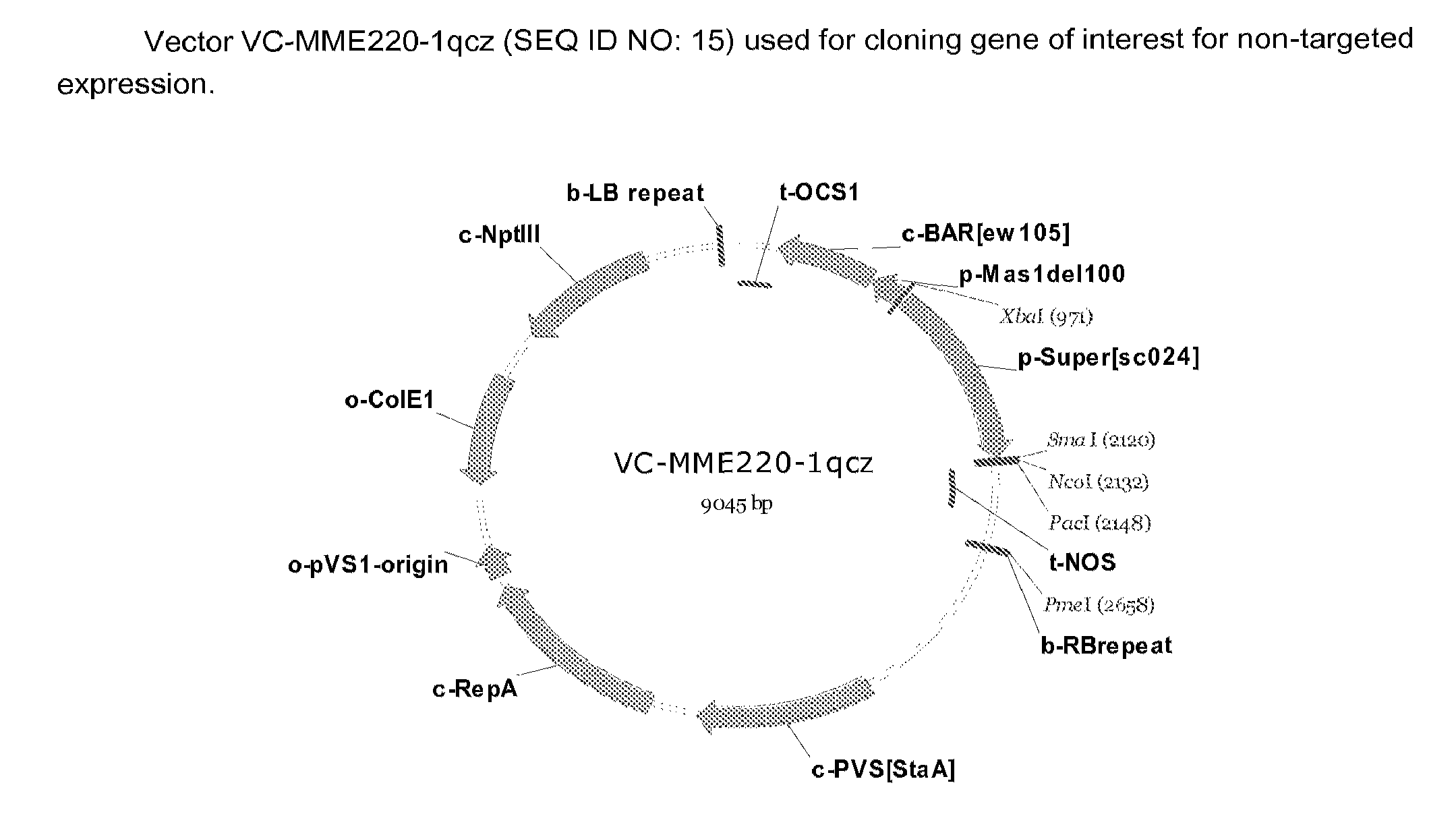
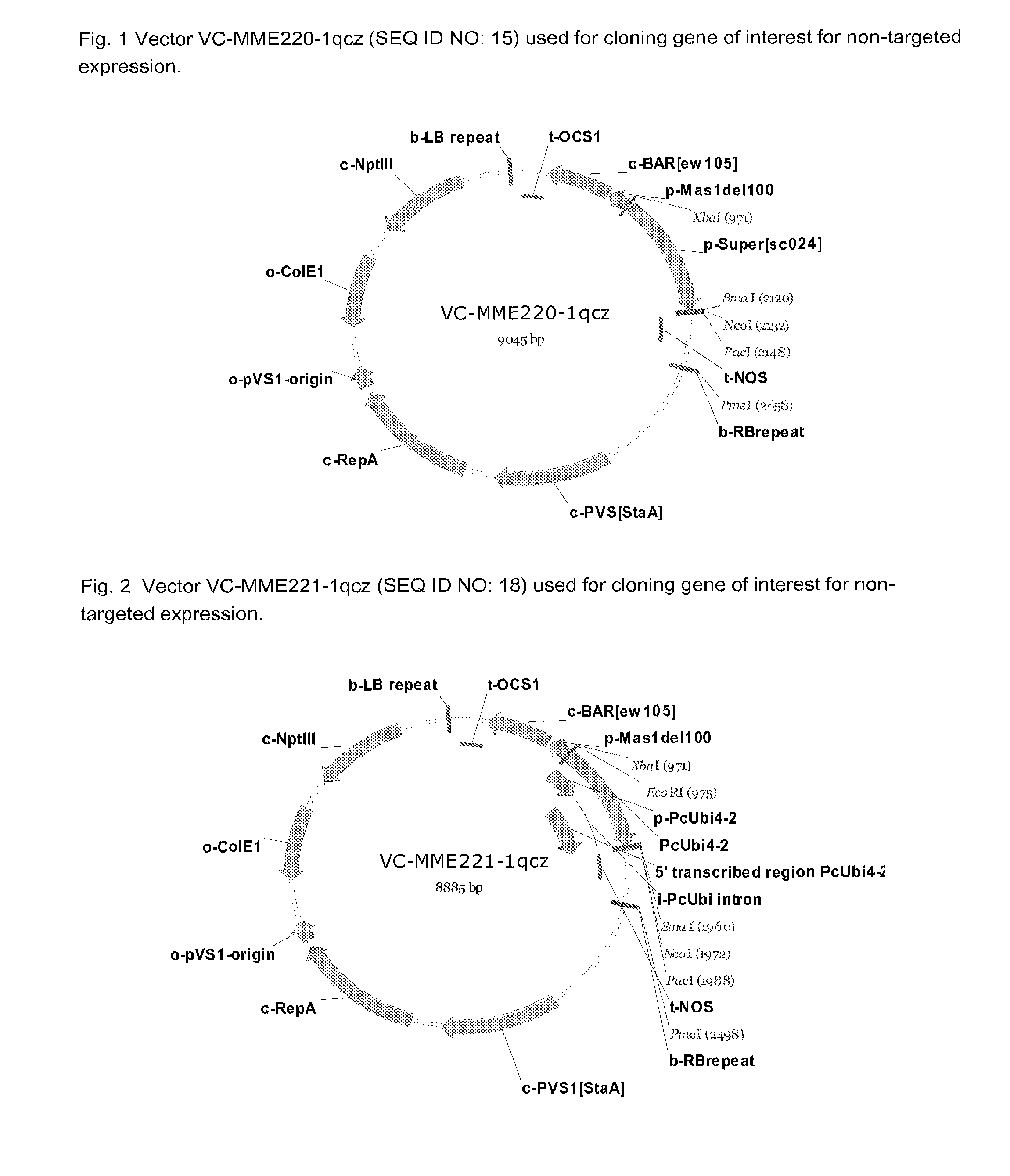
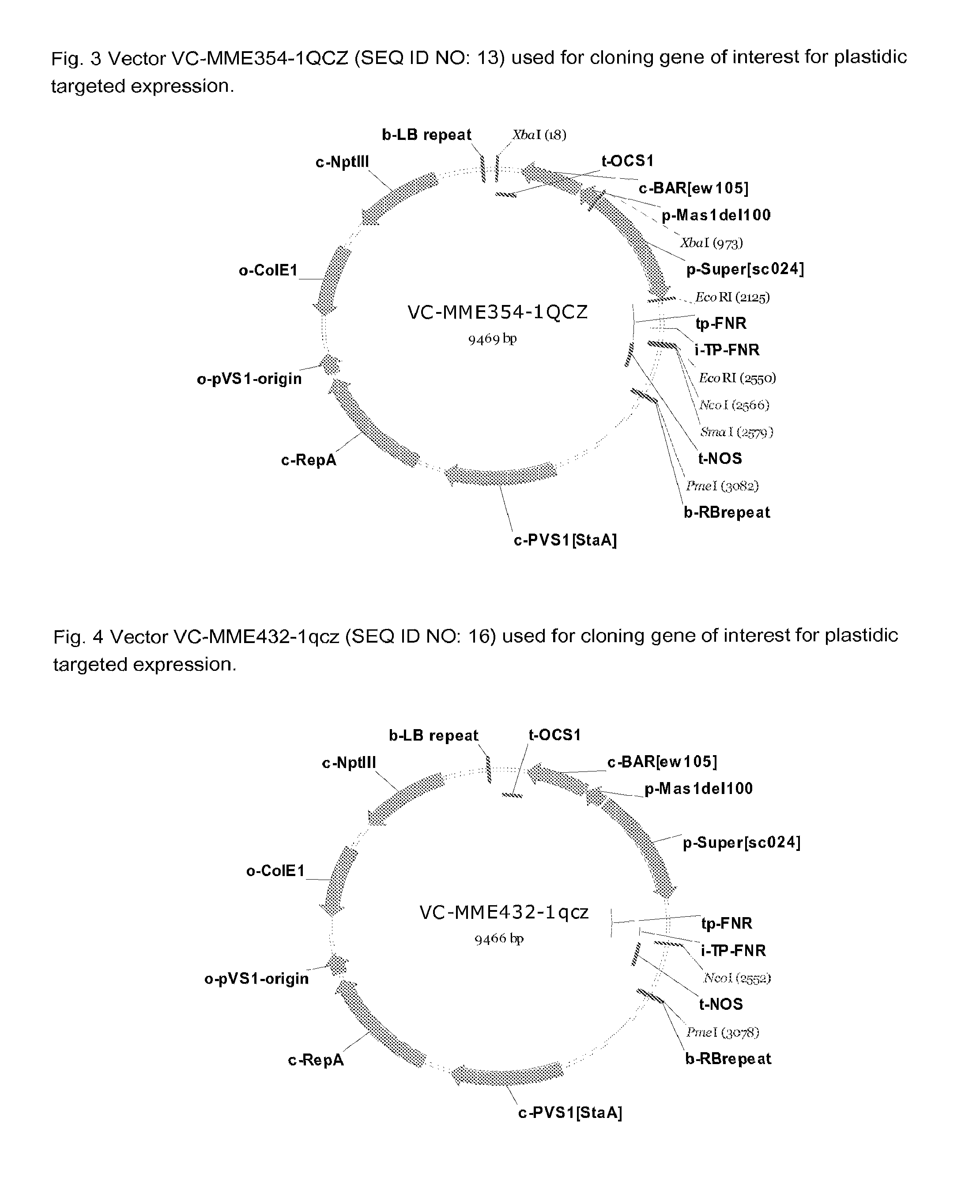
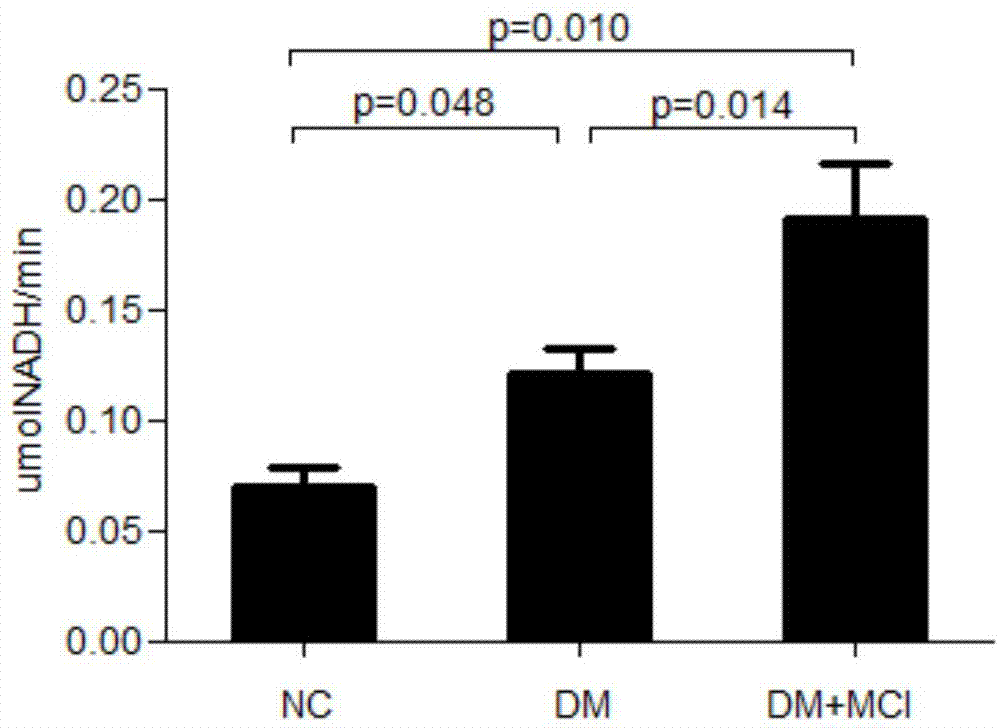
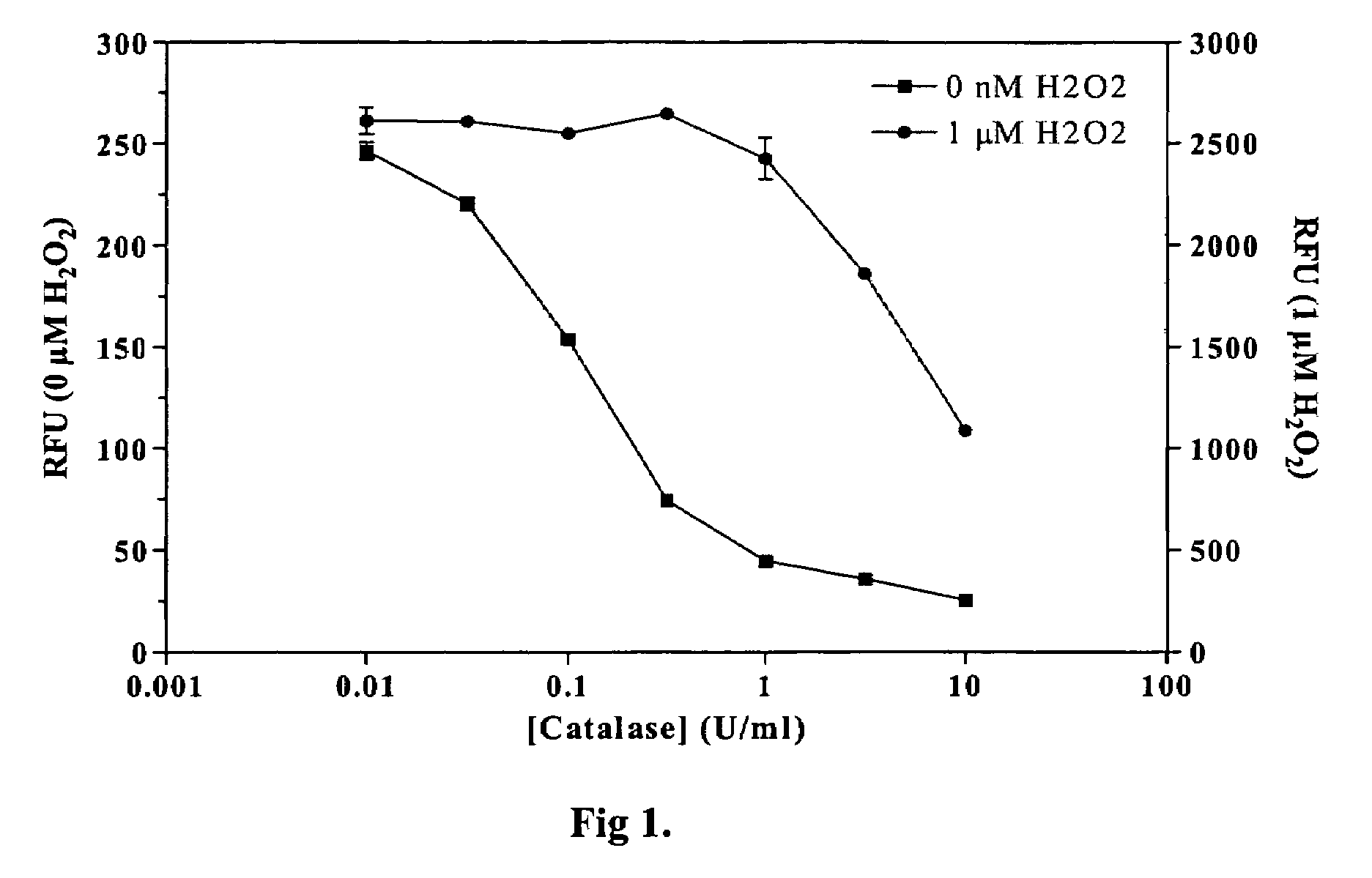
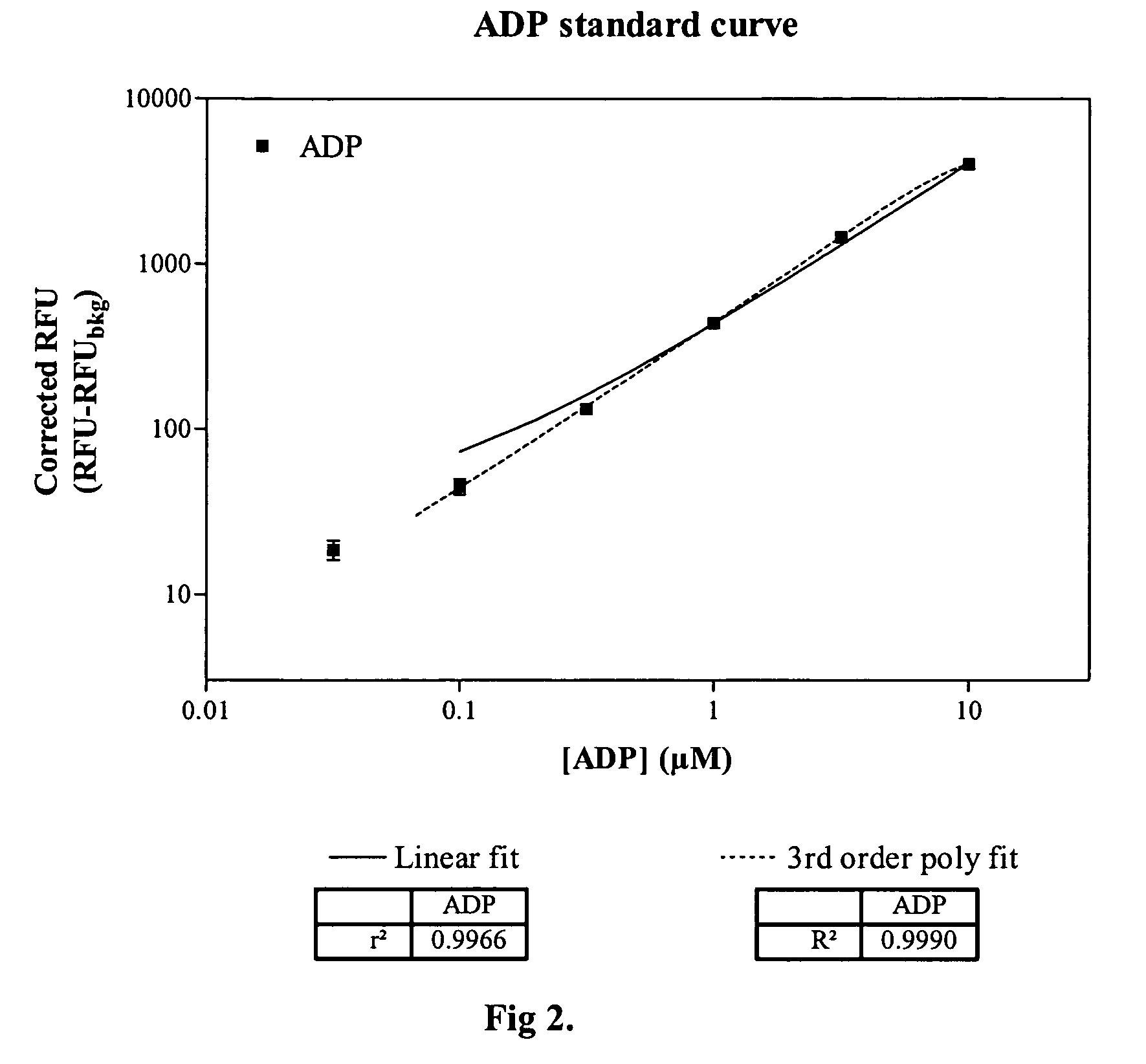
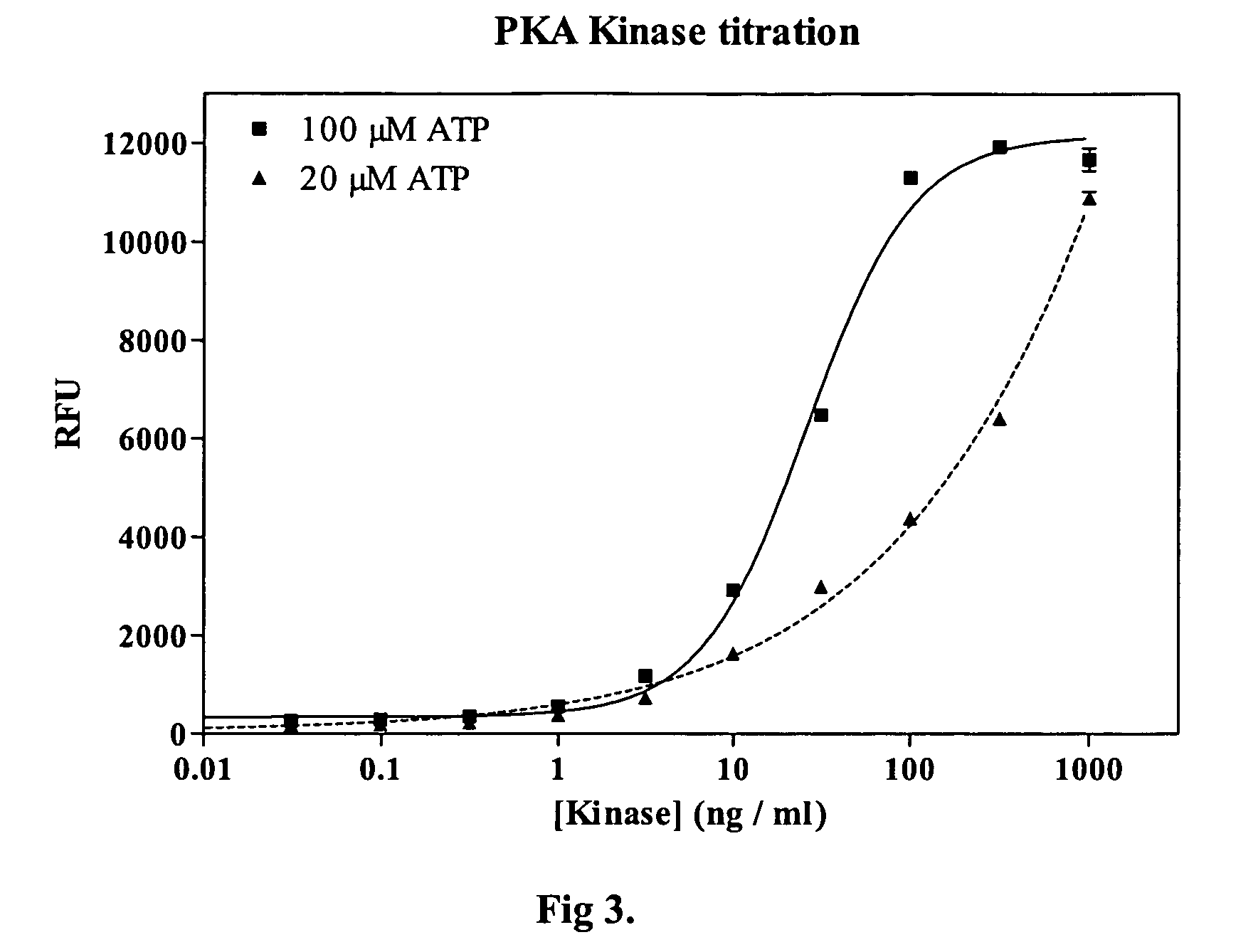
Patents
Literature
149 results about "Pyruvate kinase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pyruvate kinase is the enzyme involved in the last step of glycolysis. It catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP), yielding one molecule of pyruvate and one molecule of ATP. Pyruvate kinase was inappropriately named (inconsistently with a conventional kinase) before it was recognized that it did not directly catalyze phosphorylation of pyruvate, which does not occur under physiological conditions. Pyruvate kinase is present in four distinct, tissue-specific isozymes in animals, each consisting of particular kinetic properties necessary to accommodate the variations in metabolic requirements of diverse tissues.
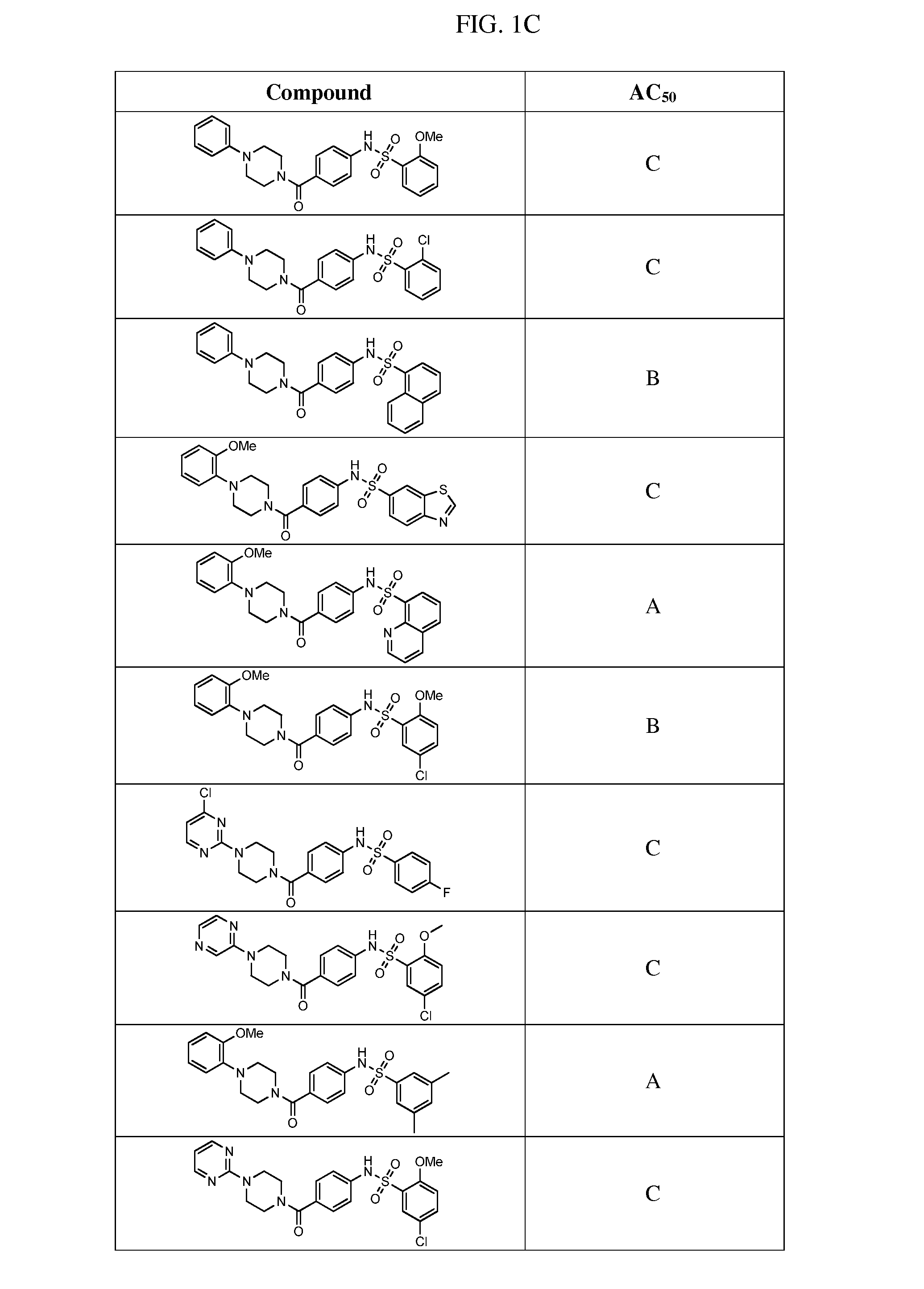
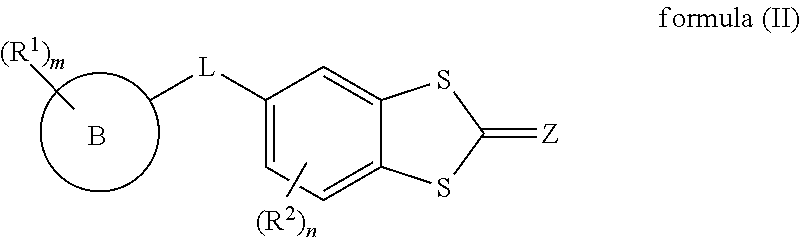
Pyruvate kinase M2 modulators, therapeutic compositions and related methods of use
Compositions comprising compounds that modulate pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) are described herein. Also described herein are methods of using the compounds that modulate PKM2 in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:AGIOS PHARM INC
Activators of pyruvate kinase m2 and methods of treating disease
ActiveUS20110046083A1Reducing endogenous down-regulationIncrease activity levelBiocideOrganic chemistrySurgeryPyruvate kinase
The invention described herein features methods, compositions, and kits for the use of activators of PKM2 for the treatment, prevention, or amelioration of diseases related to PKM2 function, including, e.g., cancer, diabetes, atherosclerosis, restenosis, obesity, autoimmune disorders, and proliferative disorders.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Therapeutic compounds and compositions
ActiveUS8785450B2Increase productionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryBiochemistryPyruvate kinase
Compounds and compositions comprising compounds that modulate pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) are described herein. Also described herein are methods of using the compounds that modulate PKM2 in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:AGIOS PHARM INC
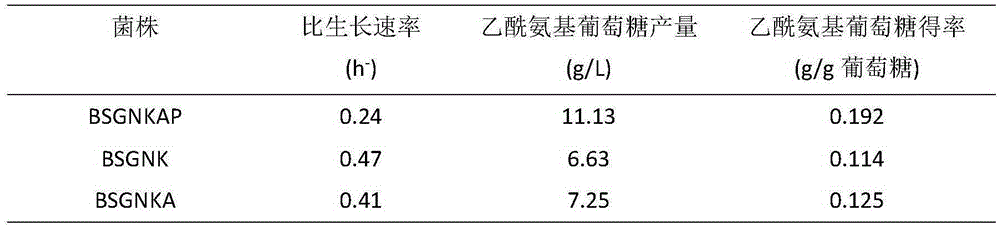
