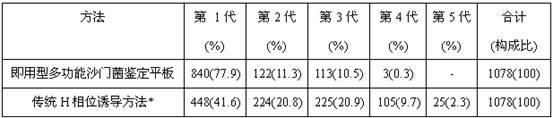
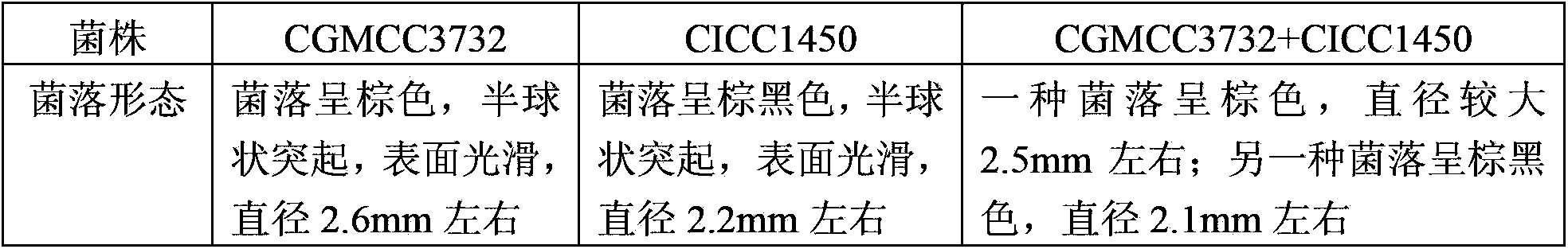
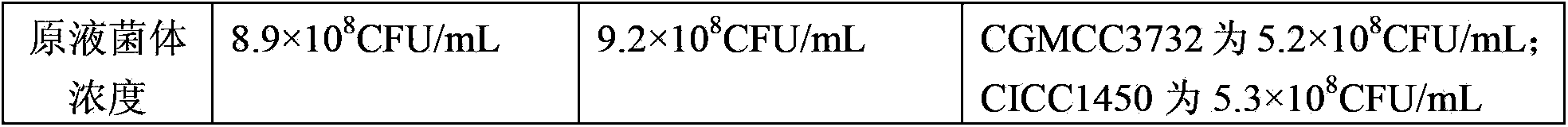Patents
Literature
78 results about "Colony morphology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
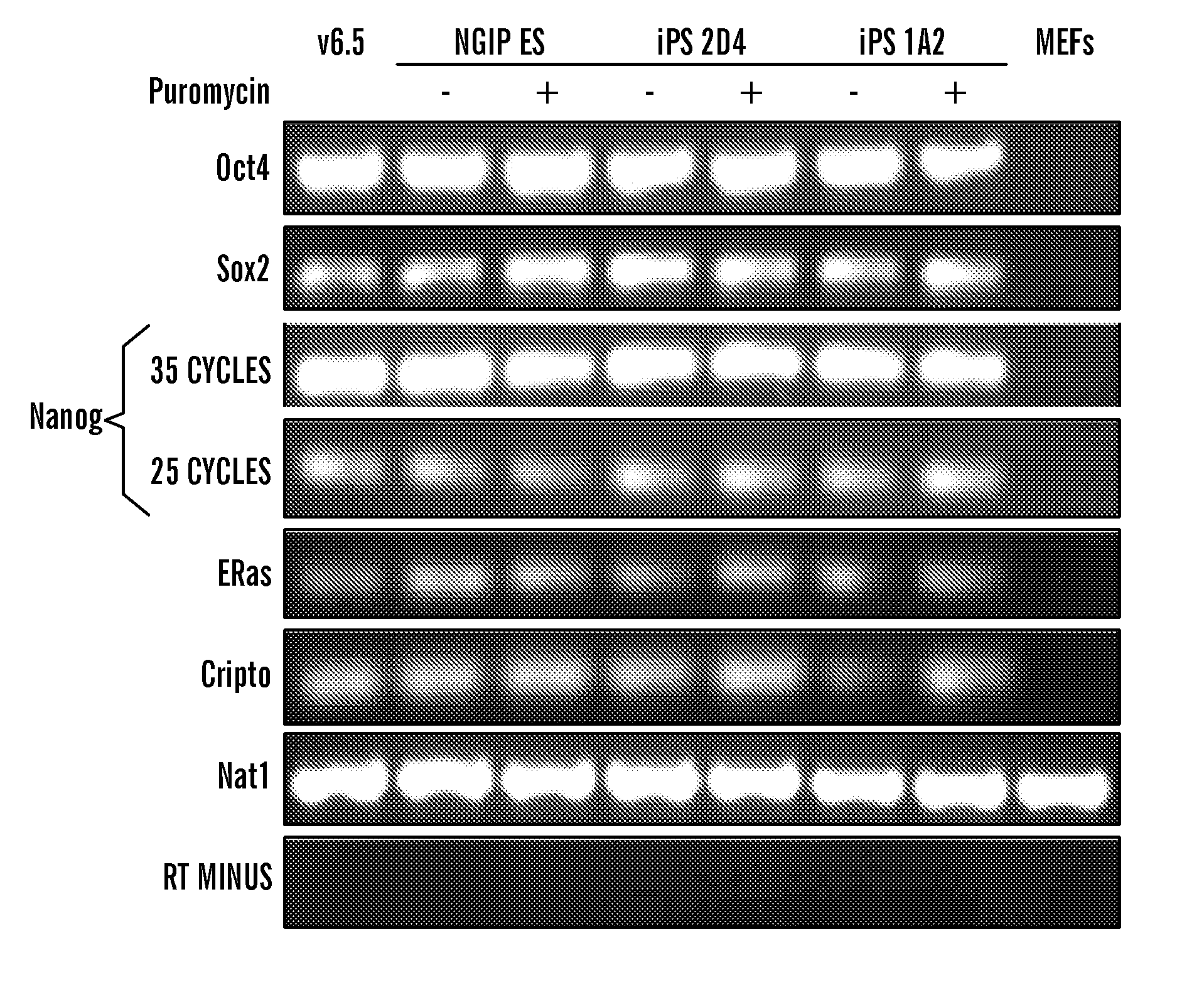
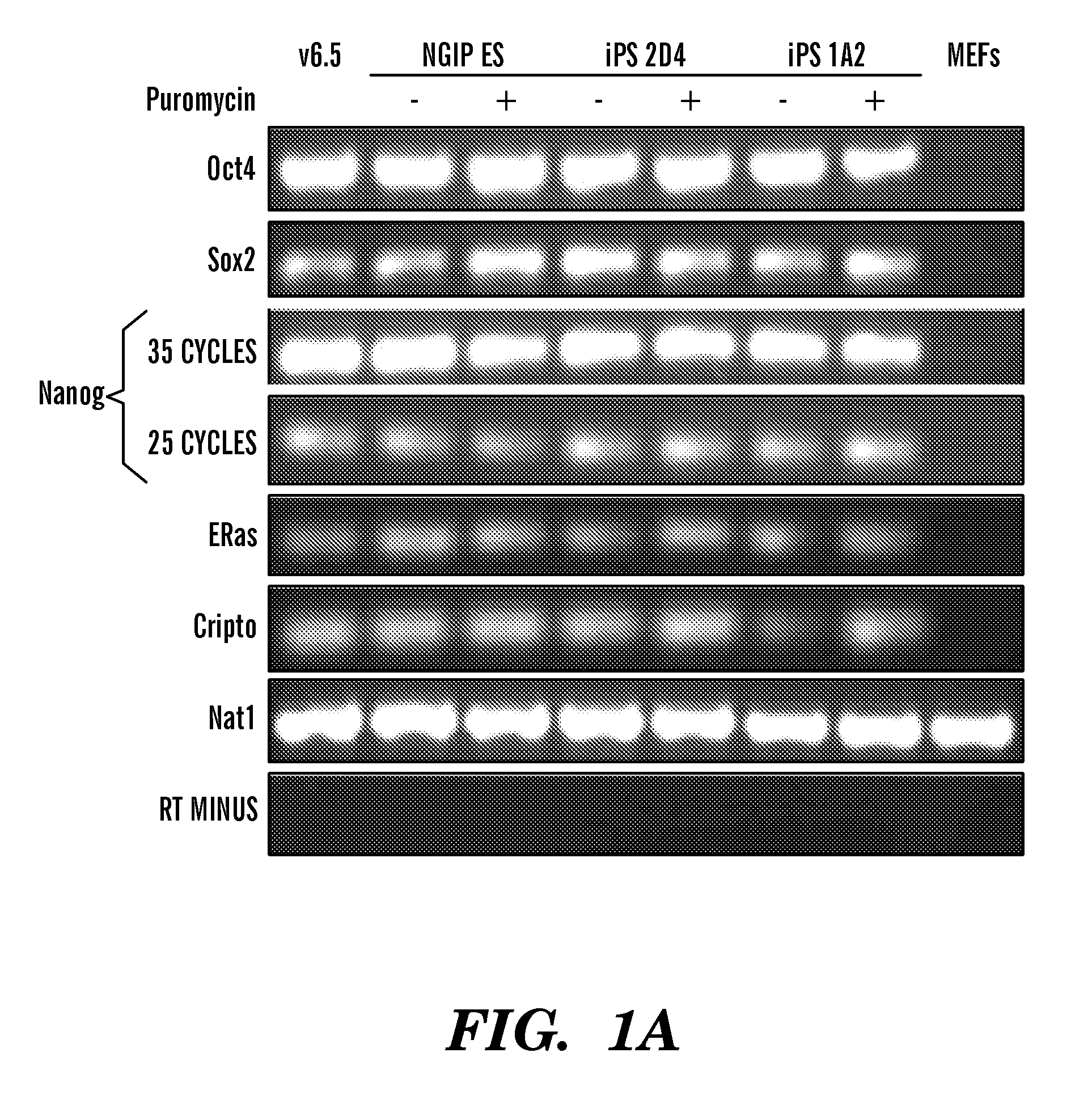
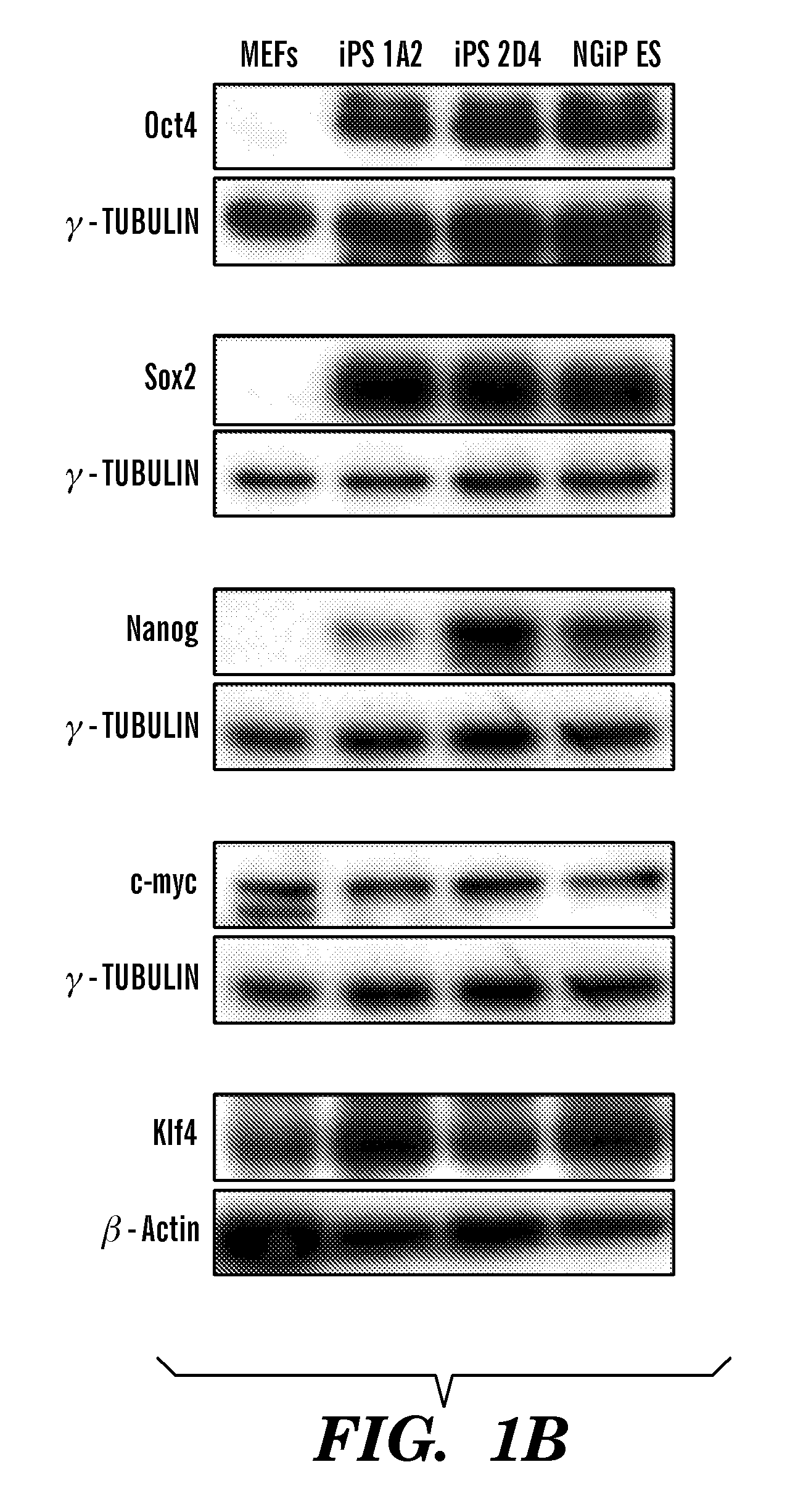
Determining colony morphology is important to characterize a bacterial colony in cultures in terms of shape, color, edge, and elevation. It is usually done by observing the colony with the unaided eye (i.e. not necessarily through microscopy). Colony morphology is one of the means in identifying bacterial species.
