Patents
Literature
280 results about "Free protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
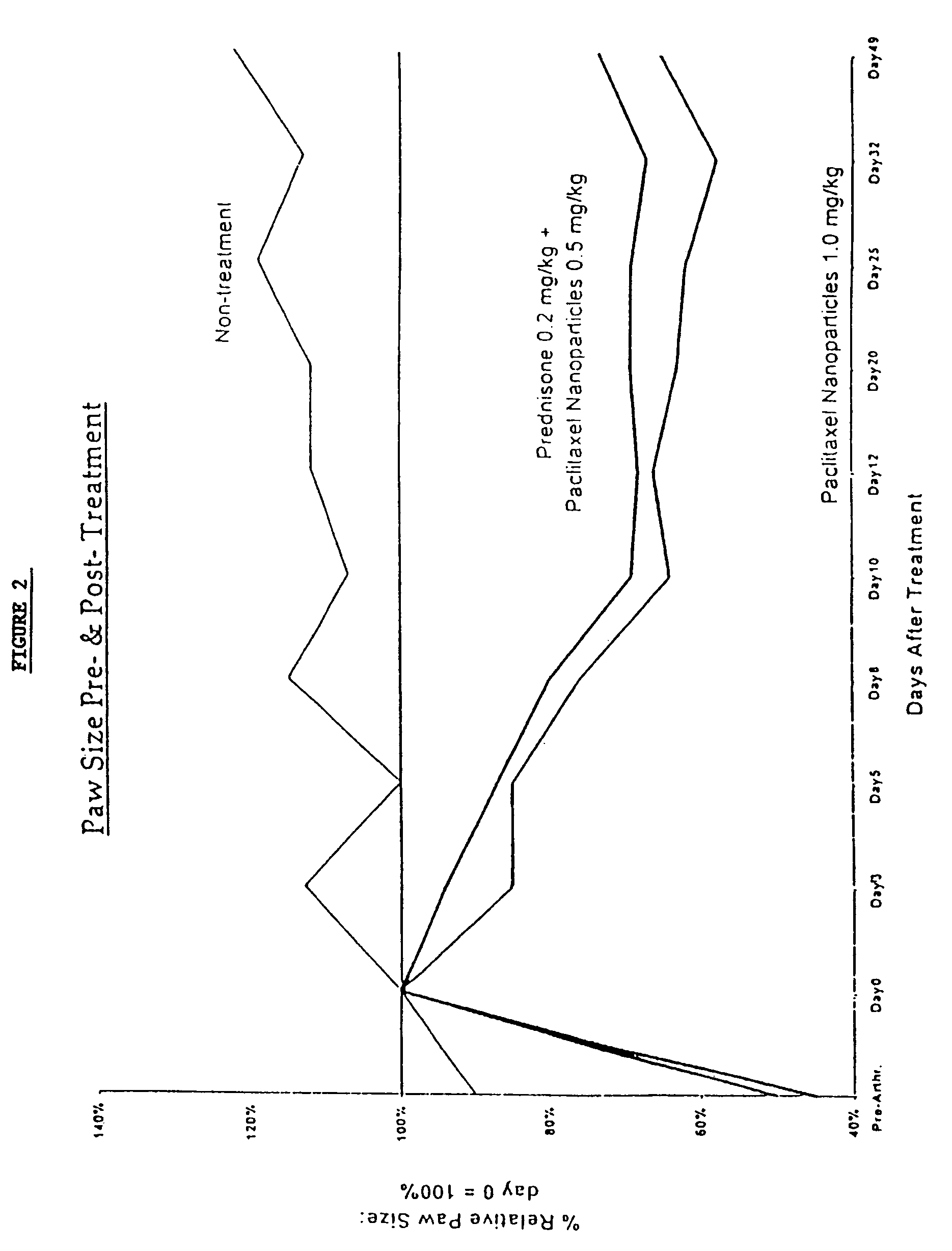
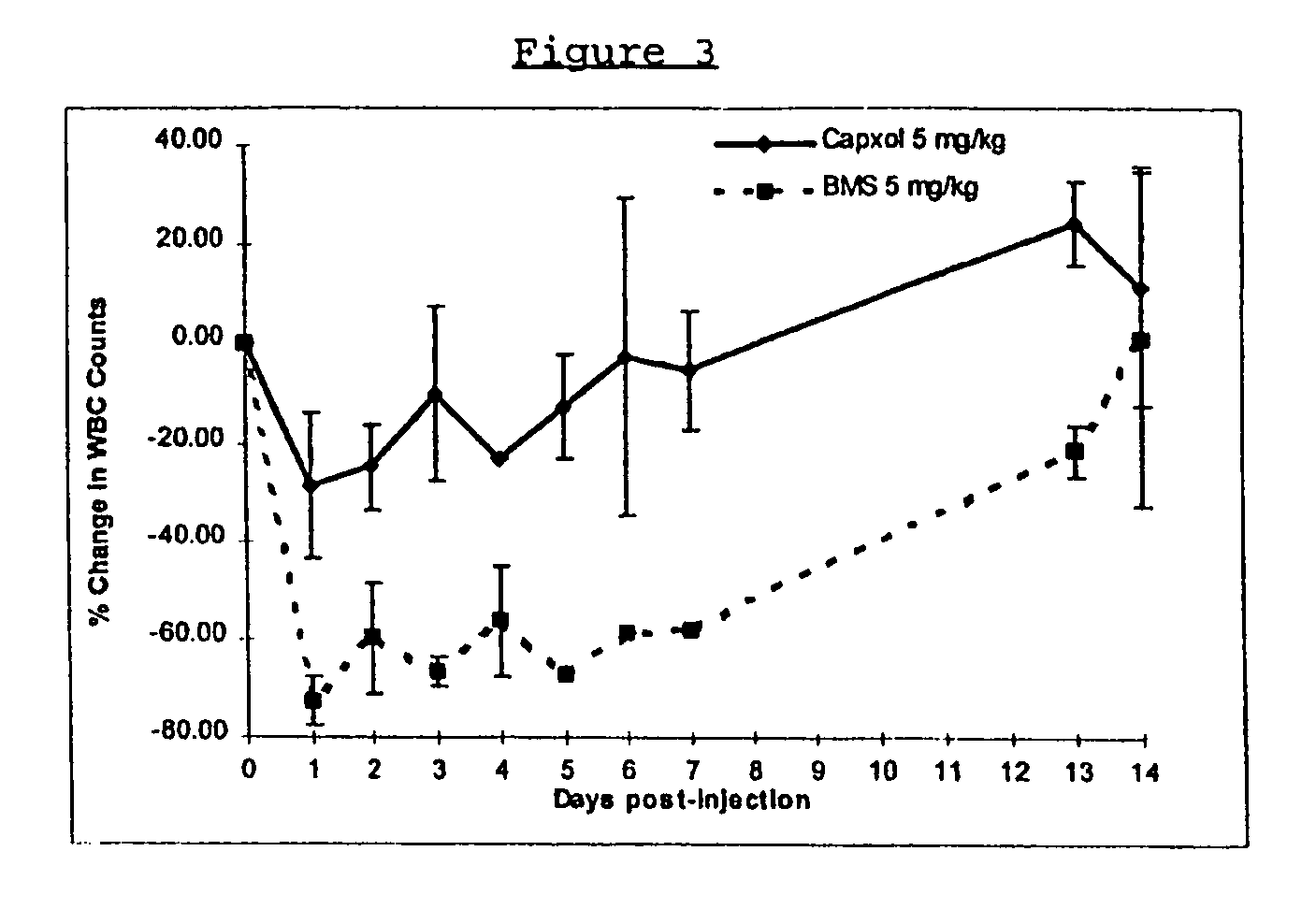
Protein stabilized pharmacologically active agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS6749868B1Low toxicityLong half-lifePowder deliveryEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsSuspended particlesFree protein
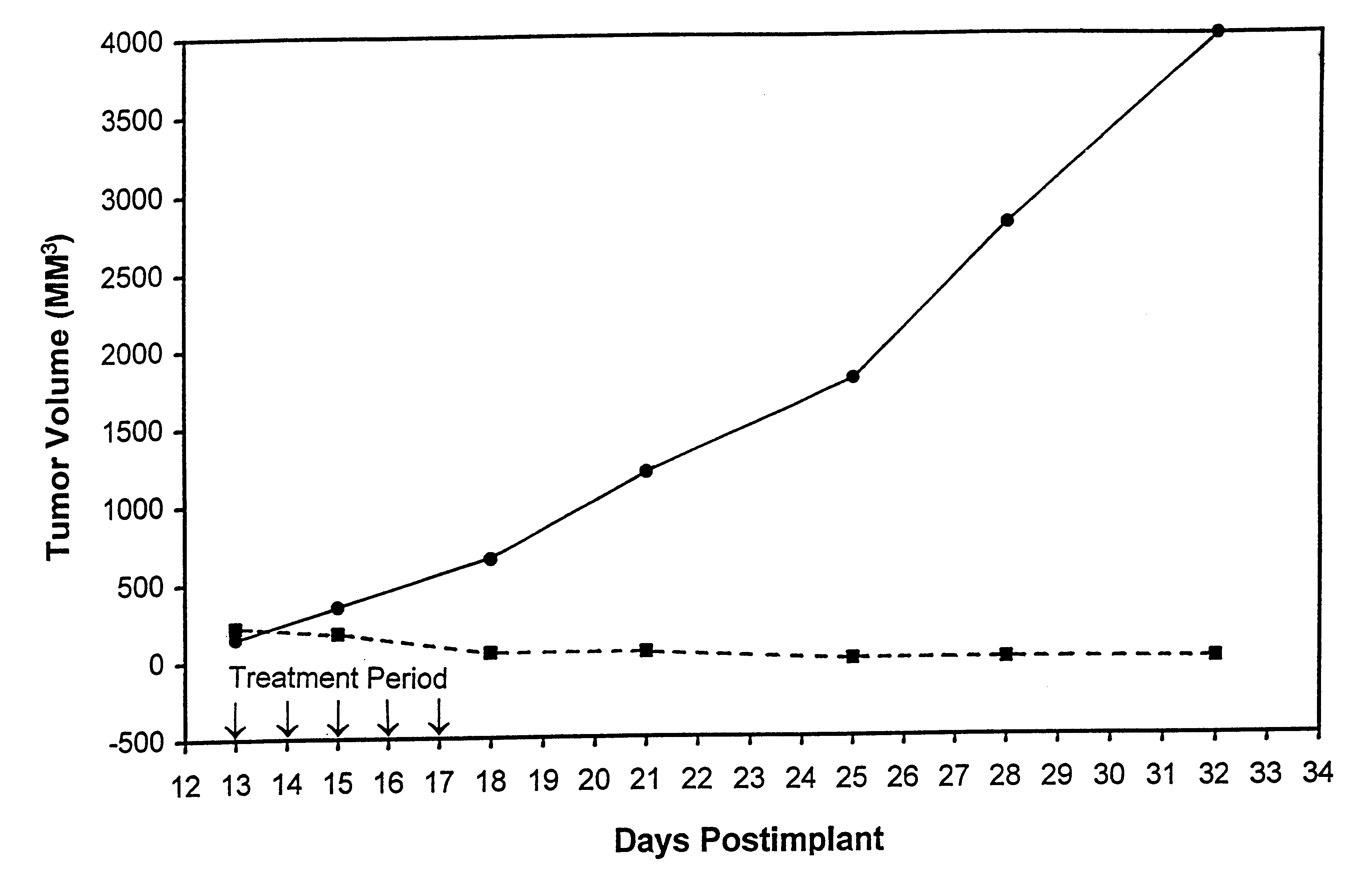
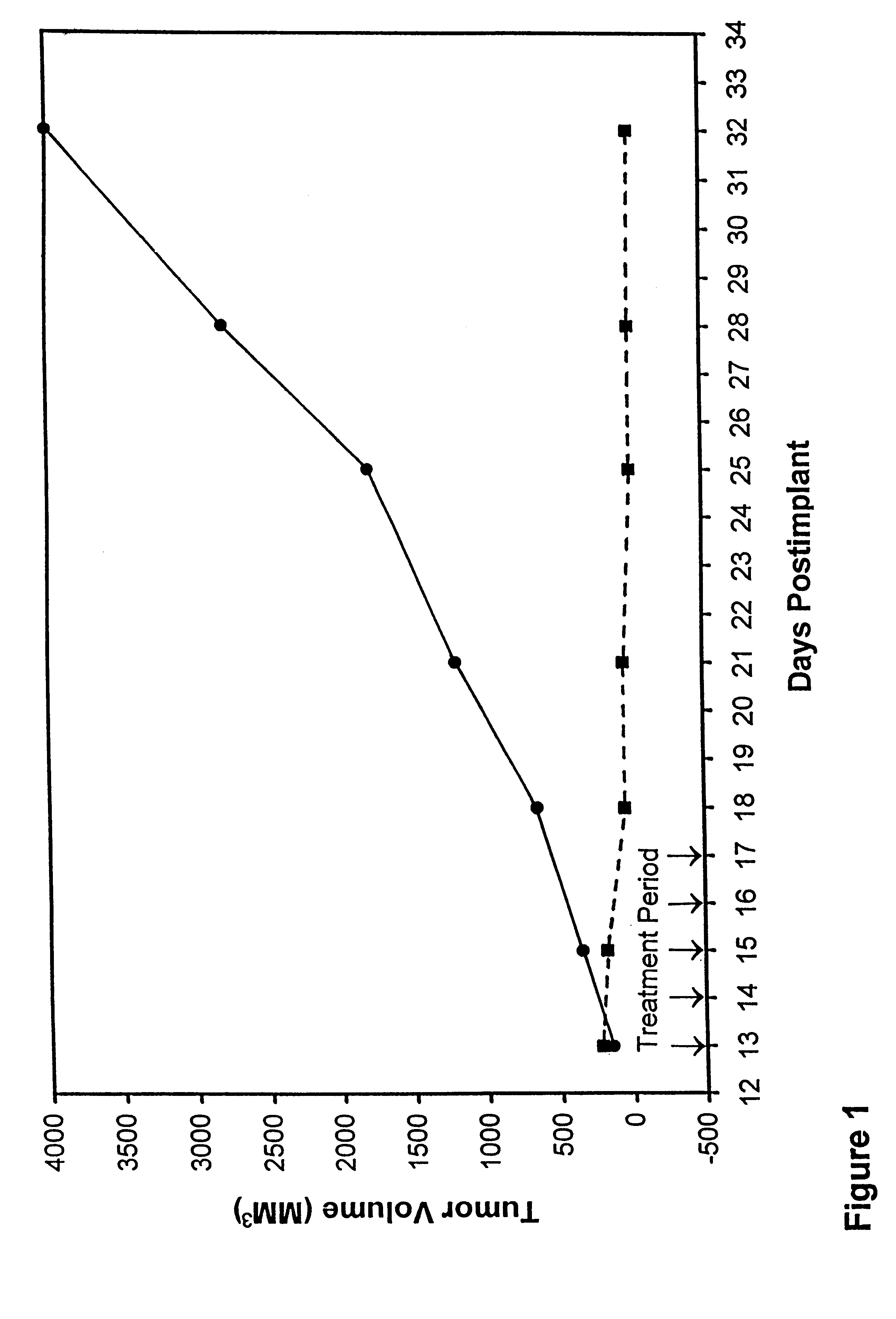
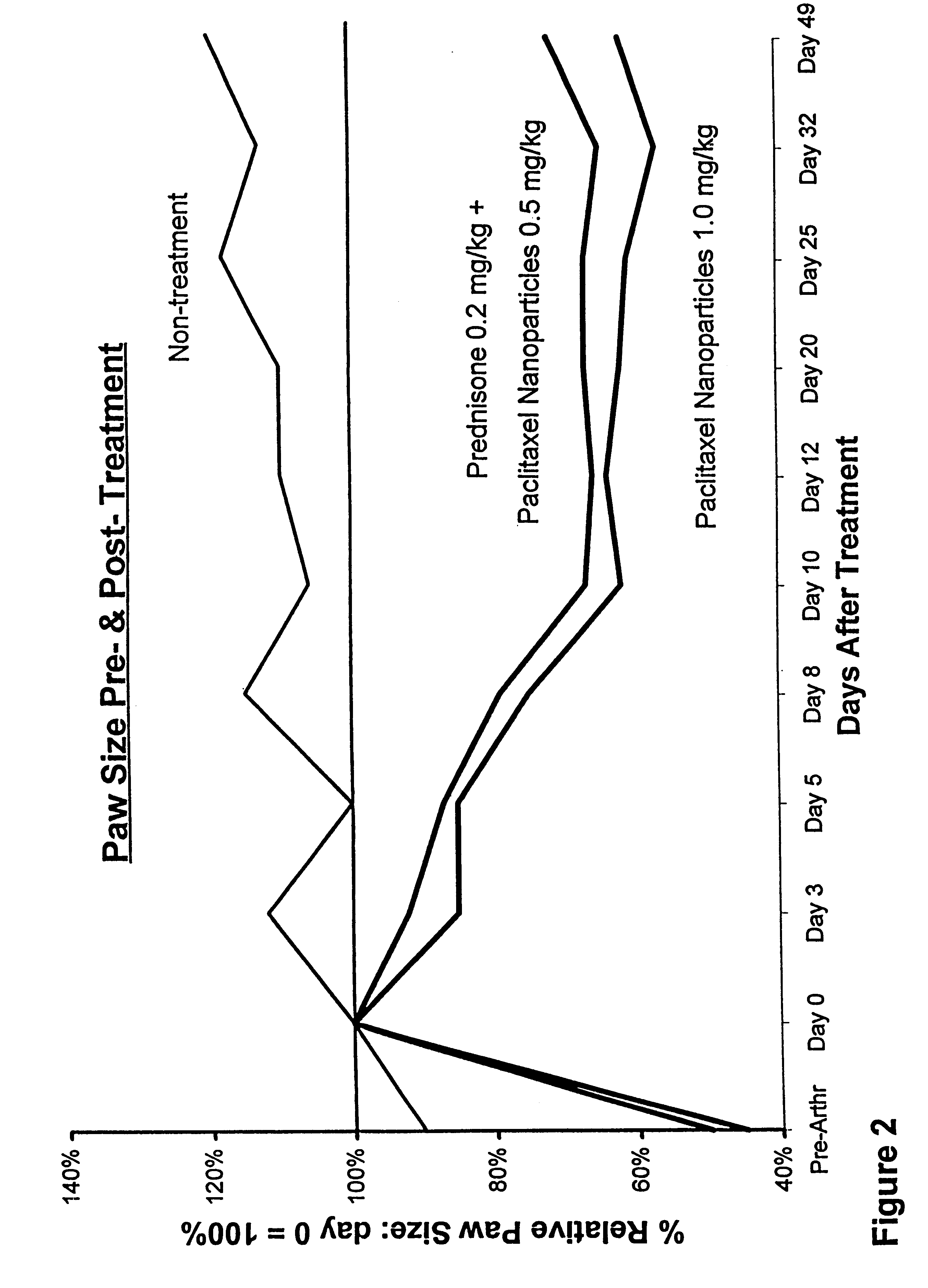
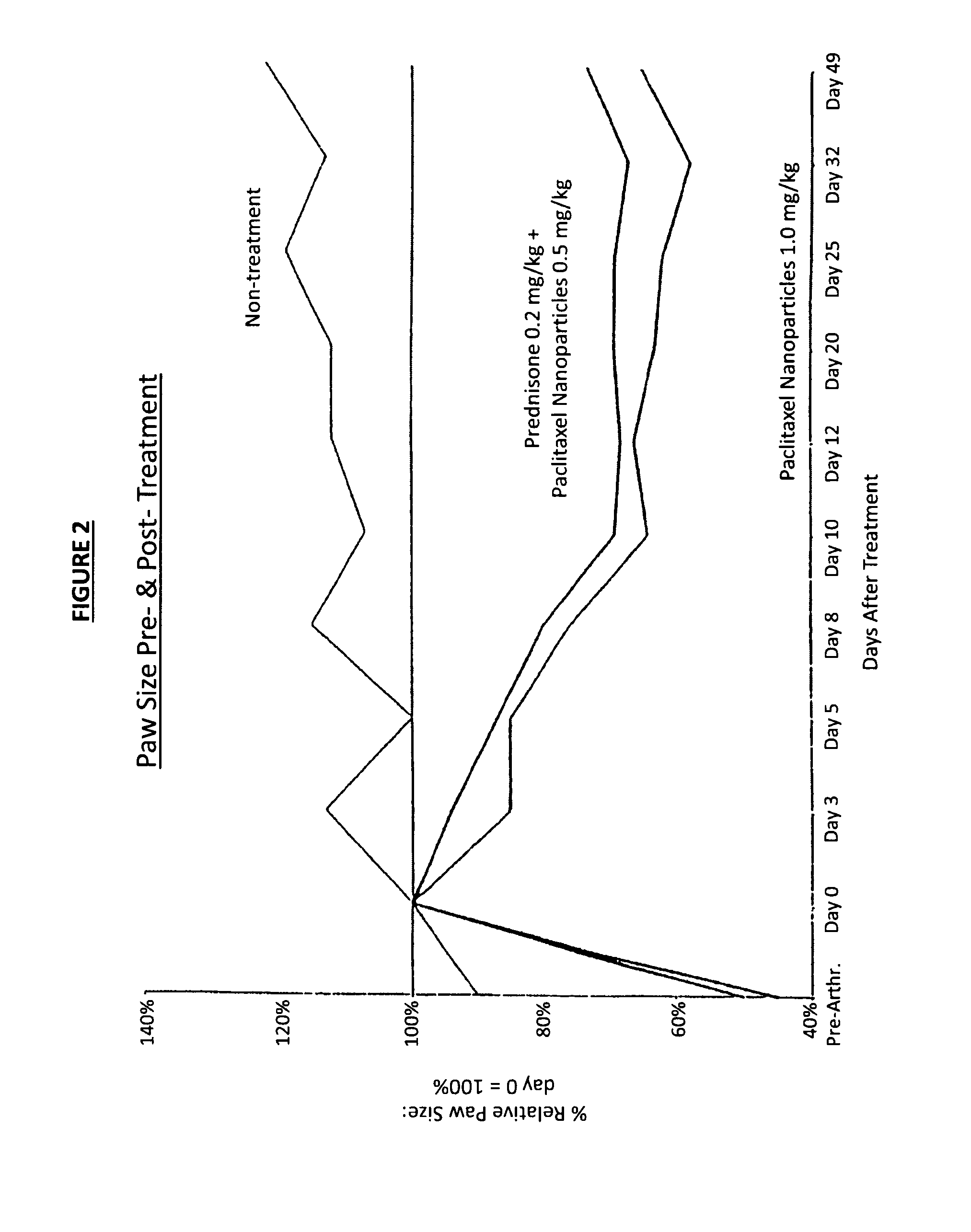
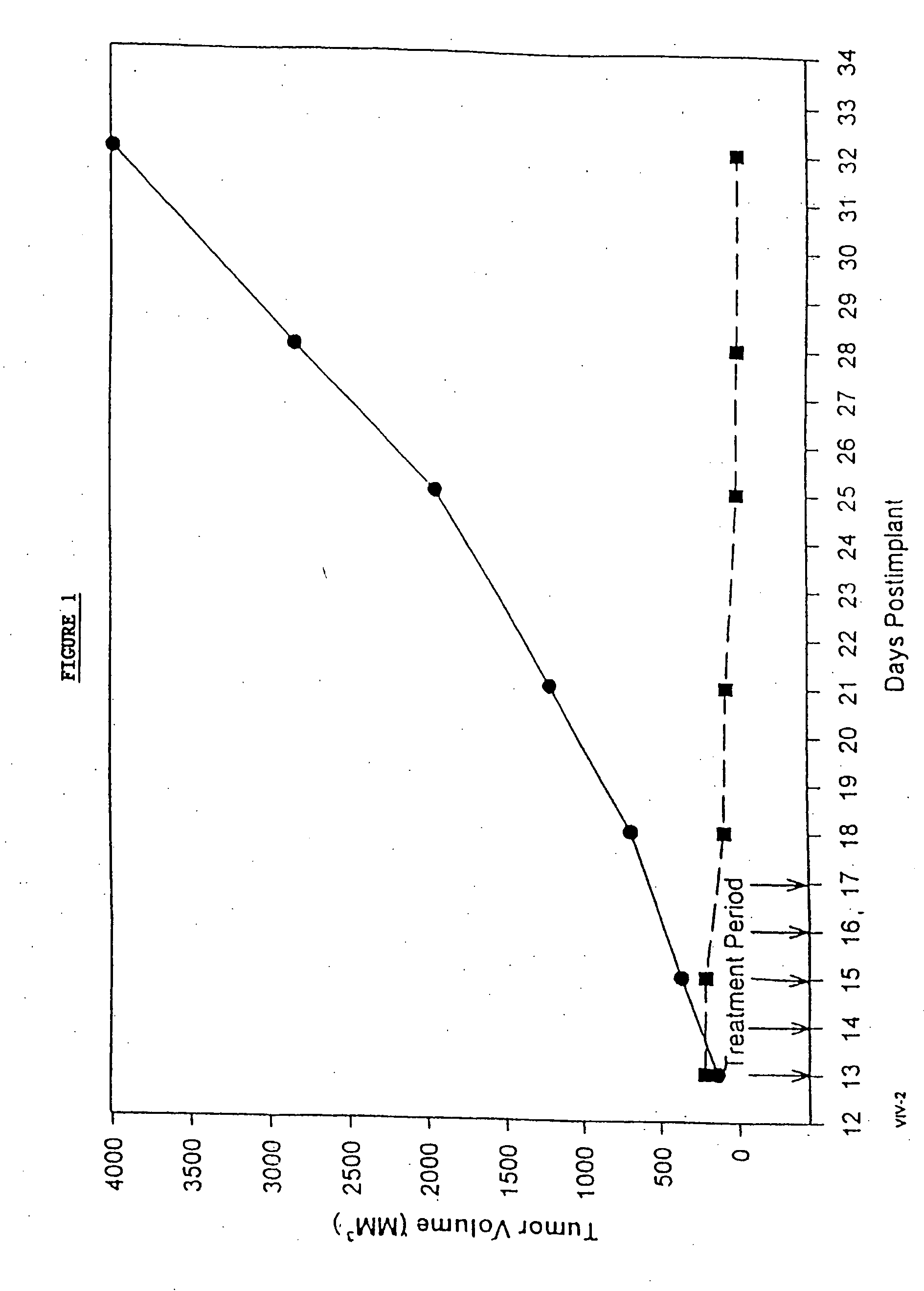
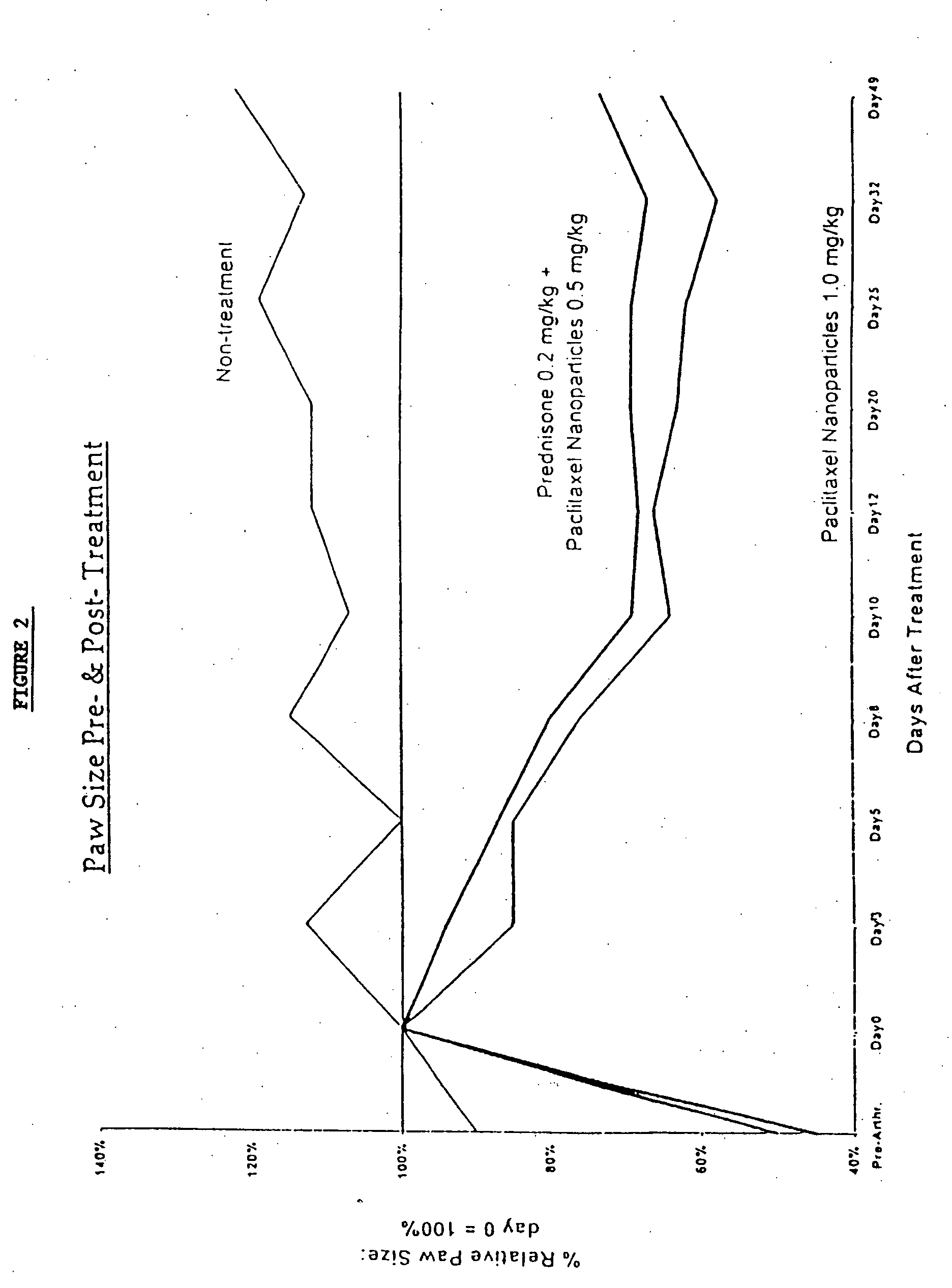
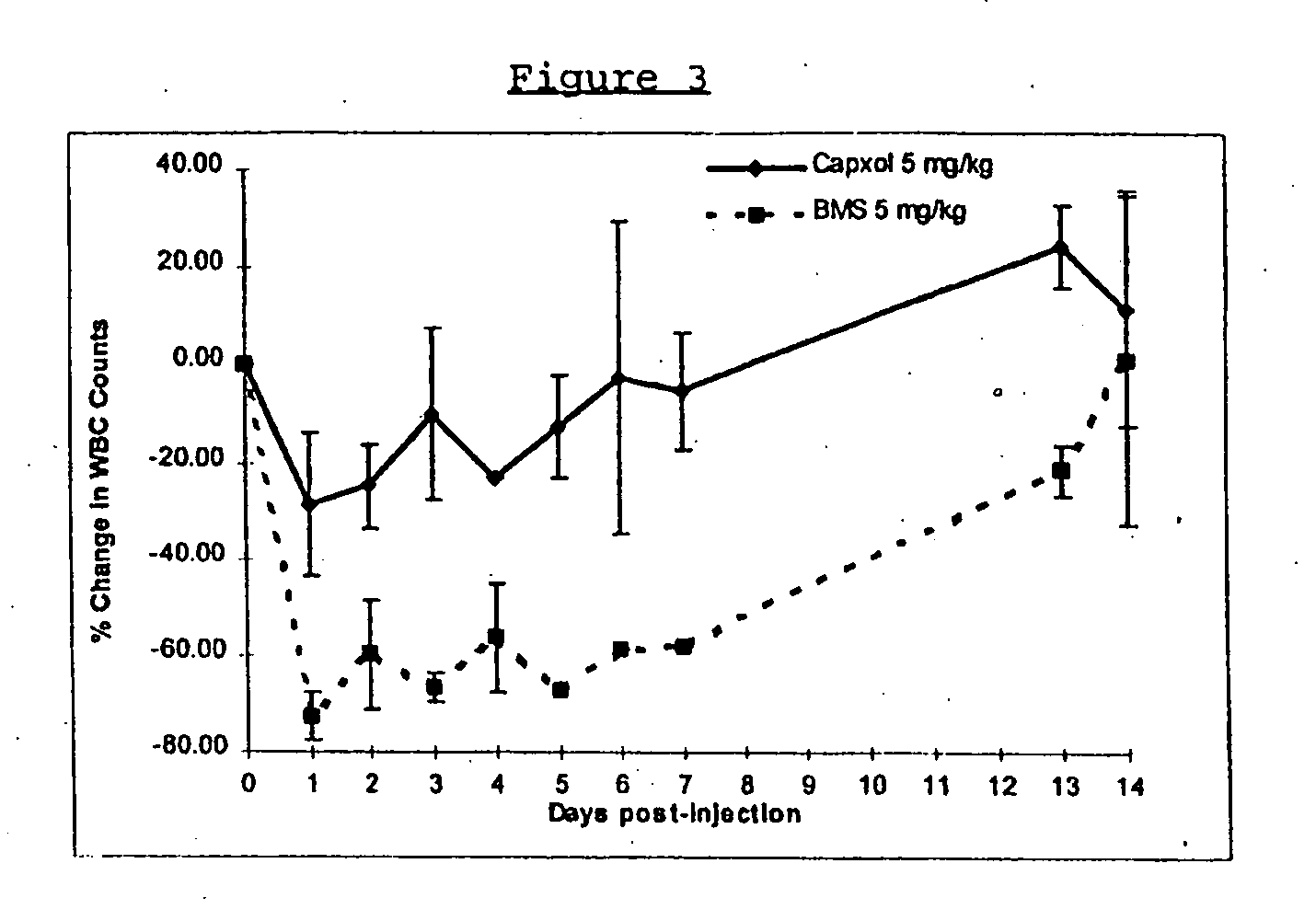
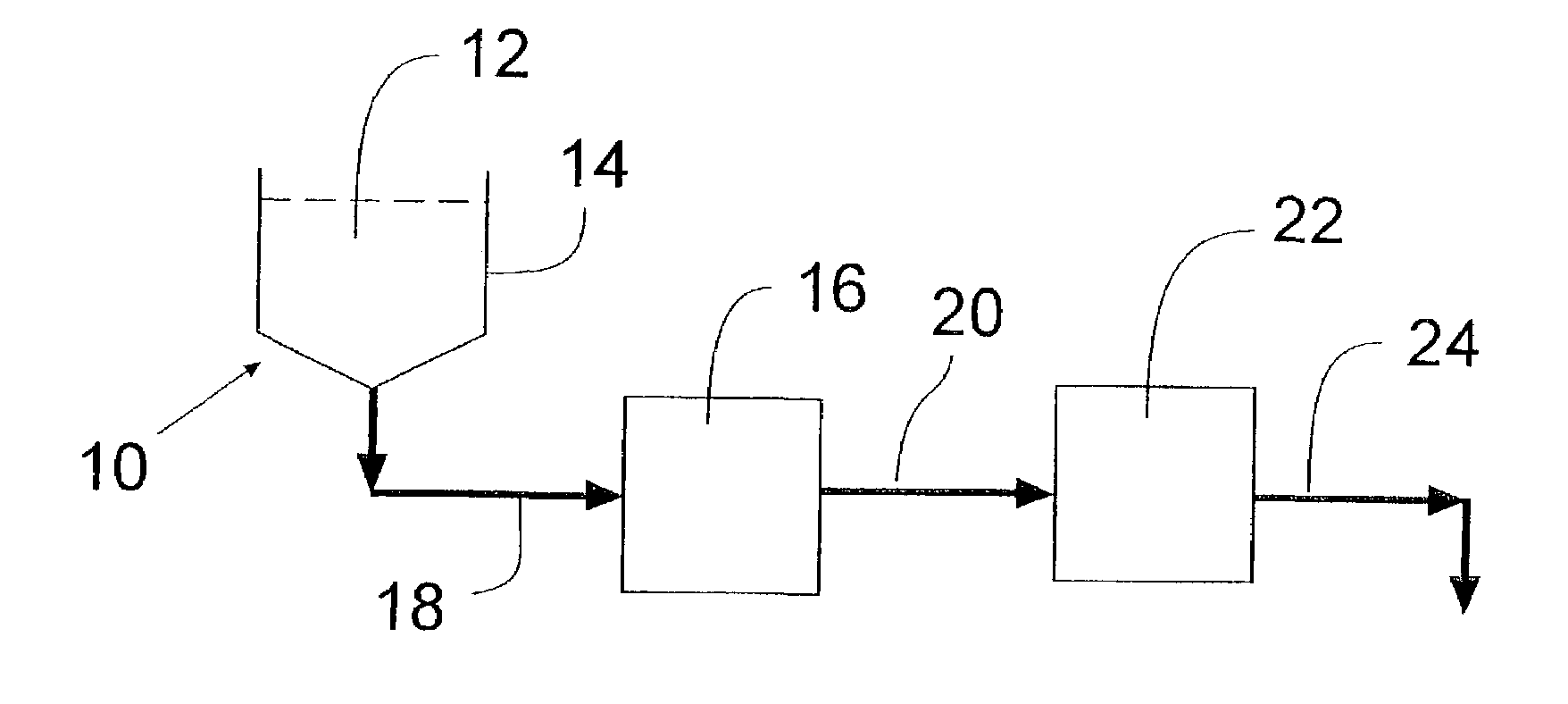
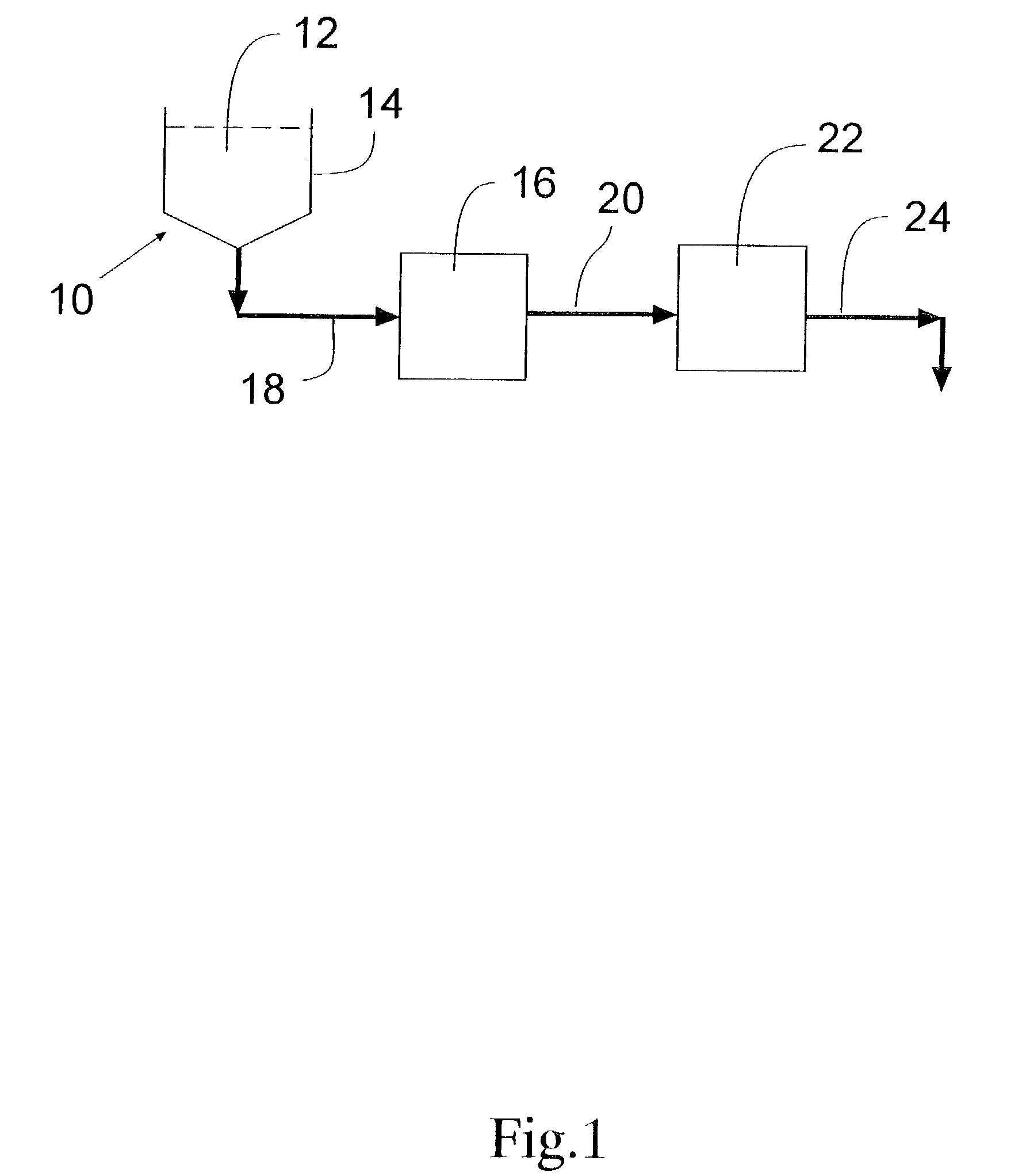
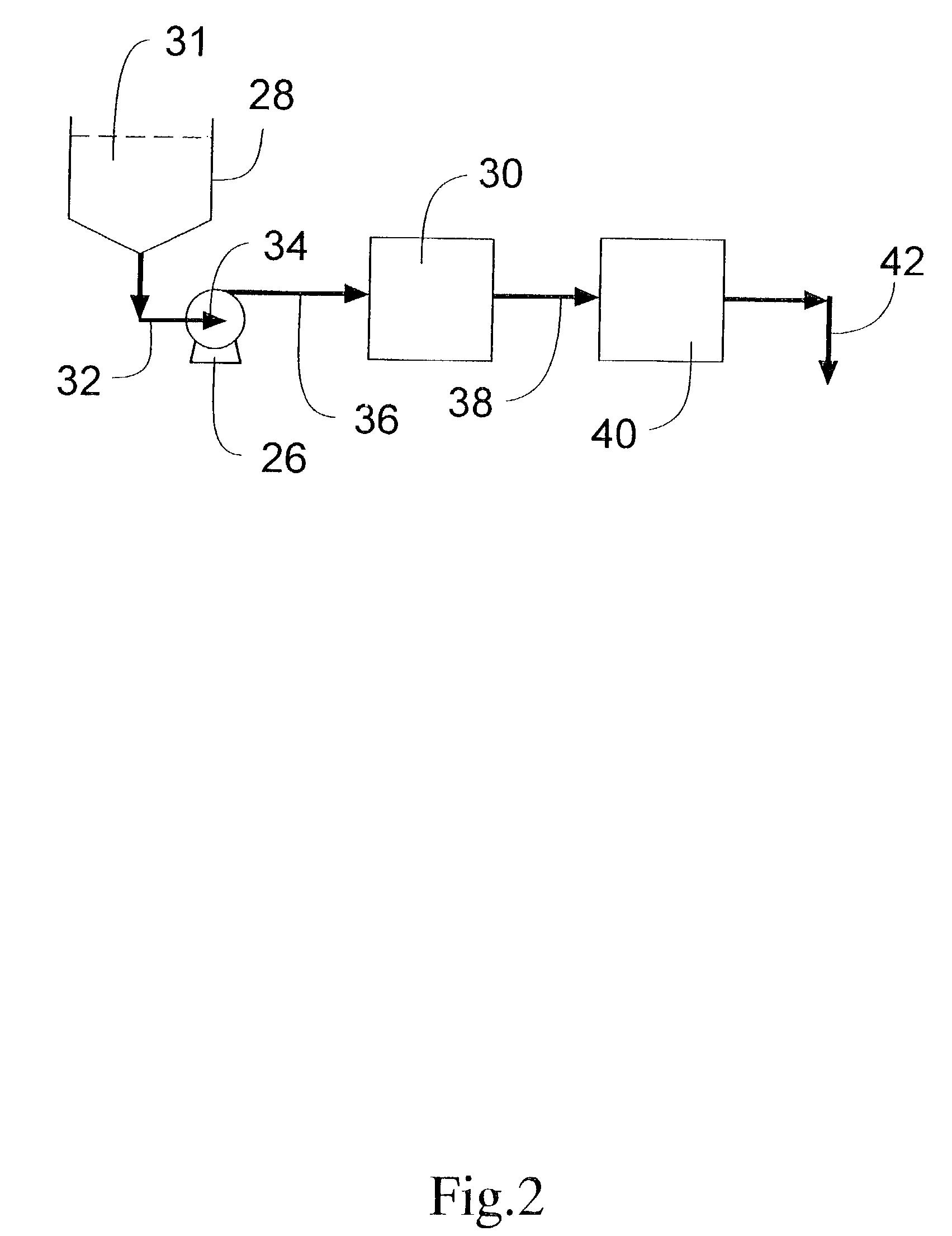
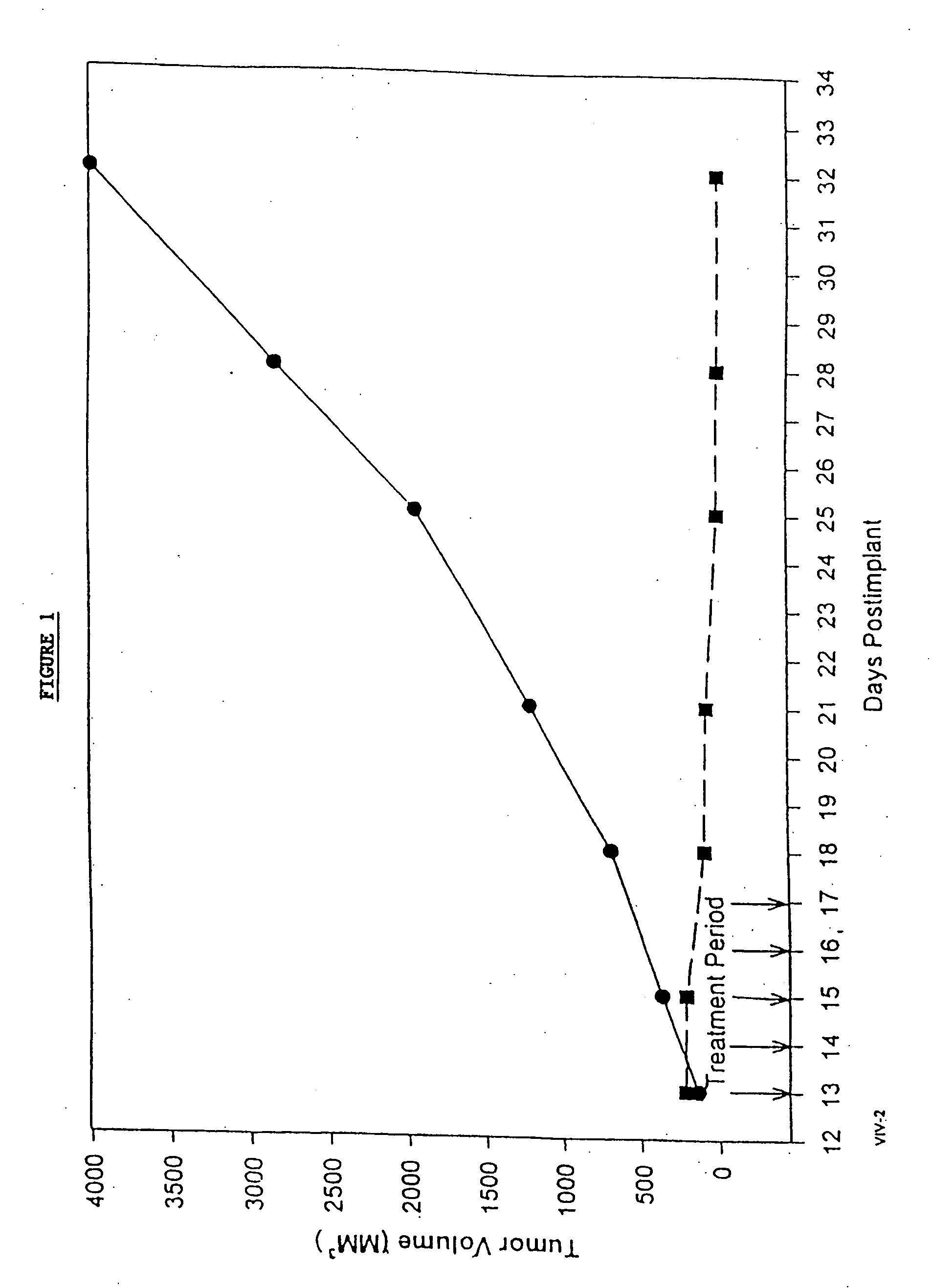
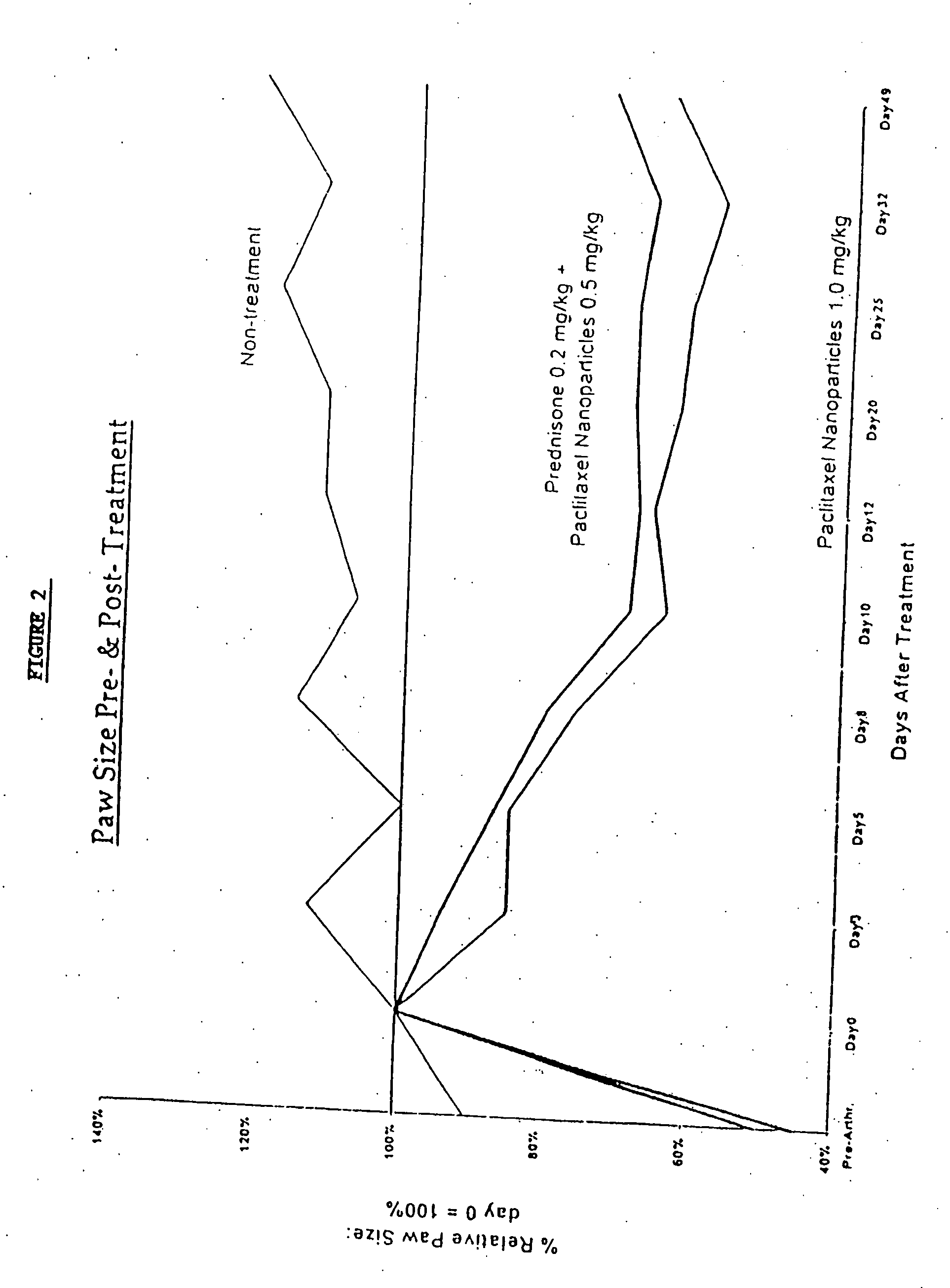
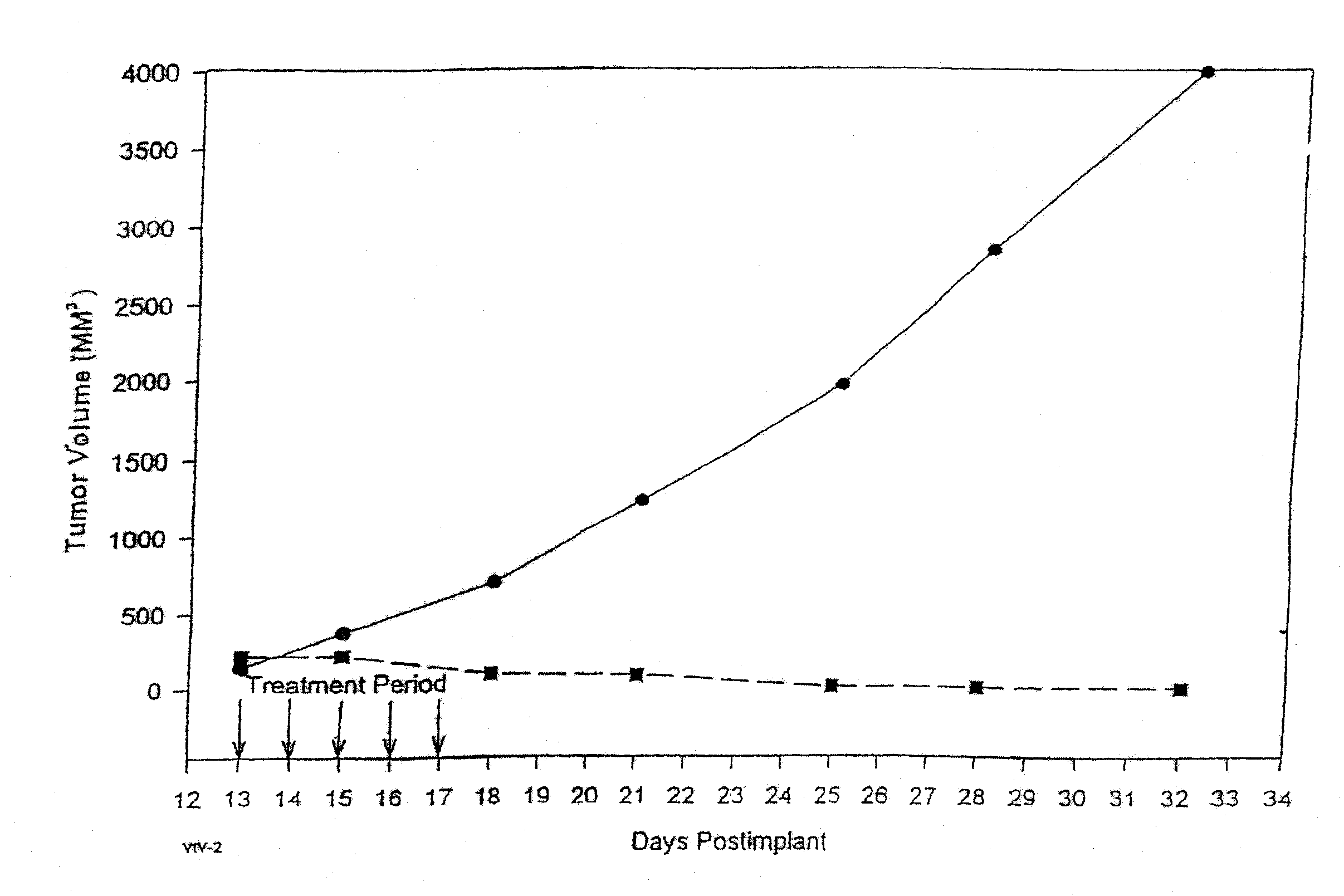
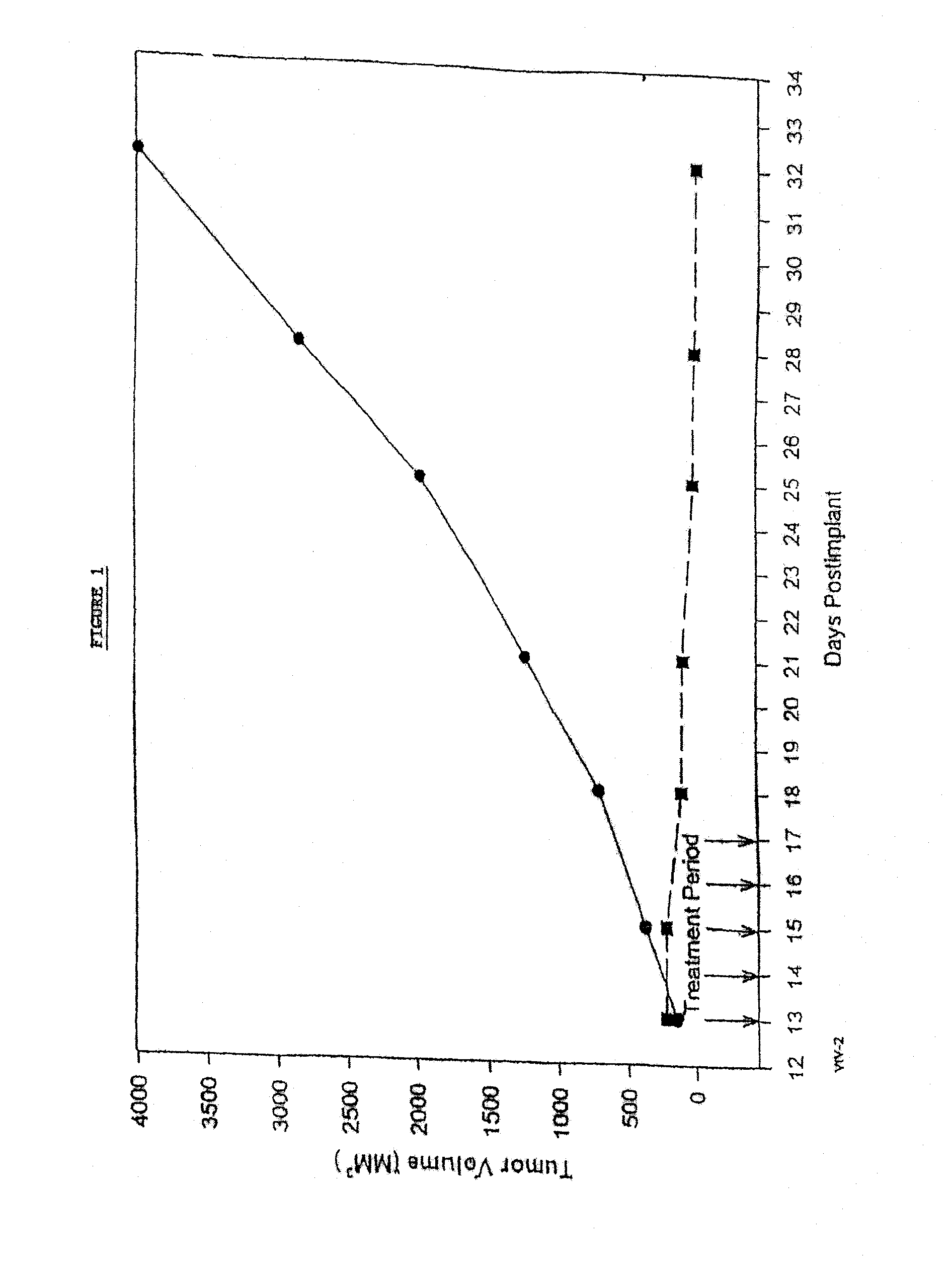
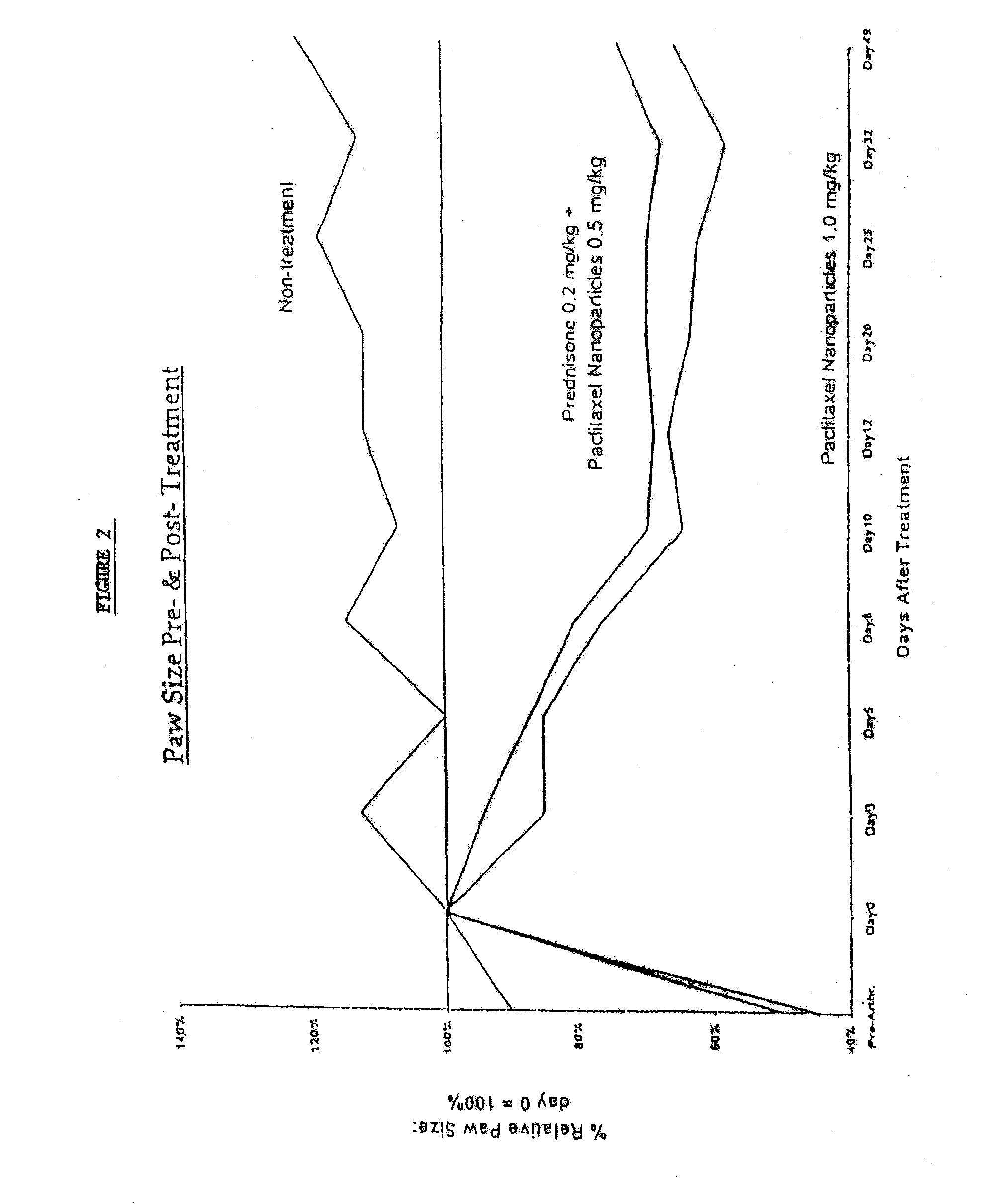
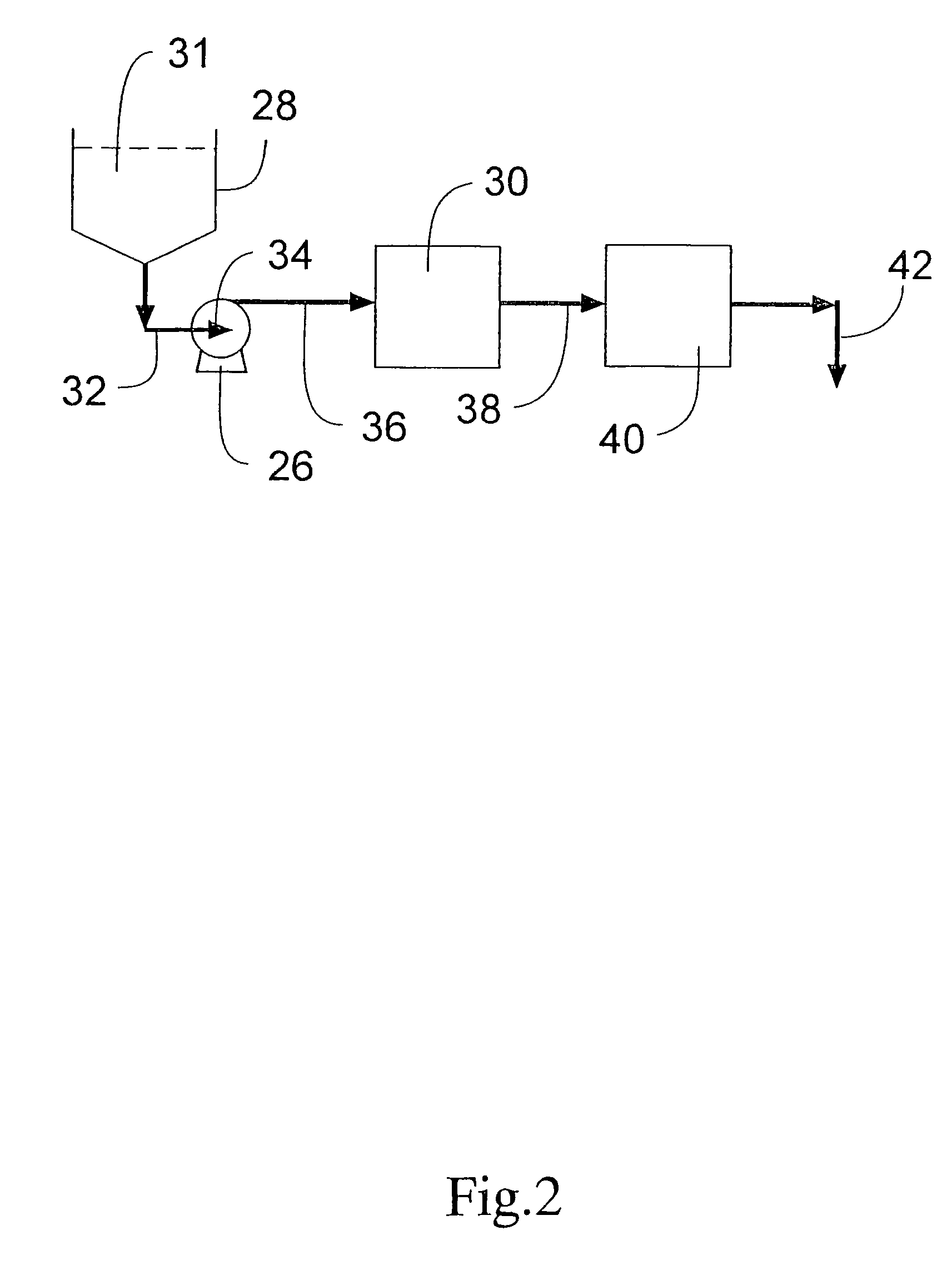
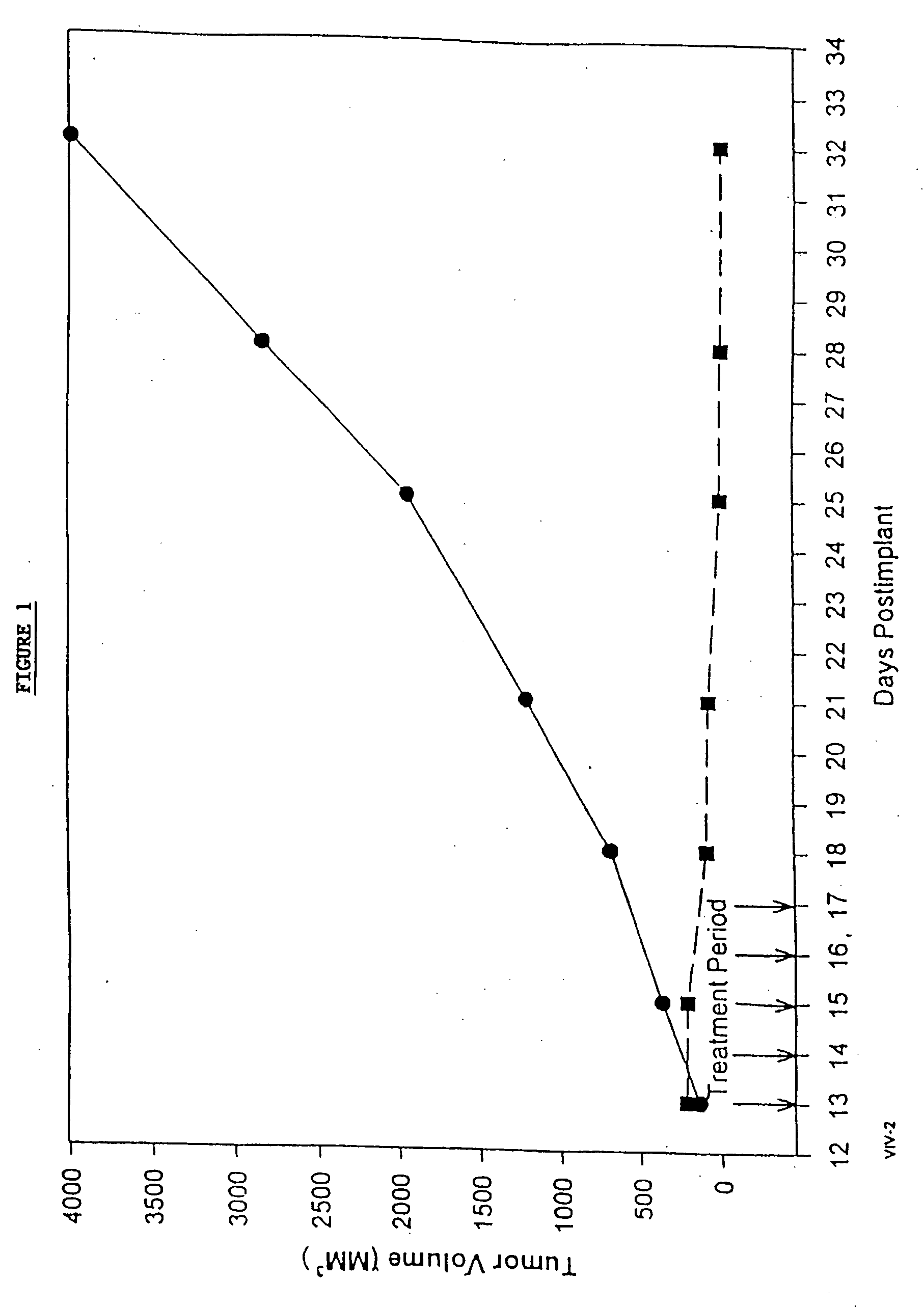
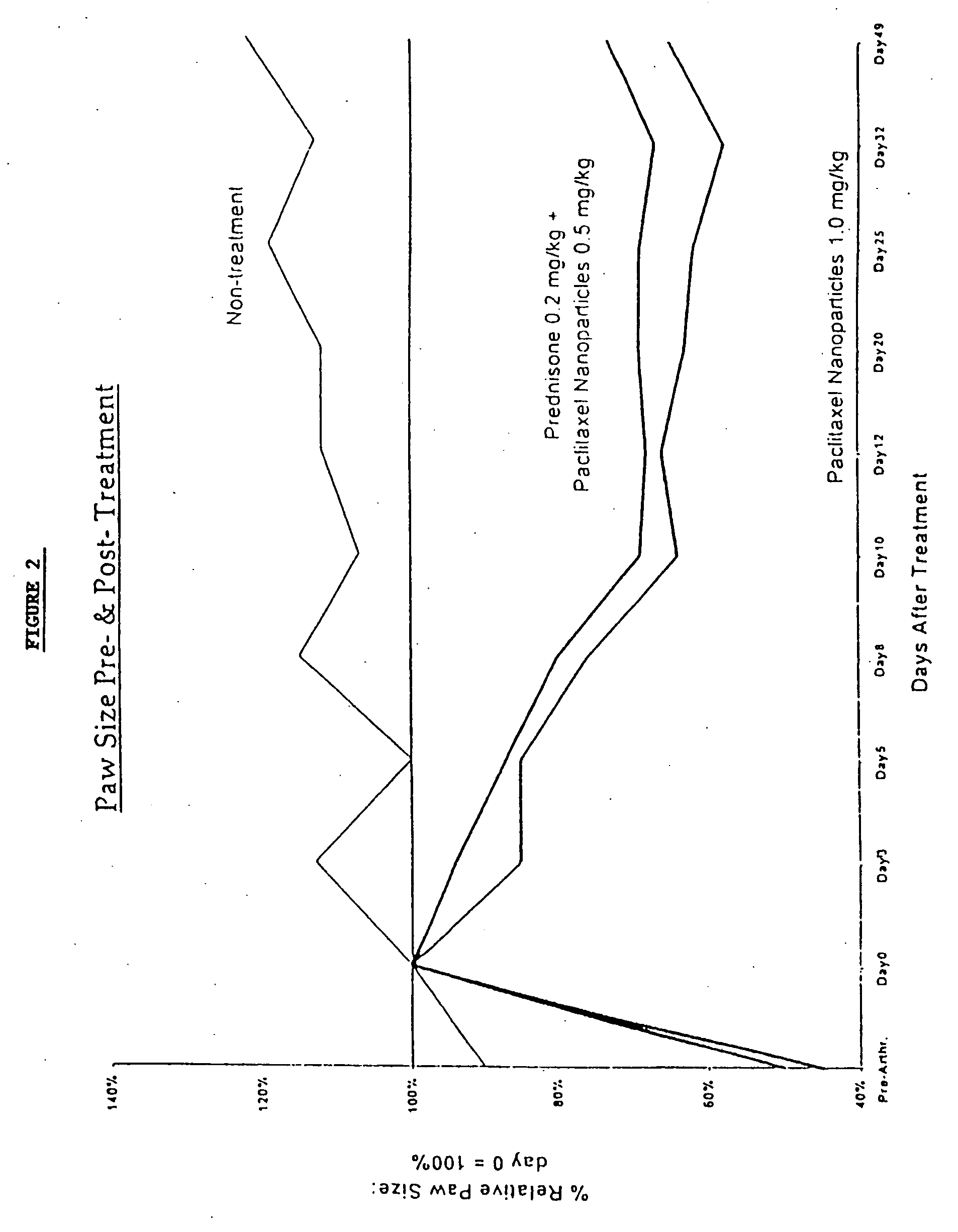
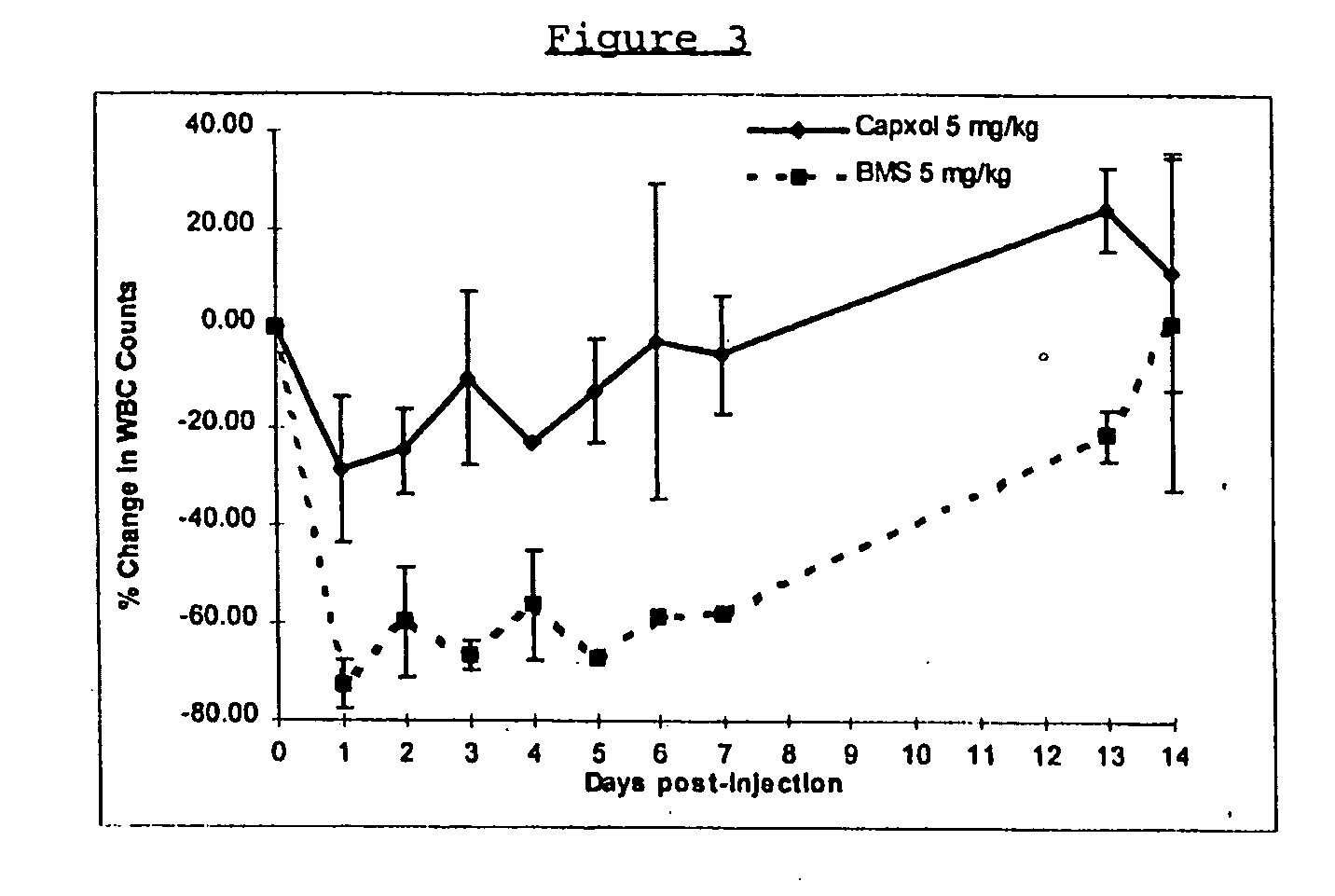
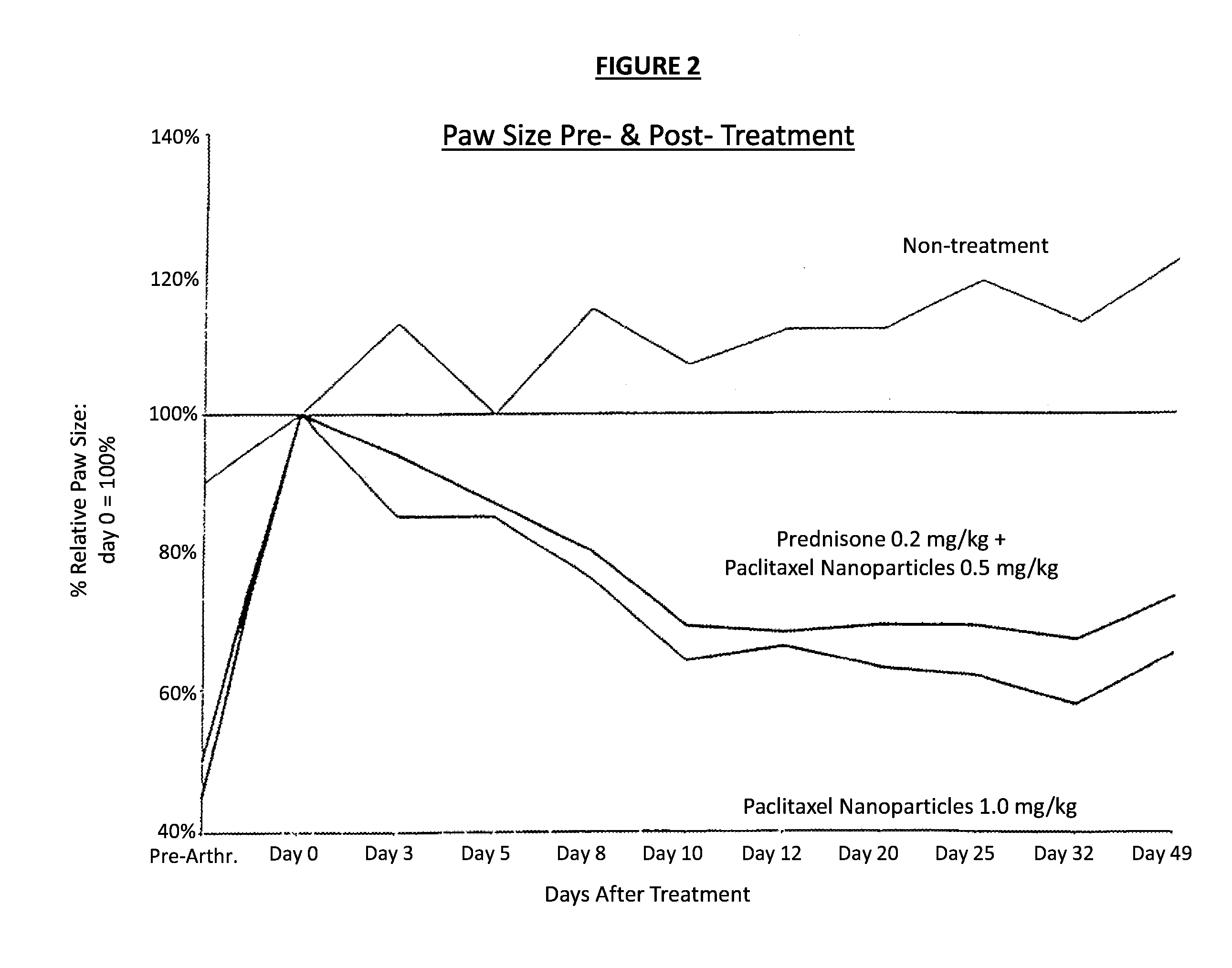