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN105255803AHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseGlucose polymers
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for efficiently synthesizing acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis, based on bacillus subtilis BSGNK, the enol phosphate type pyruvate carboxylase encoding gene pckA and pyruvate kinase encoding gene pyk (NCBI upper Gene ID: 938206) are knocked out, the BSGNK regards B.subtilis168delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nag A delta nag B delta ldh delta pta::lox <72> as the host, promoters PxylA and P43 are utilized for controlling recombinant ecpression of glmS and GNAl, and accordingly the glucose kinase encoding gene glcK is knocked out. According to the recombinant bacillus, glucose can be effectively utilized for synthesizing acetylglucosamine, the shake flask fermentation yield can reach 11.13 g / L, the yield is increased by 67.8% compared with a strain before knocking out, and a basis is provided for further improvement of bacillus subtilis for producing glucosamine of metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
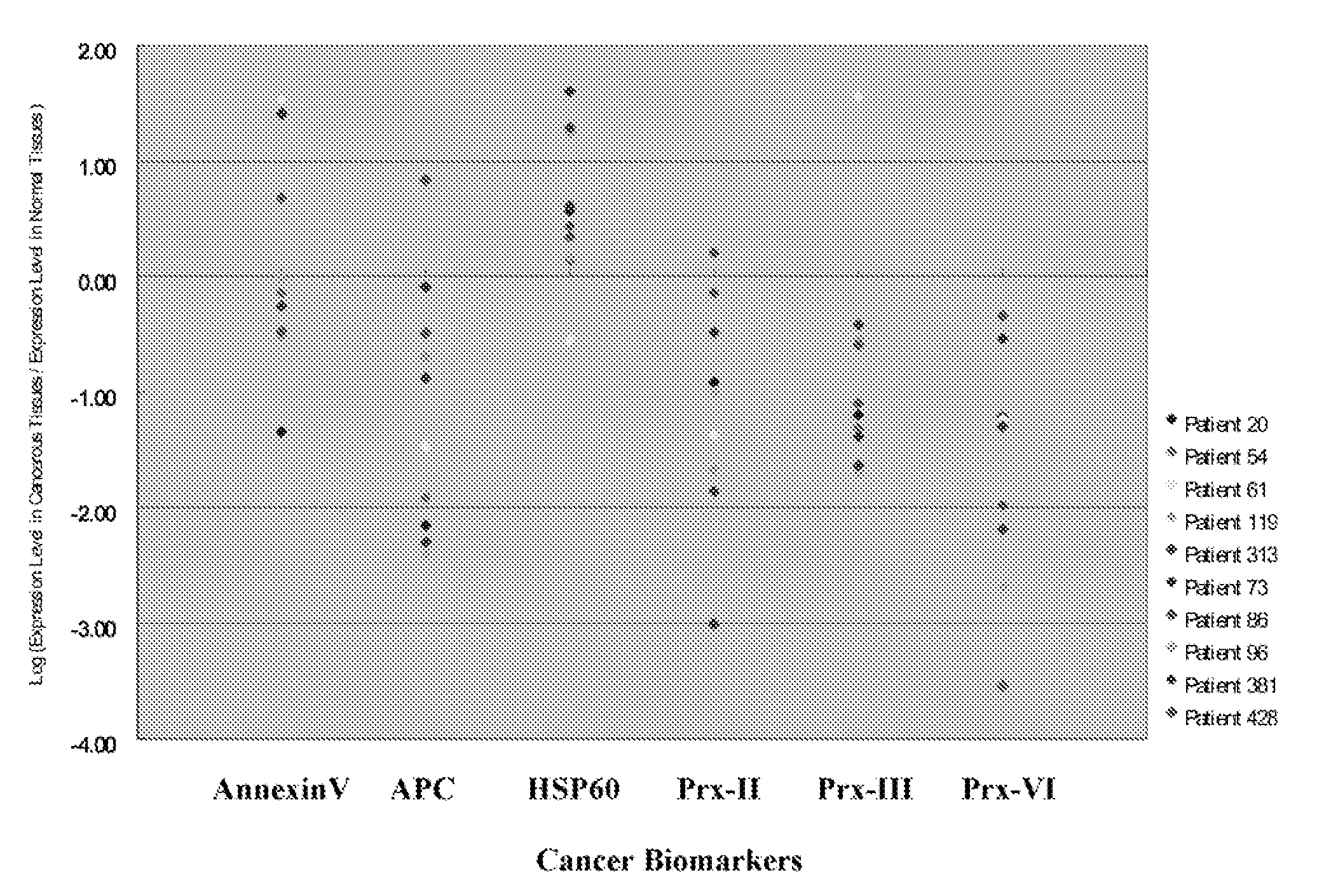
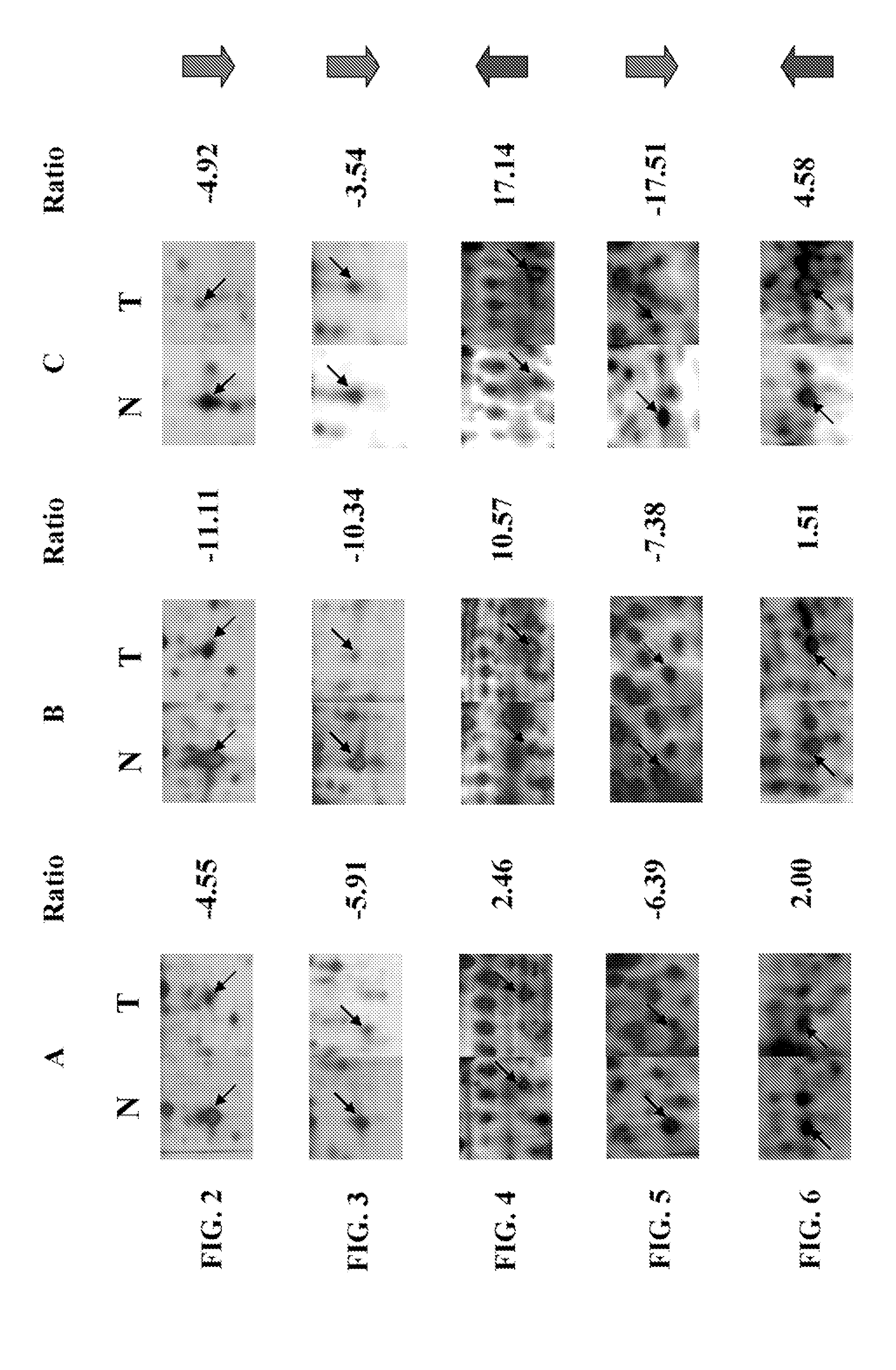
Use of biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of lung cancer
InactiveUS20100240546A1Microbiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMinichromosome maintenanceSelenium-Binding Proteins
A method for identifying, diagnosing, and monitoring cancerous lung tissues in a subject may include measuring the expression of at least one biomarker in a biological sample in the subject, and comparing the expression against a normal value. When a differential expression of the at least one biomarker between the biological sample and the normal value is more than 1.5-fold, the lung tissue sample is cancerous. The at least one biomarker is selected from the group consisting of peroxiredoxin I, peroxiredoxin II, peroxiredoxin III, peroxiredoxin IV, peroxiredoxin VI, chaperonin, amyloid-P-component, annexin V, dihydropyrimidinase-like 2 protein, glutamate carboxypeptidase, 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate mutase, thymidine phosphorylase, prolyl-4 hydroxylase, selenium binding protein 1, β-mitochondrial ATP synthase H+ transporting F1 complex, laminin-binding protein, minichromosome maintenance deficient protein 5 variant, keratin 9, keratin 10, napsin A aspartic peptidase, M2-type pyruvate kinase, and apolipoprotein A-I.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
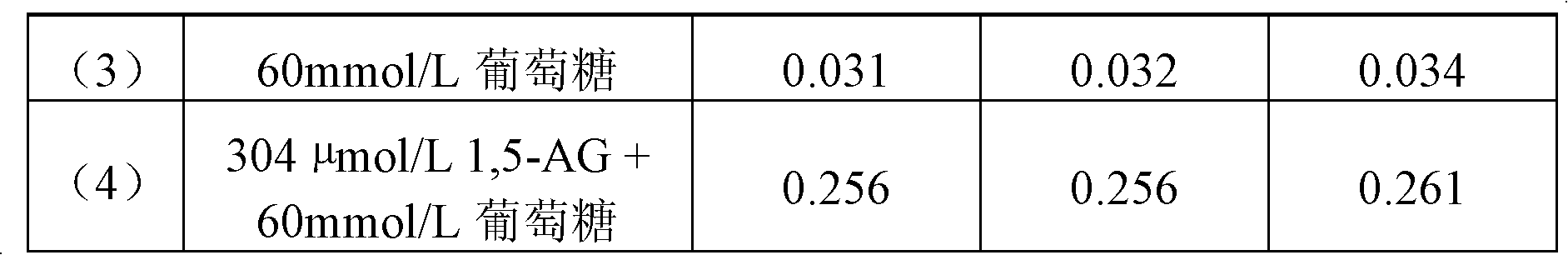
