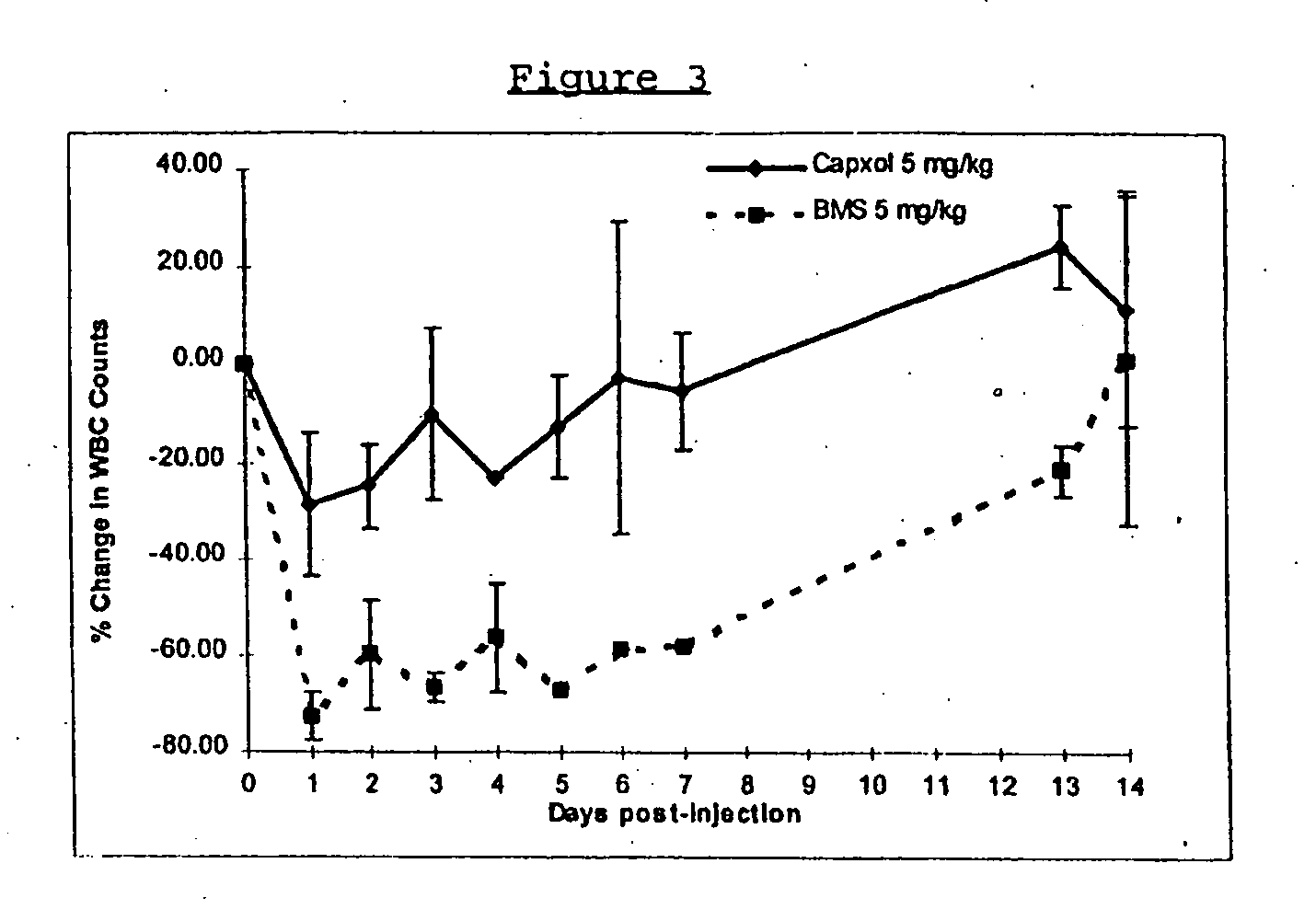
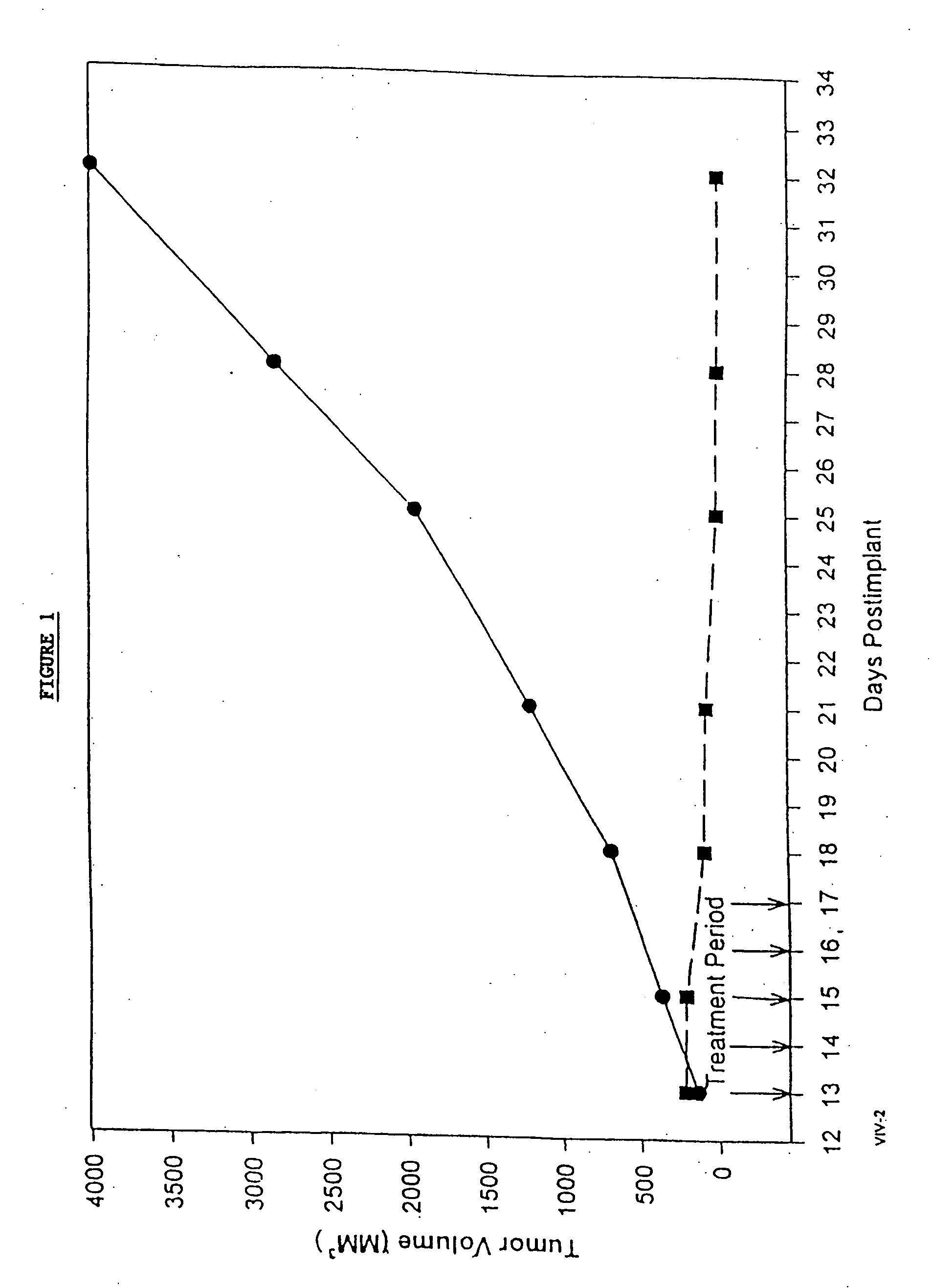
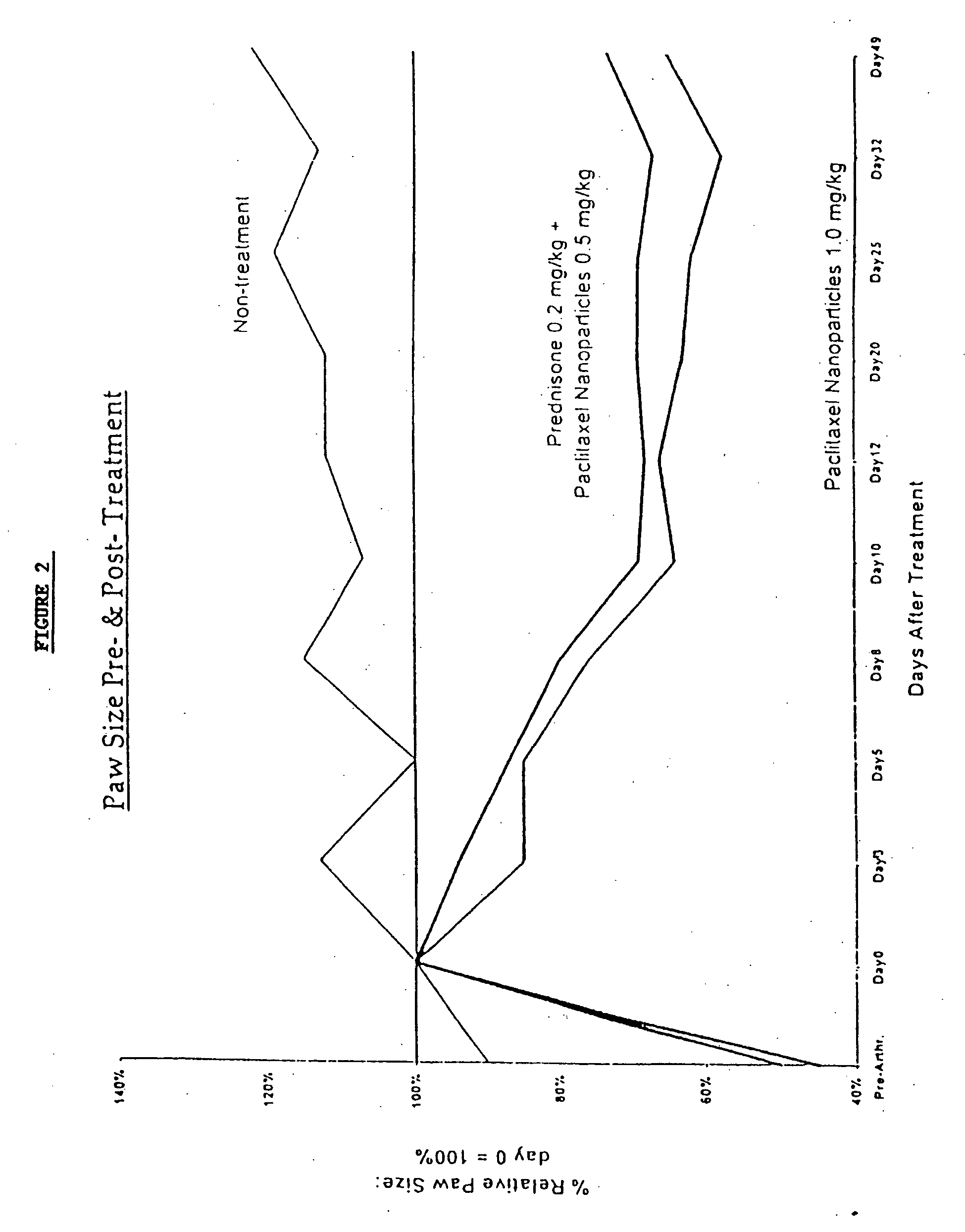
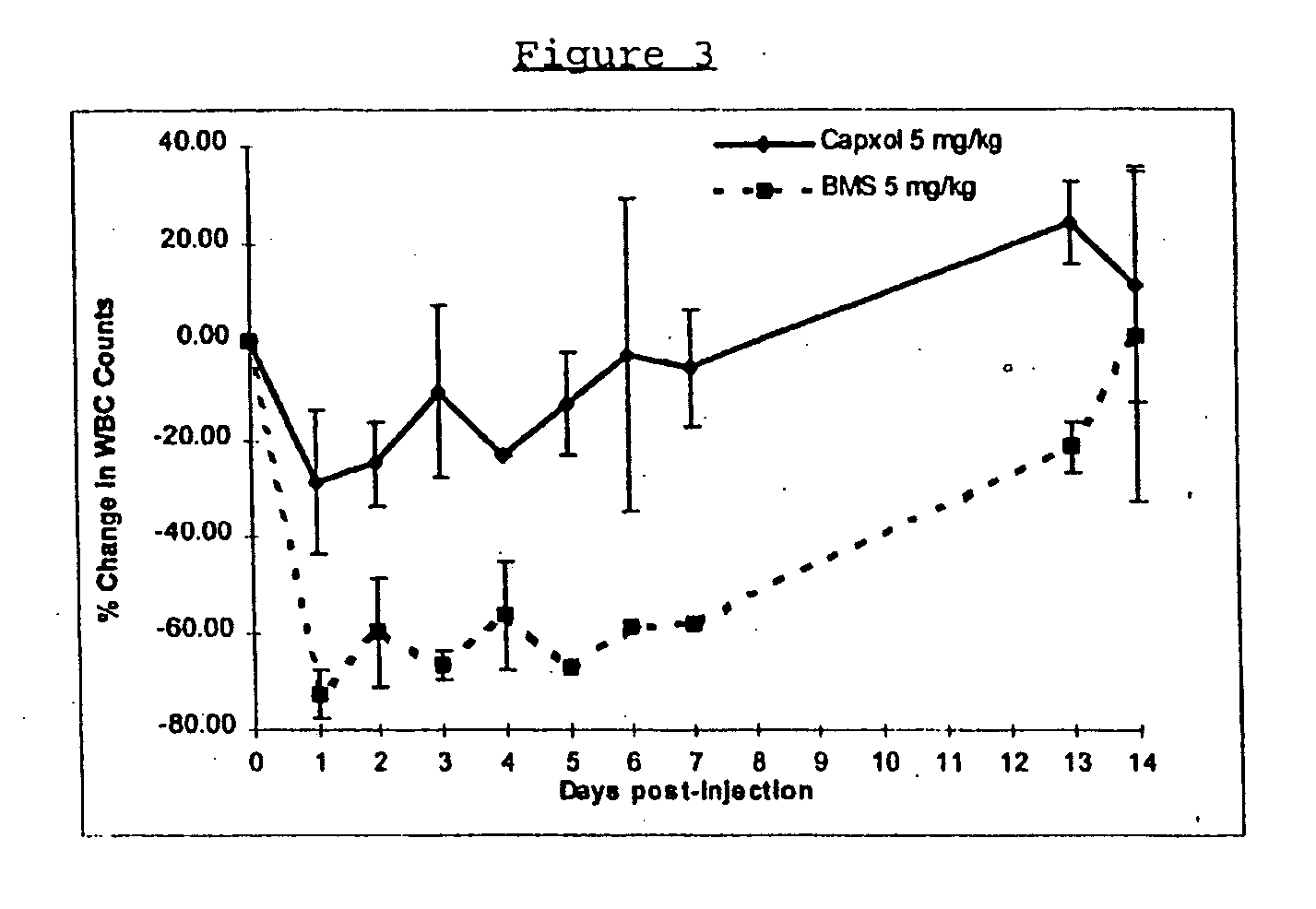
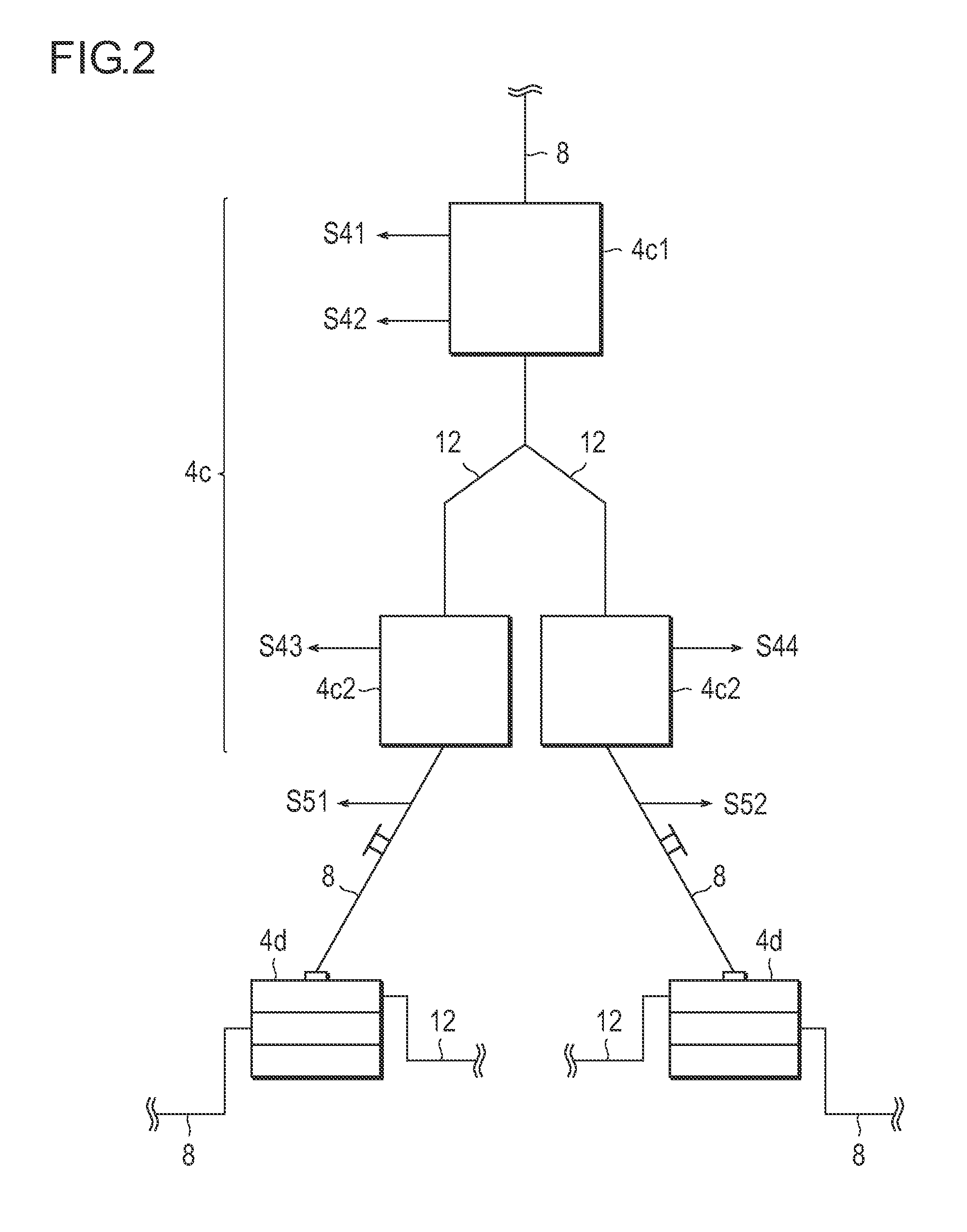
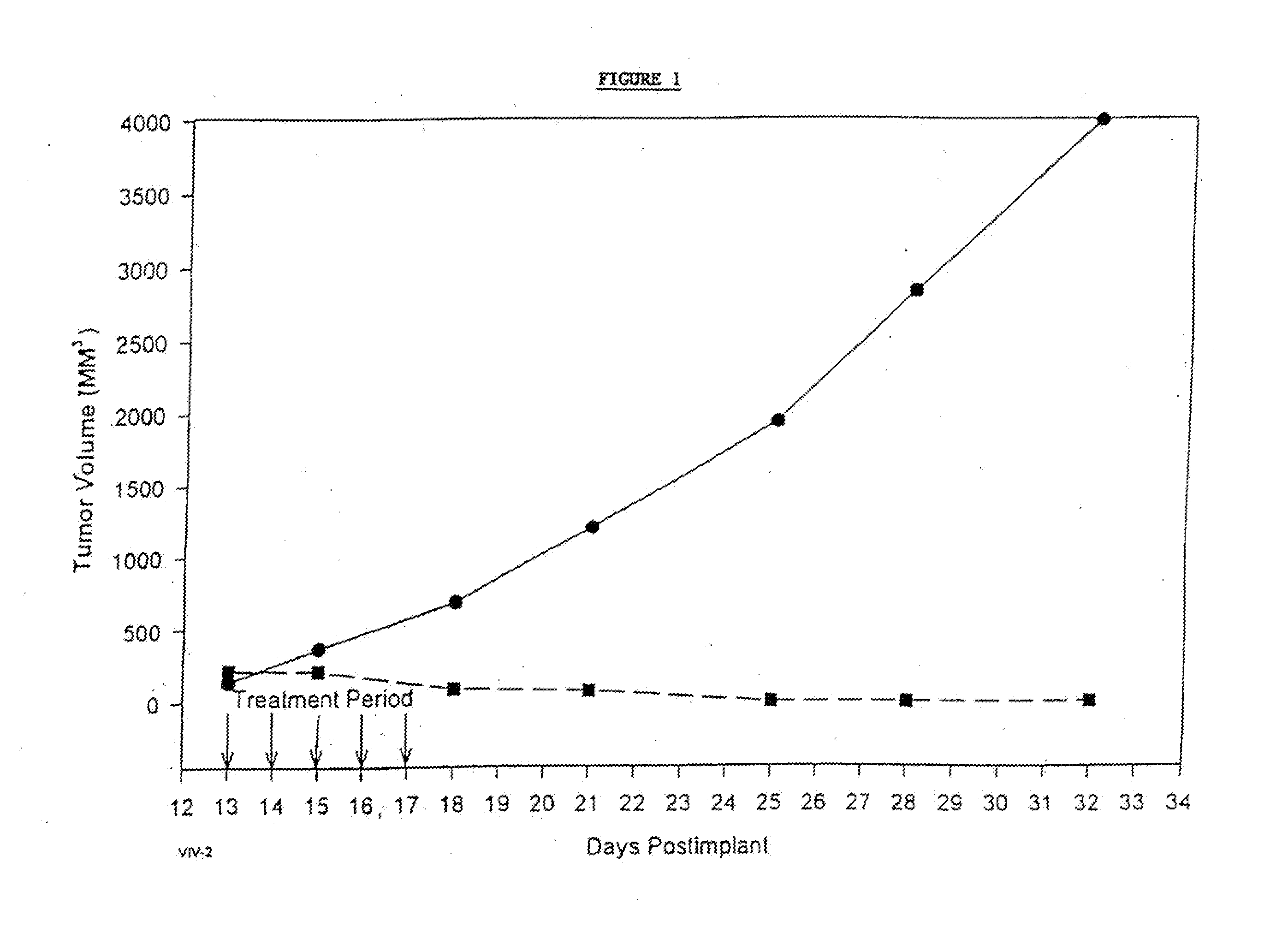
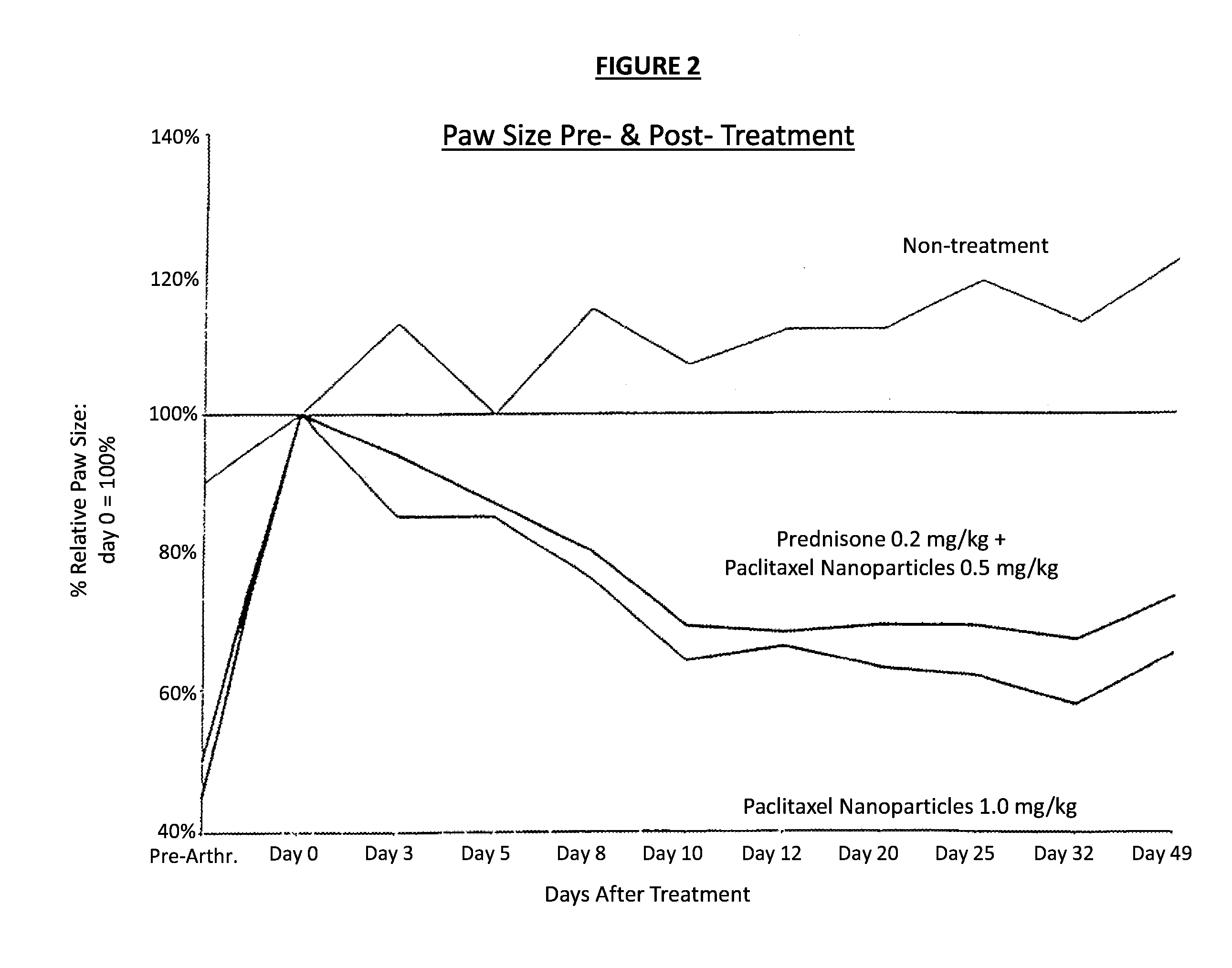
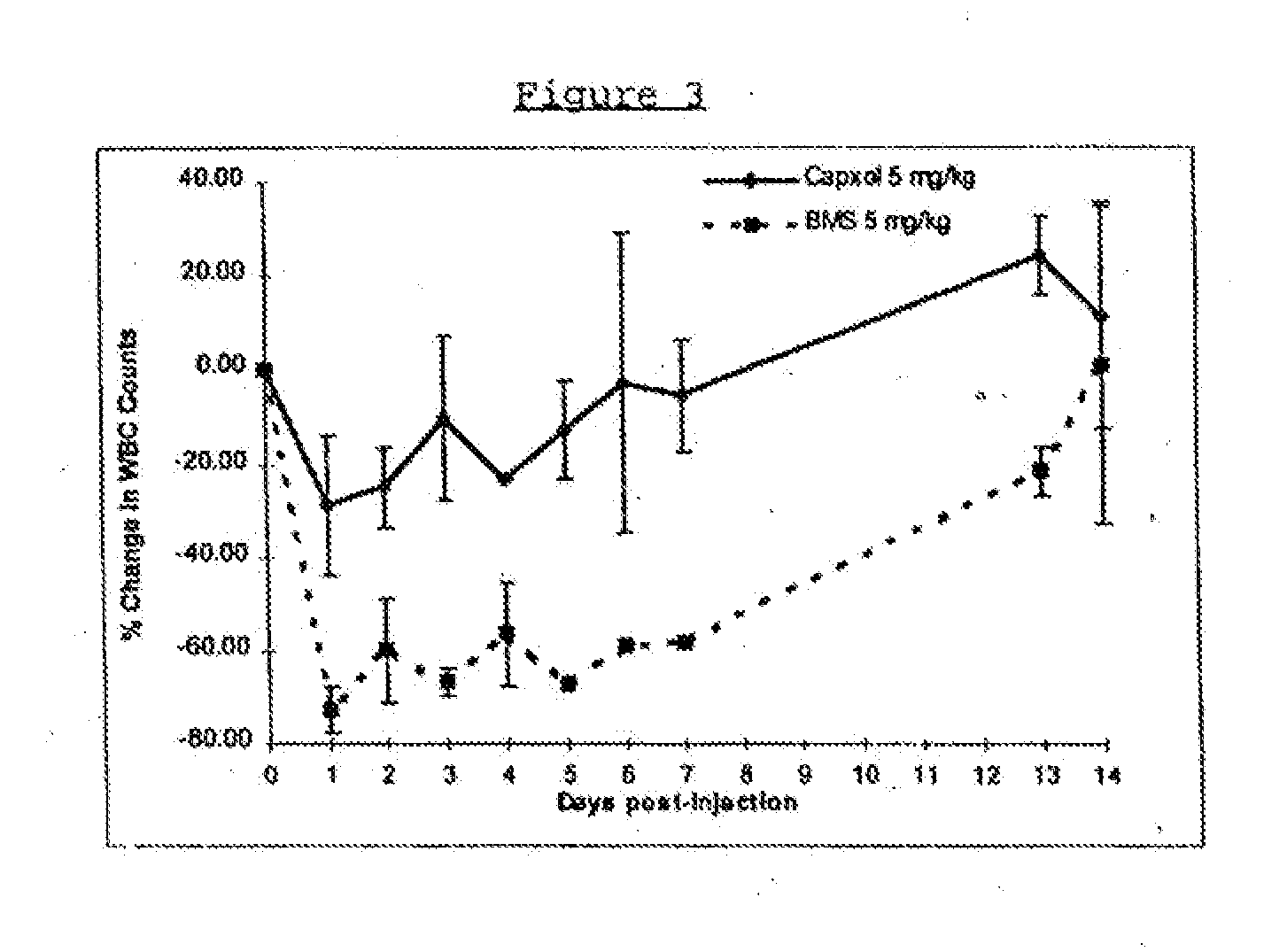
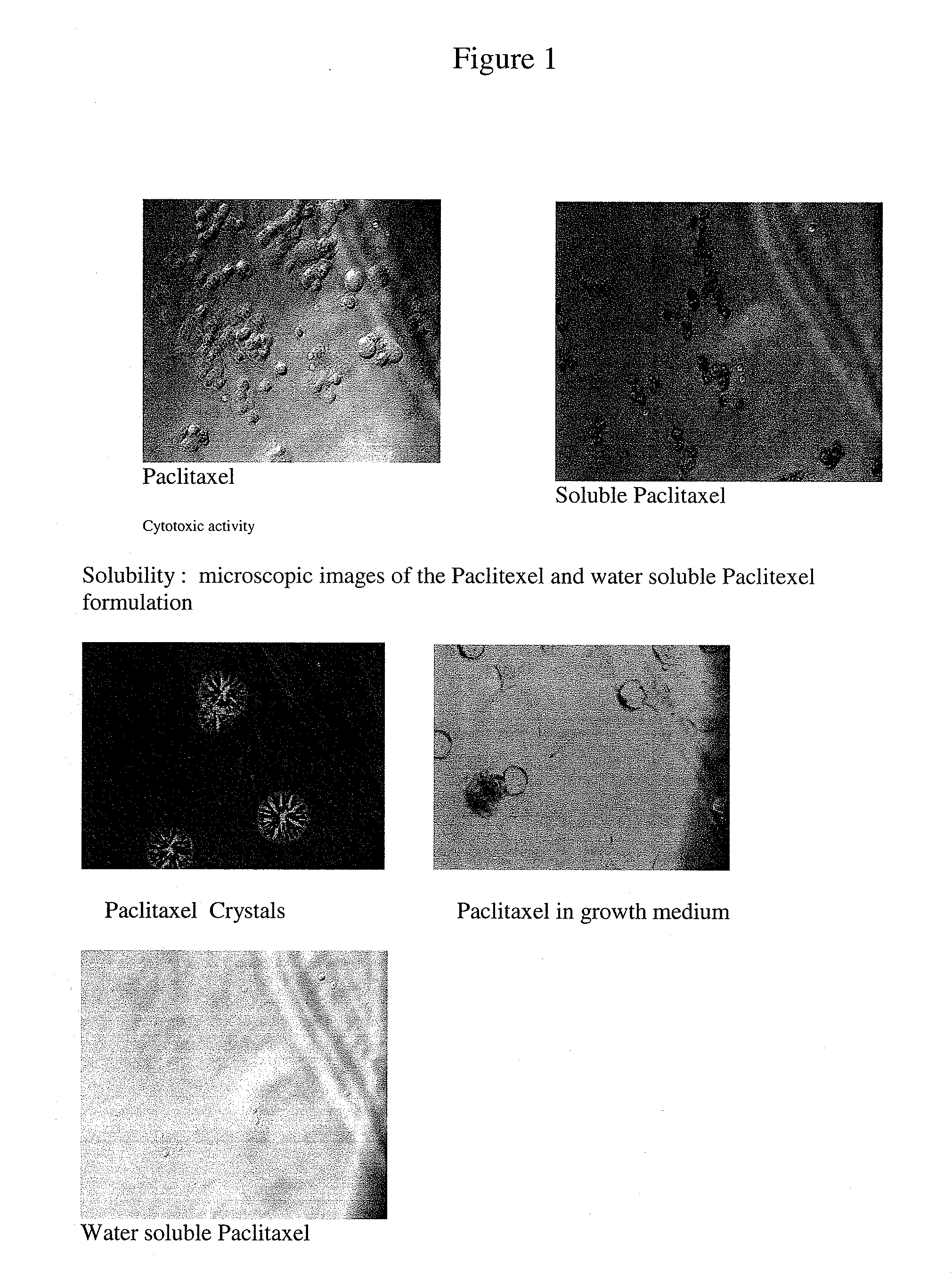
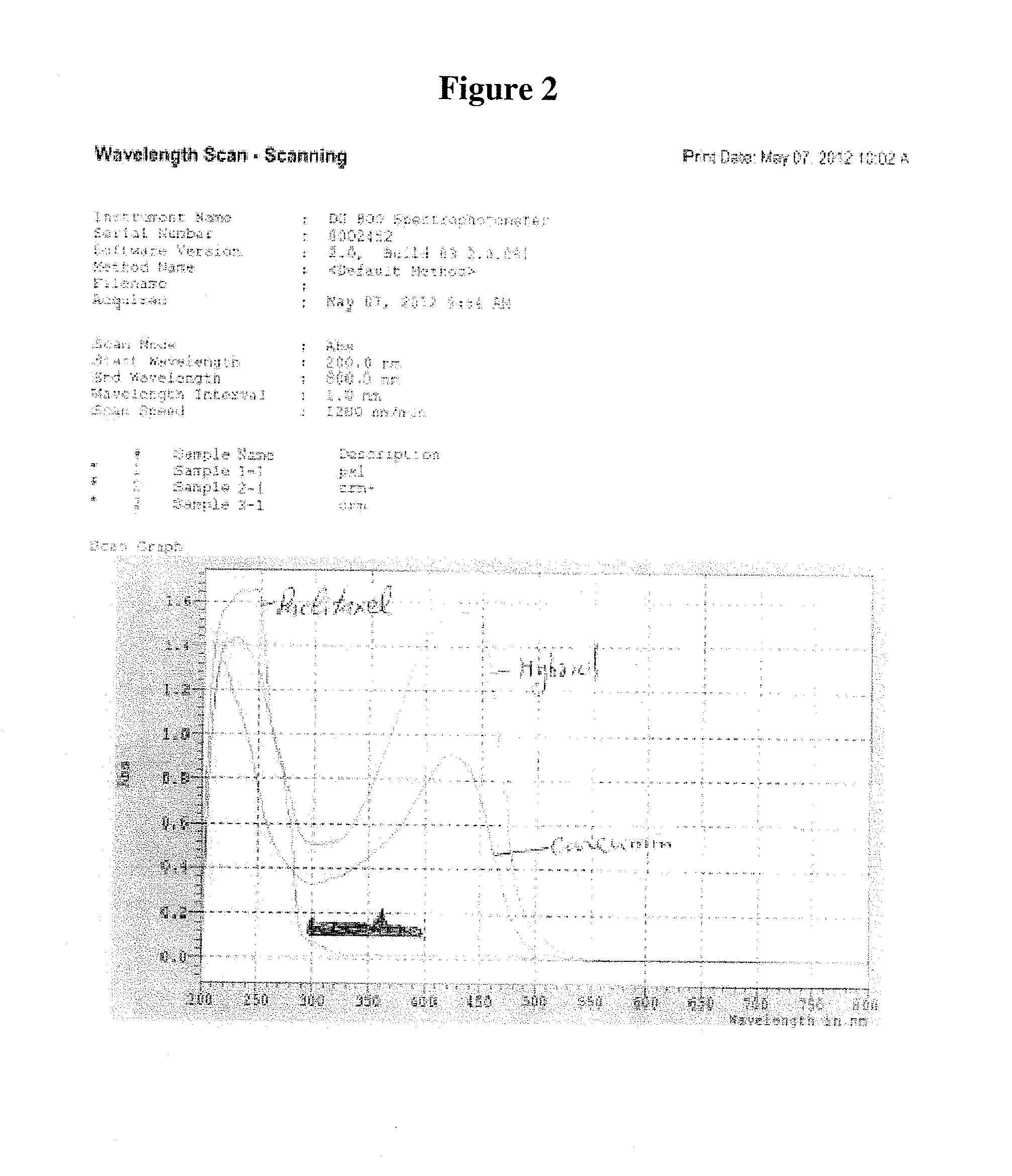
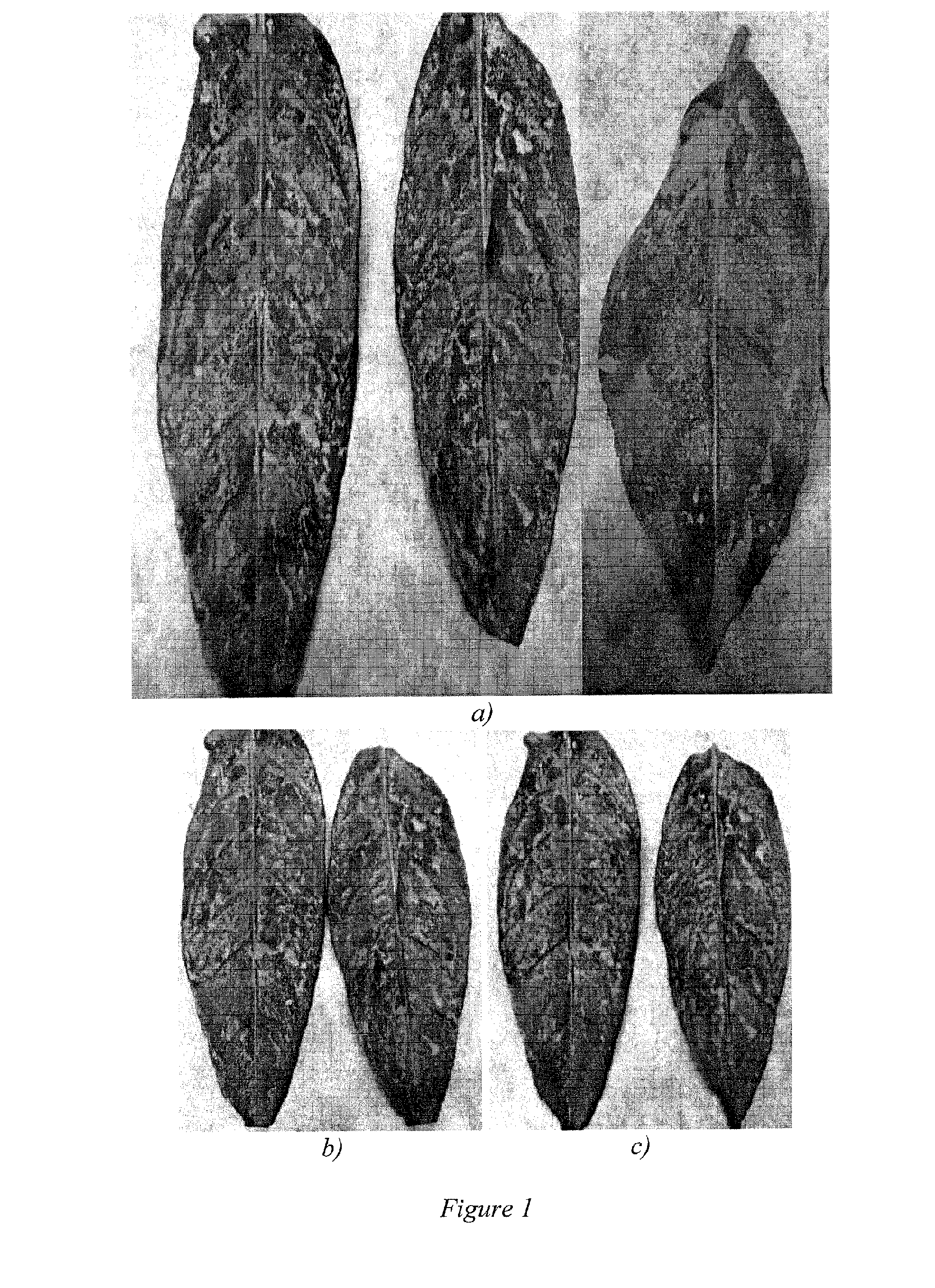Patents
Literature
47 results about "Particulate system" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Particulate Systems A division of Micromeritics Instruments is an agile and responsive organization that is dedicated to the discovery and commercialization of unique technologies in particle and material characterization. Is to develop and to seek out innovative technology that advance the science of materials and particle characterization.
