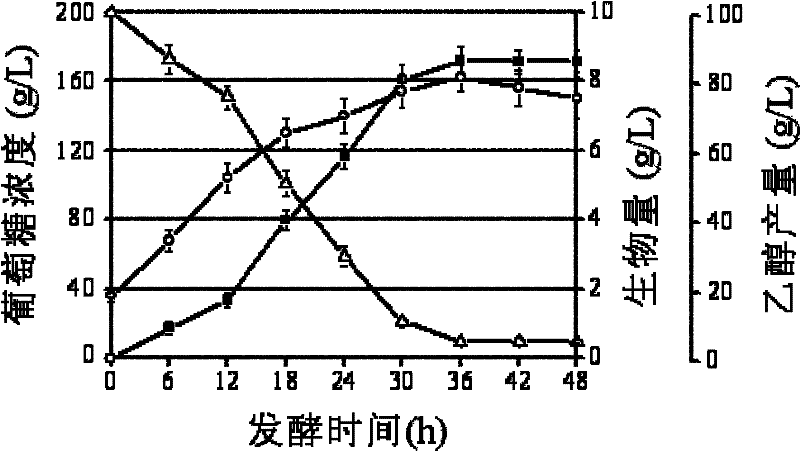
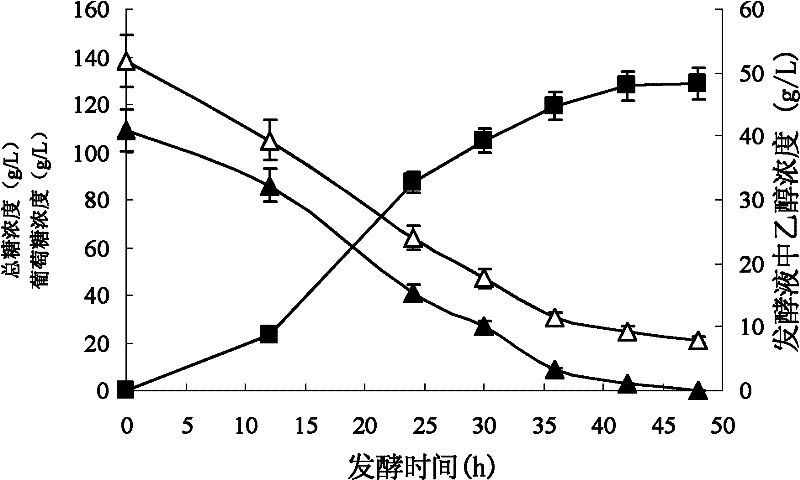
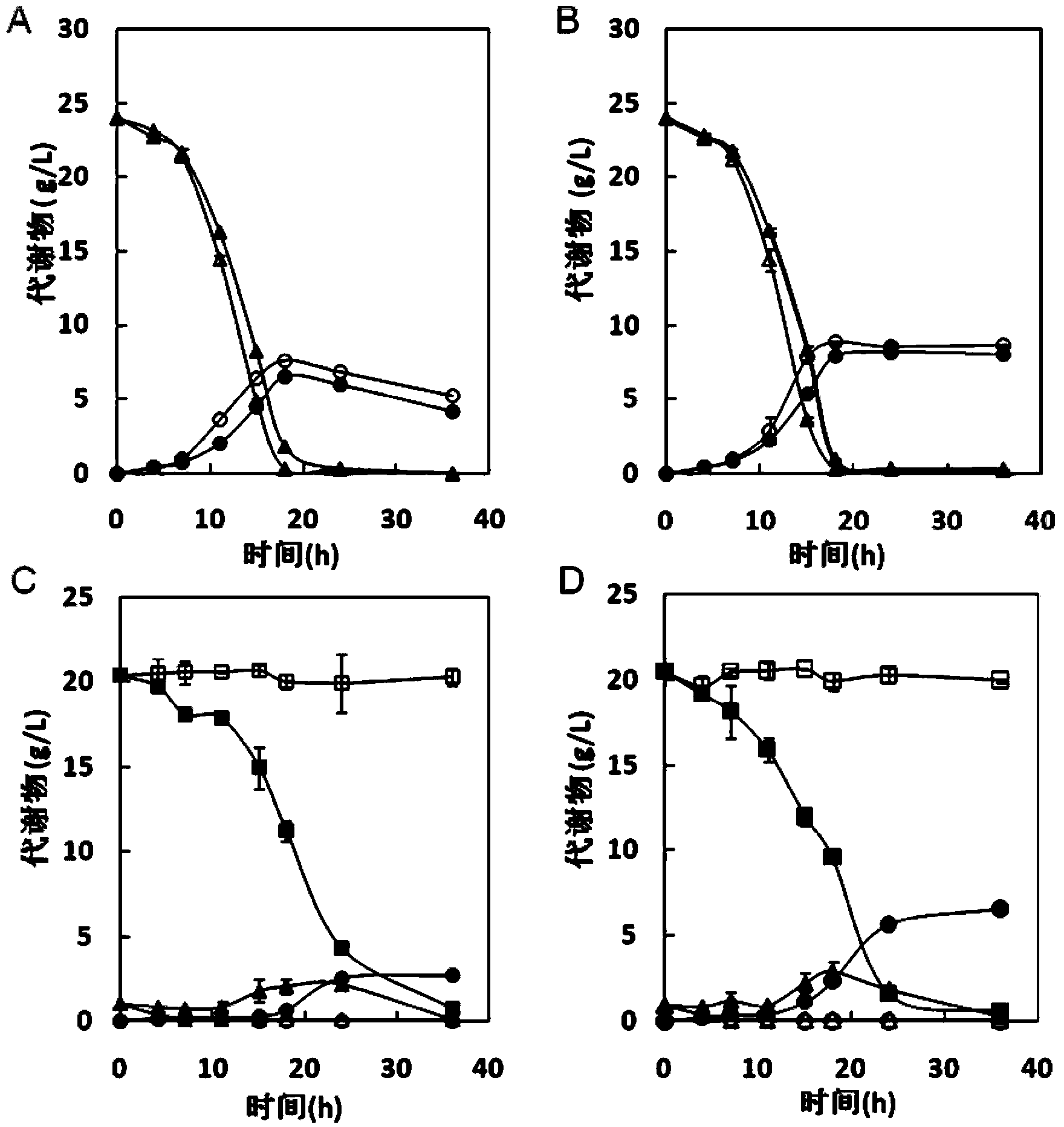
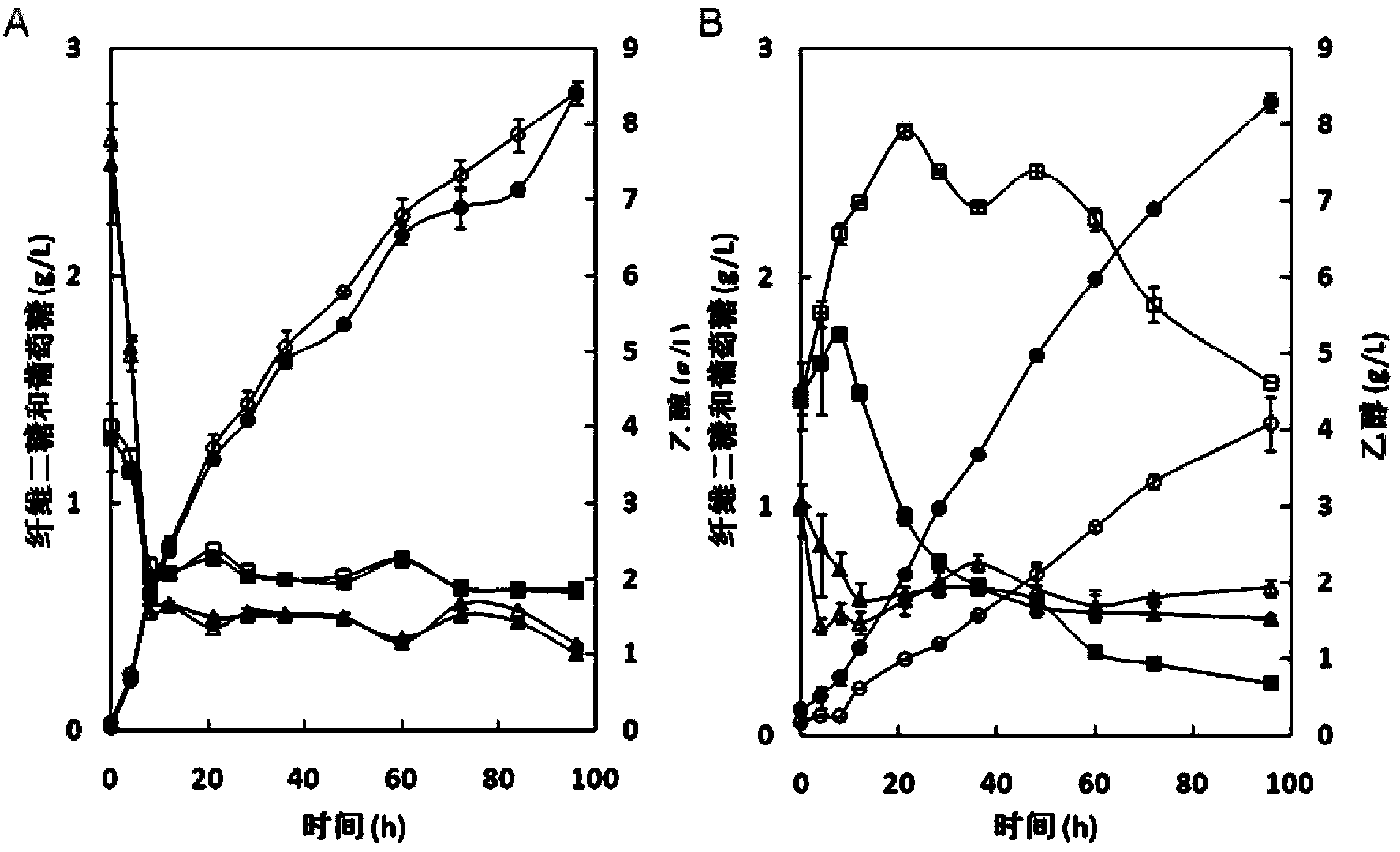
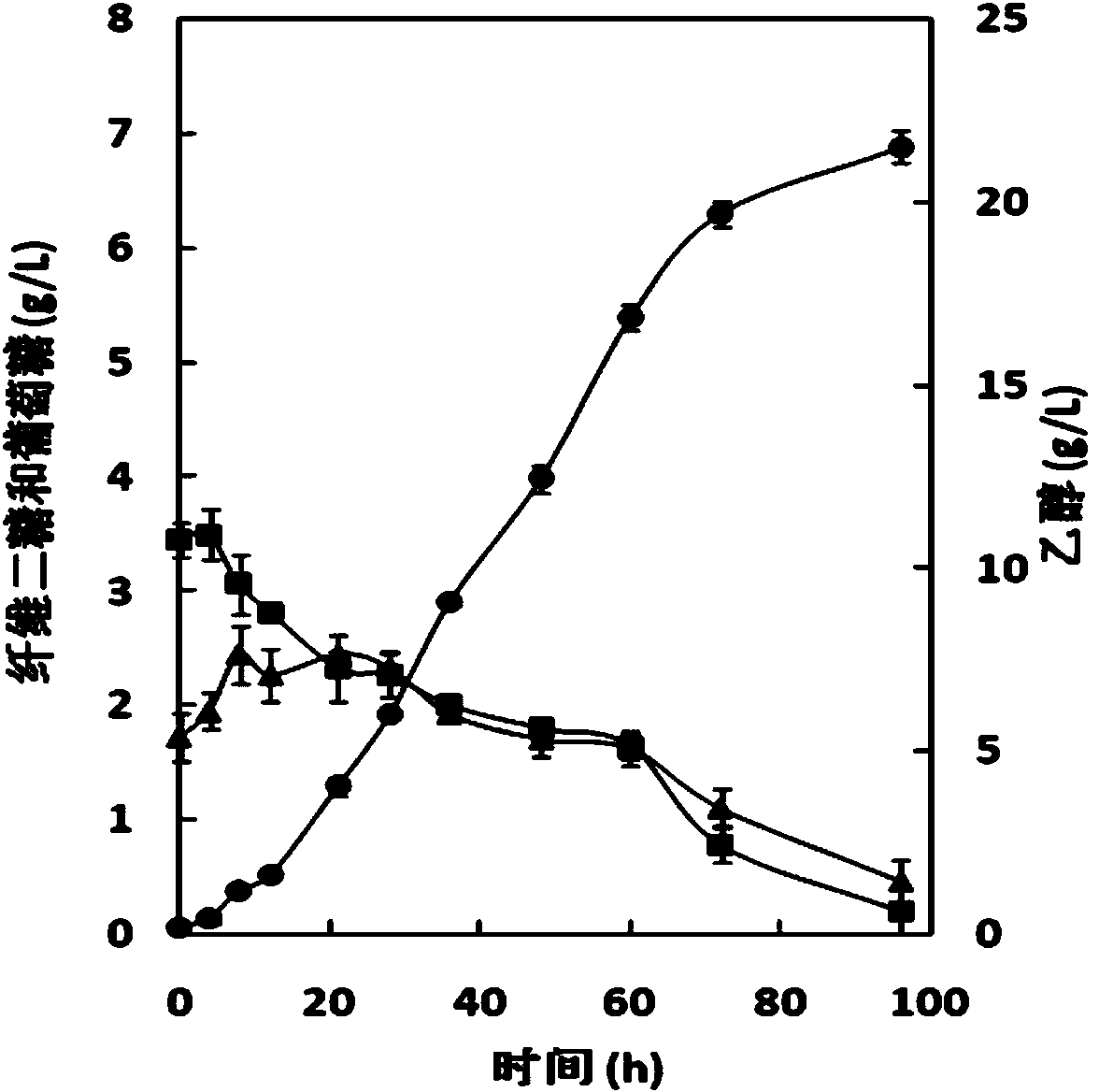
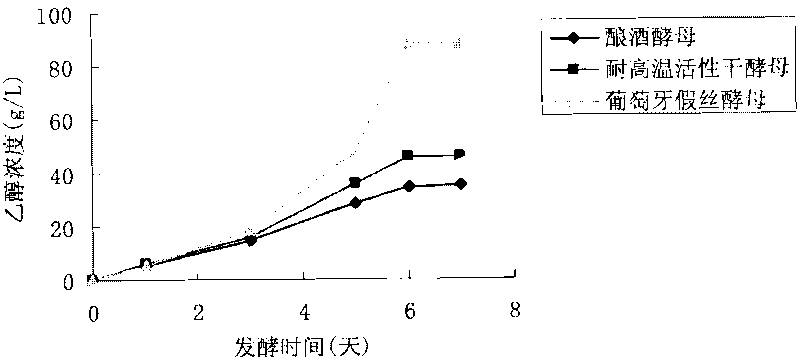
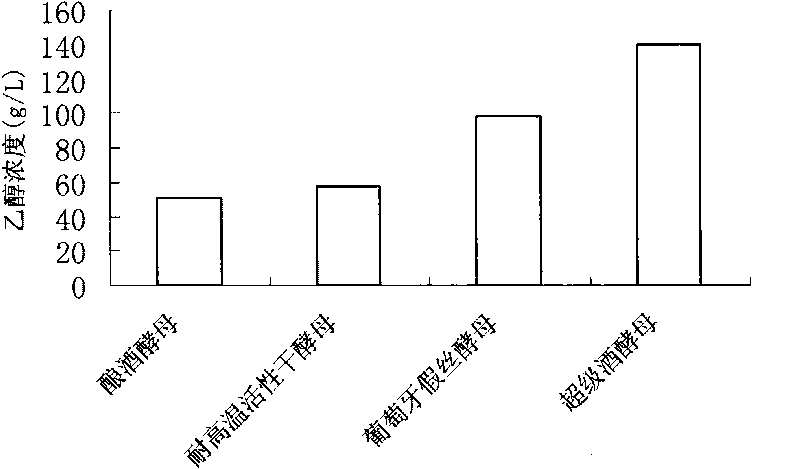
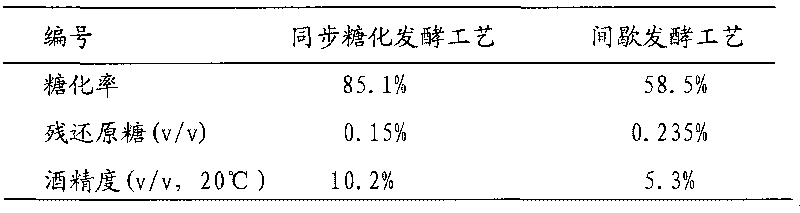
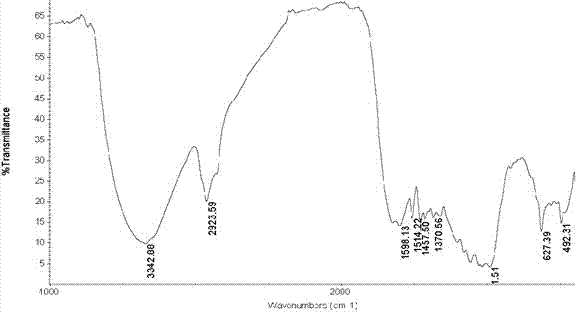
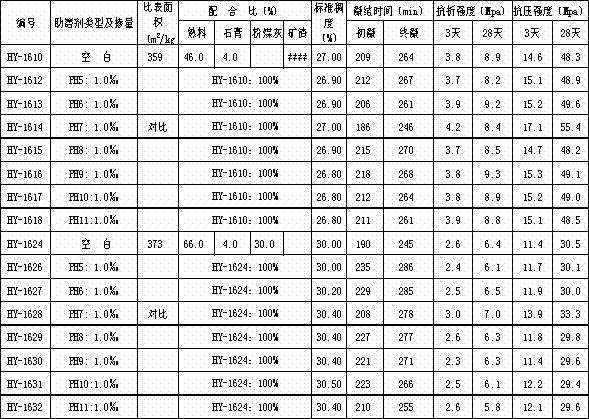
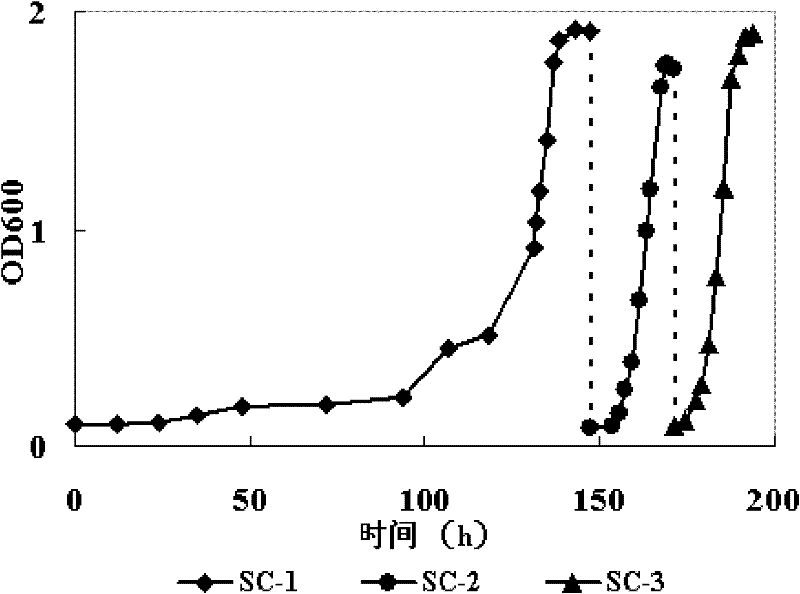
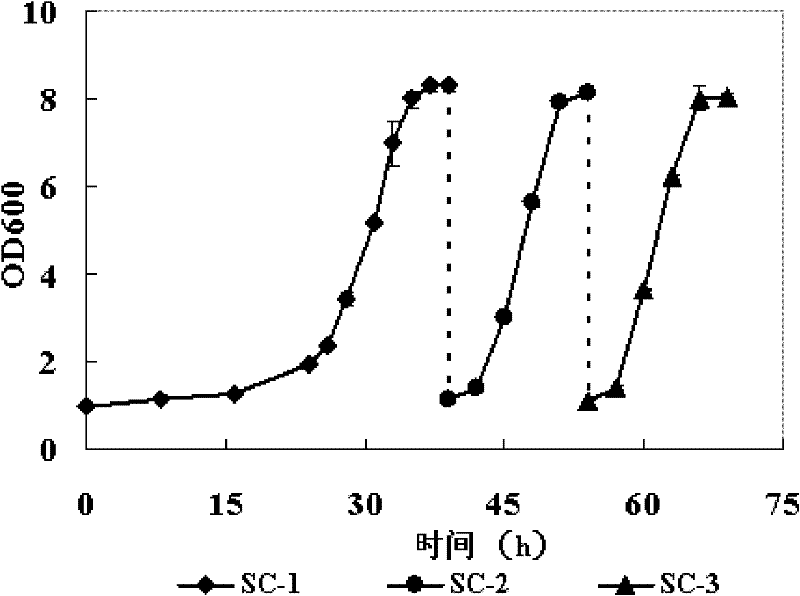
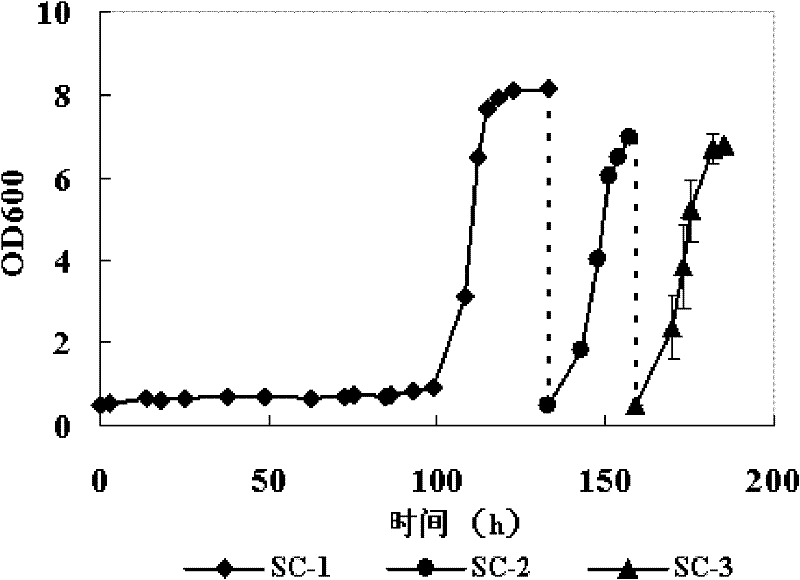
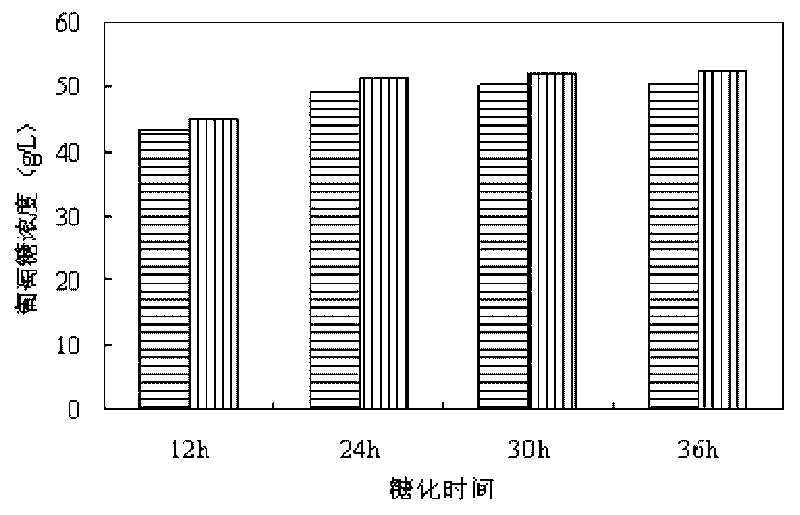
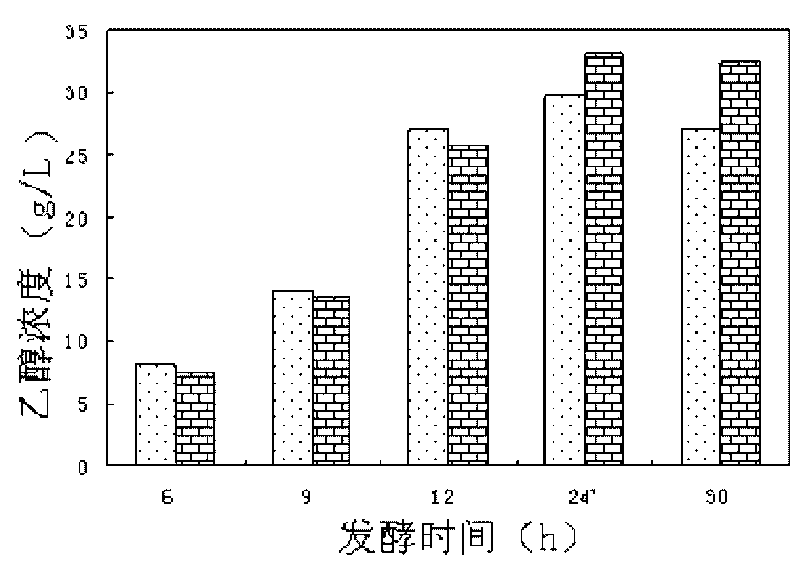
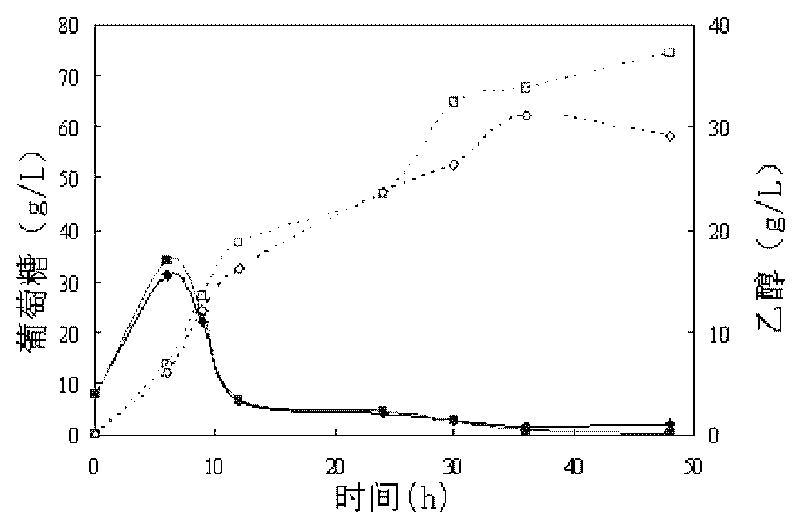
Patents
Literature
333 results about "Cellulosic ethanol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cellulosic ethanol is ethanol (ethyl alcohol) produced from cellulose (the stringy fiber of a plant) rather than from the plant's seeds or fruit. It is a biofuel produced from grasses, wood, algae, or other plants. The fibrous parts of the plants are mostly inedible to animals, including humans, except for ruminants (grazing, cud-chewing animals such as cows or sheep).
Energy crops for improved biofuel feedstocks
InactiveUS20070250961A1Low costIncrease productionBryophytesSugar derivativesDownstream processingBiofuel feedstock
The present invention is directed to improved systems and methods for reducing costs and increasing yields of cellulosic ethanol. In particular, the present invention provides plants genetically transformed for increased biomass, expression of lignocellulolytic enzymes, and simplification of harvesting and downstream processing. Also provided are methods for using these transgenic plants in the production of clean, marketable feedstocks for production of renewable fuels and chemicals and in other applications including phytoremediation.
Owner:EDENSPACE SYST CORP
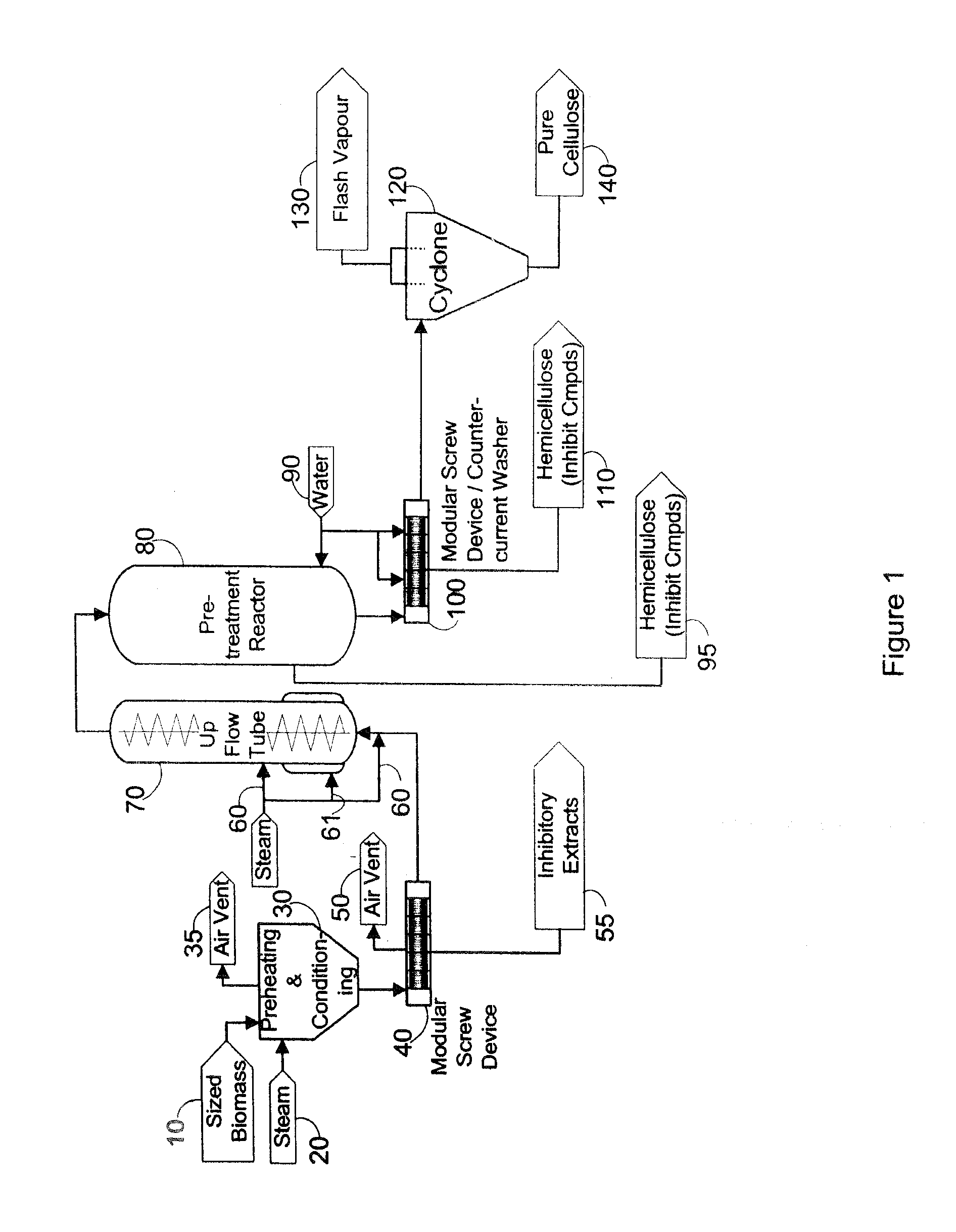
