Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with multiple-stress resistance, and application thereof in cellulose alcohol fermentation
A technology for Saccharomyces cerevisiae and alcohol fermentation, which is applied in the directions of fermentation, fungi, microorganism-based methods, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the active ethanol yield of cells, inactive and unusable yeast cells, etc., and achieves good industrial application prospects, good Effect of inhibitor tolerance, low ethanol high yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
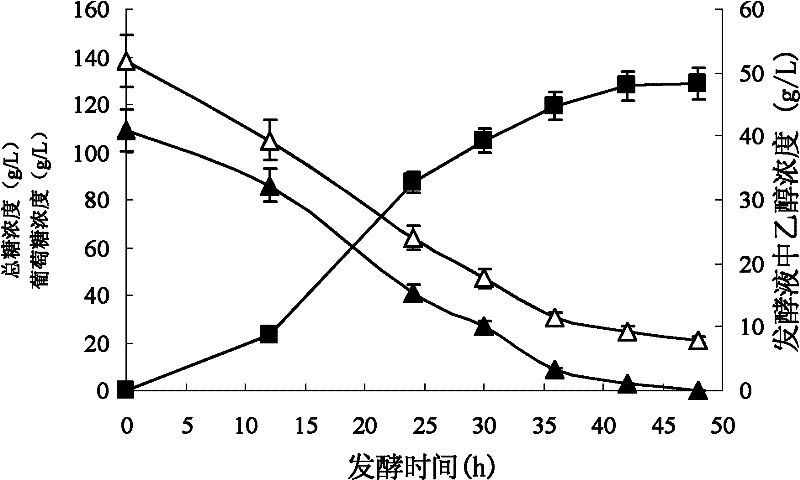
[0029] The preparation method of corn stalk hydrolyzate: Coarsely pulverize corn stalk (dry material), steam explosion for 5 minutes under 1.8MPa pressure (each process 5kg dry material); the material after steam explosion treatment is added into water, make the quality of dry material 100% The corn stalk content was 30%, cellulase (Shandong Zesheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) was added, and the amount of cellulase added was 20 FPU / g dry material, and enzymatic treatment was performed at 50° C. to obtain corn stalk hydrolyzate.
[0030] The detection method of total reducing sugar content is as follows:
[0031] (1) Preparation of solution
[0032] Dissolve 1 gram of dinitrosalicylic acid in 20ml of 2M aqueous sodium hydroxide solution and 50ml of water, then add 30 grams of potassium sodium tartrate tetrahydrate, add water to make up to 100ml, and store in a light-proof and airtight container, which is the DNS solution.
[0033] (2) Drawing of standard curve
[0034] Prepare 1...
Embodiment 1
[0044] Embodiment 1, the acquisition of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) T43
[0045] 1. Ion beam mutagenesis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain R8-10-2
[0046] Saccharomyces cerevisiae R8-10-2 has been preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CGMCC for short, address: Datun Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, China) on August 14, 2009, and the preservation number is CGMCC №. 3226 (see patent CN101633896; 200910091841.7). Saccharomyces cerevisiae R8-10-2 (CGMCC No.3226) is a yeast strain that can tolerate high concentrations of acetic acid. The strain can resist 0.8% acetic acid (volume percentage) at 30°C and 0.6% acetic acid ( Volume percentage), 40 ℃ can resist 0.2% acetic acid, the highest growth temperature is 42 ℃.
[0047] Saccharomyces cerevisiae R8-10-2 was cultured in the yeast complete medium YPD at 30°C until the mid-logarithmic phase (about 16 hours), centrifuged at 3000×g for 5 ...
Embodiment 2
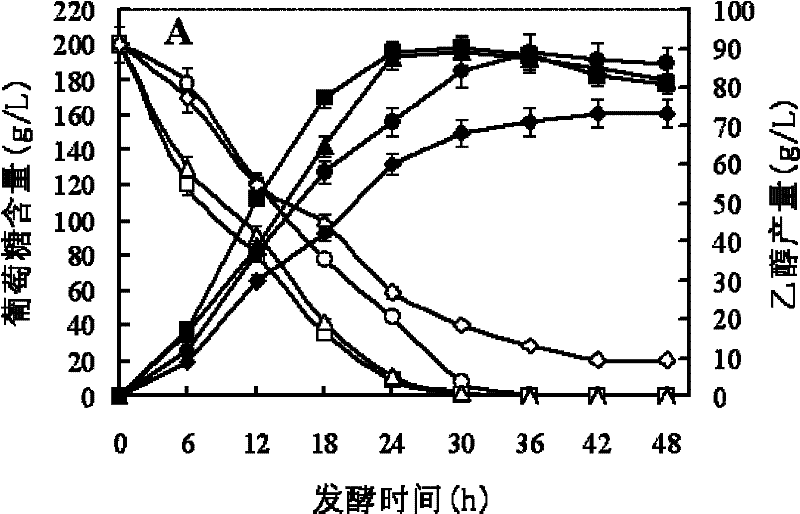
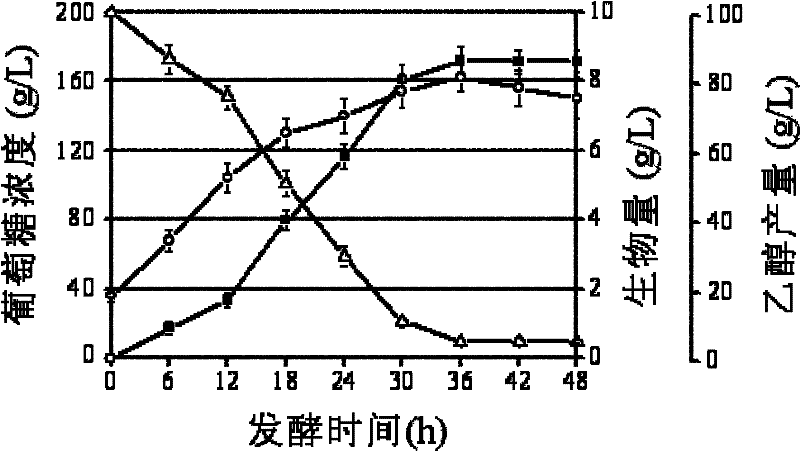
[0063] Embodiment 2, Saccharomyces cerevisiae T43 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae R8-10-2 fermentability comparison at different temperatures
[0064] Saccharomyces cerevisiae T43 and Saccharomyces cerevisiae R8-10-2 were subjected to the following experiments simultaneously (the radius of rotation of the shaker was 25 mm):
[0065] 1. Preparation of seed solution
[0066] Saccharomyces cerevisiae (T43 or R8-10-2) was inoculated in YPD medium, cultured on a shaker at 30°C (200rpm) for 18 hours, transferred to 50ml of YPD medium according to the inoculation amount of 10% (volume percentage), and shaken at 30°C The bed (200rpm) was cultivated for 20 hours, and the obtained bacterial solution was the seed solution (OD600 value was about 6.0).
[0067] 2. Fermentation to produce ethanol
[0068] The seed liquid that step one obtains is connected in the shaking flask of the 250ml that 100ml ethanol fermentation medium EFM is housed by the inoculum size of 10% (percentage by volume),...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com