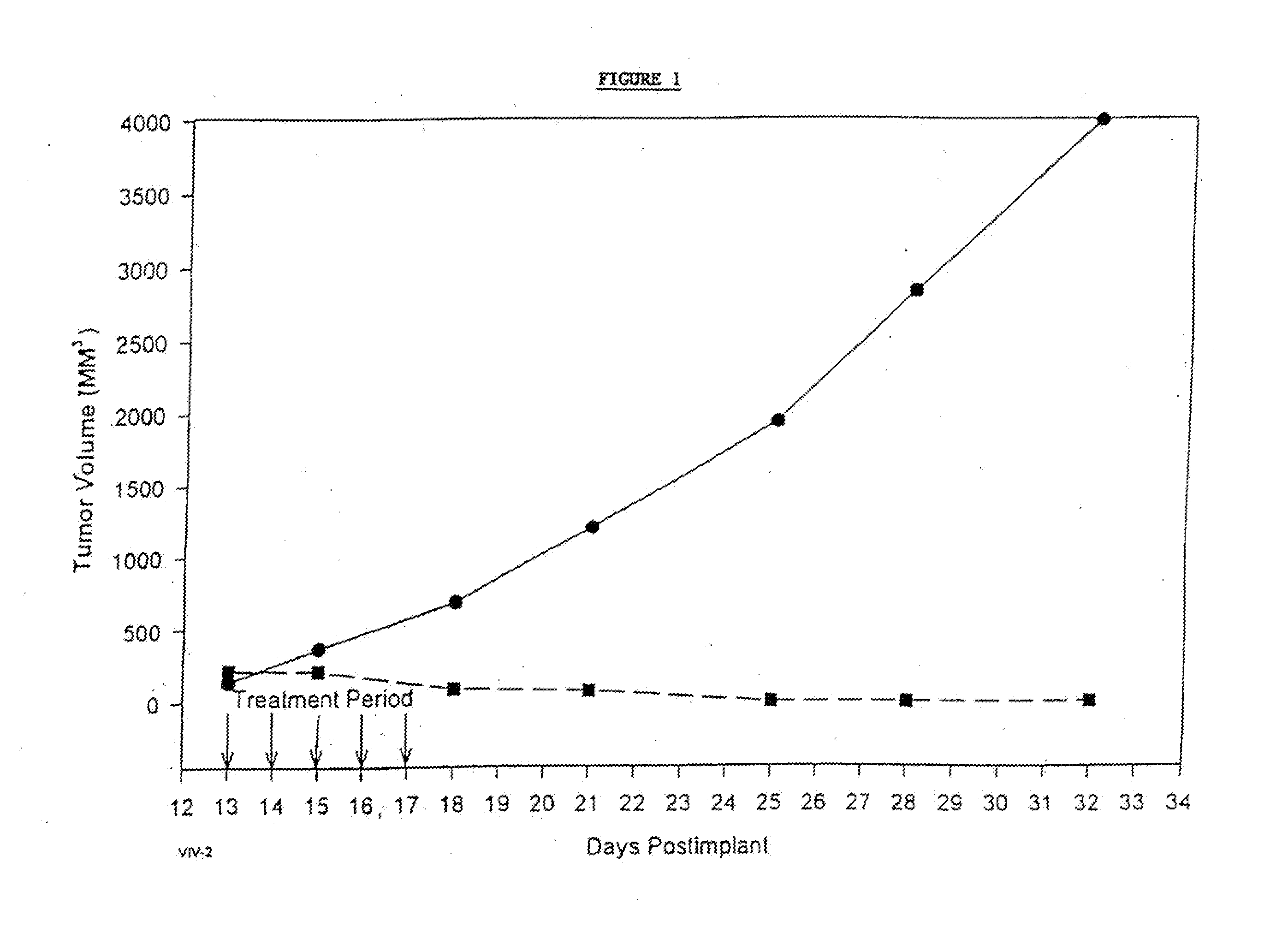
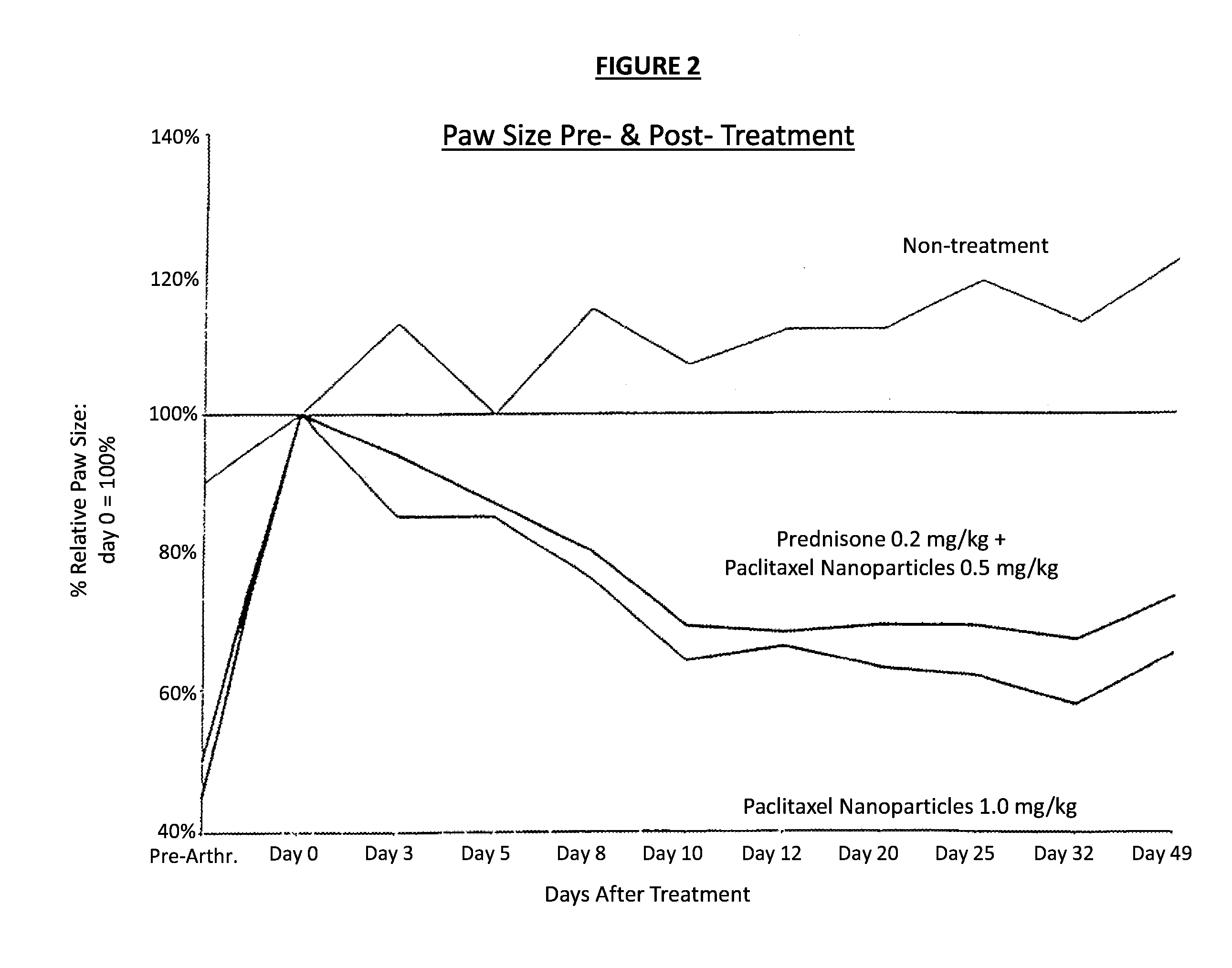
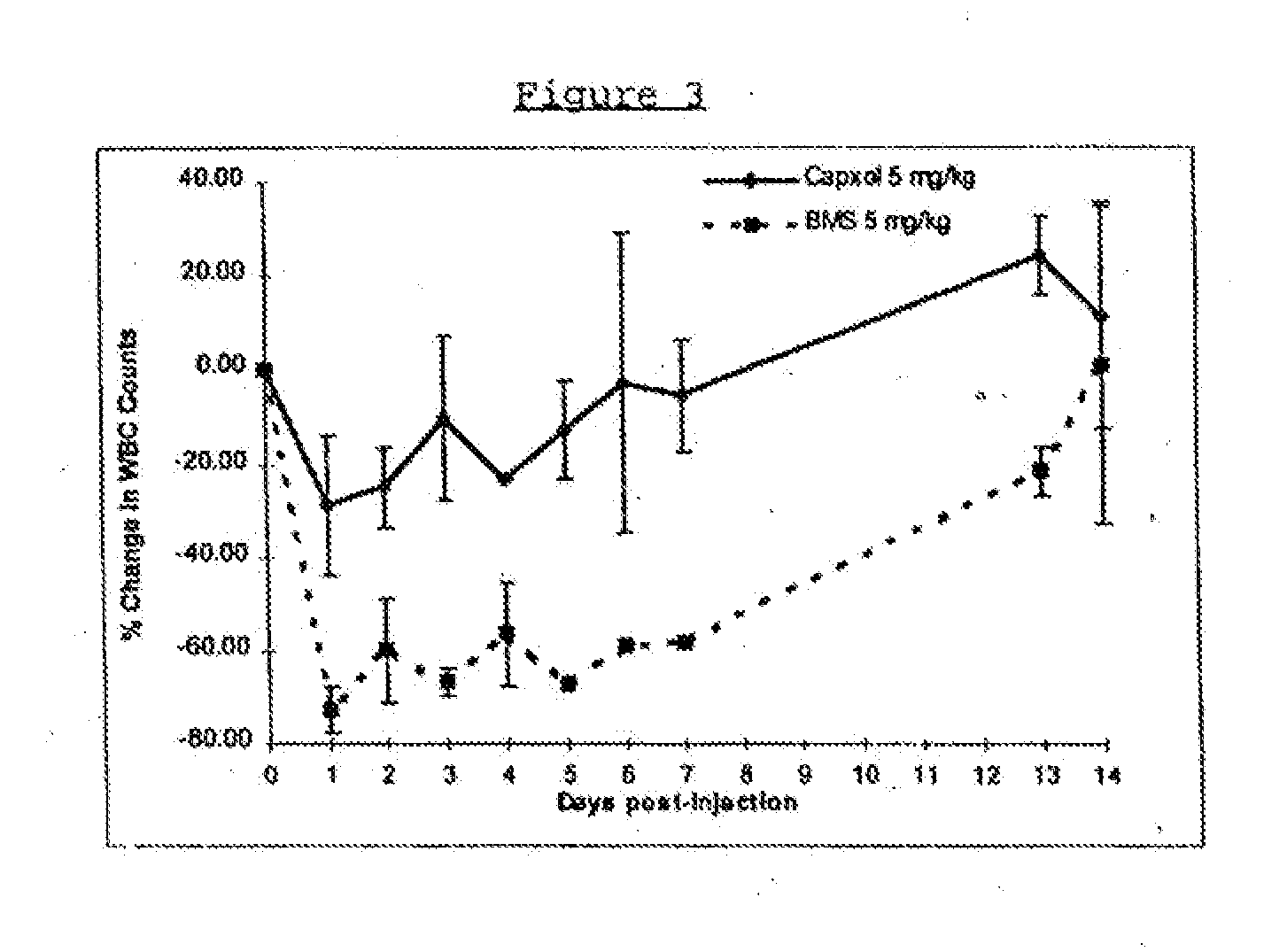
Novel formulations of pharmacological agents, methods for the preparation thereof and methods for the use thereof
a technology of pharmacological agents and formulations, applied in the direction of biocide, microcapsules, capsule delivery, etc., can solve the problems of human administration, inability to conventionally administer pharmaceuticals that are water-insoluble or poorly water-soluble, sensitive to acid environments in the stomach, etc., to reduce the incidence of severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions, reduce toxicities, and improve the effect of
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Nanoparticles by High Pressure Homogenization
[0190]30 mg paclitaxel is dissolved in 3.0 ml methylene chloride. The solution was added to 27.0 ml of human serum abumin solution (1% w / v). The mixture was homogenized for 5 minutes at low RPM (Vitris homogenizer, model: Tempest I.Q.) in order to form a crude emulsion, and then transferred into a high pressure homogenizer (Avestin). The emulsification was performed at 9000-40,000 psi while recycling the emulsion for at least 5 cycles. The resulting system was