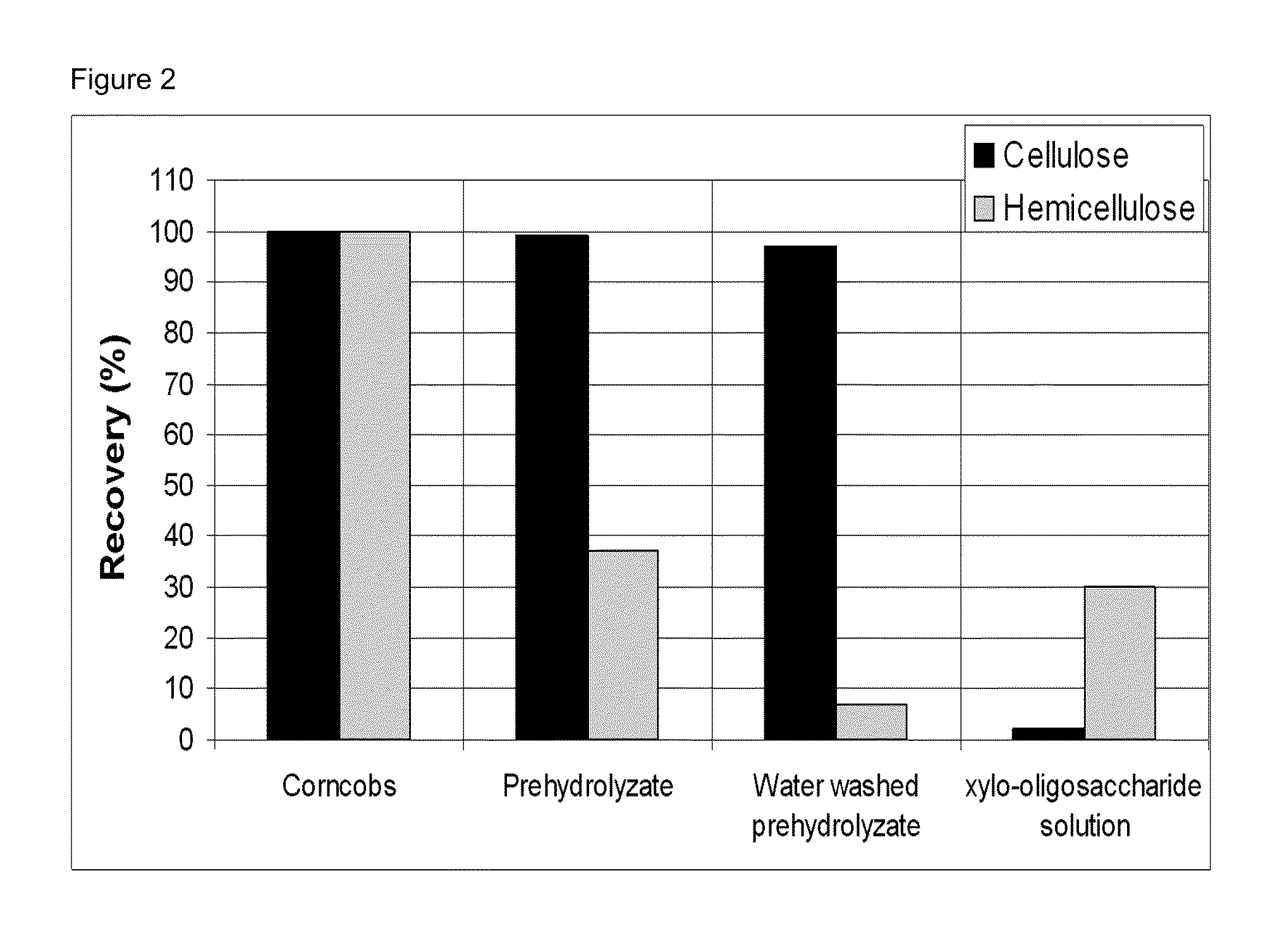
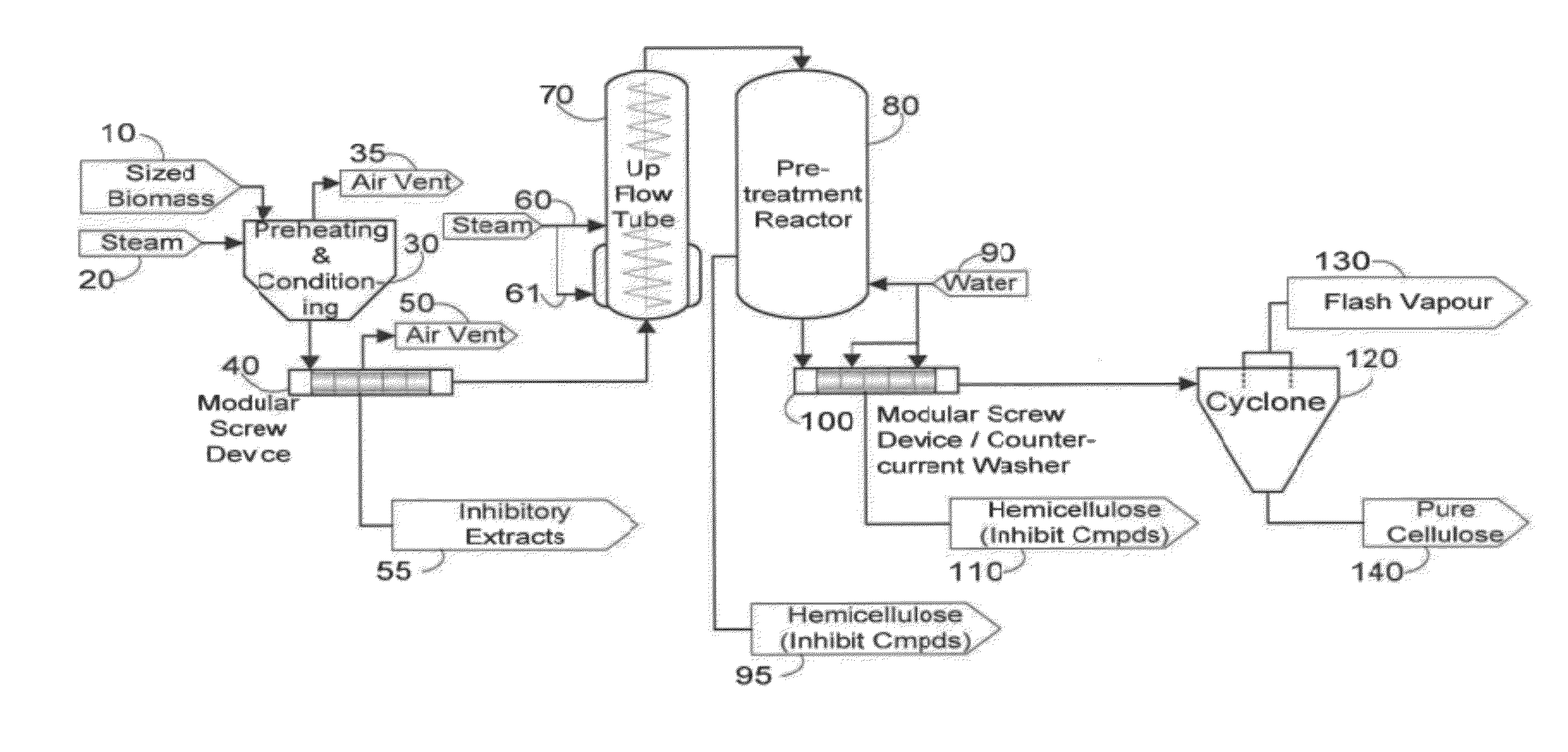
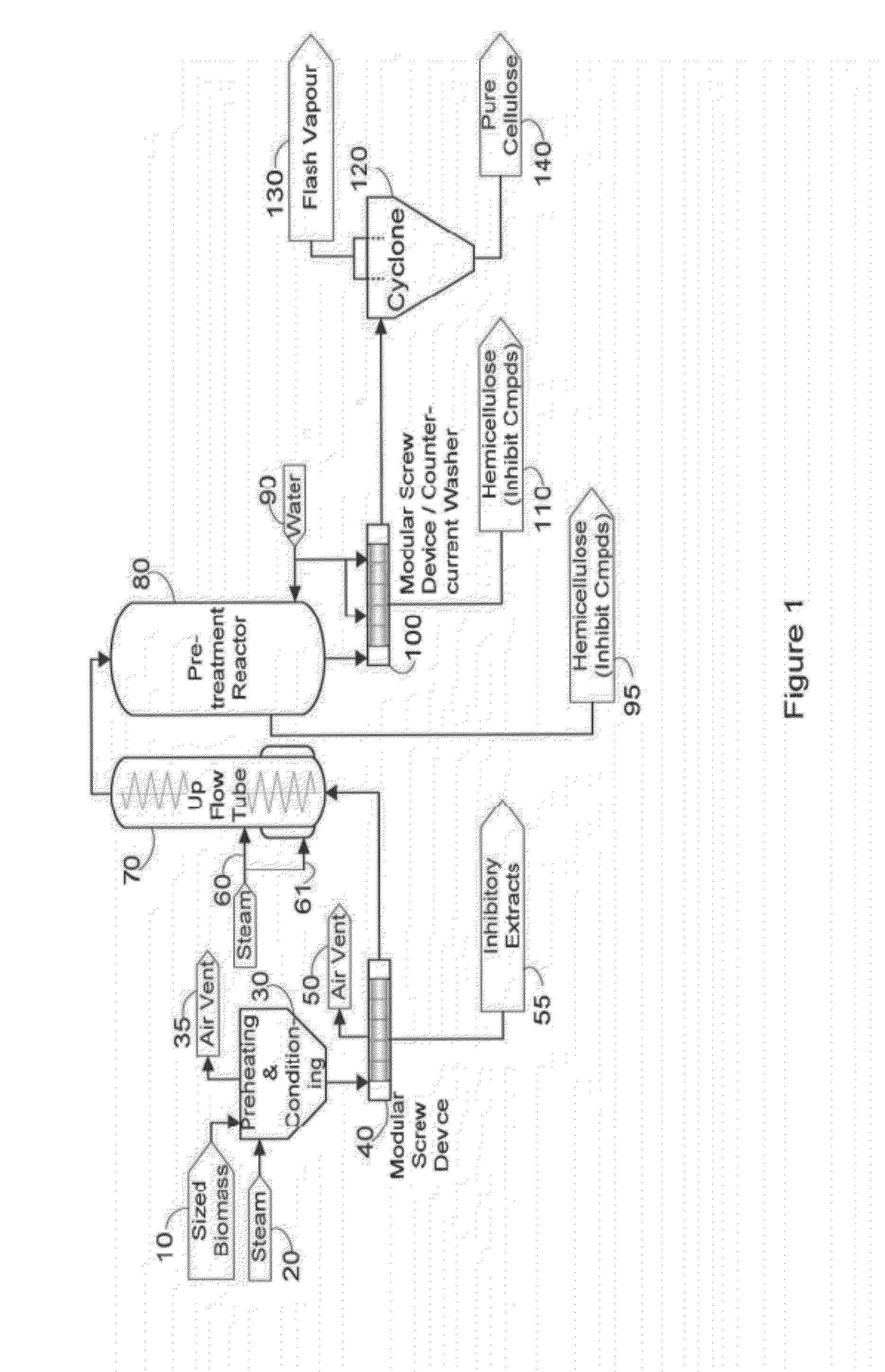
Fractionation of biomass for cellulosic ethanol and chemical production
InactiveUS20100313882A1Reduce inhibitionMore cost-effectivelyBiofuelsGlucose productionFractionationFermentation
A process is defined for the continuous steam pretreatment and fractionation of corn cobs and low lignin lignocellulosic biomass to produce a concentrated cellulose solid stream that is sensitive to enzymatic hydrolysis. Valuable chemicals are recovered by fractionating the liquid and vapor stream composed of hydrolysis and degradation products of the hemicellulose. Cellulosic derived glucose is produced for fermentation to biofuels. A hemicellulose concentrate is recovered that can be converted to value added products including ethanol.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
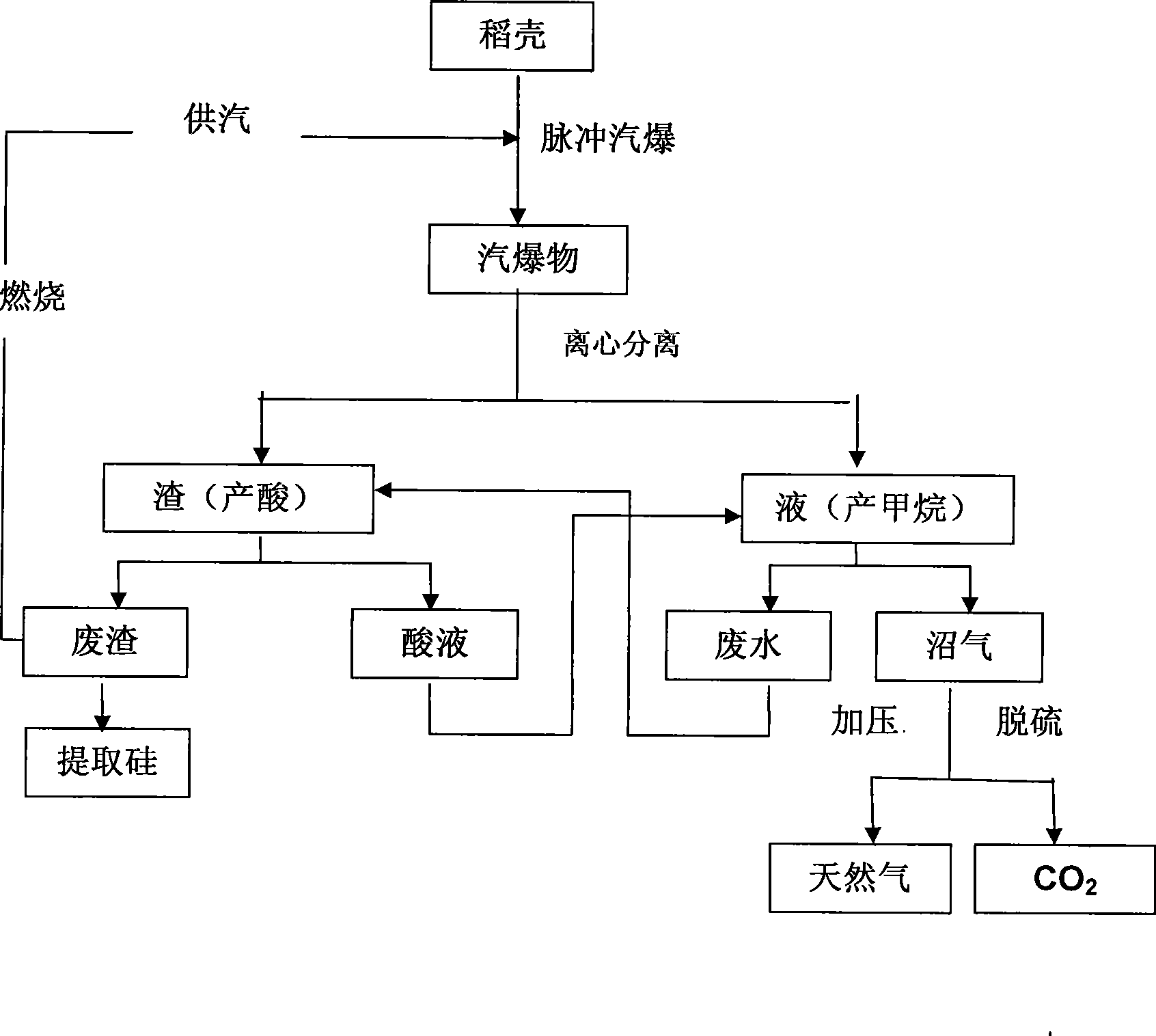
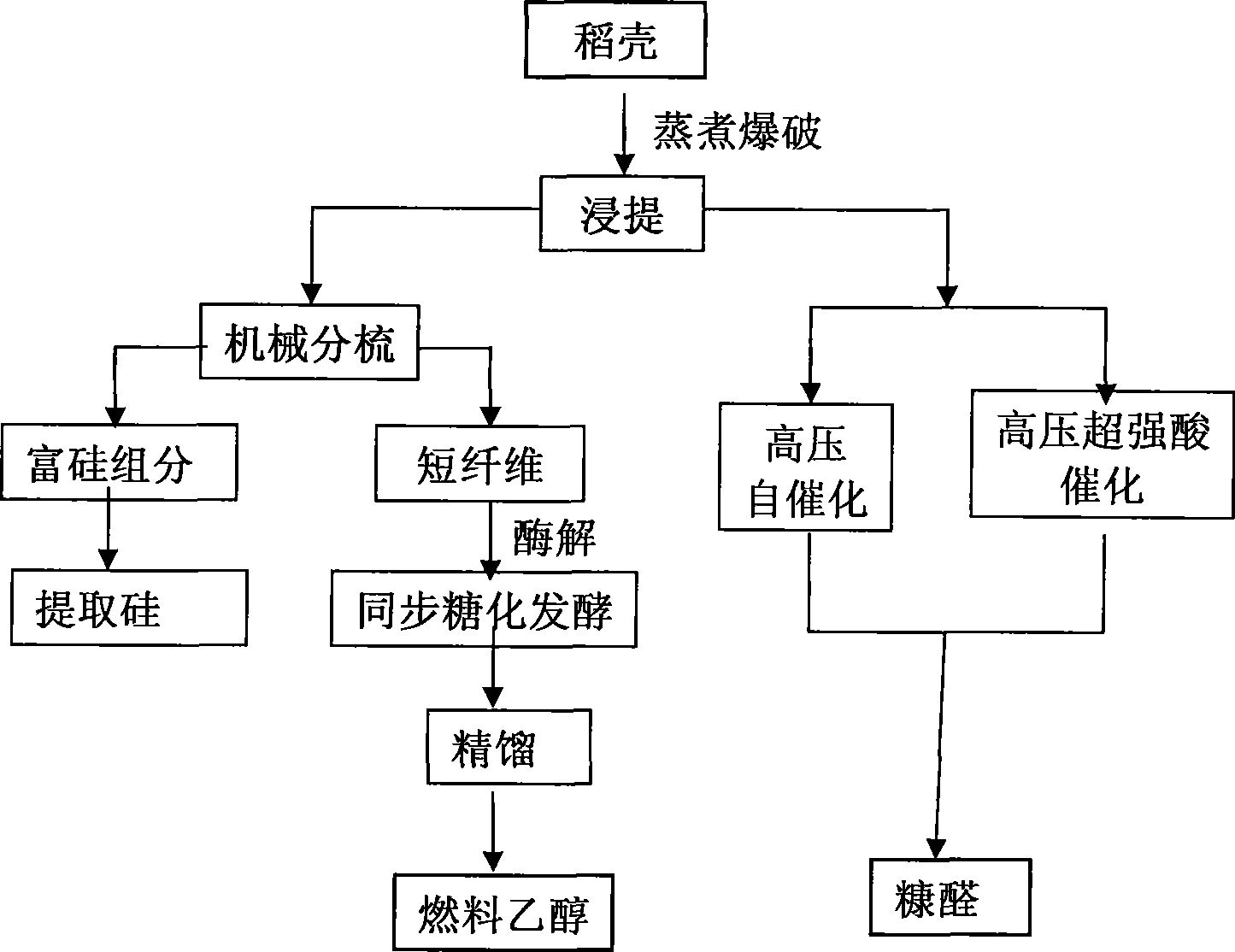
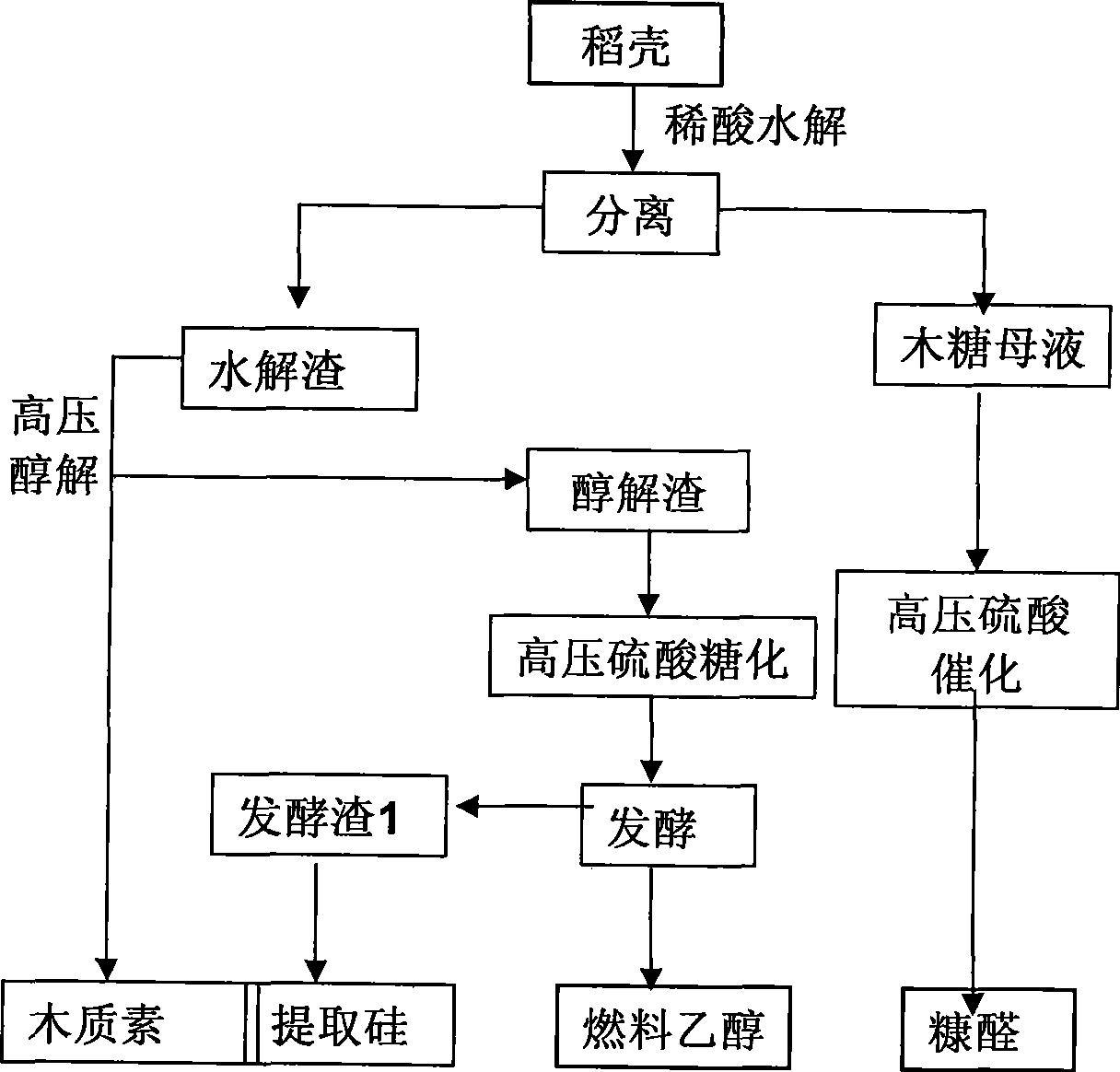
Production process of natural gas by using paddy hull
The invention relates to a production technique utilizing rice hulls to produce natural gas, which solves the problem of economically and effectively utilizing the rice hulls which are rich resources and biological materials. The technique of the invention essentially comprises the following steps: 1. Pulse gas explosion is carried out to the rice hulls and more than 90 percent of hemicelluloses in products of gas explosion are hydrolyzed while more than 85 percent of celluloses are isolated and puffed; 2. two-phase anaerobic fermentation is carried out to the products of gas explosion, thus respectively obtaining methane and acid liquor; and 3. desulfurization is carried out to the methane, thus obtaining the natural gas of the rice hulls. The technique of the invention pertains to anaerobic fermentation and has little manpower and low management