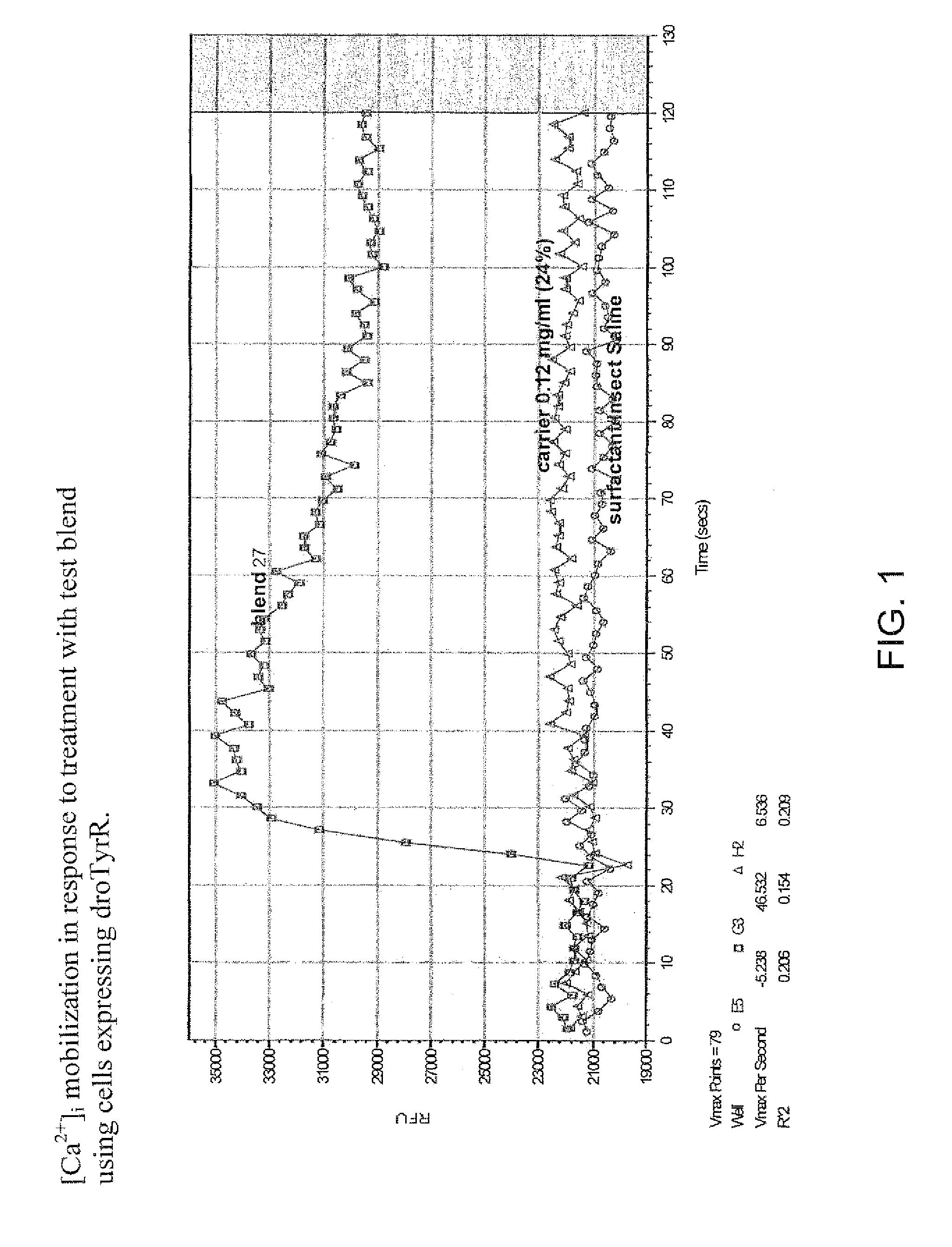
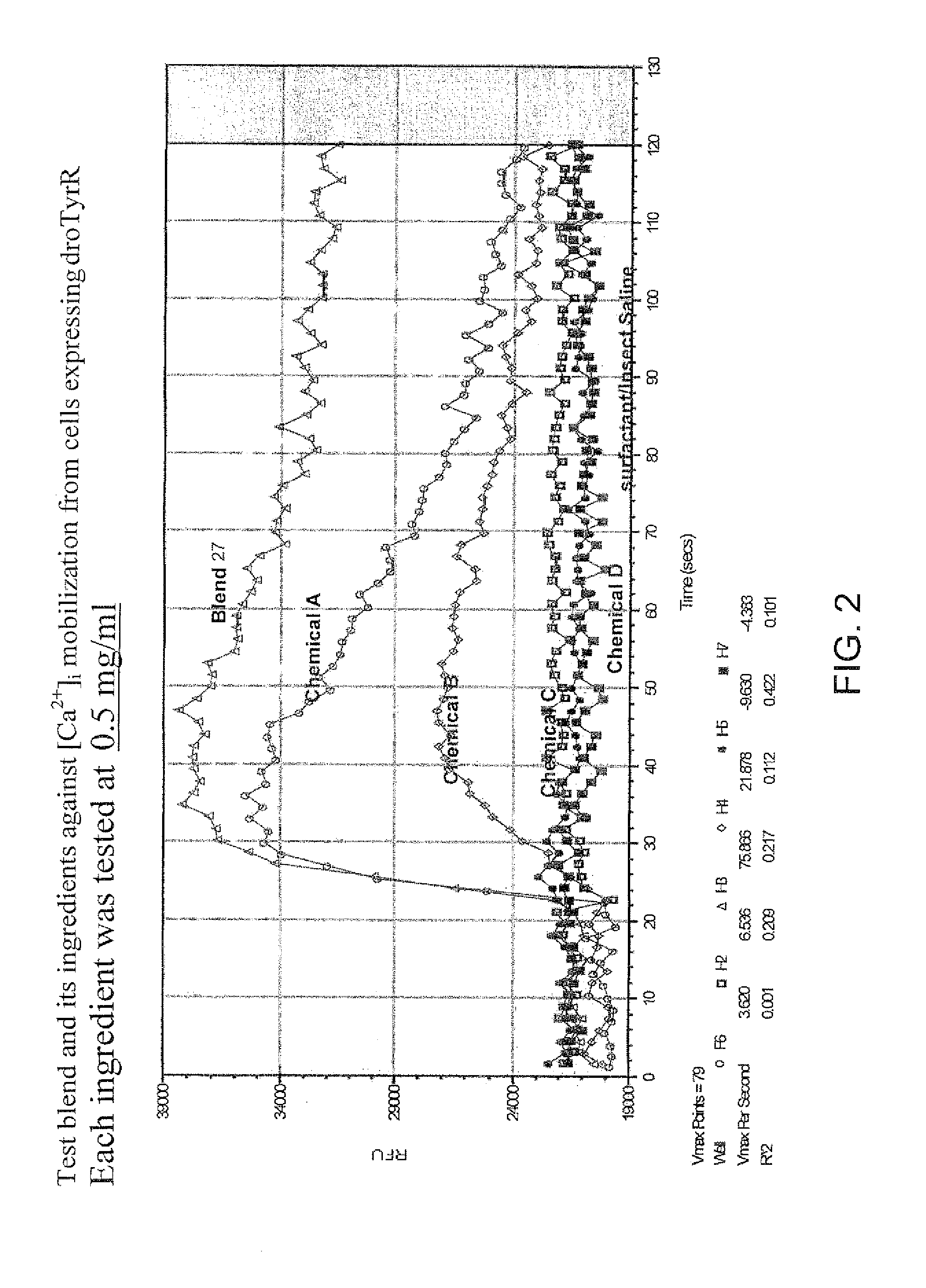
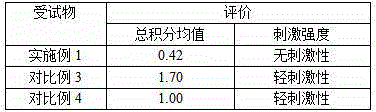
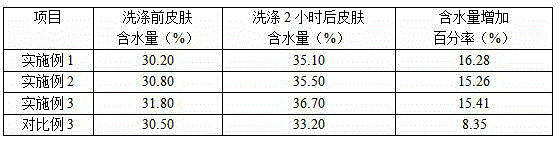
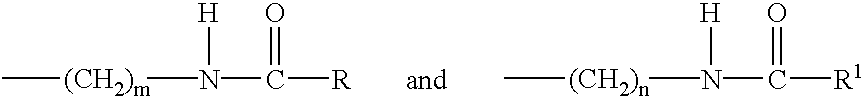Patents
Literature
666 results about "Thymol" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
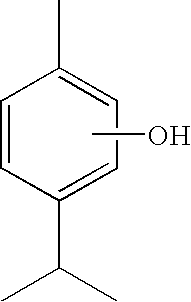
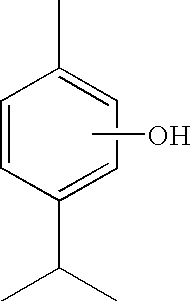
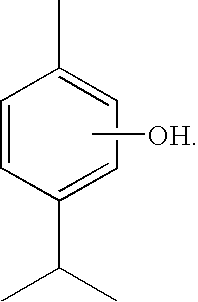
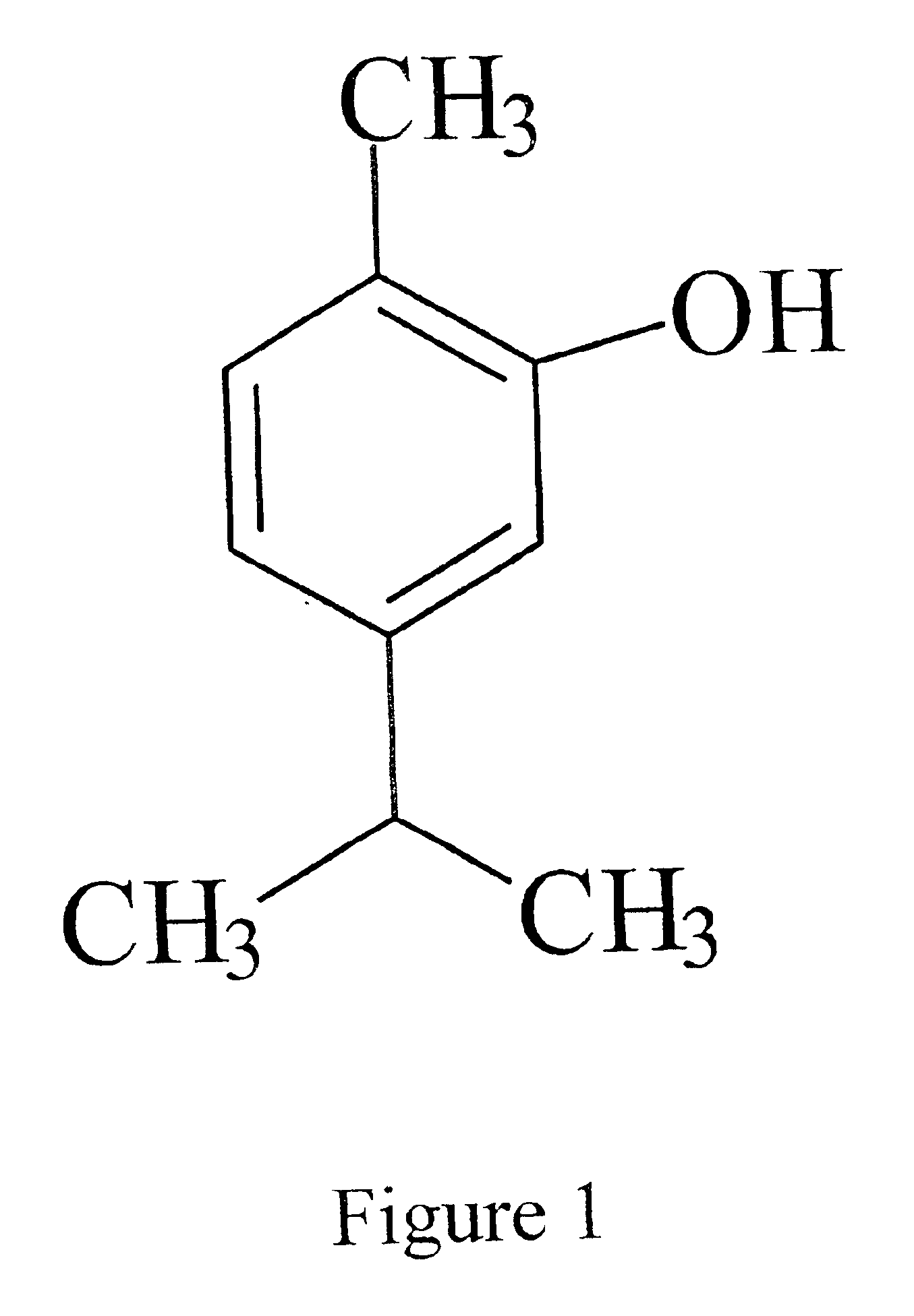
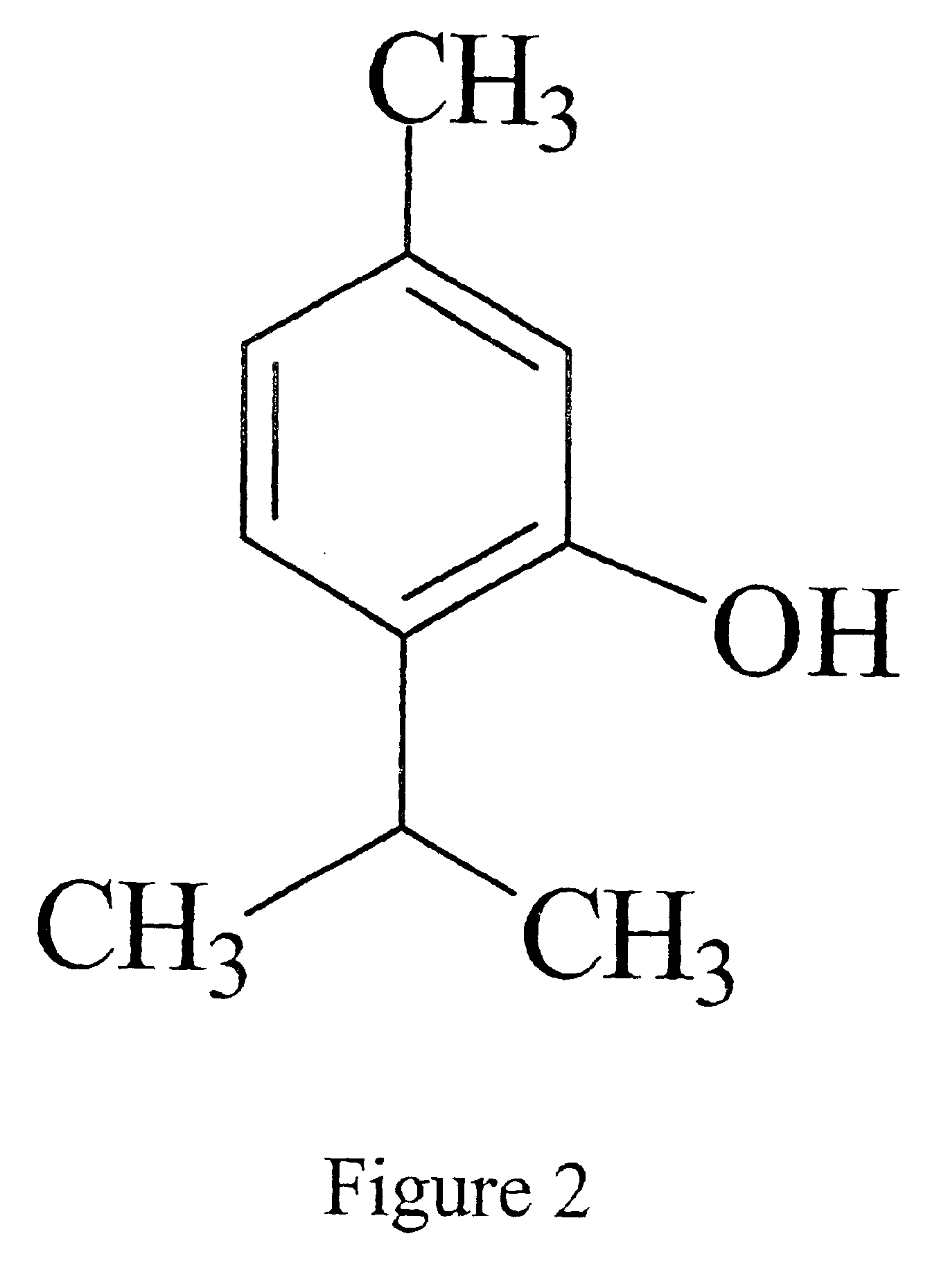
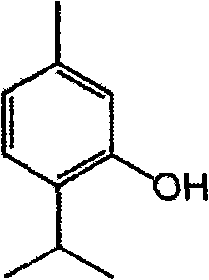
Thymol (also known as 2-isopropyl-5-methylphenol, IPMP) is a natural monoterpenoid phenol derivative of cymene, C₁₀H₁₄O, isomeric with carvacrol, found in oil of thyme, and extracted from Thymus vulgaris (common thyme), Ajwain and various other kinds of plants as a white crystalline substance of a pleasant aromatic odor and strong antiseptic properties. Thymol also provides the distinctive, strong flavor of the culinary herb thyme, also produced from T. vulgaris.
Fast dissolving orally consumable films
InactiveUS6923981B2Dissolve fastGood curative effectAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsPolymer sciencePullulan
Physiologically acceptable films, including edible films, are disclosed. The films include a water soluble film-forming polymer such as pullulan. Edible films are disclosed that include pullulan and antimicrobially effective amounts of the essential oils thymol, methyl salicylate, eucalyptol and menthol. The edible films are effective at killing the plaque-producing germs that cause dental plaque, gingivitis and bad breath. The film can also contain pharmaceutically active agents. Methods for producing the films are also disclosed.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
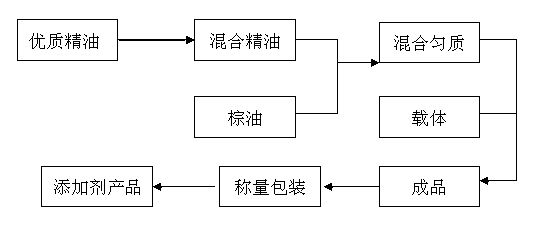
