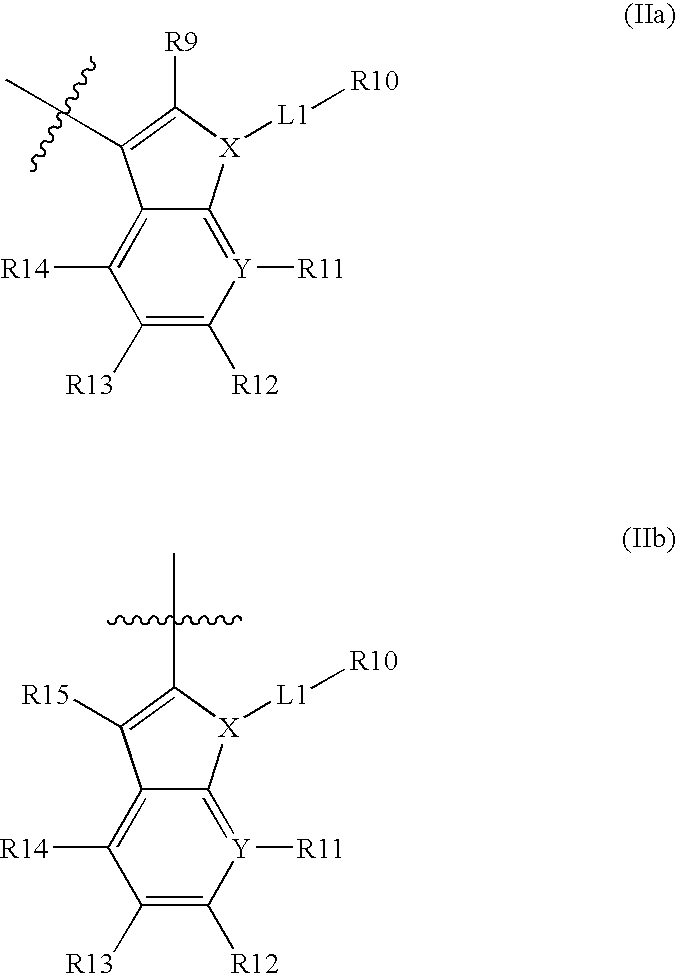
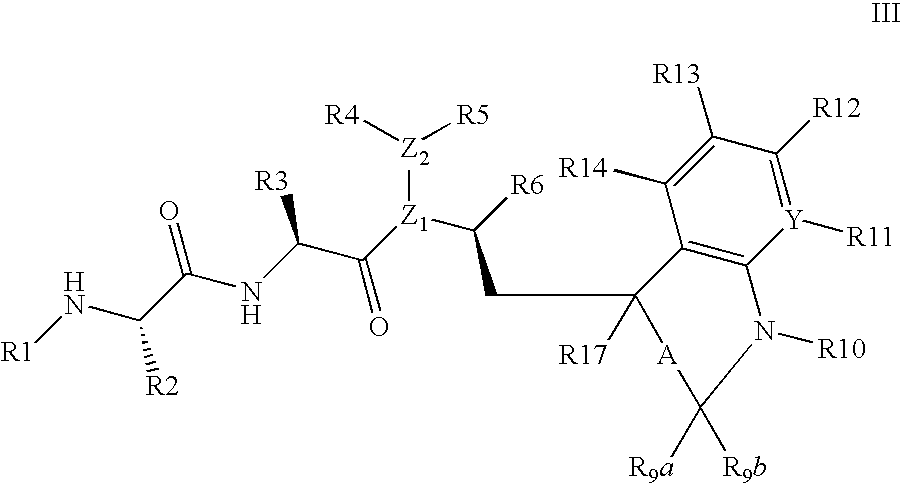
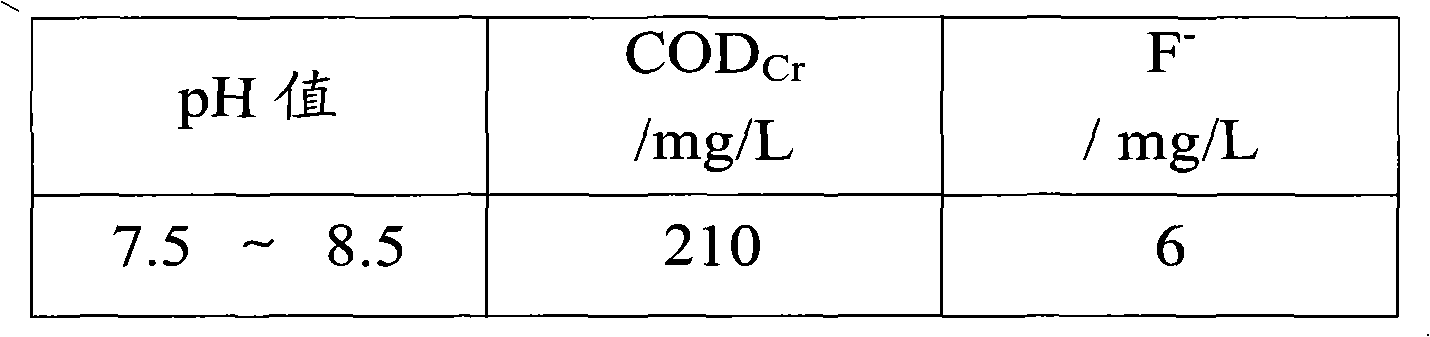Patents
Literature
288results about How to "Remove inhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Image reader and copier
InactiveUS20030179399A1Reliable preventionImprove processingImage enhancementImage analysisProgramming languageCondition Code
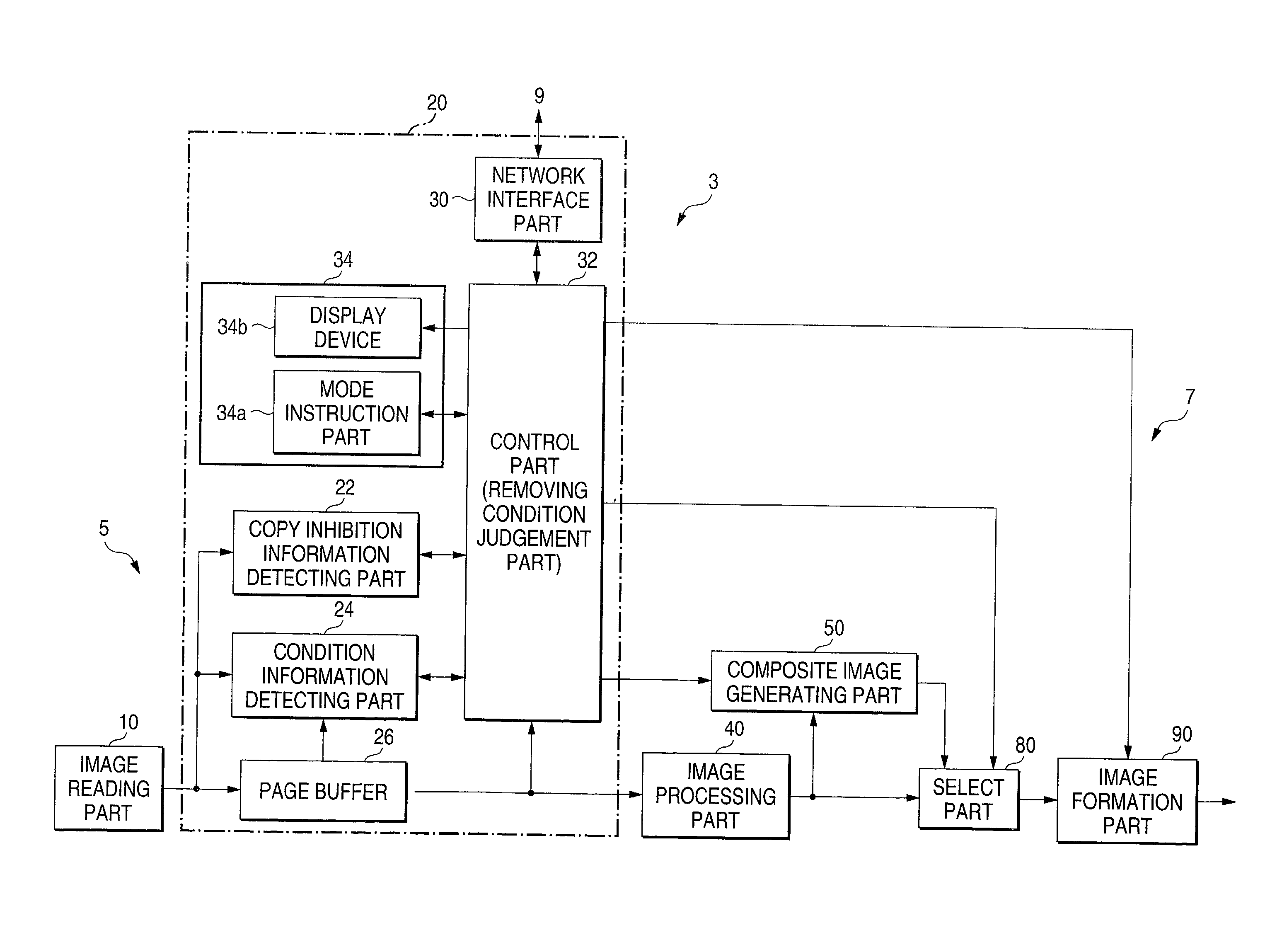
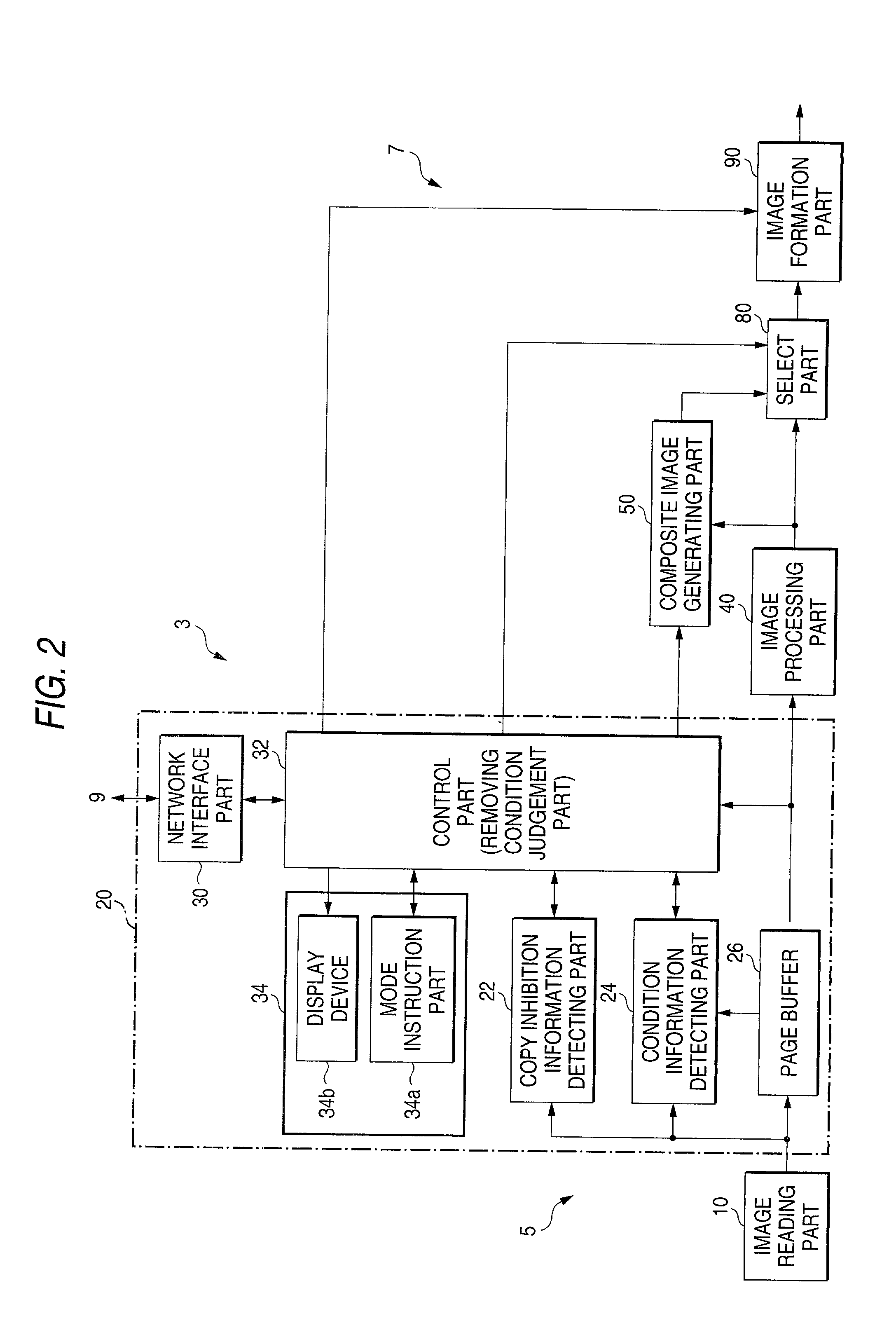
An image, in which a pattern image is arranged so as to express a control information for inhibiting copying or for removing the inhibition, is defined as an image to be read. A copy inhibition code or a condition code for removing the inhibition is assigned for the pattern image. In a "normal copy mode" of a copier, a copy inhibition information detecting part detects the copy inhibition code in an obtained image, and a controller halts the copying when the copy inhibition code is detected. A condition information detecting part detects the condition code in the obtained image. A copy mode is provided in which the copying operation is permitted when the condition matches. The controller permits copying when a condition, such as permitting a specific user to perform copying or the elapse of a predetermined day and time delimited period, is established.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
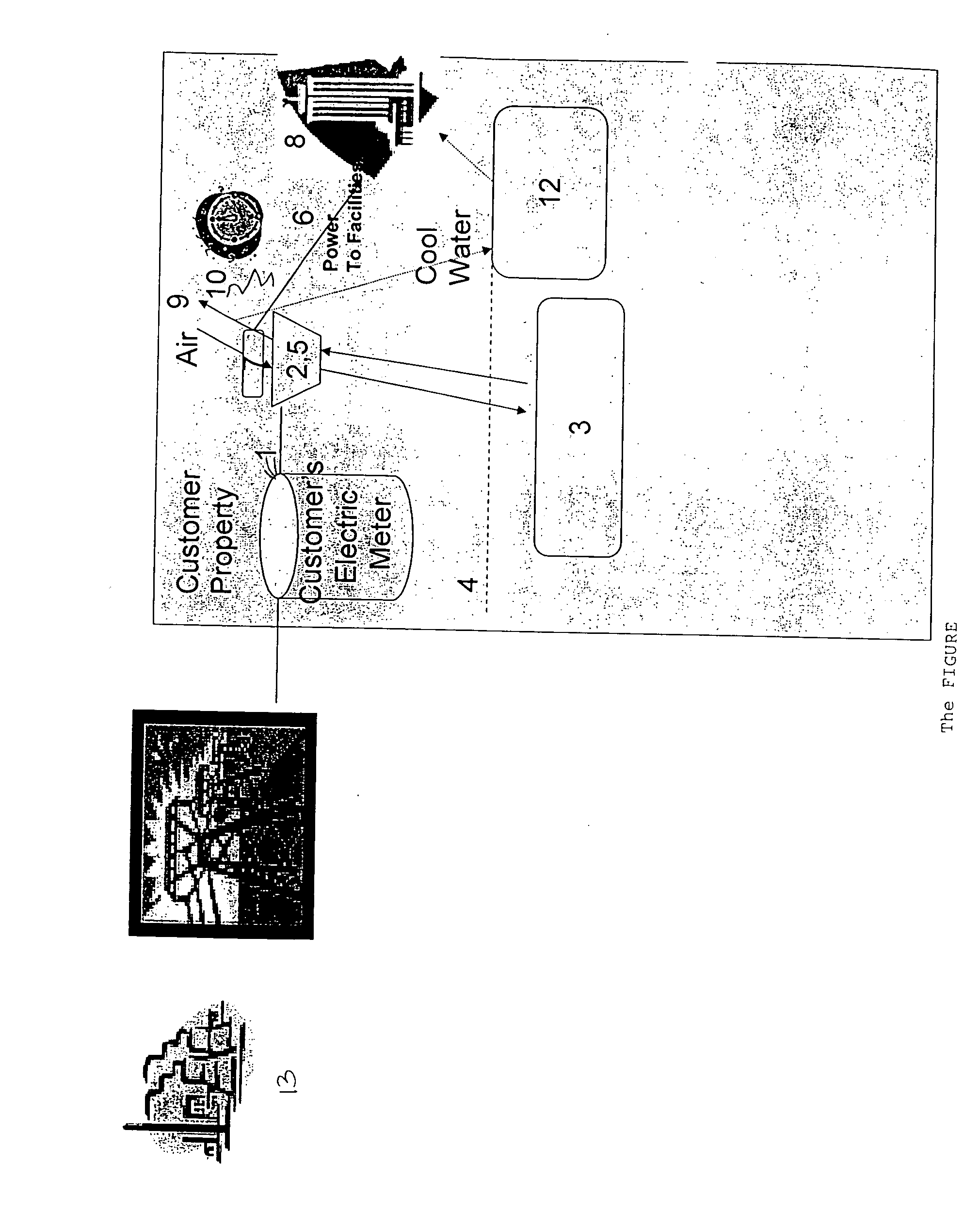
Serving end use customers with onsite compressed air energy storage systems
InactiveUS20070006586A1Easy to chargeRelieve energyGas turbine plantsMechanical power devicesElectricityCombustion
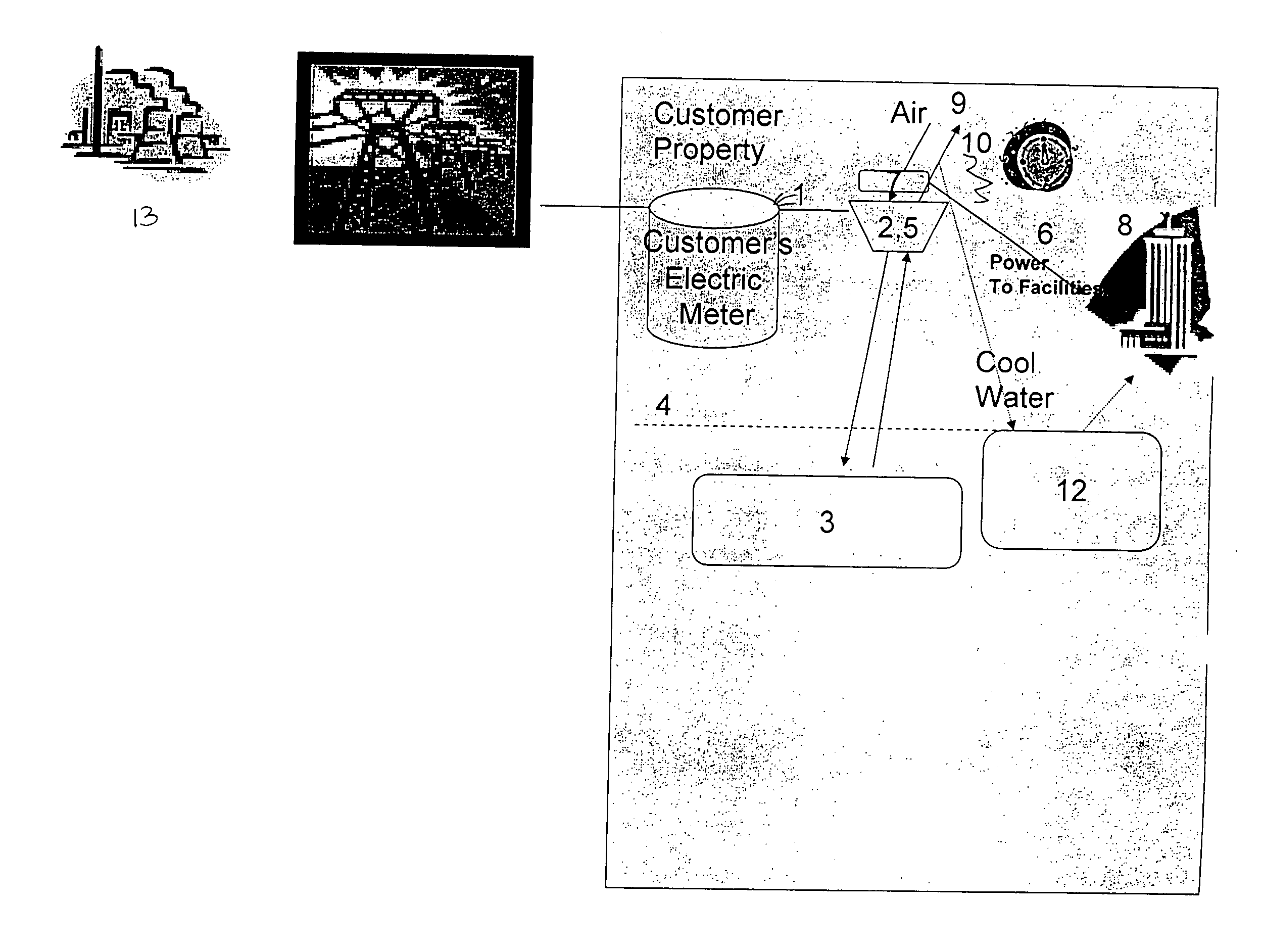
The invention relates to systems for stored compressed air without use of combustion. The systems can be installed on the customer side of the meter and creates electricity during peak hours after it has been stored in off peak hours. The invention creates a financial incentive for conserving energy costs by building compressed air storage systems which heretofore have seen little application.