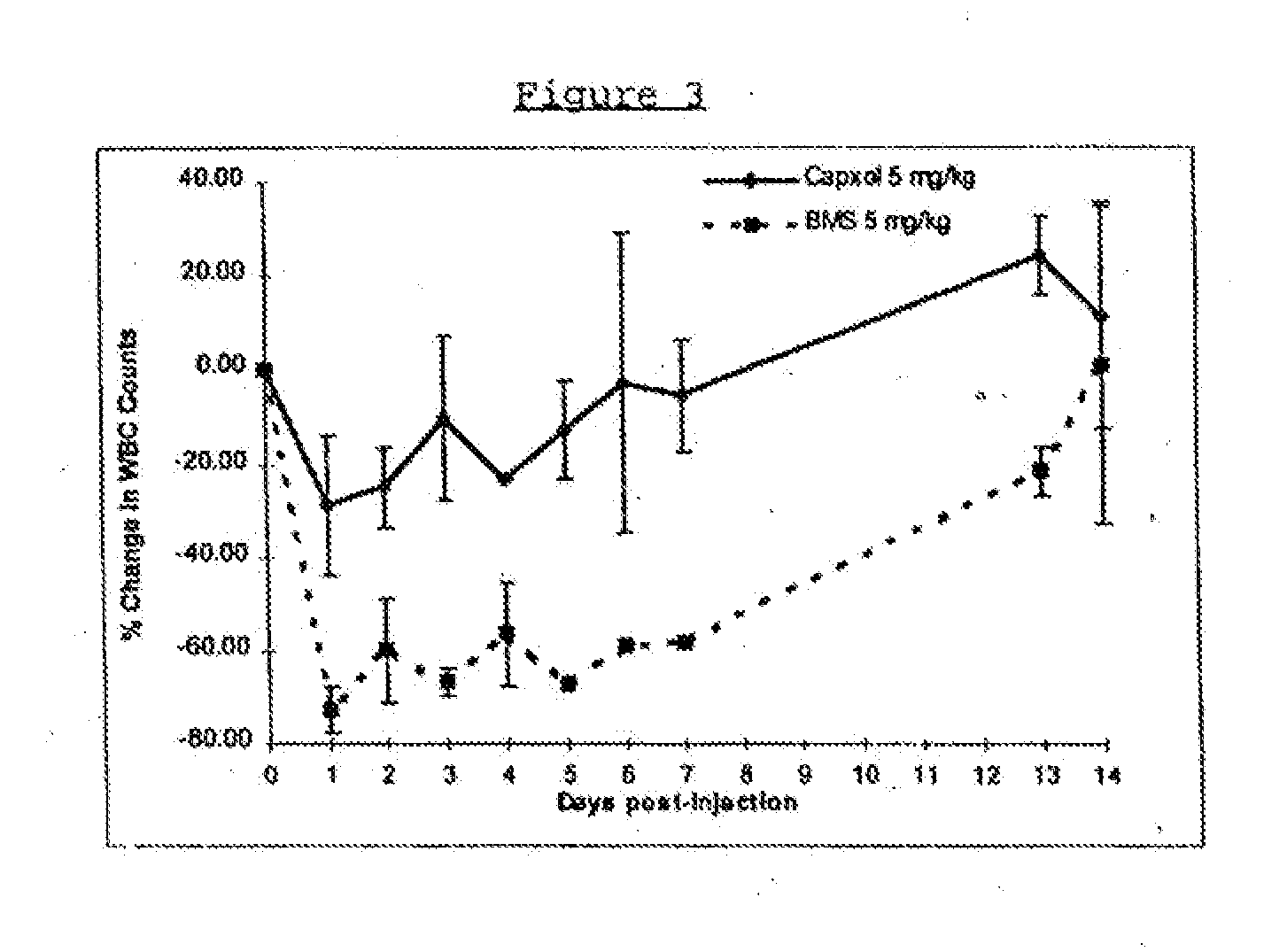
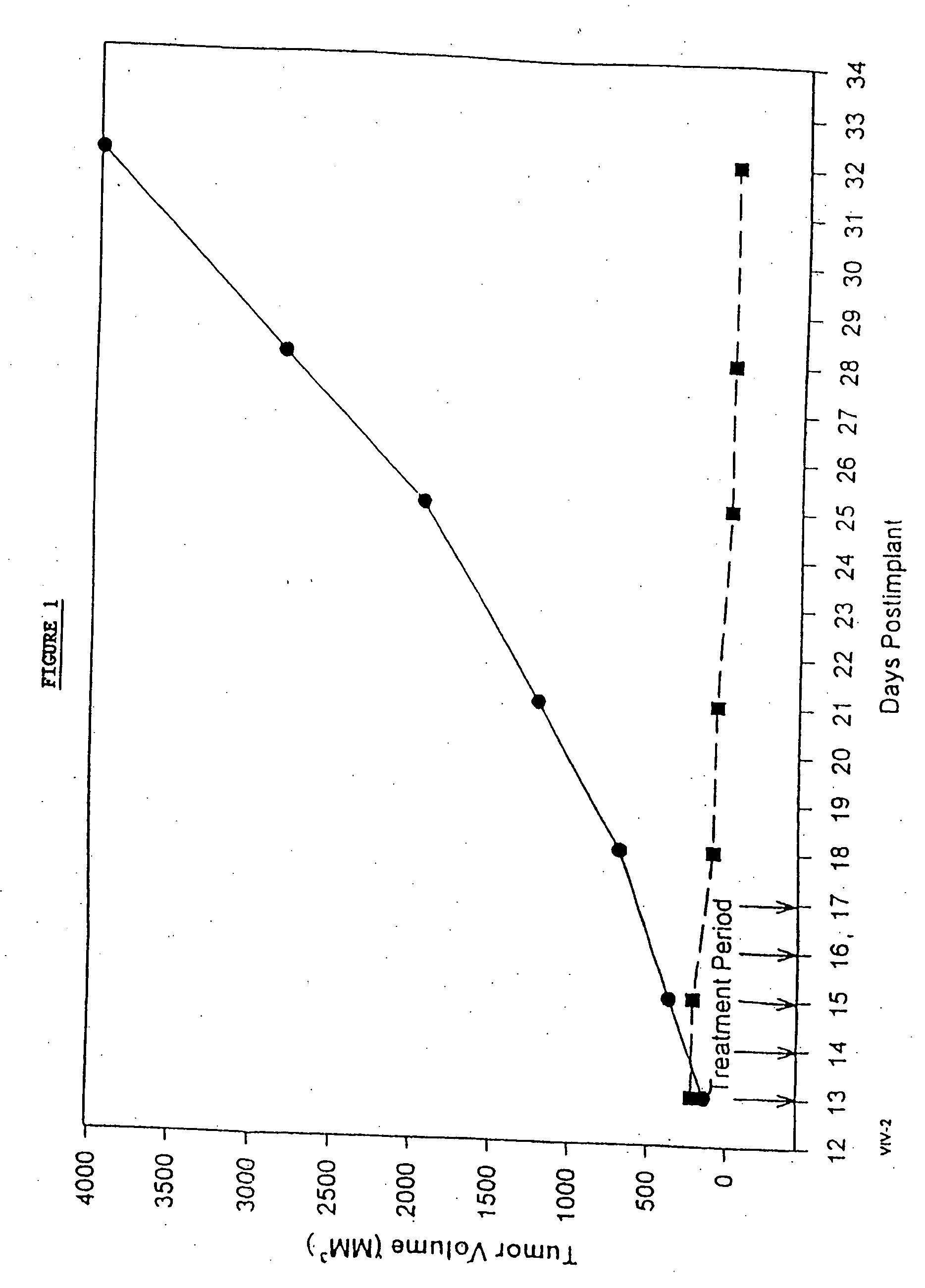
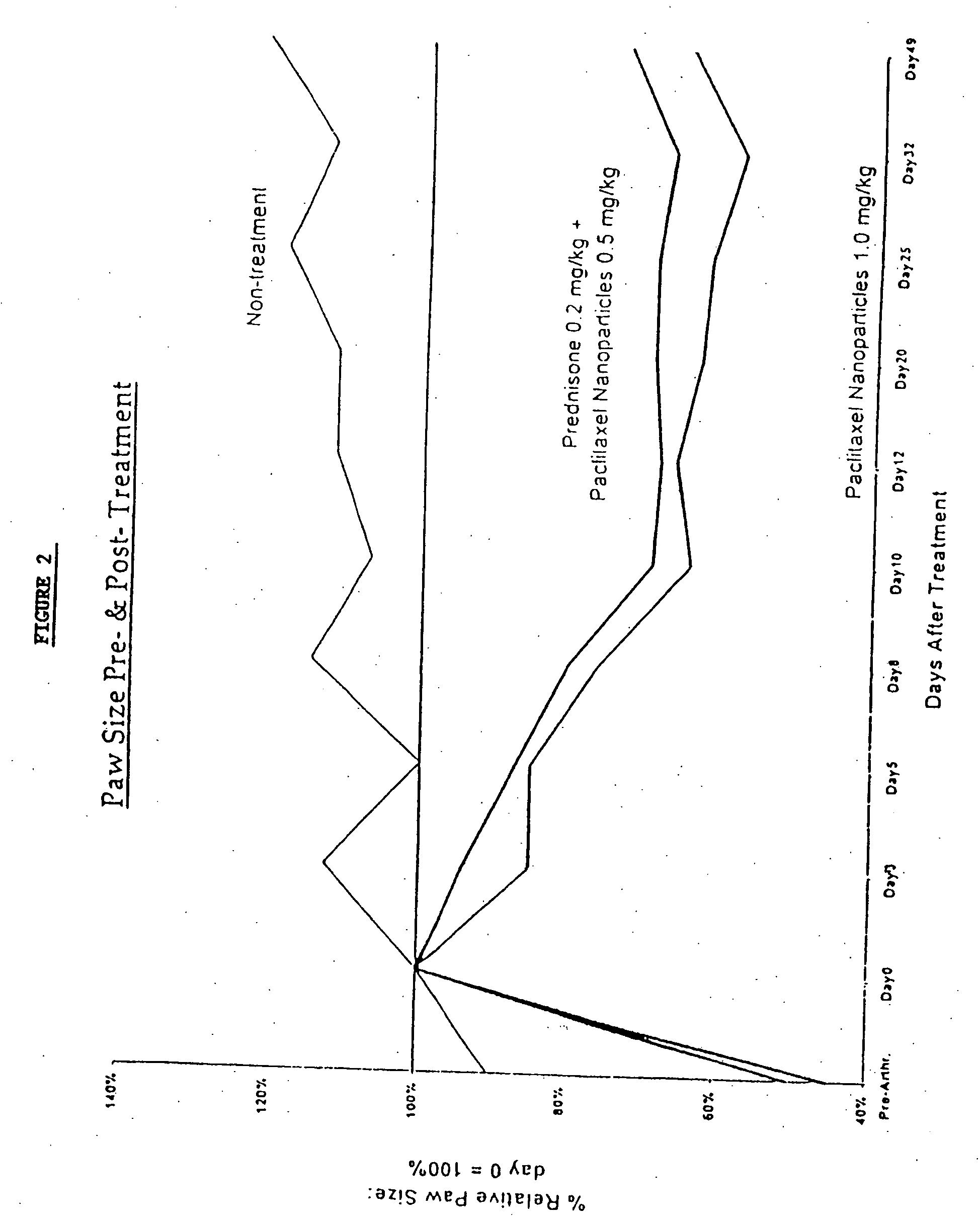
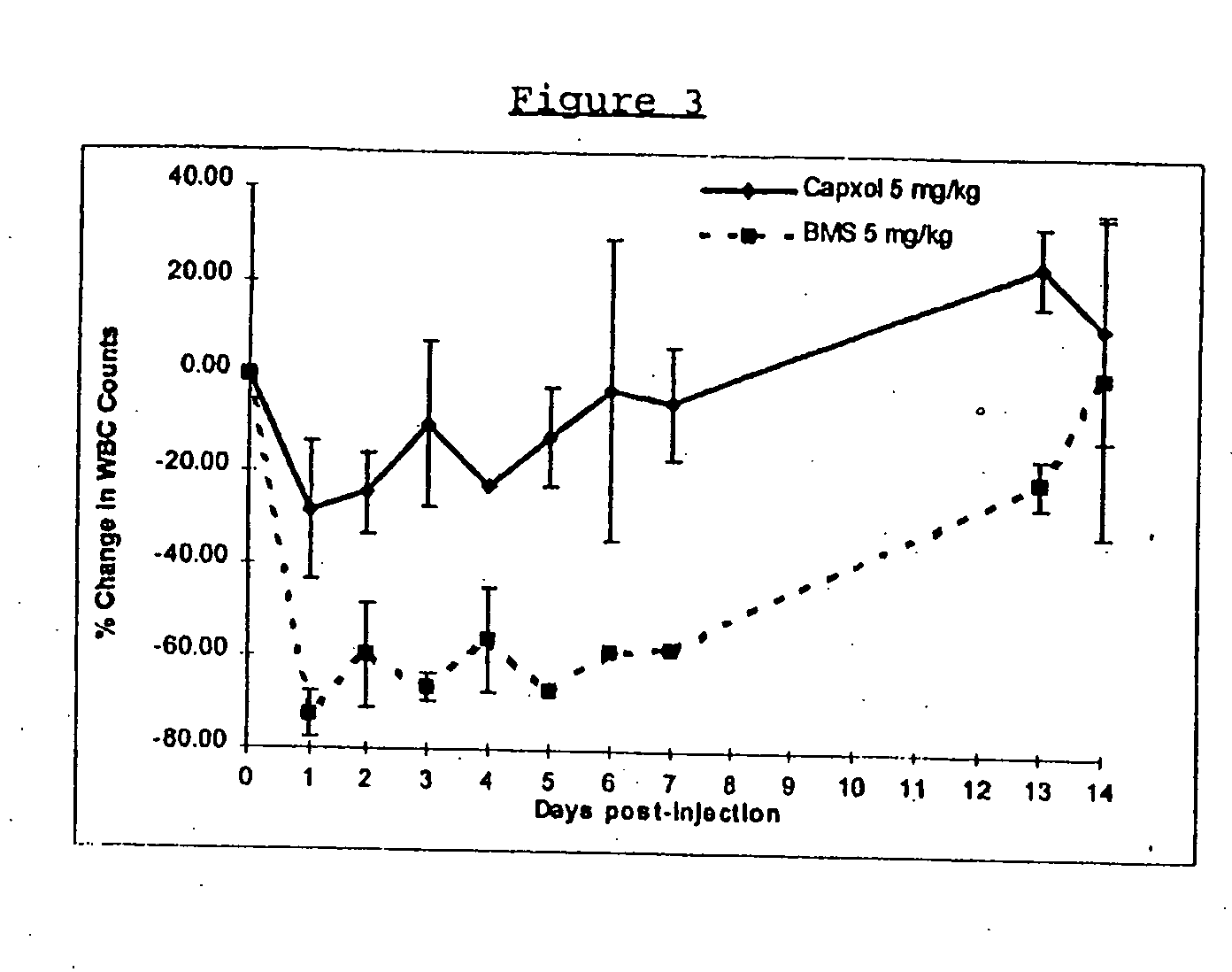
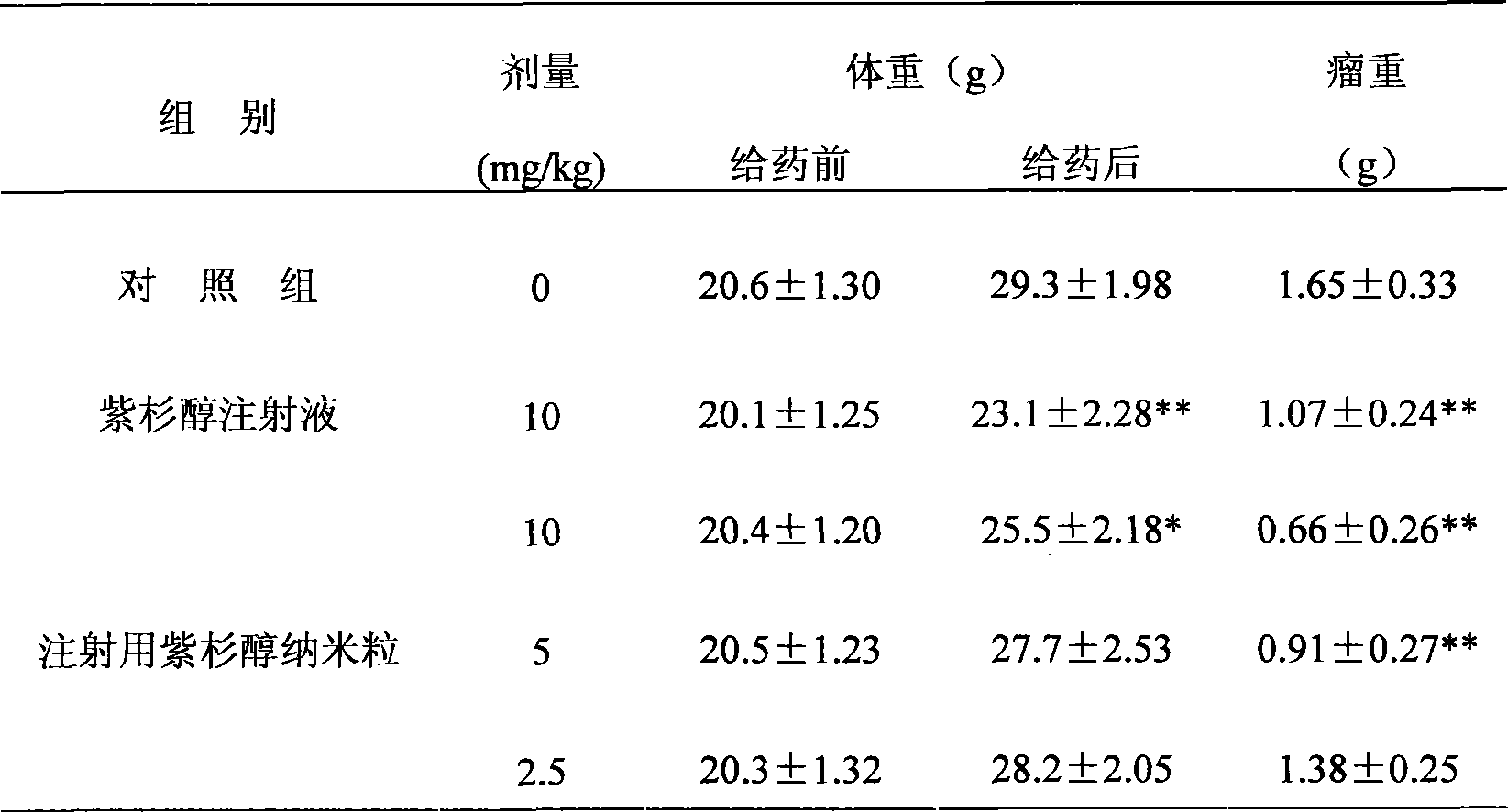
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful election of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
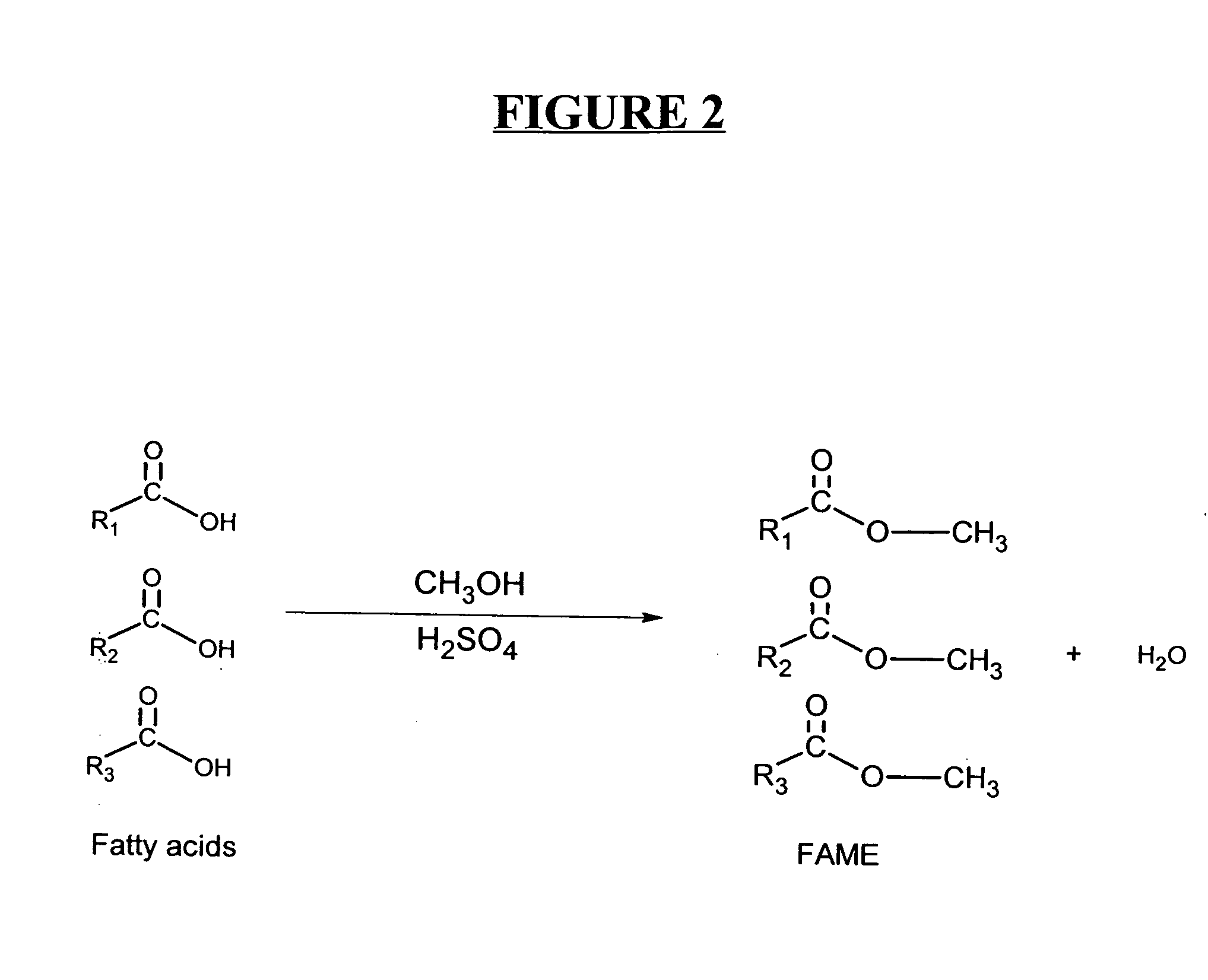
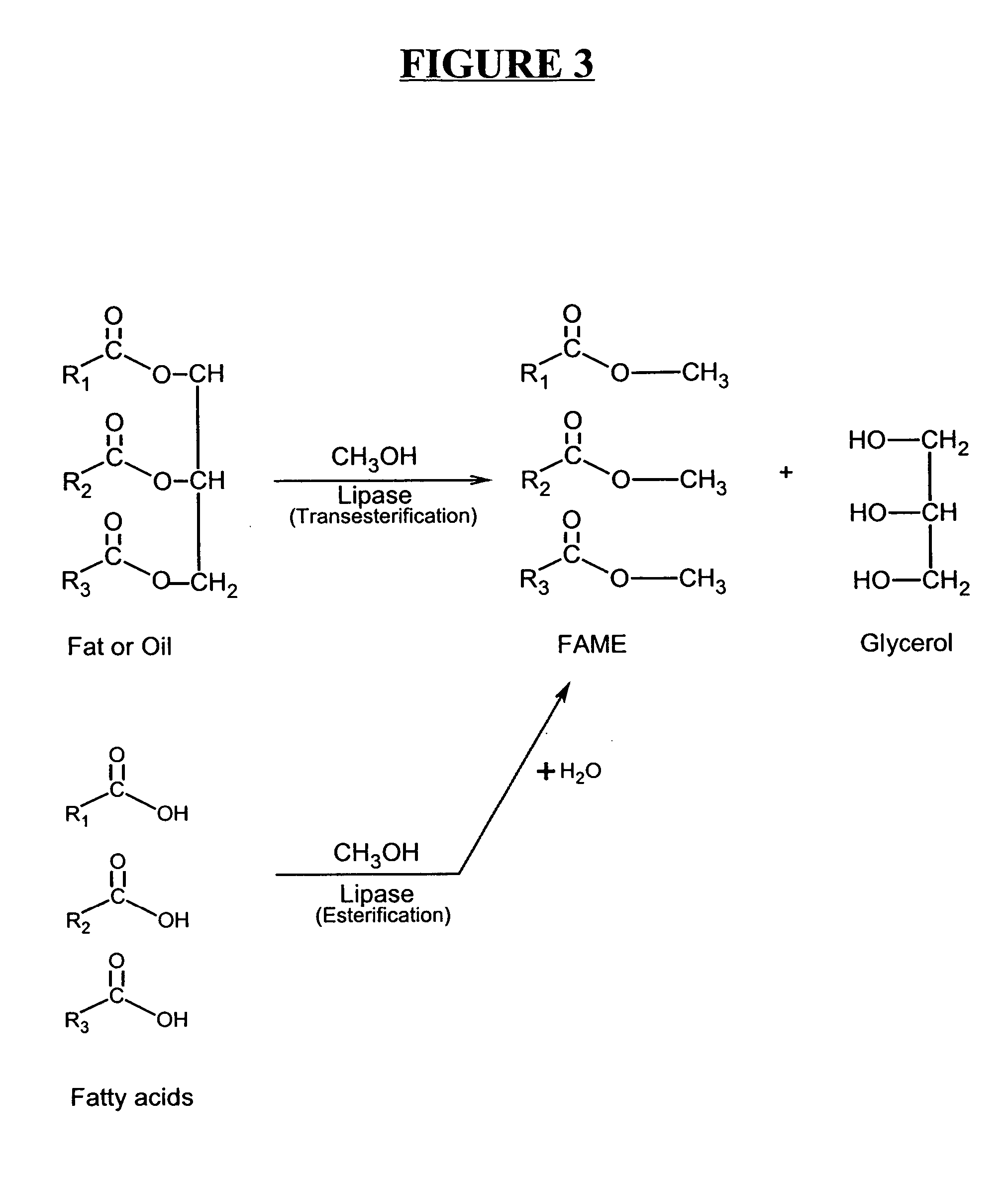
Production of biodiesel and other valuable chemicals from wastewater treatment plant sludges
ActiveUS20050112735A1Reduce the environmentPromote digestionBio-organic fraction processingByproduct vaporizationLipid formationSludge
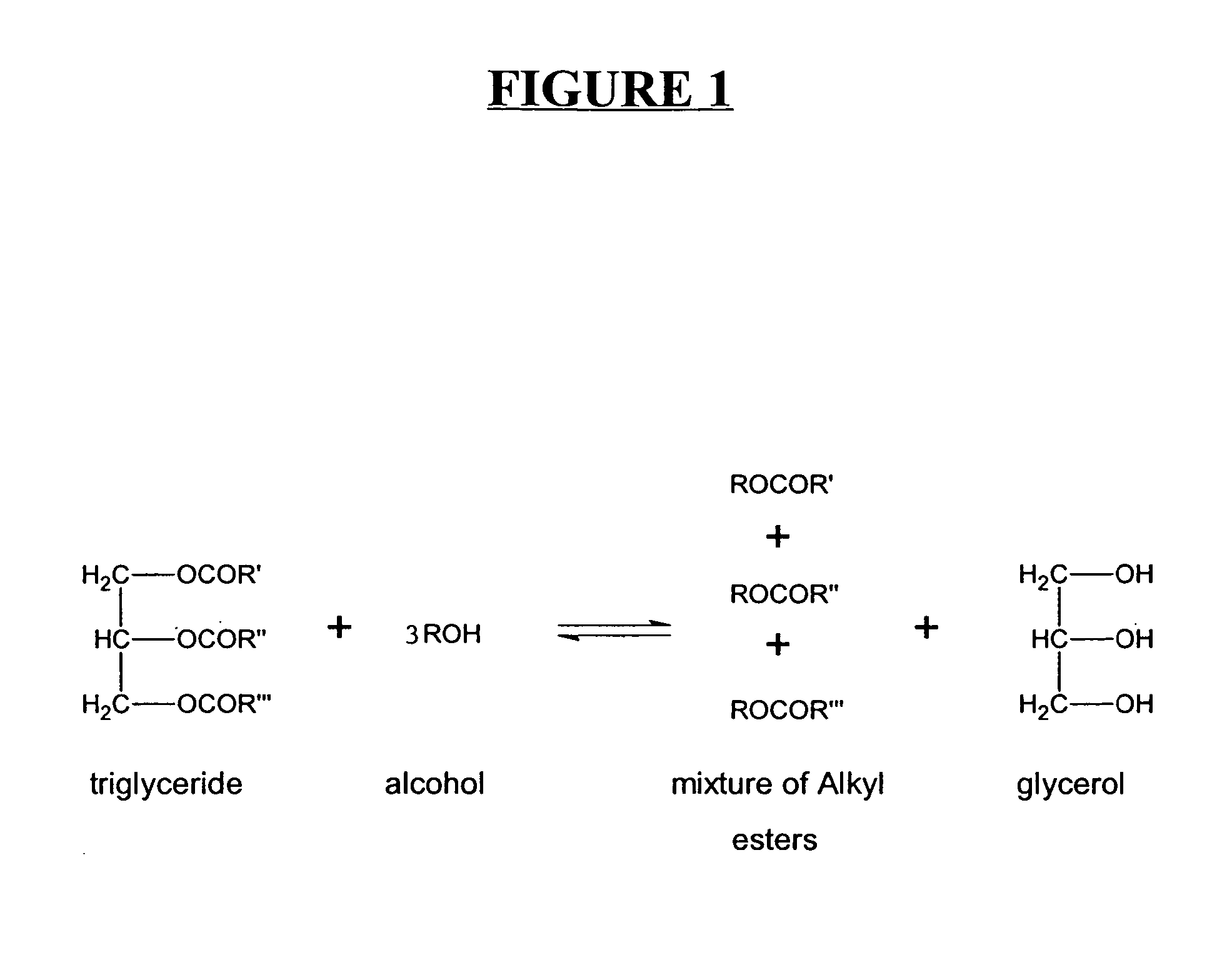
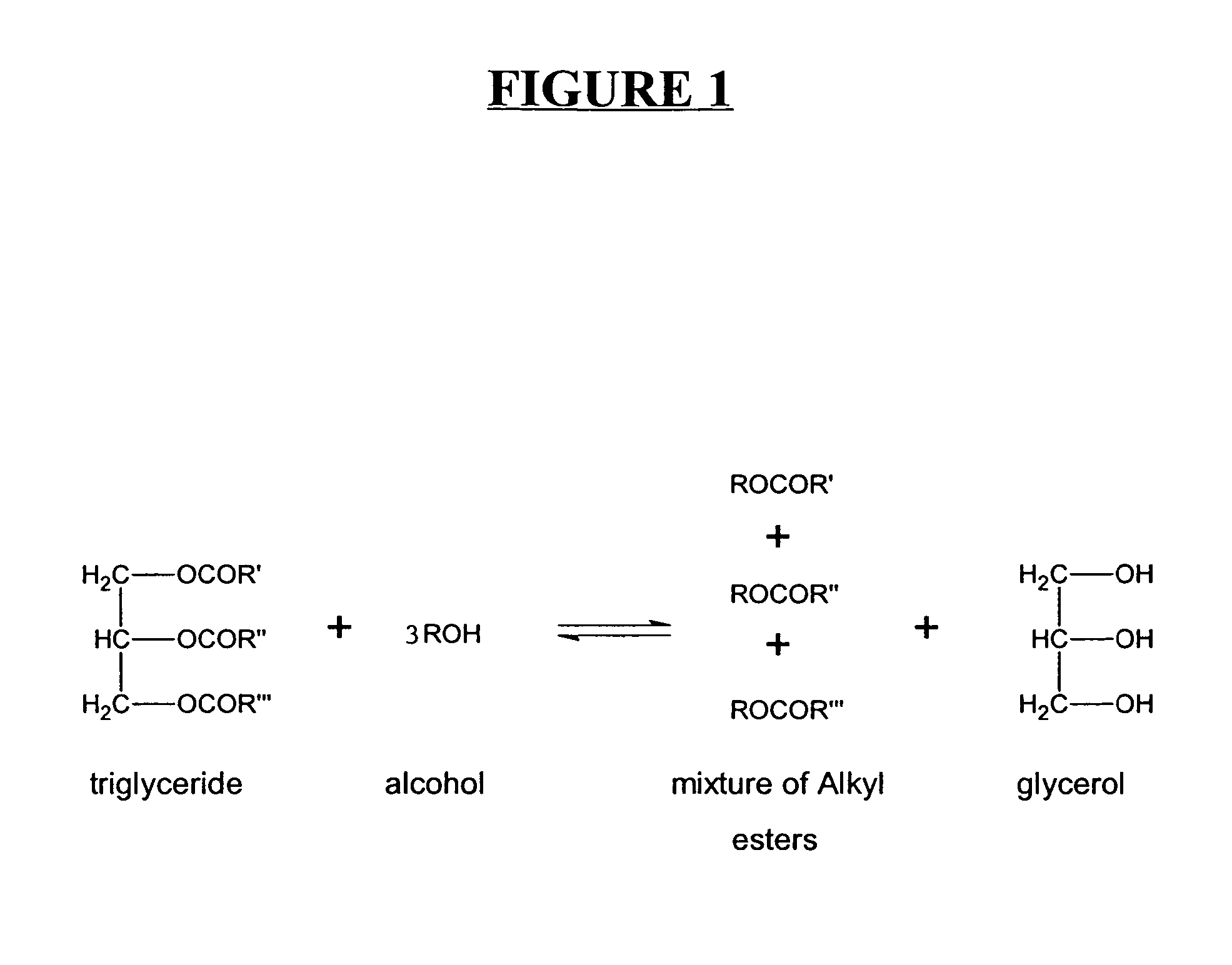
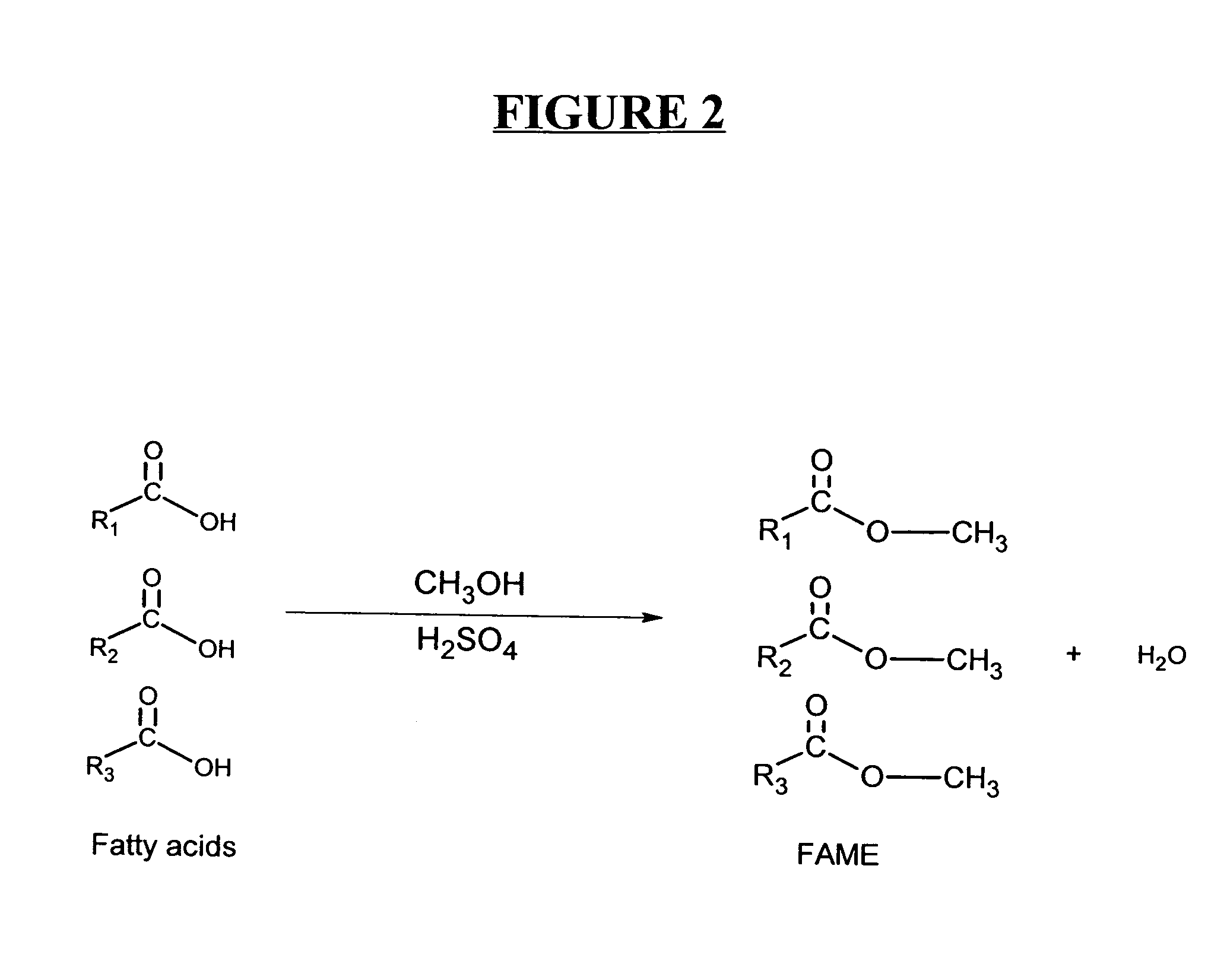
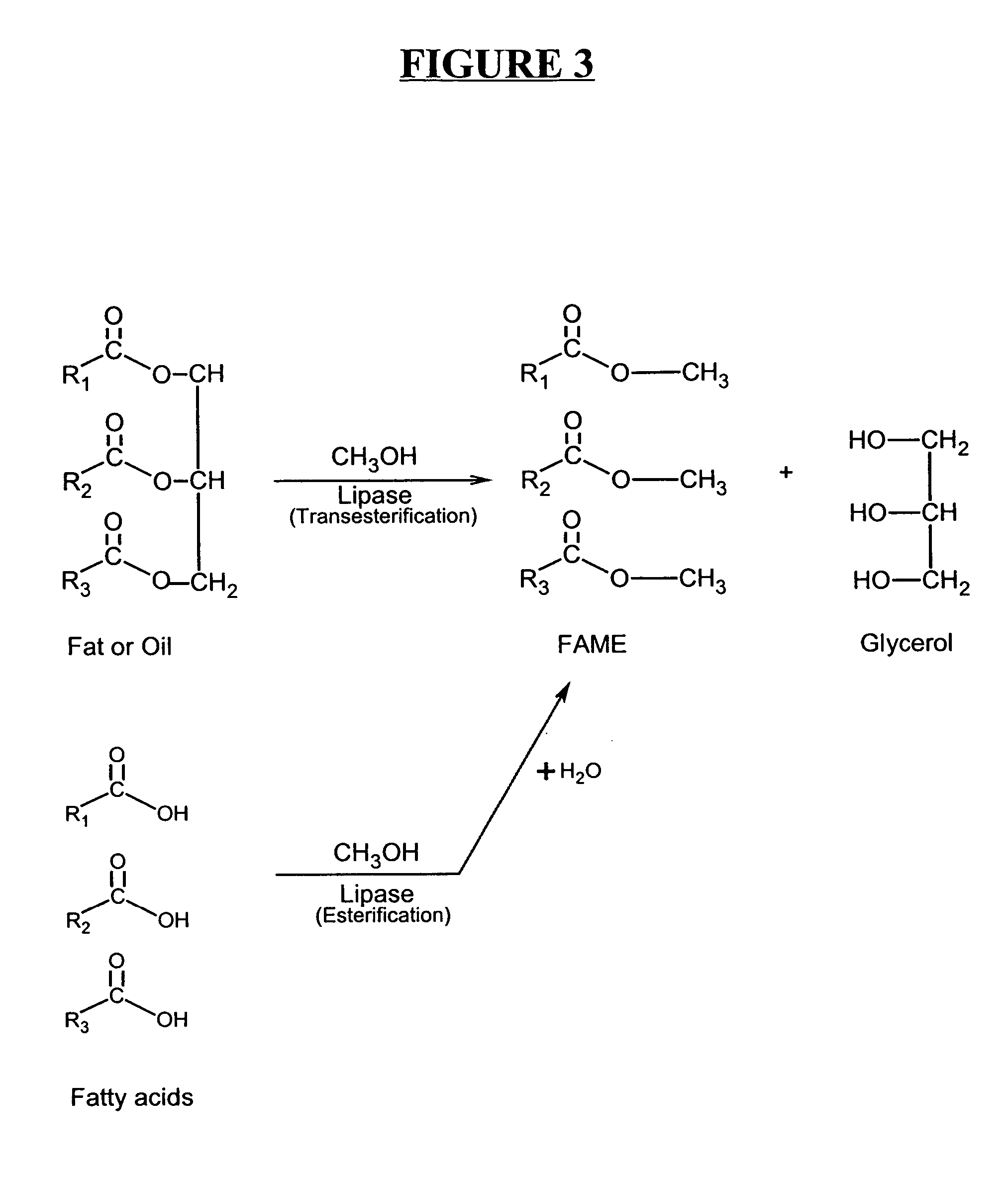
A process for producing biodiesel has been invented by first extracting lipids from the sludges generated during primary and / or biological treatment of municipal, agricultural, and industrial wastewaters using primary, secondary, and tertiary treatments followed by the transesterification of the extracted lipids using transesterification conversion into alcohol-based esters. The resulting products from this process include