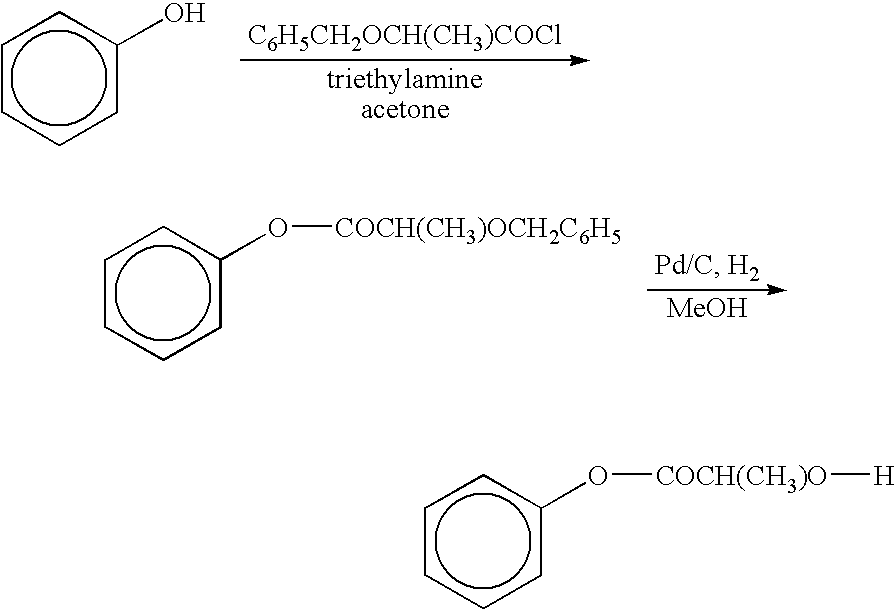
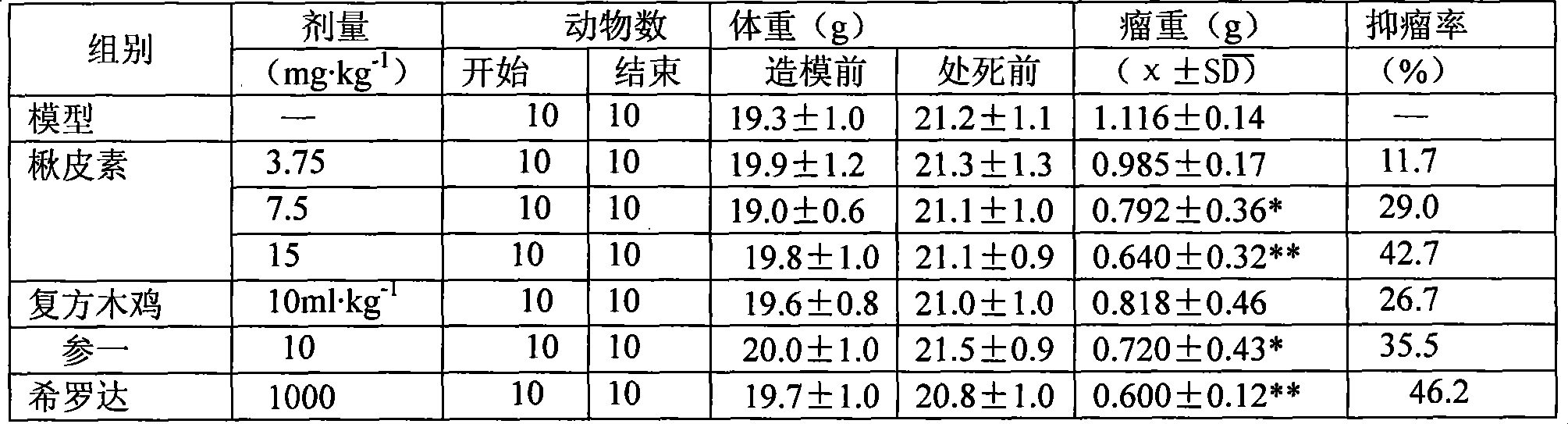
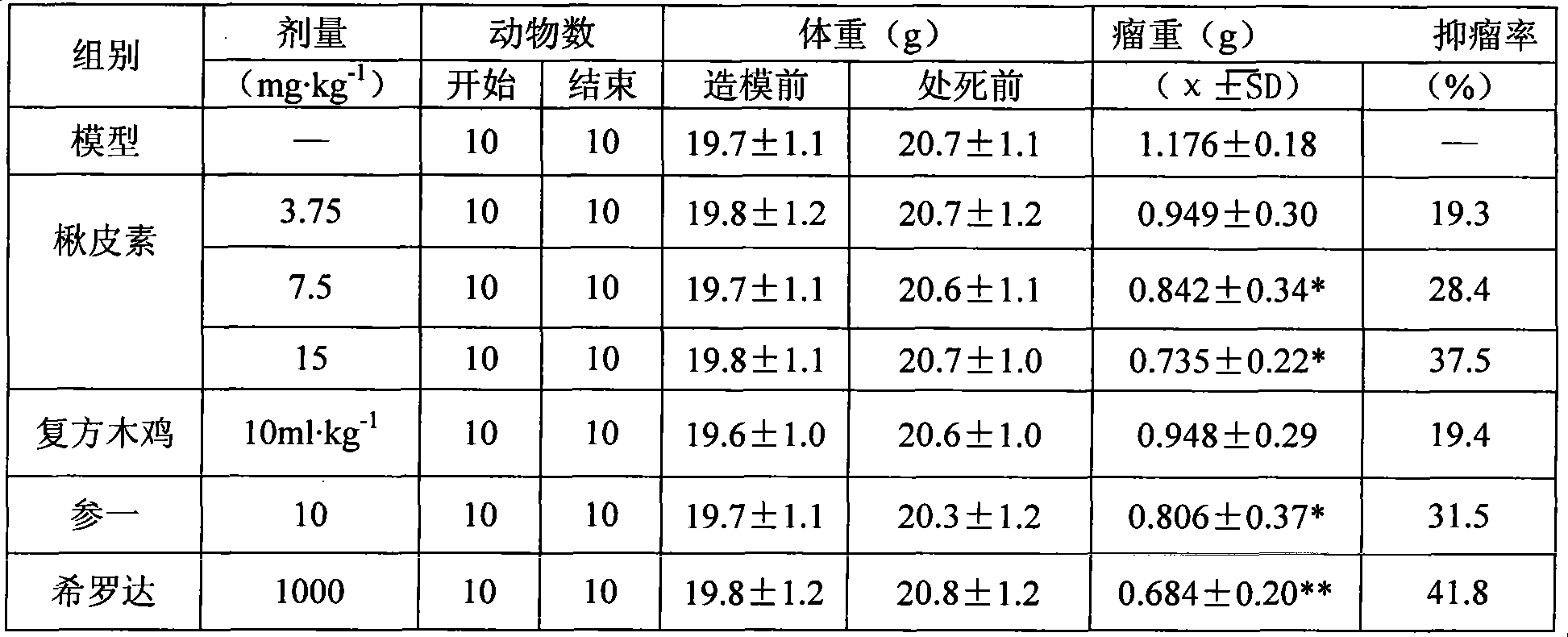
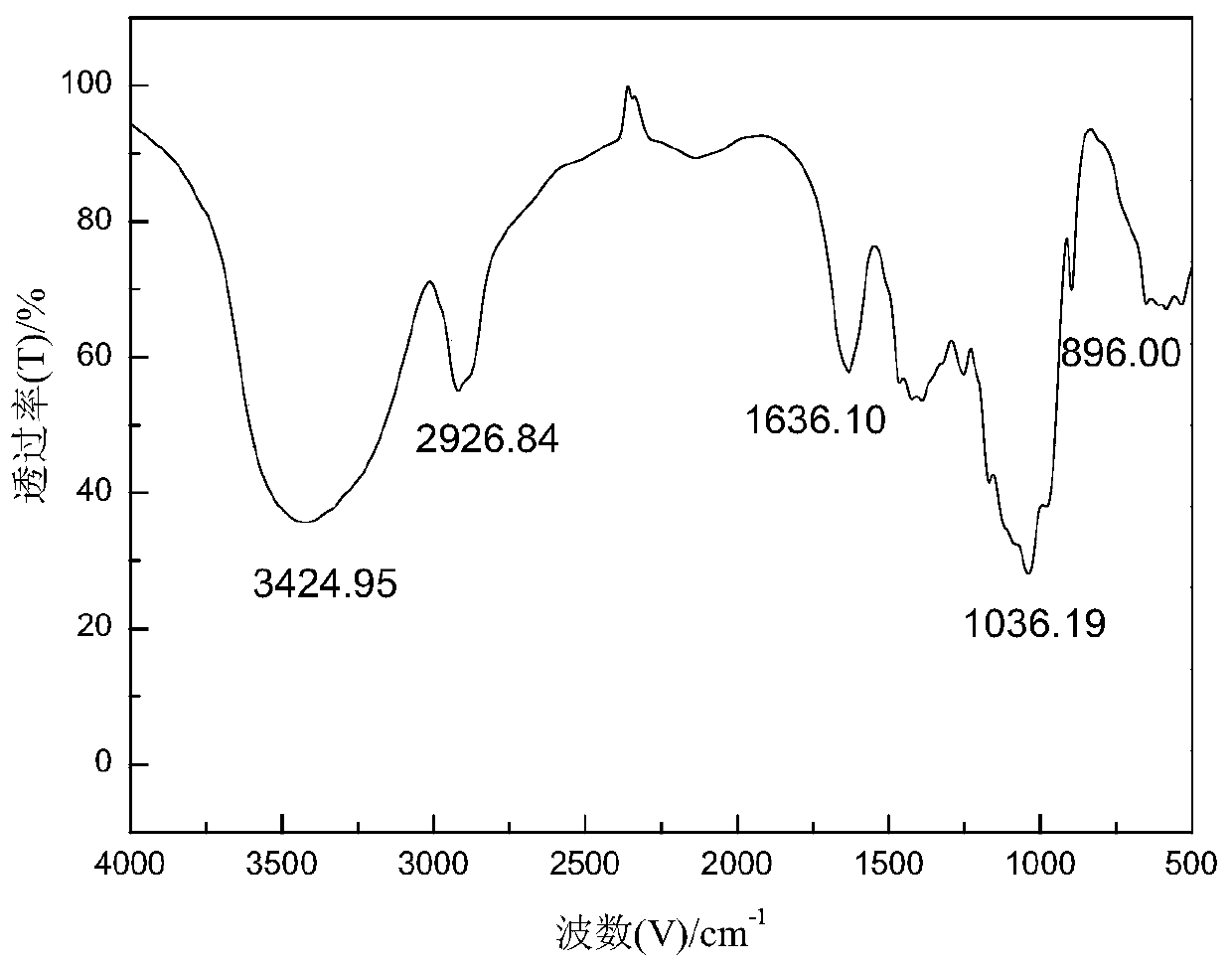
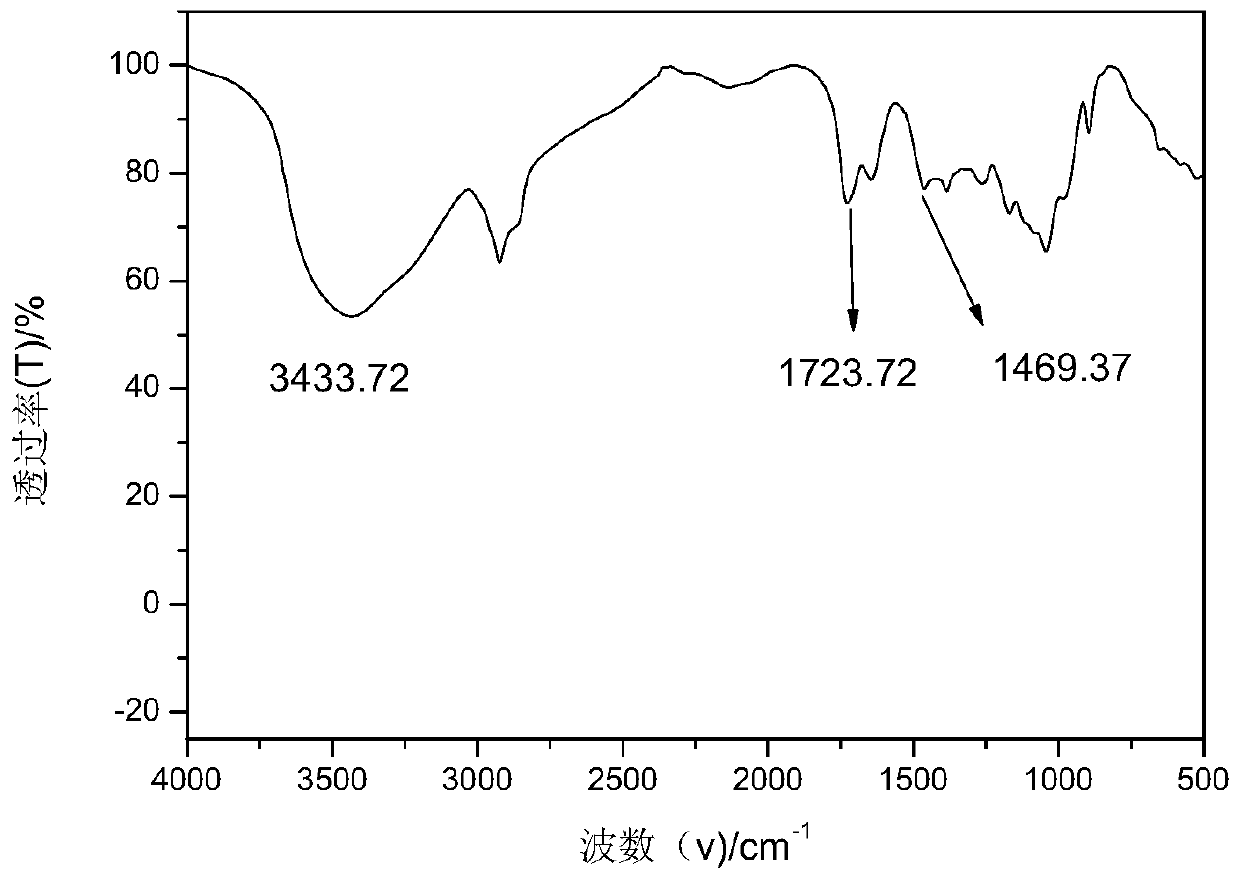
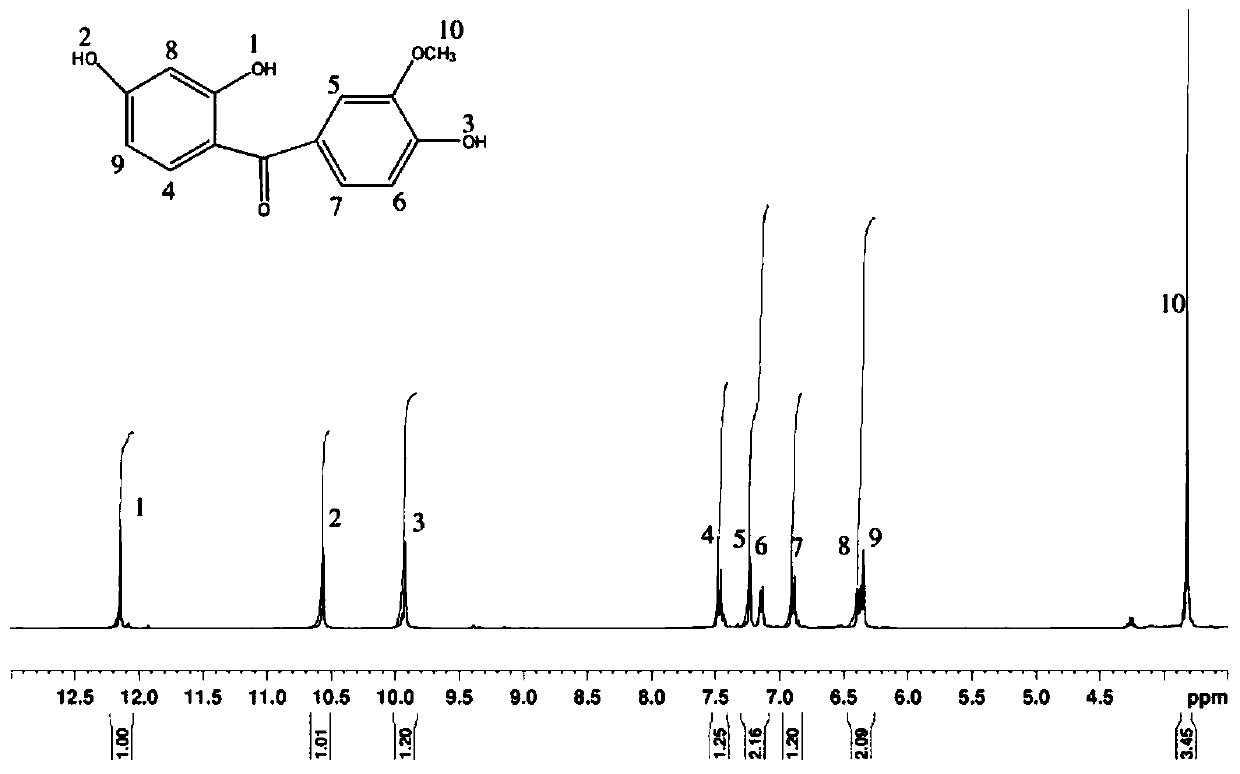
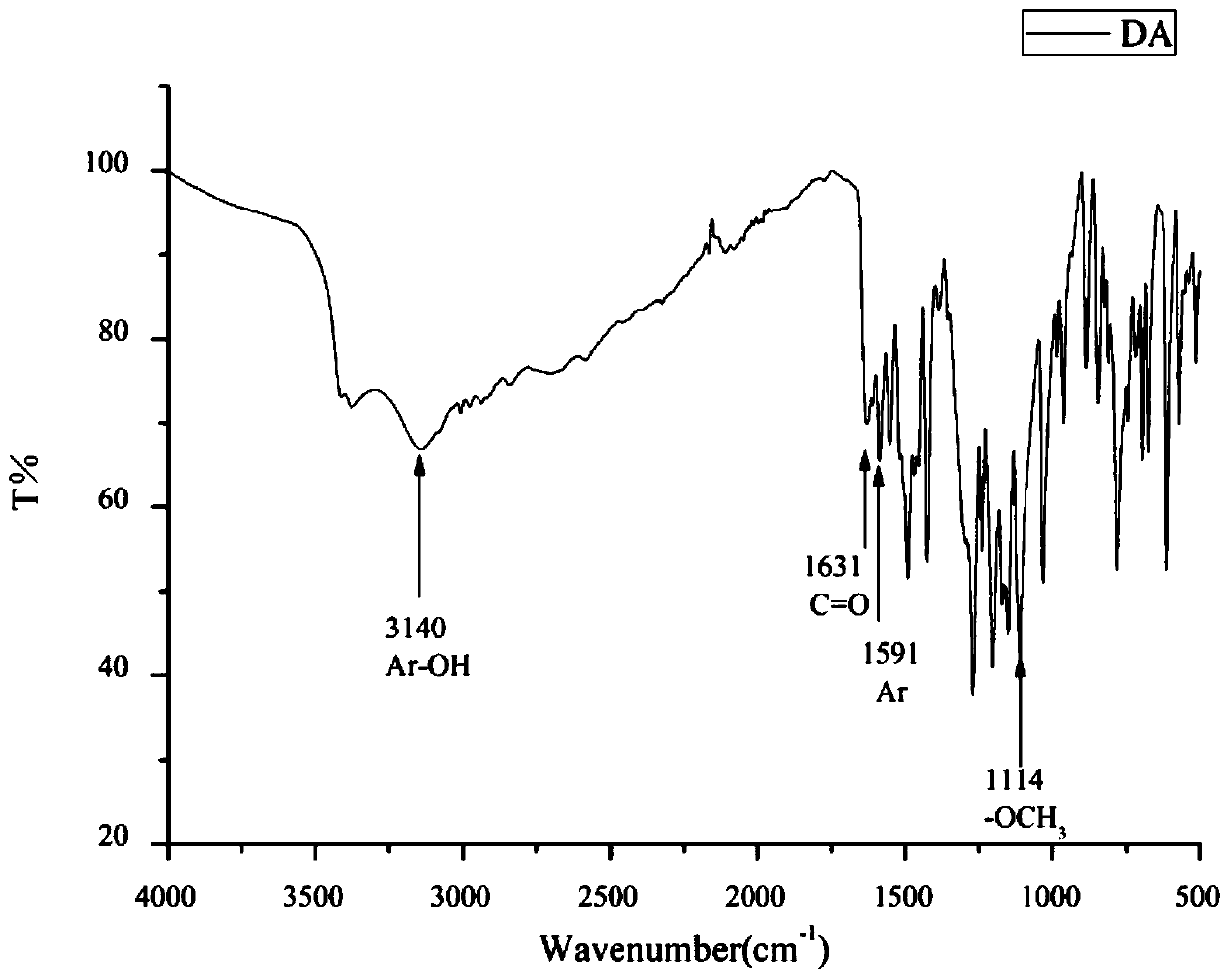
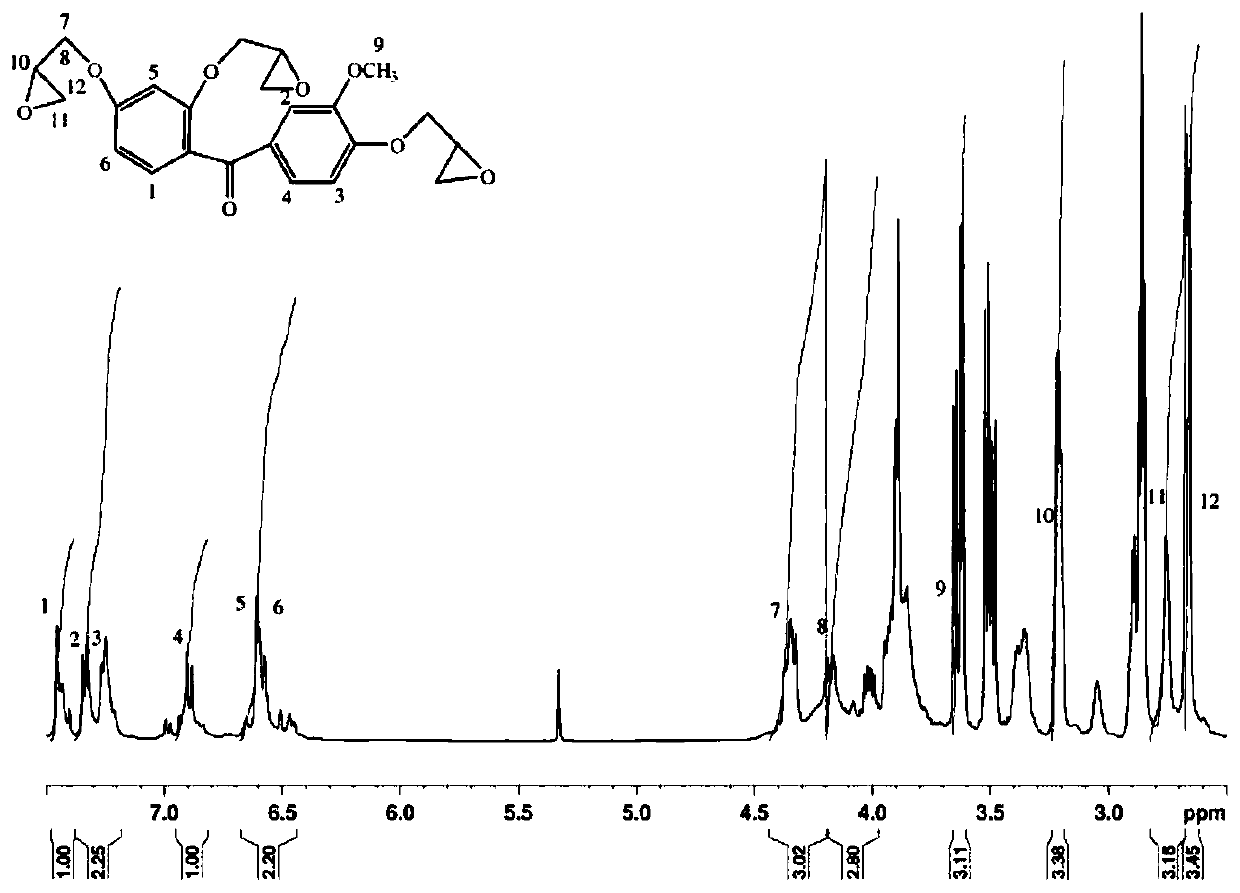
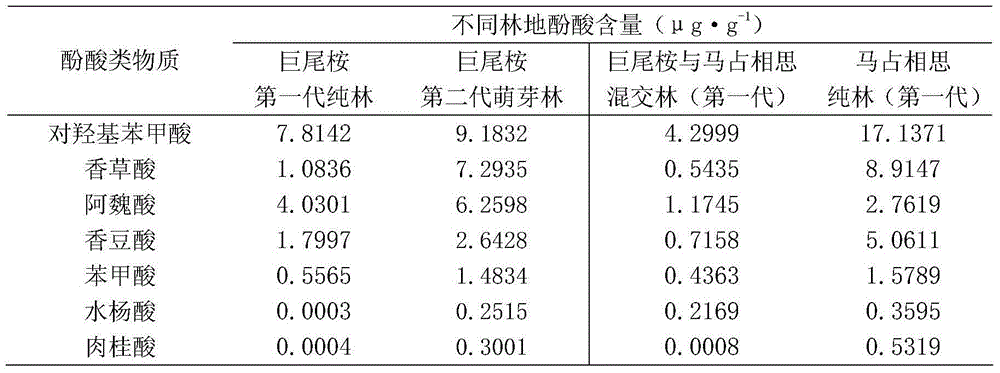
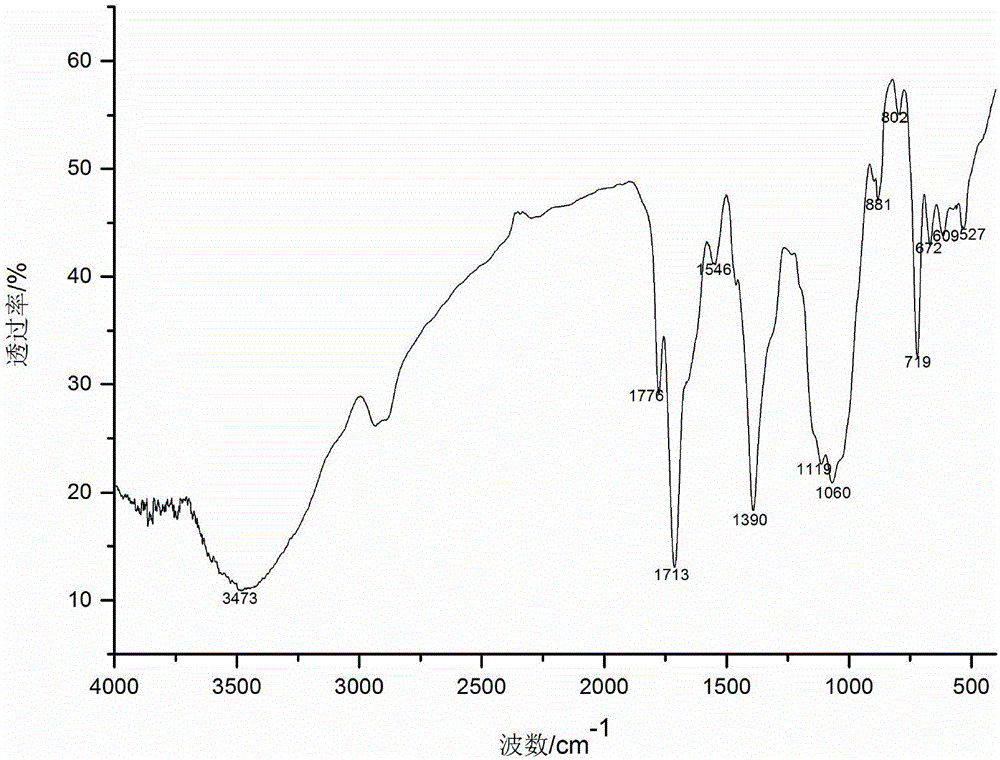
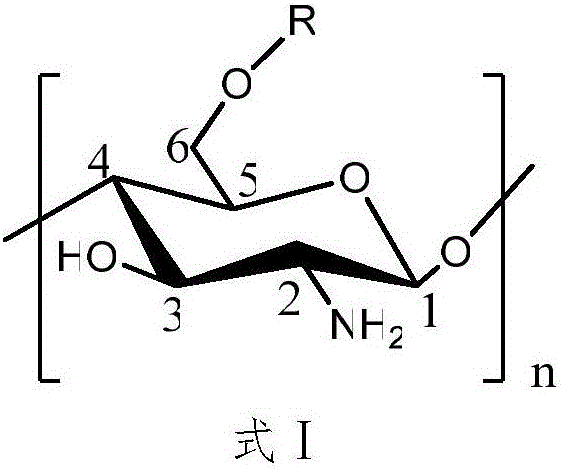