Methods of generating pluripotent cells from somatic cells
InactiveUS20100184051A1Long maintenance periodPromote recoveryGenetically modified cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementColony morphologyX chromosome
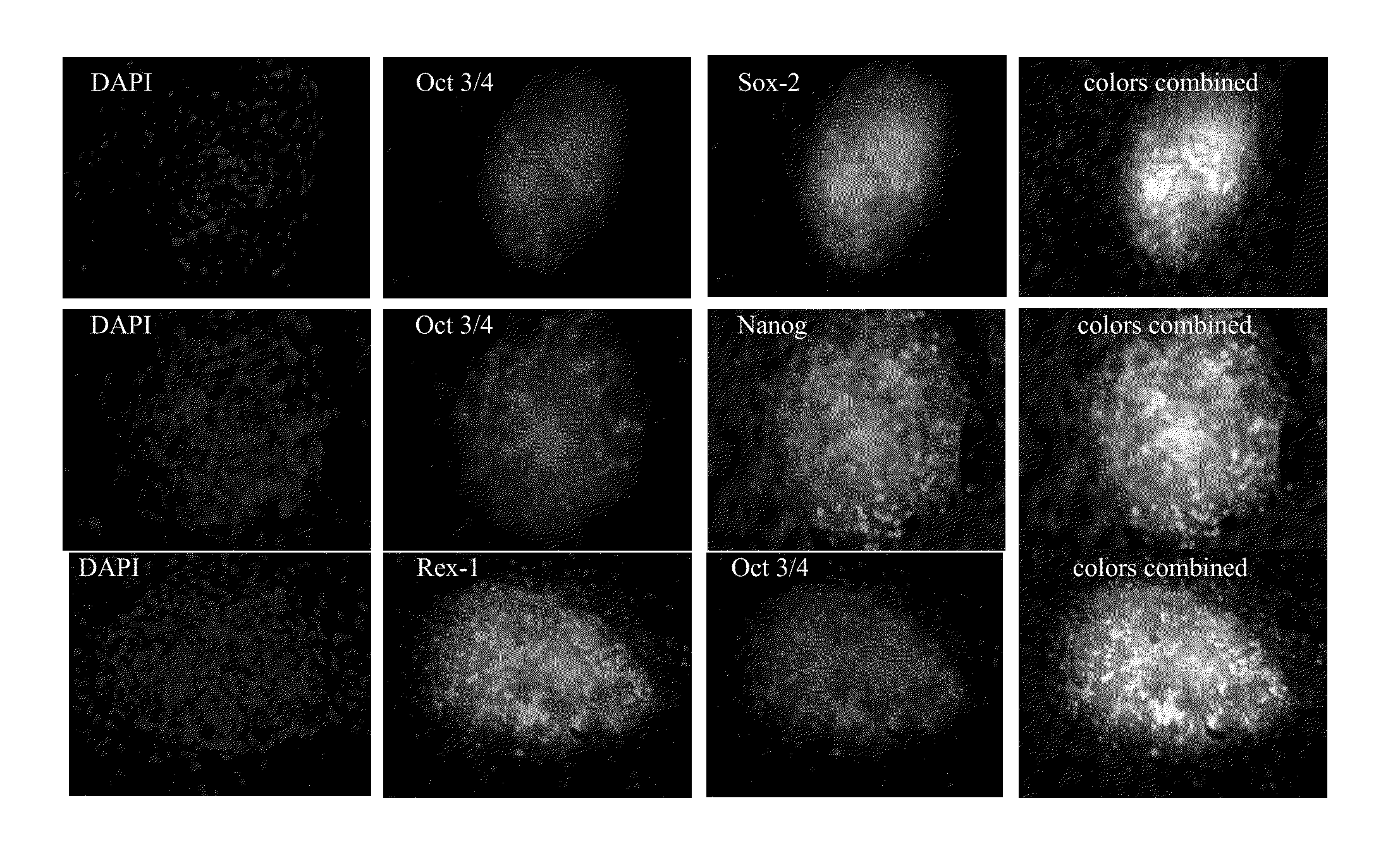
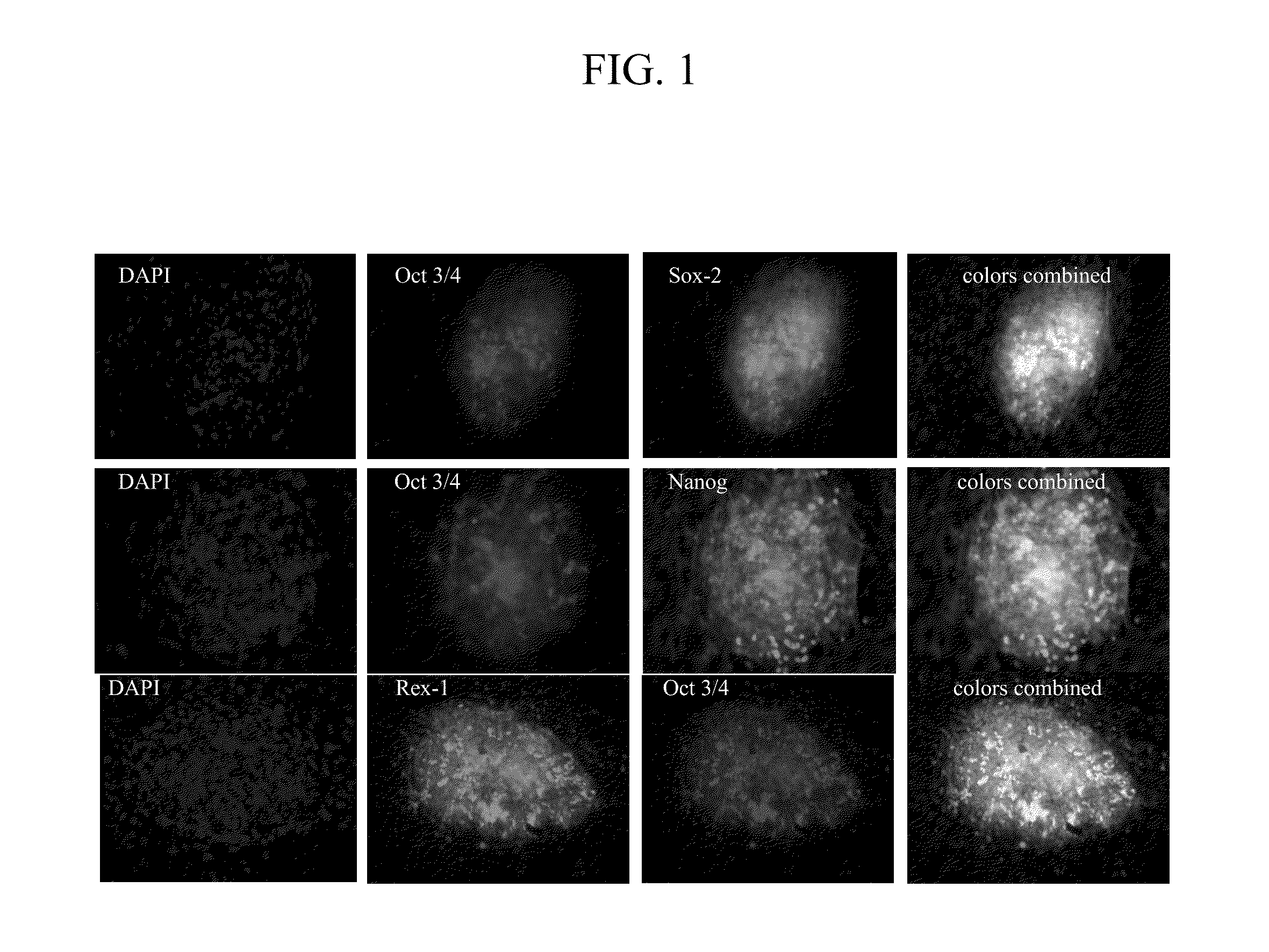
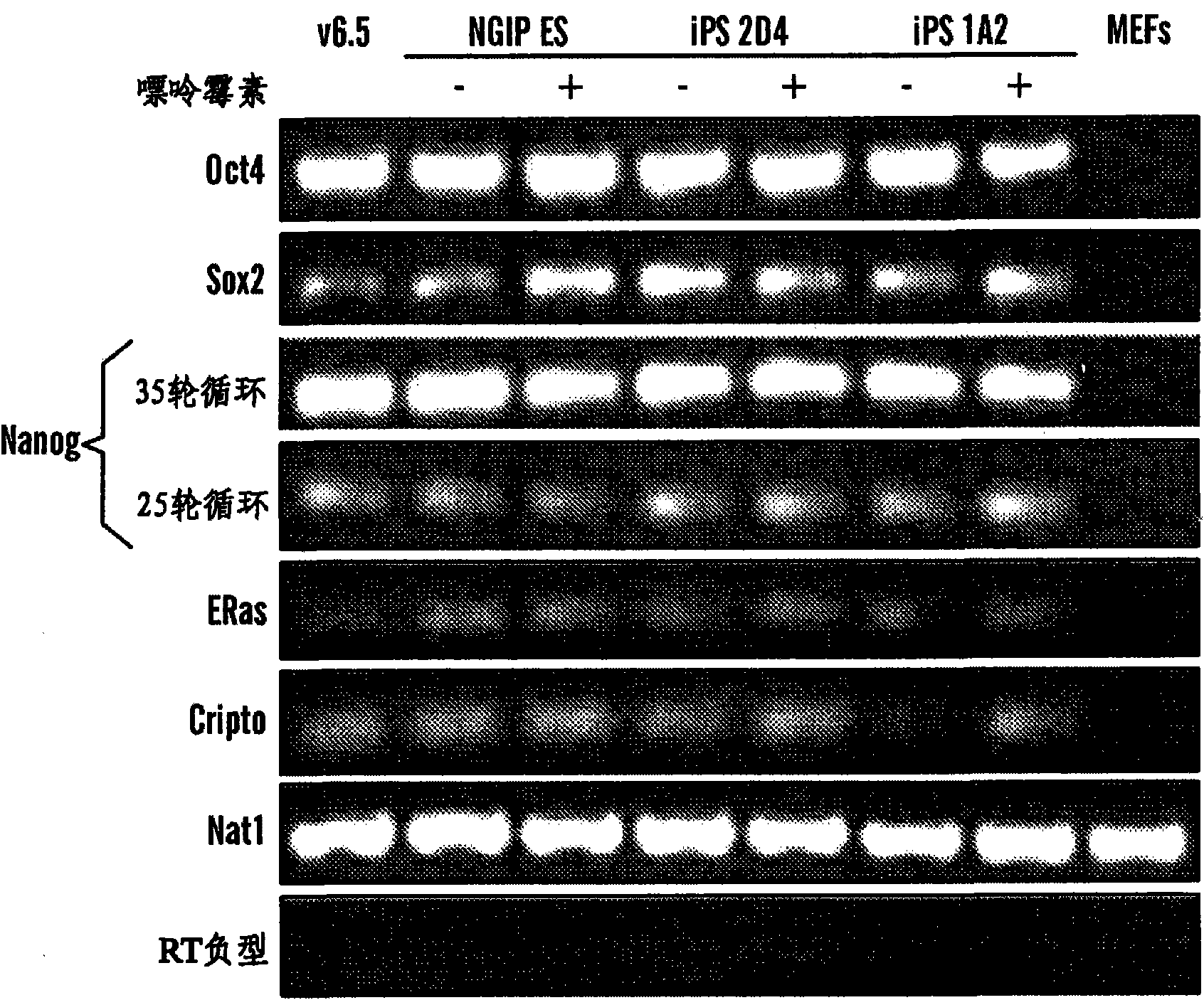
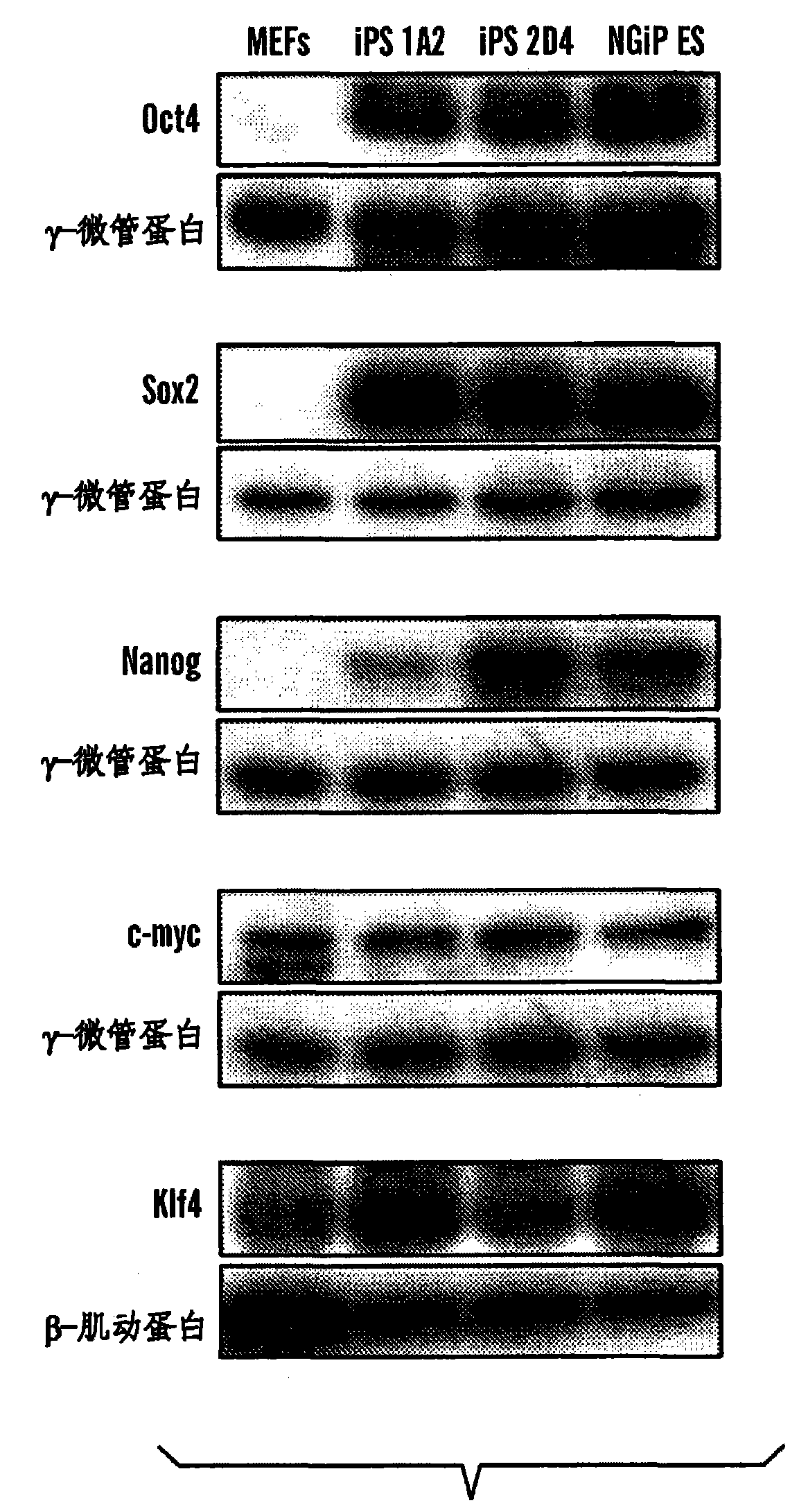
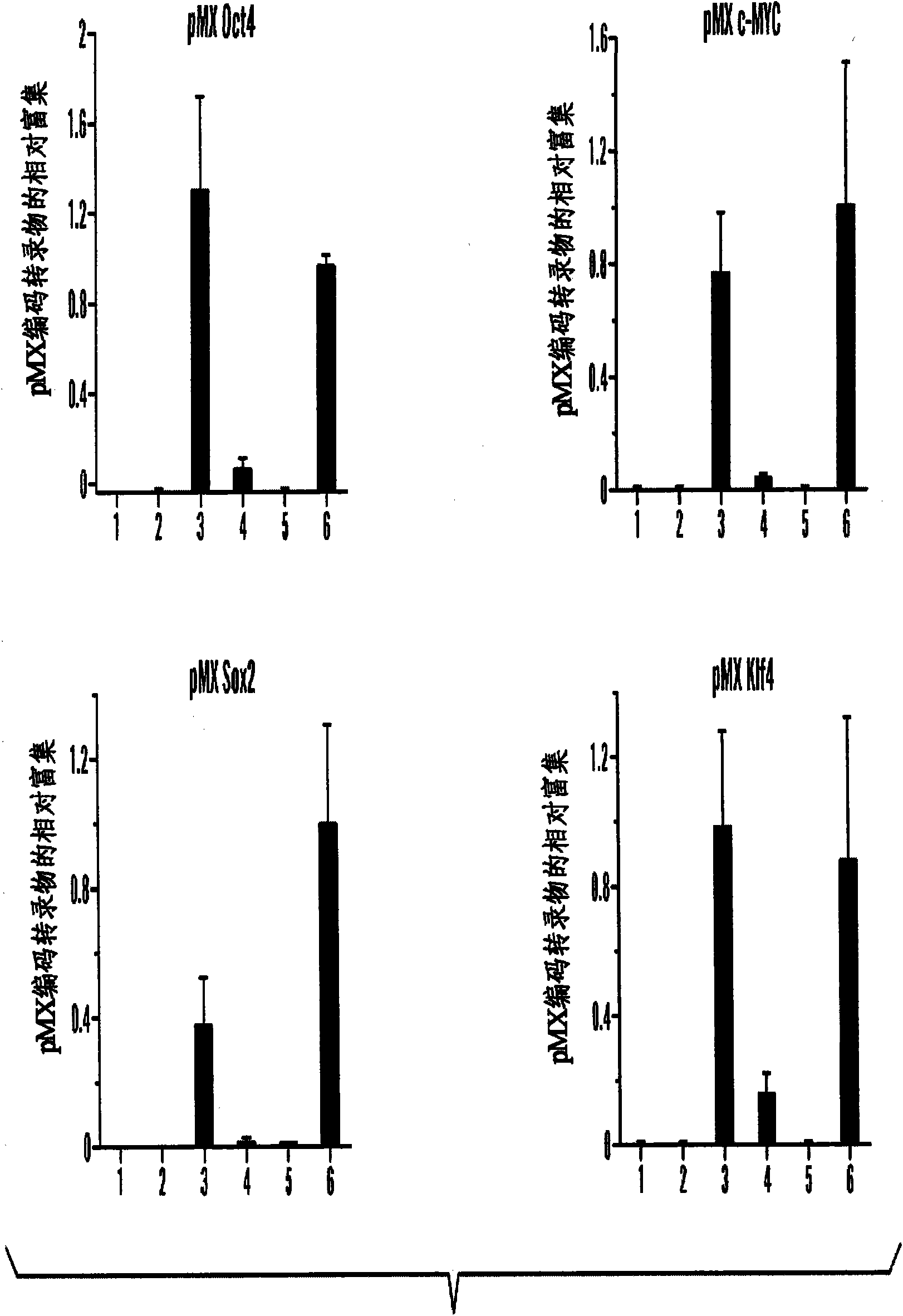
Disclosed herein are methods to select for the generation of mouse and human pluripotent stem cells during developmental reprogramming. The methods described herein relate to the selection of induced pluripotent stem cells, i.e., pluripotent stem cells generated or induced from differentiated cells without a requirement for genetic selection. Described herein are particular embodiments for selection of reprogrammed cells based on 1) colony morphology, or 2) X chromosome reactivation in female cells.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
Preparation method for Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HRH 317 and antibacterial substances thereof
InactiveCN103589655AHigh antibacterial activityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyColony morphology
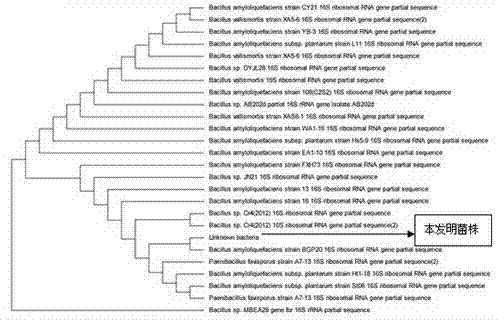
The Bacillus amyloliquefaciens HRH 317 strain separated and screened from soil is preserved on March 15th, 2013, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 7314. The strain is cultured in beef extract-peptone medium, The thalli form a large number of spores, the thalli are rod-shaped before the spores are formed, are arranged individually or in a chain, and are Gram-positive. After cluture for 3 days, the bacterial colonies are milk-white with a diameter of about 6.75mm and with wrinkles on the surfaces, have non-transparent optical characteristic, has projections and are rounded, and the edges are undulant or petaloid. During liquid standing culture, mycoderm is generated. After homology comparison with the 16SrDNA gene sequence of known strains, the homology with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens reaches 99%-100%. The phylogenetic tree of the 16 SrDNA sequence shows that the strain has the highest similarity with Bacillus amyloliquefaciens strain BGP20. After physiological and biochemical identification, the strain is identified as Bacillus amyloliquefaciens.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Bacillus cereus producing keratinase and application thereof
PendingCN107868762APromote degradationStable enzyme productionBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffMicroorganismBacillus cereus
The invention belongs to the field of microorganism, particularly relates to ((i) bacillus cereus ( / i)) Y-15 for efficiently degrading feather keratin, and further relates to application of the ((i) bacillus cereus ( / i)) Y-15. The ((i) bacillus cereus ( / i)) Y-15 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center in June 6, 2017, with the culture preservation number being CGMCCNO. 14221; the colonial morphology on a milk screening plate is as follows: bacterial colony is white and circular, the waxiness on the surface is non-transparent, and the edge is wavelike; gram staining shows a positive result, and the thallus is bacilliform. The ((i) bacillus cereus ( / i)) Y-15 screened and cultured has excellent degradation effect on keratin.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Mycoplasma bovis protein gene MbovGdpP and application thereof
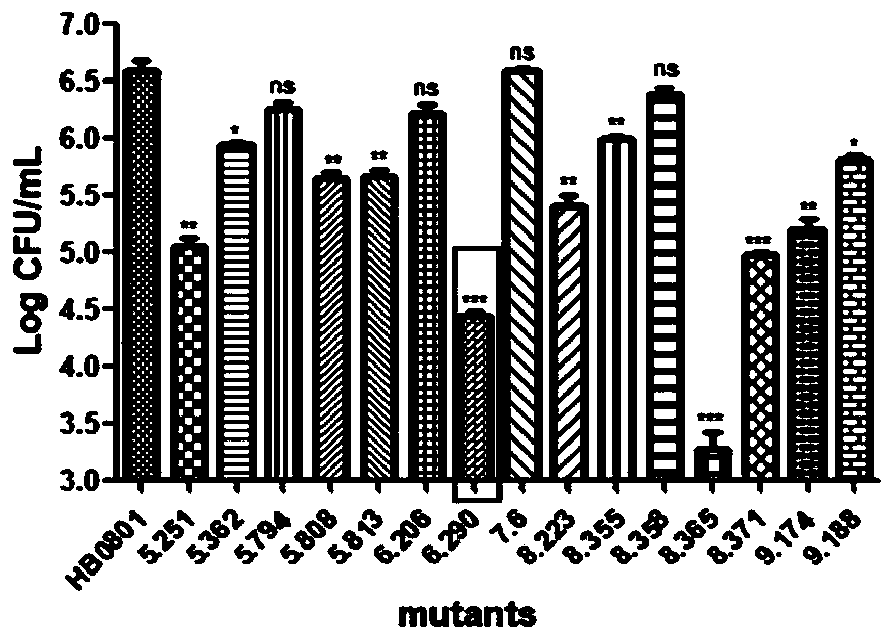
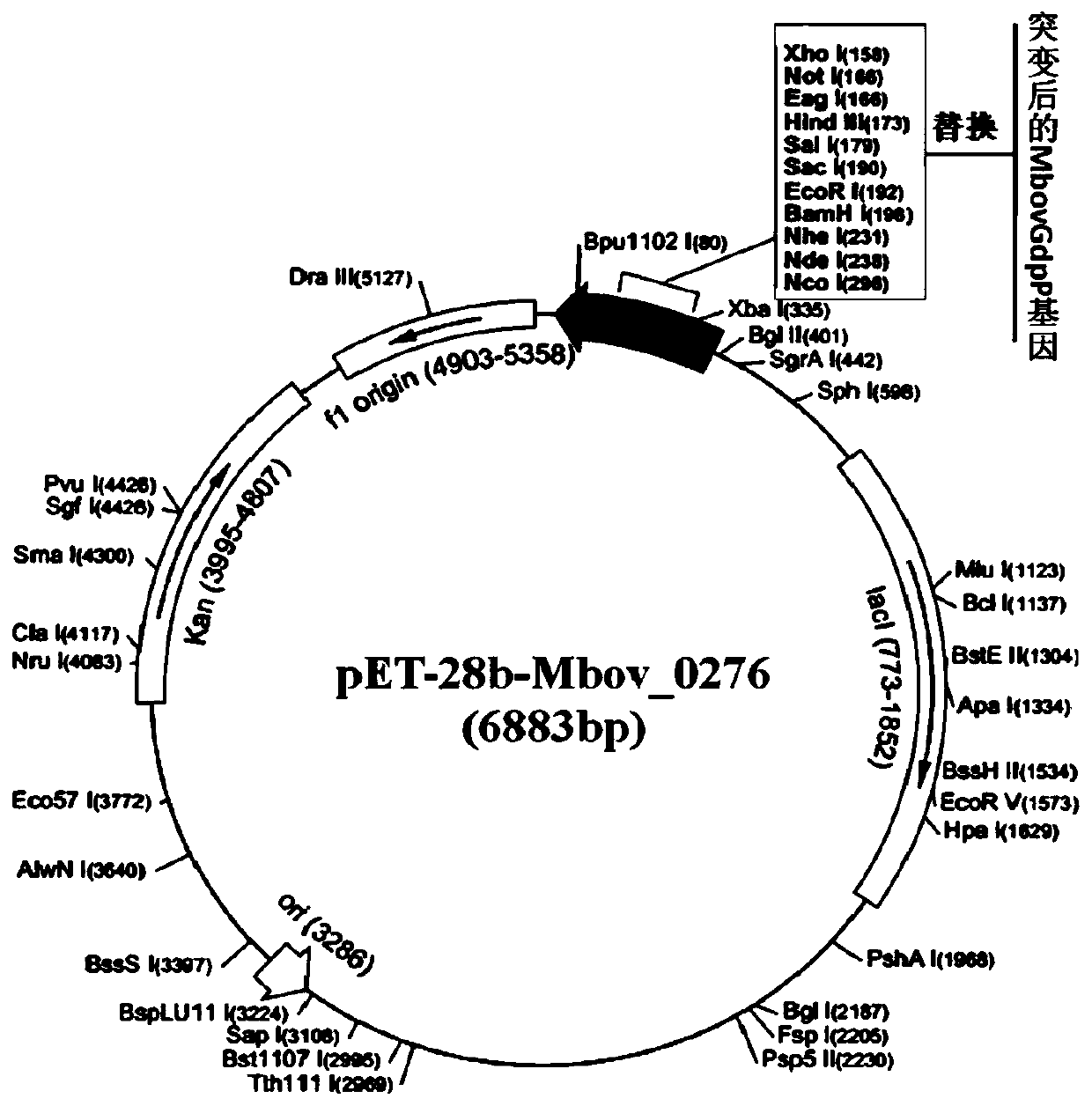
The invention belongs to the technical field of zoonosis prevention, and particularly relates to a mycoplasma bovis protein gene MbovGdpP and application thereof. Mbov_0276 is artificially synthesizedaccording to the mycoplasma bovis HB0801 genome sequence. An Mbov_0276 gene is modified for the preference of escherichia coli for codons; mycoplasma bovis tryptophan codons UGA are mutated into codons UGG for encoding tryptophan in escherichia coli to obtain escherichia coli recombinant proteins rMbovGdpP. The Mbov_0276 gene has the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1, and the ended proteinhas the sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. A mutant strain T6.290 has the growth defect phenotype, has the small colony morphology on a PPLO culture medium, reduces the adhesion of EBL cells and improvesthe sensitivity to saline ions. The mutant strain can be expected to be applied in the mycoplasma bovis pathogenesis and the preparation of immunosuppressive medicines.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from normal human mammary epithelial cells
ActiveUS20160145642A1Genetically modified cellsEpidermal cells/skin cellsColony morphologyGlandular Epithelial Cells
Described herein are reprogramming techniques allowing for production of mammary-derived iPSCs (“m-iPSCs”). The m-iPSCs described herein exhibit all the hallmarks of stem cell identity including round cluster, bright colony morphology, clonal expansion, and pluripotent marker expression (alkaline phosphatase expression, Oct-4, nanog, etc.) Further refined techniques allow for generation of m-iPSCs under essentially defined conditions.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Screening method and application of strain for producing 1,3-propanediol
ActiveCN102965323AReduce energy consumptionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSequence analysisWater baths
