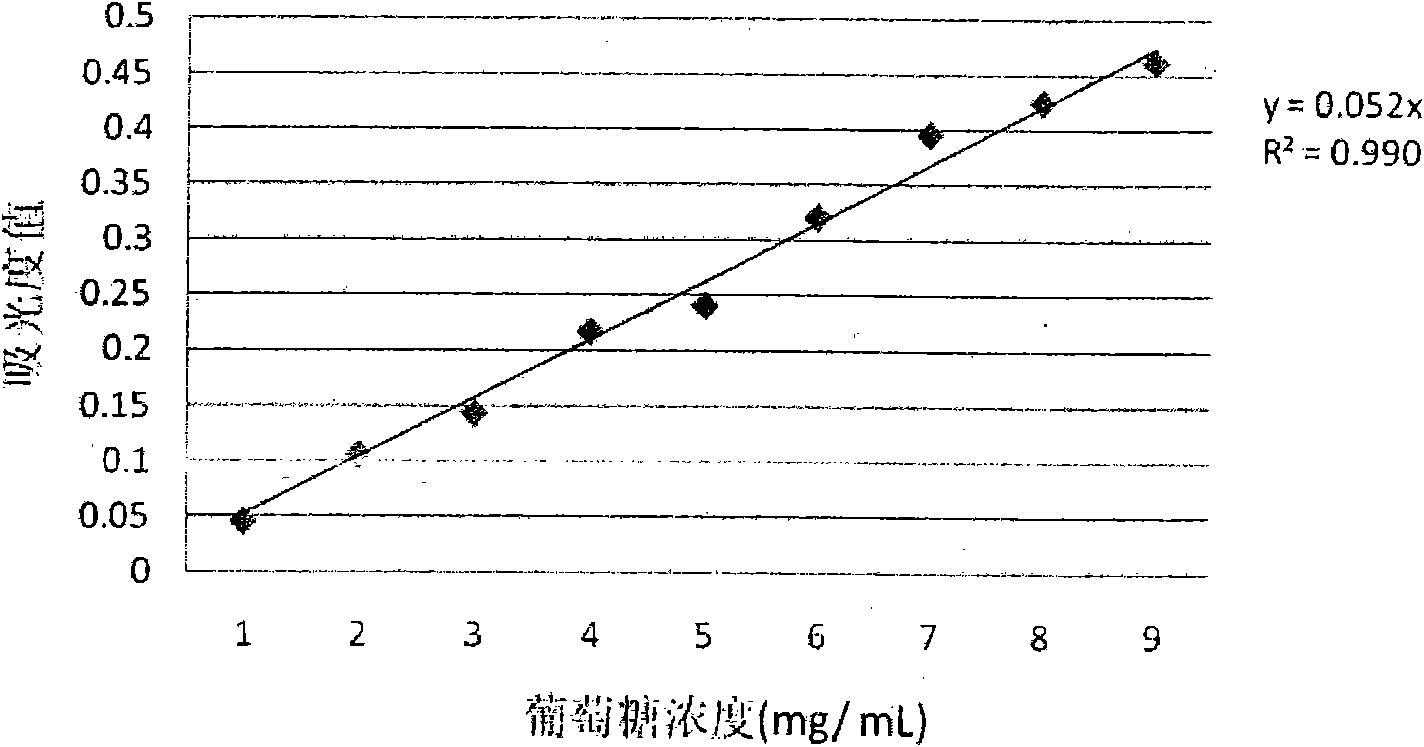
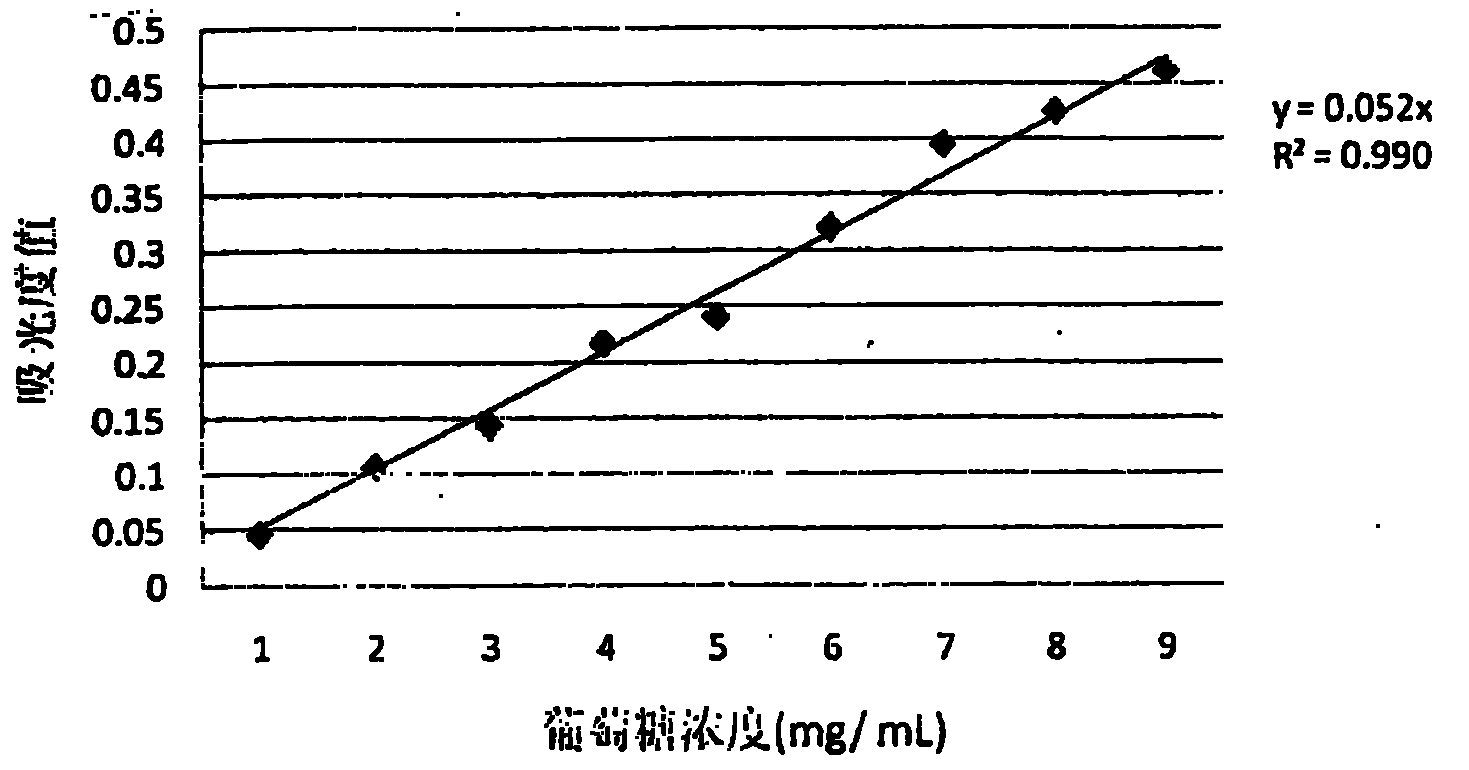
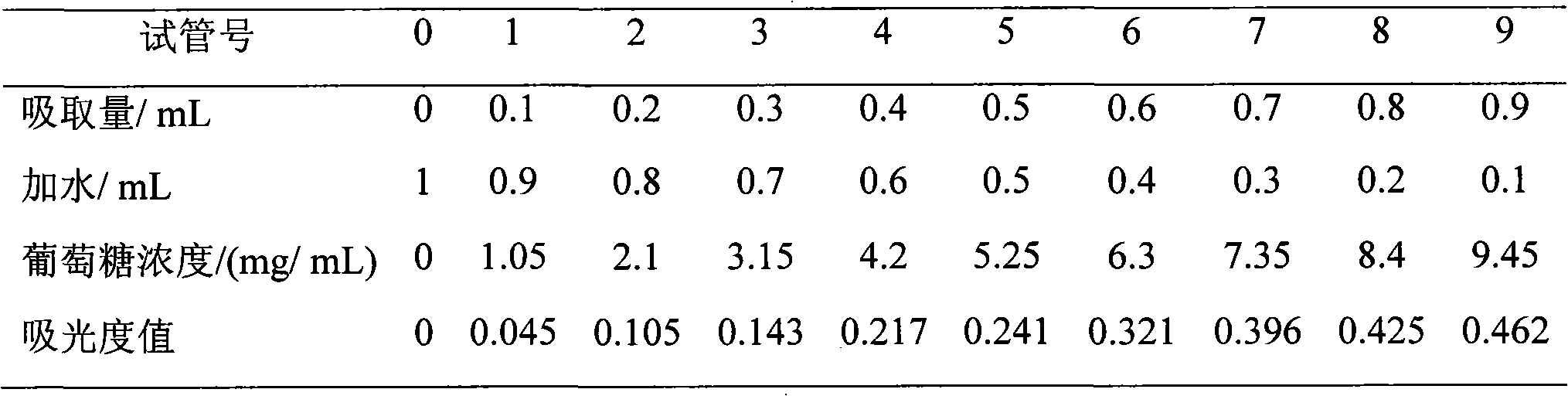
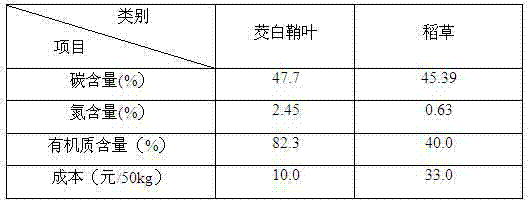
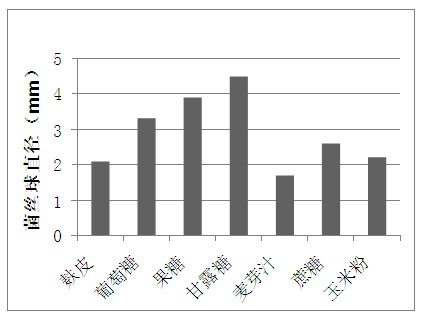
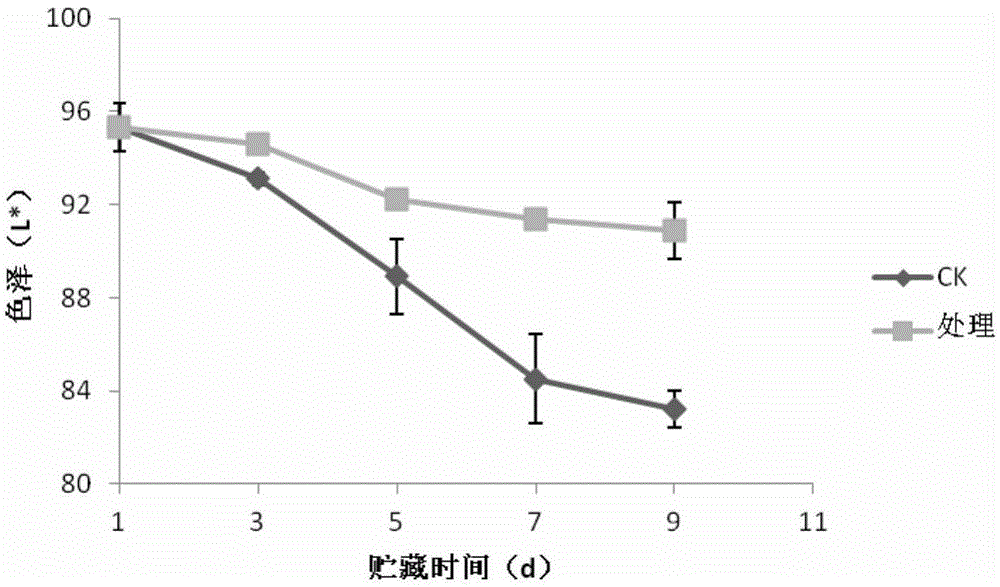
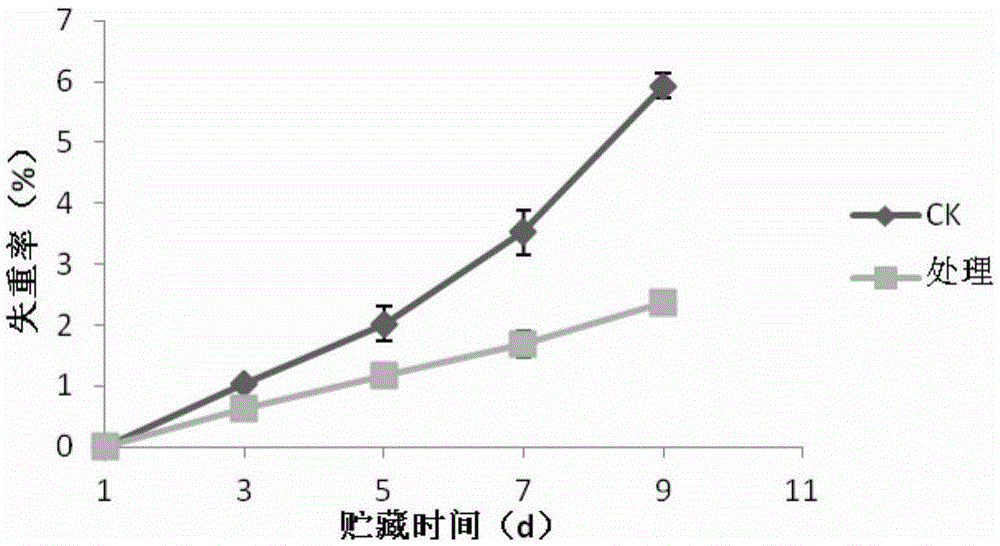