Kit for detecting 1, 5-anhydro-D-ghlcitol in human blood
ActiveCN104483487AImprove featuresImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological testingPeroxidaseSurface-active agents
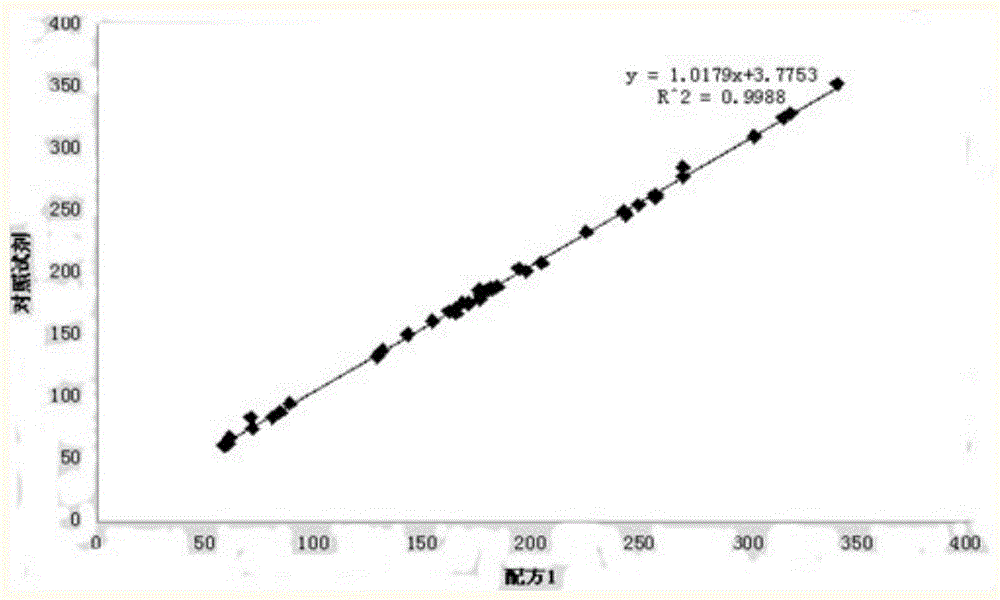
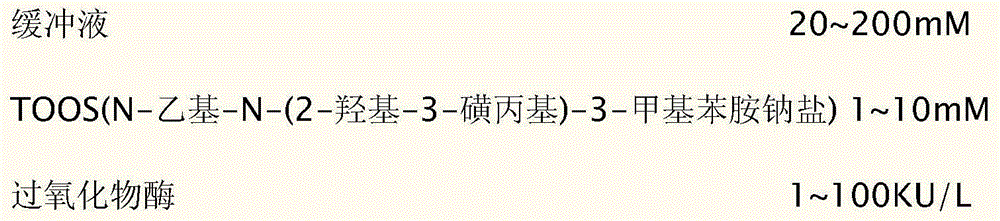
The invention discloses a kit for detecting 1, 5-anhydro-D-ghlcitol in human blood. R1 comprises components as follows: 20-200 mM of a buffer solution, 1-10 mM of 4-aminoantipyrine, 0.2-2 mM of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), 1-10 mM of PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate), 1-50 KU / L of ATP-HK, 1-50 KU / L of pyruvate kinase, 1-50 KU / L of ascorbic acid oxidase, 0.05-10 mM of sodium vanadate, 0.01%-5% of a surface active agent, 0.1%-10% of a stabilizer and 0.01%-1% of a preservative; and R2 comprises components as follows: 20-200 mM of a buffer solution, 1-10 mM of TOOS (N-ethyl-N-(2-hydroxy-3-sulfopropyl)-3-methylaniline,sodium salt), 1-100 KU / L of POD (peroxidase), 10-200 KU / L of PROD (pyranose oxidase), 0.01%-5% of a surface active agent, 0.1%-10% of a stabilizer and 0.01%-1% of a preservative. The kit has the advantages that endogenous interference of glucose, bilirubin, ascorbic acid, blood lipid and the like is effectively prevented and the stability is good.
Owner:NINGBO MEDICAL SYSTEM BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Aspergillus niger strain efficiently producing malic acid, construction method and application
ActiveCN111218408AIncreased purification process costsImprove efficiencyFungiTransferasesHexokinaseBatch fermentation
The invention relates to an Aspergillus niger gene engineering strain efficiently producing malic acid. The Aspergillus niger gene engineering strain is an Aspergillus niger gene engineering strain which knocks out a citric acid transporter gene cexA, and overexpresses a glucose transporter gene mstC, a hexokinase gene hxkA, a phosphofructokinase gene pfkA, and a pyruvate kinase gene pkiA which are derived from Aspergillus niger. The efficiency for producing malic acid of the Aspergillus niger gene engineering strain is significantly improved, the output on the eighth day through fed-batch fermentation in a fermentation tank reaches 195.72-210 g / L, a conversion rate of malic acid to glucose reaches 1.59-1.64 mol / mol, and a fermentation cycle is shorter by one day compared with a starting strain, namely the fermentation cycle is shortened from original 9 days to 8 days. An excellent strain for the preparation of malic acid by microbial fermentation methods is provided.
