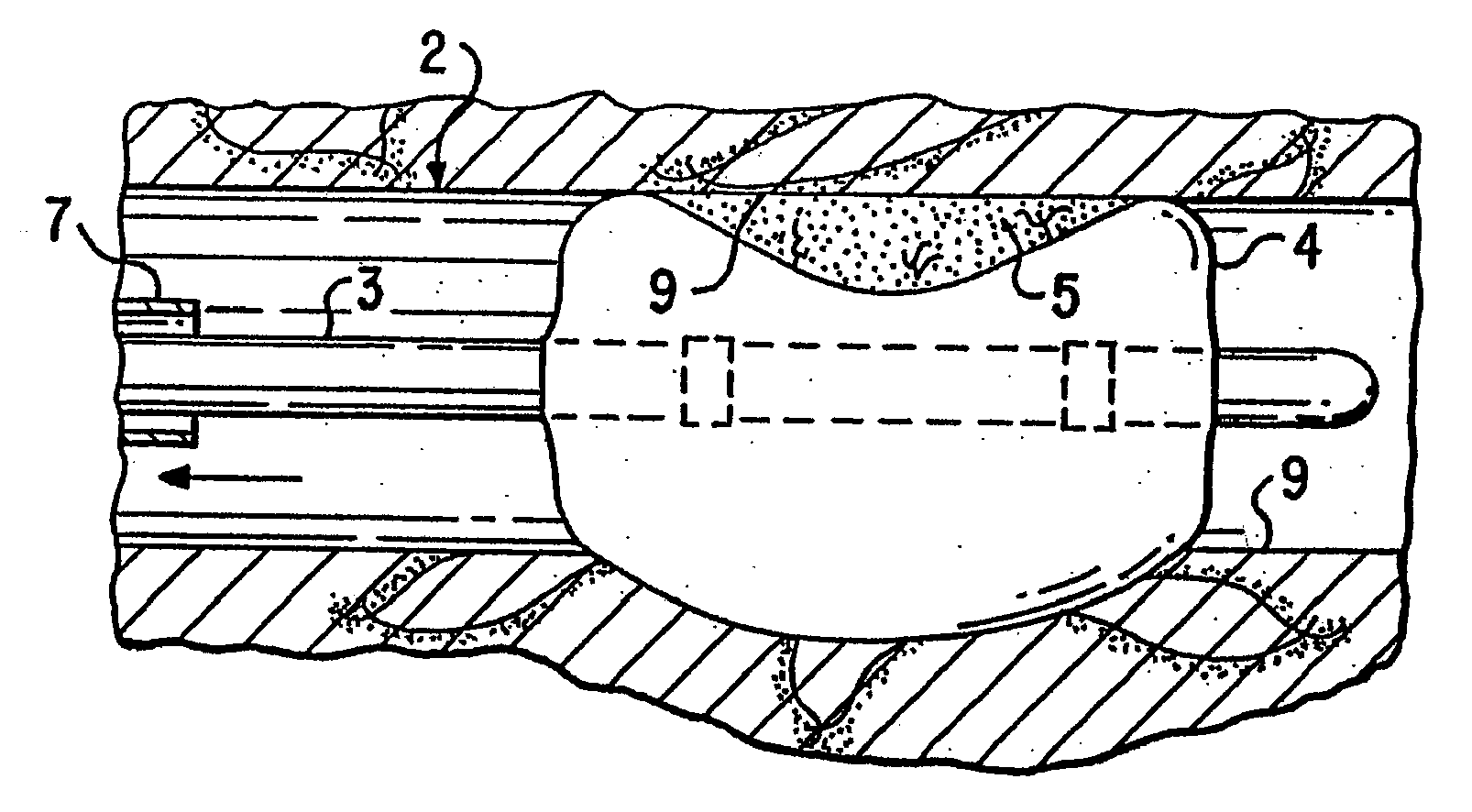
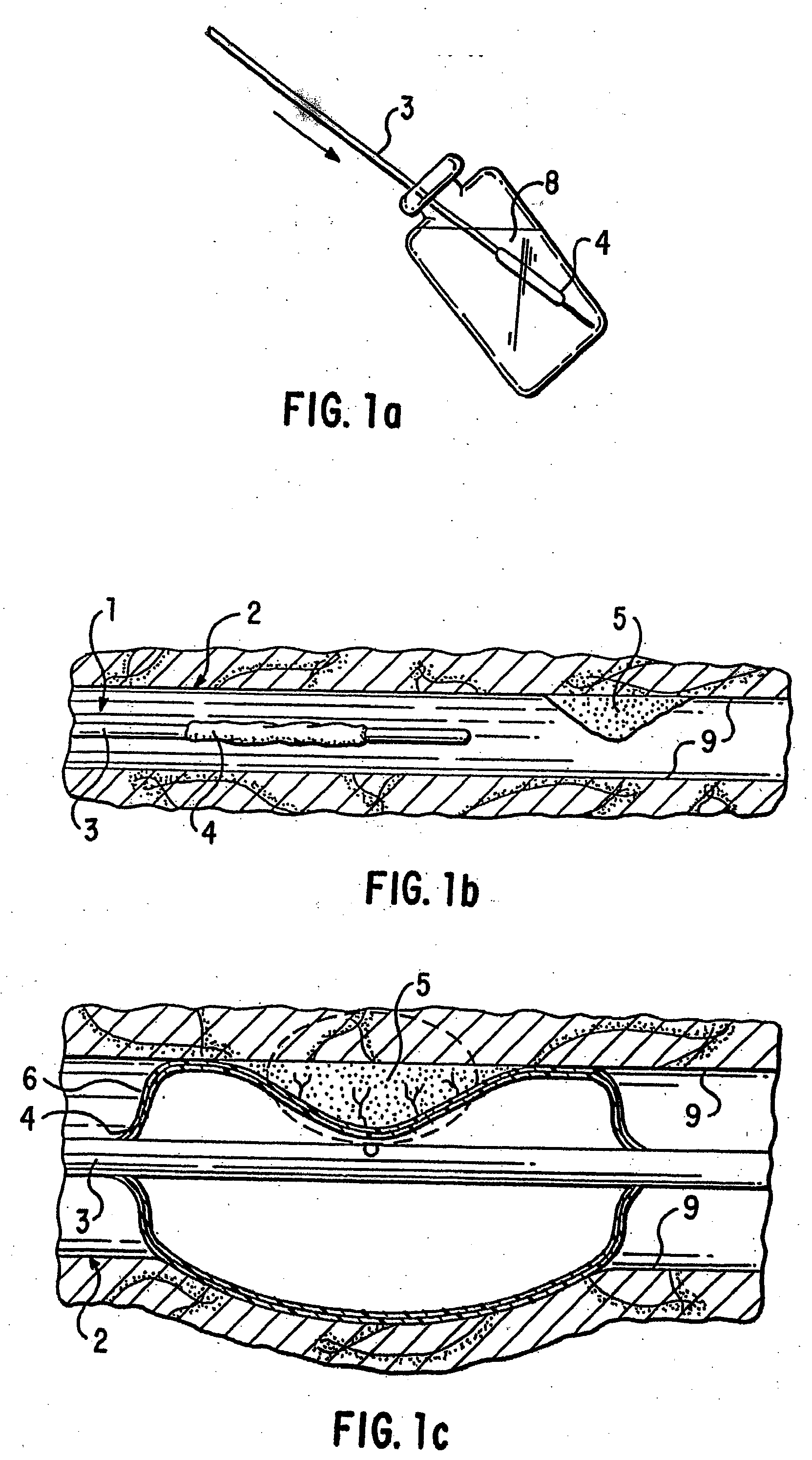
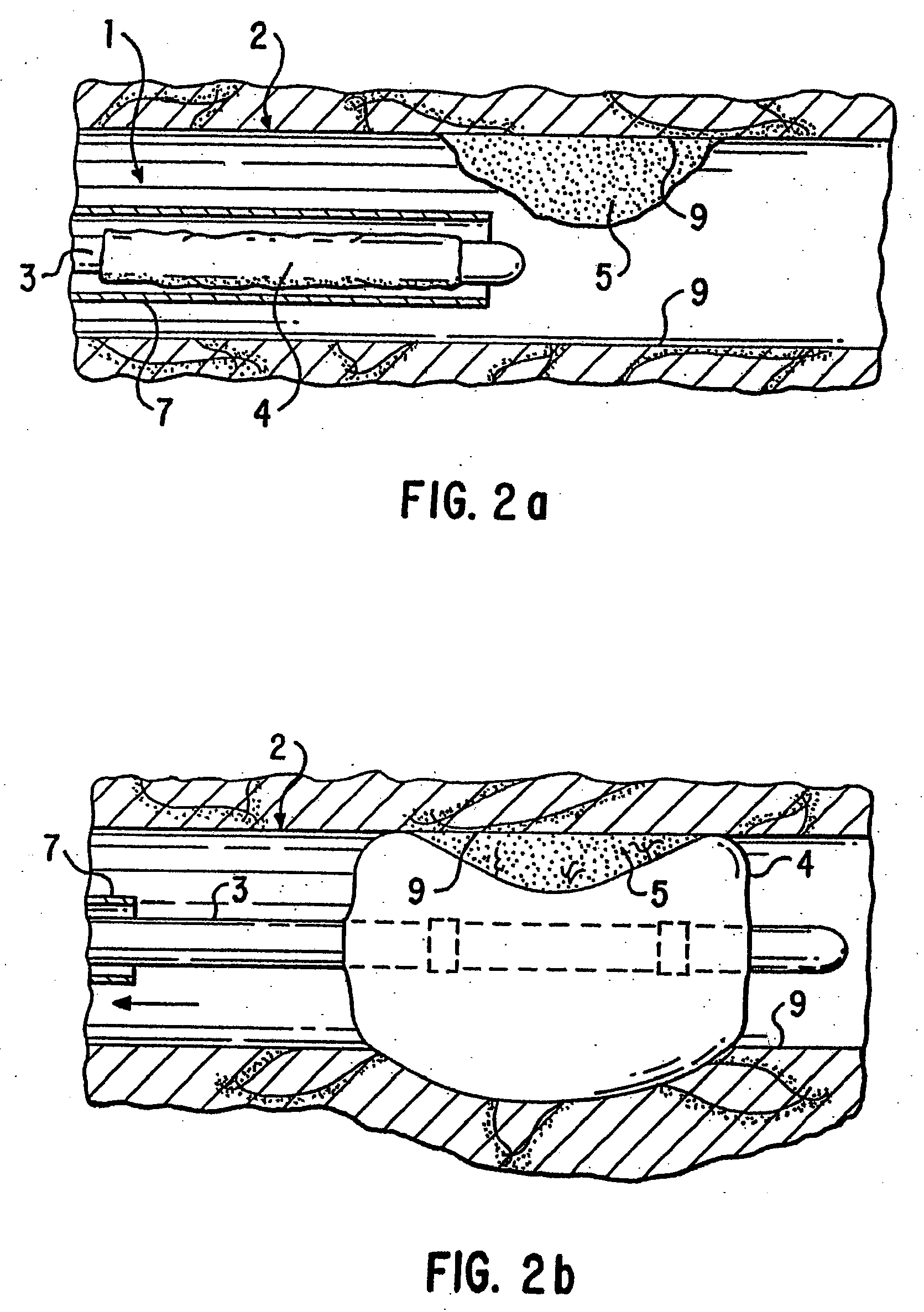
Loading and release of water-insoluble drugs
a technology of water-soluble drugs and loading and release, which is applied in the direction of prosthesis, catheters, blood vessels, etc., can solve the problems of systemic administration not being desirable, and having a limitation of being applicable to drug agents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Release Kinetics of Paclitaxel from Polyacrylic Acid-Based Coating
[0058] A 2 mg / ml solution of paclitaxel is prepared in chloroform. The solution is gently agitated until the paclitaxel is completely dissolved. The solution is applied via pipet to a balloon catheter having a polyacrylic acid-based coating and inflated to 2 atm. A total of 100 μl of solution, and hence 200 μg of paclitaxel, is applied to the catheter. The balloon catheter is then dried in air for 30 minutes and in a vacuum oven for 48 hours at 50° C. to evaporate the chloroform. The catheter is then immersed in a solution of 1% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and