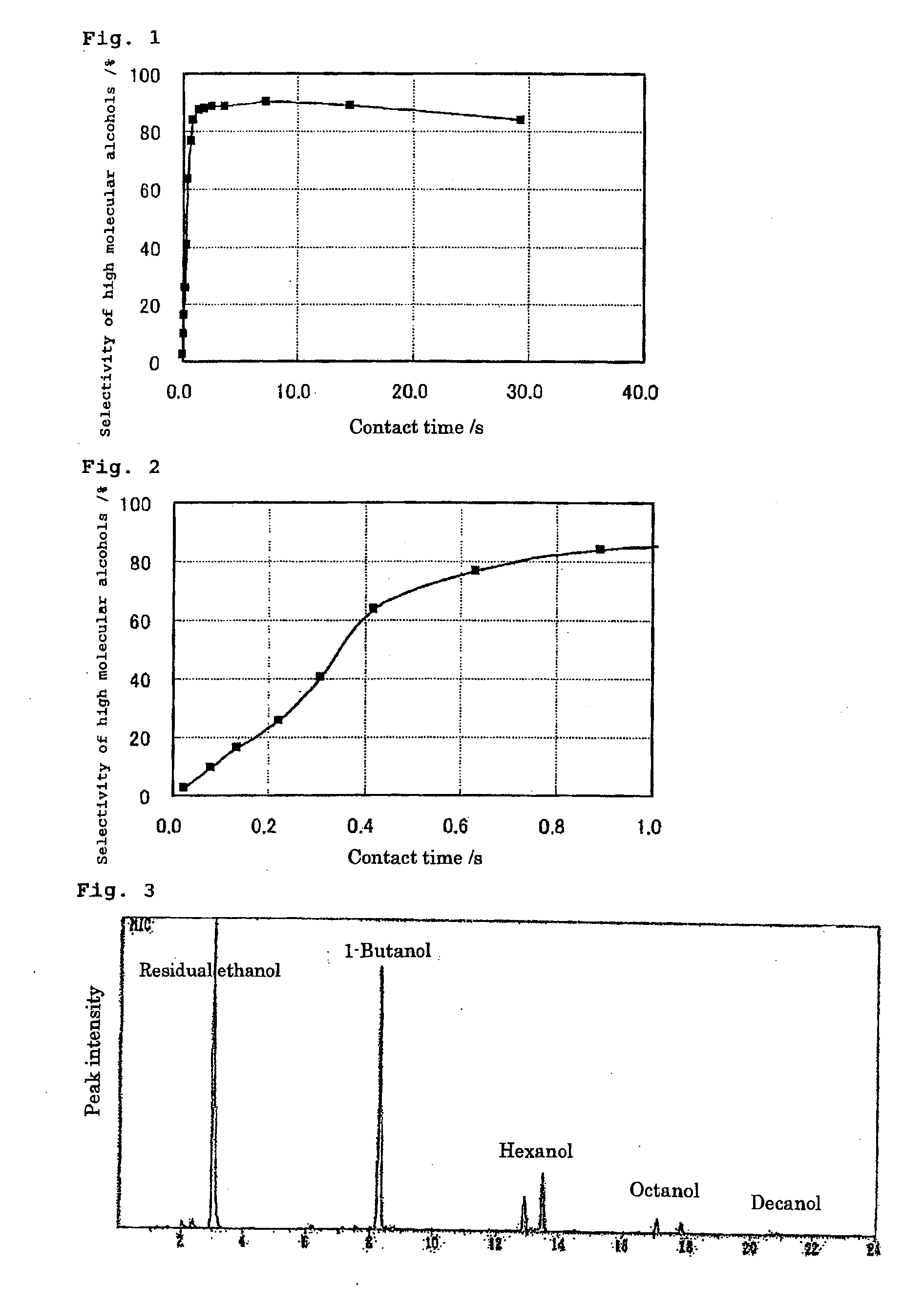
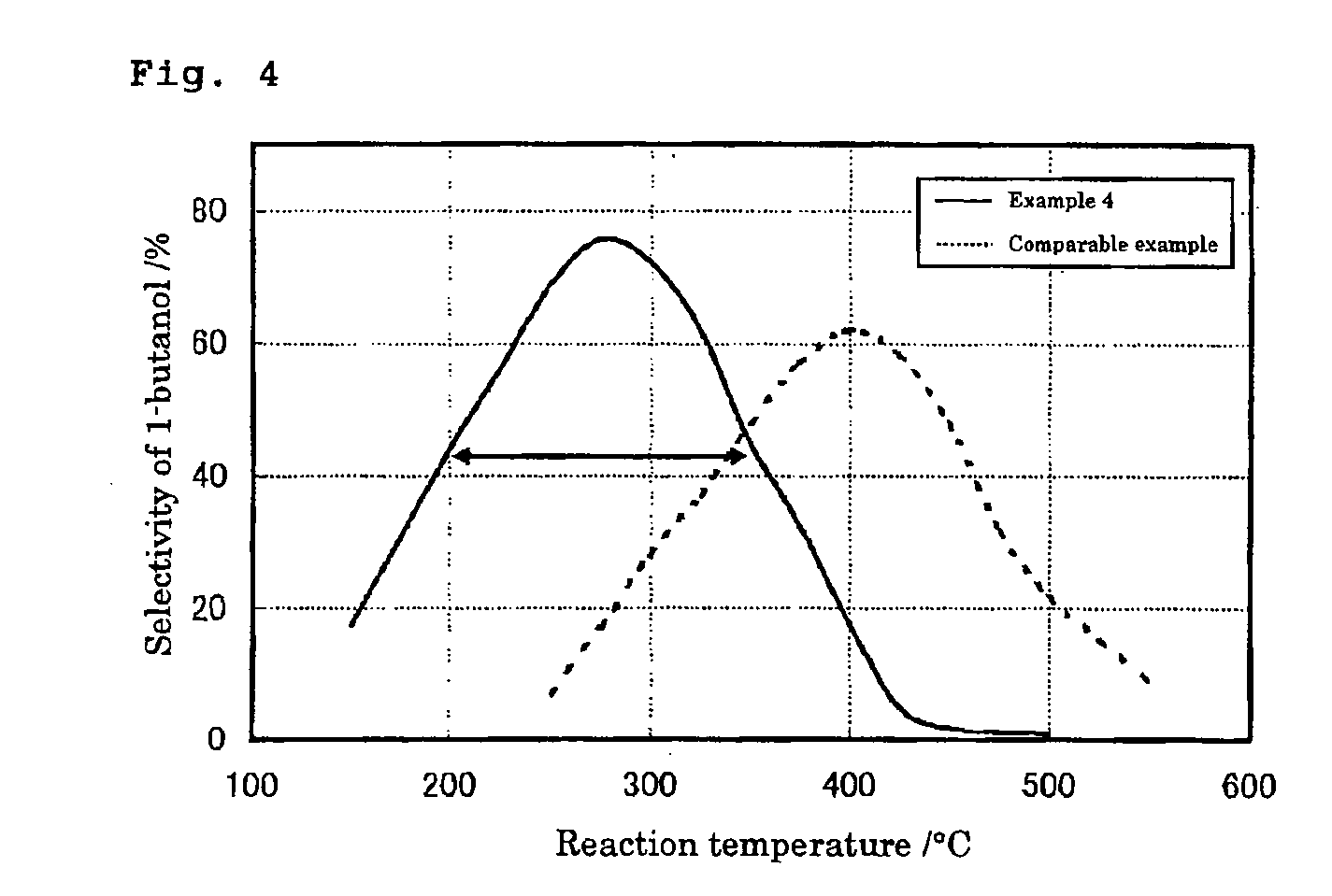
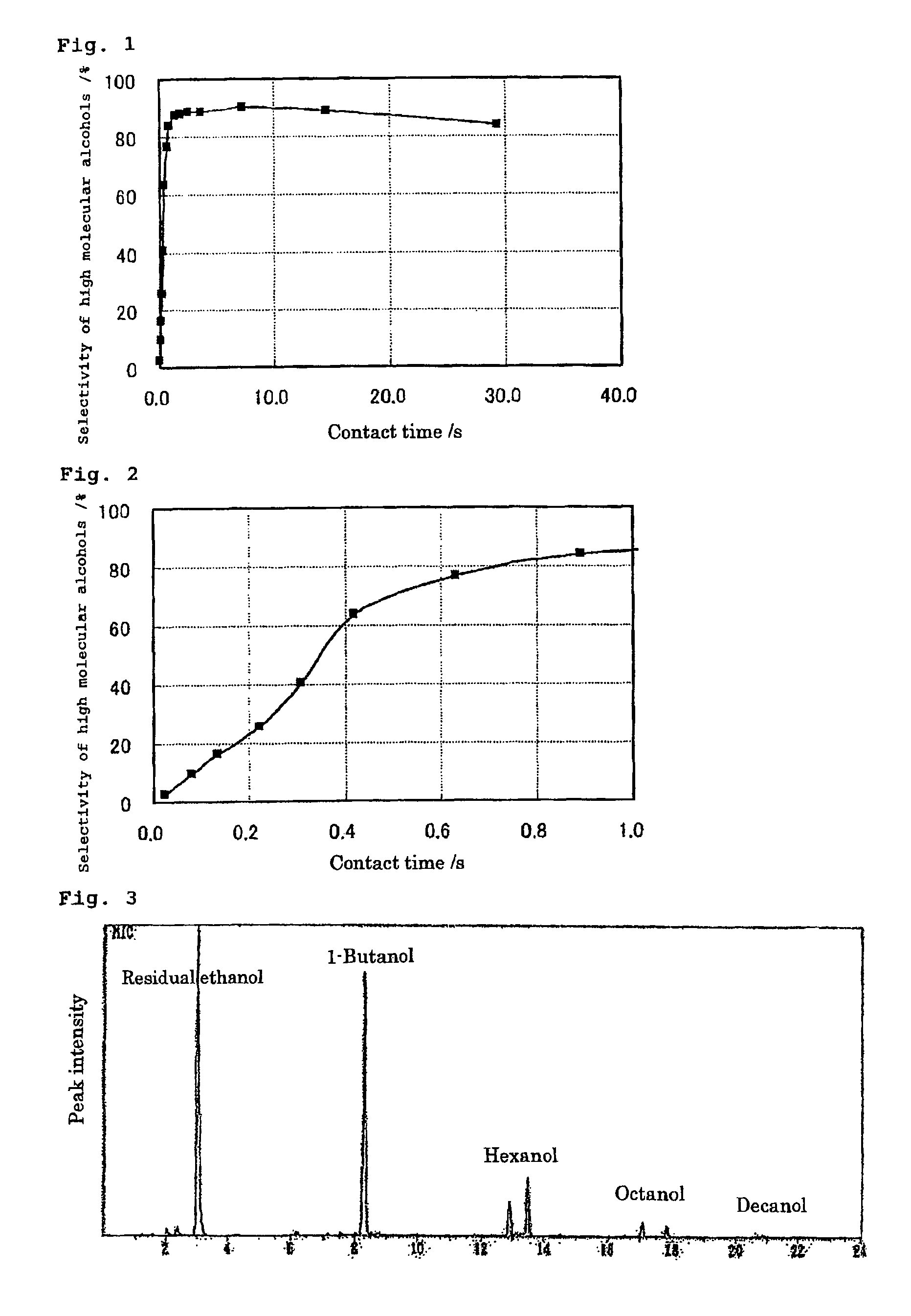
The present invention provides a production method with which high molecular alcohols having an even number of carbon atoms such as 1-butanol, hexanol, octanol and decanol, and a mixture of these are efficiently collected through clean processes with the use of ethanol as a raw material. High molecular alcohols are produced from ethanol by using calcium phosphate-based compounds such as hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, tricalcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2, calcium monohydrogen phosphate CaHPO4.(0˜2)H2O, calcium diphosphate Ca2P2O7, octacalcium phosphate Ca8H2(PO4)6.5H2O, tetracalcium phosphate Ca4(PO4)2O or amorphous calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2.nH2O as a catalyst, using ethanol as a starting material, and setting a contact time at 0.4 second or longer.