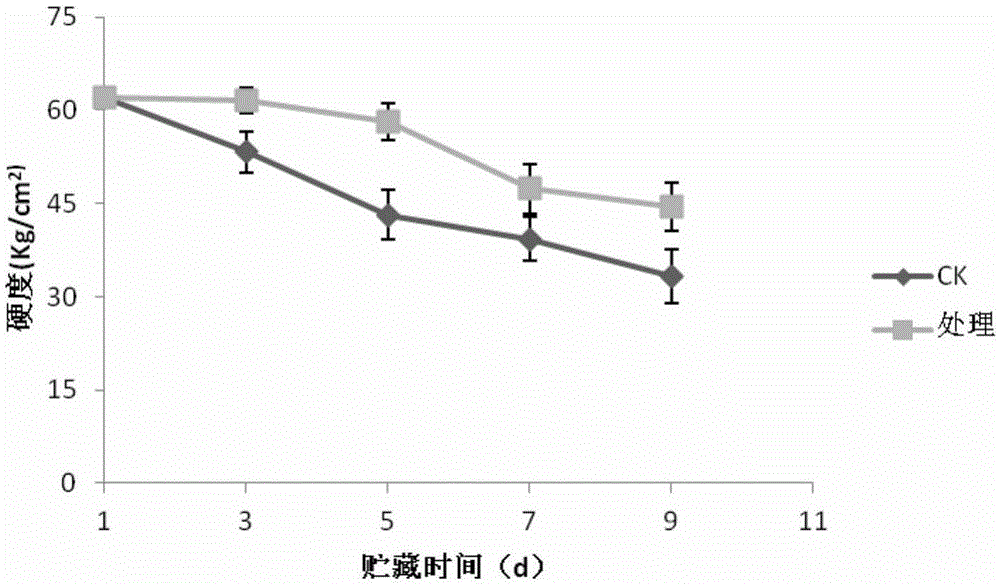
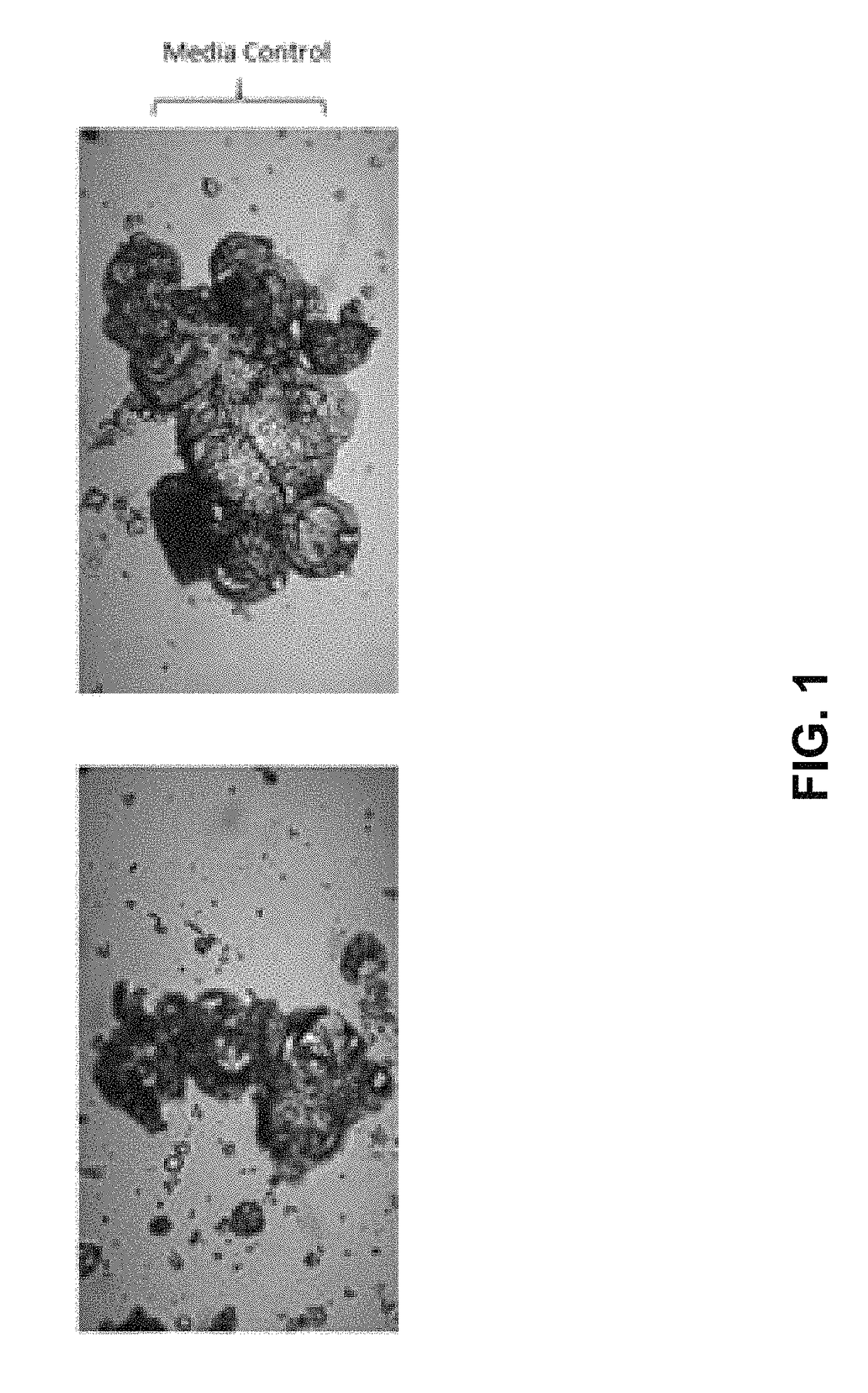
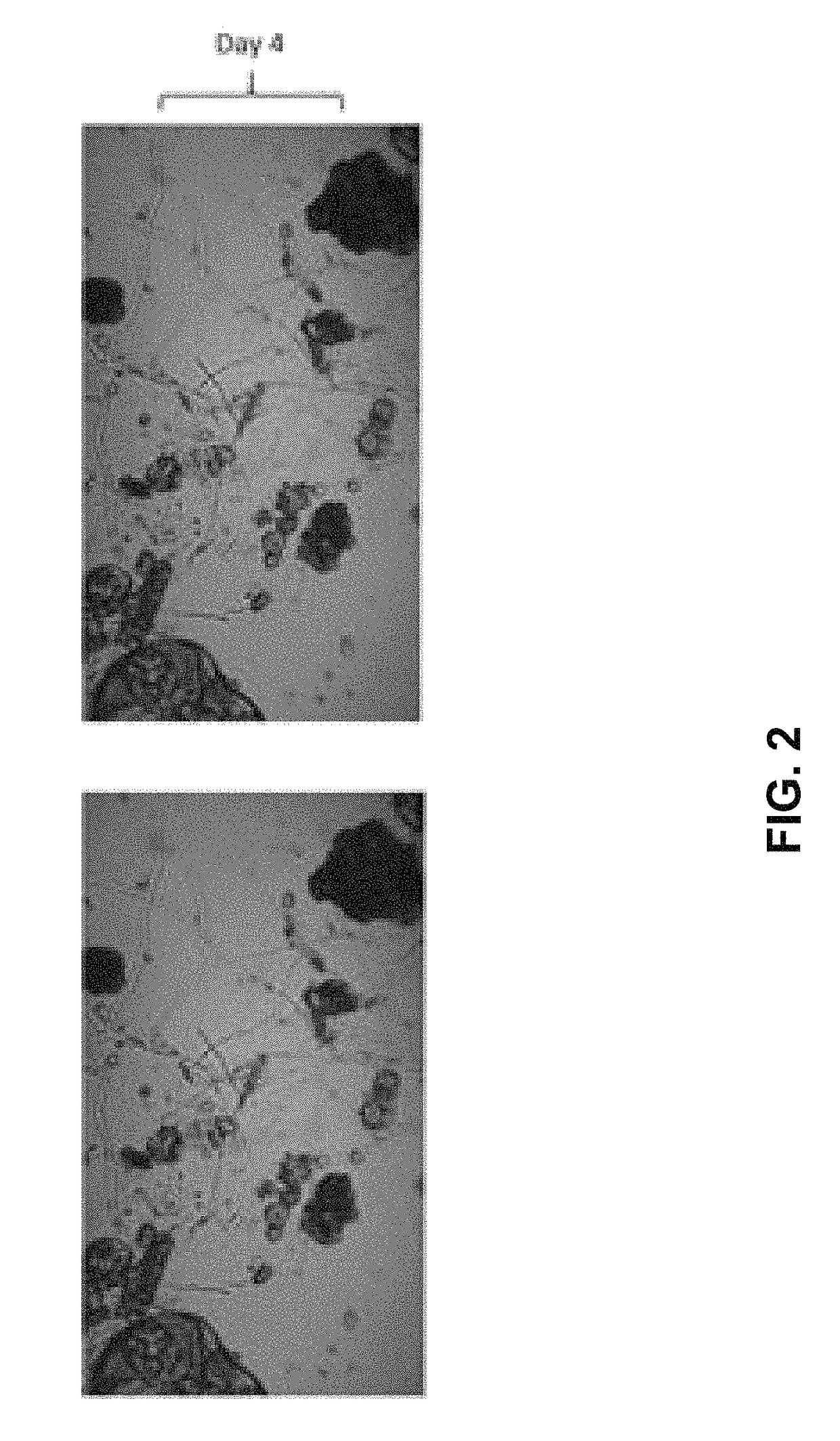
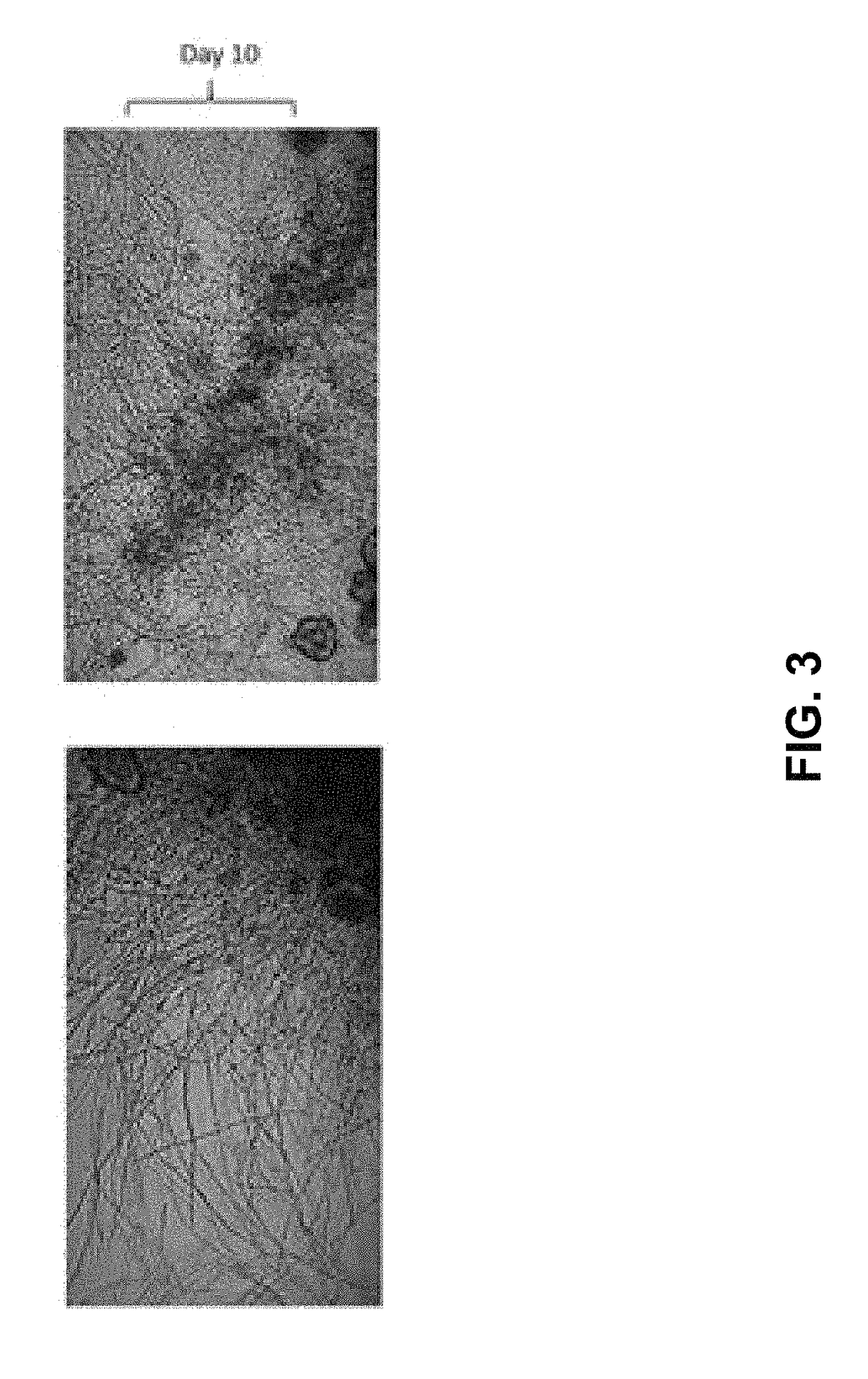
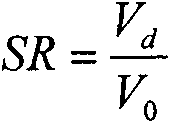Patents
Literature
453 results about "Agaricus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agaricus is a genus of mushrooms containing both edible and poisonous species, with possibly over 300 members worldwide. The genus includes the common ("button") mushroom (Agaricus bisporus) and the field mushroom (Agaricus campestris), the dominant cultivated mushrooms of the West.
