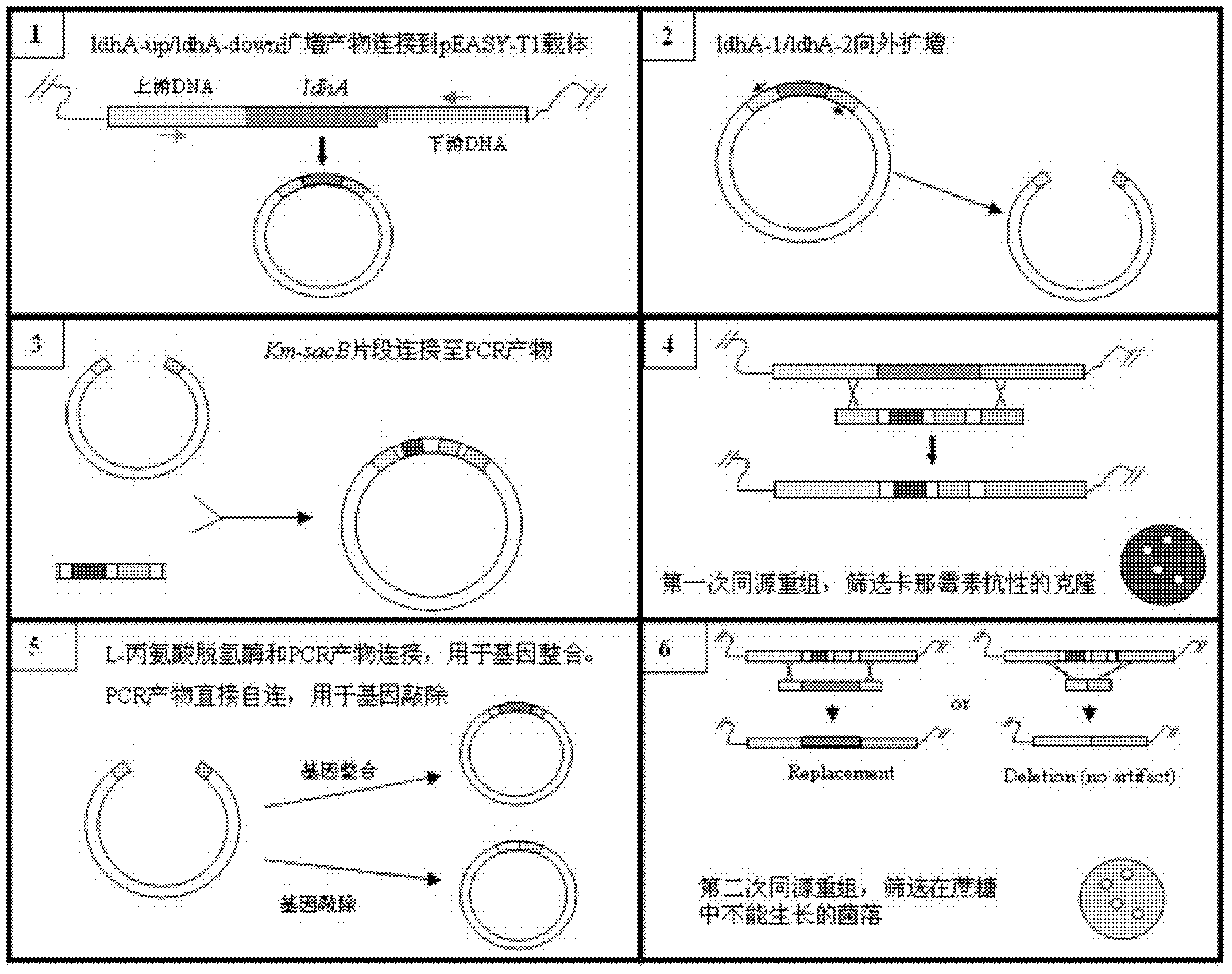
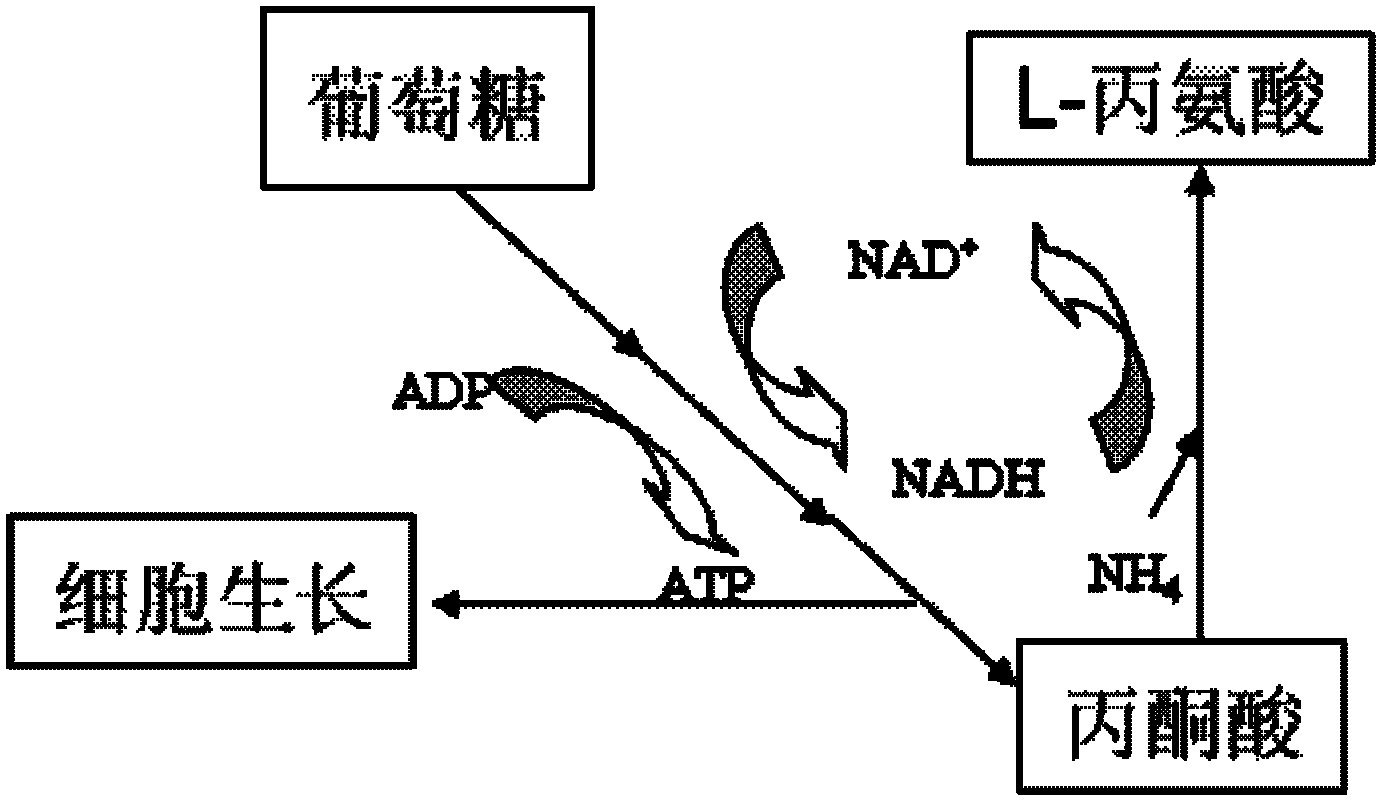
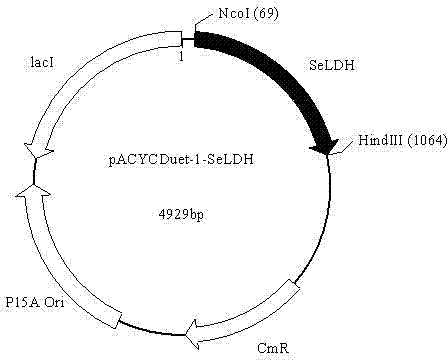
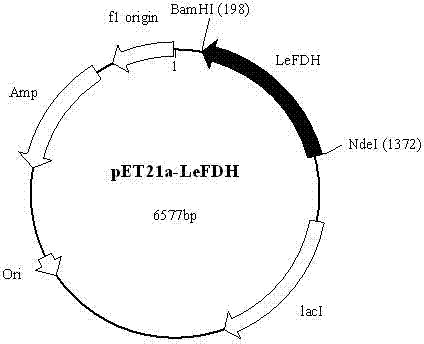
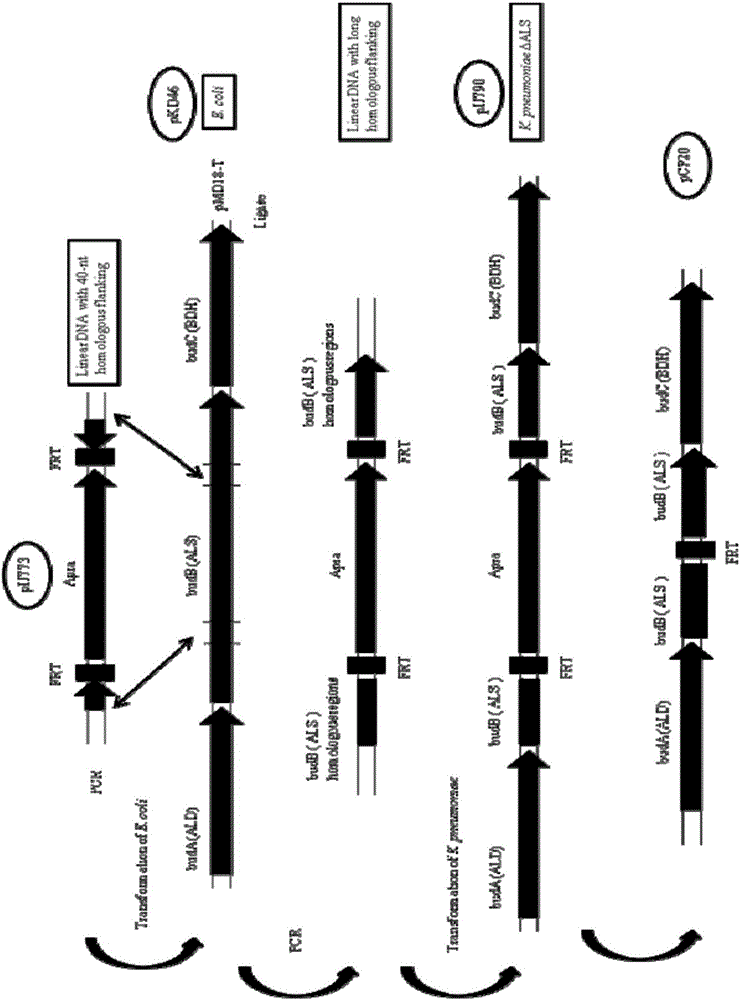
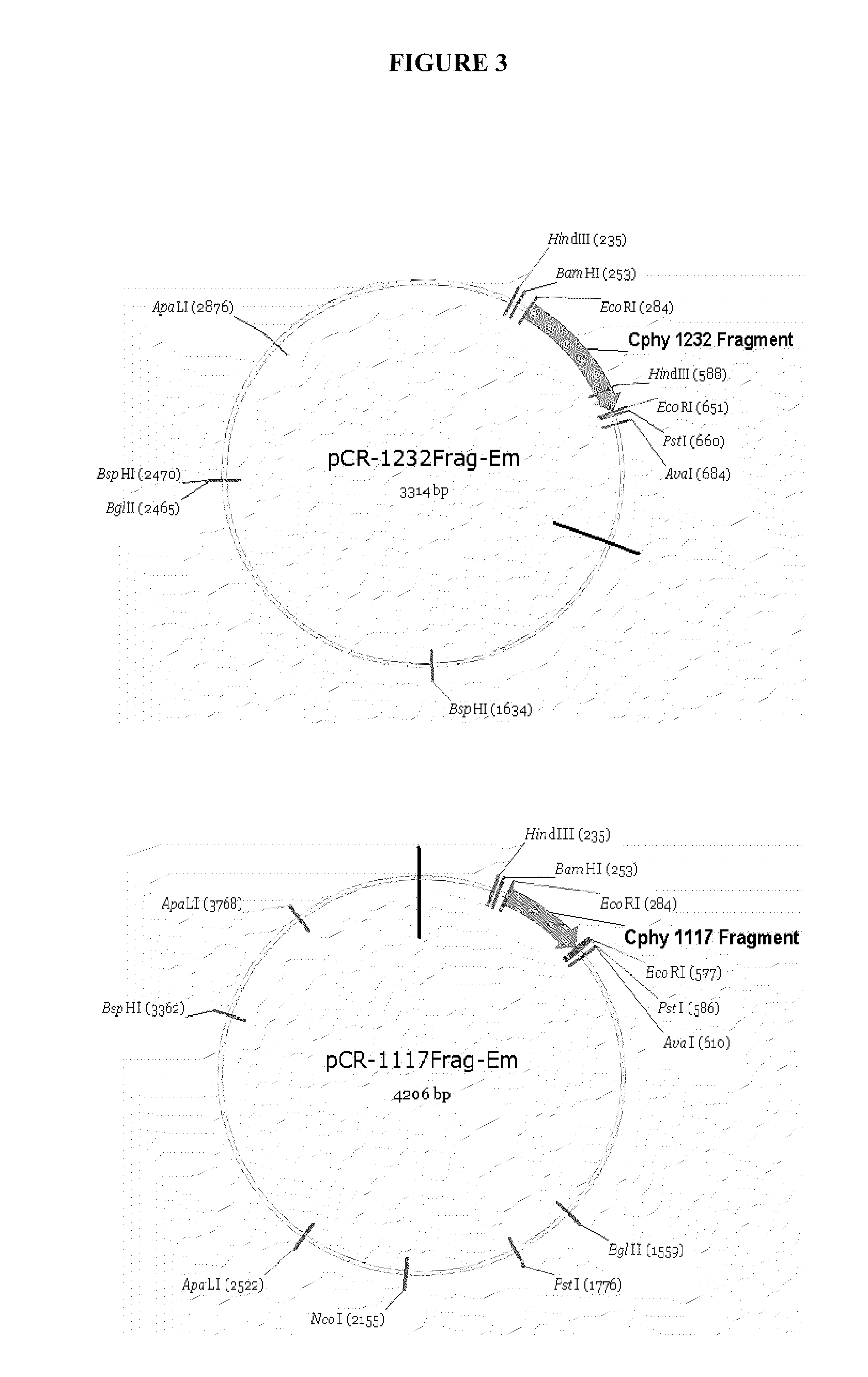
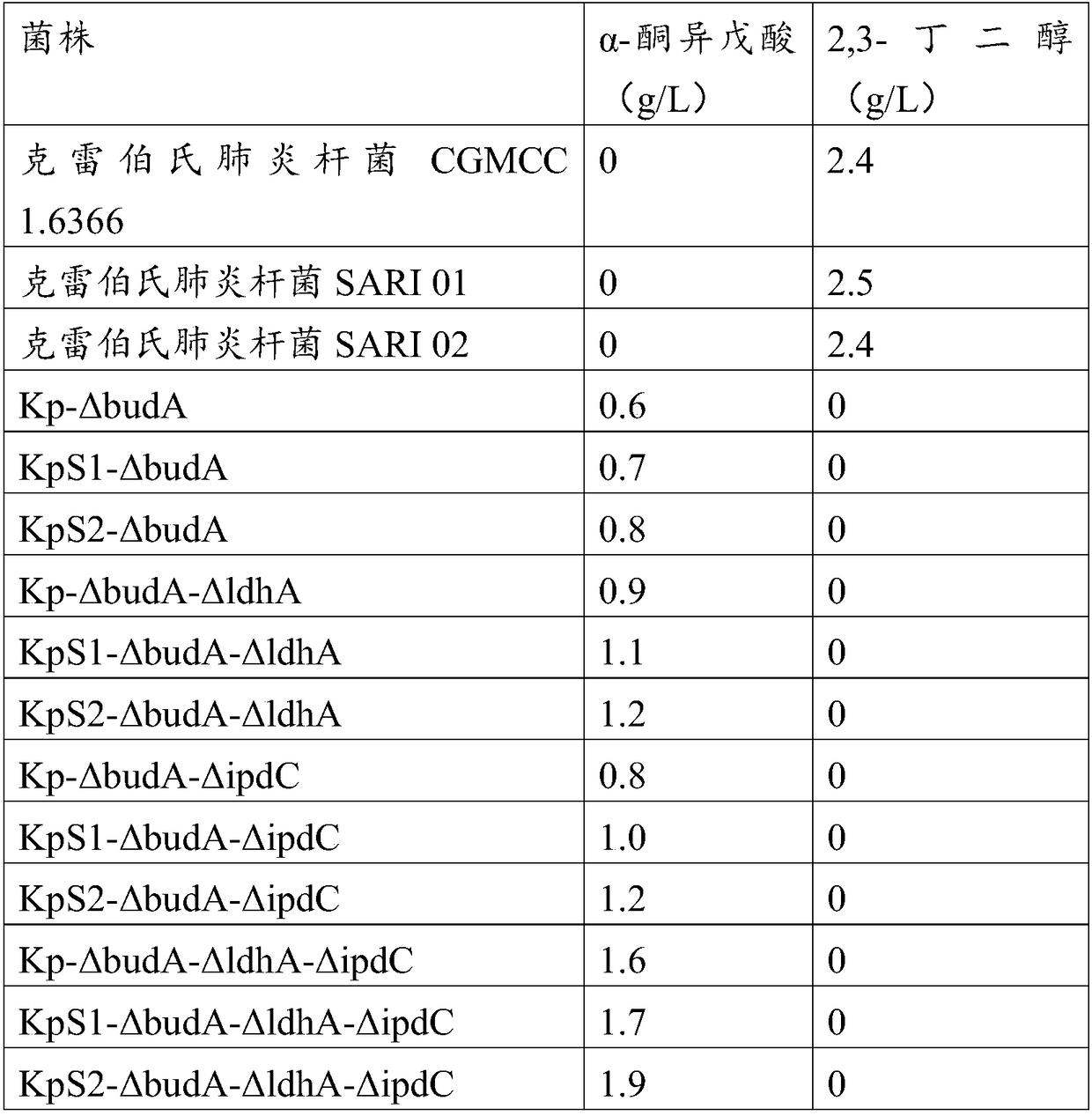
Patents
Literature
316 results about "Lactic dehydrogenase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition Lactate dehydrogenase, also called lactic dehydrogenase, or LDH, is an enzyme found in the cells of many body tissues, including the heart, liver, kidneys, skeletal muscle, brain, red blood cells, and lungs.
