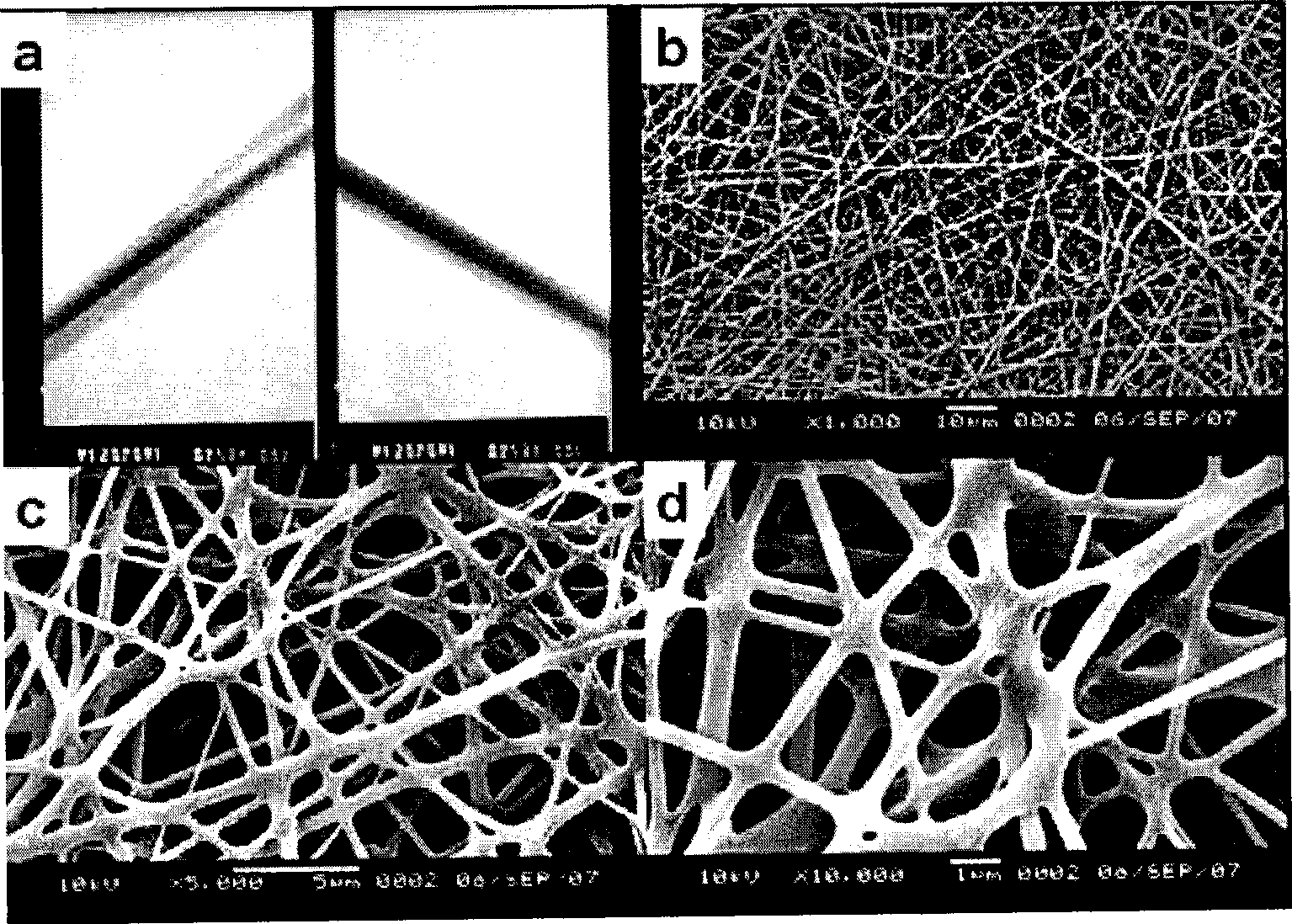
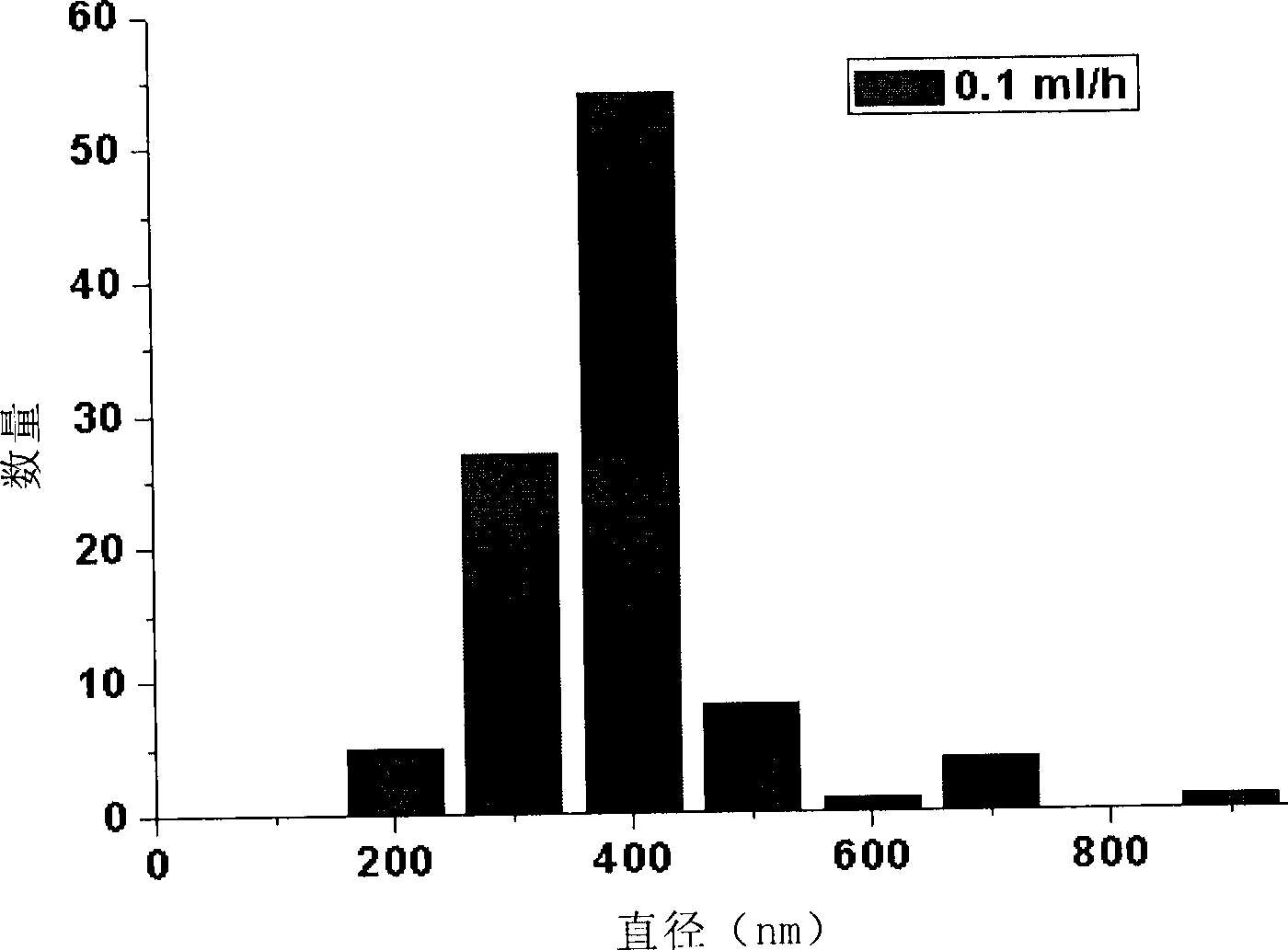
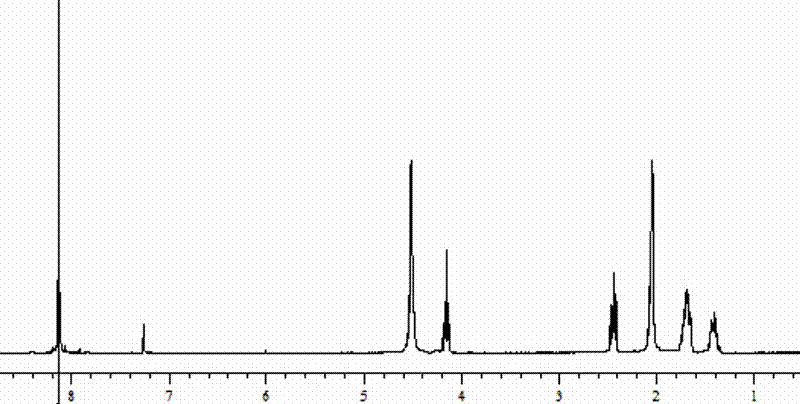
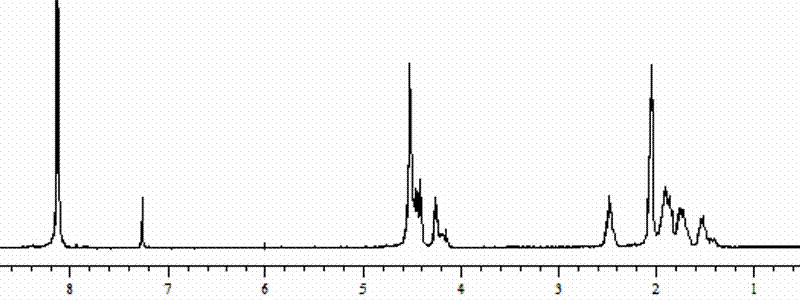
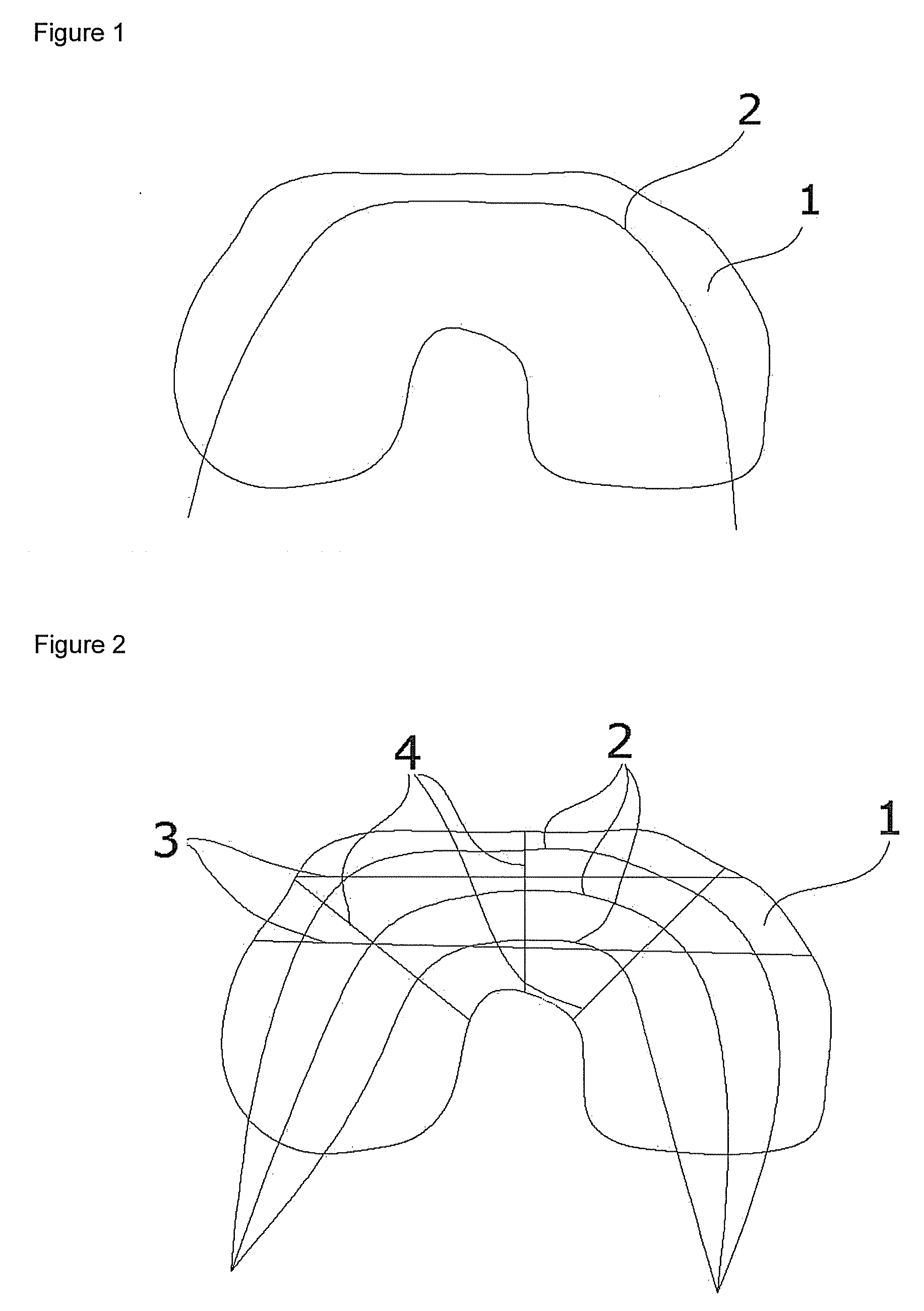
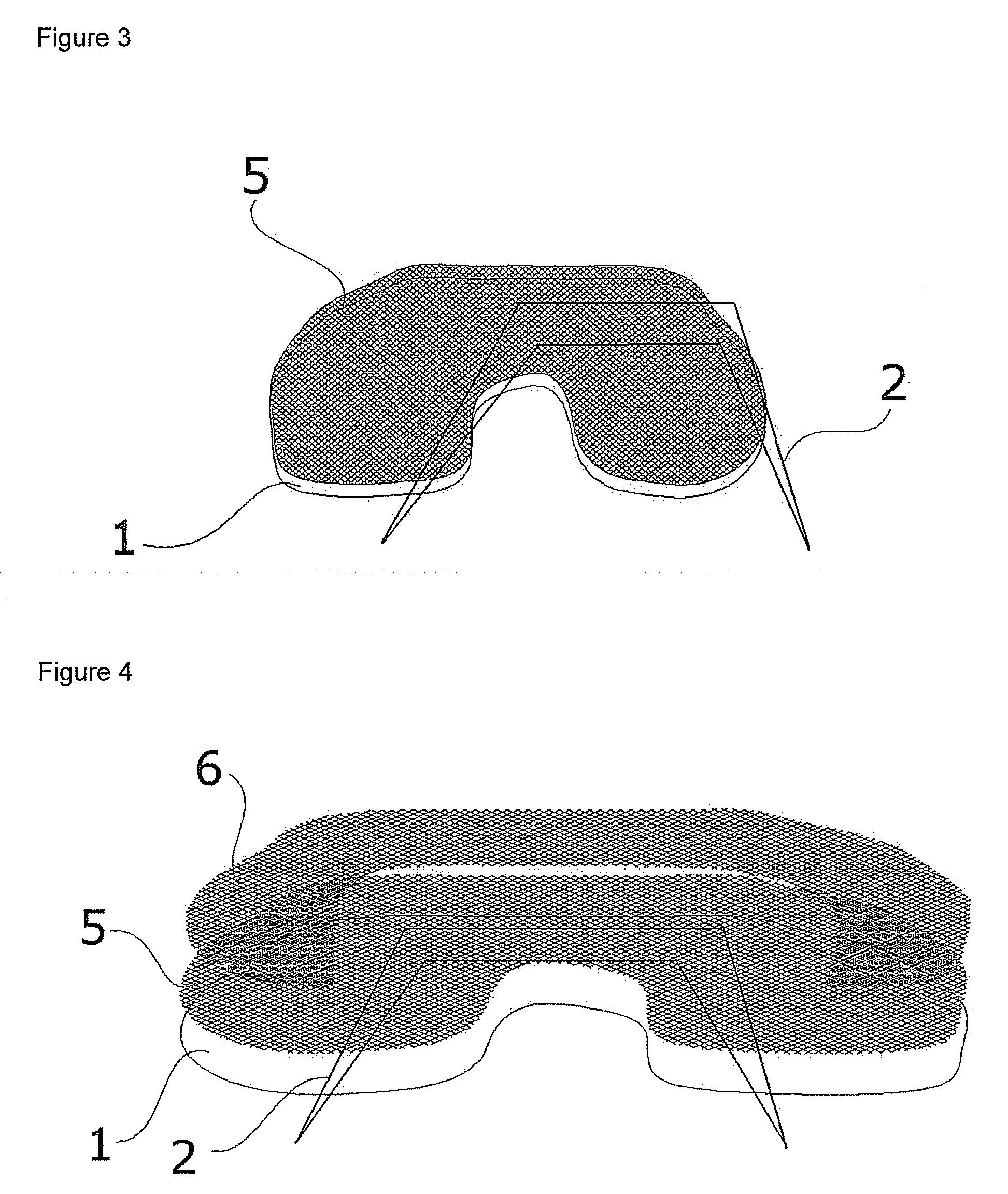
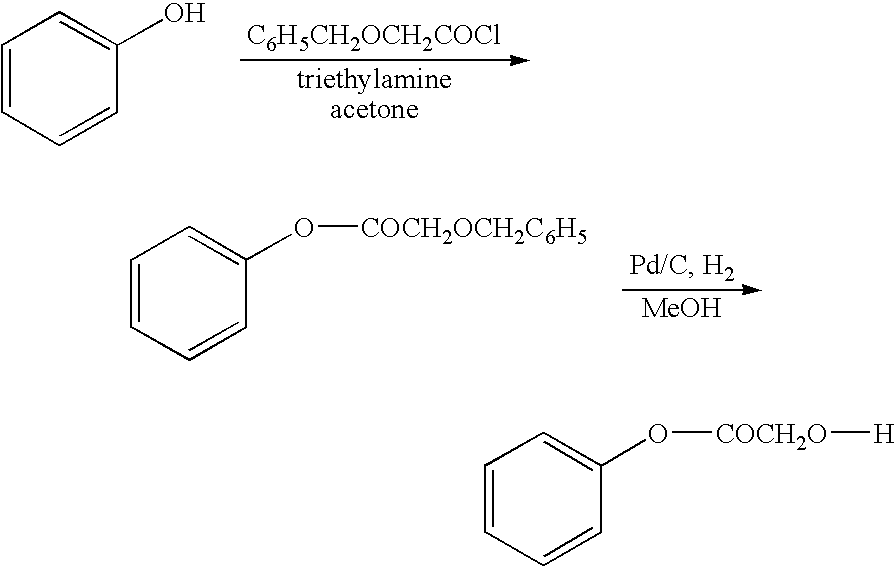
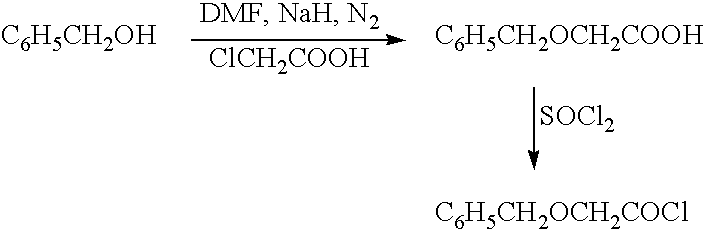Patents
Literature
1942 results about "Caprolactone" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ε-Caprolactone or simply caprolactone is a lactone (a cyclic ester) possessing a seven-membered ring. Its name is derived from caproic acid. This colorless liquid is miscible with most organic solvents and water. It was once produced on a large scale as a precursor to caprolactam.
Biocompatible compositions and methods of using same
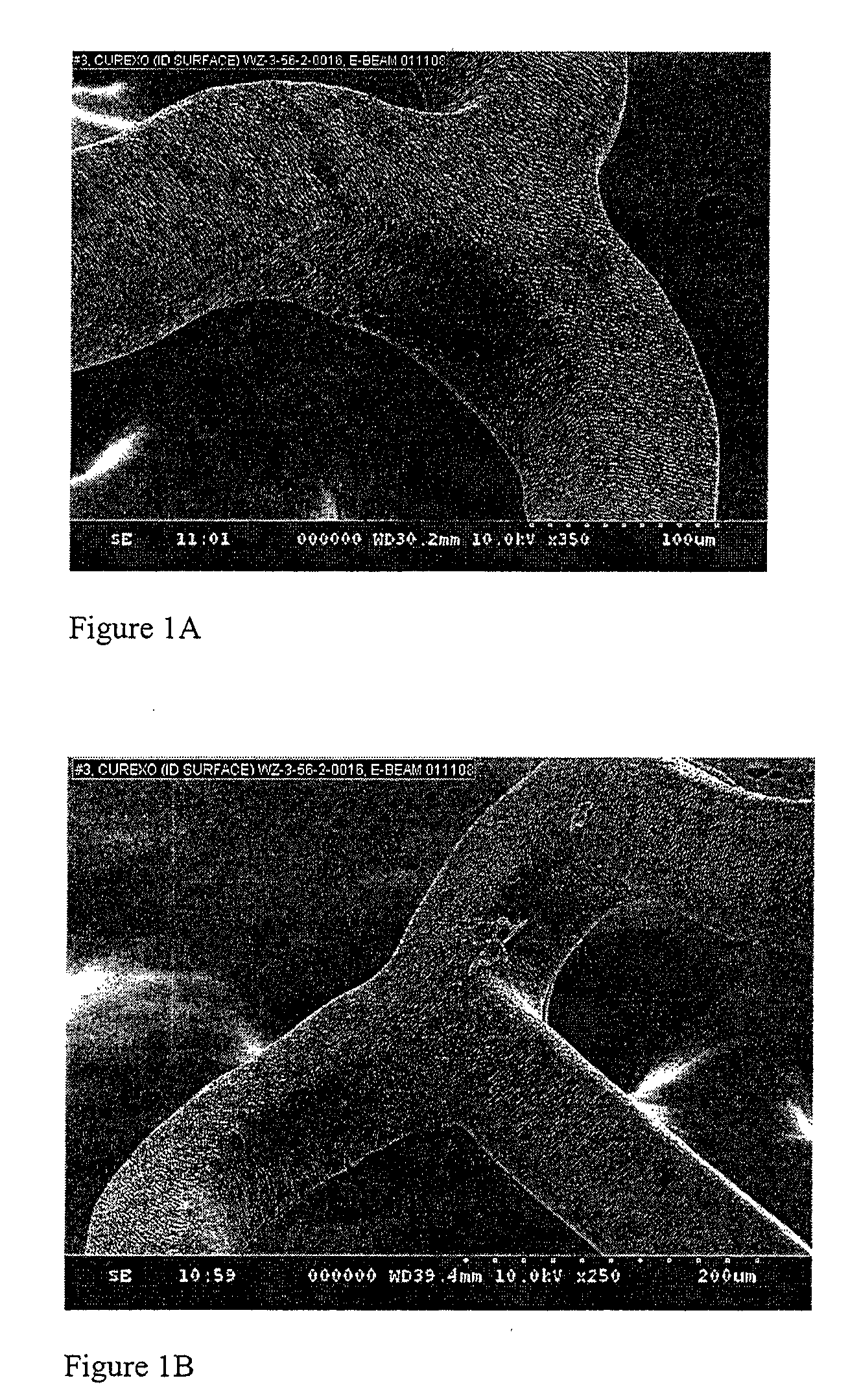
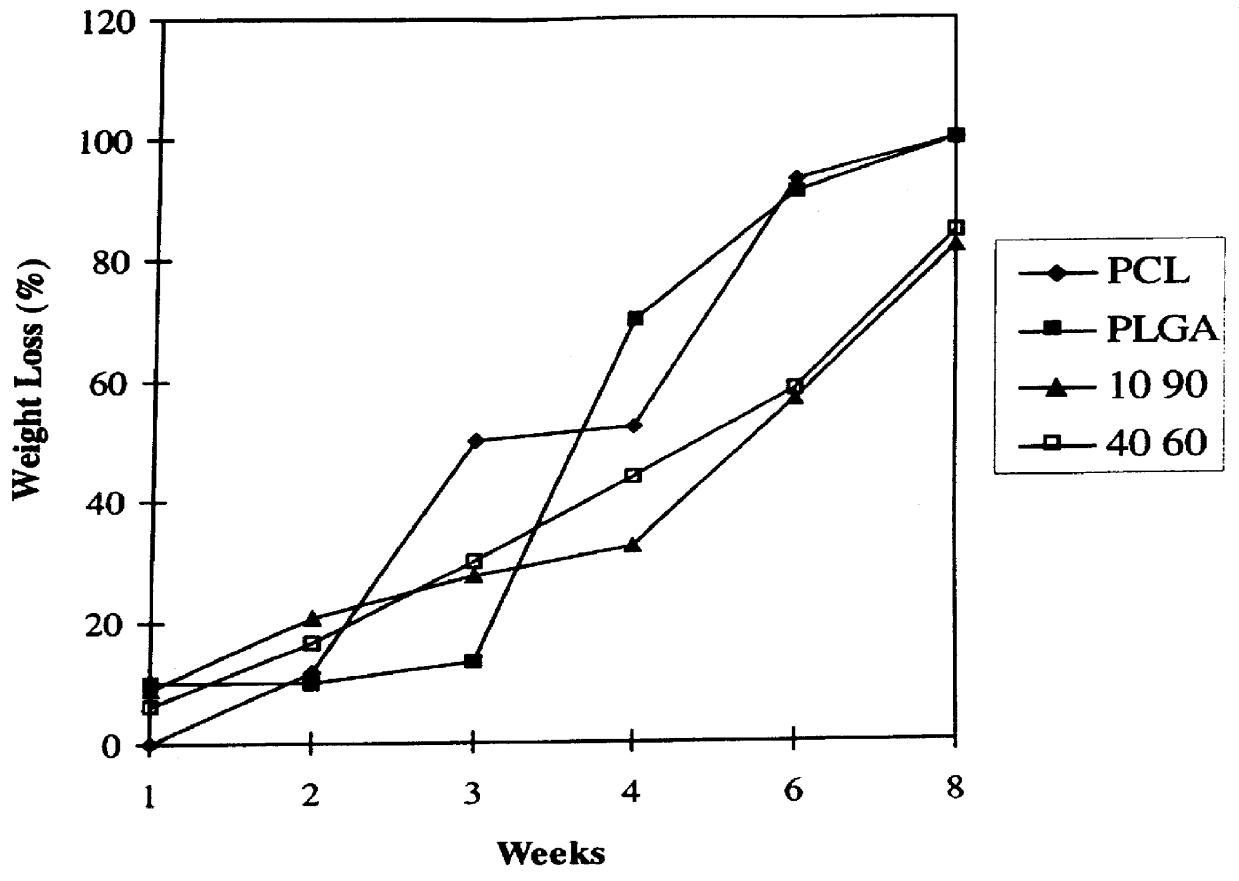
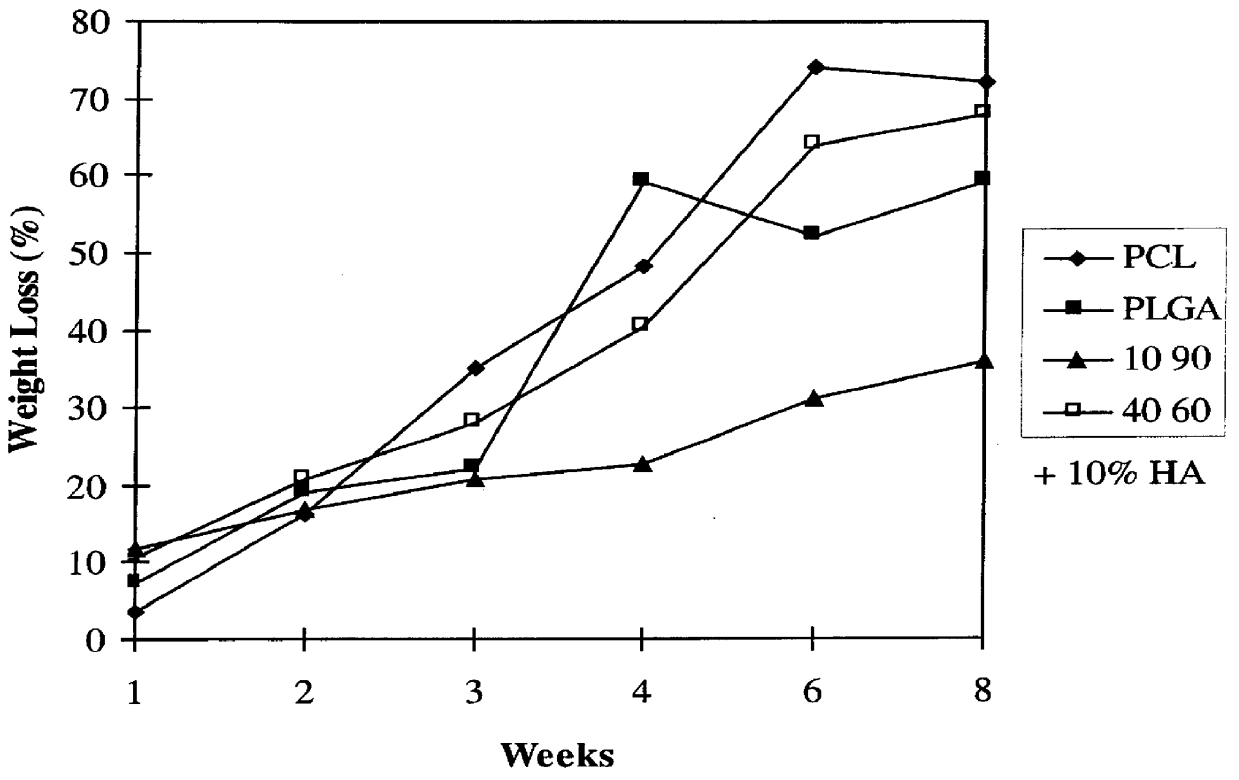
Blends of biodegradable polymers, preferably poly(caprolactone) and poly(D,L-lactic-co-glycolic) acid are discussed as well as their applications in the medical field, particularly with regard to bone tissue engineering. Preferably, hydroxyapatite ("HA") granules are incorporated into the blends and the resulting blends have desirable mechanical, physical, and biological characteristics. Even more preferably the compositions of the present invention are utilized to form osteoconductive composites that supported bone cell growth on the surface as well as throughout the scaffold.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV +1
