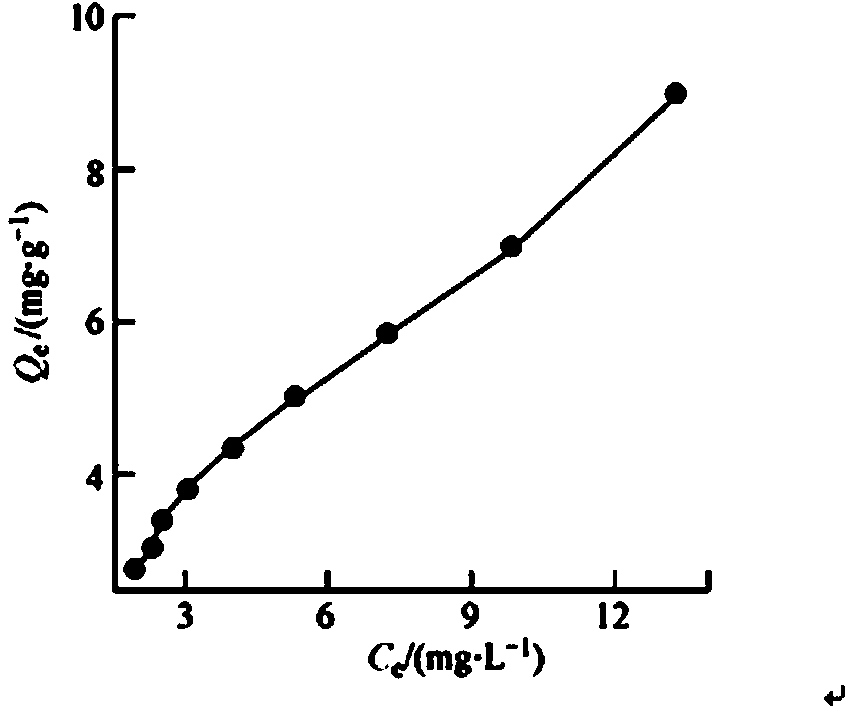Patents
Literature
120 results about "L-Glucose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
L-Glucose is an organic compound with formula C₆H₁₂O₆ or O=CH[CH(OH)]₅H, specifically one of the aldohexose monosaccharides. As the l-isomer of glucose, it is the enantiomer of the more common d-glucose.
Method for ultrasonically synthesizing hyperfluorescent carbon spots, and applications of hyperfluorescent carbon spots
InactiveCN104232084AGood water solubilityExcellent fluorescence propertiesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorLuminescent compositionsFluorescenceLuminescence
The invention discloses a method for ultrasonically synthesizing hyperfluorescent carbon spots, and applications of the hyperfluorescent carbon spots, belonging to the field of nano-luminescence materials. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a mixed solution by taking 0.1-5mol / L glucose as a carbon source, performing ultrasonic treatment to the mixed solution for 0.5-5h under the environment of pH ranging from 1 to 14; and (2) adding 0.1-5mol / L alcohol or amino acid into the mixed solution obtained in the step (1) as a modifier, and aging for 1-48h under the catalytic action of an inorganic salt catalyst, to obtain a hyperfluorescent carbon spots water solution. The method is simple to operate, pollution-free and mass production is easy to conduct.
Owner:DINGTAI HUIBEI BIOCHEM INSTR MFG
Medicinal preparation with inhibiting effect on tumor metastasis
InactiveCN101693035AGood inhibitory effectHave toxic side effectsOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsSide effectLymphatic Spread
The invention relates to a medicinal preparation with inhibiting effect on tumor metastasis, which contains steroidal saponin extractives. The effective active components of the medicinal preparation comprise the following eight steroidal saponin general extractives which are eight steroid saponins: steroidal saponin I, steroidal saponin II, dioscin, gracillin, steroidal saponin H, steroidal saponin VII, saponin A (pennogenin-3-O-alpha-L-isodulcitol-yl(1-4)-[alpha-L-isodulcitol-yl(1-2)]-alpha-L-isodulcitol-yl(1-2)-beta-D-heteroside) and saponin B (pennogenin-3-O-alpha-L-isodulcitol-yl(1-4)-[alpha-L-isodulcitol-yl(1-2)]-alpha-L-isodulcitol-yl(1-3)-beta-D-heteroside), and the effective active components of the medicinal preparation also comprise medical dressings. The weight content of the eight steroidal saponin general extractives is 5%-30%, and the weight content of the medical dressings is 70%-95%. The invention is a medicinal preparation with less toxic and side effects and inhibiting effect on tumor metastasis.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
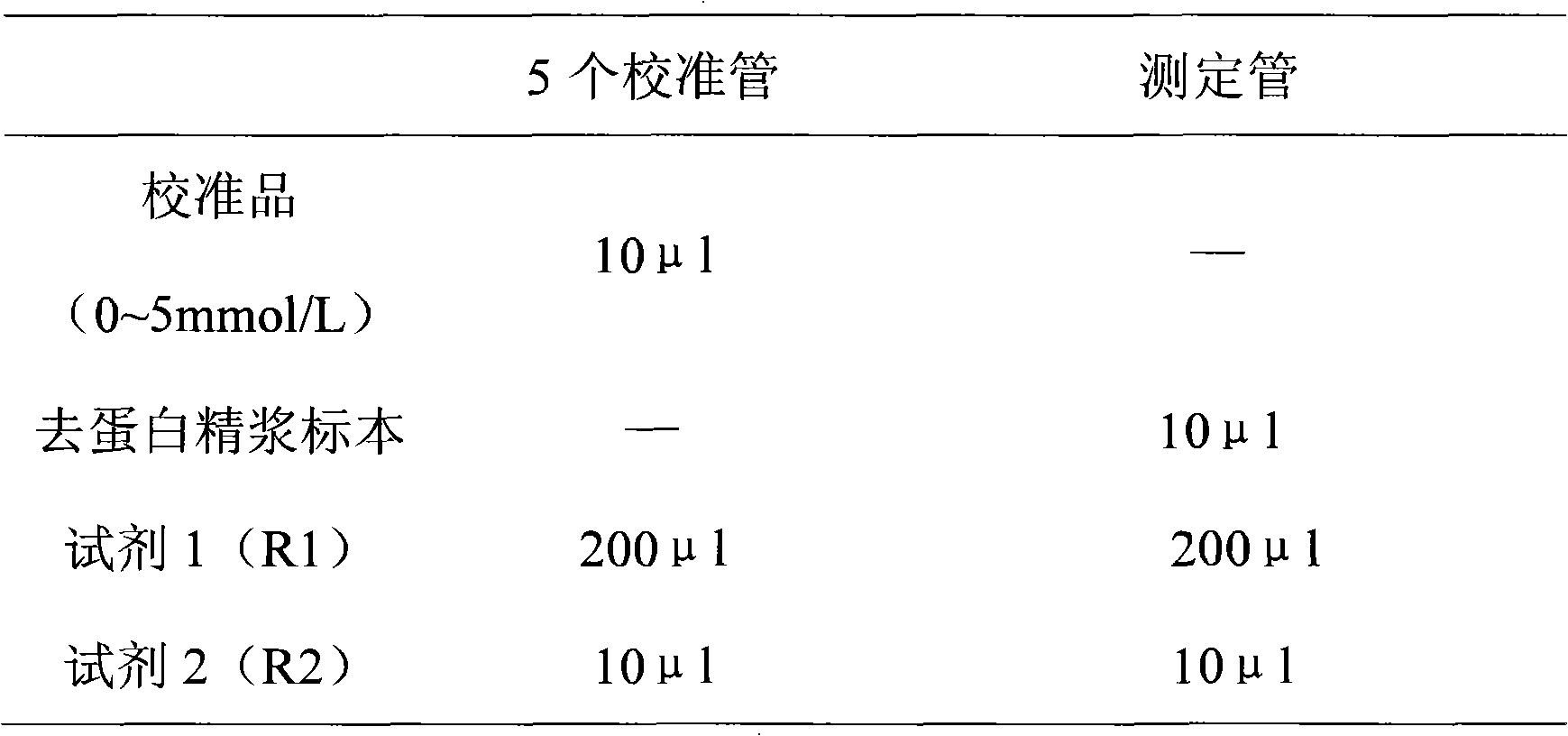
Quantitative fructose assay kit and application thereof as well as quantitative seminal plasma fructose assay method
InactiveCN102061332AEco-friendly formulaEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationPhosphateHexokinase
The invention discloses a quantitative fructose assay kit which comprises inorganic acid deproteinized extract A, inorganic base deproteinized extract B, fructose calibration solution, a reagent 1 containing 0.001-0.1mol / L adenosine triphosphate sodium salt, a reagent 2 containing 1-100KU / L hexokinase and 1-100KU / L glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, and a reagent 3 containing 0.001-0.1mol / L nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. The seminal plasma fructose assay method comprises the following steps: respectively adding the reagent 1 and the reagent 2 to deproteinized seminal plasma and the fructose calibration solution, and mixing uniformly; reacting at the temperature of 10-40 DEG C for 5-120 minutes, then reading the absorbance respectively at the wavelength of 280-400nm; adding the reagent 3 respectively, and mixing uniformly; reacting