Owner:MECHANOLOGY INC
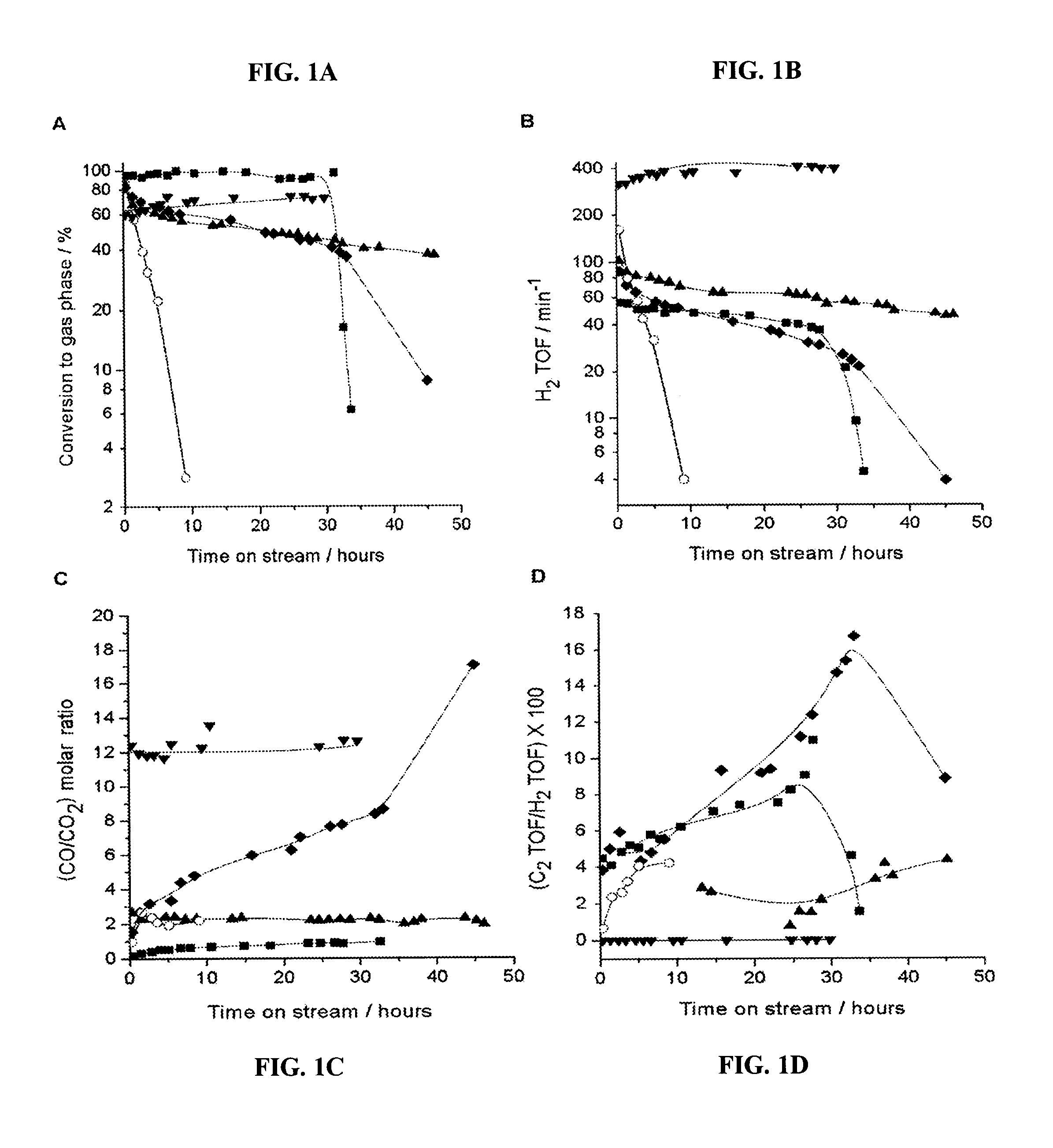
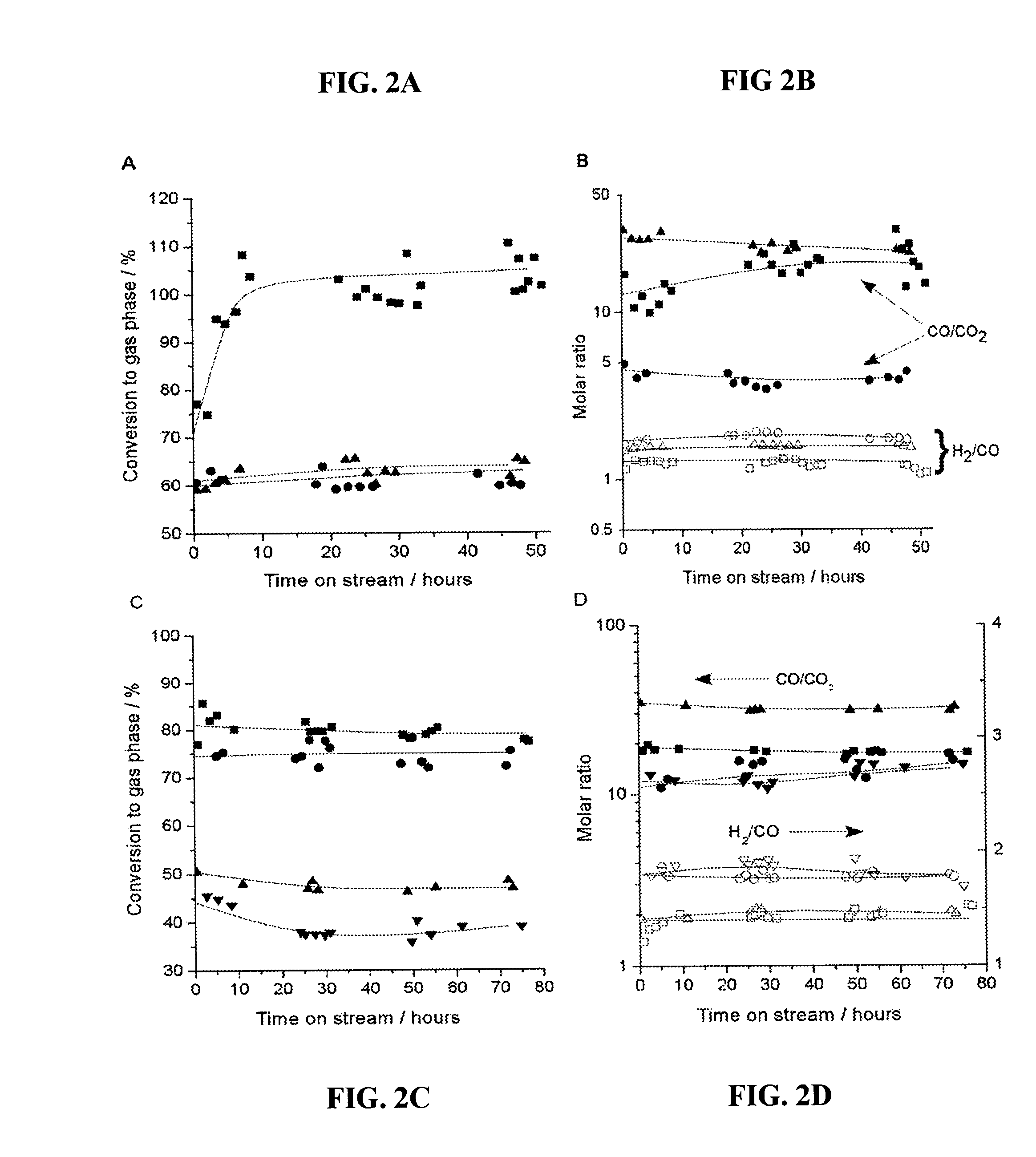
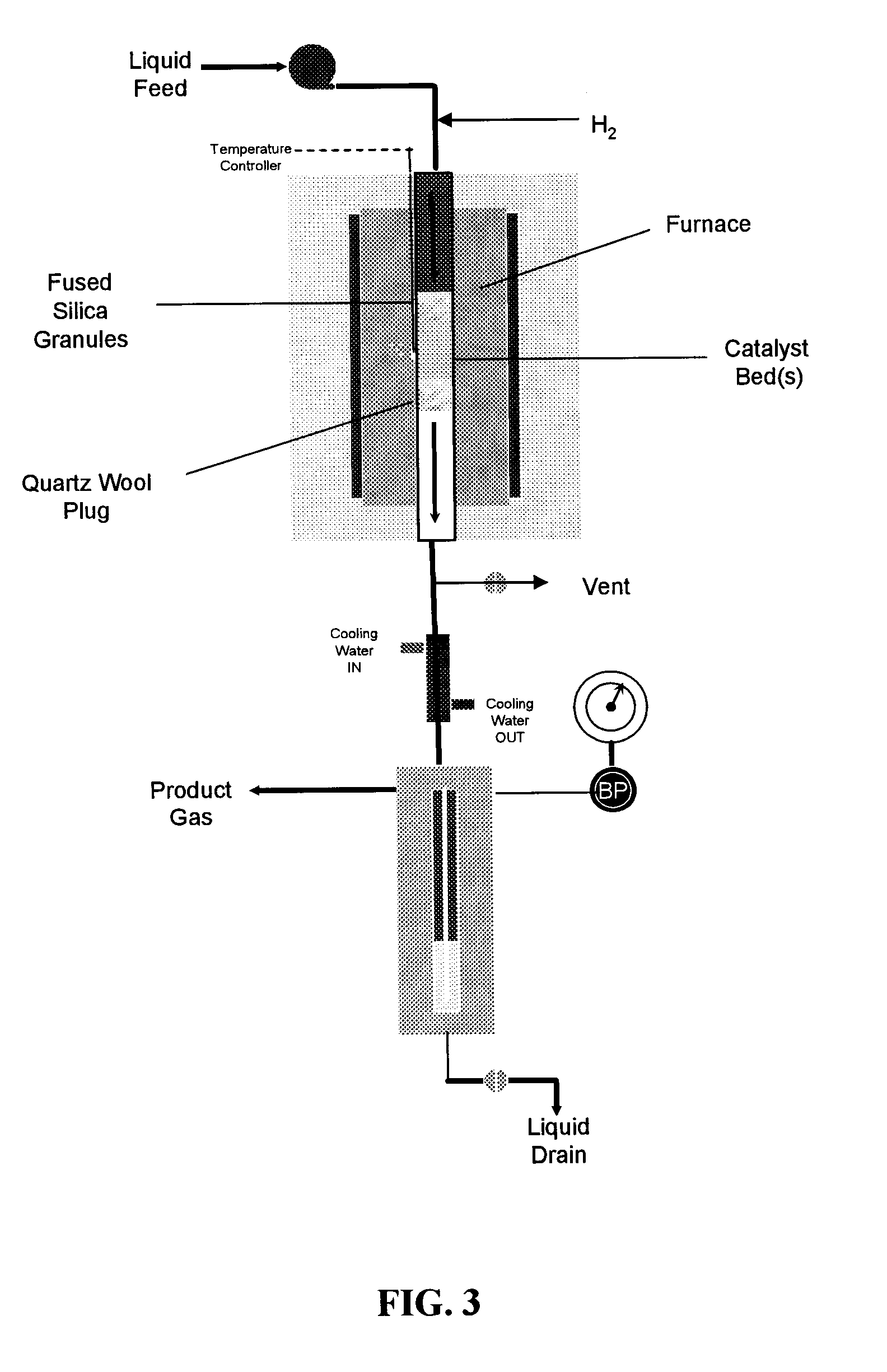
Method for producing bio-fuel that integrates heat from carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions to drive biomass gasification reactions
ActiveUS20070225383A1Improve thermal efficiencyImprove economyCatalytic crackingBiofuelsSyngasBiodiesel
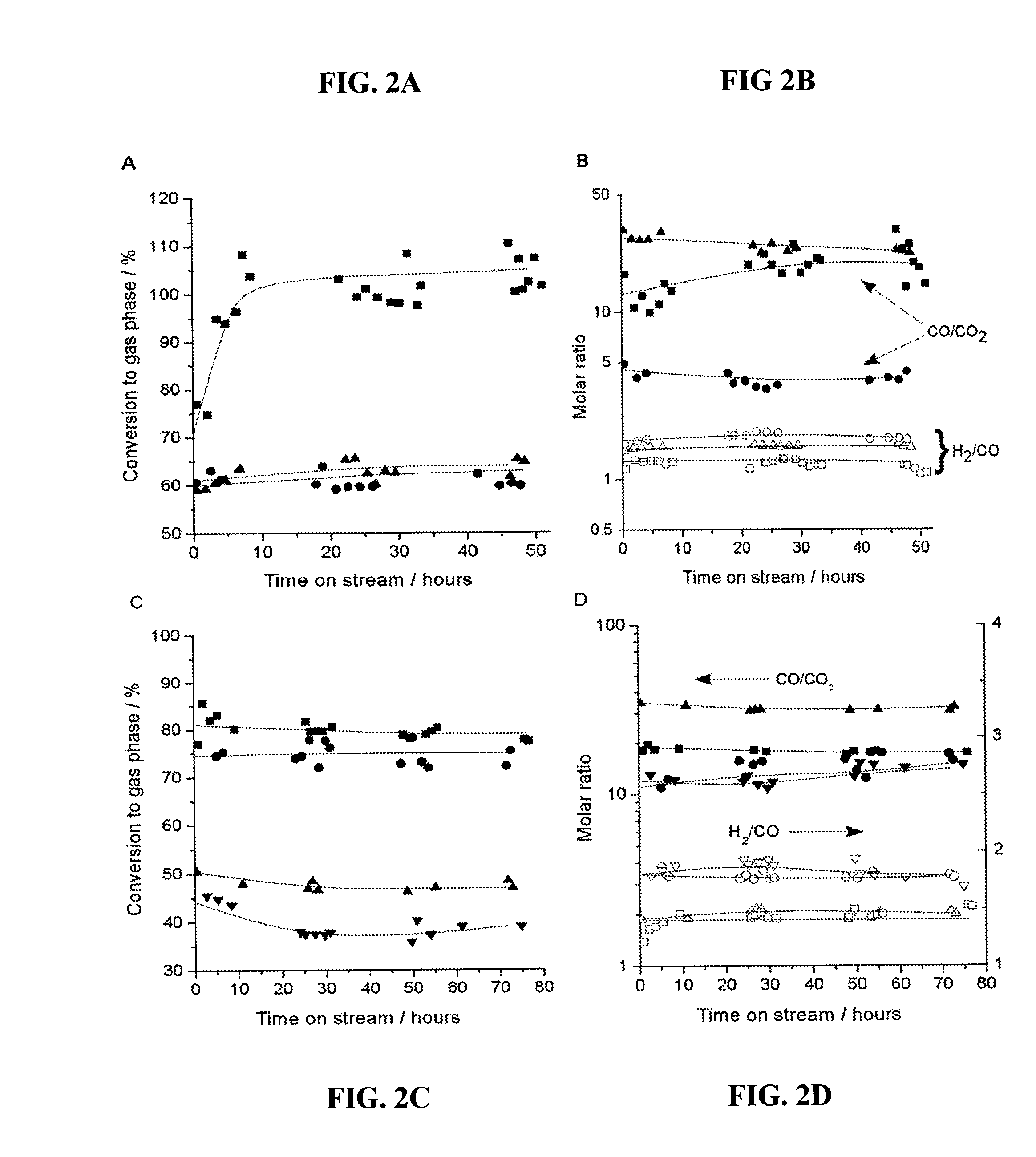
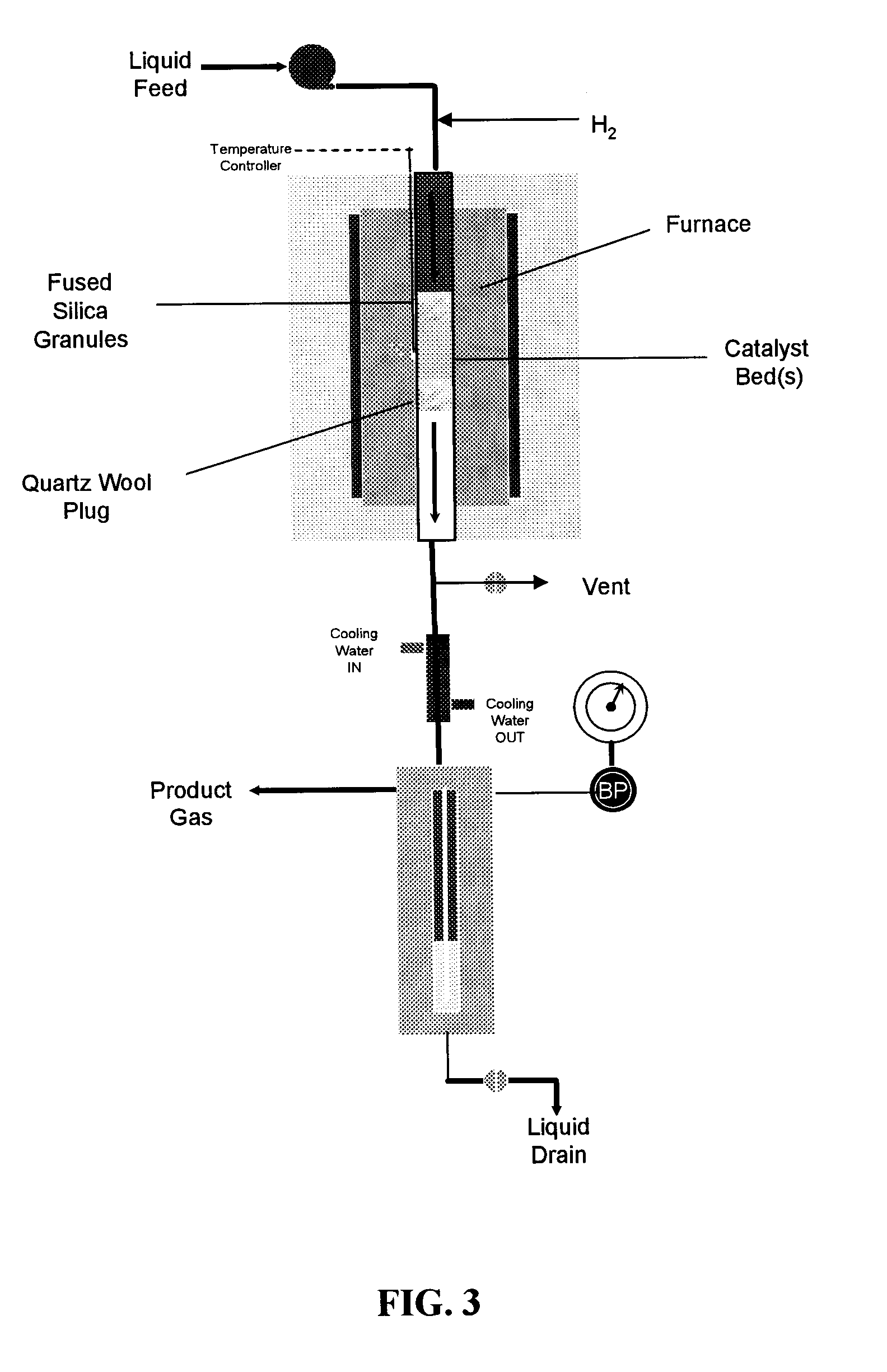
A low-temperature catalytic process for converting biomass (preferably glycerol recovered from the fabrication of bio-diesel) to synthesis gas (i.e., H2 / CO gas mixture) in an endothermic gasification reaction is described. The synthesis gas is used in exothermic carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions, such as Fischer-Tropsch, methanol, or dimethylether syntheses. The heat from the exothermic carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction is integrated with the endothermic gasification reaction, thus providing an energy-efficient route for producing fuels and chemicals from renewable biomass resources.
Owner:VIRENT +1
Treatment of proliferative disorders
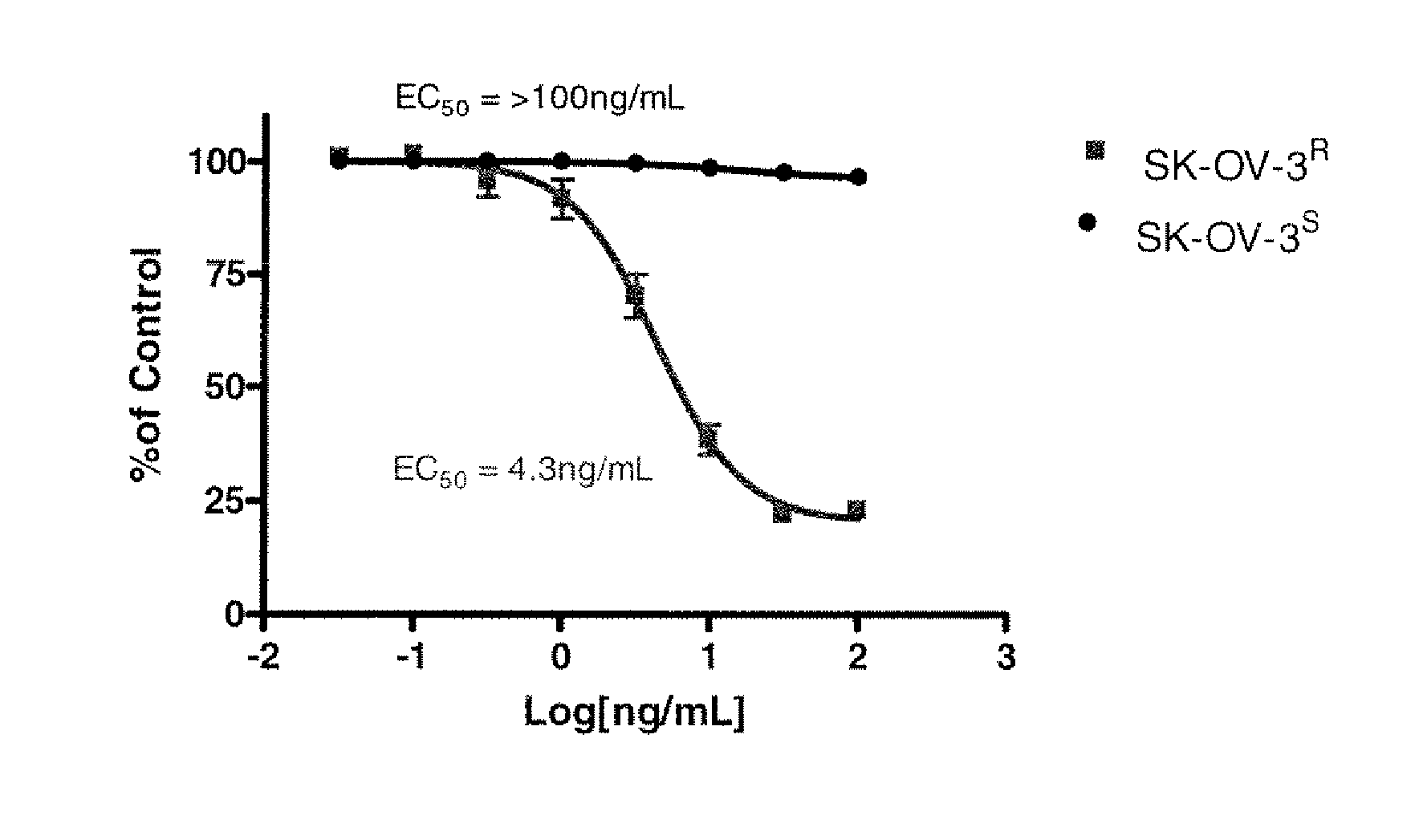
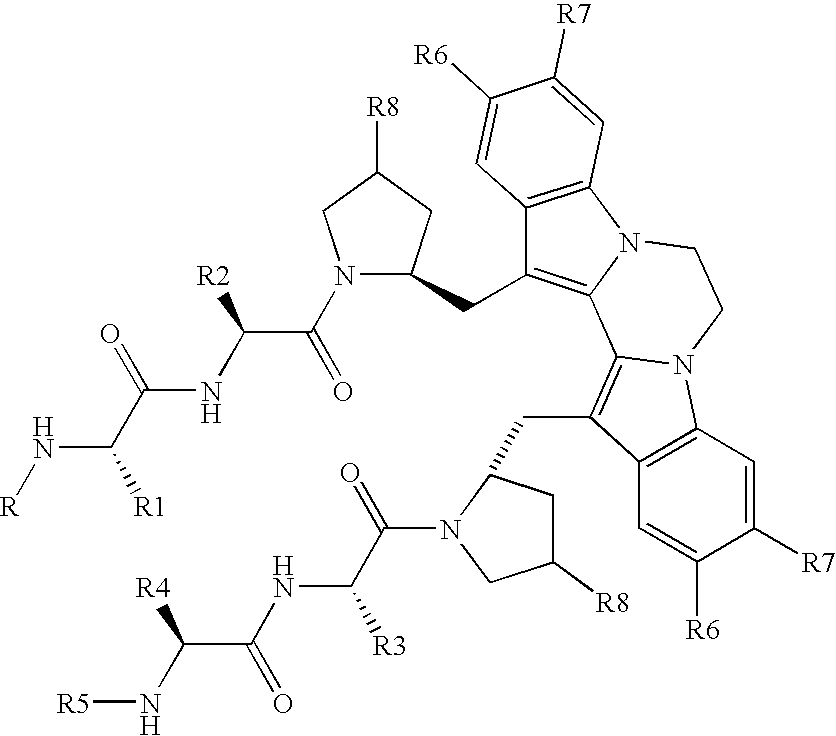
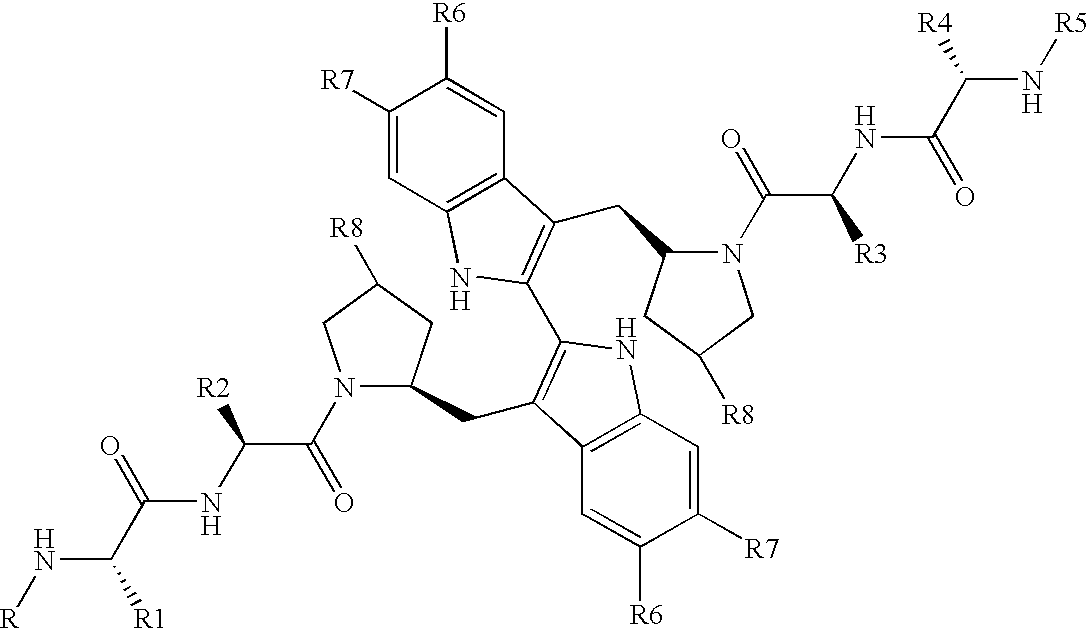
InactiveUS20070042428A1Remove inhibitionMultiple EffectsCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCancer researchProliferative disease
Owner:STAR SHOOTER +1
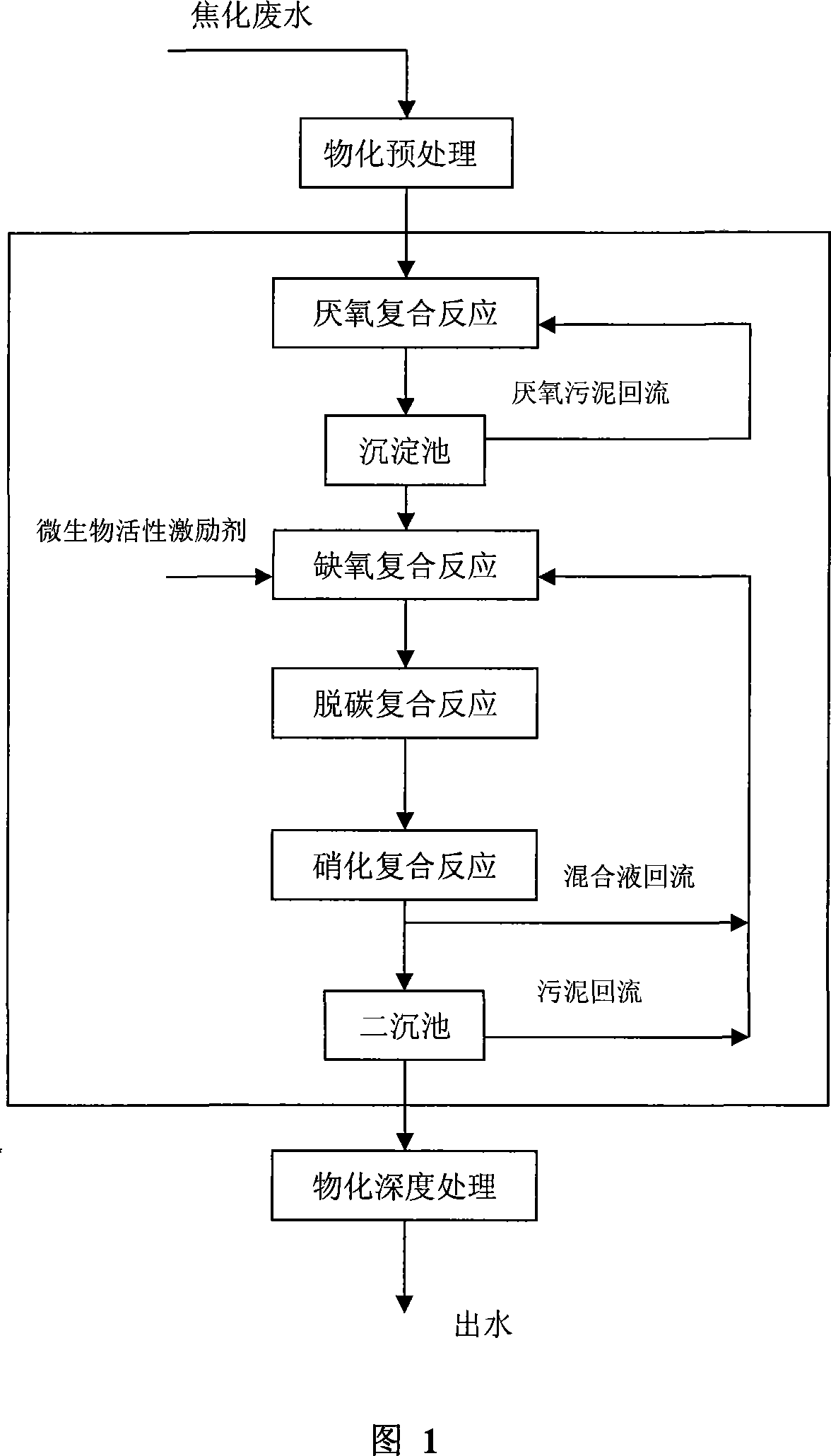
Impact-resistant multiplication combined type coking waste water treatment process
InactiveCN101113065AOptimize material compositionImprove biodegradabilityTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater treatmentWater quality
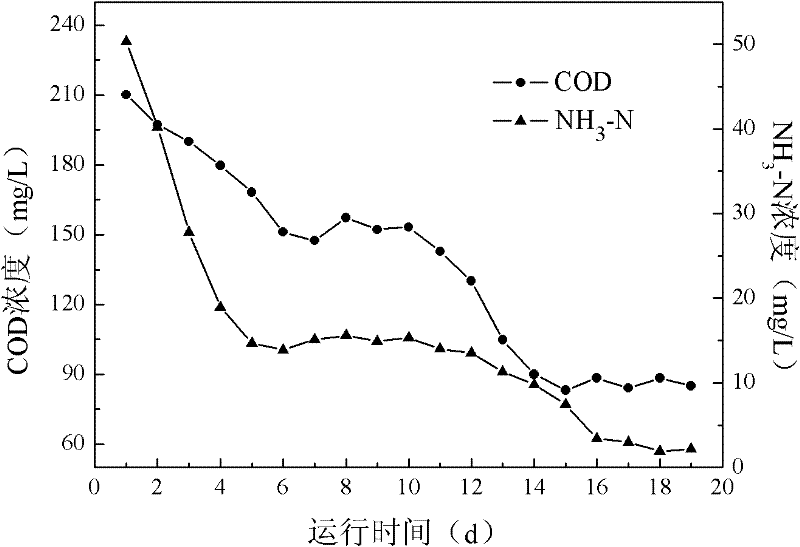
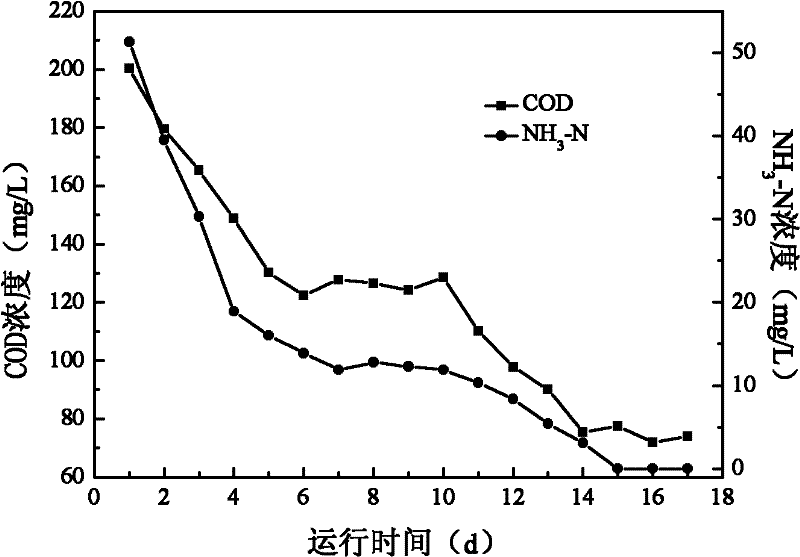
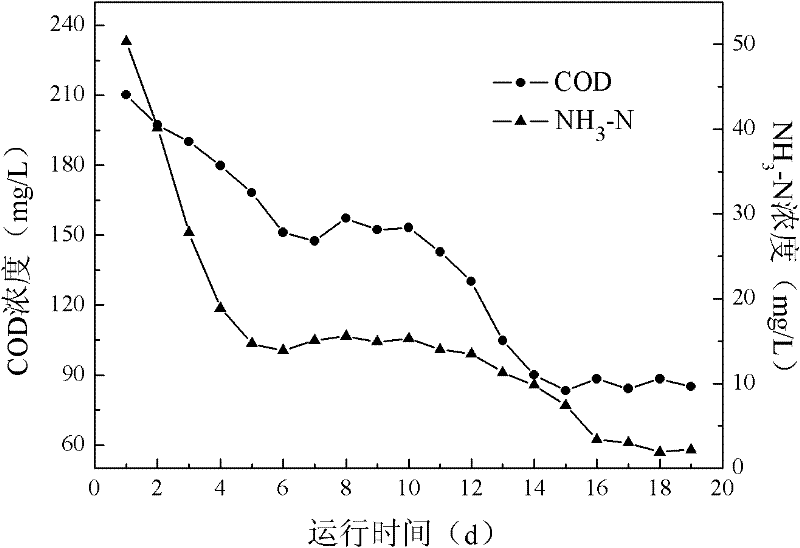
An anti-impact multiplying combination coking wastewater treatment technique relates to a treatment method of coking wastewater. The coking wastewater is first qualified by a physical-chemical pretreatment to improve biodegradable property of wastewater; the composite technology of a biological carrier of active sludge is adopted to