Patents
Literature
550 results about "Anaerobic bacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anaerobic bacteria. Anaerobic bacteria are bacteria that do not live or grow when oxygen is present. In humans, these bacteria are most commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. They play a role in conditions such as appendicitis, diverticulitis, and perforation of the bowel.
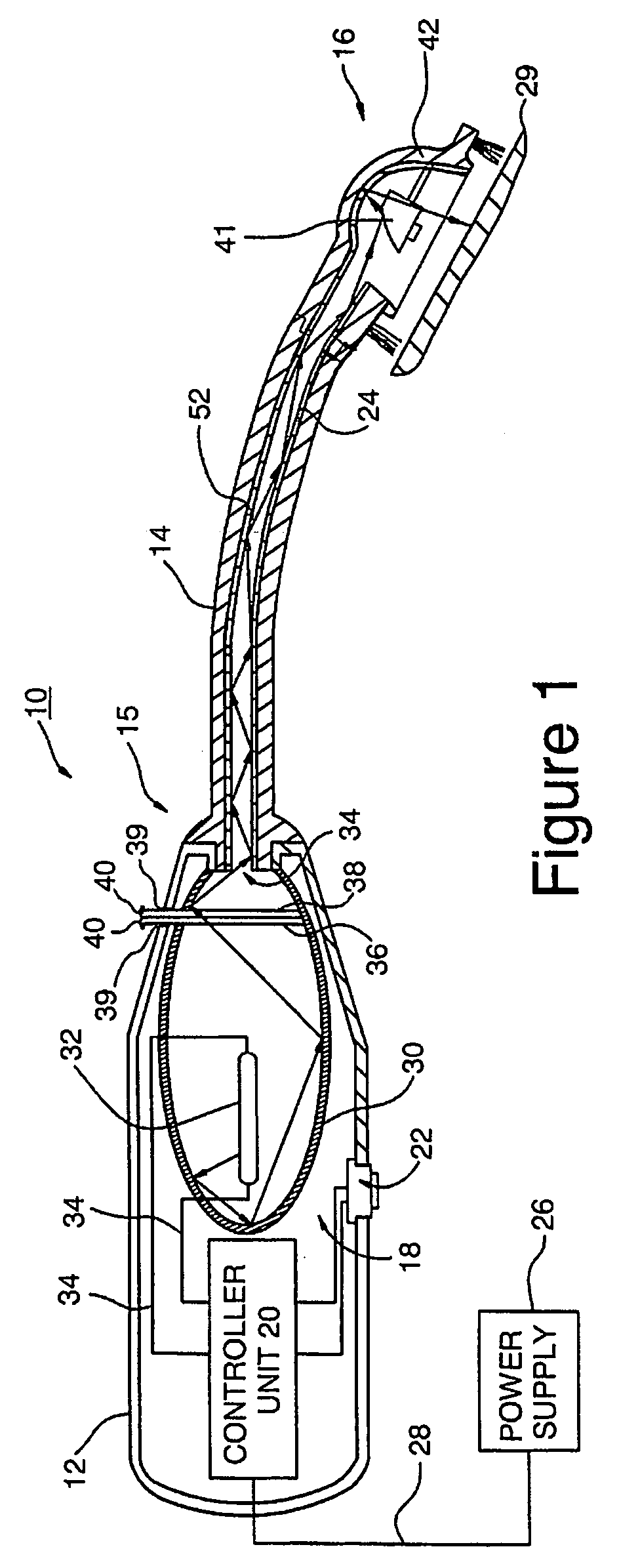
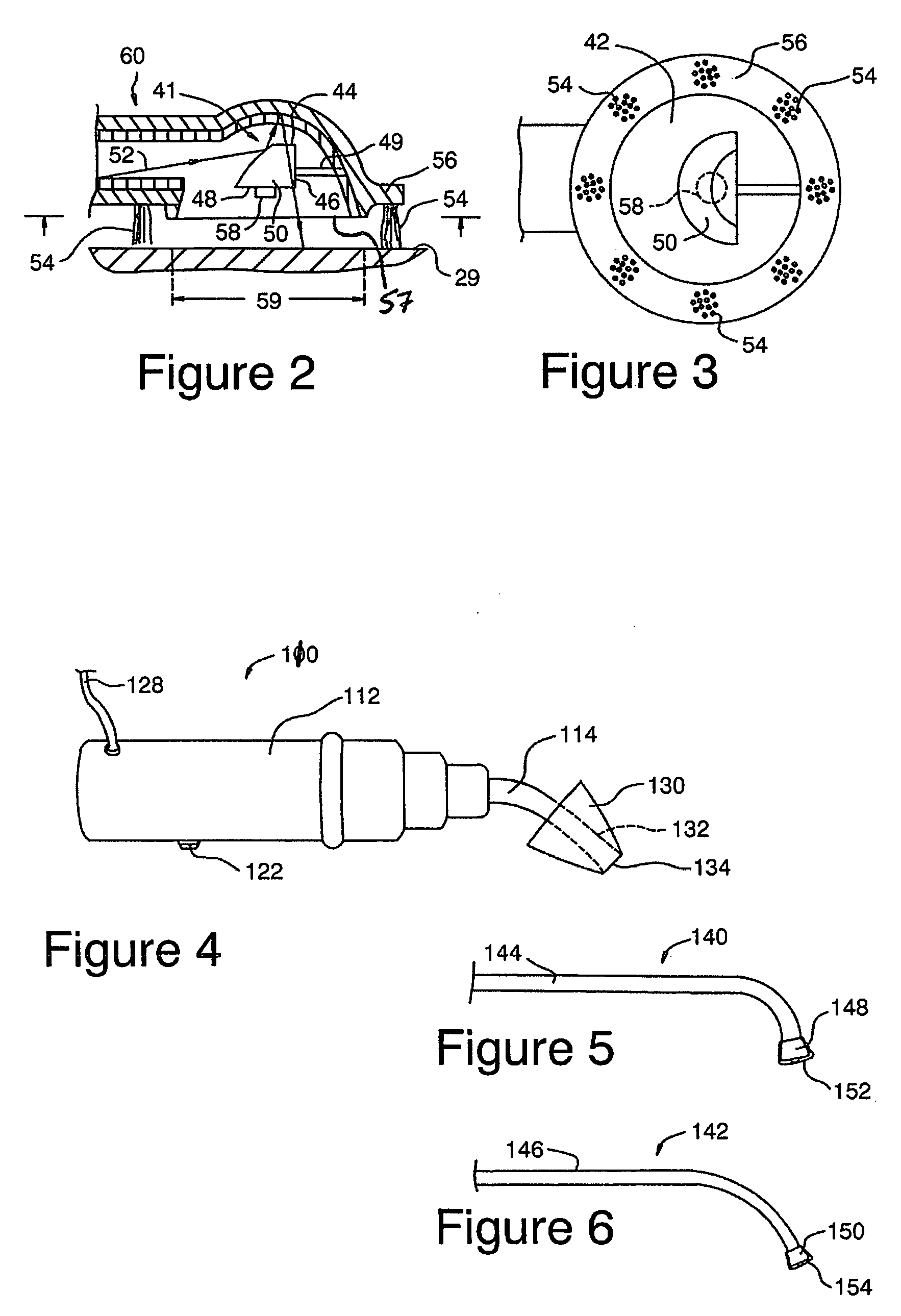
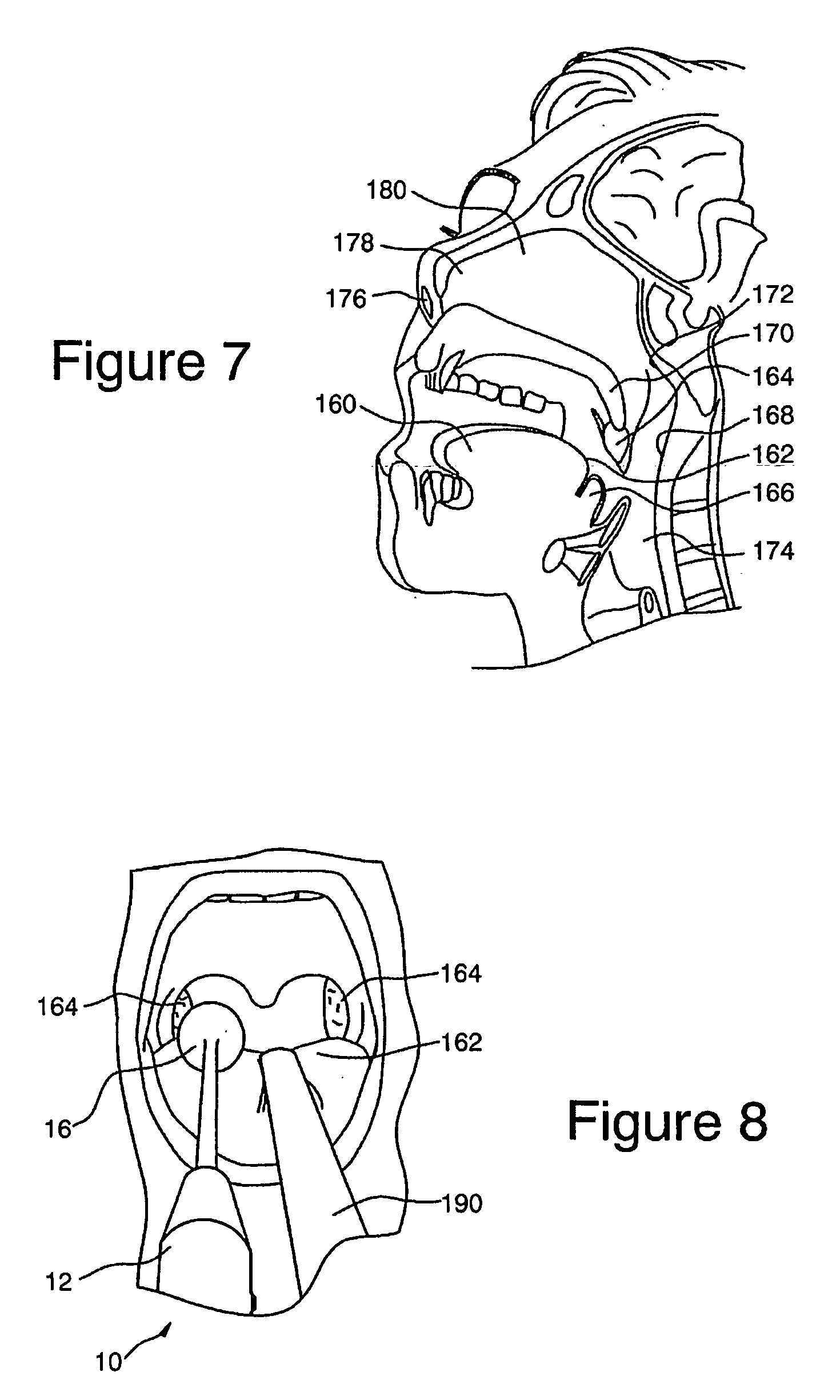
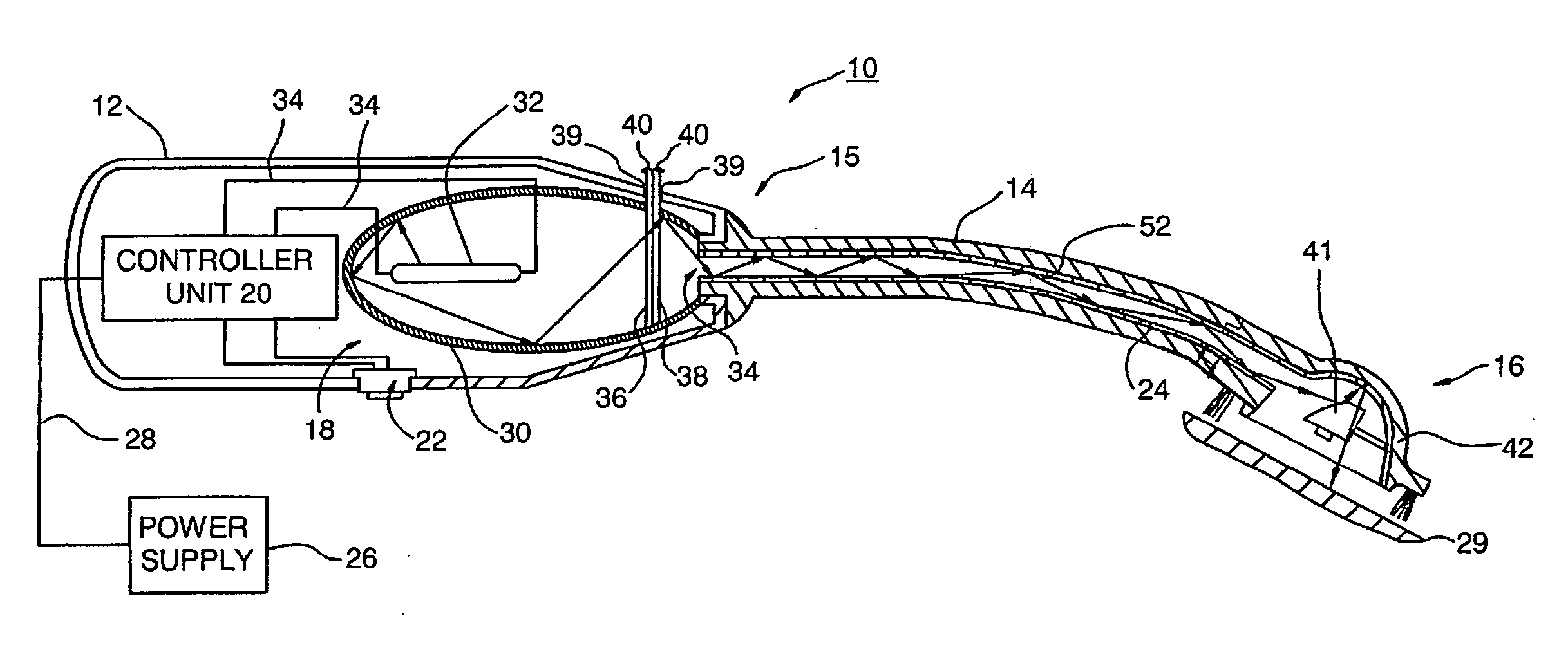
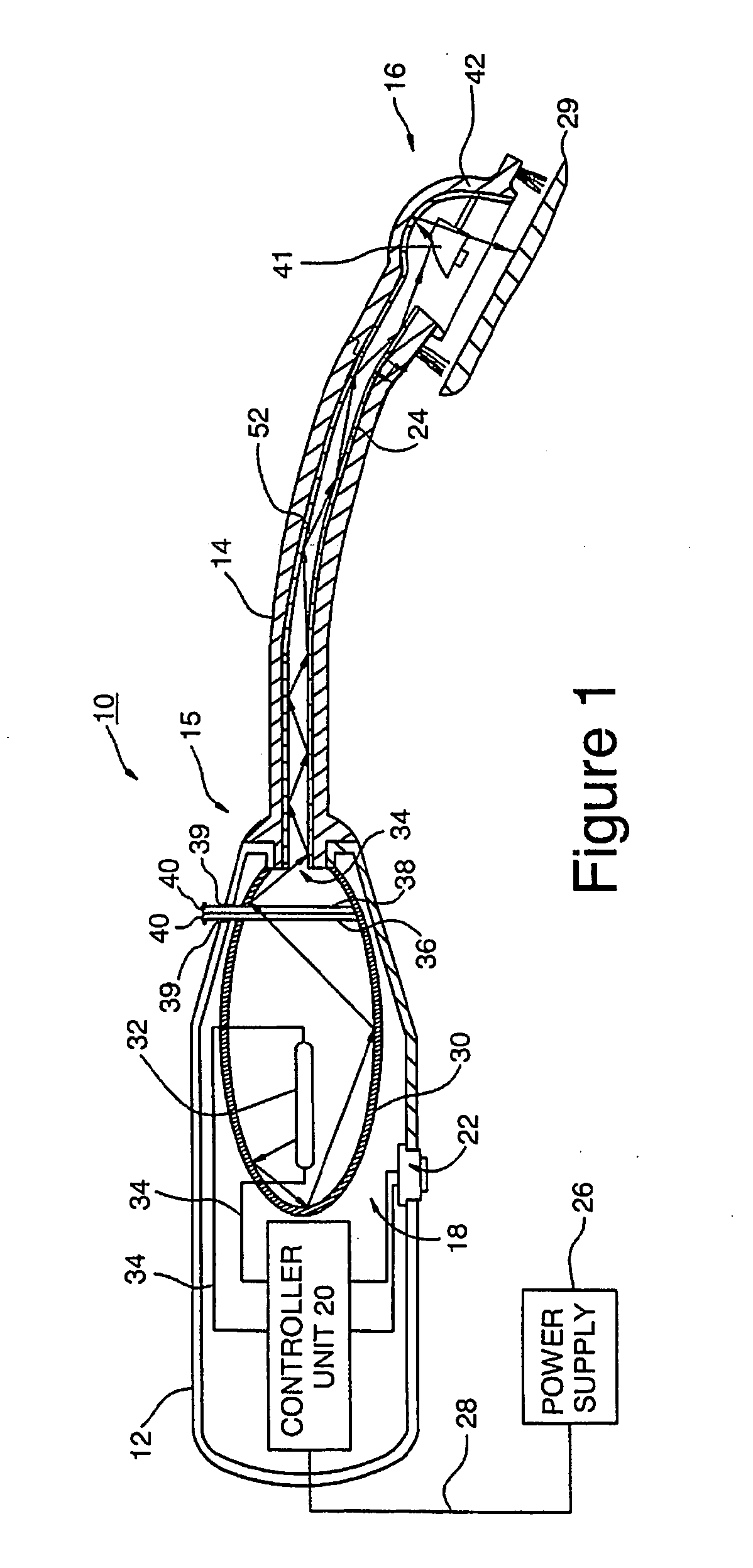
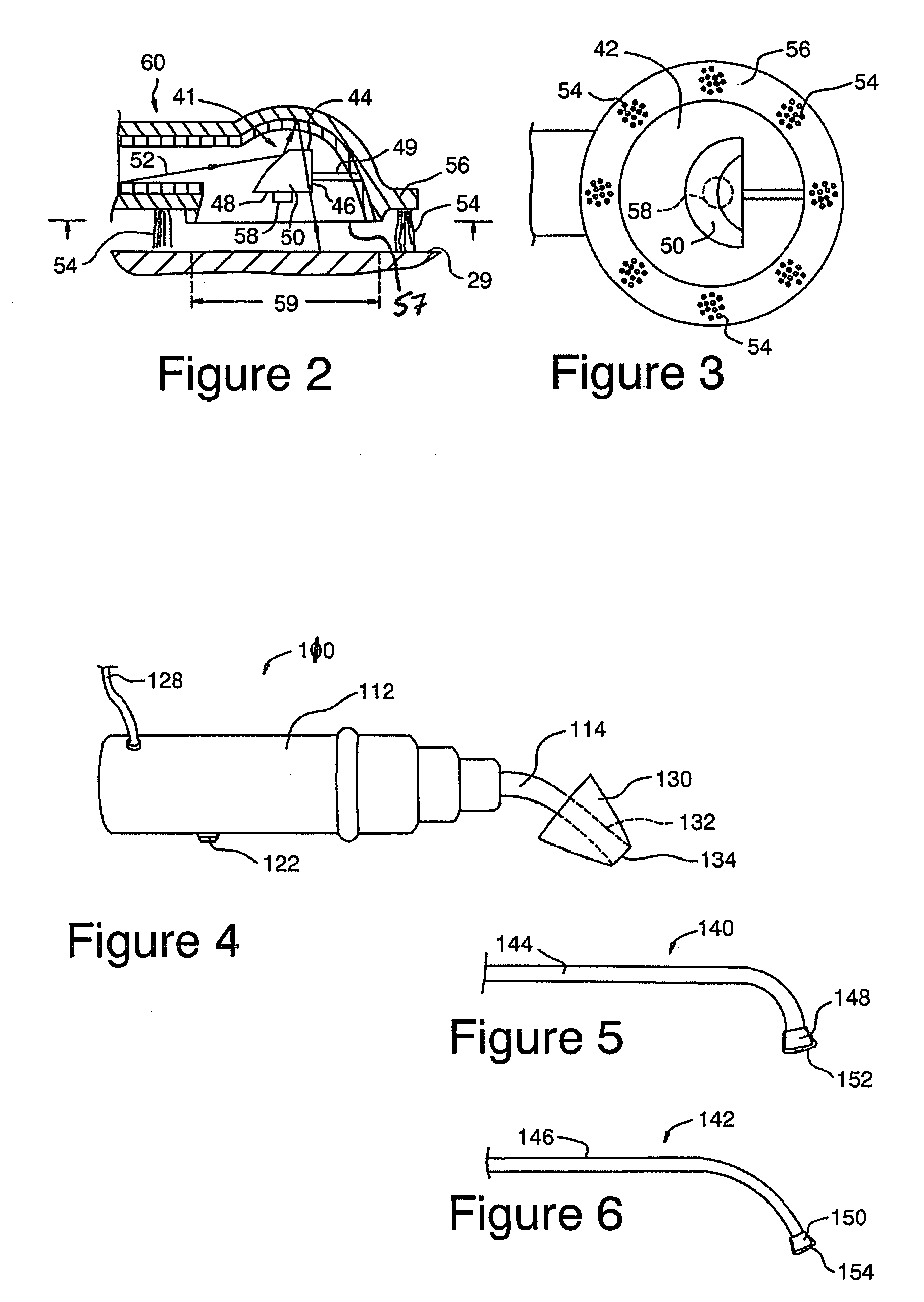
Control of halitosis-generating and other microorganisms in the non-dental upper respiratory tract
ActiveUS20060047329A1Effective controlReduce the burden onElectrotherapyDiagnosticsNon-ionizing radiationTonsil
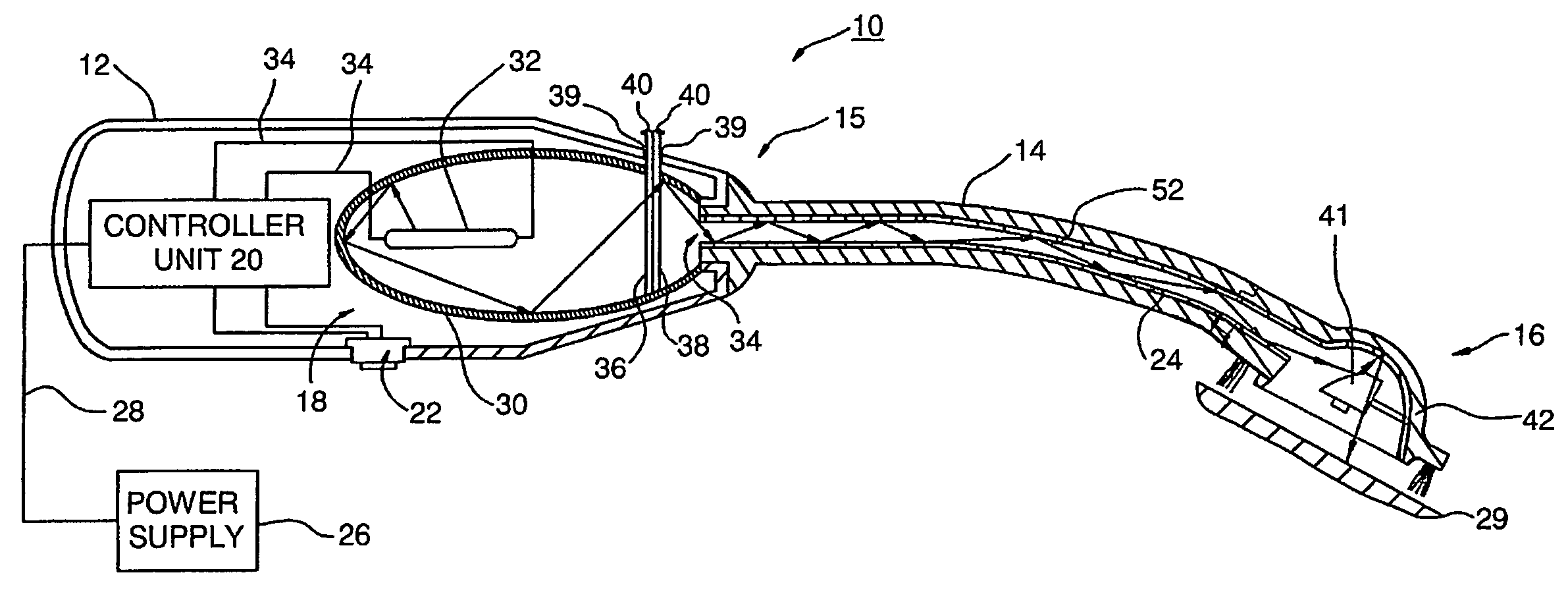
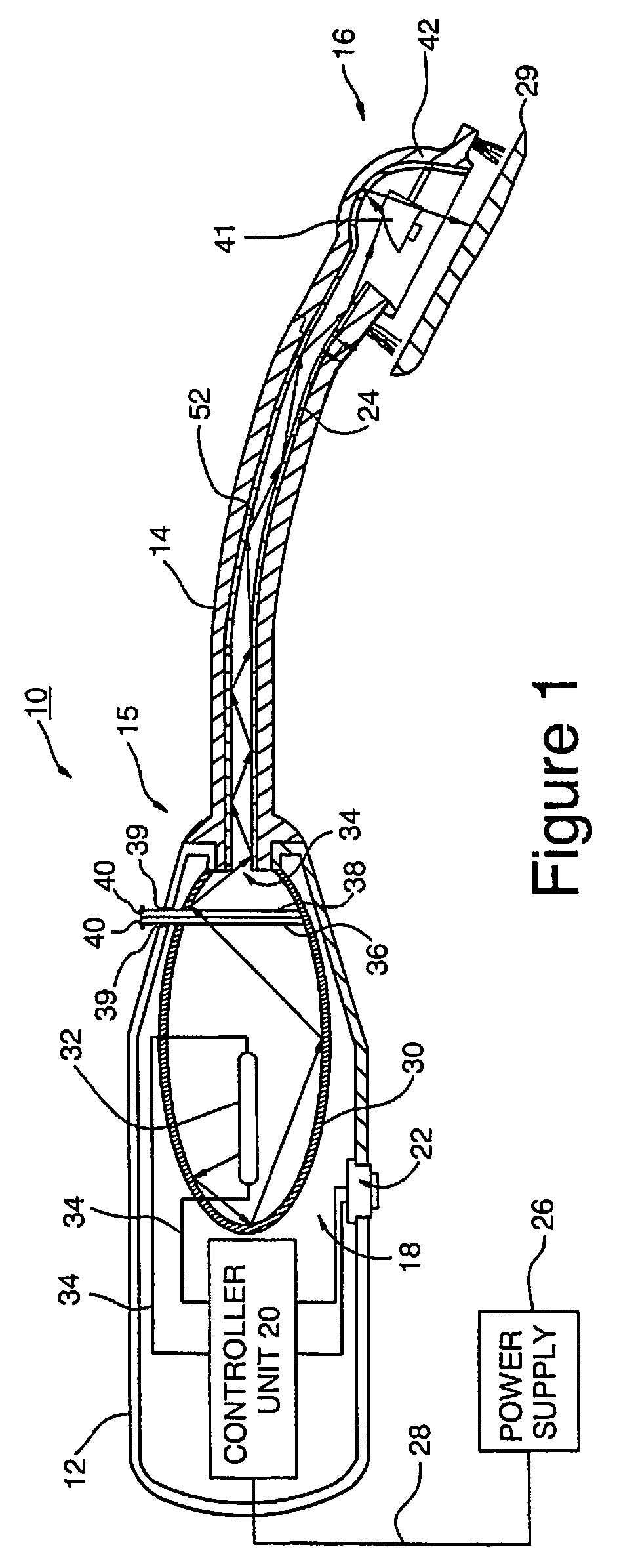
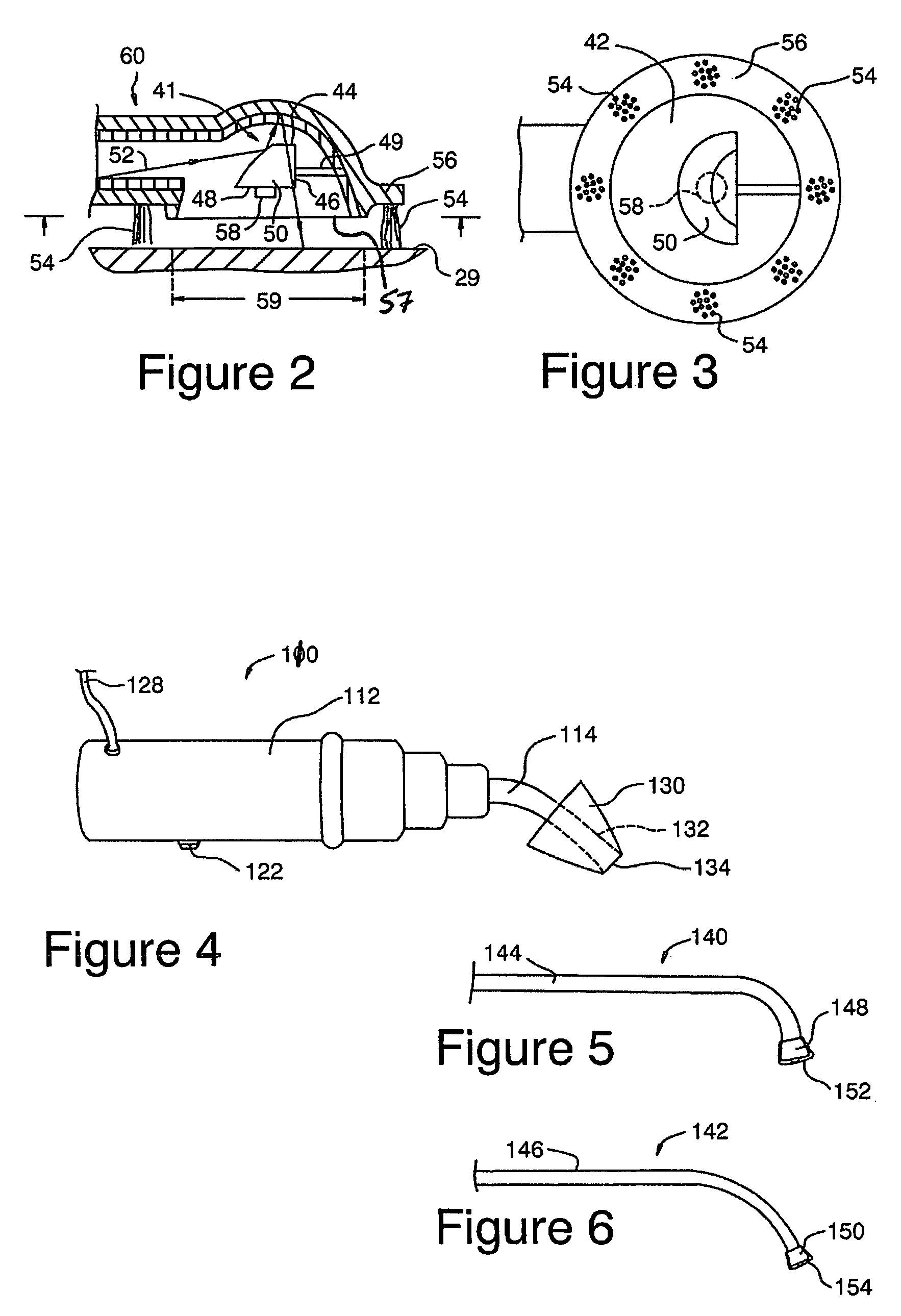
Disclosed are safe, simple and effective broad-spectrum treatments for halitosis and other microbial infections of the nondental upper respiratory tract useful to treat bacterial and other microorganism species, including anaerobic bacteria. Electromagnetic radiative energy including visible, and optionally, thermal, RF and / or microwave wavelengths, is topically applied to internal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract to destroy or incapacitate superficial microorganisms without the use of antibiotics. One useful apparatus is a handheld energy applicator having a light output head suitable for treating the back of the tongue and the tonsils and which may be interchangeably provided with extensions to reach the sinuses. The energy applicator can be supported and guided by a mounting device held between the subject's teeth, if desired. Useful embodiments of the invention include preparative treatment of the target surfaces with a photosensitizing agent such as an oxidizing agent or a complementary stain. Optionally a pre-treament procedure may be employed to remove detritus and microfloral overgrowths that may mask more deeply resident target microorganisms. Novel