Industrial cultivation method of selenium-enriched agaricus bisporus
InactiveCN101637101AIncrease productionFull of nutritionHorticultureFertilizer mixturesCaladiumAgaricus
The invention provides an industrial cultivation method of selenium-enriched agaricus bisporus, The cultivation materials comprises the materials based on the following part by weight: 100-300 parts of straw, 100-300 parts of cow dung, 0.5-1 part of urea, 0.5-1 part of ammonium bicarbonate, 0.5-1 part of superphosphate, 1-2 parts of lime, 1-2 parts of cake fertilizer, 0.1-0.3 parts of sodium selenite, etc. The invention also provides a series of industrial cultivation methods such as the preparation of mushroom seeds, the preparation of paved soil, the cultivation of the selenium-enriched agaricus bisporus, etc. The cultivation method has low cost, simple and convenient operation and easy realization, and can cultivate the agaricus bisporus with high yield and abundant nutrition, wherein the content of organic selenium generally can reach more than 0.5-1%. The selenium-enriched agaricus bisporus is dried in a drying oven till that moisture content is less than 5%, is crashed and screened to obtain the organic selenium powder; and the organic selenium powder is taken as raw materials to be matched with spirulina, lucid ganoderma, and the like, to prepare various selenium-enriched nutritious foods such as granules, troche, oral liquid, and the like, thereby having wide application range.
Owner:蛟河市黑土白云食用菌有限公司
Production method for planting agaricus bisporus by using mushroom residues of pleurotus eryngii
InactiveCN101940127AAvoid pollutionBody hair bacteria fastClimate change adaptationBioloigcal waste fertilisersCaladiumAgaricus
The invention discloses a production method for planting agaricus bisporus by using mushroom residues of pleurotus eryngii. The agaricus bisporus consists of the following substances in percentage by weight: 40 to 60 percent of mushroom residues, 20 to 40 percent of corn straws, 10 to 30 percent of cow dung, 1 to 3 percent of urea, 1 to 3 percent of lime and 0.5 to 2.5 percent of calcium superphosphate. In the production method for planting agaricus bisporus by using the mushroom residues of pleurotus eryngii, the routine production process for culturing agaricus bisporus is adopted, wherein the process comprises the following steps of: pre-wetting raw materials, piling the materials, turning over the piles, placing and laying the piled materials on a frame, fermenting the materials, seeding the materials, mycelium culture, earthing, taking out and managing the agaricus bisporus and harvesting fruit bodies. Because the mushroom residues for producing pleurotus eryngii are recycled to serve as the material for planting agaricus bisporus, environmental pollution is avoided and the aim of clean growth and environmental protection is fulfilled.
Owner:李文生
Mycellated grain and other myceliated agricultural materials to be used as animal food supplement
InactiveUS20080187574A1Improve feed conversionImprove biological activityBiocideMicroorganismsCelluloseWeight gaining
Animal feedstuff having beneficial properties is obtained by adding to a substrate one or more fungal species of the kind that excretes substances into said substrate during its growth which are beneficial to the health, growth or weight gain of an animal, or animals to which the feedstuff is intended and allowing the fungus to grow and / or ferment on the substrate. Suitable substrates are cereal grains, residue of cereal grains, agricultural primary products, agricultural waste products, and other cellulosic materials or a combination of one or more of the same. Suitable fungus species include Cordyceps species, Ganoderma species, Grifola species, Trametes Species, Lentinula species, Antrodia species, Agaricus species, Tremella species, Pleurotus species, Lentinus species, Polypore species, Agaricales species, Ascomycetes species and Basidiomycetes species. Some substrates such as certain agricultural waste products and cellulosic material are not suitable for animal consumption per se but become suitable as a result the fungal growth and fermantation by the fungus or fungi on and in them.
Owner:AMI NEWCO LLC
Method for extracting agaricus lentinan
The invention discloses a method for extracting agaricus lentinan. The method comprises the following steps: pulping agaricus bisporus; adjusting pH value of the pulp; carrying out composite hydrolysis on the pulp; passivating enzyme; carrying out microwave treatment on the pulp; preserving temperature of the pulp; filtering the pulp; centrifuging the pulp; concentrating the pulp under reduced pressure; removing protein of the pulp by an Sevage method; precipitating alcohol; centrifuging the pulp; filtering the pulp by a membrane; adsorbing the pulp by resin; desorbing the pulp; concentrating the pulp in vacuum; and drying the pulp in vacuum to obtain the agaricus lentinan. The method has the characteristics of high extraction rate and high extracting purity of the agaricus lentinan, and has no emission of pollutant in a technical process, low energy consumption and reasonable design of the process method.
Owner:BERLIN
Production method for cultivating agaricus bisporus by using pleurotus eryngii dreg
InactiveCN103130579ASolve wasteHigh nutritional valueHorticultureFertilizer mixturesNutritive valuesAgaricus
The invention relates to a production method for cultivating agaricus bisporus by using pleurotus eryngii dreg. The production method is characterized in that the cultivation base material comprises the following ingredients in percentage by mass: 50-60% of mushroom dreg, 15-25% of crop waste, 20-30% of livestock excrement, 0.01-0.02% of an auxiliary material calcium superphosphate and 0.05-0.08% of light calcium carbonate. By utilizing the method, not only is the energy waste problem solved, the production cost lowered, the working intensity alleviated, and the fermentation time shortened, but also the nutritive values of the agaricus bisporus are improved, so that the production method can be popularized and used in large scale.
Owner:盐城中绿生物科技有限公司
Methods for the Production and Use of Myceliated High Protein Food Compositions
ActiveUS20180303044A1Alter tasteAlter flavorFood ingredient as taste affecting agentFood ingredient as flavour affecting agentAgaricusDry weight
Disclosed is a method to prepare a myceliated high-protein food product, which includes culturing a fungi an aqueous media which has a high level of plant protein, for example at least 20 g protein per 100 g dry weight with excipients, on a dry weight basis. The plant protein can include pea, rice and / or chickpea. The fungi can include comprises Lentinula spp., Agaricus spp., Pleurotus spp., Boletus spp., or Laetiporus spp. After culturing, the material is harvested by obtaining the myceliated high-protein food product via drying or concentrating. The resultant myceliated high-protein food product may have its taste, flavor, or aroma modulated, such as by increasing desirable flavors or tastes such as meaty, savory, umami, popcorn and / or by decreasing undesirable flavors such as bitterness, astringency or beaniness. Deflavoring and / or deodorizing as compared to non-myceliated control materials can also be observed. Also disclosed are myceliated high-protein food products.
Owner:MYCOTECH
Selenium-rich agaricus bisporus production method using selenium-rich crop straws
InactiveCN104604519ASolving RecyclingImprove protectionCalcareous fertilisersExcrement fertilisersAgaricusBiotechnology
The present invention discloses a selenium-rich agaricus bisporus production method using selenium-rich crop straws. Selenium-rich crop straws with 50%-70% of the total weight of cultivation dry materials are mixed into the cultivation dry materials. The selenium-rich agaricus bisporus production method uses natural selenium-rich crop straws as raw materials, has a high selenium utilization and no pollution problems, and can solve the crop straw recycling problem, is environmentally friendly, is simple and easy to operate, and improves the selenium content of agaricus bisporus to 0.2-1.5 mg / kg.
