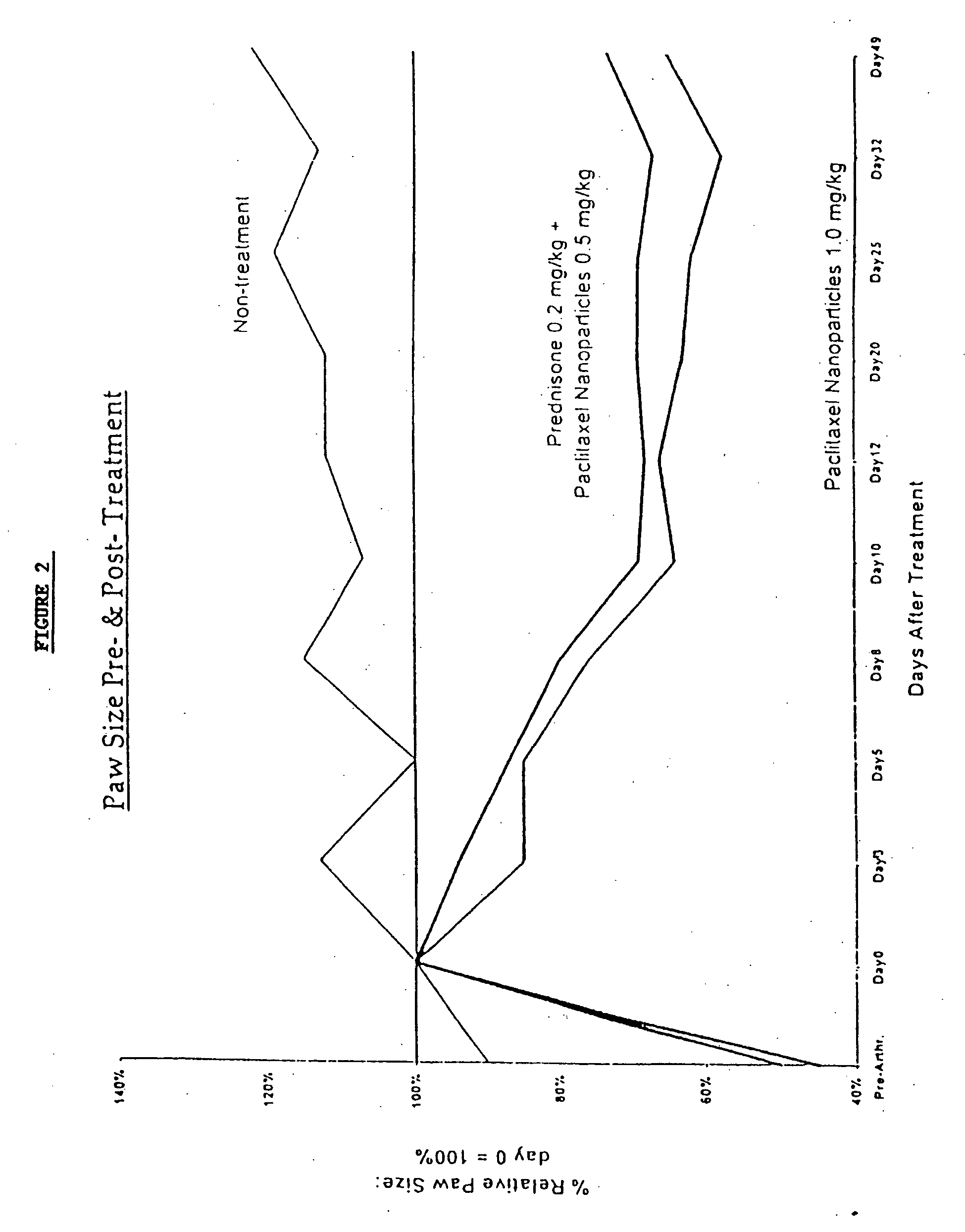
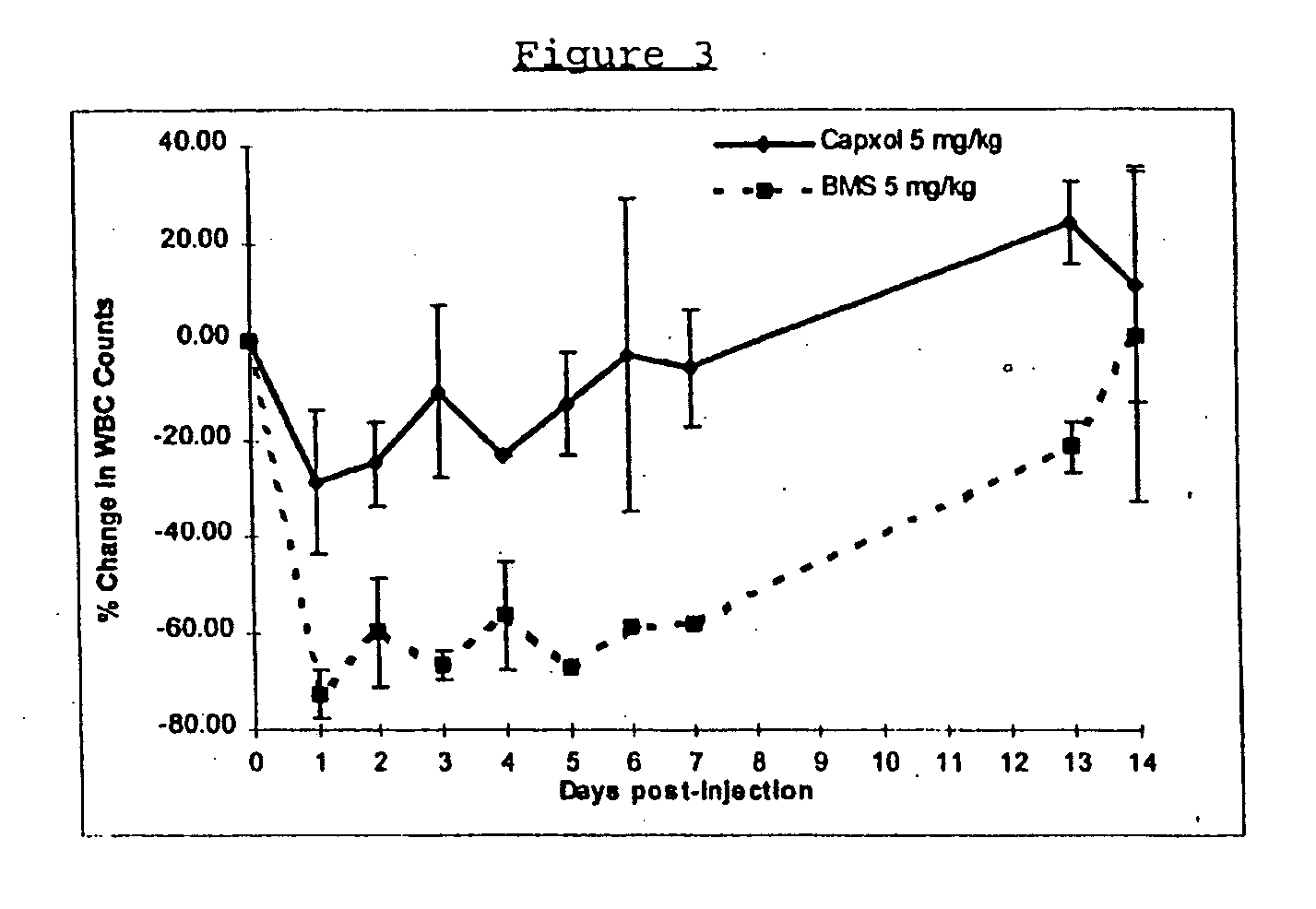
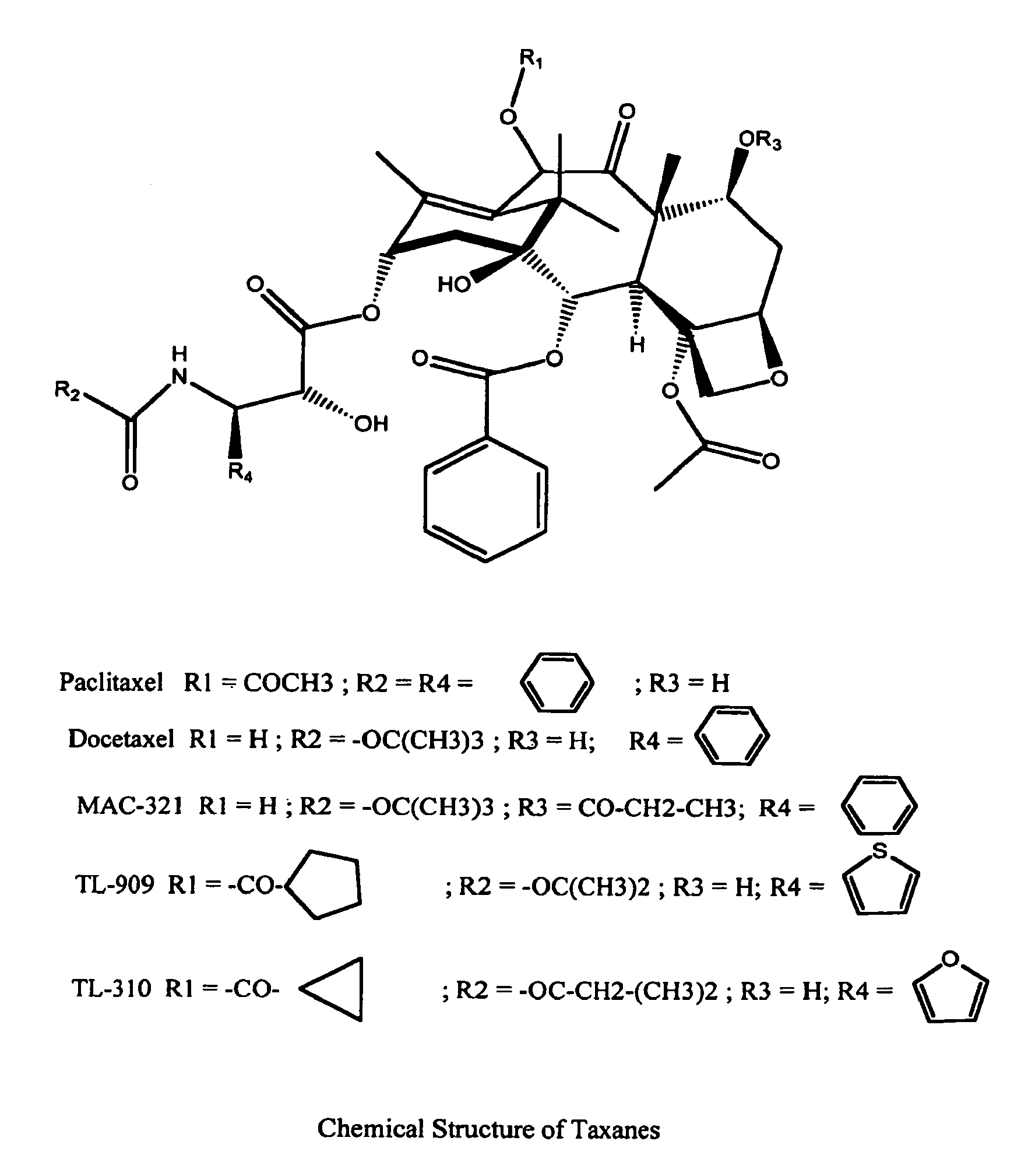
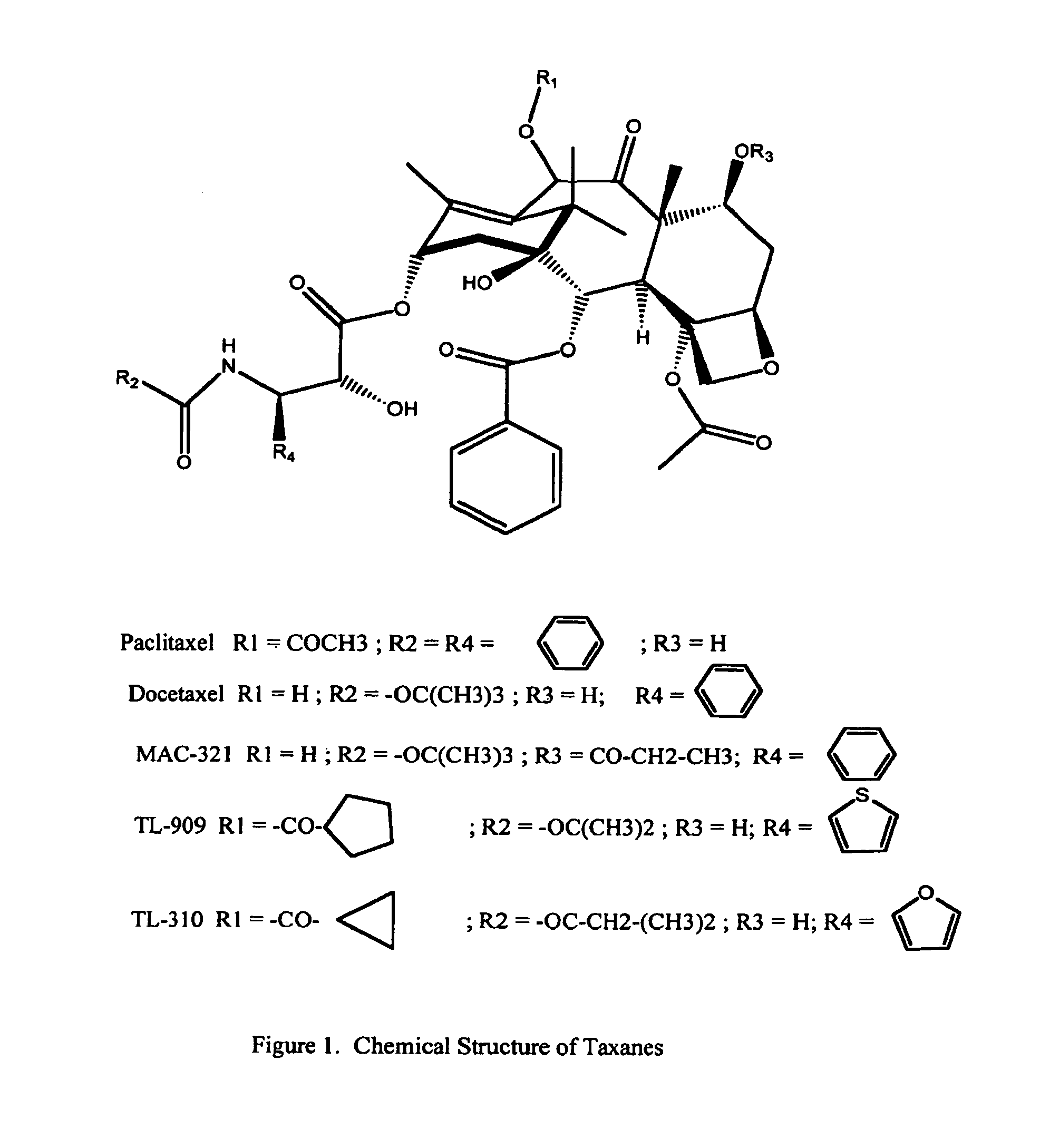
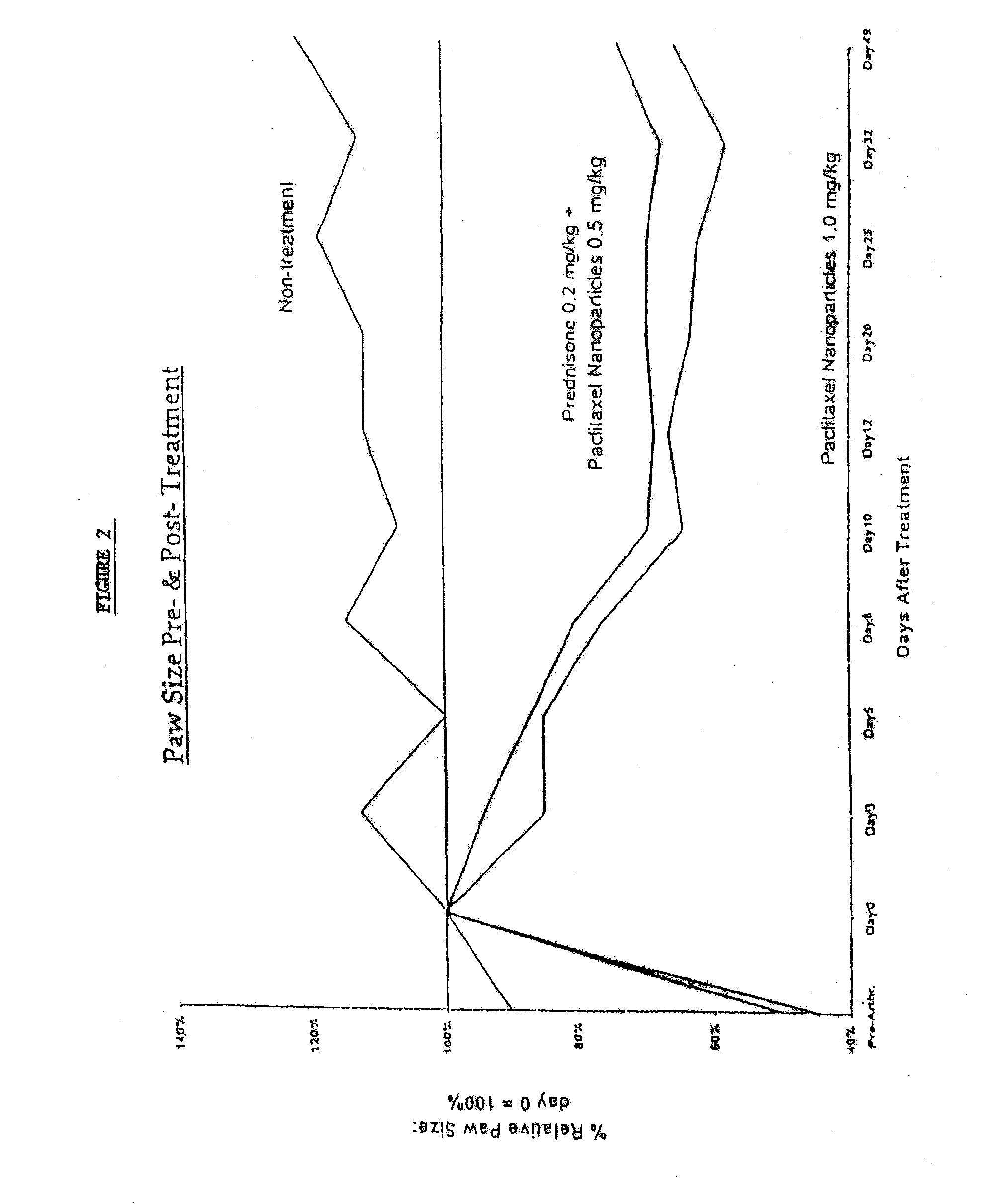
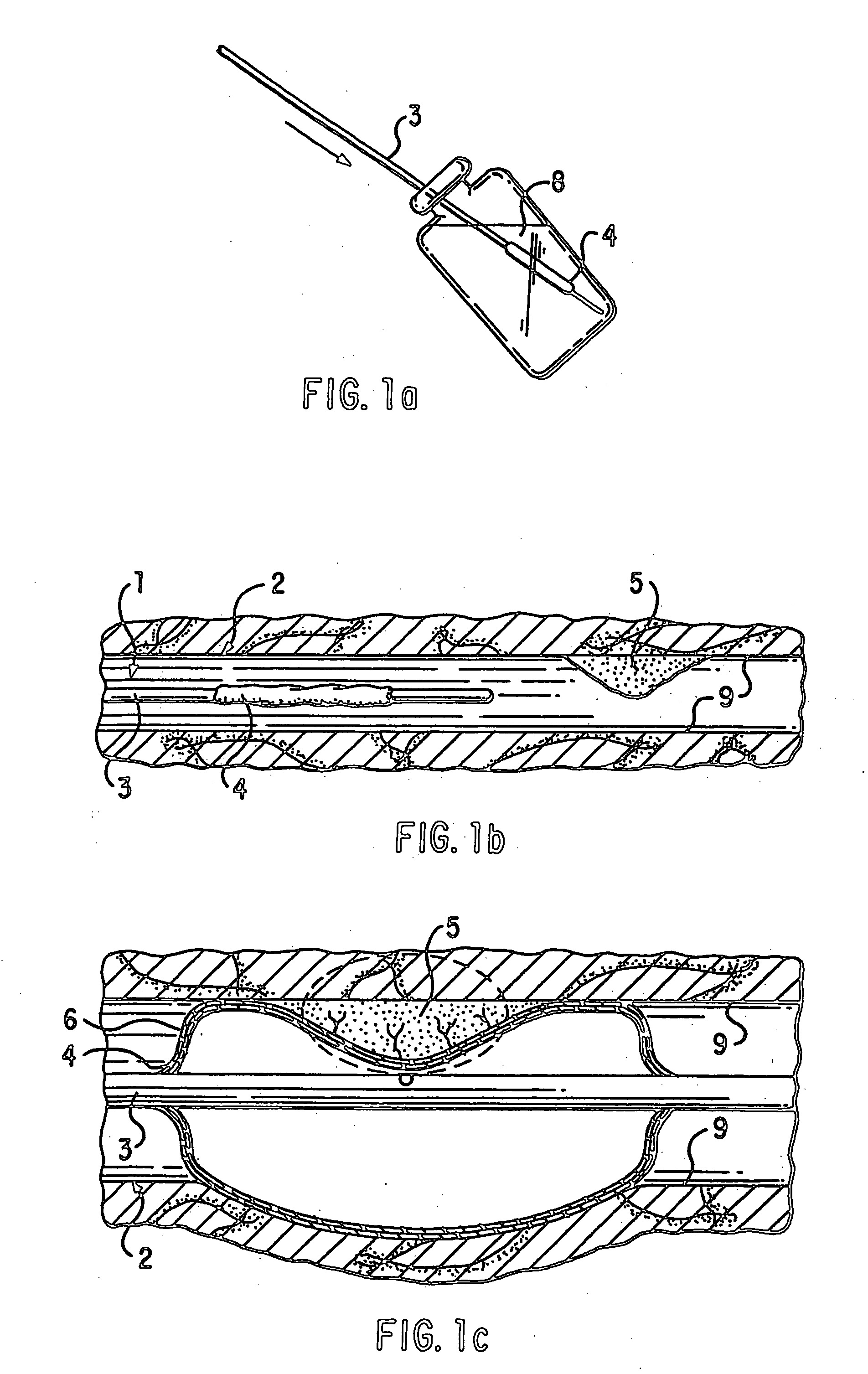
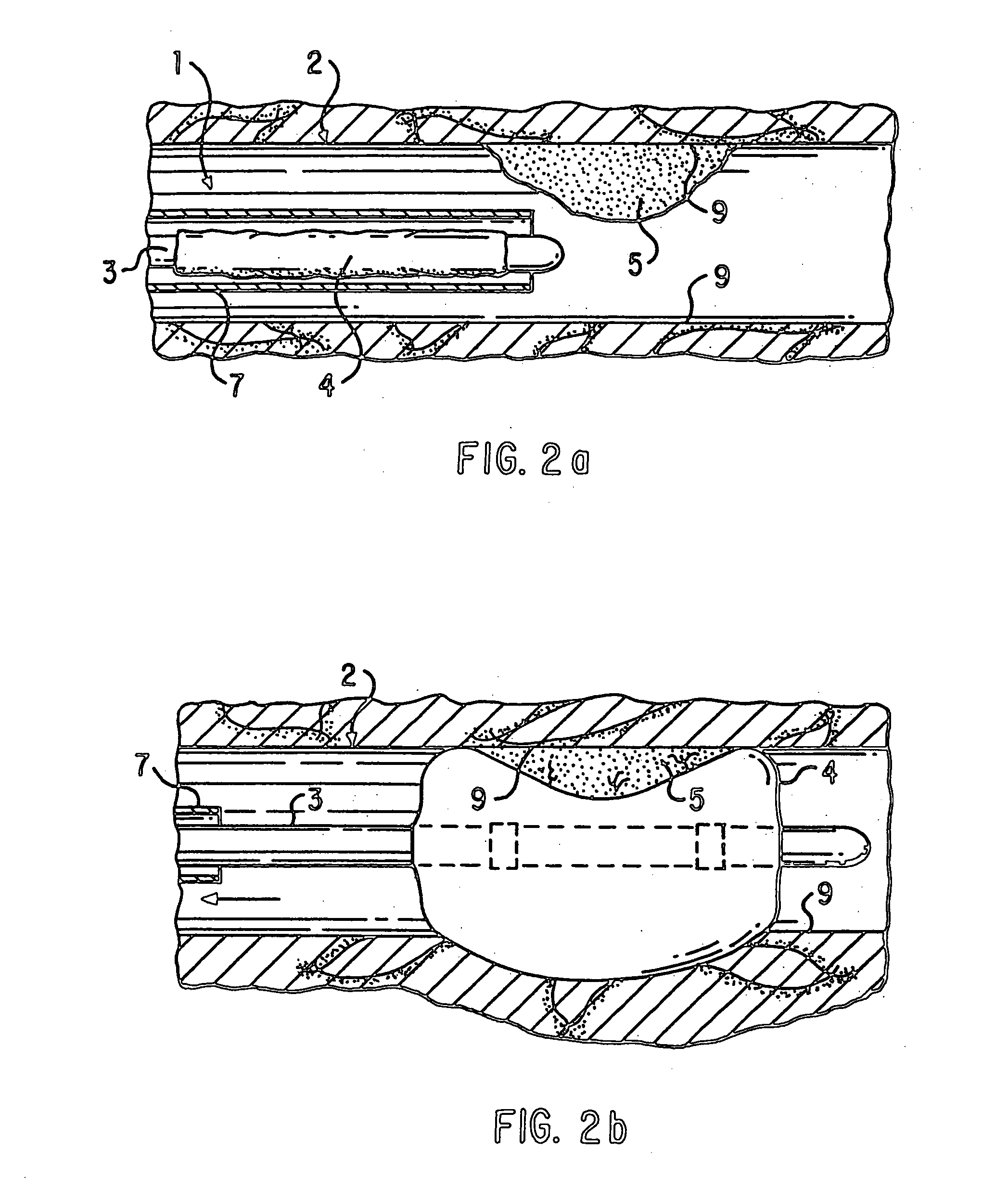
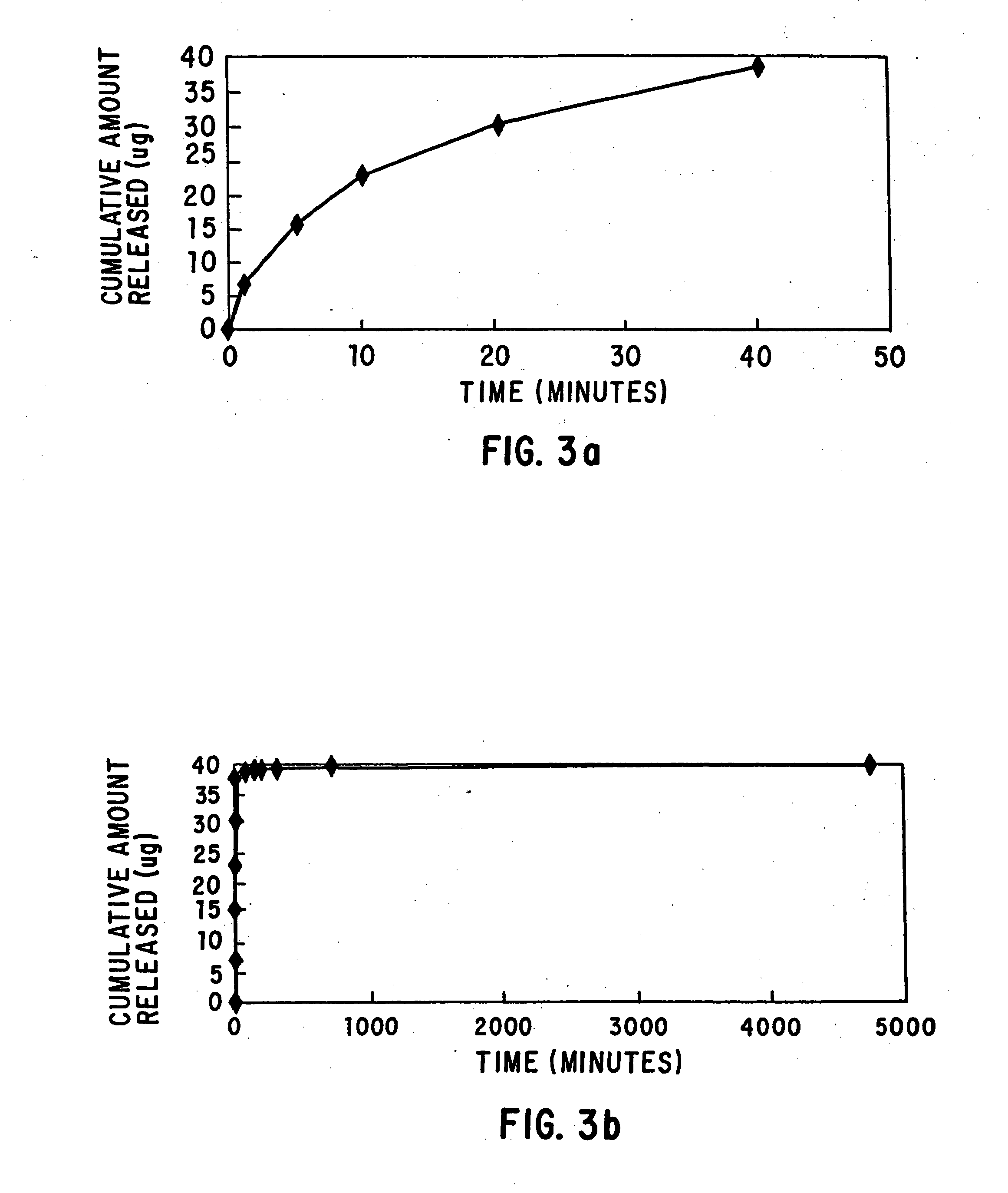
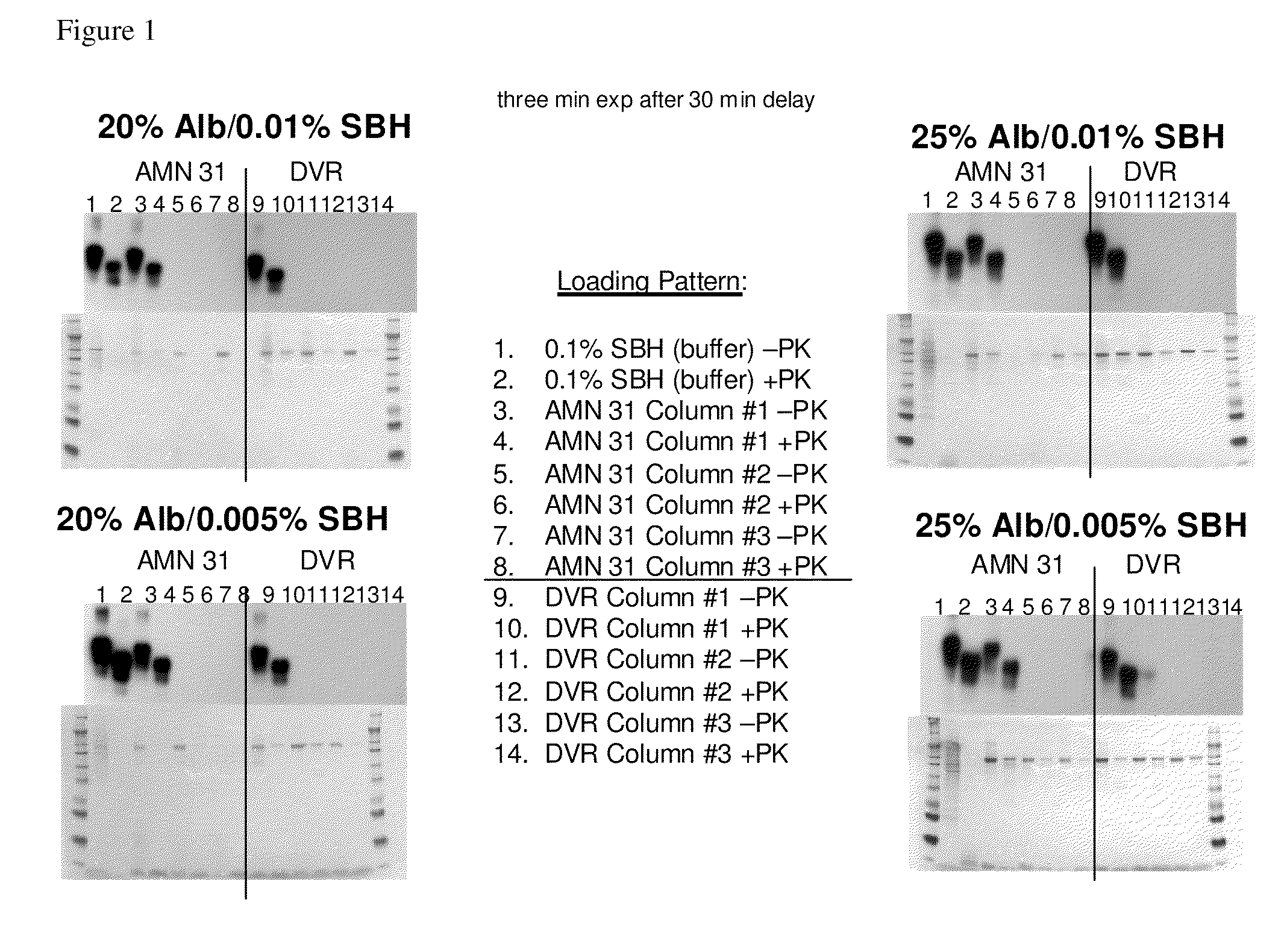
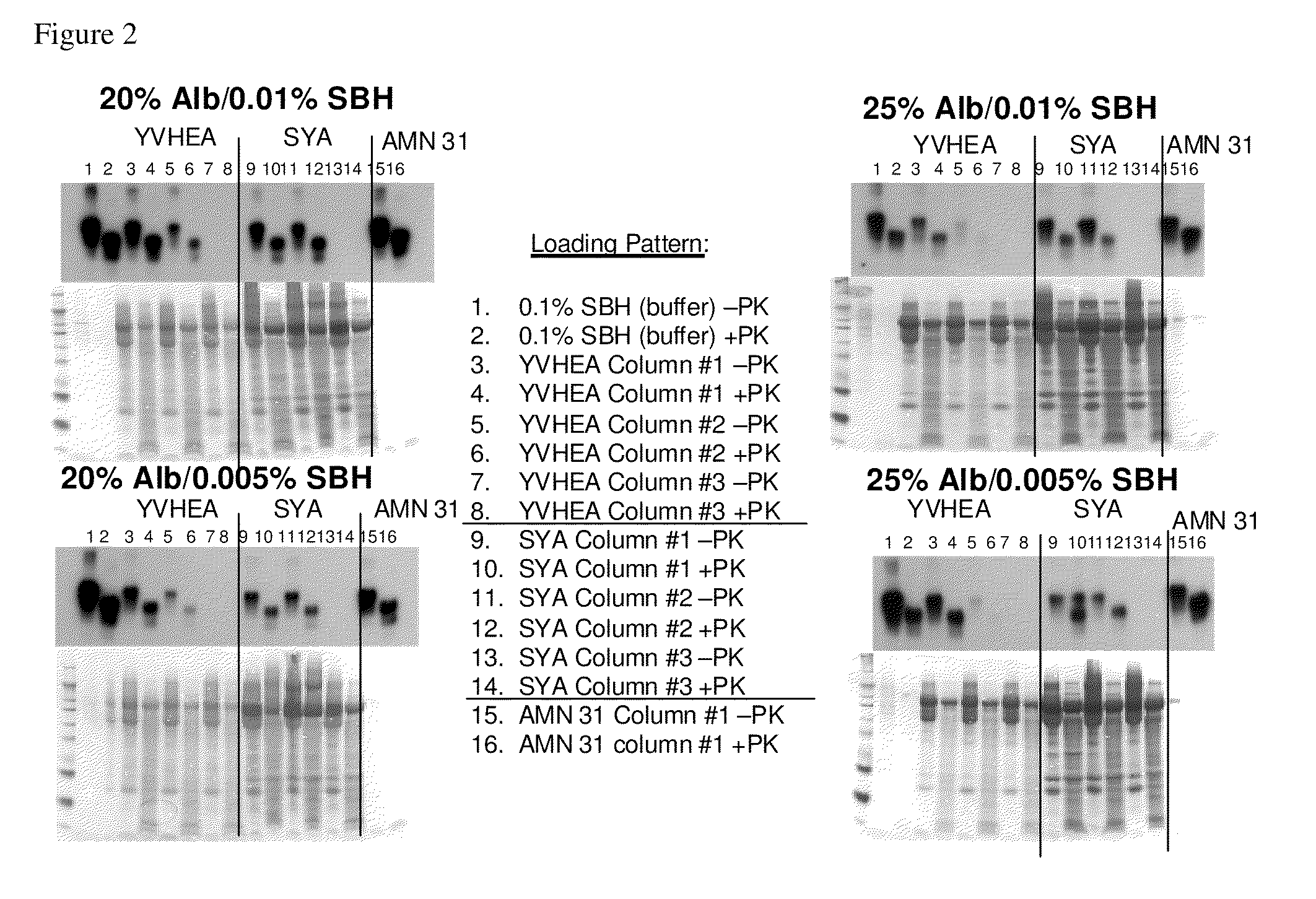
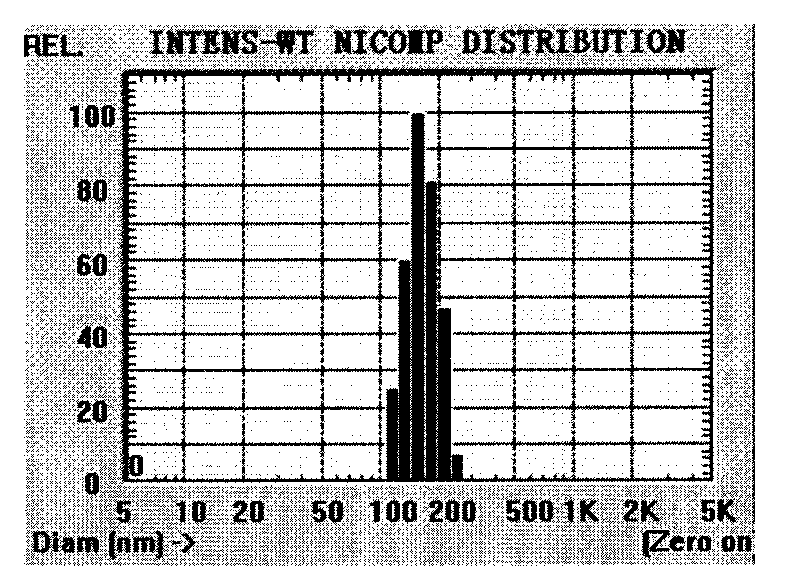
