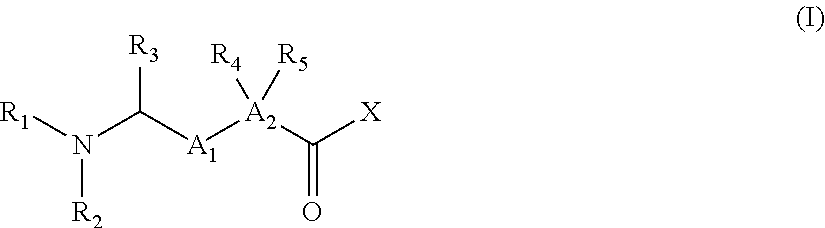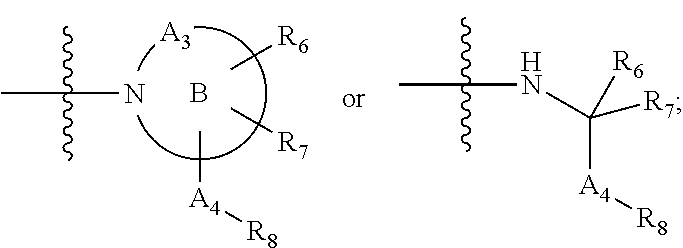Patents
Literature
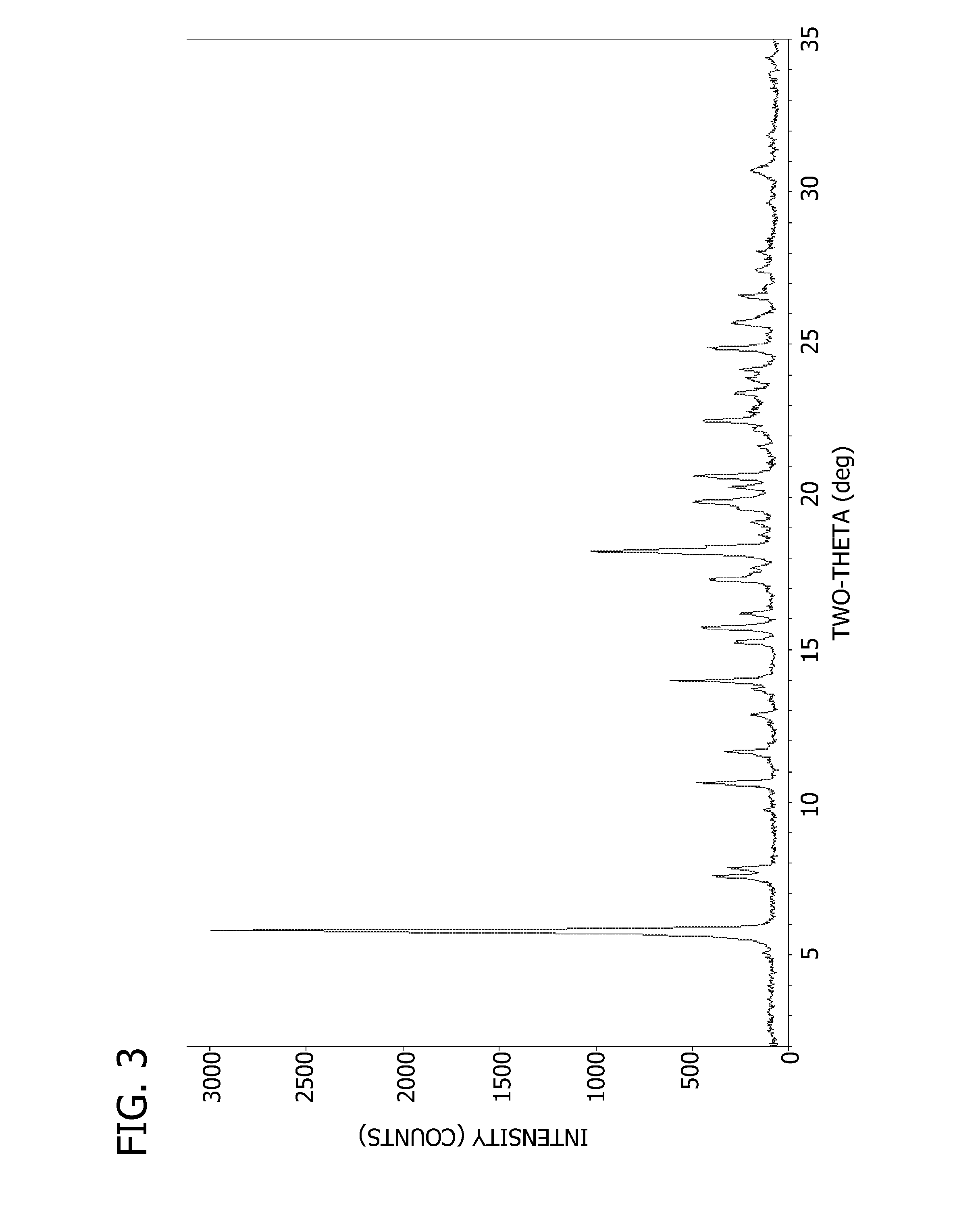
167 results about "Apoptosis inducer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apoptosis Inducers. Apoptosis inducers exhibit pro-apoptotic effects through a variety of mechanisms, including DNA cross-linking, inhibition of antiapoptotic proteins and activation of caspases. These inducers may target a specific cellular process in order to induce antitumor or antineoplastic effects.
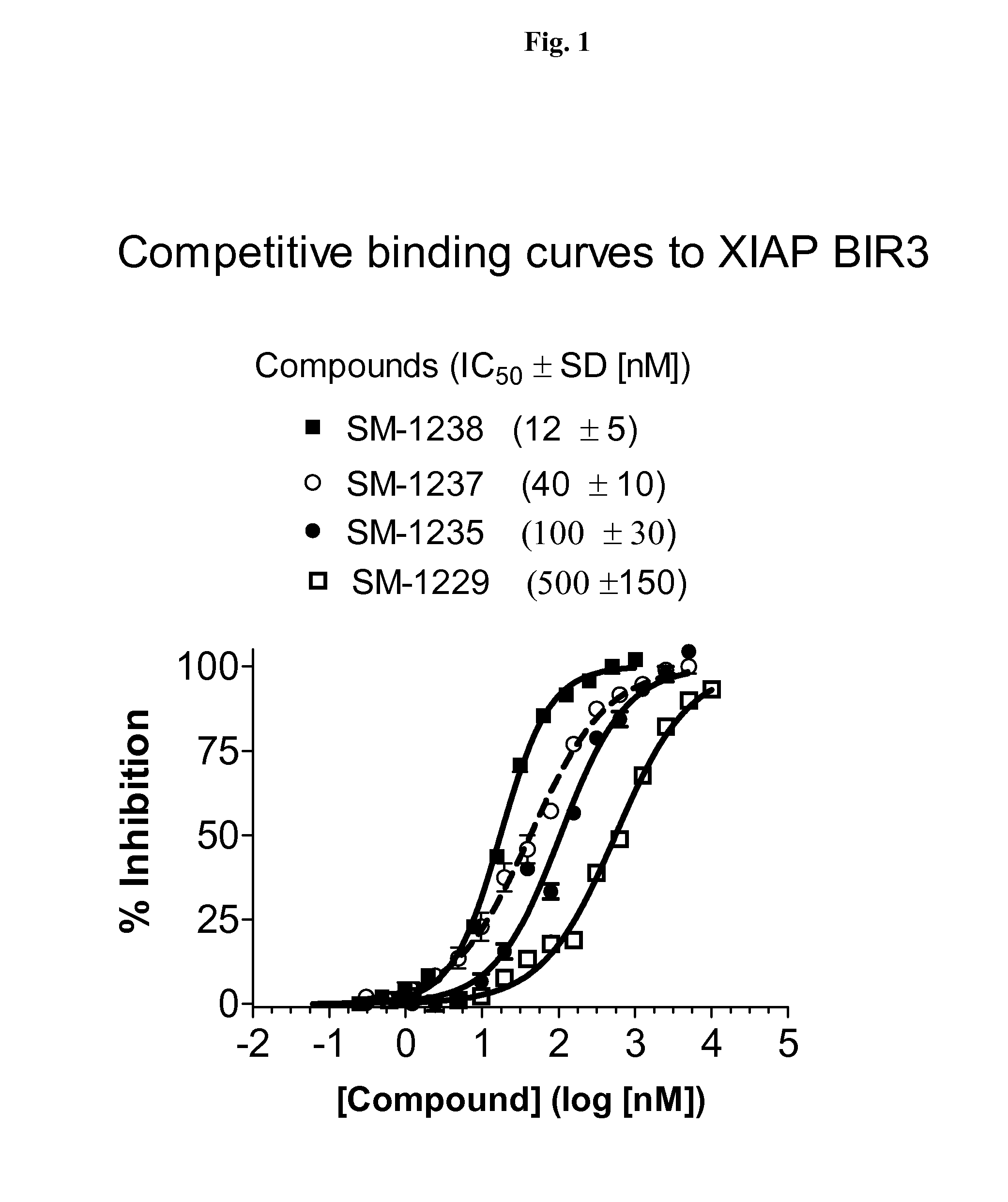
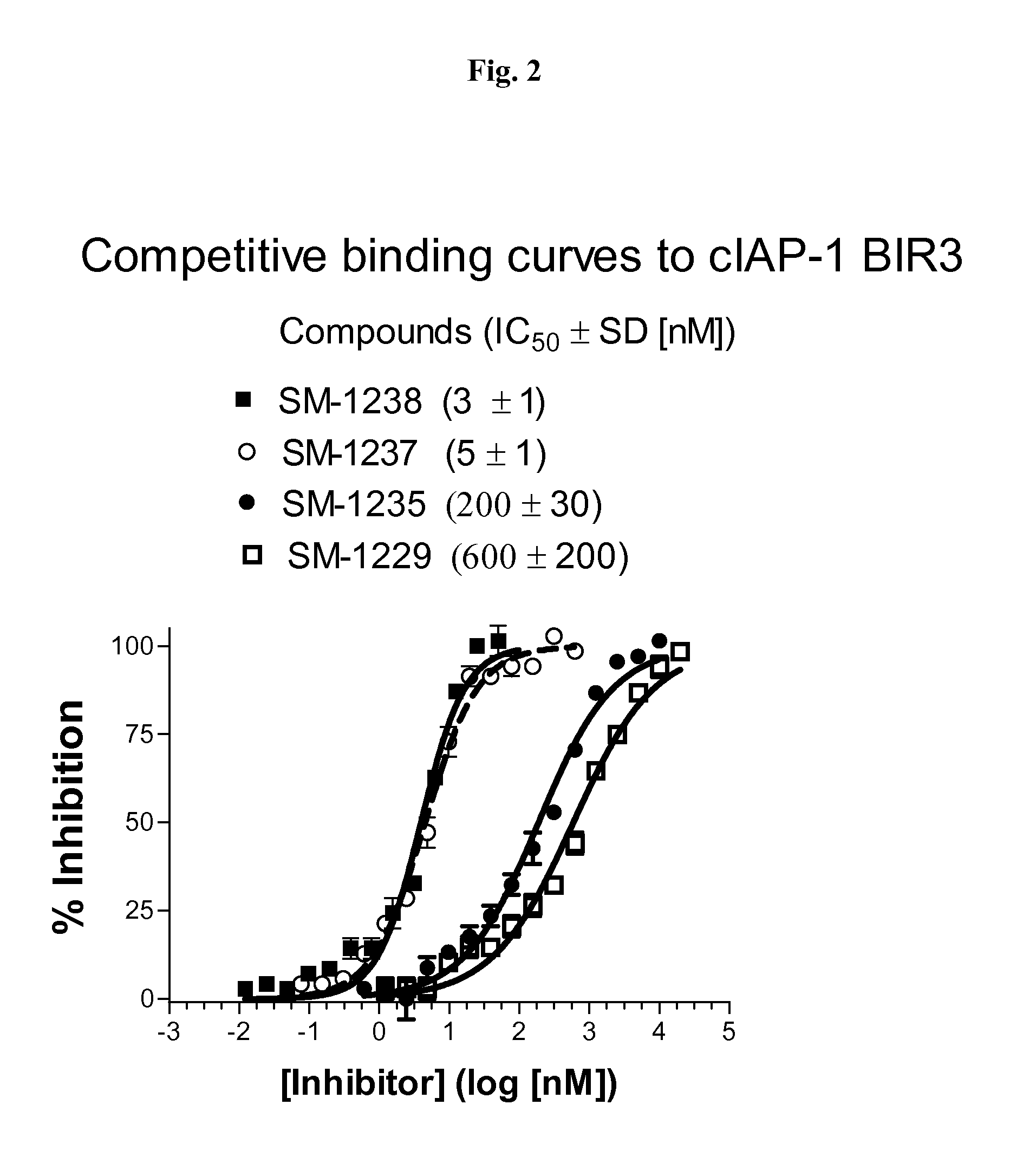
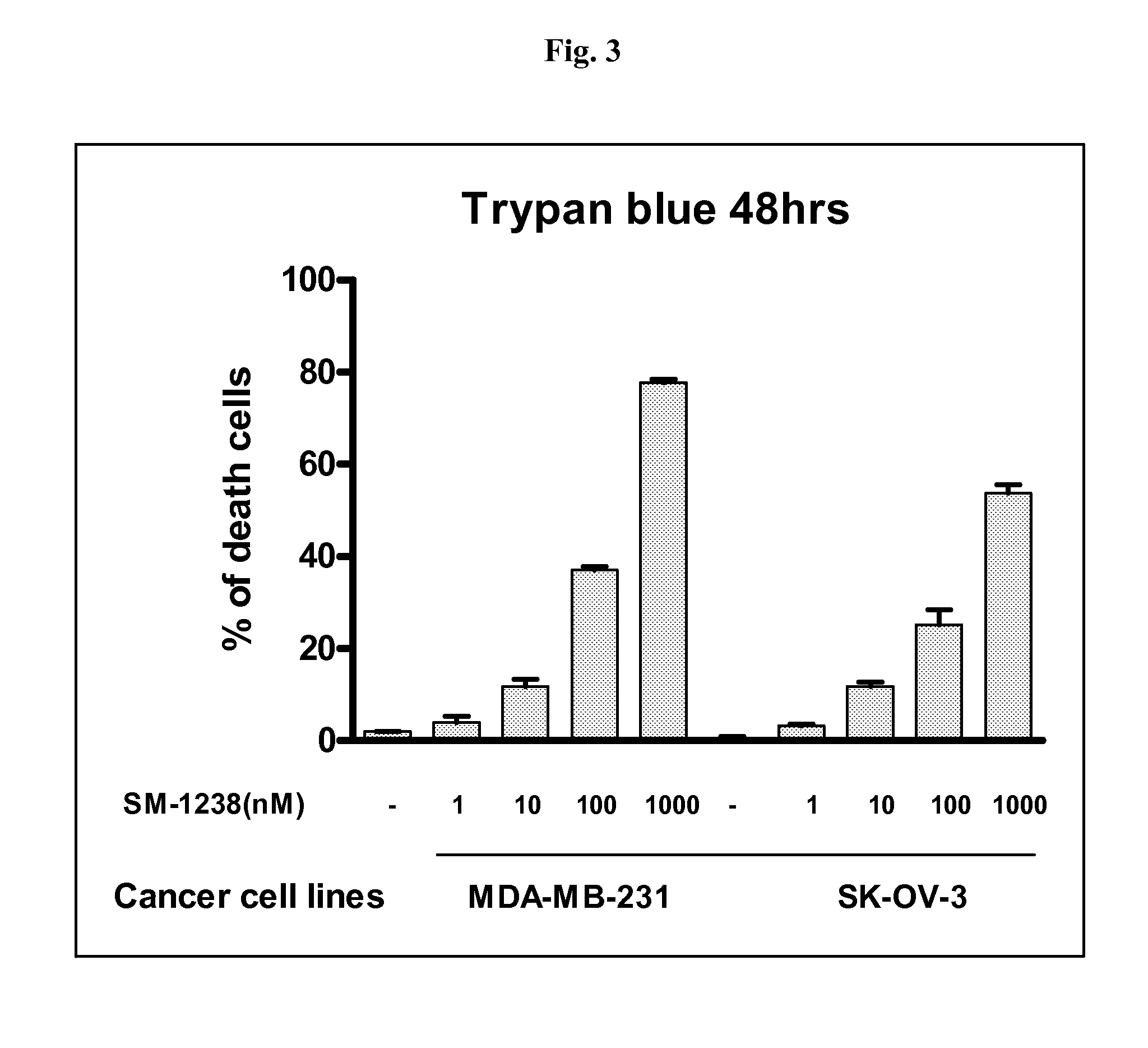
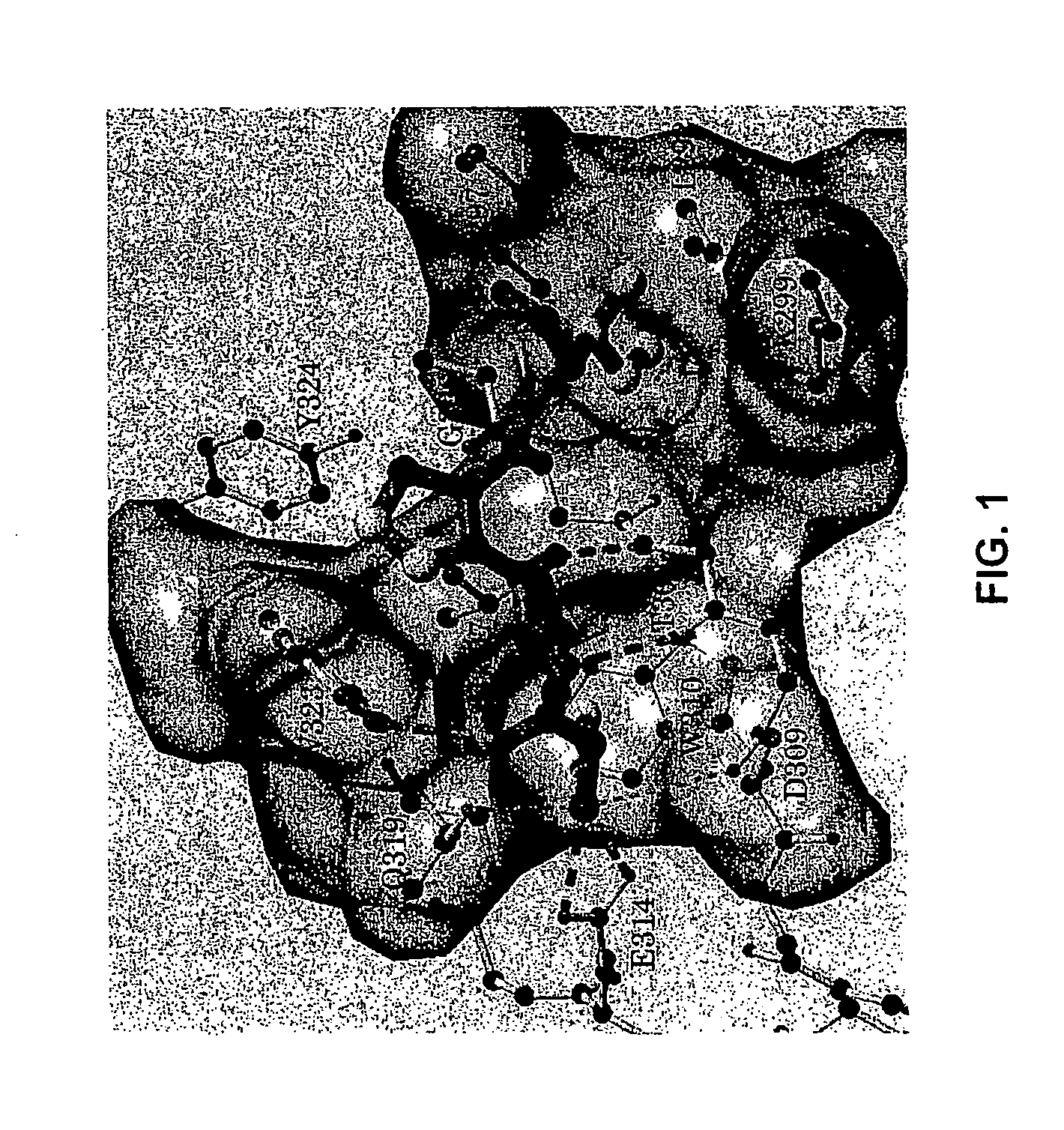
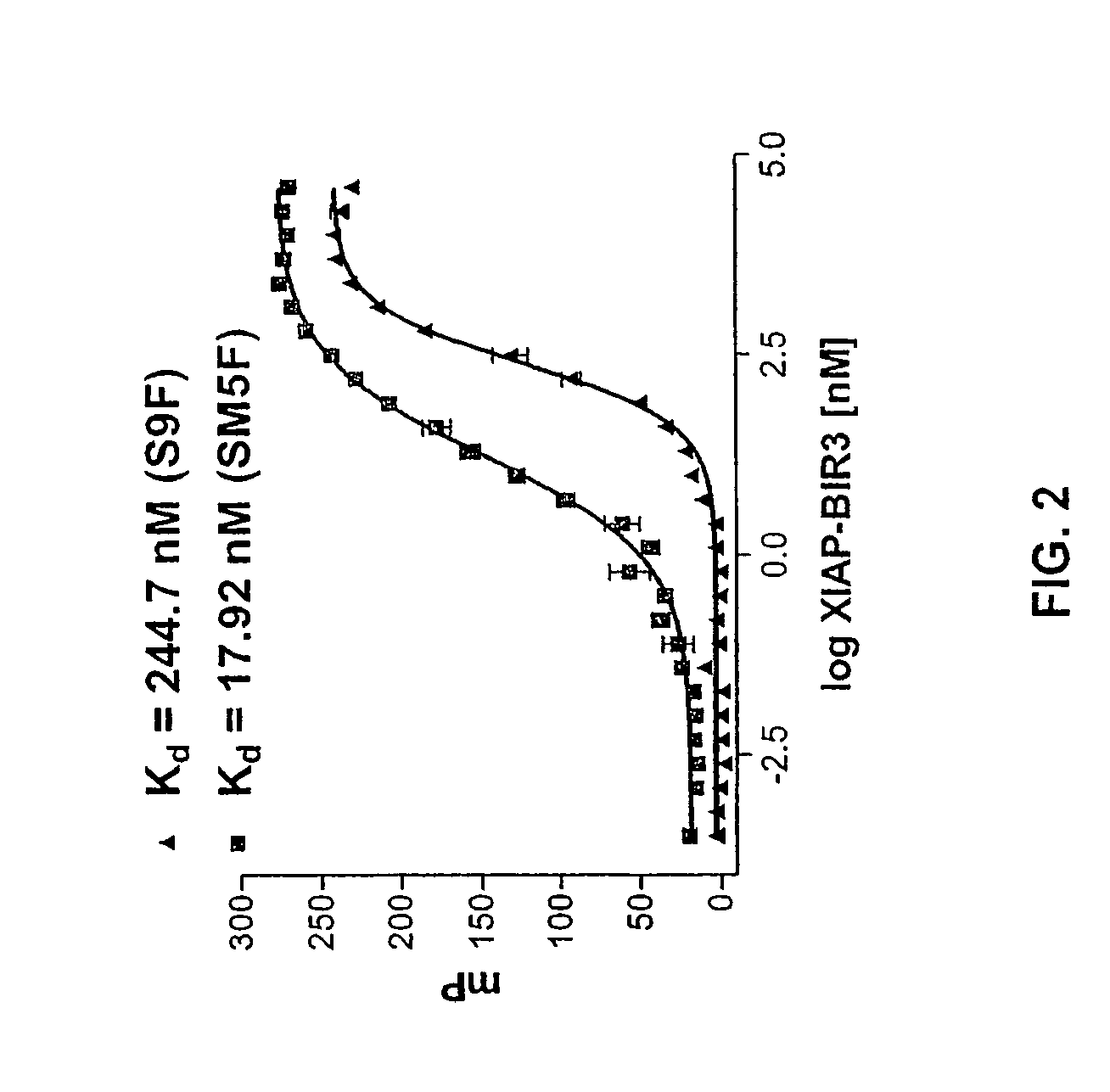
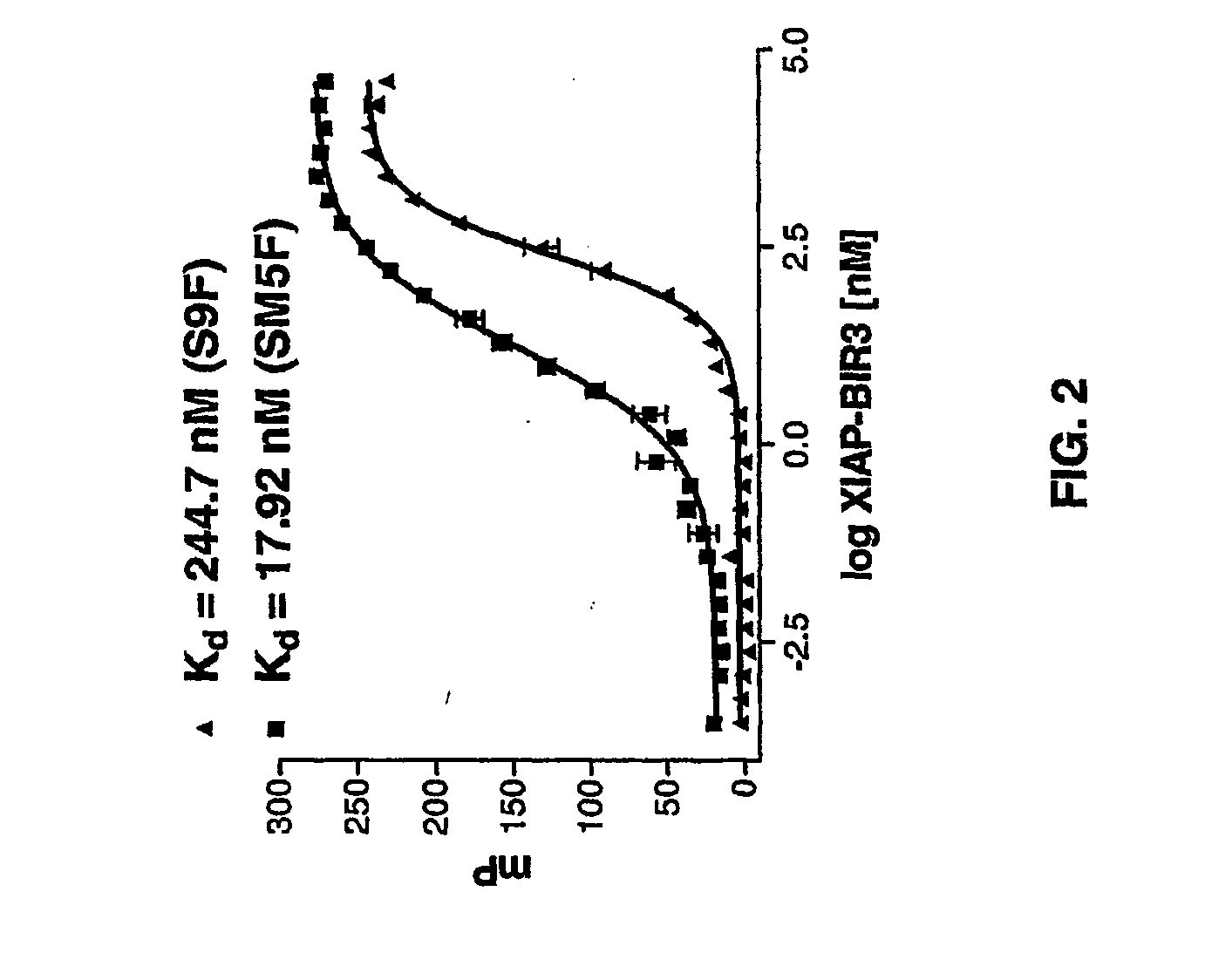
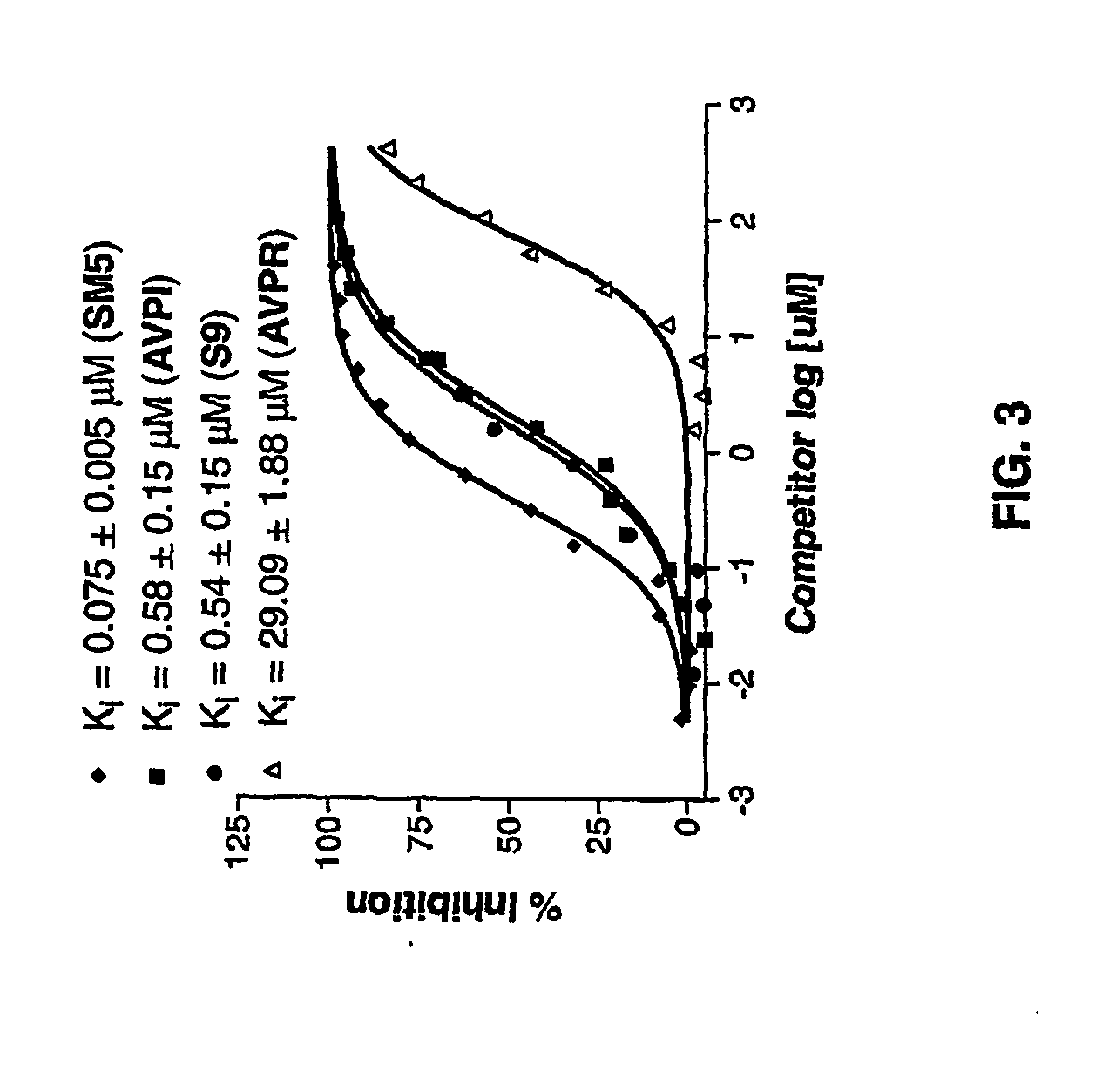
Bivalent SMAC mimetics and the uses thereof
ActiveUS20080089896A1Toxic reductionMore tolerableBiocideOrganic chemistrySmac mimeticsSensitized cell
The invention relates to bivalent mimetics of Smac which function as inhibitors of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins. The invention also relates to the use of these mimetics for inducing apoptotic cell death and for sensitizing cells to inducers of apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Conformationally Constrained Smac Mimetics and the Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20080269140A1High expressionToxic reductionDipeptide ingredientsTripeptide ingredientsSmac mimeticsSensitized cell
The invention relates to conformationally constrained mimetics of Smac which function as inhibitors of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins. The invention also relates to the use of these mimetics for inducing apoptotic cell death and for sensitizing cells to inducers of apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
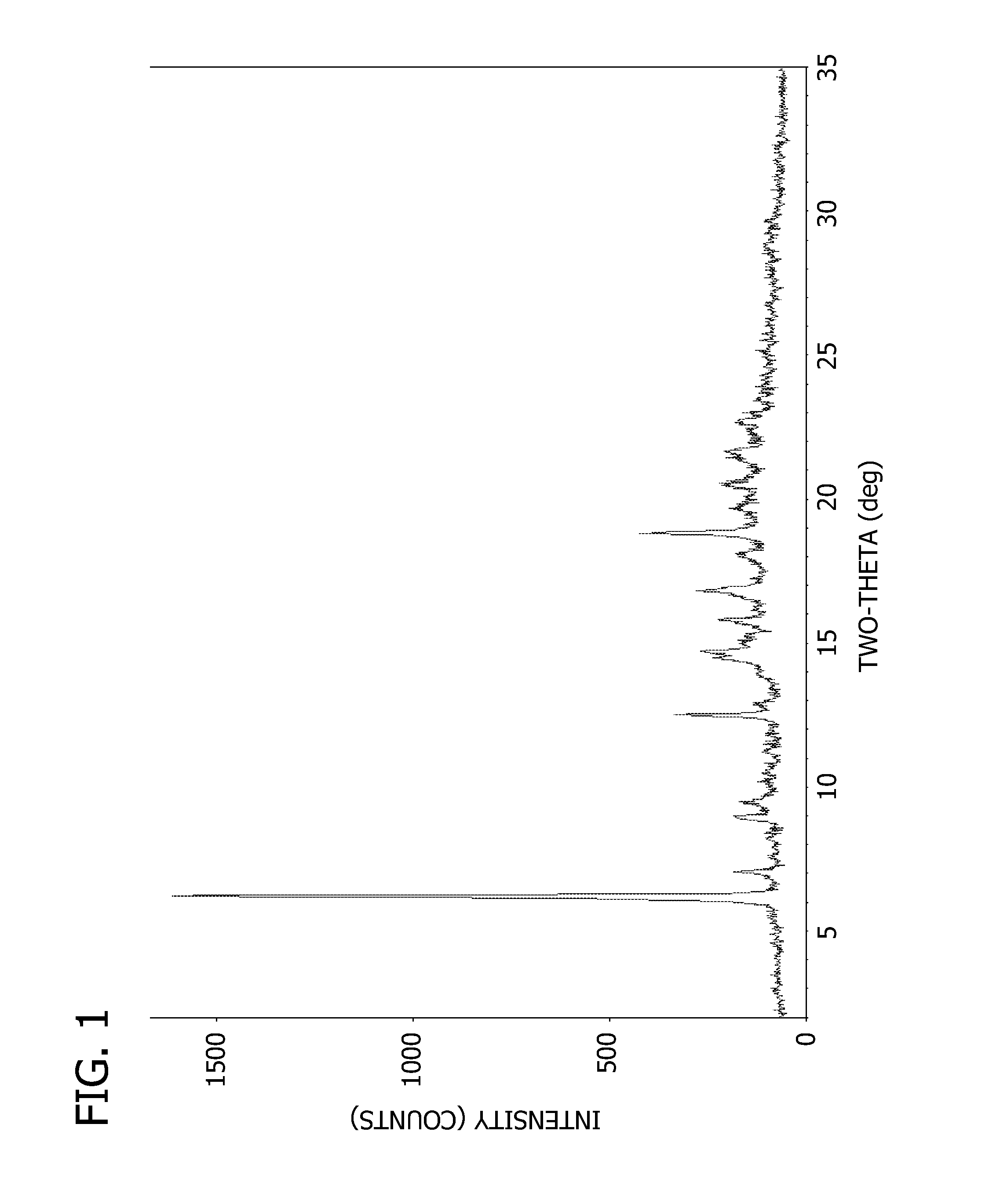
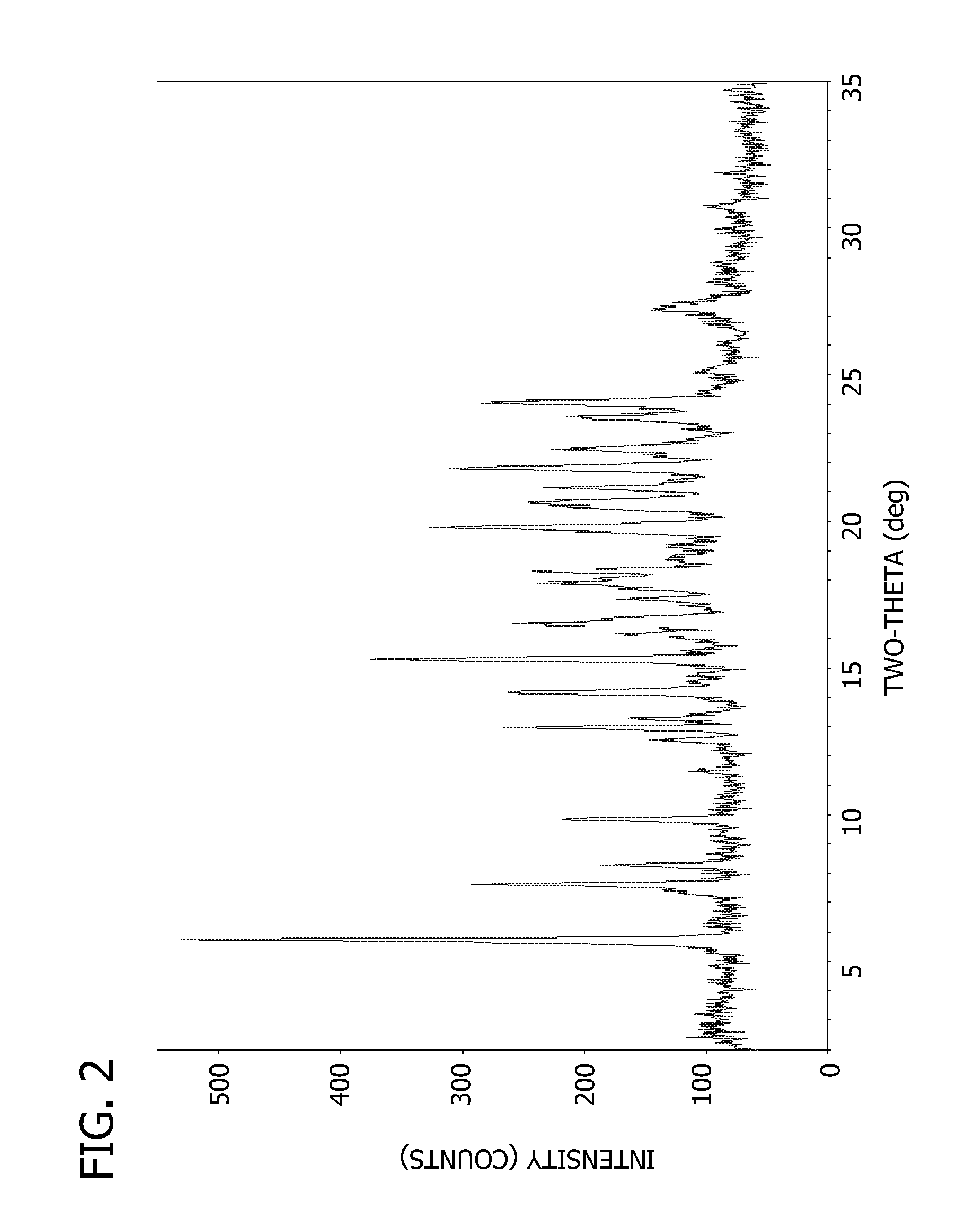
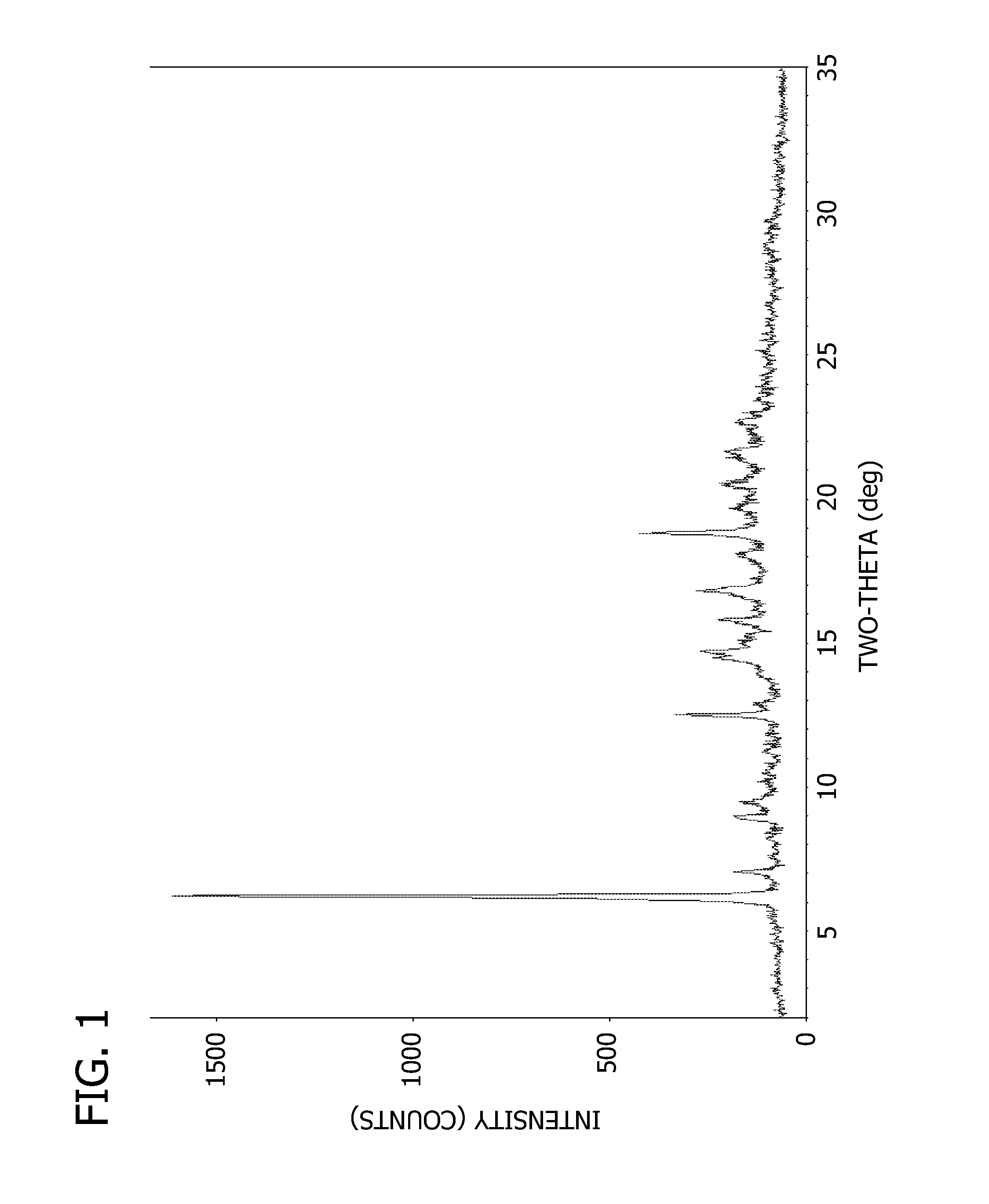
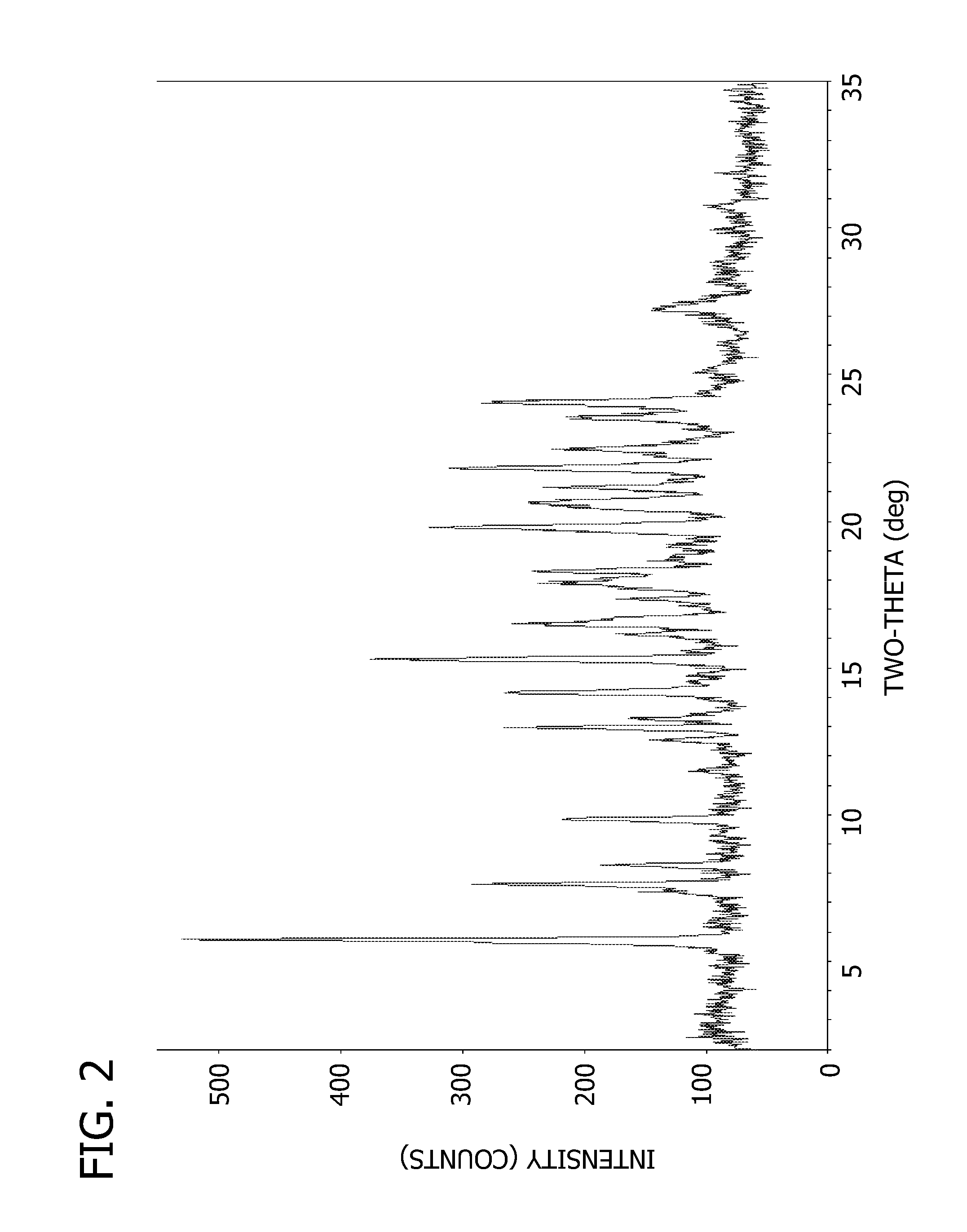
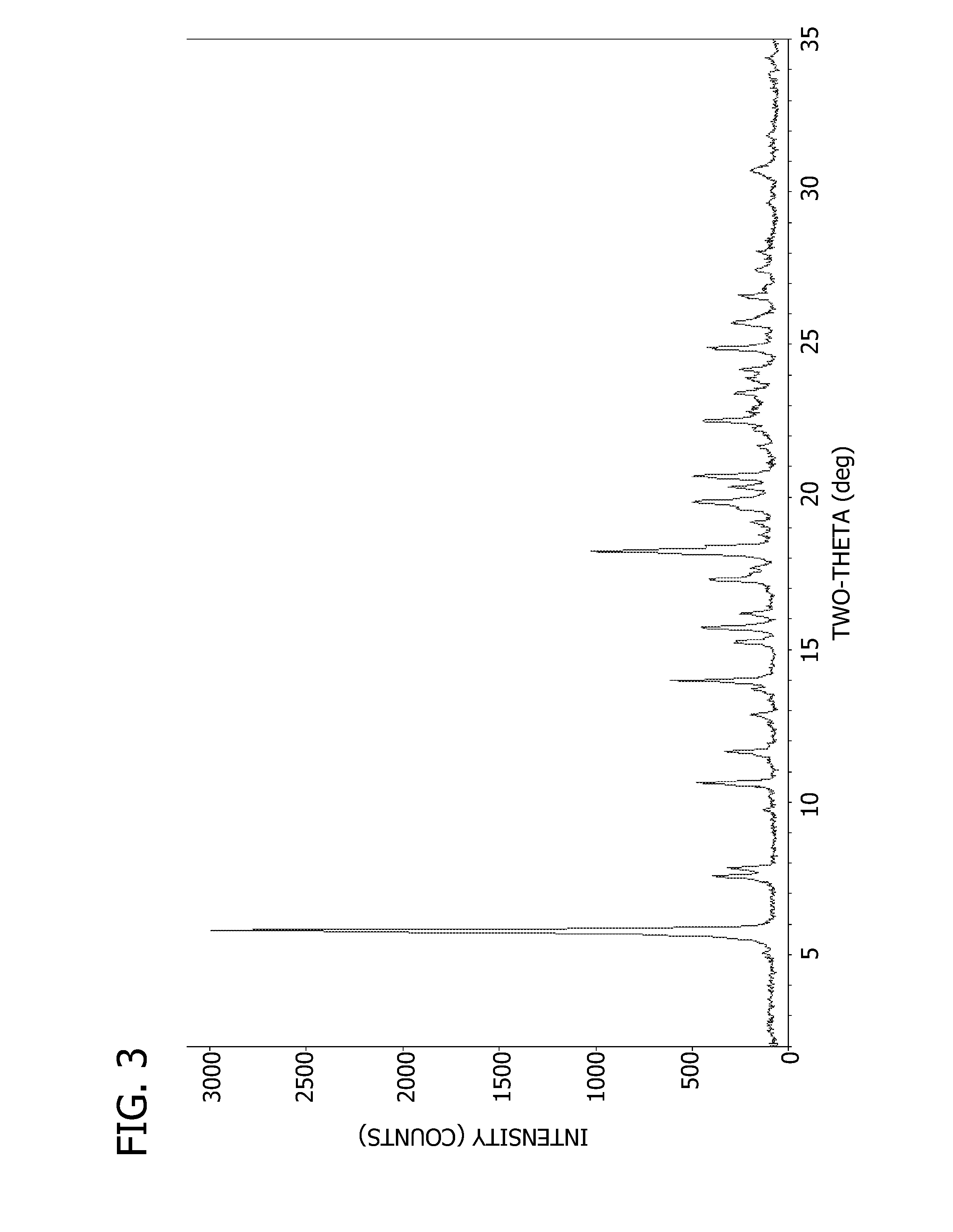
Salts and crystalline forms of an apoptosis-inducing agent