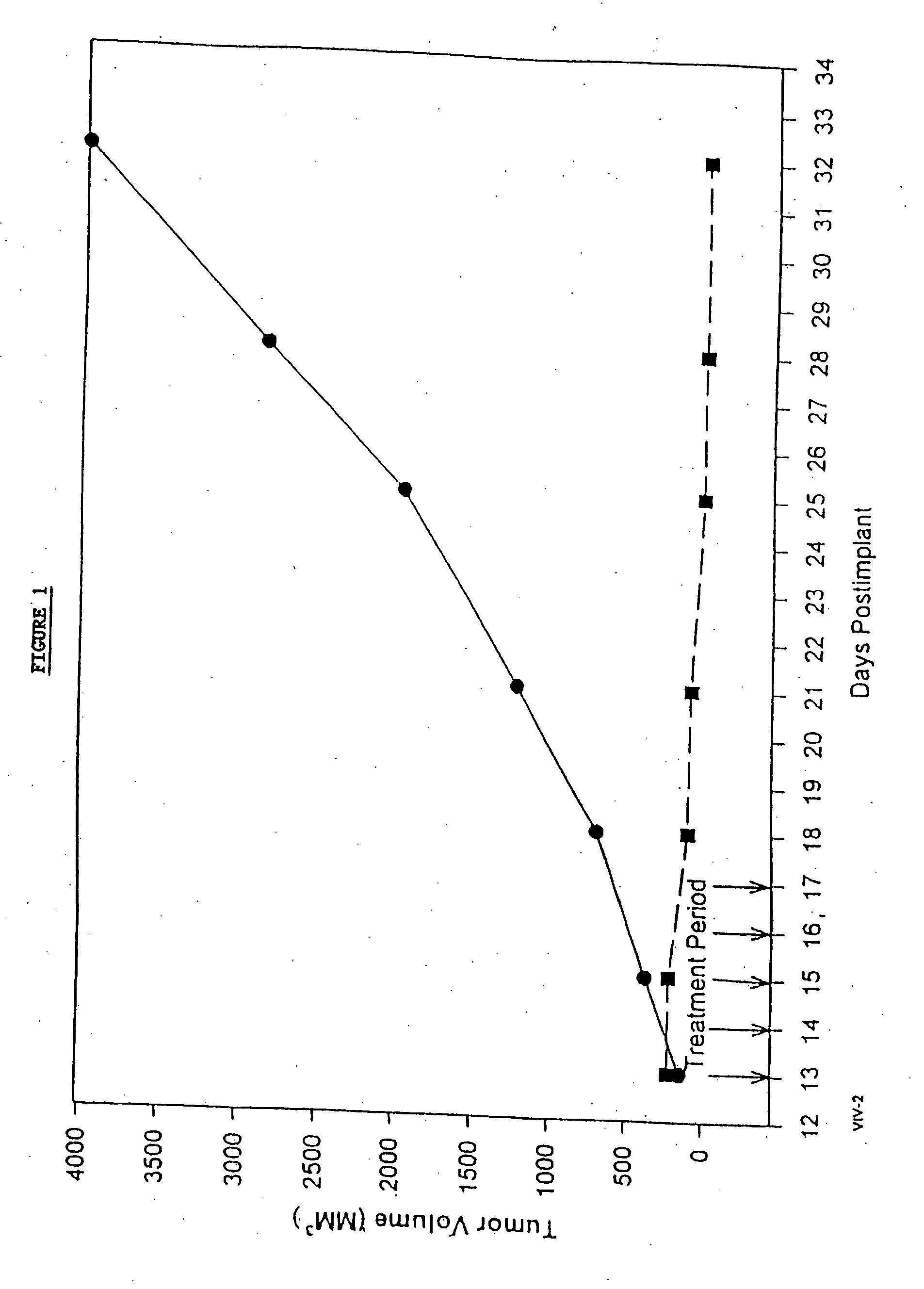
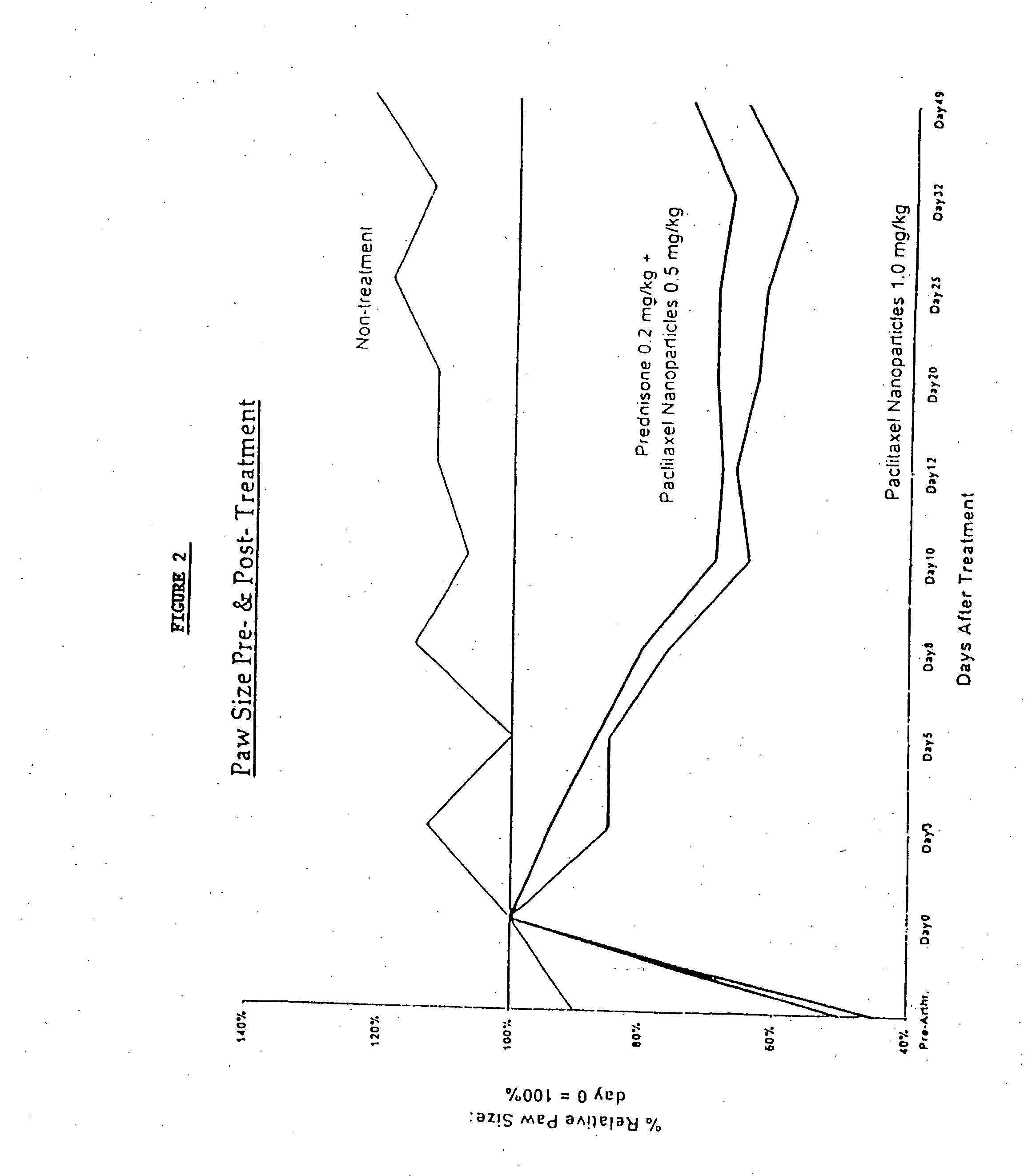
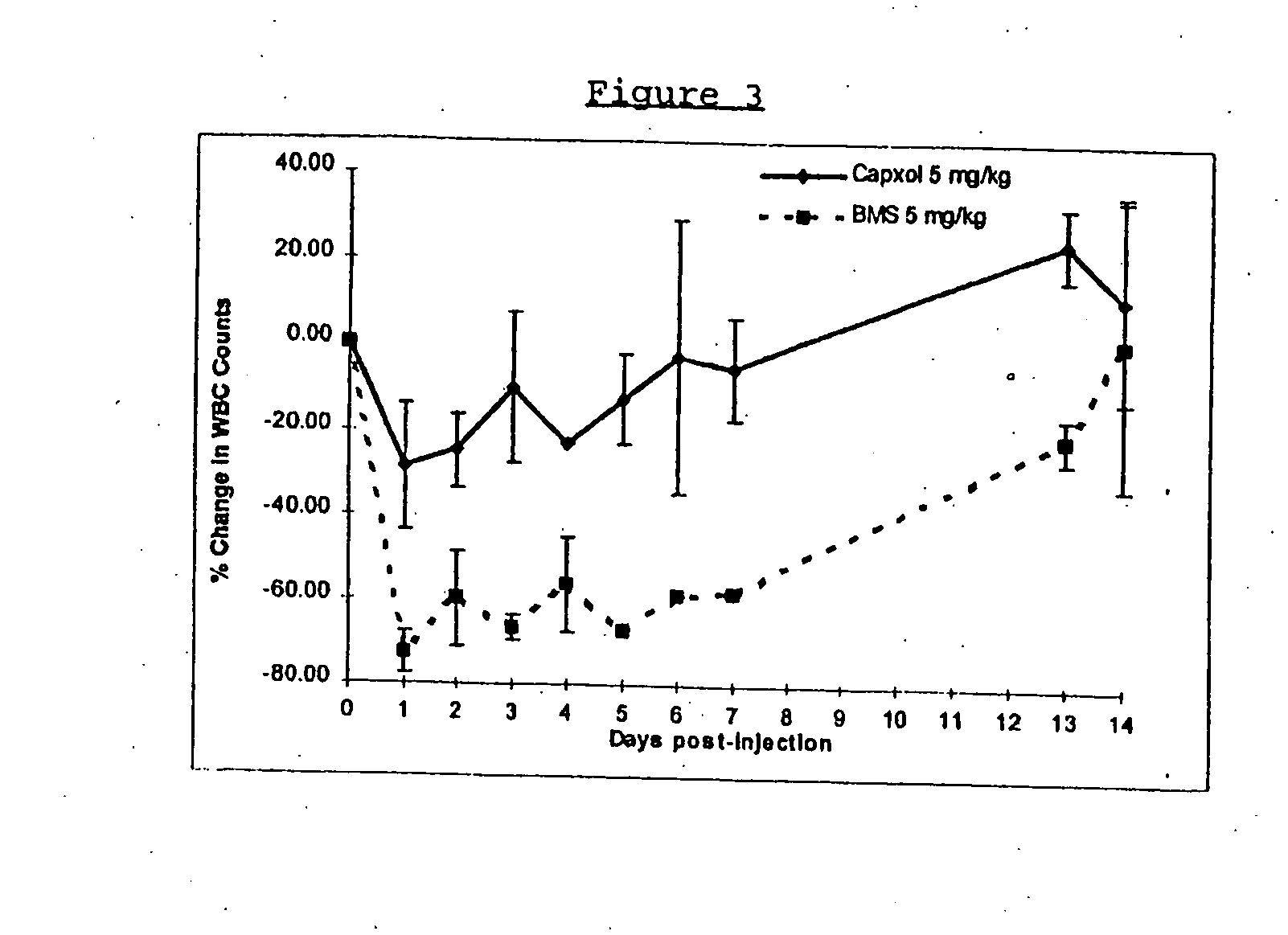
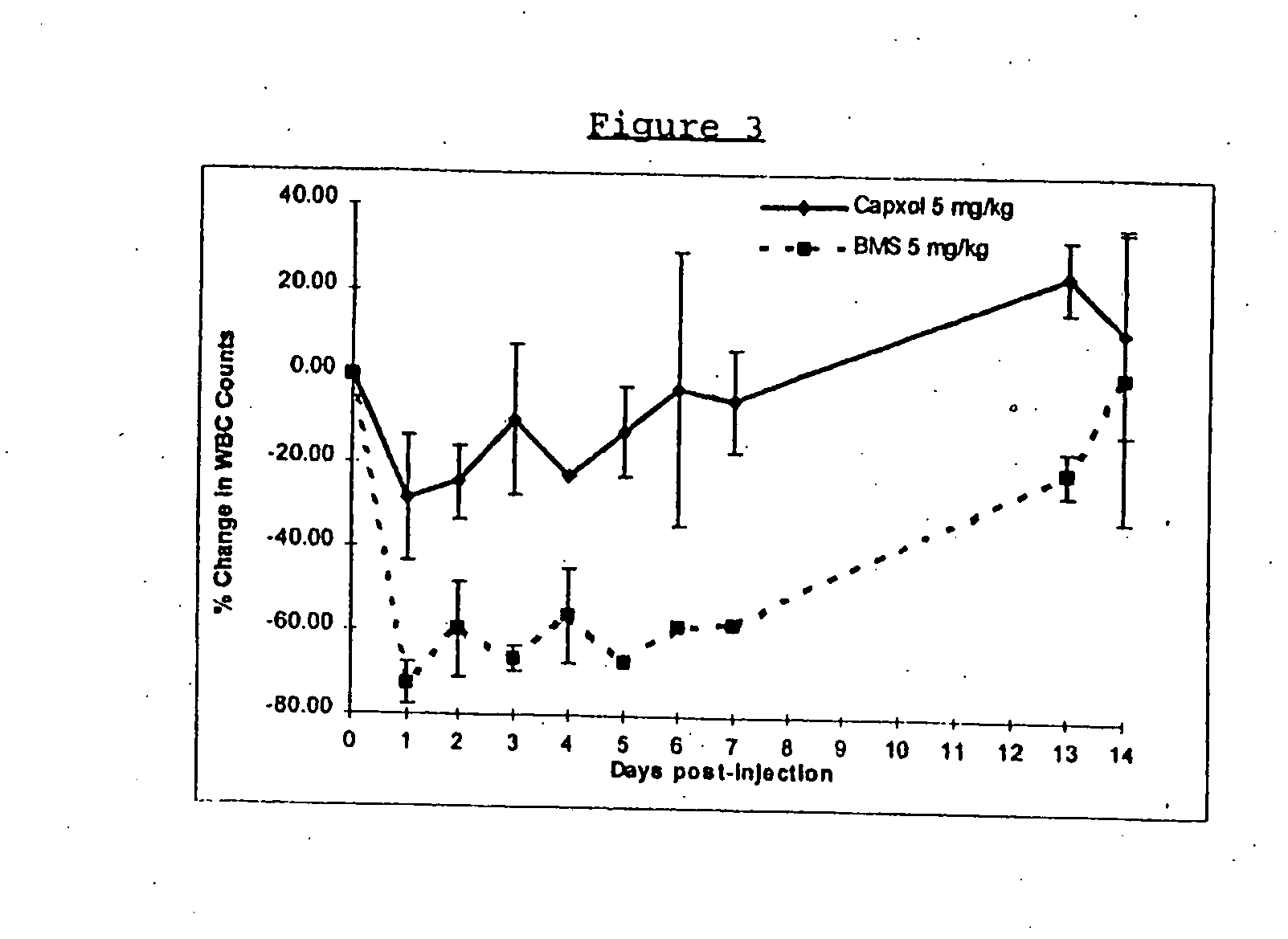
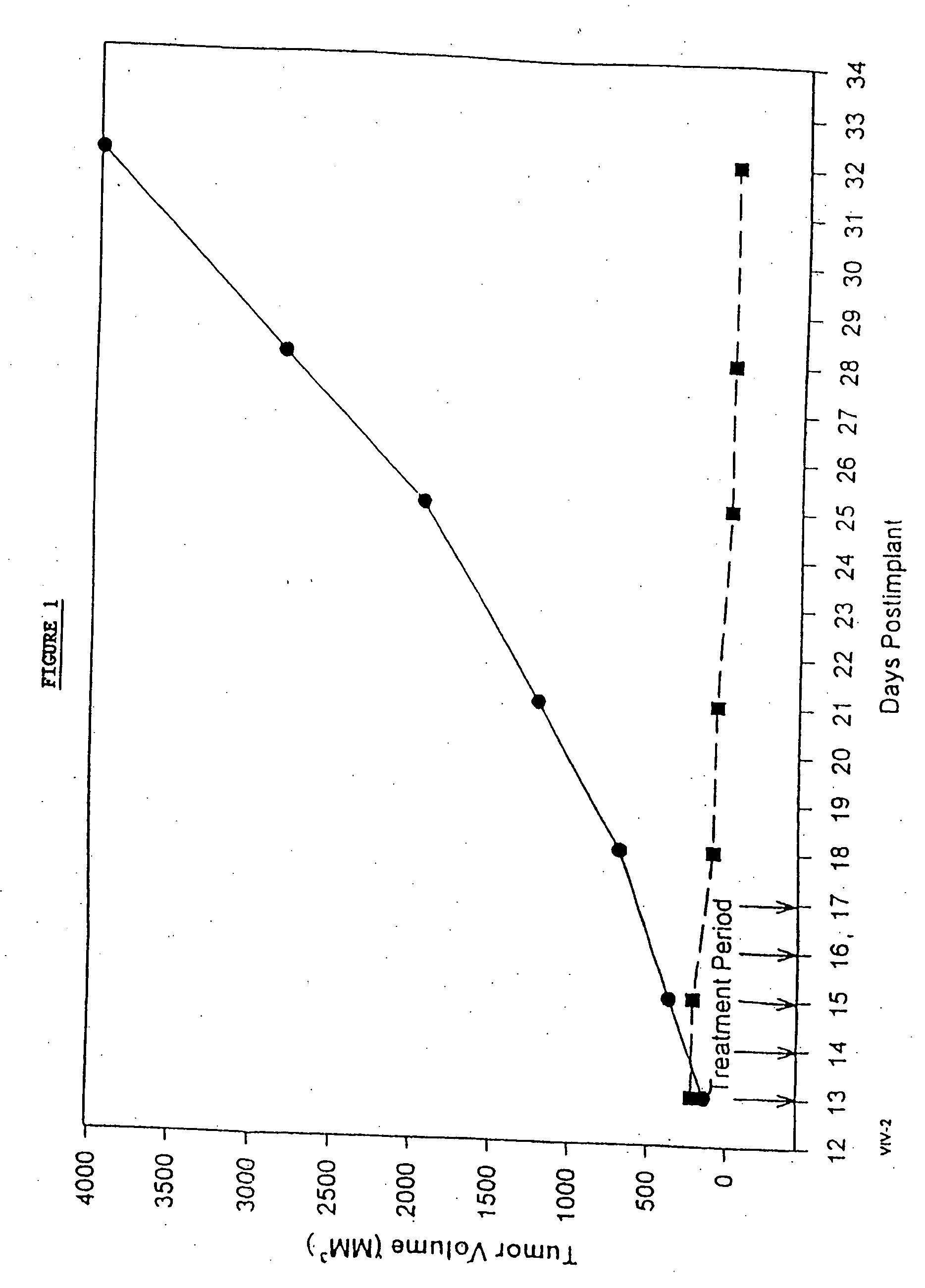
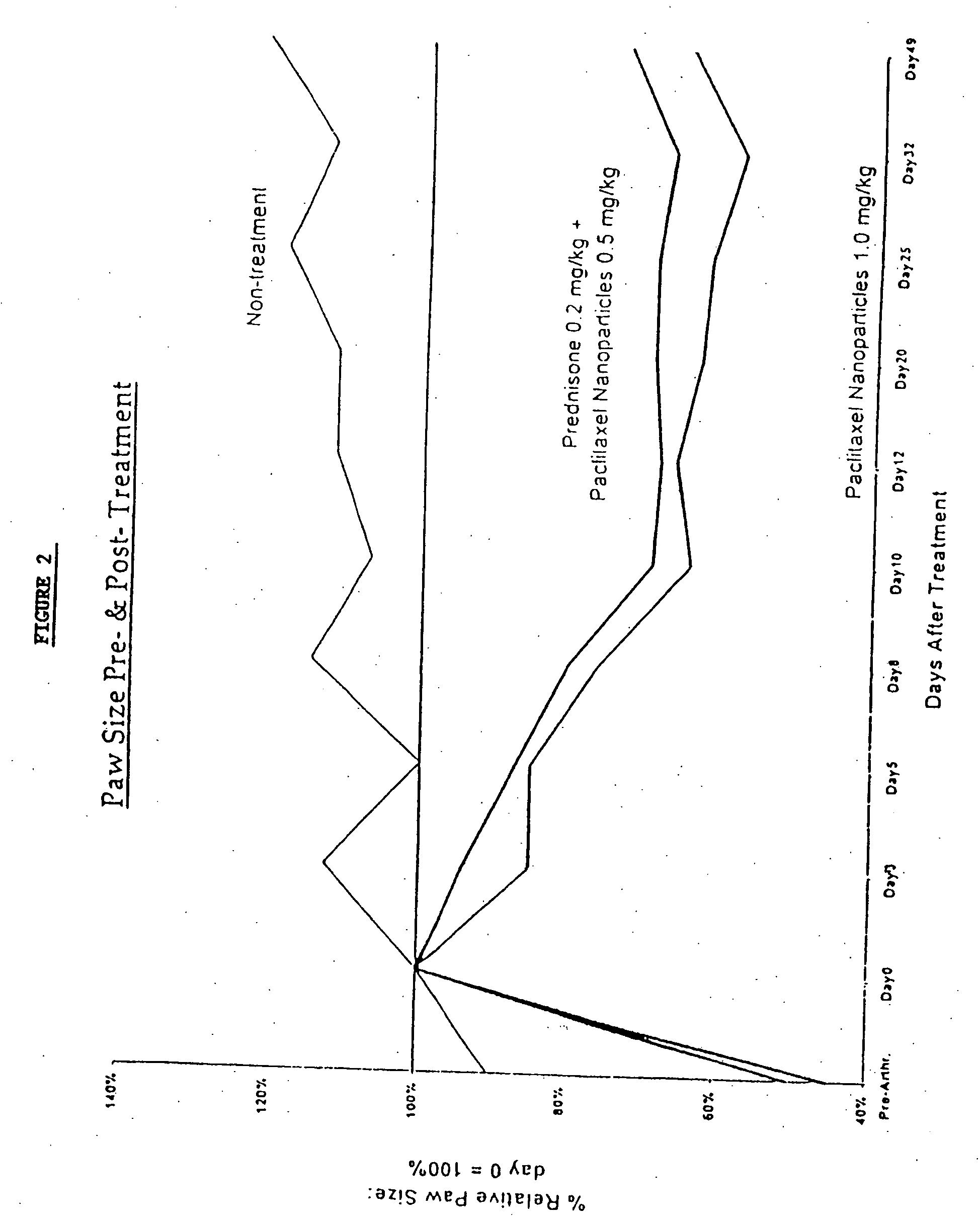
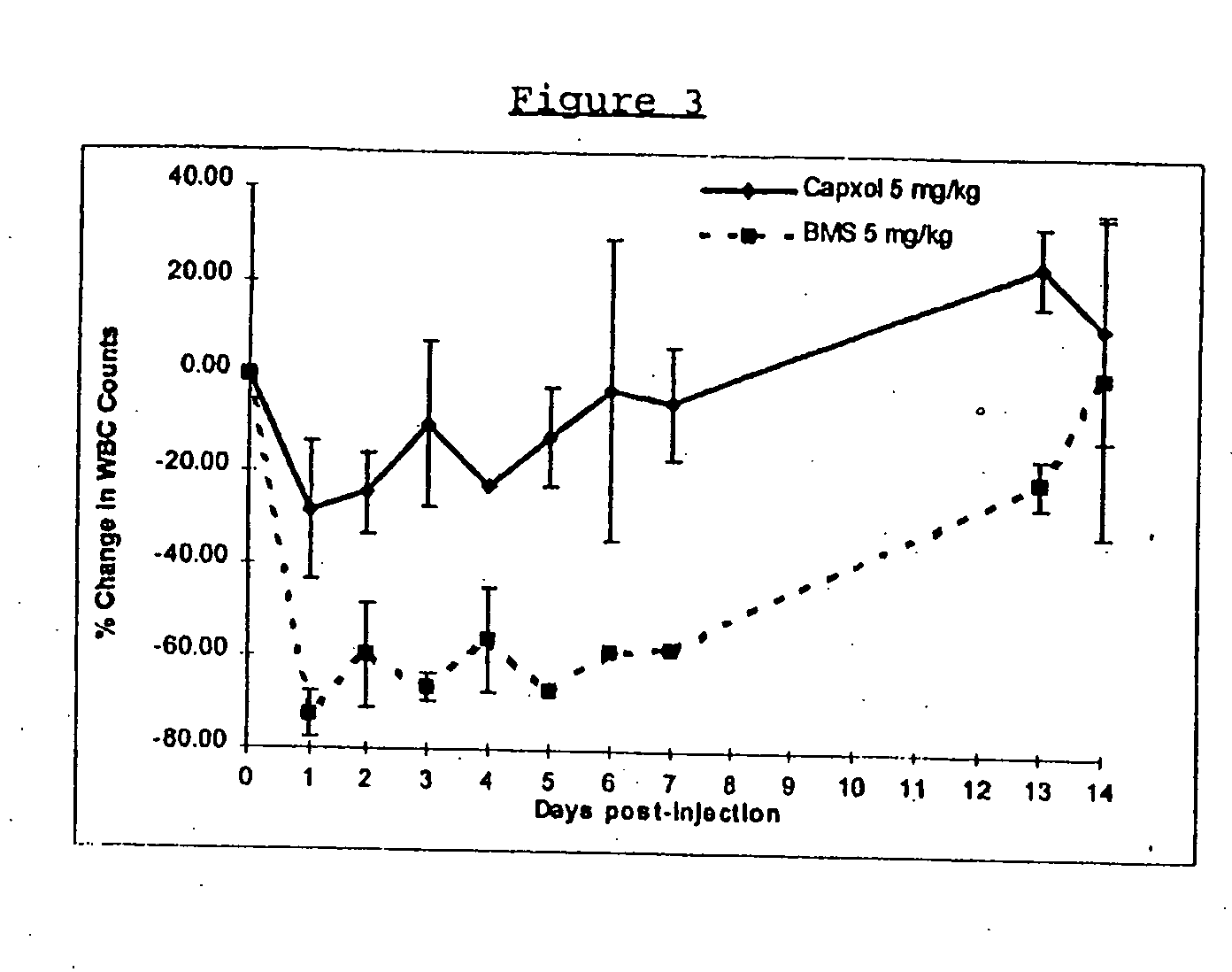
Protein stabilized pharmacologically active agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
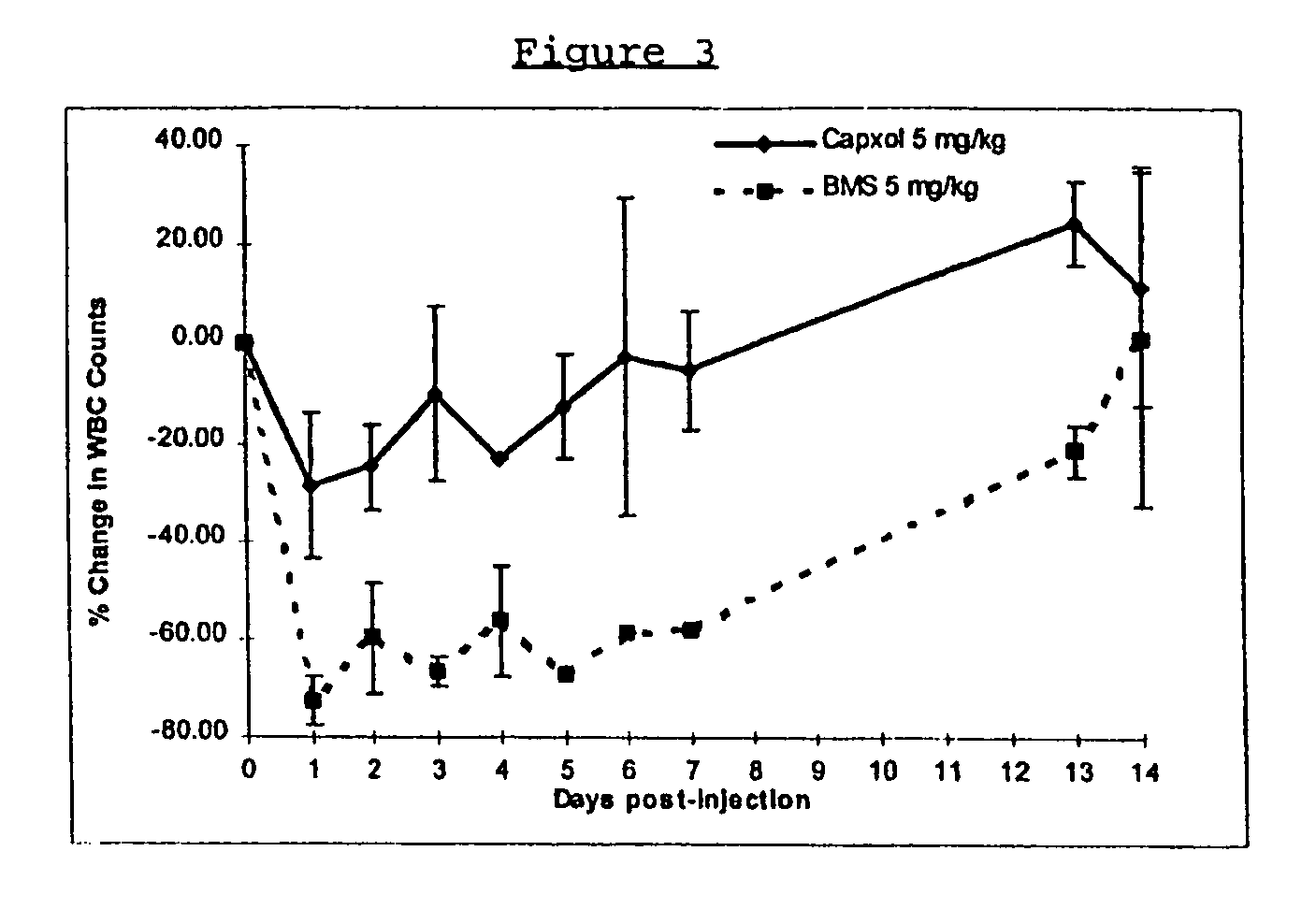
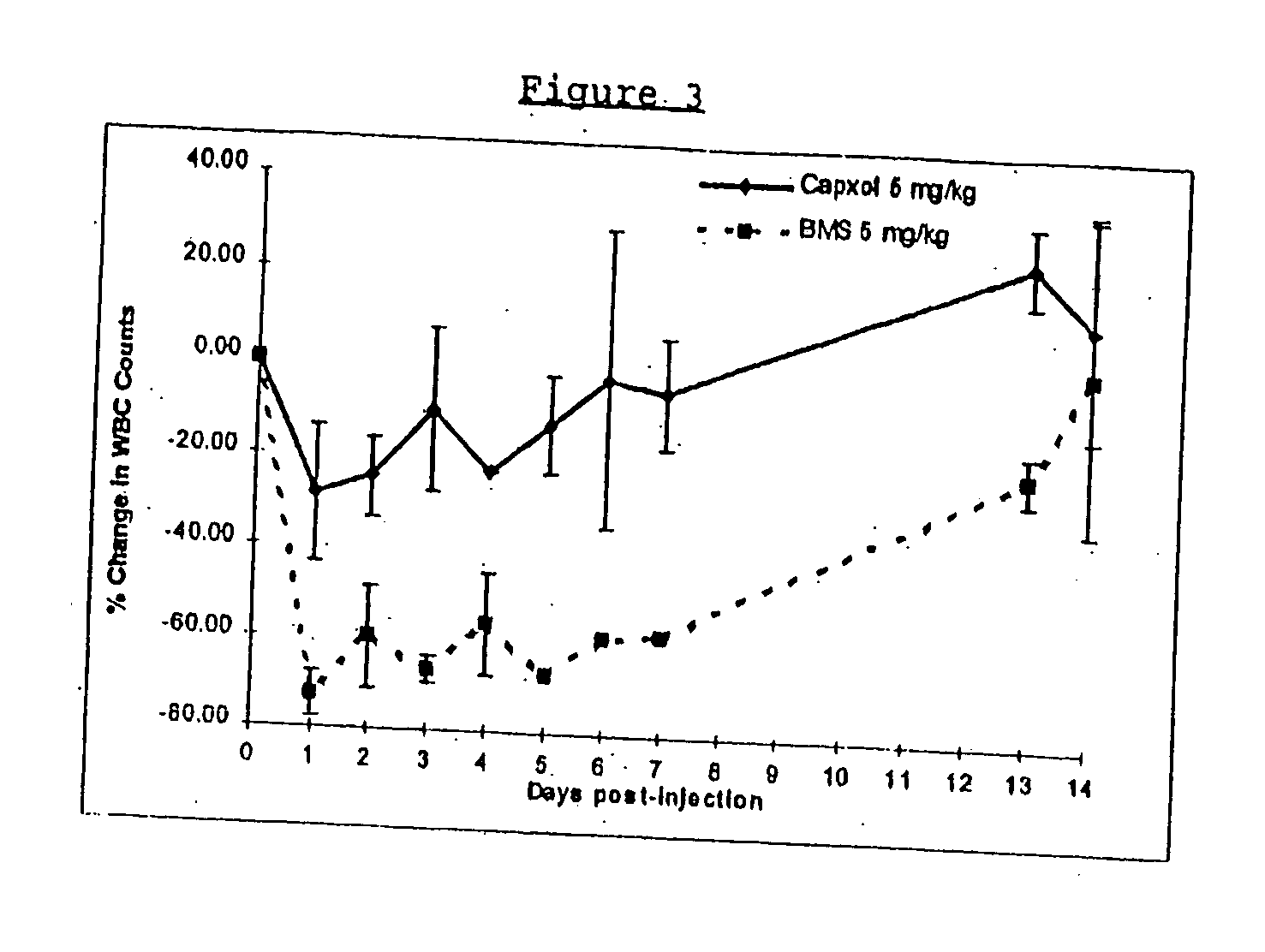
InactiveUS6749868B1Low toxicityLong half-lifePowder deliveryEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsSuspended particlesFree protein
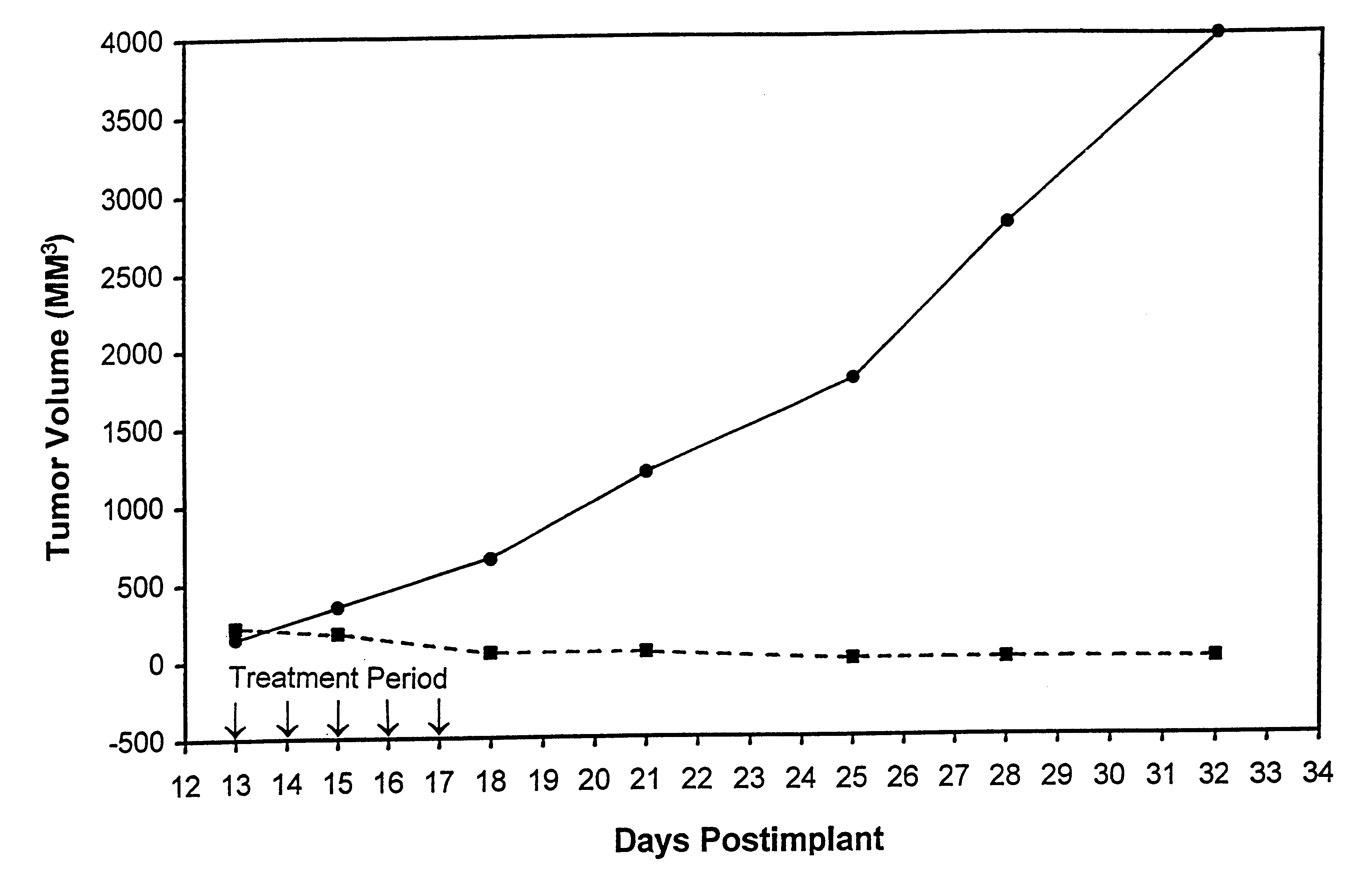
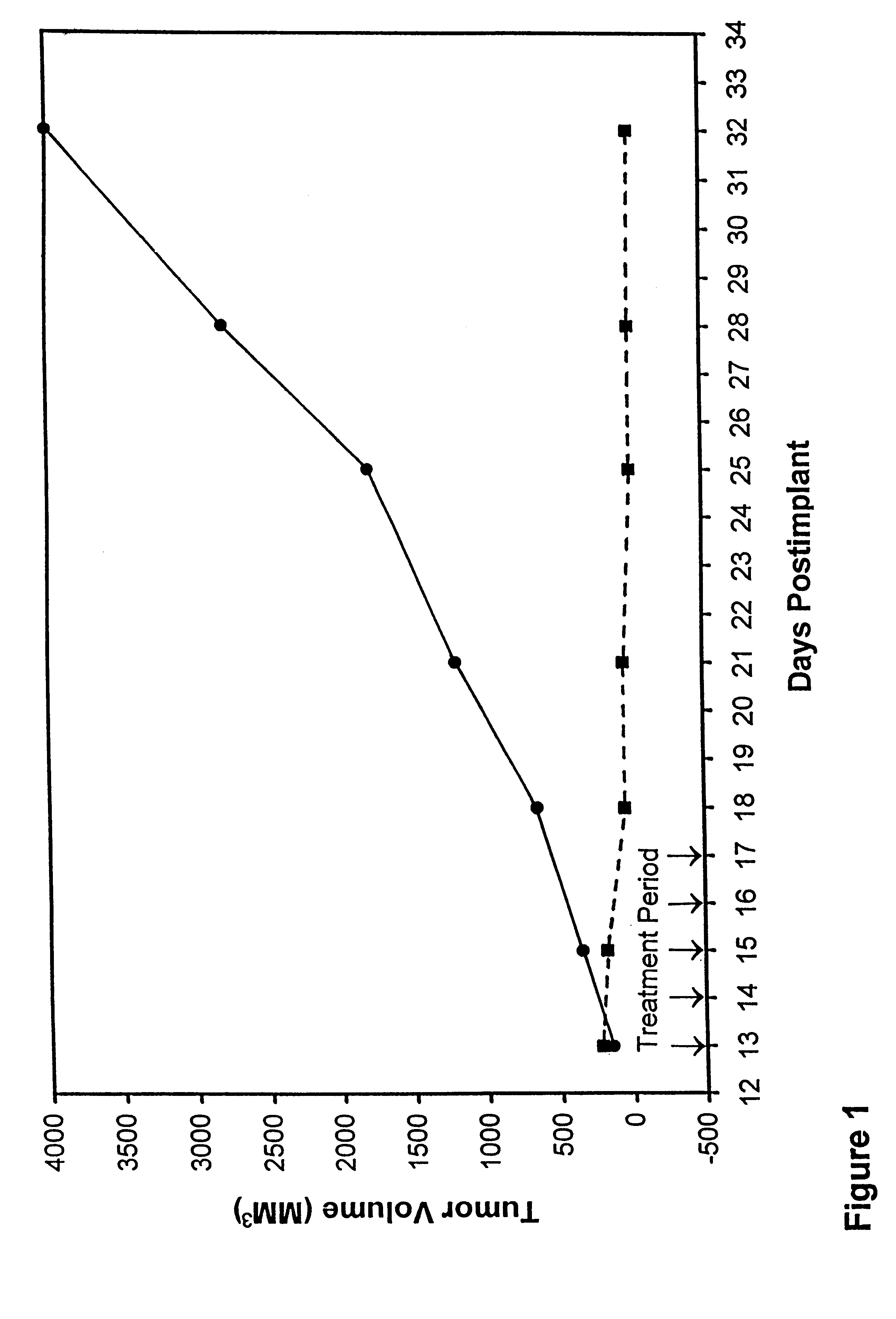
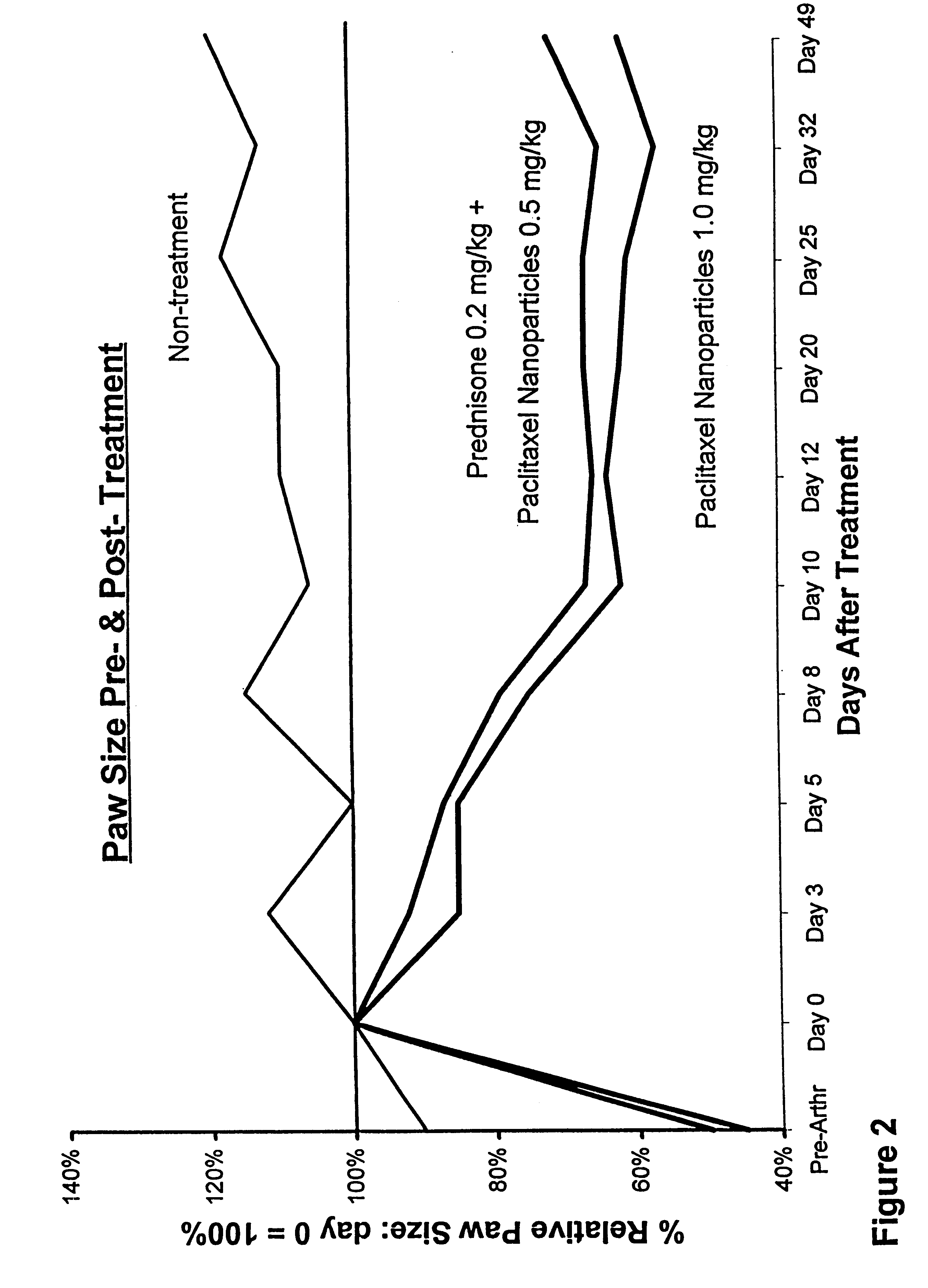
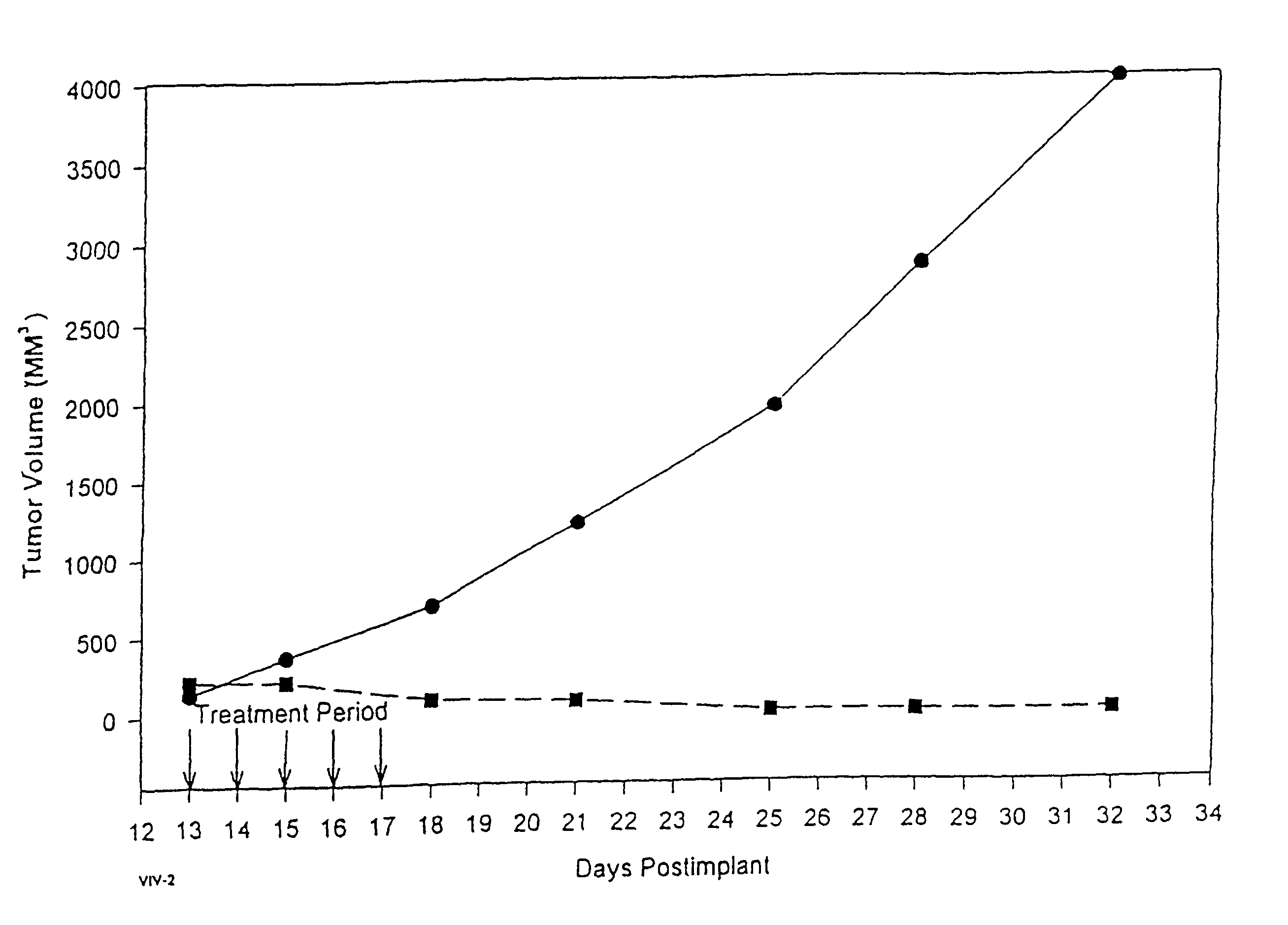
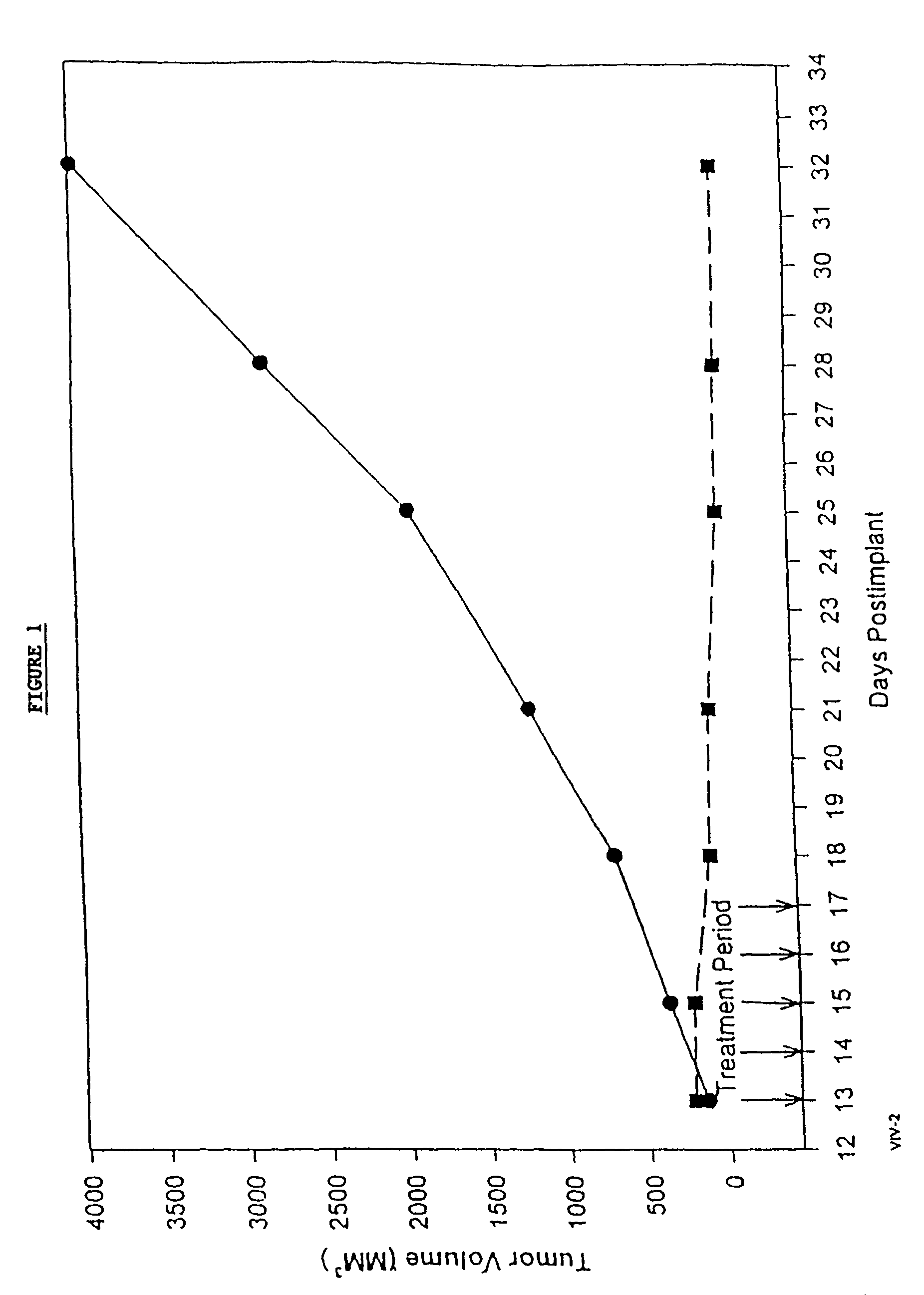
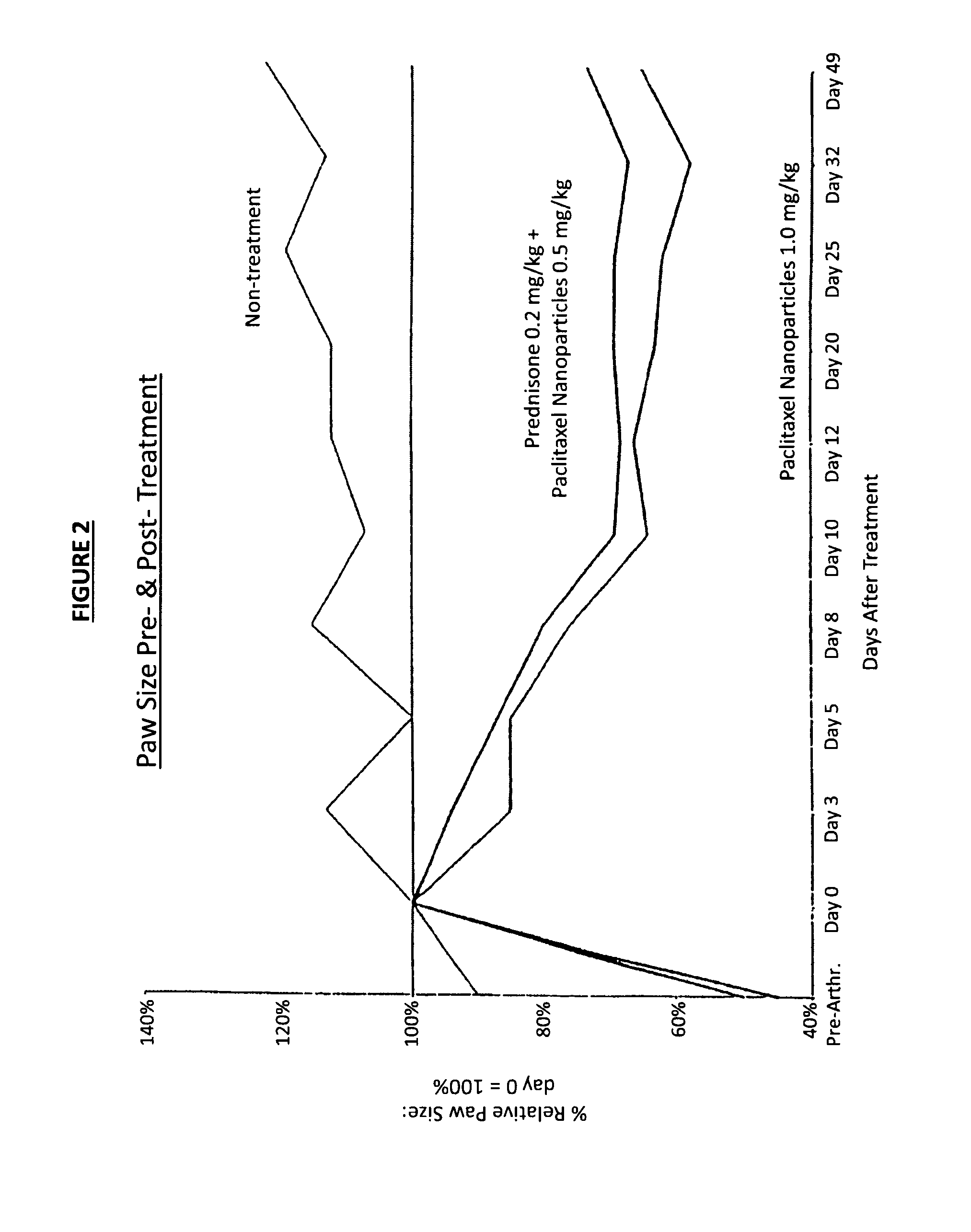
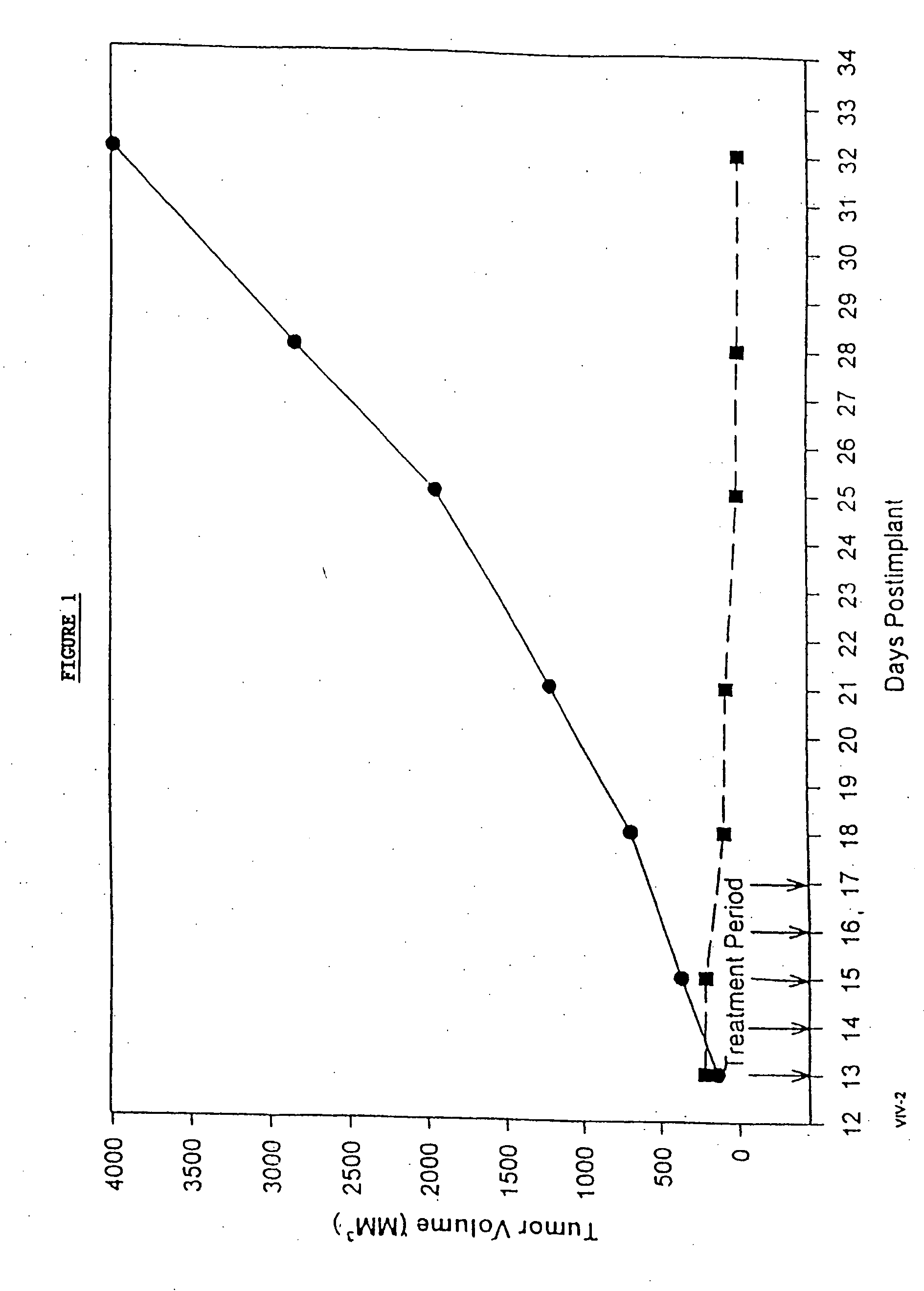
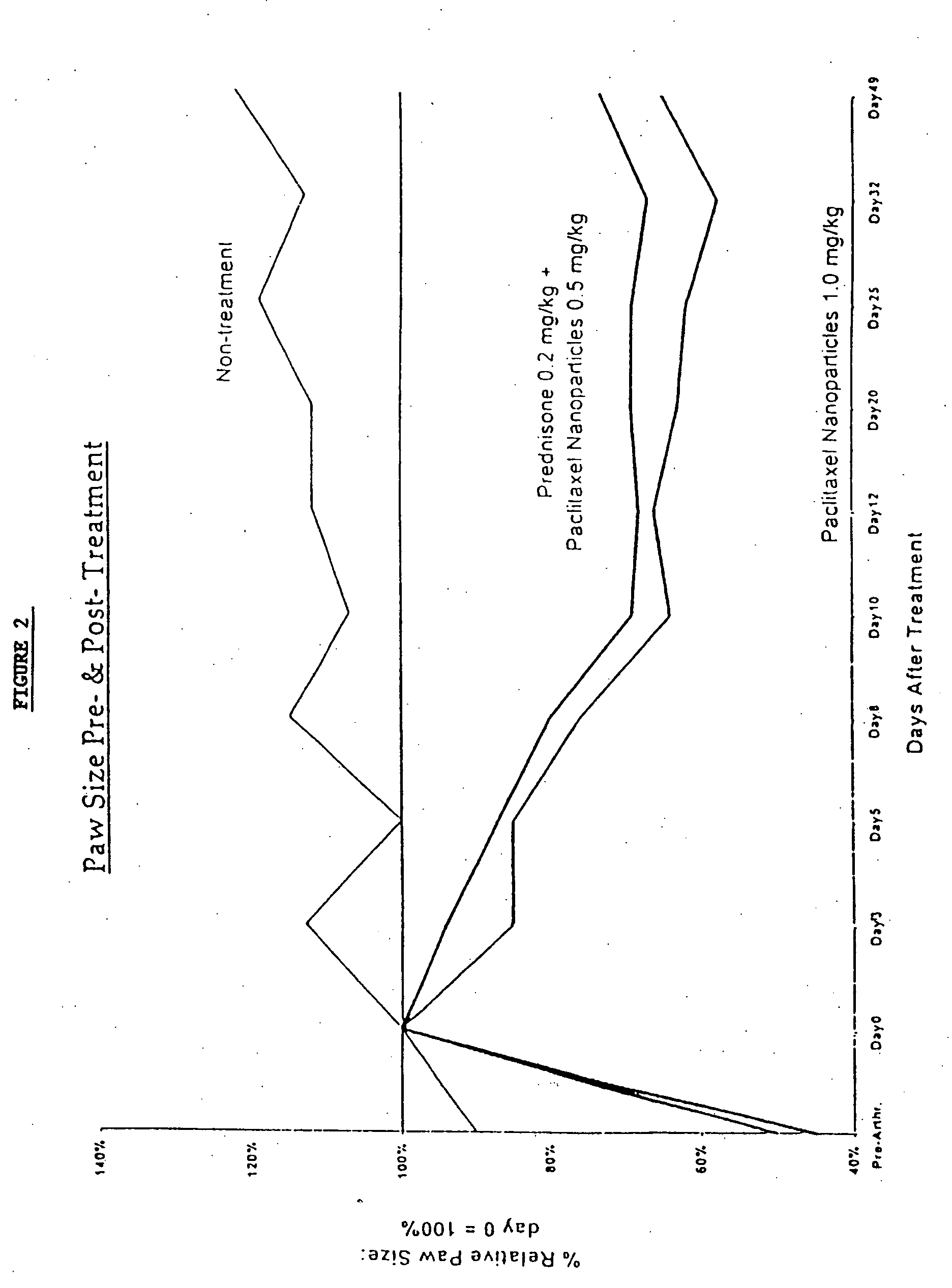
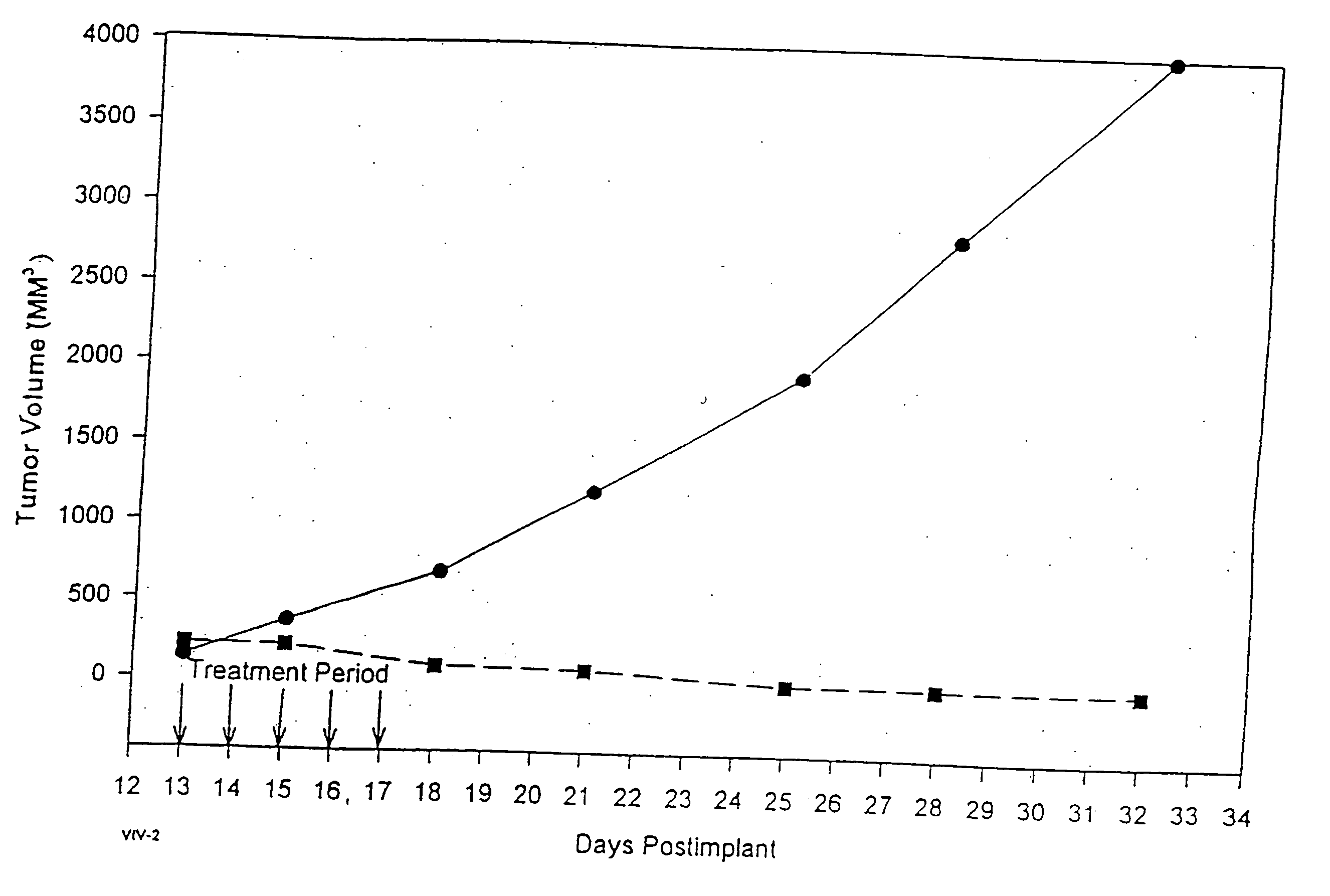
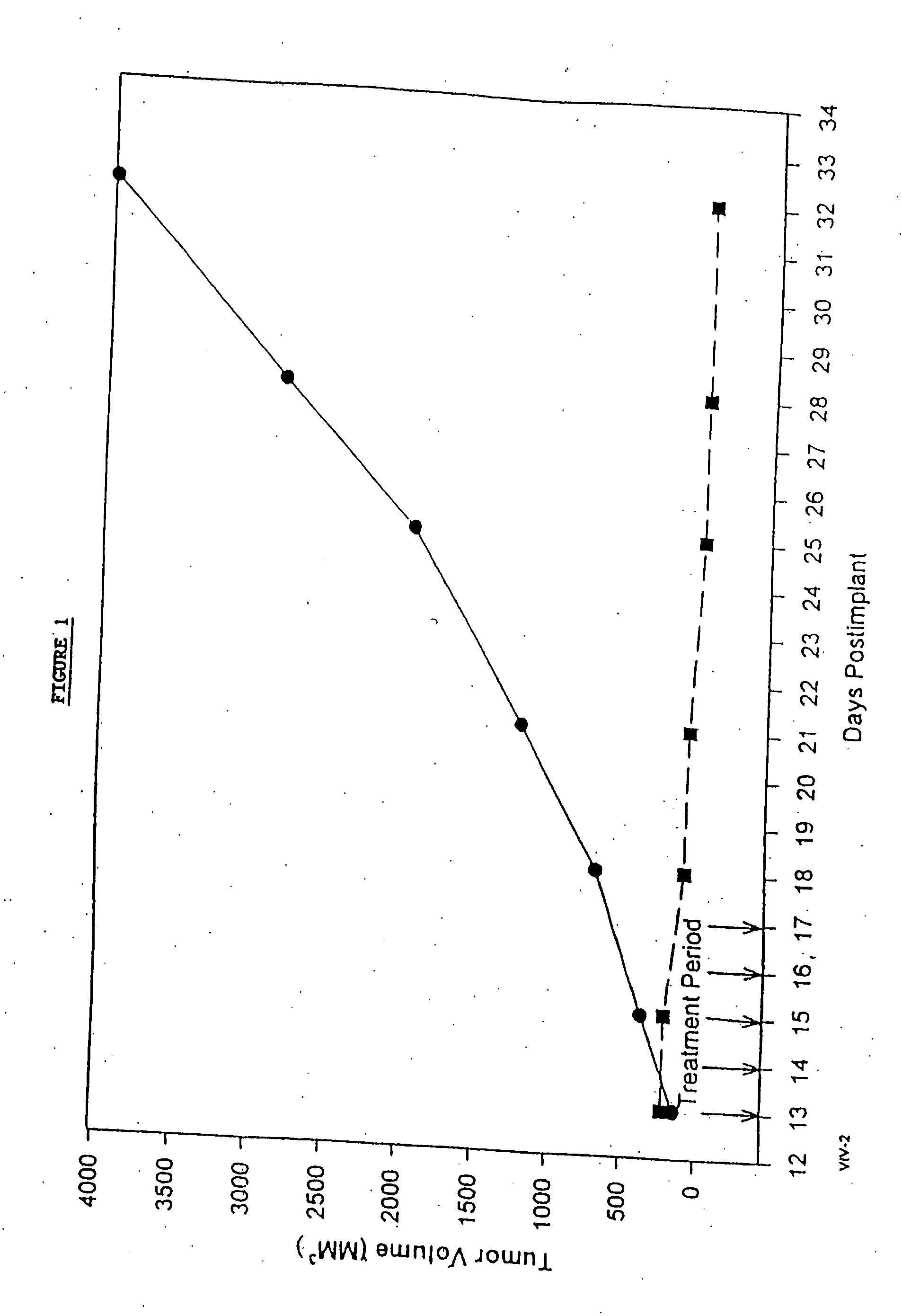
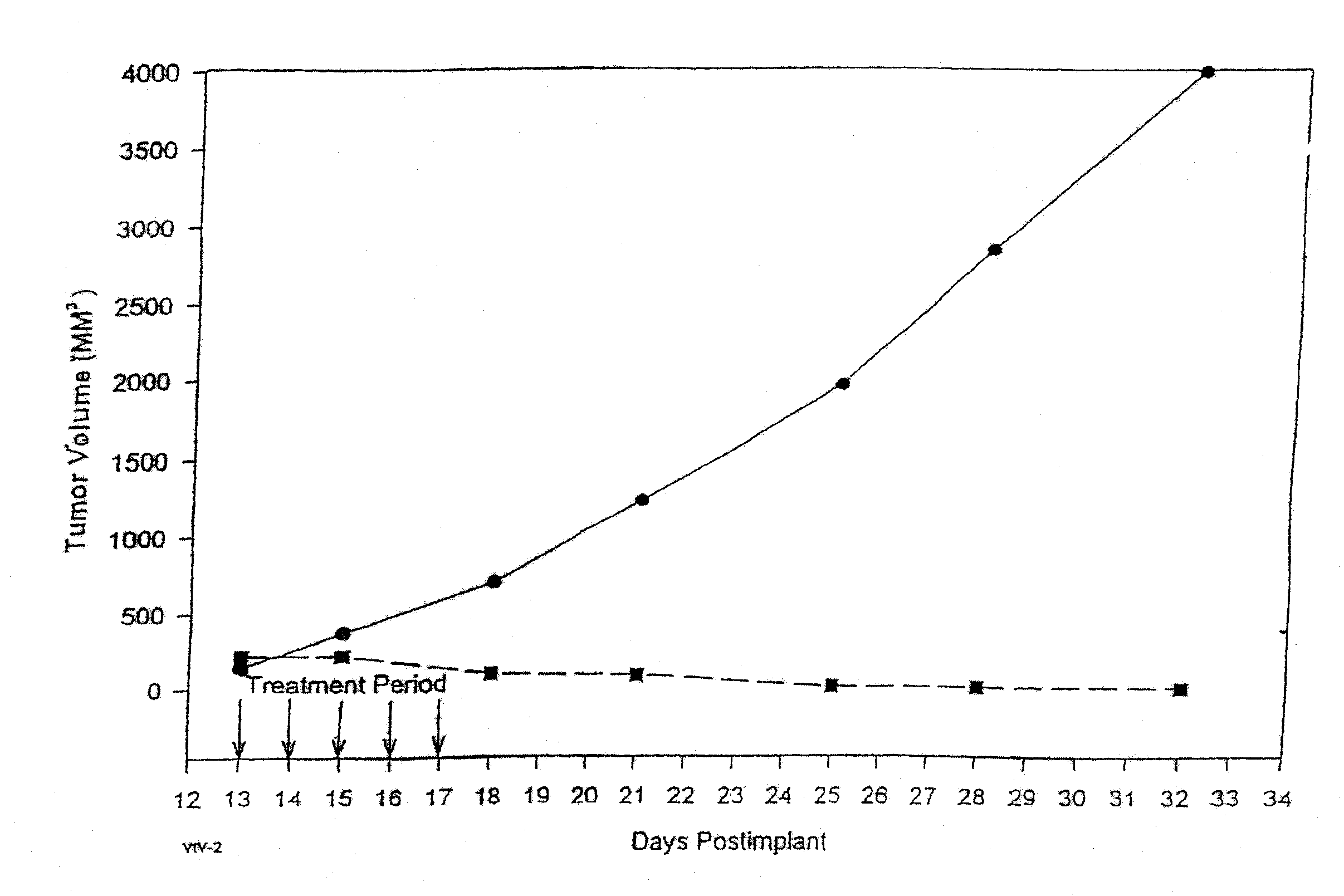
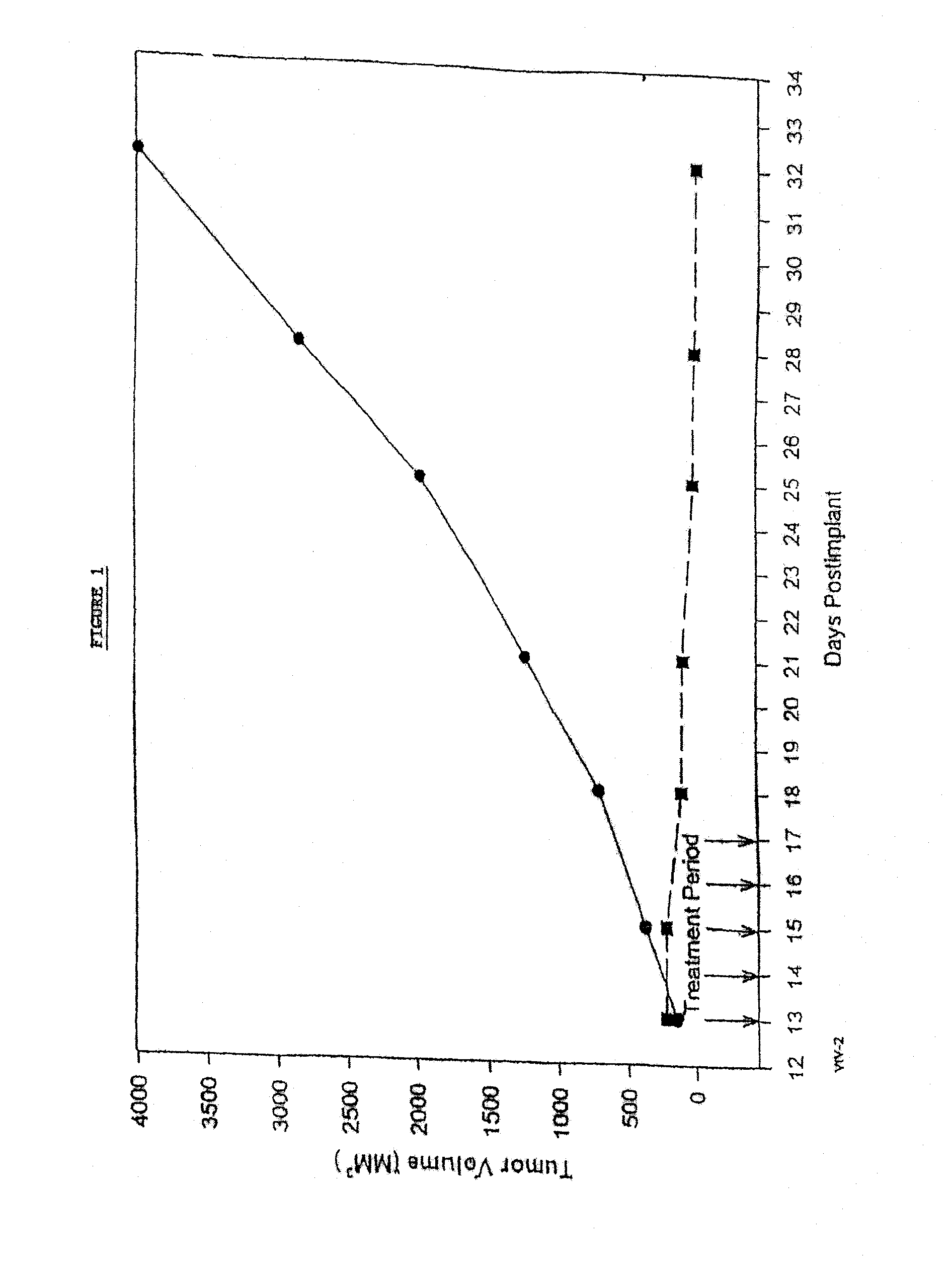
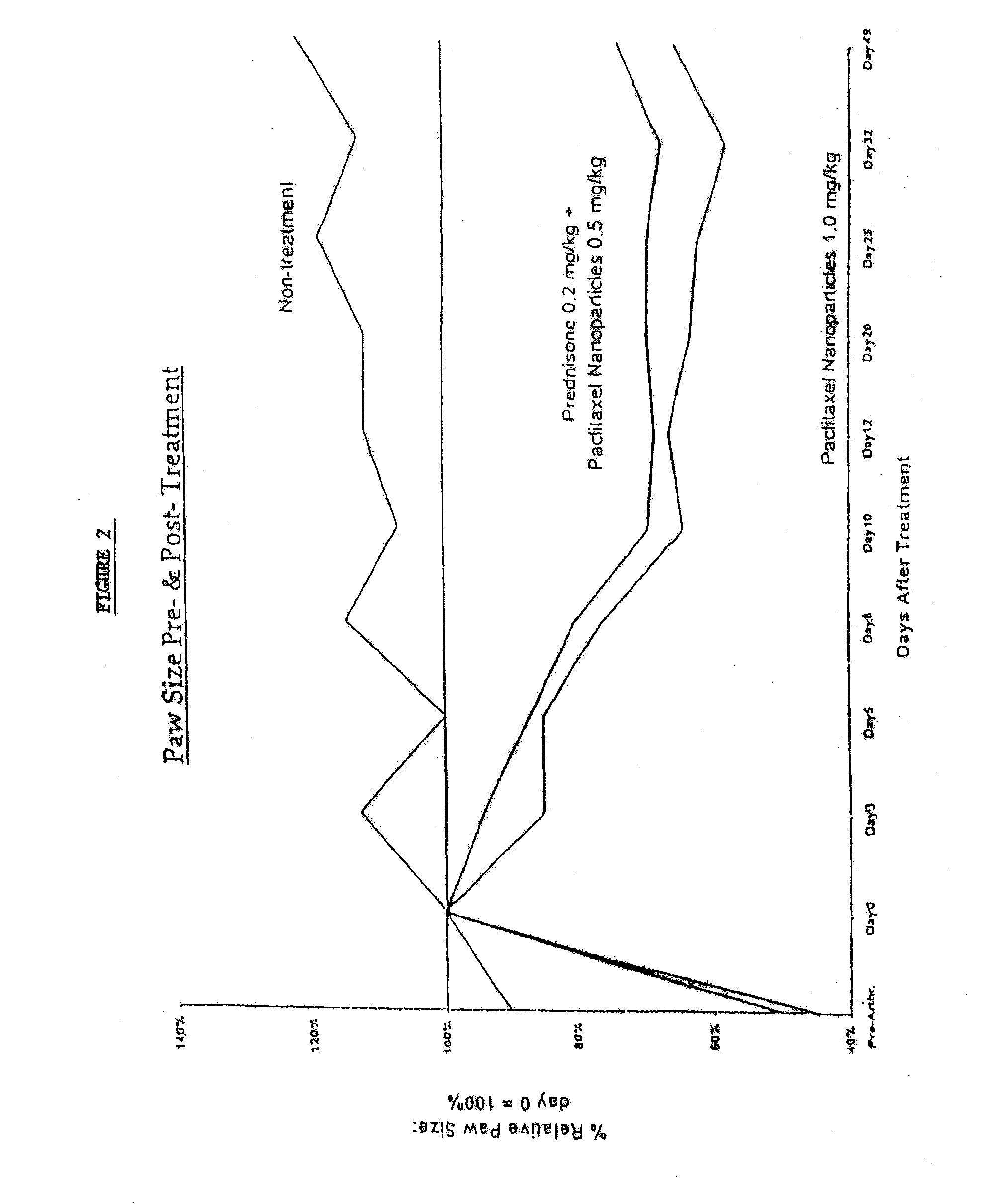
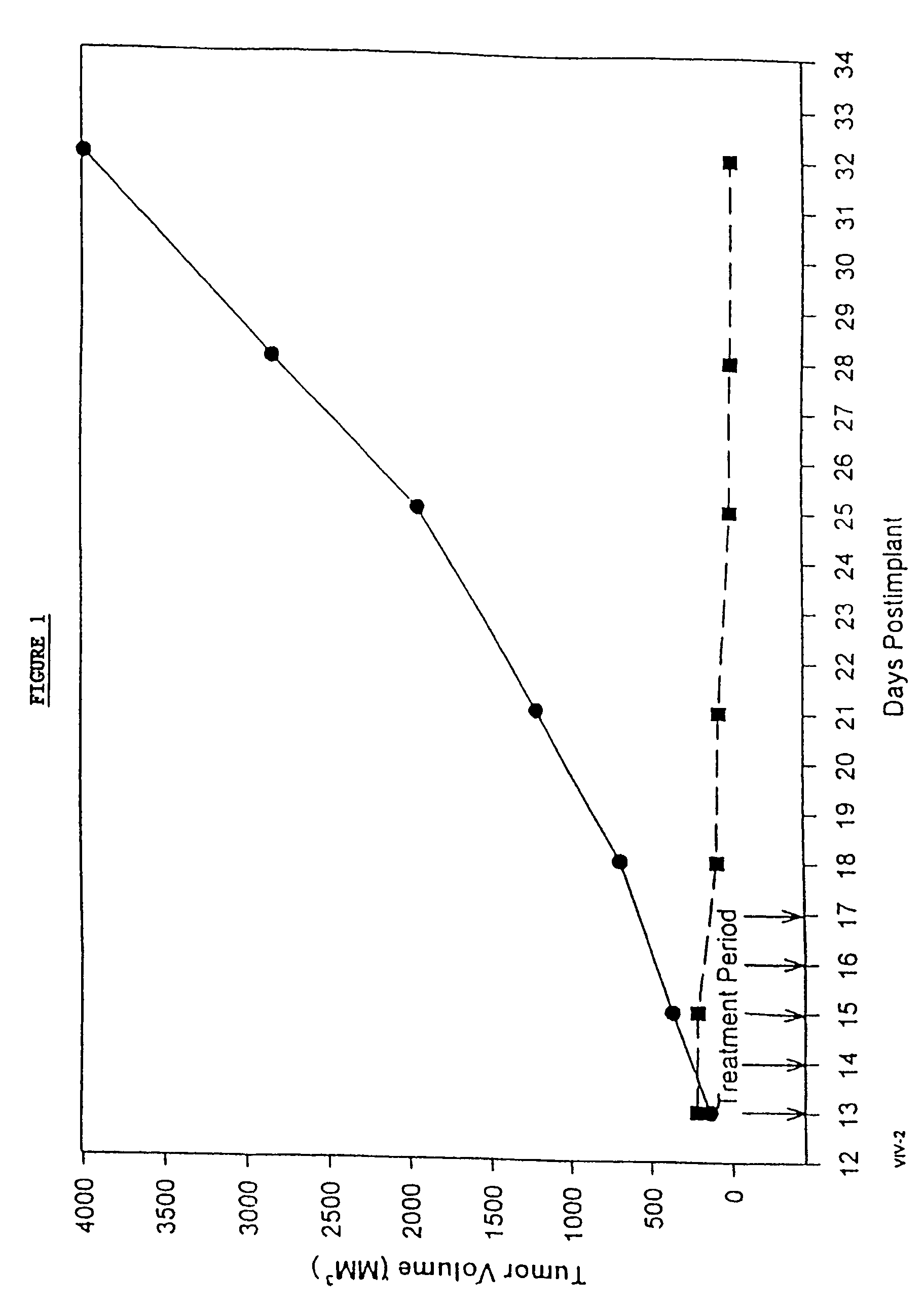
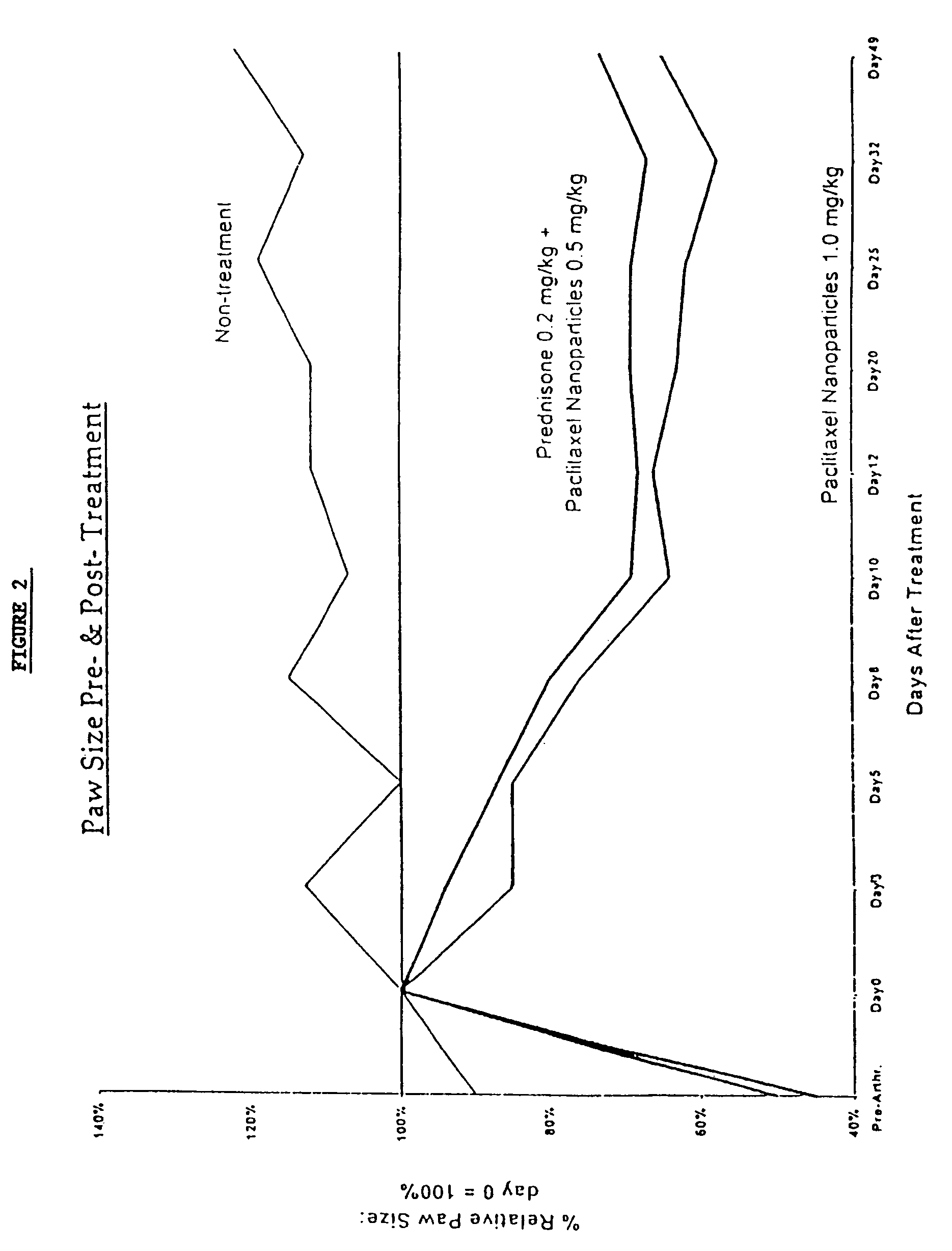
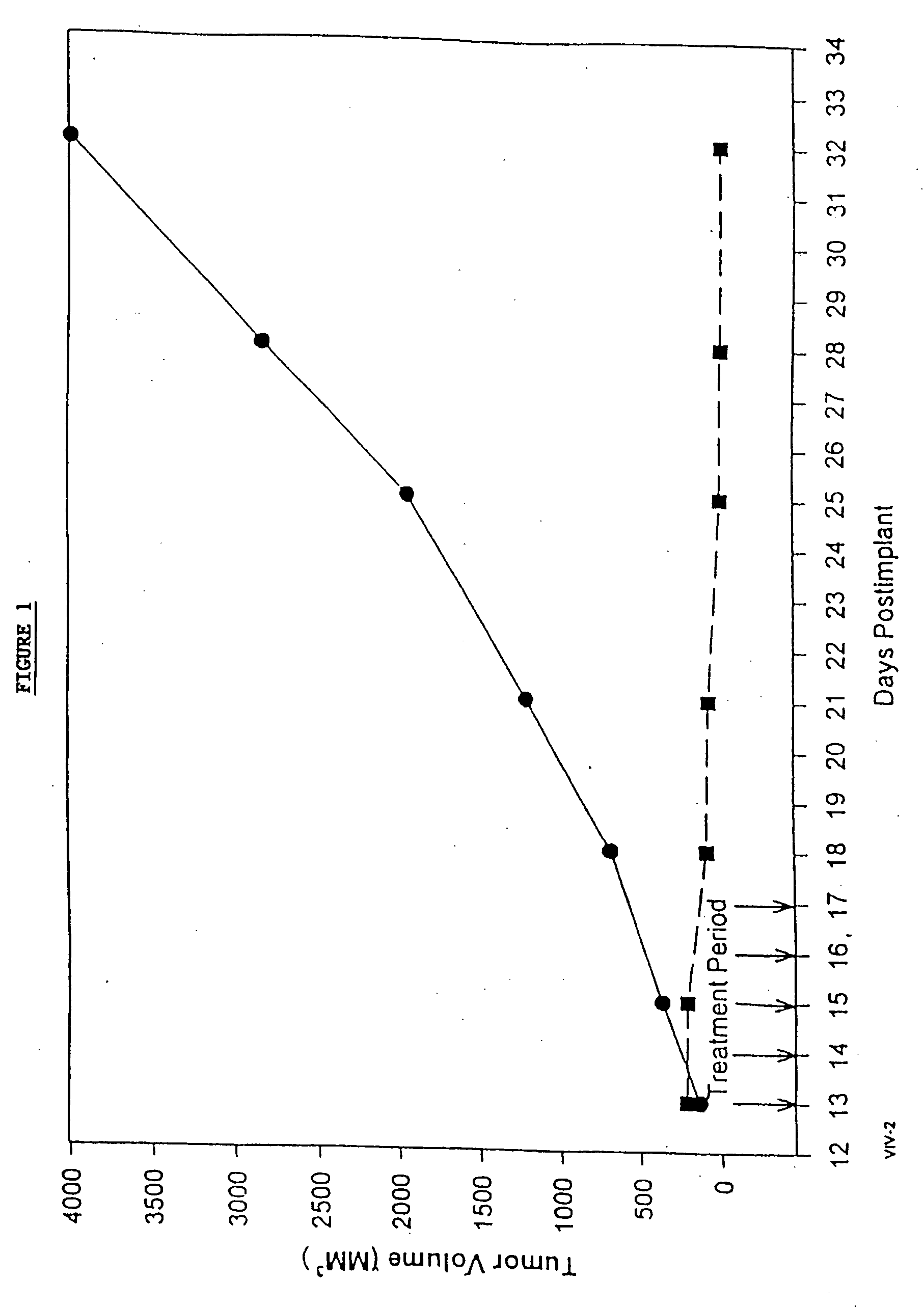
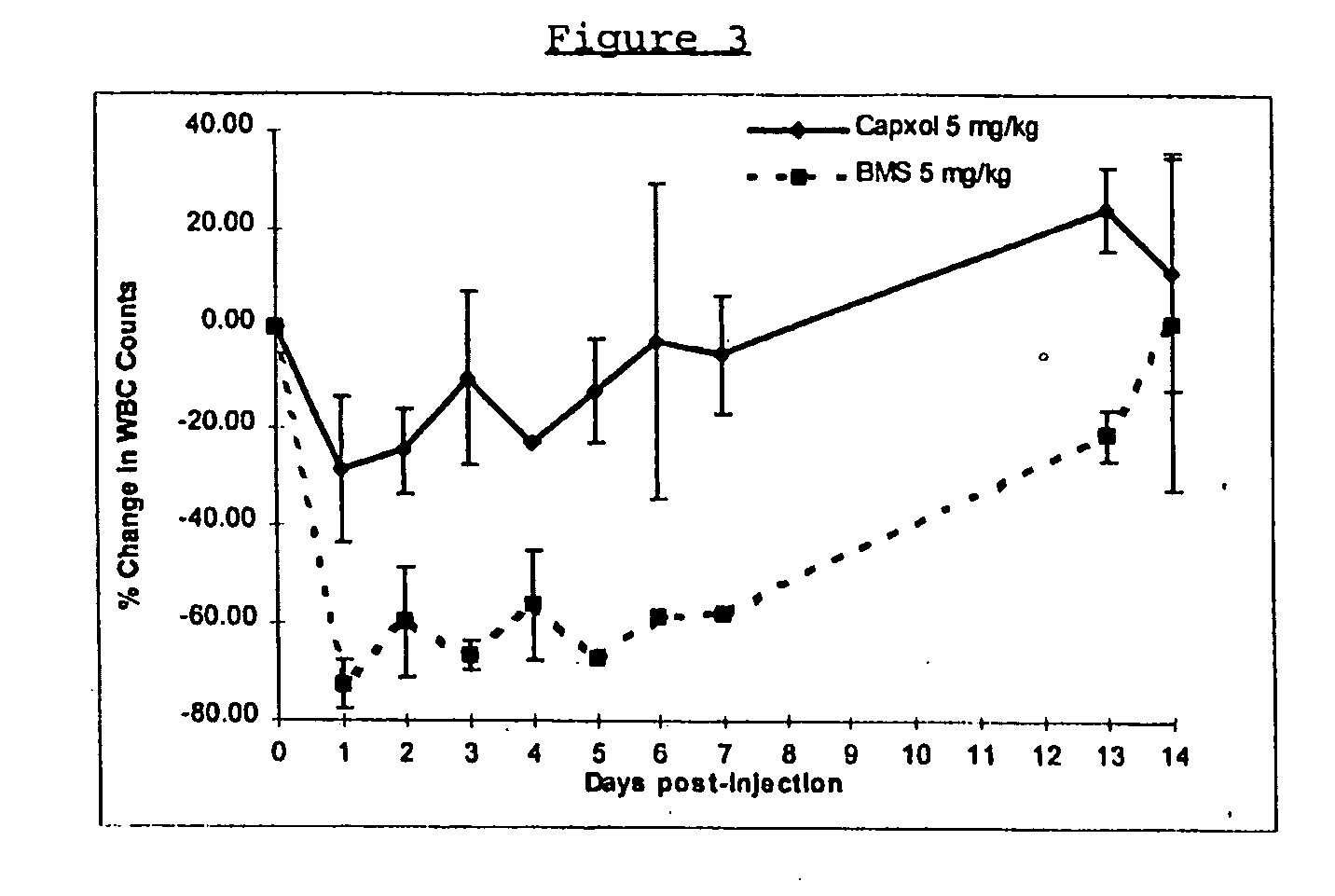
