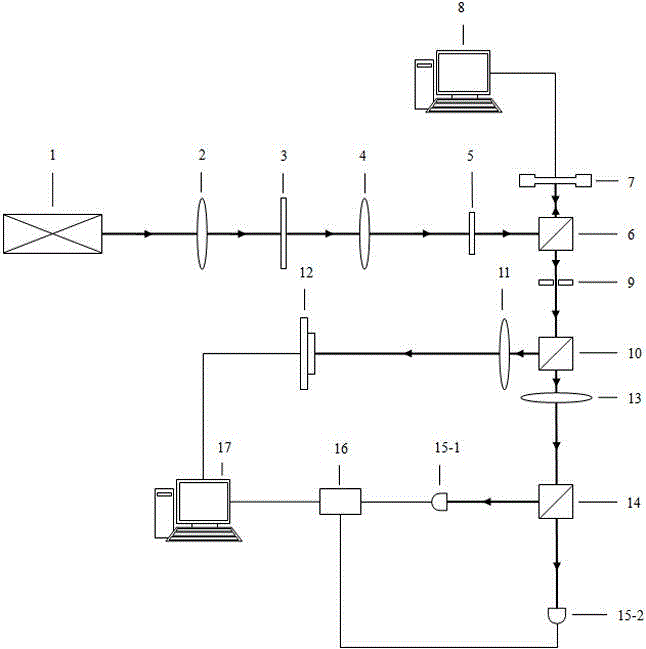
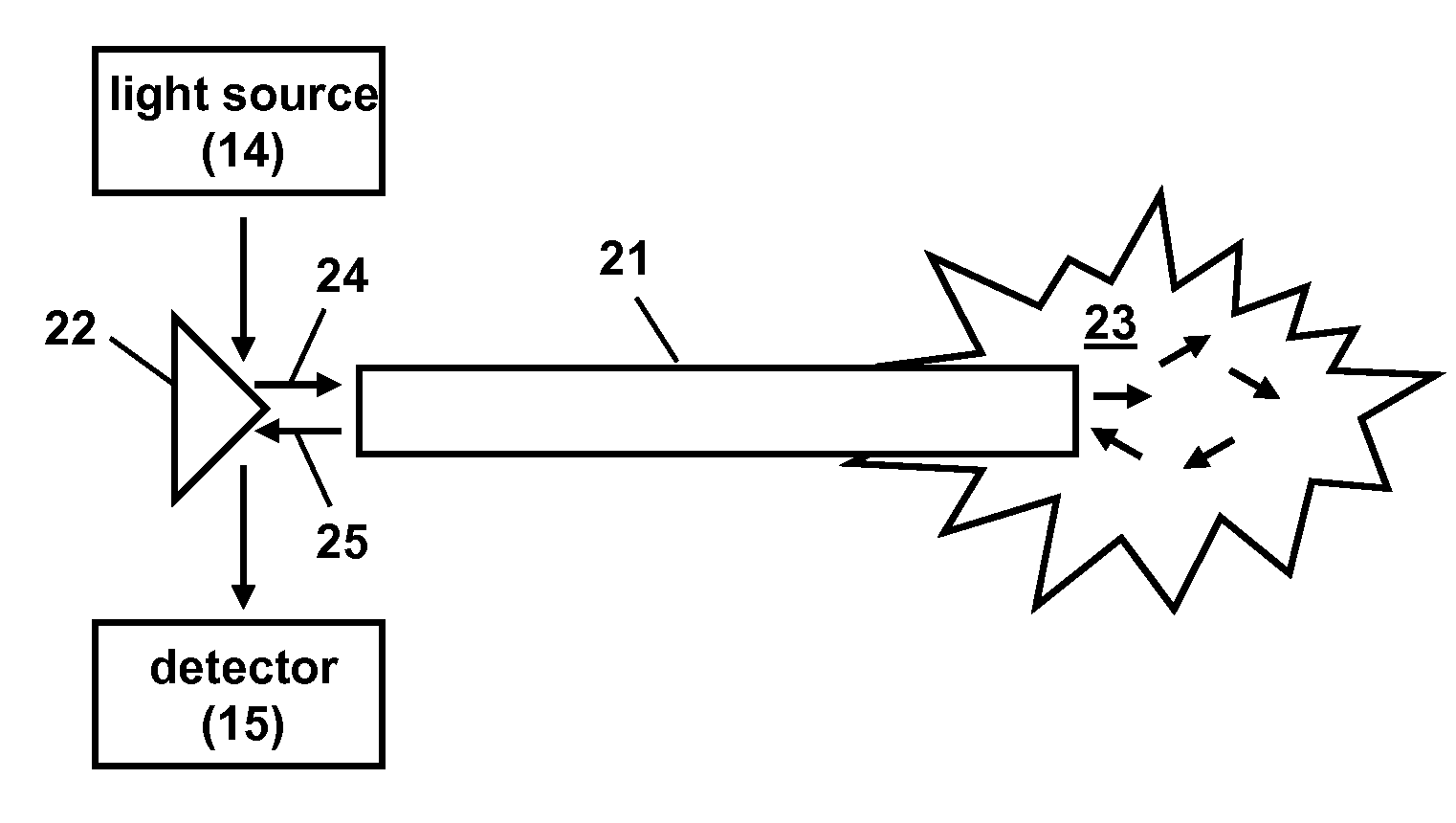
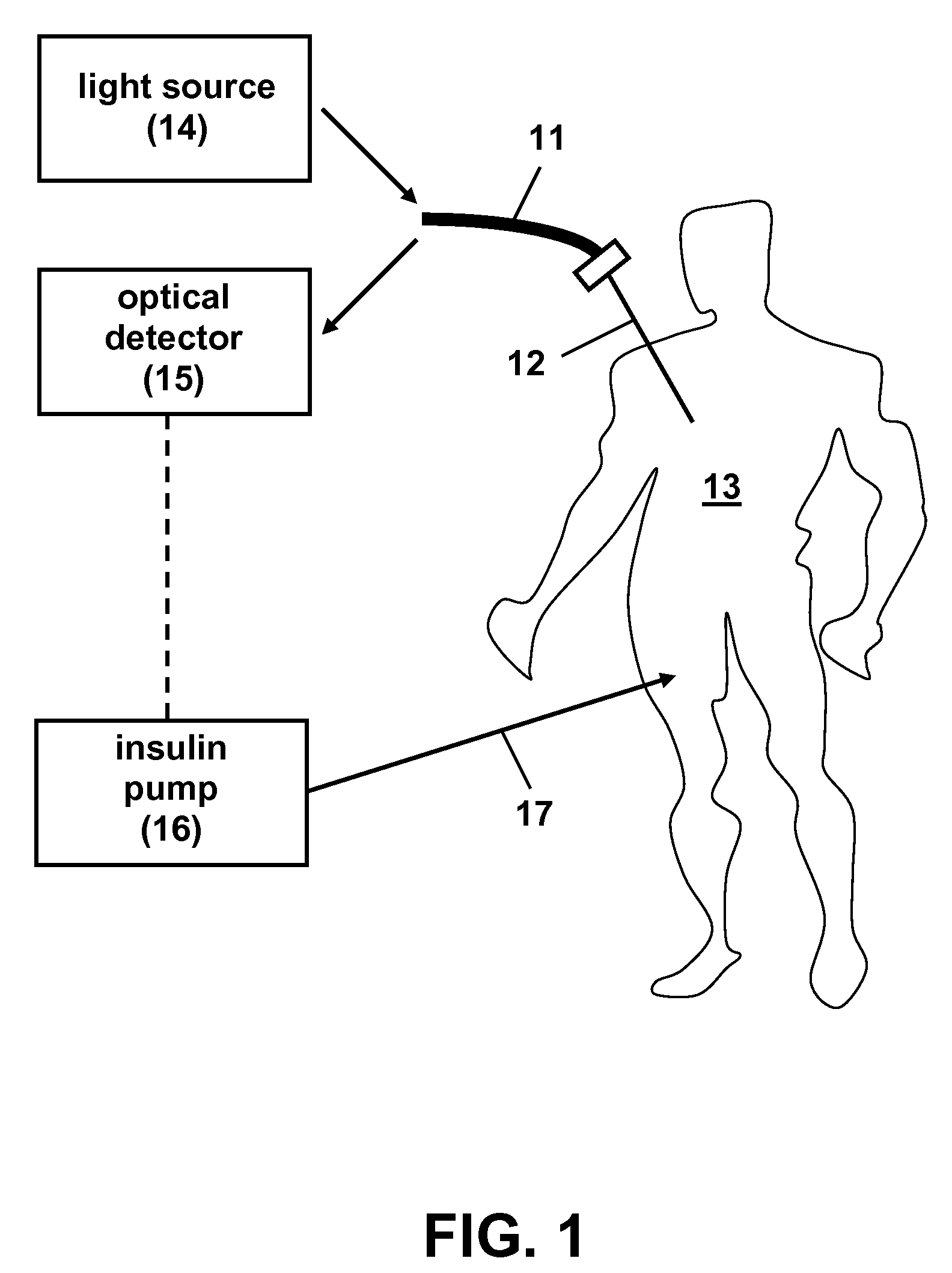
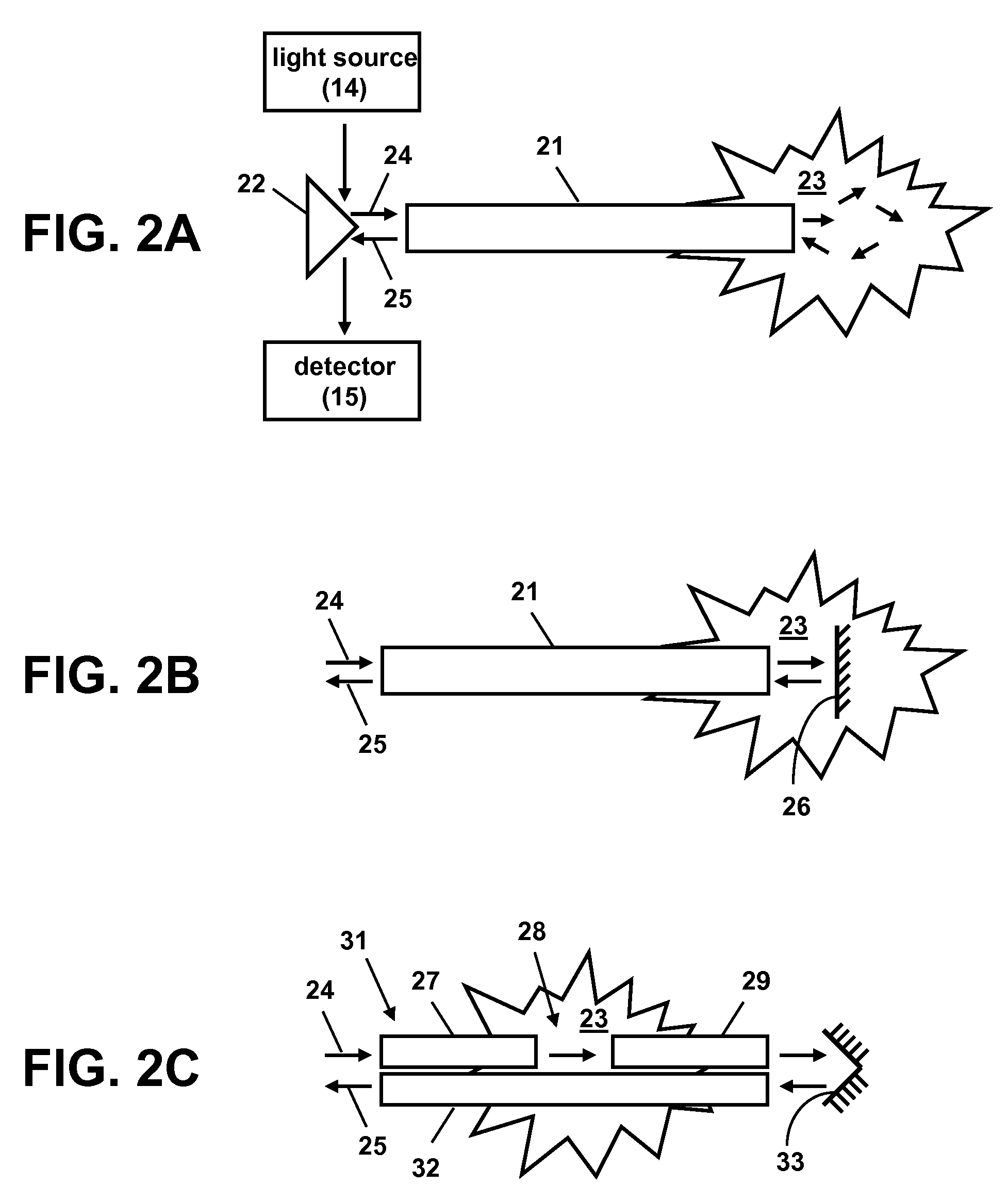
Patents
Literature
937 results about "Optical fiber probe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
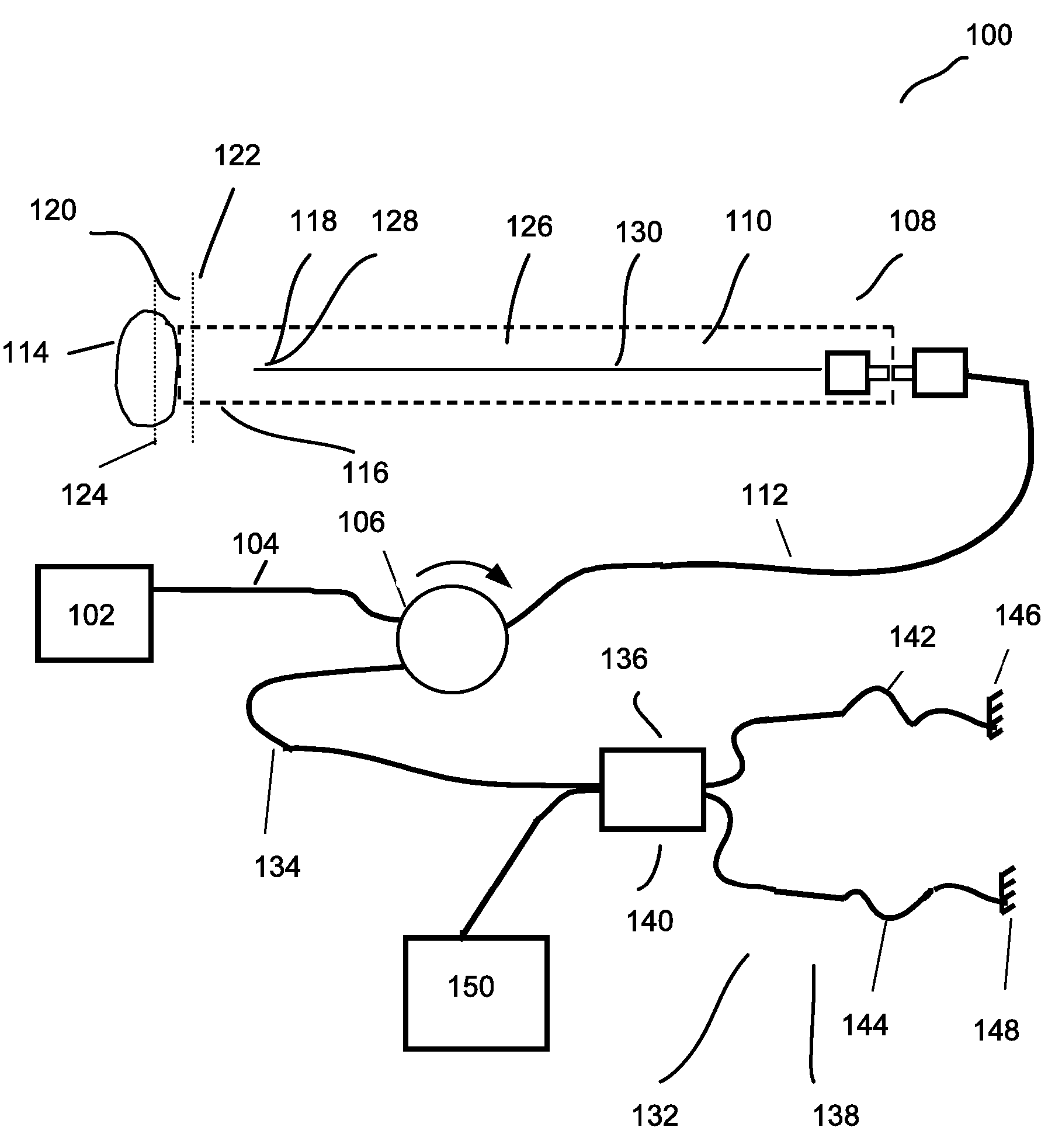
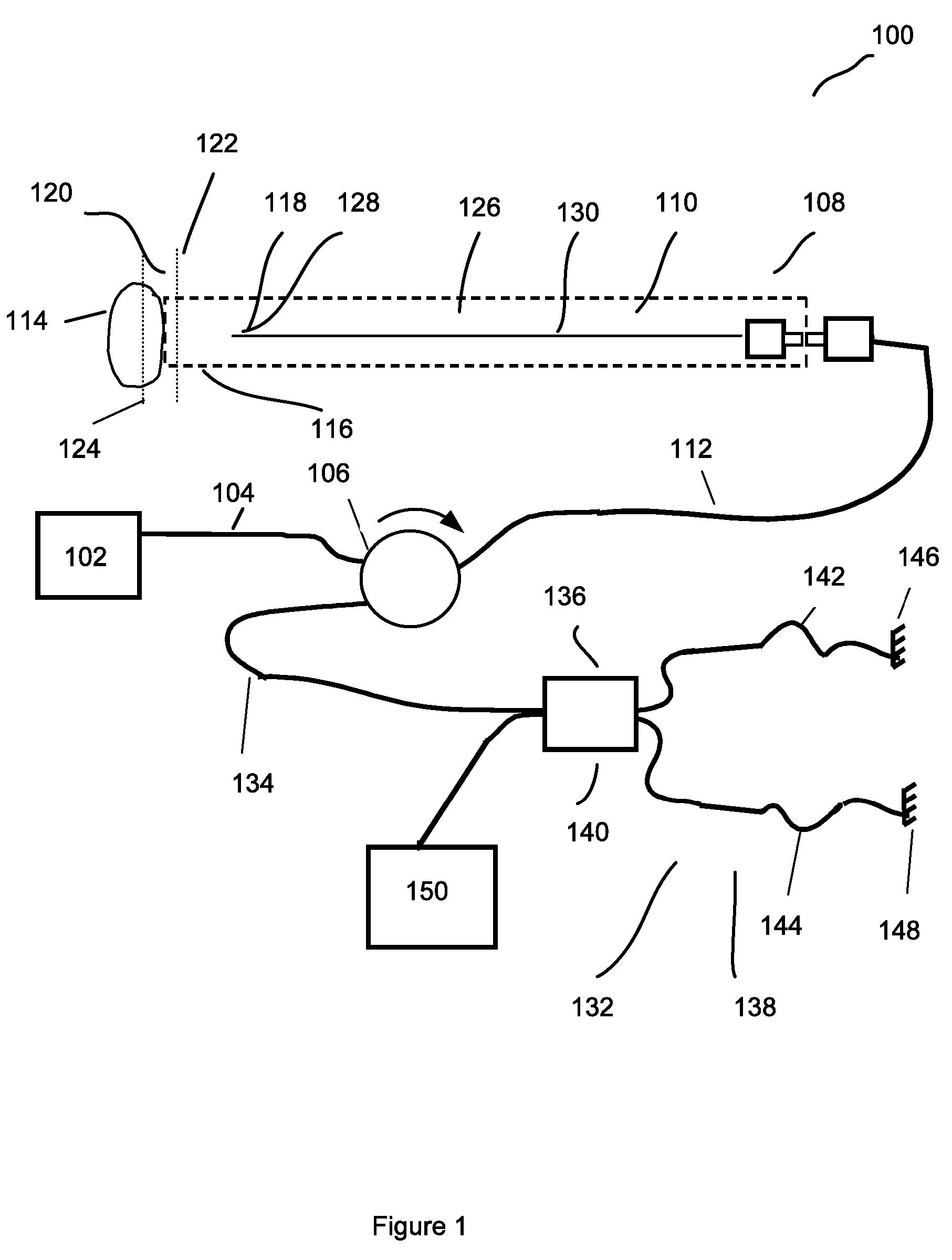
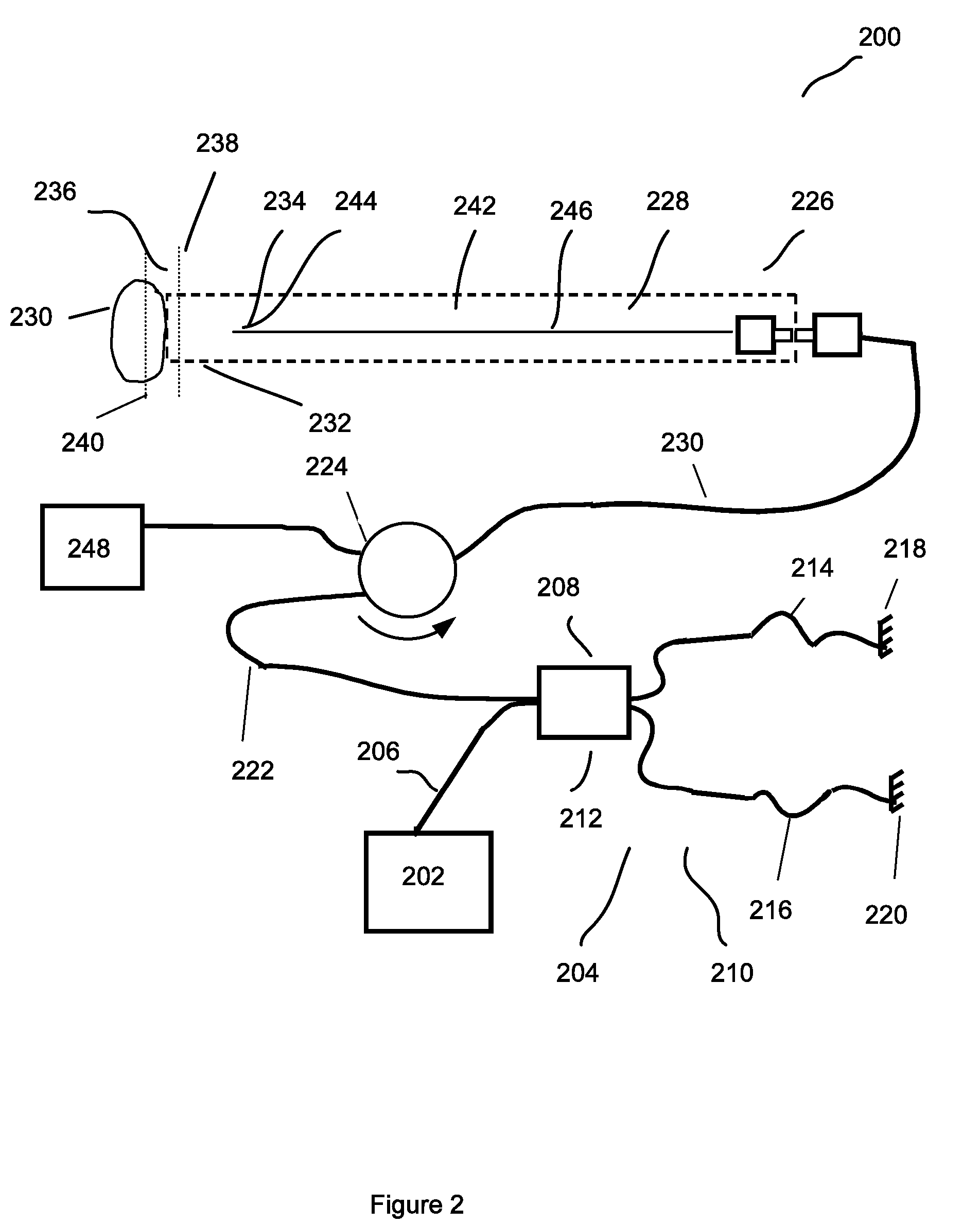
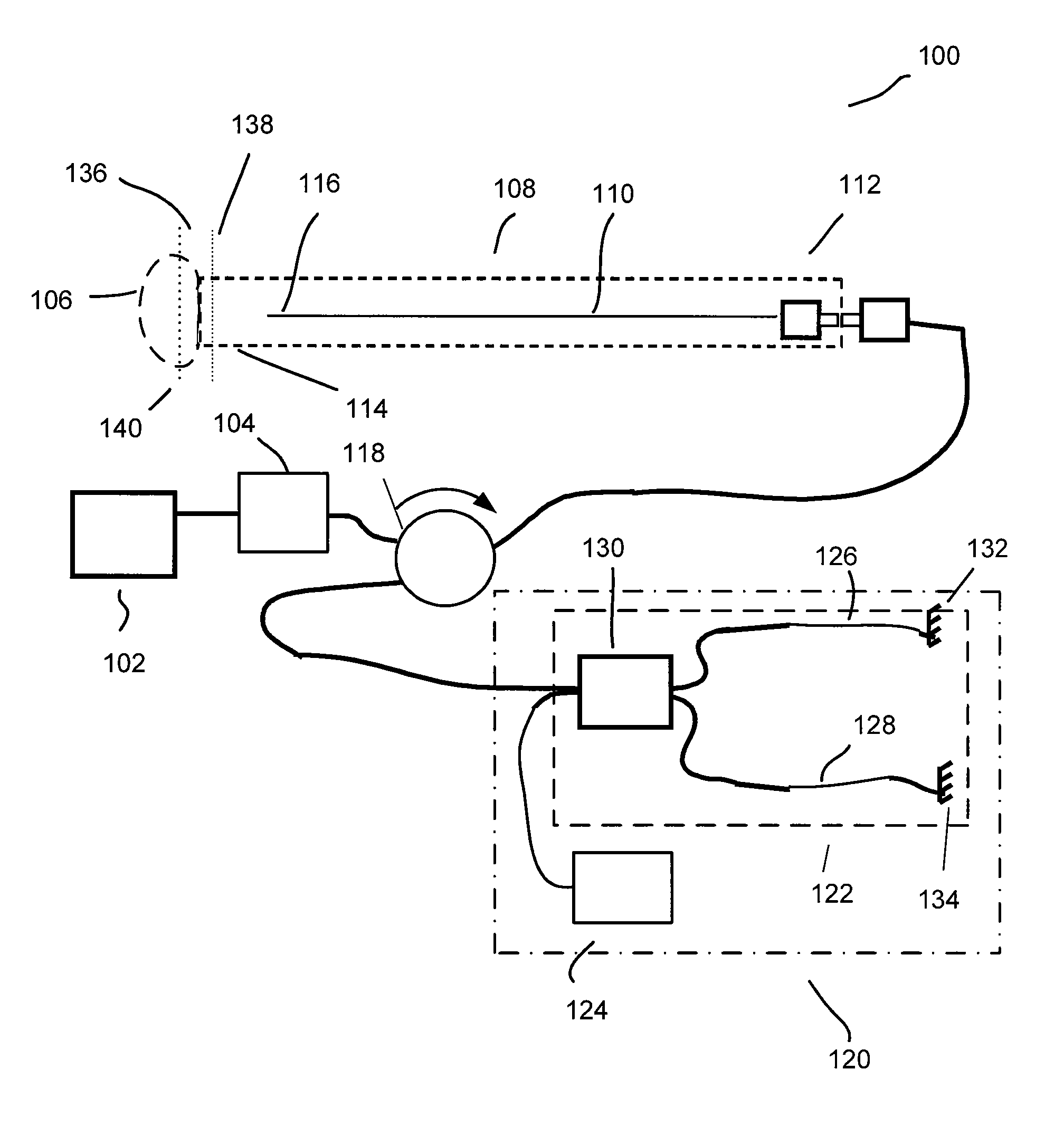
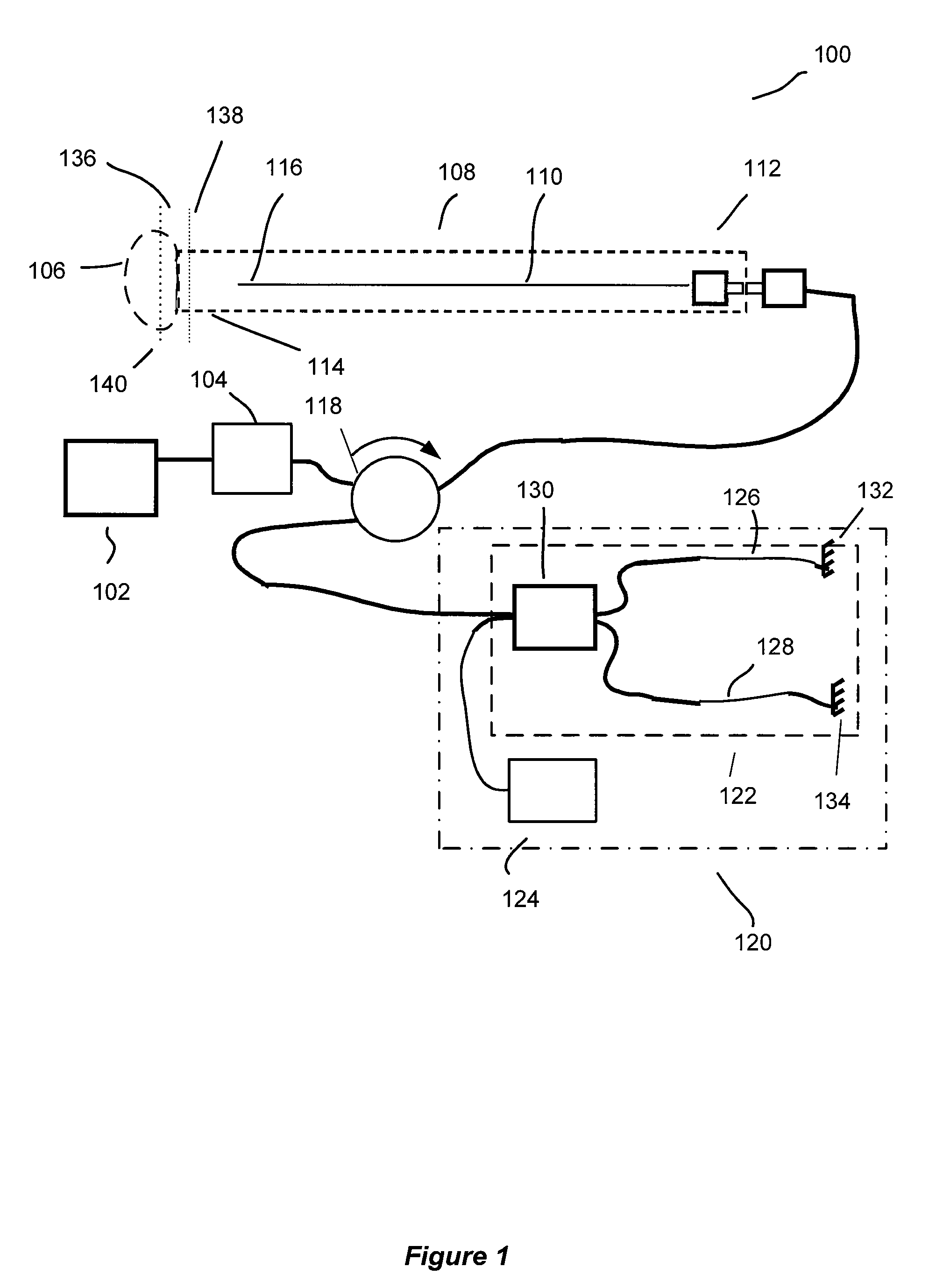
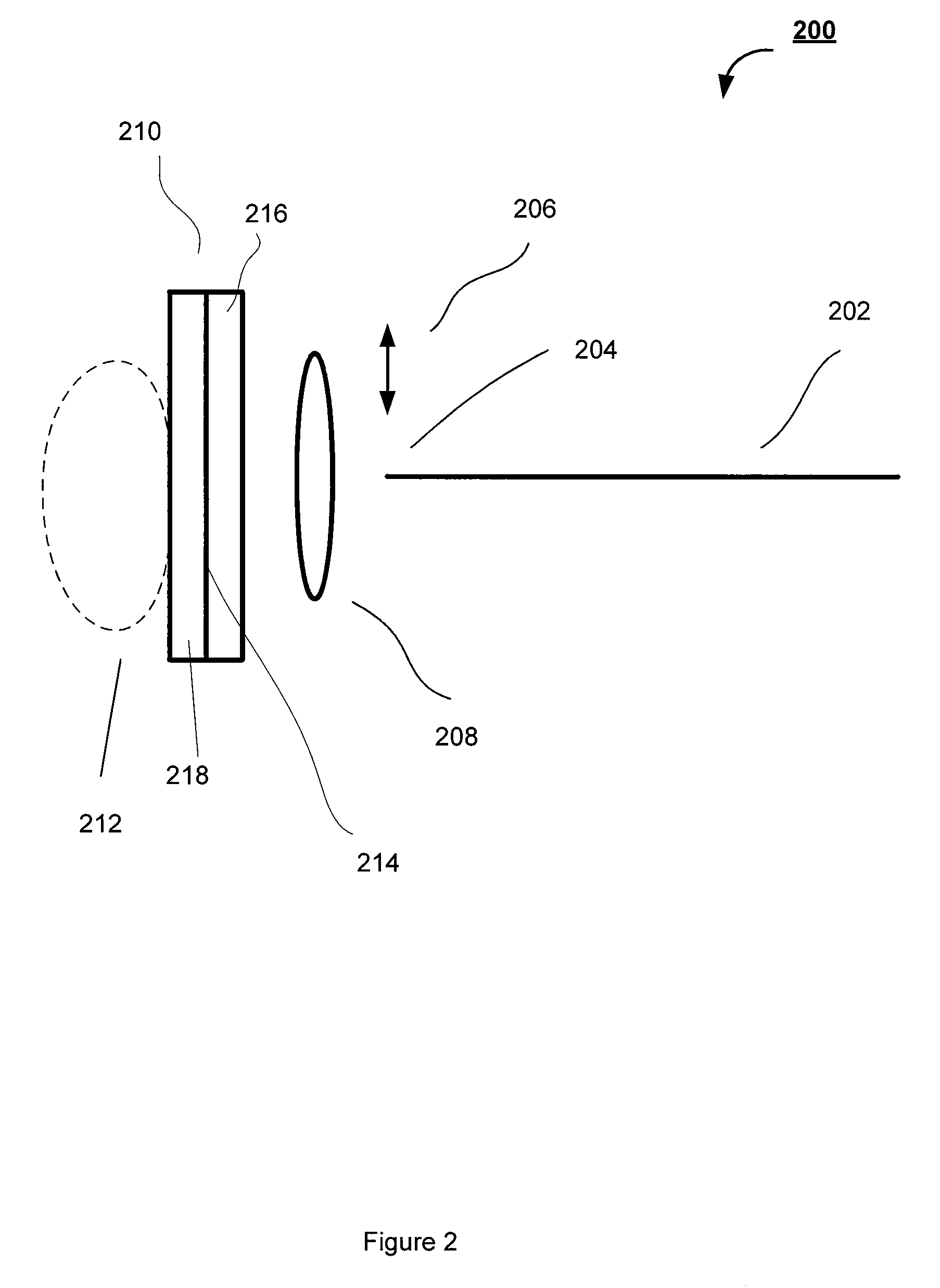
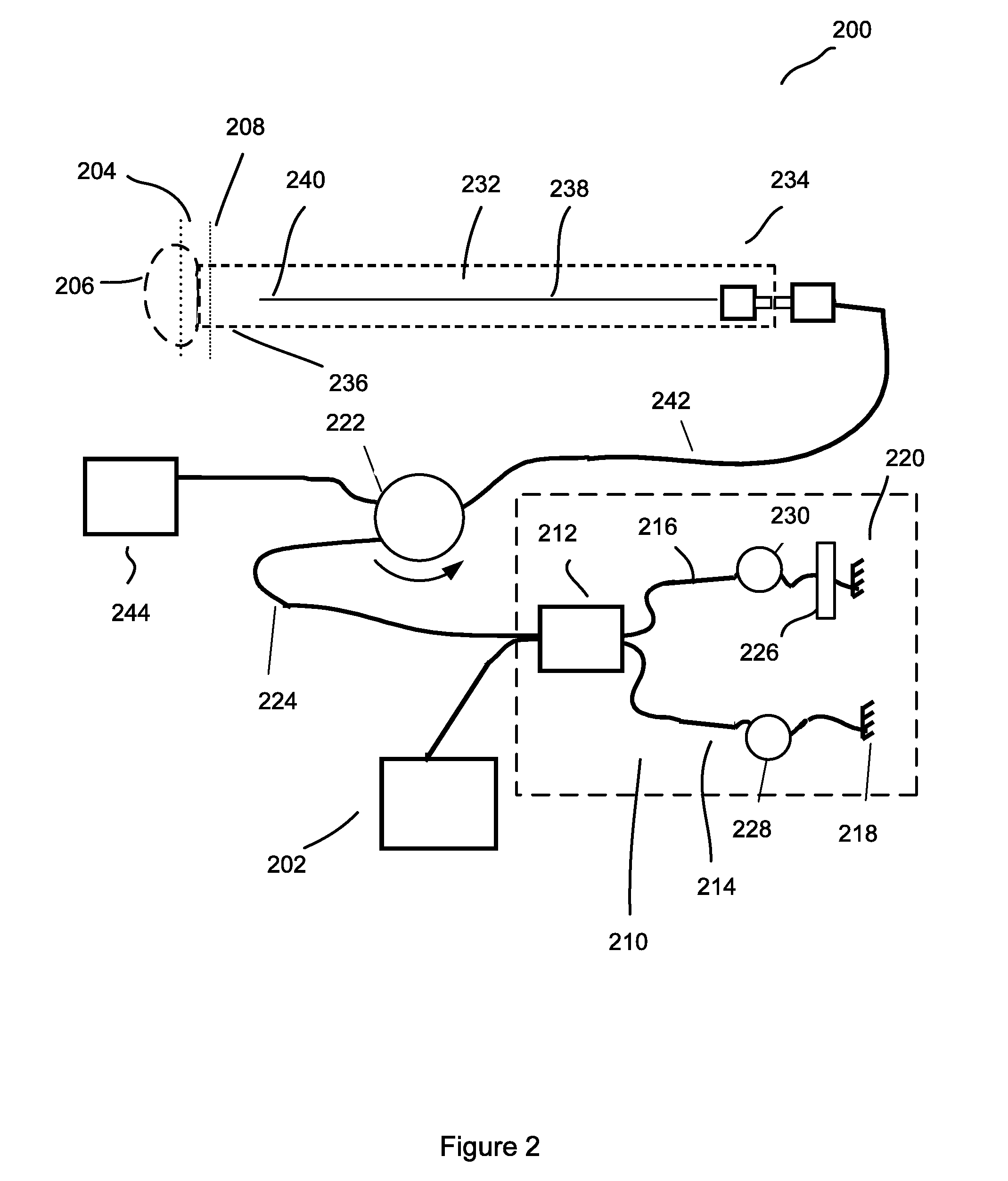
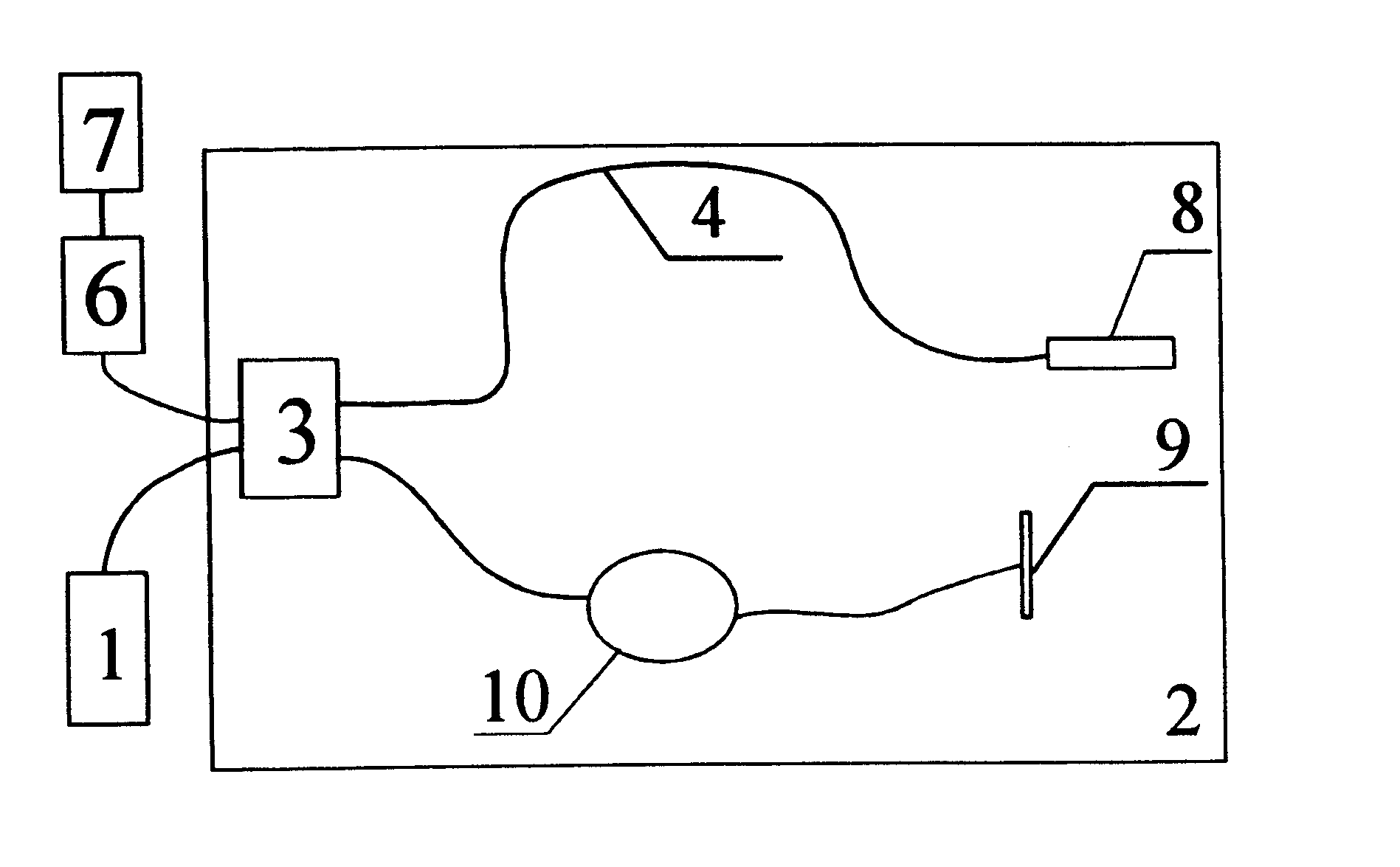
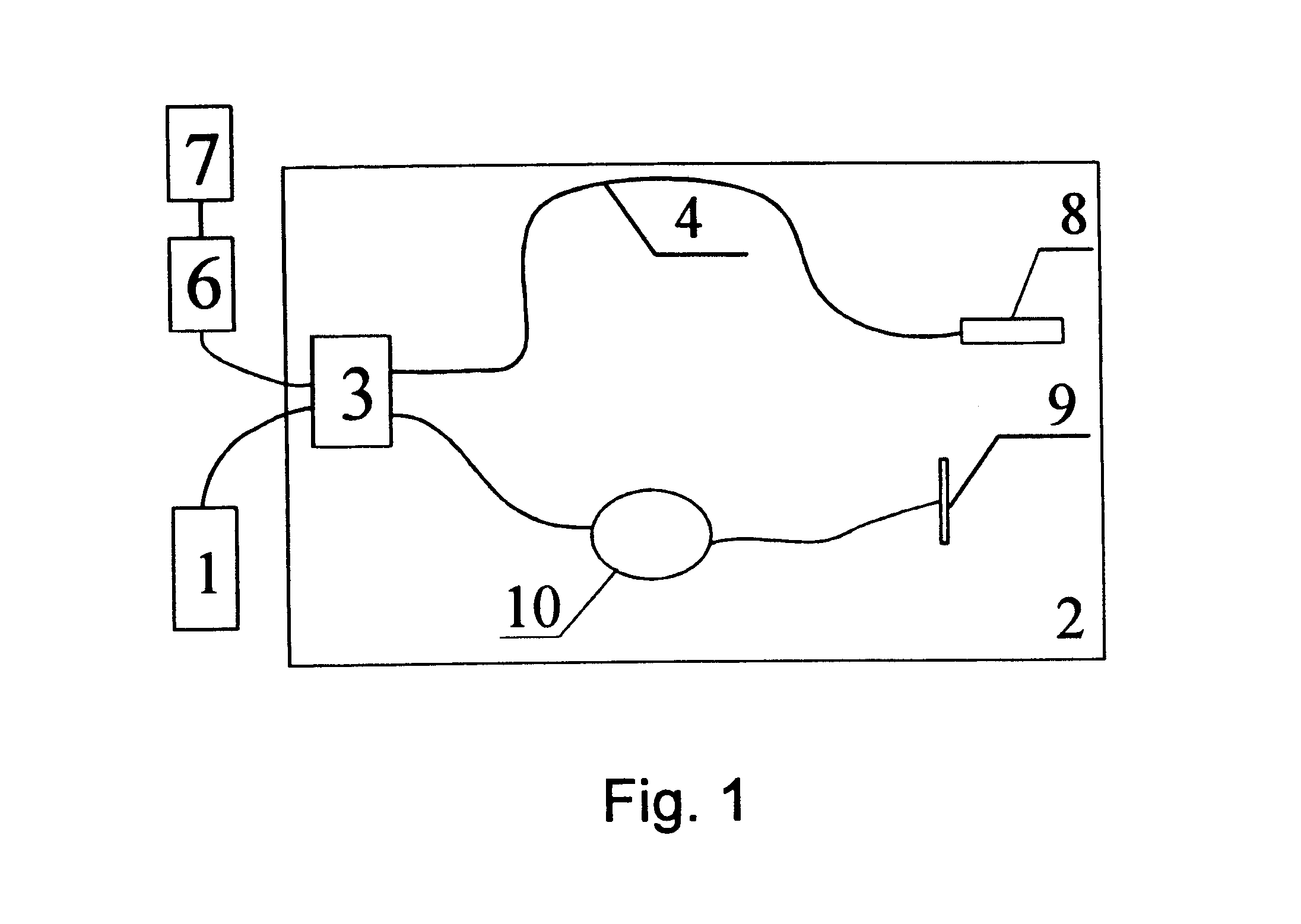
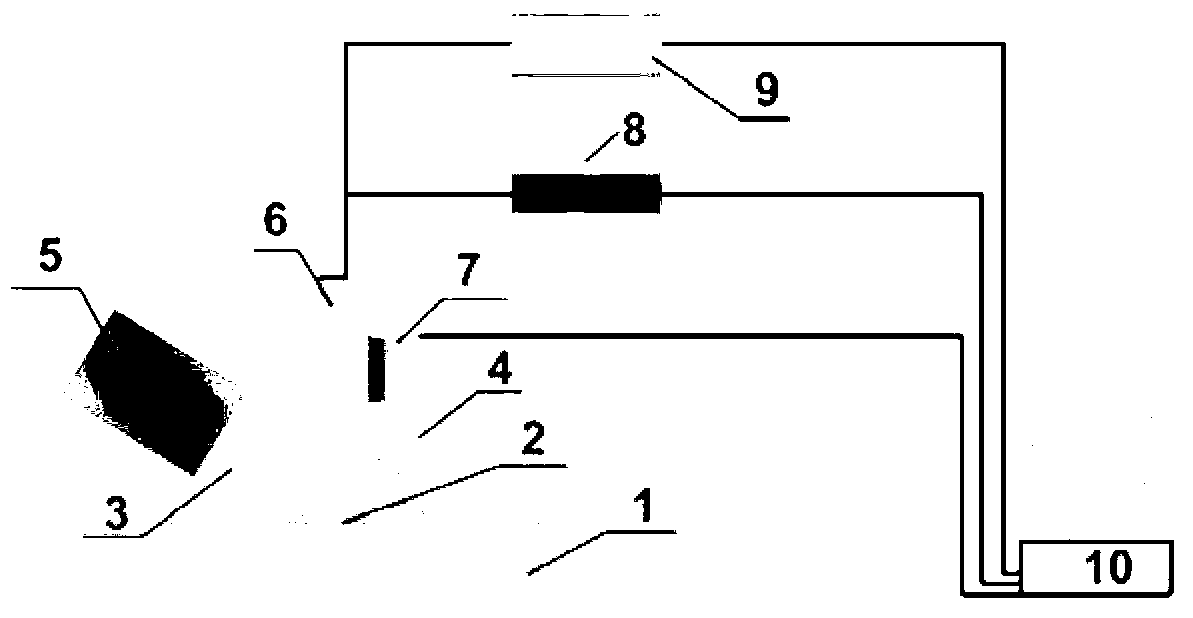
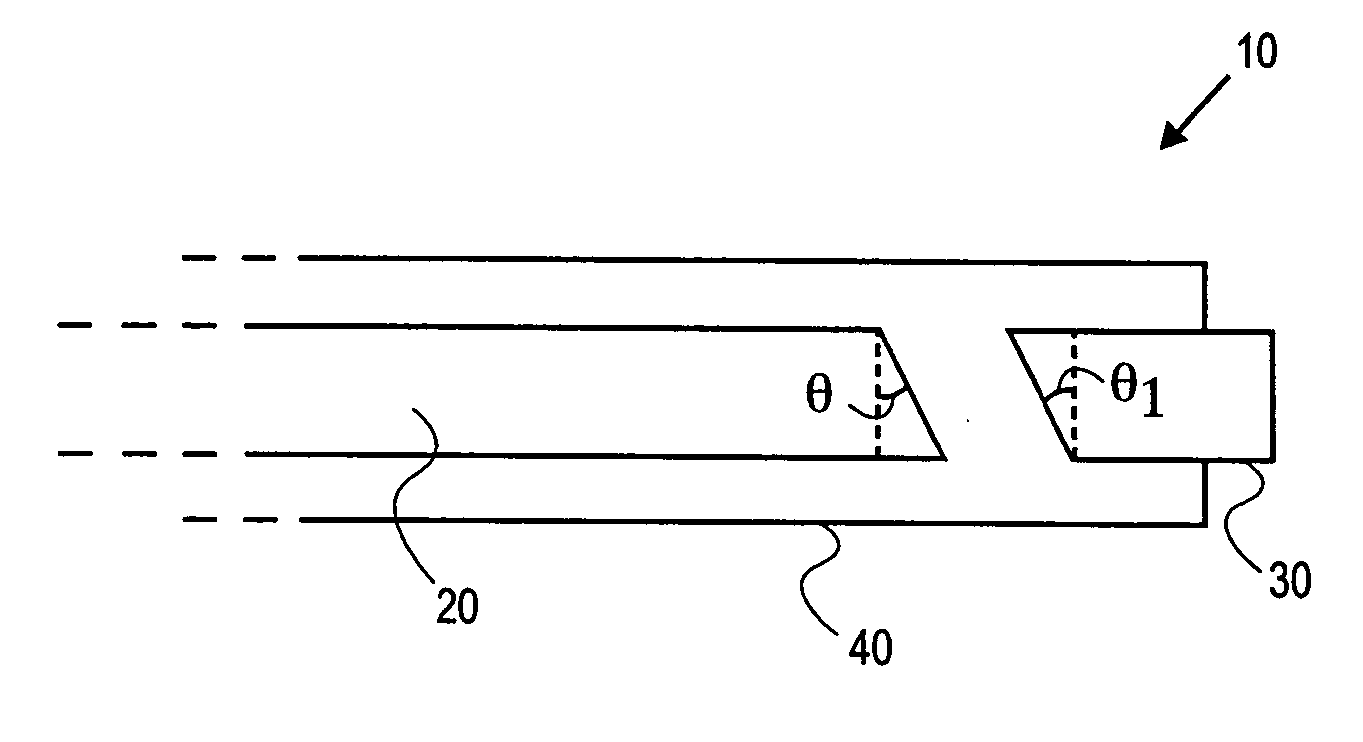
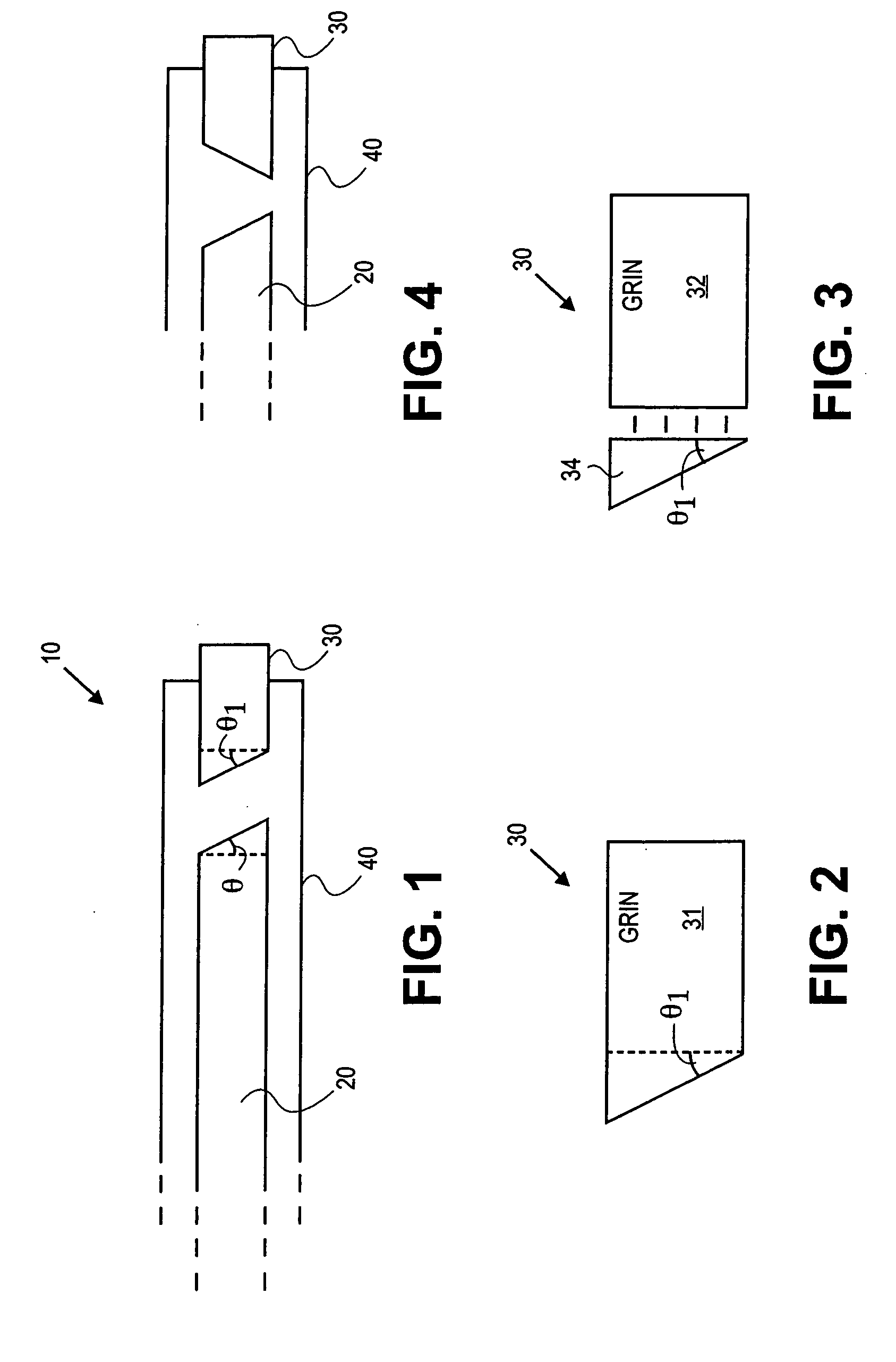
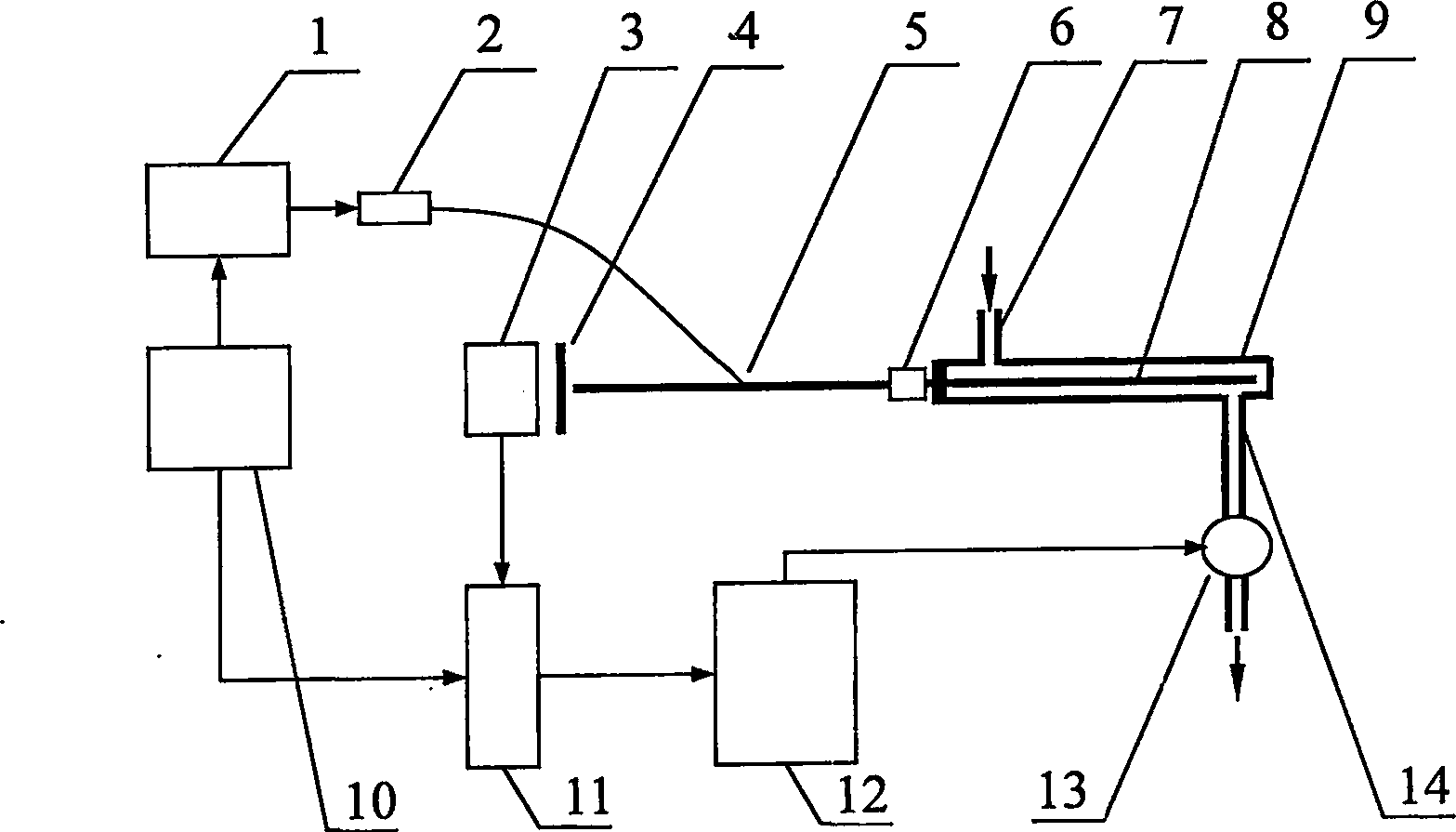
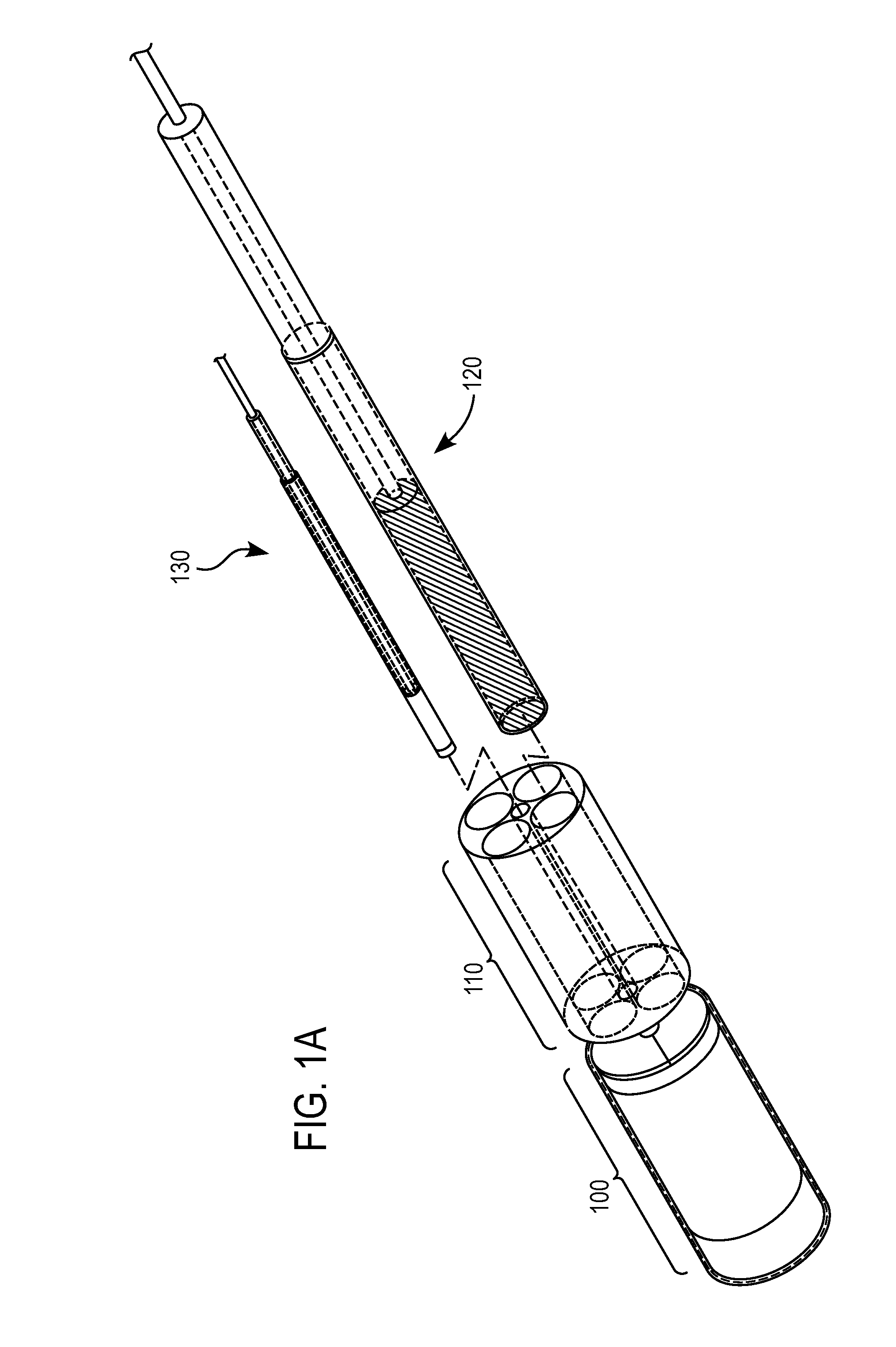
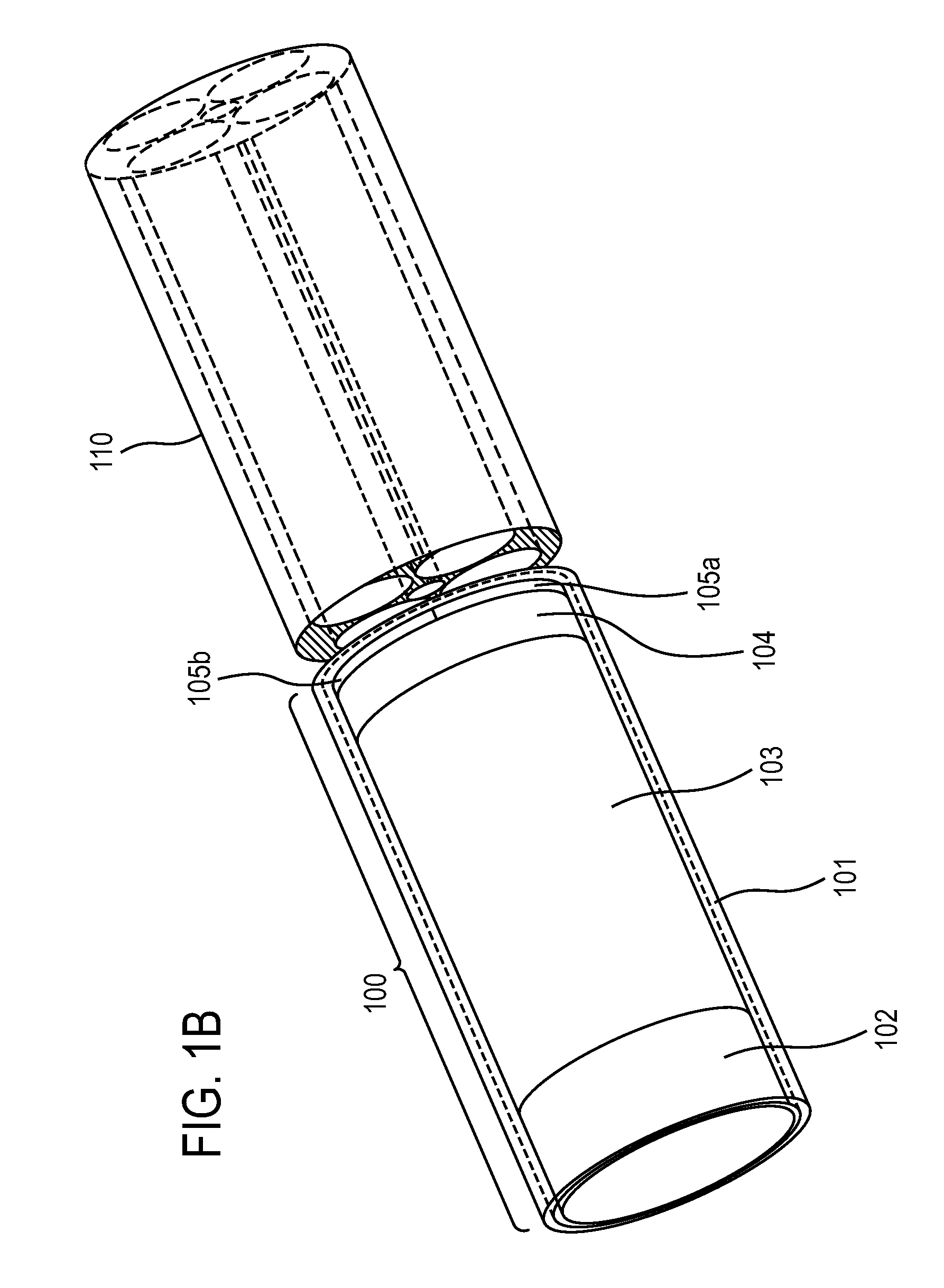
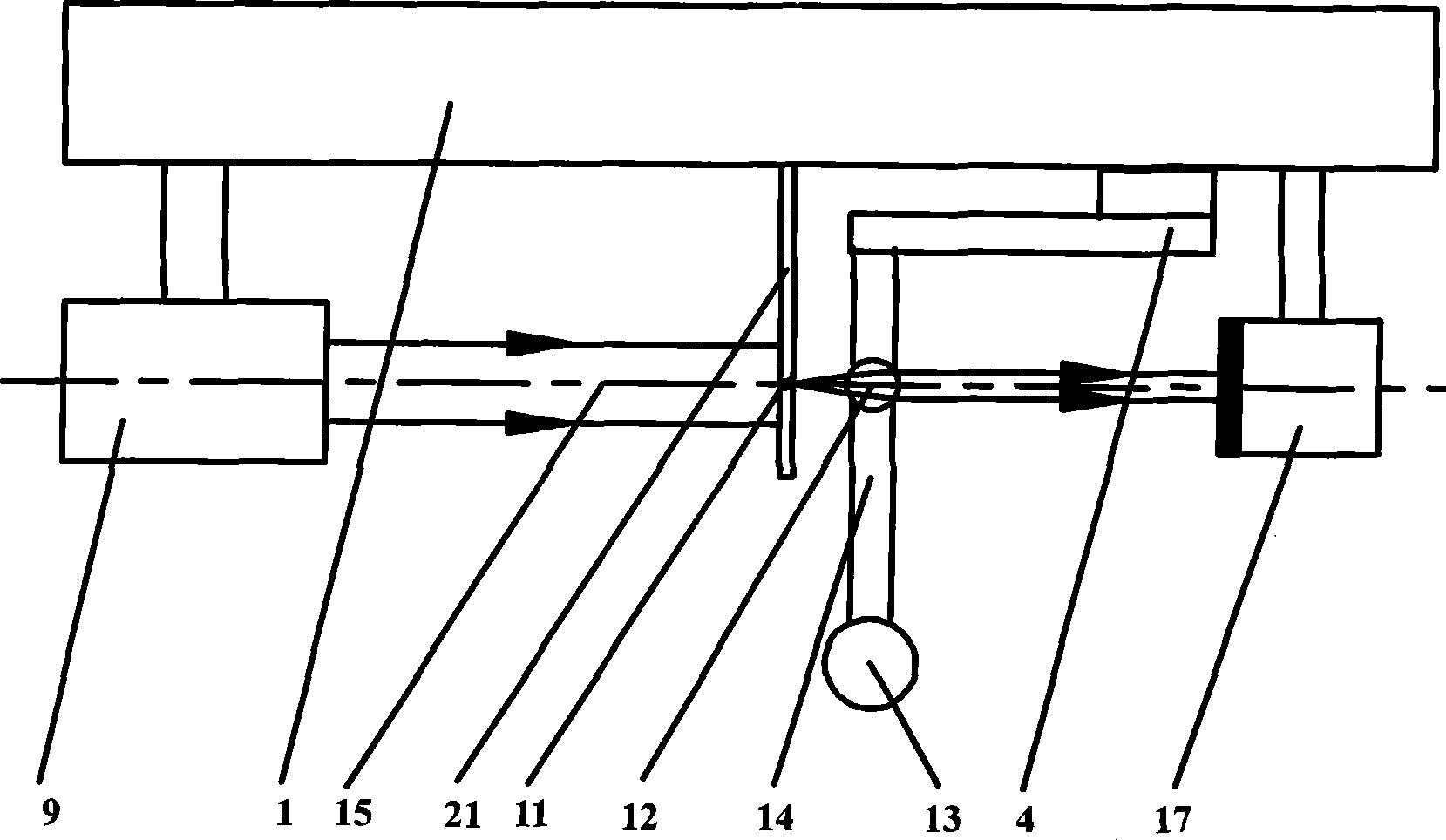
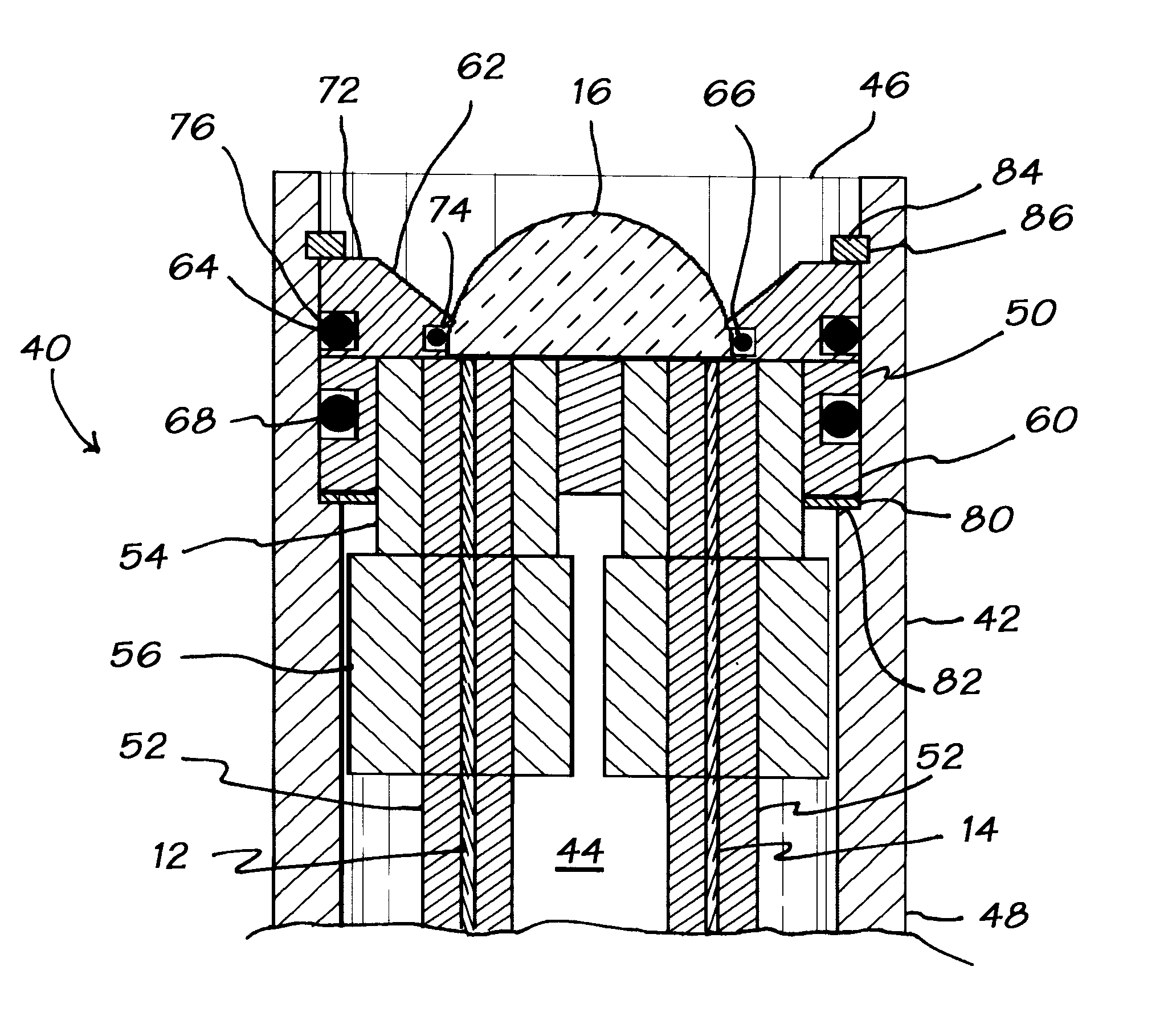
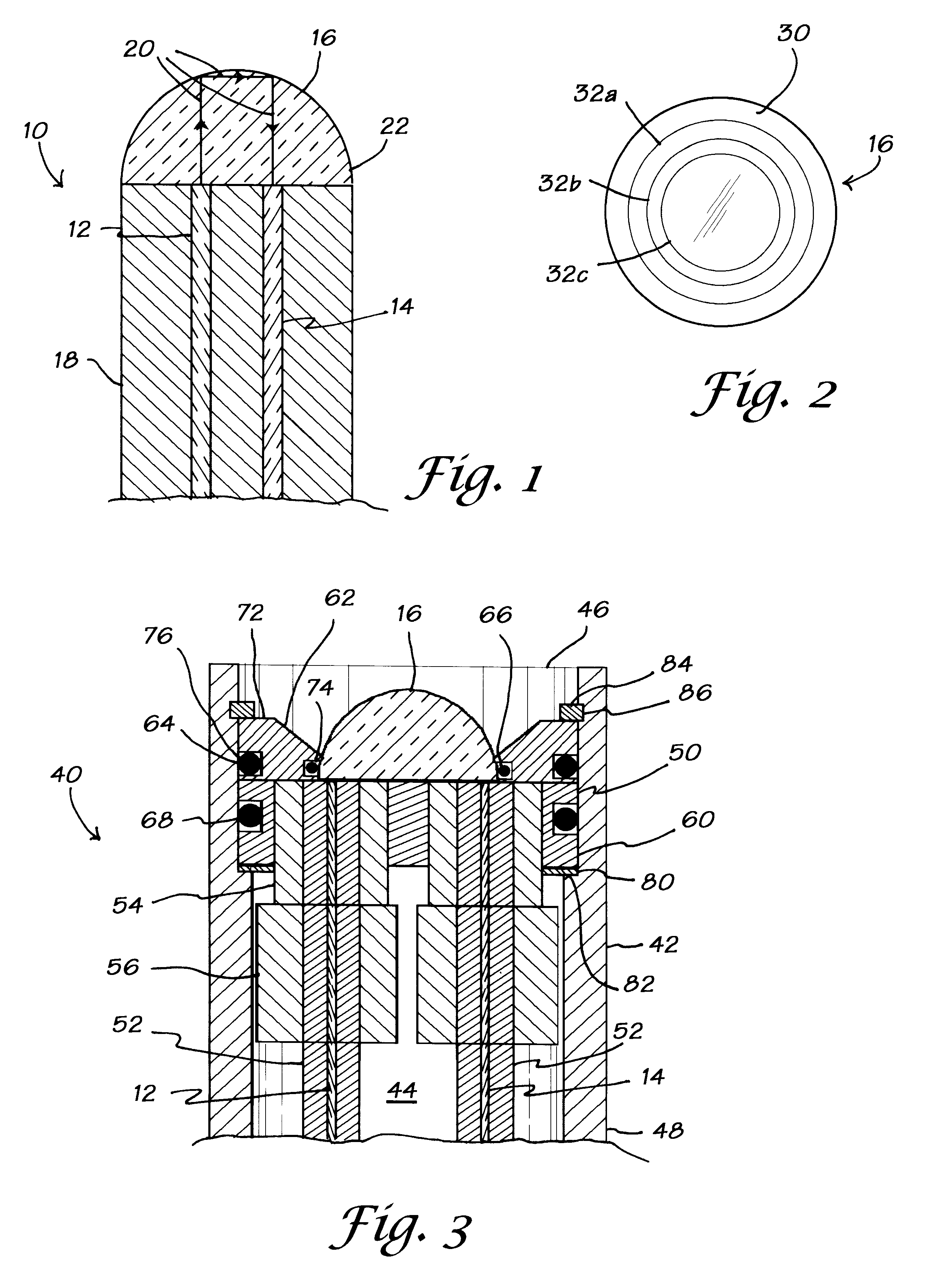
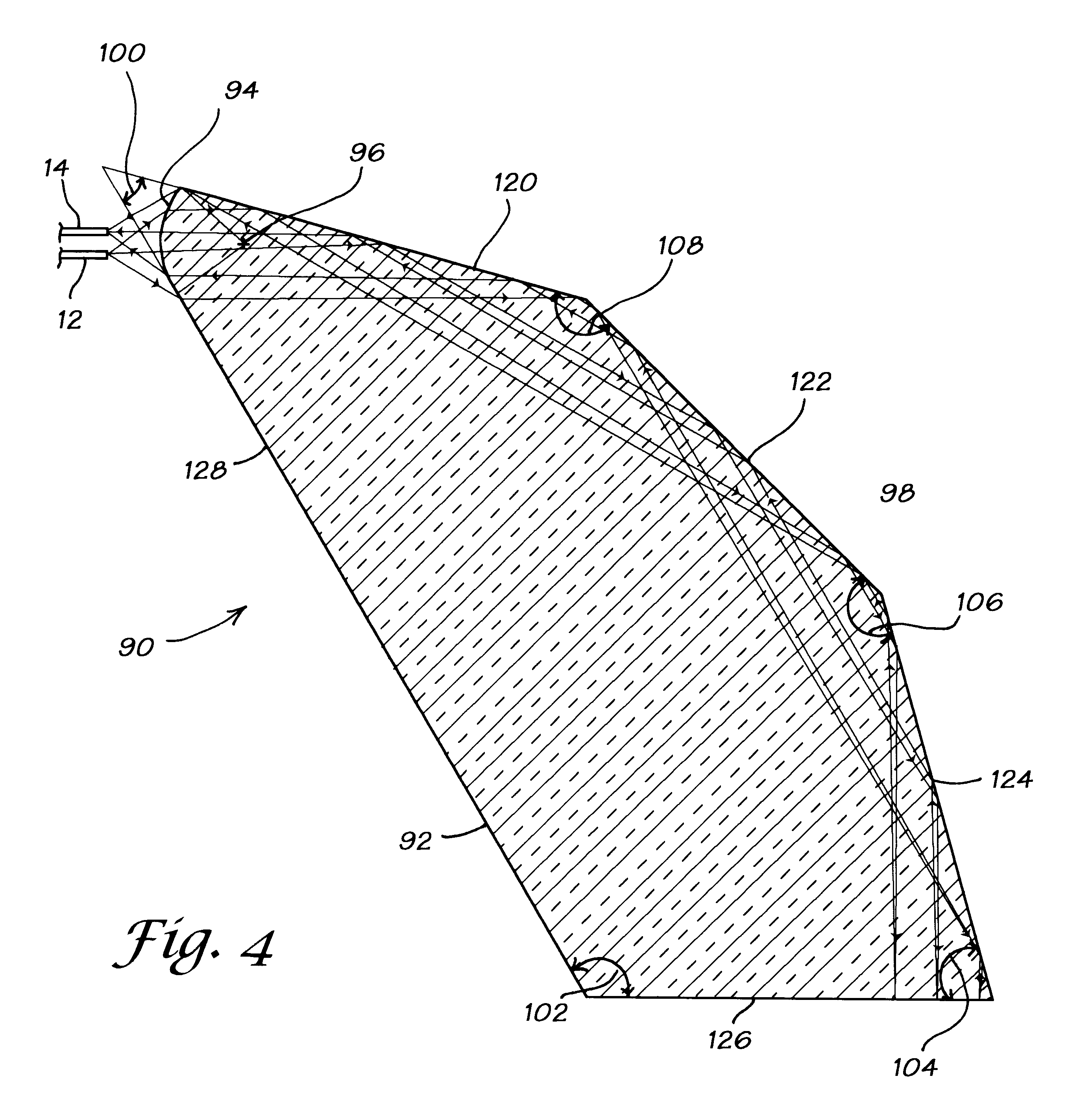
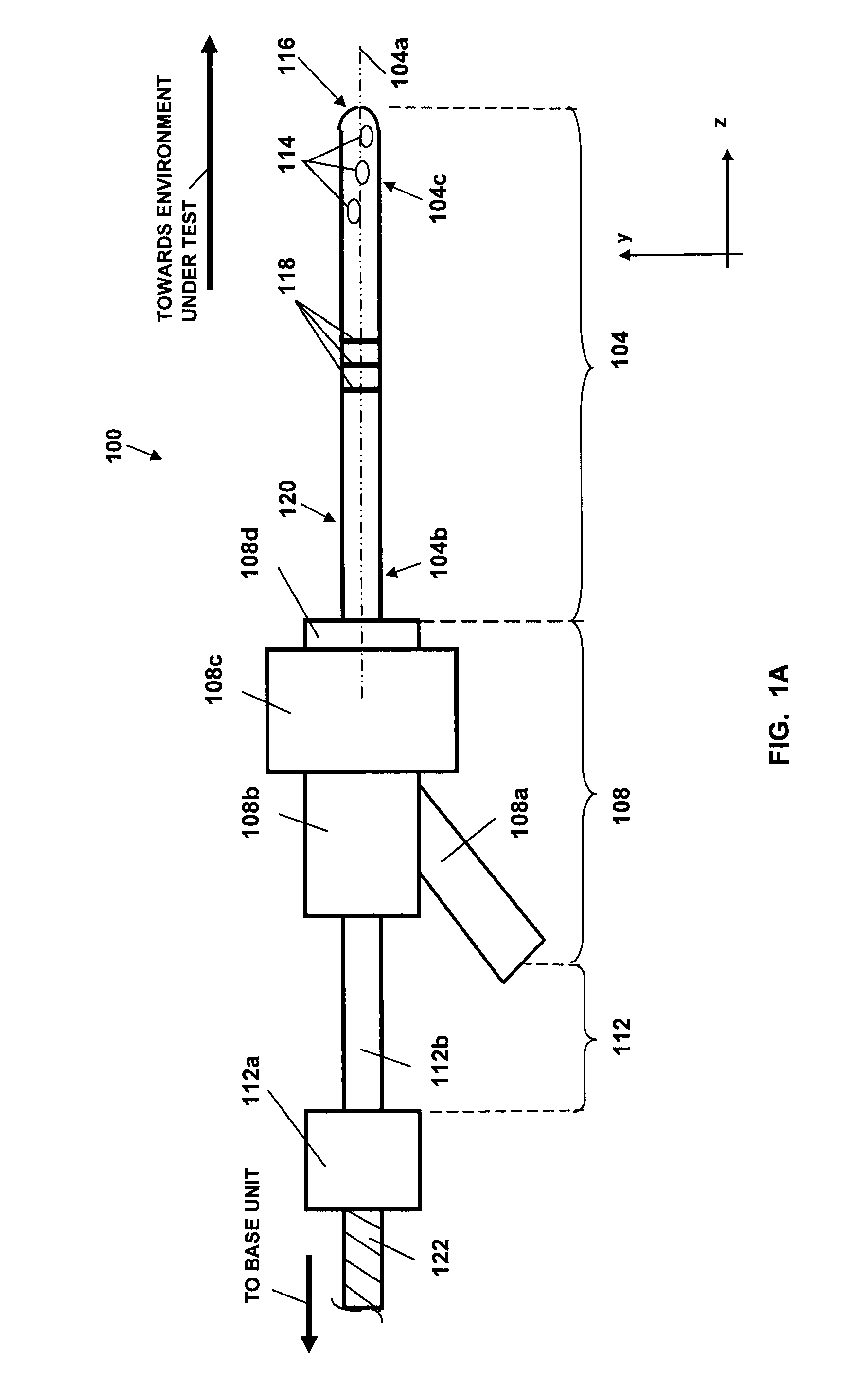
Forward scanning imaging optical fiber probe
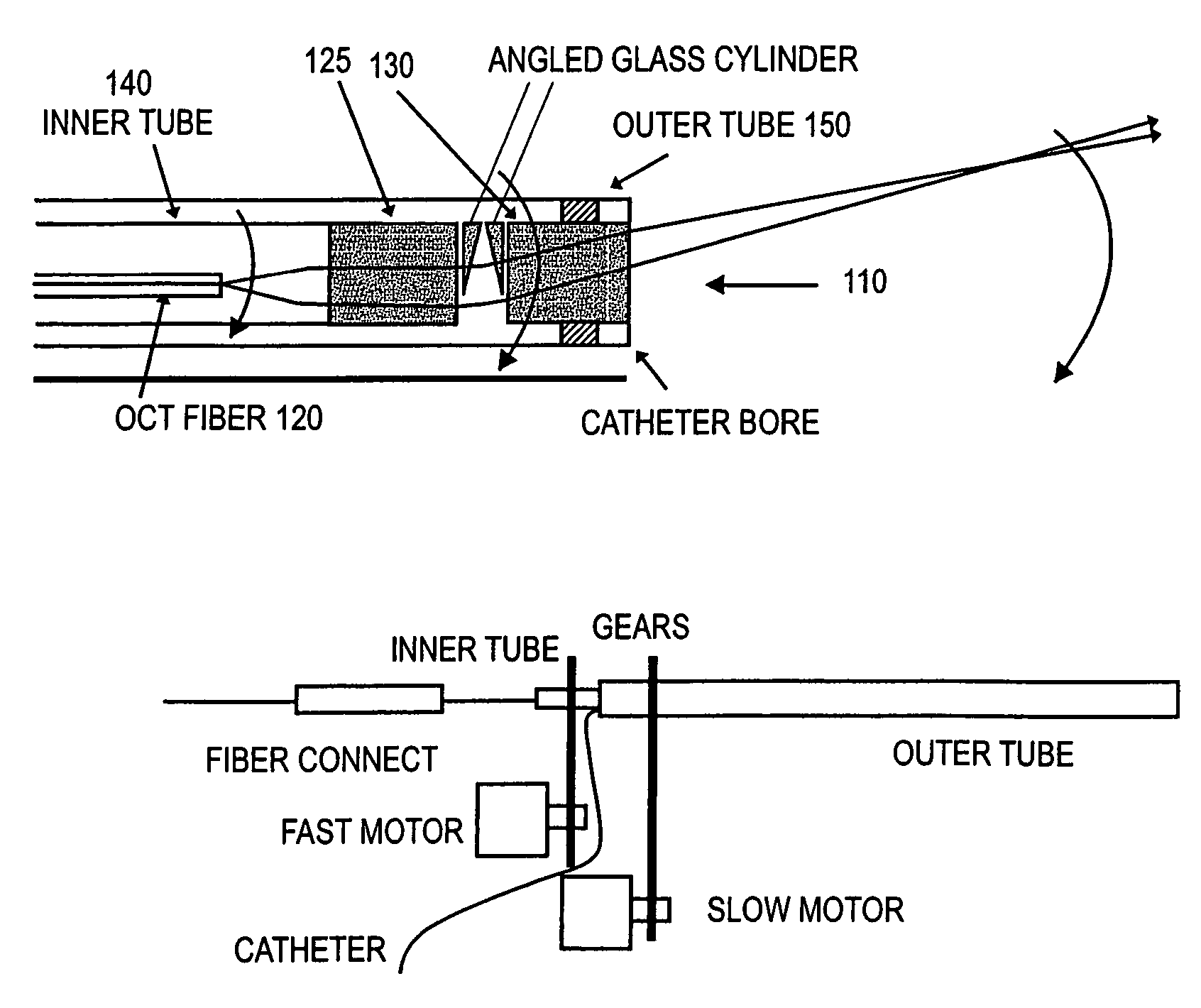
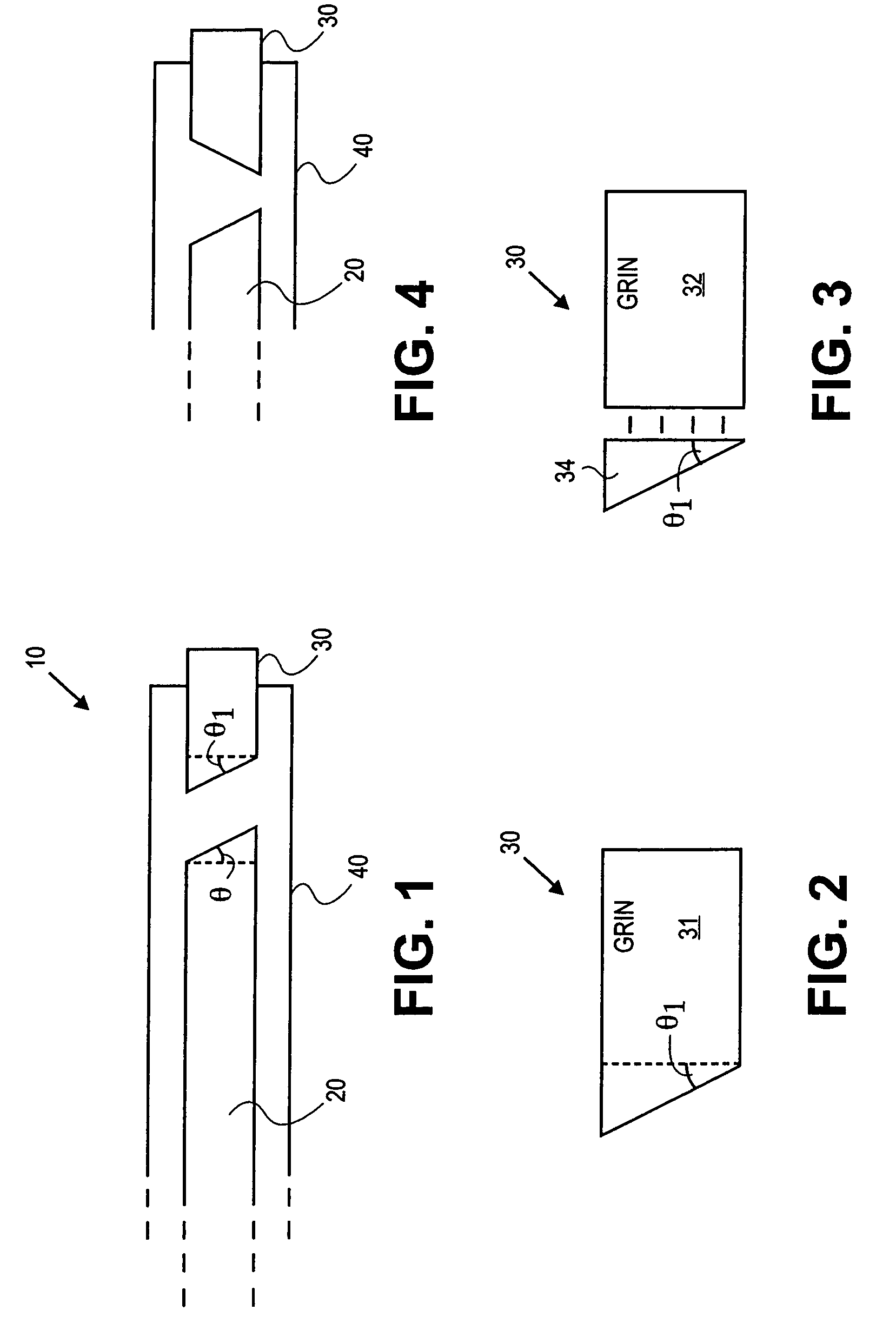
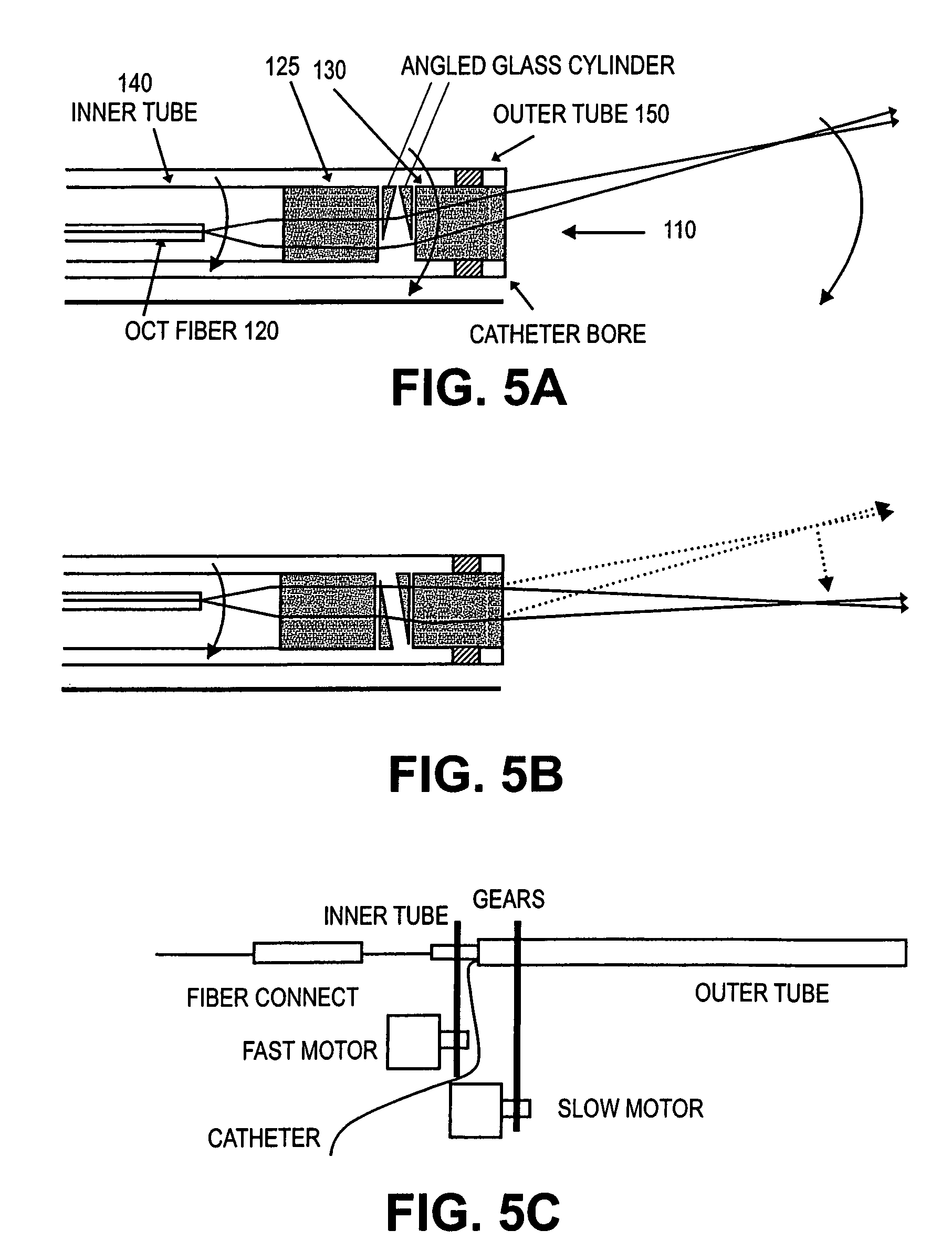
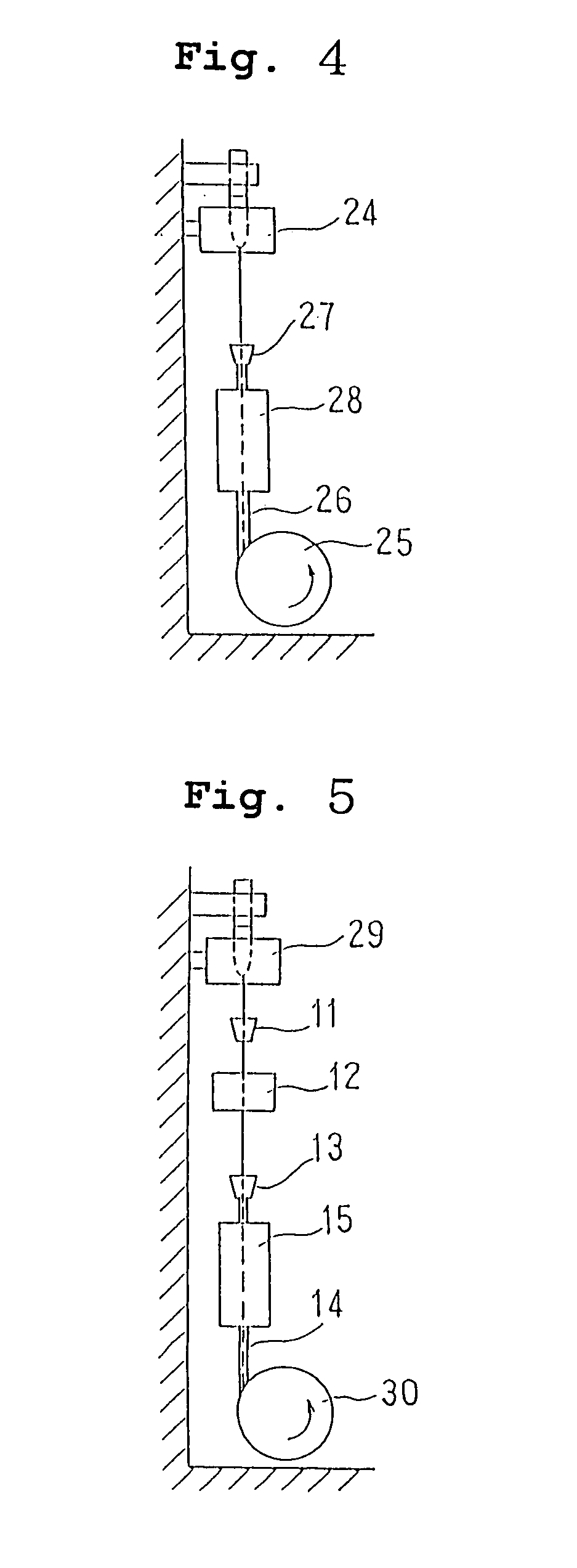
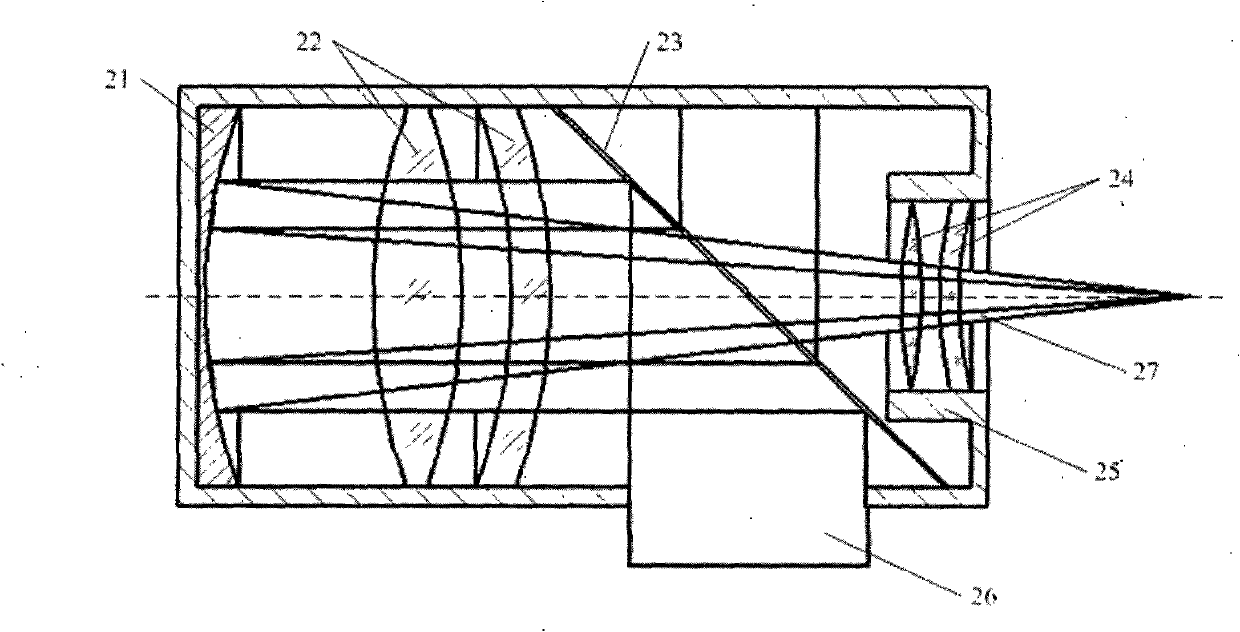
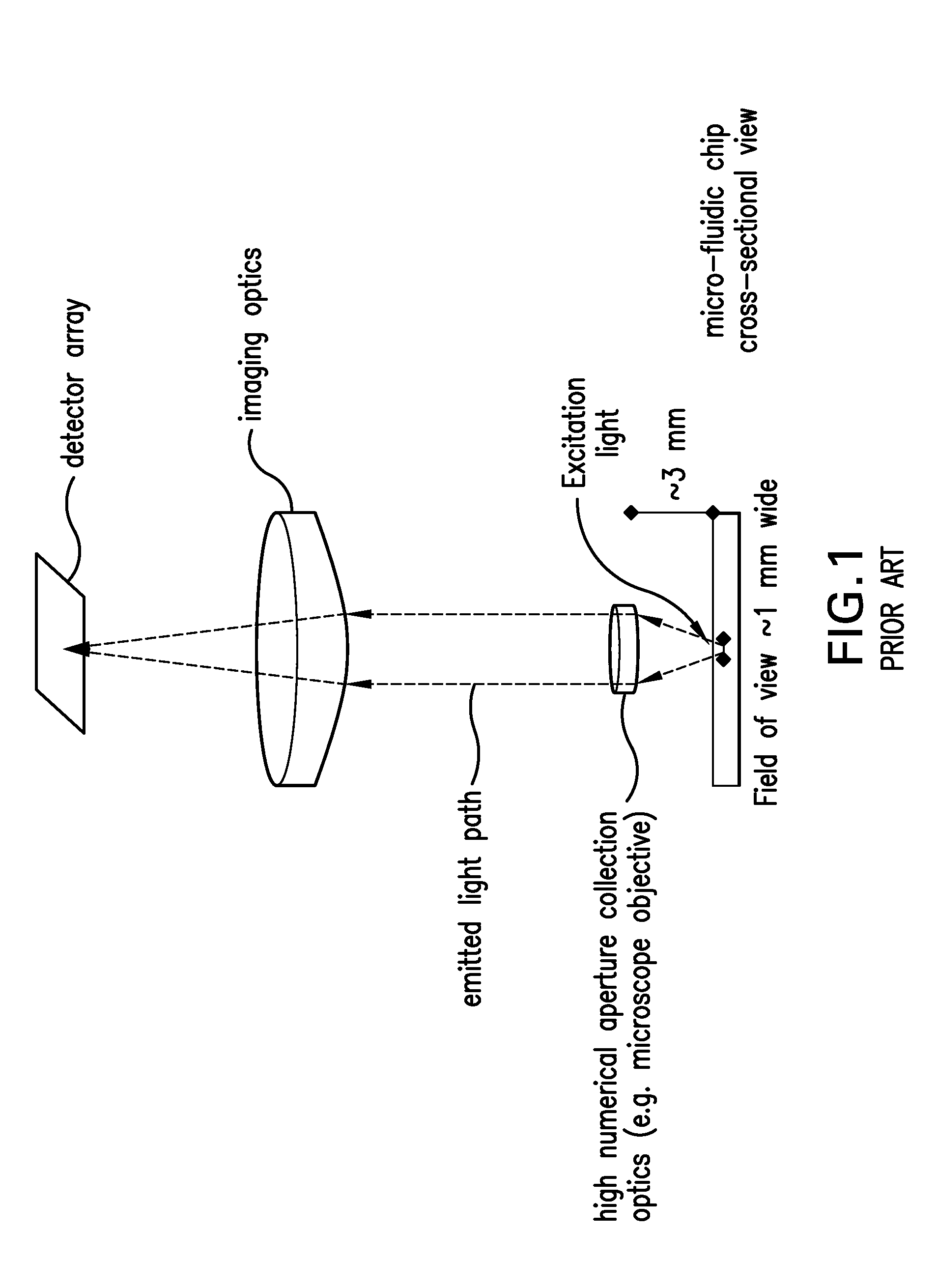
Probes, and systems and methods for optically scanning a conical volume in front of a probe, for use with an imaging modality, such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). A probe includes an optical fiber having a proximal end and a distal end and defining an axis, with the proximal end of the optical fiber being proximate a light source, and the distal end having a first angled surface. A refractive lens element is positioned proximate the distal end of the optical fiber. The lens element and the fiber end are both configured to separately rotate about the axis so as to image a conical scan volume when light is provided by the source. Reflected light from a sample under investigation is collected by the fiber and analyzed by an imaging system. Such probes may be very compact, e.g., having a diameter 1 mm or less, and are advantageous for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
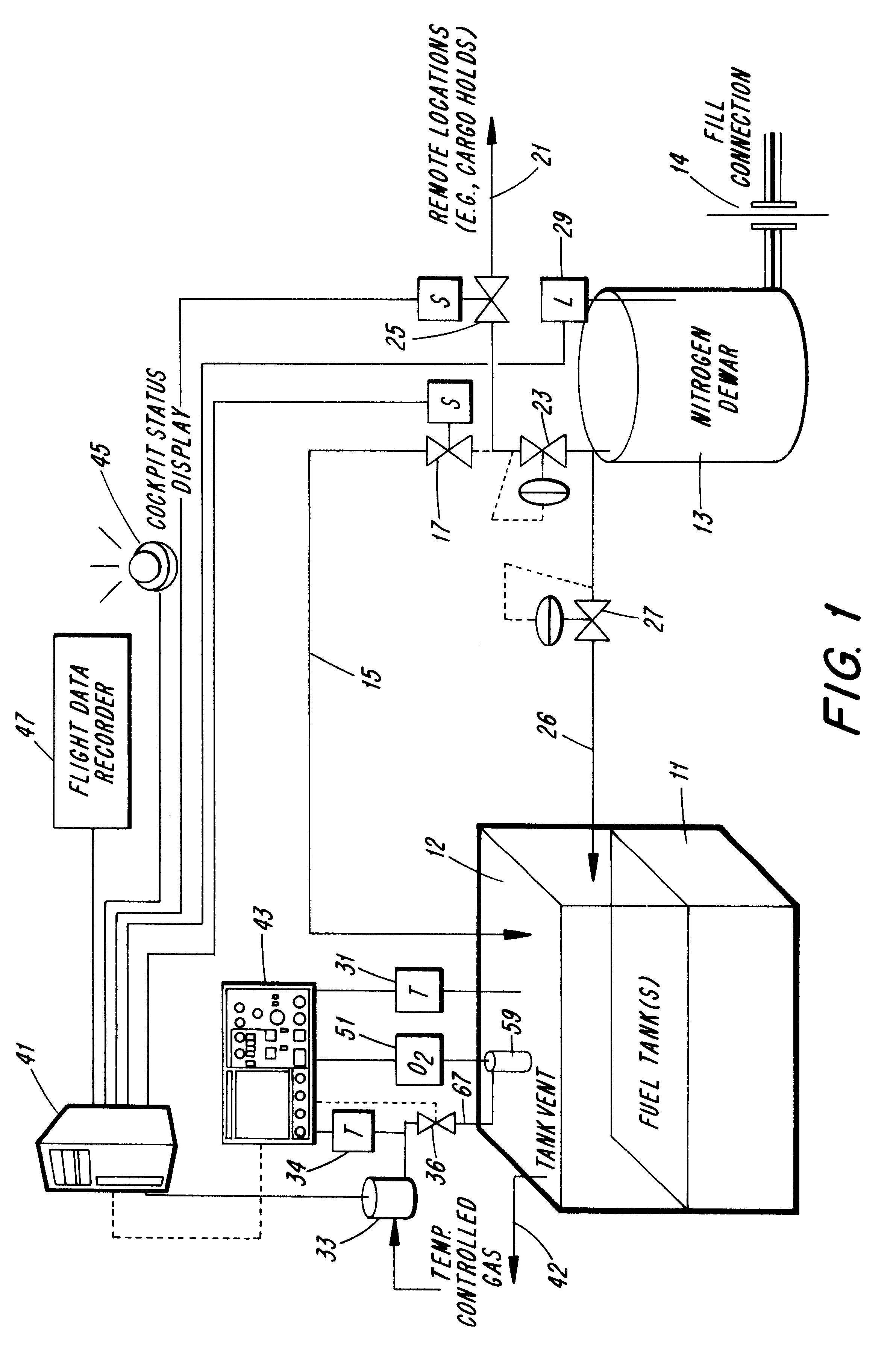
On-board fuel inerting system
InactiveUS6634598B2Effective monitoringExplosion is minimized and eliminatedPower plant fuel tanksFuel tank safety measuresUllageNitrogen gas
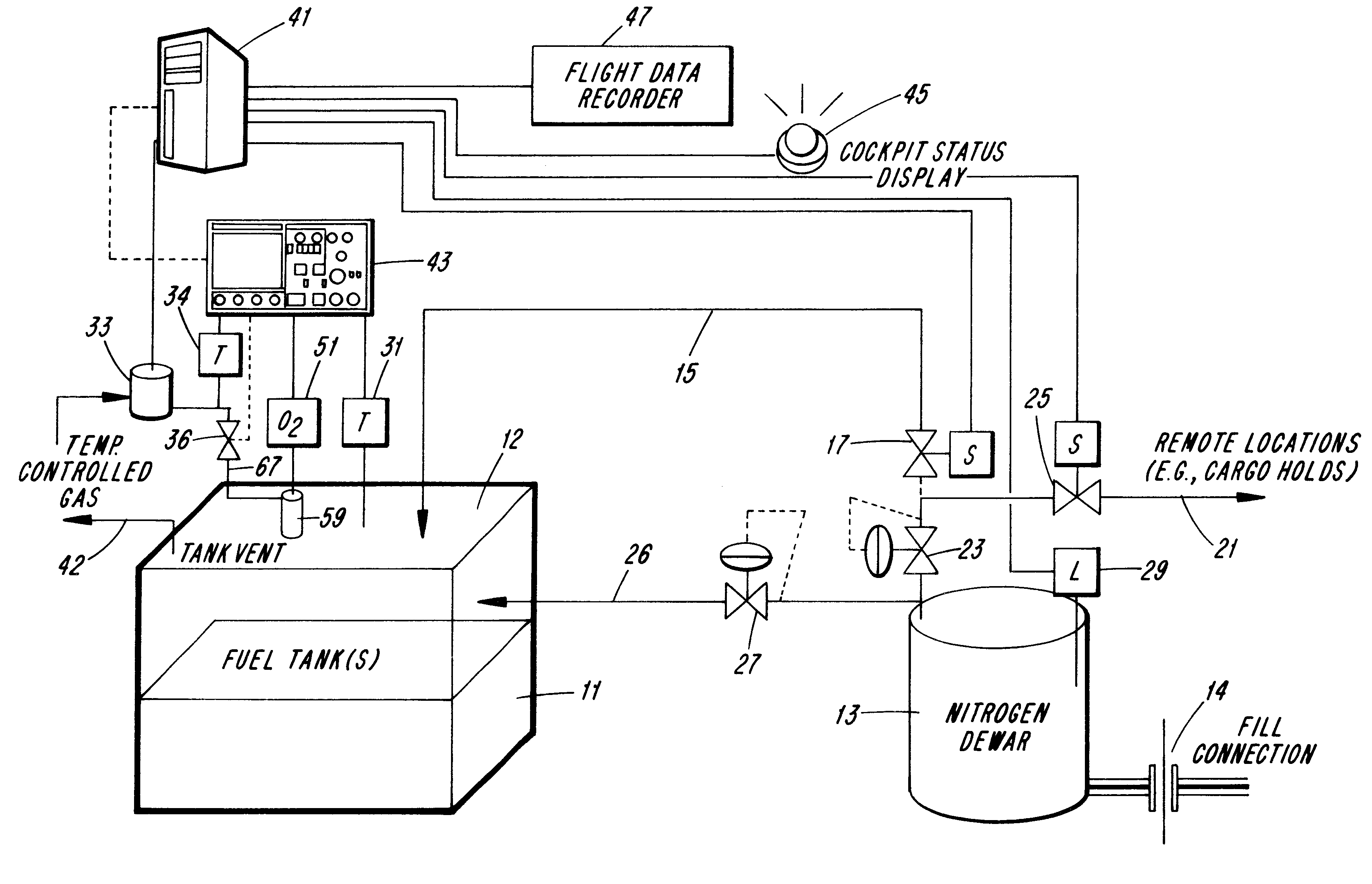
An inerting system is disclosed that is adaptable to inert the fuel tank of a vehicle, most typically an aircraft, that includes an oxygen detector to monitor the oxygen partial pressure of the vapors in the ullage (i.e., the overfuel) volume of the tank, a source of an inert gas (e.g., nitrogen) in valved communication with the ullage of the tank, and a detector for sensing the oxygen content in the ullage of the tank and controlling the flow of inert gas to the tillage to maintain that volume with a proportion oxygen that will not support combustion in the event of an ignition source or intrusion of another potentially explosive occurrence within said tank. A specific fiberoptic probe which enables monitoring oxygen content within the tank without introducing a source of electrical current within the tank is also disclosed.