cost; compared with the biomass heat energy transformation modes, such as cellulosic ethanol, biomass methanol, biological oil, pyrolytic bio-oil, biomass hydrogen production, wheat straw power generation, and the like, the transformable heat energy of biological natural gas is the highest; the technique of the invention pertains to a closed internal recycling system, which is environmentally friendly and has no pollution and high economic benefit.
Owner:浙江格义清洁能源技术有限公司
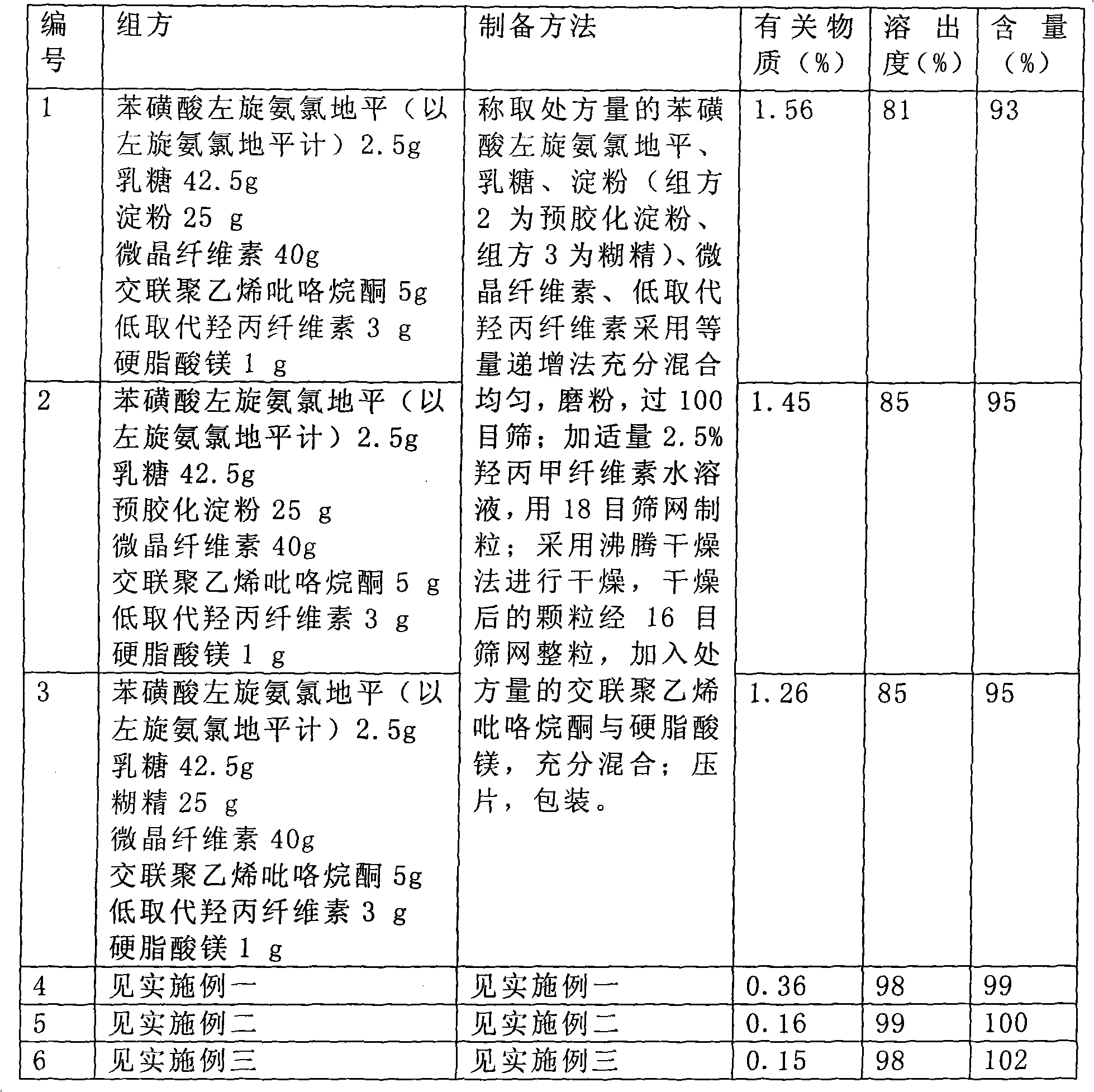
Levamlodipine besylate tablet, preparation process thereof and control method for relevant materials
ActiveCN102028662AGood treatment effectStable buckOrganic active ingredientsPill deliveryCross-linkSolubility
The invention relates to a levamlodipine besylate tablet, a preparation process thereof and a control method for relevant materials. Each 1000 levamlodipine besylate tablets provided by the invention comprise the following compositions: 2.5g of levamlodipine besylate (measured in besylate), 30 to 50g of lactose (as a filler), 20 to 40g of beta-cyclodextrin (as an inclusion agent), 25 to 45g of microcrystalline cellulose (as a disintegrating agent), 5 to 15g of cross-linked polyvinylpyrrolidone (as a disintegrating agent), 1 to 2g of magnesium stearate (as lubricant), and 50 to 80g of 2.5% HPMC (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) and 50% ethanol (as an adhesive). The levamlodipine besylate tablet provided by the invention has the advantages of making multi-item improvements on the properties of the levamlodipine besylate, increasing the solubility and apparent dissolution rate of the tablet, improving the stability of the tablet, reducing the excitability of the tablet, significantly reducing the limit of the relevant material, and having better clinical treatment effect, so that the blood pressure lowering of the patient with hypertension is more stable.
