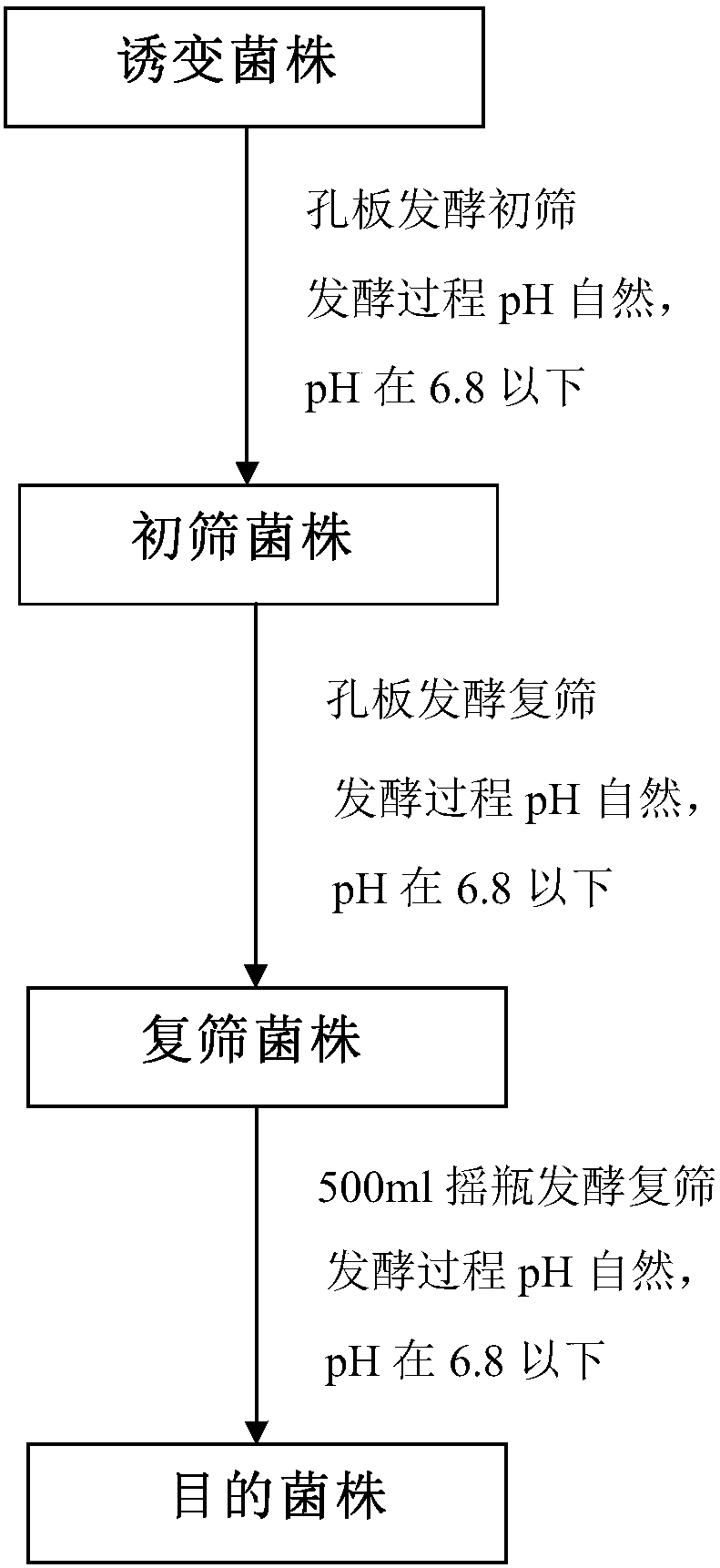
Patents
Literature
481 results about "Acidogenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
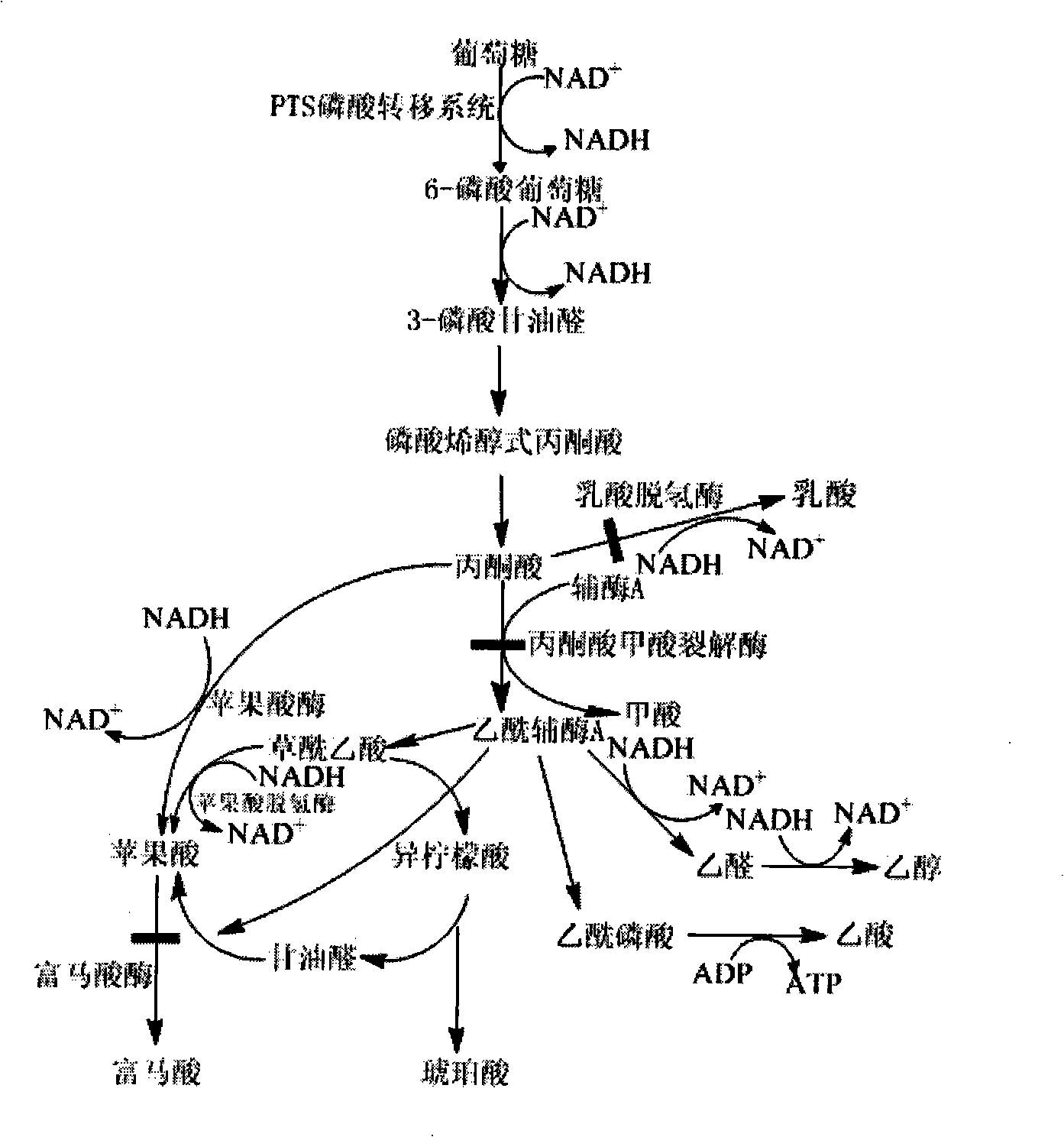
Acidogenesis is the second stage in the four stages of anaerobic digestion...
Micro-ecological preparation and application thereof
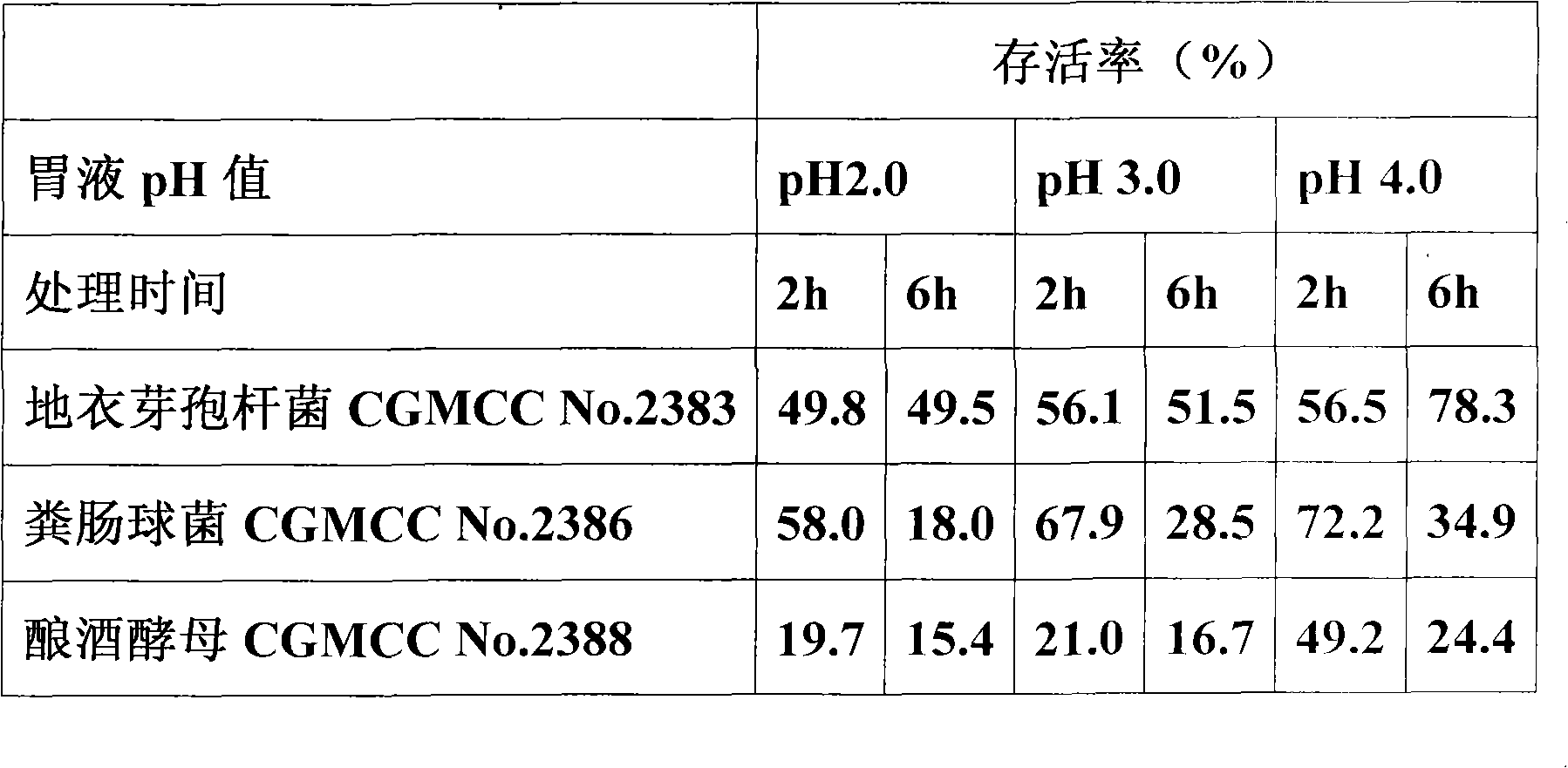
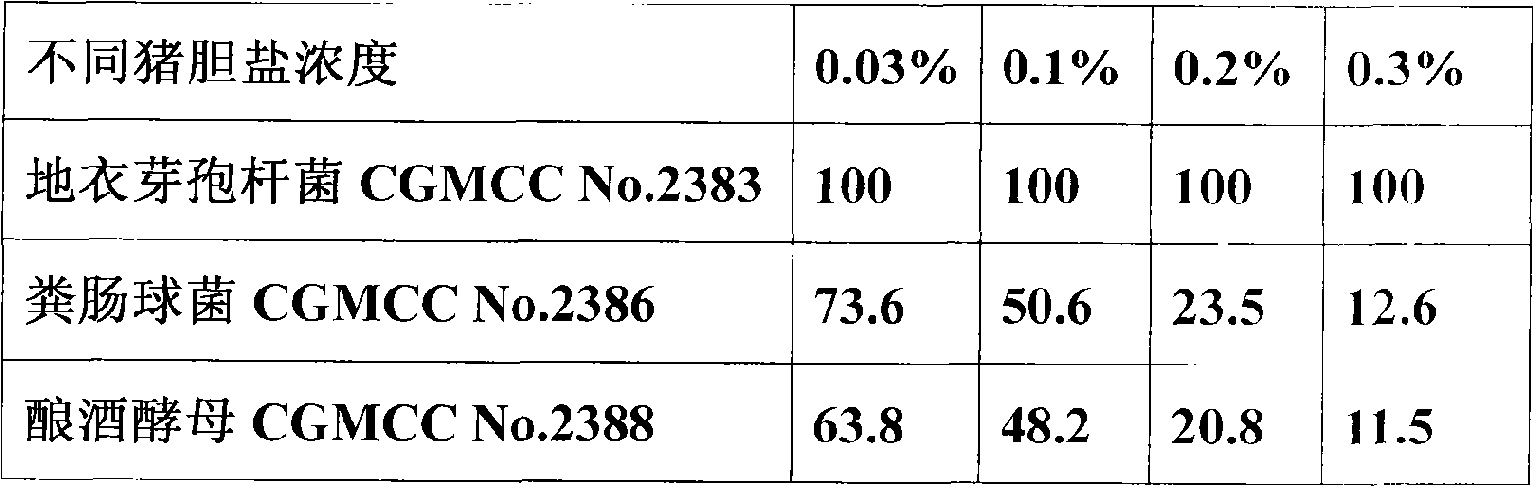
The invention relates to a micro-ecological preparation and the application thereof, in particular to a micro-ecological preparation containing a variety of probiotics and the application thereof. The micro-ecological preparation contains any three or four of the components including CGMCC No. 2383 bacillus licheniformis powder, bacillus subtilis powder, CGMCC No. 2386 enterococcus faecalis powder, lactobacillus acidophilus powder, and CGMCC No. 2388 saccharomyces cerevisiae. The micro-ecological preparation has content of live bacteria, has the adversity resistance such as gastric acid resistance, bile salt resistance, high-temperature resistance, common antibiotic resistance, and the like and the probiotic functions of producing acid and enzyme and resisting pathogenic bacteria. The variety and the proportion of the probiotics and carrier can be determined according to different kinds of animals and different animal growth phase. The micro-ecological preparation can improve the feed utilization efficiency, increase the yield of meat, eggs and milk, promote the growth of the animal, improve the immunity and the disease resistance of the animal, replace the antibiotic and improve the quality of the animal product.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG TECH GRP CO LTD +1
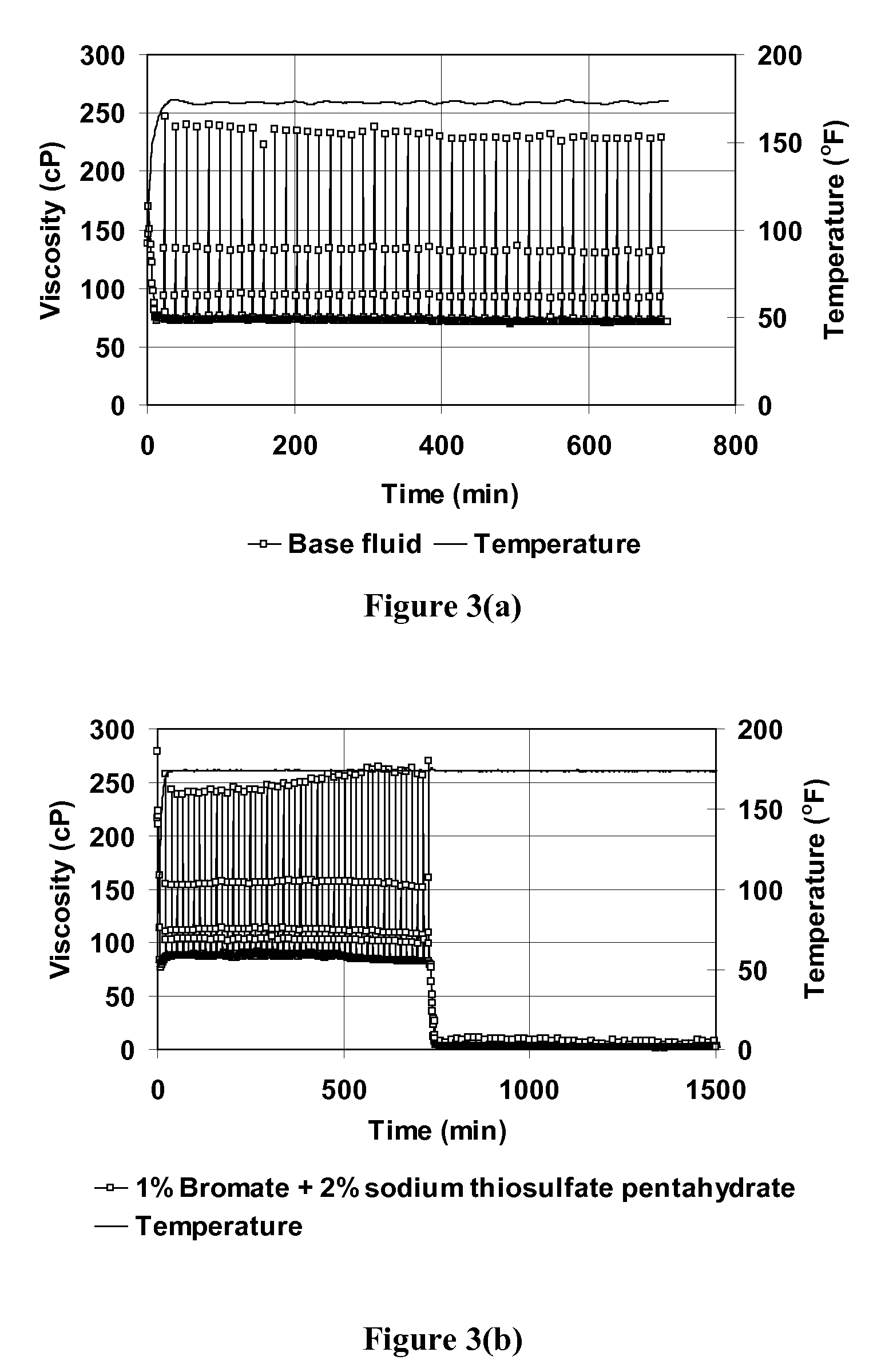
Oxidative Internal Breaker System With Breaking Activators for Viscoelastic Surfactant Fluids
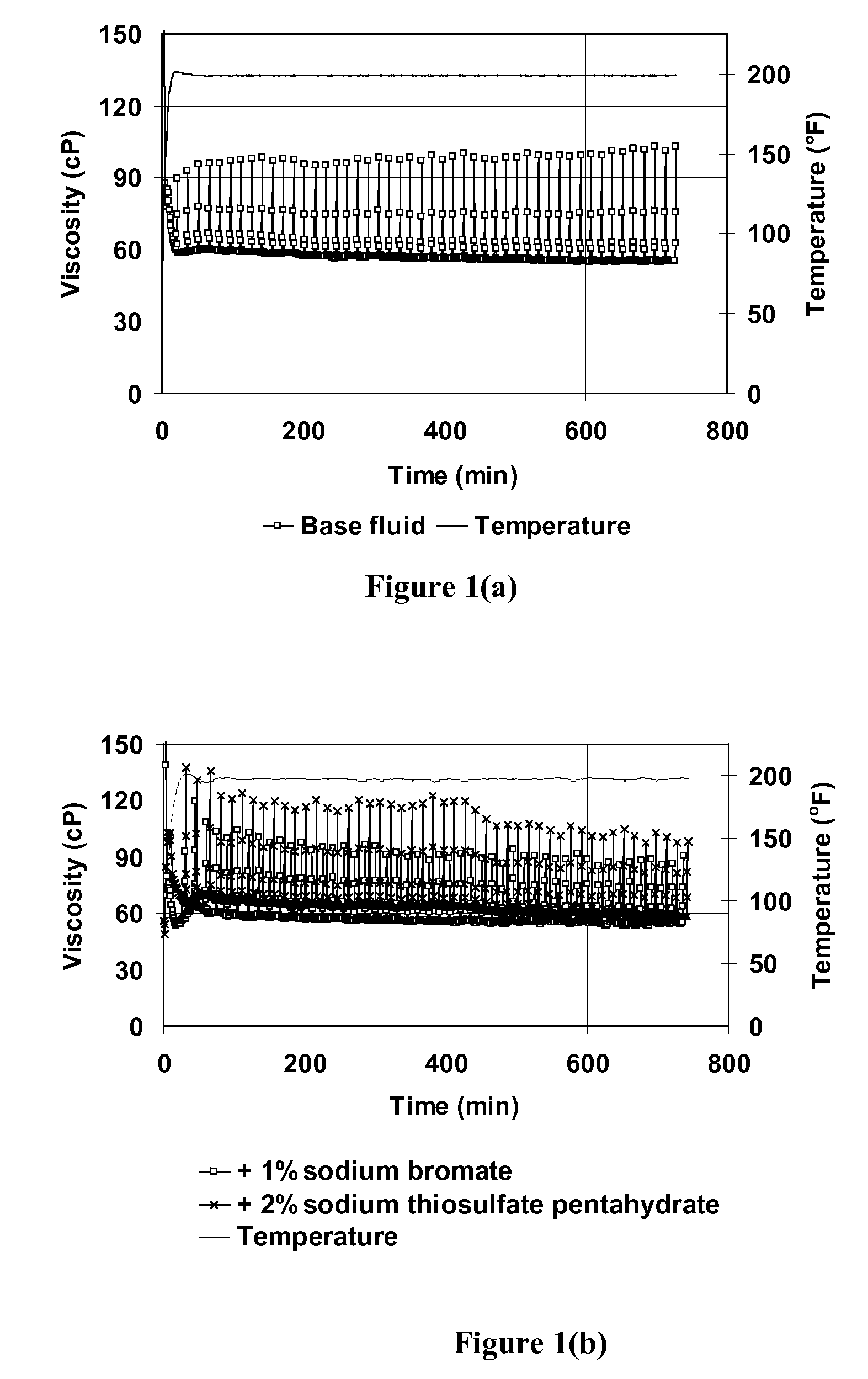
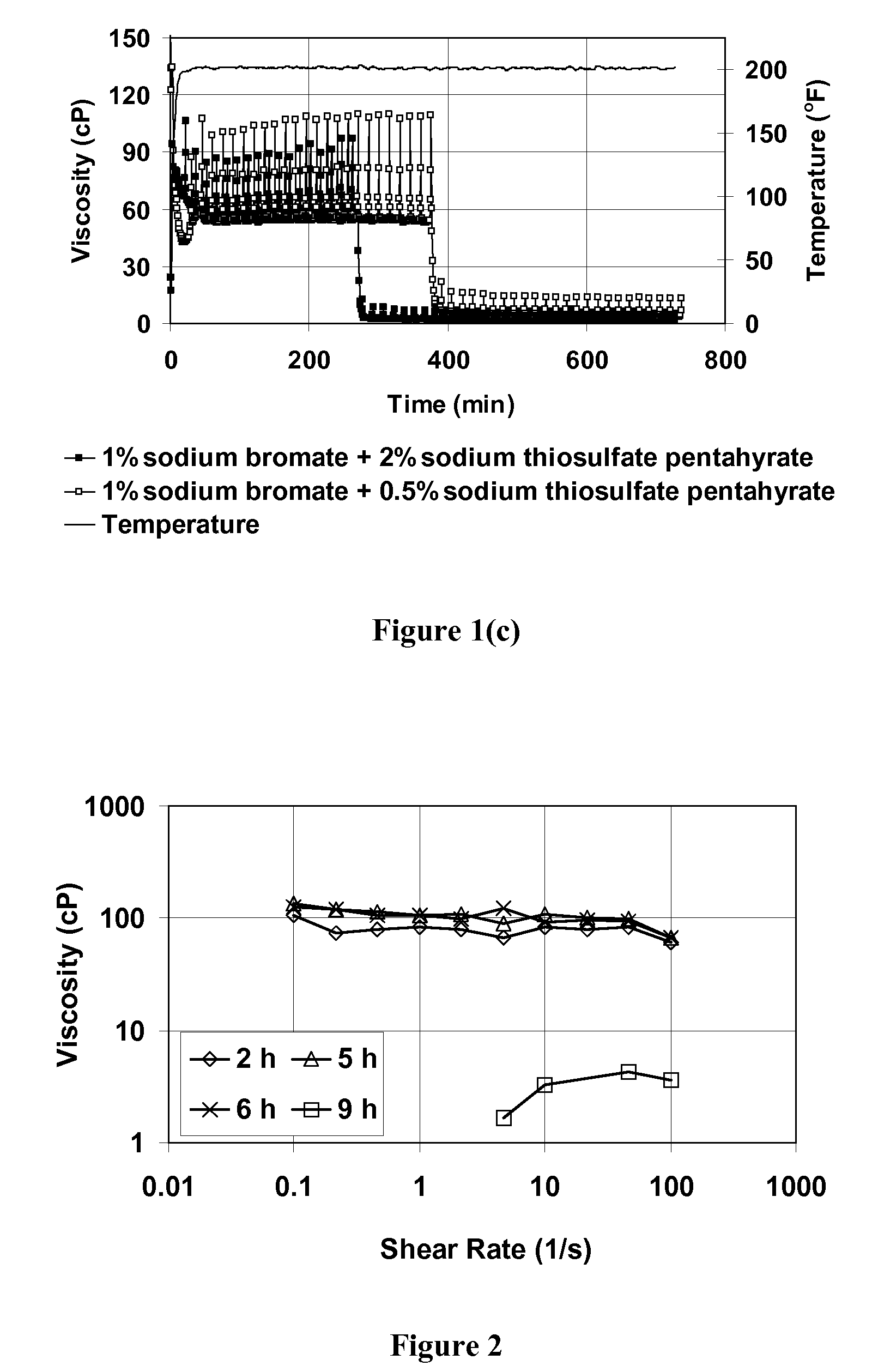
