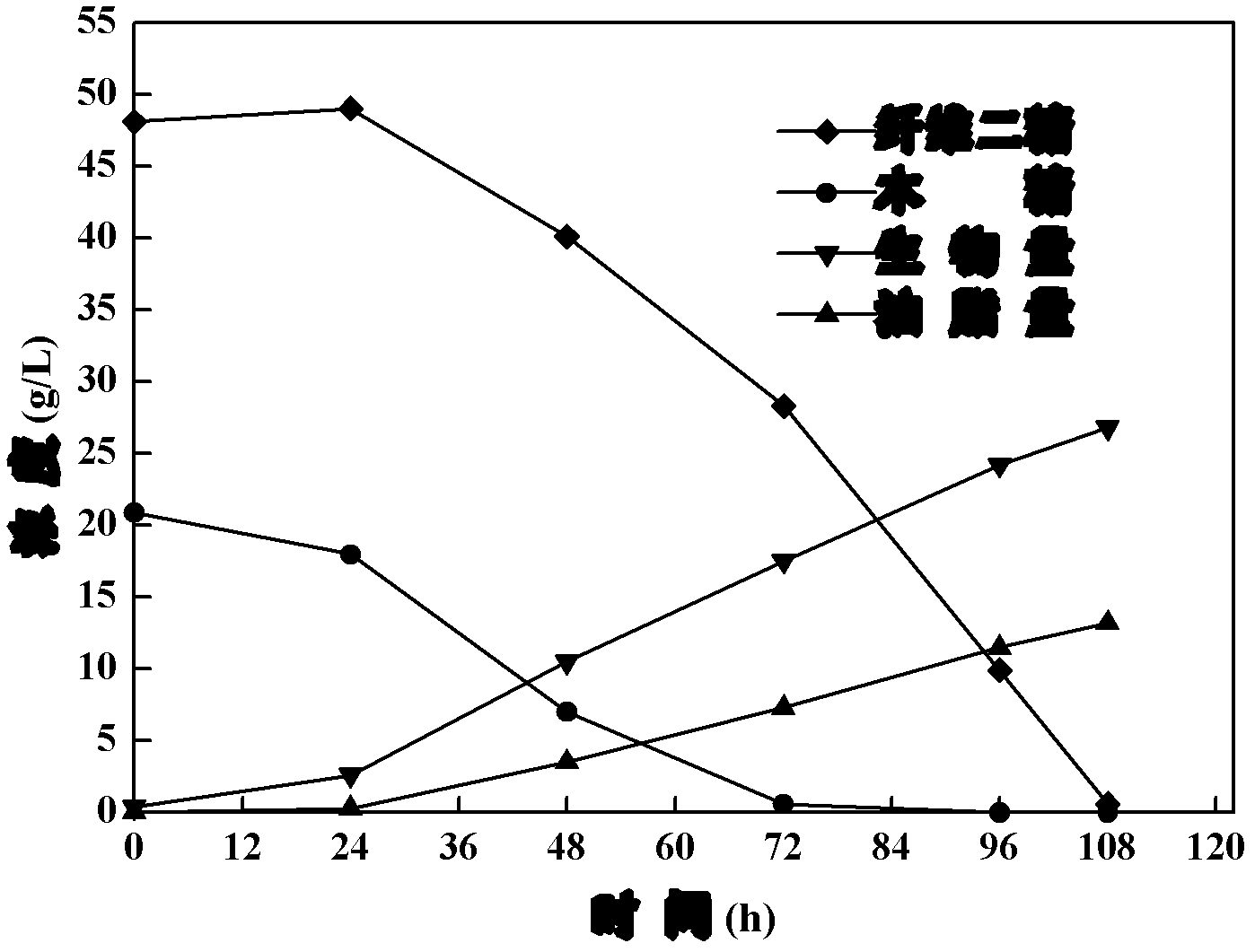
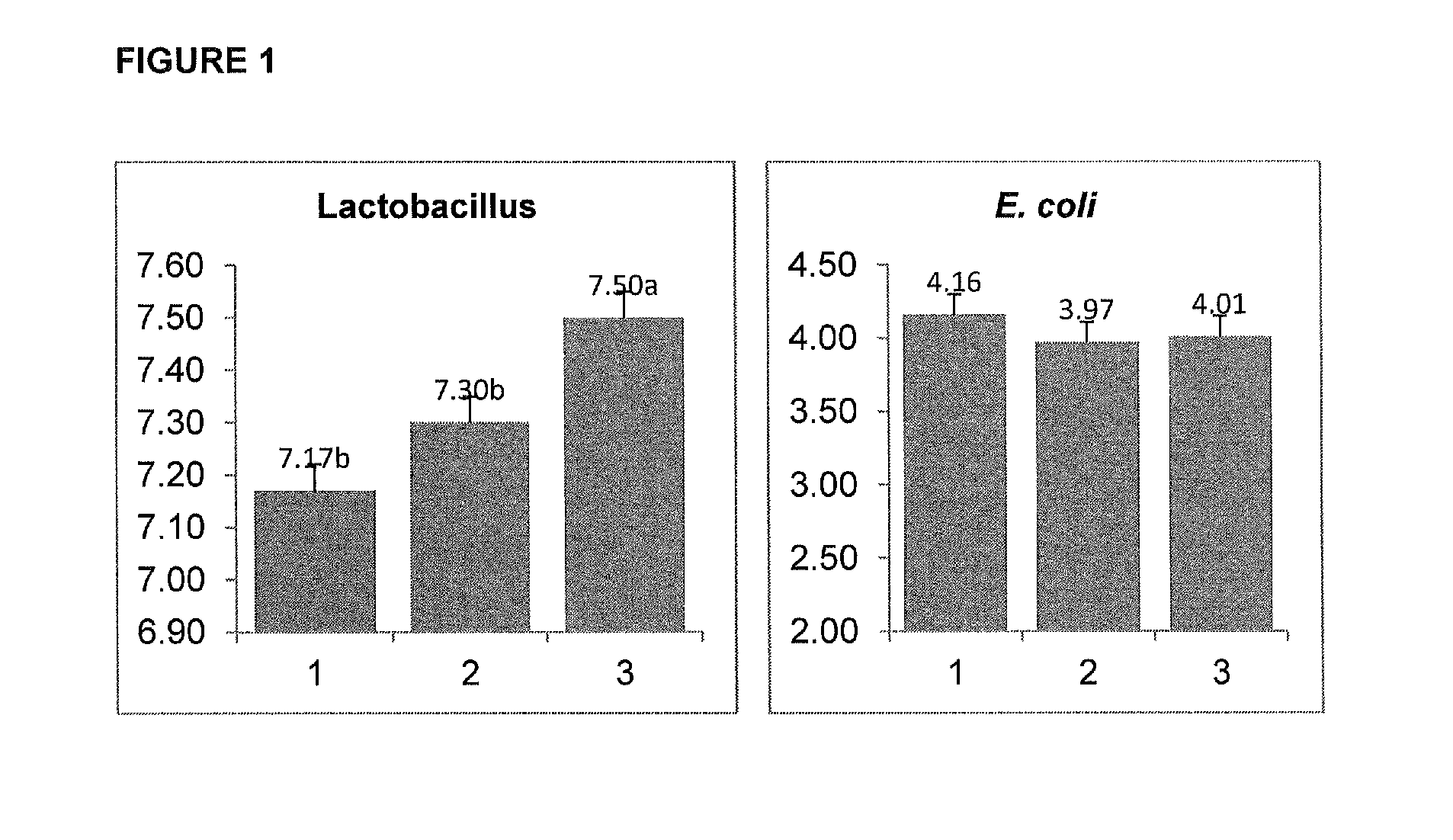
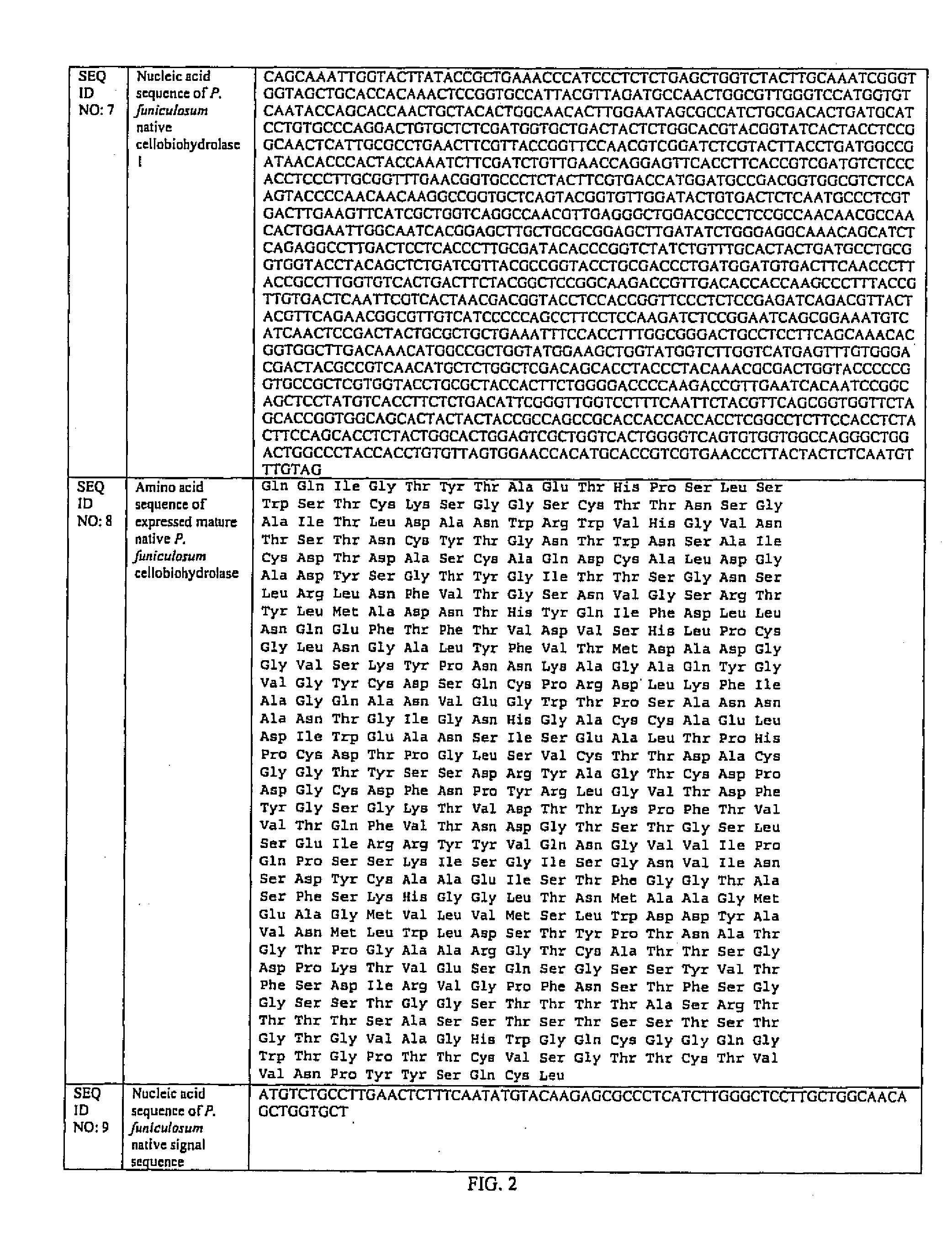
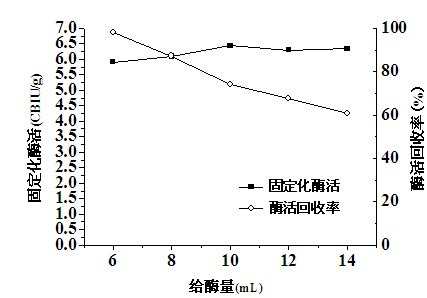
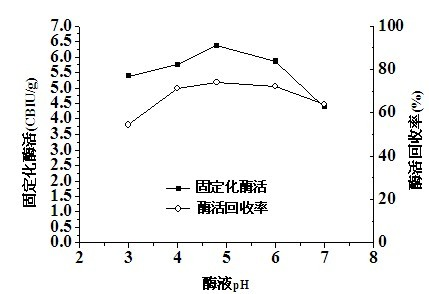
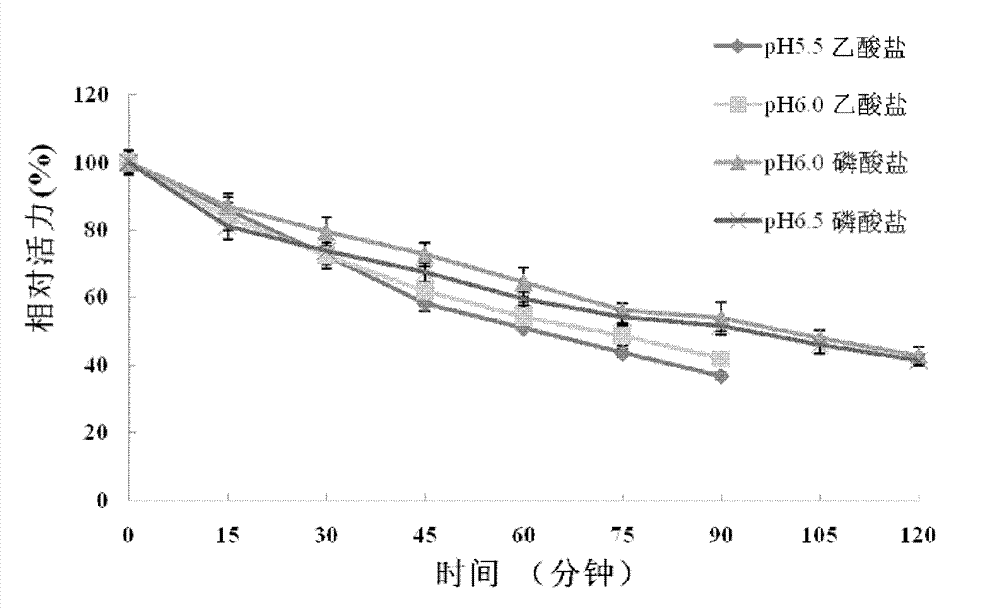
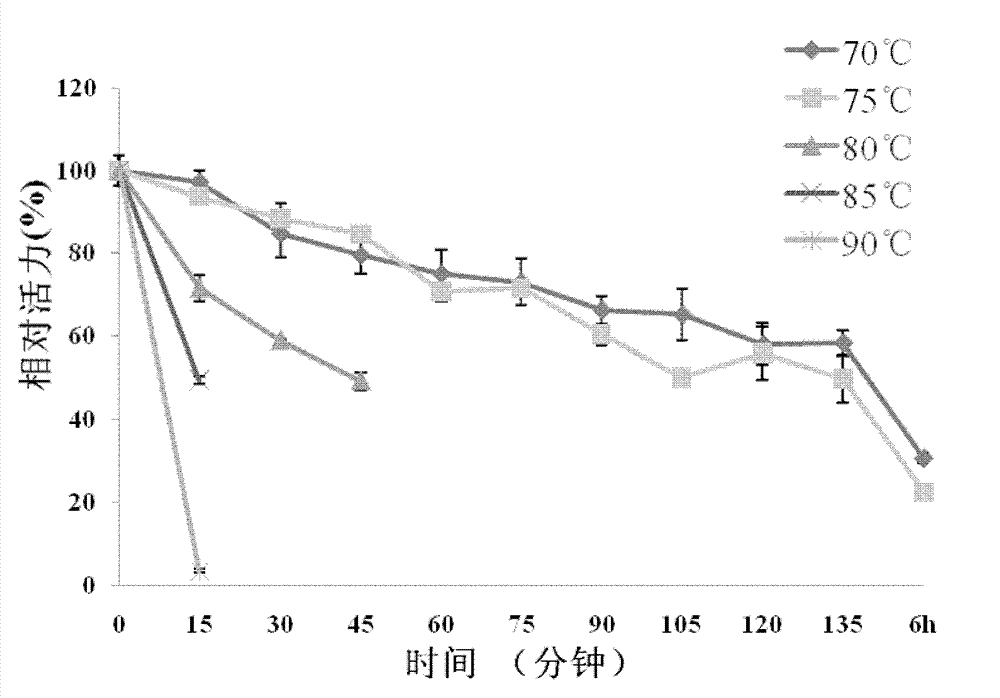
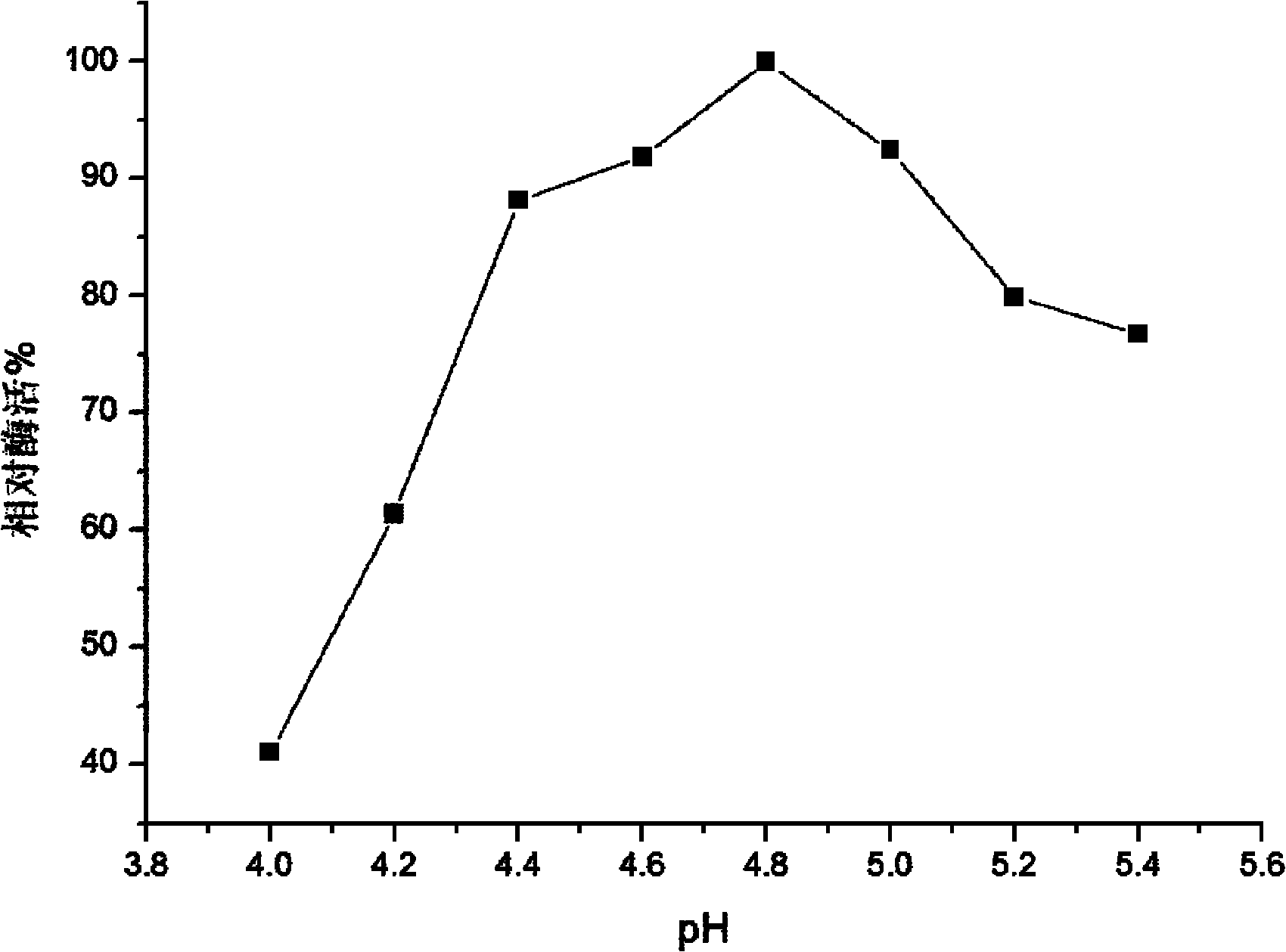
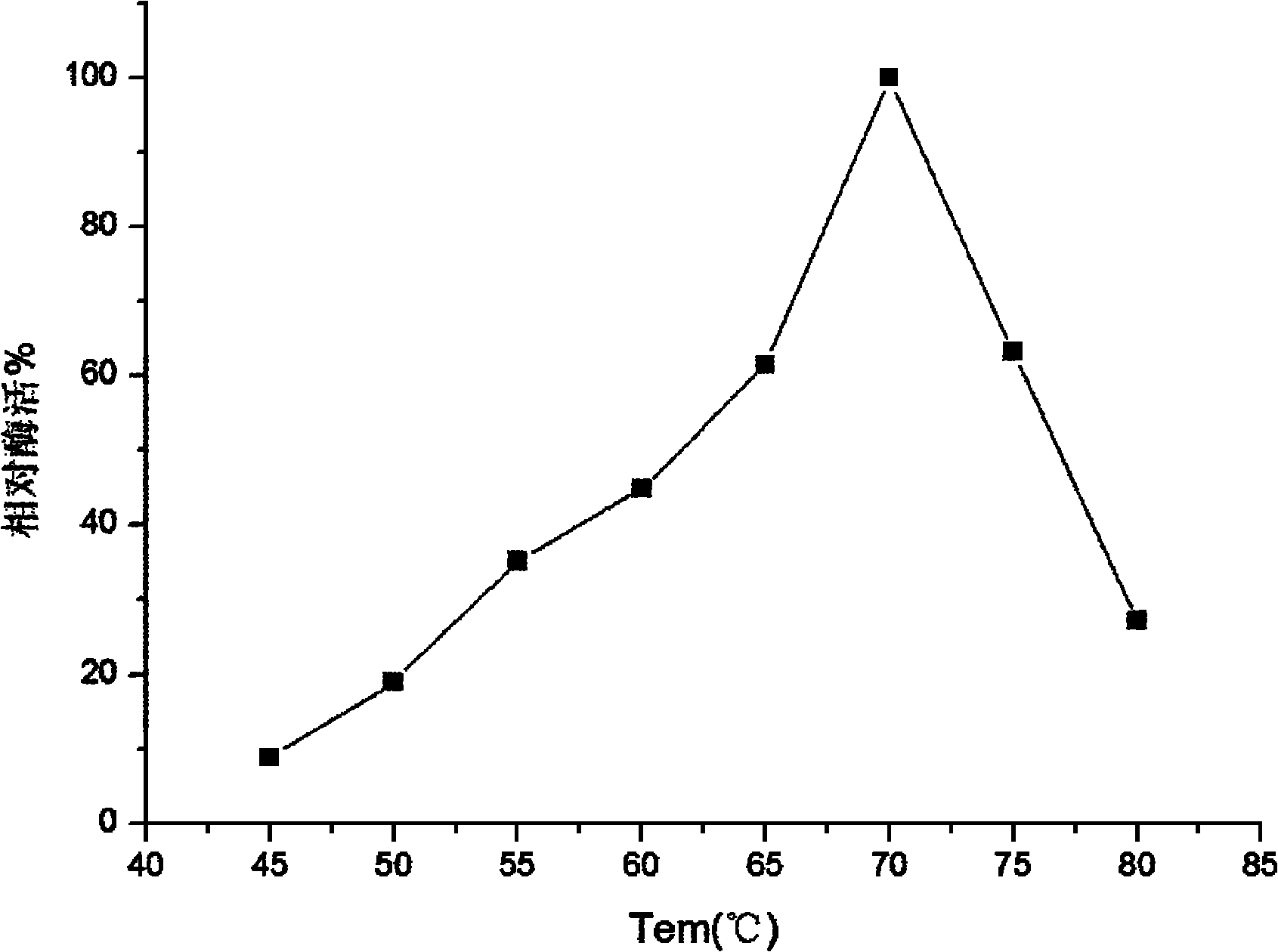
Patents
Literature
380 results about "Cellobiose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
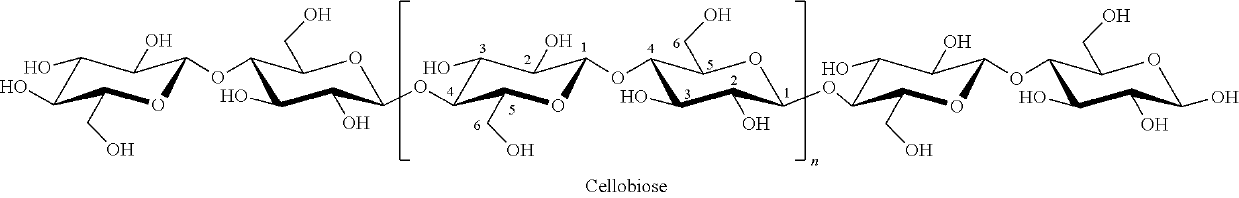
Cellobiose is a disaccharide with the formula C₁₂H₂₂O₁₁. Cellobiose, a reducing sugar, consists of two β-glucose molecules linked by a β(1→4) bond. It can be hydrolyzed to glucose enzymatically or with acid. Cellobiose has eight free alcohol (OH) groups, one acetal linkage and one hemiacetal linkage, which give rise to strong inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonds. It can be obtained by enzymatic or acidic hydrolysis of cellulose and cellulose rich materials such as cotton, jute, or paper. Cellobiose can be used as an indicator carbohydrate for Crohn's disease and malabsorption syndrome.
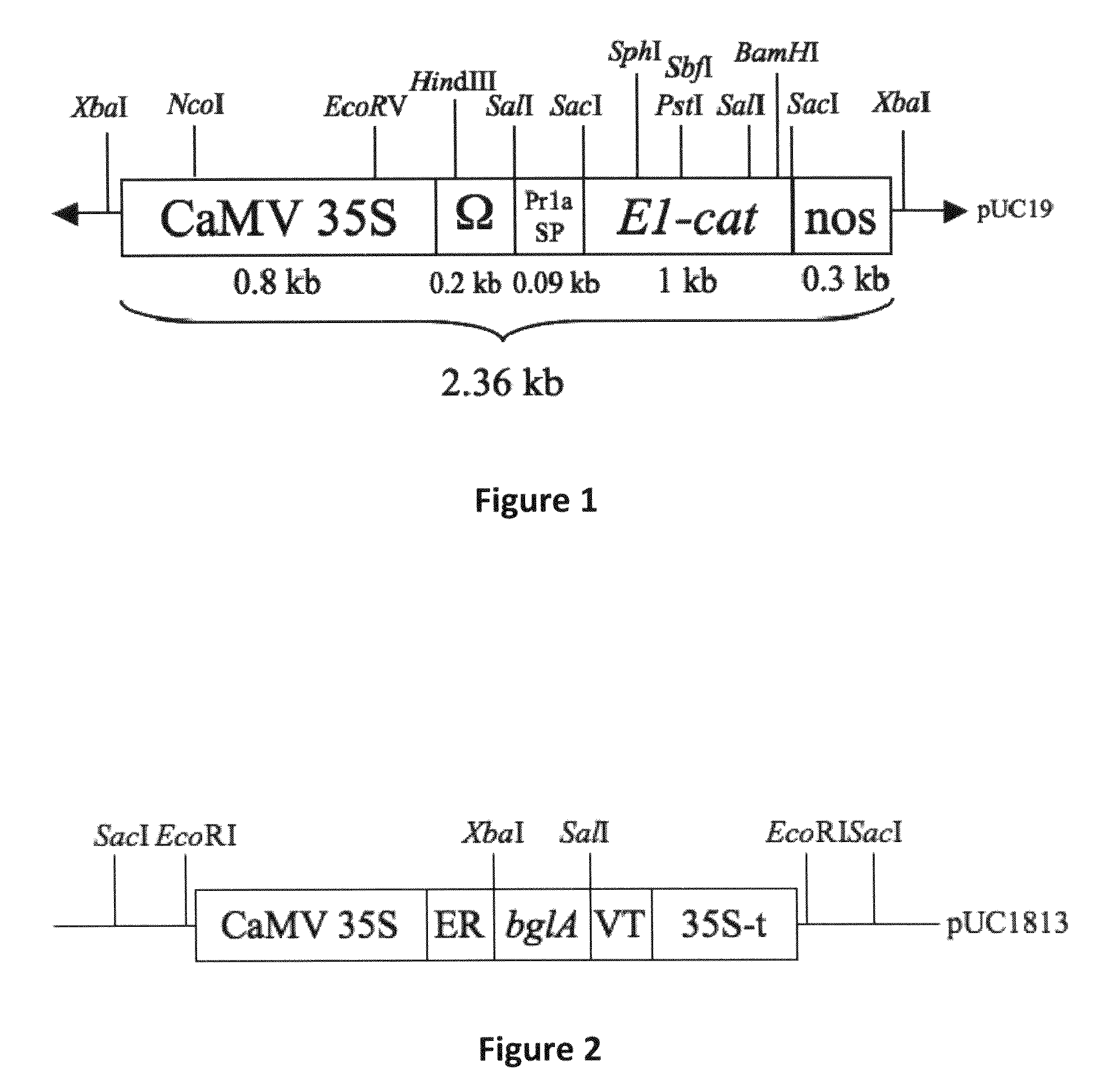
Cosmetic compositions
InactiveUS6248312B1Avoidance of high processing temperatureCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsHydrogenAcyl group
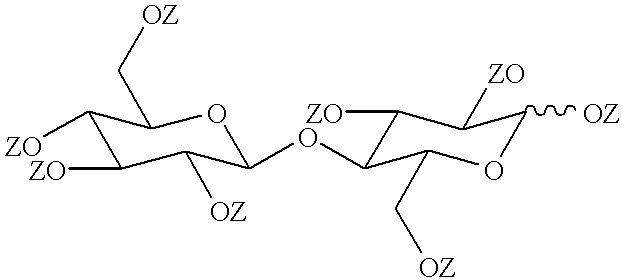
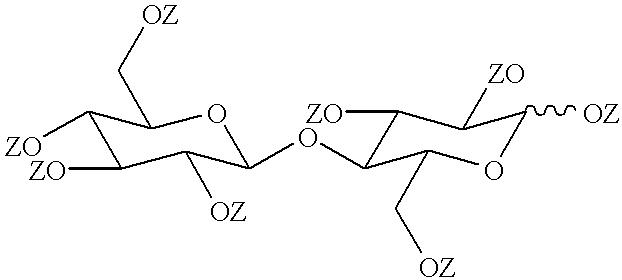
A cosmetic composition preferably an antiperspirant composition, in solid or soft-solid form has a continuous phase which contains a water-immiscible liquid carrier and also contains a structurant which is partially or fully esterified cellobiose of the formulawherein each Z is independently hydrogen or an acyl group of the formulawhere R denotes a hydrocarbyl group containing from 4 to 22 carbon atoms. Not more than half of the Z groups are hydrogen.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
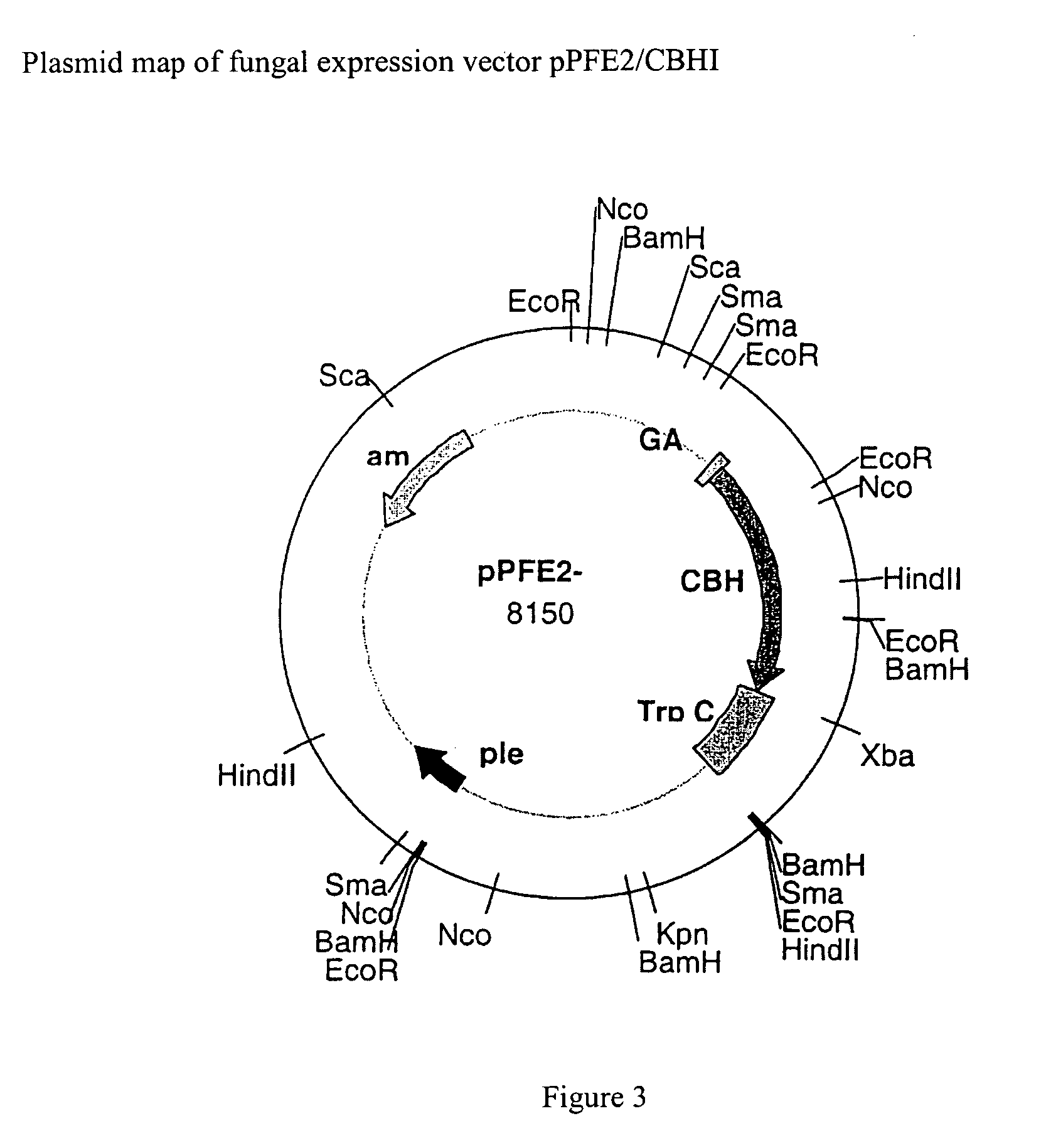
Cellobiohydrolase I gene and improved variants
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Method for increasing lignocellulose saccharification yield through multi-step enzymolysis
InactiveCN102191299AHigh yield of enzymatic hydrolysisReduce generationFermentationHydrolysateCellobiose