treatments include treatment of halitosis by destruction of bacterial species associated with halitosis, such as Atopobium parvulum, by application of non-ionizing radiative energy to the tonsils and the back of the tongue. Another embodiment comprises a candy bar incorporating a halitosis treatment lamp disposed within the candy.
Owner:VALENT MEDICAL INC
Media supplements and methods to culture human gastrointestinal anaerobic microorganisms
InactiveUS20140342438A1Enhance their axenic growthAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBacteroidesAnaerobic bacteria
A media supplement for culturing anaerobic bacteria is provided which comprises a filtrate of effluent from a chemostat vessel in which a target bacterial ecosystem has been cultured. Methods of using the supplement for culturing or isolating anaerobic microbial strains or communities, particularly anaerobic bacteria from the human gut, are also provided.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF GUELPH
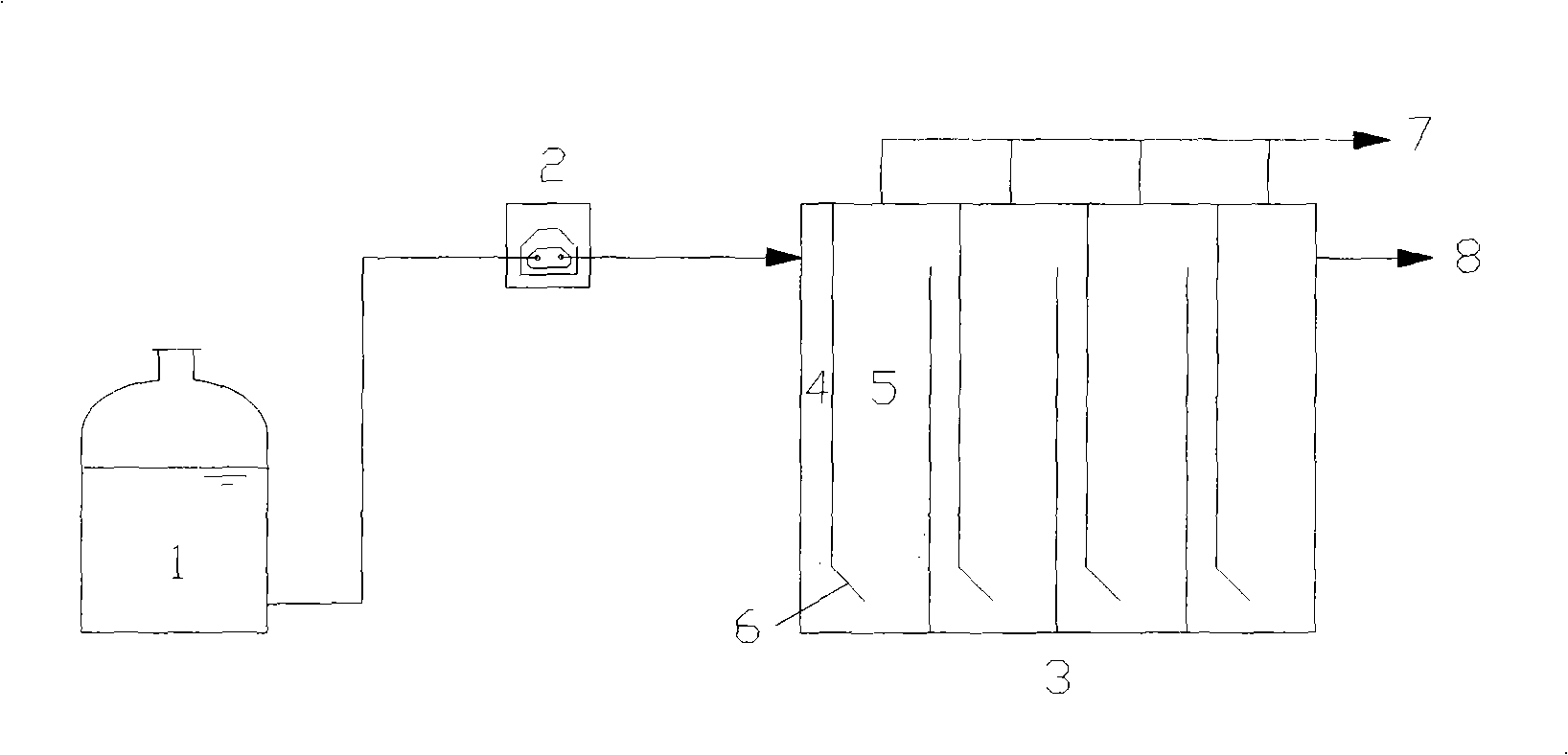
Reactor tank
ActiveUS20100320147A1Faster rateEnhanced mass transferElectrostatic separatorsSedimentation separationCavitationAnaerobic bacteria
Disclosed is an improved water treatment cavitation reactor cone. The tank operates on a continuous flow of fluids which are subjected to ultrasonic waves in combination with a high level of injected ozone. The treatment tank includes a tangential inlet that induces a rotating flow into the tank thereby increasing the mixing of the ozone within the effluent. The effluent is further treated with DC current. The treatment tank provides a cost efficient and environmentally friendly process and apparatus for cleaning and recycling fluids as contaminated as frac water, used to stimulate gas production from shale formations, as well as other types of fluids having various levels of contaminants such as aerobic and anaerobic bacteria and suspended solids. The calcium carbonate scaling tendency is reduced to an acceptable level without the use of acids, ion exchange materials, or anti scaling chemicals which is of economical and environmental significance and benefit.