phosphate buffered saline(PBS) having a pH of 7.4 for in-vitro drug release. The cumulative amount of paclitaxel released from the catheter coating yields the data shown in FIGS. 3a and 3b.
example 2
Release Kinetics of Dexamethasone from Polyacrylic Acid-Based Coating
[0059] Solutions containing 1.5 mg / ml and 200 μg / ml of dexamethasone in chloroform, are prepared by gently agitating until the dexamethasone is completely dissolved. The solutions are separately applied via dripping to separate balloon catheters having polyacrylic acid-based coatings and inflated to 2 atm. A total of 100 μl of each solution is applied to each respective catheter, corresponding to dexamethasone loadings of 1.5 mg and 200 μg, respectively. These results can be contrasted with the inability to apply substantial amounts of dexamethasone to polyacrylic acid-based coatings using aqueous solutions, in which case only about 1 μg of dexamethasone can be loaded into such coatings. The balloon catheters are then dried in a vacuum oven for 2 hours at 50° C. to evaporate the chloroform solvent. The catheters are thereafter immersed in PBS (pH=7.4) to track the release of dexamethasone over time. The cumulative...
example 3
Release Kinetic of Molsidomine from Polyacrylic Acid-Based Coating
[0060] Various solutions of molsidomine in volatile solvents are prepared and applied to balloon catheters by the methods indicated in Table I. In the “dip” application technique, each balloon catheter having a polyacrylic acid-based coating is dipped into its respective solution for 10 minutes. In the “pipet” application technique, 200 μl of solution is pipetted onto its respective coated balloon catheter while slowly turning. All samples are dried in an oven for 30 minutes at 50° C. and thereafter immersed in PBS (pH=7.4) to track the release of molsidomine over time. The cumulative amount of molsidomine released from each catheter yields the data shown in FIG. 5a and 5b.
TABLE IMolsidomine solution characterization, and methods ofapplying molsidomine solution to polymer coated catheters.Concentration (mgMolsidomine per mlApplicationSampleSolventsolvent)technique1chloroform150dip2chloroform30pipet3chloroform150pip...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com