Owner:JIANGXI SHIMEI PHARM CO LTD
Bagasse fractionation for cellulosic ethanol and chemical production
InactiveUS20120111514A1Reduce contentHigh lignin contentPretreatment with water/steamPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsEnzymatic hydrolysisFractionation
A process is defined for the continuous steam pretreatment and fractionation of bagasse to produce a concentrated cellulose solid stream that is sensitive to enzymatic hydrolysis. Valuable chemicals are recovered by fractionating the liquid and vapor stream composed of hydrolysis and degradation products of the hemicellulose. Cellulosic derived glucose is produced for fermentation to biofuels. A hemicellulose concentrate is recovered that can be converted to value added products including ethanol.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Cellulosic ethanol fermentation using adapted culture
A method for producing ethanol by fermentation includes the preparation of a starter culture, inoculation of a mash with the starter culture, fermentation of the mash, and recovery of ethanol from the mash. The starter culture includes a tallow base with Chinese tallow tree parts and water which are inoculated with micro-organisms, where the micro-organisms include yeast. The micro-organisms are grown in the tallow base, and used to inoculate the mash. The mash is then fermented, and ethanol is recovered from the mash.
Owner:ALTERNATIVE GREEN TECH +1
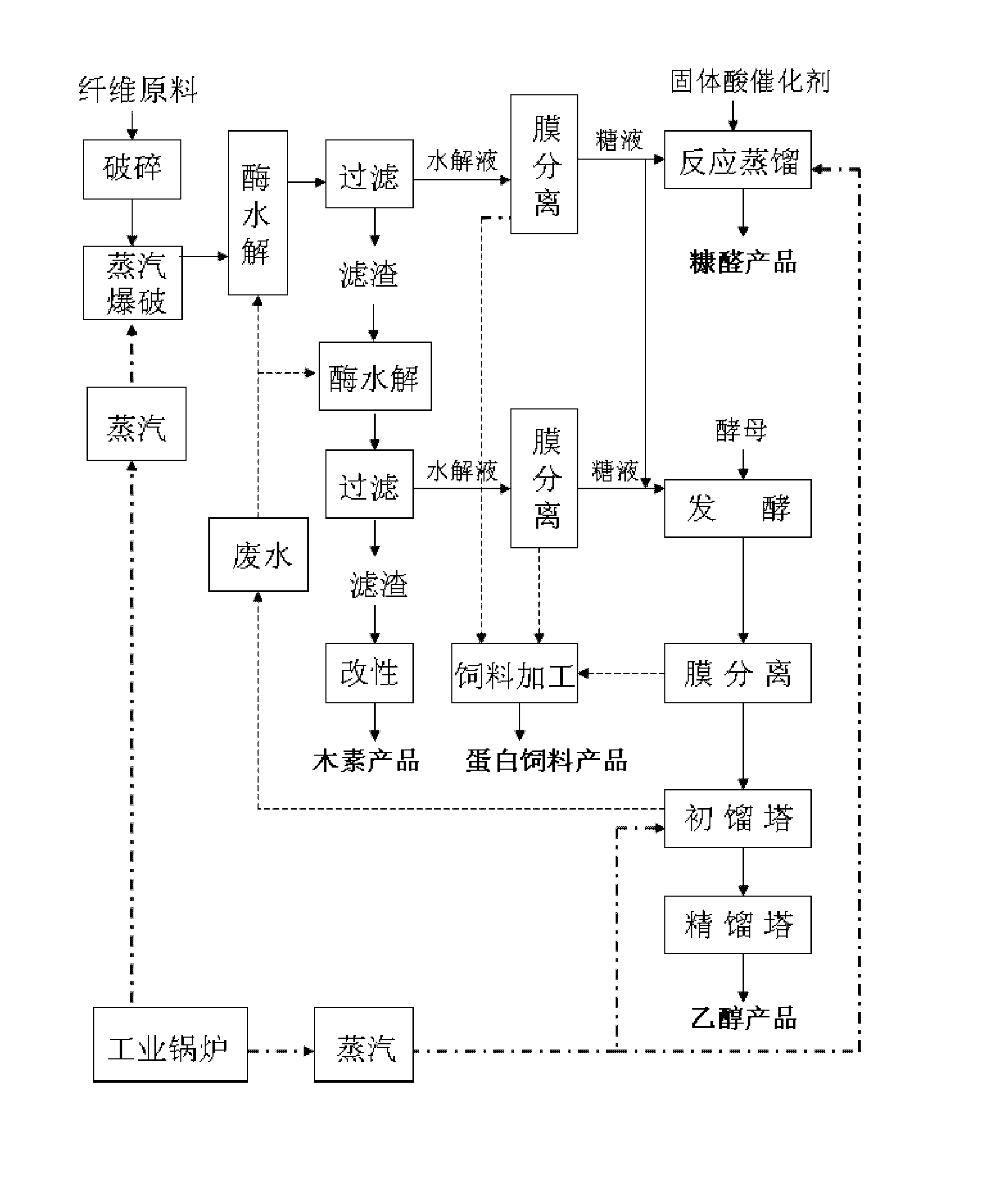
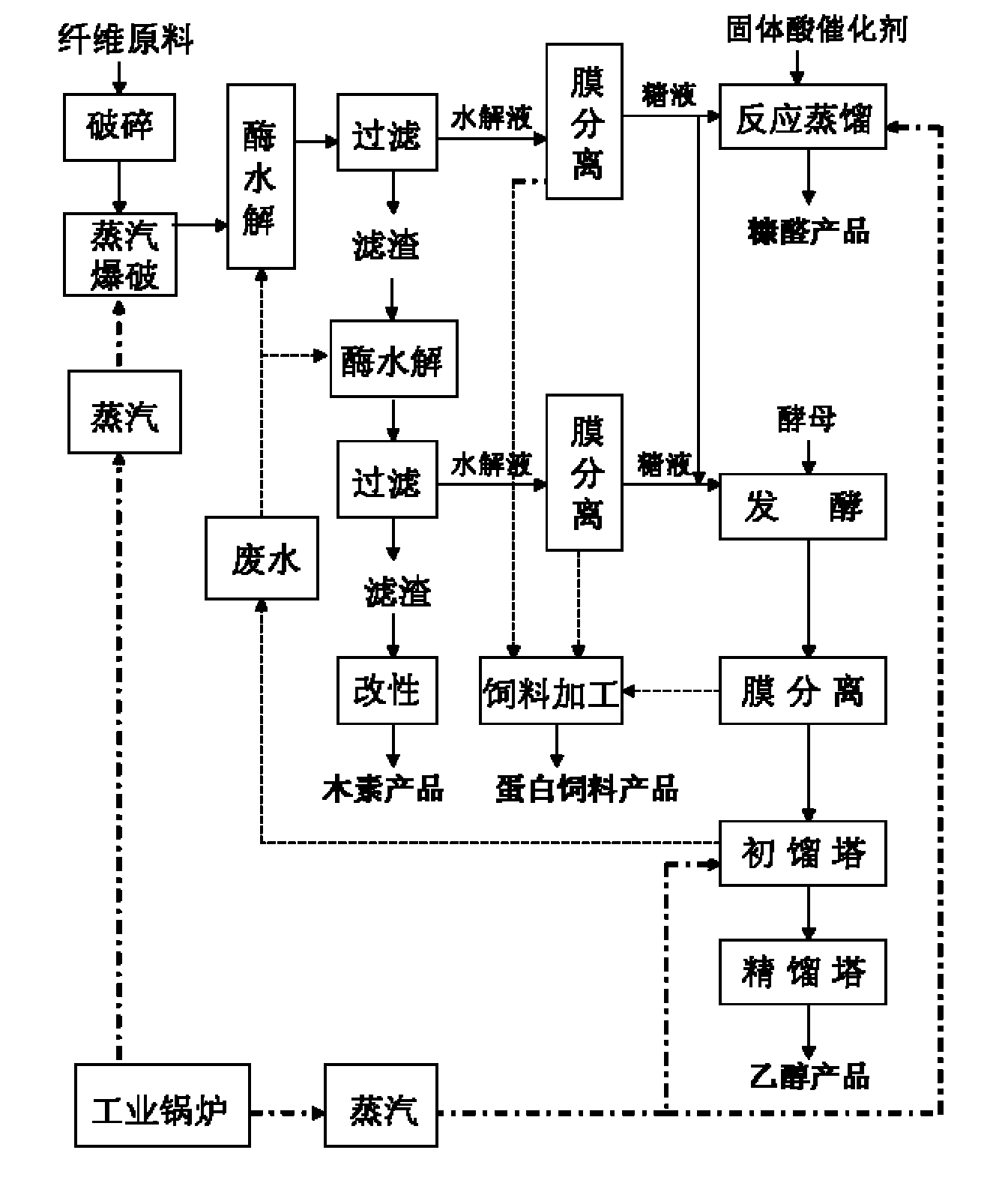
Method for coproduction of xylose, lignin and ethanol from corncobs
The invention discloses a method for the coproduction of xylose, lignin and ethanol from corncobs in the technical field of biochemical industry, comprising the following steps of: 1) hydrolyzing the corncobs under an acidic condition to obtain xylose solution and acidolysis residues; 2) performing alkaline liquor / alcohol extraction on the acidolysis residues to obtain lignin and lignin-free residues; 3) taking the lignin-free residues as an enzymolysis zymolyte, adding enzymolysis buffer solution, and performing enzymolysis using cellulase, thereby obtaining enzymolysis mixed solution; and 4) fermenting the enzymolysis mixed solution to produce ethanol solution. The method of coproduction of the invention comprehensively utilizes three components of the corncobs to obtain high value-added xylose and lignin products; and the cellulose content in the enzymolysis substrate is increased and the accessibility of the cellulase is improved, so that high transformation ratio of cellulose enzymolysis is realized. The method causes the utilization ratio of the lignocellulose raw material to be increased and the production cost of the cellulose ethanol to be reduced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Processing cellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20120040408A1Reduce processShort timeClimate change adaptationBiofuelsDownstream processingLignocellulosic biomass
Improved systems and methods for reducing costs and increasing yields of cellulosic ethanol are disclosed herein, along with plants genetically transformed for increased biomass, expression of lignocellulolytic enzyme polypeptides, and / or simplification of harvesting and downstream processing. Methods for processing biomass from these transgenic plants that involve less severe and / or less expensive pre-treatment protocols than are typically employed are also disclosed.
Owner:EDENSPACE SYST CORP +1
Bacterial strain tolerant with various inhibitors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
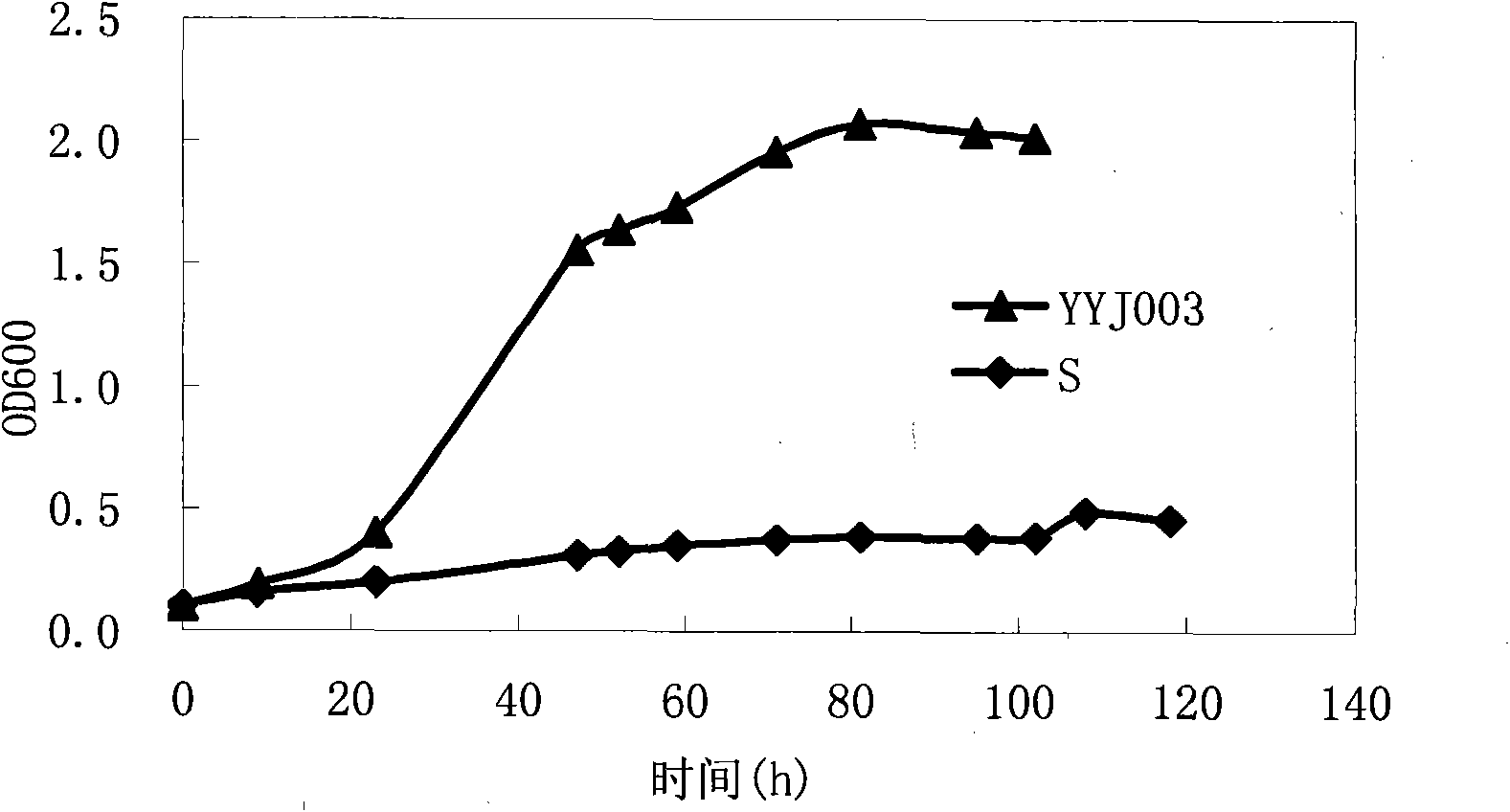
The invention discloses a bacterial strain tolerant with various inhibitors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is named as Saccharomyces cerevisiae YYJ003 and is collected in China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM) with the collection number of CGMCC NO.2757. The bacterial strain tolerant with the various inhibitors of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the invention can be in normal growth in a culture medium containing inhibitors produced by diluted acid pretreatment and can realize efficient ethanol production. The bacterial strain in the invention breaks through the bottleneck problem that a dilute acid pretreatment method is limited to produce cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Treatment method for wastewater generated in cellulosic ethanol production
ActiveCN102910777AAchieve water savingEmission reductionTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentVegetable fibersCellulosic ethanol
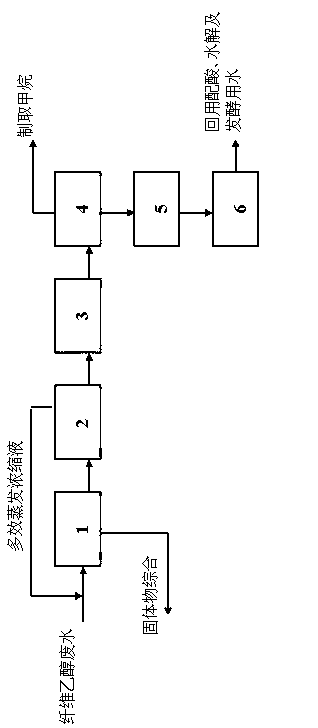
The present invention relates to a treatment method for wastewater generated in cellulosic ethanol production. The method is used for treatment and reuse of wastewater generated by using corn stalks and other plant fibers as raw materials for ethanol production, and especially for salt-containing organic wastewater. A combined process of filter pressing - multi-effect evaporation - cooling - anaerobic fermentation - aerobic biotreatment - filtration is used for treating the wastewater generated in the cellulosic ethanol production. The water flowed out after the treatment can be directly reused in the processes such as acid liquor preparation, hydrolysis and fermentation of the cellulosic ethanol production, so purposes of saving water and zero liquid discharge in the cellulosic ethanol production are reached. The method of the present invention is characterized in that recycling of all the high salt concentration wastewater can be achieved, effective recovery and comprehensive utilization of waste materials in the wastewater is obtained, high concentration organic pollutants are converted into methane and the like for resource utilization, and requirements of circular economy, clean production and the like are met.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Cellulosic ethanol distillers residues
InactiveUS20100166913A1Reduce the amount requiredImproved quality and compositionBiofuelsAnimal feeding stuffBiofuelFodder
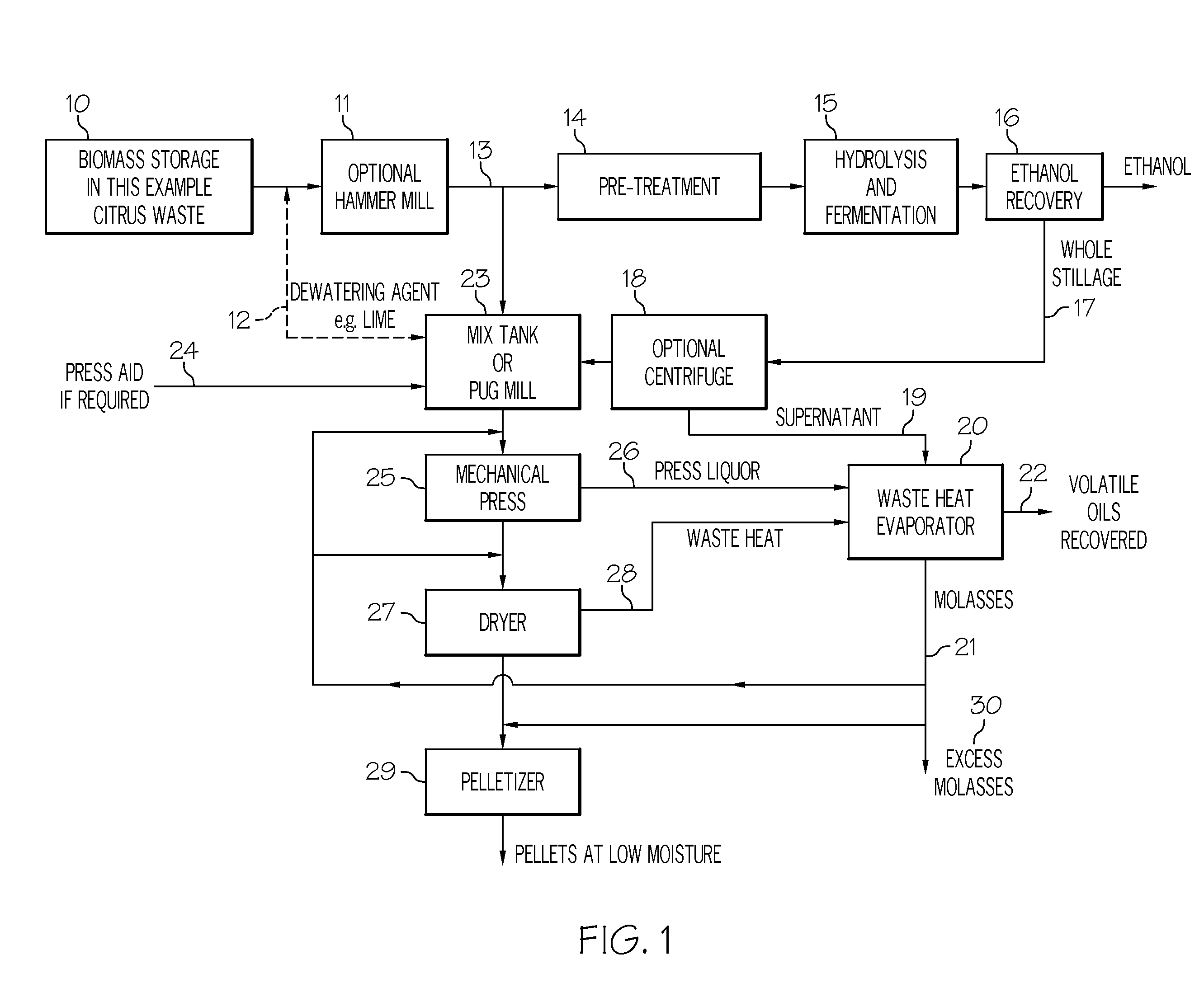
Biomass from ethanol whole stillage and processes for making same are disclosed. The process overcomes the challenge of dewatering the stillage through the use of a press aid or a mixture of the stillage and unfermented biomass. The invention further provides a system and method for producing distillers peels pellets from fermented citrus waste. The invention allows the composition characteristics of the animal feed or bio fuel to be varied and optimized by controlling the mix proportions of the feedstock.