Owner:BRISBEN WATER SOLUTIONS
Oil field water recycling system and method
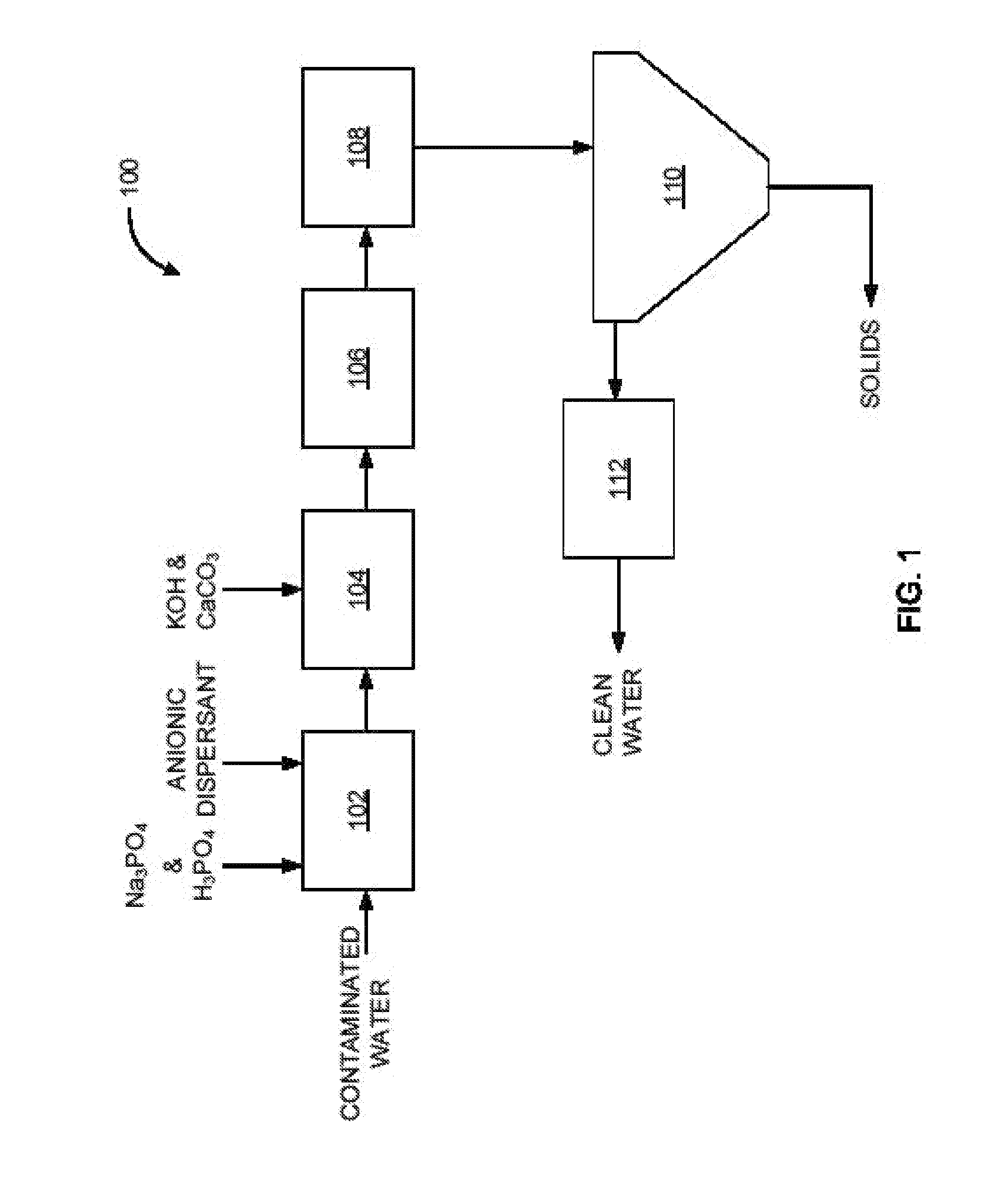
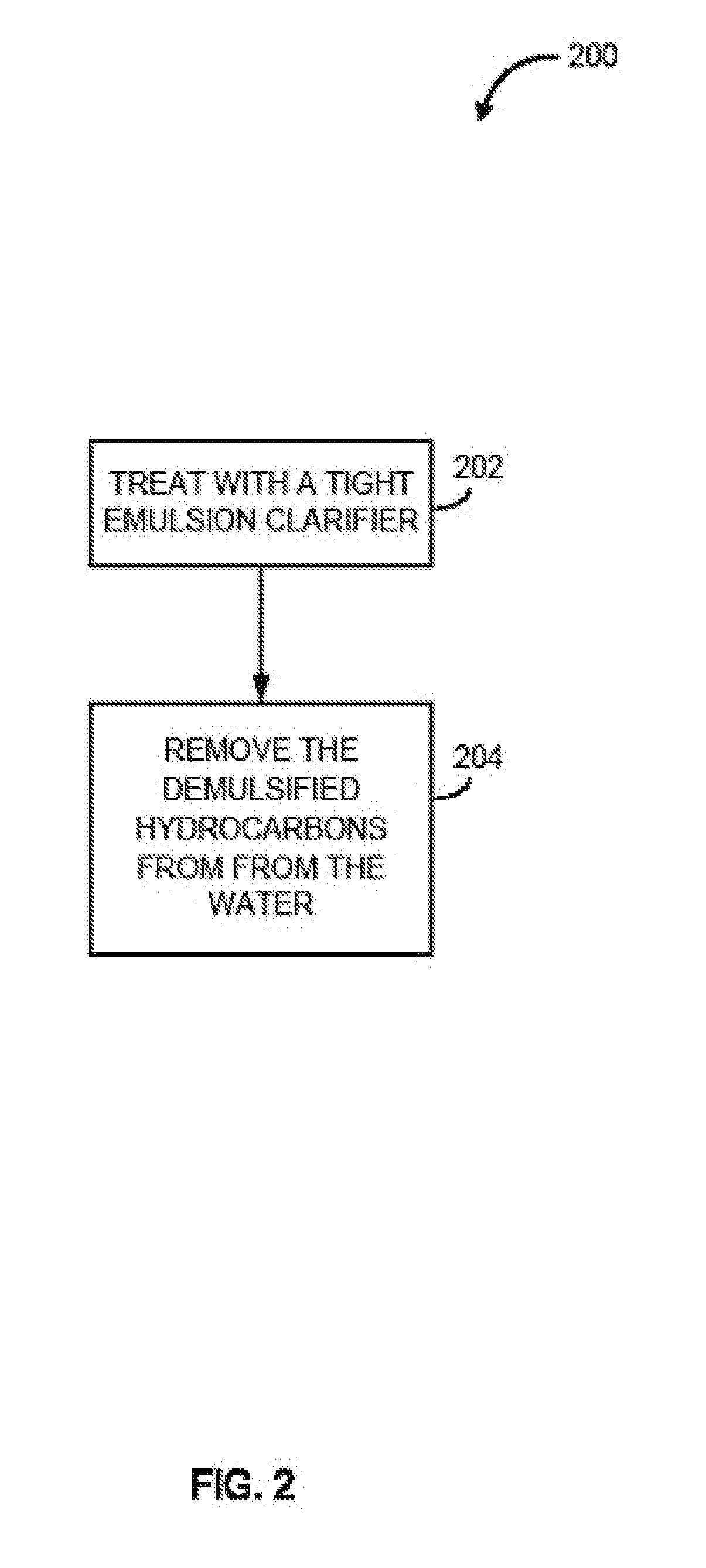
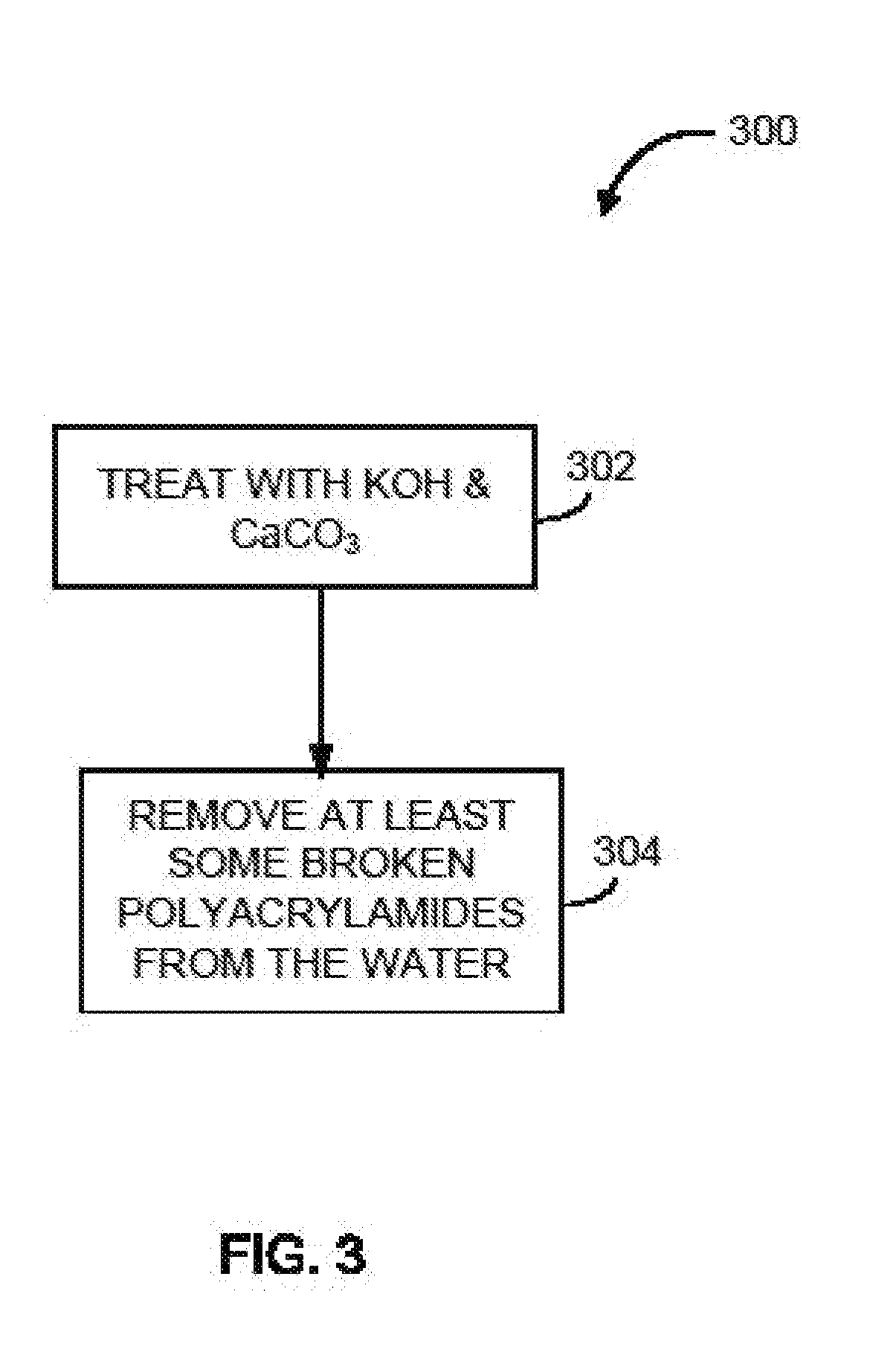
InactiveUS20110017677A1Reduce water hardnessReduce chain lengthSpecific water treatment objectivesWater contaminantsChemical treatmentAnaerobic bacteria
The disclosure describes a novel approach for treating water, such as oilfield production waste. The disclosure describes novel methods for chemically treating contaminated water, such as chemical processes for softening water, demulsifying hydrocarbons, destroying a sequestering effect on divalent cations, destroying any detectable amount or over 99% of aerobic and anaerobic bacteria, and breaking long chain polymers. The disclosure further describes novel methods for clarifying contaminated water to remove suspended solids.
Owner:EVANS THOMAS S
Control of halitosis-generating and other microorganisms in the non-dental upper respiratory tract
ActiveUS7544204B2Effective controlReduce the burden onElectrotherapyDiagnosticsNon-ionizing radiationAnaerobic bacteria
Owner:VALENT MEDICAL INC
Anaerobic bacterium as a drug for cancer gene therapy
InactiveUS20050025745A1Efficient deliveryEffective gene therapyBiocideBacteriaAbnormal tissue growthBifidobacterium
The present invention provides a bacterium belonging to the genus Bifidobacterium, by which DNA coding for a protein having an antitumor activity or DNA coding for a protein having the activity of converting a precursor of an antitumor substance into the antitumor substance is delivered to tumor tissues specifically under anaerobic conditions thereby expressing the protein encoded by the DNA, as well as a pharmaceutical composition comprising said anaerobic bacterium.
Owner:ANAEROPHARMA SCI
Antimicrobial compositions for use in products for petroleum extraction, personal care, wound care and other applications
ActiveUS20140271757A1Improve viabilityProvide benefitsBiocideCosmetic preparationsSolubilityPersonal care
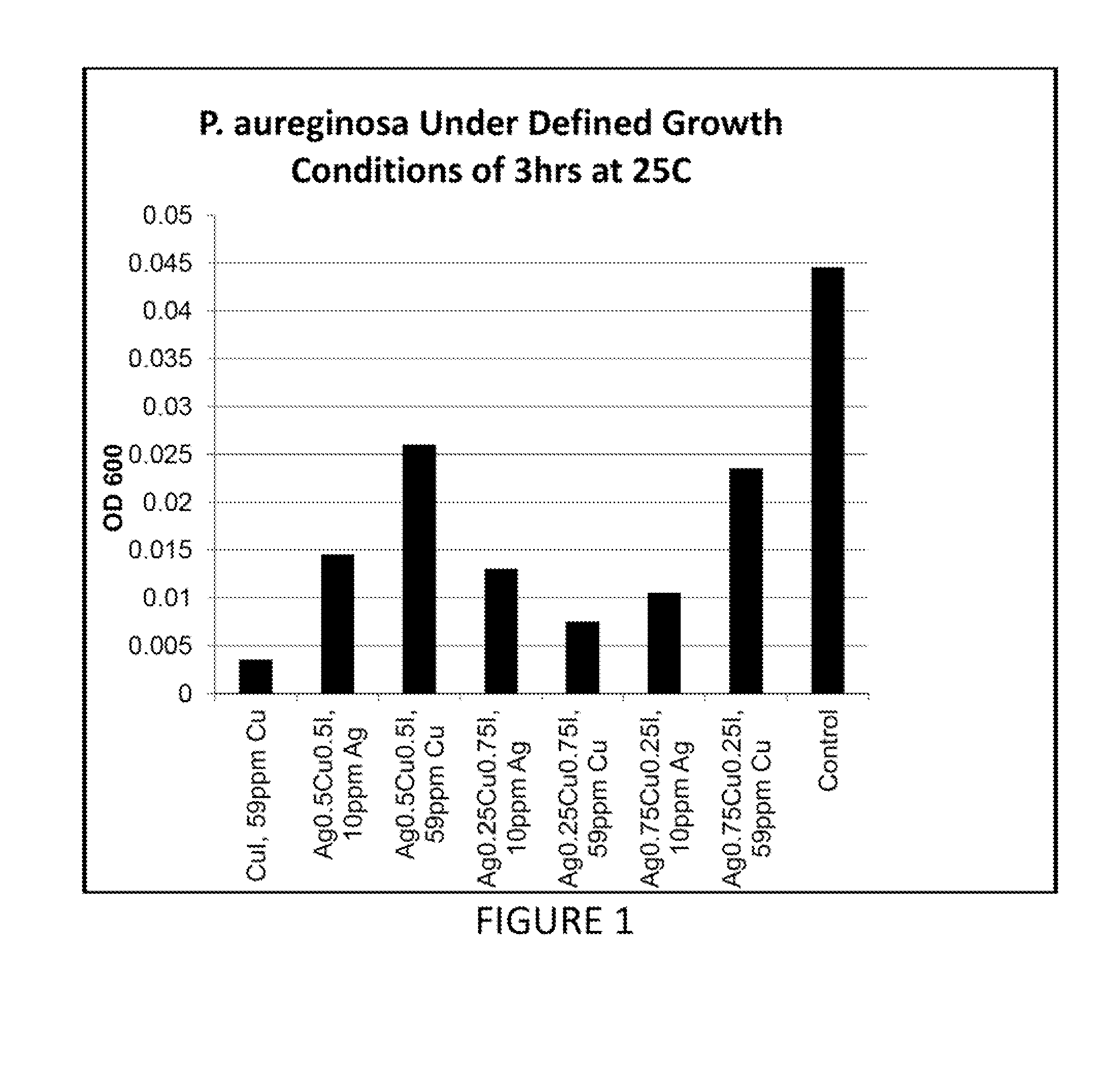
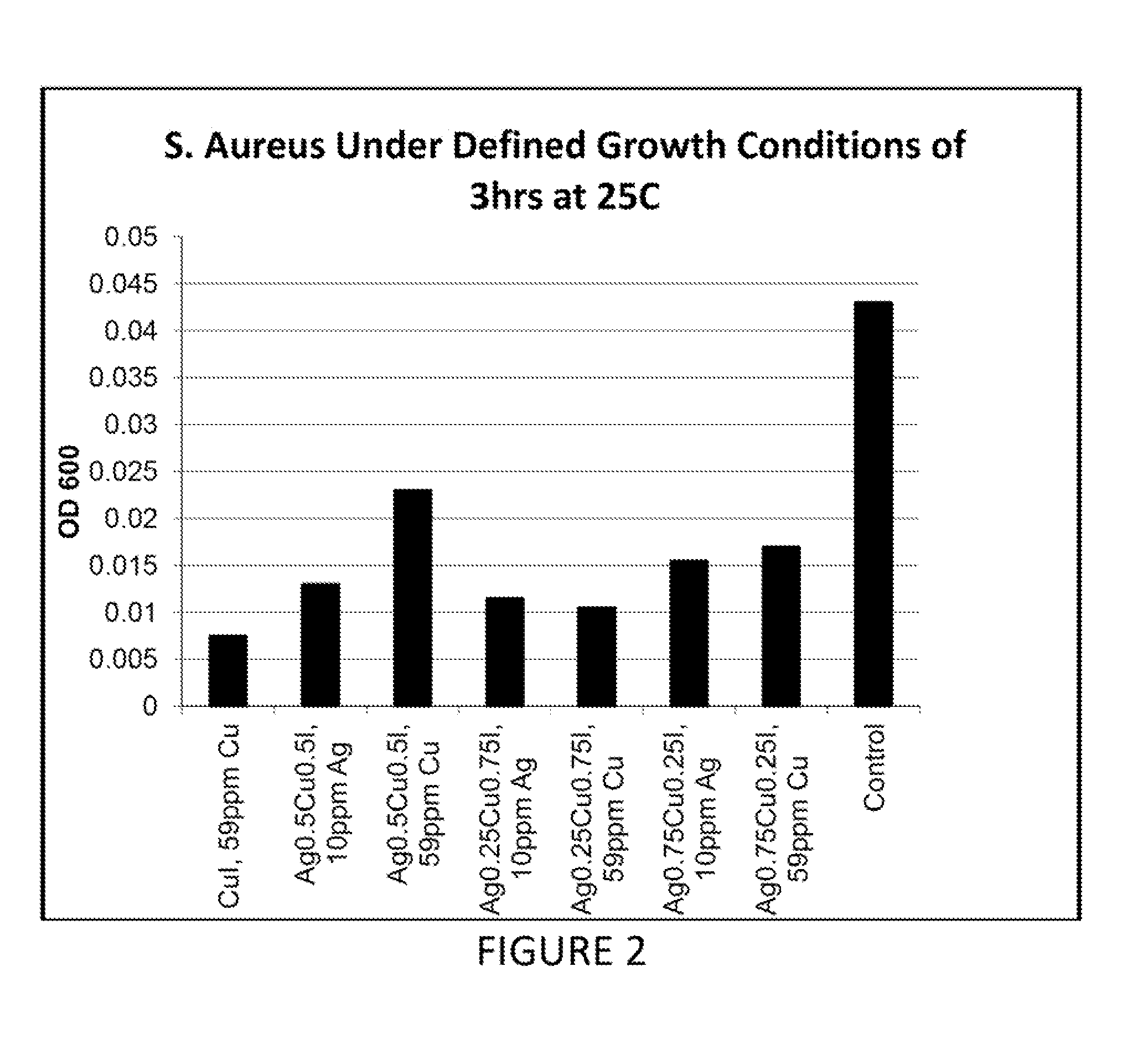
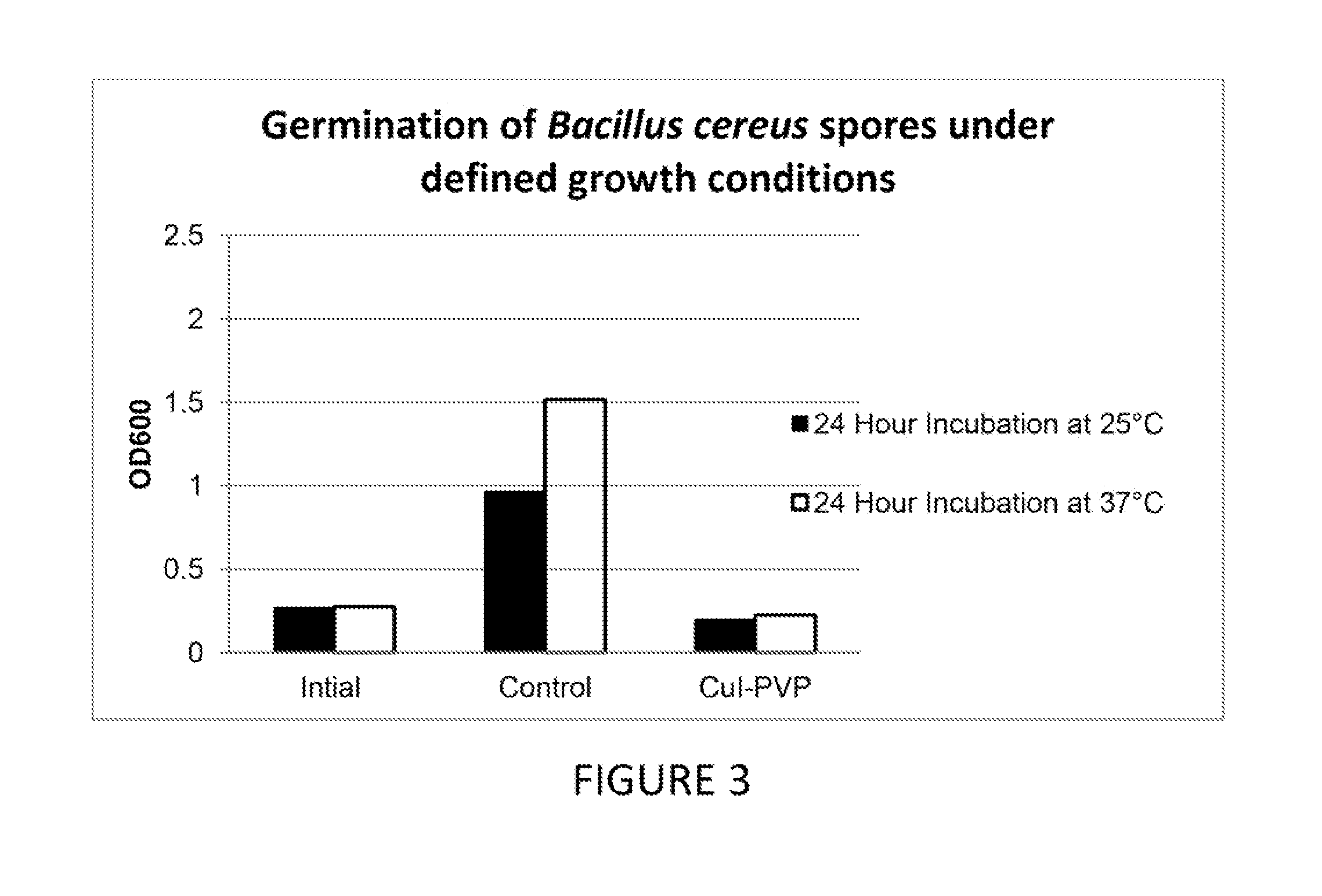
Compositions having antimicrobial activity contain surface functionalized particles comprising an inorganic copper salt which has low water solubility. These types of inorganic salts may also be introduced in porous particles to yield antimicrobial compositions. The compositions may optionally comprise additional antimicrobial agents, salts with high water solubility, organic acids, salts of organic acids and their esters. The compositions may be added to various fluids used in the petroleum extraction industry, or used as coatings on components used in this industry. These antimicrobial materials may be used for reducing both anaerobic and aerobic bacteria and are also useful for reducing corrosion of ferrous components caused by anaerobic bacteria. Although such compositions may be used for any antimicrobial application, and some of the other important uses of these compositions are in wound care, personal care and waste processing.