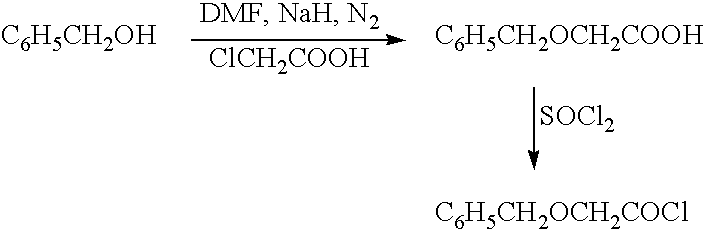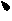Patents
Literature
158 results about "Vanillic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
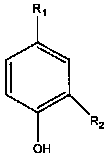
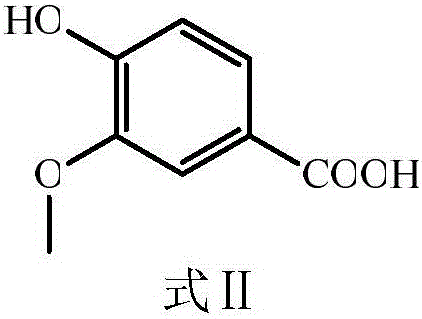
Vanillic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxybenzoic acid) is a dihydroxybenzoic acid derivative used as a flavoring agent. It is an oxidized form of vanillin. It is also an intermediate in the production of vanillin from ferulic acid.