biodiesel, glycerol, lipid-free proteins, various other useful chemicals and an aqueous-based substrate well suited for optimized digestion within subsequent biological digestion (either aerobic or anaerobic). The lipids extracted from the sludges containing high levels of microorganisms are phospholipids which can also be directly used as lecithin. The extraction of the lipids from the sludges will be performed using chemical extraction techniques with the transesterification of the extracted lipids accomplished using basic, acidic, and / or a combination of the two transesterification techniques.
Owner:MISSISSPPI STATE UNIV RES & TECH
Formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS8853260B2Improve abilitiesPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070087022A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
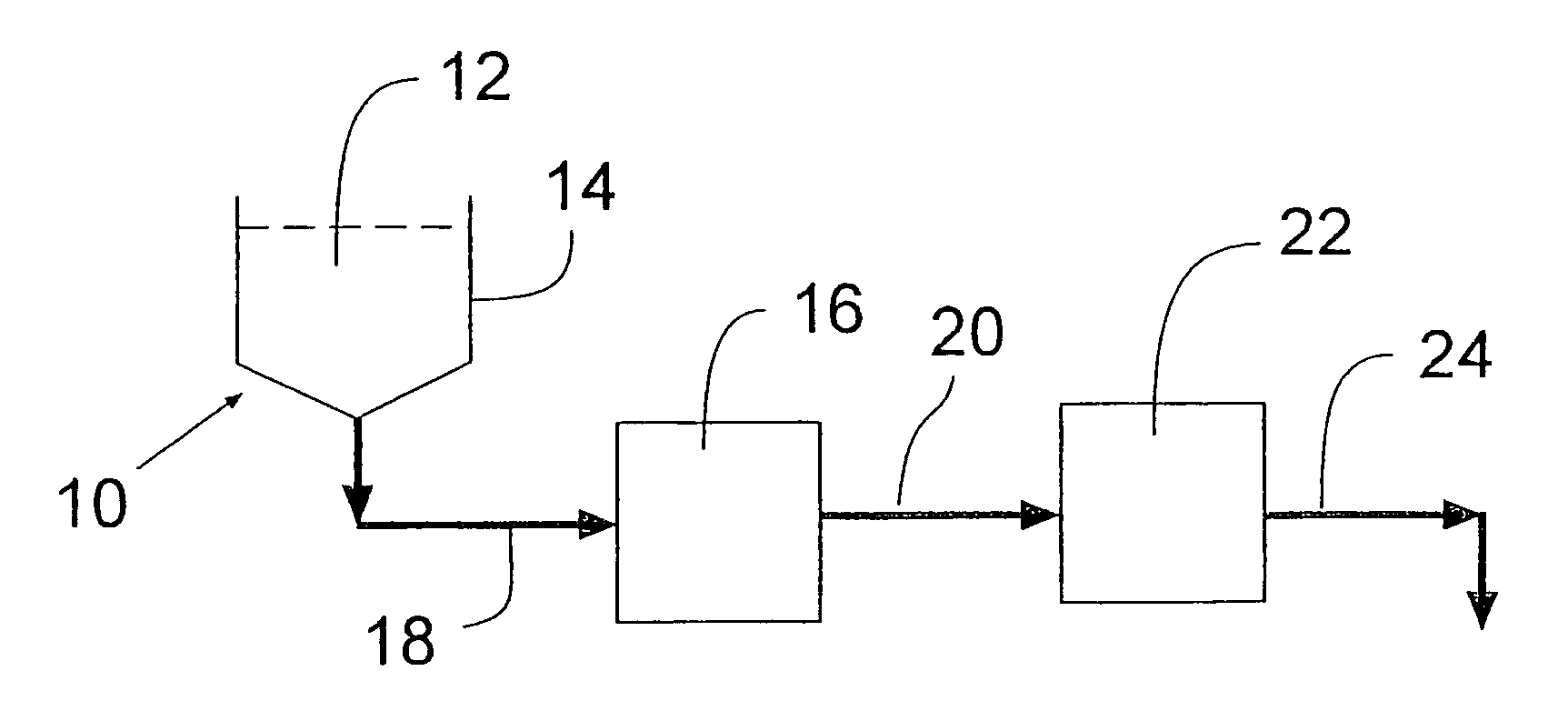
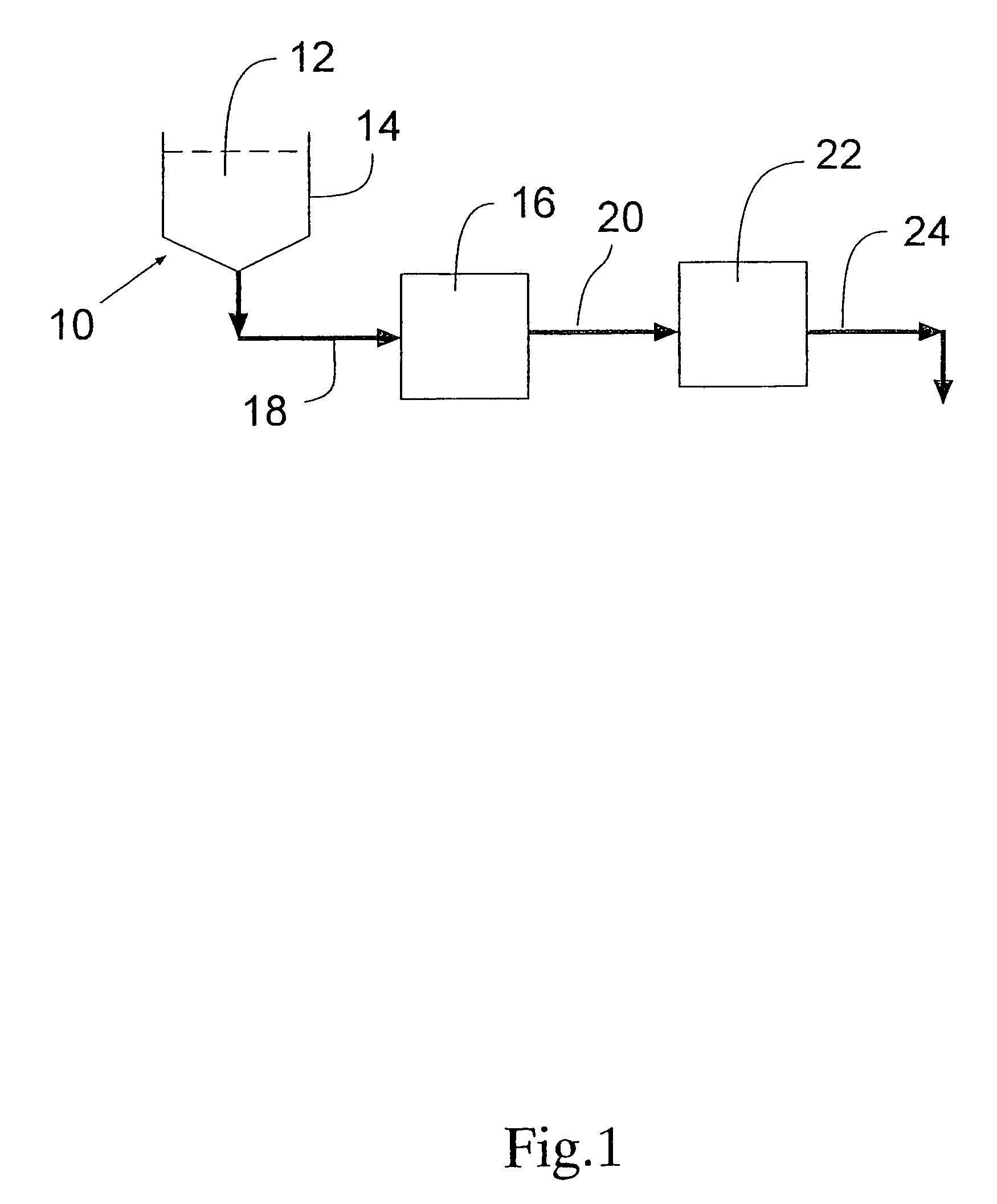
Process for removing protein aggregates and virus from a protein solution
InactiveUS7118675B2Less-expensive to purchaseLess-expensive to operateComponent separationSolvent extractionProtein solutionFree protein