under the same conditions and reading the absorbance; and calculating the difference between the absorbance read at the first time and the absorbance read at the second time, and comparing or calculating the absorbance of a seminal plasma specimen and the fructose calibration solution to obtain the concentration of the seminal plasma fructose. The kit and the method can be used for quantitative determination of fructose in sera, plasma, body fluid, food and solid extracting solution, the methodology is special, unique, clean and environment-friendly, manual operation and automatic batch assay can be realized, and the kit and the method are easy to popularize and apply clinically.
Owner:BRED LIFE SCI TECH
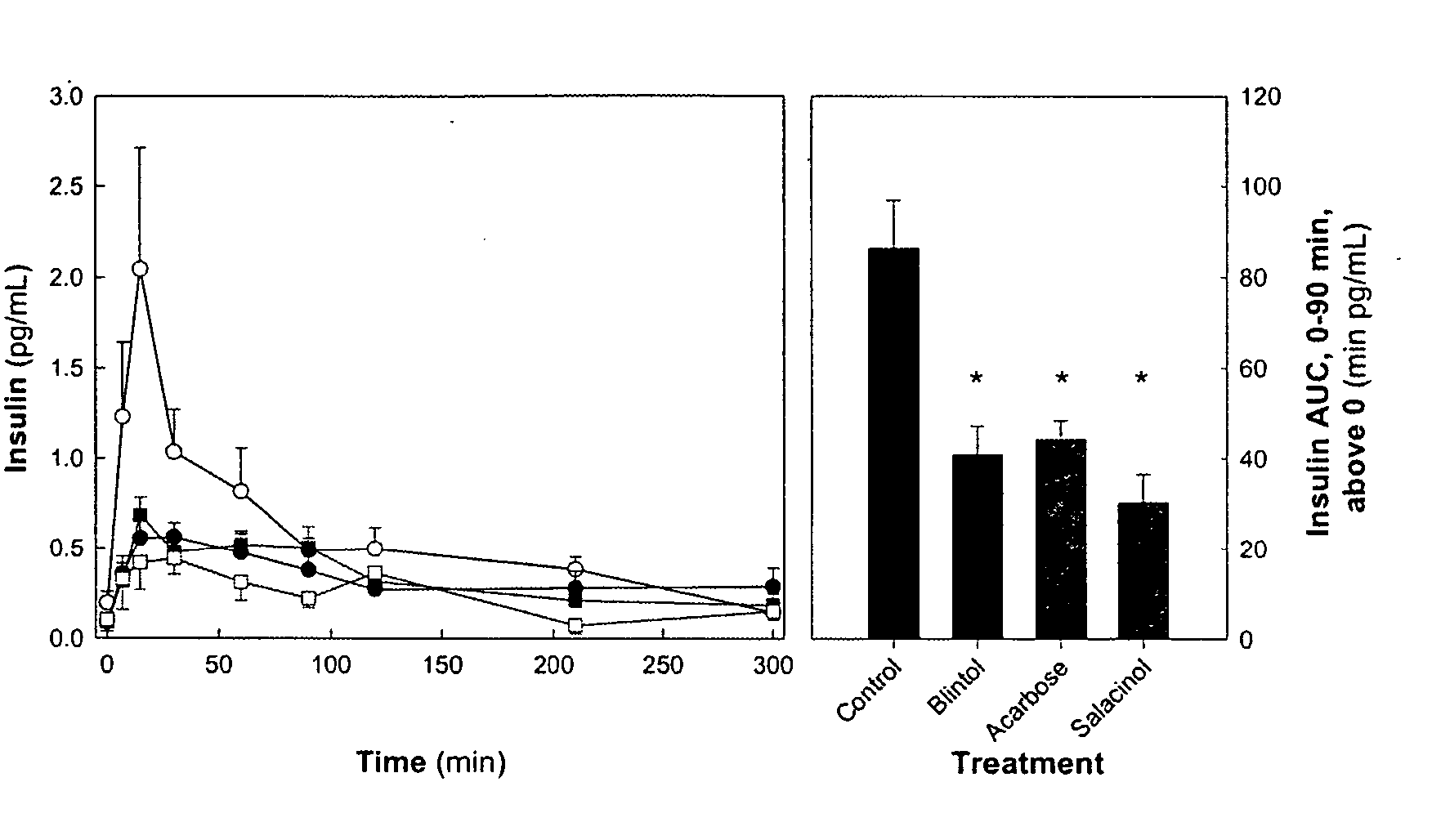
Glycosidase inhibitors and methods of synthesizing same
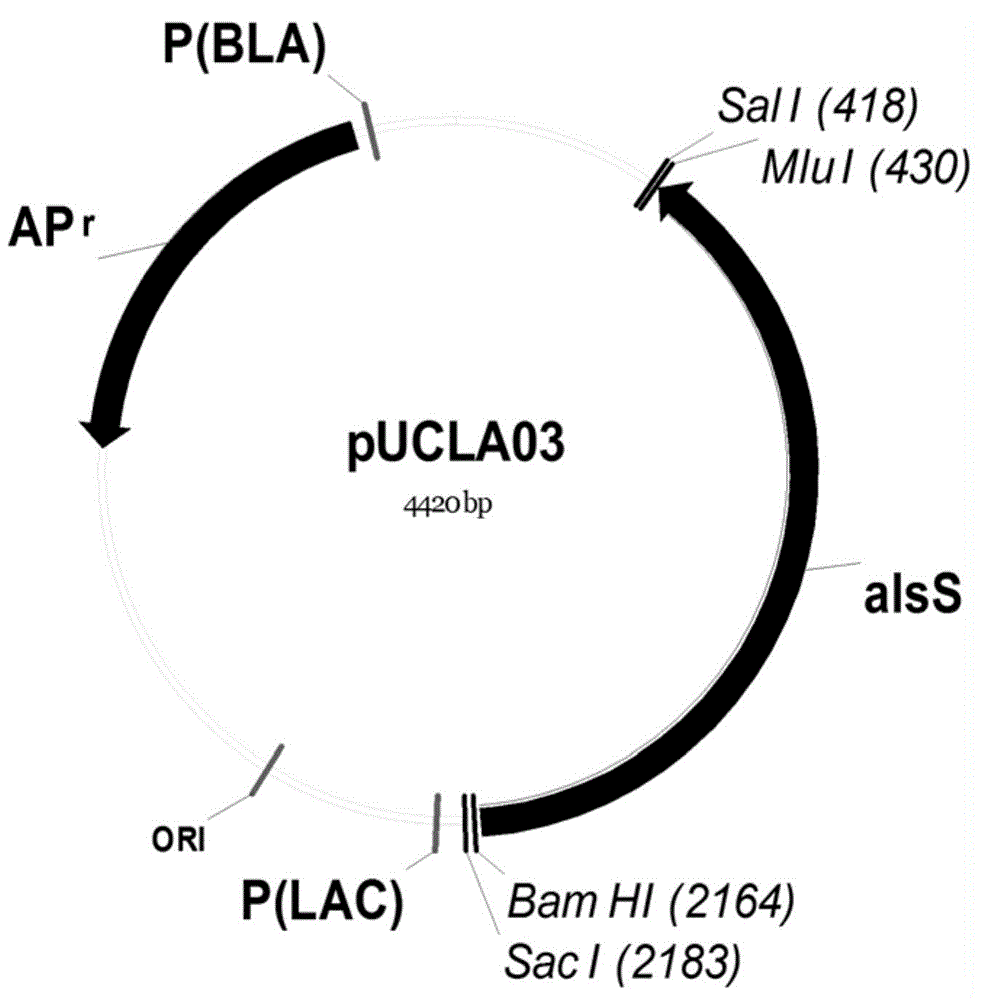
Methods for synthesizing Salacinol, its stereoisomers, and analogues, homologues and other derivatives thereof potentially useful as glycosidase inhibitors are described. In some embodiments the compounds of the invention may have the general formula (I) or (II): The synthetic schemes may comprise reacting a cyclic sulfate with a 5-membered ring sugar containing a heteroatom (X). The heteroatom preferably comprises sulfur, selenium, or nitrogen. The cyclic sulfate and ring sugar reagents may be readily prepared from carbohydrate precursors, such as D-glucose, L-glucose, D-xylose and L-xylose. The target compounds are prepared by opening of the cyclic sulfates by nucleophilic attack of the heteroatoms on the 5-membered ring sugars. The resulting heterocyclic compounds have a stable, inner salt structure comprising a heteroatom cation and a sulfate anion. The synthetic schemes yield various stereoisomers of the target compounds in moderate to good yields with limited side-reactions. Chain-extended analogues of Salacinol are also described.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
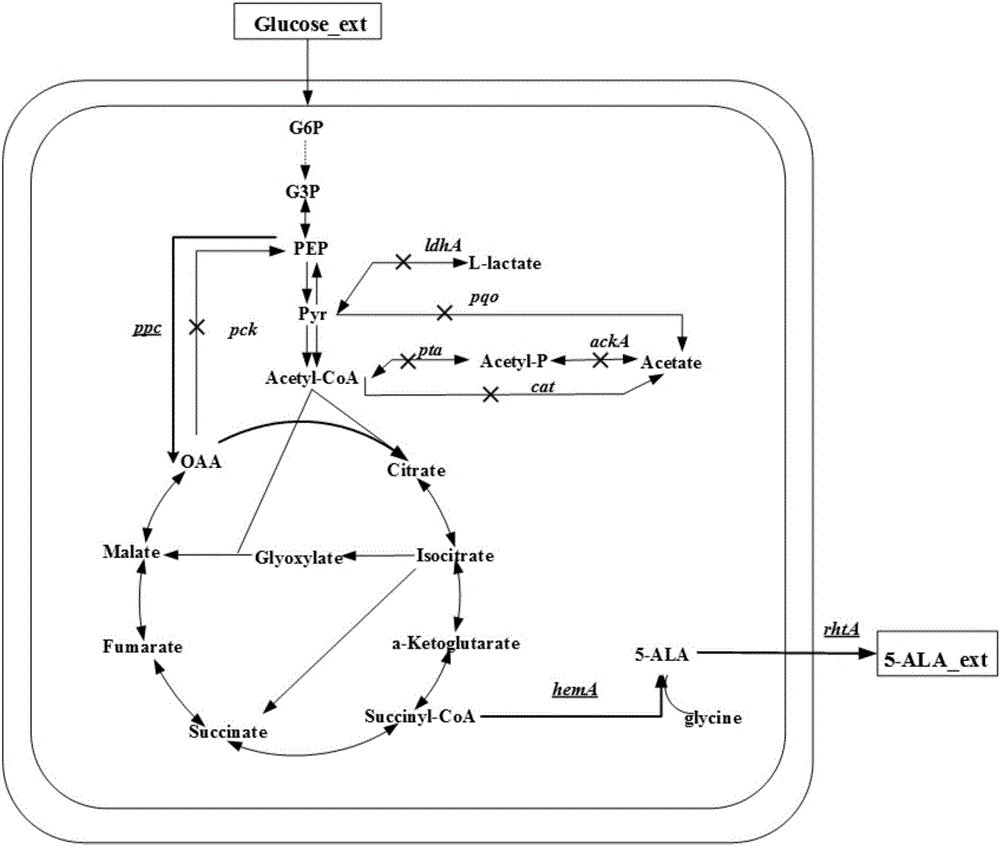
Corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain
InactiveCN106047916AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain. A construction method includes: (1) deleting a lactic dehydrogenase coding gene 1dhA and acetic acid generation genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat in corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain a strain named CB4; inserting a strong sod promoter in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc in the strain CB4 to obtain a strain CB5; deleting a gene pck in the strain CB5 to obtain a strain CB6; (2) transferring plasmid pXA and plasmid pEP2<tuf>-rhtA into the strain CB6. The strain constructed according to the method is capable of generating 2.78g / L 5-aminolevulinic acid in a culture medium with 10g / L glucose serving as a carbon source, which lays a foundation for subsequent continuous feeding of a fermentation tank to increase yield of the 5-aminolevulinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
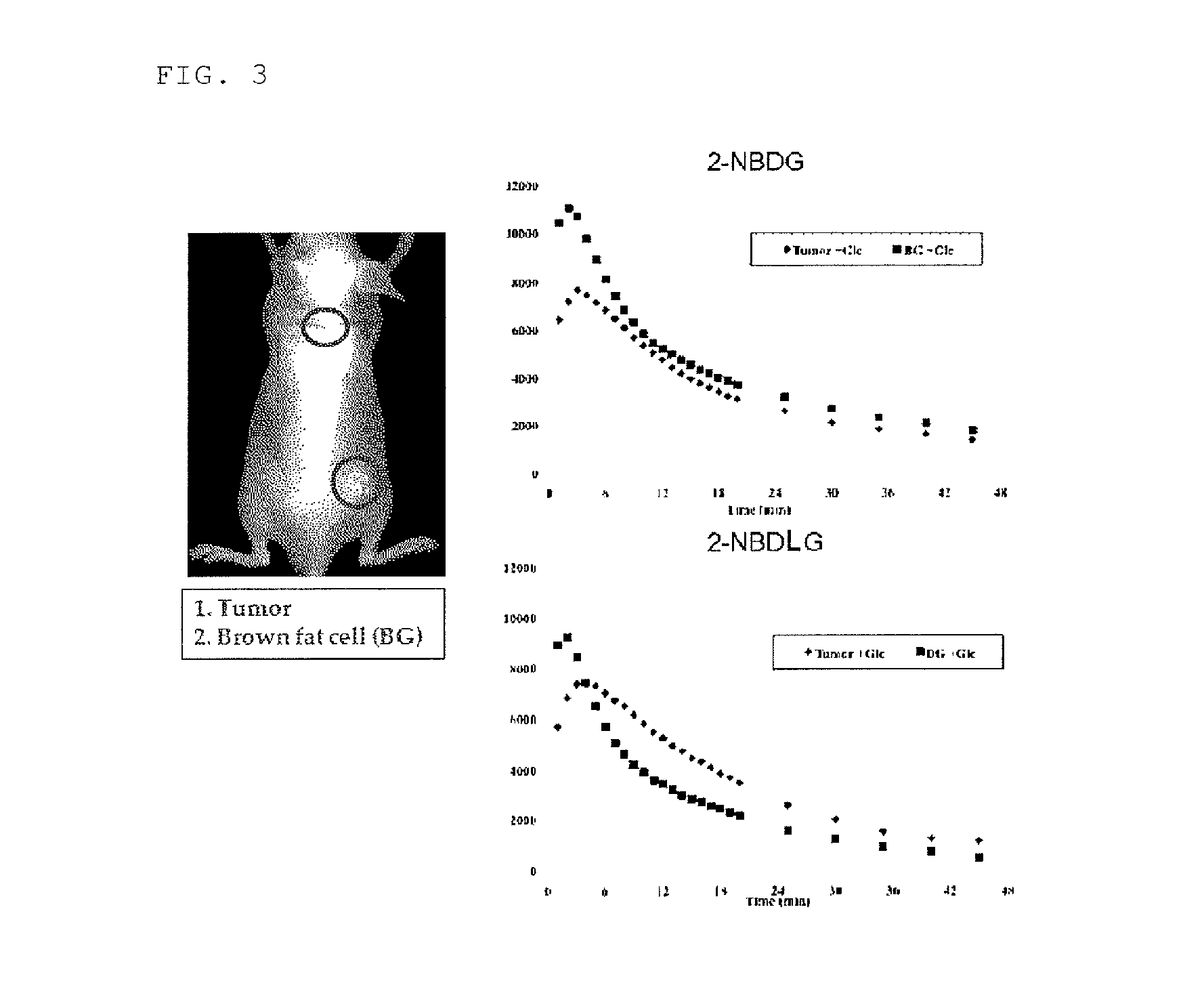
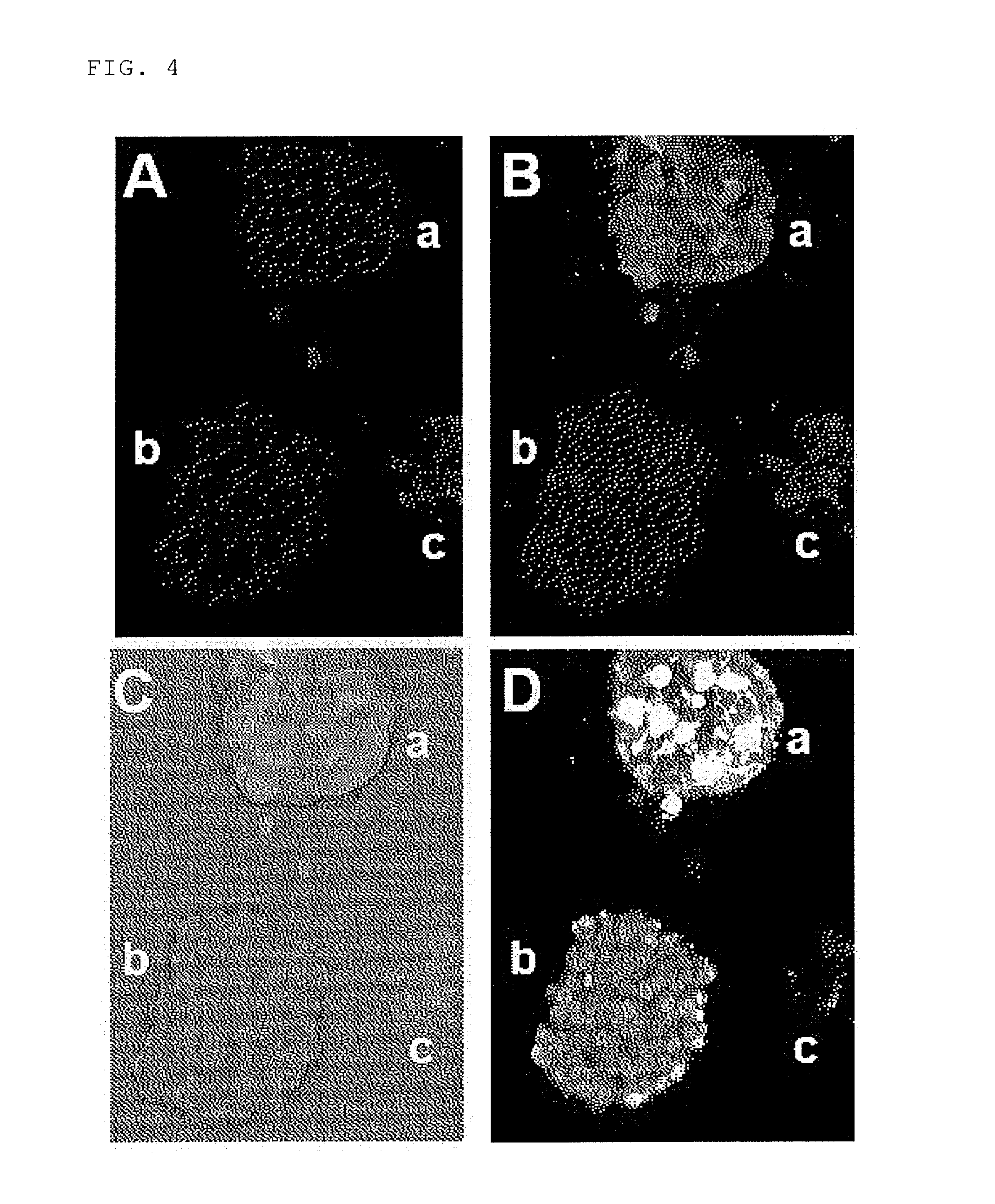
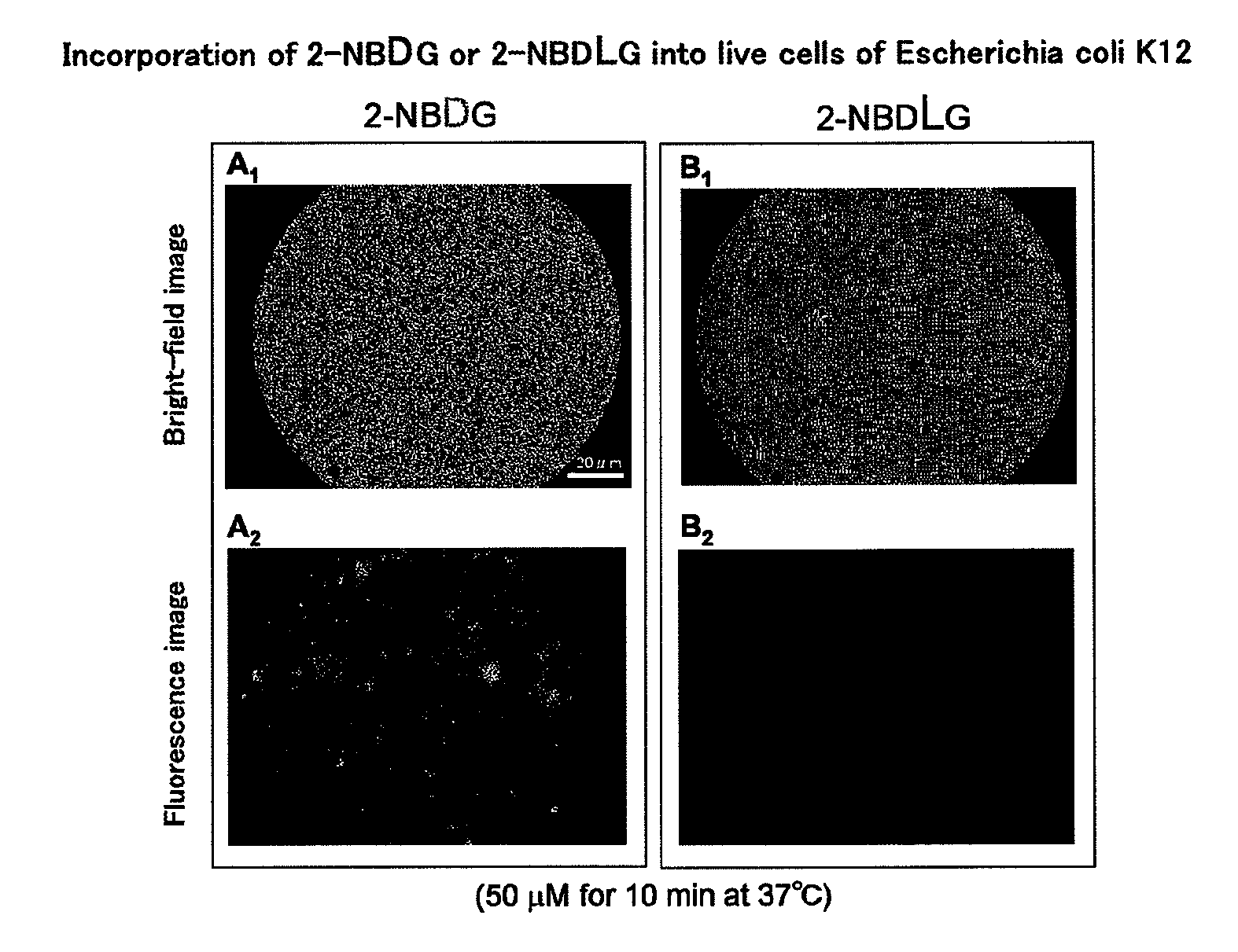
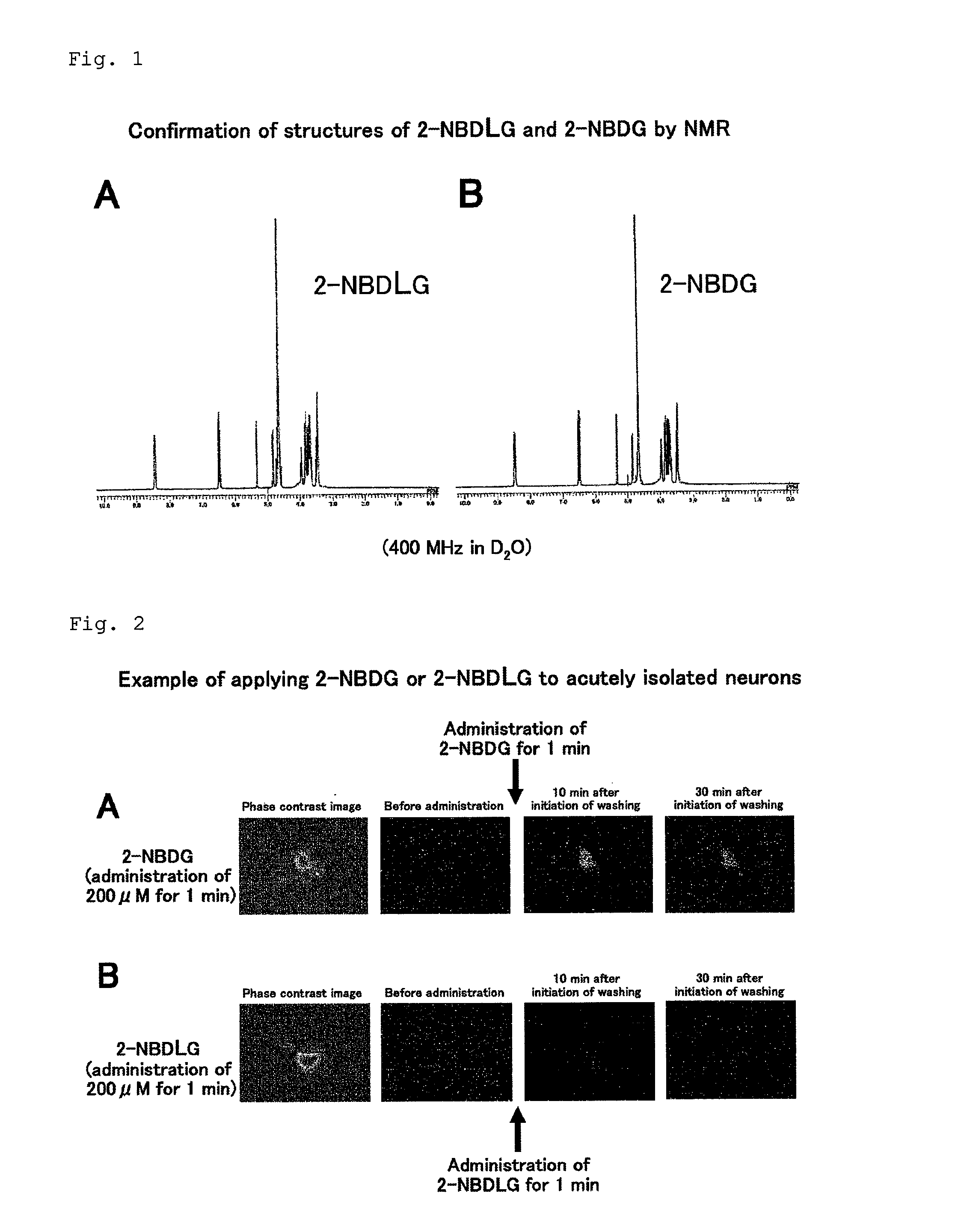
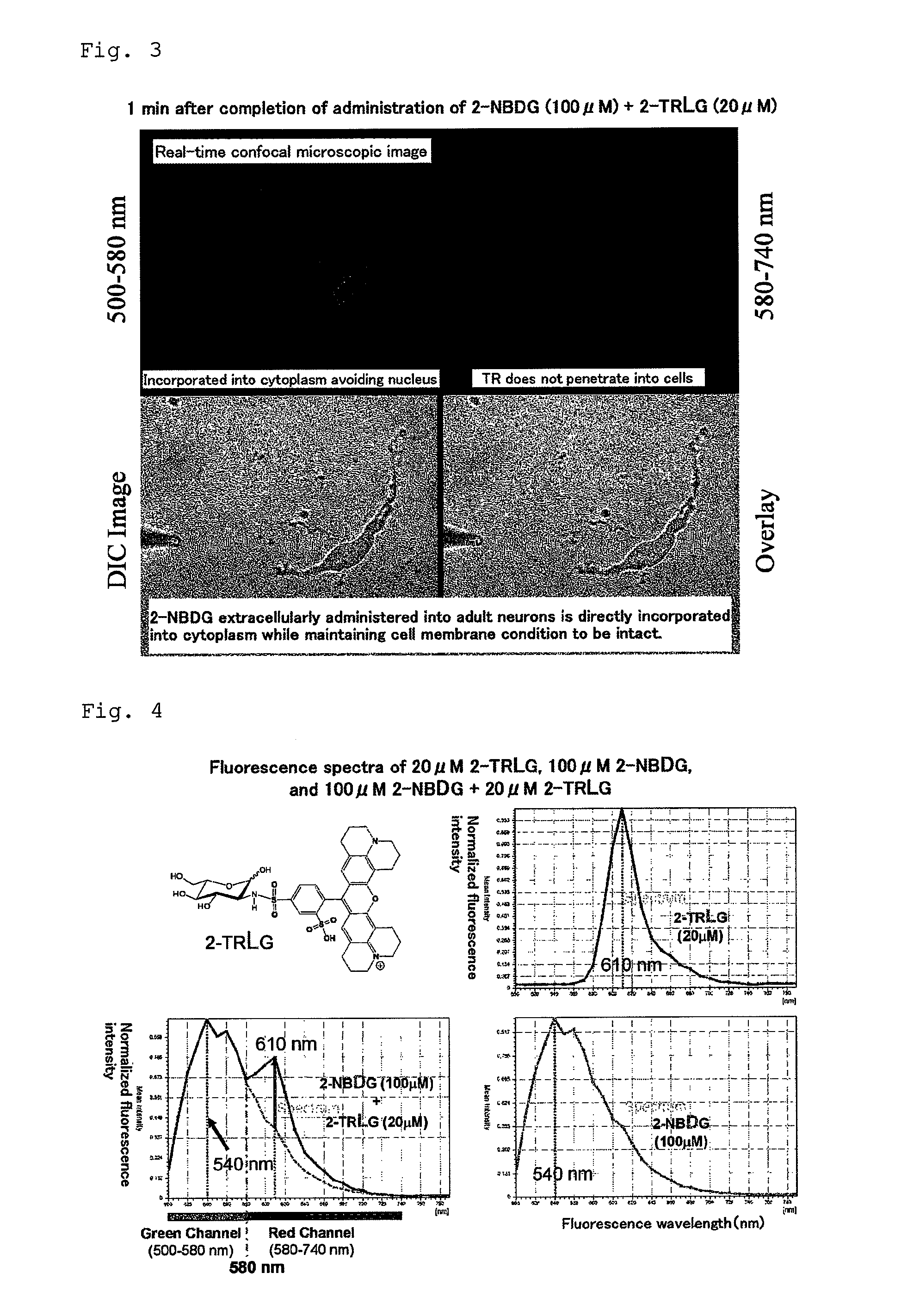
Method for detecting cancer cell using fluorescently labeled l-glucose derivative, and cancer cell-imaging agent comprising fluorescently labeled l-glucose derivative
InactiveUS20140154717A1Increase contrastMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansCancer cellNormal cell
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for highly accurately detecting a cancer cell. The method of the present invention is characterized by comprising imaging with the use of a fluorescently labeled L-glucose derivative. By using the method and imaging agent according to the present invention, a high contrast between a cancer cell and a normal cell can be obtained compared with the case that imaging is conducted with the use of a fluorescently labeled D-glucose derivative. According to this method, moreover, no fasting is needed for the determination. Thus, the imaging can be quickly carried out without imposing a burden on a patient.