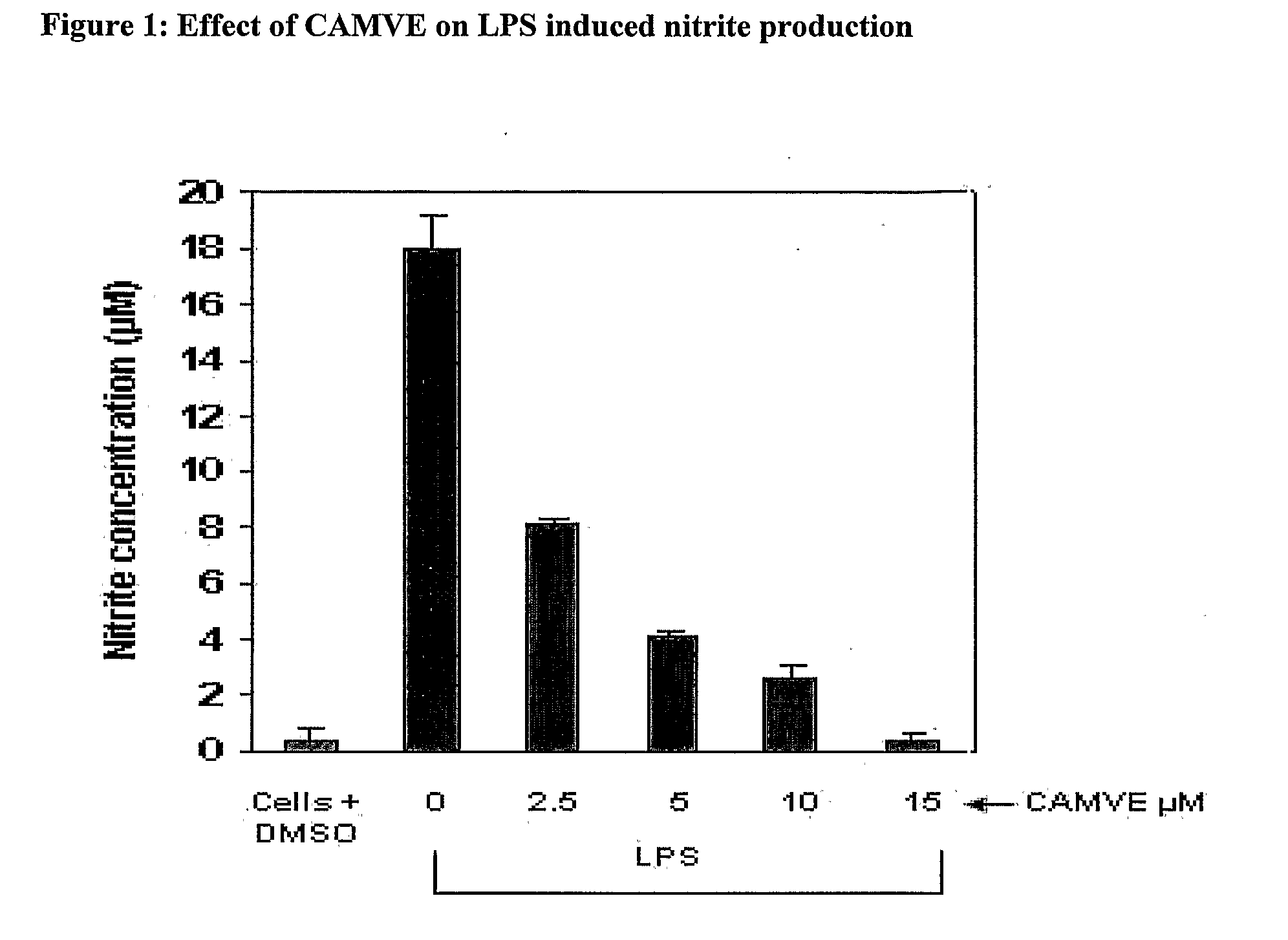
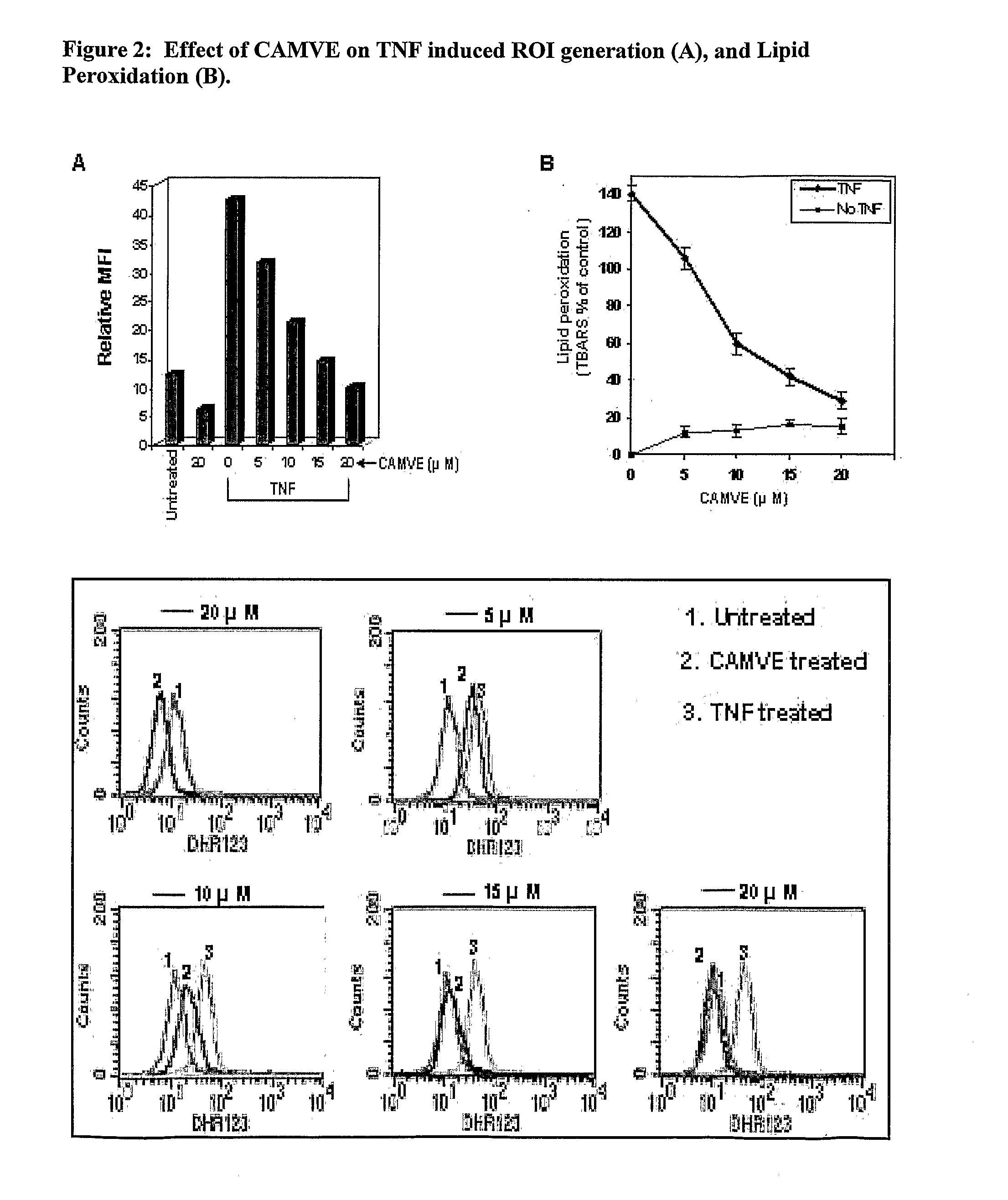
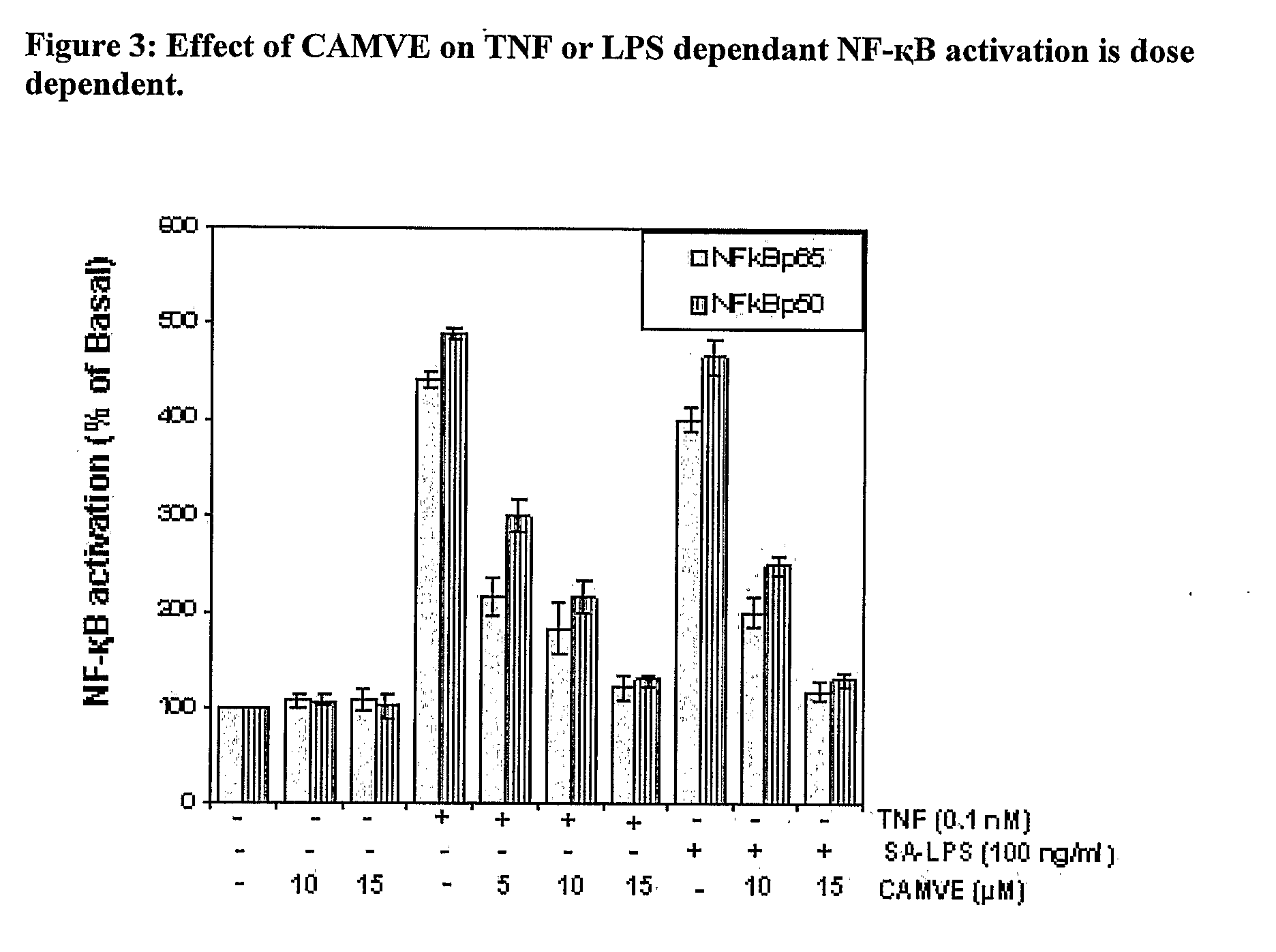
Novel chemotherapeutic agents against inflammation and cancer
InactiveUS20100168228A1Inhibit cell growthPotent activityBiocideOrganic chemistryVanillic acidInducer
Novel compounds, their methods of preparation and use in therapies related to cancer and inflammation are provided. Compounds comprise esters of cinnamic acid, vanillic acid and 4-hydroxy cinnamic acid and derivatives and salts thereof. Compounds with novel benzofuran lignan structure as a potent antimitotic agent and inducer of apoptosis are provided. Formulations and methods for treatment of diseases mediated by NF-kappaB are also provided.
Owner:RELIANCE LIFE SCI PVT
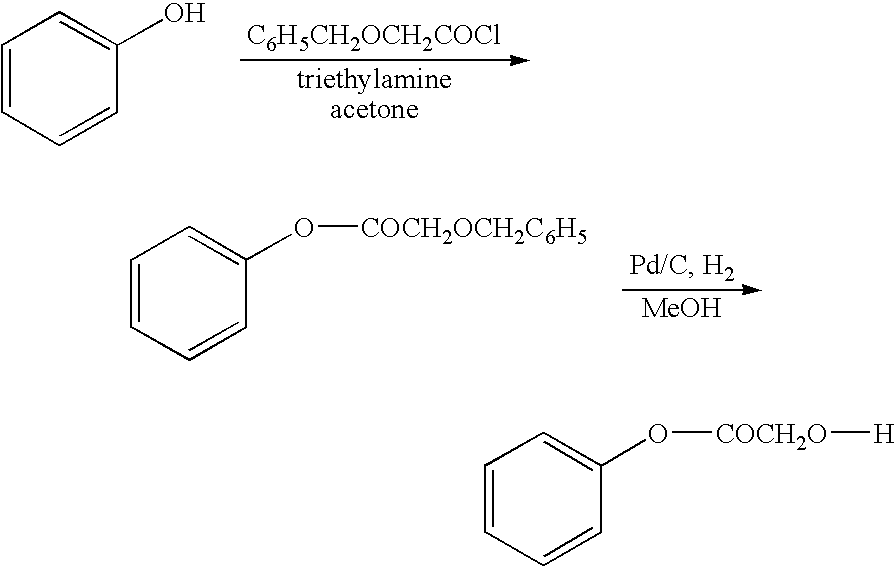
Functionalized phenolic esters and amides and polymers therefrom
InactiveUS20060173065A1Alter efficacyAlter valueBiocideOrganic chemistryBenzoic acidPhenylacetic acid
The present invention relates to a compound of the formula: R-AR—O—Y—R′Wherein R represents one or more members selected from H, alkoxy, benzyloxy, aldehyde, halogen, carboxylic acid, —NO2, —NH2, —NHCOCH3, and —NH—Y—R′, which is attached directly to AR or attached through an aliphatic chain. The carboxylic acid moiety in R includes but is not limited to the following carboxylic acids: benzoic acids, cinnamic acids, ferulic acid, caffeic acid, syringic acid, salicylic acid, vanillic acid, phenylacetic acids, phenylpropionic acids, and sinapinic acid. -AR—O— is a biologically active phenolic moiety comprising 1 to 6 substituted or unsubstituted aryl rings that are directly bonded to each other, fused together, or joined through a linking group. Y represents a member selected from: —COCH2O— (glycolic ester moiety) —COCH(CH3)O— (lactic ester moiety) —COCH2OCH2CH2O— (dioxanone ester moiety) —COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2O— (caprolactone ester moiety) —CO(CH2)mO— where m is an integer between 2-4 and 6-24 inclusive —COCH2O(CH2CH2O)n— where n is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; and R′ is either hydrogen or a benzyl or an alkyl group, the alkyl group being either straight-chained or branched. The resultant functionalized phenolic compounds, used singly or in combinations, and their polymers have controllable degradation profiles, releasing the active component over a desired time range. The polymers are useful for biomaterials and biomedical devices, wherein said biologically active phenolic moiety is a residue of a phenolic compound.