Compositions and methods are given for delayed breaking of viscoelastic surfactant gels inside formation pores, particularly for use in hydraulic fracturing. Breaking inside formation pores is accomplished without mechanical intervention or use of a second fluid. Bromate oxidizing agents are used along with selected breaking activators for the bromate breaking compounds. Useful bromate breaking activators include acid-generating breaking activators, oxidizing sulfur containing breaking activators, and reducing agent breaking activators.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Lactobacillus plantarum with function of reducing contents of biogenic amines in foods and application of lactobacillus plantarum
ActiveCN105132308AAcid resistantHas the ability to clearBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of microorganisms and discloses lactobacillus plantarum with a function of reducing contents of biogenic amines in foods and application of the lactobacillus plantarum. The lactobacillus plantarum is resistant to acids and capable of strongly removing eight types of biogenic amines (including tryptamine, phenethylamine, putrescine, cadaverine, histamine, tyramine, spermidine and spermine) in vitro. After 1*1010CFU / ml of the lactobacillus plantarum and the eight types of biogenic amines are co-cultured for 24h, wherein the concentration of each type of the biogenic amines is 100mg / L, and the total amine concentration is 800mg / L, the total amine content is reduced by 70% approximately, the content of each type of the biogenic amines is reduced by 30%-100%, and the removal rate of histamine highest in toxicity is up to 96.69%. Further, the lactobacillus plantarum is capable of lowering pH to 4 in eight hours owing to quickness in acid generation, thereby having favorable fermentation potential. The lactobacillus plantarum is used for degradation of the biogenic amines in foods, especially in fermented foods and extensive in application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