Owner:SANGI CO LTD
Ethanol production using xylitol synthesis mutant of xylose-utilizing zymomonas
InactiveUS20080187973A1Speed up the conversion processReduces glucose-fructose oxidoreductase activityBacteriaBiofuelsMutantZymomonas
Production of ethanol using a strain of xylose-utilizing Zymomonas with a genetic modification of the glucose-fructose oxidoreductase gene was found to be improved due to greatly reduced production of xylitol, a detrimental by-product of xylose metabolism synthesized during fermentation.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
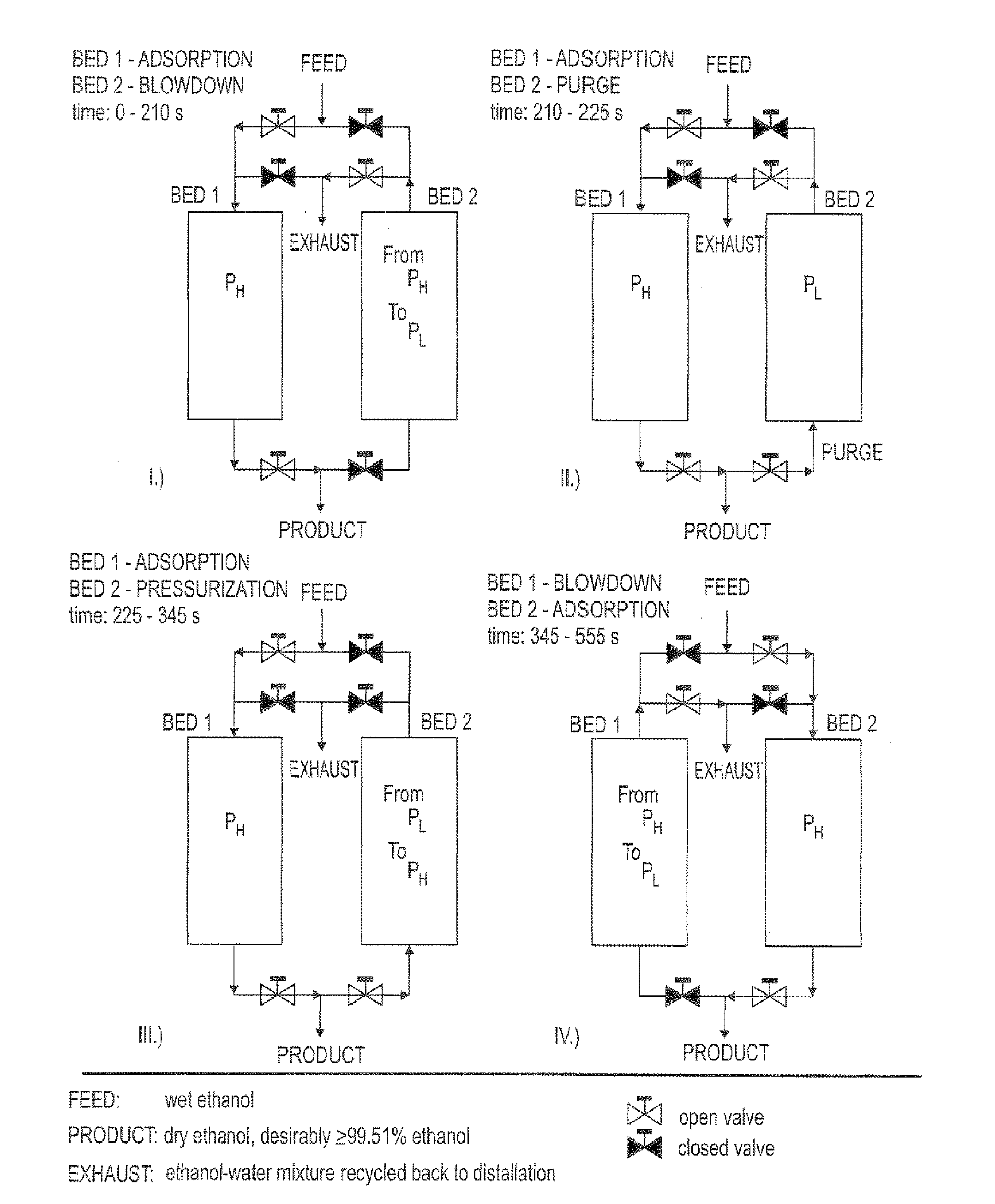
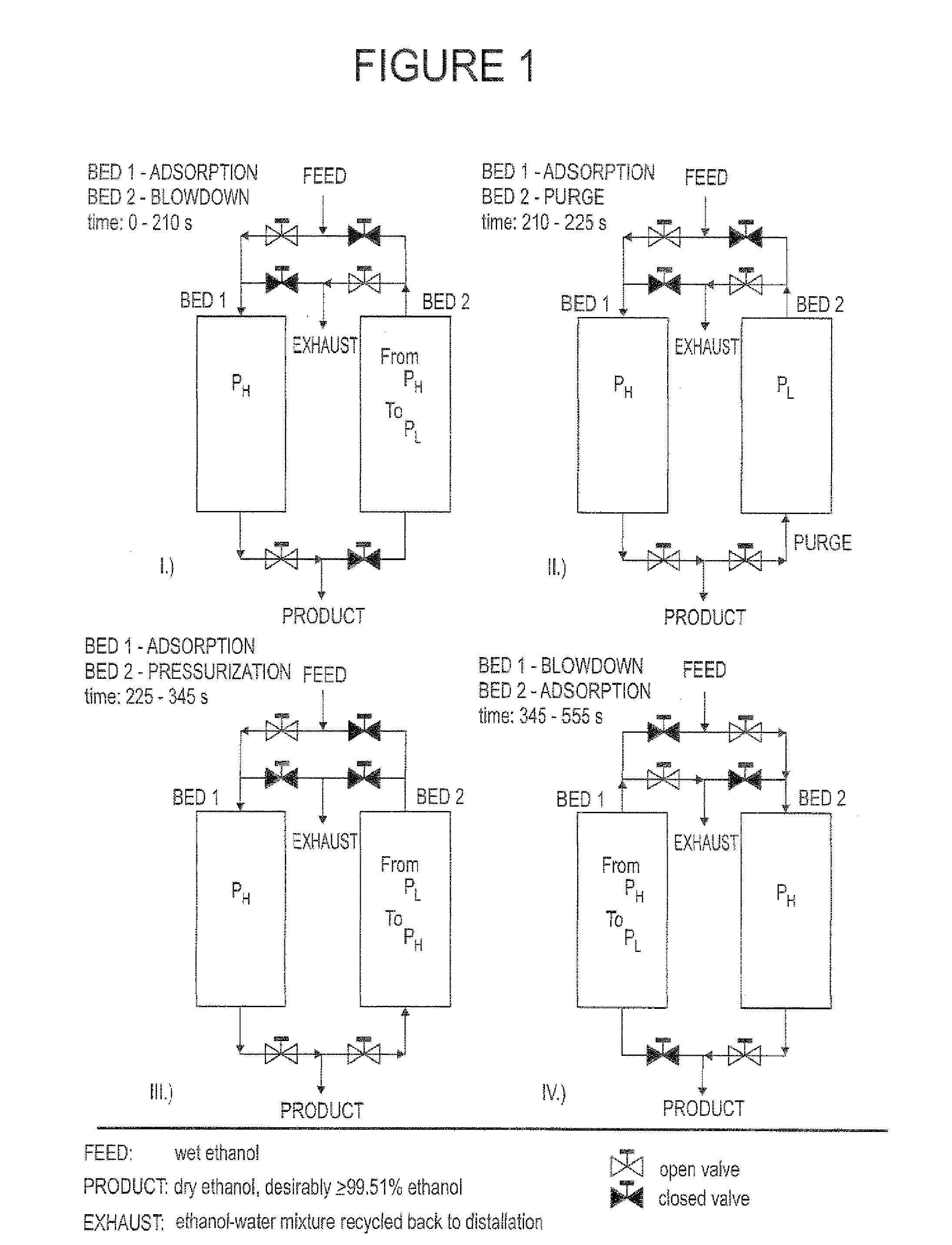
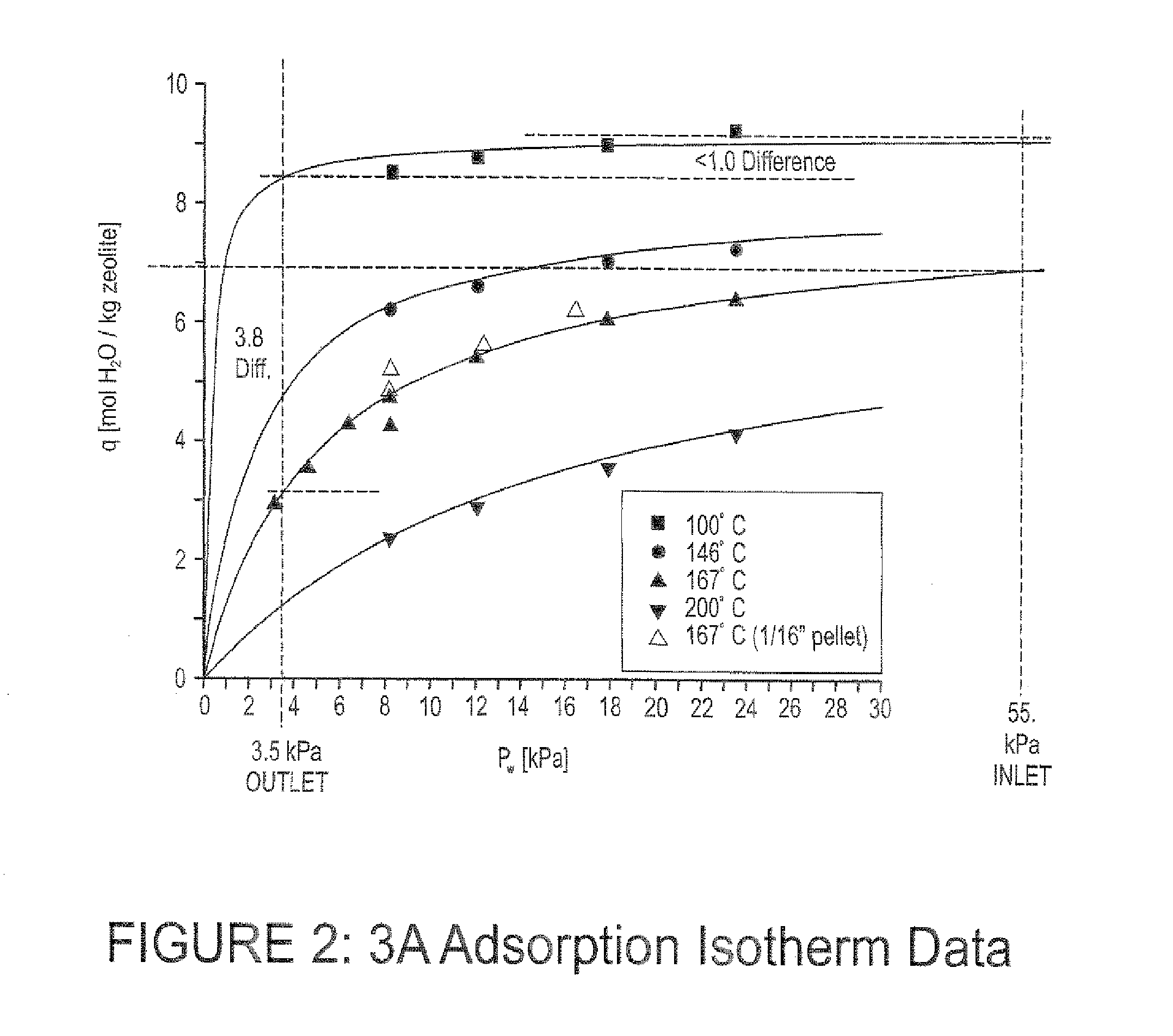
Adsorption process for the dehydration of alcohol
ActiveUS20130225880A1Increase productivityImprove performanceGas treatmentOrganic compound preparationAqueous alcoholHigh pressure
The present invention includes a process for the dehydration of ethanol by adsorption of water at elevated pressure and for the regeneration (purging) of adsorbent at a lower pressure than the pressure used for the adsorption of water where the ratio of the duration of the regeneration (purge) step to the duration of the water adsorption step is higher than 0.1 and the temperature of adsorption is greater than 260 degree Fahrenheit.
