Patents
Literature
4789results about How to "Easy to charge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
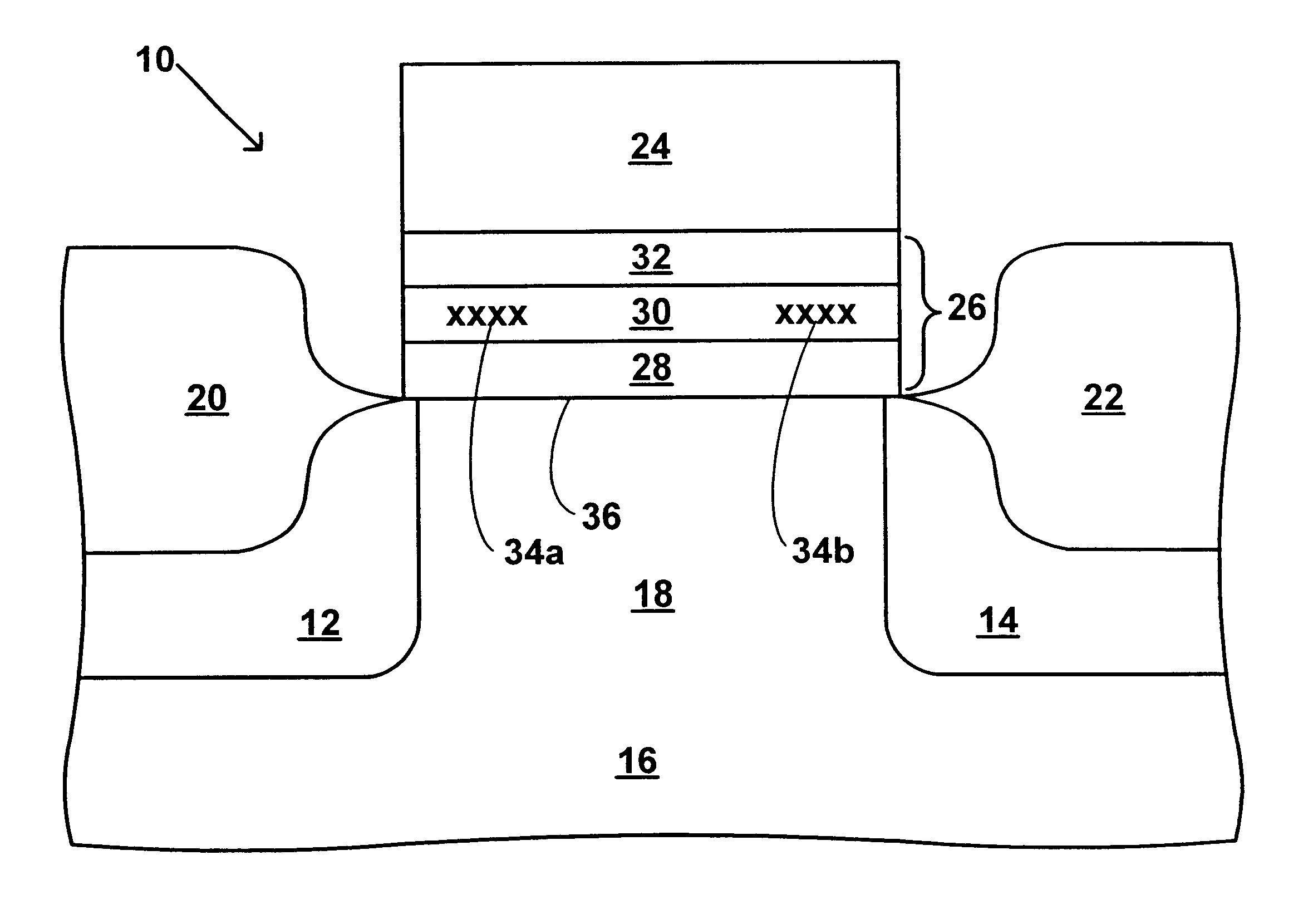
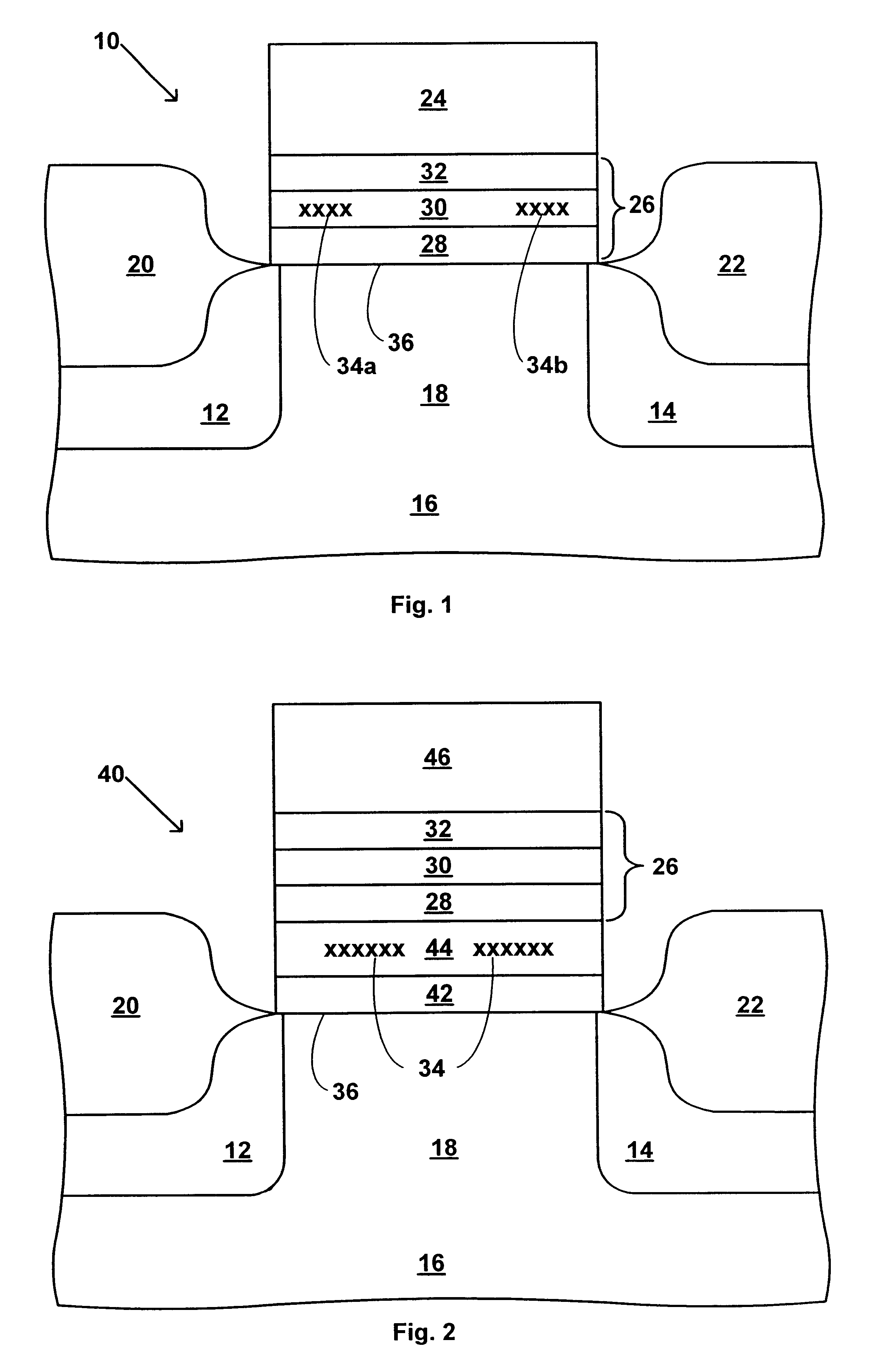
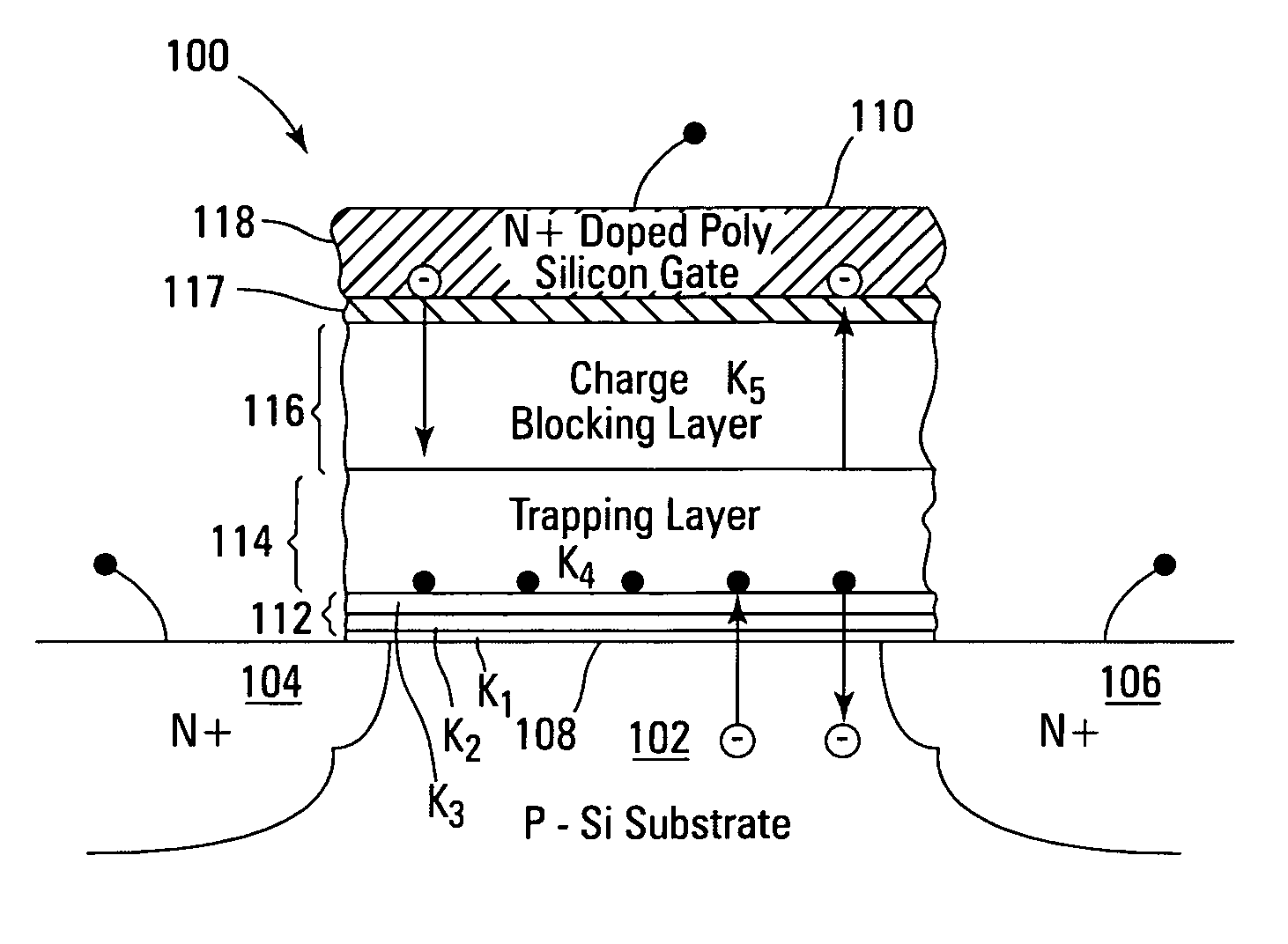
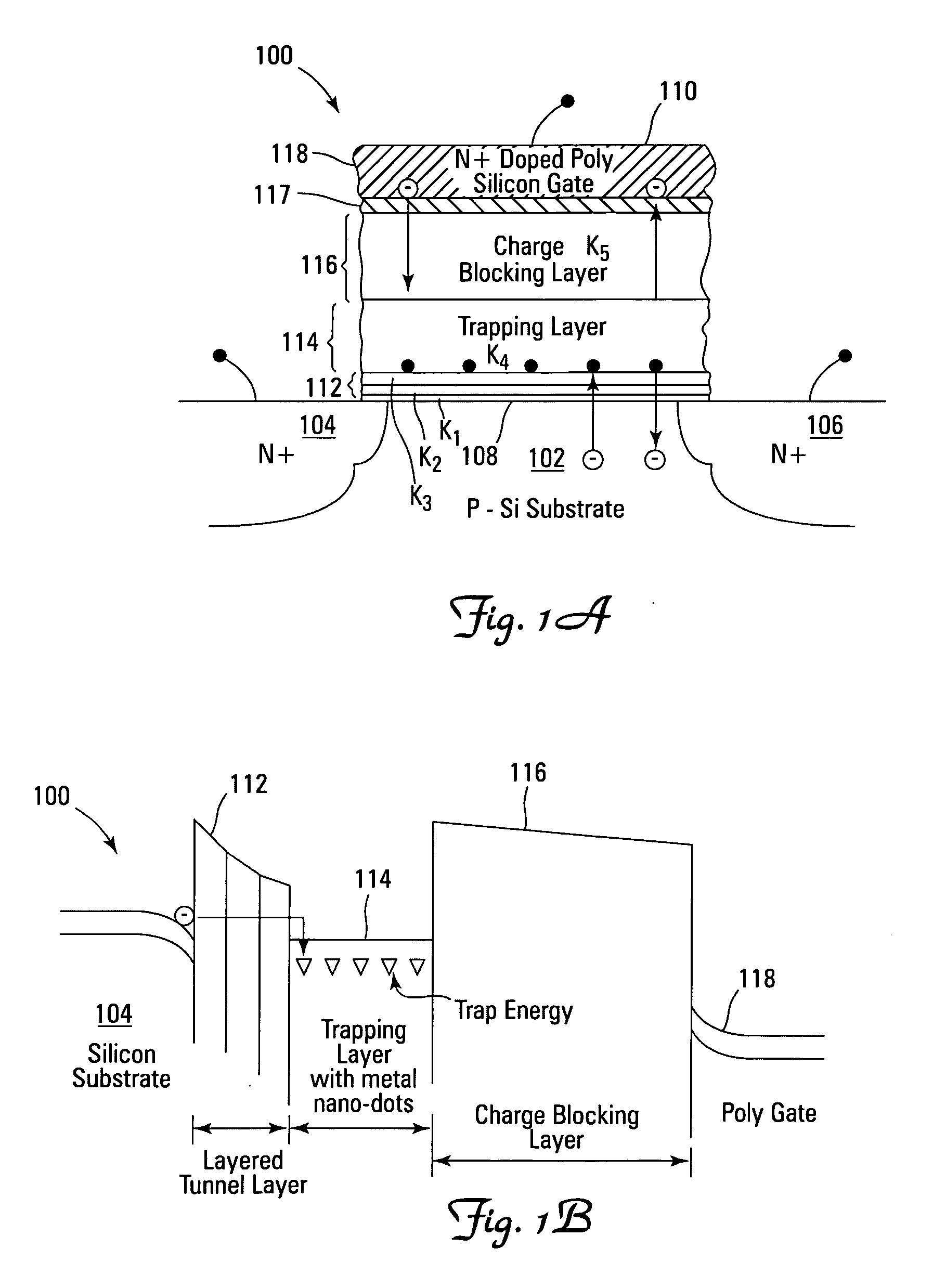
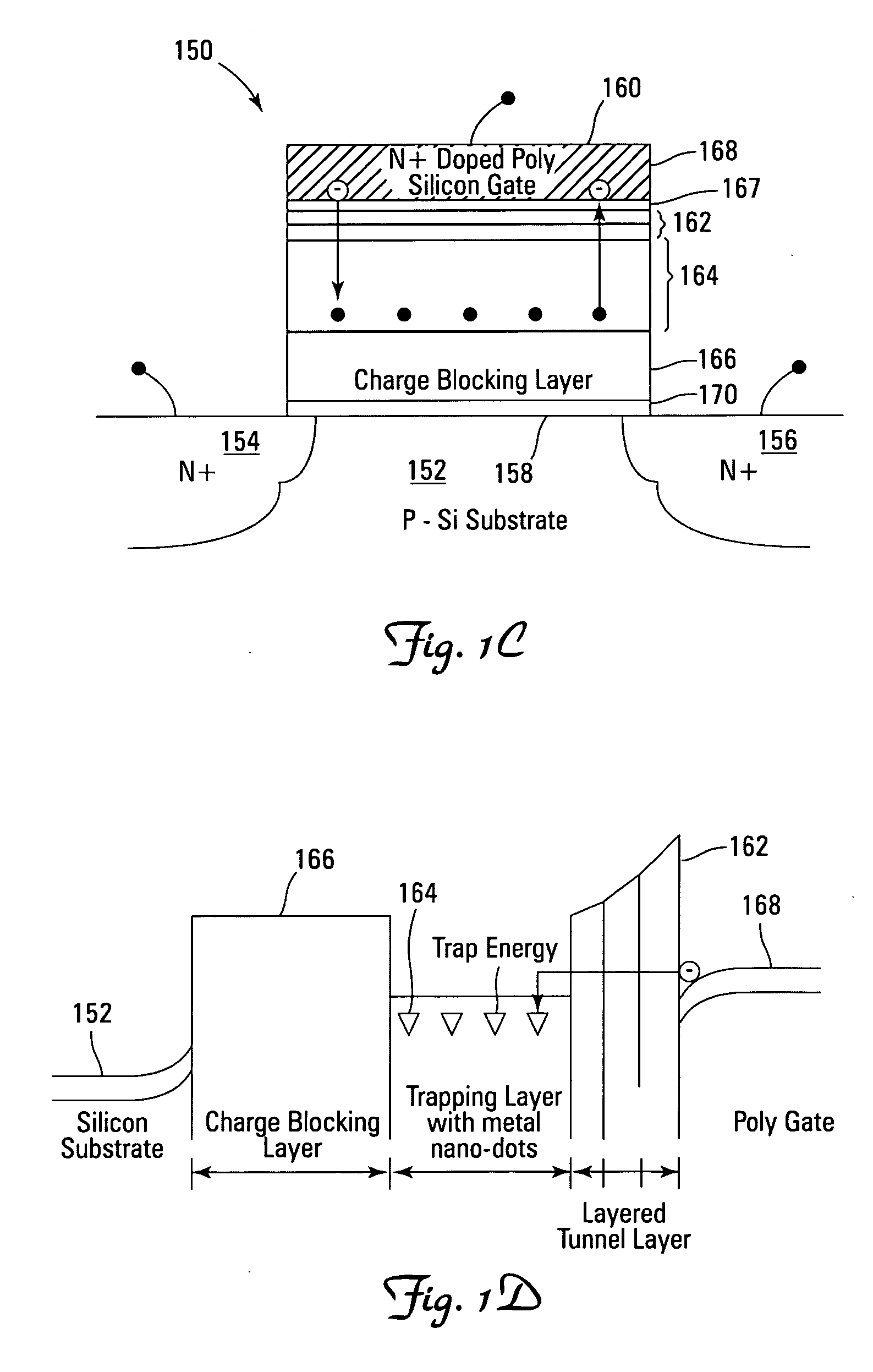
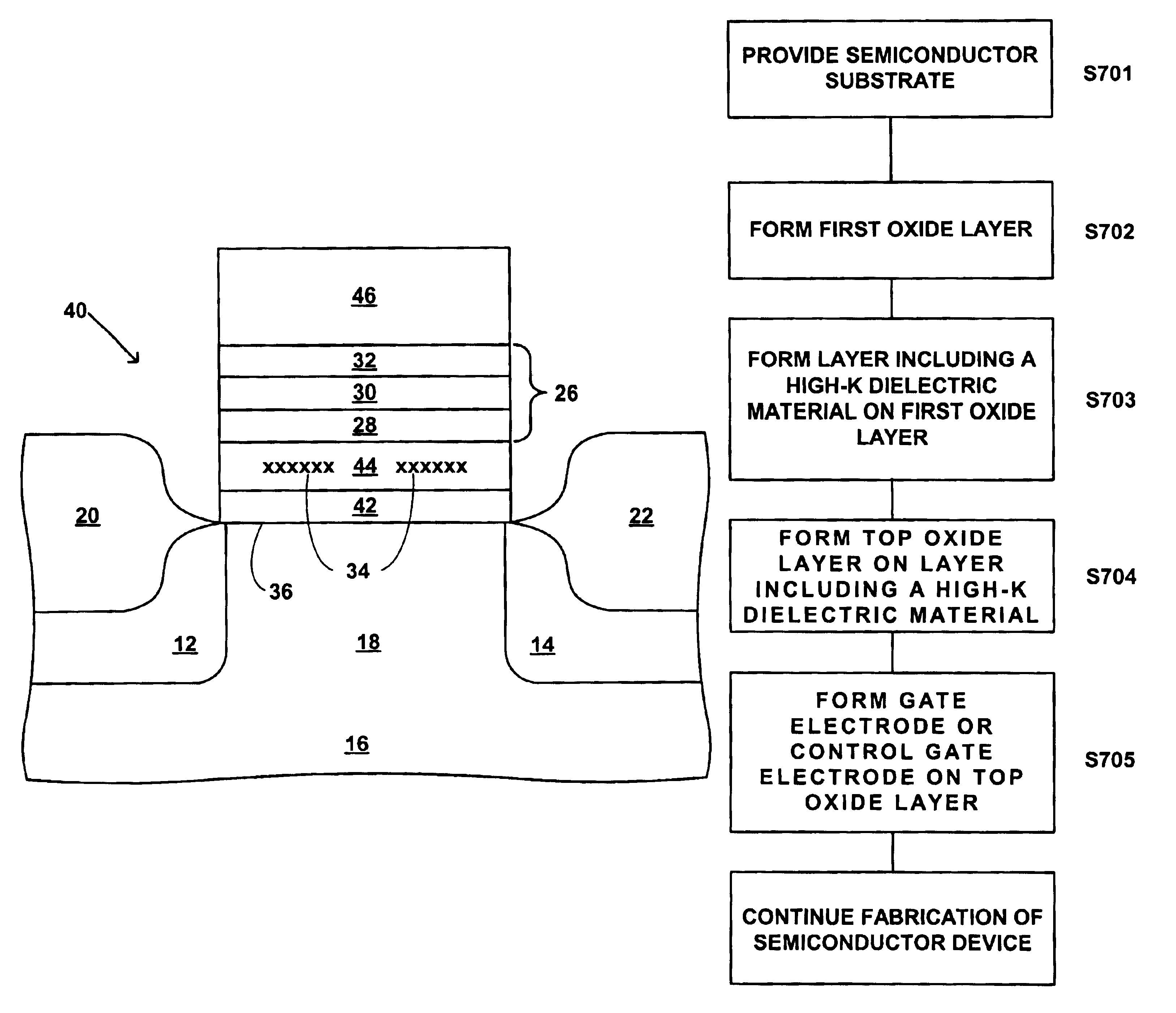
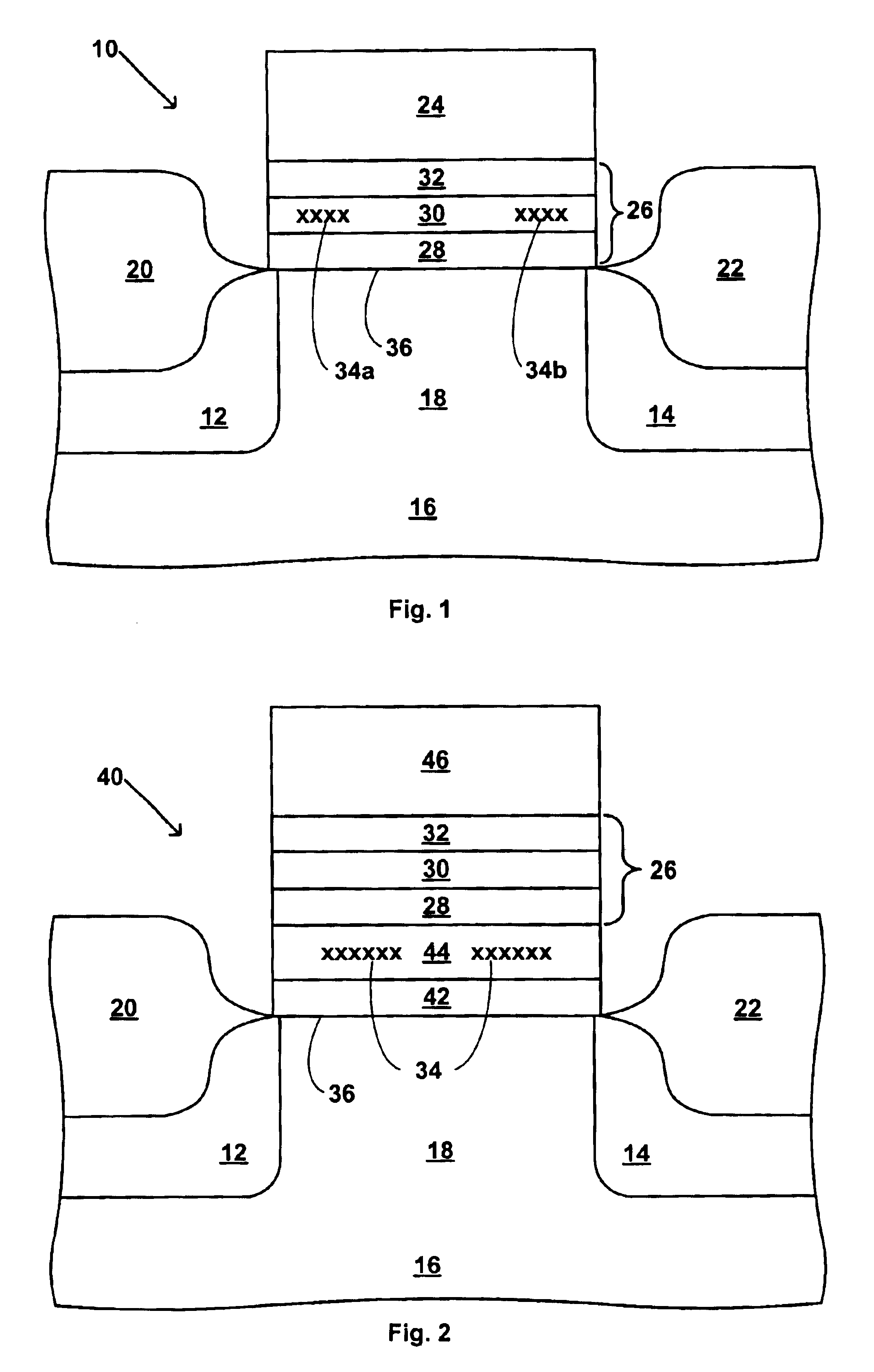
Use of high-k dielectric materials in modified ONO structure for semiconductor devices
InactiveUS6674138B1Reduced dimensionSacrificing charge trapping abilityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A process for fabrication of a semiconductor device including a modified ONO structure, including forming the modified ONO structure by providing a semiconductor substrate; forming a first oxide layer on the semiconductor substrate; depositing a layer comprising a high-K dielectric material on the first oxide layer; and forming a top oxide layer on the layer comprising a high-K dielectric material. The semiconductor device may be, e.g., a MIRRORBIT(TM) two-bit EEPROM device or a floating gate flash device including a modified ONO structure.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
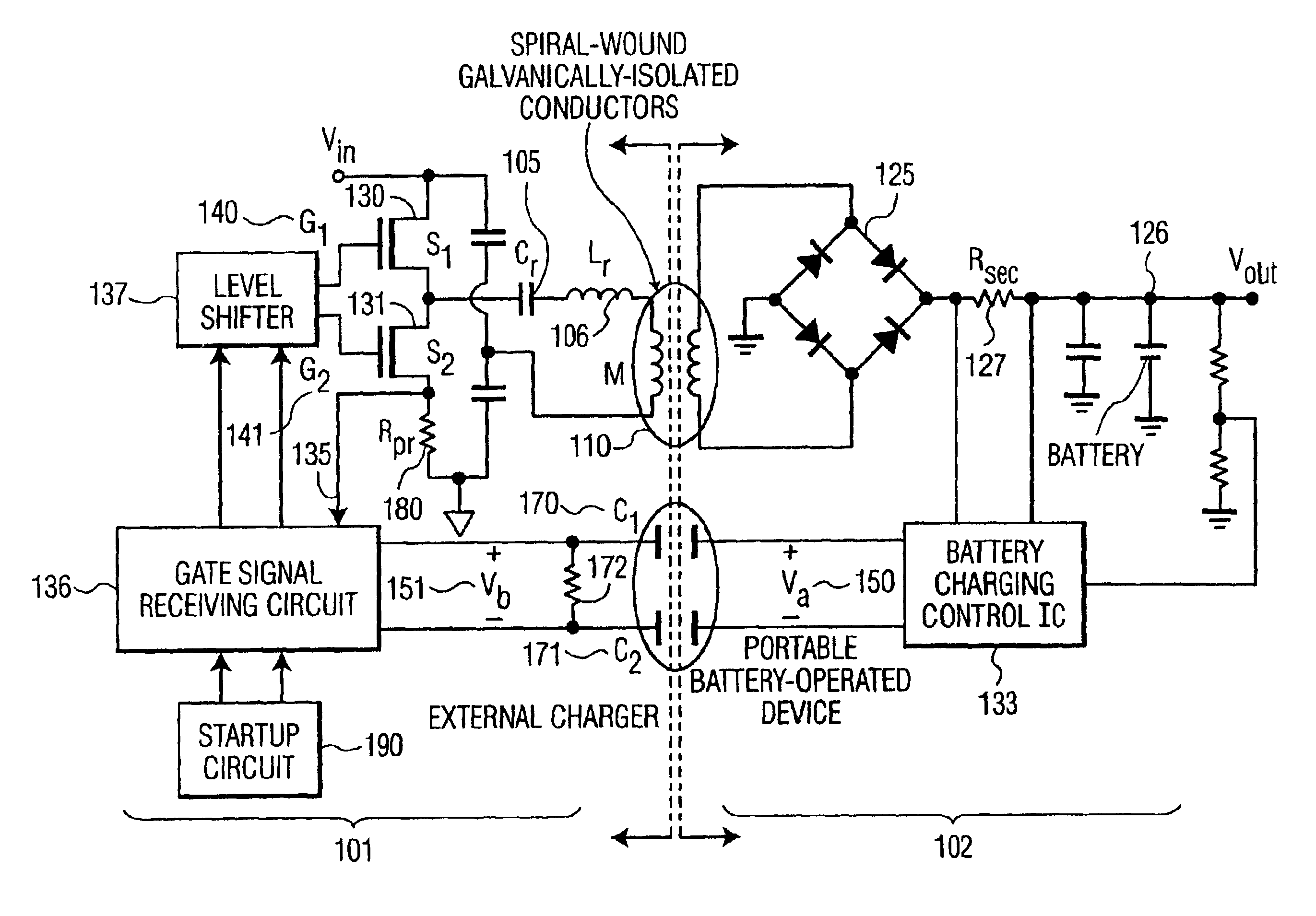
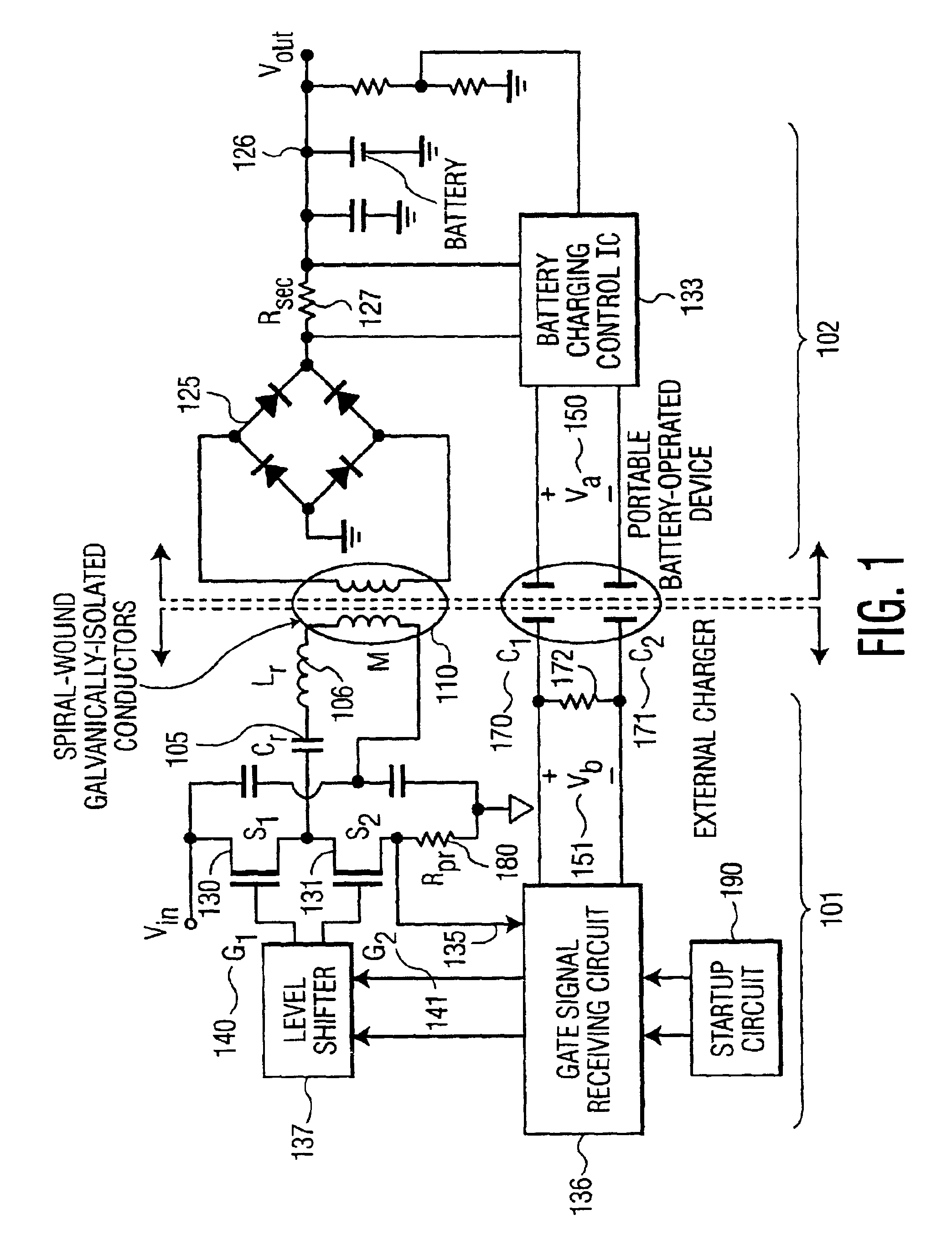
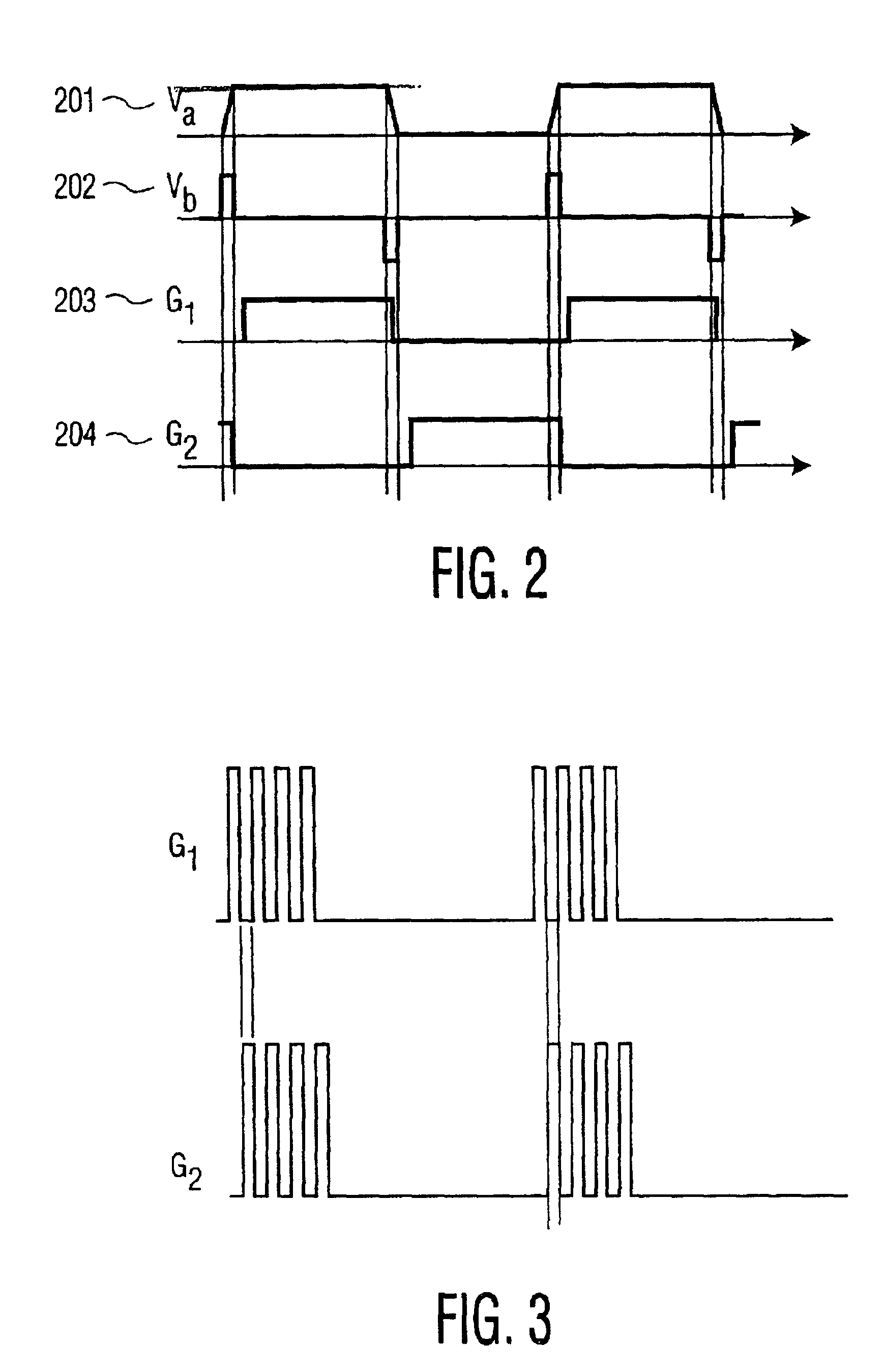
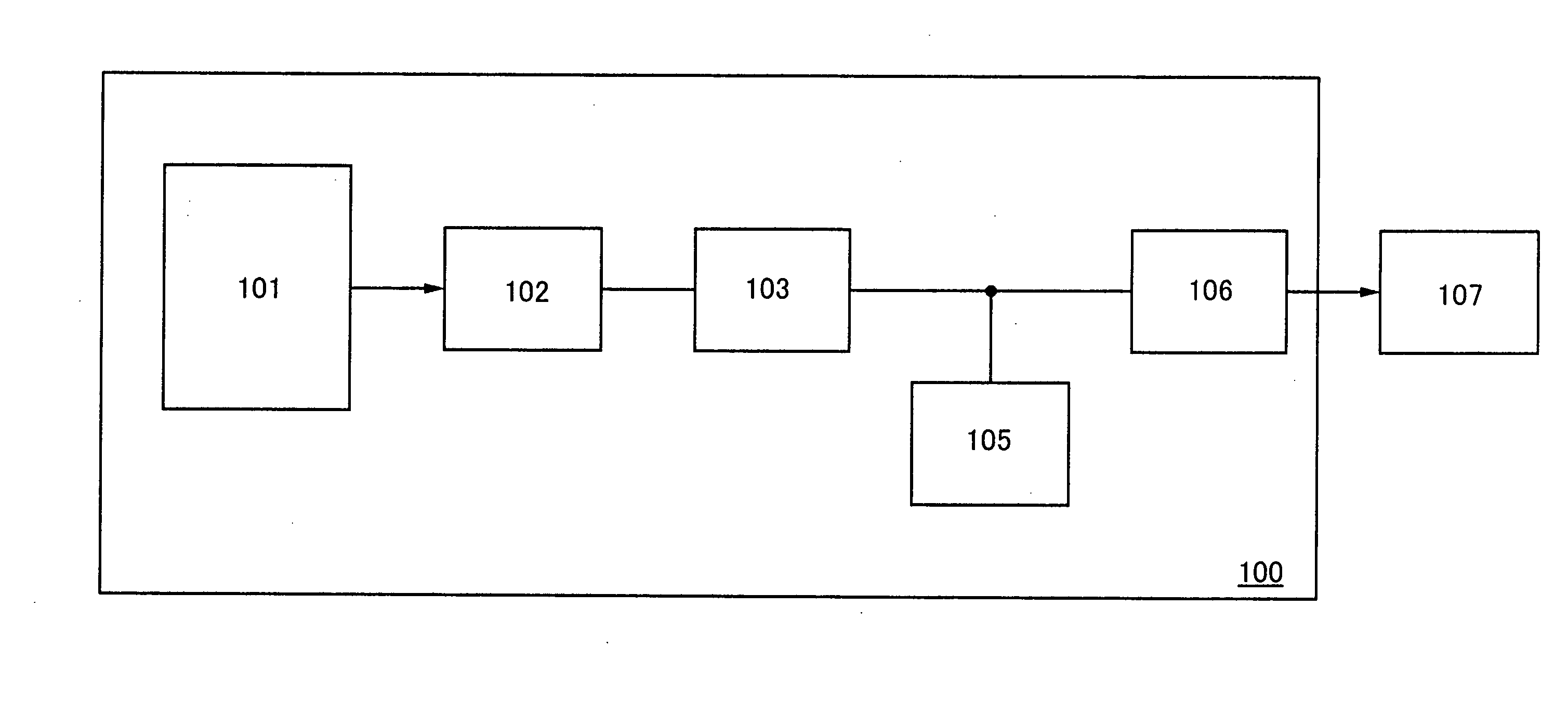
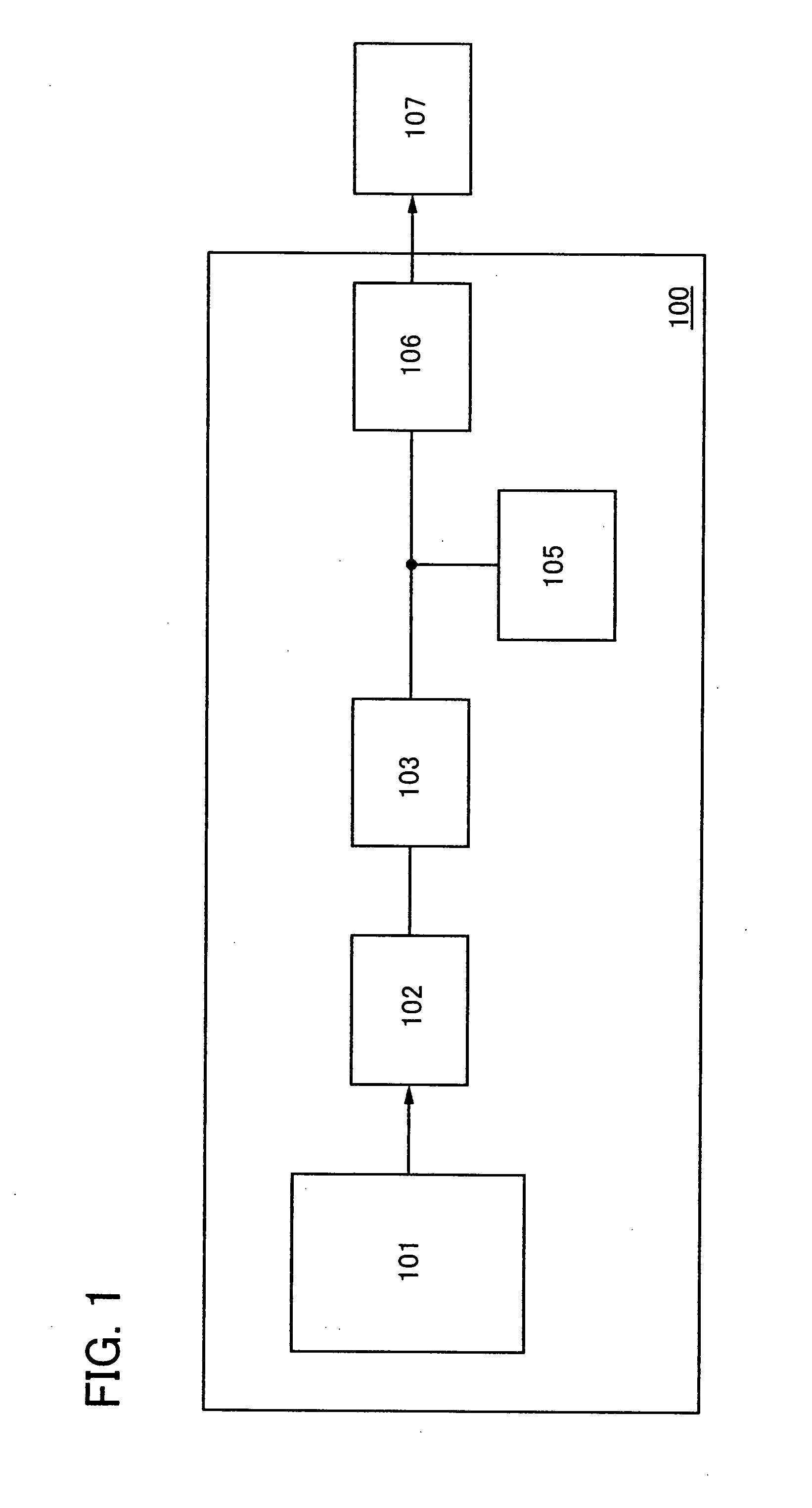
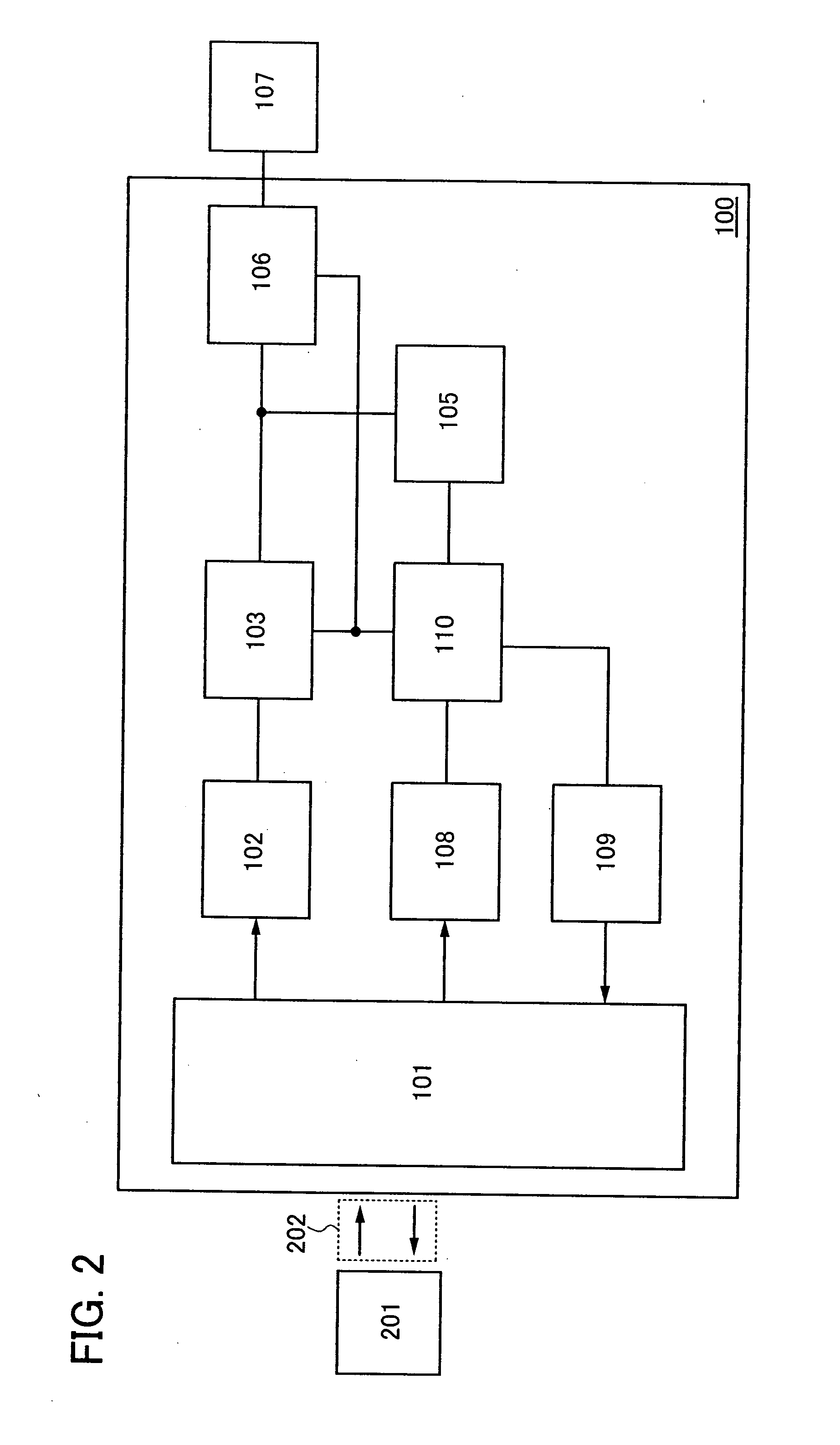
System, method and apparatus for contact-less battery charging with dynamic control
InactiveUS6844702B2Reduce complexityImprove efficiencyNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemBattery chargeEngineering
A system, method and apparatus for contact-less charging of battery operated devices, including a host charger with a power converter and resonant tank circuit and a portable device where the battery is located, with a battery charging control IC, wherein the method obviates the need for a voltage controller in each of both the host and the portable stages. The charging of the battery in the