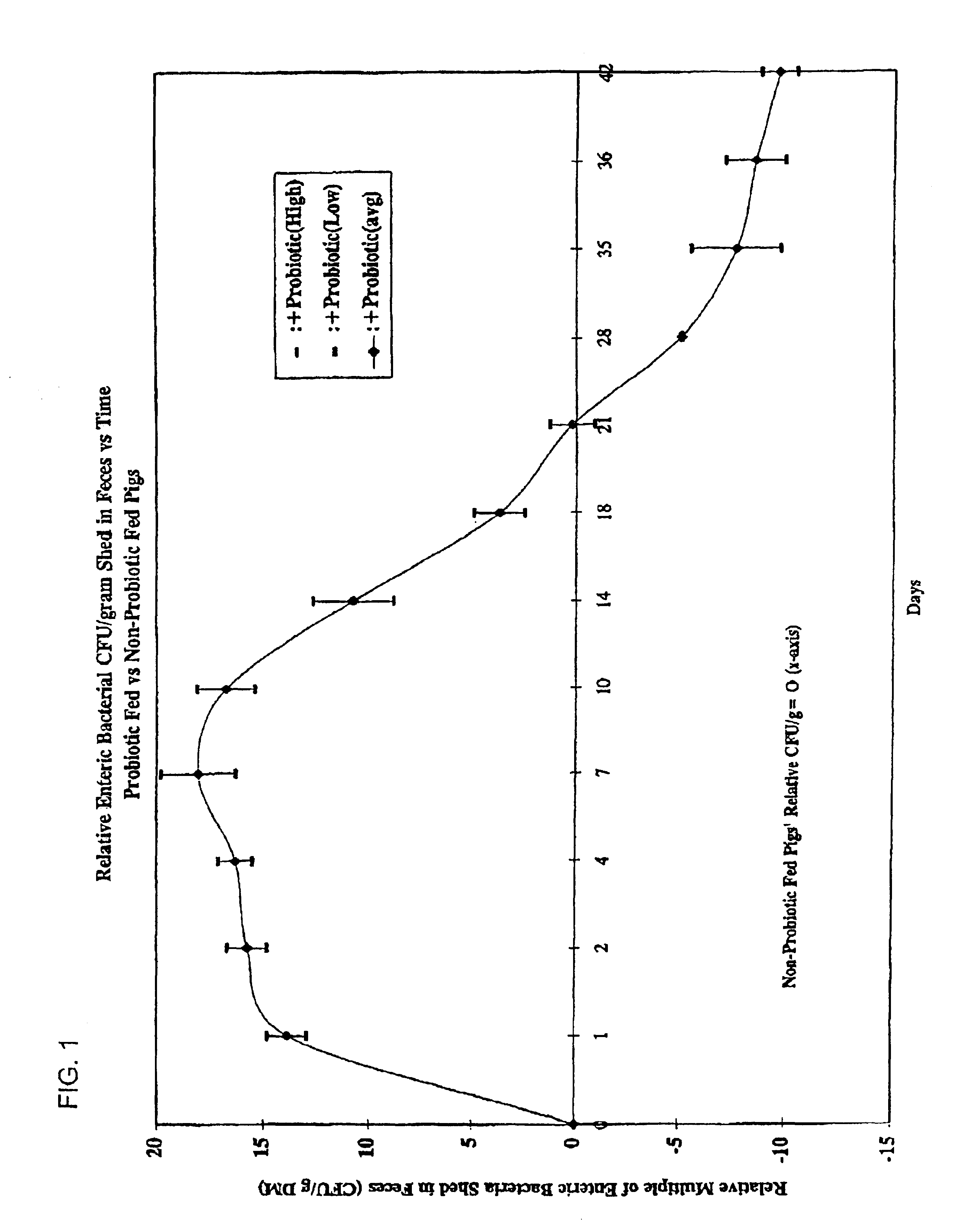
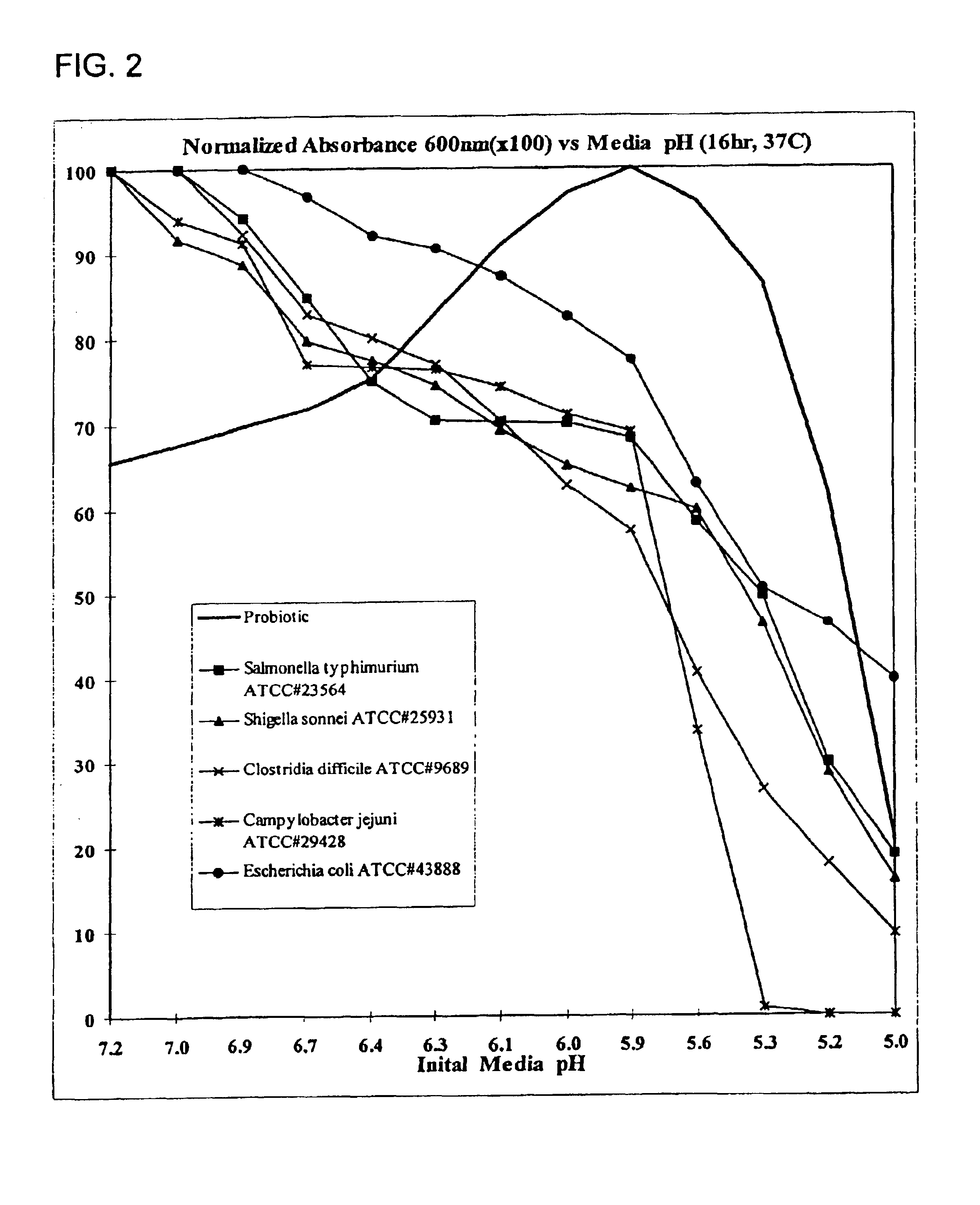
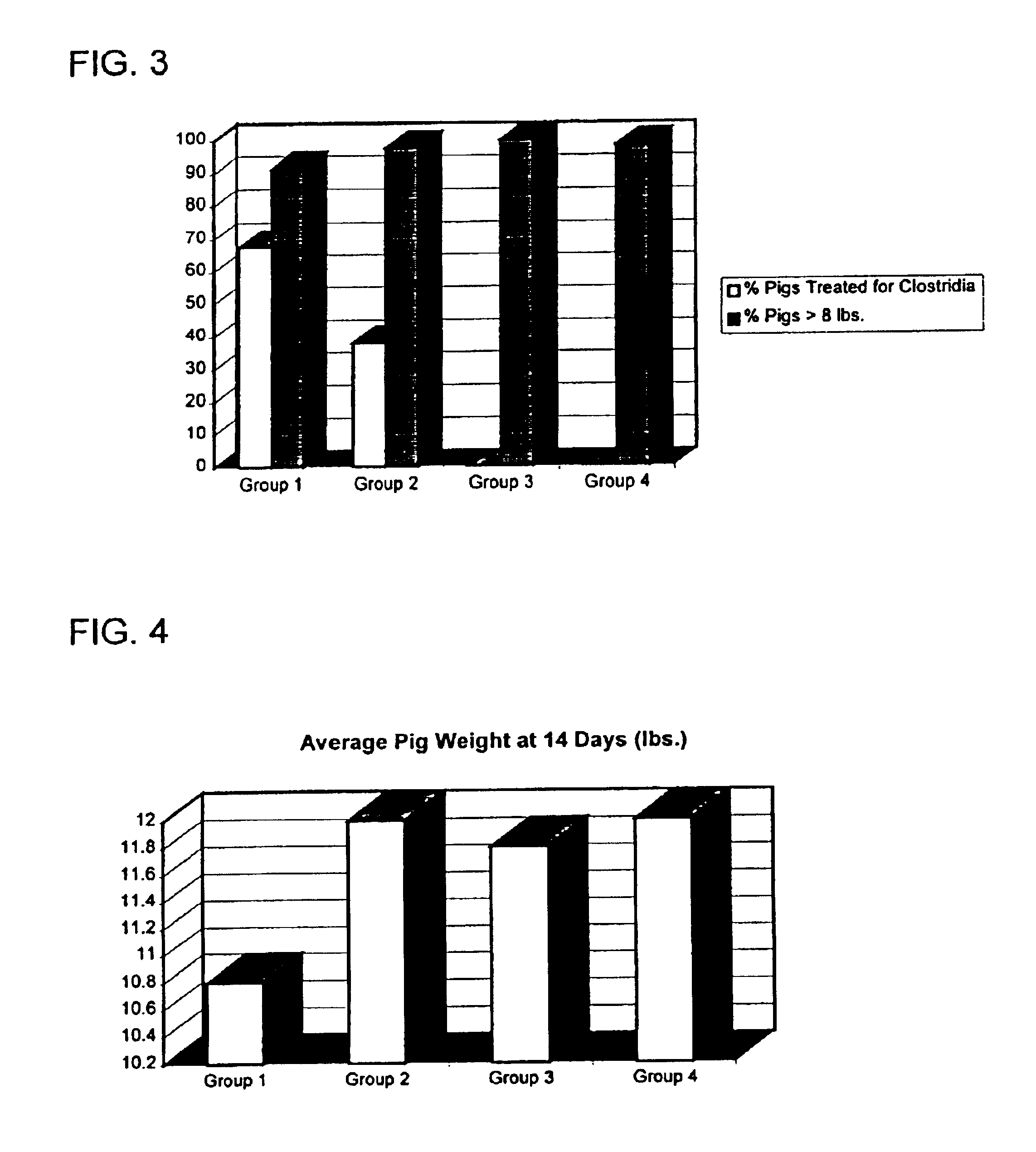
Probiotic mixture intended for monogastric animals to control intestinal flora populations
InactiveUS6841149B1Good curative effectAssist in growth and activityBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyBacteroides
A mixture of probiotics effective to reduce the contamination of enteric bacteria in humans and other monogastric animals. The mixture of probiotics includes one or more acid-producing bacteria strains and one or more yeast strains, and may advantageously be supplemented with a source of nutrients, such as prebiotics including fructo-oligosaccharides. In a preferred embodiment, said one or more bacteria strains contain Enterococcus faecium strain NCIMB #10415, and said one or more yeast strains contain NCYC #47 and CNCM I-1079.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES +1
Production of biodegradable thermoplastic materials from organic wastes
InactiveUS7141400B2Guaranteed uptimeApparatus sterilizationPlastic recyclingOrganic acidMicroorganism
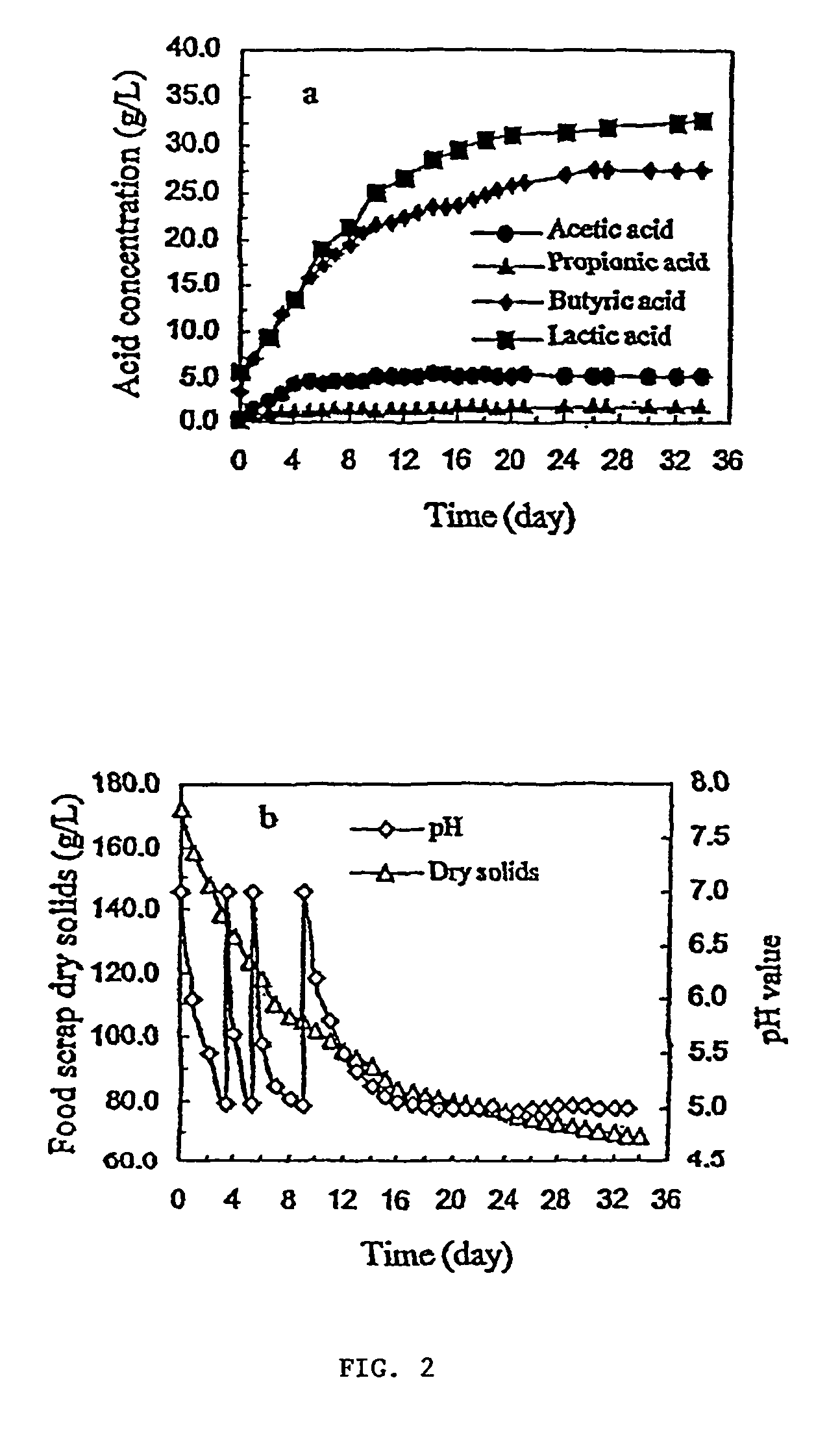
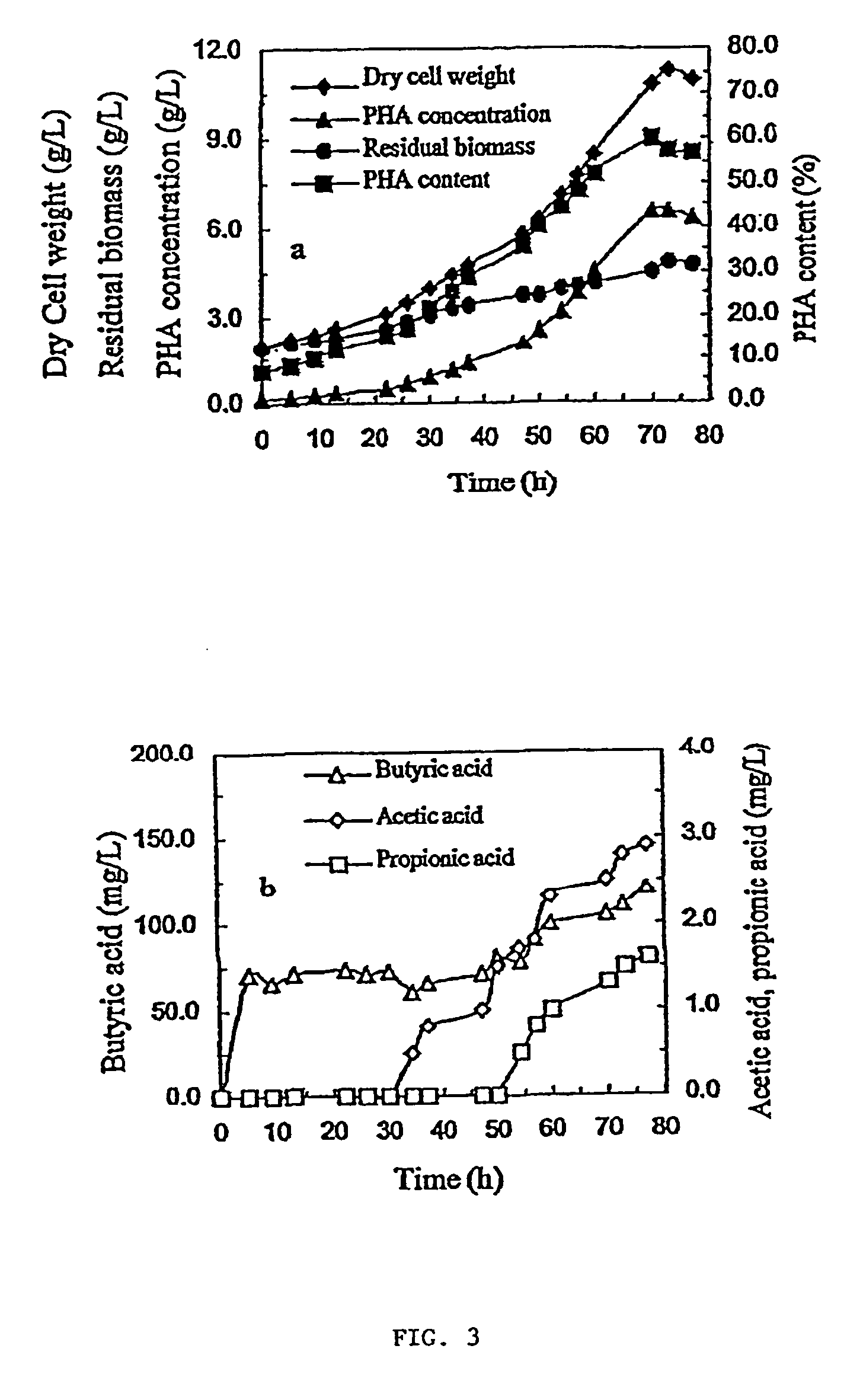
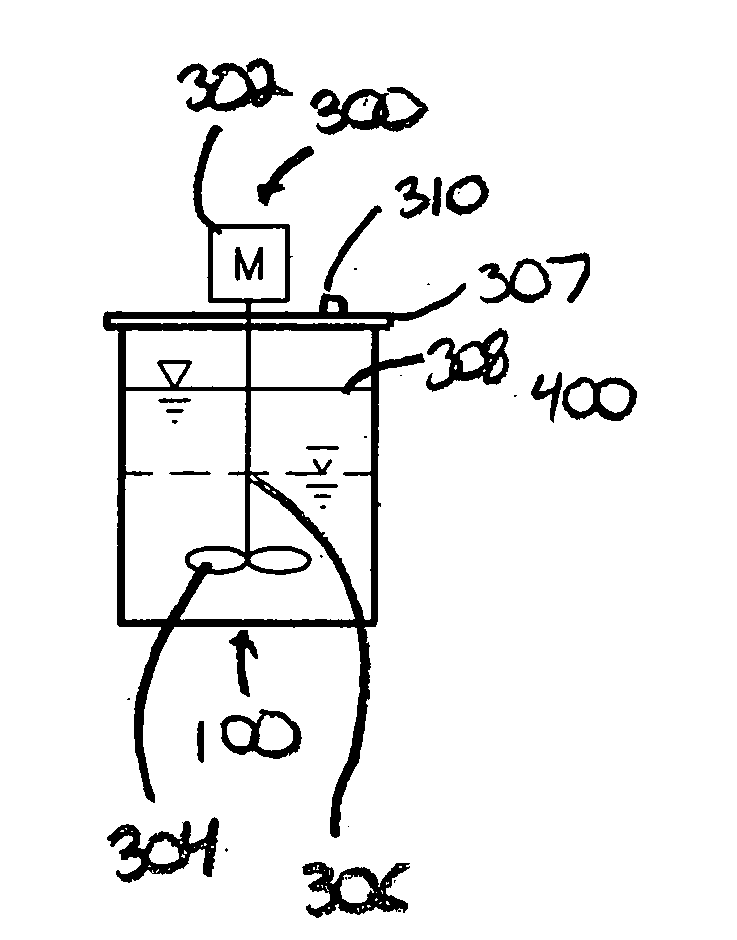
A system and method for converting organic wastes to biodegradable thermoplastic materials including polyhydroxyalkanoates is disclosed, which method includes treating the organic wastes with an acidogenic microbial population to form fermentative organic acids, and polymerization of the organic acids by PHA-producing microbial species to form PHAs. The system includes a first compartment for acidogenesis of organic wastes without oxygen, and a second compartment, for polymer synthesis by enriched cultures of species with oxygen such as R. eutropha, P. oleovorans, or mixtures thereof. The compartments are integrated with barriers that permit mass transfer of organic acids while maintaining different culture conditions in the compartments.