Owner:RCM TECH USA INC
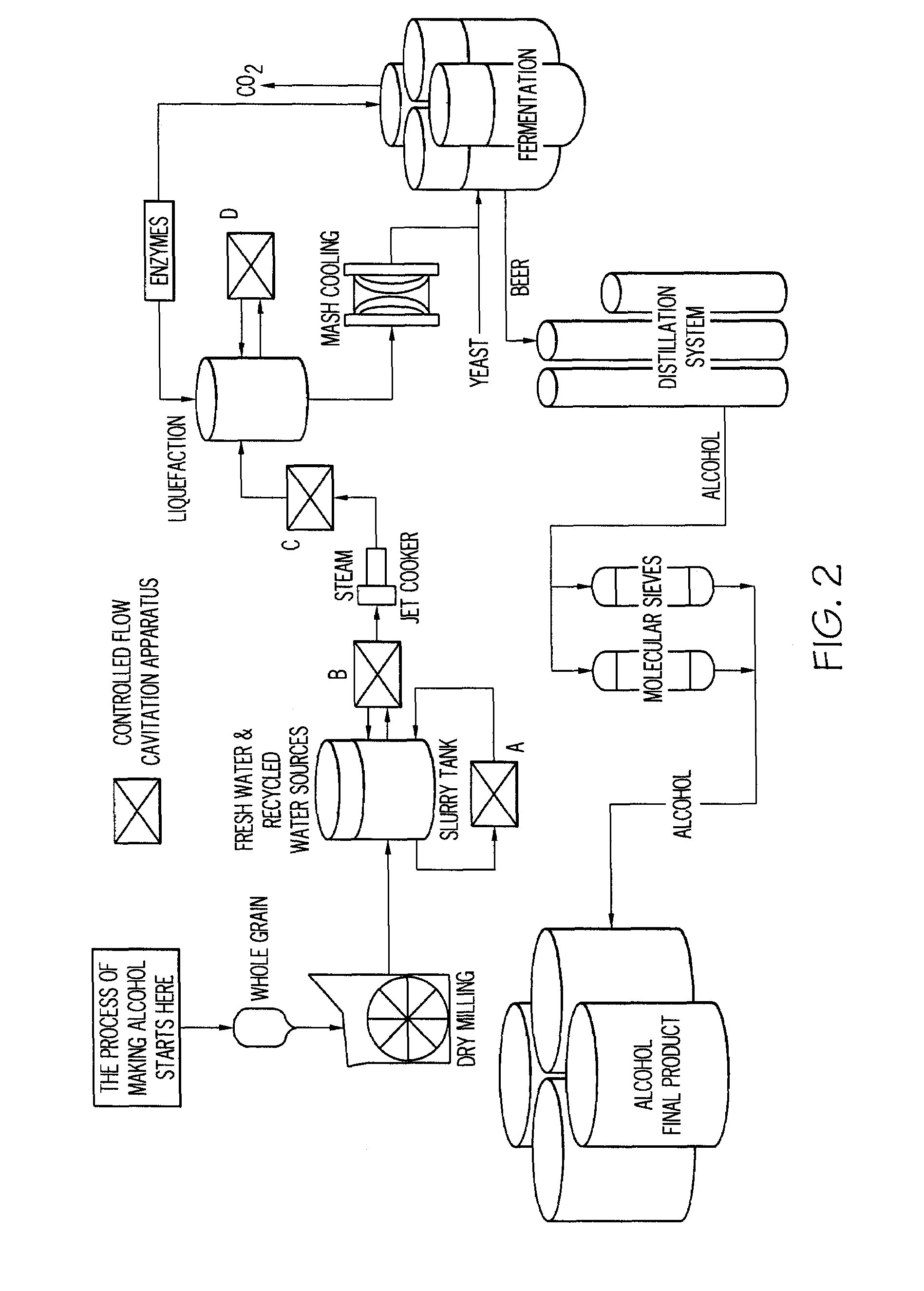
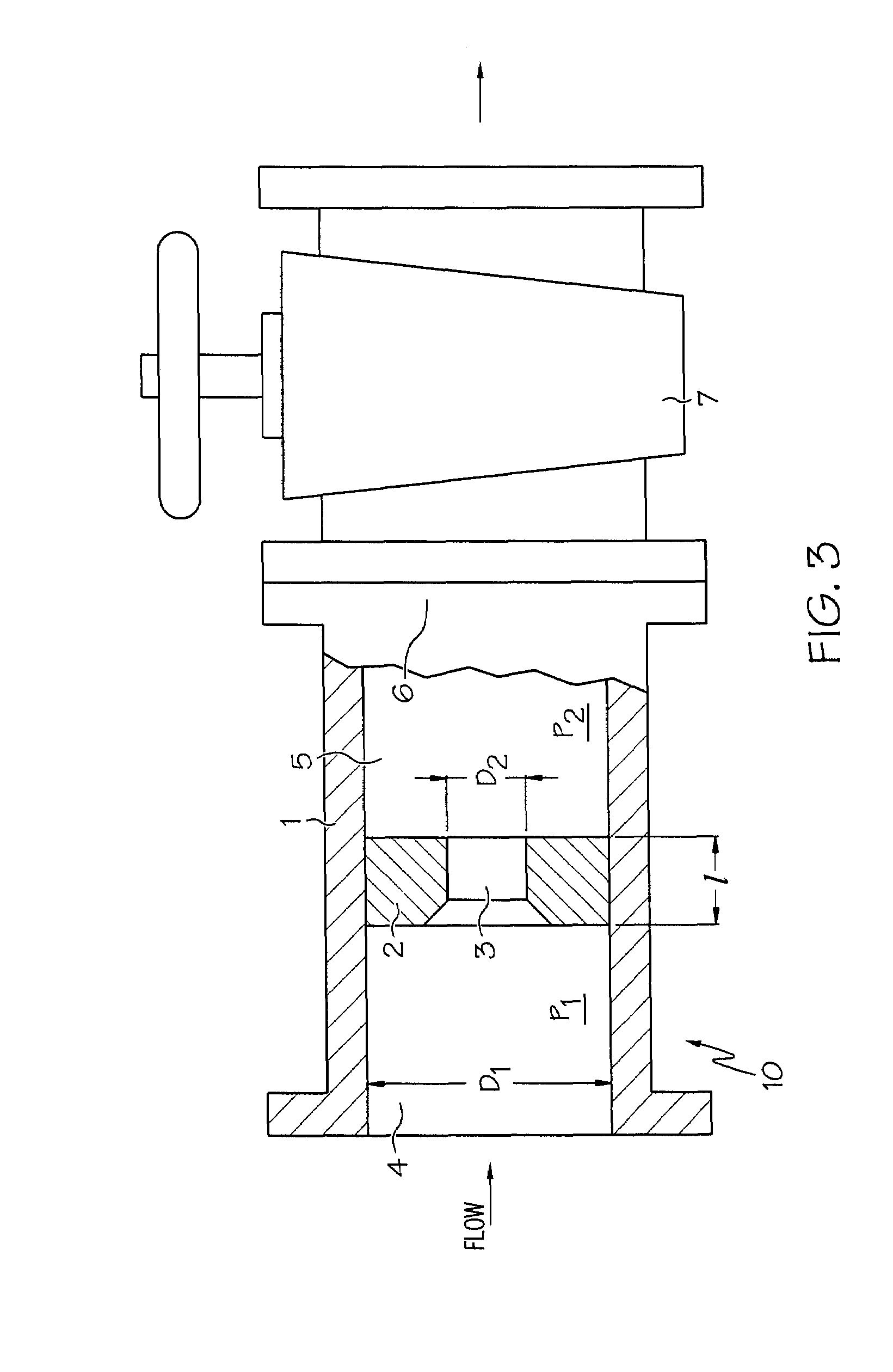
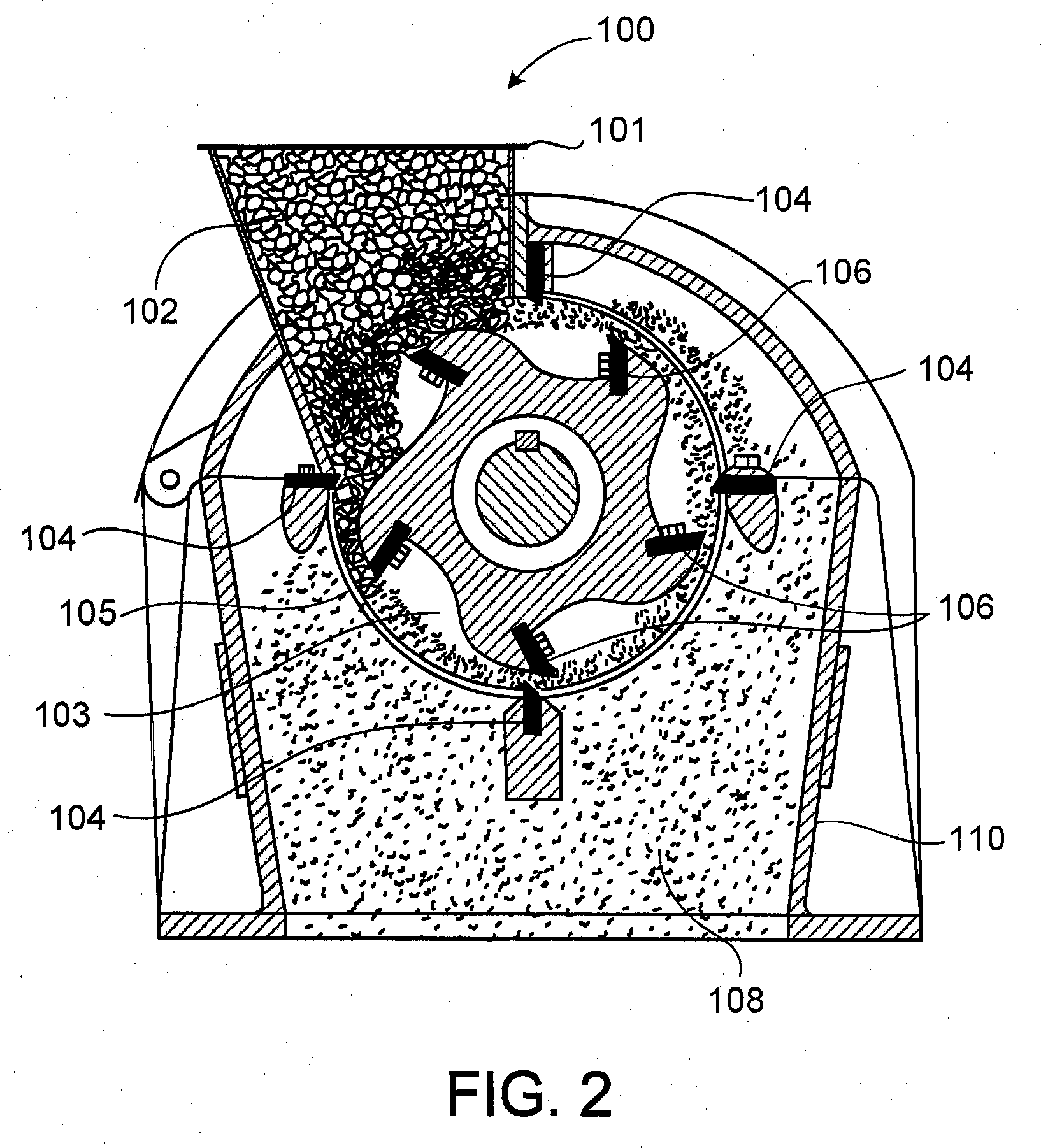
Apparatus and method for increasing alcohol yield from grain
InactiveUS7667082B2Increased ethanol productionReduce amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl flowLiquid medium
Owner:ARISDYNE STSTEMS INC
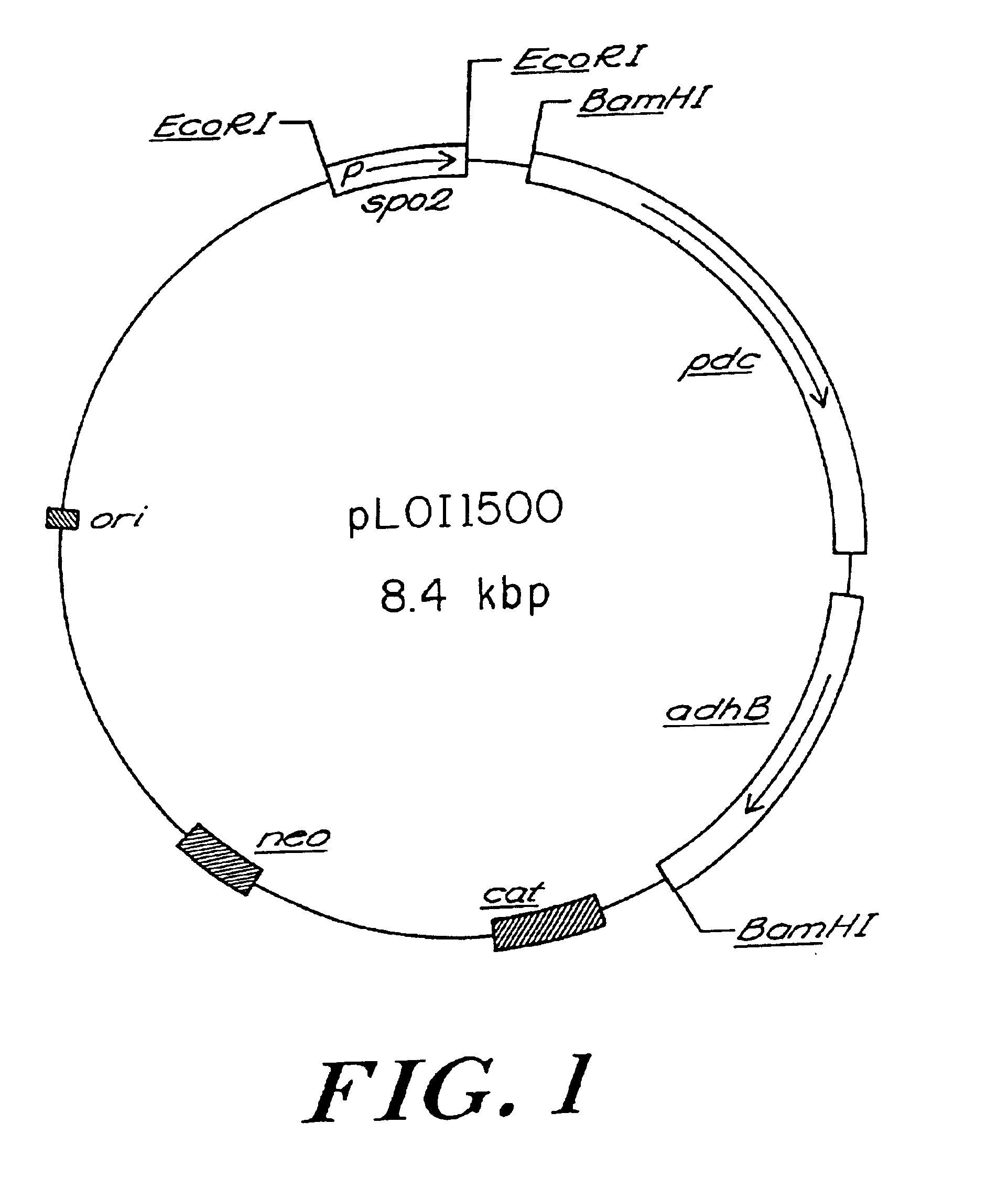
Ethanol production in recombinant hosts
InactiveUS6849434B2Reduce the amount requiredIncreased ethanol productionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHeterologousBacteroides
The subject invention concerns the transformation of Gram-positive bacteria with heterologous genes which confer upon these microbes the ability to produce ethanol as a fermentation product. Specifically exemplified is the transformation of bacteria with genes, obtainable from Zymomonas mobilis, which encode pyruvate decarboxylase and alcohol dehydrogenase.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Processes Using Antibiotic Alternatives In Bioethanol Production
ActiveUS20110230394A1Increase productionLow and no adverse environmental impactAntibacterial agentsBiocideEthanol yieldAntibacterial peptide
Methods for controlling the growth of bacteria in ethanol fermentation systems with antibiotic alternatives, which can be nonoxidizing biocides, stabilized oxidizers, or any combinations thereof, are described. As an option, a process or composition of the present invention can include one or more polycyclic antibacterial peptides. The methods can provide improvements, such as increased ethanol yields with minimal carryover of biocide into co-products of the processes.
Owner:BUCKMAN LAB INT INC
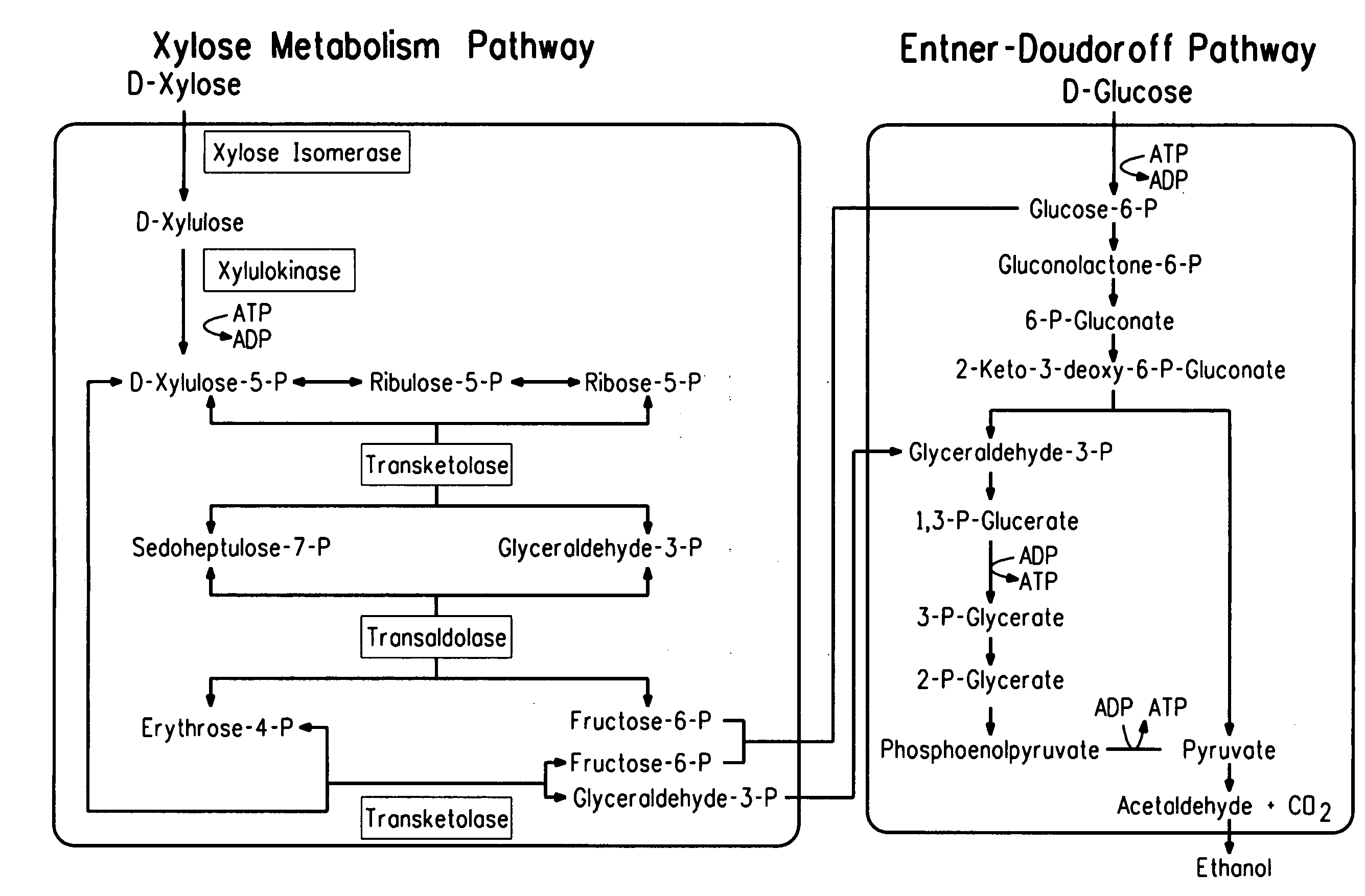
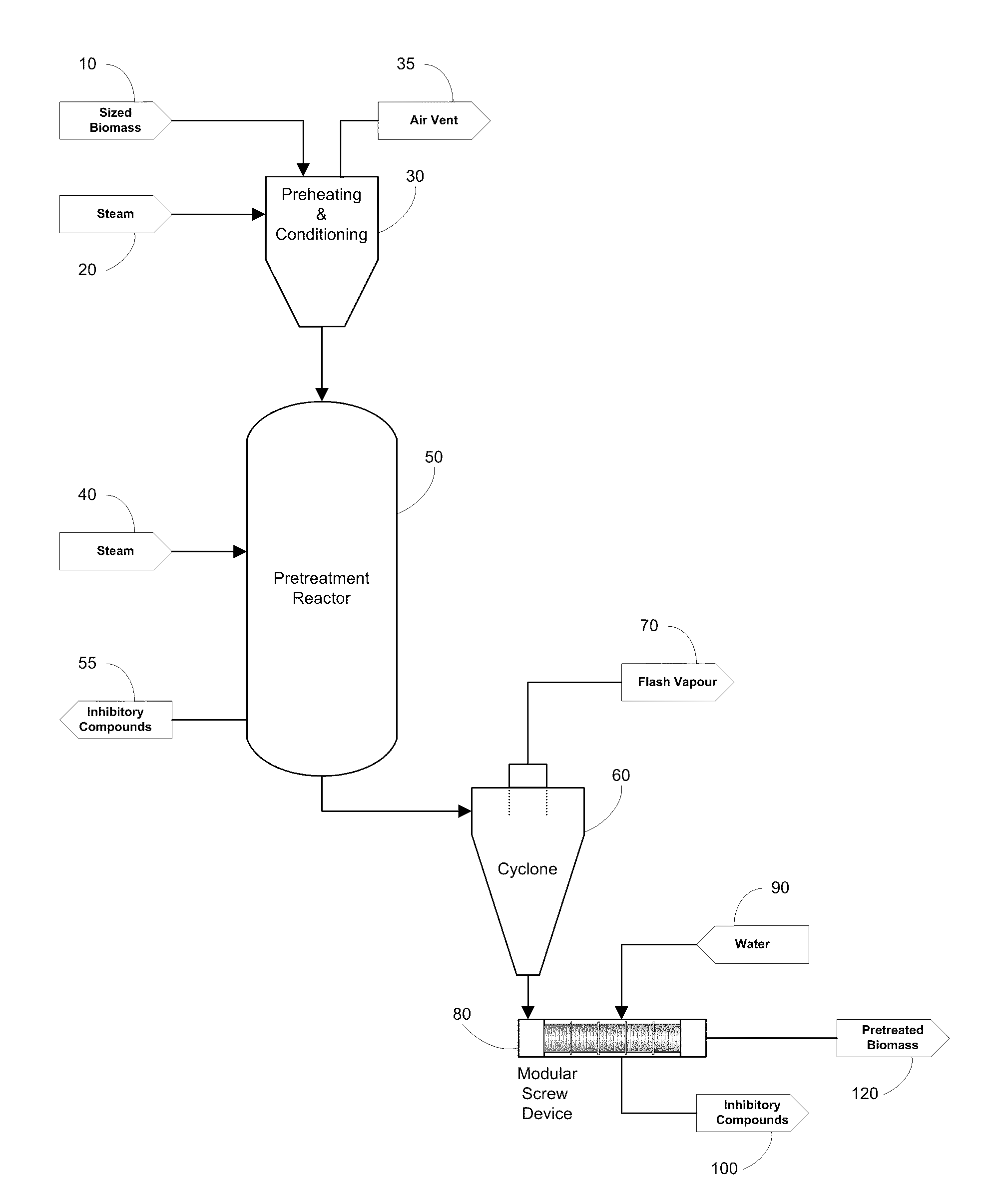
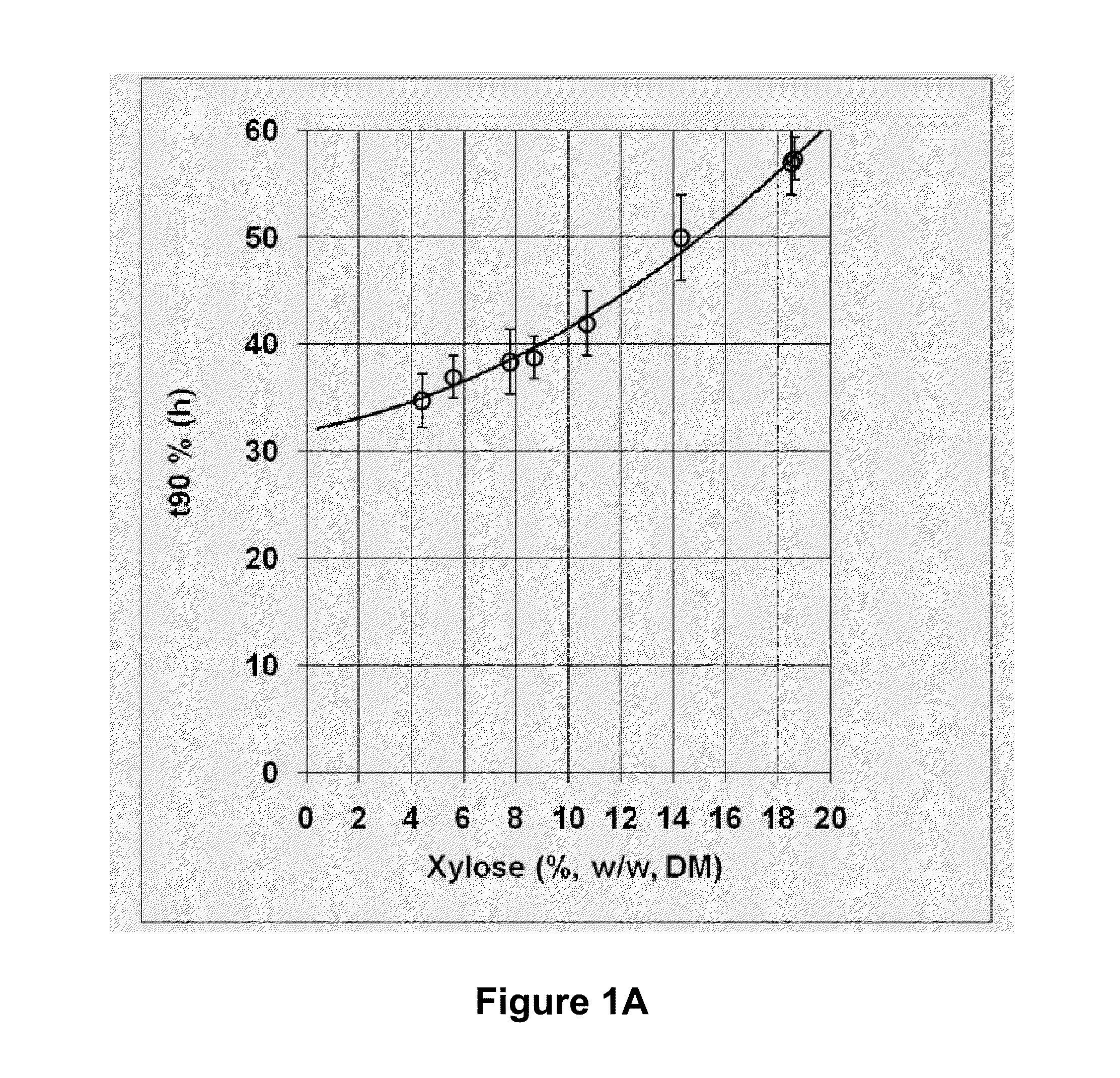
Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass through removal of inhibitory compounds
InactiveUS20100263814A1Reduce impactReducing the inhibition impact on the ratePretreatment with water/steamBiofuelsXyloseDecomposition