Owner:STEWART DAVID A
Method for producing glucose and cellobiose using cellulose complex enzyme
InactiveCN101603065AIncrease saccharification rateSatisfy productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberConcentrations glucose
A method for producing glucose and cellobiose using cellulose complex enzyme is the technology using the cellulose complex enzyme as a catalyst and realizing the high saccharification rate conversion of cellulose by adding cellulose enzyme activator at the optimized stirring speed. Glucose concentration can reach 150g / L after using cellulose enzymatic hydrolysis, and the method is a cellulose saccharification production technology with economic feasibility. With the technology used, low cost, low usage of enzyme and high saccharification rate can be realized, and the productions of cellulose alcohol and biochemical products (lactic acid, succinic acid and the like) are satisfied. In the whole technology, no beta-glucosaccharase is added additionally, no sugar concentrating device is added, and the technology is simple, the equipment cost is low and the industrialized prospect is good.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Processes for producing fluff pulp and ethanol from sugarcane
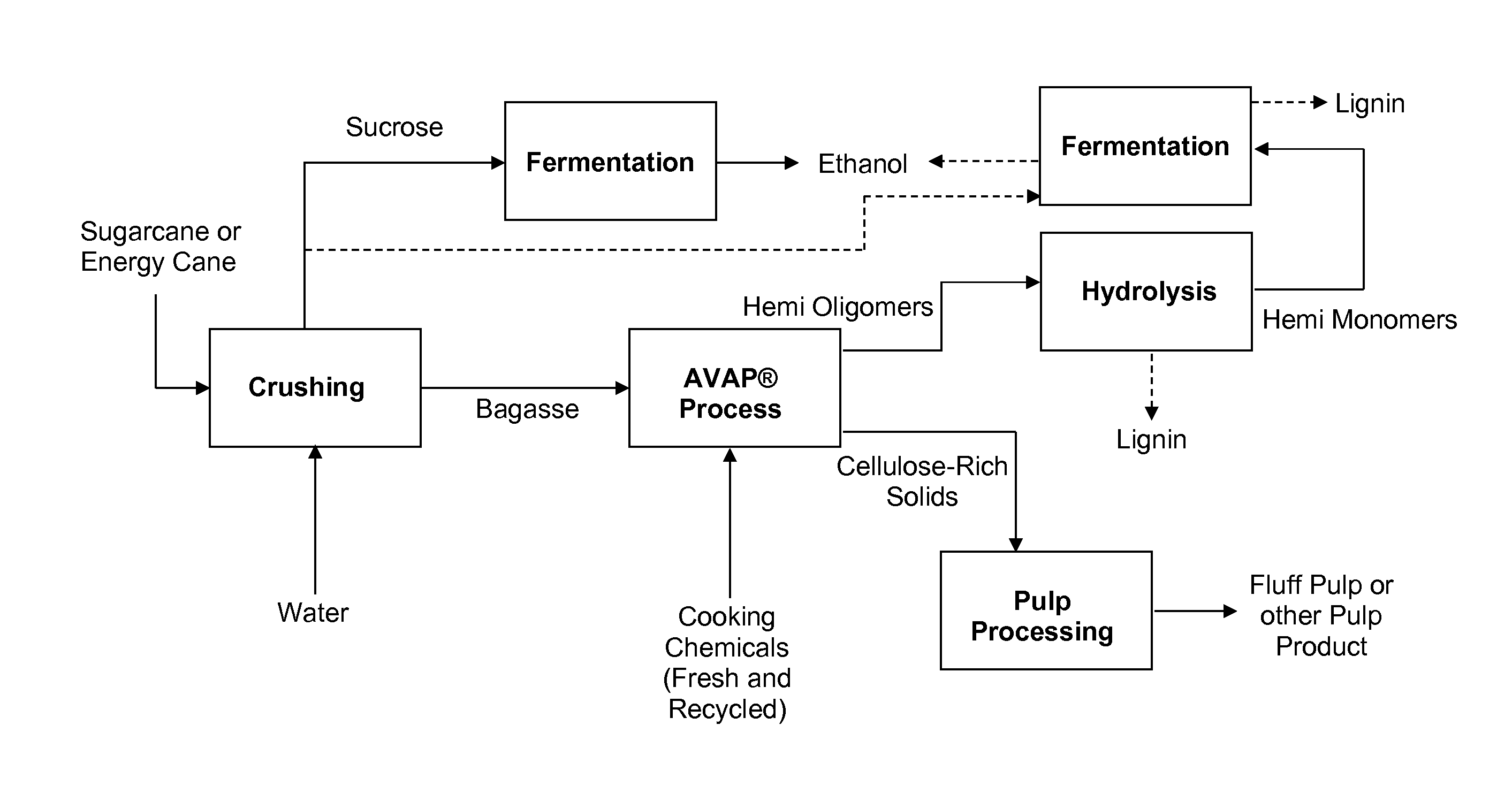
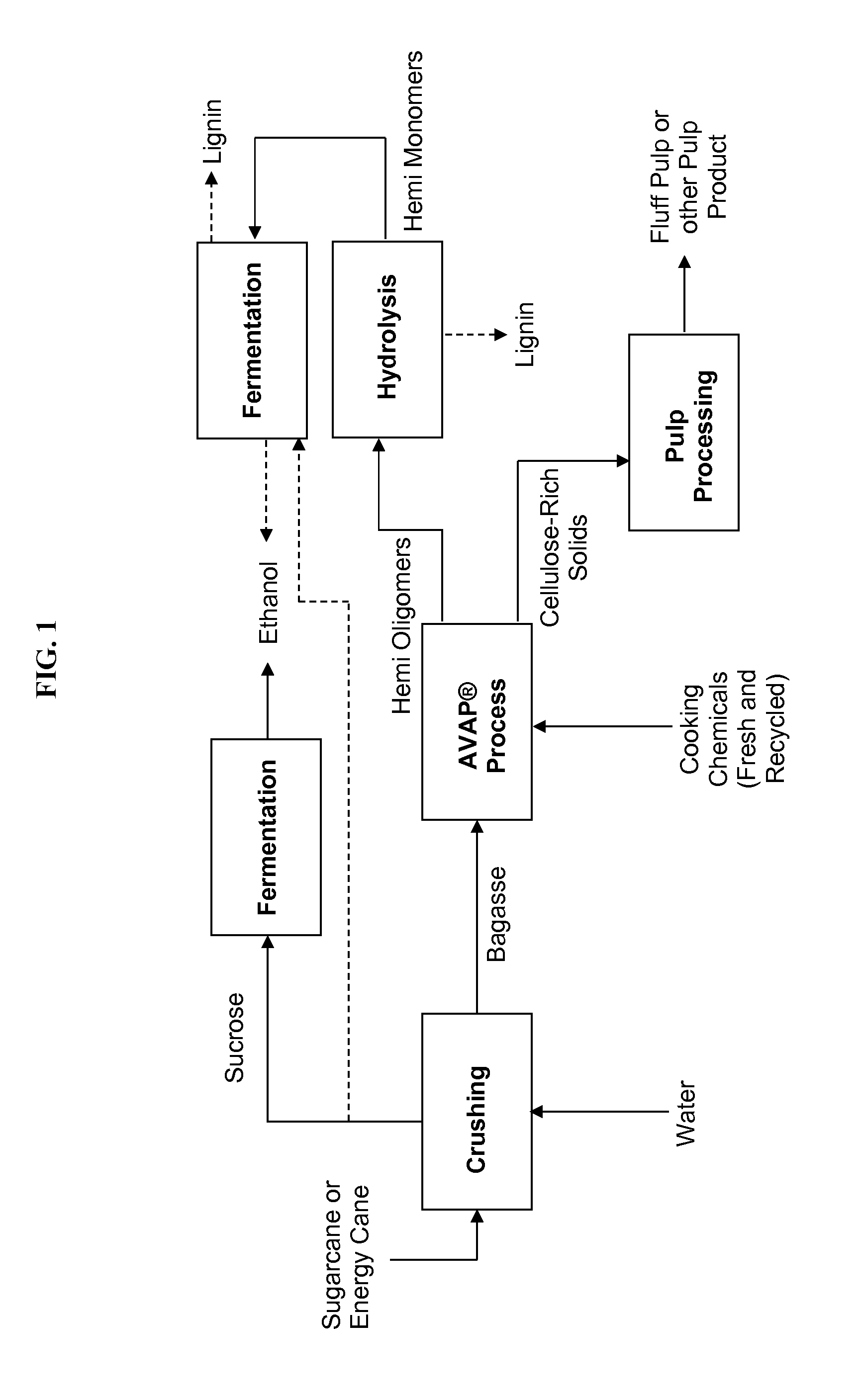
The disclosure provides a process for producing fluff pulp and ethanol from sugarcane bagasse or straw, comprising: fractionating the feedstock in the presence of an acid catalyst, a solvent for lignin, and water, to generate a solid / liquid slurry comprising cellulose-rich solids, hemicelluloses, and lignin; separating the solid / liquid slurry into a solid stream and a liquid stream; further treating the cellulose-rich solids to produce fluff pulp; hydrolyzing the hemicelluloses to generate hemicellulose monomers; and fermenting at least a portion of the hemicellulose monomers to cellulosic ethanol. Lignin is removed from the process during one or more steps and combusted to provide energy for process requirements. The process is integrated with, and provides energy to, a first-generation process that ferments sugarcane-derived sucrose to first-generation ethanol. Similar processes are possible with energy cane, corn, and other crops.
Owner:API INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
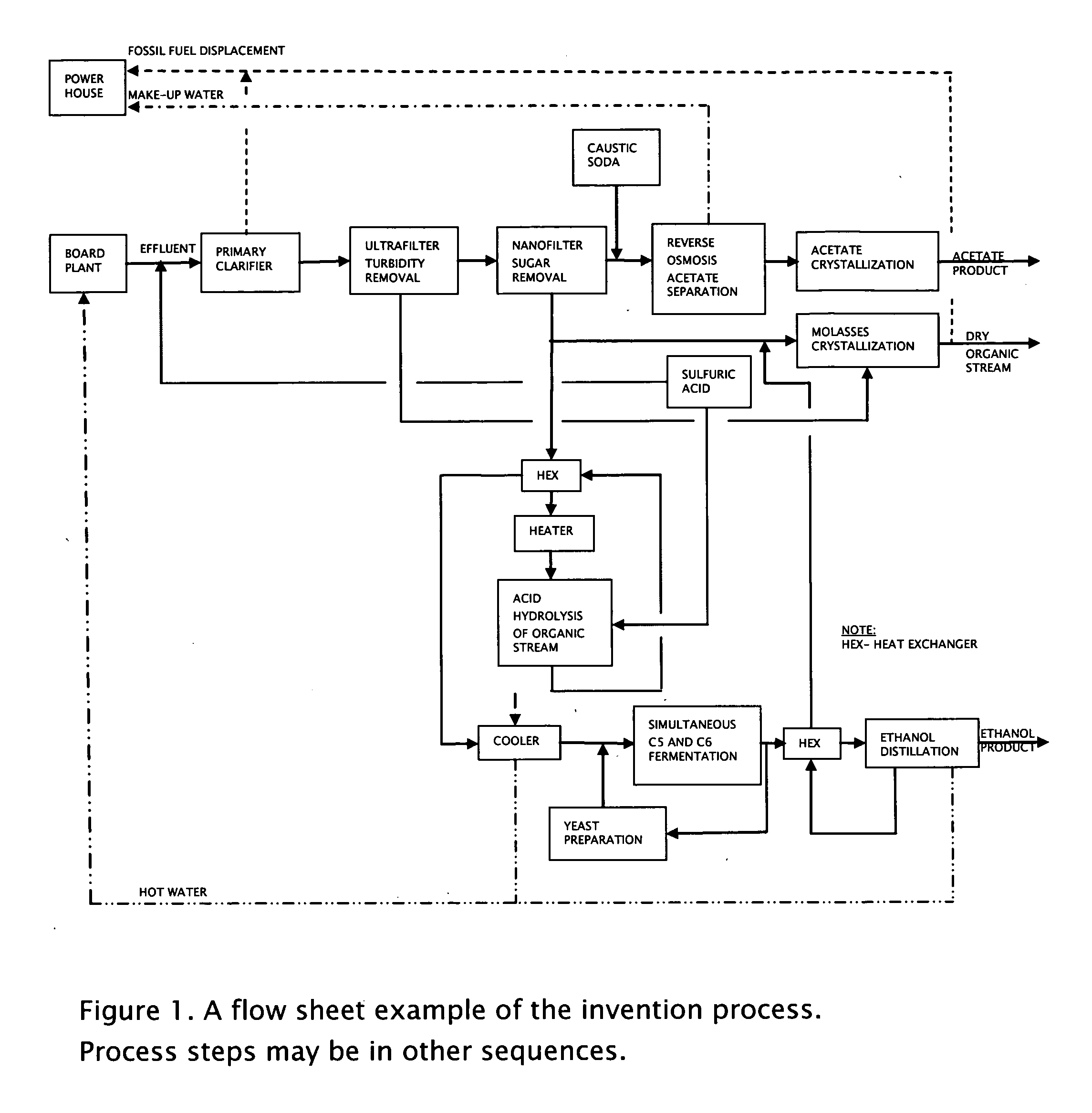
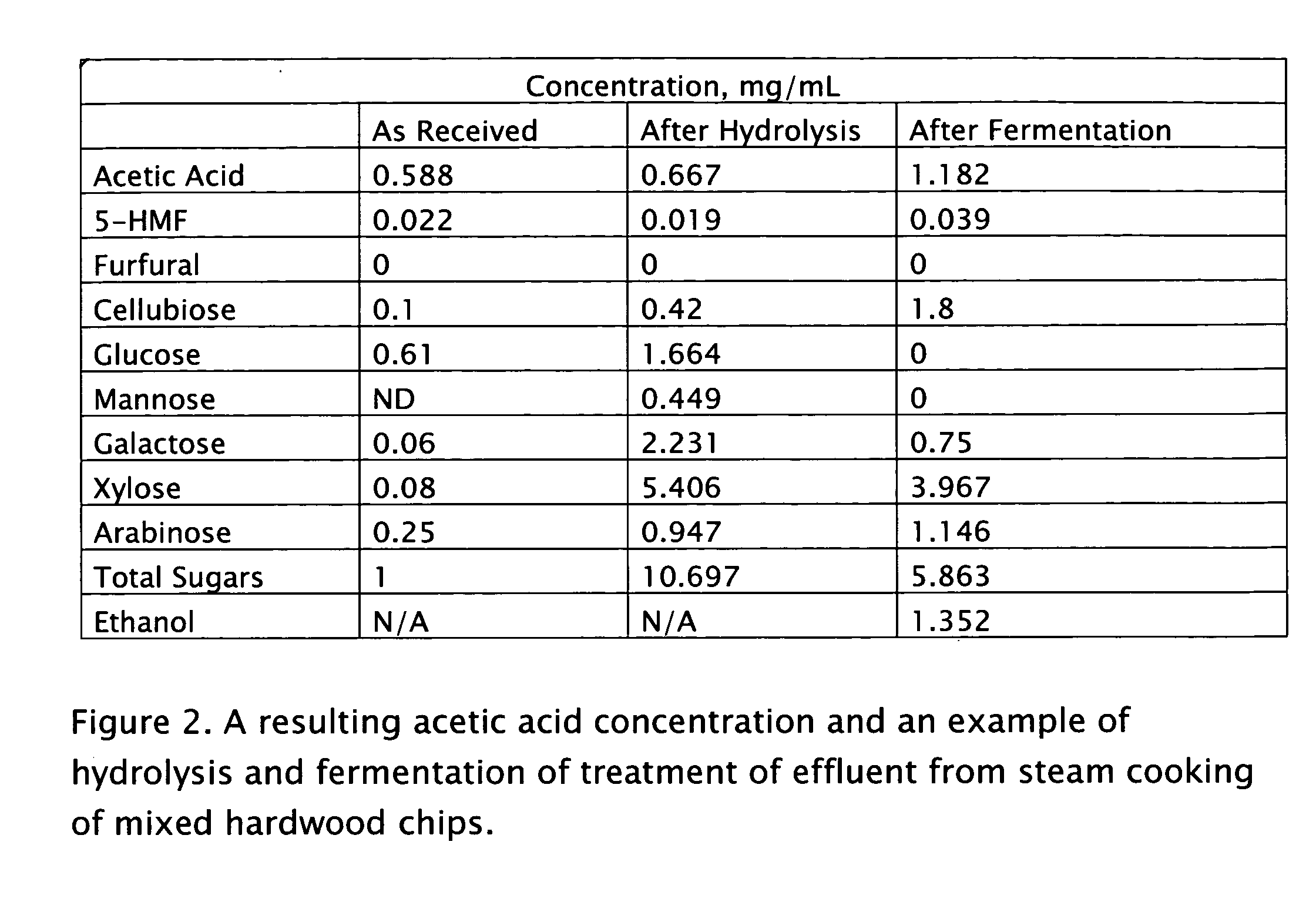
Process for obtaining biochemicals in a zero-liquid discharge plant
ActiveUS20090305374A1Minimize process energy consumptionEliminate needSugar derivativesBiofuelsFiberAcetic acid
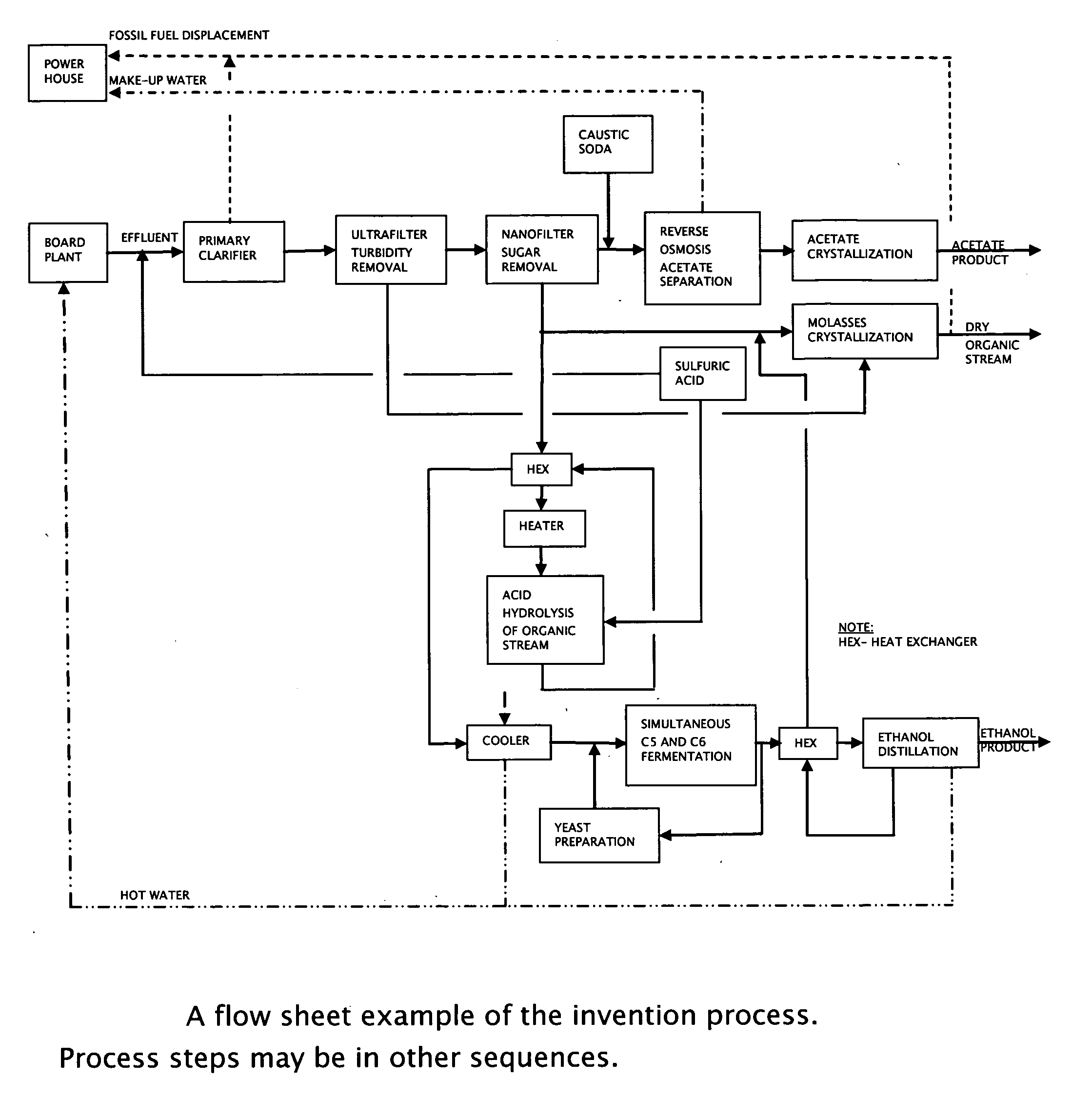
A method is presented for the production of cellulosic ethanol, acetic acid and derivatives from the extract containing fibers and hemicelluloses after steam cooking of biomass in a host plant. The process is integrated with the host plant process to minimize the effect of loss of heat value from the extracted hemicelluloses and eliminate the need for the waste water treatment plant.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Method for coproducing cellulosic ethanol, furfural, lignin and feed from plant fibers
InactiveCN102351817AReduce the degree of hydrolysisImprove hydrolysis efficiencyOrganic chemistryFood processingFiberHydrolysate
The invention provides a method for producing furfural and ethanol from plant fibers, which comprises the following steps: carrying out catalytic hydrolysis on the plant fibers, separating by filtration, and carrying out enzyme removal treatment to obtain a pentosan hydrolysate; carrying out dehydration cyclization on the hydrolysate by using a binary composite solid acid catalyst to prepare the furfural product; taking the solid residue obtained in the previous step, adding a buffer solution of which the pH value is 4-6 in a liquid-to-solid ratio of 9:1-5:1, sterilizing, adding 40-100IU of cellulase to every gram of substrate, carrying out enzymolysis for 24-48 hours, filtering out the hydrolysis residue, and removing zymoprotein from the filtrate to obtain the cellulose hydrolysate glucose solution; and adding a liquid yeast cell culture medium into the cellulose hydrolysate obtained in the previous step, sterilizing, inoculating into a 0.5-1% Saccharomyces cerevisiae seed culture liquid, carrying out fermentation and culture for 36-48 hours, and carrying out centrifugal separation to recycle the yeast cells, wherein the supernatant is the ethanol product.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV +1
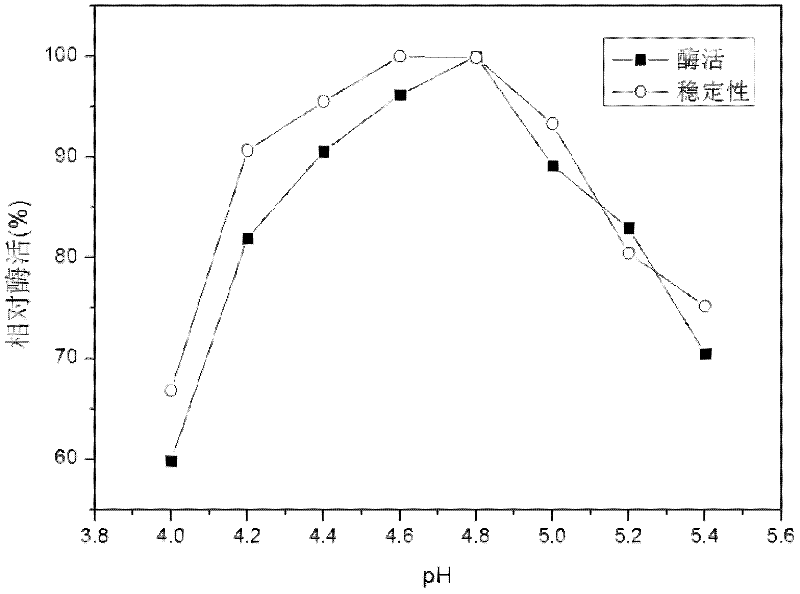
Trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and application thereof
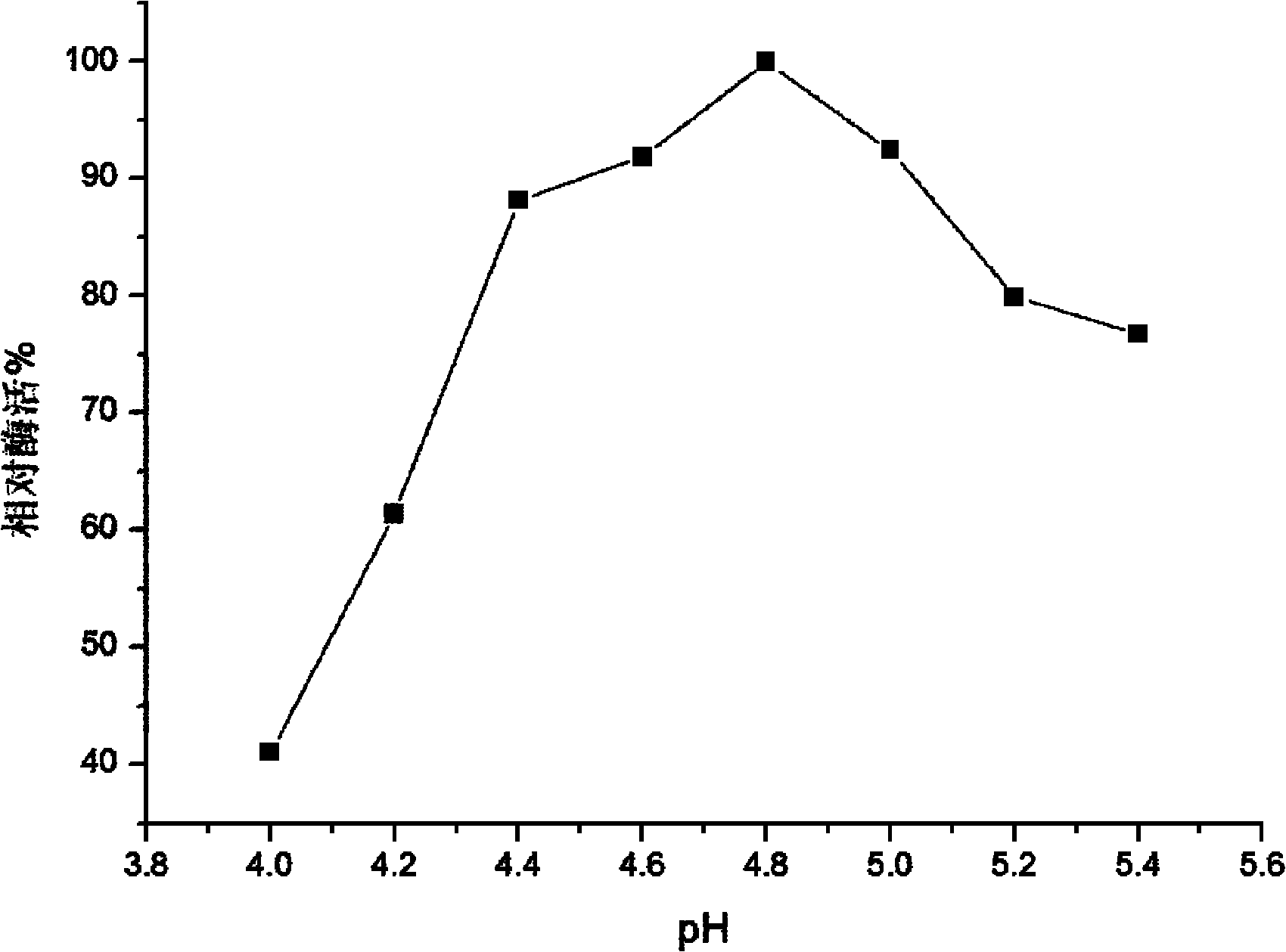
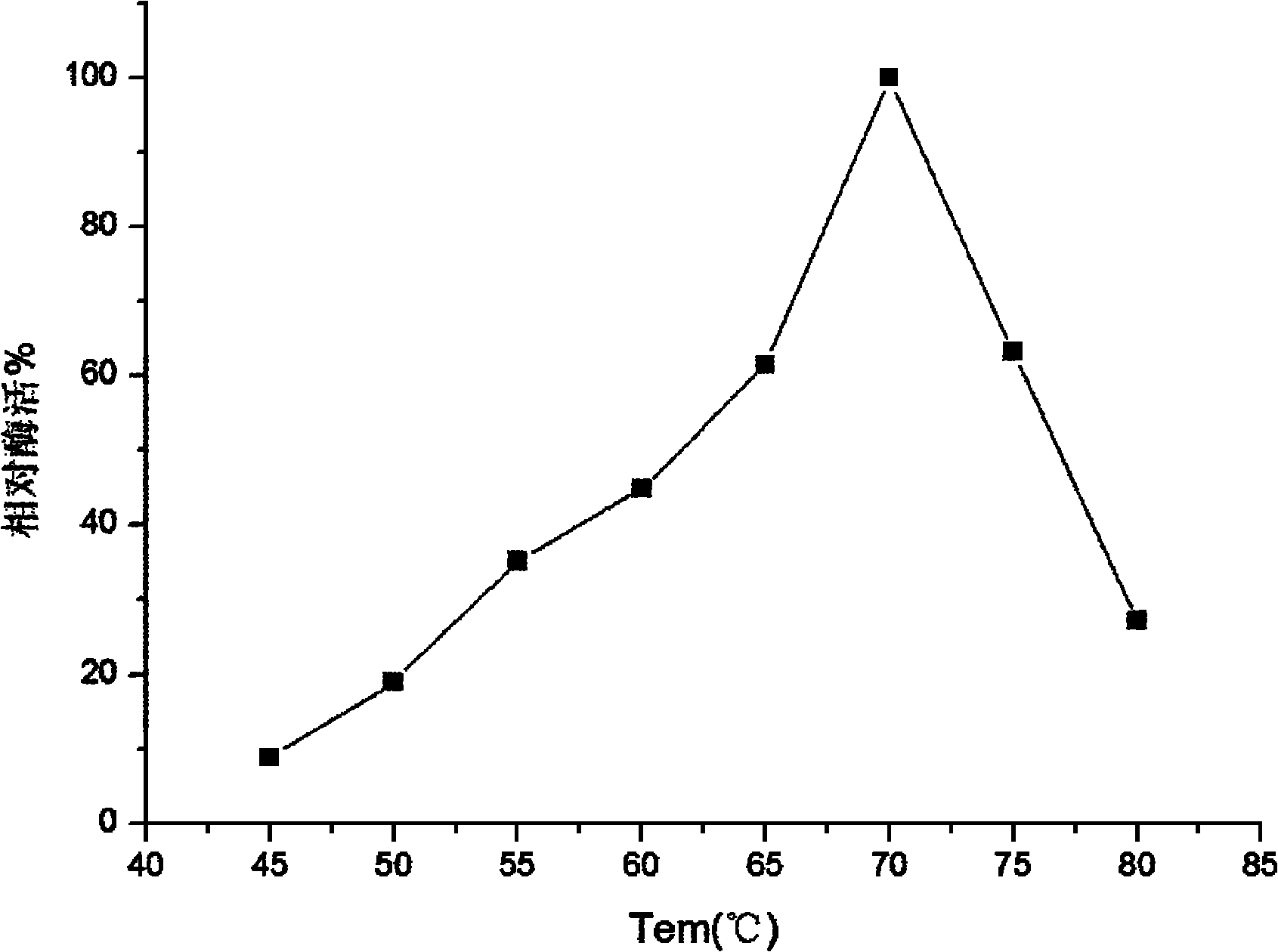
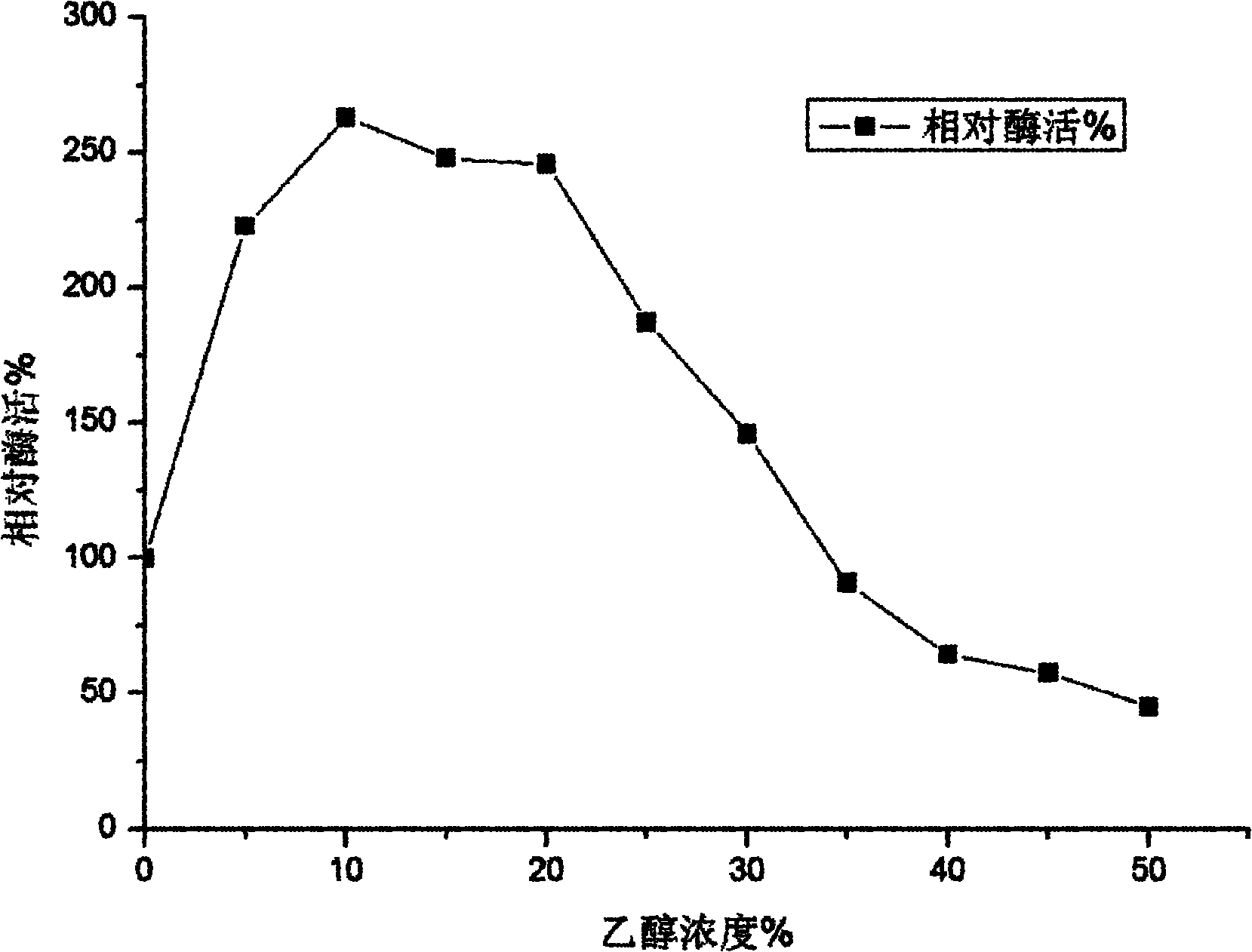
InactiveCN102080050AImprove toleranceFeedback inhibition is evidentFungiMicroorganism based processesReaction temperatureCellobiose