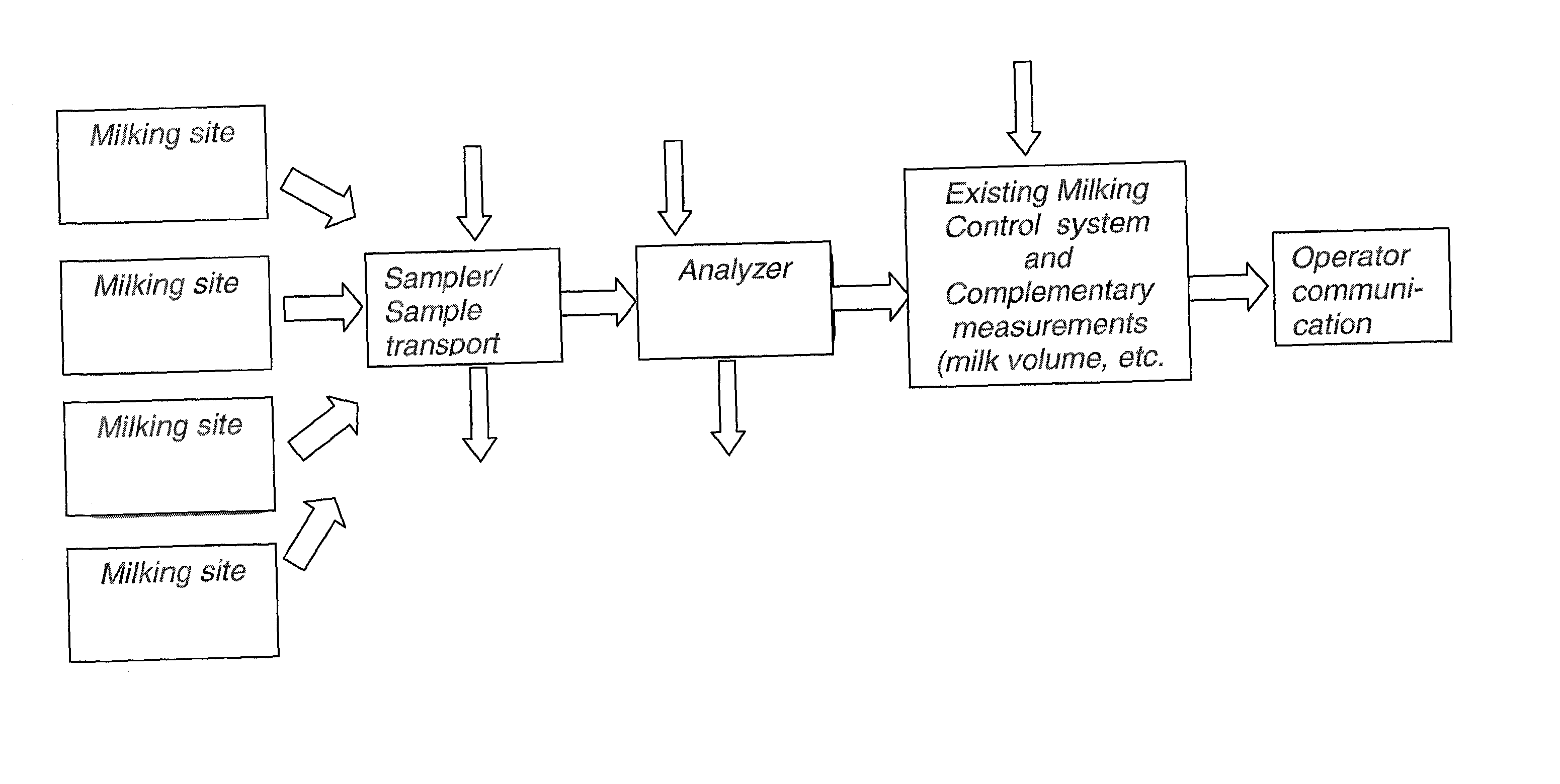
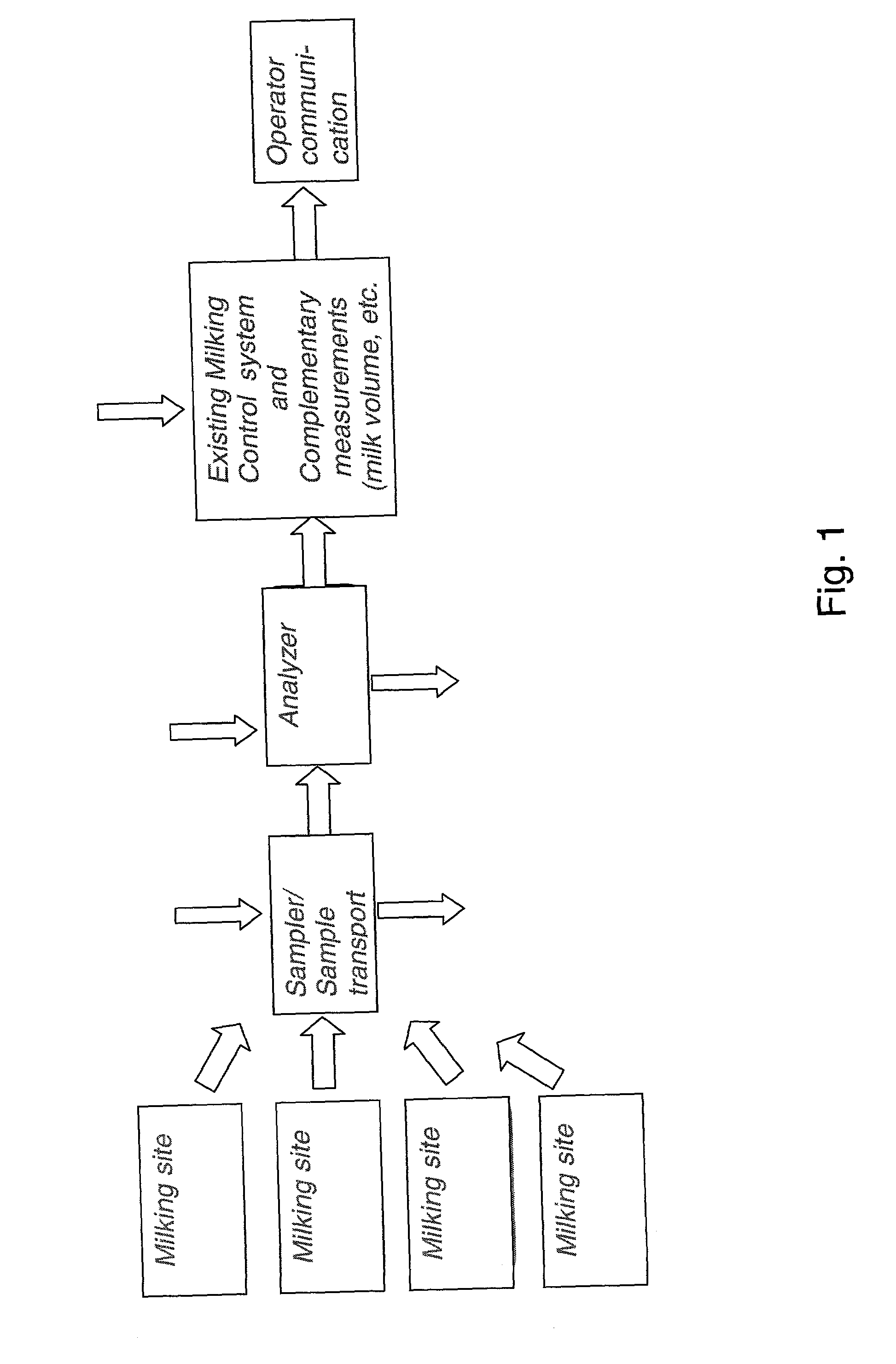
System for optimising the production performance of a milk producing animal herd
InactiveUS20020124803A1Excels in productivityImprove productivitySamplingCathetersReproductive cycleSteroid Compound
A system for optimizing the production performance of a milk producing animal herd is provided. The system comprises milk sampling means, analytical means comprising separate means for analyzing compounds or parameters that in the presence of compounds indicative of the physiological or nutritional condition of the herd member, generates detectable signals, and means for directing a part of the milk sample to each separate analyzing means which is controlled by data for the physiological and nutritional state of a herd member such that the directing means is only activated at pre-selected points in time or at pre-selected time intervals in the production and or lactation cycles. Specific compounds are compounds indicative of mastitis, including beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase (NAGase) E.C. 3.2.1.52 and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), protein balance, including milk urea nitrogen (MUN) and total protein, ketosis, including acetolactate, beta-hydroxybutyrate, acetone and lipids, fat and state in reproduction cycle, including a steroid or peptide hormone such as progesterone. Furthermore, the system comprises signal detection means for recording and processing the signals, means for data storage and data output means. Additionally there are provided methods for optimizing the production performance of a milk producing animal herd and an apparatus herefor.