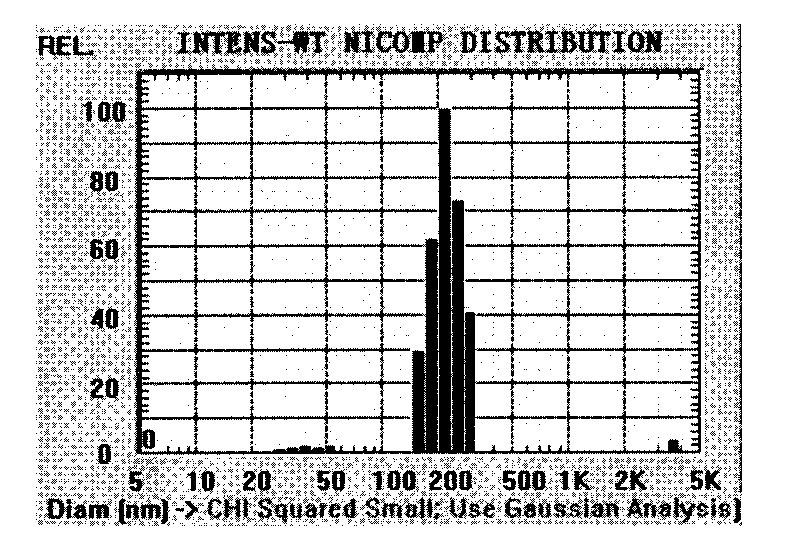
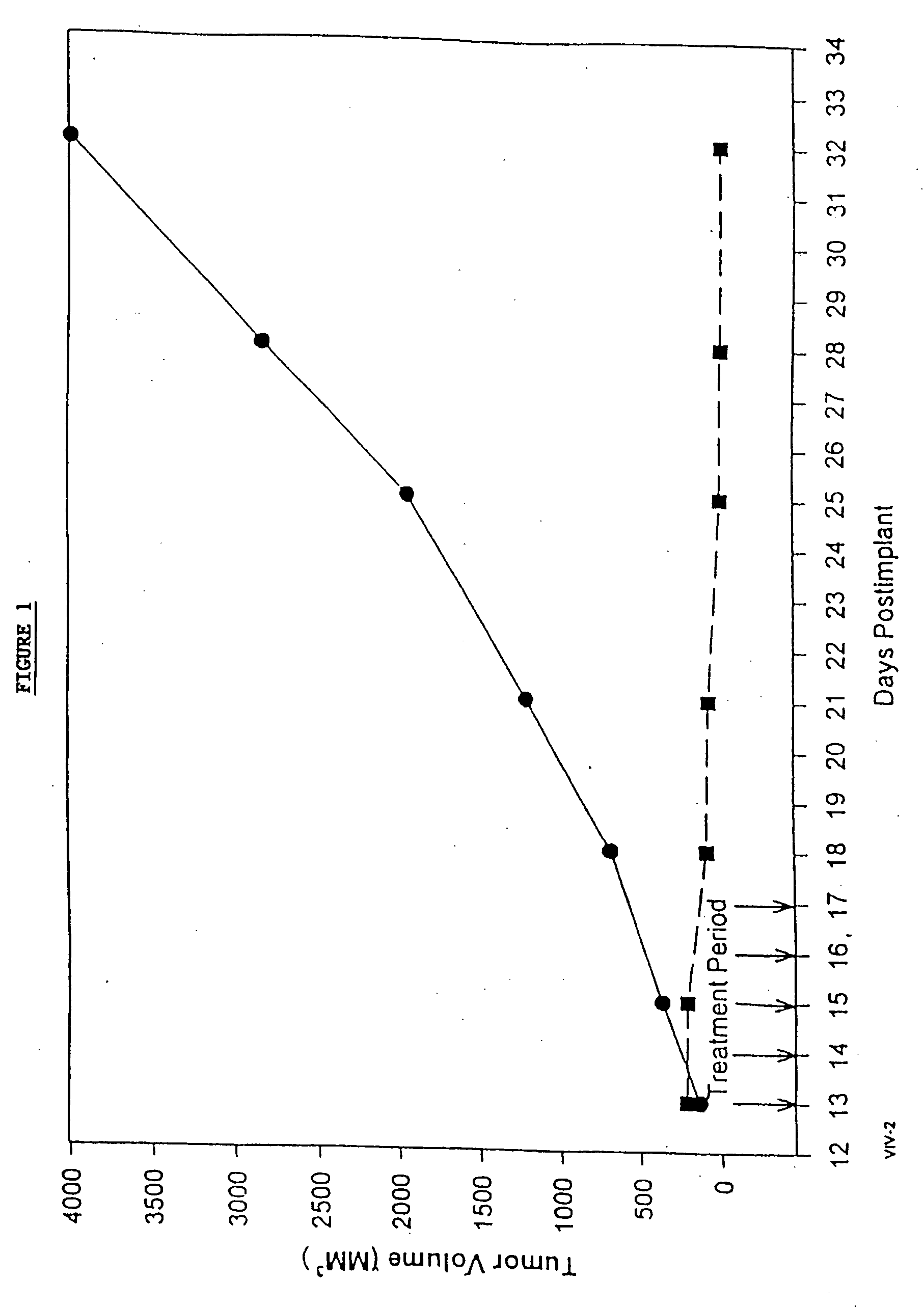
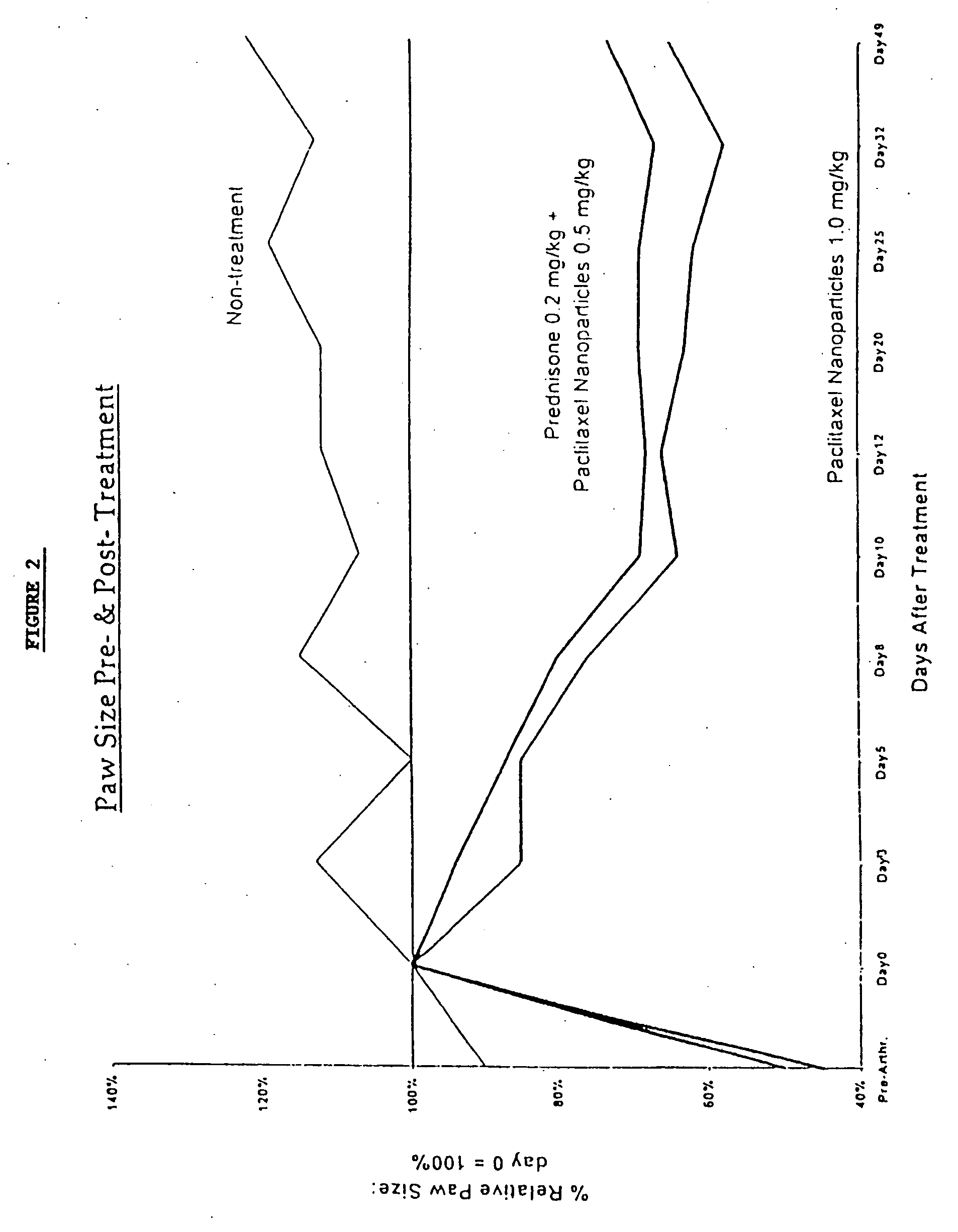
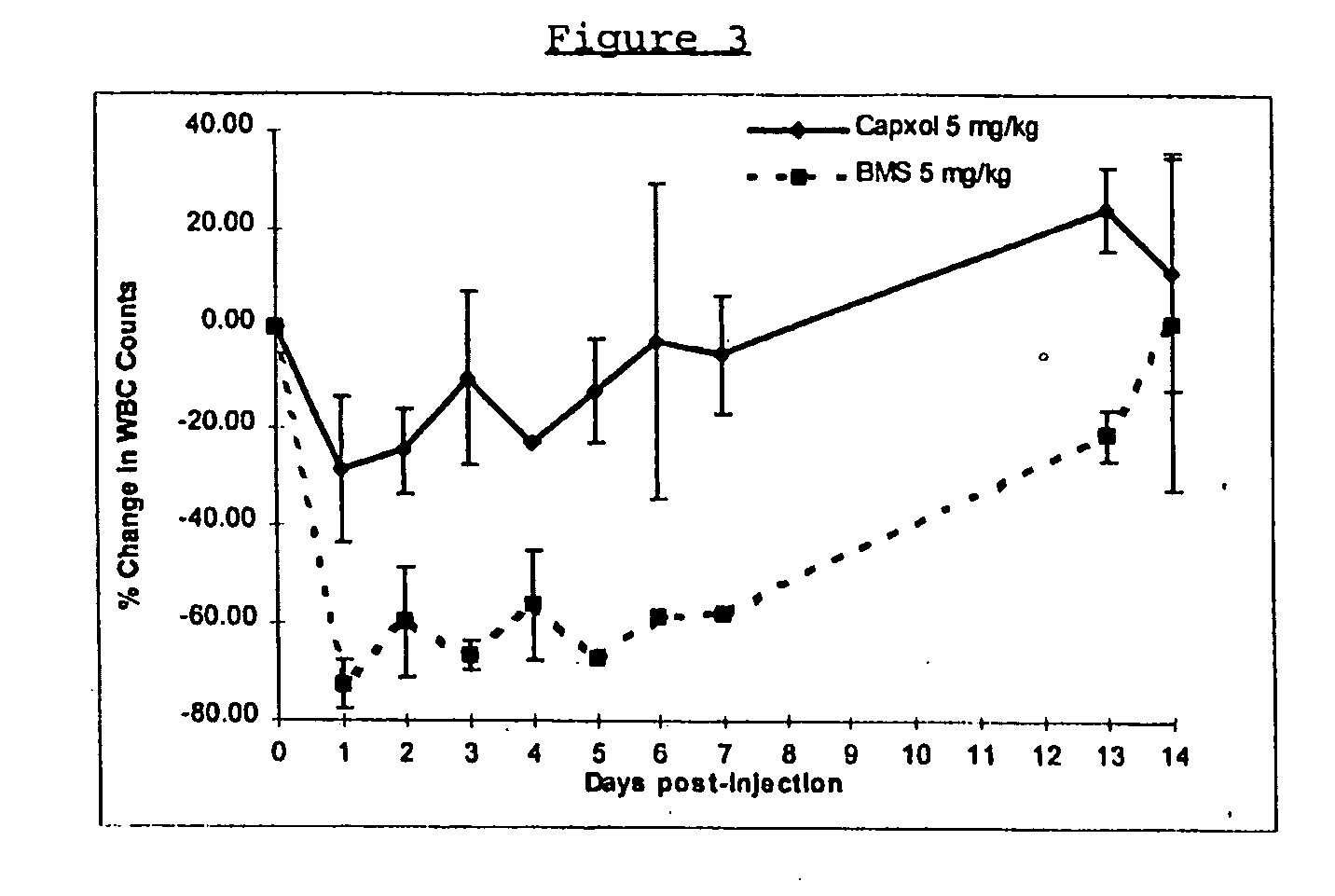
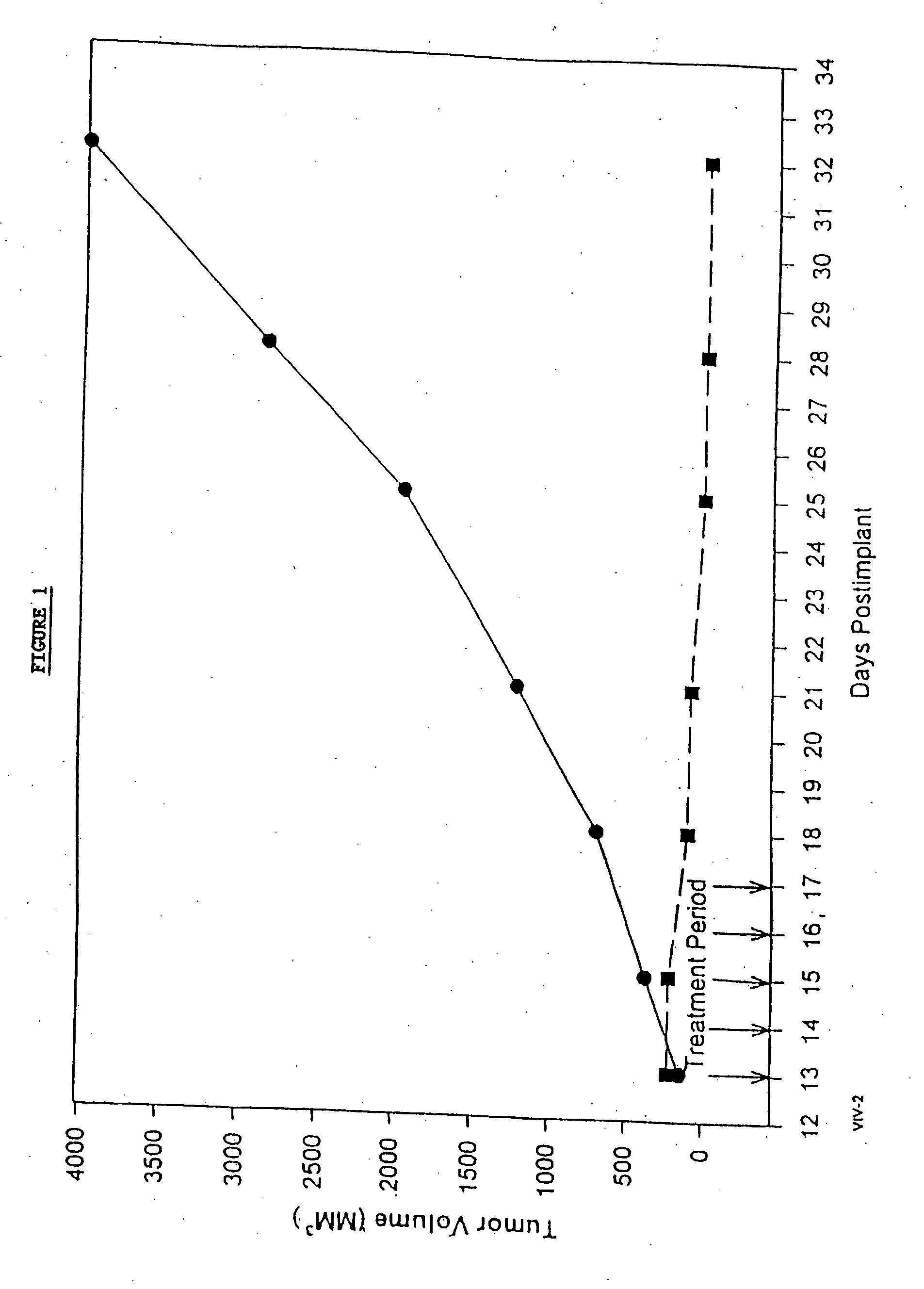
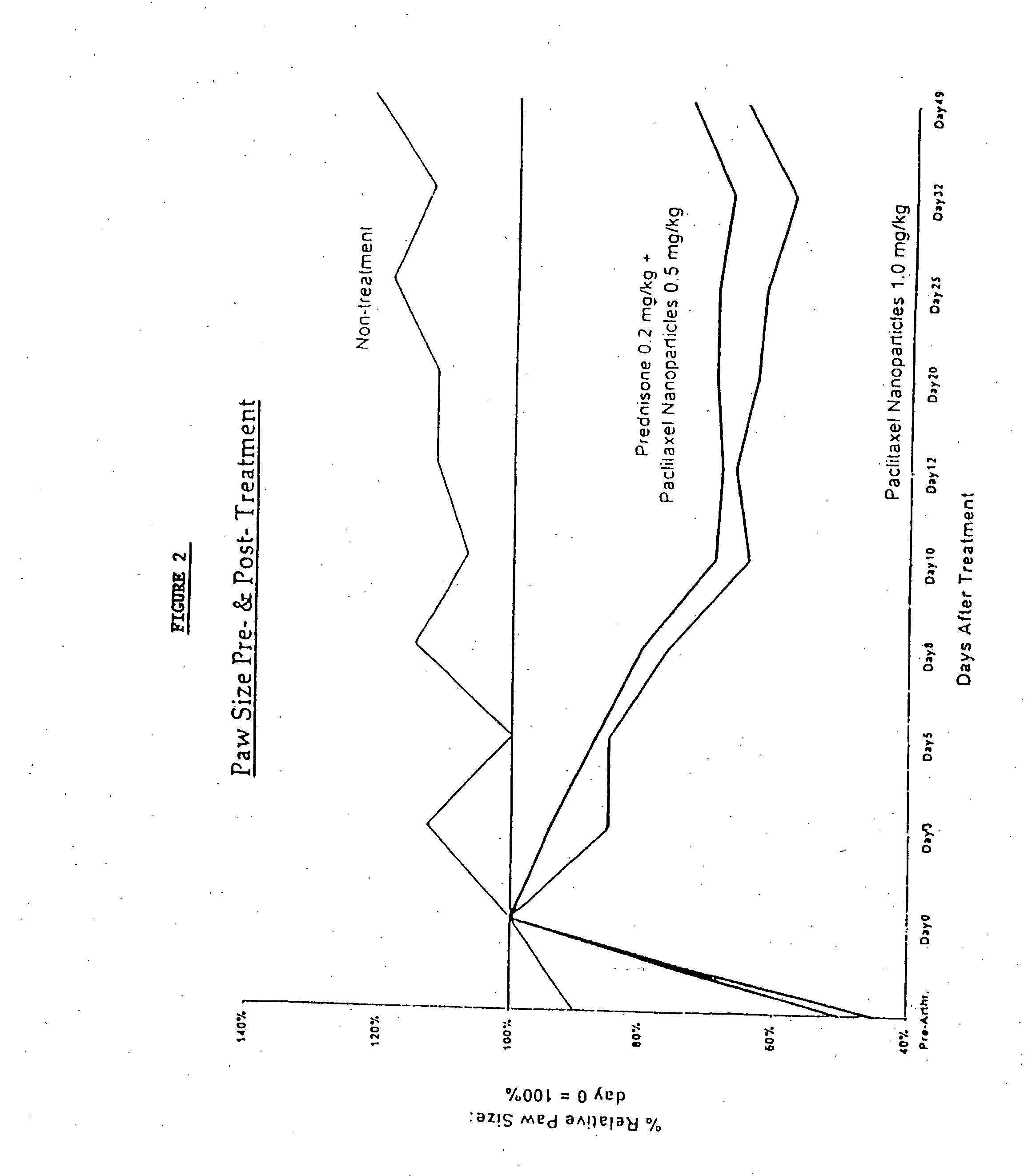
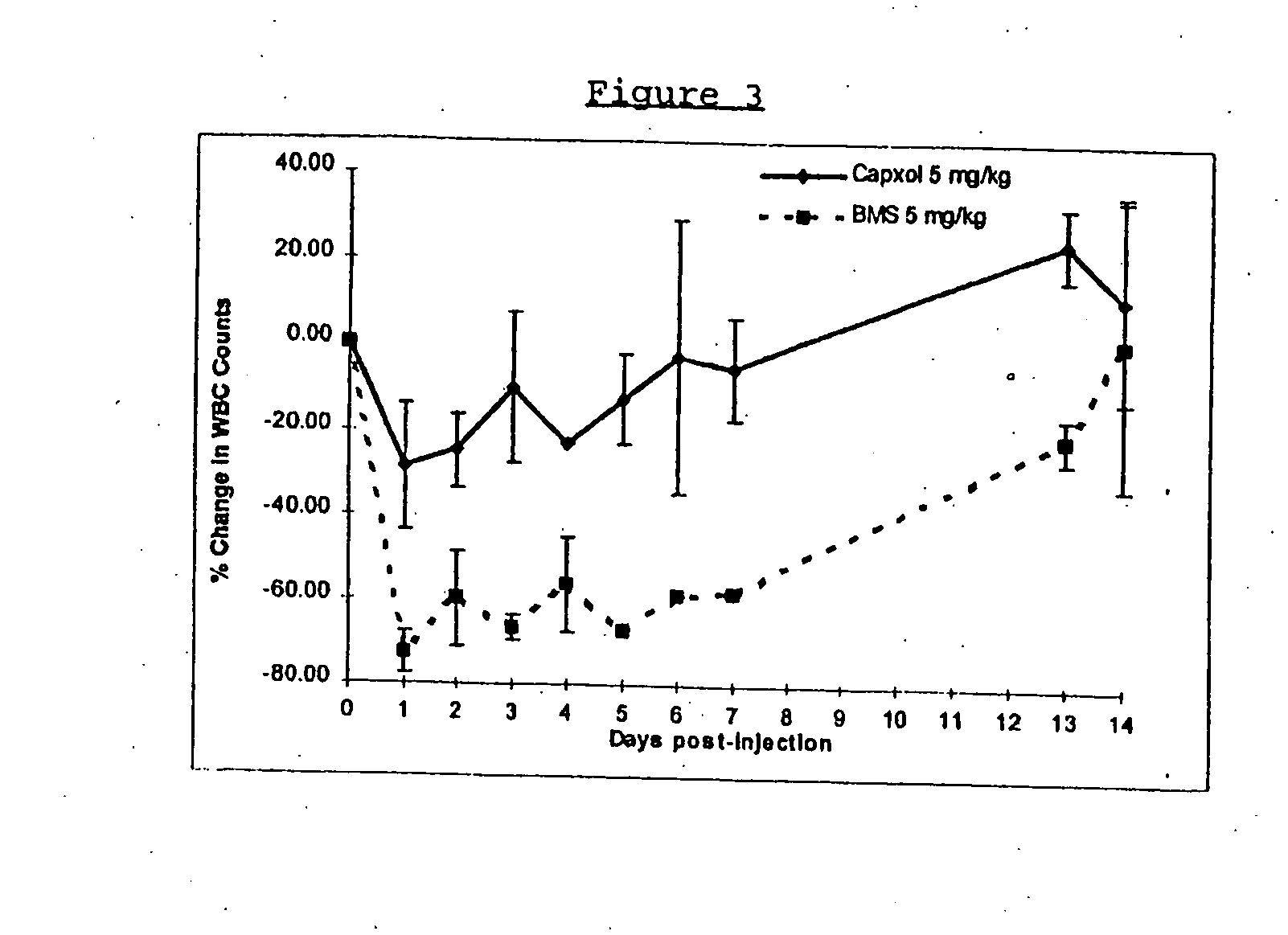
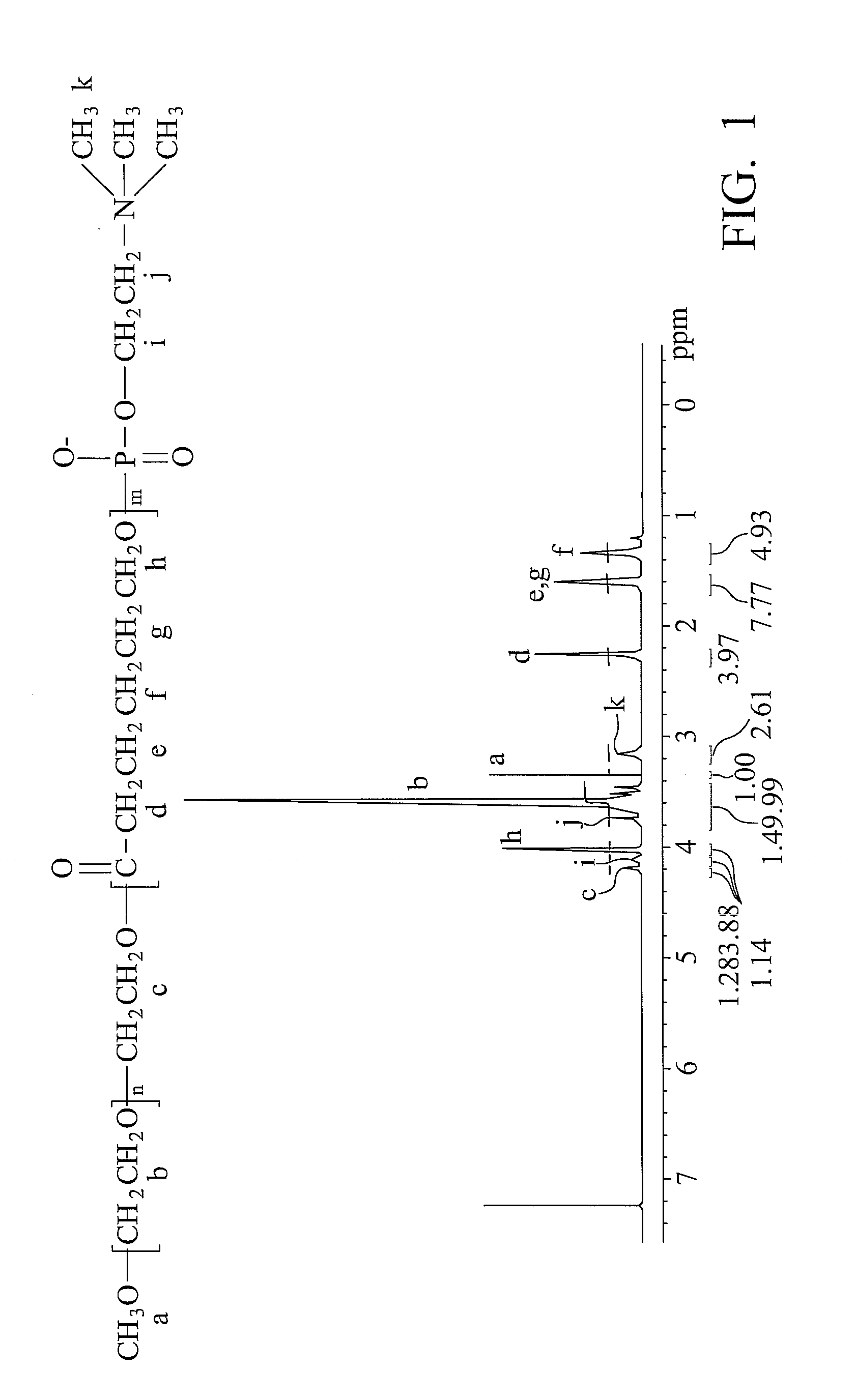
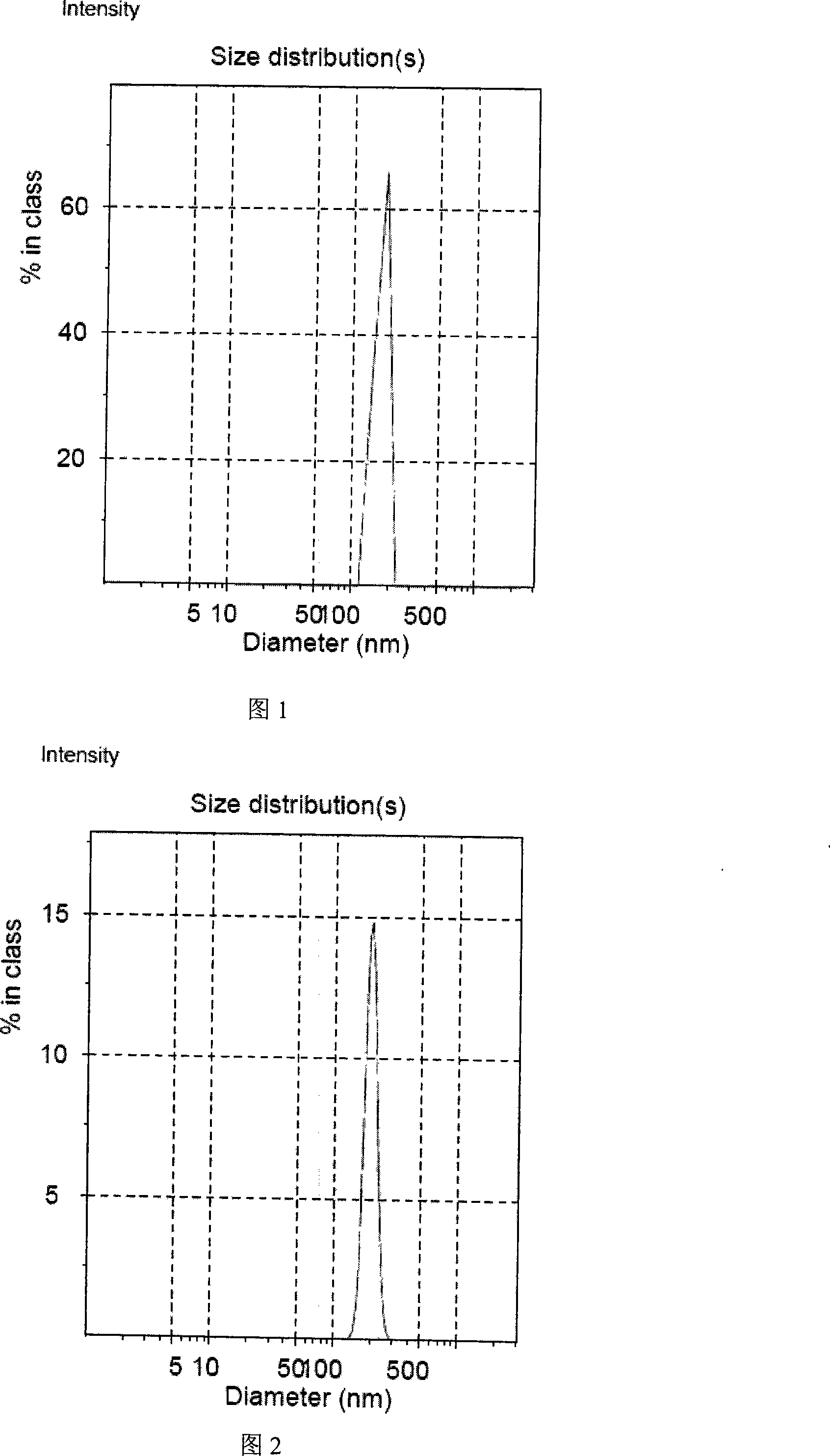
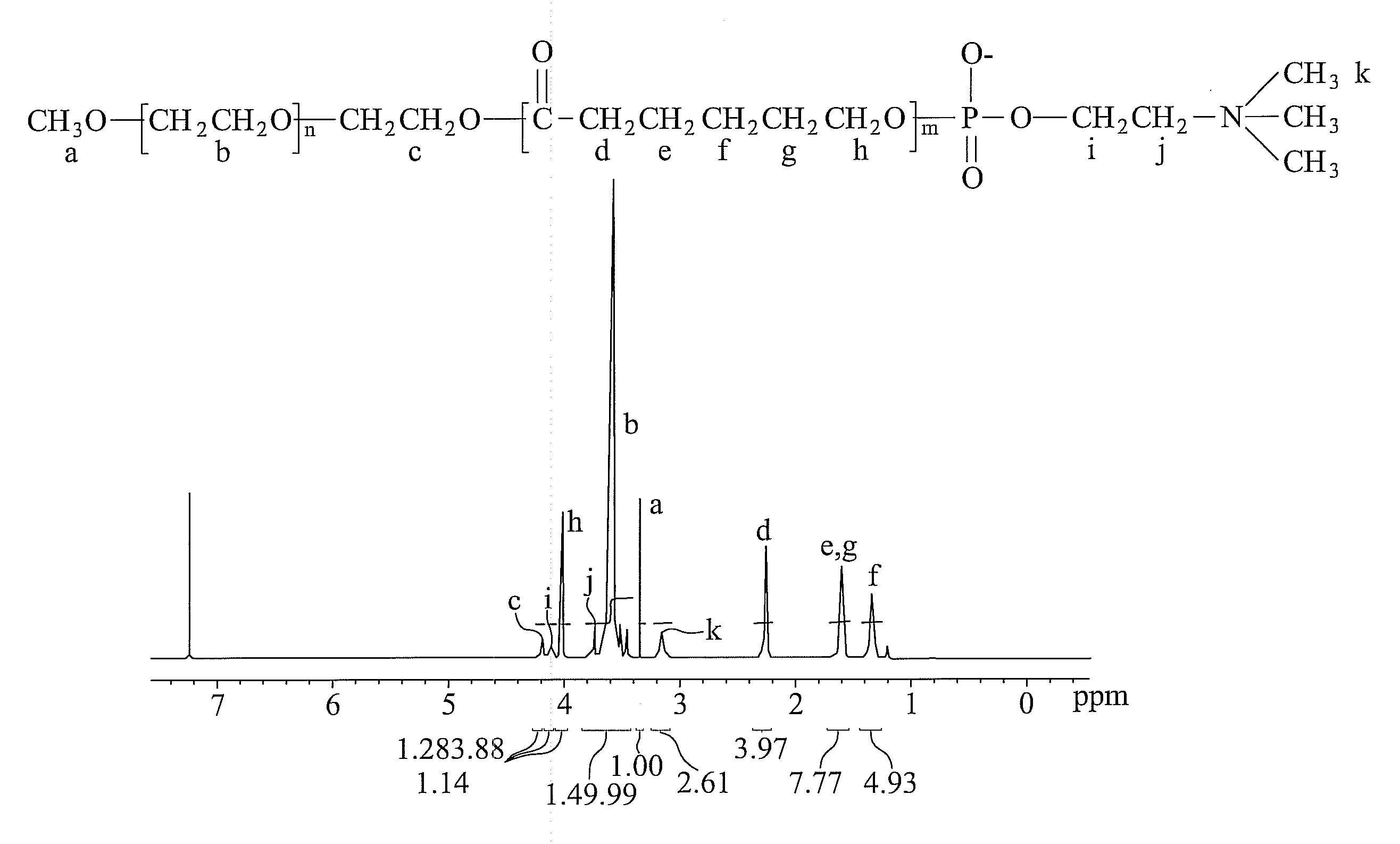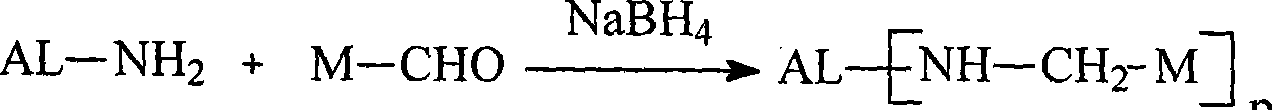Patents
