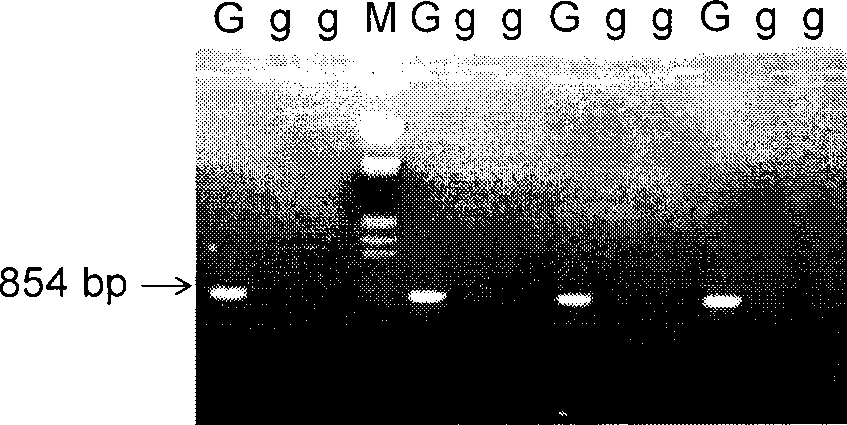Patents
Literature
183 results about "RAPD" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
RAPD (pronounced as "rapid") stands for 'Random Amplification of Polymorphic DNA'. It is a type of PCR, but the segments of DNA that are amplified are random. The scientist performing RAPD creates several arbitrary, short primers (8–12 nucleotides), then proceeds with the PCR using a large template of genomic DNA, hoping that fragments will amplify. By resolving the resulting patterns, a semi-unique profile can be gleaned from an RAPD reaction.
Mutagenic strain of cordyceps militaris and breeding method
InactiveCN101690463AGenetically stableIncrease productionFungi productsLichen productsBiotechnologyDry weight
The invention provides a mutagenic strain of cordyceps militaris and a breeding method. A new high-yield strain of cordyceps militaris is obtained by chemical mutagenesis, the preservation number thereof is CGMCC NO. 2909, and compared with original starting strain, the dry weight of mycelium is increased by 103%, the content of adenosine is increased by 536%, the content of polysaccharide is increased by 22.2%, the content of protein is increased by 55.5%, and the content of mannitol is increased by 37.5 %. The new strain of cordyceps militaris does not degenerate after more than 20 times of subculturing, has genetic stability, and utilizes the research of random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) to verify the difference on DNA level between the strain and the original starting strain. The invention also discloses the optimum process condition for extracting polysaccharide and adenosine of cordyceps militaris.
Owner:CHANGCHUN SHENGJINNUO BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
Quality assurance and identification method for high-quality strawberries
ActiveCN105203672AScientific and reliable quality evaluation systemEffective reflection of total antioxidant activityComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme GeneGenetic diversity
The invention relates to a quality assurance and identification method for high-quality strawberries, belonging to the technical field of biology. The quality assurance and identification method comprises the following steps: determining phenols and flavor substances of different varieties of strawberries by virtue of HPLC-MS and GC-MS, and establishing a chemical fingerprint chromatography database; determining the total antioxidant activity of the various strawberries by virtue of an ORAC method; analyzing blastogenesis diversity of the strawberries by utilizing RFLP, RAPD and SSR methods and combining key enzyme genes in synthetic routes of anthocyanin and polyphenol; establishing a spectrum-effect relationship between chemical fingerprint chromatography and biological activity information of the different varieties of strawberries, and analyzing the relation between hereditary basis and functional quality character of the strawberries. The high-quality variety of the strawberries is selected by combining chemical fingerprint chromatography, the effectiveness evaluation, genetic diversity analysis and the spectrum-effect relationship and is subjected to authenticity identification, so that a scientific, reliable, uniform and standard strawberry quality evaluation system is established, and technical support and scientific basis are provided for the quality control of the strawberries.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Molecular marker linked with bruchid resistance gene in mung bean