Owner:AGIENIC
Control of halitosis-generating and other microorganisms in the non-dental upper respiratory tract
InactiveUS20100076526A1Effective controlReduces gram negative bacterial burdenElectrotherapyLight therapyNon-ionizing radiationAnaerobic bacteria
Disclosed are safe, simple and effective broad-spectrum treatments for halitosis and other microbial infections of the nondental upper respiratory tract useful to treat bacterial and other microorganism species, including anaerobic bacteria. Electromagnetic radiative energy including visible, and optionally, thermal, RF and / or microwave wavelengths, is topically applied to internal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract to destroy or incapacitate superficial microorganisms without the use of antibiotics. One useful apparatus is a handheld energy applicator having a light output head suitable for treating the back of the tongue and the tonsils and which may be interchangeably provided with extensions to reach the sinuses. The energy applicator can be supported and guided by a mounting device held between the subject's teeth, if desired. Useful embodiments of the invention include preparative treatment of the target surfaces with a photosensitizing agent such as an oxidizing agent or a complementary stain. Optionally a pre-treatment procedure may be employed to remove detritus and microfloral overgrowths that may mask more deeply resident target microorganisms. Novel treatments include treatment of halitosis by destruction of bacterial species associated with halitosis, such as Atopobium parvulum, by application of non-ionizing radiative energy to the tonsils and the back of the tongue. Another embodiment comprises a candy bar incorporating a halitosis treatment lamp disposed within the candy.
Owner:KRESPI YOSEF +1
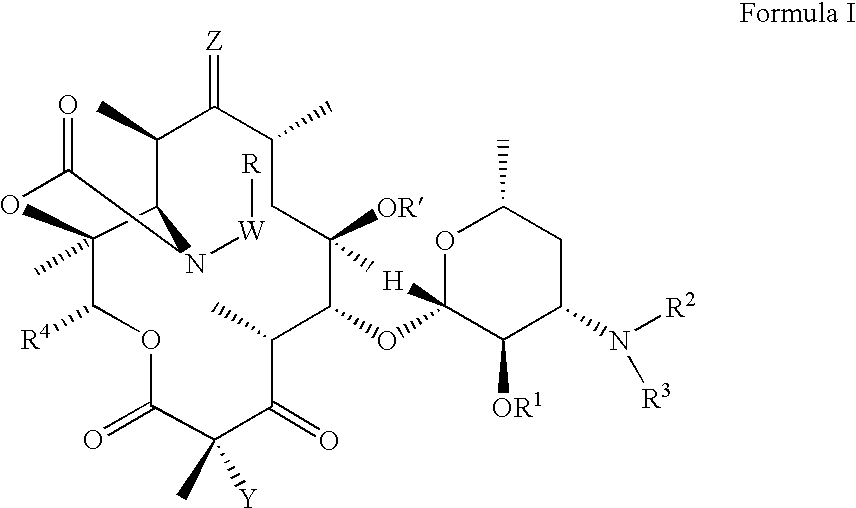
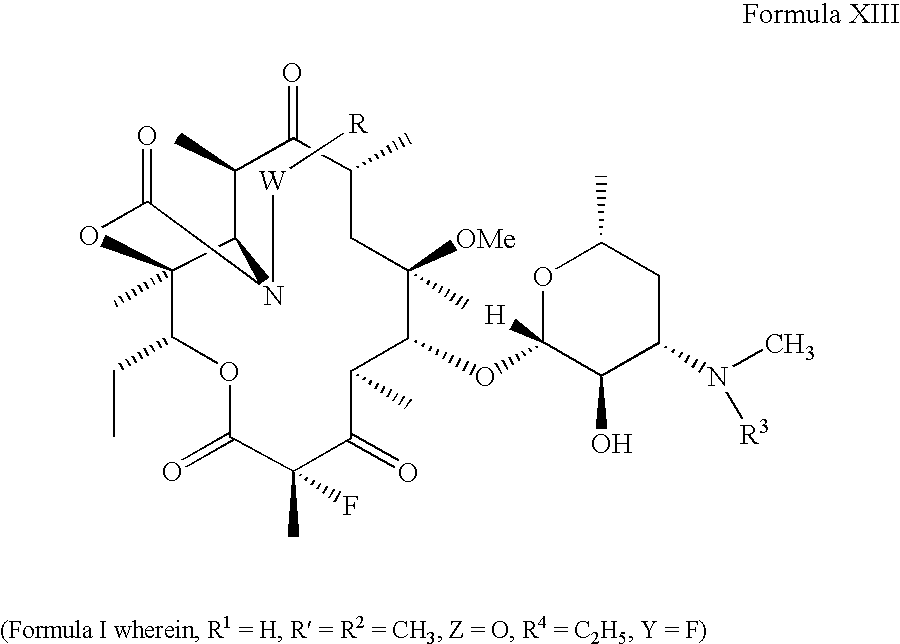
Ketolide Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents
The present invention provides ketolide derivatives, which can be used as antibacterial agents. In particular, compounds described herein can be used for treating or preventing conditions caused by or contributed to by Gram-positive, Gram-negative or anaerobic bacteria, more particularly against, for example, Staphylococci, Streptococci, Enterococci, Haemophilus, Moraxalla spp. Chlamydia spp., Mycoplasm, Legionella spp., Mycobacterium, Helicobacter, Clostridium, Bacteroides, Corynebaclerium, Bacillus or Enterobactericeae. Also provided are processes for preparing such ketolide derivatives, pharmaceutical compositions thereof, and methods of treating bacterial infections.
Owner:RANBAXY LAB LTD
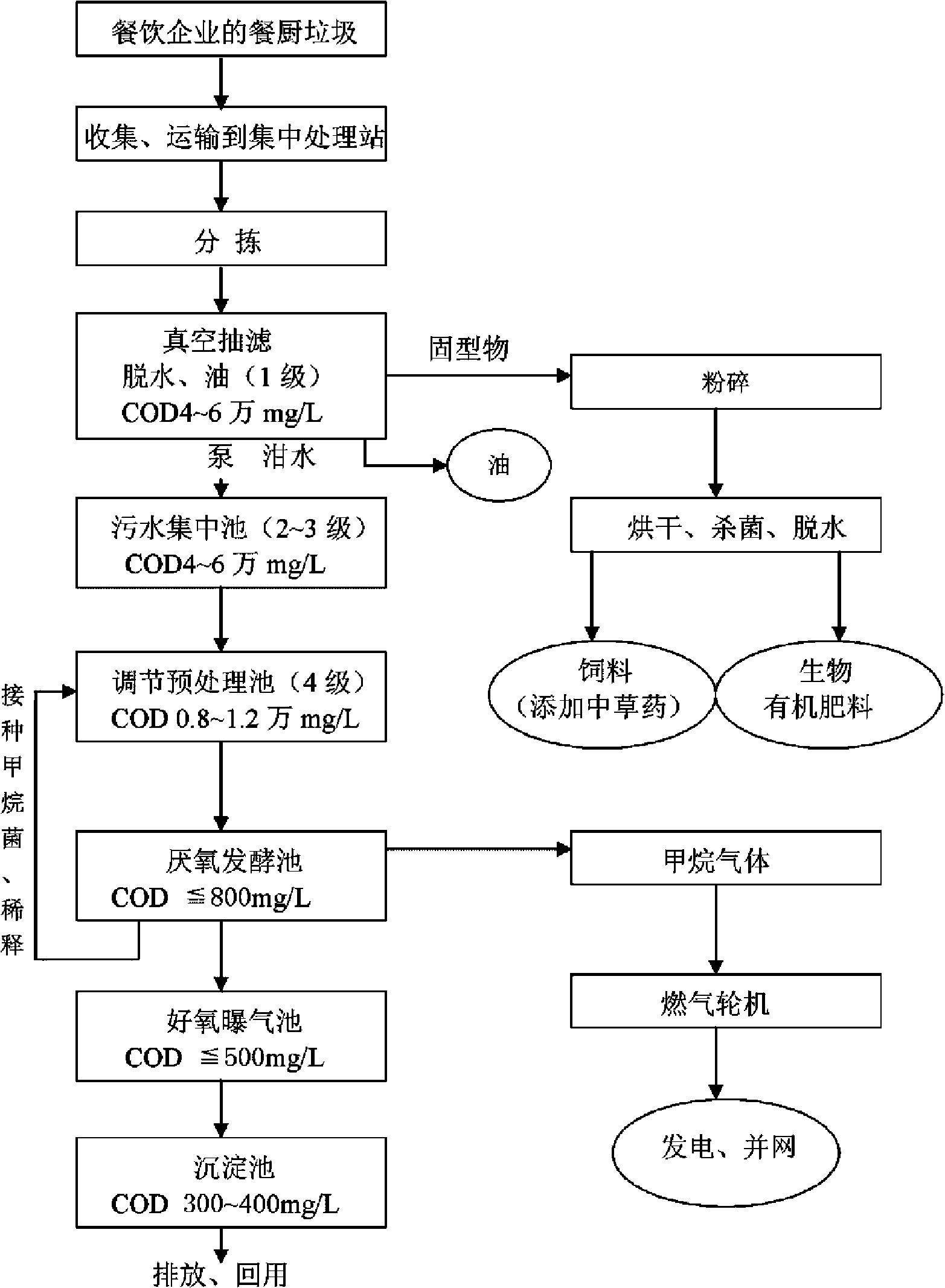
Processing method for changing restaurant and kitchen garbage into resource without environmental pollution
InactiveCN101274860AAvoid wastingEnergizeBio-organic fraction processingWaste processingThermal energyAnaerobic bacteria
The invention relates to a treating method for energy regeneration, resource recovery and pollution free of restaurant garbage, which comprises the steps that separated liquid material is pumped into a swage concentrating pool; then the concentrated liquid material is discharged into a regulating and pretreating pool, in which methane bacteria are inoculated; the pretreated liquid material is discharged into an anaerobic fermentation pool, in which anaerobic bacteria groups are added so that methane gas is generated and the overflowing liquid material from the anaerobic fermentation pool is led to enter an aerobic aerated pool for aerobic reaction; the liquid material after the aerobic reaction is discharged into a sedimentation tank for sedimentation. In the comprehensive utilization of 'swill', the disposing method of the invention carries out anaerobic fermentation and aerobic aerated biochemical treatment to transform part of the energy in the swill into bio-energy which is then transformed into heat energy and finally into electrical energy that is connected with power grid for use. The separated solid material is smashed, dried, sterilized, dehydrated and then added with Chinese herbal medicine to be processed into Chinese herbal medicine compound feeds and fertilizers; meanwhile, the treatment of energy regeneration, resource recovery and pollution free of restaurant garbage for restaurant garbage is realized.
Owner:WUXI KELUN SCI & TECH DEV
Medicinal or health care composition containing natural antimicrobials
The invention provides a medical or health-care compound and a preparation method. The compound contains at least one natural anti-bacterial agent which is separated for plants and is the soluble salt or ester formed through the extraction of the non-soluble anti-bacterial substance from plants. Further, the compound of the invention can also contain inflammation-diminishing, detumescence and anti-oxidation ingredients, as well as the preparation type auxiliary substances, Chinese medicine padding agent, etc, which are produced into a series of medicines or health-care medicines which restrain the anaerobic bacteria and effectively prevent the oxidation or aging of the human body cells. The compound of the invention can be produced into various forms, not only confined in the liquid form (for example the orally taken liquid), but also including spraying agent, liquid spraying agent, pills( e.g. buccal tablets), capsules, toothpaste, mouth clearing, etc. Moreover, the invention can be used for the health care for mouth, heart, gastrointestinal tract and joint or the treatment of the related diseases.
