Oil field thermophilic degradation long chain hydrocarbon bacillus HNMC 11117 and application thereof
A technology of 1. HNMC11117, long-chain alkanes, applied in the direction of bacteria, microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of oil-contaminated soil, etc., and achieve the goal of improving the degradation rate, improving the degradation efficiency, and improving the degradation capacity of long-chain alkanes Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
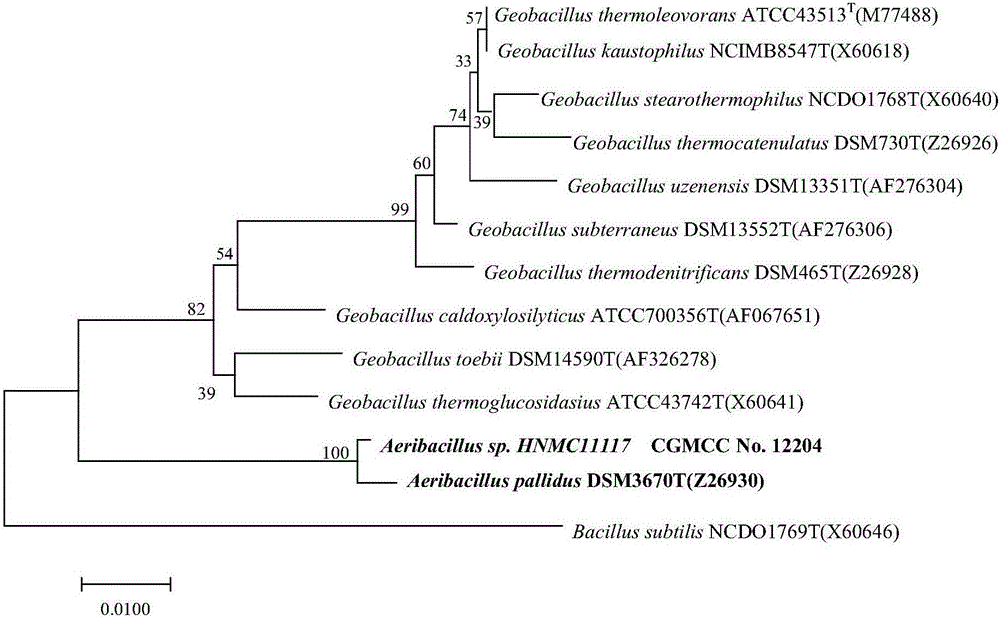
[0079] Isolation and screening of embodiment 1HNMC 11117 bacterial strain
[0080] The separation and screening method of oilfield thermophilic degrading long-chain hydrocarbon bacillus HNMC 11117 in the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0081] 1) Separation and purification: directly take the oilfield high-temperature production fluid, spread 200 μL on the plate, spread it on the H medium plate, place it in a constant temperature culture at 55°C, and observe the growth of the colony. When the colony grows stably, select the plate with clear single colony growth from the separation plate of each sample, pick out all the single colonies on the plate as much as possible, transfer all the single colonies on the plate to H medium, and culture at a constant temperature of 55 °C. Using the plate 3-section line method, single colonies were picked and purified multiple times until pure strains with consistent colony morphology were obtained.
[0082] 2) Multiple scre...
Embodiment 2
[0083] The crude oil degradation performance of embodiment 2HNMC 11117 strain
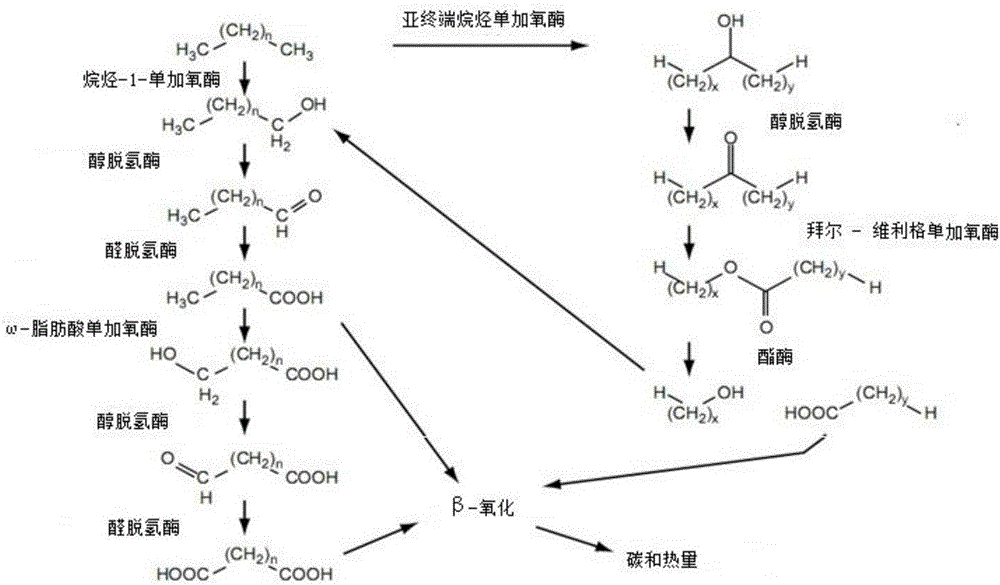
[0084] H medium, inorganic salt medium and inorganic salt medium containing 1% yeast extract were used respectively, all of which were added with 1wt% crude oil, under different conditions of temperature, salinity and pH value, 120r / min, constant temperature culture for 21 days, From the appearance of strains dispersing crude oil and the turbidity of culture solution, the optimal conditions for strains to degrade crude oil were analyzed. That is, the culture medium in some shake flasks is in a turbid state, and the crude oil has no wall-hanging phenomenon and can be completely dispersed in the liquid medium.
[0085] Based on its culture conditions and physical and chemical factors, it can be seen that the strain HNMC 11117 uses inorganic salt medium and inorganic salt medium containing 1% yeast extract as the degradation medium under the conditions of pH 7.0, 55°C, and 1.0% NaCl content. The appa...
Embodiment 3
[0091] Embodiment 3 compares with normal temperature bacterial strain crude oil degradation performance
[0092] In the present invention, with less than C 16 The liquid hydrocarbons are the only carbon source, and the basic medium is screened by liquid shake flasks. After a period of cultivation, the OD value is used to measure the final growth of the bacteria by inserting the same amount of bacteria, so as to compare with normal temperature. The growth difference between strain SHY-33 and strain HNMC 11117 was used to determine the difference in crude oil degradation performance. Liquid alkanes are n-hexane, n-octane, n-decane, dodecane, tetradecane, and hexadecane.
[0093] The strain was activated and cultured for 12 hours at the optimum temperature. Before the experiment, filter the liquid alkane with a 0.22 μm filter membrane, add 2% into the 50mL liquid shake flask screening basal medium after high temperature sterilization, and then collect the activated bacterial ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com