Feeding plant essential oil additive as well as preparation and application of additive
InactiveCN102987093AInhibition of colonizationInhibition of reproductionAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyEugenol
The invention provides a feeding plant essential oil additive. The prescription of the feeding plant essential oil additive comprises the following components by weight percent: 8.5%-12% of cinnamyl aldehyde, 2%-6.5% of thymol, 1.8%-3% of eugenol, 2%-3.5% of carvacrol, 18-30% of palm oil and 50%-60% of a carrier. The invention further provides a preparation method and application of the feeding plant essential oil additive. By reasonably proportioning different types of plant essential oils, the efficient pollution-free plant essential oil feed additive with pretty good food attraction effect is obtained, the incidence rates of diseases including diarrhea, respiratory disease complex and the like can be effectively reduced, the health level of an animal can be obviously improved, animal food intake is increased, and production efficiency is improved.
Owner:武汉索尔生物科技有限公司
Fast dissolving orally consumable film
InactiveUS20050031675A1Good curative effectEasy to adaptAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMentholPullulan
Physiologically acceptable films, including edible films, are disclosed. The films include a water soluble film-forming polymer such as pullulan. Edible films are disclosed that include pullulan and antimicrobially effective amounts of the essential oils thymol, methyl salicylate, eucalyptol and menthol. The edible films are effective at killing the plaque-producing germs that cause dental plaque, gingivitis and bad breath. The film can also contain pharmaceutically active agents. Methods for producing the films are also disclosed.
Owner:MCNEIL PPC INC
Use of organic acids and essential oils in animal feeding