do anaerobic / hypoxia / aerobic decarbonization / aerobic nitrification biochemical combination treatment; suspended or floating folding ball-shaped fillings are arranged in biochemical reactors and when micro organism traits are abnormal or a great amount of foams existing in the reactor, micro organism active incentive agents are added to the reactor in interval to improve active sludge traits and organism film quantity; finally the water is treated by a physical-chemical advanced treatment to reach a top grade standard. The invention not only strengthens the removal of COD, ammonia-nitrogen, volatile phenol and other pollutants in the coking wastewater by biochemical treatment but also resists serious water quality impact and has the advantages of quick system startup, less foams in an aeration tank, small occupying space, low operation cost and stable and effective treatment to coking wastewater.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
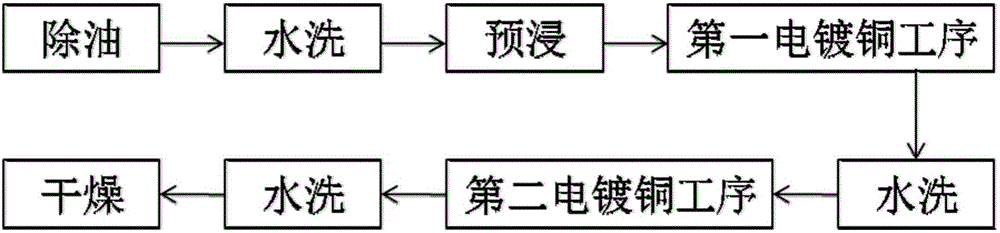
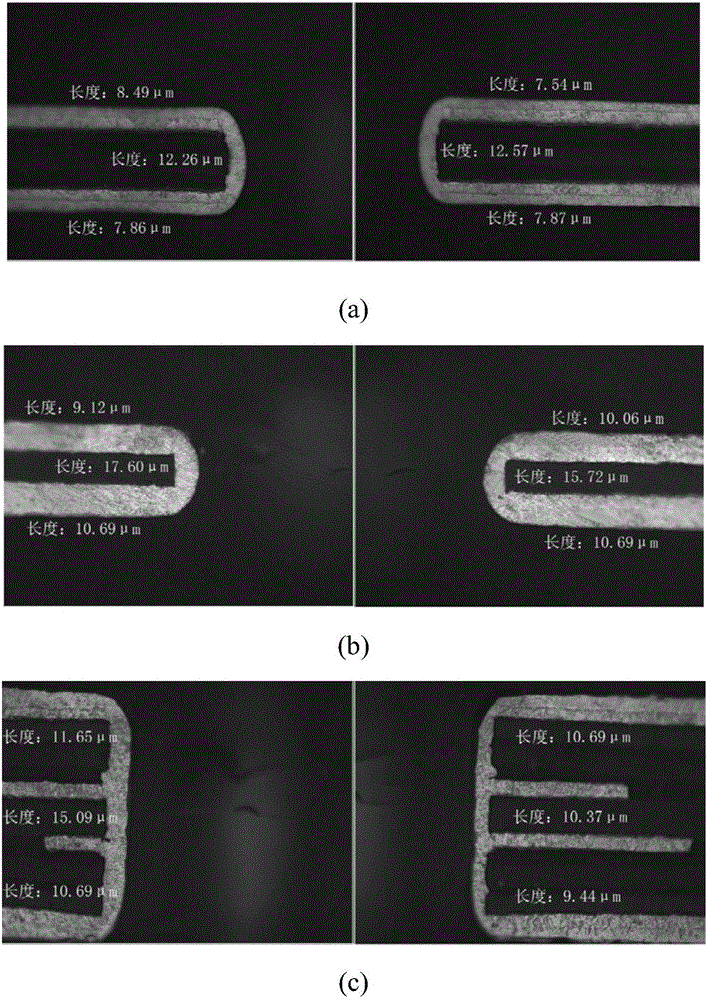
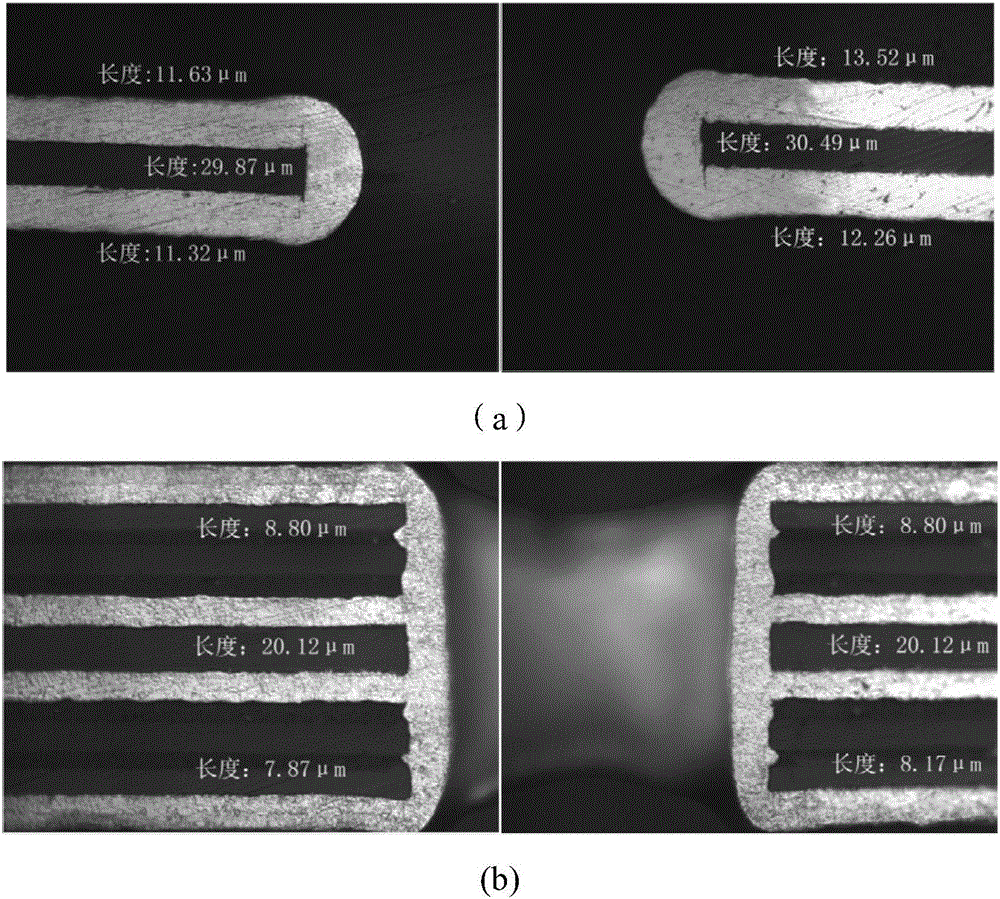
Electric copper plating liquid and electric copper plating process thereof
The invention relates to an electric copper plating liquid and an electric copper plating process thereof. The electric copper plating liquid is made with the following components: 20 g / l of copper sulfate pentahydrate, 20 g / L-300 g / L of sulfuric acid, 25 g / L-120 mg / L of chlorine ion, 0.1 mg / L-20 mg / L of a brightening agent, 1 mg / L-2000 mg / L of an inhibitor, and the balance of deionized water; the brightening agent is selected from alkyl thiol sulfonate or two of its derivatives; the inhibitor is selected from one or any of nonionic surfactants. The electric copper plating liquid of the invention enables greatly improved plating current and greatly improved throwing power (TP) of flexible board through-hole plating, TP reaching to higher than 200%, an electric copper plating layer in each hole is flat, and the quality meets various requirements of flexible board.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUANGHUA SCI TECH +1
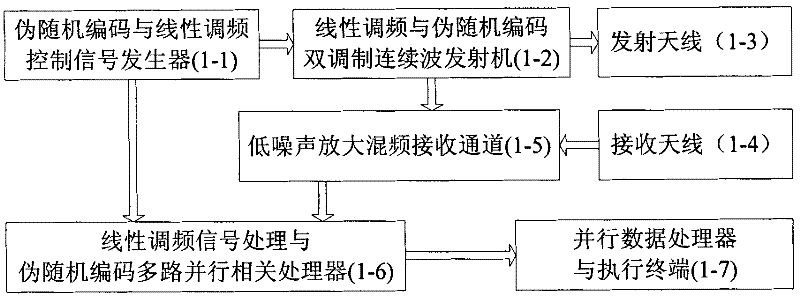
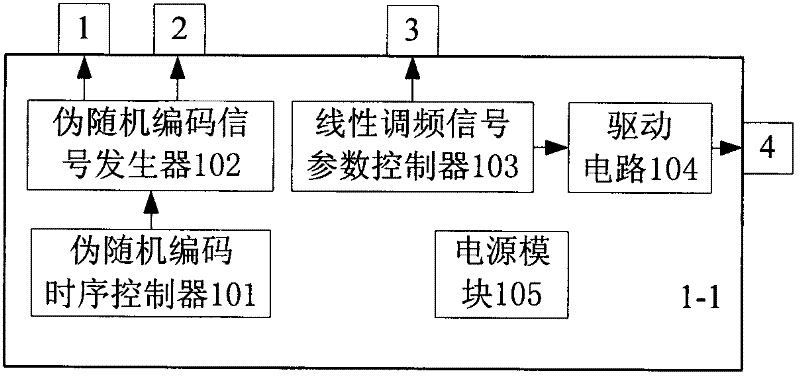