InactiveCN101358232AAssisted breeding selection with clear goalsShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationResistant genesAgricultural science
The invention relates to a molecular marker for mungbean weevil resistance gene linkage, which is used for screening mungbean weevil resistant genes. V2709, VC1973 (zhonglu No. 1) and the individual DNA of F2 separation population thereof are extracted by the CTAB method. 63 RAPD molecular markers, 100 pairs of SSR molecular markers and 28 pairs of STS molecular markers are adopted to carry out the PCR product polymorphism screening on the resistant bulk and the susceptible bulk of the two parents and the F2 progeny, and then each of F2 generation individuals is screened out the weevil resistance gene linkage marker. A RAPD primer, OPC-06 and a STS primer are found to link with a weevil resistance genes The molecular marker can target the weevil resistance gene, and the selection efficiency of weevil resistance breeding is greatly improved.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Molecular marker method for avirulence gene of rice blast
InactiveCN1952177AReveal Toxic ComponentsReveal featuresMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationPyricularia griseaParental strain
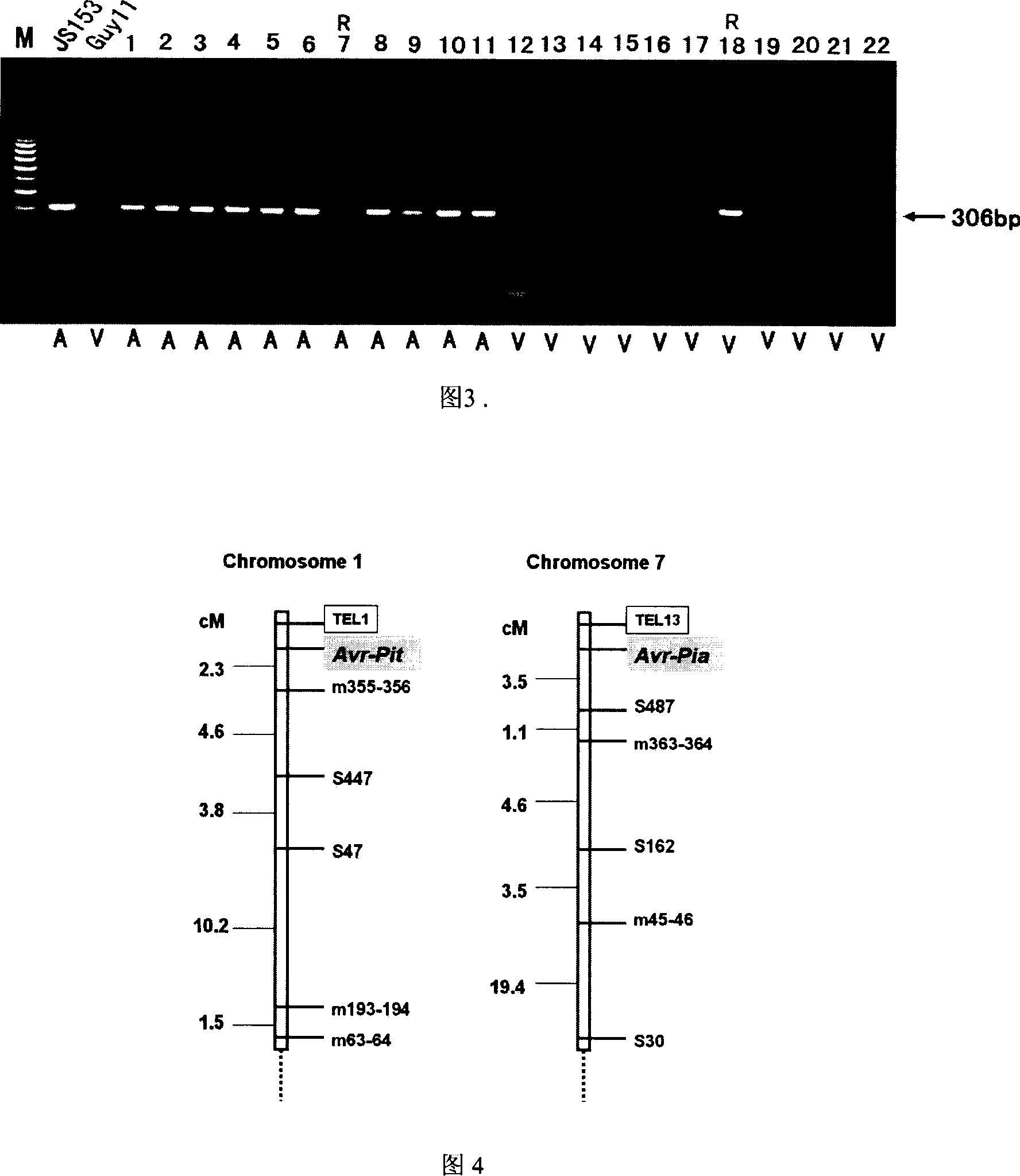
The invention of molecular labeling method of Pyricularia grisea avirulent gene belongs to the field of agricultural biotechnology. The molecular labeling technology includes performing molecular labeling to avirulent gene though assessment from two parental strains and filial generation groups of Pyricularia grisea. M355-356 labeled by SSR near NO. 1 chromosome telomere links with avirulent gene Avr-Pit with a genetic distance of 2.3cm; S487 labeled by RAPD located near NO. 7 chromosome telomere links with avirulent gene Avr-Pia with a genetic distance of 3.5cm; S361 labeled by m677-678 and RAPD located at middle of N0. 3 chromosome telomere links with Pyricularia grisea specified avirulent gene PRE1 with genetic distances of 5.9cm and 6.4. The invention can not only make use of the nontoxic gene marker as gene probe, but also set foundations for further clone of the gene through physical mapping.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
SCAR (Sequence-characterized Amplified Regions) primers and method for identifying tobacco varieties
InactiveCN102605047AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
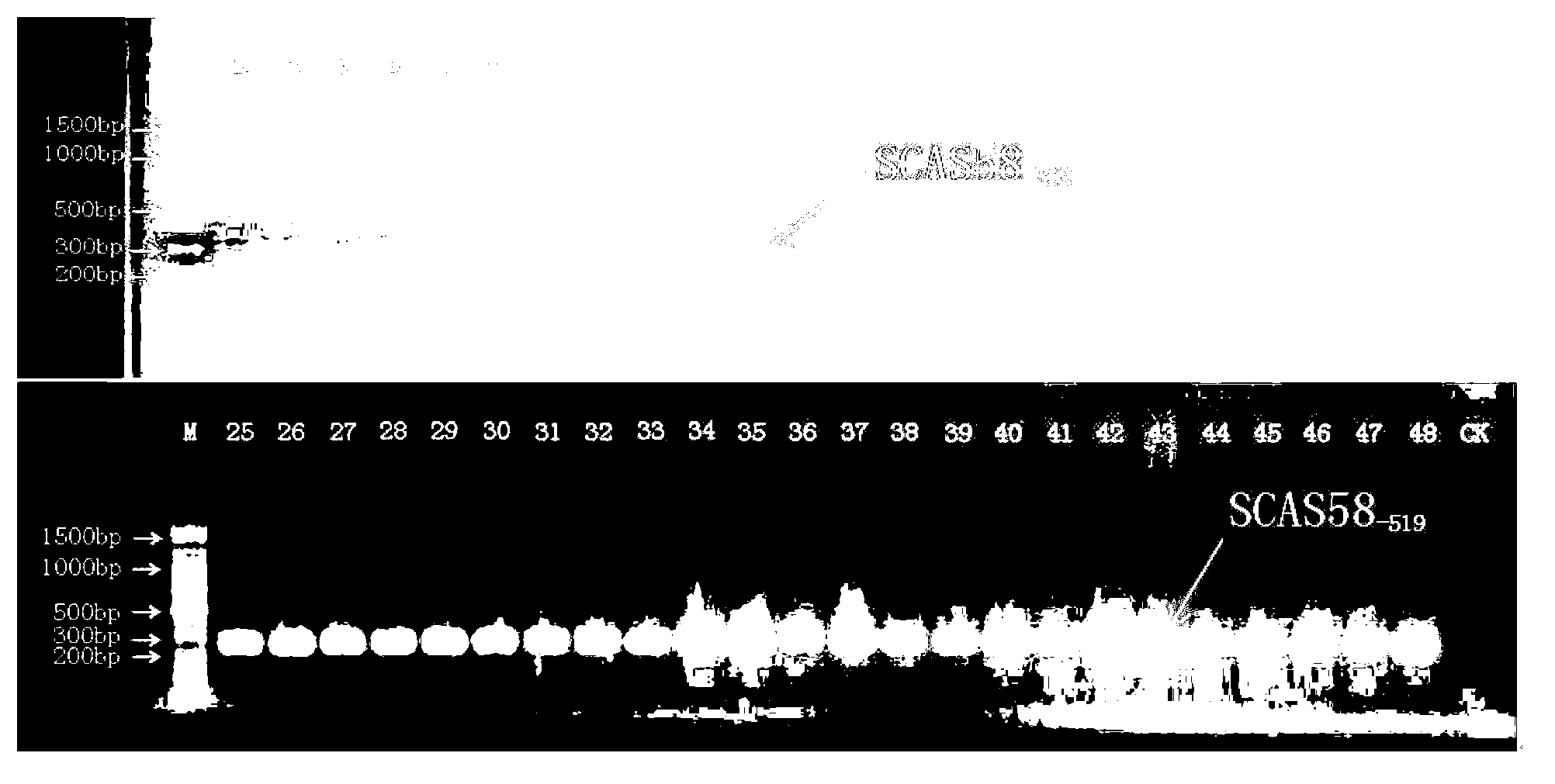
The invention discloses SCAR (Sequence-characterized Amplified Regions) marker primers and method for identifying tobacco varieties. According to the invention, twelve tobacco varieties are analyzed by RAPD (Random amplified polymorphic DNA) to obtain 6 specific fragments, and the 6 pairs of SCAR marker primers are designed on the basis of the nucleotide sequences of the 6 specific fragments. The12 tobacco varieties are as follows: Honghua Dajinyuan, K326, NC102, NC297, Yunyan85, Yunyan87, Yunyan97, China tobacco 100, flue-cured tobacco, KRK26, LJ (Long River) 911 and Nanjiang No.3. According to the invention, the method for applying SCAR markers to identification on the tobacco varieties is established; and an SCAR finger-print library for the 12 tobacco varieties is established. The method disclosed by the invention can be applied to not only field identification on cigarette raw materials, but also identification on initially-dried and redried tobacco leaves or leaf blades, so that an SCAR marking technology is successfully applied to industrial production of tobaccos.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Crested wheatgrass P genome specific sequence