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful election of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS8853260B2Improve abilitiesPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070087022A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070093547A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesFree protein
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20080160095A1Reduce morbidityLow toxicityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20080161382A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS8137684B2Improve abilitiesPromote formationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070092563A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationOrganic active ingredientsBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
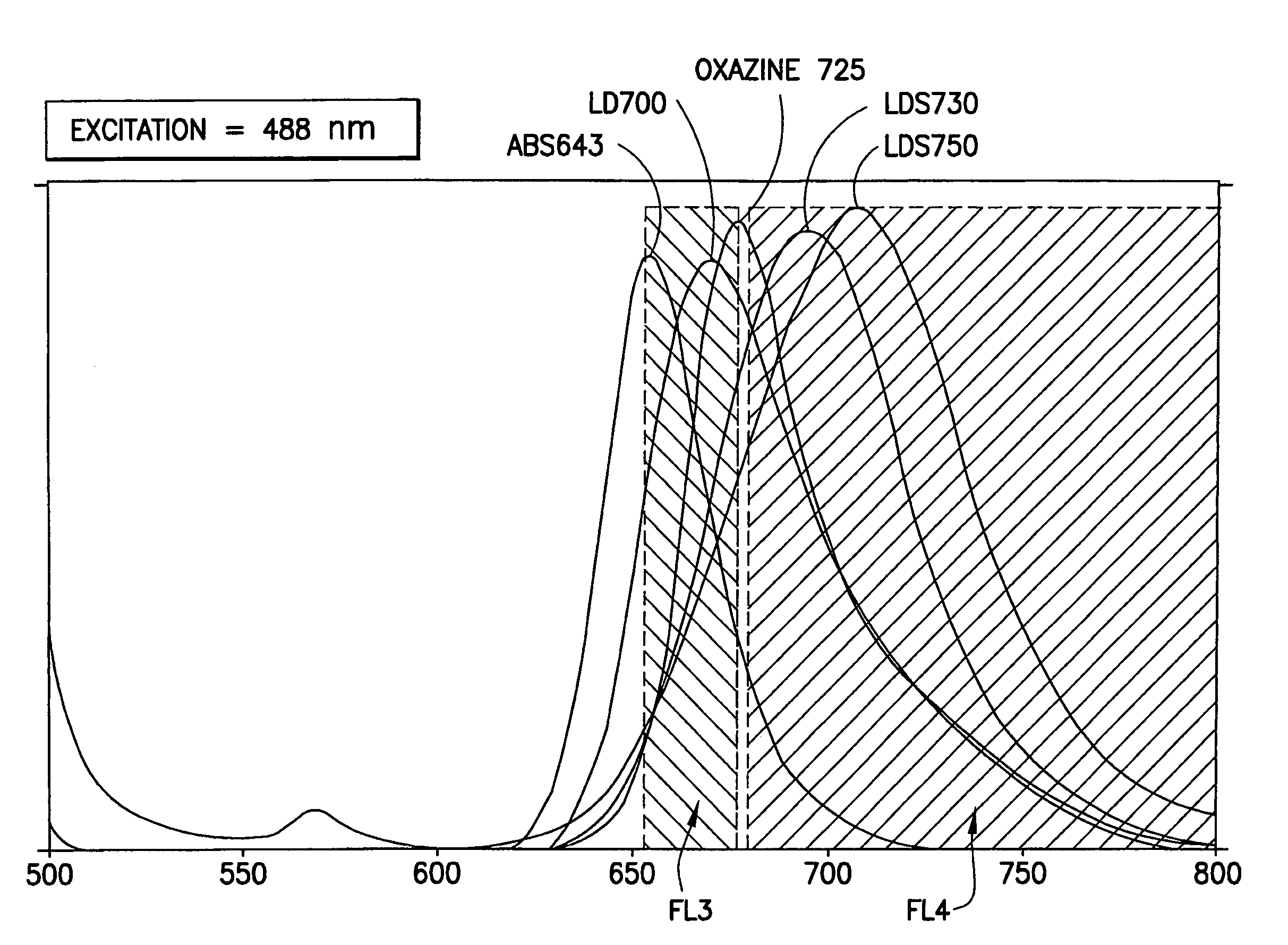
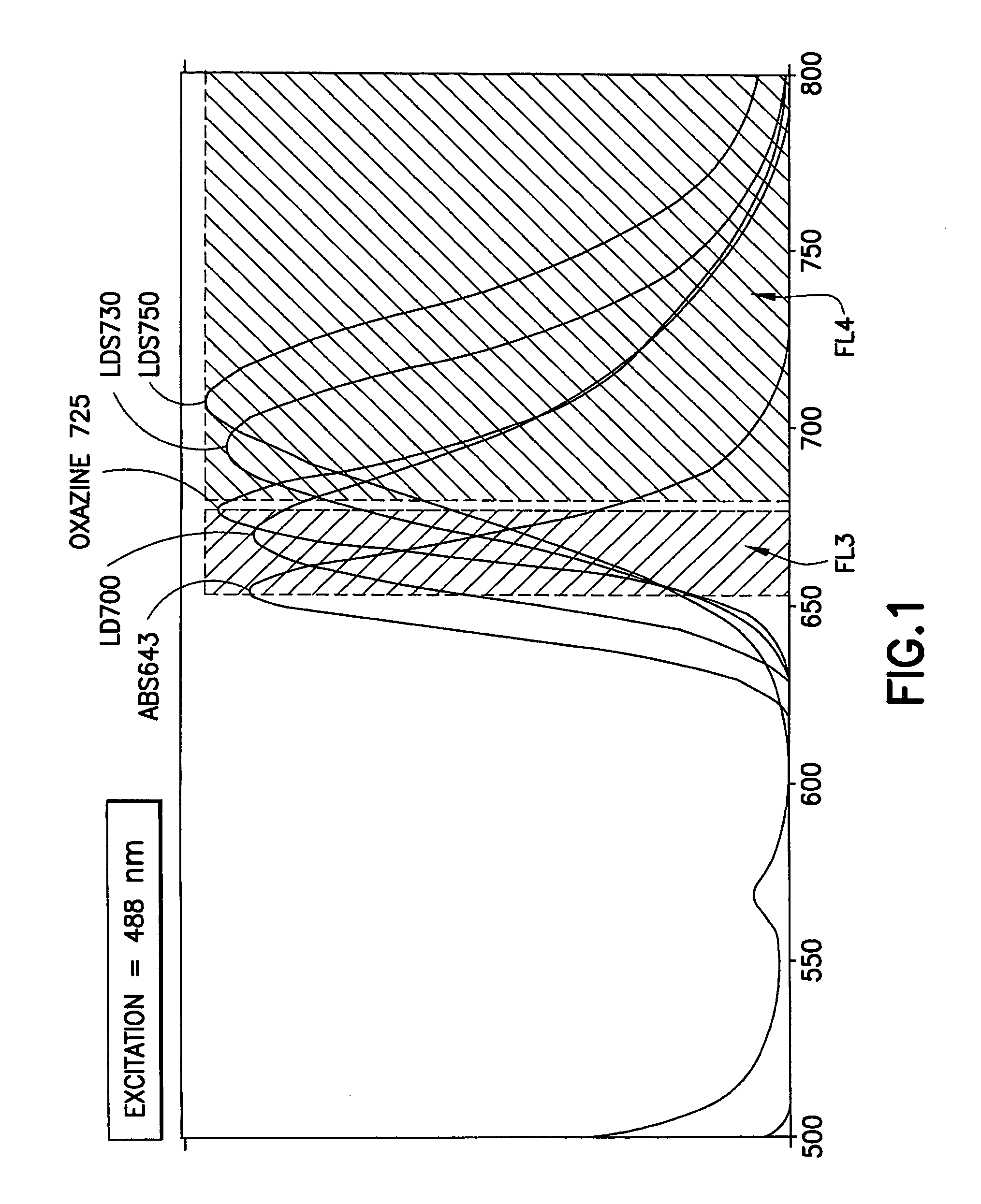
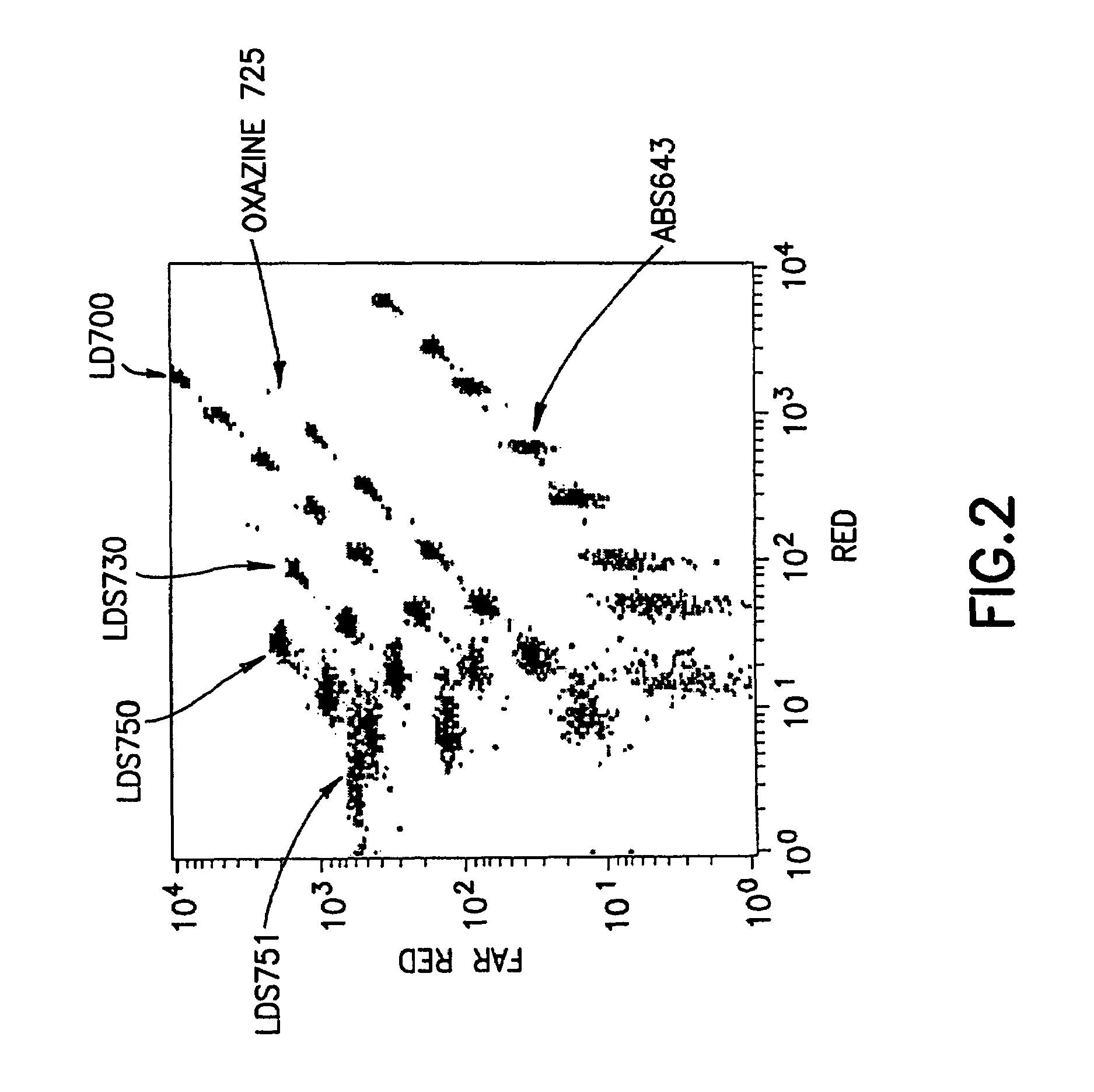
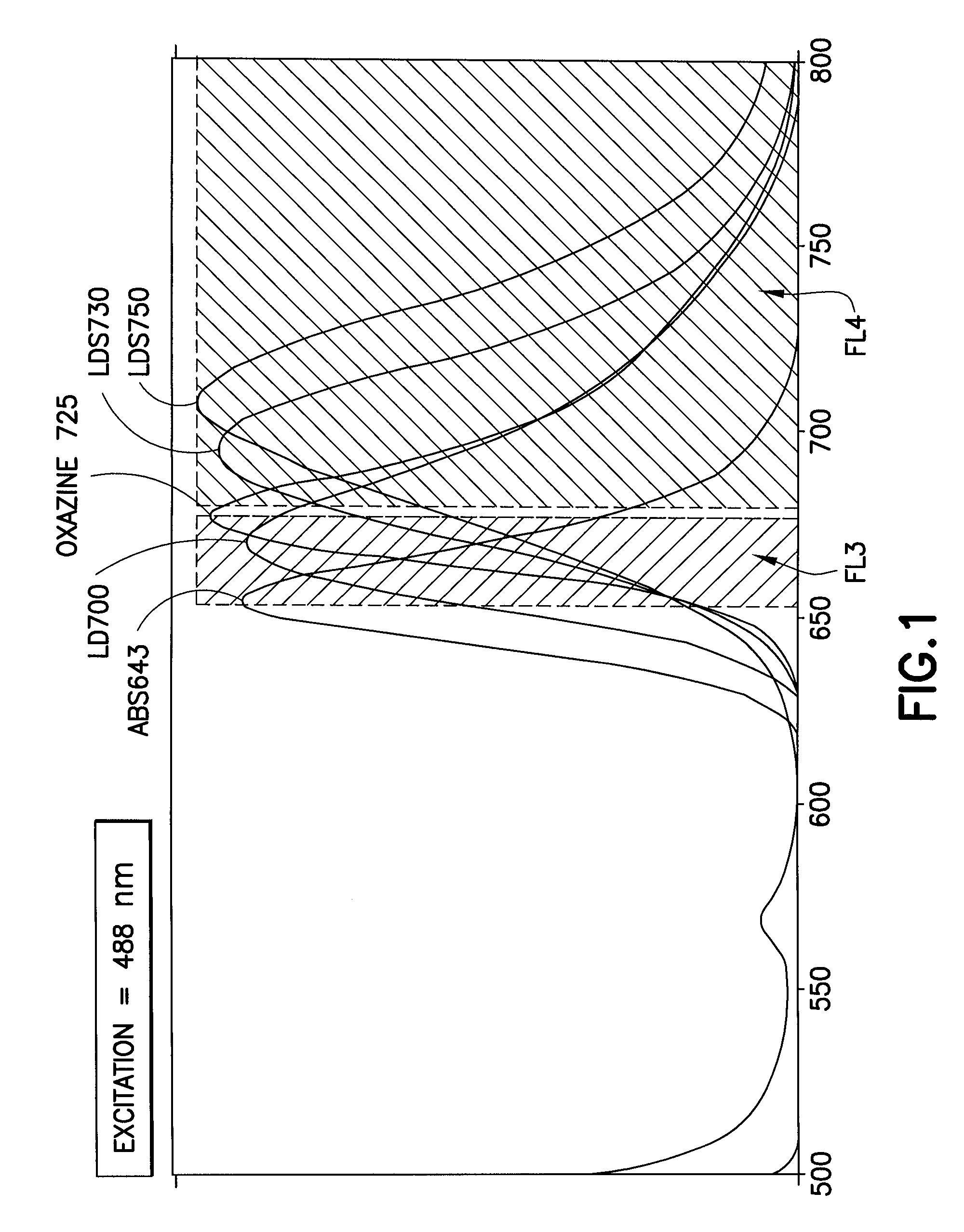
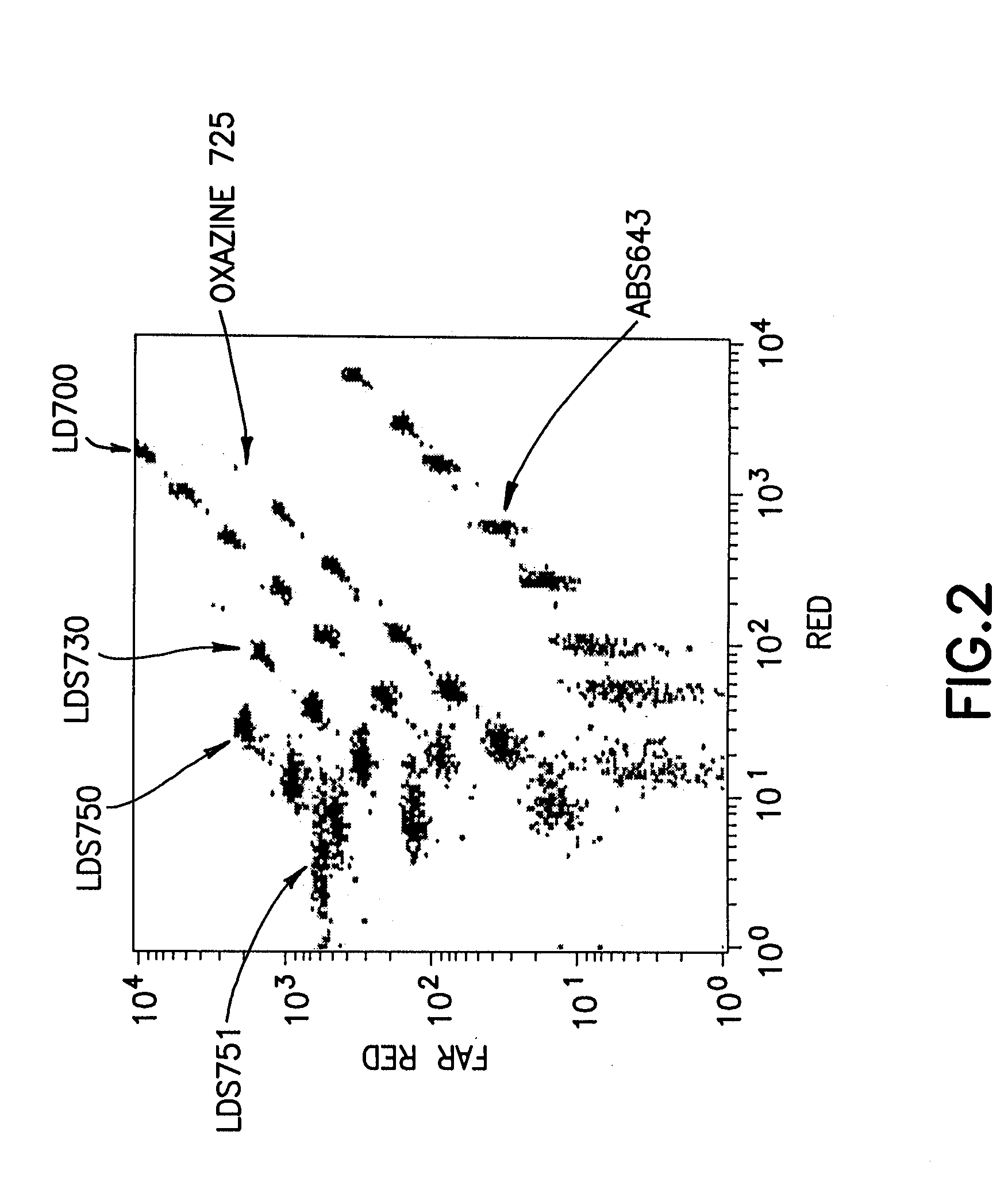
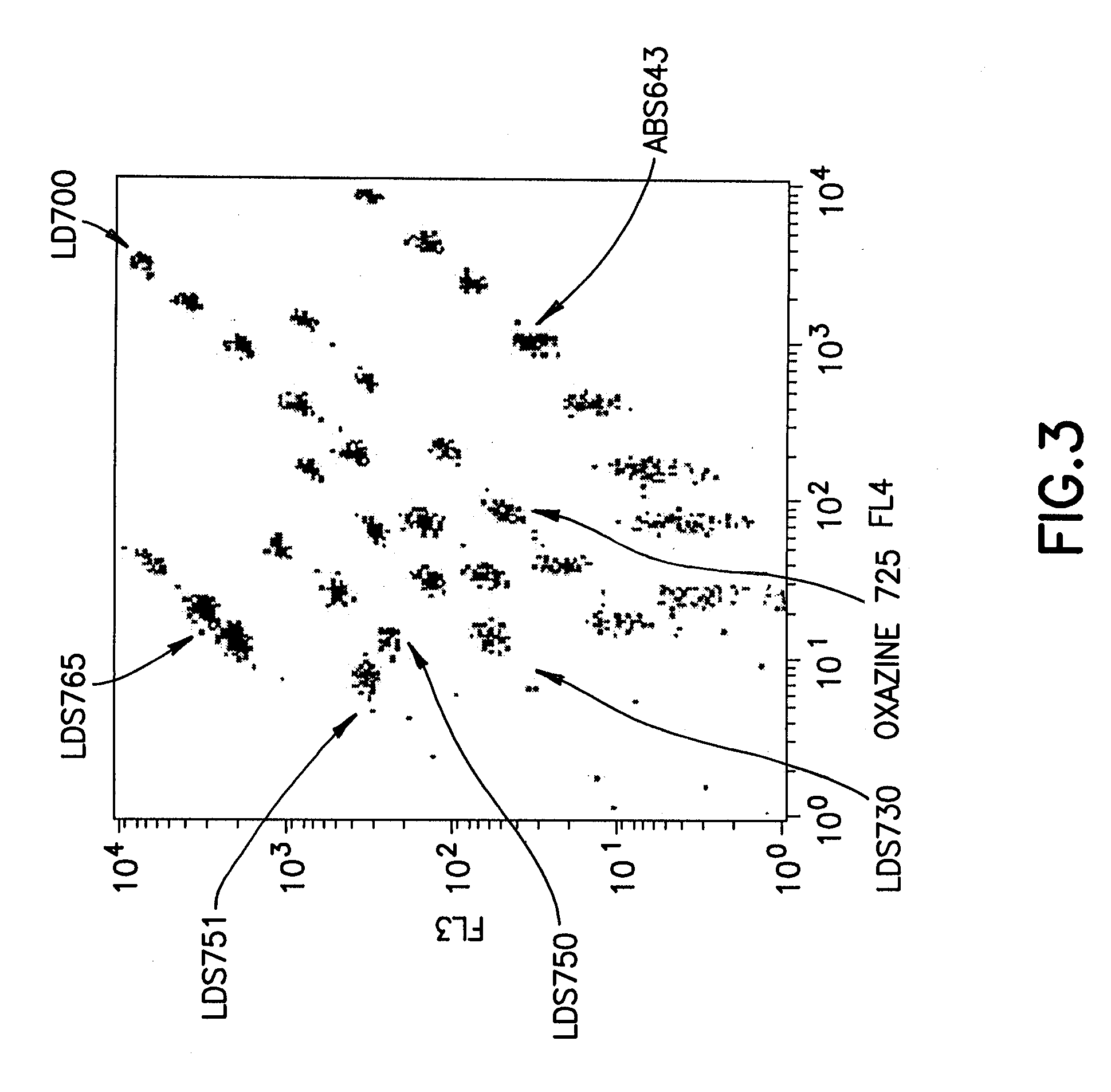
Multiplex microparticle system
ActiveUS7507588B2Simplify creationNone provides advantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMulti analyteMicroparticle
Arrays of microparticle populations, each population labeled with a single fluorescent dye, are provided for use in multiplex assays. The populations form a virtual multidimensional array wherein each microparticle is identified by fluorescence intensity in two different fluorescence detection channels. The arrays are useful in a variety of assays, including multiplex, multi-analyte