A process for the pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass is disclosed. The process is intended for use in connection with biomass to ethanol processes and is directed in particular to an economical removal of inhibitory compounds generated in biomass pretreatment, which are inhibitory to downstream hydrolysis and fermentation steps. The process includes the steps of heating the lignocellulosic biomass with steam to a preselected temperature, at a preselected pressure and for a preselected time to hydrolyze and solubilize hemicelluloses in the biomass; explosively decomposing the biomass into fibers; and extracting from the resulting reaction mixture a liquefied portion of the lignocellulosic biomass before or after explosive decomposition. The liquefied portion is extracted to remove compounds from the lignocellulosic biomass which are inhibitory to enzymatic cellulose hydrolysis and sugar fermentation to ethanol. For improved efficiency and economy, the inhibitory compounds are not completely removed. Furthermore, xylose has been found to be a good indicator compound for the general level of inhibitory compounds in the reaction mixture and the extraction step is therefore controlled on the basis of the xylose content in the reaction mixture. In particular, the extracting step is discontinued once a dry matter (dm) content of xylose, as monomer or oligomer, in the reaction mixture of 4% to 8% (w / w dm) is achieved. This most economically balances the practical need for inhibitory compound removal with the economical need to control and preferably minimize the costs of the overall ethanol production process.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Fermentation Process, Starter Culture and Growth Medium
InactiveUS20070231869A1High economicHigh environmental interestFungiBiofuelsMicroorganismCell culture media
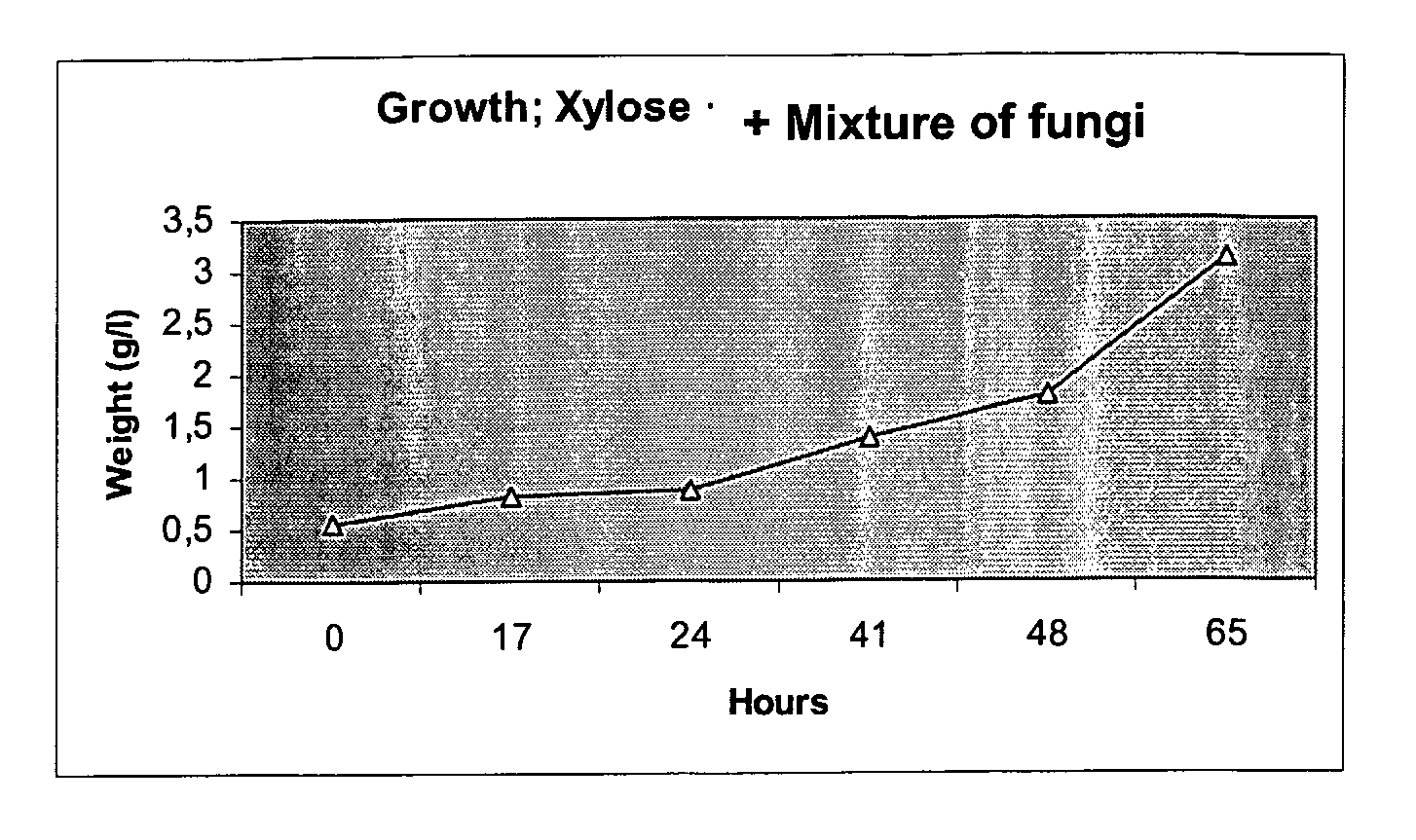
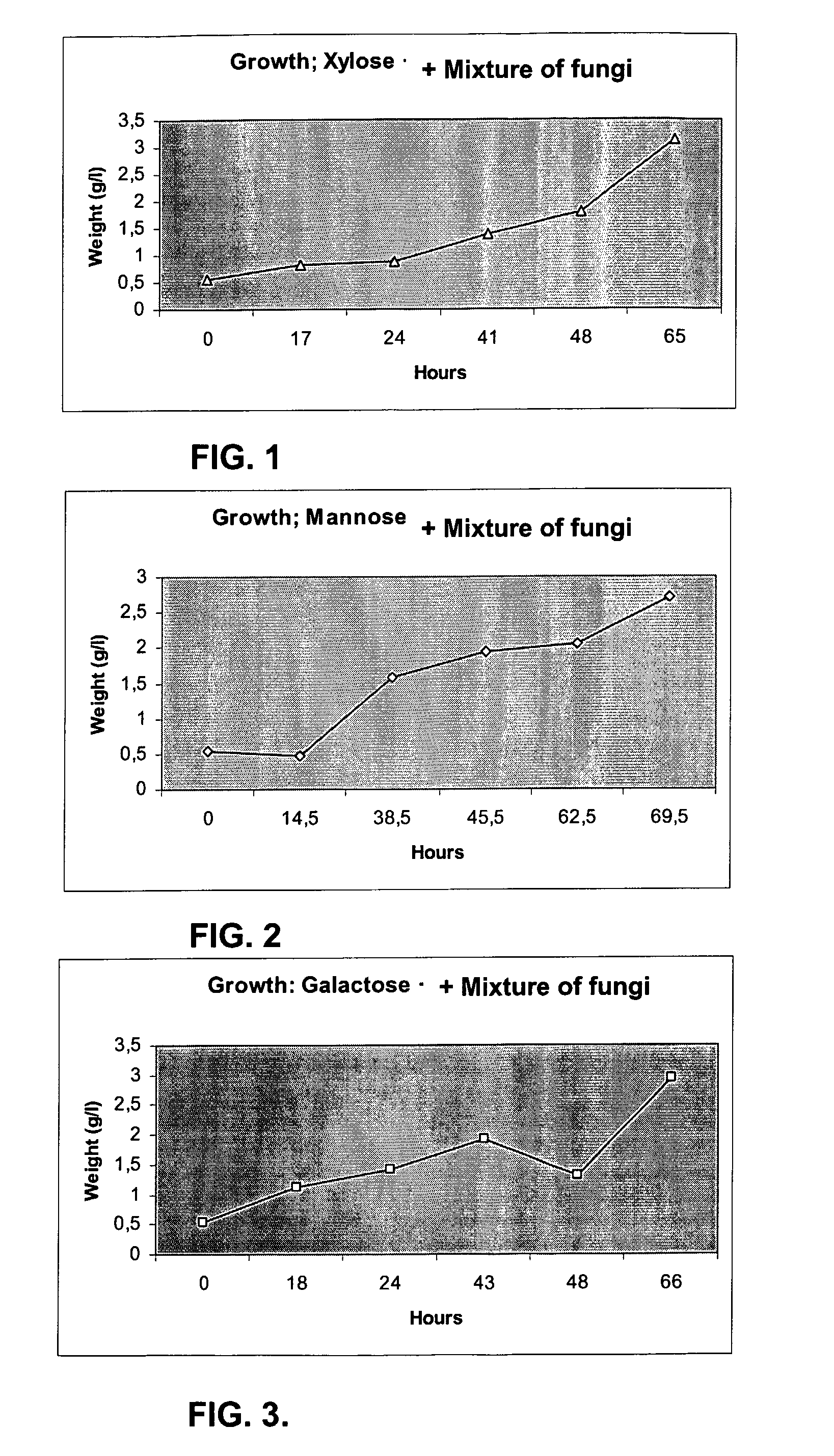
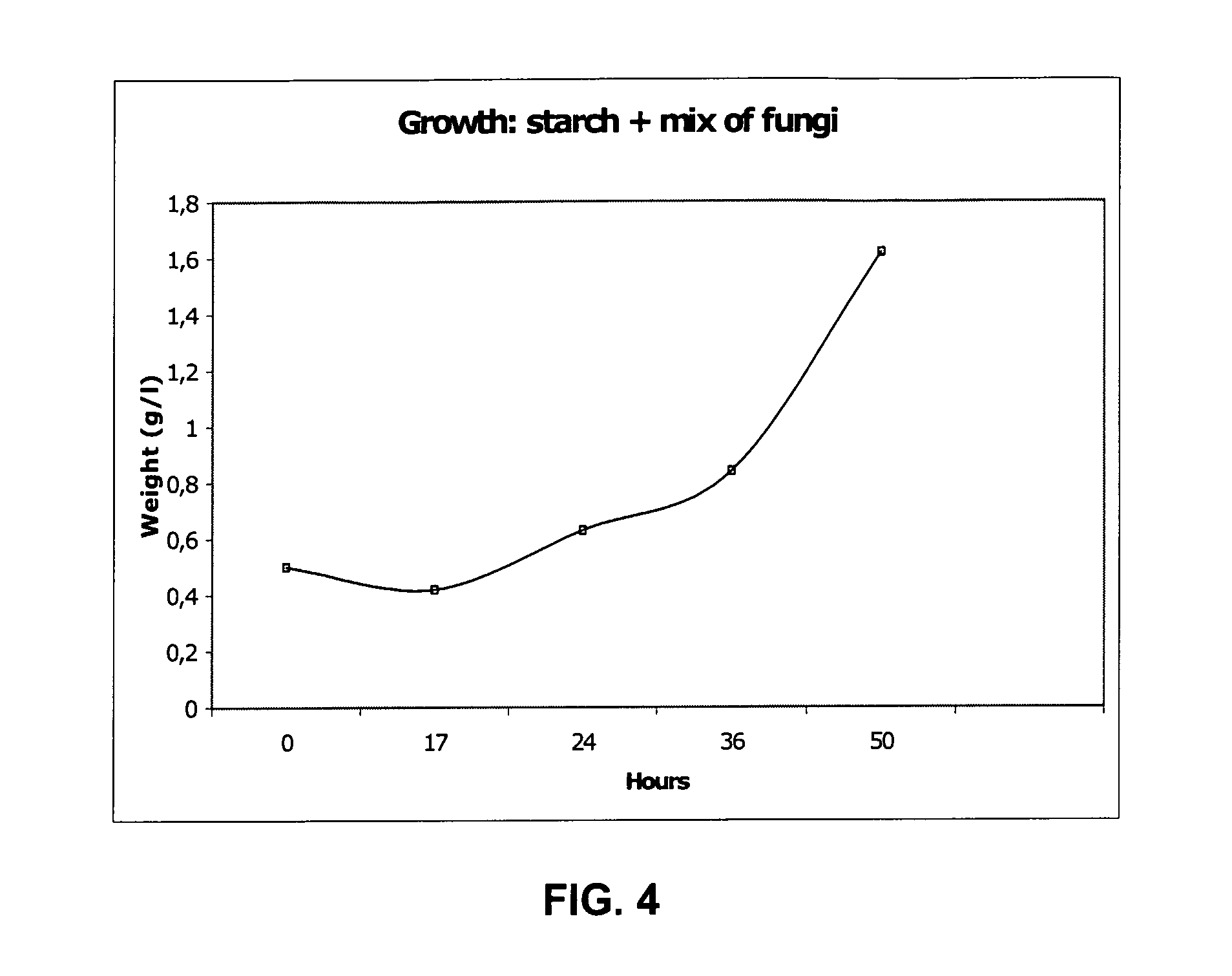
Ethanol production from biomass can be rendered more effective by the use of at least one fungus or a mix of fungi capable of fermenting pentose compounds, or both pentose as well as hexose compounds. Preferably said at least one fungus is a fungus belonging to the species Chalara sp., optionally used in combination with a second fungus belonging to the species Trametes sp. Preferably said fungus or fungi is / are used in combination with other fermenting microorganisms, such as a yeast, e.g. Saccaromyces cerevisiae.