Salts and crystalline forms of 4-(4-{[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl]methyl}piperazin-1-yl)-N-({3-nitro-4-[(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-ylmethyl)amino]phenyl}-sulfonyl)-2-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide are suitable active pharmaceutical ingredients for pharmaceutical compositions useful in treatment of a disease characterized by overexpression of one or more anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, for example cancer.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Apoptosis inducing agents and methods
Methods and compositions are disclosed for inducing differentiation and apoptosis in cells that overexpress Notch proteins. A cell fate determining function of Notch is specifically disrupted at a time when the cell is undergoing differentiation, which causes the cell to undergo apoptosis. The invention includes therapies for tumors that overexpress a Notch protein (such as Notch-1) by inducing differentiation of the cells in the tumor with a differentiation inducing agent, such as HMBA, in combination with an agent that disrupts the function of the Notch protein. At a time during which differentiation has been promoted, and the cell is susceptible to interference with the anti-apoptosis effect of Notch, the function of the Notch protein is disrupted. Disruption of Notch function can be achieved, for example, by a differentiation inducing agent, such as HMBA, combined with antibodies that specifically bind to Notch and inactivate it, for example a monoclonal antibody that recognizes Notch-1 EGF-like repeats 11 and 12, such as monoclonal antibodies A6, C11 or F3. Disruption of Notch function can also be achieved by the expression of antisense oligonucleotides that specifically interfere with expression of the Notch protein on the cell, alone or in combination with antineoplastic agents.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
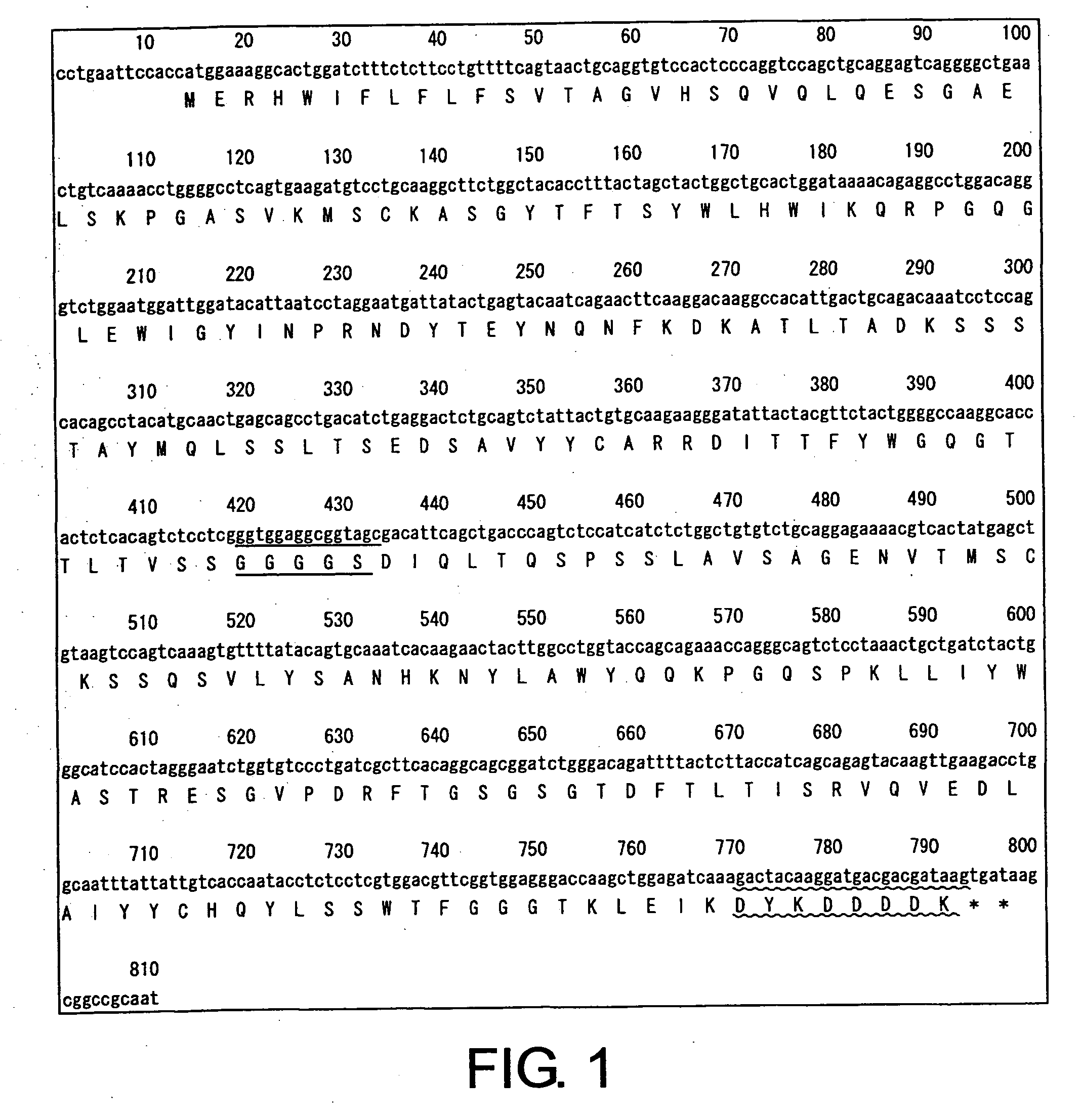
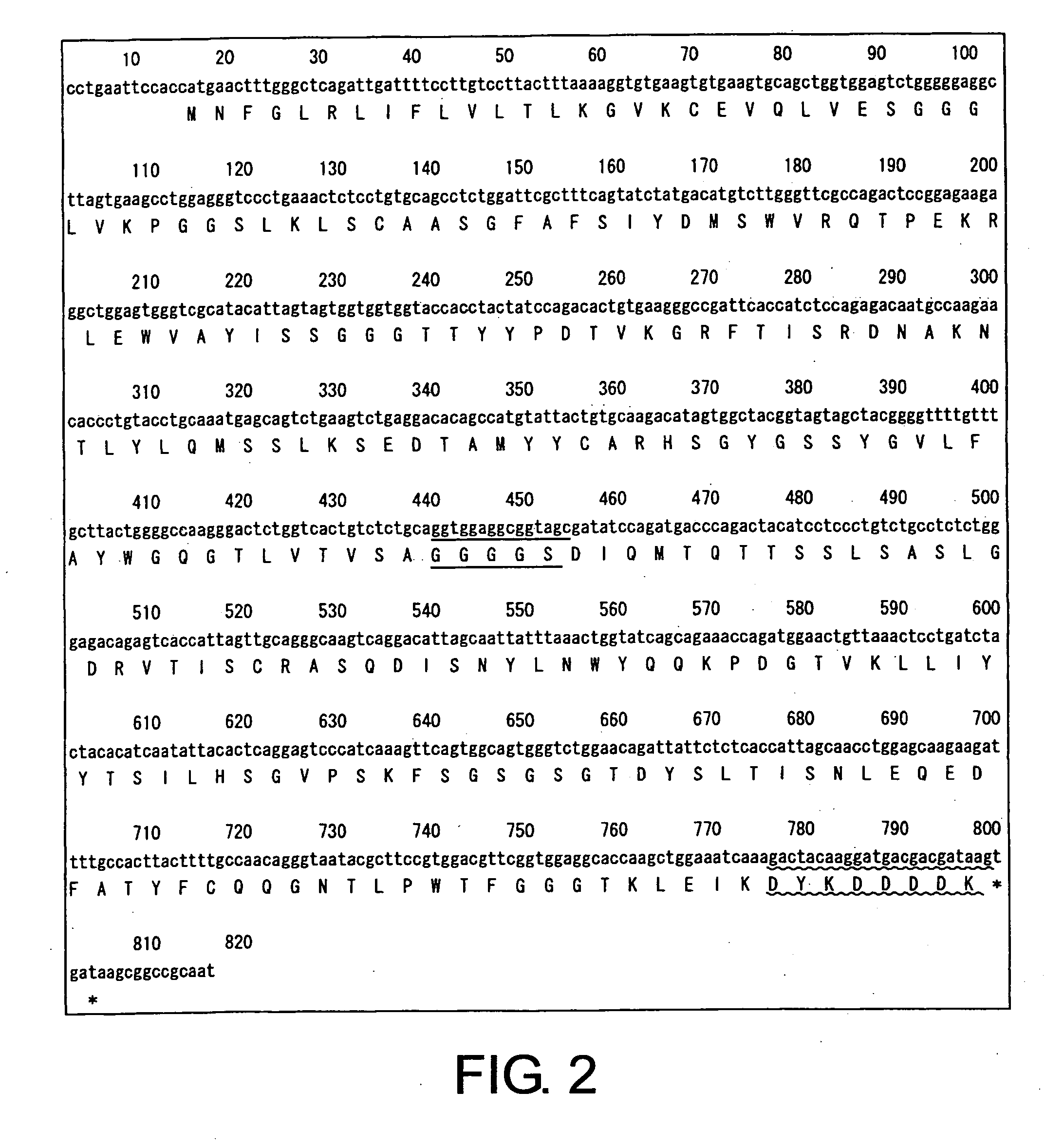
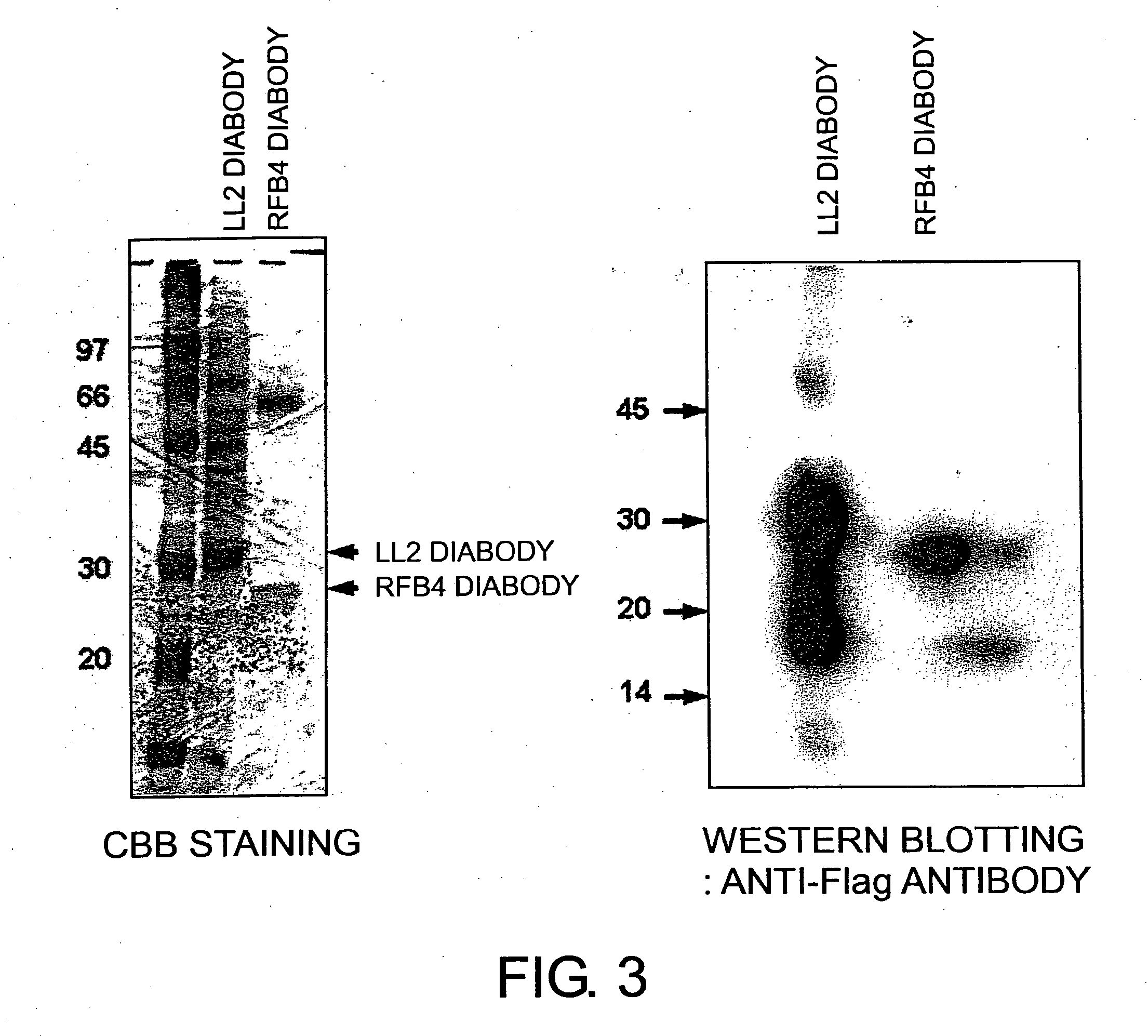
Modified antibodies against cd22 and utilization thereof
CD22 diabodies, in which heavy-chain and light-chain variable regions are linked by a 5-mer linker, were produced based on known sequence information for two types of anti-CD22 antibodies. The two diabodies produced were analyzed for their activity of binding to lymphoma cells and inducing lymphoma cell death (apoptosis). As a result, both diabodies were revealed to bind to the B-lymphoma cell line, “Raji”, and to have apoptosis-inducing activity towards Raji cells as well as towards another B-lymphoma cell line: Daudi cells. These results show that minibodies of antibodies that recognize CD22 can be used as apoptosis-inducing agents for tumor cells such as lymphoma cells.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