The present invention relates to a novel feed composition for animals, for example poultry, comprising as active ingredient benzoic acid, derivatives or metabolites thereof, in combination with a mixture of at least two active compounds selected from the group consisting of thymol, eugenol and piperine. The inventors found that in addition to the well known function of benzoic acid, this compound can be used as a potential growth promoter when it is combined with a mixture of at least two active compounds selected from the group consisting of thymol, eugenol and piperine. In particular the inventors have been able to demonstrate that a mixture of these chemical compounds present in different parts of plants, used in synergy and in combination with an appropriate amount of benzoic acid, exhibits, in totally unexpected manner, the effects sought by the present invention of improving the digestibility of poultry feed, i.e. for improving feed conversion ratio and / or daily weight gain in animal.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Pet food composition having enhanced palatability
InactiveUS20050112259A1Improve palatabilityInferior palatabilityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffFlavorAdditive ingredient
A food composition is provided for a companion animal such as a dog or cat, the food composition comprising an extract of a herb or spice that comprises at least one compound selected from thymol and carvacrol as a substantial flavorant ingredient. A method is provided for enhancing palatability of a food composition to a companion animal, the method comprising adding to the composition a palatability enhancing effective amount of an extract of a herb or spice that comprises at least one compound selected from thymol and carvacrol as a substantial flavorant ingredient. A suitable extract is essential oil of oregano.