the invention discloses an astopic sequence of crested wheatgrass P gene group, which is characterized by the following: adopting gene group DNA as mould to do PCR augmentation for RAPD primer; obtaining 1036bp nucleotide sequence; or using SCAR primer to do PCR augmentation to obtain 960bp nucleotide sequence; possessing a couple of oligonucleotide with sequence 3 and sequence 4 for SCAR primer; providing new astopic probe and molecular mark for P chromatin rapidly and exactly.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rapid identification method of genetic purity of muskmelon hybrid seeds based on PCR
InactiveCN102732621AAccurate identificationImprove the efficiency of purity identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementEnvironmental effectHybrid seed
The invention discloses a rapid identification method of genetic purity of muskmelon hybrid seeds based on PCR, characterized by respectively utilizing screened SRAP primer combination NAUSRem6 / NAUSRfc8 and / or RAPD primer NAURP401, using Haimi No.2 muskmelon parent and F1 individual genome DNA as a template to conduct PCR amplification, and using non-denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis to detect PCR amplification products; wherein only the individual plant with parent special bands can be really hybrid, and the individual plant without any parent band is false hybrid. The method provided by the invention overcomes the disadvantages of complicated operation, low accuracy and the like of conventional field purity detection, has the advantages of rapidness, simpleness, low cost, stability and reliability, immunity to the growth stages and environment, and can be one of the important detection methods of genetic purity identification of muskmelon hybrid seeds.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
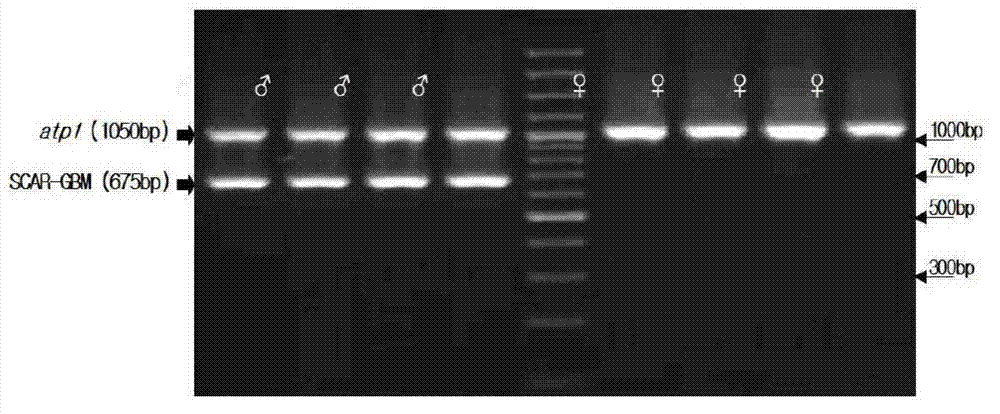
Usage of molecular marker for identifying gender of gingo
ActiveCN103374568APrevent plantingHelp productionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMultiplex pcrsScars
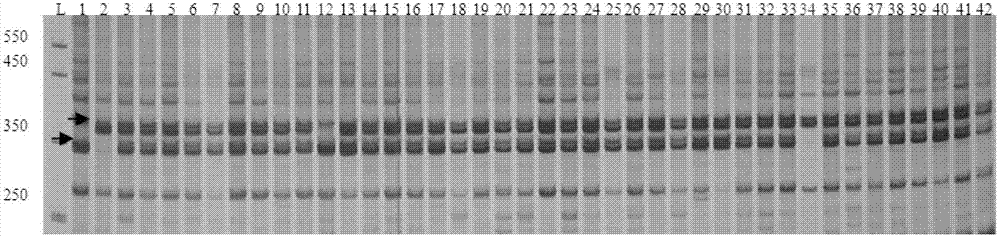
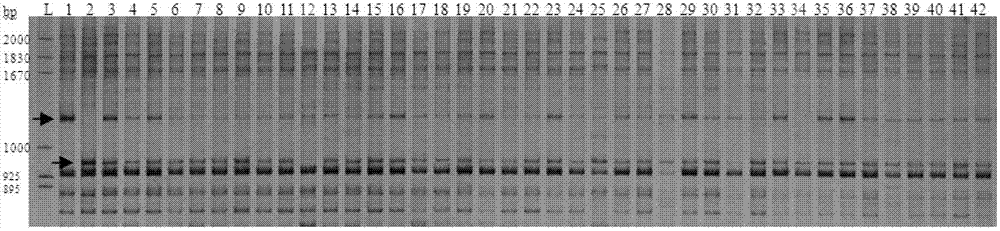
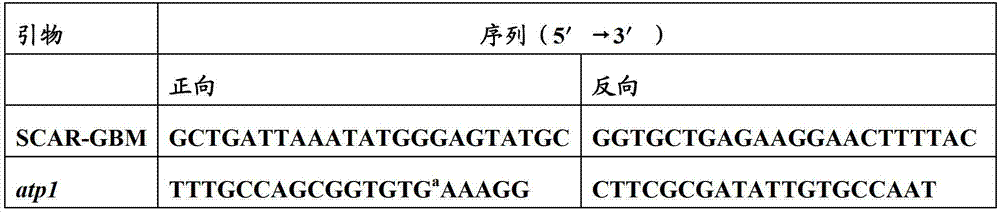
The invention relates to a molecular marker for identifying gemale plant and male plant of gingo, more particularl, the invention relates to a method for identifying gender of gingo. Compared to the usage of random primer, the method has increased stability, and compared to the dominant marker, which can provide limit information, the method is improved. According to the mehtod, the gingo male plant specificity SCAR-GBM primer and the exsisted atp1 primer of the mitochondrial DNA which is developed in the field are used at the same time for performing multiple PCR, wherein, the SCAR-GBM primer is based on the sequence development of RAPD segment which can display the heredity of gingo male plant.
