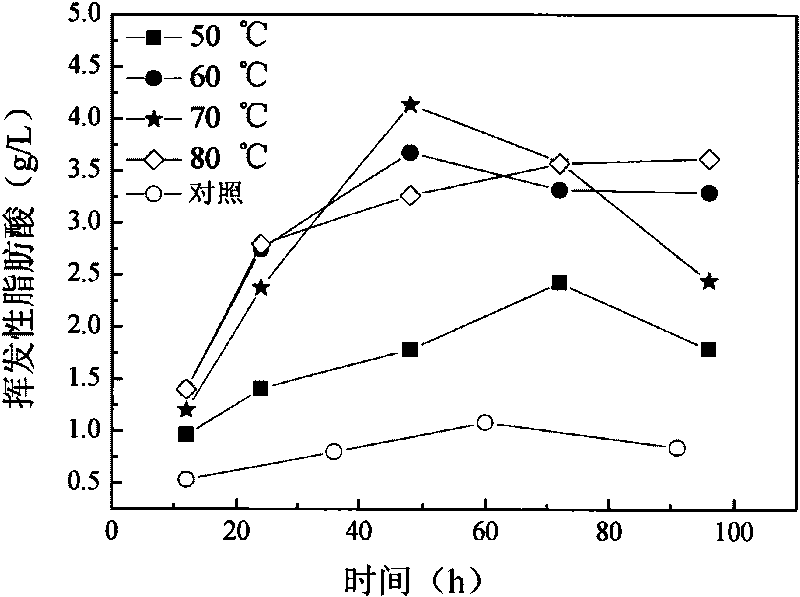
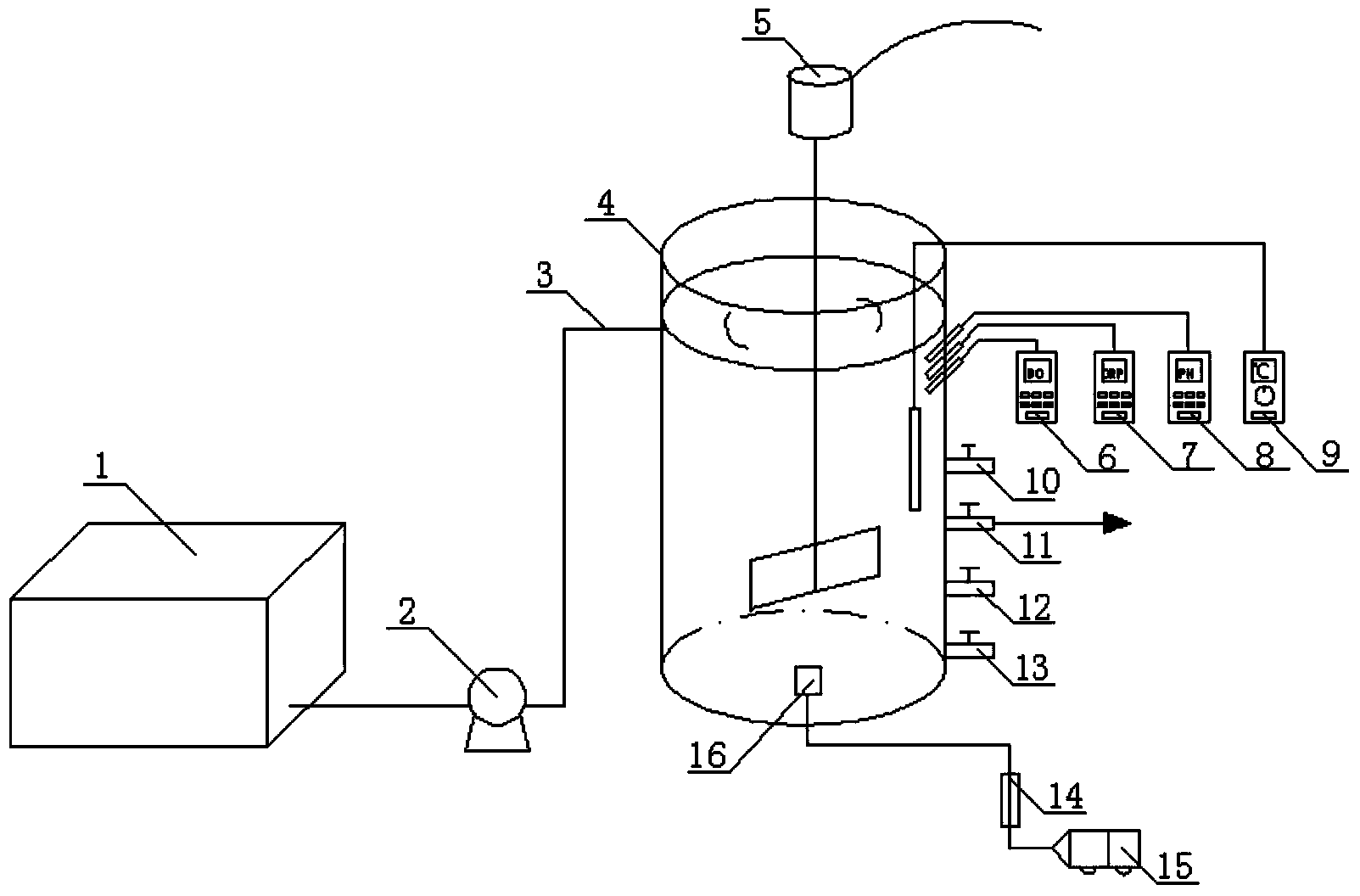
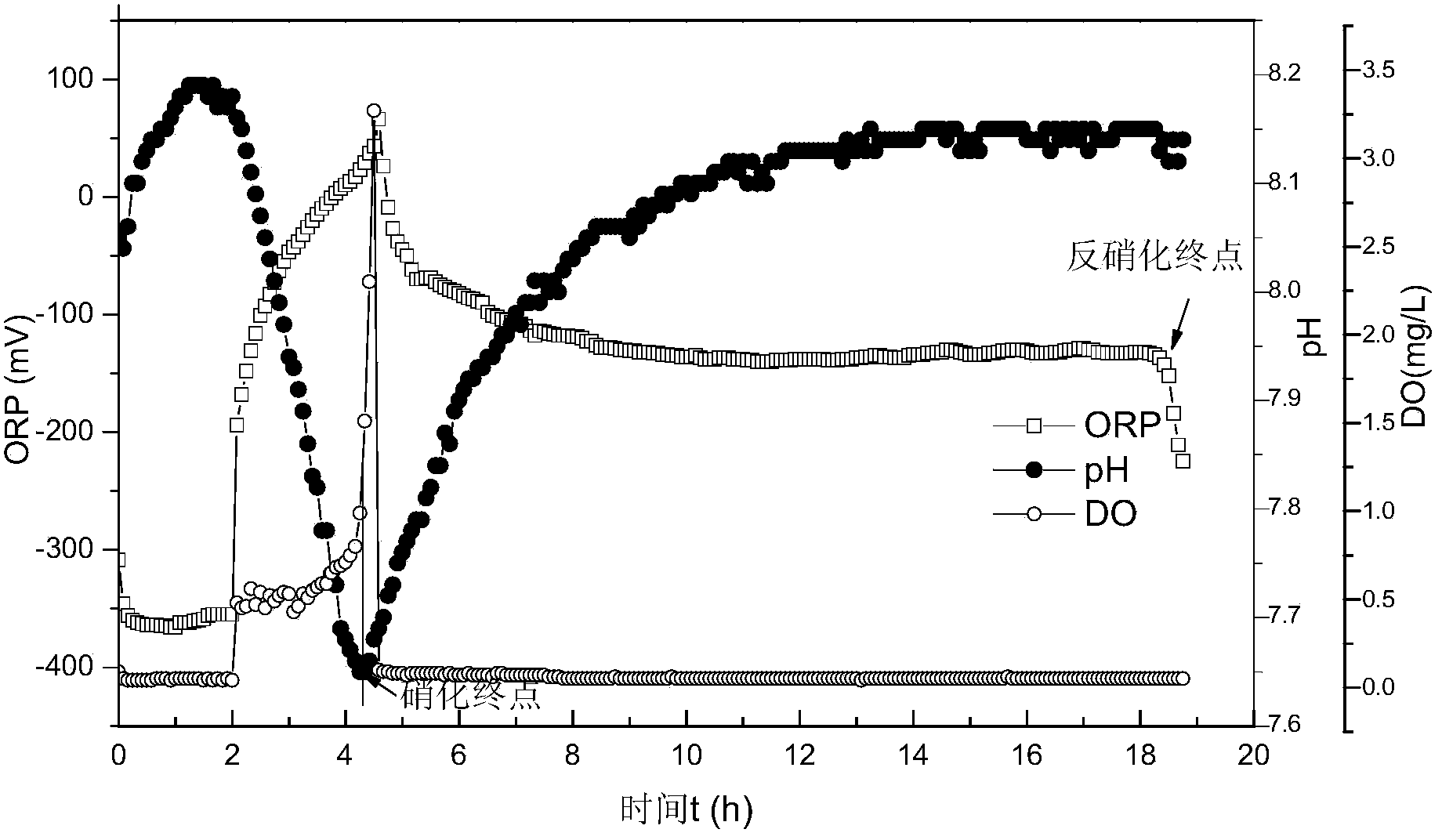
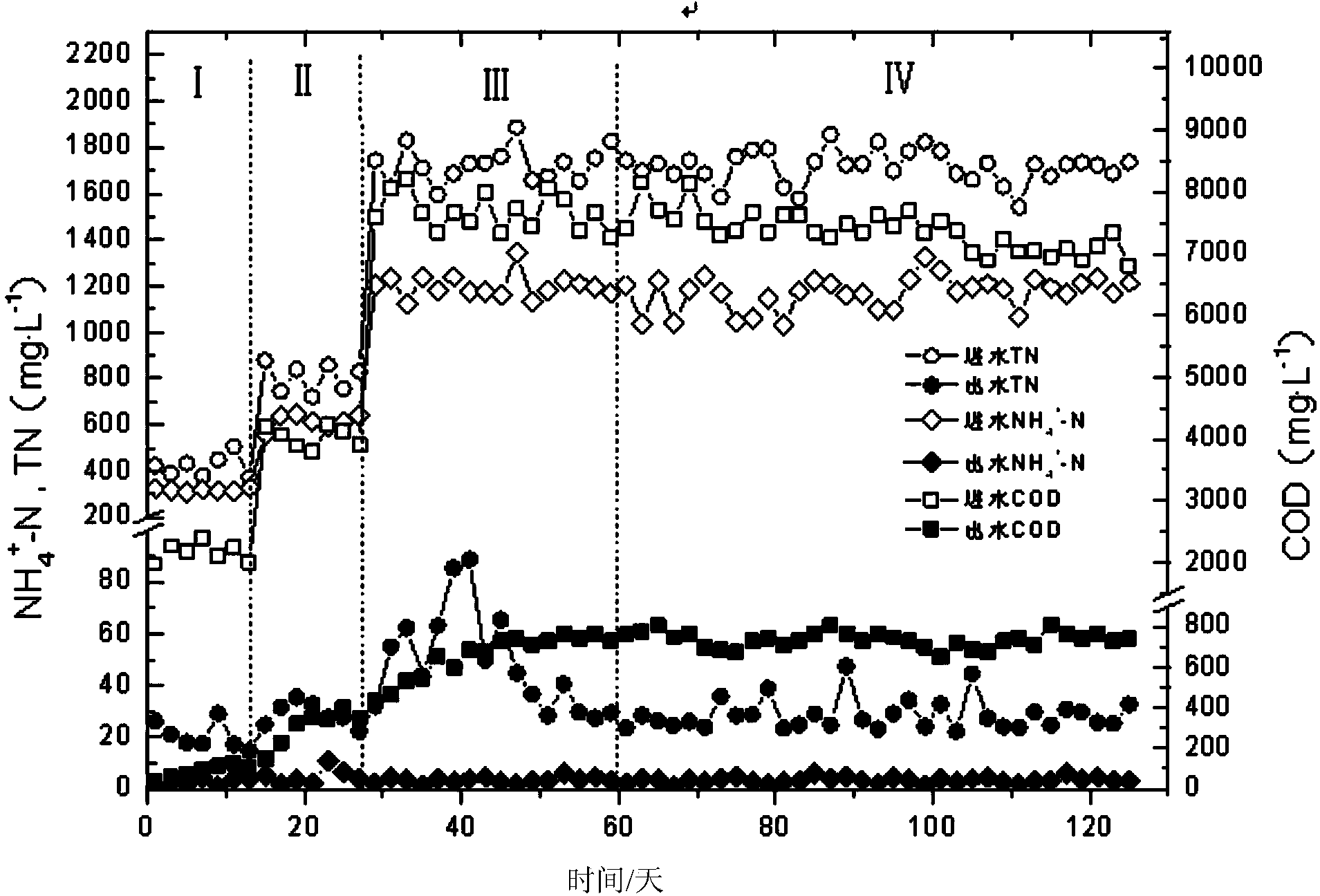
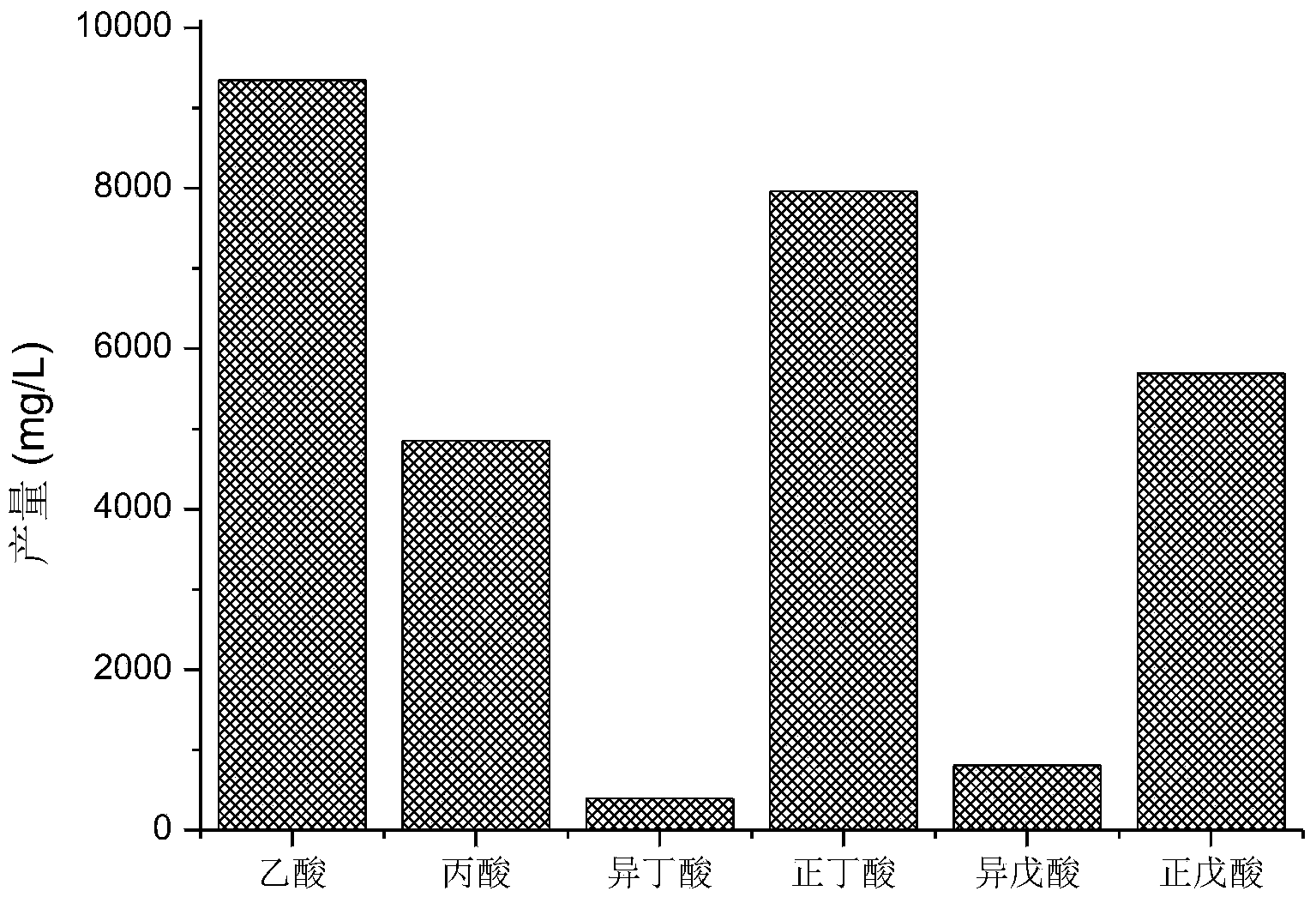Patents
Literature
412 results about "Volatile fatty acids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
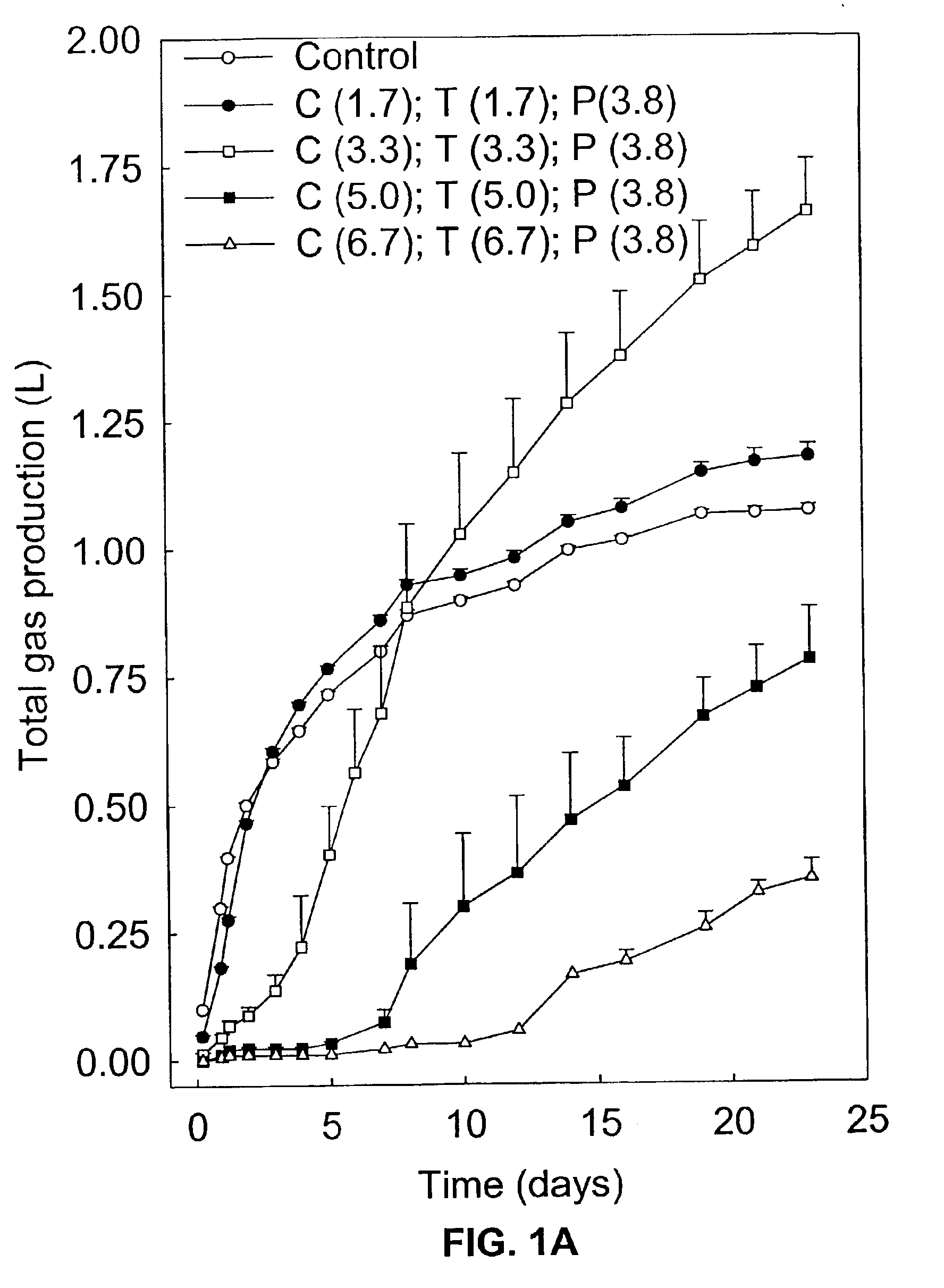
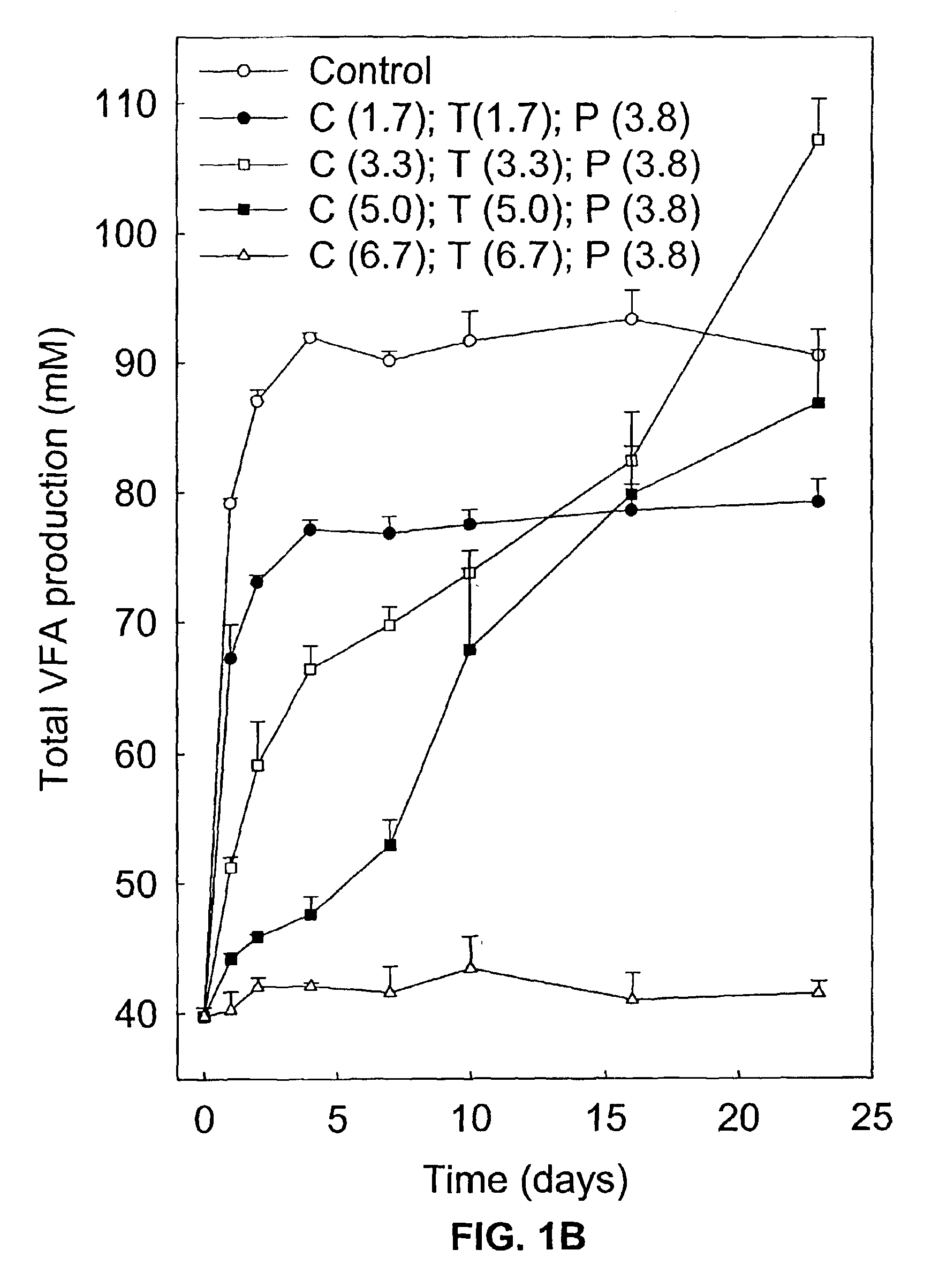
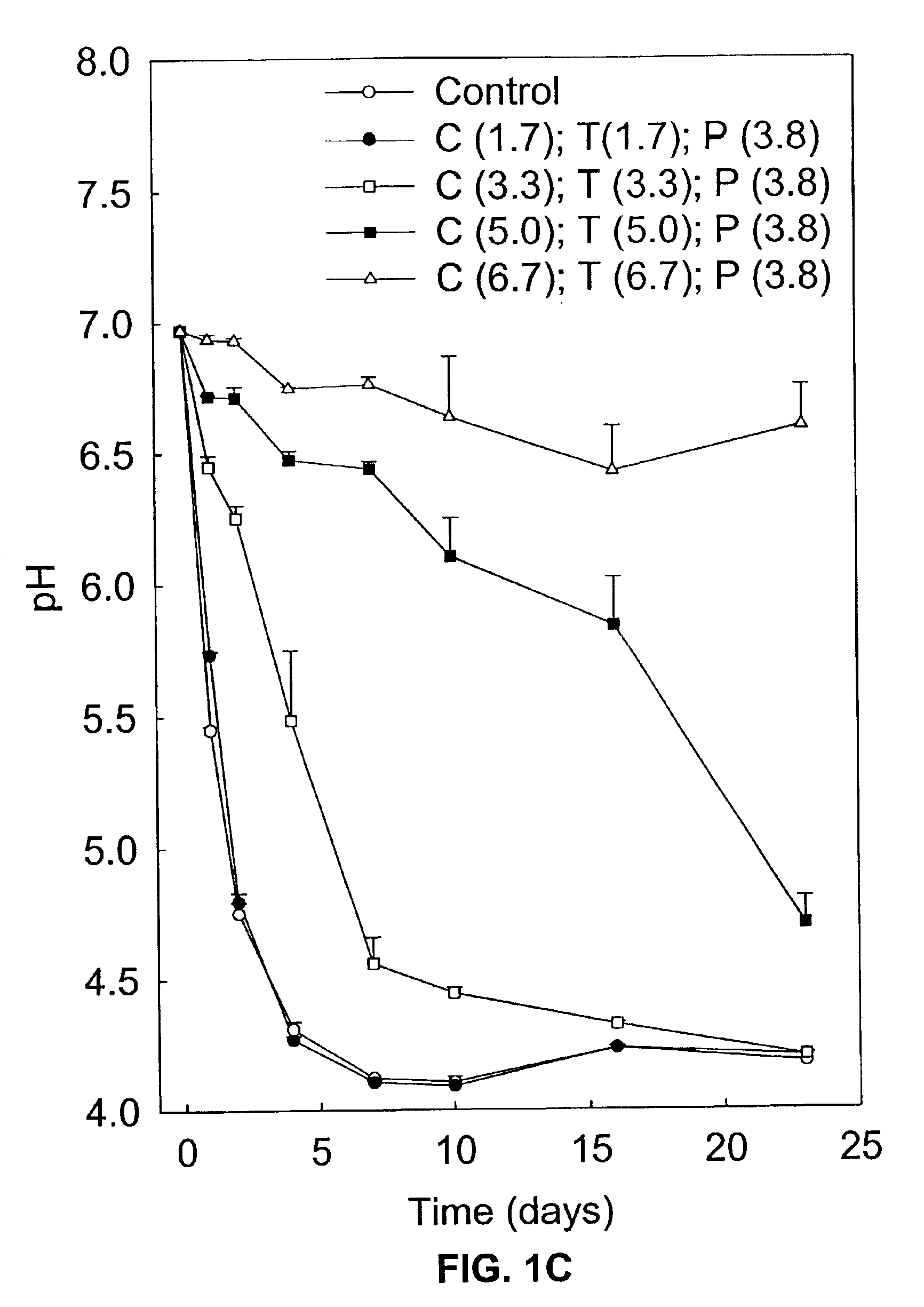
Volatile fatty acids are fatty acids with a carbon chain of six carbons or fewer. They are now usually referred to as short-chain fatty acids. ex. acetic acid, propionic acid or butyric acid They can be created through fermentation in the intestine. Examples include: Acetic acid Propanoic acid Butyric acid
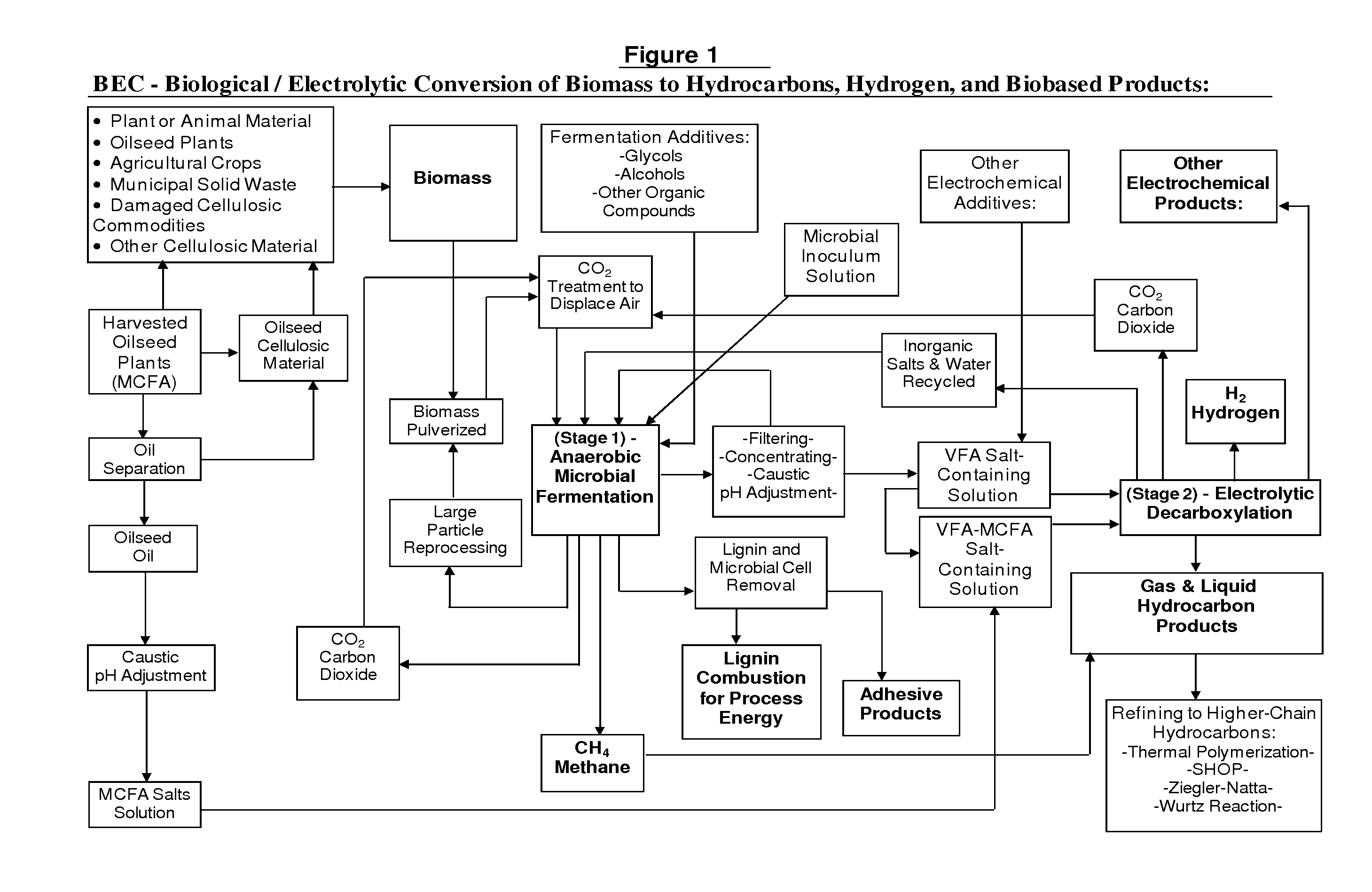
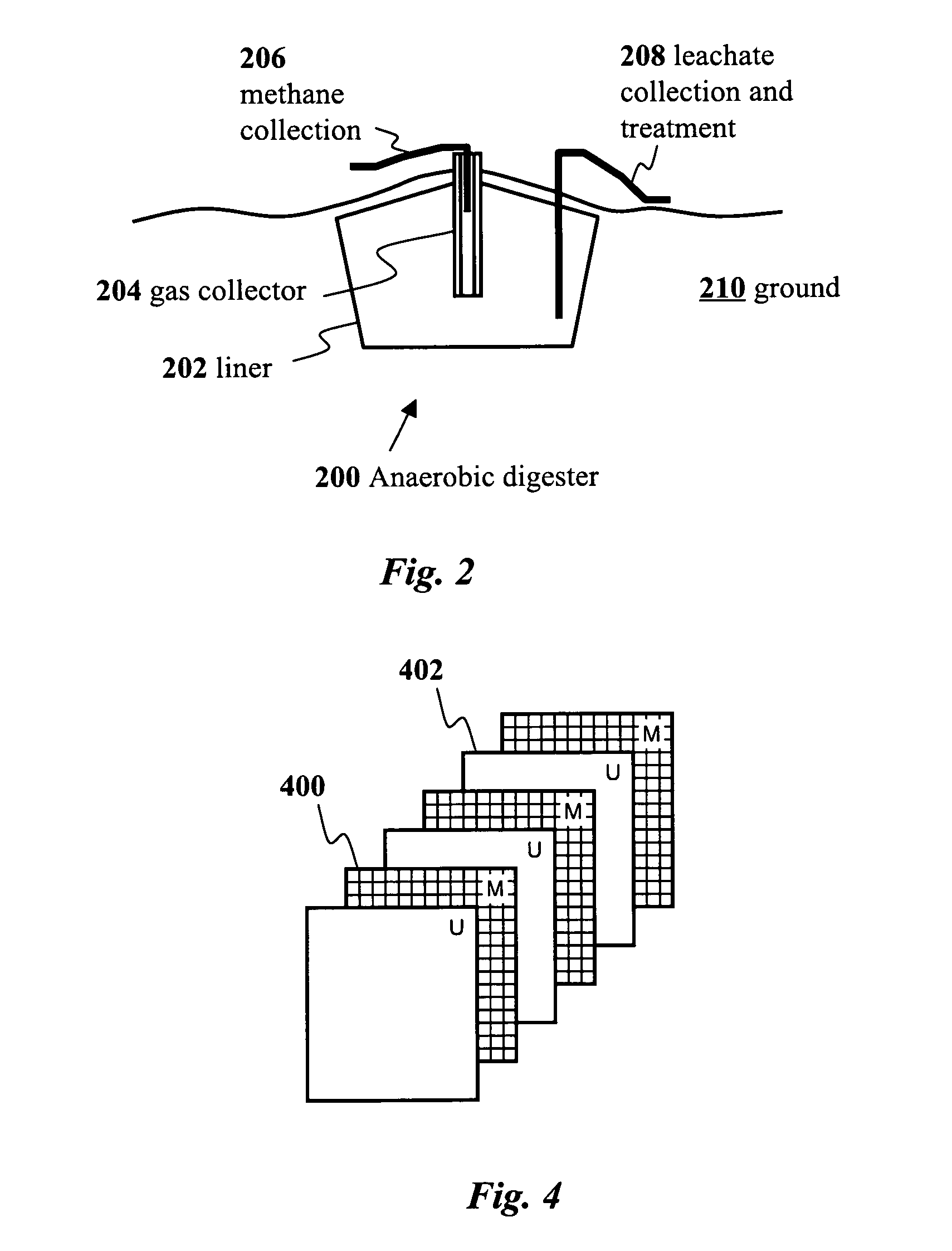
Biological/Electrolytic Conversion of Biomass to Hydrocarbons
ActiveUS20110111475A1Eliminate needInexpensive solutionElectrolysis componentsBacteriaElectrolysisSufficient time
Hydrocarbon and hydrogen fuels and other products may be produced by a process employing a combination of fermentation and electrochemical stages. In the process, a biomass contained within a fermentation medium is fermented with an inoculum comprising a mixed culture of microorganisms derived the rumen contents of a rumen-containing animal. This inoculated medium is incubated under anaerobic conditions and for a sufficient time to produce volatile fatty acids. The resultant volatile fatty acids are then subjected to electrolysis under conditions effective to convert said volatile fatty acids to hydrocarbons and hydrogen simultaneously. The process can convert a wide range of biomass materials to a wide range of volatile fatty acid chain lengths and can convert these into a wide range of biobased fuels and biobased products.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Process for enhanced recovery of crude oil from oil wells using novel microbial consortium
InactiveUS20070092930A1Enhanced Oil RecoveryEnhanced overall recoveryBacteriaWaste based fuelBiotechnologyAlcohol
The present invention provides a microbial consortium containing three hyperthermophilic, barophilic, acidogenic, anaerobic bacterial strains for enhanced oil recovery from oil reservoirs where temperatures range from 70° C. to 90√ C. The said microbial consortium is unique in producing a variety of metabolic products mainly CO2, methane, biosurfactant, volatile fatty acids and alcohols in the presence of specially designed nutrient medium. These metabolic products increase sweep efficiency of crude oil from oil bearing poles of rock formation. The present invention also provides a process for enhancing the oil recovery by in situ application of the said microbial consortium.