Owner:BEZWADA BIOMEDICAL LLC
Acorus gramineus total phenylpropanoid extraction and total phenols extraction and method for preparing simultaneously
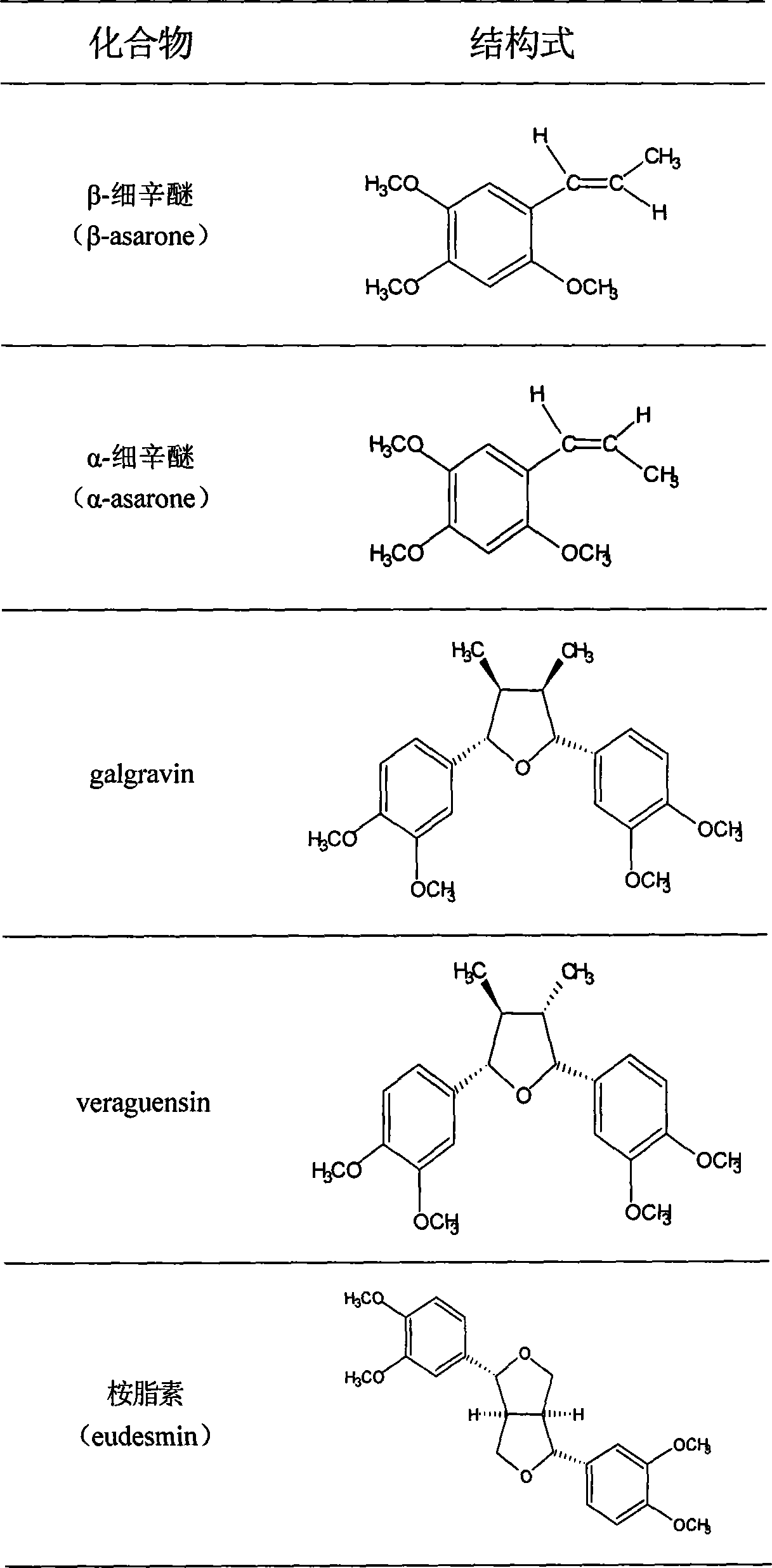
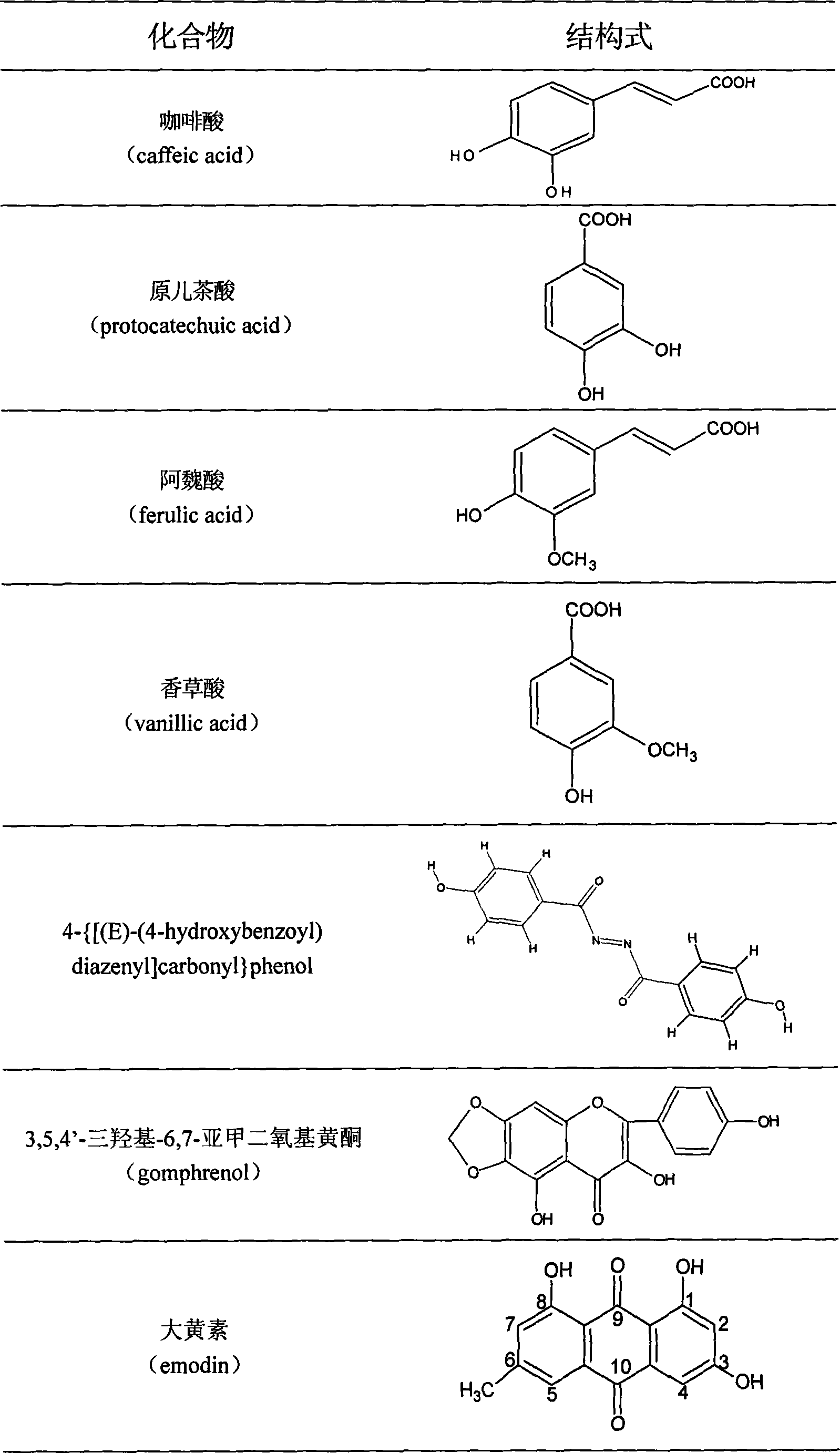
The invention discloses total phenyl propanoid extract and total phenol extract extracted from grassleaved sweetflag rhizome and its preparation method. Total phenyl propanoid extract mainly comprises beta -asaricin, alpha -asaricin, eudesmin, galgravin, veraguensin and other derivant with veraguensin as mother nuclide. Total phenol extract mainly comprises caffeic acid, protocatechuic acid, ferulic acid, vanillic acid and glucosides with vanillic acid as mother nuclide and other derivants. Total phenyl propanoid extract and total phenol extract of grassleaved sweetflag rhizome can be extracted through one or more of methods of solvent-extraction, solvent extraction, precipitation method, macroporous adsorbent resin, extraction by supercritical fluid, column chromatography, and liquid-liquid countercurrent distribution chromatography. Total percentage content of phenyl propanoids in the obtained total phenyl propanoid extract of Grassleaved sweetflag rhizome is 5-100% (w / w), wherein content of beta -asaricin and alpha -asaricin occupy 5-100% (w / w).Total percentage content of phenols in total phenol extract of grassleaved sweetflag rhizome is 5-100% (w / w), wherein content of caffeic acid and protocatechuic acid occupy 5-100% (w / w).
Owner:石任兵 +1
Compound probiotic fermentation product having effect of protecting skins, and preparation and applications thereof
ActiveCN112980892AMaintain balanceIncrease elasticityCosmetic preparationsBacteriaBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention belongs to the field of microbial fermentation, and especially relates to a fermentation metabolite having an effect of protecting skins, and a preparation method and applications thereof. The product is prepared by taking lactobacillus plantarum, lactobacillus casei, lactobacillus lactentis, bifidobacterium animalis and lactobacillus rhamnosus as fermentation strains and taking sucrose, seaweed meal, soybean meal and milk powder as fermentation raw materials through mixing and fermentation. The product contains specific fermentation metabolites, such as malonylgenistin, genistein, hyaluronic acid, irone, Preaustinoid A and daidzein, which are helpful for the enhancement of a skin protection effect; and tartaric acid, malic acid, succinic acid, salicylic acid, vanillic acid, phenylpropionic acid and other organic acid generated by fermentation can control pathogenic bacteria and spoilage microbial flora, so that skin flora balance can be maintained, and a natural antiseptic effect can be achieved. Efficacy tests show that the product has the efficacy of removing wrinkles, increasing skin elasticity, resisting inflammation and repairing skin barriers, and is significant in effect.