Owner:SUSKO KENNETH
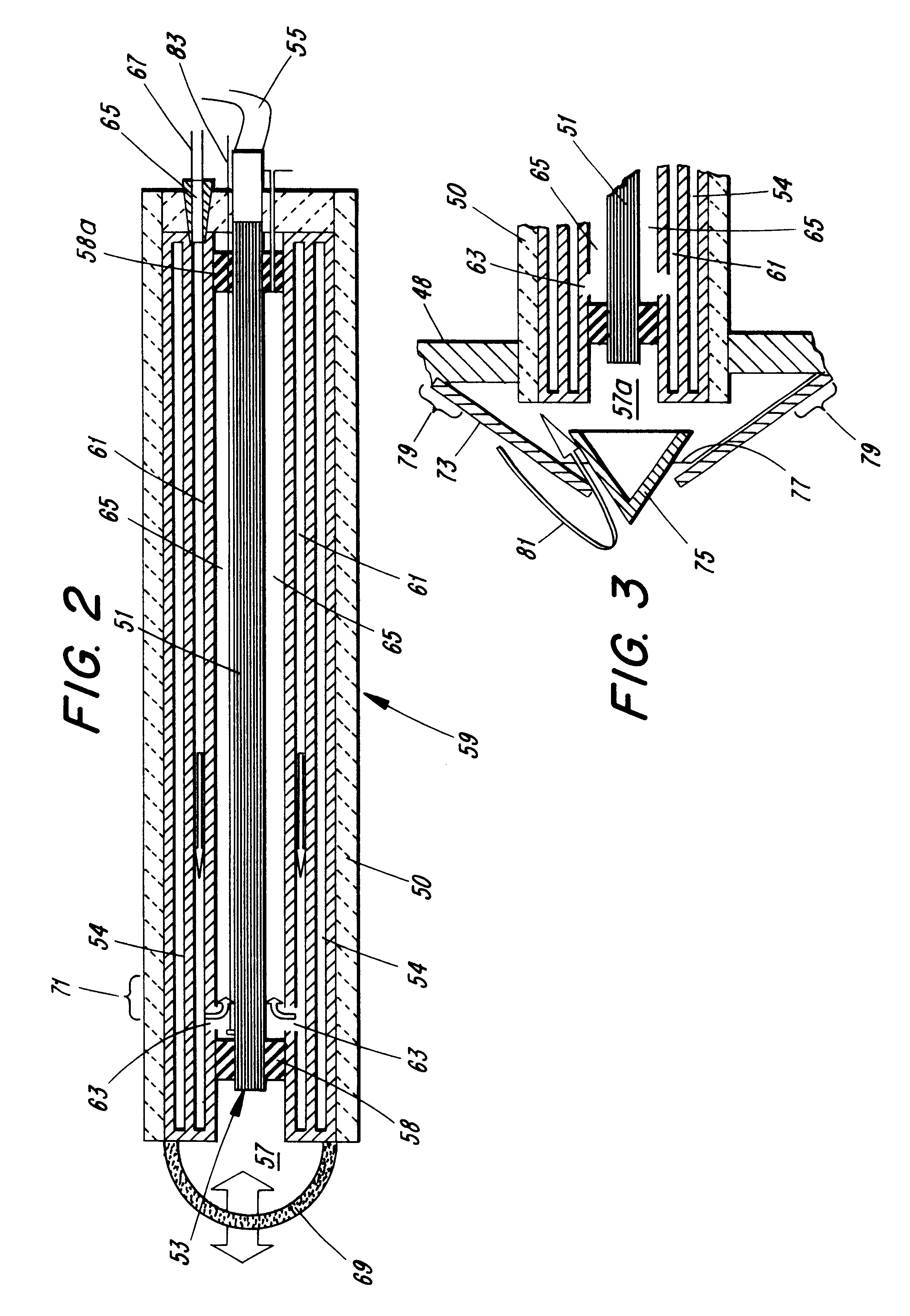
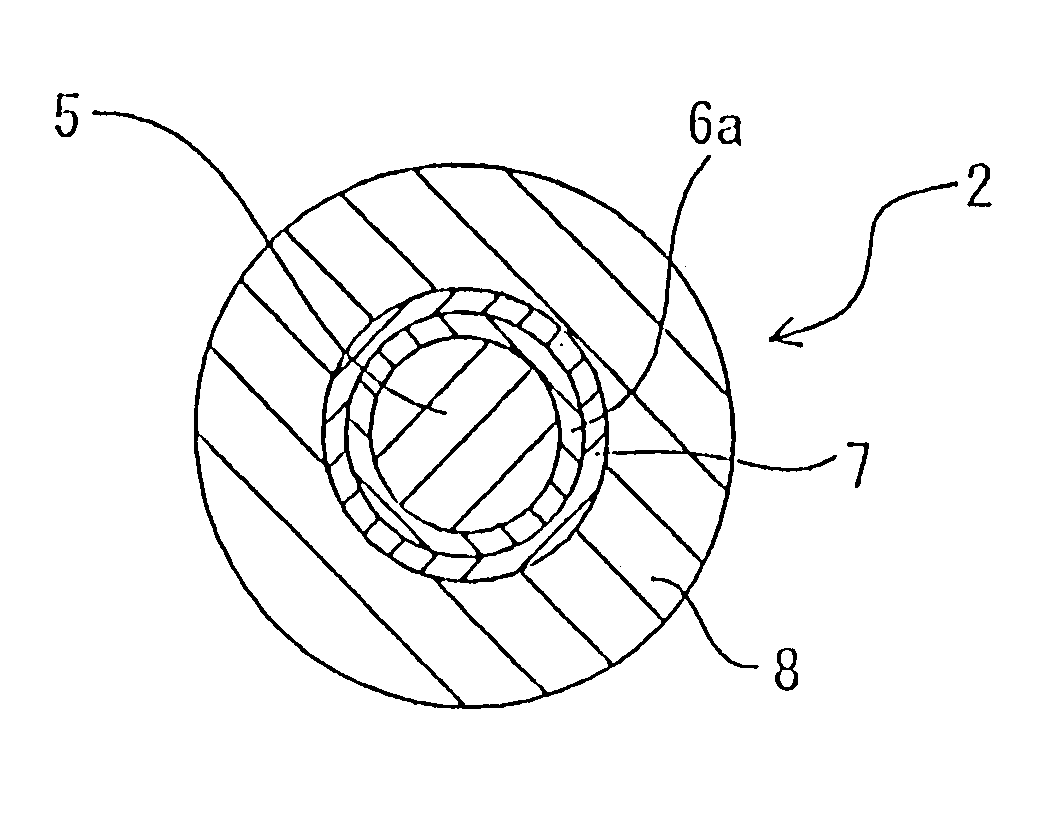
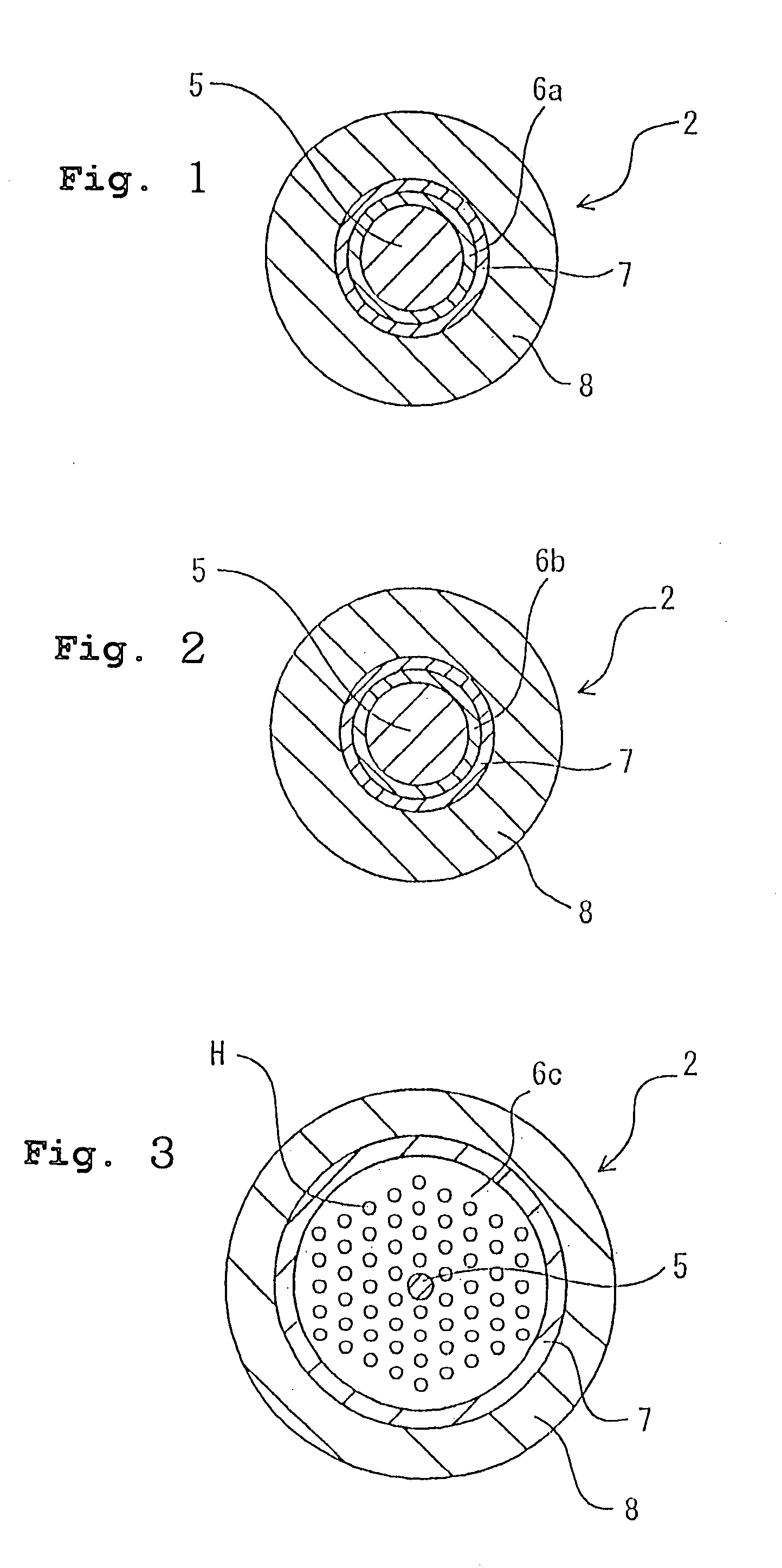
Optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray, optical fiber probe, and method of manufacturing the optical fiber probe
InactiveUS6944380B1High light transmittanceResistant to deteriorationGlass optical fibreGlass making apparatusFiberHydrogen
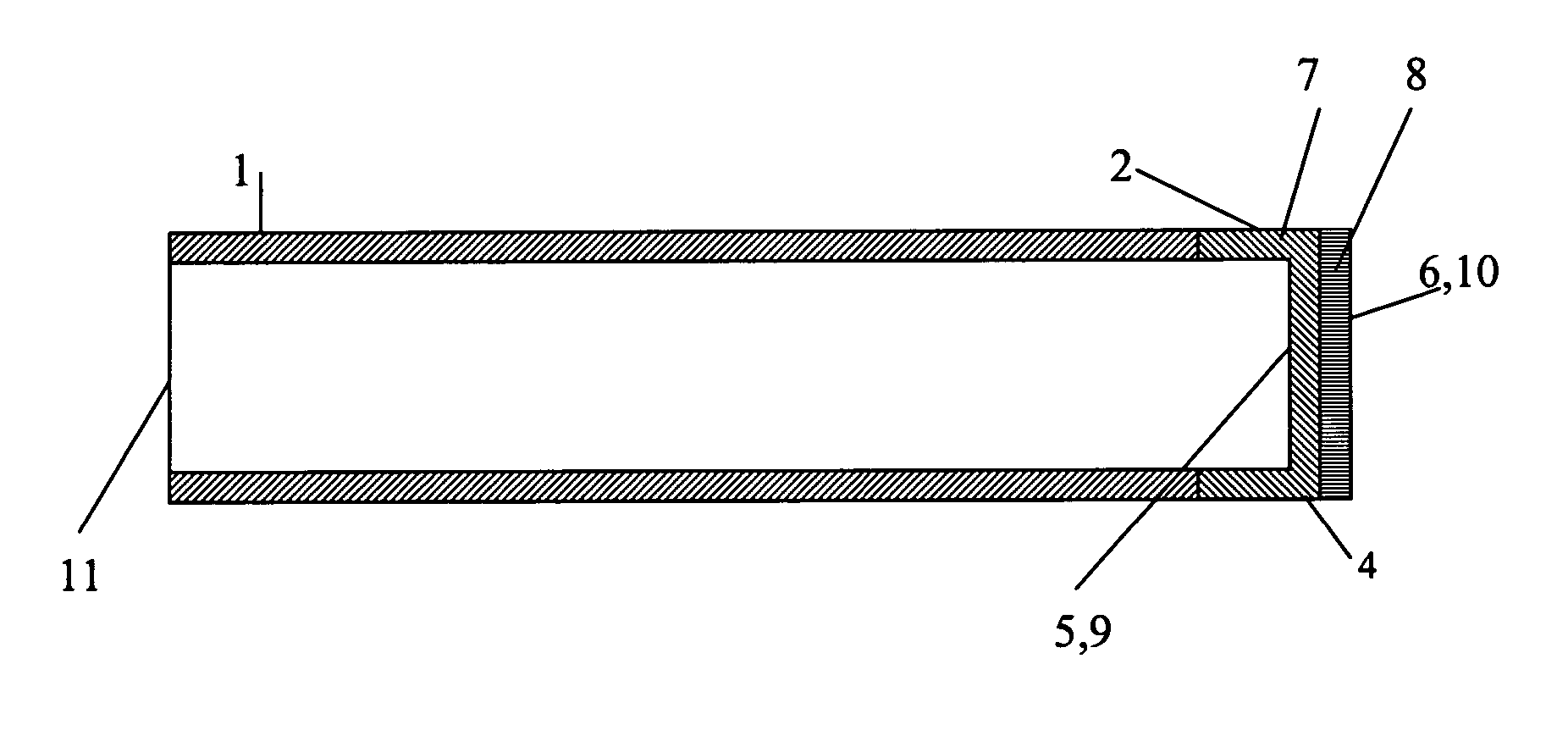
It is an object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray which has an improve transmittance and is prevented from deterioration by ultraviolet ray with which it is irradiated. It is another object of the present invention to provide an optical fiber probe which can propagate vacuum ultraviolet ray and deep ultraviolet ray at a high transmittance, is deteriorated only to a limited extent when irradiated with ultraviolet ray and can be etched to have a desired shape of the sharpened section at the fiber end.The present invention provides the optical fiber for transmitting ultraviolet ray which has a core 5 of silica glass containing a given content of fluorine and a clad 6a of silica glass containing a given content of fluorine or boron, a clad 6b of a resin which transmits ultraviolet ray or a clad 6c having air holes H. The clad may be coated with a protective layer and further with a covered layer for protection. In particular, the core, clad and protective layer have a high transmittance for ultraviolet ray and resistance to ultraviolet ray with which they are irradiated, when treated with hydrogen.An optical fiber probe 1 has an optical fiber 2 provided with a sharpened section 3 at the end, which is sharpened with an etchant solution, the sharpened section 3 being coated with a light-shielding metallic film 4.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry/tomography device
InactiveUS7428053B2Relieving the requirements to the spectral resolutionEliminate the problemInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical radiationData acquisition
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry / tomography devices include a portion of optical fiber with predetermined optical properties adapted for producing two eigen modes of the optical radiation propagating therethrough with a predetermined optical path length difference. The two replicas of the optical radiation outgoing from the portion of the optical fiber are then delivered to an associated sample by an optical fiber probe. The tip of the optical fiber serves as a reference reflector and also serves as a combining element that produces a combination optical radiation by combining an optical radiation returning from the associated sample with a reference optical radiation reflected from the reference reflector. The topology of the devices allows for registering