Owner:UNIV OF HAWAII
Lactobacillus leavening agent, preparation method thereof and special bacterial strain
InactiveCN101748082AIncrease productionHigh content of live bacteriaMilk preparationBacteriaAdditive ingredientBacterial strain
The invention discloses a lactobacillus leavening agent, a preparation method thereof and a special bacterial strain. The preservation serial number of lactobacillus is CCTCC M208151. An active constituent of the lactobacillus leavening agent is the lactobacillus. The invention also discloses a method for preparing the lactobacillus leavening agent, which comprises the following steps: firstly, leavening and culturing lactobacillus plantarum SC79 CCTCC M208151 in SC79 optimal culture medium; and secondly, collecting thallus in the step 1 and then adding a protective agent to the thallus to obtain the leavening agent. The lactobacillus leavening agent has small dosage, quick acid production speed through mixing the lactobacillus leavening agent and a harvestless exopolysacchatide yoghourt bacterial strain to prepare yoghourt, better relative viscosity, elasticity, denseness and adhesiveness than that of the conventional yogurt and small syneresis sensibility of formed sticky yogurt colloids, larger water holding capacity than that the conventional yogurt and hard whey separation.
Owner:JILIN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Two phase anaerobic contact sequencing batch reactor (ACSBR) system for treating wastewater containing simple and complex organic constituents
InactiveUS20060175252A1Improve efficiencyEfficient digestionWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesSequencing batch reactorSuspended solids
A two-phase anaerobic treatment system and method for the treatment of wastewaters containing simple and complex organic constituents is provided wherein the complex organic constituents are broken down into simple organic constituents by acidogenic bacteria in a Phase One reactor and the simple organic constituents from the Phase One reactor are converted into biogas, mainly methane, in a Phase Two reactor by methanogenic bacteria. The method includes the steps of feeding wastewater to the Phase One reactor either in an intermittent batch mode or semi-continuous mode, and withdrawing effluent from the Phase One reactor preferably in a batch mode. Effluent from the Phase One reactor is fed to the Phase Two reactor in an intermittent batch mode while effluent from the Phase Two reactor is withdrawn in a batch mode. The method minimizes the transfer of suspended solids from the Phase One reactor to the Phase Two reactor.
Owner:UPENDRAKUMAR K C +2
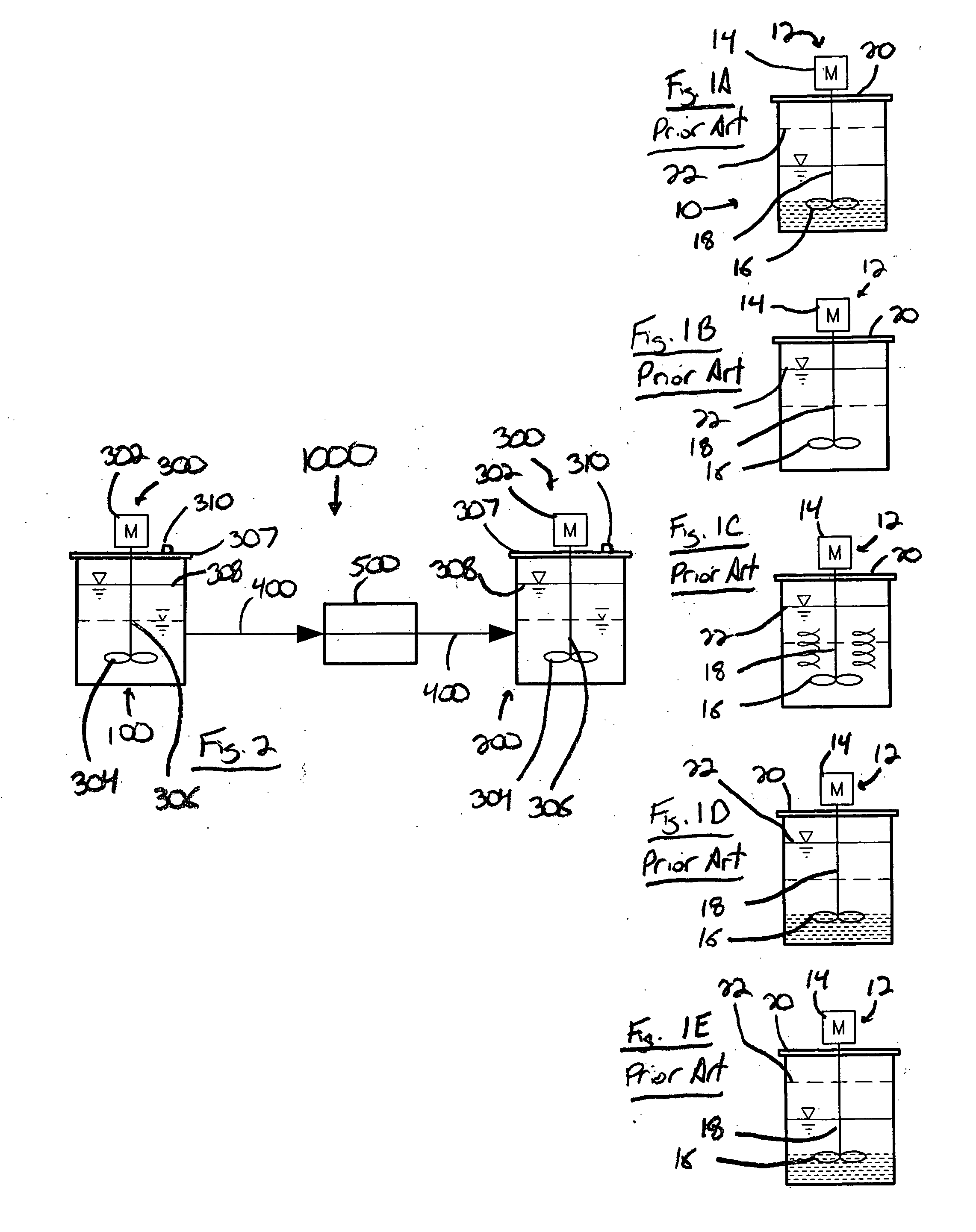
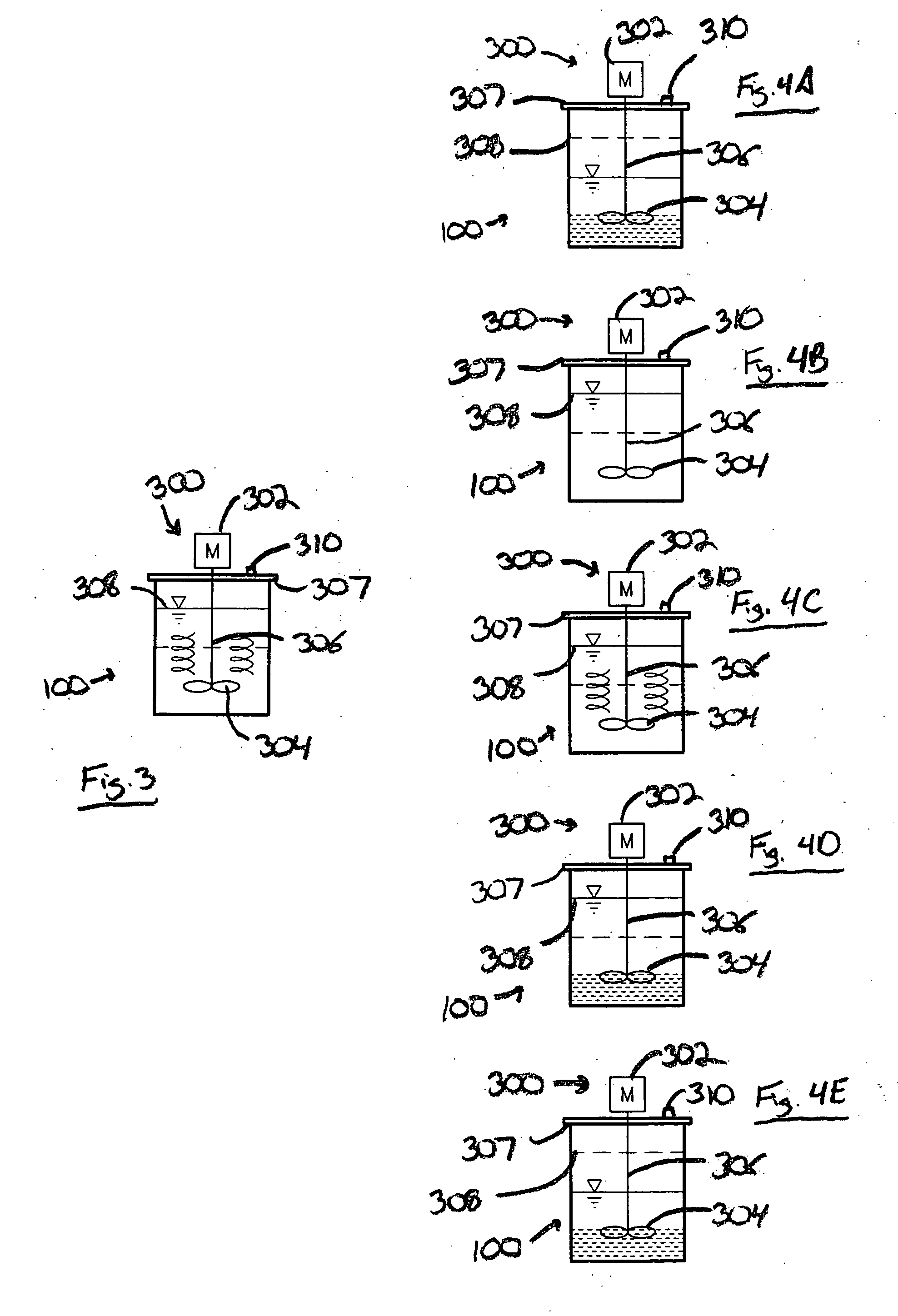
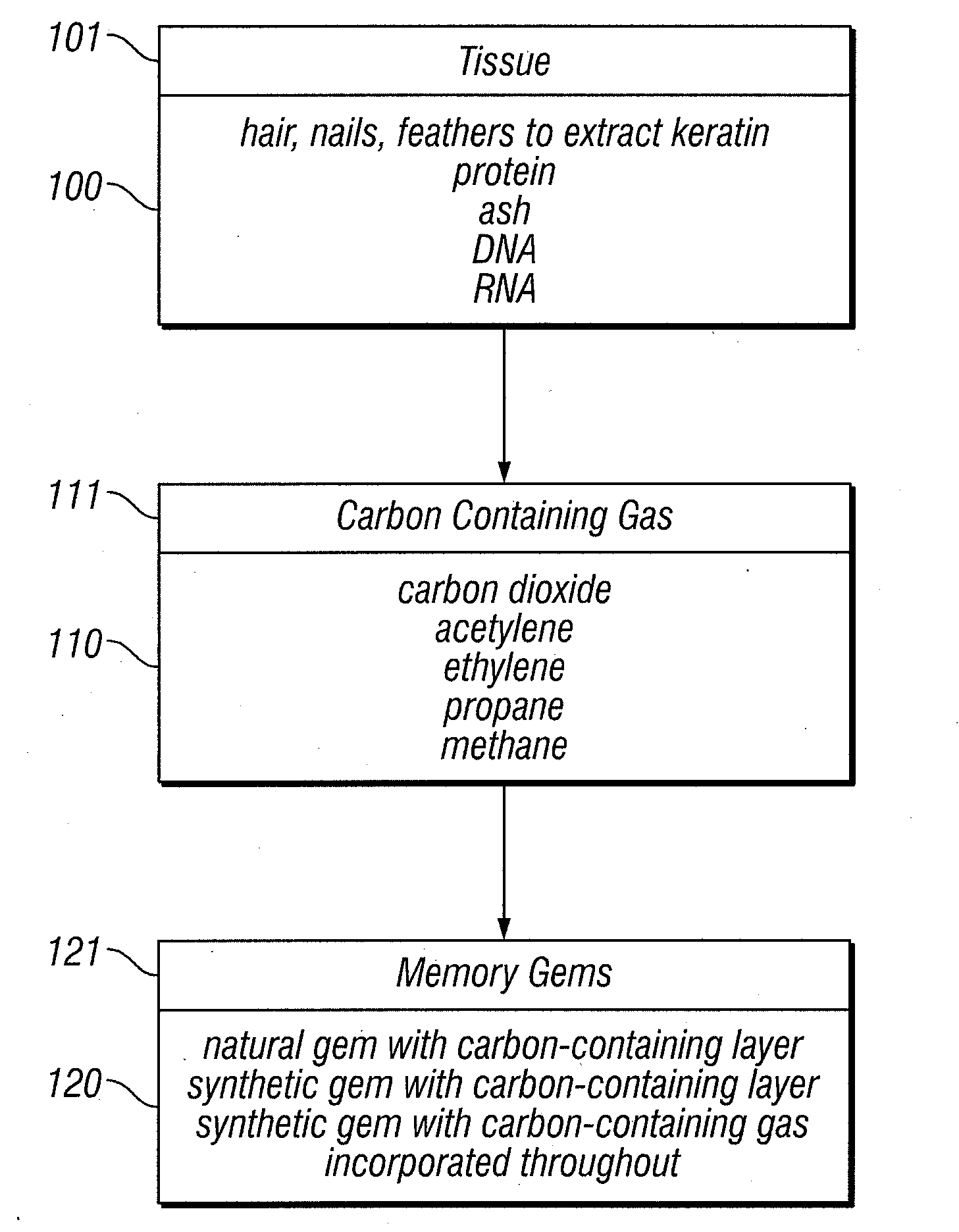
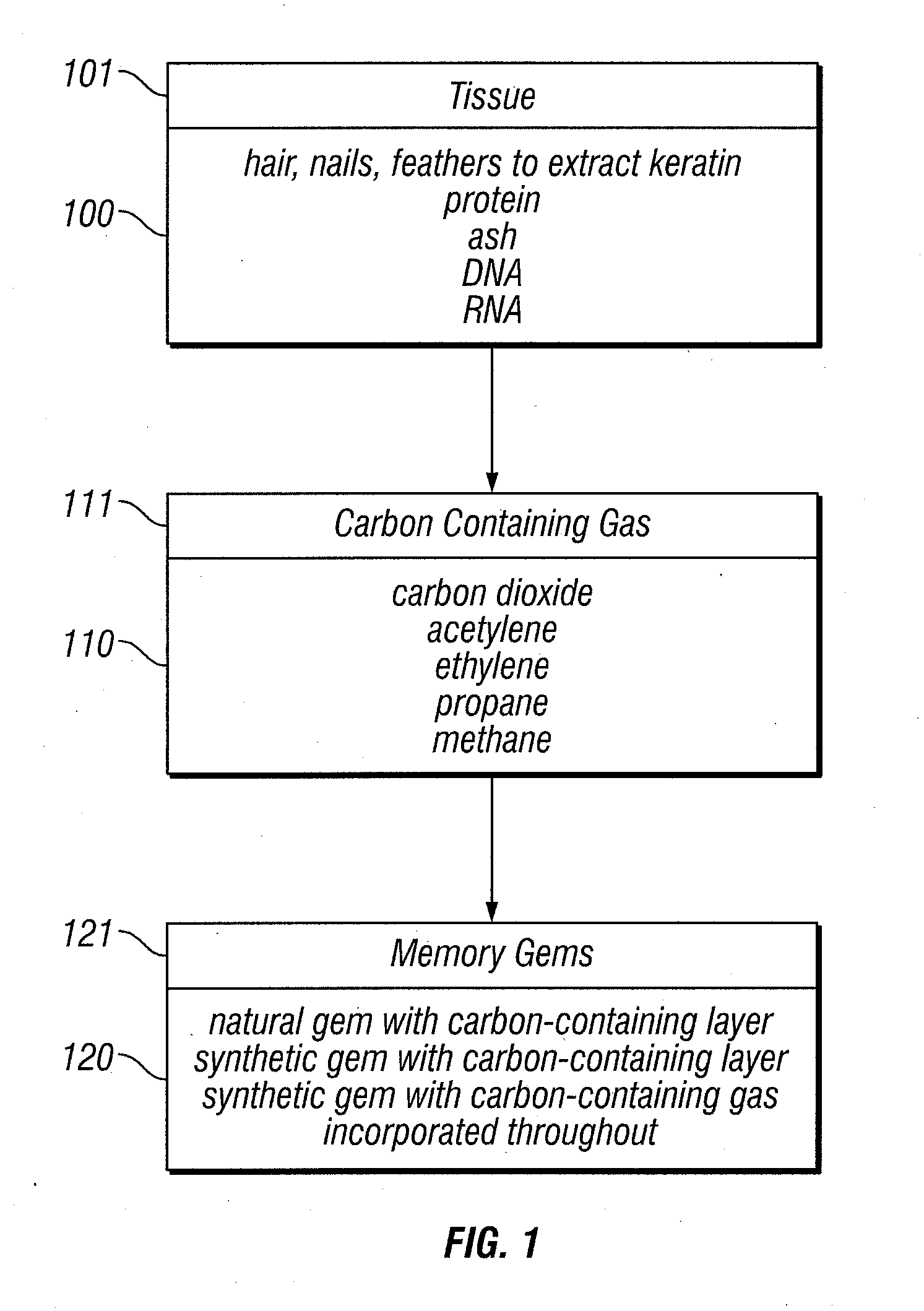
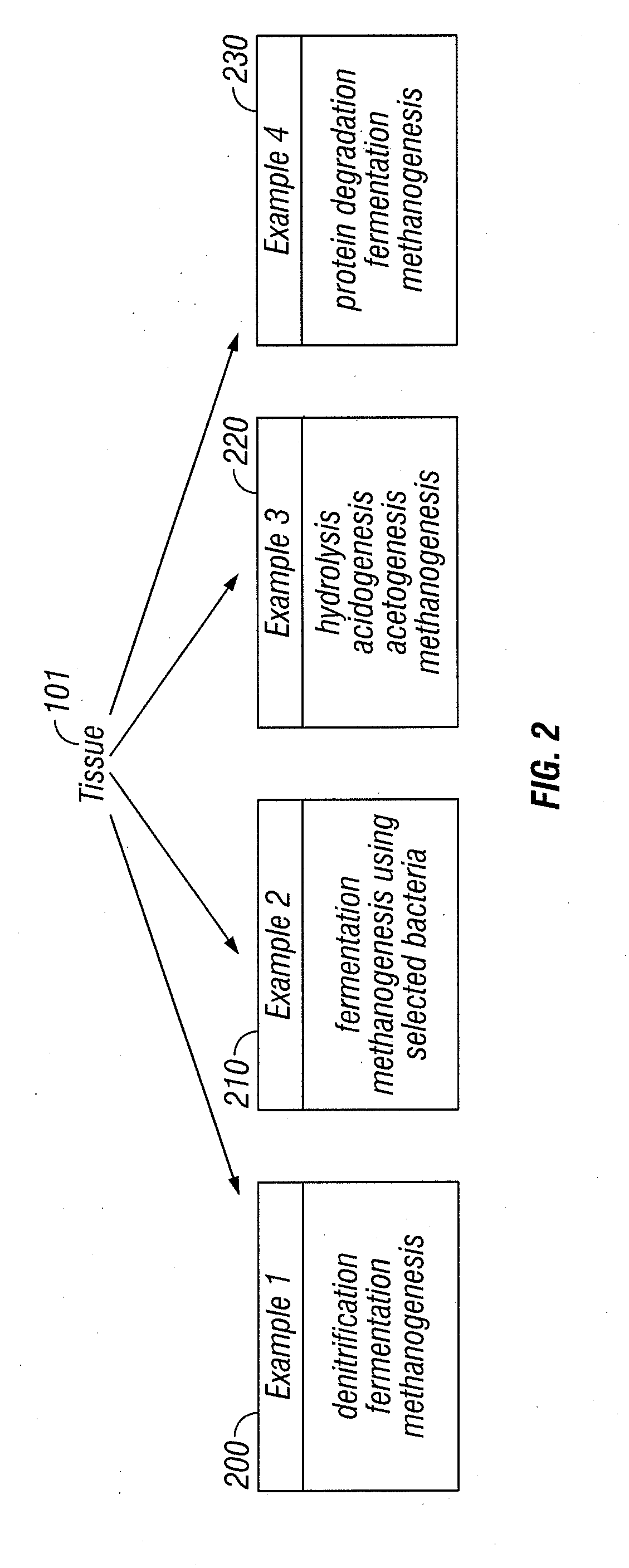
Memory gemstones
Animal or human tissue is digested to extract carbon-containing gases. The digestion process can include hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and methanogenesis. The step of denitrification can be added if too much nitrogen is produced during digestion. Digestion can also include enzymes that break down the tissue in preparation for methanogenesis. The carbon-containing gas can be added onto or be incorporated throughout a natural or synthetic diamond or other gemstone. The carbon-containing gas can be added during hydrothermal synthesis to create a gemstone with the carbon-containing gas incorporated throughout.