Owner:LATTEC
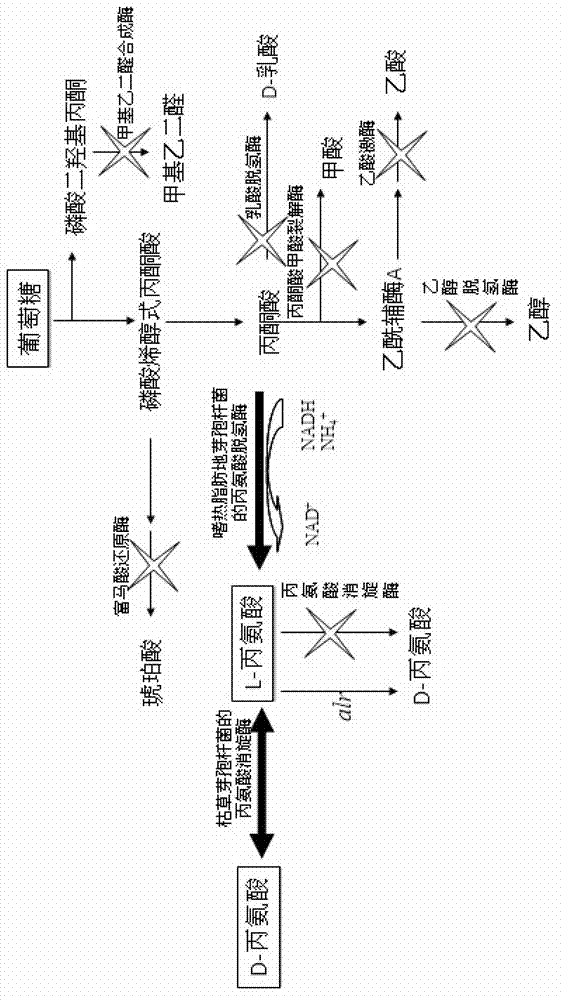
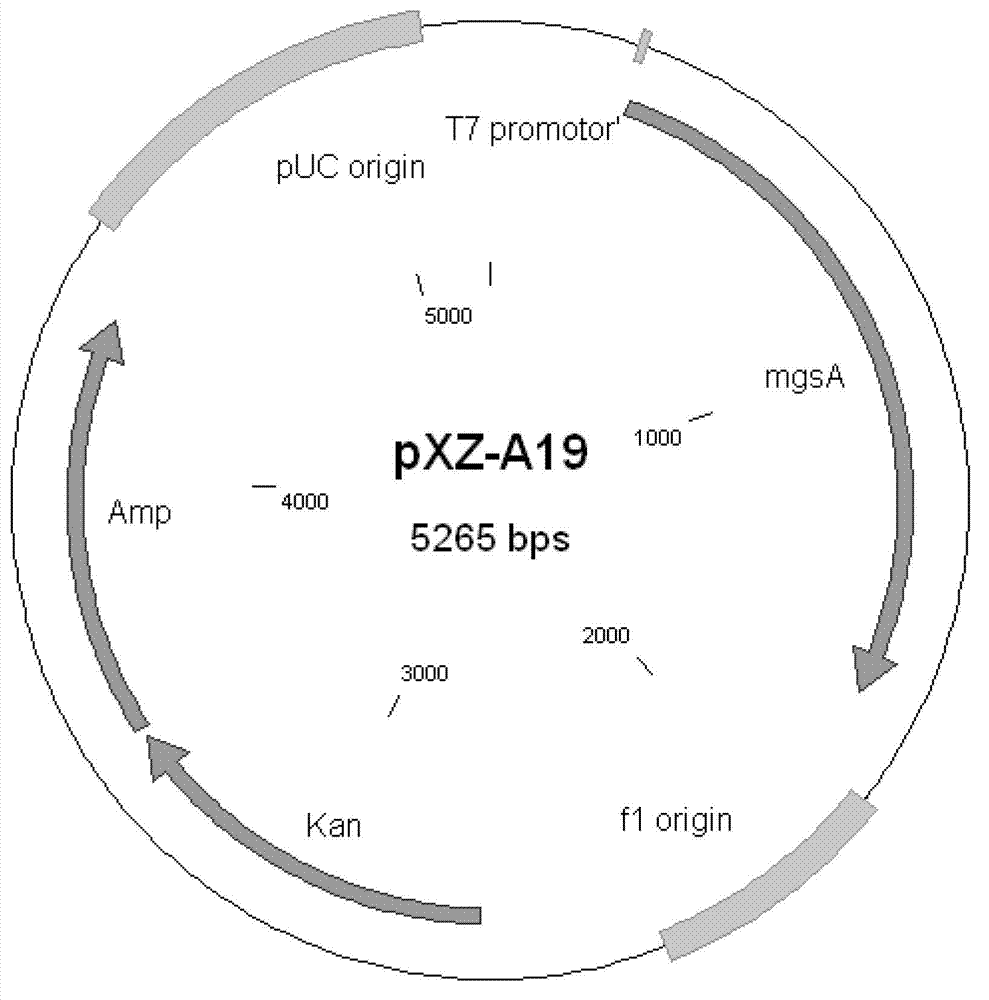
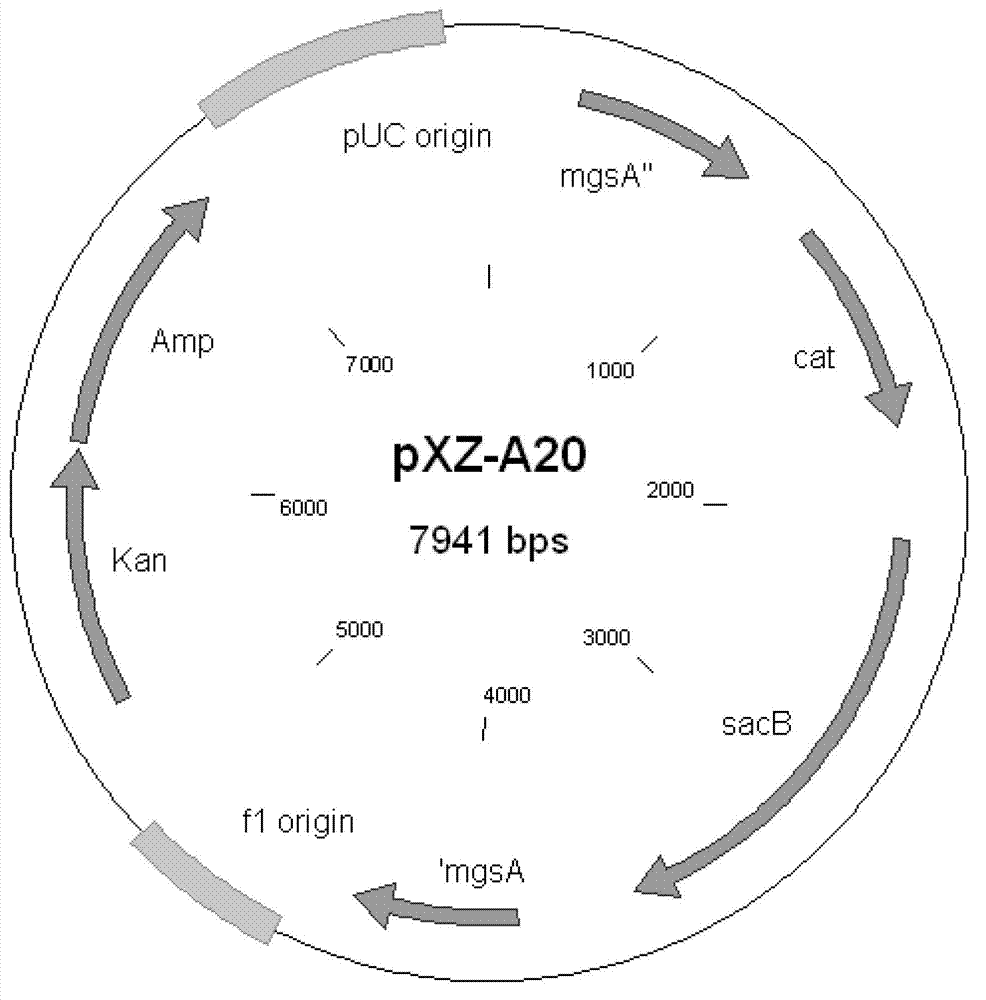
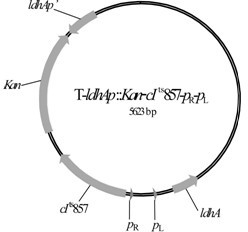
XZ-A26 bacterial strain for producing L-alanine with high yield as well as construction method and application of XZ-A26 bacterial strain
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Determination of blood ammonia content and blood ammonia diagnostic reagent kit
InactiveCN1778963AStrong specificityImprove test accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood ammoniaChemistry
The invention is about a method of measuring the content of blood ammonia, and it also concerns the reagent box of blood ammonia diagnosis. This invention belongs to the field of medical testing and measuring technology. The reagent box is consisted of buffer solution, 2ú¡ketoglutarate, reduced coenzyme, adenosine triphosphate, phosphoenolpyruvate, glutamate dehydrogenase, glutamate kinase, pyruvate kinase, lactate dehydrogenase and stabilizer. Firstly, we cause an enzyme-coupled reaction through mixing the sample and the reagent according to a certain proportion of volume; secondly, put the final reactant under the biochemical analyzer and test the absorbance variational situation (speed) of dominant wavelength; then we can get the content of blood ammonia. By using this invention, we can get the necessary measuring result with high sensitiveness and fine precision through biochemical analyzer, and the result would not be contaminated by material of internal and exogenous sources. Thus, this method can be conveniently promoted and applied.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Immobilized whole-cell catalyst and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN102260664ALow costEasy to operateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPtru catalystLisinopril
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology in the pharmaceutical industry, and discloses the preparation of an immobilized whole-cell catalyst and its application in the synthesis of a Puley intermediate (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-butyric acid. The recombinant cells containing the D-type lactate dehydrogenase gene and the formate dehydrogenase gene are established and fixed to prepare the immobilized whole cell catalyst. Using this catalyst to synthesize the intermediate (R)-2-hydroxy-4-phenyl-butyric acid of lisinopril, the reaction conditions are mild, the action is specific, and there are no by-products. It is used in medicine and food industries. value.
Owner:SYNCOZYMES SHANGHAI
Methods for the synthesis of lactic acid using crabtree-negative yeast transformed with the lactate dehydrogenase gene
InactiveUS7229805B2Considerable purificationSimpler and less-costlyFungiBiofuelsLactate dehydrogenaseTrichosporon
The invention provides methods and materials related to the production of lactic acid. Specifically, the invention provides methods for producing lactic acid using a crabtree-negative yeast, such as of the Kluyveromyces, Pichia, Candida, Trichosporon and Yamadazmya genera, which have been transformed with a lactate dehydrogenase gene.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Stable kit for detecting homocysteine
ActiveCN104198726AThe test result is accurateHigh sensitivityBiological testingPreservativeSurface-active agents
The invention provides a stable kit for detecting homocysteine. The stable kit consists of a reagent R1 and a reagent R2, wherein the reagent R1 comprises the following components: a buffering solution, a mercaptan reducing agent, lactic dehydrogenase, serine, reducing coenzyme, a surface active agent, a stabilizing agent and a preservative; and the reagent R2 comprises the following components: a buffering solution, cystathionine beta-synthase, cystathionine beta-synthase, a surface active agent, a stabilizing agent and a preservative. The stable kit provided by the invention can detect the homocysteine in serum by utilizing an enzymatic cycling method, is easy to operate, and is fast, accurate, sensitive and stable.
Owner:上海睿康生物科技有限公司
Sialidase detection kit
InactiveCN102399851ASolve complexityFix stability issuesMicrobiological testing/measurementSialidasePreservative
The invention provides a sialidase detection kit. The kit comprises a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises the components of buffer solution, neuraminidase, lactic dehydrogenase, surfactant, stabilizer and preservative; and the reagent 2 comprises the components of buffer solution, reducing coenzyme, neuraminic acid aldolase, stabilizer and preservative. The kit has accurate detection and low cost and is convenient, applicable, stable and reliable.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
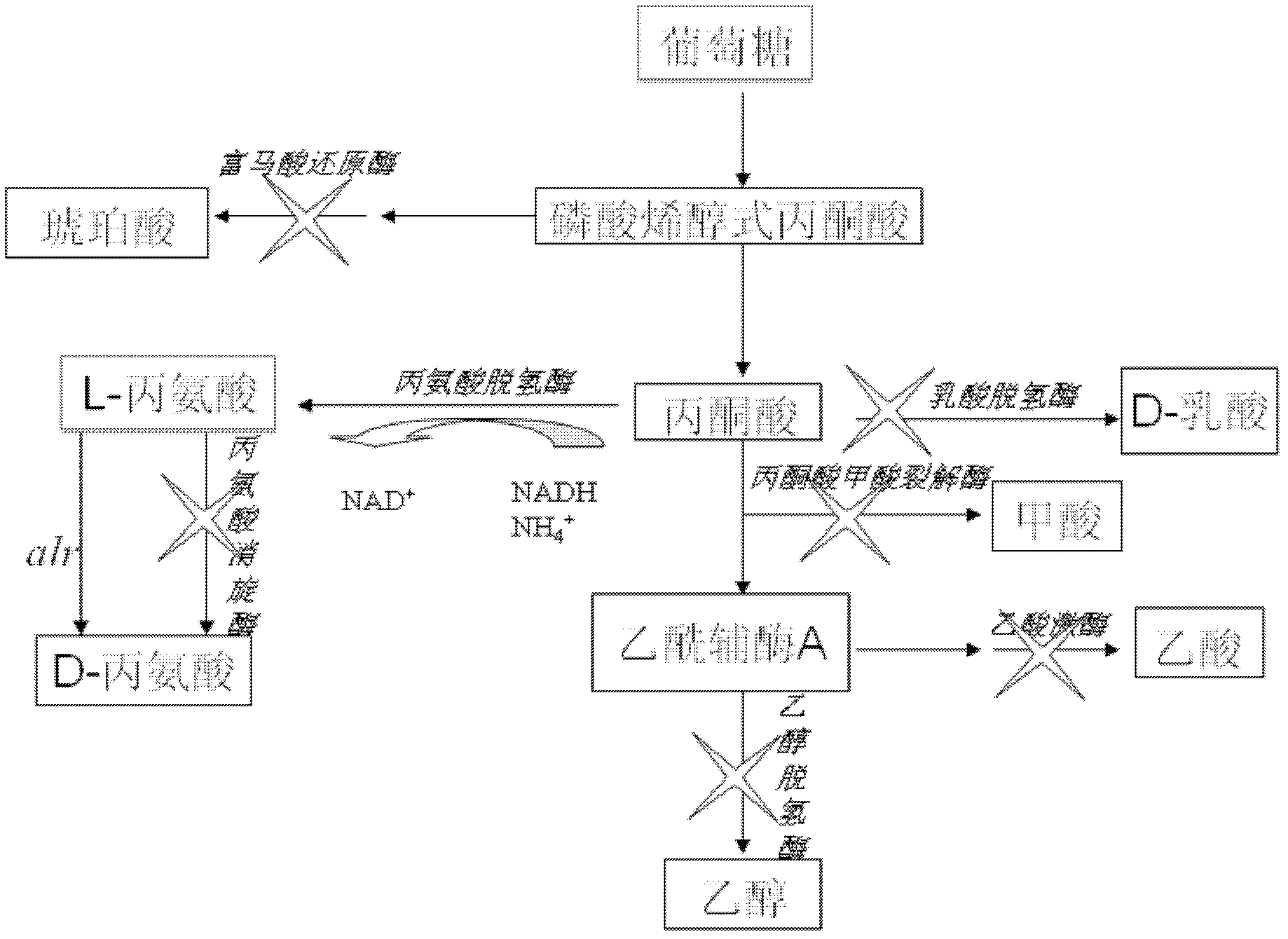
Engineering bacteria producing DL-alanine and method of producing DL-alanine by using engineering bacteria
ActiveCN103045528AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEthanol dehydrogenaseAlanine racemase
The invention discloses a strain of engineering bacteria producing DL-alanine. Lactic dehydrogenase, pyruvate formate lyase, alcohol dehydrogenase, acetic acid kinase, fumaric acid reductase, alanine racemase and methyl glyoxal synthetase of the strain of engineering bacteria producing the DL-alanine are inactivated; and exogenous L-alanine dehydrogenase gene and alanine racemase gene are integrated on the chromosome of the engineering bacteria. According to the invention, pyroracemic acid, an intermediate product of the glycolysis is converted to L-alanine by integrating the exogenous L-alanine dehydrogenase gene into the chromosome of the engineering bacteria; and an exogenous alanine racemase gene is further integrated into the chromosome, and part of the L-alanine is converted into D-alanine. Then producing the DL-alanine from raw material sugar in one step is realized, the production period of the DL-alanine is decreased and the productivity of the DL-alanine is enhanced.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
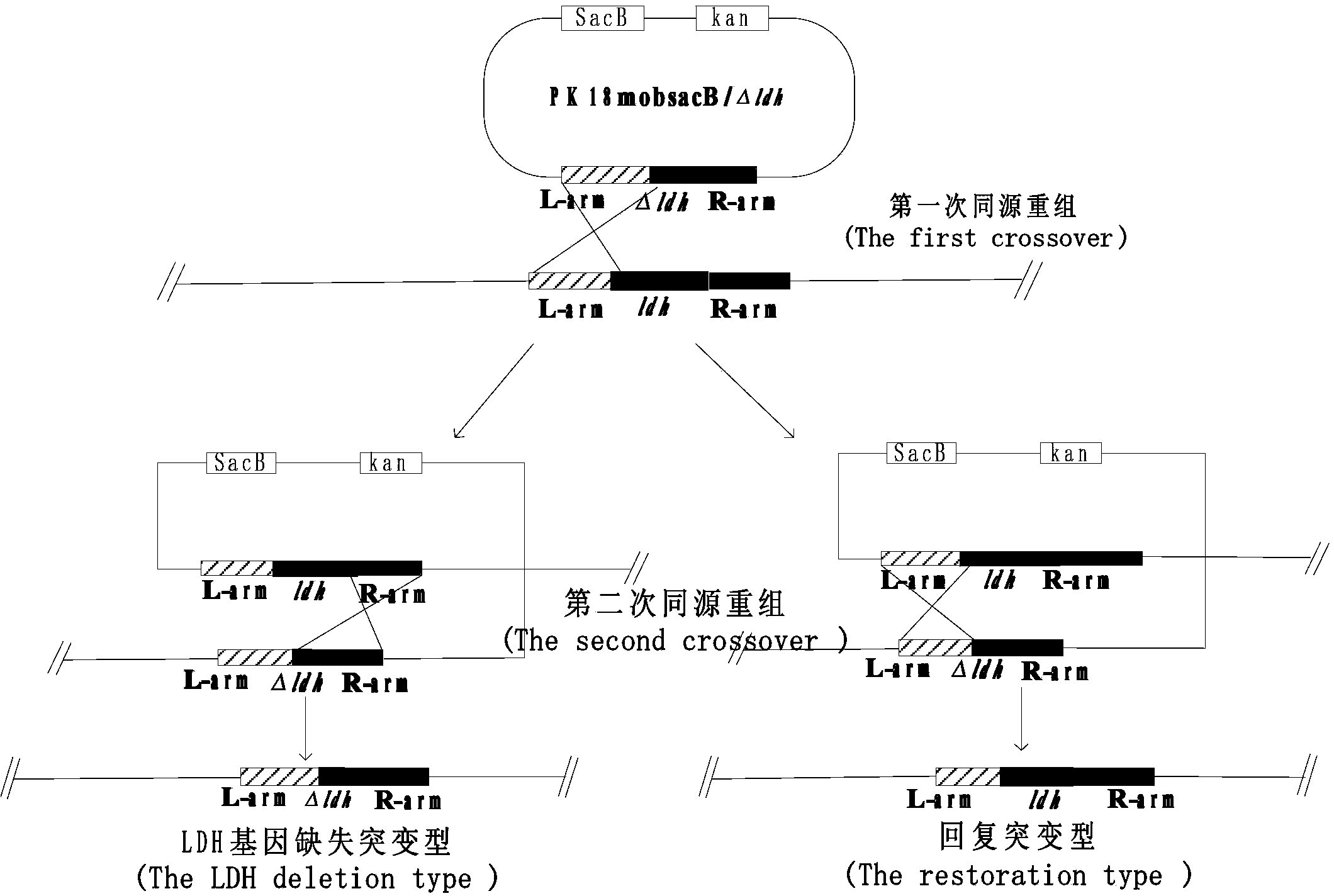
Strain producing dynamic controlling recombinant strain and method for preparing D-lactic acid with recombinant strain
ActiveCN102618478AHigh optical purityHigh yield and high optical purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
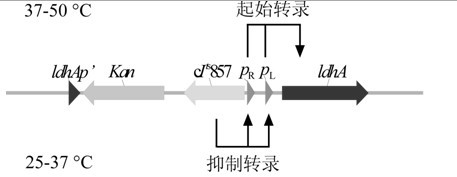