Owner:GUANGXI HEBABIZ PHARM TECH CO LTD
Microorganism bacterium agent for processing thick oil sewage and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1990854AImprove biodegradabilityAvoid incomplete treatmentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCitrobacterAnaerobic bacteria
The invention relates to the biological treatment for oil extraction wastewater, which in detail relates to a bacterial agent for treating thick oil wastewater and the method for preparing the same. The comprised components and their proportion by weight are as follows: pseudomonas aeruginosa 5-10%, bacillus subtilis 10-15%, lichen bacilli 5- 15%, Citrobacter propionate tumefaciens 10- 15%, liquid gold tumefaciens 10- 20%, annular gemma bacillus 5- 10%, wilting Bacillus pumilus 5- 10%, spherical arthrobacter 5- 10%, crabstick tumefaciens 5- 10%, and hot ground anaerobic rod baceria 10- 15%. It is prepared by activating bacteria, shake-flask culturing, expanding propagating and mixing. The cooperation action is strong, the biological surface activating agent generating- bacteria can enlarge the dissolution of hydrocarbon petroleum in water and make it is easier for hydrocarbon petroleum to contact with bacteria; the anaerobic bacteria can improve the biodegradation of thick oil wastewater; the degradation perfomace of aerobic bacteria is good and suitable for biological treatment for thick oil wastewater.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
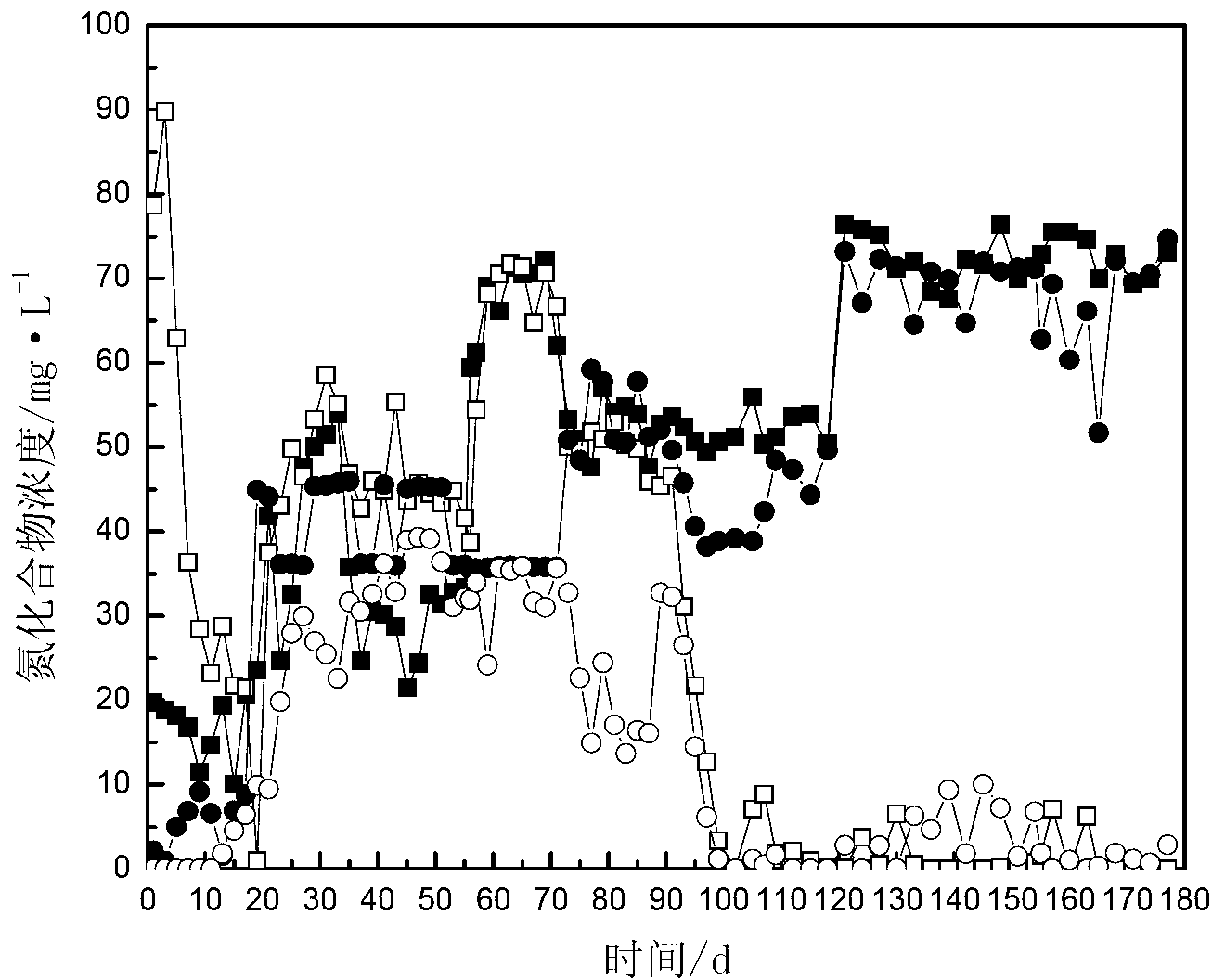
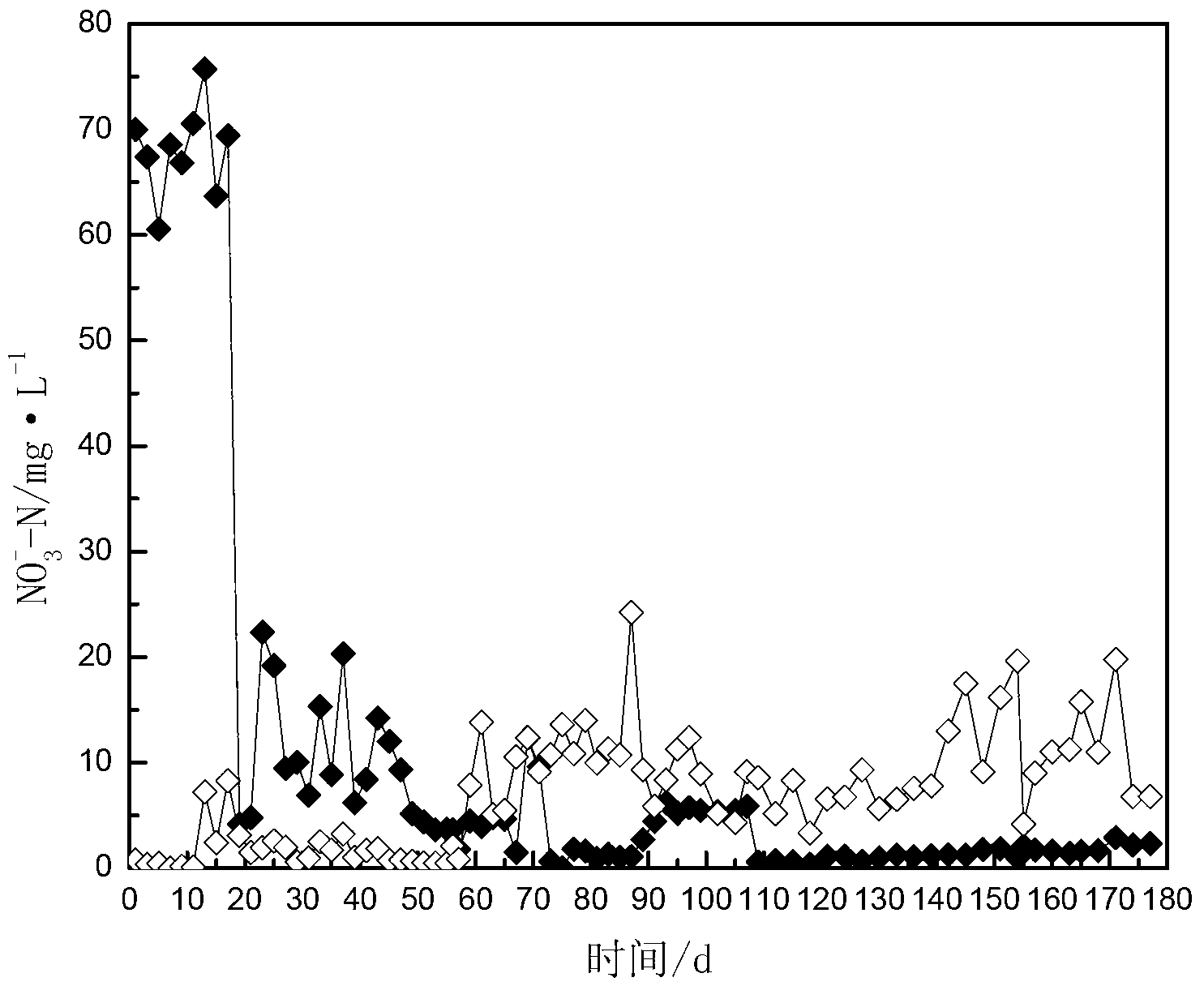
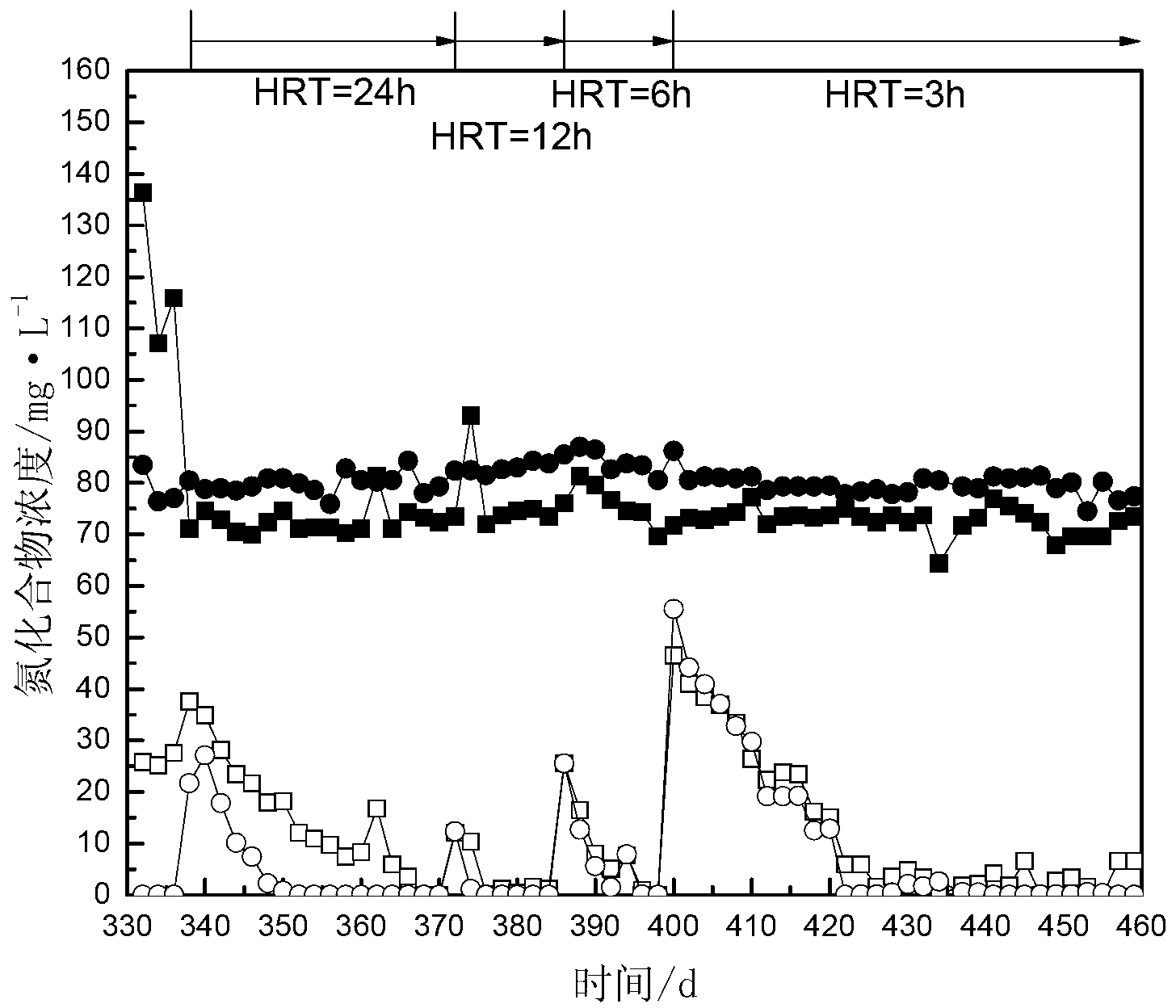
Method for anaerobic ammonia oxidation treatment of low-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater
ActiveCN101525179AAchieving oxidative denitrificationIncrease concentrationWater contaminantsWaste based fuelPeristaltic pumpAnaerobic bacteria
The invention relates to a method for the anaerobic ammonia oxidation treatment of low-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater. The method is characterized in that sludge containing anaerobic bacteria is inoculated into an anaerobic traverse baffle reactor under an anaerobic condition; the alkalescent ammonia nitrogen wastewater with 10 to 20mg / L of the concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen enters the anaerobic traverse baffle reactor by an inlet water storage bottle, and a constant-current peristaltic pump is used for controlling the hydraulic stay time to be from 24 hours to 48 hours and the reaction temperature to be from 25 DEG C to 30 DEG C; if anaerobic ammonium oxidation bacteria become dominant flora and both the removal rates of the ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen reach 80 percent for 5 days, the anaerobic traverse baffle reactor is successfully started; then, other low-concentration ammonia nitrogen wastewater enters the anaerobic traverse baffle reactor by the inlet water storage bottle, and the hydraulic stay time is controlled to be from 12 hours to 48 hours; and finally, both the removal rates of the ammonia nitrogen and the nitrite nitrogen can reach about 80 percent.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
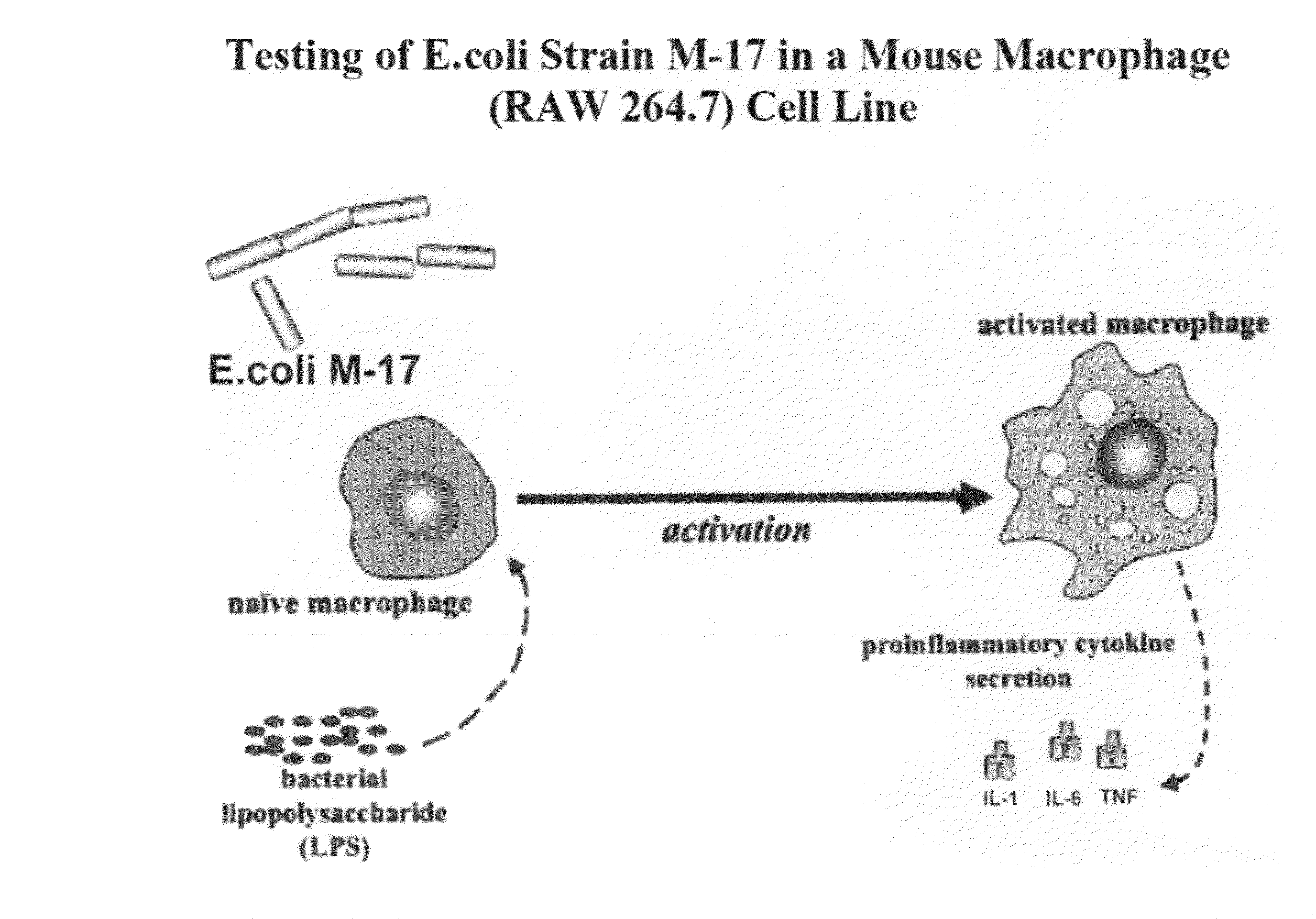
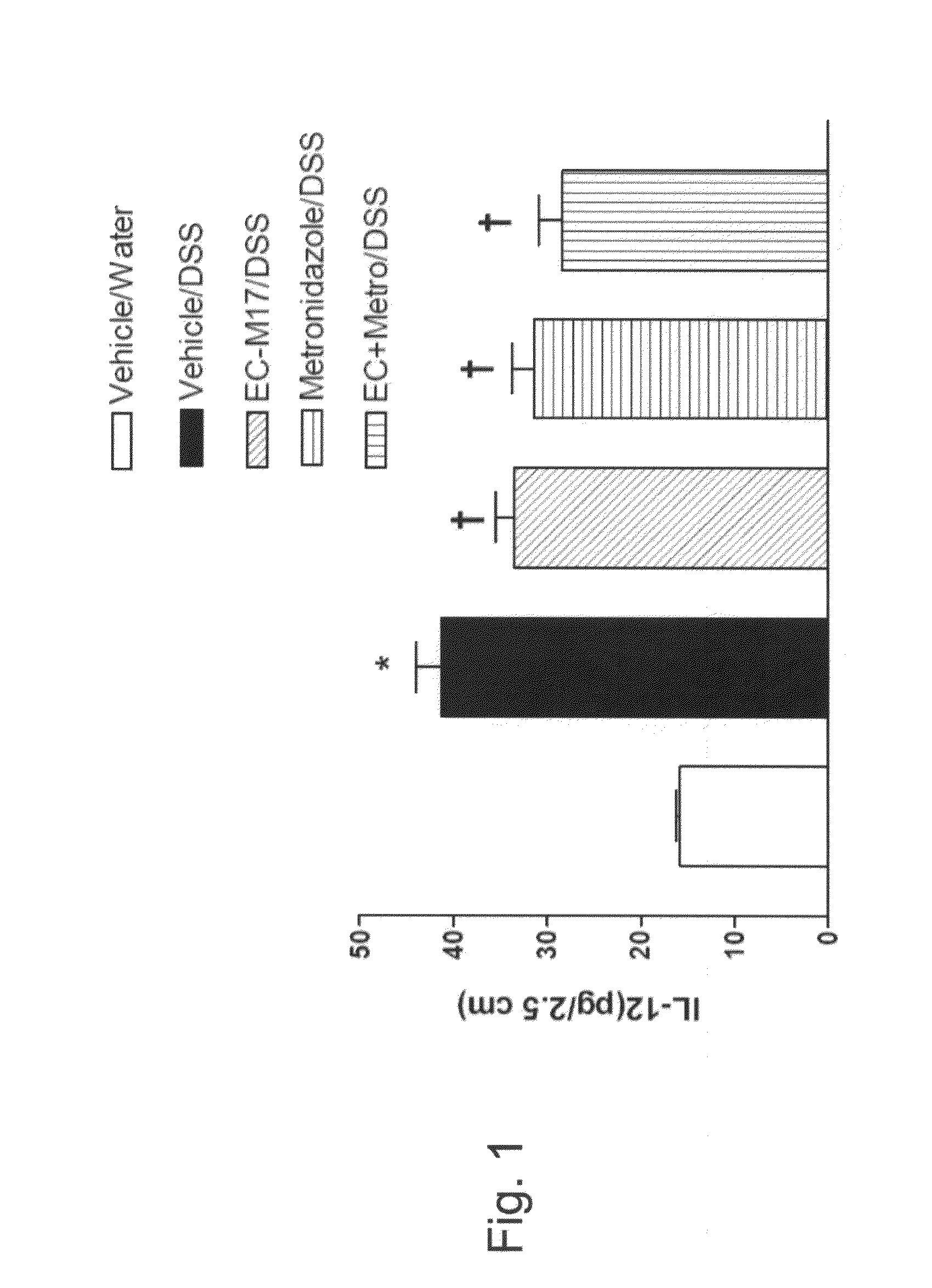
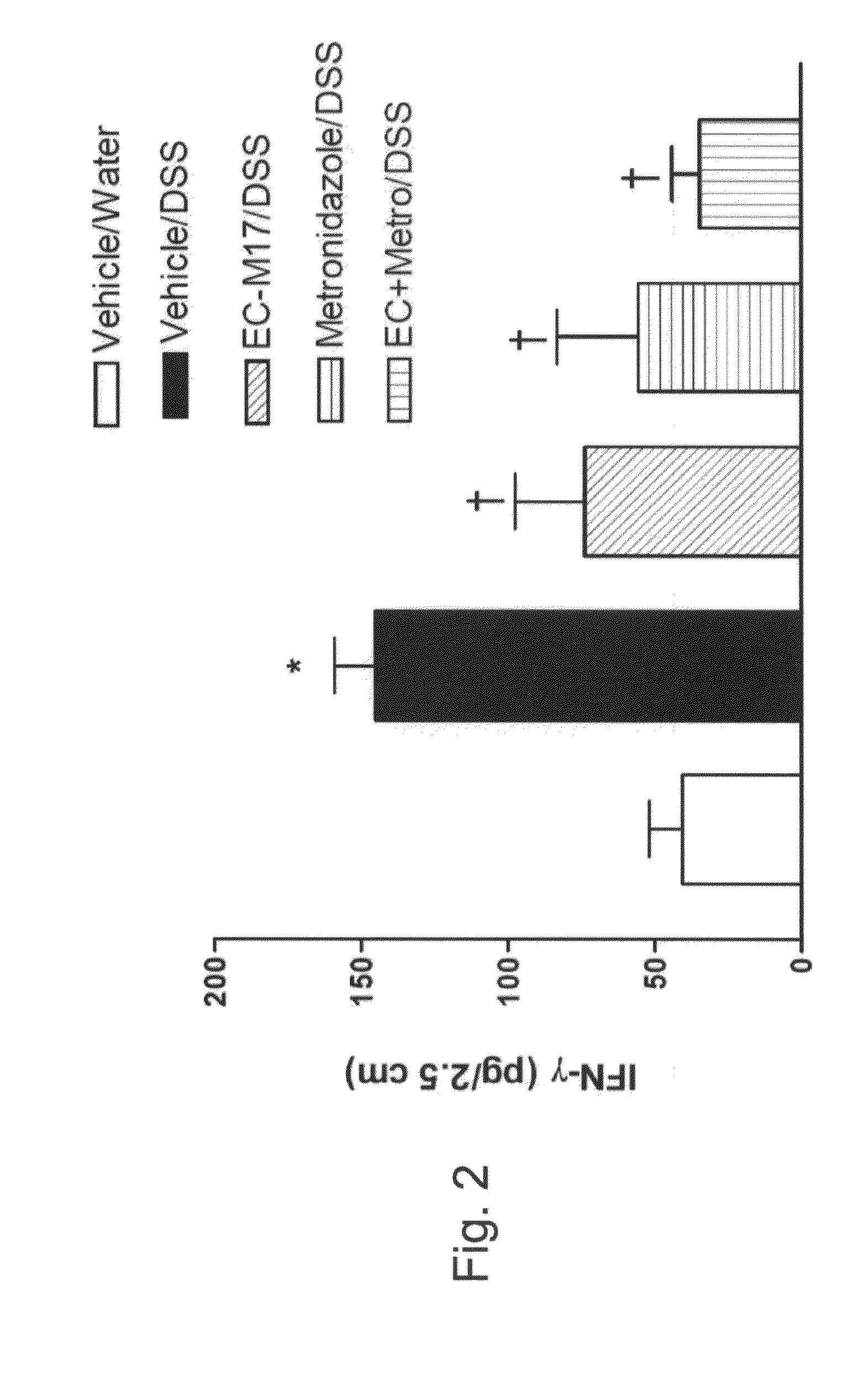
Biotherapeutic compositions comprising probiotic escherichia coli and uses thereof
Biotherapeutic compositions of a non-pathogenic bacterial strain such as M-17 and its substrains and an anaerobic bacterial antibiotic such as metronidazole, are disclosed. Further disclosed are uses of M-17 or its substrains and an anaerobic bacterial antibiotic for treating disorders caused by anaerobic bacteria, whereby such disorders include, for example, pouchitis, microbial infection, irritable bowel syndrome, inflammatory bowel disease, mucous colitis and diarrhea.