Owner:南京昊禾生物科技有限公司
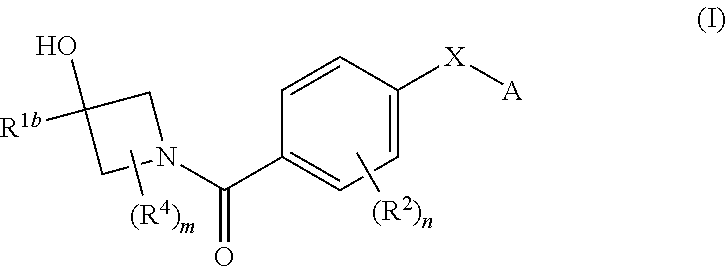
Therapeutic compounds and compositions
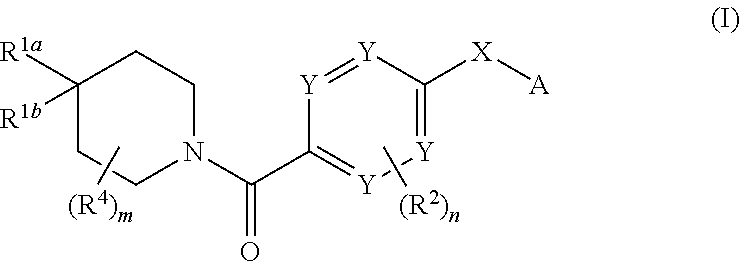
ActiveUS9108921B2Extended service lifeHigh affinityOrganic active ingredientsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDiseaseKinase
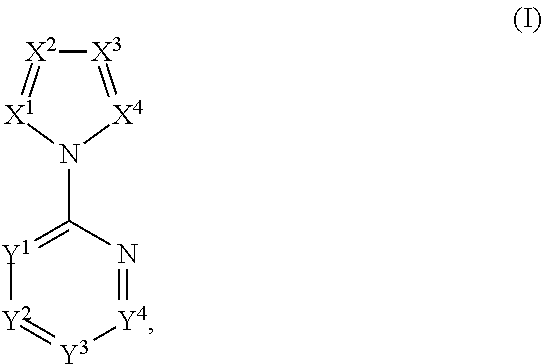
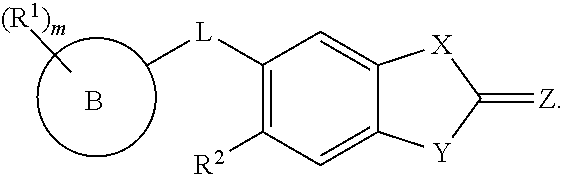
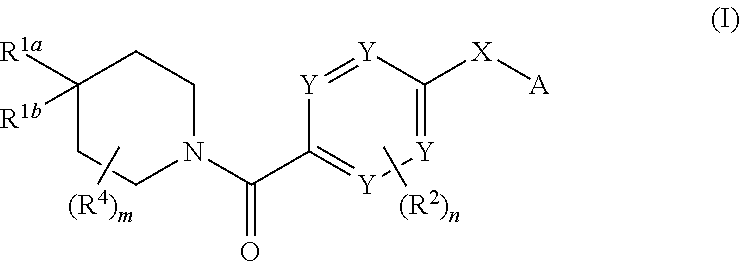
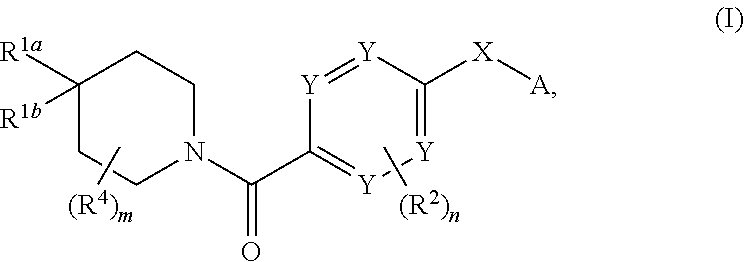
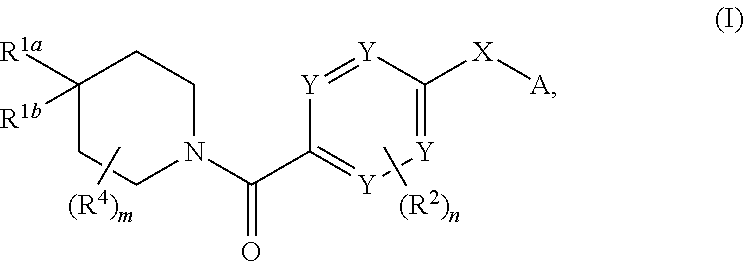
Compounds of general formula I:and compositions comprising compounds of general formula I that modulate pyruvate kinase are described herein. Also described herein are methods of using the compounds that modulate pyruvate kinase in the treatment of diseases.
Owner:AGIOS PHARM INC
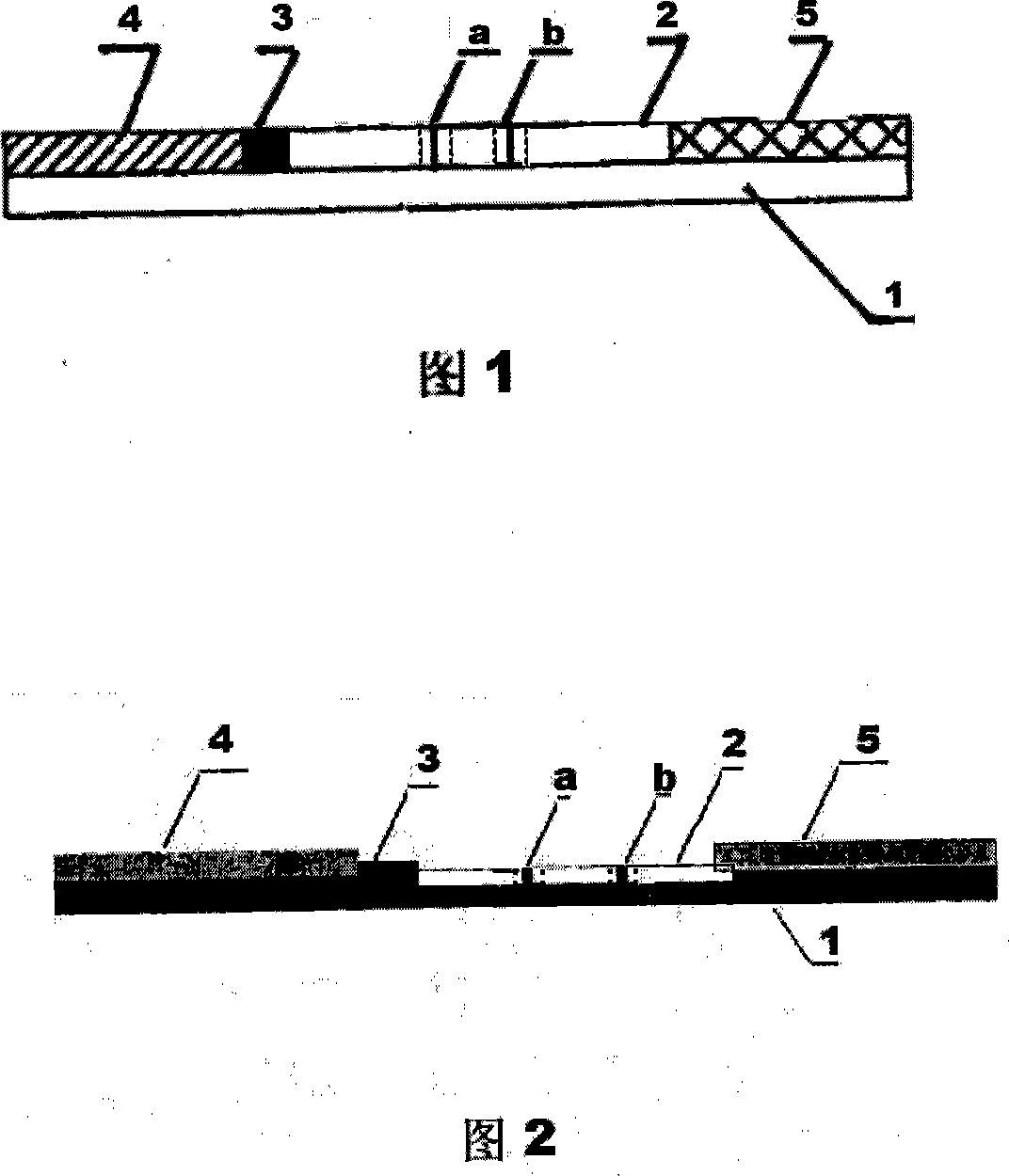
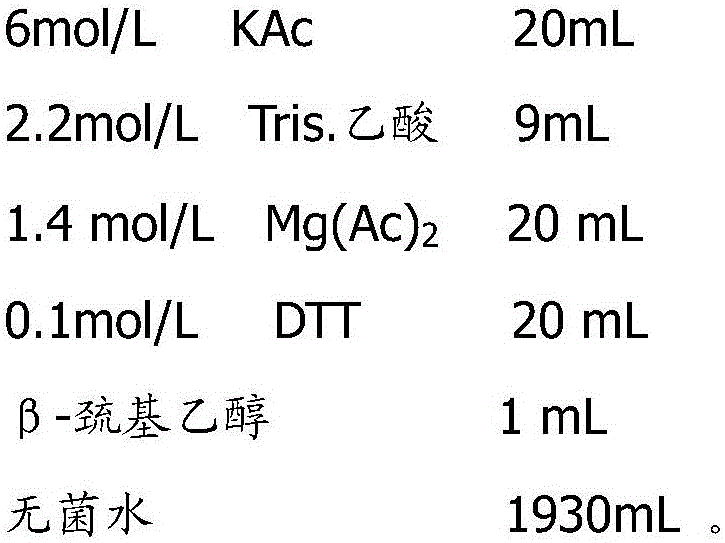
Kit for detecting knubble type M2 pyruvate kinase and preparation method thereof
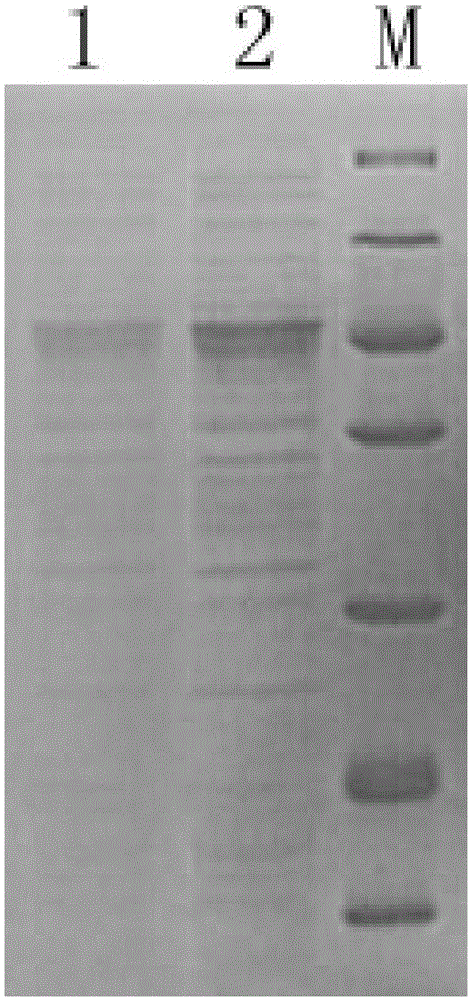
The invention relates to a test kit for detecting tumor M2 pyruvate kinase and a relative preparation method, belonging to biological medicine and medical test technical field. The inventive test kit comprises a bottom plate (1), a colorful particle conjugate pad (3), a test sample pad (4), a water absorption pad (5) and a porous filter membrane for reaction, wherein the conjugate pad is fixed with anti-tumor M2 pyruvate kinase antibody marked by colorful particles, the porous filter membrane is arranged with a test region (a) and a reference region (b), the test region covers anti-tumor M2 pyruvate kinase antibody, the reference region covers anti-mouse IgG or antigen solution. The invention can process semi-quantitatively analyze and measure tumor M2 pyruvate kinase in 10min. The test kit is portable and easy to store, with simple operation, stable method, non additional tester and enzyme and the application for quickly and simply detecting tumor M2 pyruvate kinase on solid membrane medium.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
Method for cell-free expression of signal protein and expression system
ActiveCN106011163ASolve the problem of low expressionHigh protein expressionNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliCreatine kinase
The invention relates to a method for cell-free expression of signal protein and an expression system. The method includes joining a target gene of the signal protein on a pIX3.0 vector to obtain expression plasmids; extracting escherichia coli Rosetta (DE3) by S30 buffer solution to obtain escherichia coli extract; preparing an energy supply system comprising PEP (phosphoenolpyruvic acid) / PK (pyruvate kinase), CP (phosphocreatine) / CK (creatine kinase) and glucose; preparing an amino acid mixture and a saline solution; preparing lecithin / cholesterol liposome; adding the expression plasmids into a cell-free protein expression system comprising the escherichia coli extract, the energy supply system, the amino acid mixture, the saline solution and the lecithin / cholesterol liposome for expression. The method is capable of solving the problem of small signal protein expression quantity.
Owner:CUSABIO TECH LLC
PKM2 modulators for use in the treatment of cancer
Compounds that modulate pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) are described herein. Also described herein are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds, and methods of using the compounds in the treatment of cancer.
Owner:AGIOS PHARM INC
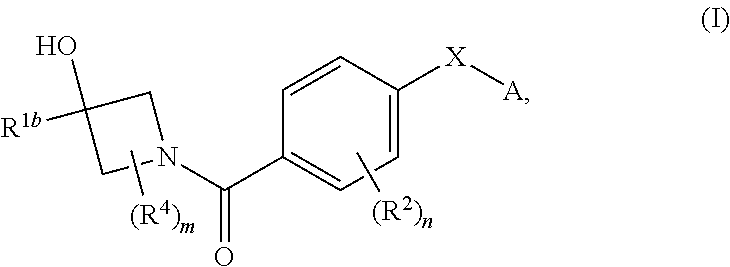
Therapeutic compounds and compositions and their use as PKM2 modulators
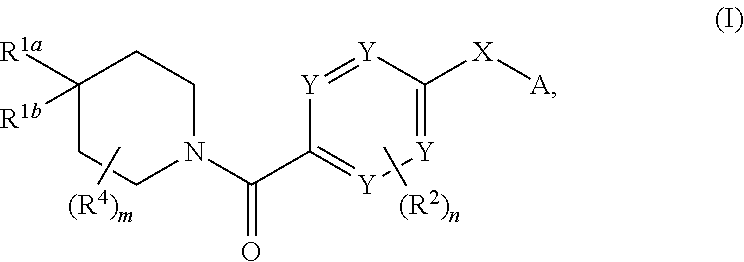
InactiveUS9458132B2Extended service lifeHigh affinityOrganic chemistryAntineoplastic agentsPyruvate kinaseStereochemistry
Compositions comprising compounds of general formula (I) that modulate pyruvate kinase are described herein. Also described herein are methods of using the compounds that modulate pyruvate kinase in the treatment of diseases.