Owner:HILLS PET NUTRITION INC
Bacterium-restraining deoxidization dual-purpose food antistaling agent and preparation thereof
The invention relates to an antibacterial deoxidizing double-effect food preservative, which is formed by combining a deoxidizer component with a bacteriostat component, wherein the deoxidizer component accounts for 60-90 percent, and the bacteriostat component accounts for 10-40 percent. The bacteriostat component comprises an adsorption carrier and an antibacterial solution. The adsorption carrier comprises salep, silicon dioxide, vermiculite, diatomaceous earth, zeolite, bentonite, fiber, etc. The antibacterial solution comprises one of or the composite mixture of edible alcohol and propylene glycol. Antibacterial synergist comprises allyl isothiocyanate, allicin, cinnamic aldehyde, cinnamic acid, carvacrol, eugenol, thymol, citral, etc. The antistaling agent integrates double protection functions of absorbing oxygen, sterilizing and inhibiting bacteria, which is remarkable in preservation effect and wide in application range.
Owner:GUANGDONG GUANGYI TECH IND
Antimicrobial composition
InactiveUS20140322147A1Inhibiting growth)Cosmetic preparationsBiocideAdditive ingredientDisinfectant
Disclosed herein are antimicrobial compositions and methods of producing an antimicrobial effect in which a citrus extract such as Biosecur® is used in combination with benzyl alcohol and one or more additional agent selected from the group consisting of lauroyl arginate / glyceryl laurate and essential oils or constituents thereof such as galangal oil, thyme oil, thymol, cinnamon leaf oil, cinnamon bark oil, lemongrass oil, orange oil, pine oil, cedarwood oil, curry leaf oil, and rosemary oil. These compositions may be used as natural preservatives for personal care products, foods, beverages, and as topical or surface disinfectants.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Cyclodextrins in dental products
InactiveUS6942848B2Reduce developmentReduce the populationOrganic active ingredientsCosmetic preparationsTriclosanMethyl salicylate
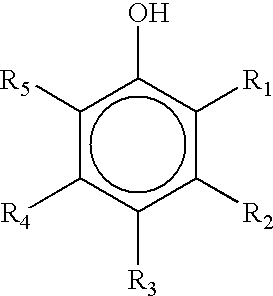
Oral rinse and dentifrice compositions, comprising a phenolic selected from the group consisting of menthol, eucalyptol, methyl salicylate, thymol, triclosan, and mixtures thereof; and a cyclodextrin selected from the group consisting of hydroxypropyl β-cyclodextrin, hydroxyethyl β-cyclodextrin, hydroxypropyl γ-cyclodextrin, hydroxyethyl γ-cyclodextrin, α-cyclodextrin, methyl β-cyclodextrin, and mixtures thereof. These compositions are useful in retarding the development of plaque, treating gingivitis, and in treating the presence of micro-organisms in the oral cavity.
Owner:MCNEIL PPC INC
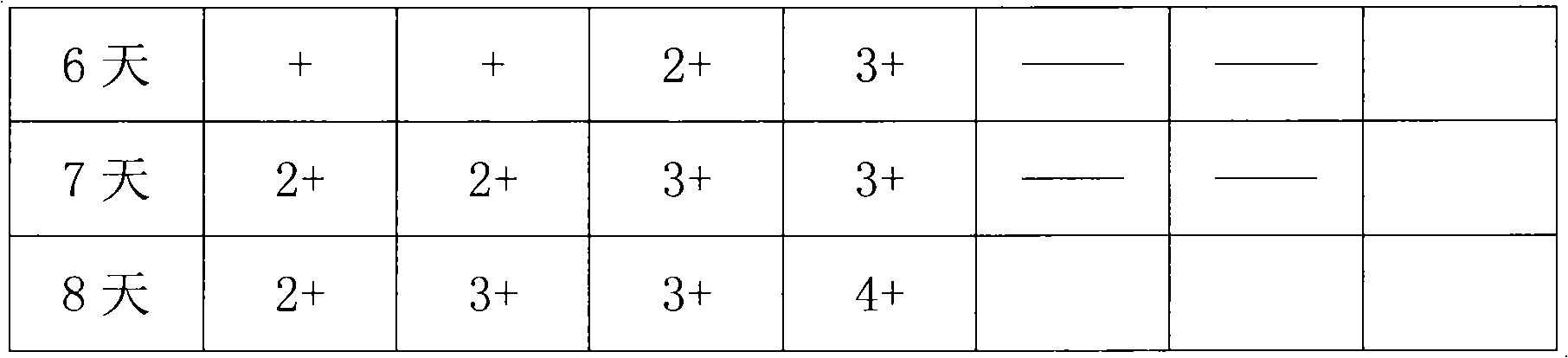
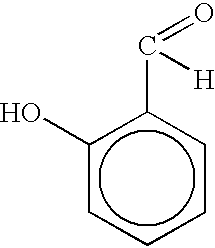
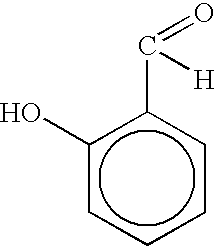
Salicylaldehyde-containing composition having antimicrobial and fragrancing properties and process for using same
InactiveUS6495512B1Alter aromaEffective amountBiocideCosmetic preparationsEscherichia coliSalicylaldehyde
Described are synergistic antimicrobial-fragrance compositions including broad spectrum antimicrobial compositions containing salicylaldehyde and at least one organoleptically-compatible antimicrobial synergism cofactor substance. The weight ratio range of salicylaldehyde:synergism cofactors substance is from 1:10 up to 10:1. The cofactor substance is such that the degree of synergism of the resultant mixture is defined according to the IFF Antimicrobial Synergism Test wherein the difference between the actual and expected antimicrobial values of the mixture is greater than or equal to a multiple of (i) 0.05 and (ii) the expected antimicrobial value of the mixture. Cofactor substances include phenolics such as cresol, caravacrol and thymol; ethyl vanillin; benzyl alcohol; indol; beta-orcinol; and terpinenol-4. Microorganisms against which the synergistic compositions are effective include:Escherichia coli;Enterococcus hirae;Pseudomonas aeruginosa;Staphylococcus aureus; andSaccharomyces cerevisae.The compositions have application in all-purpose cleaning compositions, gel-type toilet rim articles, liquid-type toilet rim articles, personal shower cleaning compositions, and body and hair care products including shower gel compositions, shampoo compositions and foam bath compositions.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES +2
Strength enhancers and method of achieving strength enhancement in an electronic vapor device
InactiveUS20170172204A1Increasing harshnessDesirable balanceTobacco treatmentTobacco devicesGrapefruit oilCayenne pepper
A pre-vaporization formulation pre-vaporization formulation for an e-vaping device, the pre-vaporization formulation including a vapor former including a combination of propylene glycol and glycerol, and an additive including at least one of capsicum, allyl isothiocyanate, piperine, isoeugenol, carvacrol, thymol, menthol, monomenthyl succinate, N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-2,3-dimethyl-2-isopropyl butanamide, horseradish oil, garlic extract, onion oil, black pepper, cayenne pepper, ginger oil, thyme oil, cinnamon bark oil, turmeric, fenugreek, cardamom, rosemary extract, grapefruit oil and andrographis extract.