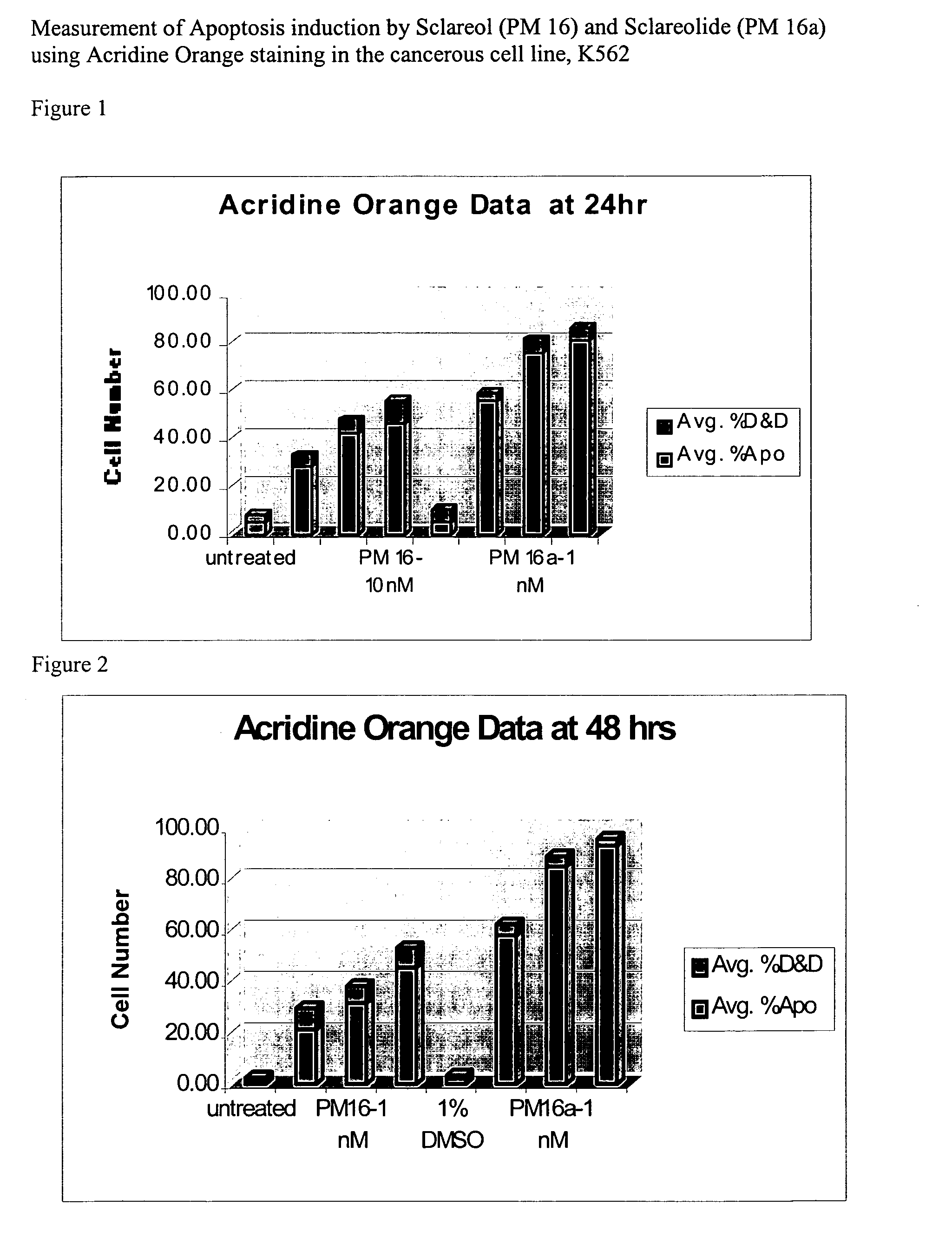
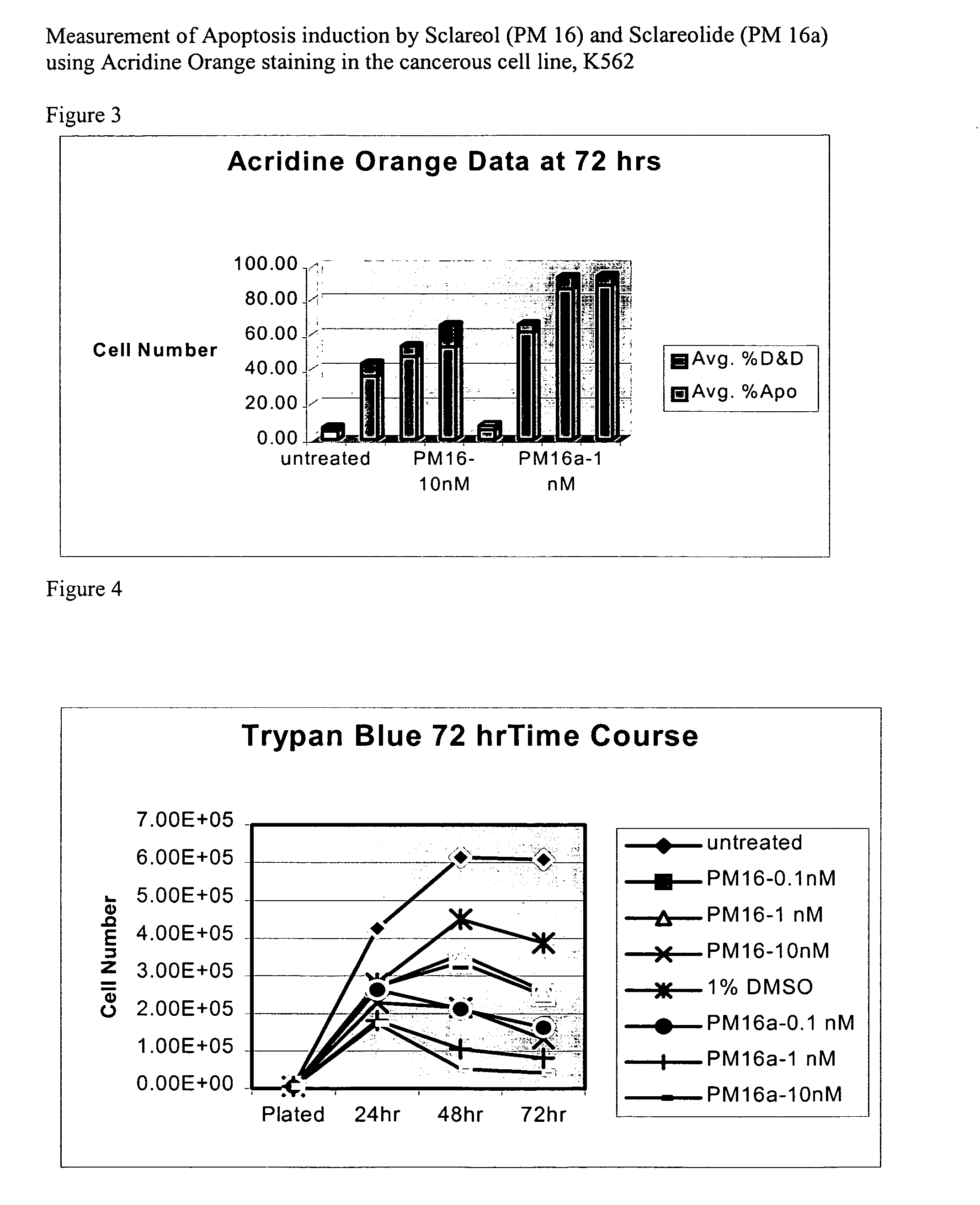
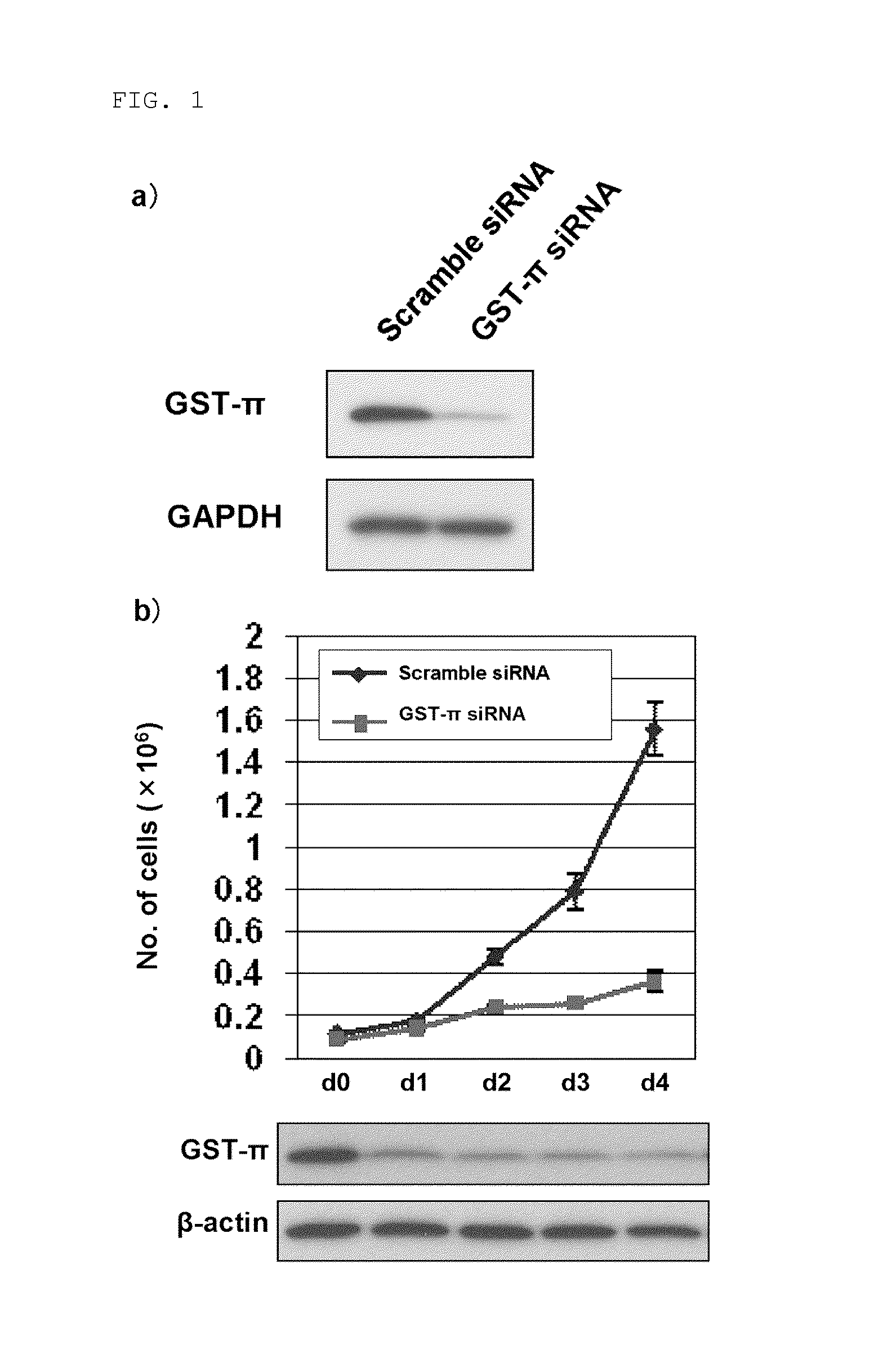
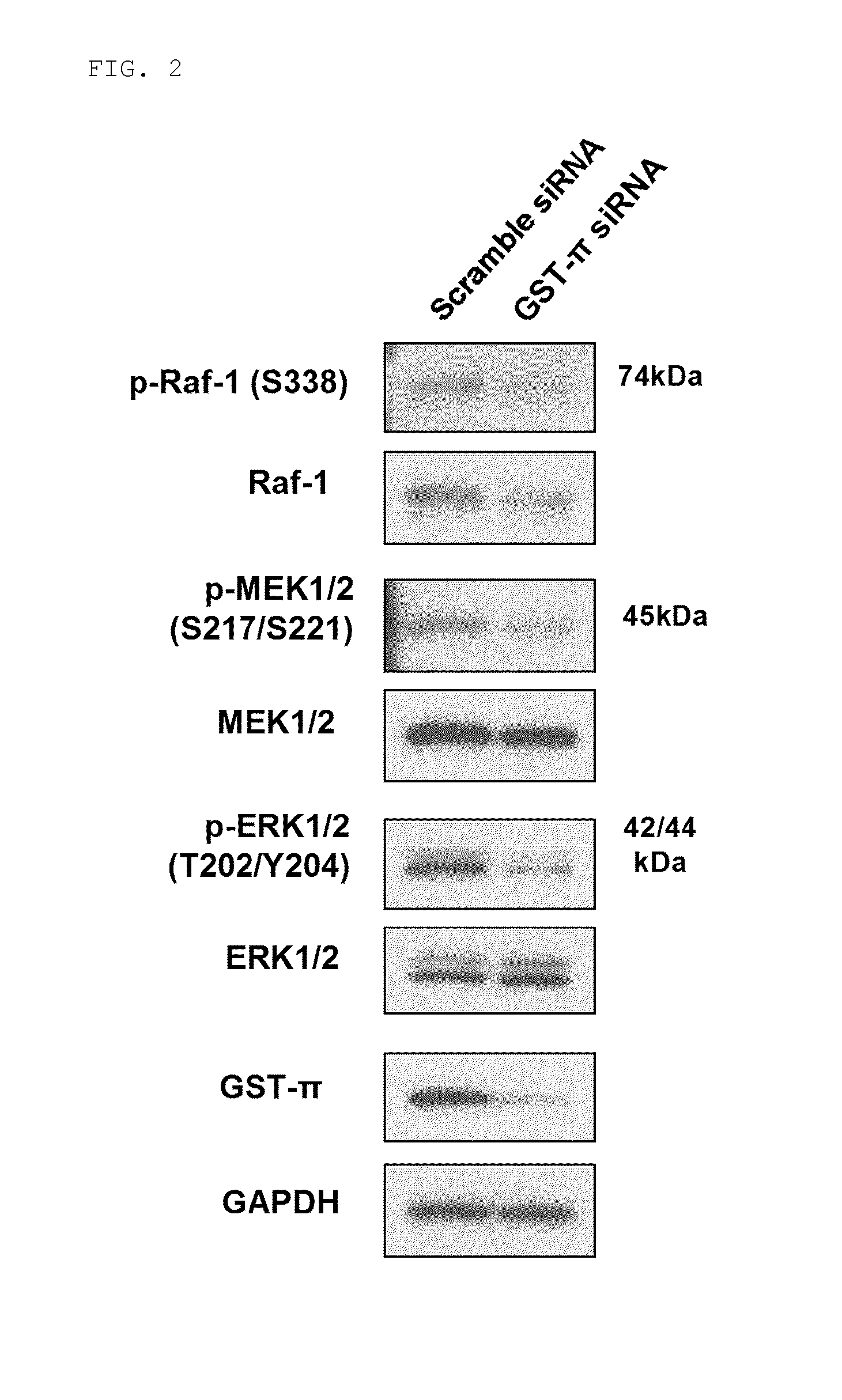
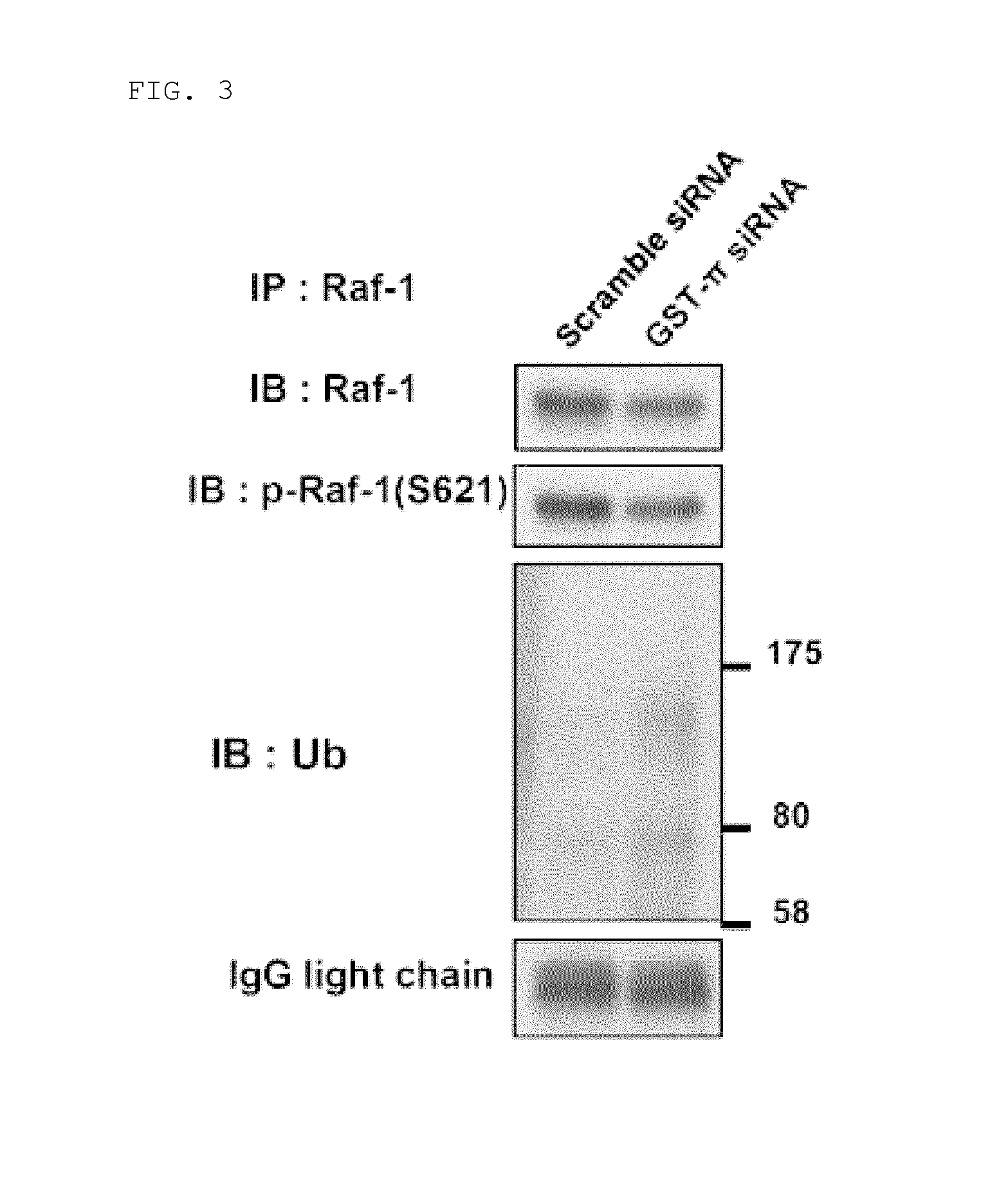
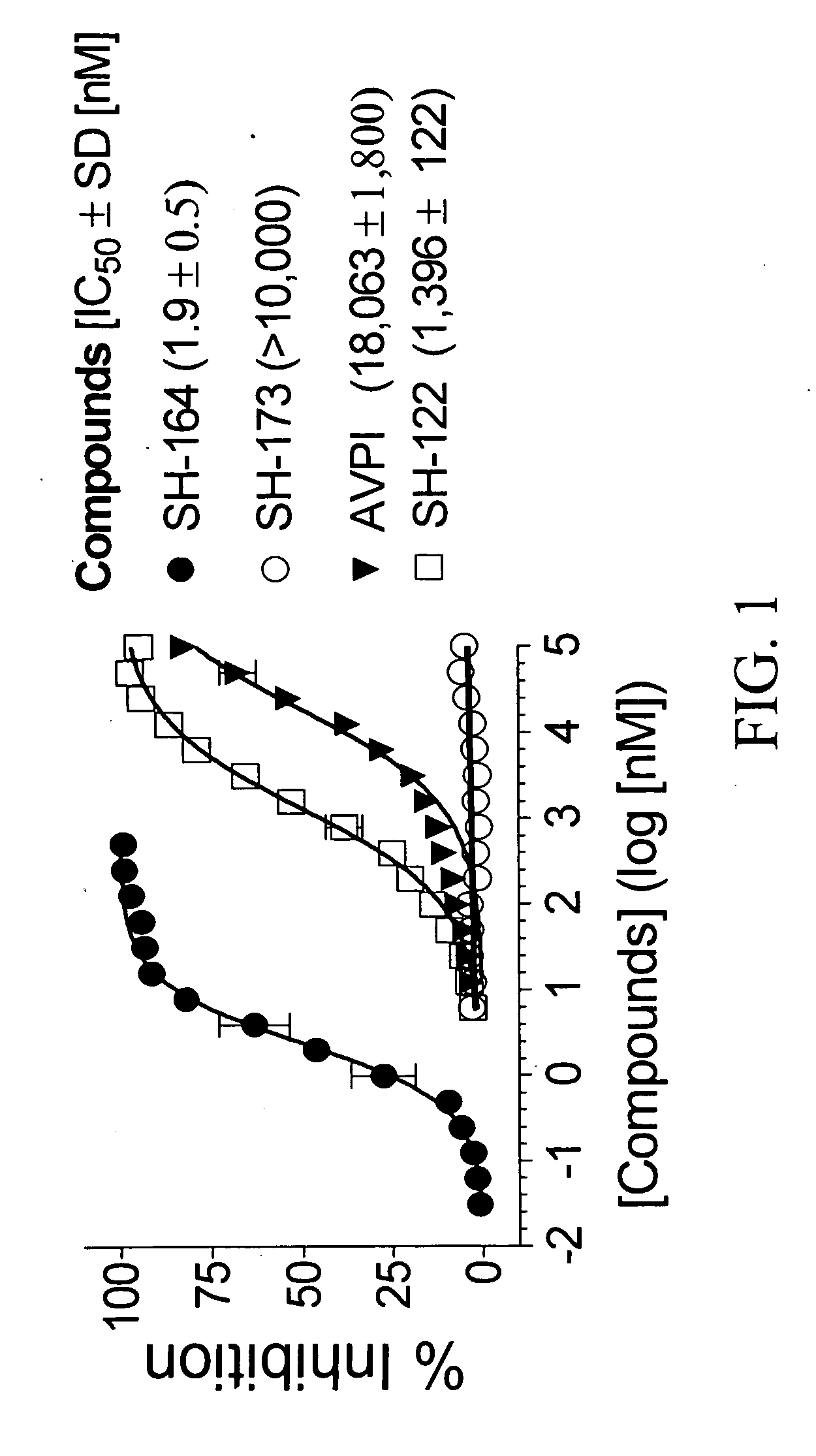
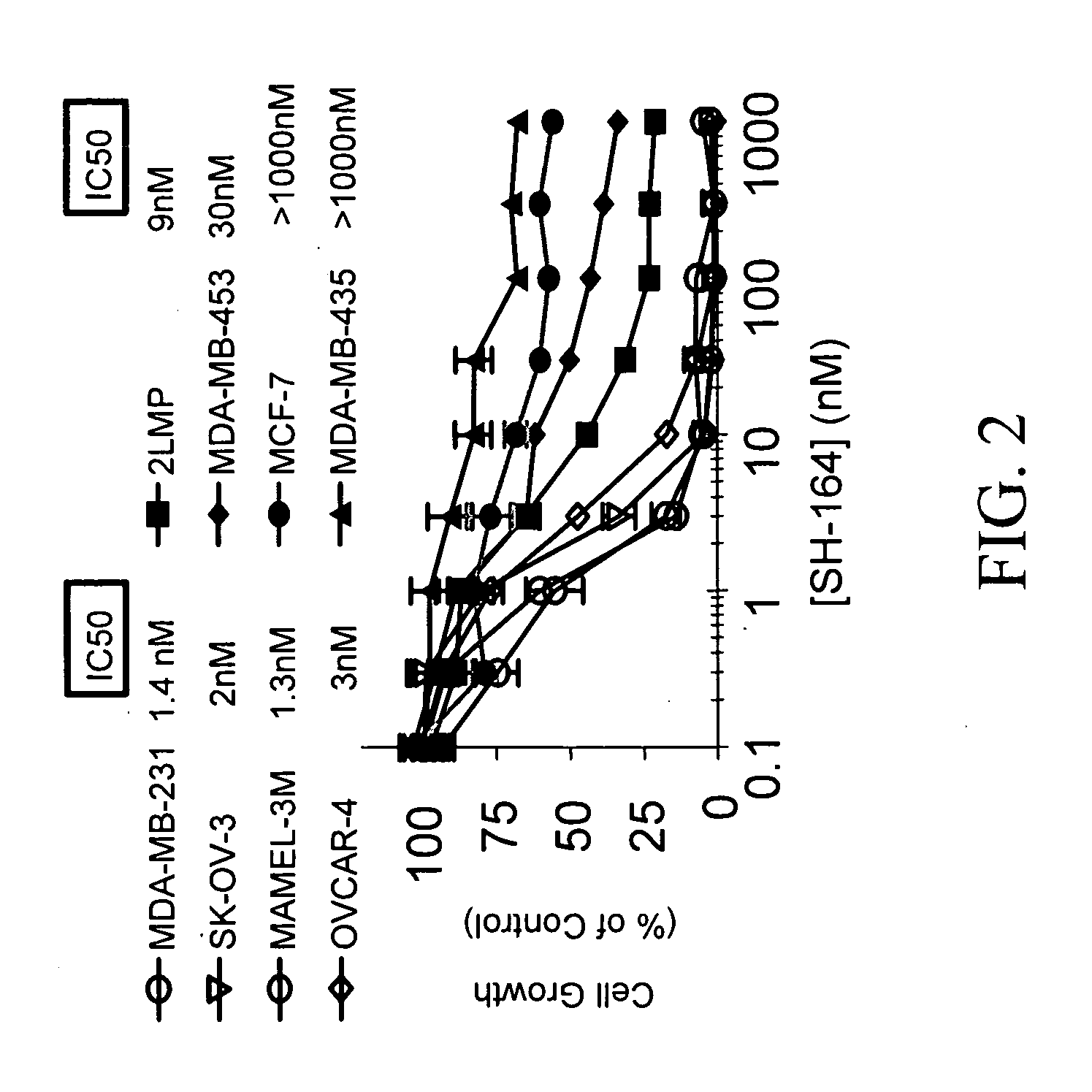
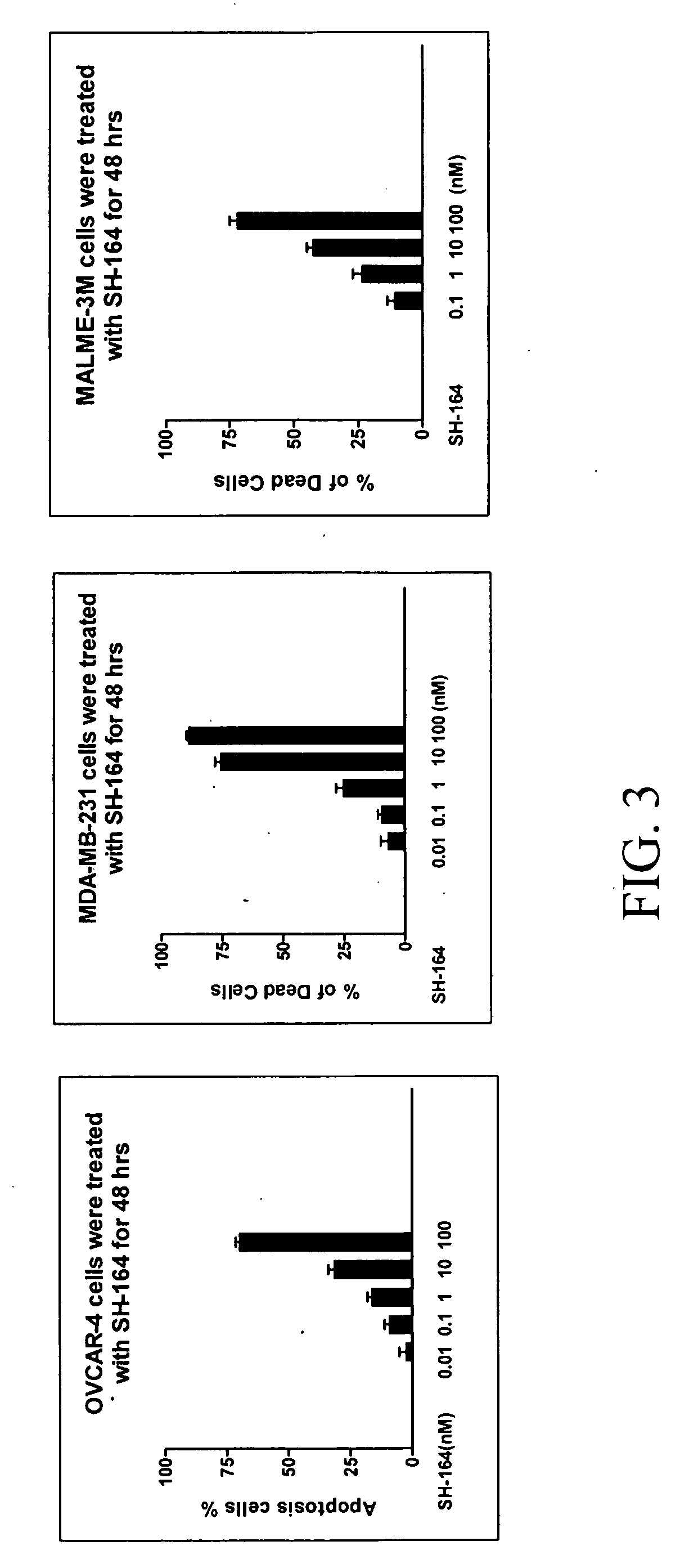
Apoptosis-inducing agent
InactiveUS20140315975A1Inhibit progressEliminate side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsTransferasesDiseaseActive component
This invention relates to: a novel use of GST-π and GST-π suppressing agents; an apoptosis-inducing agent containing as active components a drug that suppresses GST-π and a drug that suppresses autophagy; a medical composition containing said agent; and a method using said medical composition for treating diseases associated with abnormal apoptosis.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Bivalent smac mimetics and the uses thereof
ActiveUS20090123480A1Toxic reductionMore tolerableBiocideOrganic chemistrySmac mimeticsSensitized cell
The invention relates to bivalent mimetics of Smac which function as inhibitors of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins. The invention also relates to the use of these mimetics for inducing apoptotic cell death and for sensitizing cells to inducers of apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Salts and crystalline forms of an apoptosis-inducing agent
Salts and crystalline forms of 4-(4-{[2-(4-chlorophenyl)-4,4-dimethylcyclohex-1-en-1-yl]methyl}piperazin-1-yl)-N-({3-nitro-4-[(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-ylmethyl)amino]phenyl}-sulfonyl)-2-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yloxy)benzamide are suitable active pharmaceutical ingredients for pharmaceutical compositions useful in treatment of a disease characterized by overexpression of one or more anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, for example cancer.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
Conformationally Constrained Smac Mimetics And The Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080132485A1Toxic reductionMore tolerableBiocideOrganic chemistrySmac mimeticsSensitized cell