The invention discloses a screening method and application of a strain for producing 1,3-propanediol, relating to 1,3-propanediol. A screening method and application of clostridium butyricum Gen160 and the strain screening method for producing 1,3-propanediol with waste glycerol are provided. The screening method comprises the steps as follows: adding collected samples to cabbage juice, putting the samples into a water bath after an enrichment culture to kill nonsporeforms, transferring the samples to a clostridium multiplication liquid medium, carrying out an anaerobic culture and then putting the samples into the water bath again, transferring the samples to a fermentation medium, carrying out a high performance liquid chromatograph to analyze fermentation products after the anaerobic selective enrichment culture and selecting positive strains capable of producing 1,3-propanediol; separating out single colonies by a high layer agar column method; carrying out an aerobiotic culture and the anaerobic culture to remove facultative anaerobes and to obtain strict anaerobes, analyzing the fermentation products and selecting the strains to carry out 16S rDNA (ribosomal deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence analysis and identification, wherein the strains are capable of producing 1,3-propanediol and the cultural characteristics and the colonial morphologies confirm to the cultural characteristics of the clostridium butyricum consistently.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
High-throughput screening method for grape wine brewing microorganisms
ActiveCN104911114AQuick filterAccurate and Easy ScreeningFungiBacteriaColony morphologyBiotechnology
The present invention discloses a high-throughput screening method for grape wine brewing microorganisms. According to the method, high-throughput screening equipment is utilized, strains having specific colony morphology or brewing properties are subjected to primary screening on a selective solid culture medium, the obtained strains after the primary screening are subjected to micro fermentation rescreening by using a micro-pore plate, the re-screened strains are subjected to micro-fermentation, the obtained fermentation broth is subjected to metabolite analysis and multivariate statistical analysis, the re-screened strains are subjected to metabolic framework collecting grouping, the strains in different groups are subjected to small test fermentation, and physical and chemical tests and sensory evaluation are used to determine the microorganism strain suitable for the grape wine brewing. With the method of the present invention, the grape wine brewing microorganisms suitable for the specific production plate, the specific grape varieties or the brewing requirements can be quickly, accurately and easily screened so as to substantially reduce the experimental workload, save by more than or equal to 70% of the manpower, and reduce the development cycle to 4-6 months from 1-3 years.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
Medium thermophilic bacillus licheniformis strain and application thereof in treatment on high-temperature oil-bearing wastewater
InactiveCN105670956AImprove processing efficiencyThe treatment effect is obviousBacteriaHydrolasesBacillus licheniformisStaining
The invention discloses a medium thermophilic bacillus licheniformis strain and an application thereof in treatment on high-temperature oil-bearing wastewater. In the invention, a bacillus licheniformis strain is separated from petroleum-contaminated soil from Taizhou oil recovery plant of Sinopec Group Huadong Branch. The bacillus licheniformis strain is 4-5 mm in colony diameter. The colony has a round appearance with tidy edges, has a moist and smooth surface and has a slight-yellow color. The bacteria are in the shape of short bars under an oil microscopy and belong to gram-positive bacteria, have central spores and have no motility. The bacteria are 40-60 DEG C in growth temperature, preferably 50 DEG C, and is positive in both a V-P test and safranine staining and produces high temperature resistant lipase. A fermentation liquid can hydrolyte starch and produce acid. 16s DNA verification proves the bacteria belong to bacillus licheniformis. The invention also discloses the application of the medium thermophilic bacillus licheniformis strain in treatment on the high-temperature oil-bearing wastewater. A test proves the bacillus licheniformis strain can degrade petroleum hydrocarbons at high effect, can reduce energy waste when being used for treating the high-temperature oil-bearing wastewater (45-60 DEG C), and meanwhile reduces environment pollution due to volatilization of aromatic hydrocarbon during a cooling process.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Low temperature resistance straw mushroom bacterial and breeding method thereof
ActiveCN103430855AIncrease productionQuality improvementFungi productsLichen productsColony morphologyAgricultural science