Literature
162 results about "Water insoluble drug" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protein stabilized pharmacologically active agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS6749868B1Low toxicityLong half-lifePowder deliveryEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsSuspended particlesFree protein
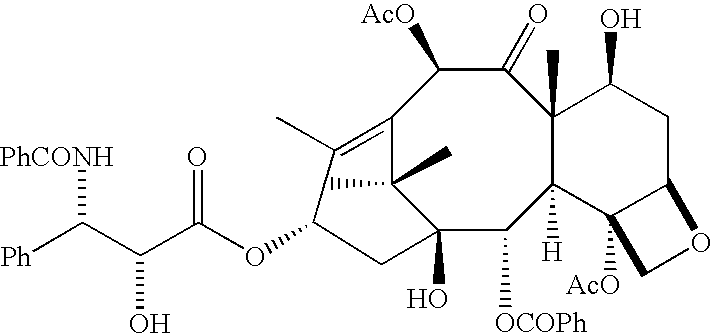
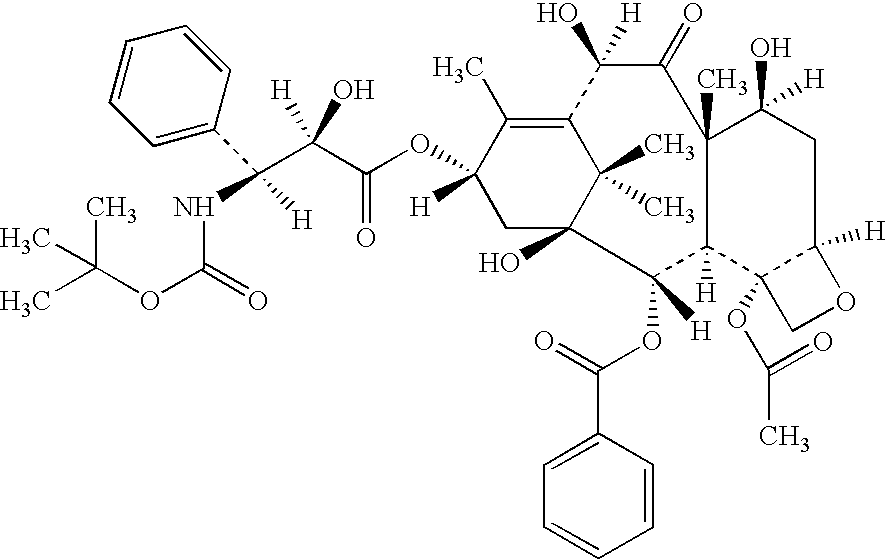
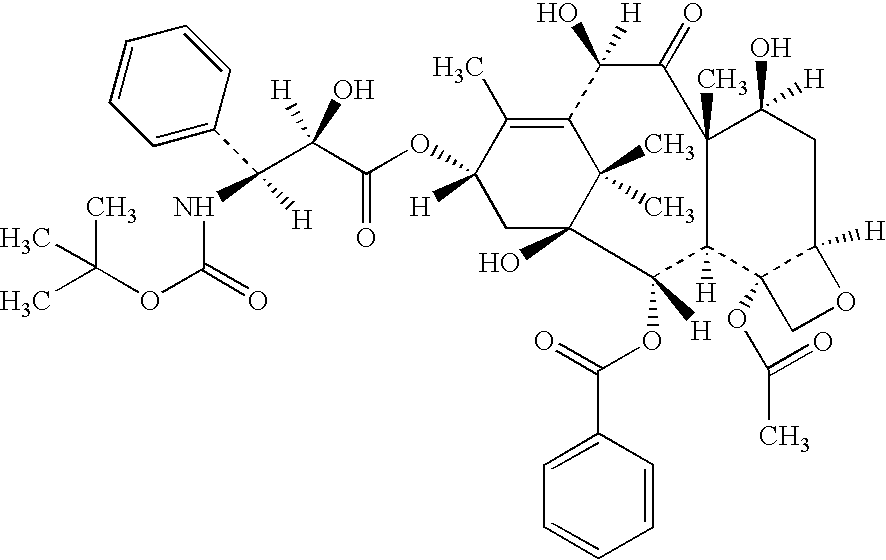
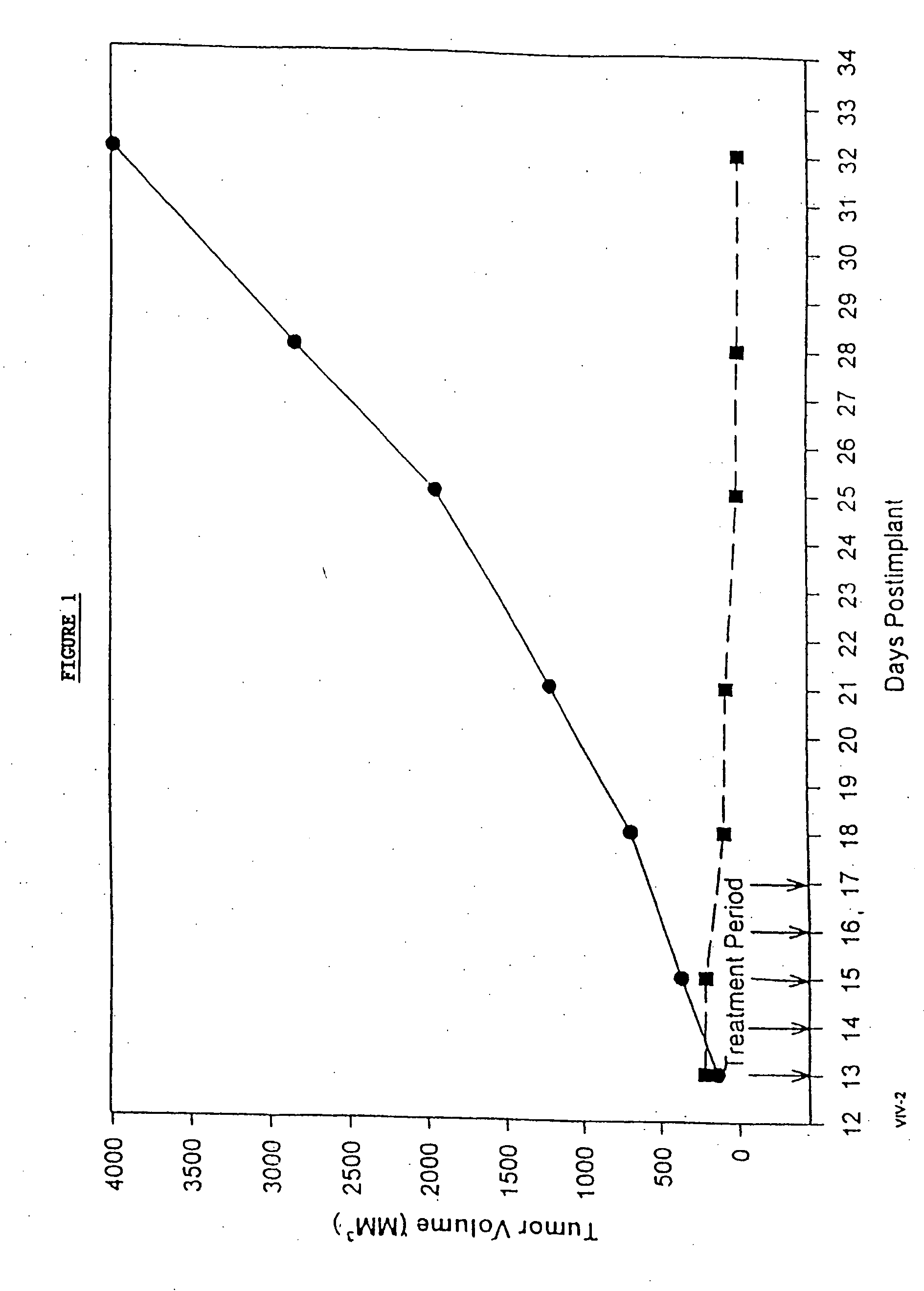
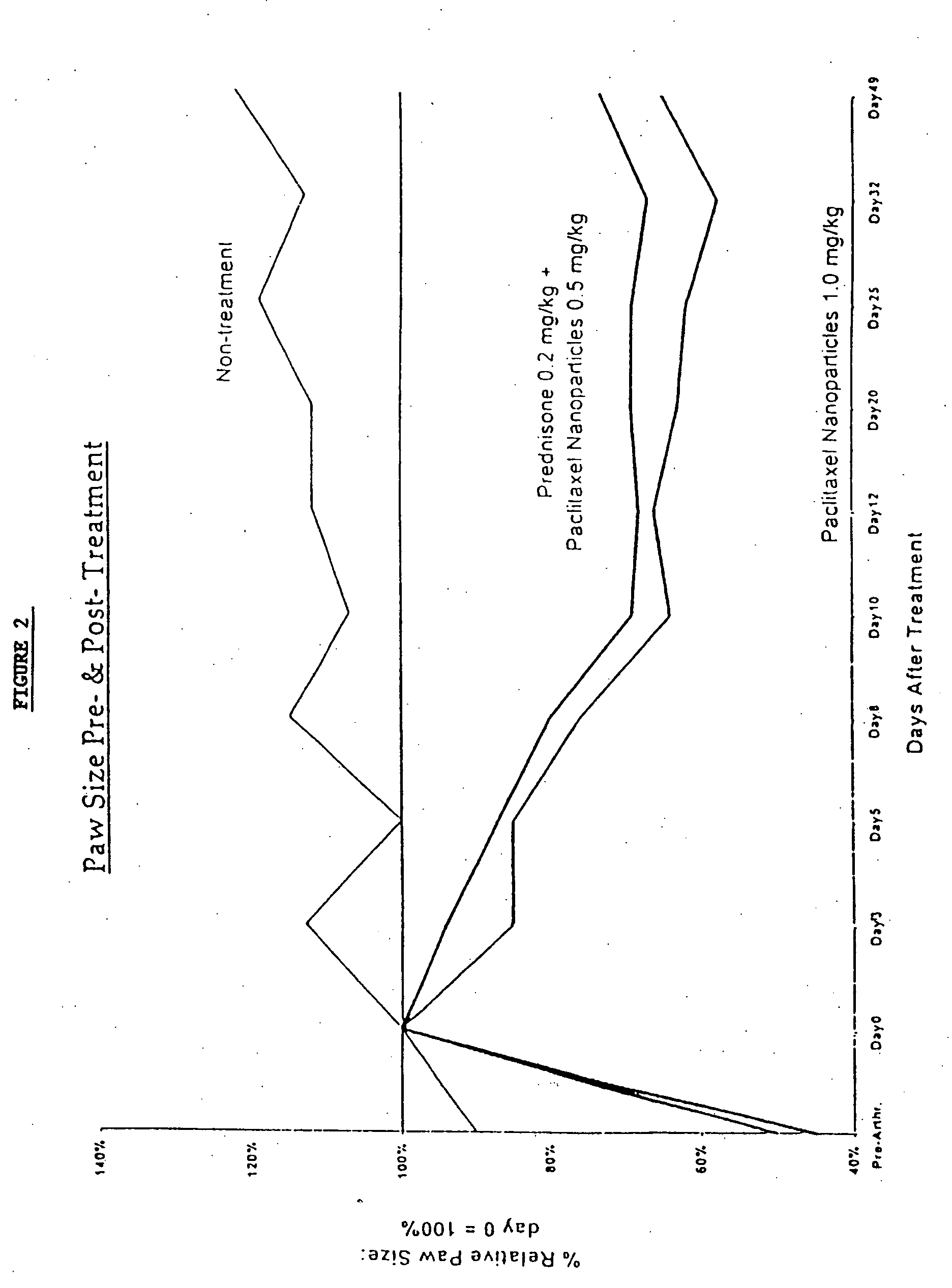
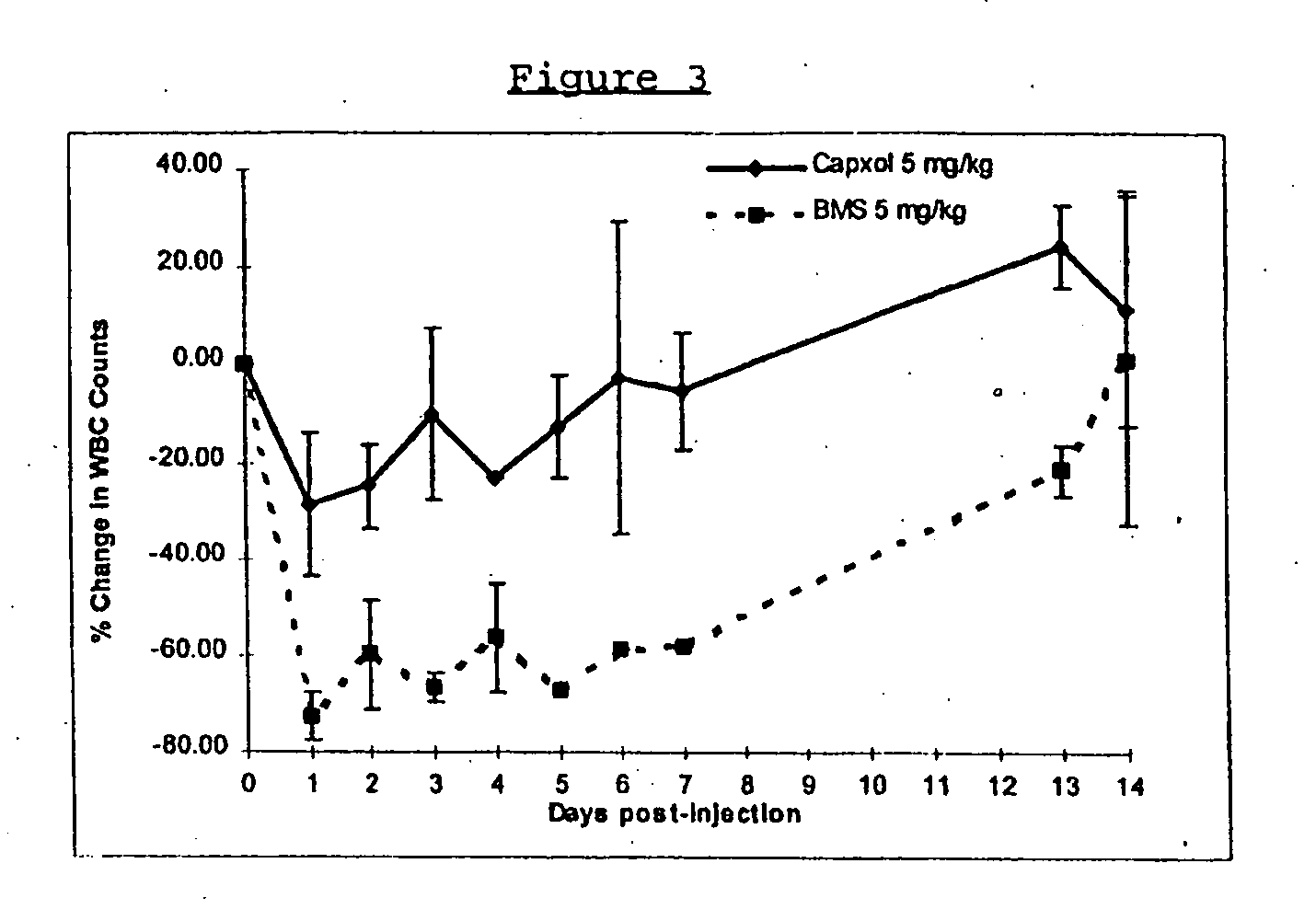
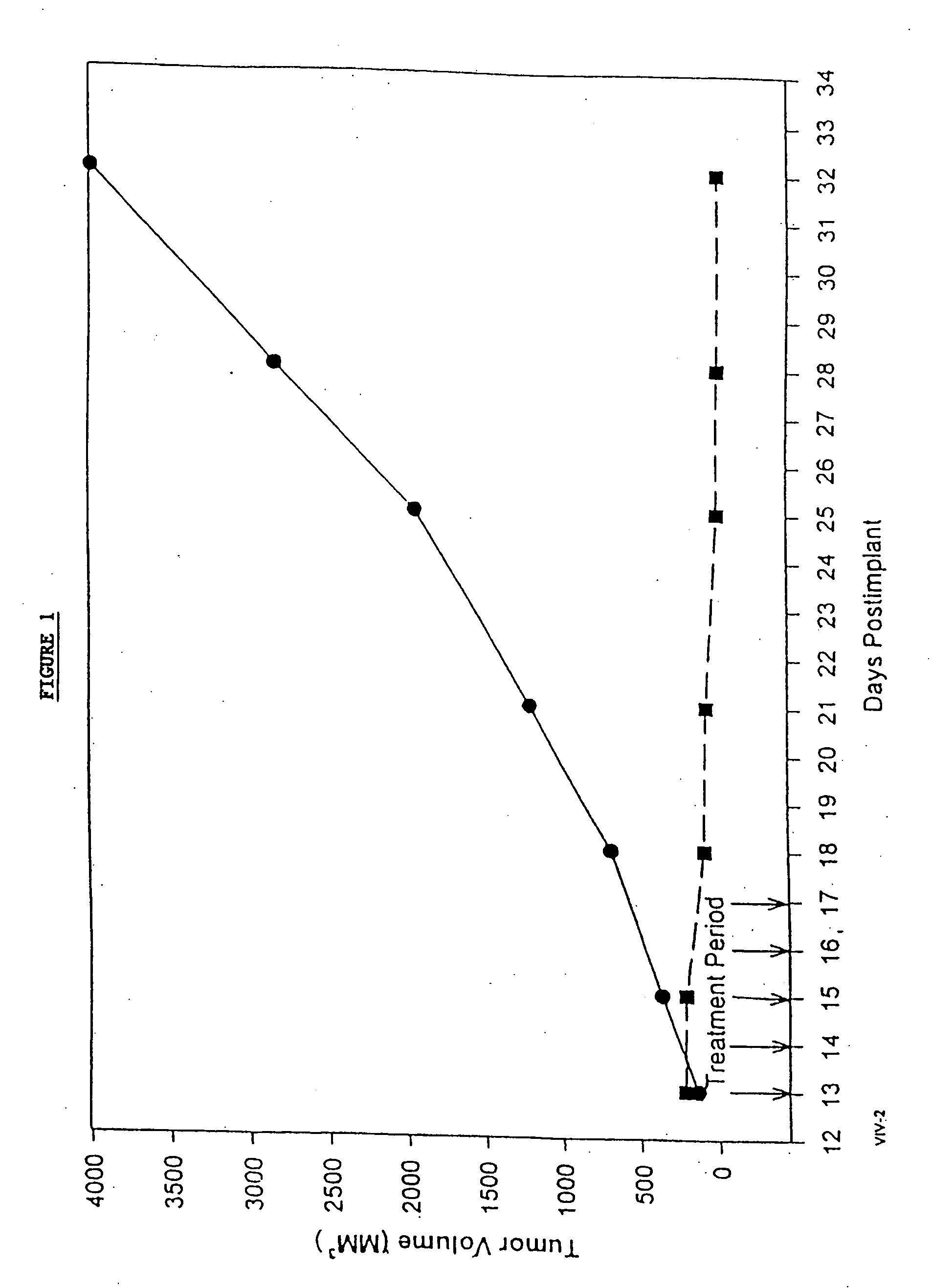
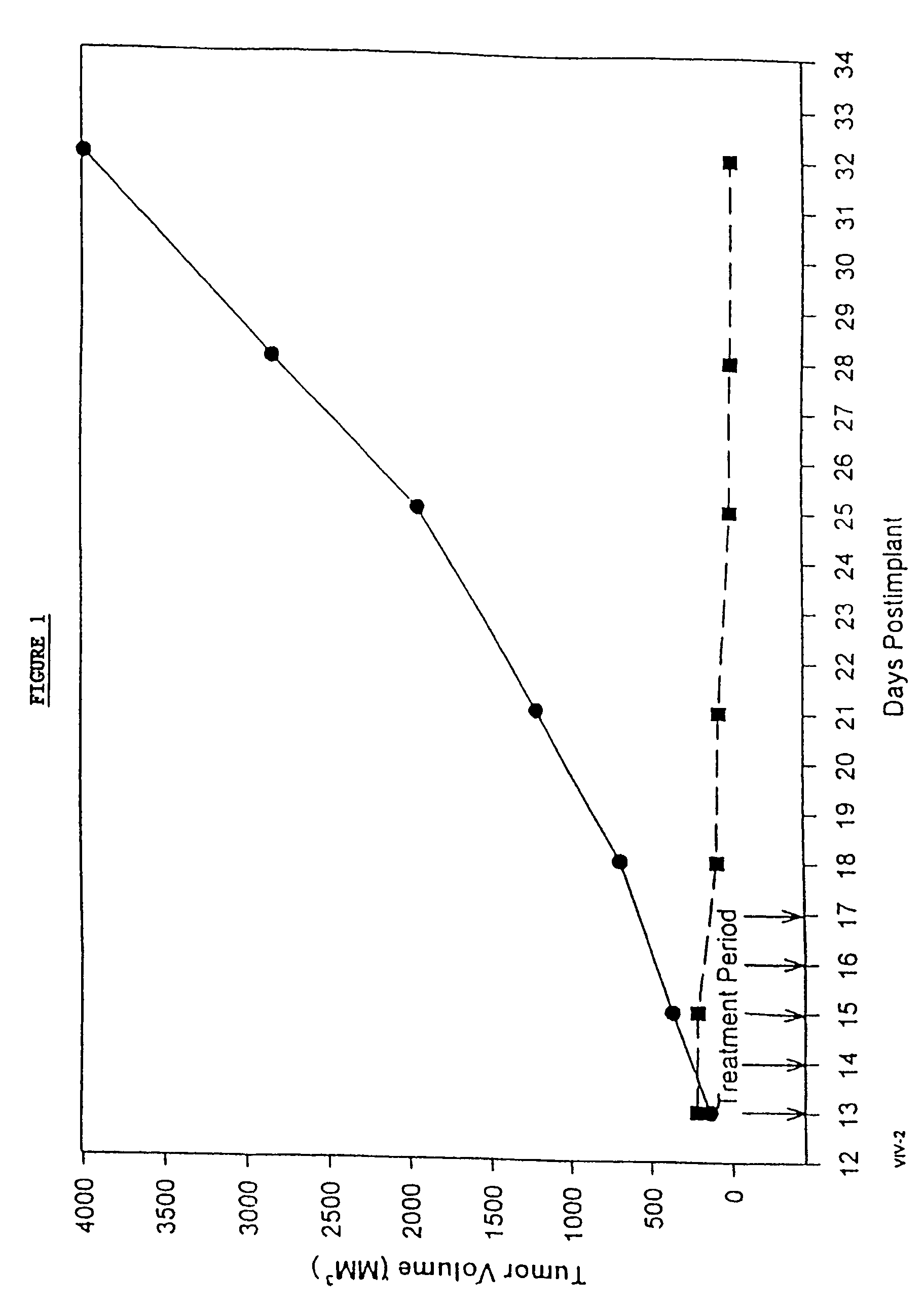
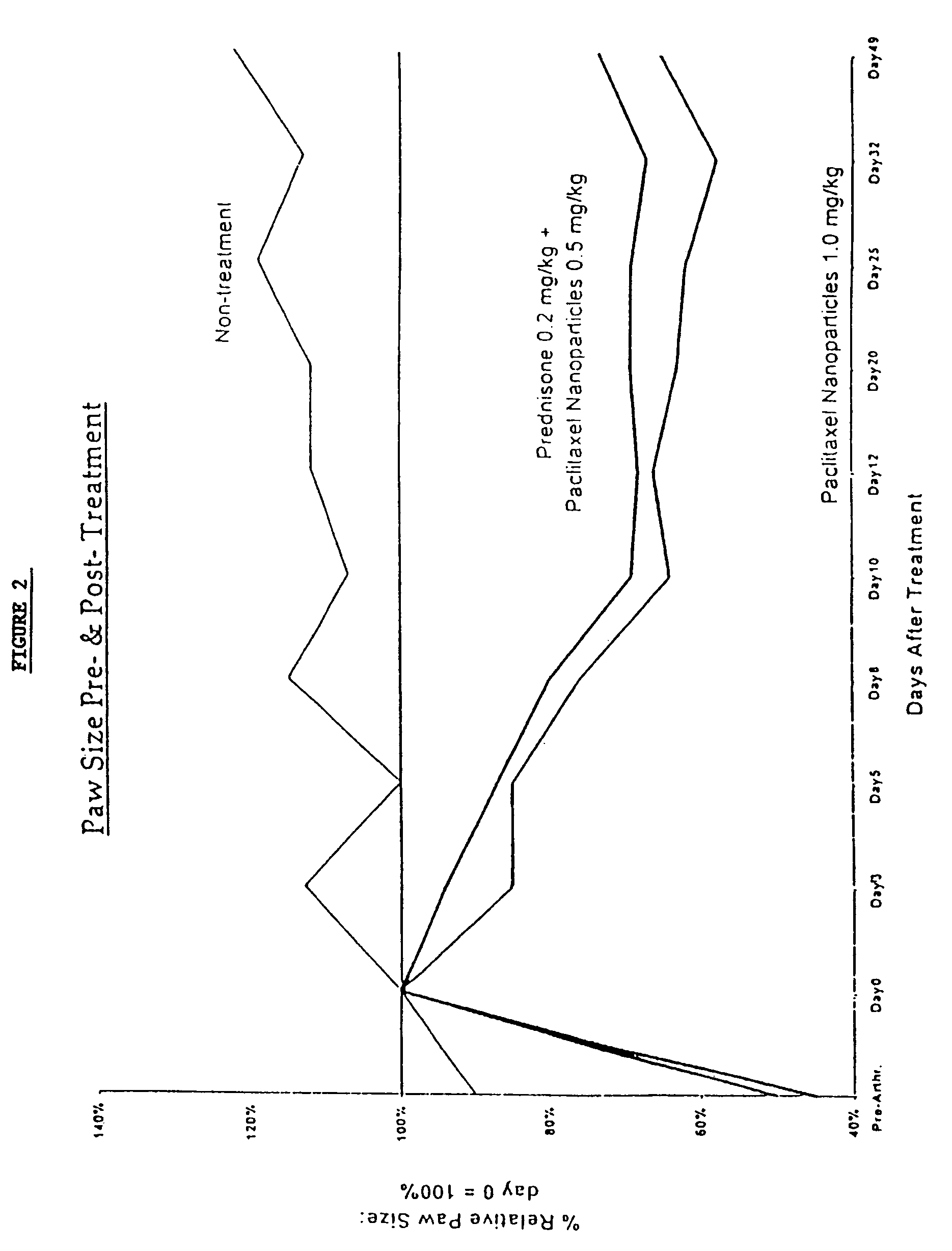
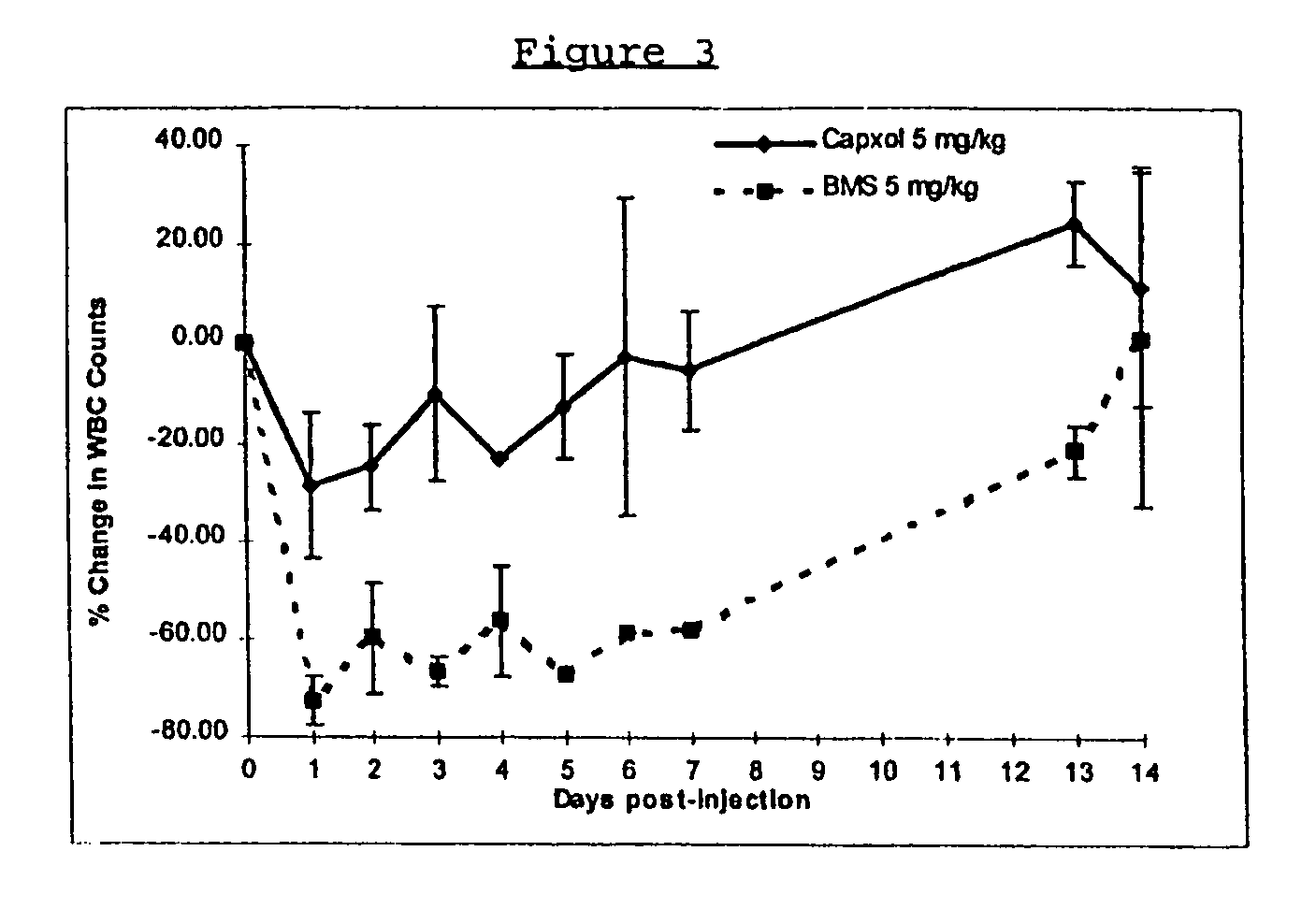
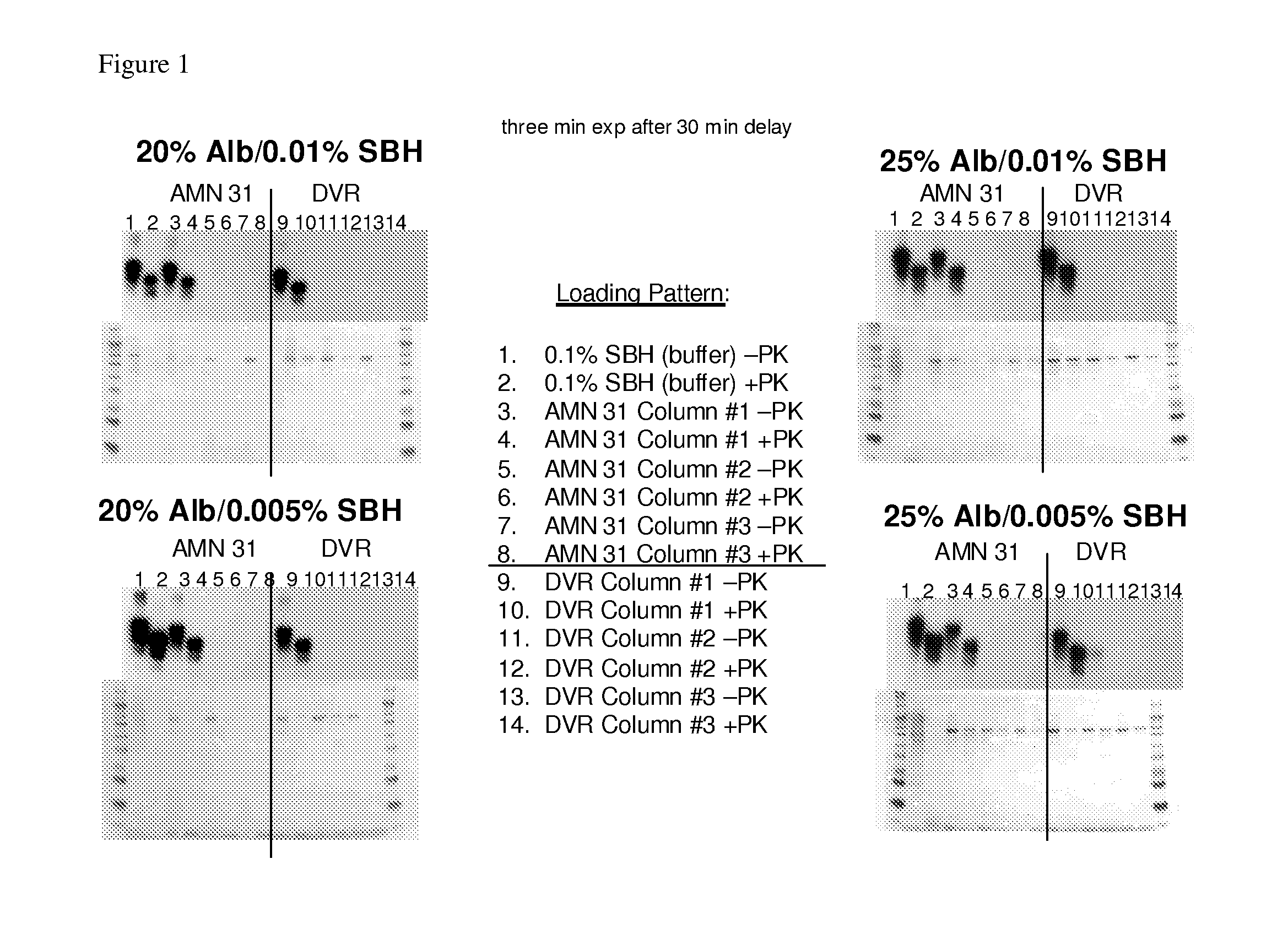
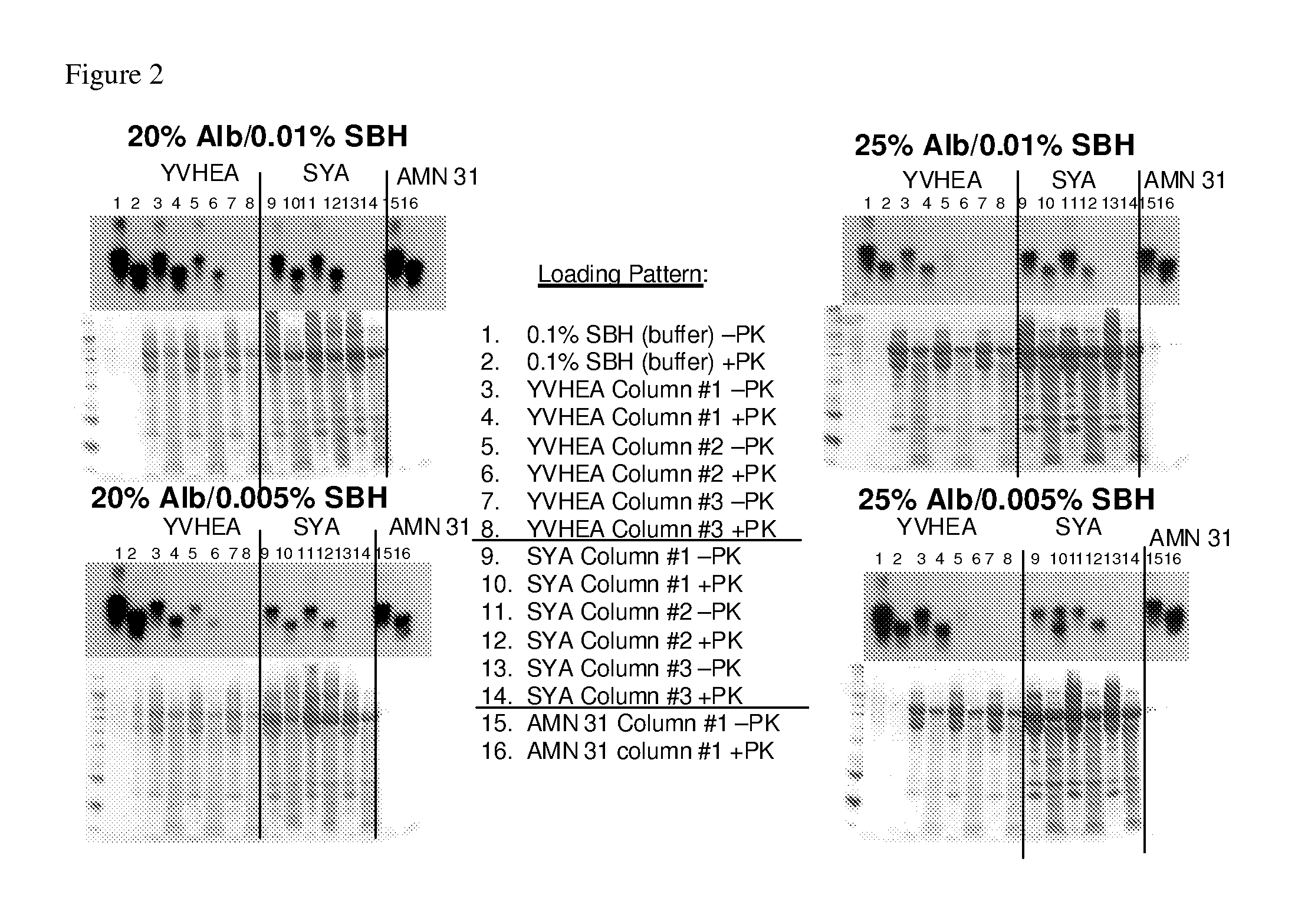