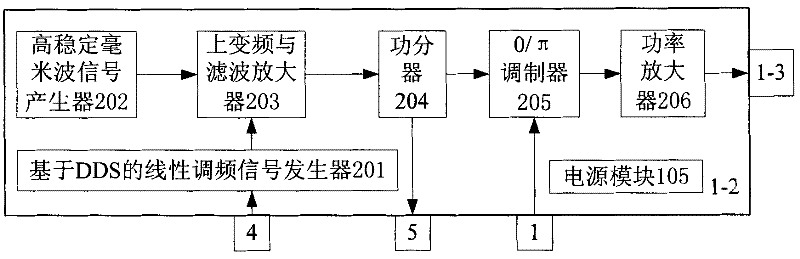
Automobile active anti-collision radar based on pseudorandom code and linear frequency modulated continuous wave
InactiveCN102162848AEnhanced inhibitory effectRemove inhibitionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLow noiseControl signal
The invention relates to an automobile active anti-collision radar based on pseudorandom code and linear frequency modulated continuous wave, belonging to the field of automobile radar, comprising a pseudorandom code and linear frequency modulated control signal generator, a pseudorandom code and linear frequency modulated continuous wave emitter, a sending antenna, a receiving antenna, a low-noise amplification mixed frequency receiving channel, a linear frequency modulated signal processing and pseudorandom code multi-path parallel correlation processor, a parallel data processor and an executing terminal. The pseudorandom code is used for modulating the phase of radar carrier wave and performing linear frequency modulation to the radar carrier wave so as to form a double-modulation emitting signal. Two systems are combined, so that the inhibition ability of interference echo is improved; the false alarm caused by false targets is removed; different codes of different automobile radars are achieved; the interference caused by the automobile radar is removed; the detection ability of the active anti-collision radar is improved; the false alarm rate is improved; and the inhibitionability under complex road condition is good.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY +1
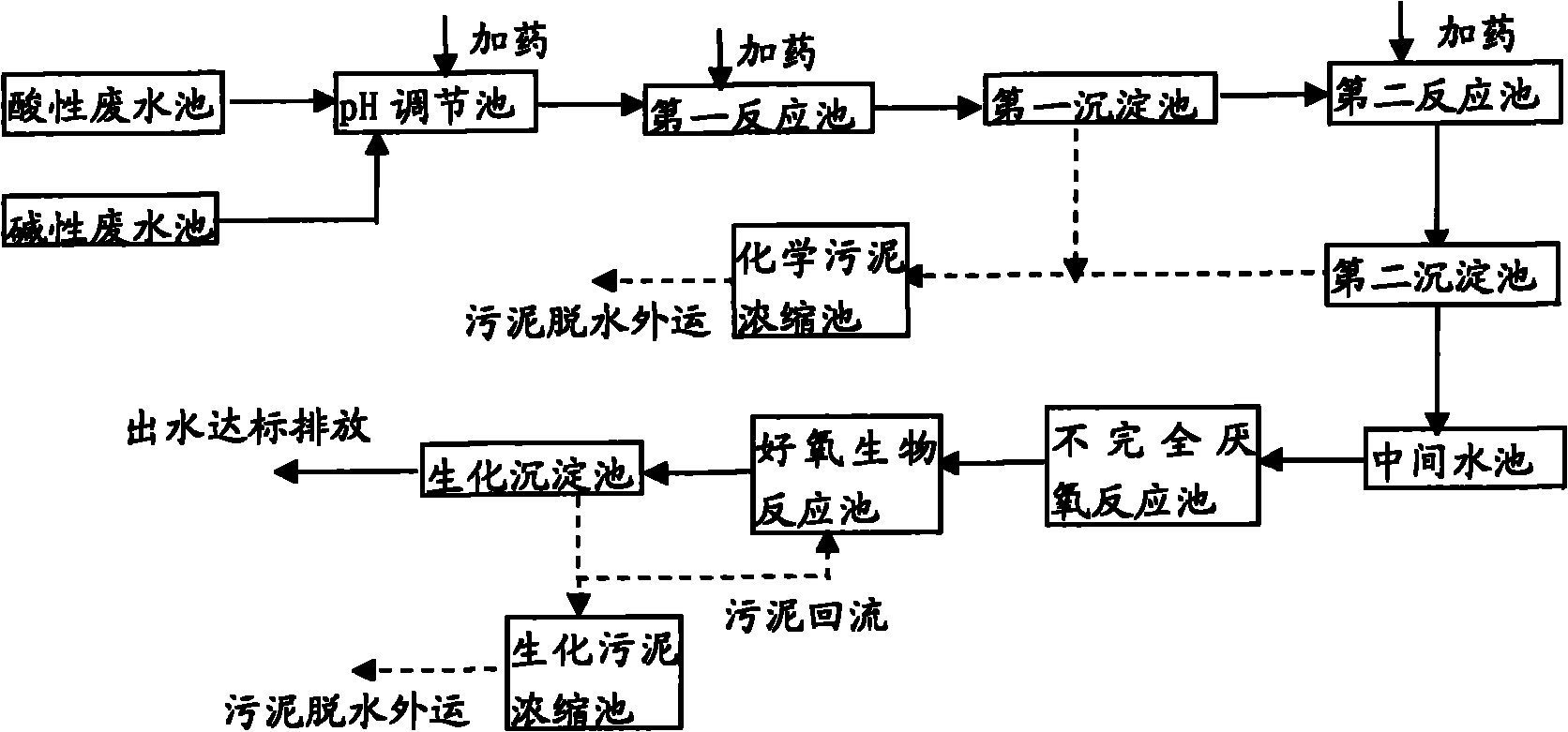
Method and system for treating industrial wastewater of photovoltaic solar cell plates
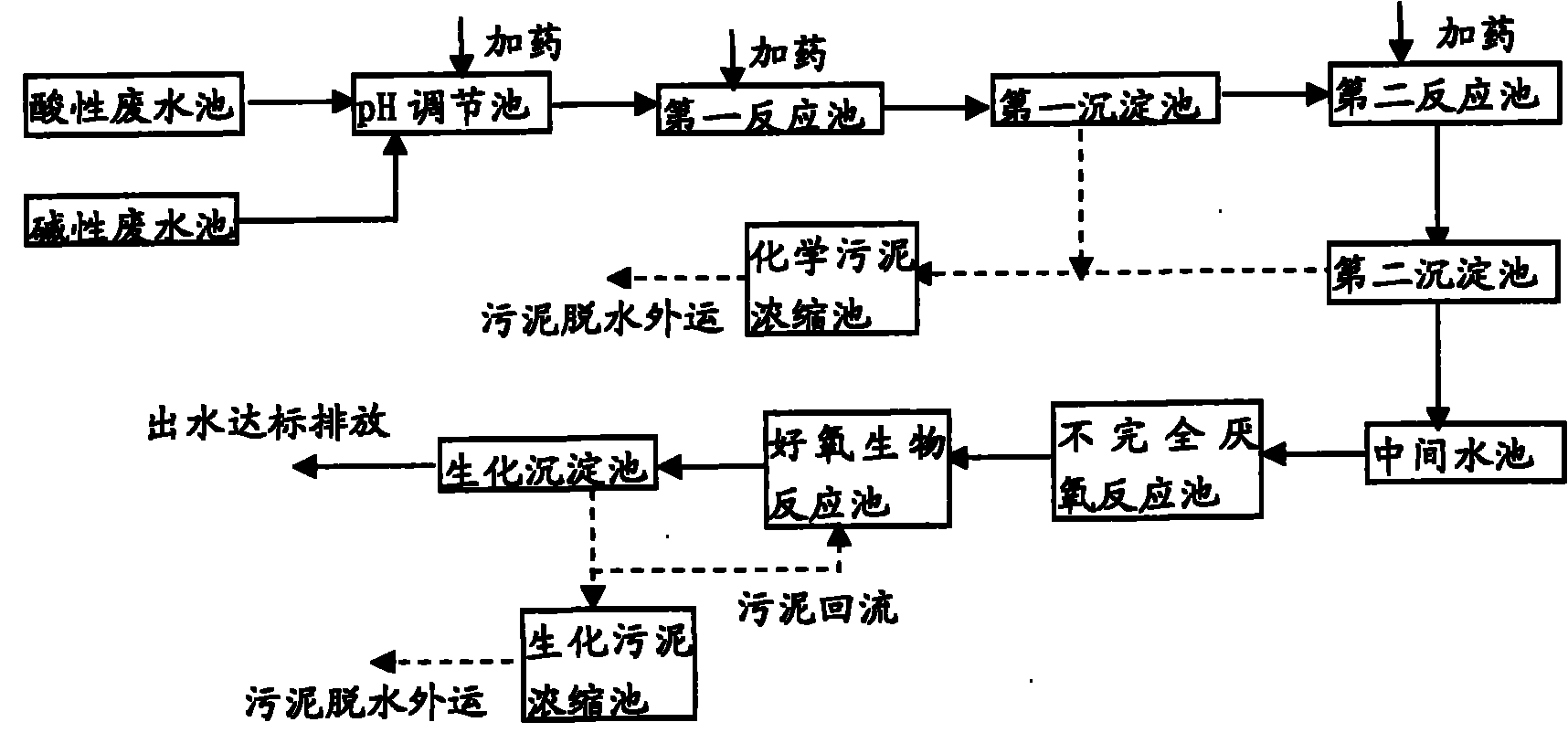
ActiveCN101973662AEfficient removalReduce concentrationGeneral water supply conservationEnergy based wastewater treatmentChemical oxygen demandStrong acids