Owner:ANHUI YULONG NEW MATERIALS TECH
Method for separating agricus bisporus polysaccharides from agricus bisporus and determining method thereof
ActiveCN101787085ALow yieldEasy to zoom inColor/spectral properties measurementsAgaricusFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a method for separating agricus bisporus polysaccharides from agricus bisporus, which comprises the following steps: carrying out vacuum freeze-drying on the agricus bisporus for 24h; extracting crude polysaccharides with hot water: adding distilled water, boiling with big fire, maintaining with slow fire, centrifuging, taking supernatant liquid, precipitating, placing back into a heating device, adding water for continuous heating till boiling, maintaining with the slow fire, re-centrifuging and taking the supernatant liquid; repeating for three times, and using the distilled water for fixing volume of the obtained supernatant liquid for standby; carrying out dual-water phase extraction operation: precisely weighing 2.66g of polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000 and 4.28g of ammonium sulfate, adding into a 50mL centrifuge tube, adding 20mL of sample diluent, and evenly mixing; simultaneously weighing 2.66g of PEG 6000 and 4.28g of ammonium sulfate, adding into the 50mL centrifuge tube, adding 20mL of distilled water, evenly mixing, and obtaining the agricus bisporus polysaccharides distributed in the PEG phase. The utilization of a dual-water phase system for extracting the agricus bisporus polysaccharides can realize the maximum yield of 80.1%, and the yield can achieve 17.45mg / g.
Owner:天津市金三农农业科技开发有限公司
Method for producing organic fertilizer by utilizing wastes of materials for planting agaricus bisporus
InactiveCN103183570AEfficient use ofSolve the breathability problemFertilizer mixturesAgaricusPotassium
The invention relates to a method for producing an organic fertilizer by utilizing wastes of materials for planting agaricus bisporus, belongs to the field of agricultural technology and is used for regulating components in the wastes of the materials for planting the agaricus bisporus so as to prepare the organic fertilizer easily absorbed by plants. The organic fertilizer produced by the method provided by the invention comprises the following effective components in parts by weight: the agaricus bisporus wastes, perlite, silica, a water-retaining agent, saw dust and a slow release fertilizer. According to the method, the wastes of the materials for planting the agaricus bisporus are utilized effectively; and the effective components are added. Therefore, nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium and trace elements in the wastes are suitable for plant growth; and the problems of air permeability, water retention and water absorptivity in the wastes are solved. The organic fertilizer is mainly suitable for vegetables, flowers, economic crops, tobaccos and the like.
Owner:敦化市吉祥农业科技有限公司
Method for increasing yield of agaricus bisporus
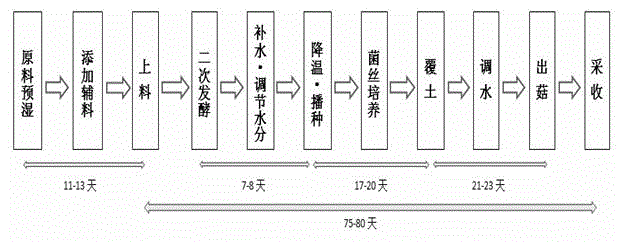
ActiveCN104920070AIncrease productionReduce pollutionCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationAgaricusFermentation
The invention discloses a method for increasing the yield of agaricus bisporus. The method includes the following steps of raw material preparation, primary fermentation, after fermentation, sowing, earthing management, fruiting management and falling rock discharge, and harvesting. According to the method, an M-shaped bed surface is arranged to increase the batch charging quantity, the heat radiating area and the unit fruiting quantity, explosive fruiting is achieved at the early stage, and finally the purpose of increasing the yield of agaricus bisporus and the purpose of increasing benefits are achieved. By the adoption of the method, resources such as agricultural production waste corncobs and farm animal excrement are fully utilized, environmental pollution is greatly lowered, and the production cost is saved.
Owner:SUQIAN AGRI SCI RES INST JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Agaricus bisporus growing fungicide and an agaricus bisporus cultivation method by using the fungicide
InactiveCN104541969ASimple structureNo pollution in the processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFungicide
The invention belongs to the technical field of edible fungi cultivation, and particularly relates to an agaricus bisporus growing fungicide and an agaricus bisporus cultivation method by using the fungicide. Active ingredients in the fungicide can generate microorganism with activated calcium carbonate (ACC) deaminase. The agaricus bisporus cultivation method comprises the steps of seed production, training material production, planting, spawn running, earthing, fruiting and harvesting. By a research of the earthing and fruiting mechanism of the agaricus bisporus, the agaricus bisporus growing fungicide is prepared, and an agaricus bisporus cultivation technology is provided; according to the technology, an earthing material is selected and replaced, the traditional soil is replaced by vermiculite with the ACC deaminase, so that the fruiting time can be ahead of time, and the fungicide has the advantages of no plant diseases and insect pests and high yield; and the vermiculite has an advantage of improving the oil structure, so that the fungicide and the cultivation method have good promotion and application value.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Agaricus bisporus cultivation material manufacturing method and agaricus bisporuscultivation method
InactiveCN105210672AHigh in nutrientsIncrease productionCalcareous fertilisersSuperphosphatesCaladiumAgaricus
The invention provides a agaricus bisporus cultivation material manufacturing method and a cultivation method, and the manufacturing method comprises the steps of the preparation of the cultivation material, bag packaging to obtain a bar, disinfection, inoculation, sterilization and fruiting; the formula of the cultivation material comprises 70% bran, 10% wheat bran, 2.5% quicklime, 1% gesso, 8% corn flour, 6% lima bean powder, 2% potato powder, 0.03% sulfate, 0.04% zinc sulfate, 0.08% calcium superphosphate, 0.2% glucose and 0.15% vitamin D; trace element and vitamin necessary to human body are added into the cultivation material, thereby raising nutrition components for the agaricus bisporus and providing a beneficial environment for agaricus bisporus's growing; a black cultivation bag is used for packaging, which is more suitable for creating a dark wet environment and the agaricus bisporus is whiter than a white plastic foil and has a much better color; and the bar is put in a production environment which is more suitable for agaricus bisporus's growth, thereby raising agaricus bisporus's output.
Owner:成都鑫万福农业开发有限公司
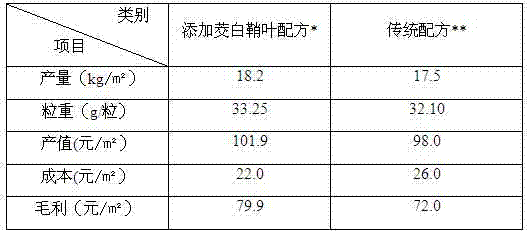
Method for cultivating agaricus bisporus by utilizing zizania latifolia turcz sheathing leaves
InactiveCN102498941ARealize resource utilizationSolve the problem of resource shortageHorticultureFertilizer mixturesAgaricusMycelium
The invention provides a method for cultivating agaricus bisporus by utilizing zizania latifolia turcz sheathing leaves. According to the cultivation method, straw in the conventional compost for the agaricus bisporus is replaced by using the zizania latifolia turcz sheathing leaves to cultivate the agaricus bisporus. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing a compost, prewetting, establishing material stack, fermenting for the first time, fermenting for the second time, cooling to room temperature, sowing, culturing for mycelium running, earthing, fruiting and harvesting. According to the method, the agaricus bisporus is cultivated by replacing the straw with the zizania latifolia turcz sheathing leaves, so that the problem of sources of raw and auxiliary materials for the agaricus bisporus is solved, the production cost is reduced, the production benefit of edible mushrooms is improved, the sustainable development of edible mushroom industry is facilitated, the zizania latifolia turcz sheathing leaves can be recycled, the pollution caused by the discharge of leftovers in the zizania latifolia turcz planting industry is relieved, the utilization value of the zizania latifolia turcz sheathing leaves is improved, and the method can create obvious economic and ecological benefit.
Owner:INST OF EDIBLE FUNGI FUJIAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
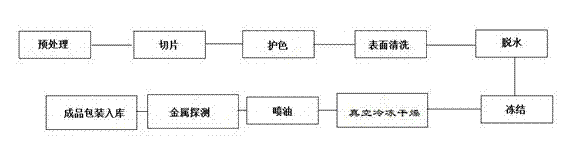
Processing method of dehydrated agaricus bisporus
InactiveCN101554185AReduce sulfur dioxideFood preparationFruits/vegetable preservation by dehydrationAgaricusChlorine dioxide
The invention discloses a processing method of dehydrated agaricus bisporus, comprising the steps as follows: getting fresh agaricus bisporus as raw materials, washing, immersing, cutting, immersing the agaricus bisporus, protecting the colour, quick-freezing, vacuum-freezing and drying the agaricus bisporus, selecting, metal-detecting and packaging the same. In the immersing and colour protecting process, the colour retention agent is composed of the following components according to mass percent: 0.1-0.15% of chlorine dioxide, 0.01-0.02% of phytic acid, 0.01-0.3% of citric acid and the balance of water. The invention has the advantages that: the moisture of product is less than or equal to 5%, the content of sulfur dioxide is less than or equal to 30 mg / kg. In the processing step, the invention does not use sulphite to protect the colour, so the invention has low content of sulfur dioxide and is healthy to human body. The appearance of the product is white or milky white and has special taste of dehydrated agaricus bisporus; the product can be directly eaten or used as seasoning to be added into instant food, such as instant noodles, instant bean vermicelli, instant soup and the like.
