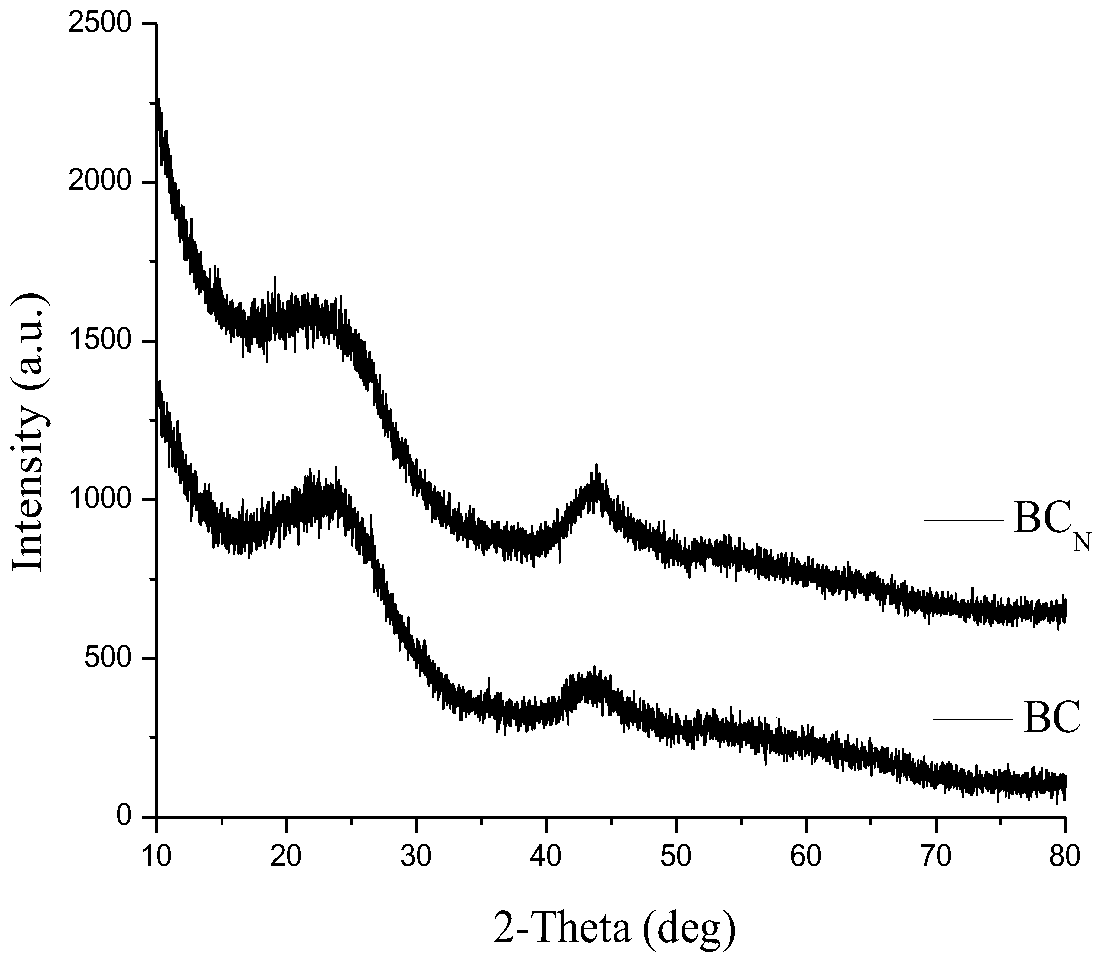
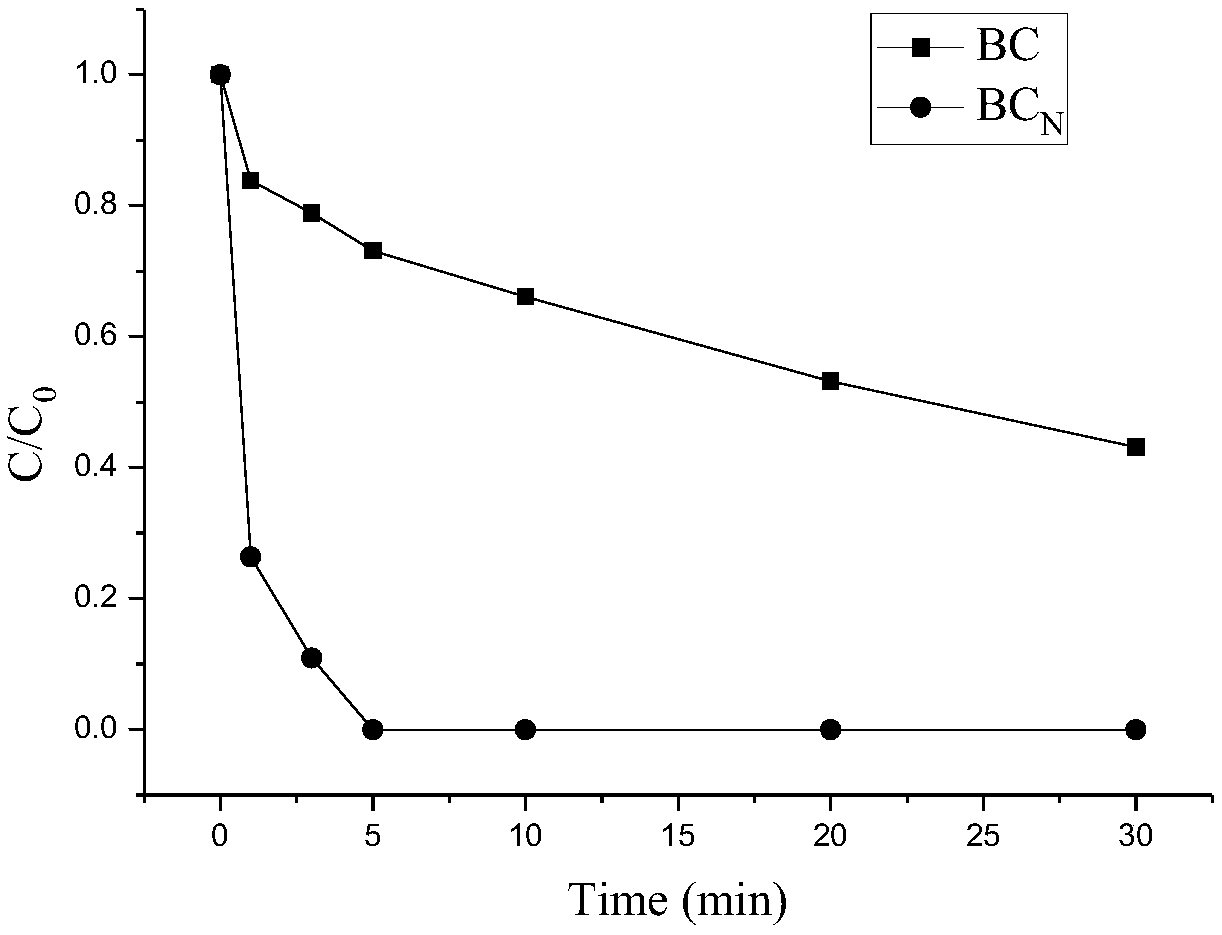
Patents
Literature
95 results about "Selective degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
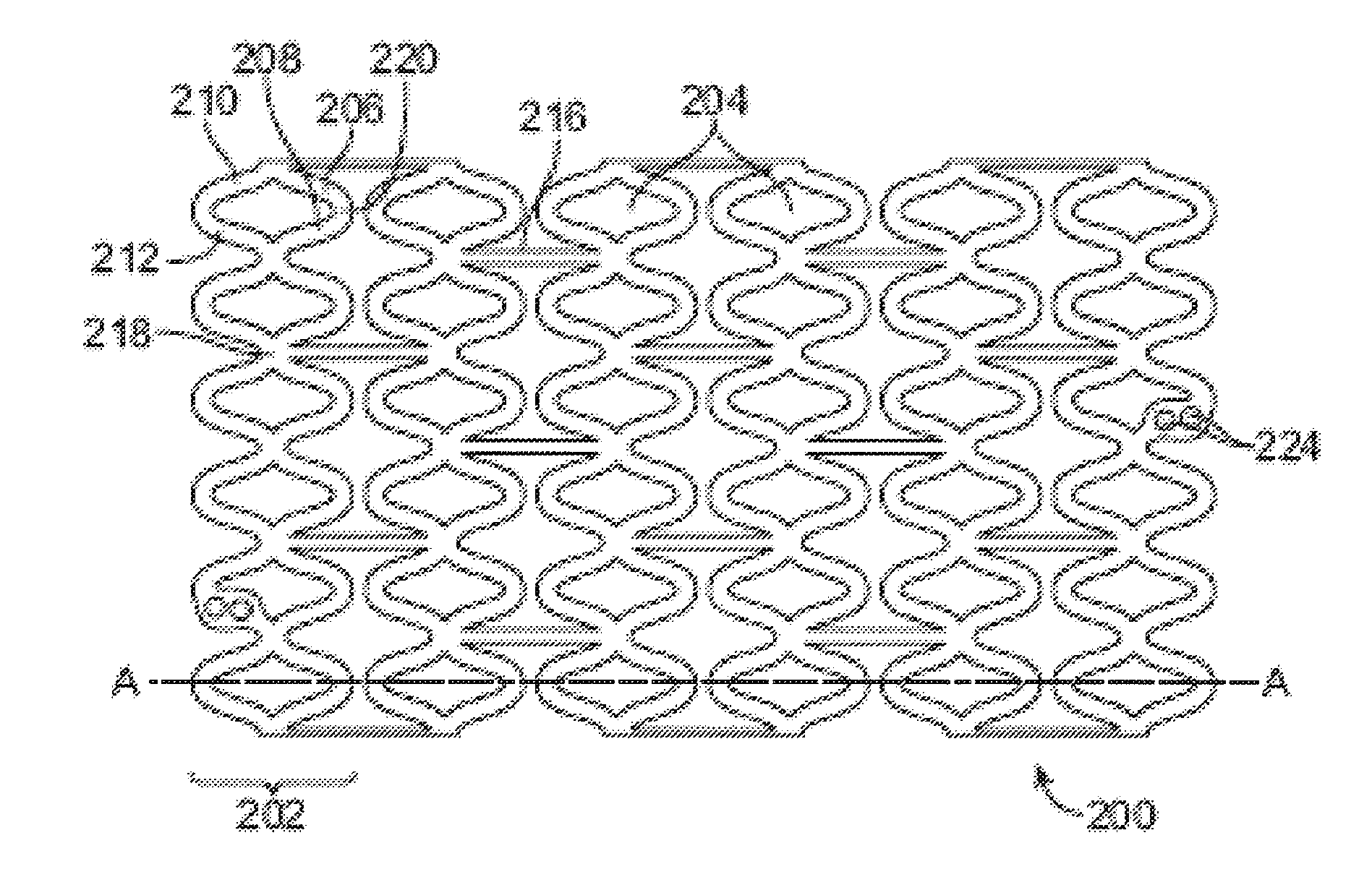
Bioabsorbable Stent With Time Dependent Structure And Properties And Regio-Selective Degradation
InactiveUS20110066225A1Promote degradationReduces tensile strength and strain to failure and fracture resistanceStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentRegioselectivity
A bioabsorbable polymeric stent with time dependent structure and properties and methods of treating a diseased blood vessel with the bioabsorable polymeric stent are disclosed. The structure and properties of the stent change with time and allow the vessel to be restored to a natural unstented state. The bioabsorbable stent loses mechanical integrity in a controlled manner due to modification of selected structural elements.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Gelatine powder modified asphalt and processing method thereof
ActiveCN101104739AImprove stabilityReduce manufacturing costBuilding insulationsPolymer scienceWaste rubber
The invention discloses a modified asphalt and a processing method of the modified asphalt. The modified asphalt of the invention contains the following components in part by weight: 50 to 92 parts by weight of base asphalt, 8 to 50 parts by weight of rubber powder, 0.1 to 5 parts by weight of first cross-linking agent, 0 to 12 parts by weight of diluent and 0 to 6 parts by weight of second cross-linking agent. The invention develops a modified asphalt prepared through desulphurization degradation and recrosslinking and the processing method of the modified asphalt through the analysis of the conditions of selective degradation process of waste rubber powder in the asphalt, the recovery of macro molecules performance of the degraded waste rubber powder in the modified asphalt and the study on the preparation technique of the modified asphalt made of the waste rubber powder. The modified asphalt can form homogeneous mixing system, the viscosity of the asphalt is reduced and the storage stability is increased.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Nucleic acid probes, their synthesis and use
ActiveUS20050221315A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesBiology
The invention provides a method of probing for a nucleic acid comprising: contacting a nucleic acid solution with an oligonucleotide probe labelled with an electrochemically active marker, providing conditions at which the probe is able to at least partially hybridise with any complementary target sequence which may be present in the nucleic acid solution, selectively degrading either hybridised, partially hybridised or unhybridised nucleic acid probe, and electrochemically determining information relating to the electrochemically active marker. The invention further provides novel molecules with use in methods of the invention.