The invention relates to conformationally constrained mimetics of Smac which function as inhibitors of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins. The invention also relates to the use of these mimetics for inducing apoptotic cell death and for sensitizing cells to inducers of apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
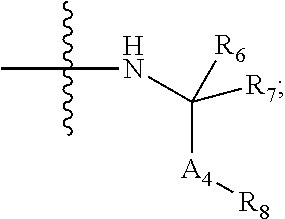
3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof
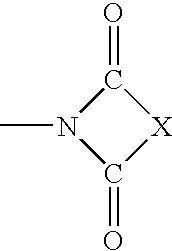
Disclosed are 3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs thereof, represented by the Formula I:wherein Ar1, R2, A, B and D are defined herein. The present invention relates to the discovery that compounds having Formula I are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention may be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
3,5-Disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof
Disclosed are 3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs thereof, represented by the Formula I:wherein Ar1, R2, A, B and D are defined herein. The present invention relates to the discovery that compounds having Formula I are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention may be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
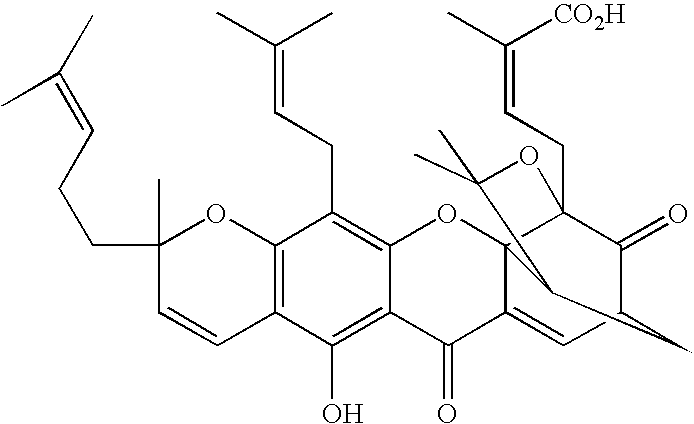
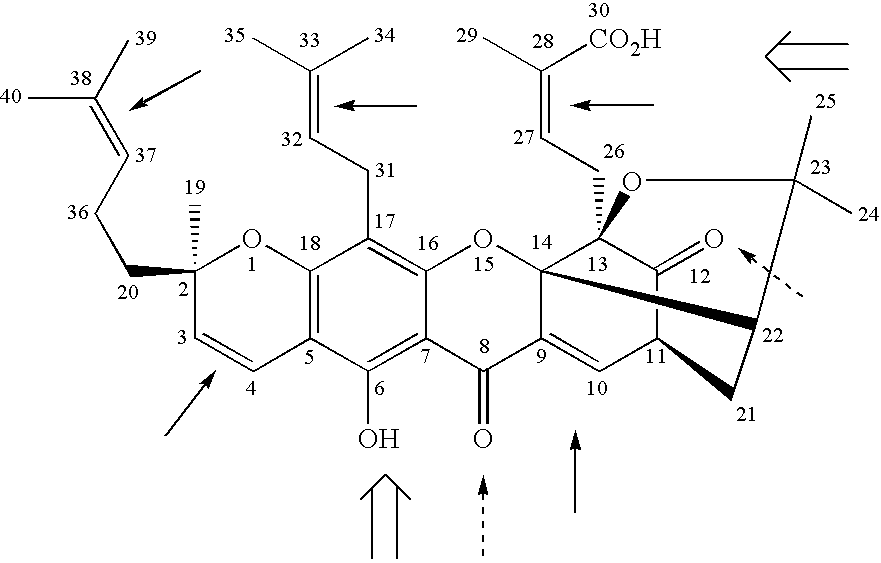
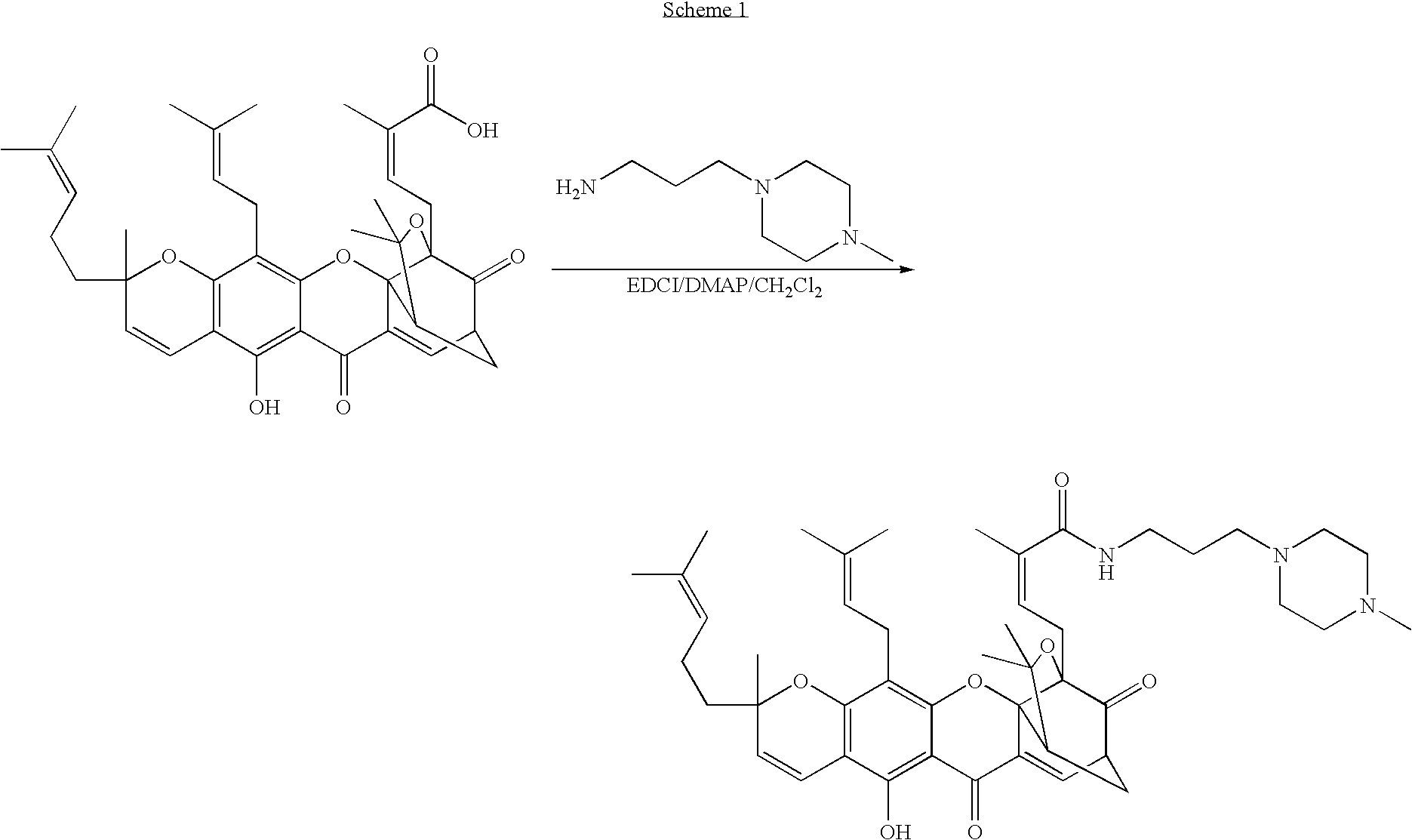
Derivatives of gambogic acid and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis
The present invention is directed to novel derivatives of gambogic acid and analogs thereof. The present invention also relates to the discovery that novel derivatives of gambogic acid are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention can be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
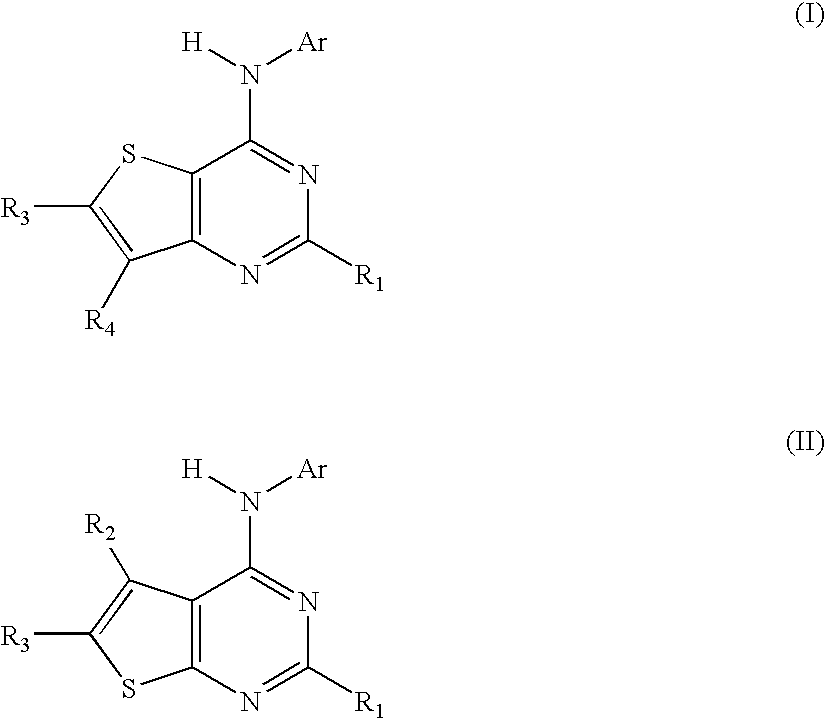
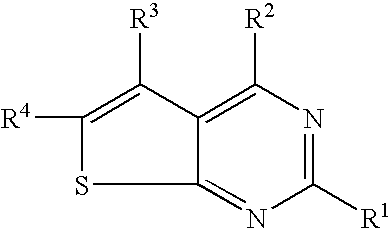
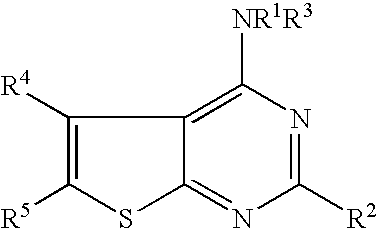
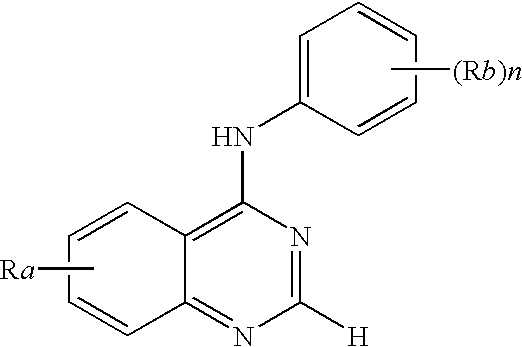
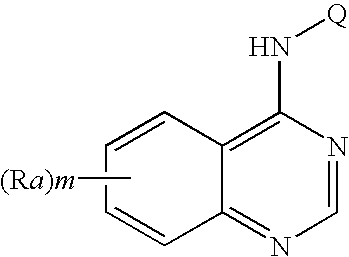
N-aryl-thienopyrimidin-4-amines and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof
Disclosed are N-aryl-thienopyrimidin-4-amines and analogs thereof, represented by the Formulae I-II: wherein Ar and R1-R4 are defined herein. The present invention relates to the discovery that compounds having Formulae I-II are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention may be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