The invention discloses a trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing a thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and an application thereof. The trichoderma viride W2 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on August 23, 2010, and the preservation number of the trichoderma viride W2 is CGMCC No.4098. The trichoderma viride W2 can produce a new beta-glucosidase, the enzymatic activity of the new beta-glucosidase reaches 346.7U / mL, the optimal reaction pH value is 4.8, the optimal reaction temperature is 70 DEG C, and the new beta-glucosidase is suitable for pyrohydrolysis and has an obvious glucose feedback inhibition effect. The ethanol the concentration of which is 10% has a maximal effect on promoting the enzymatic activity and improves the enzymatic activity of the beta-glucosidase by 1.6 times, and the resistant ability of the ethanol reaches 30%, so that the cellobiose inhibition can be effectively eliminated, the yield of the ethanol is improved by nearly 3 times, and the terminal product inhibition is effectively eliminated. Thus, the beta-glucosidase can be used for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulose raw materials, has a rare promoting effect in China, effectively increases the yield of the cellulosic ethanol, lowers the production cost, and accelerates the industrialized progress of the cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing furfural and co-producing lignin and cellulosic ethanol via plant material
ActiveCN103193737AAchieve recyclingRealize comprehensive utilizationOrganic chemistryBiofuelsFiberSlag
The invention discloses a method for preparing furfural and co-producing lignin and cellulosic ethanol via a plant material. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: (1) hydrolyzing hemicelluloses to prepare pentose; (2) preheating a pentose solution; (3) ejecting and heating; (4) dewatering and cyclizing; (5) flash-evaporating aldehyde steam to release pressure; (6) distilling; (7) rectifying in a manner of rectifying under vacuum and controlling the temperature at 98-120 DEG C to obtain a main fraction furfural; and (8) eluting lignin in pentose slag acquired in the step (1) by using an alkali liquor, acquiring delignification slag and a lignin solution, neutralizing the lignin solution to acquire the lignin, and carrying out enzymolysis on the delignification slag via cellulase to prepare the cellulosic ethanol. The method disclosed by the invention can be used for realizing cyclic utilization and comprehensive utilization of the plant materials, improving the utilization rate of raw materials, reducing the consumption of auxiliary materials and reducing the emission of wastes and reducing environmental protection pressure; and the method disclosed by the invention is a clean production and preparation process.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGLIVE BIO TECH CO LTD
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with multiple-stress resistance, and application thereof in cellulose alcohol fermentation
InactiveCN102199554AImprove toleranceEfficient conversionFungiMicroorganism based processesHydrolysateAlcohol production
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with multiple-stress resistance, and the application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain in cellulose alcohol fermentation. The invention provides a saccharomyces cerevisiae T43 CGMCC No. 4642. The saccharomyces cerevisiae T43 has strong temperature adaptability (such that cooling and heating cost is reduced during fermentation processes) and good tolerance with inhibitors in cellulose hydrolysate (such that production processes can be simplified, and fermentation time can be shortened). Therefore, the saccharomyces cerevisiae has good prospect to be adopted in industrial application. According to the present invention, the efficient conversion of glucose in corn stalk hydrolysate to ethanol can be achieved, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be directly used in present fuel ethanol production technologies and new lignocellulose ethanol technologies. With the technical scheme of the present invention, ethanol production theorugh cerevisiae fermentation of cellulose hydrolysate can be started at a high temperature. According to the present invention, low energy consumption, low material consumption, low cost and high ethanol yield can be achieved in the cerevisiae fermentation process of cellulose alcohol production. With the present invention, huge economic benefits and good social benefits are brought in.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for continuously and efficiently secreting beta-glucosidase and applications thereof
The invention provides a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for continuously and efficiently secreting beta-glucosidase, which is named Saccharomyces cerevisiae 102SB, and preserved with a Preservation No. of CGMCC No. 7450 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 11, 2013. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae disclosed by the invention can continuously and efficiently secrete beta-glucosidase in a complex non-selective medium, and the extracellular enzyme activity can reach 1005.3 U / g (dry weight). By using a characteristic that the maximum specific growth rate of cellobiose is consistent with that of glucose, the strain reaches 0.29 h<-1> under the condition of limited oxygen. In SSF taking a cellulose material as a substrate, the yield of ethanol taking microcrystalline cellulose as a substrate is increased by 110%, and the yield of ethanol taking acid-hydrolyzed corncobs as a substrate is increased by 89%. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain disclosed by the invention is of great importance in reducing the production cost of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation in the process of cellulosic ethanol production, and simplifying the production process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Production method of cellulose ethanol
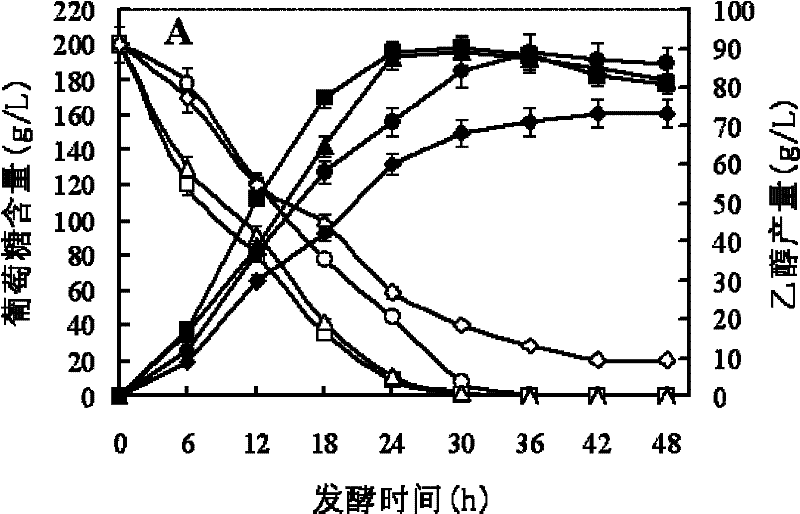