Owner:青岛元达生物科技有限公司
Lignin degradation product removing method
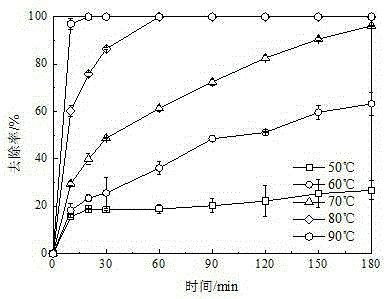
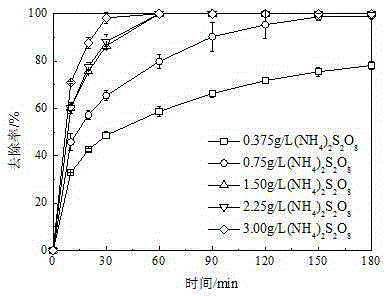
The present invention discloses a lignin degradation product removing method. According to the method, the lignin degradation products are adopted as the substrate, and the way that the persulfate is activated to generate the sulfate free radical is used to carry out oxidation removal on the lignin degradation products, wherein the activating way selects the thermal activating, and the persulfate selects ammonium persulfate as the oxidant. According to the present invention, the thermal activating way is used to activate the ammonium persulfate so as to perform the oxidation removal of the lignin degradation products, and the results show that the removal rates of vanillin, 4-hydroxybenzaldehyde, vanillic acid, 4-hydroxy benzoic acid and syringic acid achieve 100% within 1 h, and the syringic aldehyde removal rate achieves 100% within 2 h.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
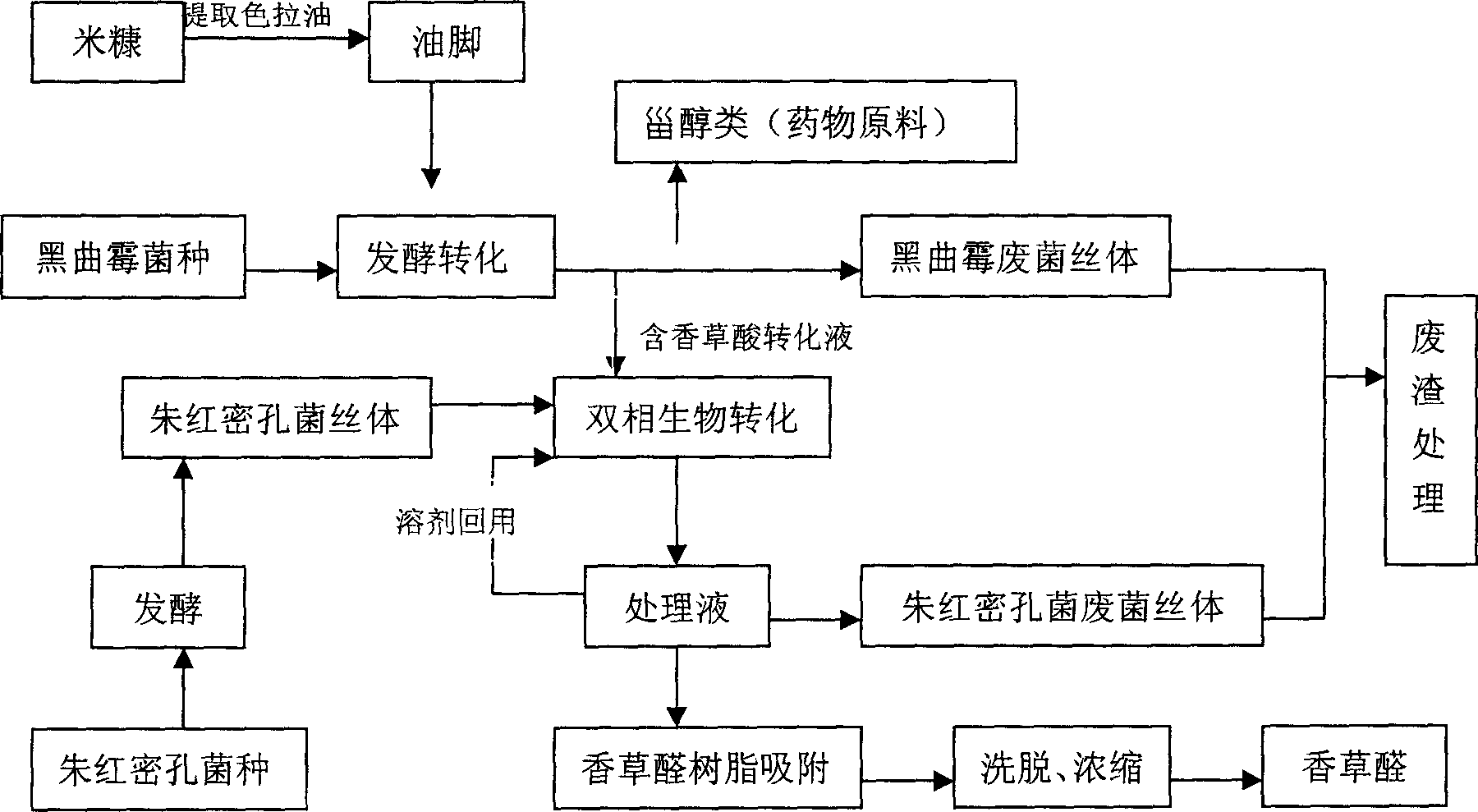
Process for producing vanillic acid and vanillic aldehyde by fermentation transforming bran foots
InactiveCN1824783AAlleviate the shortage of petrochemical resourcesReduce pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationChemical synthesisMicroorganism
The present invention provides a method capable of using wastes (oil foot) produced in the course of processing rice husk oil as raw material and utilizing microbial fermentation conversion process to produce vanillic acid and vanillic aldehyde. Said method is characterized by that it utilizes Aspergillus niger CGMCC 0774 to hydrolyze ferulic acid ester in rice husk oil foot to produce ferulic acid, and convert it into vanillic acid, then utilizes another Pycnoporuscinnabarinus CGMCC 1115 to convert the vanillic acid into vanillic aldehyde.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
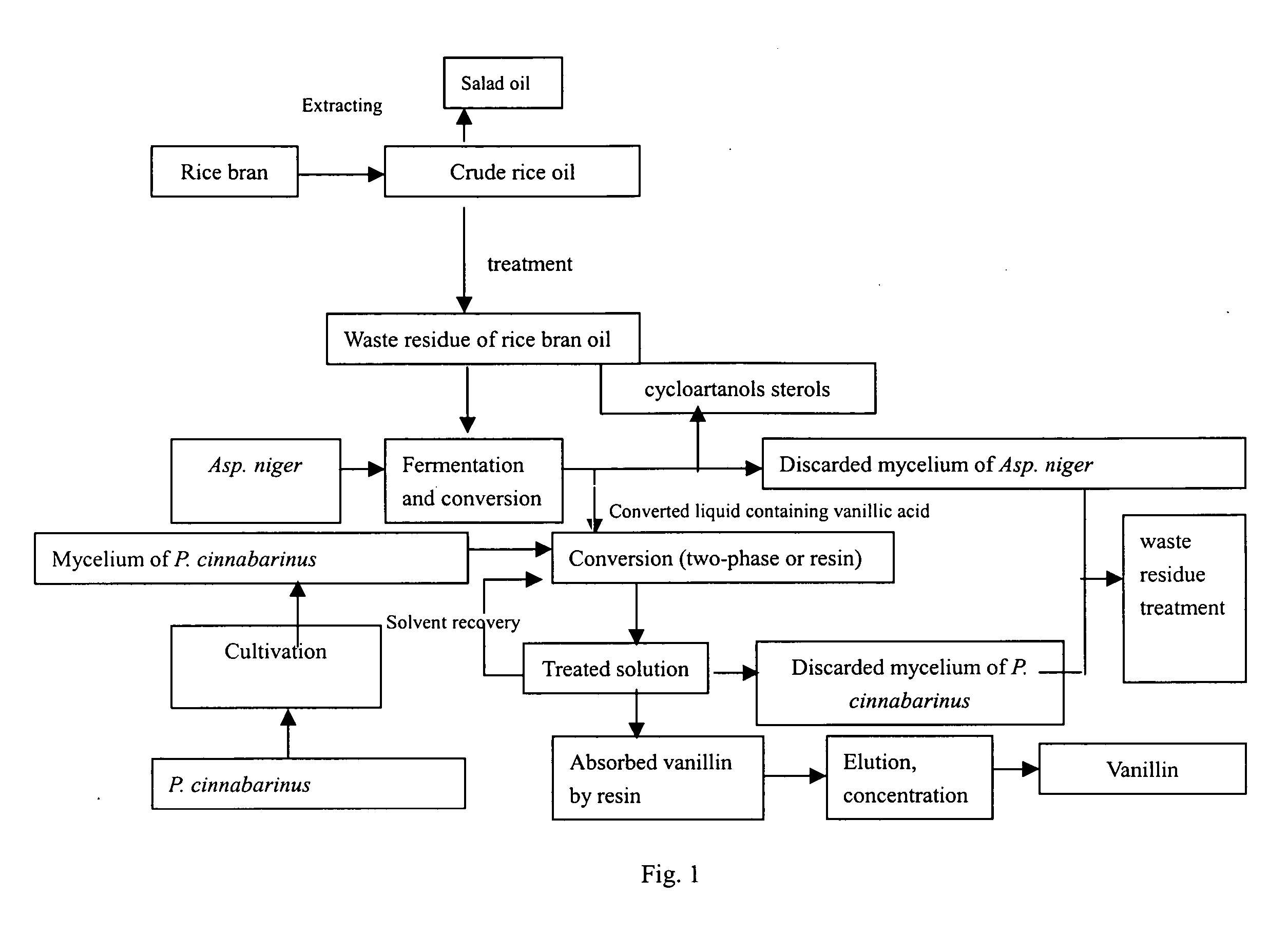
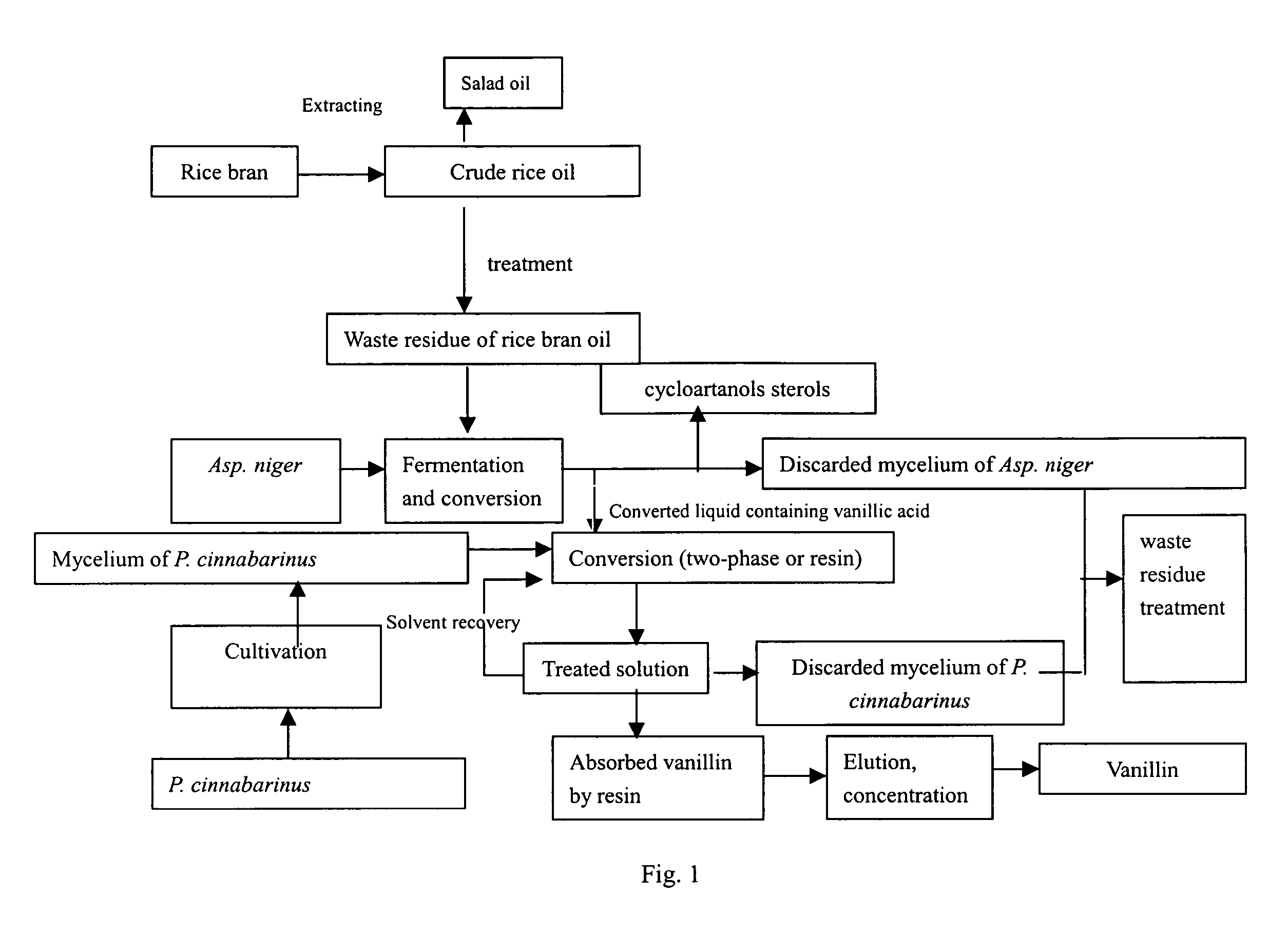
Method for the producing vanillic acid and vanillin from waste residue of rice bran oil by fermentation and biotransformation
ActiveUS20060292676A1Process safetyLow production costFungiFermentationChemical synthesisDrug biotransformation
A method for the production of vanillic acid and vanillin from waste residue (niger) of rice bran oil by microbial fermentation and biotransformation is provided. The method of the present invention comprises the steps of hydrolization of ferulic acid esters in waste residue of rice bran oil to ferulic acid and further conversion into vanillic acid using microbial strain Aspergillus niger CGMCC 0774 screened and preserved by the present inventor, followed by conversion of vanillic acid to produce vanillin using another microbial strain Pycnoporus cinnabarinus CGMCC 1115. The method for the production of vanillin according to the present invention utilizes renewable source from rice processing and alleviates the environmental pollution caused by the chemical synthesis of vanillin.
Owner:SOUTHERNYANGTZE UNIV +1
Manchurian walnut bark extract and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an extractive from juglans mandshurica maxim bark, which mainly has the following active components: 8-hydroxide radical-9, 10- anthraquinone-1- carboxylic acid, regiolone, 4, 5, 8-trihydroxy-alpha-naphthalenone-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 4, 5, 8-trihydroxy-alpha-naphthalenone-3-O-(6'-O-galloyl-group)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 1-(4'-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(3'- methoxy-4'-hydroxyphenyl) heptane-3- ethanol, 4- hydroxide radical-2, 6- syringol-1-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 4- hydroxide radical-2, 6- syringol-1-O-(6'-O-galloyl group)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, vanillic acid-4-O-(6'-O-galloyl group)-beta-D- glucopyranoside, vanillic aldehyde, vanillic acid, gallic acid, syringic acid, kaempferol and quercetin. The extractive from the juglans mandshurica maxim bark has good effects of treating hepatopathy and inhibiting the tumor growth and particularly has direct killing effect on liver cancer cells.
Owner:DANDONG MEDICINE GROUP
Method for the producing vanillic acid and vanillin from waste residue of rice bran oil by fermentation and biotransformation
A method for the production of vanillic acid and vanillin from waste residue (niger) of rice bran oil by microbial fermentation and biotransformation is provided. The method of the present invention comprises the steps of hydrolization of ferulic acid esters in waste residue of rice bran oil to ferulic acid and further conversion into vanillic acid using microbial strain Aspergillus niger CGMCC 0774 screened and preserved by the present inventor, followed by conversion of vanillic acid to produce vanillin using another microbial strain Pycnoporus cinnabarinus CGMCC 1115. The method for the production of vanillin according to the present invention utilizes renewable source from rice processing and alleviates the environmental pollution caused by the chemical synthesis of vanillin.
Owner:SOUTHERNYANGTZE UNIV +1
Melt formula
A topical composition comprises a vehicle, said vehicle including an emulsion or dispersion of water in an amount of from 50% by weight to 93% by weight; and a non-aqueous discontinuous phase in an amount of from 50% by weight to 7% by weight; at least one of a bronzer, a tanning accelerator, or a mixture thereof; and from 0.01% by weight to 5% by weight of a warming agent, based on the total weight of the composition. The warming agent comprises at least one alkyl ether of vanillyl alcohol at least one N-alkyl amide of vanillic acid; and is present in an amount effective to produce a prolonged warming sensation when applied to a user's skin. The composition is transparent to UV radiation. The composition is used for indoor tanning.
Owner:NEW SUNSHINE
Fungus with strong weed suppression effect screened from passion fruit rhizosphere soil
InactiveCN107164234AHas an anti-herb effectEnvironmentally safeBiocideFungiSalicylic acidAspergillus sydowii
The invention belongs to the field of microbial herbicides and particularly relates to weed suppression fungus screened from passion fruit rhizosphere soil. Lettuce (compositae), barnyard grass (gramineae) and lysimachia barystachys (gramineae) are taken as receptors separately, biological test is carried out on the weed suppression ability of a fungus strain fermentation liquid, and the condition that the weed suppression fungus has a very high inhibition rate on root length and plant height of two receptors is found out. The condition that protocatechuic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, salicylic acid and cinnamic acid contain phenolic acid with a weed suppression effect is detected in the fermentation liquid. The strain is named FJ-01-BXG-08. The analysis and identification results on the morphology and ITS sequence of the strain show that the strain is one of Aspergillus sydowii (aspergillus sydowii), and strong weed suppression fungus aspergillus sydowii (Aspergillus sydowii) is screened from eucalyptus soil for the first time.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Medicine for treating ischemic brain injury stroke and sequela of ischemic brain injury stroke and preparation method for medicine
The invention discloses a structural general formula of a compound LQC-T and the synthesis and the application of the compound LQC-T. Pharmacological experiments prove that the compound has an obvious effect of promoting new vessels of chick chorioallantoic membranes to grow; a compound LQC-T4 has an obvious medicinal effect of treating ischemic brain injury stroke and the sequela of the ischemic brain injury stroke; the maximal LQC-T4 single-day dose of mice is 5,400mg / kg; and the compound is extremely high in safety and can be used for preparing a medicine for treating the ischemic brain injury stroke and the sequela of the ischemic brain injury stroke after toxic responses do not occur after continuous observation within 1 to 4 days. According to the structural formula of the compound LQC-T, R is protocatechuic acid, protocatechuic aldehyde, vanillic acid, gallic acid, caffeic acid, ferulic acid and other aromatic organic acids or phenols or structural analogues of the organic acids or phenols.