A process is provided for selectively removing protein aggregates from a protein solution in a normal flow (NFF) filtration process. Preferably, it relates to a process for selectively removing protein aggregates from a protein solution in a normal flow (NFF) filtration process and virus particles from a protein solution in a two-step filtration process. In a first step, a protein solution is filtered through one or more layers of adsorptive depth filters, charged or surface modified microporous membranes or a small bed of chromatography media in a normal flow filtration mode of operation, to produce a protein aggregate free stream. The aggregate free protein stream can then be filtered through one or more ultrafiltration membranes to retain virus particles at a retention level of at least 3 LRV and to allow passage therethrough of an aggregate free and virus free protein solution.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070093547A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesFree protein
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20080160095A1Reduce morbidityLow toxicityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20080161382A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Production of biodiesel and other valuable chemicals from wastewater treatment plant sludges
ActiveUS7638314B2Reduce the environmentPromote digestionBio-organic fraction processingByproduct vaporizationSludgeFree protein
A process for producing biodiesel has been invented by first extracting lipids from the sludges generated during primary and / or biological treatment of municipal, agricultural, and industrial wastewaters using primary, secondary, and tertiary treatments followed by the transesterification of the extracted lipids using transesterification conversion into alcohol-based esters. The resulting products from this process include biodiesel, glycerol, lipid-free proteins, various other useful chemicals and an aqueous-based substrate well suited for optimized digestion within subsequent biological digestion (either aerobic or anaerobic). The lipids extracted from the sludges containing high levels of microorganisms are phospholipids which can also be directly used as lecithin. The extraction of the lipids from the sludges will be performed using chemical extraction techniques with the transesterification of the extracted lipids accomplished using basic, acidic, and / or a combination of the two transesterification techniques.
Owner:MISSISSPPI STATE UNIV RES & TECH
Formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS8137684B2Improve abilitiesPromote formationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Process for removing protein aggregates and virus from a protein solution
InactiveUS7465397B2Less-expensive to purchaseLess-expensive to operateSolvent extractionUltrafiltrationProtein solutionUltrafiltration
A process is provided for selectively removing protein aggregates from a protein solution in a normal flow (NFF) filtration process. Preferably, it relates to a process for selectively removing protein aggregates from a protein solution in a normal flow (NFF) filtration process and virus particles from a protein solution in a two-step filtration process. In a first step, a protein solution is filtered through one or more layers of adsorptive depth filters, charged or surface modified microporous membranes or a small bed of chromatography media in a normal flow filtration mode of operation, to produce a protein aggregate free stream. The aggregate free protein stream can then be filtered through one or more ultrafiltration membranes to retain virus particles at a retention level of at least 3 LRV and to allow passage therethrough of an aggregate free and virus free protein solution.