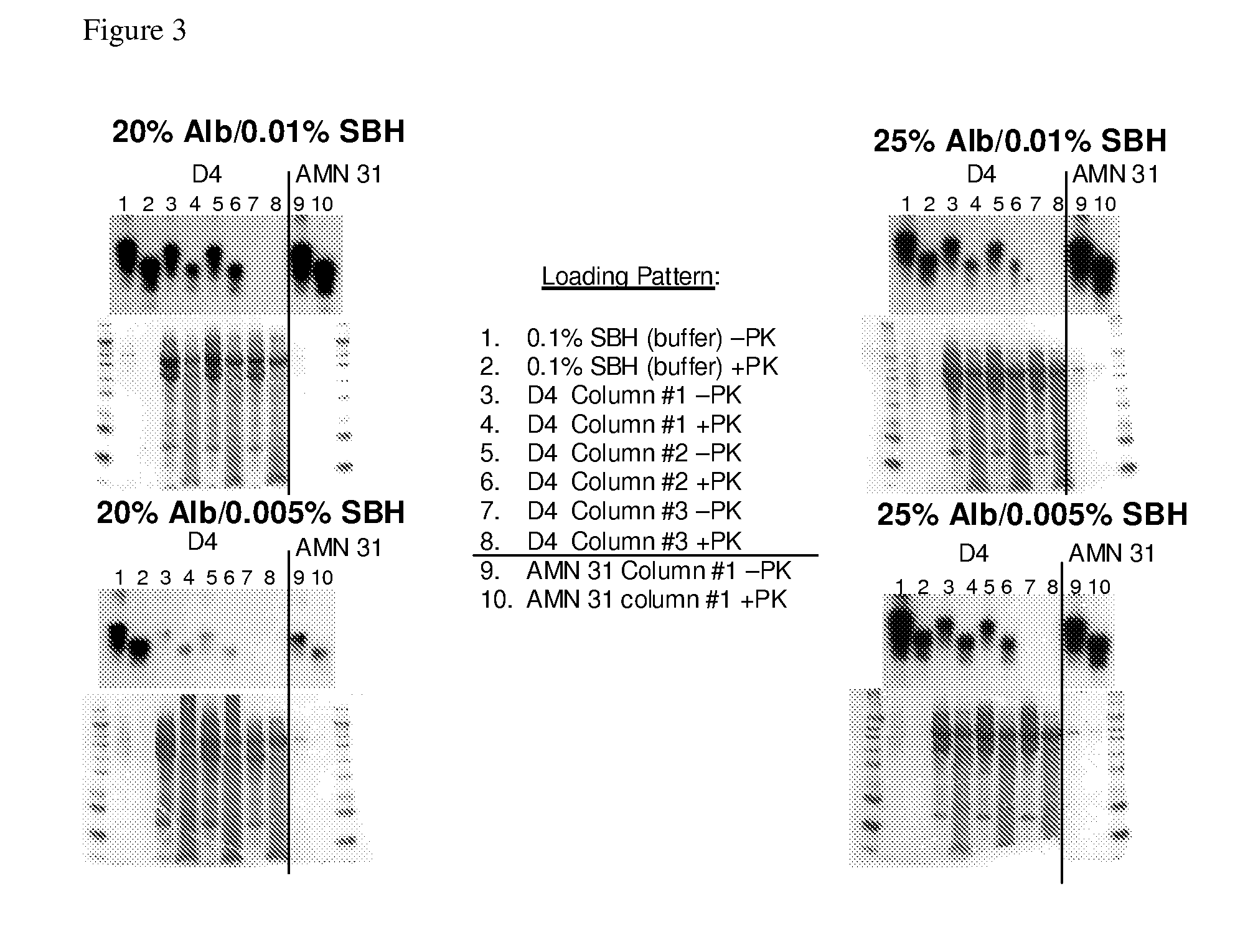
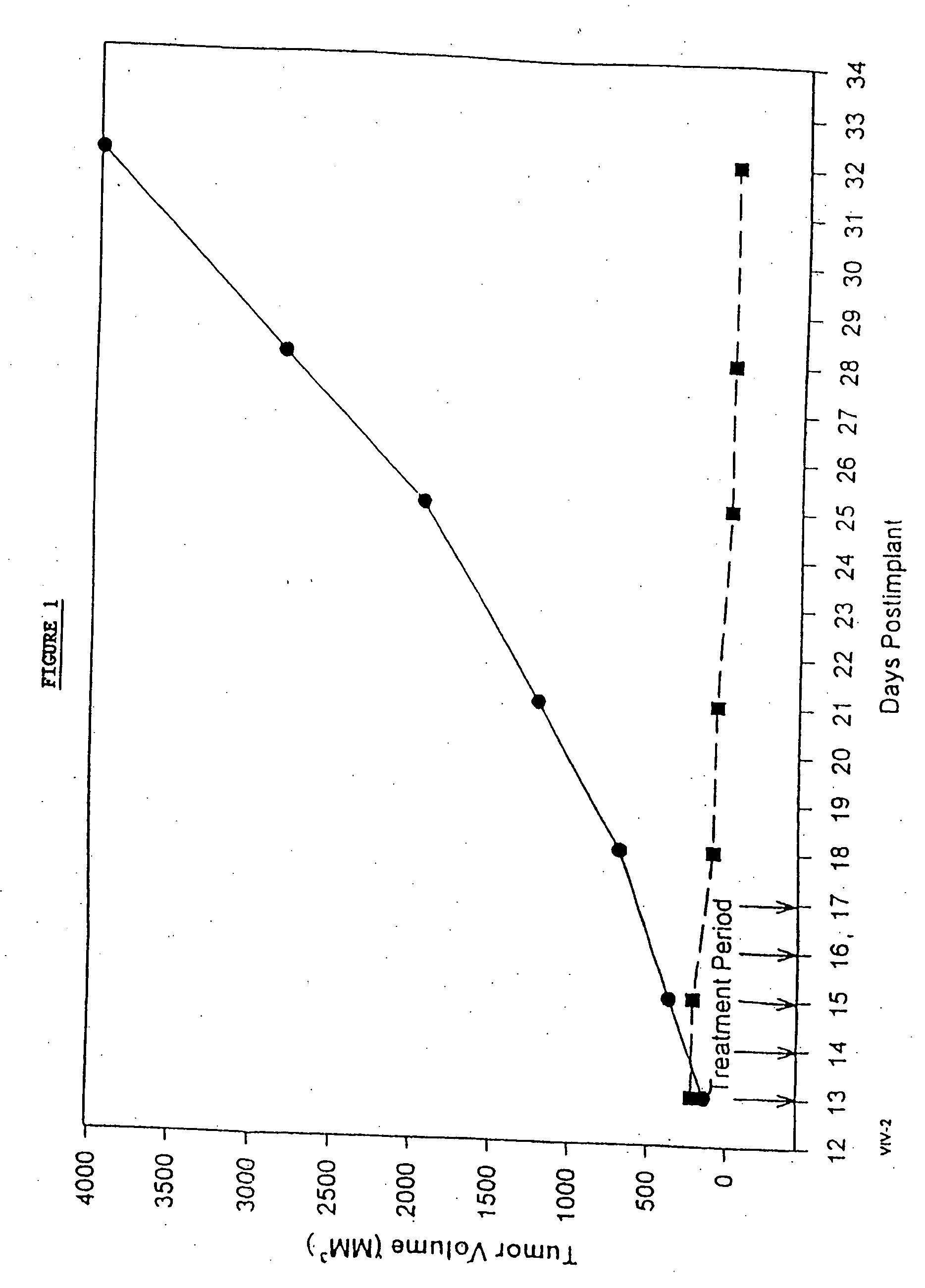
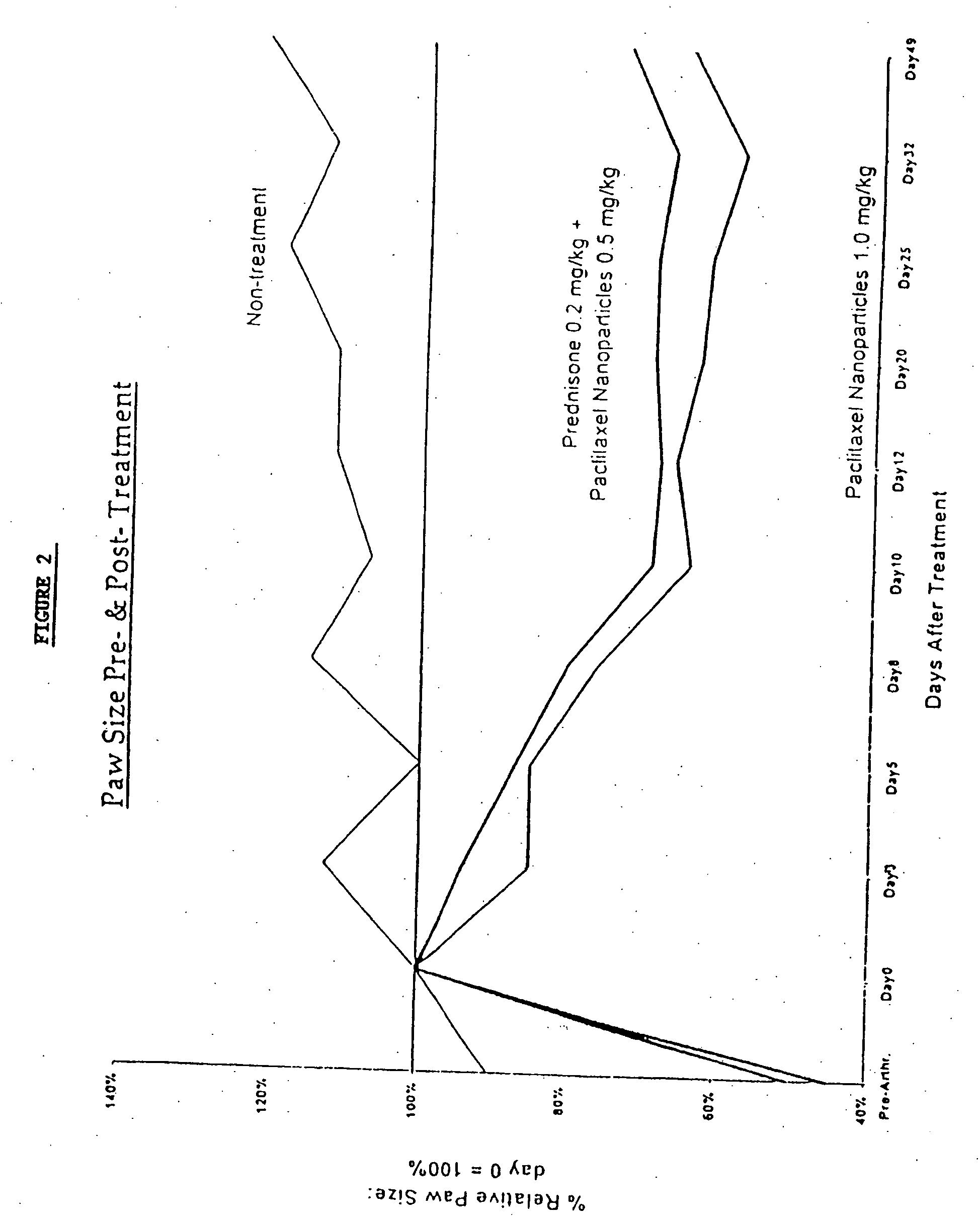
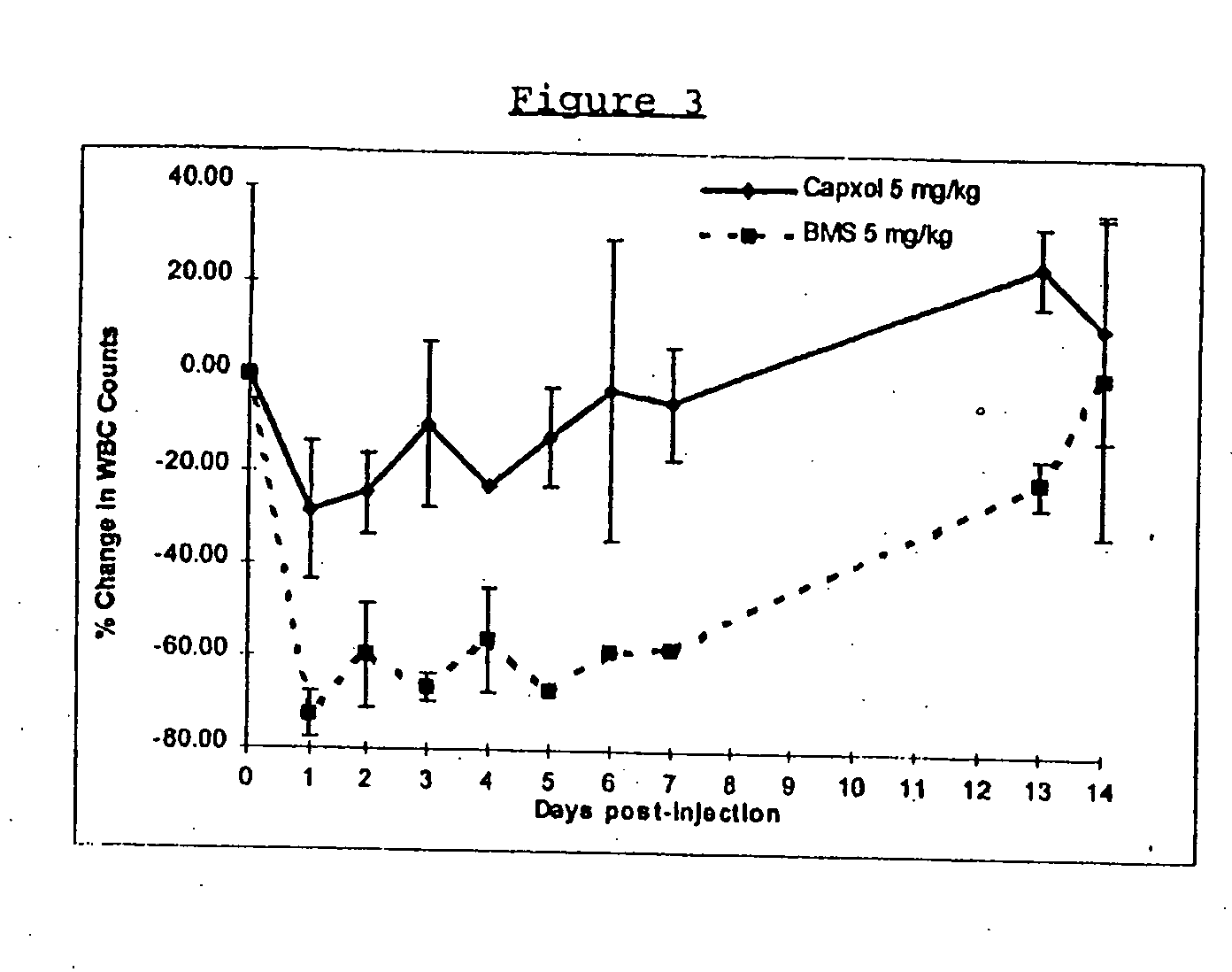
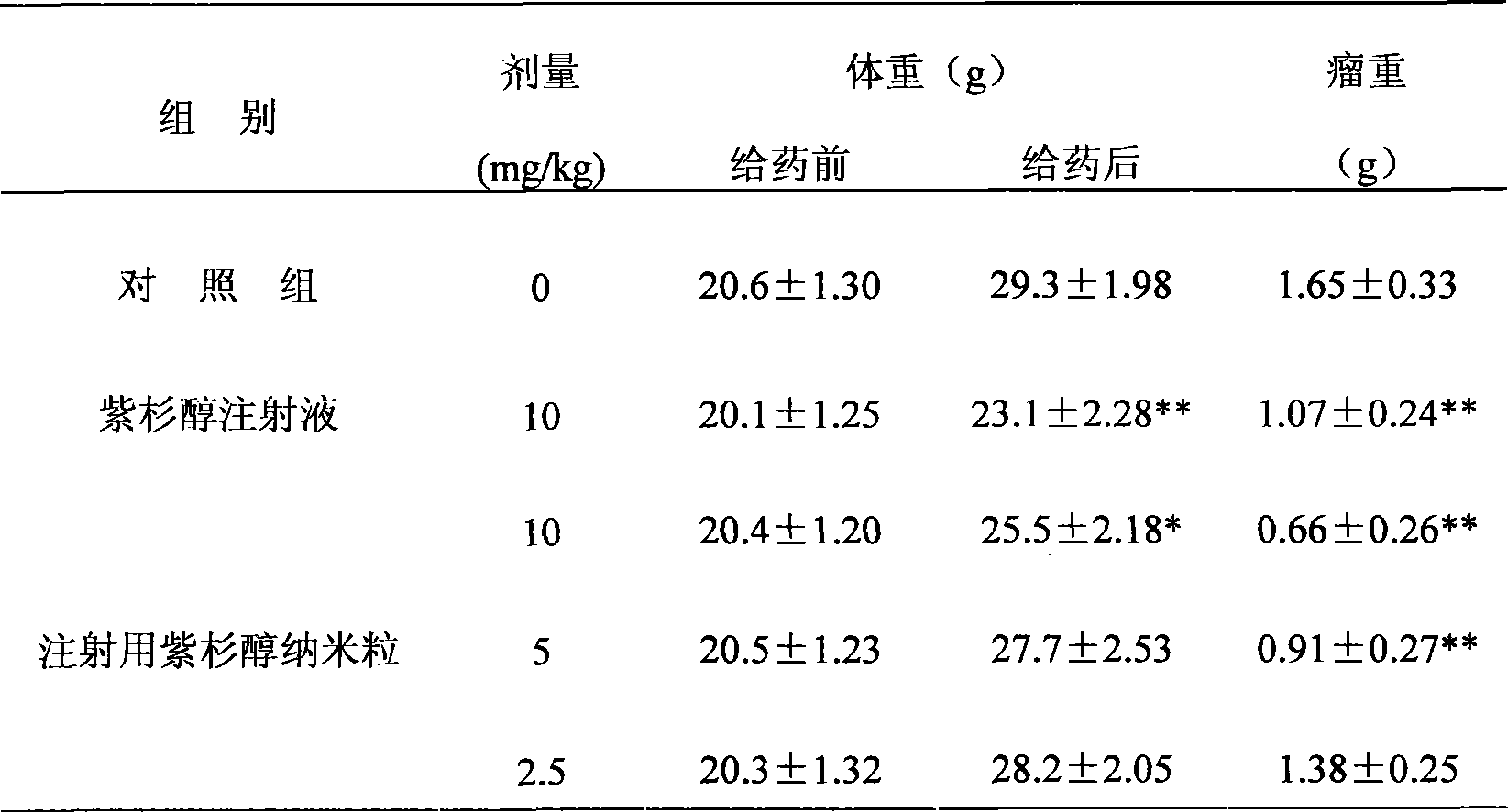
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful election of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Loading and release of water-insoluble drugs
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Low oil emulsion compositions for delivering taxoids and other insoluble drugs
ActiveUS20060067952A1Reduce oil contentNot hyperallergenicOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOil emulsionWater insoluble
The present invention provides injectable oil-in-water emulsions of taxoid drugs or other water insoluble drugs. The present invention also provides methods for preparing and using such oil-in-water emulsions.