Owner:AGIOS PHARM INC
ADP detection using an enzyme-coupled reaction
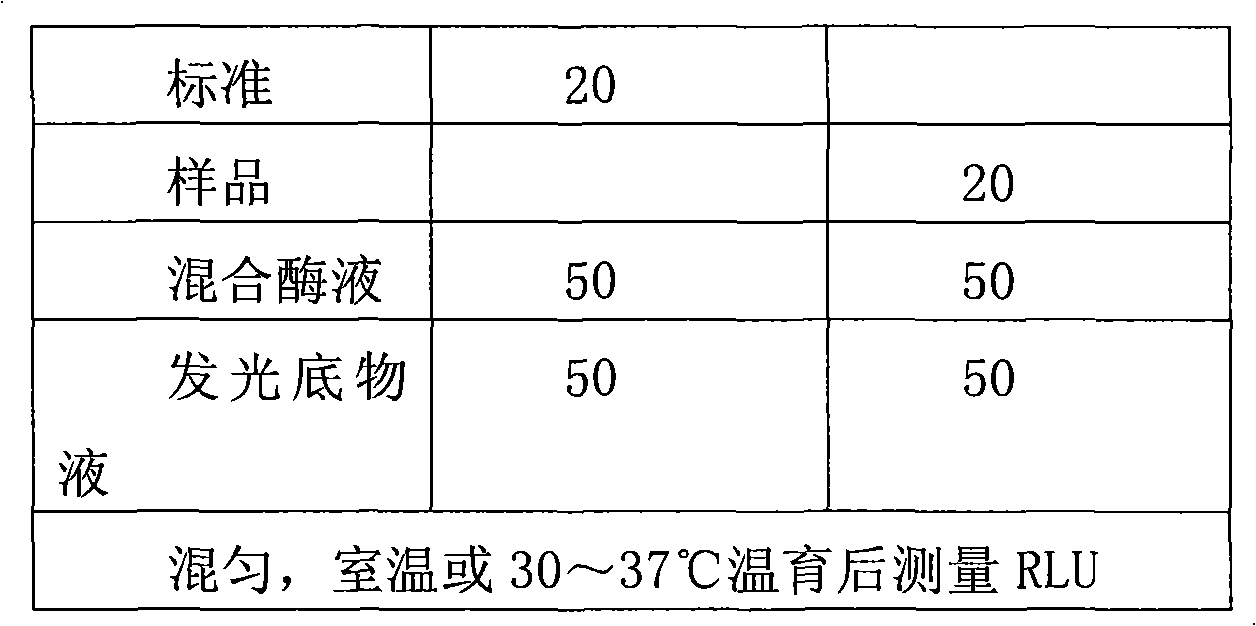
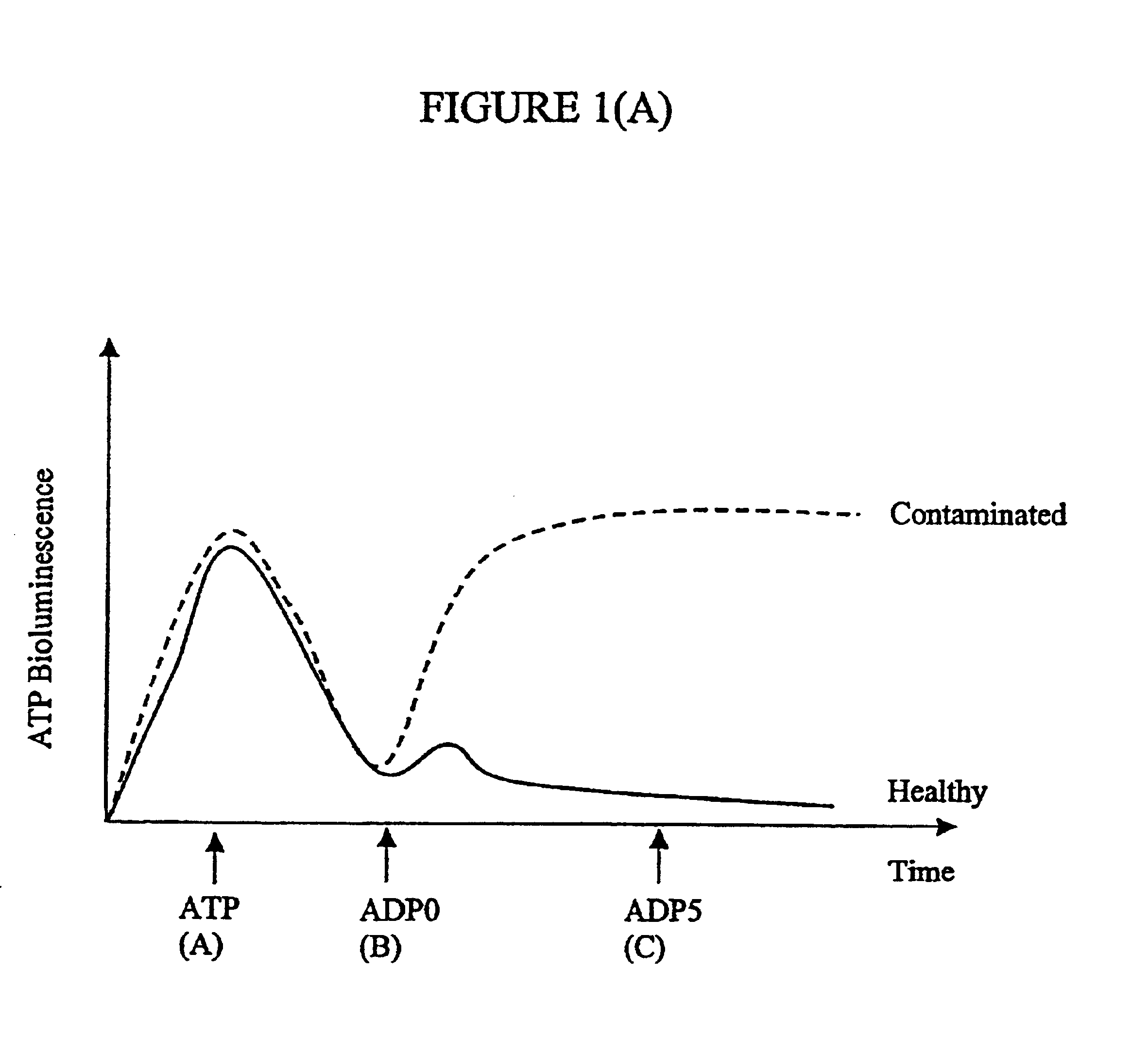
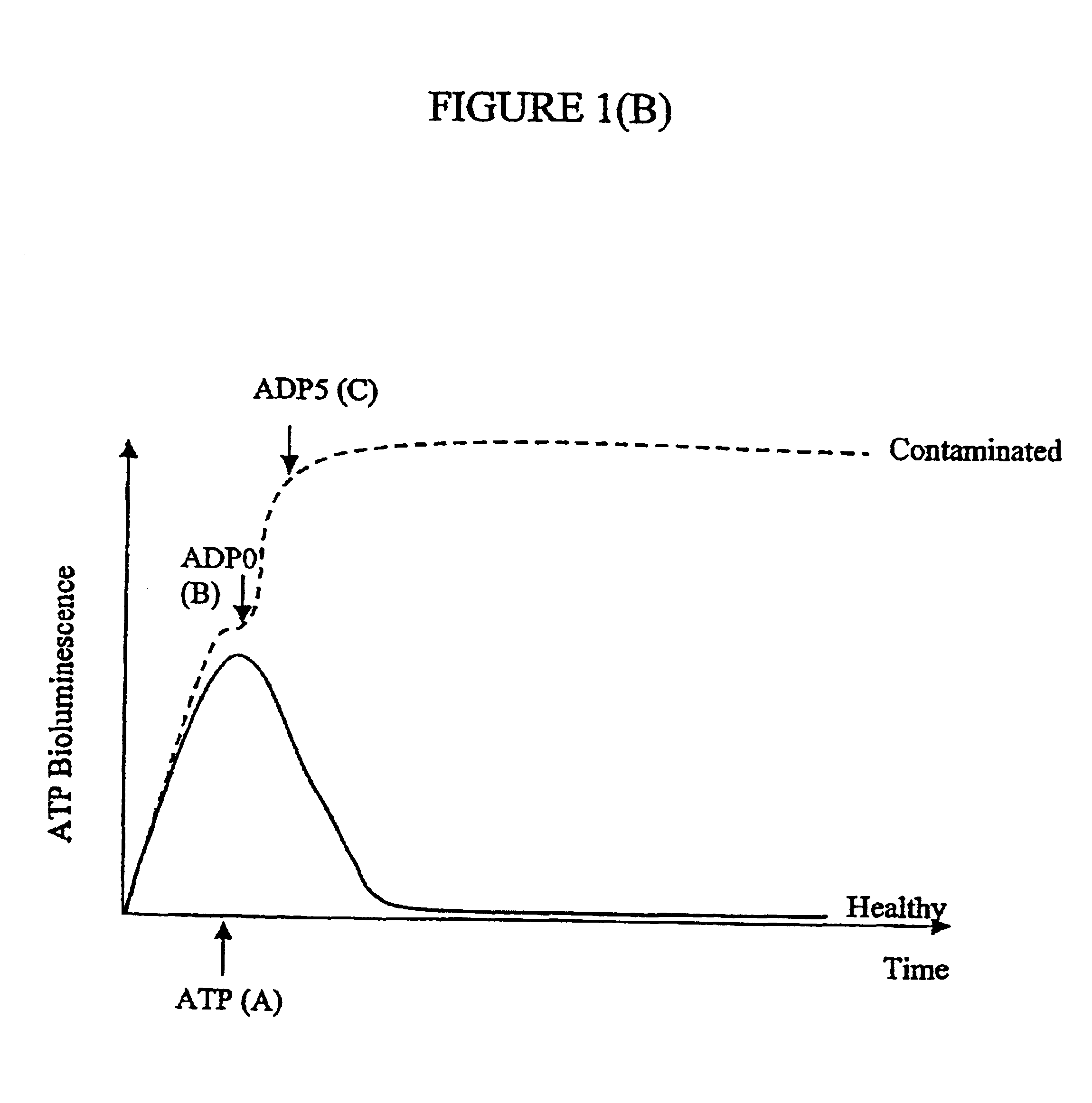
ActiveUS20060199238A1Minimize contaminationMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsFluorescencePeroxidase
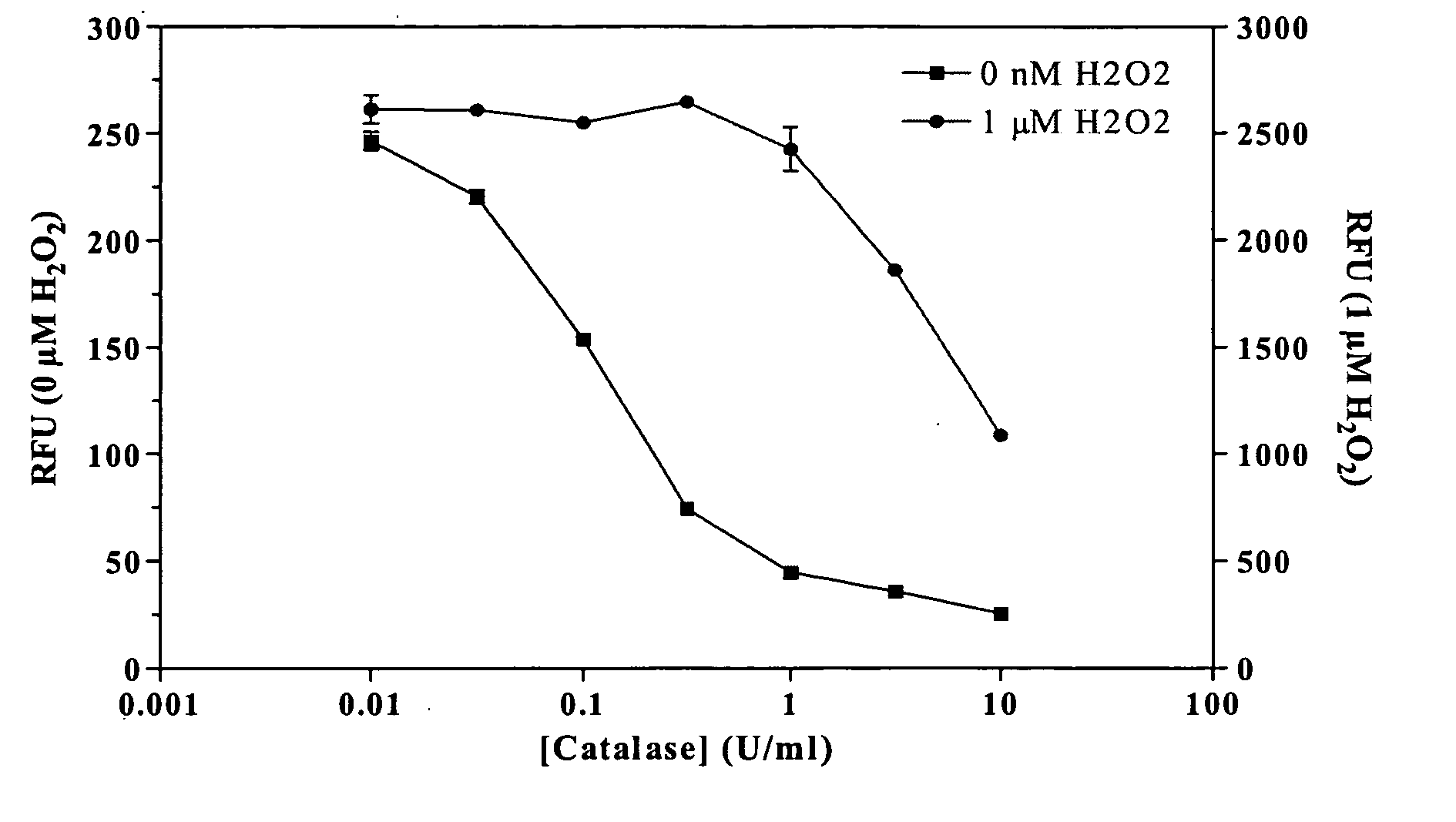
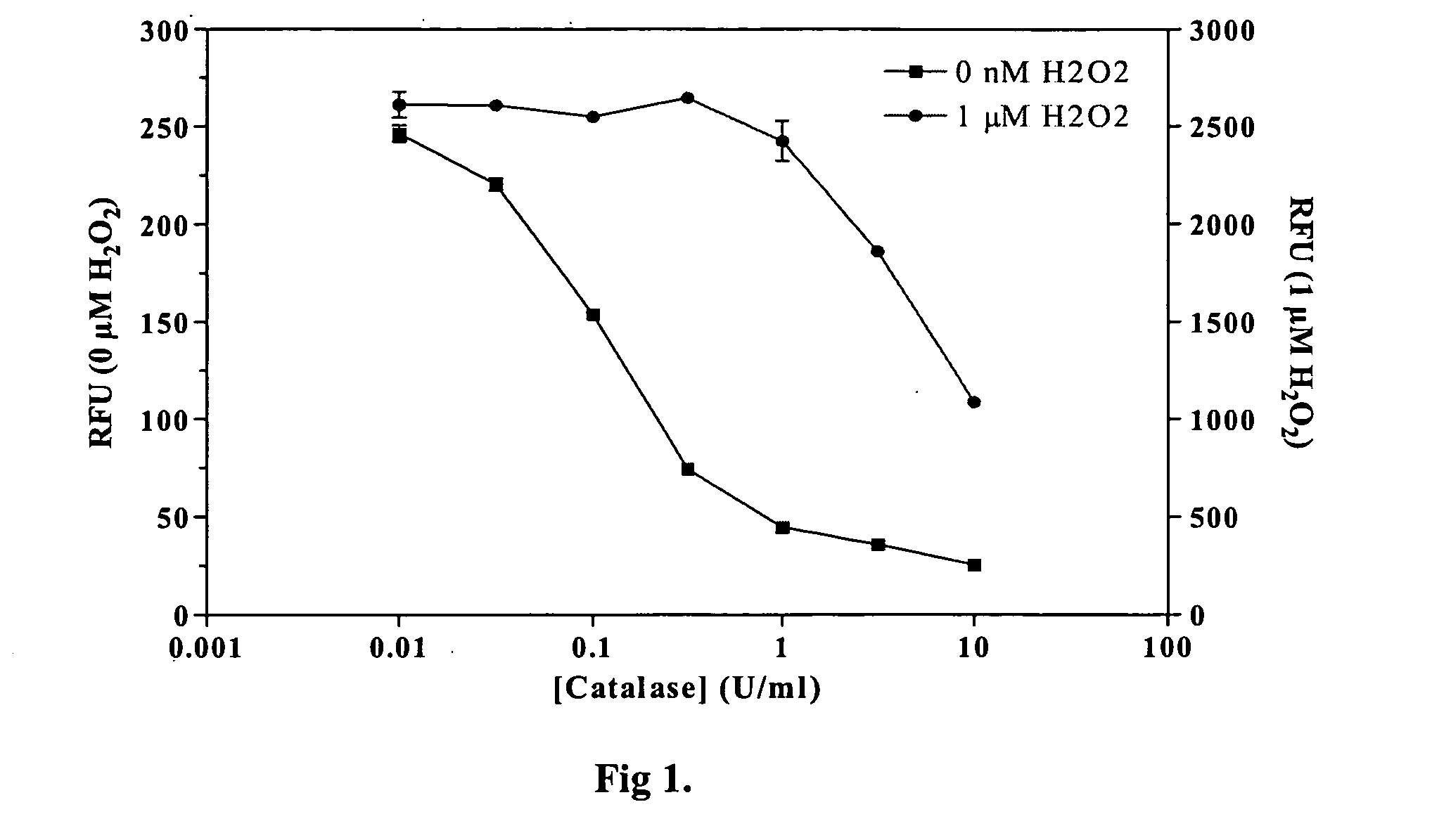
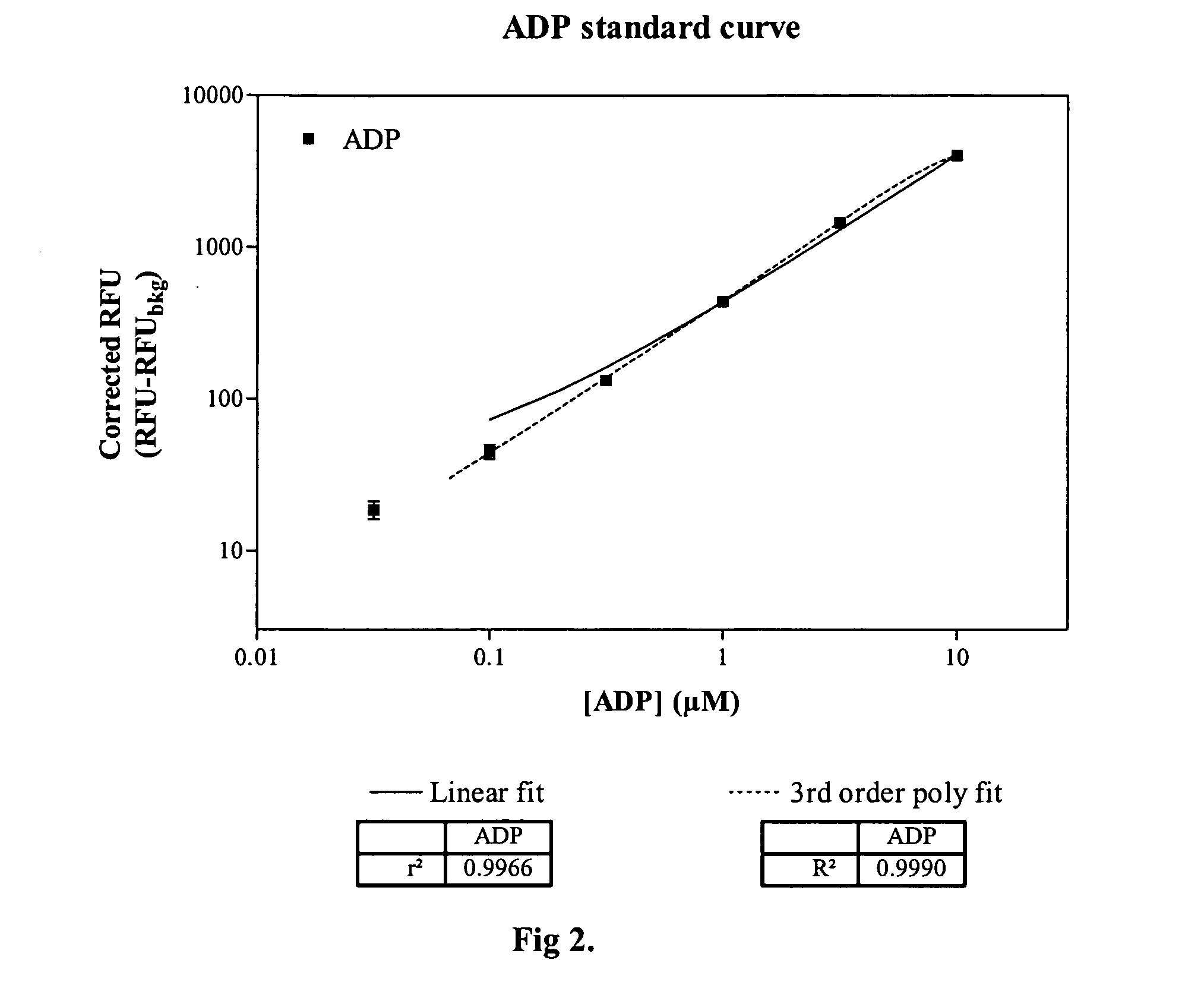
Methods and compositions are provided for determining ADP in the presence of ATP. These comprise including among the assay reagents at least one of the correcting components creatine phosphokinase and phosphocreatine, pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate, peroxidase and a non-interfering peroxidase substrate, and catalase. One aspect of the method employs formation of hydrogen peroxide from the ADP by pyruvate kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate and pyruvate oxidase. The hydrogen peroxide is then determined. A combined reagent having all of the reagents may optionally include a peroxidase when the hydrogen peroxide is to be enzymatically determined. A peroxidase substrate is added to the sample in conjunction with the peroxidase substrate reagent, the mixture incubated and depending on whether the peroxidase substrate is a fluorescer or chemiluminescer, the mixture may be illuminated with excitation light and the emitted light determined as a measure of the ADP in the sample.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Human tumor M2-type pyruvate kinase antigen determinant polypeptide and antibody and their application in diagnositic kit
ActiveCN1887901AGood antigenicityEasy to synthesizePeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAntigenHuman tumor
The present invention is one kind of human tumor M2-type pyruvate kinase antigen determinant polypeptide and antibody and their application in diagnostic kit. The human tumor M2-type pyruvate kinase antigen determinant polypeptide has one of two polypeptide segments as shown in SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2 in the sequence list. The human tumor M2-type pyruvate kinase antibody is prepared with the human tumor M2-type pyruvate kinase antigen determinant polypeptide of the present inventor. The human tumor M2-type pyruvate kinase antibody may be used in preparing extracorporeal diagnosis kit for human tumor M2-type pyruvate kinase.
Owner:深圳市安群生物工程有限公司
Composition for Lipase Activity Determination and Method of Determing Activity
InactiveUS20080038765A1Easy to useGood reproducibilityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementMonoglycerideClinical exam
[PROBLEMS] To provide lipase activity determination reagents which function by an enzymatic method. The reagents are easy to use in an ordinary clinical examination, have excellent handleability, and are excellent in accuracy and reproducibility. [MEANS FOR SOLVING PROBLEMS] Lipase activity is determined with any of reagents which comprise a low-concentration buffer and a diglyceride dissolved therein. The diglyceride is used as a substrate for lipase, whereby the liquid reagents can have long-term storage stability. One of the reagents converts a monoglyceride yielded by a lipase reaction into glycerol with the aid of monoglyceride lipase, and further contains glycerol kinase, pyruvate kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, reduced NAD, ATP, and phosphoenol pyruvate. Another reagent converts a monoglyceride yielded by a lipase reaction into glycerol with the aid of monoglyceride lipase, and further contains glycerol kinase, glucose, ADP-dependent hexokinase, glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase, oxidized NAD or oxidized NADP, and ATP. A further reagent converts a monoglyceride yielded by a lipase reaction into glycerol with the aid of monoglyceride lipase, and further contains glycerol kinase, glycerol-3-phosphate oxidase, peroxidase, and a dye which colors in the presence of hydrogen peroxide.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI PHARMA
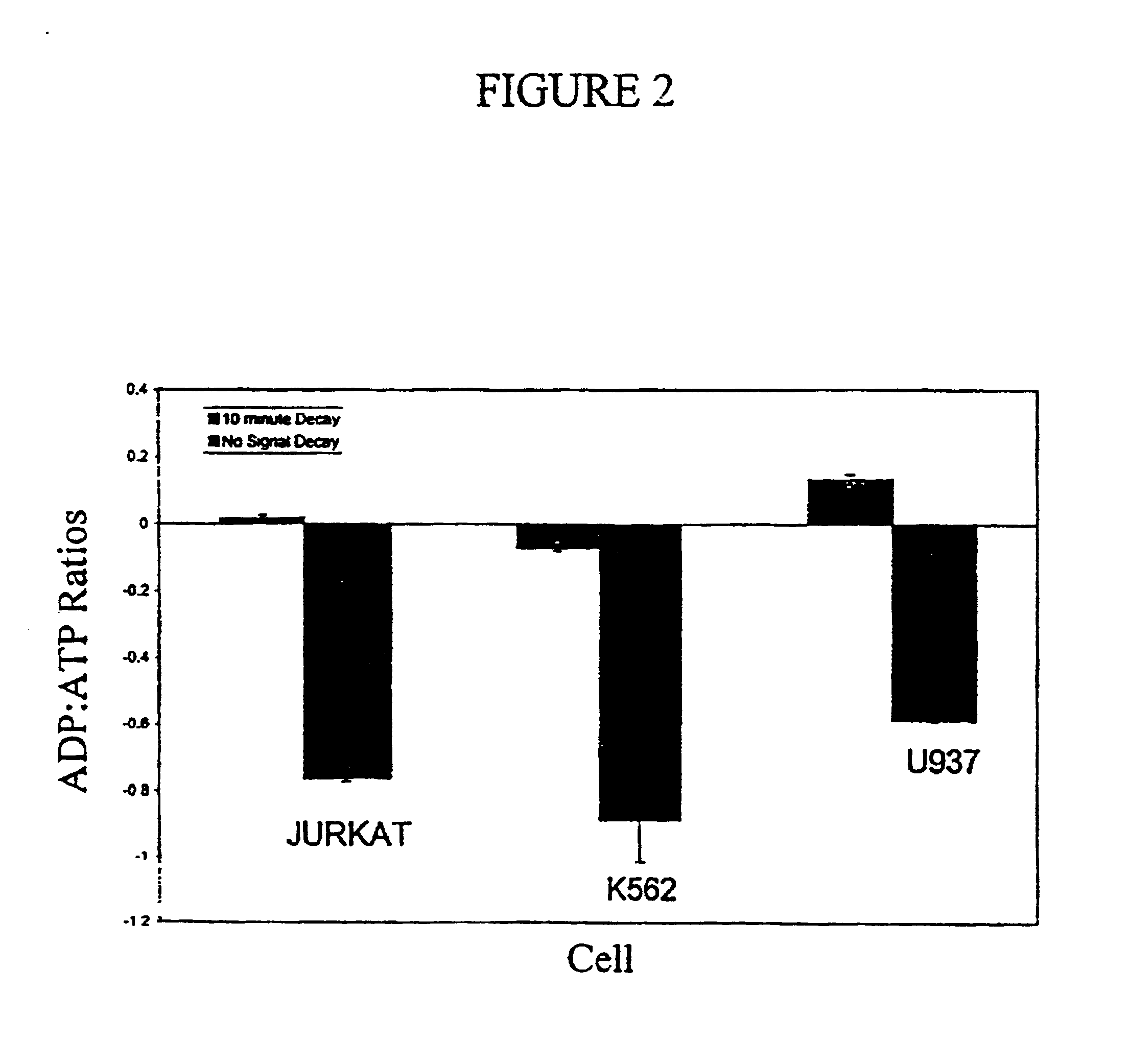
ATP-metry based on intracellular adenyl nucleotides for detecting and counting cells, use and implementing method for determining bacteria in particular devoid of atp