Owner:ATLAS GENETICS
Supporting membranes on nanometer-scale self-assembled films
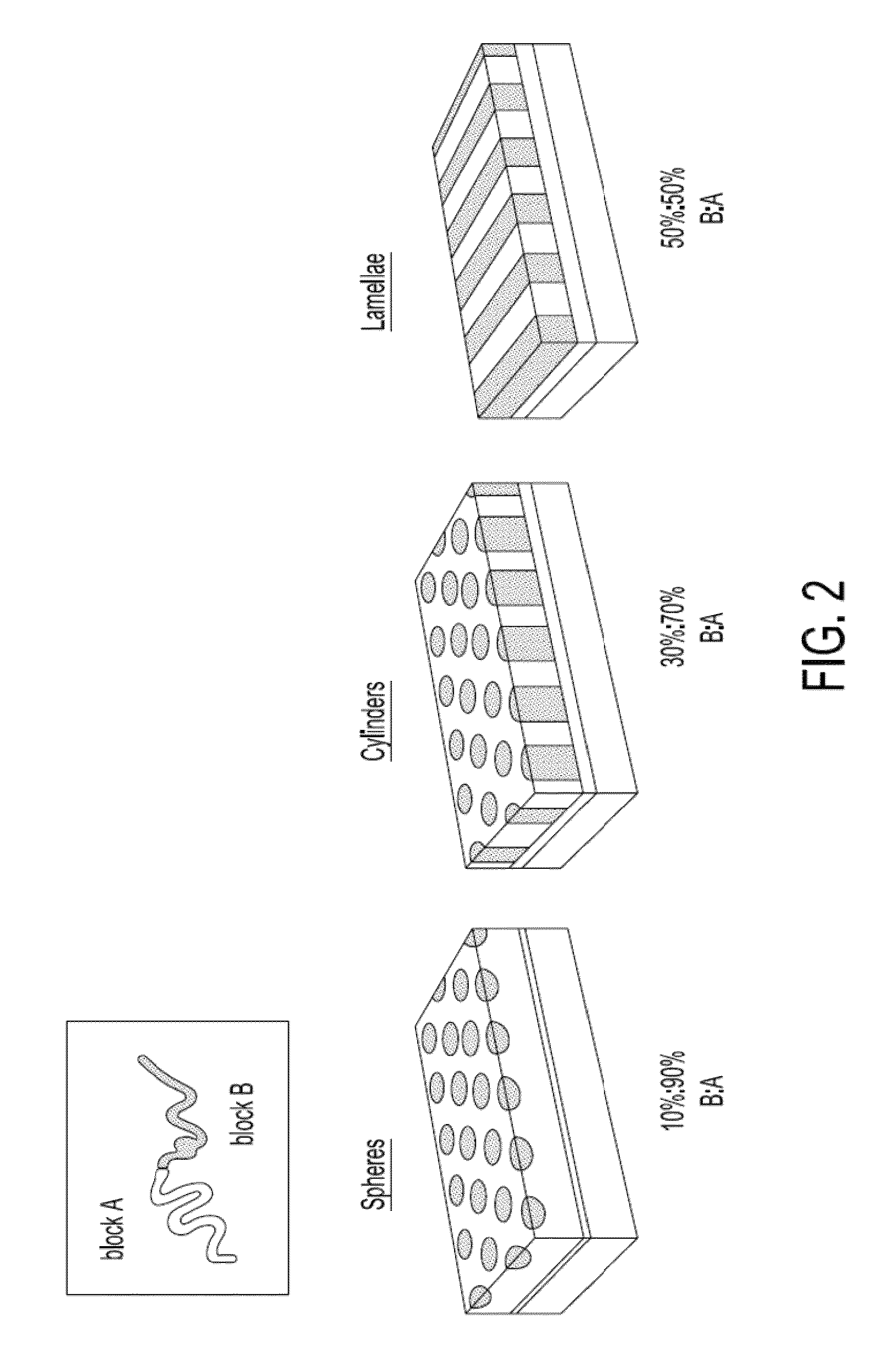
Block copolymer lithography has emerged as an alternative lithographic method to achieve large-area, high-density patterns at resolutions near or beyond the limit of conventional lithographic techniques for the formation of bit patterned media and discrete track media. In one embodiment, a structure comprises a plurality of nanostructures extending upwardly from a substrate and a porous membrane extending across upper ends of the plurality of nanostructures. A method, according to another embodiment, comprises forming a block copolymer layer on a substrate, inducing self assembly of the block copolymer layer, selectively degrading a block polymer from the block copolymer layer, forming a porous membrane over the block copolymer layer, and removing a portion of the block copolymer layer for defining a plurality of nanostructures extending upwardly from the substrate after forming the porous membrane over the block copolymer layer. Other systems and methods are disclosed as well.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Selective degradation of videos containing third-party content
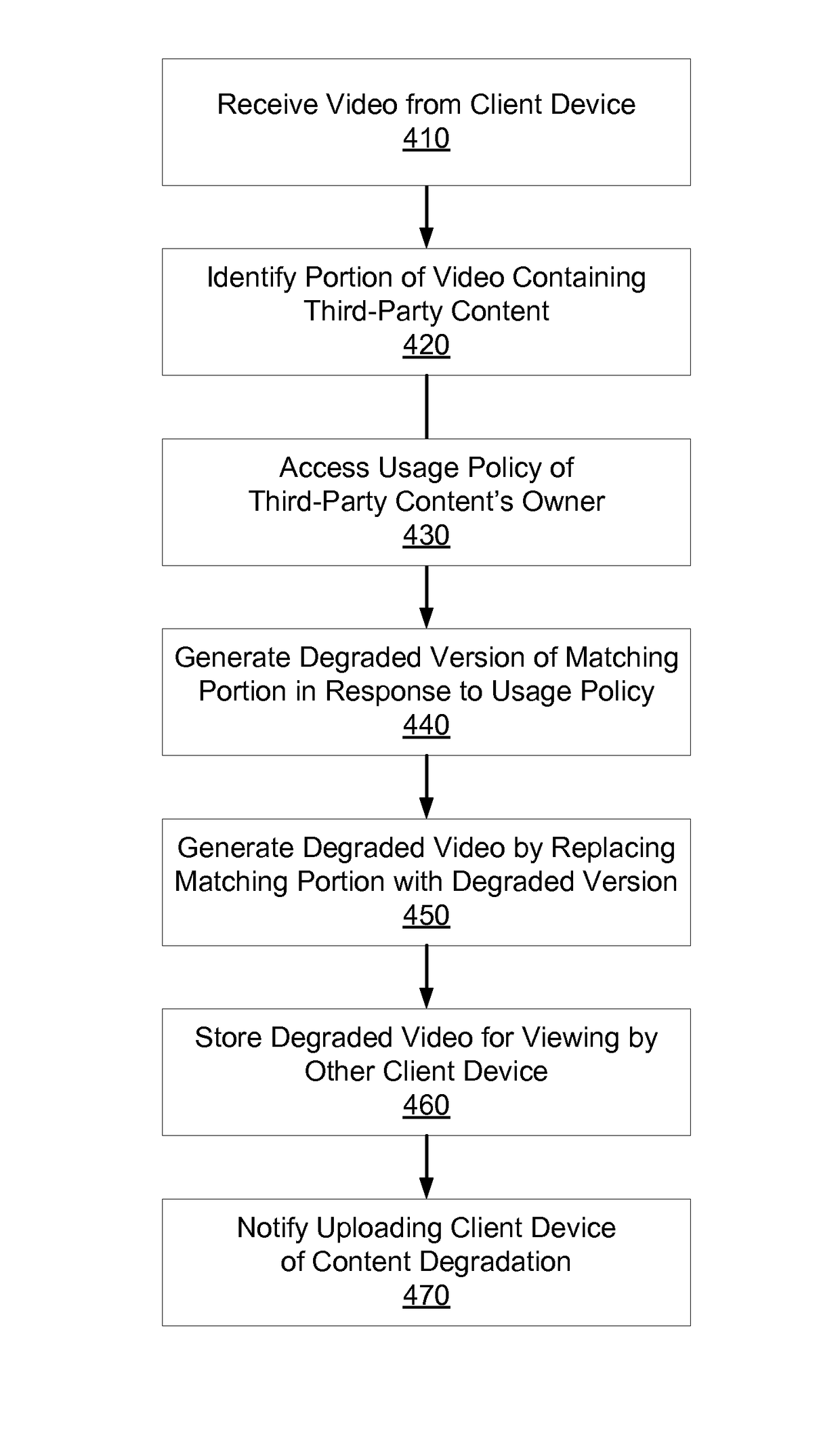
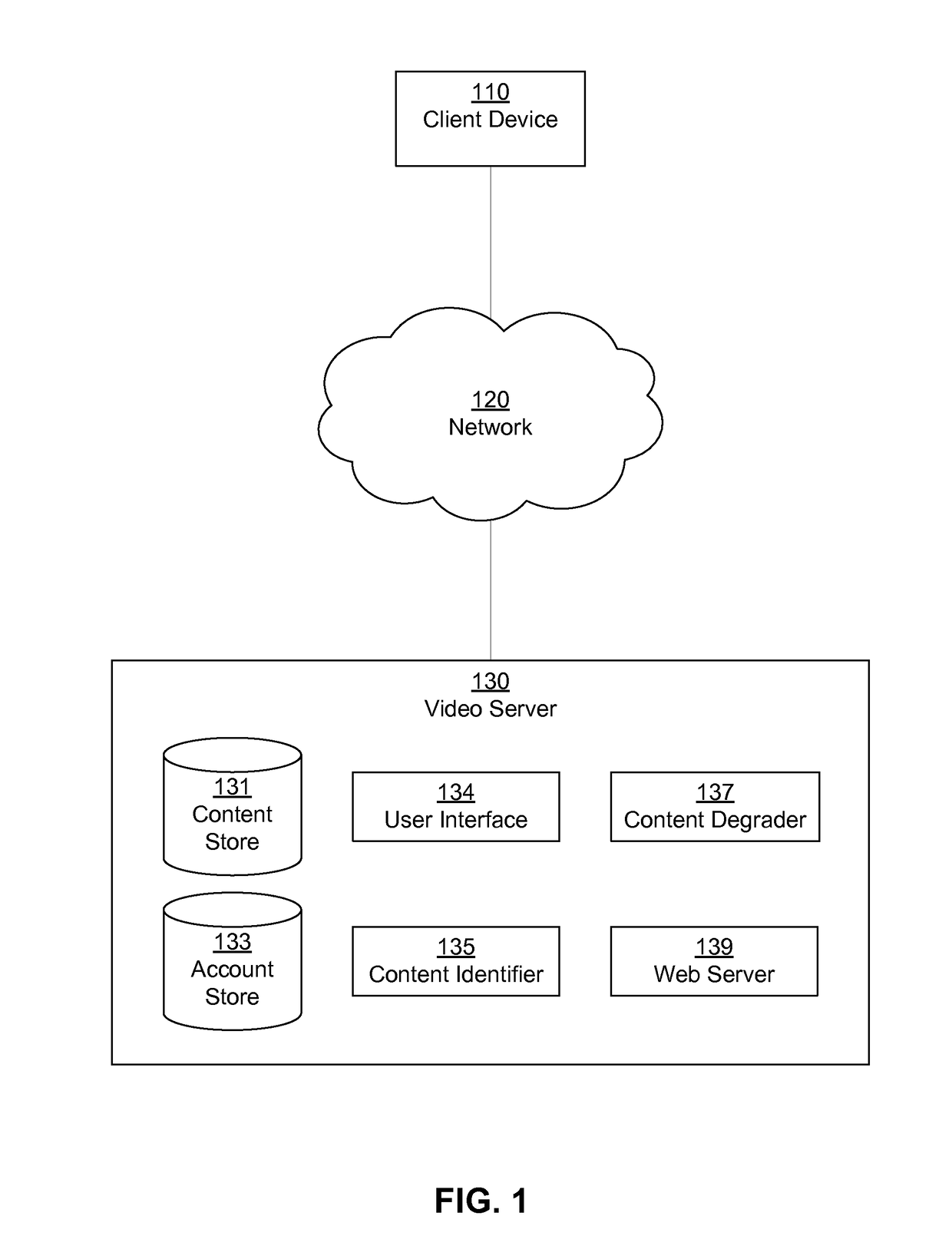
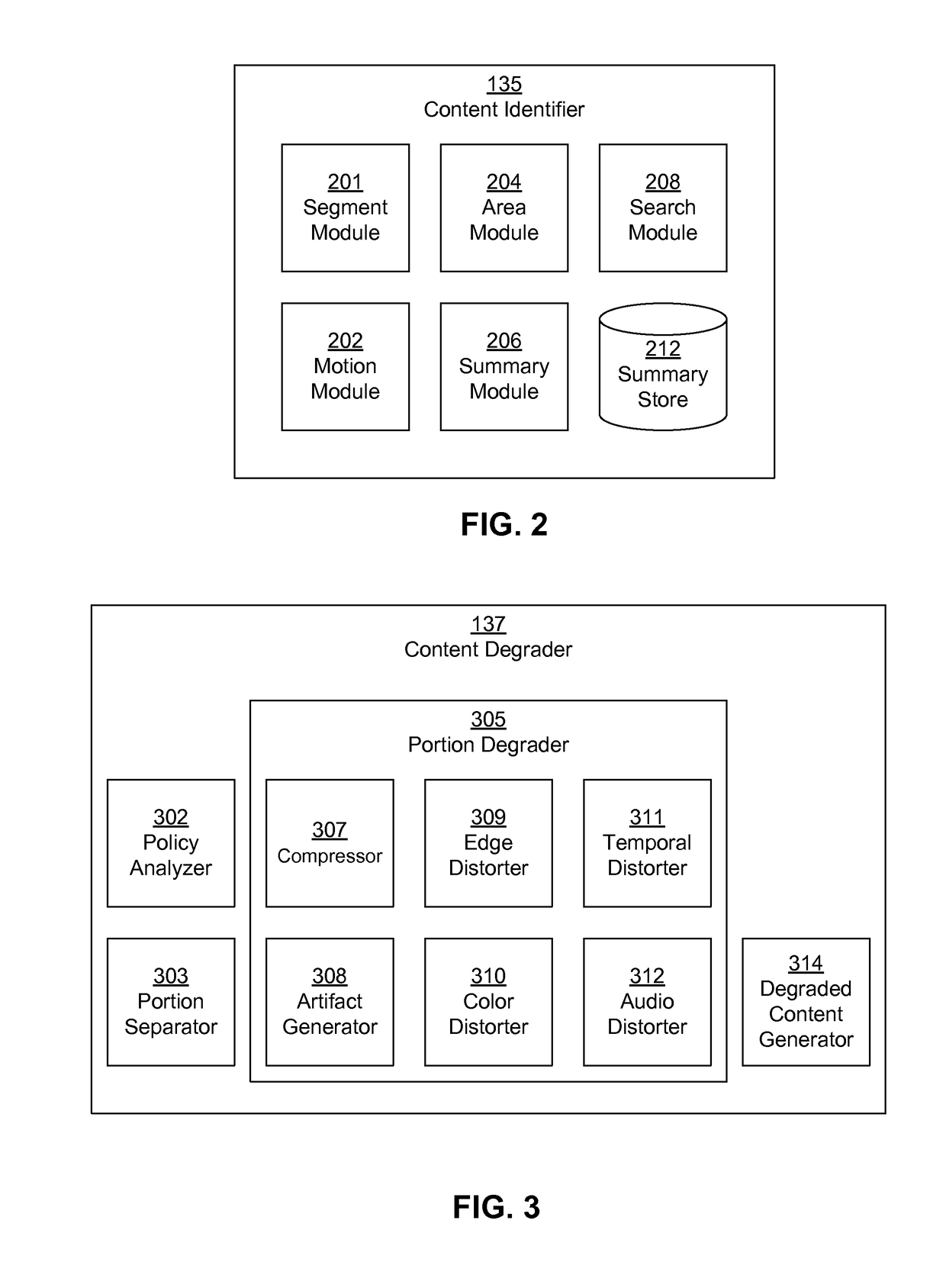
A video server receives an uploaded video and determines whether the video contains third-party content and which portions of the uploaded video match third-party content. The video server determines whether to degrade the matching portions and / or how (e.g., extent, type) to do so. The video server separates the matching portion from original portions in the uploaded video and generates a degraded version of the matching content by applying an effect such as compression, edge distortion, temporal distortion, noise addition, color distortion, or audio distortion. The video server combines the degraded portions with the original portions to output a degraded version of the uploaded video. The video server stores and / or distributes the degraded version of the uploaded video. The video server may offer the uploading user licensing terms with the content owner that the user may accept to reverse the degradation.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method of treatment with a bioabsorbable stent with time dependent structure and properties and regio-selective degradation
InactiveUS8425587B2Promote degradationReduces tensile strength and strain to failure and fracture resistanceStentsSurgeryBioabsorbable stentMechanical integrity
A bioabsorbable polymeric stent with time dependent structure and properties and methods of treating a diseased blood vessel with the bioabsorable polymeric stent are disclosed. The structure and properties of the stent change with time and allow the vessel to be restored to a natural unstented state. The bioabsorbable stent loses mechanical integrity in a controlled manner due to modification of selected structural elements.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
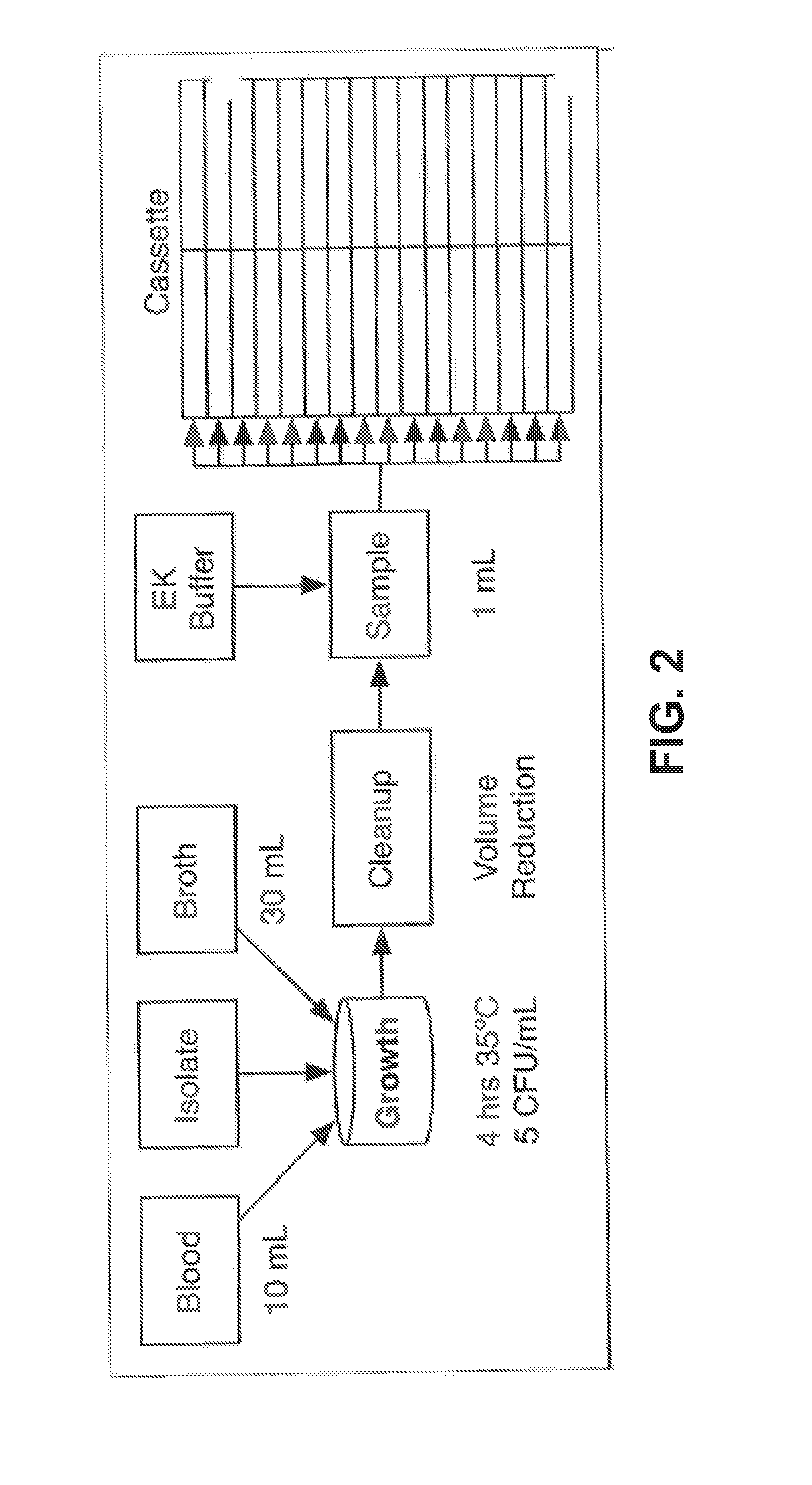
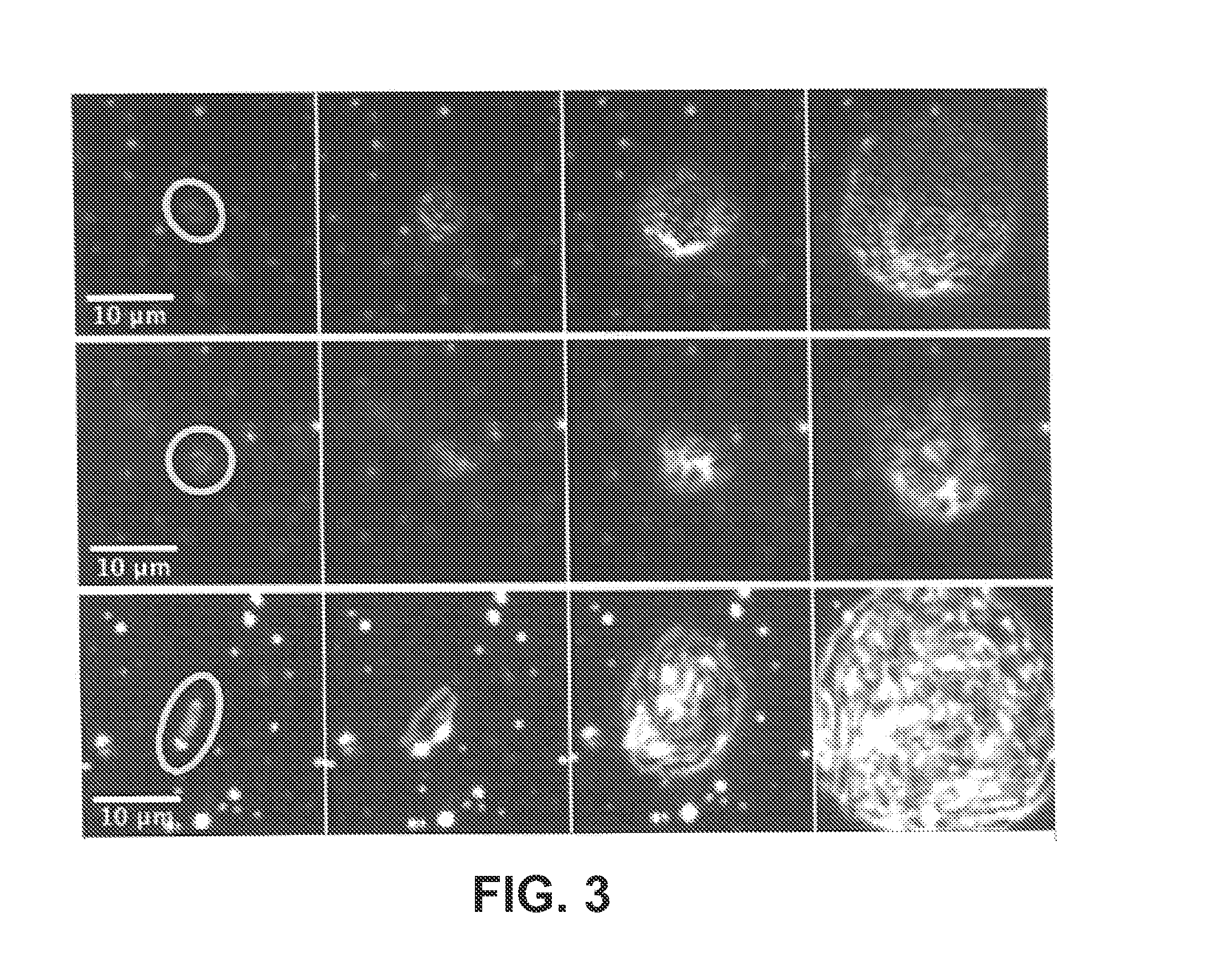
Same-day blood culture with digital microscopy
InactiveUS20150225762A1Inhibit microbial growthReduce and prevent depressionMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceCord blood cultureBiological cell
Generally provided are methods for rapid culture of microorganisms in a sample, including methods for growth and recovery of live microbial cells directly from a sample. Various features include enabling growth of microorganisms in a sample along with a reduction of sample debris that may interfere with microorganism detection, and reduction in toxicities that may inhibit microorganism growth. Further methods for selectively degrading non-viable microbial cells, are provided, for enhanced detection of viable microbial cells following a growth period.
Owner:ACCELERATED MEDICAL DIAGNOSTICS INC
Method for improving sweetness of stevia sugar
InactiveCN101691389AIncrease sweetnessSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationMicroorganismAdditive ingredient
Stevioside is a novel sweeter which is extracted from stevia leaves, and the stevioside in the stevia leaves mainly comprises two components of stevioside and rebaudioside A. The sweetness and mouthfeel of the rebaudioside A are both excellent, while the stevioside has certain lingering bitterness; and as the structure and nature of the rebaudioside A are approximate to the structure and nature of the stevioside, the separation of rebaudioside A and stevioside features high cost and great technical difficulty. In the invention, microorganisms are transformed for 20h-150h under the conditions that the concentration of the stevioside is 0.01%-5% (W / W), the temperature is 25-80 DEG C, the quantity of inverting enzyme or bacterial solution is 0.1%-10% (W / W), and the pH value is 2.0-7.0, and the stevioside contained in the rebaudioside A solution can be selectively degraded, thus obtaining high purity rebaudioside A containing no stevioside. The biotransformation method used in the invention has temperate conditions, does not use toxic methanol and other chemicals or macroporous resin with high cost, thus being a novel technology with safety, greenness and environmental friendliness.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
4-substituted naphthalimide compound and use thereof