portable device is controlled by a charging controller therein, which is in continual electric communication with the host, whose output power the control IC dynamically monitors and controls. In one embodiment, component count is minimized but battery charging is not optimized when the battery voltage is very low. In the other embodiment, charging efficiency is maximized regardless of the output voltage of the battery.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
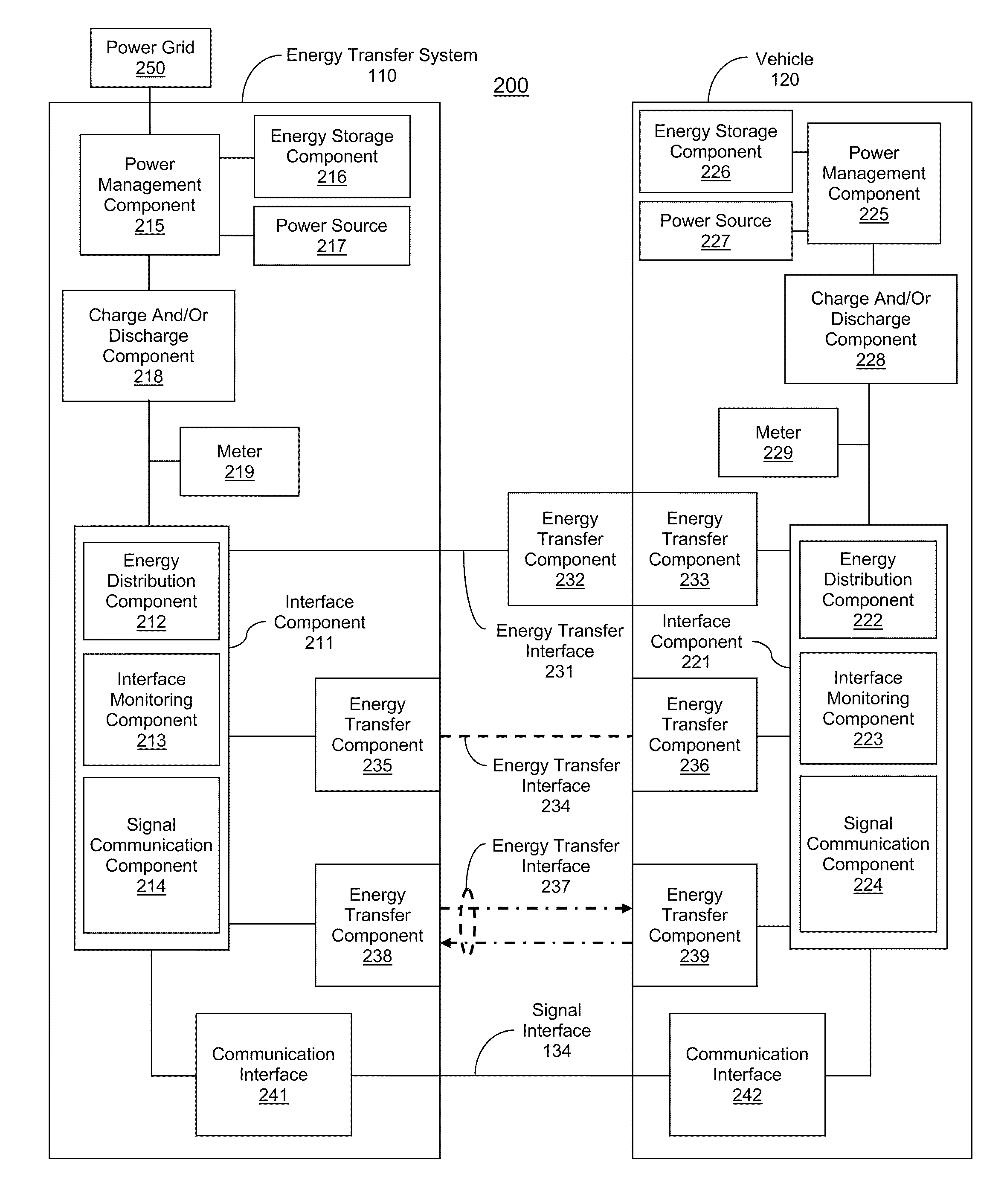
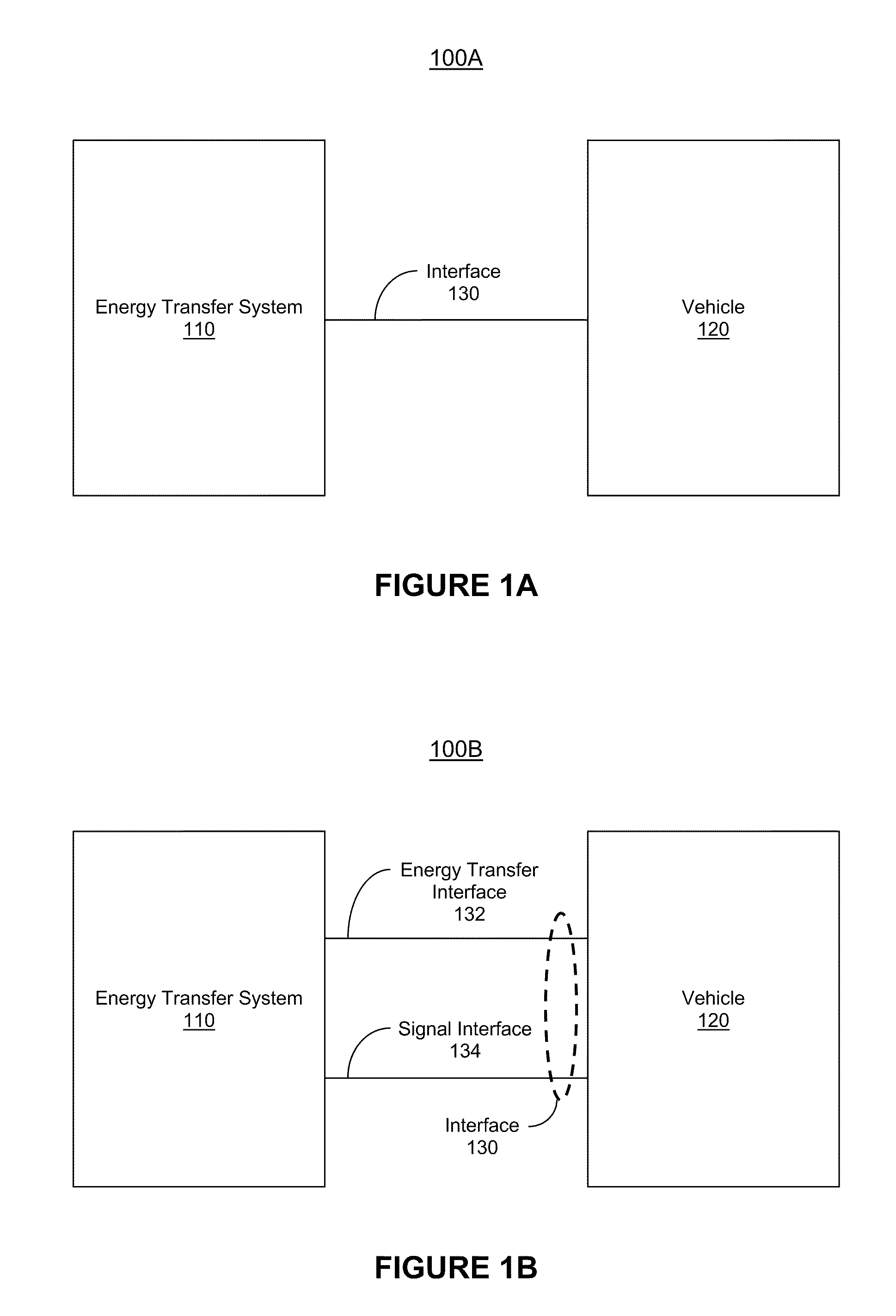
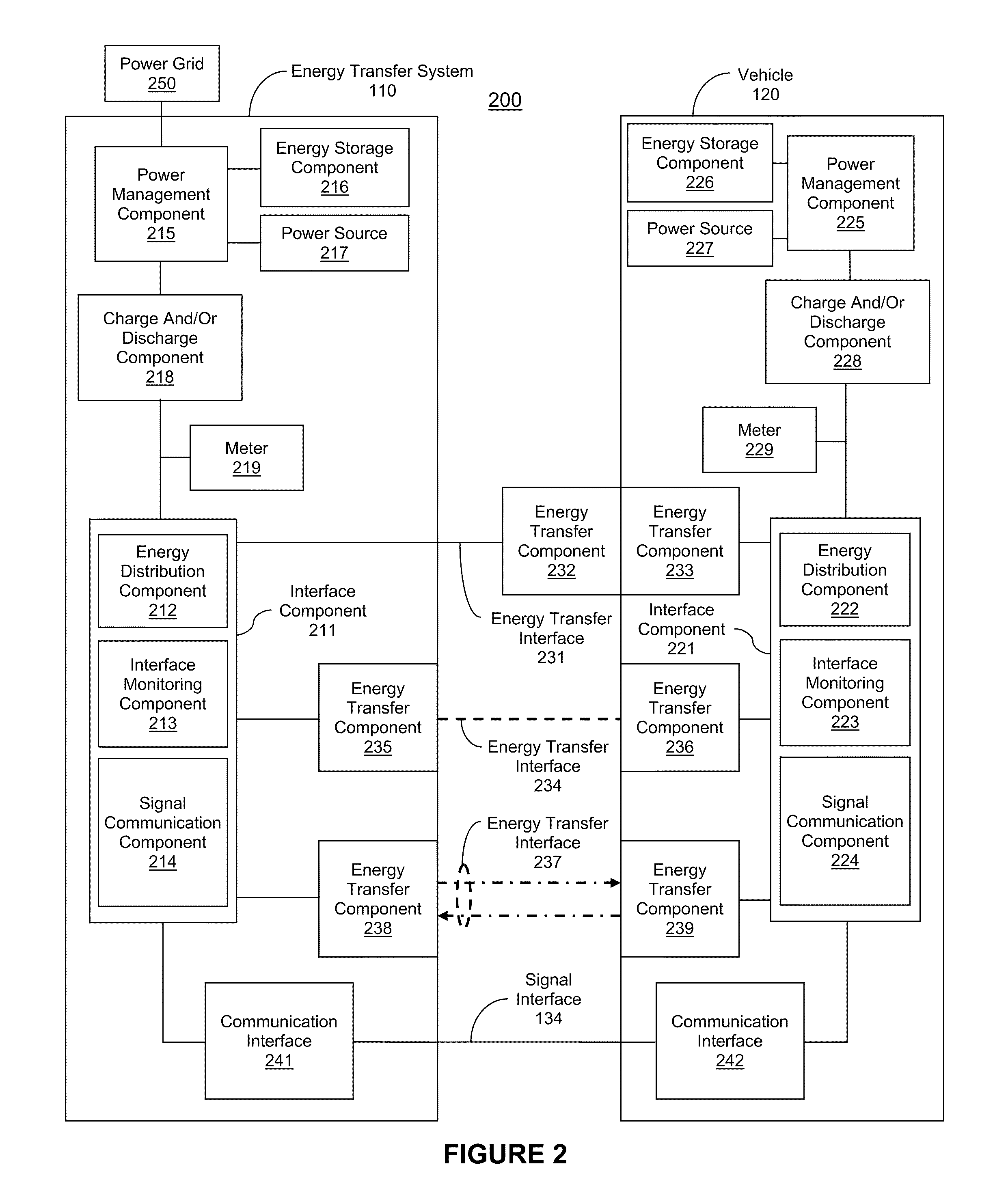
Managing an energy transfer between a vehicle and an energy transfer system
InactiveUS20110302078A1Easy to chargeEfficient chargingLevel controlVolume/mass flow measurementEnergy transferEngineering
Owner:FAILING BRYAN MARC
Novel low power non-volatile memory and gate stack
ActiveUS20060261401A1High charge blocking barrierExcellent charge retentionTransistorNanoinformaticsCharge retentionLow voltage
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that facilitate the use of band-gap engineered gate stacks with asymmetric tunnel barriers in reverse and normal mode floating node memory cells in NOR or NAND memory architectures that allow for direct tunnel programming and erase, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The low voltage direct tunneling program and erase capability reduces damage to the gate stack and the crystal lattice from high energy carriers, reducing write fatigue and enhancing device lifespan. The low voltage direct tunnel program and erase capability also enables size reduction through low voltage design and further device feature scaling. Memory cells of the present invention also allow multiple bit storage. These characteristics allow memory device embodiments of the present invention to operate within the definition of a universal memory, capable of replacing both DRAM and ROM in a system.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
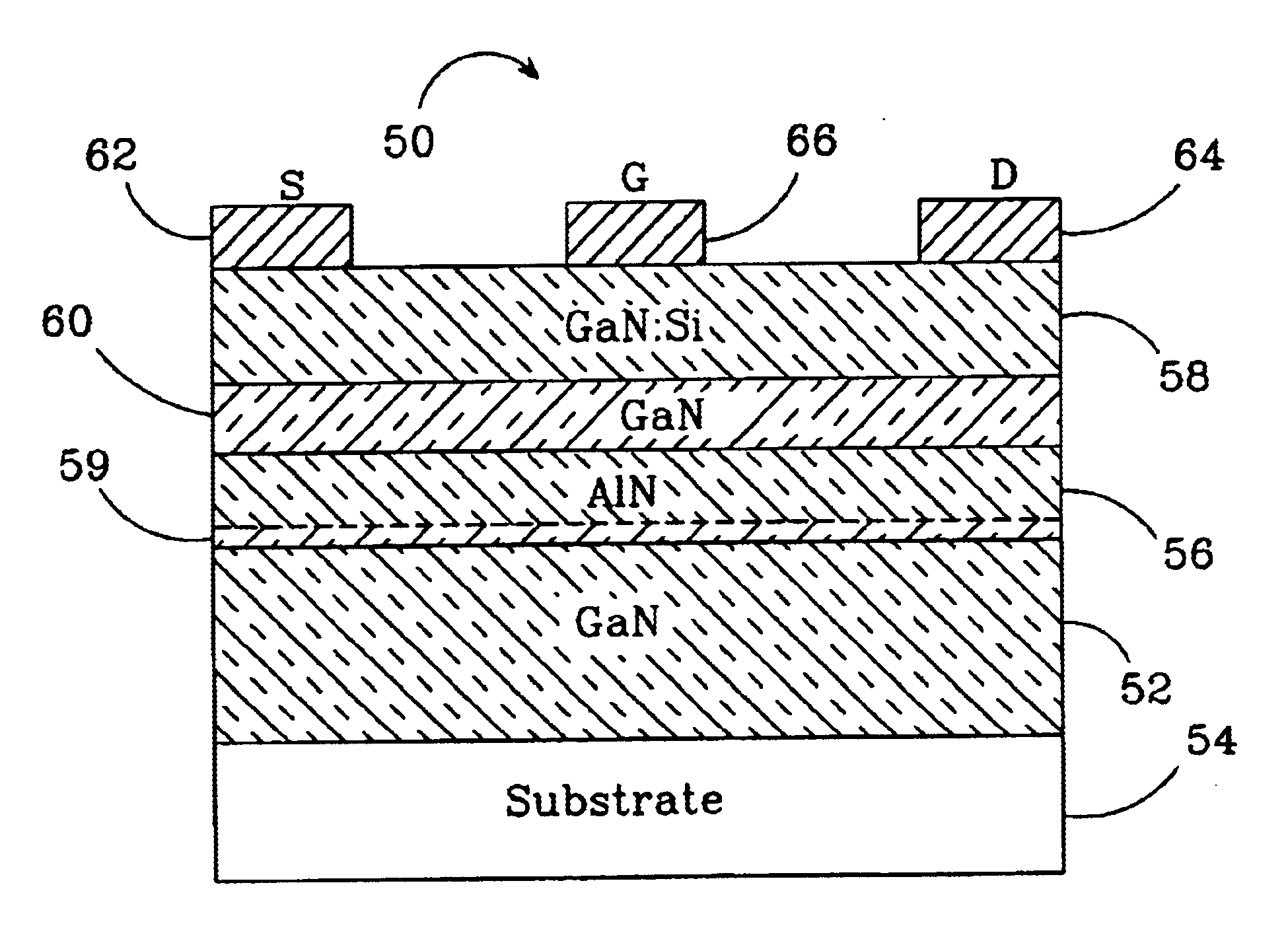
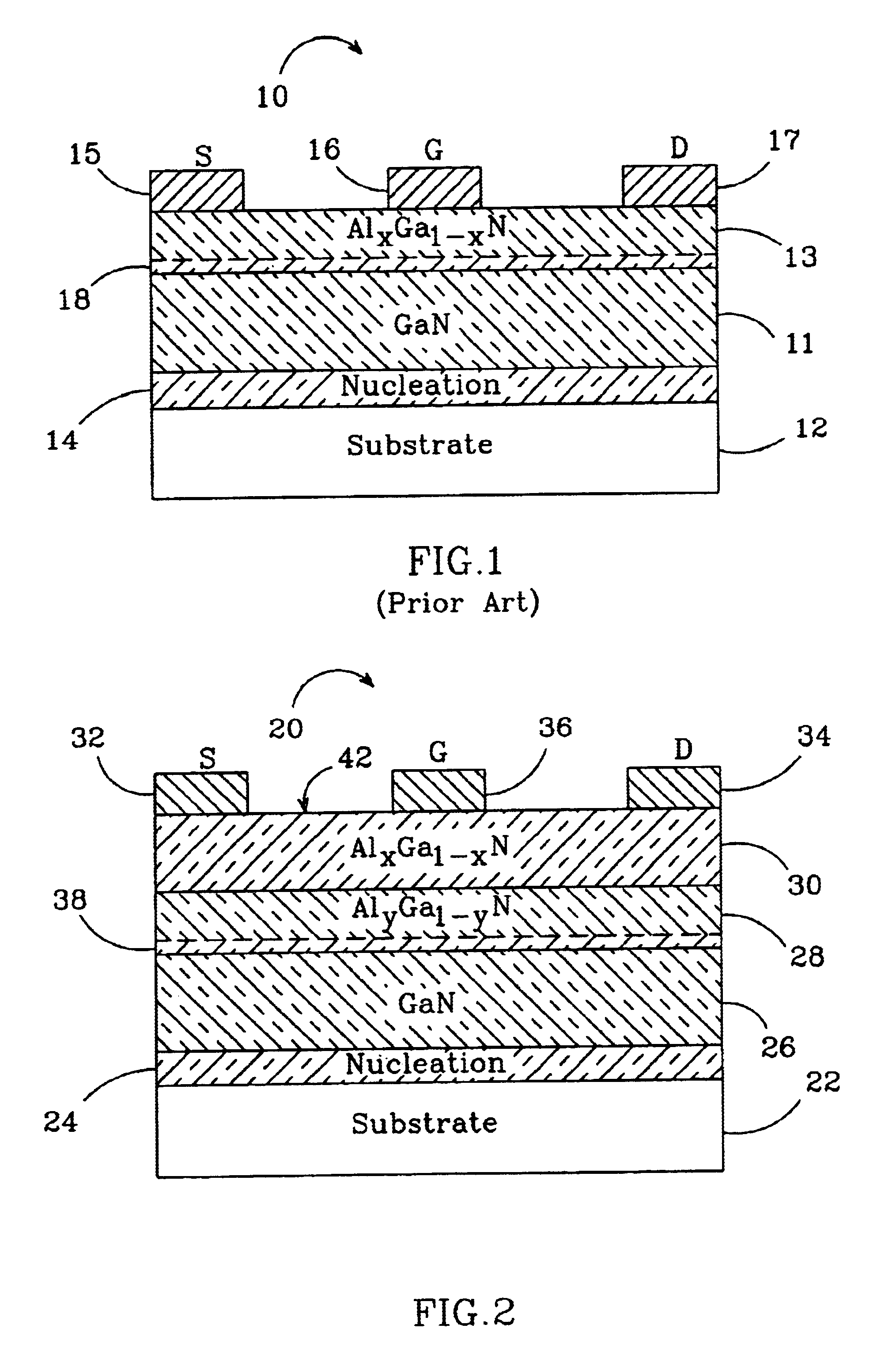