Owner:SWETREE TECHOLOGIES AB
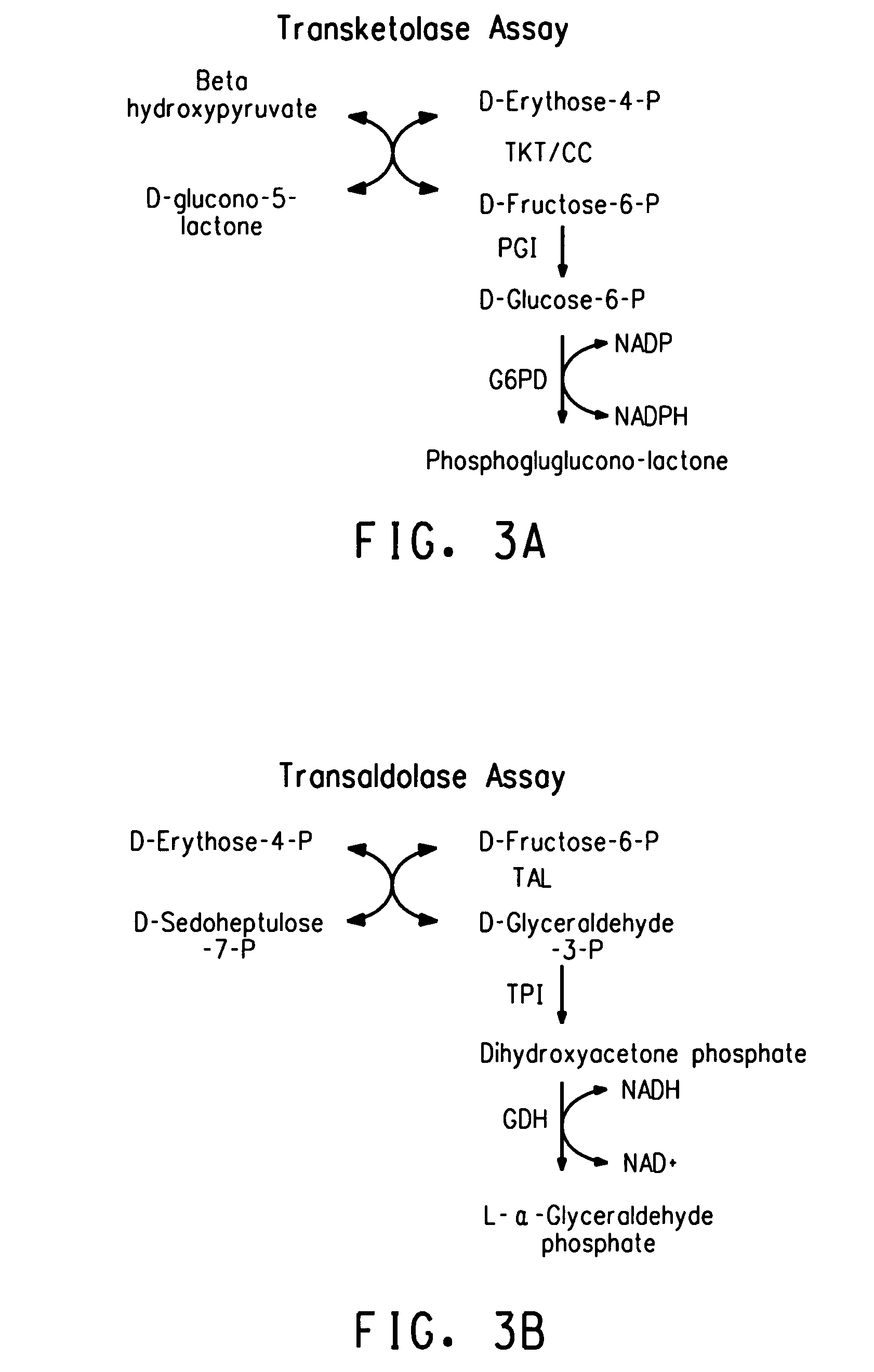
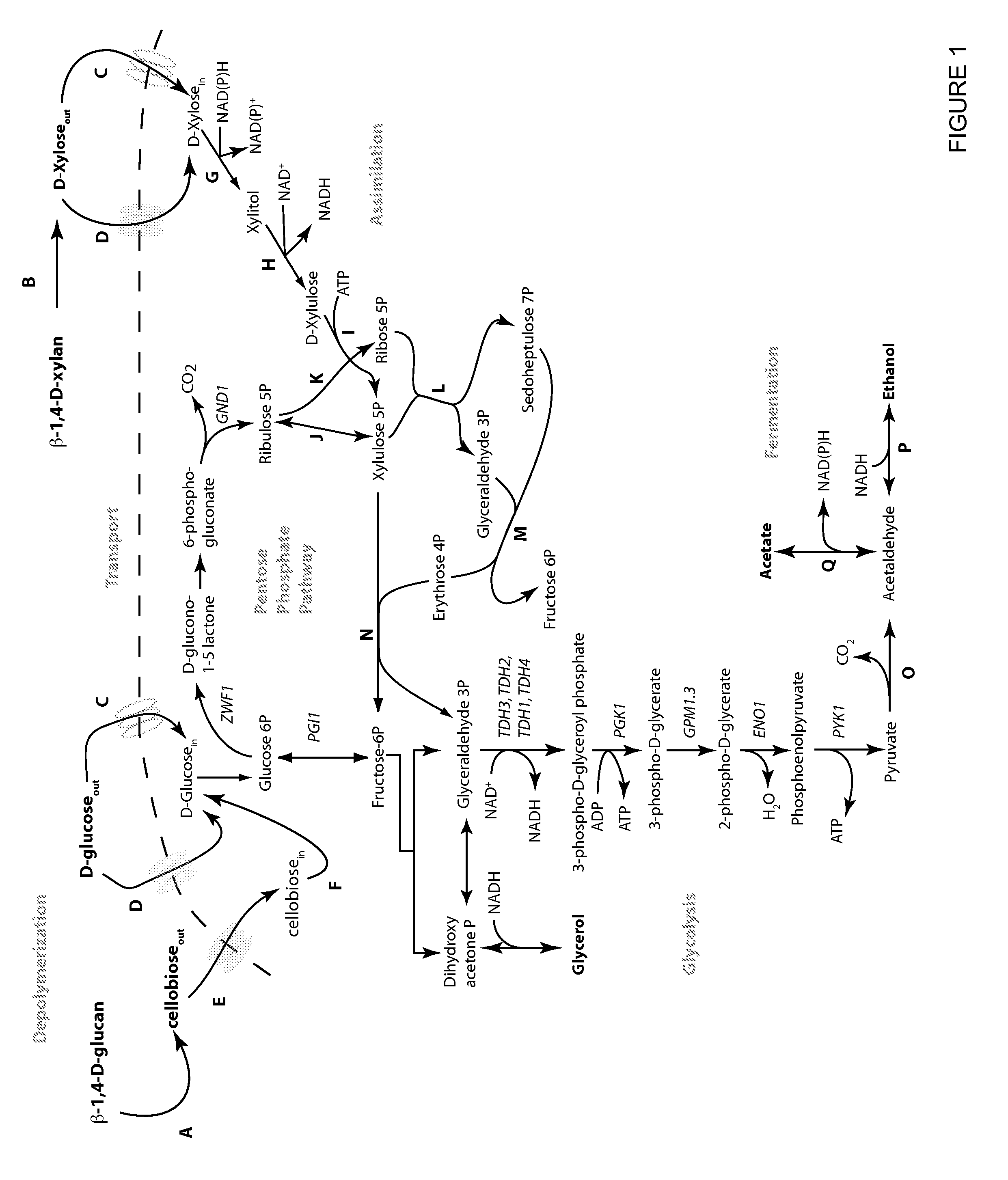
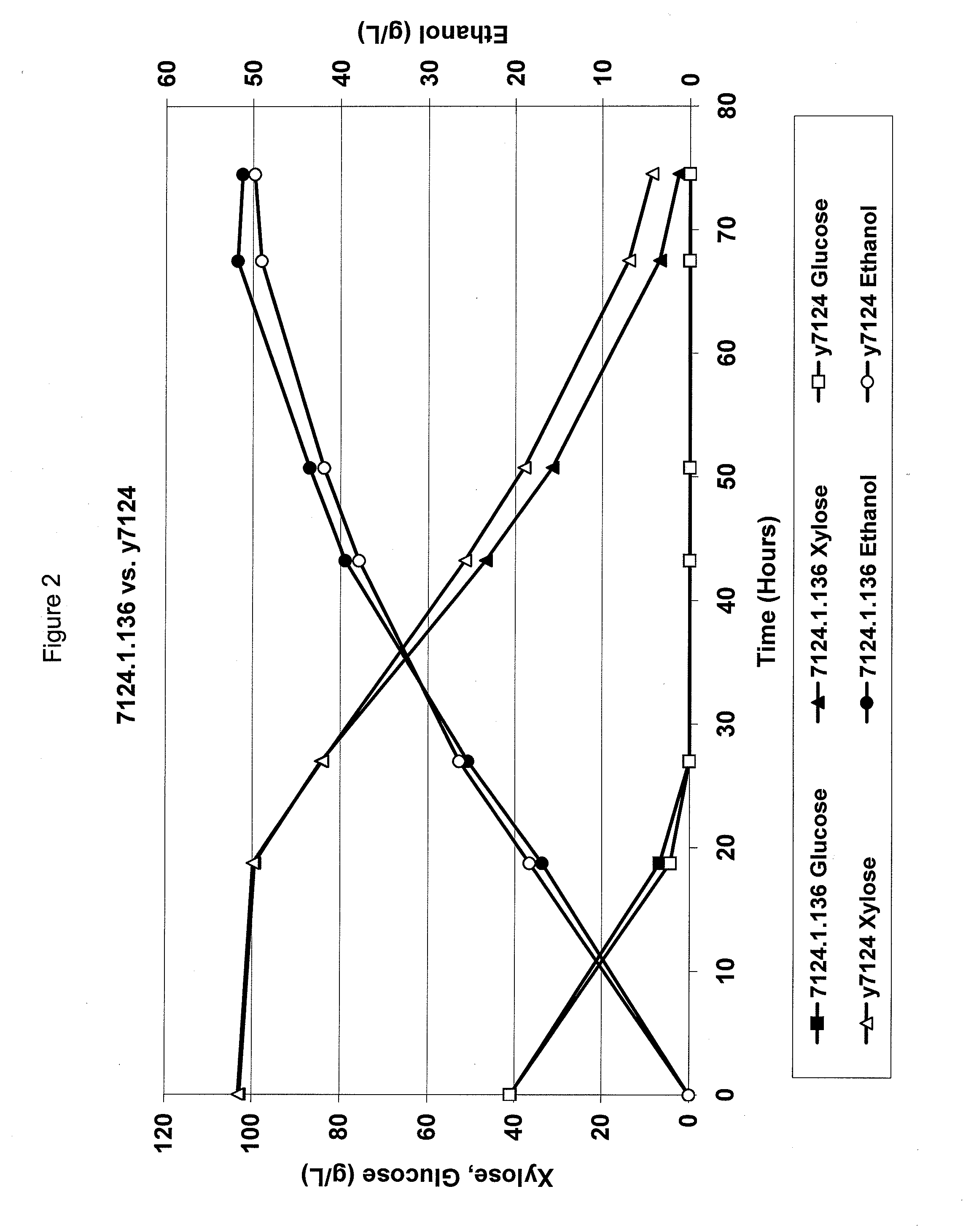
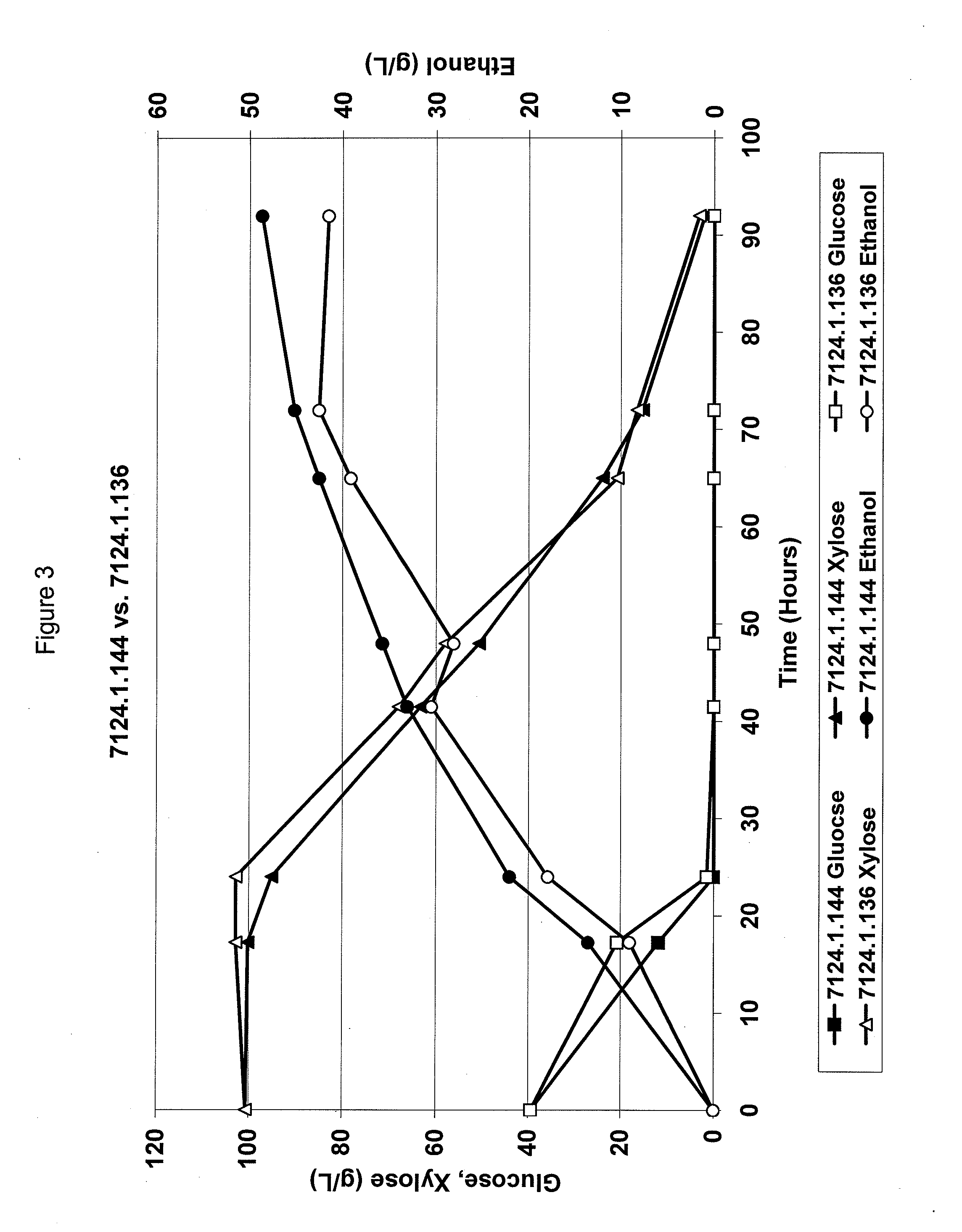
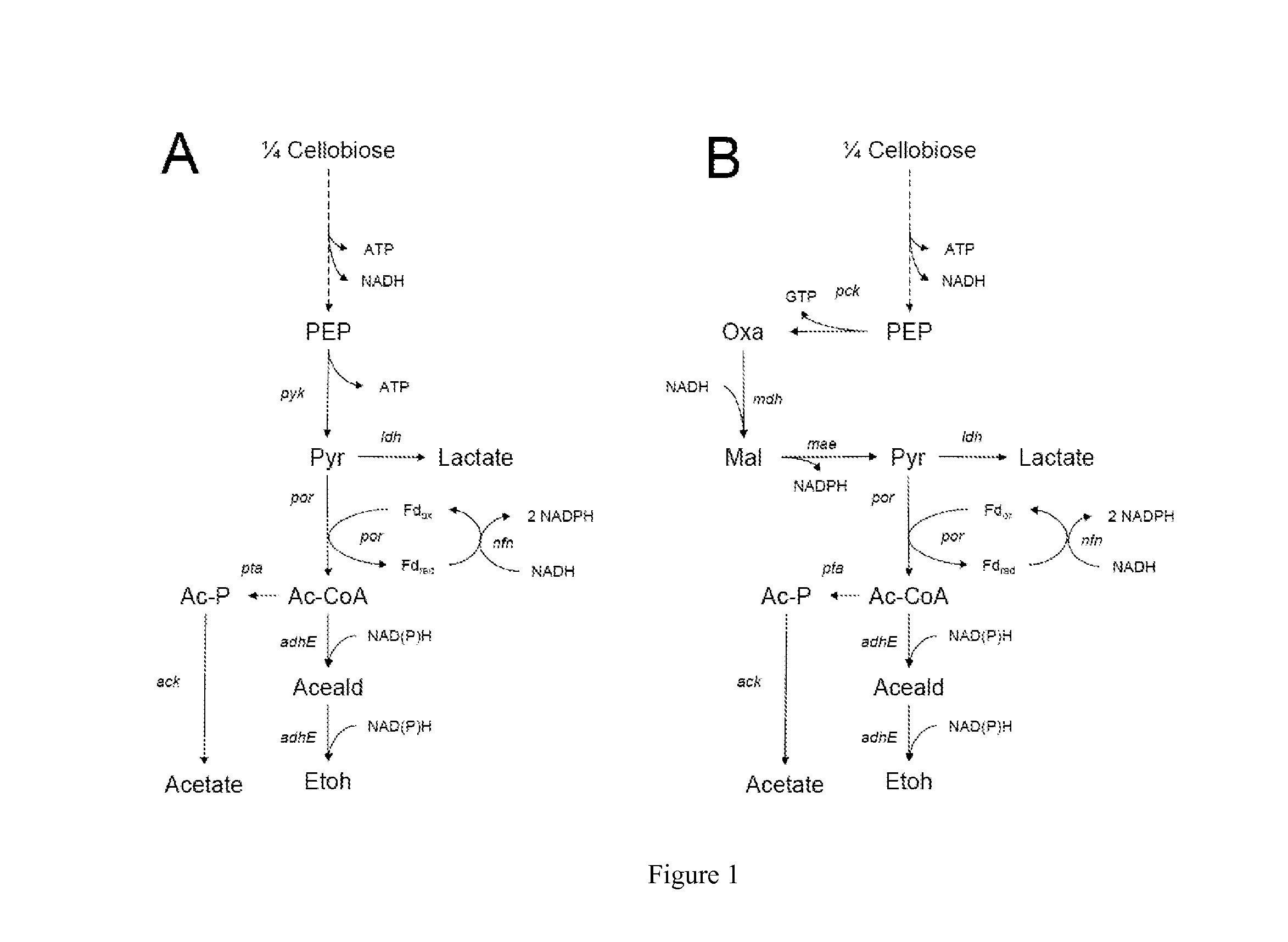
Metabolically engineered yeasts for the production of ethanol and other products from xylose and cellobiose
InactiveUS20110262983A1Increase expressionIncreased ethanol productionFungiTransferasesXyloseCellobiose
Owner:US SEC AGRI
Engineering Microorganisms to Increase Ethanol Production by Metabolic Redirection
ActiveUS20140356921A1Increased ethanol productionRedirecting carbon fluxBacteriaBiofuelsCelluloseMicroorganism
The present invention provides for the manipulation of carbon flux in a recombinant host cell to increase the formation of desirable products. The invention relates to cellulose-digesting organisms that have been genetically modified to allow the production of ethanol at a high yield by redirecting carbon flux at key steps of central metabolism.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF DARTMOUTH COLLEGE THE +1
Apparatus and method for increasing alcohol yield from grain
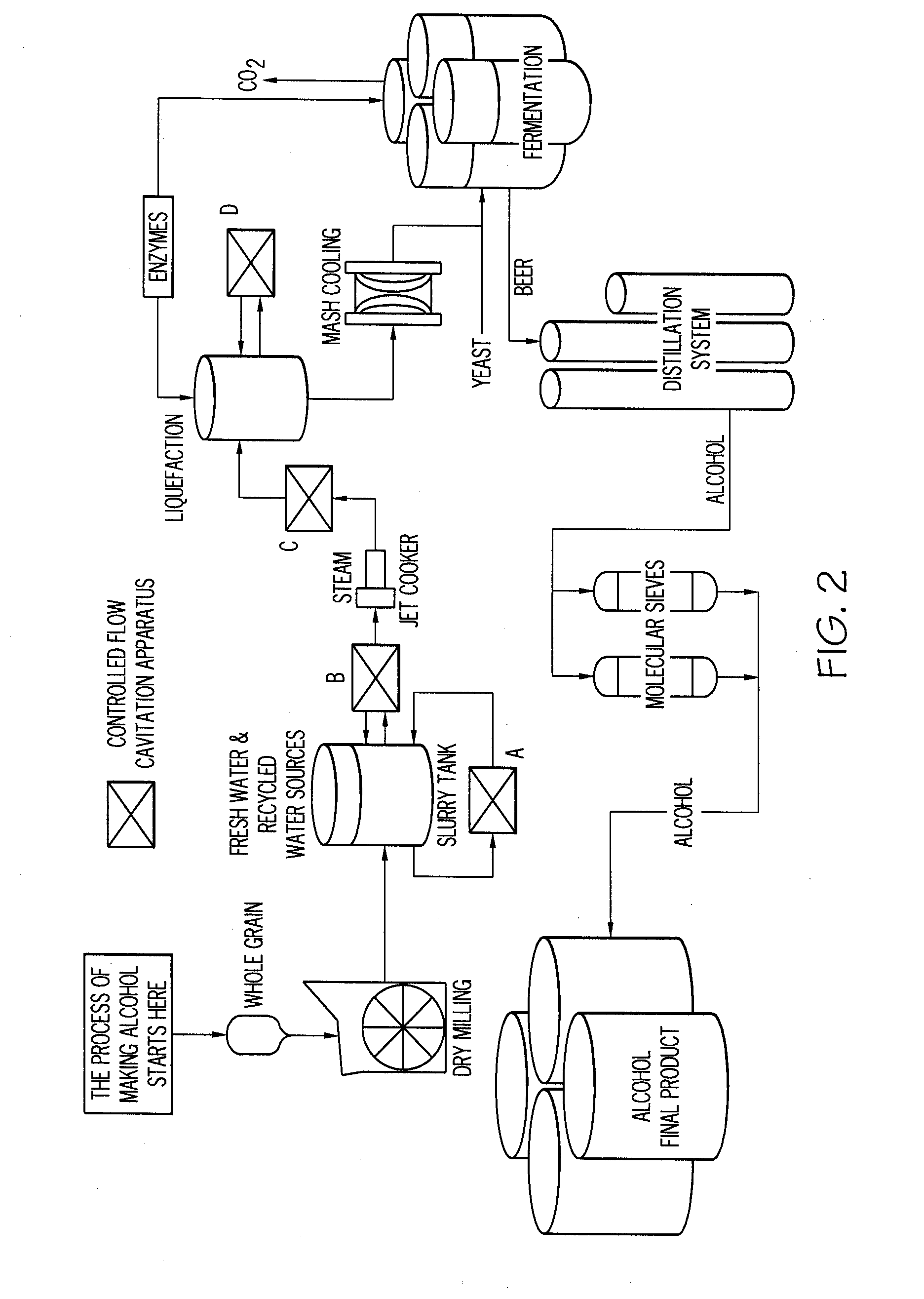
InactiveUS20080281131A1Increased ethanol productionReduce amountBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl flowCavitation
A method comprising applying a controlled flow cavitation apparatus to an alcohol production process in order to increase alcohol yield. A grain-based liquid medium comprising grain and a liquid carrier can be passed through a controlled flow cavitation apparatus at a velocity capable of generating a hydrodynamic cavitation zone where the grain size can be reduced. One or more controlled flow cavitation apparatuses can be applied at various points of an alcohol production process, such as a starch-to-ethanol production process.
Owner:ARISDYNE STSTEMS INC
Process for the preparation of stable yeast crystals for enhanced production of ethanol
InactiveUS6420146B1Reduce product inhibitionEasy to processMilk preparationFungiYeastCell culture media