A Strain producing dynamic controlling recombinant strain and a method for preparing D-lactic acid with the recombinant strain belong to the technical field of genetically engineered agricultural microorganisms. The recombinant strain is named (Escherichia coli)B0013-070B, and is preserved in the China center for type culture collection, and the preservation number is CCTCCNO:M2012071. A lactate dehydrogenase gene promoter ldhAp in the genome of the strain is replaced with a culture environment / nutritional factors control-type promoter. Through the utilization of the recombinant strain, fermentation is conducted for 28 to 40 hours in stages at 25 to 50 DEG C, and the level of producing D-lactic acid reaches 12.5%; the optical purity lives up to 99.9%; and the chemical purity reaches to 98.4%. The dynamic controlling to the D-lactic acid dehydrogenase encoding gene expression on D-lactic acid high-producing strain B0013-070 chromosomes is conducted, so that the gene expression is controlled only through changing the fermentation temperature during the D-lactic acid production process to achieve the purpose of efficiently synthesizing D-lactic acid through taking glucose as a raw material. After simple modification, the invention can be used for producing important microbial metabolites in other industries.
Owner:SHANDONG BAISHENG BIOTECH
Lactic dehydrogenase detection kit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102766677AAvoid interferenceReduce distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementPreservativeTurbidity
The invention discloses a lactic dehydrogenase detection kit and a preparation method of the kit. The kit disclosed by the invention consists of a reagent I and a reagent II which are independent each other, wherein the components of the reagent I comprise a biobuffer, a metal ion complex, a lactic dehydrogenase reactive substrate, a surfactant, a lactic dehydrogenase activity activating agent, a preservative and water; and the components of the reagent II comprise a biobuffer, a nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidation state, a surfactant, a preservative and water. The detection kit disclosed by the invention adopts a dual reagent mode to effectively avoid the interference of the nonspecific reaction and synchronously furthest reduce the interference of the sample turbidity, thereby guaranteeing the stable and reliable measurement result; and the detection kit has the advantages of good stability, high precision, wide linear testing range, good repeatability, and strong anti-interference performance and the like. In addition, the detection kit disclosed by the invention does not need to pre-dilute the sample in the detecting process, thereby being convenient for clinical use, simple and fast to operate, and suitable for an automatic biochemical analyzer.
Owner:WUHAN LIFE ORIGIN BIOTECH LTD
Application of antiplatelet thrombolysin in preparation of medicine for treating thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
PendingCN105833255ARecovery levelLower levelPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood disorderAnti plateletThrombasthenia
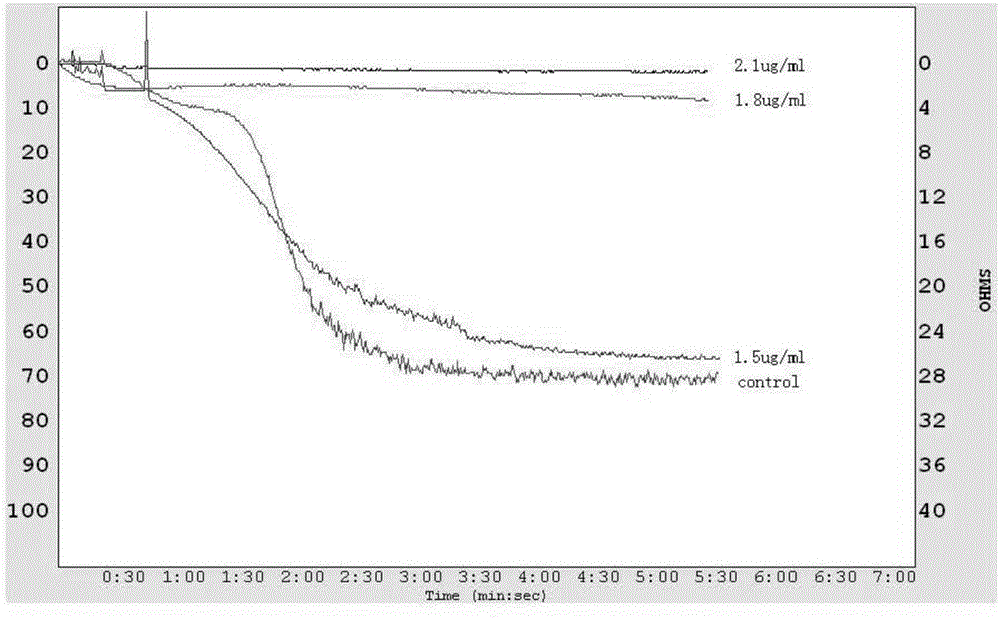
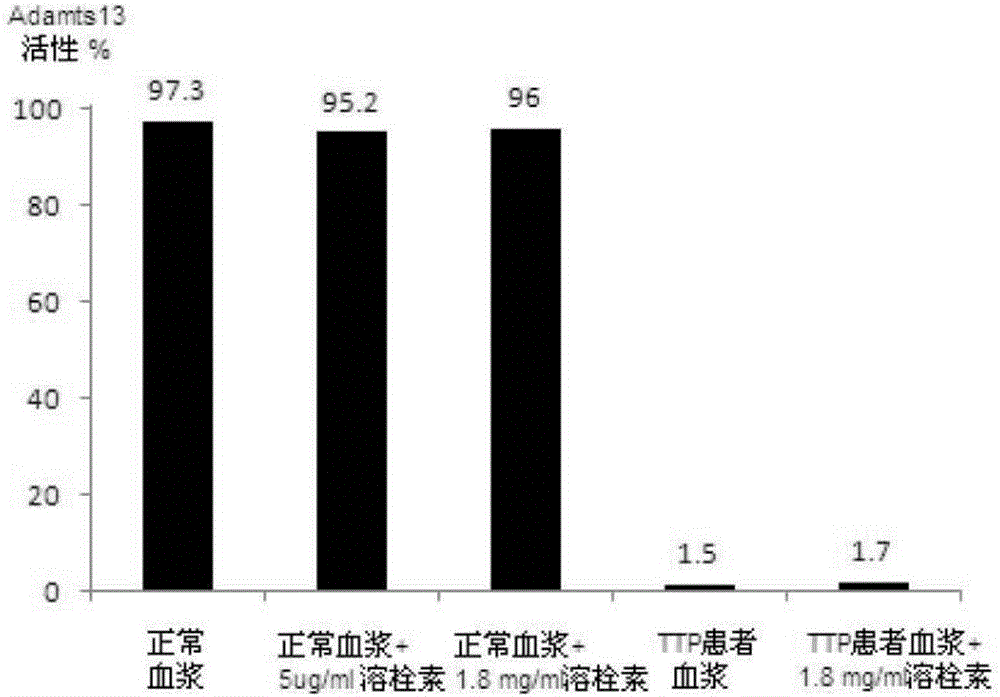
The invention relates to the field of medicines and especially relates to an application of antiplatelet thrombolysin in preparation of a medicine for treating thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). The antiplatelet thrombolysin limits adhesion and aggregation of platelets, recovers levels of the platelets, erythrocytes and hemoglobin, reduces level of lactic dehydrogenase and effectively inhibits thrombocytopenia and cleaved-cell hemolyticanemia, thereby treating the TTP. The antiplatelet thrombolysin has great clinical application prospect.
Owner:ZHAOKE PHARMA HEFEI
Application of Inonotus obliquus polysaccharide components in preventing and controlling chronic pancreatitis
InactiveCN105147717AIncrease contentReduce accumulationOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticAmylaseHydroxyproline
The invention discloses application of Inonotus obliquus polysaccharide components in preventing and controlling chronic pancreatitis and belongs to the technical field of medicaments. The Inonotus obliquus polysaccharide components are applicable to preventing and controlling chronic pancreatitis. The Inonotus obliquus polysaccharide components which are 0.4g / kg of mouse weight are effective in increasing the content of superoxide dismutase in pancreatic glands of mice with chronic pancreatitis and decreasing accumulation of malondialdehyde and meanwhile are capable of reducing IL-1Beta and IFN-Nu in serum, and effective in decreasing the contents of amylase and lactic dehydrogenase and decreasing synthetic hydroxyproline. An application method of Inonotus obliquus polysaccharide components alleviate the condition of chronic pancreatitis in terms of immunity and metabolic regulation; compared with methods such as accumulated heat and dyspepsia conditioning in traditional Chinese medicine and medicated analgesia and surgery in western medicine, the method has the advantages that no toxic or side effect occurs, surgical pain is avoided, a treatment course is short, treatment is safe and convenient, and the effect of preventing and treating chronic pancreatitis in mice is significant.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Immunochromatographic test strip for rapidly detecting malaria and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102087294AHigh sensitivityImprove test accuracyBiological testingAgainst vector-borne diseasesLap jointLatex particle
The invention discloses an immunochromatographic test strip for rapidly detecting malaria and a preparation method thereof. The test strip is formed by sticking a sample pad, a labeling pad, a coating membrane and absorbent paper to a substrate in sequence through lap joint, wherein colored latex particle labeled plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein II monoclonal antibody and non-plasmodium falciparum lactic dehydrogenase monoclonal antibody are coated on the labeling pad; the coating membrane comprises detection regions and a control region; the detection regions are coated by plasmodium falciparum histidine-rich protein II monoclonal antibody and non-plasmodium falciparum lactic dehydrogenase monoclonal antibody with epitopes different from the epitopes of the monoclonal antibodies on the labeling pad; and the control region is coated by an anti-mouse IgG (immunoglobulin G) monoclonal antibody. The test strip improves the accuracy and convenience of malaria screening, is simple and convenient to operate and has the advantages of rapidness, simpleness, convenience and intuition.