Owner:BLUE MOON GEM
In-situ acid stimulation of carbonate formations with acid-producing microorganisms
InactiveUS20140202684A1Reduce decreaseFluid removalDrilling compositionMicroorganismEnvironmental engineering
Methods of treating a subterranean formation penetrated by a wellbore of a well, wherein the subterranean formation includes carbonate. The methods can include the following steps of: (1) optionally, fracturing the subterranean formation; (2) optionally, acidizing the subterranean formation with a Bronsted-Lowry acid; (3) treating the subterranean formation with an acid-producing microorganism, a nutrient for the microorganism, and, if needed, a suitable electron acceptor for respiration by the microorganism; (4) optionally, flushing the wellbore with a wash fluid to push the microorganism deeper into the subterranean formation and wash it away from the metal tubulars of the well; (5) preferably, shutting-in the well for a required incubation period for in-situ acid generation by the microorganism; and (6) preferably, after the shut-in, flowing back fluid from the subterranean formation into the wellbore.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Lactobacillus plantarum CQ02-108 and application thereof to preparation of fermented sausages
ActiveCN108949645AInhibition of reproductionGrowth inhibitionSugar food ingredientsBacteriaEscherichia coliStaphylococcus cohnii
The invention discloses lactobacillus plantarum CQ02-108 and application thereof to preparation of fermented sausages. The lactobacillus plantarum CQ02-108 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on July 17, 2018; and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 16121. The lactobacillus plantarum CQ02-108 can be used for producing proteinase and rapidly producing acid, does not cause viscosity, produce gas, produce biological amine, produce H2O2, produce H2S and produce pigments, and also has the advantages of high-salt concentration tolerance, high acidity tolerance, inhibition of growth of escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus, bile salt resistance and gastric juice tolerance. When the lactobacillus plantarum CQ02-108 is used for fermenting the sausages, the quantity of viable bacteria of lactic acid bacteria in the fermented sausages can be remarkably improved and the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value of the sausages is reduced; and the growth ofharmful bacteria is inhibited and the quality of the fermented sausages can be remarkably improved.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Novel constructed high-yield malic acid gene engineering and method for producing malic acid
The invention discloses a method for constructing strain Escherichia coli JM127 in high product malic acid gene project and acid producing method thereof. The constructing method mainly includes deactivating or knocking out enzyme with ability to make malic acid dehydrate and pyruvate degrade, and over-expressing enzyme regenerated by NAD. A two-stage fermentation experiment using a constructed Escherichia coli is carried out, which includes steps of: (1) inoculating activated Escherichia coli into enrichment medium, aerobically culturing to enhance biomass; (2) after treating the bacteria liquid membrane obtained by aerobic culture, introducing it into LB culture medium containing 20-100 g / L glucose and a definite content of carbonate, anaerobically fermenting to produce malic acid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
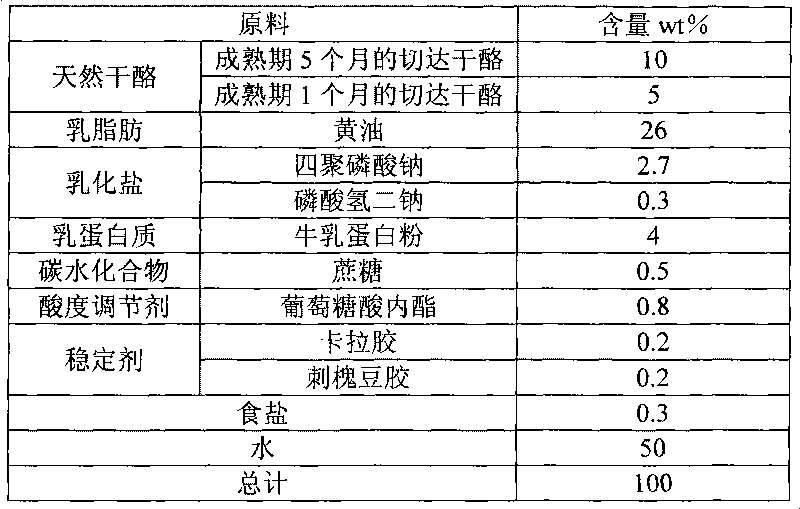
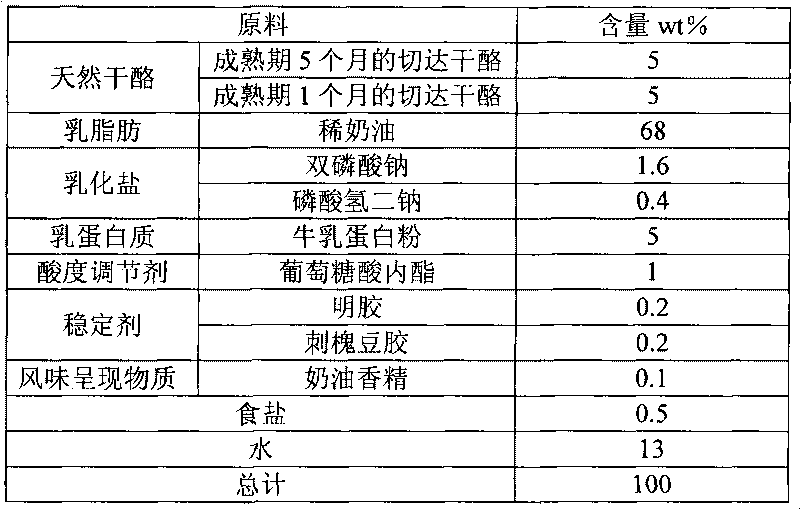
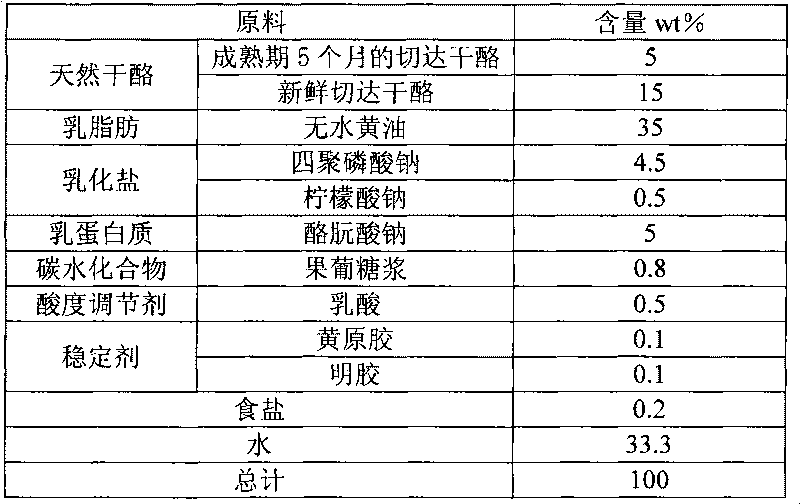
Method for preparing regenerated cream cheese and obtained cheese
The invention discloses a method for preparing regenerated cream cheese, which comprises the following steps: (1) melting and mixing raw materials comprising natural cheese, milk fat, milk protein, emulsifying salt, carbohydrates, edible salt, stabilizer and water in addition to fermentation acid-producing yak milk type cheese; (2) low-temperature acid-adding process; (3) pasteurization; (4) homogenization process; and (5) fast cooling. The invention can overcome the defects of all aspects of the natural cream cheese process, the existing regenerated cream cheese process, the conventional regenerated cheese process and the like and provides the method for preparing the regenerated cream cheese; compared with the traditional natural cheese production process, the method is greatly simplified and has the advantages of simple production process, small equipment input and short production cycle, thereby having great advantages on the cost, leading a product to have high additional value, leading the better raw materials of the product to have relative advantages on the cost and being more realistic and convenient when in real production. Compared with the natural cheese, the senses of the prepared regenerated cream cheese are better.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
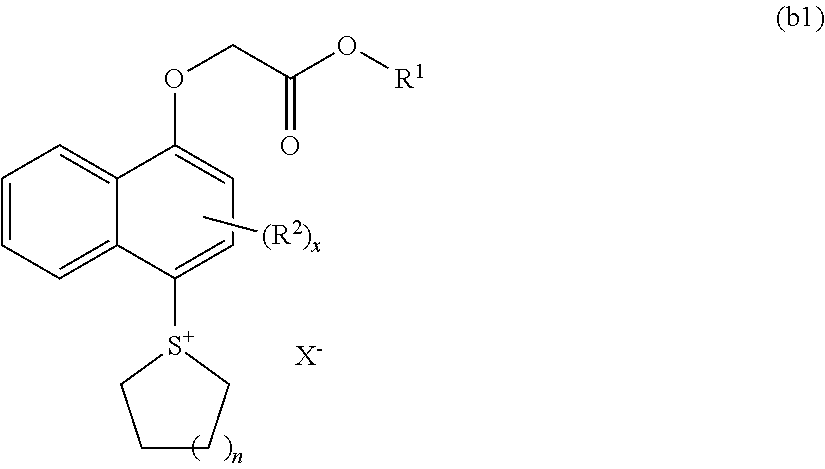
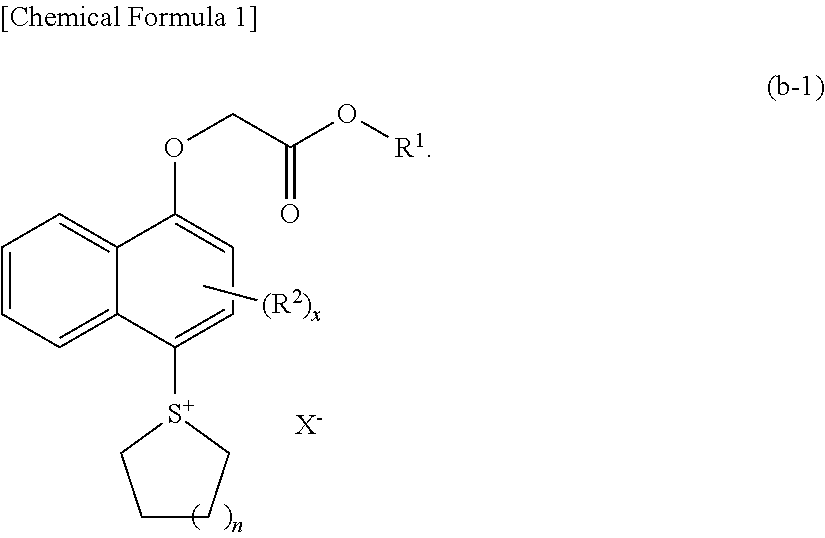
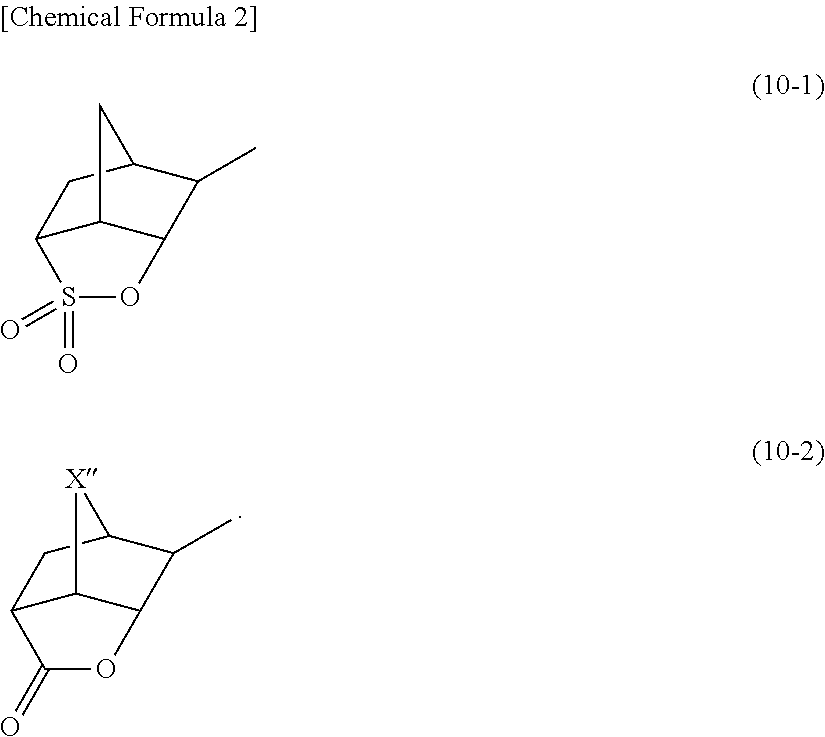
Resist composition, method of forming resist pattern, novel compound, and acid generator
InactiveUS20120015297A1High transparencyImprove propertiesOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsSolubilityChemical compound
A compound represented by general formula (b1); an acid generator including the compound; and a resist composition including a base component (A) which exhibits changed solubility in an alkali developing solution under action of acid and an acid-generator component (B) which generates acid upon exposure, the acid-generator component (B) including an acid generator (B1) including a compound represented by general formula (b1), wherein R1 represents a hydrogen atom, a linear, branched or cyclic alkyl group of 1 to 10 carbon atoms or a heterocyclic group of 1 to 10 carbon atoms; R2 represents a linear or branched alkyl group of 1 to 10 carbon atoms; x represents an integer of 0 to 6; n represents an integer of 0 to 3; and X− represents an anion.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Production method of microbial preparation by symbiotic fermentation of lactic acid bacteria and saccharomycetes
The invention discloses a production method of a microbial preparation by symbiotic fermentation of lactic acid bacteria and saccharomycetes. The production method is characterized by comprising the following steps: carrying out symbiotic assemblage screening on lactic acid bacteria and saccharomycetes separated from an Inner Mongolia dairy product kumiss to select a set of enterococcus faecium HE5 and brewer yeast J-4 with mutual promotion, wherein the viable count of the lactic acid bacteria reaches 2.88*10<9>CFU (Colony-Forming Unit) / mL when enterococcus faecium HE5 and brewer yeast J-4 screened are cultivated on an optimized skimmed milk culture medium, the viable count of the saccharomycetes reaches 3.3*10<8>CFU / mL, and double bacteria culture is better to promote the growing effect of lactic acid bacteria; and freezing and drying the cultivated and harvested double bacteria to obtain the microbial preparation by symbiotic fermentation of lactic acid bacteria and saccharomycetes. The microbial preparation is good in symbiotic effect and strong in acid-producing capacity.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Microorganism bacterium agent for treating leather wastewater and preparation method thereof
PendingCN106834158APromote degradationStrong resistance to changeFungiBacteriaBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a microorganism bacterium agent and a preparation method thereof, and relates to a composite bacterium agent and a preparation method thereof. The composite bacterium agent can be used for efficiently removing a large amount of COD (chemical oxygen demand), ammonia and nitrogen in leather wastewater. The composite bacterium agent is prepared from mycobacterium, microbacterium, acinetobacter, pichia pastoris, lactobacillus, klebsiella oxytoca and a liquid culture medium. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1, activating the bacteria strains of raw materials; 2, enriching and culturing; 3, mixing the bacterium strains according to a weight ratio, and adding into the liquid culture medium, so as to obtain the composite bacterium agent. The composite bacterium agent has the advantages that the biological activity is high, the growth speed is high, the leather wastewater can be treated under the low temperature condition, the removal rate of organic matter can be obviously increased, the contents of COD, ammonia and nitrogen in the leather wastewater are effectively decreased, and the effect is obvious.