The invention provides a process for the preparation of stable yeast crystals for enhanced production of ethanol, said process comprising the steps of culturing yeast Sacchromyces spp. in a growth medium, obtaining immobilized yeast heads, separating and dehydrating the stable yeast crystals, adding the stable yeast crystals to a 5-8% molasses solution and incubating the said crystals for a period ranging between 6-48 hours at a temperature ranging between 24-32° C. to obtain activated stable yeast heads to obtain crystals which are separated in a fermentation broth containing molasses and having a total reducing sugar concentration in the range of 10-30% and recovering the ethanol from the fermentation broth by known methods.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
High-yielding ethanol yeast and method for improving quality of traditional fermented foods through symbiotic fermentation of high-yielding ethanol yeast and ester-producing yeast
ActiveCN109810910AIncreased ethanol productionOptimizing the Culture Conditions of Symbiotic FermentationFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationHydrolysateEthyl acetate
The invention relates to a saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 strain for high-yielding ethanol and a symbiotic fermentation culture method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 strain and a Wickerhamomyces anomalus Y3604 strain for high-yielding ethyl acetate as well as application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 strain. The saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 was preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 20th, 2017, with a preservation number of CGMCC No.14828; the similarity of 26S rDNA D1 / D2 sequence of the saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 strain to 26S rDNA D1 / D2 sequence of other saccharomyces cerevisiae strains; symbiotic fermentation of two yeast strains in a sorghum enzymatic hydrolysate culture medium by a standing or shaking mode has the advantages that the content of the ethyl acetate is favorably improved and the contents of flavor substances such as total ester, beta-phenylethanol and isoamyl alcohol also can be improved. In a solid brewing system, the symbiotic fermentation of the two strains can enhance the characteristics of ester-improving and flavor-enhancing of yeast. The symbiotic fermentation method of the two strains, disclosed by the invention, can be applied to the brewing industries, having demands on the ethyl acetate, such as Baijiu, yellow rice wine and soy sauce.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Corn and fiber refining