Owner:KERALA FOREST RES INST
Method for separating cotton chloroplast DNA
InactiveCN101117634AQuality improvementHigh yieldFermentationPlant genotype modificationSucroseSaccharum
The present invention belongs to the cotton genetic engineering technical field, in particular to a new method for separating the chloroplast DNA of cotton. The present invention includes: young and tender leaves are taken as material, and are fully homogenated by a common domestic juicer, four kinds of buffer solutions of A, B, C, and D are utilized, the leaves are centrifuged at a general velocity, and the cotton chloroplast DNA pure can be finally obtained successively by the separating and the cracking of the chloroplast as well as the separating and the purifying of the chloroplast DNA (cpDNA). The quality of the chloroplast DNA prepared and separated by the present invention is higher, and the UV spectrophotometer measuring shows that the D260 nm / D280 nm of a DNA sample prepared by the present invention is set between 1.6 and 1.8; the leaf sample yields up to 1-10 microgram cpDNA per gram. After being verified, taking the separated cpDNA as the template can completely satisfy the common molecular biological operation needs such as the specific enzyme restriction, the RAPD, the PCR, the clone of target gene sequences, and so on. Compared with the prior art, the present invention does not need a hypervelocity centrifugal machine, and equipments and steps of centrifugalization through the sucrose density gradient are also not needed.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Purity testing method for tomato hybrid based on PCR technology
InactiveCN101017151AClear bandGood repeatabilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementRelationship - FatherPcr ctpp
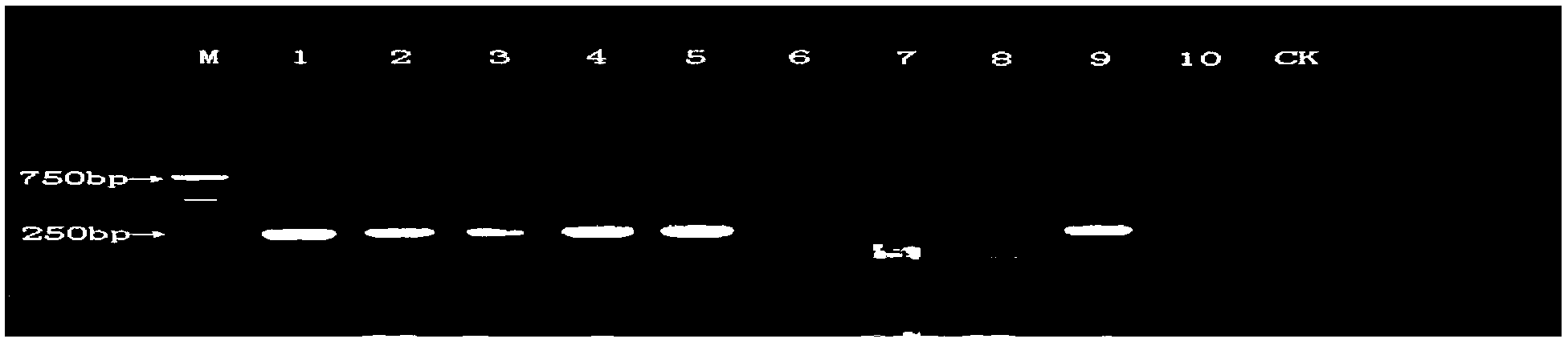
This invention relates to one tomato mixture purification test method based on PCR technique in biological technique field, which comprises the following steps: using product mixture tomato Shu power 8 as subject to extend molecule label filtering to identify one RAPD and one SSR label object of local abnormal band; RAPD label generate mother property label of NAURP409800 and father property label of NAURP4091100; SSR label lead object property mother label of NAUSSRTOM47140 and father label of NAUSSRTOM 47148.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A method for quickly distinguishing grape varieties by using rapd
InactiveCN102277444AEnables early identificationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementVitis viniferaAgricultural science
The invention discloses a method for quickly distinguishing grape varieties by utilizing RAPD, and belongs to the field of molecular biology molecular markers. This method can completely distinguish 28 grape varieties through the design of 11 RAPD random primers. The primers are screened for stability and polymorphism, and the optimal annealing temperature is determined; The bands construct the map relationship of the corresponding differentiated varieties. This method is easy to operate, fast and accurate, and 7 PCRs can distinguish 28 grape varieties at the molecular level. With primers of any two species, the method can realize the early identification of seedlings and has wide versatility in other species.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Rapid detection method of heterodera avenae wollenweber LAMP and application of detection method
InactiveCN103045751AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseHeterodera avenae
The invention relates to a rapid detection method of heterodera avenae wollenweber LAMP and application of the detection method. Five LAMP primers, namely HA5-F3, HA5-B3, HA5-FIP, HA5-BIP and HA5-LB are designed and screened according to a heterodera avenae wollenweber random amplified polymorphic dna (RAPD) sequence obtained by cloning; and an LAMP reaction system is configured and optimized. By performing DNA extraction, loop-mediated isothermal amplification, amplified product developing and observation on the heterodera avenae wollenweber, the heterodera avenae wollenweber can be rapidly detected. The detection method is high in specificity, low in cost and convenient to operate, and has high application values on rapid detection of the heterodera avenae wollenweber and early and field diagnosis of the heterodera avenae wollenweber diseases.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Seed production and culture method for cyprinoid with short growth circle
InactiveCN101223865AUnique growthCarp with a short growth cycle have unique morphologically uniqueClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaDiseaseCarp
The invention discloses a seed production and culture method of a carp with short growth period and comprises the steps of the selection of breeding parent, which determines Jinxin female carp and Ukrainian scaled male carp as seed production parents through the RAPD technology, grouping of the male and female parents with a proportion of 1 to 1.2-1.5, reproduction of fish seeds by the methods of artificial flushing, natural spawning or artificial insemination, incubation in the step of which artificial fish egg collectors with naturally produced eggs and artificial fish egg collectors with fertilized ovum through artificial dousing are delivered to a pond for natural incubation or the fertilized ovum through artificial insemination is doused in the waxed pond bottom and then placed into a ring channel for incubation after being collected and washed, and initial culture and commercial fish culture: each Mu of pond can culture 2,000-2,200 pieces of summer fingerlings or 1200-1400 pieces of spring fingerlings and is matched with silver carp fingerlings or spring fingerlings which account for 20 percent of the main culture objects. The fish can be cultured in the current year. The carp with short growth period cultured by the method of the invention has the advantages of unique shape, rapid growth, strong disease resistance and high yield.
Owner:HUANXIN FIELD OF AQUATIC PROD & FINE BREED TIANJIN
Fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized molecular marker and application thereof
InactiveCN103060322ARapid identificationQuick checkMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationFusarium oxysporumStrain specificity
The invention discloses a fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) marker (SEQ.ID.No.1), an SCAR (sequence characterized amplified region) marker (SEQ.ID.No.2) obtained by transforming the RAPD marker and application of the molecular markers in pathogenic bacteria identification and pathogenetic tissue detection. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention has fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized strain specificity, consistency and stability, can distinguish difference between the specialized strain and other specialized pathogenic bacteria, can identify fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized pathogens and plays an important role in identification of the fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized strain, so that a foundation is laid for building a special, quick, high-sensitivity, stable and reliable molecular detection technical system for fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized pathogenic bacteria. By applying the molecular marker disclosed by the invention, the defects that workload is high and cycle is long in the conventional fusarium oxysporum bitter gourd specialized pathogenic bacterium identifying and distinguishing process can be overcome, and quick and accurate identification and detection on pathogens are realized.