The invention relates to a method for increasing the lignocellulose saccharification yield through multi-step enzymolysis. The method comprises the following main steps: 1) pretreating wood fiber raw material; 2) adding one or more of bio-degrading enzymes in the pretreated wood fiber stepwise or simultaneously, removing the extract component or lignin in the raw material to change the fiber structure of the raw material; 3) adding one or more of hemicellulose degrading enzymes in the lignocellulose which is removed extract or lignin through enzymolysis stepwise or simultaneously, extracting pentose in the raw material; and 4) filtering fiber residue obtained in the step 3) through the enzymolysis, and adding cellulase and / or cellobiase to hydrolyze continuously and obtain glucose hydrolysate. By adopting the method, each component can be recycled and the total reducing sugar yield can be increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
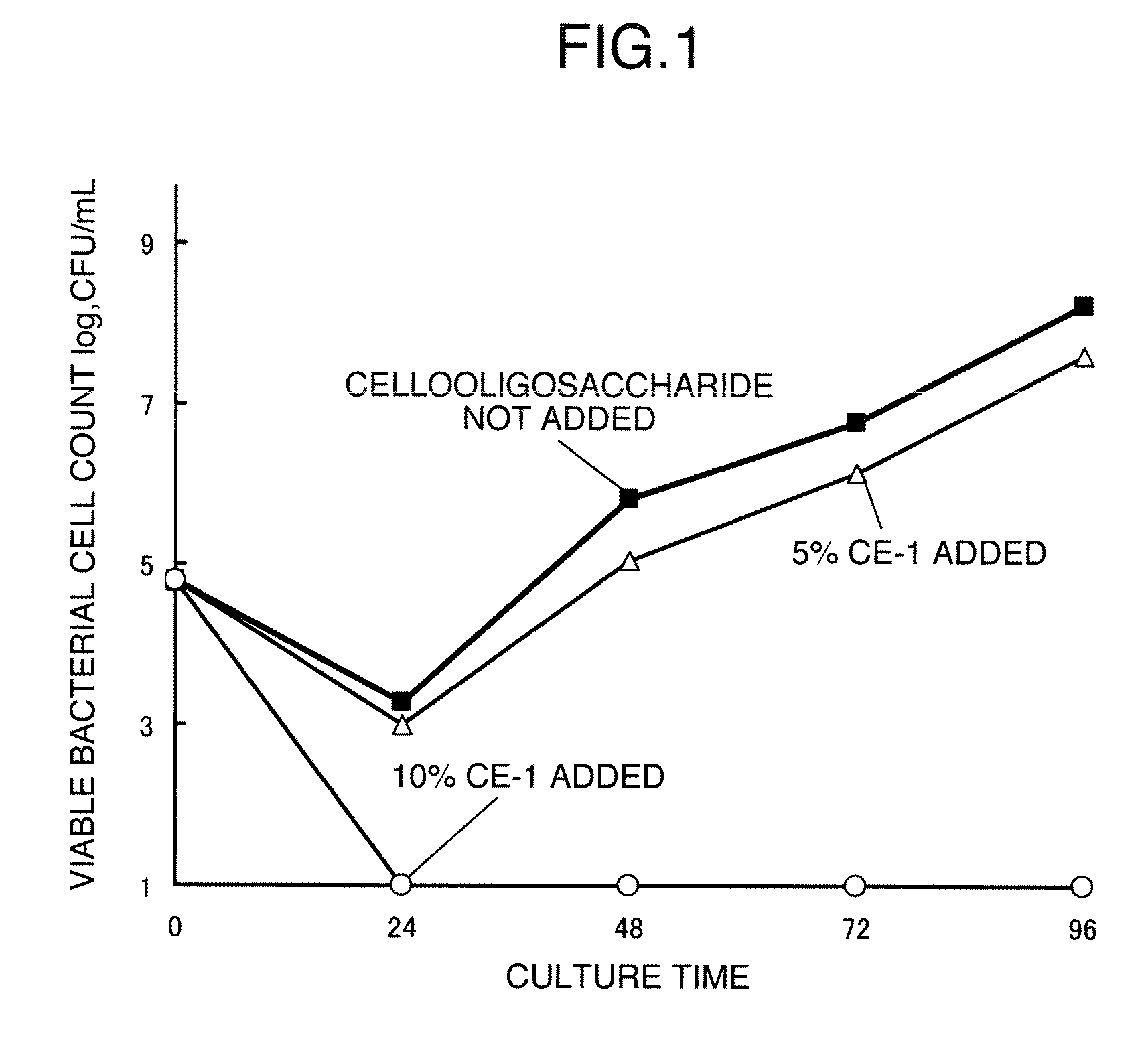
Cellooligosaccharide-Containing Composition
InactiveUS20090232892A1To promote metabolismEnhance skin barrier functionAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryAdditive ingredientMedicine
Disclosed is a cellooligosaccharide composition comprising, as the main ingredient, at least one cellooligosaccharide selected from the group consisting of cellobiose, cellotriose, cellotetraose, cellopentaose and cellohexaose, which is in the powdery form having an average L / D value of 3.0 or lower, a bulk density of 0.80 g / mL or lower and an angle of repose of 60° or lower.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Cosmetic compositions
InactiveUS20050244441A1Improve stabilityReduce fragranceCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEmulsionMedicine
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
Oil production microbe culture method
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production of ethanol from agronomic crop fibre castoff
The invention belongs to a method for preparing ethyl hydrate by improved agronomic crop fabric wastes which is more economy for preparing ethyl hydrate by integrated utilization. The improved method comprises acid and caustic pretreating the agronomic crop wastes, color removing and concentrating crystal the xylose, enzyme treatmenting the ligno-cellulose, alcohol(ic) fermentation and rectification the hydrolytic decomposition sugar. The chemical