assays for the simultaneous detection of two or more analytes by, for example, flow cytometry, and a labeling reagents in, for example, microscopy. The use of singly-dyed microparticles to form multidimensional arrays greatly simplifies the creation of multiplex assays.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070116761A1Reduce morbidityReduce decreaseBiocidePowder deliverySuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
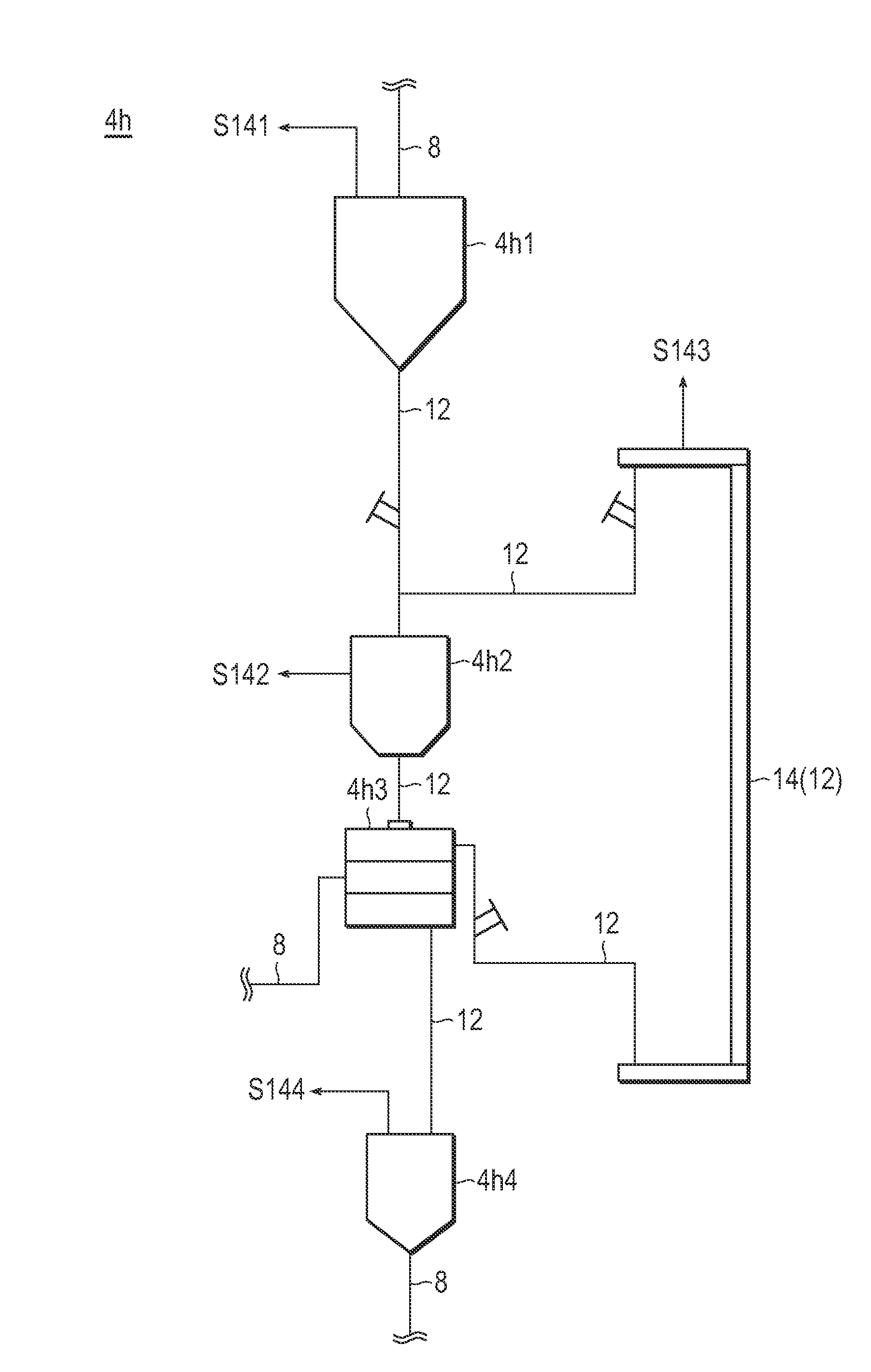
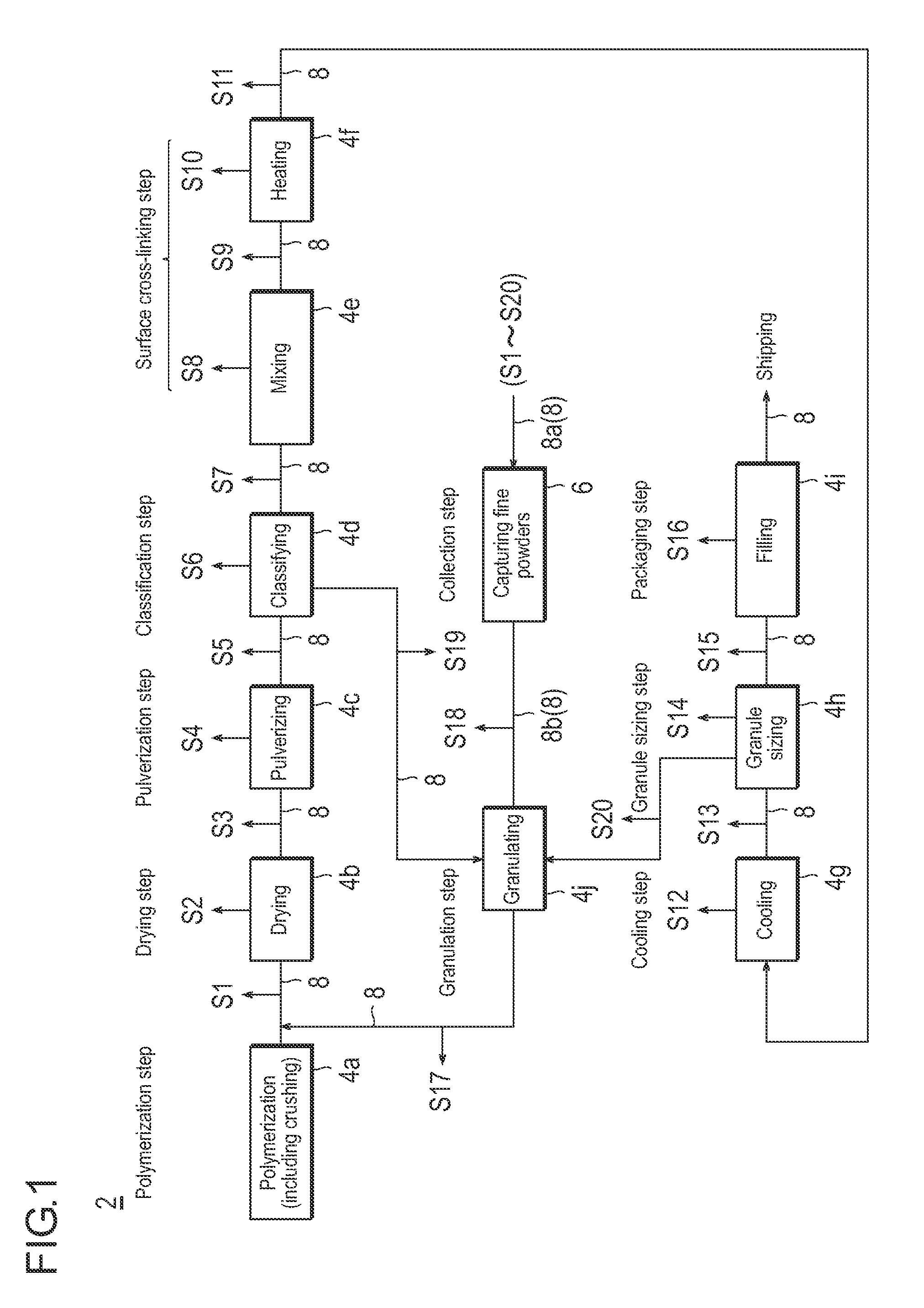
Method for producing particulate water - absorbing agent composed principally of water absorbing resin
ActiveUS20110009590A1Improve trapping efficiencyMaintain good propertiesSolid materialProduction rateParticulates
Provided is a production method for the particulate water-absorbing agent, which can contribute to property enhancement, and further improvement of productivity or the like, as well. One example of the production method for the particulate water-absorbing agent relevant to the present invention includes the polymerization step for obtaining a polymer gel; the drying step for drying the polymer gel to obtain a dried substance; the pulverization step for pulverizing the dried substance or the polymer gel to obtain the particulate water-absorbing resin; the classification step for sieving the particulate water-absorbing resin; the granule sizing step for granule sizing the particulate water-absorbing agent obtained from the particulate water-absorbing resin; and the transporting step for transporting the products produced in each of the steps to other steps. Preferably, one or more steps selected from the pulverization step, the classification step, the granule sizing step and the transporting step after the pulverization step are set under reduced pressure state.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20150104521A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSuspended particlesWater insoluble
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Systems and Methods for Detecting Gases, Airborne Compounds, and Other Particulates
InactiveUS20160274025A1Artificial lifeColor/spectral properties measurementsParticulatesFeature extraction algorithm
Systems and methods for detecting gases, airborne compounds, and other particulates, are provided. The system detects materials of interest, including but not limited to, volatile organic compounds, aerosols, particulates, and biological and other pathogens in a three dimensional volume over an area of interest. The system detects the concentration of analytes of interest in the presence of atmospheric contaminants. Data points form a three-dimensional “point cloud” to which particle swarm optimization and feature extraction algorithms are applied, providing leak detection, mapping of chemical plumes, and short-term and long-term flux measurements, among other functions.