Owner:GUANGXI ZHUANG AUTONOMOUS REGION ACAD OF AGRI SCI
RAPD-SCAR839 label for identifying group E chromosome of thinopyrum elongatum and application of same
InactiveCN102373291AEasy to identifyEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTriticeaeNucleotide
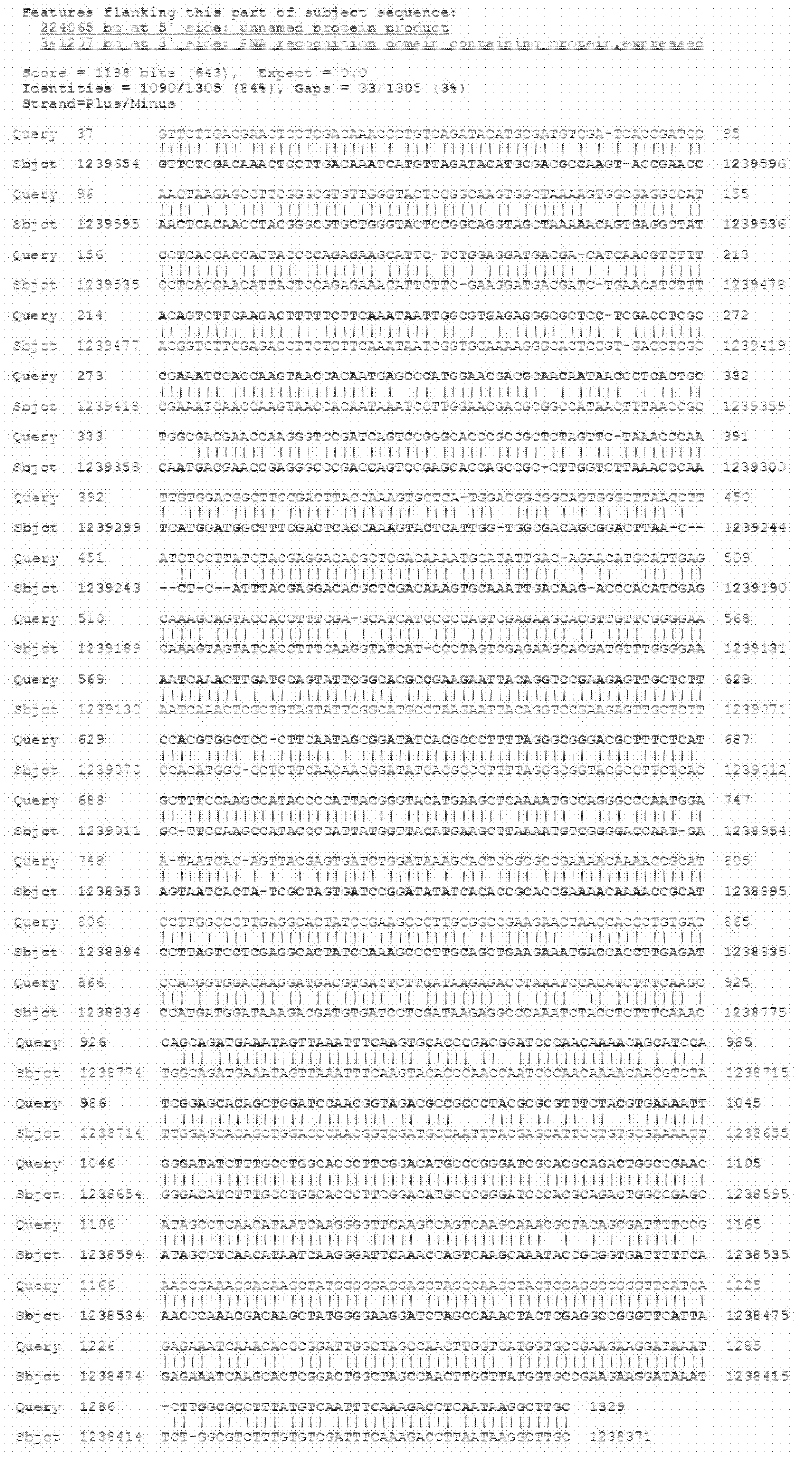
The invention discloses an RAPD-SCAR83 label for identifying group E chromosome of thinopyrum elongatum and application of the same. A nucleotide sequence of the group E chromosome is as shown in SEQ. ID. NO. 2 or SEQ. ID. NO. 5. In the invention, specific RAPD segments are screened to obtain through an RAPD-SCAR method, and are converted into stable SCAR labels; and amplification of the RAPD labels is detected. When the label of the group E chromosome of the thinopyrum elongatum provided by the invention is adopted, a solid foundation is laid for quickly identifying a 2E or 3E chromatin or chromosome of the thinopyrum elongatum under the genetical background of wheat through the detection of the SCAR labels, and a very convenient and quick means is also provided for molecular marker-assisted breeding.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Field hyperspectral rapd measurement system
InactiveCN107748140AEasy to operateSuitable for field workColor/spectral properties measurementsEngineeringOptical fiber probe
The invention discloses a field hyperspectral rapid measurement system. The system comprises a first support rod (1), a second support rod (2), an instrument package and an optical fiber probe (3); and the optical fiber probe (3) is sleeved with a sleeve (4), the external of the sleeve (4) is movably connected with a first rotating shaft (5) and a second rotating shaft (6), the instrument packageincludes a system host, and a hyperspectral measurement instrument host, a system power supply and a display which are connected with the system host, and the optical fiber probe (3) is connected withthe hyperspectral measurement instrument host; and a circular track (7) is arranged on the second support rod (2), and a range finding sensor (8) is arranged on the circular track (7). The field hyperspectral rapid measurement system has the advantages of simple structure, low cost, simplicity in operation, and accurate measurement result.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
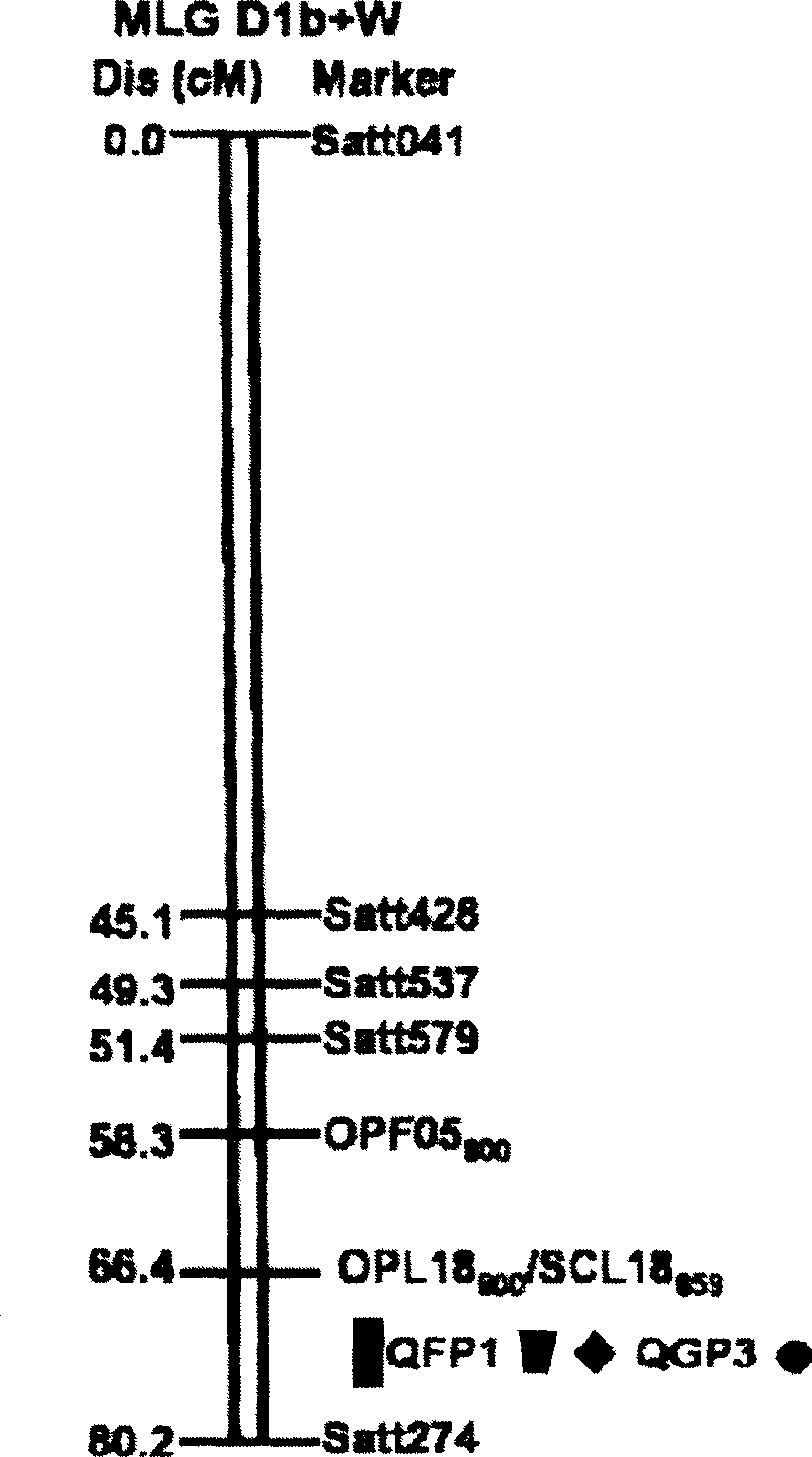
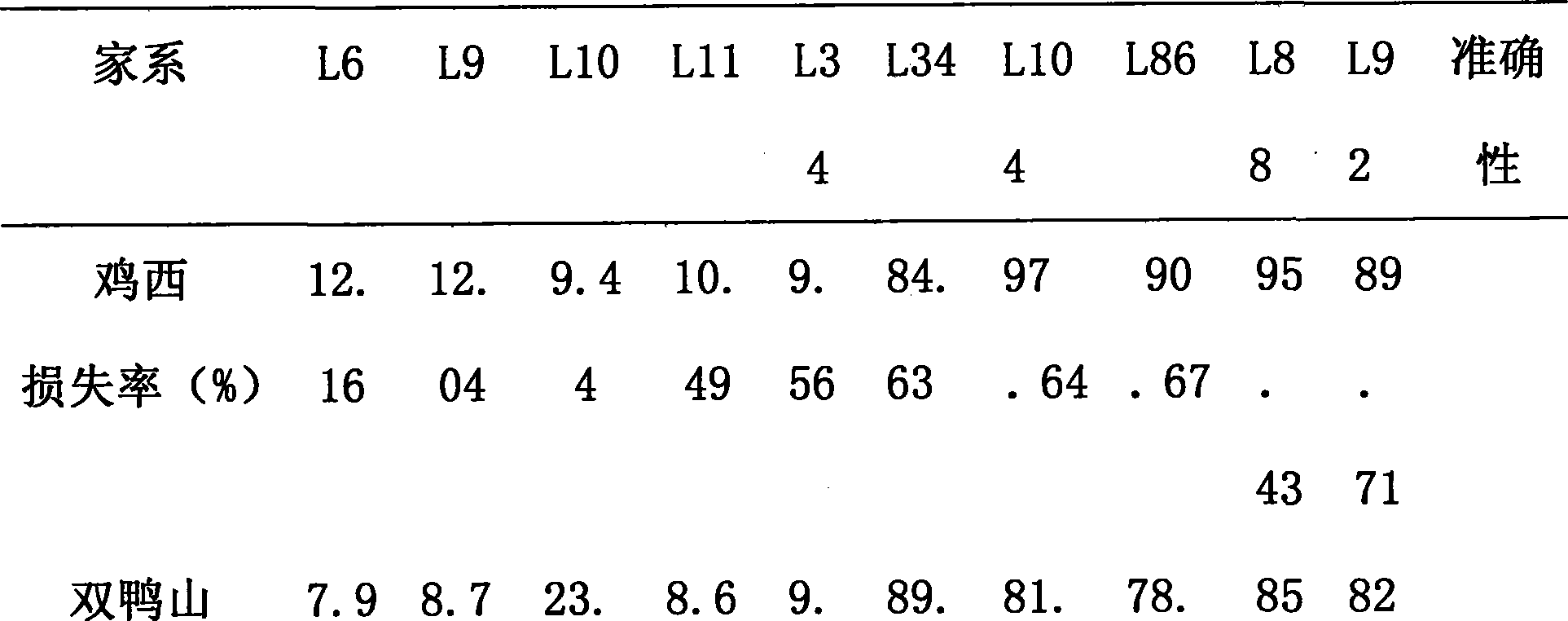
Method for determining soybean phytophthora root rot resistant quantitative trait loci and use of the loci
InactiveCN101372710AReduce manpowerReduce material wasteMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant genotype modificationLoss ratePhytophthora sp.
The invention discloses a method for determining quantitative trait loci (QTL) for soybean phytophthora root rot tolerance and the application of the loci, comprising the following steps: carrying out analysis (genotype data analysis) upon the DNA of the descendant of the disease tolerant variety (female parent) and the infected strain (male parent) by utilizing random primer (RAPD), repeat sequence primer (SSR) and sequence characteristic application range primer (SCAR); conducting inoculation identification upon the descendant with home and aboard mixed strain and having statistics upon the disease loss rate (phenotype data analysis); calculating the existent threshold of quantitative trait loci (QTL) for soybean phytophthora root rot tolerance with regression algorithm and detecting whether there are quantitative trait loci (QTL) for soybean phytophthora root rot tolerance with WinQTLCarter2.0; and finally judging whether the genealogies or derived varieties have the quantitative trait loci (QTL) by detecting the DNA of parent and genealogies or derived varieties thereof. The invention can detect whether the genealogies or derived varieties have disease tolerance so as to speed up the seed selection for varieties (strains) of soybean phytophthora root rot tolerance.