Owner:GUANGZHOU WONDFO BIOTECH
Method for producing phenyllactic acid through whole-cell transformation of phenylalanine
InactiveCN108277190AThe solution steps are cumbersomeLow resolutionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemical synthesisPhenylalanine
The invention discloses a method for producing a phenyllactic acid through whole-cell transformation of phenylalanine, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The method successfullyconstructs an L-amino acid deaminase, L-lactic dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase co-expressed strain. Phenyllactic acid of 30 g / L is produced through the whole-cell transformation of phenylalanine, and the transformation rate is 100%. The establishment of a whole-cell transformation system solves the problems of complicated steps, low yield and environment pollution in the chemical synthesis of the phenyllactic acid as well as the problem of low transformation rate in the production of the alpha-oxoglutarate through the enzymatic conversion, the phenyllactic acid is produced through a one-step method at high yield without pollution, and a certain theoretical foundation is laid for the subsequent industrial production.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain
InactiveCN106047916AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylasePhosphoric acid
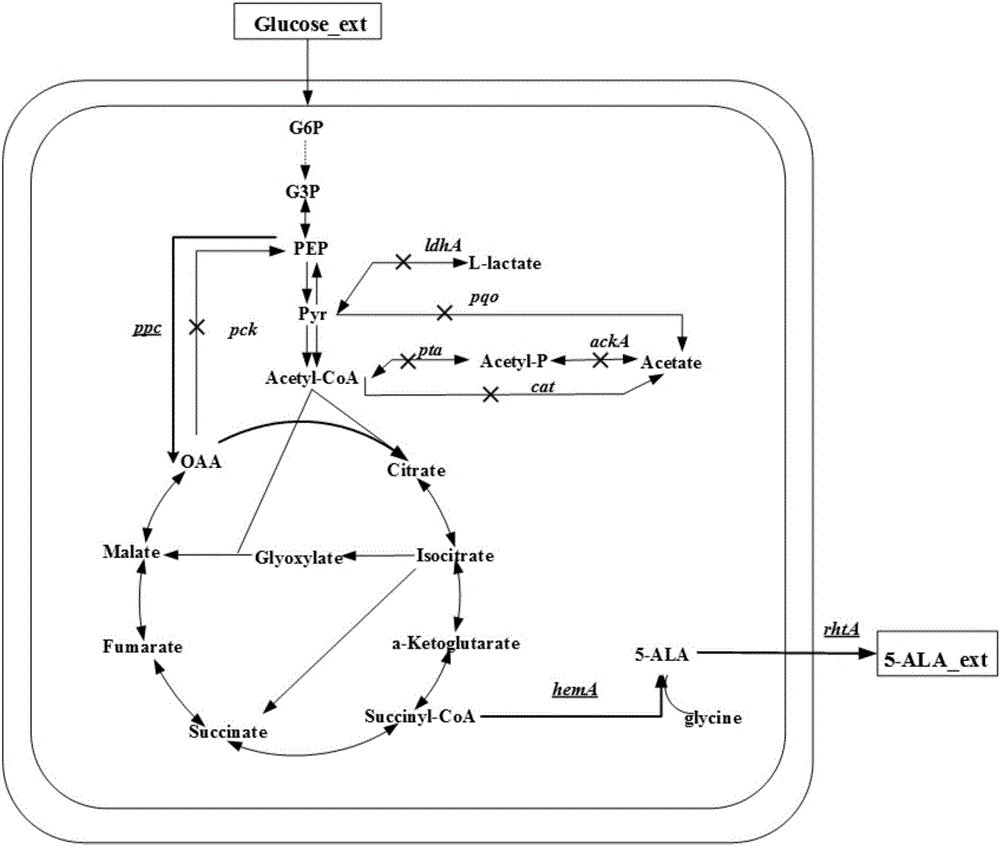
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum strain for production of 5-aminolevulinic acid and construction and application of corynebacterium glutamicum strain. A construction method includes: (1) deleting a lactic dehydrogenase coding gene 1dhA and acetic acid generation genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat in corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain a strain named CB4; inserting a strong sod promoter in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase coding gene ppc in the strain CB4 to obtain a strain CB5; deleting a gene pck in the strain CB5 to obtain a strain CB6; (2) transferring plasmid pXA and plasmid pEP2<tuf>-rhtA into the strain CB6. The strain constructed according to the method is capable of generating 2.78g / L 5-aminolevulinic acid in a culture medium with 10g / L glucose serving as a carbon source, which lays a foundation for subsequent continuous feeding of a fermentation tank to increase yield of the 5-aminolevulinic acid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Double-gene knockout engineering bacteria and construction method and application thereof in fermentation production of 1,3-propylene glycol
InactiveCN105936915AReduce synthesisIncrease percentageBacteriaTransferasesLactate dehydrogenaseMetabolite
The invention discloses double-gene knockout engineering bacteria and a construction method and an application thereof in fermentation production of 1,3-propylene glycol. A D-lactic dehydrogenase gene and an alpha-acetolactate synthetase gene in a genome of a wild type strain for production of 1,3-propylene glycol are knocked out to obtain the engineering strain; the wild type strain for production of 1,3-propylene glycol takes glycerol as a raw material for fermentation production of 1,3-propylene glycol. The engineering bacteria obtained after simultaneous knockout of the two genes of lactic dehydrogenase and acetolactate synthetase are applied in the process of fermentation-process production of 1,3-propylene glycol; the accounting proportion of 1,3-propylene glycol in a fermentation liquid in metabolites is