Owner:INSTITUE OF RESERVOIR STUDIES +1
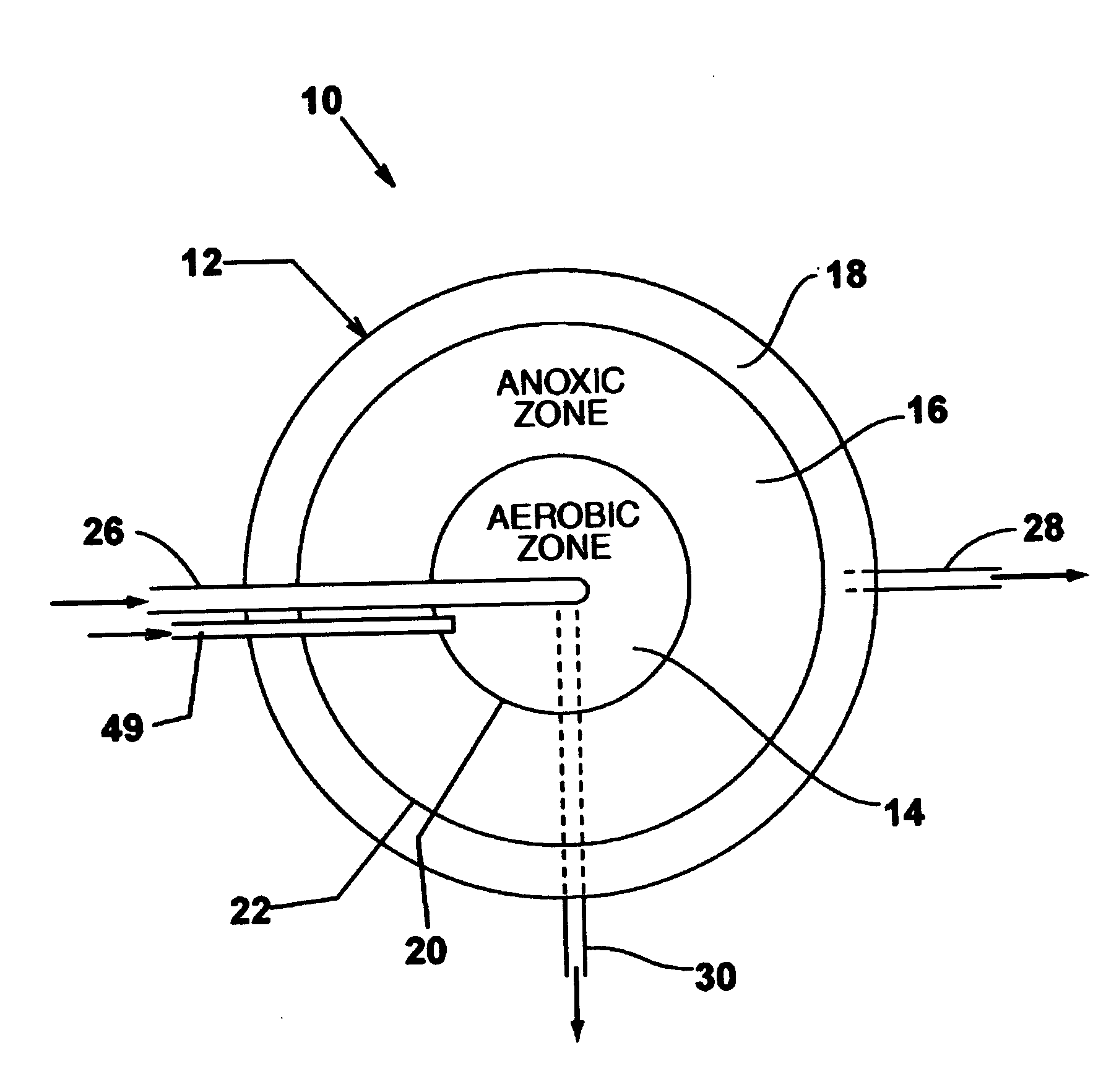
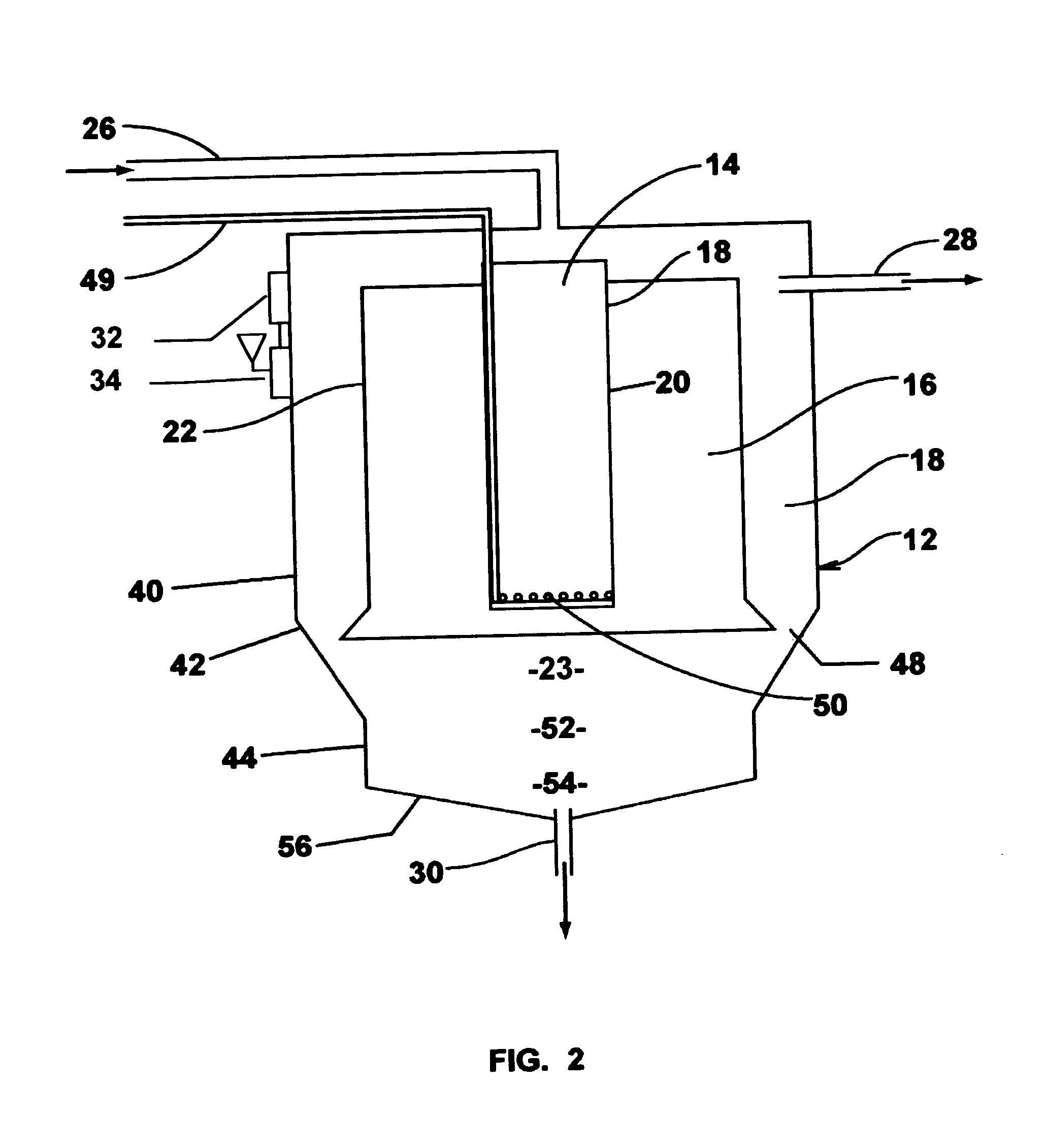
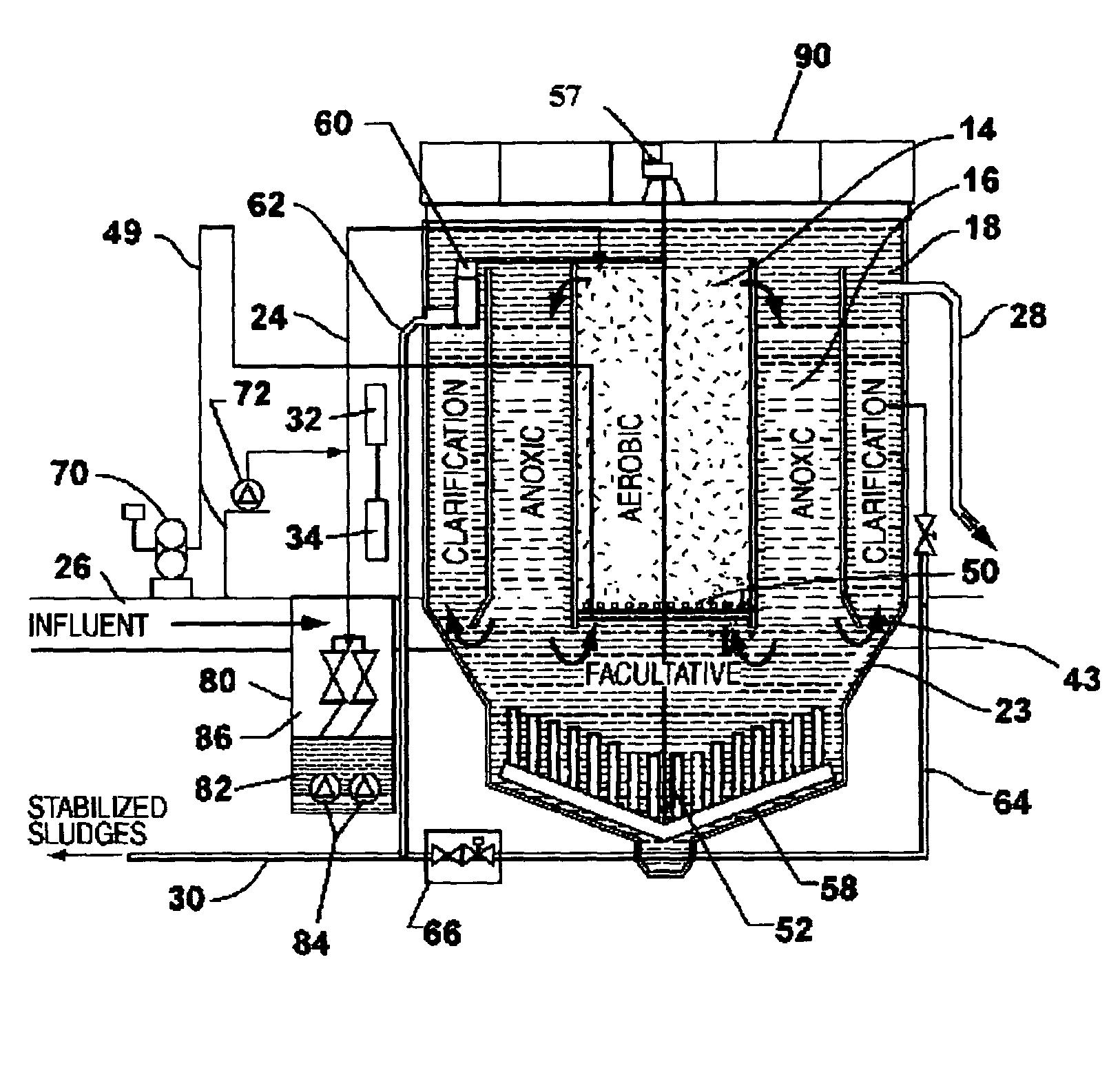
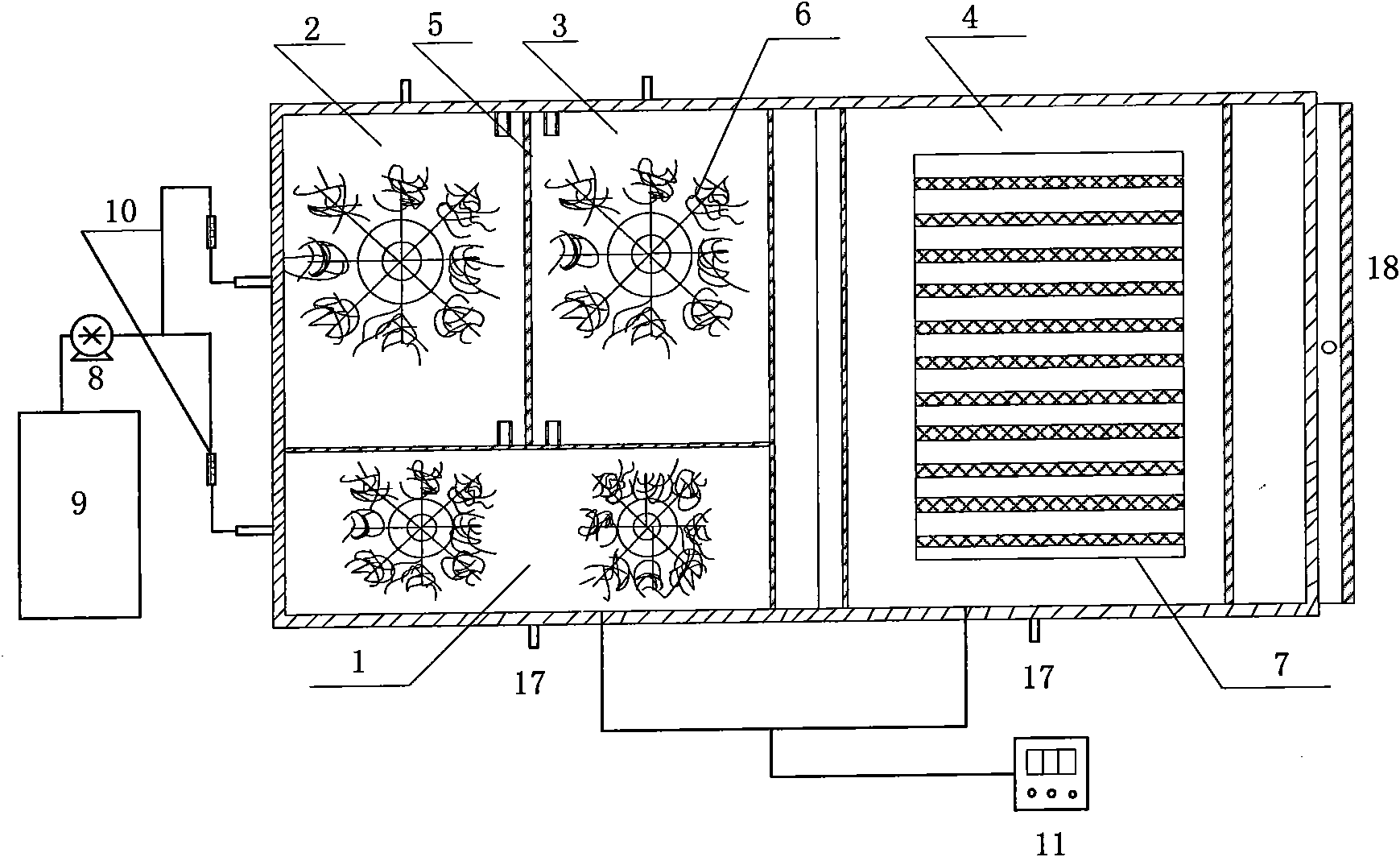
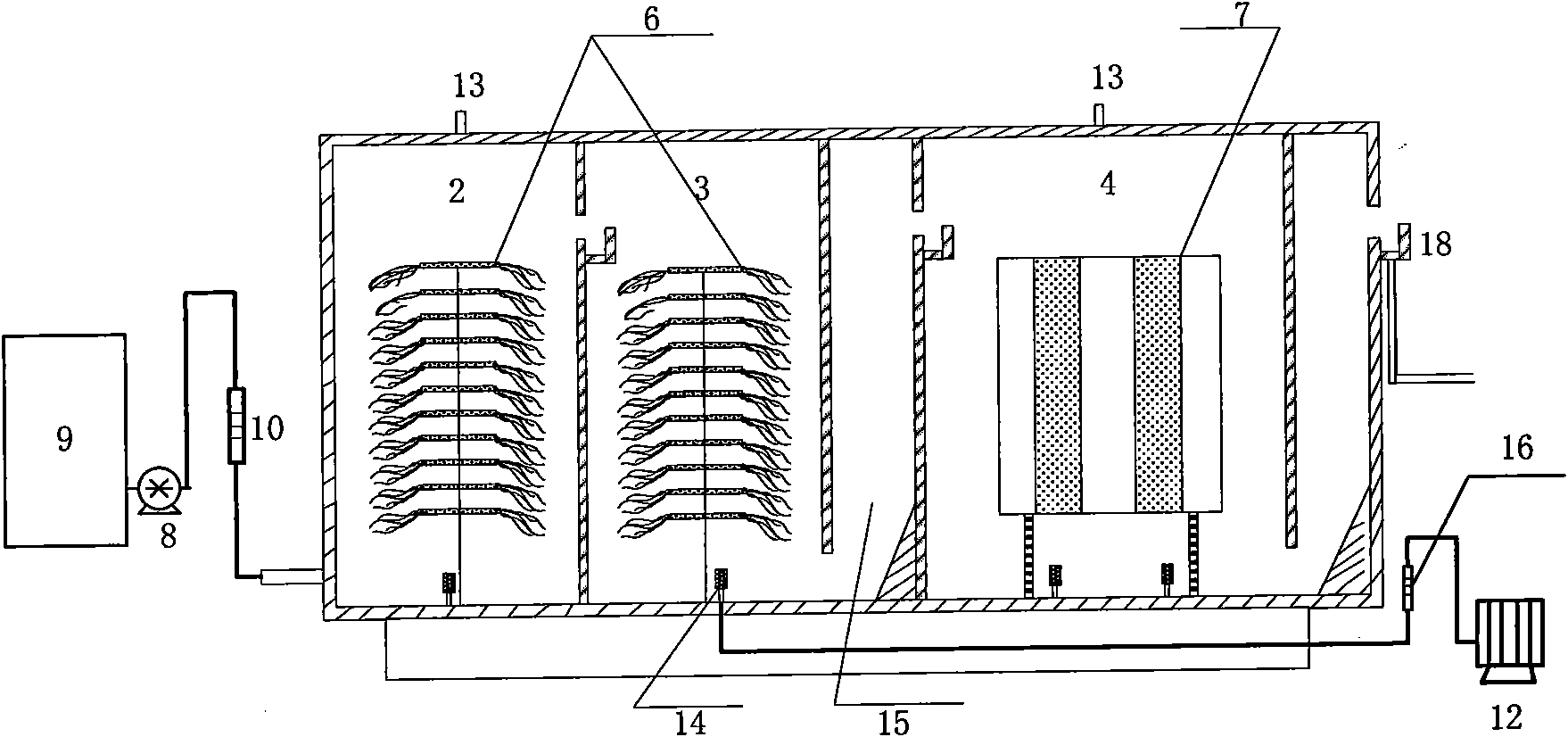
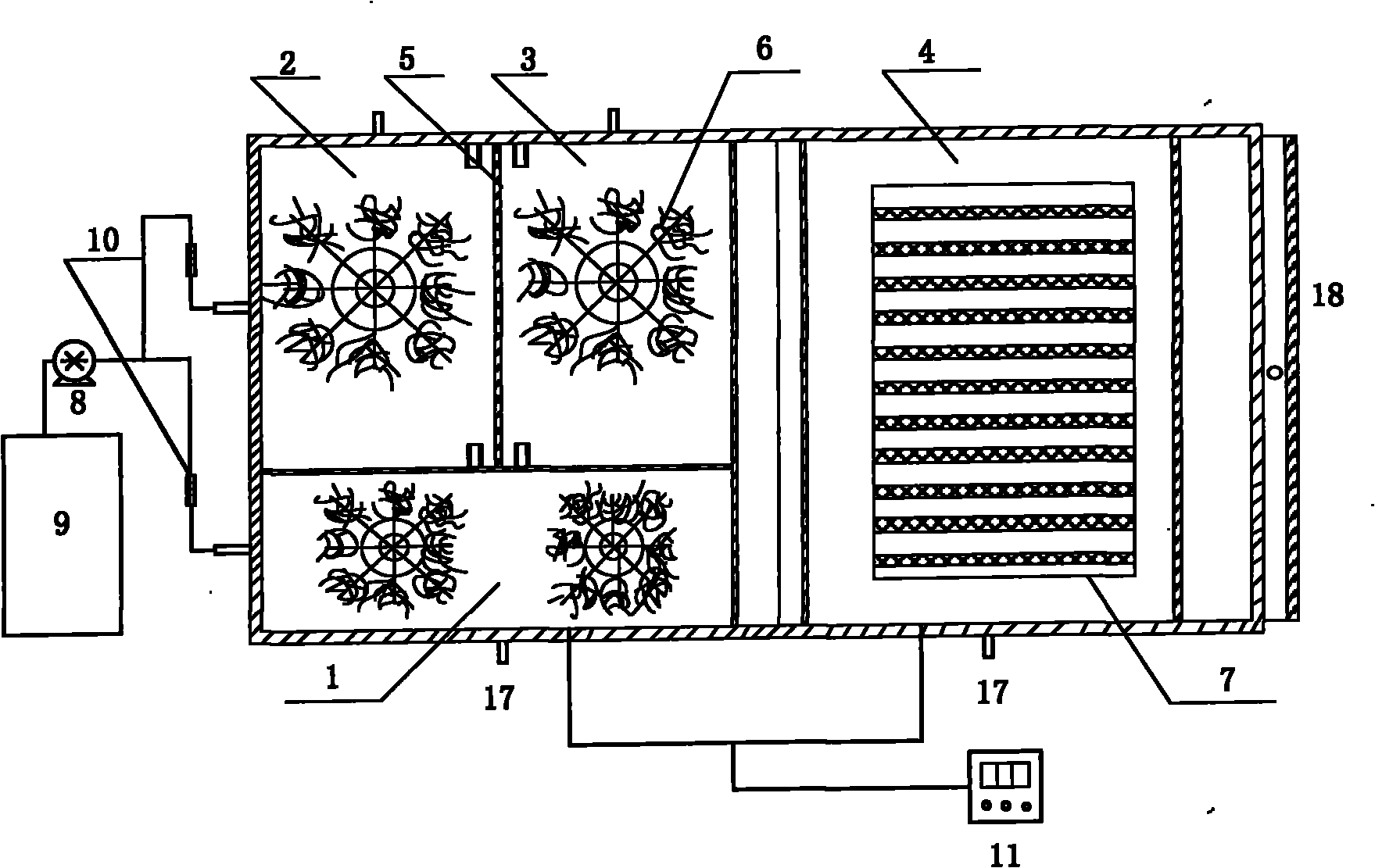
Single vessel multi-zone wastewater bio-treatment system
ActiveUS20050040107A1Suitable for processingSemi-permeable membranesTreatment using aerobic processesSingle vesselNitrate
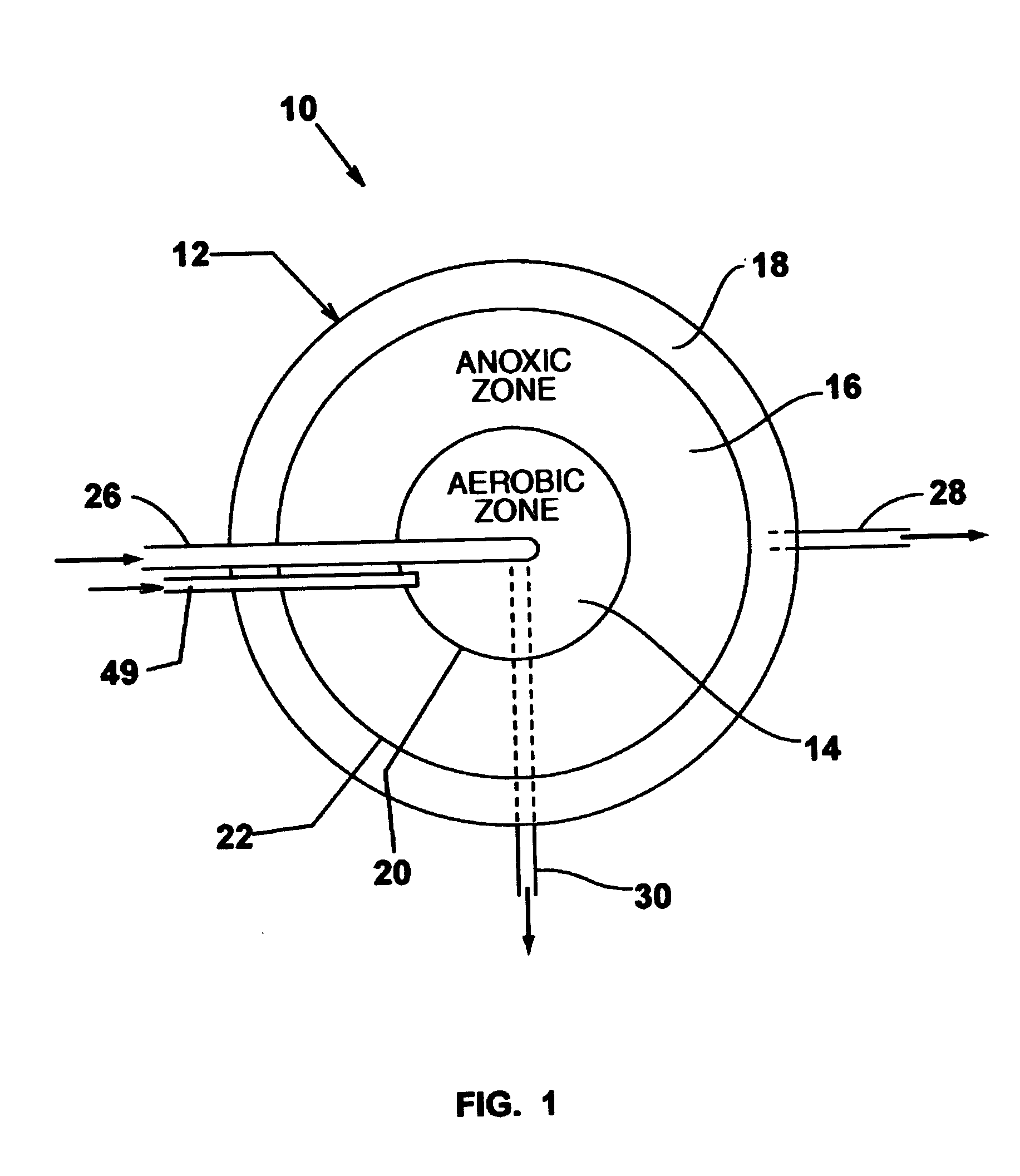
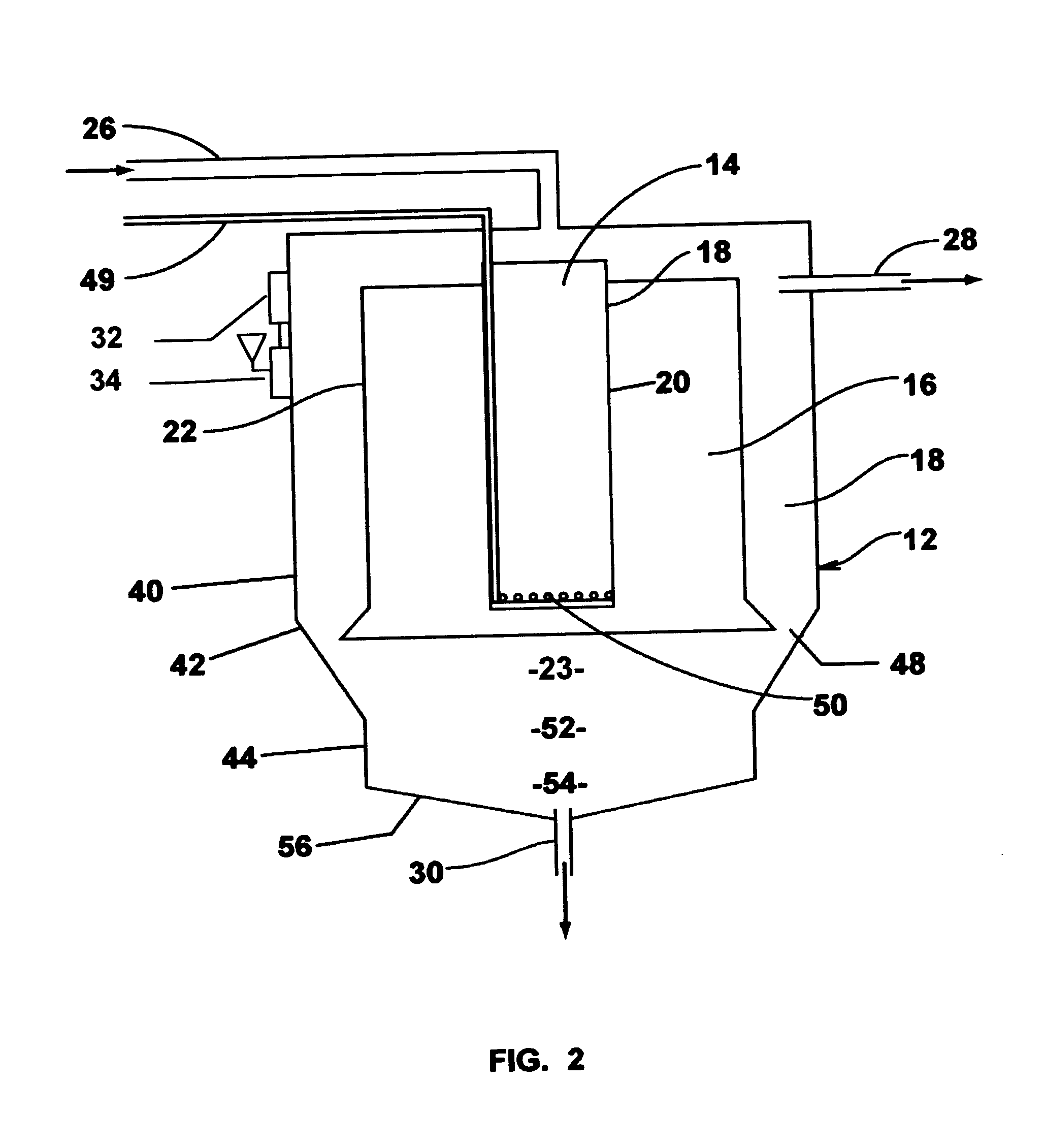
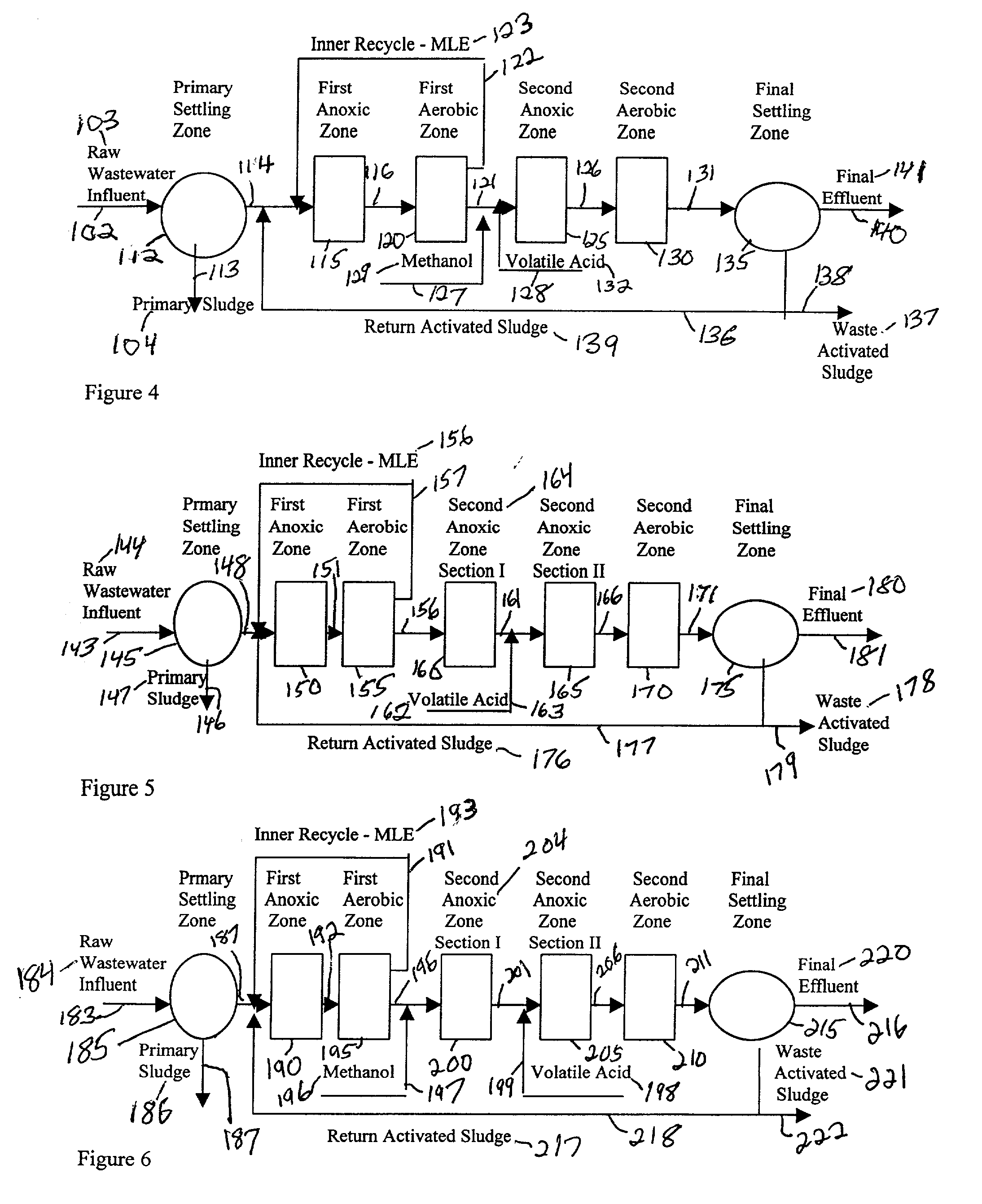
A process for treating wastewater and a system for practicing the process includes: providing a plurality of zones within a single vessel wastewater treatment system; feeding wastewater into the system; maintaining an aerobic zone in the upper central portion of the vessel; feeding air into the aerobic zone for oxygenation and creating an upflow; maintaining an annularly disposed anoxic zone about said aerobic zone; causing the upflow from the aerobic zone to produce a downflow in the anoxic zone; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the aerobic zone; maintaining an annularly disposed clarification zone about said anoxic zone for clarified liquid, including an upflow; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the clarification zone; maintaining a facultative transition zone below the upper aerobic, anoxic and clarification zones; maintaining an anaerobic zone below the facultative zone for absorbing solids settled by gravity and synthesizing volatile fatty acids; withdrawing substantially clarified liquid from the upflow of the clarified liquid zone; withdrawing substantially solids from about the bottom of the anaerobic zone; employing the aerobic zone for breaking down carbon chains and oxidizing volatile fatty acids dispersed from the anaerobic zone; interacting the aerobic and anoxic zones for the removal of nitrates; and interacting the aerobic, anaerobic ananoxic zones for the removal of phosphorus.
Owner:KASPARIAN ANN
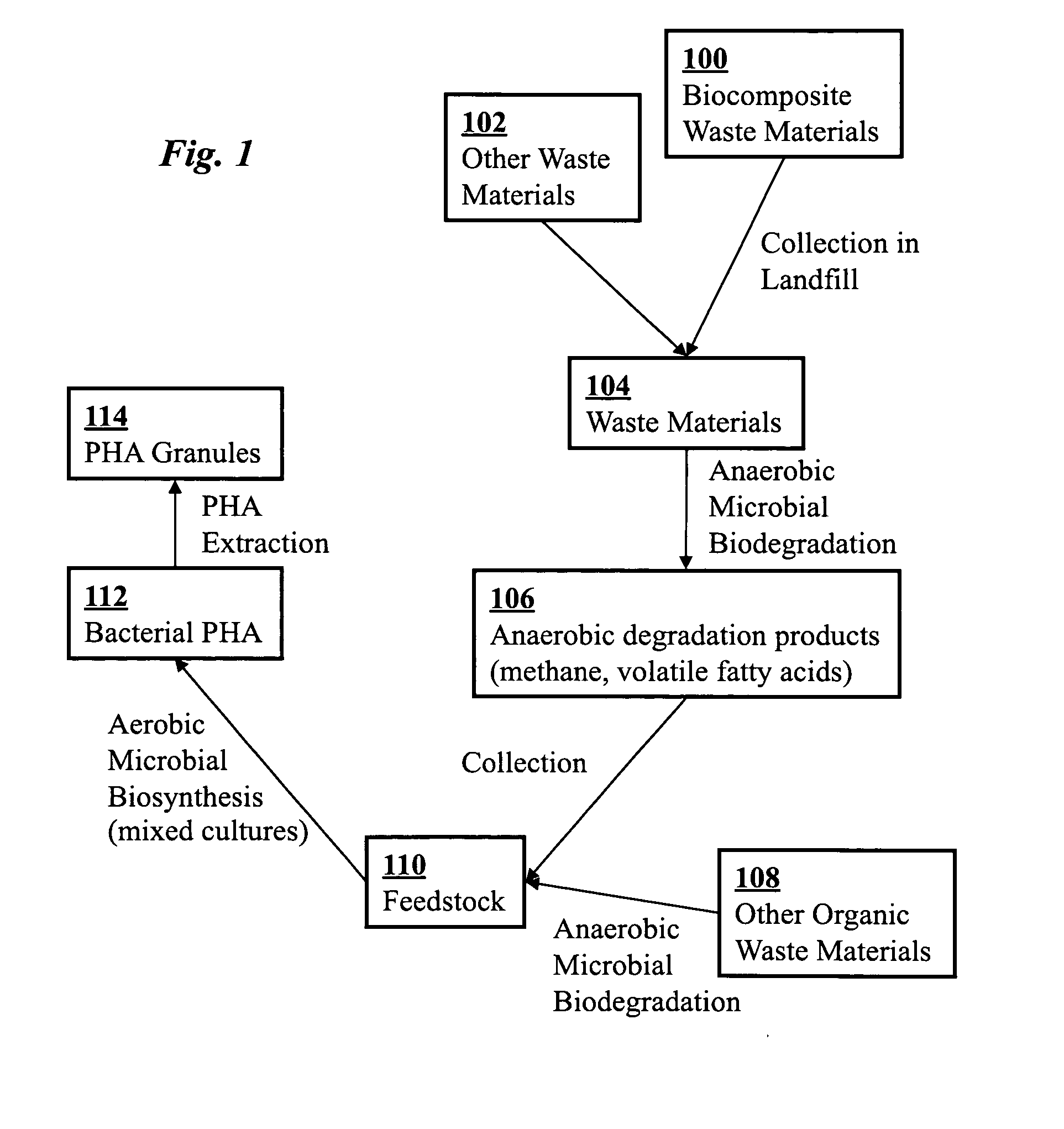
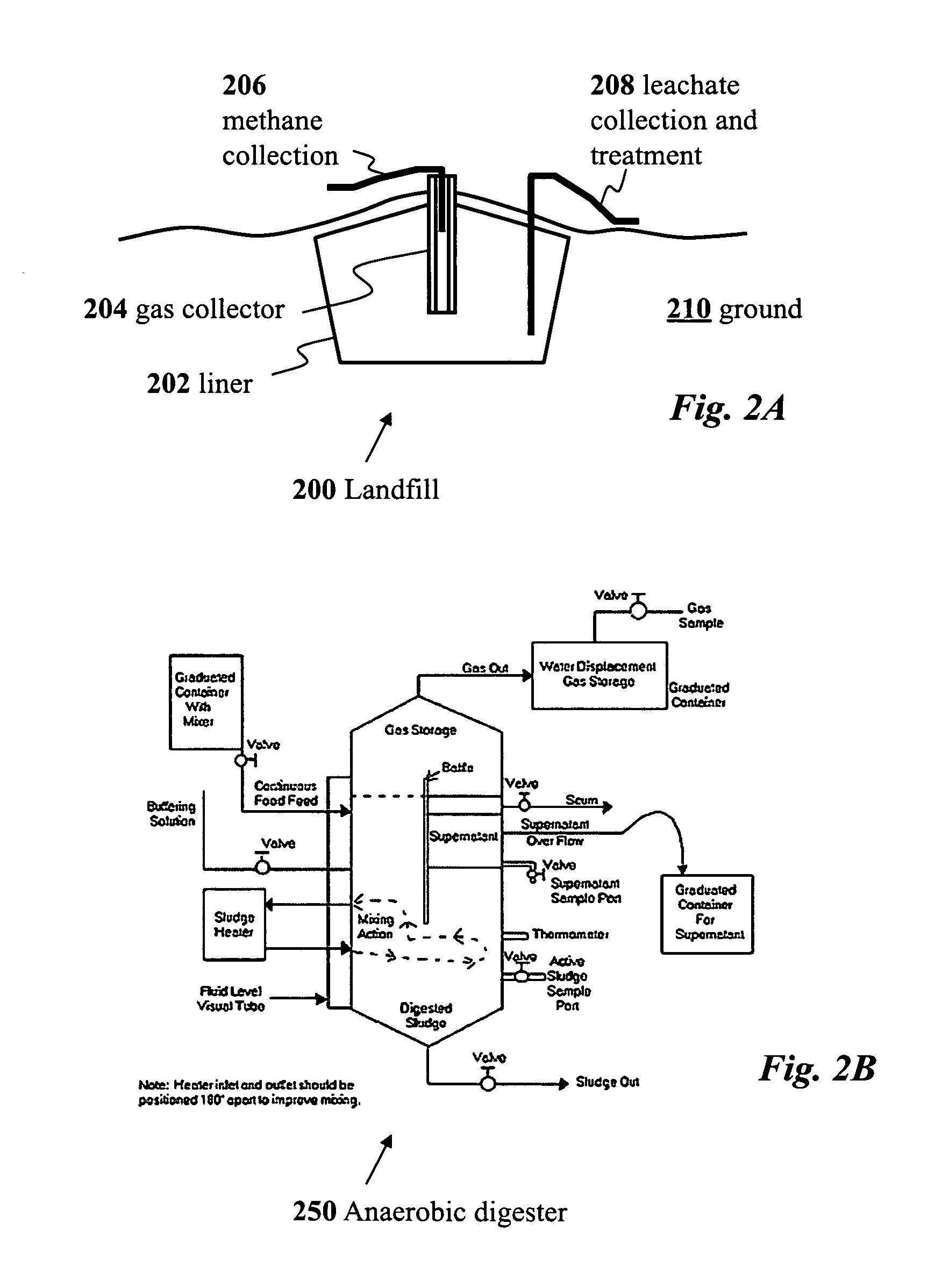
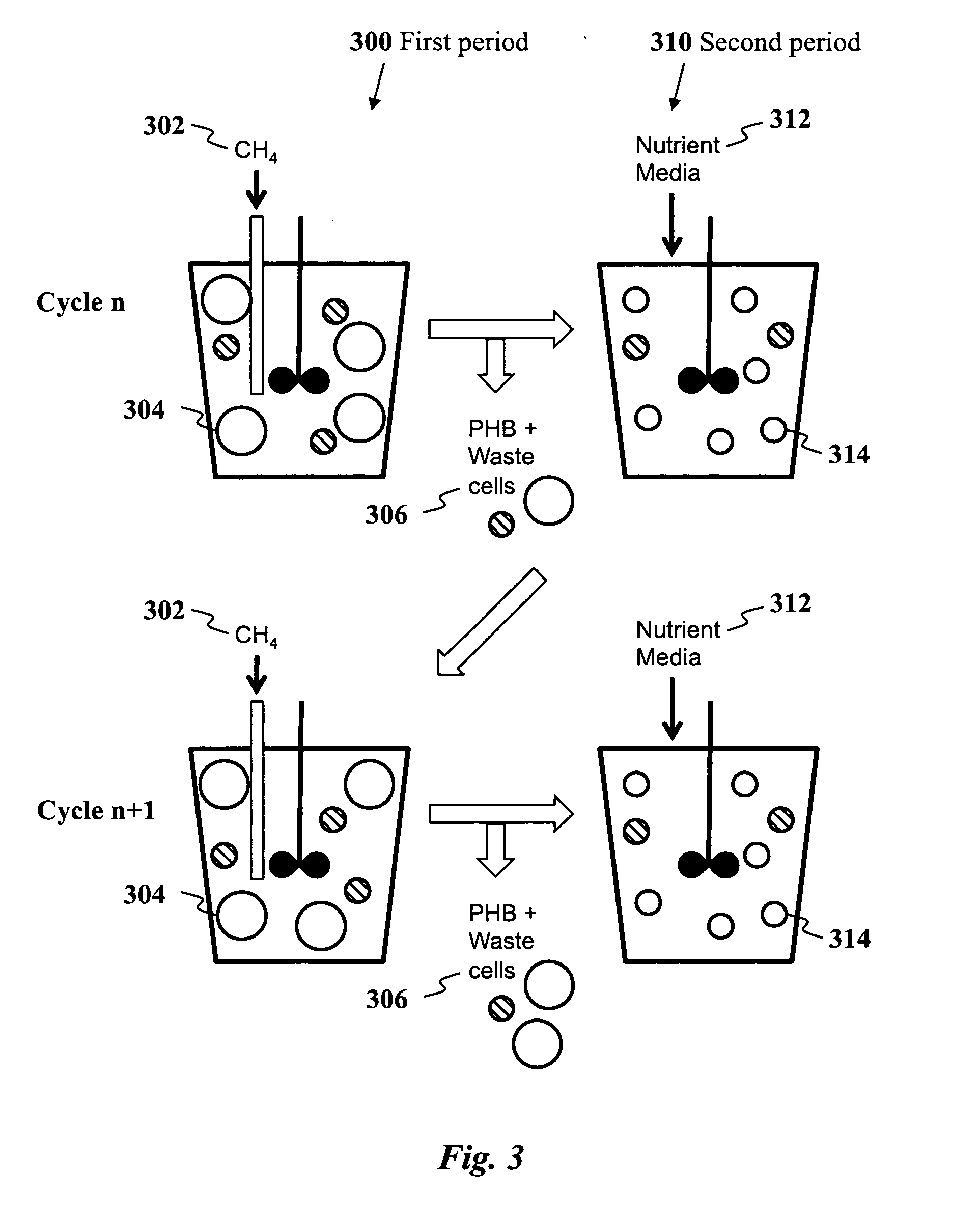
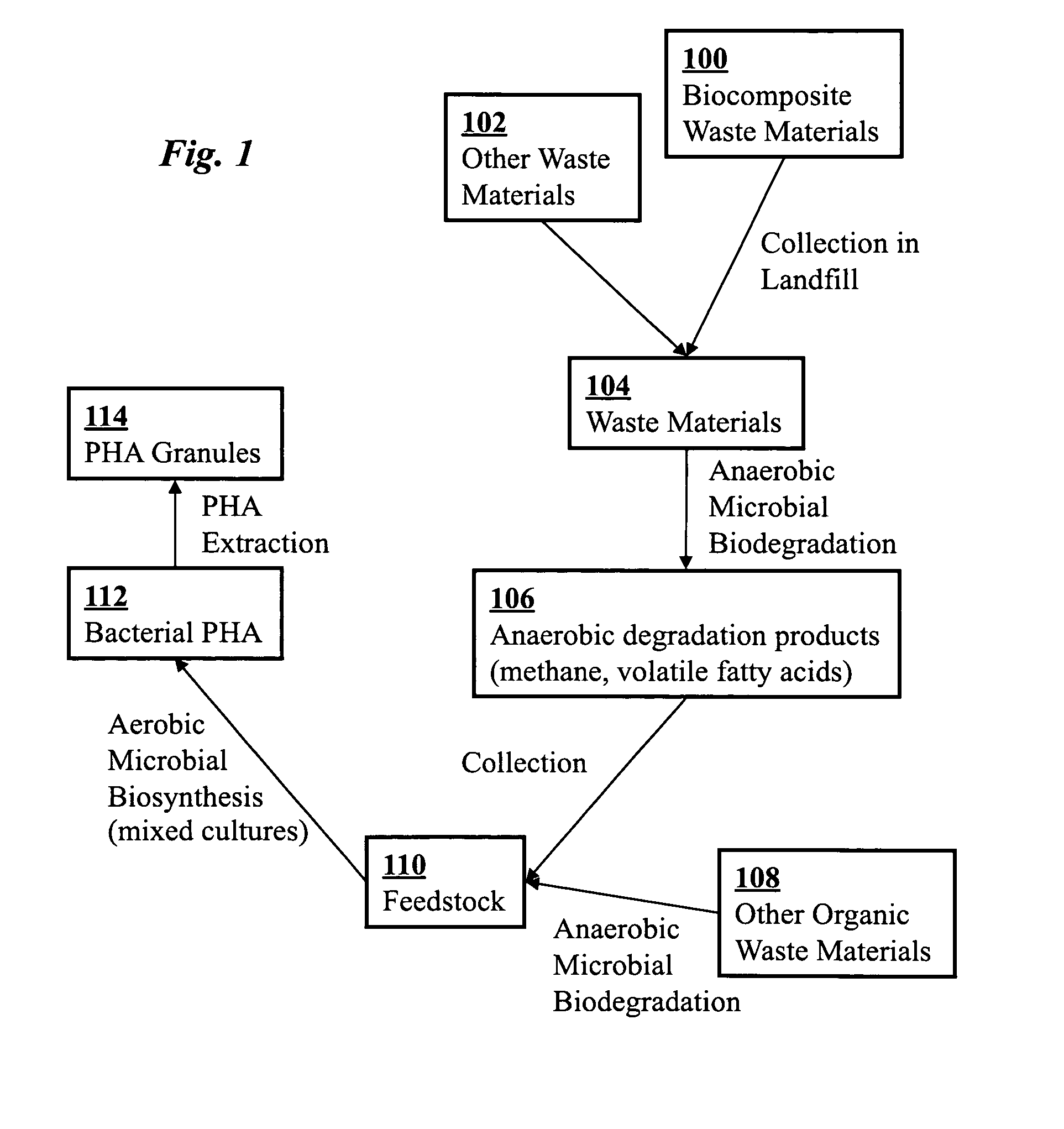
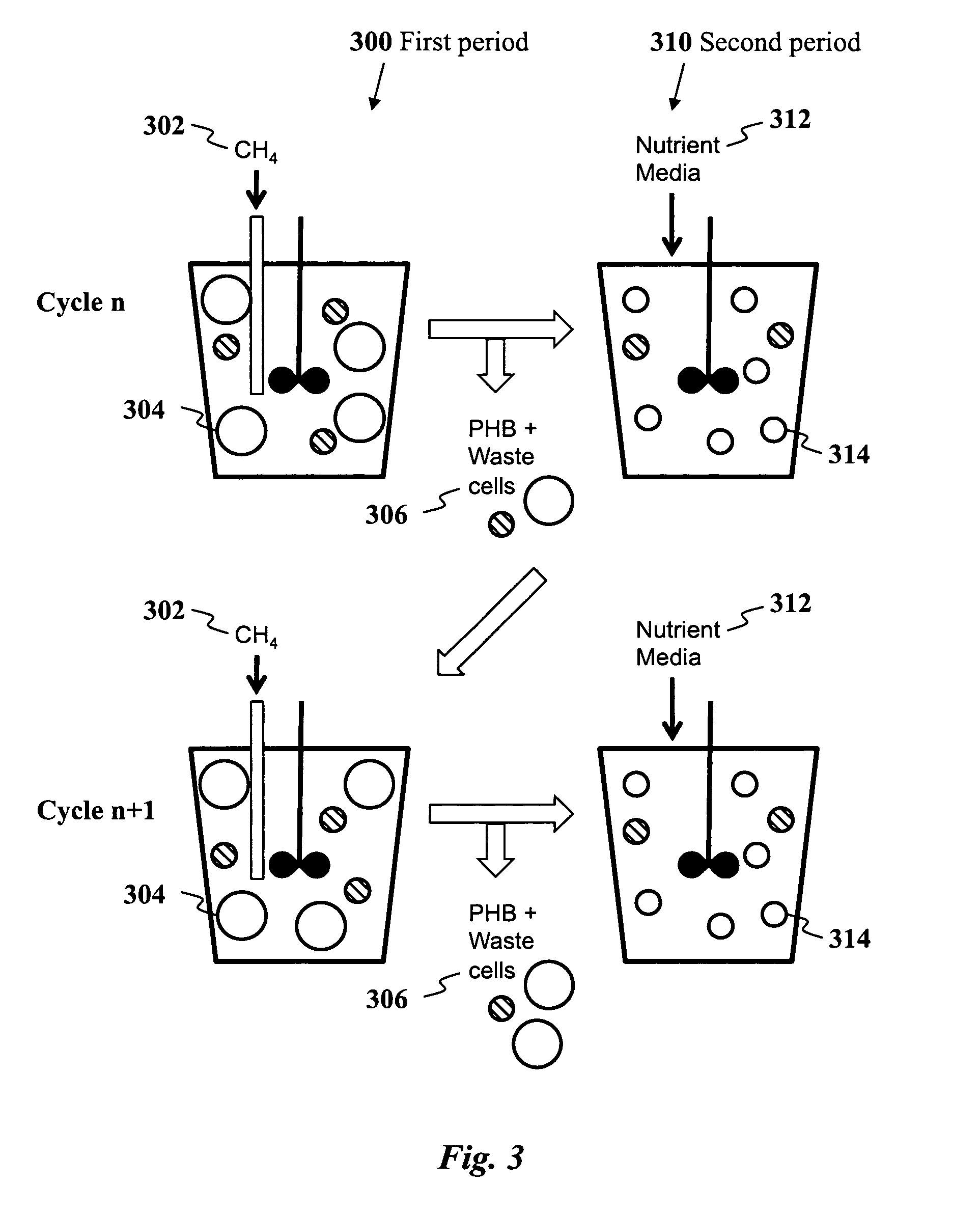
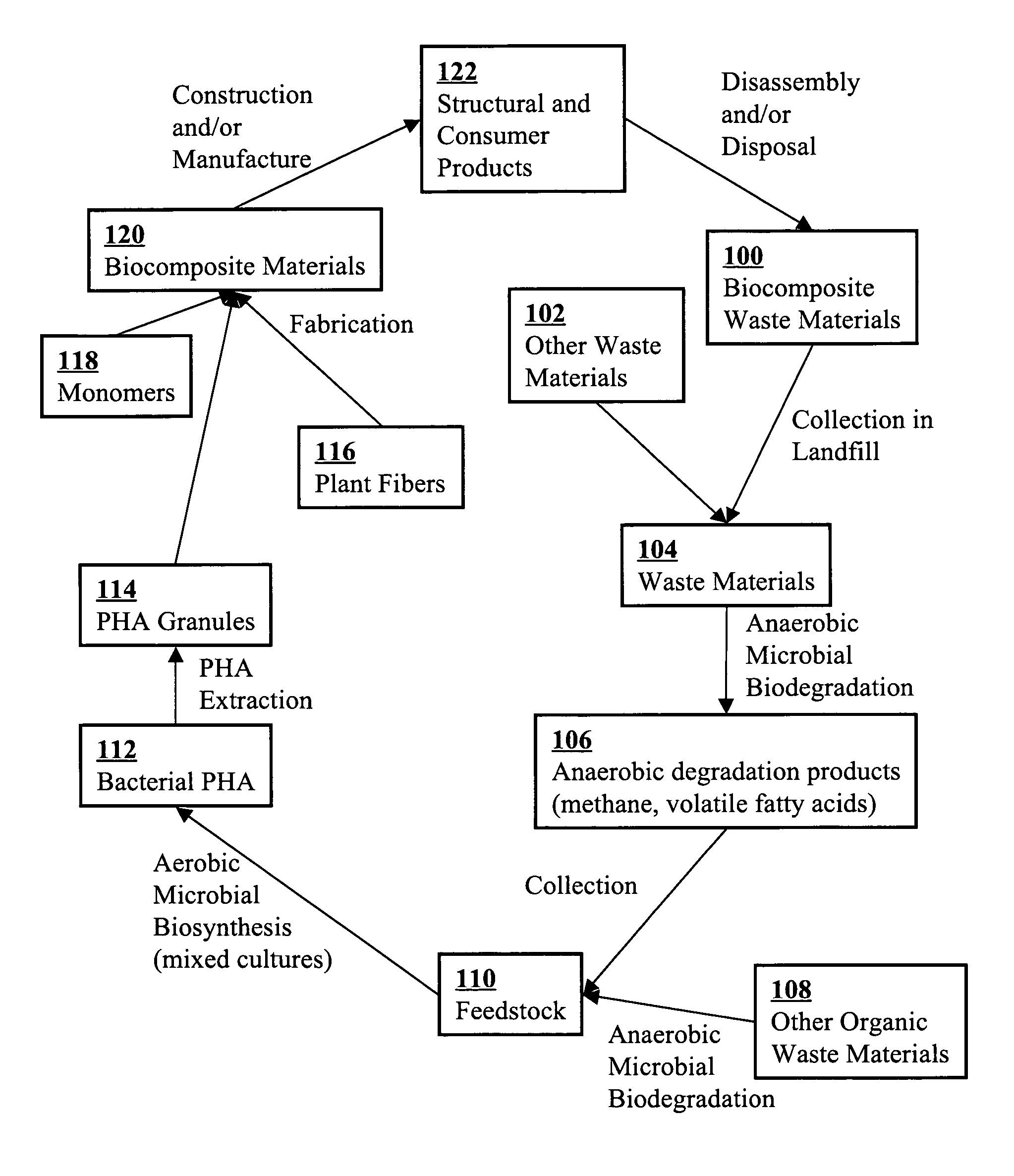
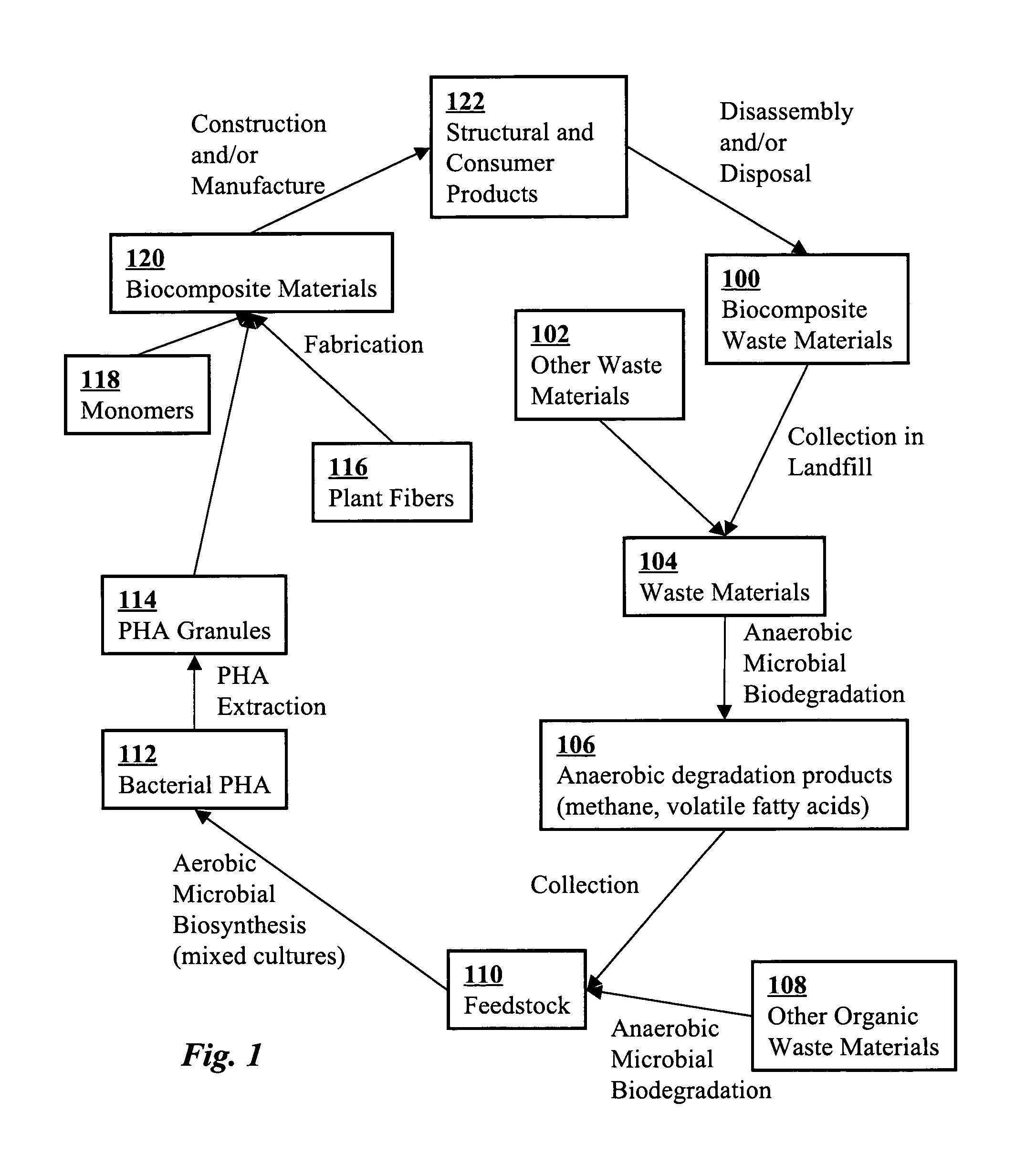