Owner:HIROSAKI UNIVERSITY +2
Fortified soft drink for hangover relief
InactiveUS20070184152A1Relief of hangover symptomsFood ingredient functionsFood preparationSodium bicarbonateVitamin C
A soft drink and method of producing a soft drink that is a fortified, normally zero calorie beverage, formulated with natural flavors such as lemon or berry that can be formulated from L-Gluamine, sodium bicarbonate, a potassium salt like potassium chloride or potassium gluconate, caffeine with optional B vitamins, folic acid and vitamin C added for fortification along with a sweetener. This drink mixture can help reduce or eliminate symptoms of a hangover caused by alcohol consumption as well as supply a large portion of the recommended daily requirements for some vitamins and minerals.
Owner:DTK
Method for evaluating specific incorporation of d-glucose into cells
ActiveUS20110189708A1Accurately evaluating the specific incorporation of D-glucoseSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementD-GlucoseCell strain
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for accurately evaluating the specific incorporation of D-glucose into cells. The present invention as a means for achieving the object is characterized by comprising contacting a D-glucose derivative that has a fluorescent chromophore in the molecule and is specifically incorporated into cells and an L-glucose derivative that has a fluorescent chromophore in the molecule with different cells in the same cell strain to be evaluated, respectively, comparing the fluorescence emitted by the D-glucose derivative that has a fluorescent chromophore in the molecule and is specifically incorporated into cells with the fluorescence emitted by the L-glucose derivative that has a fluorescent chromophore in the molecule, and evaluating the specific incorporation of D-glucose into cells relative to L-glucose by taking the difference between the two kinds of fluorescence intensities.
Owner:ORBIO CORP +1
Endophytic bacillus amyloliquefaciens capable of generating a large number of antagonistic tobacco bacterial wilt active materials
ActiveCN105296386AEnhanced inhibitory effectEnhance colonization abilityBiocideBacteriaAmyrisNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial pesticides and discloses endophytic bacillus amyloliquefaciens BG2 capable of generating a large number of antagonistic tobacco bacterial wilt active materials. The endophytic bacillus amyloliquefaciens BG2 is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO. M 2015173. The invention further discloses the potting application of the bacterial strain, identification of generated antibiotic substances and high-yield fermentation process optimization of the bacterial strain. The bacterial strain has high colonization capacity in tobacco plant tissue and rhizosphere soil of the tobacco plant tissue, can generate antagonistic tobacco bacterial wilt active materials, can restrain various pathogenic fungi, and can be produced more widely at low cost and applied effectively. It is found through isolation purification and identification analysis of antipathogen active materials that the active components of the bacterial strain are mainly lipopeptid surfactin homolog and protein. The invention further provides a high-yield fermentation process of the bacteriostatic active materials. The process is characterized in that 10-100 g / L bean pulp, 5-50 g / L glucose, 1-10 g / L K2HPO4, 0.05-1.00 g / L CaCl2 and 0.05-1.00 g / L MgSO4 are adopted, pH is 7.2-7.4, culture temperature is 25-40 DEG C, inoculum size is 1-5%, liquid volume is 10-100 ml / 250 ml, inoculum age is 6-18 h, and fermentation is conducted for 24-60 h.