Owner:SMS SENSORS INC
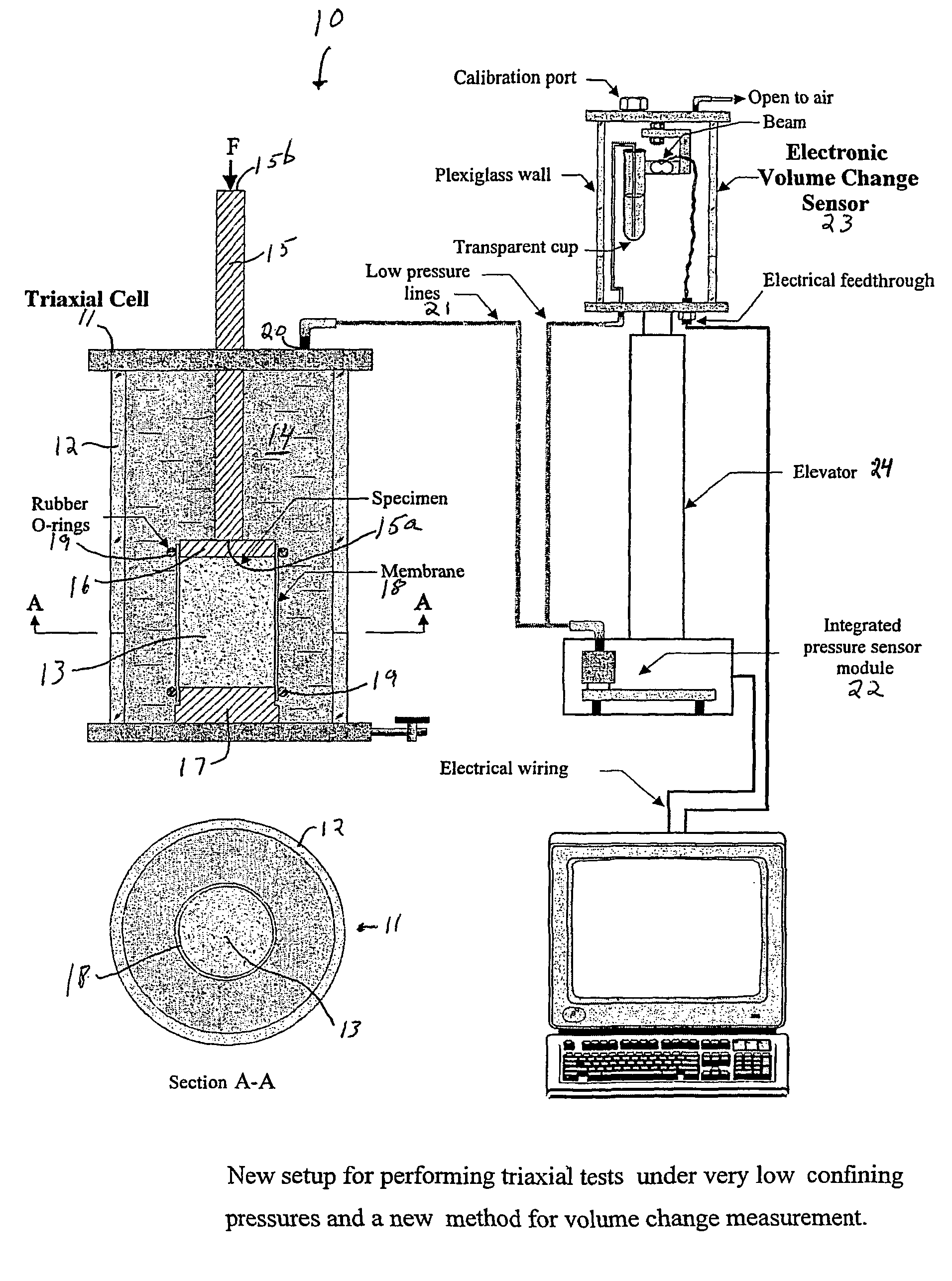
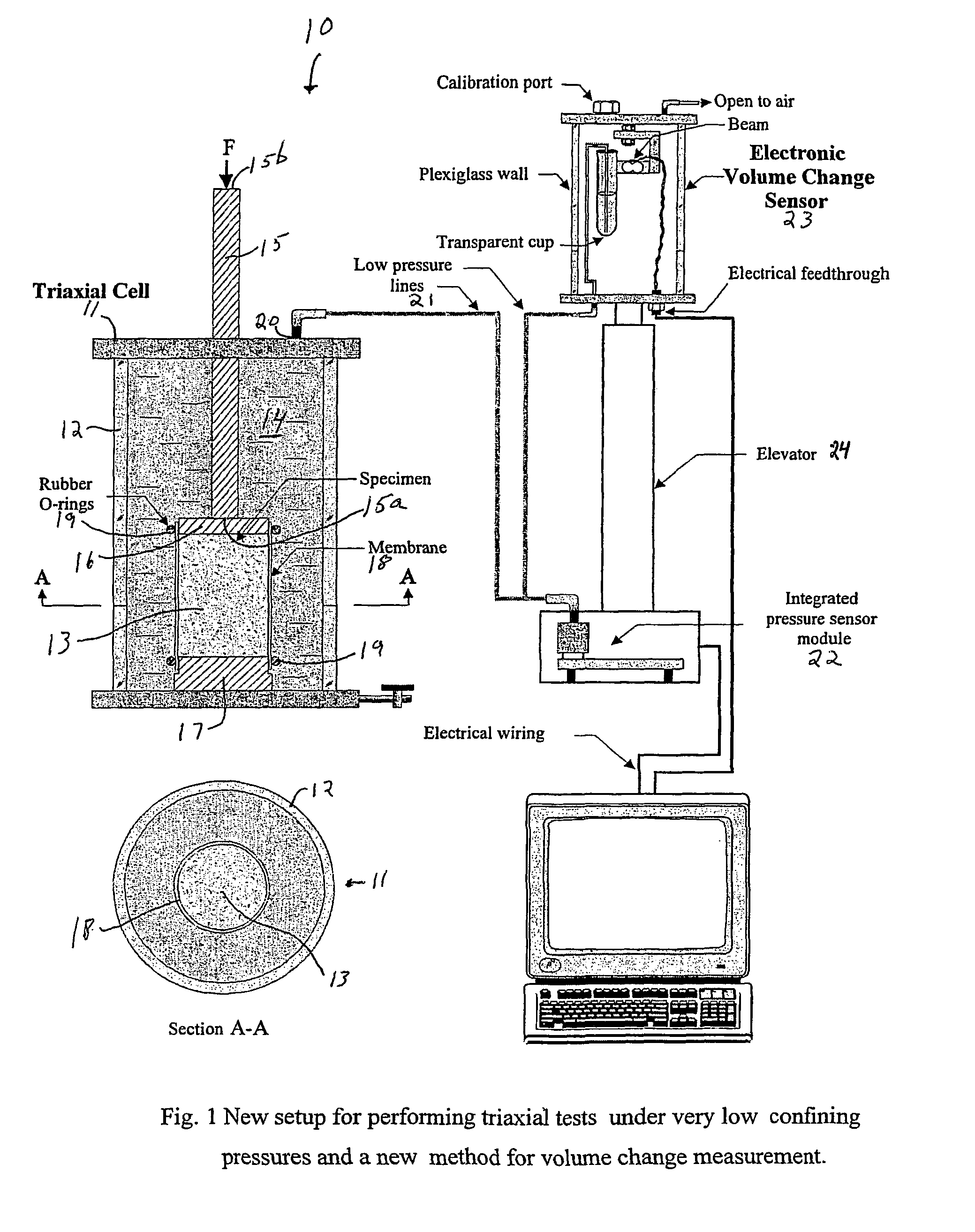
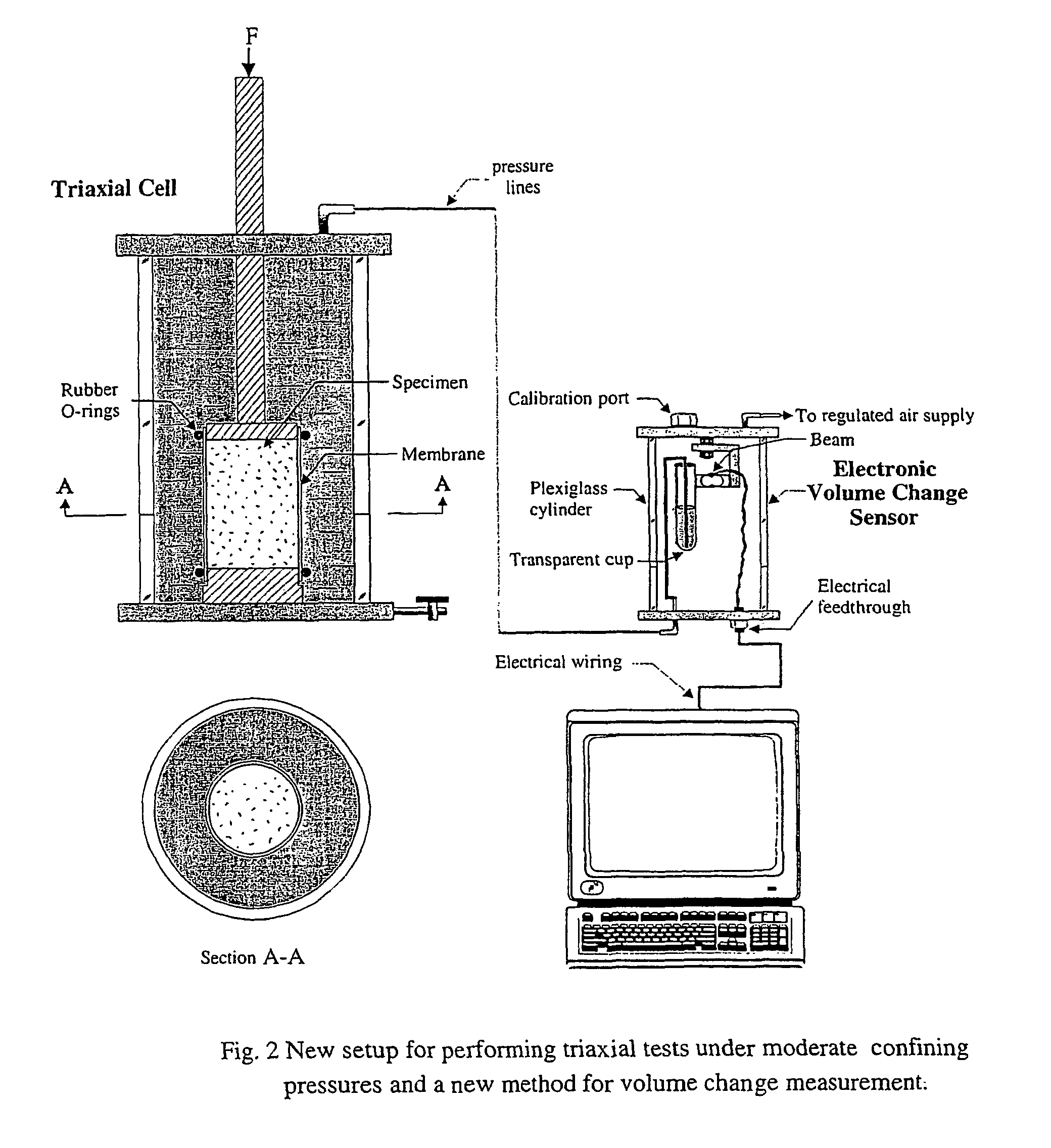
Enhanced triaxial tester with volume change device for measurement of flow properties of dry cohesive particulate systems under low confining pressures
InactiveUS7143653B2Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityFlow propertiesMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesParticulatesVolume variation
Disclosed is a triaxial system for testing particulate matter under substantially dry triaxial load conditions comprising: a housing means fillable with confining fluid for providing confining pressure on a sample of dry particulate matter to be tested, the housing having a channel for introduction therein and removal therefrom of the confining fluid, a load piston sealingly extends for providing a load on the sample, sample mounting means for mounting the sample within the housing, the sample mounting means including a top end platen for mounting at the top and a button end platen for disposition at the bottom of the sample, at least one flexible, impermeable membrane for enclosing the surface of the sample other than its ends, fluid passage means connecting the housing to a volume change sensor for freely delivering confining fluid thereto, and a volume change sensor adapted to measure the volume of confining fluid delivered thereto through the fluid passage means. Also disclosed is a test method for employing the above system to test particulate matter.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070117862A1Eliminate side effectsHigh anticancer activityPowder deliveryBiocideSuspended particlesFree protein
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Composition for wood treatment comprising an injectable aqueous wood preservative slurry having sparingly-soluble biocidal particles and pigments
InactiveUS20090293761A1Inhibition of agglomerationLimited solubilityFireproof paintsBiocideNickel saltHue
Owner:OSMOSE
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070122465A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationPowder deliveryBiocideSuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
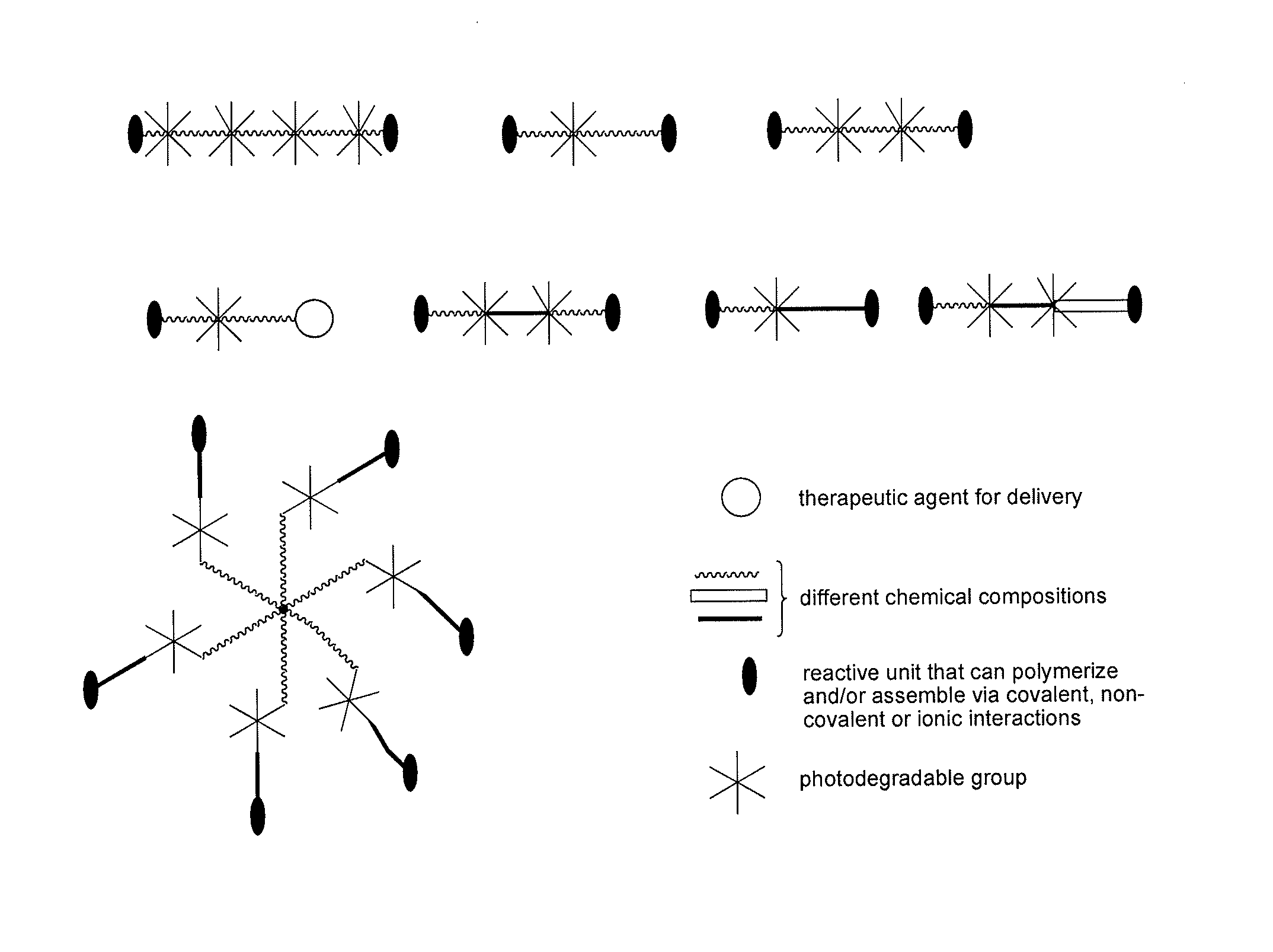
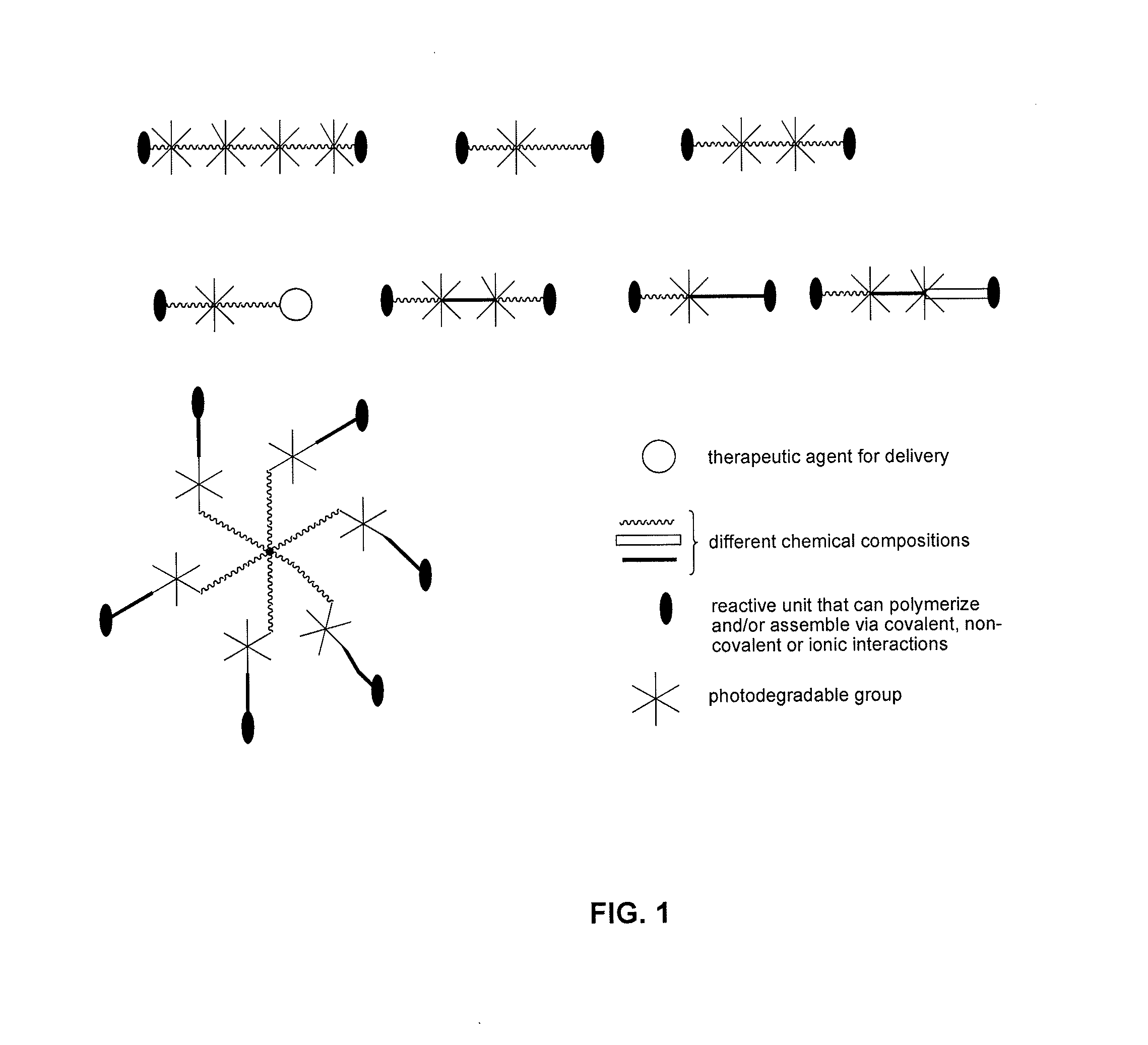
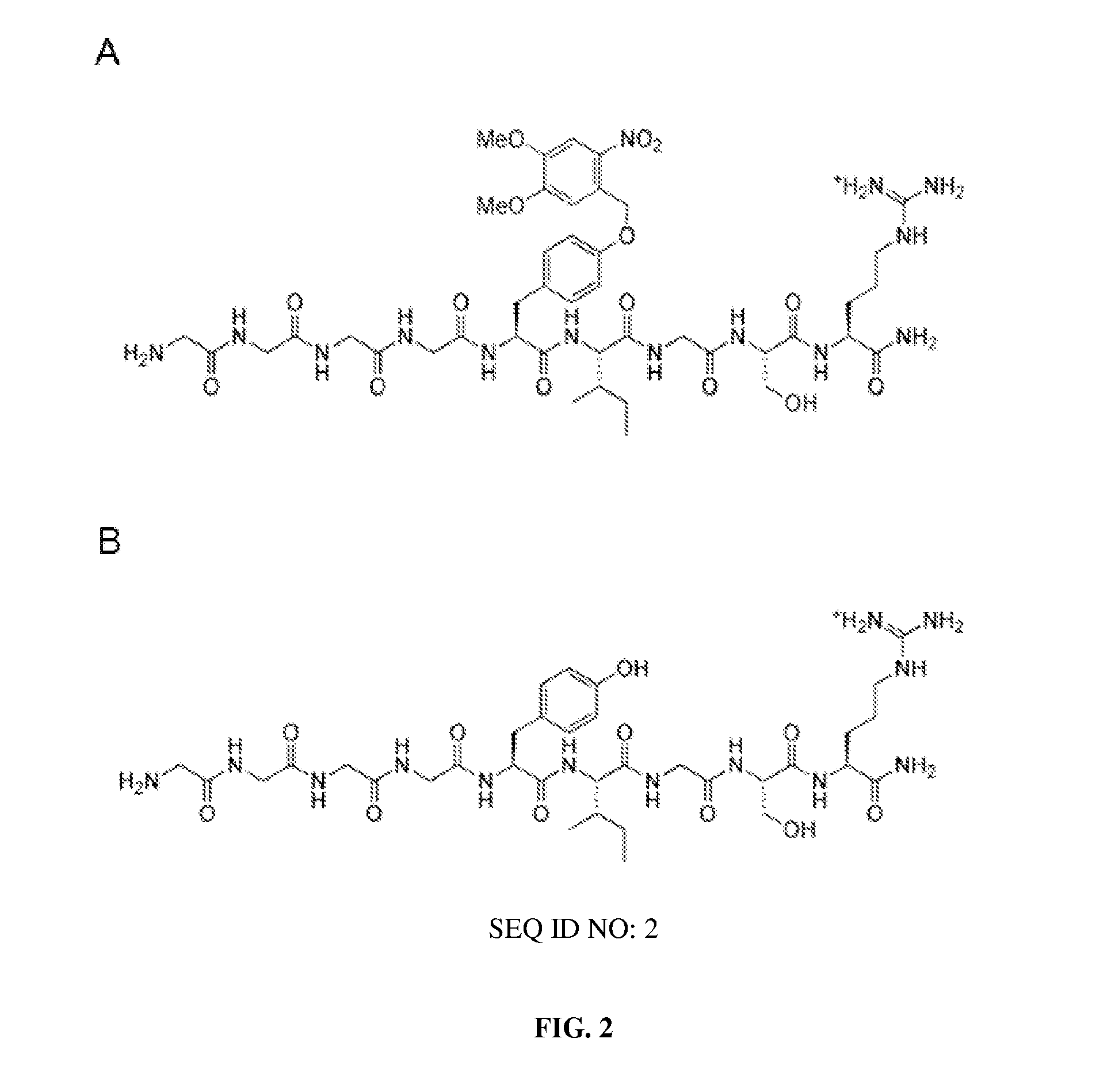
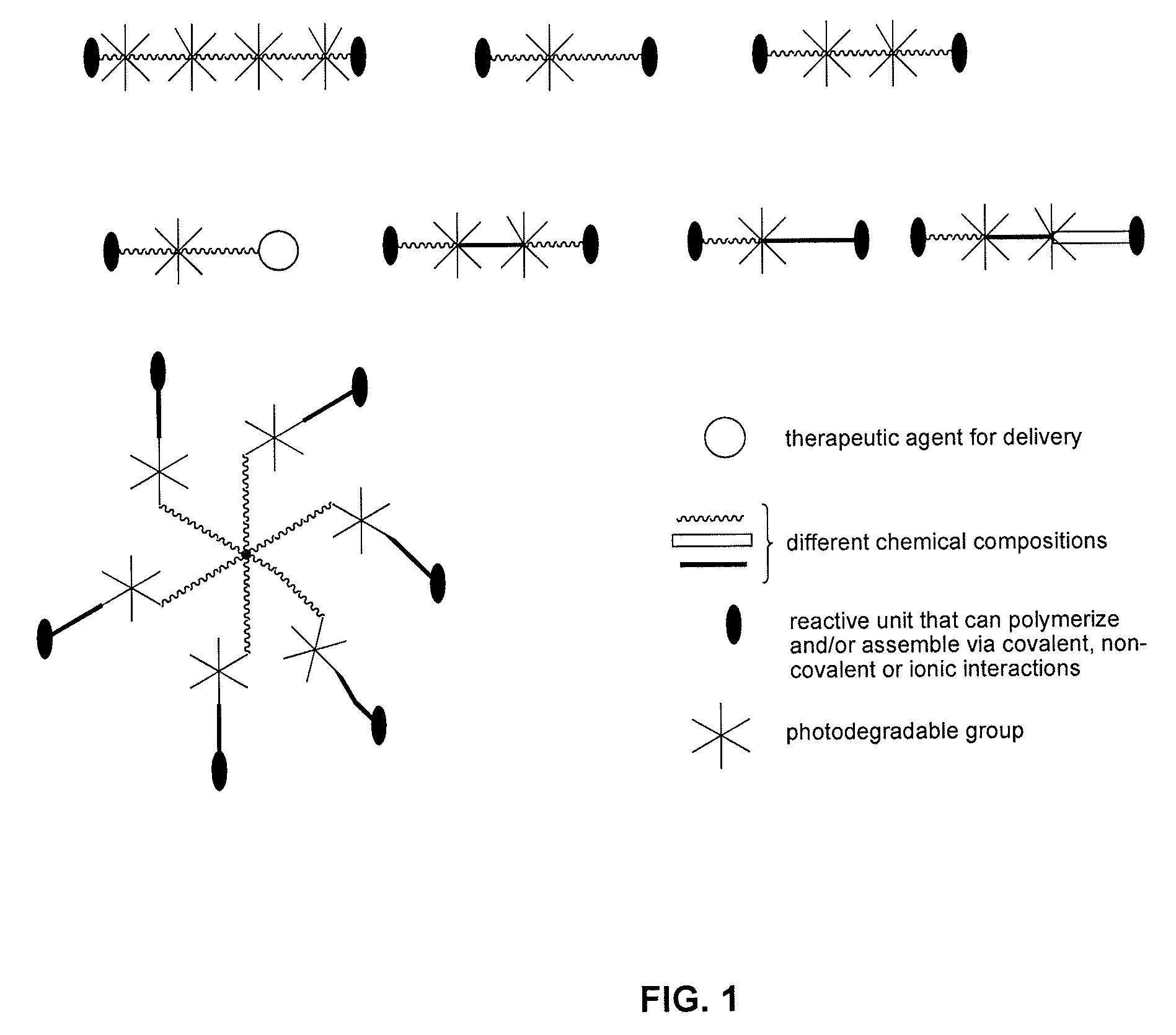
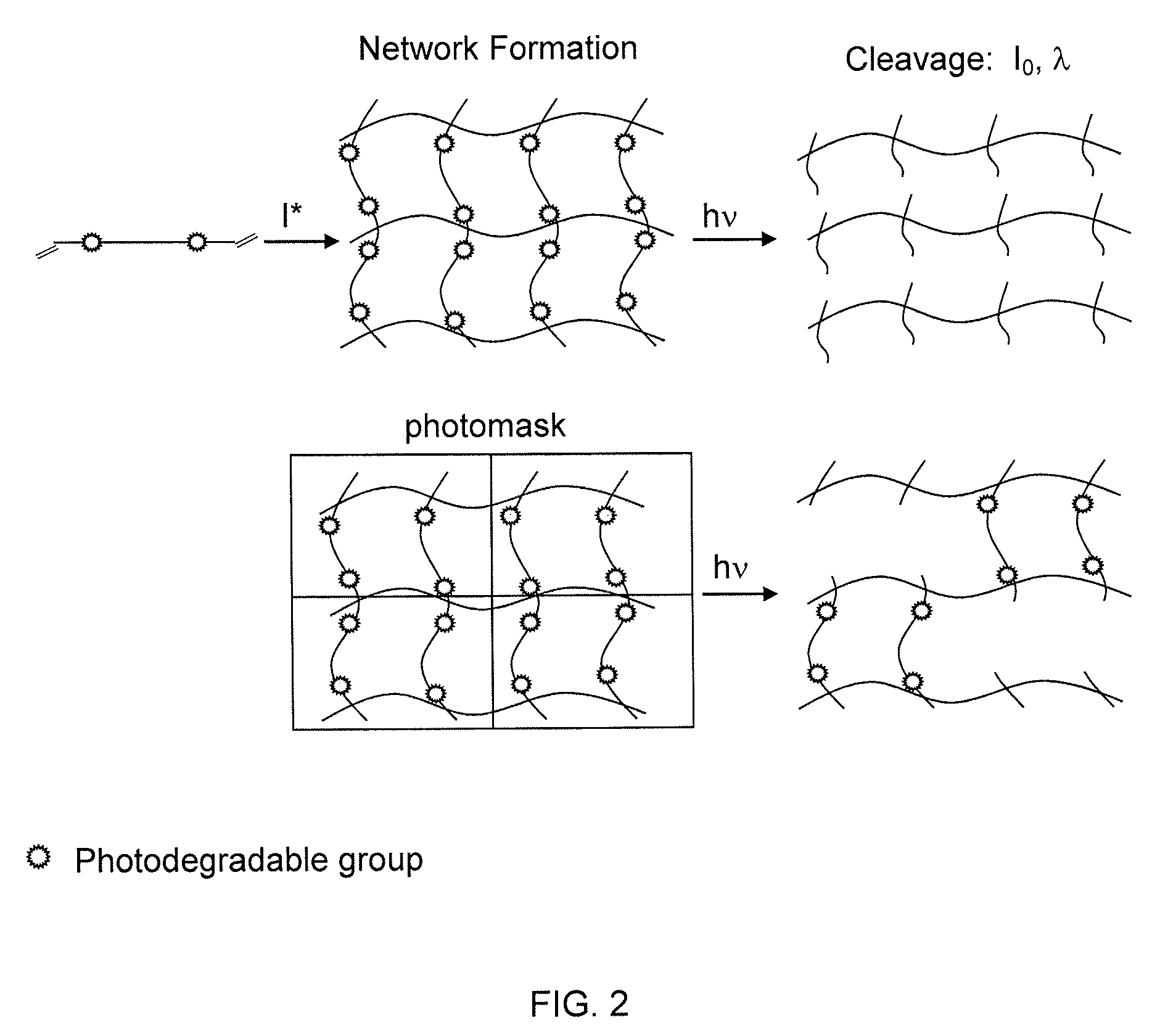
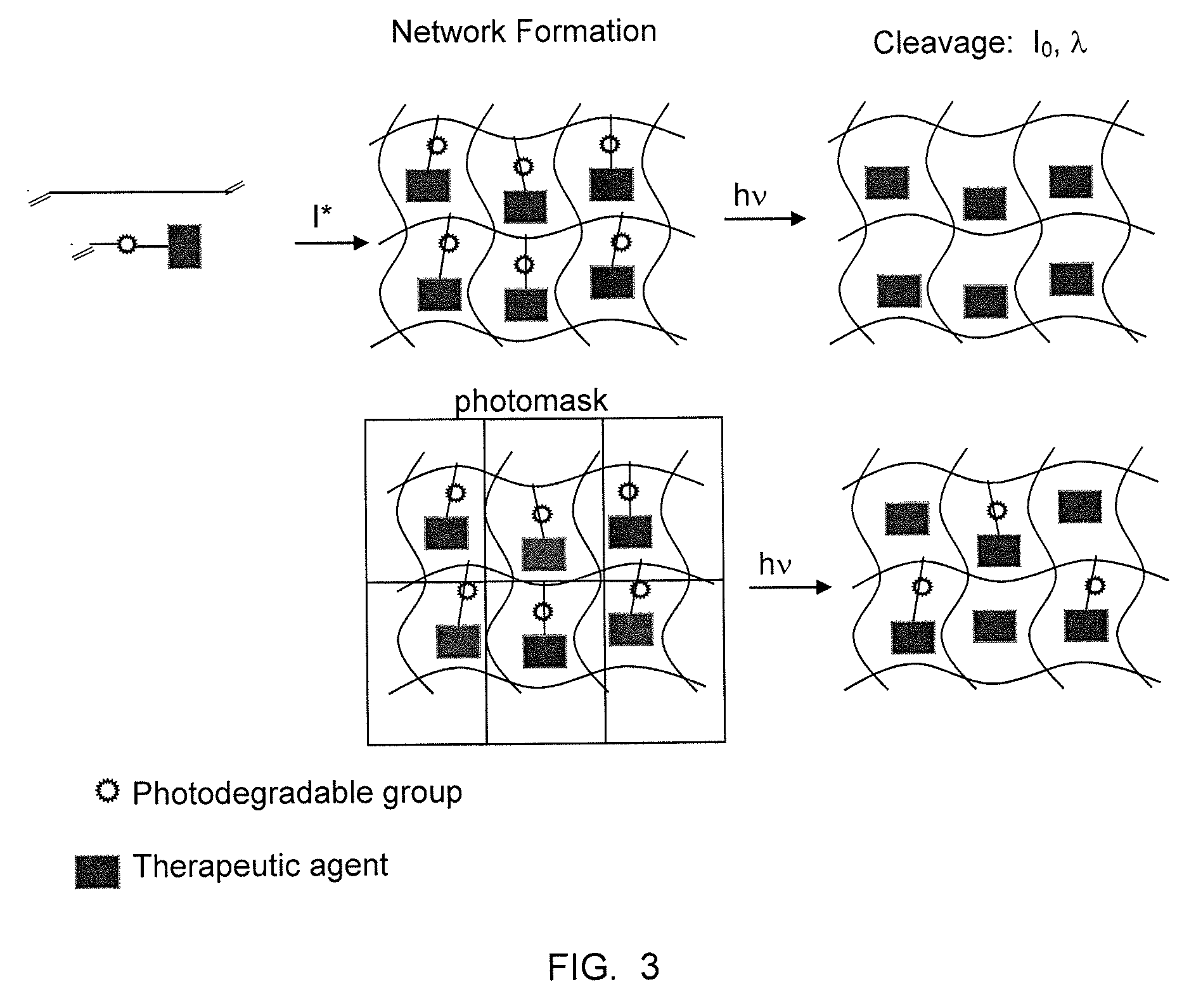
Photodegradable groups for tunable polymeric materials
ActiveUS20140031285A1Sure easyEasy to useDrug photocleavagePeptide/protein ingredientsMean diameterFluorescence
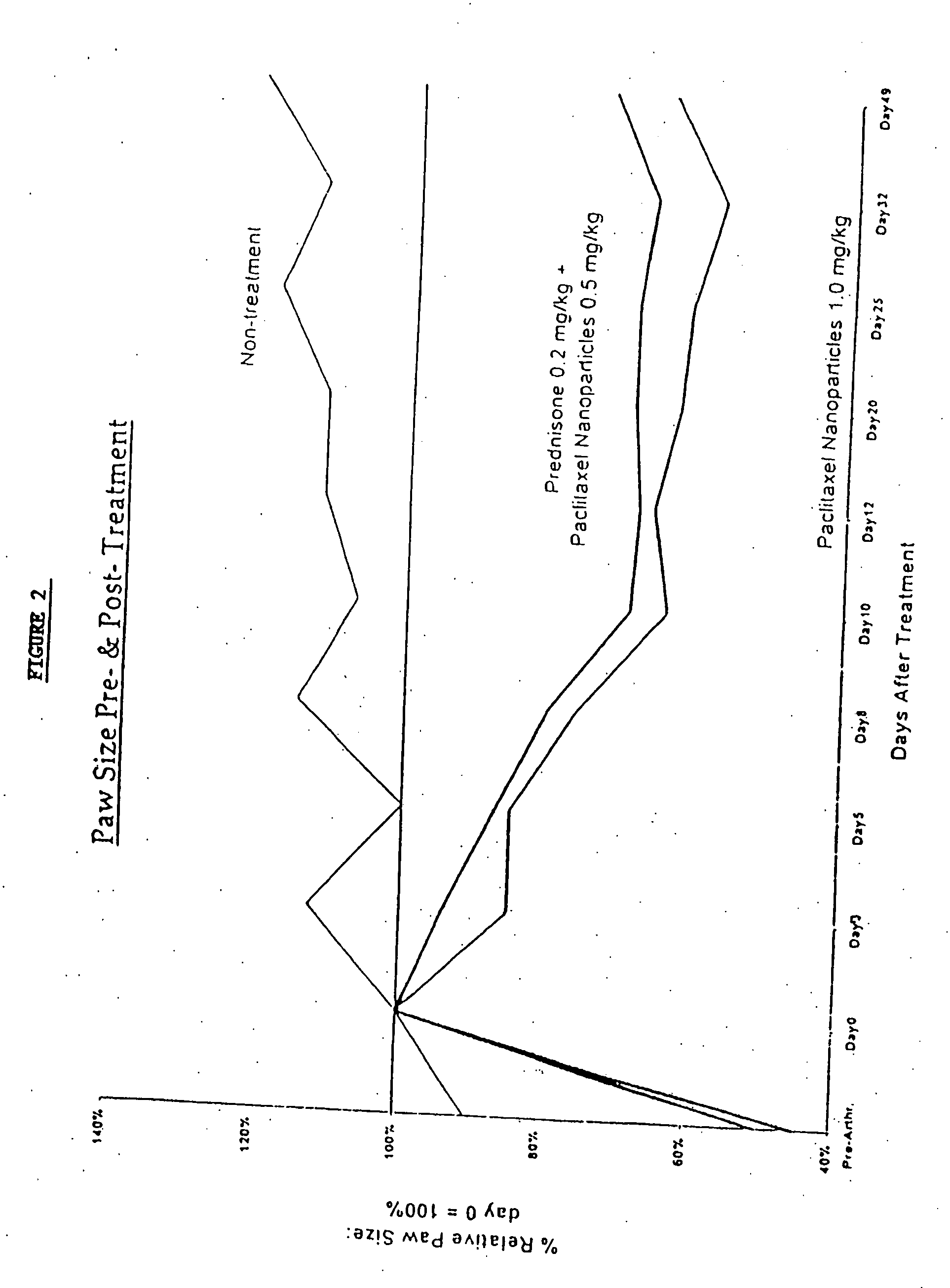
Here, we present a photodegradable microparticle system that can be employed to entrap and deliver bioactive proteins to cells during culture. By using a photosensitive delivery system, experimenters can achieve a wide variety of spatiotemporally regulated release profiles with a single microparticle formulation, thereby enabling one to probe many questions as to how protein presentation can be manipulated to regulate cell function. Photodegradable microparticles were synthesized via inverse suspension polymerization with a mean diameter of 22 μm, and degradation was demonstrated upon exposure to several irradiation conditions. The protein-loaded depots were incorporated into cell cultures and release of bioactive protein was quantified during the photodegradation process. This phototriggered release allowed for the delivery of TGF-β1 to stimulate PE25 cells and for the delivery of fluorescently labeled Annexin V to assay apoptotic 3T3 fibroblasts during culture. By incorporating these photoresponsive protein delivery depots into cell culture, new types of experiments are now possible to test hypotheses about how individual or multiple soluble factors might affect cell function when presented in a uniform, temporally varying, or gradient manner.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Device and method for combusting particulate substances
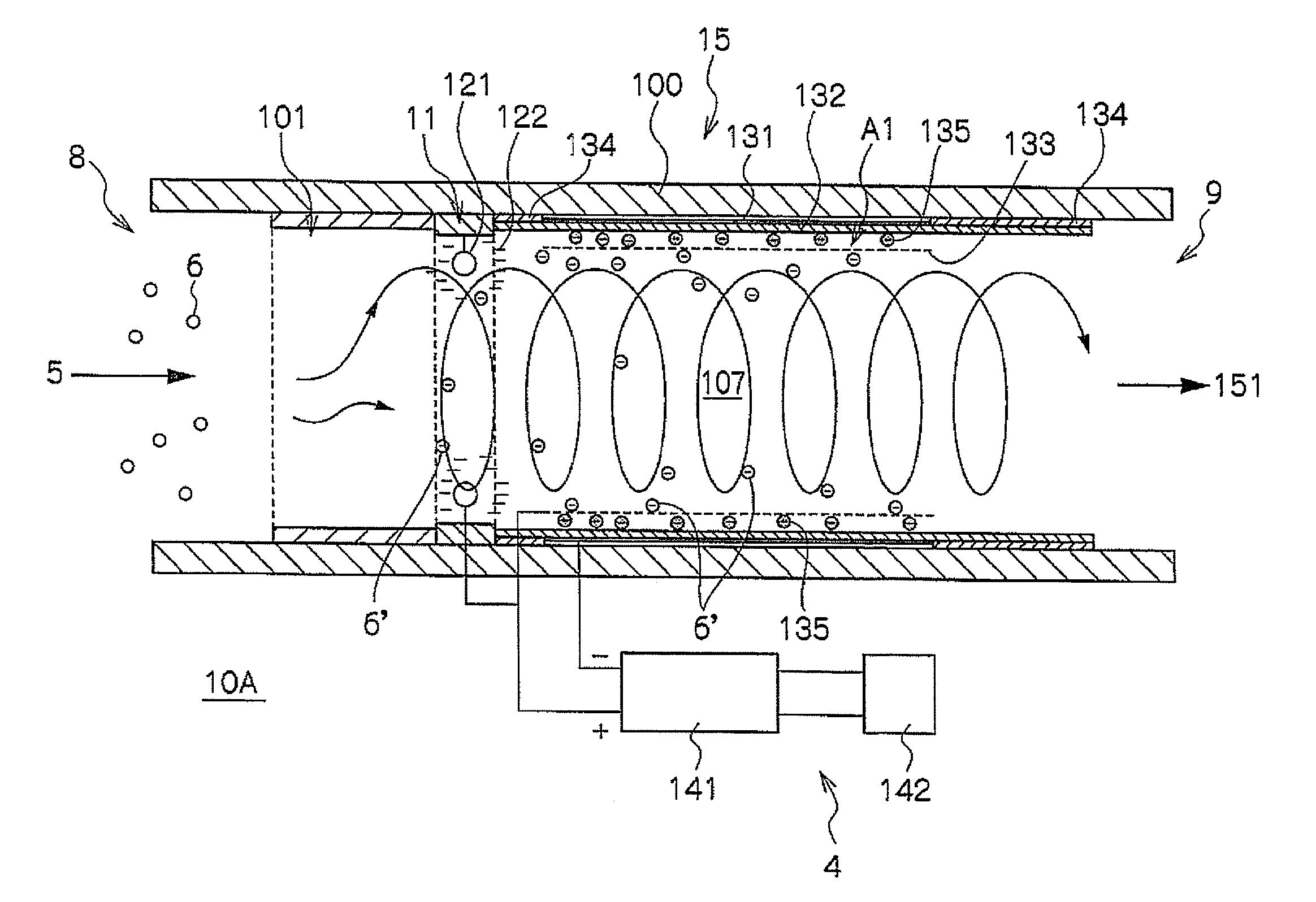
InactiveUS20120124969A1Improve combustion efficiencyShorten speedExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusParticulatesElectric discharge
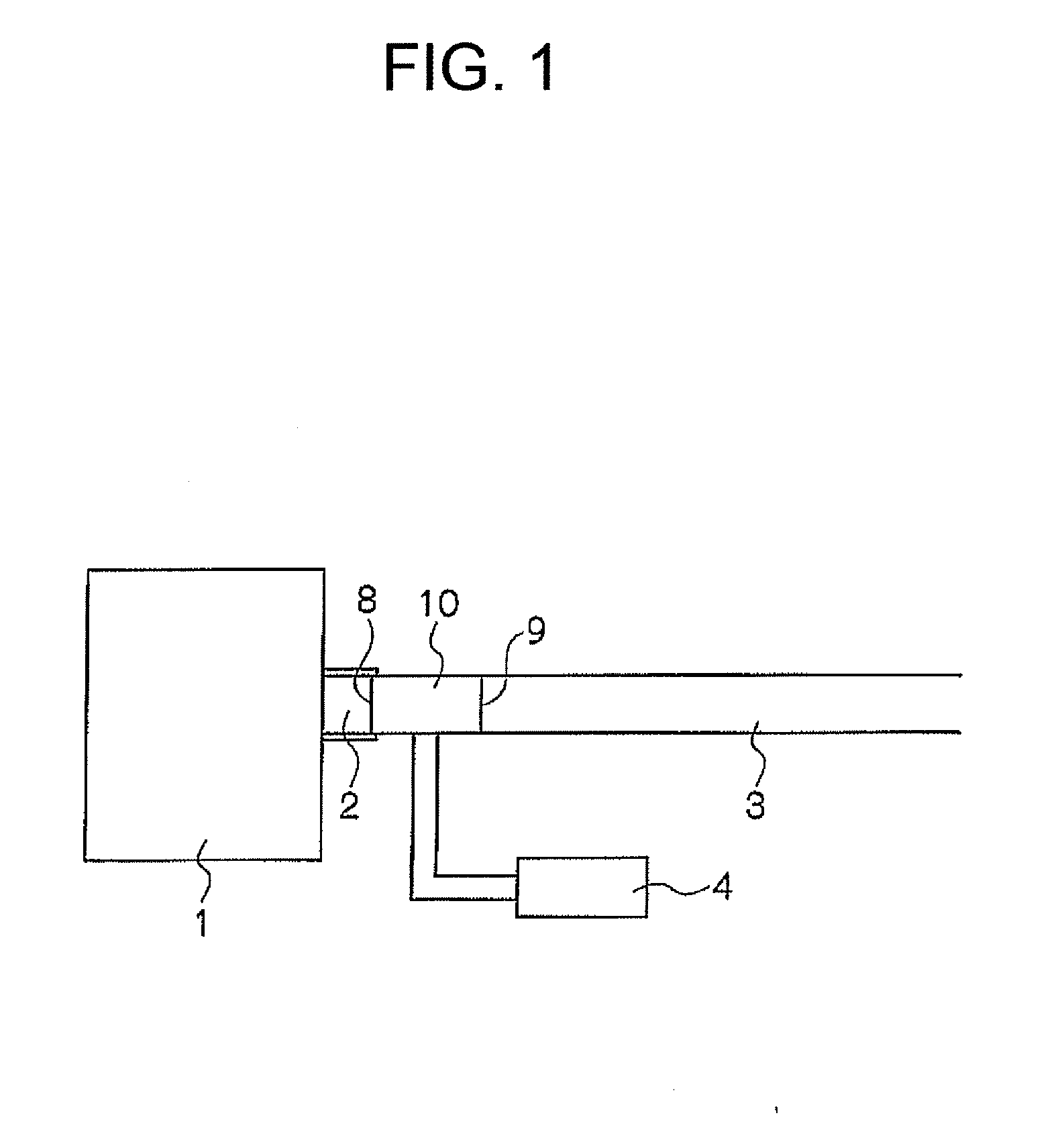
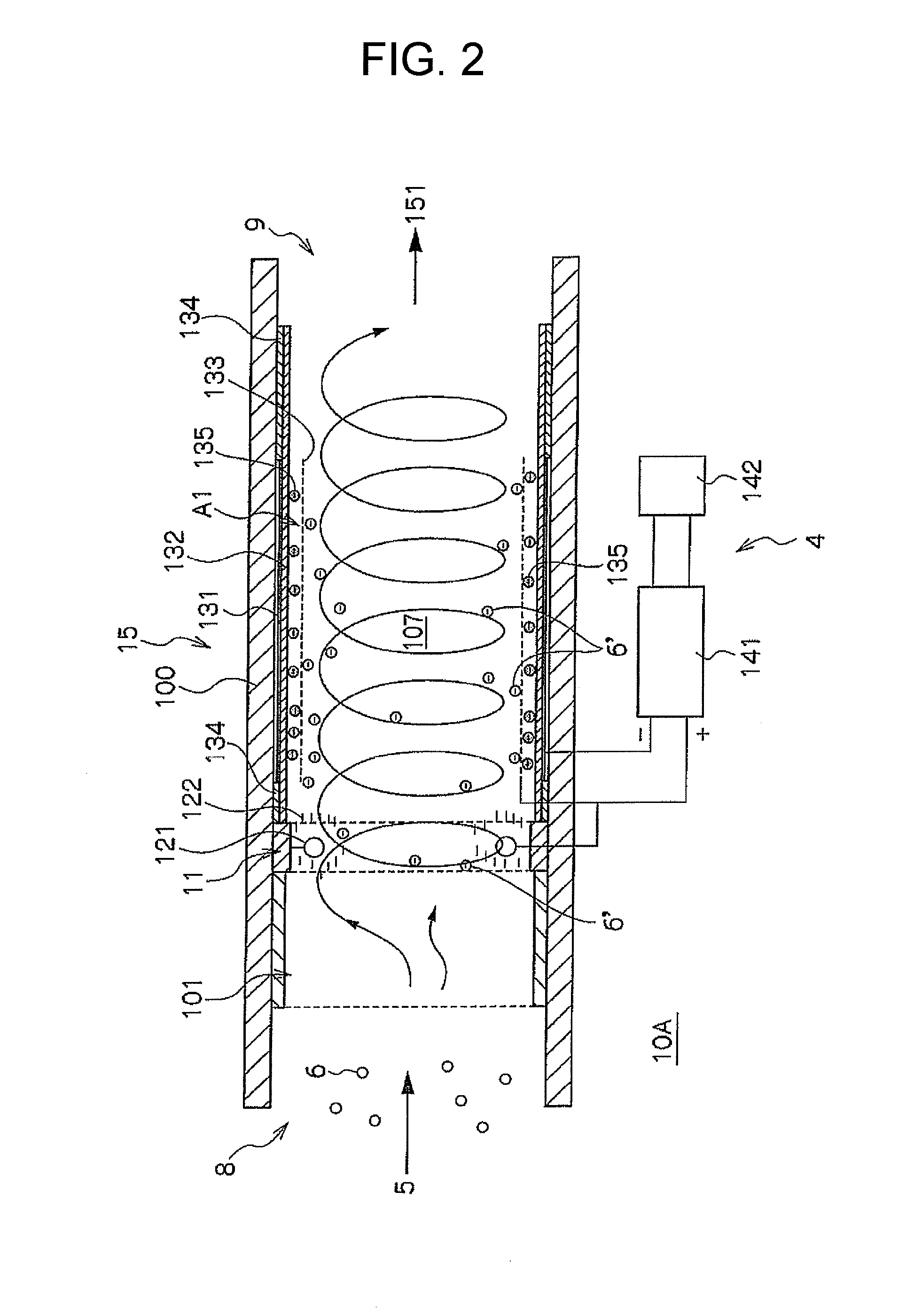
It is possible to provide a device and a method for combusting particulate substances which particulate matters discharged from an internal combustion engine can be effectively combusted, and the device configuration is simple and does not become large and heavy. The combustion device has: an introduction portion 8 used to introduce a particulate matter-containing gas 5 discharged from the exhaust port of an internal combustion engine; a charging unit 11 which is provided on the downstream side of the introduction portion 8, and in which all or part of the particulate matters 6′ are e negatively charged by bringing the particulate matter-containing gas into contact with; an electric discharge unit 15 which is provided in an insulation pipe 100 which is connected to the downstream side of the charging unit 11, and in which the particulate matters 6′, all or part of which are negatively charged, are introduced into a silent discharge area A1 and are combusted with an increased retention time, the silent discharge area being generated between an anode and a cathode; a discharge portion 9 which is connected to the insulation pipe 100 at the downstream side of the electric discharge unit and which discharges the combusted gas; and a power source unit which applies an electric field to the charging unit and the electric discharge unit.