Wound healing polymer compositions and methods for use thereof
The present invention provides bioactive polymer compositions that can be formulated to release a wound healing agent at a controlled rate by adjusting the various components of the composition. The composition can be used in an external wound dressing, as a polymer implant for delivery of the wound healing agent to an internal body site, or as a coating on the surface of an implantable surgical device to deliver wound healing agents that are covalently attached to a biocompatible, biodegradable polymer and / or embedded within a hydrogel. Methods of using the invention bioactive polymer compositions to promote natural healing of wounds, especially chronic wounds, are also provided. Examples of biodegradable copolymer polyesters useful in forming the blood-compatible, hydrophilic layer or coating include copolyester amides, copolyester urethanes, glycolide-lactide copolymers, glycolide-caprolactone copolymers, poly-3-hydroxy butyrate-valerate copolymers, and copolymers of the cyclic diester monomer, 3-(S)[(alkyloxycarbonyl)methyl]-1,4-dioxane-2,5-dione, with L-lactide. The glycolide-lactide copolymers include poly(glycolide-L-lactide) copolymers formed utilizing a monomer mole ratio of glycolic acid to L-lactic acid ranging from 5:95 to 95:5 and preferably a monomer mole ratio of glycolic acid to L-lactic acid ranging from 45:65 to 95:5. The glycolide-caprolactone copolymers include glycolide and ε-caprolactone block copolymer, e.g., Monocryl or Poliglecaprone.