Owner:AKRIA CLIENT SERVICES LLC
Bactericidal preparation
InactiveUS20040014818A1Aving "antibiotic" effectivenessAntibacterial agentsBiocideMethyl benzeneButylated hydroxytoluene
A bactericidal preparation in the form of a solution, cream or ointment is disclosed. The preparation comprises a liquid compounded from photosynthesized hydrocarbons, isolates from hydrocarbons, 2-hydroxy-1-isopropyl-4-methyl-benzene (thymol) and butylated hydroxytoluene.
Owner:BOECK BETTY +1
Pest control using natural pest control agent blends
ActiveUS20110135764A1Increase volumeBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsMethyl salicylateBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Embodiments of the invention relate to a composition for controlling a target pest, wherein the composition includes at least two active ingredients selected from the group consisting of thymyl acetate, linalyl acetate, amyl butyrate, anise star oil, black seed oil, p-cymene, geraniol, isopropyl myristate, d-limonene, linalool, lilac flower oil, methyl salicylate, alpha-pinene, piperonal, piperonyl alcohol, tetrahydrolinalool, thyme oil white, thyme oil red, thymol, vanillin, and winter-green oil, wherein the composition causes synergistic control of the target pest.
Owner:TYRATECH +1
Analgesic and refreshing herbal composition and a process for preparing the same
The invention provides an analgesic and refreshing herbal composition useful as dentrifrices, said composition comprising 50-60% Wt. of betle extract (from Piper betle leaves); 40-50% Wt. of one or more group I essential oil selected from Levender officinal, Dementholised oil (ex-Mentha arvensis), Fennel oil and Ocimum gratissimum; 3.5-6% Wt. of one or more group II essential oils and their isolates selected from Ocimum Sanctum, Pulegone (ex Mentha pulegonium), Carvone (ex. Dill seed) and Menthol (ex. Mentha arvensis); 1-5% Wt. of one or more group III essential oils selected from Camphor, turpentine oil, Cedarwood oil and Safrole oil, along with 0.5-2% Wt. of Thymol and 0.25-1% Wt. of preservative / antioxidant, and a process for preparing the composition.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Antibacterial soap-based shower gel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104800123AImprove antibacterial propertiesGood moisturizing effectCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsShower gelGlycerol