The invention relates to low temperature resistance straw mushroom bacterial and a breeding method thereof, wherein starting bacterial library construction, straw mushroom protoplast preparation and mutagenesis, mutation bacterial library construction, and straw mushroom protoplast inactivation and fusion are performed to finally screen rearrangement bacterial with characteristics of low temperature resistance maintaining, no significant growth speed change, no significant colony morphology change and no significant color change to obtain the low temperature resistance bacterial, wherein the biological preservation number is CCTCC NO:M2013207. The low temperature resistance straw mushroom has the following characteristics that: normal fruiting can be achieved, genetic stability is good, mycelium has vitality after storing for 42 h at a temperature of 0 DEG C, a fruiting body can be stored for 28 h at a temperature of 10 DEG C, low temperature resistance of the straw mushroom fruiting body is substantially increased, and the difficult problem that the existing straw mushroom fruiting body can not subjected to low temperature preservation is solved so as to substantially increase a yield and quality of the straw mushroom, effectively expand the straw mushroom planting season, and improve economic benefits.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
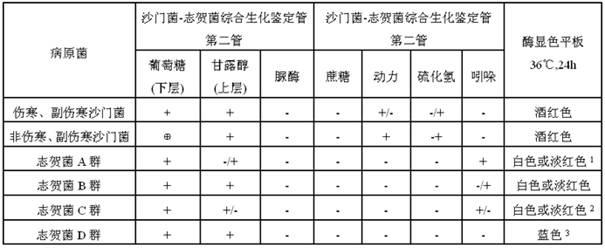
Kit for synchronously separating and identifying salmonella and shigella as well as preparation and application
InactiveCN102031281AImprove timelinessImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyColony morphology
The invention relates to a method for synchronously separating and identifying salmonella and shigella in enteric pathogenic bacteria, which mainly solves the technical problems of high detection-missing rate, complicated identification step, high cost and unintuitive screening result in the existing method for separating the salmonella and the shigella. The kit comprises: 1) a TSB (Trypticase Soy Broth) serving as an universal-type non-selective proliferous liquid; 2) a 10-folds concentrated TSB serving as a 10-folds concentrated universal-type non-selective proliferous liquid; 3) a selenite brilliant green-sulfanilamide proliferous liquid serving as a salmonella proliferous liquid; 4) a shigella proliferous liquid; 5) a xylose lysine deoxycholate agar plate; 6) a salmonella chromogenic agar plate; 7) a salmonella-shigella comprehensive biochemical identification tube comprising a first test tube and a second test tube; 8) a hydrogen sulphide filter paper strip; and 9) an indole filter paper strip. In the invention, typical colonial morphology corresponding to the growth of a selective isolation medium, simple biochemistry and reaction combination test of a specific enzyme and a substrate are adopted to identify two kinds of enteric pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Method for brewing soybean sauce by adding halotolerant bacteria to reduce content of free tyrosine in sauce mash
ActiveCN111423988AAvoid the risk of white spotsReduce contentFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyColony morphology
The invention provides a method for brewing soybean sauce by adding halotolerant bacteria to reduce the content of free tyrosine in sauce mash, and in particular relates to a method for screening andseparating halotolerant bacteria consuming tyrosine. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) detecting the tyrosine content of sauce mash in different high-salt dilute fermentation tanks, selecting sauce mash of which the content of free tyrosine is most obviously reduced than the content of tyrosine in the initial fermentation stage, separating out a strain from the sauce mash, and culturing the strain by using a high-salt culture medium to obtain a halotolerant bacterium original strain; (2) observing the colony form and the thallus microscopic form of the halotolerant bacteria; (3) performing expanding culture on the halotolerant bacteria original strain to obtain a halotolerant bacterium solution; and (4) inoculating the halotolerant bacterium solution into sauce mash containing high free tyrosine for constant-temperature fermentation, and screening out sauce mash with the free tyrosine content less than 100mg / 100g, wherein halotolerant bacteria corresponding to the used bacterium solution are halotolerant bacteria capable of consuming tyrosine. According to the invention, the tyrosine-consuming halotolerant bacteria are separated out for the soybeanpaste brewing process, so that the amount of tyrosine in the later fermentation stage can be reduced, and the risk of white spots generated in the soybean paste can be reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG MEIWEIXIAN FLAVORING & FOOD
Fusion method for protoplast of Cordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris
InactiveCN103266101AEffective fusion methodIncrease success rateFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyColony morphology
The invention provides a fusion method for protoplast of Cordyceps sinensis and Cordyceps militaris. The method is characterized by performing enzymatic hydrolysis for mycelia cells of the Cordyceps sinensis and the Cordyceps militaris to prepare the protoplast, performing thermal inactivation for the protoplast of the Cordyceps sinensis, performing UV-inactivation for the protoplast of the Cordyceps militaris, using a PEG-mediated chemical fusion method, fusing the protoplast of the Cordyceps sinensis and the Cordyceps militaris, and obtaining the fusion strain through colony morphology, an antagonism test and an RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) integrated verification. The method can effectively fuse the protoplast of the Cordyceps sinensis and the Cordyceps militaris to obtain the new strain as an artificial substitute for the Cordyceps sinensis, thereby providing an effective method for breeding objective strains by protoplast fusion.
