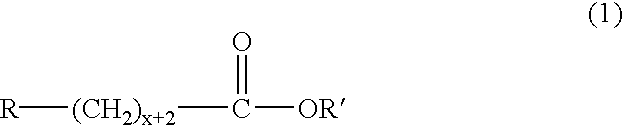Patents
Literature
251 results about "PHA biosynthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
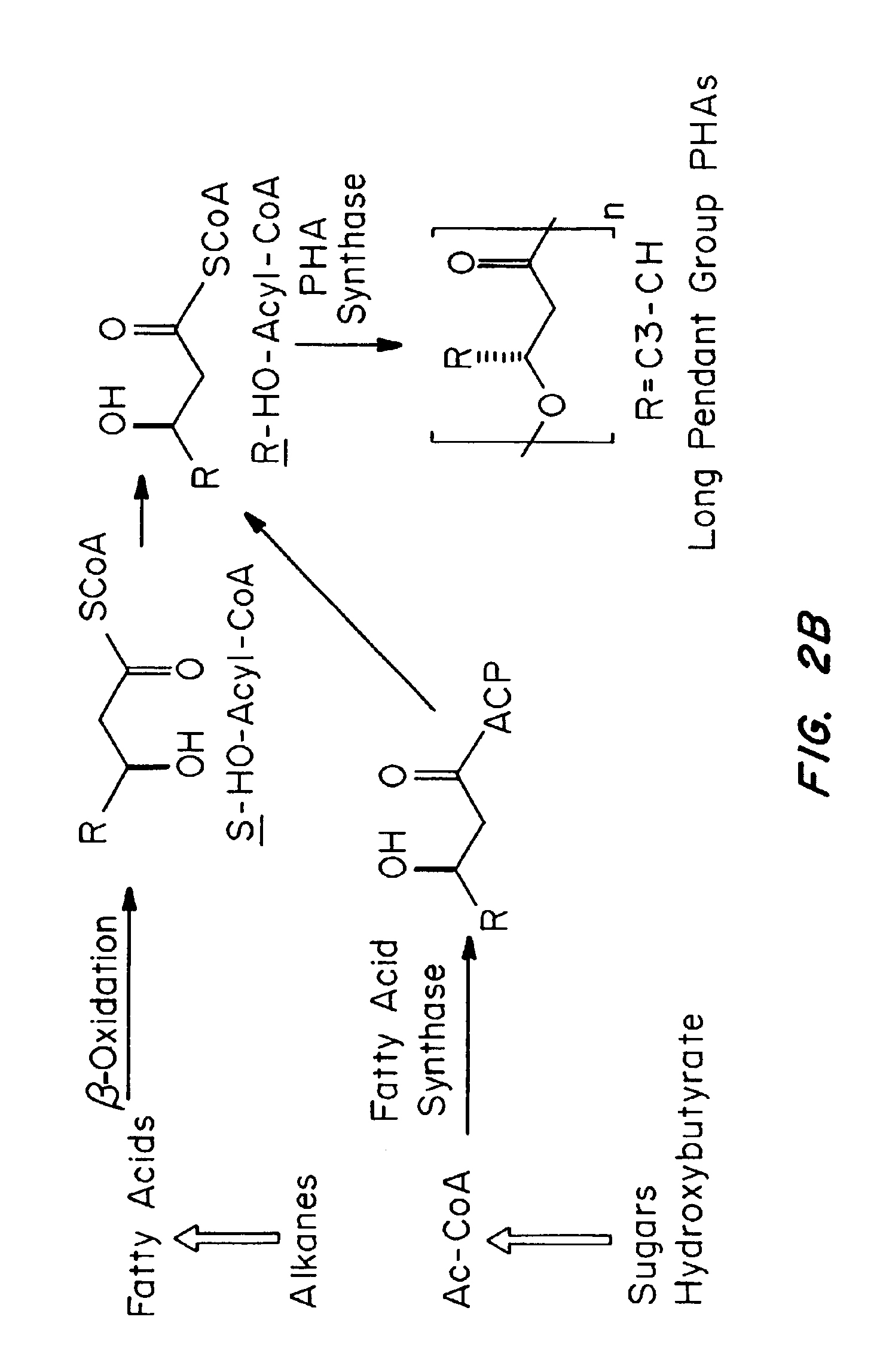
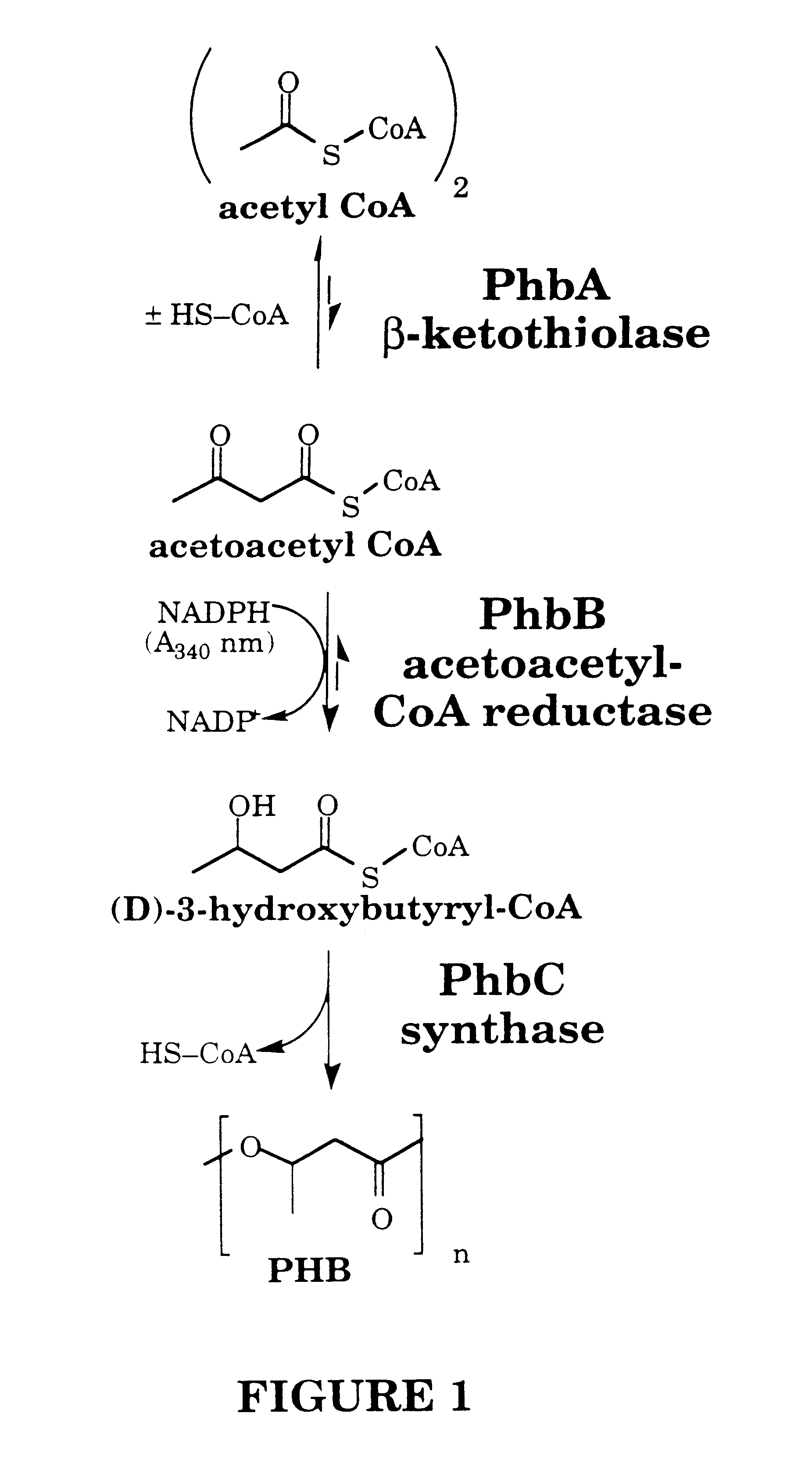
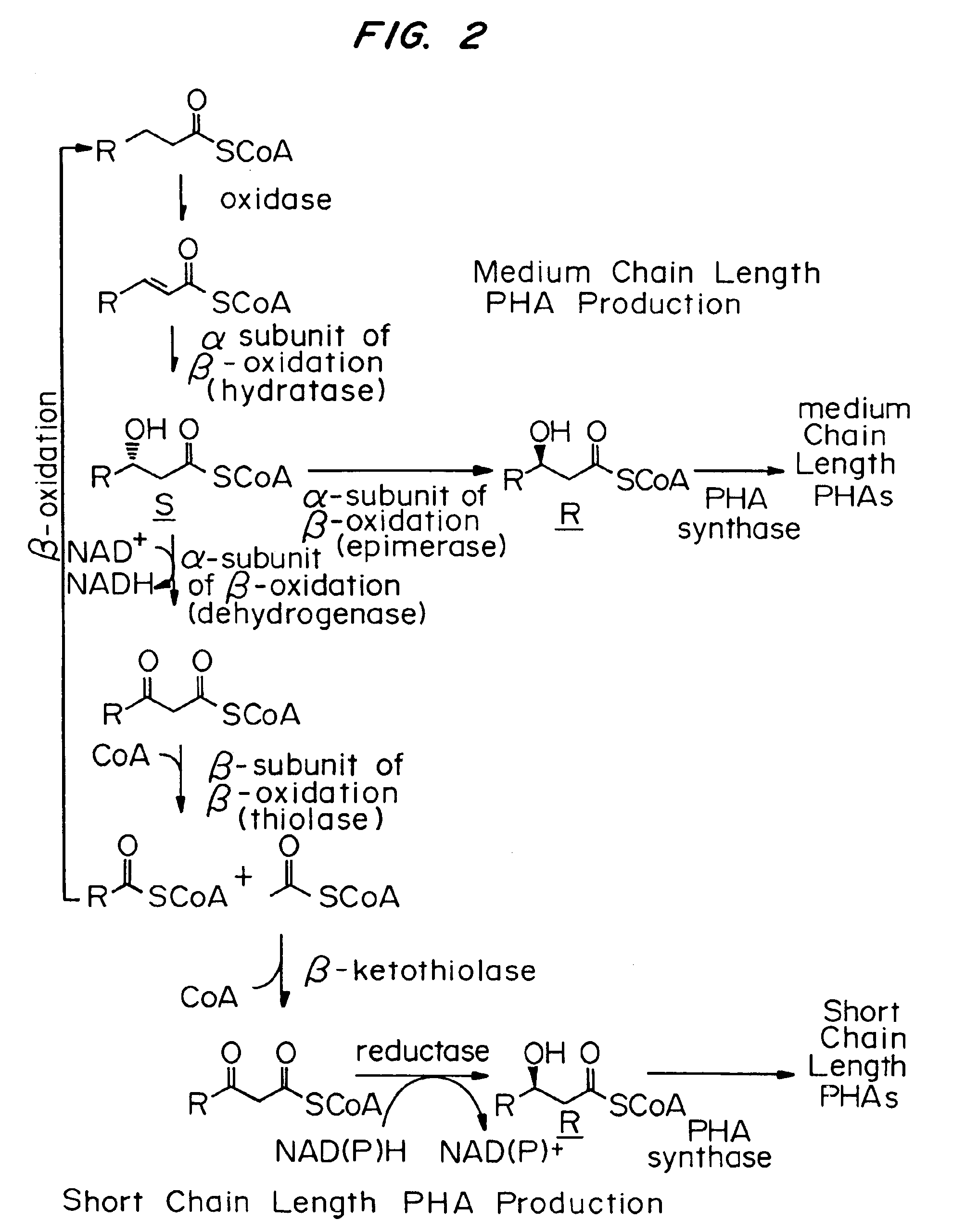
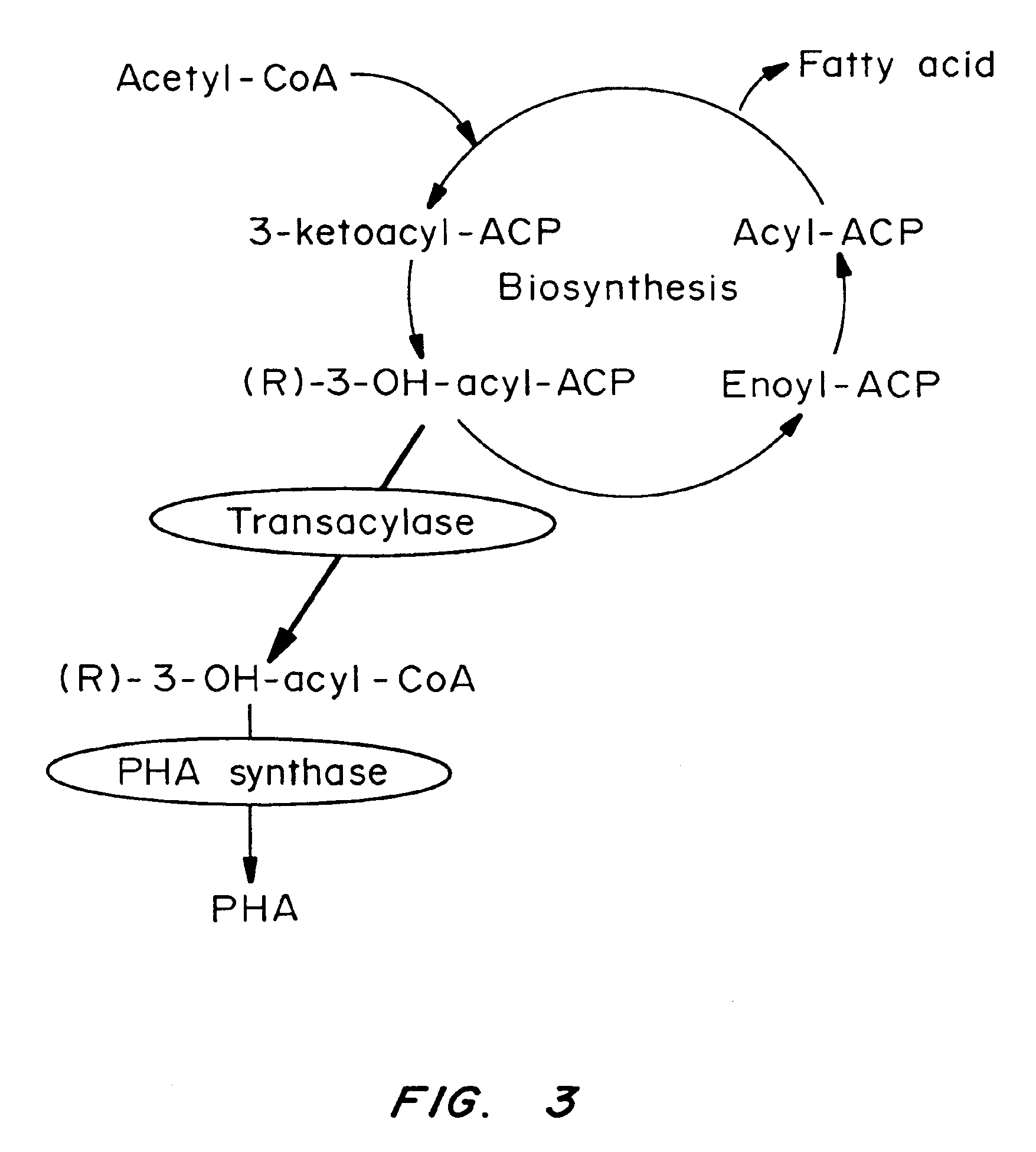
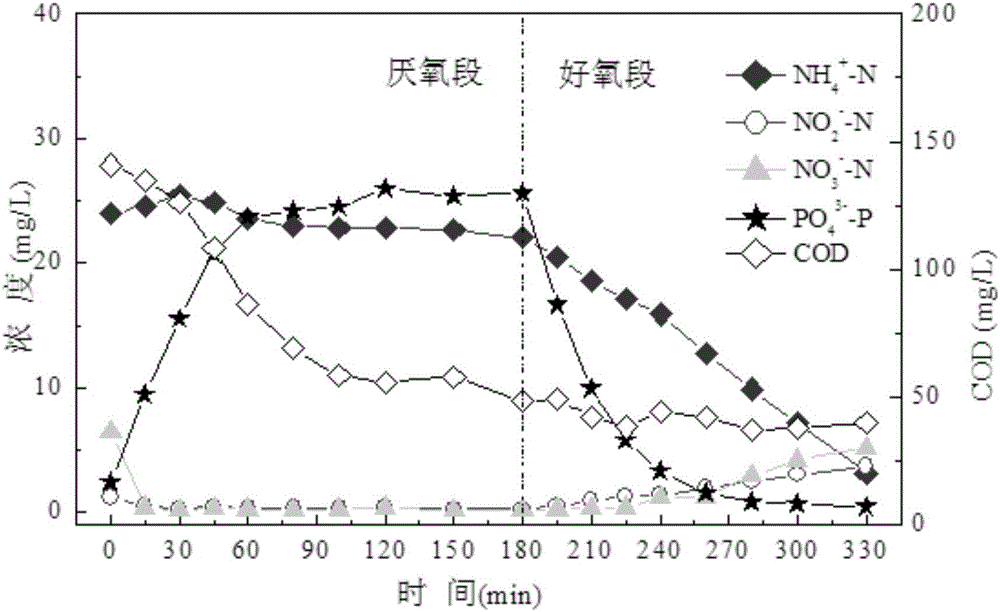
The biosynthesis of PHA is usually caused by certain deficiency conditions (e.g. lack of macro elements such as phosphorus, nitrogen, trace elements, or lack of oxygen) and the excess supply of carbon sources.