pretreatment process comprises using 0.1-10alcaine, vitriol oil, phosphoric acid, volatility organic acid and mixture of the above acid, and 1-5Óalcarea lime, ammonia spirit and mixture of the above alkali in order to carry out in moment. The temperature of acid pretreatment is from normal temperature to 120 DEG C, and time is 1-8 hours. The pretreatment final liquor is used for color removing, concentrating and crystallization. The pretreatment final slag is hydrolyzed by cellulase and cellase at the temperature of 40 to 60 DEG C for 12-14 hours. The fermentation time of prehydrolysis or prehydrolysis while fermentation are 48 hours or so.
Owner:徐佳珊 +3
Feed additive composition
InactiveUS20150216203A1Improve performanceImprove feed conversionMilk preparationBiocideAlglucerasePentagalacturonic acid
A feed additive composition comprising a direct fed microbial (DFM), in combination with a xylanase (e.g. endo-1,4-β-d-xylanase) and a β-glucanase (and optionally a further fibre degrading enzyme), wherein the DFM is selected from the group consisting of an enzyme producing strain; a C5 sugar-fermenting strain; a short-chain fatty acid-producing strain; a fibrolytic, endogenous microflora-promoting strain; or combinations thereof. The DFM may be selected from the group consisting of: Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS3BP5, Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS442, B. subtilis AGTP BS521, B. subtilis AGTP BS918, Bacillus subtilis AGTP BS1013, B. subtilis AGTP BS1069, B. subtilis AGTP 944, B. pumilus AGTP BS 1068 or B. pumilus KX11-1, Enterococcus faecium ID7, Propionibacterium acidipropionici P169, Lactobacillus rhamnosus CNCM-1-3698, Lactobacillus farciminis CNCM-1-3699, a strain having all the characteristics thereof, any derivative or variant thereof, and combinations thereof and the further fibre degrading enzyme may be selected from the group consisting of a cellobiohydrolase (E.C. 3.2.1.176 and E.C. 3.2.1.91), a β-glucosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.21), a β-xylosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.37), a feruloyl esterase (E.C. 3.1.1.73), an α-arabinofuranosidase (E.C. 3.2.1.55), a pectinase (e.g. an endopolygalacturonase (E.C. 3.2.1.15), an exopolygalacturonase (E.C. 3.2.1.67) or a pectate lyase (E.C. 4.2.2.2)), or combinations thereof.