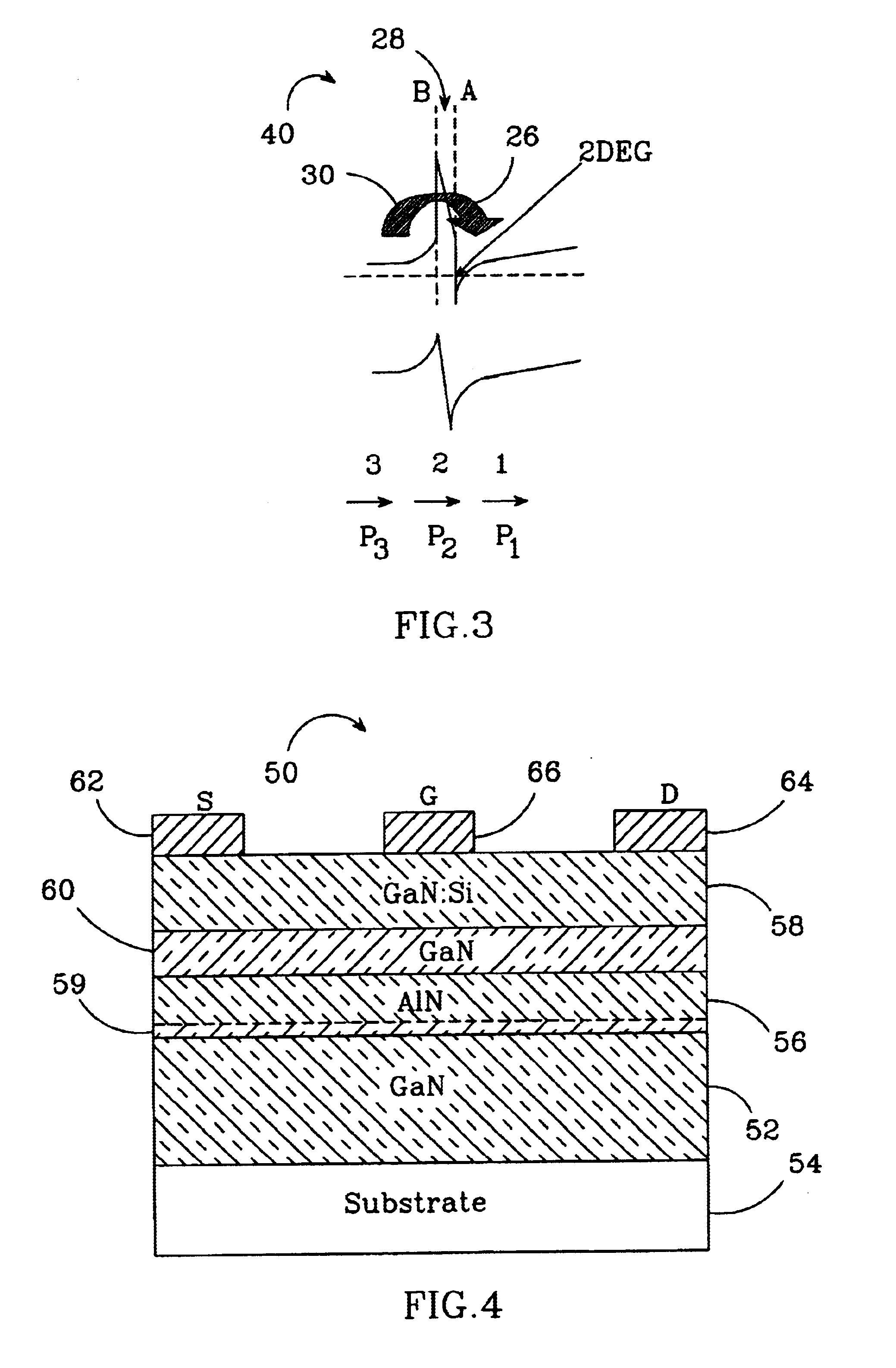
Group-III nitride based high electron mobility transistor (HEMT) with barrier/spacer layer
InactiveUS6849882B2High piezoelectric chargeReduction in piezoelectric scatteringSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh electronNucleation
A Group III nitride based high electron mobility transistors (HEMT) is disclosed that provides improved high frequency performance. One embodiment of the HEMT comprises a GaN buffer layer, with an AlyGa1−yN (y=1 or y 1) layer on the GaN buffer layer. An AlxGa1−xN (0≦x≦0.5) barrier layer on to the AlyGa1−yN layer, opposite the GaN buffer layer, AlyGa1−yN layer having a higher Al concentration than that of the AlxGa1−xN barrier layer. A preferred AlyGa1−yN layer has y=1 or y˜1 and a preferred AlxGa1−xN barrier layer has 0≦x≦0.5. A 2DEG forms at the interface between the GaN buffer layer and the AlyGa1−yN layer. Respective source, drain and gate contacts are formed on the AlxGa1−xN barrier layer. The HEMT can also comprising a substrate adjacent to the buffer layer, opposite the AlyGa1−yN layer and a nucleation layer between the AlxGa1−xN buffer layer and the substrate.
Owner:CREE INC +1
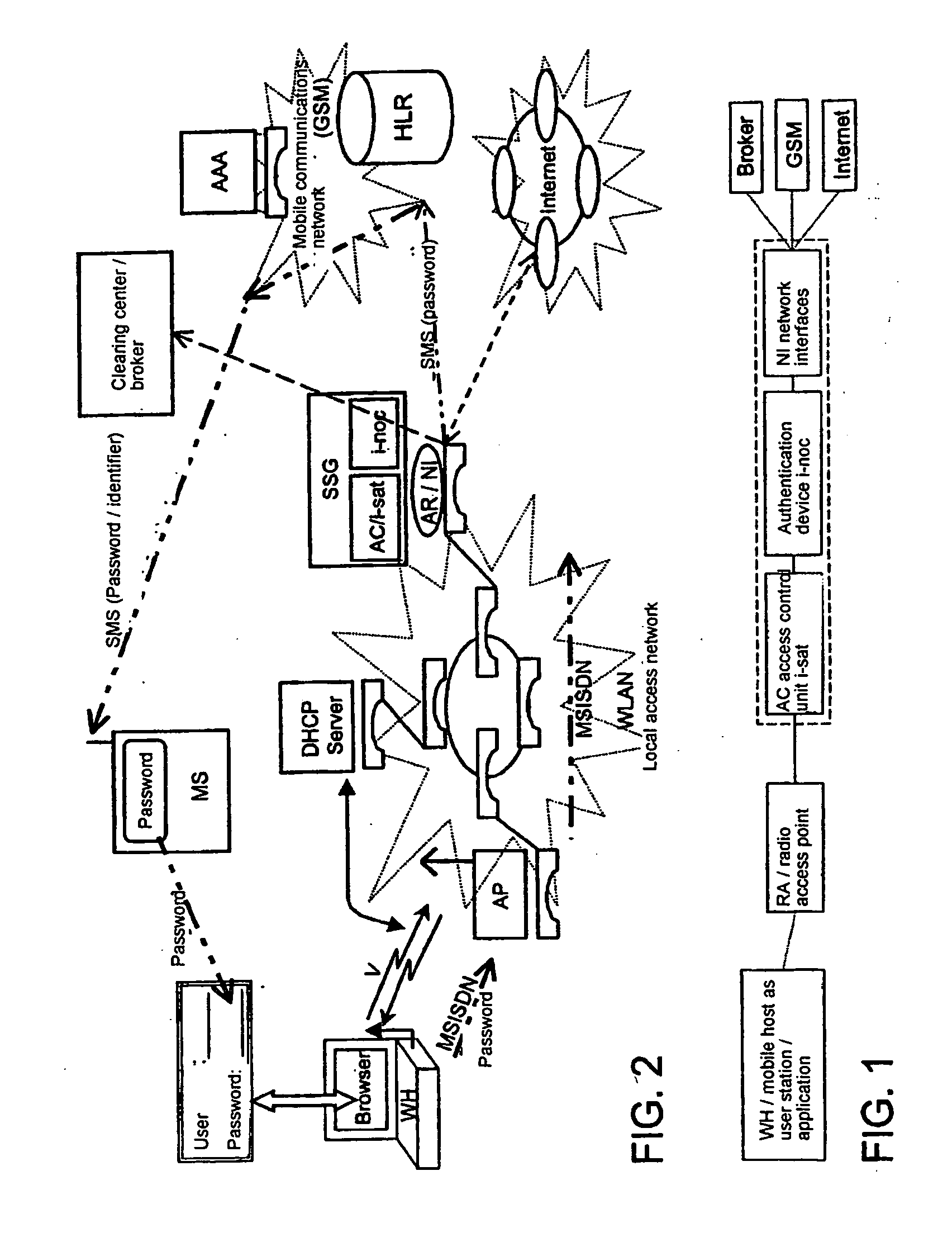
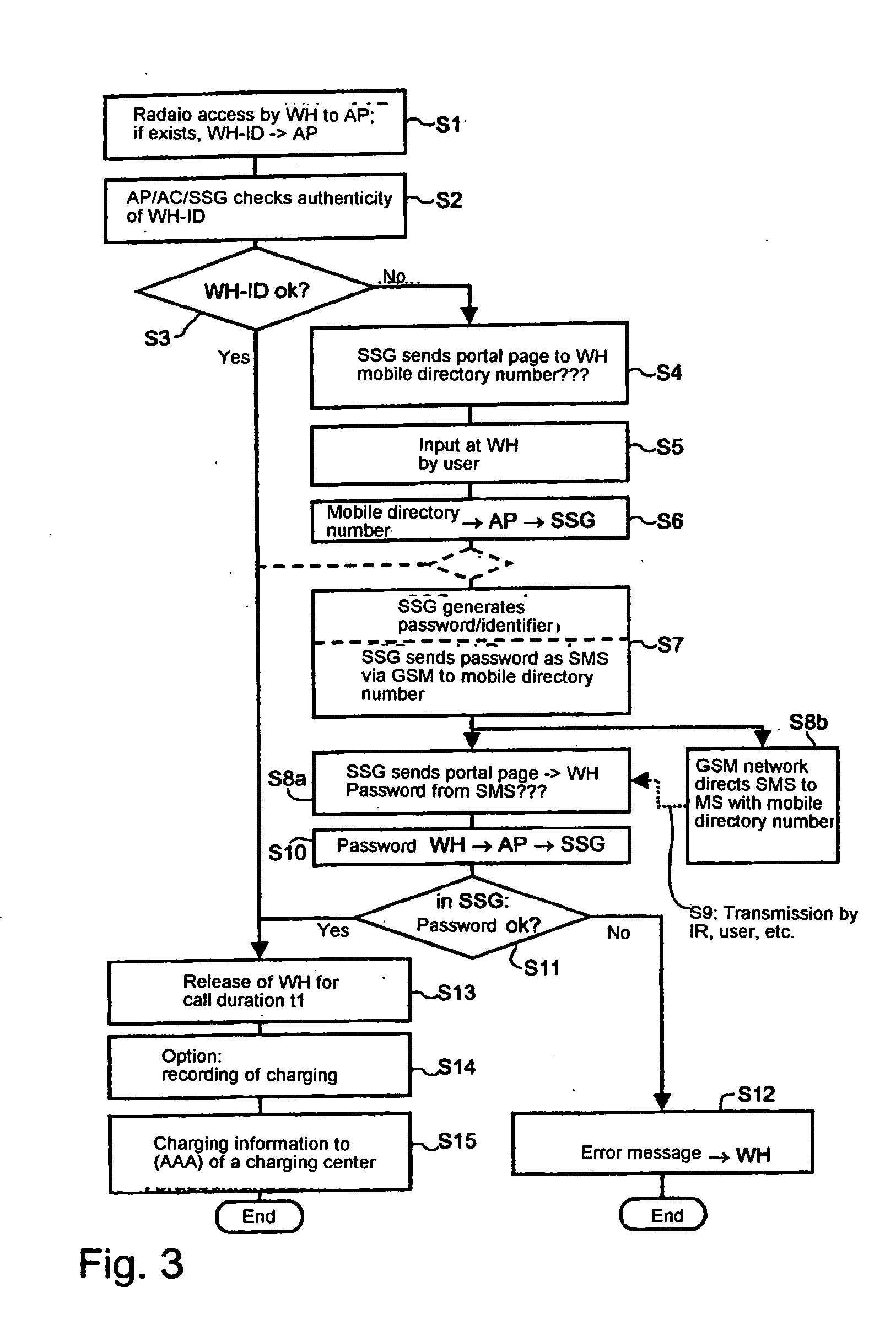
Method and device for authenticated access of a station to local data networks in particular radio data networks
ActiveUS20050048950A1Authentication is simpleEasy to chargeMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionRadio equipmentCommunications system
The invention relates to methods, devices and systems for the authenticated access to a data network by means of a station (WH) compatible with a data network (WLAN), which permit an authentication of the station and user. A device, for example a mobile radio device, is used for the above, which is authenticated in another system. In addition to the authentication, in particular a charging of services in a data network or another communication system (GSM) which is accessible by means of the data network is thus possible.