Owner:薪火炙药(北京)科技有限公司
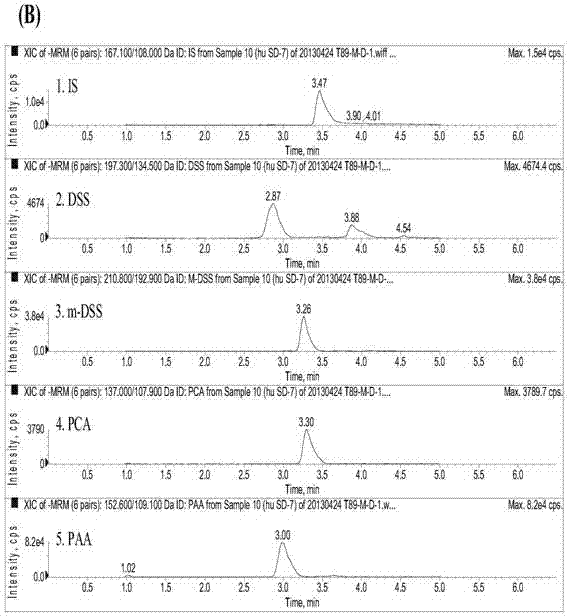
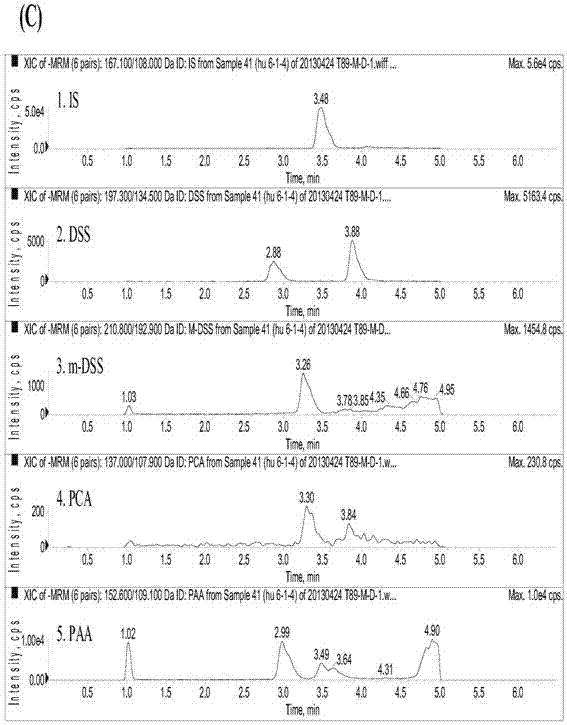
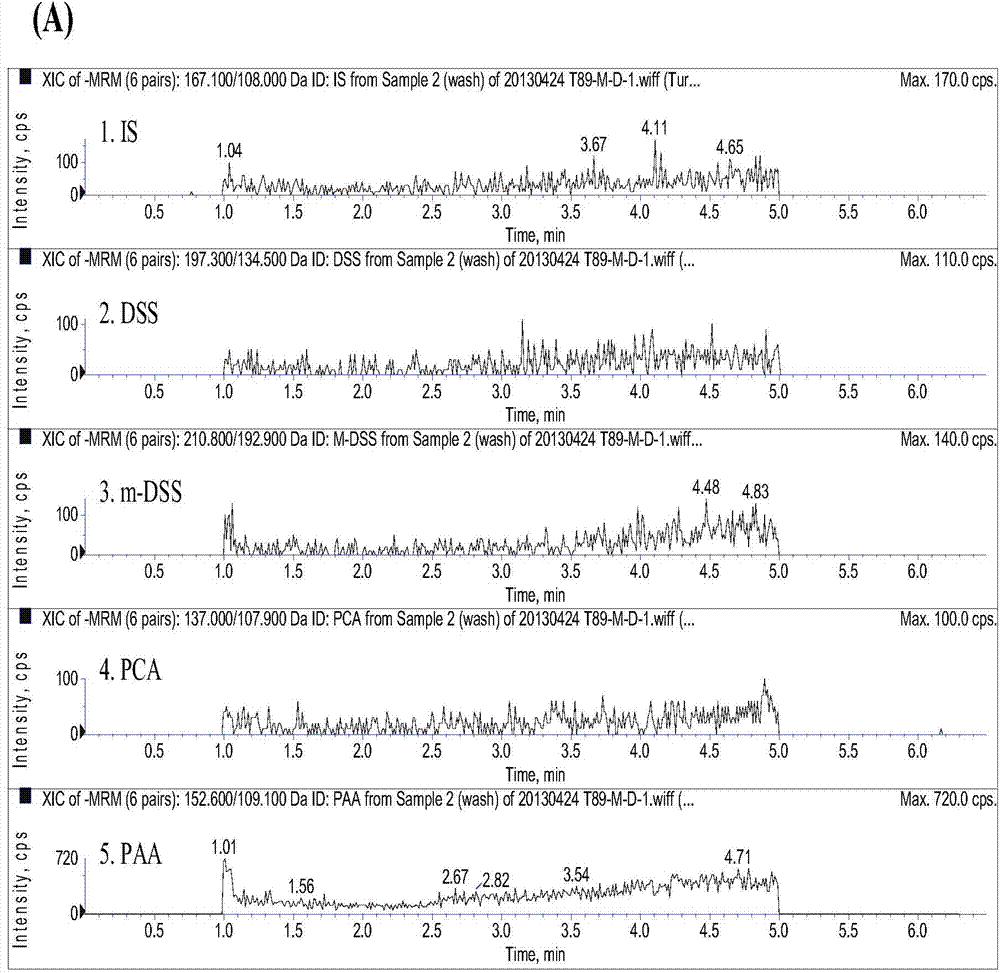
Method for measuring danshensu, m-methyl-danshensu, protocatechualdehyde, and protocatechuic acid in human blood plasma
The invention relates to a method for measuring drug contents, particularly to a method for measuring danshensu, m-methyl-danshensu, protocatechualdehyde, and protocatechuic acid in the human blood plasma. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparation of reference substance storing solutions: weighting reference substances of danshensu, m-methyl-danshensu, protocatechualdehyde, and protocatechuic acid, and dissolving the reference substances with methanol to obtain reference substance storing solutions of danshensu, m-methyl-danshensu, protocatechualdehyde, and protocatechuic acid; 2) preparation of an internal standard solution: dissolving an internal standard substance of vanillic acid with methanol to obtain the internal standard solution; 3) a treatment method of a blood plasma sample: taking the blood plasma sample, adding the internal standard solution, methanol, hydrochloric acid, and ethyl acetate into the blood plasma sample, performing uniform mixing, performing centrifugation of the obtained mixture to obtain a supernatant ethyl acetate layer, drying the ethyl acetate layer, re-dissolving the ethyl acetate layer with methanol, and performing centrifugation of the obtained solution to obtain supernatant liquid of the blood plasma sample; and 4) content measurement: by adopting LC-MS / MS chromatography, injecting the reference substance storing solutions and the supernatant liquid of the blood plasma sample into a chromatographic instrument to obtain a chromatogram, and calculating concentrations of danshensu, m-methyl-danshensu, protocatechualdehyde, and protocatechuic acid in the human blood plasma according to the areas of chromatographic peaks in the chromatogram.
Owner:TIANJIN TASLY PHARMA CO LTD
Compositions comprising derivatives of essential oil compounds and use in personal care products
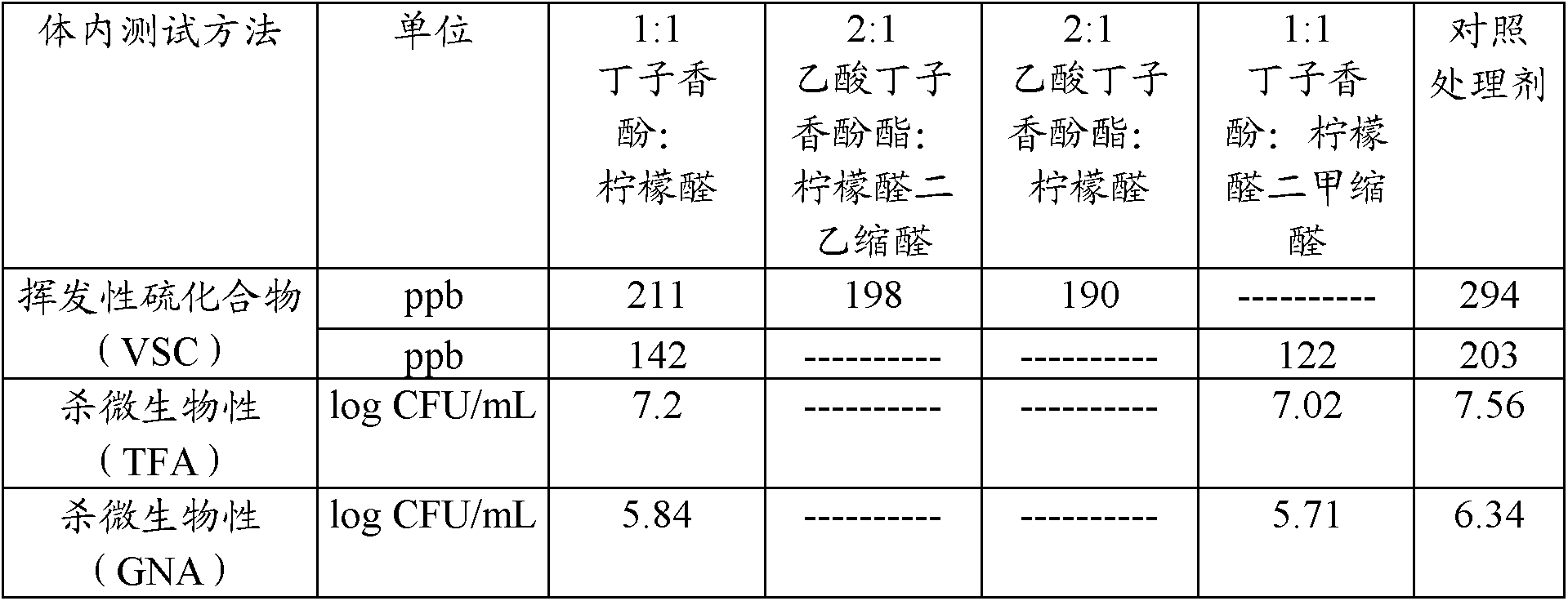
Compositions containing one or more derivatives of essential oil compounds for use in personal care compositions, such as compositions for oral, throat and skin care are disclosed. These derivatives include acetals of parent essential oil aldehydes and ketones; esters or ethers of parent essential oil alcohols and phenolics; and esters of parent essential oil acids. Examples of parent essential oil aldehydes and ketones include citral, cinnamic aldehyde, anisaldehyde, vanillin, ethyl vanillin, heliotropin, carvone, and menthone. Examples of parent essential oil alcohols and phenolics include thymol, eugenol, isoeugenol, dihydroeugenol, carvacrol, carveol, geraniol, nerol, vanillyl alcohol, heliotropyl alcohol, anisyl alcohol, cinnamyl alcohol and ss-ionol. Examples of parent essential oil acids include anisic acid, cinnamic acid, vanillic acid and geranic acid.; The present compositions comprising essential oil derivatives are useful as base flavor or base perfume for incorporation into personal care products and to provide other benefits including antimicrobial efficacy. Optionally the compositions will contain additional antimicrobially- or anti-inflammatory-effective components including those also derived from plant essential oils or synthetic versions thereof.