Owner:MEDIVAS LLC
Polymer coating for medical devices
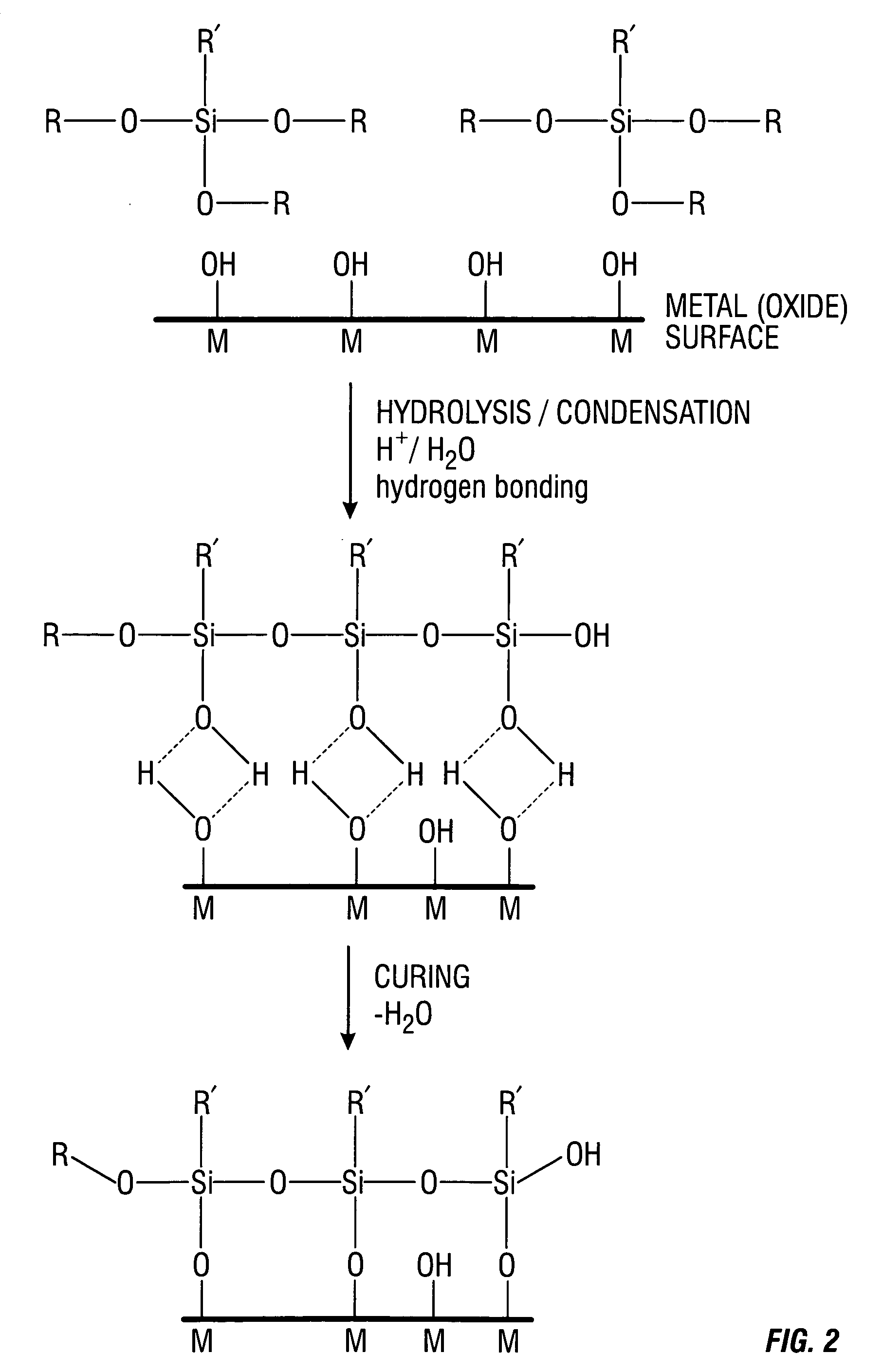
Coatings are provided in which surfaces may be activated by covalently bonding a silane derivative to the metal surface, covalently bonding a lactone polymer to the silane derivative by in situ ring opening polymerization, and depositing at least one layer of poly(lactide-co-caprolactone) copolymer on the bonded lactone. Biologically active agents may be disposed with the poly(lactide-co-caprolactone) copolymer layers. Such coated surfaces may be useful in medical devices, in particular stents.
Owner:CV THERAPEUTICS INC
Bioabsorbable and biocompatible polyurethanes and polyamides for medical devices
ActiveUS20060188547A1Low toxicitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsAbsorbable polymersPolyester
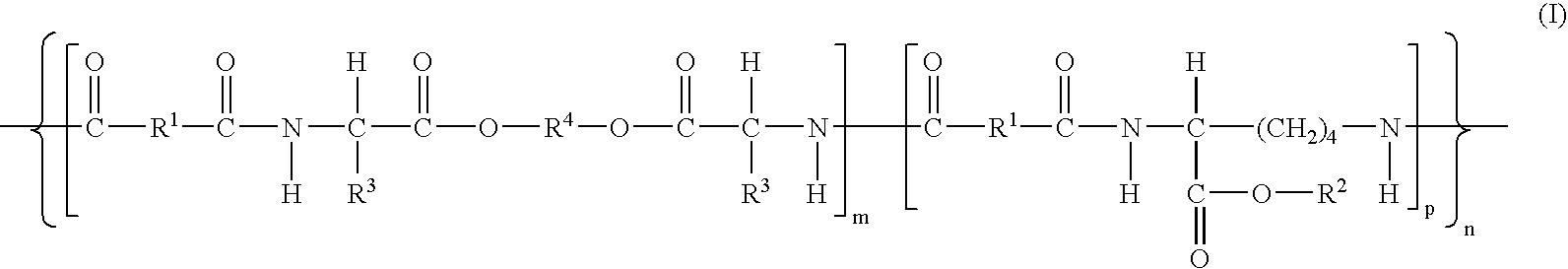
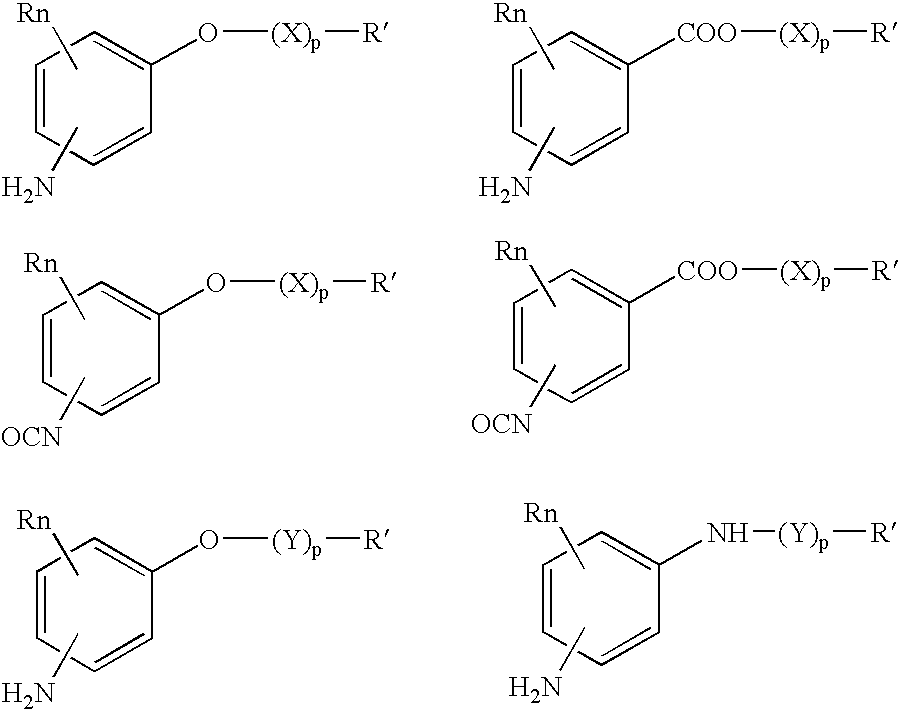
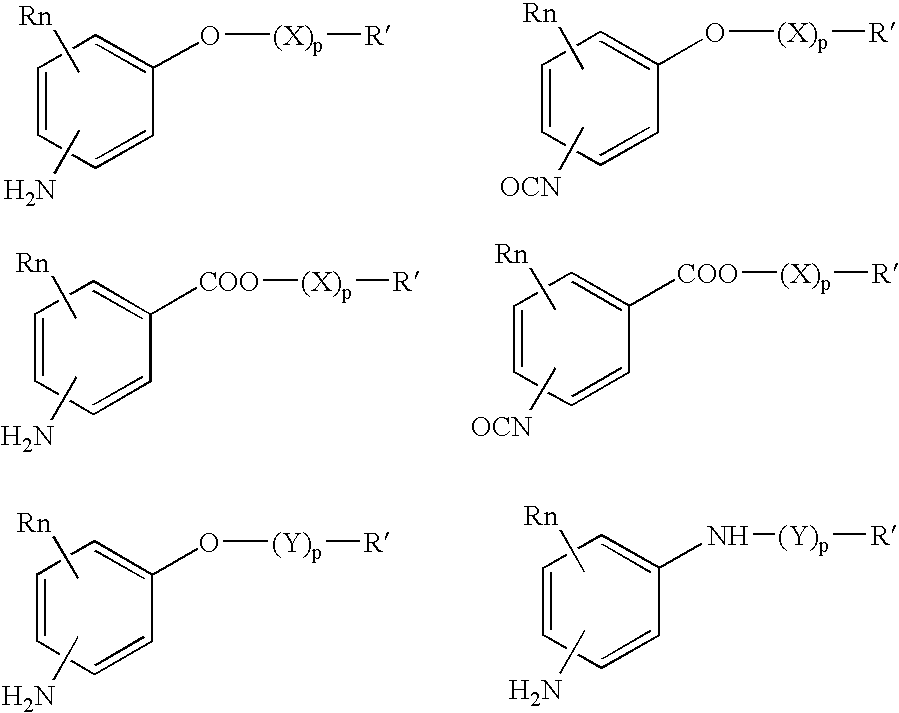
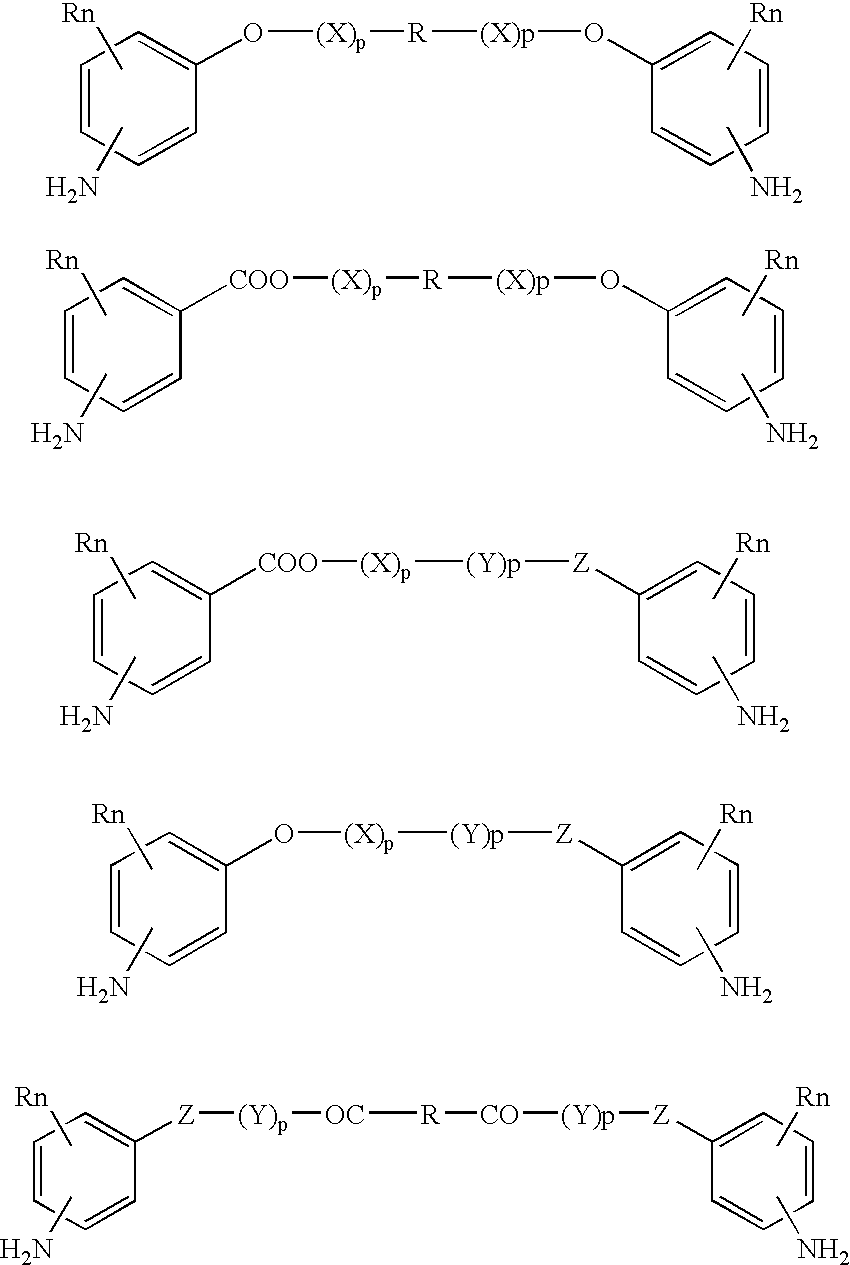
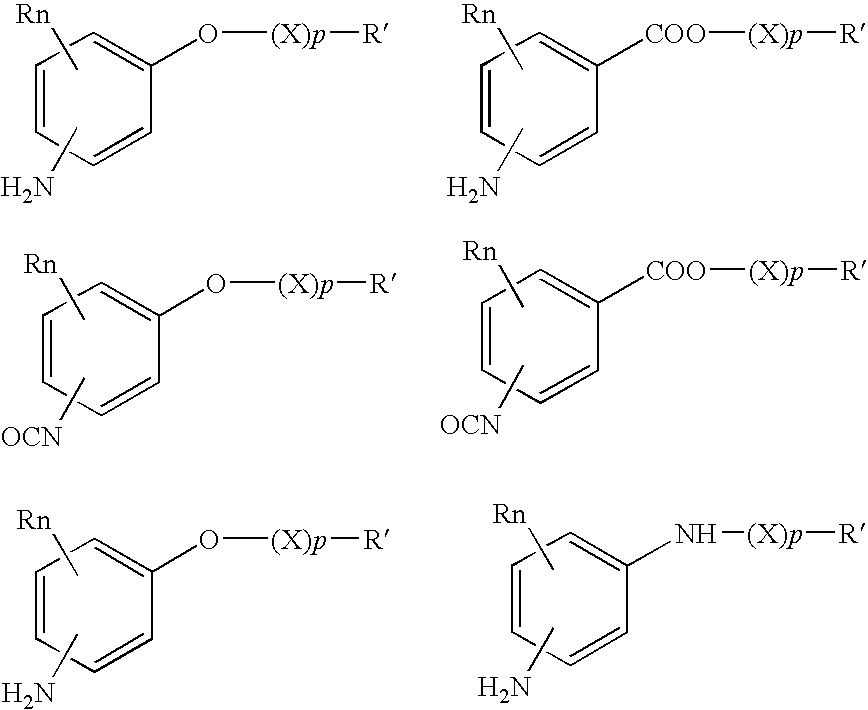
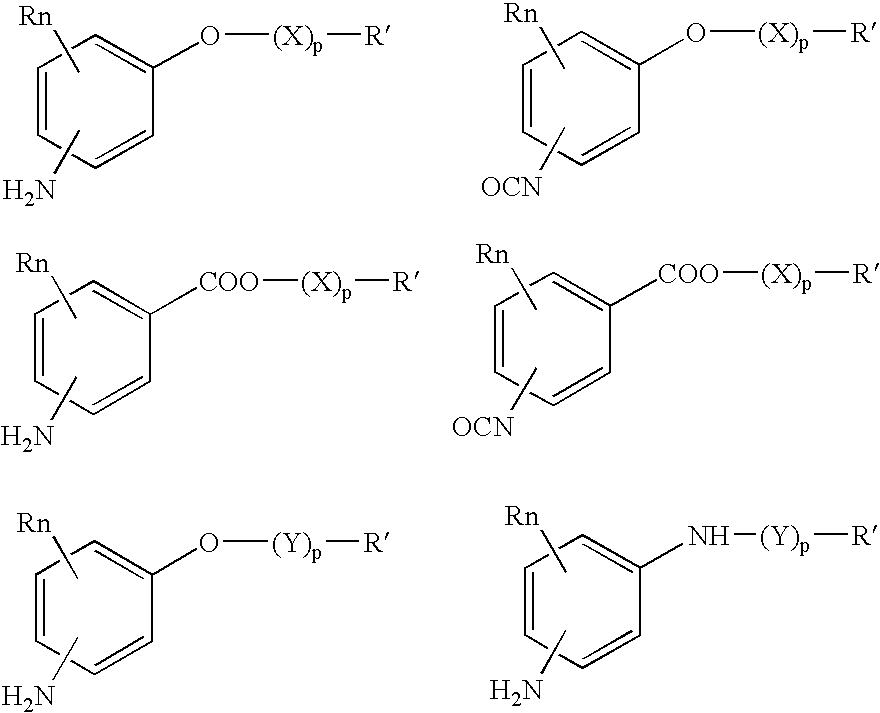
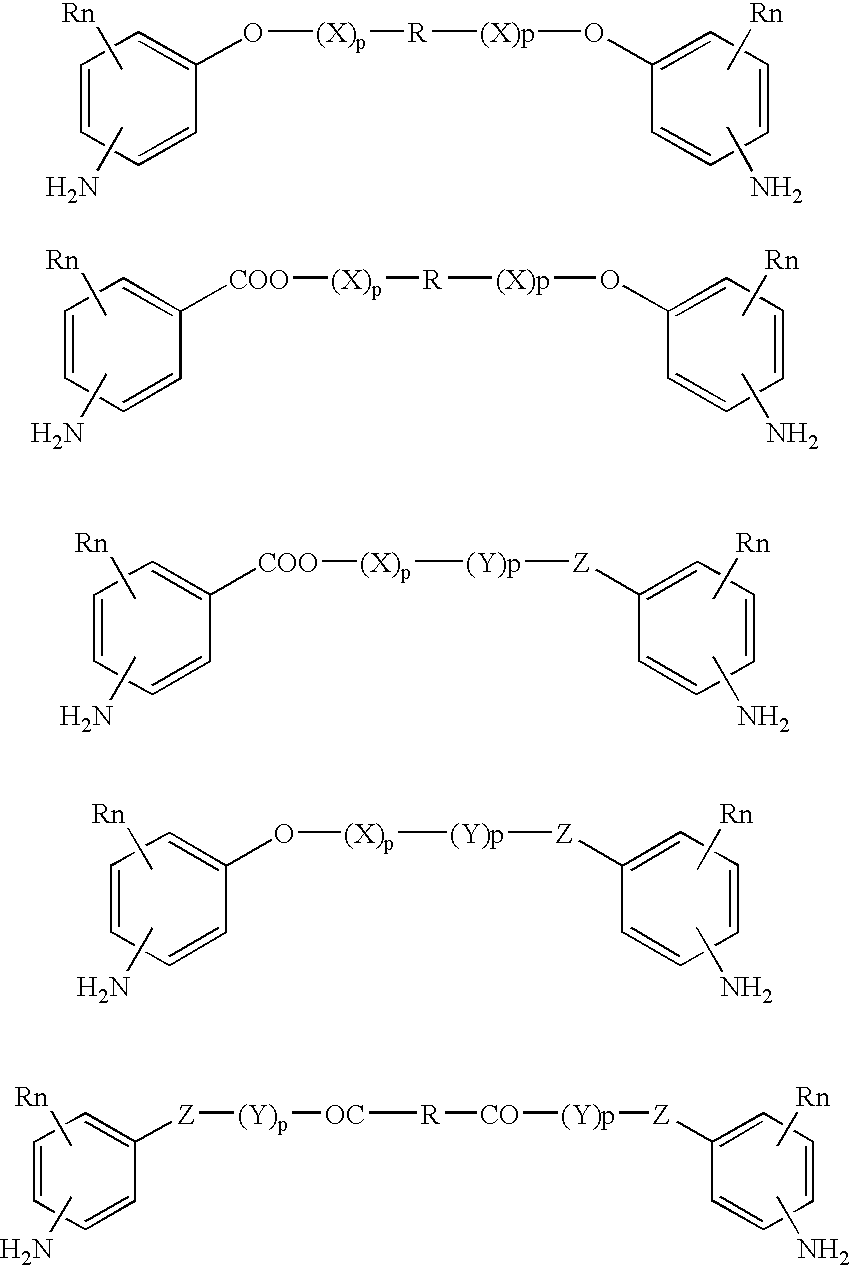
Absorbable polyurethanes, polyamides and polyester urethanes prepared from at least one compound selected from: or the diamines and diisocyanates thereof, wherein each X represents a member independently selected from —CH2COO— (glycolic acid moiety), —CH(CH3)COO— (lactic acid moiety), —CH2CH2OCH2COO— (dioxanone), —CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COO— (caprolactone moiety), —(CH2)yCOO— where y is one of the numbers 2, 3, 4 or 6-24 inclusive, and —(CH2CH2O)z′CH2COO— where z′ is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; each Y represents a member independently selected from —COCH2O— (glycolic ester moiety), —COCH(CH3)O— (lactic ester moiety), —COCH2OCH2CH2O— (dioxanone ester), —COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2O— (caprolactone ester), —CO(CH2)mO— where m is an integer between 2, 3, 4 or 6-24 inclusive, —COCH2O(CH2CH2O)n— where n is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; R′ is hydrogen, benzyl or an