Conformationally constrained Smac mimetics and the uses thereof
InactiveUS7674787B2Toxic reductionMore tolerableBiocideOrganic chemistrySmac mimeticsSensitized cell
The invention relates to conformationally constrained mimetics of Smac which function as inhibitors of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins. The invention also relates to the use of these mimetics for inducing apoptotic cell death and for sensitizing cells to inducers of apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Conformationally constrained Smac mimetics and the uses thereof
ActiveUS7932382B2Toxic reductionMore tolerableAntineoplastic agentsHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsSmac mimeticsSensitized cell
The invention relates to conformationally constrained mimetics of Smac which function as inhibitors of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins. The invention also relates to the use of these mimetics for inducing apoptotic cell death and for sensitizing cells to inducers of apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Bivalent Smac mimetics and the uses thereof
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
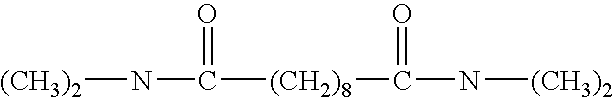
4-substituted naphthalimide compound and use thereof
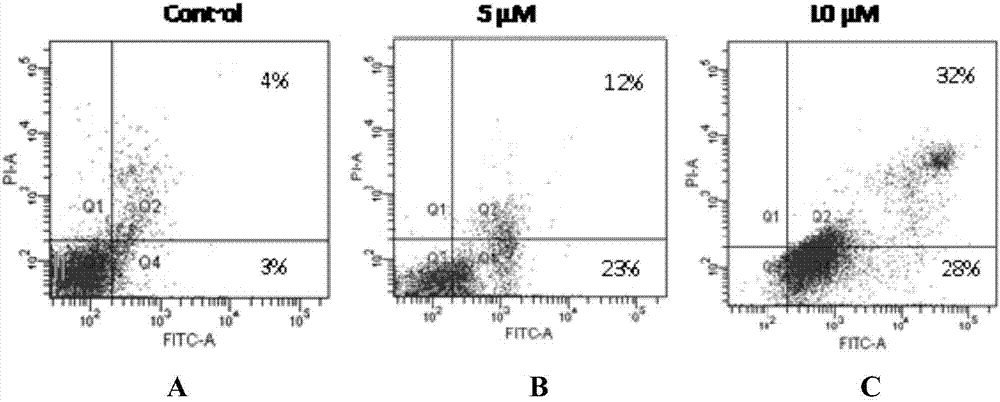
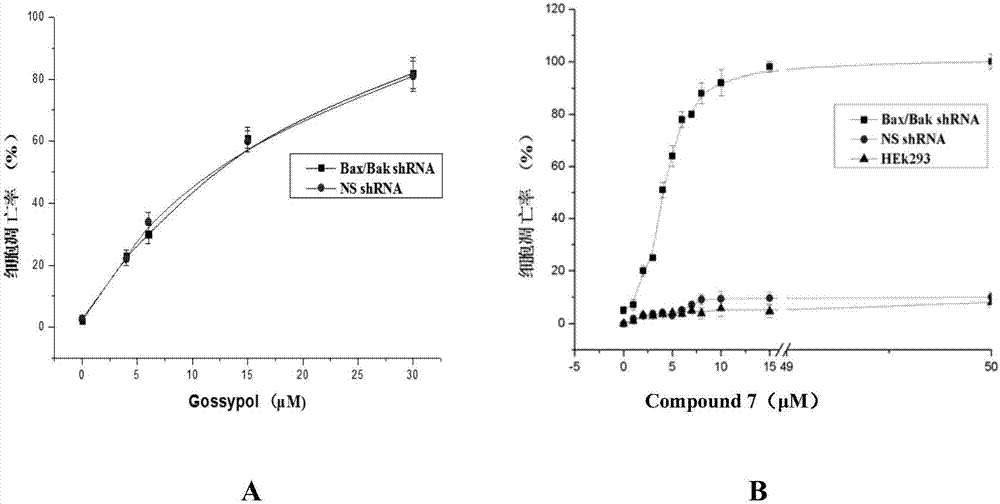
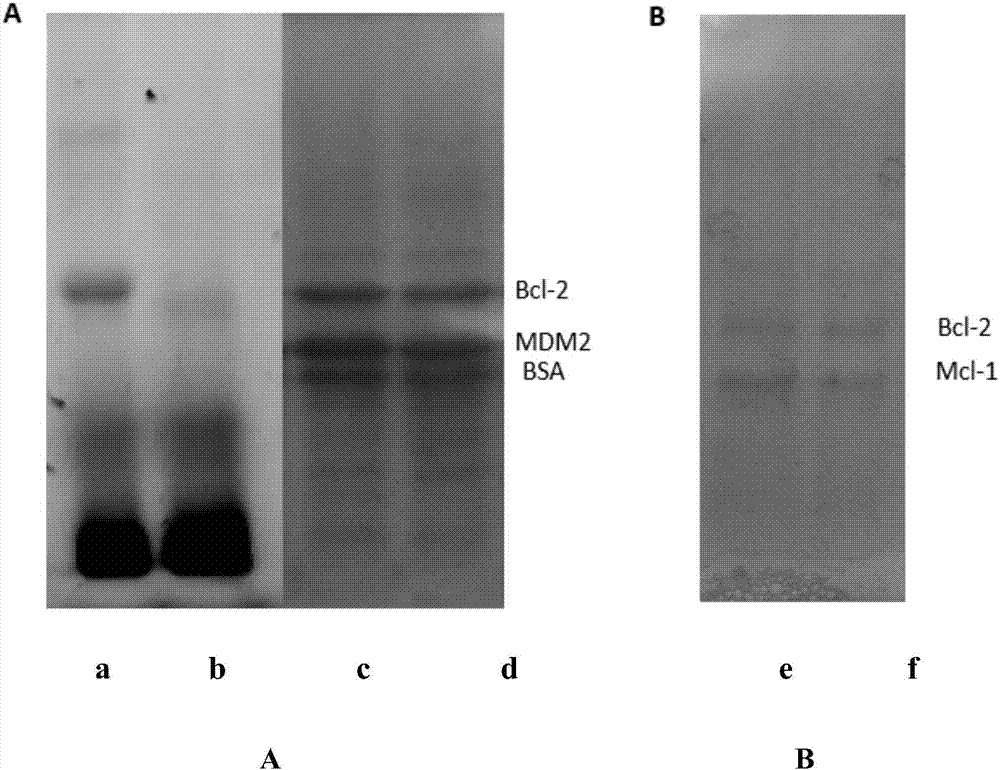
The invention provides a 4-substituted naphthalimide compound and a use thereof. The compound has a structure shown in the general formula I. The compound can competitively bind and antagonize with Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins in vitro and in cells so that apoptosis is induced and thus the compound is a high activity apoptosis inducing agent and an antitumor compound. The derivative based on the compound can be used as a bifunctional molecule for external and intracellular recognition, separation, enrichment and fluorescence detection of Bcl-2 family proteins or can be used as a PROTAC bifunctional complex for intracellular selective degradation of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins so that the level of the Bcl-2 family proteins in living cells can be adjusted and controlled.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Tumor targeting drug-loaded particles