Owner:TIANJIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Achromobacter strain with monomethylamine degradation ability and application thereof
ActiveCN107904188AHas the ability to degrade monomethylamineBacteriaWater contaminantsColony morphologyAchromobacter xylosoxidans
The invention discloses an achromobacter strain with monomethylamine degradation ability and application thereof. The name of the strain is Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 which is preserved in theChina Center for Type Culture Collection at Wuhan University, No. 299, Bayi Road, Wuchang District, Wuhan, Hubei Province, China. The preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2017285. The preservation dateis May 24, 2017. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 is Gram-negative and rod-shaped, has a round colony morphology, is light yellow and opaque, and has a smooth surface and a colony diameter of 1-2 mm. The Achromobacter xylosoxidans GDUTAN5 can be applied to environmental remediation for degradation of monomethylamine in the environment and has a high degradation rate. When the substrate concentration is 5 mg / L, the degradation rate can reach 92.3% after 96 h of degradation.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
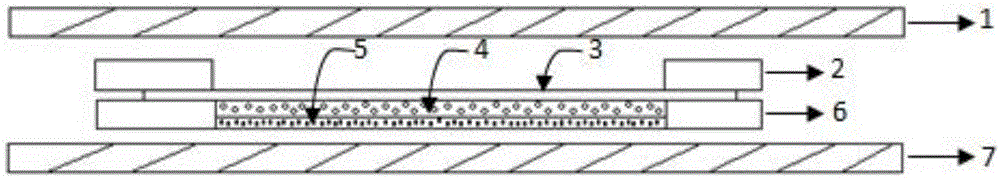
Total bacterial count test piece and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN106520542AEasy to identifyConvenient statisticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNational standardEngineering
The invention relates to a total bacterial count test piece and a manufacturing method thereof. The total bacterial count test piece comprises a carrier structure and further includes two layers of gaskets, an upper layer base material and a lower layer base material. The carrier structure is formed by combining a nonwoven and a filter film. The total bacterial count test piece can contain 500 [mu]l of liquid. The total bacterial count test piece manufactured through the manufacturing method can count red bacterial colonies after a liquid sample is inoculated and cultivation is conducted under the condition of 37 DEG C for 48 h. Through the contrast experiment result of a test piece method and a national standard method, the effects can be known that the experimental bacteria detection conformity of the test piece can reach 105%, and the practical sample total bacterial count detection conformity of the test piece can reach 89% or above. Bacterial colony counting is conducted through the test piece, operation is simple and convenient, bacterial colony forms are good, and results are accurate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
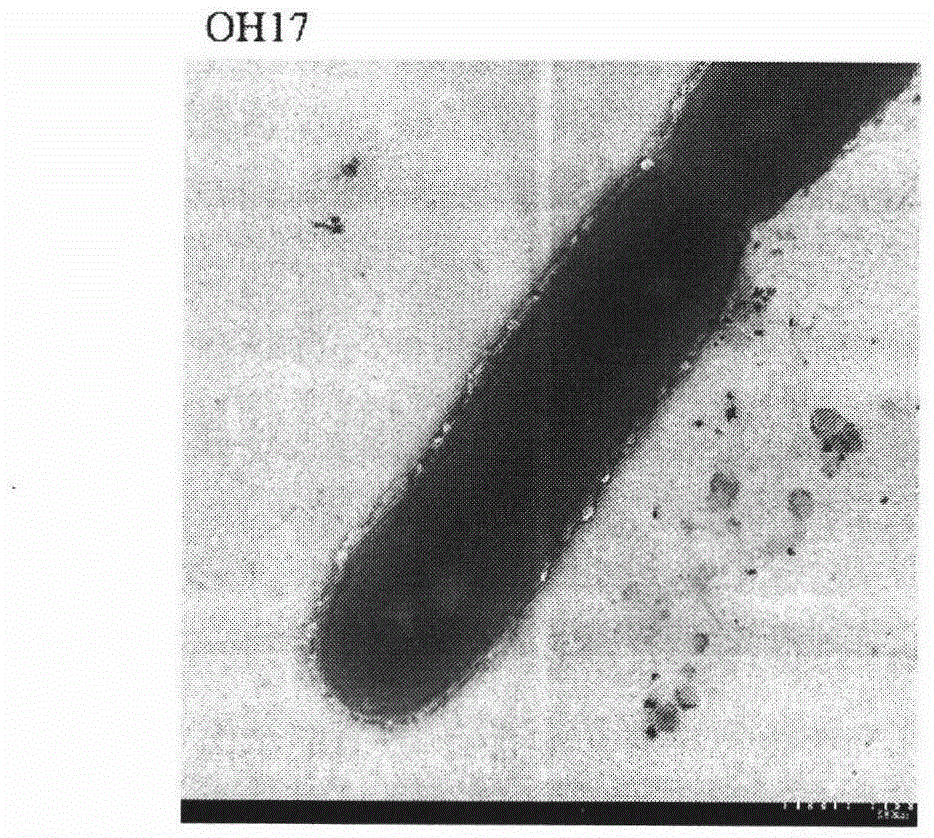
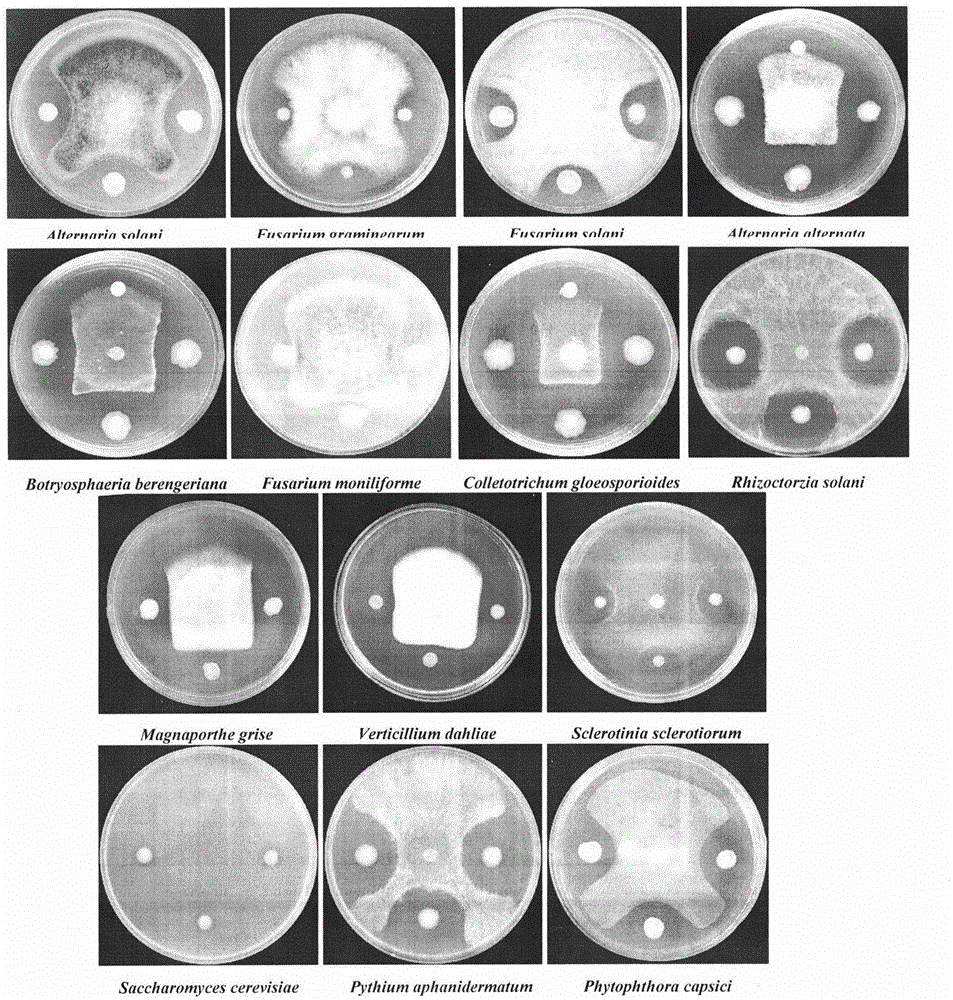
Separation and identification of Lysobacter gummosus OH17 with wide spectrum and high efficiency antagonistic action on plant pathogenic fungi and oomycete
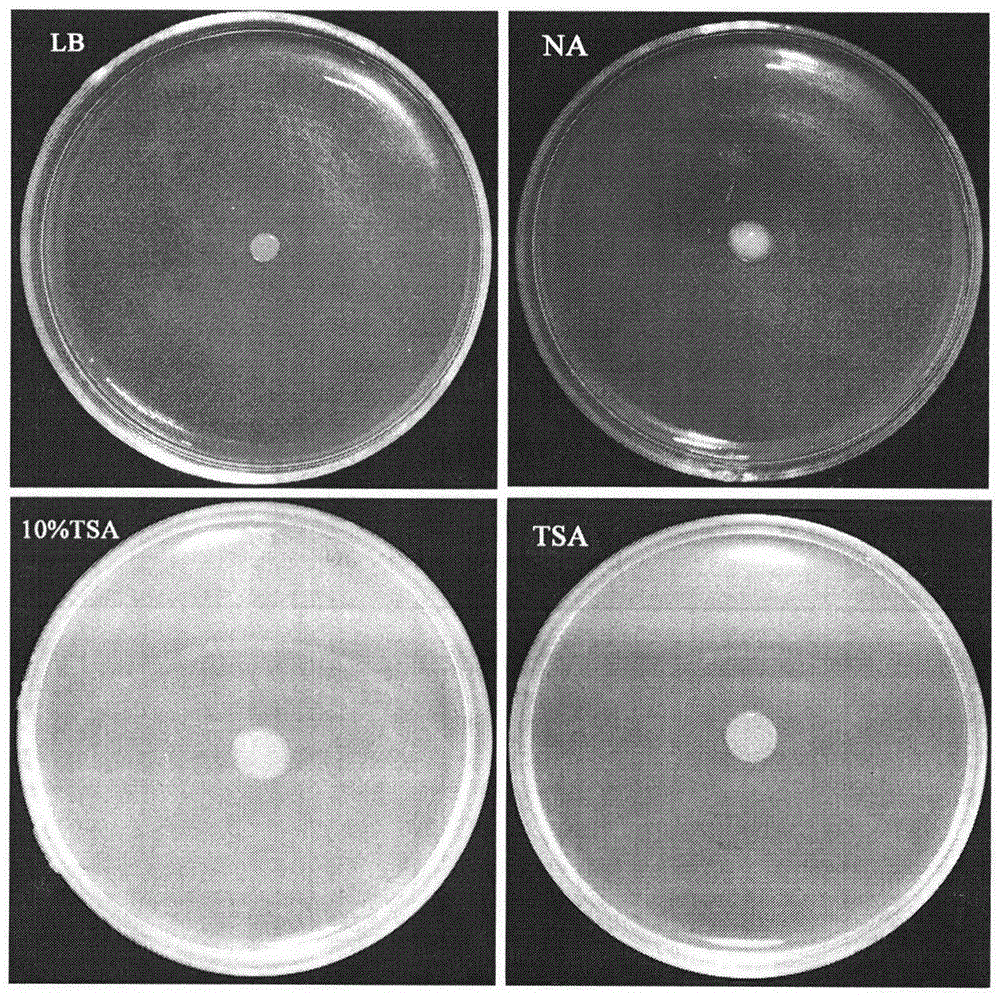
The invention relates to a biocontrol bacterium strain OH17 with good antagonistic activity for plant pathogenic fungi and oomycete. The bacterial strain is characterized in that: the bacterial strain is Lysobacter gummosus, which belongs to Lysobacter of Xanthomonadaceae, with CGMCC No. 8649. The form of the bacterium colony is as follows: the bacterium colony presents different forms on different mediums, for example, the bacterium colony is in light yellow color on a NA medium, the thallus surface is smooth with luster, and the surface is protruding; the bacterium colony is always in yellow color on an LB medium with slow growth; the bacterium colony is white on a 10% TSA medium with flat surface; the bacterium colony does not grow on any TSA medium. The bacterium is gram-negative and in a rod shape without any flagellum. The optimum growth temperature is 28 DEG C. The bacterial strain has a wide spectrum and high efficiency antagonistic action on plant pathogenic fungi and oomycete.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
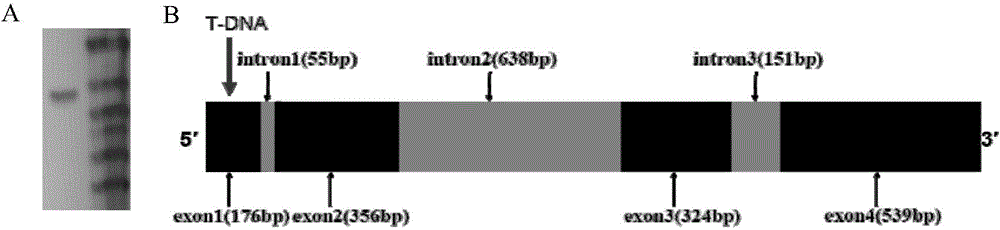
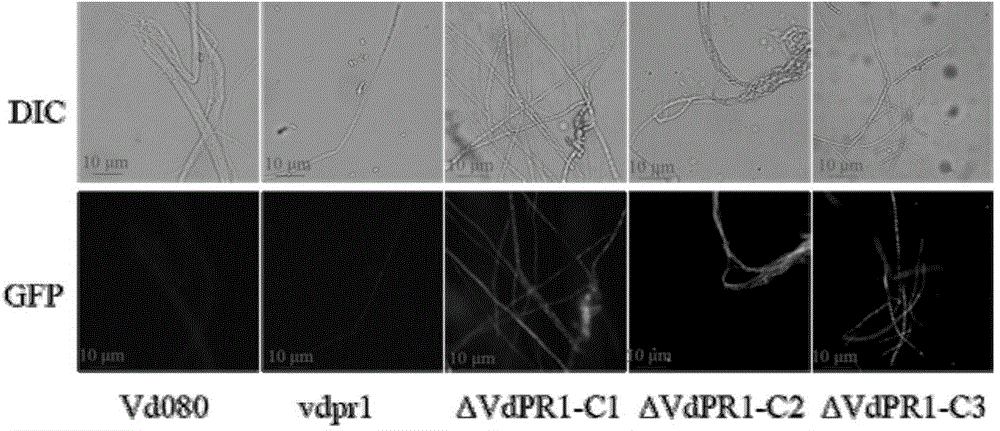
Applications of verticillium dahlia pathogenicity related gene VdPR1 as anti-verticillium dahlia target gene
ActiveCN104818287AReduce outputHigh activityMicroorganism based processesDepsipeptidesColony morphologyVerticillium species
The present invention relates to the field of plant diseases, particularly to applications of verticillium dahlia pathogenicity related gene VdPR1 as the anti-verticillium dahlia target gene. According to the present invention, the colony morphology, the growth rate, the extracellular enzyme activity and the pathogenicity of the knockout mutant [delta]VdPR1 and the complementary mutant [delta]VdPR1-C are determined, and are subjected to compared analysis with various indexes of the wild type, such that it is determined that the VdPR1 gene is the verticillium dahlia pathogenicity related gene, is associated with microsclerotium production and melanin accumulation, and provides promotion effects for activities of cellulase and protease.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Chlorine resistant strain V430 and its screening method
InactiveCN1900272AEfficient degradationBacteriaWater/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The present invention relates to a kind of chlorine tolerant microbe and its screening process. The chlorine tolerant microbe strain is Staphylococcus saprophyticus V430 in the preservation number of CCTCC No. M205145. The Staphylococcus saprophyticus V430 has circular opaque colony shape with lug and smooth edges; spherical single, paired or piled cells of d in 0.6-0.9 micron without flagellum; no motion, no endogeneous spore, gram positive and anaerobic property; and optimal growth pH value of 6.0-7.5 and temperature of 25-45 deg.c. It can survive in high chlorine ion concentration environment and degrade high concentration organic pollutant effectively.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Reprogramming normal and cancerous human cell lines into human induced poluripotent stem cells by co-electroporation with living xenopus laevis frog oocytes
InactiveUS20110143415A1Rapid reprogrammingCell differentiationArtificial cell constructsColony morphologyGene delivery
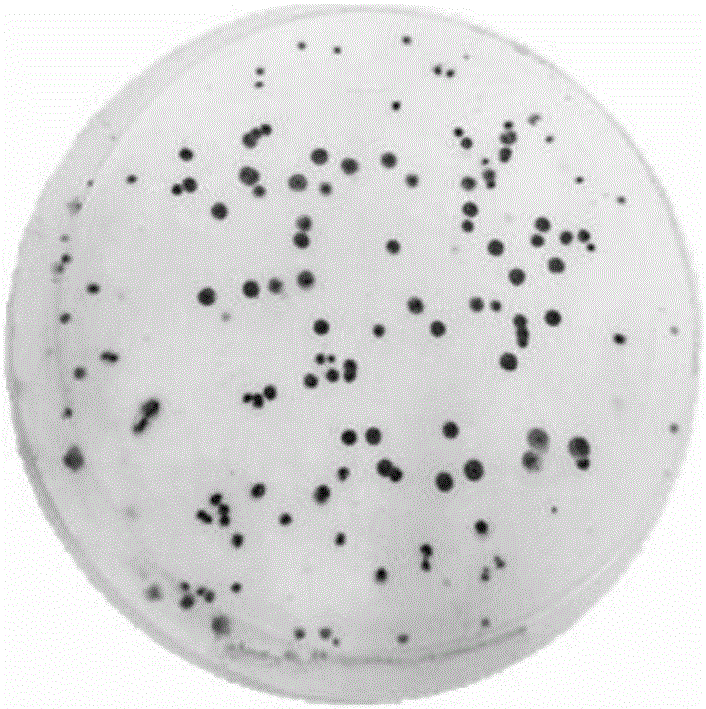