a cross-polarized or a parallel-polarized component of the optical radiation reflected or backscattered from the associated sample. Having the optical path length difference for the two eigen modes of the optical radiation (which is an equivalent of an interferometer offset in previously known devices) differ from the reference offset in the devices of the present invention allows for relieving the requirements to the spectral resolution of the FD OCT engine and / or data acquisition and processing system, and substantially eliminates depth ambiguity problems.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometer and common path frequency domain optical coherence tomography device
InactiveUS7426036B2Improve fluencyImprove signal-to-noise ratioInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansData acquisitionHandling system
Common path frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry / tomography devices with an additional interferometer are suggested. The additional interferometer offset is adjusted such, that it is ether less than the reference offset, or exceeds the distance from the reference reflector to the distal boundary of the longitudinal range of interest. This adjustment allows for relieving the requirements to the spectral resolution of the frequency domain optical coherence reflectometry / tomography engine and / or speed of the data acquisition and processing system, and eliminates depth ambiguity problems. The new topology allows for including a phase or frequency modulator in an arm of the additional interferometer improving the signal-to-noise ratio of the devices. The modulator is also capable of substantially eliminating mirror ambiguity, DC artifacts, and autocorrelation artifacts. The interference signal is produced either in the interferometer or inside of the optical fiber probe leading to the sample.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Polarization-sensitive common path optical coherence reflectometry/tomography device
Polarization sensitive common path OCT / OCR devices are presented. Optical radiation from a source is converted into two cross-polarized replicas propagating therethrough with a predetermined optical path length difference. The two cross-polarized replicas are then delivered to an associated sample by a delivering device, which is, preferably, an optical fiber probe. A combination optical radiation is produced in at least one secondary interferometer by combining a corresponding portion of an optical radiation returning from the associated sample with a reference optical radiation reflected from a tip of an optical fiber of the optical fiber probe. Subject to a preset optical path length difference of the arms of the at least one secondary interferometer, a cross-polarized component, and / or a parallel-polarized component of the combined optical radiation, are selected. The topology of the devices allows for time domain, as well as for frequency domain registration.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Common path systems and methods for frequency domain and time domain optical coherence tomography using non-specular reference reflection and a delivering device for optical radiation with a partially optically transparent non-specular reference reflector