Owner:PROCTER & GAMBLE CO
Clostridium beijerinckii with high stress resistance and application thereof
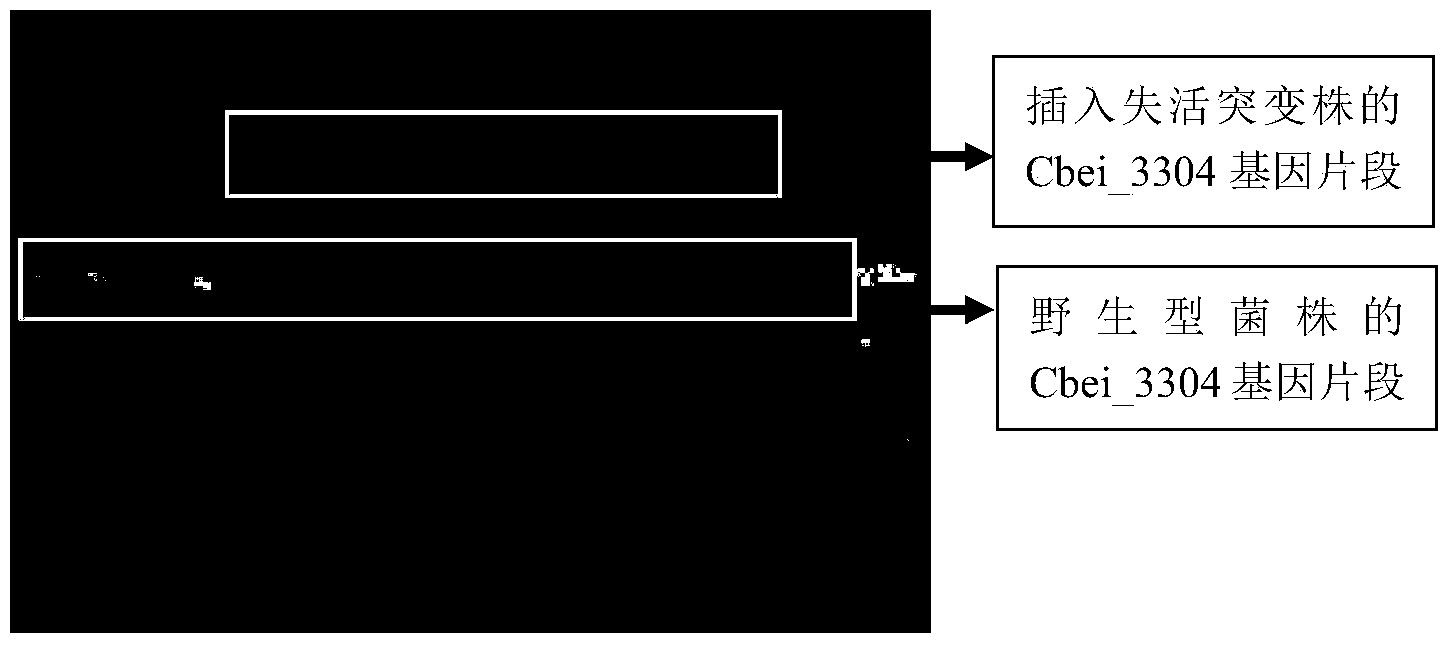
InactiveCN103911334AEfficiently improve stress resistanceImprove stress resistanceBacteriaBiofuelsBiotechnologyVanillic acid
The invention discloses clostridium beijerinckii with high stress resistance and an application of the clostridium beijerinckii. A gene Cbei_3304 of the clostridium beijerinckii strain with high stress resistance cannot be expressed normally, and a normal Cbei_3304 protein function is deleted, so that the clostridium beijerinckii has high stress resistance to toxic substances such as ferulic acid and vanillic acid, also has high stress resistance to toxic substances in virus-carrying wood fiber acidolysis sugar liquor, and can be used for producing butyl alcohol through fermentation very well. The invention provides a simple and efficient method for improving stress resistance of the clostridium beijerinckii. The clostridium beijerinckii which has high stress resistance to the toxic substances in the virus-carrying wood fiber acidolysis sugar liquor and can be used for efficiently producing butyl alcohol can be obtained by only enabling the clostridium beijerinckii to delete the normal Cbei_3304 protein function, so as to be helpful in promoting the efficient utilization of wood fiber resources.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL BIOENGINEERING INST (GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST)
Application of phenolic acid compounds in preparation of bleeding stopping and stasis eliminating medicaments
InactiveCN102210667AHas the effect of stopping bleeding and removing blood stasisInhibit aggregationHydroxy compound active ingredientsSexual disorderGallic acid esterChlorogenic acid
The invention discloses application of a phenolic acid compounds in preparation of bleeding stopping and stasis eliminating medicaments. The phenolic acid compounds mainly comprise chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, coumaricacid, vanillic acid, cinnamic acid, syringic acid, protocatechuric acid, gallic acid, ferulic acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, hydroquinone or pyrocatechol and medicinal salts thereof. Experiments show that the phenolic acid compounds have the functions of stopping blood and eliminating stasis; one or more of the active ingredients is applied to preparing the bleeding stopping and stasis eliminating medicaments which are used for preventing and treating menorrhagia, artificial abortion, postpartum hemorrhage and dysfunctional uterine bleeding of women.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Active part of Sambucus williamsii Hance for reducing risk of bone-related diseases of menopausal women and application thereof
ActiveCN101773490AImprove bone lossHigh densityEther/acetal active ingredientsSkeletal disorderFood additiveGlycerol
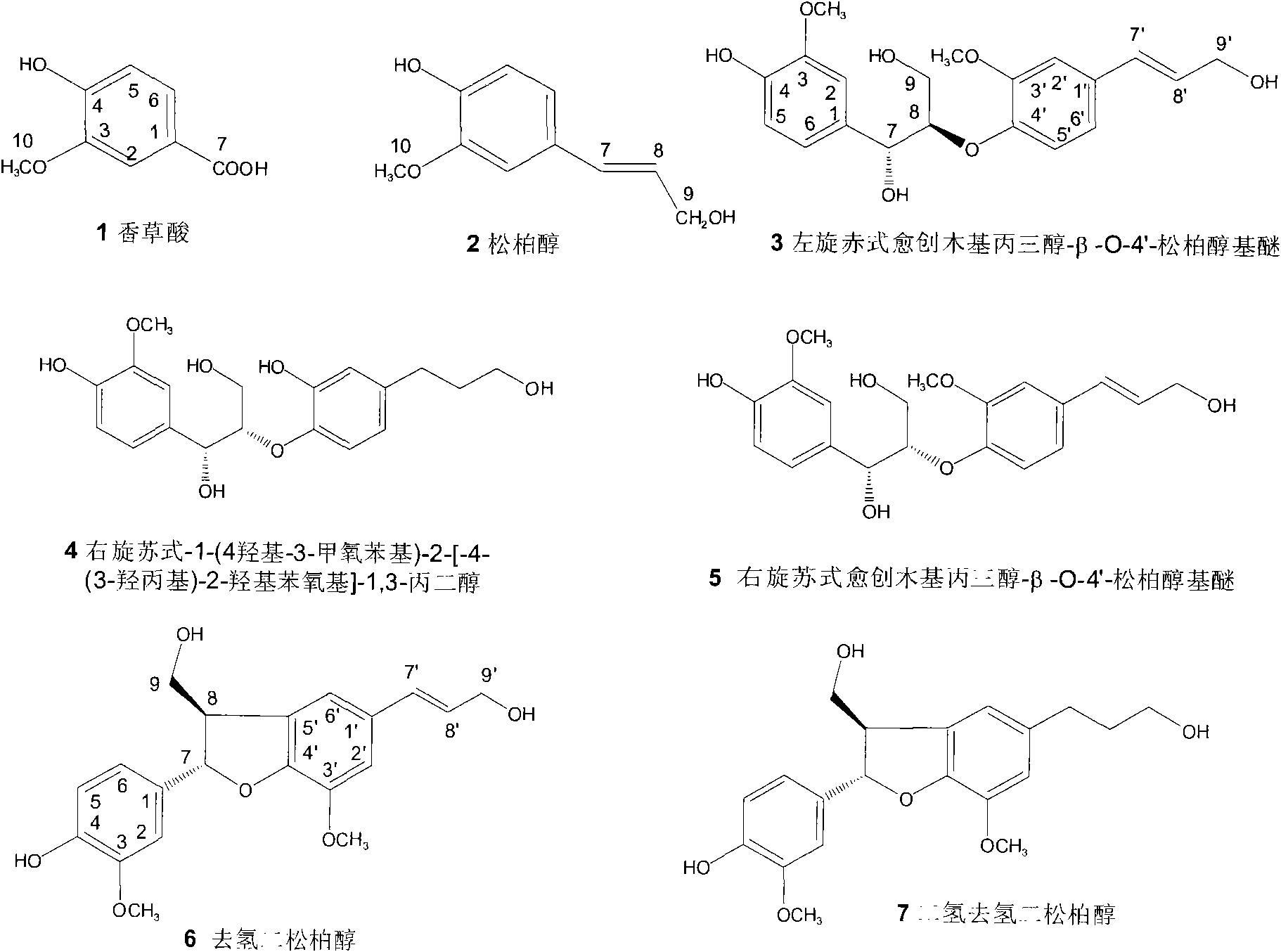
The invention discloses an active part of Sambucus williamsii Hance with the effect of reducing bone mass loss after menopause. The active part has definite chemical components and mainly comprises seven compounds: vanillic acid, coniferol, levo erythro form guaiacyl glycerol-beta-O-4'-coniferyl alcohol ether, dextro threo form-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-2-[-4-(3-hydroxypropyl)-2-hydroxyphenoxy]-1,3-propanediol, dextro threo form guaiacyl glycerol-beta-O-4'-coniferyl alcohol ether, coniferyl alcohol dehydrogenase and dihydro-coniferyl alcohol dehydrogenase. The active part can remarkably reduce the bone loss of ovariectomized mice, increase bone density of thighbone and shinbone, increase bone volume, does not increase the weight of uterus, and is a component for safely and effectivelyrelieving and improving various symptoms of the bone-related diseases of the menopausal women. The invention has the advantages of providing the active part of the Sambucus williamsii Hance which canbe used for preparing a medicament, food or a food additive for preventing and treating the bone-related diseases after menopause.
Owner:THE HONG KONG POLYTECHNIC UNIV SHENZHEN RES INST +1
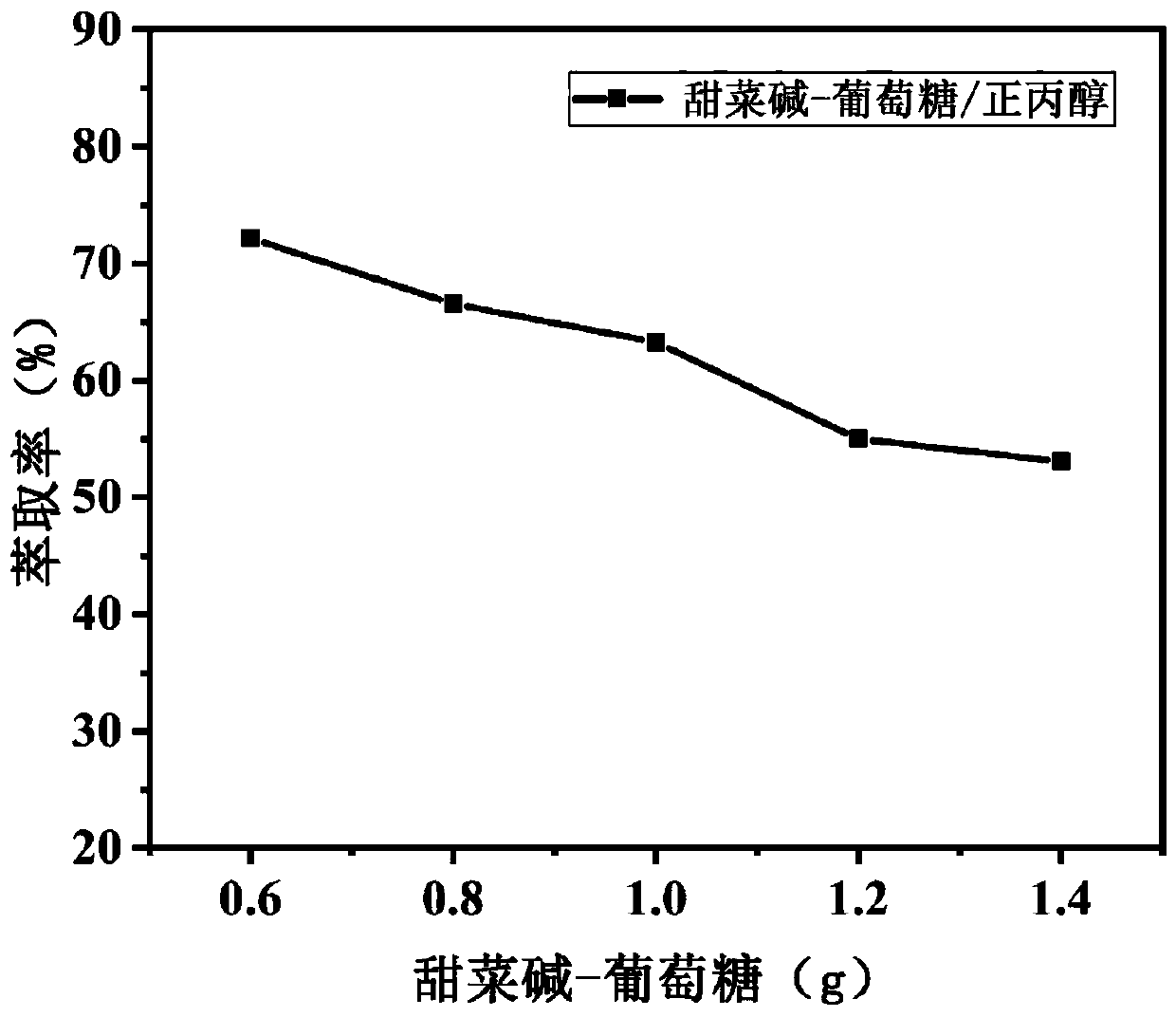
Method for extracting vanillic acid by using deep-eutectic solvent/normal propyl alcohol aqueous two-phase system
ActiveCN111087299ALow costWide range of synthetic raw materialsCarboxylic compound separation/purificationVanillic acidN-Propyl alcohol
The invention discloses a method for extracting vanillic acid by using a deep-eutectic solvent / normal propyl alcohol aqueous two-phase system. According to the method, extraction solvents including adeep-eutectic solvent and normal propyl alcohol are mixed to jointly construct the aqueous two-phase system, salts in a conventional aqueous two-phase system are replaced, and the salting-out problemof a salt-containing system is avoided. According to the method, the deep-eutectic solvent and normal propyl alcohol are added into an aqueous solution of vanillic acid to form the aqueous two-phase extraction system with a lower phase rich in the deep-eutectic solvent and an upper phase rich in the normal propyl alcohol, and vanillic acid is extracted into the upper phase. The purpose of enriching and recovering the vanillic acid from the aqueous solution is achieved by utilizing the deep-eutectic solvent / normal propyl alcohol aqueous two-phase system, the deep-eutectic solvent can be recycled, the process is simple, and cost is low.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
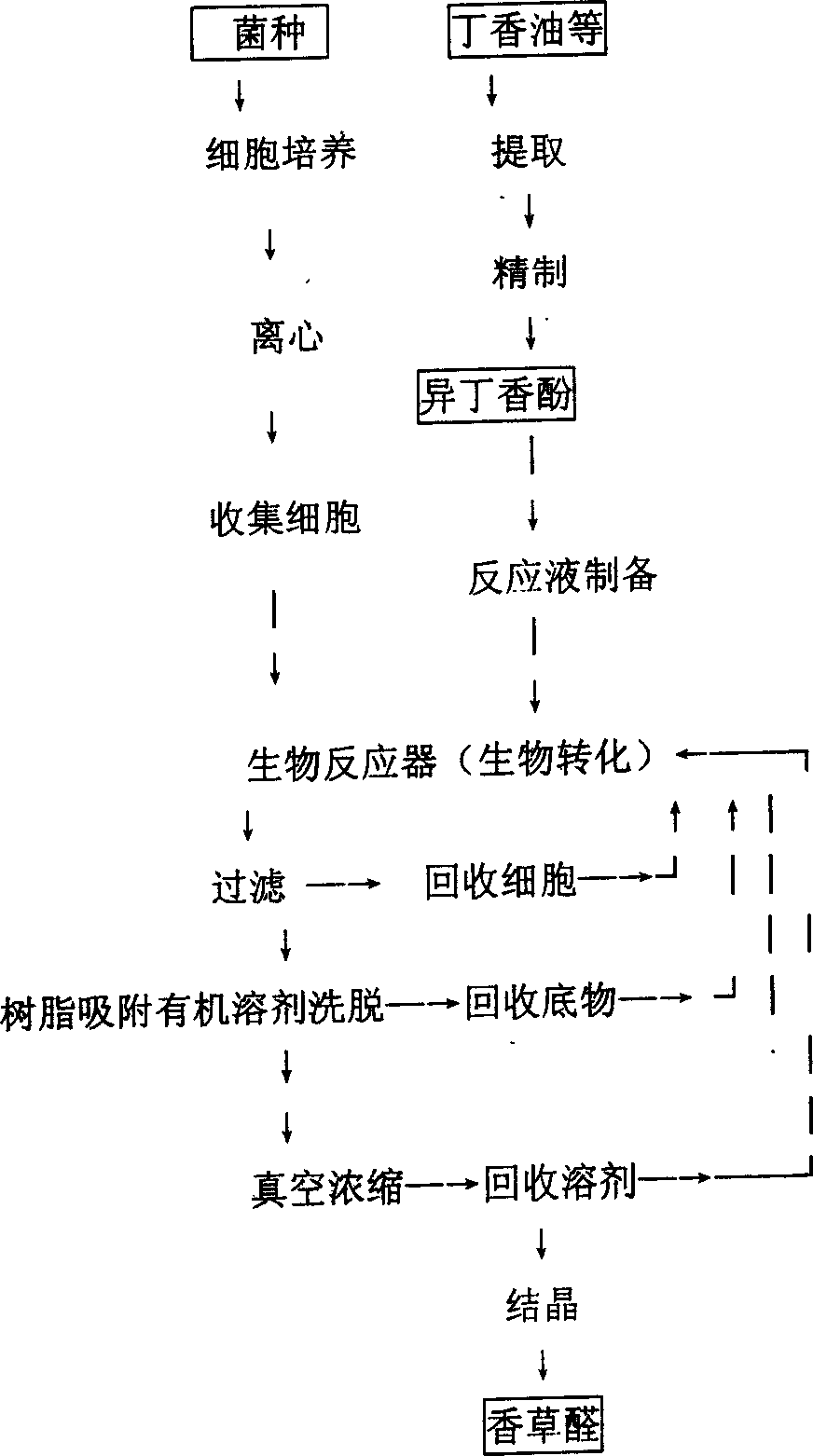
Fungus and method for preparing vanillin from isoeugenol converted by microorgan
InactiveCN1712518AReduce the content of harmful substancesEasy to trainBacteriaMicrobial transformationDouble phase
Vanillin bacteria from microbial conversion isobutyl aromatic phenol and its production are disclosed. The process is carried out by fermentation culturing under optimizing condition, converting isobutyl aromatic phenol for 24í½96hrs from fermentation liquor or free cell or fixed cell with conversion liquor containing vanillic acid 2í½4g / L, conversion reacting for 72hrs in water-organic solvent double-phase system with vanillin concentration 32.5g / L in organic phase, adsorbing vanillin in conversion liquor from resin, extracting from ethyl acetate and obtaining light yellow crystalline vanillin powder. Extraction rate reaches 87%, purity of product reaches 98.1% and recovery rate reaches 93.4%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Effective parts of schisandra bee pollen and application thereof in liver injury prevention
The invention relates to effective parts of schisandra bee pollen and the application thereof in liver injury prevention. The effective parts are obtained through extracting the schisandra bee pollen using ethanol, and the active ingredients and the content are gallic acid 15.78+ / -1.64 mg / kg, protocatechuic acid 54.78+ / -5.09 mg / kg, vanillic acid 64.21+ / -5.13 mg / kg, p-coumaric acid 57.32+ / -5.25 mg / kg, quercetin 273.63+ / -20.84 mg / kg, hesperidin 741.56+ / -76.8 mg / kg, kaempferol 387.34+ / -35.65 mg / kg, and galangin 487.35+ / -47.24 mg / kg. The inventor has found that the antioxidant activity of the schisandra bee pollen is higher than that of all known commercial bee pollen, and that the schisandra bee pollen can be used for preparing medicine or health care food for preventing liver injury caused by carbon tetrachloride.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV +1
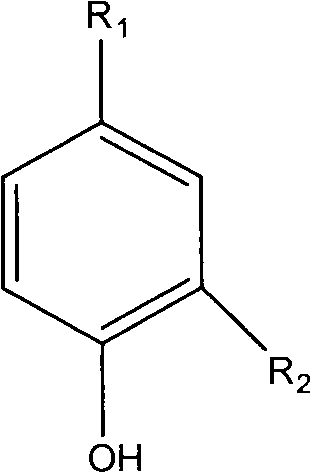
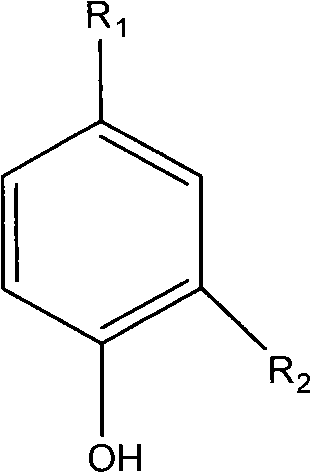
Phenolic acid compound and use thereof in the preparation of anticomplementary medicaments
InactiveCN101817746AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryChemical structureNatural product
The invention relates to a phenolic acid compound and use thereof in the preparation of anticomplementary medicaments. The phenolic acid compound has a chemical structure formula shown in the specification; when R1 is COOH, and R2 is OCH3, the compound is vanillic acid; and when R1 is-CH=CH-COOH, and R2 is H, the compound is para-hydroxycinnamic acid. The invention has the advantages that the phenolic acid compound is directly extracted from natural product, and the compounds of vanillic acid and para-hydroxycinnamic acid have better inhibition function to the classical pathway of a complement system.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Plasmid, transformants and process for production of 3- carboxymuconolactone
ActiveUS8211683B2High yieldHigh-yield and inexpensive fermentative productionBacteriaOxidoreductasesVanillic acidMuconic acid
Owner:FORESTRY & FOREST PRODS RES INST
Synthesis method of active bagasse xylan vanillate-g-HEMA/MAA/EA