The invention provides a 4-substituted naphthalimide compound and a use thereof. The compound has a structure shown in the general formula I. The compound can competitively bind and antagonize with Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins in vitro and in cells so that apoptosis is induced and thus the compound is a high activity apoptosis inducing agent and an antitumor compound. The derivative based on the compound can be used as a bifunctional molecule for external and intracellular recognition, separation, enrichment and fluorescence detection of Bcl-2 family proteins or can be used as a PROTAC bifunctional complex for intracellular selective degradation of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 proteins so that the level of the Bcl-2 family proteins in living cells can be adjusted and controlled.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Artificial antibody type titanium dioxide (TiO2)/ boron-doped diamond (BDD) membrane electrode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104047019AImprove photocatalytic efficiencyImprove oxidation capacityWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsElectrodesAntibody typesMolecular recognition
The invention relates to an artificial antibody type titanium dioxide (TiO2) / boron-doped diamond (BDD) membrane electrode and a preparation method thereof, the electrode is in p-n heterostructure, the electrode uses boron-doped diamond (BDD) as a substrate, uniform dense fusiform TiO2 particles are on the surface of the BDD, the particle size of the TiO2 particles is 50-100nm, a modification layer with a thickness of 5 to 10 mum is formed by the densely covered TiO2 particles; the preparation method of the artificial antibody type titanium dioxide (TiO2) / boron-doped diamond (BDD) membrane electrode is as follows: using of the boron-doped diamond as the substrate, low temperature liquid phase deposition of TiO2 with a target pollutant molecular imprinting on the surface of the substrate, and removal of target pollutant molecules. Compared with the prior art, the artificial antibody type titanium dioxide (TiO2) / boron-doped diamond (BDD) membrane electrode prepared by the method both has the p-n heterostructure and target pollutant molecular recognition ability, has excellent photoelectrocatalytic integrative performance and high selectivity degradation ability, has the advantages of simple preparation process, can be effectively used for removal of organic pollutants with low concentration, low tendency to biochemistry and high toxicity, and has extensive economic and social benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Molecular imprinting catalytic membrane capable of selectively degrading ciprofloxacin and preparation method
ActiveCN106955726AHighly selective degradation effectEasy to separatePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSelective degradationCarbonate
The invention provides a molecular imprinting catalytic membrane capable of selectively degrading ciprofloxacin and a preparation method. The preparation method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing graphite-like nitrogen carbonate g-C3N4; step 2, preparing a noble metal loaded semiconductor composite material; and step 3, preparing the molecular imprinting catalytic membrane capable of selectively degrading the ciprofloxacin. The material prepared by the preparation method can effectively realize the aims of preferably selectively adsorbing and degrading target pollutants in a mixed sewage system; post-treatment is simple, a photocatalyst is conveniently recycled for a plurality of times and secondary pollution is effectively avoided; and the molecular imprinting catalytic membrane has the advantage of selectively treating antibiotic wastewater very well.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Synthetic method of TiO2 composite photocatalyst with high selective degradation
InactiveCN101491757AHigh selectivityImprove degradation efficiencyWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPhotocatalytic reactionDichlorophenol
The invention provides a method for synthesizing TiO2 composite photocatalyst with high selectivity and degradation function, belongs to the technical field of new material synthesis, and solves the problem of low selectivity in the prior photocatalysis reaction. The method for synthesizing the TiO2 composite photocatalyst with the high selectivity and the degradation function comprises the following steps: a, preparing titanium dioxide colloidal sol; b, performing hydrolytic condensation; and c, preparing the TiO2 composite photocatalyst. The TiO2 composite photocatalyst synthesized by the method for synthesizing the TiO2 composite photocatalyst with the high selectivity and the degradation function has high selectivity; and the method has the advantages of quick degradation and high degradation efficiency for 2, 4-dichlorophenol, and the like.
Owner:TAIZHOU UNIV
Assays and Apparatus for Detecting Electrochemical Active Markers in an Electric Field
InactiveUS20150159203A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesElectrochemistry
The invention provides a method of probing for a nucleic acid comprising: contacting a nucleic acid solution with an oligonucleotide probe labelled with an electrochemically active marker, providing conditions at which the probe is able to at least partially hybridise with any complementary target sequence which may be present in the nucleic acid solution, selectively degrading either hybridised, partially hybridised or unhybridised nucleic acid probe, and electrochemically determining information relating to the electrochemically active marker. The invention further provides novel molecules with use in methods of the invention.