Owner:北京市科学技术研究院资源环境研究所
High-temperature-resistant acetic acid bacteria and application thereof in production of acetic acid through fermentation
ActiveCN103614318APromote energy saving and emission reductionReduce fermentation cooling costsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant Acetobacter pasteurianus strain and an application thereof in production of acetic acid through fermentation. The strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.8189. The acetic acid bacteria disclosed by the invention can grow and generate acid at 25-45 DEG C; the strain and ethanol serving as a main raw material are used to produce acetic acid through liquid submerged fermentation, and the temperature and ventilation volume during fermentation are controlled in three stages; the concentration of acetic acid obtained after fermentation can reach 60-180g / L, and the acid conversion rate of ethanol reaches 85-101%. The production of acetic acid through fermentation is performed by using the high-temperature-resistant acetic acid bacteria, and a relatively high fermentation temperature is adopted, so that the consumption of cooling electricity and cooling water is reduced, relatively high production efficiency is achieved at the same time, and the production cost is reduced. The high-temperature-resistant acetic acid bacteria and a fermentation process thereof are suitable for production of a variety of table vinegar including food vinegar, fruit vinegar and the like through fermentation.
Owner:广东天地壹号食品研究院有限公司 +1
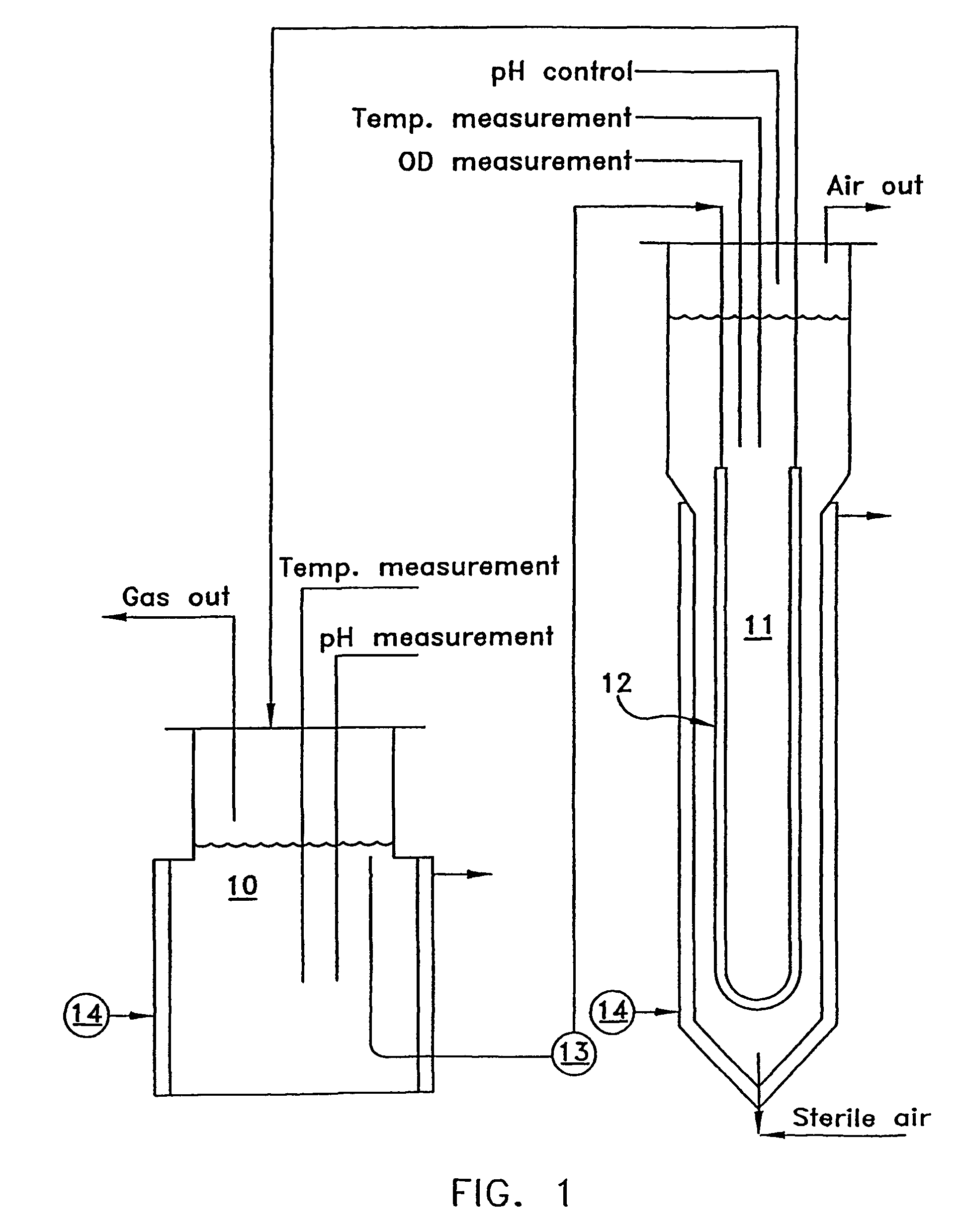
Sustained microbial production of hydrogen gas from diluted fruit juice
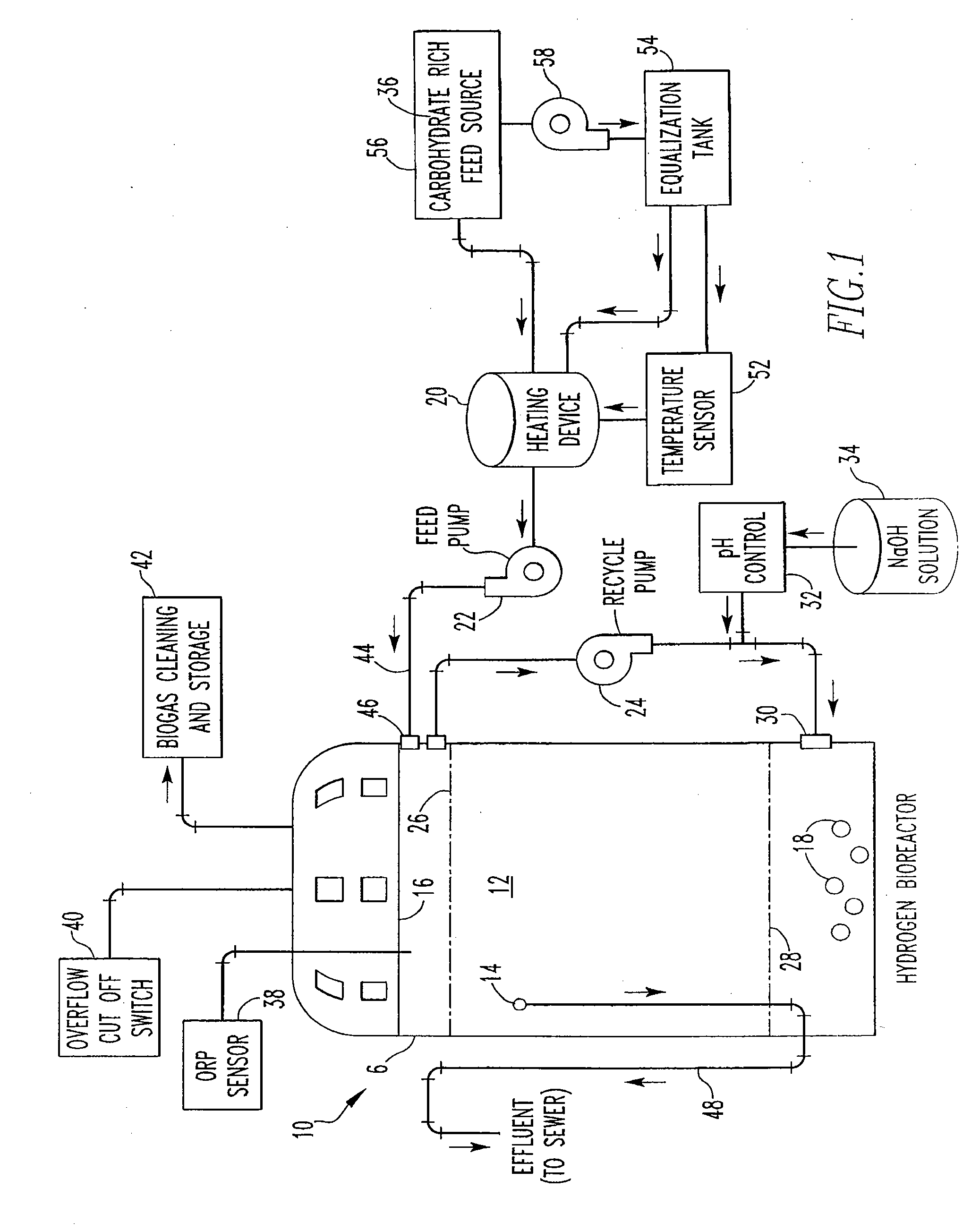
InactiveUS20070178570A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismHydrogen
The present invention provides an apparatus and method for the production of hydrogen based on the capture of metabolic by-products of hydrogen-producing microbacteria, in which a bioreactor is maintained in an environment conducive to the growth of hydrogen-producing microbacteria and the production of hydrogen and at the same time is restrictive to the growth of undesirable microorganisms such as methanogens and the production of methane. The present invention utilizes concentrated growth of hydrogen-producing microbacteria such as Klebsiella oxytoca. The invention provides a simple and cost-effective way to produce hydrogen by selectively harnessing hydrogen-producing microbacteria utilizing glucose-based solutions while substantially eliminating methane-producing microbacteria.
Owner:NANOLOGIX INC
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof to kitchen wastes
ActiveCN106047762AHigh activity proteaseImprove salt toleranceBacteriaSolid waste disposalSalt resistanceMicroorganism
The invention provides bacillus subtilis which is classified and named bacillus subtilis CY-4 and is preserved in Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences at No. 3 Yard, No. 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing, on May 13, 2016, the postal code is 100101, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.12447. The invention further provides application of the bacillus subtilis to kitchen wastes. The bacillus subtilis has the activities of highly-active proteases, amylases and oil hydrolases, degrades glucose-produced acid and contains thermophilic bacteria with high salt resistance and acid resistance, and through the effective combination with a carrier, the weight of the bacillus subtilis put into the kitchen wastes can be quickly and effectively reduced to 85 percent.
Owner:BIOMAX ECOLOGICAL ENG
Town multi-element organic waste for preparing biogas and method for preparing biogas from same
InactiveCN105755052AAchieve complete fermentationImprove utilization efficiencyWaste based fuelFermentationLivestock manureBiogas production
The invention relates to a method for preparing biogas, in particular to town multi-element organic waste for preparing biogas and a method for preparing biogas from the town multi-element organic waste.The problems existing in the prior art that materials are single, the degradation efficiency is low, the biogas yield is low, energy consumption is high, and operation is not stable are solved.According to the method, the multi-element organic waste is subjected to different preprocessing, and the degrading capacity of fermentation microorganisms for waste is improved.As for straw materials with the long fermentation period, firstly, microbial populations in livestock manure are utilized for performing hydrolysis treatment on the straw materials, then, the straw materials are transferred into an acid production reaction system to be mixed with other materials for fermentation so as to keep pace with materials which are subjected to a reaction rapidly, all the materials can be subjected to the hydrolysis and acidification steps so as to enter the methane production stage at the same time, fermentation is completed, and therefore complete fermentation of the materials is achieved.The operation is simple and easy to implement, the biogas production efficiency of fermentation raw materials is effectively improved, the selection range of the fermentation raw materials is enlarged, and the disposal intensity of organic solid waste in a town is increased.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading nicosulfuron and applications thereof
ActiveCN106591168AResidue reductionReduce production and use costsBacteriaWater contaminantsAntibiotic YBiology
The invention discloses rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading nicosulfuron and applications thereof. The invention provides a strain namely rhodococcus ruber YMHL-1 capable of degrading residual nicosulfuron in wastewater, and the identification shows that the strain belongs to Rhodococcus. The strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, CGMCC in February 9th, 2015; and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 10542. The main biological characteristics are as follows: the Gram staining reaction is negative; the bacterial colony is in an orange yellow color, is in a round shape, and is opaque, the surface of the bacterial colony is rough and dry; the cell is in a sphere shape or short bar shape, does not have any flagellum, is motionless, and does not generate any spore; the strain is aerobic and chemoheterotrophic and cannot liquefy gelatin and hydrolyze starch; the enzyme contact reaction is positive, the V.P. reaction is positive, the methyl red reaction is negative; the strain cannot degrade casein, cannot reduce nitrates; and the strain can produce acids from glucose, can utilize glucose, fructose, and citrates, cannot utilize mannose, arabinose, and raffinose, and can reduce more than 90% of antibiotics in water through direct application.