The invention discloses a process for treating industrial wastewater of photovoltaic solar cell plates. The process comprises the following steps of: collecting wastewater, namely collecting acid wastewater and alkaline wastewater respectively; regulating pH, namely adding strong acid or strong base into the acid wastewater, alkaline wastewater or acid-alkaline mixed wastewater mixed by the acid wastewater and the alkaline wastewater, and regulating the pH value to be between 8.0 and 8.5 to form conditioning fluid; defluorinating the conditioning fluid and / or removing chemical oxygen demand (COD) from the conditioning fluid, wherein the defluorinating step means throwing calcium salt into the conditioning fluid so as to remove fluorion from the wastewater, and the COD removing step means performing incomplete anaerobic reaction on the conditioning fluid; performing aerobic biological treatment; and sequentially completing the steps to discharge the wastewater meeting the discharge standard. The invention provides a treatment process aiming at the water quality characteristics of the industrial wastewater of the photovoltaic solar cell plates and main design operational parameters.By a treatment system, the fluorion can be effectively removed, the fluorion concentration of effluent can be reduced to be below 10mg / L, and the wastewater CODCr is below 300mg / L and meets the discharge standard. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a system for treating the industrial wastewater of the photovoltaic solar cell plates.
Owner:BEIJING GUOHUAN TSINGHUA ENVIRONMENT ENG DESIGN & RES INST CO LTD BEIJING CHINA
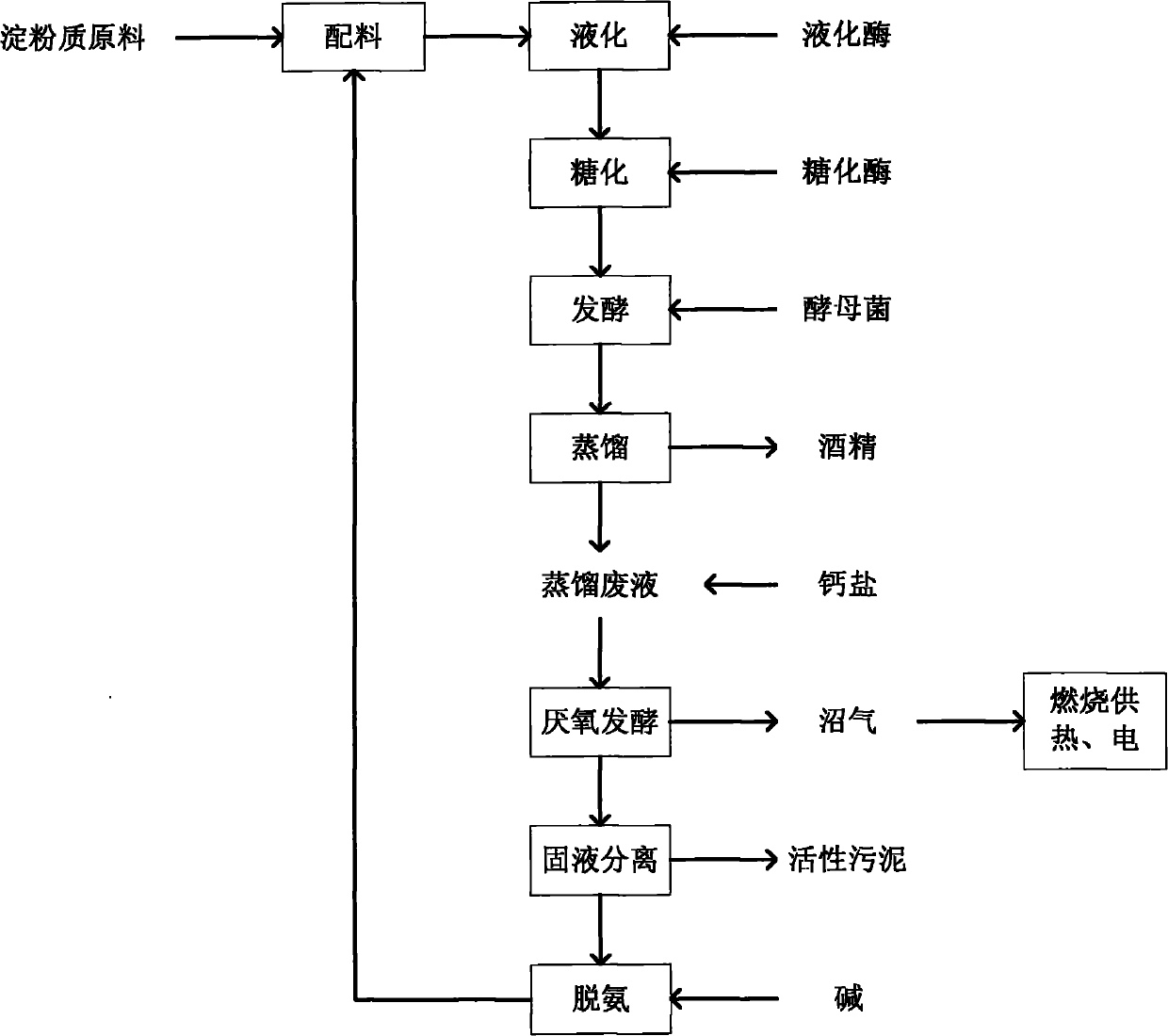
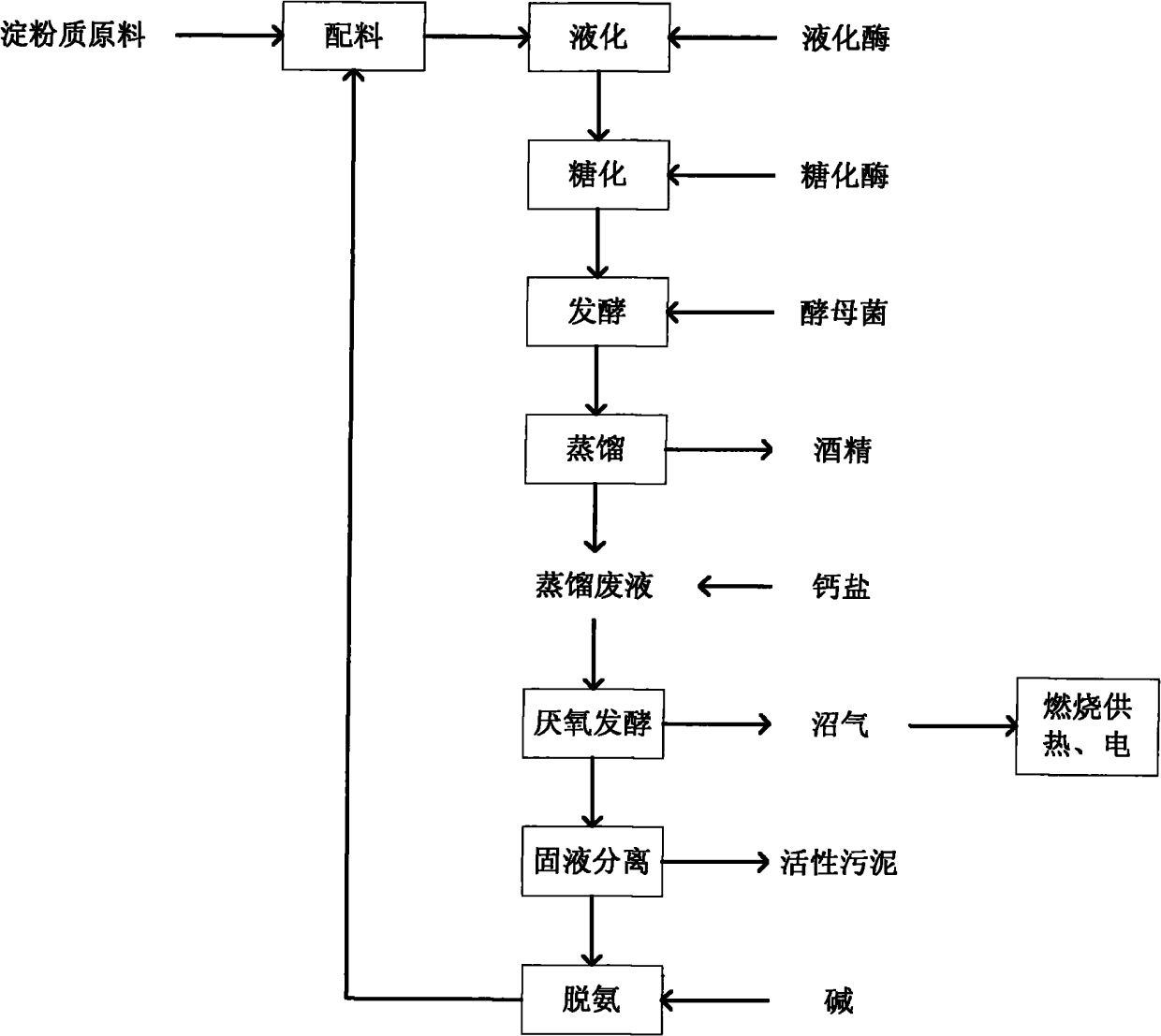
Method for industrial production of ethyl alcohol by using straw or corn or Chinese sorghum straw
InactiveCN101041834AReduce pollutionIncreased degradation rateBiofuelsFermentationBiotechnologyAlcohol
The invention discloses a processing craft with rice straw or corn or sorghum straw to produce industrial alcohol, which comprises the following steps: pressing the rice straw and straw to brick; disposing with 60Co-gama ray of 0.5-2.0X106Gy or electron-beam accelerator; grinding with mechanical; screening through 200 order sieve; leaching with hot water; stripping lignin with alcohol; degrading enzyme; separating 1-2 mu m cord hole film; synchronous-saccharifying saccharomyces cerevisiae and pichia; dispersing and yeasting; dewatering and separating the alcohol; getting the product.