Use of selection pressures to enable microbial biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates from anaerobic degradation products
InactiveUS20090317879A1Cost of producingImprove the level ofWaste based fuelFermentationVolatile fatty acidsMethane gas
A method for inexpensive and efficient PHA biosynthesis includes operating a sequencing bioreactor in alternating phases of nutrient deprivation and carbon feedstock deprivation to select for robust PHA-producing microbes. Preferably, the bioreactor is operated in a non-sterile manner with mixed cultures of methanotrophs. The method also preferably uses periodic biomass-wasting (PHA harvesting) at the end of the carbon feed phase, gradually lengthening the time period of carbon deprivation phase to create a penalty for rapid PHA degradation and incentive for PHA accumulation. Also, bacterial enrichment cultures may be introduced periodically. The PHA-accumulating bacteria are preferably grown on common anaerobic degradation products, specifically volatile fatty acids, such as acetate and propionate, and methane gas. The PHA has useful applications in bioplastics and other products.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
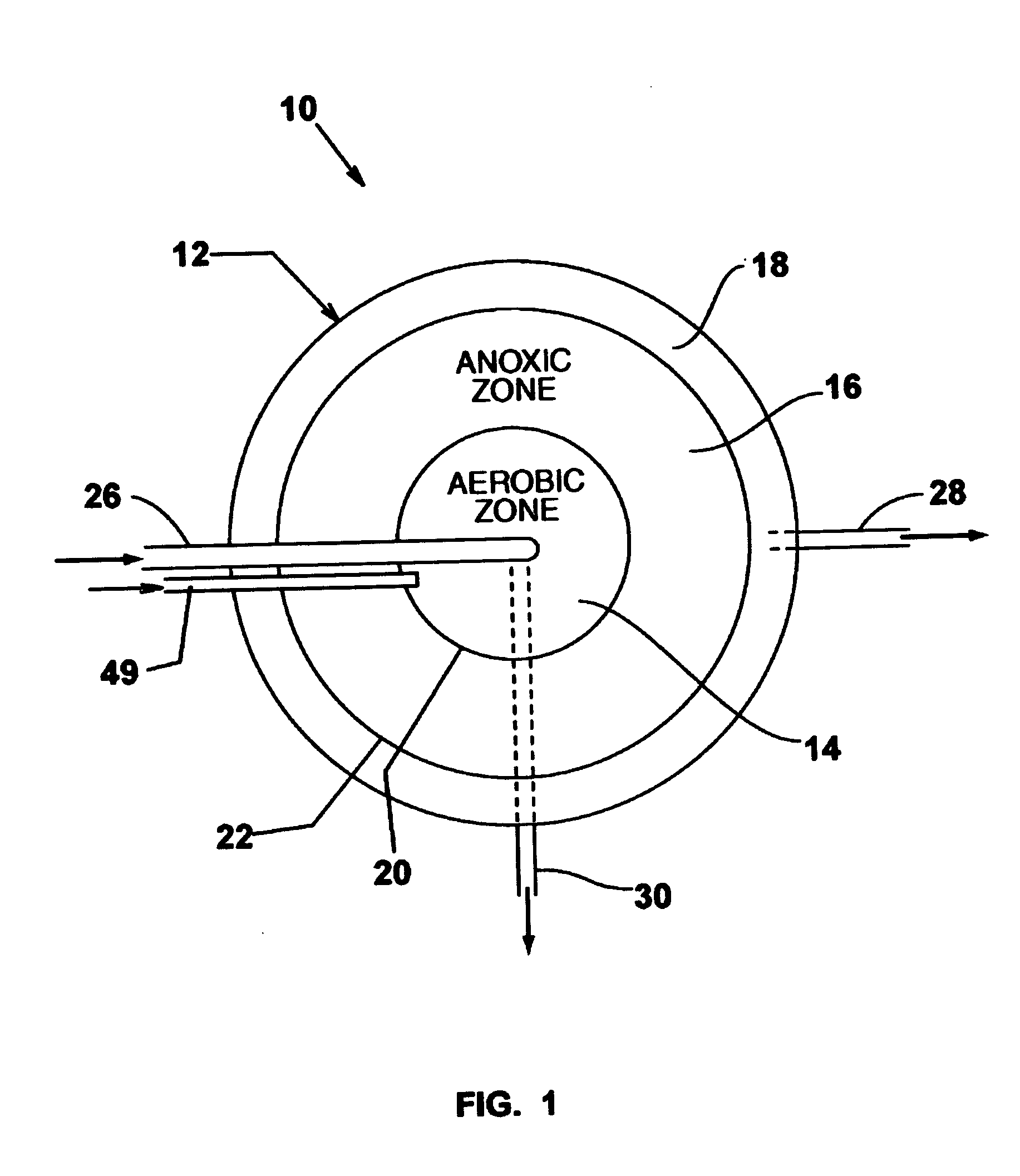
Single vessel multi-zone wastewater bio-treatment system
ActiveUS7008538B2Suitable for processingTreatment using aerobic processesMixing methodsSingle vesselNitrate
A process for treating wastewater and a system for practicing the process includes: providing a plurality of zones within a single vessel wastewater treatment system; feeding wastewater into the system; maintaining an aerobic zone in the upper central portion of the vessel; feeding air into the aerobic zone for oxygenation and creating an upflow; maintaining an annularly disposed anoxic zone about said aerobic zone; causing the upflow from the aerobic zone to produce a downflow in the anoxic zone; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the aerobic zone; maintaining an annularly disposed clarification zone about said anoxic zone for clarified liquid, including an upflow; causing at least a portion of the downflow from the anoxic zone to pass into the upflow of the clarification zone; maintaining a facultative transition zone below the upper aerobic, anoxic and clarification zones; maintaining an anaerobic