Owner:DUPONT NUTRITION BIOSCIENCES APS
Cellobiohydrolase I gene and improved variants
InactiveUS20030170861A1Reducing glycosylationImprove toleranceSugar derivativesTissue cultureGlucanaseNucleic acid sequencing
A nucleic acid molecule having a nucleic acid sequence that encodes a linker region of exoglucanase, said nucleic acid sequence comprising the nucleic sequence 5'-GGCGGAAACCCGCCTGGCACCACC-3'.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Novel cellobiohydrolase enzymes
Provided are isolated cellobiohydrolases comprising a modified Glycoside Hydrolase (GH) Family 7 catalytic domain, a GH Family 7 catalytic domain and a modified Family 1 carbohydrate binding module (CBM), or both a modified Family 7 catalytic domain and a modified Family 1 CBM. Such isolated cellobiohydrolases exhibit from 45% to about 99.9% amino acid sequence identity to amino acids 1-436 of SEQ ID NO: 1 or to amino acids 1-438 of SEQ ID NO: 2 and improved activity on process substrates. Also provided are genetic constructs and genetically modified microbes for expressing the isolated cellobiohydrolases, a process for producing the isolated cellobiohydrolases, cellulase enzyme mixtures comprising the isolated cellobiohydrolase and a process for hydrolysing a cellulosic substrate with such cellulase enzyme mixtures.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
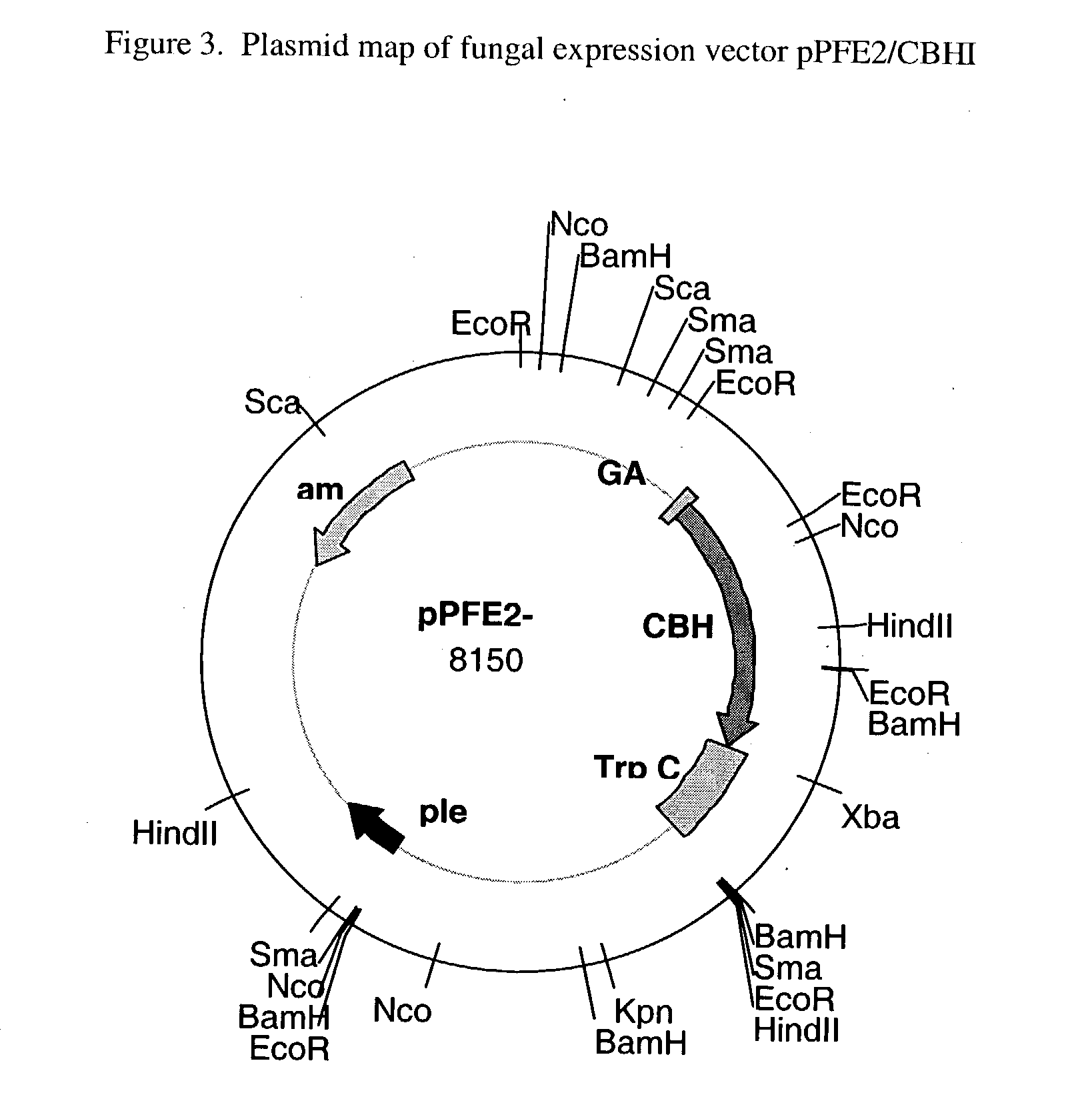
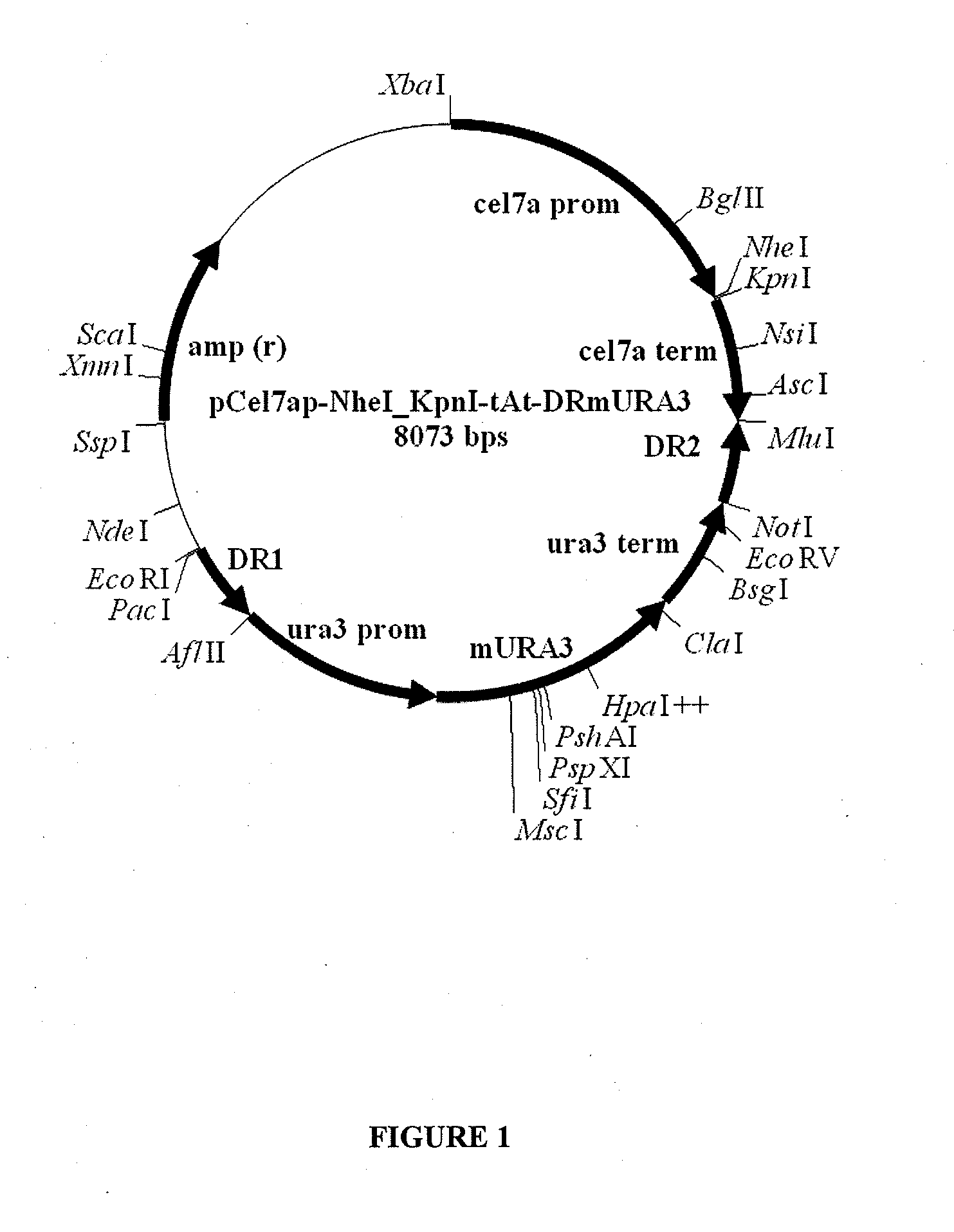
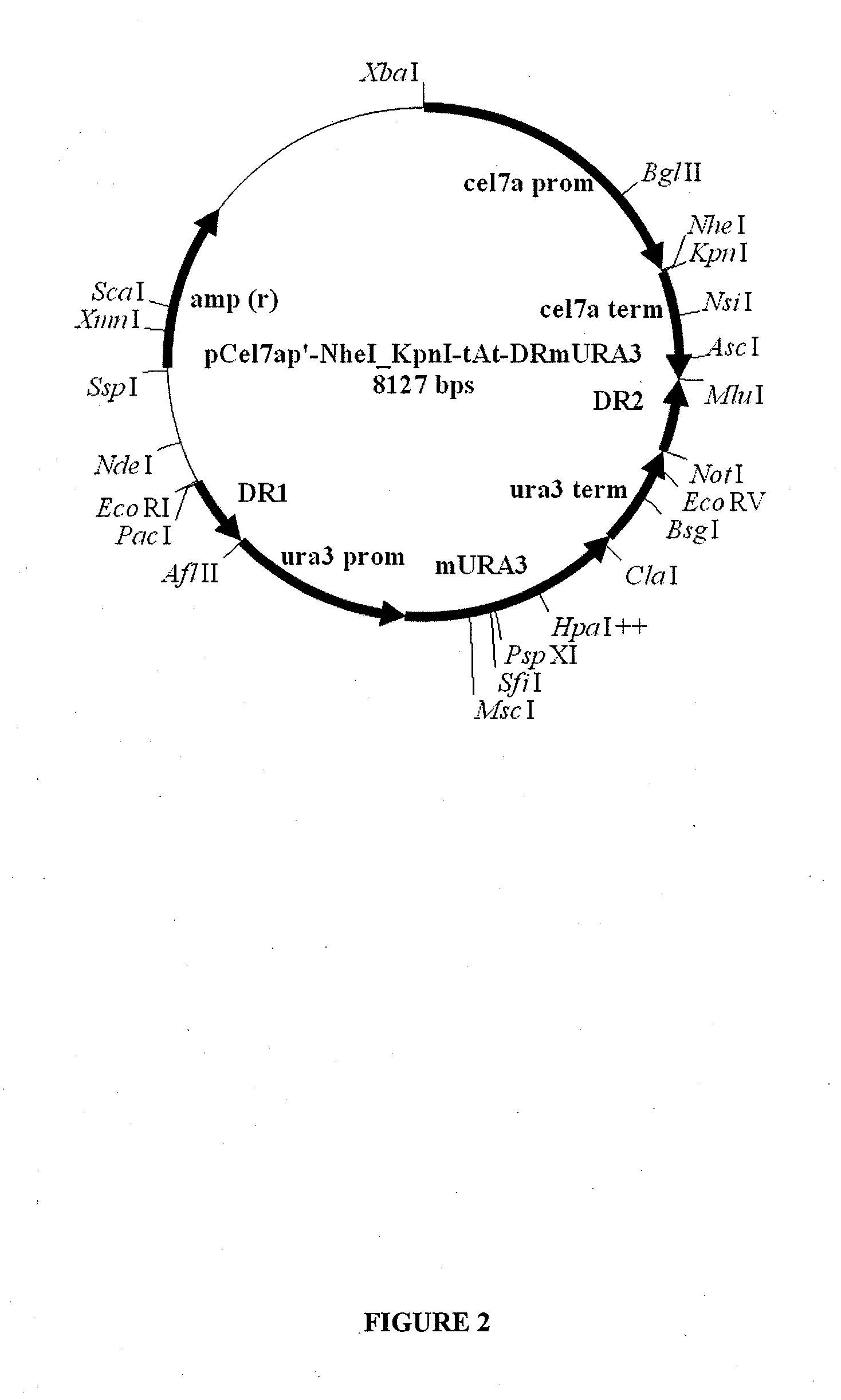
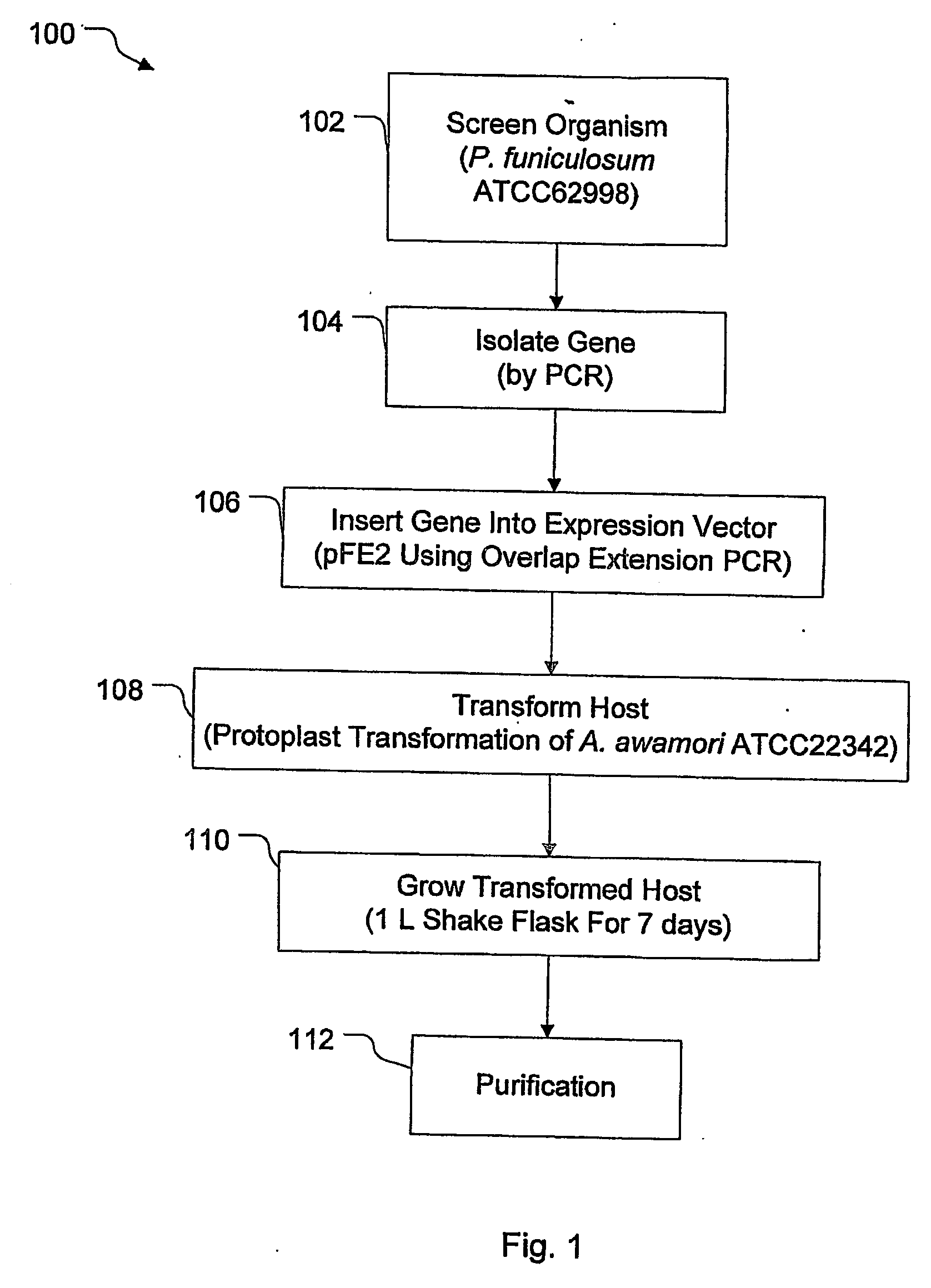
Superactive cellulase formulation using cellobiohydrolase-1 from penicillium funiculosum
ActiveUS20070148730A1Improve specific performanceImprove performanceFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyGlucanase
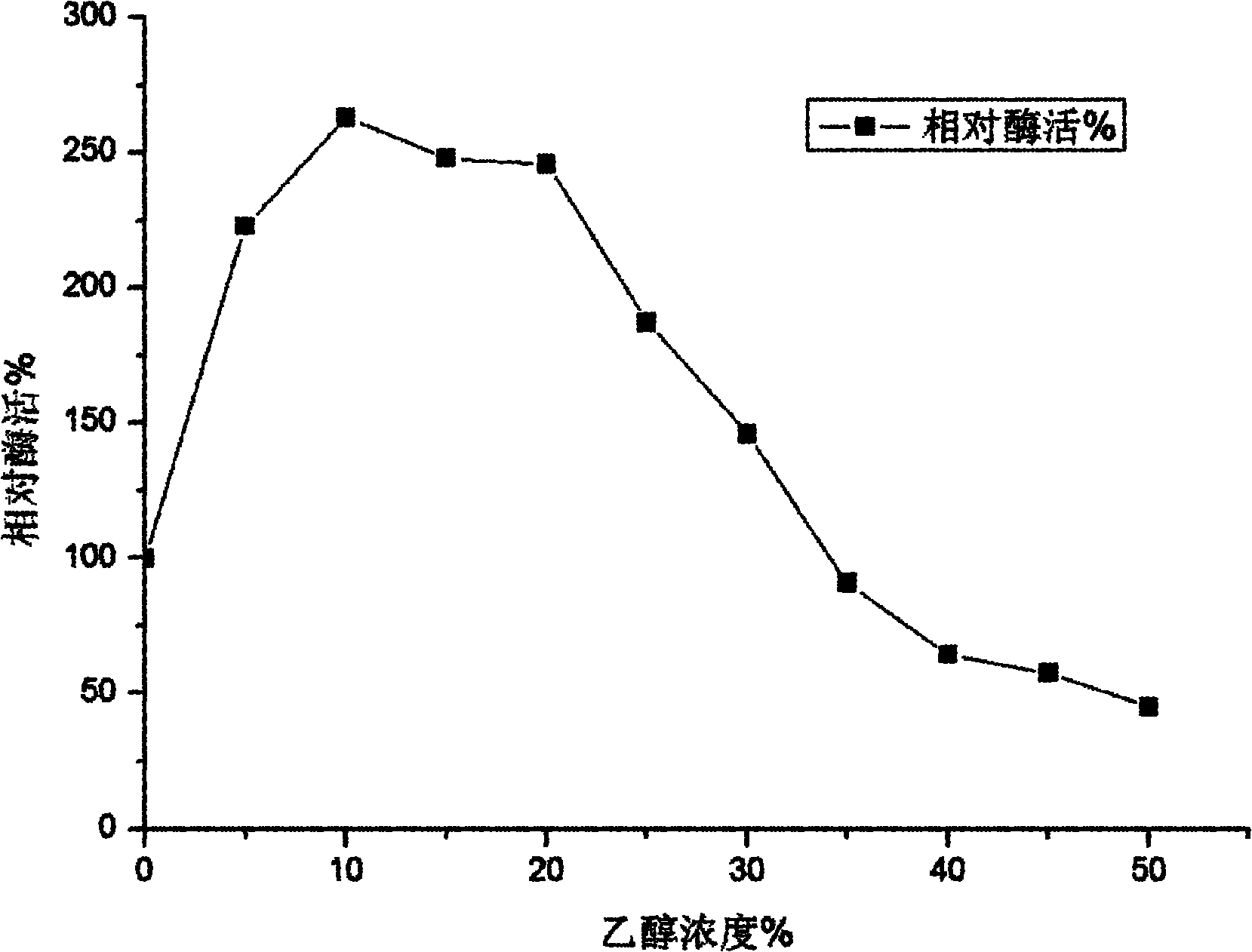
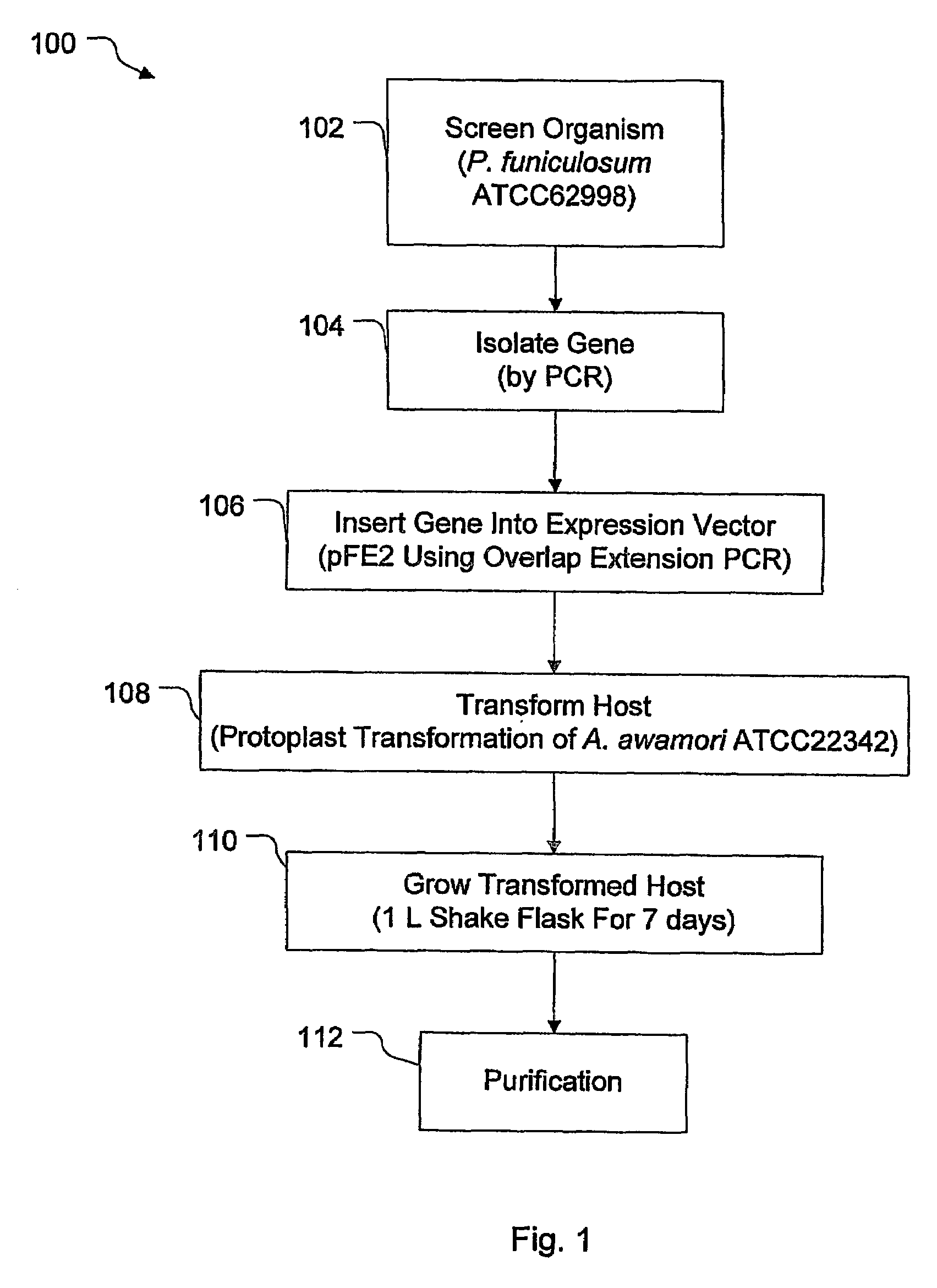
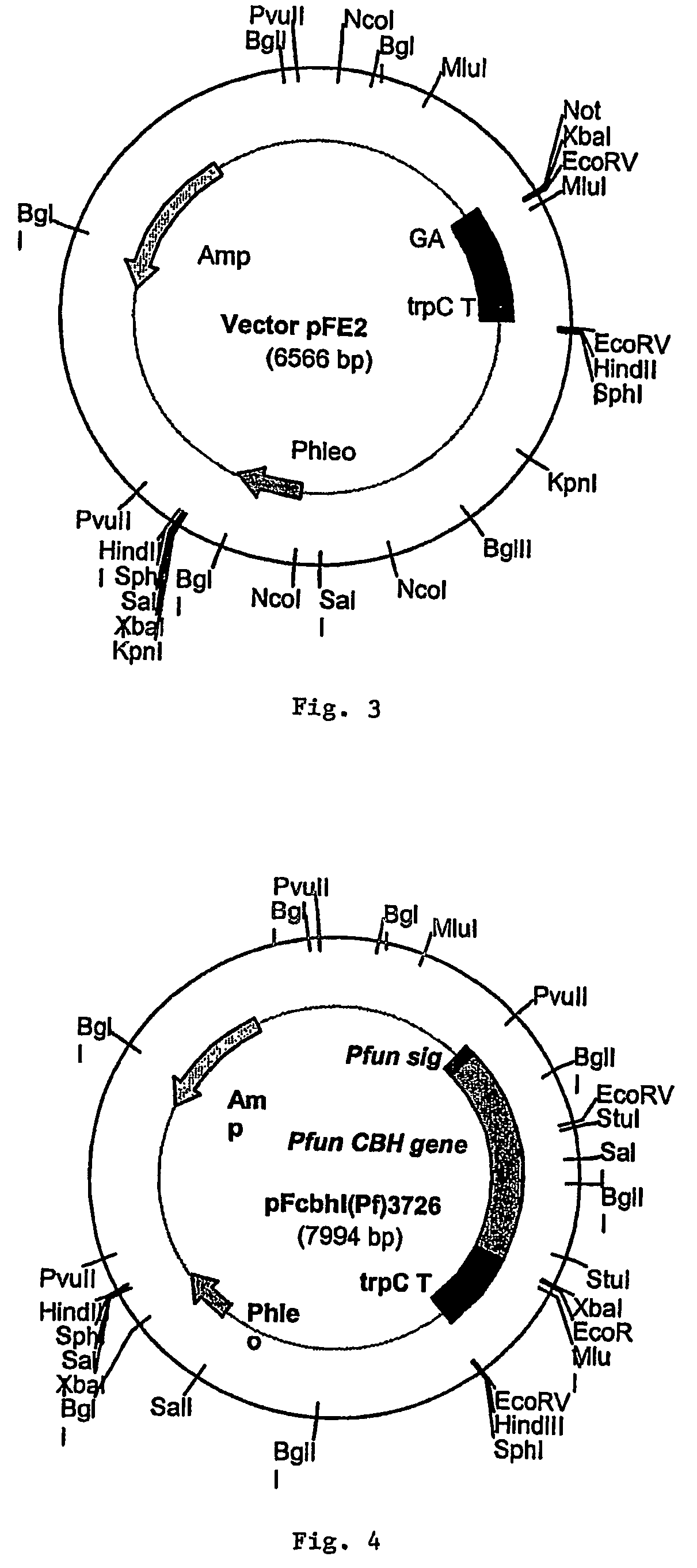
Purified cellobiohydrolase I (glycosyl hydrolase family 7 (Cel7A) enzymes from Penicillium funiculosum demonstrate a high level of specific performance in comparison to other Cel7 family member enzymes when formulated with purified EIcd endoglucanase from A. cellulolyticus and tested on pretreated corn stover. This result is true of the purified native enzyme, as well as recombinantly expressed enzyme, for example, that enzyme expressed in a non-native Aspergilllus host. In a specific example, the specific performance of the formulation using puriified recombinant Cel7A from Penicillium funiculosum expressed in A. awamori is increased by more than 200% when compared to a formulation using purified Cel7A from Trichoderma reesei.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Wood fibrous material coupled enzymatic saccharification method
The invention relates to a wood fibrous material coupled enzymatic saccharification method which mainly comprises the following steps that: (1) crushed wood fibrous material is primarily pre-treated, and hemicellulose is hydrolyzed into monosaccharides or oligosaccharides solution through dilute acid or water treatment; (2) the solution in step (1) is separated from solid, residue is filtered, and hydrolyzed sugar solution and filtered residue are respectively prepared; (3) the filtered residue is cooked and delignified through a caustic soda method, a sulfate method or a sulphite method; and (4) the cellulose product which is prepared from the cooking in step (3) and is insoluble in reaction solution is filtered and mixed with the hydrolyzed sugar collected in step (2), the pH value is adjusted to be 3 to 7, cellulase, xylanase and cellobiase are added in to be hydrolyzed, and fermentable sugar is prepared. The wood fibrous material coupled enzymatic saccharification method not only reduces a neutralization step required by a one-step treatment (acid or alkali) process, but also improves the utilization rate (reducing sugar yield) of the wood fibrous material.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for immobilizing beta-glucosidase and hydrolyzing straw cellulose by cooperating beta-glucosidase with cellulase