Owner:湖南省原子能农业应用研究所 +1
Dimeric iap inhibitors
InactiveUS20080020986A1Remove inhibitionMultiple EffectsAntibacterial agentsBiocideSmac mimeticsDimer
Owner:TETRALOGIC BIRINAPANT UK
Detection kit for quickly identifying donkey skin, horse skin and mule skin
ActiveCN104046700AIncrease productionHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementCreatine kinaseFluorescence
The invention discloses a detection kit for quickly identifying donkey skin, horse skin and mule skin, which is used for accurately identifying donkeys, horses, mules and jennets by creatively applying 16SrRNA genes of CKM (creatine kinase) karyogene (nDNA) and mitochondrial genome DNA (mtDNA) at the same time from genetic background of the horses, the donkeys and the mules. The kit adopts an molecular beacon probe (MB) method to carry out a quintuple multicolor fluorescence quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection technology, and also can detect donkey, horse, mule and jennet components; and moreover, the kit is added with exogenous internal reference as an interior label, can detect and avoid false negative results produced by PCR inhibitor contained in a sample. The quintuple multicolor fluorescence quantitative PCR is used for detecting in the same tube without opening a cover, so that the detection kit is not easy to pollute, and is accurate and stable, simple to operate, extremely high in sensitivity, strong in specificity, and the like, and therefore, a novel way is explored for identifying the donkey skin, horse skin and mule skin.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Fixed enzyme membrane reactor, preparation thereof and method for producing biological diesel oil by the same
InactiveCN101235351ANot easy to desorbHigh specific surface areaLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBio-feedstockImmobilized enzymeMembrane reactor
The invention relates to an immobilized enzyme membrane reactor and the preparation thereof and a method for producing bio-diesel. The method comprises filling superfine fiber complex film in a die whose inside and outside are double cylindrical shape to form a film reactor, injecting activating agent solution and lipase solution in the film reactor in turn through adopting a cross-flow filtration mode, leading lipase to be chemically fixed on superfine fiber membrane surface, getting an enzyme membrane reactor which is fixed with lipase, respectively injecting mixed solution of animal and vegetable oil and carbinol in the inner side and the outer side of the superfine fiber complex film, doing catalytic alcoholysis reaction on fiber membrane surface, and producing bio-diesel. The enzyme gathering catalysis of the method of the invention is integral with a membrane separation process, and the method of the invention simplifies manufacturing technique, and meanwhile, the method of the invention overcomes inhabitation of lower alcohol to enzymatic activity in the process of catalyzing, the immobilized enzyme membrane reactor can be repeatedly used, which can achieve continuous production, improves production efficiency, and has excellent industrial application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
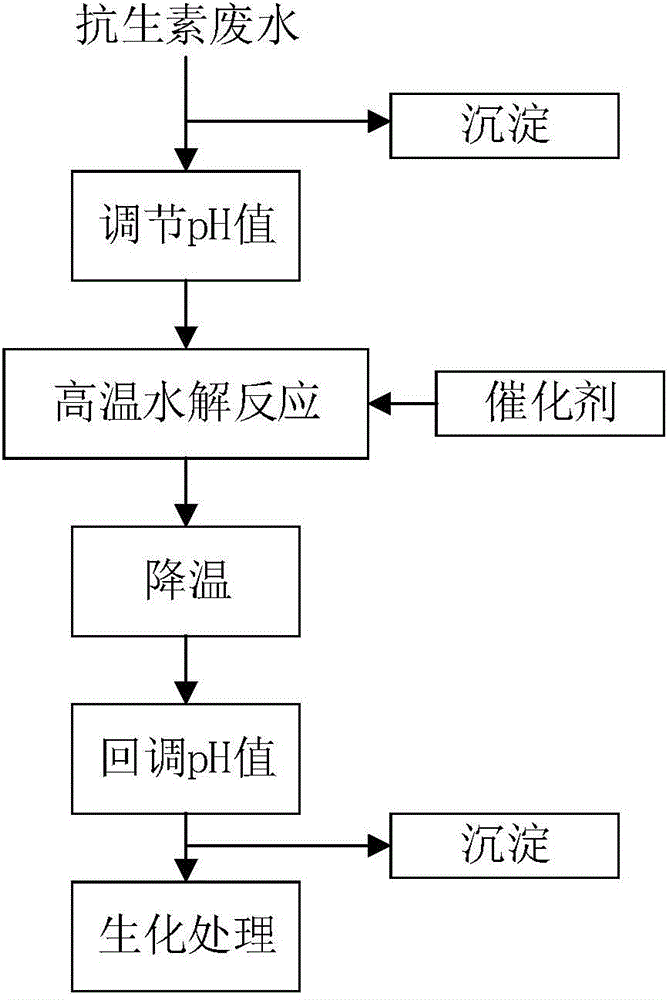
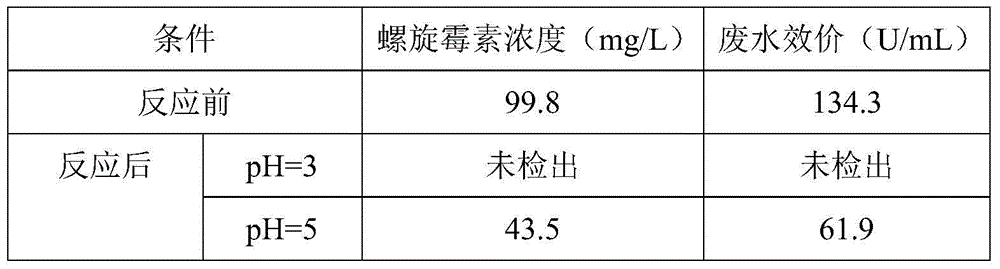
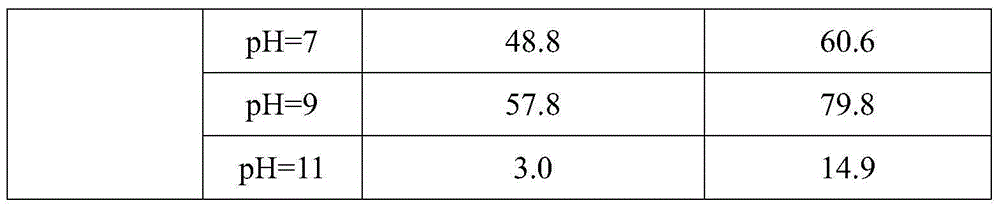
Pretreatment method for removing antibiotics in ferment antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater
ActiveCN105084442ALower titerEfficient decompositionMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by heatingMicroorganismResistant bacteria
The invention provides a pretreatment method for removing antibiotics in ferment antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater. The method removes antibiotics in the ferment antibiotic pharmaceutical wastewater mainly through adjustment of the pH value of the wastewater and high-temperature catalytic hydrolysis, and the treated pharmaceutical wastewater without antibiotics can enter a subsequent biochemical treatment process for treatment. The method provided by the invention can basically remove antibiotics in the pharmaceutical wastewater, reduce inhibition effect of high-concentration antibiotics on microbes, lower down difficulty in treatment of the wastewater by using the subsequent biochemical process and decrease generation of drug-resistant bacteria and drug-resistant genes in subsequent biochemical treatment.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing bio-fuel that integrates heat from carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions to drive biomass gasification reactions
ActiveUS7872054B2Improve thermal efficiencyImprove economyCatalytic crackingBiofuelsBiodieselCarbon–carbon bond
A low-temperature catalytic process for converting biomass (preferably glycerol recovered from the fabrication of bio-diesel) to synthesis gas (i.e., H2 / CO gas mixture) in an endothermic gasification reaction is described. The synthesis gas is used in exothermic carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions, such as Fischer-Tropsch, methanol, or dimethylether syntheses. The heat from the exothermic carbon-carbon bond-forming reaction is integrated with the endothermic gasification reaction, thus providing an energy-efficient route for producing fuels and chemicals from renewable biomass resources.
Owner:VIRENT +1
Method for separating agricus bisporus polysaccharides from agricus bisporus and determining method thereof
ActiveCN101787085ALow yieldEasy to zoom inColor/spectral properties measurementsAgaricusFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a method for separating agricus bisporus polysaccharides from agricus bisporus, which comprises the following steps: carrying out vacuum freeze-drying on the agricus bisporus for 24h; extracting crude polysaccharides with hot water: adding distilled water, boiling with big fire, maintaining with slow fire, centrifuging, taking supernatant liquid, precipitating, placing back into a heating device, adding water for continuous heating till boiling, maintaining with the slow fire, re-centrifuging and taking the supernatant liquid; repeating for three times, and using the distilled water for fixing volume of the obtained supernatant liquid for standby; carrying out dual-water phase extraction operation: precisely weighing 2.66g of polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000 and 4.28g of ammonium sulfate, adding into a 50mL centrifuge tube, adding 20mL of sample diluent, and evenly mixing; simultaneously weighing 2.66g of PEG 6000 and 4.28g of ammonium sulfate, adding into the 50mL centrifuge tube, adding 20mL of distilled water, evenly mixing, and obtaining the agricus bisporus polysaccharides distributed in the PEG phase. The utilization of a dual-water phase system for extracting the agricus bisporus polysaccharides can realize the maximum yield of 80.1%, and the yield can achieve 17.45mg / g.
Owner:天津市金三农农业科技开发有限公司
Method for treating erythromycin thiocyanate wastewater
ActiveCN103011526AGood removal effectRemove inhibitionMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterChemistryActivated sludge system
The invention relates to a method for treating industrial wastewater and application of the method, belonging to the field of wastewater treatment. The method for treating wastewater comprises the steps: conducting yeast treatment, catalysis microelectrolysis, two-phase anaerobic treatment, CASS (Cyclic Activated Sludge System) method treatment, advanced oxidization and biological aerated filter to industrial wastewater. In the method for treating wastewater, the treatment units are reasonably combined, COD and ammonia nitrogen removal efficiency is high, and the wastewater treated by using the method can meet the demand of up-to-standard emission or backwater recycling. The method for treating the wastewater is low in running cost, very applicable to treatment of antibiotic industrial wastewater, especially to treatment of erythromycin thiocyanate wastewater, thus the method has wide industrial application prospects.
Owner:SHANDONG NEWTIME PHARMA
Method for producing alcohol by taking anaerobic effluent as ingredient water
ActiveCN102115764AEliminate potential hazardsImprove stabilityBiofuelsMultistage water/sewage treatmentLiquid wasteSulfate radicals
The invention relates to a method of an alcohol production process in which anaerobic effluent is taken as ingredient water. The method comprises the following steps of: mixing raw materials with deaminized anaerobic effluent in a specified material to water ratio; adjusting pH value and adding liquefied enzyme, heating, digesting and liquefying; cooling, and adding saccharified enzyme for saccharifying; lowering the temperature, inoculating and fermenting; distilling; precipitating sulfate radicals before performing anaerobic treatment on the distilled effluent obtained by distilling; and performing anaerobic treatment on the distilled effluent, and performing deamination treatment to obtain ingredient water for fermenting a next batch of alcohol. By adopting method, the running stability of the process in which the anaerobic effluent is taken as the ingredient water is enhanced, the content of hydrogen sulfide in marsh gas obtained by fermenting anaerobic marsh gas is lowered, and subsequent use of the marsh gas is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
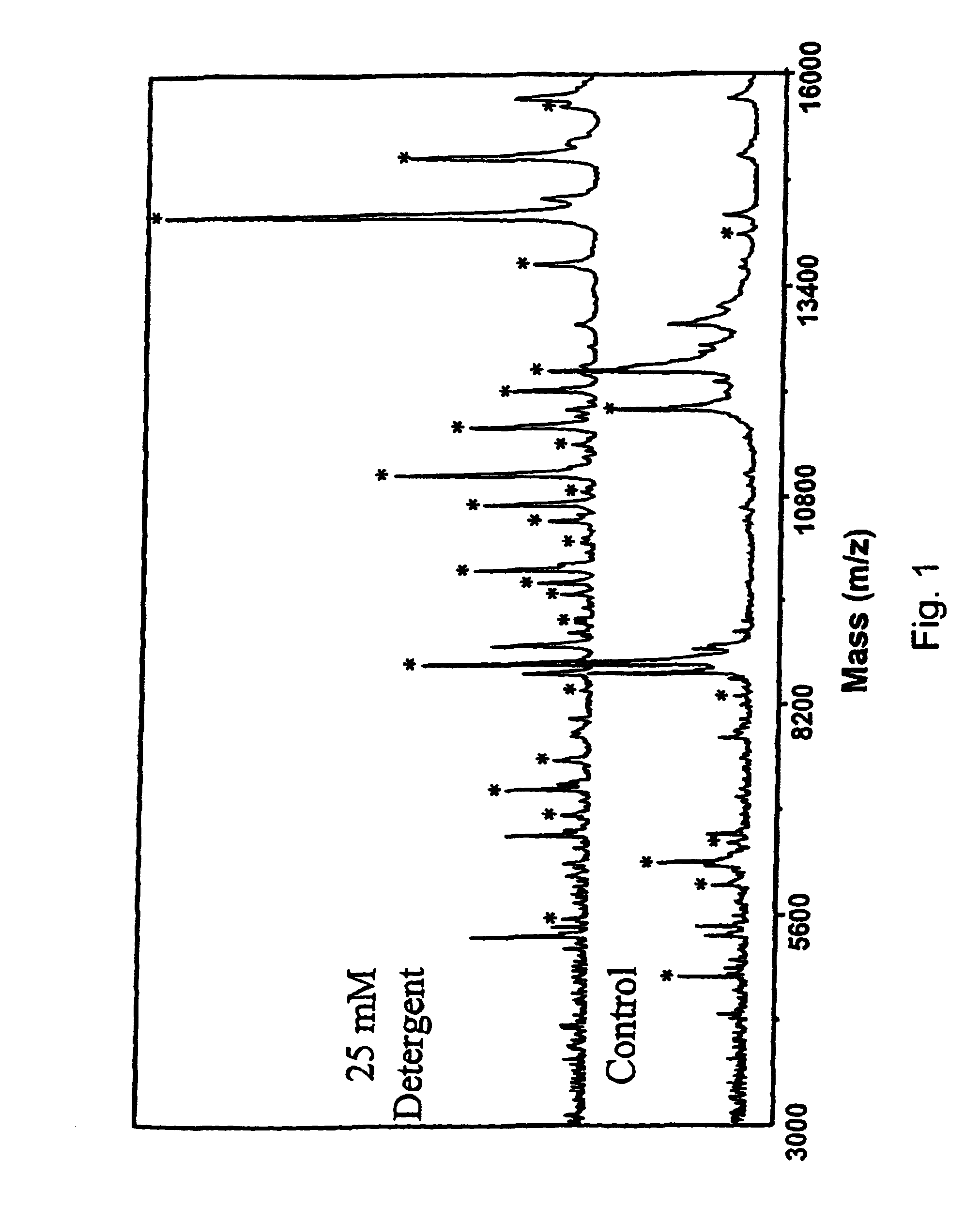
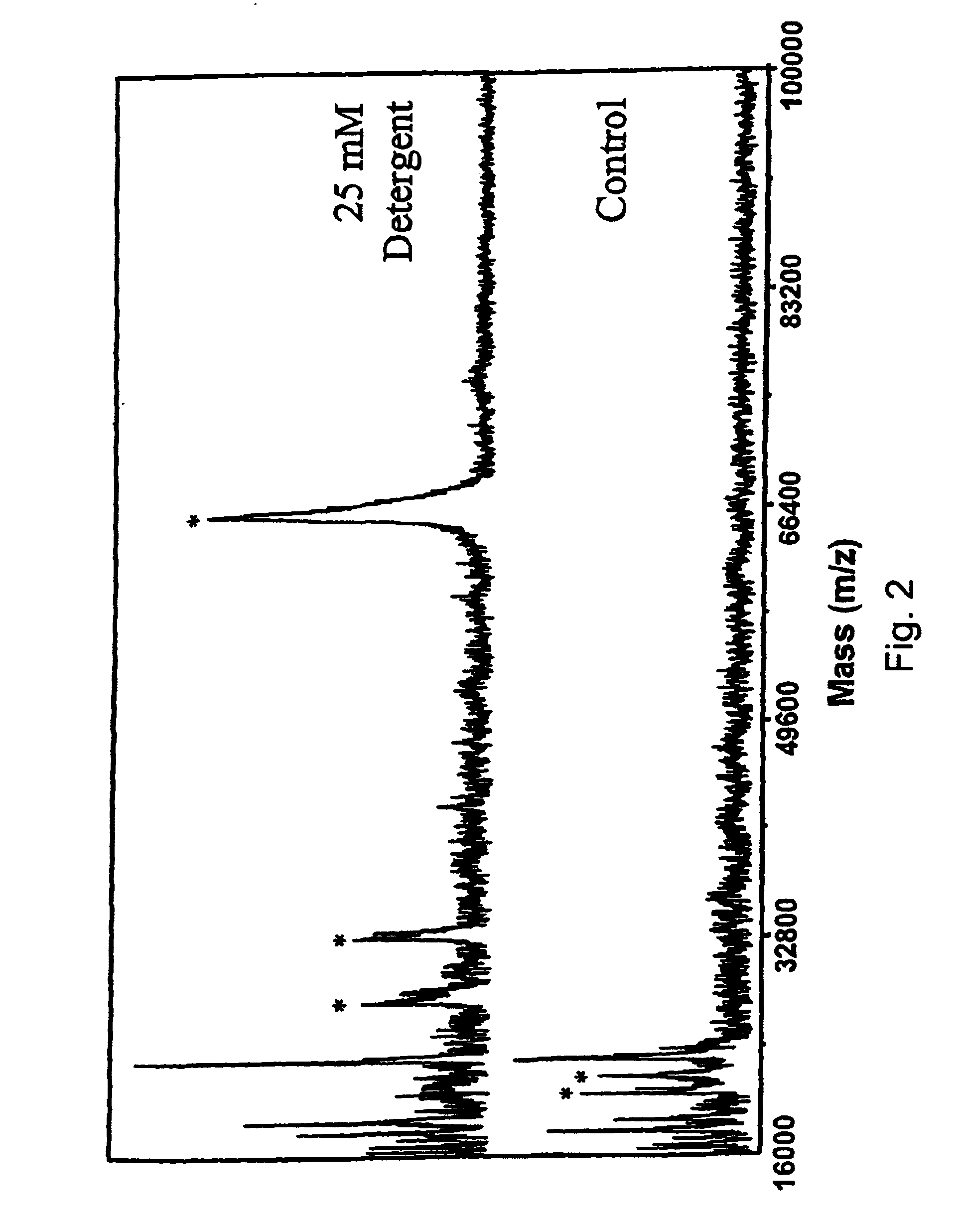
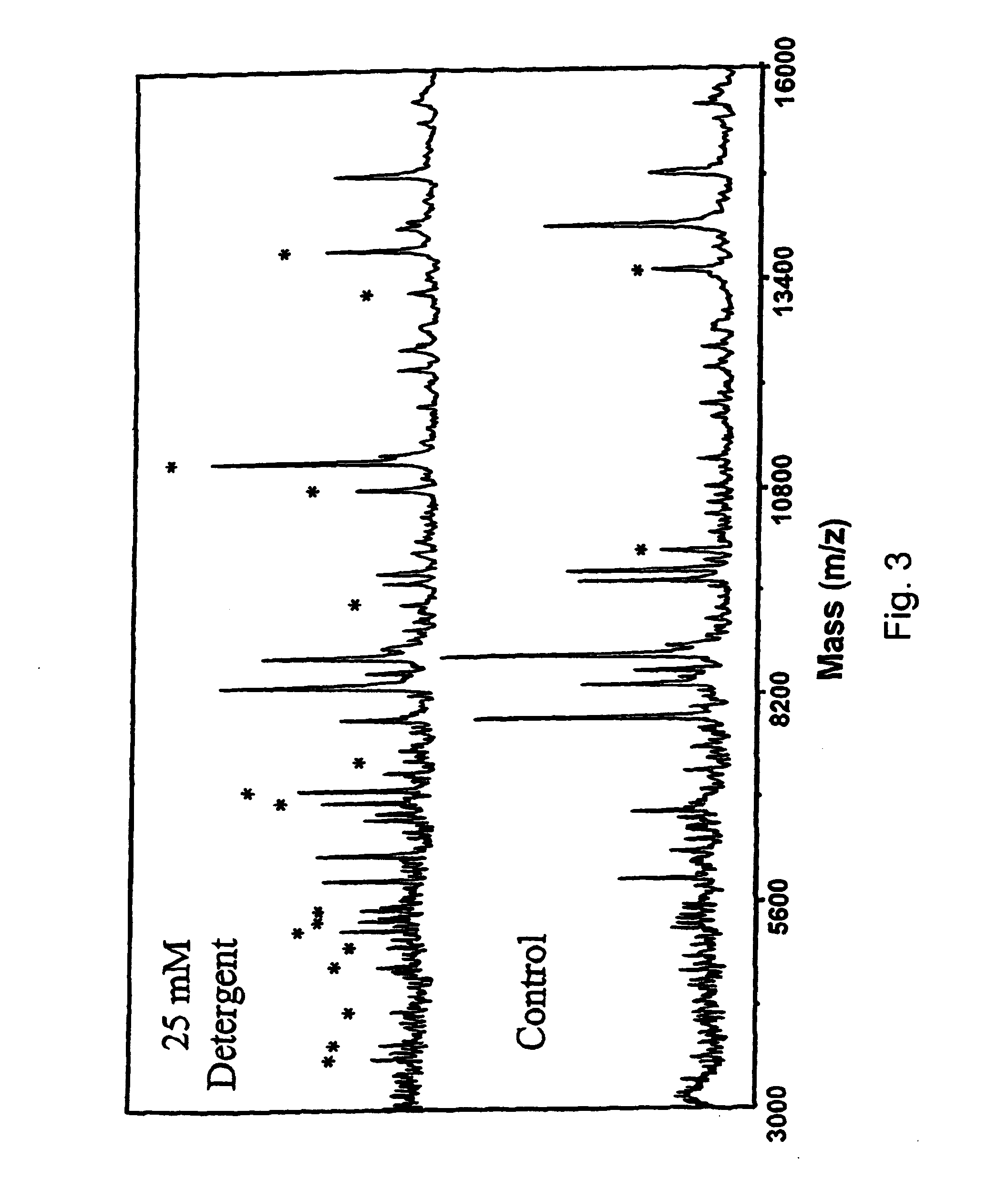
Cleavable surfactants and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7074936B2Increase in signal intensityEliminate effectSilicon organic compoundsPhosphatide foodstuff compositionsMaldi msAnalytical chemistry
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
IAP inhibitors
InactiveUS20080021066A1Improve efficiencyIncrease effectivenessBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsChemistrySmac mimetics
Owner:TETRALOGIC BIRINAPANT UK
Method for increasing methane production efficiency in organic waste anaerobic process
ActiveCN102140001APromote hydrolysisImprove metabolic activityGas production bioreactorsWaste based fuelGeneration rateFeces
The invention discloses a method for increasing methane production efficiency in organic waste anaerobic process. The method is characterized in that powder containing no less than 15% of free ferric iron oxides is added into an anaerobic biochemical system to be uniformly blended, wherein the anaerobic biochemical system produces methane by utilizing organic wastes; and ferric ions released when microbes reduce the ferric iron oxides in the anaerobic process can promote the activity of anaerobic bacteria such as methane bacteria and the like, thus increasing the production rate and yield of methane by utilizing organic wastes. The method can be widely used for increasing the methane production rate and yield of an energy utilization system for biogas production of municipal domestic waste, agriculture product processing wastes, excess sludge of sewage treatment plants, feces of intensifying raising farms and the like and improves the utilization rate of renewable energy sources of organic wastes.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Dimeric IAP inhibitors
InactiveUS7985735B2Remove inhibitionMultiple EffectsAntibacterial agentsBiocideSmac mimeticsStereochemistry
Owner:TETRALOGIC BIRINAPANT UK
Preparation method of lactic acid streptostacin
ActiveCN101113463AHigh yieldIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationUltrafiltrationSolid matter
A preparation method of nisin relates to the preparation method of small active peptides and solves the shortages of low output of nisin and protein using rate in the existing separating preparation method of nisin. The nisin is prepared by the steps that: 1. clean air is pumped from the bottom of fermentation solution and bubbles are collected: 2. bubbling treatment is carried out: 3. foaming liquid is filtered: 4. ultrafiltration is done: 5. salting out is done: 6. centrifugation is done, then solid matters are dissolved again and spayed and dried, thereafter the nisin is obtained. The production bacteria of the invention are in the logarithmic phase and have strong growth capacity and keep growing during bubble collecting course to continuously produce nisin and improve the production capacity of production bacteria and output of nisin. The invention collects bubble during the foaming course, solves the problem of the inhibiting effect of products on production bacteria during fermentation and improves the using rate of protein and output of products in fermentation solution.