Owner:UTSUNOMIYA UNIV
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070122468A1Improve abilitiesPromote formationBiocidePowder deliverySuspended particlesActive agent
In accordance with the present invention, there are provided compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water insoluble pharmacologically active agents (such as the anticancer drug paclitaxel) in which the pharmacologically active agent is delivered in the form of suspended particles coated with protein (which acts as a stabilizing agent). In particular, protein and pharmacologically active agent in a biocompatible dispersing medium are subjected to high shear, in the absence of any conventional surfactants, and also in the absence of any polymeric core material for the particles. The procedure yields particles with a diameter of less than about 1 micron. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions (e.g., addition of a polar solvent to the organic phase), and careful selection of the proper organic phase and phase fraction, enables the reproducible production of unusually small nanoparticles of less than 200 nm diameter, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a redispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of water-insoluble drug coated with a protein, and free protein to which molecules of the pharmacological agent are bound. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable (in the form of molecules bound to the protein), and part of the agent is present within particles without any polymeric matrix therein.
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
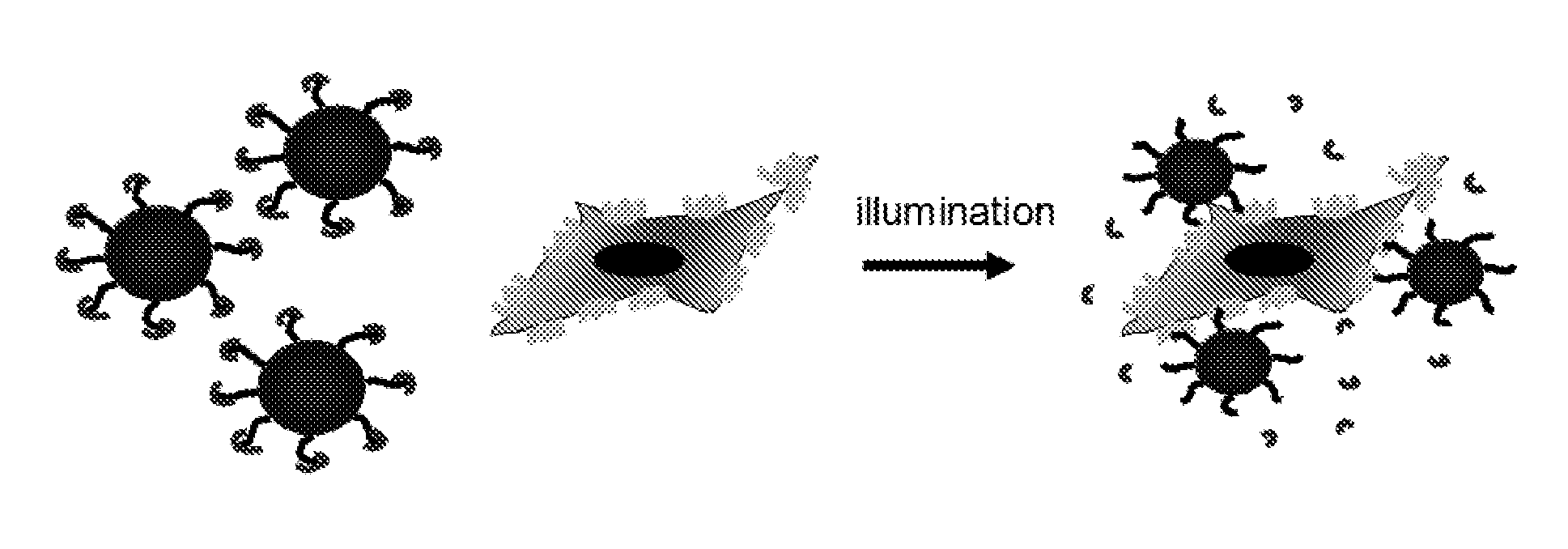
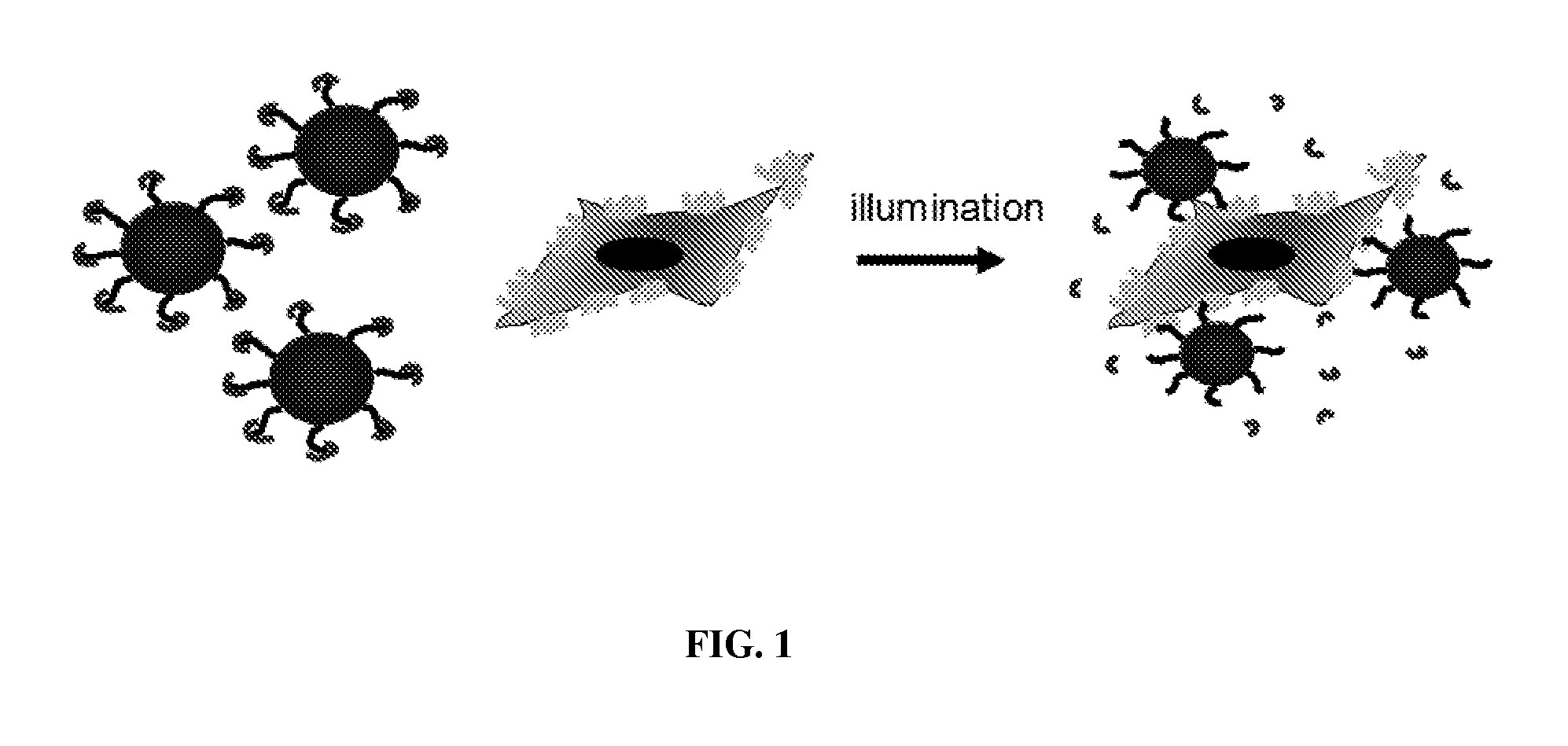
Phototriggered nanoparticles for cell and tissue targeting
InactiveUS20130004522A1Sufficient amountPowder deliveryDrug photocleavageTissue targetingLight irradiation
The present invention relates, in part, to a novel and simple particulate system that targets and binds any tissue selectively upon light illumination. The particulate system can be used for targeted delivery of substances to predefined cells or tissues in an individual.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +2
Method and system for monitoring of a physical quantity related to a particulate mass in at least one exhaust pipe
ActiveUS20170030245A1Accurate and reliable monitoringCost-effective and reliableInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusParticulatesProcess engineering
Methods and systems are provided to monitor a quantity relating to particulate mass M in at least one exhaust pipe arranged downstream of a combustion engine. A first determination device determines a reduction Δ of a pressure difference dP over at least one or several particulate filters, arranged downstream of the combustion engine. This reduction Δ is related to a pressure difference dPref over one or more corresponding reference particulate filters. A second determination device determines a quantity related to the particulate mass M, based on the determined reduction Δ of the pressure difference dP and a predetermined correlation between the reduction Δ and the quantity related to the particulate mass M, so that use of soot sensors in the exhaust pipe may be avoided. A comparison device compares the quantity with a defined threshold value Mth and a providing device provides indications related to the comparison.
Owner:SCANIA CV AB
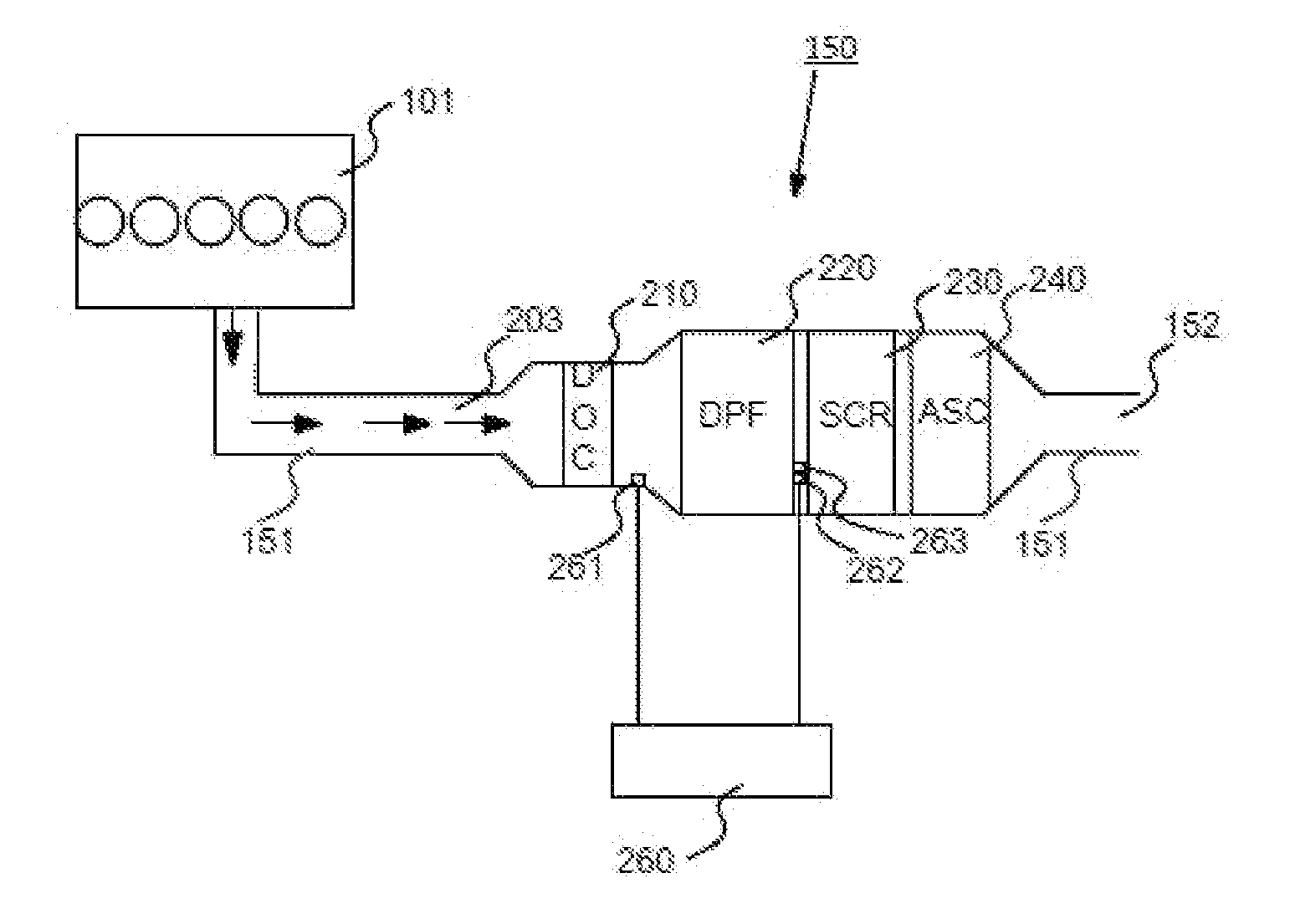
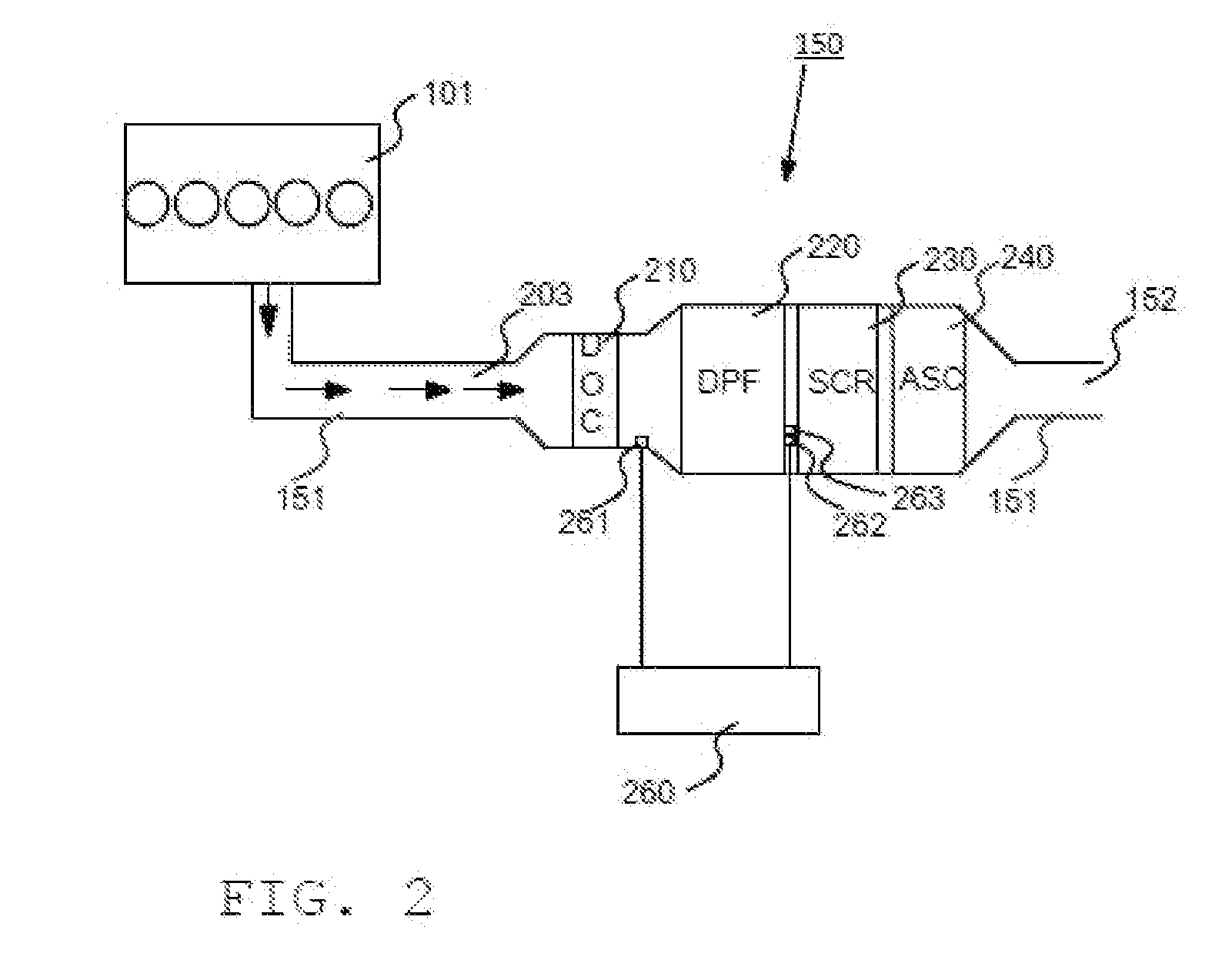
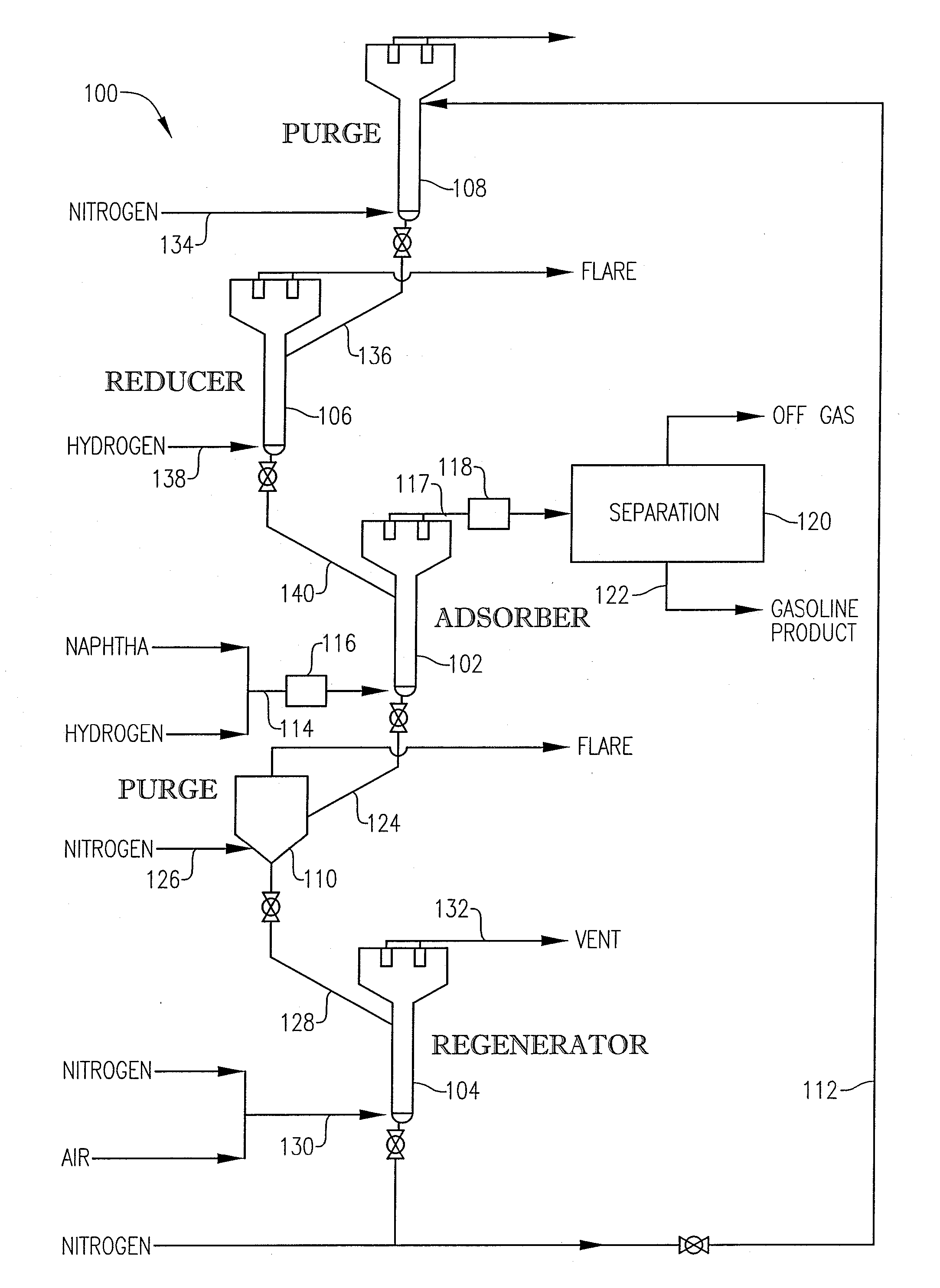
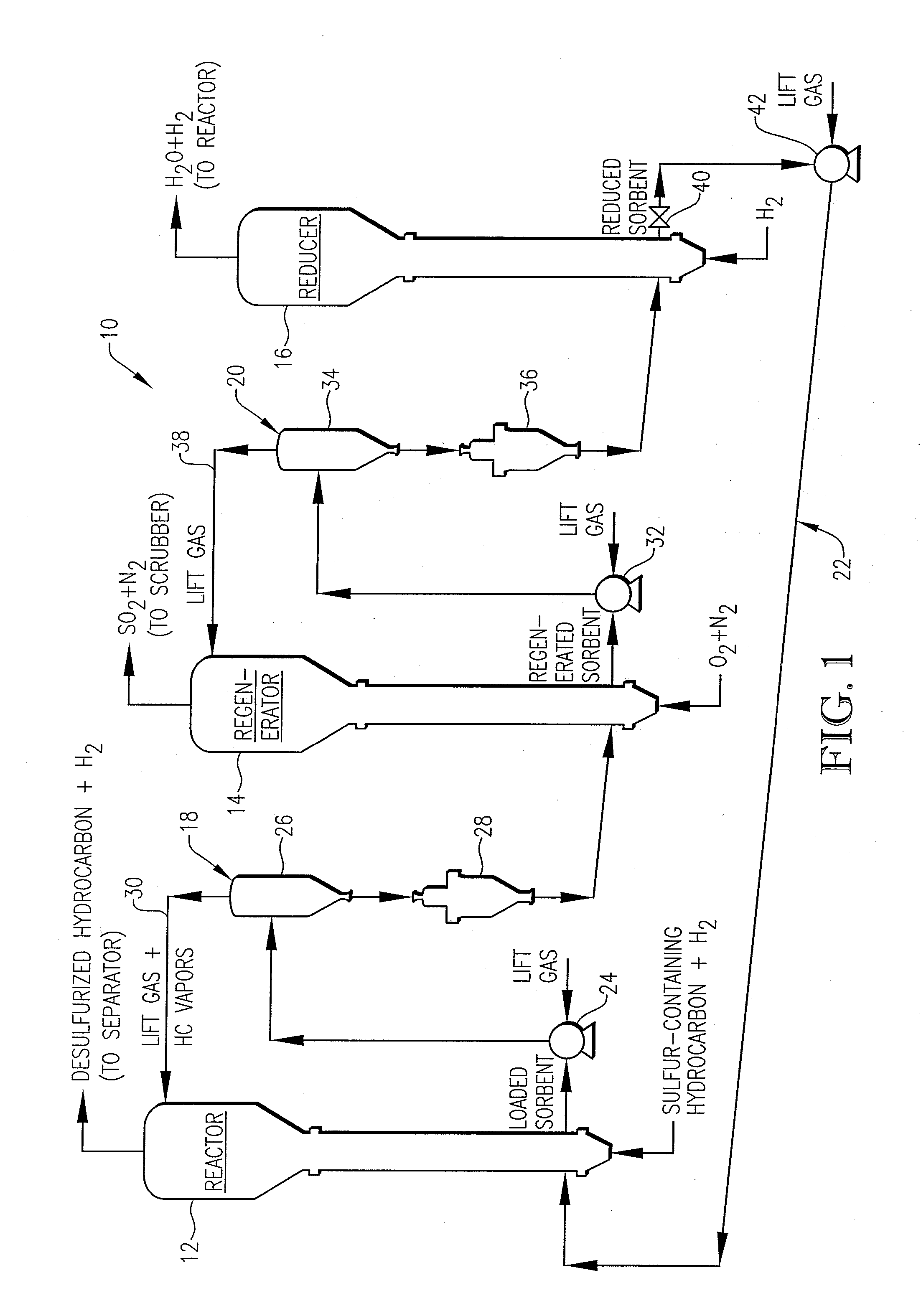
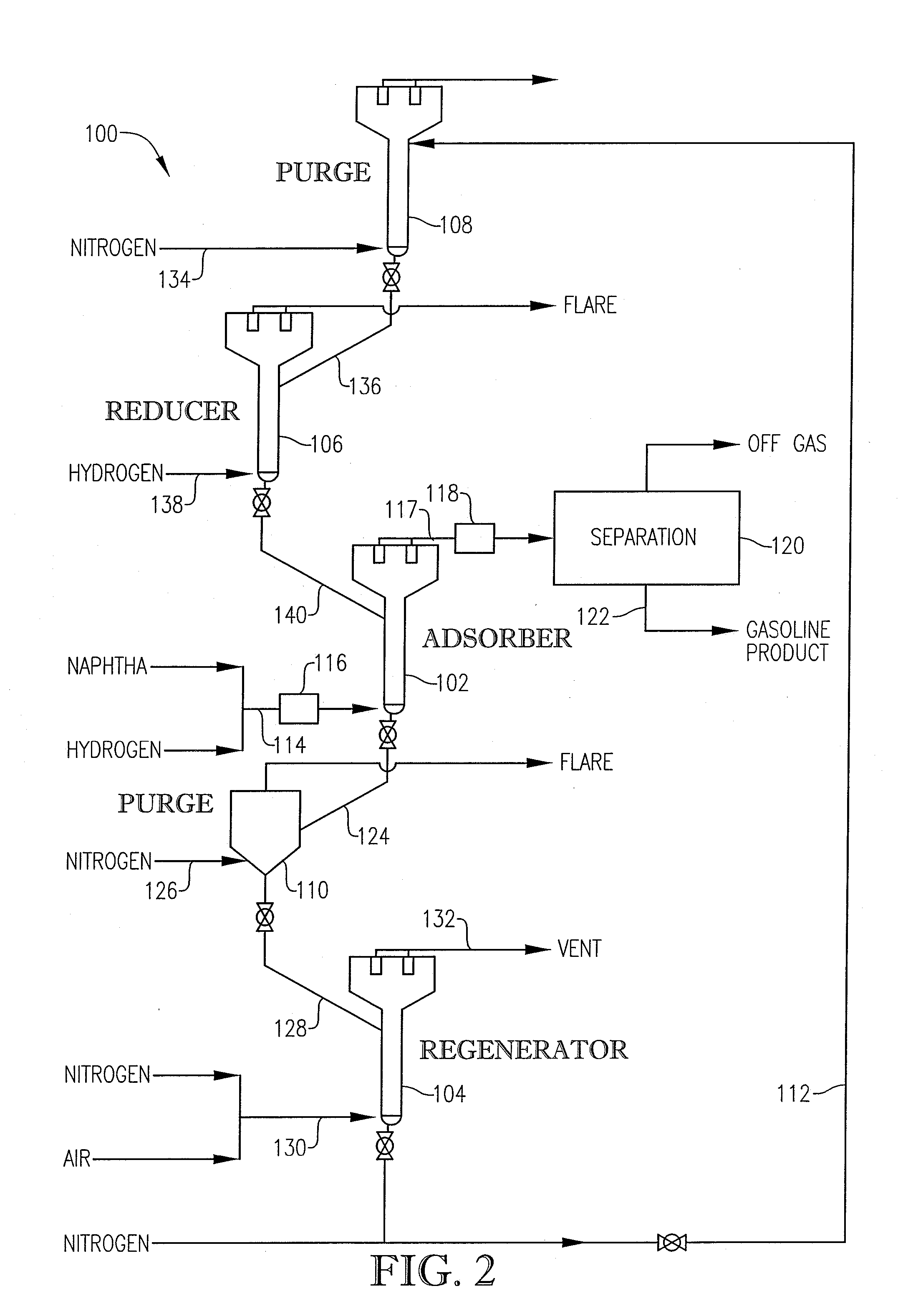
Desulfurization With Octane Enhancement
InactiveUS20070225156A1Increased octaneMinimizing octane lossRefining with non-metalsMolecular sieve catalystsFluidized bedSorbent
A desulfurization system employing a system of fluidizable and circulatable solid particles to desulfurize a hydrocarbon-containing fluid in a fluidized bed reactor. The solid particulate system includes solid sorbent particles operable to remove sulfur from the hydrocarbon-containing fluid stream and solid catalyst particles operable to enhance the octane of the resulting desulfurized hydrocarbon-containing fluid stream. The solid particulate system can be circulated between a reactor, regenerator, and reducer, to thereby allow for substantially continuous desulfurization in the reactor.