InactiveCN102533717AEasy to shapeUniform shapeOn/in organic carrierFermentationAlglucerasePropanoic acid
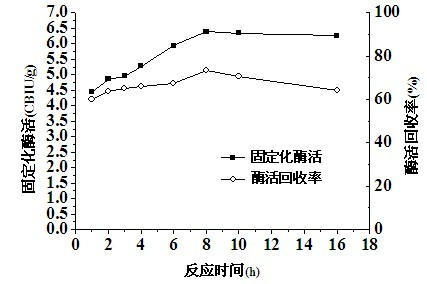
The invention relates to a method for immobilizing beta-glucosidase and hydrolyzing straw cellulose by cooperating the beta-glucosidase with cellulase, belonging to the technical field of biocatalysis. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) dissolving chitosan into a propionic acid solution to form a transparent and homogeneous colloid, mixing and stirring the colloid with Fe3O4 grains, dropwise adding a NaOH solution to obtain magnetic microspheres, and carrying out crosslinking on the magnetic microspheres in a glutaraldehyde solution to obtain an immobilized carrier; (2) adding the immobilized carrier into a beta-glucosidase solution for adsorption to obtain a magnetic immobilized beta-glucosidase, hydrolyzing a cellobiose substrate by using the magnetic immobilized beta-glucosidase, and measuring the enzyme activity of the magnetic immobilized beta-glucosidase; and (3) degrading maize straws by coordinating the magnetic immobilized beta-glucosidase with the cellulase. The immobilized beta-glucosidase prepared by the method has the characteristics of homogeneous shape, large specific surface area, high mechanical strength, high enzyme activity and easiness in recovery; and the immobilized beta-glucosidase can hydrolyze the straw cellulose by coordinating with the cellulase to increase the yield of hydrolyzed sugar, and the stability in repeated use is good, so that the cost for the enzymatic hydrolysis of the straw cellulose can be lowered.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
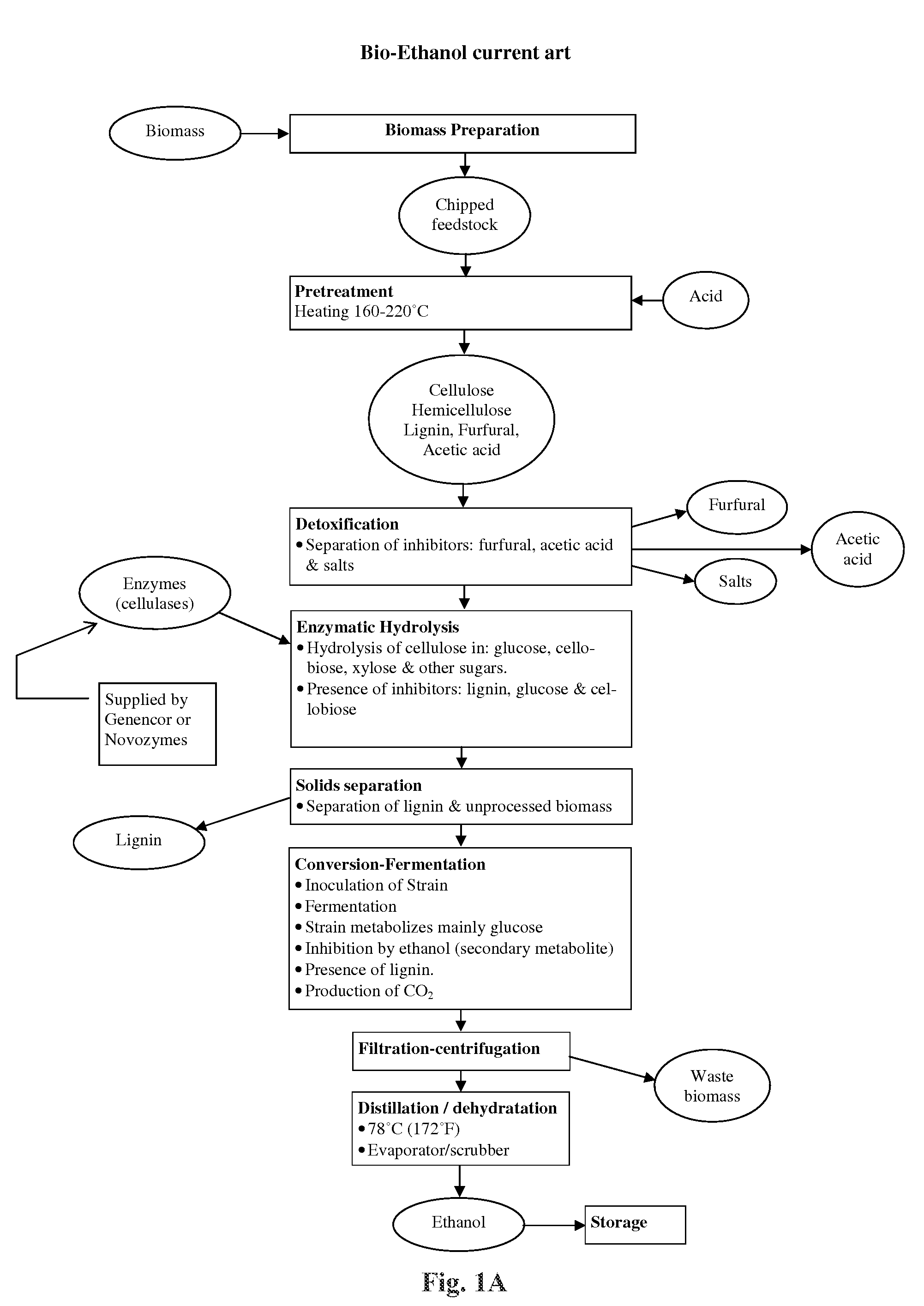
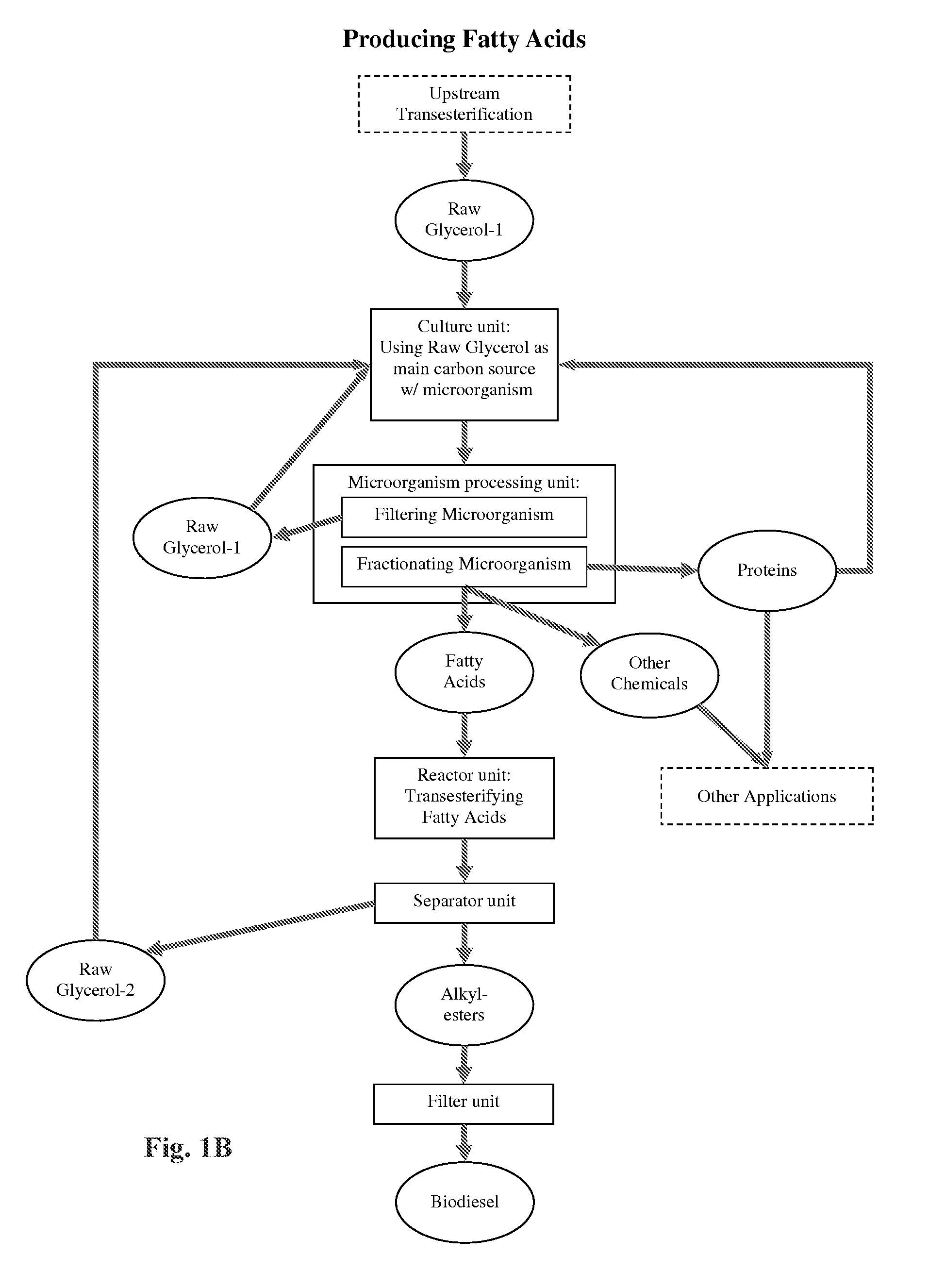
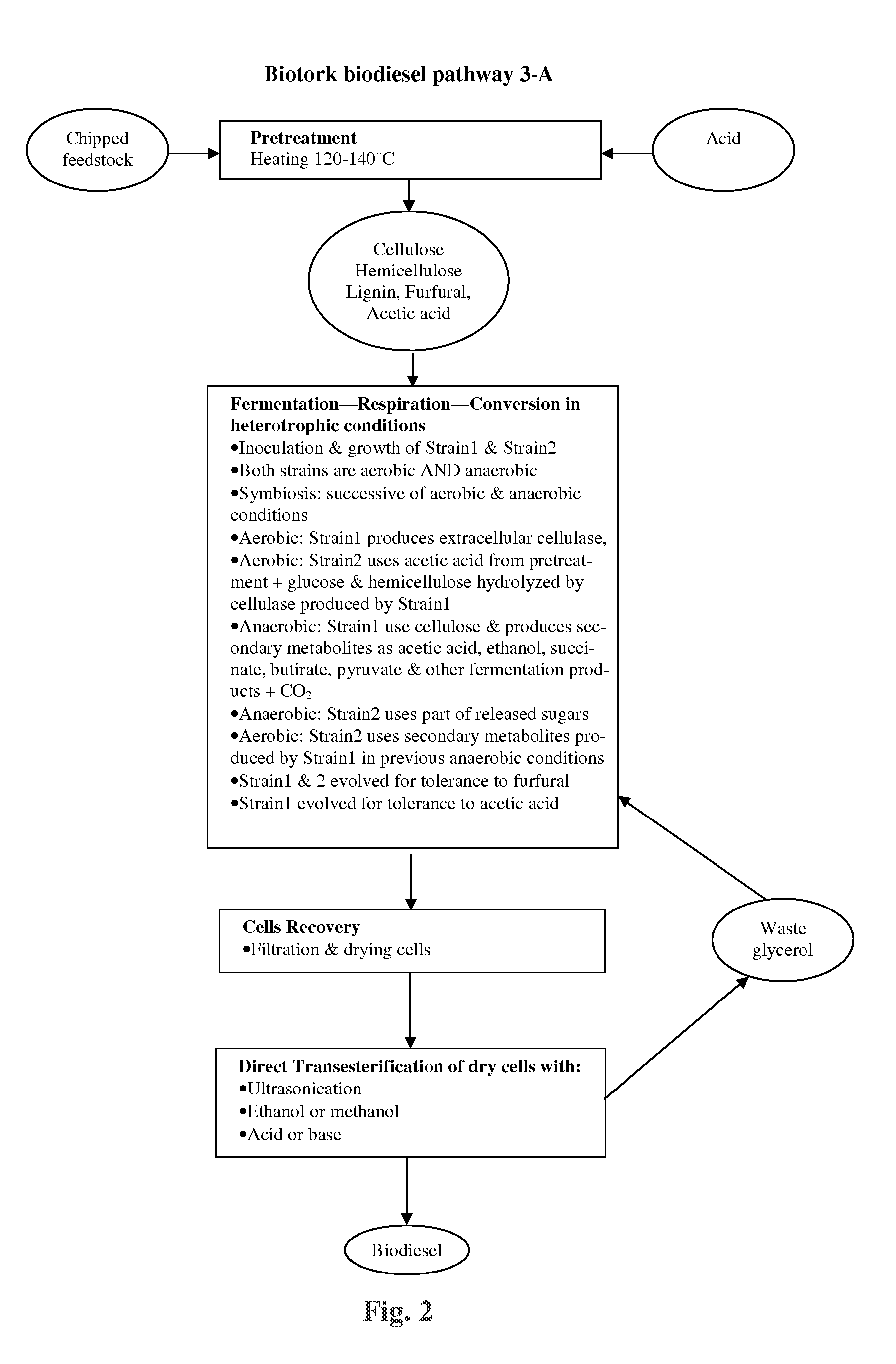
Method of producing fatty acids for biofuel, biodiesel, and other valuable chemicals
The present invention relates to a method of producing fatty acids, by inoculating a mixture of at least one of cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin with a microorganism strain and an algae strain, and growing said inoculated strains under successive aerobic-heterotrophic and either anaerobic-phototrophic or anaerobic-heterotrophic conditions creating symbiosis between the strains. Under a first aerobic-heterotrophic condition, the microorganism strain produces extracellulases that hydrolyze cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin, to produce sugars, such as glucose, cellobiose, xylose, mannose, galactose, rhamnose, arabinose or other hemicellulose sugars that are metabolized by the algae strain which also metabolizes acetic acid, glucose and hemicellulose from pretreatment. Then, either under a subsequent anaerobic-heterotrophic condition, the microorganism uses cellulose and produces fermentation products, and the algae strain uses part of the released sugars and exhibits a slower growth rate, or under a further anaerobic-phototrophic condition, the microorganism uses cellulose and produces fermentation products and CO2, and the algae strain uses the CO2 and part of the released sugars and the at least one fermentation product. Under a further aerobic-heterotrophic condition, the algae strain uses the fermentation products produced by the microorganism strain in a previous anaerobic step to produce one or more fatty acids, and the microorganism strain continues to produce extracellulases. The microorganism and algae strains are evolved for tolerance to furfural. The fatty acids can optionally be recovered and used for production of biodiesel fuel.