zone below the facultative zone for absorbing solids settled by gravity and synthesizing volatile fatty acids; withdrawing substantially clarified liquid from the upflow of the clarified liquid zone; withdrawing substantially solids from about the bottom of the anaerobic zone; employing the aerobic zone for breaking down carbon chains and oxidizing volatile fatty acids dispersed from the anaerobic zone; interacting the aerobic and anoxic zones for the removal of nitrates; and interacting the aerobic, anaerobic ananoxic zones for the removal of phosphorus.
Owner:KASPARIAN ANN
Wastewater treatment process
InactiveUS20010045390A1Improve efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesActivated sludgeVolatile fatty acids
Owner:KIM SUNGTAI +2
Synergistic composition and method for odor control
InactiveUS20060006121A1Improve dehydration effectEasy to controlSpecific water treatment objectivesWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationWaste streamVolatile fatty acids
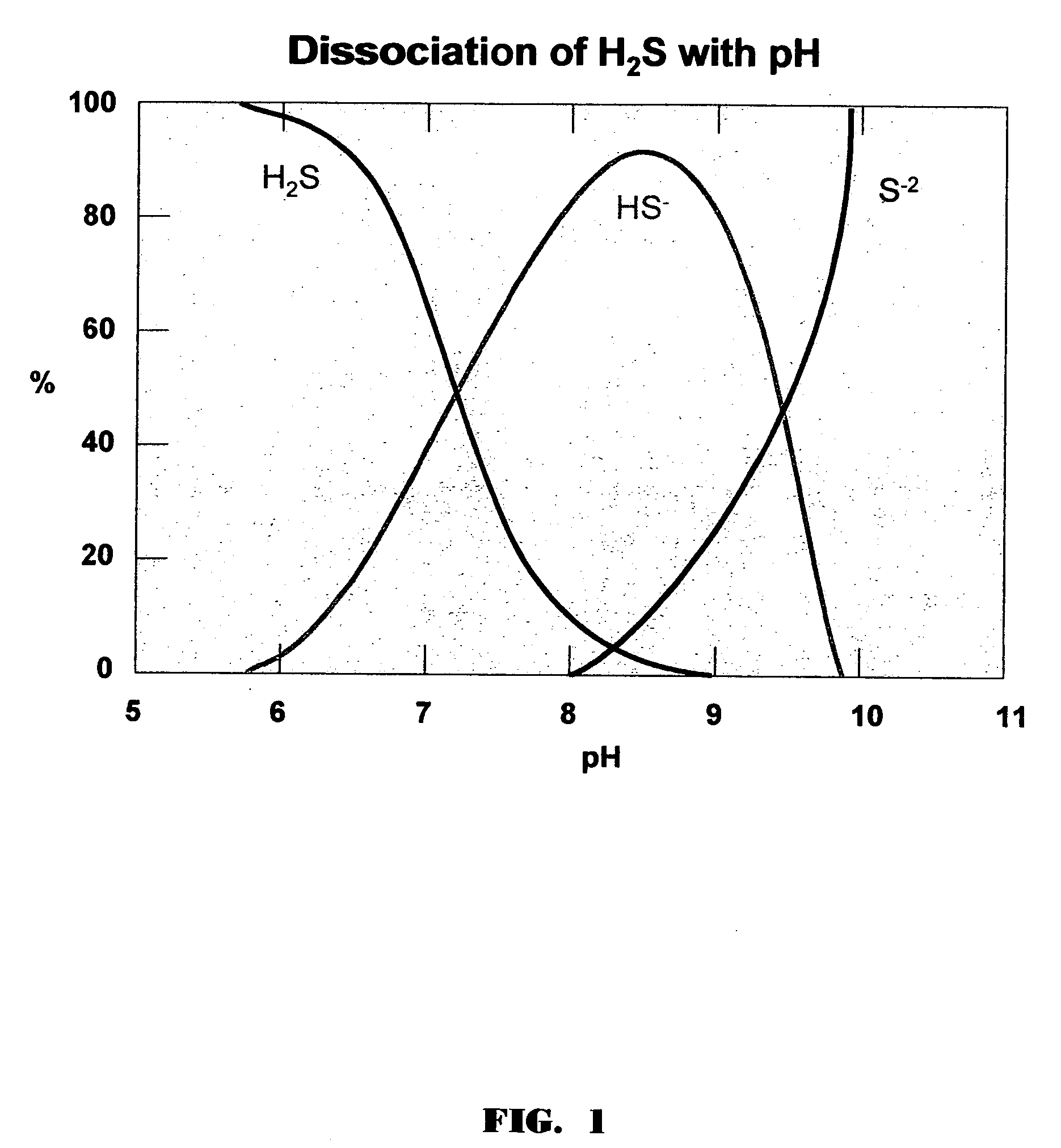
A synergistic composition and method is provided for controlling odor from waste products. The composition comprises a combination of magnesium hydroxide and a sulfide-consuming compound. The method includes adding a sufficient amount of the composition to a waste stream to provide sufficient sulfide-consuming compound to effect immediate removal of sulfide. The composition incorporates a pH elevating and buffering compound, which both increases and buffers the pH. The increased pH serves to reduce both the volatile sulfide species and the volatile fatty acid (VFAs) species. The elevated pH also promotes the growth of naturally occurring bacteria which metabolize the sulfide to an innocuous form. Finally, addition of the composition drives the pH into a range where the growth of sulfide producing bacteria is inhibited. The mixture has surprisingly been found to be synergistic with respect to both control of chemical species that produce odors and corrosion of metals commonly found in sludge dewatering equipment.
Owner:SIEMENS WATER TECH CORP
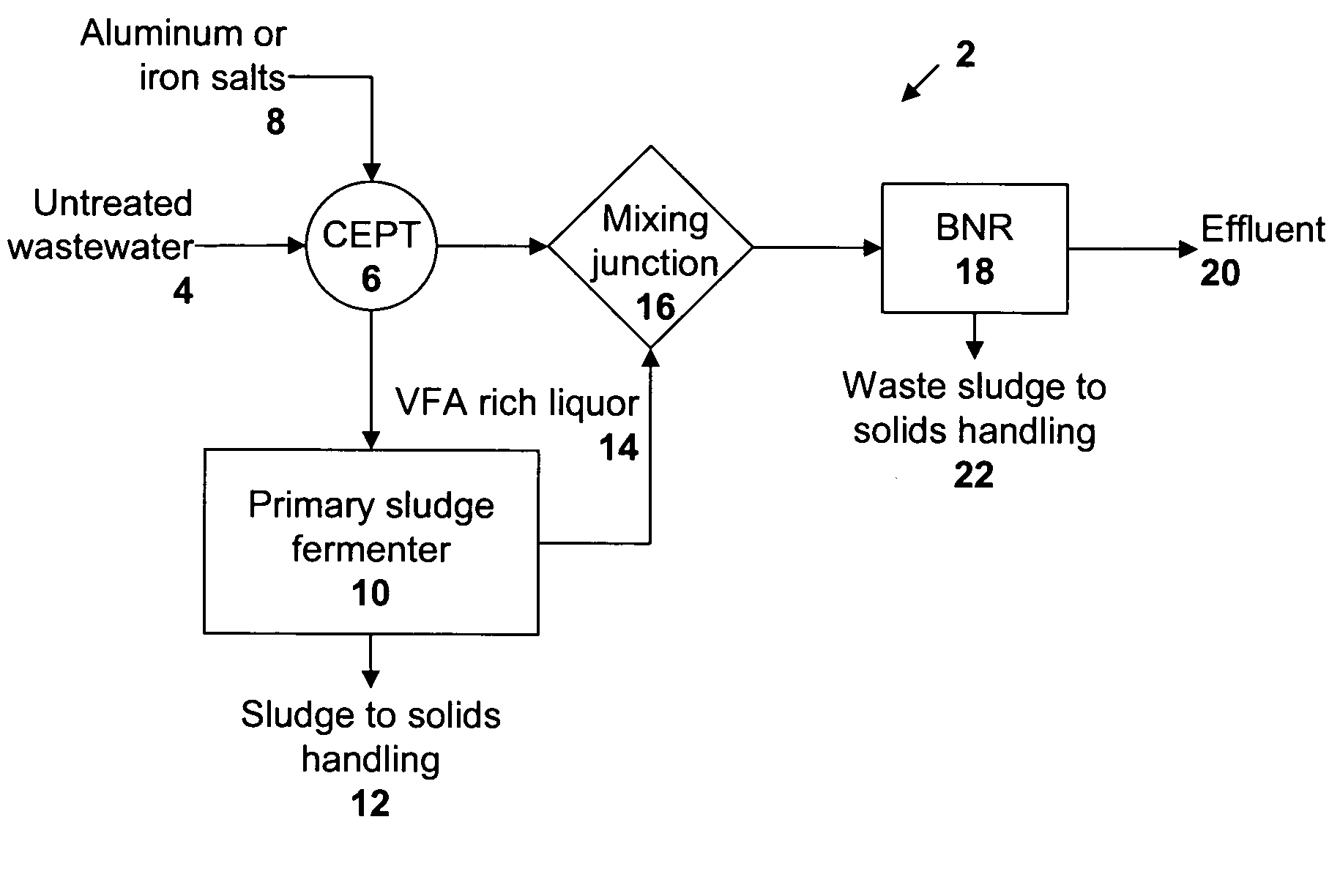
Method and system for treating wastewater
InactiveUS20130134089A1Water treatment parameter controlSpecific water treatment objectivesActivated sludgeVolatile fatty acids
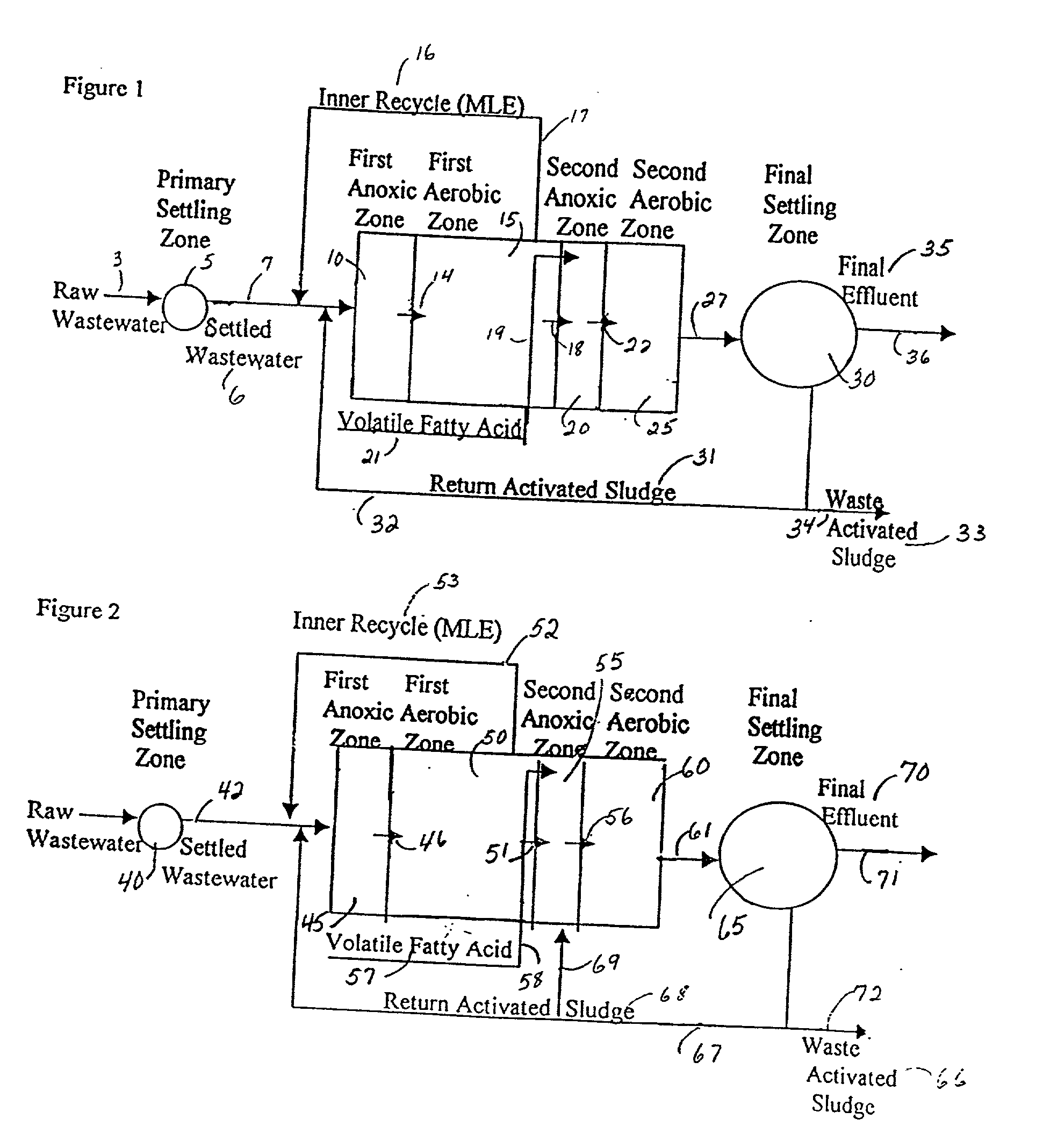
