Taxadol slow release nano-particle, its preparation method and application
A paclitaxel and nanoparticle technology, which can be applied in pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations with inactive ingredients, and medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc., can solve problems such as low quality of life and dyspnea, and achieve increased release and increased drug release. , to maintain the effect of effective therapeutic concentration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
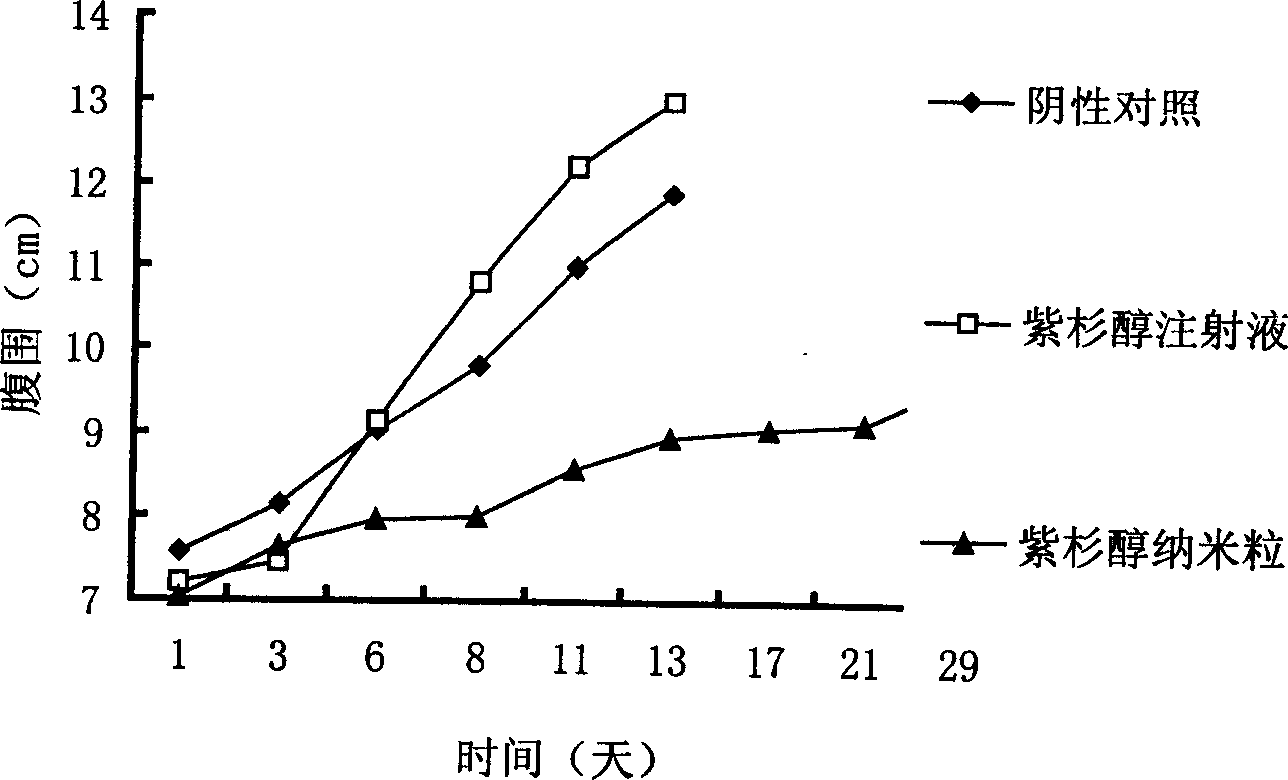
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Polyε-caprolactone can be commercially available or self-prepared.
[0030] The preparation method of polyε-caprolactone:
[0031] 1. Under the protection of nitrogen, put caprolactone and stannous octoate in proportion (1-12:0.001-0.1) into a three-necked flask, seal it, stir and mix evenly, and vacuum degassing: room temperature, vacuum <80Pa, time 5 -15 minutes, and then filled with high-purity nitrogen;
[0032] 2. Transfer the mixed raw materials to the polymerization kettle under the protection of nitrogen, repeat the above vacuum degassing and nitrogen replacement process, close the ventilation valve after filling the nitrogen gas for the last time, and put the polymerization kettle in a constant temperature oven at 100-300°C for polymerization 24-96 hours.
[0033] After the polymerization is completed, the polymer is extruded from the discharge valve at the bottom of the polymerization kettle, cooled and solidified at room temperature.
Embodiment 2
[0035] The preparation method of paclitaxel slow-release nanoparticles:
[0036] The method of preparing nano-controlled release system includes polymerization reaction method and polymer material dispersion method. The former is emulsion polymerization and interfacial polymerization technology prepared by polymerization reaction using different monomers; the latter is such as emulsification-solvent evaporation method using high molecular polymer The method of preparation. In the present invention, the nanoparticles are prepared by a solvent substitution method. Compared with the commonly used emulsification-solvent evaporation method, the solvent substitution method is easy to operate, does not require high-speed emulsification or ultrasonic stirring, and requires low energy consumption.
[0037](1) 63 grams of molecular weight are 20,000 to 30,000 polyε-caprolactone, 6 grams of poloxamer 188 and 25 grams of paclitaxel dissolved in 4000 milliliters of acetone;
[0038] (2) ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] The preparation method of paclitaxel slow-release nanoparticles:
[0044] (1) 90.25 grams of polylactic acid with a molecular weight of 20,000 to 30,000, 2 grams of poloxamer 407 and 5 grams of paclitaxel were dissolved in 3000 milliliters of acetone;
[0045] (2) According to the ratio of 1:4 by volume, the solution made in step (1) is added to the poloxamer 188 aqueous solution with a molecular weight of 110,000 at a mass percentage concentration of 0.5%, and the addition speed is 5ml / min;
[0046] (3) Remove acetone under reduced pressure at 10°C;
[0047] (4) 0°C, 20000rpm, centrifuge for 20min, collect the solidified nanoparticles, wash with distilled water, and centrifuge once to remove Poloxamer 188 in the nanoparticle suspension;
[0048] (5) freeze-drying to obtain paclitaxel sustained-release nanoparticles.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com