Owner:DE CRECY EUDES
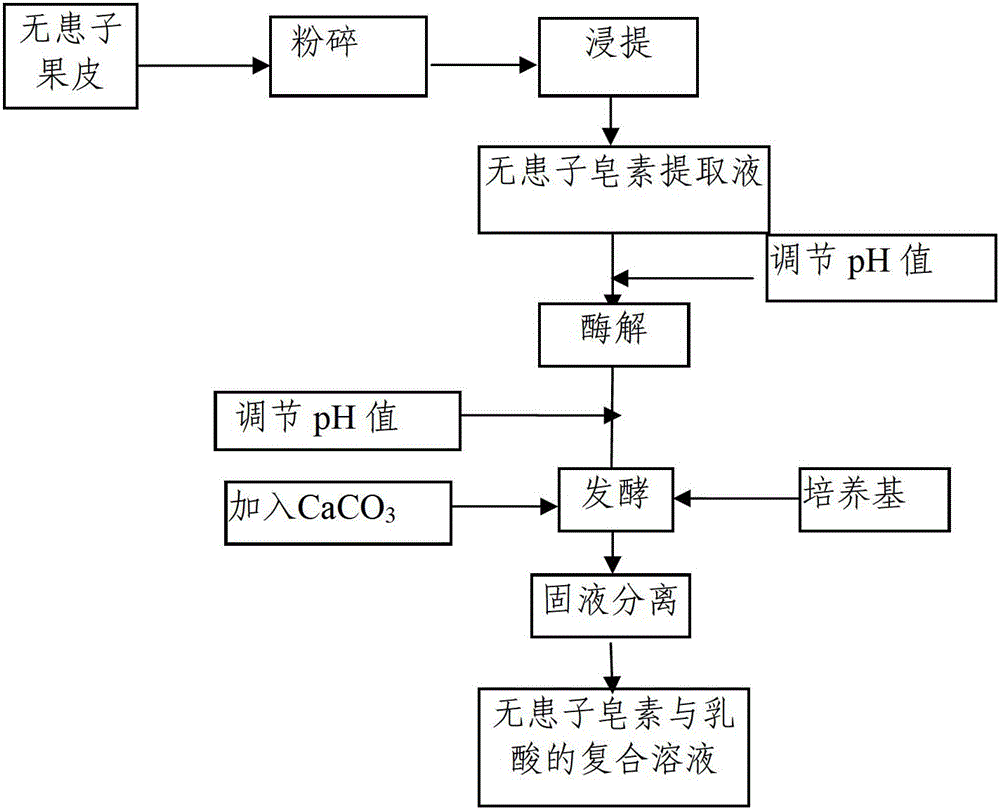
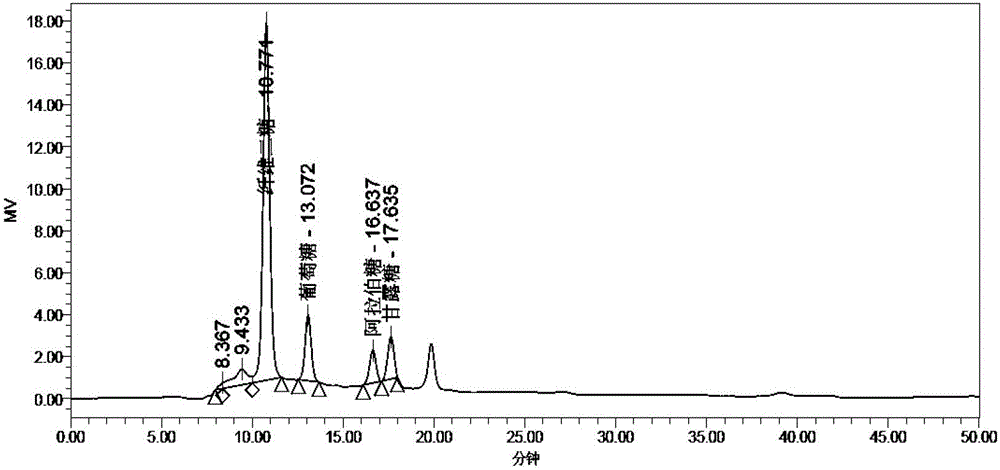
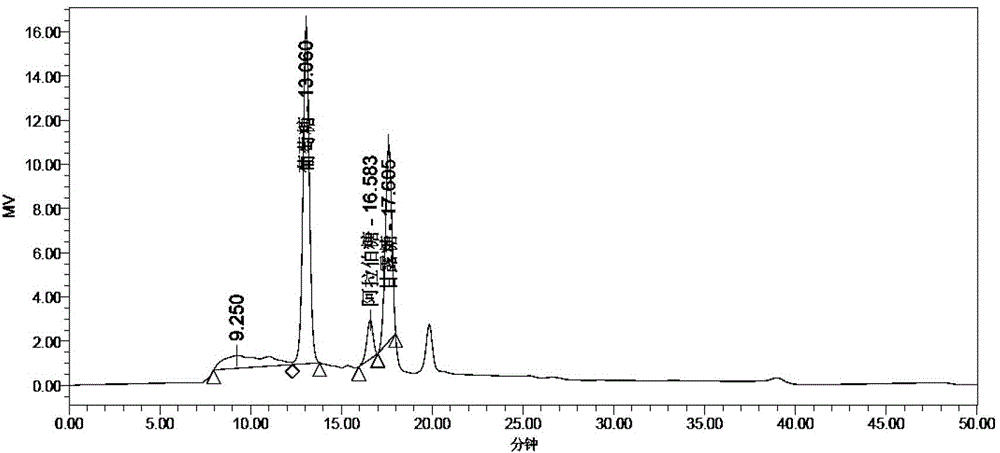
Fermentation and refining method for sapindus mukurossi saponin extract
ActiveCN102719491ARealize high-value utilizationTake advantage ofSugar derivativesSteroidsBiotechnologyLiquid product
The invention provides a fermentation and refining method for sapindus mukurossi saponin extract, which includes the following steps: sapindus mukurossi extract is enzymatically saccharified, and lactic acid bacteria are then used for inoculation and fermentation. The invention also provides a fermented and refined product of the sapindus mukurossi saponin extract. According to the characteristic of the sapindus mukurossi peel extract containing high-density cellobiose and mannose, in the fermentation and refining method, the sapindus mukurossi peel extract is enzymatically saccharified and fermented to convert carbohydrates and a small amount of protein in the sapindus mukurossi peel extract into lactic acid, consequently, sapindus mukurossi peels are sufficiently utilized, the compound product of sapindus mukurossi saponin and lactic acid is obtained, and the high-value utilization of sapindus mukurossi fruits is realized. According to the method, carbohydrates, protein and other interfering impurities in the aqueous sapindus mukurossi extract are directly converted into active components in the final product, the quality of the prepared refined sapindus mukurossi liquid product is stable, the purity of the refined sapindus mukurossi liquid product is high, and the refined sapindus mukurossi liquid product can be used in the preparation of liquid detergent or other liquid products.
Owner:广州德谷个人护理用品有限公司
Transgenic monocot plants encoding beta-glucosidase and xylanase
Plant proteins isolated from monocot plants from transformation of the monocot plant with DNA at least 80% homologous to the bglA gene encoding β-glucosidase from a rumen bacterium which is Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens H17c and targeted to a subcellular compartment. The transformed plant is ground after the β-glucosidase has been accumulated, and the protein is extracted or used directly with the ground plant material to degrade cellobiose, in particular, to produce sugars used in fermentations, particularly to produce ethanol. Also, a gene at least 80% homologous to DNA XYL1 gene encoding a xylanase is also provided in a transformed plant and used to produce sugars.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Feed fermentation agent and fermented feed
InactiveCN104605167AEnhance physical fitnessImprove the immunityAnimal feeding stuffPichia pastorisBiotechnology
The invention discloses a feed fermentation agent and a fermented feed, the feed fermentation agent includes the following components by mass: 20-25% of pichia pastoris, 15-20% of lactobacillus, 10-15% of enterococcus faecalis, 3-10% lactobacillus plantarum, 10-15% of cellobiose lactobacillus and 15%-25% a compound enzyme agent. The fermented feed is a fermented product of soybean meal, corn and wheat bran, mulberry-rich plants and a mixture of mulberry-rich plants and soybean meal by use of the feed fermentation agent, after fermentation of the soybean meal or corn or wheat bran and other traditional feed by use of the feed fermentation agent, harmful materials such as accumulated stool and the like cumulated in pig intestines can be decomposed and removed by cooperation of crude fiber in the traditional feed and microorganism, so that the intestinal absorption efficiency of nutrients can be provided.