alkyl group, the alkyl group being either straight-chained or branched; p is an integer between 1 and 4, inclusive; and Rn represents one or more members selected from H, alkoxy, benzyloxy, aldehyde, halogen, carboxylic acid and —NO2, which is attached directly to an aromatic ring or attached through an aliphatic chain. Absorbable polymers prepared from these compounds are useful for drug delivery, tissue engineering, tissue adhesives, adhesion prevention and other implantable medical devices.
Owner:BEZWADA BIOMEDICAL LLC
Bioabsorbable and biocompatible polyurethanes and polyamides for medical devices
Absorbable polyurethanes, polyamides and polyester urethanes prepared from at least one compound selected from:or the diamines and diisocyanates thereof, wherein each X represents a member independently selected from —CH2COO— (glycolic acid moiety), —CH(CH3)COO— (lactic acid moiety), —CH2CH2OCH2COO— (dioxanone), —CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COO— (caprolactone moiety), —(CH2)yCOO— where y is one of the numbers 2, 3, 4 or 6-24 inclusive, and —(CH2CH2O)z′CH2COO— where z′ is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; each Y represents a member independently selected from —COCH2O— (glycolic ester moiety), —COCH(CH3)O— (lactic ester moiety), —COCH2OCH2CH2O— (dioxanone ester), —COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2O— (caprolactone ester), —CO(CH2)mO— where m is an integer between 2, 3, 4 or 6-24 inclusive, —COCH2O(CH2CH2O)n— where n is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; R′ is hydrogen, benzyl or an alkyl group, the alkyl group being either straight-chained or branched; p is an integer between 1 and 4, inclusive; and Rn represents one or more members selected from H, alkoxy, benzyloxy, aldehyde, halogen, carboxylic acid and —NO2, which is attached directly to an aromatic ring or attached through an aliphatic chain. Absorbable polymers prepared from these compounds are useful for drug delivery, tissue engineering, tissue adhesives, adhesion prevention and other implantable medical devices.