Owner:BIOBALANCE
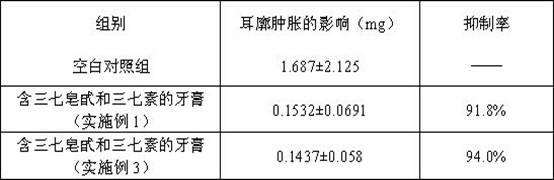
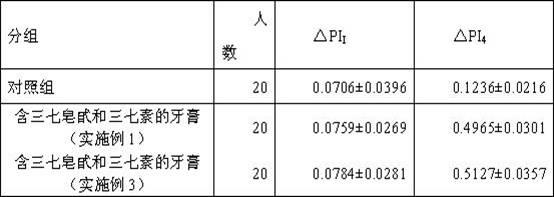
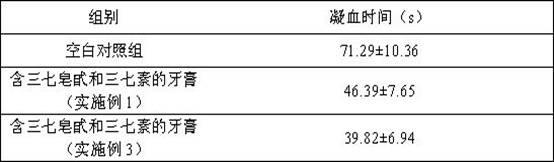
Toothpaste containing dencichine and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102379827AGood hemostatic effectEasy to useAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsSide effectAnaerobic bacteria
The invention relates to toothpaste containing dencichine, which is characterized in that the toothpaste is prepared by adding arasaponin and dencichine into a toothpaste matrix, wherein the weight percent of the arasaponin is 0.2-1.2% and the weight percent of the dencichine is 0.01-1.0%. The toothpaste according to the invention can kill pyococcus, candida albicans, staphylococcus aureus, anaerobic bacteria and other pathogens which can cause gingivitis, periodontitis, canker sores, halitosis, ngival hamorrhage, caries and other symptoms in the oral cavity and eliminate the peculiar smell in the oral cavity. The effective rate for the gingivitis and the ngival hamorrhage achieves 94.6%; and the effective rate for the canker sores achieves 89%, and the efficacy is significant. The toothpaste has no toxicity or side effects, is safe to use and can prevent drug resistance. The toothpaste has significant efficacy for the gingivitis, the ngival hamorrhage, the canker sores and the like. The hemostatic effect of the toothpaste is well promoted. Sanchi extract and the dencichine are simultaneously used in the toothpaste, thereby enabling the effects of relieving pain and preventing thegingivitis, the ngival hamorrhage and the pain of the toothpaste to be more significant.
Owner:YUNNAN PHYTOPHARML
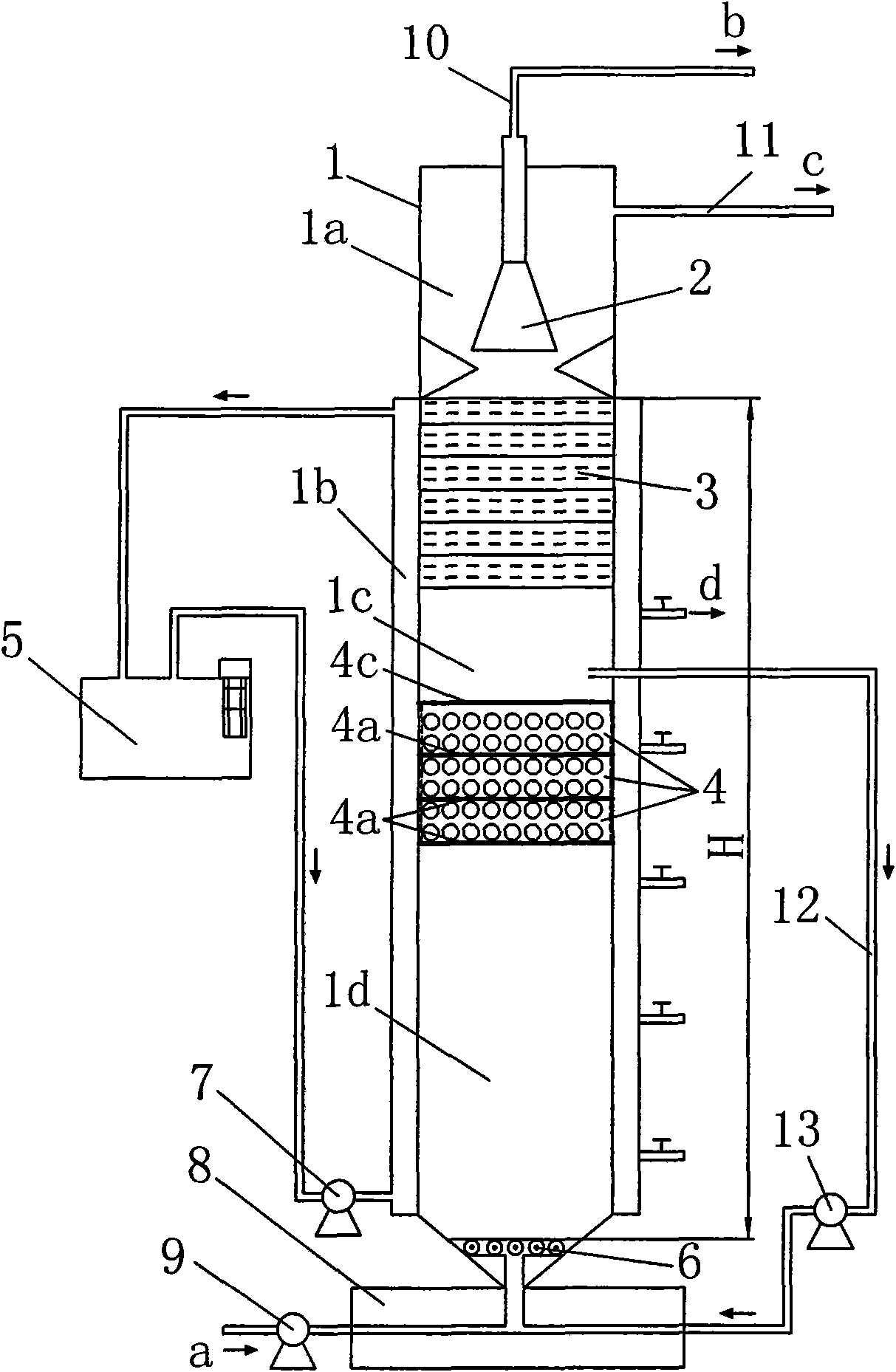
Anaerobic built-in zero-valent iron reactor
InactiveCN101591064AAvoid defectsReasonable structureTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesAnaerobic bacteriaDecomposition
The invention discloses an anaerobic built-in zero-valent iron reactor, which belongs to the technical field of water treatment. The reactor is provided with two to six zero-valent iron packing layers between a water distributor and a biofilter material layer to form a suspended sludge area positioned between the biofilter material layer and the zero-valent iron packing layers and a sludge expansion area positioned between the zero-valent iron packing layers and the water distributor. The suspended sludge area is connected to a water inlet pipeline on the lower part of an anaerobic reactor through a circulating pipeline and a circulating pump. The outside of the anaerobic reactor is provided with a set of hydraulic circulating pipelines to improve the water flow velocity in a carrier sludge layer and the suspended sludge area so as to improve the decomposition rate of anaerobic bacteria on organic substances; the reactor has a reasonable structure and good working performance, can limit the expansion and floating loss of a bottom sludge layer, can improve the degradation capability on the organic substances, achieve high removal rate of the organic substances, and realize the quick startup of sewage at the same time; and late experiments show that the reactor can realize the successful startup of chemical saline wastewater within 43 days and keeps steady operation at subsequent stages.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Five-layer coverage forced reduction in-situ mineralization restorative method
ActiveCN107363083AAvoid pollutionReduce penetrationSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationSolubilityReaction layer
The invention provides a five-layer coverage forced reduction in-situ mineralization restorative method, and belongs to the technical field of mine environment ecological restoration. A five-layer structure involved in the method particularly comprises a non-pollution new soil layer, a clay sealing layer, a biomass reduction sealing layer, a main reaction layer and an original tailing layer. The method comprises the steps that organic matter in biomass on the main reaction layer is taken as the reducing agent, arsenic in a high oxidation state is reduced into arsenic in a low oxidation state or in a reduced state under the effect of anaerobic bacteria, and sulphur in a high oxidation state is reduced into sulphur in a reduced state, so that the minerals of realgar, orpiment and the like are formed again; and meanwhile, a large amount of iron is reduced to form iron pyrite, arsenopyrite, pyrrhotite and other minerals with the low solubility, and the heavy metals of Pb<2+>, Zn<2+>, Cu<2+>, Hg<2+>, Cd<2+>, Sb<3+> and the like form galena, blende, copper pyrites, cinnabar, greenockite, stibnite and other sulfide minerals with the extremely low solubility, so that mine heavy metal pollution in-situ mineralization restoration is achieved.
Owner:北科蕴宏环保科技(北京)有限公司
Broad spectrum and anaerobic bacteria-resistant pharmaceutical composition
The invention provides a pharmaceutical composition capable of treating various diseases caused by anaerobic bacteria such as fungi, viruses and bacilli. Raw materials for the pharmaceutical composition comprise gastrodia rhizome, pinellia rhizome, liquidambar fruit, common clubmoss, rhizoma atractylodis, eupatorium and lysimachia. The pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention has a significant curative rate for treating various chronic diseases caused by anaerobic bacteria such as fungi, viruses and bacilli. Besides, the pharmaceutical composition provided by the invention has low cost and no side or toxic effect.
Owner:肖鸣春
Tea tree oil mouth wash and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101991521AEffective in treating infectionsTreat infectionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAnaerobic bacteriaAntibacterial property
The invention relates to mouth wash and a preparation method thereof, in particular to tea tree oil mouth wash with the functions of bacteriostasis, inflammation diminishing and hemostasis and a preparation method thereof. The tea tree oil mouth wash comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.01 to 30 percent of tea tree oil, 0.01 to 20 percent of propylene glycol (for medicine or food), 0.01 to 20 percent of Tween-60, 30 to 99.97 percent of distilled water and few additives. In the invention, the tea tree oil is added into the mouth wash, so that the mouth wash can be taken, has no toxic nor side effects, has a wide-spectrum antibacterial property, has high capability of killing many anaerobic bacteria and non-anaerobic bacteria, can reduce gingival inflammation and promote canker sore coalescence, has a remarkable effect of alleviating throat pain and is safe and nonirritating.
Owner:AGRI PRODS PROCESSING RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method of producing organic fertilizer by fermentation of poultry and animal faeces
InactiveCN1556071APreserve activityReasonable workmanshipBio-organic fraction processingClimate change adaptationBiotechnologyFowl
A process for preparing organic fertilizer from the dung of domestic animals and the droppings of fowls through proportioning mixing them with organic waste and assistant to obtain culture medium inoculating composite microbial seeds composed of aerobic, facultative and anaerobic bacteria, stacking, fermenting at 15-70 deg.C, granulating, and fermenting again. Its advantages are low cost and high bioactivity.
Owner:吕鸣捷
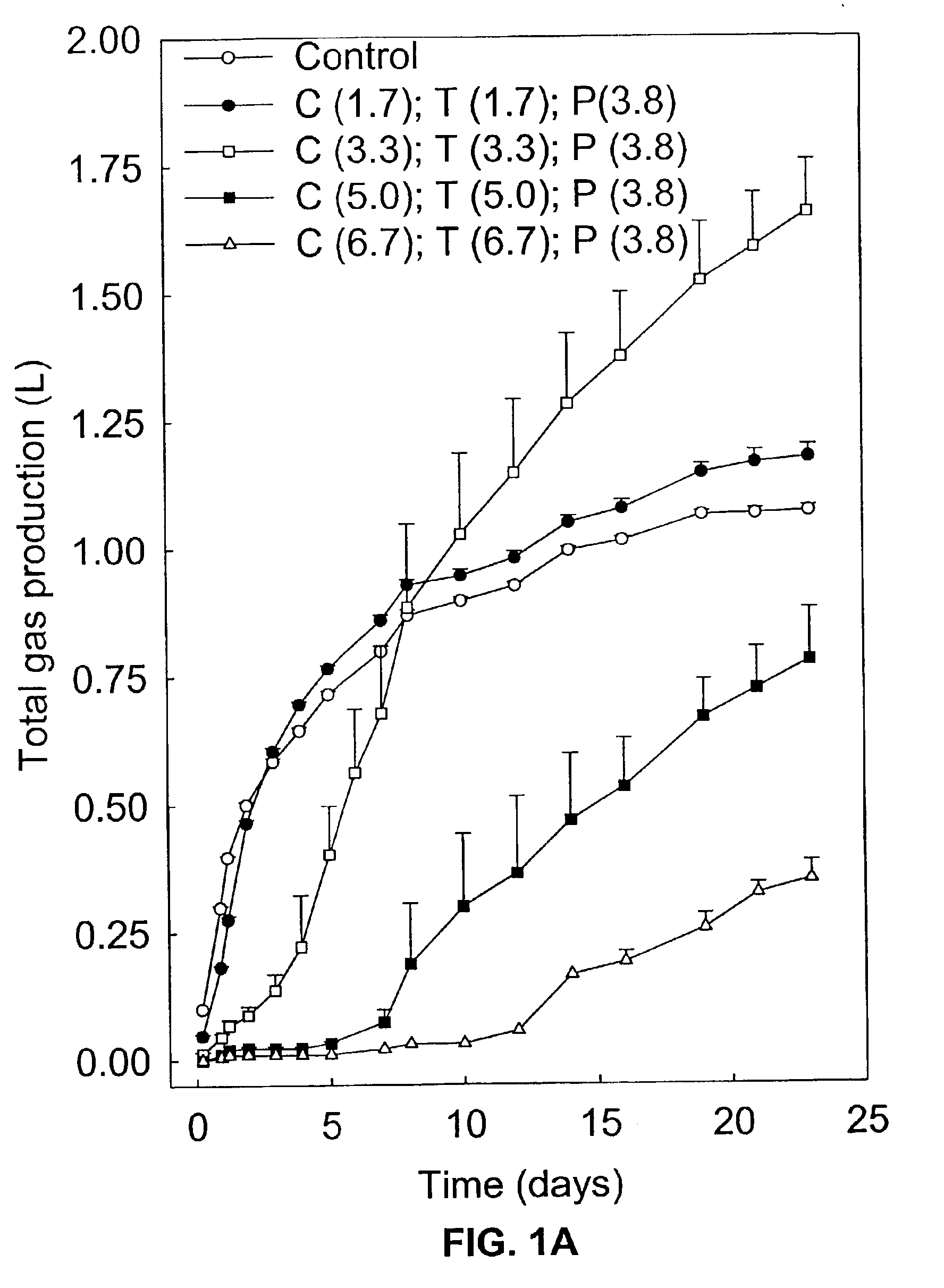
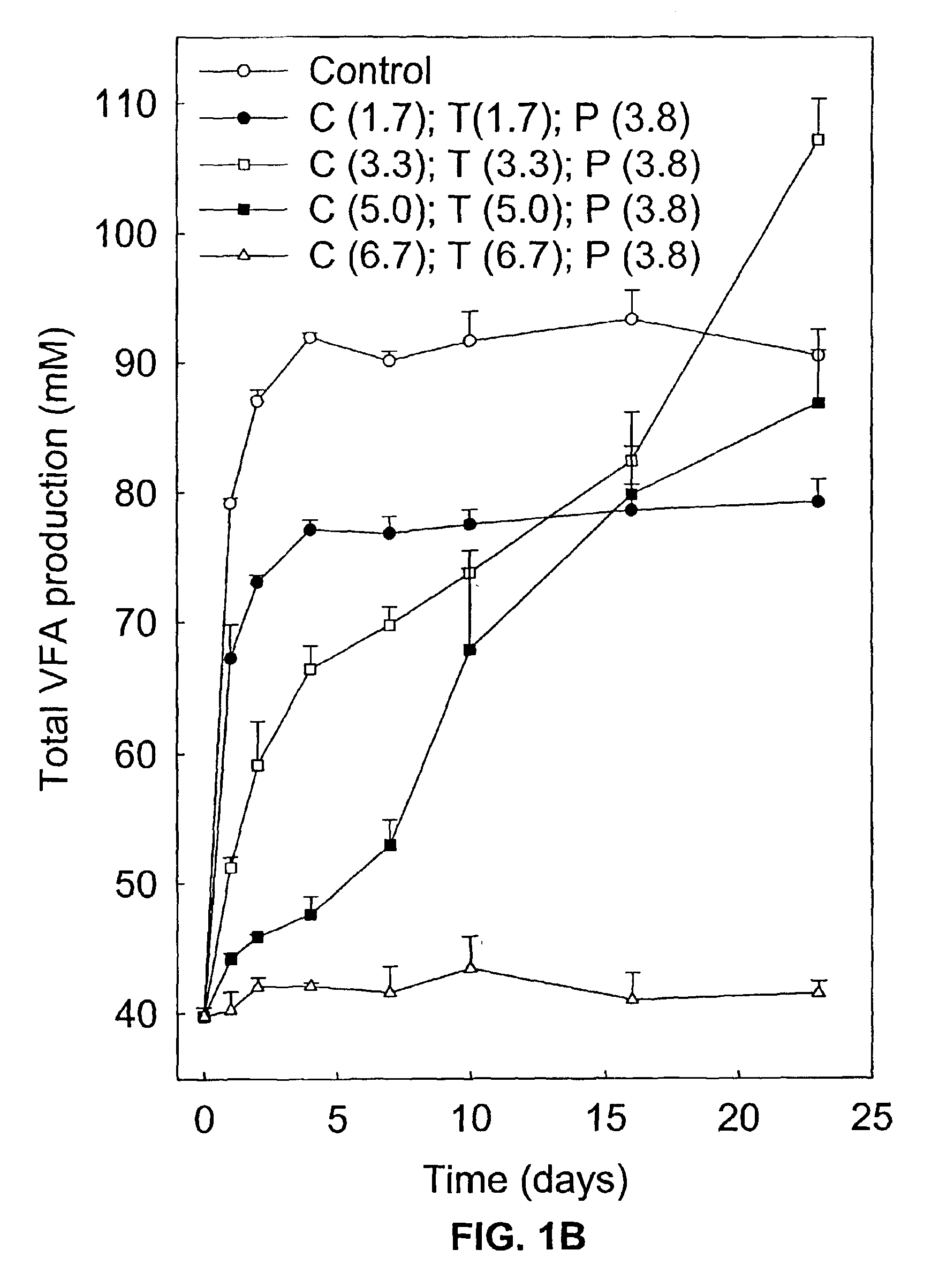
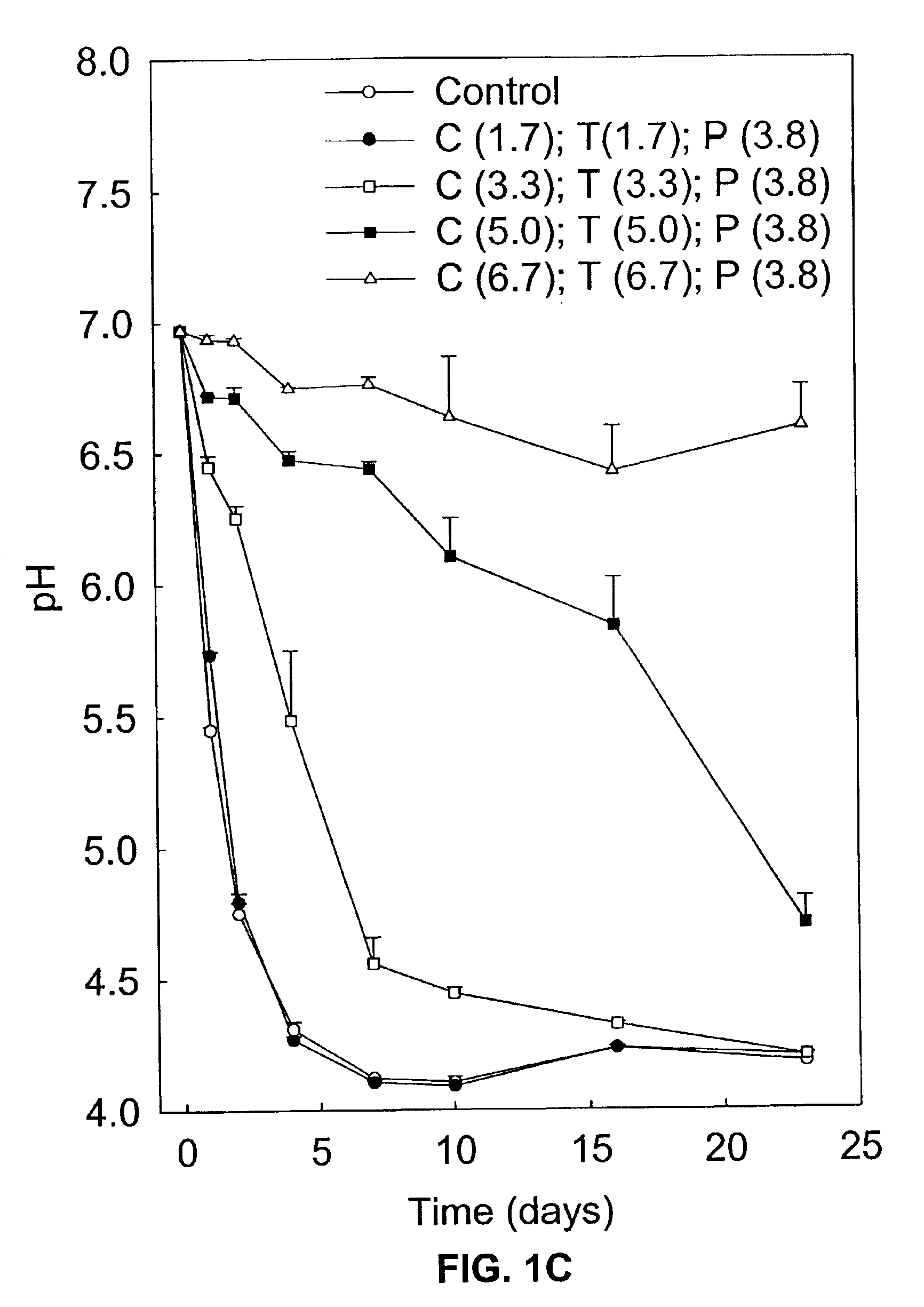
Incorporation of anaerobic bacteria in feed formulation
InactiveUS20060008861A1Good effectMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal feeding stuffSporeAnaerobic bacteria
Anaerobic bacteria are incorporated in a feed such that they provide a benefit to the consuming animal. Anaerobic bacteria can be viable and colonize the gut to provide this benefit by displacing harmful bacteria, secreting a particular agent (e.g., enzyme, antibiotic or bioactive compound), binding or sequestering harmful organisms or compounds, or providing a beneficial physical effect. Anaerobic bacteria can also be added n a non-viable form wherein the added bacteria provide a benefit to the consuming organism by delivering preformed compounds such as enzymes, bioactive agents, or polymers. Recombinant anaerobes can be utilized for any of the above purposes. Feeds can contain naked bacteria, spores, treated bacteria such as encapsulated, coated or freeze dried bacteria, in order to maintain either viability or stability of the active function.