increased, synthesis of lactic acid and 2,3-butylene glycol are simultaneously greatly reduced, and other by-products are not significantly increased. In the process of microbiological fermentation-process production of 1,3-propylene glycol, the role in improving the accounting proportion of 1,3-propylene glycol synthesized by the engineering bacteria and reducing the proportion of the synthesized by-products are played, the production cost is facilitated to be reduced, and the engineering bacteria have important application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
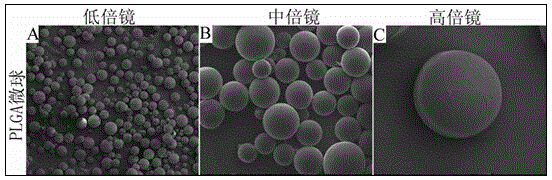
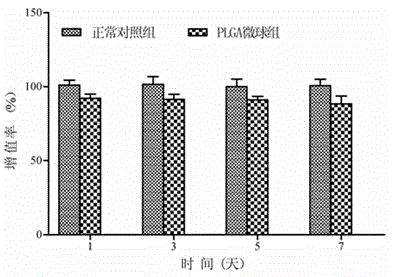
Blank PLGA microspheres and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104448356ANo toxicityDoes not affect growth activityProsthesisBiologic scaffoldPolyvinyl alcohol
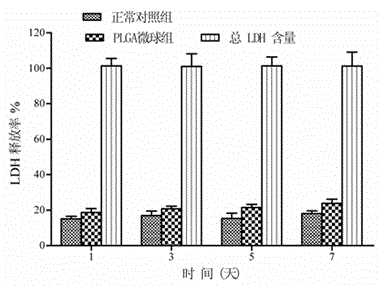
The invention provides blank polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer microspheres which are prepared by a water-oil-water emulsion process. The PLGA microspheres are prepared from PLGA powder by using excellent dissolving capacity of dichloromethane and emulsification of polyvinyl alcohol. Through representation observation and particle size determination of the microspheres, the diameter and the surface sign of a biological scaffold material are obtained; and the diameters of the PLGA blank microspheres accord with the injection size. Through CCK-8 determination and lactic dehydrogenase determination, the microspheres have no toxicity on attached mesenchymal stem cells, and do not affect the growth activity. Compared with chitosan particles, the microspheres are simple in preparation method, high in repetitive rate, clear structure, and easy to degrade in a living body, do not affect microenvironment metabolism, and can used as good cell carriers for different treatment targets in tissue regeneration engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods for the synthesis of lactic acid using crabtree-negative yeast transformed with the lactate dehydrogenase gene
The invention provides methods and materials related to the production of lactic acid. Specifically, the invention provides methods for producing lactic acid using a crabtree-negative yeast, such as of the Kluyveromyces, Pichia, Candida, Trichosporon and Yamadazmya genera, which have been transformed with a lactate dehydrogenase gene.
Owner:CARGILL INC
Lactic acid-producing engineering bacteria, constructing method thereof and application thereof
InactiveCN101886048ABreak through the bottleneck of productionBreak through the bottleneckFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyBacterial strain
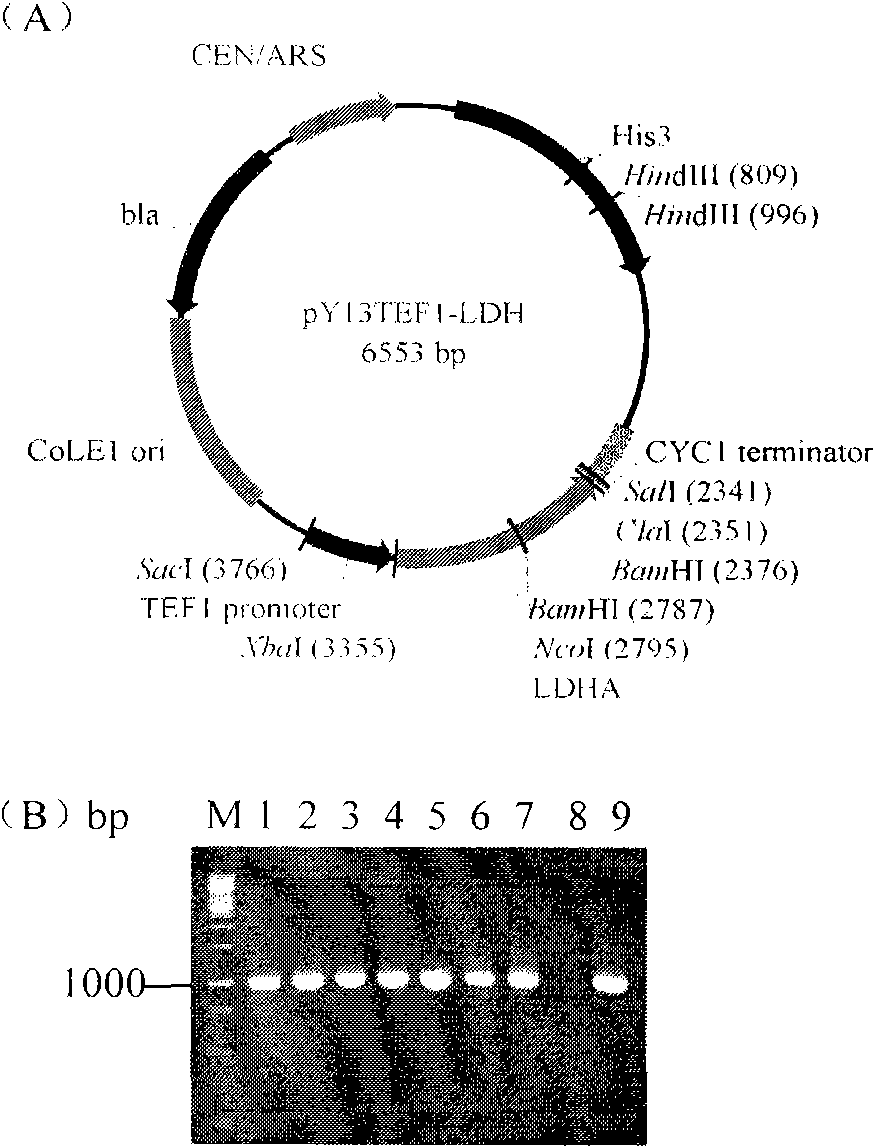
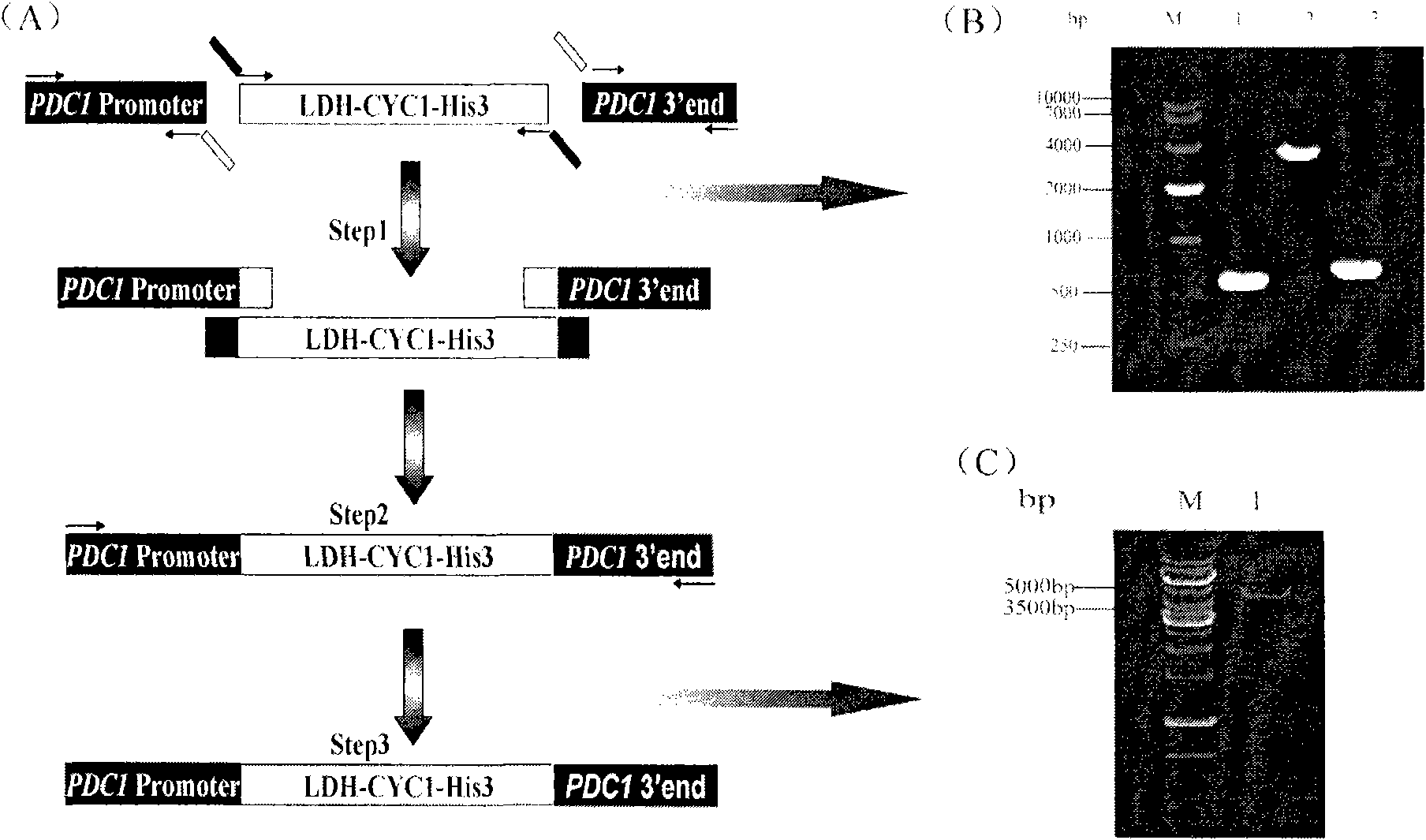
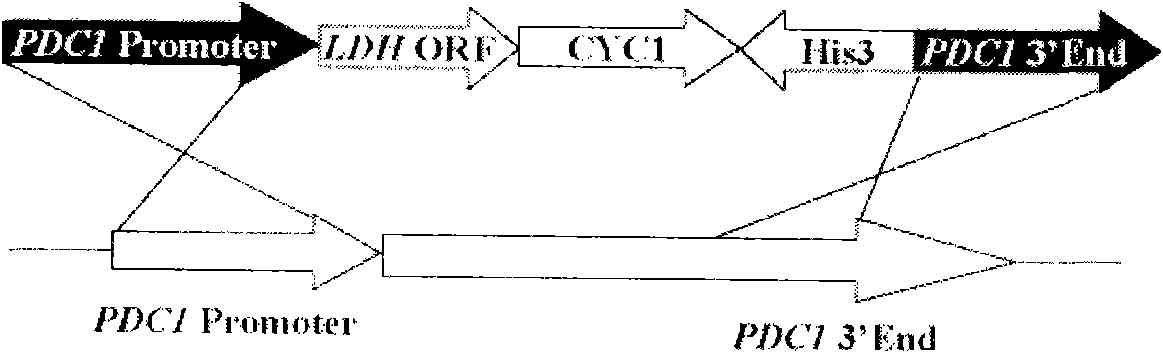
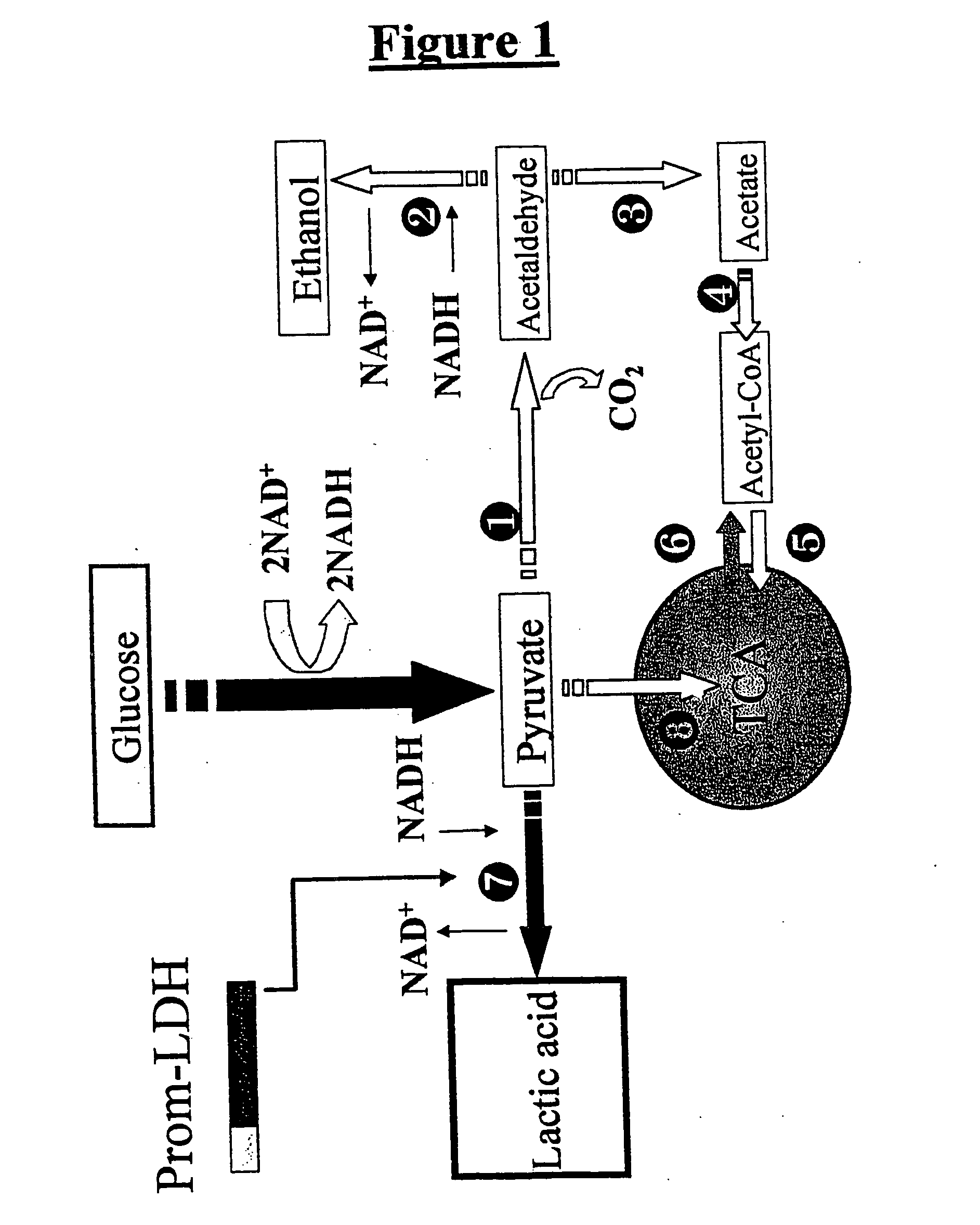
The invention discloses lactic acid-producing engineering bacteria, a constructing method thereof and application thereof, and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. In the genetic engineering bacterial strain provided by the invention, gene segments of lactic dehydrogenase (LDH), which are derived from Bovine, are integrated into S.cerevisiae genome by a homologous recombination method, and the pyruvic decarboxylase (PDC1) gene of the bacterial strain is silenced. The engineering bacterial strain obtained by constructing is used for fermenting and producing the lactic acid; after fermentation for 100 hours, the yield of the lactic acid reaches 15g / L, and the yield of ethanol is reduced by 45 percent less than a parent strain, namely 16.2g / L; and the engineering bacteria has a wide application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Yeast strains for the production of lactic acid