Owner:武汉康绿达生物科技有限公司
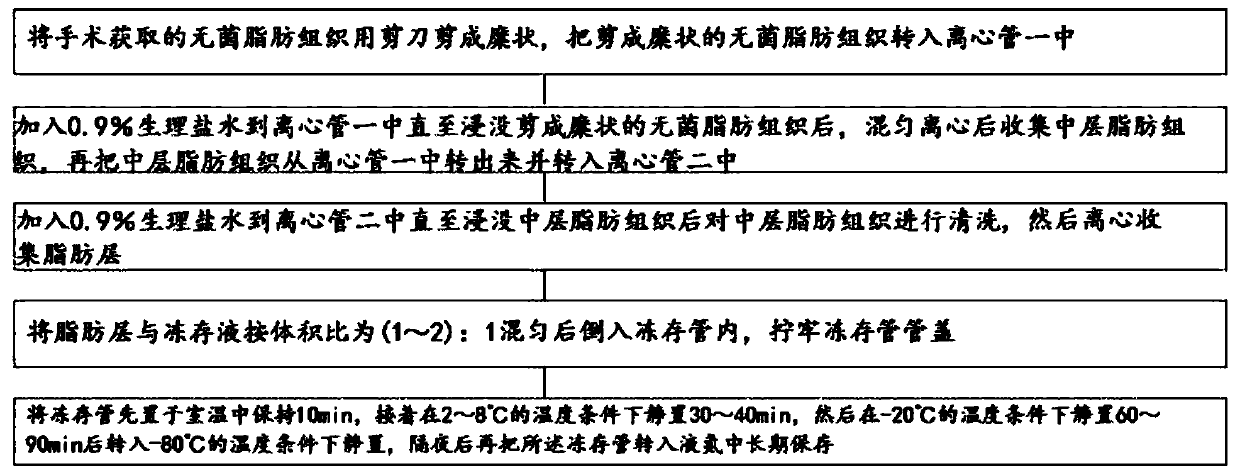
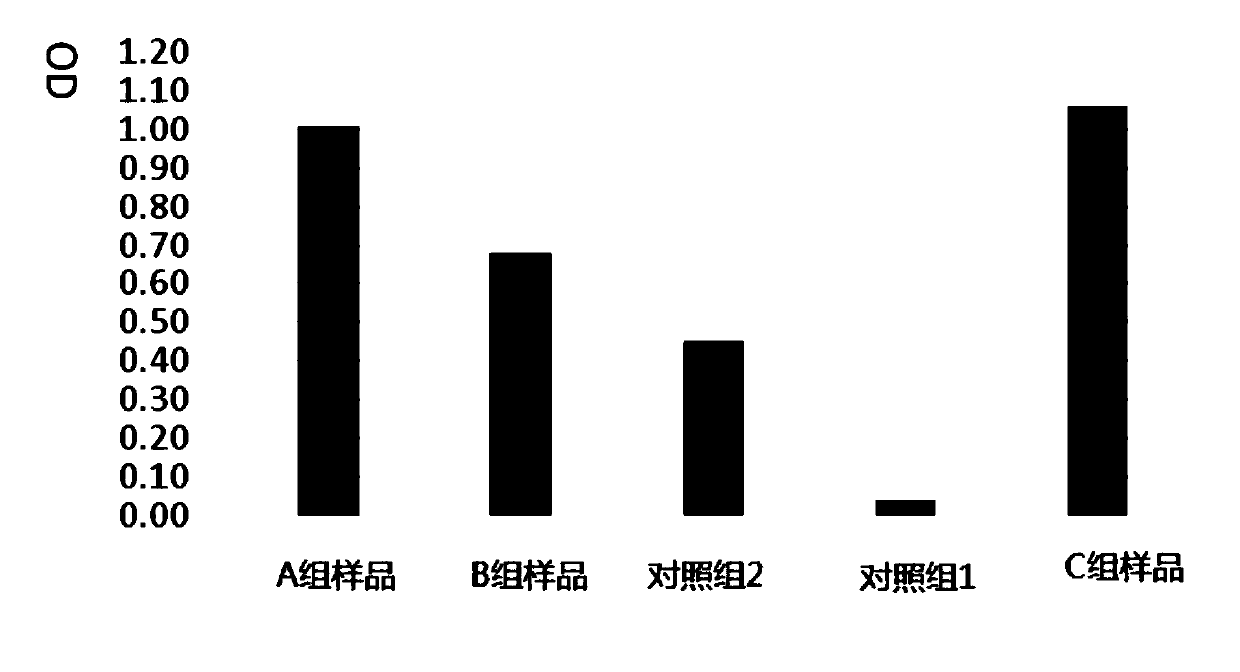
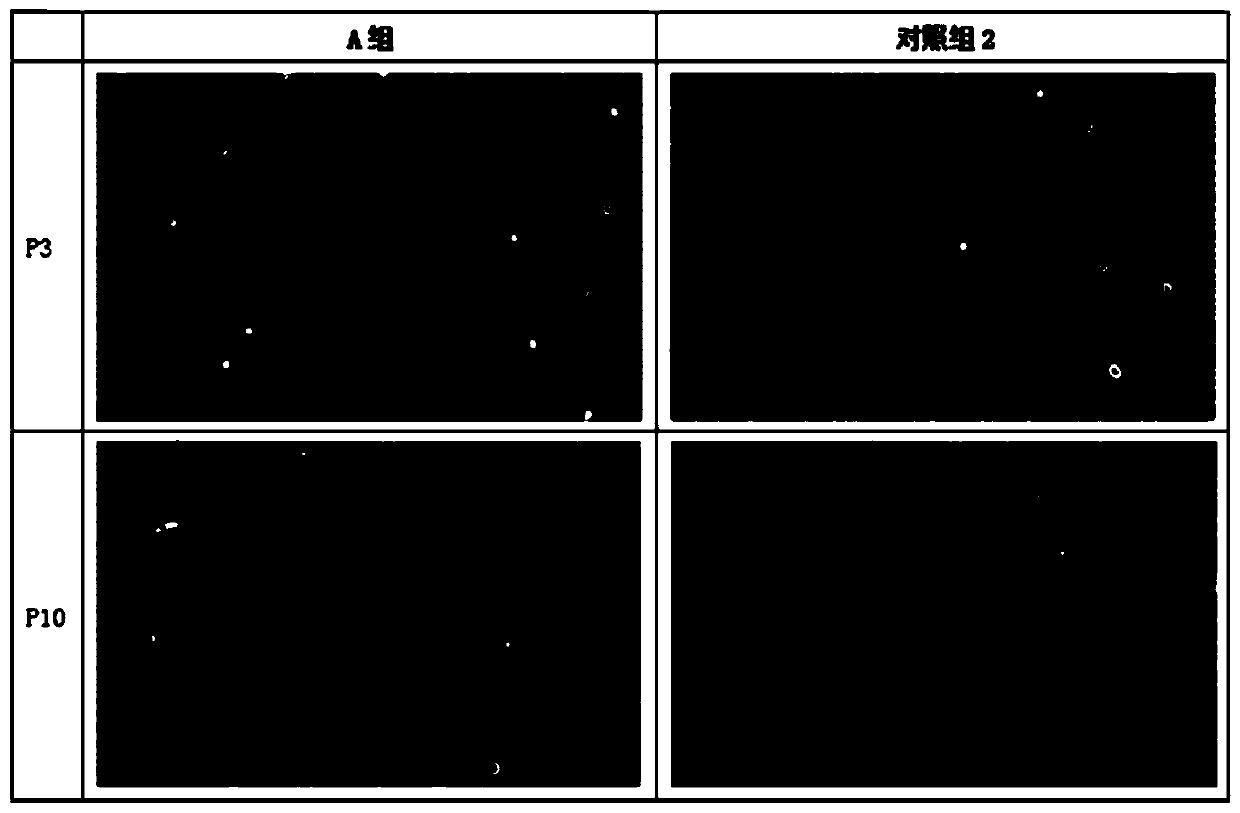
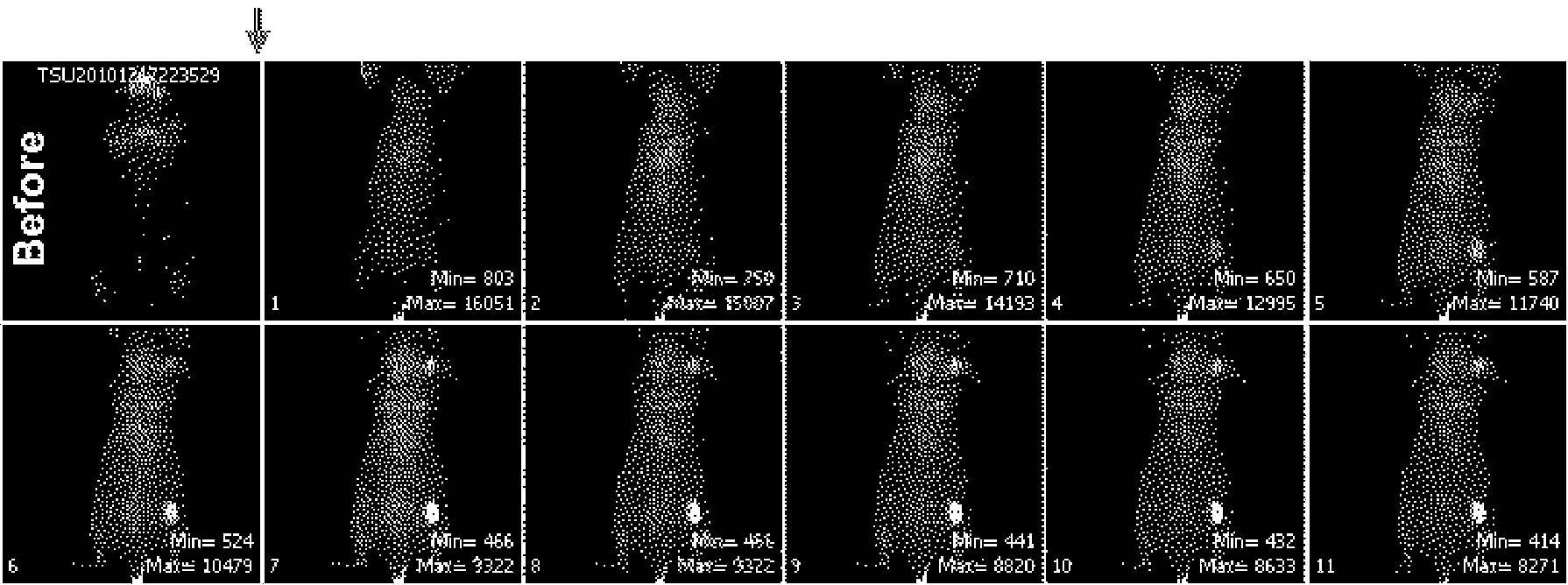
Adipose tissue cryopreservation liquid at clinical application level and cryopreservation method
Adipose tissue cryopreservation liquid at a clinical application level and a cryopreservation method. The adipose tissue cryopreservation liquid at the clinical application level comprises 15-50-mmol / L saccharose, 15-50-mmol / L mannitol injection, 1-5-mmol / L glucose injection, 1-3-mol / L adenosine injection, 0.5-5-mmol / L reduced glutathione, 1-4.5-mol / L trehalose and 0.1-1-mmol / L EDTA-2Na; and the components are mixed to form mixed liquid, and the mixed liquid is the adipose tissue cryopreservation liquid at the clinical application level. By means of the adipose tissue cryopreservation liquid,in combination with the cryopreservation method thereof, at the clinical application level, the defect of adverse reaction due to 2-[4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethanesulfonic acid (HEPES), phenol red, DMSO, animal serum, blood platelet extracts and the like which are used in the prior art is effectively overcome.
Owner:陕西医赛尔生物科技有限公司
Method for detecting cancer cell using fluorescently labeled L-glucose derivative, and cancer cell-imaging agent comprising fluorescently labeled L-glucose derivative
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for highly accurately detecting a cancer cell. The method of the present invention is characterized by comprising imaging with the use of a fluorescently labeled L-glucose derivative. By using the method and imaging agent according to the present invention, a high contrast between a cancer cell and a normal cell can be obtained compared with the case wherein imaging is conducted with the use of a fluorescently labeled D-glucose derivative. According to this method, moreover, no fasting is needed for the determination. Thus, the imaging can be quickly carried out without imposing a burden on a patient.
Owner:ORBIO CORP +1
Isobutanol synthetic strain construction method implemented by guiding adjustment of intracellular reducing power based on genomic scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN104630250AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSynthetic biologyIsobutanol synthesis
The invention provides an isobutanol synthetic strain construction method implemented by guiding the adjustment of intracellular reducing power based on a genomic scale metabolic network model. Based on the genomic scale metabolic network model, by adopting flow balance analysis and metabolic minimum adjustment analysis, the action law of different reconstruction modes of an intracellular reducing power metabolism to strain growth and isobutanol synthesis is simulated, and according to phenotypic coefficients, a conclusion that glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key target spot of the intracellular reducing power adjustment of an isobutanol synthetic strain is obtained. By using a synthetic biological artificially-regulated element, an NADP+ depended glycerin-3-phosphate dehydrogenase metabolic pathway is built and adjusted so as to match and balance the intracellular reducing power metabolism, thereby obtaining an efficient isobutanol synthetic strain. The intracellular NADPH / NADP ratio of the strain reaches 0.4-0.8, and when 20-50 g / L glucose as a substrate is adopted for carrying out batch fermentation, the yield of isobutanol can reach over 8 g / L in 36 h, which is increased by over 60%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Kit for extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from white cells in human whole blood
ActiveCN103710338AImprove extraction efficiencySimple extraction efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationWhite blood cellRed blood cell
The invention provides a kit for extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from white cells in human whole blood. The kit comprises a red blood cell lysis buffer and a DNA extracting solution, wherein the red blood cell lysis buffer comprises the following components: 4.5-5.5mmol / L sodium chloride, 0.8-1.2 percent (v / v) triton 100, 300-340mmol / L glucose and 0.008-0.012mol / L tri-hydroxymethyl aminomethane. The kit provided by the invention can be used for solving the defect of an existing kit for extracting the DNA in human whole blood white cells. The invention provides a kit for quickly extracting the DNA from white cells in the human whole blood, and the kit is simple and quick in operation, high in extraction efficiency, safe to use, and low in manufacture cost. By applying the kit, the DNA in white cells of a clinical whole blood sample for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology detection can be rapidly extracted, and DNA in white cells and DNA of viruses in the white cells in whole blood are extracted.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Glycosidase inhibitors and methods of synthesizing same
A method for synthesizing Salacinol, its stereoisomers, and analogues, homologues and other derivatives thereof potentially useful as glycolsidase inhibitors. The compounds of the invention may have the general formula (I) or (II): The synthetic schemes comprise reacting a cyclic sulfate with a 5-membered ring sugar containing a heteroatom (X). The heteroatom preferably comprises sulfur, selenium, or nitrogen. The cyclic sulfate and ring sugar reagents may be readily prepared from carbohydrate precursors, such as D-glucose, L-glucose, D-xylose and L-xylose. The target compounds are prepared by opening of the cyclic sulfates by nucleophilic attack of the heteroatoms on the 5-membered ring sugars. The resulting heterocyclic compounds have a stable, inner salt structure comprising a heteroatom cation and a sulfate anion. The synthetic schemes yield various stereoisomers of the target compounds in moderate to good yields with limited side-reactions.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
Optimized technological method for amplifying recombinant adenovirus by using bioreactor
The invention relates to the biotechnology field and in particular relates to a comprehensively optimized technological method for amplifying recombinant adenovirus. The method is used for amplifying human embryonic kidney cells (HEK293) by using poly-fiber paper carriers through a bioreactor; in this way, the whole set of process flow of adenovirus replication and amplification is established. The optimized technological method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: under the condition of comprehensively adapting to type 5 adenovirus replication and amplification system, utilizing a DMEM culture medium containing 10% of blood serum at the cell culture stage, utilizing a DMEM culture medium containing 20% of blood serum in 20 hours after virus inoculation absorption; employing a blood serum-free culture medium added with 0.25% of lactoalbumin hydrolysate at the virus collecting stage, and simultaneously, supplementing 2g / L glucose every 20 hours. The way of batch collection and batch liquid exchange is adopted; and the method enables the optimized process to achieve high virus titer on the basis of reducing the later-stage purification difficulty and meeting the requirements of biological products. Therefore, the optimized process established by the invention an efficient recombinant adenovirus amplification process having excellent repeatability, and is suitable for any bioreactor with the poly-fiber paper as the carriers to amplify the recombinant adenovirus.