Owner:BEZWADA BIOMEDICAL LLC
Hydrogel Porogents for Fabricating Biodegradable Scaffolds
InactiveUS20080206308A1Rheologic propertyElimination of porogen leaching stepPowder deliveryBiocideBiodegradable scaffoldBiodegradable hydrogels
Hydrogel microparticles with entrapped liquid are used as the porogen to reproducibly form interconnected pore networks in a porous scaffold. In one embodiment, a biodegradable unsaturated polymer, a crosslinking agent, and a porogen comprising biodegradable hydrogel microparticles are mixed together and allowed to form a porous scaffold in an mold or in a body cavity. Example biodegradable unsaturated polymers include poly(propylene fumarate) and poly(e-caprolactone-fumarate). The cosslinking agent may be a free radical initiator, or may include a free radical initiator and a monomer capable of addition polymerization. Example hydrogel microparticles include uncrosslinked or crosslinked collagen , an uncrosslinked or crosslinked collagen derivative, and an uncrosslinked or crosslinked synthetic biodegradable polymer such as oligo(poly(ethylene glycol) fumarate).
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
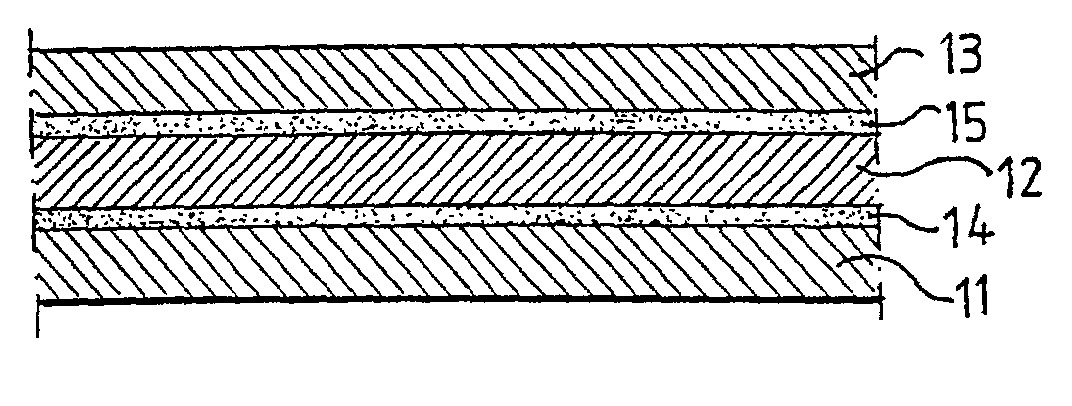
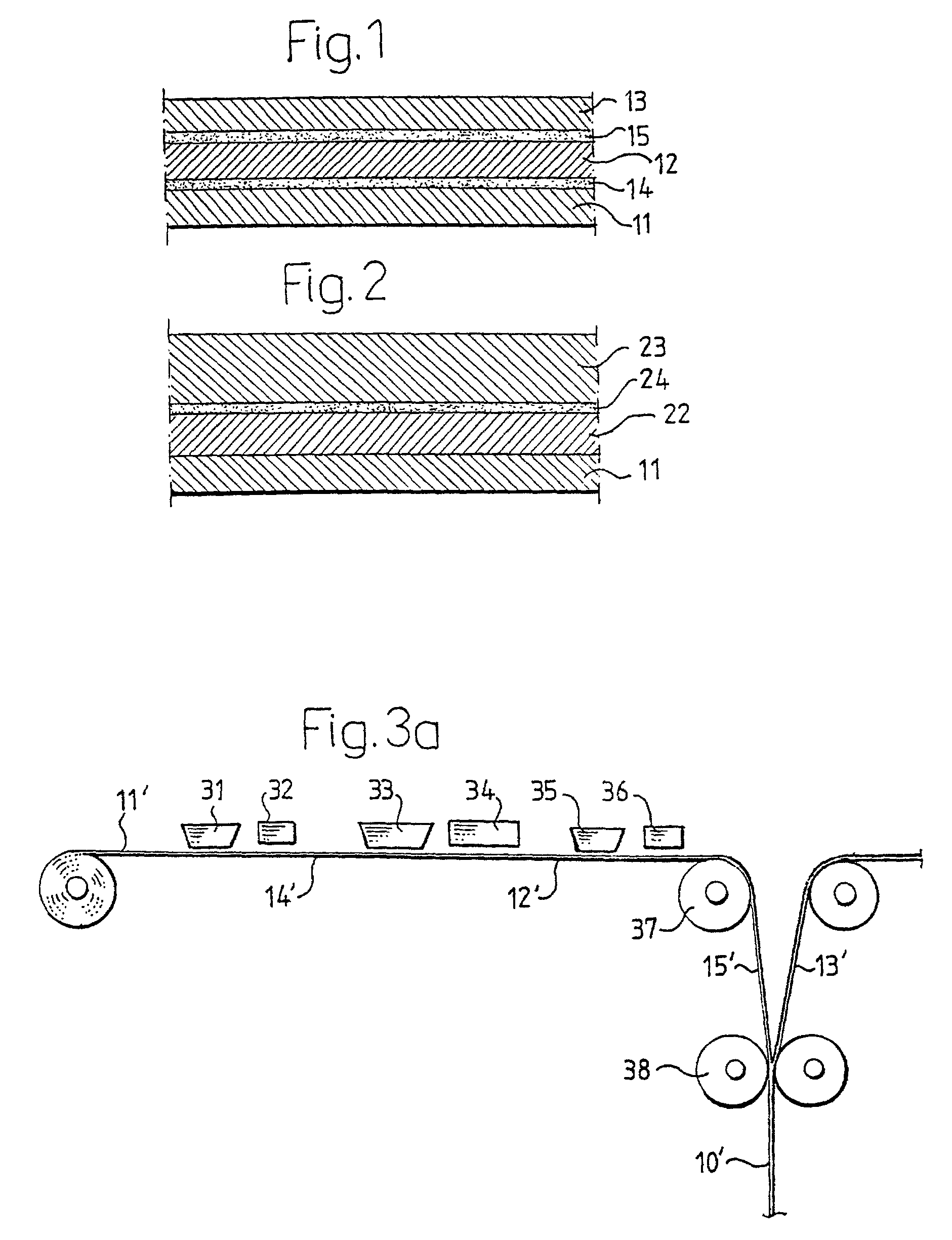
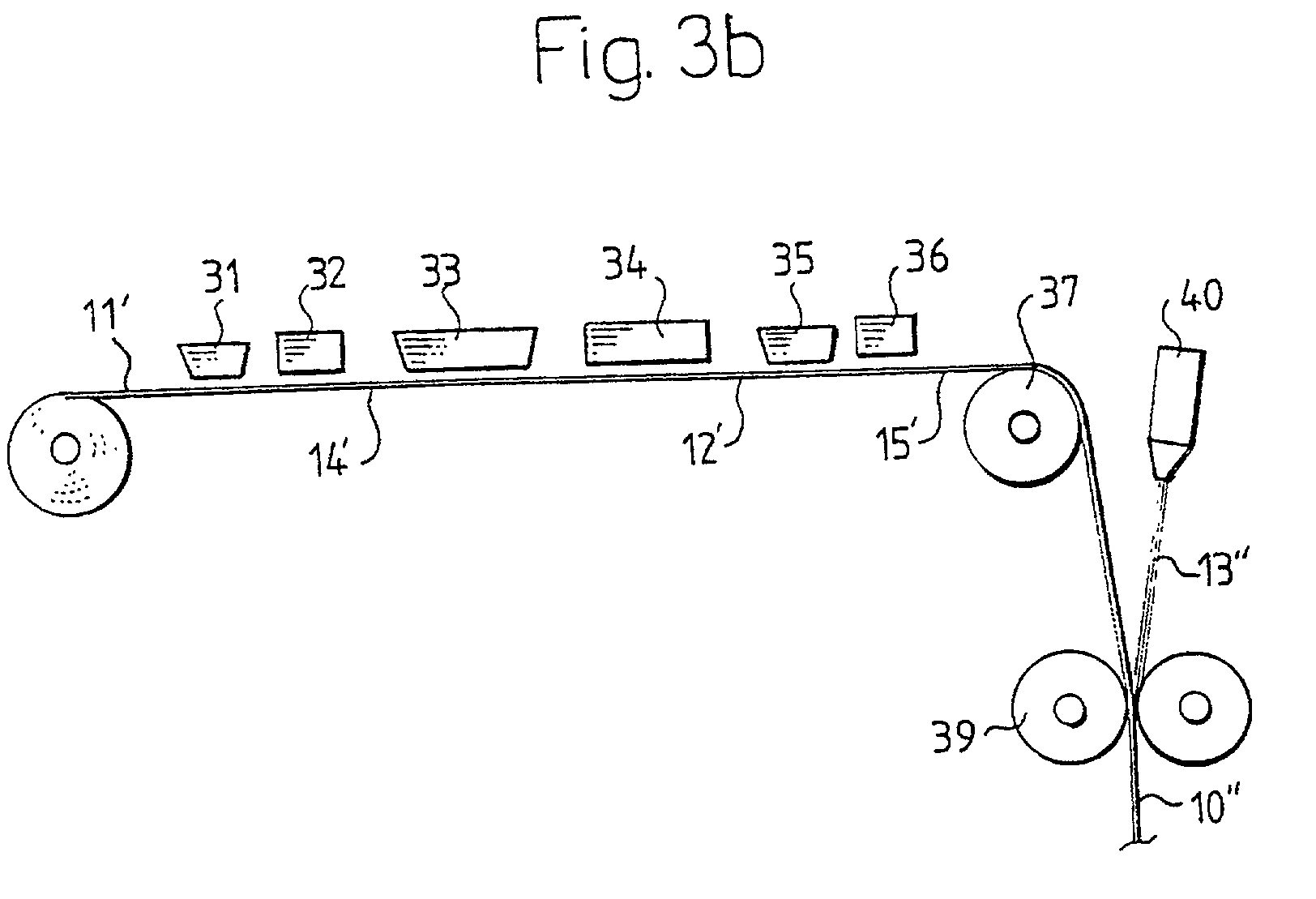
Biodegradable packaging laminate, a method of producing the packaging laminate, and packaging containers produced from the packaging laminate
InactiveUS20020127358A1Improve adhesionExcellent gas barrier performanceAdhesive processesLiquid surface applicatorsLactideBiopolymer
Packaging laminate for packages for liquid foods having excellent liquid and oxygen gas barrier properties in which all included layers are biodegradable. The packaging laminate includes at least one liquidtight layer (11, 13) of homo or copolymers of monomers selected from a group consisting of lactic acid, glycol acid, lactide, glycolide, hydroxy butyric acid, hydroxy valeric acid, hydroxy caproic acid, valerolactone, butyrolactone and caprolactone, as well as an oxygen gas barrier layer (12) of ethylene vinyl alcohol, polyvinyl alcohol, starch or starch derivatives. The oxygen gas barrier layer is preferably applied by a dispersion coating process. The layers may be laminated directly to one another or indirectly by means of interjacent adhesive layers. The packaging laminate may also include a core layer of, for example, paper or paperboard, or a biopolymer. The invention also realises a method of producing the biodegradable packaging laminate according to the invention.
Owner:TETRA LAVAL HLDG & FINANCE SA
Bioabsorbable blends and surgical articles therefrom
InactiveUS7138441B1Excellent flexibiltyExcellent Adhesive PropertiesSuture equipmentsSurgical adhesivesCyanoacrylatePolymer science
Blends made of bioabsorbable materials including glycolide, lactide, caprolactone, dioxanone, trimethylene carbonate, alkylene glycols, esteramides, etc., and polymers and copolymers thereof with cyanoacrylates are described. Processes for making the polymers and surgical articles made totally or in part from such polymers, including sutures, are also described.
Owner:UNITED STATES SURGICAL CORP
Adhesion-Preventive Film
InactiveUS20080090936A1Good flexibilityProvide effectSuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsLactideCaprolactone
An adhesion-preventive film is provided that is excellent in flexibility and can prevent cracks from occurring. The adhesion-preventive film contains a copolymer of lactide and caprolactone. The lactide and the caprolactone of the copolymer has a mole ratio in the range of 65:35 to 80:20. Even when this adhesion-preventive film is used in a curved state in vivo or is wound around an affected part such as a tendon, for example, it can provide an adhesion-preventive function for a sufficiently long period without cracking.
Owner:JMS CO LTD
Heat curable adhesive composition, article, semiconductor apparatus and method
InactiveUS20080090085A1Lose resistanceLose strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSynthetic resin layered productsEpoxySemiconductor chip
Provided are a heat curable adhesive composition and an adhesive article suited for dicing of a semiconductor and die-bonding of the diced semiconductor chip, and a semiconductor apparatus and a process for preparing a semiconductor apparatus using the adhesive composition and article. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a heat curable adhesive composition comprising a caprolactone-modified epoxy resin and a tack reducing component. Another embodiment of the present invention provides an adhesive article comprising a heat curable adhesive layer of a heat curable adhesive composition comprising a caprolactone-modified epoxy resin, a tack reducing component, and a backing layer carrying said adhesive layer on at least a portion of the backing layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Method for preparing caprolactone from cyclohexanone by catalytic oxidation
InactiveCN101307045AHigh yieldHigh selectivityOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCyclohexanoneHalogen
The invention relates to a method for preparing caprolactone through cyclohexanone catalytic oxidation. The method comprises the following steps that: raw materials, namely cyclohexanone, oxidant, solvent and catalyst, are respectively added to a reaction vessel; the reaction vessel is heated to at a temperature between 40 and 100 DEG C; constant temperature reaction is carried out for 1-15 hours; after the reaction is finished, the raw materials are cooled and separated, and then a finished product of caprolactone can be obtained, wherein the catalyst contains 50-100 percent of zinc oxide and 50-0 percent of other metallic oxide in weight percentage; the solvent is nitrile; the oxidant is hydrogen peroxide or peracetic acid. High caprolactone yield and selectivity can be obtained by adopting the method provided by the invention; meanwhile, the catalyst used in the method is low in price, easy to get and simple to prepare, contains no halogen element, has high stability, and can be used repeatedly.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Ternary mixture of biodegradable polyesters and products obtained therefrom
InactiveUS6841597B2RapidityImproves UV stabilitySynthetic resin layered productsPaper coatingPolymer scienceBiodegradable polyester
The invention relates to a mixture of biodegradable polyesters comprising: (A) a polyhydroxy acid of the poly-ε-caprolactone type and its copolymers, (B) aliphatic polyester, and (C) a polymer of polylactic acid, in which the concentration of (A) varies with respect to (A+B) in the range between 40 and 70% by weight, and the concentration of (C) with respects to (A+B+C) lies between 2 and 30%.