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6838493B2High porosityReduce probabilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Medical devices and applications of polyhydroxyalkanoate polymers
InactiveUS6867247B2Reduce probabilityHigh porositySuture equipmentsStentsTissue repairBiocompatibility Testing
Devices formed of or including biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoates are provided with controlled degradation rates, preferably less than one year under physiological conditions. Preferred devices include sutures, suture fasteners, meniscus repair devices, rivets, tacks, staples, screws (including interference screws), bone plates and bone plating systems, surgical mesh, repair patches, slings, cardiovascular patches, orthopedic pins (including bone filling augmentation material), adhesion barriers, stents, guided tissue repair / regeneration devices, articular cartilage repair devices, nerve guides, tendon repair devices, atrial septal defect repair devices, pericardial patches, bulking and filling agents, vein valves, bone marrow scaffolds, meniscus regeneration devices, ligament and tendon grafts, ocular cell implants, spinal fusion cages, skin substitutes, dural substitutes, bone graft substitutes, bone dowels, wound dressings, and hemostats. The polyhydroxyalkanoates can contain additives, be formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones, or can be chemically modified, all to alter the degradation rates. The polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions also provide favorable mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and degradation times within desirable time frames under physiological conditions.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Polyhydroxyalkanoates of narrow molecular weight distribution prepared in transgenic plants
Methods for the biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoate homopolymers and copolymers are described. In a preferred embodiment, the polymers have a single mode molecular weight distribution, and more preferably have a distribution of between about 2 and about 4, and most preferably about 2.1 or 2.5.
Owner:METABOLIX
Polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions having controlled degradation rates
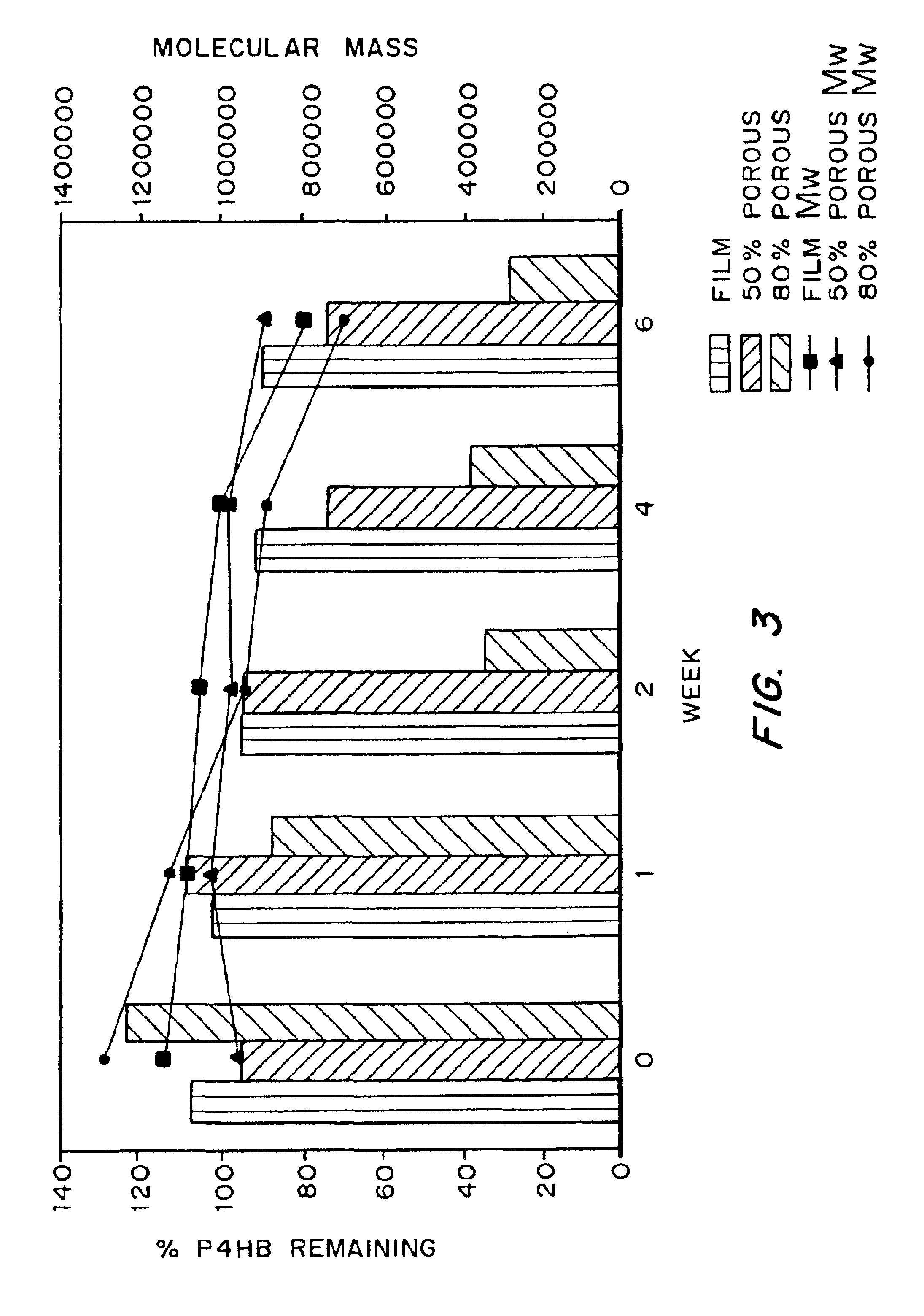
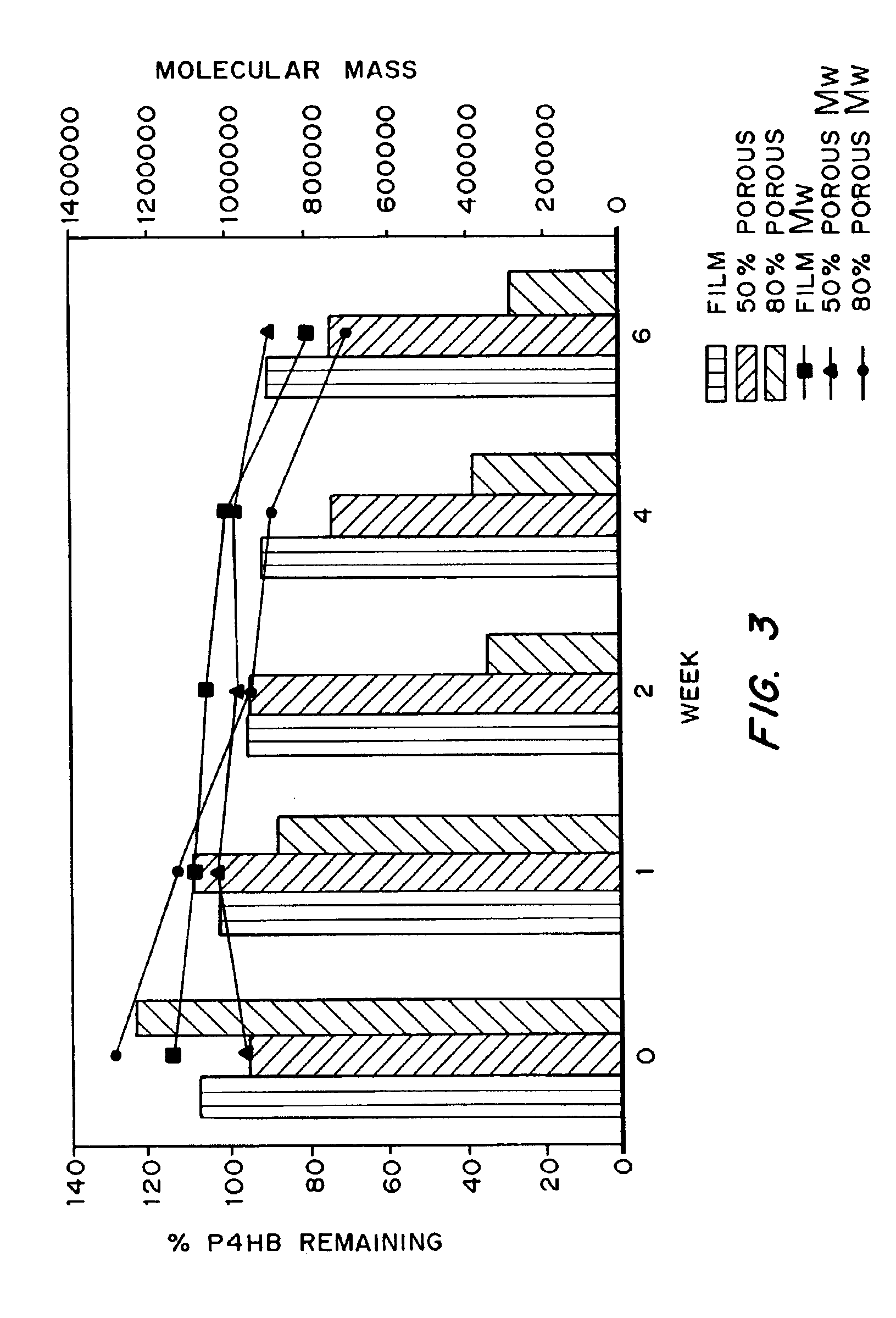
Biocompatible polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions with controlled degradation rates have been developed. In one embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates contain additives to alter the degradation rates. In another embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates are formed of mixtures of monomers or include pendant groups or modifications in their backbones to alter their degradation rates. In still another embodiment, the polyhydroxyalkanoates are chemically modified. Methods for manufacturing the devices which increase porosity or exposed surface area can be used to alter degradability. For example, as demonstrated by the examples, porous polyhydroxyalkanoates can be made using methods that creates pores, voids, or interstitial spacing, such as an emulsion or spray drying technique, or which incorporate leachable or lyophilizable particles within the polymer. Examples describe poly(4HB) compositions including foams, coatings, meshes, and microparticles. As demonstrated by the examples, these polyhydroxyalkanoate compositions have extremely favorable mechanical properties, as well as are biocompatible and degrade within desirable time frames under physioogical conditions. These polyhydroxyalkanoate materials provide a wider range of polyhydroxyalkanoate degradation rates than are currently available. Methods for processing these materials, particularly for therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic applications, or into devices which can be implanted or injected, are also described.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Method for making devices using polyhydroxyalkanoate having pyrogen removed
InactiveUS7244442B2Physical improvementGood chemical propertiesSuture equipmentsBiocideSolubilityChemical structure
Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from which pyrogen has been removed are provided for use in numerous biomedical applications. PHAs which have been chemically modified to enhance physical and / or chemical properties, for targeting or to modify biodegradability or clearance by the reticuloendothelial system (RES), are described. Methods for depyrogenating PHA polymers prepared by bacterial fermentation processes are also provided, wherein pyrogens are removed from the polymers without adversely impacting the polymers' inherent chemical structures and physical properties. PHAs with advantageous processing characteristics, including low melting points and / or solubility in non-toxic solvents, are also described. PHAs are provided which are suitable for use in in vivo applications such as in tissue coatings, stents, sutures, tubing, bone and other prostheses, bone or tissue cements, tissue regeneration devices, wound dressings, drug delivery, and for diagnostic and prophylactic uses. Properties which are selected for include degradability, elasticity, inclusion of functional groups or derivatized groups, which can in turn be used to attach targeting agents, and bioadhesion.
Owner:TEPHA INC
Polyhydroxylkanoates as well as blending modification for copolymer thereof and polylactic acid
The invention discloses a PHBV with good performance and a copolymer of PHBV and PLA and the preparation technique method. The invention is characterized in that 1 per cent to 99 per cent of PHAs, 1 per cent to 99 per cent of PLA1 and other additives 0-40 per cent are put in a mixer for 1 to 30 minutes, and then put in an electricity hot blast drying oven a temperature ranging from 40 to 100 DEG C for 2 to 48 hours after being mixed equally. The dried compound is plastified in a double screw extruder, the highest temperature of the double screw extruder is between 90 and 180 DEG C according to the the different content of PHAs and the temperature of the mouth mold is between110 to 170 DEG C. The material extruded from a die head is cooled, stretched and grained to form the complete biodegradation aggregate. The resin consisting of PHBV and copolymer of PHBV and PLA is able to be used for producing the thin films, plates and sheet materials and injected mold to plastic materials. The compound has biological degradability and good machining performance. The target product of the compound has excellent mechanical properties and can be used for replacing the petroleum base plastic to be widely used for packing, agriculture, medical material, electron, chemical industry concerning products for daily use, etc.
Owner:深圳市奥贝尔科技有限公司
Slow-release fertilizer with effect of soil remediation and remediation method of soil polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons
ActiveCN101928188AImprove repair efficiencyImprove biological activityContaminated soil reclamationFertilizer mixturesSolubilityPhytoremediation
The invention discloses slow-release fertilizer with the effect of soil remediation, which is prepared by polyhydroxyalkanoates which can be completely biodegraded, organic and inorganic nutrients and other substances, by slow-releasing the organic and inorganic nutrients, microorganism propagation and sustained and rapid growth of plants can be promoted, the bioactivity and water solubility of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons are quickened, and simultaneously, the defects of fertilizer loss and repeated fertilization can be avoided, thereby saving the cost and enhancing the soil remediation efficiency. The invention also discloses a soil pollution remediation method by utilizing the slow-release fertilizer, plants with the remediation effect are planted in the soil with the slow-release fertilizer, and efficient, environment-friendly and sustained remediation of the soil polluted by the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) can be realized by utilizing the microorganism-plant remediation technology.