The invention discloses an antibacterial soap-based shower gel and a preparation method thereof. The shower gel comprises the following ingredients: thymol, salicylic acid, plants extracts, ethyl alcohol, propylene glycol, erythritol, lauric acid, myristic acid, palmitic acid, potassium hydroxide, glycol distearate, dihexyl sodium sulfosuccinate, cocamidopropyl betaine, sodium cocoyl glycinate, polyquaternium-7, polyglyceryl fatty acid ester composition, ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid tetrasodium, sodium chloride, citric acid, essence, a preservative and water. The antibacterial soap-based shower gel is soft and friendly to skin, can effectively resist bacteria and moisturize skin and is particularly applicable to people with thicker cuticle, high grease secretion, skin pruritus and tinea corporis.
Owner:WALCH GUANGZHOU COMMODITY
Antimicrobial therapeutic compositions and method of use
InactiveUS6921539B2Enhanced broad based antimicrobial activityEasy to useBiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsMicroorganismProcaine
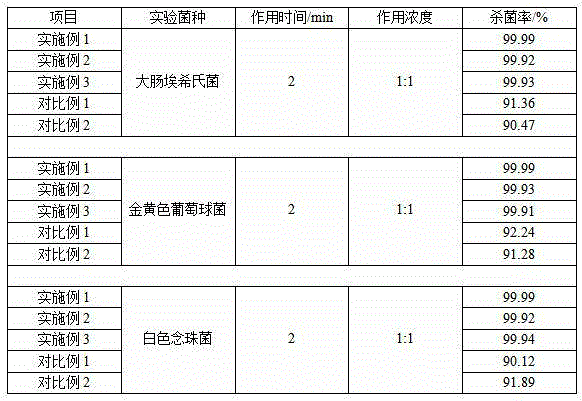
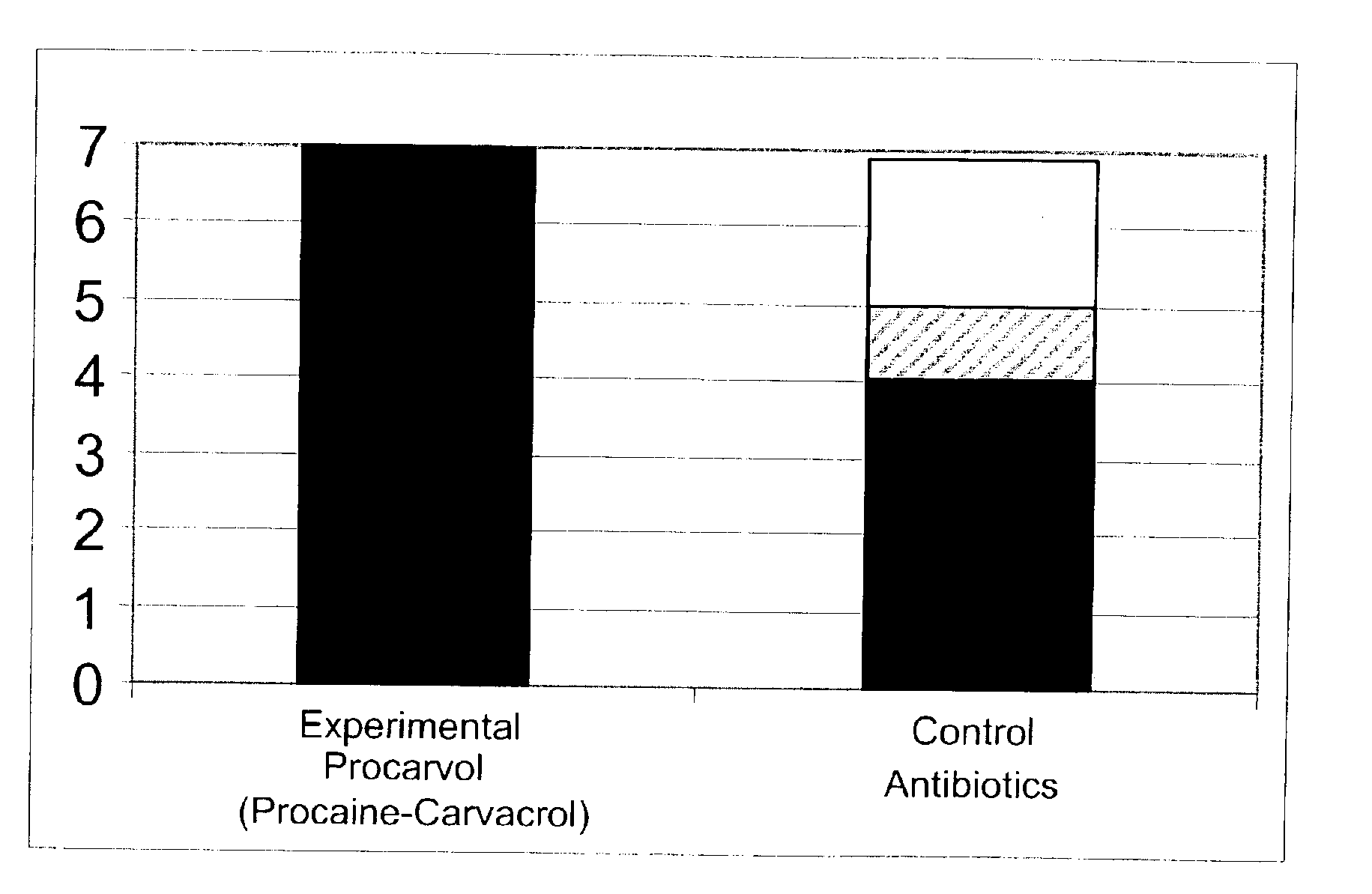
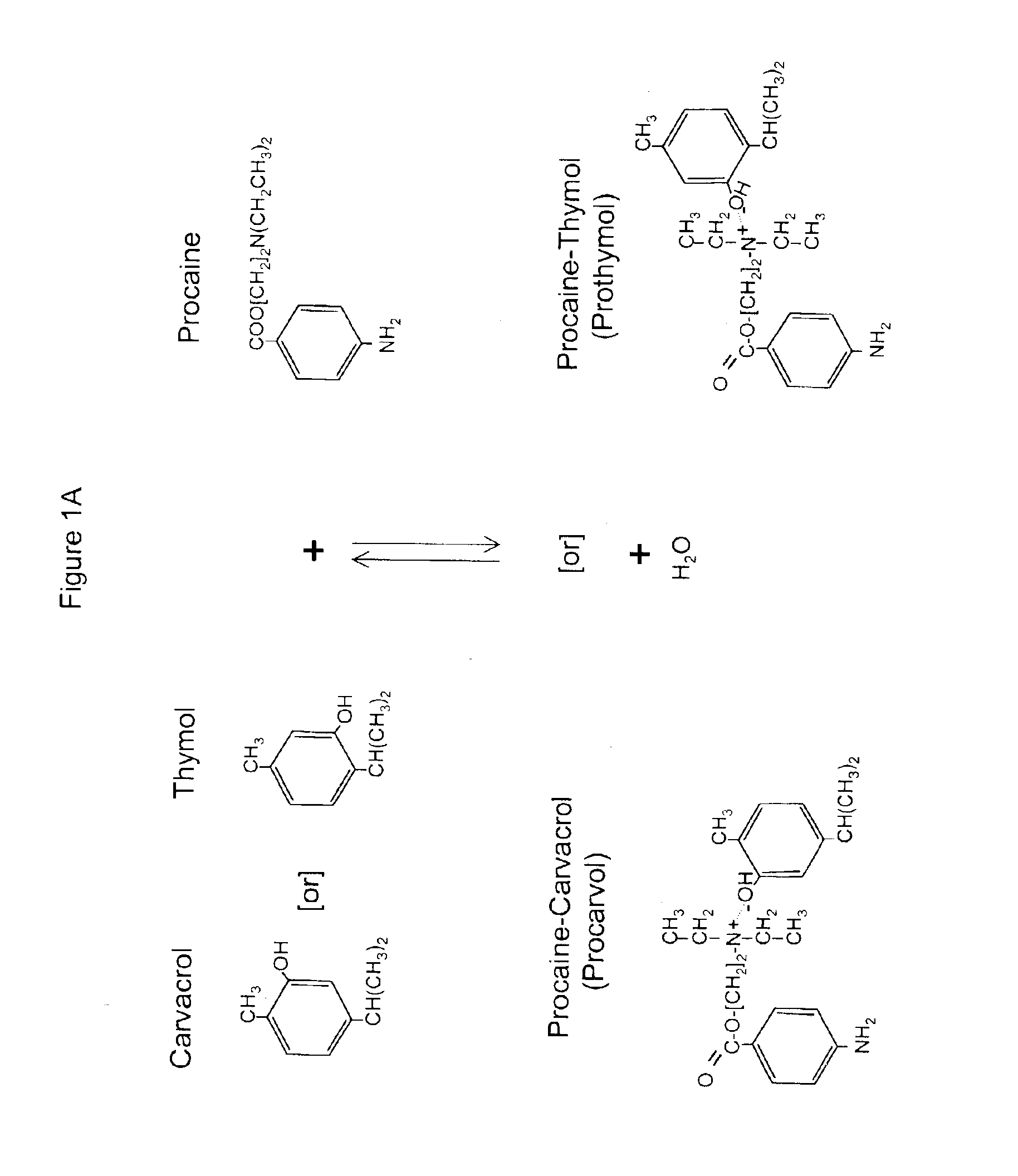
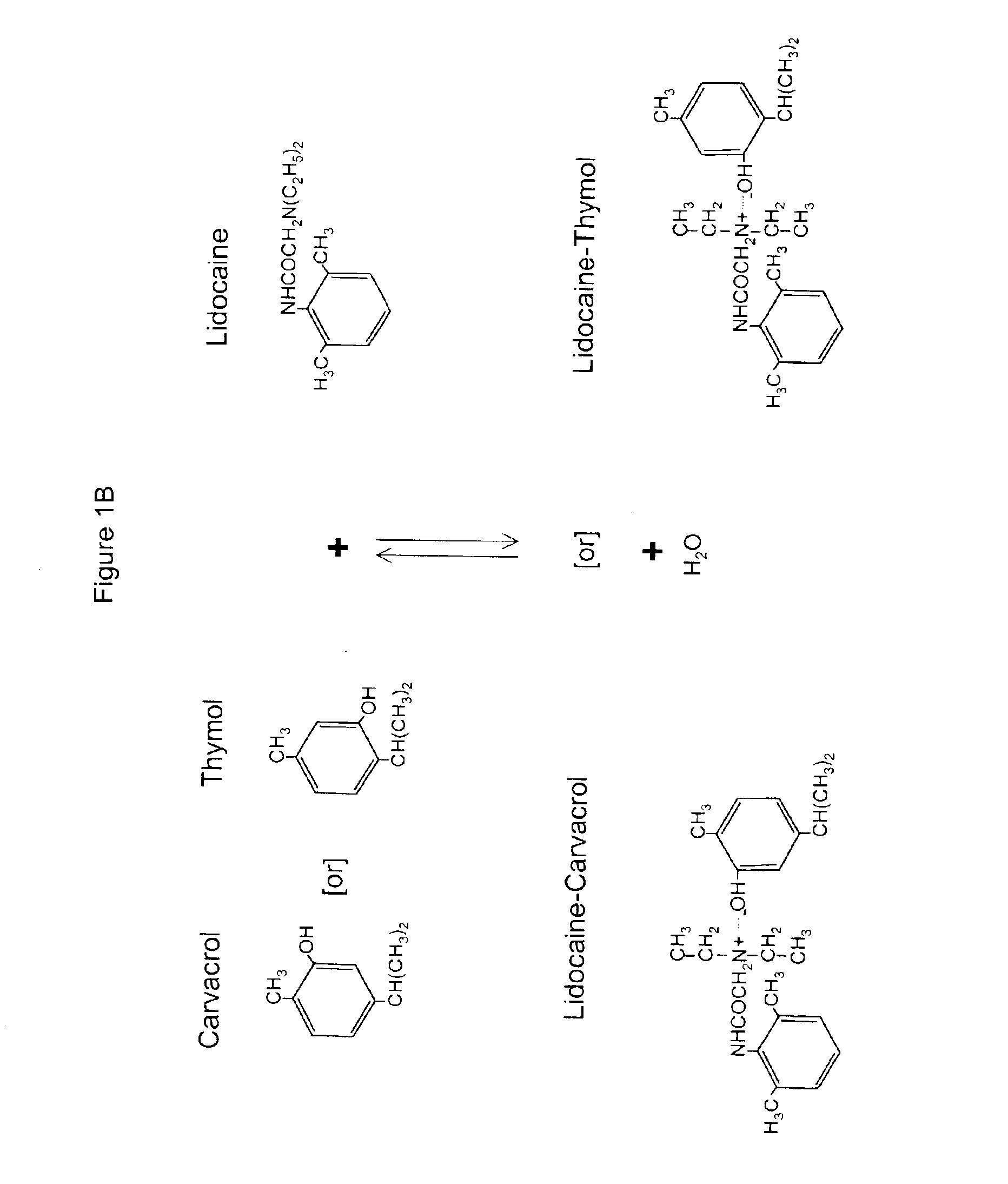
The invention provides therapeutic antimicrobial compositions and methods for their use based on natural organic phenolic compounds combined with pharmacological agents. The antimicrobial activities of each carvacrol and thymol are believed to be enhanced, while the pharmacological properties of procaine and related compounds are added to provide their unique properties to facilitate usefulness and effectiveness in humans. The therapeutic compositions are active against bacterial, fungal, and protozoan infections. The forms of the invention are intended to treat various internal infections through parenteral, subcutaneous, intradermal, intravenous, and intramuscular injections. They are also intended as useful agents to treat microbial infections that have become resistant to conventional anitibiotics as well as secondary opportunistic infections.