The invention discloses a production method of cellulose ethanol, which comprises the following steps of: (1) adding a culture medium containing the raw materials of cellulose and / or hemicellulose into a fermentation reaction kettle; (2) adding cellulase into the fermentation reaction kettle and inoculating Candidalusitaniae; and (3) carrying out synchronous diastatic fermentation under the combined action of the cellulase and the Candidalusitaniae and separating to obtain the cellulose ethanol. The Candidalusitaniae used for the synchronous diastatic fermentation in the invention has higher ethanol tolerance and higher ethanol throughput rate and can prepare the cellulose ethanol by the synchronous diastatic fermentation with high efficiency through taking the cellulose and the hemicellulose as the raw materials under the combined action of the cellulase.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
Modified sodium lignin sulfonate and application thereof as cement grinding aid
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
A method for obtaining yeast strains tolerant to multiple inhibitors
ActiveCN102296034AImprove toleranceAchieve in situ detoxificationFungiMicroorganism based processesHydrolysateYeast strain
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a yeast strain with the tolerance on various inhibitors, which comprises the following steps of: inoculating an activated saccharomyces cerevisias strain into a subculturing medium containing a cellulosic hydrolysate inhibitor to culture; after separating cell growing to a stationary phase, inoculating the obtained strain into the same fresh subculturing medium containing the cellulosic hydrolysate inhibitor to culture; and obtaining the strain in the stationary phase, i.e. the yeast strain with the tolerance on the various inhibitors. The yeast strain with the tolerance on the various inhibitors, which is obtained by the method disclosed by the invention, has improved tolerance on the cellulosic hydrolysate inhibitor and has stable growth traits, so that the in situ detoxification of hydrolysate is realized. The method has important significance for promoting the industrial production of cellulose ethanol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Improved method of excess calcium hydrate detoxification during cellulose ethanol production
InactiveCN101693905AImprove fermentation effectReduce dosageBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesDetoxification methodFermentation
A method for improving the detoxification of excess calcium hydrate during cellulose ethanol production relates to the method for improving the detoxification of the excess calcium hydrate. The invention solves the problems of big dosage of calcium hydroxide and low converting rate of cellulose ethanol of existing detoxification methods of the excess calcium hydrate, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a steam explosion straw, secondly, preparing filtrate A and a filter residue, thirdly, preparing filtrate B, fourthly, placing the filtrate B into the residue and adjusting the PH, then carrying out the damp-heat disinfection, adding cellulose and saccharomyces cerevisiae, then carrying out the saccharifying and fermentation, namely completing the improvement of the detoxification of the excess calcium hydrate during cellulose ethanol production. The invention not only reduces the dosage of the calcium hydrate, and the dosage is only 50%-60% of that of the prior art, but also improves the conversion rate of the cellulose ethanol to 84%-95% from the original 75%-79%, and can be widely applied in the production technologies. The method of the invention has the advantages that the required equipment is simple, and the cost of raw materials is low.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
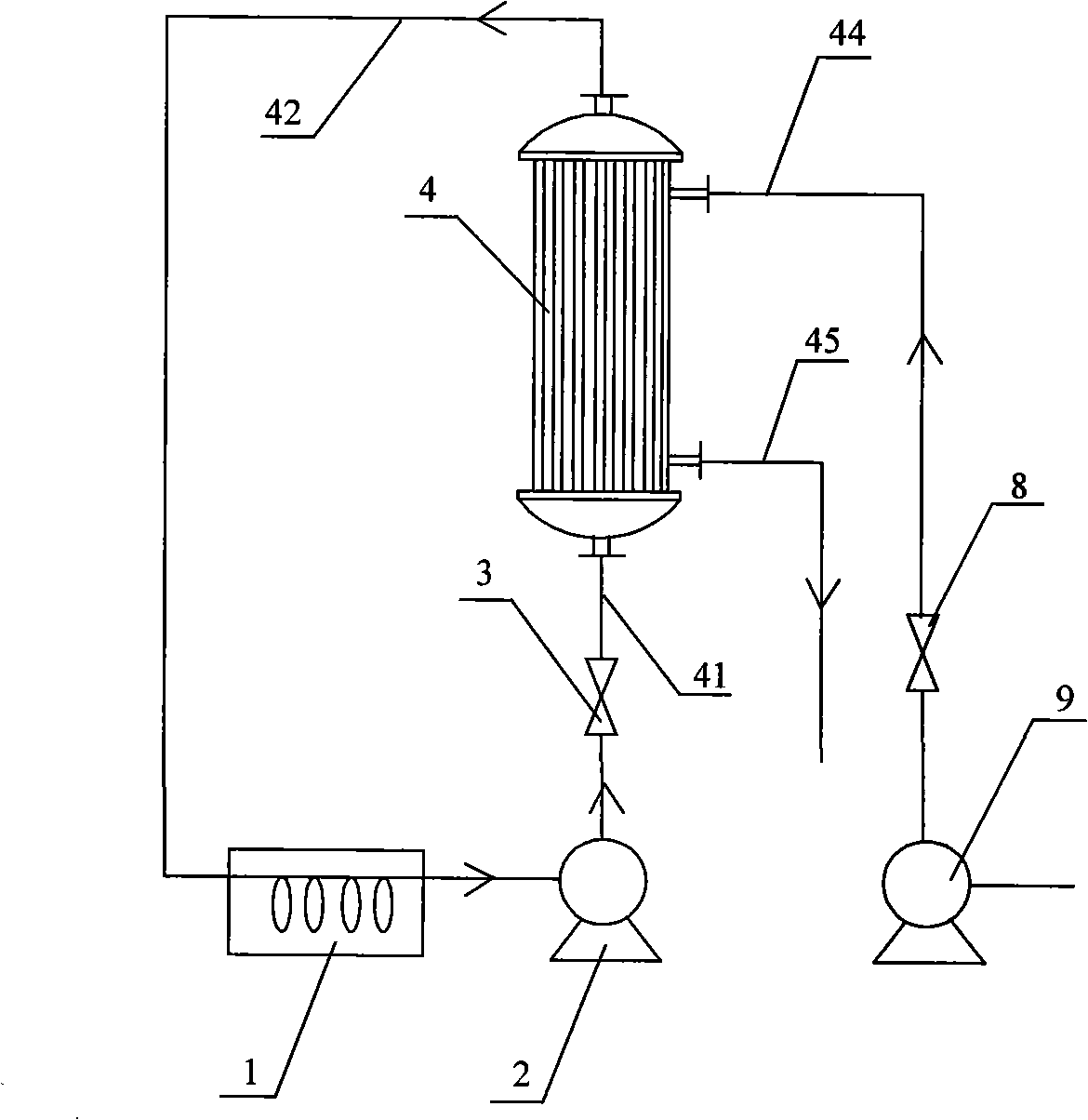
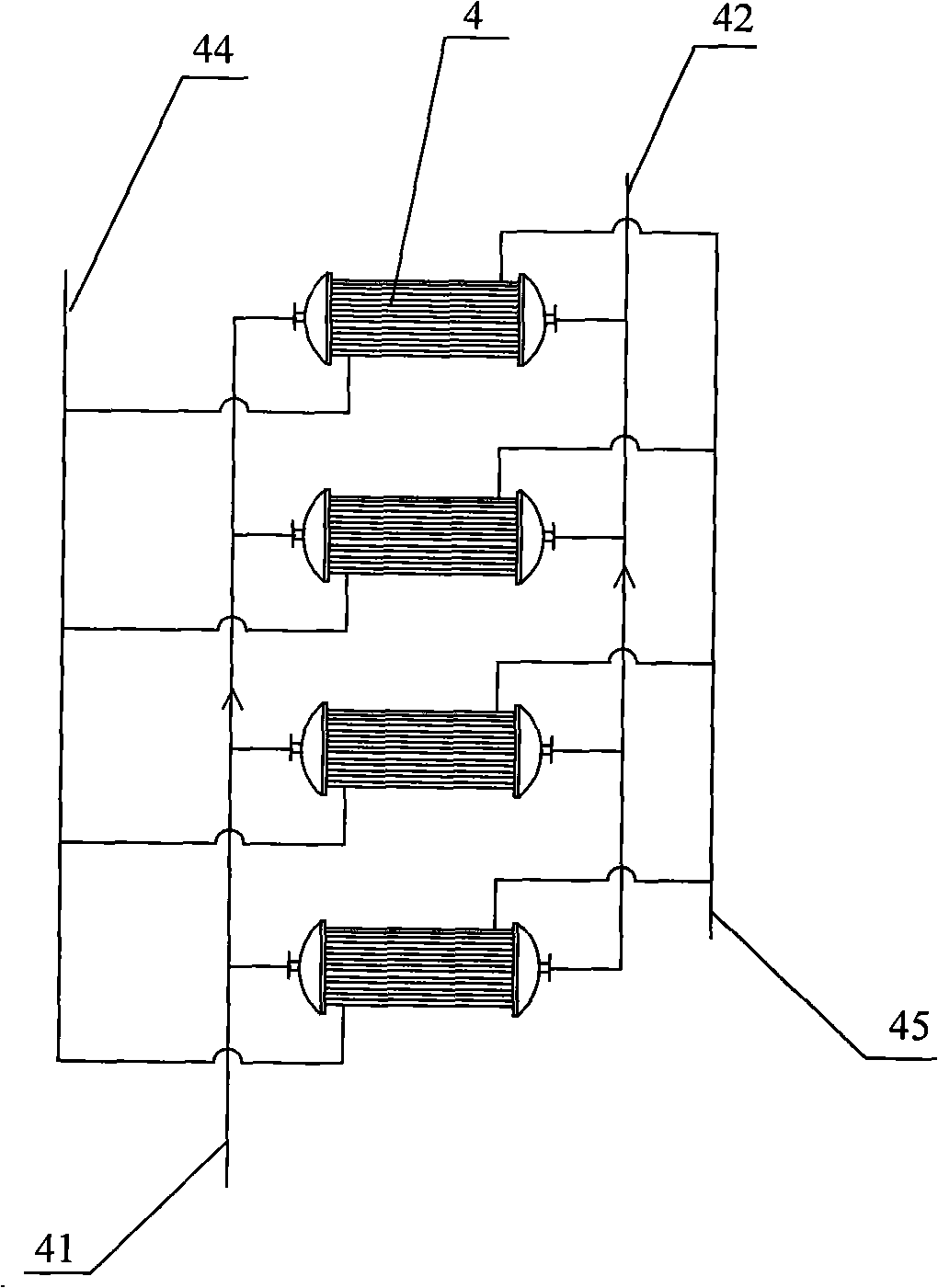
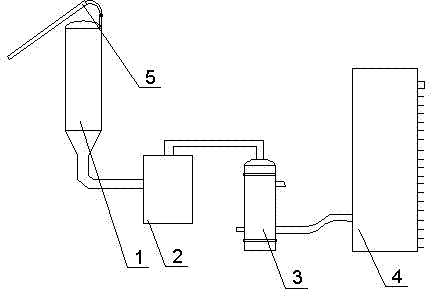
Transverse tube continuous cooking and steam explosion apparatus for biomass cellulosic ethanol
ActiveCN103132359AImprove dehydration efficiencyConsistent moistureDigestersPaper material treatmentFiberSpiral blade
The invention discloses a transverse tube continuous cooking and steam explosion apparatus for biomass cellulosic ethanol, which is provided with a preevaporation spiral tube and a transverse cooking tube, wherein the preevaporation spiral tube is connected with the transverse cooking tube through a spiral cork press and a T-shaped tube; the transverse cooking tube comprises an evaporation tube, a central shaft and a spiral blade; the evaporation tube is communicated with a steam input pipeline; the spiral blade comprises multiple spiral blade sections which have unequal thread pitches and unequal diameters; the edges of the spiral blade sections having small diameters are provided with shift teeth; every two neighboring ones among the shift teeth are respectively inclined towards the two sides; an outlet of the transverse cooking tube is connected with a horizontal blanking unit; a spiral blade of a feeding screw of the horizontal blanking unit is transversely arranged; and the horizontal blanking unit is connected with a pressurizing jet and explosion unit. The invention can realize large-scale production, ensures that raw materials are uniformed in cooked rate and straw fibers are pulverized and physically shaped into fine and soft pieces through steam explosion, and completely increases the late enzymolysis saccharification yield; and steam and a water source can be recycled, thereby saving the energy and reducing the consumption.