Owner:SHENZHEN ECOMANN BIOTECH
Polyhydroxyalkanoates of narrow molecular weight distribution prepared in transgenic plants
InactiveUS6091002ATransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesEthylene HomopolymersGMO Plants
Owner:METABOLIX
Green process and compositions for producing poly(5HV) and 5 carbon chemicals
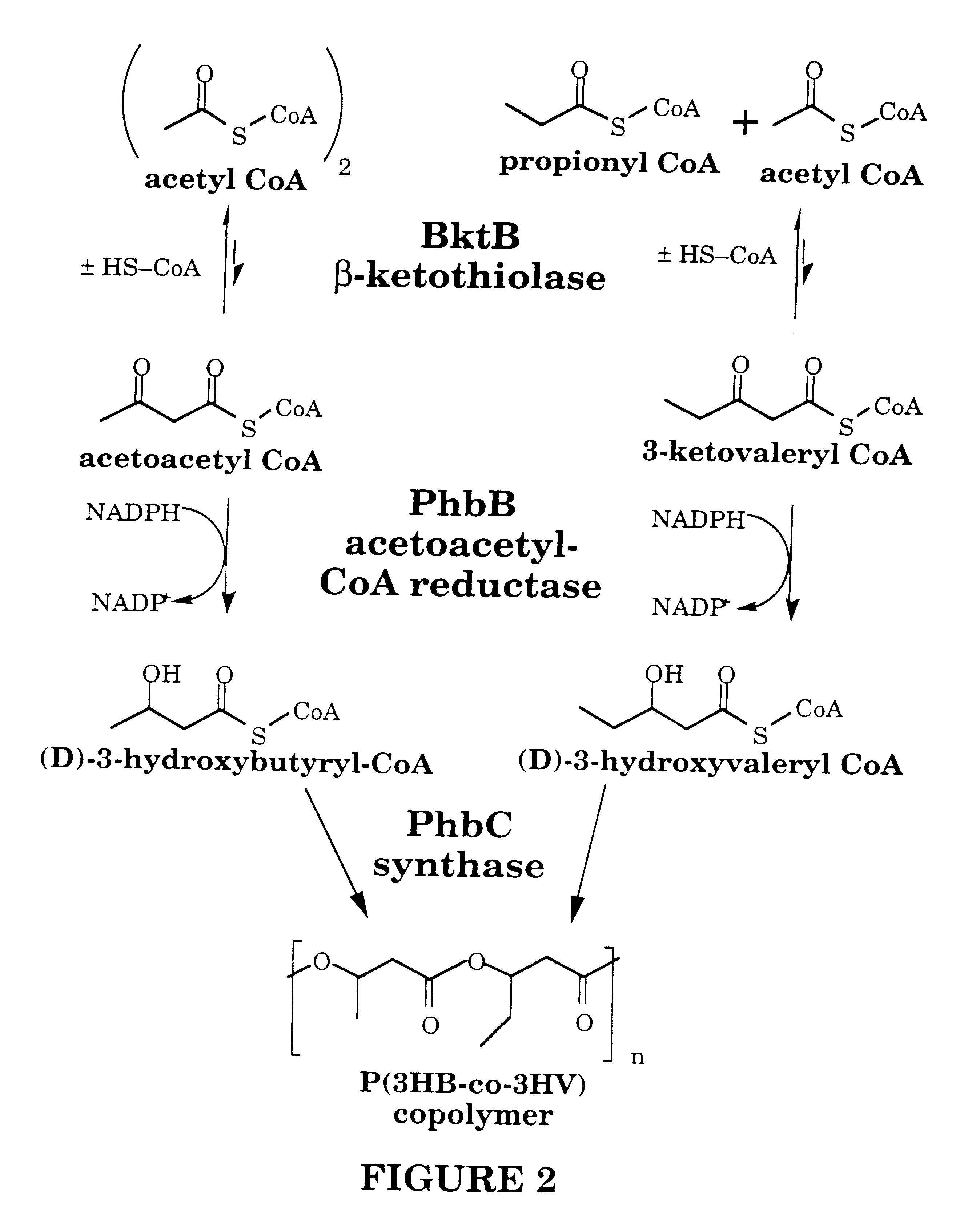
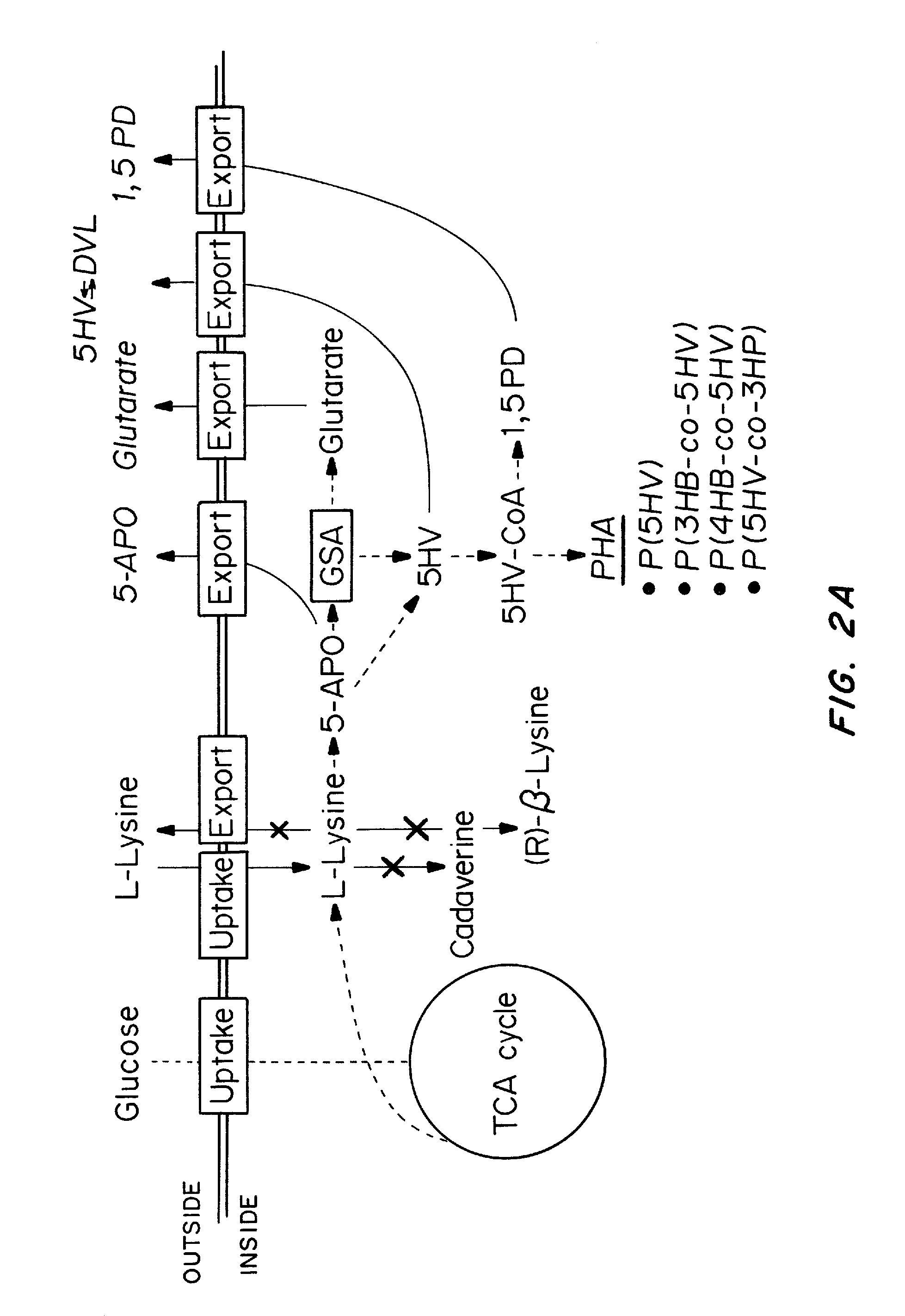
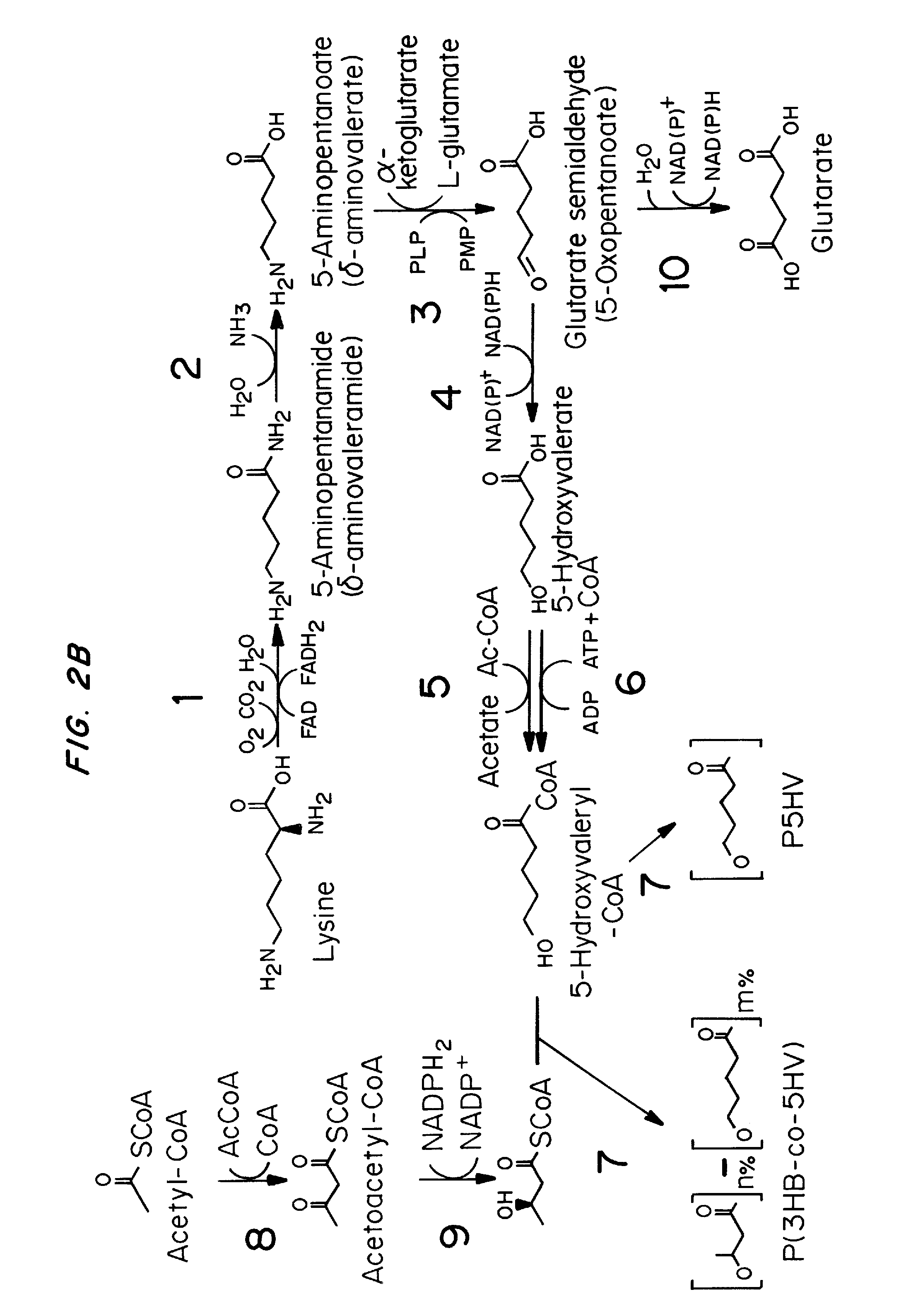
Recombinant hosts for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates and methods of producing polyhydroxyalkanoates from renewable carbon substrates are provided. Certain recombinant hosts that produce 5 carbon chemicals such as 5-aminopentanoate (5AP), 5-hydroxyvalerate (5HV), glutarate, and 1,5 pentanediol (PDO) are also provided. One embodiment provides a recombinant host expressing a gene encoding a heterologous enzyme selected from the group consisting of a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5-hydroxyvalerate-CoA (5HV-CoA) transferase, wherein the host produces a polymer containing 5-hydroxyvalerate. Preferably, the host expresses both a polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase and a 5HV-CoA transferase. The host can be prokaryotic or eukaryotic. A preferred prokaryotic host is E. coli. The polymers produced by the recombinant hosts can be homopolymers or copolymers of 5-hydroxyvalerate. A preferred copolymer is poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-5-hydroxyvalerate).
Owner:CJ CHEILJEDANG CORP
Recombinant cell producing 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid
ActiveUS20110171702A1Less stressfulFew stepsMicroorganismsFermentationAcetoacetyl coenzyme AWild type
The invention relates to a cell which has been genetically modified so as to be capable of producing more 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid or more polyhydroxyalkanoates containing 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid monomer units than its wild type, characterized in that 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid or polyhydroxyalkanoates containing 2-hydroxyisobutyric acid monomer units are produced via acetoacetyl-coenzyme A as intermediate and 3-hydroxybutyryl-coenzyme A as precursor.