Owner:ATLAS GENETICS
Micro-nano bubble generating device and method and application thereof in dye wastewater treatment
ActiveCN109304108AReduce noiseEasy to operateFlow mixersWater treatment compoundsMicro nanoOrganic matter
The invention provides a micro-nano bubble generating device and method and application thereof in dye wastewater treatment. The micro-nano bubble generating device provided by the invention comprisesa pressure dissolved gas tank, a gas and liquid mixing pump, a jet ejector and a water box. By adjusting the gas suction volume of the gas and liquid mixing pump and the jet ejector, the device provided by the invention can generate a large number of micro-nano bubbles with a slow rising speed and a diameter between 100nm and 300nm. Aiming at the problems of deep chroma, high COD content and difficult degradation of dye wastewater, the high-efficiency oxygenation and hydroxyl radical-producing properties of the micro-nano bubbles can non-selectively degrade organic matters in water, and the foam generated in the degradation process can be relieved by finely adjusting temperature, salt concentration, defoamer concentration and the like. The micro-nano bubble generating device and method provided by the invention have very high application value in dye wastewater treatment.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
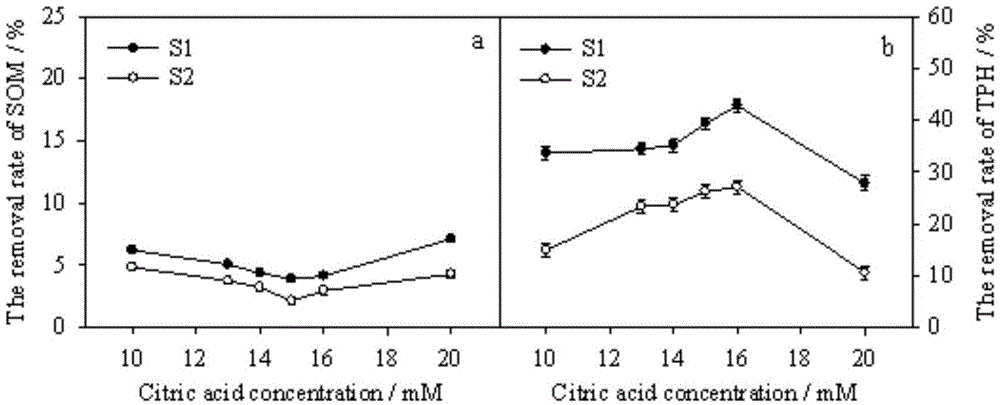
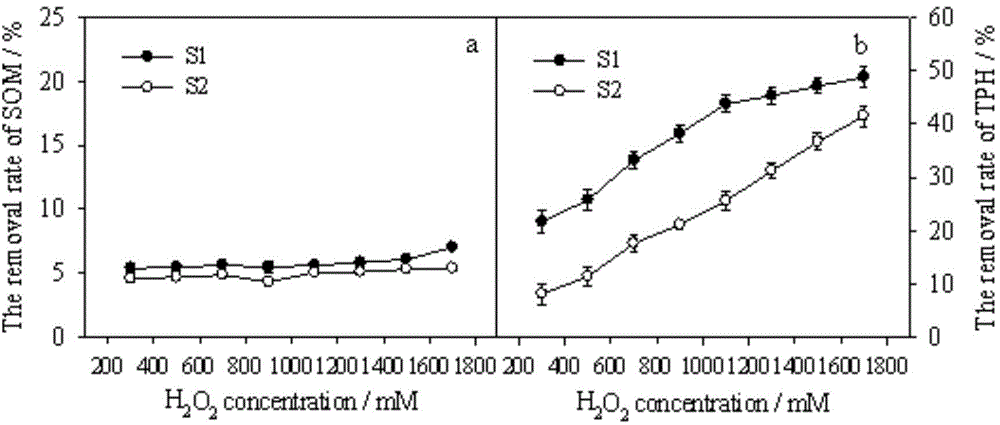
Selective degradation method for petroleum pollutants in soil rich in organic matters
ActiveCN104889152AHigh removal rateReduce oxidationContaminated soil reclamationFenton reagentPetroleum
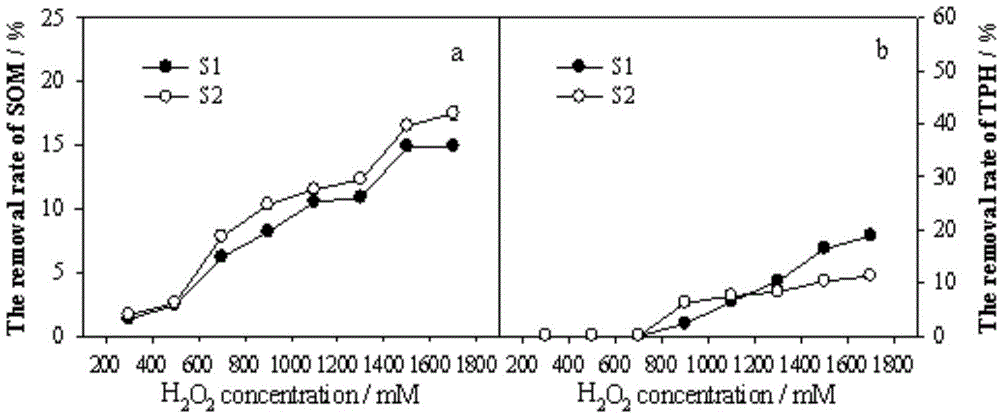
The invention provides a selective degradation method for petroleum pollutants in soil rich in organic matters. According to the selective degradation method, a Fenton reagent consisting of hydrogen peroxide and Fe<2+> is taken as an oxidization reagent; and a complex solution of citric acid and calcium chloride is added into a Fe<2+> solution in the Fenton reagent and used as a selective regulator to improve selective oxidative degradation of the Fenton reagent to the petroleum pollutants. TPH (total petroleum hydrocarbons) are selectively degraded by the Fenton reagent, so that the TPH removal rate is increased, the oxidization of SOM (soil organic matter) is reduced, the stability and the utilization rate of hydrogen peroxide in a Fenton system can be improved, and the service life of a hydroxyl radical is prolonged.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
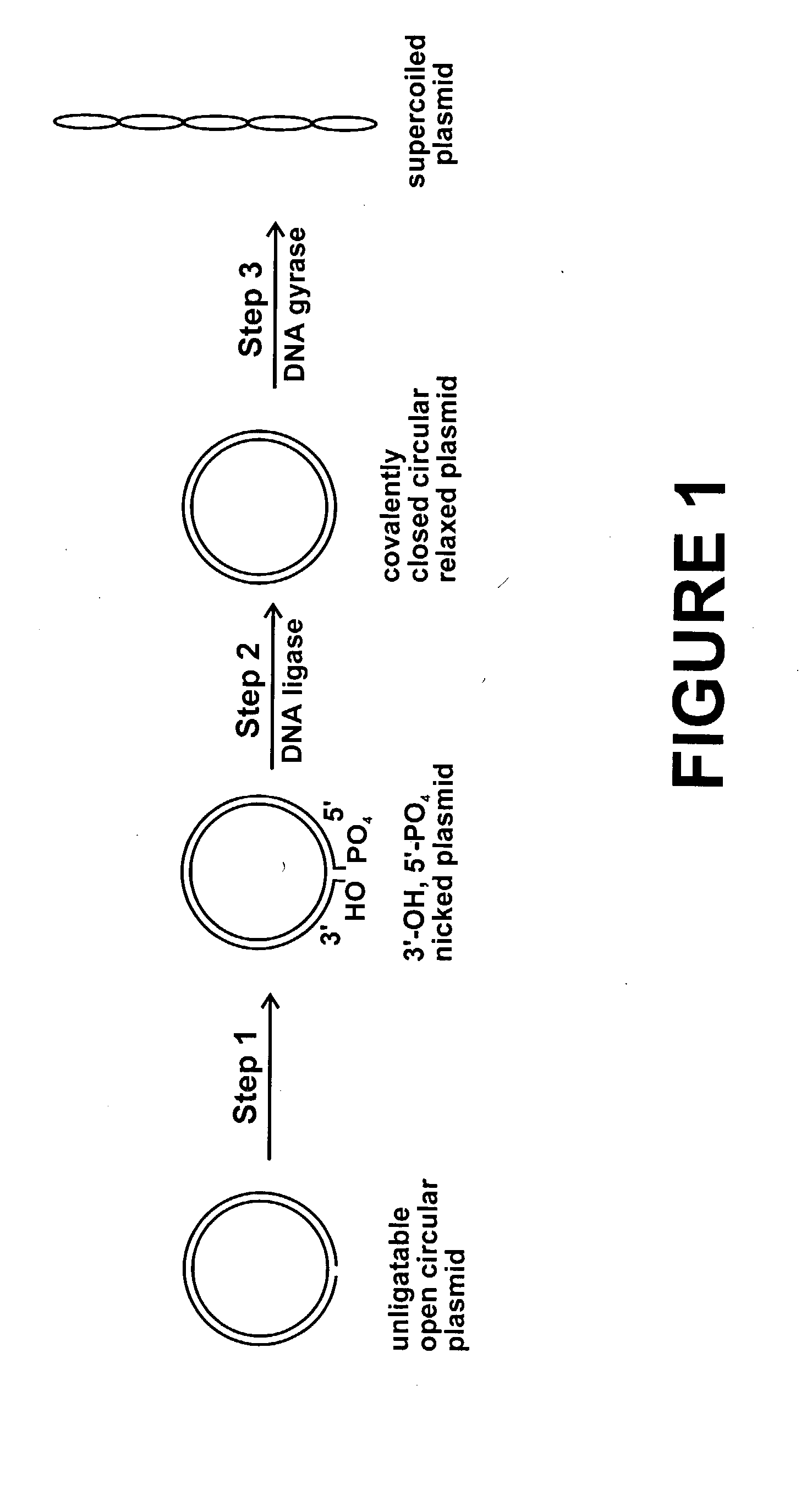
Method for plasmid preparation by conversion of open circular plasmid
InactiveUS20040191871A1Increase percentageFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionNucleotidePhosphoric acid
In accordance with the invention, there is provided a method for preparing plasmid from host cells which contain the plasmid, comprising the steps: (a) preparing a cleared lysate of the host cells, wherein the cleared lysate comprises unligatable open circular plasmid, wherein the open circular plasmid is not 3'-hydroxyl, 5-phosphate nicked plasmid; (b) incubating the unligatable open circular plasmid with one or more enzymes in the presence of their appropriate nucleotide cofactors, whereby the unligatable open circular plasmid is converted to 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid; (c) incubating the 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid with DNA ligase in the presence of DNA ligase nucleotide cofactor, whereby 3'-hydroxyl, 5'-phosphate nicked plasmid is converted to relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid; and (d) incubating the relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid with DNA gyrase in the presence of DNA gyrase nucleotide cofactor, whereby relaxed covalently closed circular plasmid is converted to negatively supercoiled plasmid. Preferably, the enzymatic steps (b), (c), and (d) are performed in a single step using an enzyme mixture comprising DNA polymerase, DNA ligase, and DNA gyrase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises a 3' terminus deblocking enzyme, such as exonuclease III or 3'-phosphatase. Preferably, the mixture further comprises one or more regenerating enzymes and a high energy phosphate donor, whereby the nucleotide by-products of the nucleotide cofactors generated by DNA ligase and DNA gyrase are converted to back to nucleotide cofactor. Preferably, the enzyme mixture further comprises one or more exonucleases, such as ATP dependent exonuclease, whereby linear chromosomal DNA is selectively degraded.
Owner:HYMAN EDWARD DAVID
Compound eluting agent for repairing organic matter and heavy metal compound contaminated soil, leaching method of compound eluting agent and eluting agent recycling process
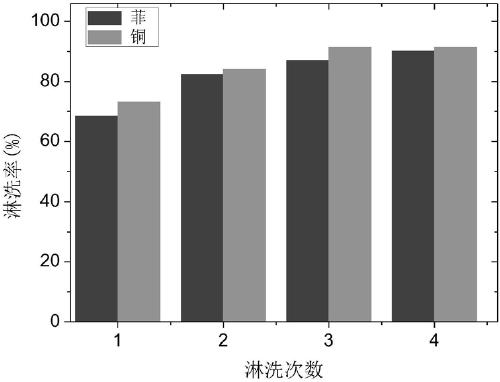
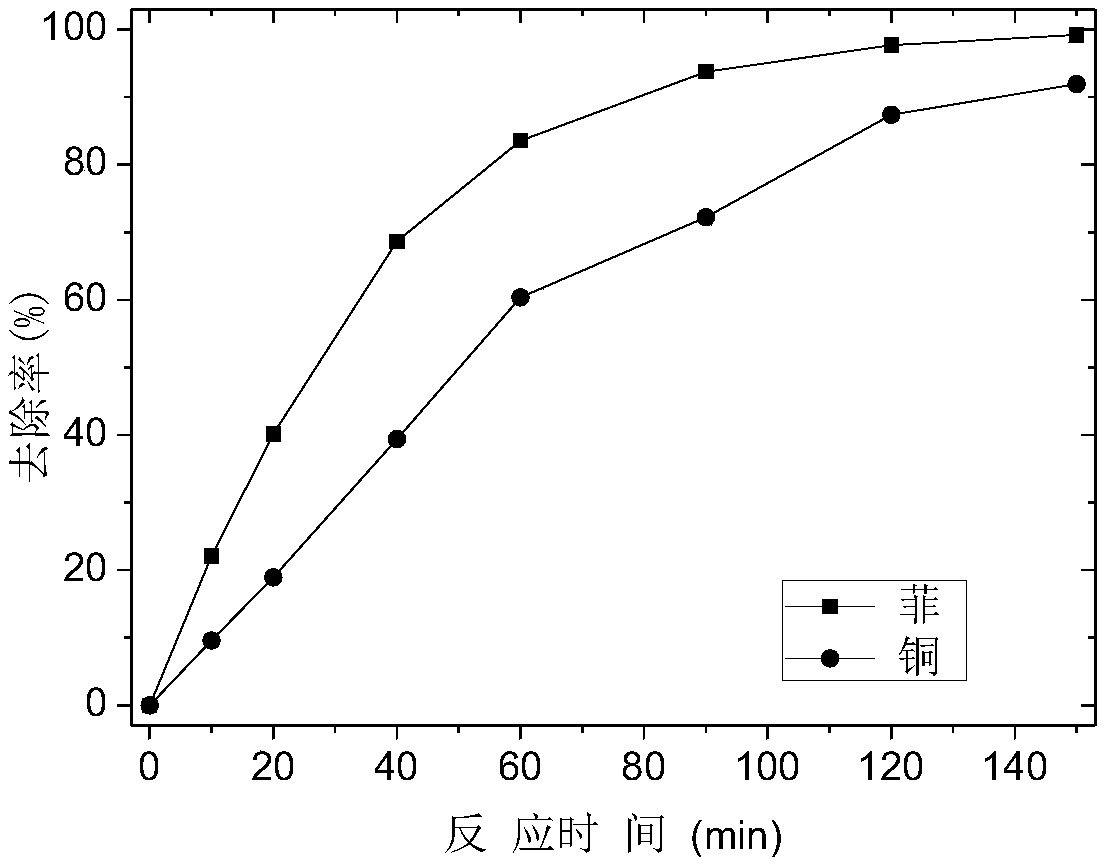
InactiveCN109207154AEffective rinse removalImprove rinsing efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersHeavy metal compoundPersulfate
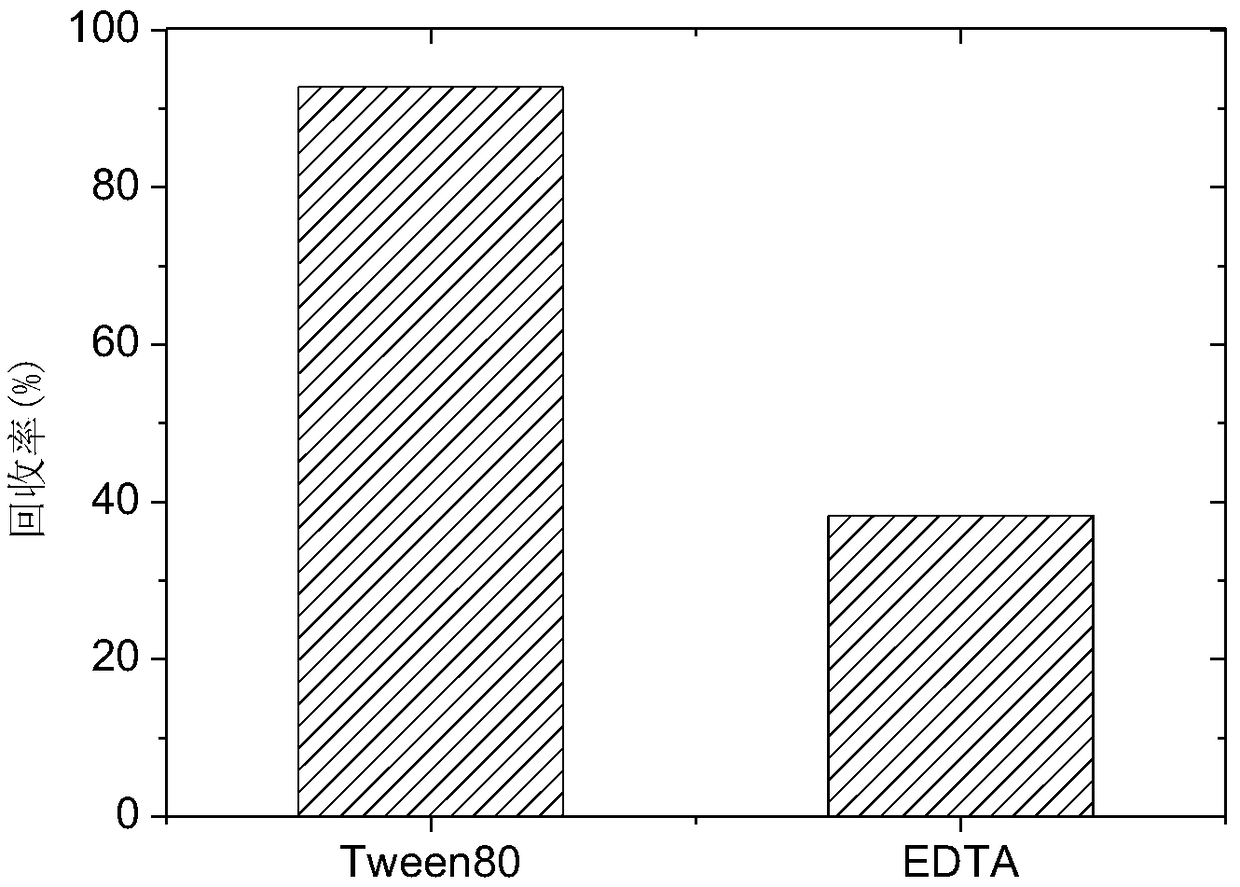