Owner:EUROVLOOT +2
Coccidiosis and clostridial disease prophylactic and/or therapeutic feed for coccidiosis and clostridial disease
InactiveUS20080160000A1Decrease in breeding yieldDeterioration in productivity caused by coccidiosis or clostridial disease can be preventedAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseTreatment effect
There is provided an animal feed, an anticoccidial agent, and an anticlostridial agent having less harm and an excellent prophylactic and / or therapeutic effect for coccidiosis and clostridial disease. Also provided is a prophylactic and / or therapeutic feed for coccidiosis containing pinene, thymol, eugenol, and limonene; an anticoccidial agent containing pinene, thymol, eugenol, and limonene as active ingredients; a clostridial disease prophylactic and / or therapeutic feed containing pinene, thymol, eugenol, and limonene; and an anticlostridial agent containing pinene, thymol, eugenol, and limonene as active ingredients.
Owner:MARUBENI NISSHIN FEED CO LTD
Pesticidal compounds and compositions
InactiveUS6844369B2Growth inhibitionReduce in quantityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideNatural sourceChemistry
Owner:VAN BEEK NATURAL SCI LLC
Feed supplements for ruminants including essential oil compounds and organic acids
InactiveUS20080032021A1Improve palatabilityImprove scalabilityAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsOrganic acidAdditive ingredient
A livestock and poultry feed additive composition includes at least one essential oil derived from at least one of an herb and a spice and containing thymol and carvacrol as its main ingredients, at least one organic acid derived from at least one of citric, fumaric, fulvic and humic acid and an organic pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The total amount of the essential oil in the composition is present in an amount between five percent and forty percent (5% and 40%) by weight of the composition, the total amount of the organic acid in the composition is present in an amount between fifty percent and eighty-five percent (50% and 85%) of the composition by weight and the remainder of the composition consists of the organic pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:FALTYS GARY L +1
Thymol mite-killing microemulsion and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101601382AEffective controlIncrease contactBiocideAnimal repellantsTetranychus pierceiEmulsion
The invention discloses a thymol mite-killing microemulsion and a preparation method thereof. The microemulsion comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 5 to 25 percent of thymol, 10 to 20 percent of solvent, 10 to 20 percent of emulsion, 0.5 to 3 percent of stabilizer, and 1 to 5 percent of antifreeze agent, and the balance of water. The microemulsion has broad spectrum of killing mites, can effectively prevent and control various agricultural pest mites, such as Tetranychus cinnabarinus, Tetranychus piercei McGregor, Oligonychus biharensis and the like, and is safe and low in toxicity. The microemulsion has simple production process, easy preparation and low cost.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Method and compositions for treatment of fungal nail disease
Compositions for the treatment of fungal nail disease (onychomycosis), including camphor, menthol, eucalyptus and thymol are described. The ingredients are natural and very effective in treating the nail fungus.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Antiperspirant compositions
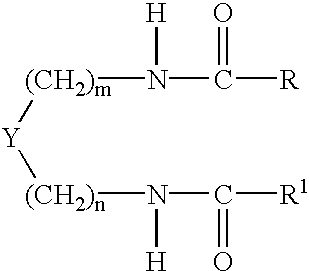
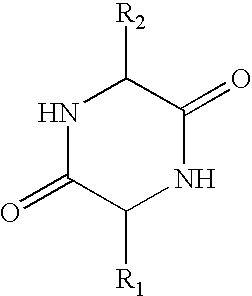
Clear solid suspension antiperspirant compositions comprise 0.5 to 50% by weight of a particulate antiperspirant active material of which less than 50% by weight of its particles are below 110pm diameter and a refractive index of from 1.49 to 1.57 at 22° C. is suspended in a water-immiscible carrier liquid of which at least 50% by weight is selected from liquid non-volatile silicone oils and liquid alkyl-aryl esters and not more than 25% by weight of the carrier liquid comprises a volatile silicone oil. The carrier liquid and the antiperspirant have refractive indexes which differ by no more than 0.02 at 22° C and the structurant which solidifies the carrier liquid comprises a fibre-forming non-polymeric structurant, and preferably an N-acyl aminoacid amide such as GPl and / or a cyclodipeptide such as a thymol derivative of (2S-cis)-(-)-5-benzyl-3,6-dioxo-2-piperazine acetic acid.