Owner:ROHM GMBH
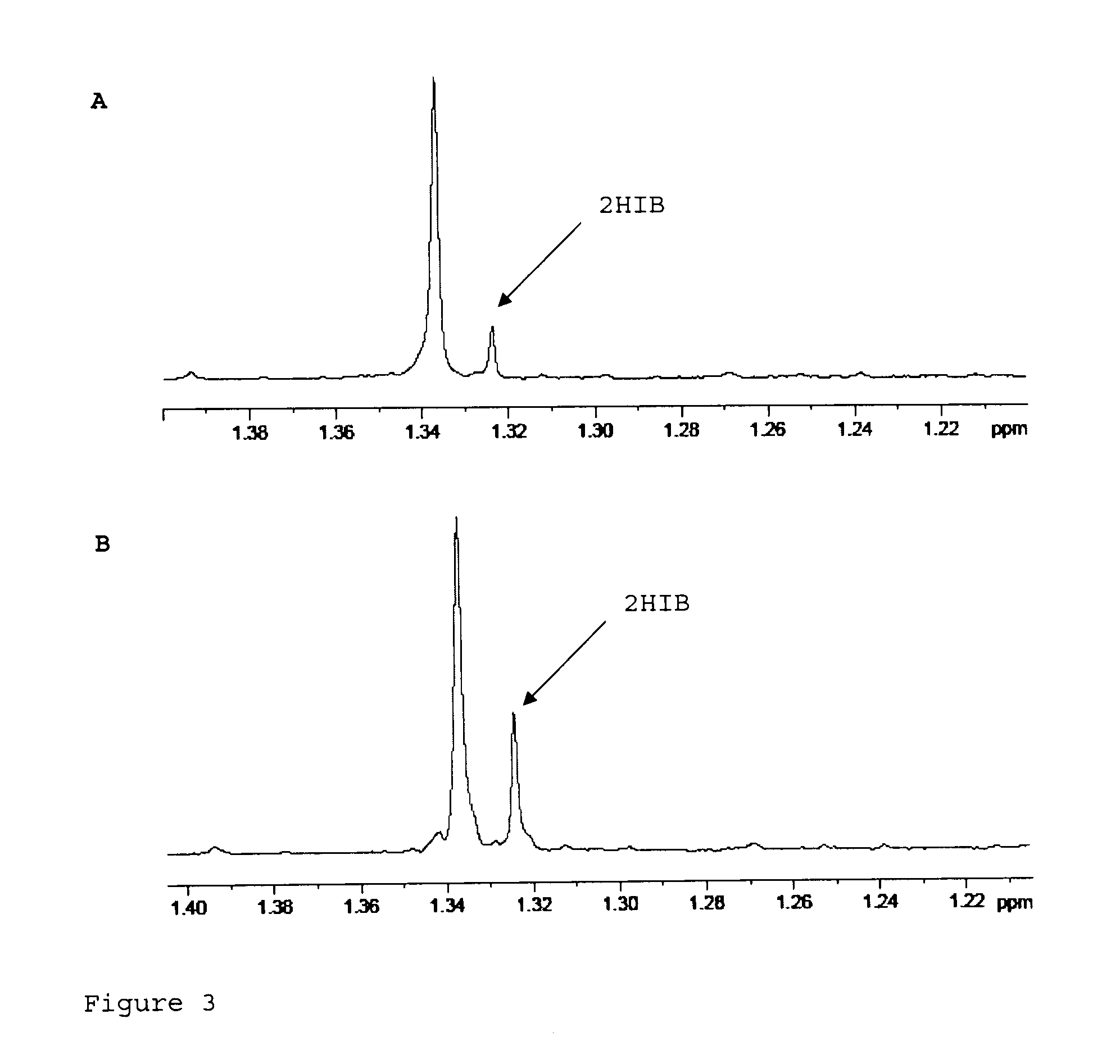
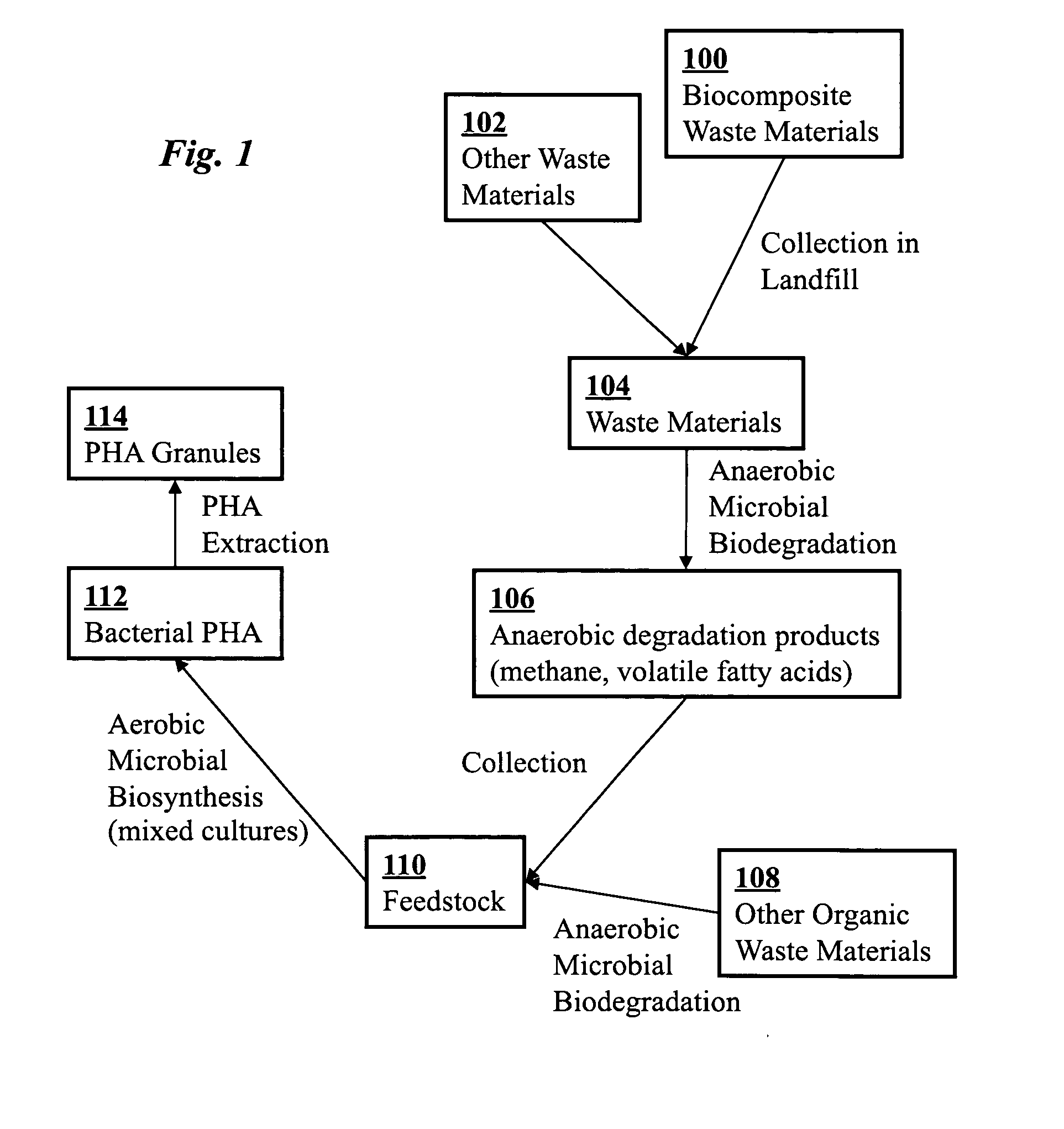
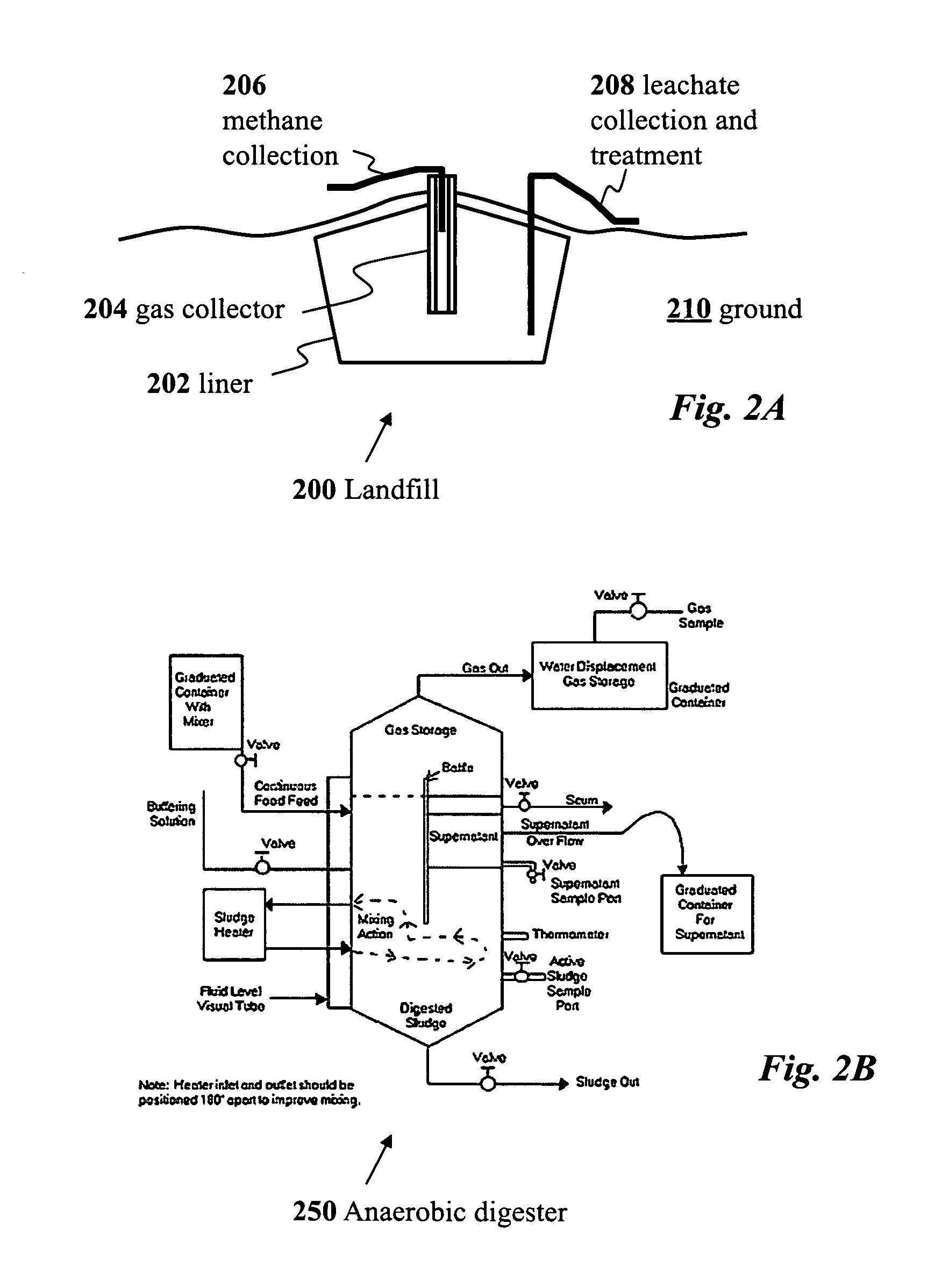
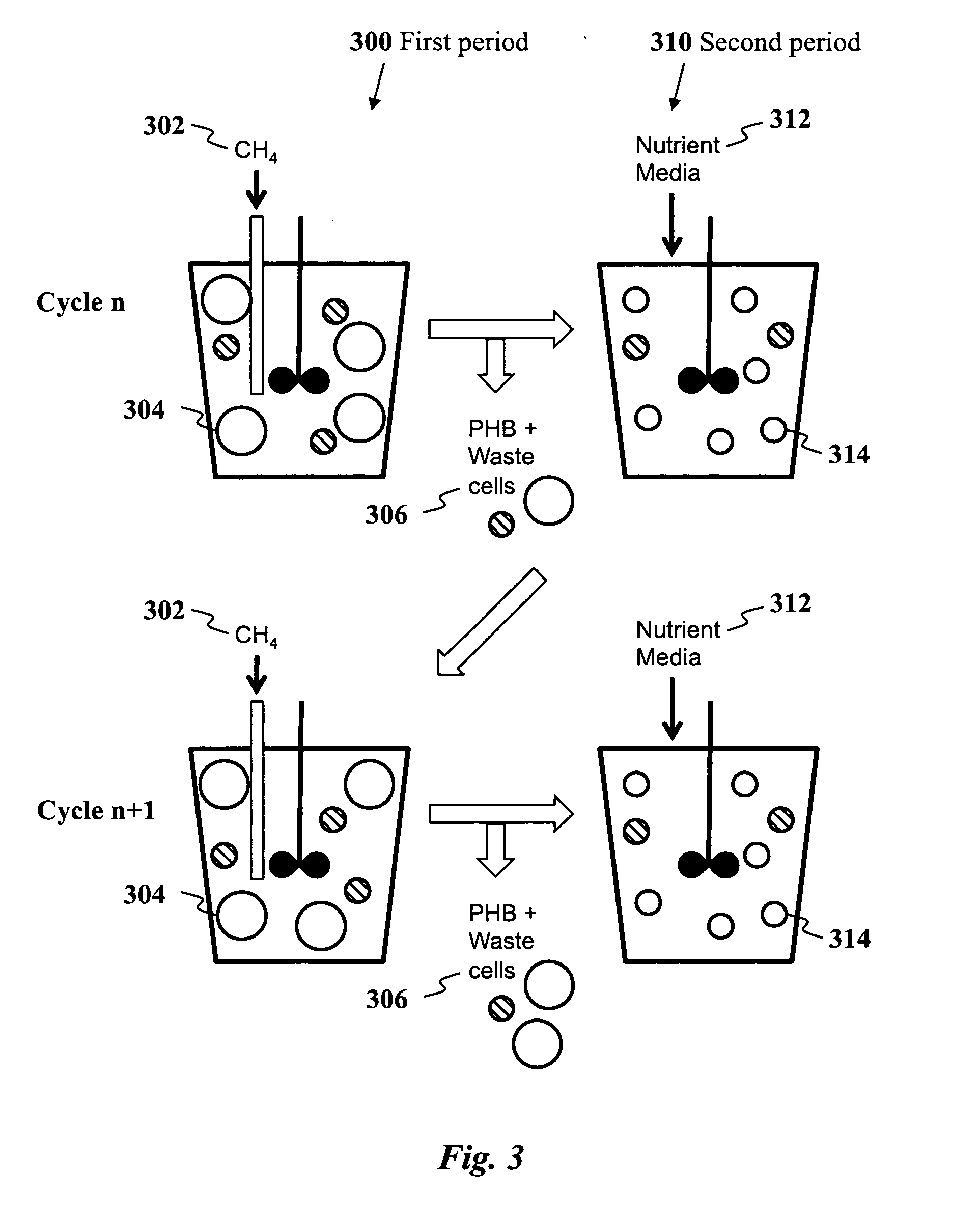
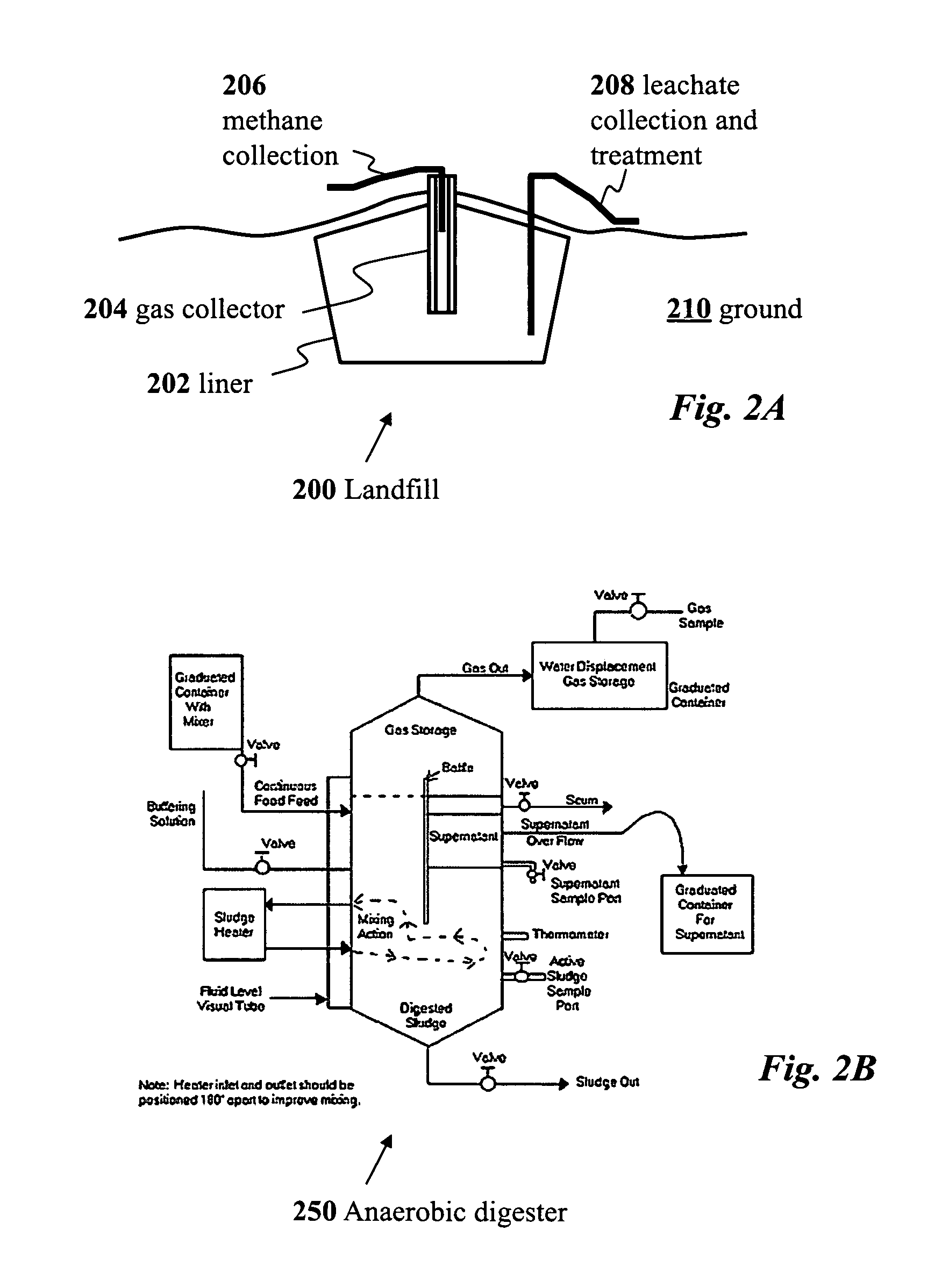
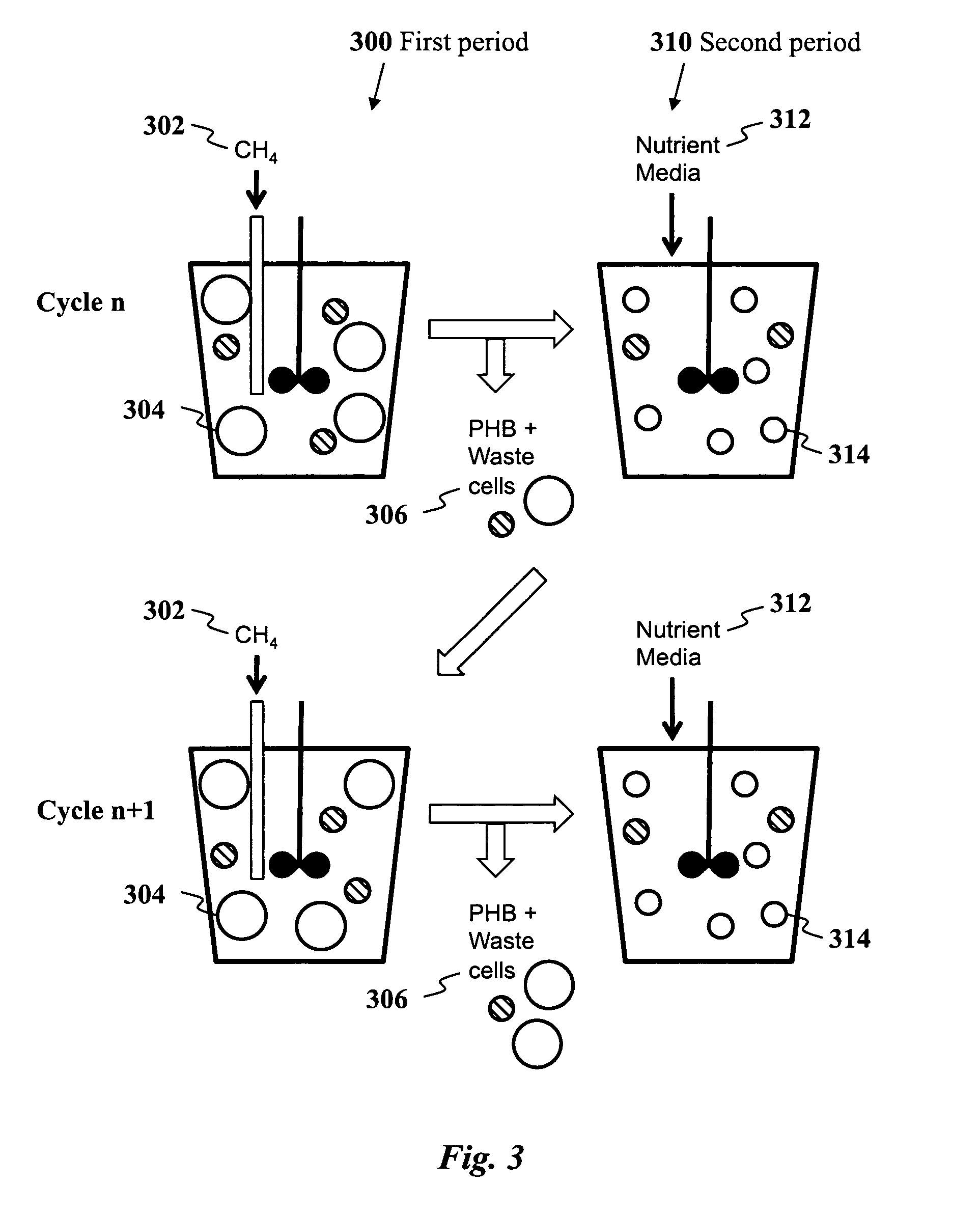
Use of selection pressures to enable microbial biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates from anaerobic degradation products
InactiveUS20090317879A1Cost of producingImprove the level ofWaste based fuelFermentationVolatile fatty acidsMethane gas
A method for inexpensive and efficient PHA biosynthesis includes operating a sequencing bioreactor in alternating phases of nutrient deprivation and carbon feedstock deprivation to select for robust PHA-producing microbes. Preferably, the bioreactor is operated in a non-sterile manner with mixed cultures of methanotrophs. The method also preferably uses periodic biomass-wasting (PHA harvesting) at the end of the carbon feed phase, gradually lengthening the time period of carbon deprivation phase to create a penalty for rapid PHA degradation and incentive for PHA accumulation. Also, bacterial enrichment cultures may be introduced periodically. The PHA-accumulating bacteria are preferably grown on common anaerobic degradation products, specifically volatile fatty acids, such as acetate and propionate, and methane gas. The PHA has useful applications in bioplastics and other products.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Polyhydroxyalkanoate production method
ActiveUS20130337516A1Reduce carbon input costWide availabilityFermentationCarbon sourceMaterials science
Provided are processes for the production and high efficiency processing of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from carbon sources comprising carbon-containing gases or materials.