The invention discloses an eluting agent for repairing organic matter and heavy metal compound contaminated soil, an eluting method of the compound eluting agent and an eluting agent recycling method,wherein the eluting agent is prepared by compounding Tween 80 and EDTA. The eluting method comprises the following steps: adding the eluting agent into the contaminated soil, oscillating, mixing, centrifugally separating an eluting solution, adding the compound eluting agent solution again into the soil subjected to first-time eluting, performing secondary elution, and repeating for four times. The eluting agent recycling method comprises the following steps: transferring the separated eluting solution into a photoelectric recovery device, adding sodium persulfate and sodium sulfate electrolytes, turning an ultraviolet lamp and a power supply for photoelectric treatment for 2.5 hours to selectively degrade organic matters in the eluting solution and recover heavy metals. The compound solution of the Tween 80 and EDTA-2 Na is used, a plurality of times of continuous eluting are carried out, a photoelectric synergistic persulfate method is adopted to regenerate the eluting agent, and the organic matter and heavy metal compound contaminated soil can be effectively repaired synchronously. The method has the characteristics of simple process, convenience operation, short time consumption, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for degrading polybrominated diphenyl ethers using surface active agent solubilization combined with UV technique
InactiveCN101461989AShort reaction timeImprove efficiencyChemical protectionWater bathsSelective degradation
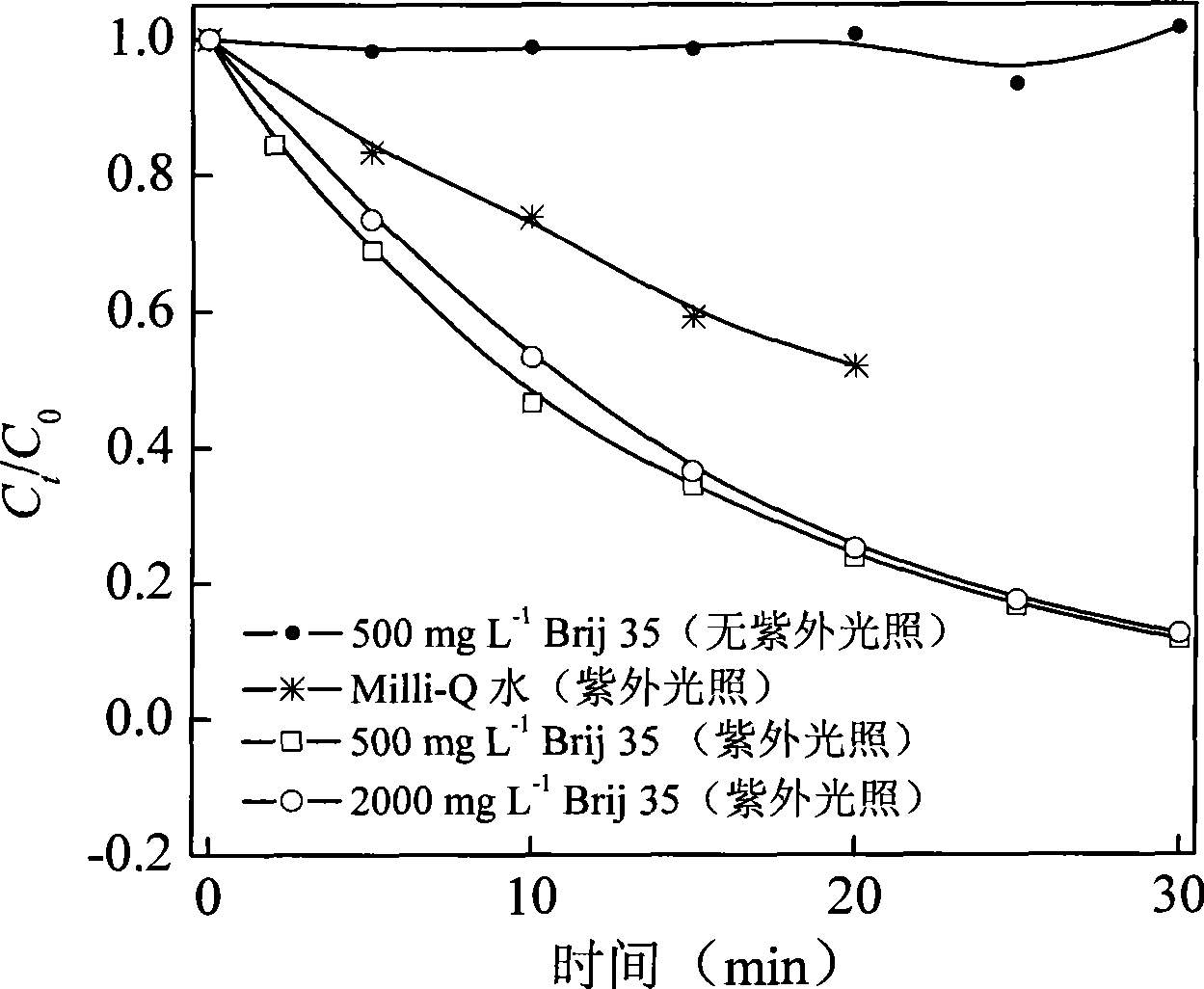
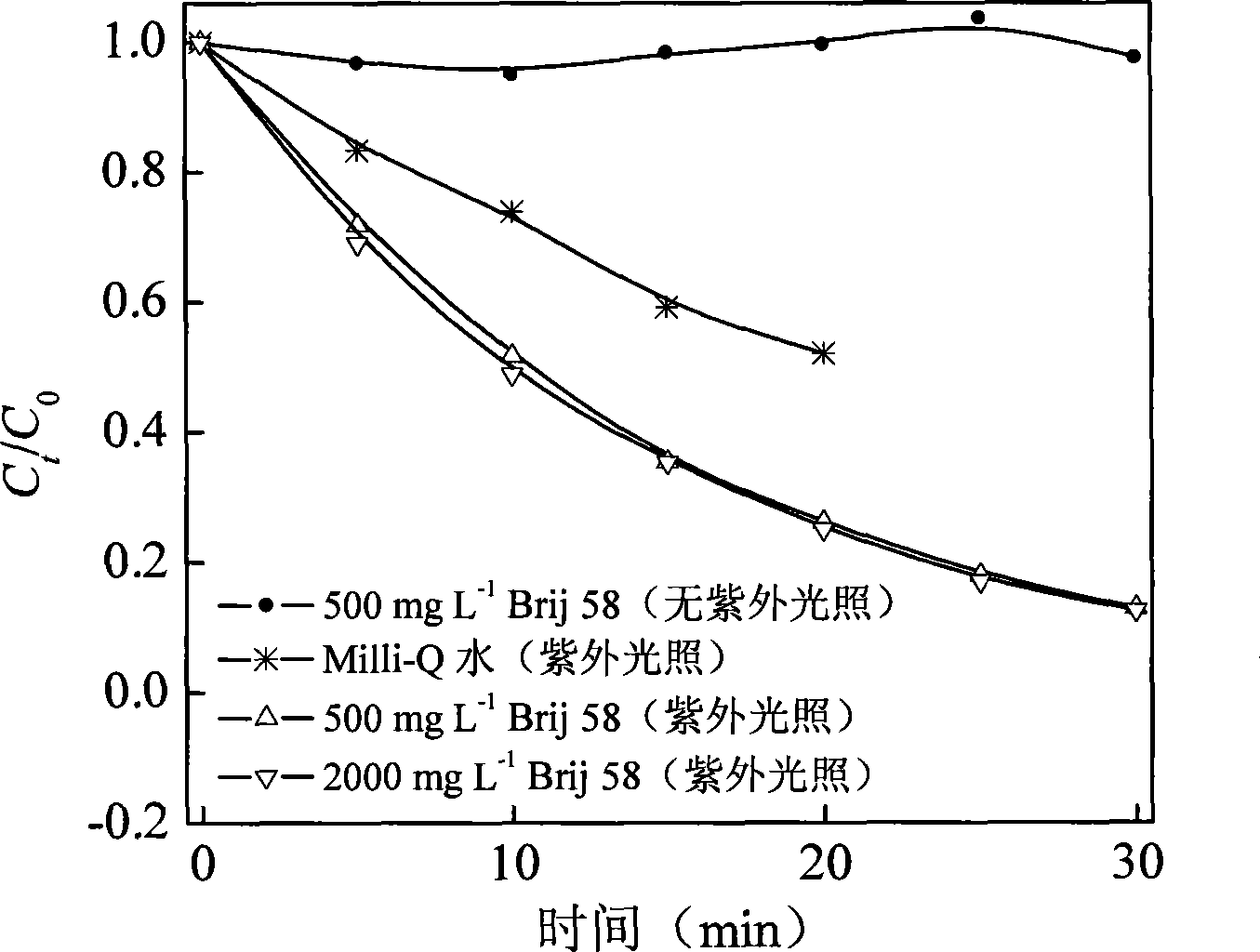
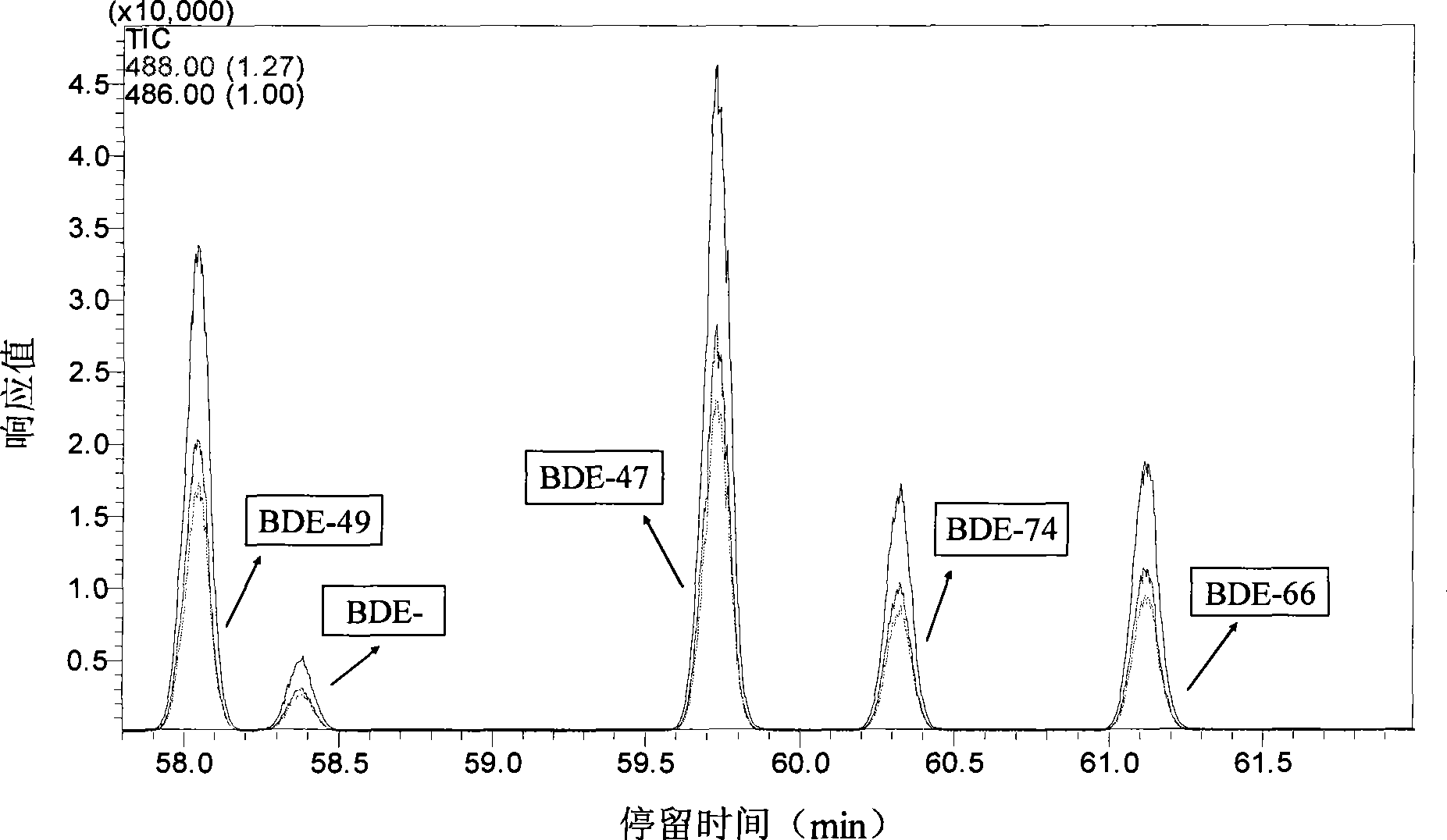
The invention discloses a method for degrading polybrominated diphenyl ether by combining surfactant solubilization and UV technology, which belongs to the technical field of environment-friendly halogenated aryl hydrocarbon organic pollutant treatment. The method adopts the technical proposal that surfactant solubilization of 2,2',4,4',5-pentabromated diphenyl ether is improved in a hydrophobic environment provided by nonionic surfactant micelle (Brij 35 or Brij 38) under the conditions of normal temperature and pressure, water bath and ultrasonic sound; and the 2,2',4,4',5-pentabromated diphenyl ether which is dissolved in a surfactant solution is subjected to UV advanced treatment at normal temperature and pressure and then subjected to stepwise debromination reaction or intermolecular elimination and annulation reaction to generate intermediate products, namely PBDEs from monobromo to tetrabromo and polybrominated dibenzofuran (PBDFs) from monobromo to tetrabromo. The whole technology has short time consumption and high efficiency, and the method can selectively degrade target pollutant without damaging a surfactant, provides convenience for recycling of the surfactant, and has good application prospect in the aspect of remediation of soil polluted by the PBDEs in electronic waste recycling sites.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method and application of molecular print catalytic membrane for selectively degrading tetracycline
InactiveCN106552620AHighly selective degradation effectAchieving identifiabilityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesWastewaterPhotocatalytic degradation
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a molecular print catalytic membrane for selectively degrading tetracycline. The preparation method mainly comprises the steps that 1, an Ag@Au@TiO2 catalyst is prepared; 2, dispersion liquid of the Ag@Au@TiO2 catalyst is prepared; 3, a casting solution is further prepared through the dispersion liquid of the Ag@Au@TiO2 catalyst; 4, a blend membrane is prepared on a glass plate through the casting solution; and 5, the molecular print catalytic membrane for selectively degrading the tetracycline is prepared through the blend membrane. Through the photocatalytic degradation process of the prepared molecular print catalytic membrane for selectively degrading the tetracycline, the purposes of selectively recognizing, adsorbing and catalytically degrading target pollutants can be achieved effectively, aftertreatment is simple and convenient, the effective degradation efficiency of the target substances is improved, and the preparation method has the advantage of higher selectivity of treatment of antibiotic wastewater.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Imprinting-doped mesoporous TiO2 microspheres and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102658210AStable in natureExtended service lifeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAbsorption capacitySynthesis methods
The invention provides a synthesis method and application for imprinting-doped mesoporous TiO2 microspheres. The synthesis method includes dissolving 1-5ml of titanium source substances into 100-200ml of organic solution, adding 0.1-0.3g of catalytic into the organic solution, adding 0.1-0.5g of target molecules used as imprinting molecules while stirring the mixture, and further adding metal salt with the molar ratio ranging from 0.1% to 8% relative to a titanium source so as to introducing doping ions; and continuing stirring for 1-12 hours, then enabling the solution to react in a high-temperature and high-pressure kettle at the temperature ranging from 80 DEG C to 180 DEG C for 3-6 hours, centrifugally washing to obtain white solid, placing the white solid in a muffle furnace at the temperature ranging from 400 DEG C to 450 DEG C, keeping the temperature for 2-4 hours and then obtaining the imprinting-doped mesoporous TiO2 microspheres. The prepared materials are used for degrading target organic pollutant in water, have higher photocatalytic activity as compared with pure TiO2(P25), and are capable of selectively degrading the target pollutant. In addition, the imprinting-doped mesoporous TiO2 microspheres have a wider photoresponse range as compared with pure TiO2 undoped with imprinting, and have high visible light absorption capacity.