Owner:EMD MILLIPORE CORP
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070092563A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070116761A1Reduce morbidityReduce decreaseBiocidePowder deliverySuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20150104521A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
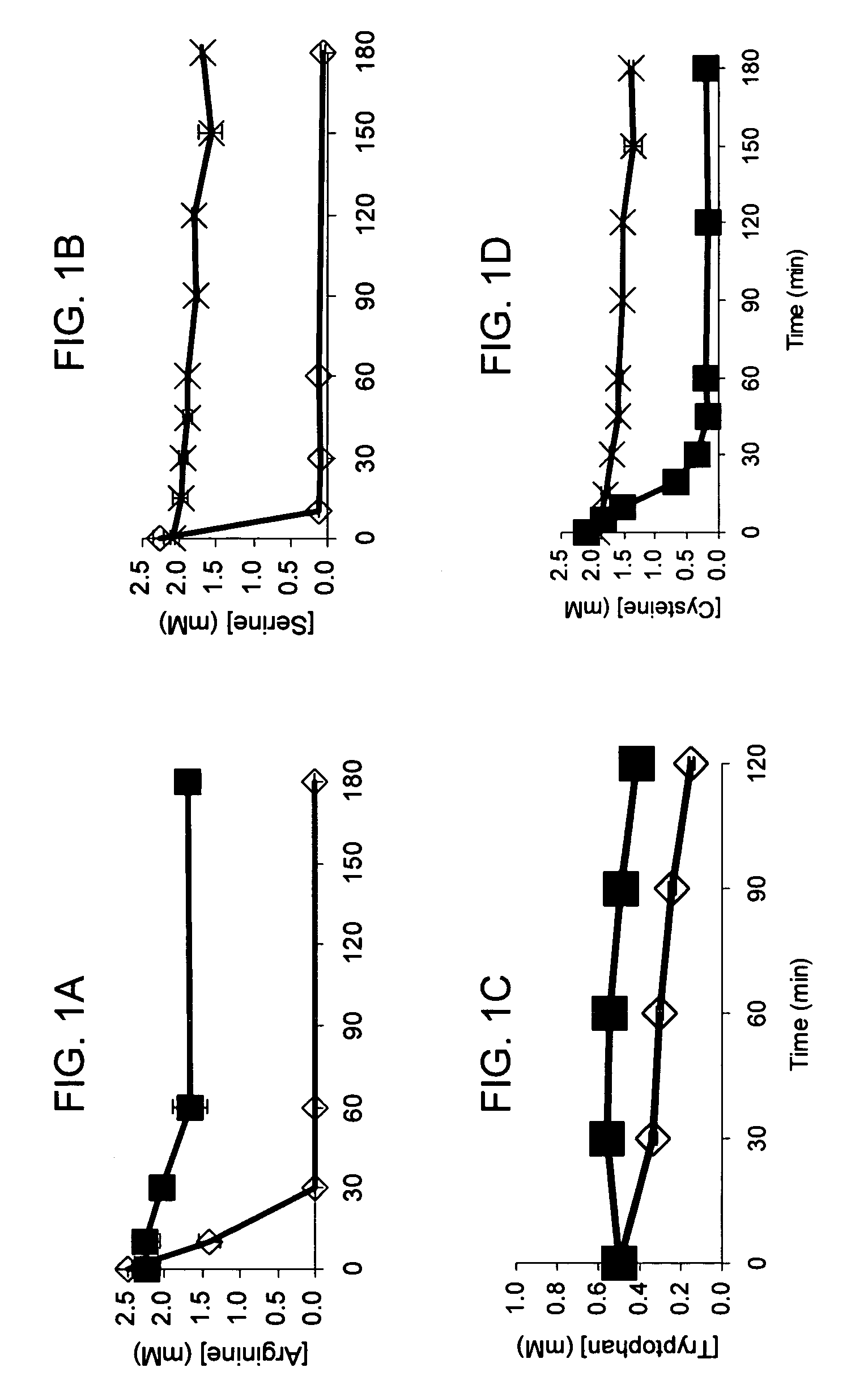
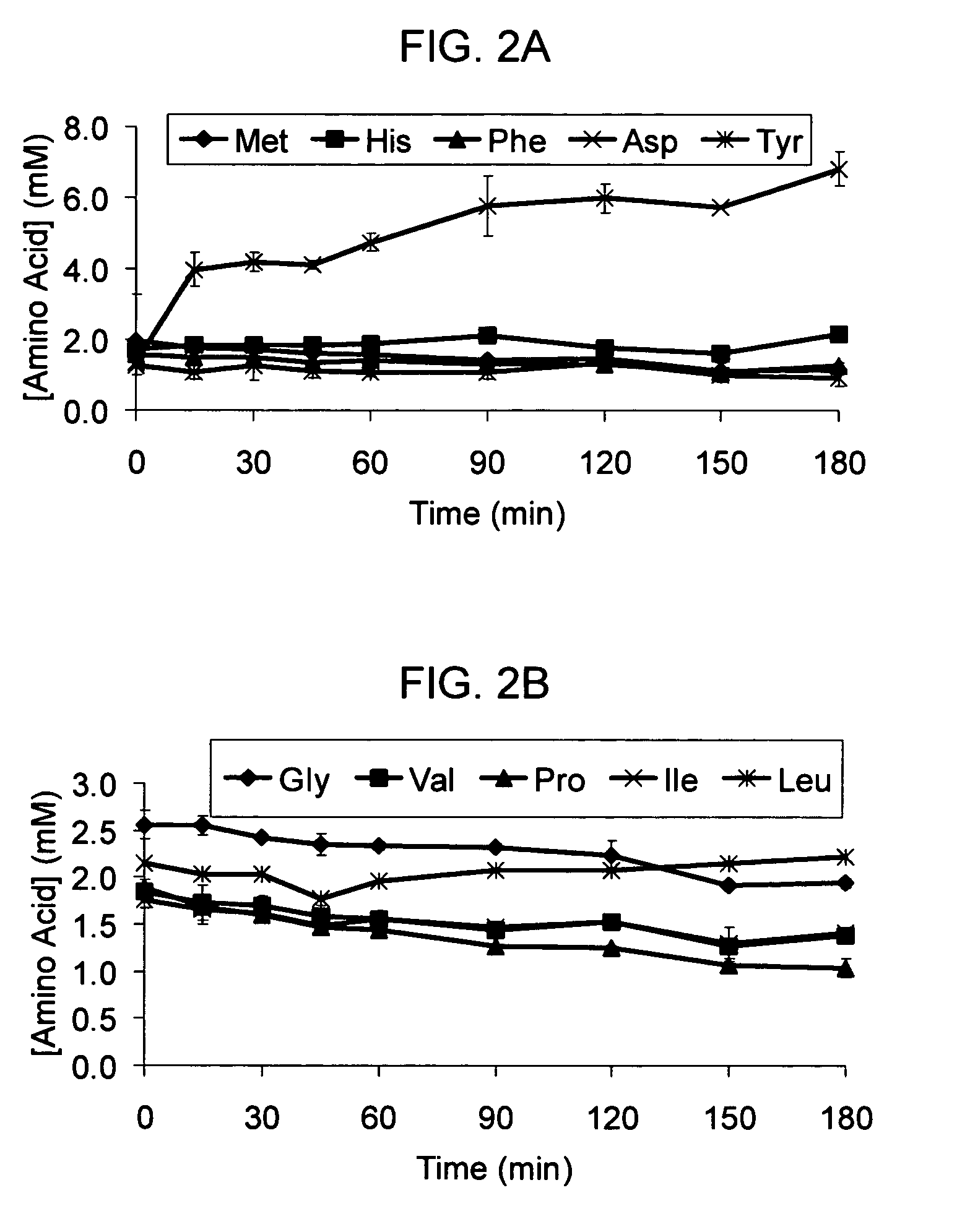
Total amino acid stabilization during cell-free protein synthesis
Compositions and methods are provided for the enhanced in vitro synthesis of protein molecules, by optimizing the metabolism of amino acids present in the reaction mix, preferably all amino acids in the reaction mixture. By performing synthesis with extracts from genetically modified microbial strains that are deficient in multiple amino acid metabolizing enzymes reduces the enzymatic activities responsible for catalyzing these reactions and improves the overall yield of synthesis.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070117862A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityPowder deliveryBiocideSuspended particlesFree protein
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070122465A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationPowder deliveryBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel nano preparation with stable protein and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101385857AShort operating timeStable productionOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsWater insolubleFree protein
The invention discloses a novel nano preparation with stable protein, as well as a preparation method and a purpose thereof. The invention is characterized in that: a protein coating is formed from albumin and other materials containing sulphydryl or disulfide bond through the cross linking of the disulfide bond; the protein coating contains free protein or protein derivatives which associate(s) with the protein coating, wherein, part of insoluble drugs are contained in the protein coating and part of such drugs are associated with the free protein or the protein derivatives, and the average diameter of protein coating particles is not more than 1 micron. The purpose of the preparation is to send water insoluble drugs into the bodies of living things.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Optimized in vitro cell-free protein synthesis system and application
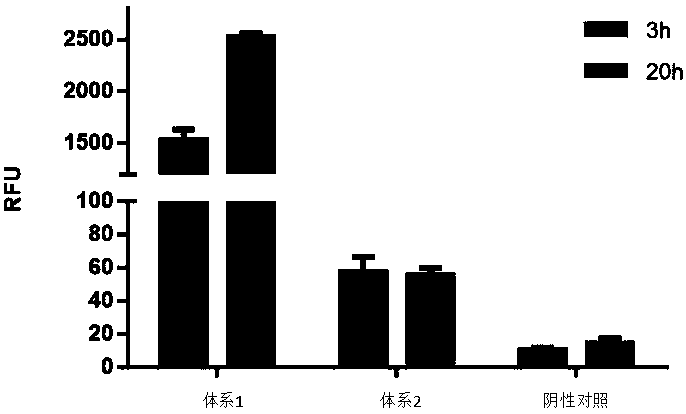
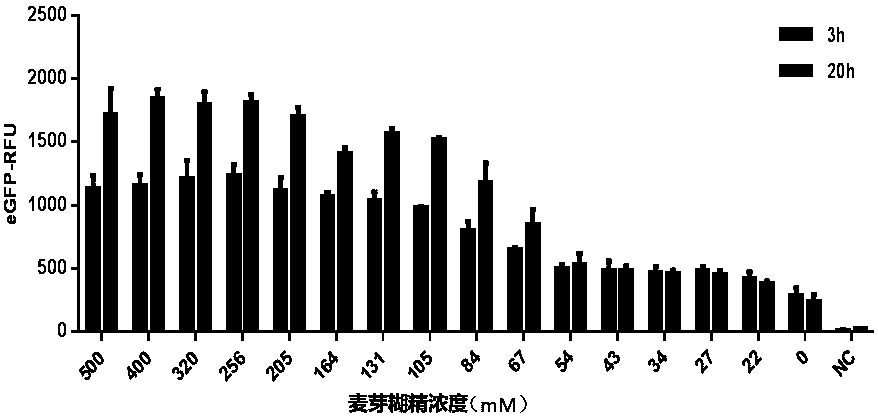
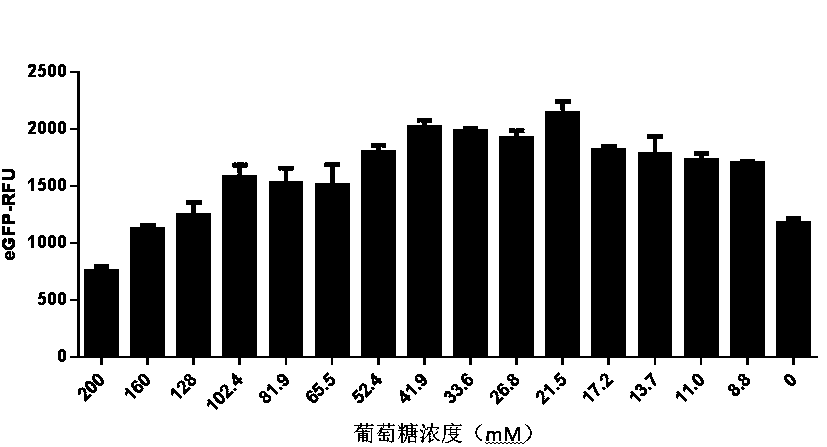
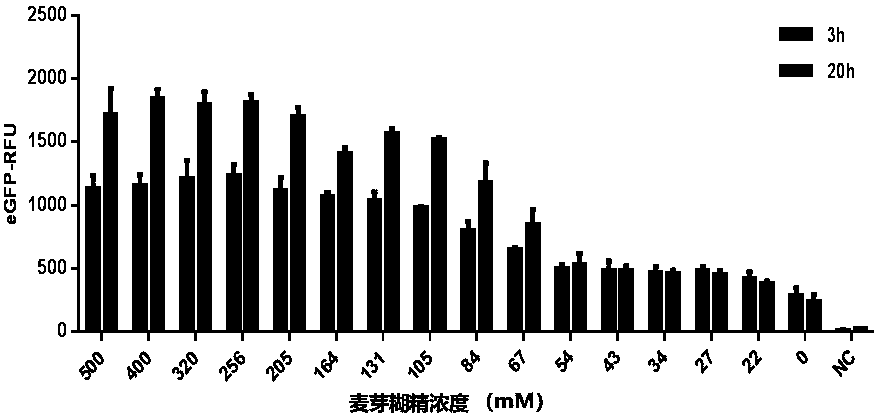
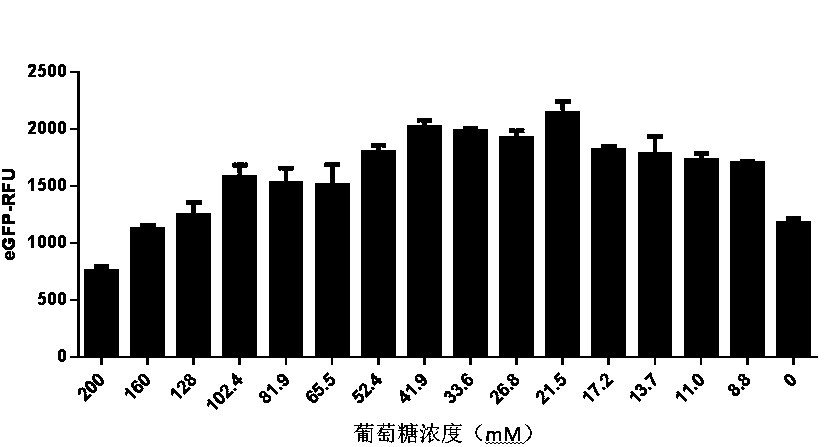
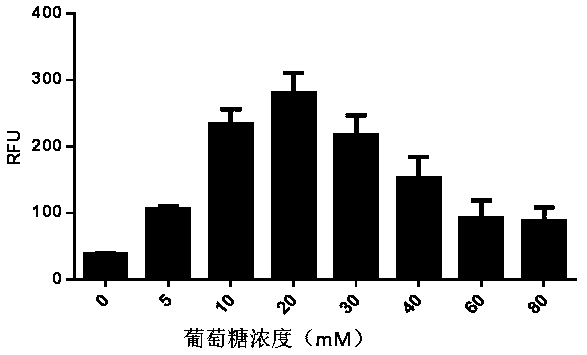
ActiveCN111378708AIncrease productionLow costFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetCell free
The invention discloses an optimized in vitro cell-free protein synthesis system. The system comprises a cell extract, a carbohydrate material, a phosphate compound, a buffering agent and a DNA molecular template for encoding an exogenous protein, wherein the cell extract is a yeast cell extract inserted into a T7 RNA polymerase gene; the carbohydrate material is a mixture of glucose and maltodextrin; the buffering agent is a trihydroxymethyl aminomethane buffering agent; and the DNA molecule template is prepared by a nucleic acid isothermal amplification method, and a sequence as shown in SEQID NO.1 is inserted into the upstream of the coding sequence of the exogenous protein in the DNA molecular template. By optimizing, the cost of in vitro protein synthesis is reduced and the yield ofthe target protein is increased.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
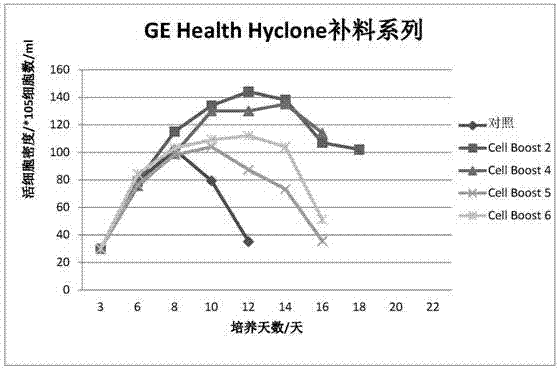
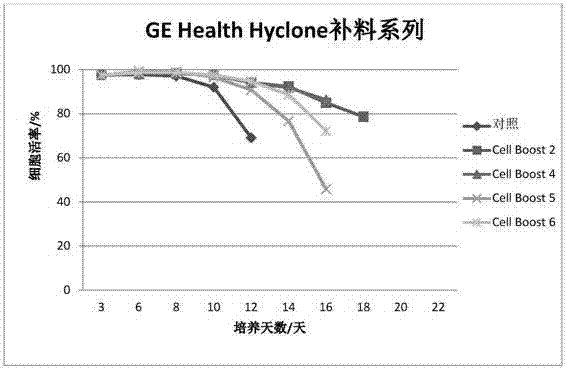
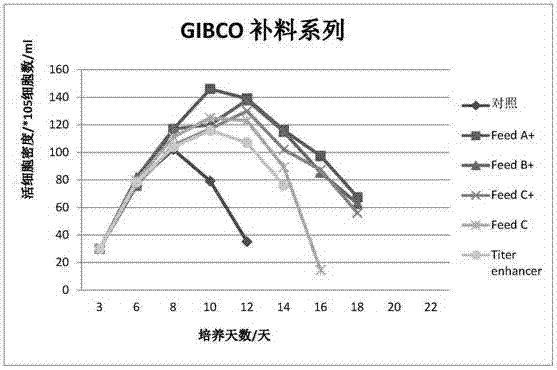
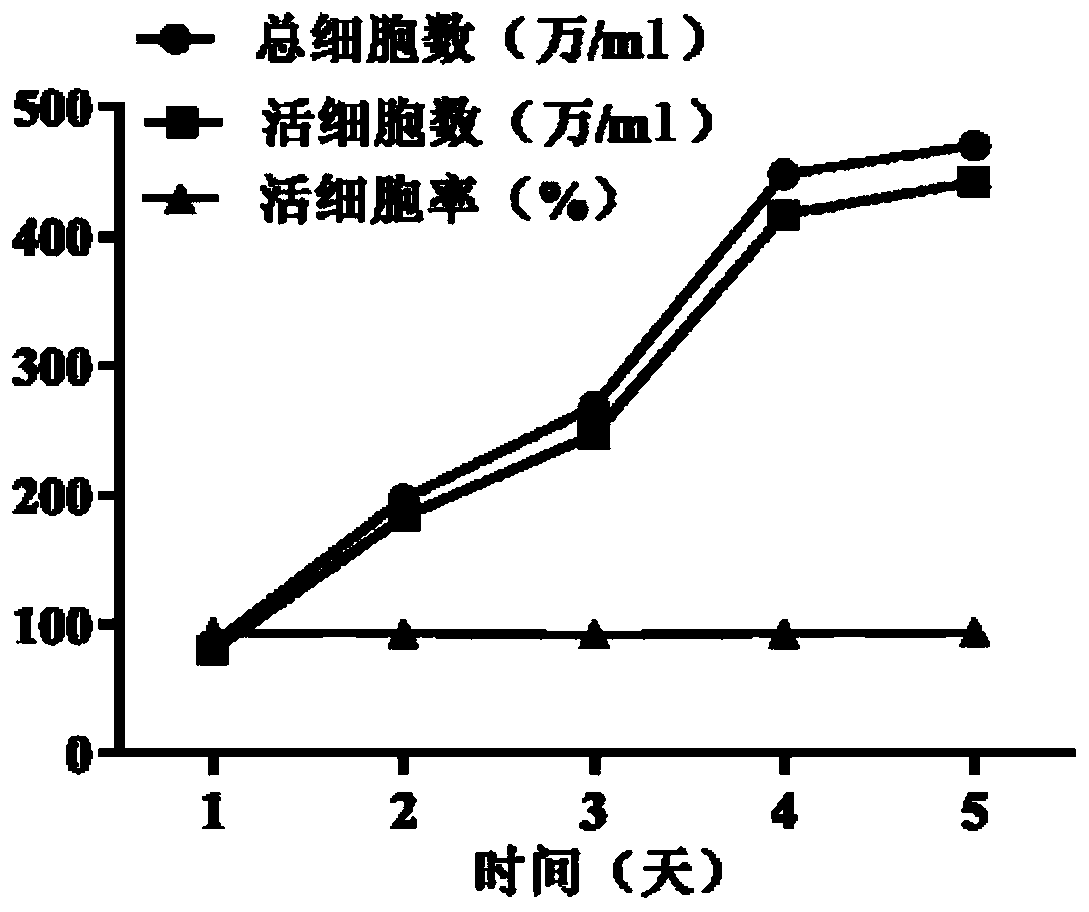
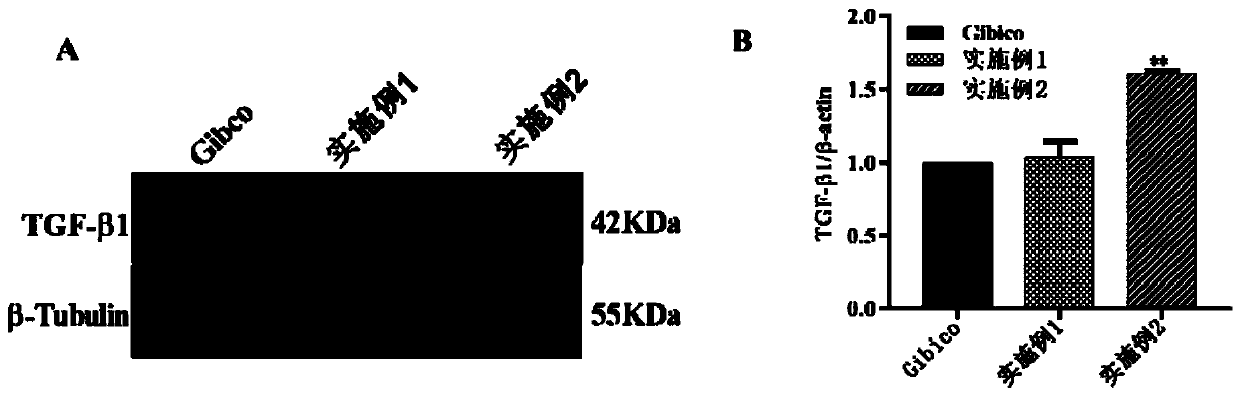
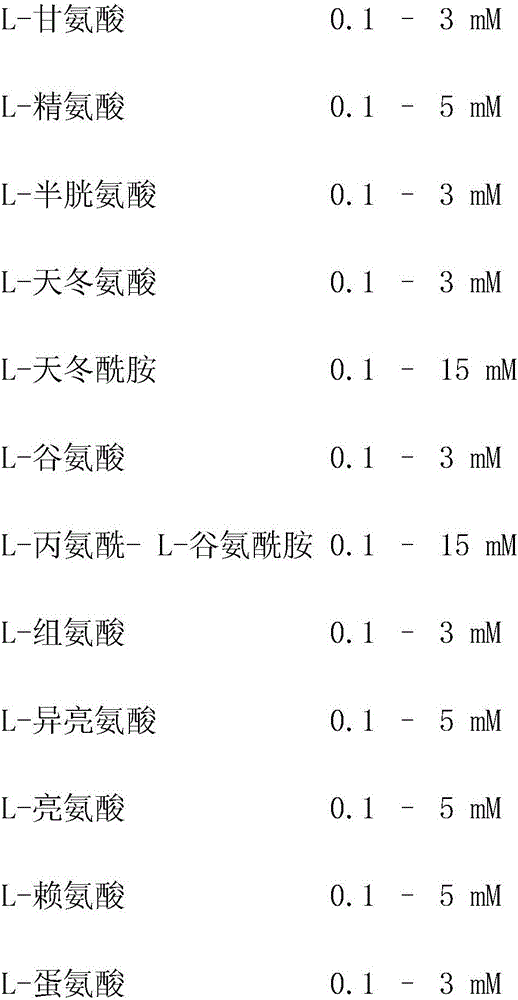
Serum-free protein-free feed culture medium as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107460159AReduce the risk of contaminationRich varietyCulture processArtificial cell constructsPollutionCulture mediums
The invention relates to a serum-free protein-free high-efficiency feed culture medium as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The feed culture medium comprises amino acids, inorganic salts, trace elements, vitamins, carbohydrates and other organic matters. Moreover, the culture medium does not contain any glutamine. Since the feed culture medium contains serum-free protein-free animal-source-free components, the viral pollution risk can be greatly reduced, and downstream purification is facilitated. Meanwhile, since the culture medium is full in types of formula components and balanced in proportion, the culture medium can be applicable to high-density culture and high-protein expression of multiple CHO cell strains.