Owner:ADVANCED BIONUTRITION CORP
Method of treating a hydrocarbon bearing formation
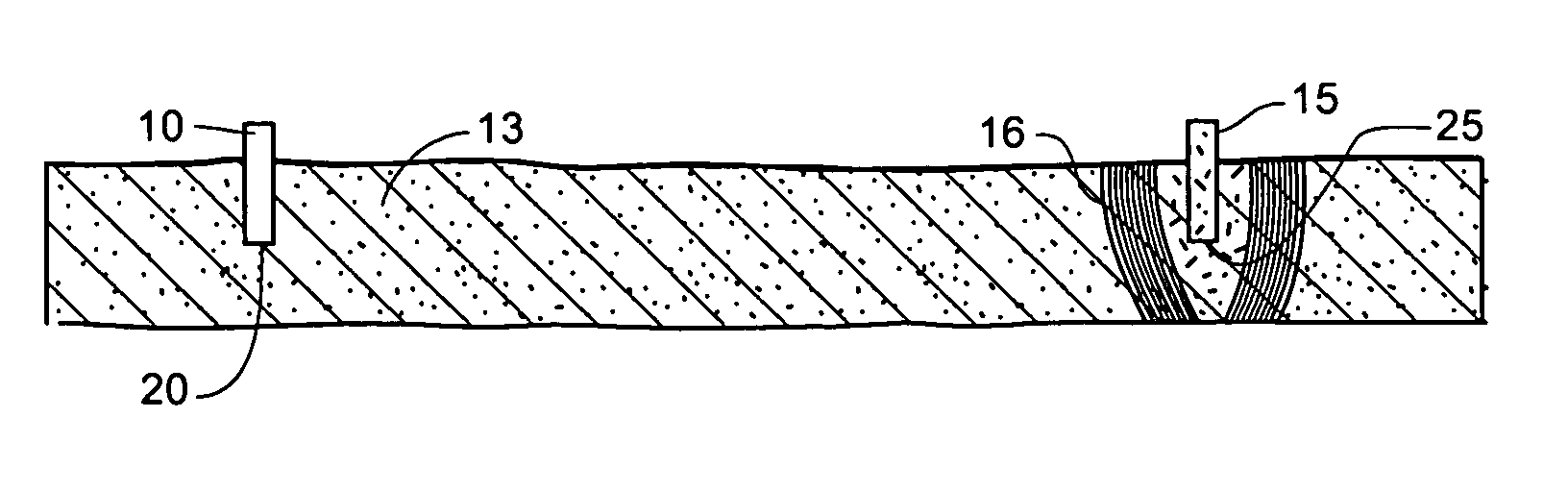
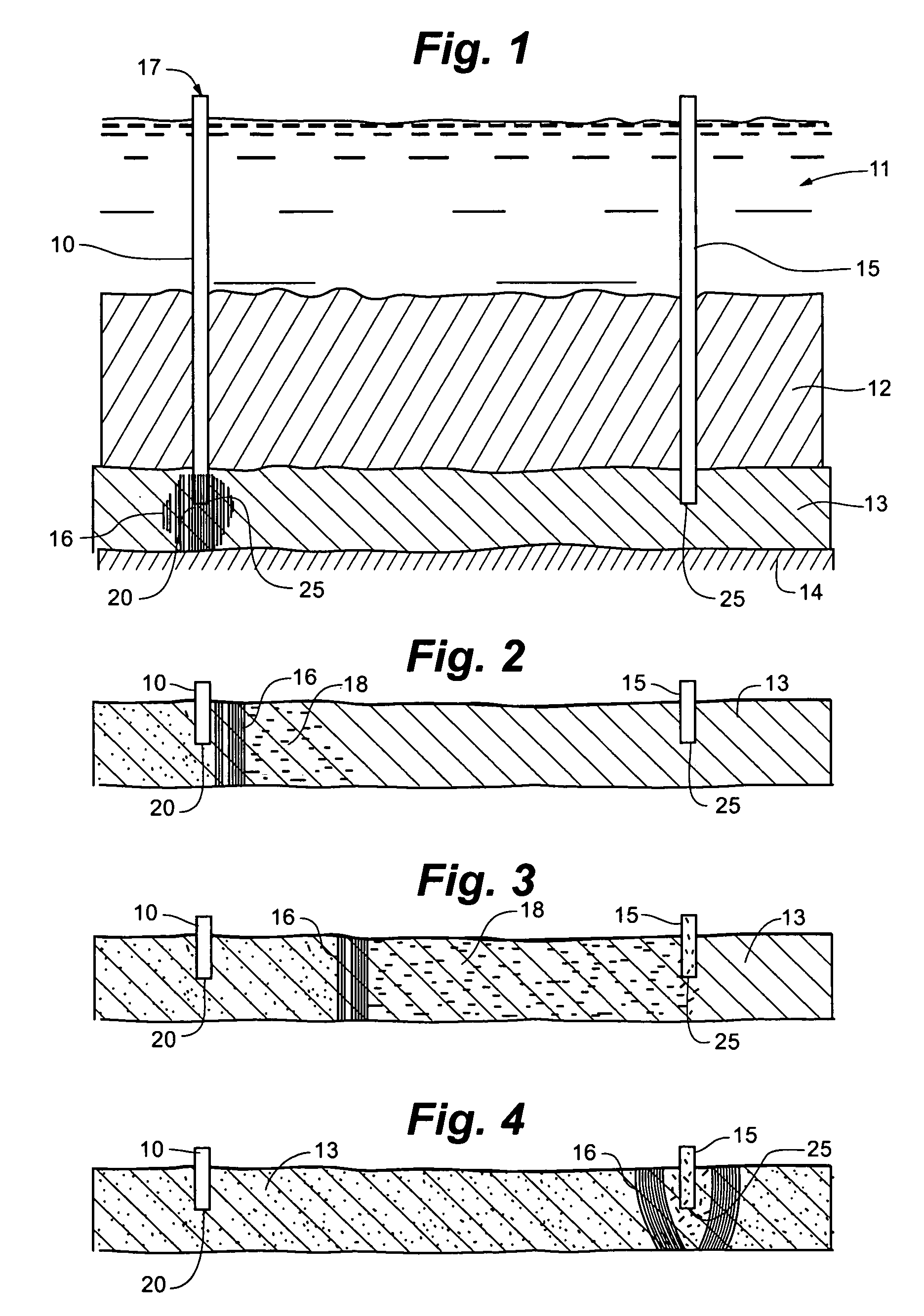
InactiveUS7124817B1Efficient removalMinimize exposureFluid removalDrilling compositionControlled releaseNitrate
A method of treating a hydrocarbon-bearing measure such as an oil-bearing rock formation (13). The method comprises: injecting water containing a source of vitamins, phosphates and an electron acceptor such as nitrate into the formation at first location (10) and allowing anaerobic bacteria, which are either already present in the formation (13) or which are introduced simultaneously to multiply using the oil as their main carbon source. This establishes a biomass layer (16) which acts to dissociate the oil from the rock formation (13). The dissociated oil is removed via an outlet (15). The vitamins are supplied by means of a controlled-release medium.
Owner:STATOIL ASA PETRO SA (NO)
Three-dimensional floating bed for purification of black and odorous rivers and building method
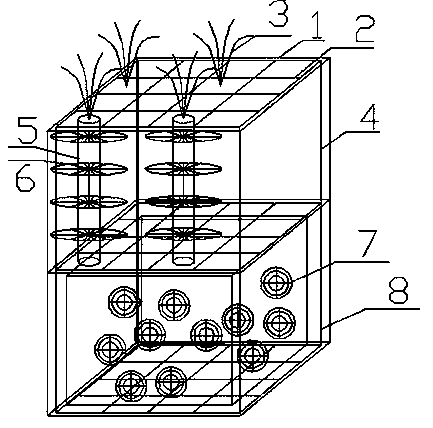
ActiveCN103663712AImprove governance effectEliminate degradationClimate change adaptationTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesRough surfaceAnaerobic bacteria
The invention provides a three-dimensional floating bed for purification of black and odorous rivers and a building method for the three-dimensional floating bed. A fence formed by PVC pipes and polyvinyl net is divided from top to bottom into an upper layer of floating plant growing region, a middle layer of artificial medium region and a lower layer of artificial medium region, wherein water plants with relatively developed root systems are planted on the upper layer; a biological membrane is formed on the middle layer by hanging pieces with rough surfaces and acts together with the root region of the plants on the upper layer, and organic substances are decomposed by oxygen generated by the plants; floating filler net is hung on the lower layer, and is filled with anaerobic bacteria according to different forming reasons of the black and odorous rivers, wherein the anaerobic bacteria are attached to an artificial hanging membrane, and domesticated to achieve high tolerance and degradation capability to pollutants. The three-dimensional floating bed provided by the invention has the advantages as follows: the manufacturing method of the floating bed is simple and convenient, the cost is lower, and the three-dimensional floating bed has an enhanced improvement effect on black and odorous rivers with high pollutant burdens.