InactiveUS7821643B2Stable levelScattering properties measurementsUsing optical meansOptical radiationSpherical shaped
Provided are common path frequency domain and time domain OCT systems and methods that use non-specular reference reflection for obtaining internal depth profiles and depth resolved images of samples. Further provided is a delivering device for optical radiation, preferably implemented as an optical fiber probe with a partially optically transparent non-specular reflector placed in the vicinity of an associated sample. High frequency fringes are substantially reduced and a stable power level of the reference reflection is provided over the lateral scanning range. The partially optically transparent non-specular reflector is implemented as a coating placed on the interior surface of the optical probe window including spots of a metal, or a dielectric coating, separated by elements of another coating or just spaces of a clean substrate. In an alternative embodiment, the scattering elements are made 3-dimensional, having, for example, a spherical shape.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
Common path time domain optical coherence reflectometry/tomography device
InactiveUS7538886B2Reduce necessityInterferometersMaterial analysis by optical meansOptical radiationTomography
In common path time domain OCT / OCR devices optical radiation from a source is first split into two replicas, which are then delivered to an associated sample by an optical fiber probe. The tip of the optical fiber probe serves as a reference reflector and also serves as a combining element that produces a combination optical radiation by combining an optical radiation returning from the associated sample with a reference optical radiation reflected from the reference reflector. The topology of the devices eliminates the necessity of using Faraday mirrors, and also allows for registering a cross-polarized component of the optical radiation reflected or backscattered from the associated sample, as well as a parallel-polarized component.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
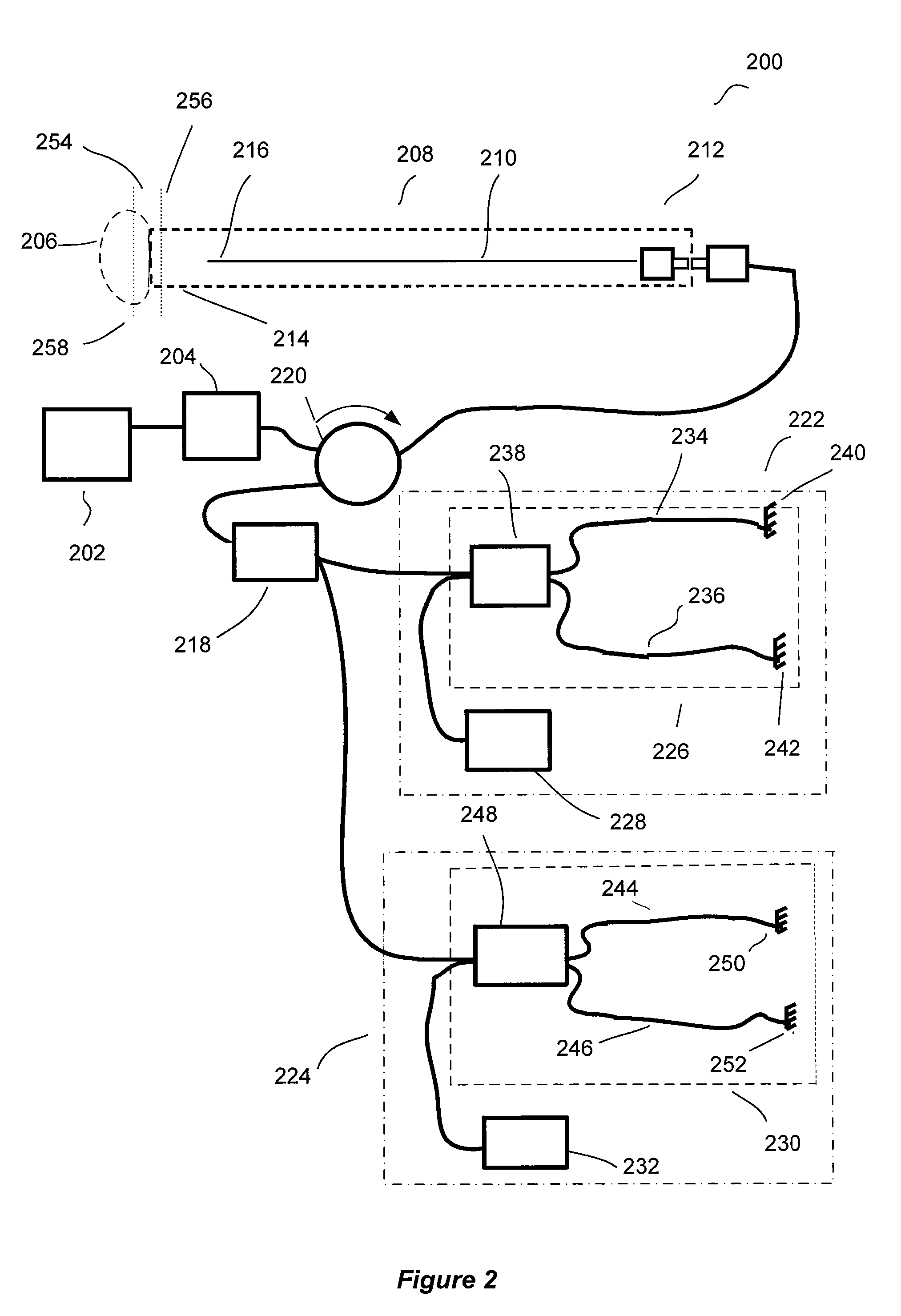
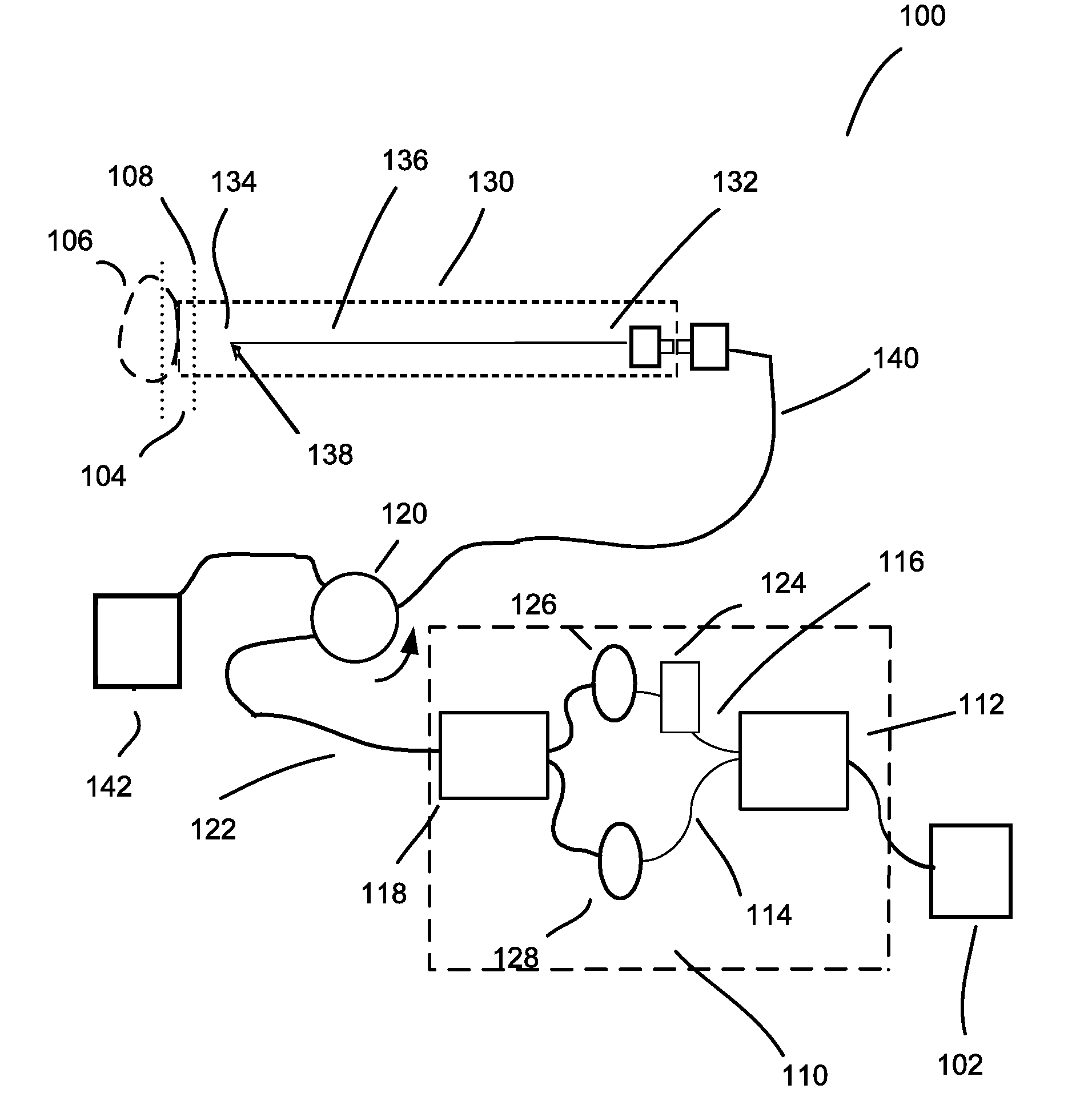
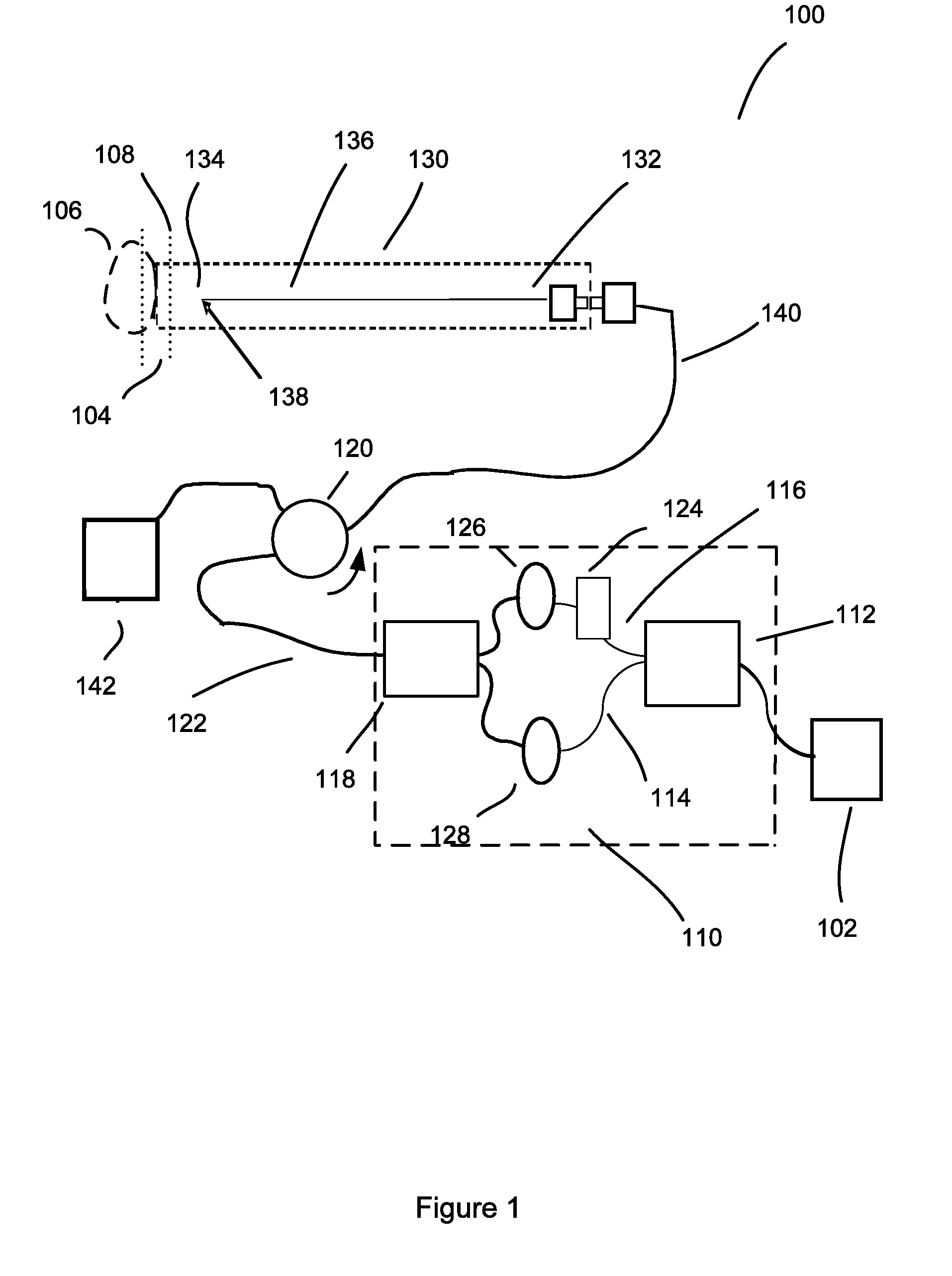
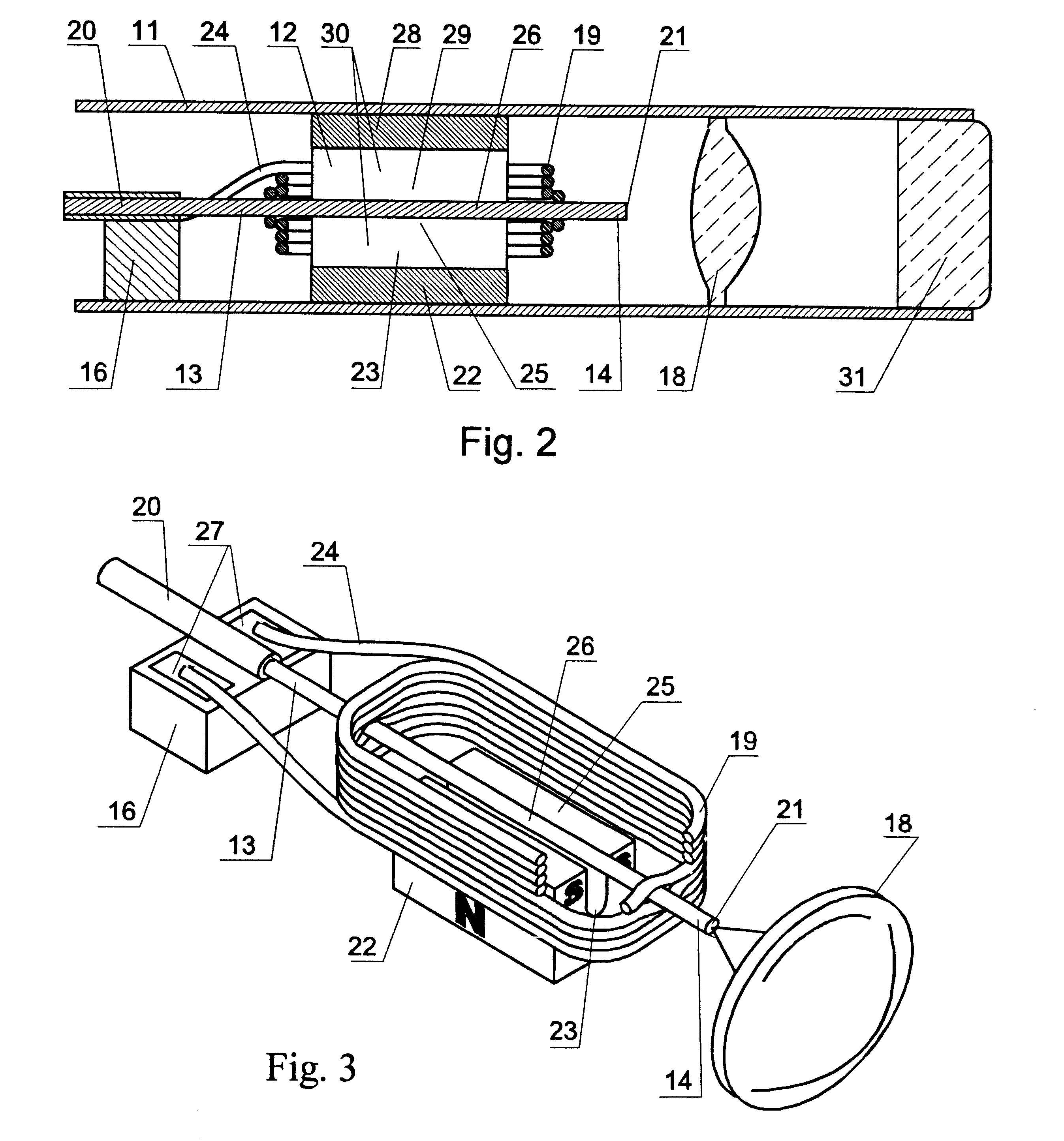
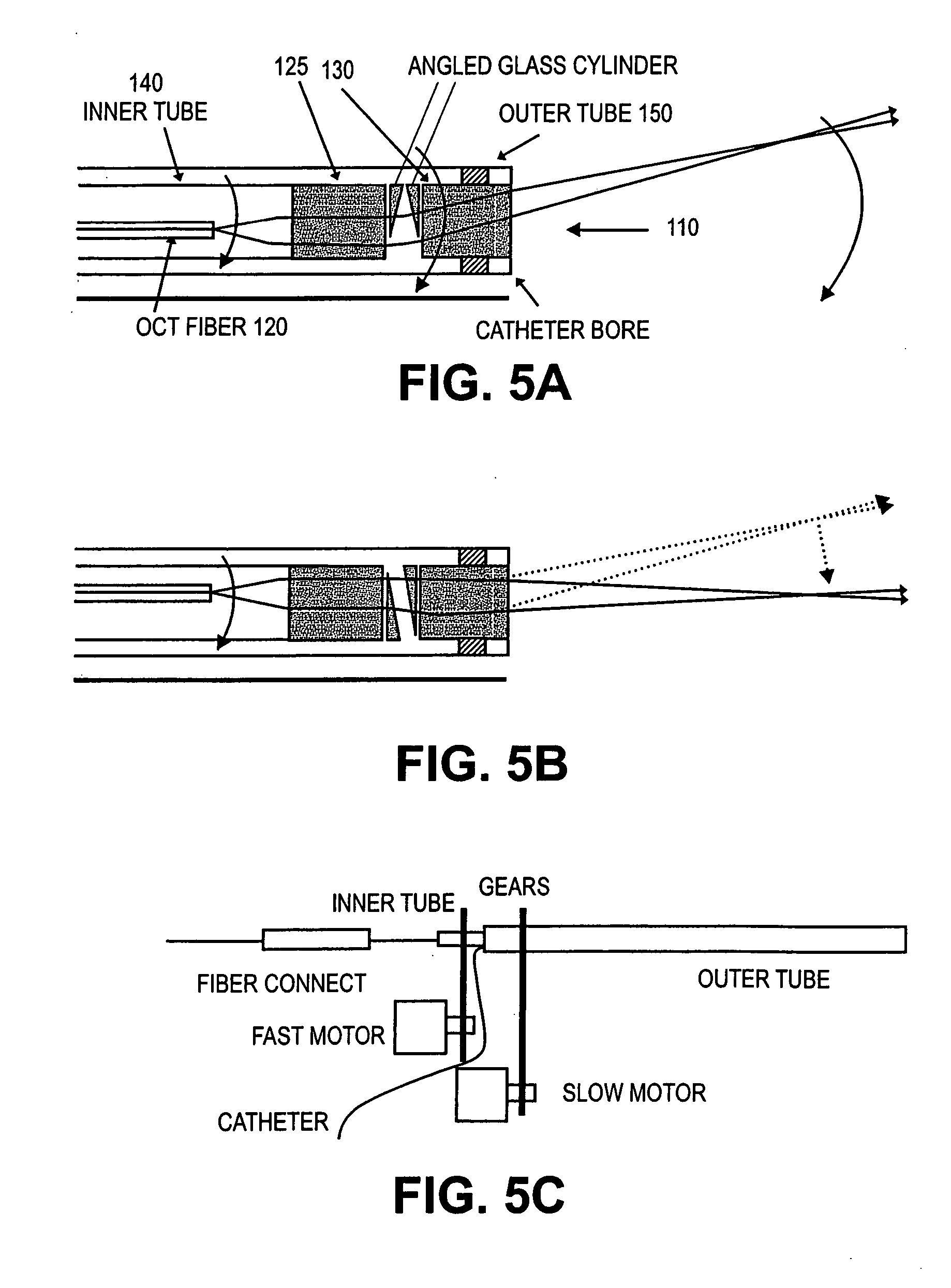
Optical coherence tomography apparatus, optical fiber lateral scanner and method for studying biological tissues in vivo
InactiveUS6608684B1Data augmentationIncrease spaceInterferometersSurgeryElectrical conductorBasal membrane
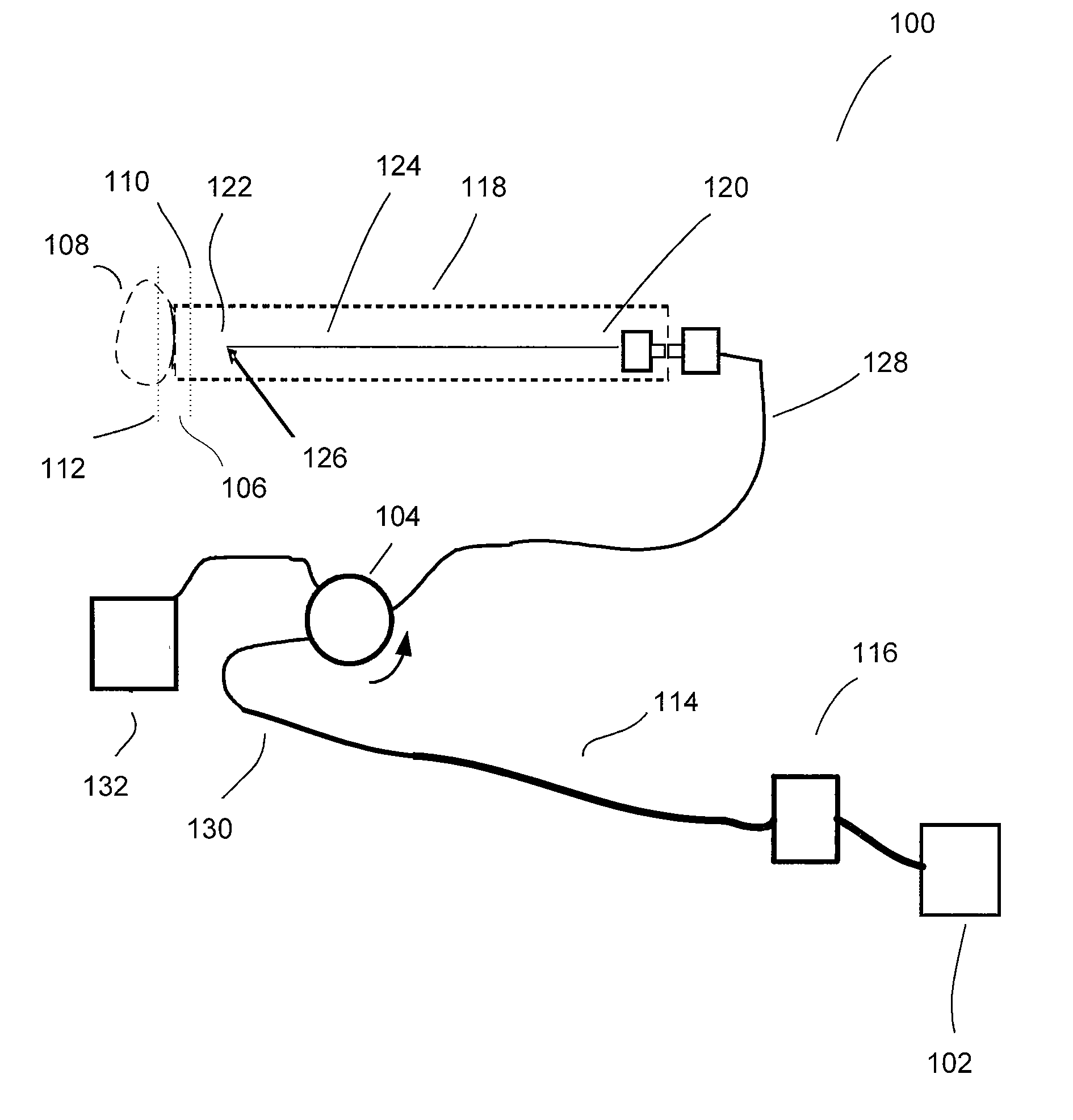
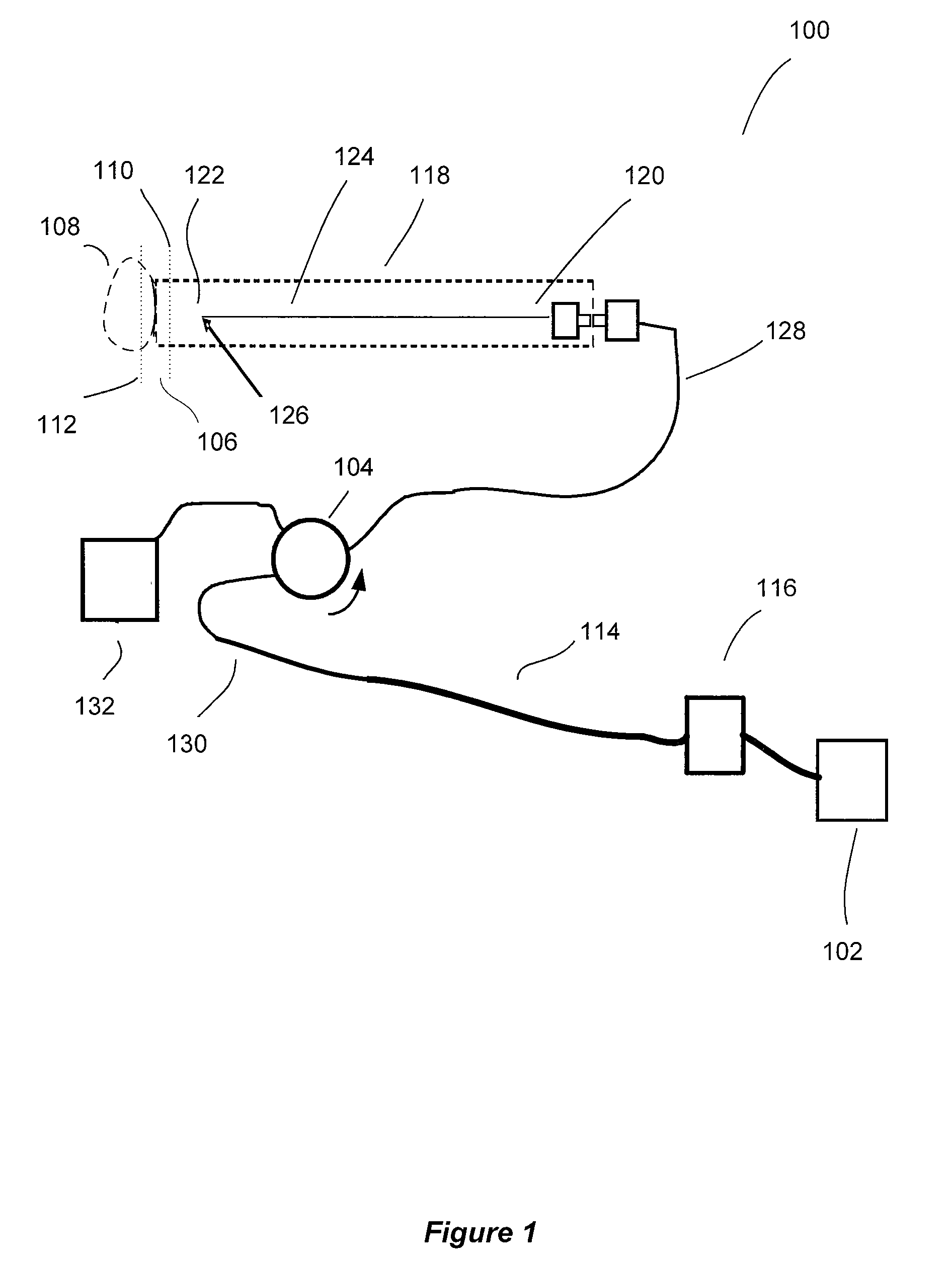
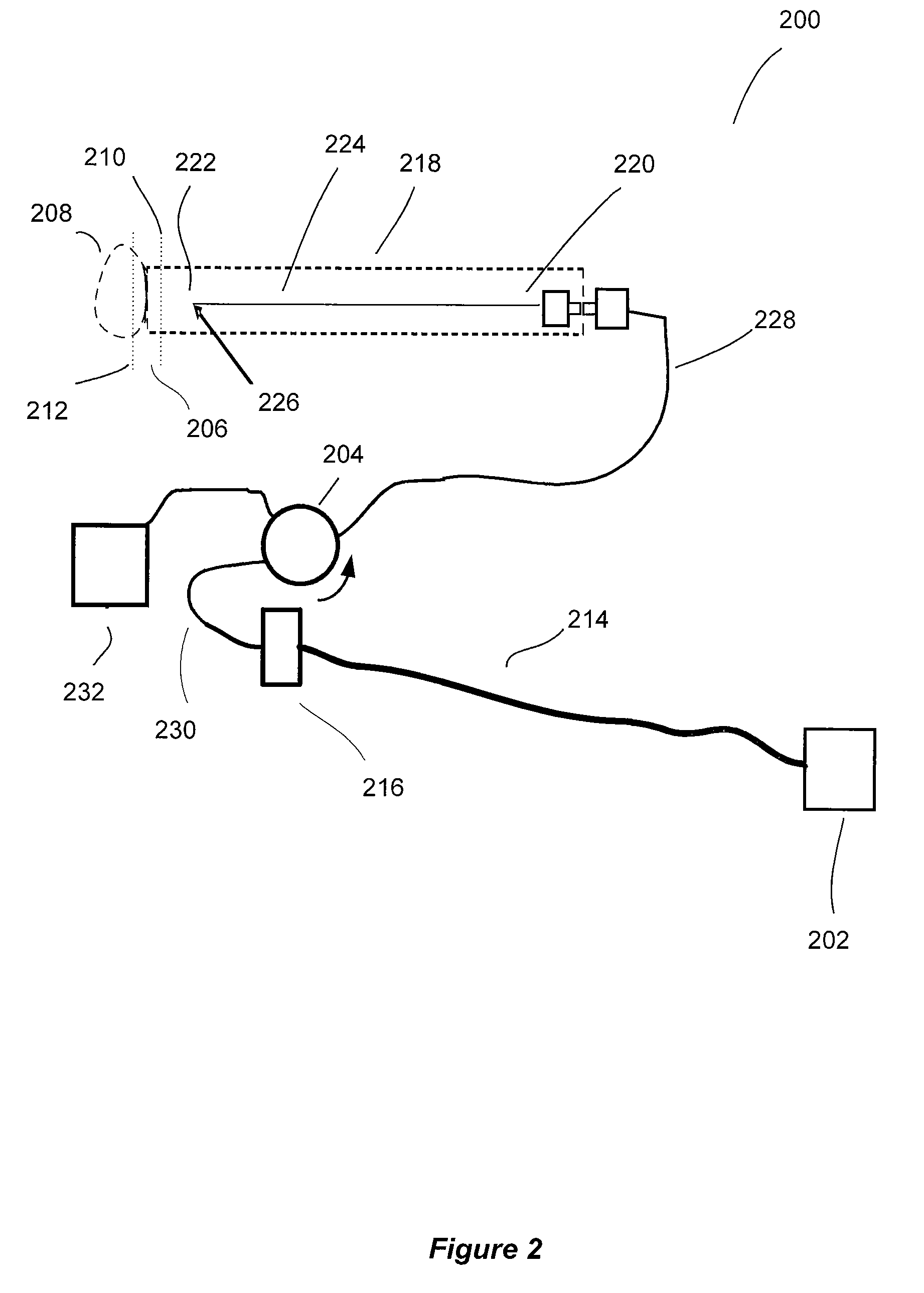
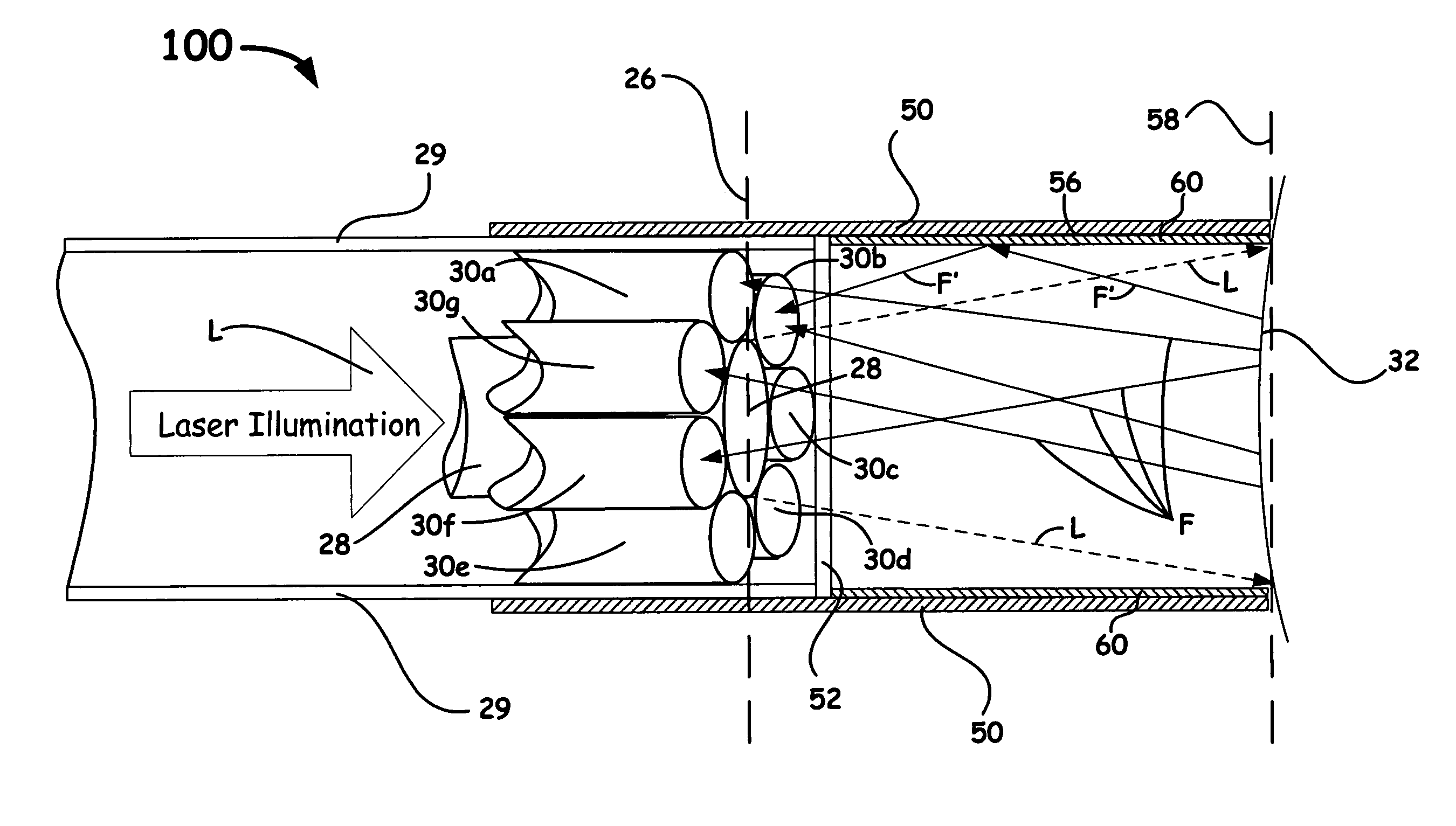
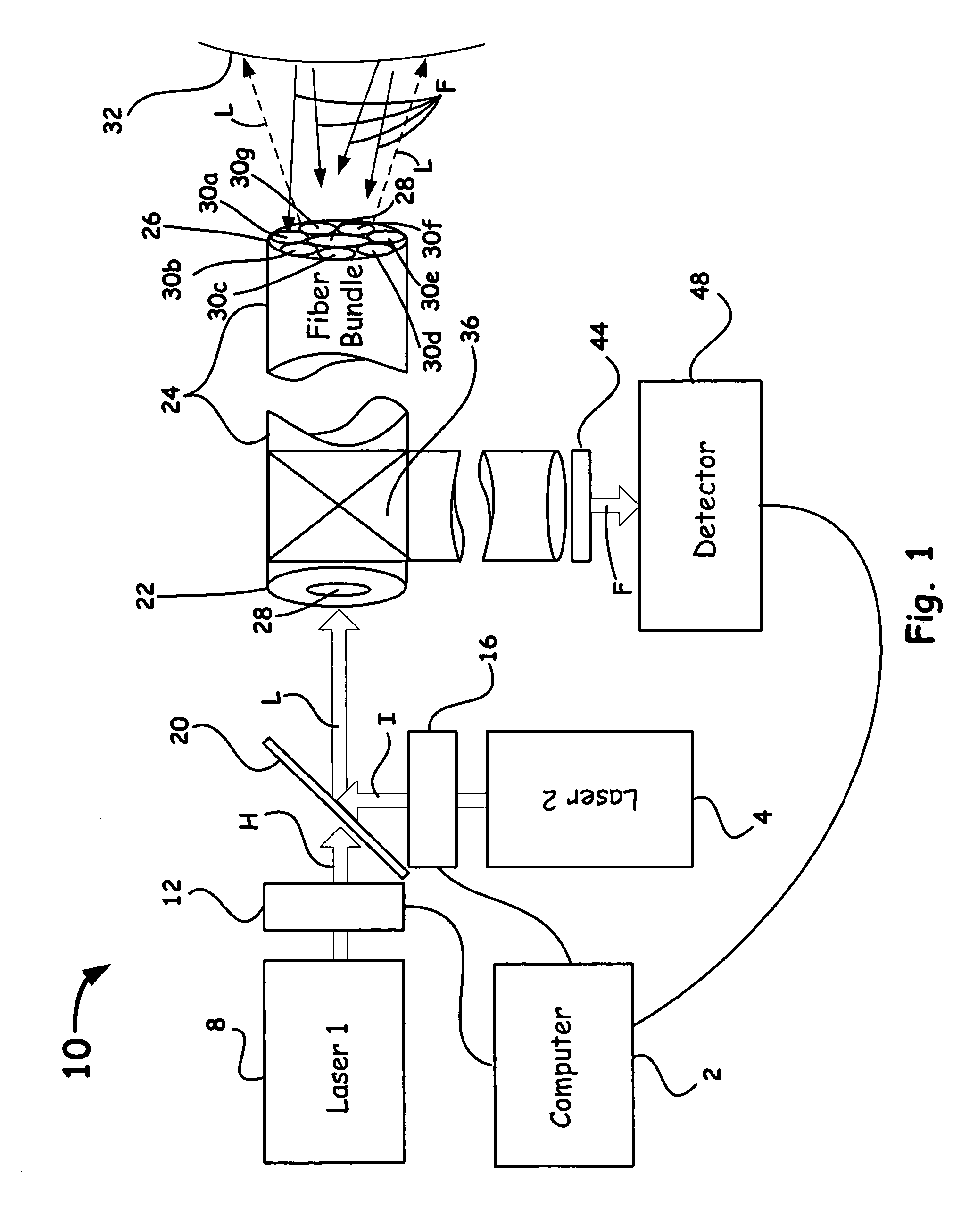
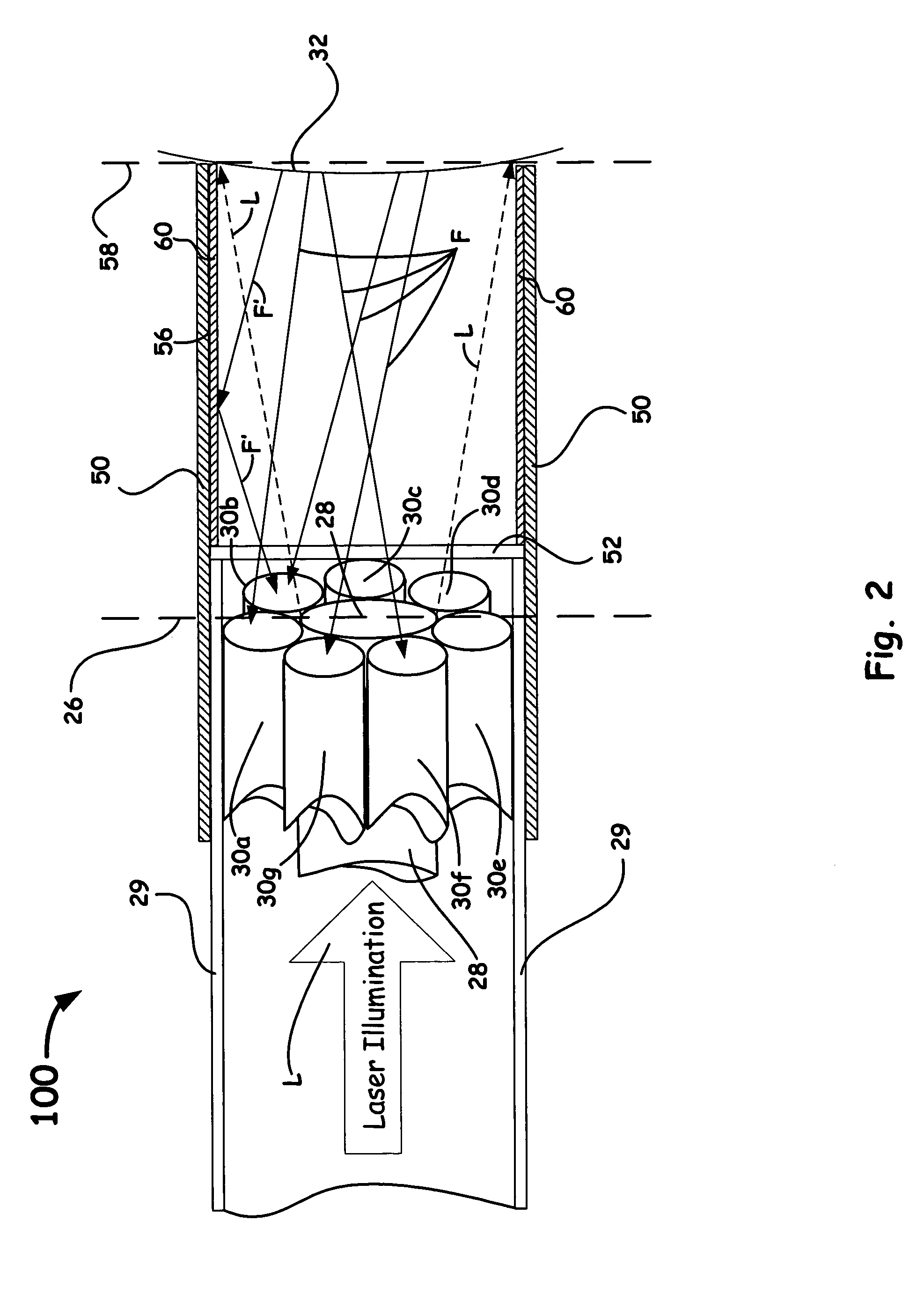