Owner:李 文滨
Radish cytoplasmic male sterility molecular markers and method for assisting selective breeding using same
The invention discloses radish cytoplasmic male sterility molecular markers and a method for assisting selective breeding using same. The method comprises the steps of: based on genome DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of fertility separated F2 generation and first backcross generation of white radish cytoplasmic sterility material as templates, carrying out RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA) analysis and multiple repeated tests to screen to obtain two RAPD markers, namely S88-1526 and S1344-415, linked with the radish cytoplasmic sterility fertility restorer gene, wherein the S88-1526 and S1344-415 markers are respectively located at both sides of the restorer gene and have the genetic distances of 4.2cm and 6.9cm, respectively. Furthermore, the RAPD marker S88-1526 is successfully transformed into SCAR (Sequence Characterized Amplified Region) marker scar-88. Linkage analysis shows that the cross-over value between the marker scar-88 and the restorer gene is 4.28%, and the corresponding genetic distance is 4.24cm. The radish cytoplasmic male sterility molecular markers can be used for performing assisted selection of early molecular markers during radish cytoplasmic male sterility breeding, so as to accelerate the breeding progress.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Three-stage amplifying method of inventing novel germplasm of drupe fruit tree utilizing distant hybridization
The present invention provides three-stage amplification method as one kind of system method capable of overcoming incompatibility and sterility in distant hybridization of stone fruit tree. The three-stage amplification method includes electrostatic field treatment of male parent pollen, adopting female parent with self-compatibility or high natural bearing rate and pollination in bell blooming period; salving hybrid young embryo in MS culture medium with BA and IAA to obtain more hybrid; and inducing multiple bud and proliferation culture in MS+BA+IAA+vitamin C culture medium to avoid gene type loss. The test seedling is rooting cultured and RAPD identified before being transplanted in field. One series of new stone fruit tree germ plasm has been created via the said method.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
DNA Molecular Marker Identification Technique to Distinguish Polygonum cephalum and Polygonum nepal
InactiveCN102296118AReliable identificationStable identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMedicinal herbsResearch Object
The present invention takes Polygonum cephalum, a representative national medicine in Guizhou, as the research object, explores the use of RAPD analysis method to analyze the genetic diversity of Polygonum cephalum and Polygonum nepalensis; and on the basis of RAPD experiments, converts the RAPD method into SCAR markers, It provides an accurate, reliable, rapid and stable method for the identification of Polygonum cephalum and Polygonum nepalensis.