Owner:郭旭华
Method for producing glucose and cellobiose using cellulose complex enzyme
InactiveCN101603065AIncrease saccharification rateSatisfy productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberConcentrations glucose
A method for producing glucose and cellobiose using cellulose complex enzyme is the technology using the cellulose complex enzyme as a catalyst and realizing the high saccharification rate conversion of cellulose by adding cellulose enzyme activator at the optimized stirring speed. Glucose concentration can reach 150g / L after using cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis, and the method is a cellulose saccharification production technology with economic feasibility. With the technology used, low cost, low usage of enzyme and high saccharification rate can be realized, and the productions of cellulose alcohol and biochemical products (lactic acid, succinic acid and the like) are satisfied. In the whole technology, no beta-glucosaccharase is added additionally, no sugar concentrating device is added, and the technology is simple, the equipment cost is low and the industrialized prospect is good.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
High-efficiency and low-cost fermentation feed processing method based on bean dregs and application
The invention belongs to the field of biological feed, and relates to a high-efficiency and low-cost fermentation feed processing method based on bean dregs and application; the processing method comprises the steps of activating a strain to obtain fermentation seed liquid of bacillus, yeast and lactic acid bacteria; mixing the bean dregs with bran or rice bran, then adding sucrose, adding cellulase, cellobiase, glucoamylase, xylanase, mannanase and beta-glucanase, mixing to obtain a primary aerobic fermentation medium, inoculating the bacillus fermentation seed liquid and the yeast fermentation seed liquid for primary aerobic fermentation, obtaining a primary fermentation mixture after fermentation, and then inoculating the lactic acid bacteria fermentation seed liquid for anaerobic fermentation under sealed conditions to obtain a finished product; an bacteria-enzyme cooperative fermentation and aerobic and anaerobic step-by-step fermentation mode is adopted, the fermentation is completed, the conversion degree of soybean peptide is high, the removal rate of trypsin inhibitor is 85% or above, each mycotoxin is lower than the feed hygiene limit standard of China; the feed is good in palatability, and favored by animals, and the economic efficiency is high.
Owner:浙江康星生物科技有限公司
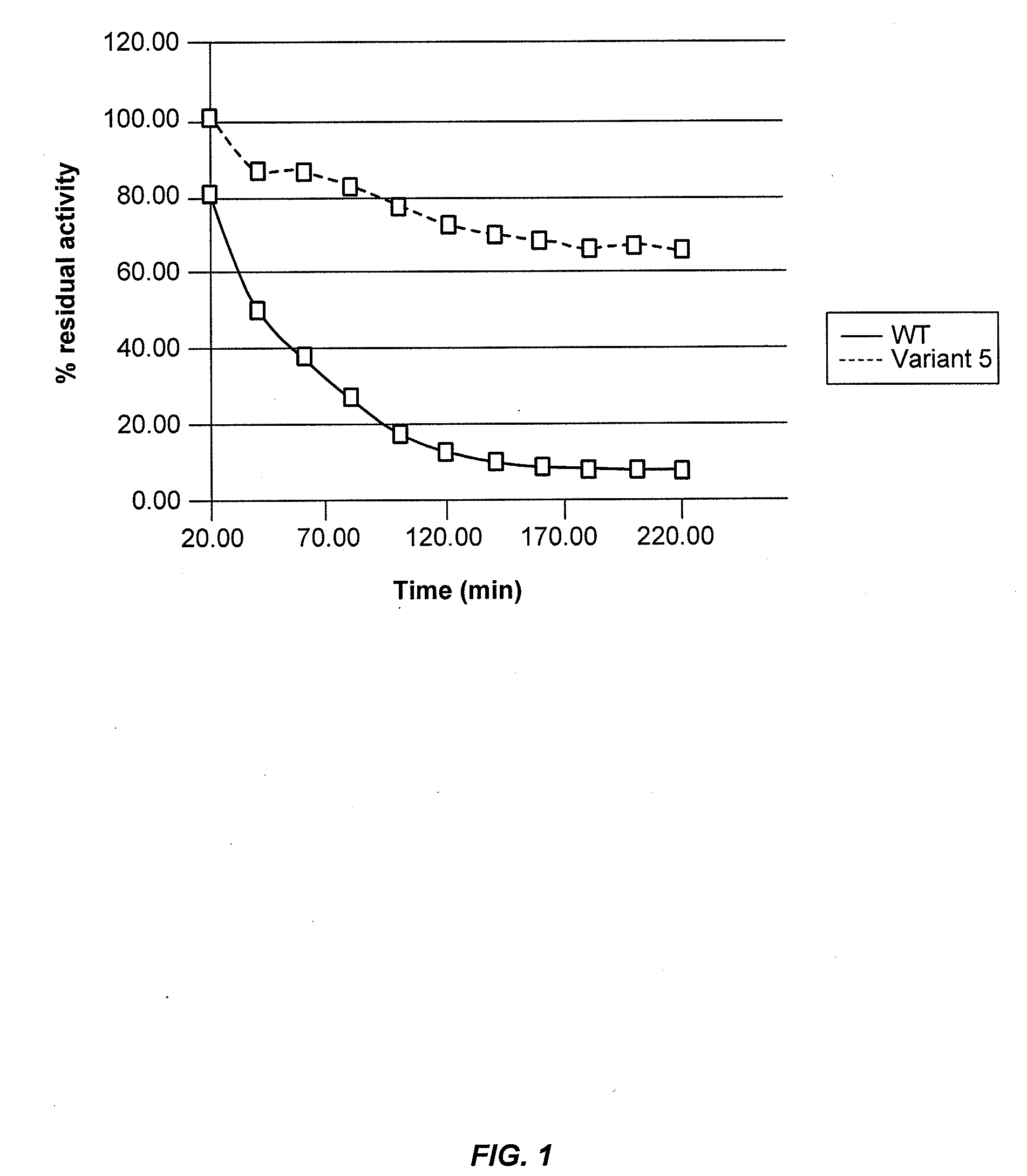
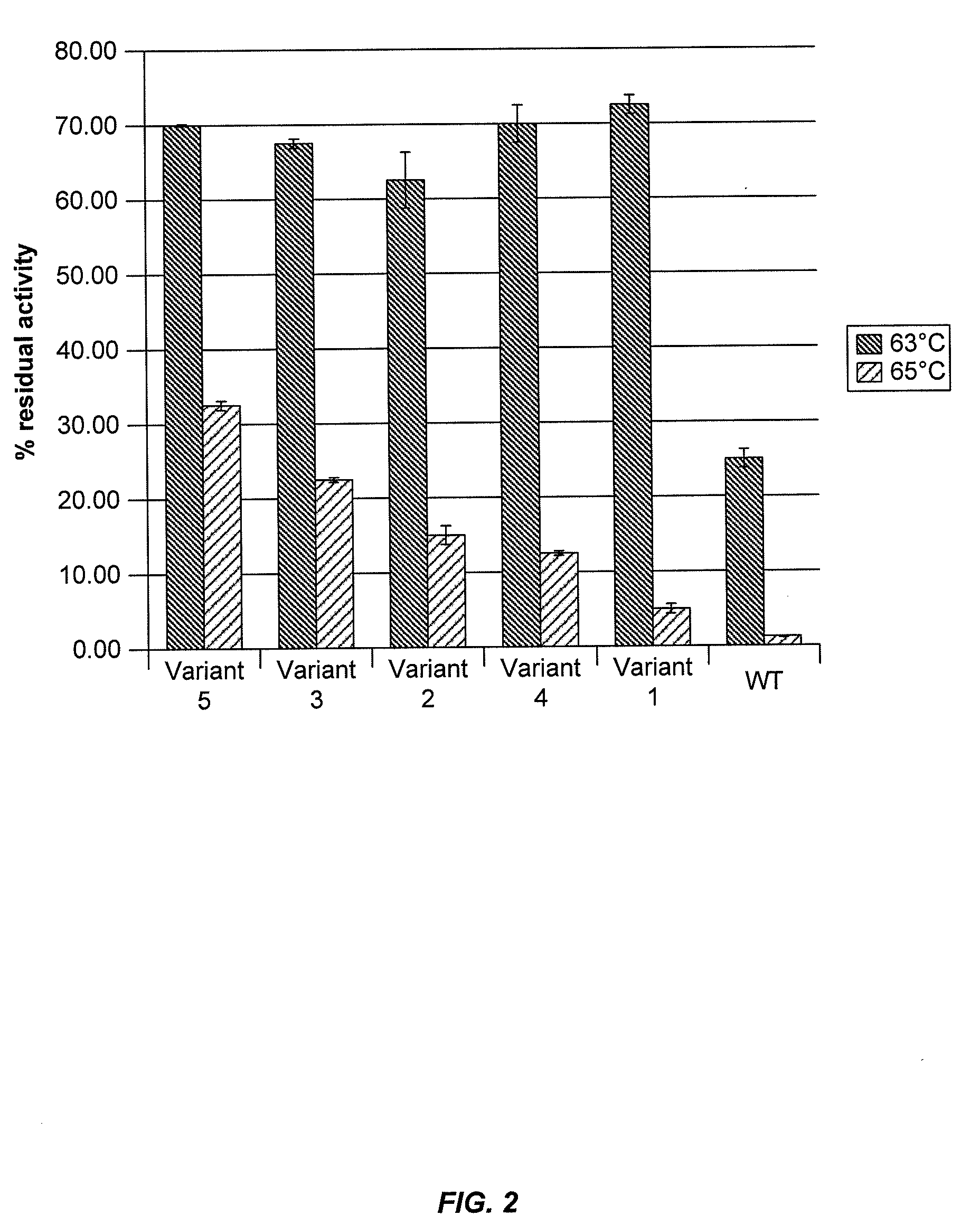
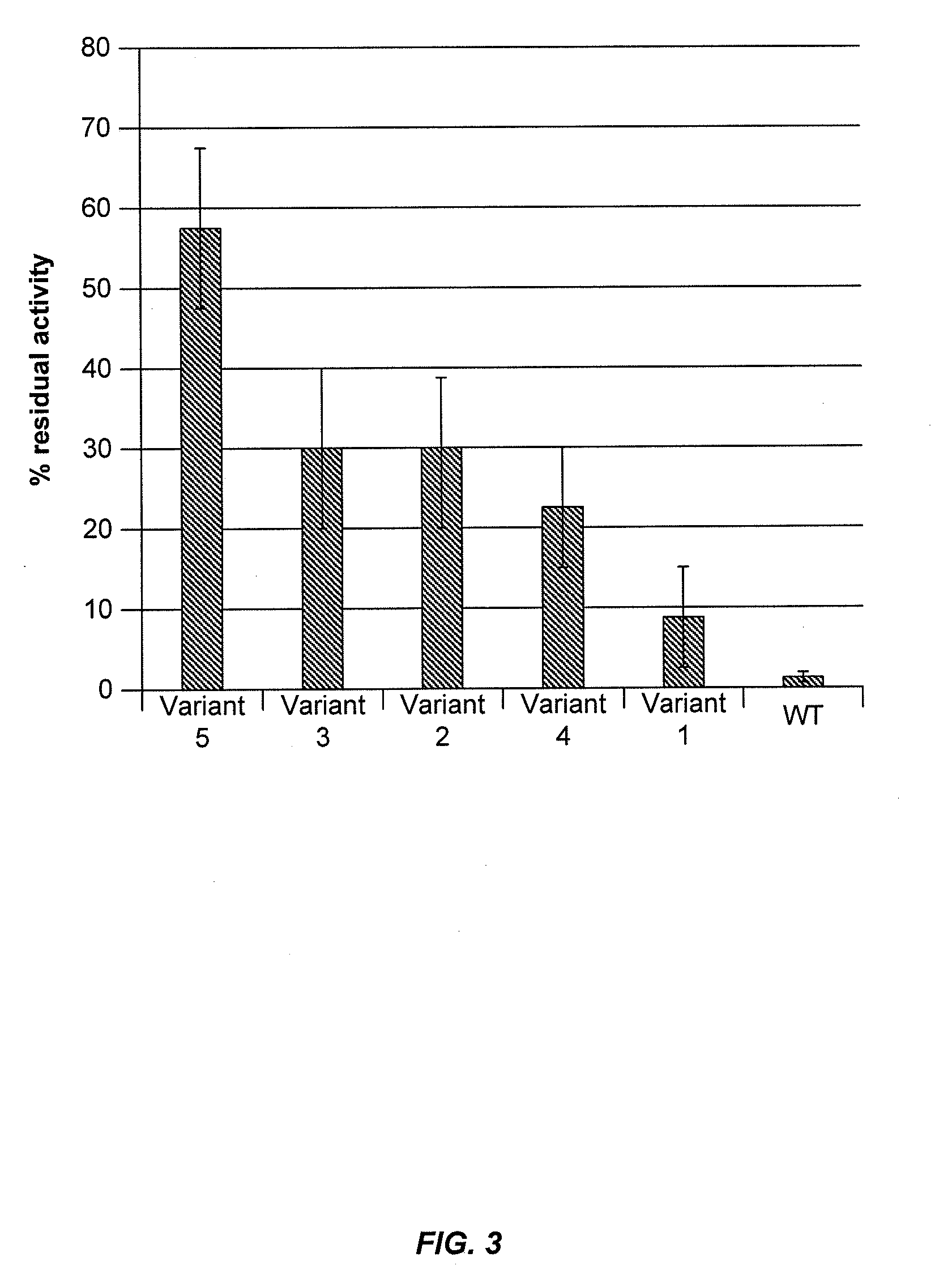
Cellobiohydrolase variants
The invention relates to recombinant expression of variant forms of C1 CBH1a and homologs thereof, having improved thermostability, low-pH tolerance, specific activity and other desirable properties. Also provided are methods for producing ethanol and other valuable organic compounds by combining cellobiohydrolase variants with cellulosic materials.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Oxidized cellulose-based material, method for obtaining same and use thereof as compress
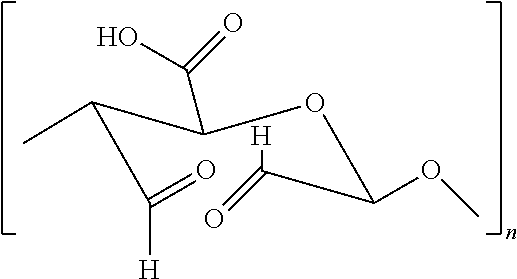
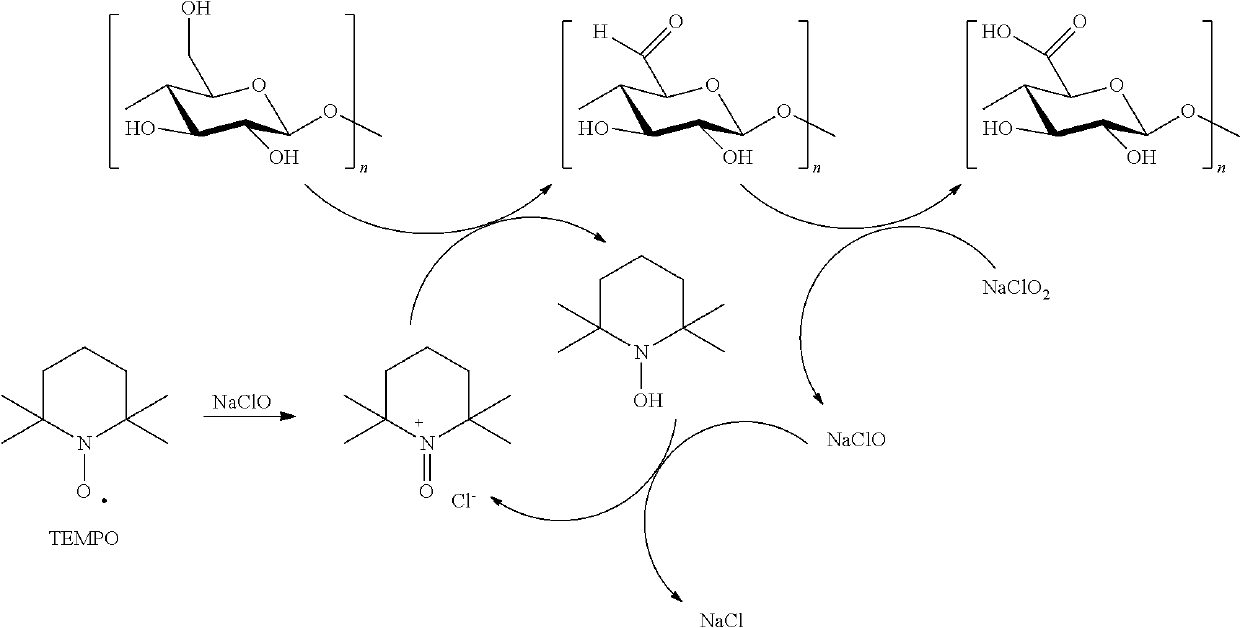
The present invention relates to a method of obtaining a solid material based on a polymer having its cellobiose units exhibiting the following characteristics:at least some of the cellobiose units have at least one carboxylic acid function attached to the C6 carbon, the other C6 carbons having a primary alcohol function attached thereto; andat least some of the cellobiose units have at least one of the two rings open between the C2 and C3 carbons, the other C2 and C3 carbons forming a ring and having an alcohol function attached thereto.Such a material, advantageously a textile, may be used as a compress.