InactiveUS20080014607A1Less expensiveMeet needsMicrobiological testing/measurementLuciferinIntracellular
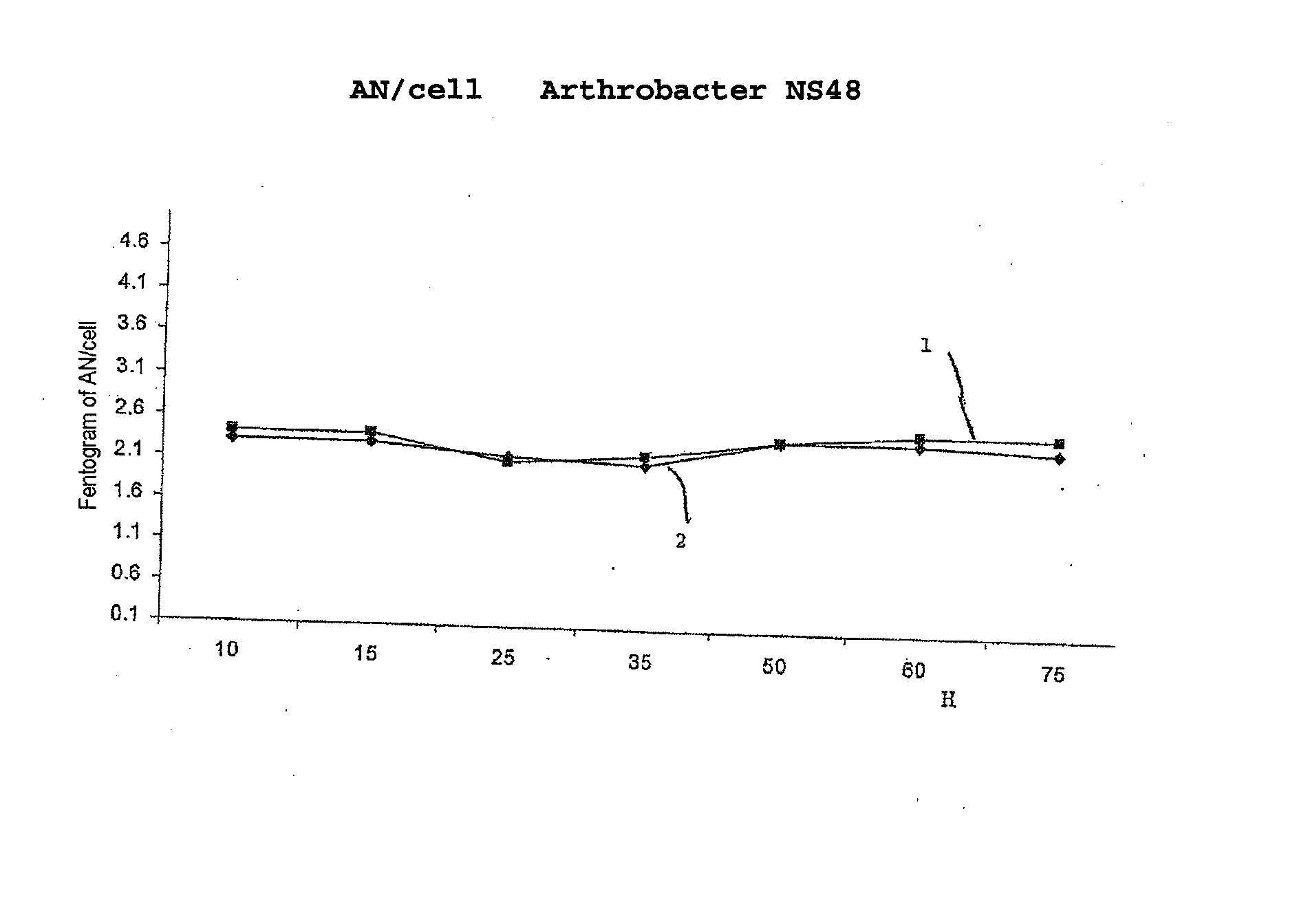
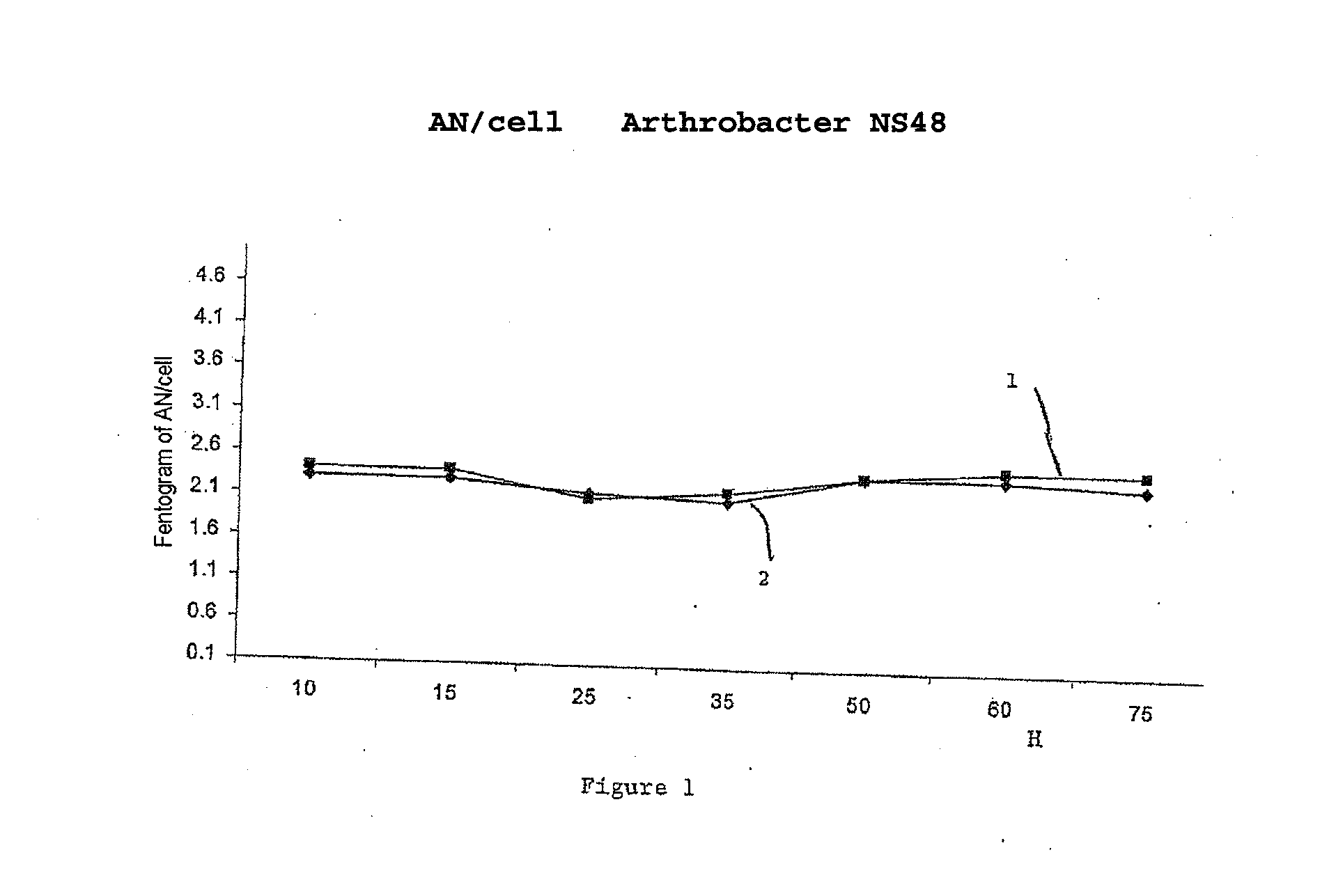
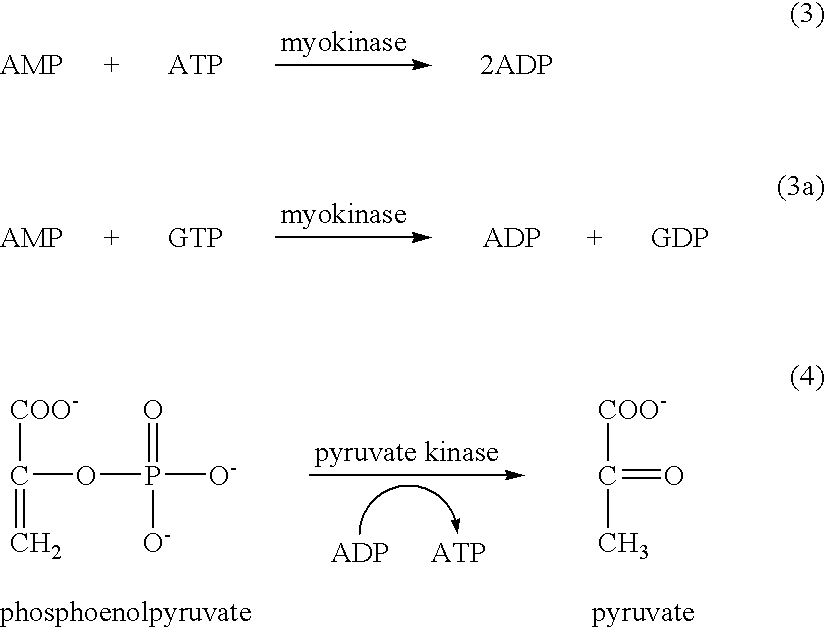
The invention concerns the use of bioluminescence dependent on the reaction (1): luciferin+ATP+O2+Mg2++luciferase→oxyluciferin+photons for detecting and counting living cells of a given species potentially present in a liquid sample, said use being characterized in that it consists in measuring the total free intracellular adenyl nucleotides (AN) content, expressed in ATP form, of living cells of a given non-viral species, taking into account the fact that the sum of free intracellular ATP, ADP and AMP of said family is constant according to the relationship (2): [AN]=[ATP]+[ADP]+[AMP]=Cte after transforming the free intracellular ATP, ADP and AMP by using myokinase and pyruvate kinase, said measurement being performed (i) without adding ATP and (ii) after adding a known amount of ATP. The invention also concerns a method for detecting and counting cells by ATP-metry.
Owner:TESTLIFE TECH
Method for detecting blood lactic acid in vitro by using chemiluminescence method
InactiveCN101639446AHigh sensitivityMinimum minimumMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceO-Phosphoric AcidGlycerol
The invention discloses a method for detecting blood lactic acid in vitro by using a chemiluminescence method, which is characterized in that LD is utilized to catalyze L-lactic acid and NAD<+> to generate pyruvate and NADH, the pyruvate and ADP generate ATP under the catalysis of pyruvate kinase (PK), ATP and glycerol generate glycerol-3-phosphoric acid and ADP under the catalysis of GK, the glycerol-3-phosphoric acid is acted by GPO to obtain H2O2, and H2O2 is catalyzed by HPR to enable luminol to emit light; the size of light signals is in positive correlation with the concentration of thepyruvate, i.e. the bigger the concentration of the lactic acid is, the stronger the emitted light signals are; the concentration of the lactic acid can be conjectured by recording the light signals; and the lactic acid with the known concentration is used for detecting the light signals to make a dose-response curve, and the content of the lactic acid of an unknown sample can be calculated throughthe curve. In the invention, a chemiluminescence substance replaces a colored substance to achieve the purposes of sensitivity, stability, wide range and safety. The method can be used for preparinga corresponding commercial kit for quantitatively detecting the lactic acid in body fluids such as whole blood, plasma, cerebrospinal fluid, urine, gastric juice and the like.
Owner:福建省洪诚生物药业有限公司
Assay of micro-organisms in cell cultures
InactiveUS6951723B2Convenient and easy screeningImprove the level ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatments3D cell cultureAbsolute level
Micro-organisms which over-produce ATPase, especially mycoplasmas in a sample of a cell culture, are detected by making use of the ATPase activity to convert cellular or externally added ATP to ADP. The decrease in ATP externally added or the increase or absolute level of ADP produced from cellular ATP can then be detected or measured. For example, if a reagent such as phosphenol pyruvate / pyruvate kinase is added to convert that ADP back to ATP, the resulting high level of ATP can be detected bioluminescently using the reaction: Luciferin+luciferase enzyme+ATP→hv+products.
Owner:LUMITECH UK
Plants with Increased Yield
A method for producing a plant with increased yield as compared to a corresponding wild type plant whereby the method comprises at least the following step: increasing or generating in a plant or a part thereof one or more activities of a polypeptide selected from the group consisting of 26S proteasome-subunit, 50S ribosomal protein L36, Autophagy-related protein, B0050-protein, Branched-chain amino acid permease, Calmodulin, carbon storage regulator, FK506-binding protein, gamma-glutamyl-gamma-aminobutyrate hydrolase, GM02LC38418-protein, Heat stress transcription factor, Mannan polymerase II complex subunit, mitochondrial precursor of Lon protease homolog, MutS protein homolog, phosphate transporter subunit, Protein EFR3, pyruvate kinase, tellurite resistance protein, Xanthine permease, and YAR047C-protein.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