Owner:YUNNAN UNIV
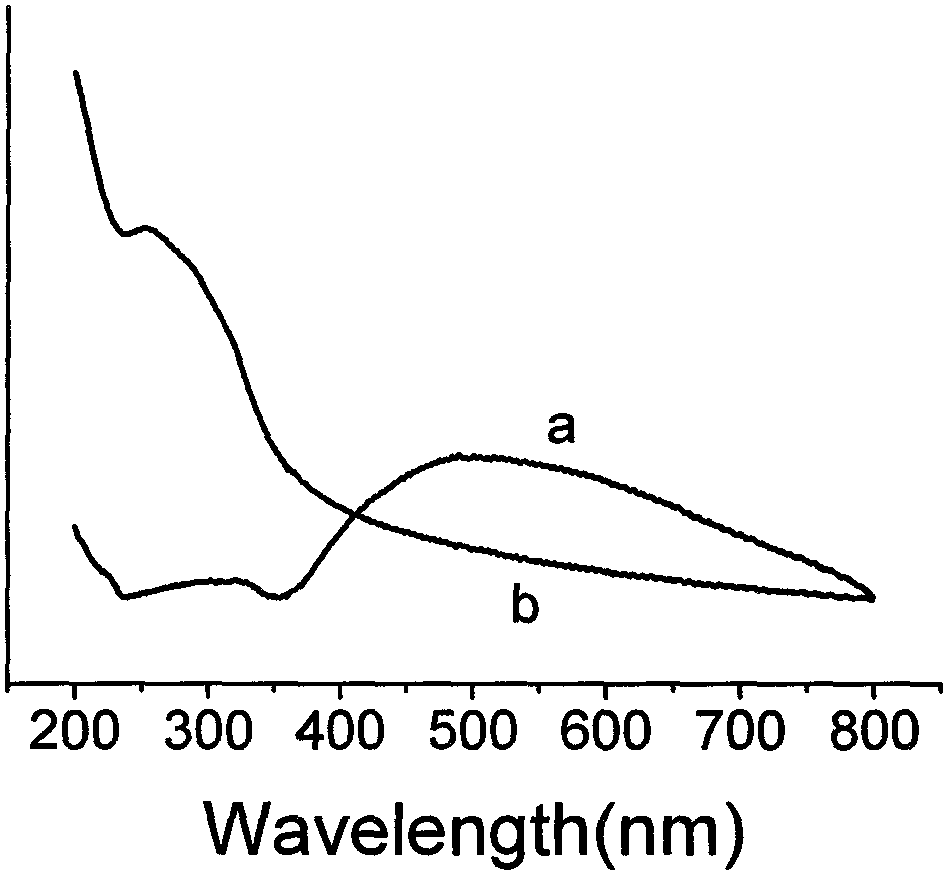
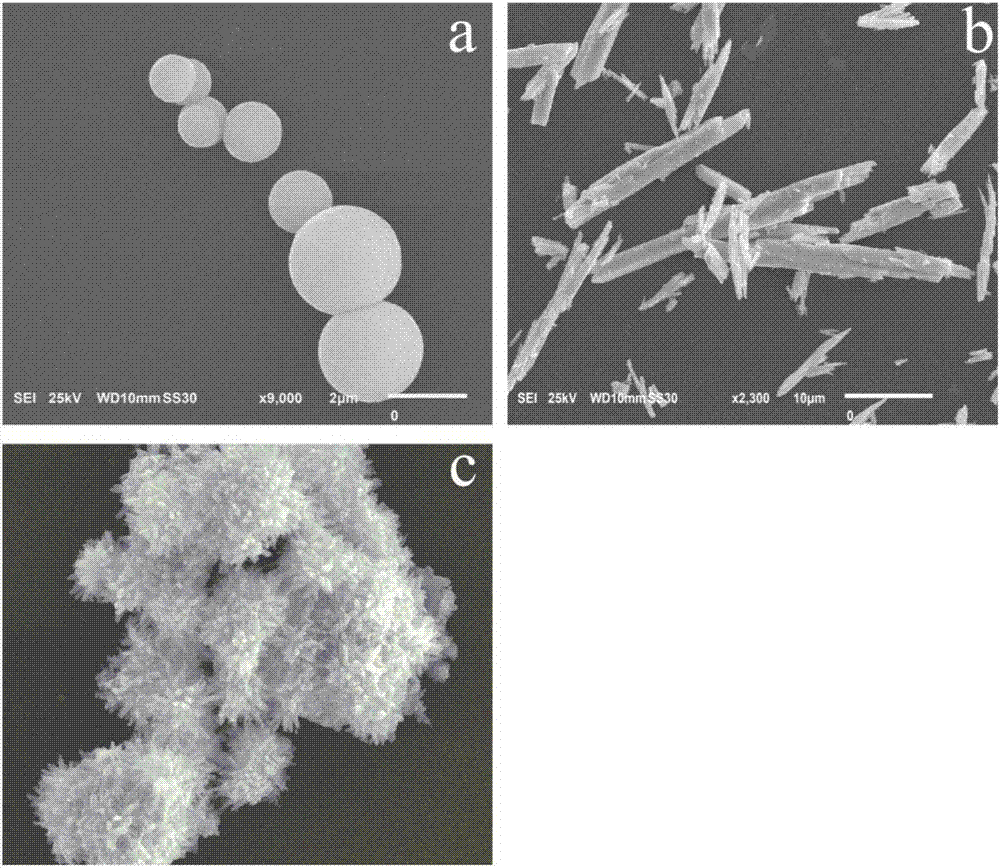
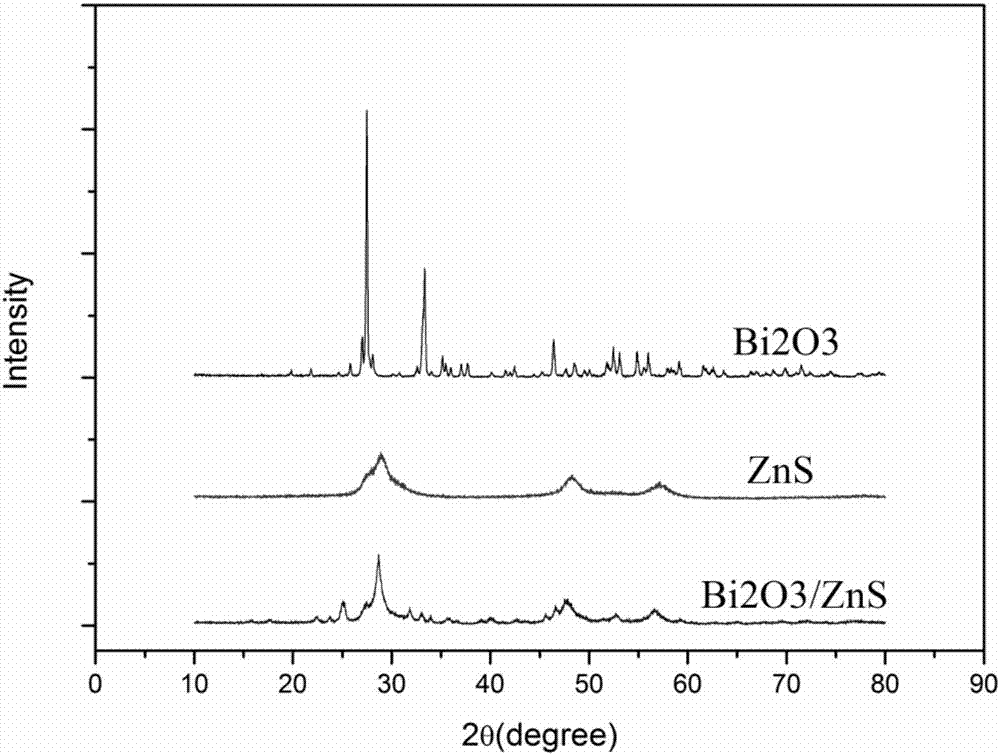
ZnS/Bi2O3 heterojunction molecularly-imprinted photocatalytic membrane, preparation method and application
ActiveCN106955718AEfficient degradationHighly selective degradation effectPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationHeterojunctionWastewater
The invention provides a ZnS / Bi2O3 heterojunction molecularly-imprinted photocatalytic membrane, a preparation method and an application. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a Bi2O3 photocatalyst; (2) preparing a ZnS / Bi2O3 heterojunction photocatalyst; and (3) preparing a ZnS / Bi2O3 heterojunction molecularly-imprinted photocatalytic membrane. The prepared ZnS / Bi2O3 heterojunction molecularly-imprinted photocatalytic membrane for selectively degrading rhodamine B has the advantages that in the process of photocatalytic degradation, the purposes of selective recognition, absorption and catalytic degradation of target pollutants can be effectively realized, the aftertreatment is simple and convenient, the efficiency of effective degradation of target substances is improved, and the selective treatment of dye waste water is stronger.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Solid photocatalyst with visible-light response and selectivity as well as preparation method and application of solid photocatalyst
InactiveCN103721753AImprove stabilityHigh photoactivityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsHigh concentrationTin dioxide
The invention discloses a solid photocatalyst with visible-light response and selectivity as well as a preparation method and application of solid photocatalyst. The solid photocatalyst comprises metal semiconductor nanoparticles and a metal complex loaded on the metal semiconductor nanoparticles, wherein the metal semiconductor nanoparticles are selected from at least one of titanium dioxide, tin dioxide, zinc oxide and cadmium sulfide; central metal ions of the metal complex are selected from platinum (II), ruthenium (II) or iron (II), and a ligand in the metal complex is an organic or inorganic ligand; in the solid photocatalyst, the mass content of the metal complex is 1-100mg / g. The solid photocatalyst can be used for selective degradation treatment of low-concentration toxic phenolic pollutants in various low-toxin high-concentration pollutants and selective oxidation of organic matters, also can be used for treating industrial wastewater, and has the characteristics of simple preparation process and high catalytic efficiency.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Nitrogen-doped carbon material, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109647474AHigh reactivityImprove removal efficiencyPhysical/chemical process catalystsWater contaminantsD-GlucoseNitrogen source
The invention belongs to the field of carbon materials, and concretely relates to a nitrogen-doped carbon material, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The prearatio method comprisesthe following steps: calcining glucose used as a raw material in an inert atmosphere using melamine used as a nitrogen source to a certain temperature to obtain a carbon substrate, mixing the carbon substrate with melamine in an aqueous solution according to a certain ratio, performing heating and stirring, drying the obtained material, and calcining the dried material in the inert atmosphere at alow temperature in order to obtain the nitrogen-doped carbon material. The preparation method has the advantages of simplicity, low energy consumption and low cost, and the nitrogen-doped carbon material has a very high reactivity, and can selectively degrade a plurality of organic pollutants, so the technical problems of complexity and high cost of preparation methods of the nitrogen-doped carbon material in the prior art and the technical problem of limited ability to degrade the organic pollutants in the environment are solved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