Owner:ZHEJIANG PUKANG BIOTECH
Microbial complex microbial agent for degrading lactic acid
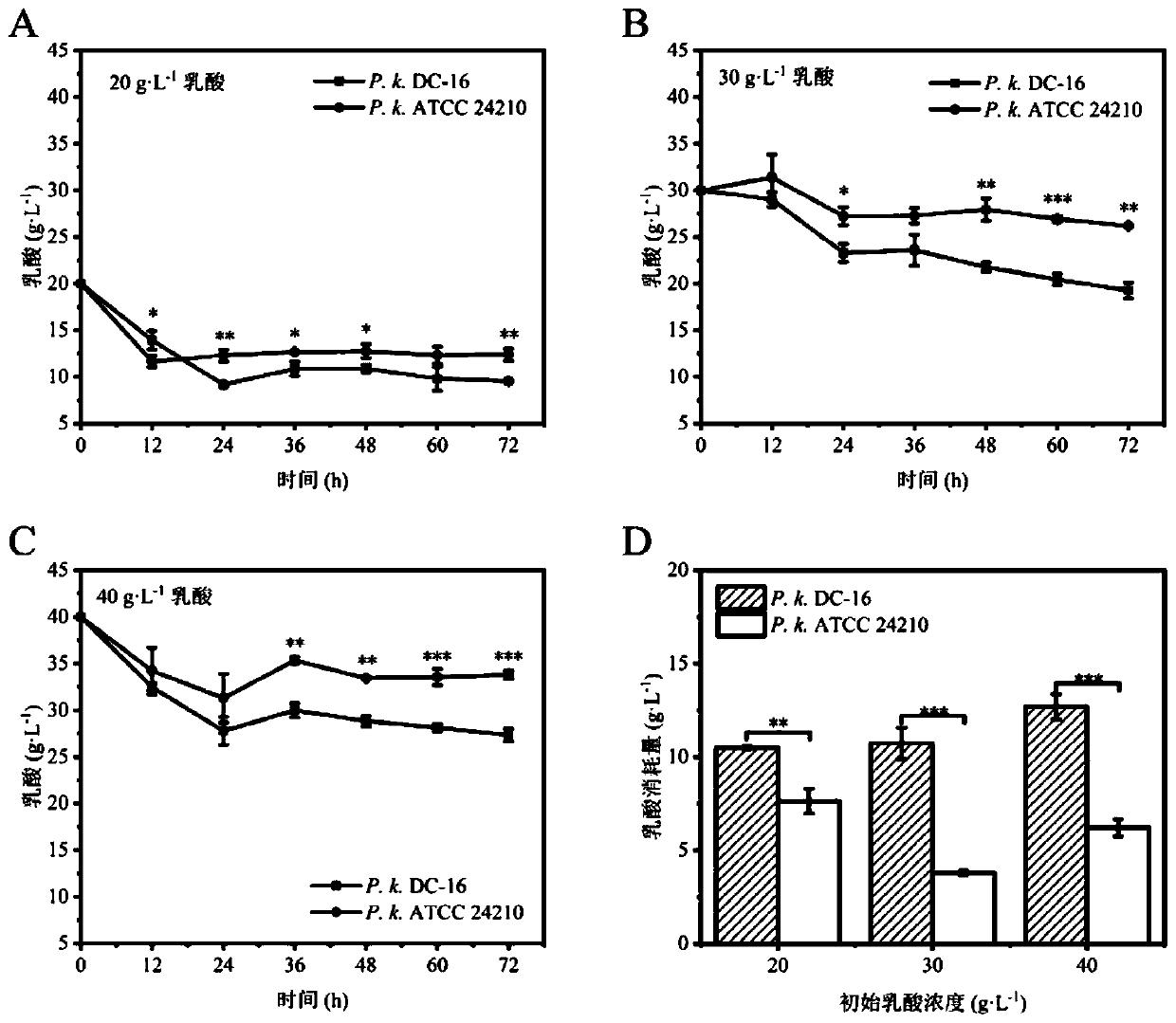
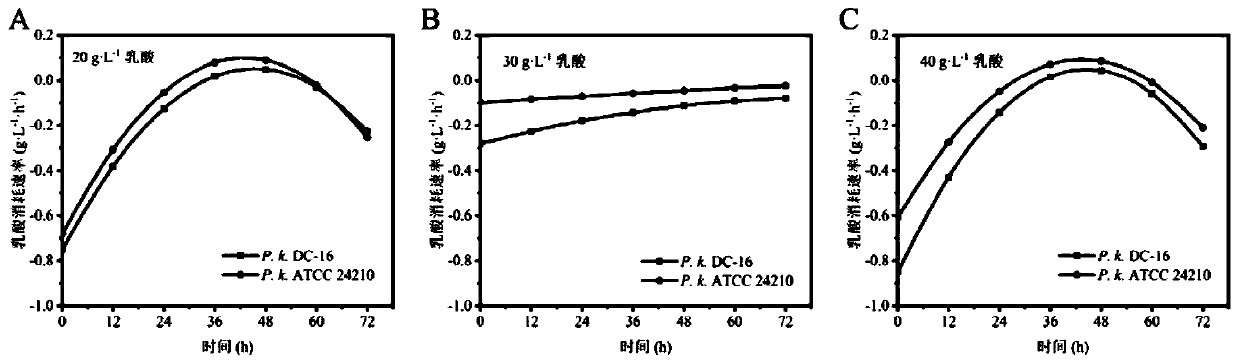
ActiveCN111254085APromote degradationRelieve Lactic Acid StressBiocideFungiBiotechnologyMicrobial agent
The invention discloses a microbial complex microbial agent for degrading lactic acid, and belongs to the technical field of microbes. The degradability of the pichia kudriavzevii provided by the invention to the lactic acid is up to 12.69 g / L, and is 2.04 times that of a model strain; at the same time, the strain can metabolize ethanol, and the OD600 can reach 4.48 after the strain is fermented in a sorghum juice culture medium at 30 DEG C and 200 rpm for 3 days; after fermentation is performed for 60 h, 58 g / L glucose in the sorghum juice culture medium can be completely depleted, and 13.06g / L ethanol can be produced; and the pichia kudriavzevii can relieve lactic acid pressure in a fermentation system when degrading the lactic acid, so that saccharomyces cerevisiae can grow and be metabolized to produce liquor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
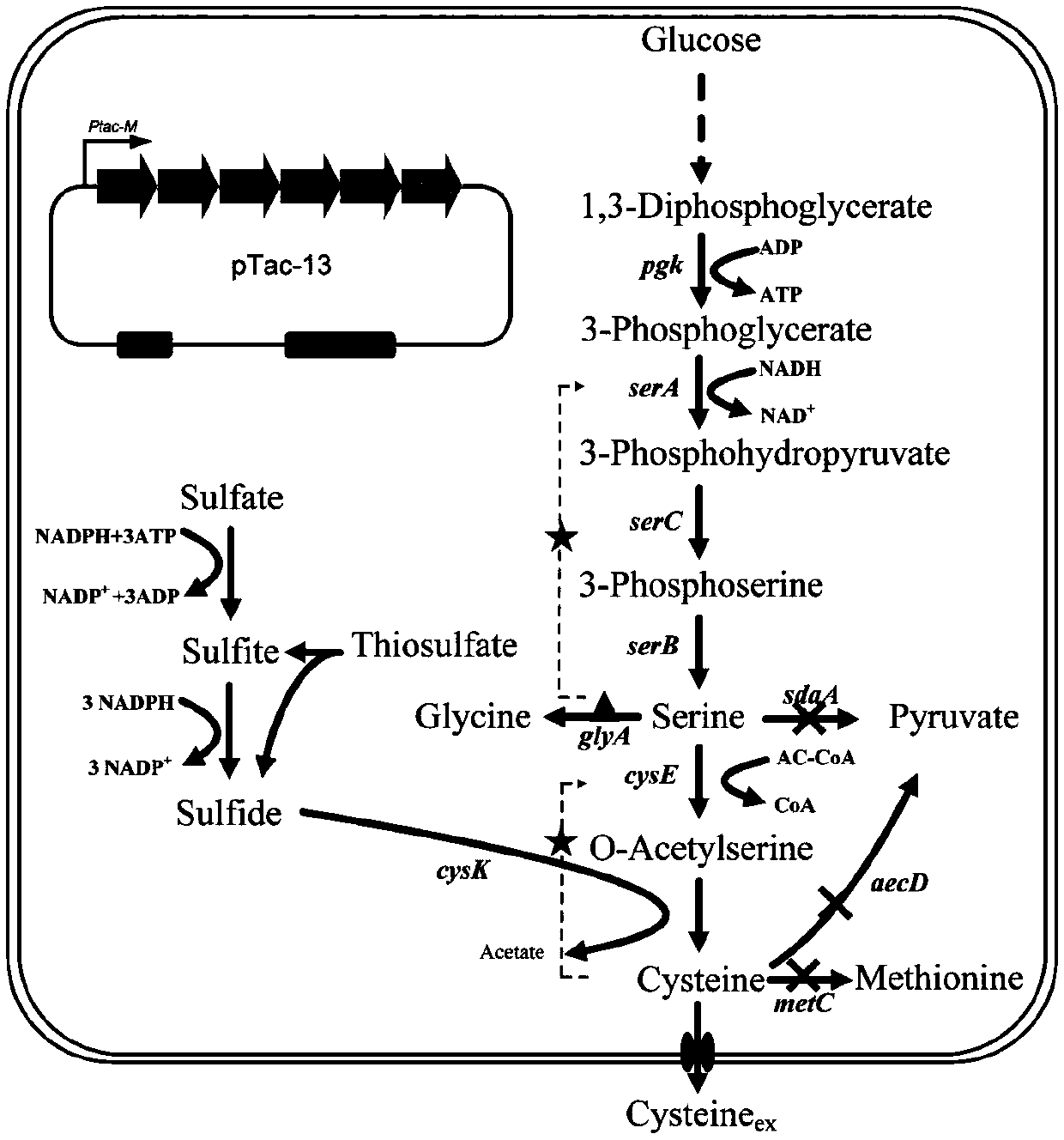
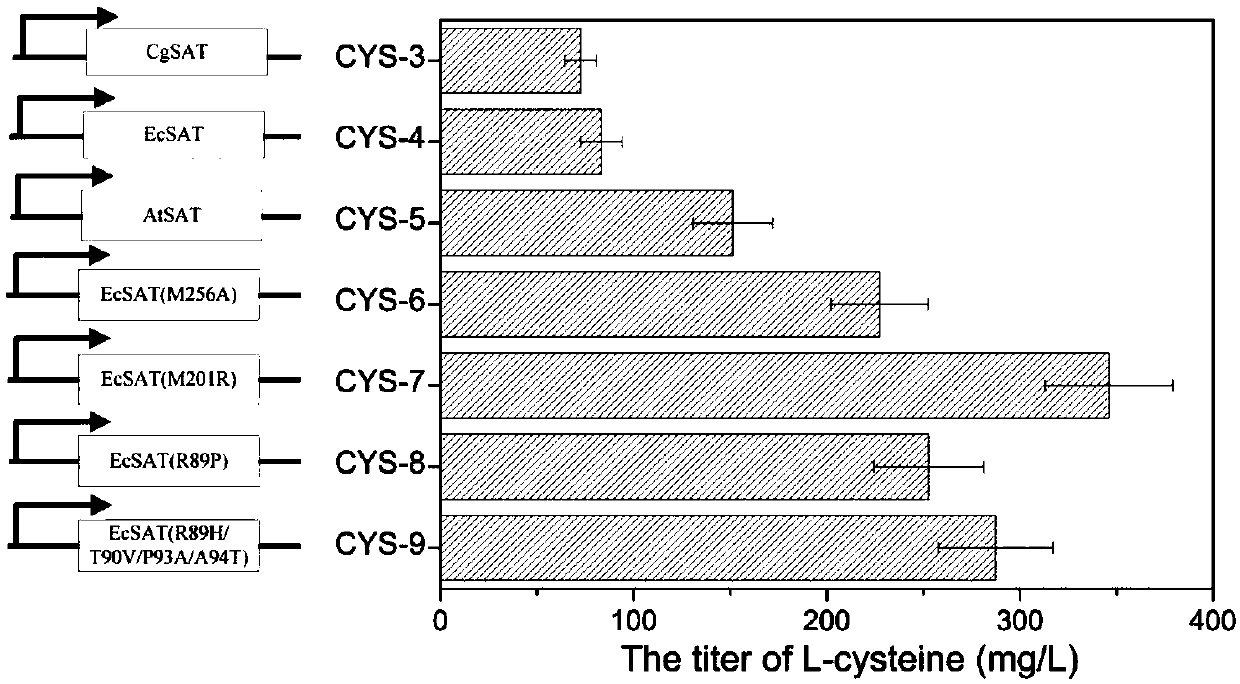
Method for high-yield production of L-cysteine by metabolic engineering modification of corynebacterium glutamicum
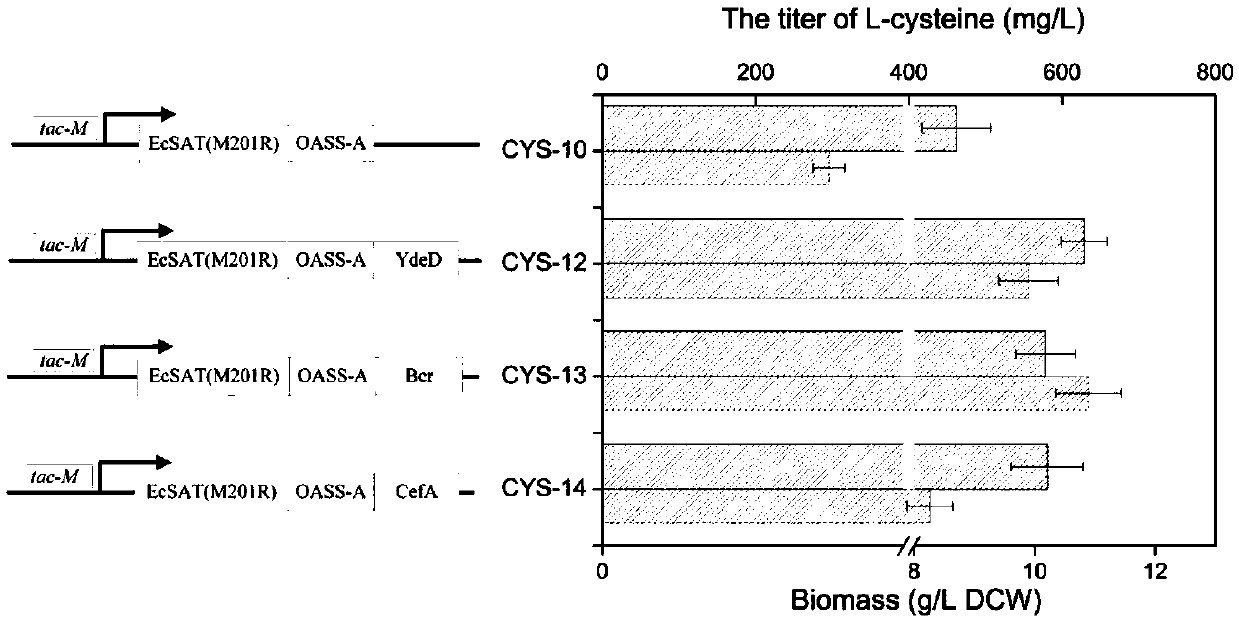
The invention provides a method for high-yield production of L-cysteine by metabolic engineering modification of corynebacterium glutamicum. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out an L-cysteine desulfhydrase gene aecD while overexpressing a serine acetyltransferase gene cysE to obtain an L-cysteine accumulation strain; respectively overexpressing the serine acetyltransferase genescysE of escherichia coli and arabidopsis thaliana, and obtaining EcysE(M201R) most beneficial to L-cysteine synthesis after activity comparison; respectively overexpressing L-cysteine transporter proteins from escherichia coli and pantoea ananatis, and comparing the influences of different transporter proteins on the yield of L-cysteine to obtain a transporter protein Bcr most beneficial to L-cysteine secretion; promoting the synthesis of L-cysteine by improving the level of a precursor L-serine; and finally fermenting for 3-4 days by using 50-60 g / L glucose as a substrate, wherein the contentof L-cysteine reaches 800-1000 mg / L.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Banana fusarium oxysporum culture medium and application thereof
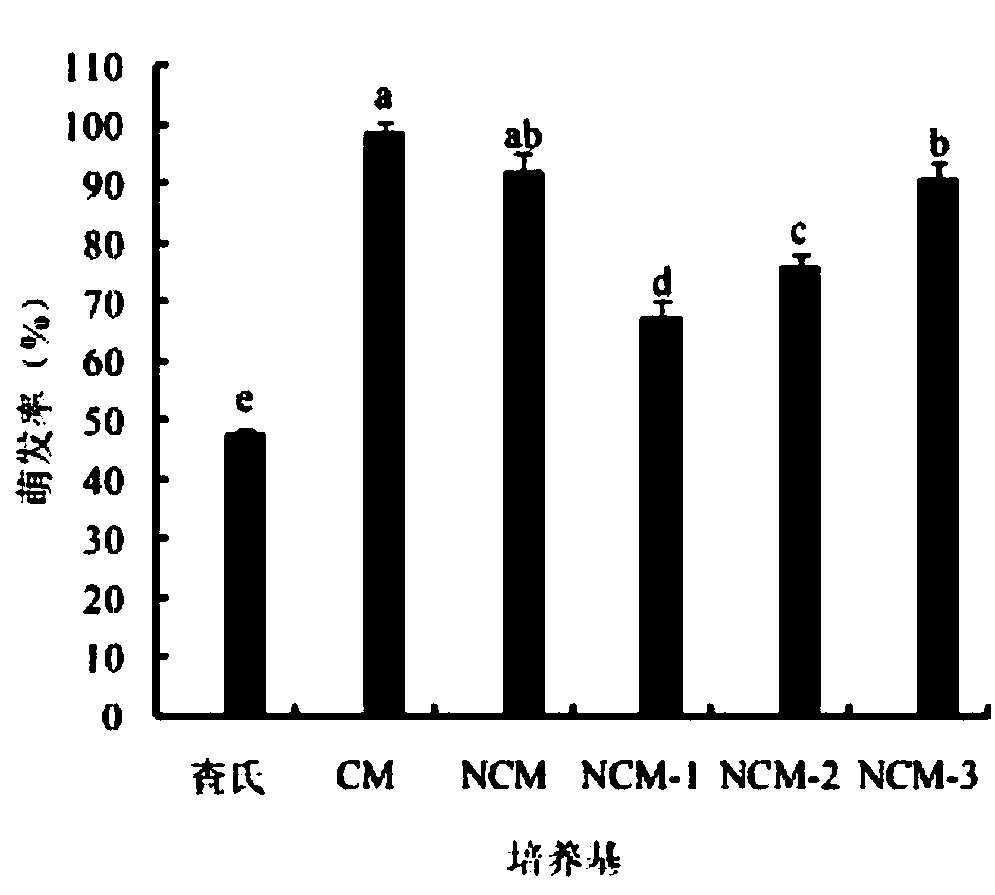
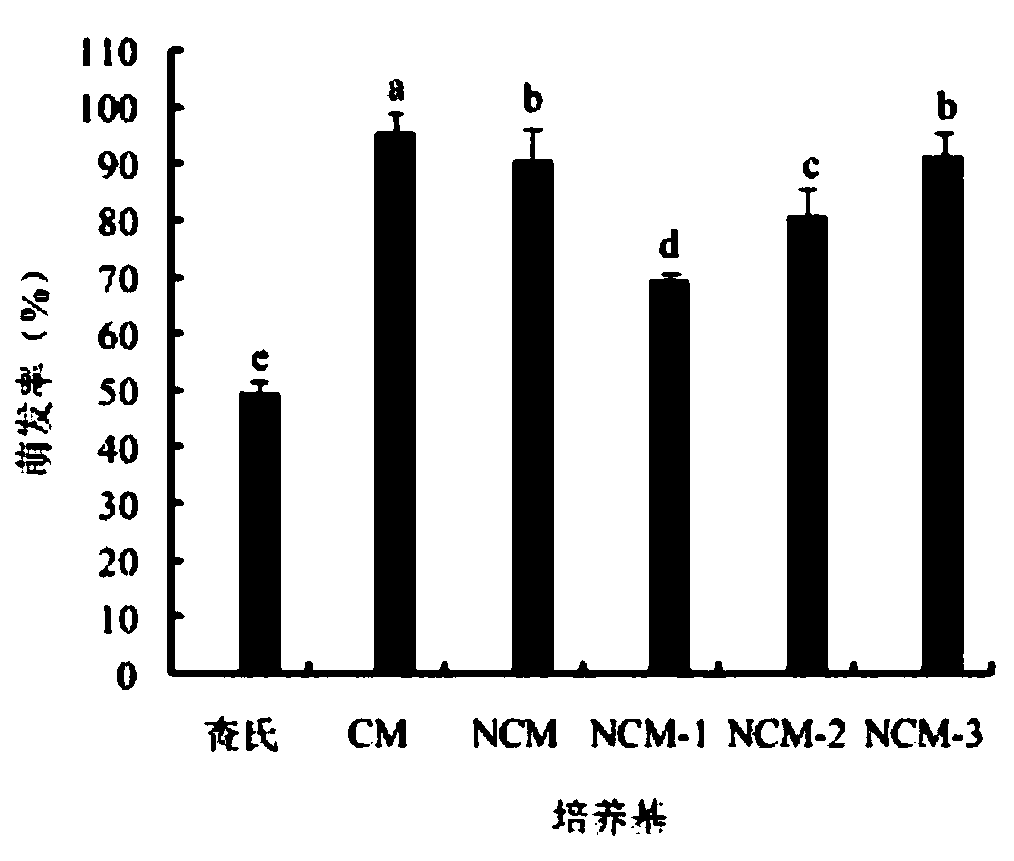
ActiveCN107641599ASimple manufacturing methodPromote germinationFungiMicroorganism based processesCulture mediumsL-Glucose
The invention discloses a banana fusarium oxysporum culture medium and application thereof. The culture medium comprises the following components: 10g / L glucose, 2-8g / L aspartic acid, 5% by volume of20*nitrate, 0.5% by volume of 200*ferric salt, 0.1% by volume of 1000*vitamins and 0.1% by volume of 1000*trace elements, and the pH value of the culture medium is 6.2-6.5. By adopting the culture medium disclosed by the invention, germination of banana fusarium oxysporum conidium is promoted, interference of macromolecule proteins is avoided, and analysis on banana fusarium oxysporum secretion proteins is facilitated.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
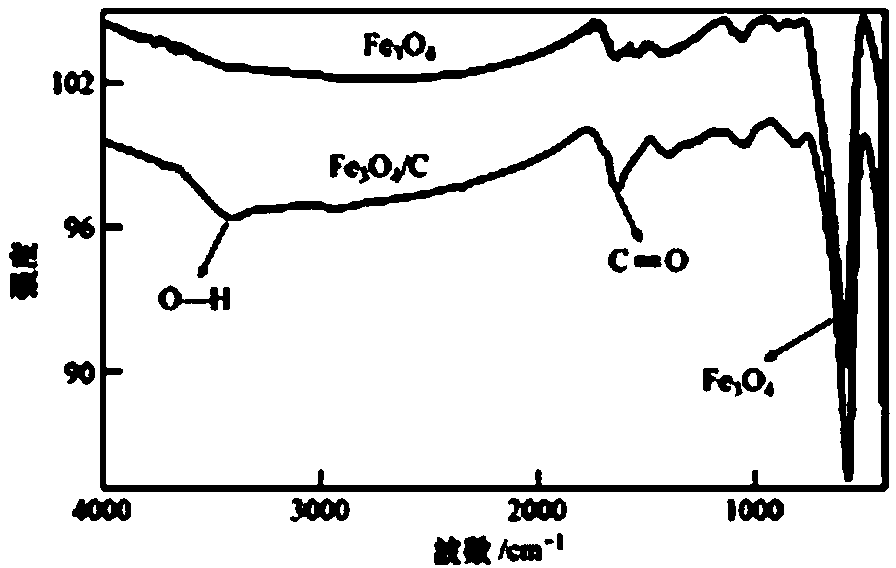
Preparation method of Fe3O4/ C nanoparticles
InactiveCN103506078AUniform sizeSimple methodOther chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesNanoparticleDistilled water
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of Fe3O4 / C nanoparticles. The preparation method of the Fe3O4 / C nanoparticles comprises the following steps: (1) dissolving 1.35 g of FeCl3.6H2O into 40 ml of ethylene glycol, adding 3.6 g of NaAc.3H2O and 1.0 g of polyethylene glycol (PEG-4000) in sequence, uniformly mixing, reacting for 8 hours at 200 DEG C, and cooling to obtain Fe3O4; (2) dispersing the prepared Fe3O4 into 0.1 mol / L HNO3, washing with distilled water, and redispersing the acidified Fe3O4 into 8 mL of 0.5 mol / L glucose, transferring the suspension to a reactor, reacting for 4 hours at 170 DEG C, cooling, washing repeatedly with water and ethanol, and drying to obtain the Fe3O4 / C nanoparticles. The preparation method has the advantages of easy obtainment of raw materials, nontoxicity and simpleness.
Owner:SHAANXI SHENGMAI PETROLEUM
Semicontinuous fermentation method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by lactic acid bacteria
InactiveCN102108370AGuaranteed productionReduce dosageMicroorganism based processesFermentationSolventOxygen
The invention discloses a semicontinuous fermentation method for producing gamma-aminobutyric acid by lactic acid bacteria, which comprises the following steps: inoculating lactic acid bacteria onto an Man, Rogosa and Sharpe gelatin (MRSG) culture medium; and fermenting in a mode of segmental substrate addition, segmental temperature control and segmental oxygen control to obtain gamma-aminobutyric acid, wherein the solvent of the MRSG culture medium is water, and the solute comprises the following materials at concentration: 7 to 12g / L glucose, 20 to 30g / L peptone, 30 to 40g / L beef extract, 0.05 to 1g / L manganese sulfate, 0.01 to 0.05g / L vitamin B, and 2 to 5g / L sodium glutamate. When the method provided by the invention is adopted, the yield of the gamma-aminobutyric acid can reach 13.1to 38.7g / L.