The present invention relates to the analysis of the internal structures of objects using optical means. According to the invention there were designed an apparatus suited for optical coherence tomography (OCT), an optical fiber lateral scanner (15), which is a part of said apparatus and is incorporated into an optical fiber probe (8), and a method for studying biological tissue in vivo, which allows for making a diagnostics of the biological tissue under, study on basis of the state of the basal membrane (46). The moving part of lateral scanner (15) of sampling arm (4) of interferometer (2) is arranged comprising a current conductor (19), which envelopes a magnetic system (17) in the area of one of its poles (25) and an optical fiber (13), which is rigidly fastened to current conductor (19), whereas optical fiber (13) serves as a flexible cantilever, allowing to miniaturize the optical fiber probe (8). Constructing magnetic system (17) as two permanent magnets (22, 28) which are aligned at their analogous poles (25, 29), and placing optical fiber (13) in a throughhole (30), the throughhole (30) being formed by the facing grooves made in said analogous poles (25, 29) of permanent magnets (22, 28), ensure optimization of the design of optical fiber probe (8), the body (11) of said optical fiber probe (8) having limited dimensions. Optical fiber probe (8) is placed at the distal end of an instrumental channel of an endoscope or borescope. Studying of biological tissue in vivo with the aid of the developed apparatus allows for non-invasive diagnostics of biological tissue on basis of the state of basal membrane (46).
Owner:IMALUX CORP
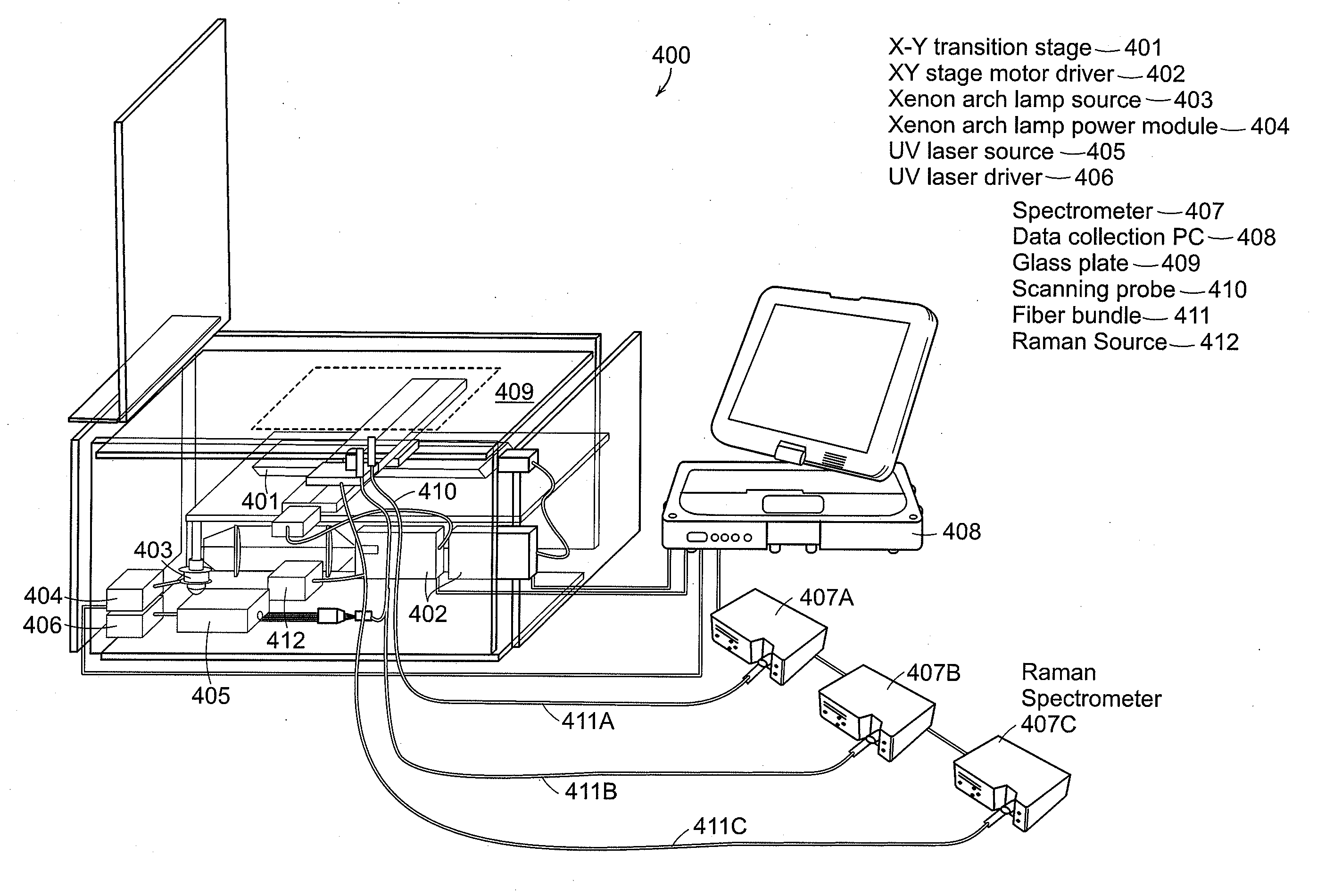
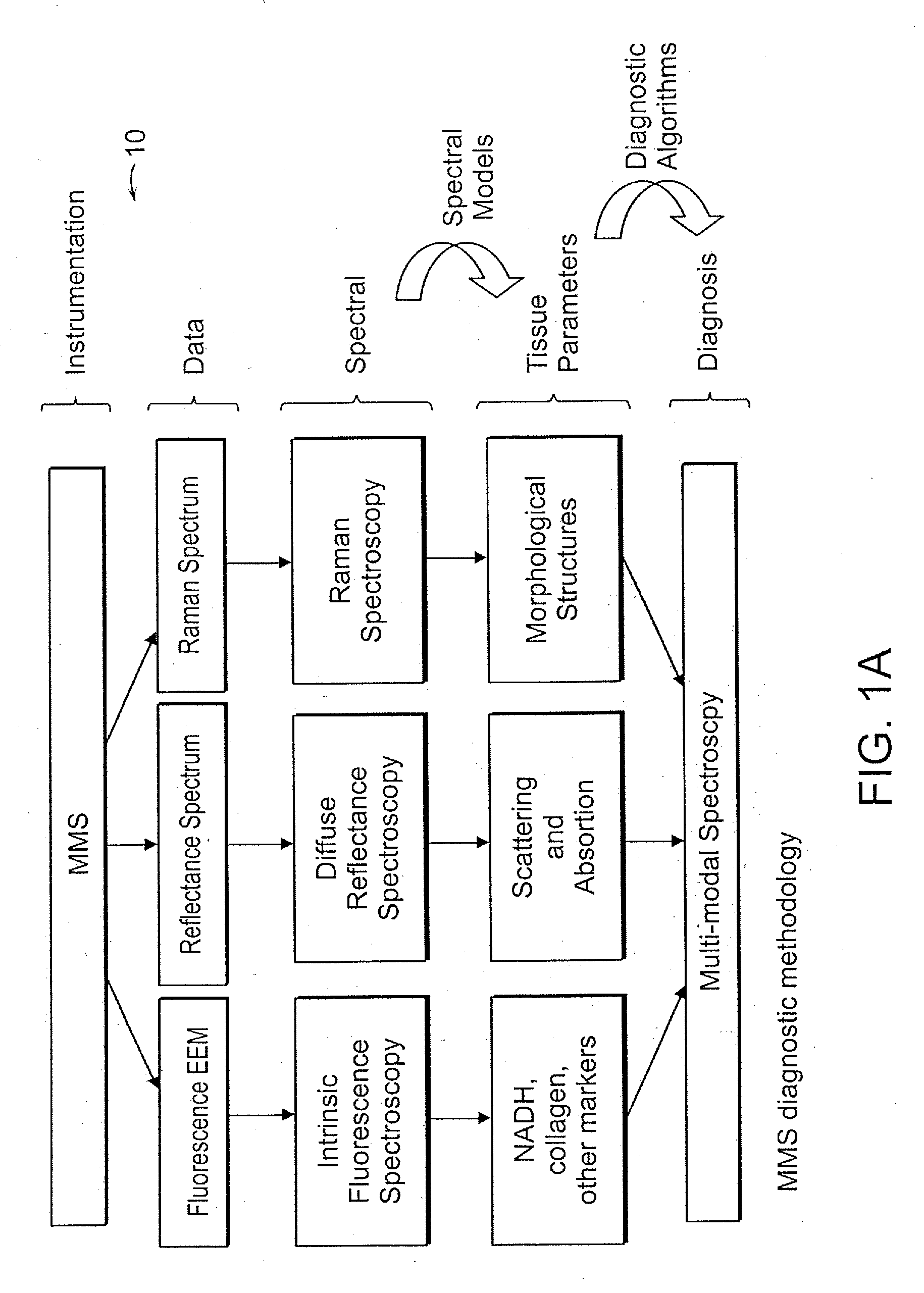
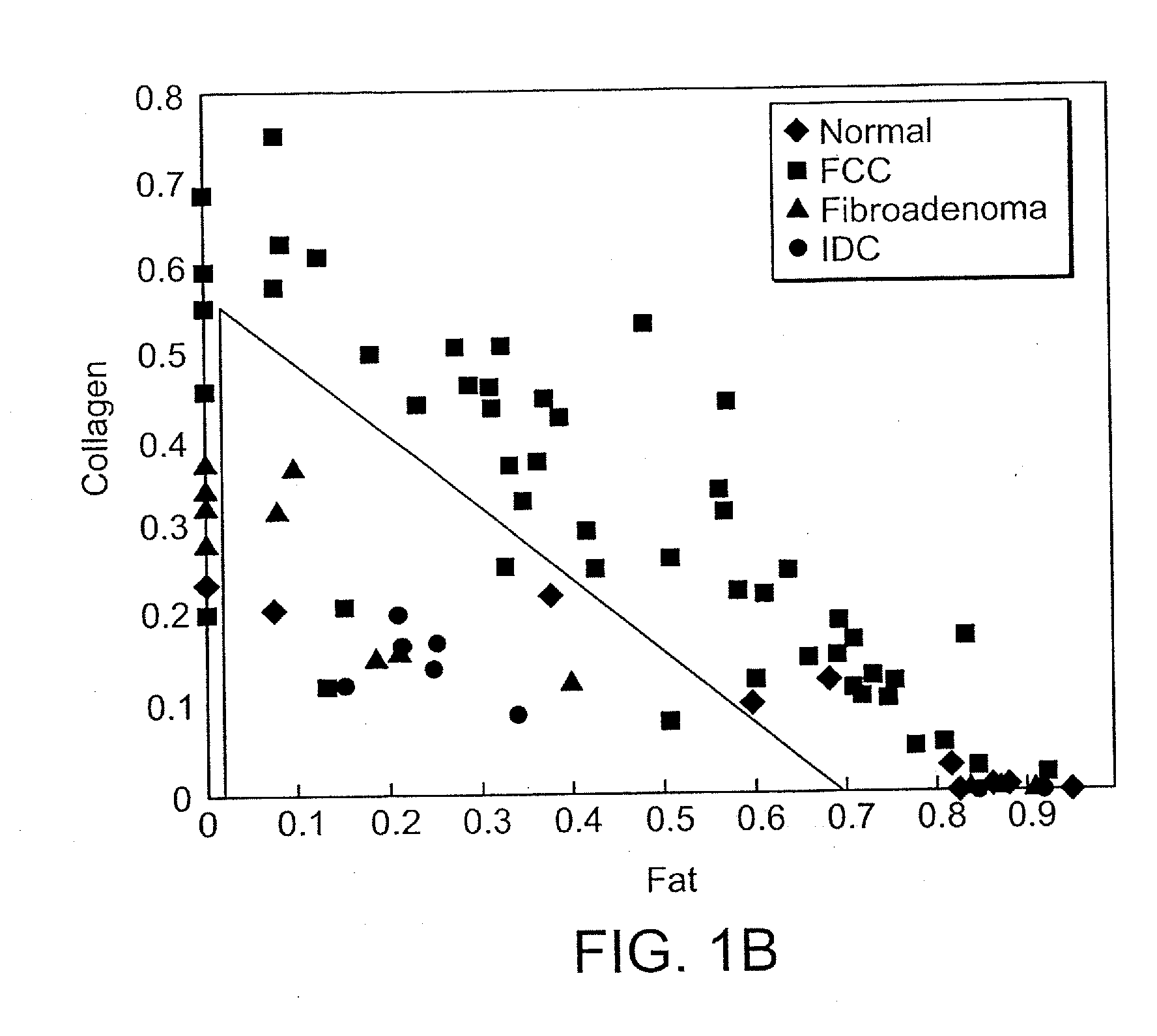
Portable optical fiber probe-based spectroscopic scanner for rapid cancer diagnosis
InactiveUS20120302892A1Overcoming distortionImprove accuracyDiagnostics using spectroscopyDiagnostics using fluorescence emissionDiseaseReflectance spectroscopy
A multimodal probe system for spectroscopic scanning of tissue for disease diagnosis. The system can use diffuse reflectance spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy for the detection of cancerous tissue, such as tissue margin assessment.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope, electrochemical testing device and leveling system
InactiveCN102798735AAchieve positioningAchieve levelingScanning probe microscopyDesorptionMetal particle
The invention provides a pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope, an electrochemical testing device and a leveling system. The pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope is characterized by using an optical fiber probe, wherein metal nanometer particles for decoration are arranged at the pinpoint of the optical fiber probe, incident lights are transmitted inside the optical fiber probe which is provided with the metal nanometer particles for decoration, and the distance between the pinpoint and a sample adopts a light intensity control mode; and the pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope is a localized surface plasmon resonance dark-field coupling device which utilizes the near-field