InactiveCN110194817AImprove antioxidant capacityImprove antibacterial properties(Hydroxyethyl)methacrylateSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a synthesis method of active bagasse xylan vanillate-g-HEMA / MAA / EA. The method includes: taking bagasse cassava starch as the main raw material, adopting vanillic acid as the esterifying agent, and carrying out catalytic synthesis of bagasse xylan vanillate in an N, N-dimethylacetamide organic solvent; and then using ammonium persulfate-sodium bisulfate as the initiator, and adopting hydroxyethyl methylacrylate / methacrylic acid / ethyl acrylate (HEMA / MAA / EA) as the mixed graft monomer to prepare the target product bagasse xylan vanillate-g-HEMA / MAA / EA. The product synthesized by the method provided by the invention improves the biological activity of raw bagasse xylan, and the introduced vanillic acid, HEMA, MAA and EA groups can improve the antioxidation, antimicrobial, antitumor and other biological activity of bagasse xylan.
Owner:GUILIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of biological basic characteristic type flame-retardant epoxy resin
The invention provides a preparation method of biological basic characteristic type flame-retardant epoxy resin. The preparation method comprises the following steps: reacting vanillic acid with resorcinol to obtain trihydric alcohol containing a benzophenone structure, further introducing an epoxy group through a phenolic hydroxyl group to obtain a bio-based epoxy monomer with a structure similarto that of DGEBA used in general industry, and mixing and curing the bio-based epoxy monomer and a curing agent under certain conditions to obtain the flame-retardant bio-based epoxy resin. The resinis wide in raw material source, environmentally friendly, simple in synthesis process, high in thermal stability and good in flame retardant property, the carbon residue amount at 800 DEG C can reach35%, the limit oxygen index can reach 34% at most, and the vertical combustion grade reaches the V-0 grade.
Owner:INST OF CHEM IND OF FOREST PROD CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY +1
Inonotus obliquus probiotic enzyme and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105495551AHigh health medical efficacyYeast food ingredientsFood ingredient functionsInonotus obliquusAlkaloid
The invention discloses an inonotus obliquus probiotic enzyme and a preparation method thereof. The inonotus obliquus probiotic enzyme is a fermented product obtained by fermenting inonotus obliquus and brown rice through Shimamoto bacteria with the addition of honey. According to the inonotus obliquus probiotic enzyme, by taking the inonotus obliquus and the brown rice as main raw materials for fermenting and taking the Shimamoto bacteria as a zymophyte, a plurality of enzymes, such as polysaccharide, fuscoporine, inotodiol, a plurality of oxidized triterpenoids, trametenolic acid, a plurality of lanosterol type triterpenoids, folate derivatives, aromatic vanillic acid, syringic acid and gamma hydroxybenzoic acid, a tannin compound, steroid and alkaloid, can be obtained through enzymolysis. The inonotus obliquus probiotic enzyme has a relatively good healthcare medicinal effect.
Owner:于蜀豪 +1
Method for detecting types and contents of soil phenolic acids in eucalyptus forest land
InactiveCN104597164ASimple and fast operationThe detection process is fastComponent separationBenzoic acidAutosampler
The invention relates to a method for detecting types and contents of soil phenolic acids in a eucalyptus forest land. The method comprises the following steps: sampling a soil sample in a forest land and bringing back to a laboratory for later use; preparing a phenolic acid mixed standard solution, injecting into efficient high performance liquid chromatography, determining proper wavelength and chromatographic conditions, carrying out linear regression according to phenolic acid concentration and peak area of a map to draw a standard curve; preparing a sample solution for test, and obtaining a sample solution by adding a NaOH solution, centrifugalizing, acidifying by virtue of hydrochloric acid, removing humic acid, filtering and the like; and feeding the sample by using an automatic sampler, measuring according to the chromatographic condition, recording the peak area, and calculating the types and contents of soil phenolic acids according to the standard curve of the phenolic acid mixed solution. The detection method provided by the invention is simple to operate, high in detection speed, high in sensitivity, strong in accuracy, good in repeatability and suitable for detecting the types and contents of p-hydroxybenzoic acid, vanillic acid, ferulic acid, cumaric acid, benzoic acid, salicylic acid and cinnamic acid in forest land soil.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Chitosan grafted vanilloyl-based derivative and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106117392AGood water solubilityImprove biological activityEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideSolubilityVanillic acid
The invention discloses a chitosan grafted vanilloyl-based derivative and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps that vanillic acid serves as the raw material, and vanillic acid reacts with thionyl chloride to prepare aroyl chloride; an amino protection product N-phthaloyl chitosan of the chitosan and aroyl chloride are subjected to a reaction of nucleophilic substitution firstly, an acylate product 2-N-phthalyl-6-O-vanilloyl chitosan is generated, amino protection of the product is removed in a hydrazine hydrate solution, and the 6-O-vanilloyl chitosan product is obtained. For the obtained target product, vanilloyl is introduced, an active amino group of the chitosan is reserved simultaneously, the original physicochemical property of the chitosan is improved, and the solubility is improved; meanwhile, the bioactivity is improved, the antibacterial spectrum is broadened, the antibacterial activity is enhanced, and therefore the application range of the chitosan grafted vanilloyl-based derivative is expanded.
Owner:HENAN INST OF SCI & TECH
Red date brandy aging method
InactiveCN104877885AAccelerated agingPromoting rational processing and utilizationAlcoholic beverage preparationVanillic acidChemistry
The invention discloses a red date brandy aging method and belongs to the technical field of wine brewing. Red date brandy is promoted to be aged by adopting an oak, and total phenol content is obviously increased to be as high as 300-332mg / l; a free phenol comprises, by weight, 10-12mg / L of gallic acid, 3-5mg / L of vanillic acid, 3-4mg / L of syringic acid, 4-5mg / L of syringaldehyde, 10-12mg / L of ferulic acid, 10-15mg / L of benzoic acid and 4-5mg / L of salicylic acid. The red data brandy is moderate in wine color, soft and rich in flavor, amber in color, the chroma (OD value) ranges from 0.9 to 1.4, PH (potential of hydrogen) ranges from 4.0 to 4.5, total acid ranges from 0.8g / l to 0.9g / l, and total ester ranges from 0.7g / l to 1.0g / l. The aging method specifically includes: cutting the oak into oak blocks 15-20mm in length, 7-10mm in width and 3-6 in thickness; moderating the oak blocks for 90-120 minutes under the temperature ranging from 180DEG C to 220DEG C; during aging, adding the oak blocks by 9-18g / l and aging the oak blocks for 3-6 months under the temperate ranging from 18DEG C to 26DEG C to obtain wine which is end wine. A very important role is played in promoting reasonable processing utilization of oak resources and adjusting red date brandy processing production structure, and great significance is achieved for sustainable development of agricultural economy of red date producing areas in China is achieved.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
Amycolatopsis sp. and application thereof
ActiveCN113637607AHigh molar yieldHigh vanillinBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyVanillic acid
The invention relates to amycolatopsis sp. and application thereof. The amycolatopsis sp. HM-141 (the preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.22871) disclosed by the invention is applied to production of vanillin by taking ferulic acid as a substrate. Experiments confirm that the amycolatopsis sp. HM-141 uses ferulic acid as a substrate to produce vanillin, the molar conversion rate can reach up to 87%, impurities (or byproducts) in the product are obviously lower than that in the prior art, the detection amount of vanillin alcohol is 0, the detection amount of vanillic acid is as low as 0.25 g / L, and the amycolatopsis sp. HM-141 has obvious advantages.
Owner:SHAANXI HEALTHFUL BIOLOGICAL ENG
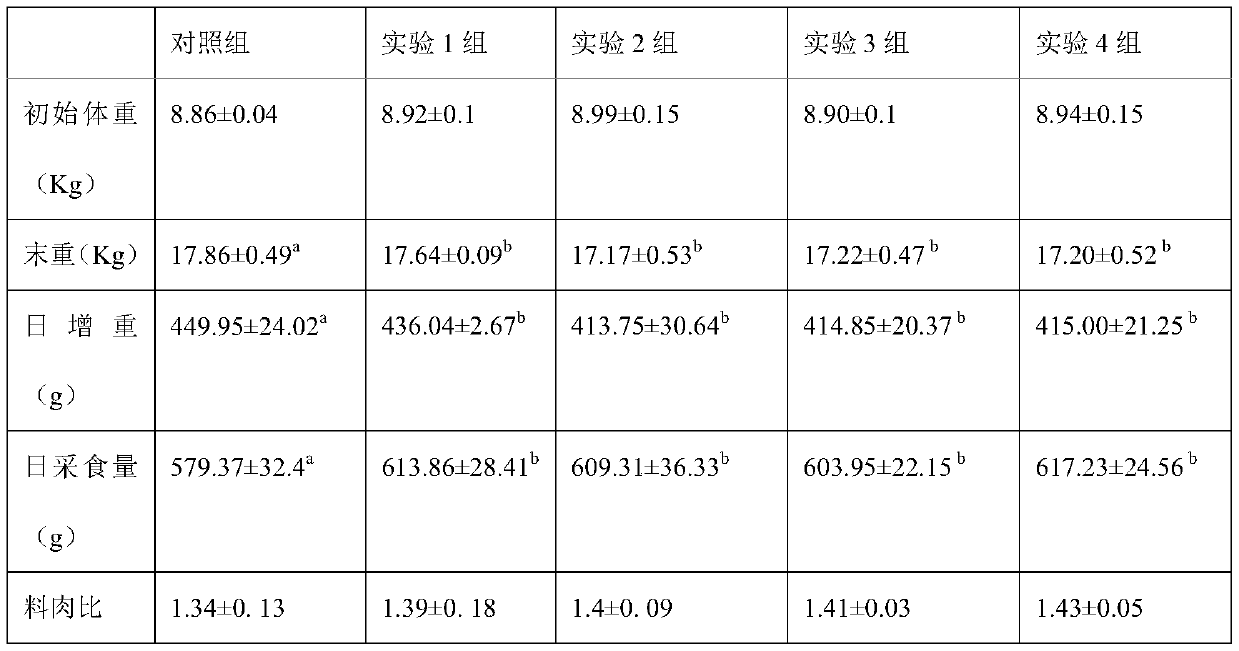
Weaned piglet feed
InactiveCN110574839AAlleviate adverse diseasesImprove antioxidant capacityAccessory food factorsPhosphateChemistry
The invention relates to weaned piglet feed. The weaned piglet feed is mainly prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 0.01-0.06 part of vanillic acid, 0.0001-0.0011 part of copper chloride hydroxide, 0.01-0.09 part of zinc oxide, 0.0111-0.555 part of ferrous sulfate, and 0.00050-0.00229 part of manganese sulfate, and in addition, the weaned piglet feed mainly further comprises corn, puffed corn, soybean meal, puffed soybeans, fish meal, whey powder, soybean oil, dicalcium phosphate, stone powder, table salt, lysine hydrochloride, methionine, threonine, tryptophan, compound vitamins, potassium iodide and sodium selenite. According to the formula of the weaned piglet feed, weaning stress in weaned piglets can be reduced, absorption of mineral elements is promoted, and thegrowth performance of the piglets is improved.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com