Owner:山东水晶生物科技股份有限公司
Debonding protectant, method for preparing monocell suspension with high survival rate and application of debonding protectant
PendingCN111235090AGood effectShorten the timeCell dissociation methodsPancreatic cellsBiotechnologyAnimal science
Owner:CHENGDU DAOSHENG BIOTECH CO LTD
Hemodialysis concentrate
InactiveCN108066356AAvoid hypoglycemiaBlood sugar avoidancePharmaceutical delivery mechanismAluminium/calcium/magnesium active ingredientsSodium bicarbonateHaemodialysis machine
The invention discloses hemodialysis concentrate. The hemodialysis concentrate comprises a hemodialysis concentrated solution A and a hemodialysis concentrated solution B and is prepared from 208.0-212.0 g / L sodium chloride, 5.0-5.5 g / L potassium chloride, 6.0-8.0 g / L calcium chloride, 3.5-4.0g / L magnesium chloride, 7.0-11.5 g / L glacial acetic acid, 82.0-86.0 g / L sodium bicarbonate and 35.0-41.0 g / L or 70.0-82.0 g / L glucose (containing one molecule of crystal water). The hemodialysis concentrate needs to be used in cooperation with a dialysis machine, and is prepared from the hemodialysis concentrated solution A, the hemodialysis concentrated solution B and dialysis water at a dilution ratio of 1:1.225:32.775. The hemodialysis concentrate provides a better choice for patients suffering from hypoglycemia dialysis, the steps are simplified, the working efficiency is improved, and the operation is easy and convenient.
Owner:济泰(上海)生物科技有限公司
Control method for efficient production of calcium gluconate by microbial fermentation
InactiveCN103352090AReal-time controlReal-time control of adding speedMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention discloses a control method for efficient production of calcium gluconate by microbial fermentation. The method includes: taking a gluconic acid high-producing strain as the starting strain, conducting seed culture, then transferring the strain into a fermentation tank to perform fermentation production of calcium gluconate, and during fermentation, according to an online measured oxygen transfer coefficient (Kla), automatically controlling the adding speed and adding amount of 500g / L glucose and nutrients. The method realizes direct, real-time and accurate control of a calcium gluconate fermentation process.
Owner:山东福洋生物科技股份有限公司
High production method for glycerol with multi-step zymotechnics
ActiveCN101343643APost extraction easyRaise the scaleMicroorganism based processesFermentationYeastConcentrations glucose
Disclosed is a high-yield method for using a multi-step fermentation method to manufacture glycerin, which belongs to the technical field of biochemical industry. Through adjusting the ventilation capacity and the rotating speed, the fermentation can be divided into four stages for staged-fermentation with the process steps: a hyperosmotic yeast starter liquid which accounts for 5 to 10 percent of the inoculation amount according to the volume is added into an initial fermentation medium containing 250 g / l to 380 g / l glucose concentration, and the aerobic fermentation is performed under the condition of 30 DEG C to 40 DEG C; the ventilation capacity is turned up every 6 hours to finally reach 0.6 vvm to 3.5 vvm, the stirring rate reaches 70 rpm to 600 rpm, when the glucose concentration is lower than 30 g / l to 50 g / l, the multi-step fermentation enters the third stage of fermentation, when the ventilation capacity is turned down every 4 hours to 6 hours to finally reach 0 vvm, the stirring rate reaches 10 rpm to 50 rpm, the multi-step fermentation enters the forth stage of anaerobic fermentation, and when the glucose concentration is lower than 2 g / l, the fermentation stops. After the fermentation is finished, the fermentation liquor undergoes solid-liquid separation, and the glycerin is prepared into products through separation and purification. The invention has the advantages that the residual sugar is obviously reduced at the later stage of fermentation, and the glycerin is not re-consumed.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
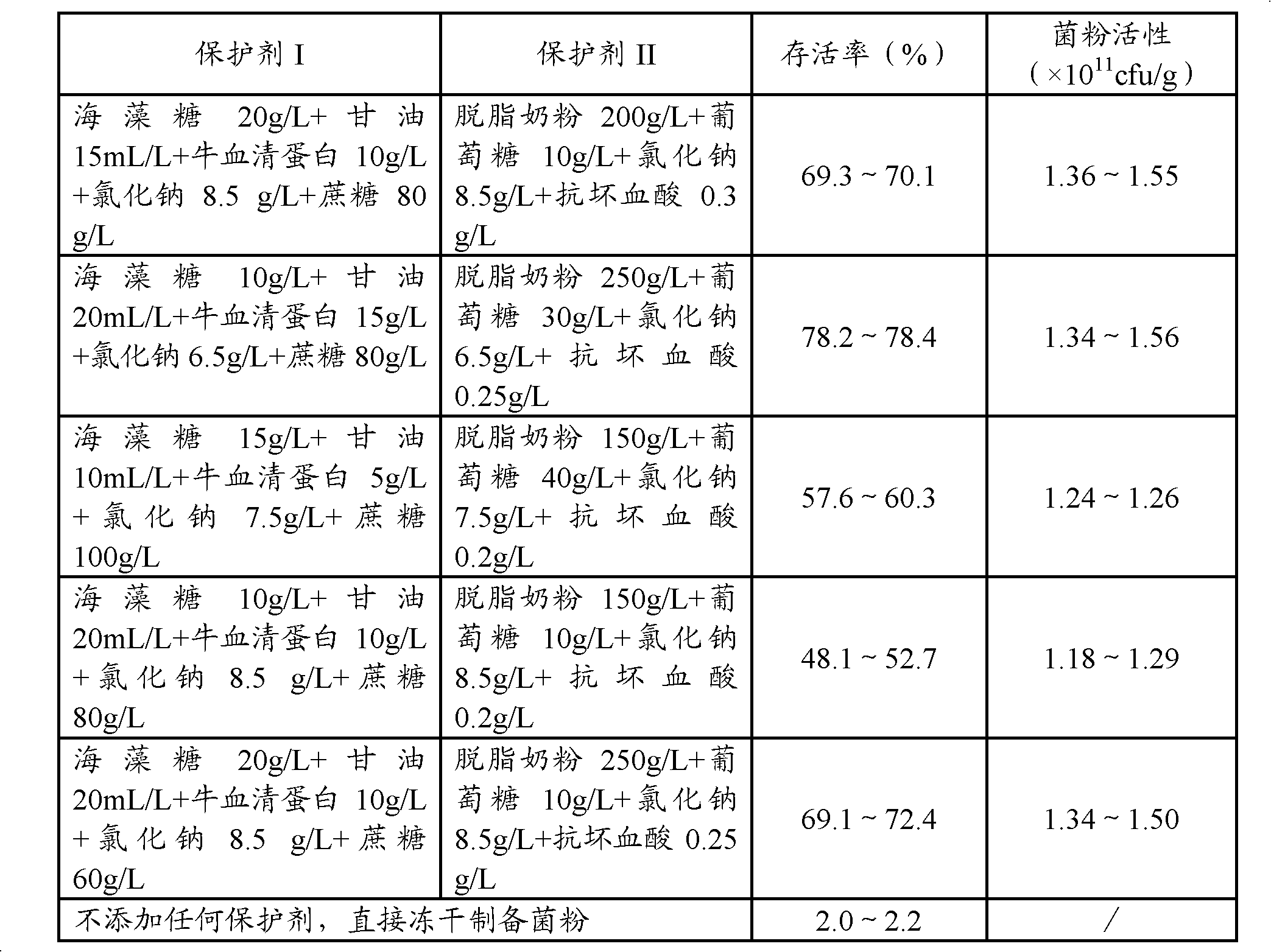
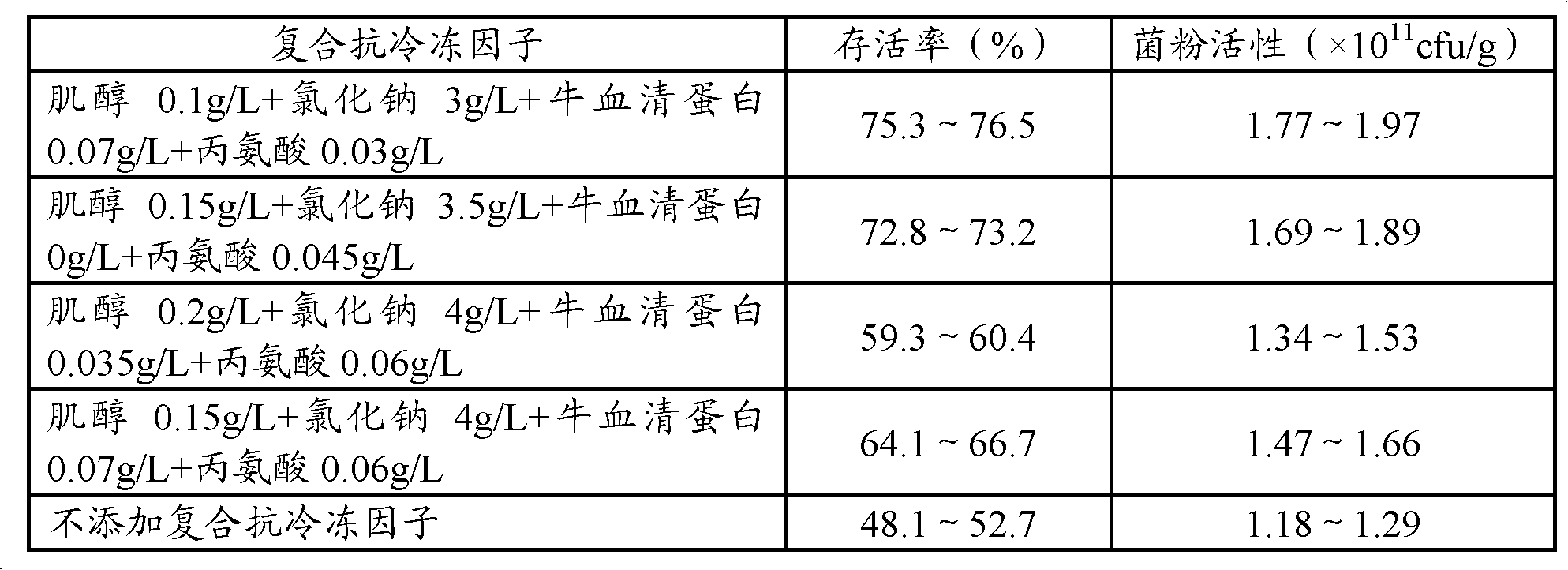
Method for preparing lactobacillus acidophilus powder by freeze-drying in vacuum
ActiveCN101962616AImprove survival rateMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationSucroseFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a method for preparing lactobacillus acidophilus powder by freeze-drying in vacuum. The method comprises the following steps of: adding lactobacillus acidophilus into a culture medium for culturing the lactobacillus acidophilus; after centrifugal collection of thalli, washing the thalli with physiological saline and centrifuging to remove clear liquid; after preparing the thalli into bacterial suspension by using a protecting agent I; adding a protecting agent II; and finally performing freeze-drying, wherein the formula of the protecting agent I comprises the following components: 10 to 20g / L trehalose, 10 to 20 g / L glycerol, 5 to 15 g / L bovine serum albumin, 6.5 to 8.5g / L sodium chloride and 60 to 100 g / L sucrose; and the formula of the protecting agent II comprises the following components: 150 to 250g / L skim milk powder, 10 to 40g / L glucose, 6.5 to 8.5g / L sodium chloride, and 0.2 to 0.3g / L ascorbic acid. The survival rate of the lactobacillus acidophilus powder prepared by the invention is up to 99.9 percent.