Owner:NOVAMONT SPA
Ternary mixture of biodegradable polyesters and products obtained therefrom
InactiveUS20040092672A1RapidityMaintain transparencyFlexible coversWrappersPolymer scienceBiodegradable polyester
The invention relates to a mixture of biodegradable polyesters comprising: (A) a polyhydroxy acid of the poly-epsilon-caprolactone type and its copolymers, (B) aliphatic polyester, and (C) a polymer of polylactic acid, in which the concentration of (A) varies with respect to (A+B) in the range between 40 and 70% by weight, and the concentration of (C) with respects to (A+B+C) lies between 2 and 30%.
Owner:NOVAMONT SPA
Drug-Impregnated Encasement
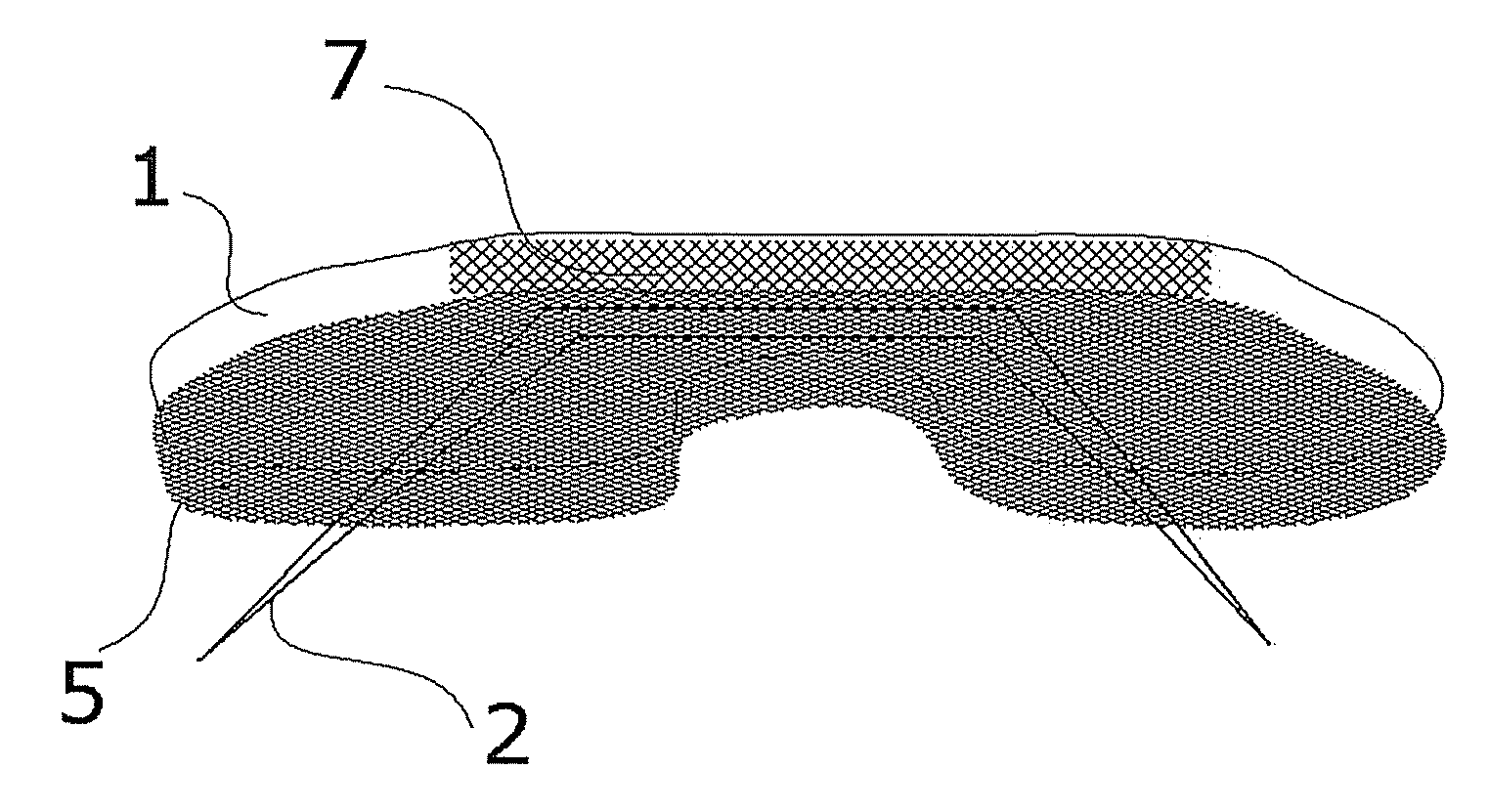
A drug-impregnated sleeve for encasing a medical implant is provided. In one embodiment, the sleeve may include a body made of a biologically-compatible material that defines an internal cavity configured to receive the medical implant. In one embodiment, the biologically-compatible material is bioresorbable. The body may include a plurality of apertures, such as perforations or holes, extending from the cavity through the body. The sleeve may further include a first end, a second end, and a drug impregnated into the resorbable sheet. In one possible embodiment, the first end of the sleeve may be open for receiving the medical implant therethrough and the second end may be closed. The implant may be encased in the sleeve and implanted into a patient from which the drug is dispensed in vivo over time to tissue surrounding the implantation site. In one embodiment, the body is made from at least one sheet of a biologically-compatible material, hi one embodiment, the sleeve may be made in least in part from caprolactone to add stretchability to the sleeve.
Owner:SYNTHES GMBH
High strength fibers of L-lactide copolymers epsi-caprolactone and trimethylene carbonate and absorbable medical constructs thereof
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably epsi-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 25%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.4 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Surgical sutures made of mono- or multifilament yarns of the present copolymers will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
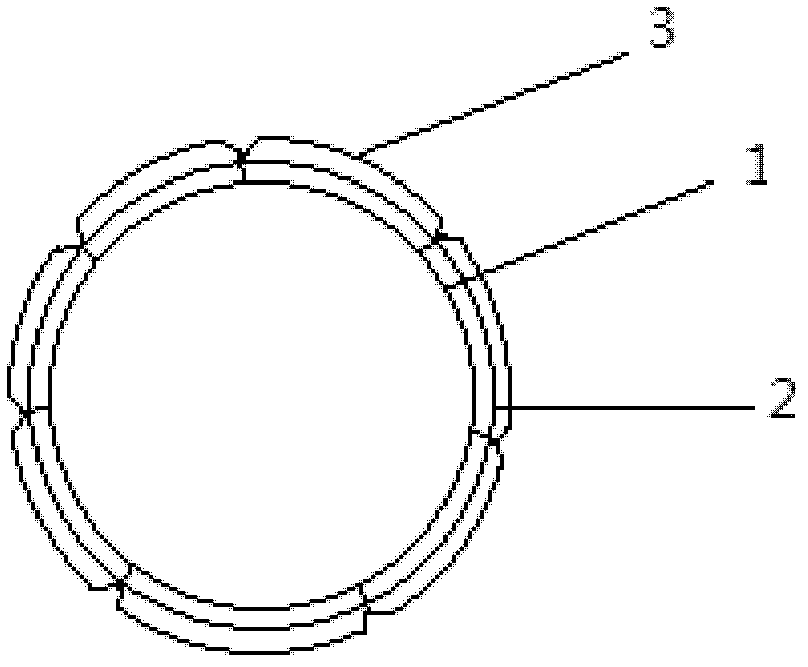
Blood vessel stent and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a blood vessel stent, which comprises an inner layer, a middle layer and an outer layer. The inner layer is made of an electrostatic spinning screen blended by silk fibroin and PLCL (caprolactone), the middle layer is made of an electrostatic spinning screen blended by silk fibroin and PLCL and is sleeved outside the inner layer, the outer layer is a silk fibroin braided hose and sleeved outside the middle layer, and the inner layer, the middle layer and the outer layer are connected in a stitching manner so that intermittent annular spaces are respectively formed between the inner layer and the middle layer and between the middle layer and the outer layer. The blood vessel stent has fine biological compatibility, can be used for repairing of small-bore blood vessels, and can be matched with blood vessels of hosts due to the compliance thereof.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
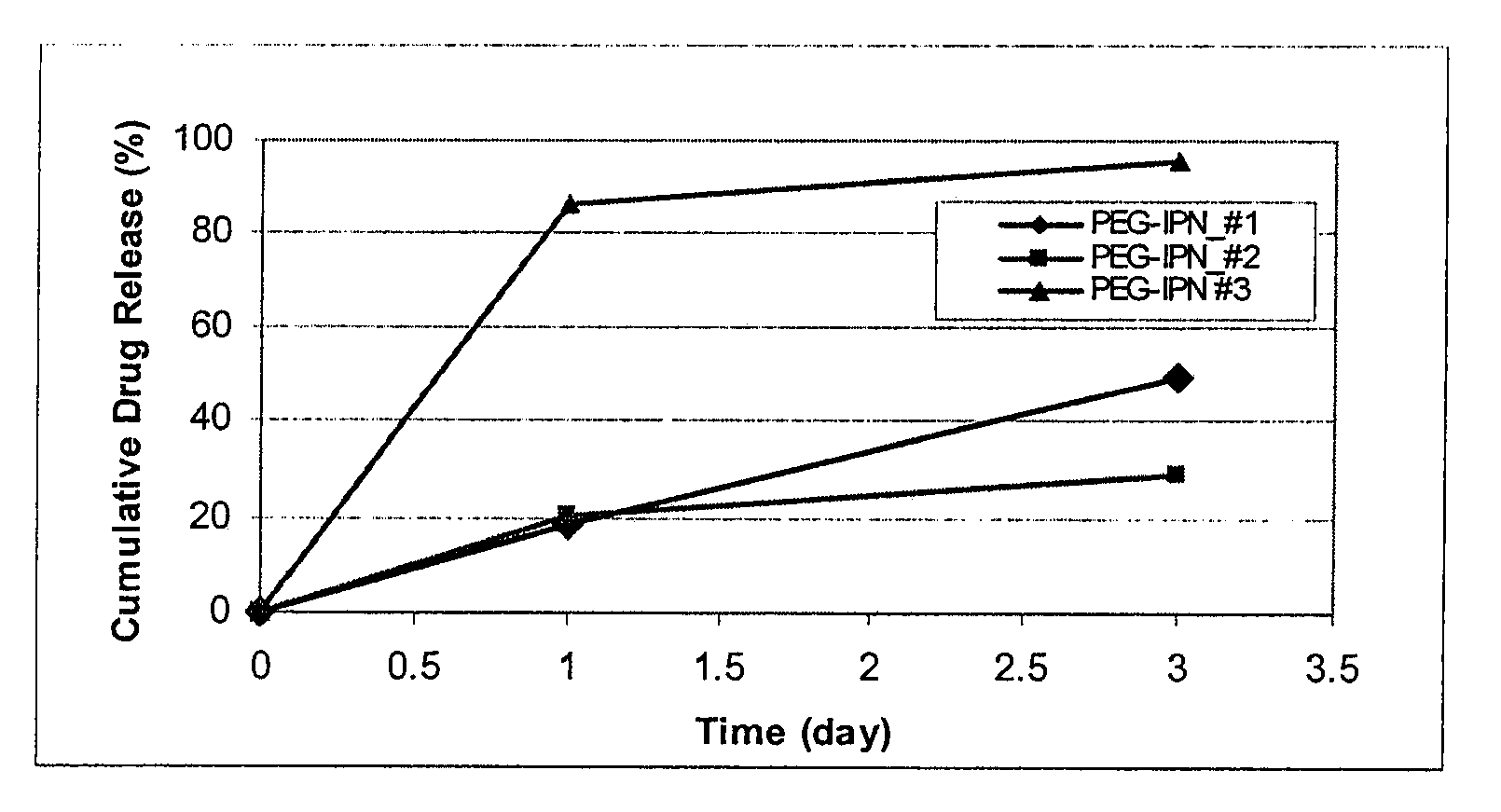
Coating comprising poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (lactide-glycolide-caprolactone) interpenetrating network
Methods for fabricating coatings for implantable medical devices are disclosed. The method comprises forming a coating on an implantable device comprising an interpenetrating network or semi-interpenetrating network. The interpenetrating network or semi-interpenetrating network comprises poly(ethylene glycol) and an aliphatic polyester copolymer. It is also provided an implantable device and a method of using the implantable device.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Implantable elastomeric caprolactone depot compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070184084A1Reduce dosing frequencyPatient compliance is goodAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsControlled releaseElastomer
Methods and compositions for systemically or locally administering a beneficial agent to a subject are described, and include, for example, implantable elastomeric depot compositions that can be injected into a desired location and which can provide controlled release of a beneficial agent over a prolonged duration of time. The compositions include a biocompatible, elastomeric caprolactone copolymer, a biocompatible solvent having low water miscibility that forms an elastomeric viscous gel with the polymer and limits water uptake by the implant, and a beneficial agent.