Owner:HUBEI XINMEIXIANG FOODS
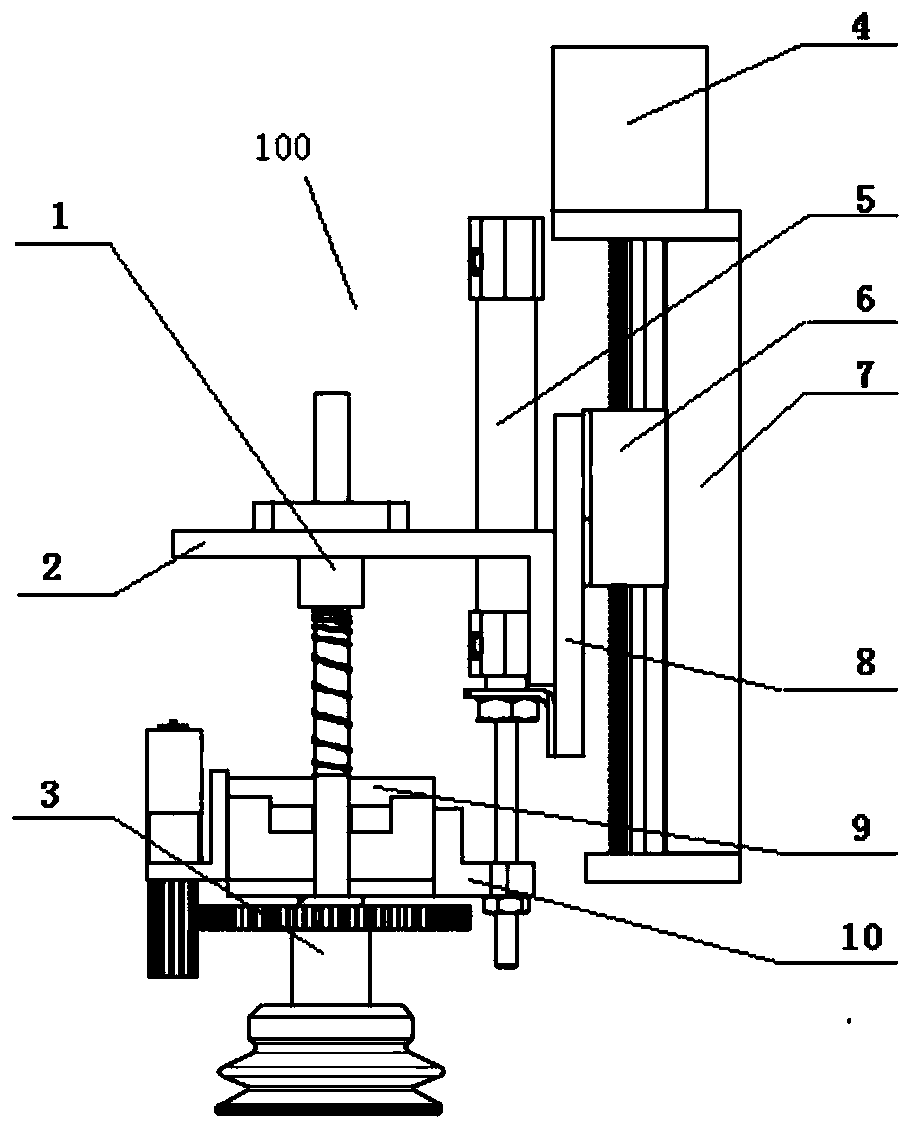
Two-section lifting self-adaptive flexible picking mechanism
PendingCN111011112AReduce volumeRotary controls are compactCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationAgaricusAgricultural engineering
The invention provides a two-section type lifting self-adaptive flexible picking mechanism. The two-section type lifting self-adaptive flexible picking mechanism comprises a flexible tail end pickingmechanism (3), a sliding sleeve and sliding rod lifting mechanism (1) and a linear position movement lifting mechanism (7). By means of the two-section lifting structure, the contradiction that in actual industrial production, due to the fact that the height space of a culture frame is small, a common single-section lifting mechanism cannot meet the requirement for the large picking change stroke,and picked agaricus bisporus can be conveyed to a collecting conveying belt to be collected at a high speed is solved; and high-efficiency harvesting of actual industrial intelligent picking of the agaricus bisporus is facilitated. The lifting self-adaptive flexible picking mechanism can adapt to large picking stroke, is high in flexibility and compact in structure, well solves the key problem ofefficient harvesting of industrial actual production of edible mushrooms, and is beneficial to well promoting the industrialization process of intelligent agaricus bisporus picking. The method is also suitable for picking edible mushrooms with similar cultivation modes such as Portobello mushroom and straw mushrooms.
Owner:SHANGHAI SECOND POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Antiviral activity from medicinal mushrooms
InactiveUS20050238655A1Reduce usageUseful in treatmentSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideAgaricusMedicine
Compounds having unique antiviral properties are prepared from medicinal mushroom mycelium, extracts and derivatives. The compositions are derived from Fomitopsis, Piptoporus, Ganoderma resinaceum and blends of medicinal mushroom species and are useful in preventing and treating viruses including Pox and HIV viruses.
Owner:TURTLE BEAR HLDG LLC
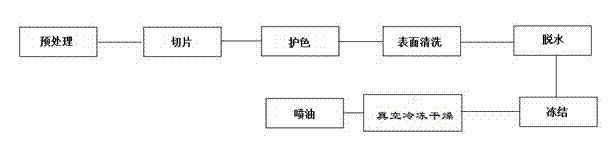
Preparation method of freeze-drying oil-injection sliced agaricus bisporus
InactiveCN102960428AReduce exposureEasy to storeFruits/vegetable preservation by coatingAgaricusAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a preparation method of free-drying oil-injection sliced agaricus bisporus. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preprocessing, slicing and protecting color and also comprises the steps of sterilizing, cleaning surfaces, dewatering, freezing, conducting vacuum freeze-drying and injecting oil. The freeze-drying oil-injection sliced agaricus bisporus prepared by the method does not damage the original color, aroma and taste and shape of a product; the nutrition ingredients can not be lost, the production efficiency is high, and the yielding rate is high; and the prepared sliced agaricus bisporus has low water content (below 4%) so as to be light in weight, and is easy to store.
Owner:四川江茂食品有限公司
Method applying wood rotting fungus dregs to industrial cultivation of agaricus bisporus
InactiveCN104604532AShorten the timeIncrease profitSuperphosphatesCultivating equipmentsAgaricusEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of edible fungus cultivation and particularly relates to a method applying wood rotting fungus dregs to industrial cultivation of agaricus bisporus. The formulation of substrate adopted in the method comprises 69-98.5% of the wood rotting fungus dregs, 0-29% of cow dung, 0.6-0.7% of salt, 0.3-0.4% of calcium superphosphate, 0.3-0.4% of light calcium and 0.3-0.5% of lime, and temperature control is implemented in the cultivation process. The wood rotting fungus dregs are used for industrial cultivation of the agaricus bisporus, cost can be saved greatly, overall economic benefits are increased, and industrial cultivation of the agaricus bisporus is realized. The mushroom dreg waste after production of the wood rotting fungi is utilized effectively, so that utilization ratio of raw materials is increased. Due to the fact that industrial cultivation of the agaricus bisporus is added with temperature control facilities as compared with conventional cultivation, time from sowing to fruiting of the agaricus bisporus can be saved, the waste can be used for producing organic fertilizer or directly used as fertilizer to improve soil fertility after being treated simply, and the overall thinking of circular agriculture is conformed to.
Owner:福建绿宝食品集团有限公司
Method for liquid fermentation cultivation of Agaricus bisporus strain
The invention discloses a method for liquid fermentation cultivation of Agaricus bisporus strain, which includes: firstly, inoculating activated slant culture 0.5cm2 into a 250mL culture bottle containing 60-120mL of liquid medium, controlling temperature to be 21-27 DEG C, shaking at 90-180rpm, culturing for 5-7 days to obtain primary shaking strain, transferring primary seeds accounting for 5-10% of the inoculation amount to secondary culture liquid for cultivation, transferring cultured secondary shaking liquid strain to tertiary culture liquid for cultivation, and sequentially performing all levels of cultivation to obtain seed broth by the same methods; and secondly, inoculating the seed broth accounting for 5% of the inoculation amount into a 10L fermentation jar containing 6L of fermentation medium for cultivation, and culturing at 25 DEG C for 5-6 days. The method is characterized by short production cycle, uniform fungus age, low production cost and simplicity in inoculation, a test tube of strain can be multiplied by 200000 times by five levels of cultivation, the secondary liquid strain is evidently faster than traditional solid spawn in growth speed, and the speed is increased by 33%. In addition, the growth speeds of all levels of the liquid strain are nearly equal, the average fullness time is 27.5 days, and the method is absolutely applicable to practice of factory production.