coupling function of the nanometer metal particles at the pinpoint of the probe and a metal substrate material. The microscope can be used for researching basic surface and interface chemical problems such as a double-electric-layer structure of a substrate surface, adsorption / desorption behaviors and multi-phase catalysis. In addition, based on the LSPR (Localized Surface Plasmon Resonance) distance sensitiveness principle, the pinpoint enhanced dark-field microscope can be applied to a three-probe horizontal sensor to perform self-adaptive leveling on a nanometer processing platform.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Forward scanning imaging optical fiber probe
Probes, and systems and methods for optically scanning a conical volume in front of a probe, for use with an imaging modality, such as Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT). A probe includes an optical fiber having a proximal end and a distal end and defining an axis, with the proximal end of the optical fiber being proximate a light source, and the distal end having a first angled surface. A refractive lens element is positioned proximate the distal end of the optical fiber. The lens element and the fiber end are both configured to separately rotate about the axis so as to image a conical scan volume when light is provided by the source. Reflected light from a sample under investigation is collected by the fiber and analyzed by an imaging system. Such probes may be very compact, e.g., having a diameter 1 mm or less, and are advantageous for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Biosensor of full fiber optic evanescent wave
InactiveCN1873450AReduce energy lossImprove transfer efficiencyCoupling light guidesFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceData treatment
The invention relates to a full optical fiber instant passing wave biology sensor technology to realize biological detection by using laser to excite the biology material to emitting. The feature is that the laser transferring and fluorescence receiving path of the sensor contains an optical fiber probe, a single and multiple optical fiber coupler. The laser from the laser emitting device would send to the end of the single-mode optical fiber, and the other end coupling to multimode fiber. One end of the multimode fiber connects to fiber probe, and the other end locating in the light incidence end of fluorescence collecting and data processing device. The invention could decrease the consumption, improve coupling efficiency and decrease optical discrete element and simplify instrument structure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Fiber optic probes utilizing grin lenses for spatially precise optical spectroscopy
The invention provides improved fiber optic probe assemblies which utilize a configuration of gradient index (GRIN) lenses to deliver light to a focal point and collect light for analysis from the same focal point. Also provided are methods for manufacturing the probe assemblies and related methods of spatially precise spectroscopy using the probe assemblies.