Owner:DURECT CORP
Heat curable adhesive composition, article, semiconductor apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050224978A1Lose heat resistanceLose shear strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEpoxySemiconductor chip
Provided are a heat curable adhesive composition and an adhesive article suited for dicing of a semiconductor and die bonding of the diced semiconductor chip, and a semiconductor apparatus and a process for preparing a semiconductor apparatus using the adhesive composition and article. In one embodiment, the present invention provides a heat curable adhesive composition comprising a caprolactone-modified epoxy resin and a tack reducing component. Another embodiment of the present invention provides an adhesive article comprising a heat curable adhesive layer of a heat curable adhesive composition comprising a caprolactone-modified epoxy resin, a tack reducing component, and a backing layer carrying said adhesive layer on at least a portion of the backing layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Injection-moldable thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer
InactiveUS6521164B1Reduces intermolecular hydrogen bondingPromote sportsCoatingsThermoplastic polyurethaneDiol
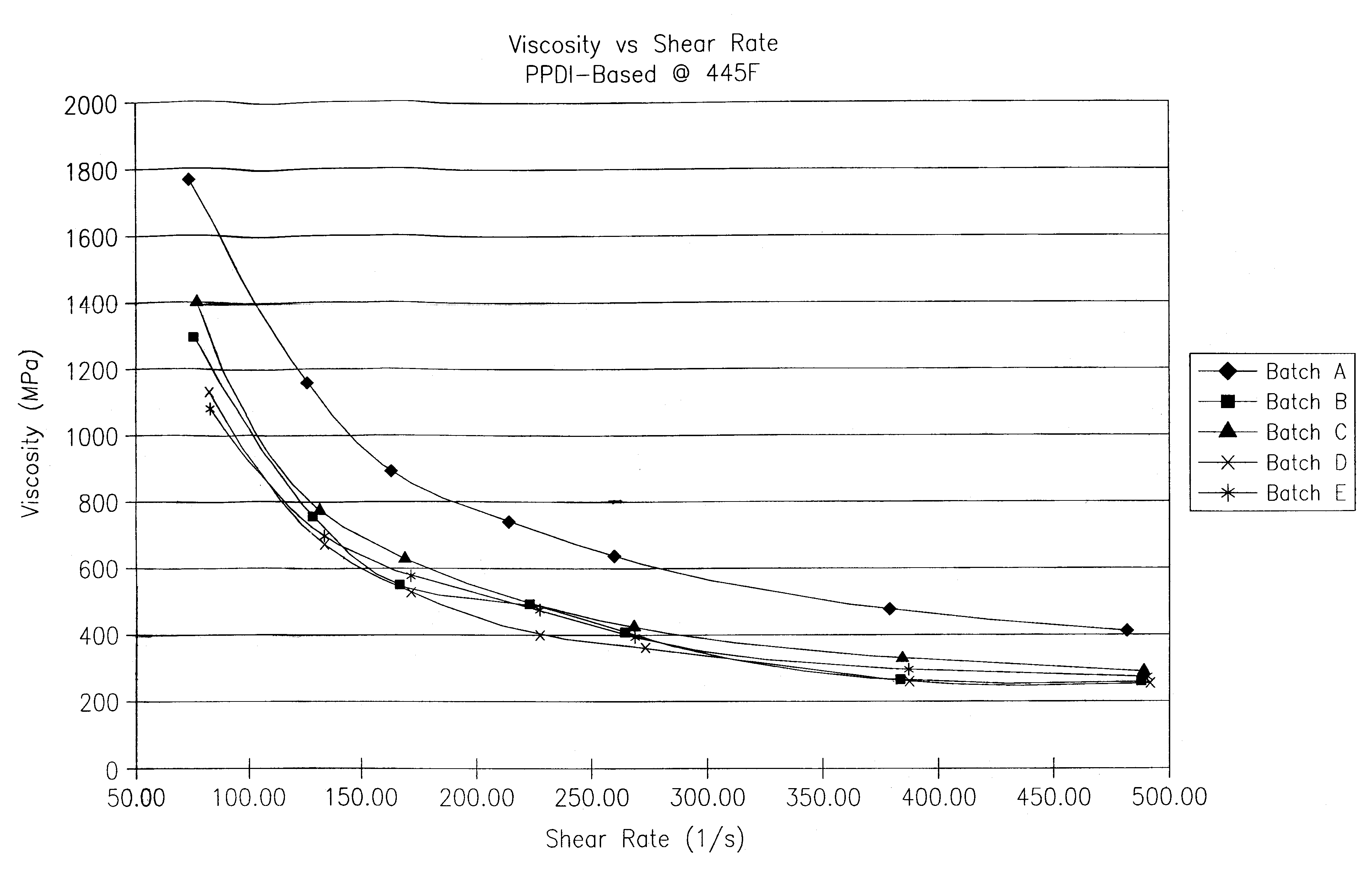
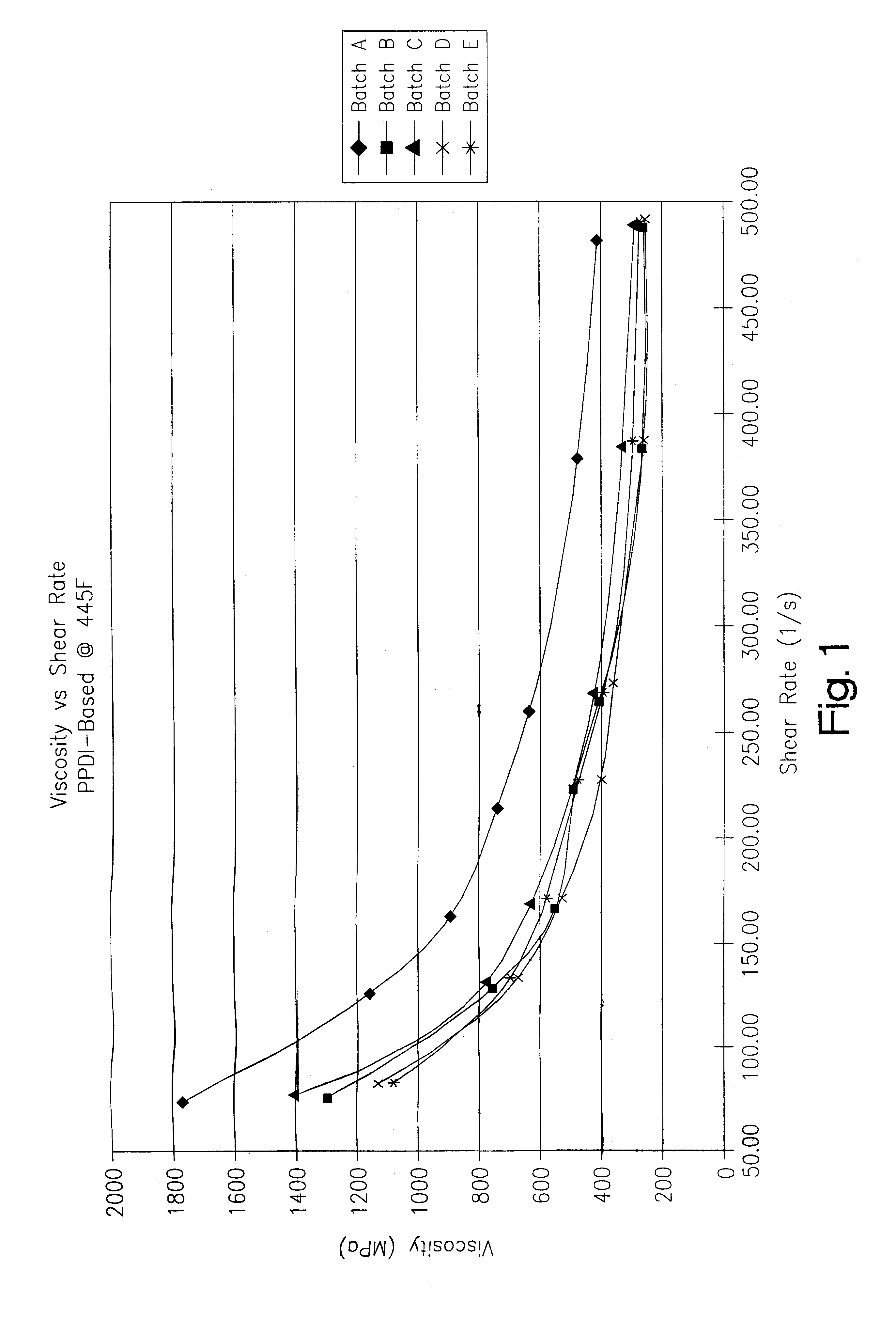
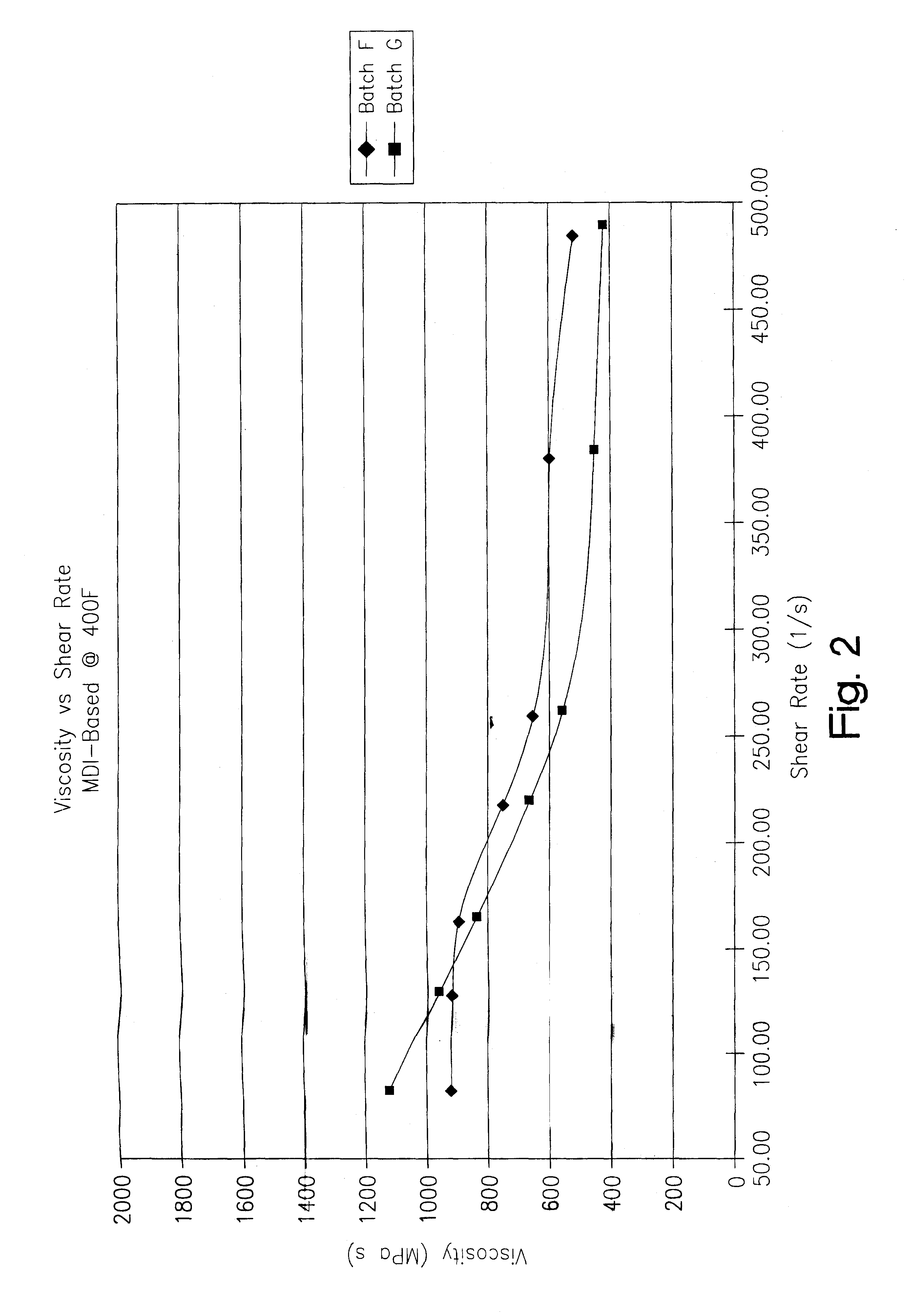
A thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) elastomer and p-phenylene diisocyanate (PPDI) / polycaprolactone-based composition therefor having a unique chain extender combination for improved injection moldability. The elastomer is formed as the reaction product of: (A) from about 60 to 80% by weight of a hydroxyl-terminated poly(caprolactone) diol; (B) from about 17 to 22% by weight of a p-phenylene diisocyanate; (C) from about 3 to 10% by weight of a first hydroxyl-functional chain extender; and (D) less than about 2% by weight of a second hydroxyl-functional chain extender different from the first chain extender, the second chain extender being selected as effective to modify the crystallinity of the elastomer.
Owner:PARKER INTANGIBLES LLC
High strength fibers of l-lactide copolymers, epsilon-caprolactone, and trimethylene carbonate and absorbable medical constructs thereof
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably ε-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 20%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.1 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Surgical sutures made of mono- or multifilament yams of the present copolymers will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Nerve catheter as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101439205APromote regenerationHigh porosityFilament/thread formingCatheterMedicineActive component
The invention discloses a nerve duct and a preparation method as well as use thereof. The nerve duct is composed of 'shell-core' structured nanofiber, a core layer of the 'shell-core' structured nanofiber contains a biological active component, and a shell layer of the 'shell-core' structured nanofiber contains a biodegradable material; the inside diameter of the nerve duct is 0.5-5.0mm, and the outside diameter thereof is 1.0-6.0mm; the biological active component is a neurotrophic factor; and the biodegradable material is selected from one or more than one of the following components: polylactic-co-glycolic acid (PLGA), poly(lactic acid-caprolactone copolymer) (P (LLA-CL)) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) (PHB) or polyphosphoester (PPE).
Owner:SHANGHAI SIXTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Method for preparing polyester-polyester blocked copolyester
The invention discloses a method for preparing polyester-polyester blocked copolyester, which comprises the following steps: (1) synthesizing an aromatic polyester hard segment to obtain a prepolymer P1 with a number-average molecular weight in the range of 500-10,000g / mol; (2) synthesizing an aliphatic polyester soft segment to obtain a prepolymer P2, wherein the prepolymer P2 can also be obtained by ring-opening polymerization of caprolactone monomer, and the number-average molecular weight of the prepolymer P2 is in the range of 500-10,000g / mol; (3) carrying out polycondensation reaction of the aromatic polyester oligomer and the aliphatic polyester oligomer: mixing the esterified product P1 and the esterified product P2, adding antioxidant, catalyst, passsivator and chain expander, allowing reaction at 220-260 DEG C to obtain a polyester-polyester block polyester elastomer. The catalysts used in the steps (1) and (2) are selected from titanium-containing organic substances. The method disclosed by the invention has the following advantages: (1) because the aliphatic polyester soft segment is introduced, the product has both the mechanical properties of the rigid aromatic polyester hard segment and the flexibility of the soft segment; and (2) because a number of assistants are added, the good chain expansion effect is achieved, and the reaction conditions are controlled.