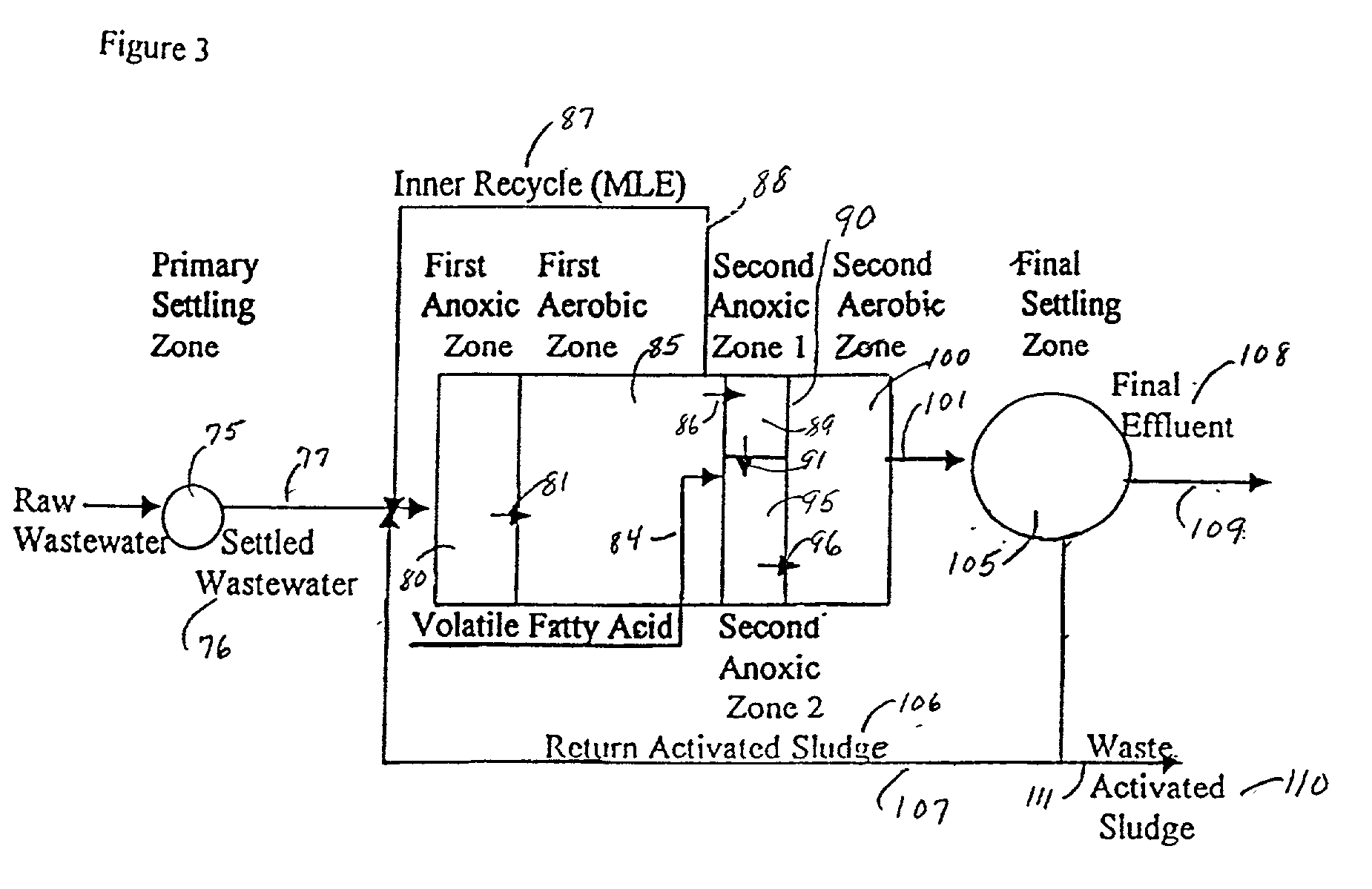
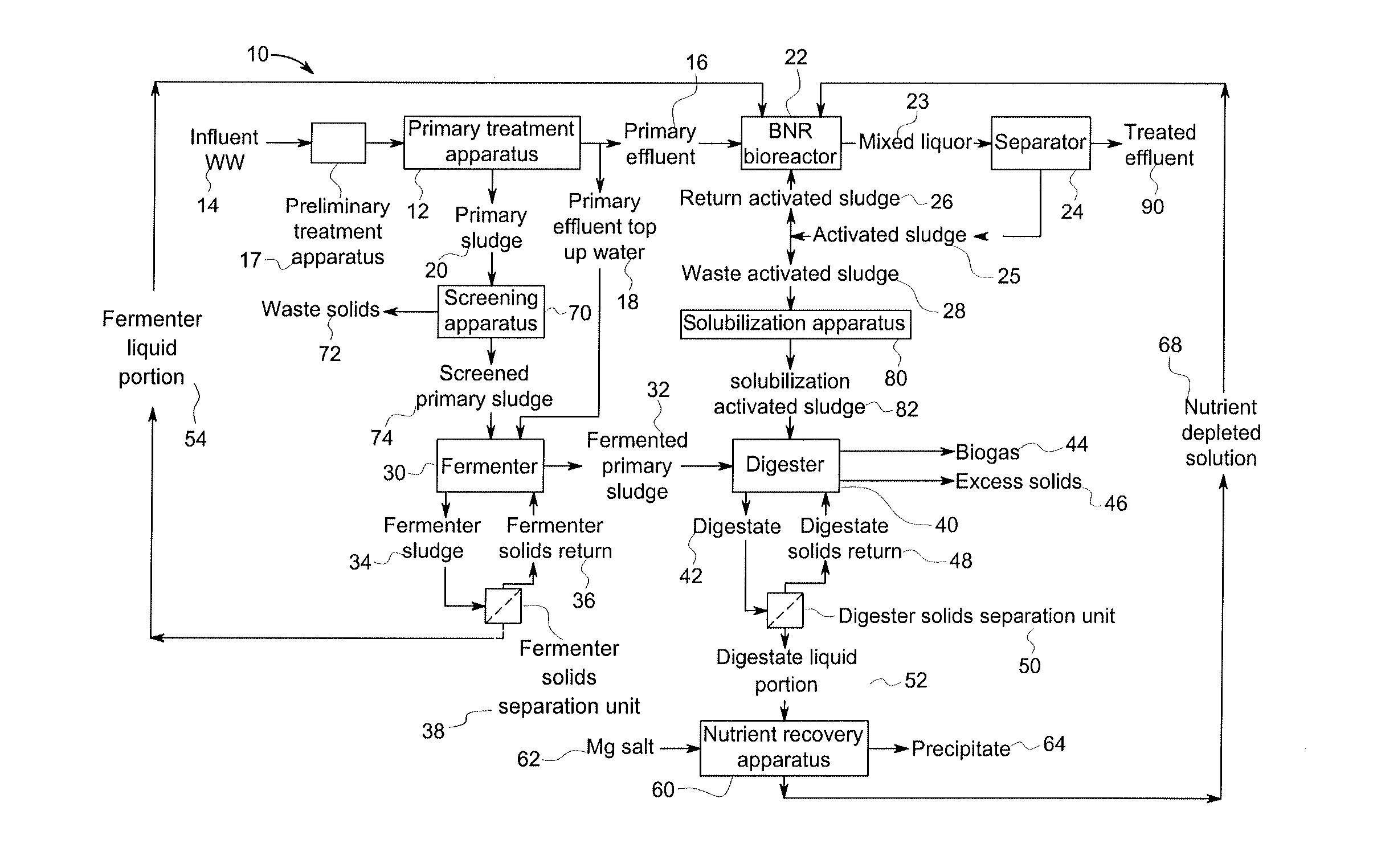
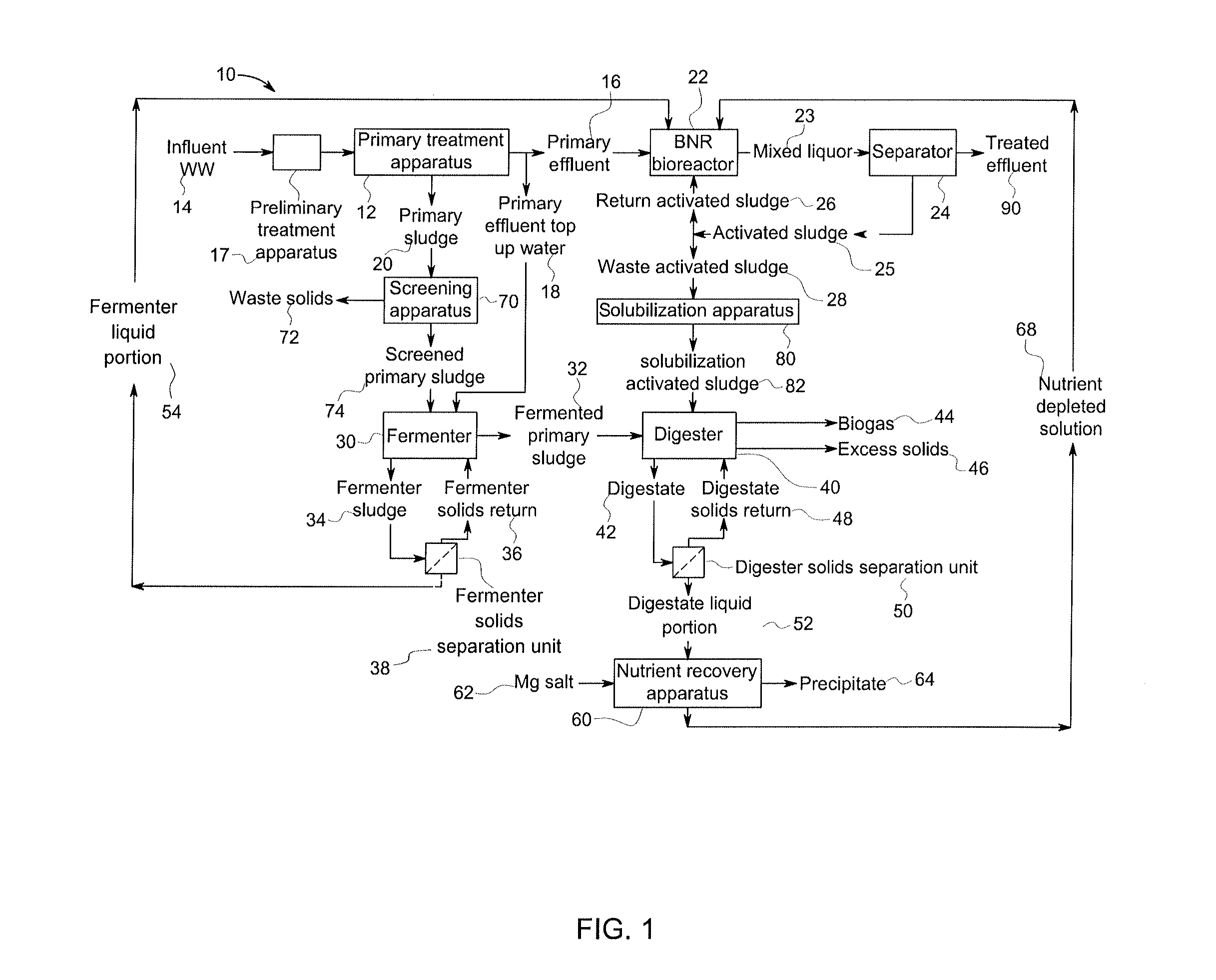
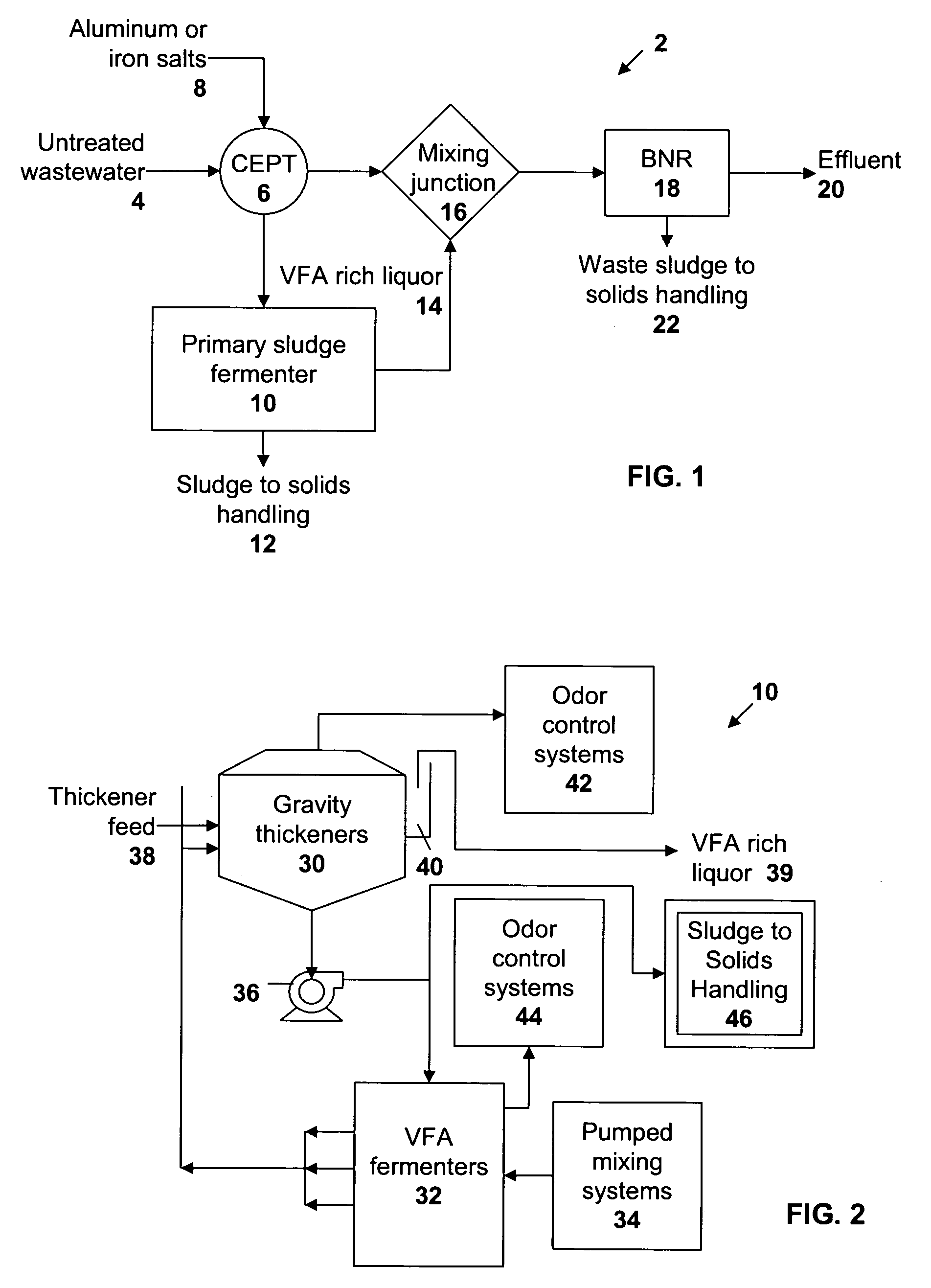
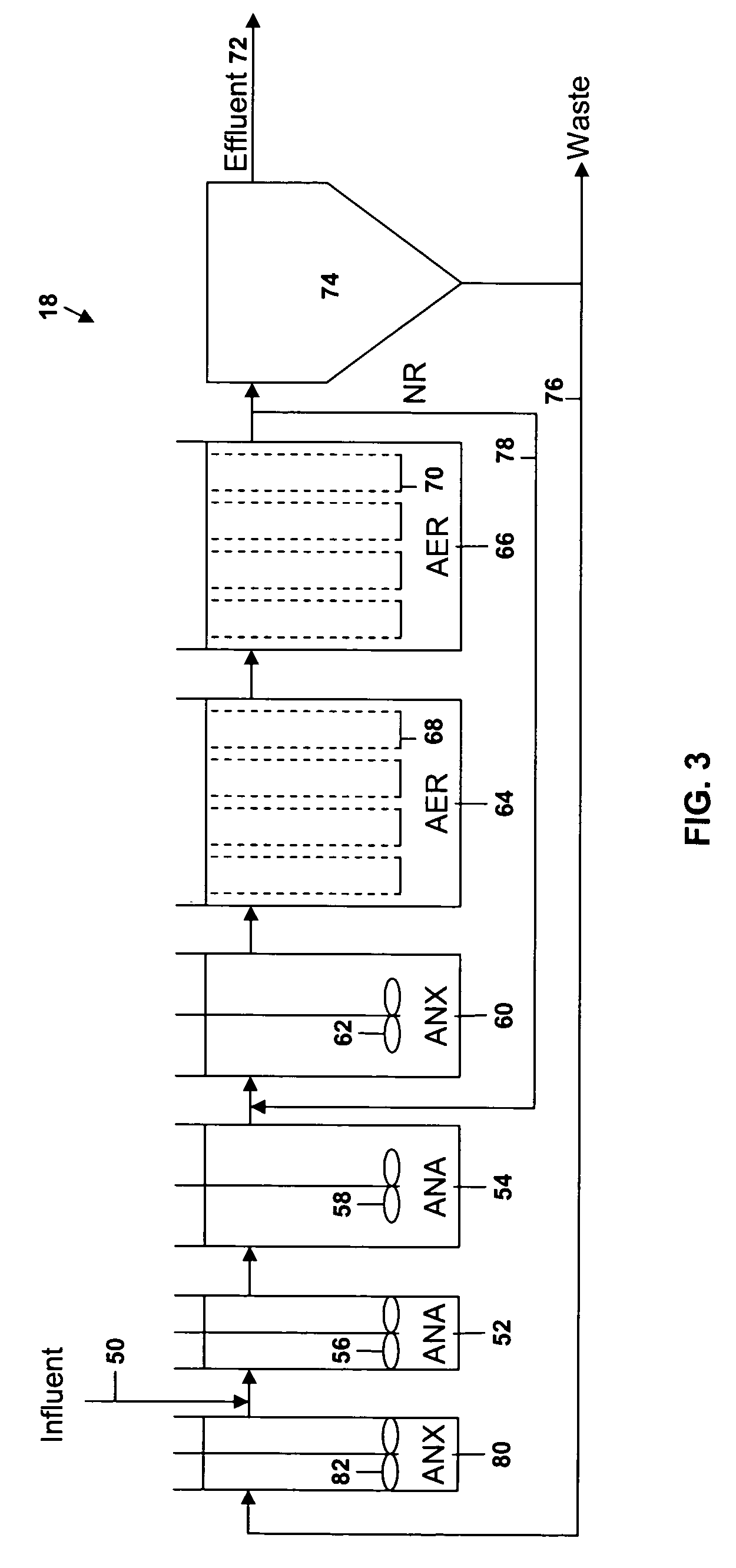
A wastewater treatment process uses enhanced primary treatment to remove suspended solids from raw wastewater. Primary sludge is treated in a fermenter. Primary effluent is treated by biological nutrient removal (BNR) to produce a treated effluent and waste activated sludge (WAS). The WAS is treated in an anaerobic digester, which also treats sludge from the fermenter. Anaerobic digestate is separated to provide a liquid effluent. The liquid effluent is stripped of phosphorous and returned to the BNR as a source of readily biodegradable carbon. Liquid in the fermenter may also be separated to provide a liquid rich in volatile fatty acids (VFAs). This liquid is returned to the BNR when additional VFAs are required.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
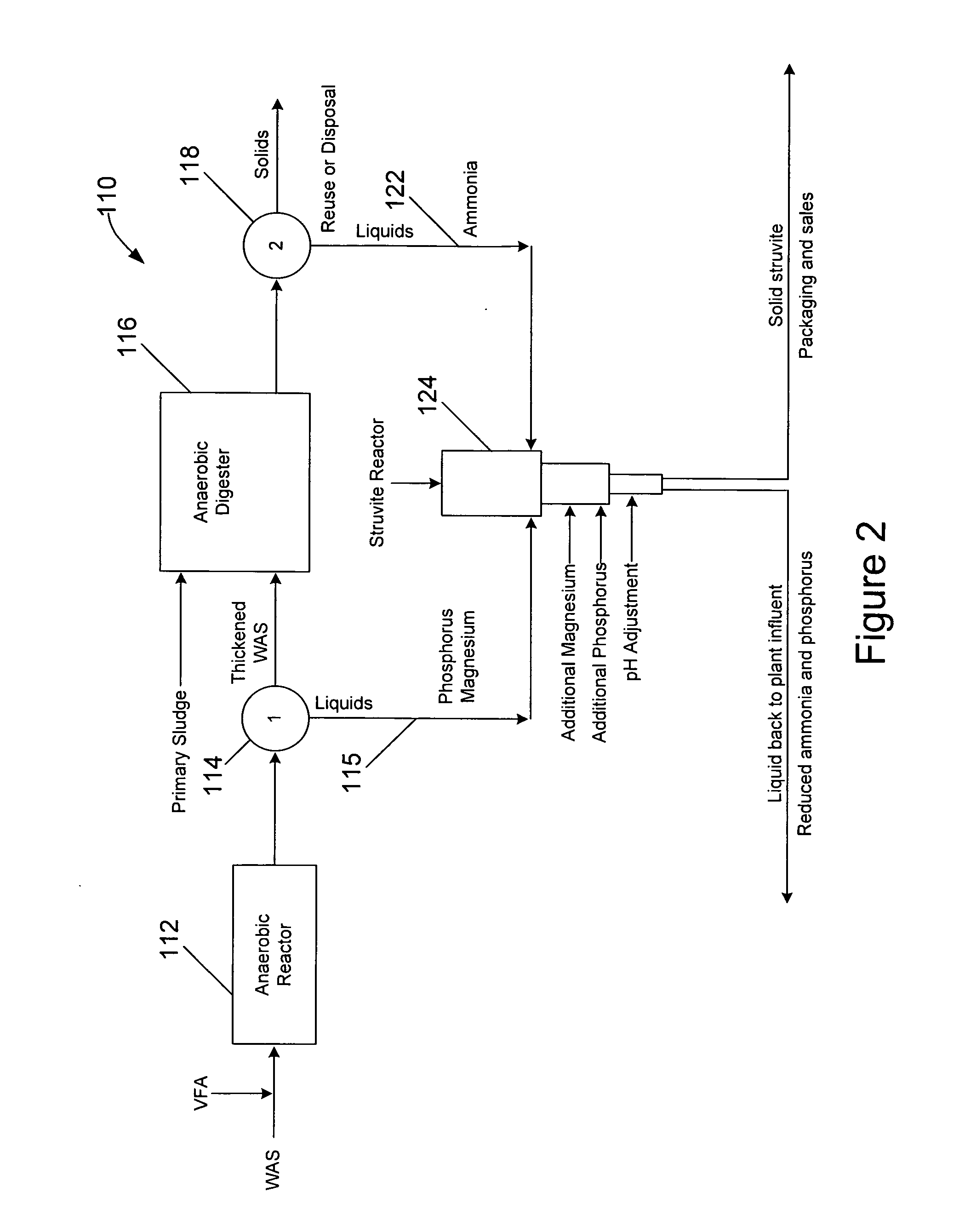
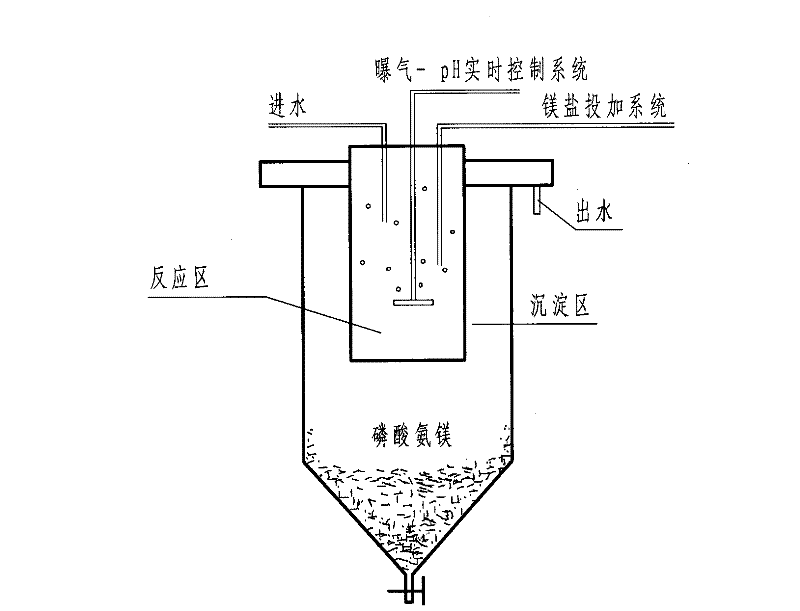
Waste activated sludge phosphorus and magnesium stripping process and struvite production system
ActiveUS20100170845A1Reduce productionBio-organic fraction processingTreatment using aerobic processesActivated sludgeMicroorganism
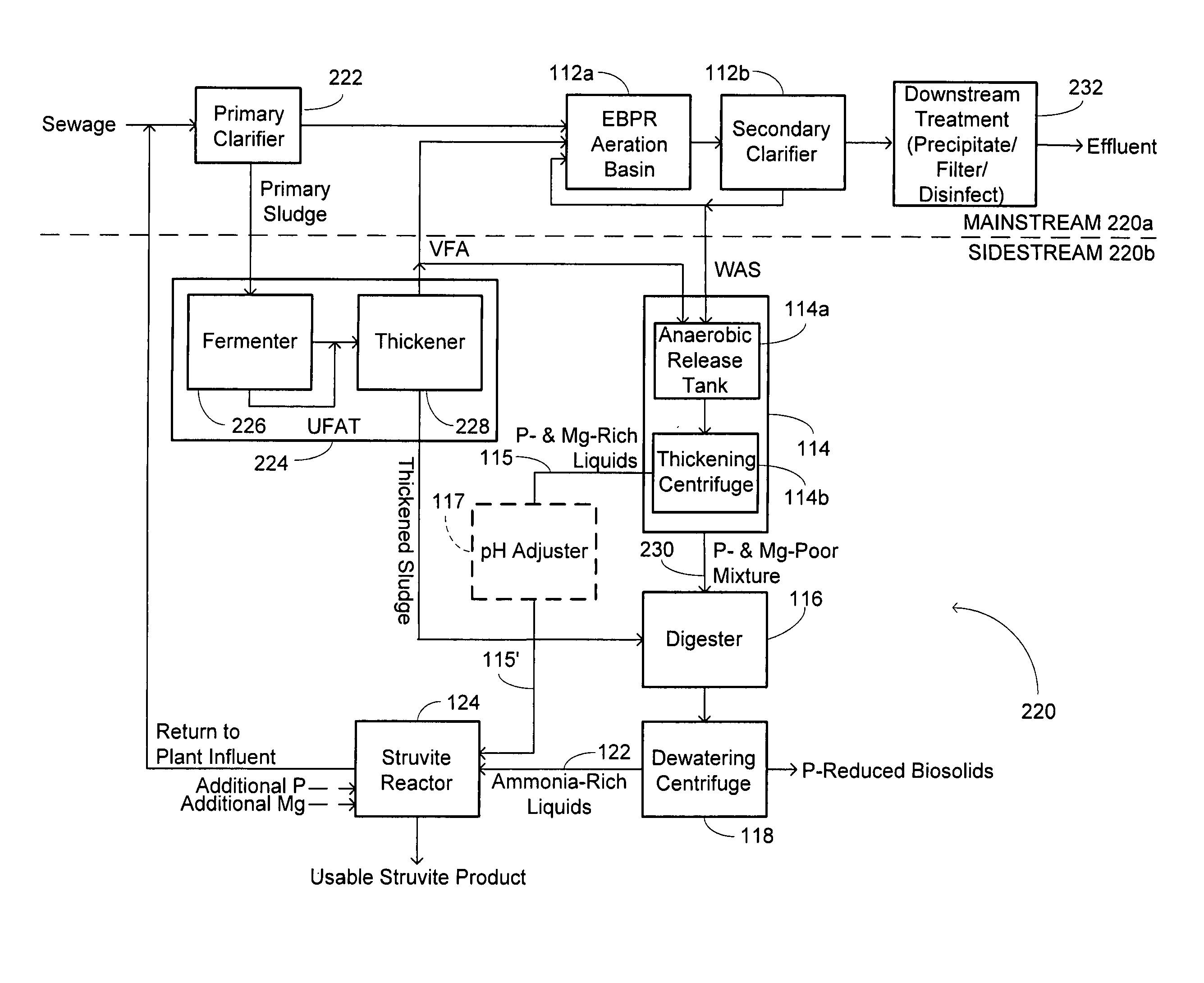
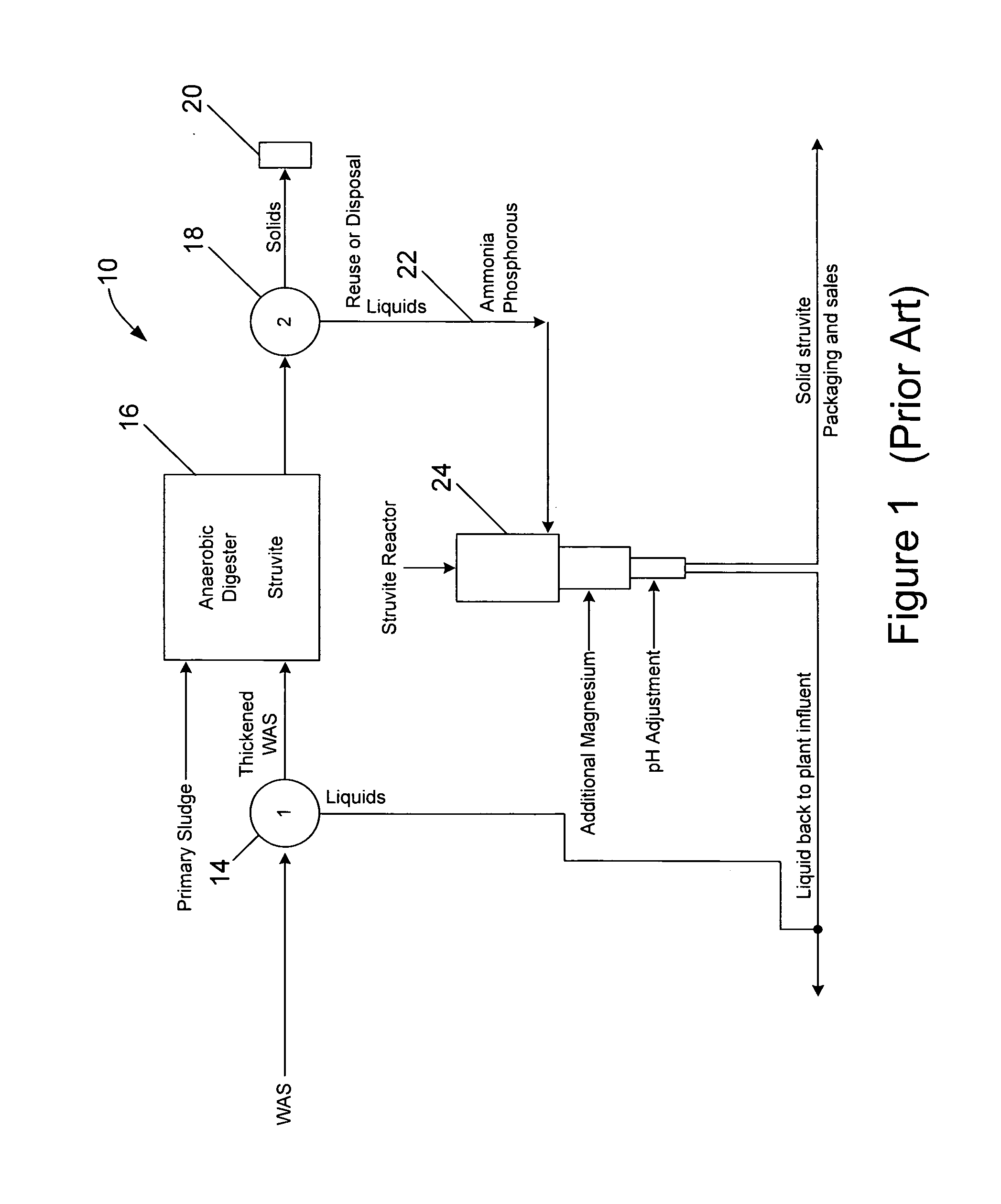
A method of treating a mixture of microorganisms with readily biodegradable carbon compounds (RBCs) in the form of one or more volatile fatty acids (VFAs), by first inducing the mixture microorganisms to release phosphorus and magnesium which is then tapped o as the mixture is thickened, to produce a phosphorus / magnesium-nch liquid and a phosphorus / magnesium-reduced treated mixture This treated mixture is placed in an anaerobic digester where ammonia is formed, but combines very little with phosphorus or magnesium Next the high-ammonia mixture is dewatered to produce an ammonia-rich liquid, which is combined with the phosphorus and magnesium-rich liquid and reacted to form struvite In one preferred embodiment, VFAs are formed in situ via an upstream unified fermentation and thickening (UFAT) process and added to the waste sidestream to strip phosphorus and magnesium found therein In another preferred embodiment a usable struvite product is harvested.