Owner:江苏众友兴和菌业科技有限公司
Culture base material for cultivating agaricus bisporus by edible fungus production waste and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102531723ABroaden sources of raw materialsThe formula is reasonable and reliableBio-organic fraction processingOrganic fertiliser preparationAgaricusBiotechnology
The invention provides a culture base material for cultivating agaricus bisporus by edible fungus production waste and a preparation method thereof. The culture base material comprises the following raw material and auxiliary materials: the raw material is edible fungus production waste; the auxiliary materials comprise cotton seed hull, corn cob, wheat bran, plaster, lime, urea, calcium superphosphate and sugar, wherein the culture base material comprises the following materials in percentage by weight: 15+ / -1 percent of corn cob, 15+ / -1 percent of cotton seed hull, 12+ / -1 percent of wheat bran, 1+ / -0.1 percent of plaster, 3+ / -0.1 percent of lime, 1+ / -0.1 percent of urea, 2+ / -0.1 percent of calcium superphosphate, 0.5+ / -0.1 percent of sugar, 0.5+ / -0.1 percent of fermentation promoter and the balance of edible fungus production waste. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: weighing the corn cob, the cotton seed hull, the wheat bran, the plaster, the lime, the urea, the calcium superphosphate, the sugar, the fermentation promoter and the edible fungus production waste according to weight percentage; preparing; pre-wetting; mixing the raw material and the auxiliary materials; performing primary fermentation; bagging; and sterilizing under normal pressure to prepare the culture base material for cultivating agaricus bisporus. The culture base material has the advantages of rational formula, and simple and reliable preparation method; the cultivated agaricus bisporus has reliable quality, is low in cost and has good market prospect.
Owner:天津市绿谷农庄农产品种植有限公司
Culturing substrate for industrially cultivating agaricus bisporus and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102093105AImprove ventilationReduce manufacturing costFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyAgaricus
The invention discloses a culturing substrate for industrially cultivating agaricus bisporus and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the technical field of cultivation of edible fungi. In the technical scheme, the culturing substrate consists of raw materials and auxiliary materials such as corn straws, wheat straws, chicken manure and gypsum, and is prepared by material preparation, mixing, primary fermentation and secondary fermentation; and the culturing substrate has the nitrogen content of between 2.0 and 2.2 percent, the pH value of between 7.5 and 8.2, the water content of between 65 and 70 percent, the total sugar content of between 10 and 18 percent and the reducing sugar content of between 0.3 and 0.9 percent, is deep brown, contains a large number of visible actinomyces, is non-sticky when held by hands, is elastic, smells like the flavor of bread, has small tension and can be scattered and broken by the hands, and over 65 percent of wax is removed from the straws. Compared with the prior art, the culturing substrate has the advantages of expanding the raw material source of the agaricus bisporus culturing substrate, realizing local acquisition of materials, lowering the production costs of raw materials and enhancing economic benefits; moreover, the culturing substrate has a reasonable formula, reliable physical and chemical property indexes and good social and economic benefits, is fully accordant with the growth requirement of the agaricus bisporus, and increases the yield of the agaricus bisporus in each square meter area by 6.96 kilograms and the profit in each square meter area by 63.96 yuan compared with those of the prior art.
Owner:中国农业大学烟台研究院
Selenium-rich agaricus bisporus cultivation material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104557305APositive and beneficial technical effectsRaw material ratio is reasonableCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingAgaricusDrug biotransformation
The invention relates to a selenium-rich agaricus bisporus cultivation material and a preparation method thereof. The cultivation material consists of the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 50 to 60 percent of straw, 15 to 25 percent of selenium-rich alfalfa meal, 15 to 25 percent of corncob, 1 to 2 percent of calcium carbonate, 1 to 3 percent of calcium superphosphate, 1 to 3 percent of gypsum powder and 1 to 3 percent of lime powder. According to the selenium-rich agaricus bisporus cultivation material provided by the invention, the proportion of the raw materials is reasonable; the nutrition is balanced; the C / N meets the cultivation requirement of agaricus bisporus; the biotransformation efficiency and the selenium utilization rate are high; the selenium content of the agaricus bisporus produced by utilizing the cultivation material according to the conventional cultivation method is 0.15 mg / kg to 3.0 mg / kg, and is 30 to 60 times that of the common agaricus bisporus; the agaricus bisporus is rich in nutrition, is a very good selenium supplement green health product, and is wide in development prospect.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & ECONOMY
Edible mushroom fresh keeping agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105410167AImprove anti-corrosion performanceExtend freshnessNatural extract food ingredientsFruits/vegetable preservation by coatingAgaricusSuillus
The invention discloses an edible mushroom fresh keeping agent and a preparation method thereof. The edible mushroom fresh keeping agent is prepared from the following components: sarcodon quel fruiting body enzyme extraction liquid, dictyophora echinovolvata fruiting body enzyme extraction liquid and chitosan in the weight ratio of the sarcodon quel fruiting body enzyme extraction liquid, to the dictyophora echinovolvata fruiting body enzyme extraction liquid and the chitosan being 0.5-2:0.25-1.25:0.5-1.5. The preparation method comprises the following steps of uniformly mixing the sarcodon quel fruiting body enzyme extraction liquid, the dictyophora echinovolvata fruiting body enzyme extraction liquid and the chitosan so as to obtain a target edible mushroom fresh keeping agent. The edible mushroom fresh keeping agent disclosed by the invention is safe, non-toxic, edible, good in antiseptic effect, and long in fresh keeping time. Agaricus bisporus painted with the edible mushroom fresh keeping agent disclosed by the invention for keeping fresh, is stored in the environment of 8-12 DEG C, and after being stored for 9 days, the color, the hardness, and the mouth feel of the agaricus bisporus are not changed basically. Bolete painted with the edible mushroom fresh keeping agent disclosed by the invention, for keeping fresh, is stored in the environment of 1-3 DEG C, and after being stored for 19 days, the hardness and the mouth feel of the bolete are changed little. The edible mushroom fresh keeping agent disclosed by the invention is used for fresh keeping of edible mushrooms, so that the depletion of products is greatly reduced, and the sale benefits are increased.
Owner:云南云菌科技(集团)有限公司
Method for cultivating edible fungus using wormcast as earth covering material
InactiveCN101480137ATaking into account cost issuesClimate change adaptationExcrement fertilisersAgaricusBiology
The invention discloses a method for cultivating the edible fungus by taking worm-cast as soil-covering material, which belongs to the technical field of edible fungus cultivation in the agricultural technology. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, the daily manure is selected and is fully digested and absorbed by earthworms to generate worm-cast as the soil-covering material, the worm-cast is evenly mixed with loam and soddy soil, the soil covering is performed when the filler absorption of the mycelium of the agaricus bisporus reaches 8 to 12 cm, water is prayed to keep the soil covering layer humid, finally, when the mycelium climbs to the surface of the soil covering layer, the ventilation is carried out, and the fruiting water is spouted to promote the formation of the anlage of the agaricus bisporus. The invention takes account of the granular structure, the air permeability and the microorganisms of the soil-covering material from the aspect of the water-retaining capacity of the soil-covering material as well as the cost of the soil-covering material, solves the problem that the soil-covering material of the current agaricus bisporus is inappropriate and promotes the positive development of the agaricus bisporus industry.
Owner:江苏省天健生物科技有限公司
Special biofertilizer for cucumbers and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103524228AObvious benefits of increasing productionHas insecticidal effectFertiliser formsFertilizer mixturesAgaricusEcological environment
The invention discloses a special biofertilizer for cucumbers. The biofertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-55 parts of cucumber stems, 30-35 parts of pig manure, 20-25 parts of phosphogypsum, 20-32 parts of spent mushroom compost, 8-10 parts of peat soil, 6-10 parts of plant ash, 15-20 parts of poultry feather, 8-12 parts of borax and 0.5-1.2 parts of microbial fermented matters. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the special biofertilizer for cucumbers. Compared with the prior art, the biofertilizer has the advantages that the biofertilizer can protect the ecological environment and the farmland soil, is easily absorbed by crops, has obvious yield increase benefit, integrates double functions of fertilization and sterilization, is low in cost and is environment-friendly and pollution-free.