Owner:HANGZHOU GRAND BIOLOGIC PHARMA INC
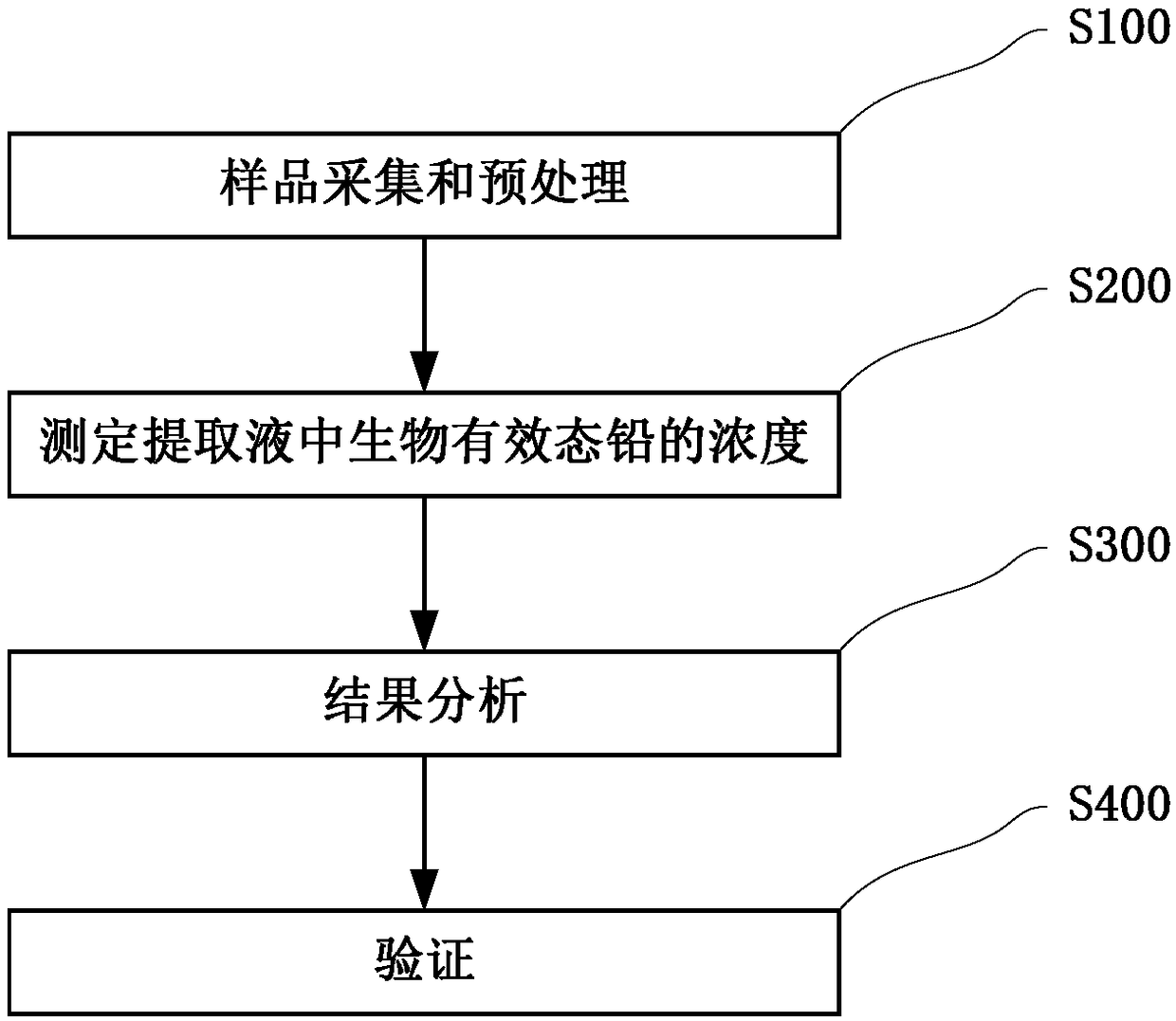
Method for detecting bioavailable lead in soil
ActiveCN109387411AAcid-base damage is smallPrevent curingPreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsBiologyStrontium chloride
A method for detecting bioavailable lead in soil comprises the following steps: s100, collecting and pretreating a sample, to be more specific, collecting the soil, air-drying the collected soil at room temperature, grinding, sieving by a 200-mesh sieve to prepare the soil sample, weighing 1-5 g of the soil sample, and putting the soil sample into a 250 ml polytetrafluoroethylene centrifugal cup,respectively adding 25 ml of a 1 mol / L strontium chloride solution and 25 ml of a 0.5mol / L glucose solution, stirring by a constant-temperature magnetic stirrer, centrifuging by a centrifugal machine,taking supernate, filtering the supernate with a filtering membrane to obtain an extracting solution, and diluting the extracting solution to a scale by using a HNO3 solution with the concentration of 1%; s200, determining the concentration of the bioavailable lead in the extracting solution, to be more specific, establishing a standard curve used for determining the different concentrations of the bioavailable lead by adopting an atomic absorption spectrometer through a flame atomic absorption method, and measuring the concentration of the bioavailable lead in the extracting solution throughthe standard curve by adopting the atomic absorption spectrometer; and s300, analyzing results, to be more specific, according to the measured mass of the soil sample and the measured concentration of the extracting solution, calculating the content of the bioavailable lead in the measured soil sample.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
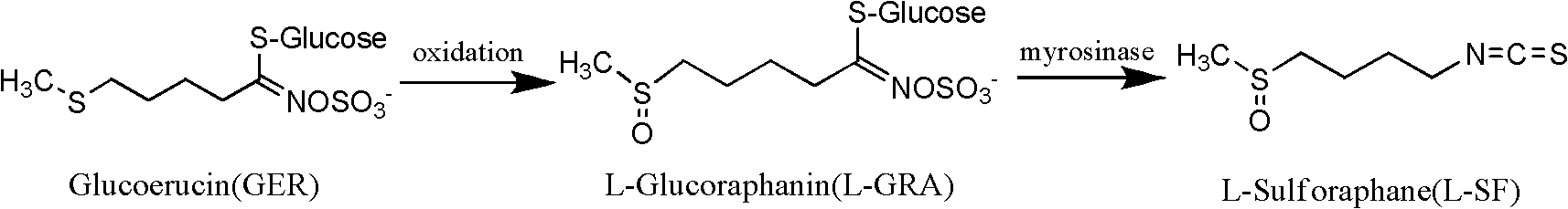
Method for preparing sulforaphane by using glucoerucin
The invention relates to a method for preparing sulforaphane by using glucoerucin, comprising the following steps: (1) preparing glucoerucin; (2) preparing L-glucose sulforaphane: adding sulforaphane obtained by the step (1), (+)-L-diethyl tartrate, alkoxy titanium or alkoxy vanadium compound in a mixed solution of methanol, ethanol and ethyl acetate to obtain a product of L-glucose sulforaphane;(3) taking broccoli seeds and crushing, filtering through gauze to obtain a filtrate, adding ammonium sulfate in the filtrate at a temperature of 4 DEG C with a saturation of 55 %, mixing uniformly, centrifuging the precipitate to dissolve the precipitate in deionized water, and dialyzing overnight to obtain a crude enzyme of hydrolase; and (4) purifying the L-glucose sulforaphane. The method aims at overcoming the disadvantages of high cost of raw materials, low yield of sulforaphane and the like. According to the invention, sesame seeds which are cheaply obtained are used as raw materials, thus the cost of the raw materials is one fifth that of broccoli seeds, and the sulforaphane yield obtained by using sesame seeds is 3 times the yield obtained by using broccoli seeds.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
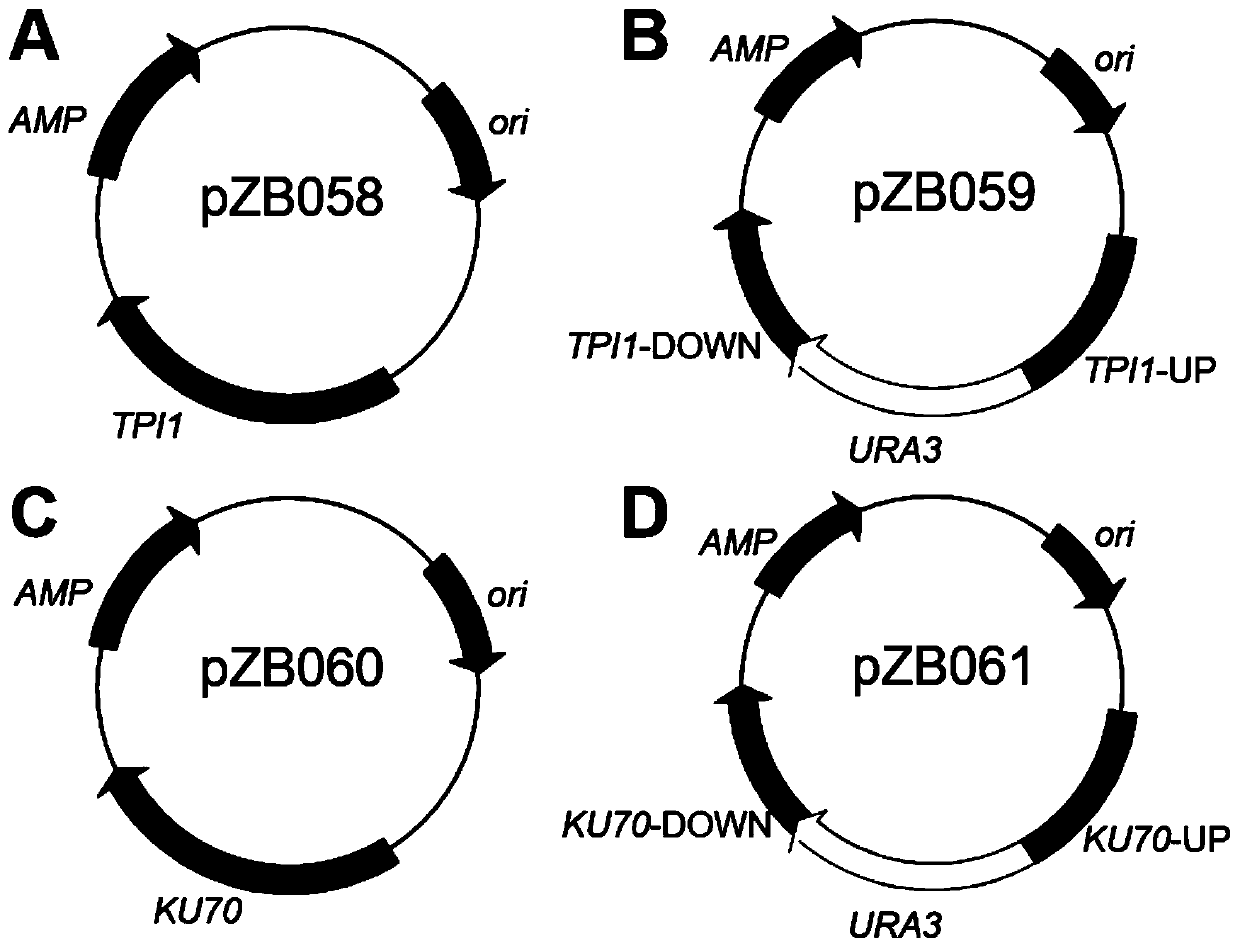
Construction and application of heat-resistant yeast engineering bacteria capable of producing glycerine under high temperature aerobiotic condition