Using electroporation, it is possible to activate the natural reprogramming potential of living Xenopus laevis oocytes and pass it on to donor cells placed with eggs in one electroporation chamber. We demonstrated that co-electroporation at 150 v / cm / 25 μF of mature oocytes with ˜105 cells / ml of suspension of various normal and cancerous human cell lines, such as bone marrow stromal cells, foreskin fibroblasts, pre-adipocytes, CD4+ T-lymphocytes, cheek cells, cervical carcinoma (HeLa) cells and breast adenocarcinoma (MCF-7) cells, reprograms donor cells into iPSc-like cells, which form colonies on irradiated MEF feeders. The iPSc-like cells generated by this study resemble human embryonic stem cells in colony morphology and expression of stem cell-associated transcription factors, including Oct3 / 4, Nanog, SOX-2, Rex-1, TRA-1-60 and SSEA-1. New method obviates the use of retroviral or lentiviral gene delivery vectors and other “non-parental” reprogramming approaches.
Owner:PAYLIAN SERGEI
Methods of generating pluripotent cells from somatic cells
InactiveCN101802172AGenetically modified cellsCell culture active agentsColony morphologyPluripotential stem cell
Disclosed herein are methods to select for the generation of mouse and human pluripotent stem cells during developmental reprogramming. The methods described herein relate to the selection of induced pluripotent stem cells, i.e., pluripotent stem cells generated or induced from differentiated cells without a requirement for genetic selection. Described herein are particular embodiments for selection of reprogrammed cells based on 1) colony morphology, or 2) X chromosome reactivation in female cells.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
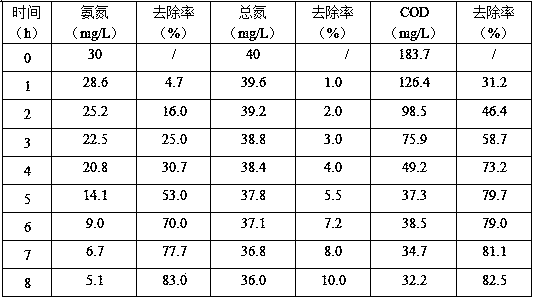
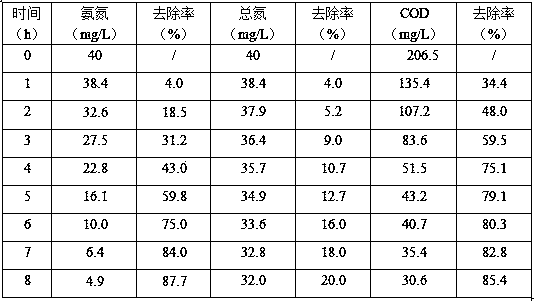
Rhodotorula mucilaginosa for removing total nitrogen in sewage and application of rhodotorula mucilaginosa
ActiveCN111196632AEfficient removalEfficient degradationWater treatment parameter controlFungiColony morphologyRhodotorula
The invention discloses rhodotorula mucilaginosa for removing total nitrogen in sewage and application of the rhodotorula mucilaginosa. The rhodotorula mucilaginosa NBUY-9 is is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection on December 5, 2019, the preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 20191015, the rhodotorula mucilaginosa grows on a YPD flat plate without seawater salinity, the bacterial colony morphology characteristic is orange red, the surface is round, smooth, wet and opaque, the strain can grow in a relatively wide pH range of 2.5 to 9.0, and the optimal growth temperature is 20-30DEG C. The rhodotorula mucilaginosa can be applied to preparation of a total nitrogen removal agent, an ammonia nitrogen removal agent and a COD removal agent in domestic sewage and preparation of anammonia gas degradation agent in industrial waste gas, and has the advantages that ammonia nitrogen, total nitrogen and COD in the sewage can be efficiently removed at the same time, and ammonia gas components in the industrial waste gas can be efficiently degraded.
Owner:湖北宜水生物科技有限公司
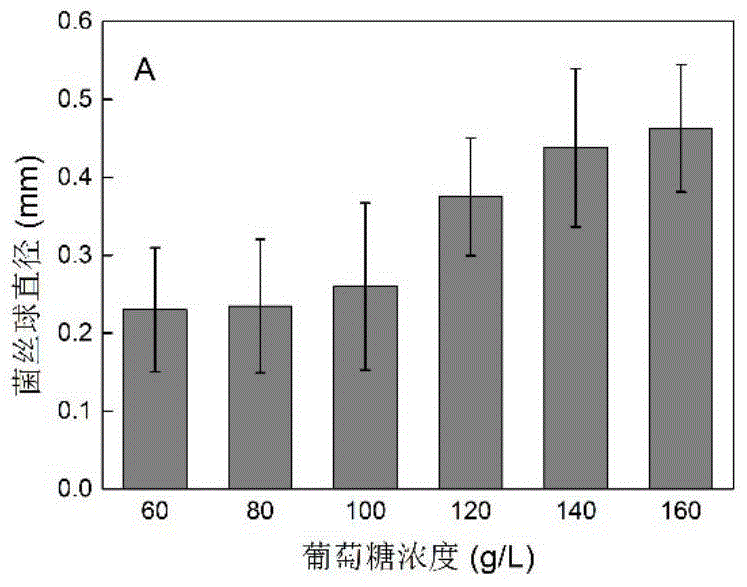
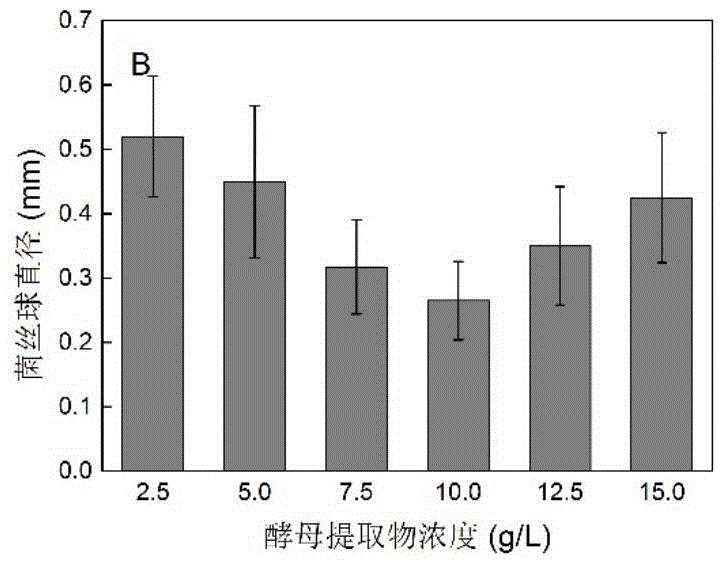
Method for increasing kojic acid yield of Aspergillus oryzae
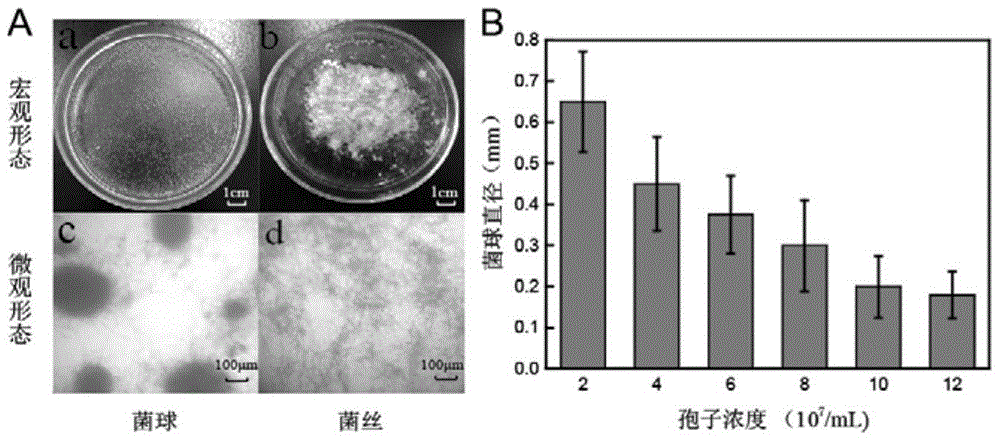
The invention provides a method for increasing kojic acid yield of Aspergillus oryzae, and belongs to the technical field of fermentation engineering. Specifically, the method changes the concentration and inoculation conditions for culturing key components to control a spherical colony morphology of the Aspergillus oryzae (bacteria in the best shape for acid production), thereby increasing the yield of kojic acid. When the mycelial morphology is spherical, A.oryzae has significantly higher acid production than the mycelia, and reaches kojic acid yield up to 15.11g / L. Meanwhile, the mycelial pellet has diameter in the range of 0.25-0.35mm, and the accumulated amount of kojic acid in unit cell is up to 0.778g / g. The method optimizes the concentrations of glucose and yeast extract and concentration of spores in a seed medium, and controls the size of the mycelial pellet, thereby increasing unit cell Kojic acid yield of Aspergillus oryzae. The invention has good application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for screening and immobilizing efficient petroleum hydrocarbon degradation flora
InactiveCN103320346AEasy to transportRepair pollutionBacteriaSeawater treatmentColony morphologyScreening method
The present invention relates to a method for screening and immobilizing efficient petroleum hydrocarbon degradation flora, wherein the method is applicable for offshore petroleum pollution environment remediation. According to the method, a lot of petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacterial are enriched, acclimatized and separated from petroleum pollution sea area sediments, the n (n is more than or equal to 3) strains of the bacterial with strong growth activity, different colony morphologies and different cell morphologies are selected, a petroleum hydrocarbon degradation rate of the single strain of the bacterial is determined, 16SrDNA molecule identification is performed on the bacterial, the n strains of the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacterial are subjected to mixing culture, the (n-1) strains of the bacterial are randomly selected from the n strains of the bacterial, and are combined to form n groups of different combinations to carry out mixing culture, the optimal combination of the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacterial is determined, and the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation flora with the optimal combination is prepared into immobilized bacterial balls to be stored so as to provide a spare use for offshore petroleum pollution environment remediation. The method is an efficient petroleum hydrocarbon degradation flora screening method with characteristics of science, rationality, simplness, feasibility, and meeting of optimal combination principle, wherein the efficient petroleum hydrocarbon degradation flora can be immobilizedly embedded into the ball shape, petroleum pollution impact can be buffered, and petroleum pollution biodegradation efficiency can be increased.