A composition for delivering a tumor therapeutic agent to a patient includes a fast-release formulation of a tumor apoptosis inducing agent, a slow-release formulation of a tumor therapeutic agent, and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. An apoptosis-inducing agent in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier may be administered before or concomitantly therewith. Nanoparticles or microparticles (e.g., cross-linked gelatin) of the therapeutic agent (e.g., paclitaxel) also may be used. The nanoparticles or microparticles may be coated with a bioadhesive coating. Microspheres that agglomerate to block the entrance of the lymphatic ducts of the bladder to retard clearance of the microparticles through the lymphatic system also may be employed. This invention also uses drug-loaded gelatin and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles and microparticles to target drug delivery to tumors in the peritoneal cavity, bladder tissues, and kidneys.
Owner:AU JESSIE L S +1
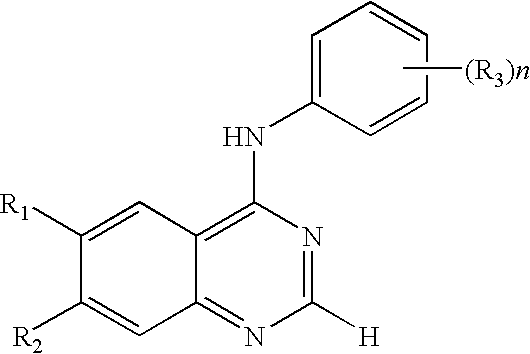
Compounds and therapeutical use thereof
Disclosed are 4-arylamino-quinazolines and analogs thereof effective as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. The compounds of this invention are useful in the treatment of a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC +1
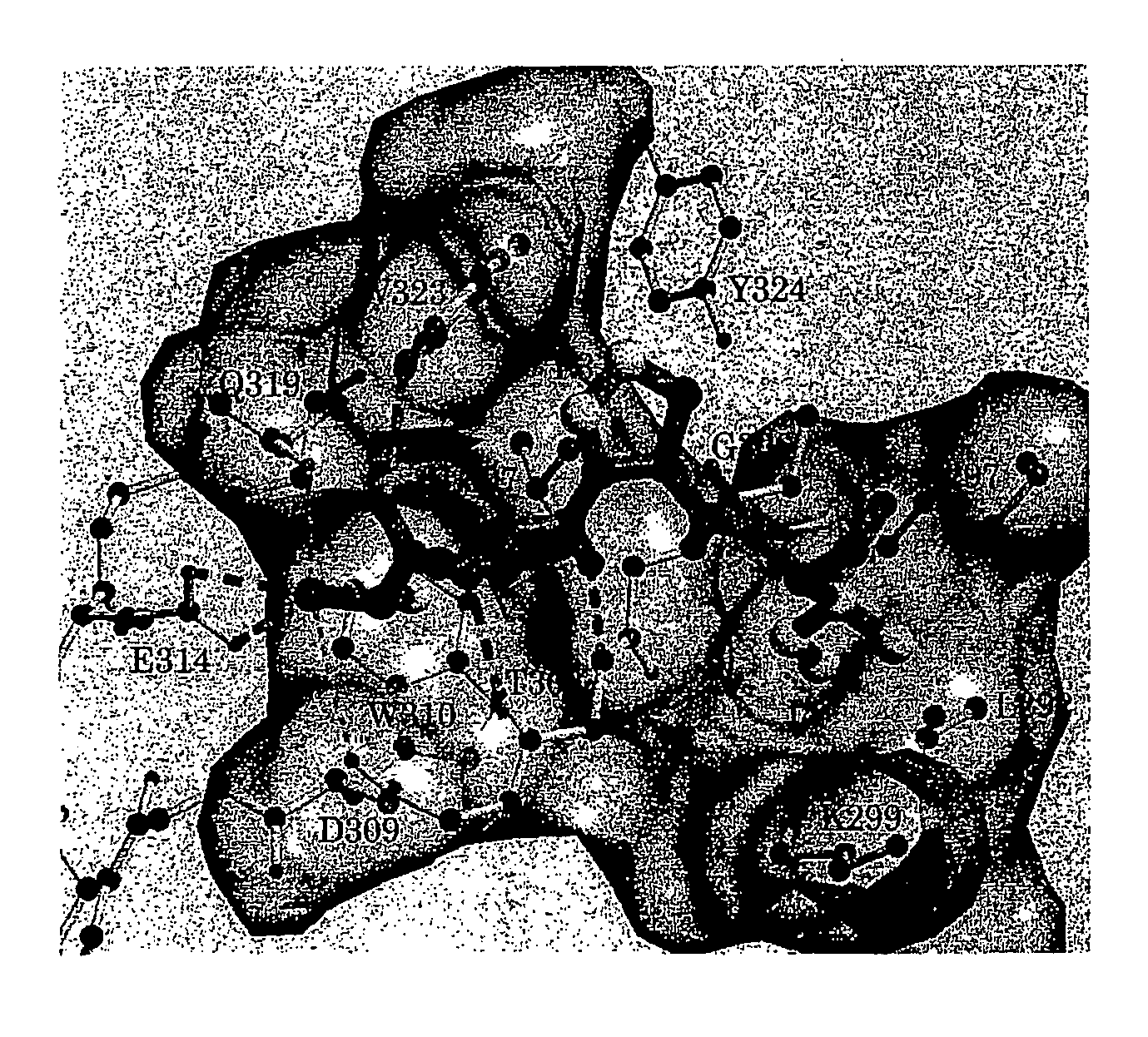
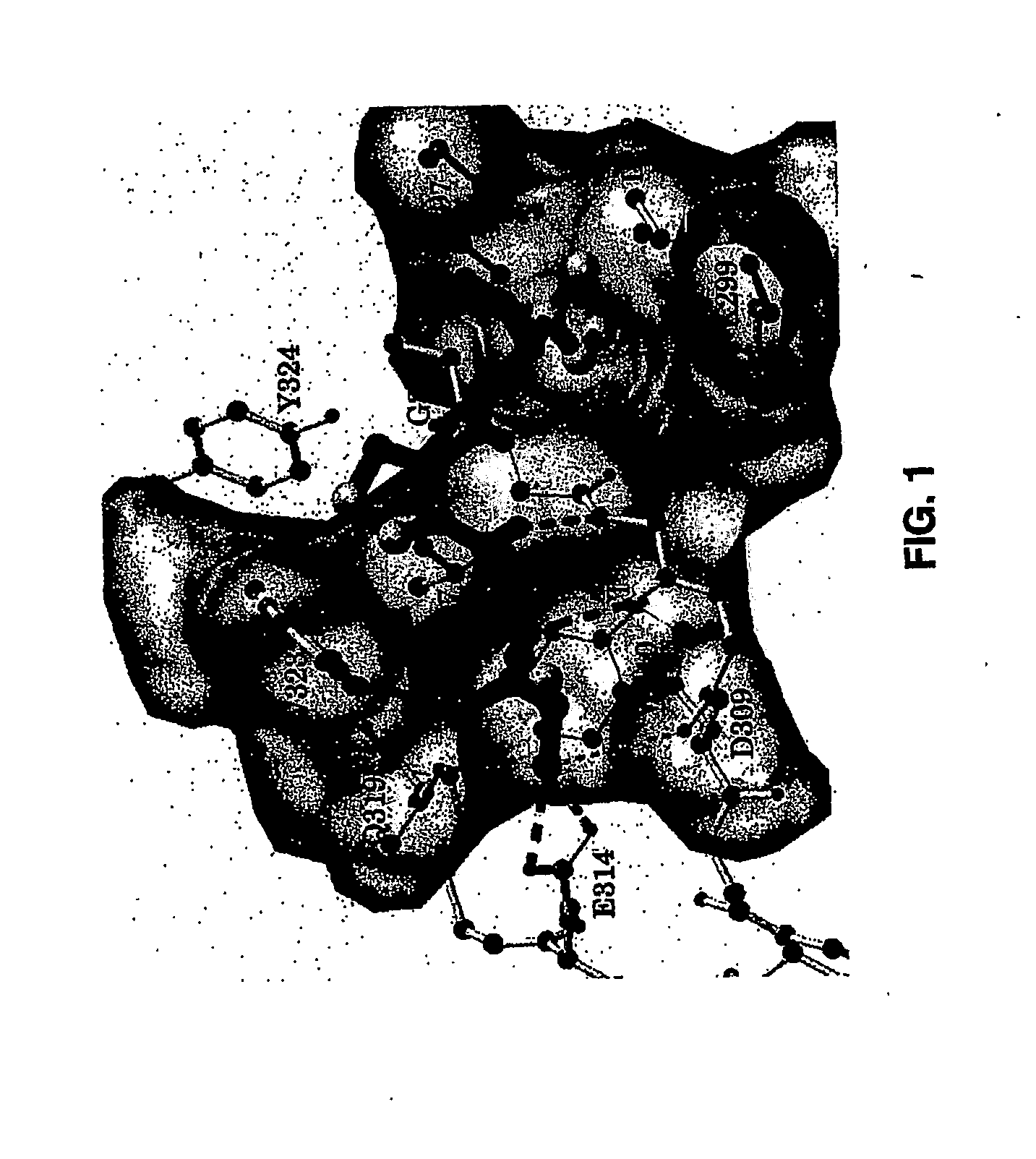
Iap binding compounds
The present invention relates to compounds of formula (I), or pharmaceutically acceptable salts, solvates or prodrugs thereof, that bind to Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins (IAPs). The compounds of the invention may be used as diagnostic and therapeutic agents in the treatment of proliferative diseases, such as cancer, for promoting apoptosis in proliferating cells, and for sensitizing cells to inducers of apoptosis. The present invention furthermore provides a polymeric compound of formulas (VI) or (VII), comprising either at least two monomeric units of compounds of formula (I), or at least one monomeric unit of a compound of formula (I) and an entity E. The present invention further relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said compounds of formulas (I), (VI), and (VII) and the use of said compounds in medicine.