Owner:CHINA PETROCHEMICAL CORP
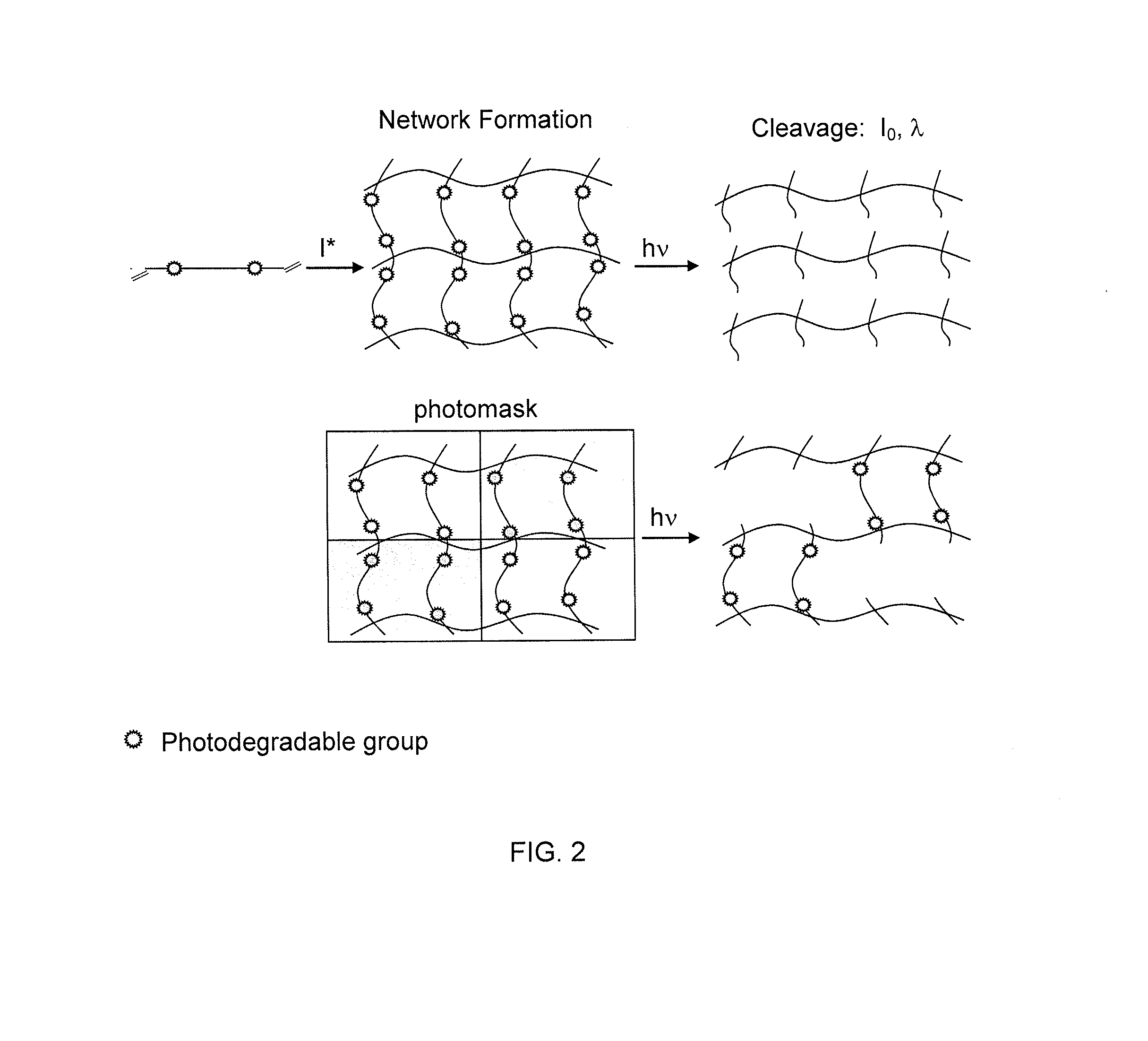
Photodegradable groups for tunable polymeric materials
Here, we present a photodegradable microparticle system that can be employed to entrap and deliver bioactive proteins to cells during culture. By using a photosensitive delivery system, experimenters can achieve a wide variety of spatiotemporally regulated release profiles with a single microparticle formulation, thereby enabling one to probe many questions as to how protein presentation can be manipulated to regulate cell function. Photodegradable microparticles were synthesized via inverse suspension polymerization with a mean diameter of 22 μm, and degradation was demonstrated upon exposure to several irradiation conditions. The protein-loaded depots were incorporated into cell cultures and release of bioactive protein was quantified during the photodegradation process. This phototriggered release allowed for the delivery of TGF-β1 to stimulate PE25 cells and for the delivery of fluorescently labeled Annexin V to assay apoptotic 3T3 fibroblasts during culture. By incorporating these photoresponsive protein delivery depots into cell culture, new types of experiments are now possible to test hypotheses about how individual or multiple soluble factors might affect cell function when presented in a uniform, temporally varying, or gradient manner.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
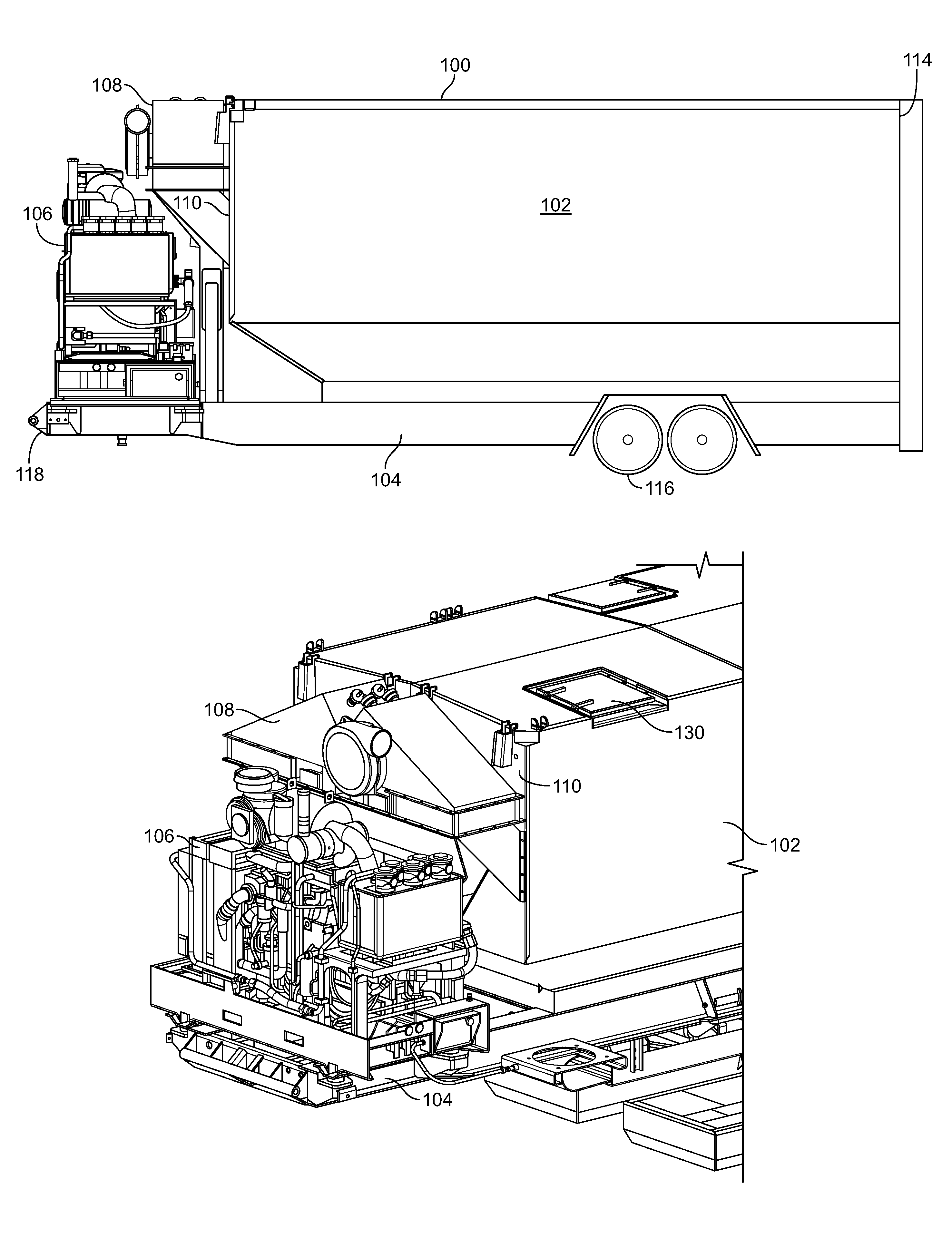
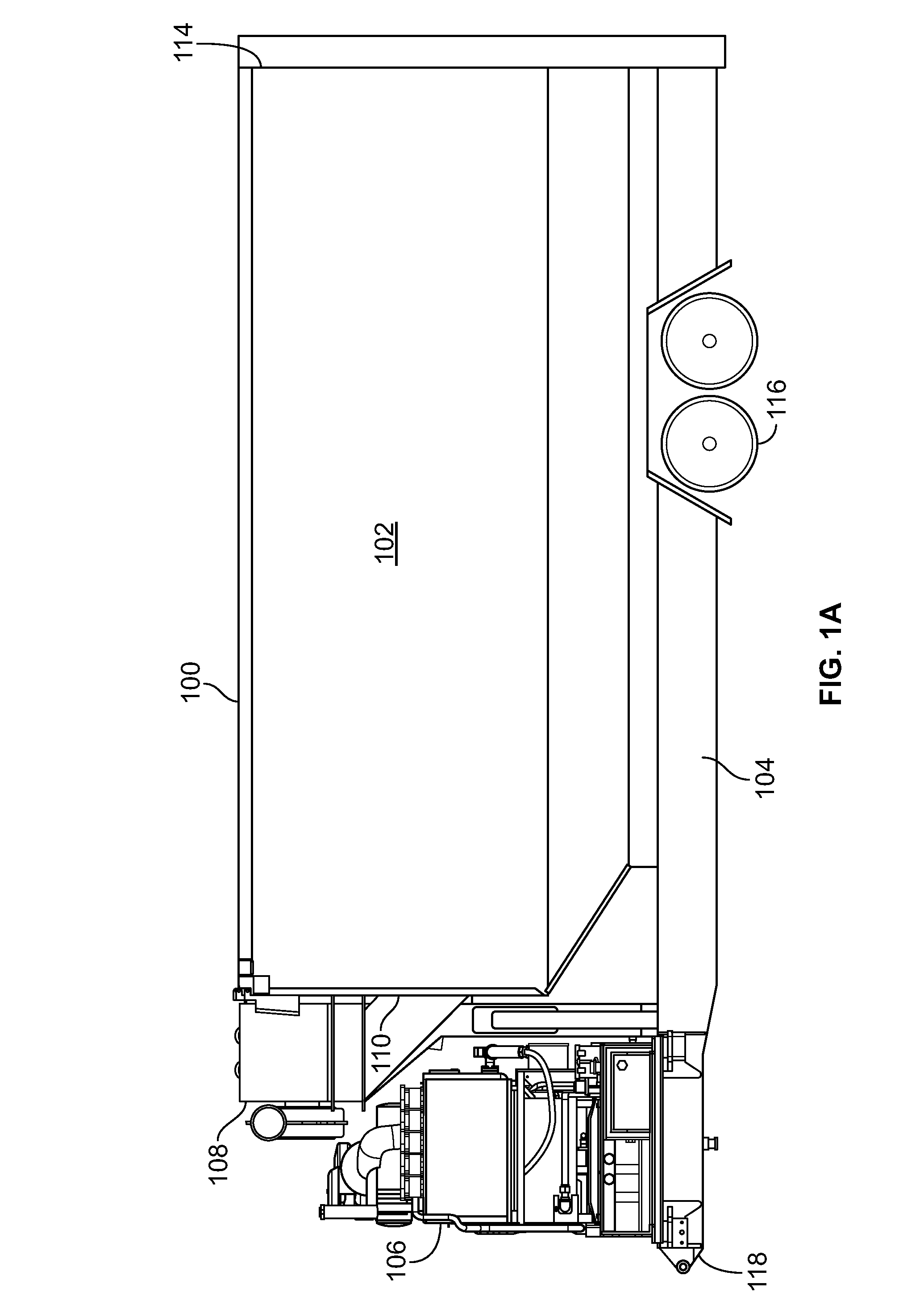
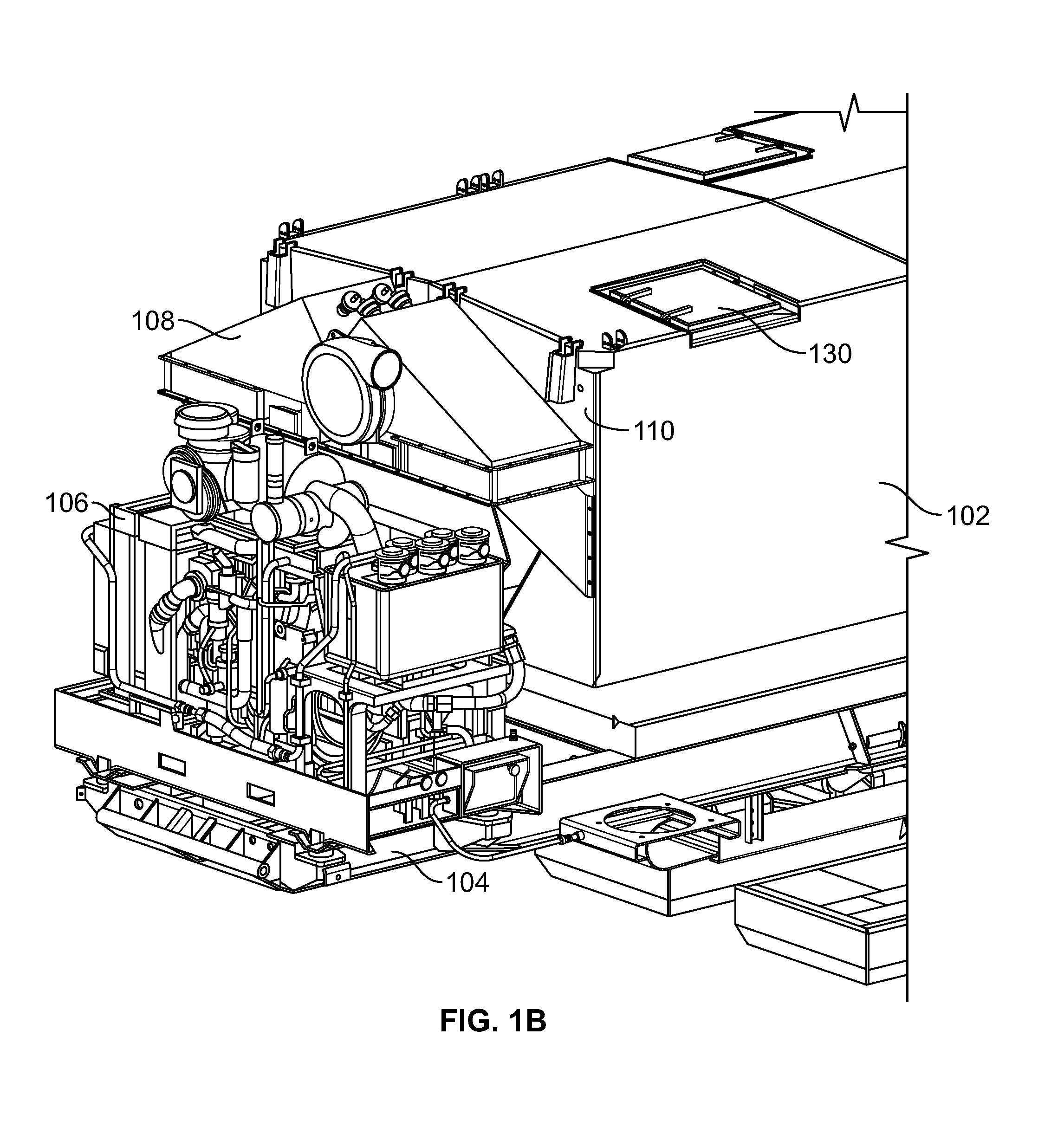
Filtration system for a particulate storage fracking trailer
A fracking trailer includes a particulate storage enclosure to receive a mixture of particulate and air in an interior of the particulate storage enclosure having a front end and a rear end. The fracking trailer also includes a filtration system connected to the particulate storage enclosure at the front end to filter particulate from the air in the mixture and exhaust filtered air.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Particulate delivery systems
The present invention provides particulate delivery systems comprising plurality of particles comprising fenugreek gum and at least one pharmaceutically acceptable excipient. The particulate delivery systems of the present invention are used for the delivery of therapeutic, immunologic or diagnostic agents, and the like.
Owner:RUBICON RES PTY LTD
Multiplex microparticle system
ActiveUS20090163378A1Simplify creationNone provides advantagesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMulti analyteMicroparticle
Arrays of microparticle populations, each population labeled with a single fluorescent dye, are provided for use in multiplex assays. The populations form a virtual multidimensional array wherein each microparticle is identified by fluorescence intensity in two different fluorescence detection channels. The arrays are useful in a variety of assays, including multiplex, multi-analyte assays for the simultaneous detection of two or more analytes by, for example, flow cytometry, and a labeling reagents in, for example, microscopy. The use of singly-dyed microparticles to form multidimensional arrays greatly simplifies the creation of multiplex assays.
Owner:U S SMOKELESS TOBACCO COMPANY LLC
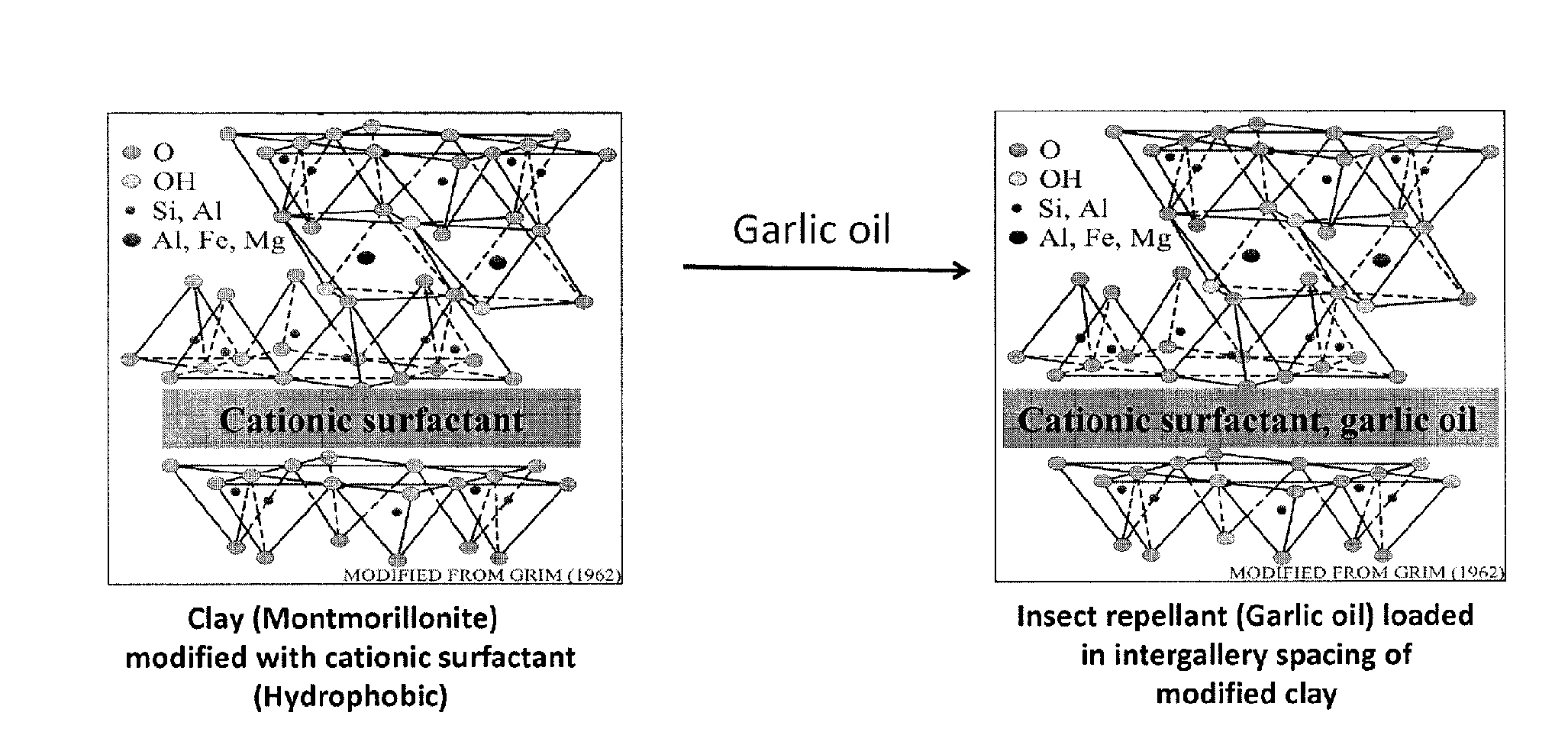
Engineered particulate systems for controlled release of pesticides and repellants
Nanoengineered particulate coatings (NPCs) comprise a multiplicity of particulate hosts that are infused with a nanophase comprising a surfactant and at least one guest. The particulate hosts can be clay particles, the surfactant can be a cationic surfactant, and the guest can be an insect repellant. For example, montmorillonite particles infused with hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and garlic oil form NPCs that may be used to form an emulsion or suspension for spraying on citrus trees to repel Asian Citrus Psyllid.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Method for manufacturing particulate water-absorbing agent and particulate water-absorbing agent
ActiveUS7919564B2Excellent liquid diffusibility and liquid permeabilityResidue reductionAbsorbent padsBandagesParticulatesAqueous solution
The present invention provides a method for manufacturing a particulate water-absorbing agent which has excellent liquid diffusibility and liquid permeability, and whose amount of residual monomers is reduced. The method for manufacturing the particulate water-absorbing agent of the present invention includes a step of surface-crosslinking, in the presence of an organic crosslinking agent, water-absorbing resin particles obtained through at least a step of polymerizing an aqueous solution of unsaturated monomers, and in or after the polymerizing step, a reaction system is mixed with peroxide. Thus, it is possible to obtain the particulate water-absorbing agent which has excellent liquid diffusibility and liquid permeability and whose amount of residual monomers is small, that is, it is possible to obtain the particulate water-absorbing agent which is highly functional and highly safe.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
Pharmaceutical compositions for the delivery of substantially water-insoluble drugs
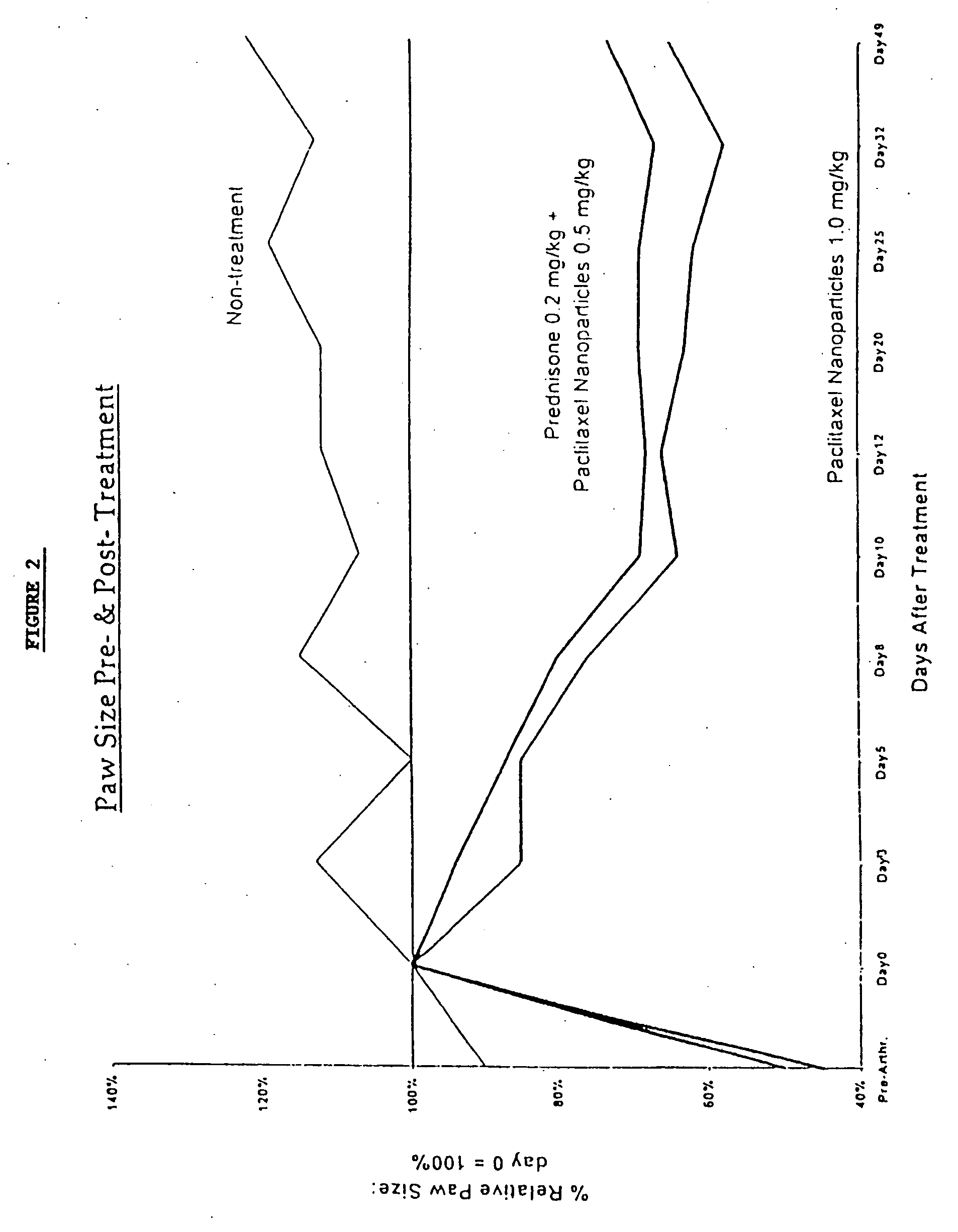
The subject invention relates to compositions and methods useful for the in vivo delivery of substantially water-insoluble drugs, like taxol. The use of specific composition and preparation conditions enables the reproducible production of unusually water-soluble formulation, which can be sterile-filtered. The particulate system produced according to the invention can be converted into a re-dispersible dry powder comprising nanoparticles of drug. The innovation is also based on the fact that complementary partner is also an active drug but may have a different mode action with respect to primary molecule of the hybrid drug. The complementary molecule has multiple properties like antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, cox-2 inhibitors, etc. This results in a unique delivery system, in which part of the pharmacologically active agent is readily bioavailable.
Owner:SINGH MEWA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com