Owner:MONARCH NETWORKING SOLUTIONS LLC
Method and apparatus for wireless charging an electronic device
ActiveUS20140055098A1Minimize impactOptimal charging efficiencyNear-field transmissionCircuit monitoring/indicationEngineeringElectromagnetic radiation
A wireless charging method for an electronic device using an electromagnetic radiation (EMR) circuit is provided. The wireless charging method includes receiving an event input through the EMR circuit, controlling an input function according to a signal received through the EMR circuit in response to an input event, and controlling a wireless charging of a target device or electronic device using energy generated through the EMR circuit in response to a charge event.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Power storage device
InactiveUS7714535B2Increase power storageMeet growth needsTransistorBatteries circuit arrangementsControl storeControl circuit
In the field of portable electronic devices in the future, portable electronic devices will be desired, which are smaller and more lightweight and can be used for a long time period by one-time charging, as apparent from provision of one-segment partial reception service “1-seg” of terrestrial digital broadcasting that covers the mobile objects such as a cellular phone. Therefore, the need for a power storage device is increased, which is small and lightweight and capable of being charged without receiving power from commercial power. The power storage device includes an antenna for receiving an electromagnetic wave, a capacitor for storing power, and a circuit for controlling store and supply of the power. When the antenna, the capacitor, and the control circuit are integrally formed and thinned, a structural body formed of ceramics or the like is partially used. A circuit for storing power of an electromagnetic wave received at the antenna in a capacitor and a control circuit for arbitrarily discharging the stored power are provided, whereby lifetime of the power storage device can be extended.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Retroreflective electrophoretic displays and materials for making the same
InactiveUS7071913B2High level controlDisorientingMechanical clocksStatic indicating devicesCelluloseOptical property
Disclosed herein are novel electrophoretic displays and materials useful in fabricating such displays. In particular, novel encapsulated displays are disclosed. Particles encapsulated therein are dispersed within a suspending, or electrophoretic, fluid. This fluid may be a mixture of two or more fluids or may be a single fluid. The displays may further comprise particles dispersed in a suspending fluid, wherein the particles contain a liquid. In either case, the suspending fluid may have a density or refractive index substantially matched to that of the particles dispersed therein. Finally, also disclosed herein are electro-osmotic displays. These displays comprise at least one capsule containing either a cellulosic or gel-like internal phase and a liquid phase, or containing two or more immiscible fluids. Application of electric fields to any of the electrophoretic displays described herein affects an optical property of the display.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Retroreflective electrophoretic displaya and materials for making the same
InactiveUS20050035941A1High level controlDisorientingMechanical clocksStatic indicating devicesChemistryElectric field
Disclosed herein are novel electrophoretic displays and materials useful in fabricating such displays. In particular, novel encapsulated displays are disclosed. Particles encapsulated therein are dispersed within a suspending, or electrophoretic, fluid. This fluid may be a mixture of two or more fluids or may be a single fluid. The displays may further comprise particles dispersed in a suspending fluid, wherein the particles contain a liquid. In either case, the suspending fluid may have a density or refractive index substantially matched to that of the particles dispersed therein. Finally, also disclosed herein are electro-osmotic displays. These displays comprise at least one capsule containing either a cellulosic or gel-like internal phase and a liquid phase, or containing two or more immiscible fluids. Application of electric fields to any of the electrophoretic displays described herein affects an optical property of the display.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Non-spherical cavity electrophoretic displays and methods and materials for making the same
InactiveUS7109968B2High level controlEasy to chargeStatic indicating devicesNanoinformaticsCelluloseOptical property
Disclosed herein are novel electrophoretic displays and materials useful in fabricating such displays. In particular, novel encapsulated displays are disclosed. Particles encapsulated therein are dispersed within a suspending, or electrophoretic, fluid. This fluid may be a mixture of two or more fluids or may be a single fluid. The displays may further comprise particles dispersed in a suspending fluid, wherein the particles contain a liquid. In either case, the suspending fluid may have a density or refractive index substantially matched to that of the particles dispersed therein. Finally, also disclosed herein are electro-osmotic displays. These displays comprise at least one capsule containing either a cellulosic or gel-like internal phase and a liquid phase, or containing two or more immiscible fluids. Application of electric fields to any of the electrophoretic displays described herein affects an optical property of the display.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
Display methods and apparatus
InactiveUS20060250325A1Easy dischargeEasy to chargeStatic indicating devicesOptical light guidesDisplay deviceComputer science
Owner:SNAPTRACK
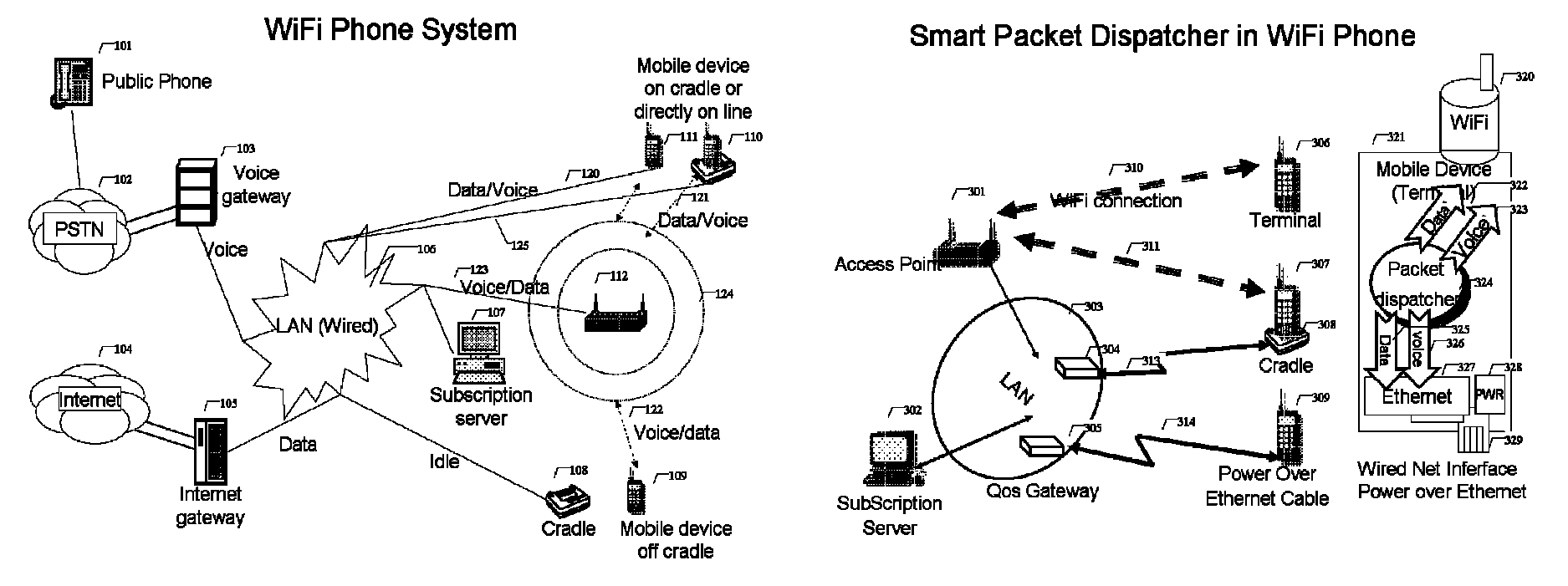
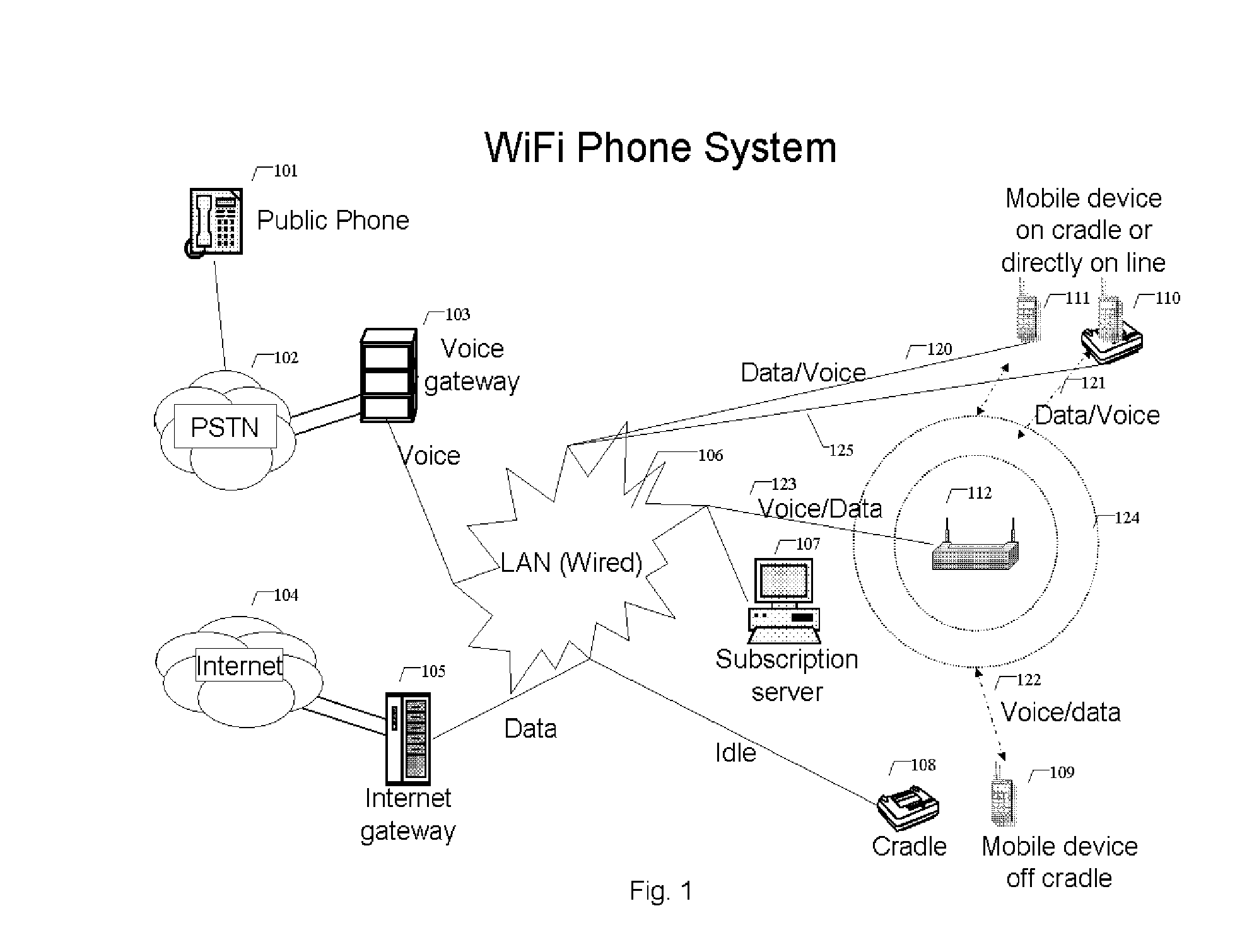
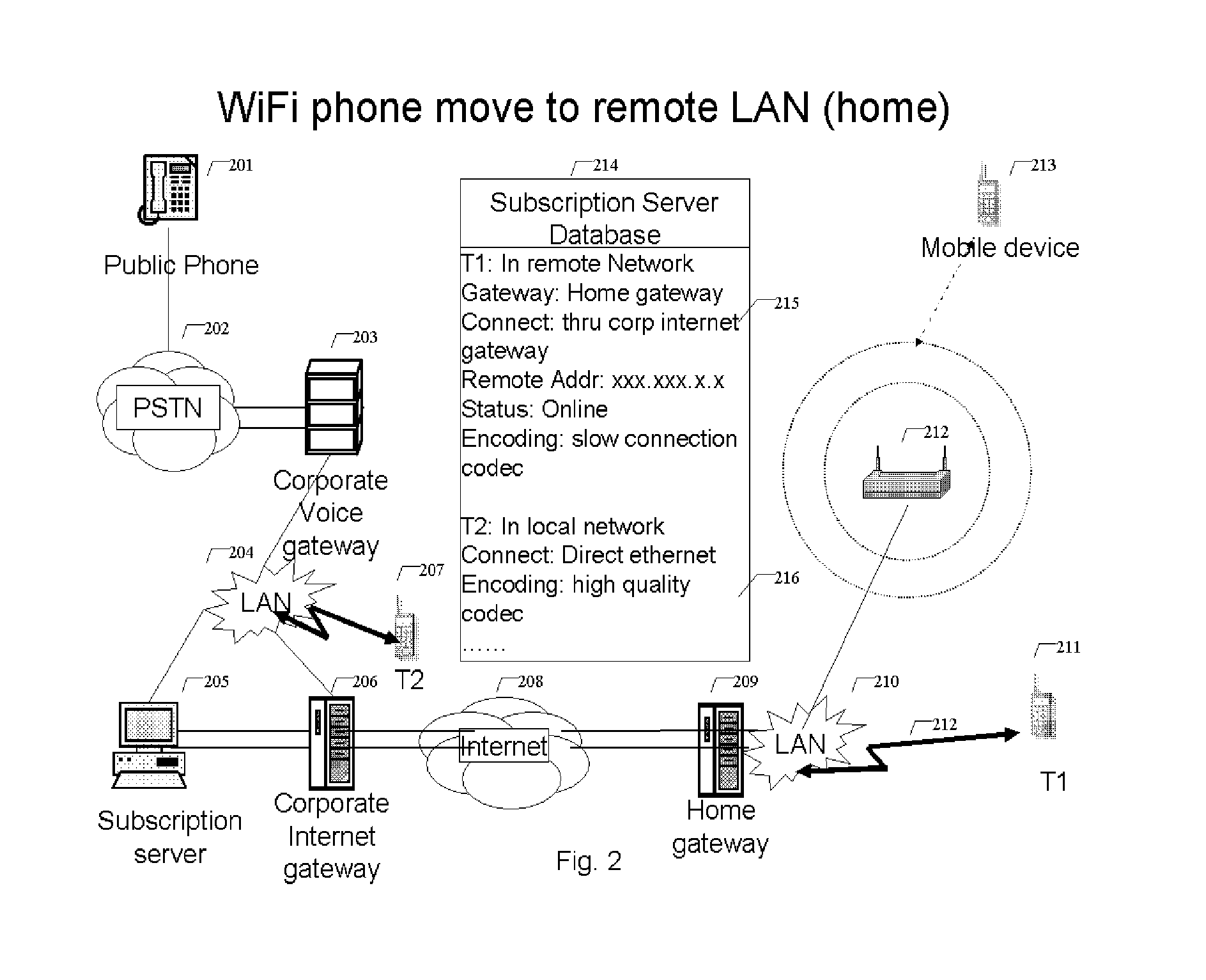
WiFi phone system
ActiveUS8503340B1Small rangeFast transferNetwork topologiesSubstation equipmentQuality of serviceData stream
A voice communication system over WiFi 802.11 network includes: WiFi phone devices, subscription servers and wireless access points. Through voice and data gateways the system can transfer both voice and data streams through WiFi; Phone devices with both wired and WiFi wireless interfaces can automatically switches between wired network and wireless network through WiFi access points. Subscription server maintains the current status of each device every time it changes location. Voice packets are prioritized over regular data packets and dispatched to different network interface by smart packet dispatcher. Quality of service for voice conversation over WiFi is achieved by various methods: piggy-tail method and ACK enhancements and other improvements to reduce delay and latency of real time voice packets.
Owner:XU YONGYONG
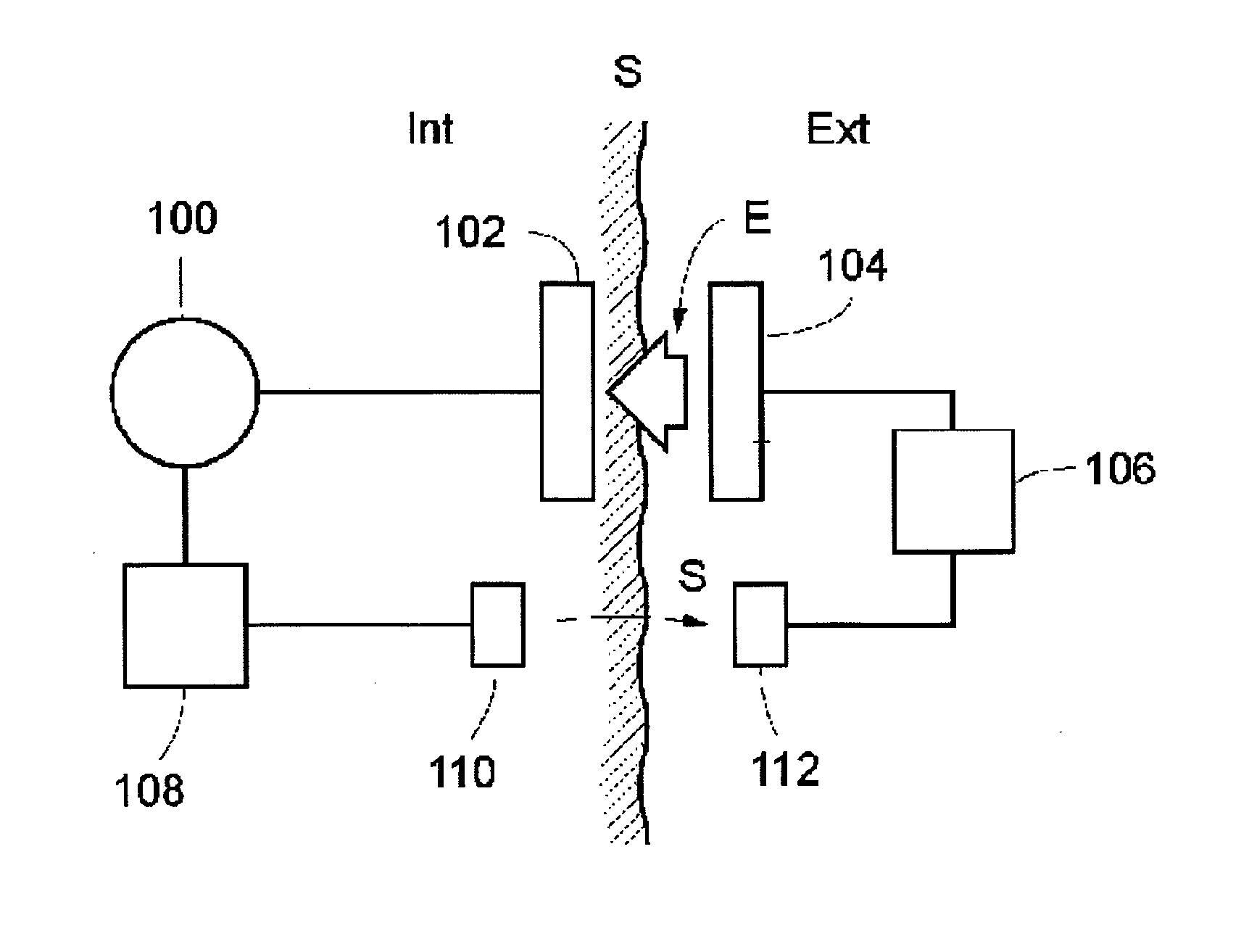
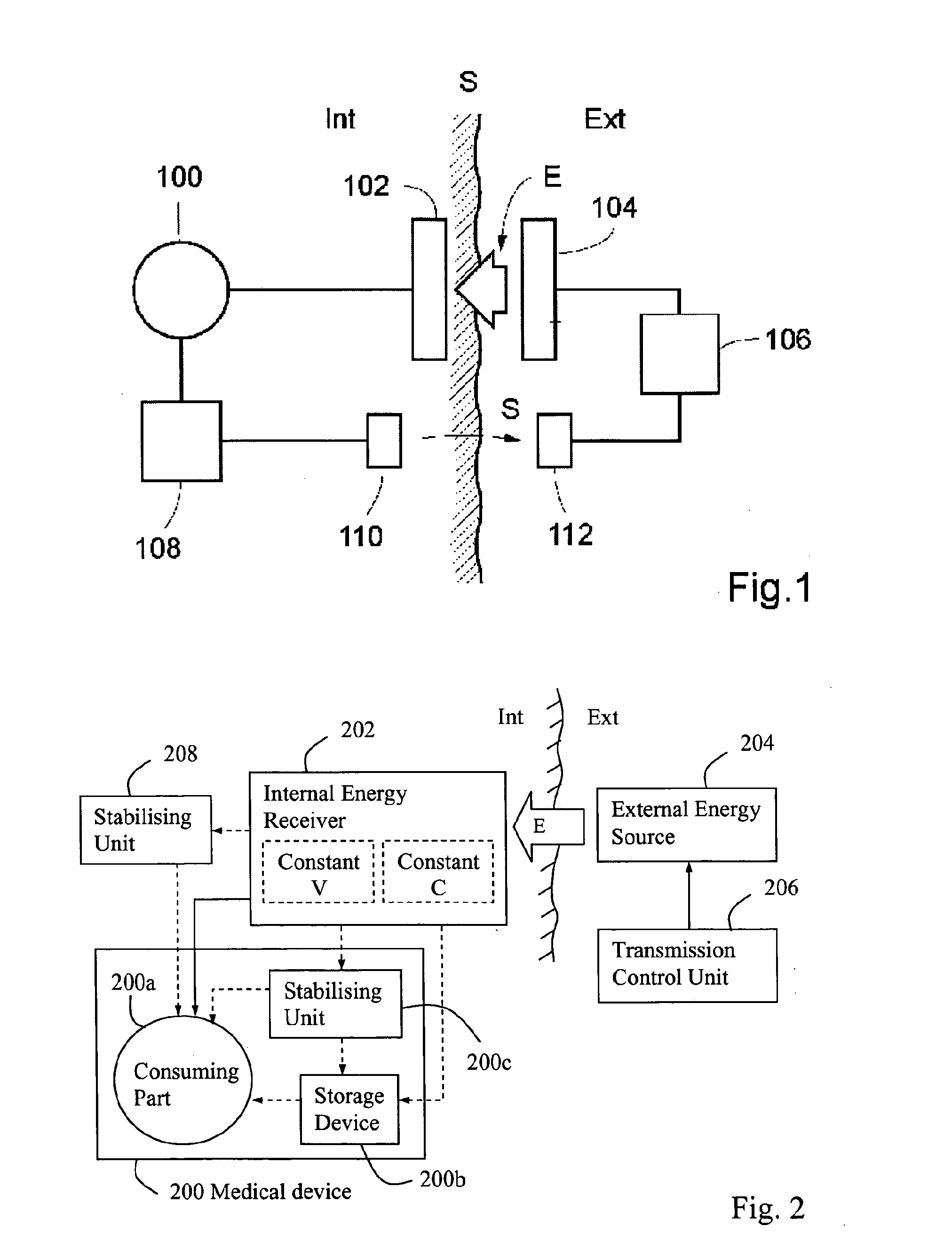
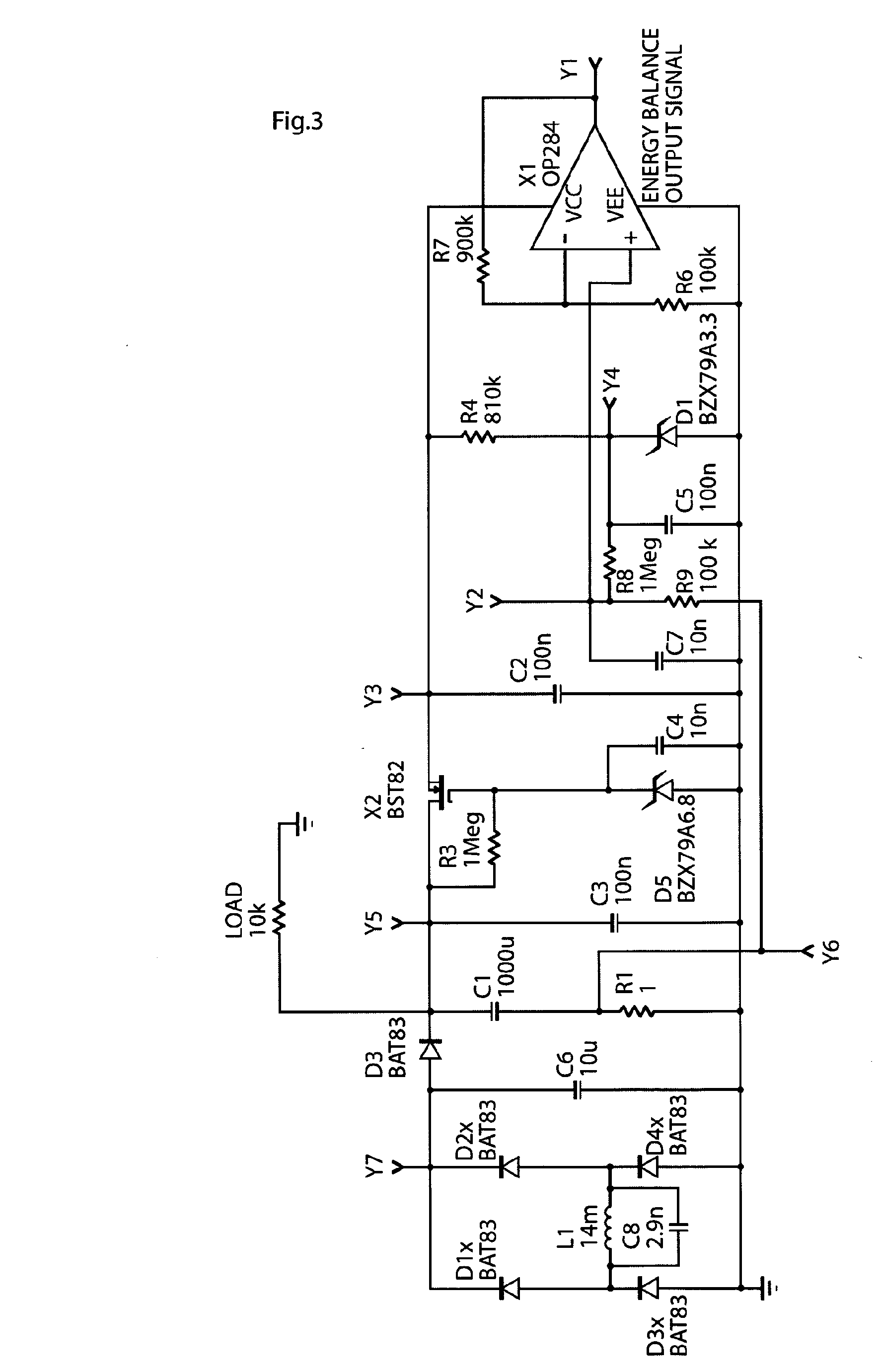
Method and apparatus for supplying energy to a medical device
ActiveUS20100234922A1High energy charging rateFast chargingNear-field transmissionElectrotherapyInternal energySupply energy
In a method and apparatus for supplying wireless energy to a medical device (100) implanted in a patient, wireless energy is transmitted from an external energy source (104) located outside a patient and is received by an internal energy receiver (102) located inside the patient, for directly or indirectly supplying received energy to the medical device. An energy balance is determined between the energy received by the internal energy receiver and the energy used for the medical device, and the transmission of wireless energy is then controlled based on the determined energy balance. The energy balance thus provides an accurate indication of the correct amount of energy needed, which is sufficient to operate the medical device properly, but without causing undue temperature rise.