Owner:合肥科友生物科技有限公司
Methods for the production and use of myceliated high protein food compositions
Disclosed is a method to prepare a myceliated high-protein food product, which includes culturing a fungi an aqueous media which has a high level of protein, for example at least 20 g protein per 100 g dry weight with excipients, on a dry weight basis. The fungi can include Pleurotus ostreatus, Pleurotus eryngii, Lepista nuda, Hericium erinaceus, Lentinula edodes, Agaricus blazeii, Laetiporus sulfureus and combinations thereof. After culturing, the material is harvested by obtaining the myceliated high-protein food product via drying or concentrating. The resultant myceliated high-protein food product may have its taste, flavor, or aroma modulated, such as by increasing desirable flavors or tastes such as meaty, savory, umami, popcorn and / or by decreasing undesirable flavors such as bitterness, astringency or beaniness. Deflavoring and / or deodorizing as compared to non-myceliated control materials can also be observed. Also disclosed are myceliated high-protein food products.
Owner:MYCOTECH
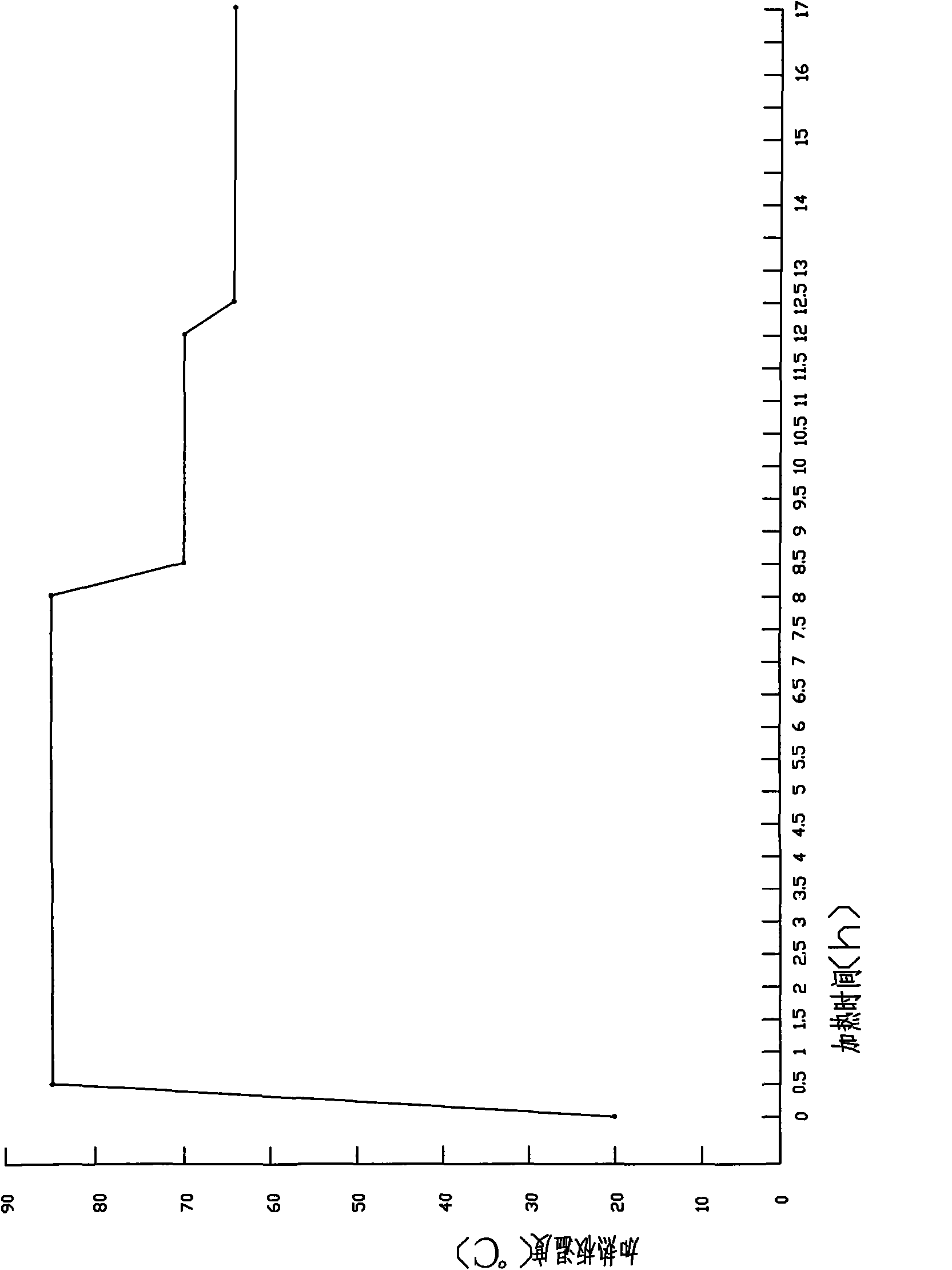
Method for uniformly drying agaricus bisporus slices through variable-frequency ultrasound-assisted impregnation pretreatment and vacuum microwaves
ActiveCN104304426AImprove uniformity of vacuum microwave dryingUniform colorFruits/vegetable preservation by dehydrationDielectricAgaricus
The invention relates to a method for uniformly drying agaricus bisporus slices through variable-frequency ultrasound-assisted impregnation pretreatment and vacuum microwaves, and belongs to the field of deep processing of agricultural products. The method comprises the following steps: cleaning agaricus bisporus and cutting into 5-8mm thick slices, protecting color by using a mixed solution of vitamin C, citric acid and calcium chloride, and carrying out variable-frequency staged ultrasound impregnation treatment on the color-protected agaricus bisporus slices: a first stage: putting the agaricus bisporus slices in clear water according to a ratio of agaricus bisporus slice to water of 1:5, and setting the water temperature to 45-50 DEG C, the ultrasonic frequency to 45KHz, the ultrasonic power to 120-150W, and the treatment time to 30-40min; a second stage: taking out the agaricus bisporus slices and putting into a mixed solution of 50-60% by mass fraction of sucrose and 5% by mass fraction of salt according to a ratio of agaricus bisporus slice to mixed solution of 1:10, and setting the water temperature to 35-40 DEG C, the ultrasonic frequency to 100KHz, the ultrasonic power to 210-240W and the treatment time to 40-50min; finally, carrying out vacuum microwave drying, and setting the microwave transmitting power to 15-20W / g, the degree of vacuum to 70-80kPa and the drying time to 15-25min. The agaricus bisporus slices subjected to variable-frequency ultrasound-assisted impregnation treatment has uniformly distributed dielectrics; when the vacuum microwave drying is carried out, a material is uniformly heated in a microwave field, and moisture is rapidly evaporated, so that the dried agaricus bisporus slice is uniformly distributed in color and luster, and is uniform in shape and better in rehydration.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
A kind of preparation method of xylitol bisporus preserved fruit
The invention discloses a preparation method of bisporus bisporus preserved fruit with xylitol, which provides a new way for bisporus bisporus edible. Soak the cleaned Agaricus bisporus in hot water at 70°C-80°C for 20 minutes to remove moisture from the Agaricus bisporus; put the soaked Agaricus bisporus into cold water to cool; put the cooled Agaricus bisporus and xylitol sugar into vacuum cooking In the can making, vacuum cooking is carried out at a vacuum degree of 0.08MPa and a temperature below 105°C until the Agaricus bisporus is sugared; the vacuum-boiled Agaricus bisporus is immersed in a vacuum environment with a vacuum degree of 0.06MPa-0.08MPa 12 hours to make the sugar uniform; wash the Agaricus bisporus with warm water to remove the surface syrup, and then dry it until the water content is about 20% and soften; dry the softened Agaricus bisporus for the second time to obtain the finished product, which will be made The preserved fruit of Agaricus bisporus is picked up and unqualified products are packed.
Owner:邢涛
Physiologically active composition and preparing method thereof
An object of the present invention is to provide a mixed composition of a herbal medicine with an effective physiological activity. The composition comprises an extract component from any one of a carpophore, a mycelium and a culture from more than two kinds of the Basidiomycete fungi selected from a group comprising a fungus belonging to Basidiomycetes Aphyllophorales Ganoderma Ganodermaceae, a fungus belonging to Basidiomycetes Polyporaceae Coriolus, a fungus belonging to Basidiomycetes Agaricales Agaricaceae Agaricus, and a fungus belonging to Basidiomycetes Agaricales Hymenochaetaceae Phellinus and an extract component from a root of a plant belonging to Araliaceae, and has an oxidation-reduction potential sufficient to express the antitumor effect and hypoglycemic effect.
Owner:GOINO TADASHI
Agaricus bisporus SSR molecular marker specific primer system and application thereof
ActiveCN105255882AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular identificationAgaricus
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com