Owner:CAPTAIN JRT
Sensing method and device for micro inner cavity size and three-dimensional coordinate based on two-dimensional micro-focus collimation
InactiveCN101520313AGenerate displacement sensitivityEfficient extractionUsing optical meansPoint lightThree dimensional measurement
The invention relates to a sensing method and a device for micro inner cavity size and three-dimensional coordinate based on two-dimensional micro-focus collimation, belonging to the technical filed of precise instrument manufacture and measurement, in particular to a sensing method and a device for micro and complex inner cavity size and three-dimensional coordinate in the filed of sub-macroscopy, which is especially suitable for the three-dimensional detection of blind holes with large depth-diameter ratio. The device combines a micro spherical biconvex lens and an optical fiber probe measuring rod, and establishes a point light two-dimensional micro-focus collimation imaging light path by using the micro spherical biconvex lens, thereby realizing the high magnification and the sensing for the three-dimensional displacement of the optical fiber probe measuring rod by utilizing the light path. The invention has the characteristics of small measured force of a single optical fiber probe, easy miniaturization, large measured depth-diameter ratio, simple system structure, good real-time performance, easy practical application, and has obvious advantages for carrying out the quick and ultra-precise measurement and calibration for the inner cavity micro-size and the three-dimensional coordinate. Especially, the top of the resolution capability can reach the deep sub-nanometer magnitude, and an absolute zero position exists in the three-dimensional measurement direction.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fiber optic probe for attenuated total internal reflection spectrophotometry
InactiveUS6205272B1Scattering properties measurementsCoupling light guidesFiberTotal internal reflection
A fiber optic probe for ATIR (Attenuated Total Internal Reflection) spectrophotometry. The probe includes a housing that contains an optical element or lens, a light-transmitting fiber that directs incident light to the lens, a light-receiving fiber that receives reflected light from the sample interface, a coupler for holding these components in precise alignment, and a flexible armor casing that provides strain relief and protection for the optical fibers. The lens is shaped and dimensioned so that light from the transmitting fiber is reflected at the interface between the lens and the surrounding medium (such as a liquid to be analyzed). The reflected light is transmitted via the transmitting fiber to a suitable spectrophotometer, where the light signal is recorded and analyzed to determine the composition of the sample. The probe is particularly suitable for analyses of fluids and slurries with high optical absorbance.
Owner:INTERNAL REVENUE SERVICE
Method for measuring partially coherent vortex light beam topological charge number
InactiveCN102944312AEasy to implementEasy to measureOptical measurementsBeam splitterCorrelation function
The invention discloses a method for measuring partially coherent vortex light beam topological charge number. A measured light beam passes through an imaging convex lens and then passes through a beam splitter to be divided into a transmission light beam and a reflection light beam, optical fiber scanning probes of two single-photon counters are respectively arranged at the centers of the transmission light beam and the reflection light beam, the position of a single-photon counter optical fiber probe is fixed, the position of the other single-photon counter optical fiber probe is regulated to perform point-by-point scanning measurement, correlation function values of the two beams on measuring position points are recorded, a spatial distribution image of a fourth-order correlation function is output through computer processing according to fourth-order correlation function relationship of partially coherent laguerre-gaussian beams, and the topological charge number of the beam to be measured is obtained through the number of dark rings on the image. The method is based on the fourth-order correlation function, a novel method for measuring the partially coherent vortex light beam topological charge number is provided, an adopted measuring device is simple in light path and easy to achieve, measuring method is simple, data processing is convenient, and result is reliable.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Indwelling Fiber Optic Probe for Blood Glucose Measurements
InactiveUS20090088615A1The instrumentation is simpleLong measurement timeMedical devicesPressure infusionFiberVein
An indwelling fiber optic probe can be used to make in vivo blood glucose measurements through a central venous catheter. The fiber optic probe can operate in the near-infrared spectral region. The optical measurement can be backscattering, transmission, or a combination of both, depending on the optical configuration.
Owner:LUMINOUS MEDICAL
Ultra-high-precision freezing detecting device and real-time freezing thickness detecting method thereof
ActiveCN103940352AAchieve ultra-high precision detectionAccurate Freezing RateDe-icing equipmentsUsing optical meansSpectrum analyzerMicrometer
The invention discloses an ultra-high-precision freezing detecting device and a real-time freezing thickness detecting method thereof. The ultra-high-precision freezing detecting device comprises a wideband light source, a spectrum analyzer, an optical fiber coupler, a film-coated optical fiber, an optical fiber polarization controller, an optical switch and optical fiber probes. The wideband light source and the spectrum analyzer are connected to a port a and a port b which are located on the same side of the optical fiber coupler through optical fibers respectively. The film-coated optical fiber is installed on the optical fiber polarization controller and connected to a port c located on the other side of the optical fiber coupler. The input end of the optical switch is connected to a port d of the optical fiber coupler and the output end of the optical switch is connected with the optical fiber probes. The ultra-high-precision freezing detecting device can realize ultra-high-precision detection of a micrometer-level-thickness ice layer on the surface of an object and accurately forecast the freezing rate. In addition, the device is high in integration degree, low in cost, capable of realizing distributed real-time detection, particularly suitable for airplane freezing detection, capable of realizing safety early warning and capable of being widely applied to other fields in need of freezing condition detection or monitoring.
Owner:浙江虹鑫光电科技有限公司
Handheld near-infrared probe for nondestructive internal quality testing of fruit and detection method
InactiveCN101799401AEasy to collectImprove final detection efficiencyPoint-like light sourceScattering properties measurementsHand heldWavelength
The invention relates to a handheld near-infrared probe for nondestructive internal quality testing of fruit and a detection method. The optical fiber probe consists of four LED light sources with different waverlengths, a detection optical fiber, an automatic sampling control system, a light source stabilizing circuit, a digital temperature and humidity sensor, a circular lug boss, a darkening ring, a soft rubber ring, a switch, a circuit box and a shell. The probe has the characteristics of high stability, simple structure, low cost and spectra collecting controllability, and can be widely used for on-line monitoring and on-site sampling of fruit. A voice system and a wireless transmission system can be used for realizing the humanization and easy operation of equipment and effectively expand application space.
Owner:EAST CHINA JIAOTONG UNIVERSITY
Apparatus and method for nondestructive optical constant imaging of dermatosis tissue of human body
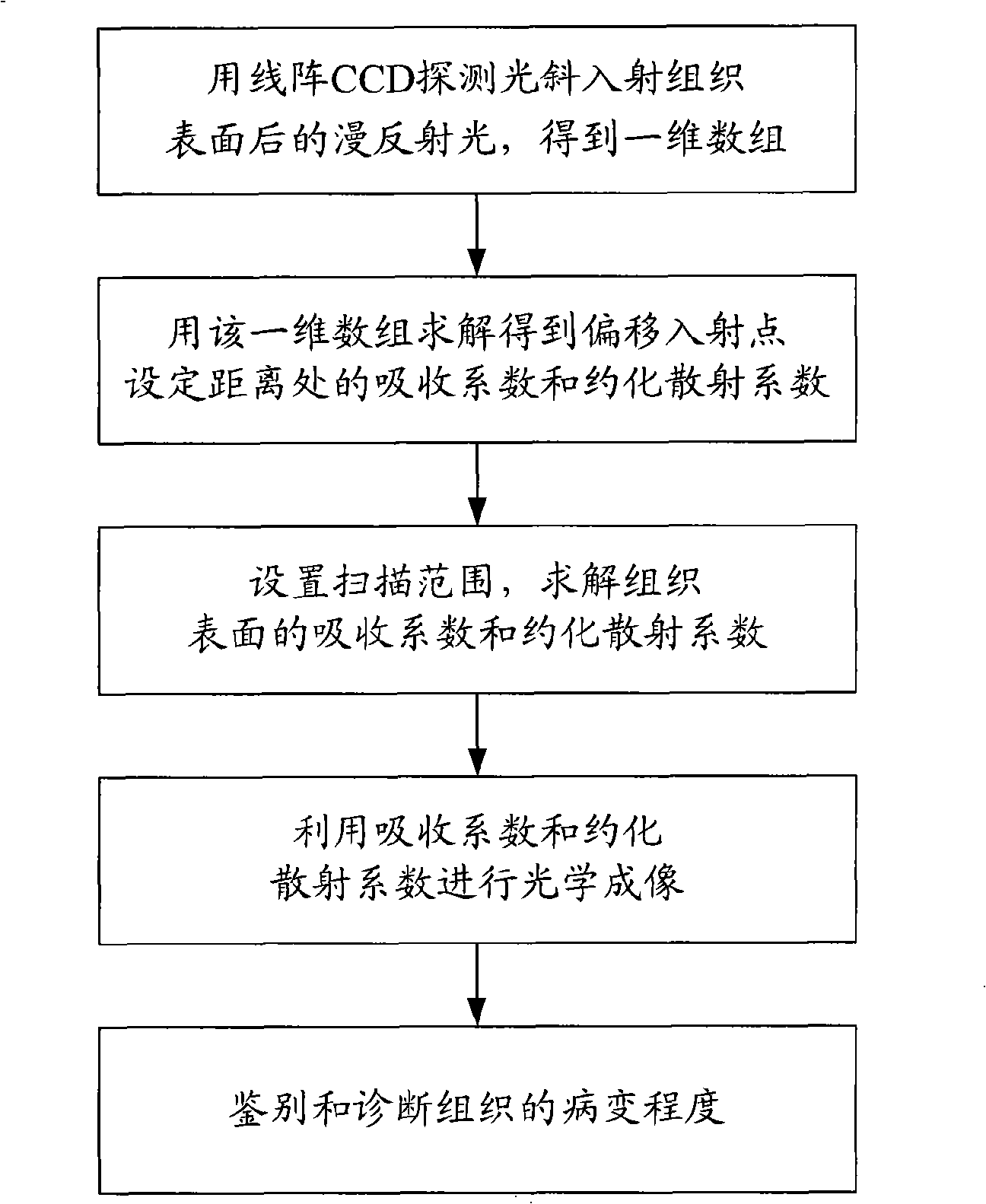
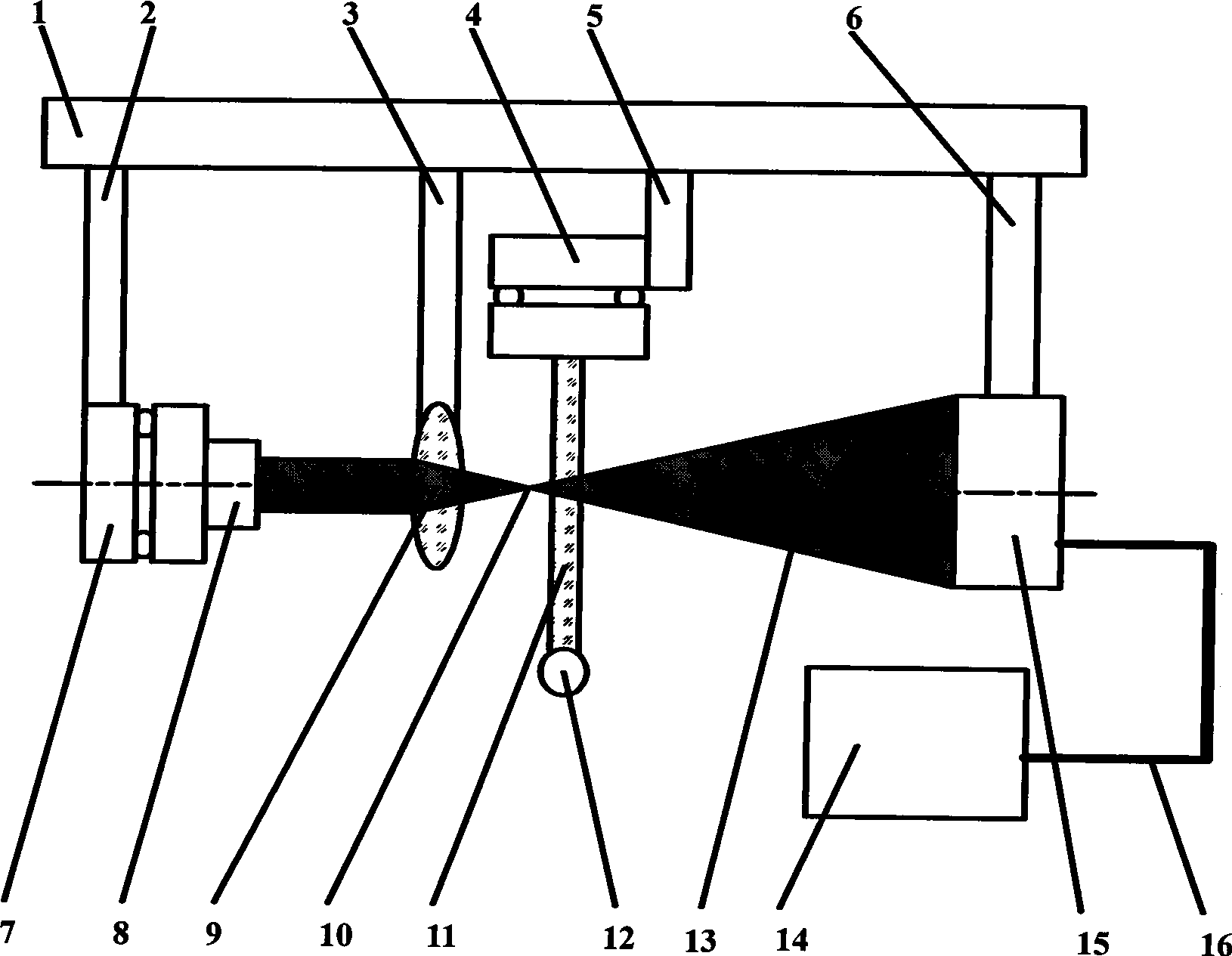
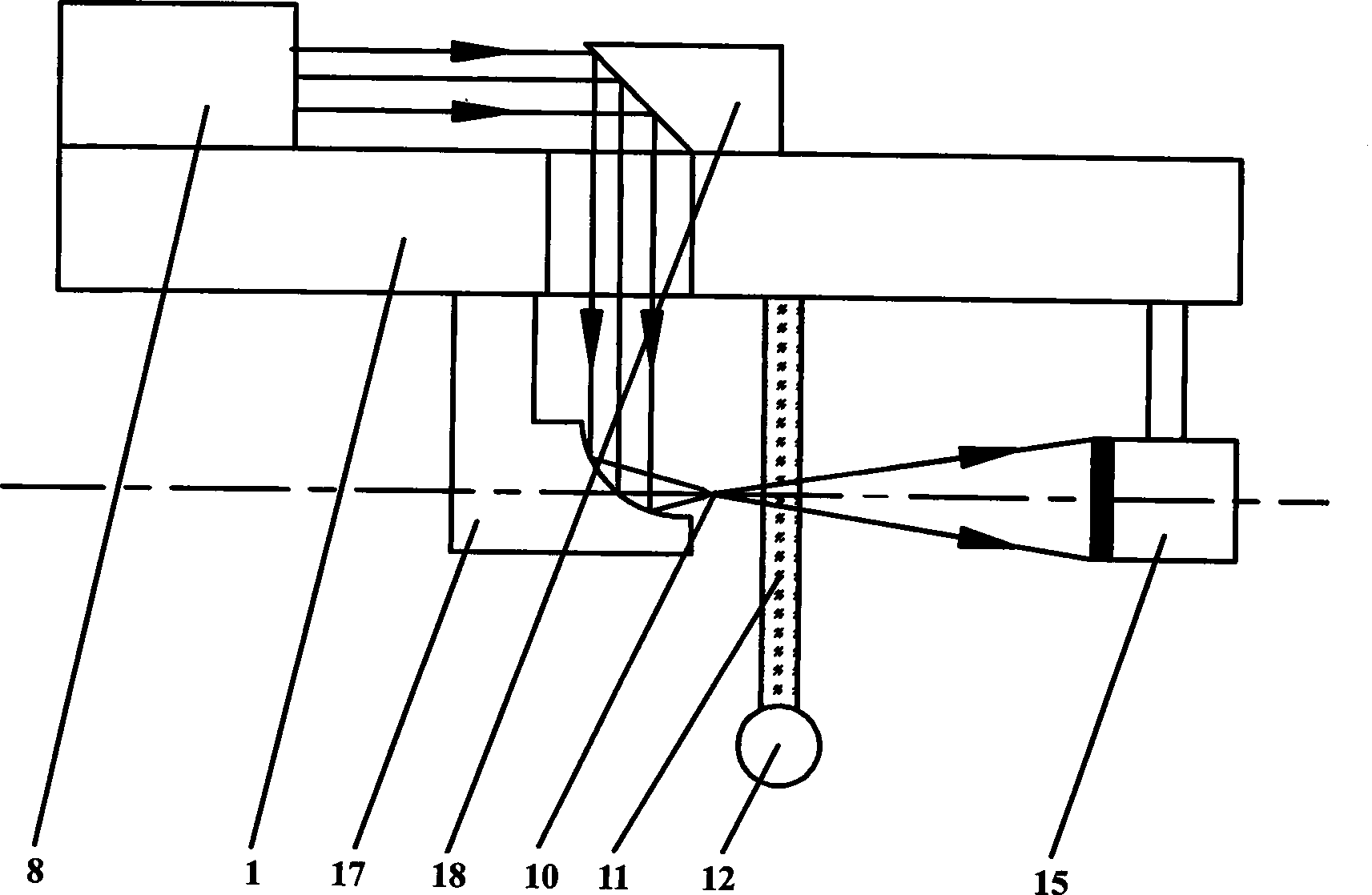
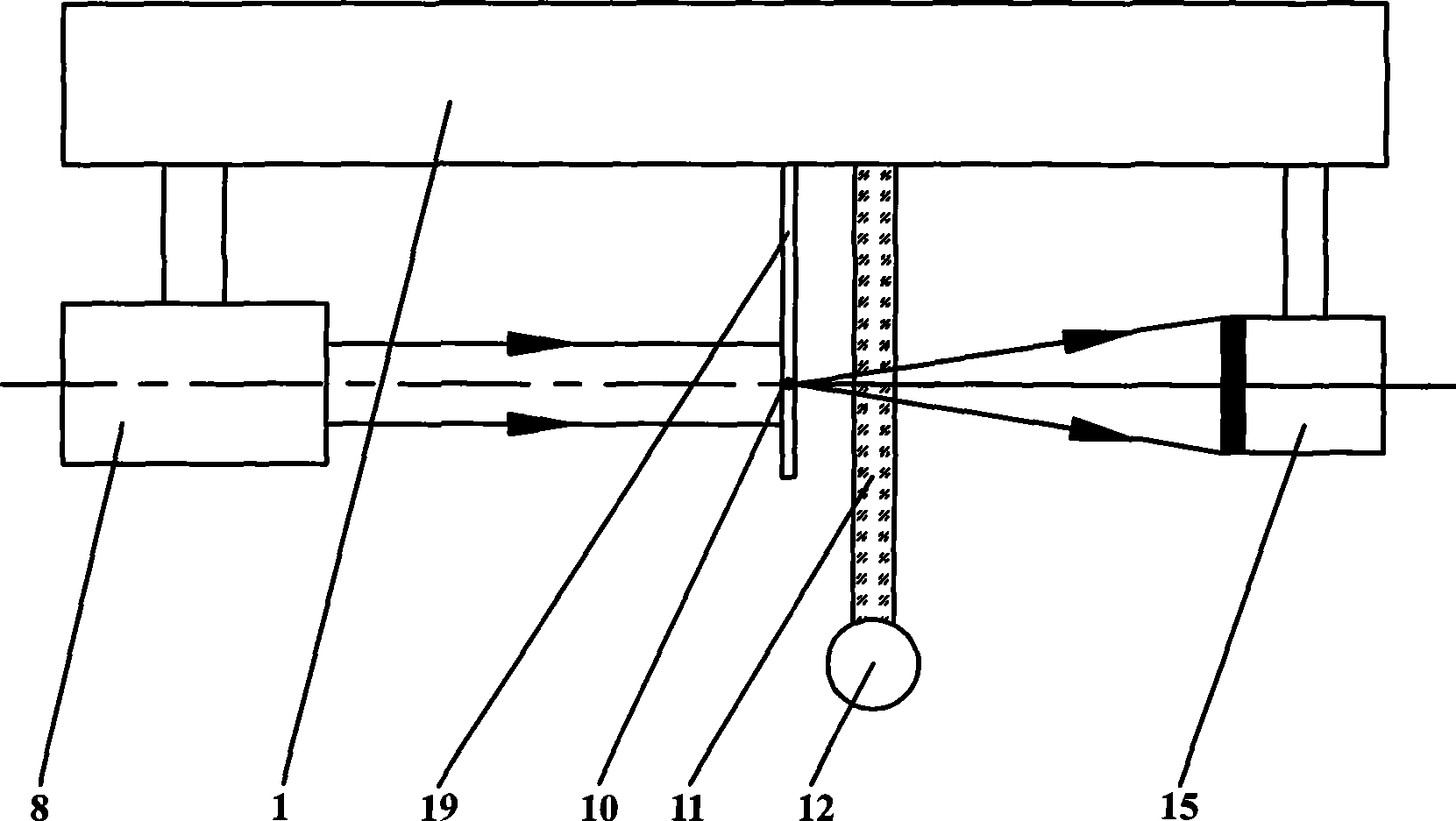
InactiveCN101313847AHigh resolutionImprove clarityScattering properties measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyFiber
The invention relates to a device for carrying out the nondestructive optical constant imaging of a human body cutis pathologic tissue and a method thereof. The device comprises a tungsten halogen lamp, an incident fiber optic probe, a line array CCD for receiving diffused reflection light, and a grating spectrograph, an amplification filter circuit, an A / D conversion circuit, a computer and a computer-controlled three-dimensional traveling table which are connected in turn through an optical fiber. The invention uses the line array CCD optical measurement device detecting the obliquely incident diffused reflection light to detect the human body cutis tissue, uses a Monte Carlo statistical method limited by characteristic parameters to conversely compute the values of the absorption coefficient and the reduction scattering coefficient at each two-dimensional space coordinates of the detected cutis tissue, then uses the grating spectrograph to carry out spectrum, and respectively images through the absorption coefficient and the reduction scattering coefficient and simultaneously detects the detected human body pathologic tissue and a healthful tissue around the pathologic tissue. Then the optical constants of the pathologic tissue and the healthful tissue are compared to see difference or the optical constant of the pathologic tissue is compared with a healthful human body tissue sample, thereby carrying out the diagnosis and identification of diseases.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Sensing method and device for micro inner cavity and two-dimensional coordinate based on one-dimensional micro-focus collimation
InactiveCN101520314AHigh speed extractionEasy to handleUsing optical meansDiameter ratioMiniaturization