Owner:CLEAN WATER SERVICES
Use of selection pressures to enable microbial biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates from anaerobic degradation products
InactiveUS8030021B2Cost of producingImprove the level ofWaste based fuelFermentationVolatile fatty acidsMethane gas
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Bacterial poly(hydroxy alkanoate) polymer and natural fiber composites
ActiveUS7887893B2Improve bindingImprove performanceLayered productsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVolatile fatty acidsResin matrix
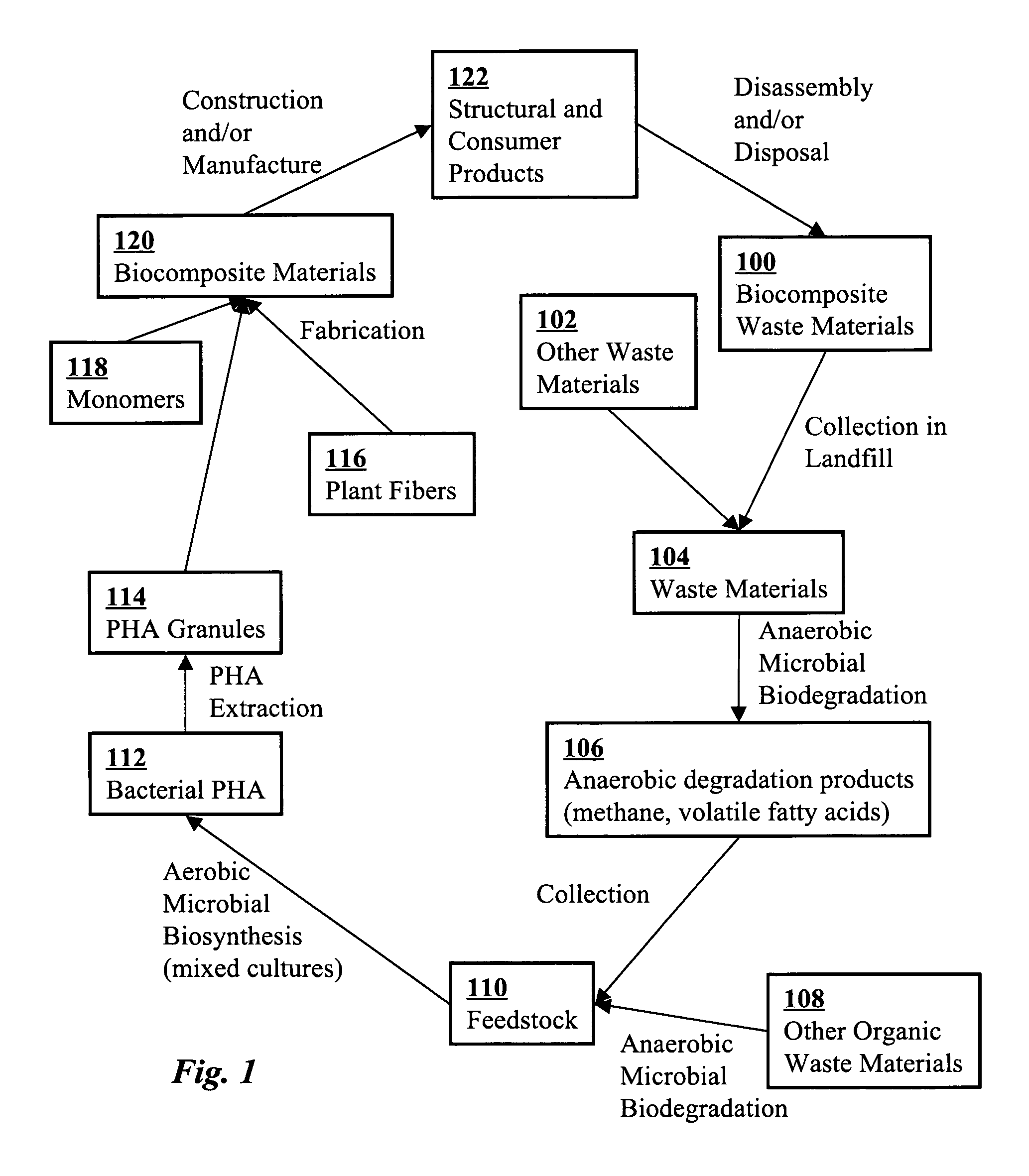
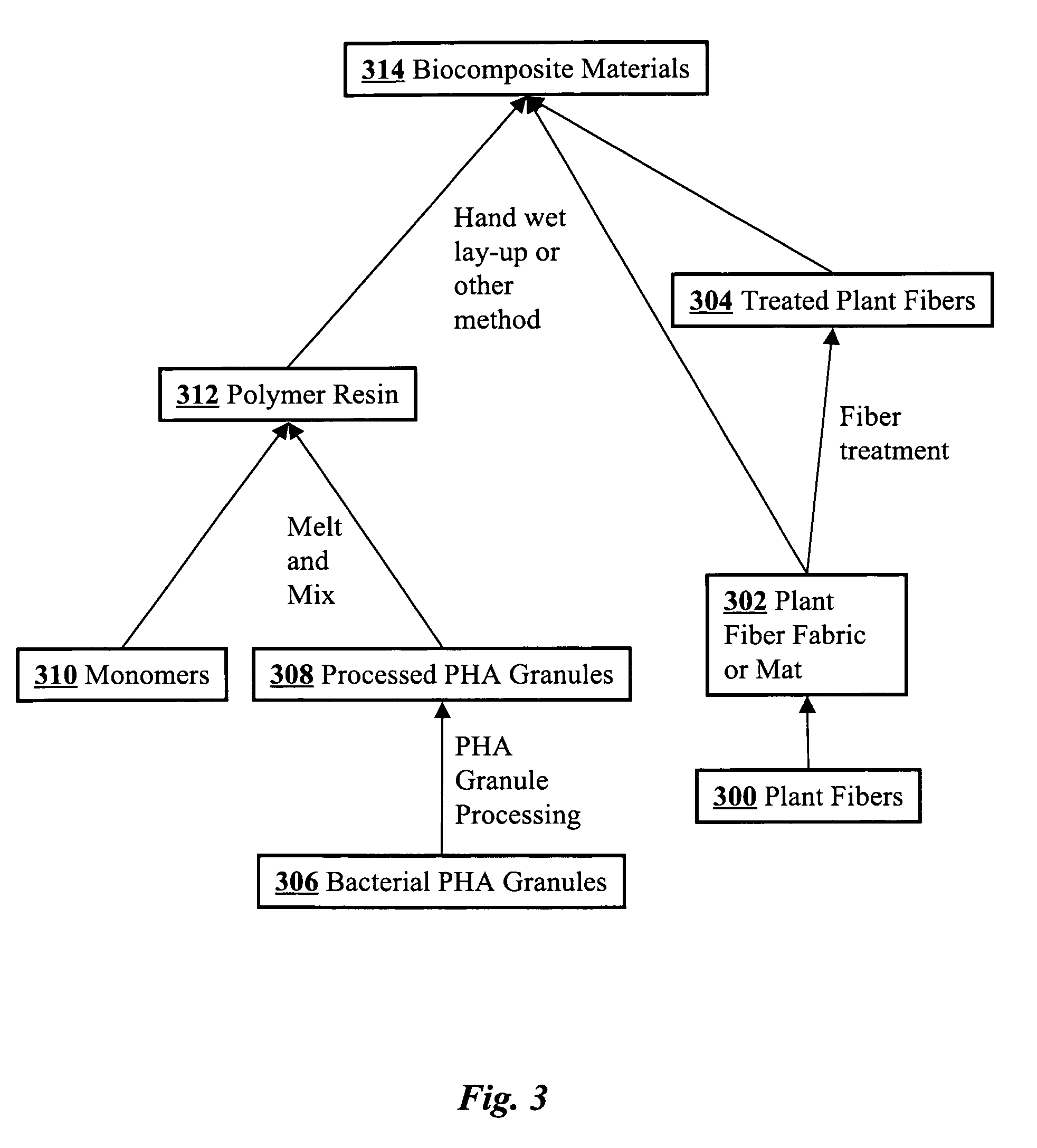
A biocomposite is produced from natural fiber fabrics embedded in a matrix of biosynthetic polyhydroxy-alkanoate (PHA) polymers. The PHA is synthesized using aerobic microbial biosynthesis using mixed bacterial cultures and a feedstock containing anaerobic degradation products such as methane and volatile fatty acids derived from microbial biodegradation of organic waste materials, which may include waste biocomposites. Monomers may be added to the synthesized PHA polymer to control mechanical properties of the resulting biocomposite. The natural fibers and / or PHA may be pretreated using various techniques to improve the bond between the fibers and the PHA resin matrix and water absorption resistance of the fibers. The composite may be a laminate of treated and untreated fabric layers, or differently treated layers, to achieve good in-service performance as well as rapid and / or optimal biogas production when taken out of service and put in an anaerobic environment to degrade.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
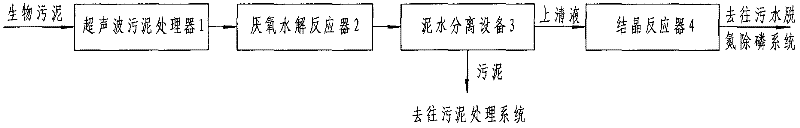
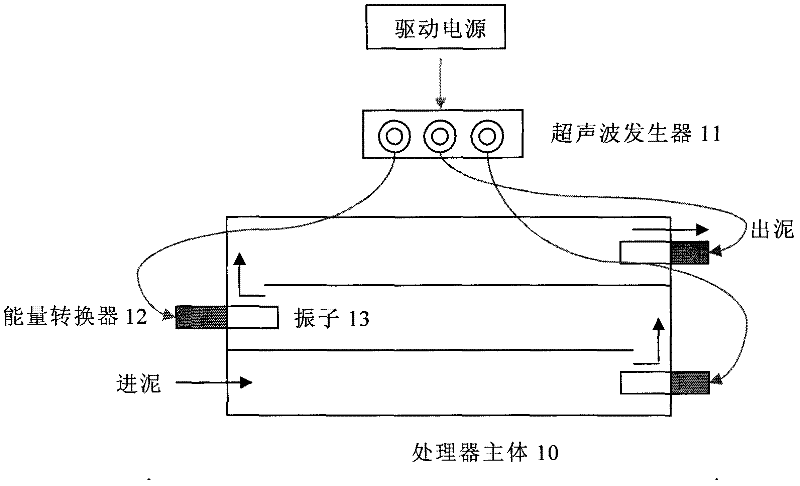
System and method for obtaining carbon source by utilizing ultrasonic enhanced sludge hydrolysis
InactiveCN102229463AImprove efficiencyIncrease speedBiological sludge treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentPropanoic acidUltrasonic cavitation
The invention relates to a system and method for obtaining a carbon source by utilizing ultrasonic enhanced sludge hydrolysis. The biological sludge in a municipal sewage plant is used as a raw material; the flocculation structure and cell wall of the sludge are firstly damaged by utilizing a waterpower shear force generated by an ultrasonic cavitation effect; the sludge after ultrasonic preprocessing is added to an anaerobic hydrolysis reactor; and under anaerobic conditions, macromolecular solid organic matters are finally converted into volatile fatty acids (VFAs) such as acetic acid, propionic acid, butyric acid and the like through a series of biological hydrolytic action. In the invention, the efficiency and velocity for a sludge to release a carbon source are improved by utilizing the coupling of ultrasonic processing and anaerobic hydrolysis processes, and the N (nitrogen) and P (phosphorus) which are released by hydrolysis are effectively eliminated and recovered by utilizing a crystallization method. The invention can solve the problem of carbon source insufficiency of the existing denitrification and dephosphorization process and realizes the stabilization and resource of the sludge to some extent. Simultaneously, because the hydrolysis velocity of the sludge is enhanced, the hydrolysis time of the sludge is greatly shortened and the investment and operating cost of engineering are lowered.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL RES INST OF ENVIRONMENT PROTECTION
Bacterial poly(hydroxy alkanoate) polymer and natural fiber composites
ActiveUS20080160567A1Improve bindingGood in-service performanceLayered productsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVolatile fatty acidsResin matrix
A biocomposite is produced from natural fiber fabrics embedded in a matrix of biosynthetic polyhydroxy-alkanoate (PHA) polymers. The PHA is synthesized using aerobic microbial biosynthesis using mixed bacterial cultures and a feedstock containing anaerobic degradation products such as methane and volatile fatty acids derived from microbial biodegradation of organic waste materials, which may include waste biocomposites. Monomers may be added to the synthesized PHA polymer to control mechanical properties of the resulting biocomposite. The natural fibers and / or PHA may be pretreated using various techniques to improve the bond between the fibers and the PHA resin matrix and water absorption resistance of the fibers. The composite may be a laminate of treated and untreated fabric layers, or differently treated layers, to achieve good in-service performance as well as rapid and / or optimal biogas production when taken out of service and put in an anaerobic environment to degrade.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
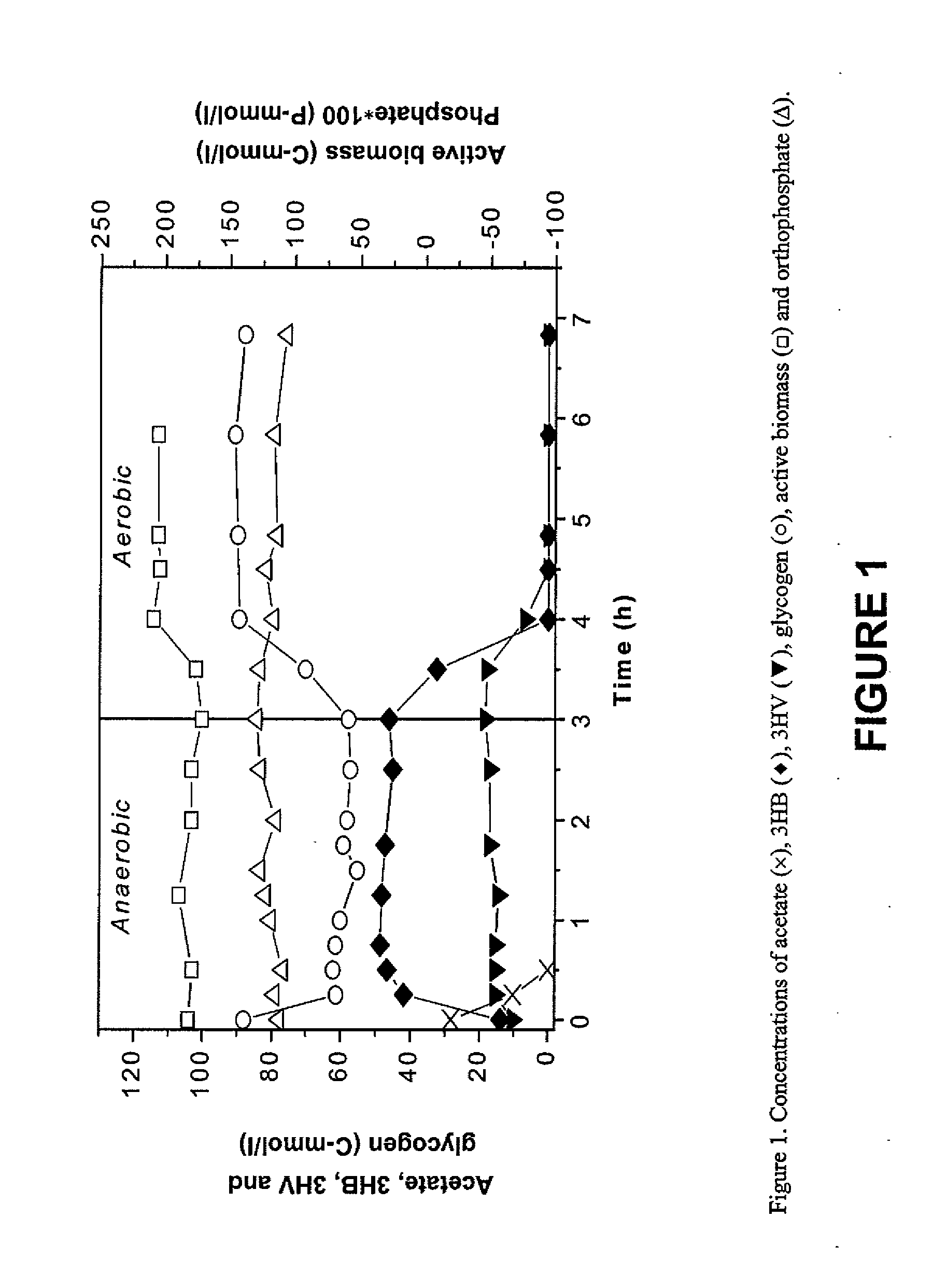
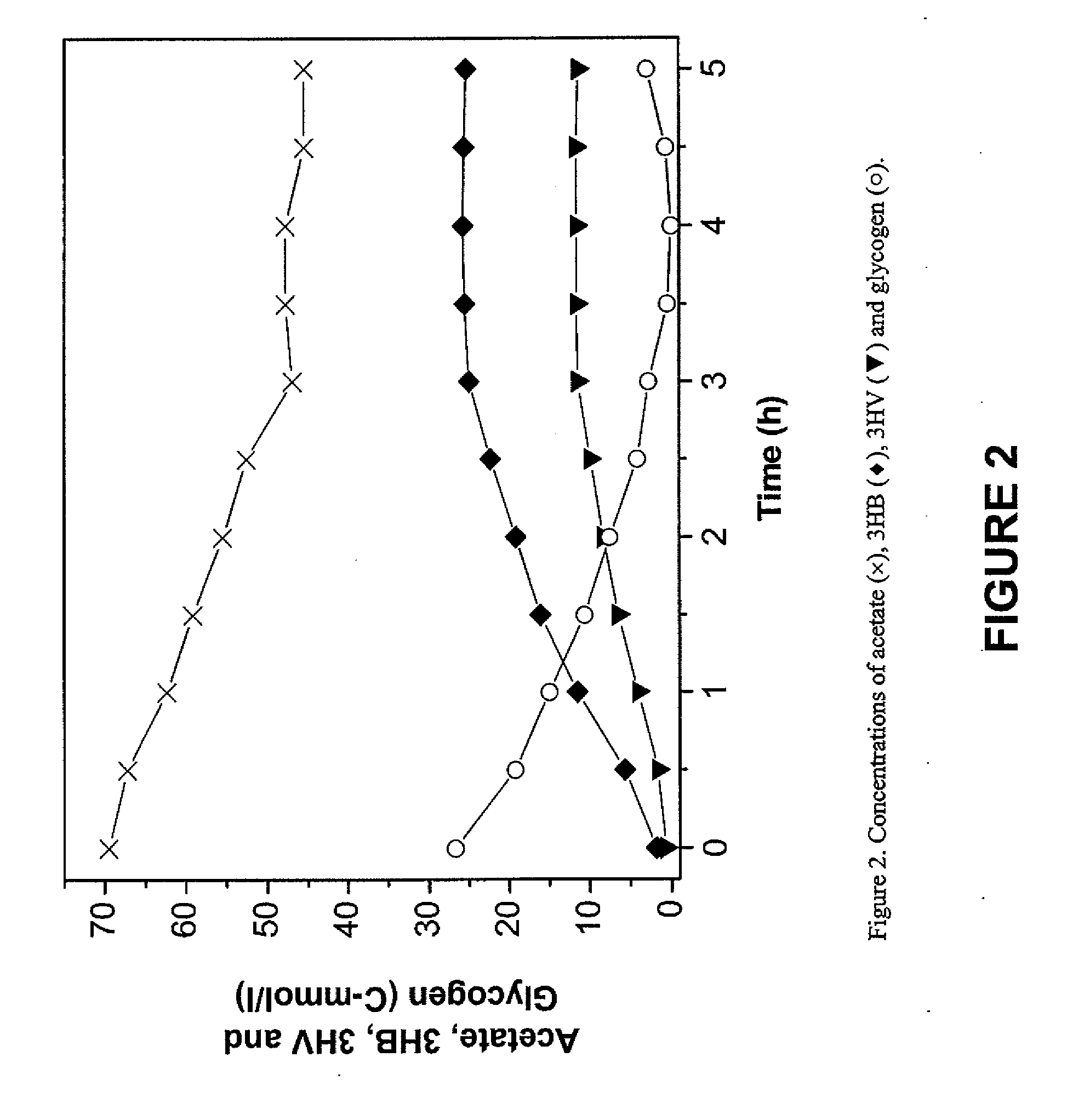
Process for Maximizing PHA Production in Glycogen Accumulating Organisms
InactiveUS20100200498A1High load rateHigh level of intracellularBacteriaSolid waste disposalBiological bodyAnaerobic aerobic
A process is provided for increasing the production of PHA in a mixed culture biomass. In a first stage of the process, organic material associated with a substrate is converted to volatile fatty acids. In the case of a wastewater treatment process, if the wastewater includes sufficient volatile fatty acids (VFAs) to support the process, then it is unnecessary to convert organic material to VFAs. In a second stage of the process, an anaerobic-aerobic selection process is utilized to select glycogen accumulating organisms that cause these organisms to proliferate and dominate the open mixed culture biomass. By providing relatively high organic loading in the form of VFAs in the anaerobic treatment phase of the selection process, glycogen accumulating organisms having a relatively high level of stored glycogen are produced. In a third stage, the PHA accumulation process is practiced where the glycogen rich organisms are fed VFAs under anaerobic or aerobic conditions or combinations thereof. Through the consumption of externally supplied VFAs and internally stored glycogen, relatively high levels of PHA in the biomass are produced. Thereafter PHA is separated from the residual biomass.
Owner:VEOLIA WATER SOLUTIONS & TECH SUPPORT
Process for enhanced recovery of crude oil from oil wells using novel microbial consortium
InactiveUS7484560B2Low viscosityEnhanced overall recoveryBacteriaWaste based fuelBiotechnologyMetabolite
The present invention provides a microbial consortium containing three hyperthermophilic, barophilic, acidogenic, anaerobic bacterial strains for enhanced oil recovery from oil reservoirs where temperatures range from 70° C. to 90√ C. The said microbial consortium is unique in producing a variety of metabolic products mainly CO2, methane, biosurfactant, volatile fatty acids and alcohols in the presence of specially designed nutrient medium. These metabolic products increase sweep efficiency of crude oil from oil bearing poles of rock formation. The present invention also provides a process for enhancing the oil recovery by in situ application of the said microbial consortium.
Owner:INSTITUE OF RESERVOIR STUDIES +1
Sewage treatment system
InactiveUS6893566B2Lower cost of capitalReduce operating costsSludge treatment by thermal conditioningSolid waste disposalActivated sludgeWaste stream
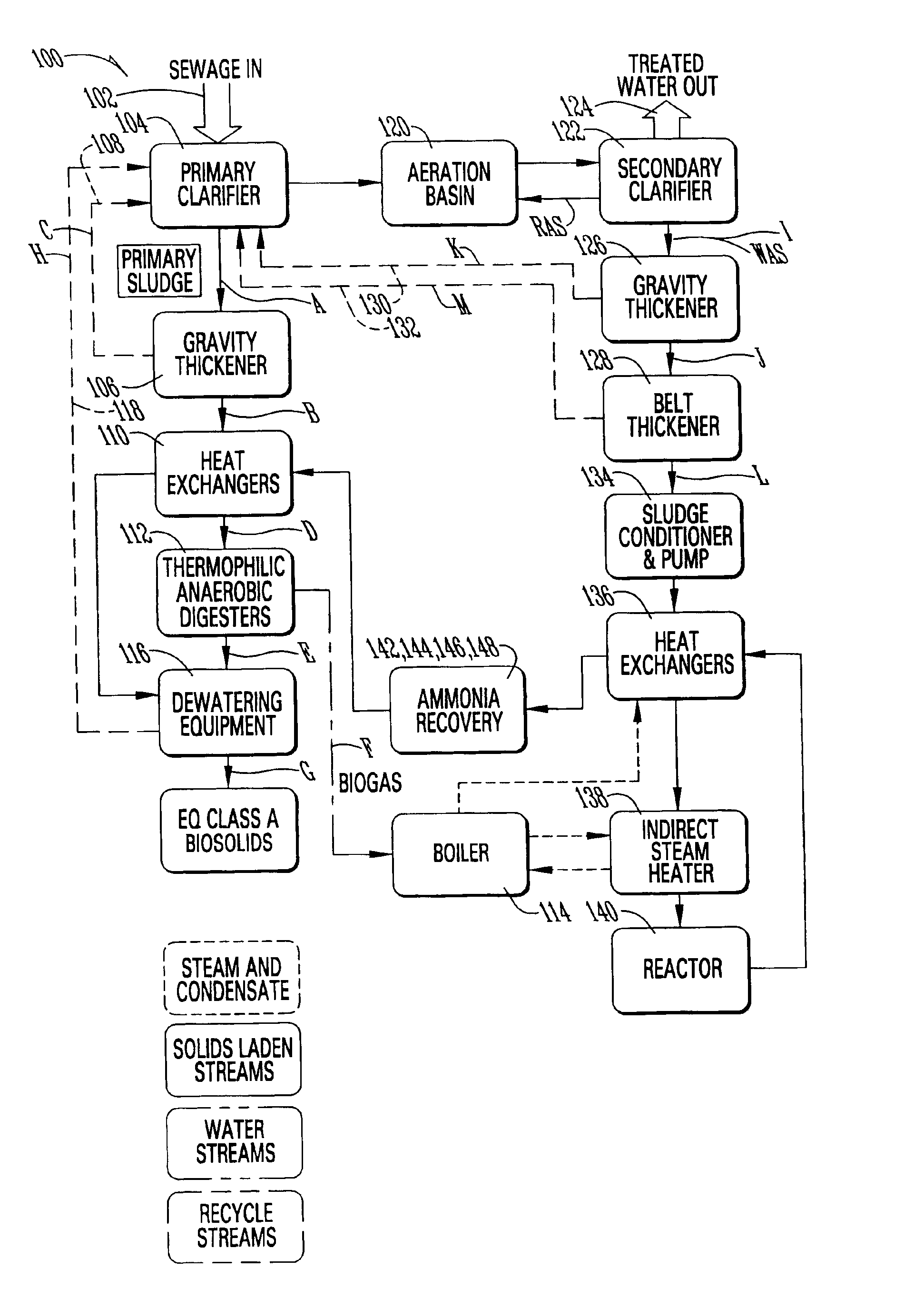
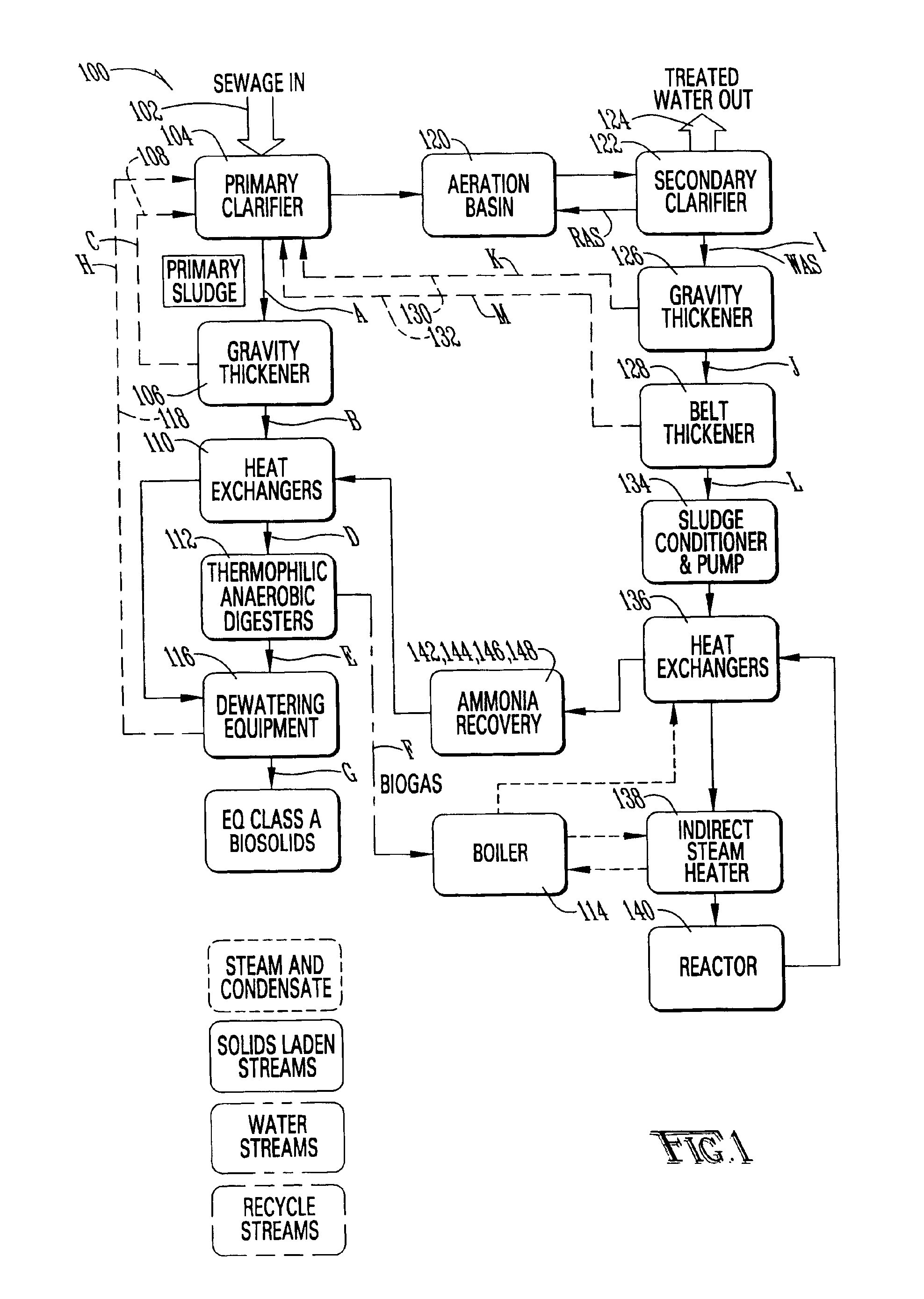
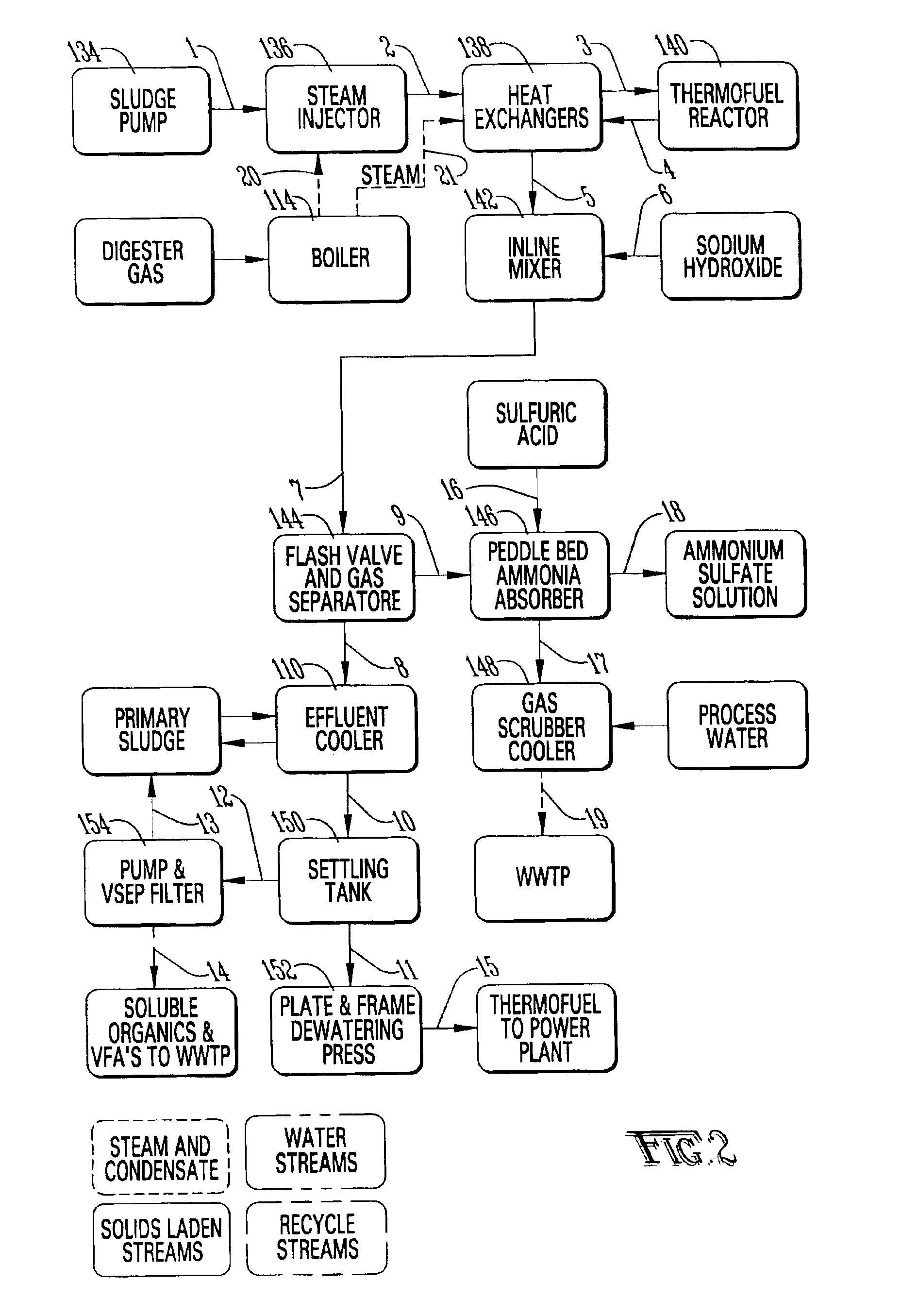
A sewage treatment system is disclosed in which a waste stream is separated into a primary sludge and water effluent, and the primary sludge is anaerobically digested and dewatered to produce a Class A biosolid. The water effluent is aerobically digested and separated to provide a waste activated sludge. The waste activated sludge is heated in a two-stage process with steam injection and indirect steam before it is passed to a hydrothermal process. The pH of the treated waste activated sludge is then increased, and the nitrogen is stripped and recovered as an ammonium salt. A low nitrogen stream with volatile fatty acids and soluble organics is then separated and fed to the aerobic digester. Biogas generated during anaerobic digestion provides energy for heating the waste activated sludge for the hydrothermal process, and reject heat from the hydrothermal process heats the primary sludge for thermophilic anaerobic digestion.