Owner:QIQIHAR ANTAI BIOLOGICAL ENG
Trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and application thereof
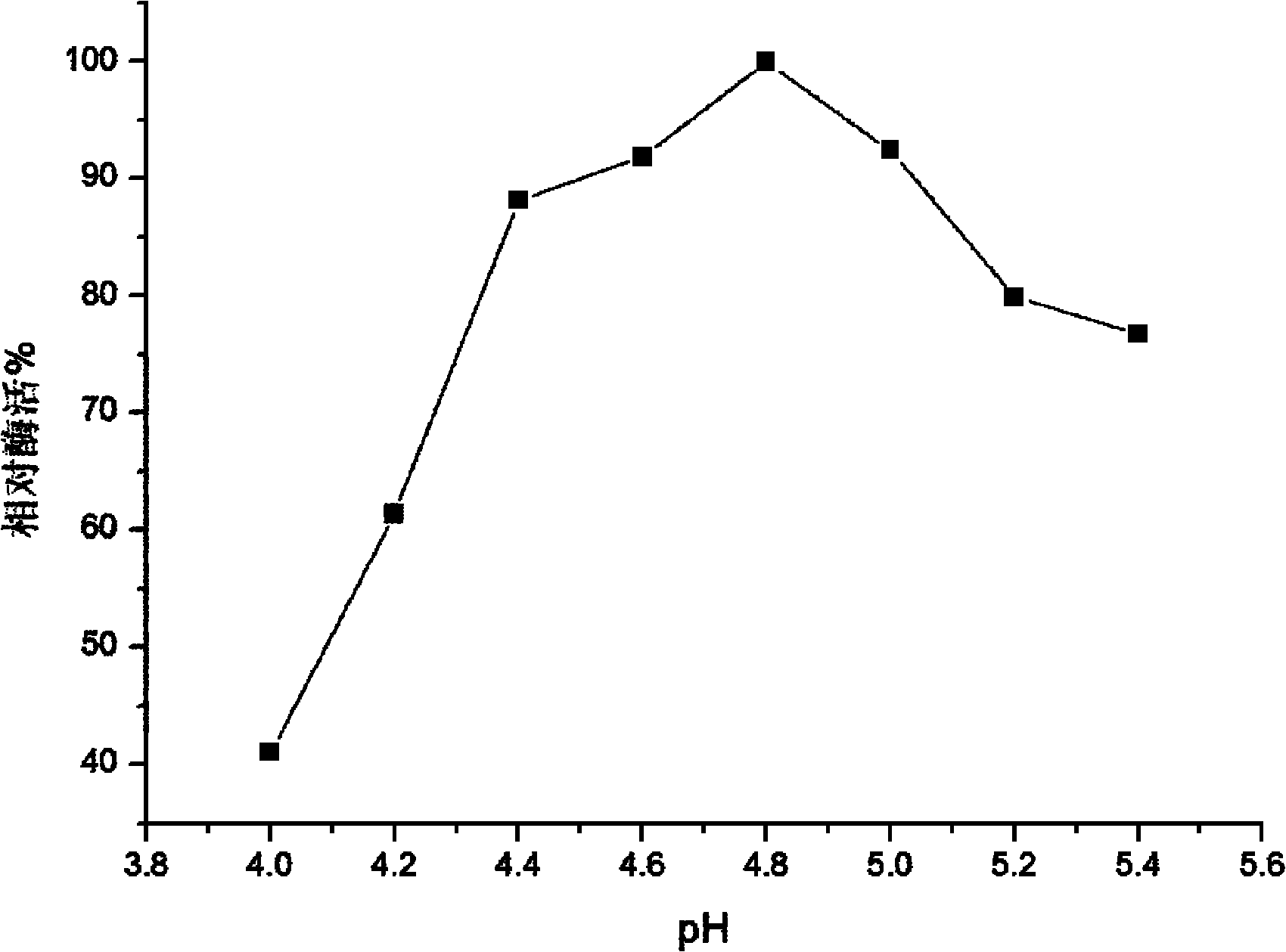
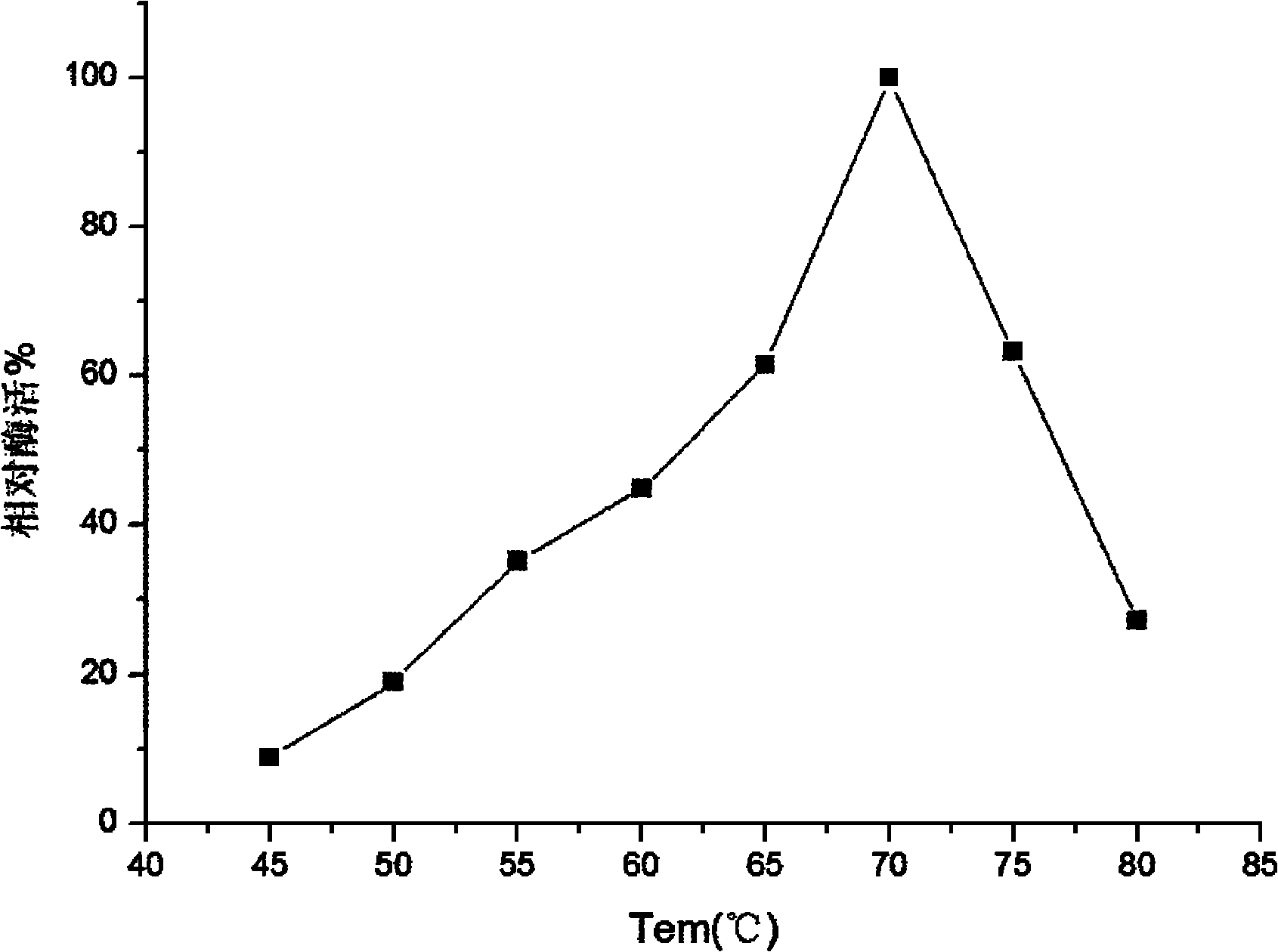
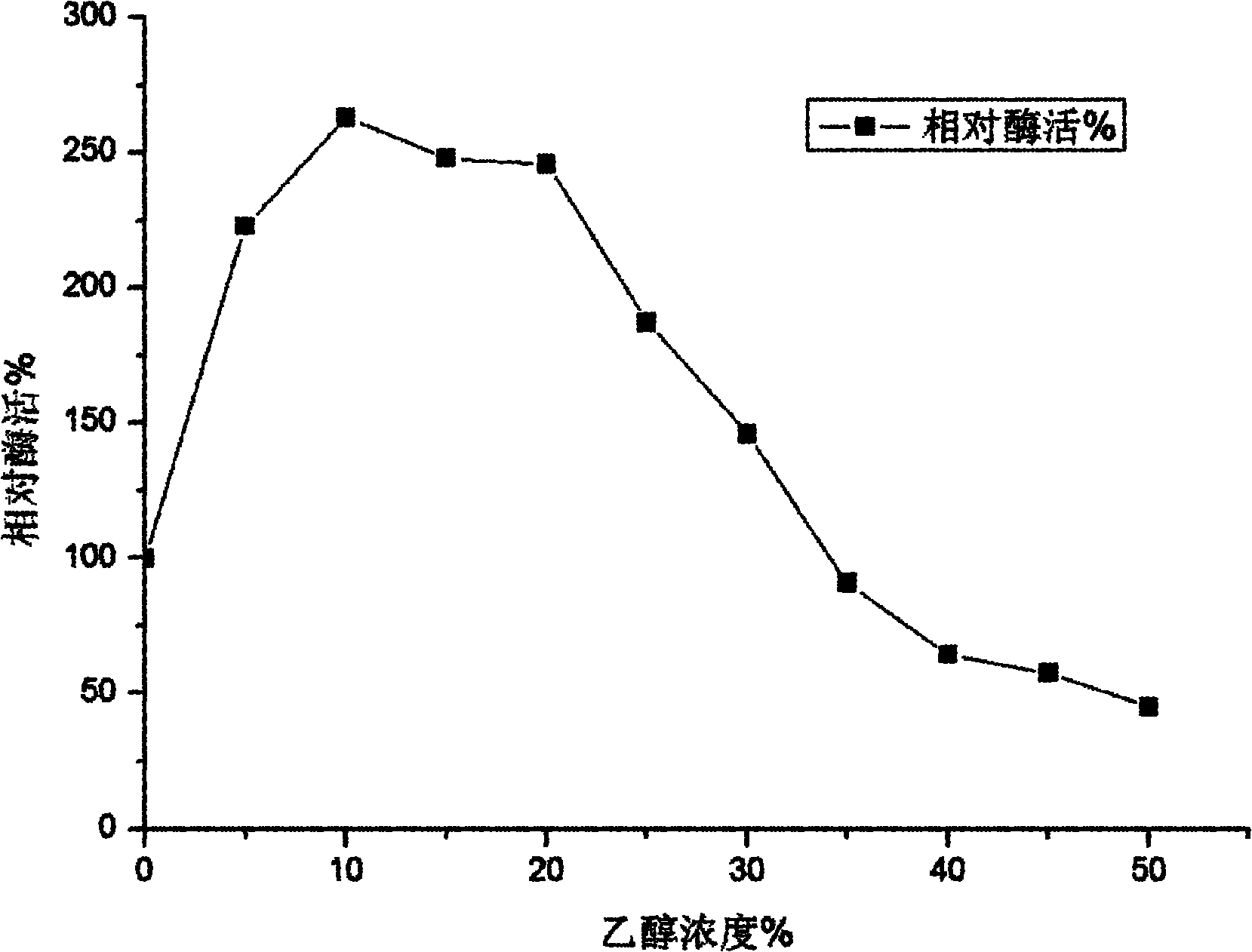
InactiveCN102080050AImprove toleranceFeedback inhibition is evidentFungiMicroorganism based processesReaction temperatureCellobiose
The invention discloses a trichoderma viride W2 capable of producing a thermophilic ethanol-resistant beta-glucosidase and an application thereof. The trichoderma viride W2 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on August 23, 2010, and the preservation number of the trichoderma viride W2 is CGMCC No.4098. The trichoderma viride W2 can produce a new beta-glucosidase, the enzymatic activity of the new beta-glucosidase reaches 346.7U / mL, the optimal reaction pH value is 4.8, the optimal reaction temperature is 70 DEG C, and the new beta-glucosidase is suitable for pyrohydrolysis and has an obvious glucose feedback inhibition effect. The ethanol the concentration of which is 10% has a maximal effect on promoting the enzymatic activity and improves the enzymatic activity of the beta-glucosidase by 1.6 times, and the resistant ability of the ethanol reaches 30%, so that the cellobiose inhibition can be effectively eliminated, the yield of the ethanol is improved by nearly 3 times, and the terminal product inhibition is effectively eliminated. Thus, the beta-glucosidase can be used for simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of lignocellulose raw materials, has a rare promoting effect in China, effectively increases the yield of the cellulosic ethanol, lowers the production cost, and accelerates the industrialized progress of the cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
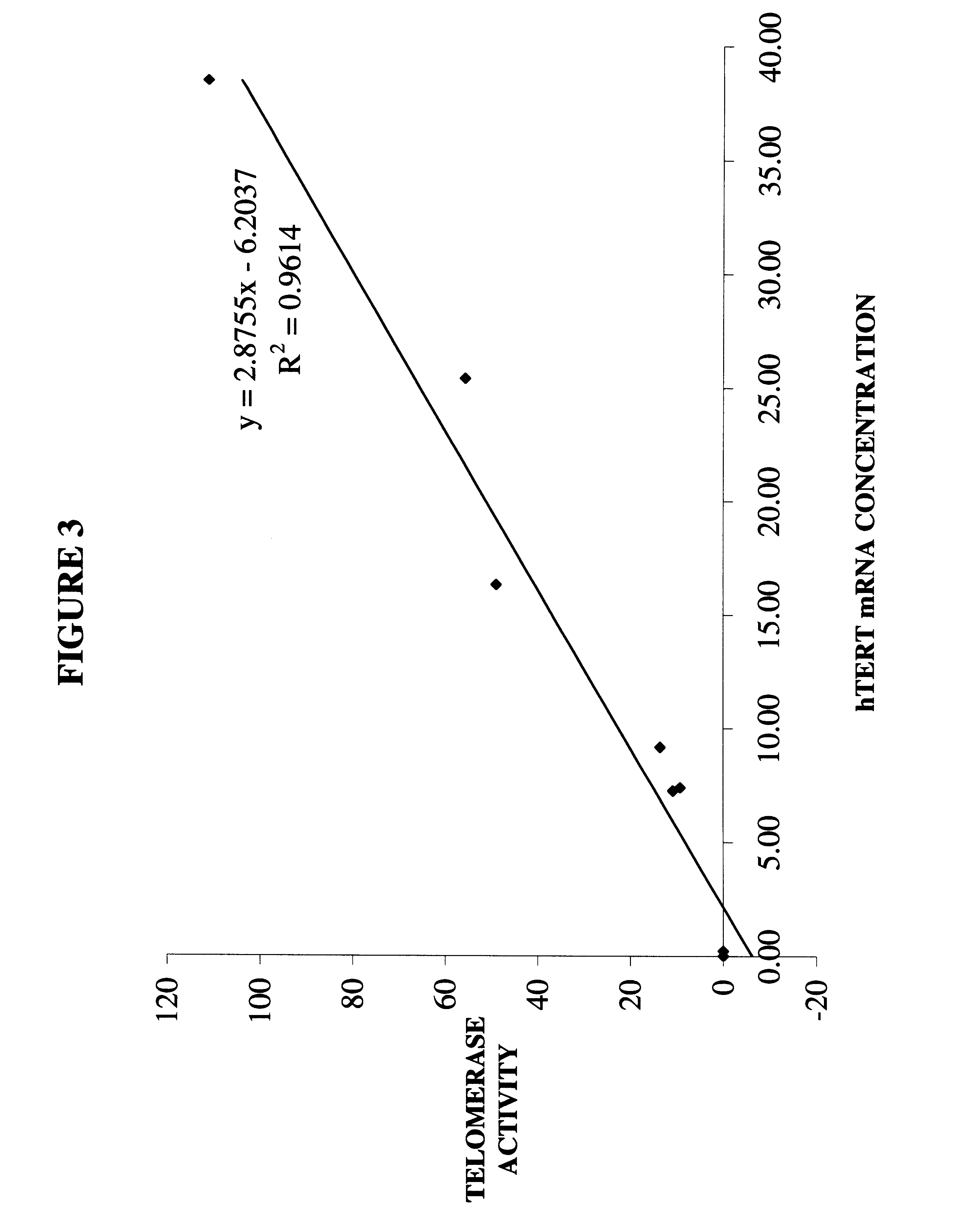
Quantitation of hTERT mRNA expression
InactiveUS6664046B1Accurate estimateEfficient and specific amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHtert mrnaBiology
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Nucleic acid amplification in the presence of modified randomers
InactiveUS20090269766A1Remove inhibitionEasy to useMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzymesHot start PCRPolymerase L
The present invention is directed to a composition comprising a DNA Polymerase which is preferably thermostable, Deoxynucleotides, at least one primer oligonucleotide or a pair of amplification primers, and randomized 5-8 mer oligonucleotide, characterized in that said oligonucleotide comprises a modification with an organic hydrophobic moiety Such a composition is specifically useful for performing hot start PCR.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
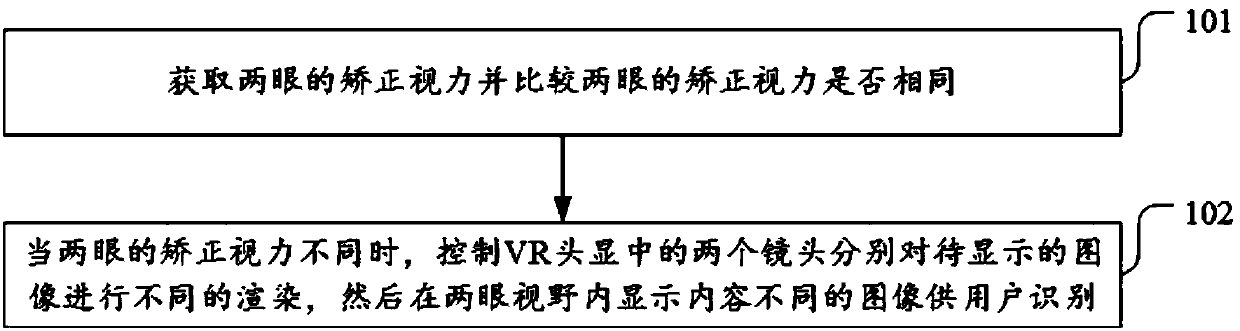
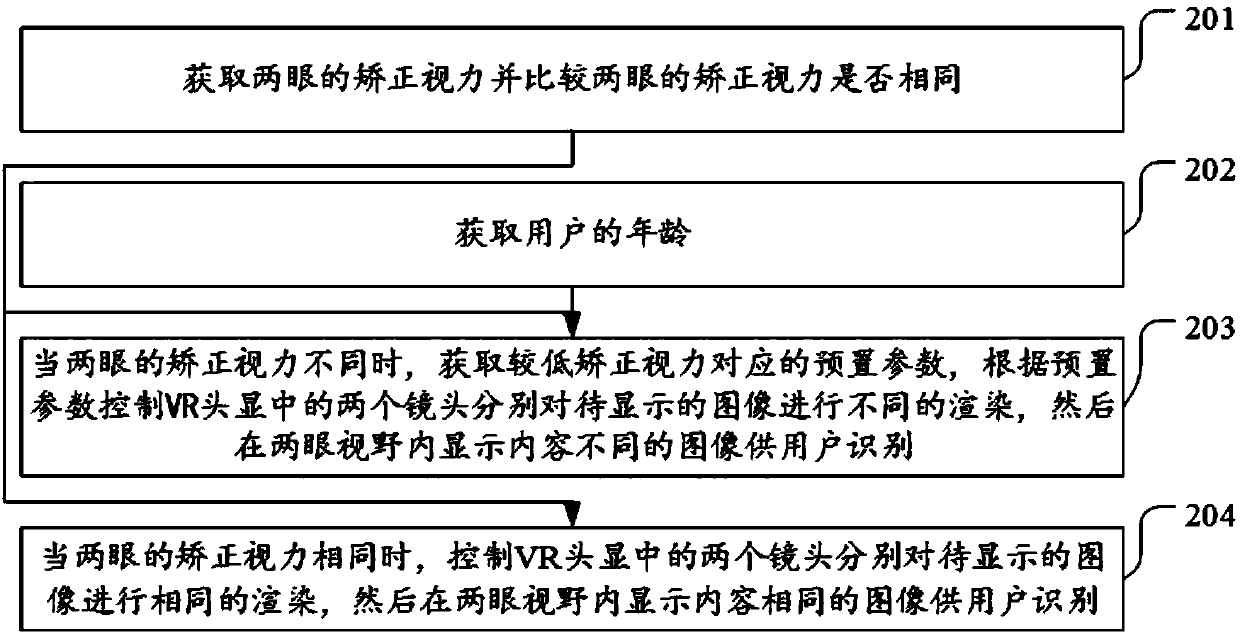
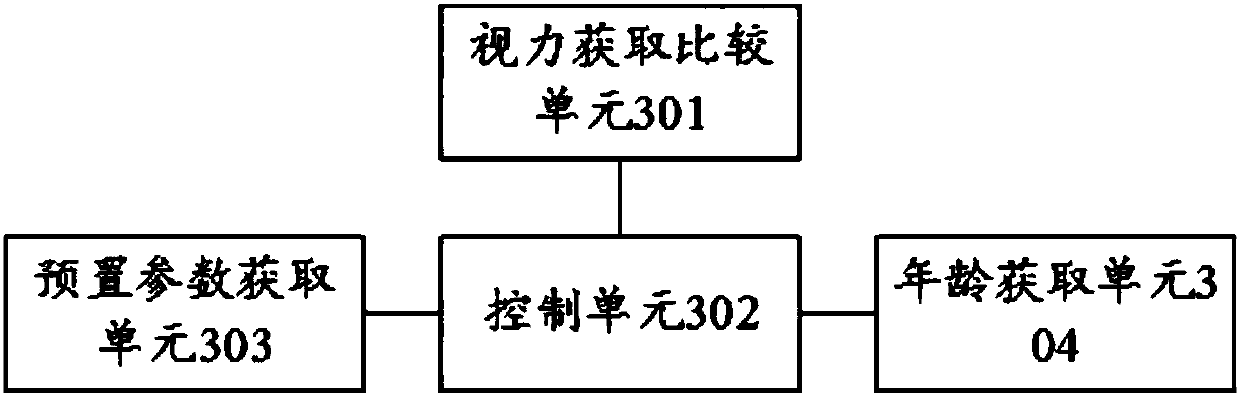
Vision training method, device and equipment
InactiveCN107669455AReduce inhibitionReduce or even eliminate inhibitionEye exercisersCamera lensDisplay device
The invention discloses a vision training method, device and equipment. The method comprises the steps of obtaining corrected visual acuity of two eyes of a user, and judging whether or not the visualacuity of one eye is equal to that of the other eye through comparison; when the visual acuity of one eye is different from that of the other eye, controlling two cameras in a VR headset display device to render images to be displayed differently, and then displaying the images with different contents in views of the two eyes to be recognized by the user, wherein compared with the image in the view of the eye with higher corrected visual acuity, the image in the view of the eye with lower corrected visual acuity has more objects and / or has an image background which is in a visual-stimulationdynamic change mode, and thus the image stimulation received by the eye with the lower corrected visual acuity is stronger than that received by the eye with the higher corrected visual acuity. Through the vision training method, device and equipment, the defect that only vision of the two eyes can be improved but the prohibition problem between the two eyes cannot be solved by training the two eyes with a cover method is overcome.
Owner:广州视景医疗软件有限公司
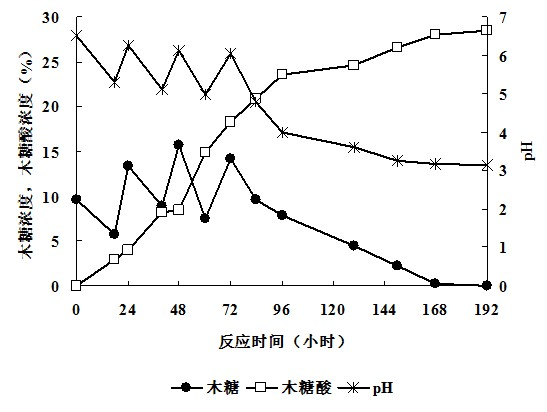
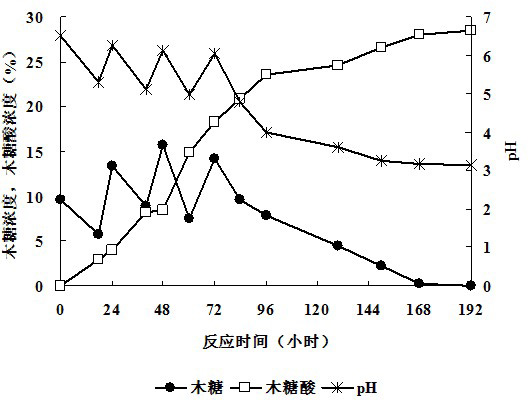
Method for preparing xylonic acid (salt) through whole-cell high-efficiency catalysis of xylose transformation
InactiveCN102676608AIncrease the reaction concentrationIncrease concentrationMicroorganism based processesFermentationGluconic acidTransformation ratio
The invention discloses a method for preparing xylonic acid (salt) through whole-cell high-efficiency catalysis of xylose transformation. The method comprises the following steps of: adding an initial reaction matrix into a liquid deep-layer ventilation reaction system; inoculating gluconabacteriumoxydonas; stirring and ventilating to continuously react; keeping dissolved oxygen concentration of the reaction system not less than 10 percent; adding xylose or xylose solution into the reaction system in a semi-continuous or continuous batch adding mode; controlling mass concentration of xylose in the reaction system to be not greater than 25 percent; synchronously adjusting and controlling the pH value to be not less than 2.8; stopping adding when the mass concentration of the xylose accumulatively added into the reaction system reaches 30 percent; and continuously performing full catalytic reaction to obtain a transformed product, i.e., the xylose acid (salt) product. According to the method, the maximum value of the accumulative concentration of the substrate xylose can reach 30 percent, the maximum utilization rate of the xylose exceeds 99 percent, the maximum concentration value of the fermentation product, i.e., the xylose acid (salt), can reach 29.8 percent, and the transformation ratio of the xylose acid (salt) can reach 100 percent.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for preparing fuel of ethanol from immobilized mixed strain fermented cellulosic hydrolysate