Owner:NEWLIGHT TECH
Slow release fertilizer having soil remediation function and soil contamination remediation method
ActiveCN101928179AReduce the frequency of fertilizationImprove repair efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationFertilizer mixturesBiologyNutrients substances
The invention discloses a slow release fertilizer having a soil remediation function. The slow release fertilizer is prepared by mixing fully-biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates and organic and inorganic nutrient substances. The fully-biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates is slowly degraded under the actions of soil microorganisms to provide nutrient substances needed by the growth of the soil microorganisms so as to promote the ionization effects of the soil microorganisms on heavy metals and release the organic and inorganic nutrient substances by slow degradation so as to promote durable and rapid growth of plants and improve soil remediation efficiency. The invention also discloses a soil contamination remediation method for using the slow release fertilizer. High-efficiency, environmentally-friendly and durable remediation of heavy metal-contaminated soil is realized by planting plants having hyper-accumulation capability to absorb and extract the heavy metals in the soil to which the slow release fertilizer is applied.
Owner:SHENZHEN ECOMANN BIOTECH
Sewage purifier and sewage purification method
ActiveCN101928069AIncrease reproductive rateImprove purification effectSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentPurification methodsMetal salts
The invention discloses a sewage purifier, which comprises polyhydroxyalkanoate, diatomite, humic acid, a bioactivator, inorganic metal salt and other substances. The invention also discloses a sewage purification method by utilizing the sewage purifier. A completely biodegradable material polyhydroxyalkanoate is used as a sustained material of the bioactivator, and the completely biodegradable material is slowly degraded and releases the bioactivator so as to realize the long-term high-efficiency purification function of the bioactivator; and by combining the effects of aquatic plants, phosphorus, nitrogen, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and heavy metals in the sewage are purified and treated, so the sewage purifier has better sewage treatment effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN ECOMANN BIOTECH
Multi-gene expression constructs containing modified inteins
InactiveUS7026526B2Other foreign material introduction processesFermentationEucaryotic cellPoly-A RNA
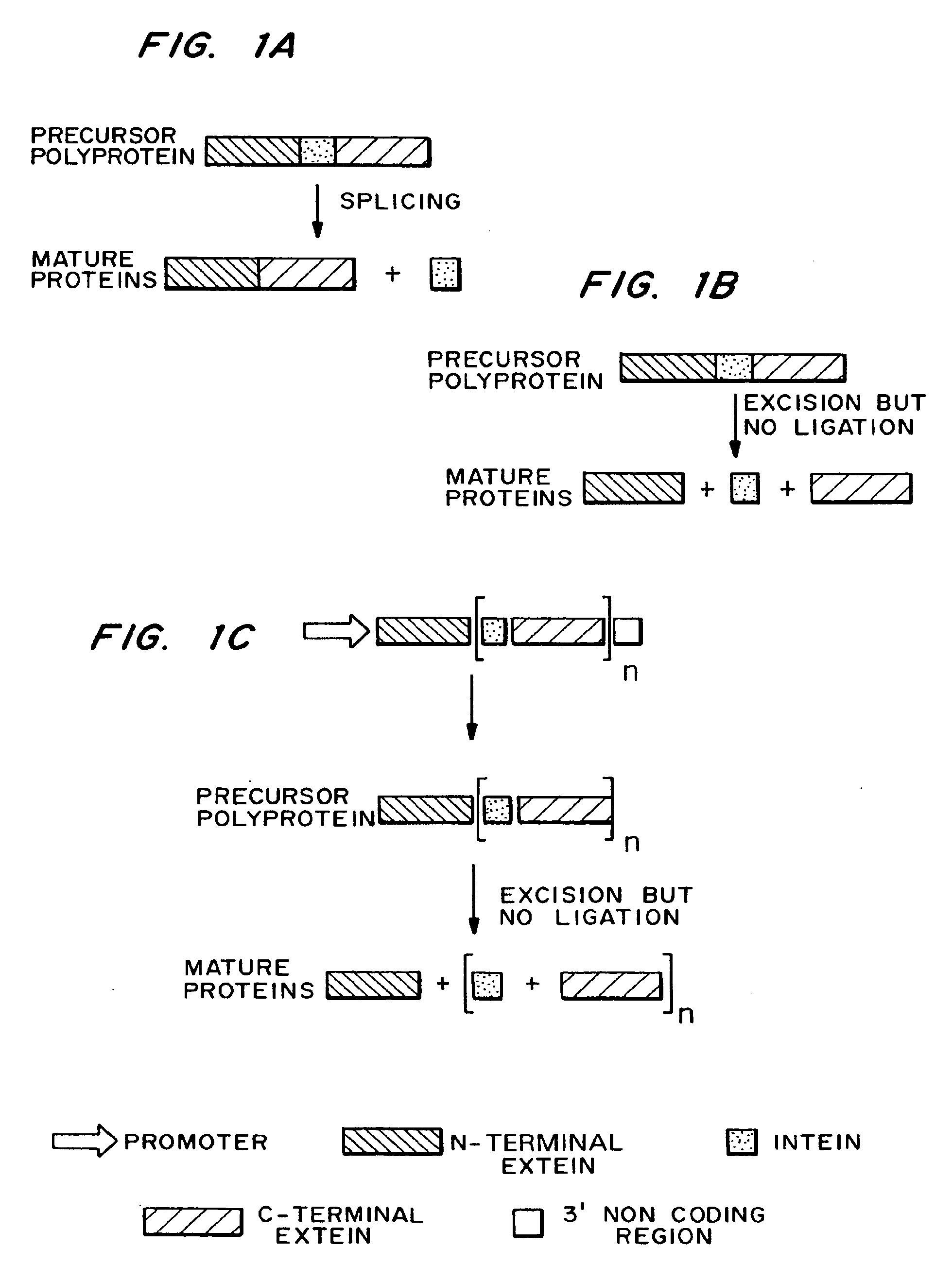
Methods and constructs for the introduction of multiple genes into plants using a single transformation event are described. Constructs contain a single 5′ promoter operably linked to DNA encoding a modified intein splicing unit. The splicing unit is expressed as a polyprotein and consists of a first protein fused to an intein fused to a second protein. The splicing unit has been engineered to promote excision of all non-essential components in the polyprotein but prevent the ligation reactions normally associated with protein splicing. Additional genetic elements encoding inteins and additional proteins can be fused in frame to the 5′-terminus of the coding region for the second protein to form a construct for expression of more than two proteins. A single 3′ termination sequence, such as a polyadenylation sequence when the construct is to be expressed in eucaryotic cells, follows the last coding sequence. These methods and constructs are particularly useful for creating plants with stacked input traits, illustrated by glyphosate tolerant plants producing BT toxin, and / or value added products, illustrated by the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates in plants.
Owner:METABOLIX
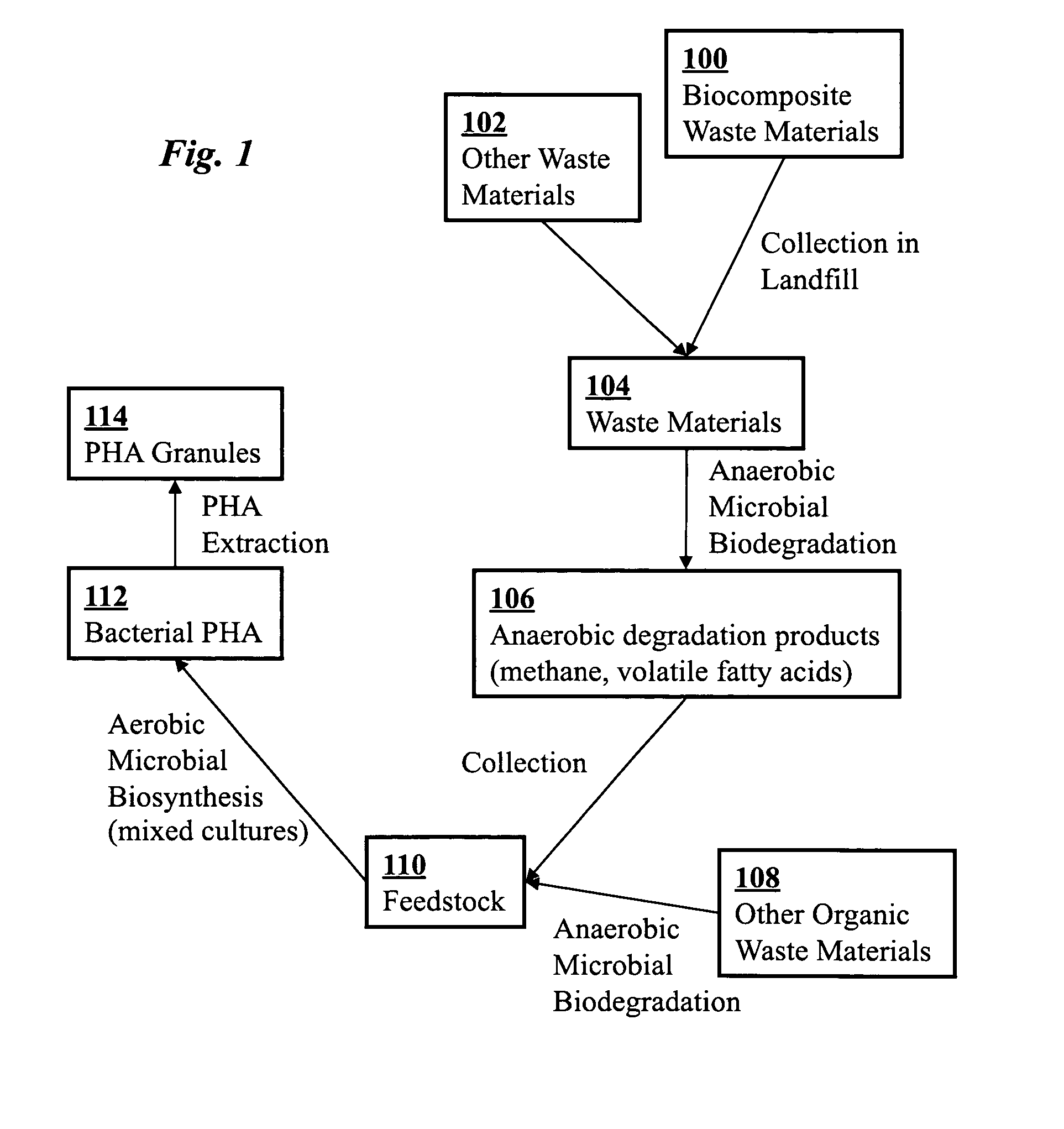
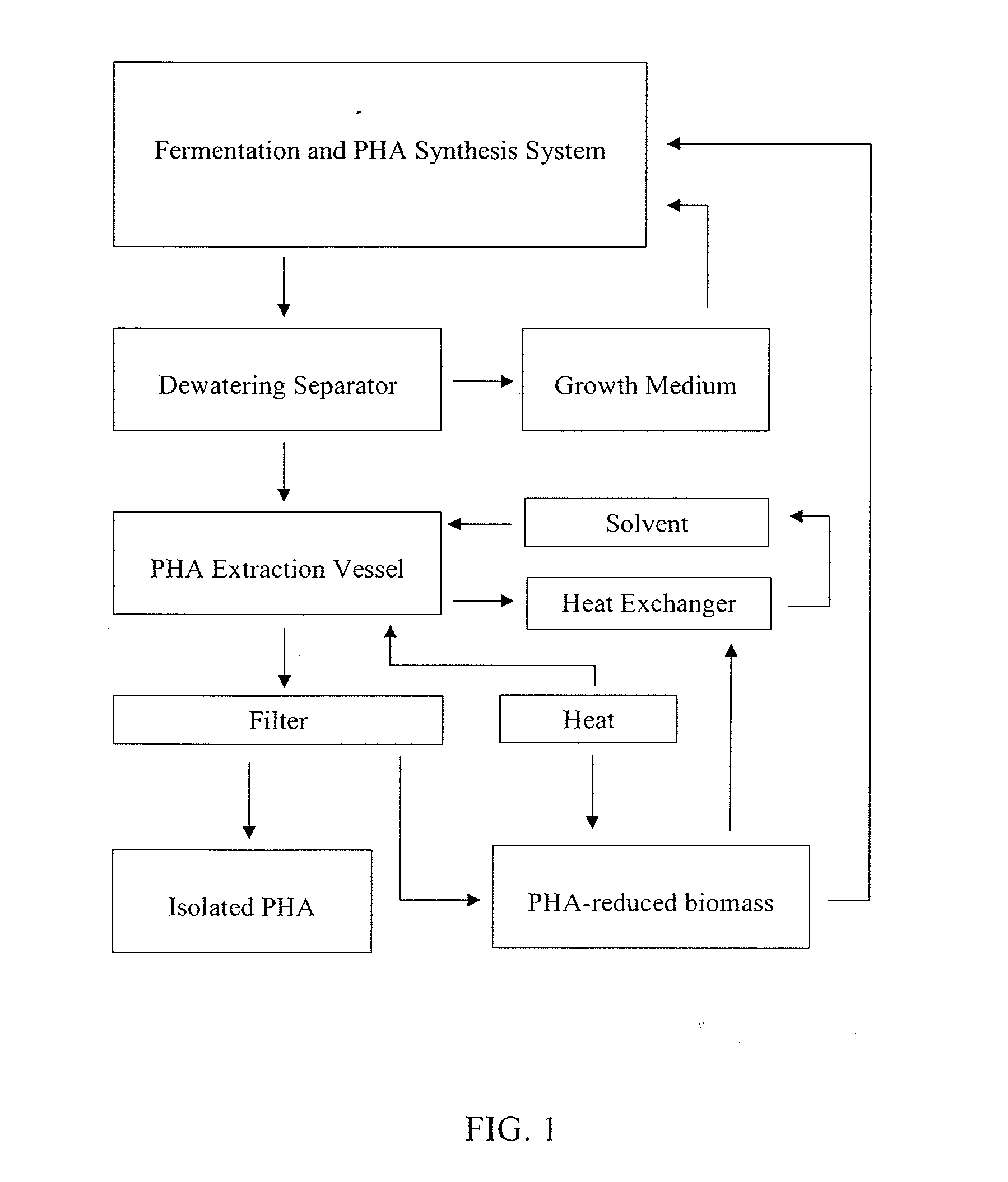
Production of biodegradable thermoplastic materials from organic wastes
InactiveUS7141400B2Guaranteed uptimeApparatus sterilizationPlastic recyclingOrganic acidMicroorganism
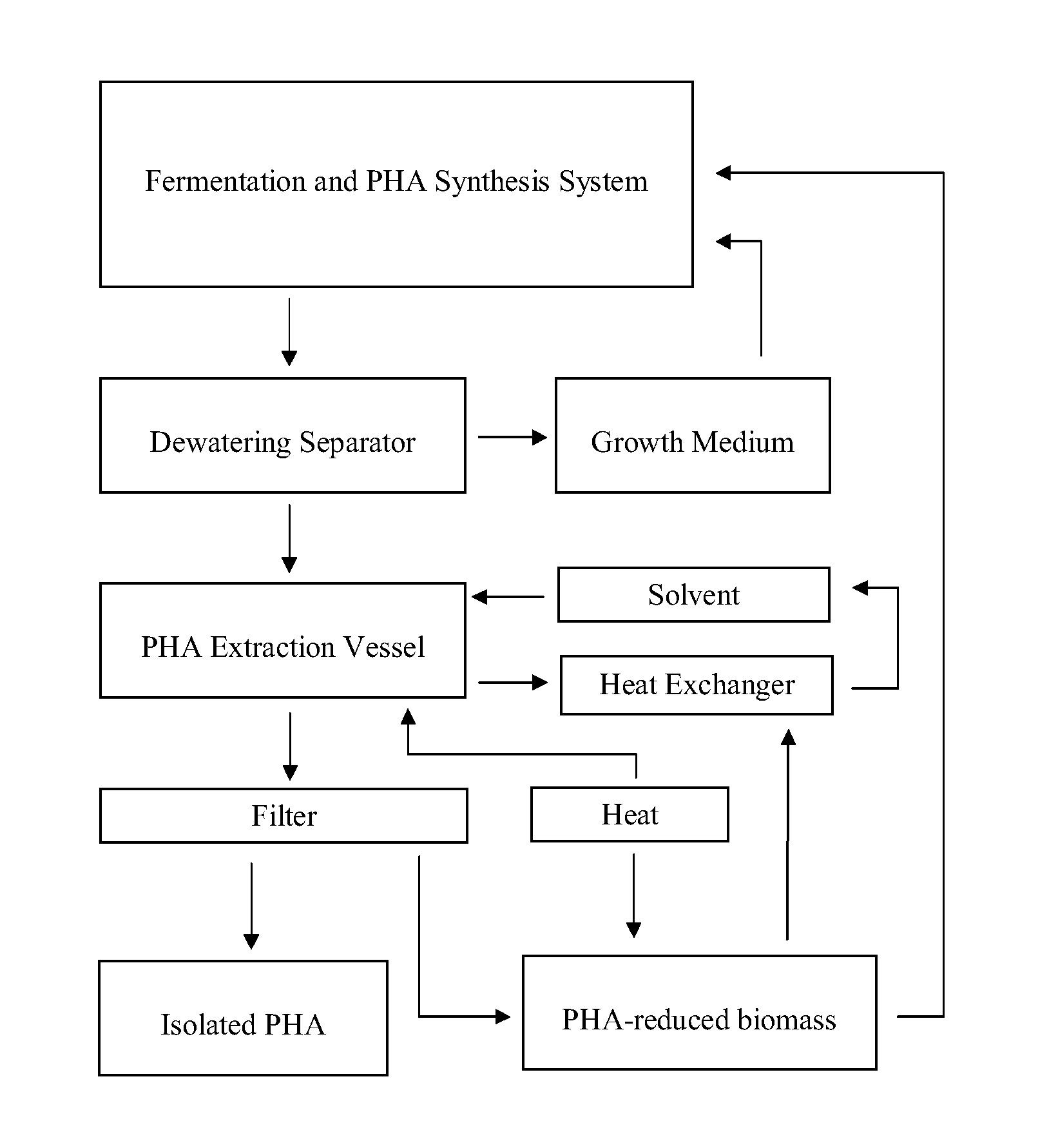
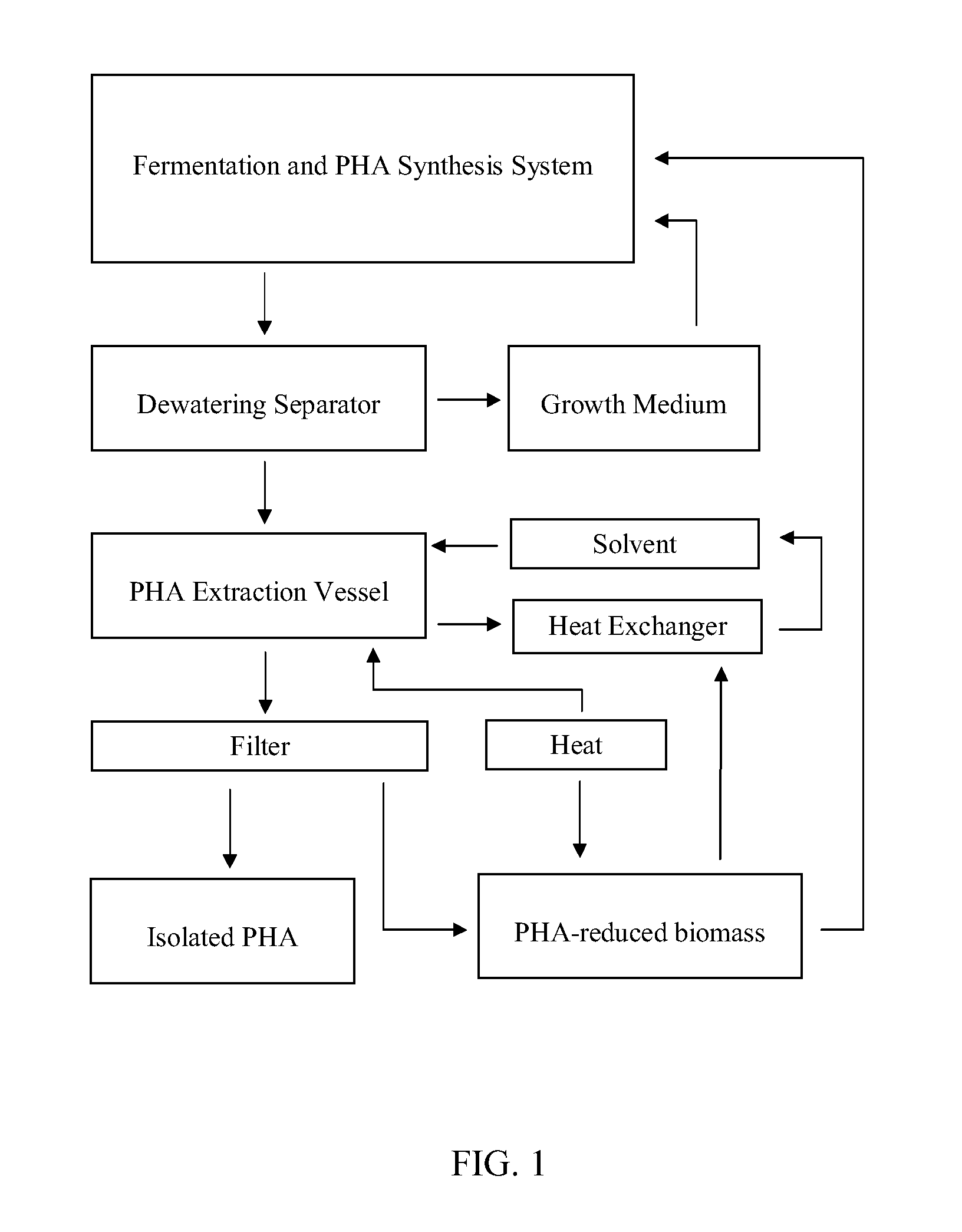
A system and method for converting organic wastes to biodegradable thermoplastic materials including polyhydroxyalkanoates is disclosed, which method includes treating the organic wastes with an acidogenic microbial population to form fermentative organic acids, and polymerization of the organic acids by PHA-producing microbial species to form PHAs. The system includes a first compartment for acidogenesis of organic wastes without oxygen, and a second compartment, for polymer synthesis by enriched cultures of species with oxygen such as R. eutropha, P. oleovorans, or mixtures thereof. The compartments are integrated with barriers that permit mass transfer of organic acids while maintaining different culture conditions in the compartments.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Completely-biodegradable mulching film material and mulching film