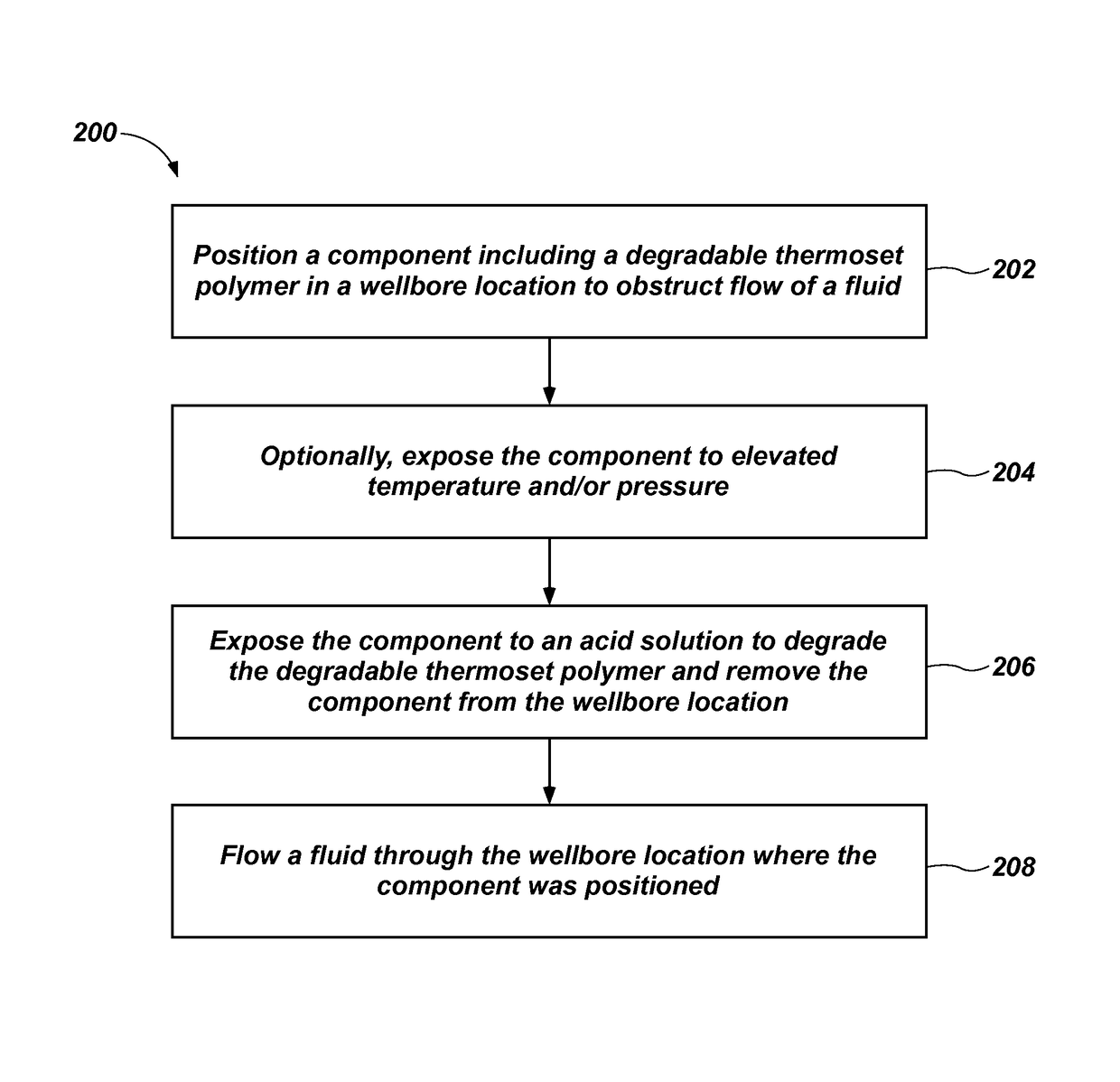
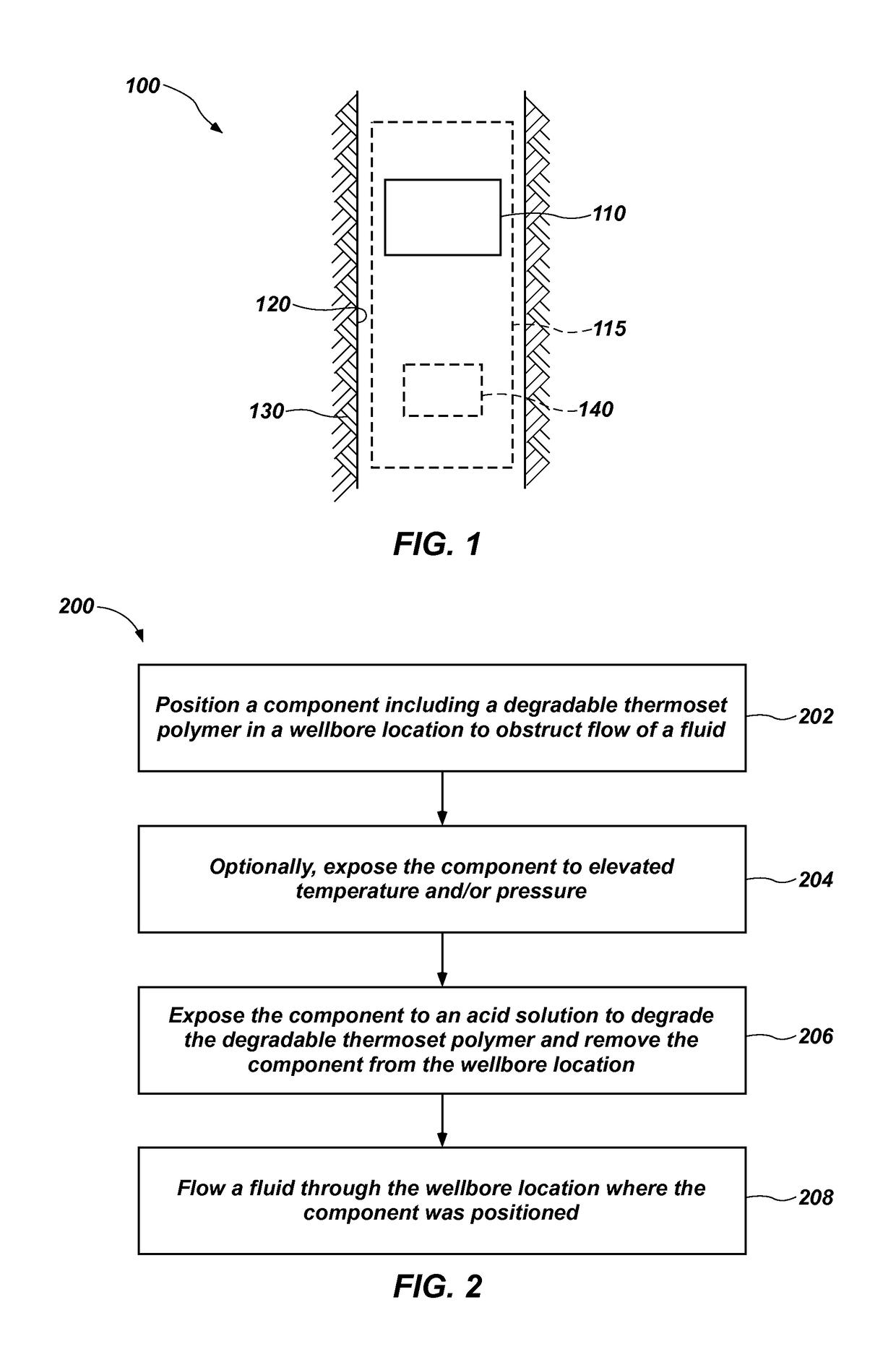
Methods of using a degradable component in a wellbore and related systems and methods of forming such components
Methods of using a component in a subterranean wellbore include positioning a component including a degradable thermoset polymer material in a wellbore location, obstructing flow with the component, exposing the component to an acidic solution to degrade the selectively degradable thermoset polymer material and to remove the component from the wellbore location, and flowing a fluid through the wellbore location where the component was positioned. Methods of forming a component of a wellbore system include forming at least a portion of the component to comprise a degradable thermoset polymer material. Wellbore systems include at least one component including a selectively degradable thermoset polymer material. The selectively degradable thermoset polymer material may be a polyhexahydrotriazine (“PHT”) material.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Normalized cDNA library of ocean medaka specific tissue and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101851786AEasy to analyze and studyEasy to filterMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism librariesCDNA libraryTotal rna
The invention discloses a normalized cDNA library of ocean medaka specific tissues and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of cDNA libraries. The library is prepared from one or more specific tissues of ocean medaka. The preparation method of the normalized cDNA library comprises the following steps: extracting total RNA of the specific tissues of the ocean medaka, synthesizing cDNA polynucleotide products, re-hybridizing after cDNA denaturation, selectively degrading double-stranded components, amplifying normalized cDNA components through PCR and inserting amplified products in carriers. The normalized cDNA library of ocean medaka specific tissues lays a foundation for greatly finding and researching the expressing genes of the ocean medaka, and is of a great significance to the deep research on the expressing markers of the ocean medaka specific tissues.
Owner:香港城市大学深圳研究院
Compositions and methods for treating cdk4/6-mediated cancer
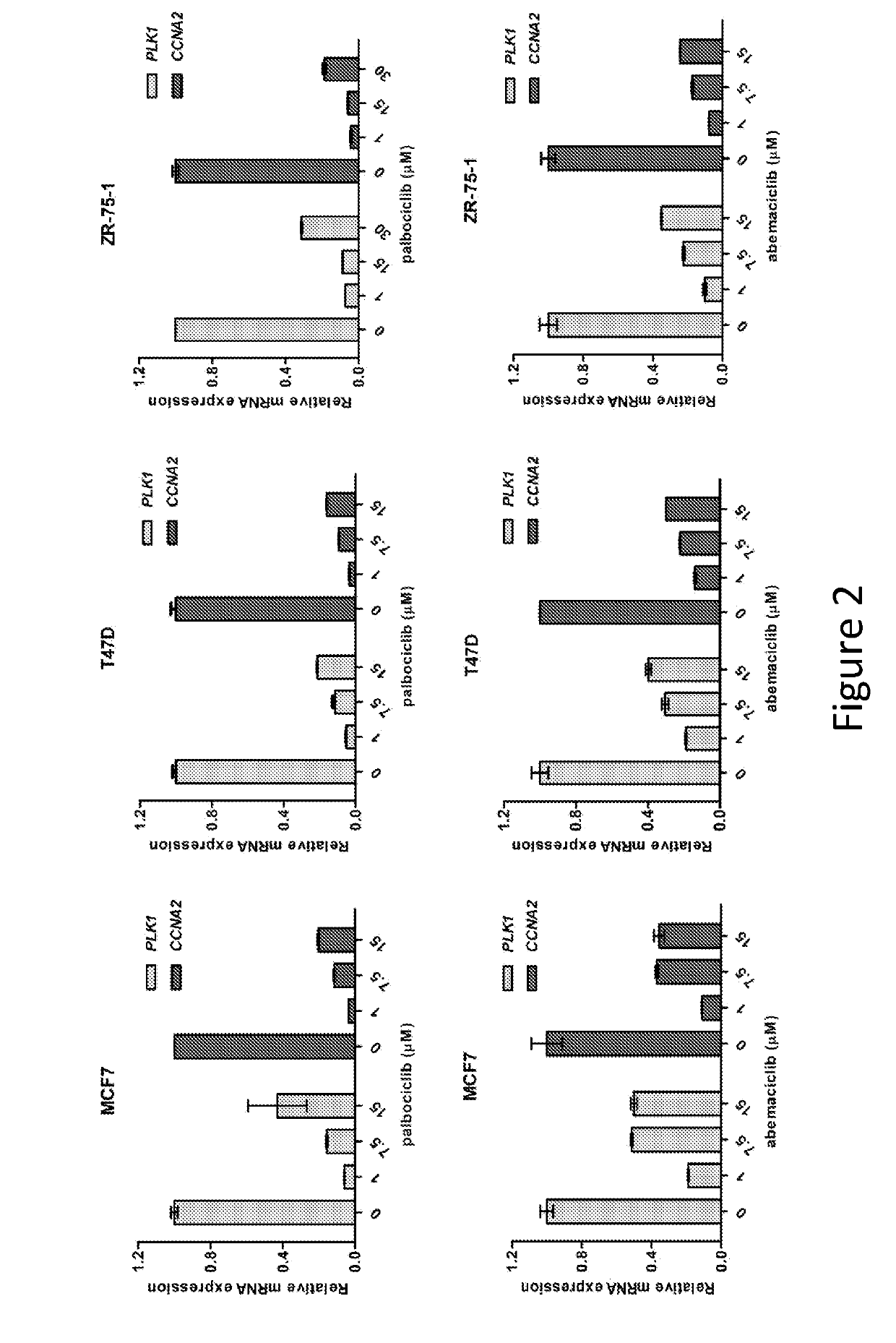
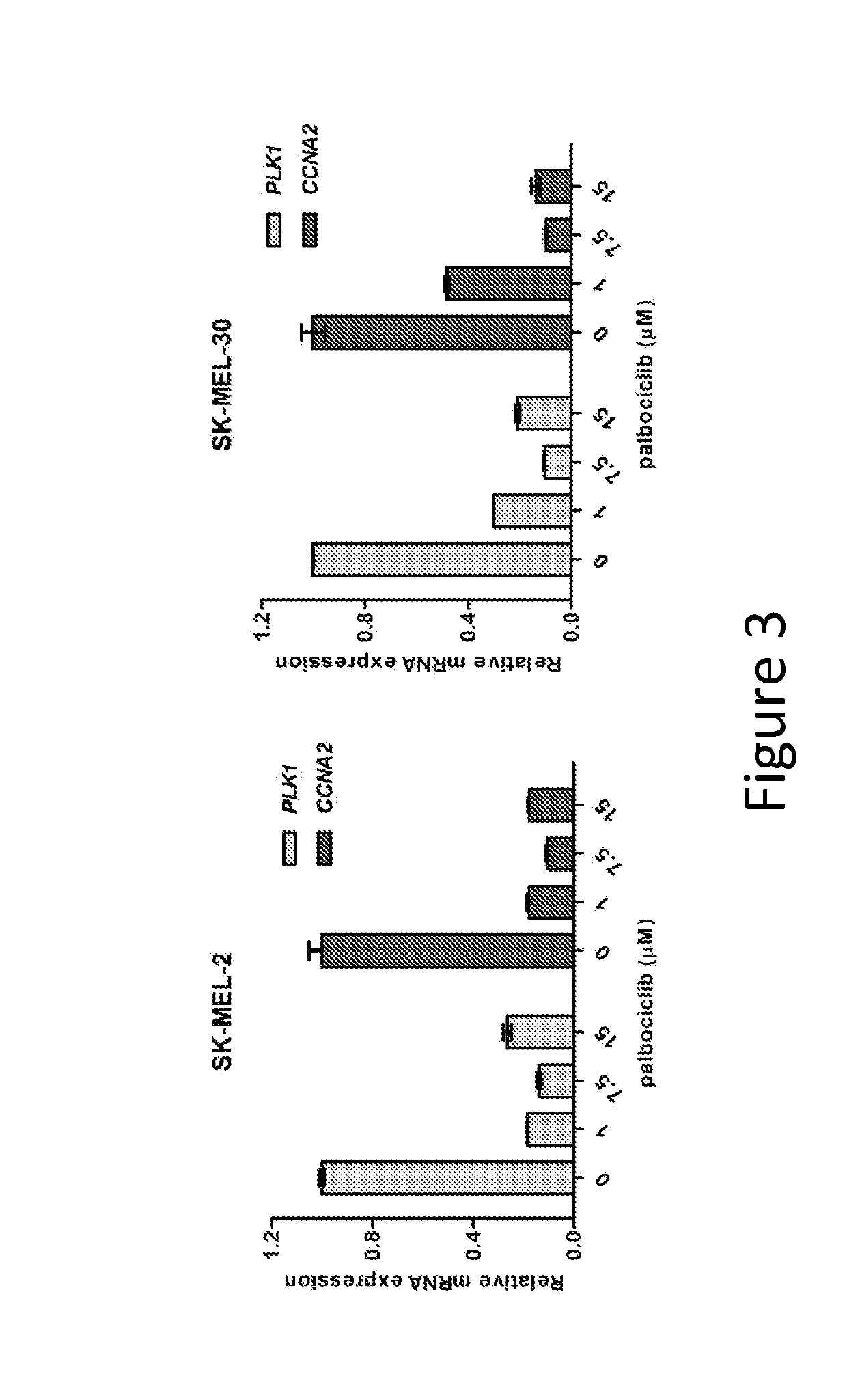
ActiveUS20190336503A1Effective therapyOrganic chemistryPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineSelective degradation
Methods for designing heterobifunctional small molecules which selectively degrade / disrupt CDK4 / 6 and compositions and methods of using such degraders / disruptors to treat CDK4 / 6-mediated cancer are provided.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
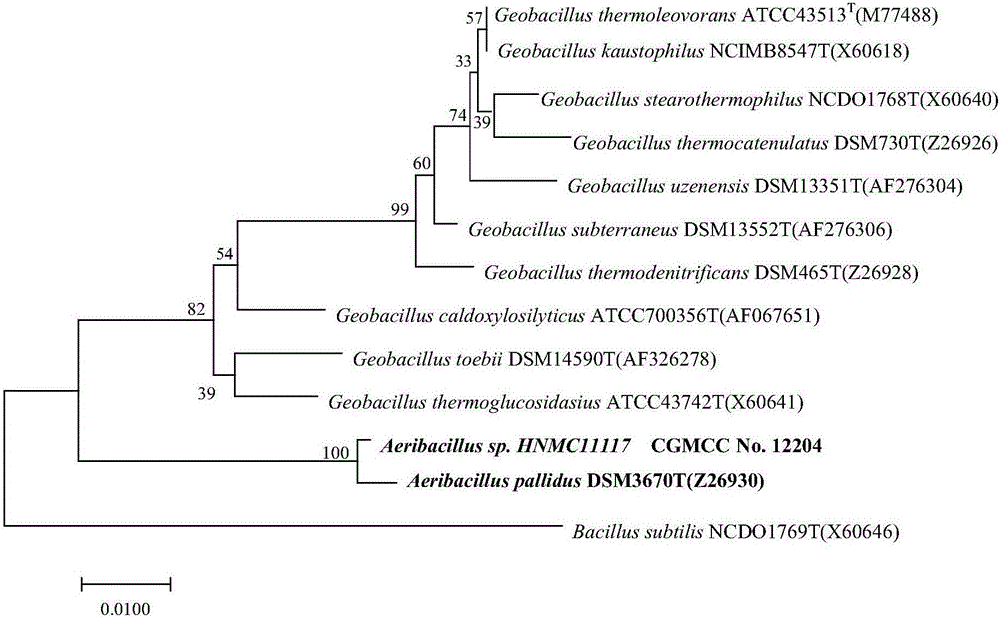
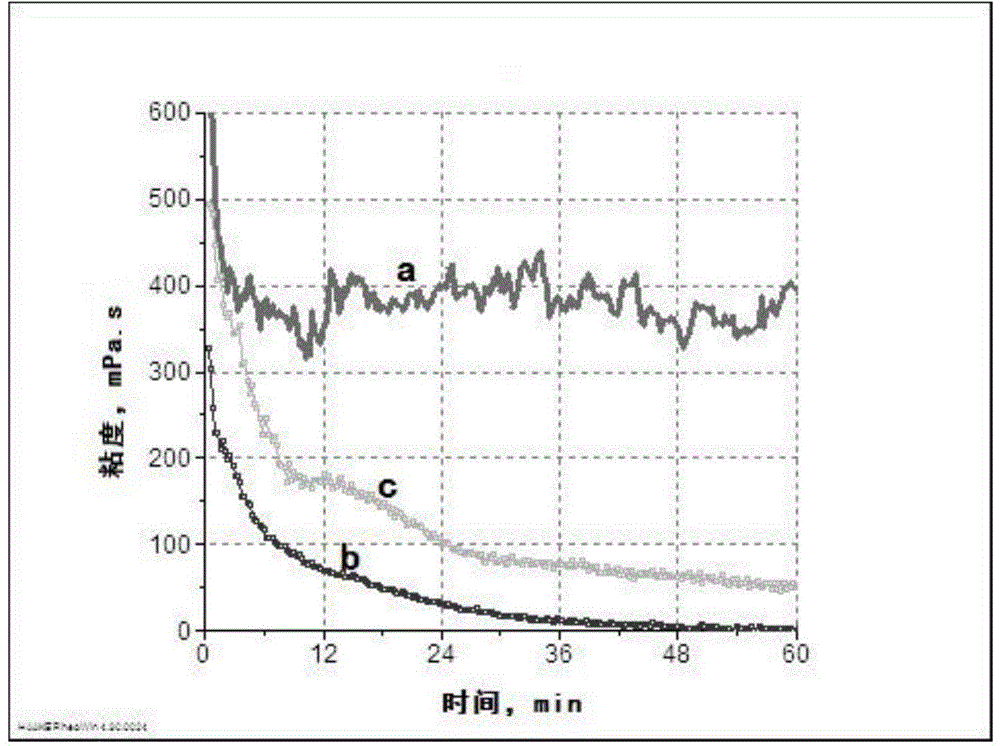
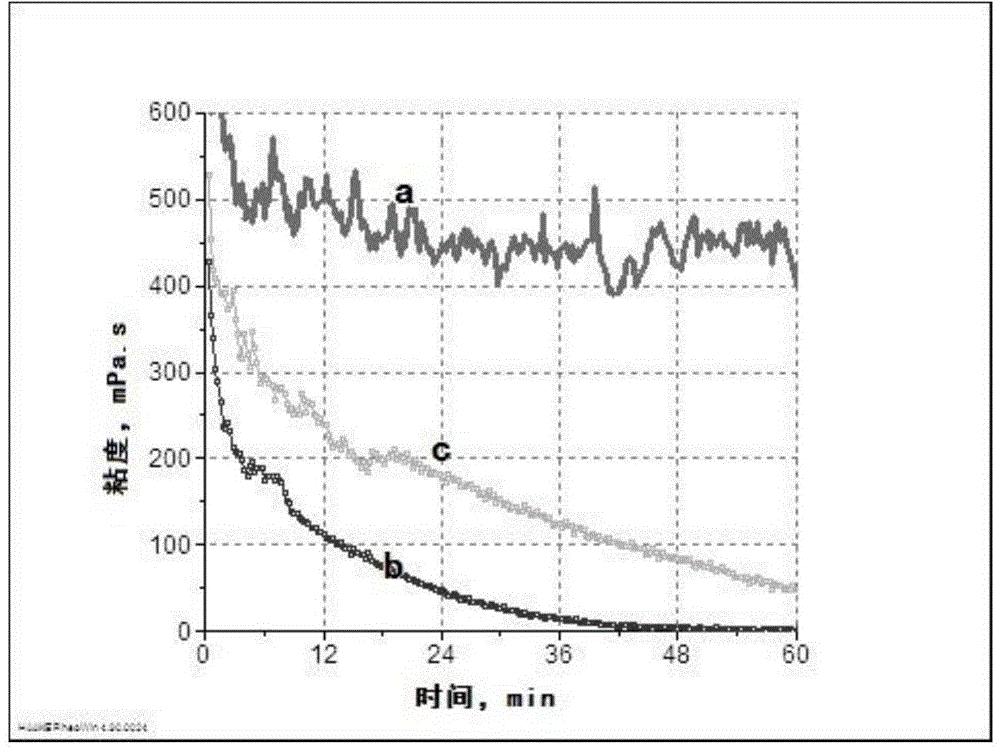
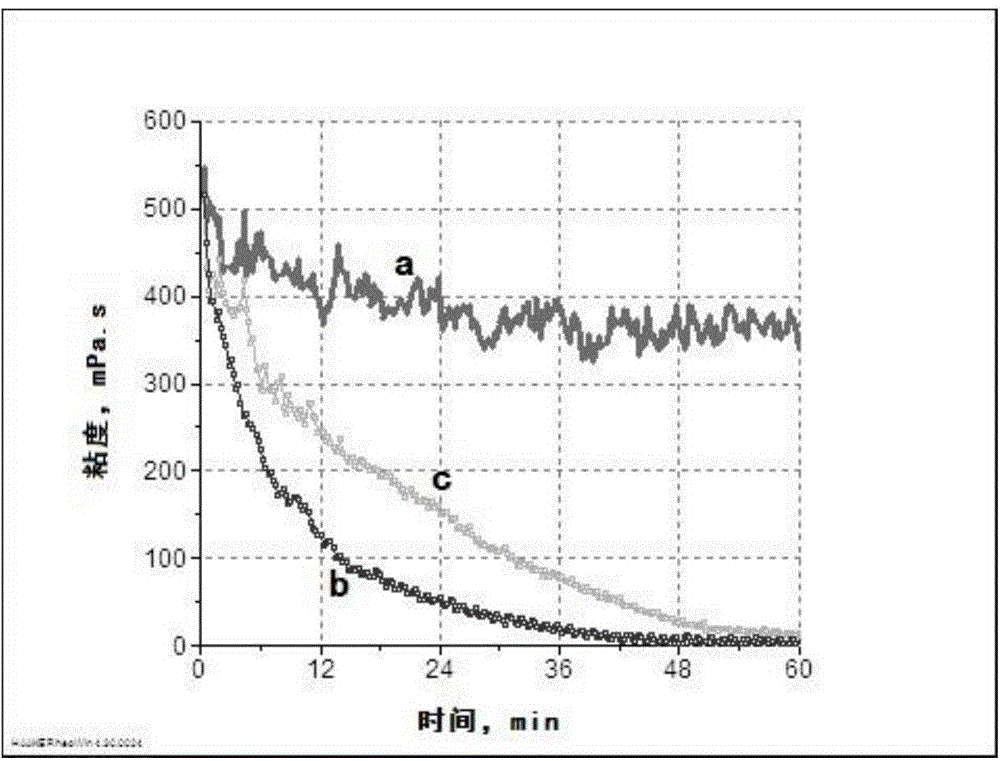
Oil field thermophilic degradation long chain hydrocarbon bacillus HNMC 11117 and application thereof
InactiveCN105861388AImprove degradation rateImprove degradation efficiencyBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationAlkaneOil field
The invention discloses an oil field thermophilic degradation long chain hydrocarbon bacillus HNMC 11117 and application thereof. The preservation number of the bacterial strain is CGMCC No.12204. Extraction liquid of an air inflation well with the oil deposit bottom layer temperature larger than 60 DEG C in Henan Zhongyuan Oil Field is used as an isolation sample, separation, purification, screening and recheck are performed, and the effective bacterial strain being HNMC 11117 bacterial strain which has the selectable degradation effect on alkane with the chain length of C16-C30 is obtained. The bacterial strain can be used for improving oil recovery at high temperature, repairing soil polluted by oil and other fields.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