Owner:CHEN ANDREW XIAN
Formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS8853260B2Improve abilitiesPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070087022A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Dosage unit for sublingual, buccal or oral administration of water-insoluble pharmaceutically active substances
ActiveUS20100008985A1Disperse fastEfficient packagingBiocidePowder deliveryWater insolubleProphylactic treatment
One aspect of the invention relates to a pharmaceutical dosage unit for sublingual, buccal, pulmonary or oral administration, said dosage unit having a weight of 20-500 mg and comprising 1-80 Wt. % of a microgranulate that is distributed throughout a solid hydrophilic matrix; said microgranulate being characterised in that it: has a volume weighted average diameter of 5-100 m; contains at least 0.01 wt. %, preferably at least 0.1 wt. % of one or more water-insoluble pharmaceutically active substances; contains at least 10 wt. %, preferably at least 20 wt. % of an emulsifier component; and is capable of forming a micro-emulsion upon contact with saliva or water. The dosage units of the present invention achieve the inherent benefits of oral delivery whilst at the same time realising a high transmucosal absorption rate of the cannabinoids contained therein. Other aspects of the present invention relate to the use of the aforementioned dosage units in the therapeutic or prophylactic treatment and to a process for the manufacture of said dosage units.
Owner:ECHO PHARM BV (NL)
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070093547A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesFree protein
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Solid nanoparticle formulation of water insoluble pharmaceutical substances with reduced ostwald ripening
ActiveUS8728527B2Good dispersionReduced and substantially no particle growthBiocideOrganic active ingredientsDocetaxel-PNPDocetaxel
The present invention belongs to the fields of pharmacology, medicine and medicinal chemistry. The present invention provides novel pharmaceutical compositions composed of solid nanoparticles dispersed in aqueous medium of substantially water insoluble pharmaceutical substances such as docetaxel with reduced Ostwald ripening.
Owner:AUSTIN BIOSCIENCES CORP
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20080160095A1Reduce morbidityLow toxicityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
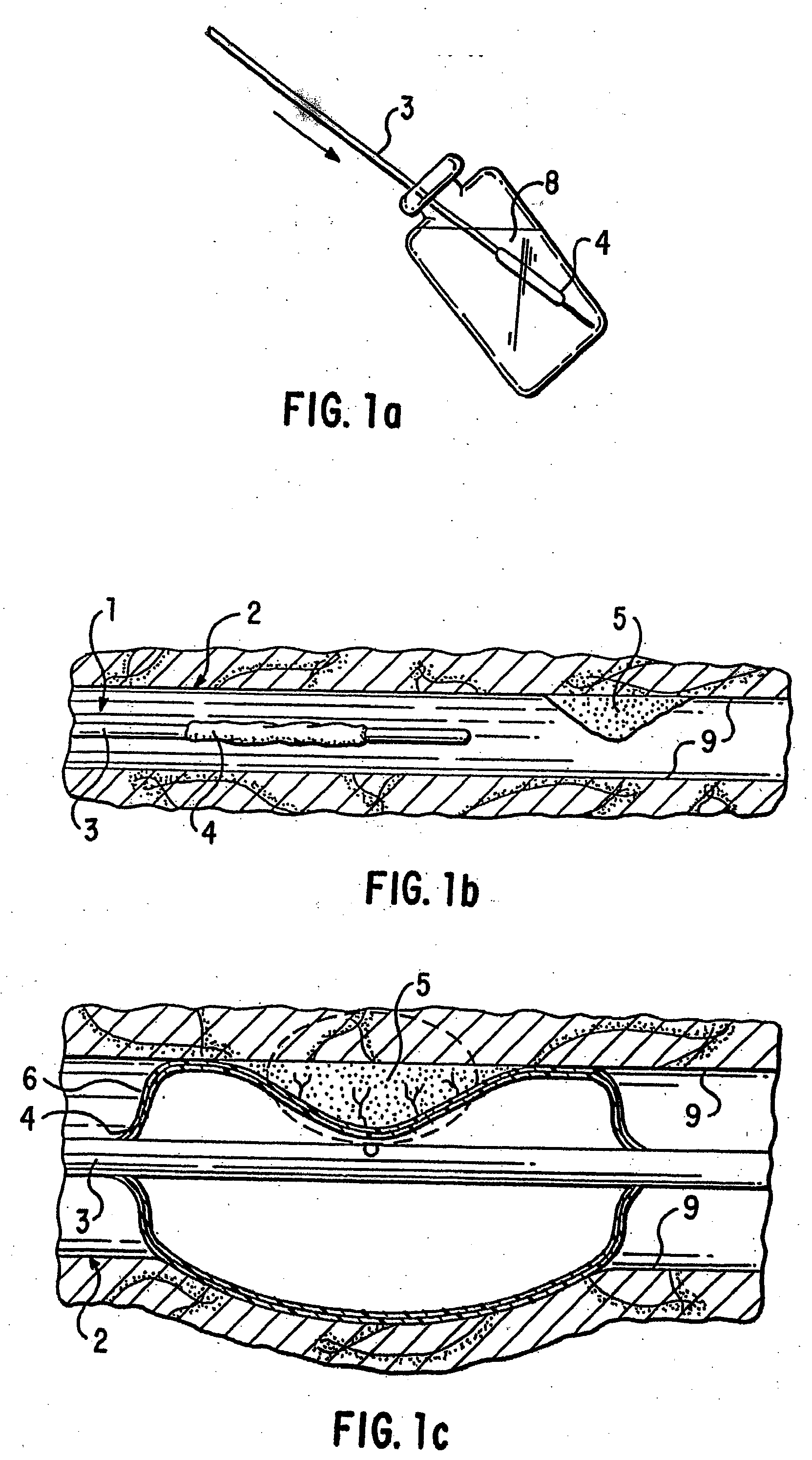
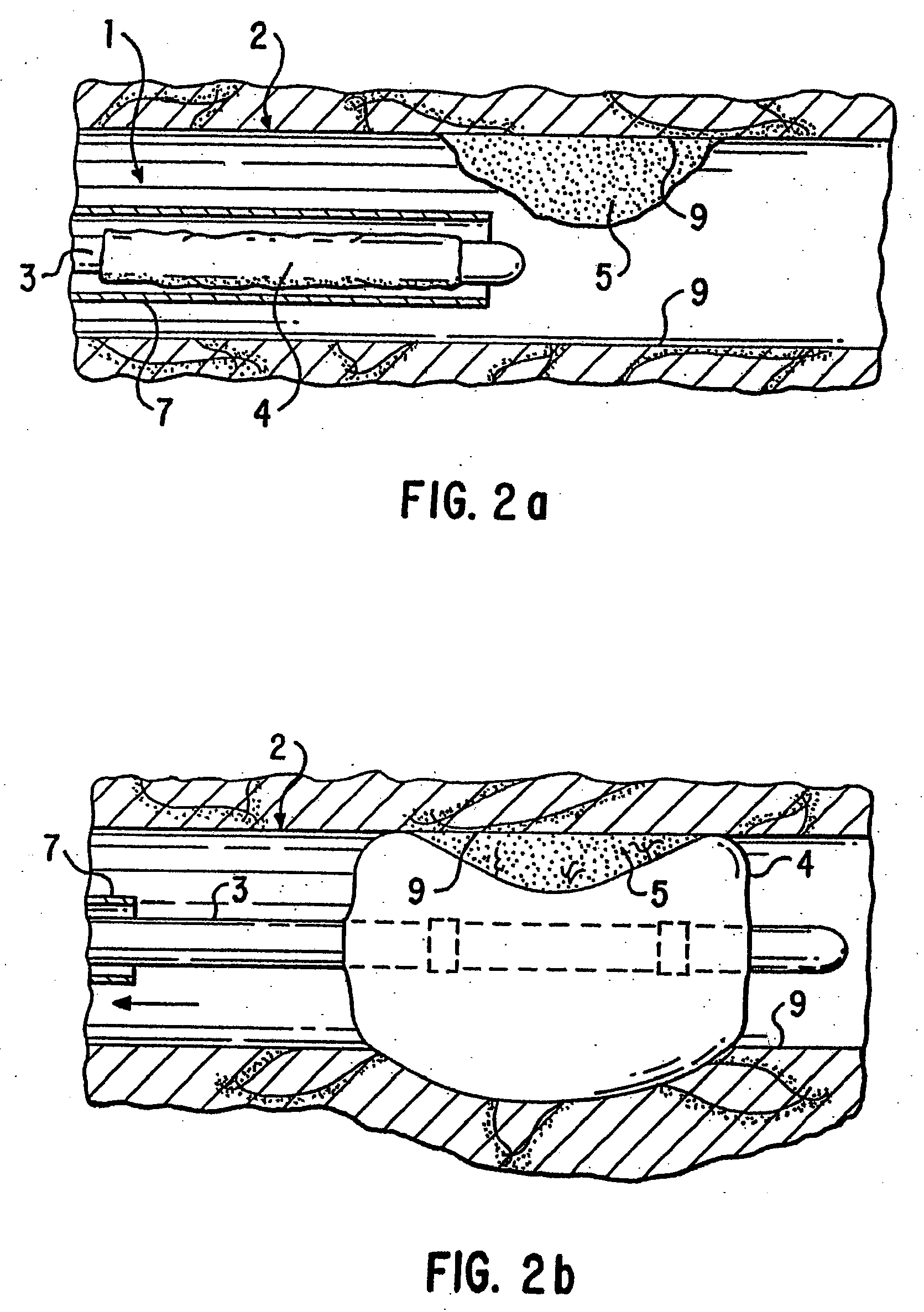
Drug formulations for coating medical devices
The present invention relates to oil-based formulations of hydrophobic drugs for the uniform coating of medical devices such as vascular stents and balloons. Another aspect of the present invention is an intravascular medical device having an oil-based coating suitable for delivering a water-insoluble drug, comprising one or more of an anti-oxidant, an anti-inflammatory and an anti-restenotic agent.
Owner:REVA MEDICAL LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20080161382A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
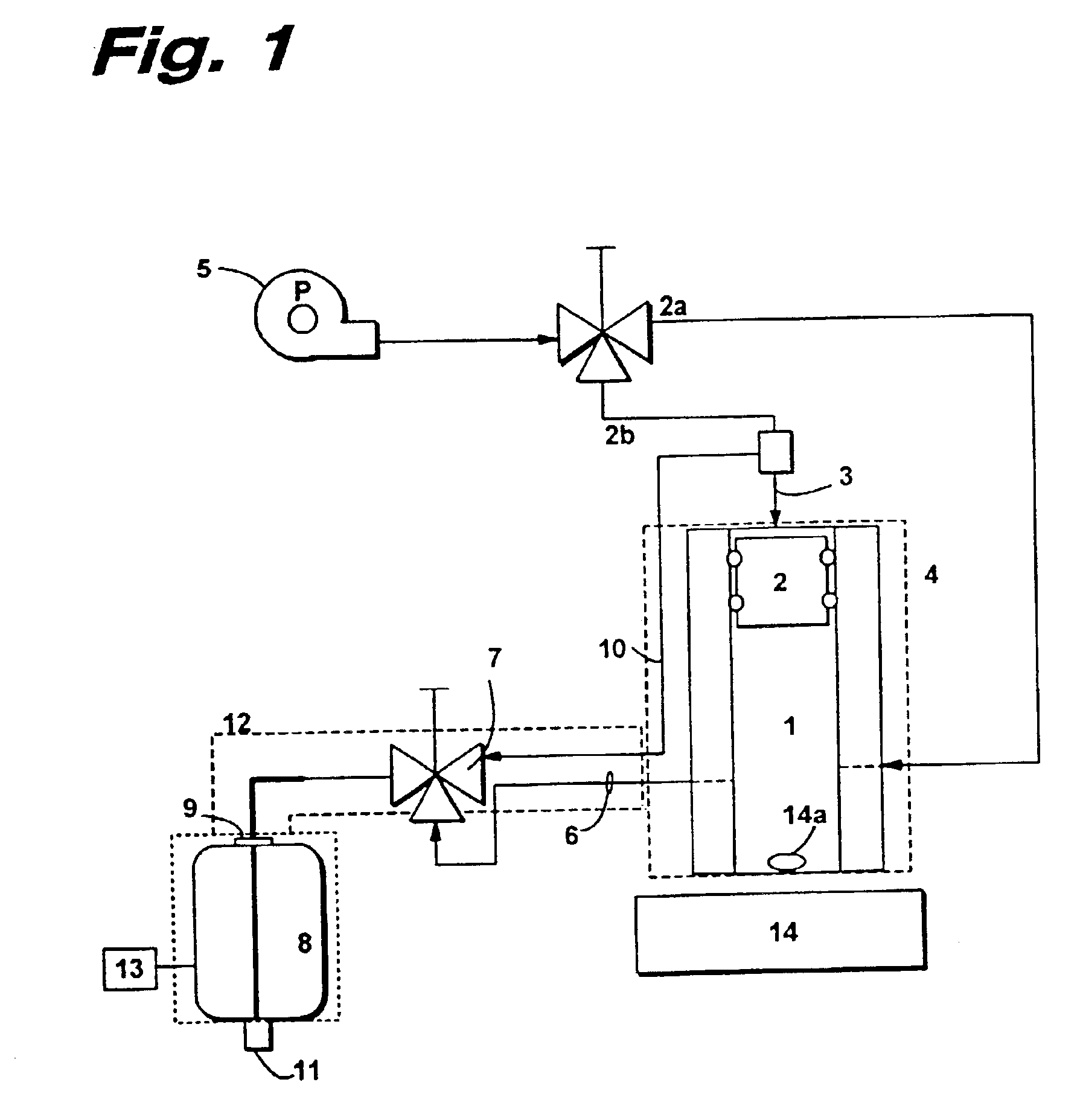
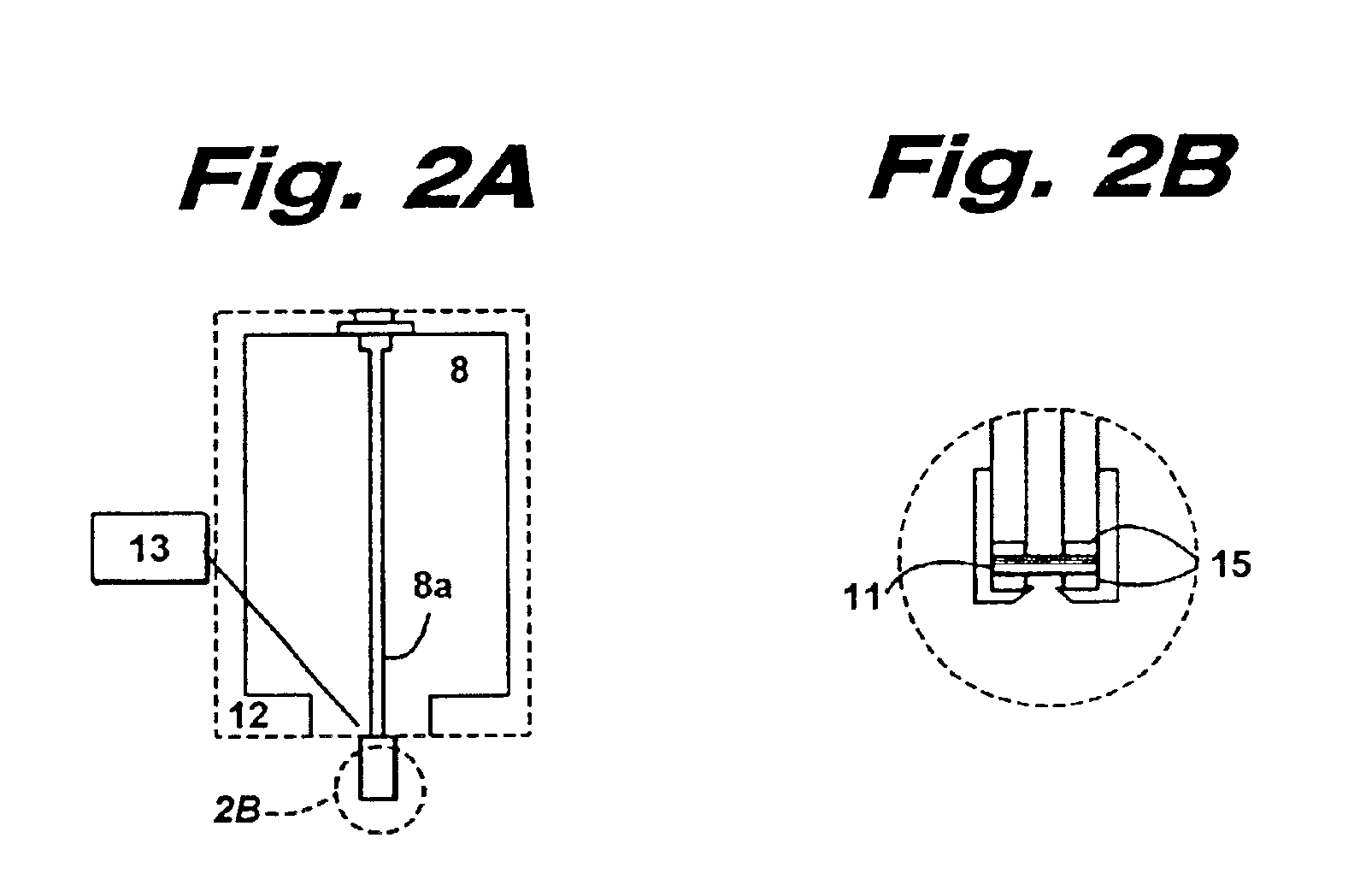
Loading and release of water-insoluble drugs
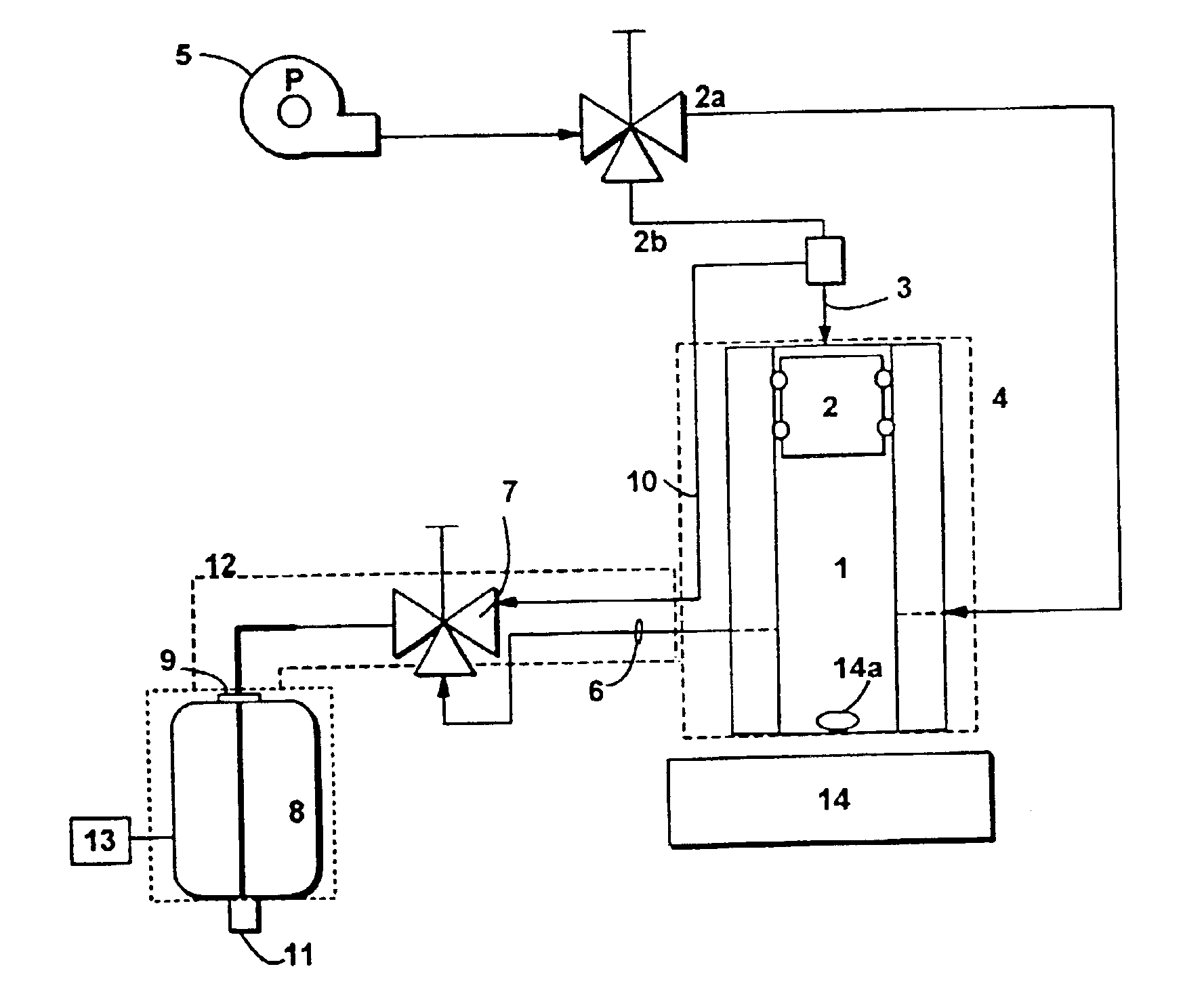
A medical device, polymer composition, and method for delivering substantially water-insoluble drugs to tissue at desired locations within the body. At least a portion of the exterior surface of the medical device is provided with a polymer coating. Incorporated in the polymer coating is a solution of at least one substantially water-insoluble drug in a volatile organic solvent. The medical device is positioned to a desired target location within the body, whereupon the drug diffuses out of the polymer coating.