Owner:NATIONAL MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENTRE
Multi-inhibitor stress tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae as well as preparation method and application thereof
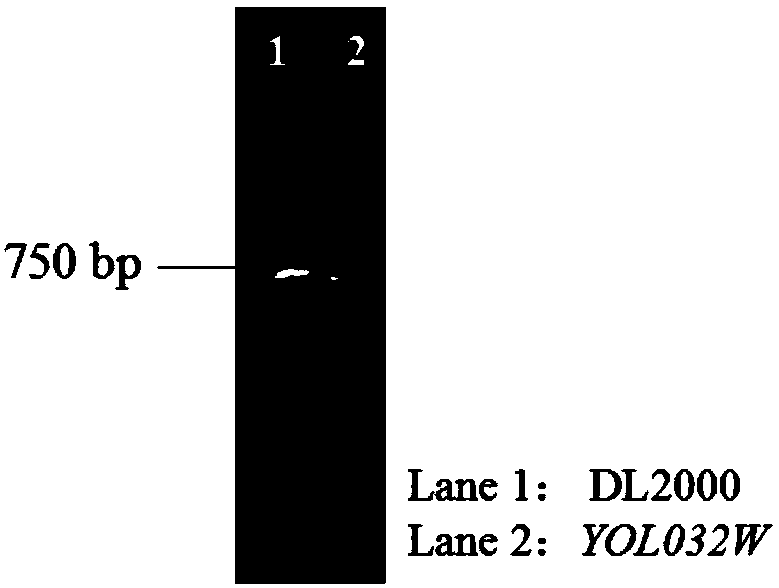
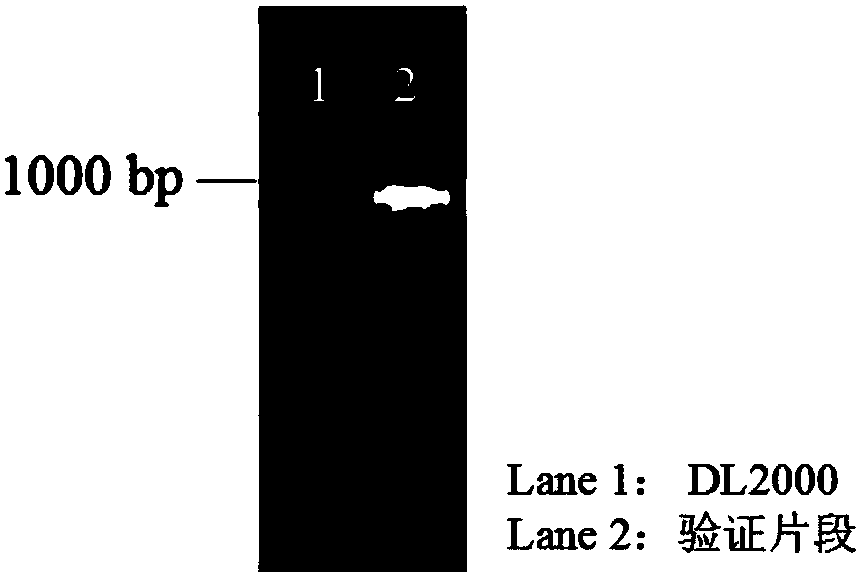
ActiveCN107937297AHigh Ethanol Fermentation EfficiencyPromote growthFungiBiofuelsColony morphologyBacteroides
The invention relates to the field of microbial biotechnology, in particular to a multi-inhibitor stress tolerant saccharomyces cerevisiae as well as a preparation method and application thereof. Themain technical scheme is as follows: the name of the strain is S288C-YOL032W, the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC No.13926, the strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on March 24, 2017; and the strain carries a YOL032W gene with a GenBank accession number of NM_001183286.1. The saccharomyces cerevisiae strain is a unicellular fungus which is generally oval and round. The colony morphology is similar to that of bacteria, but is larger and thicker, and the strain is milky white, and has a wet and sticky surface. The nutrient mode is a heterotrophic facultative anaerobic mode. The strain is free and milky white when growing in a culture medium. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C-YOL032W provided by the invention can have goodgrowth and higher ethanol fermentation performance under the environmental stress condition of containing high-concentration acetic acid, furfural and vanillin respectively.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Apricotskin-skin residue vinegar acetic bacterium as well as separating-purifying method and application method thereof
InactiveCN103173381AImprove alcohol resistanceImprove fermentation performanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyColony morphology
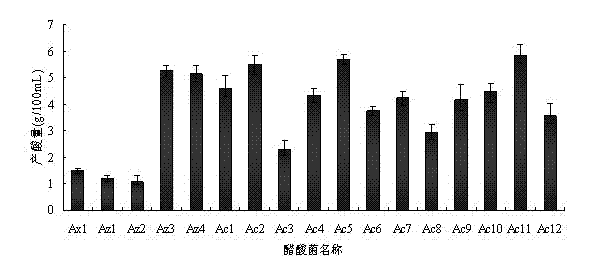
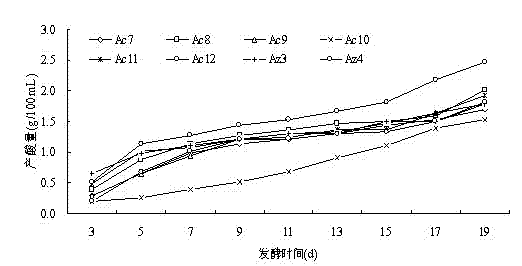
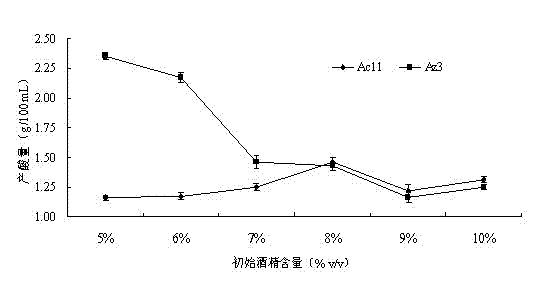
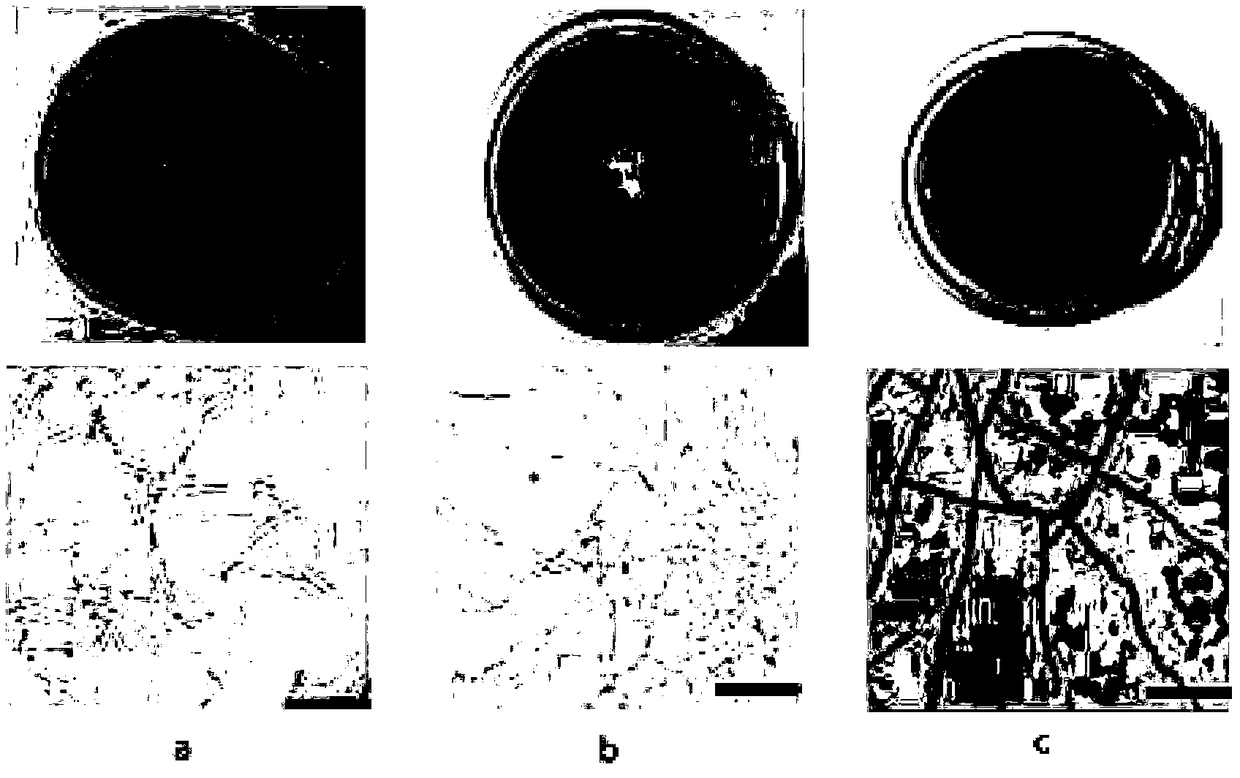
The invention discloses an apricotskin-skin residue vinegar acetic bacterium and a method of utilizing the strain to prepare apricotskin-skin residue vinegar. The name of the strain is bacillus aceticus (acetobacterpomoru strain LMG18848), which belongs to acetomonas and named as Ac11; the bacillus aceticus is stored in a common microorganism center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, wherein the storage number is CGMCC No.6938 and survival demonstration is provided; the apricotskin-skin residue vinegar acetic bacterium is easy to grow in an environment containing alcohol, wherein the colonial morphology is circular bacterial colony which is regular at the edge, smooth on the surface, milk white and bumped; and the diameter of the circular bacterial colony is 0.5mm-1mm; the individual form of the bacterial colony is shaped like a short rod; and the bacterial colony is arranged individually, in pair, in the form of a file or a chain to form ram-negative bacterium. According to the apricotskin-skin residue vinegar acetic bacterium and the method of utilizing the strain to prepare apricotskin-skin residue vinegar disclosed by the invention, acetic bacterial strain growing well is screened out from apricotskin-skin residue natural fermentation liquor and is an acetic strain with good tolerance and excellent fermentation performance. The apricotskin-skin residue vinegar produced by utilizing the strain has a typical apricot flavor.