Owner:NUEVOLUTION AS
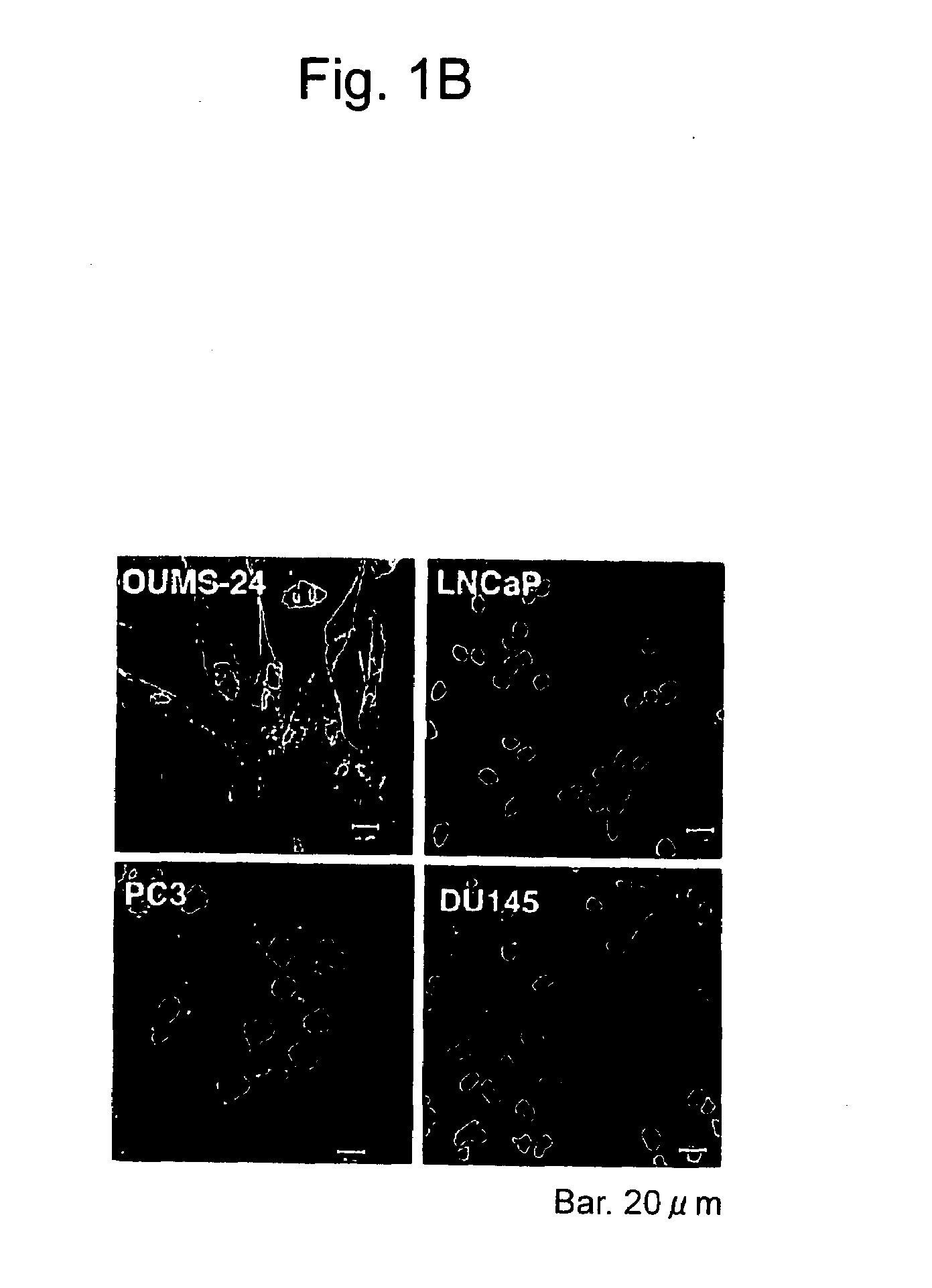
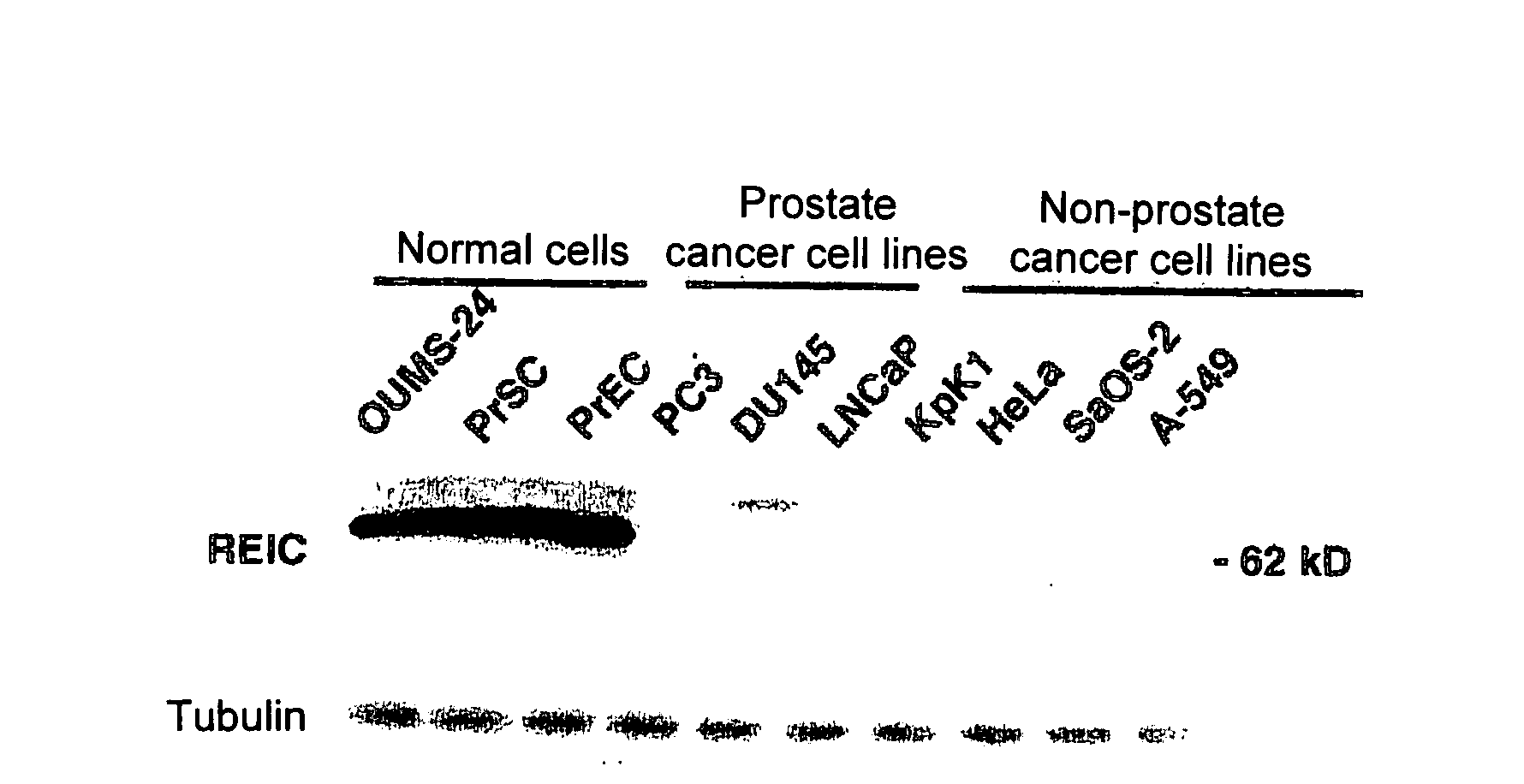
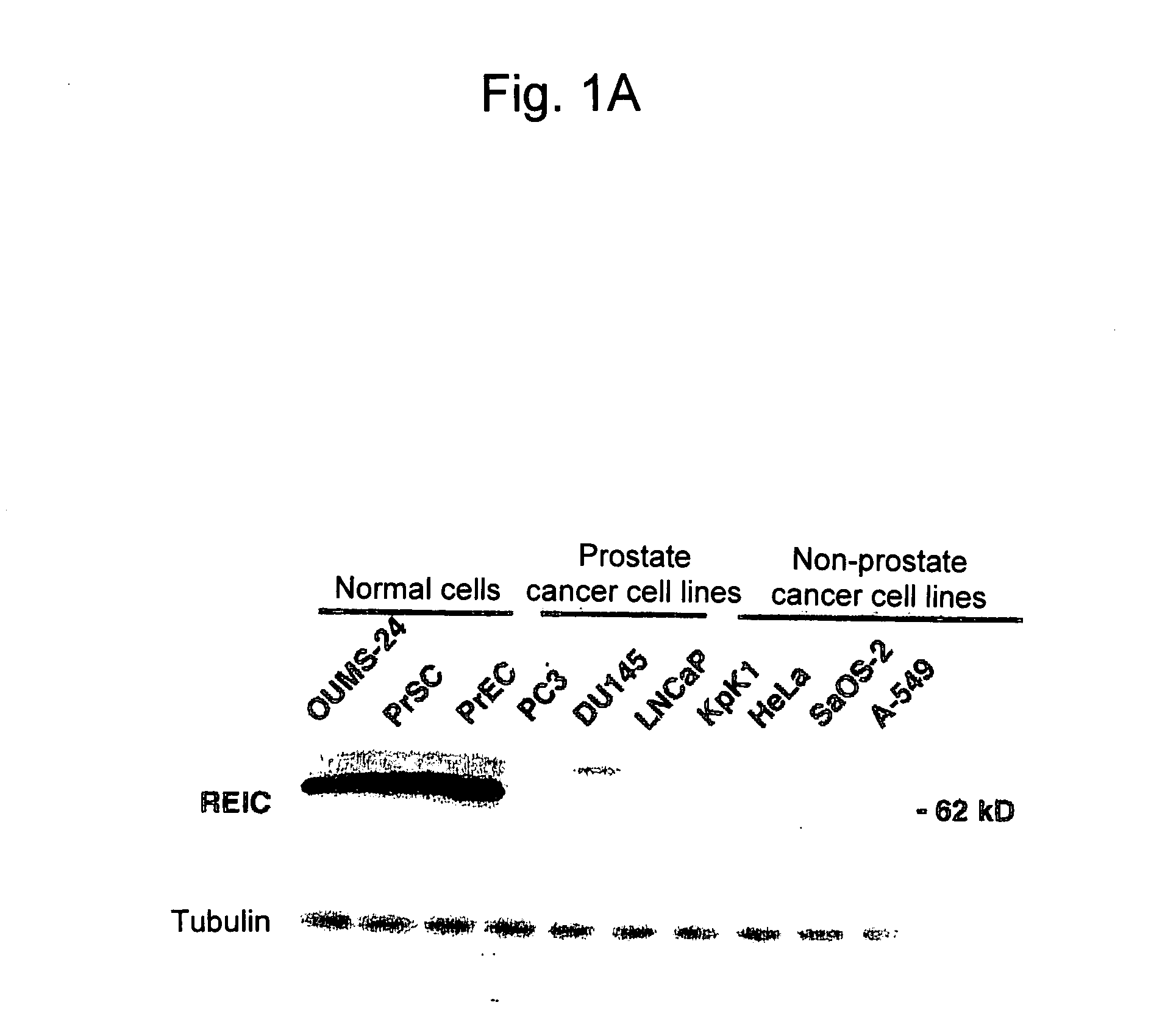
Apoptosis-Inducing Agent for Prostate Cancer Cells
InactiveUS20090005538A1Reduced expression levelInhibit prostate cancerPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesProstate cancer cellLymphatic Spread
According to the present invention, an apoptosis-inducing agent for prostate cancer comprising REIC / Dkk-3 DNA or an REIC / Dkk-3 protein, and a therapeutic agent for prostate cancer and an agent for inhibiting prostate cancer metastasis that comprise such apoptosis-inducing agent are provided.An apoptosis-inducing agent for prostate cancer, comprising, as an active ingredient, an REIC / Dkk-3 protein (a) or (b) or REIC / Dkk-3 DNA (c) or (d):(a) a protein consisting of the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2;(b) a protein consisting of an amino acid sequence derived from the amino acid sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 2 by substitution or deletion of 1 or more amino acids;(c) DNA consisting of the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1; or(d) DNA that hybridizes under stringent conditions to DNA consisting of a nucleotide sequence complementary to the nucleotide sequence represented by SEQ ID NO: 1 and encodes a protein having apoptosis activity; anda therapeutic agent for prostate cancer comprising such apoptosis-inducing agent are provided
Owner:KUMON HIROMI +3
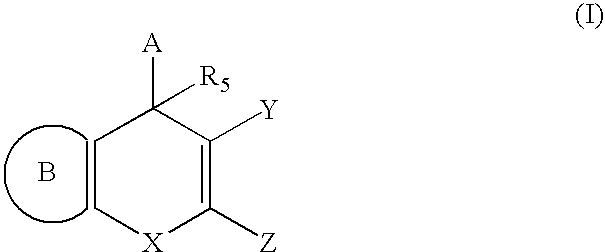
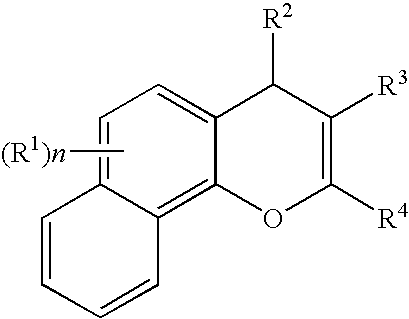
Substituted 4H-chromene and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof
InactiveUS6906203B1Treating preventing amelioratingOrganic chemistryAntipyreticInducerApoptosis inducer
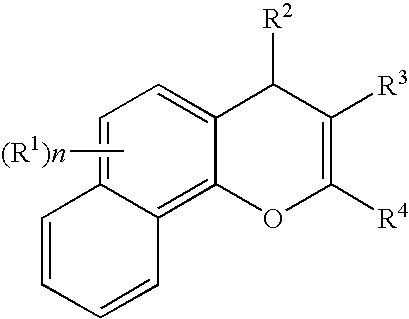
The present invention is directed to substituted 4H-chromene and analogs thereof, represented by the general Formula I: wherein A, B, X, Y, Z and R5 are defined herein. The present invention also relates to the discovery that compounds having Formula I are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention can be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
Thio/oxo-naphthalimide compound and application thereof
The invention provides a thio / oxo-naphthalimide compound and application thereof. The compound has a structure shown as a general formula I. The compounds are capable of realizing competitive binding and antagonism of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins in vitro and in cells so as to induce cell apoptosis, and refer to a type of apoptosis inducers and antitumor compounds with extremely high activities. In addition, the derivative designed based on the compound can serve as a bifunctional molecule and is capable of recognizing, separating, enriching and realizing fluorescence detection of Bcl-2 family proteins; or the derivative can serve as a PROTAC bifunctional complex for selectively degrading the Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins in the cells, so that the level of the Bcl-2 family proteins in living cells is regulated. The structural formula is as shown in the specification.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
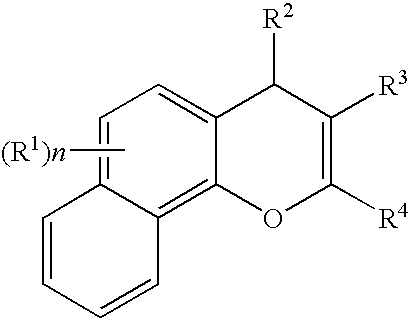
Substituted 4h-chromens, 2h-chromenes, chromans and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof
The present invention is directed to substituted 4H-chromenes, 2H-chromenes, chromans and analogs thereof, represented by the general Formula (I) wherein R5, A, B, X, Y, Z and dotted lines are defined herein. The present invention also relates to the discovery that compounds having Formula (I) are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. Therefore, the activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis of this invention can be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC +1
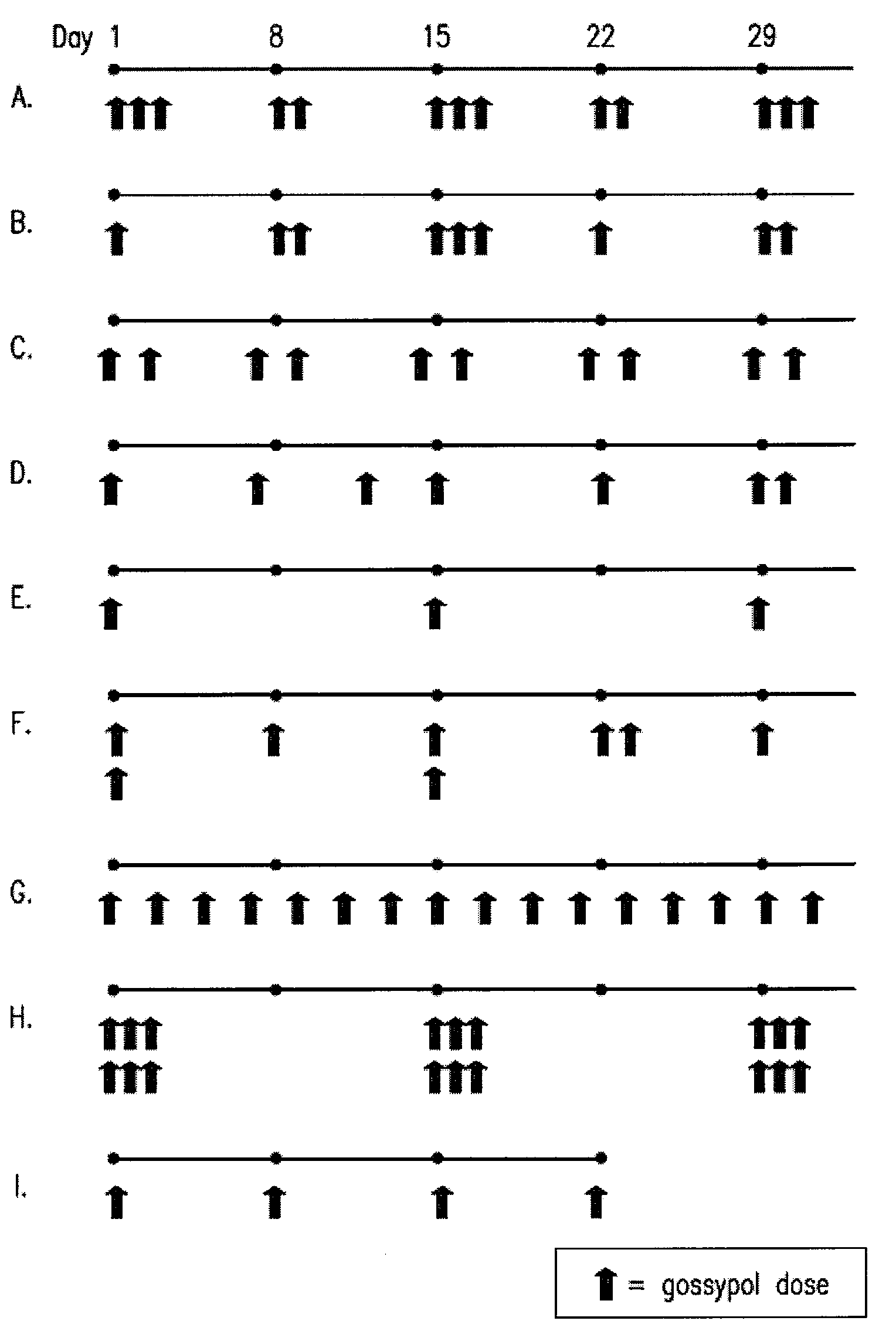
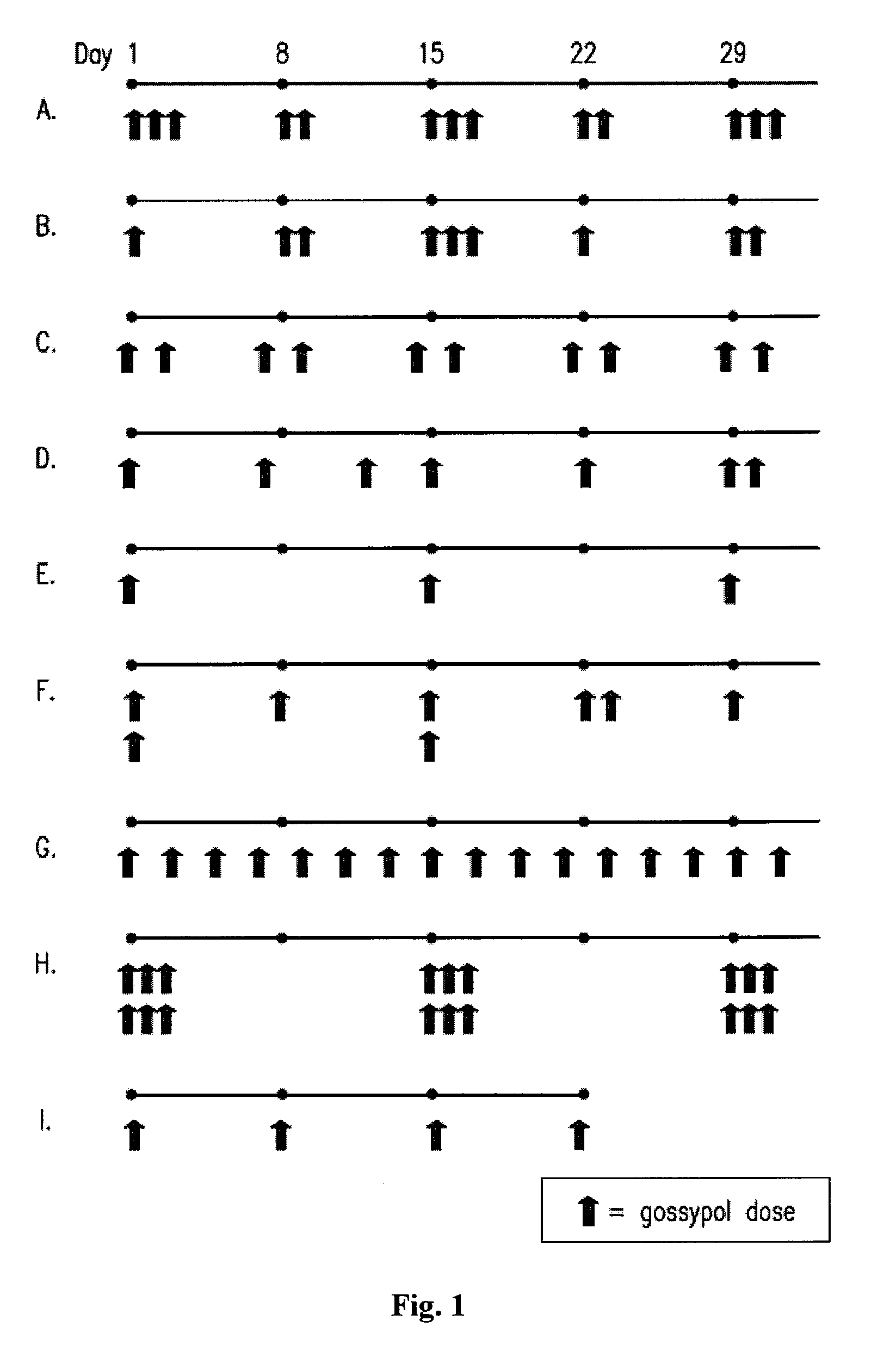
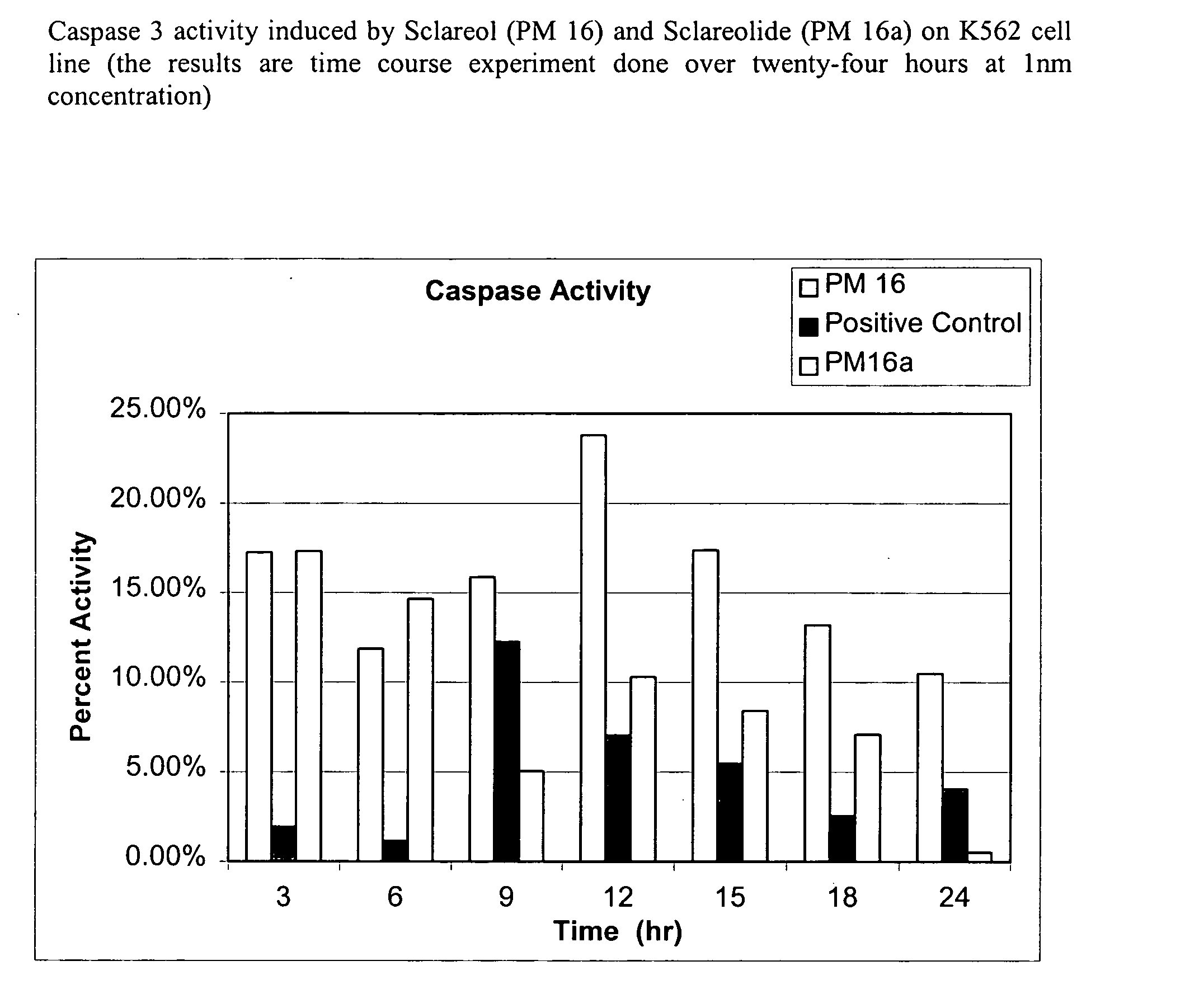
Pulsatile Dosing of Gossypol for Treatment of Disease
InactiveUS20090175869A1Reduction in adverse eventsInhibitory activityBiocideHeavy metal active ingredientsDiseaseInducer
This invention relates to pulsatile dose administration of gossypol, a gossypol-related compound or pharmaceutical compositions thereof for treating diseases, disorders and conditions responsive to gossypol or gossypol-related compound, inhibiting the activity of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, inducing apoptosis in cells and increasing the sensitivity of cells to inducers of apoptosis.