Enzyme treatment and recycling method for protein fibers in waste textiles
ActiveCN103556475ATake advantage ofProcess greenPlastic recyclingBiochemical treatment with enzymes/microorganismsFiltrationPre treatment
The invention relates to an enzyme treatment and recycling method for protein fibers in waste textiles. The provided method aims to effectively realize the recycling of the protein fibers in the waste textiles. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the enzyme treatment and recycling method for the protein fibers in the waste textiles sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) continually carrying out following treatment steps on the waste textiles containing the protein fibers; (2) adding oxidordeuctase into dyed textiles which are directly treated by a direct dye, an active dye, an insoluble azo pigment or a cationic dye, and carrying out pre-treatment; (3) adding protease into the waste textiles treated by the step (2), and carrying out selective degradation on the protein fibers; and (4) carrying out solid-liquid separation on a substance treated by the step (3); carrying out ultra-filtration separation on the protease in a degraded solution and reutilizing, wherein a degraded product is used for producing relative products; and physically recycling the residual solid textiles.
Owner:浙江省轻工业品质量检验研究院
Bio-enzyme gel breaker, and applications thereof
The invention relates to bio-enzyme gel breaker and applications thereof. The bio-enzyme gel breaker is an aqueous solution of beta-mannanase, alpha-galactosidase, and a cross-linking agent. According to an application method, by volume, 80 to 120 parts of a fracturing fluid base solution is mixed with 5 to 10 parts of the bio-enzyme gel breaker, and after gel forming, an obtained mixture is taken as a fracturing fluid. According to applications, galactosidase is used for removing a part of galactose residues on the side chains of galactomannan, so that mannose glycosidic bonds on the main chain of galactomannans are exposed, and then degradation effect of mannanase is adopted for selective degradation of galactomannan. Combination of the above two enzymes is capable of realizing high-efficiency rapid gel breaking of the fracturing fluid, reducing molecular weight of gel breaking products greatly, and reducing reservoir damage.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Enzyme treatment and recycling method for cellulosic fibers in waste textiles
ActiveCN103556474ATake advantage ofGreen recyclingBiochemical fibre treatmentPlastic recyclingUltrafiltrationFiltration
The invention relates to an enzyme treatment and recycling method for cellulosic fibers in waste textiles. The provided method aims to effectively realize the recycling of the cellulosic fibers in the waste textiles. According to the technical scheme provided by the invention, the enzyme treatment and recycling method for the cellulosic fibers in the waste textiles sequentially comprises the following steps: (1) qualitatively determining the variety of fibers in the waste textiles and the variety of dyes; (2) adding oxidordeuctase into dyed textiles which are directly treated by a direct dye, an active dye, an insoluble azo pigment or a cationic dye, and carrying out pre-treatment; (3) adding cellulase into the waste textiles treated by the step (2) and carrying out selective degradation on the cellulosic fibers; and (4) carrying out solid-liquid separation on a substance treated by the step (3); carrying out ultra-filtration separation on the cellulase in a degraded solution and reutilizing, wherein a degraded product is used for sugar fermentation to produce relative products; and physically recycling the residual solid textiles.
Owner:浙江省轻工业品质量检验研究院
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com