Owner:HANSHAN NORMAL UNIV
Ginkgo endophytic fungus and application thereof
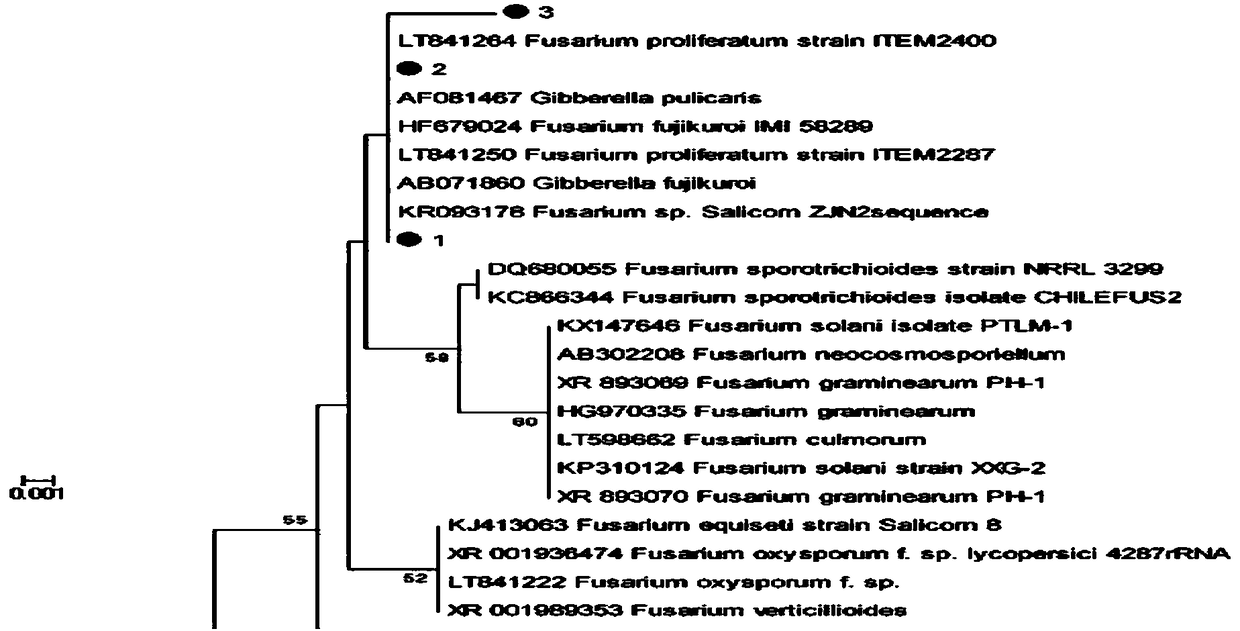
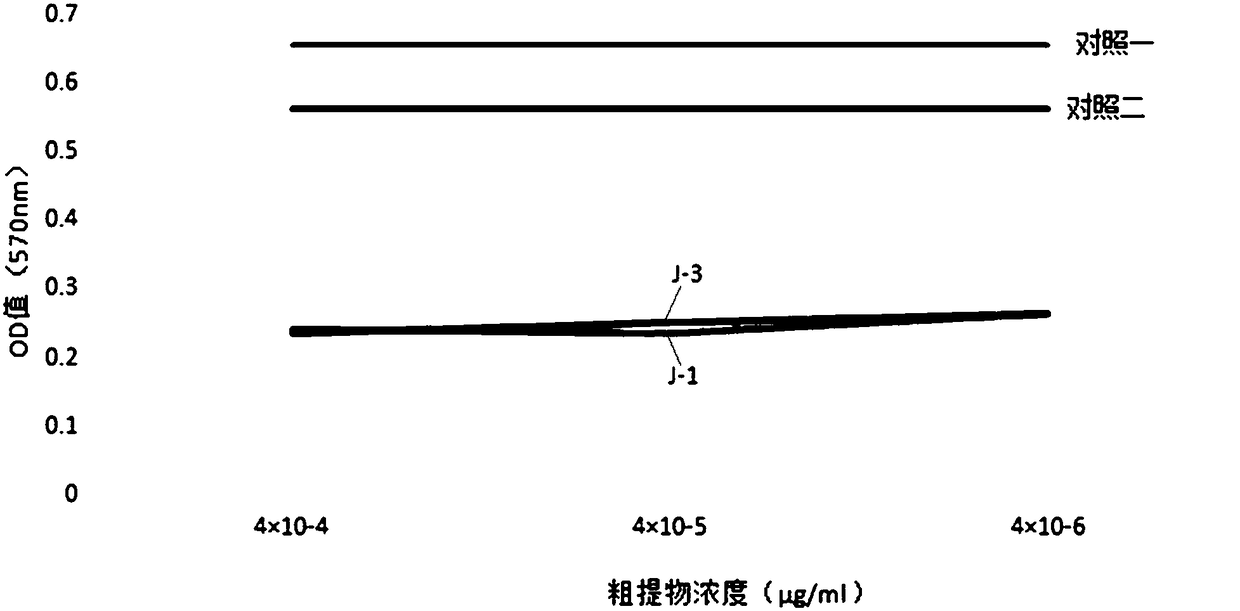
The invention discloses a ginkgo endophytic fungus and an application thereof. The ginkgo endophytic fungus fusarium proliferatum DZHQ1 with anti-tumor activity is separated from ginkgo bark, the species of a strain is judged with a colony morphology and 18sRNA sequencing combination method, the anti-cervical cancer activity of a crude extract of the strain is detected with MTT assay, and finally,secondary metabolites of the strain with inhibition rate being higher than 50% are separated with a semi-preparative HPLC method. Accordingly, compound monomers with anti-tumor activity can be further screened.
Owner:德州汇洋生物科技有限公司
Clostridium welchii and application thereof
InactiveCN110106109AImprove enrichment capacityImprove tolerancePlant growth regulatorsBiocideColony morphologyMicroorganism
The invention provides clostridium welchii. The preservation number of the clostridium welchii is CCTCC NO.M2019204. A microorganism is screened from a domesticated water hyacinth root by an inventor,it is found that the strain has very strong resistance to heavy metals, and the strain is identified as the clostridium welchii by colony morphology, biochemistry and 16S rDNA sequencing analysis. The clostridium welchii can improve the enrichment capacity of water hyacinths to heavy metals including at least one of Cd, Zn, Mn, Ni, Cu and Pb. Meanwhile, IAA and ACC deaminase can be released to promote the growth of the water hyacinths.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
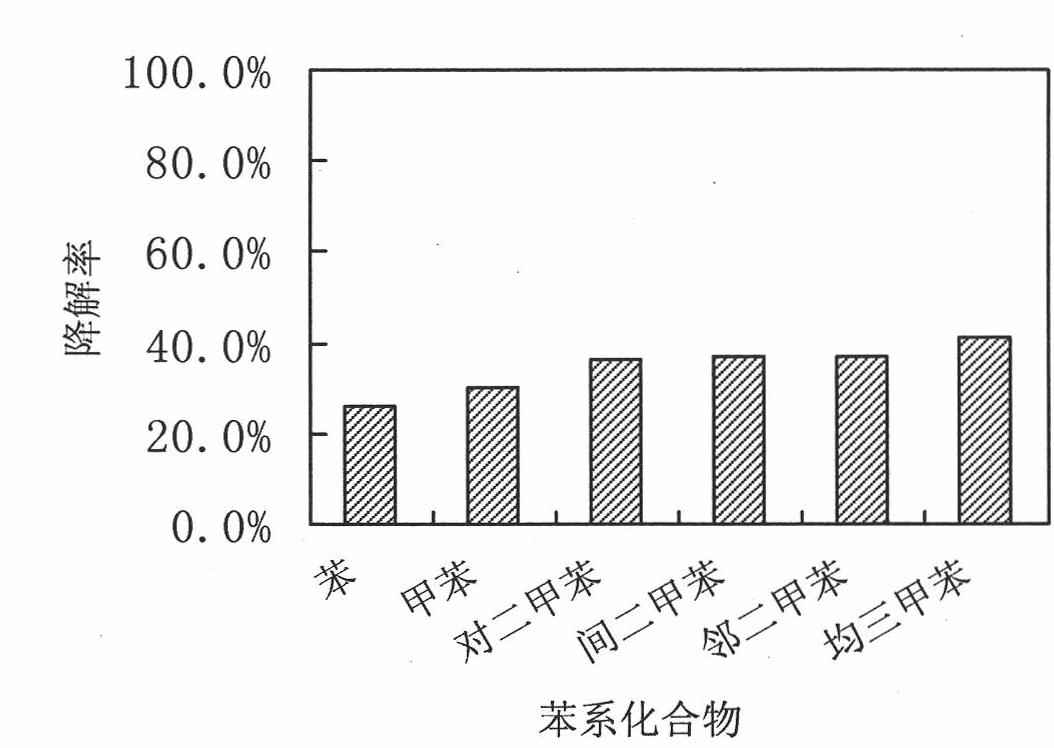
Benzene series compound facultative anaerobic degrading bacterium
The invention belongs to the technical field of degrading microorganisms and relates to a benzene series compound facultative anaerobic degrading bacterium which is characterized in that the invention is microbacterium schleiferi HBSD-C CCTCC No. M209284 and is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection at November 27, 2009, and the preservation number is CCTCC No. M209284. The invention has the colony morphology that the benzene series compound facultative anaerobic degrading bacteria is pale yellow, circular, semi-transparent and sunken and has tidy edge and smooth surface; a cell is in a shape of a straight bar and is gram-positive and immobile; and the invention has the main biochemical characteristics that the benzene series compound facultative anaerobic degrading bacterium is oxidase-positive, catalass-positive, nitrate reduction positive, gelatin hydrolysis negative and facultative anaerobic, utilizes glucose, fructose and sucrose without utilizing maltose and grows under the temperature of 4-41 DEG C. The invention can degrade benzene, toluene, xylene and mesitylene under the anaerobic condition and has the degradation rate of 25.9-41.2 percent on benzene series compound 3d with the concentration of 175.8mg / L.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Kit of ready-to-use salmonella identification plate, preparation method and use method
InactiveCN102031282AReduce random errorShorten appraisal report timeMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesAntigenSerotype
The invention relates to a method for synchronously identifying a specificity enzyme-substrate phenotype and a serum subtype of salmonella in intestinal pathogenic bacteria, which mainly solves the technical problems of the traditional salmonella identification method has complicated identification steps, higher cost, inaccurate serum identification result caused by nonuniform antigen induction or culturing materials, delayed report time, and the like. The kit of a ready-to-use salmonella identification plate comprises: (1) a salmonella specificity enzyme-substrate screening culture medium, (2) a selective culture medium aiming at the salmonella specificity O-phase antigen growth, and (3) a selective culture medium aiming at the salmonella specificity H-phase antigen growth. In the invention, the typical colonial morphology is generated by utilizing an enzyme-reaction substrate, and the salmonella O antigen and H antigen are simultaneously cultured, therefore, the method is beneficial to the serotype identification of the salmonella.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Method for isolation and identification of bacillus circulans
ActiveCN110468067AGood for separation and identificationEffective screeningBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementColony morphologyBenzylpenicillin potassium
The invention provides a method for isolation and identification of bacillus circulans, wherein the method comprises the following steps: (1) environmental bacteria containing bacillus circulans is subjected to selective enrichment culture by a selective enrichment culture medium, the proliferation of non-bacillus circulans is reduced, and the bacillus circulans is highly efficiently proliferates,wherein the selective enrichment culture medium is a modified tryptone soybean broth culture medium containing cephalosporin antibiotics and benzylpenicillin potassium; and (2) the bacterial solutionobtained in the step (1) is cultured in a Columbia blood agar plate containing antibiotics, and the strains having hemolytic ring appearing are isolated and are identified according to the colony morphology. The method can further use the molecular biological method to identify the strains isolated in the step (2). The method can simply and quickly isolate and identify bacillus circulans from theenvironmental bacteria, and has high screening precision.
Owner:NANJING INST OF PROD QUALITY INSPECTION
Culture medium composition, culture medium and viable bacteria counting method for strain
ActiveCN103911298AControl contentTo achieve the purpose of jointly counting live bacteriaFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementColony morphologyNitrogen source
The invention discloses a culture medium composition, which contains a nitrogen source. The culture medium composition is characterized in that the nitrogen source contains urea and / or amino acid, in terms of nitrogen element, urea and / or amino acid account for more than 80wt% of the total content of the nitrogen source, and based on the total weight of the culture medium composition, in terms of nitrogen element, the total content of the nitrogen source is 0.02-15wt%. The invention also discloses a culture medium, which contains the culture medium composition provided by the invention and water, wherein the culture medium composition and the water are in a weight ratio of 1:20-30. In addition, the invention discloses a viable bacteria counting method for a strain. The method includes: subjecting the strain to plate culture on the culture medium provided by the invention, and conducting plate counting on the cultured strain. By means of the method provided by the invention, viable bacteria counting on different strains can be carried out according to different colony morphologies and colors.
Owner:COFCO NUTRITION & HEALTH RES INST +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com