Owner:KINGFA SCI & TECH CO LTD +2
Method for improving water resisting performance of polyvinyl alcohol film from polycaprolactone and polylactic acid
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Bioabsorbable Polymeric Compositions and Medical Devices
The present invention comprises a stent forming a plurality of meandering elements comprising a blend formed from a polymer. The polymer comprises poly-L-lactide, poly-D-lactide or mixtures thereof and a copolymer moiety comprising poly-L-lactide or poly-D-lactide linked with ε-caprolactone or trimethylcarbonate. The poly-L-lactide or poly-D-lactide sequence in the copolymer moiety is random with respect to the distribution of ε-caprolactone or trimethylcarbonate and the copolymer moiety molecular weight ranges from about 1.2 IV to about 4.8 IV. The meandering elements may be stretched to a modulus ranging from about 250000 PSI to about 550,000 PSI, one segment of the meandering element has a decreased cross-sectional area and may have a wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) 2θ values of ranging from about 1 to about 35. In various embodiment, two, three or n segments of the meandering element have a decreased cross-sectional area and may also have a wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) 2θ values of ranging from about 1 to about 35 after stretching. In another embodiment, all segments of the meandering element have a decreased cross-sectional area and may also have a wide-angle X-ray scattering (WAXS) 2θ values of ranging from about 1 to about 35 after stretching. The meandering element may comprise a helical winding, a circumferential winding or stent ringlet. The properties of the bioabsorbable polymers allow for both crimping and expansion of the stent. The crystal properties of the bioabsorbable polymers may change during crimping and / or expansion allowing for improved mechanical properties such as tensile strength and slower degradation kinetics.
Owner:ORBUSNEICH MEDICAL PTE LTD
Microemulsions with adsorbed macromolecules and microparticles
InactiveUS8206749B1Powerful toolStimulate immune responseAntibacterial agentsDigestive systemHydroxybutyric acidAdjuvant
Microparticles with adsorbent surfaces, methods of making such microparticles, and uses thereof, are disclosed. The microparticles comprise a polymer, such as a poly(α-hydroxy acid), a polyhydroxy butyric acid, a polycaprolactone, a polyorthoester, a polyanhydride, and the like, and are formed using cationic, anionic, or nonionic detergents. The surface of the microparticles efficiently adsorb biologically active macromolecules, such as DNA, polypeptides, antigens, and adjuvants. Also provided are compositions of an oil droplet emulsion having a metabolizable oil and an emulsifying agent. Immunogenic compositions having an immunostimulating amount of an antigenic substance, and an immunostimulating amount of an adjuvant composition are also provided. Methods of stimulating an immune response, methods of immunizing a host animal against a viral, bacterial, or parasitic infection, and methods of increasing a Th1 immune response in a host animal by administering to the animal an immunogenic composition of the microparticles, and / or microemulsions of the invention, are also provided.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Biocompatible Material and Prosthetic Device Made Thereof for the Replacement, Repair and Regeneration of Meniscus
Herein described is a biocompatible material comprising a polymer matrix based on hyaluronic acid derivatives and poly-εCaprolactone, the process for preparing this material, a prosthetic device constituted by this biocompatible material and a reinforcing material, the process for preparing the prosthetic device, and its use for the partial or total replacement of meniscus, and regeneration of the meniscal fibrocartilage.
Owner:PROF LUIGI AMBROSIO
Functionalized phenolic esters and amides and polymers therefrom
InactiveUS20060173065A1Alter efficacyAlter valueBiocideOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidPhenylacetic acid
The present invention relates to a compound of the formula: R-AR—O—Y—R′Wherein R represents one or more members selected from H, alkoxy, benzyloxy, aldehyde, halogen, carboxylic acid, —NO2, —NH2, —NHCOCH3, and —NH—Y—R′, which is attached directly to AR or attached through an aliphatic chain. The carboxylic acid moiety in R includes but is not limited to the following carboxylic acids: benzoic acids, cinnamic acids, ferulic acid, caffeic acid, syringic acid, salicylic acid, vanillic acid, phenylacetic acids, phenylpropionic acids, and sinapinic acid. -AR—O— is a biologically active phenolic moiety comprising 1 to 6 substituted or unsubstituted aryl rings that are directly bonded to each other, fused together, or joined through a linking group. Y represents a member selected from: —COCH2O— (glycolic ester moiety) —COCH(CH3)O— (lactic ester moiety) —COCH2OCH2CH2O— (dioxanone ester moiety) —COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2O— (caprolactone ester moiety) —CO(CH2)mO— where m is an integer between 2-4 and 6-24 inclusive —COCH2O(CH2CH2O)n— where n is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; and R′ is either hydrogen or a benzyl or an alkyl group, the alkyl group being either straight-chained or branched. The resultant functionalized phenolic compounds, used singly or in combinations, and their polymers have controllable degradation profiles, releasing the active component over a desired time range. The polymers are useful for biomaterials and biomedical devices, wherein said biologically active phenolic moiety is a residue of a phenolic compound.
Owner:BEZWADA BIOMEDICAL LLC
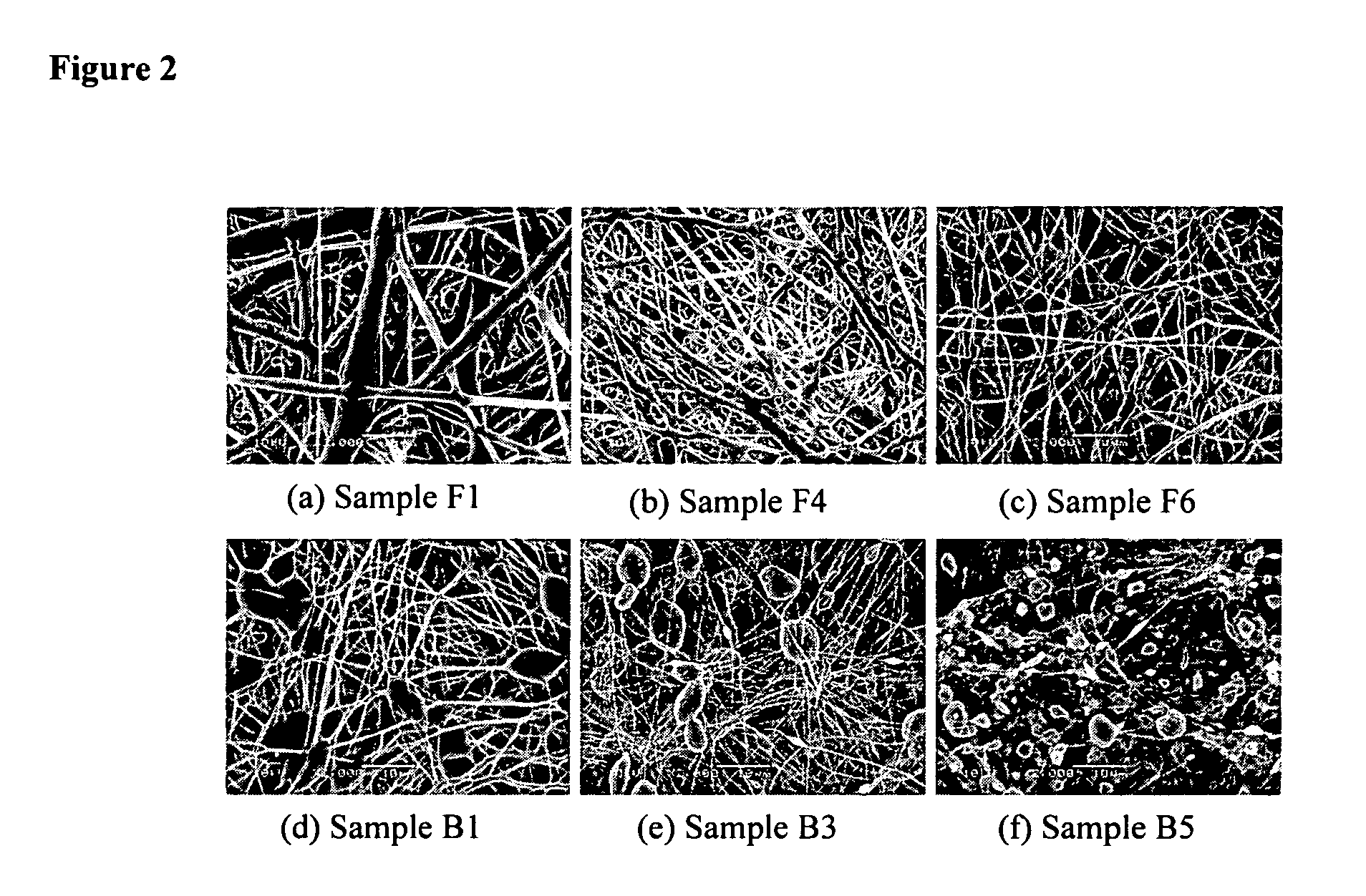
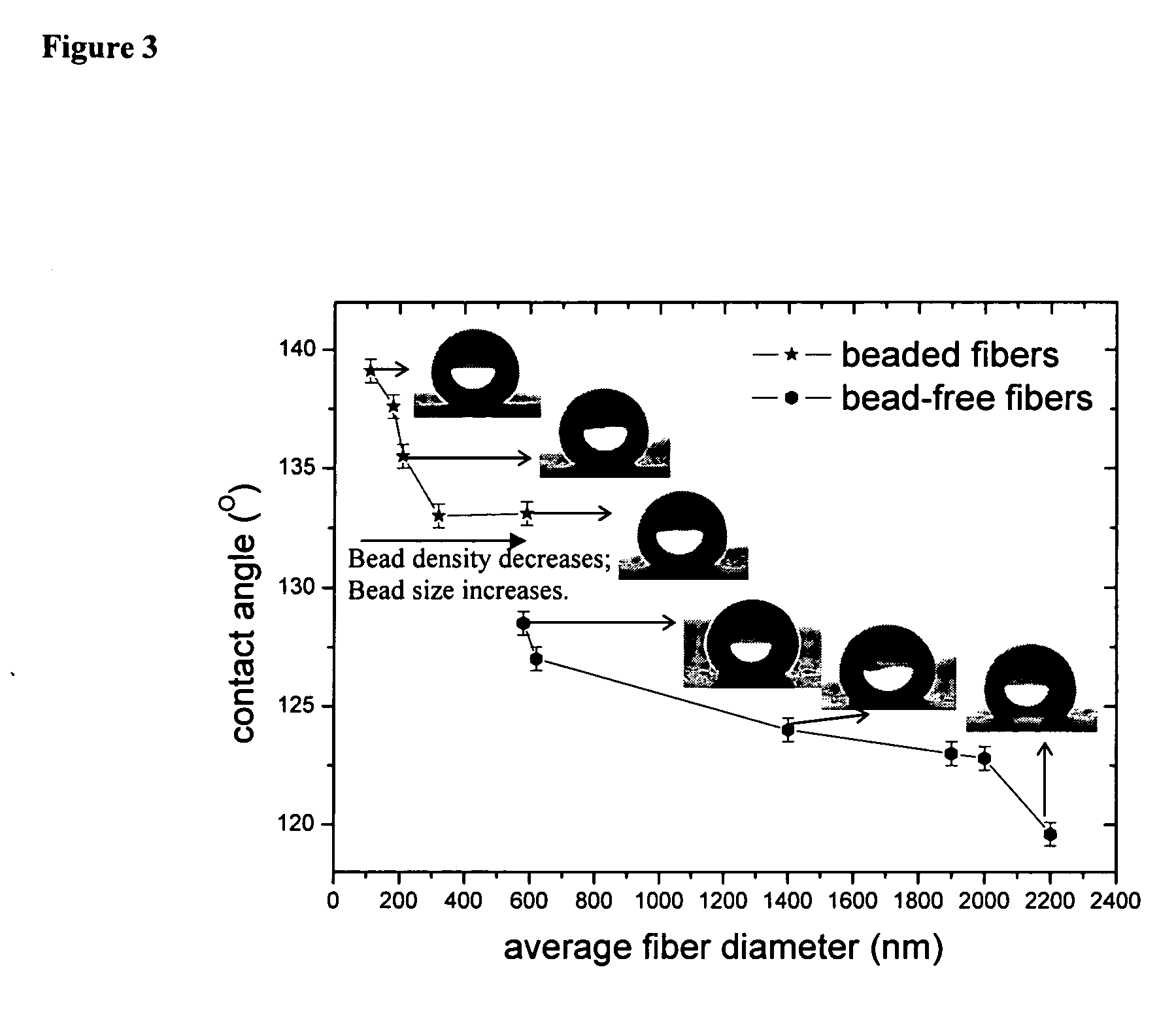
Superhydrophobic fibers produced by electrospinning and chemical vapor deposition
Disclosed is a versatile method to produce superhydrophobic surfaces by combining electrospinning and initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD). A wide variety of surfaces, including electrospun polyester fibers, may be coated by the inventive method. In one embodiment, poly(caprolactone) (PCL) was electrospun and then coated by iCVD with a thin layer of hydrophobic polymerized perfluoroalkyl ethyl methacrylate (PPFEMA). In certain embodiments said coated surfaces exhibit water contact angles of above 150 degrees, oleophobicities of at least Grade-8 and sliding angles of less than 12 degrees (for a water droplet of about 20 mg).
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Coated, slow-absorbing textile constructs for sutures and tissue engineering
The present invention is directed to crystalline copolymers of l-lactide and a minor portion of a cyclic monomer, preferably epsi-caprolactone or trimethylene carbonate or both. The present copolymers have a melting temperature of at least 150° C. and a crystallinity of at least 20%. Preferred are high molecular weight copolymers having an inherent viscosity of at least 1.1 dl / g. A variety of surgical constructs may be formed from the present copolymers. Disclosed are coated surgical constructs including sutures made of multifilament yarns of the present copolymers and coated with nitrogenous copolyesters which will bioabsorb in less than three years and will maintain at least 50% of their initial strength three weeks post-operatively.
Owner:POLY MED
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com