Owner:UNILEVER HOME & PERSONAL CARE USA DIV OF CONOPCO IN C
Plant essential oil composition for fumigating and killing grain aspergillus flavus
InactiveCN102144666AKilling excellentInhibition excellentSeed preservation using chemicalsBiotechnologySalicylaldehyde
The invention discloses a plant essential oil composition for fumigating and killing grain aspergillus flavus. The composition is prepared by utilizing plant or plant essential oil containing cinnamic aldehyde, citral, thymol and salicylaldehyde or by utilizing synthetic identical materials, wherein the parts by weight of the four components in the composition are respectively as follows: 5-20 parts of cinnamic aldehyde, 15-35 parts of citral, 35-60 parts of thymol and 10-35 parts of salicylaldehyde. The composition has the advantages that: the drawing materials are natural, safe and non-toxic; and the volatile essential oil components are easy to diffuse; and the gas of the volatile essential oil is used for fumigating and killing to ensure that the composition needs not be in direct contact with grains and only needs to be put at a corner of a warehouse or a closed container to play a role in efficiently killing the grain aspergillus flavus.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Spicy spice for kretek blasting bead, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104804871ACover up bad breathMake up for distortionTobacco treatmentEssential-oils/perfumesIsoeugenolGuaiacol
The invention provides a spicy spice for a kretek blasting bead, a preparation method and application thereof. The spicy spice is characterized in that the spicy spice is prepared by mixing the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 2 to 5 percent of clove bud oil, 0.5 to 1 percent of eugenol, 0.01 to 0.03 percent of thymol, 0.2 to 0.8 percent of beta-caryophyllene, 0.2 to 0.8 percent of guaiacol, 0.5 to 1 percent of isoeugenol, 0.1 to 0.5 percent of vanillin, 0.5 to 1 percent of benzyl alcohol, and the balance of a solvent. The spicy spice can not only cover adverse chemical smell produced by wall materials and package solvent when the kretek blasting bead is pinched, but also provide spicy fragrance coordinated with the fragrance of the tobacco, makes up the situation of distortion of clove fragrance during burning of the kretek, and enables the kretek to have conformable and natural spicy fragrance.
Owner:HUBEI CHINA TOBACCO IND +2
Additives for animal food
InactiveUS20140037698A1Improving productive parameterReduce morbidityAntibacterial agentsBiocideStimulantBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The present invention relates to the combination of organic acid salts with at least one active ingredient of plant origin, preferably essential oils, partially protected with vegetable fats and / or oils, which prevent these active ingredients from being digested by stomach enzymes during the digestive process. The sodium salts of short-chain acids, preferably salts of butyric, acid are preferred. The preferred essential oils are ginger, piperine, oregano, garlic, thymol, carvacrol, cinnamaldehyde and / or any combinations thereof. The combination of organic acid salts and the essential oils protected with vegetable fats and / or oils, are used as powerful promoters or stimulants for animal growth, as organic bactericides against pathogenic bacteria present in said animals and as modulators of immune response thereof.
Owner:NOREL
Alcohol-free slightly-alcoholic oral care composition and a process for preparing same
InactiveUS20130224125A1Extends antimicrobial efficacy of coatingImprove efficacyCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAlcohol freeWater insoluble
An aqueous, heat and cold stable, non-alcoholic or slightly-alcoholic microemulsion based antimicrobial mouthwash composition with improved antimicrobial efficacy. The composition comprises a unique water-soluble matrix composite, at least one water-immiscible or water-insoluble antimicrobial agent, and optionally, a preservative or preservative system, a weak carboxylic acid, a coloring agent and other additives. Examples of antimicrobial agents include menthol, thymol, eucalyptol and / or methyl salicylate. A process for preparing the oral care composition is also disclosed.
Owner:ISP INVESTMENTS INC
Wipe Coated with a Botanical Emulsion having Antimicrobial Properties
An oil-in-water emulsion that is environmentally friendly and also exhibits antimicrobial activity is provided. More specifically, the oil phase of the emulsion includes a botanical oil derived from a plant (e.g., thymol, carvacrol, etc.). Because the botanical oil tends to leach out of the emulsion during storage and before it is used in the desired application, a water-dispersible polymer is also employed in the aqueous phase of the emulsion to enhance long term stability of the oil and, in turn, antimicrobial efficacy. Without intending to be limited by theory, it is believed that the water-dispersible polymer can effectively encapsulate the botanical oil within the emulsion and inhibit its premature release. Once the emulsion is formed, water can then be removed so that it becomes a substantially anhydrous concentrate. In this manner, the water-dispersible polymer will not generally disperse before use and prematurely release the botanical oil. When it is desired, moisture may simply be re-applied to the concentrate to disperse the polymer and activate the release of the botanical oil. Of course, to provide the optimum degree of biocompatibility, the water-dispersible polymer is also a “biopolymer” that is biodegradable and / or renewable.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Taste masking of phenolics using citrus flavors
InactiveUS6235267B1Inhibit harshnessReduce developmentCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsTriclosanAdditive ingredient
An oral rinse, dentifrice, or oral gel composition comprising:a) about 0.01 weight % to about 5 weight % of a citrus flavor, citrus flavor ingredient, or mixtures thereof;b) about 0.01 weight % to about 5 weight % of a phenolic, said phenolic selected from the group consisting of menthol, eucalyptol, methyl salicylate, thymol, triclosan, and mixtures thereof; andc) an orally acceptable carrier.The claimed composition is useful in retarding the development of plaque, treating gingivitis, and reducing the viable population of micro-organisms in the oral cavity of a mammal.
Owner:MCNEIL PPC INC
Chemical composition and method for cold and sinus relief
InactiveUS20060210482A1Safe and effective reliefSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideSinusitisNasal passage
A chemical composition and method for treatment of the common cold, sinusitis and other conditions associated with nasal congestion is provided. The chemical composition is made of predetermined concentrations of thymol, alcohol, eucalyptol, menthol, methyl salicylate, a preservative, saline solution and a buffer. The method includes the step of administering the chemical composition of the invention via either intranasal instillation, oral inhalation or intermittent positive pressure breathing. Administration of the chemical composition via the method of the invention clears the nasal passages and alleviates the symptoms of the common cold, sinusitis, and related conditions.
Owner:CASSARA JOHN
Reduction of odor gases from waste using plant-derived oils
InactiveUS6902726B1Reduce productionPromoting lactic acid accumulationOrganic chemistryMicroorganismsVolatile fatty acidsAnaerobic bacteria
Plant-derived oils, carvacrol and thymol, when added to human or animal waste reduce the production of gas and short-chain volatile fatty acids, and the viability of total anaerobic bacteria and fecal coliforms. In an embodiment, carvacrol or thymol are combined with eugenol.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
Method of preparing thymol
InactiveCN101402551ASolution to short lifeGood choiceOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationReaction temperatureFixed bed
The invention provides a method for preparing thymol at normal pressure. The method adopts resordinol and isopropanol as raw materials, and the reaction is carried out in a fixed bed reactor, and a catalyst is filled into the reactor. The method is characterized in that the mol ratio of resordinol to isopropanol is between 1:1 and 1:6; the reaction temperature is between 200 and 350 DEG C; the reaction time is 4 to 7 hours; the reaction is carried out at the normal pressure; and the reactants are in a gas state, and the carrier gas is inert gas not taking part in the reaction. The catalyst is Gamma-Al2O3 which undergoes the following process: stirring and soaking Gamma-Al2O3 in sulphuric acid; filtrating, drying and roasting the Gamma-Al2O3; and then carrying out cooling, tabletting and sieving on the Gamma-Al2O3 to take 100 to 80 meshes of finished product for standby. The method solves the defects in the prior art, and has the characteristics that the reaction conditions are easily satisfied; and the reaction can be carried out at the normal pressure, and the method has little byproducts, good selectivity, long service life of the catalyst, and the like. The method has higher use value.
Owner:广东省石油化工研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com