Owner:FORSELL PETER
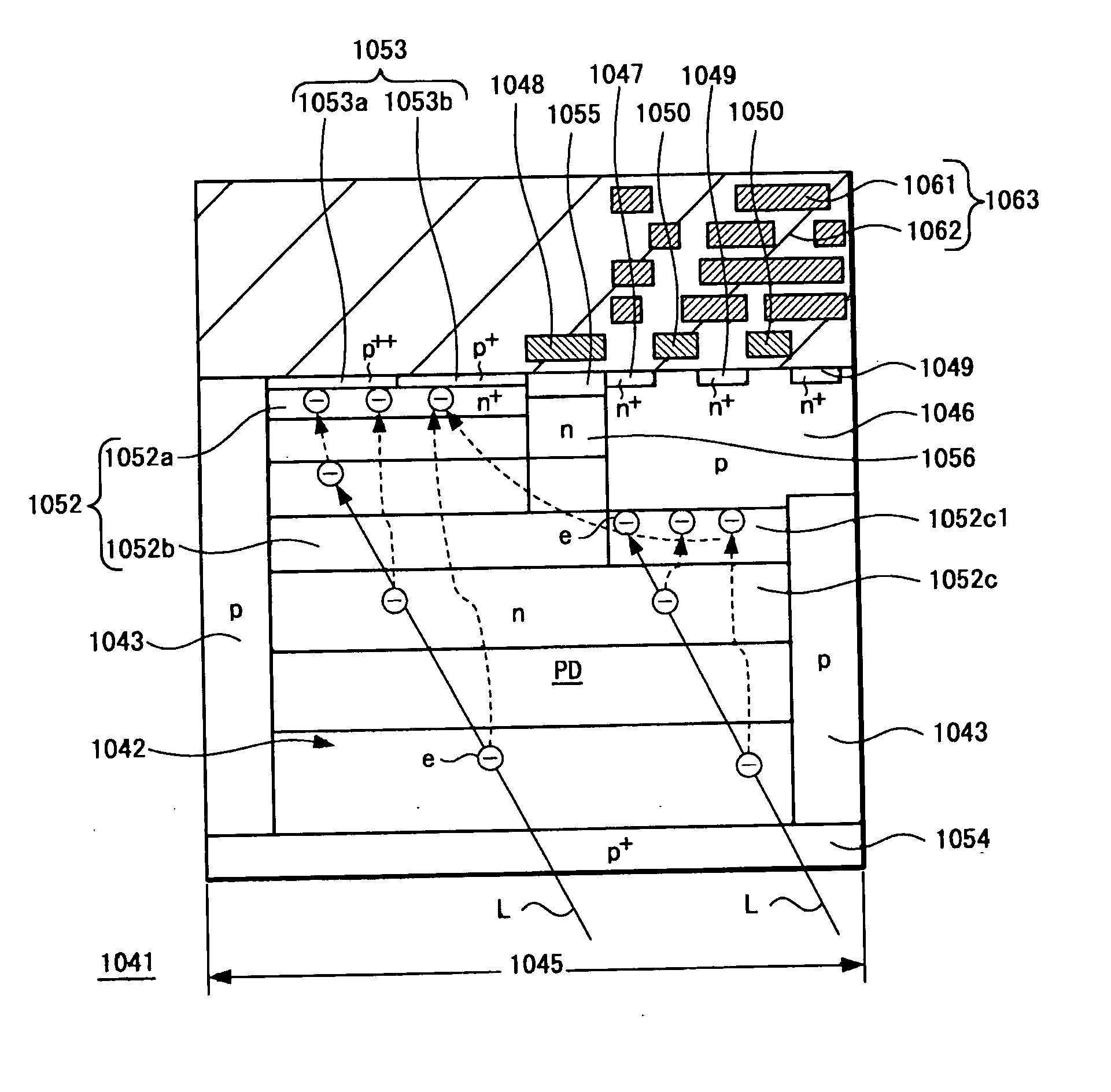
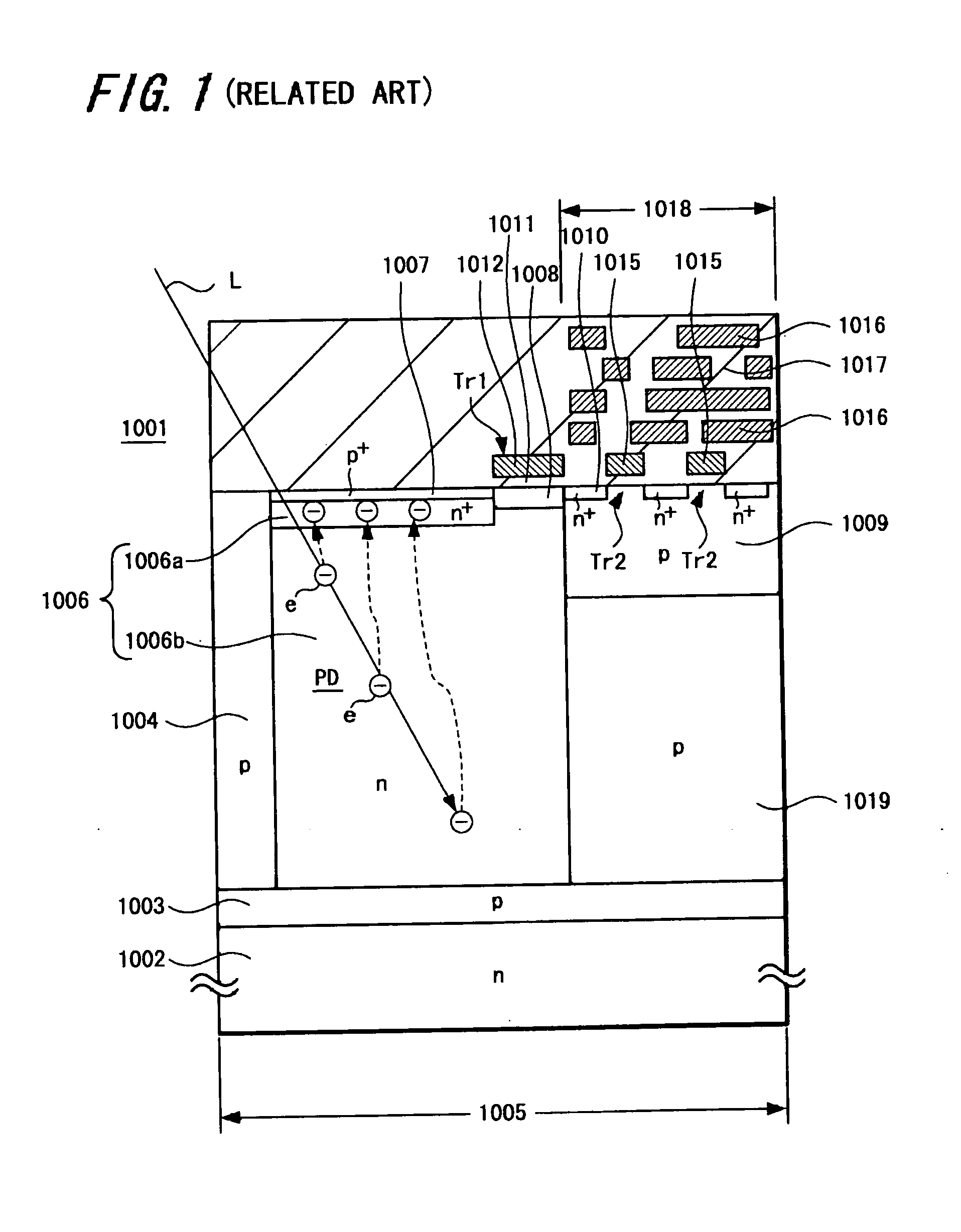
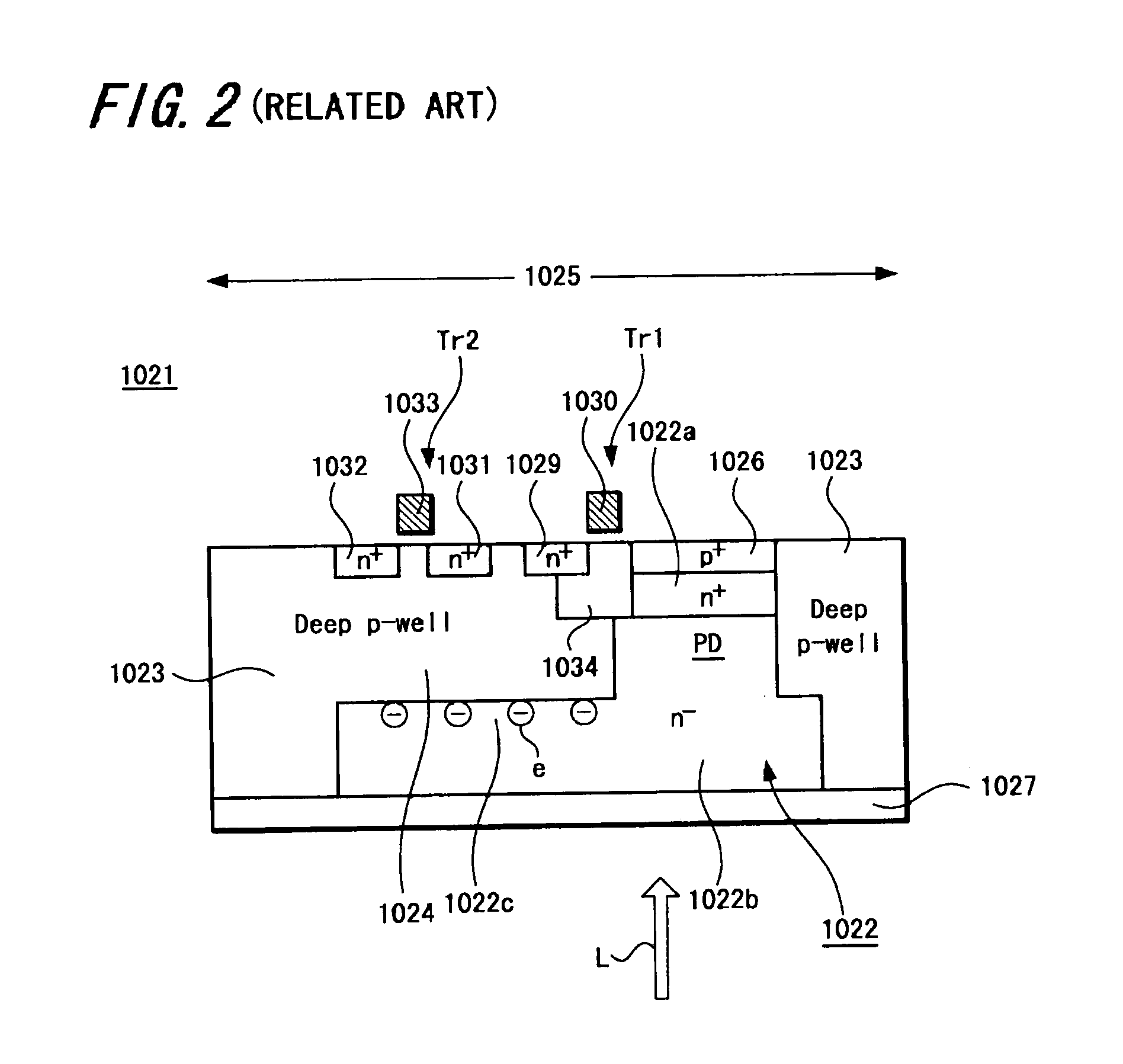
Solid-state image pickup device, electronic apparatus using such solid-state image pickup device and method of manufacturing solid-state image pickup device
ActiveUS20060197007A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce sensitivityConveyorsCleaningEngineeringElectron
A back-illuminated type solid-state image pickup device (1041) includes read circuits (Tr1, Tr2) formed on one surface of a semiconductor substrate (1042) to read a signal from a photo-electric conversion element (PD) formed on the semiconductor substrate (1042), in which electric charges (e) generated in a photo-electric conversion region (1052c1) formed under at least one portion of the read circuits (Tr1, Tr2) are collected to an electric charge accumulation region (1052a) formed on one surface side of the semiconductor substrate (1042) of the photo-electric conversion element (PD) by electric field formed within the photo-electric conversion element (PD). Thus, the solid-state image pickup device and the camera are able to make the size of pixel become very small without lowering a saturation electric charge amount (Qs) and sensitivity.
Owner:SONY CORP
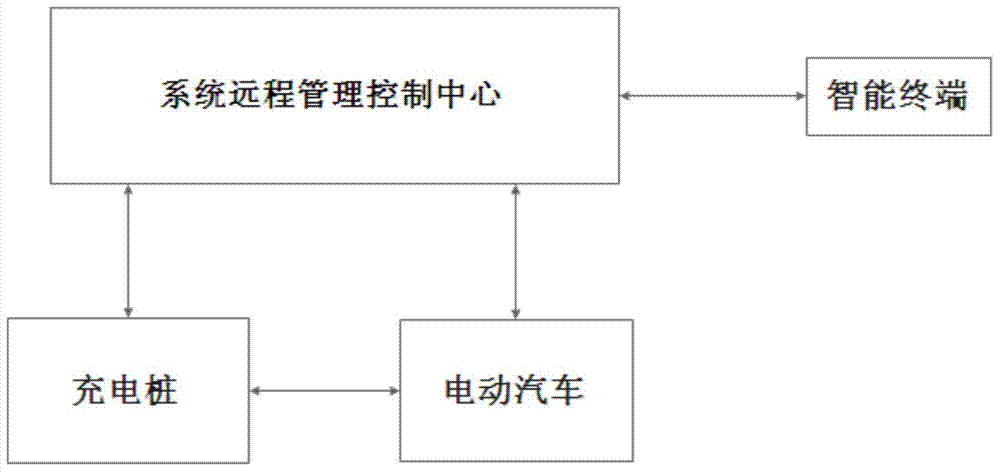
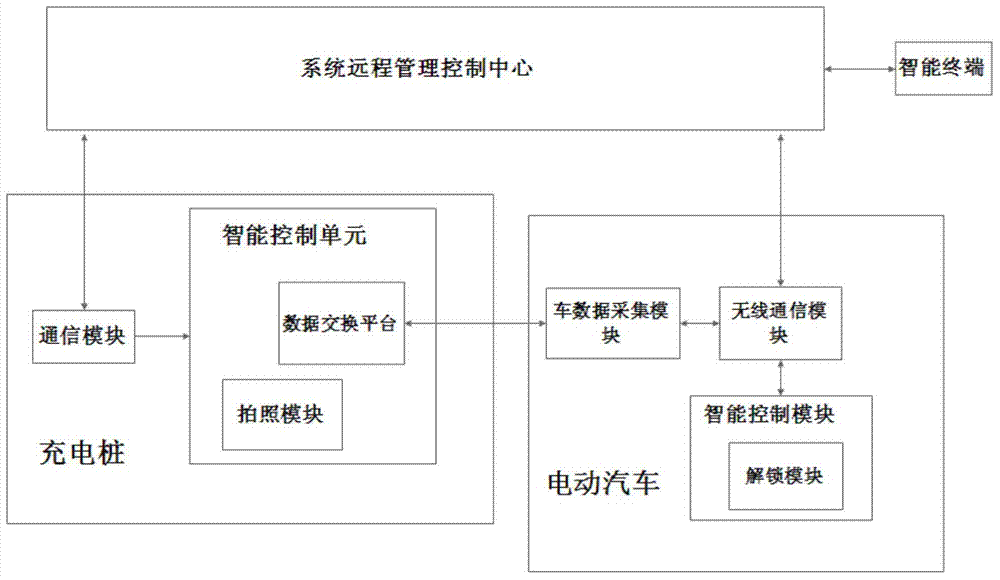
Electric vehicle lease management system on basis of charging piles and lease management method implemented by electric vehicle lease management system
InactiveCN104282088AGuarantee the safety of usePrevent and resolve theftApparatus for meter-controlled dispensingElectric vehicle charging technologyInformation networksComputer module
The invention discloses an electric vehicle lease management system on the basis of charging piles. The electric vehicle lease management system comprises a system remote management control center, electric vehicles, the charging piles and intelligent terminals. A vehicle battery data acquisition module, a wireless communication module and an intelligent control module are mounted on each electric vehicle; an intelligent control unit and a communication module are mounted on each charging pile, each intelligent terminal is wirelessly communicated with the system remote management control center, and the wireless communication module of each electric vehicle is wirelessly communicated with the system remote management control center. The electric vehicle lease management system has the advantages that lease systems which are used by vehicle lease users and management staffs can be conveniently and quickly implemented by the aid of modern information network technologies, the users can order lease application and check relevant lease information via the intelligent terminals or directly via computers at any time in any places, and the management staffs can monitor various indexes such as electric vehicle location data and battery data in real time, and prompting effects can be timely realized.
Owner:WUHU HENGTIAN YIKAI SOFTWARE TECH CO LTD
Lipid particles on the basis of mixtures of liquid and solid lipids and method for producing same
InactiveUS8663692B1Promote formationImprove stabilityPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsLipid particleSolid content
The invention relates to drug-free or drug-loaded lipid particles of a mixed matrix made of solid and liquid lipids, and to a method for producing highly concentrated lipid particle dispersions of solid-liquid particles having a lipid content of from 30% to 95% or a solids content of from 30% to 95% (lipid and stabilizer), which in contrast to biamphipileic cremes are integer particles, and / or which upon dilution of the highly concentrated particle dispersions with the outer phase result in free-flowable particle dispersions.
Owner:PHARMASOL
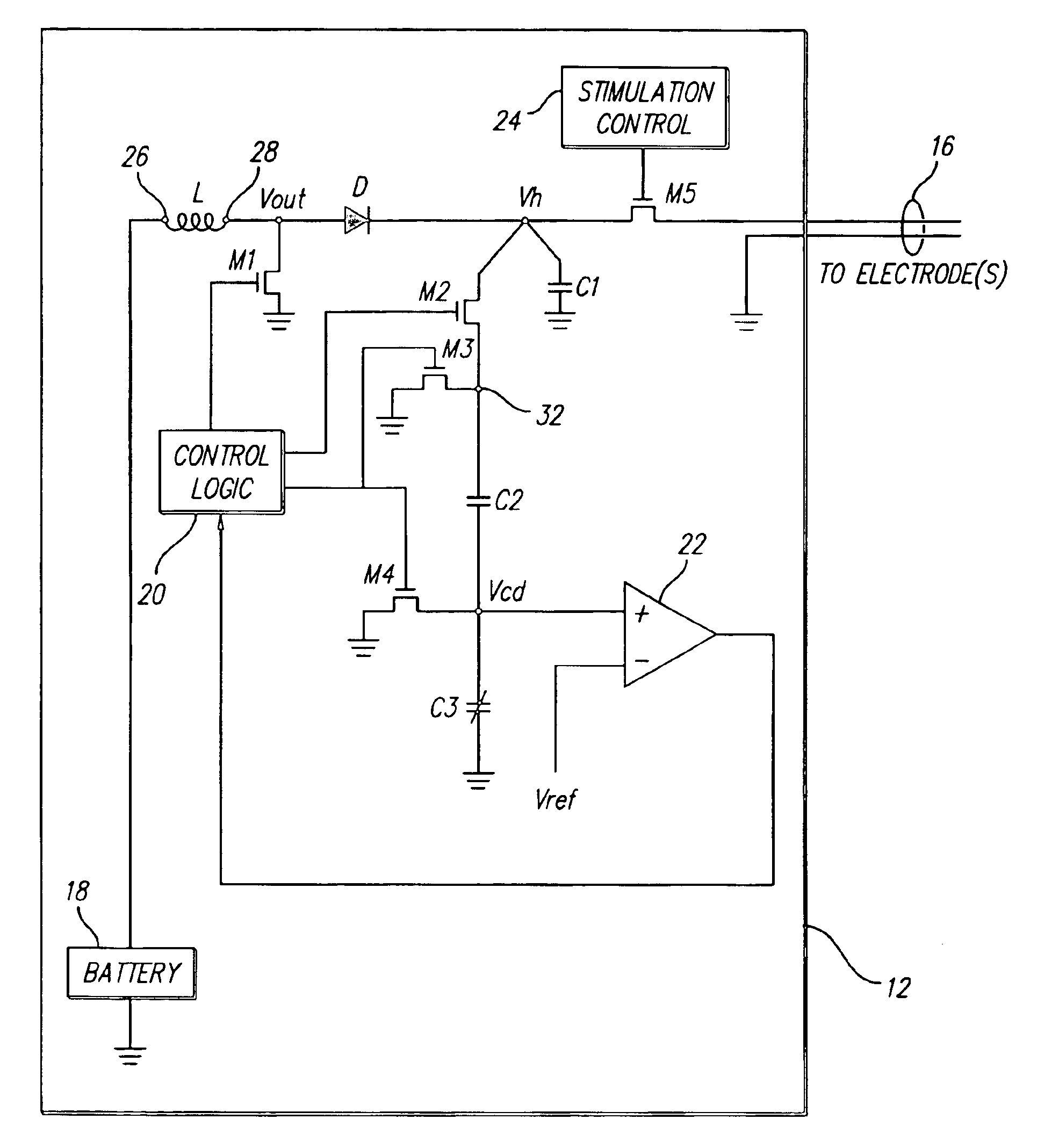