Owner:SYMATESE
Novel high-temperature beta-glucosidase, its coding gene and application
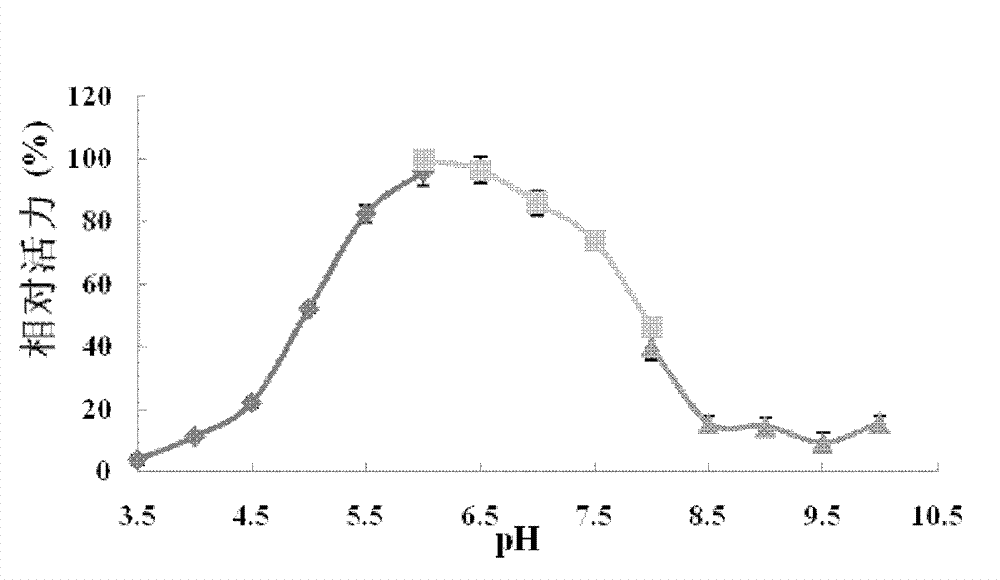
The invention relates to novel beta-glucosidase, and its coding gene and application. The invention further relates to an expression vector and host cells which contain the coding gene. The invention also relates to a method for using the beta-glucosidase to hydrolyze cellobiose generated in the process of cellulose degradation to glucose. The beta-glucosidase disclosed herein has the characteristics of high temperature resistance and good stability under neutral and alkaline conditions, and can be well applied in industrial production.
Owner:CAS CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR PLANT SCI
Trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and application thereof
InactiveCN102080050AImprove toleranceFeedback inhibition is evidentFungiMicroorganism based processesReaction temperatureCellobiose
The invention discloses a trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing a thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and an application thereof. The trichoderma viride W2 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on August 23, 2010, and the preservation number of the trichoderma viride W2 is CGMCC No.4098. The trichoderma viride W2 can produce a new beta-glucosidase, the enzymatic activity of the new beta-glucosidase reaches 346.7U / mL, the optimal reaction pH value is 4.8, the optimal reaction temperature is 70 DEG C, and the new beta-glucosidase is suitable for pyrohydrolysis and has an obvious glucose feedback inhibition effect. The ethanol the concentration of which is 10% has a maximal effect on promoting the enzymatic activity and improves the enzymatic activity of the beta-glucosidase by 1.6 times, and the resistant ability of the ethanol reaches 30%, so that the cellobiose inhibition can be effectively eliminated, the yield of the ethanol is improved by nearly 3 times, and the terminal product inhibition is effectively eliminated. Thus, the beta-glucosidase can be used for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulose raw materials, has a rare promoting effect in China, effectively increases the yield of the cellulosic ethanol, lowers the production cost, and accelerates the industrialized progress of the cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compound type biological flocculating agent two-stage fermentation method
InactiveCN1597571AAvoid partial lossShort processBacteriaWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationCelluloseFiber
A two-stage fermenting process for preparing composite biologic flocculant includes such steps as physically and chemically pretreating cellulose, preparing culture liquid, adding inorganic salt, regulating pH value, sterilizing, adding cellulose gradating bacteria to convert cellulose to glucose and cellodiase, and adding flocculant generating bacteria.
Owner:哈尔滨益生环境技术有限公司
Enzymolysis treatment method of algae
The invention provides an enzymolysis treatment method of algae. The method comprises the steps of material preparation, pretreatment, enzyme treatment and centrifugating. In the enzyme treatment step, the adopted enzyme is a composite enzyme which comprises proteinase, cellulase and pectinase in a mass ratio of 3:1:2. The proteinase is any one of papain, bromelin, carboxypeptidase and chymopapain. The cellulase is any one of cellobiohydrolase, endoglucanase, beta-glucosaccharase and cellobiase. The pectinase is any one of protopectinase, lyase and polygalacturonase. According to the enzymolysis treatment method of algae, the extraction rate of sodium alginate is 38.0-50.9%, and the extraction rate of alga glycine is 7.5-11.8%.
Owner:SHANDONG HETIANWANG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing bio-ethanol by taking seaweed processing waste as raw material
InactiveCN101701225AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyOpportunity for facilitationMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberCellulose compounds
The invention relates to a method for preparing bio-ethanol by taking seaweed processing waste as raw material, which is characterized by comprising the steps: selecting the seaweed processing waste, and pretreating the raw material by sulfuric acid or hydrogen peroxide; then, adding cellulase or cellobiase for cellulose compound enzymolysis, and filtering enzymolysis liquid to remove insoluble components; and finally, supplementing inorganic salt, inoculating saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and carrying out alcoholic fermentation under the anaerobic condition. The original structure of algae cellulose is changed by the pretreatment process, and the action probability between the cellulose and degrading enzyme can be promoted, so that the enzymolysis efficiency of the cellulose is improved; furthermore, after the cellulose is treated by the compound enzymolysis of the cellulase and the cellobiase, the feedback inhibition of the cellobiose for the cellulose can be effectively eliminated, the content of glycolysis sugar of yeast can be improved, and the yield of alcoholic fermentation is further improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Cleaning And/Or Treatment Compositions
InactiveUS20090181874A1Effective and efficient bleachingCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsFiberCellobiose
This invention relates to compositions comprising certain cellobiose dehydrogenase enzymes and processes for making and using such compositions, including the use of such compositions to clean and / or treat a situs.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Superactive cellulase formulation using cellobiohydrolase-1 from Penicillium funiculosum
ActiveUS7449550B2Increase heightImprove specific performanceSugar derivativesMicroorganismsBiotechnologyGlucanase
Purified cellobiohydrolase I (glycosyl hydrolase family 7 (Cel7A) enzymes from Penicillium funiculosum demonstrate a high level of specific performance in comparison to other Cel7 family member enzymes when formulated with purified EIcd endoglucanase from A. cellulolyticus and tested on pretreated corn stover. This result is true of the purified native enzyme, as well as recombinantly expressed enzyme, for example, that enzyme expressed in a non-native Aspergillus host. In a specific example, the specific performance of the formulation using purified recombinant Cel7A from Penicillium funiculosum expressed in A. awamori is increased by more than 200% when compared to a formulation using purified Cel7A from Trichoderma reesei.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
High glucose resistance beta-glucosidase-CBD fusion enzyme, and expression gene and application thereof
ActiveCN103045565AImprove bindingEfficient degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationFiber
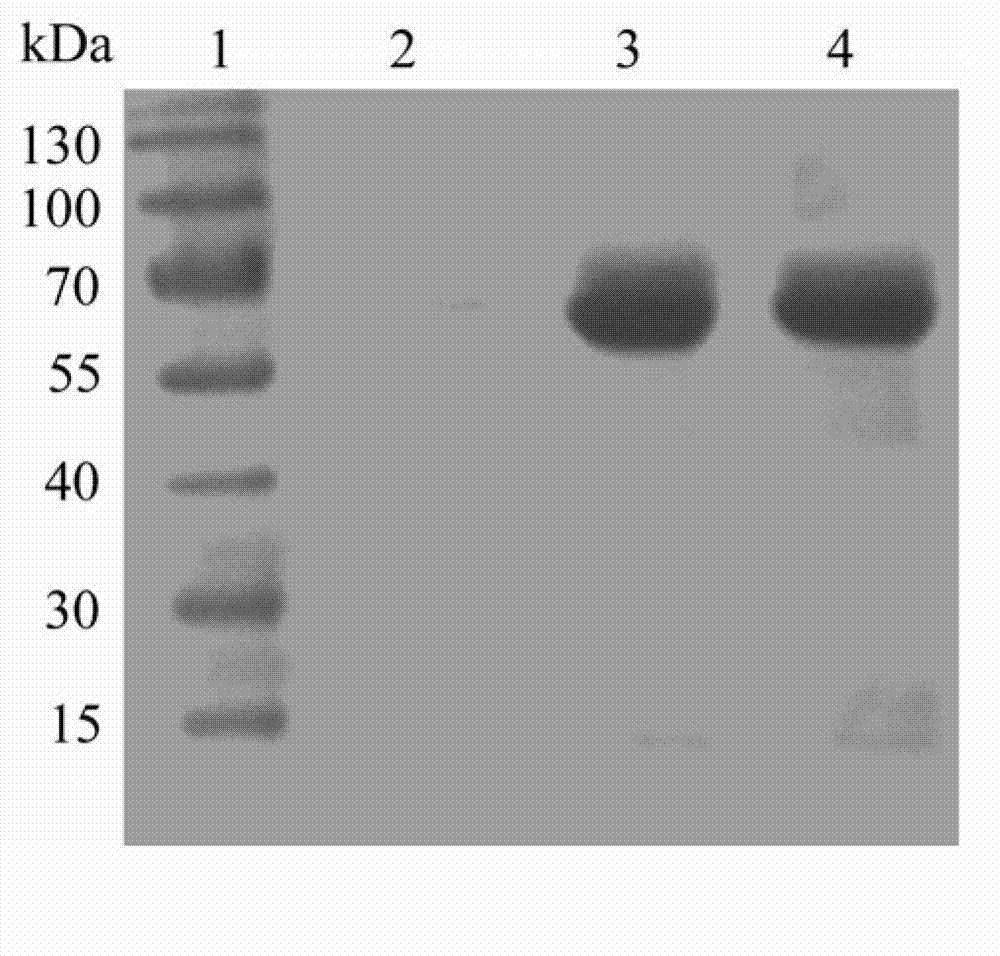
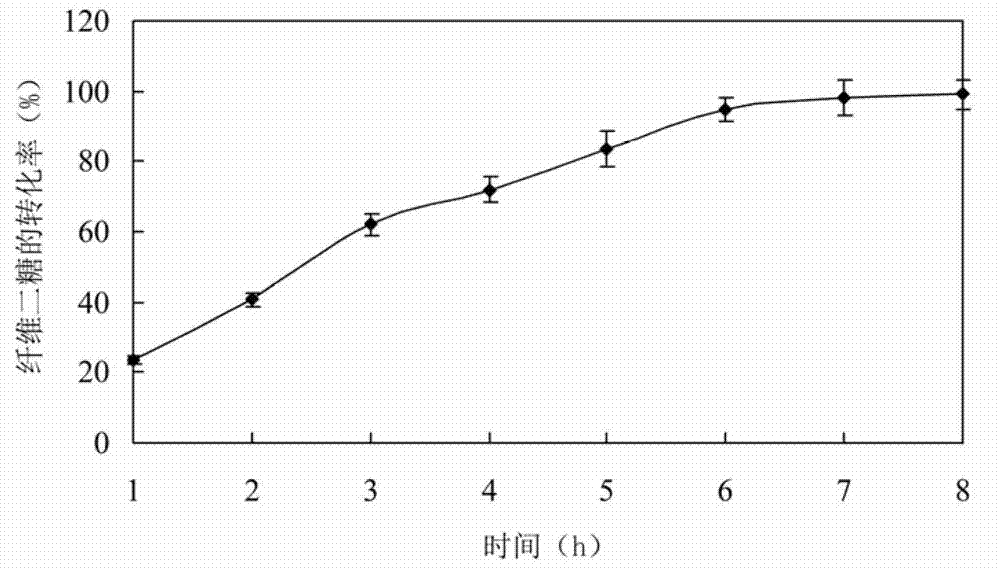
The invention relates to a high glucose resistance beta-glucosidase-CBD fusion enzyme, and expression gene and application thereof. The amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1. Compared with the conventional beta-glucosidase enzyme, the fusion enzyme (BGL-CBD) provided by the present invention has the following characteristics: (1) higher cellulose binding ability, wherein the fusion enzyme (1 [mu]g / [mu]L) is incubated with 4 wt% of microcrystalline cellulose for 30min, and 98% of fusion enzyme is adsorbed by cellulose; (2) effectively degrading cellobiose, wherein the degradation rate of 10 wt% of the cellobiose by the fusion enzyme (0.15 [mu]g / [mu]L) within 8 h is 95%; and (3) resistance for high concentration glucose, wherein the glucose tolerance factor Ki is 1000 mmol / L.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for continuously and efficiently secreting beta-glucosidase and applications thereof
The invention provides a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for continuously and efficiently secreting beta-glucosidase, which is named Saccharomyces cerevisiae 102SB, and preserved with a Preservation No. of CGMCC No. 7450 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 11, 2013. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae disclosed by the invention can continuously and efficiently secrete beta-glucosidase in a complex non-selective medium, and the extracellular enzyme activity can reach 1005.3 U / g (dry weight). By using a characteristic that the maximum specific growth rate of cellobiose is consistent with that of glucose, the strain reaches 0.29 h<-1> under the condition of limited oxygen. In SSF taking a cellulose material as a substrate, the yield of ethanol taking microcrystalline cellulose as a substrate is increased by 110%, and the yield of ethanol taking acid-hydrolyzed corncobs as a substrate is increased by 89%. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain disclosed by the invention is of great importance in reducing the production cost of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation in the process of cellulosic ethanol production, and simplifying the production process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com