InactiveUS7488390B2Increased ethanol productionIncrease the number ofJuice extractionBiofuelsSugarHemicellulose
Plant materials such as corn kernels which contain starch and fiber comprising cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, and pectin are refined. The starch, cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin are converted to sugars which are then fermented to ethanol. Additional sources of starch and fiber are optionally added to the refining process to further increase the yield of ethanol.
Owner:LANGHAUSER ASSOC
Method of synthesizing higher-molecular alcohol
ActiveUS8080695B2Efficient collectionIncreased ethanol productionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationSynthetic Polymeric MacromoleculesOctanol
The present invention provides a production method with which high molecular alcohols having an even number of carbon atoms such as 1-butanol, hexanol, octanol and decanol, and a mixture of these are efficiently collected through clean processes with the use of ethanol as a raw material. High molecular alcohols are produced from ethanol by using calcium phosphate-based compounds such as hydroxyapatite Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, tricalcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2, calcium monohydrogen phosphate CaHPO4.(0˜2)H2O, calcium diphosphate Ca2P2O7, octacalcium phosphate Ca8H2(PO4)6.5H2O, tetracalcium phosphate Ca4(PO4)2O or amorphous calcium phosphate Ca3(PO4)2. nH2O as a catalyst, using ethanol as a starting material, and setting a contact time at 0.4 second or longer.
Owner:SANGI CO LTD
Designer organisms for photosynthetic production of ethanol from carbon dioxide and water
InactiveUS7973214B2Higher solar-to-ethanol energy-conversion efficiencyWeaken energyUnicellular algaeBiofuelsCellulosePlant cell