Owner:孟周强
Concentration method for sugar liquid in cellulose alcoholic fermentation
InactiveCN101270372ASolve the problem of energy consumptionSolve problems such as easy cokingBiofuelsDistillationSuspended particlesFiltration
The invention discloses a concentration method of sugar solution in ethanol fermentation of cellulose. Firstly the sugar solution which is removed of suspended particles is obtained via membrane filtration, then membrane distillation technology is adopted, i.e. the sugar solution of temperature of 40 to 70 DEG C is introduced from one side of a hydrophobic membrane module, then the water in the sugar solution penetrates through the wall of microporous membrane on the hydrophobic membrane module in the vapor status, diffuses into the other side and condensates, thereby realizing the concentration of the sugar solution. Adopting the method of the invention to concentrate the sugar solution in the ethanol fermentation of cellulose has the advantages of the good concentration effect and the low energy consumption.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
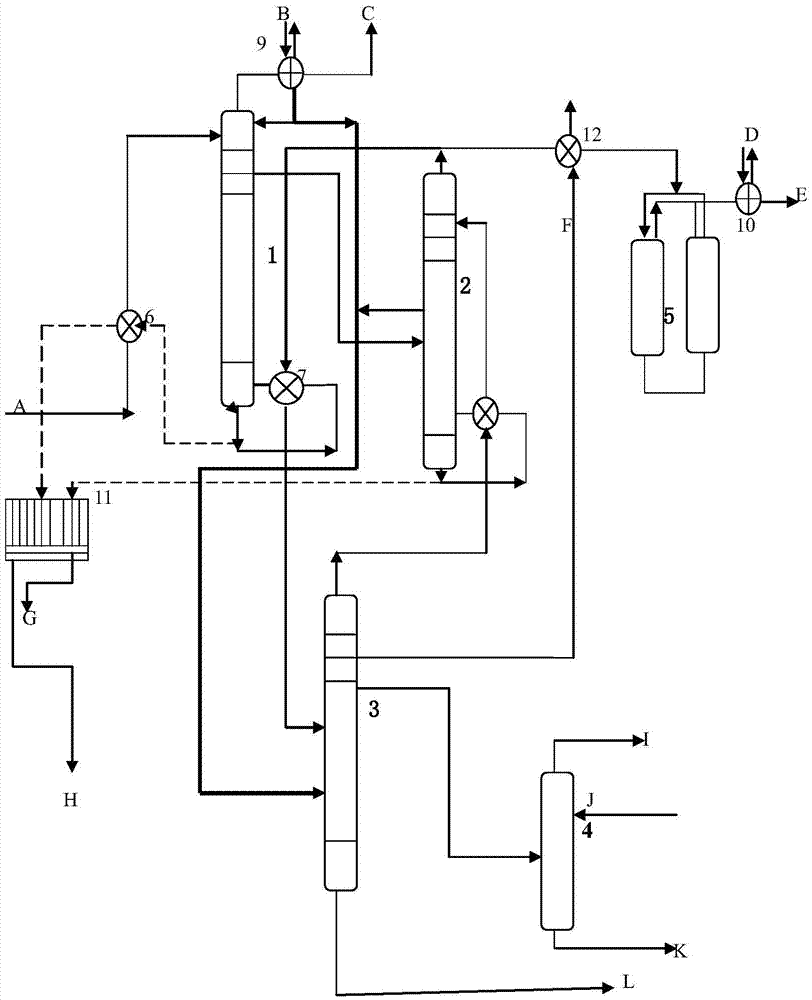
Cellulosic ethanol distilling method
ActiveCN106928026AEfficient recyclingHigh recovery rateOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationCellulosic ethanolChemistry
The invention relates to the field of cellulosic ethanol purification, and discloses a cellulosic ethanol distilling method. The method includes steps of delivering the heated fermenting mash to a first distilling tower to distill, extracting first ethanol steam from the tower roof, and extracting a first ethanol mixture from the side line of the first distilling tower; condensing the first ethanol steam extracted from the tower roof and forming ethanol condensate; back-flowing a part of ethanol condensate, and delivering the other part of ethanol condensate to a third distilling tower to distill; delivering the first ethanol mixture extracted from the side line of the first distilling tower to a second distilling tower to distill; extracting the second ethanol steam from the second distilling tower roof, delivering a part of second ethanol steam to a third distilling tower to distill, and dewatering the other part of second ethanol steam. The method provided by the invention can effectively recycle cellulosic ethanol with high purity and high yield from the fermented mash of the cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +2
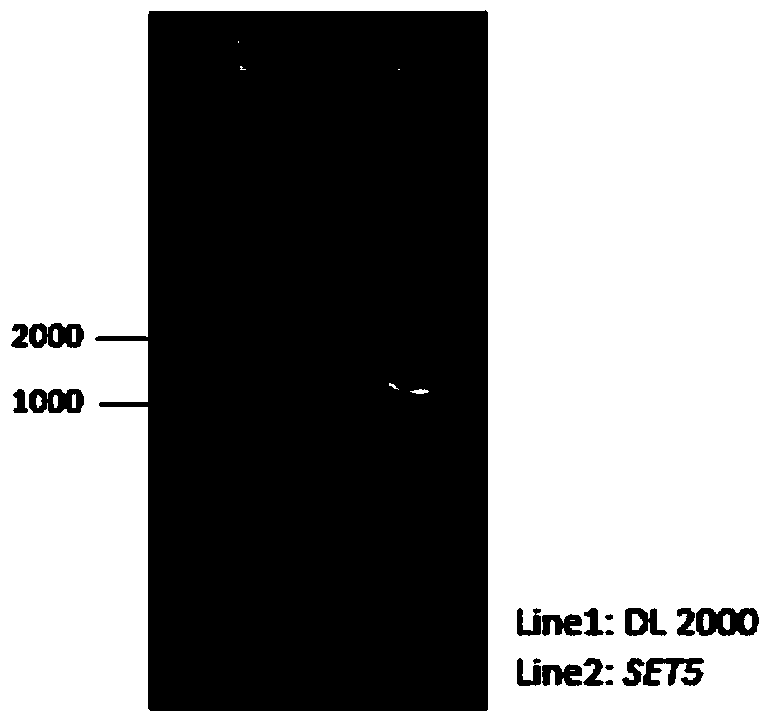
Recombined saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with stress tolerance
InactiveCN103849576APromote growthHigh Ethanol Fermentation EfficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationMicroorganism
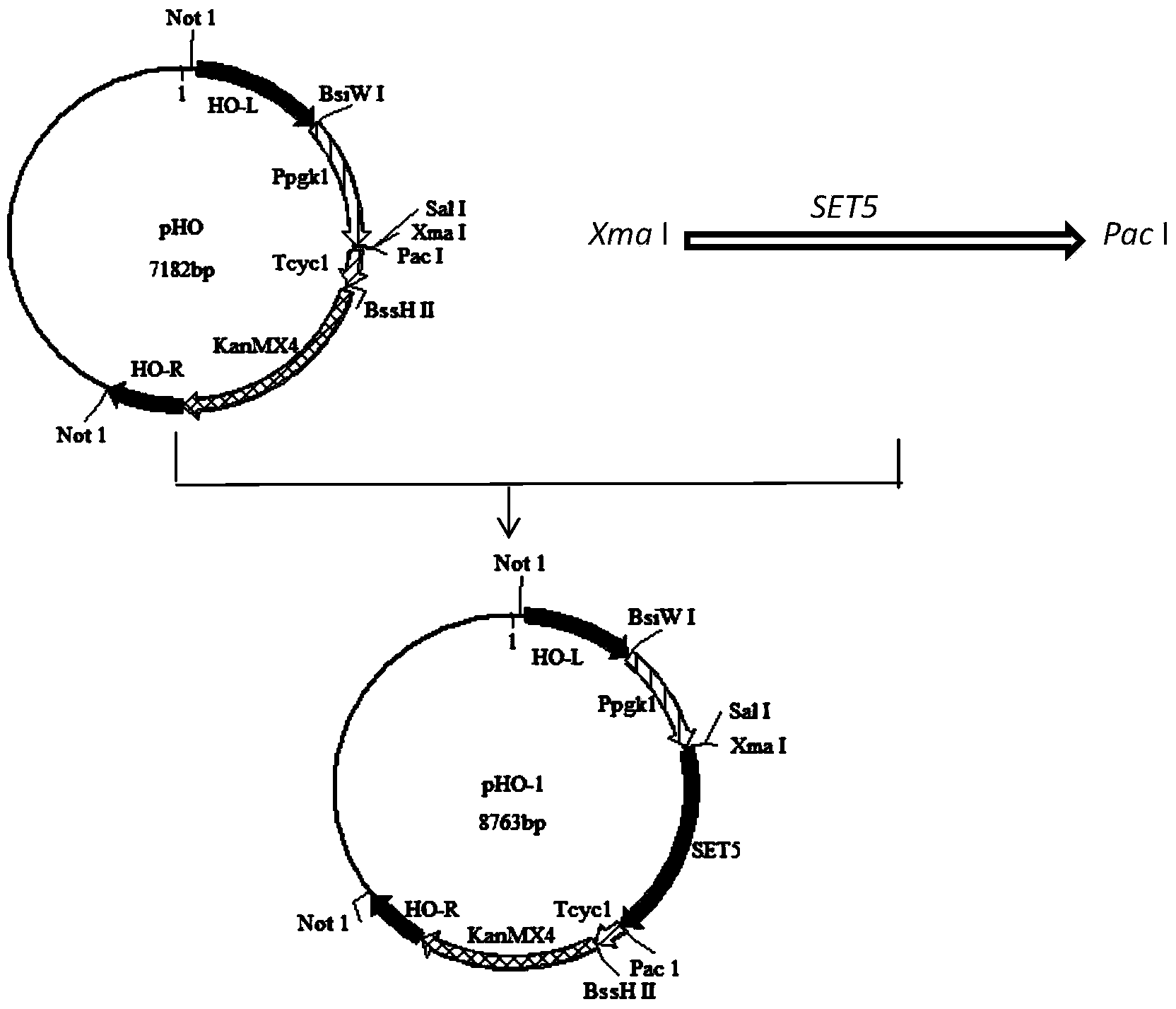
The invention discloses recombined saccharomyces cerevisiae (4126-SET5) with stress tolerance and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The strain is classified and named as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the accession number of the strain is CGMCC No.8724, and the strain is preserved in the common microorganism center of China microorganism strain preservation administration committee, wherein the address of the preservation enterprise is 3#, Yard No.1, West Beichen Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing City, and the preservation data is Jan 15th, 2014. The invention discloses a gene engineering construction method of the recombined strain 4126-SET5, and the method comprises acquisition of a gene, construction of a chromosome integration vector and the growth condition of the strain under various environmental stress conditions, including on a flat plate containing high-concentration acetic acid, hydrogen peroxide and ethanol and under a high temperature condition. Compared with a contrast strain of an empty integration vector, the recombined saccharomyces cerevisiae 4126-SET5 can be rapidly fermented in the presence of 5g / L of acetic acid, thereby not only providing theoretical support for further research on tolerance mechanism of the saccharomyces cerevisiae but also being used as a good strain for fermentation of cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Steam explosion straw material collection and energy utilization technology
InactiveCN103045656AIncrease temperatureReduce contentBiofuelsFermentationDecompression chamberWastewater
The invention belongs to the technical field of cellulosic ethanol production process steam explosion pretreatment, and discloses a steam explosion straw material collection and energy utilization technology, comprising the concrete steps of: (1) feeding the crushed straw into a blasting vessel by mechanical means; (2) feeding high pressure steam with a pressure of 1.2-4.0 MPa into the blasting vessel; (3) keeping pressure for the blasting vessel for 10-120 min; (4) opening the blasting vessel to eject the material to achieve separation of the material and the steam; (5) feeding the steam from the step (4) into a decompression chamber, and discharging organic molecule containing steam from the top of the decompression chamber and into the a condenser; (6) feeding a liquid formed by the steam of the step (5) through the condenser to the wastewater treatment process, and feeding the exhaust gas into an absorption tower for subsequent exhaust absorption. The technology enables steam explosion byproducts to be scientifically collected and used, makes fully use of exhaust heat, and is easy to promote and use.
Owner:河南天冠纤维乙醇有限公司
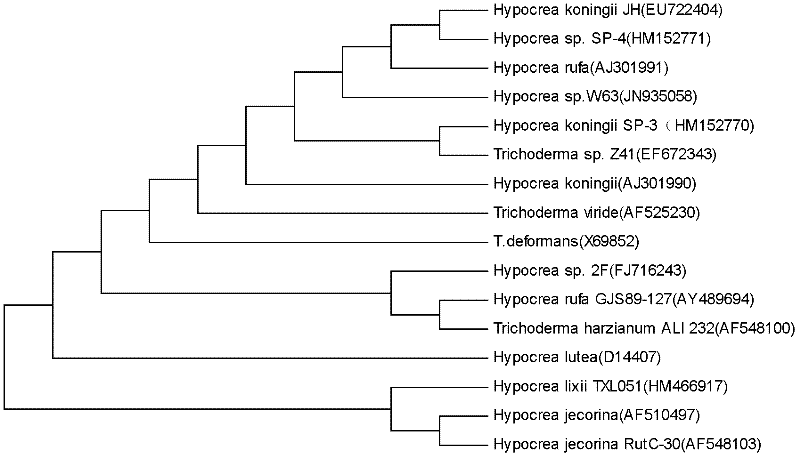
Hypocrea for producing mesophile ethanol-tolerant beta-glucosidase highly and application of hypocrea
The invention discloses hypocrea for producing mesophile ethanol-tolerant beta-glucosidase highly and application of the hypocrea. The hypocrea is conserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on September 1st, 2011, and the conservation No. is CGMCC No. 5209. The hypocrea can produce novel beta-glucosidase, wherein the enzyme activity of the beta-glucosidase is up to 482.1U / ml, the pH value of the optimum reaction is 4.8, the optimum reaction temperature is 70 DEG C, and the enzyme activity is high in stability at the temperature of 50 DEG C, so the beta-glucosidase is suitable for pyrohydrolysis; ethanol of which the concentration is 10 percent has the maximum promotion effect on the enzyme activity, and the enzyme activity of the beta-glucosidase is improved by nearly 1 time; and the ethanol of which the concentration is less than 30 percent in a reaction system does not inhibit the enzyme activity, and when biomass raw materials are hydrolyzed, the inhibition of cellobiose can be eliminated effectively, so that the yield of the ethanol is improved, and the inhibition of terminal products is eliminated. The production cost of cellulosic ethanol can be reduced, and the industrialized progress of the cellulosic ethanol is accelerated.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
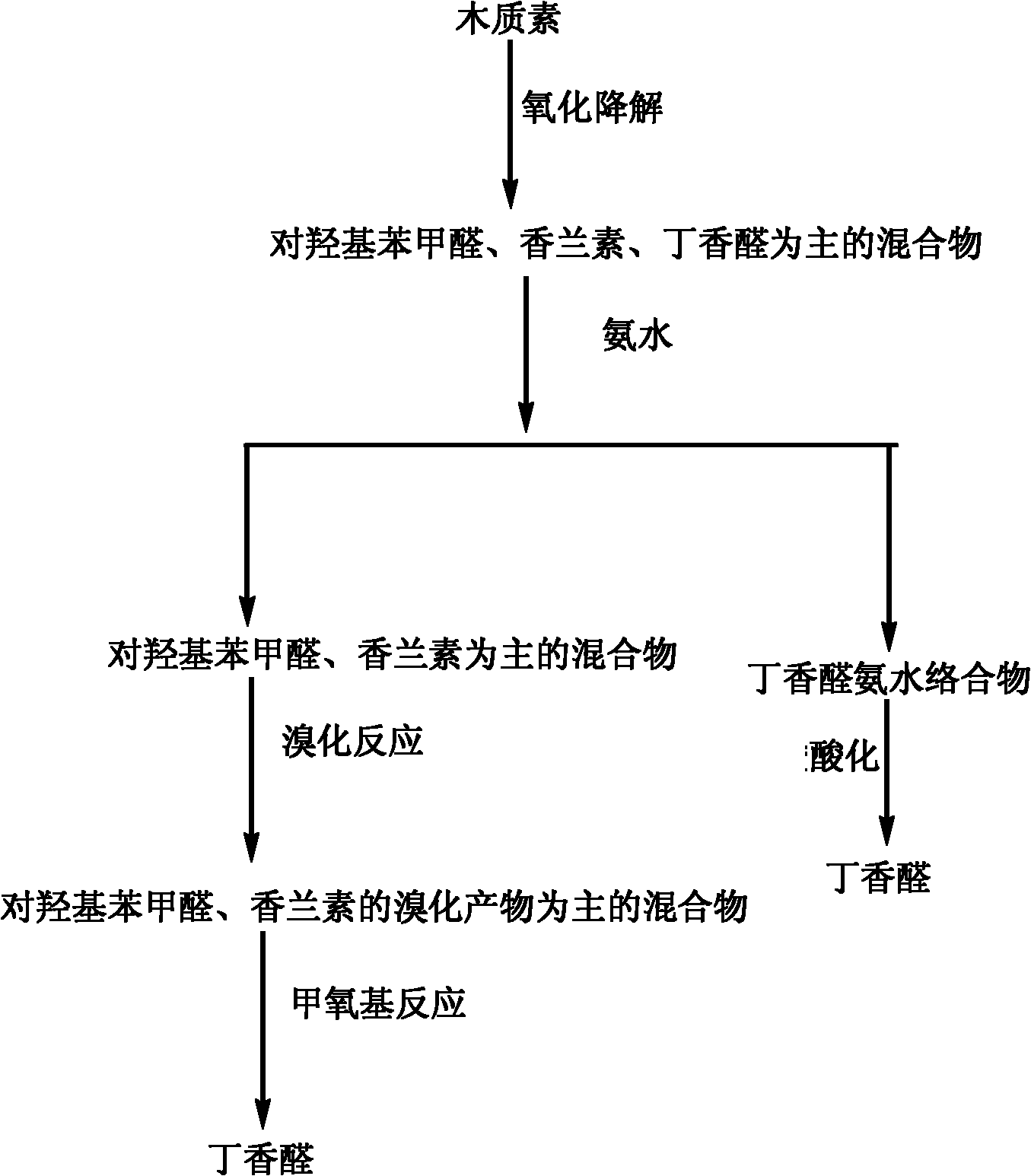
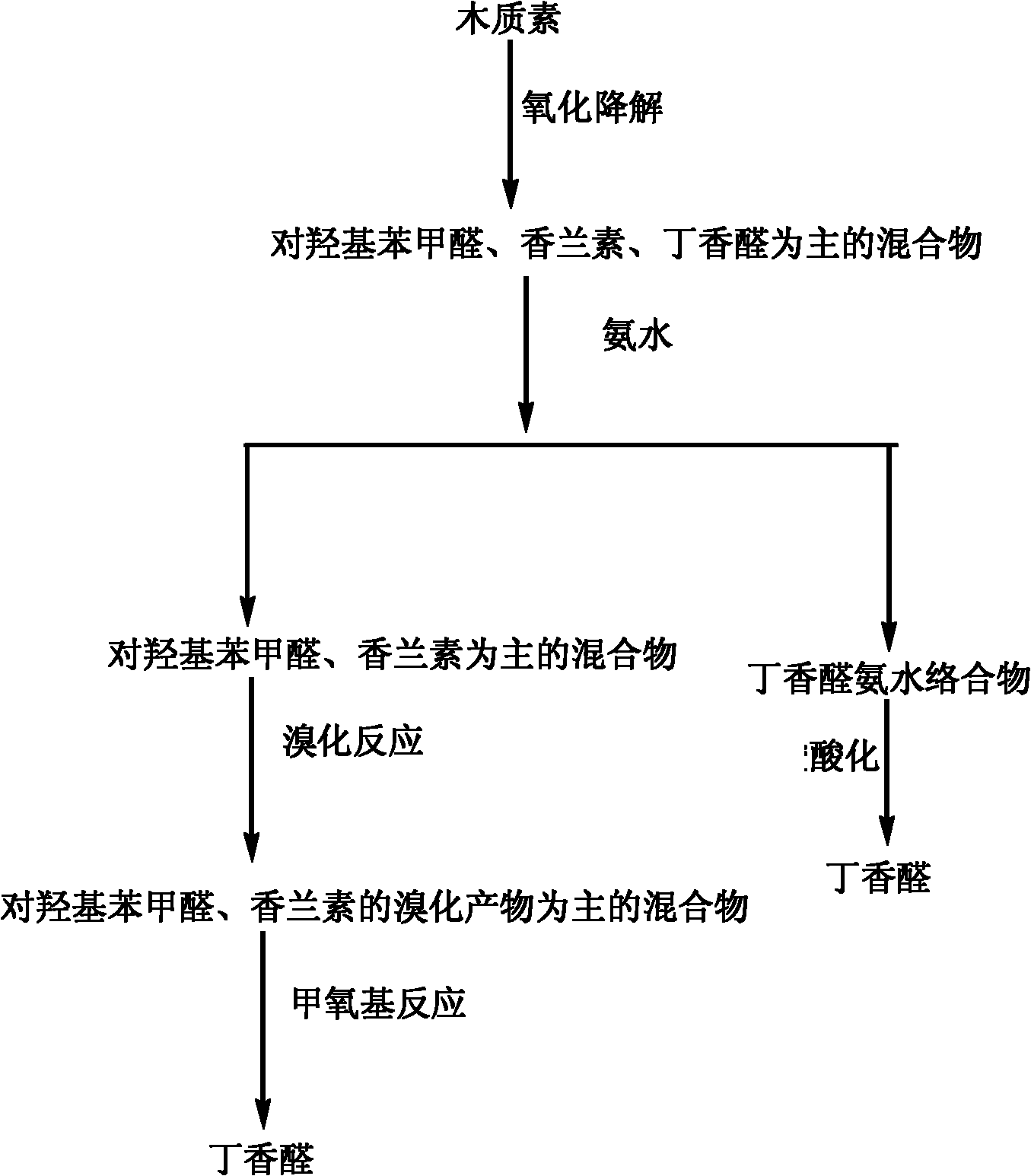
Method for preparing syringaldehyde by oxidative degradation of lignin
InactiveCN102146025AIncrease profitLow costOrganic compound preparationCarbonyl compound separation/purificationSodium methoxideFiber
The invention relates to a method for preparing syringaldehyde by oxidative degradation of lignin, which comprises the following steps of: 1) dissolving an oxidative degradation product solid of the lignin by using an organic solvent, adding ammonia water to obtain a syringaldehyde and ammonia water complex precipitate, performing centrifugal separation, and acidifying the complex precipitate to obtain syringaldehyde; and 2) evaporating to dryness under reduced pressure and centrifuging to obtain ammonia water mixed solution, performing bromination on the obtained solid substance and elemental bromine or bromine hydride solution, and performing methoxylation reaction on the bromination product and sodium methoxide under the catalysis of cuprous salt to obtain the syringaldehyde. By the steps, the oxidative degradation product of the lignin is all converted into the same product, namely the syringaldehyde, the yield of the syringaldehyde is 50-60 percent, the utilization rate of lignocellulosic materials is improved, the cost of cellulose alcohol and papermaking industry is reduced, and the method has important meaning for realizing high value-added industrial development of the lignin and industrialization of cellulose ethanol and promoting agricultural sustainable development.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com