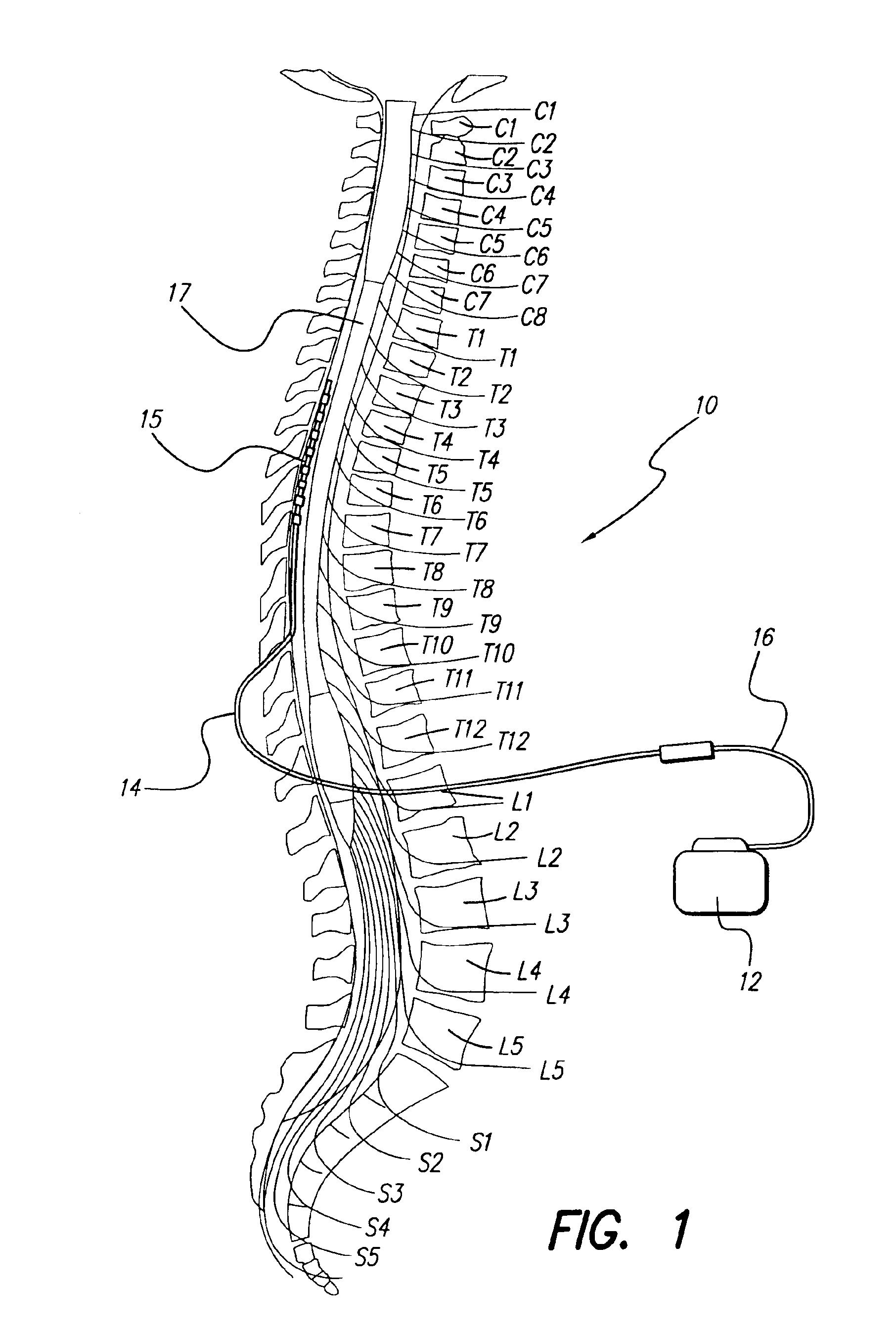
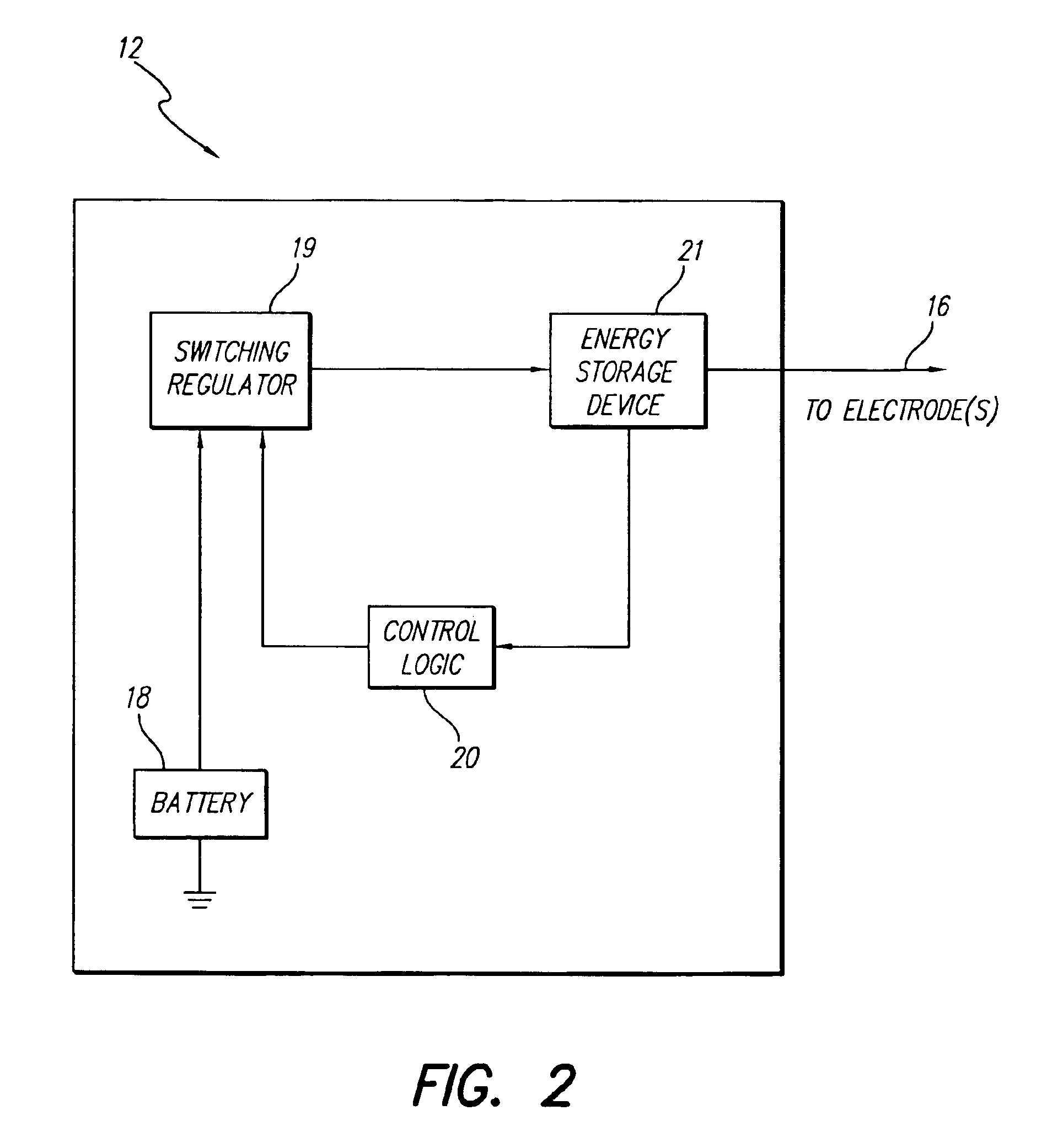
Switching regulator for implantable spinal cord stimulation
An improved switching regulator for implantable medical devices includes a control circuit with a capacitor divider to conserve energy, and selectable duty cycles to efficiently match the duty cycle to the charge level in a holding capacitor. The switching regulator charges the holding capacitor to commanded voltage levels, and the holding capacitor provides current for tissue stimulation. The commanded voltage level is reached by “pumping-up” the holding capacitor with the output of the switching regulator. For control purposes, the high voltage (i.e., the voltage across the holding capacitor) is divided between a fixed capacitor and a variable capacitor, and the voltage between the fixed capacitor and the variable capacitor (i.e., the divided voltage) is compared to a reference voltage. The result of the comparison is used to turn-off the switching regulator once the commanded voltage level is reached. The switching duty cycle is set to one of two values. At start-up, or when the output voltage drops below a determined threshold, a low duty cycle is used. Once the output voltage reaches the threshold, a higher duty cycle is used.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
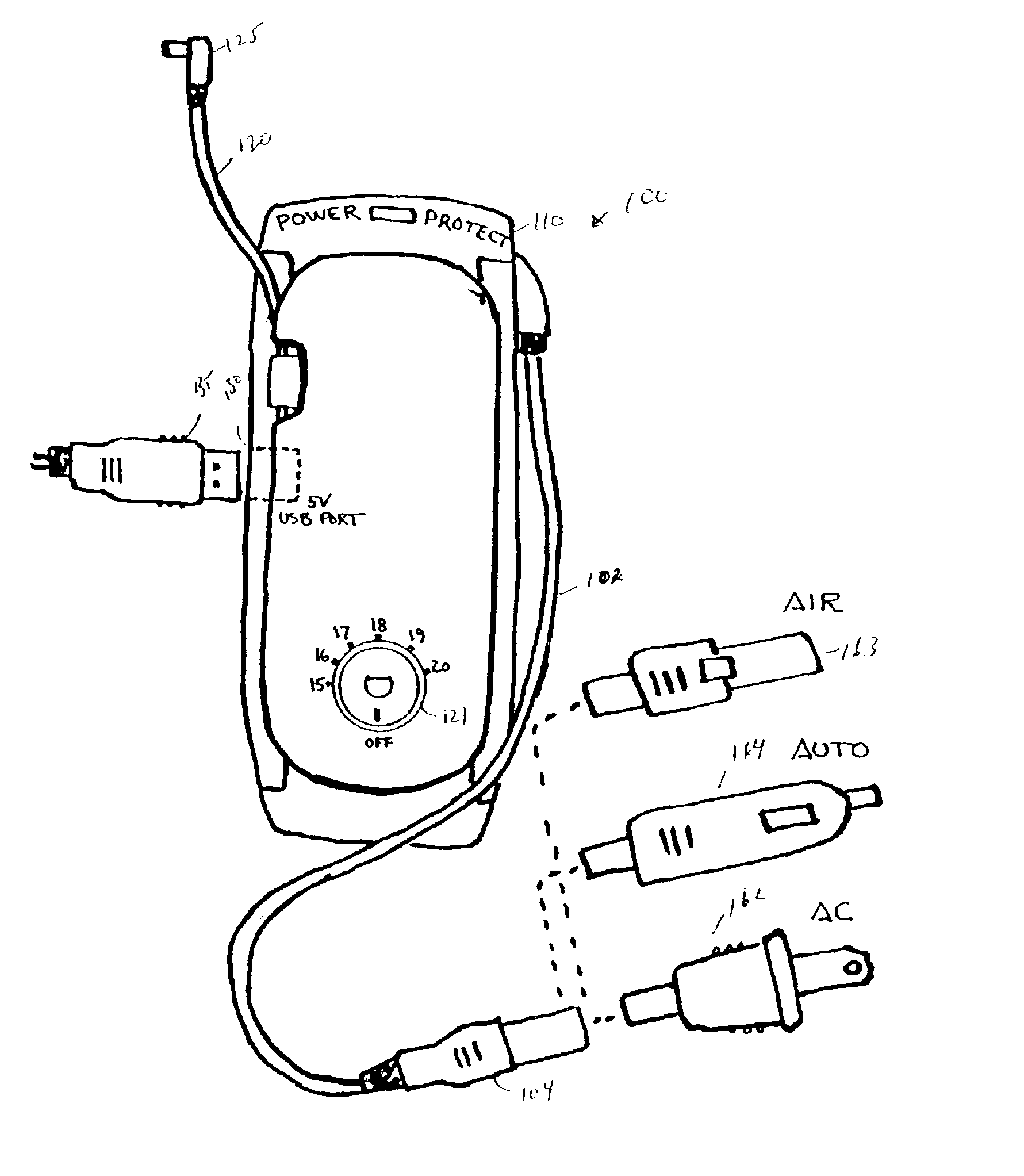
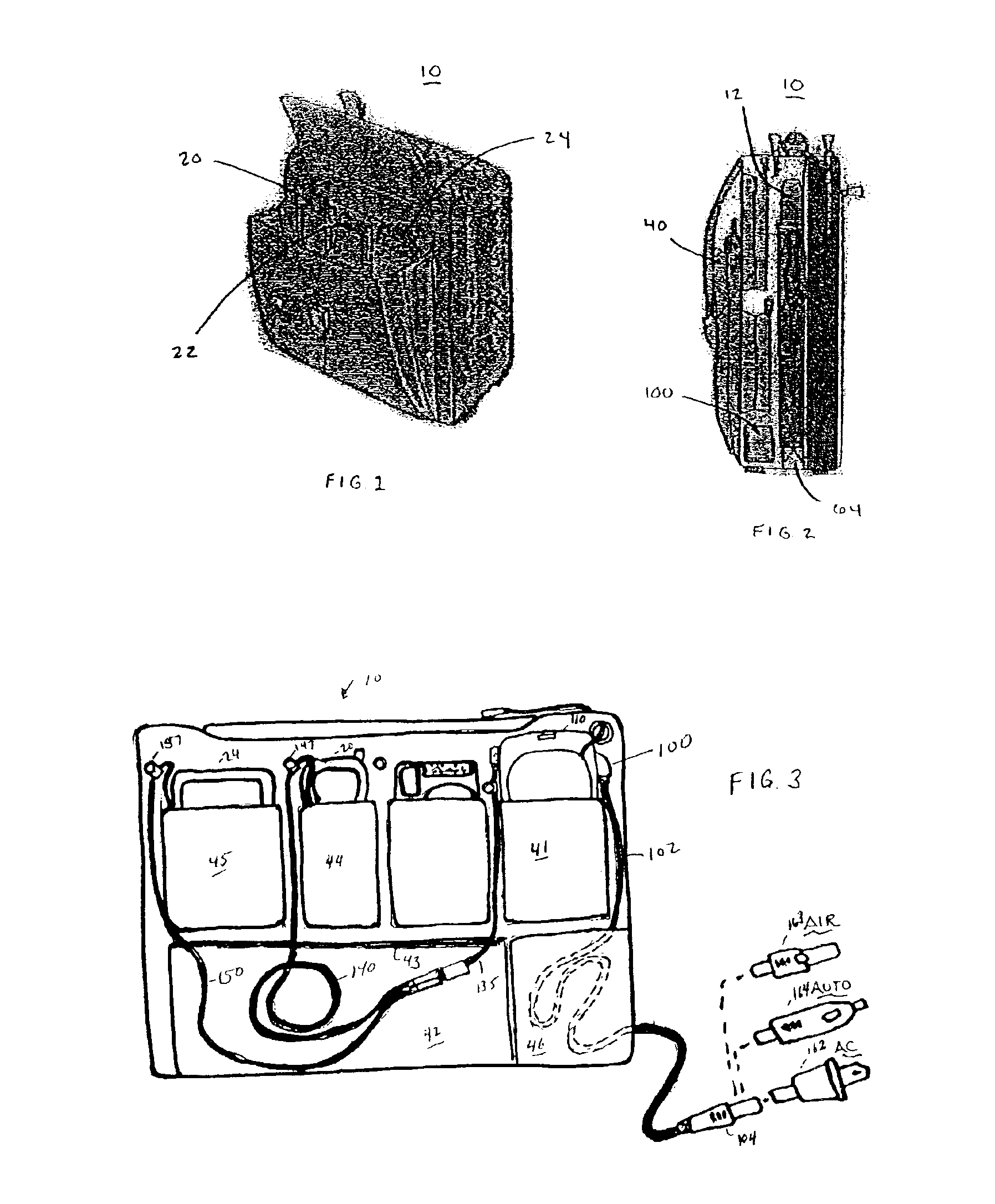
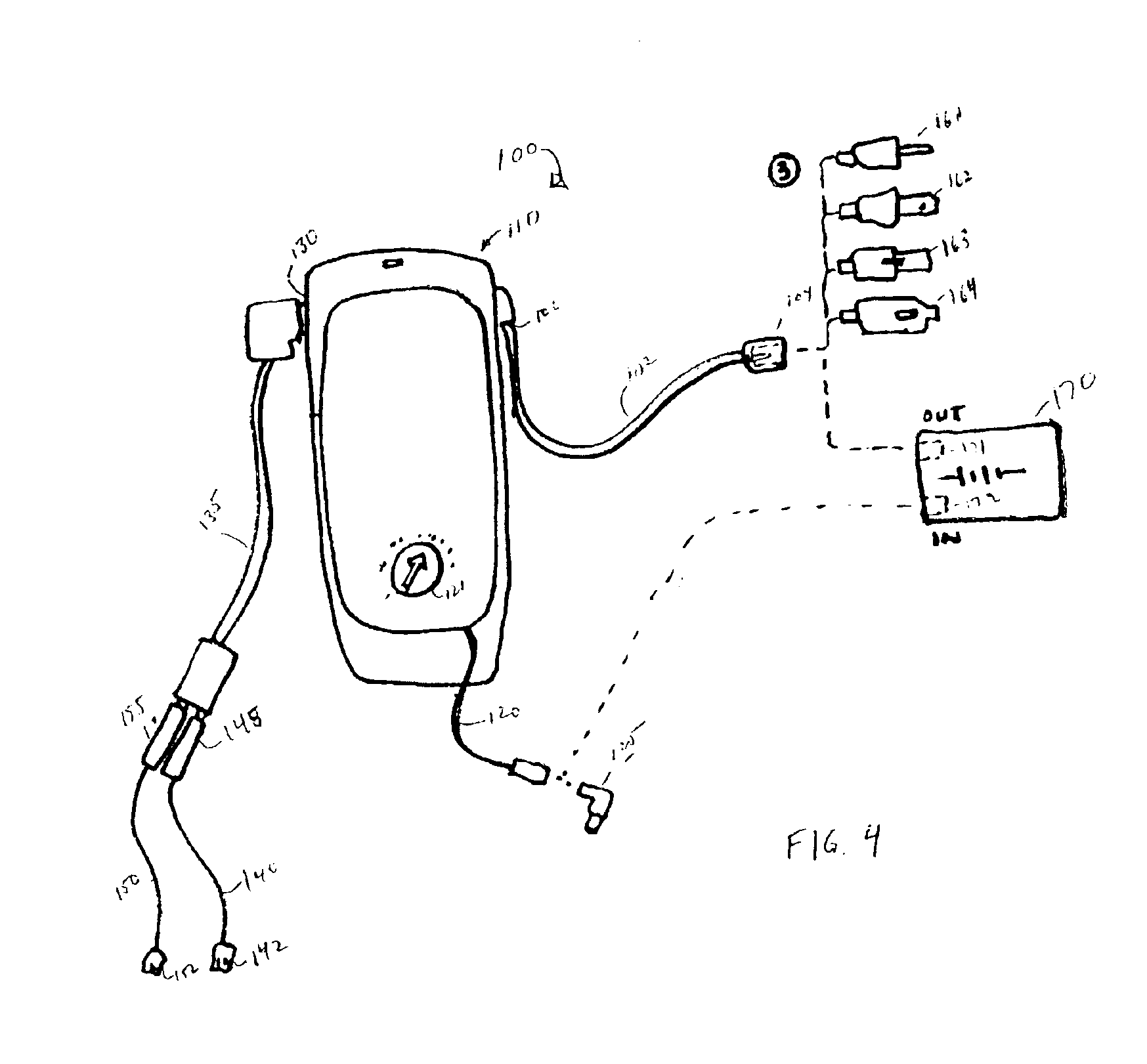
Universal multiple device power adapter and carry case
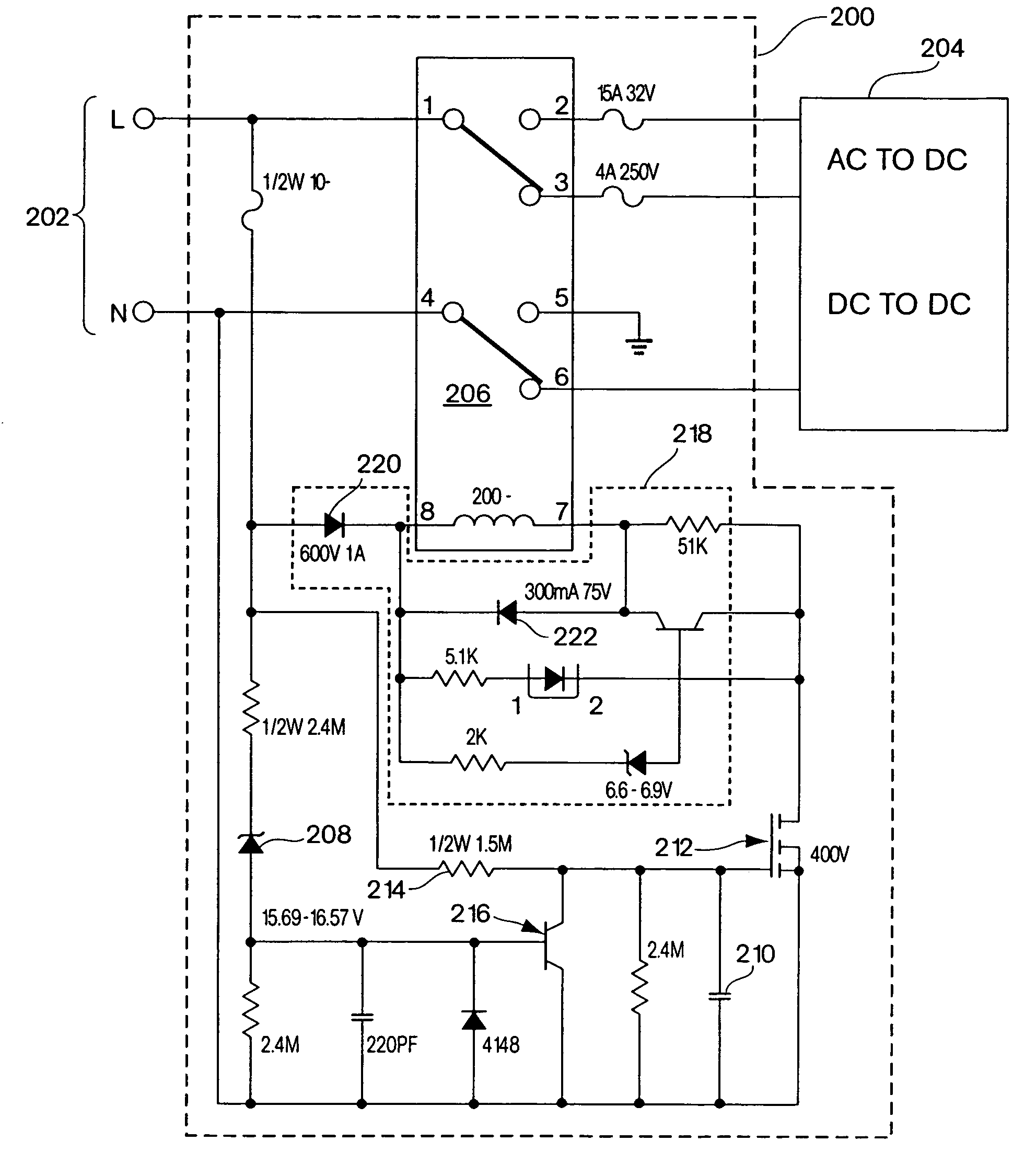
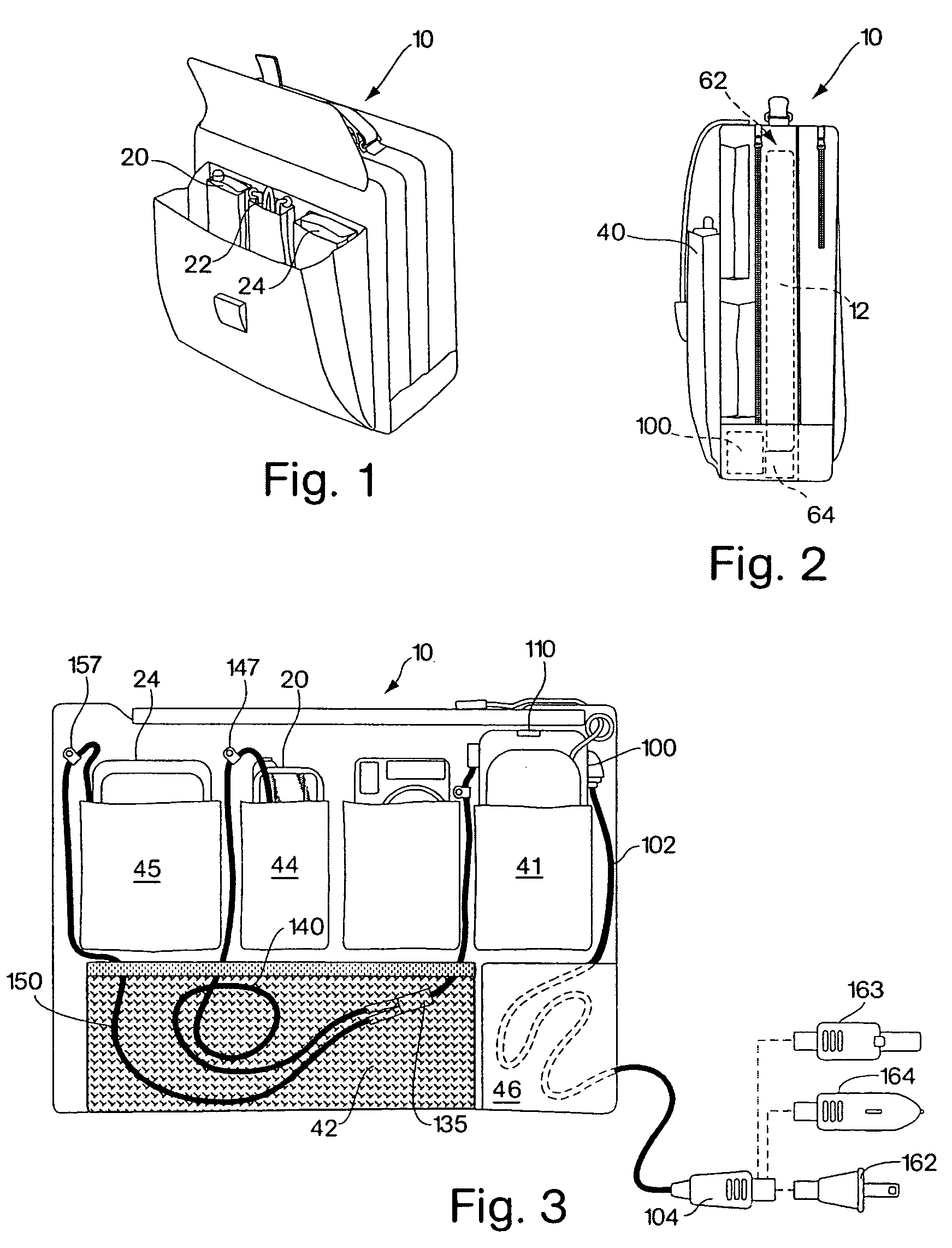
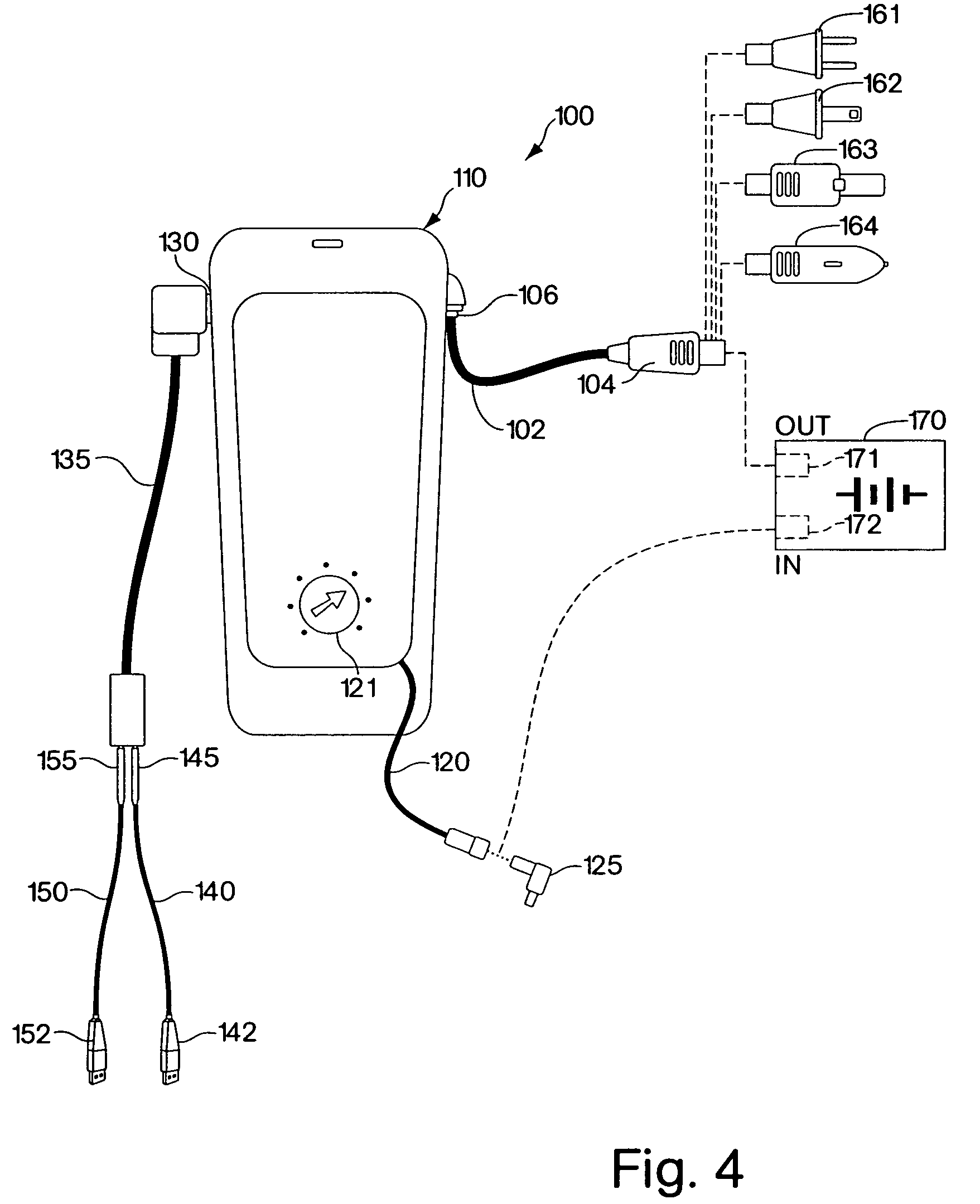
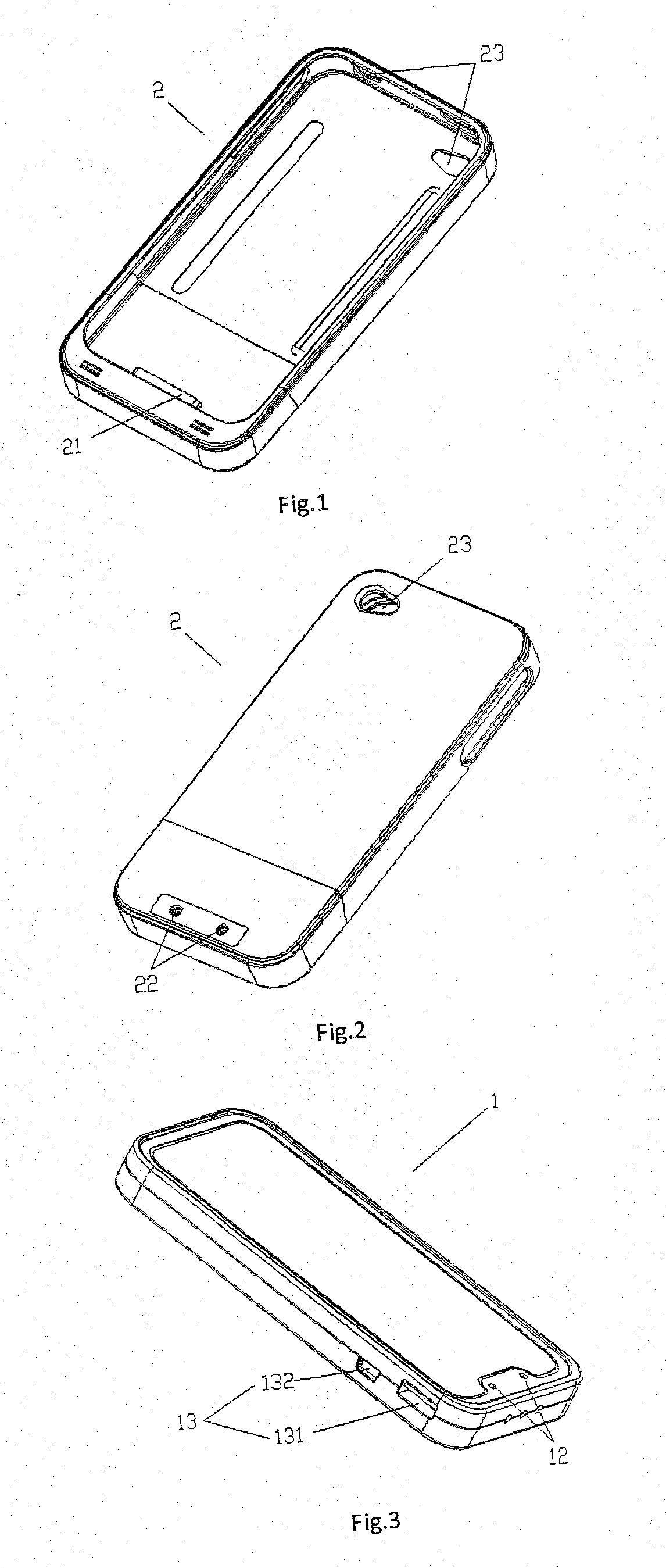
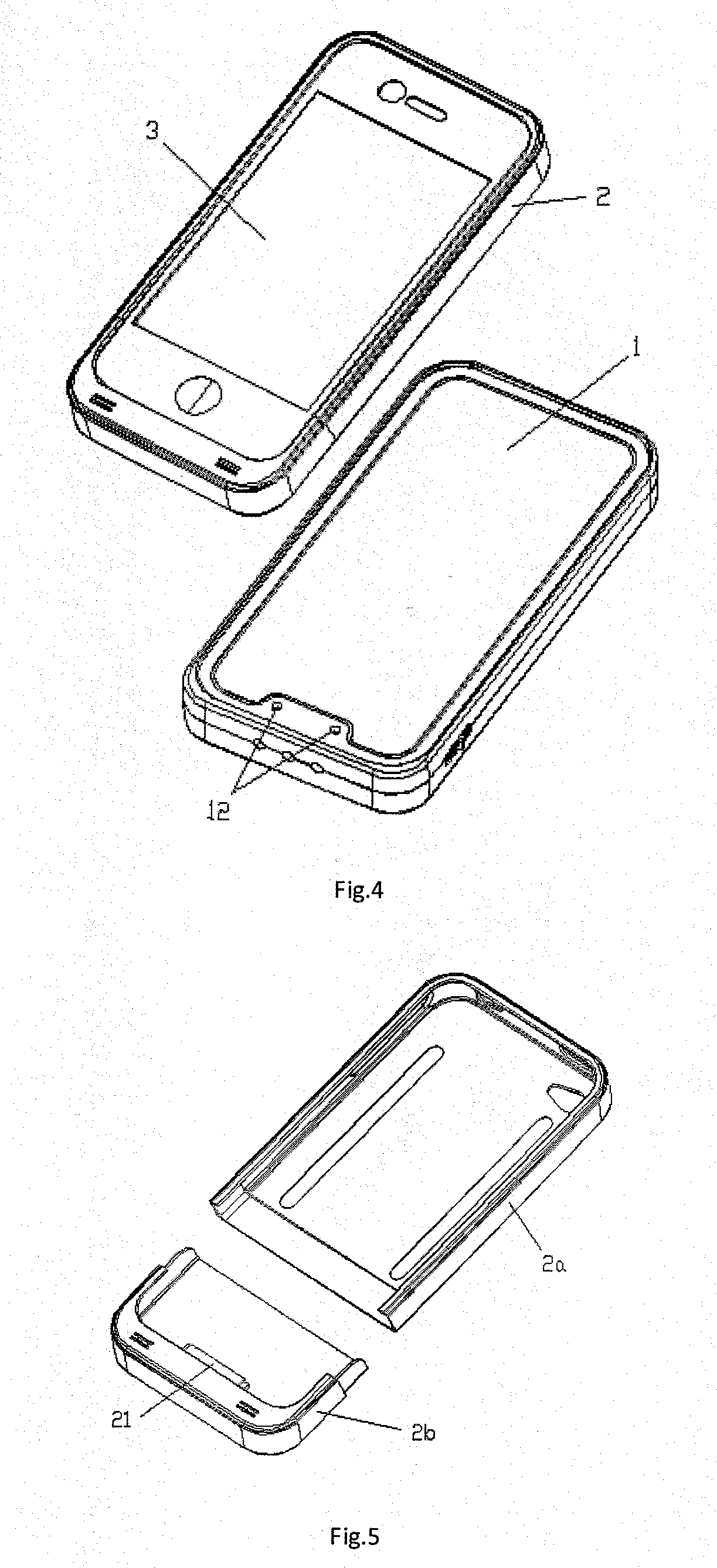
InactiveUS6894457B2Easy to chargeEasy accessCoupling device connectionsBatteries circuit arrangementsMultiple deviceEngineering
The present invention is directed to a carrying case with an integrated power supply system for providing power to multiple electronic devices from a single power source. In addition to allowing quick access and storage of various electronic devices, the carrying case also allows the individual electronic devices to be easily connected to the power source and eliminates the need to carry multiple charging cords. In certain embodiments, the power supply system further includes an additional battery or other power source, which increases the runtime of connected electronic devices and reduces the need to carry additional individual batteries for the individual devices. With different connectors on the input to the power system, different AC or DC power sources may be utilized. Different connectors can also be used to provide power to different electronic devices.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
Universal multiple device power adapter and carry case
InactiveUS7224086B2Easy to chargeEasy accessCoupling device connectionsBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power systemElectrical battery
The present invention is directed to a carrying case with an integrated power supply system for providing power to multiple electronic devices from a single power source. In addition to allowing quick access and storage of various electronic devices, the carrying case also allows the individual electronic devices to be easily connected to the power source and eliminates the need to carry multiple charging cords. In certain embodiments, the power supply system further includes an additional battery or other power source, which increases the runtime of connected electronic devices and reduces the need to carry additional individual batteries for the individual devices. With different connectors on the input to the power system, different AC or DC power sources may be utilized. Different connectors can also be used to provide power to different electronic devices.