Owner:FASSBENDER ALEXANDER G
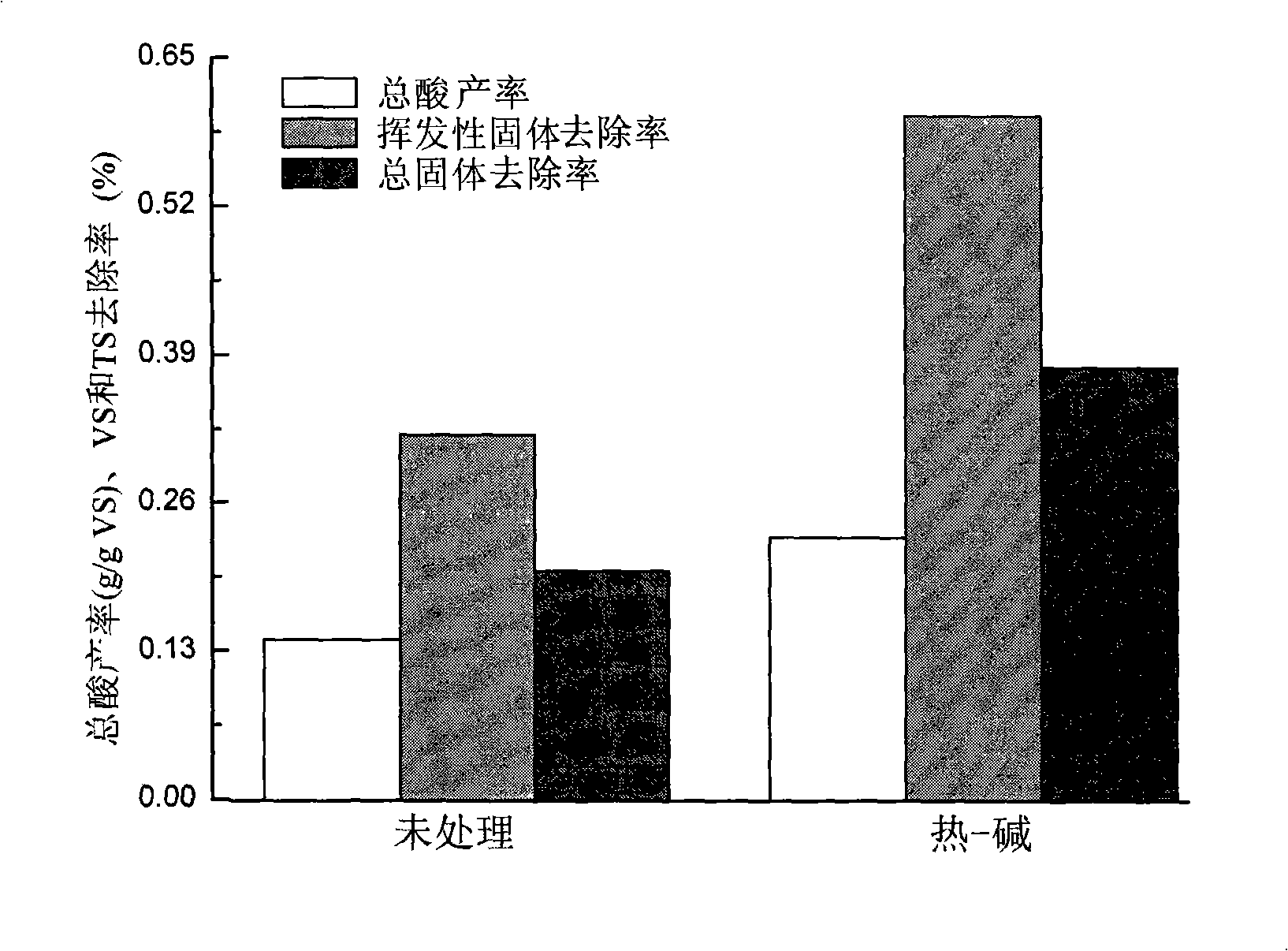
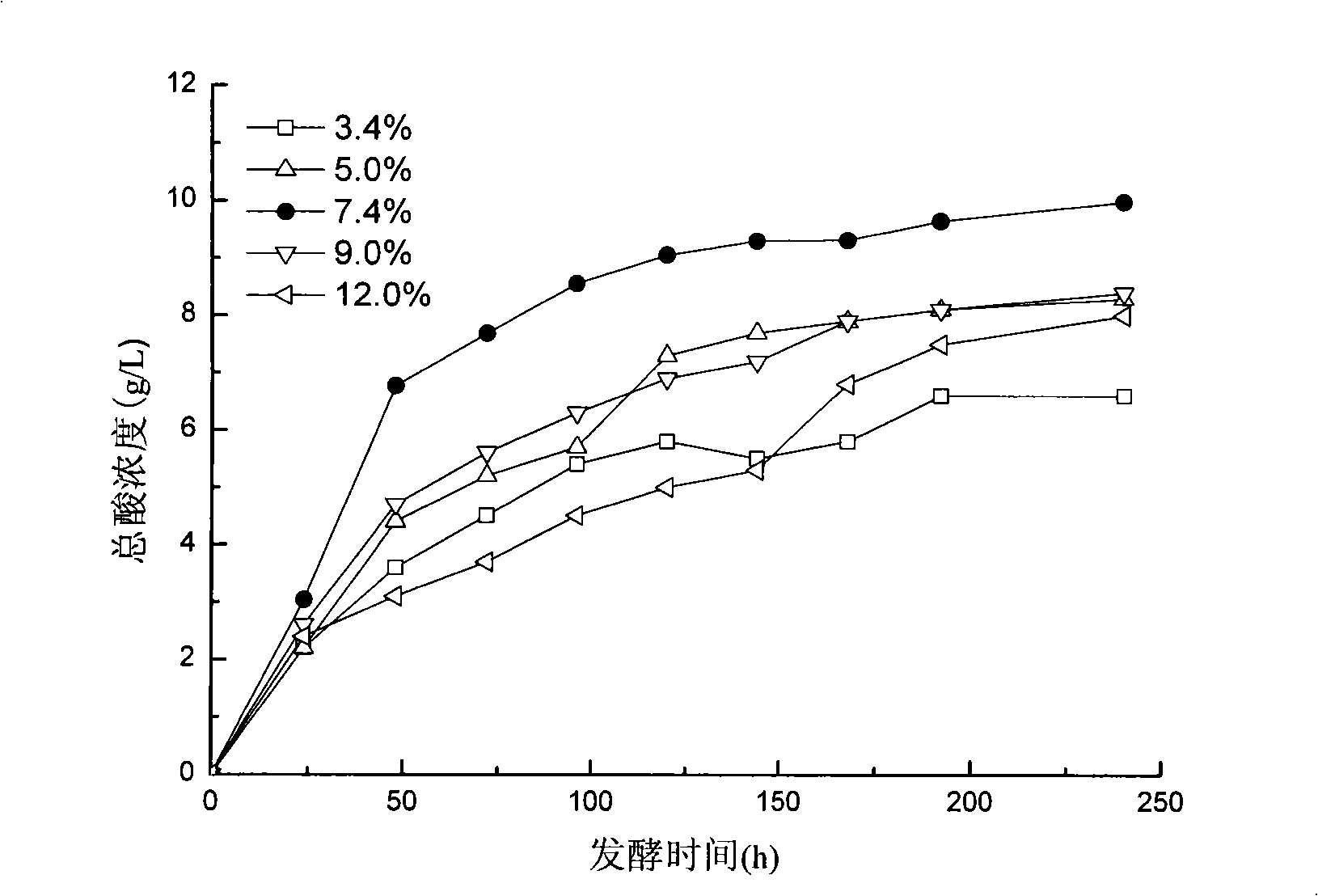
Method for preparing volatile fatty acid with high solid concentration organic castoff heat-alkali preprocessing post anaerobic fermentation
InactiveCN101314783AHigh yieldShorten the fermentation cycleWaste based fuelFermentationVolatile fatty acidsGram
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing volatile fatty acid by using sludge as substrate
InactiveCN101705256ARealize resourcesIncreased rate of hydrolytic acidificationFermentationVolatile fatty acidsHydrolysis
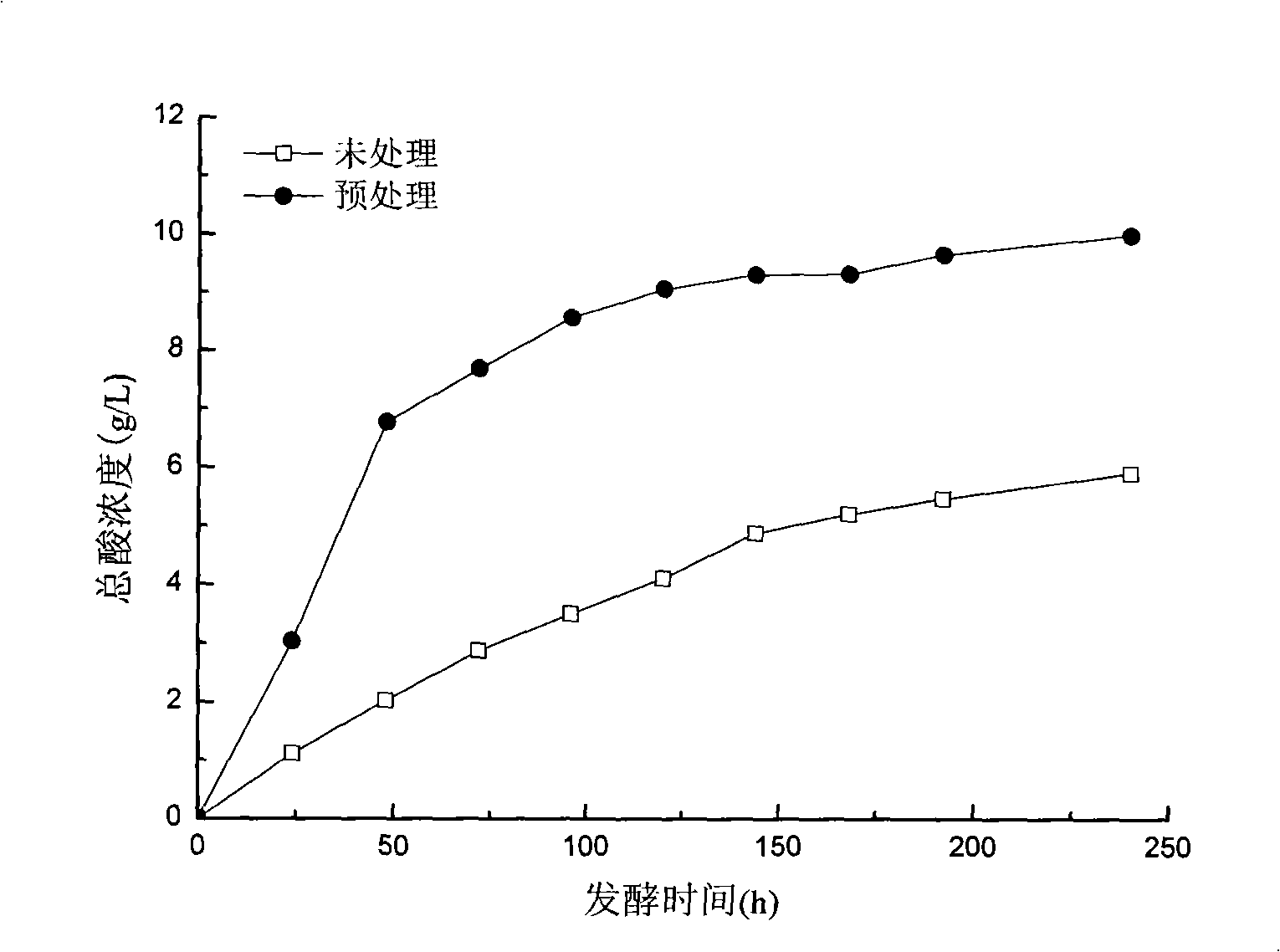
The invention provides a method for producing volatile fatty acid by using sludge as a substrate and relates to a fatty acid. The method comprises the following steps of: using mixed sludge of primary sludge and residual sludge of a sewage treatment plant as a raw material, adding sodium hydroxide, stirring the mixture, naturally cooling to a room temperature after heating, and adjusting a pH value with hydrochloric acid until neutral; and using anaerobic sludge as an inoculum, stirring the anaerobic sludge under an anaerobic condition, and carrying out anaerobic fermentation to obtain the volatile fatty acid. The method produces acid by using the residual sludge of the urban sewage treatment plant, realizes reclamation of the sludge, reduces pollution of organic matters in the sludge to environment at the same time, and is a recycling economic mode of the urban sewage treatment plant. The hydrolysis acidification rate of the sludge is greatly improved and the volatile fatty acid is accumulated in a short time in a pretreatment way. Meanwhile, because of greatly improving the hydrolysis rate of the sludge and shortening anaerobic fermentation time of the sludge, the method has significance for improving and optimizing the conventional sludge treatment systems and reducing investment and running cost.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for deep denitrification of metaphase landfill leachate through single-stage SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) post denitrification treatment
ActiveCN103755028AStart fastThe reaction device is simpleTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesVolatile fatty acidsEmission standard
The invention discloses a method for deep denitrification of metaphase landfill leachate through single-stage SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) post denitrification treatment, which belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment by using biochemical process. Aiming at the characteristics that the landfill leachate is high in organism concentration, high in ammonia concentration, high in C / P ratio (grater than 200), the invention discloses a real-time control method with the combination of 'anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic' operation modes, and SBR post denitrification is achieved. Under long-term domestication, glycan bacteria (GAO) can be enriched, volatile organic acids (VFA (Volatile Fatty Acid)) in water are converted into poly-beta-hydroxy-alkanoic acid ester (PHA) through glycogen glycolysis at an anaerobic stage by using GAO, in an aerobiotic stage (the dissolved oxygen is less than 0.8mg / L), when partial nitrification is carried out, most part of PHA is converted into glycogen, and in the anoxic stage, the residual PHA and the glycogen are utilized to perform carbon source denitrification, so that the effluent meets the latest national emission standard. The method has the advantages of simple devices, rapid starting, freedom of external carbon source, good denitrification effect, simplicity in operation, low cost and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Reduction of odor gases from waste using plant-derived oils
InactiveUS6902726B1Reduce productionPromoting lactic acid accumulationOrganic chemistryMicroorganismsVolatile fatty acidsAnaerobic bacteria
Plant-derived oils, carvacrol and thymol, when added to human or animal waste reduce the production of gas and short-chain volatile fatty acids, and the viability of total anaerobic bacteria and fecal coliforms. In an embodiment, carvacrol or thymol are combined with eugenol.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF AGRI THE
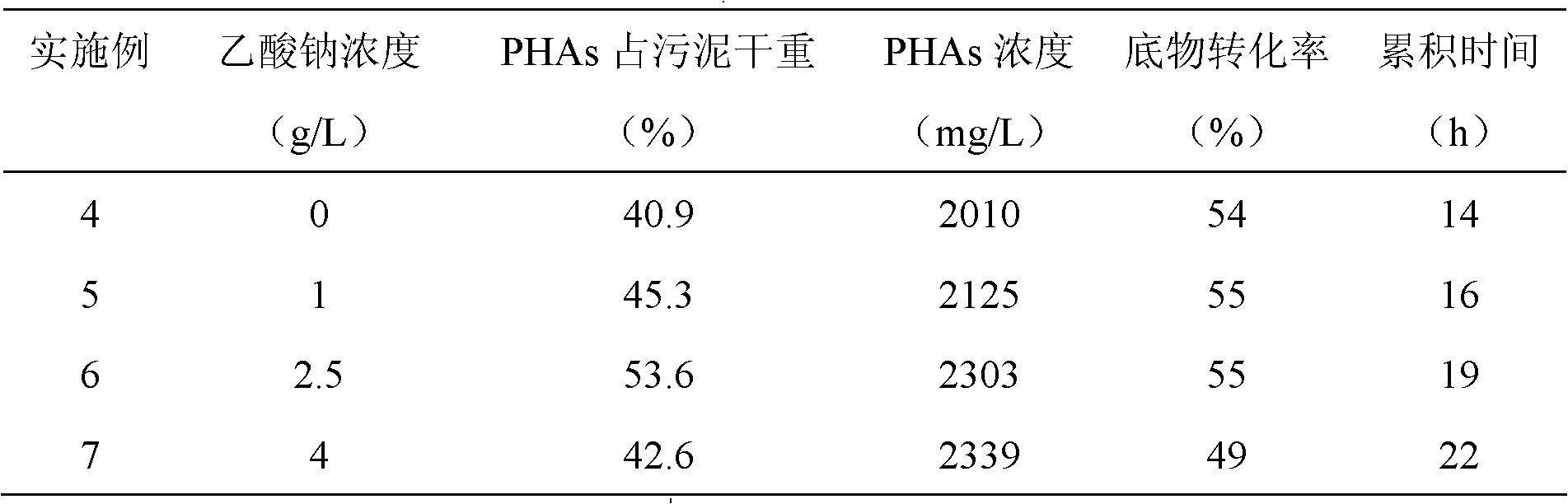
Method for synthesizing polyhydroxyalkanoate by using residual sludge broth as substrate
ActiveCN102505025ARealize resourcesReduce manufacturing costSludge processingFermentationSodium acetateVolatile fatty acids
The invention provides a method for synthesizing polyhydroxyalkanoate by using a residual sludge broth solution as a substrate, and relates to a synthesis method of polyhydroxyalkanoate. The method comprises the following steps: putting urban aerobic active sludge into a sludge domestication device to domesticate for one domestication period according to a sequence of water intake, aerobic aeration, sludge discharging, precipitating and water discharging, wherein the aeration amount is controlled to be between 1 and 3L / L / min in aerobic aeration, and the domestication is continuously carried out for 18-22 periods to obtain the active sludge stabilized through domestication; putting the urban residual sludge into a reactor, adding sodium hydroxide, carrying out hot alkali pretreatment, and regulating the pH value to be neutral; inoculating anaerobic sludge, stirring to perform anaerobic fermentation, and separating to obtain volatile fatty acid fermentation stock; and putting the active sludge stabilized through domestication into a synthesis reactor, adding the volatile fatty acid fermentation stock, synthesizing polyhydroxyalkanoate by virtue of sludge, regulating the pH value to be neutral, and adding sodium acetate utilized as an external carbon source under an intermittent aeration condition so as to synthesize the polyhydroxyalkanoate.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
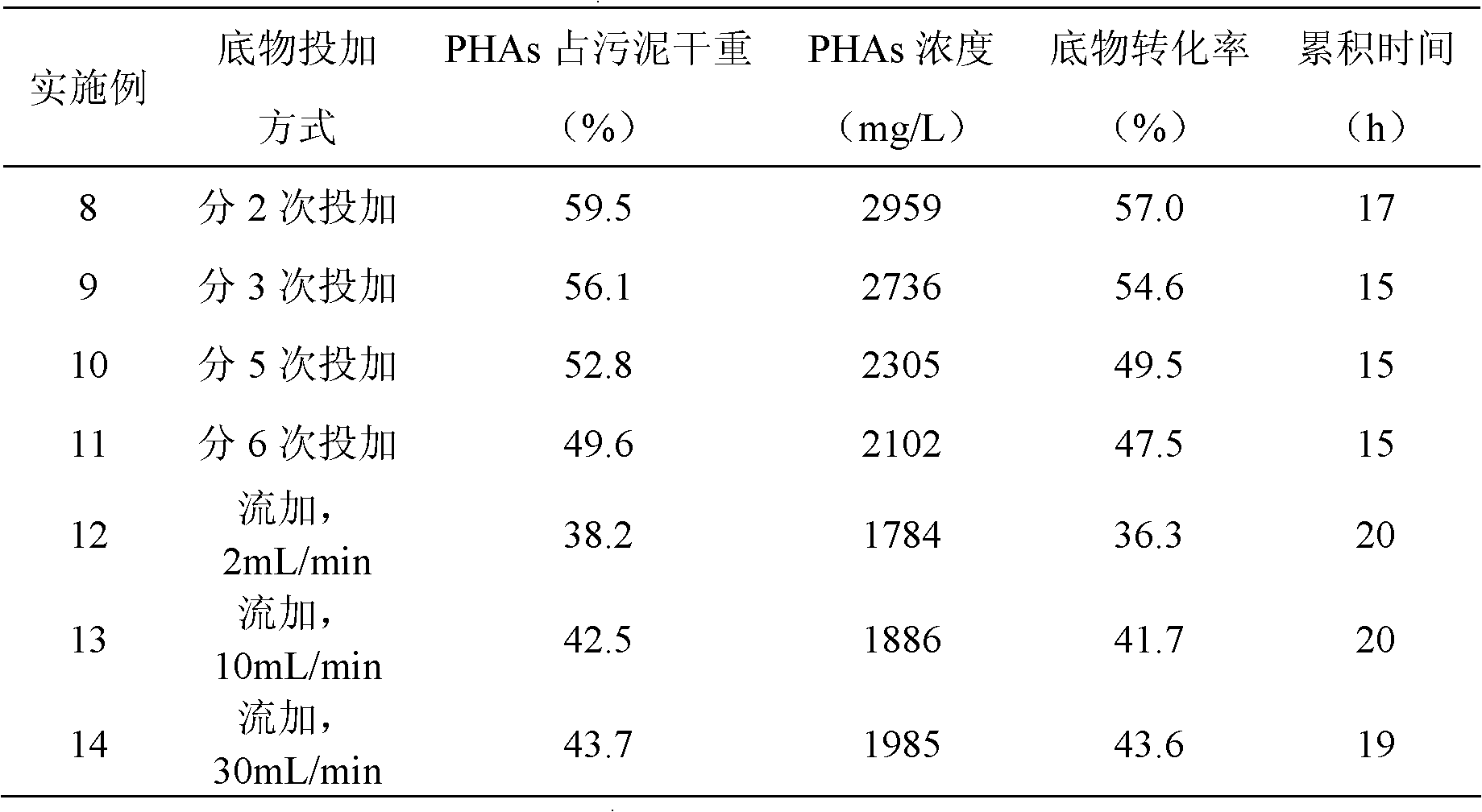
Method for producing short-chain volatile fatty acids by utilizing kitchen wastes and short-chain volatile fatty acids
InactiveCN104498541AIncrease productionGood denitrification and phosphorus removalFermentationBiotechnologyVolatile fatty acids
The invention discloses a method for producing short-chain volatile fatty acids by utilizing kitchen wastes and the short-chain volatile fatty acids. The method specifically comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing and stirring the kitchen wastes serving as a fermentation substrate and sludge serving as an inoculum, thereby obtaining a fermentation matrix; and adding alkyl polyglucosides into the fermentation matrix, and performing anaerobic fermentation under a stirring condition. The reduction, recycling and innocent treatment of the kitchen wastes are realized, and the method has the advantages of low operating cost, high profit, high yield of the short-chain volatile fatty acids and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
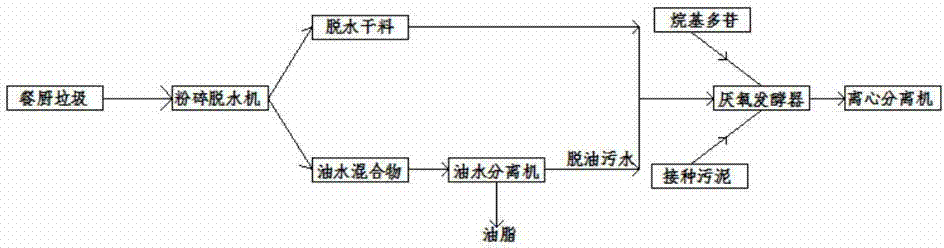
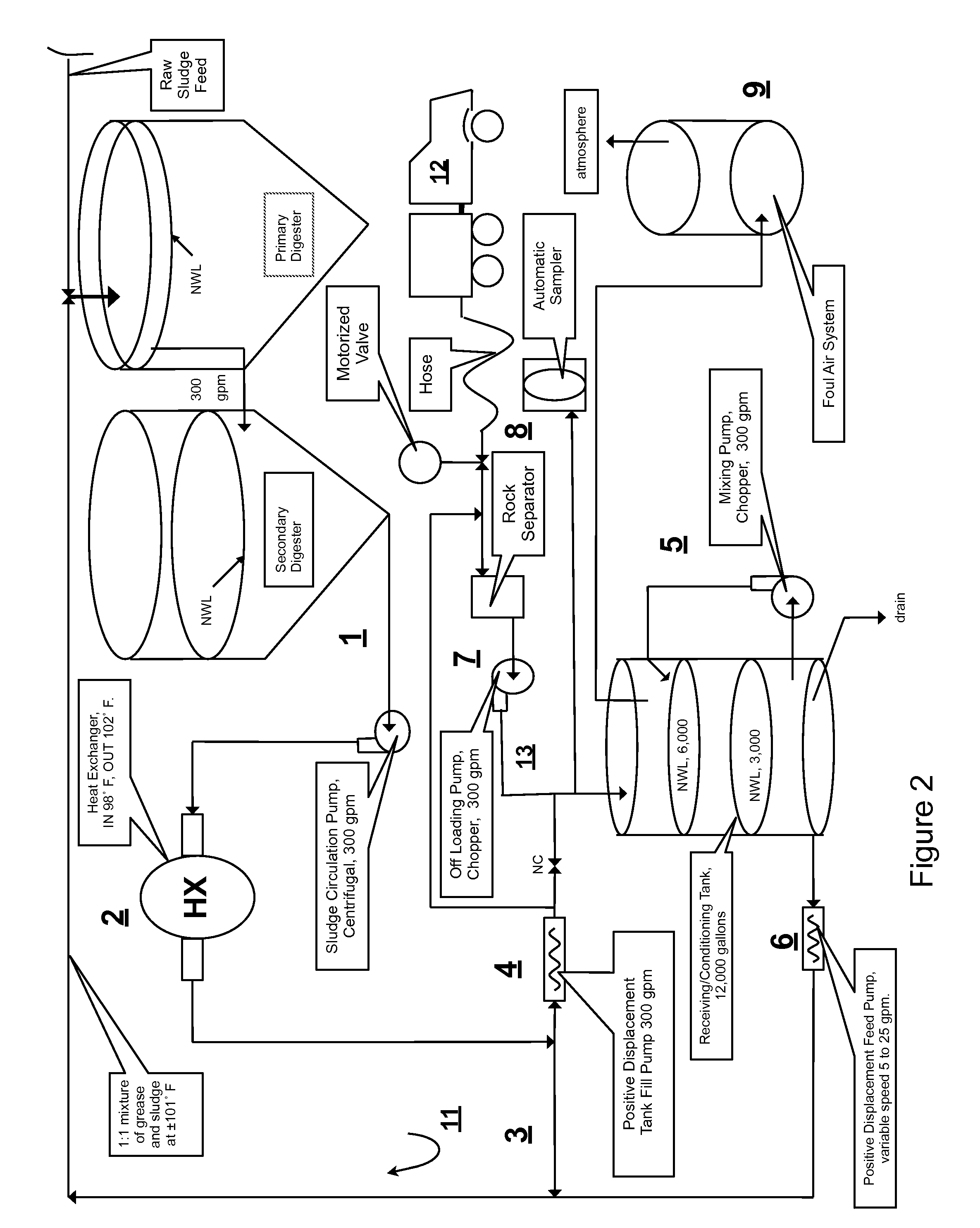
Integrated cogeneration wastewater sewage and waste polar fats/ oils/ greases/waxes (FOG) waste treatment method and facility
InactiveUS20080203014A1Rule out the possibilityLow solidsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsGeneral water supply conservationOil and greaseVolatile fatty acids
Integrated sewage or digestible wastes, and fats, oils, greases and waxes (FOG) waste treatment methods, systems and facilities include a slipstream loop incorporating circulation pumps, hot water heat exchangers and conventional anaerobic digesters for continuously circulating actively digesting sludge at a rate to preclude solid settlement accumulation as a warm flowable slurry source. The warmed actively digesting sludge is pumped from the slipstream loop through a rock trap into a delivery / input loop both for aiding transport or delivery of FOG waste to, and for partially filing a closed receiving / conditioning holding tank, where the warmed actively digesting sludge softens and liquefies the FOG wastes offloaded into the holding tank for further treatment at a desired treatment temperature range (whether psychrophilic, mesophilic, or thermophilic). The contents of the closed receiving / conditioning holding tank are continuously mixed by a bottom-top recirculation chopper pump to pre-treat the FOG wastes, liquefying and decreasing solids particle size allowing acidogens in the actively digesting sludge to pre-digest such wastes producing volatile fatty acids, some biogas and a highly bioreactive, flowable feedstock slurry. The produced highly bioreactive, flowable feedstock slurry can then injected back into the actively digesting sludge slipstream loop at a controlled rate where the resultant mixture then is introduced, together with raw sewage or other digestible wastes, into input or head ends of waste treatment systems having anaerobic digesters for digestion of solids and steady-state methane production. Advantages of the integrated system relate to a partial digestion of the FOG in the reaction / holding tank generating volatile fatty acids that suppress expression of methane producing methagens in the holding tank, increased steady-state methane production and significantly reduced solids volume of treated digestible wastes (sewage) and FOG wastes.