Yeast strains transformed with at least one copy of a gene coding for lactic dehydrogenase (LDH) and further modified for the production of lactic acid with high yield and productivities, are described.
Owner:TATE & LYLE INGREDIENTS AMERICAS INC
Reagent for detecting myocardial infarction and application of reagent
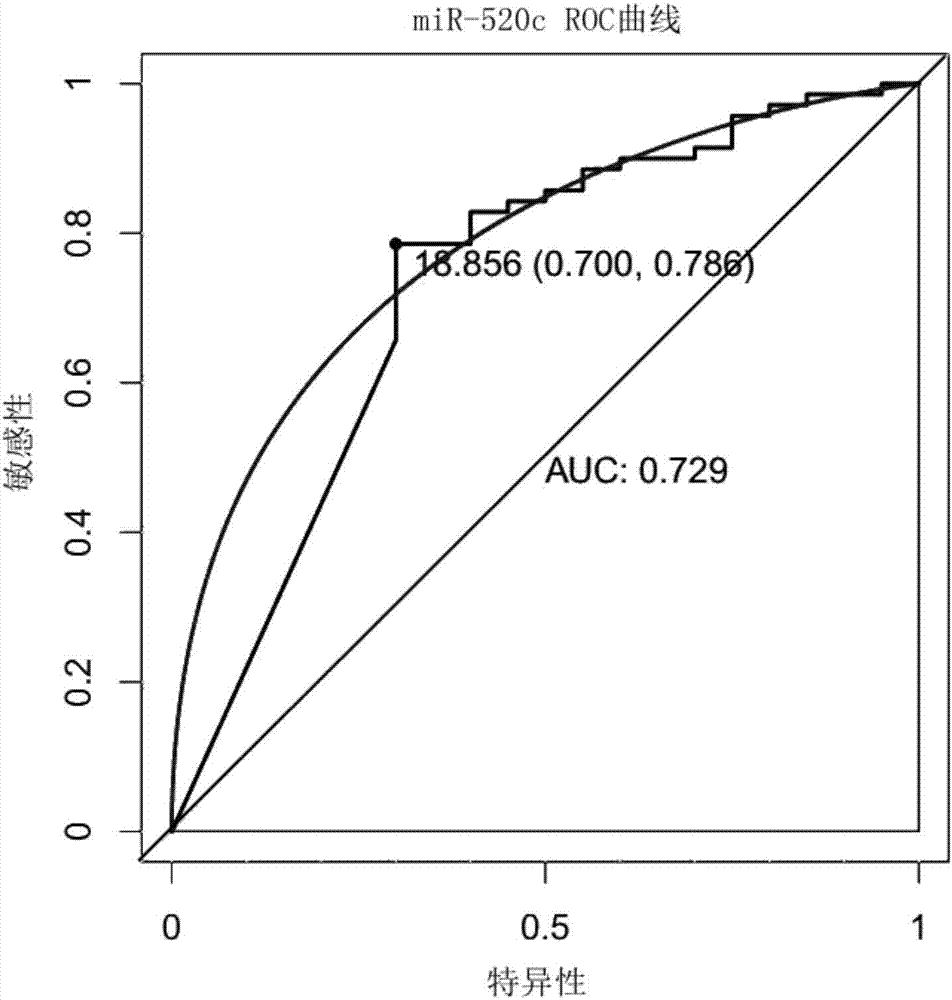
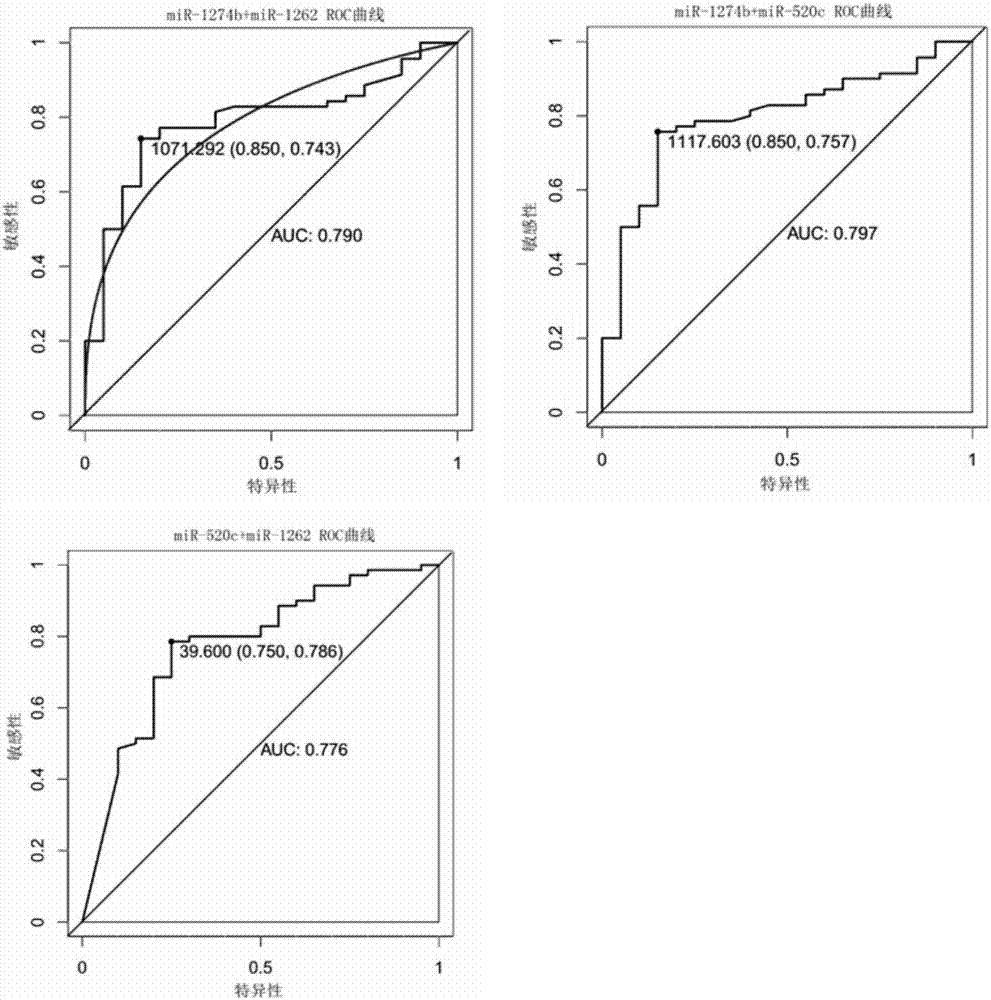
The invention relates to a reagent for detecting myocardial infarction and the application of the reagent and particularly relates to a reagent for detecting miR-520c and application of the reagent in preparing reagents for detecting myocardial infarction. Because of specificity, sensitivity and the like, conventional myocardial infarction diagnosis biochemical indexes such as creatine kinase, lactic dehydrogenase and myoglobin are limited in clinical application. On the basis of a high-flux sequencing method, a molecular marker miR-520c tightly associated with myocardial infarction is obtained. The molecular marker and conventional biochemical indexes are supplemented by each other, defects of single detection methods are overcome, and bases are made for precise clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Owner:QINGDAO MEDINTELL BIOMEDICAL CO LTD
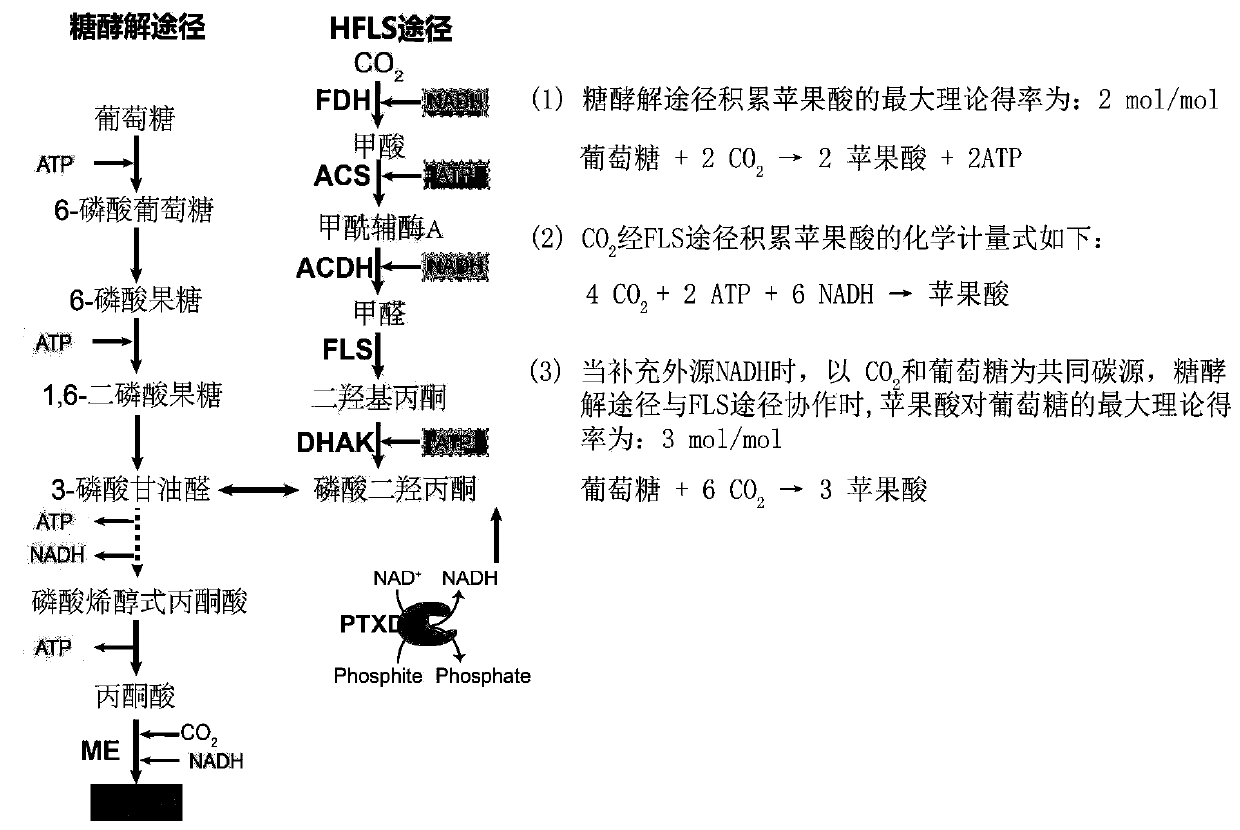
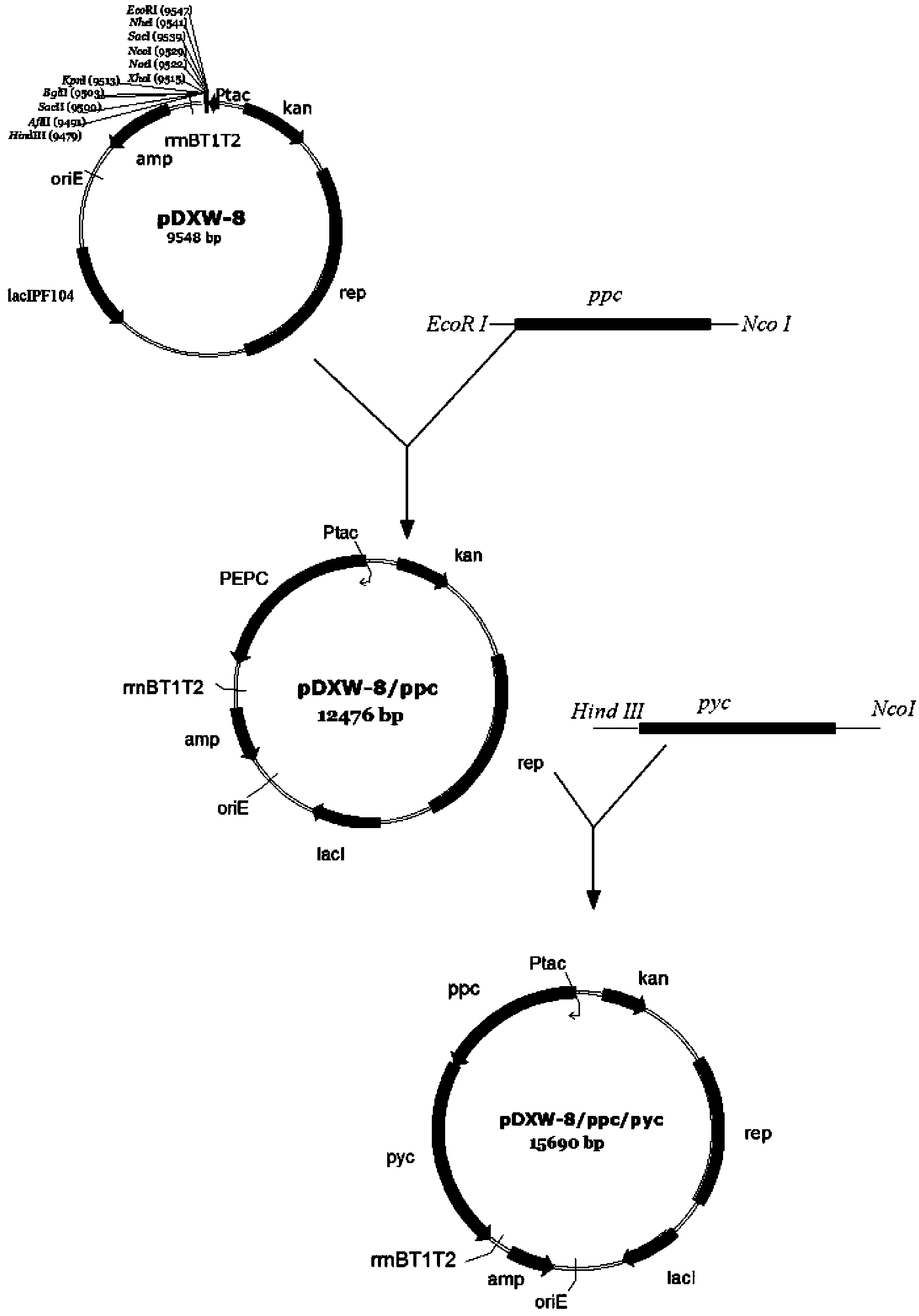
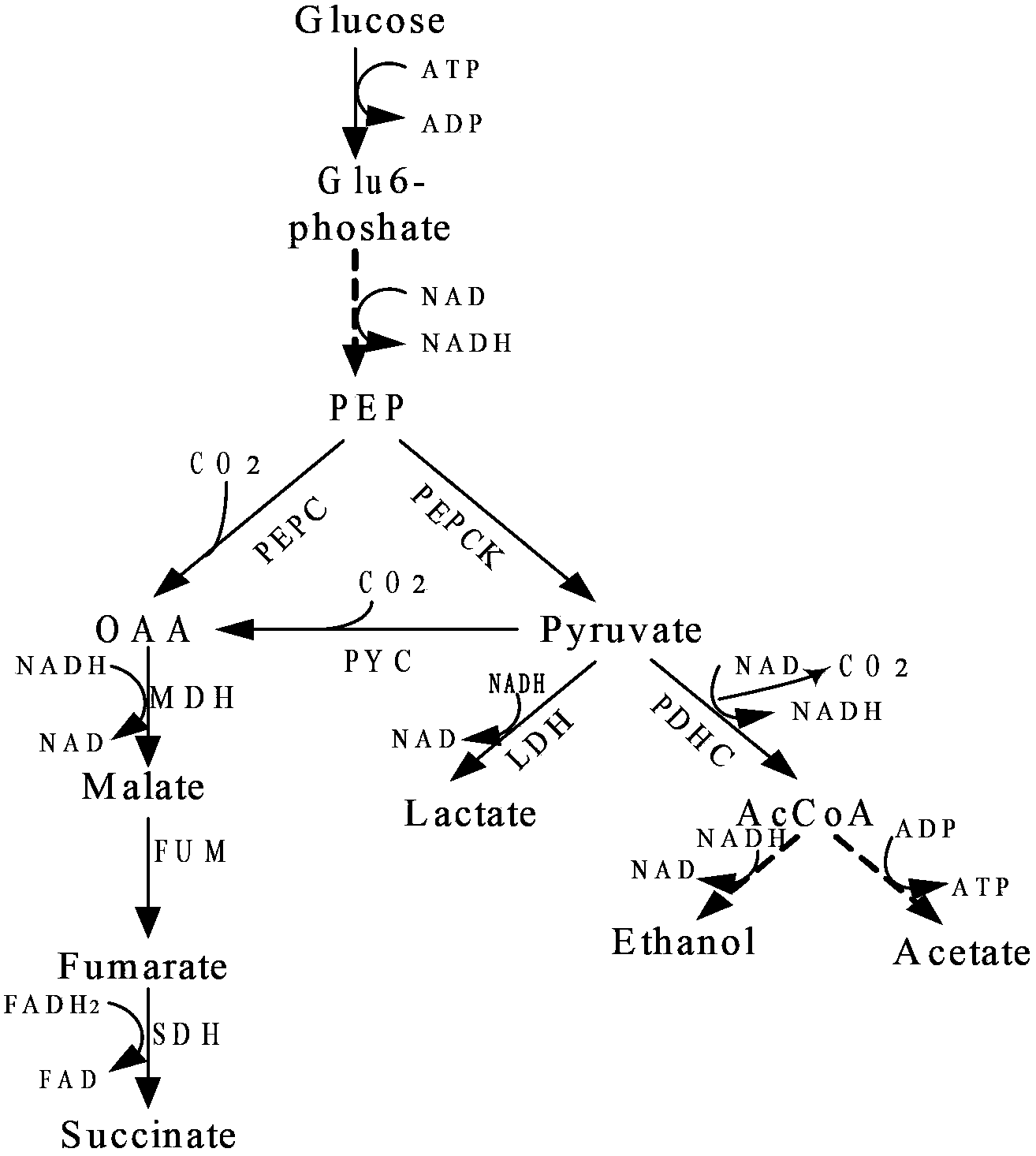
Construction and application of Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for immobilizing CO2 and producing malic acid
ActiveCN110951660APromote accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliPhosphorous acid
The invention discloses construction and application of Escherichia coli engineering bacterium for immobilizing CO2 and producing malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation. The engineeringbacterium is a strain obtained by carrying out gene engineering modification on Escherichia coli MG1655. The genetic engineering transformation is as follows: 1, knocking out a fumarate reductase gene, a fumarase gene, a lactic dehydrogenase gene and an ethanol dehydrogenase gene, and carrying out free over-expression on formate dehydrogenase, acetyl coenzyme A synthetase, acylated acetaldehyde dehydrogenase, formaldehyde lyase, dihydroxyacetone kinase, malic enzyme and phosphorous acid oxidordeuctase so as to obtain a strain GH0407. The strain is used for fermentation production of malic acid, CO2 and glucose are used as co-substrates for anaerobic fermentation for 72 h, the malic acid yield reaches 39 g / L, the yield is 1.53 mol / mol, and malic acid is not accumulated in an original starting strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
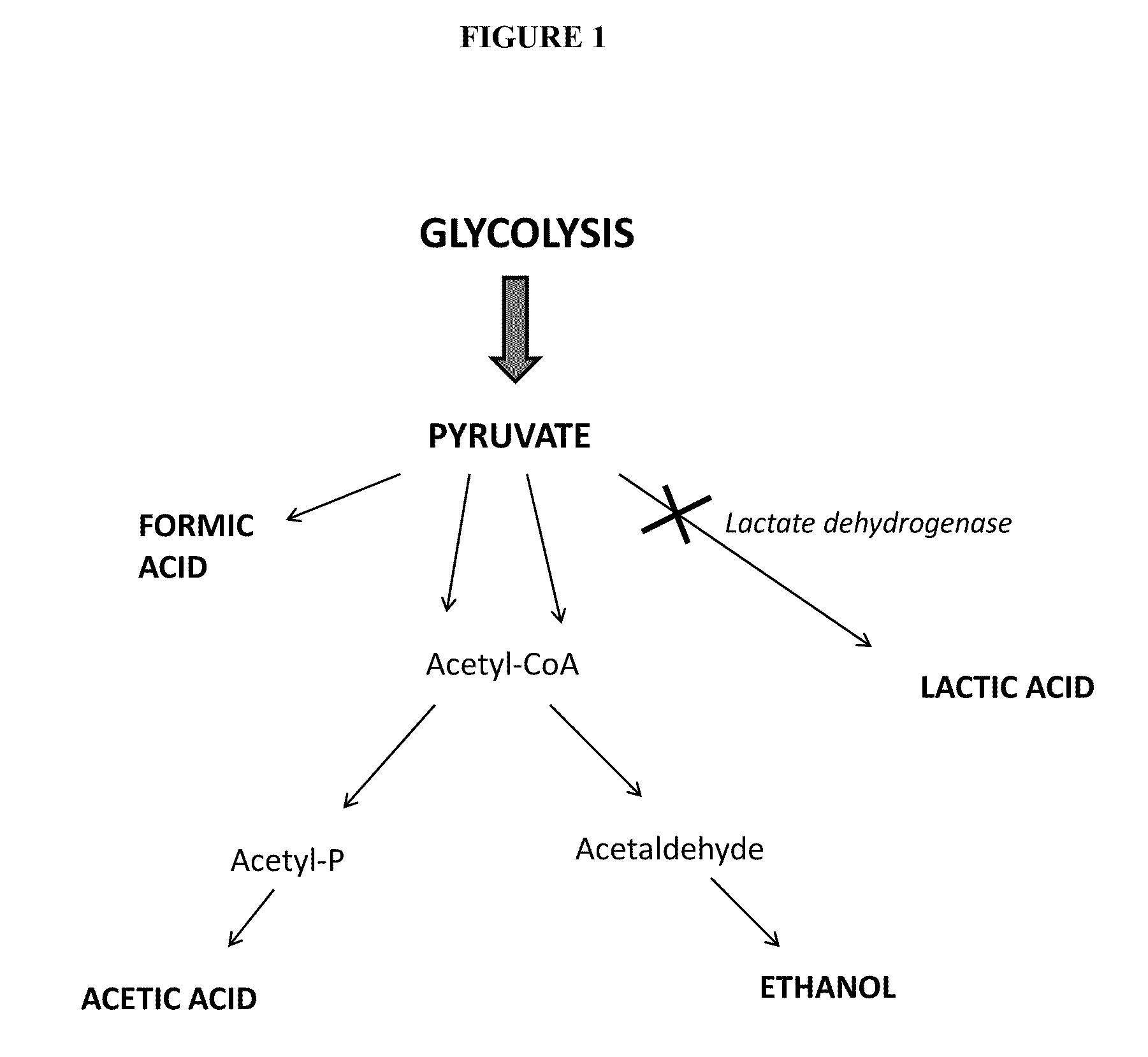
Microorganisms with inactivated lactate dehydrogenase gene (LDH) for chemical production
InactiveUS20110230682A1Reduced capacity to synthesizeIncrease productionBacteriaSugar derivativesLactate dehydrogenaseMicroorganism
This invention provides systems and methods for the increased production of ethanol and other chemical compounds by recombinant Clostridium species whereby the recombinant species are genetically-engineered to disrupt lactate dehydrogenase activity and to hydrolyze and ferment carbonaceous biomass and synthesize compounds of commercial value without production of lactic acid.