Owner:SCI MED LIFE SYST
Formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS8137684B2Improve abilitiesPromote formationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Prion free nanoparticle compositions and methods of making thereof
InactiveUS20100297243A1Increase shearImprove conditionsPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsNanoparticleWater insoluble
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Polyethylene glycol-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-polylysine nano-delivery system, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101732723AEffective targeted deliveryPowder deliveryGenetic material ingredientsTumor targetingPolyethylene glycol
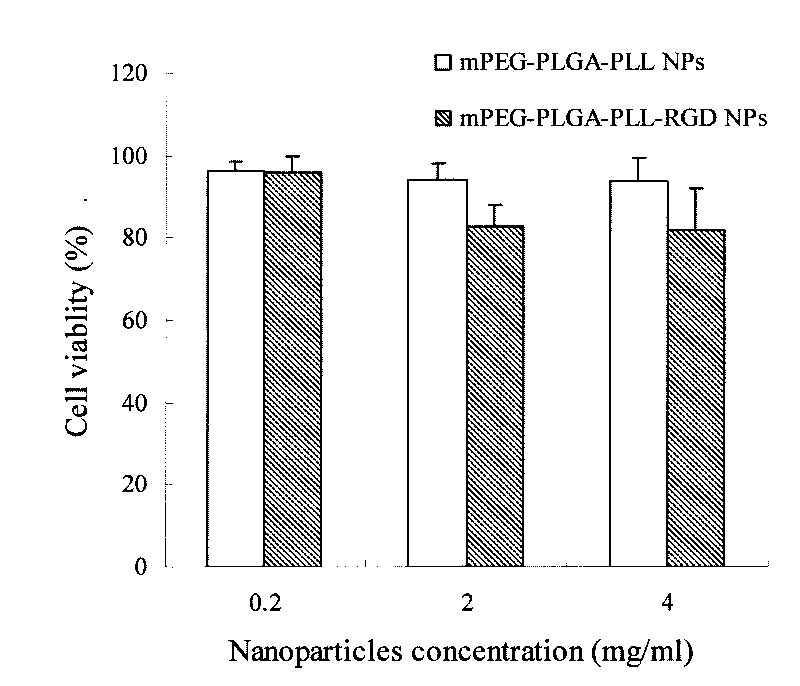
The invention belongs to the nanotechnical field, and discloses preparation of a methoxy polyethylene glycol-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-polylysine(mPEG-PLGA-PLL) cationic polymer nano-drug delivery system and application thereof. The nano-drug delivery system can have multi-functional characteristics such as tumor targeting, reversing drug resistance and medical diagnosis functions through modification, and can be used for supporting organic medicaments, water-soluble medicaments, non-water-soluble medicaments, or developers for diagnosis. The preparation method is simple and convenient, is suitable for mass production, and is particularly suitable for the preparation of targeting drug delivery systems.
Owner:森心(上海)科技有限公司
Mouth cavity quick dissolving quick disintegrating freeze-dried tablet and its preparing method
InactiveCN1473562AFast disintegrationPrevent "throat stuck" phenomenonAntibacterial agentsPill deliveryThroatFreeze-drying
The oral cavity quick dissolving and quick disintegrating freeze dried tablet for children includes at least one medicinal active component and at least one medicinal stuffing, adhesive and other supplementary material. It is loose and porous tablet in network structure and prepared through common freeze drying process. The said medicinal active component may be different children's medicines, such as antibiotic, antipyretic, analgesic, cough stopping and phlegm eliminating medicine, cold medicine, etc. Bitter or excitant medicine may be coated and water insoluble medicine is prepared intofine powder of 50 micron below size for stable dispersion in liquid. The present invention has fast disintegration, no jamming in throat, simple preparation process and low cost.
Owner:刘辉
Transdermal delivery system for water insoluble drugs
InactiveUS7395111B2Minimal irritationMinimal sensitizationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideWater insolubleWater insoluble drug
Owner:SYNERON MEDICAL LTD
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070092563A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070116761A1Reduce morbidityReduce decreaseBiocidePowder deliverySuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Amphiphilic block copolymers and nanoparticles comprising the same
An amphiphilic block copolymer is disclosed. The amphiphilic block copolymer includes one or more hydrophilic polymers, one or more hydrophobic polymer, and one or more zwitterions. The invention also provides a nanoparticle and carrier including the amphiphilic block copolymer for delivery of water insoluble drugs, growth factors, genes, or water insoluble cosmetic substances.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20150104521A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Prion free nanoparticle compositions and methods of making thereof
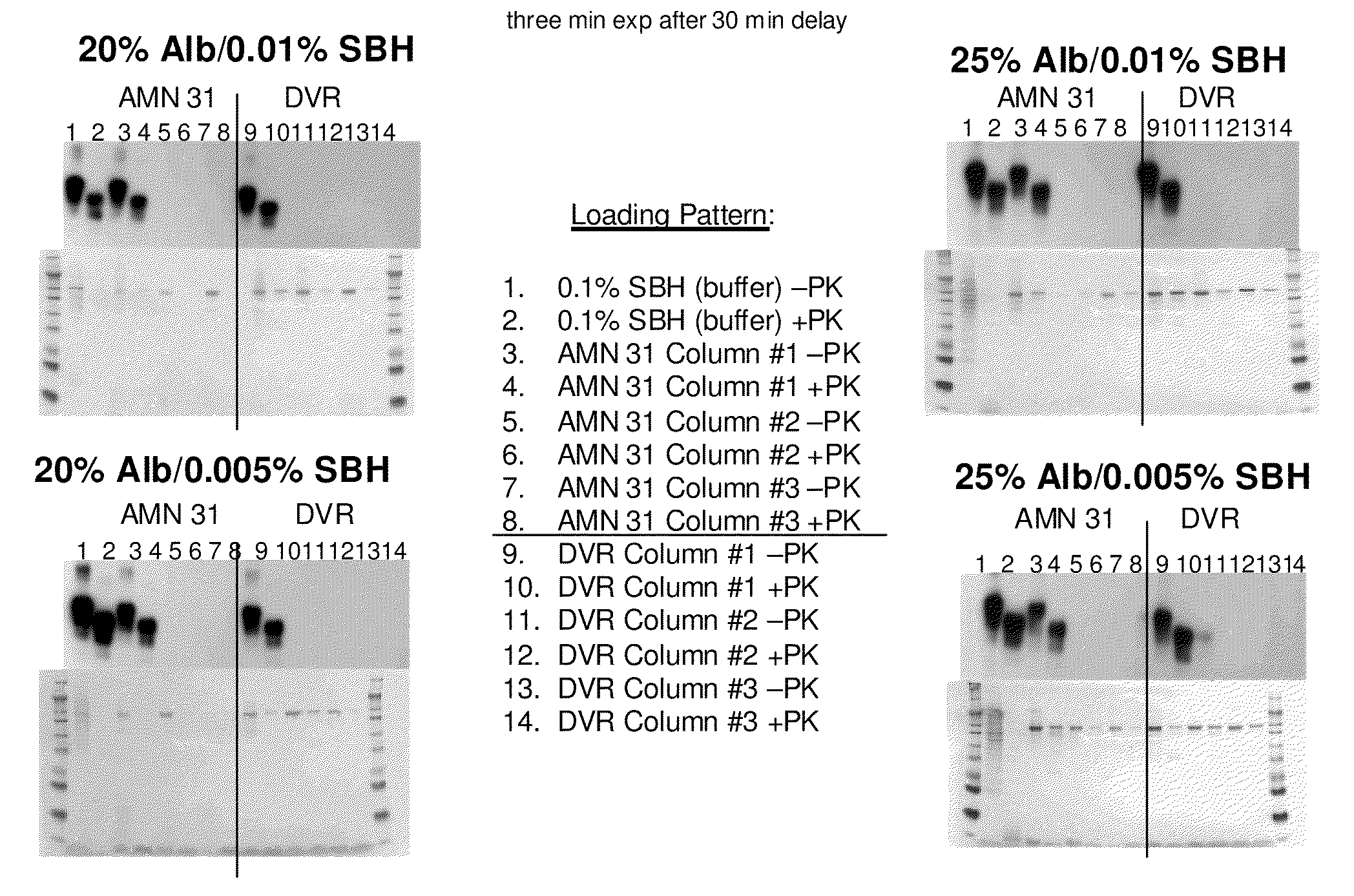
The present invention provides prion-free compositions comprising nanoparticles comprising albumin and substantially water insoluble drugs. Also provided are methods of making prion-free compositions and methods of removing prion proteins from the nanoparticle compositions. Methods of using the compositions, as well as kits useful for carrying out the methods are also provided.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Insoluble drug delivery
InactiveUS6974593B2Robust and scalableWide rangeOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryWater insolubleWater insoluble drug
Particles of water insoluble biologically active compounds, particularly water-insoluble drugs, with an average size of 100 nm to about 300 nm, are prepared by dissolving the compound in a solution then spraying the solution into compressed gaz, liquid or supercritical fluid in the presence of appropriate surface modifiers.
Owner:JAGOTEC AG
Drug-releasing graft
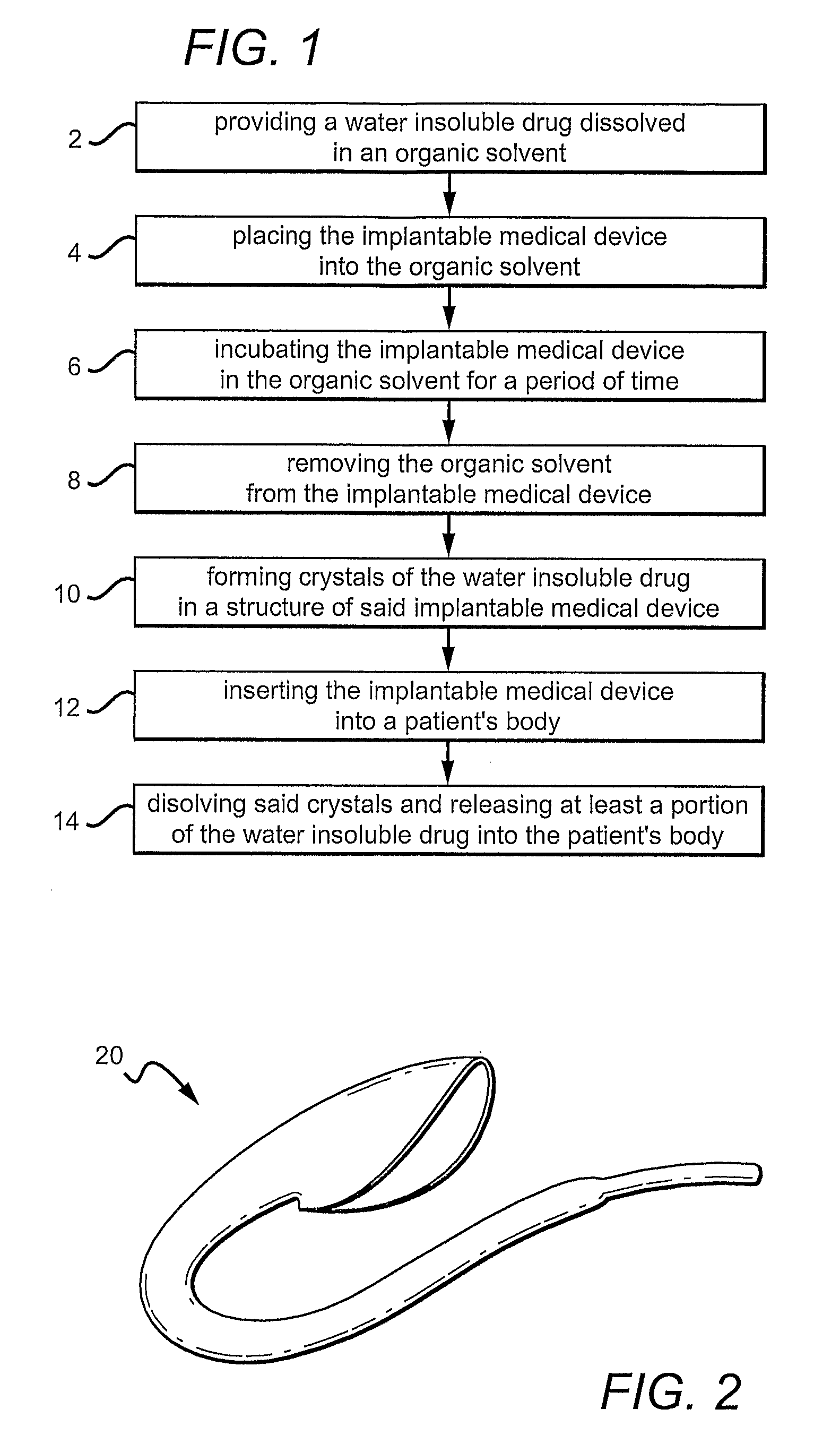
InactiveUS20100268321A1Minimize partial impairmentAvoid occlusionBiocideStentsMedicineWater insoluble
A method of incorporating drugs into an implantable medical device. In one variation, water insoluble drugs are used to form crystals within the porous structure of the device. Upon implantation, the drug crystals dissolve slowly and release the drug into the surrounding tissue. In one example, a water insoluble drug is crystallized within the pores of an ePTFE vascular graft.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Pharmaceutical composition comprising nanocrystals
ActiveUS20140302132A1Small sizePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsWater insolubleWater soluble
The present invention relates to processes for the manufacture of suspensions comprising one or more water soluble or water insoluble pharmaceutical or nutraceutical active ingredients with a particle size in the range of from 0.01 to 10 micron. More specifically, suspensions prepared by this process can be used to formulate pharmaceutical compositions, especially in liquid fill capsules.
Owner:MW ENCAP
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070117862A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityPowder deliveryBiocideSuspended particlesFree protein
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Oil-in-oil nonaqueous microemulsion used as medicine carrier and its medicine prepn
ActiveCN101019833AEasy to manufactureExpand the range of speciesBiocideAnthropod material medical ingredientsControlled releaseWater insoluble
The present invention discloses oil-in-oil nonaqueous microemulsion used as medicine carrier and its medicine preparation. The oil-in-oil nonaqueous microemulsion consists of oil phase I, oil phase II, surfactant and co-surfactant, and can dissolve water insoluble medicines to prepare microemulsion. The nonaqueous microemulsion has the advantages of no hydrolysis and long effective period, slow or controlled release of medicine, nanometer level dispersion of water insoluble medicine and obviously raised bioavailability. For example, the present invention can obtain bioavailability of puerarin microemulsion and puerarin sol as high as 40.41 % and 52.68 % separately.
Owner:HEFEI LIFEON PHARMA
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070122465A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationPowder deliveryBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel nano preparation with stable protein and preparation method and use thereof
InactiveCN101385857AShort operating timeStable productionOrganic active ingredientsMacromolecular non-active ingredientsWater insolubleFree protein
The invention discloses a novel nano preparation with stable protein, as well as a preparation method and a purpose thereof. The invention is characterized in that: a protein coating is formed from albumin and other materials containing sulphydryl or disulfide bond through the cross linking of the disulfide bond; the protein coating contains free protein or protein derivatives which associate(s) with the protein coating, wherein, part of insoluble drugs are contained in the protein coating and part of such drugs are associated with the free protein or the protein derivatives, and the average diameter of protein coating particles is not more than 1 micron. The purpose of the preparation is to send water insoluble drugs into the bodies of living things.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Biological degradable albumin derivant, pharmacy composition, preparation and application of the same
InactiveCN101220093AFlat surfaceImprove uniformitySerum albuminPharmaceutical delivery mechanismWater insolubleWater insoluble drug
The invention relates to a bio-degradable alb derivative and the related pharmaceutical combinations; wherein, the derivative introduces alkyl, or fatty acyl or deoxycholic acid in the alb skeleton to enable the amphiphilic property and form a nano-micelle by self-organization in water, and can enwrap the drugs through the double effects of the hydrophobic group, the alb molecular chain and the drugs, thereby substantially improving the drug enwrapping ability of the alb and prolonging the stability time. The excipient can be used as the carrier for organic drugs, water-insoluble drugs or dugs with poor water solubility and the carrier of amphipathic drugs, and for the administration inside the vein or muscle injection and oral administration. The preparation method of the bio-degradable alb derivative and the related pharmaceutical combinations is simple and of mature techniques, which is suitable for large scale continuous production.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com