Owner:MAGNER JOSEPH A +1
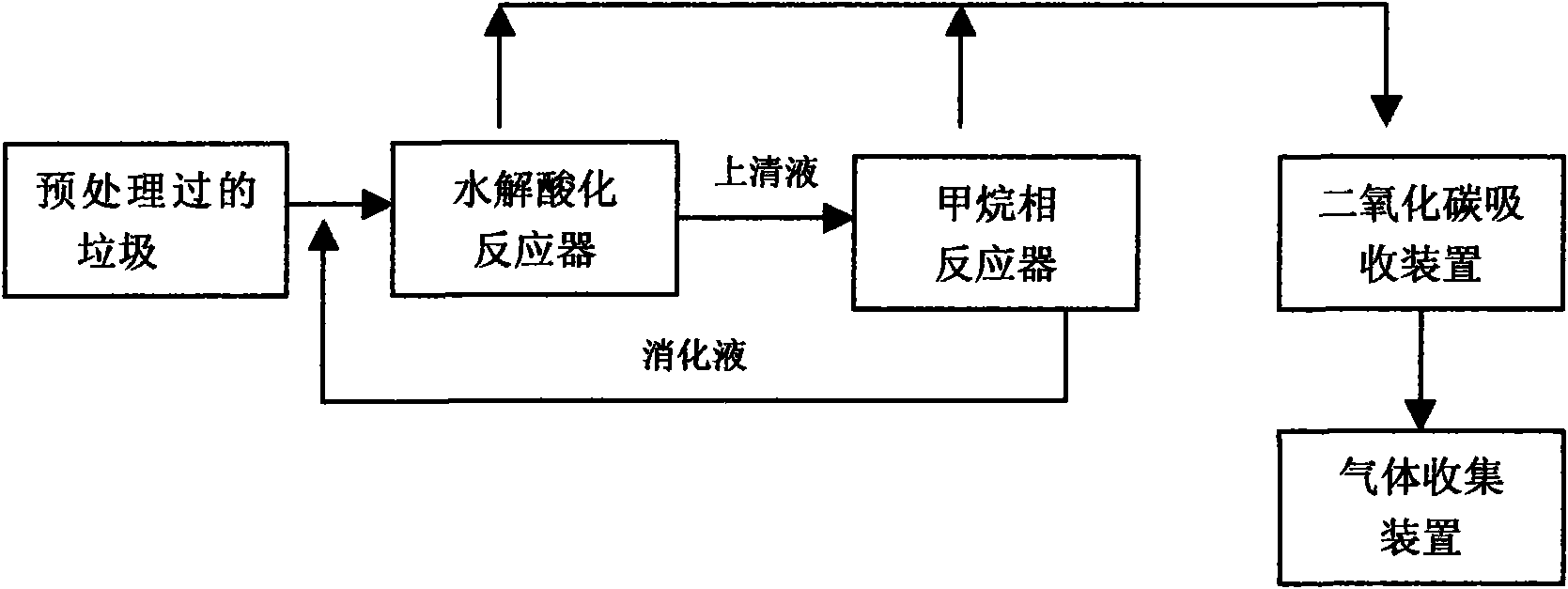
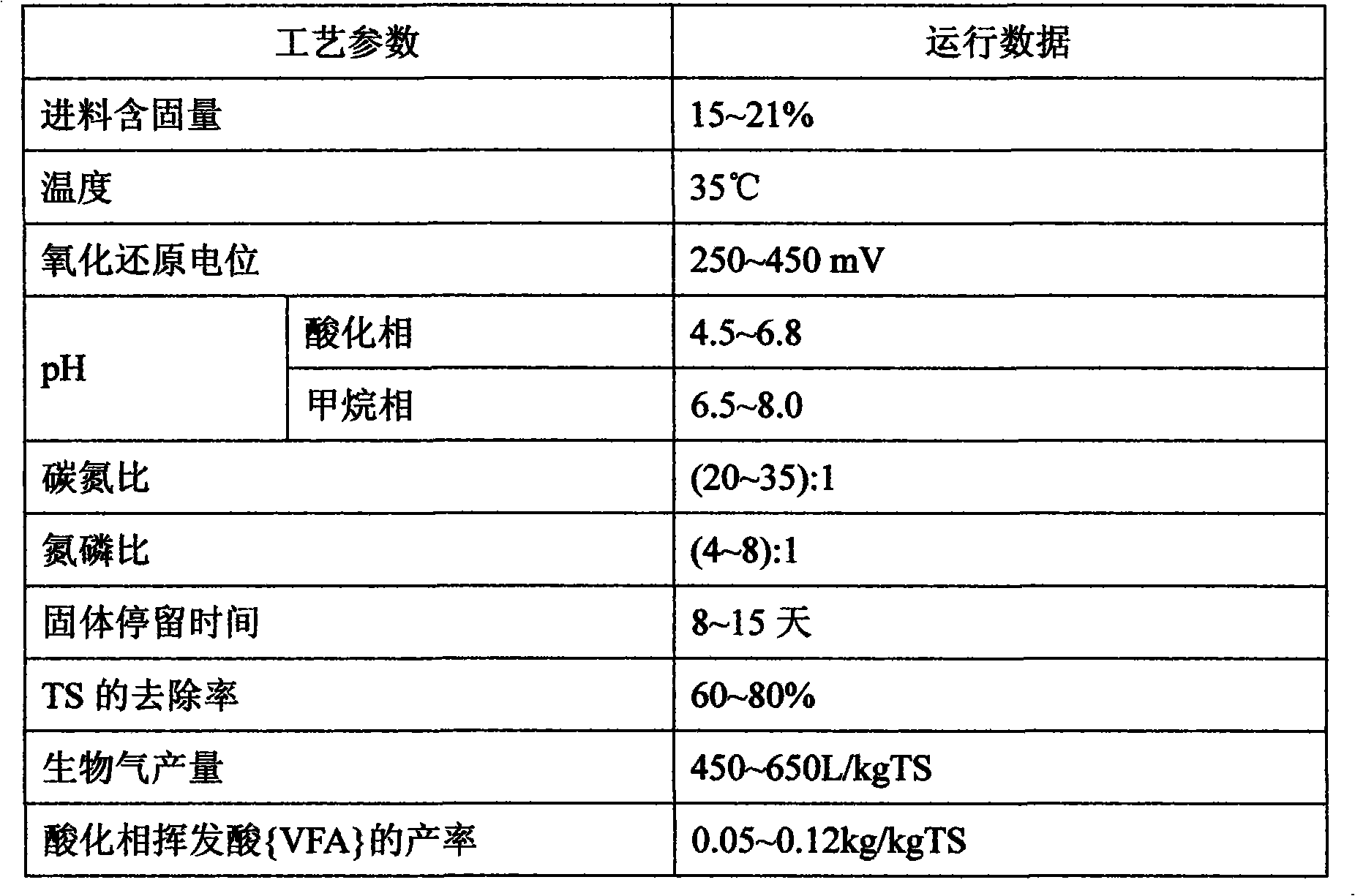
Two-phase wet-type anaerobic digestion treatment method of food waste
InactiveCN101862747AInhibitory activityLow operating costSolid waste disposalVolatile fatty acidsProduct gas
The invention relates to a two-phase wet-type anaerobic digestion treatment method of food waste, which adopts an intermittent two-stage wet-type anaerobic digestion process aiming at food waste treatment characteristics: the solid-liquid separation is simultaneously achieved when crushed food waste is put in a hydrolysis acidification reactor to carry out acidification, acidified liquid enters into a methane-phase reactor to carry out continuous digestion, digested gas passes through a methane and carbon dioxide detector and a carbon dioxide absorber in sequence and finally enters into a gas collection device, and effluent water digestion liquid of a methane phase is recycled to an acidification phase. In the invention, the solid-liquid separation is simultaneously realized in the hydrolysis acidification process, therefore, the production ratio of volatile fatty acid is increased, and the hydraulic retention time of the acidification phase is reduced; effluent water of the methane phase is recycled to the acidification phase so as to dilute the input concentration and be capable of adjusting the pH value of the acidification reaction, therefore, the operation cost is saved, the pH value is easy to control, and the acidification effect is remarkably enhanced.
Owner:上海派升环保科技有限公司
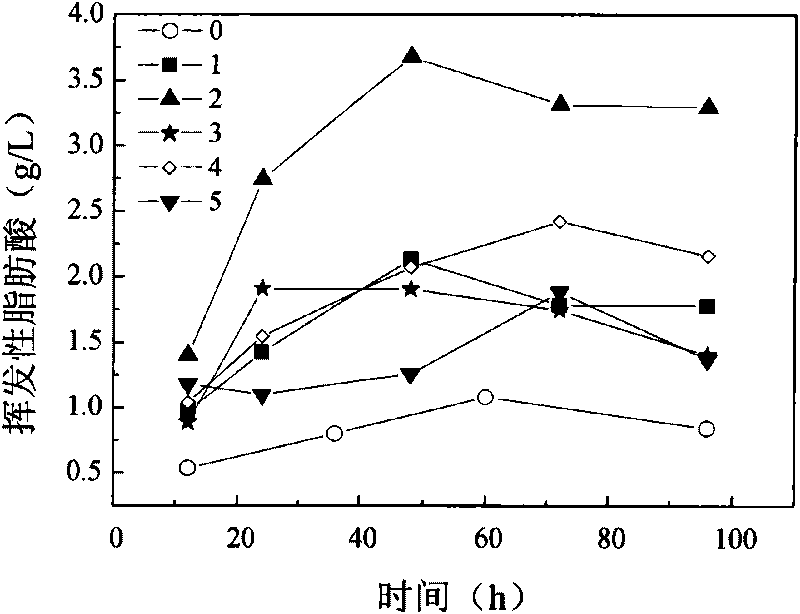
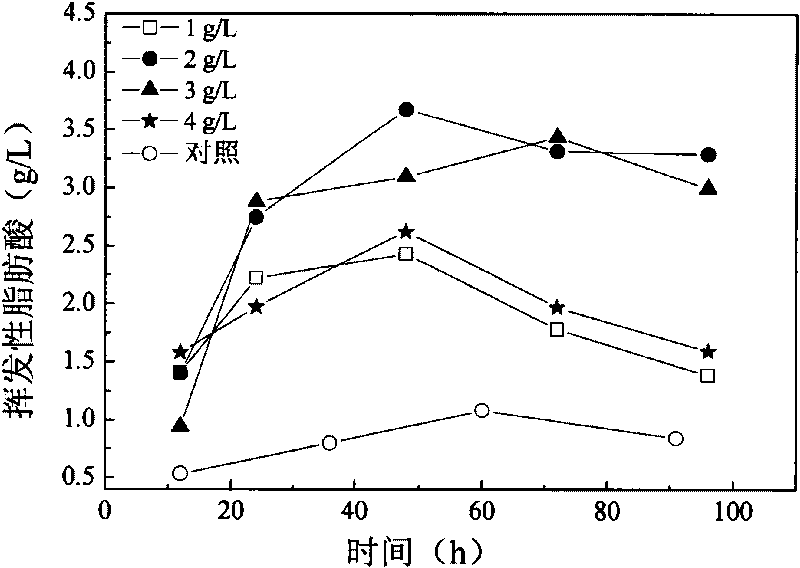
Short-chain volatile fatty acid and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a short-chain volatile fatty acid and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method for the short-chain volatile fatty acid comprises the following steps of employing sludge as a fermentation substrate; adding sodium nitrite into the fermentation substrate, performing pretreatment in an acid environment, and performing anaerobic fermentation under an alkaline condition to obtain the short-chain volatile fatty acid. According to the short-chain volatile fatty acid and the preparation method thereof, the sludge of a sewage treatment plant is taken as a raw material, and is jointly treated by virtue of free nitrite pretreatment and alkaline anaerobic fermentation, and the concentration of free nitrite in the system, the pretreatment time, the fermentation pH value and the action of microorganisms in the sludge are controlled to maximally convert undissolved sludge organic matters in the sludge into the short-chain volatile fatty acid, so that the yield of the volatile fatty acid produced from the sludge is further increased on the basis of resourcefully utilizing the sludge and reducing environmental pollution caused by the sludge, and the reaction time is shortened; the short-chain volatile fatty acid and the preparation method thereof have the advantages of high product yield, simple preparation method, energy conservation, consumption reduction, low running cost and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
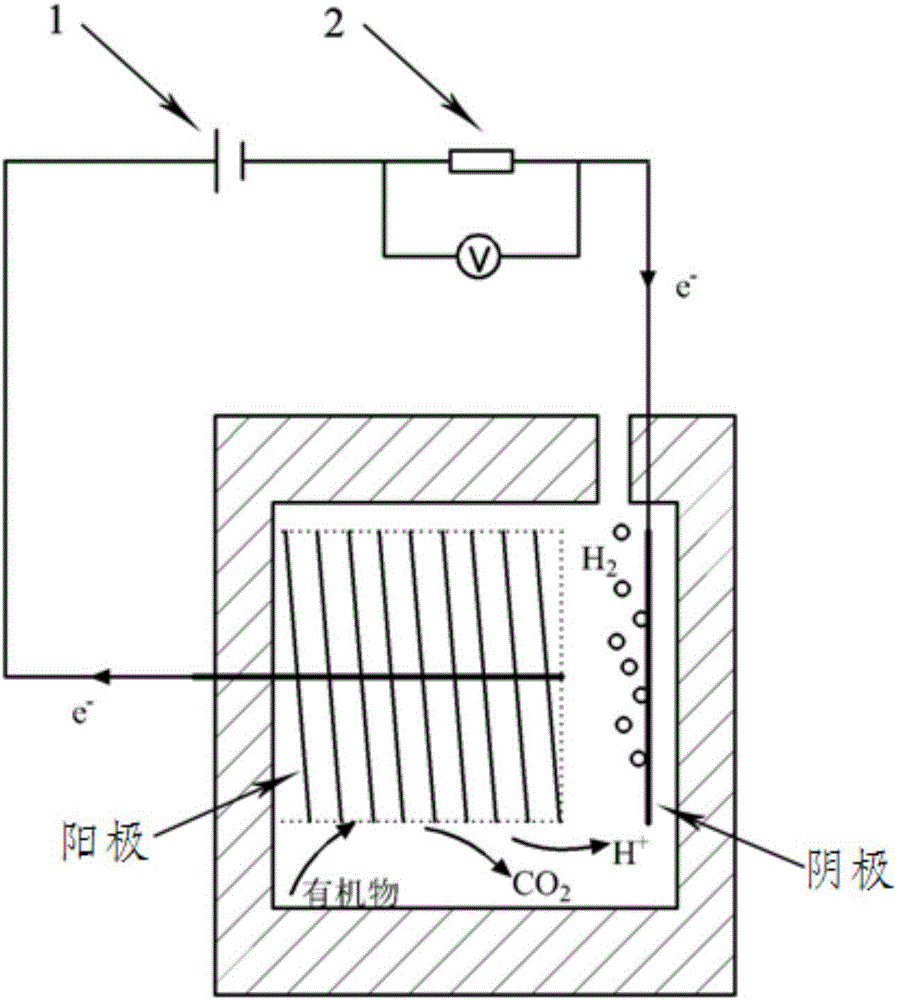
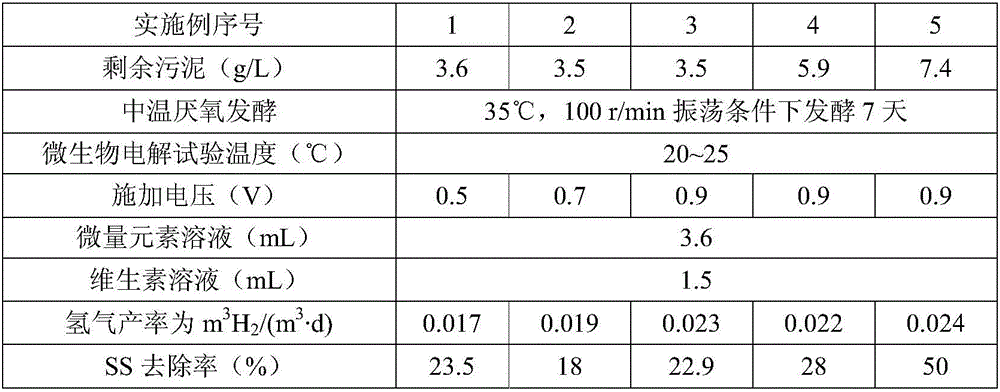
Method for producing hydrogen from residual sludge by anaerobic fermentation and microbial electrolysis cell coupling
ActiveCN106011176AAchieve stabilizationFully degradedSludge treatmentSpecific water treatment objectivesSludgeVolatile fatty acids
The invention discloses a method for producing hydrogen from residual sludge by anaerobic fermentation and microbial electrolysis cell coupling. The method comprises the following steps: S1, enriching anode electricity production bacteria by taking the residual sludge as an inoculums and using a double-chamber microbial fuel cell at the temperature of 20 to 25 DEG C, wherein when an external resistance voltage value of the microbial fuel cell tends to be stable and at least three cycles recur, enrichment of anode microorganisms is completed; S2, performing anaerobic fermentation on the residual sludge at the temperature of 35 DEG C under an oscillation condition for 7 days, to obtain residual sludge pretreated by medium-temperature anaerobic fermentation; S3, operating a single-chamber microbial electrolysis cell by taking the pretreated residual sludge as a substrate at the temperature of 20 to 25 DEG C under external voltage of 0.5 to 0.9 V, to produce hydrogen from the residual sludge. According to the method, products, such as volatile fatty acid, a carbohydrate and proteins, obtained by anaerobic fermentation of the residual sludge and a microbial electrolysis technology are used to produce hydrogen from small-molecule organic matters in fermentation supernate, so that reutilization of fermentation final products is realized.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
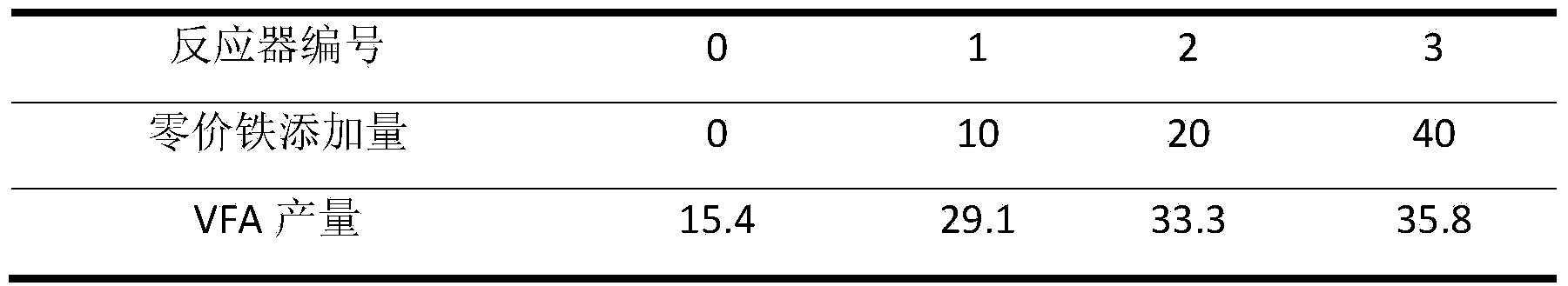
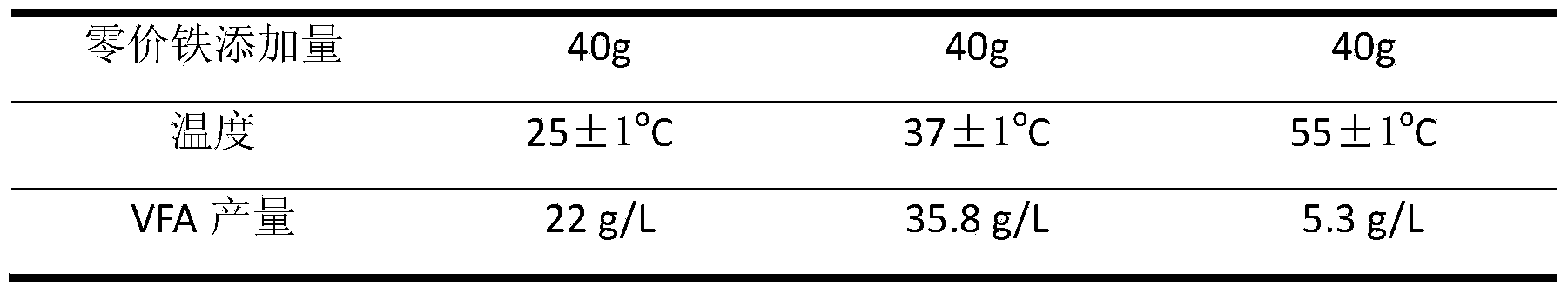
Method for producing volatile fatty acid through promoting anaerobic fermentation of kitchen wastes
InactiveCN103555775AReduce processing costsReduce investment and operating costsFermentationAcetic acidPropanoic acid
The invention relates to a method for producing volatile fatty acid through promoting the anaerobic fermentation of kitchen wastes. The method comprises the steps of firstly, crushing the kitchen wastes to be up to the particle size of 1-5mm; then, regulating the content of solids to 100mg / L; next, placing the crushed kitchen wastes into an anaerobic fermentation reactor, adding 10-40g / L of marketing zero-valent iron with the particle size of 800 meshes, fermenting at the temperature of 15-40 DEG C for 4-17 days while stirring at the rotating speed of 120r / min, centrifuging, recycling the zero-valent iron in filter residues, and taking out the residual organic components to be composted or used as a liquid fertilizer to obtain the volatile fatty acid with the yield of 29.1-35.8g / L in a supernatant liquid, wherein the volatile fatty acid is detected to contain 32% of acetic acid, 17% of propionic acid, 27% of n-butanoic acid and 20% of n-pentanoic acid when the yield of the volatile fatty acid in the supernatant liquid is 29.1g / L. Compared with the conventional anaerobic fermentation for the kitchen wastes, the method has the advantages that the content of the volatile fatty acid in the supernatant liquid is increased by 2.3-13 times, the recycling of the kitchen wastes is effectively realized, and the method is low in cost, high in speed and high in social, economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Low energy consumption integrated hydrolysis-denitrifying ammoxidation process for treating low C/N ratio wastewater
InactiveCN101891334AGood removal effectReduce outputTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentVolatile fatty acidsSludge
The invention provides a low energy consumption integrated hydrolysis-denitrifying ammoxidation process for treating low C / N ratio wastewater, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment in environment engineering. The process is characterized in that: a second hydrolysis region and an aerobic denitrification region are connected in series to provided a nitrate nitrogen electron acceptor for the denitrifying ammoxidation process; the second hydrolysis region is connected in parallel to provide volatile fatty acid and ammonia nitrogen; and autotrophic nitrogen removal without an additional carbon source can be realized in the denitrifying ammoxidation reacting region finally. The process has the advantages of improving the nitrogen pollutant removal effect without the additional carbon source, reducing aeration energy consumption and sludge yield, and reducing greenhouse gas emission compared with the traditional denitrification process; and the design of a modular reactor guided by an integrated baffle and the flow design without sludge return can effectively reduce floor area, and greatly reduce operation complexity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Chemically enhanced primary sludge fermentation method
ActiveUS6982036B2Easy to separateImprove the level ofSludge processingSeparation devicesChemical treatmentIron salts
A method of treating wastewater to increase effluent volatile fatty acid content consisting of providing wastewater to a primary treatment vessel and adding a select quantity of a chemical, typically an aluminum or iron salt, to the wastewater, enhancing the separation of organic matter. Separated organic matter is then removed from the chemically treated wastewater forming a primary sludge and a primary effluent. A portion of the primary sludge is fermented to form a volatile fatty acid rich liquor. The volatile fatty acid rich liquor may then be used with the primary effluent, directed to a bioreactor, thereby forming a volatile fatty acid enriched bioreactor feed. The volatile fatty acid enriched influent may be further treated through known biological phosphorous and nitrogen removal methods.
Owner:CH2M HILL
A method for strengthening denitrification and dephosphorization by hydrolyzing and fermenting mixed sludge from sewage plant
ActiveCN104118971BPromote degradationSimple structureMultistage water/sewage treatmentActivated sludgeVolatile fatty acids
The invention creatively provides a method for strengthening nitrogen and phosphorus removal by using the hydrolysis and fermentation of mixed sludge of a sewage plant. According to the method, part of activated sludge returns to a primary sedimentation tank and is mixed with primary sedimentation sludge, so as to be subjected to precipitation and concentration, the precipitated and concentrated mixed sludge enters a hydrolysis tank which can consist of a separate reactor and can also consist of two series reactors, and is subjected to hydrolysis and fermentation in the hydrolysis tank, so as to produce easily-degradable organic matters (rbCOD) or volatile fatty acids (VFAs), and after the process is completed, a hydrolyzed mixed solution which is rich in VFA, or supernatant is introduced into an anaerobic tank or anoxic tank of a biological pool, thereby realizing the aim of strengthening nitrogen and phosphorus removal. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the carbon source insufficiency of inlet water can be effectively improved, the biological nitrogen and phosphorus removal function can be strengthened, and the addition of an external commercial carbon source is reduced or canceled; the method is applicable to the new construction of sewage plants and is also applicable to the upgrading and reconstruction of the existing sewage plants.
Owner:刘智晓
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com