Owner:SCHNEIDER ELECTRIC IT CORP
Use of high-K dielectric material in modified ONO structure for semiconductor devices
InactiveUS6803272B1Reduced dimensionSacrificing charge trapping abilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorSemiconductor device
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
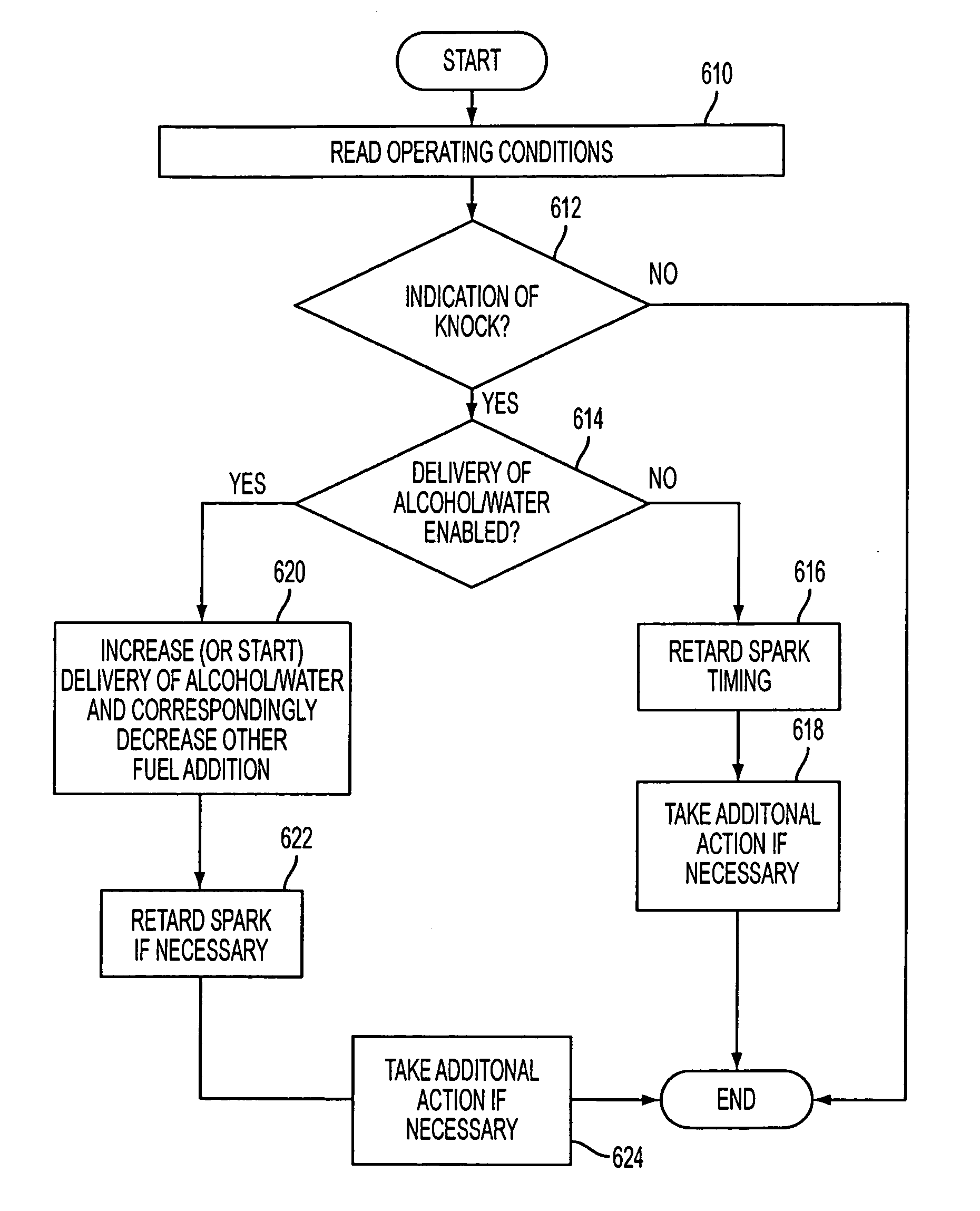
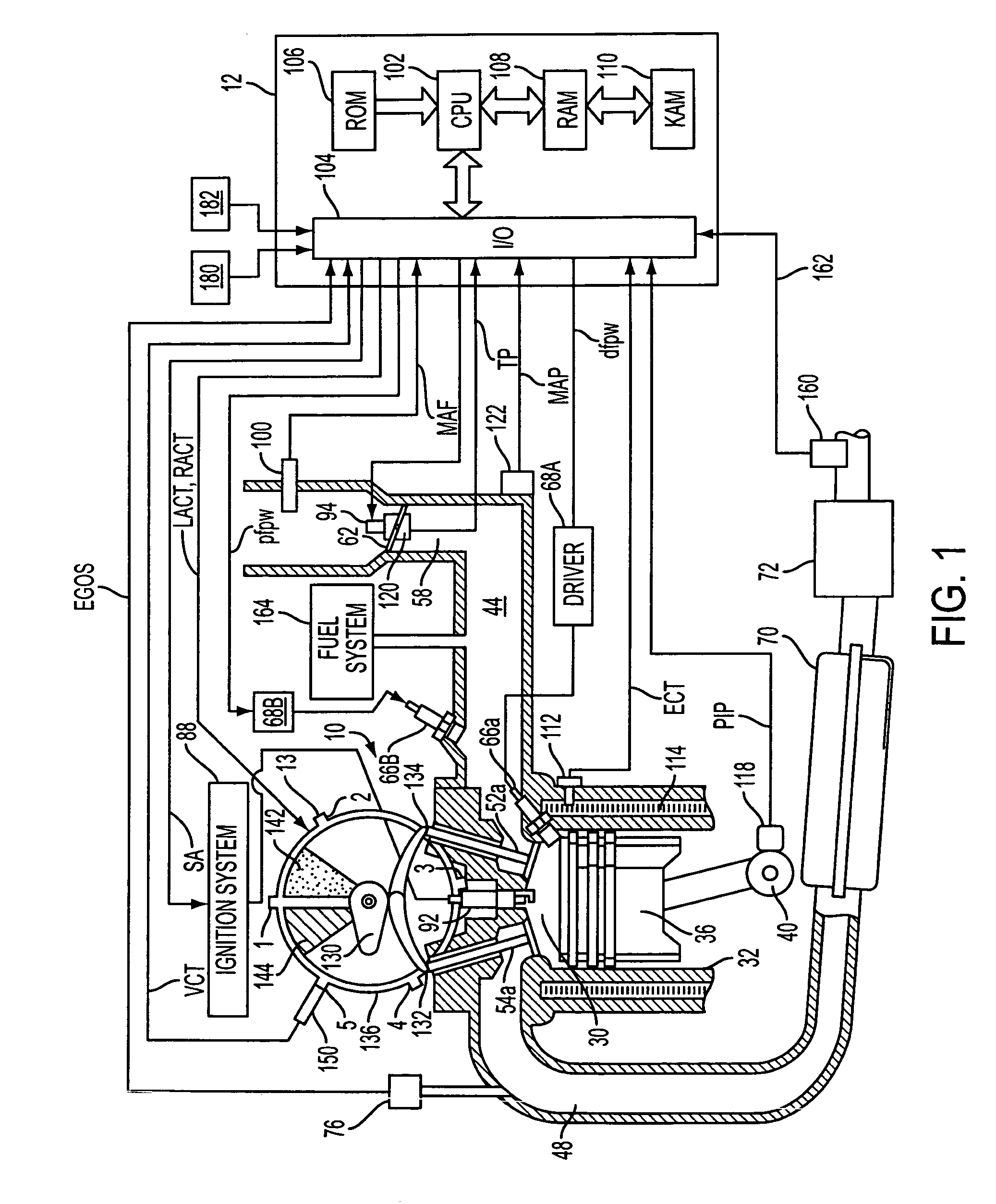
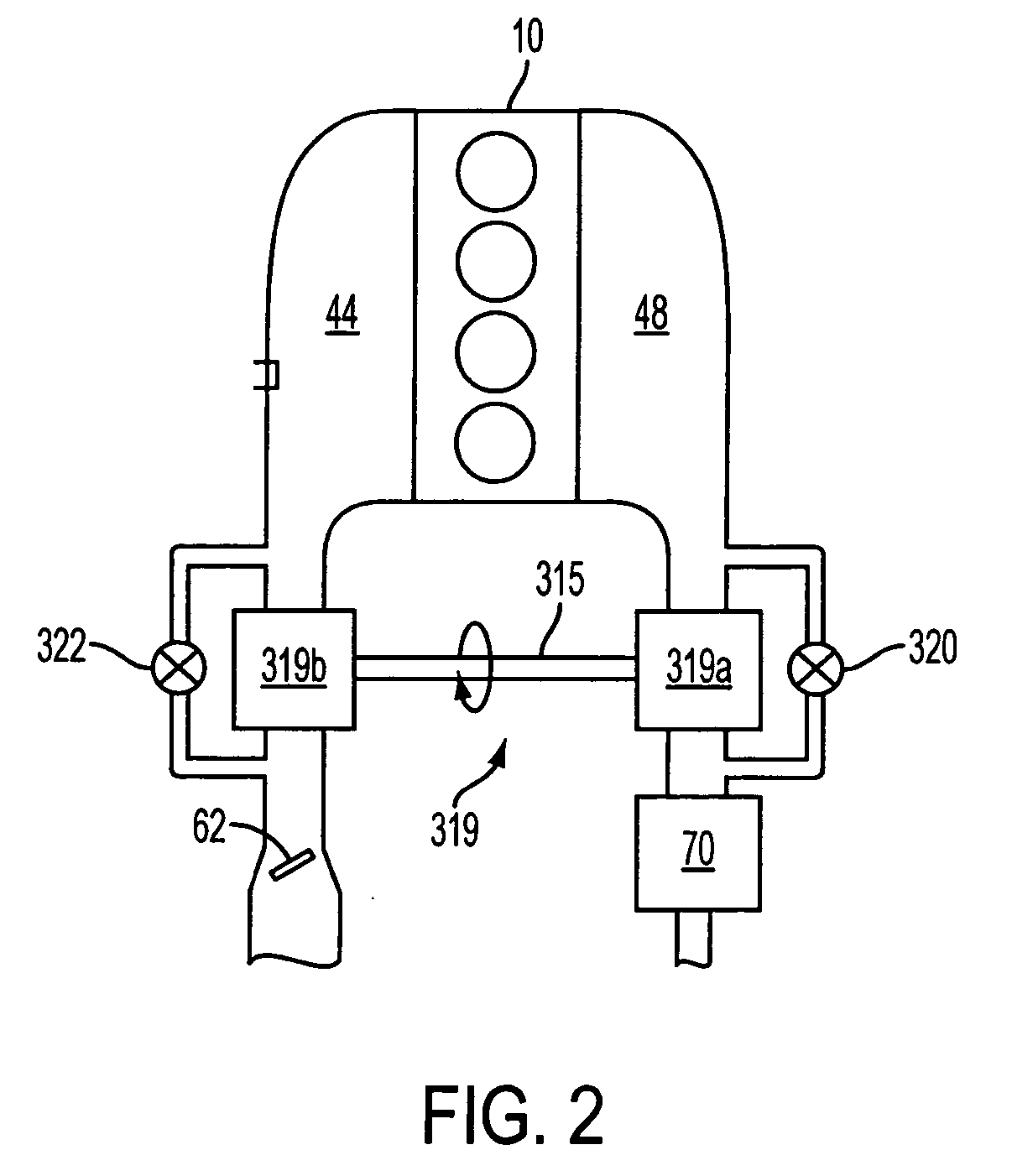
Control for alcohol/water/gasoline injection
ActiveUS20070119391A1Low costImprove charge cooling effectInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelAlcoholGasoline
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
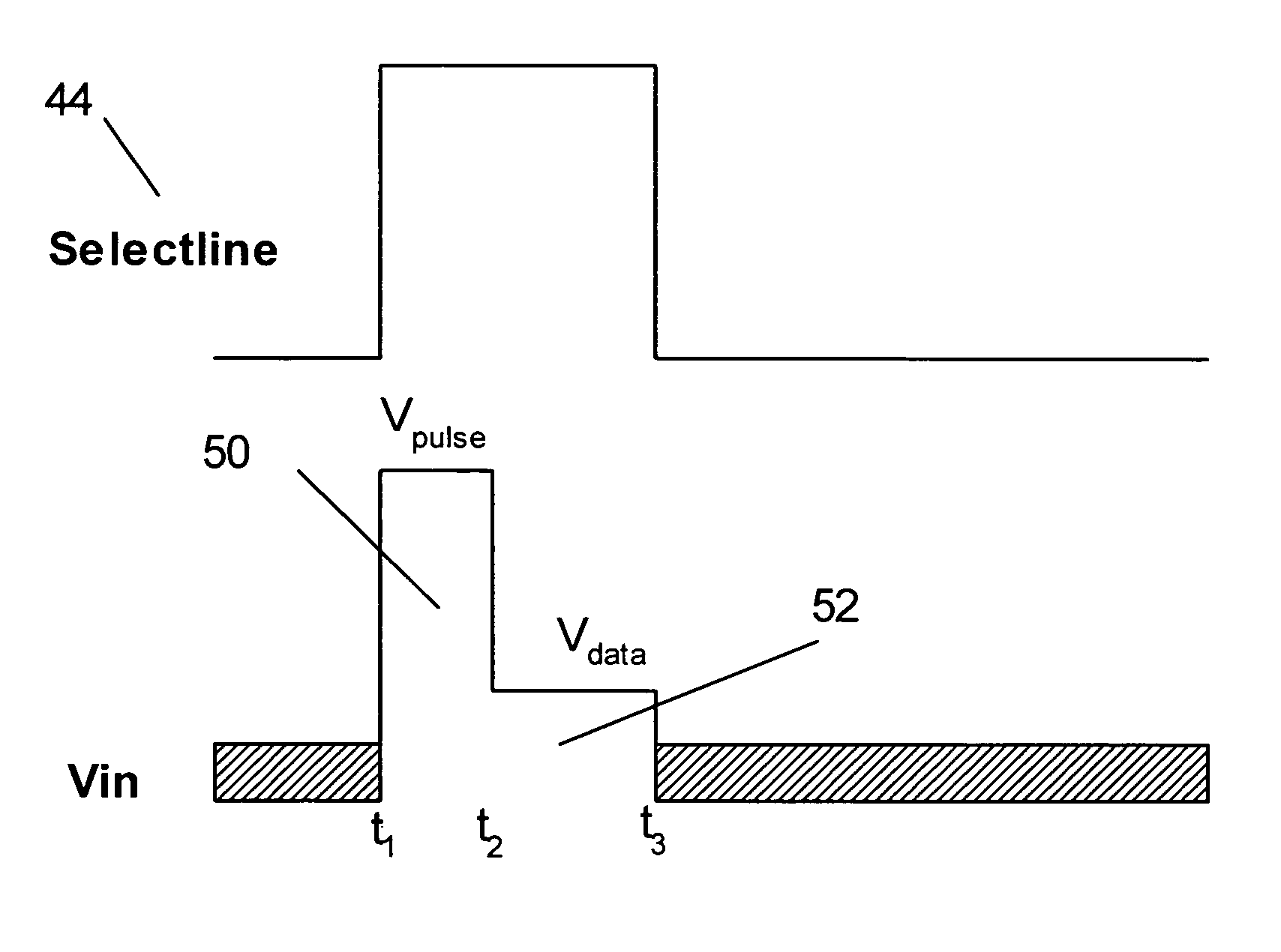
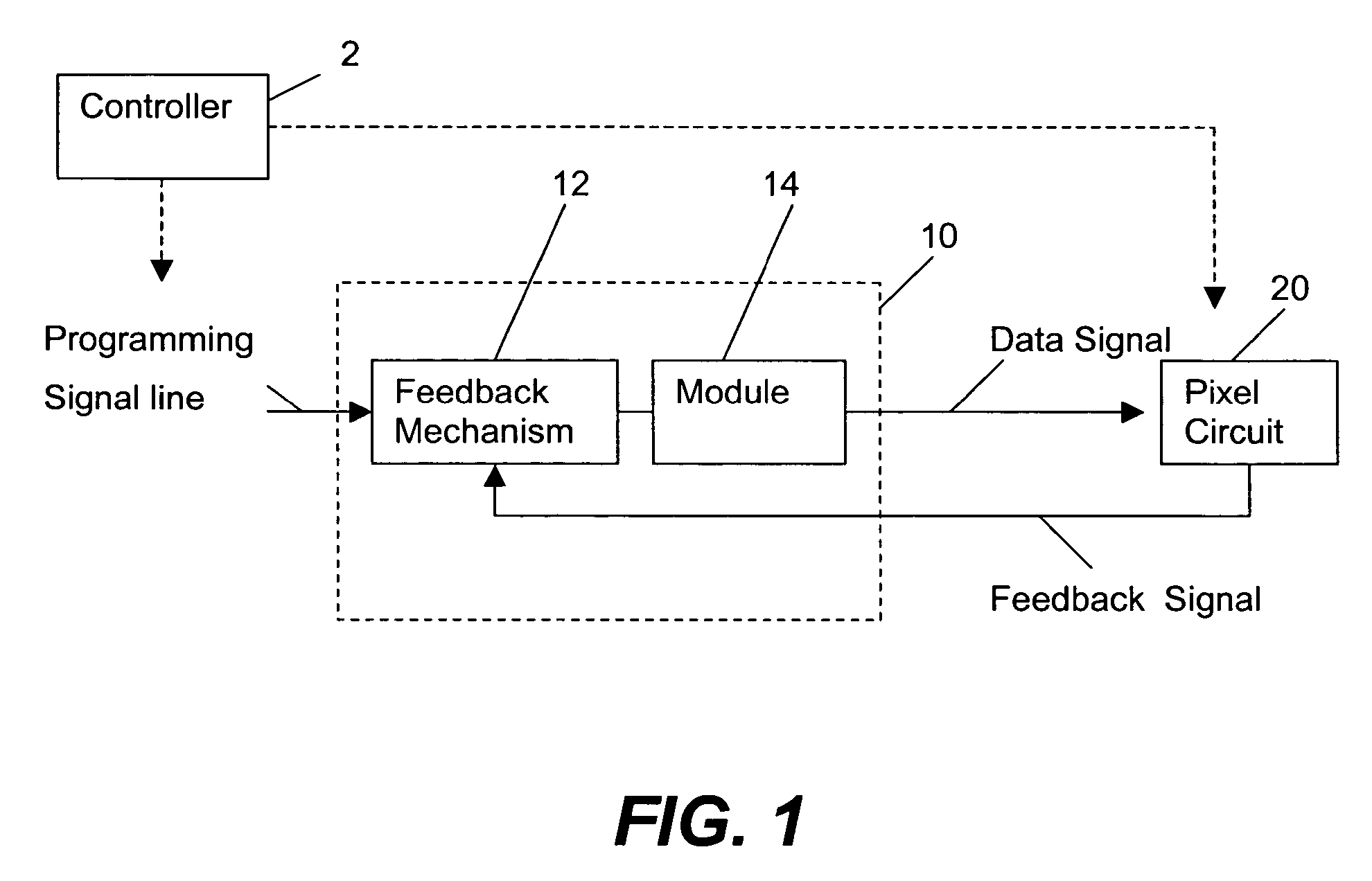
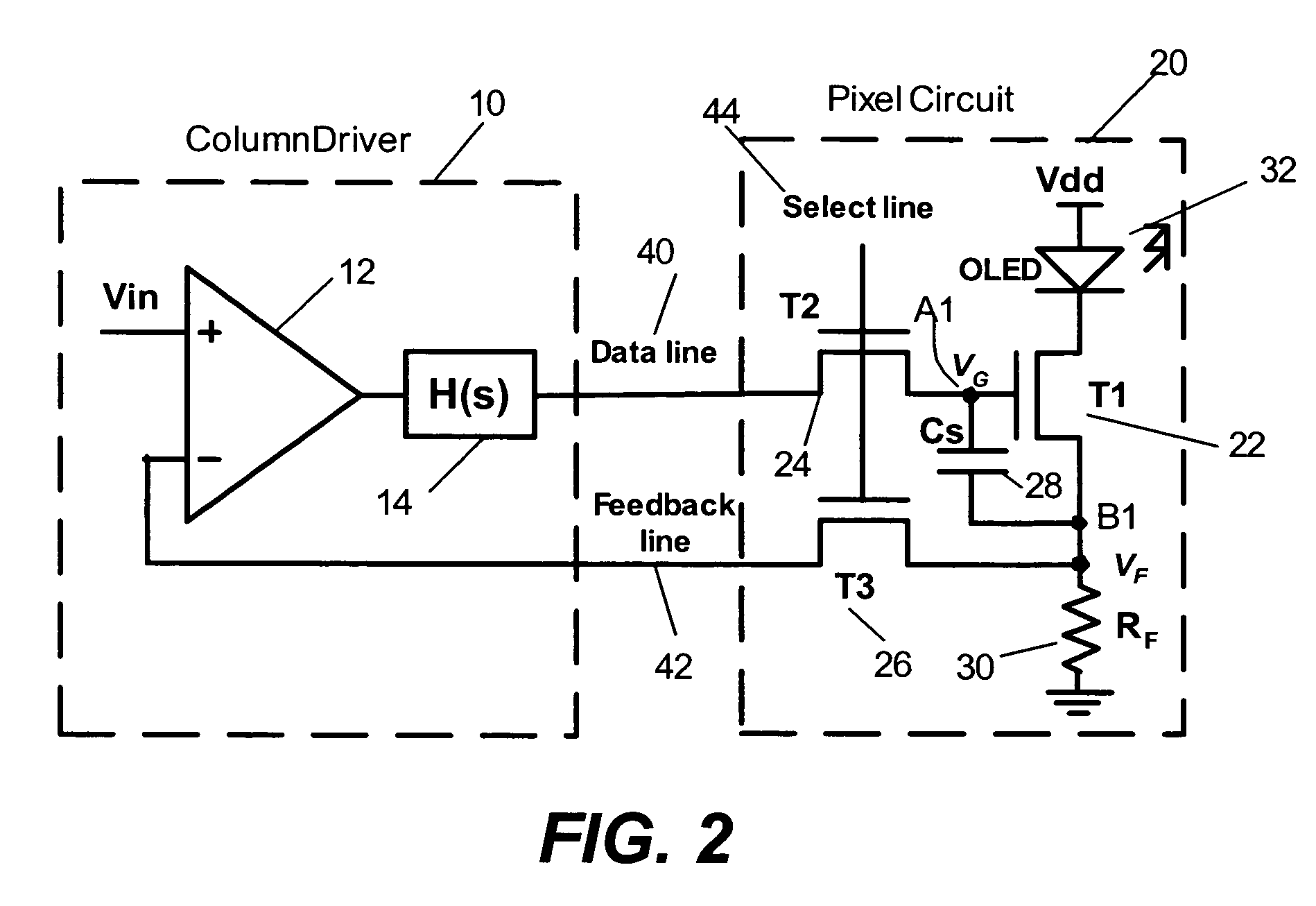
Method and system for driving a pixel circuit in an active matrix display
ActiveUS8223177B2Reduced settling timeEasy to chargeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixSignal on
A method and system for driving a pixel circuit in an active matrix display is provided. The system implements a feedback driving scheme to enhance programming speed of the pixel circuit. The system includes a column driver for driving the pixel circuit with feedback. A controller controls a signal on a programming signal line during a programming cycle. For example, the driver may include a model for reducing the settling time of a pixel current. During the programming mode, an accelerating pulse may be provided to accelerate the programming of the pixel circuit.
Owner:IGNIS INNOVATION
Confidential information management system and information terminal for use in the system
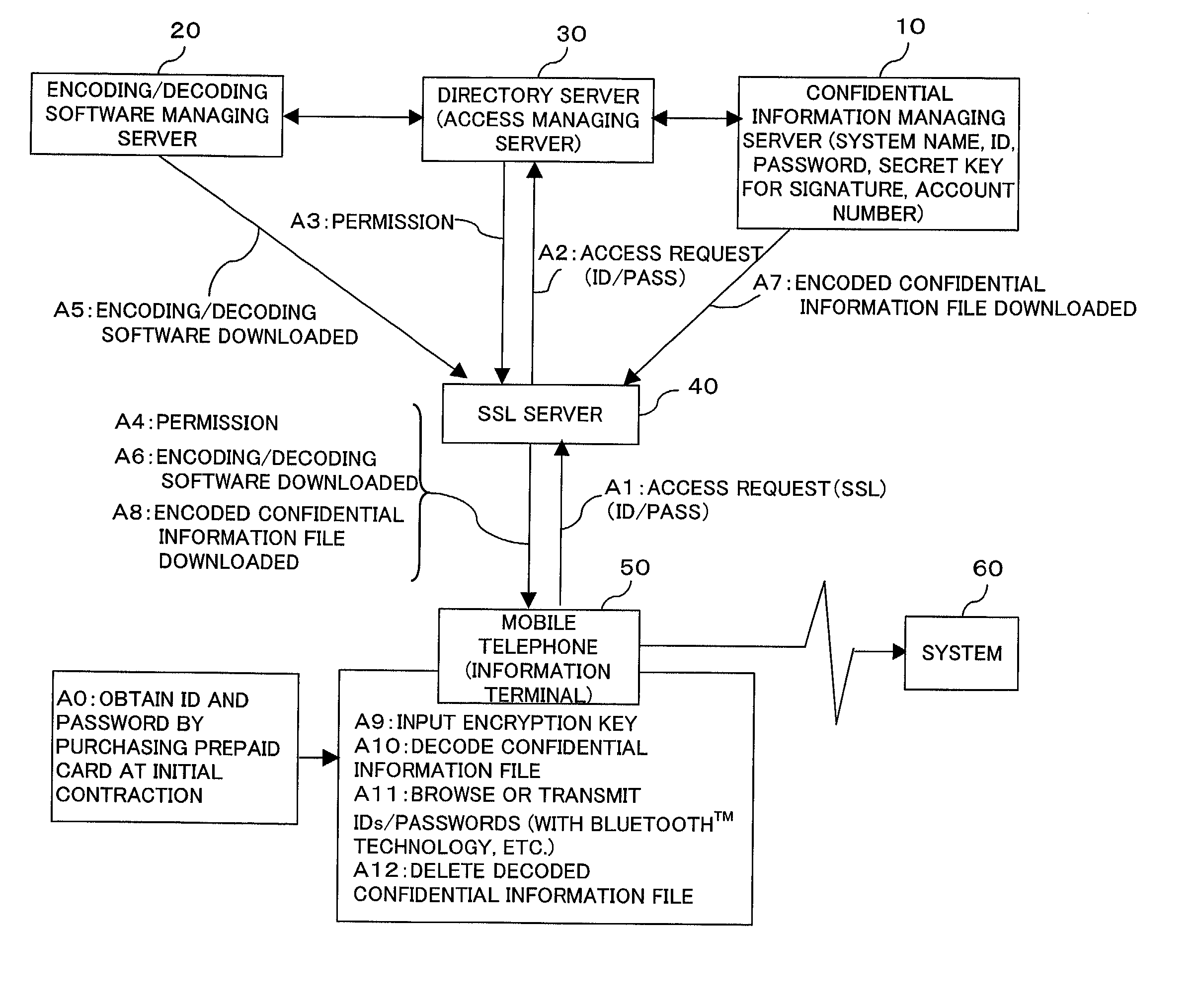
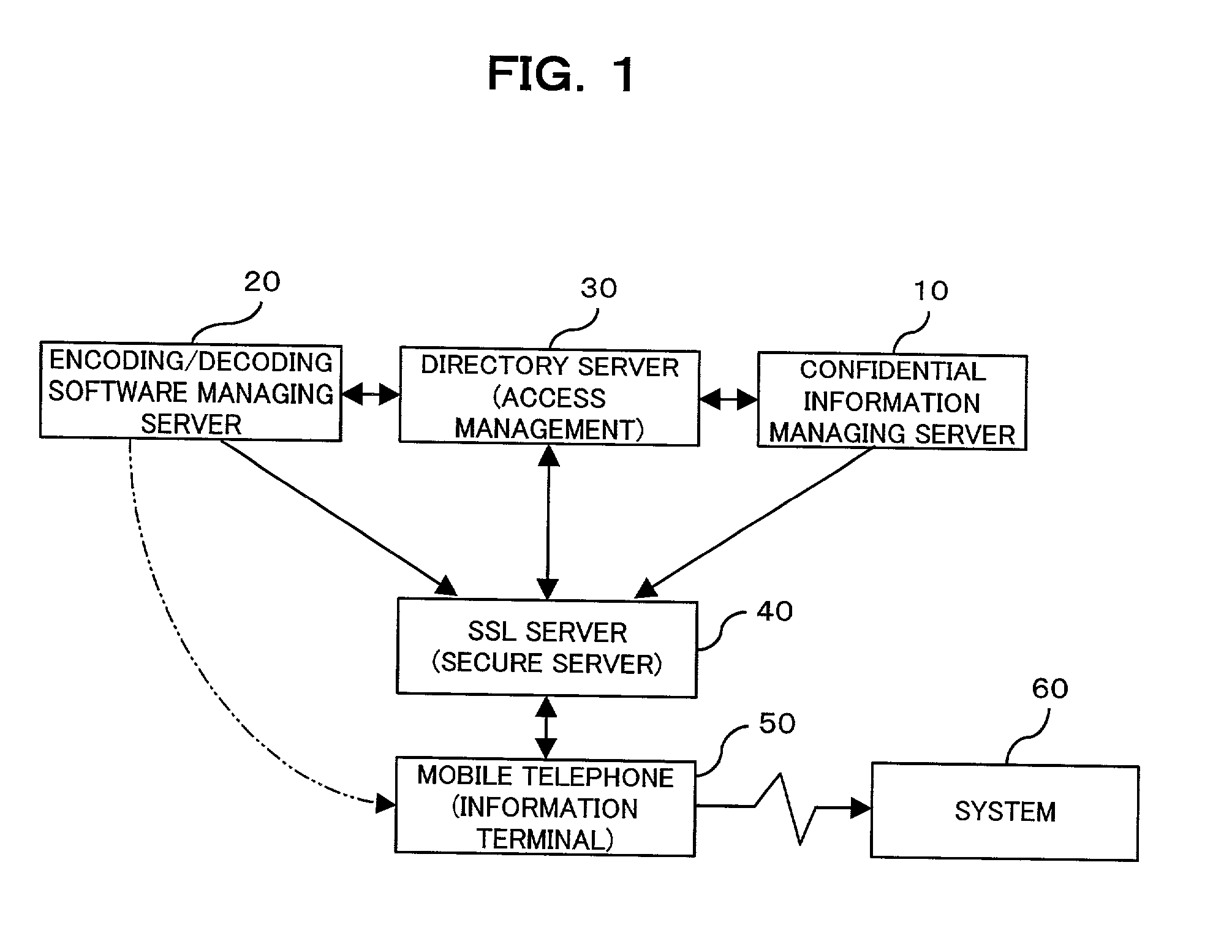
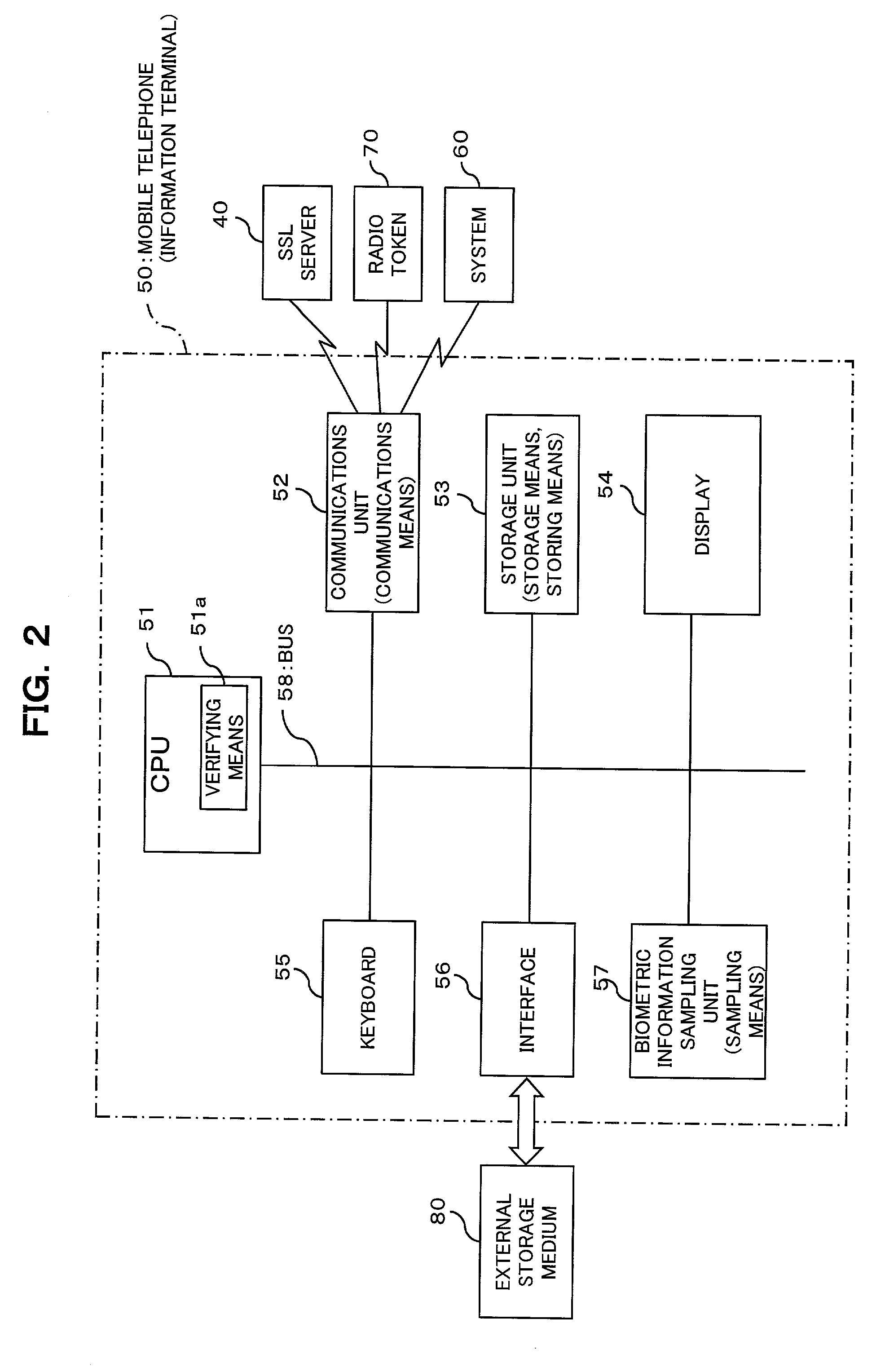
InactiveUS20030004881A1Simplify user operationsAvoid problemsUser identity/authority verificationUnauthorized memory use protectionUser verificationInternet privacy
The present invention provides a confidential information management system which allows users to securely obtain confidential information files containing various confidential information, which files are securely stored in the present system, anywhere and anytime, using a minimum of confidential information. A confidential information file and encoding / decoding software are downloaded to an information terminal from a confidential information managing server and an encoding / decoding software managing server, respectively, so that the confidential information file is decoded on the information terminal by using the encoding / decoding software. The present system is applicable to various (computer) systems which store and manage confidential information (ID numbers, passwords, encryption keys, digital certificates, etc.) for use in user verification.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Use of a Metal Complex as an N-Dopant for an Organic Semiconducting Matrix Material, Organic of Semiconducting Material and Electronic Component, and also a Dopant and Ligand and Process for Producing same
ActiveUS20090212280A1Low oxidation potentialEasy to chargeGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCarbanionValence electron
A method of using a metal complex as an n-dopant for doping an organic semiconducting matrix material in order to alter the latter's electrical characteristics is provided. In order to provide n-doped organic semiconductors with matrix materials having a low reduction potential, while achieving high conductivities, the n-dopant is a neutral electron-rich metal complex with a neutral or charged transition metal atom as a central atom and having at least 16 valence electrons. The complex can be polynuclear and can possess at least one metal-metal bond. At least one ligand can form a π complex with the central atom, which can be a bridge ligand, or it can contain at least one carbanion-carbon atom or a divalent atom. Methods for providing the novel n-dopants are provided.