Owner:GUIZHOU WARMEN PHARMA
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection method of specificity of botrytis cinerea
InactiveCN103146812AExtended service lifeStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesGel electrophoresisBotrytis squamosa
The invention discloses a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detection method of specificity of botrytis cinerea. The PCR detection method of the specificity of the botrytis cinerea includes the following steps of obtaining specificity fragment of the botrytis cinerea according to randomly amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) marks, designing amplification primer pair sequences, B1SE11f and B1SE11r, extracting sample deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), conducting amplification through the PCR method, detecting an amplification product through gel electrophoresis, and judging whether the sample contains botrytis cinerea, wherein the judging is conducted according to the fact that the sample contains the botrytis cinerea when the electrophoresis result appears an amplification band on 327bp. The PCR detection method of the specificity of the botrytis cinerea can detect DNA of 0.4-nanogram botrytis cinerea, distinguish the botrytis cinerea from other fungus and relative genus fungus of the botrytis cinerea, and be directly applied to field detection. The PCR detection method of the specificity of the botrytis cinerea is short in detection time, low in cost, distinctive in detection result and simple in result judgment.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
SCAR label of Chinese cabbage orange leaf-head and its use in auxiliary selective breeding
The present invention discloses one kind of SCAR label of orange Chinese cabbage leaf bulb and its application in auxiliary selective breeding. The auxiliary selective breeding method includes adopting the genome of color Chinese cabbage, common white Chinese cabbage and their second filial generation segregating colony as the template, RAPD analysis and repeated experiments to screen out RAPD marker linked with the orange leaf bulb of color Chinese cabbage and convert into one specific SCAR marker successfully. It is found through linked analysis that the linking distance between the marker and the orange leaf bulb is 3.7cm. The SCAR marker may be used in molecular auxiliary selective breeding of orange leaf bulb character of Chinese cabbage.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Anther culture method for indica japonica hybrid rice
ActiveCN103782908AImprove flower cultivation efficiencyLarge group sizePlant tissue cultureHorticulture methodsAge limitGenetic engineering
The invention discloses an anther culture method for indica japonica hybrid rice. The method comprises the following steps: sampling, identifying a microspore development period, low-temperature pretreatment, young wheatear sterilization, anther inoculation, still dark cultivation at 25+ / - 2 DEG C until the diameter of embryonic callus is 2-3mm; carrying out a redifferentiation stage to form complete regenerated plants with haploid or double haploids. The double haploids are good breeding materials, and can be directly used for breeding of new varieties or varietal improvement; the breeding age limit is greatly shortened; the selection efficiency is improved; the double haploids also are ideal materials for molecular markers, such as amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP), restricted fragment length polymorphisms (RFLP), randomly amplified polymorphic deoxyribonucleic acid (RAPD) and the like, genetic map drawing, and researches on animal evolution, genetic analysis, plant gene cloning and screening, genetic engineering breeding and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NONGKE SEED IND
Molecular marking method of corn hybrid incompatibly gene
InactiveCN101423871AImproved germplasmSpeed up the breeding processMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisPollen
The invention provides a method for molecularly marking maize cross incompatibility genes, and the molecular marker in the method has the following specific nucleic acid base sequence: (1) SCAR / S2055 / 854 marked positive direction: 5' CAGGTTCCATTGGAACCCTA 3'; and reverse direction: 5' TCAGACCAATACTCCGGTC 3'; and (2) SCAR / M16P22 / 303 marked positive direction: 5' GAGTAACACTCAGAATAAGC 3'; and reverse direction: 5' CATGCAGATTGGCTGCTGCTG 3'. The method for molecularly marking the maize cross incompatibility genes comprises the following steps: carrying out extraction of maize genetic group DNA, mark analysis of RAPD or AFLP polymorphism, PCR amplification, purification, clone and order checking, wherein a RAPD marker is converted into an SCAR marker; the nucleic acid base sequence marked by SCAR / S2055 / 854 is used as a primer to carry out PCR reaction; an individual containing Ga gene has a characteristic strip of 854bp through electrophoretic test; or an AFLP marker is converted into the SCAR marker; the nucleic acid base sequence marked by SCAR / M16P22 / 303 is used as a primer to carry out PCR reaction; and an individual containing Ga gene has a characteristic strip of 303bp through electrophoretic test. The method has the advantages that the method can be used for maize variety breeding, can protect the maize variety from intermixing of other maize pollen by the cross incompatibility of the maize, thereby improving the purity and quality of the variety.
Owner:BOHAI UNIV
Quick molecular detection method of novel mycelium T4 injecting wheat stripe rust with AABBDDXX
InactiveCN103667451AStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesMyceliumStripe rust
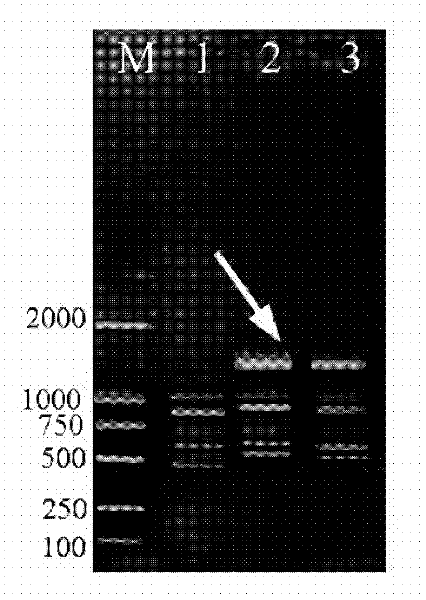
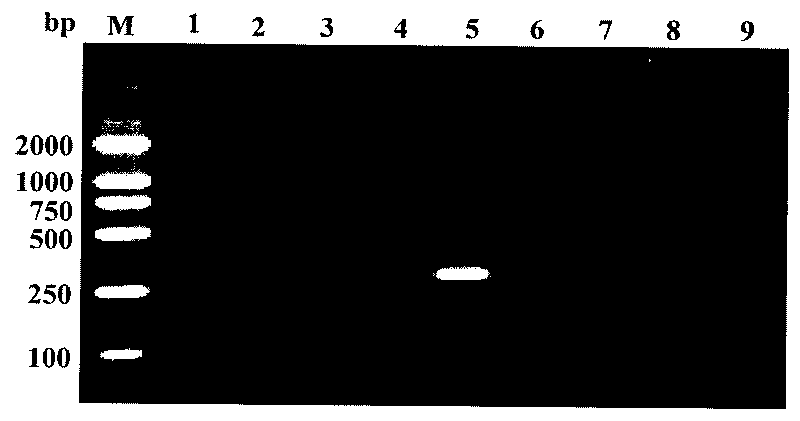
The invention discloses a quick molecular detection method of a novel mycelium T4 injecting wheat stripe rust with AABBDDXX. The method comprises the following steps: screening to obtain two specific RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA) marks S1311 and S1363 of T4 by use of 189 RAPD random primers among the novel mycelium T4, epidemic strains of wheat stripe rust CYR29, CYR31, CYR32, CYR33 and Su11-4 and a novel mycelium V26 injecting an anti-stripe rust gene Yr26; recovering, purifying, cloning and sequencing the specific stripes, designing an SCAR (Sequence Characterized Amplified Regions) primer according to the sequencing result, and successfully converting the RAPD marks to stable SCAR marks T4SP8-1 / T4SP8-2 (the sequence is 5'GGGCGTGGATGAAGAG-3' / 5'-GGAGCAGAAGCAGGTTT3'); stably amplifying the specific stripe of the novel mycelium T4 at 700bp by the marks. The specific SCAR marks T4SP8-1 / T4SP8-2 of the novel mycelium T4 provided by the invention can be used for realizing quick molecular detection of the novel mycelium T4 in an early stage in a large field so as to understand the variation dynamic condition of the pathogenic bacteria, thereby providing a reliable technical support and a theoretical foundation for prophylaxis and treatment policy of the mycelium and the wheat stripe rust.