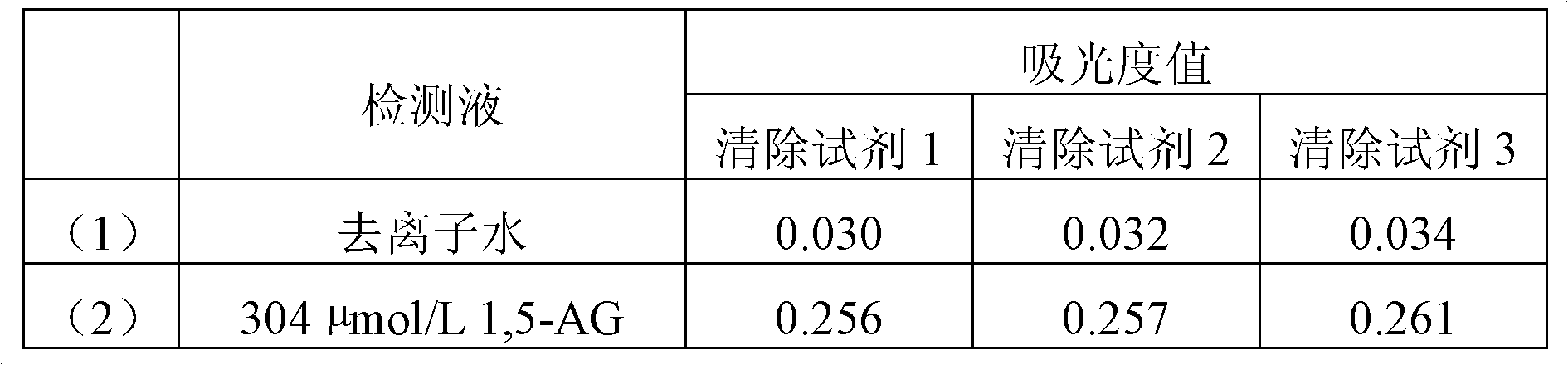
High-concentration glucose removal method and kit for determining serum 1,5 anhydro-D-glucitol based on pyranose oxidase method
The invention discloses a high-concentration glucose removal method for determining serum 1,5 anhydro-D-glucitol based on a pyranose oxidase method, which comprises the following steps: preparing a 2-morpholinoethanesulfonic acid (MES) buffer solution having a pH value of 6.0-9.0, wherein the MES buffer solution contains a certain amount of glucokinase (GK), glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADP), pyruvate kinase (PK), phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP); and adding into a serum sample containing glucose (Glu), and reacting at 20-50 DEG C for 3-5 minutes, wherein the GK converts the Glu into glucose-6-phosphoric acid (G6P) in the presence of the ATP, and adenosine diphosphate (ADP) is generated at the same time; the G6P is further converted into glucose-6-phosphate lactone (G6PL) by the G6PD in the presence of the NADP+; and the ADP generated in the reaction is converted into ATP again under the action of thePK in the presence of the PEP. The glucose removal agent prepared by the method can be stably stored at 2-8 DEG C for 14 months, and can be used for a clinical biochemical autoanalyzer extensively used at present.
Owner:浙江夸克生物科技有限公司
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent and isothermal nucleic acid amplification method
ActiveCN105543402ASimplify the amplification reaction processLower requirementMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LHelicase
The invention provides an isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent. The isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent is characterized by comprising components as follows: 100-800 mM of a Tris-HCl buffer solution, 10-150 mM of sodium chloride, 10-150 mM of potassium chloride, 10-50 mM of magnesium chloride, 5-15 mM of dithiothreitol, 5%-20% of polyvinylpyrrolidone, 10-20 mM of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), 1-5 mM of dNPTs, 10-50 mM of phosphoenolpyruvate, 500-1,500 ng / mu l of pyruvate kinase, 10-500 ng / mu l of BSA (bovine serum albumin), 25-200 pmol of each primer in a primer group, 50-200 ng / mu l of T4 bacteriophage DNA helicase gp41 protein, 100-500 ng / mu l of streptomyces coelicolor recA protein, 200-1,000 ng / mu l of single-strand binding protein and 50-200 ng / mu l of escherichia coli DNA polymerase I. The invention further provides an isothermal nucleic acid amplification method. According to the isothermal nucleic acid amplification reaction reagent and the isothermal nucleic acid amplification method, nucleic acid amplification under the isothermal condition at the lower temperature is realized, and a traditional nucleic acid amplification reaction process is greatly simplified.
Owner:刘国宪
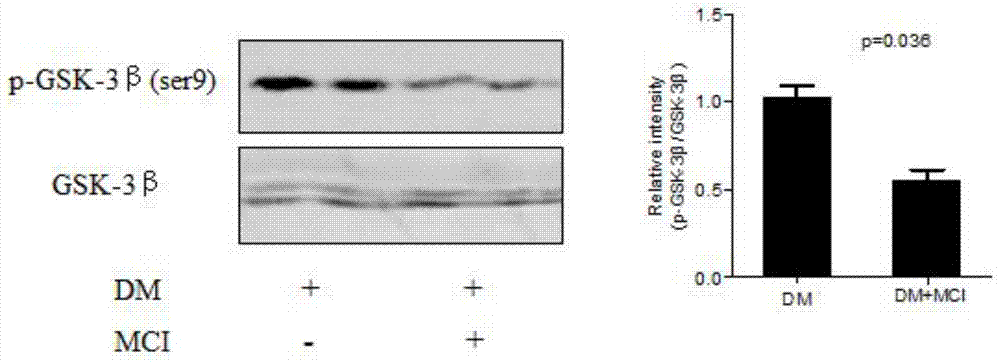
Novel serology biomarker GSK3beta detection method for cognitive impairment of diabetic
The invention provides a novel serology biomarker GSK3beta detection method for cognitive impairment of a diabetic. The method comprises an enzyme activity assay method and a relative quantification dot-blot method. According to the enzyme activity assay method, a GSK-3beta enzyme activity assay kit of GENMED is applied; GSK-3beta phosphorylation is performed under the suppression of GSK-3alpha; along with oxidation reaction of reduced form of nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotid (NADH), a pyruvate kinase and lactic dehydrogenase continuous circulation method reaction system adopts the spectrophotometric method to measure the peak value change after oxidization so as to reflect GSK 3beta activity in a sample. The dot-blot method transfers blood platelet protein to an NC film according to the antigen and antibody fixation reaction principle and then utilizes antibody to perform detection. The novel serology biomarker GSK3beta detection method is used for studying GSK-3beta protein and enzyme activity expression in the diabetic blood and is expected to become a serology biomarker for early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD).