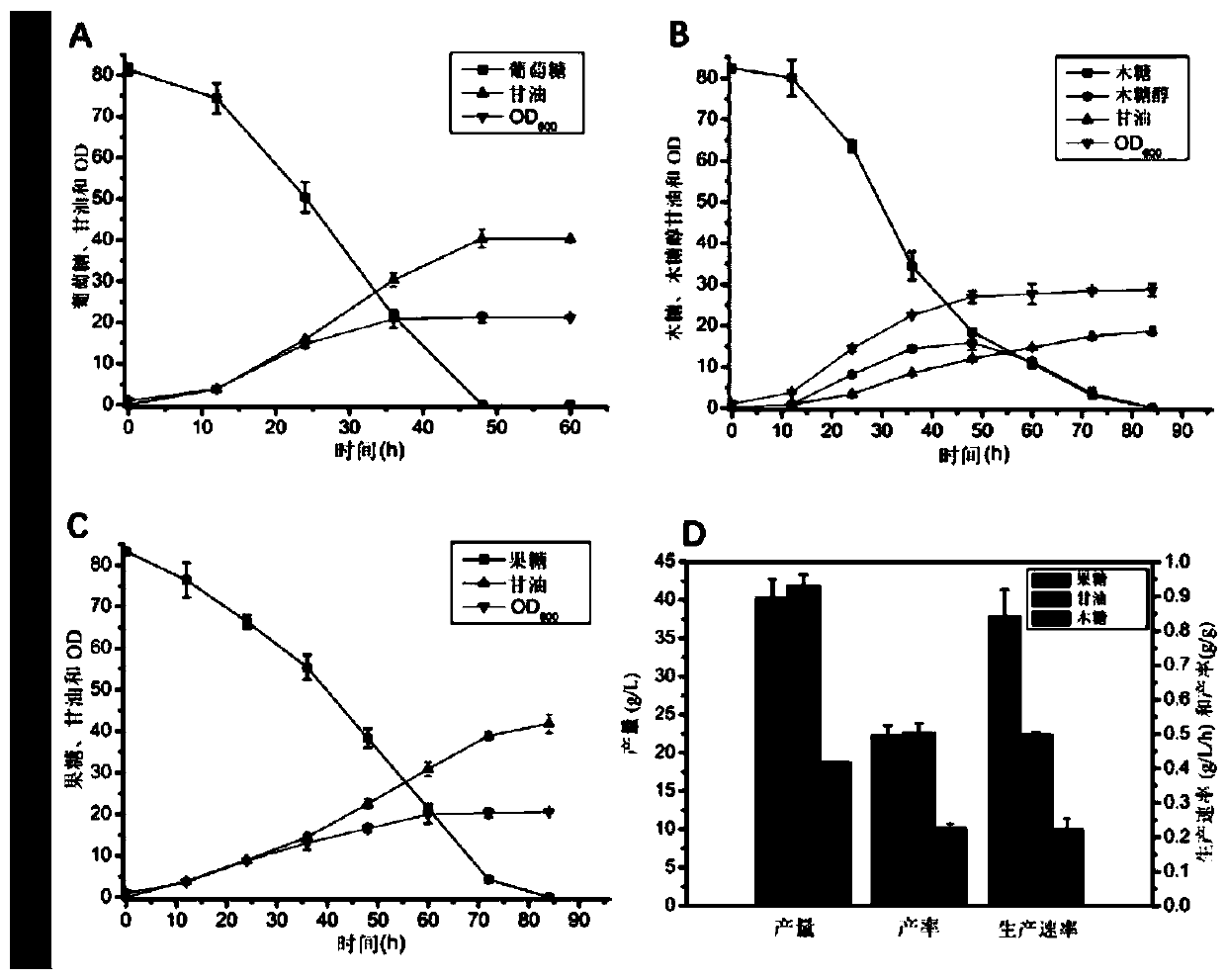
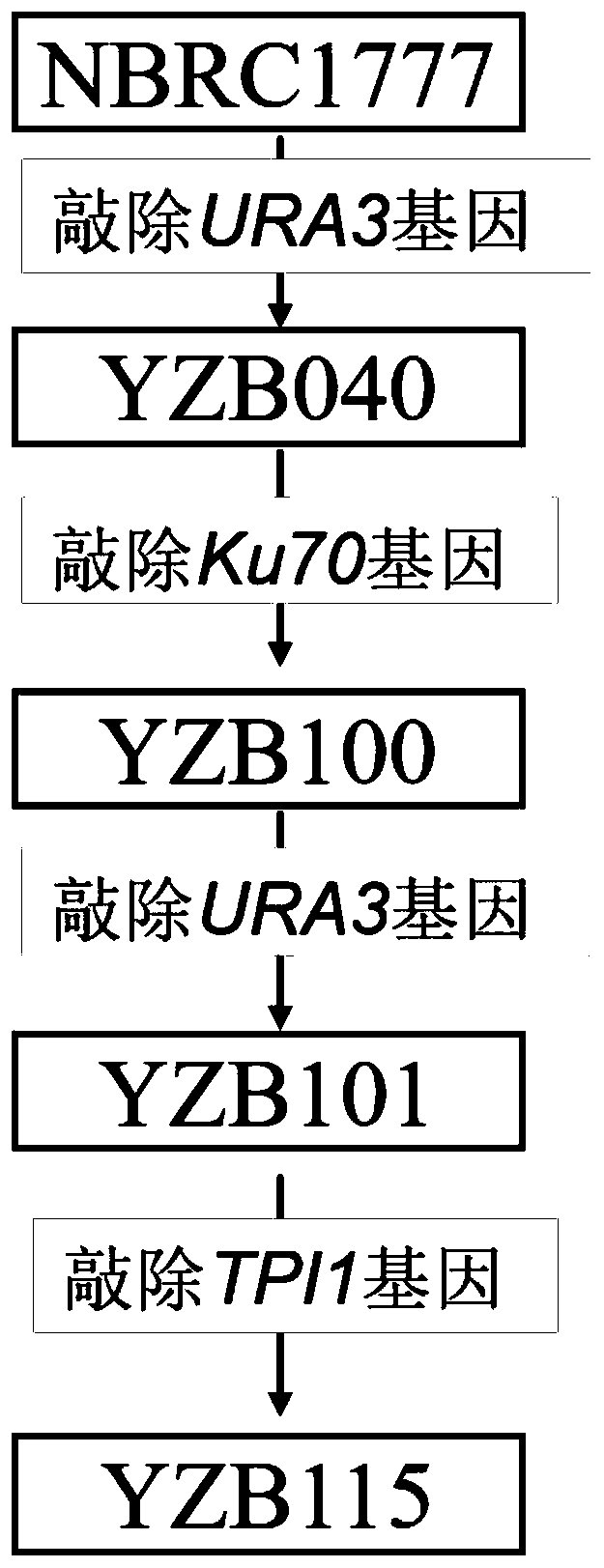
The invention discloses construction and application of heat-resistant yeast engineering bacteria capable of producing glycerine under high temperature aerobiotic condition. A heat-resistant kluyveromyces marxianus is used as a platform, methods of genetic engineering, metabolic engineering and the like are utilized, a strain having triose phosphate isomerase (TPI1) deletion is constructed, and the constructed strain has the capacity of efficiently producing the glycerine through efficient utilization of glucose, levulose and xylose under the high temperature aerobiotic condition. The obtainedkluyveromyces marxianus strain YZB115 produces 40.32 g / L glycerine through 80g / L glucose, produces 41.84 g / L glycerine through 80g / L levulose and 18.64g / L glycerine through 80g / L xylose under the aerobiotic condition of 42 DEG C, the production rates are respectively 0.84g / L / h, 0.50g / L / h and 0.22g / L / h, the yields are respectively 0.50g / g, 0.50g / g and 0.23g / g, in the fermentation process of the constructed engineering strain, a by-product namely ethanol is not produced, and xylitol is not accumulated when the operation of producing the glycerine through fermentation of xylose is ended.
Owner:HUAIBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Medicinal nano silver paste and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104721227AOvercoming chaosHigh strengthInorganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSilver pasteMetallurgy
The invention discloses a formula and preparation method of high-purity medicinal nano silver paste. According to the formula and preparation method of the high-purity medicinal nano silver paste, specific high-purity spherical ultrafine nano silver powder and the medicinal nano silver paste are selected. According to the indexes of the specific high-purity spherical ultrafine nano silver powder, the silver purity is larger than or equal to 99.99 percent, the silver shape is spherical, and the silver particle size ranges from 0.1 nm to 10 nm. According to the formula of the medicinal nano silver paste, the medicinal nano silver paste comprises 1 g / L to 2 g / L glucose, 1 g / L to 2 g / L nano-silver, 996 g / L to 998 g / L pure water. The preparation method of the medicinal nano silver paste comprises dispersing, stirring, atomizing, collecting and liquid taking.
Owner:HUNAN GUANGGU NANO SCI & TECH
Klebsiella sp. and application thereof
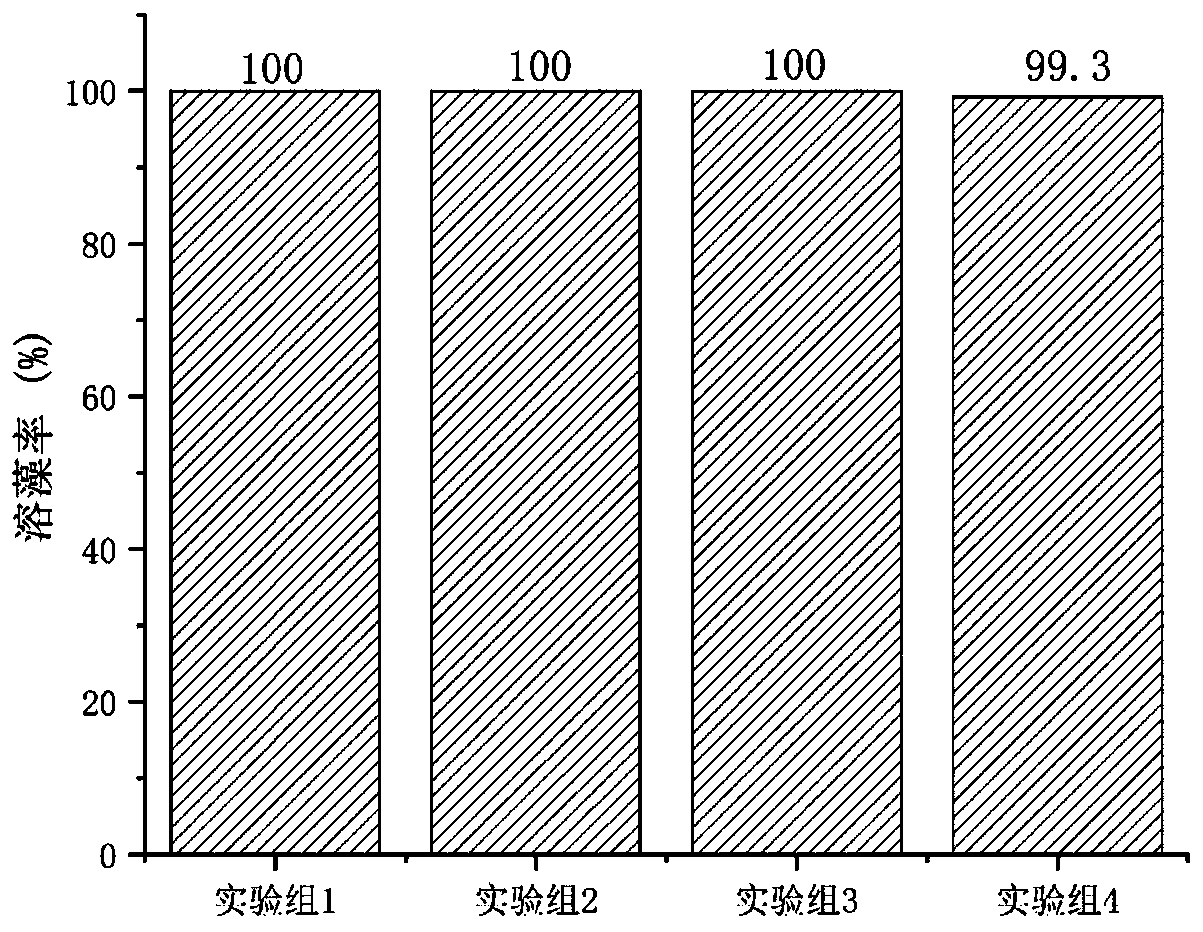
ActiveCN110484472ACompletely killDamage structureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBlue green algaeCyanus
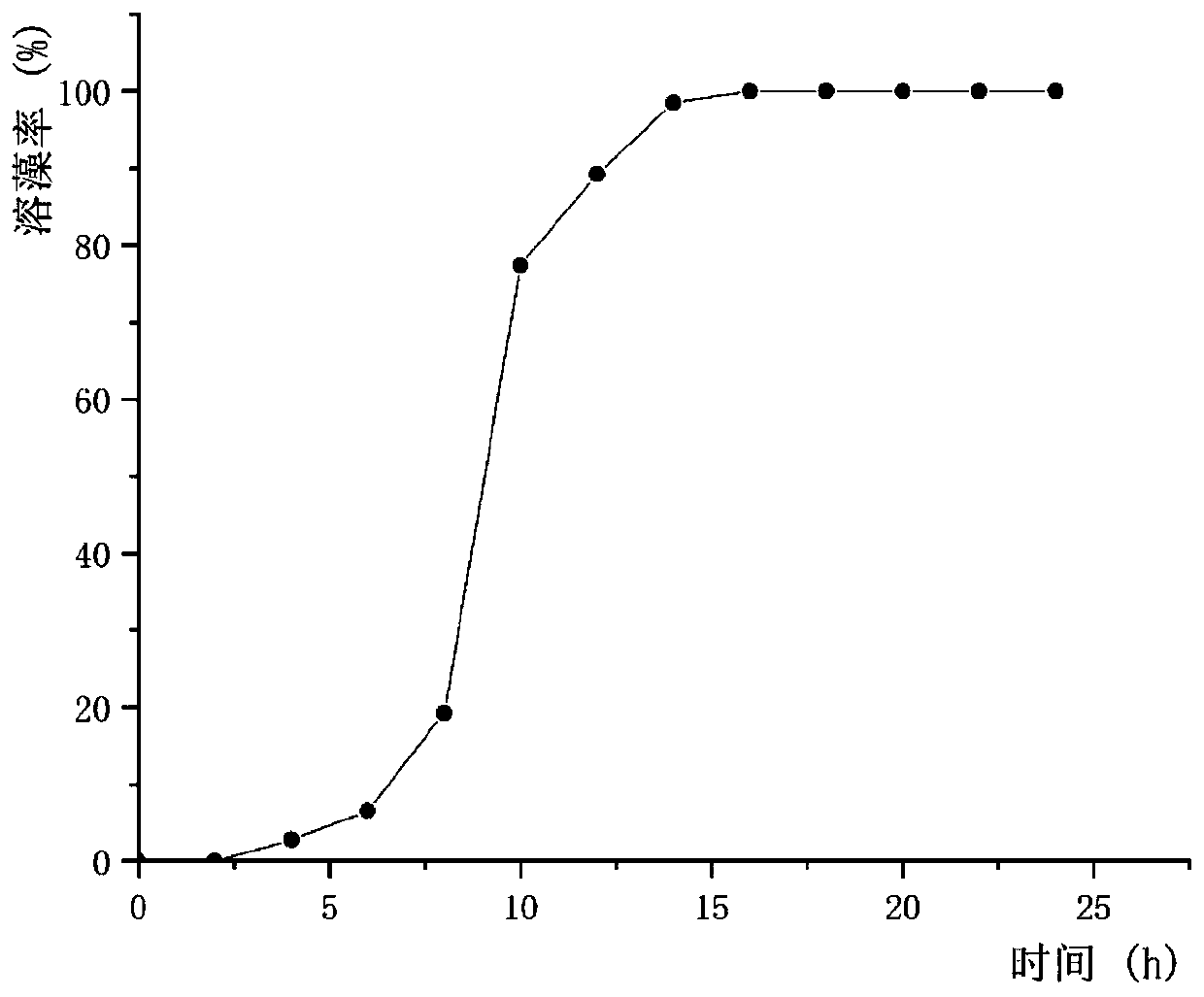
The invention relates to a Klebsiella sp. and its application. The Klebsiella sp. DHU-S1 has the preservation number of CGMCCC No. 18075, and its nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1. The Klebsiella sp. is used for dissolving and killing blue-green algae in a water body. The most suitable algae-dissolving conditions of the strain are as follows: inoculation amount is 10%, pH is 7.0, temperature is 25 DEG C, and 10g / L glucose is added as a supplementary carbon source. Under the conditions, the dissolution rate of blue-green algae by the Klebsiella sp. reaches 100%.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com