InactiveCN103937179ANo residueTo increase productionClimate change adaptationPlant protective coveringsPlastic mulchPoly(butylene succinate)
The invention discloses a completely-biodegradable mulching film material which contains one kind or several kinds of compounds which are selected from a group consisting of polyhydroxy alkanoates, polylactic acid, poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate), poly(butylene-scuccinate / adipate) and poly(butylene-scuccinate). By adopting the completely biodegradable mulching film material, the yield of crops can be greatly improved, the mulching film material can be completely biodegradable without residues of a mulching film, and the yield of crops can be continuously increased.
Owner:山东省意可曼科技有限公司
Use of selection pressures to enable microbial biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates from anaerobic degradation products
InactiveUS8030021B2Cost of producingImprove the level ofWaste based fuelFermentationVolatile fatty acidsMethane gas
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
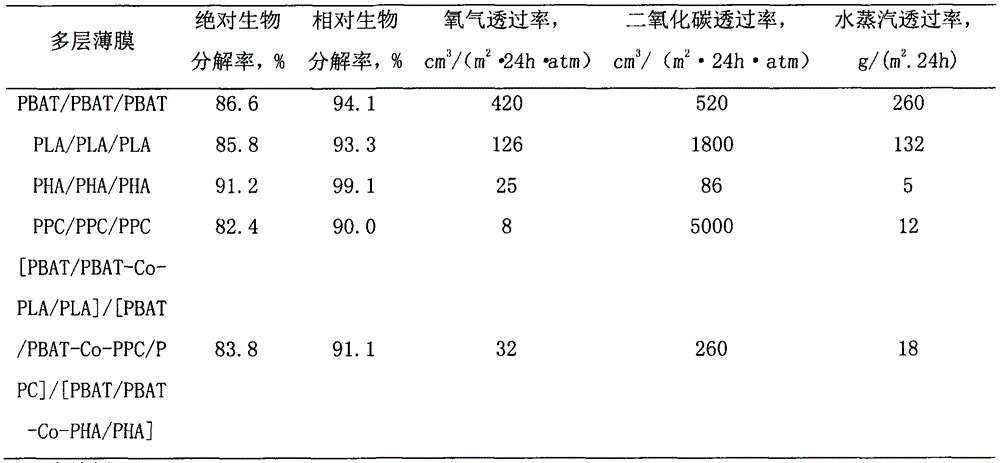
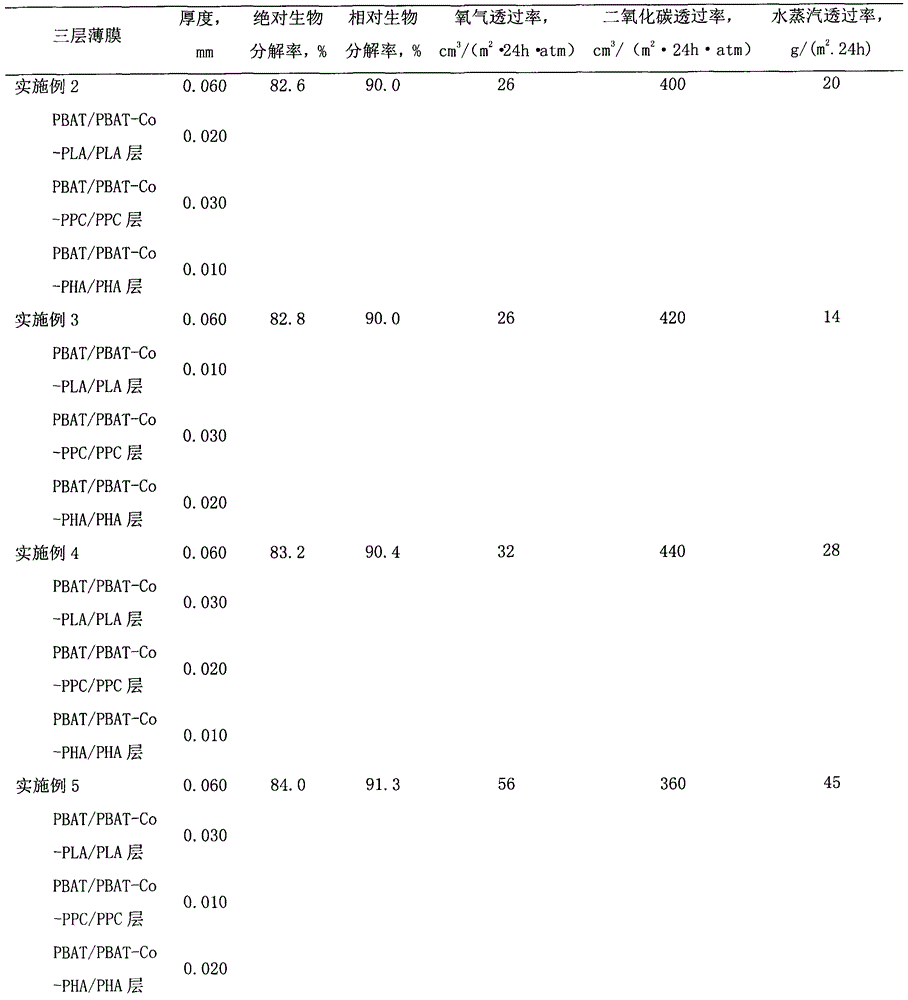
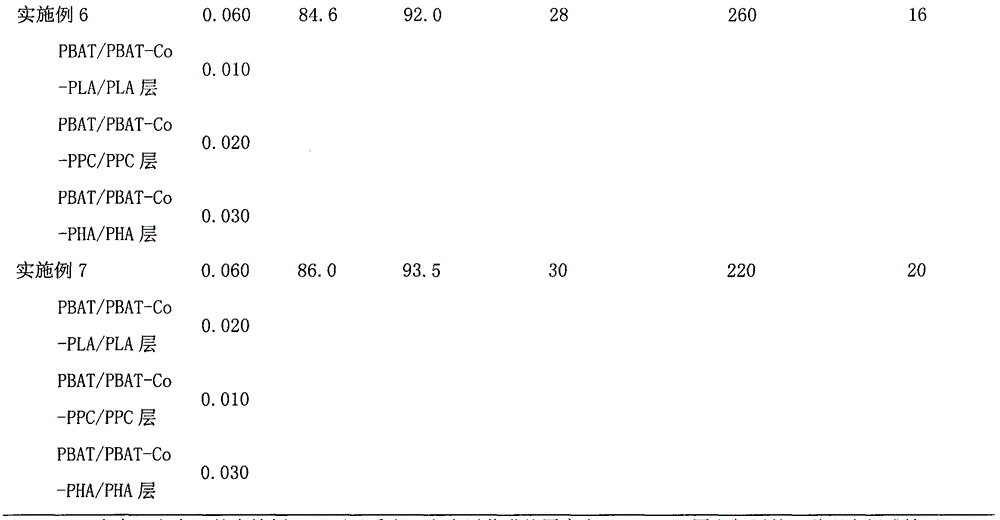
Biodegradable multilayer material with adjustable gas transmission rate and preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN104691067AStable physical propertiesNot easy to layerFlexible coversWrappersWater vaporOxygen
The invention relates to a biodegradable multilayer material, which can be a thin film material or a sheet material. The biodegradable multilayer material at least comprises one of an adipic butanediol terephthalate copolymer (PBAT) / PBAT-chain extender-polypropylene carbonate (PBAT-Co-PPC) / PPC blend layer, a PBAT / PBAT-chain extender-polylactic acid (PBAT-Co-PLA) / PLA blend layer and a PBAT / PBAT-chain extender-polyhydroxyalkanoate (PBAT-Co-PHA) / PHA blend layer, and blend resins are respectively prepared through twin-screw reactive extrusion. The multilayer material is produced by using extrusion and coextrusion methods, has a function that the transmission rates of oxygen, carbon dioxide and water vapor can be adjusted, and can be applied to the packaging field and the agriculture field, and especially applied to food packaging, pharmaceutical packaging, and ground film mulching.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
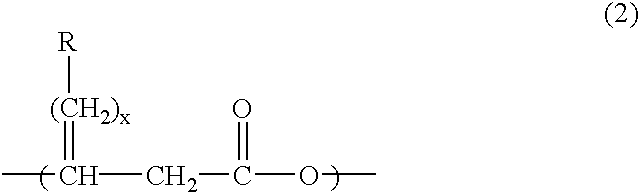
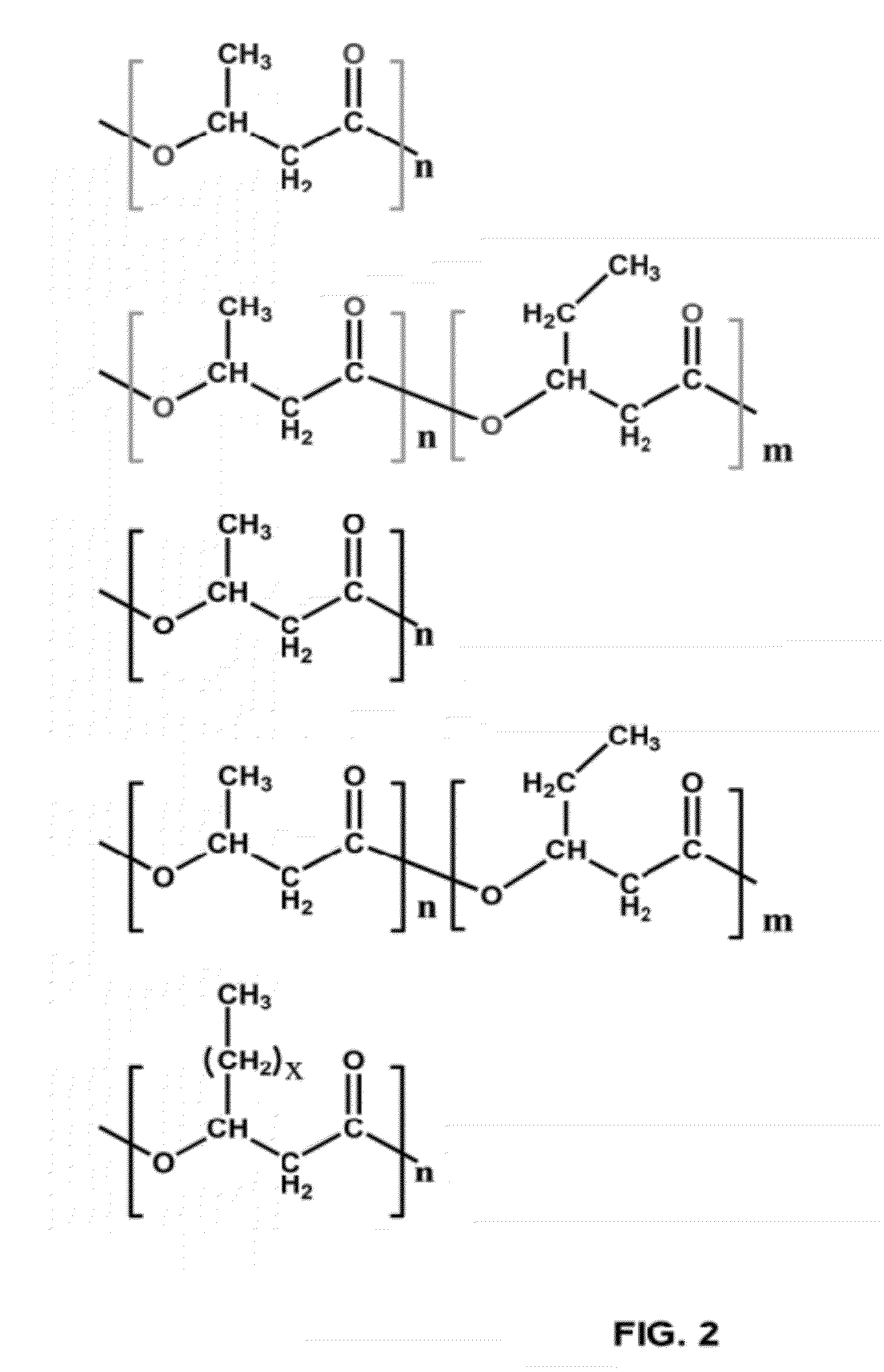
Production method of polyhydroxyalkanoate from substituted fatty acid ester as raw material
InactiveUS6867023B2Easy to getEasy to synthesizeOrganic chemistryBacteriaMicroorganismCulture mediums
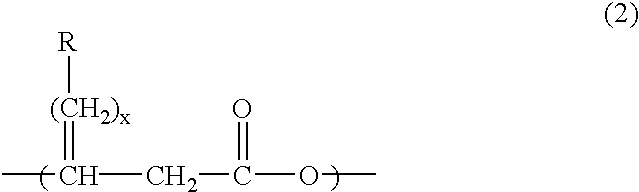
Polyhydroxyalkanoates comprising a monomer unit having the following chemical formula (2): (where the reference characters R represents an arbitrarily selected substituent and x represents an integer of 0 to 8) is produced by culturing a microorganism in a culture medium containing a substituted fatty acid ester having the following chemical formula (1): (where the reference characters R and R′ separately denote an optional substituent and x represents an integer of 0 to 8). The microorganism is capable of taking the substituted fatty acid ester into the cells and synthesizing the desired polyhydroxyalkanoate in the culture medium.
Owner:CANON KK
Biodegradable preservative film material and preservative film
InactiveCN103059529AGood oxygen barrier functionAppropriate water vapor transmission rateFruit and vegetables preservationOxygenFilm material
The invention discloses a biodegradable preservative film material which contains polyhydroxyalkanoate. The invention also discloses a preservative film prepared by the material, wherein the preservative film has a proper penetration rate and a good oxygen blocking function, so that some fruits and vegetables can retain proper moisture but not be contact with oxygen to prolong the preservative time; and in addition, the biodegradable preservative film material has a good preservative effect, and can be completely biodegraded after the preservative film is discarded after use, and pollution to the environment is not caused.
Owner:山东省意可曼科技有限公司
Completely biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanote / poly(butylene succinate) blending alloy
The invention discloses a full biodegradable N-poly-ester / poly butylene succinate blending alloy, which is characterized in that the blending alloy is prepared from N-poly-ester, poly butylene succinct, starch, filler and the other auxiliary agents. The blending alloy uses the heat resistance, good processing and forming property, higher crystallizing property, good tensile strength and impact toughness of the poly butylene succinate to improve the defects of poor heat resistance, serious processing and forming viscous, slow crystallization and lower mechanical strength of the N-poly-ester, and reduce the cost and widen the application range, the obtained blending alloy has good comprehensive performance, and can be applied in the fileds of blowing film, extruding sheets, injecting one-off environmental supplies and medical treatment.