Owner:QTEROS INC
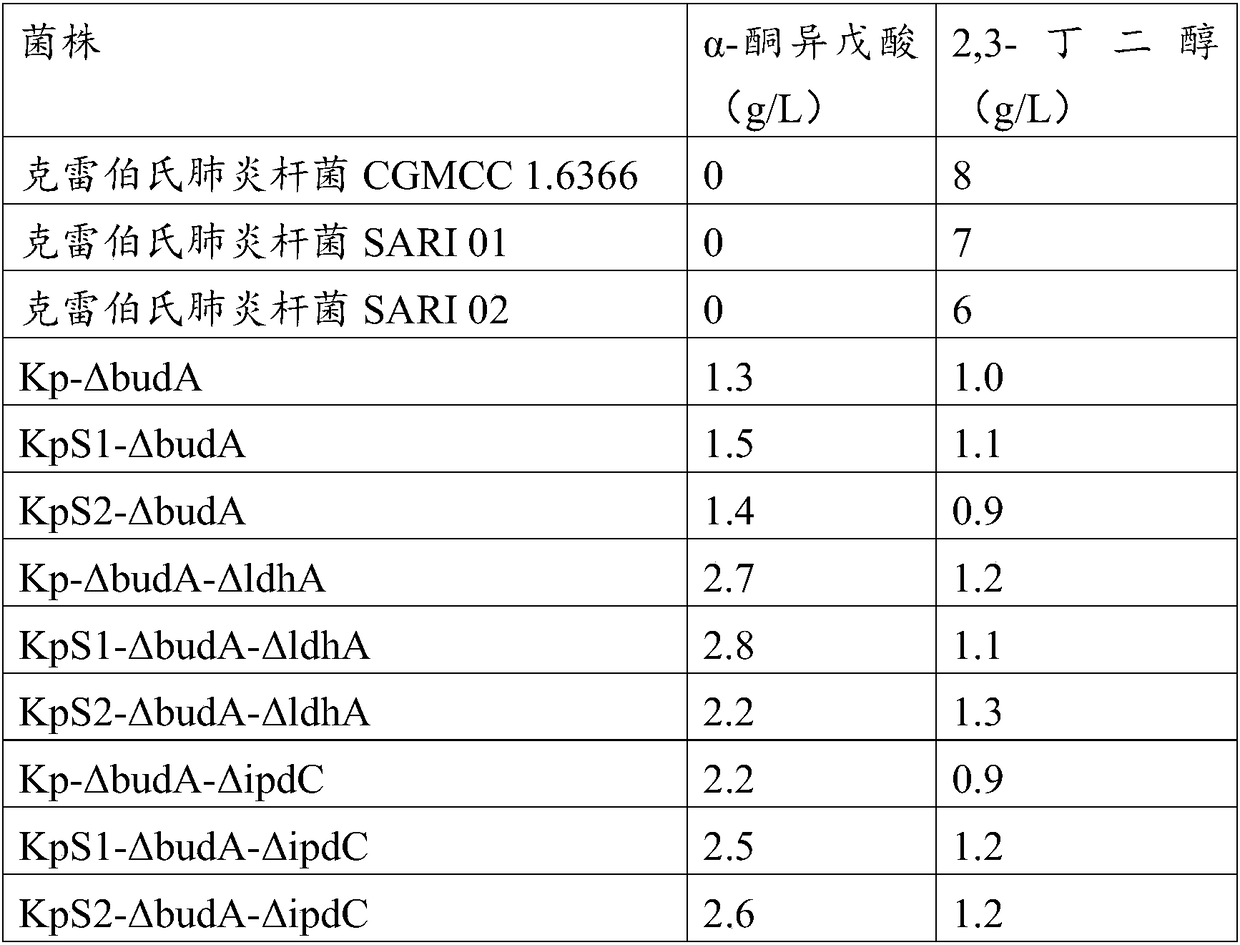
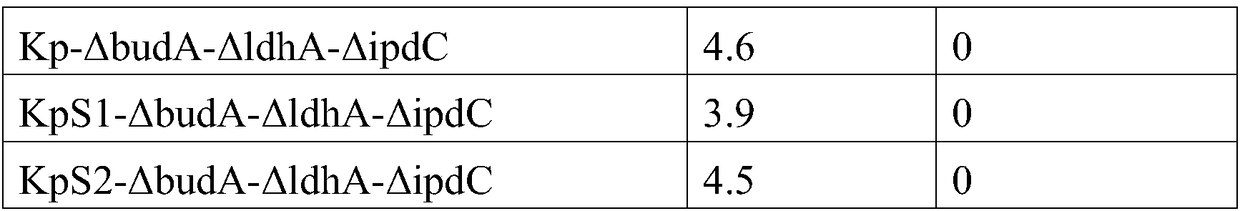
Method for improving alpha-ketoisovaleric acid yield of Klebsiella pneumoniae, and modified strain
ActiveCN108570438AHigh genetic stabilityRaw material conversion rate is highBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCarbon sourceAcetolactate decarboxylase
The invention discloses a method for improving the alpha-ketoisovaleric acid yield of Klebsiella pneumoniae, and a modified strain. The method comprises: inactivating acetolactate decarboxylase in Klebsiella pneumoniae, or simultaneously inactivating indole-3-pyruvate decarboxylase and / or lactate dehydrogenase, wherein the Klebsiella pneumoniae inactived with the enzyme is the modified strain; andinoculating the modified Klebsiella pneumoniae in a carbon source culture medium, and carrying out fermentation culture, wherein the carbon source in the culture medium is converted into alpha-ketoisovaleric acid by the modified Klebsiella pneumoniae during the fermentation culture. According to the present invention, with the method, the exogenous gene is not introduced into the modified strain,such that the strain has high genetic stability, the final concentration of the product is high, and the range of the raw material is wide.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Homocysteine diagnosis/determination reagent (kit) and homocysteine concentration determination method
InactiveCN101762517AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsEnzymatic ColorimetryWavelength
The invention relates to a homocysteine diagnosis / determination reagent (kit) using enzyme-colorimetry and enzyme-linked method technology. Meanwhile, the invention also relates to a homocysteine concentration determination method, reagent compositions and components, which belong to the technical filed of medical test and determination. The reagent (kit) of the invention mainly includes: buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, serine, cystathionine Beta synthase, cystathionine Beta catenase, lactic dehydrogenase and stabilizing agent; samples and reagent are mixed according to a certain volume ratio to generate a series of enzymatic reactions; then the reactants are arranged under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer to detect the decreasing degree of absorbance at the 340nm position of a dominant wave so as to measure and calculate the concentration of the homocysteine.
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Yeast and Method of Producing L-Lactic Acid
Yeast includes an introduced gene coding a Homo sapiens- or frog-derived L-lactate dehydrogenase.It is possible to produce lactic acid, which has a variety of applications, efficiently and more cost-effectively by using the yeast and the method of producing lactic acid by using the yeast.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Aspartate transaminase mitochondrial isozyme detection kit
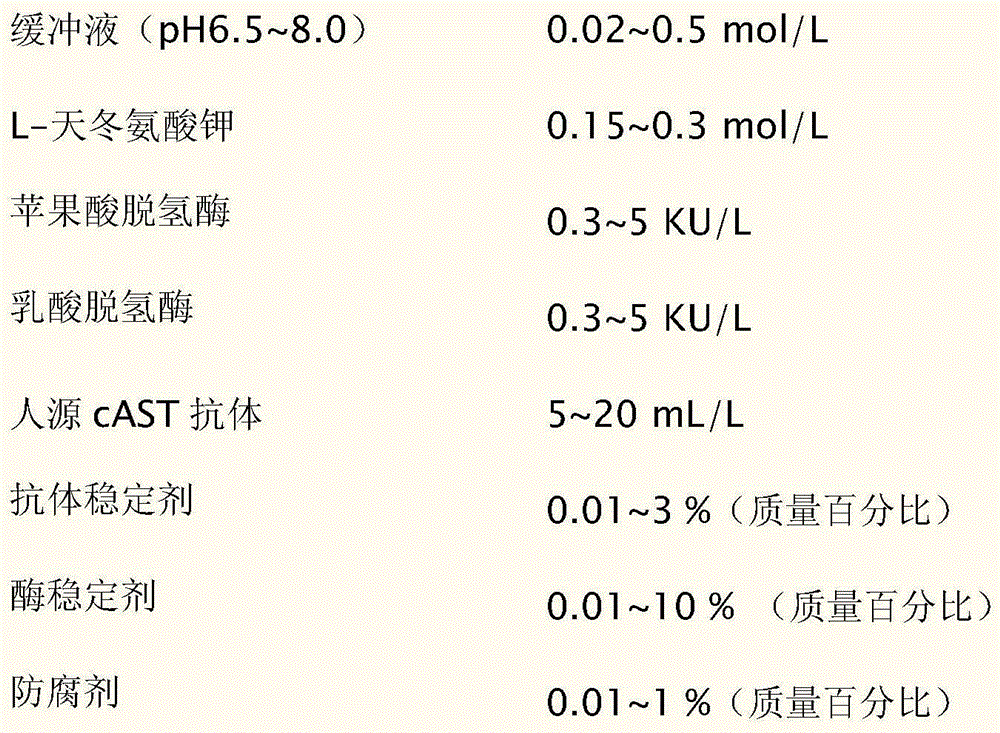
The invention discloses an aspartate transaminase mitochondrial isozyme detection kit, comprising: reagents 1: 0.02-0.5mol / L of buffer solution of which pH value is 6.5-8.0, 0.15-0.3mol / L of L-potassium aspartate, 0.3-5KU / L of malic dehydrogenase, 0.3-5KU / L of lactic dehydrogenase, 5-20mL / L of human cAST antibody, 0.01-3% of antibody stabilizer, 0.01-10% of enzyme stabilizer and 0.01-1% of preservative; and reagents 2: 0.02-0.5mol / L of buffer solution of which pH value is 7.0-9.0, 0.005-0.02mol / L of alpha-ketoglutarate, 0.1-0.5mmol / L of reduced coenzyme I, 0.01-1% of preservative and 0.01-10% of reduced coenzyme I stabilizer. The kit has the advantage of good stability.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Fatigue-relieving traditional Chinese medicine health product and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104825791ADefinite curative effectNo side effectsAntinoxious agentsUnknown materialsEpimediumLycium barbarum fruit
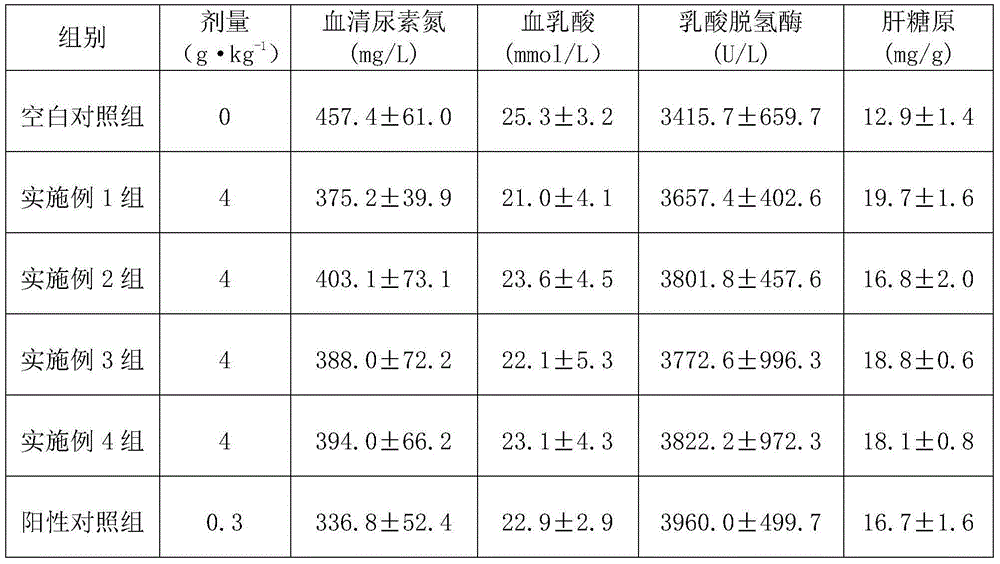
The invention discloses a fatigue-relieving traditional Chinese medicine health product, which is composed of the following seven traditional Chinese herbals: ginseng, processed rhizoma polygonati, wolfberry, raspberry, maca, epimedium, and cervus elaphus antler. The pharmacodynamic test result show that the health product can prolong the load swinging time of mice, the contents of hepatic glycogen and lactic dehydrogenase are increased, the contents of serum urea nitrogen and blood lactic acid are reduced, and the health product has a prominent fatigue relieving effect.
Owner:HUBEI GOLDEN EAGLE BIOTECH
Corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for highly producing succinic acid and building method thereof
InactiveCN103509747AIncrease productionReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharic acidPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium for anaerobic conversion to produce succinic acid, and a building method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. A pyruvate carboxylase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum and phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from escherichia coli are cloned to corynebacterium glutamicum (ATCC13032); a lactate dehydrogenase gene of the corynebacterium glutamicum is knocked out in a homologous recombination manner. By adopting the lactic dehydrogenase-defective corynebacterium glutamicum for coexpression of a carboxylase gene, anaerobic production of succinic acid is carried out in a cell reutilization manner, so that the yield of succinic acid can be greatly improved; the yield can be up to 75g / L; the conversion rate of saccharic acid is 75%; the corynebacterium glutamicum engineering bacterium has a good application prospect; a fermentation model, especially a fermentation model for cell reutilization is built according to the optimum condition for biological transformation of succinic acid; the acid-production performance in repeated batch transformation process of cells can be basically kept stable.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
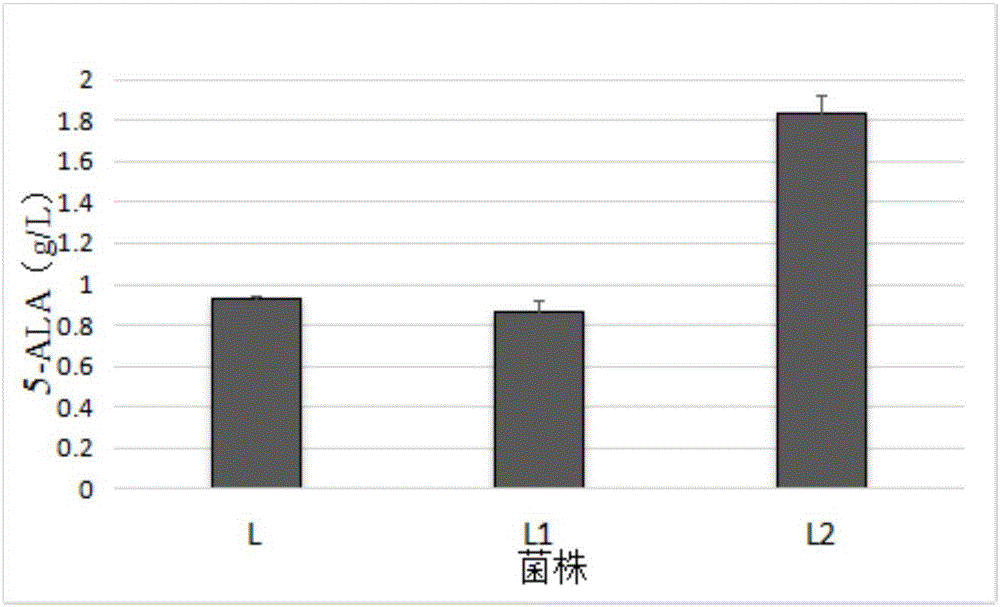
Corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid
InactiveCN106434513AEasy to transportIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPhosphoenolpyruvate carboxylaseAminolevulinic acid synthase
The invention discloses a corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid. An establishing method comprises steps as follows: (1) a lactic dehydrogenase encoding gene ldhA and acetic acid producing genes pta-ackA, pqo and cat are knocked out from corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 1303, and a strain CG4 is obtained; an sod promoter is inserted in front of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase encoding gene in the CG4, and a strain CG5 is obtained; a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase encoding gene pck is knocked out from the CG5, and a strain CG6 is obtained; (2) plasmids of an overexpressed 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase gene are transferred into the CG6, and a recombinant strain L is obtained; (3) 5-aminolevulinic acid transport protein plasmids are transferred into the L. The recombinant strain can promote 5-aminolevulinic acid to be transported outside corynebacterium glutamicum cells, and the yield of 5-aminolevulinic acid is 112.3% higher than that of a contrast strain.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com