InactiveCN101555494AIncrease profitImprove fermentation effectBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesXyloseSide product
The invention relates to a method for preparing fuel of ethanol from immobilized mixed strain fermented cellulosic hydrolysate, which is characterized by utilizing mixed strains of P. tannophilus and S. cerevisilae to graft into diluted acid hydrolysate and fermenting the mixed solution by a supplemented material batch fermentation mode. The method is realized by the following steps: (1) domestication of the P. tannophilus and the S. cerevisilae; (2) immobilization of the mixed strains by calcium alginate; (3) multiplication culture of the immobilized mixed strains; and (4) supplemented material batch fermentation of the immobilized mixed strains. The immobilized mixed strains can be fermented while using xylems and glucose in the hydrolysate for fermentation, thereby the fermentation period is shortened, the utilization ratio of the xylose and the glucose is improved and the ethanol concentration is increased; the immobilized mixed strains can be repeatedly used and have strong anti-hybrid bacteria capability; the supplemented material batch fermentation mode is applied to hydrolysate with cellulose raw material for producing the fuel of ethanol, thereby reducing inhibiting factors in the hydrolysate; and the method is beneficial to thoroughly eliminating the inhibition on substrates, diluting poisonous metabolite, reducing contaminated bacterial, controlling the fermentation time and preventing the generation of side products.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Microbial composite functional bacterial agent for treating coking wastewater and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102337214AEfficient degradation abilityRemove inhibitionFungiBacteriaChemical oxygen demandEmission standard
The invention particularly relates to a microbial composite functional bacterial agent for treating coking wastewater and a preparation method thereof. According to the technical scheme, the microbial composite functional bacterial agent comprises the following microbes: 15-20wt% of n-hexadecane degrading bacteria, 20-30wt% of phenol degrading bacteria, 10-15wt% of pyridine degrading bacteria, 8-12wt% of chinoline degrading bacteria, 5-10wt% of carbazole degrading bacteria, 15-20wt% of naphthalene degrading bacteria and 8-12wt% of anthracene degrading bacteria. The microbial composite functional bacterial agent has the characteristics that: the composite functional bacterial agent prepared from artificially bred functional strains is added to an original biochemical treatment device, thus the removing capability of refractory organic matters in the coking wastewater is greatly improved and the contents of COD (chemical oxygen demand) and NH3-N in the coking biochemical effluent can both reach national first-level emission standard. The microbial composite functional bacterial agent has strong environment adaptability, good cooperativity, and broad application prospects in bioaugmentation of coking wastewater.
Owner:武钢集团有限公司 +1
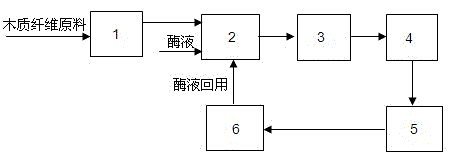
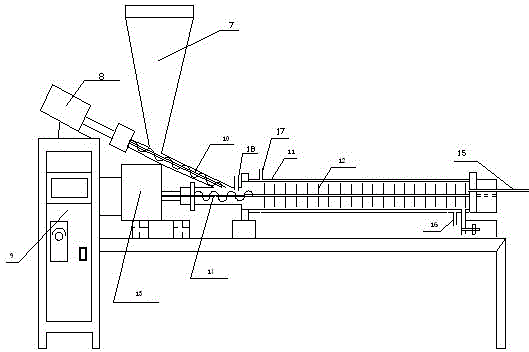
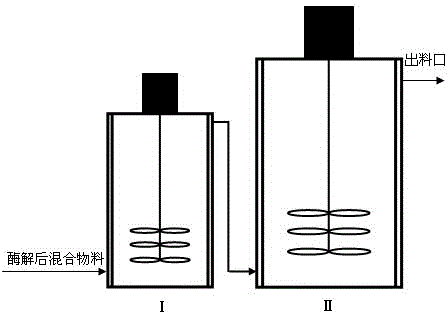
Method for producing ethanol by continuous enzymolysis and fermentation of lignocellulose
The invention relates to a method for producing ethanol by continuous enzymolysis and fermentation of lignocelluloses. The method comprises the following steps: (1) a pretreated lignocellulose raw material and an enzyme solution are added in proportion into an enzymolysis reactor with a screw device to carry out continuous enzymolysis; (2) the materials enter a fermentation tank I after enzymolysis, and microzyme is inoculated to carry out simultaneous saccharification and fermentation at 30-38 DEG C; (3) the materials in the fermentation tank I enter a fermentation tank II, and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation are continuously carried out at 39-44 DEG C; (4) the fermented materials undergo reduced pressure distillation; and (5) the distilled materials undergo solid-liquid separation, and an enzyme-containing liquid phase is reused in the step (1). By the use of the screw device, continuous supply and continuous enzymolysis of the raw materials are realized, and enzymolysis efficiency is enhanced. As simultaneous saccharification and fermentation are carried out at different temperatures, enzymolysis efficiency is further improved and yield of ethanol is then raised. The finally-obtained enzyme solution can be directly reused in the enzymolysis process, thus reducing production cost.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com