Owner:NOVALED GMBH
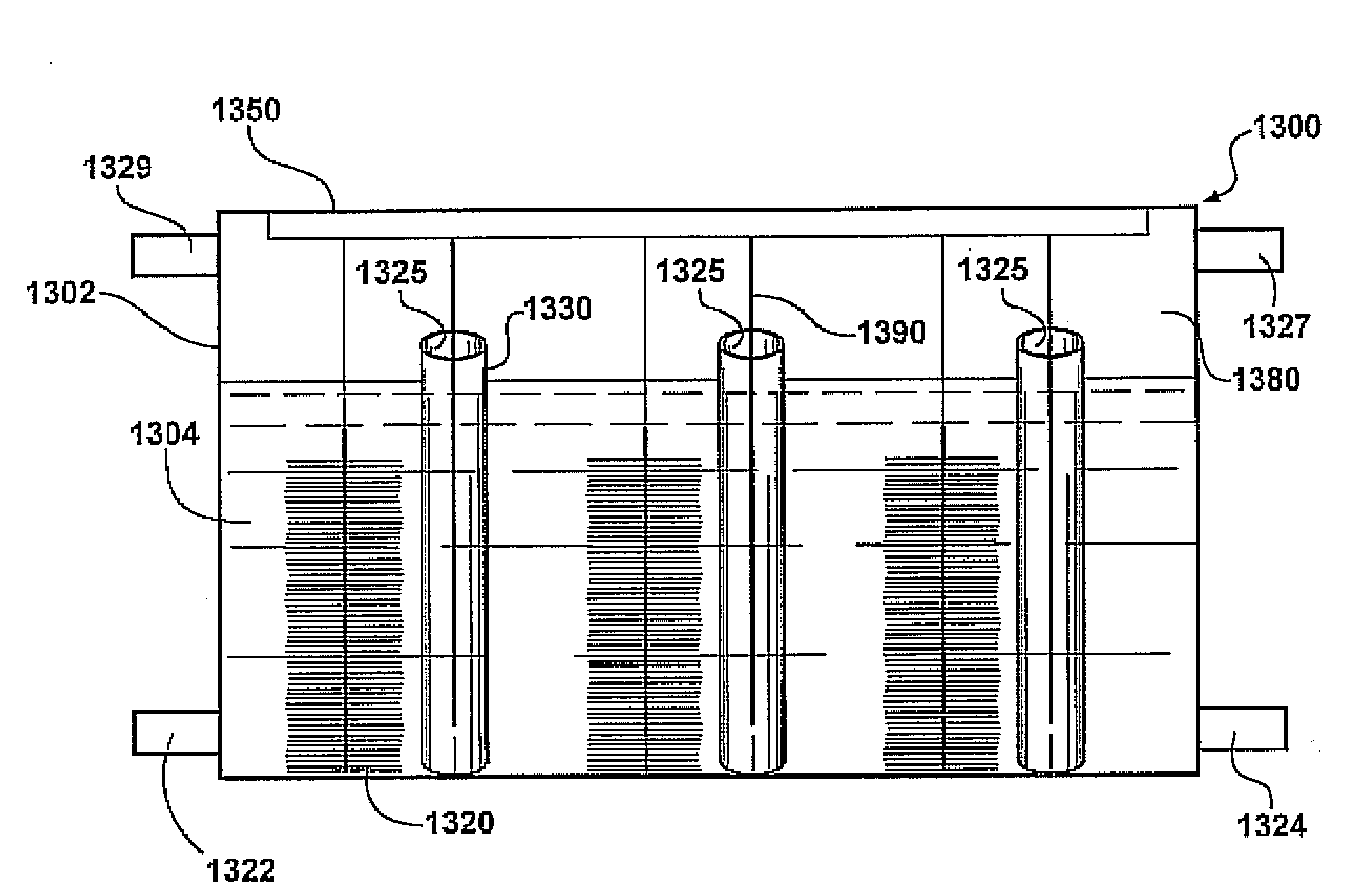
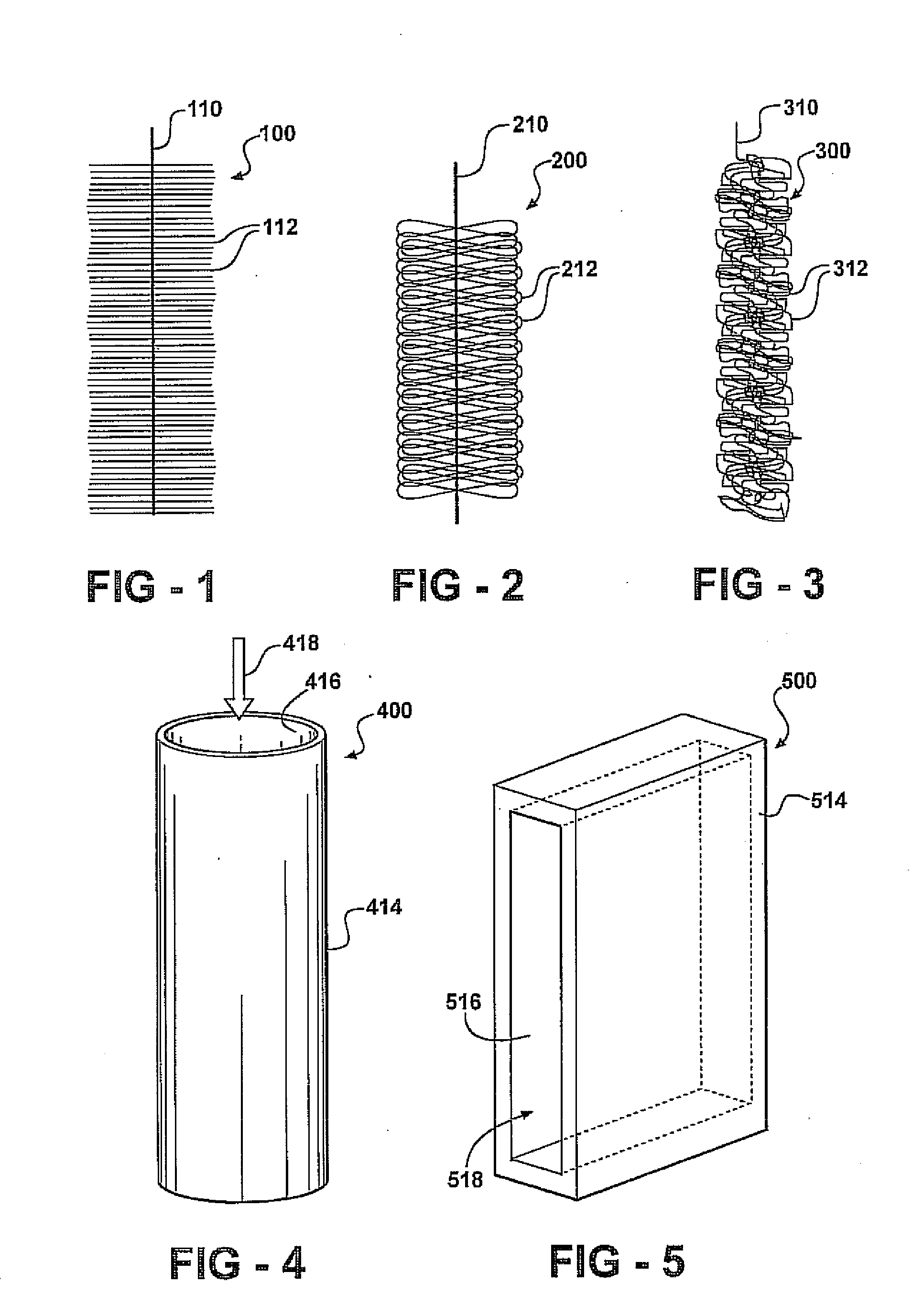
Energy storage device
ActiveUS20100203362A1Reduce heatImprove conductivityLead-acid accumulatorsCapacitor and primary/secondary cellsTin dioxideConductive materials
An energy storage device comprising at least one negative electrode, wherein each negative electrode is individually selected from (i) an electrode comprising negative battery electrode material; (ii) an electrode comprising capacitor electrode material; (iii) a mixed electrode comprising either—a mixture of battery and capacitor electrode material or—a region of battery electrode material and a region of capacitor electrode material, or—a combination thereof, and wherein the energy storage device either comprises at least one electrode of type (iii), or comprises at least one electrode of each of types (i) and (ii),—at least one positive electrode, wherein the positive electrode comprises positive battery electrode material and a charging ability-increasing additive, such as one or a mixture of: (a) carbon nanomaterial, vapour grown carbon fibre, fullerene, or a mixture thereof, and (b) tin dioxide conductive materials.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG +1
Data repository and method for promoting network storage of data
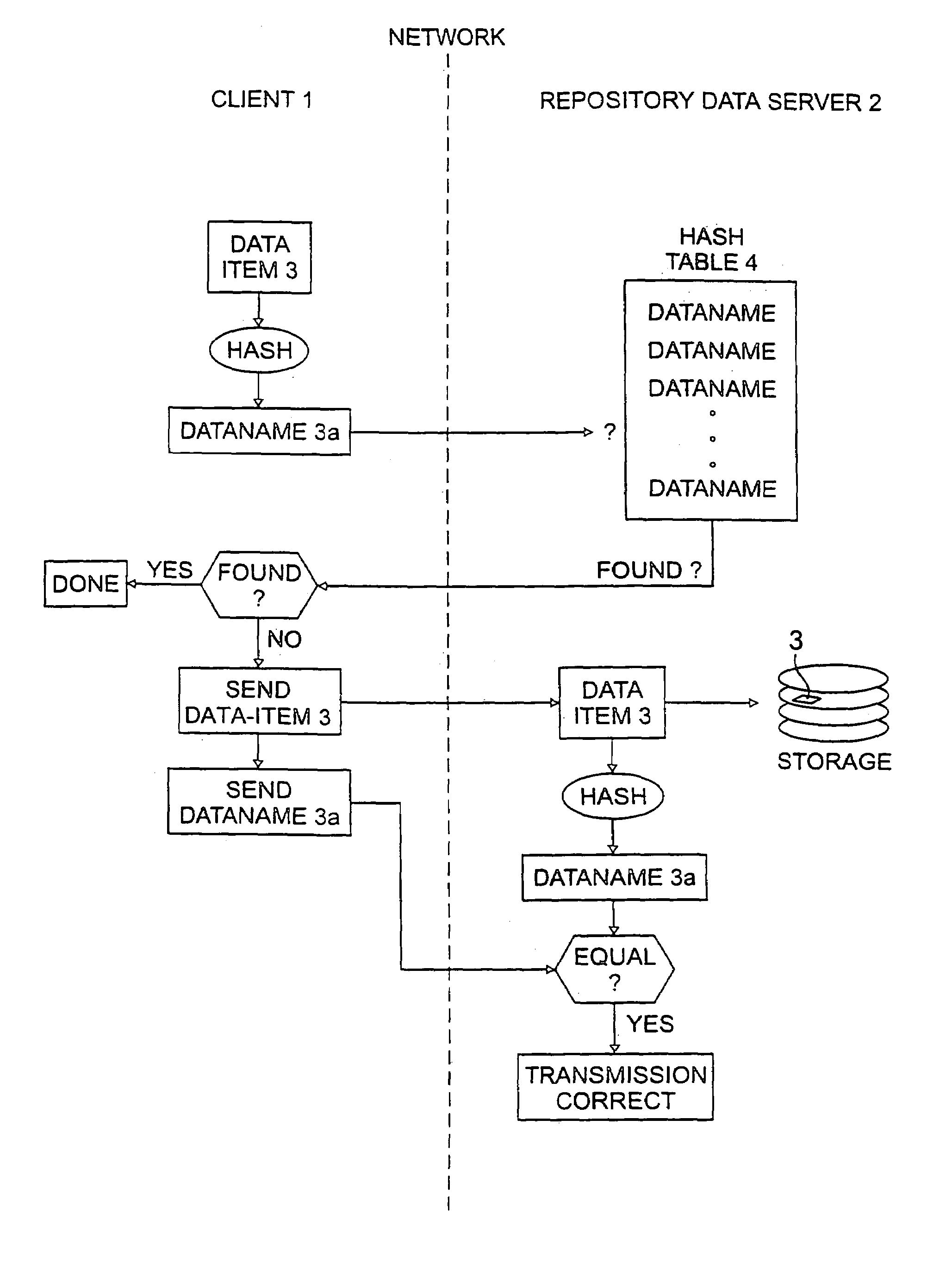
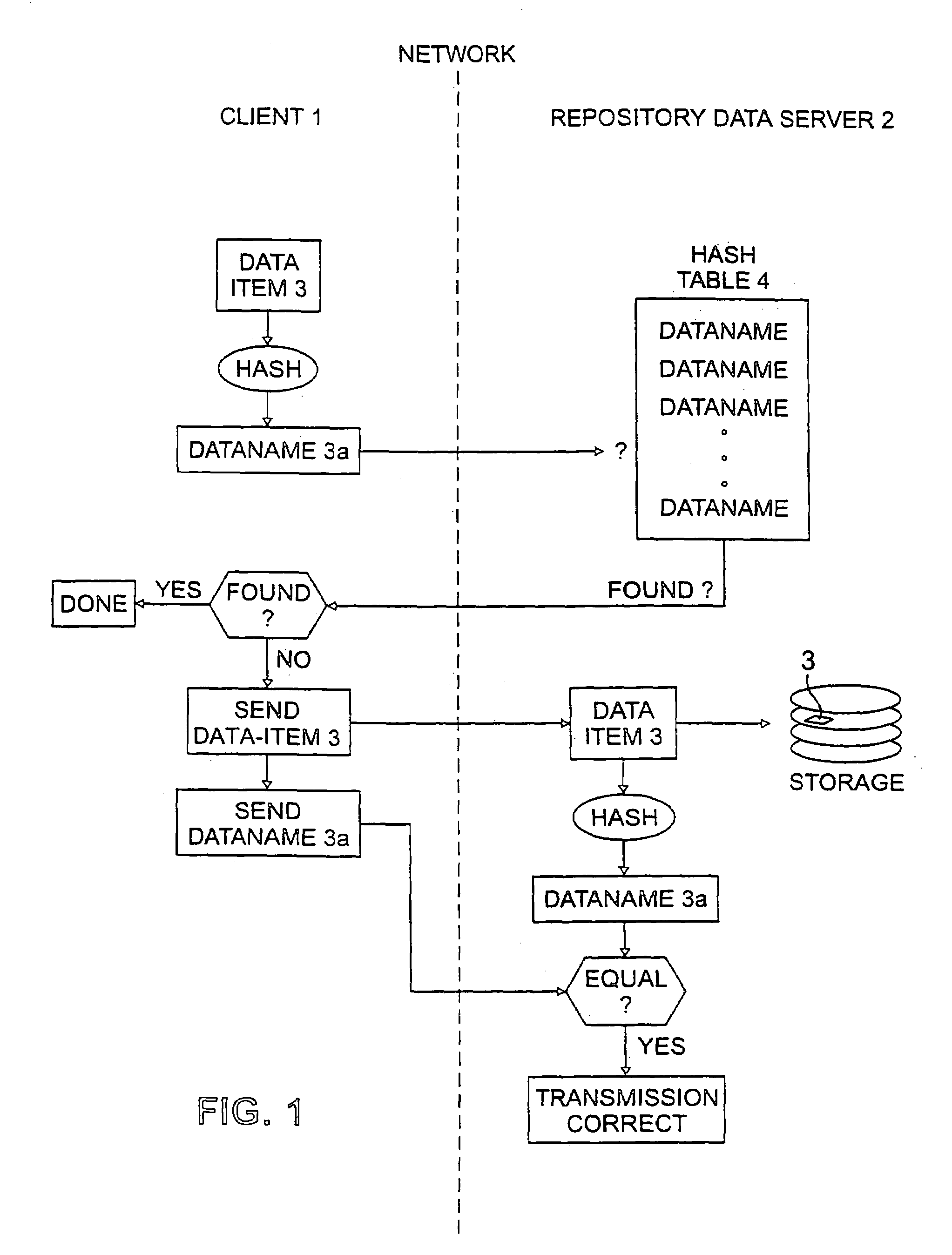
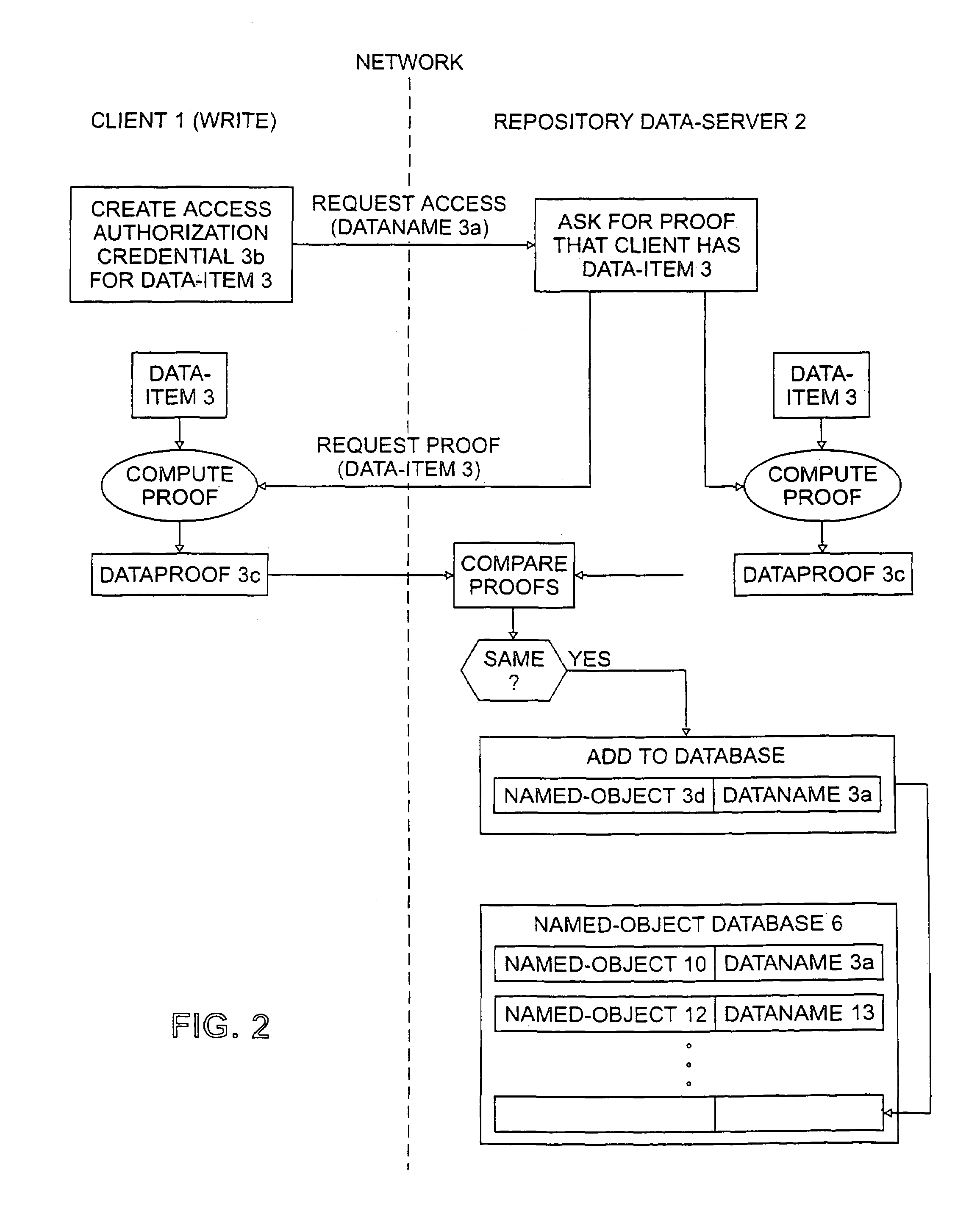
InactiveUS7124305B2Reduced likelihoodReduced versionDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsFull dataClient-side
In general, the invention features methods by which more than one client program connected to a network stores the same data item on a storage device of a data repository connected to the network. In one aspect, the method comprises encrypting the data item using a key derived from the content of the data item, determining a digital fingerprint of the data item, and storing the data item on the storage device at a location or locations associated with the digital fingerprint. In a second aspect, the method comprises determining a digital fingerprint of the data item, testing for whether the data item is already stored in the repository by comparing the digital fingerprint of the data item to the digital fingerprints of data items already in storage in the repository, and challenging a client that is attempting to deposit a data item already stored in the repository, to ascertain that the client has the full data item.
Owner:RED HAT
Wireless power storage device, semiconductor device including the wireless power storage device, and method for operating the same
InactiveUS20080079396A1Increased durabilityIncrease frequency of useBatteries circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemElectricityEngineering
To simplify charging of a battery in a power storage device which includes the battery. Further, to provide a wireless power storage device which can transmit and receive information without the task of replacing a battery for drive power supply, which becomes necessary when the battery depletes over time, being performed. An antenna circuit, a battery which is electrically connected to the antenna circuit via a rectifier circuit, and a load portion which is electrically connected to the battery are provided. The battery is charged when an electromagnetic wave received by the antenna circuit is input to the battery via the rectifier circuit, and discharged when electrical power which has been charged is supplied to the load portion. The battery is charged cumulatively, and the battery is discharged in pulses.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
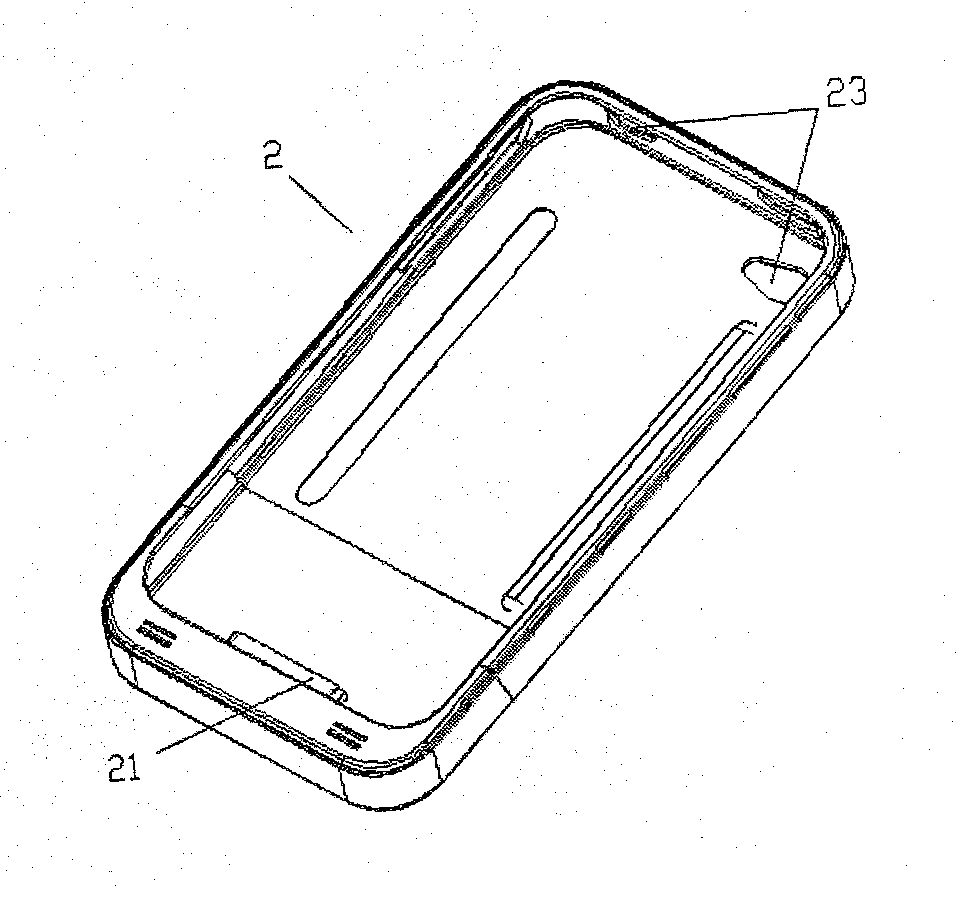
Wireless charging equipment for mobile phones
InactiveUS20120088555A1Effective protectionEasy to chargeSubstation equipmentTransmissionElectricityEngineering
The present invention provides a wireless charging equipment for mobile phones for mobile phones. The charging equipment comprises a protection cover with a switch port and a charger with an internal battery arranging therein. The mobile phone is enveloped in the protection cover, one end of the switch port is electrically connected with the socket of the mobile phones while the other end is electrically connected with the charger which is detachable from the switch port, the mobile phone then could be charged via the electricity provided by the internal battery. The charging equipment is facilitated to carry, when travelling to some places where it is not easy to find somewhere to charge, people can charge the mobile phone by using the internal battery of the present invention so as to extent the working time of the mobile phone. When charging is not processing, the protection cover of the present invention can serve as a common mobile phone protection cover, avoiding the mobile phone from scratching or crashing. Moreover, contact points are positioned on the protection cover and the charger of the present invention, The contact points can be designed in a consistent pattern, enabling different mobile phones to charge by using the same charger and protection cover, thereby it can be universally used.
Owner:HU JIANZHONG
Electrodes and methods for microbial fuel cells
InactiveUS20080292912A1Raise the potentialImprove performanceTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesCell electrodesMicrobial fuel cellFuel cells
Methods of improving a performance parameter of a microbial fuel cell are provided according to embodiments of the present invention which include heating an electrode and exposing the heated electrode to ammonia gas to produce a treated electrode characterized by an increased positive surface charge on the electrode surface. Improved performance parameters include increased maximum power density, increased coulombic efficiency, increased volumetric power density and decreased microbial fuel cell operation time to achieve maximum power density
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com