The present invention provides a revolutionary photosynthetic ethanol production technology based on designer transgenic plants, algae, or plant cells. The designer plants, designer algae, and designer plant cells are created such that the endogenous photosynthesis regulation mechanism is tamed, and the reducing power (NADPH) and energy (ATP) acquired from the photosynthetic water splitting and proton gradient-coupled electron transport process are used for immediate synthesis of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) directly from carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O). The ethanol production methods of the present invention completely eliminate the problem of recalcitrant lignocellulosics by bypassing the bottleneck problem of the biomass technology. The photosynthetic ethanol-production technology of the present invention is expected to have a much higher solar-to-ethanol energy-conversion efficiency than the current technology and could also help protect the Earth's environment from the dangerous accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Chaotic fermentation of ethanol
InactiveUS20050170483A1Improve productivityUnstable environmentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiotechnologyControl system
A method and apparatus for fermentation of ethanol. A method comprises selecting a desired fermentation on process with oscillatory process characteristics, providing a fermentor and a biocatalyst, feeding a substrate to the fermentor, and fermenting under chaotic conditions. An apparatus comprises a fermentor, a process control system capable of operating the fermentor under chaotic conditions, and a membrane selective for ethanol. The invention can be applied to other catalytic processes.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Systems and methods for producing biofuels and related materials
InactiveUS20100151546A1Increase productionIncreased ethanol productionBacteriaBiofuelsOrganic acidClostridium phytofermentans
Clostridium phytofermentans cells (American Type Culture Collection 700394T) and all other strains of the species can ferment materials such as biomass into useful products and coproducts, such as ethanol, hydrogen and organic acids. Compositions that include Clostridium phytofermentans are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com