Owner:沐联环境科技(重庆)股份有限公司
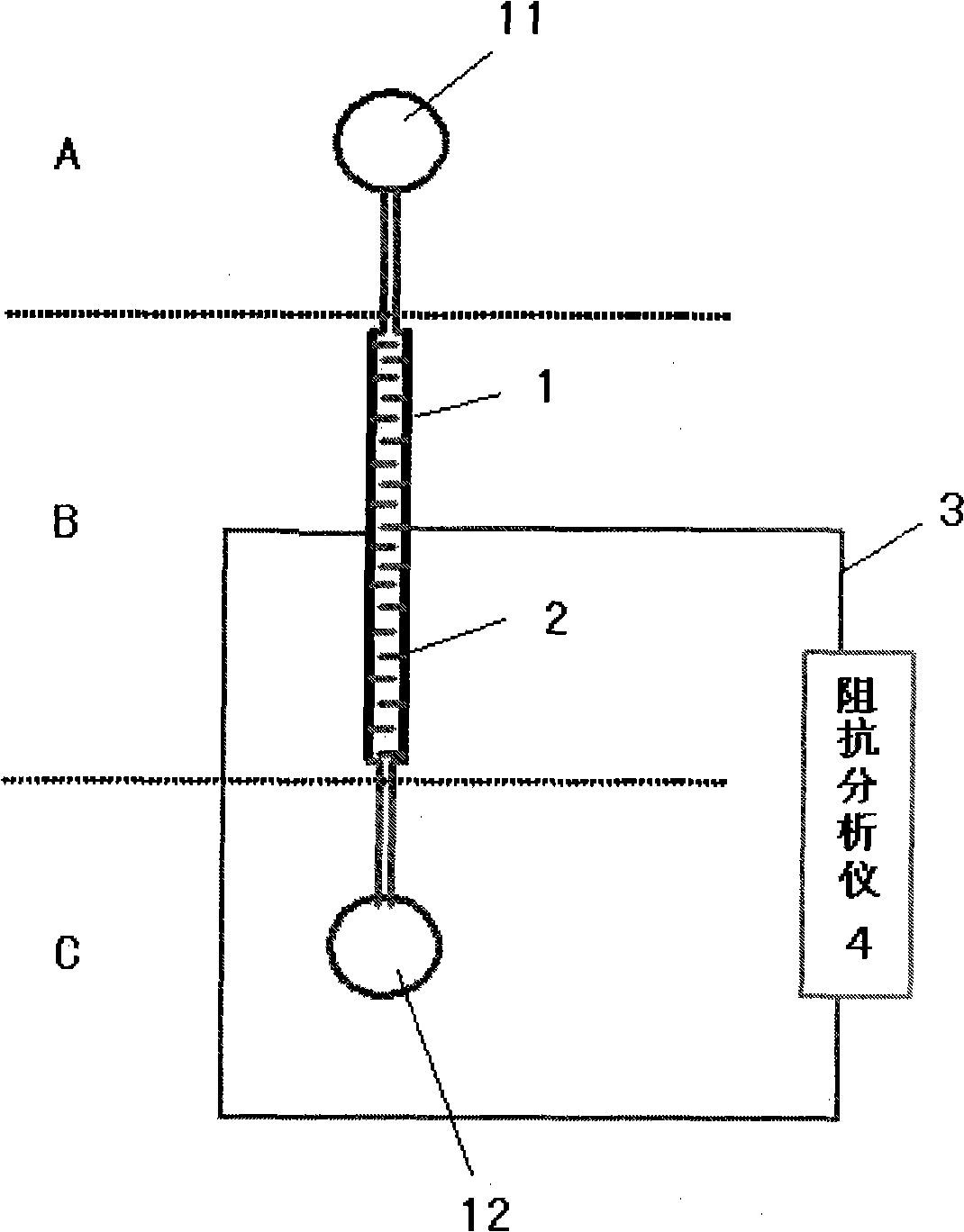
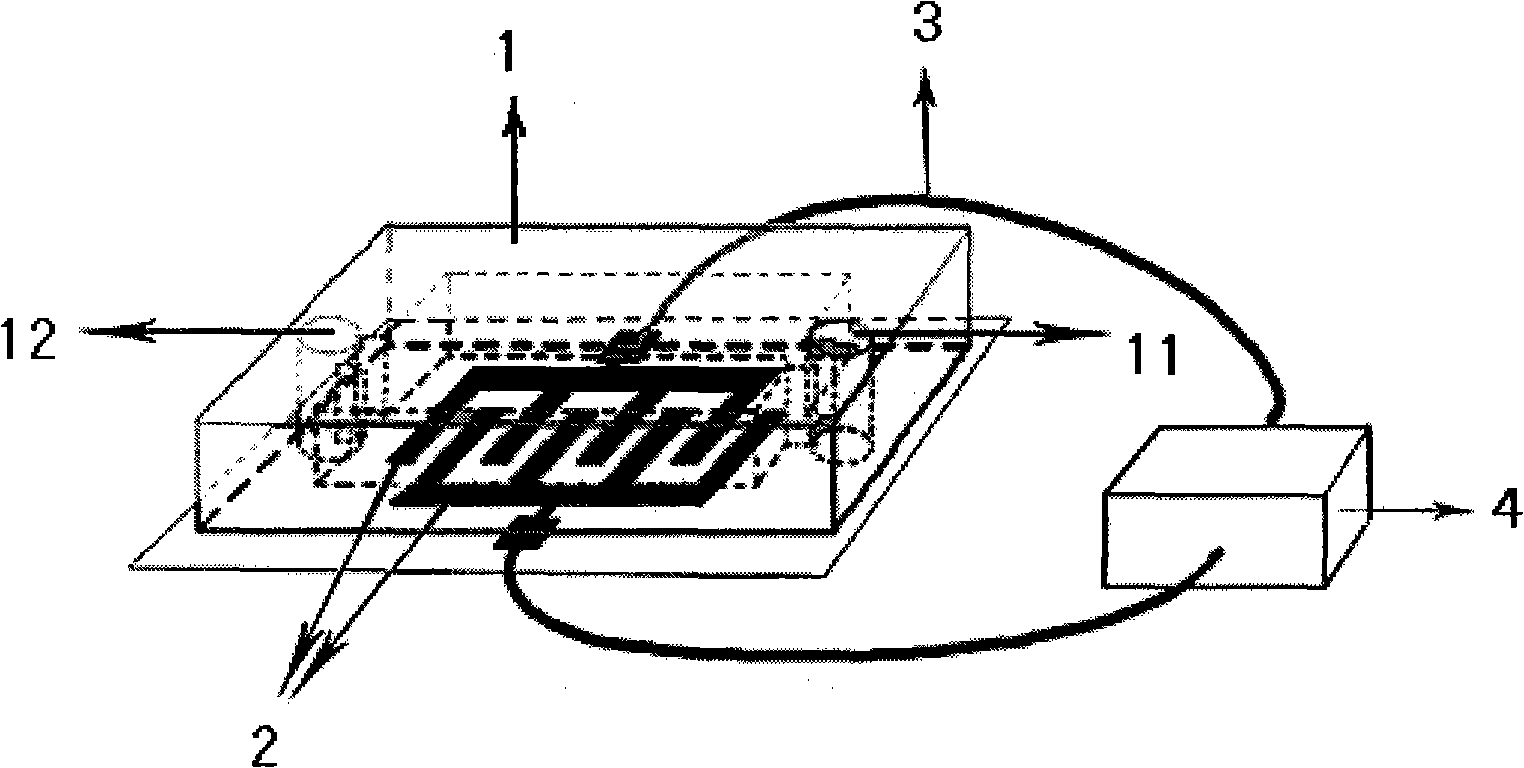
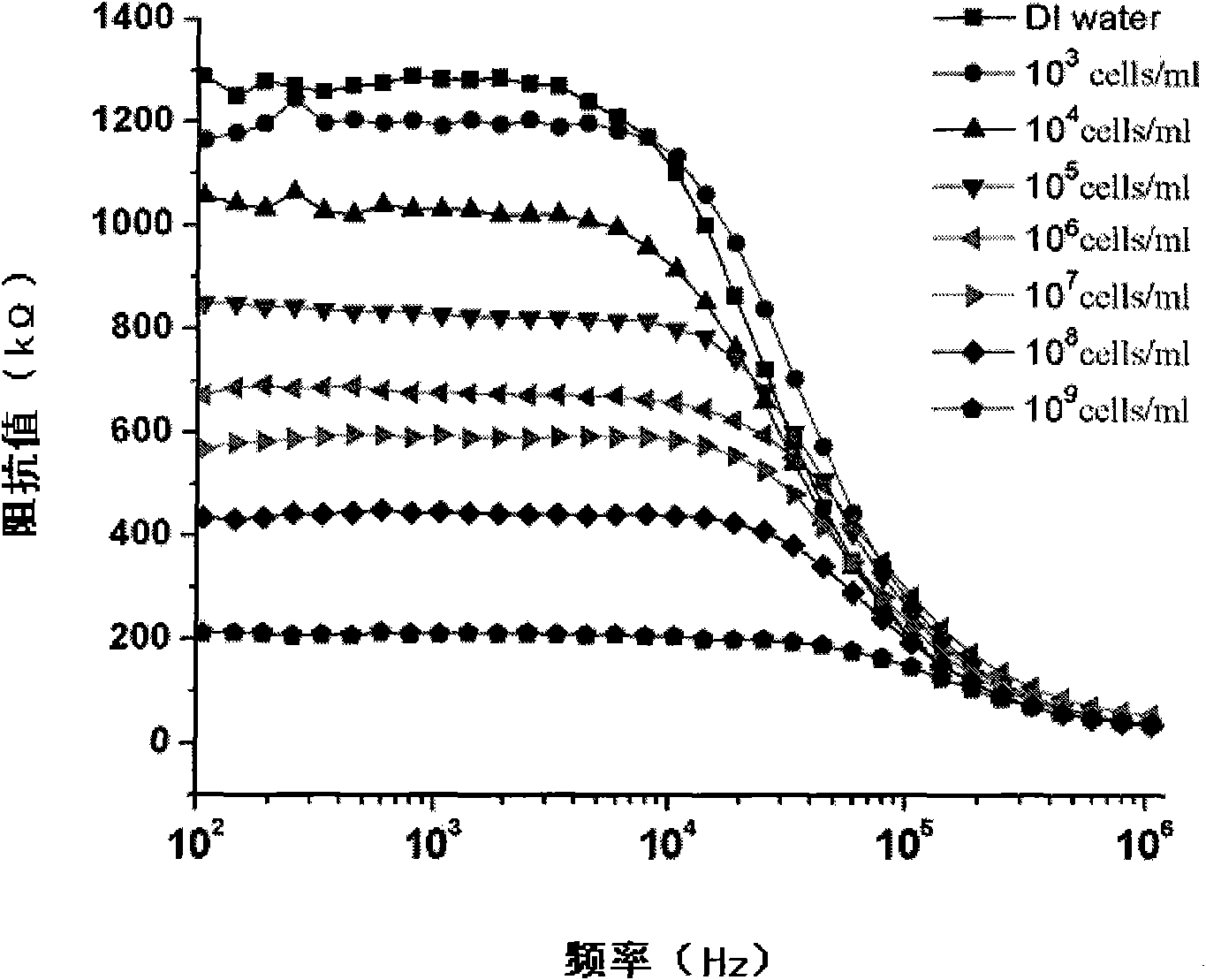
Method for detecting bacteria by using electrochemical impedance principle and microfluidic chip
InactiveCN101788515AEasy to integrateMiniaturizationMaterial resistanceData displayAnaerobic bacteria
The invention relates to a method for detecting bacteria by using the electrochemical impedance principle and a microfluidic chip. The method comprises the following steps of 1) arranging one microfluidic chip and determining the functional relation between the system impedance value and the bacterial concentration by using a standard; 2) filling bacteria samples to be detected in a sample inlet of the microfluidic chip and flushing to remove the redundant samples; 3) connecting an impedance analyzer with a conductive electrode in a microfluidic chip detecting zone, reading data displayed in the impedance analyzer and recording the measured impedance value of the bacteria sample; 4) calculating the number of the target bacteria in the bacteria sample according to the determined functionalrelation of the system impedance value and the bacterial concentration. The complex processing for the samples, particularly for the anaerobic bacteria samples, is unnecessary, the required equipmentis simple, the detection is quick, the cost is saved, the integration and miniaturization are easy, and the invention creates favorable conditions for realizing individualization of bacteria detection and real-time in vivo detection of the bacteria so as to better promote and maintain the human health.
Owner:BEIJING STOMATOLOGY HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV +2
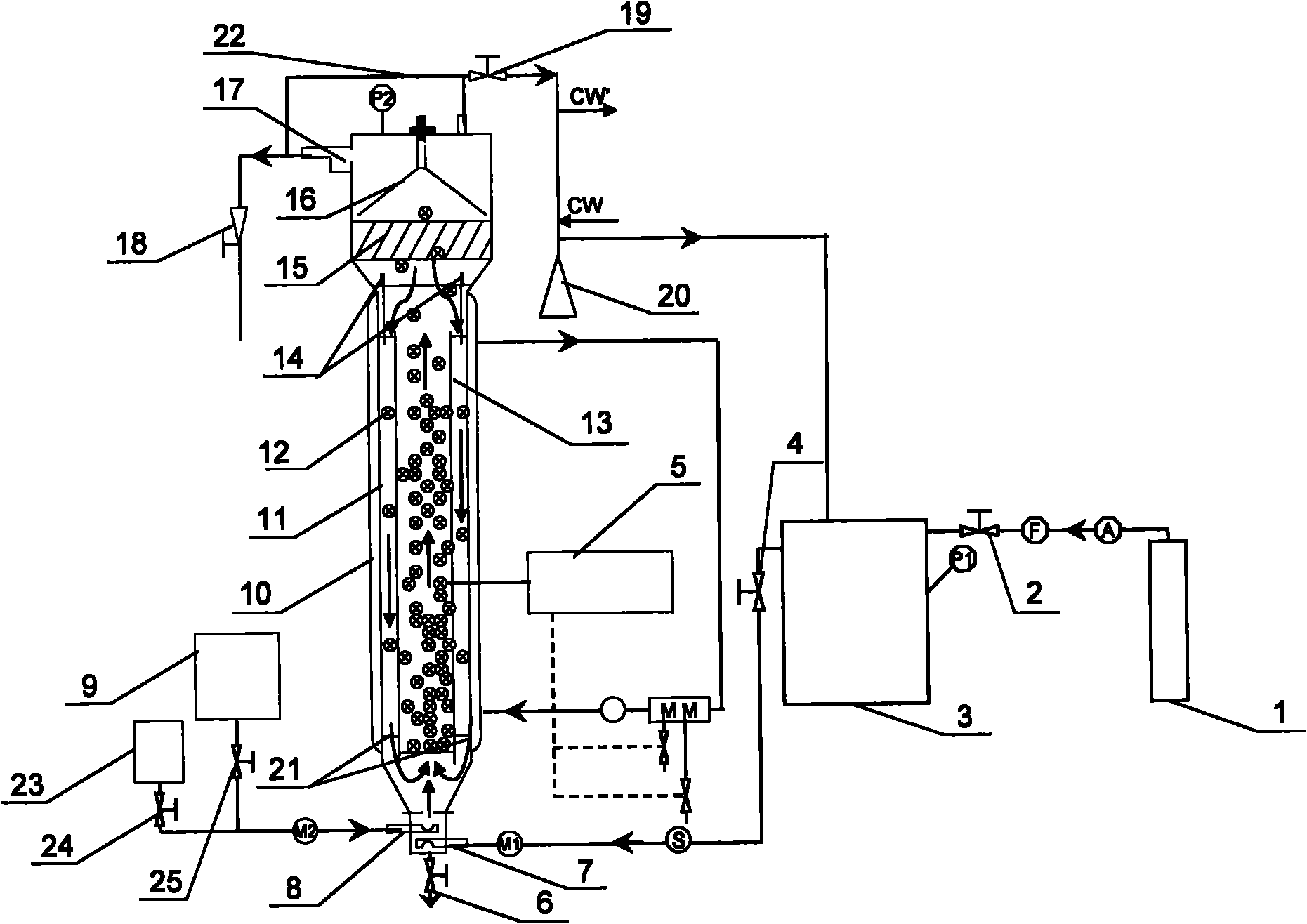
Method and device for producing organic acid or alcohol by fermenting synthetic gas
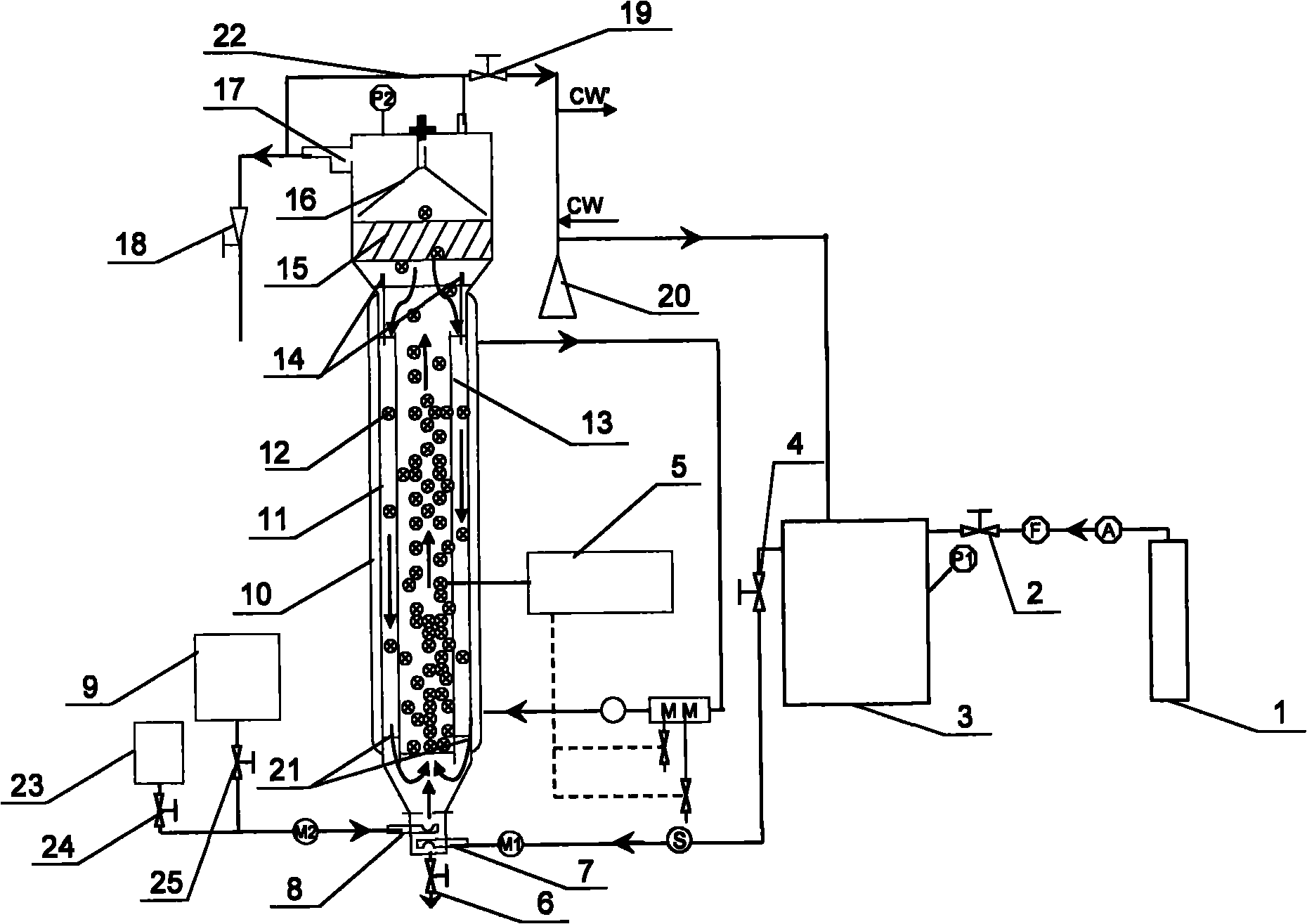
The invention relates to a method for producing organic acid or alcohol by fermenting synthetic gas, which comprises the following steps: (1) adding anaerobic bacteria capable of metabolizing CO, H2 and CO2 to produce organic acid or alcohol into a reactor filled with inert particles which are used as a vector; (2) introducing synthetic gas, which is composed of one or more of CO, H2 and CO2, into the reactor, enabling the vector to be in a fluidized state and keep the fluidized state, thoroughly mixing the anaerobic bacteria and the vector, and fermenting; and (3) adding a liquid culture medium into the reactor, and flushing the suspended anaerobic bacteria out of the reactor, so that the microbes attached to the surface of the vector form a biomembrane. The invention also provides a device for implementing the method. The invention fully utilizes the characteristic of high mass transfer efficiency of the solid / liquid internal circulation fluidized bed, and is assisted by the gas external circulation technology, thereby realizing high-efficiency conversion from synthetic gas into organic acid or alcohol.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Stalk microbe feed additive and its prepn
InactiveCN101066092ALower pH valueInhibition of colonizationAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsMicroorganismFeed conversion ratio
The present invention relates to stalk microbe feed additive and its preparation. After stalk as solid culture medium is crushed, gas exploded, added with water, sterilized, microwave treated and cooled, mixed bacterial seed culture liquid is sprayed for solid fermentation in anaerobic fermenting tank and aerobic fermenting tank to obtain anaerobic bacterial seed and aerobic bacterial seed. Through further fermentation with the anaerobic bacterial seed and aerobic bacterial seed in certain ratio, stalk microbe feed additive is prepared. The stalk microbe feed additive can raise feed converting rate, promote animal's growth, raise animal's disease resistance and produce other positive effects.
Owner:张培举
Reduction of odor gases from waste using plant-derived oils
InactiveUS6902726B1Reduce productionPromoting lactic acid accumulationOrganic chemistryMicroorganismsVolatile fatty acidsAnaerobic bacteria
Plant-derived oils, carvacrol and thymol, when added to human or animal waste reduce the production of gas and short-chain volatile fatty acids, and the viability of total anaerobic bacteria and fecal coliforms. In an embodiment, carvacrol or thymol are combined with eugenol.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Methods of and Formulations for Reducing and Inhibiting the Growth of the Concentration of Microbes in Water-Based Fluids and Systems Used with Them
ActiveUS20100298275A1Maximize synergyEffective controlBiocidePhosphorous compound active ingredientsWater basedPhosphonium
The present invention provides methods and formulations for reducing or inhibiting increase in the concentration of microbes in a water-based fluid. The methods and formulations of the present invention use glutaraldehyde and a hydroxymethyl-substituted phosphorus compound selected from the group consisting of tetrakis(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium salts, C1-C3 alkyl- and alkenyltris(hydroxymethyl)phosphonium salts and tris(hydroxymethyl)phosphine, in a ratio of hydroxymethyl-substituted phosphorus compound to glutaraldehyde in the range of about 2:1 to about 7:1, or about 3.5:1 to about 7.5:1. The methods and formulations of the present invention can be useful in treating water contaminated with aerobic or anaerobic bacteria in oilfield, natural gas field and other industrial applications.
Owner:NUTRITION & BIOSCIENCES USA 1 LLC
Normal-temperature starting domestication method for anaerobic ammoxidation reactor with low-dissolved-oxygen inflow water
InactiveCN102701445AWide variety of sourcesEasy accessTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesStart timeSludge
The invention discloses a normal-temperature starting domestication method for an anaerobic ammoxidation reactor with low-dissolved-oxygen inflow water and relates to the starting domestication method of a reactor. The method aims to solve the problems that starting time of the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor is long, and that the dissolved oxygen in the inflow water brings the adverse effect on the anaerobic ammoxidation process and causes high energy consumption. The method comprises the following steps: 1, culturing a denitrification biomembrane; 2, starting the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor; and, 3, domesticating the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor. The method provided by the invention uses the denitrification biomembrane as the secondary seed sludge and starts the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor within 100d successfully; under the condition that the inflow water contains 1-1.5mg / l of dissolved oxygen, the method provided by the invention can domesticate microflora in which the aerobic bacteria and anaerobic bacteria are co-existing. The method provided by the invention reduces the operation temperature of the anaerobic ammoxidation reactor from 35 DEG C to (19-22) DEG C, and greatly reduces the operation cost; meanwhile, the reactor system still operates stably and realizes high denitrification effect.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for preparing granular ammonia oxidative mud with anaerobic bacteria from mixed mud
InactiveCN1583600AImprove performanceHigh volume loadTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSustainable biological treatmentAnaerobic bacteriaSewage
A process for using sludge mixture to culture the granular sludge used for anaerobic ammoxidation reactor includes such steps as mixing the granular anaerobic sludge with active aerobic sludge, loading the mixture in flow-up anaerobic reactor, preparing simulative sewage, pumping it in said reactor from its bottom, and running for a certain time while controlling the flow speed, temp and pH value.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com