Common path systems and methods for frequency domain and time domain optical coherence tomography using non-specular reference reflection and a delivering device for optical radiation with a partially optically transparent non-specular reference reflector
a frequency domain and time domain optical coherence tomography technology, applied in the field of common path systems and methods for frequency domain and time domain optical coherence tomography using non-specular reference reflection and a delivering device for optical radiation with a partially optically transparent non-specular reference reflector, can solve the problems of serious frequency domain oct problems, the cost of telecentric optical systems is more expensive and difficult to assemble and align, and the implementation of critical dimensions of optical probes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
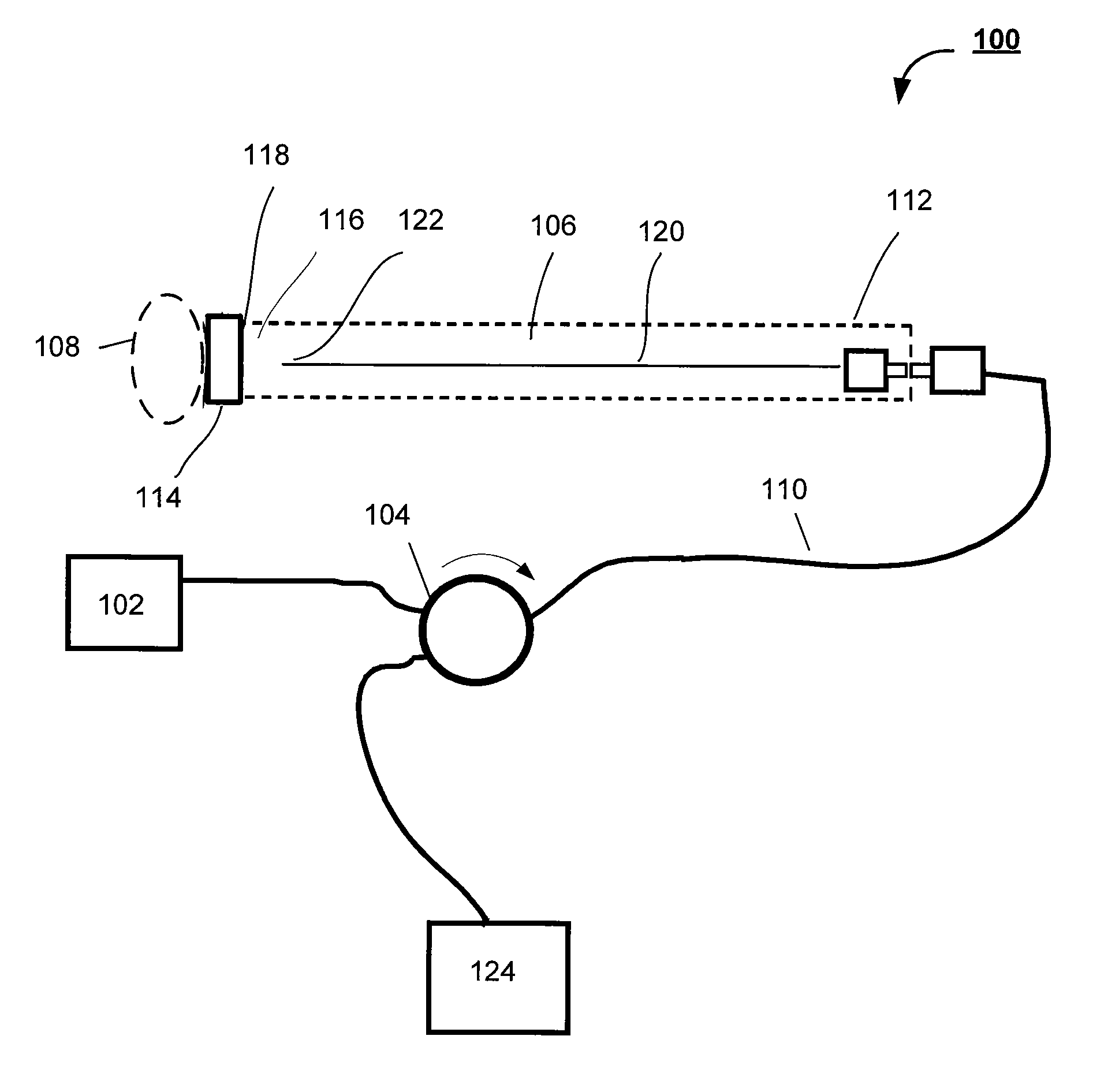
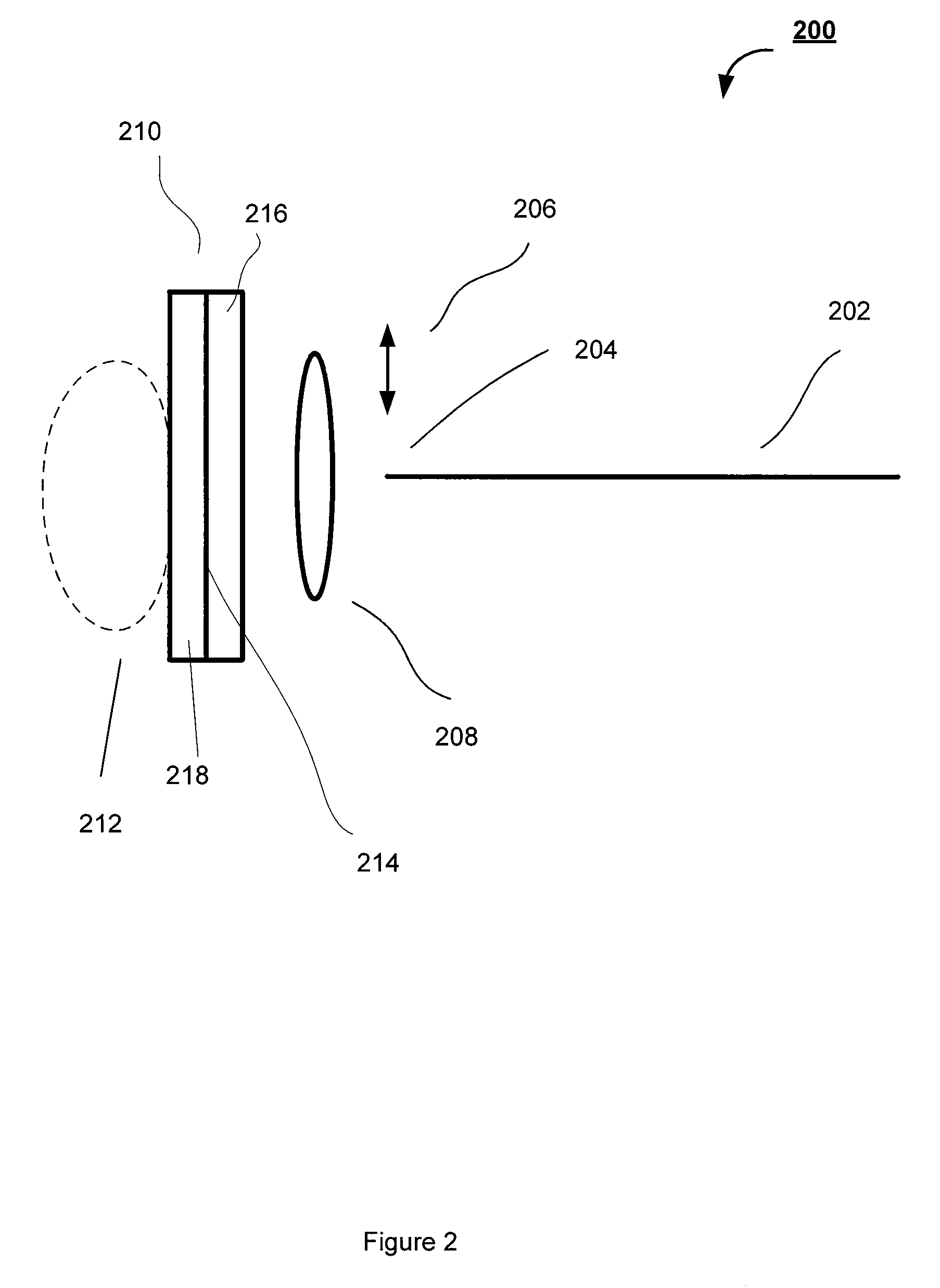
[0028]The subject application is directed to systems and methods for visualizing subsurface regions of samples, and more specifically, to common path systems and methods for frequency domain and time domain optical coherence tomography (OCT) using a partially optically transparent non-specular reference reflector for providing internal depth profiles and depth resolved images of samples. The subject application is also directed and to a device for delivering optical radiation to an associated sample, preferably implemented as an optical fiber probe with a partially optically transparent non-specular reflector. The delivering device of the subject application is capable of being efficiently used in common path frequency domain and time domain reflectometry, as well. The common path frequency domain and time domain OCT devices are illustrated herein by means of examples of optical fiber devices, although it is evident that they may be implemented with the use of bulk optic elements. T...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com