Owner:JIANGSU NANZI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION SCI & TECH
Method for preparing caproic acid through two-phase process anaerobic fermentation
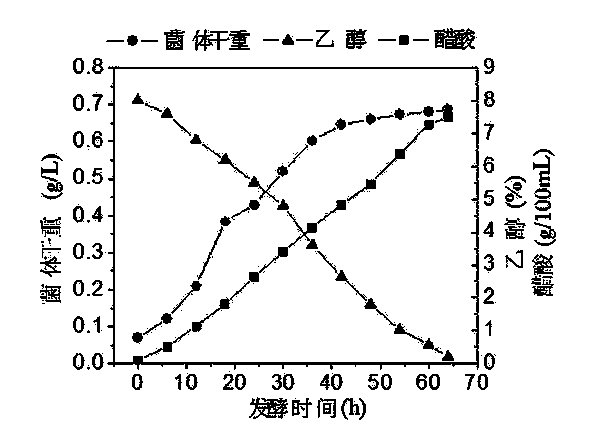
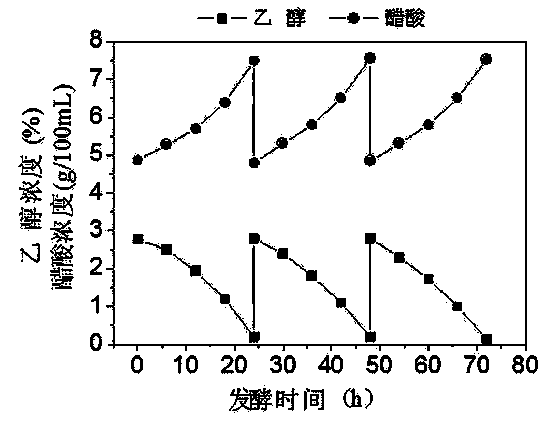
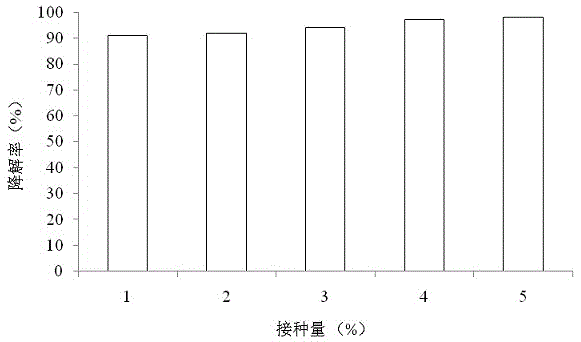
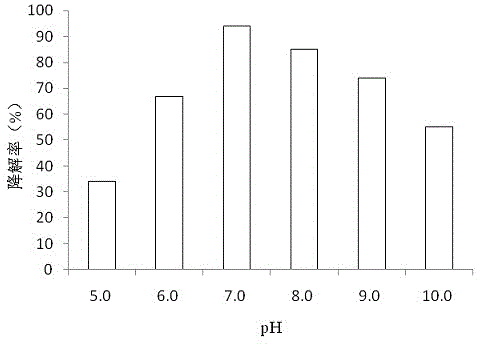
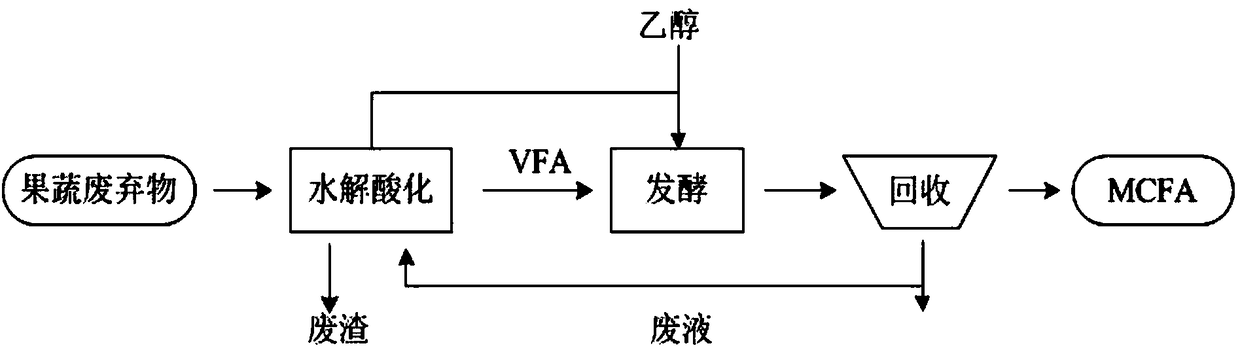
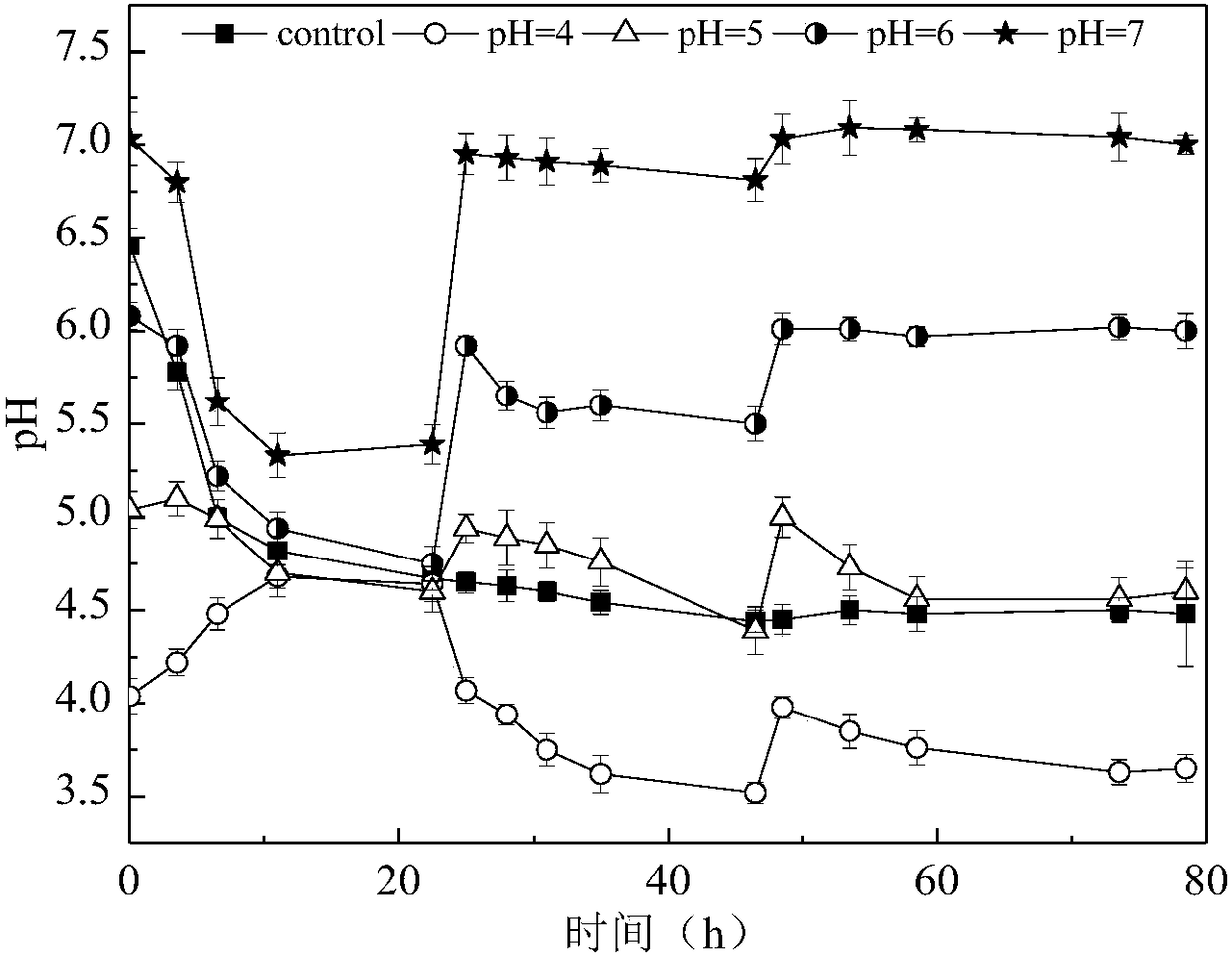
The invention discloses a method for preparing caproic acid through two-phase process anaerobic fermentation, and belongs to the technical field of waste resource treatment techniques and environment-friendly purification treatment. The method utilizes fruit and vegetable waste as an acidogenic-phase substrate, and the fruit and vegetable waste serving as the acidogenic-phase substrate builds a stable acidogenic fermentation system at the temperature of 35 DEG C and with the pH value being 6.0; the acidogenic-phase fermented liquid serves as a substrate, the caproic acid yield can reach 12.85g.L<-1> under the conditions that the temperature is 30 DEG C, the pH value is 6.8-7.0, the alcohol acid ratio is 4 to 1, that is, the ethyl alcohol additive amount is 17.22g.L<-1>, and thus efficientgeneration of caproic acid is achieved.
Owner:江苏道同环境科技有限公司
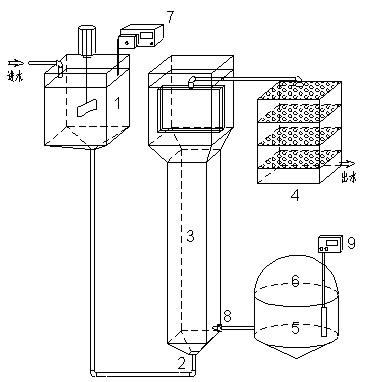
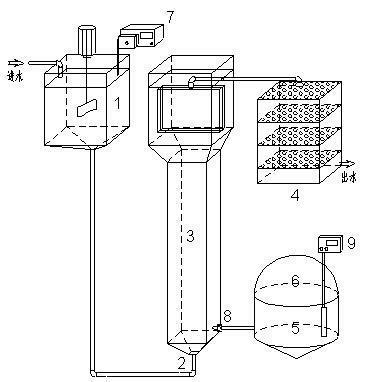
Solid-liquid two-phase anaerobic fermentation apparatus and method
ActiveCN105861306AImprove efficiencyAvoid inhibitionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAutomatic controlBiogas production
The invention relates to a solid-liquid two-phase anaerobic fermentation apparatus and method. The solid-liquid two-phase anaerobic fermentation apparatus comprises a solid-producing acid fermentation reactor, a liquid-producing methane reactor, an acid-producing fermentation liquor collecting tank, a biogas slurry collecting tank, a cyclic heating device, a methane meter, a blender, a sewage pump, a liquid level sensor, a temperature sensor and an automatic control cabinet. The solid-liquid two-phase anaerobic fermentation apparatus and method has the advantages that a liquid-phase fermentation device is small in size, fast in temperature rising, good in insulation and low in energy consumption; the apparatus is small in space occupation, low in investment, and about 20% of the investment can be saved as compared with traditional wet fermentation; the apparatus and method is suitable for recycling use of organic wastes of pig manure, straw, vegetable residues, kitchen wastes, municipal wastes and the like, and the apparatus and method is water saving, free of biogas slurry discharge, free of secondary pollution and the like, and substrate conversion rate and volume biogas production are high.
Owner:AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION INST OF MIN OF AGRI
Lactobacillus johnsonii, and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102839136AImprove Gut HealthIncrease production capacityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryMicroorganismFeces
The invention discloses a Lactobacillus johnsonii, and a preparation and application thereof, and discloses an optimal culture medium for the strain and a preparation method of a freeze-dried preparation of the strain. The microbial preservation number of the Lactobacillus johnsonii ZLJ010 is CGMCC No.5762. The strain is definite in hereditary basis, and has the characteristics of good growth performance and high acid production, acid resistance, heat resistance and bacterium inhibition capabilities. When being used as a feed additive for sows, the freeze-dried preparation of the strain can improve the intestinal tract health of the sows, reduce the number of harmful bacteria in feces, enhance the body immunity and increase the production performance of the sows.
Owner:BEIJING ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE & FORESTRY SCIENCES
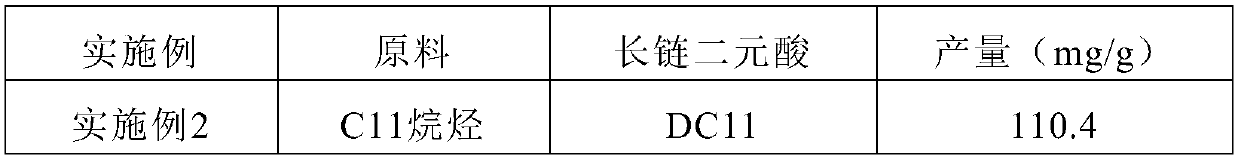
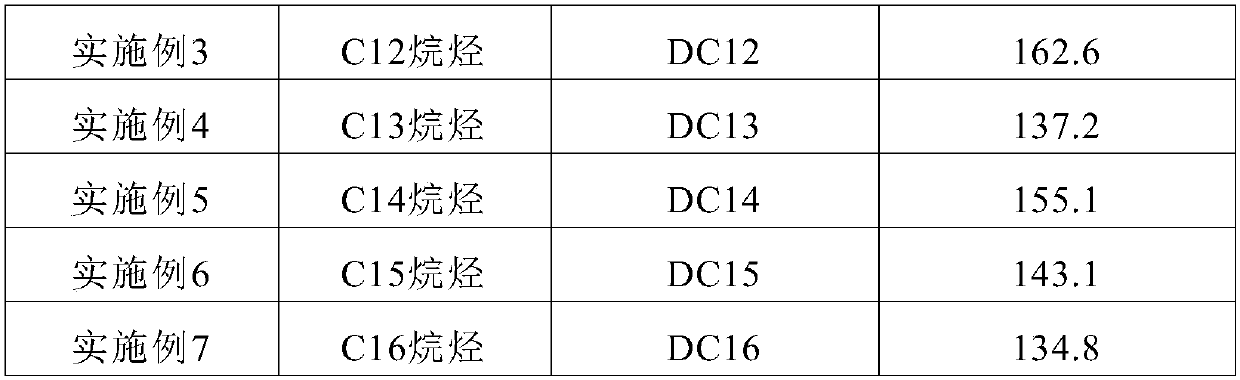
Candida tropicalis and application thereof, and production method for long chain diprotic acid
PendingCN110218661AReduce dosageSimple extraction processFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobial agentCandida tropicalis
The invention discloses a candida tropicalis strain CAT H1614, a microbial agent comprising the same and an application thereof, and a method for producing long chain diprotic acid by fermentation anda preparation method of the long chain diprotic acid. The candida tropicalis strain CAT H1614 of the invention can maintain high vitality for a long time in an environment with a pH lower than 7.0, thereby being particularly suitable for production of the long chain diprotic acid by a biological method, acid production is rapid during fermentation, the yield is high, and a fermentation cycle canalso be reduced. The fermentation method and the preparation method of the long chain diprotic acid provided by the invention have significant cost advantages, can effectively alleviate pressure on resources and environment, and thus have very obvious industrialization value advantages.
Owner:CATHAY R&D CENT CO LTD +1
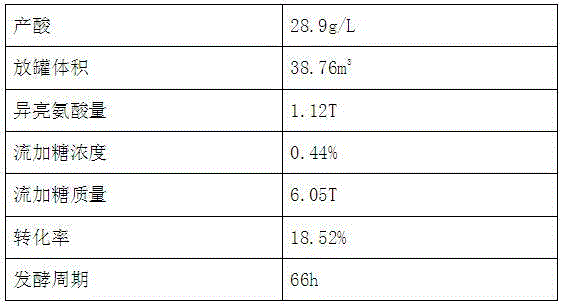
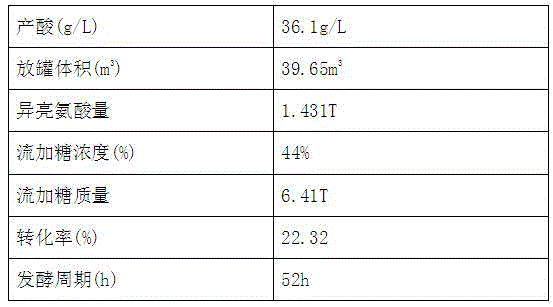
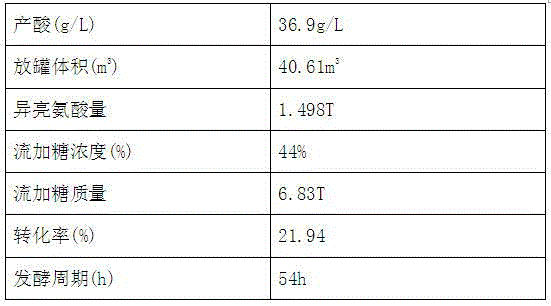
Fermentation method for improving yield of isoleucine
The invention discloses a fermentation method for improving the yield of isoleucine. The fermentation method comprises the following steps: culturing microorganisms, fermenting, separating fermentation liquor, carrying out ion exchange on fermentation supernatant, deaminizing with a deamination tower, decolorizing with activated carbon and crystallizing by evaporating. Because the corn steep liquor which serves as a hydrolysis liquor in the culture medium and accounts for 40% of the total weight of the culture medium replaces the hydrochloric acid adopted by the traditional method to regulate the pH value, the corrosion of the hydrochloric acid to the stainless steel tank is avoided. In addition, because biotin and VB1 are used as growth factors in the process, the viscosity of the fermentation liquor can be reduced, the respiratory metabolism of the microorganisms can be promoted, and the down-stream finished product can be extracted easily. By adopting the fermentation method disclosed by the invention, a good fermentation index can be achieved, the yield of the isoleucine which is a metabolite can be improved significantly, the average yield of the isoleucine can be up to 36.9g / L and can be increased by 30% compared with that of the metabolite isoleucine obtained by adopting the original method, the conversion rate of the metabolite isoleucine can be increased by 2-4%, and the fermentation cycle can be shortened by 10 hours.