Owner:山东省意可曼科技有限公司
Modified polyurethane suspended filler and preparation method and application thereof
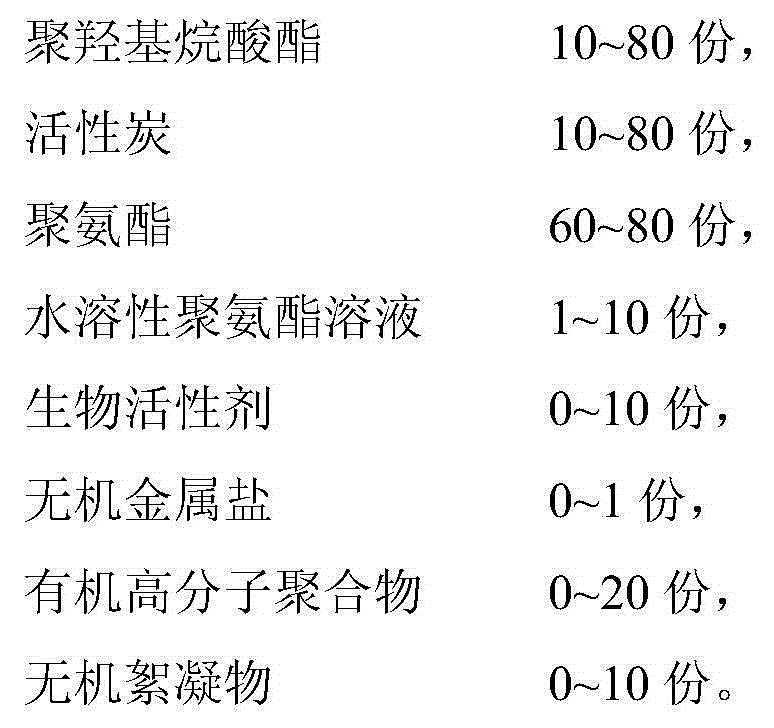
ActiveCN104961227AImprove and optimize the ecosystemImprove effectivenessSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentActivated carbonPorosity
The invention discloses modified polyurethane suspended filler which comprises, by weight, 10 parts to 80 parts of polyhydroxyalkanoate, 10 parts to 80 parts of activated carbon, 60 parts to 80 parts of polyurethane, 1 part to 10 parts of water-soluble polyurethane solutions, 0 part to 10 parts of bioactivator, 0 part to 1 part of inorganic metal salt, 0 part to 20 parts of organic high-molecular polymer and 0 part to 10 parts of inorganic flocculate. A preparation method of the modified polyurethane suspended filler includes the steps of taking the 10 parts to 80 parts of polyhydroxyalkanoate, the 10 parts to 80 parts of activated carbon, the 0 part to 10 parts of bioactivator, the 0 part to 1 part of inorganic metal salt, the 0 part to 20 parts of organic high-molecular polymer and the 0 part to 10 parts of inorganic flocculate, dissolving the mixture in the 1 part to 10 parts of water-soluble polyurethane solutions, soaking the 60 parts to 80 parts of polyurethane in the solution to obtain the loaded polyurethane suspended filler, and conducting secondary drying after primary drying is conducted to obtain the modified polyurethane suspended filler. The modified polyurethane suspended filler has the advantages of being high in porosity and large in specific area.
Owner:HEFEI JIKUN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
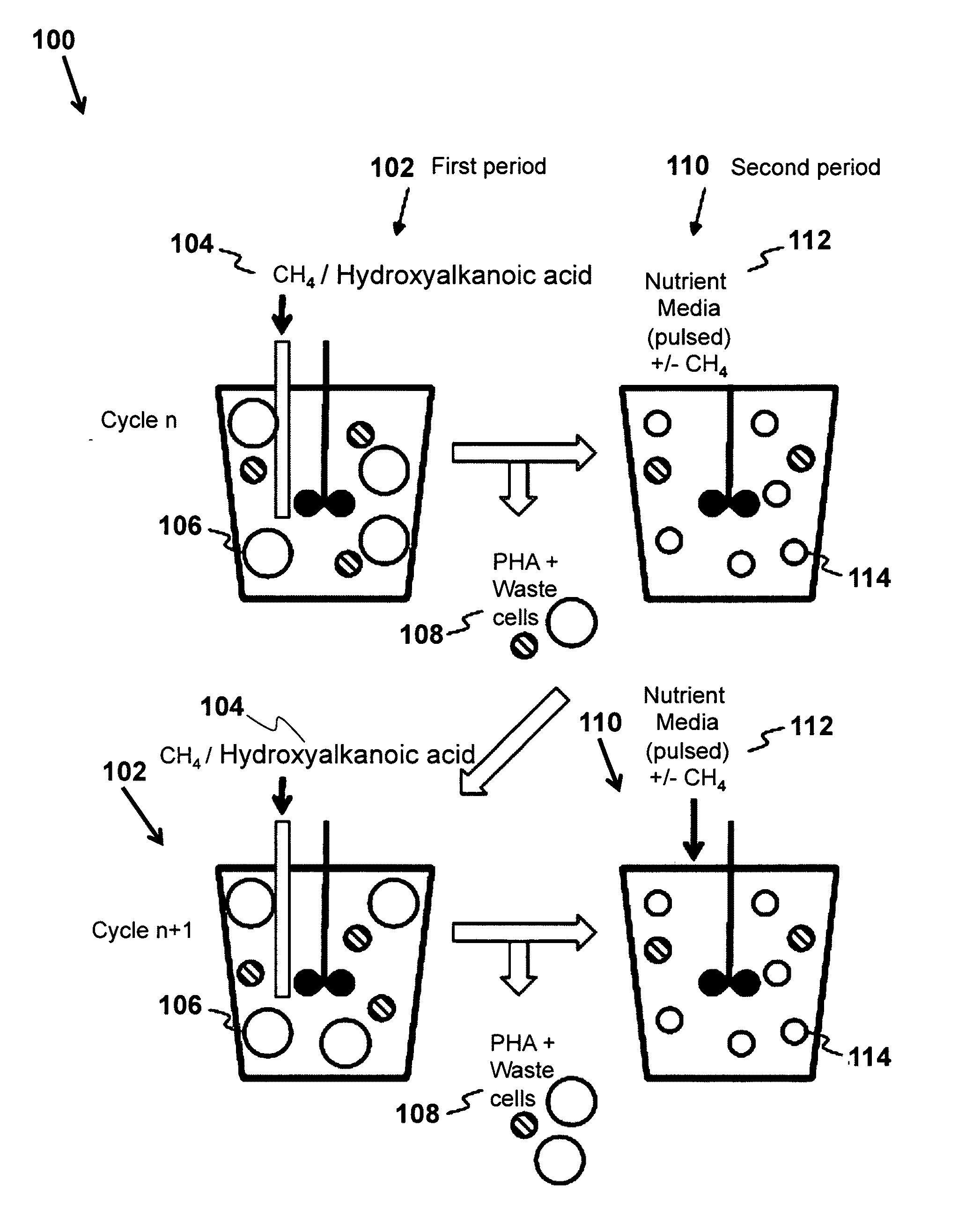
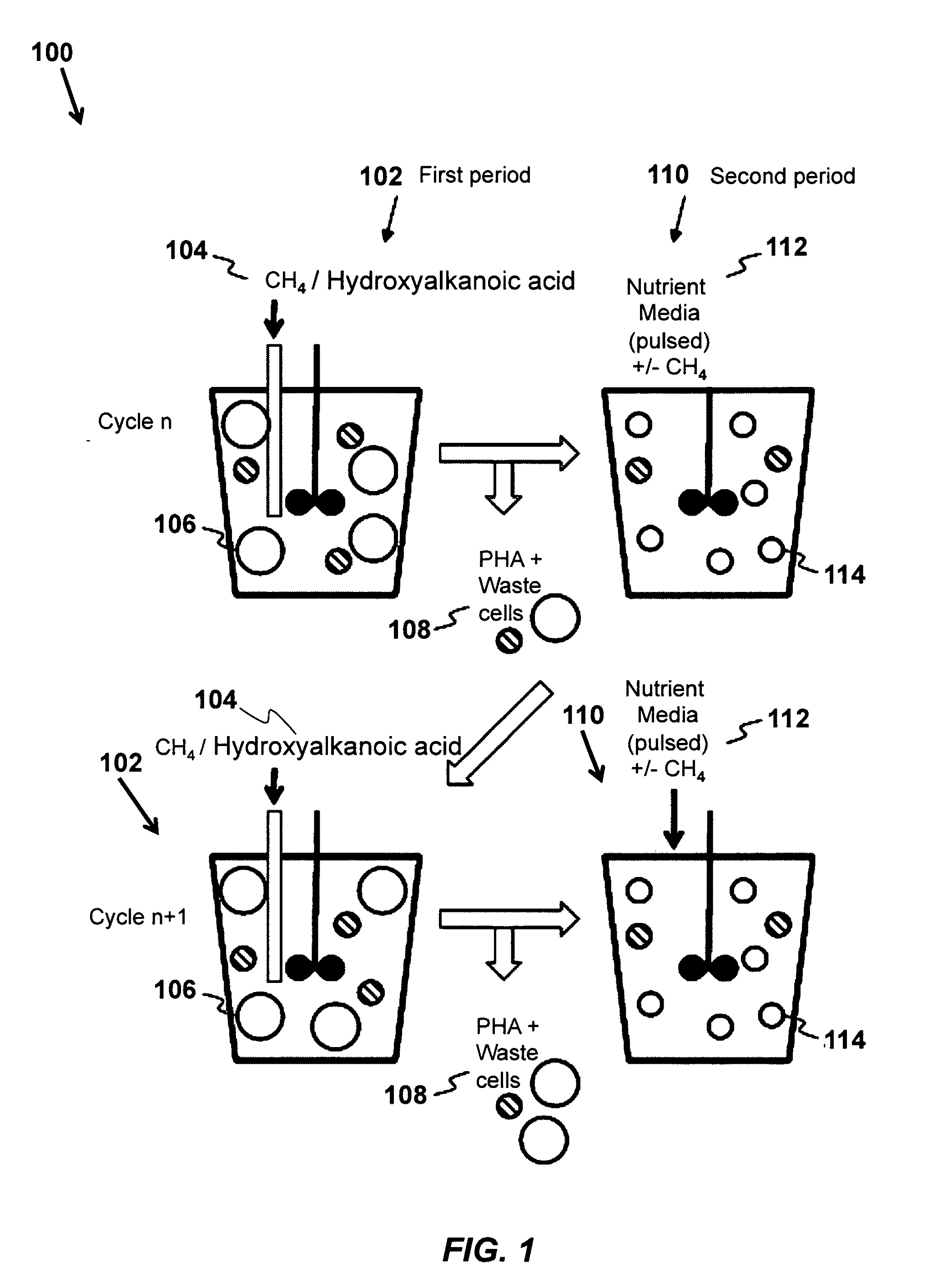
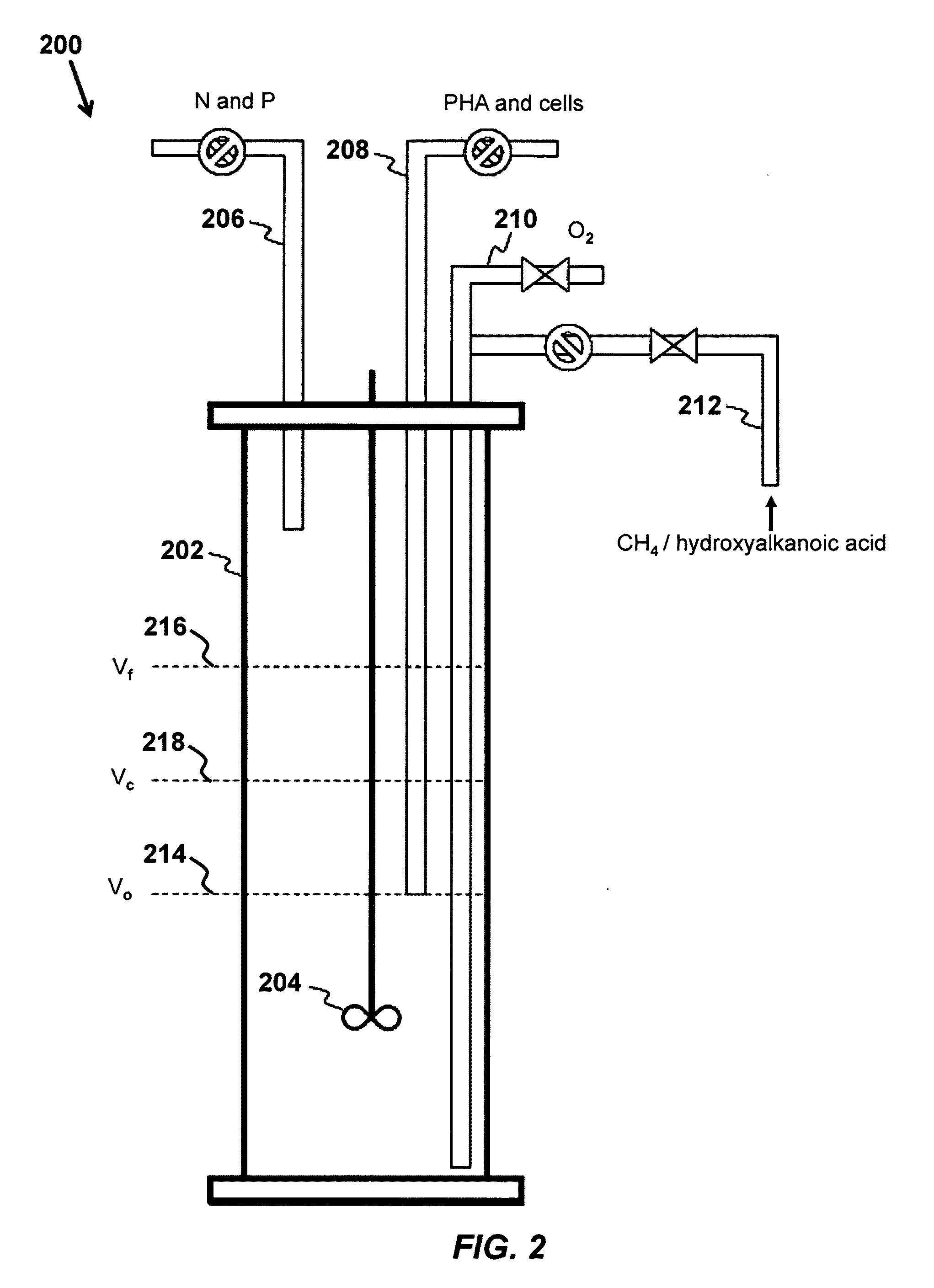
Use of hydroxyalkanoic acids as substrates for production of poly-hydroxyalkanoates by methane-oxidizing bacteria
A method of biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) is provided that includes providing a type II methanotrophic bacteria, and disposing the type II methanotrophic bacteria in an unbalanced growth condition, where the unbalanced growth condition includes a nutrient-deficient media and a hydroxyalkanoic acid, and where the nutrient-deficient media has an absence of an essential nutrient required for cell replication of the type II methanotrophic bacteria.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Biodegradation expanded plastic and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN101245175ANo difficult recycling issuesNo atmosphere damage problemThermal insulationCopolymer
The invention relates to a biological degradation foamed plastic which comprises the following components and contents: polylactic acid resin: 100 portions; polylactic acid plasticizer: 10 to 20 portions; polyhydroxy alkanoates multipolymer: 10 to 50 portions; corn starch: 20 to 60 portions; foaming agent: 8 to 17 portions; blowing promoter: 2 to 4 portions; lubricant: 0.8 to 1.2 portions; antiager: 0.45 to 0.70 portion, and the amount is calculated by weight. The biological degradation foamed plastic of the invention also provides a manufacturing method for manufacturing the biological degradation foamed plastic. The biological degradation foamed plastic is characterized by low density, high specific strength, good shock absorption performance and complete biological degradation, can be applied not only in the shock absorption packages of industrial products, such as domestic appliances, electron, instruments, industrial fittings and glass / ceramic etc., but also in a field that needs heat preservation and thermal insulation, thus the biological degradation foamed plastic of the invention is a new environmental-friendly packaging material.
Owner:陈俭秋
Method for degradation of nucleic acids and use thereof
ActiveUS7435567B2High viscositySimple and easy mannerBiomass after-treatmentFermentationMicroorganismDecomposition
The present invention provides a method to efficiently degrade nucleic acids, which result in a viscosity increase of the solution thereof on the occasion of decomposition or solubilization of microbial cells, in an easy and simple manner in the step of recovering various useful substance produced by a microorganism, and a use thereof. The product recovery method of the present invention make the product recovery from within microbial cells with ease under relatively mild conditions, because, by bringing living microbial cells into contact with a little amount of hypochlorous acid or a salt thereof, autodigestion of nucleic acids is induced and following decomposition of microbial cells or viscosity increase of the solution thereof after dissolution is inhibited. The method of the present invention is particularly preferred in recovering polyhydroxyalkanoates, which are biodegradable polymers, from microbial cells.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Device and method capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from sewage in low C/N ratio by coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification
ActiveCN105923772AHigh degree of enrichmentAerobic phosphorus uptakeWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesAmmonia-oxidizing bacteriaLow oxygen
The invention discloses a device and a method capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from sewage in a low C / N ratio by coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification and belongs to the field of biological sewage treatment. After entering an SBR coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and denitrification, sewage is first subjected to anaerobic stirring, and GAOs (glycogen-accumulating organisms) and PAOs (phosphorus-accumulating organisms) absorb organic carbon sources from the sewage and synthesize an internal carbon source PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) to be stored in bodies; then the sewage is subjected to low-oxygen aeration stirring, AOB (ammonia oxidizing bacteria) play a role in shortcut nitrification to convert ammonia nitrogen into nitrite nitrogen, and the PAOs decompose the PHA for aerobic phosphorus accumulation so as to create a hypoxic microenvironment beneficial to that the GAOs and the PAOs use the nitrite nitrogen produced during shortcut nitrification for endogenous denitrification and denitrifying phosphorus removal respectively. The method coupling enhanced biological phosphorus removal with simultaneous shortcut nitrification and endogenous denitrification is capable of realizing simultaneous phosphorus and nitrogen removal from the sewage in the low C / N ratio without addition of a carbon source, so that oxygen consumption and energy consumption are reduced and urban sewage treatment costs are saved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Process for the production of polyhydroxyalkanoates
InactiveUS20120165500A1Maximize penetration of lightHigh light transmittanceMicroorganismsFermentationPolymerizationPolyhydroxyalkanoates
Embodiments of the invention relate generally to processes for the production and processing of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) from carbon sources. In several embodiments, PHAs are produced at high efficiencies from carbon-containing gases through the utilization of a regenerative polymerization system.
Owner:NEWLIGHT TECH
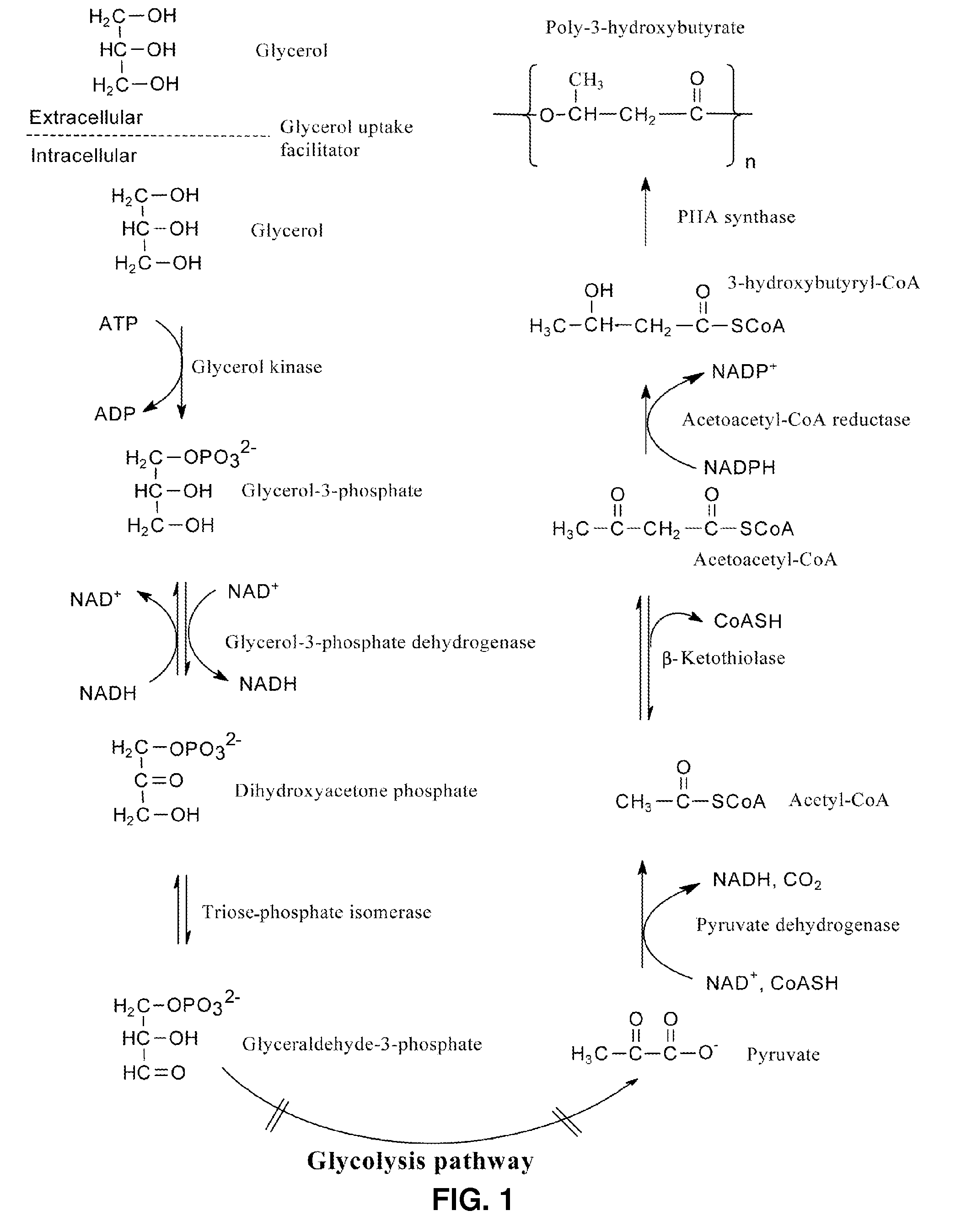
Methods for producing polyhydroxyalkanoates from biodiesel-glycerol
Methods are provided for producing biodegradable polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) with desired geometry, molecular mass, mechanical and / or physical-chemical properties from glycerol, an inexpensive carbon source and byproduct of the biodiesel industry. Microorganisms capable of converting carbon to PHA can be used to convert biodiesel-glycerol to poly-3-hydroxybutyrate (PHB) or other monomer or copolymer PHAs via fermentation. The microorganisms are cultured in a medium comprising glycerol as a primary carbon source and one or more low molecular mass organic acids as a secondary carbon source. Biomass can be harvested from the culture medium and crude PHA extracted and purified, thereby recovering purified PHA with the desired property. After PHA isolation, a nucleating agent can be added to improve certain physical-chemical properties of the PHA, e.g., crystallization temperature, to enhance performance of the PHA during injection molding.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Medical biology degradable magnesium alloy composite material
InactiveCN102652840AControl degradation timeEnhance memoryCoatingsProsthesisSurface layerUltimate tensile strength
The invention relates to a novel degradable medical magnesium alloy composite material. The medical magnesium alloy composite material provided by the invention has the characteristics of high strength, good temperature memory and controllable degradation velocity and can be used in the field of orthopedic implantation. The composite material is characterized in that the composite material contains Mg-Al-Zn magnesium alloys, wherein the content of Al is 0.5-3.5wt% and the content of Zn is 0.5-1.8wt%; besides, the magnesium alloy material can contain a few impurities including Fe, Mn, Cu and Ni, wherein the total of the impurities is not greater than 0.3wt%; and a medical biology degradable material exists on the surface layer of the composite material and can be a pure carbon dioxide copolymer, pure polyhydroxyalkanoate or a blend of the carbon dioxide copolymer and polyhydroxyalkanoate, which has to be medically purified before use.
Owner:吉林金源北方科技发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com