Owner:ASCENTA THERAPEUTICS
Dimer citrinin compounds and preparation and use thereof
The invention relates to a preparation method and a use of two dimer citrinin compounds. The dimer citrinin compounds with novel structures are produced by adopting Penicillium Citrinum HGY1-5 in samples collected from a crater. Tests prove that the compounds can be used as a cell proliferation inhibitor, an apoptosis inducer or an anti-tumor agent.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Acenaphthene heterocyclic compound and its cell fading inducing and anti-tumor use
InactiveCN1304370CGrowth inhibitionOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryInducer CellsTumor cell apoptosis
The present invention relates to a kind of amino group or halogen substituted 8-oxy-8H-acenaphthenee[1, 2-b] pyrrolyl-9-nitrile derivatives and their biological use. They are applied mainly in intracorporeal and extracorporeal inducing cell apoptosis and as anticancer compound. These compounds are 3, 6-disubstituted, 3-disubstituted or 6-substituted 8-oxy-8H-acenaphthenee[1, 2-b] pyrrolyl-9-nitrile derivatives. They can induce tumor cell apoptosis and block cell period in the dosage dependent mode within the wide concentration range of 0.01-10 micro mole. The highest activity compound B1 has IC50=0.17 micro mole (0.56 micro gram). When they are used in animal tumor model body, they can inhibit tumor growth obviously in inducing cell apoptosis mode. Therefore, the present invention is one kind of apoptosis inducing agent and antitumor compound with high activity.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Heteroaryl-substituted bicyclic smac mimetics and the uses thereof
ActiveUS20110046189A1High expressionMore tolerableBiocideOrganic chemistrySmac mimeticsSensitized cell
The invention relates to heteroaryl-substituted bicyclic mimetics of Smac which function as inhibitors of Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins. The invention also relates to the use of these mimetics for inducing apoptotic cell death and for sensitizing cells to inducers of apoptosis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
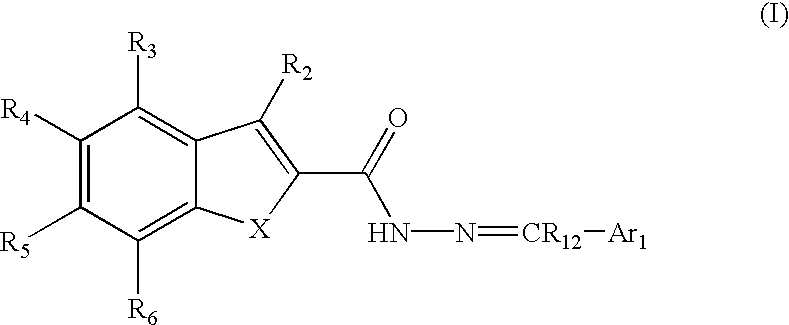
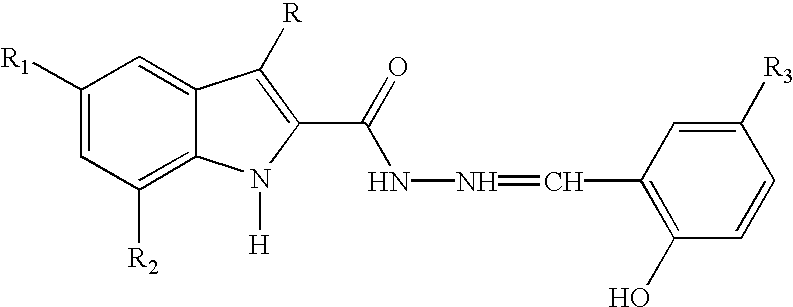
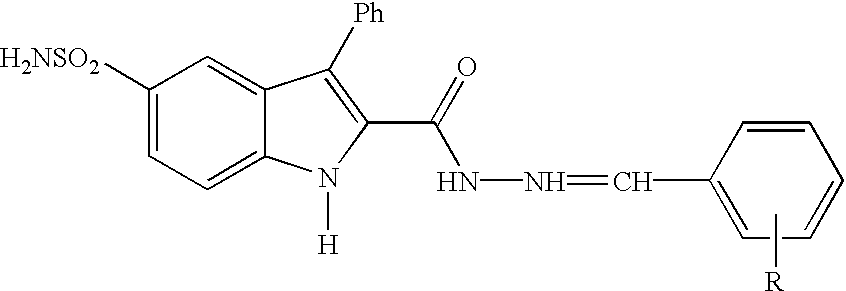
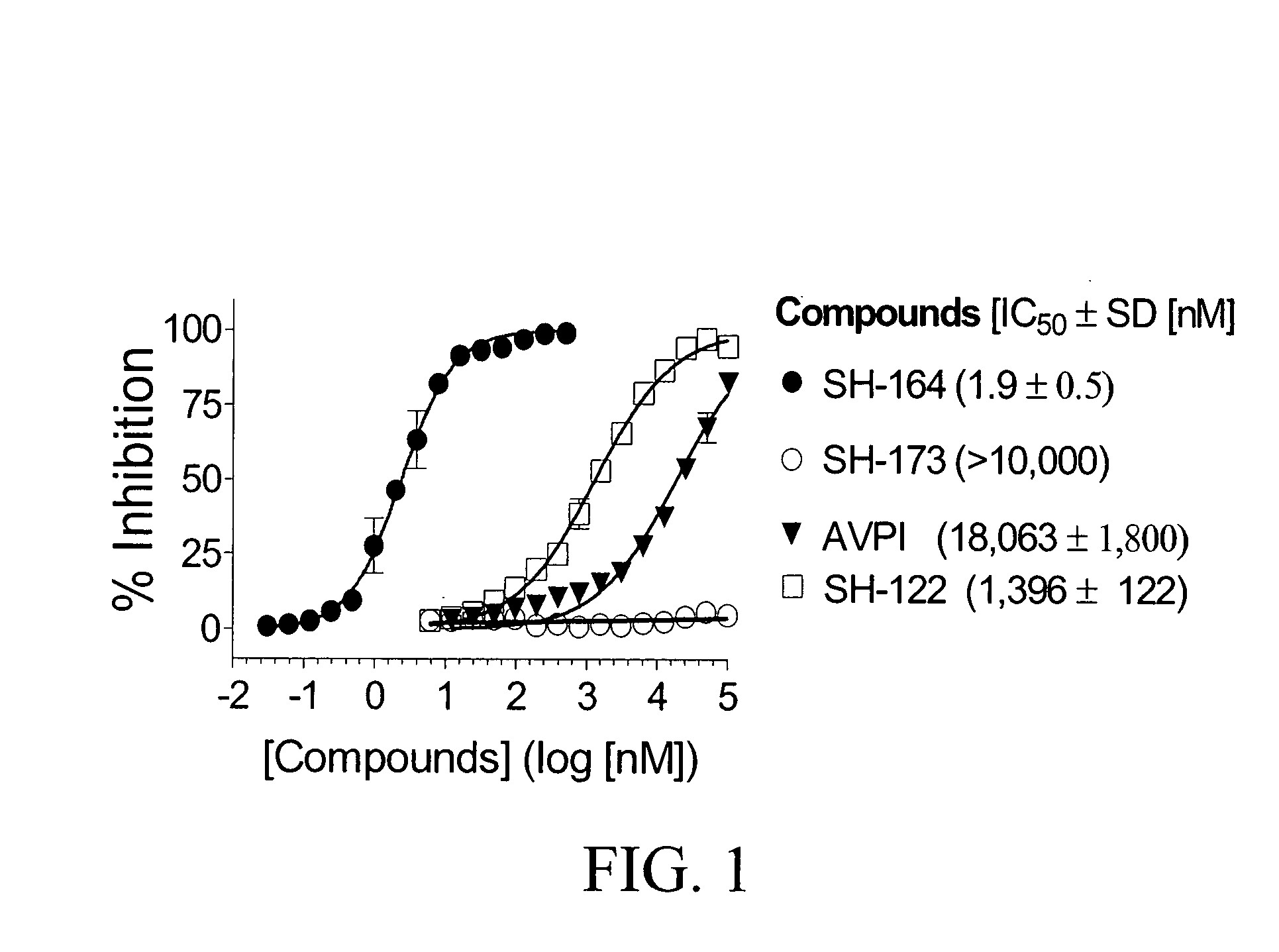
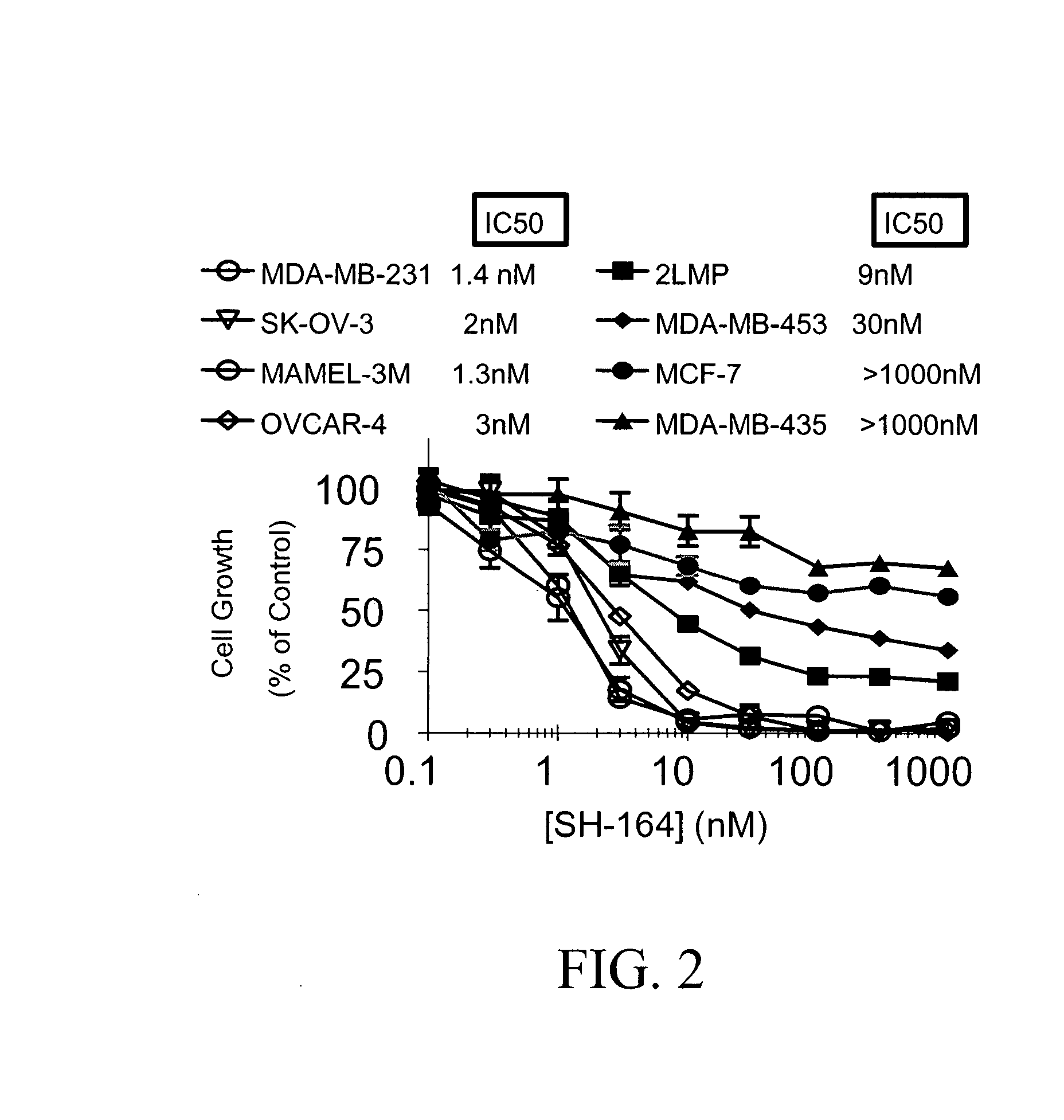
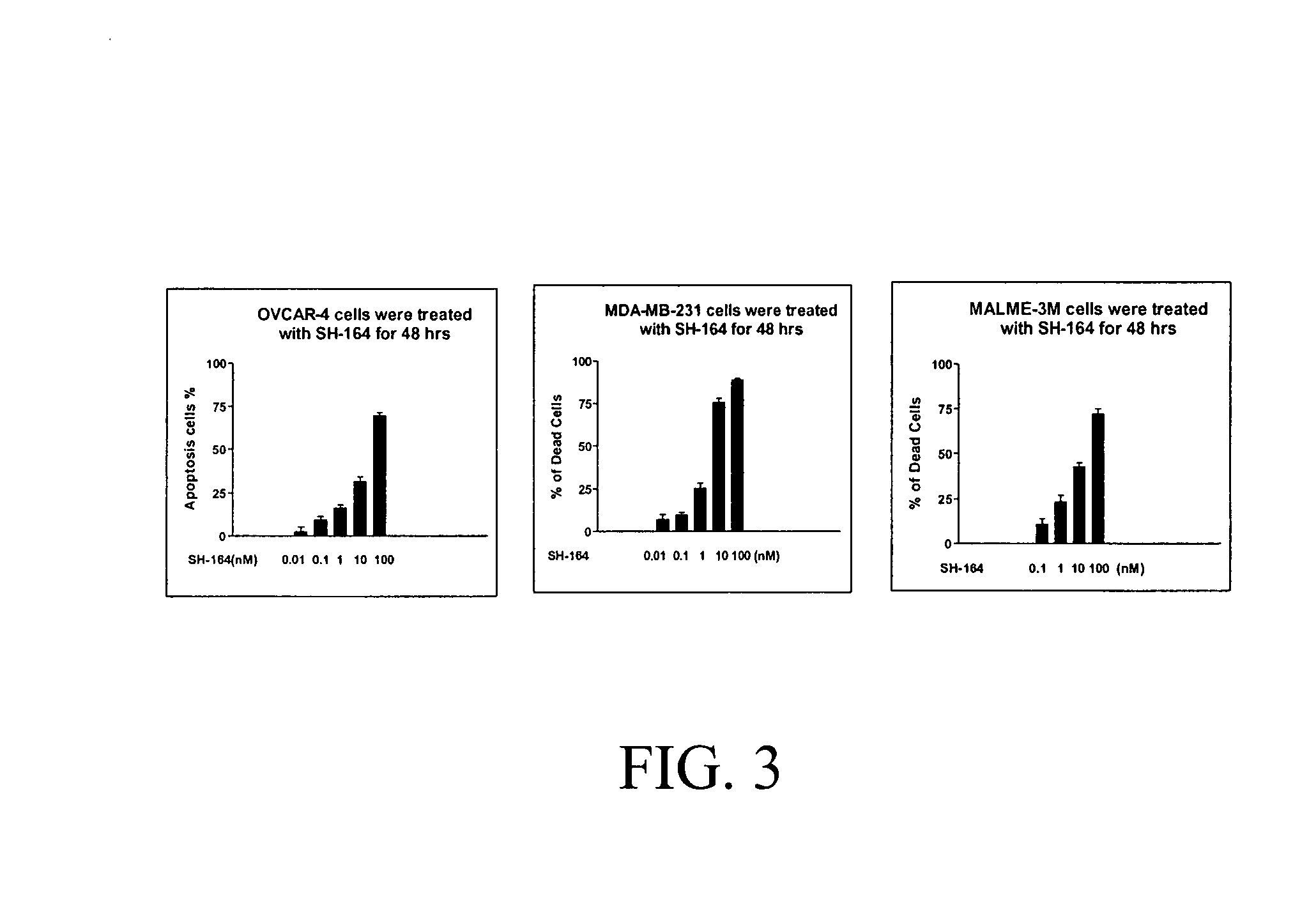
Substituted indole-2-carboxylic acid benzylidene-hydrazides and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof
The present invention is directed to substituted indole-2-carboxylic acid benzylidene-hydrazides and analogs thereof, represented by the general Formula I: 1 wherein X, Ar.sub.1, R.sub.2-R.sub.6 and R.sub.12 are defined herein. The present invention also relates to the discovery that compounds having Formula I are activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis. The compounds of this invention may be used to induce cell death in a variety of clinical conditions in which uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells occurs.
Owner:CYTOVIA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

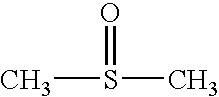
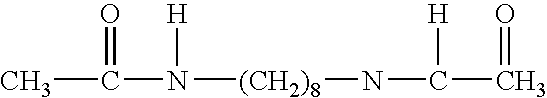
![3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof 3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/48af0cf9-bcee-443c-b772-e23fd87dddd1/US07317029-20080108-C00001.png)
![3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof 3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/48af0cf9-bcee-443c-b772-e23fd87dddd1/US07317029-20080108-C00002.png)
![3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof 3,5-disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/48af0cf9-bcee-443c-b772-e23fd87dddd1/US07317029-20080108-C00003.png)
![3,5-Disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof 3,5-Disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/439e030b-234e-4cd7-9537-32fb6c0d143d/US07144876-20061205-C00001.png)
![3,5-Disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof 3,5-Disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/439e030b-234e-4cd7-9537-32fb6c0d143d/US07144876-20061205-C00002.png)
![3,5-Disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof 3,5-Disubstituted-[1,2,4]-oxadiazoles and analogs as activators of caspases and inducers of apoptosis and the use thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/439e030b-234e-4cd7-9537-32fb6c0d143d/US07144876-20061205-C00003.png)