Owner:HENAN JULONG BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
Acid-producing Klebsiella bacterium and uses thereof
InactiveCN101063095AReduce outputIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesUltravioletKlebsiella species
The invention discloses a generating acid klebsiella and appliance, which is characterized by the following: setting the preserved number at CCTCC NO: M 207023; adopting ultraviolet and diethyl sulfate; composite-treating strain CCTCC NO: M 207023; seeding on selective solid medium with bromide of sodium and sodium bromate; culturing; sorting single bacterial colony; yeasting; preparing 2, 3-butylene glycol. This invention possesses simple operation, low cost, high efficiency and short period, which can increase receiving ratio of 2, 3-butylene glycol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
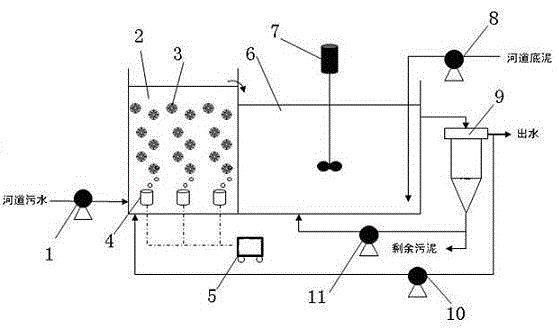
Method and device for performing combined treatment on sewage and bottom mud in black-odor riverway
ActiveCN105417687ARealize processingAchieve stabilizationTreatment using aerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentPhosphateSludge
The invention relates to a method for performing combined treatment on sewage and bottom mud in a black-odor riverway. The method includes the following steps that sewage in the black-odor riverway is collected into a reaction tank, organic matter in the water is degraded through microorganisms, ammonia nitrogen in the water is converted into nitrate nitrogen, bottom mud in the riverway is mixed in the water, treatment is performed through acid production bacteria and denitrifying bacteria, and nitrate nitrogen in water and heavy metal and phosphate in the bottom mud are removed. Then, proper anaplerosis is performed on the treated water and the treated sludge. Meanwhile, a device applying the method is disclosed. The device comprises an aerobiotic MBBR reaction tank and a riverway bottom mud fermentation coupling denitrifying pool which are adjavcently connected. The method and the device are reasonable in design, the technology is advanced, riverway sewage treatment and riverway bottom mud treatment can be coupled in one system, sewage and sludge can be treated at the same time, the treatment efficiency is improved, and secondary pollution is eliminated.
Owner:JIANGSU YULONG ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Process and device of low energy consumption sewage treatment based on carbon source recovery
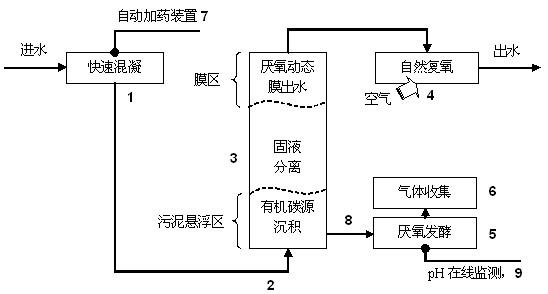
ActiveCN102557349AImprove settlement performanceFacilitate solid-liquid separationMultistage water/sewage treatmentBiological sludge treatmentVolatile fatty acidsMembrane bioreactor
The invention relates to a process and a device of low energy consumption sewage treatment based on carbon source recovery, which belong to the technical field of sewage (waste water) treatment. A process flow comprises a rapid coagulating basin, an anaerobic dynamic membrane-bioreactor, an effluent natural reoxygenation machine, an anaerobic digestion reactor and a gas collector. High efficient flocculation of low concentration organic sewage is carried out in the rapid coagulating basin, solid-liquid separation of the low concentration organic sewage is carried out in the anaerobic dynamic membrane-bioreactor, natural reoxygenation of effluent is carried out, and water quality stably achieves the national second grade discharge standard. Simultaneously, recovered low-quality carbon sources (anaerobic sludge) enter the anaerobic digestion reactor to finally enable energy matters in the sewage to be recovered in a mode of high-quality carbon sources of volatile fatty acids (VFAs) or methane and the like through a hydrolyzing-fermenting and producing acids-producing the methane approach. By means of coupling between a sewage treatment method and an anaerobic organism treatment process, high efficient treatment of the low concentration organic sewage is achieved in a short hydraulic retention time. The high efficient treatment of the low concentration organic sewage can be carried out on the condition of normal temperature, and energy conservation and consumption reduction of the sewage treatment can be achieved to the greatest extend.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV +1
Lactic acid bacteria starter, acidified milk prepared by using lactic acid bacteria starter, and preparation method of acidified milk
ActiveCN104726358AModerate acidityLow in lactoseMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyLactic acid bacterium
The invention provides a lactic acid bacteria starter, which contains Lactobacillusdelbrueckiisubsp.bulgaricus with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 2922 and Streptomycesthermophilus with a preservation number of CGMCC No. 2915. The lactic acid bacteria starter can perform good lactose degradation capability during a fermentation process of the acidified milk, a combination of Lactobacillusdelbrueckiisubsp.bulgaricus with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 2922 and Streptomycesthermophilus with the preservation number of CGMCC No. 2915 is used for solving the problem of beta-galactosidase vitality and acidogenesis under a conventional fermentation technology, and percent hydrolysis of lactose in an acidified milk can be ensured. The invention also provides the acidified milk prepared by using lactic acid bacteria starter, and a preparation method of the acidified milk.
Owner:蒙牛乳制品(天津)有限责任公司
Municipal sludge pretreatment method enhancing sludge anaerobic fermentation acid production
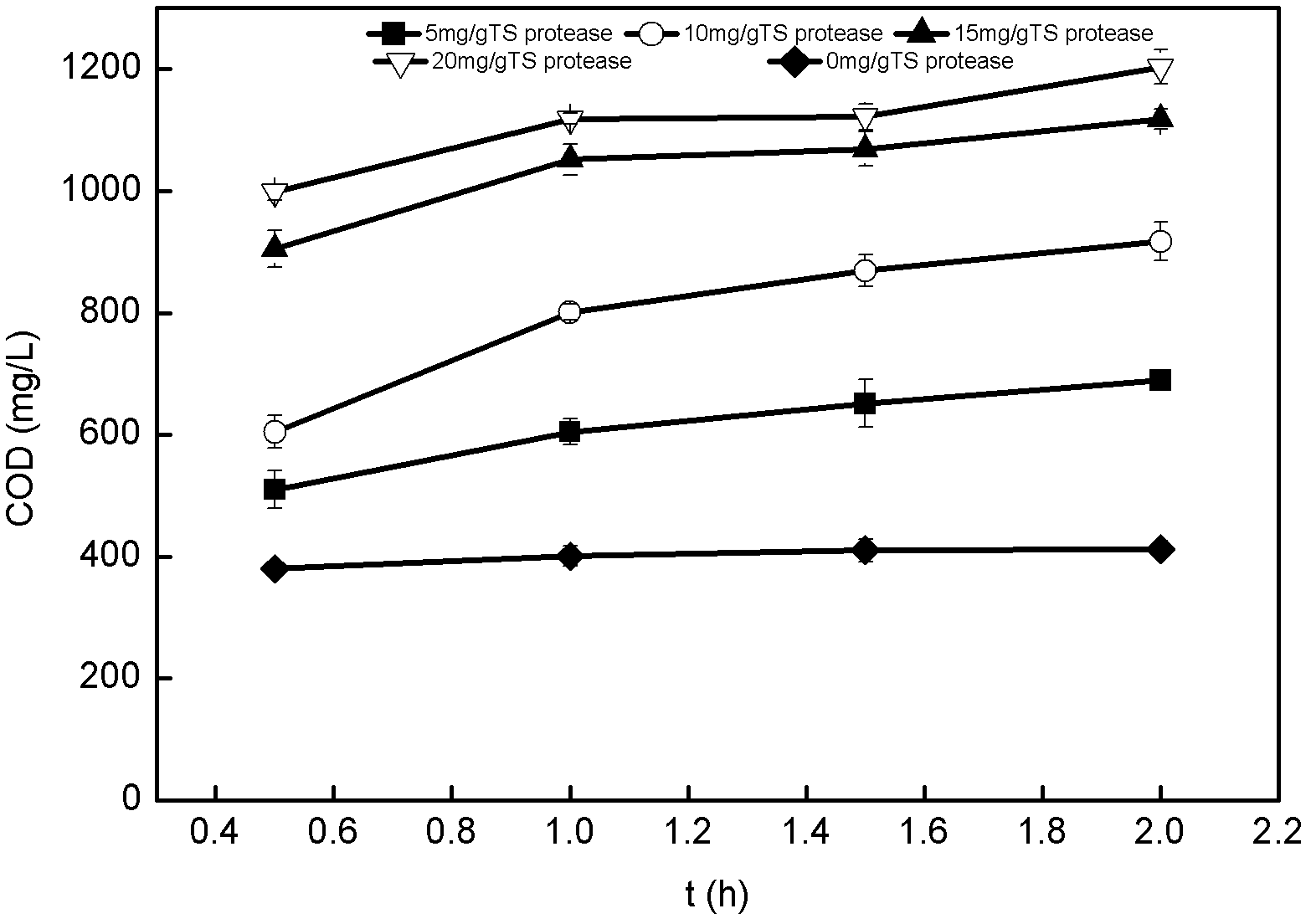
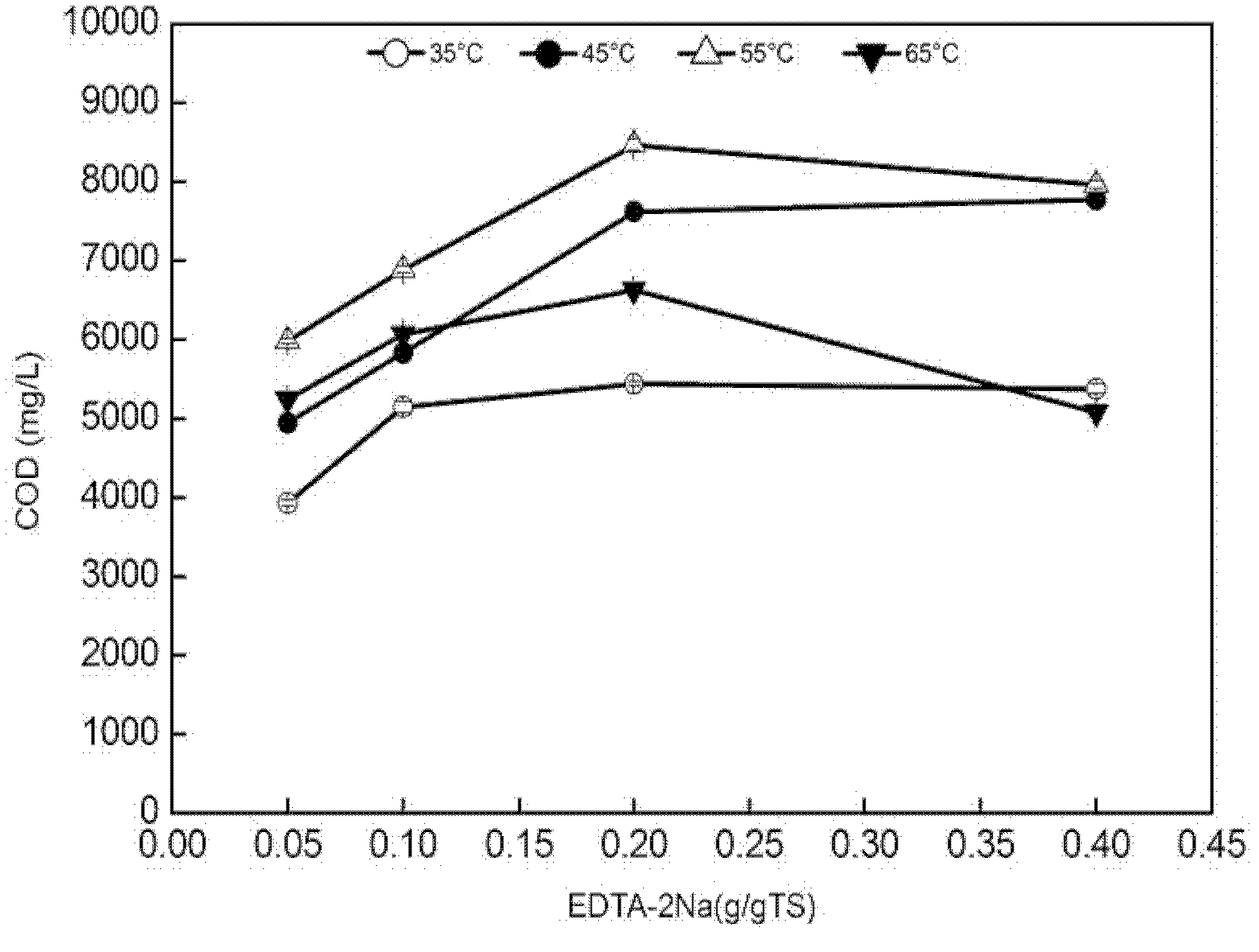
ActiveCN102583917AIncrease concentrationReduce the amount requiredBiological sludge treatmentNeutral proteaseChemical oxygen demand
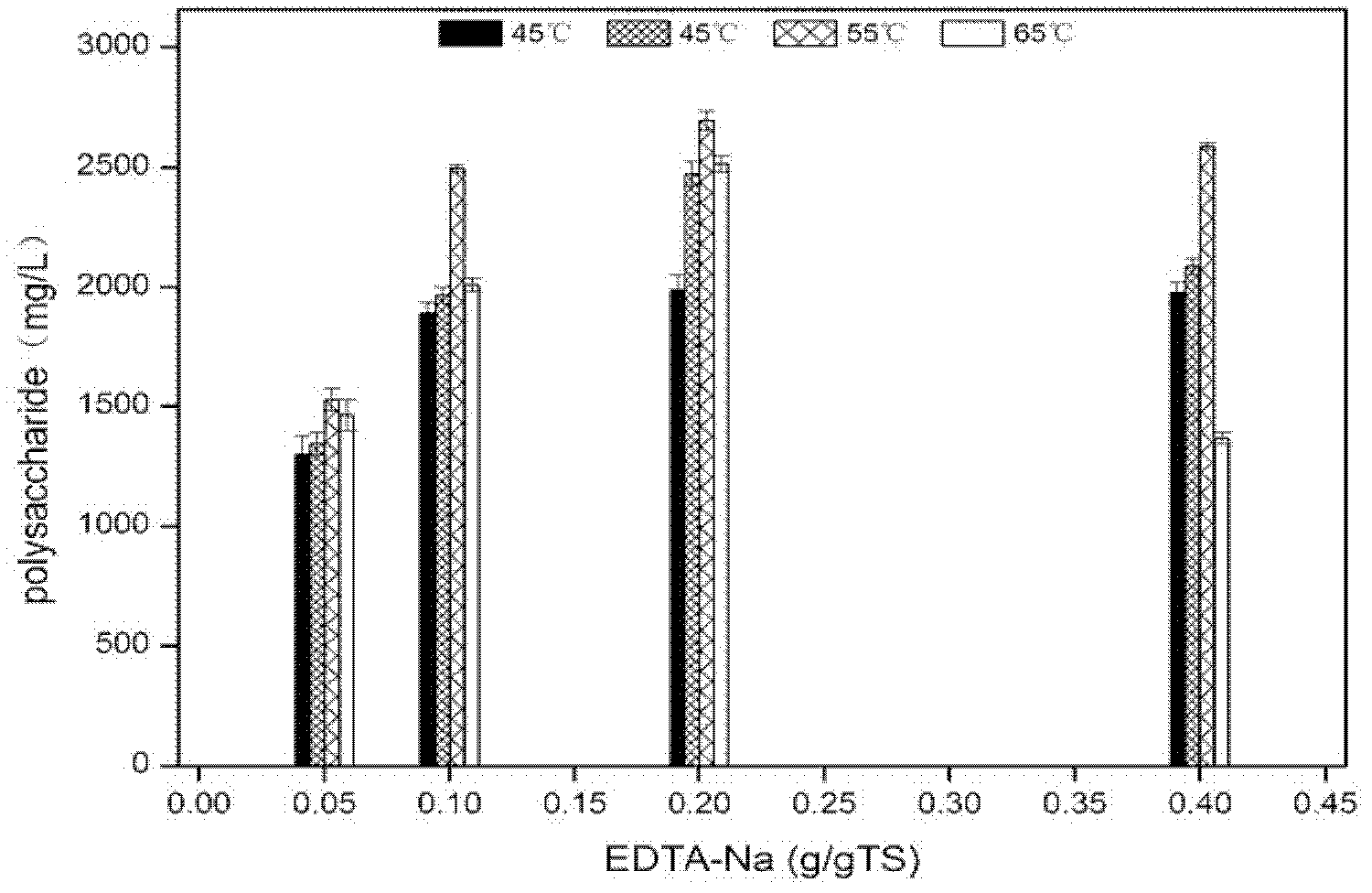
The invention discloses a municipal sludge pretreatment method enhancing sludge anaerobic fermentation acid production. The method enables sludge cells to rupture, enables organic matter to be released and converted in a superior-quality mode to the most extent and remarkably increases the quantity of organic acid produced through follow-up anaerobic fermentation by jointly inputting neutral protease and ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt (EDTA-2Na) and adjusting potential of hydrogen (pH) and reaction temperature. Test results show that by means of the municipal sludge pretreatment method, the concentration of soluble chemical oxygen demand (SCOD) in sludge is improved by 18.0-20.0 times, the concentration of polysaccharide is improved by 11.0-13.0 times, and the concentration of protein is improved by 1.5-2.5 times. The municipal sludge pretreatment method has the advantages of being moderate in reaction condition, high in efficiency, high in sludge quantity reducing degree and the like. A new method and idea is provided for the purpose of finally achieving recycling, reduction and harmlessness of excess sludge.
Owner:南京特克赛环保科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com