Owner:上海多宁生物科技股份有限公司
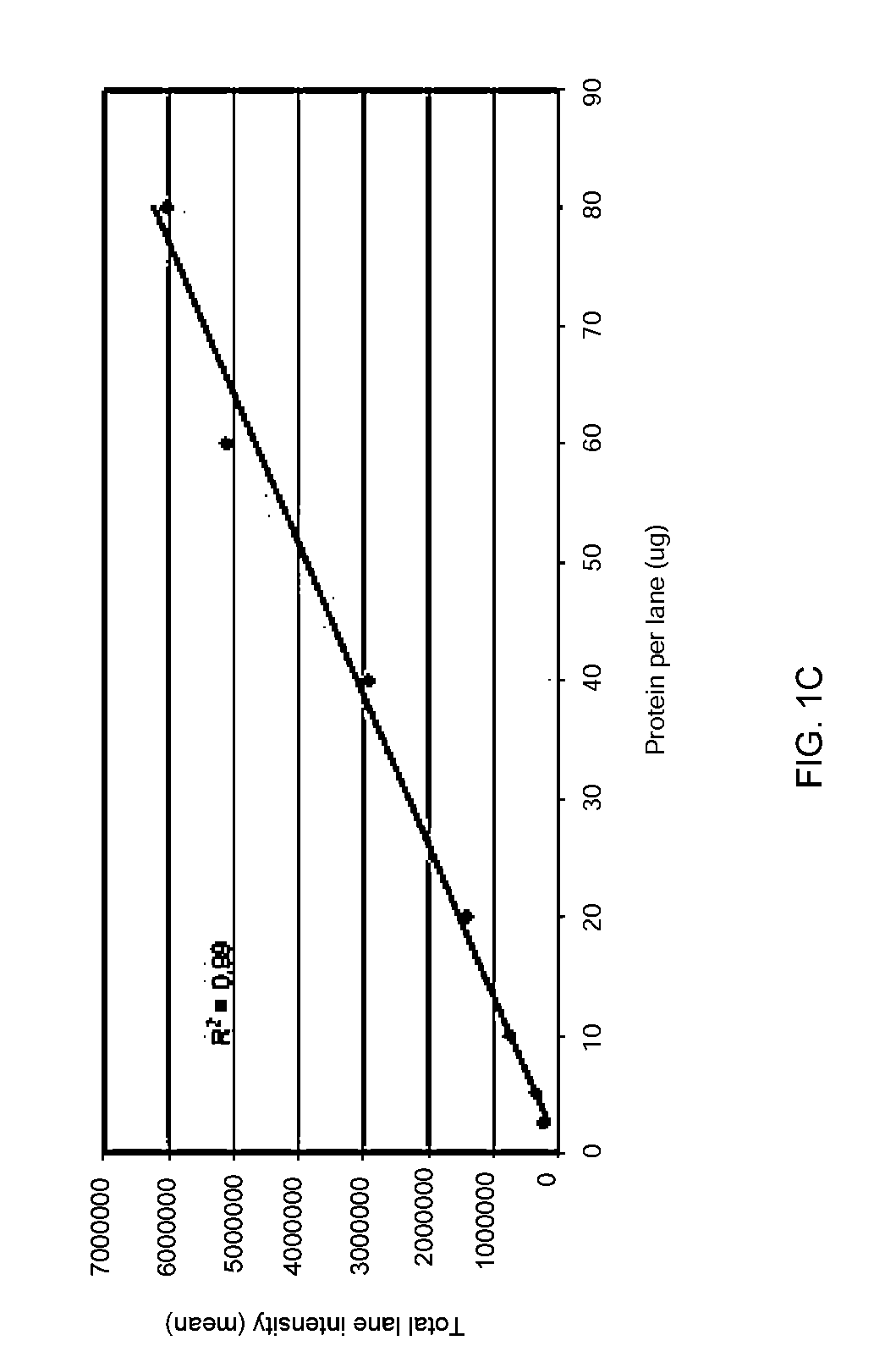
Stain-free protein quantification and normalization
Disclosed herein are methods of protein quantification and normalization using haloalkylated tryptophan fluorescence. Complex protein samples, i.e., samples that each contain 1,000 or more distinct proteins, from diverse sources that do not have common protein profiles are treated with a halo-substituted organic compound (i.e. haloalkane) that reacts with tryptophan residues to form fluorescent products. Irradiation of the samples with ultraviolet light and the detection and quantification of the resultant fluorescent emissions from all proteins in each sample are then used to obtain comparative values for total protein content among the various samples. The values thus obtained are found to be valid indications of comparative total protein content, despite the fact that the tryptophan levels vary widely among the various proteins in any single sample and the samples, due to the diversity of their origins, tend to differ among themselves in the identities and relative amounts of the proteins that they contain. Protein samples are also normalized to correct for differences in sample dilution, sample loading, and protein transfer inconsistencies, by using stain-free detection of total protein in each of the samples, or detection of subsamples within each sample.
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Protein-radical biogum fiberboard and the manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101564864AHigh curing temperatureHigh viscosityProtein adhesivesFlat articlesFiberboardFormaldehyde free
The invention relates to a protein-radical biogum fiberboard and a manufacturing method thereof. As the protein radical biogum fiberboard adopts formaldehyde-free protein radical biogum as an adhesive, the formaldehyde emission is far less than that of board products manufactured by urea-formaldehyde glue or phenolic glue. The advanced manufacturing method ensures that the boards produced have excellent hydrolytic resistance and can effectively avoid phenomenon of delamination or barbotage of the boards.
Owner:SHANGHAI HONGHAN CHEM TECH
In-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system and application thereof
The present invention discloses an in-vitro cell-free protein synthesis system. The system comprises cell extract, carbohydrate and a phosphate compound, wherein the carbohydrate is maltodextrin, lactose, or a combination of the maltodextrin and glucose, or a combination of the lactose and the glucose, or a combination of the maltodextrin, the lactose and the glucose. ATP is provided for an in-vitro reaction by low-cost substances such as the glucose, the maltodextrin and the lactose instead of energy sources such as phosphoenolpyruvic acid, phosphocreatine and acetyl phosphate, so that whilethe cost is reduced, a mode of providing energy by slow release prolongs the reaction time and increases the yield of target protein.
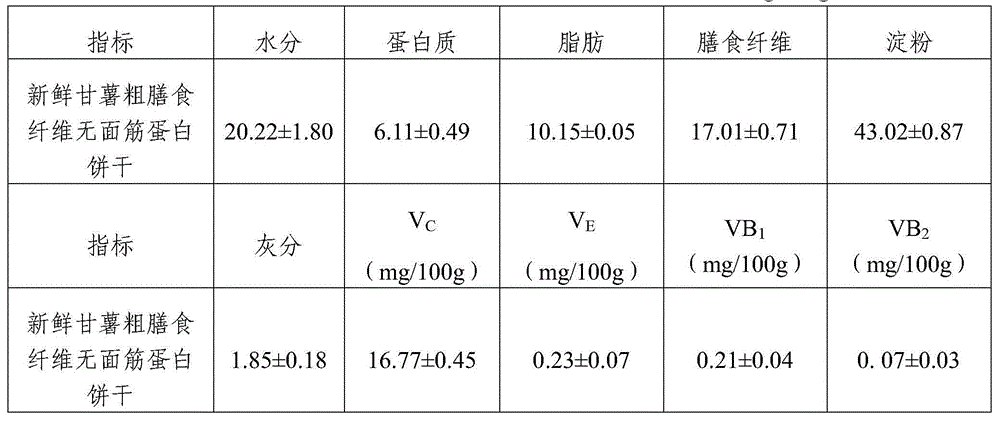
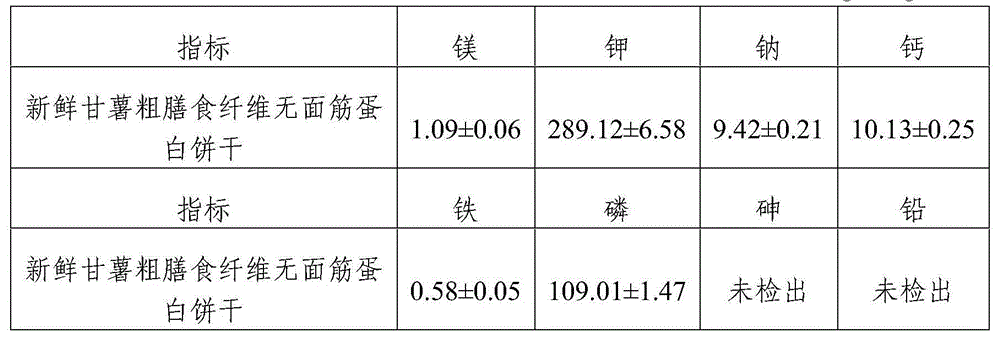
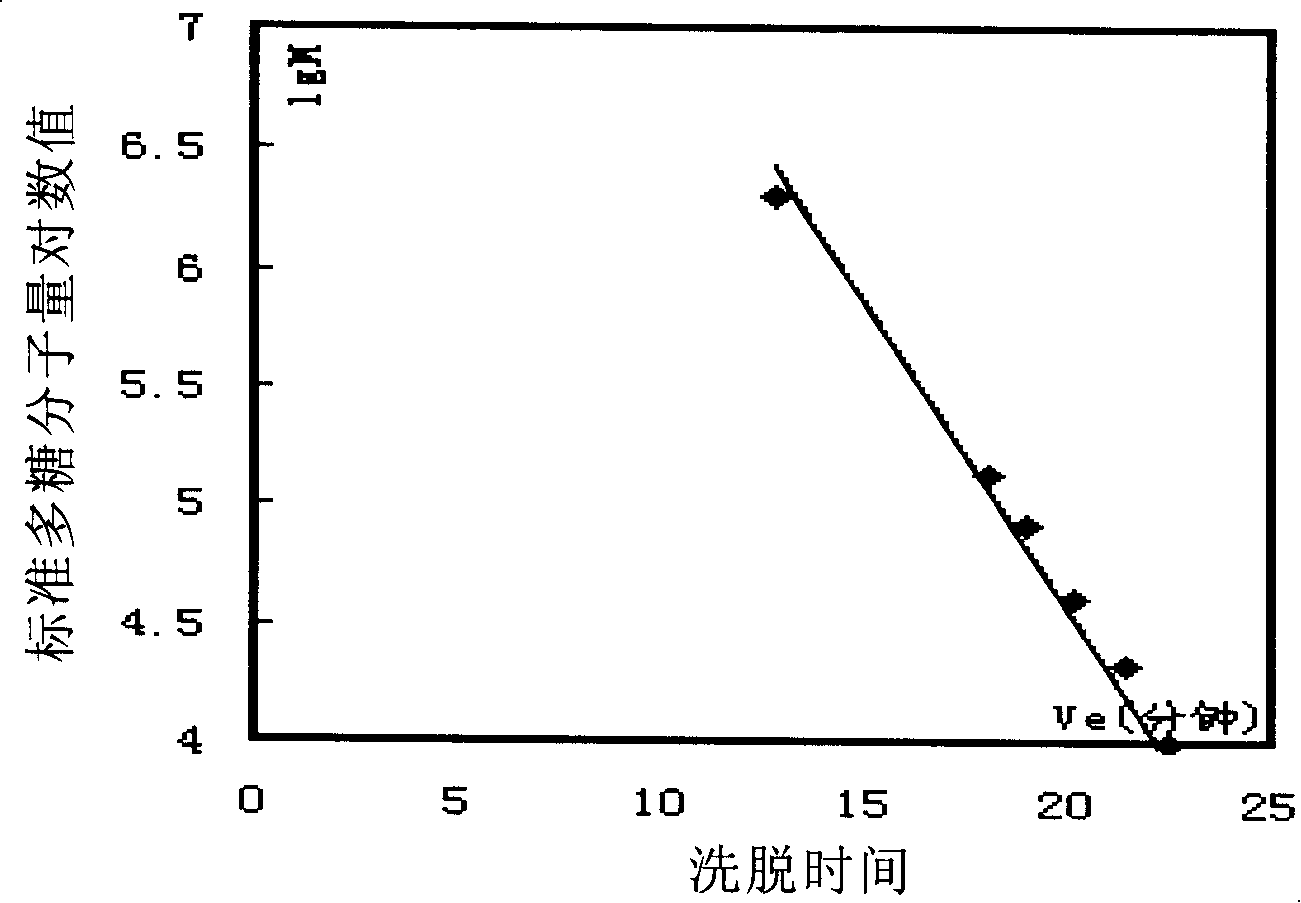
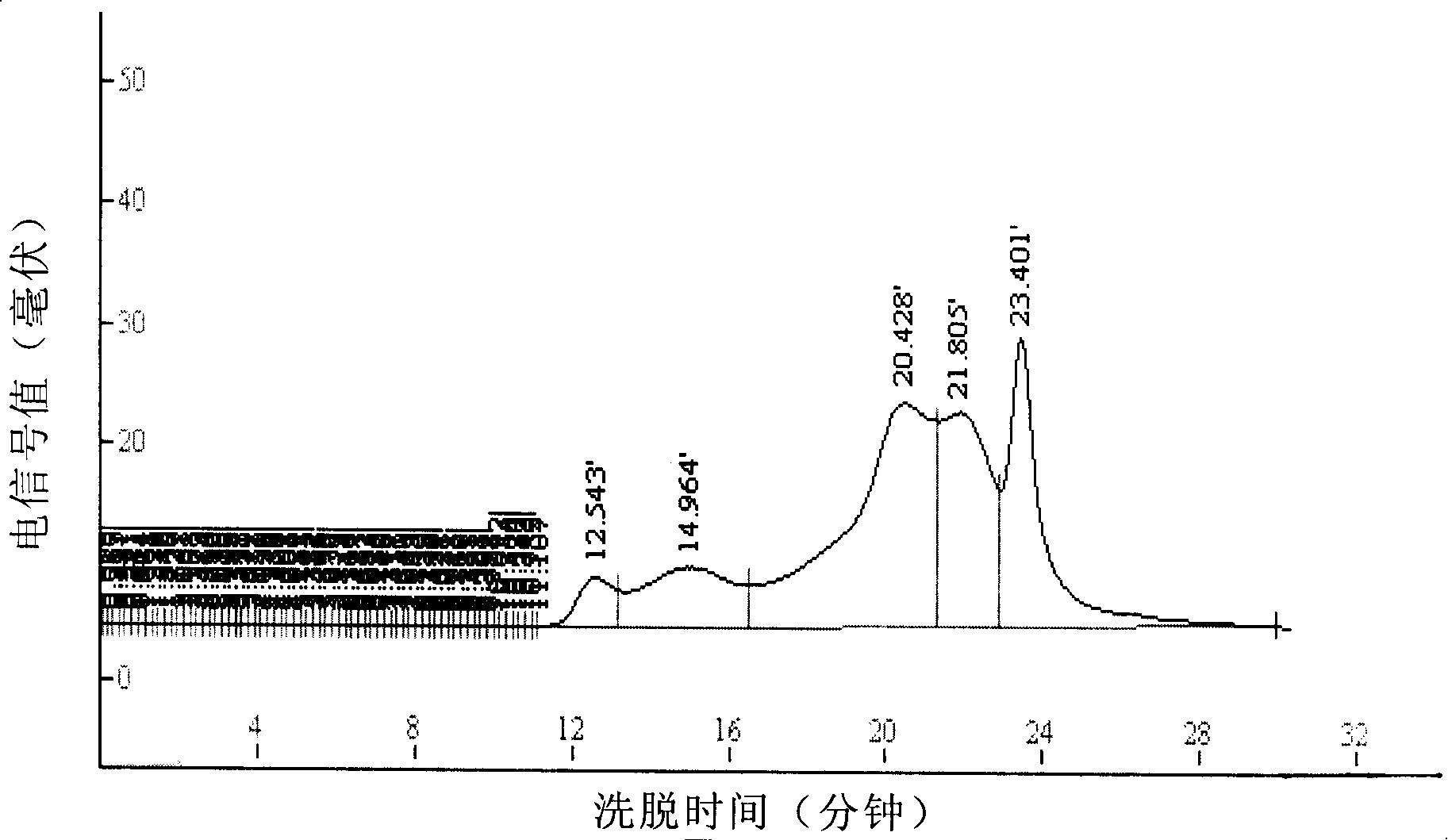
Gluten-free protein biscuit manufactured by sweet potato coarse dietary fibers and preparation method of gluten-free albumen cookie
The invention provides a gluten-free protein biscuit manufactured by sweet potato coarse dietary fibers and a preparation method of the gluten-free protein biscuit. Raw materials for manufacturing the gluten-free protein biscuit include sweet potato coarse dietary fiber starchy flour, sweet potato coarse dietary fiber superfine powder, sweet potato coarse dietary fiber nano-powder, sweet potato modified starch, extrusion sweet potato coarse dietary fiber powder, sweet potato coarse dietary fiber microwave treatment powder, sweet potato starch, food gum, plant source polyphenol, albumen, sugar, salt, baking soda, ammonium bicarbonate, edible oil, water and the like. The weight ratio of the raw materials is 10-40: 10-40: 10-20: 4-12: 5-12: 5-13: 0.5-6: 0.1-3: 0.1-0.7: 1-3: 0.5-25: 0.1-3: 0.1-1: 0.1-0.5: 14-34: 20-69. The sweet potato coarse dietary fiber gluten-free protein biscuit manufactured by the method has unique flavor of a sweet potato, is crisp in taste, golden in color and rich in protein, coarse fibers, vitamin, mineral elements and the like, and has fine nutrition and health care functions.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Extractive of locust tree microellobosporia, preparation method and uses thereof
ActiveCN101204405AThe active ingredient is clearQuality is easy to controlPeptide preparation methodsFungi medical ingredientsSide effectFree protein
The invention discloses an extraction of sophora japonica ear fermentation substance, which is a medicine for treating oncosis, consisting free protein, polyferose and proteoglycan.The invention also discloses a preparation method and the pharmaceutical application for the extraction.The extractive of sophora japonica ear fermentation substance provided by the invention is characterized by definite active component, controllable quality, high purity active components which have a reliable treatment effect for treating all kinds of oncosis and almost no side effect.The preparation method provided by the invention has a simple technology and the products made by the method enriches active ingredient further.
Owner:QIDONG GAITIANLI MEDICINES
Monitoring a dynamic system by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20110262946A1Increasing recombinant protein productionSuppression problemBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementCell freeFree protein
The present invention provides a method for monitoring of profile changes of components in a dynamic system such as a cell-free in vitro protein synthesis system by using liquid chromatography (LC) combined with mass spectrometry (MS). In an additional aspect, this invention provides a method for enhancing the yield and / or reproducibility in a cell-free protein synthesis system by modulating the level and / or activity of a protein component that has regulatory effects on the system.
Owner:SUTRO BIOPHARMA
Method for removing protein of Brazil mushroom crude polysaccharide
InactiveCN1821274AHigh removal rateReduce pollutionPeptide preparation methodsOrganic solventFree protein
The present invention relates to the method of removing protein from crude Brazil mushroom polysaccharide. The crude Brazil mushroom polysaccharide is column chromatography separated with at least one kind of weak acid cation resin or weak alkali anion resin to separate free protein from polysaccharide. The method of the present invention has short operation time of 3-5 hr, high protein eliminating rate, less polysaccharide loss, no use of organic solvent. less environmental pollution, low cost and reusablility of ion exchange resin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Serum-free protein-free culture medium supporting HEK293 cell suspension culture and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111304149AEasy to separate and purifyReduce pollutionCulture processArtificial cell constructsBiotechnologyFree protein
The invention discloses a serum-free protein-free culture medium supporting HEK293 cell suspension culture and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of cellengineering. According to the serum-free protein-free culture medium disclosed by the invention, different nutrient substances are selected according to the nutritional requirements of in-vitro growthof cells so as to replace animal serum, and the proportion of the different nutrient substances is reasonably adjusted. By further adding an anti-shearing force substance and an anti-caking substance, high-density suspension culture of HEK293 cells can be maintained without supplementing serum, and the normal form of the cells is maintained, so that the cells are dispersed and not caked, meanwhile, the normal growth speed is maintained, and the transfection and expression of target genes are facilitated.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV +1
Three spiral lentinan with anti-cancer activity and its preparation and use
InactiveCN1613876AAntitumor activityOvert immune functionOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsAcetic acidSaline water
This invention relates to three-spiral lentina with beta-(1-3)-D-glucan having 20-30%(1-6) chain connected glucose side chains as main chain. It shows three chains in water, with average molecular weight of 20,000-200,000. It is produced by: cutting dry shiitake, removing fat by Suo extraction, soaking in normal saline, centrifuging, extracting remains at 100-130 degrees C, centrifuging, extracting remains in water solution of NaOH / NaBH4, adding acetic acid into extracting liquid to neutralize, decoloring supernatant, removing free protein, dialyzing, concentrating, and frozen drying. It has higher anti-tumor activity and can be used to prepare medicines or health-care products for improving immune ability and antitumor.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Serum-free protein-free cell culture medium
ActiveCN106635953AHigh expressionReduce manufacturing costAnimal cellsCulture processBiotechnologyVaccine Production
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, specifically discloses a serum-free protein-free cell culture medium, and aims to provide a serum-free protein-free cell culture medium capable of supporting the growth of high density cells. The culture medium comprises amino acids, vitamins, inorganic salts, trace elements, carbohydrates, other chemical compounds, polyamine (or derivatives of polyamine), and hydrolysate. The manufacturing cost is low. The stability is high, the live cell density and cell survival rate are extremely high, and the culture medium is suitable for culture cells for recombinant protein and vaccine production.
Owner:昆明润什生物科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com