transferred into a Rotary evaporator, and methylene chloride was rapidly removed at 40° C., at reduced pressure (30 mm Hg), for 20-30 minutes. The resulting dispersion was translucent, and the typical diameter of the resulting paclitaxel particles was 160-220 (Z-average, Malvern Zetasizer).
[0191]The dispersion was further lyophilized for 48 hrs without adding any cryoprotectant. The resulting cake could be easily reconstituted to the original dispersion by addition of...
example 2
Use of Conventional Surfactants and Proteins Results in Formation of Large Crystals
[0192]The following example demonstrates the effect of adding surfactants which are used in the conventional solvent evaporation method. A series of experiments was conducted employing a similar procedure to that described in Example 1, but a surfactant such as Tween 80 (1% to 10%) is added to the organic solvent. It was found that after removal of the methylene chloride, a large number of paclitaxel crystals is obtained having an average size of 1-2 micron, as viewed by light microscopy and under polarized light. The crystals grow within a few hours to form very large needle-like crystals, with a size in the range of about 5-15 micron. A similar phenomenon is observed with other commonly used surfactants, such as Pluronic F-68, Pluronic F-127, Cremophor EL and Brij 58.
[0193]From these results it can be concluded that the conventional solvent evaporation method utilizing conventional surfactants in co...
example 3
Use of Conventional Surfactants Alone Results in Formation of Large Crystals
[0194]This example demonstrates that it is not possible to form nanoparticles while using conventional surfactants, without a polymeric core material, with pharmacologically active agents which are soluble in polar, water immiscible solvents (e.g. chloroform).
[0195]30 mg Taxol is dissolved in 0.55 ml chloroform and 0.05 ml ethanol. The solution is added to 29.4 ml of Tween 80 solution (1% w / v), which is presaturated with 1% chloroform. The mixture is homogenized for 5 minutes at low RPM (Vitris homogenizer, model: Tempest I.Q.) in order to form a crude emulsion, and then transferred into a high pressure homogenizer (Avestin). The emulsification is performed at 9000-40,000 psi while recycling the emulsion for at least 6 cycles. The resulting system was transferred into a Rotary evaporator, and the chloroform was rapidly removed at 40° C., at reduced pressure (30 mm Hg), for 15-30 minutes. The resulting disper...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com