Owner:李强 +2
Spiraling whitefly specificity SCAR primer, detecting method and reagent case thereof
InactiveCN101693924AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationRibonucleotide synthesisRibonucleotide
The invention relates to the field of the molecular biology, in particular to a spiraling whitefly specificity SCAR primer, a detecting method and a reagent case thereof. According to the ribonucleotide sequence of the spiraling whitefly specificity SCAR primer, showing in SEQ- ID- No: 1 and 2, the invention designs a pair of specificity primers according to the unique genome DNA sequence of spiraling whitefly, and the primers only have the proliferation ability for spiraling whitefly, which is a supplement and improvement for spiraling whitefly RAPD technological detecting method.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for establishing cauliflower hybrid seed DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fingerprint spectrum and application thereof
InactiveCN102108395AProtection of legal rightsAccurate identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementHybrid seedTest material
The invention discloses a method for establishing a cauliflower hybrid seed and a parent DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) fingerprint spectrum and the application thereof. The establishment method comprises the following steps: 1) extracting and purifying cauliflower DNA; 2) using the obtained high-purity cauliflower DNA as a template for performing RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) and SRAP (sequence-related amplified polymorphism) analysis; and 3) selecting selective polymorphism amplified bands to construct the DNA fingerprint spectrum of a tested material; and the cauliflower hybrid seed and parents thereof in the DNA fingerprint spectrum have specific DNA fingerprints which can be mutually differentiated. The DNA fingerprint spectrum is represented in the form of a diagram, thereby being relatively intuitive to look and being easy to understand; and the DNA fingerprint spectrum is converted to the digital representation form, thereby being convenient to be identified, read and analyzed by a computer. The method can be applied in identification of seed purity of the cauliflower hybrid seed, the result is accurate and reliable, and the detection is rapid.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Molecular markers for identifying high temperature-resistant porphyra haitanensis strain and construction method for molecular markers
InactiveCN102660646AThe result is accurateReliable resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparation3-deoxyriboseElectrophoresis
The invention discloses molecular markers for identifying a high temperature-resistant porphyra haitanensis strain and a construction method for the molecular markers and relates to porphyra haitanensis. The molecular markers for identifying the high temperature-resistant porphyra haitanensis strain are Z-26-600 and Z-26-360. The construction method comprises the following steps of: collecting porphyra haitanensis materials; extracting total deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA); performing random amplified polymorphic (RAPD) sweep analysis; performing electrophoresis detection of an RAPD amplification product; performing gel extraction on specific bands and recovering, and sequencing; designing sequence characterized amplified region (SCAR) maker primes; and verifying SCAR markers. A method foridentifying the high temperature-resistant strain by using the SCAR markers comprises the following steps of: collecting the porphyra haitanensis materials; extracting total DNA; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification; performing electrophoresis detection of a PCR amplification product; and judging according to a result.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Pair of tuta absoluta specific SS-COI primers, and rapid PCR detection method and kit
ActiveCN103131699AImprove accuracyHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationTuta absolutaGenetics
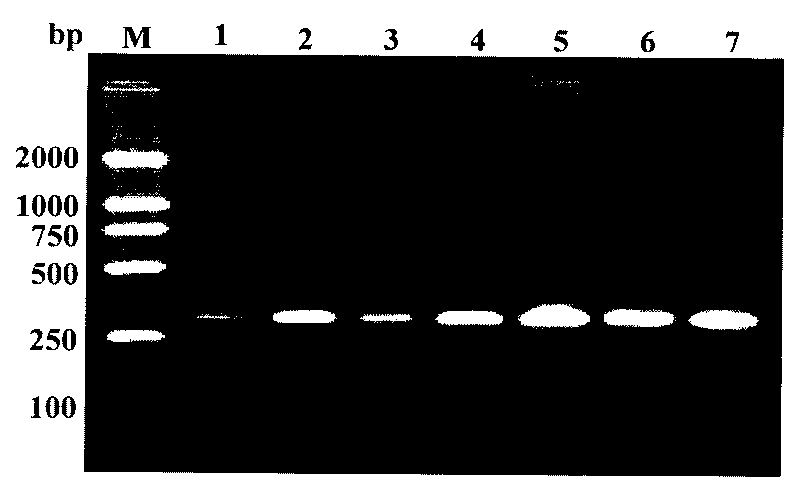
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and relates to a pair of tuta absoluta specific SS-COI primers, a rapid PCR detection method, and a kit. According to the invention, according to specific mitochondrial DNA sequence of tuta absoluta, a pair of specific primers is designed. The primers only have amplification capacities upon tuta absoluta, wherein an amplification product size is 256bp. The primers also have good detection method upon single egg and adult residues. The pair of primers is a supplementation and improvement to tuta absoluta RAPD and rDNA ITS, and mtDNA COI technical detection methods. Also, an SS-COI PCR technology is adopted, such that detection accuracy is improved, and detection time is saved. The primers and the method can be popularized in our ports in a form of a kit.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Primers and method for quickly distinguishing orange varieties
InactiveCN102492774AImprove stabilityEmbody early identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMolecular levelTree shaped
The invention discloses primers and a method for quickly distinguishing orange varieties, and belongs to the field of molecular marking in molecular biology. The method comprises the steps of: designing RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic Deoxyribonucleic Acid) random primers according to the gene sequences of the orange, and screening to obtain 16 random primers; extracting DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of a plurality of orange varieties, and diluting for later use; and amplifying the DNA of the unknown orange varieties by utilizing the random primers one by one, distinguishing out the variety with unique characteristic band, and building a tree-shaped identification figure. According to the invention, 48 orange varieties can be distinguished on a molecular level through a plurality of PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), the practicability of RAPD molecular marking utilizing 11 base primers in plant variety identification is embodied to a certain extent, and the obtained tree-shaped identification figure is more illustrative than the clustering tree, namely the primers for distinguishing any two varieties can be found out according to the variety identification figure; and the method can realize early identification of orange seedlings, and has wide universality in other species.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com