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant microbe capable of yielding N-acetylneuraminic acid and application of recombinant microbe
ActiveCN113122491AReduce manufacturing costIncrease the level of fermentation productionBacteriaTransferasesNeuraminic acidMicrobiology
The invention relates to the technical field of microbial fermentation and particularly discloses a recombinant microbe capable of yielding N-acetylneuraminic acid and application of the recombinant microbe. According to the recombinant microbe provided by the invention, compared with an original strain, the recombinant microbe has lowered expression of pyruvate kinase and / or enzymatic activity; the pyruvate kinase is pyruvate kinase I and / or pyruvate kinase II; and the original strain is a microbe capable of synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid. Compared with the original strain capable of synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid, the recombinant microbe provided by the invention has lowered expression of the pyruvate kinase and / or enzymatic activity. The recombinant microbe is especially adapted for generating the N-acetylneuraminic acid through carrying out fermentation culture by using a cheap low-carbon raw material, i.e., glucose. According to the recombinant microbe provided by the invention, the fermentation level of synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid is high, the production cost of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is reduced remarkably, and thus, the recombinant microbe has industrialized potentials.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
ADP detection using an enzyme-coupled reaction
ActiveUS7410755B2Minimize contaminationMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulinsFluorescencePeroxidase
Methods and compositions are provided for determining ADP in the presence of ATP. These comprise including among the assay reagents at least one of the correcting components creatine phosphokinase and phosphocreatine, pyruvate kinase and phosphoenolpyruvate, peroxidase and a non-interfering peroxidase substrate, and catalase. One aspect of the method employs formation of hydrogen peroxide from the ADP by pyruvate kinase, phosphoenolpyruvate and pyruvate oxidase. The hydrogen peroxide is then determined. A combined reagent having all of the reagents may optionally include a peroxidase when the hydrogen peroxide is to be enzymatically determined. A peroxidase substrate is added to the sample in conjunction with the peroxidase substrate reagent, the mixture incubated and depending on whether the peroxidase substrate is a fluorescer or chemiluminescer, the mixture may be illuminated with excitation light and the emitted light determined as a measure of the ADP in the sample.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Method for measuring 1,5-anhydroglucitol by oxidase
InactiveCN103725749AEliminate distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementPhosphoric acidGlucose polymers
The invention relates to a method for measuring 1,5-anhydroglucitol by oxidase, which can be widely applied in the field of medical and biochemical technologies. The method comprises the following steps of: converting glucose (Glu) in a sample into fructose-6-phosphate (Fru-6-P) by glucokinase (GK) and phosphoglucose isomerase (PGI), and establishing an ATP regeneration system by pyruvate kanise (PK) and phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) in the system so as to ensure that Glu is converted into Fru-6-P. In the sample, 1,5-AG reacts in the presence of pyranose oxidase (PROD) to produce 1,5-fructosan (1,5-AF) and H2O2, and then H2O2 is colored and quantified via a Trinder's system..
Owner:WENZHOU PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Kit for detecting avian onfectious synovitis antibody and preparation method
The invention provides an ELISA kit for detecting avian onfectious synovitis antibody. The kit adopts the ELISA kit for detecting the avian onfectious synovitis antibody, based on avian onfectious synovitis pyruvate kinase (PYK) recombinant protein as envelope antigen. The invention further provides a preparation method of the envelope antigen of the kit, namely PYK protein. The PYK protein prepared through the method has excellent reactogenicity, and the ELISA detection kit provides an effective method for the diagnosis of avian onfectious synovitis and the detection of an antibody level after immunization, and has an obvious promotion effect on the prevention research on avian onfectious synovitis.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Kalium ion diagnosis/measuring reagent kit and kalium ion concentration determination method
InactiveCN101464299AFast measurementImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsPotassiumEnzymatic Colorimetry
The invention relates to a kit for diagnosing / measuring potassium (ions) by utilizing the technologies of the enzymic colorimetry and the enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. The invention further relates to a method, a principle and the composition and the components of a reagent for measuring the concentration of the potassium (ions), and belongs to the technical field of medical / food / environmental inspection and measurement. The main components of the kit include a buffer solution, reduced coenzyme, adenosine diphosphate, a phosphoenolpyruvic acid, coenzyme A, pyruvate kinase, pyruvate oxidase, NADH peroxydase and a stabilizer. Through mixing a sample and the reagent by a certain volume ratio, a series of enzymatic reactions occur, then the reactant is placed under an ultraviolet / visible light analyzer, and the velocity of the decrease in absorbance at 340 nm of the dominant wavelength is detected, thereby measuring the concentration of potassium (ions).
Owner:SUZHOU ANJ BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
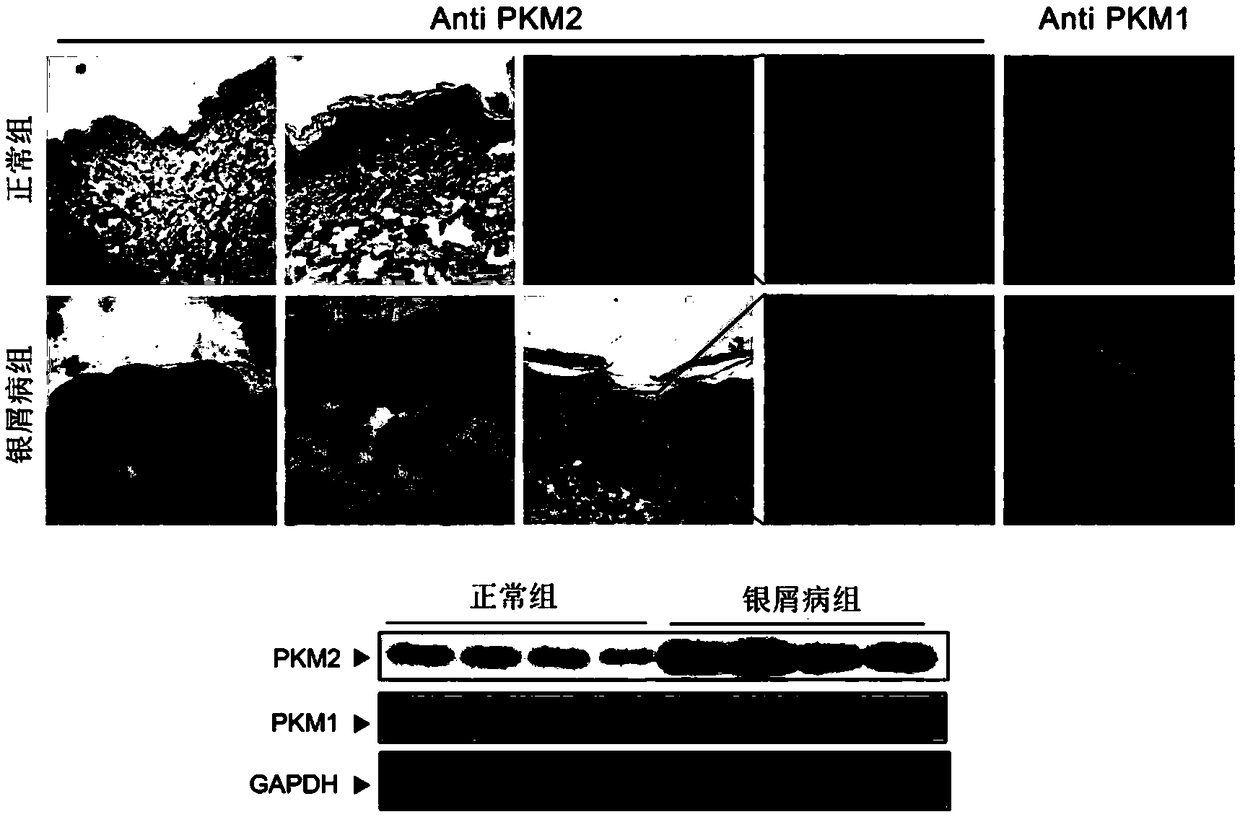
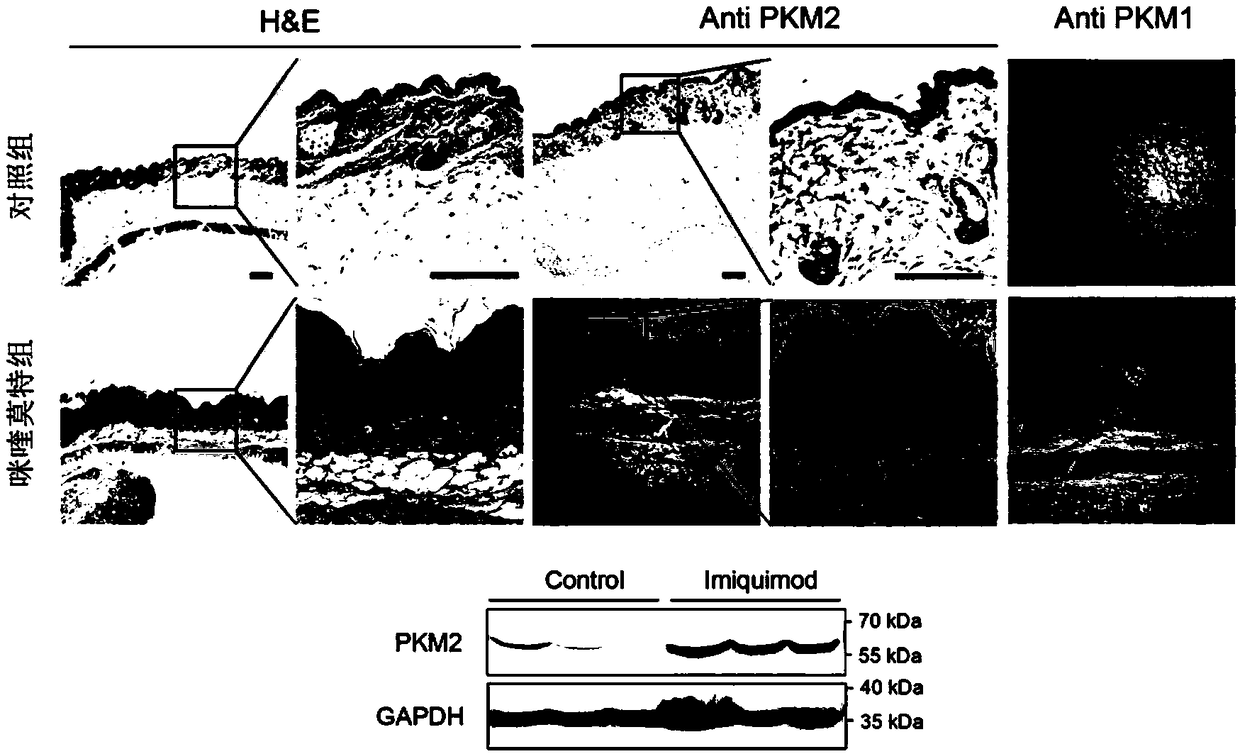
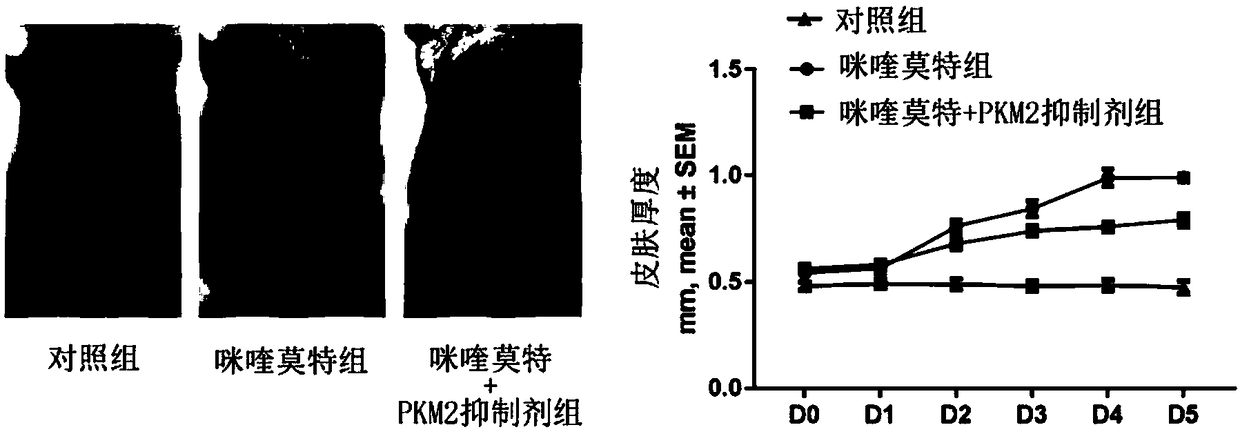
Application of M2 pyruvate kinase as drug target in preparation of drugs for prevention and treatment of psoriasis
InactiveCN108653736AInhibit hyperproliferationStop progressOrganic active ingredientsDermatological disorderMedicineDrug target
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
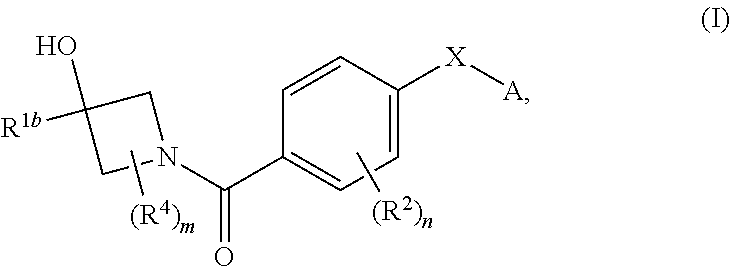
Therapeutic compounds and compositions
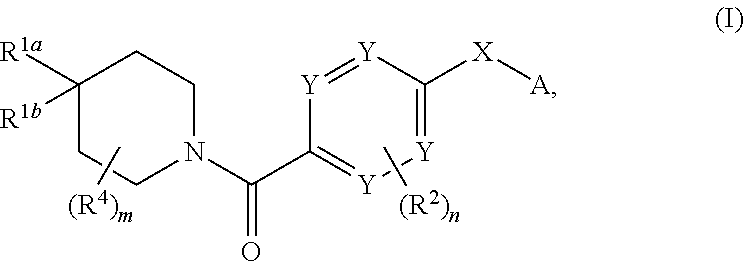
ActiveUS20140288081A1Extended service lifeHigh affinityBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsDiseaseKinase
Compounds of general formula I:and compositions comprising compounds of general formula I that modulate pyruvate kinase are described herein. Also described herein are methods of using the compounds that modulate pyruvate kinase in the treatment of diseases.
Owner:AGIOS PHARM INC
Compounds, Methods, and Treatments for Abnormal Signaling Pathways for Prenatal and Postnatal Development
The present invention relates to prevention of congenital deformations. The invention further relates to cancer inhibition and prevention. The invention further relates to methods and compositions to modulate, antagonize, or agonize disparate signaling pathways that may converge to regulate patterning events and gene expression during prenatal development, post-natal development, and during development in the adult organism. The invention also relates to activators or deactivators of pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2) for the treatment, prevention, or amelioration of diseases related to PKM2 function.
Owner:JENNINGS BARBARA BROOKE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com