The invention relates to a sensing method and a device for micro inner cavity and two-dimensional coordinate based on one-dimensional micro-focus collimation, belonging to the technical filed of precise instrument manufacture and measurement, in particular to a sensing method and a device for micro and complex inner cavity structure size and two-dimensional coordinate in the filed of sub-macroscopy, which is especially suitable for the measurement of micro-holes with large depth-diameter ratio. By using the structure characteristics of super large curvature and micro-cylindrical lens of an optical fiber probe measuring rod, a point light source one-dimensional micro-focus collimation imaging light path is established, thereby realizing the high magnification and the sensing of the two-dimensional displacement of the optical fiber probe measuring rod by utilizing the light path. The invention has the characteristics of small measured force of a single optical fiber probe, easy miniaturization, large measured depth-diameter ratio, simple system structure, good real-time performance, easy practical application, and has obvious advantages for carrying out the quick and ultra-precise measurement and calibration for the inner cavity micro-size and the two-dimensional coordinate. Especially, the top of the resolution capability can reach the deep sub-nanometer magnitude, and an absolute zero position exists in the two-dimensional measurement direction.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Photon crystal optical-fiber probe sensor based on nano grain surface increasing Raman spectrum
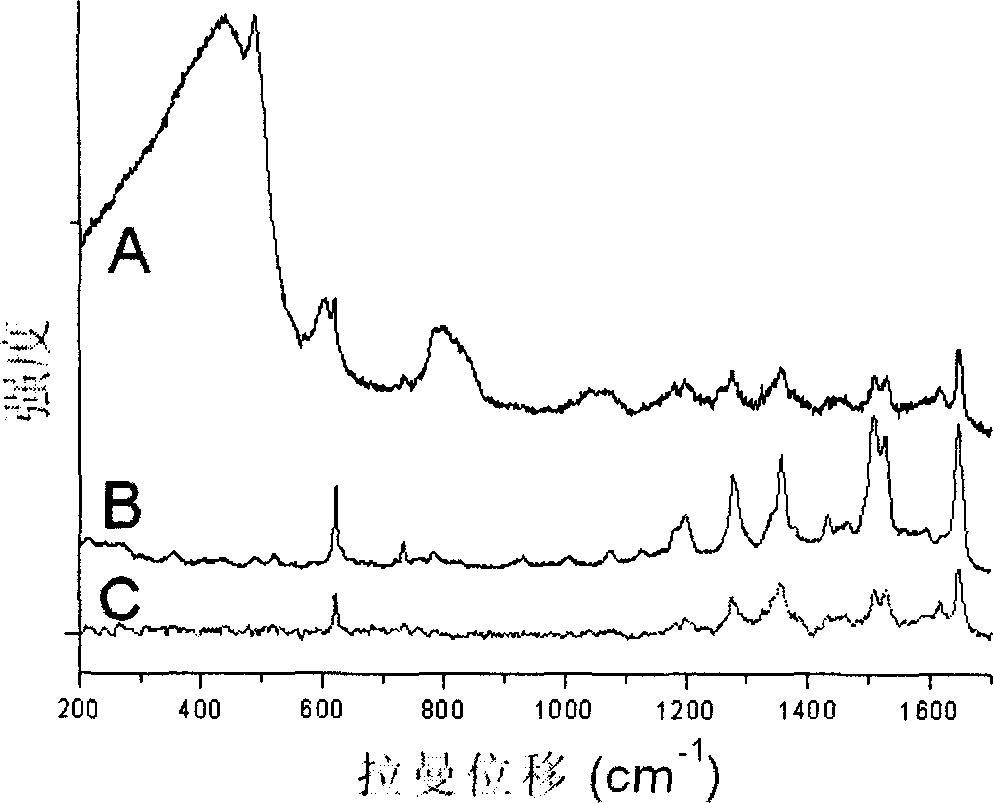
InactiveCN1815197AImprove performanceHigh signal to noiseRaman scatteringReal time analysisSignal light
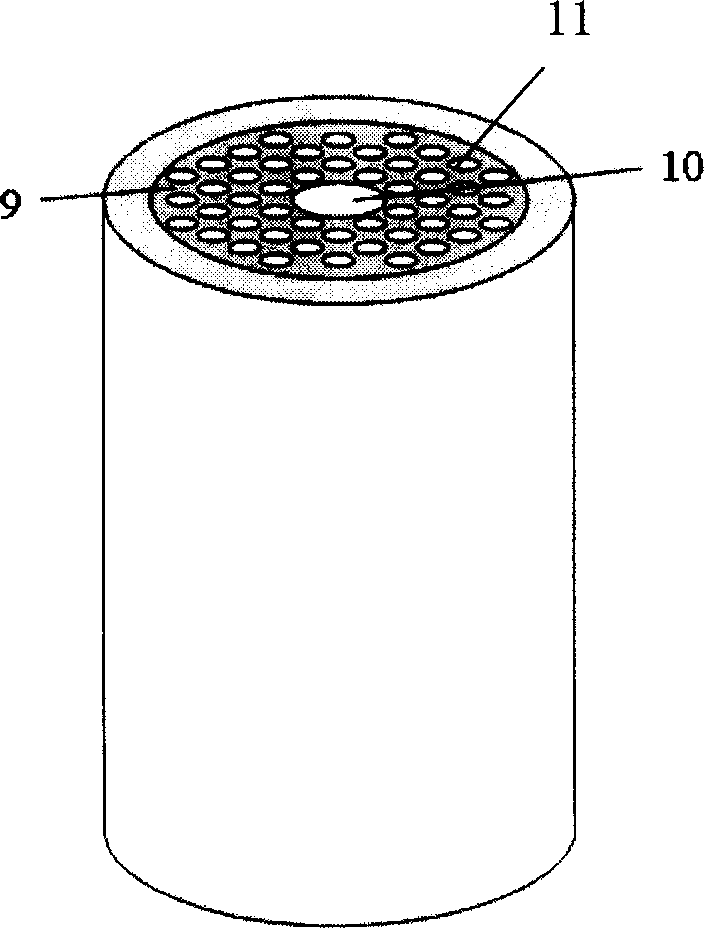
Present invention discloses photons crystal optical fiber probe transducer based on nano particle surface enhancing Raman spectra belonging to laser Raman spectra detection technique. Combining photons crystal optical fiber PCF and SERS spectral technique to obtain PCF-SERS probe transducer having SERS activity, PCF-SERS probe covered with cycle arranged airport, the inner wall of central light guiding air core on PCF-SERS probe end having SERS activity nano metal granule. Said invention can be used in gas and liquid molecule detection with low background noise and high sensitivity, and making exciting light and SERS signal light existing steady mode field in PCF to realize very transmission loss, thereby suitable for on line analysis, real-time analysis, living body analysis, and in situ detecting etc.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Orthogonal light path two-dimensional micro-focus collimation and three-dimensional coordinate sensor
InactiveCN102589422ACapable of direction detectionEliminate dependenciesUsing optical meansCouplingMiniaturization
The invention relates to an orthogonal light path two-dimensional micro-focus collimation and three-dimensional coordinate sensor, belonging to a sensor. A first to a seventh connecting frames are arranged on an assembly platform in sequence; a four-dimensional adjusting frame, a spectroscope, a refracting-reflecting type long-focus system A, a refracting-reflecting type long-focus system B, a photoelectric receiver B and a photoelectric receiver A are respectively assembled on the first to the seventh connecting frame; a laser source is assembled on the four-dimensional adjusting frame; an optical fiber probe measuring bar provided with an optical fiber probe measuring head is arranged on a five-dimensional adjusting frame; and the photoelectric receiver A and the photoelectric receiver B are respectively connected with a data acquisition processor through data transmission lines. The orthogonal light path two-dimensional micro-focus collimation and three-dimensional coordinate sensor has the characteristics of zero coupling of two-dimensional sensing information, capability of carrying out detection in the two-dimensional direction, small measuring force, easy minimization, large measured ratio of pit-depth to pit-diameter, good real-time property and easy application, and has remarkable advantages in implementation of rapid and ultra-precise measurement and calibration on micro inside dimensional and three-dimensional coordinates.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Optical spectroscopy for the detection of ischemic tissue injury
InactiveUS7587236B2Diagnostics using spectroscopyScattering properties measurementsMedicineSpectroscopy
An optical method and apparatus is utilized to quantify ischemic tissue and / or organ injury. Such a method and apparatus is non-invasive, non-traumatic, portable, and can make measurements in a matter of seconds. Moreover, such a method and apparatus can be realized through optical fiber probes, making it possible to take measurements of target organs deep within a patient's body. Such a technology provides a means of detecting and quantifying tissue injury in its early stages, before it is clinically apparent and before irreversible damage has occurred.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Systems and methods for monitoring the amplification of DNA
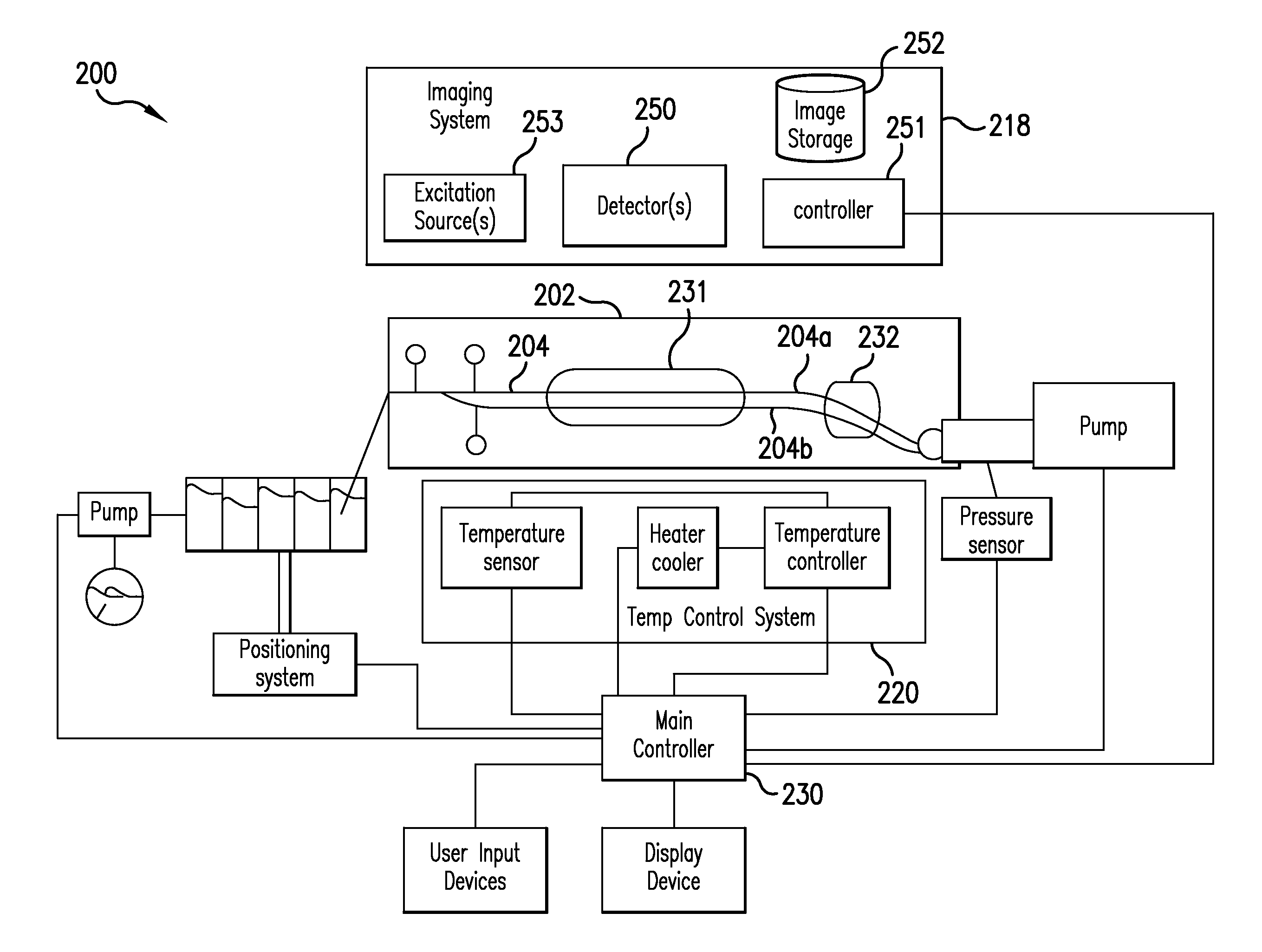
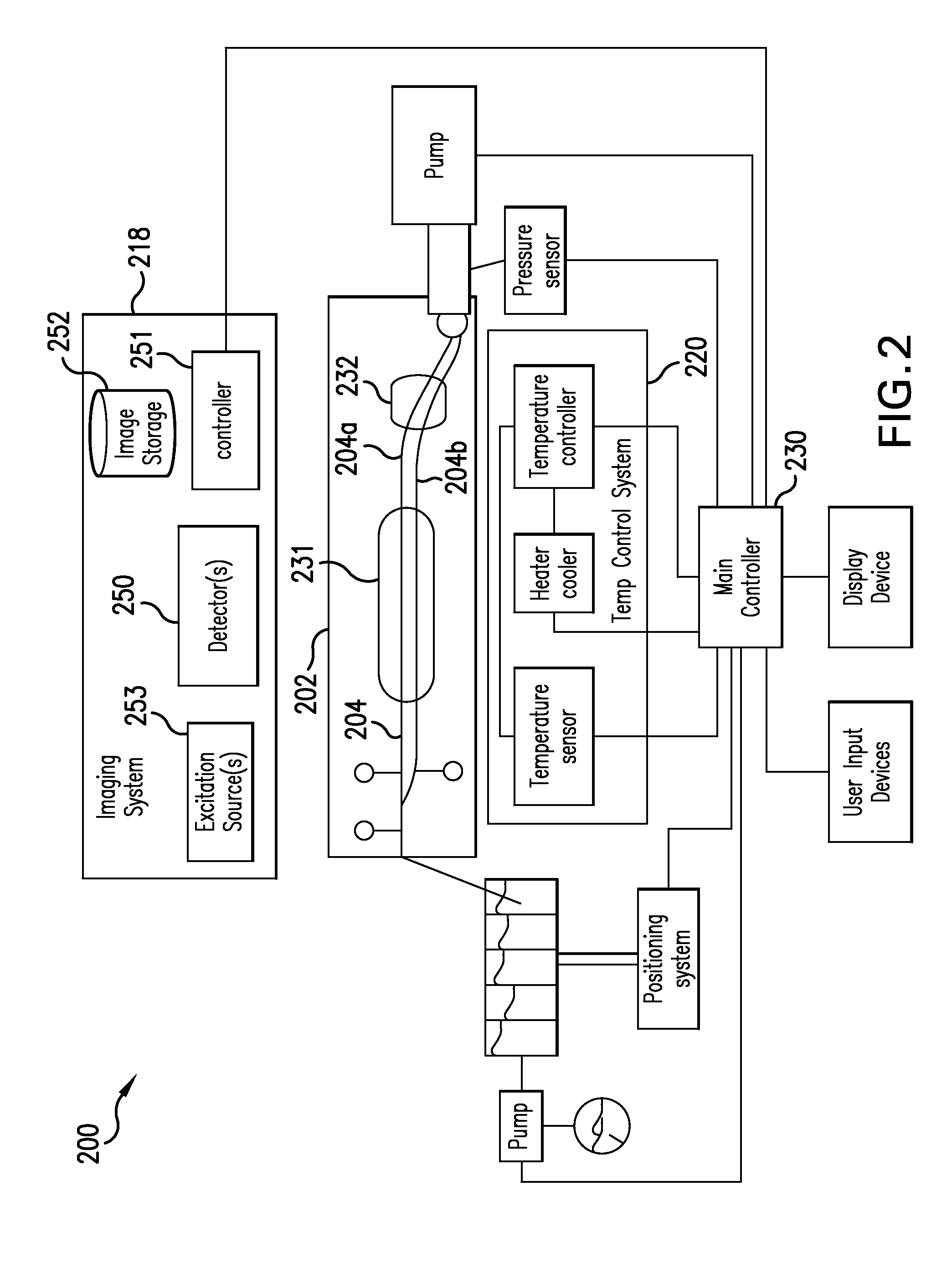
ActiveUS20090317806A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiologyFiber
A system and method for amplifying and detecting nucleic acids are disclosed. In one embodiment, the system includes: a microfluidic device comprising a channel for receiving a sample of solution containing real-time PCR reagents; a temperature control system configured to cycle the temperature of the sample; an excitation source for illuminating the sample; a fiber optic probe comprising (i) an optical fiber having a distal end and a proximal end and (ii) a probe head connected to the distal end of the optical fiber and positioned between the distal end of the optical fiber and the channel; and a detector configured to detect emissions exiting the proximal end of the optical fiber.
Owner:CANON USA
Protector for a fibre-optic catheter
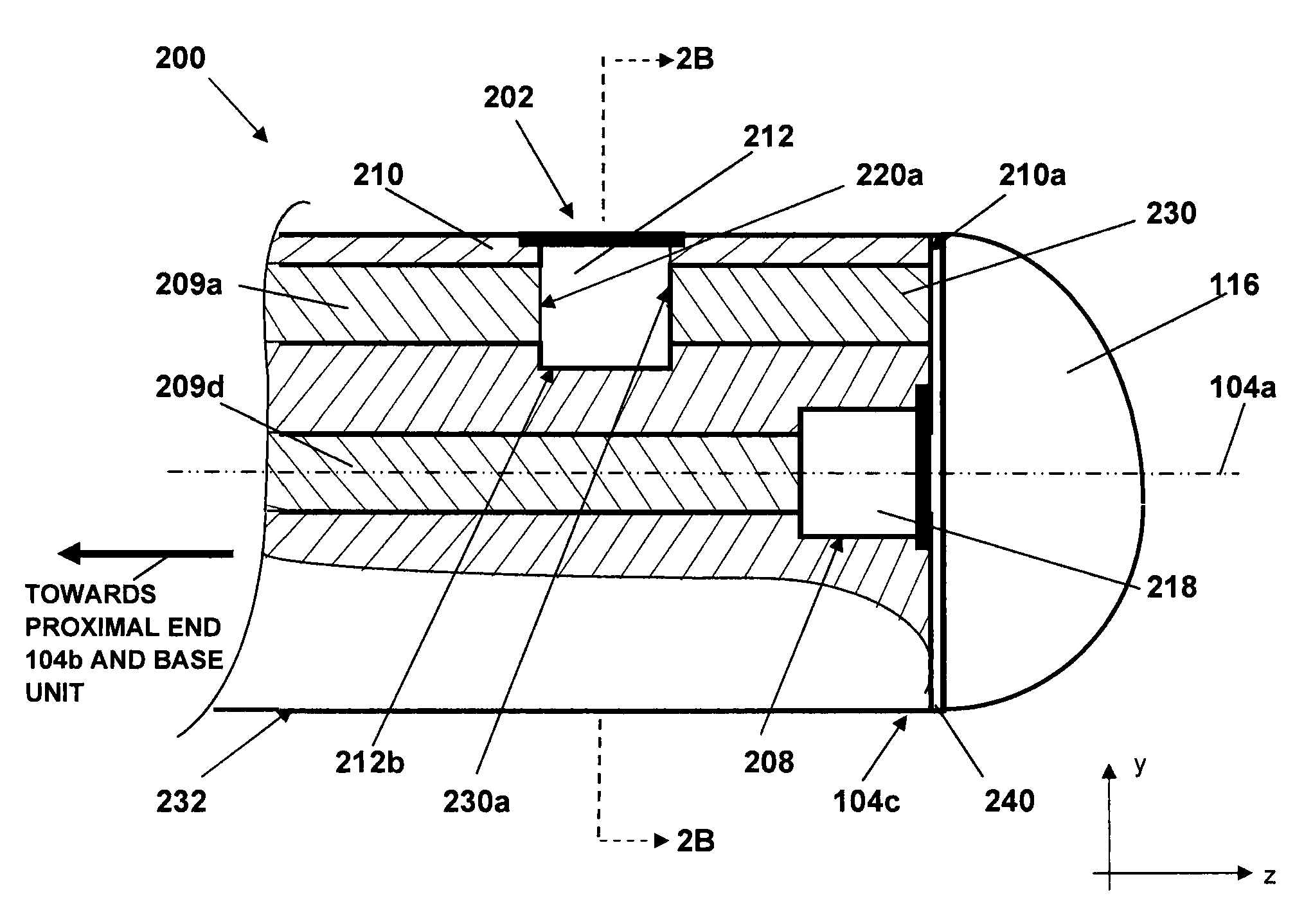
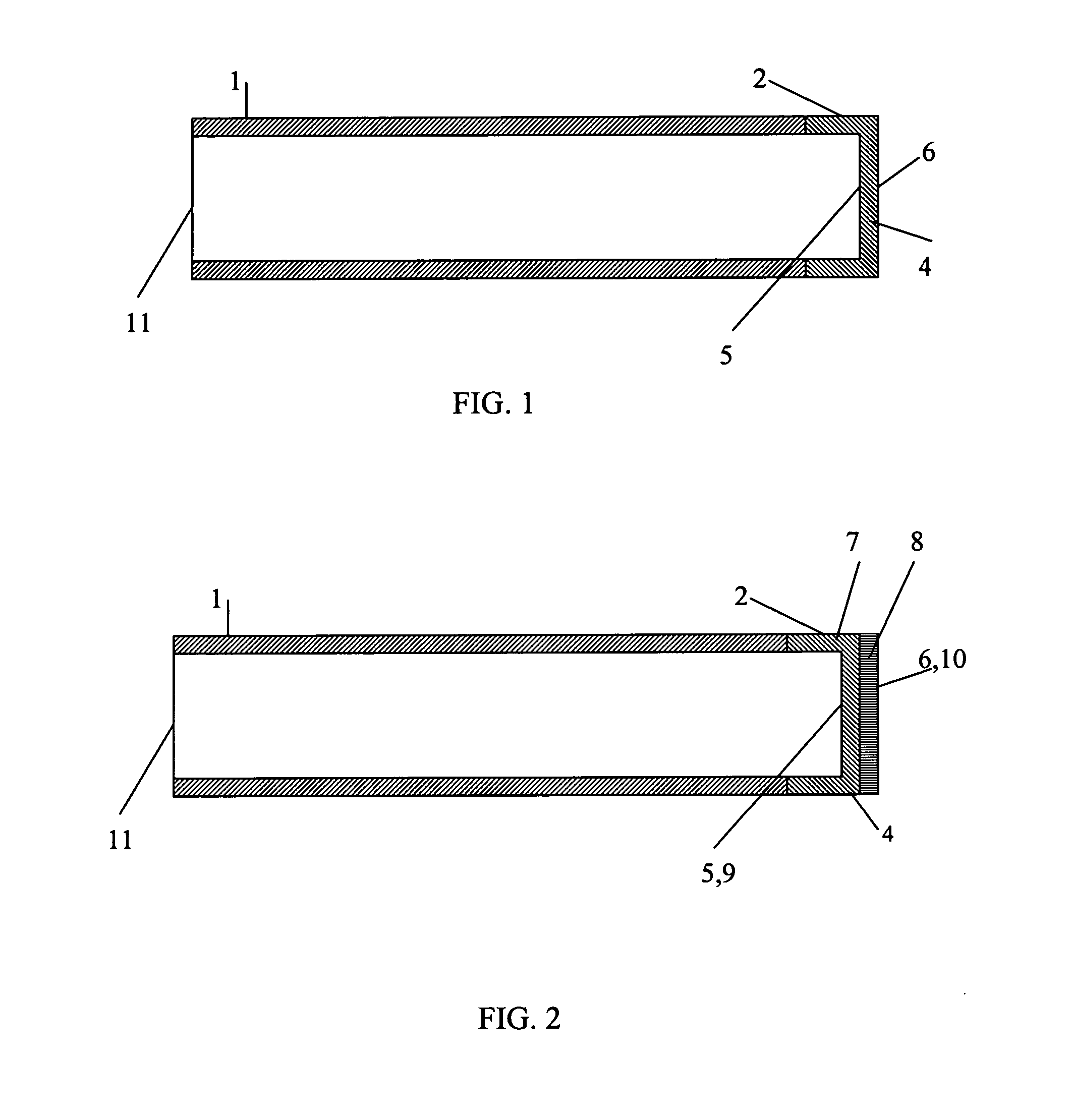
The invention presents modifications of a protector design for an optical fiber probe intended for studying an object. The object being studied can be a biological tissue, namely, a biological tissue of a living body, for example, an internal cavity of a living body. The invention ensures an effective optical contact between an end face of a distal part of the optical fiber probe and the object being studied. In a preferred embodiment the later is achieved by designing an inner surface of a protector window capable of forming a temporary adhesive contact with the end face of the distal part of the optical fiber probe under a pressure of an axial force exerted on the optical fiber probe placed inside a sheath. Herewith, an outer surface of the protector window is designed capable of forming a temporary adhesive contact with the object being studied under the pressure of the axial force exerted on the optical fiber probe placed inside the sheath. To accomplish this in one embodiment the protector window is made of a pliable and resilient material, for example, of a cured optical gel. In another embodiment the protector window is configured as at least a bilayer structure. Additionally, in a preferred embodiment the layers, one of whose surfaces form either the inner or the outer surface of the protector window, are made of a pliable and resilient material, such as a cured optical gel. This prevents the protector window from sliding over the surface of the object being studied and at the same time ensures an effective optical contact between the end face of the distal part of the optical fiber probe and the object being studied. The cured optical gel can be jelly-like or rubber-like. The values of the refractive indexes of the protector window material at the operating wavelength or at least of the layer facing the interior cavity of the sheath and of the layer, one of whose surfaces forms the outer surface of the protector window, are chosen taking into account the values of refractive indexes of the distal part of the optical fiber probe and of the object being studied.
Owner:IMALUX CORP
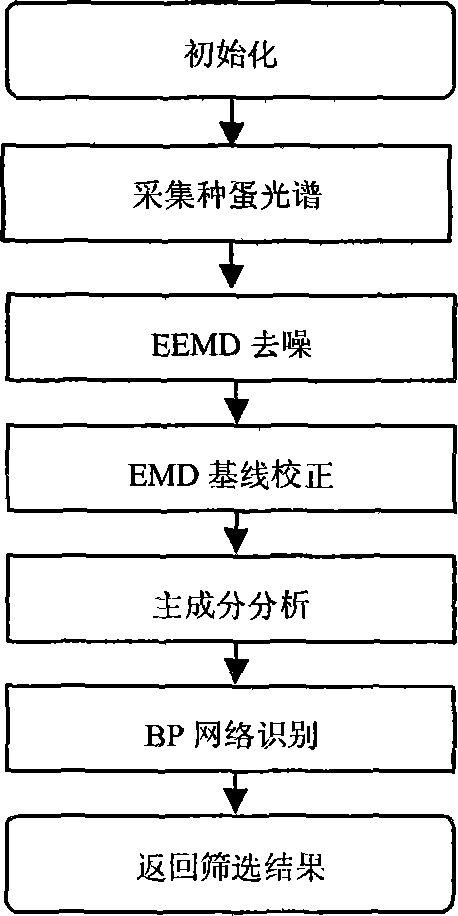
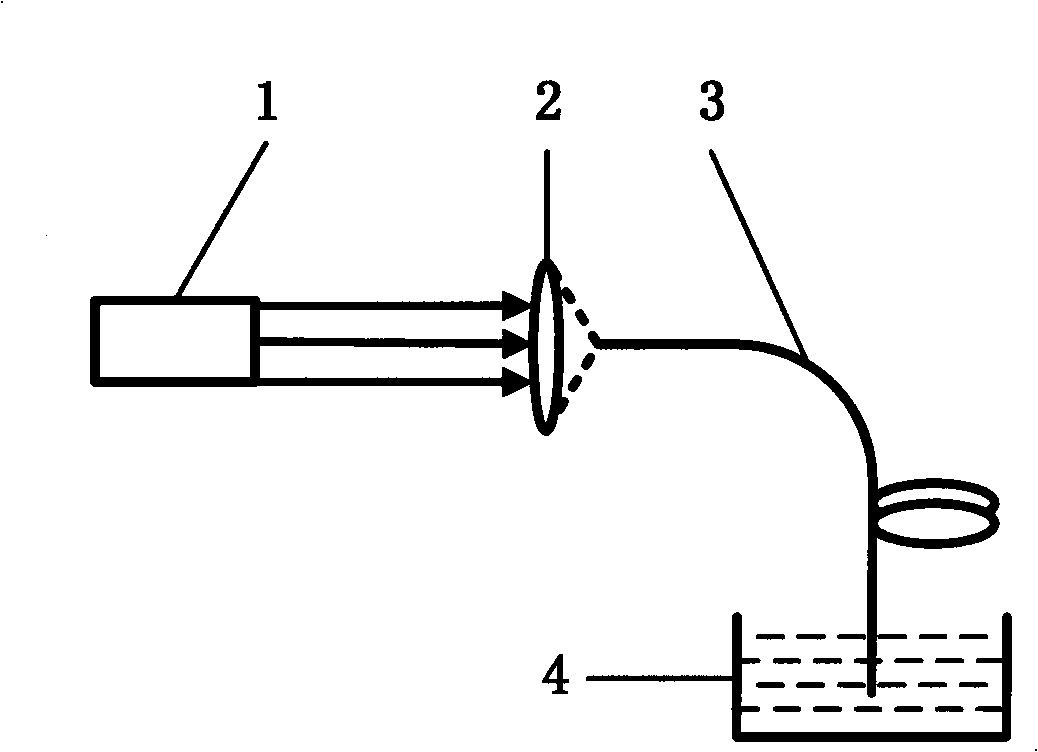
Gender identification method for chick embryo in near-infrared hatching egg at earlier stage of incubation
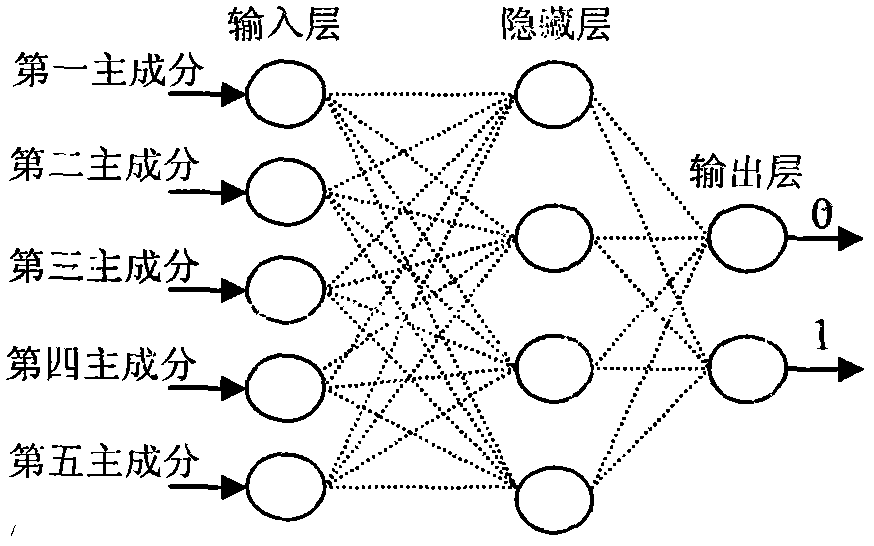
InactiveCN103472008AImprove efficiencyHigh precisionColor/spectral properties measurementsNerve networkDecomposition
The invention discloses a gender identification method for a chick embryo in a near-infrared hatching egg at earlier stage of incubation, and belongs to a hatching egg detection technology. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a near-infrared spectrum of a hatching egg through an optical fiber probe and a Fourier near-infrared spectrometer in a dark room, decomposing the near-infrared spectrum of the hatching egg by an overall mean empirical mode, removing high-frequency characteristic mode components to remove noise, removing low-frequency characteristic mode components by a method based on empirical mode decomposition to achieve baseline correction, extracting main components of spectral data as input variables of a nerve network so as to finish the identification, wherein the output value of the nerve network is 0 or 1. According to the method, the gender identification efficiency and accuracy of the hatching egg at earlier stage of incubation are high, the incubation cost is reduced, and the development of layer chicken and meat chicken feeding production is facilitated.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG BAYI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing surface enhanced Raman scattering optical fiber probe
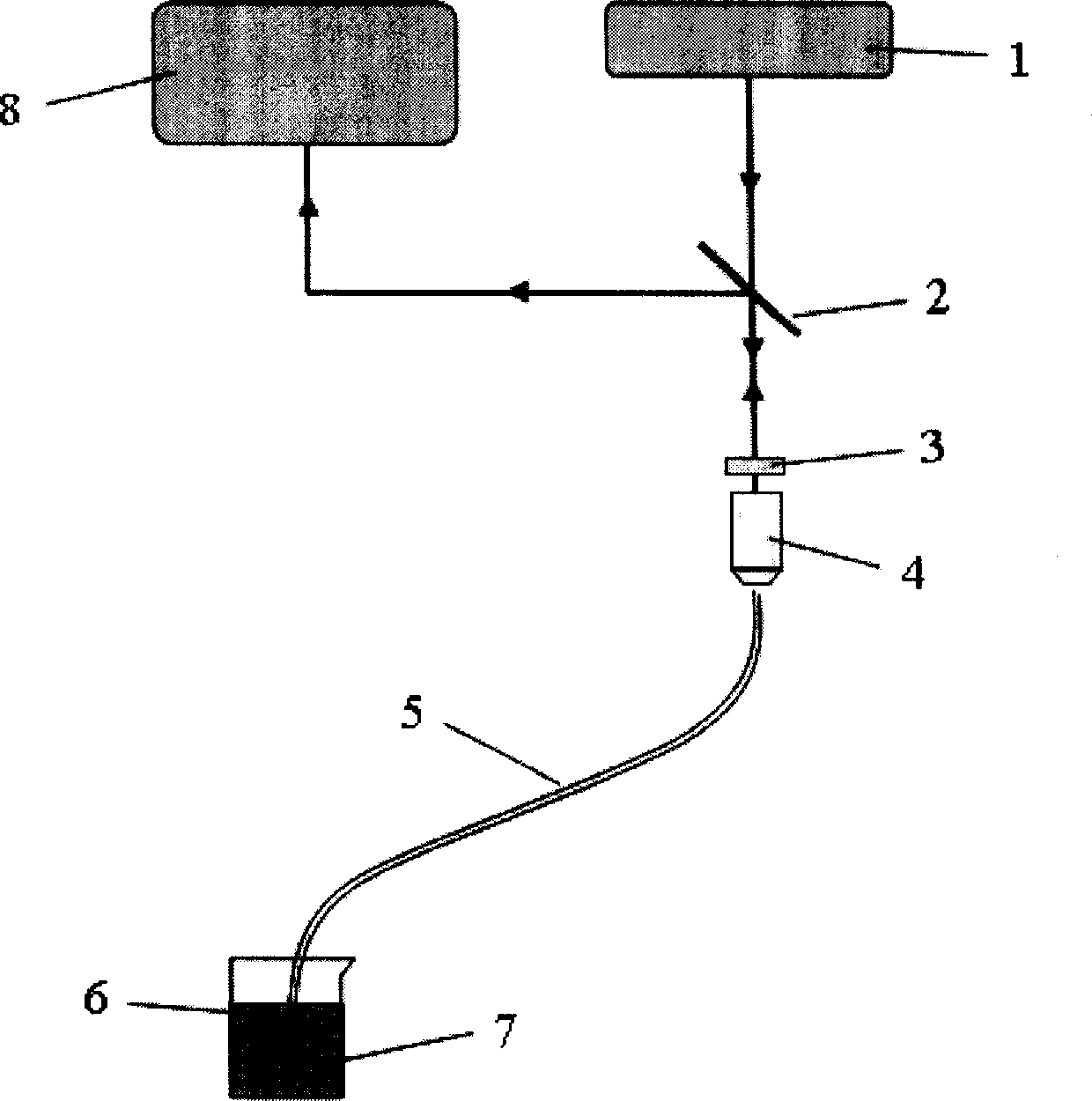
InactiveCN101539522AAdjust detection performanceSimple preparation processRaman scatteringFiberOptical fiber probe
The invention relates to a method for preparing a surface enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) optical fiber probe, which comprises the steps as follows: the laser-transmitting characteristic of optical fiber is utilized to form an optical field with graded distribution on the fiber end surface; the remote end of the optical fiber is immersed in a reaction solution containing a reducing agent and soluble metal salt; under laser radiation, metal cations in the reaction solution are reduced into metal nano particles, and the particles are adhered on the core field of the fiber end surface under the gradient force action of the optical field to form a deposition pattern with distribution being the same as the laser mode field of the remote end surface of the optical fiber and then taken as a substrate needed by surface enhanced Raman detection, thus obtaining the optical fiber probe applied to SERS detection. The method utilizes the laser power, action time and optical spot profile of laser on the fiber end surface to respectively control the size of the metal nano particles and the deposition shape thereof at the fiber end surface, thus providing a new method for controlling the properties of the surface enhanced Raman probe.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com