Patents
Literature
214 results about "Central venous catheter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
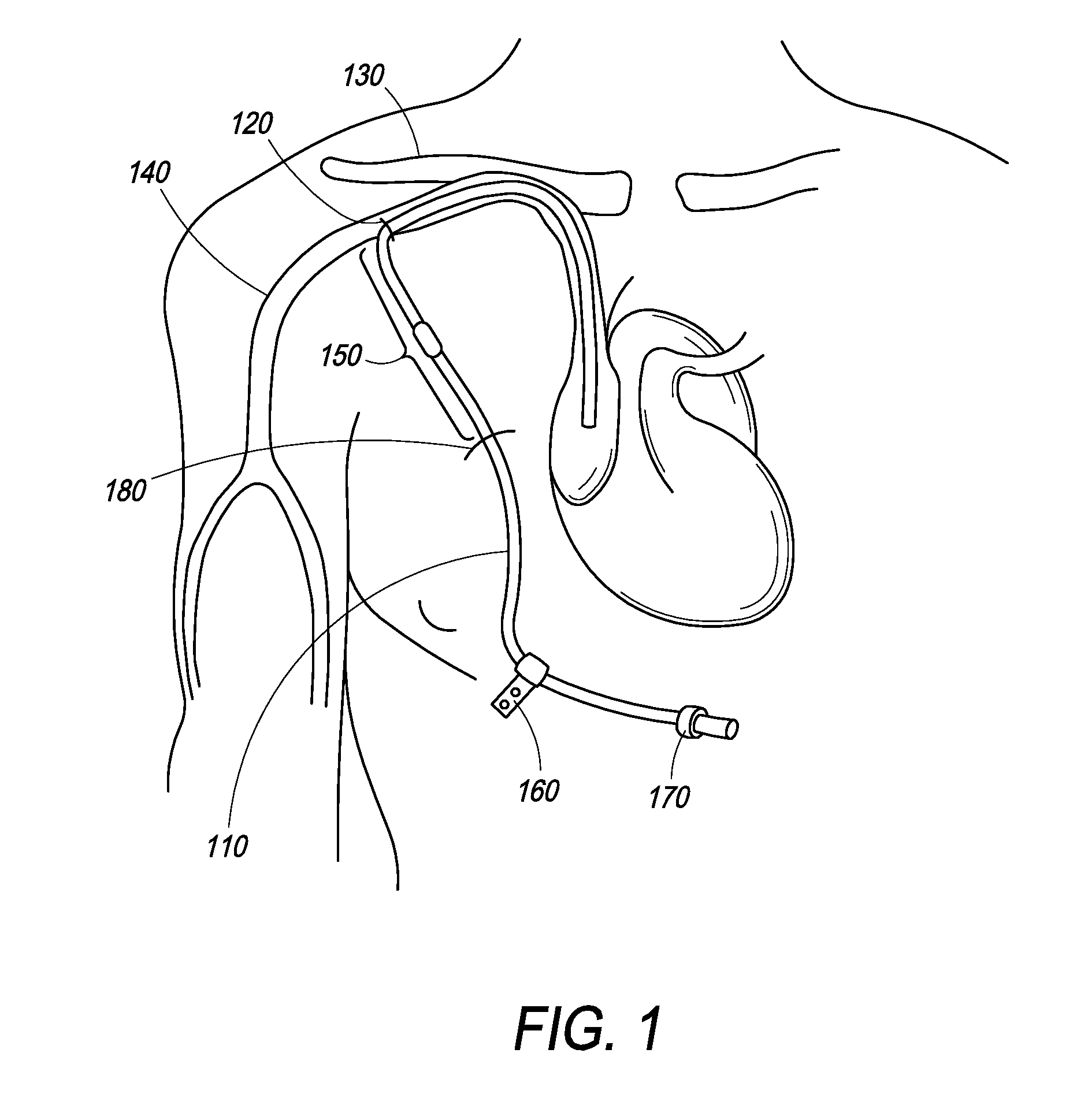
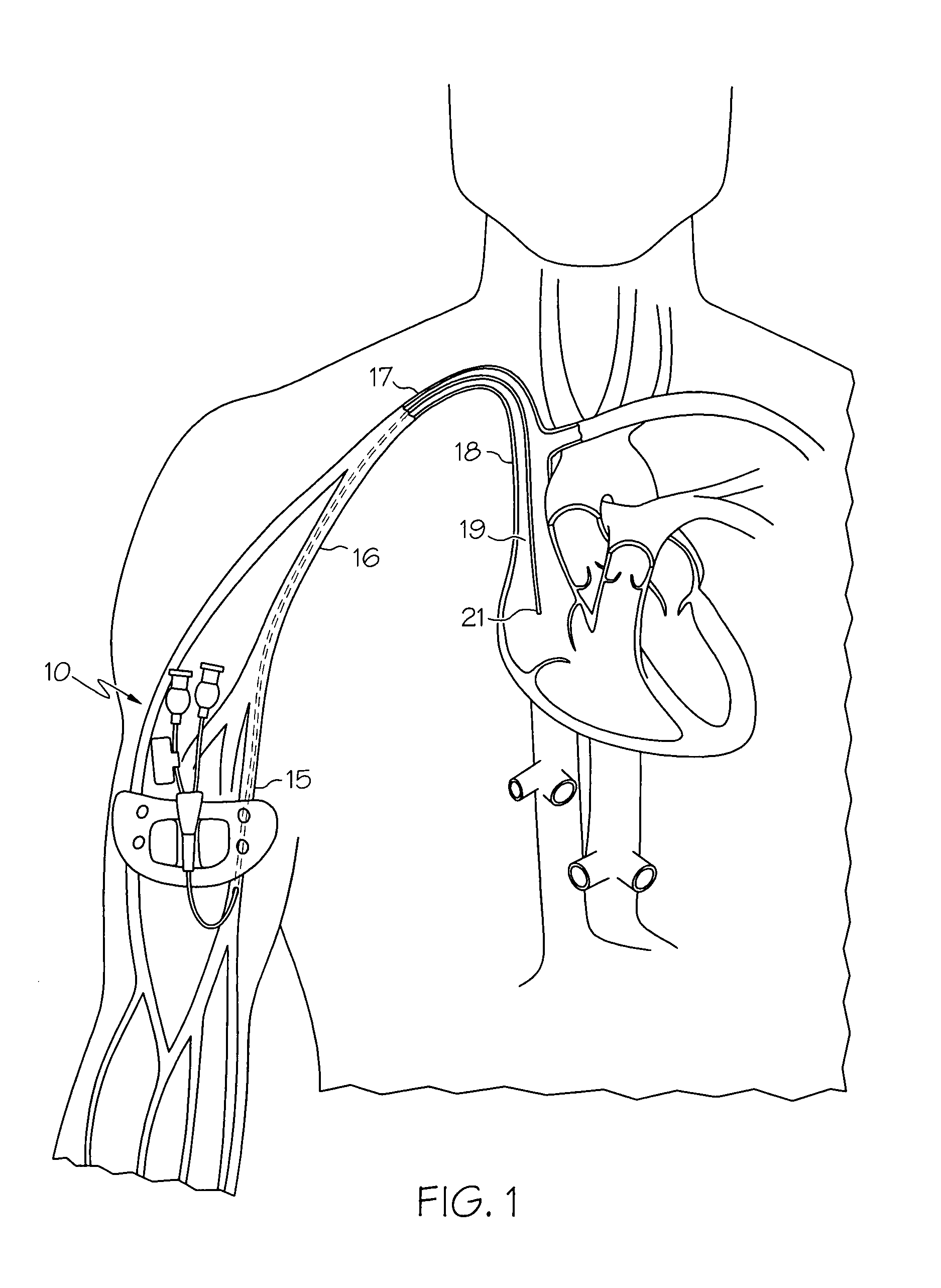
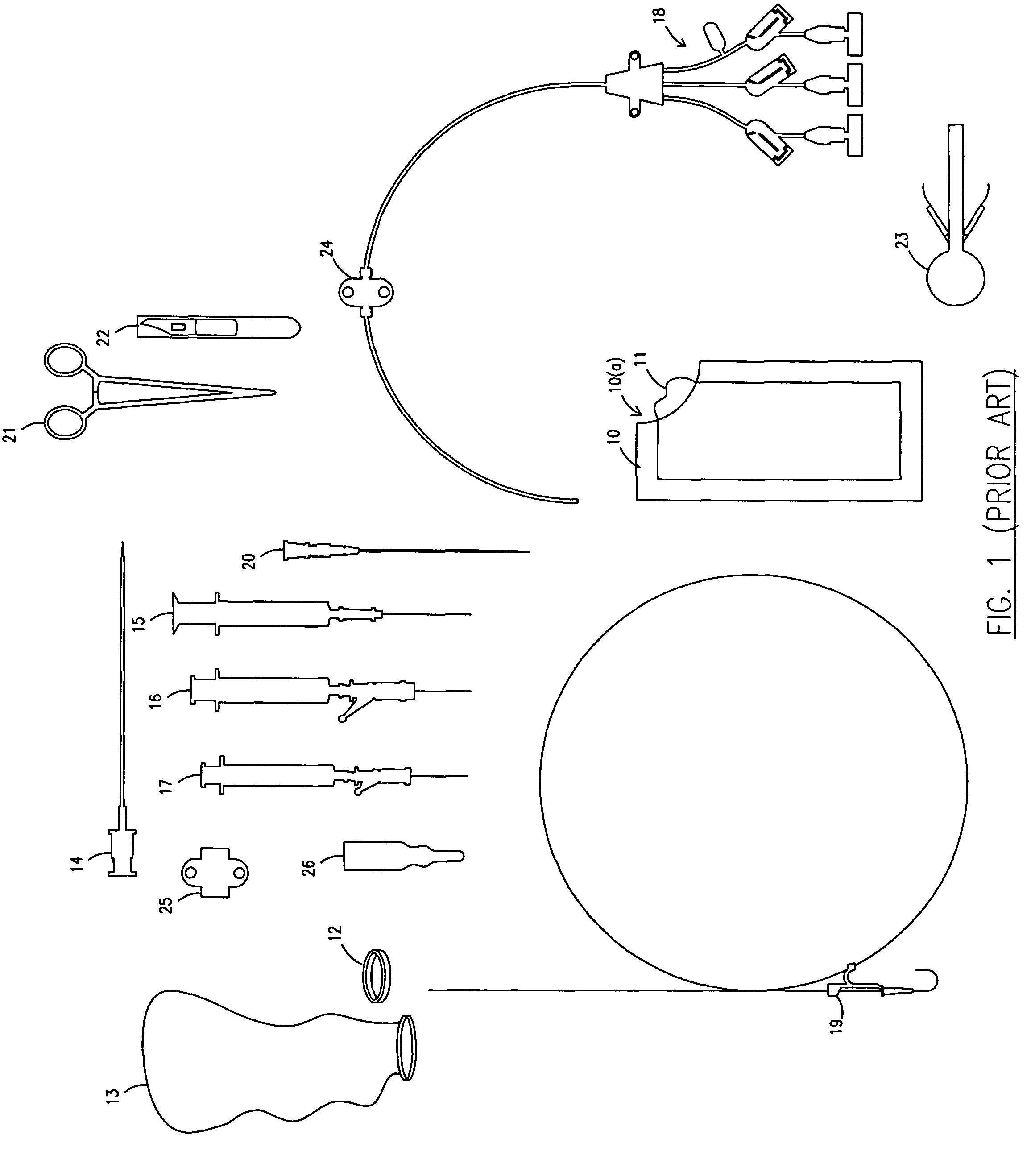
A central venous catheter (CVC), also known as a central line, central venous line, or central venous access catheter, is a catheter placed into a large vein. Catheters can be placed in veins in the neck (internal jugular vein), chest (subclavian vein or axillary vein), groin (femoral vein), or through veins in the arms (also known as a PICC line, or peripherally inserted central catheters). It is used to administer medication or fluids that are unable to be taken by mouth or would harm a smaller peripheral vein, obtain blood tests (specifically the "central venous oxygen saturation"), and measure central venous pressure.
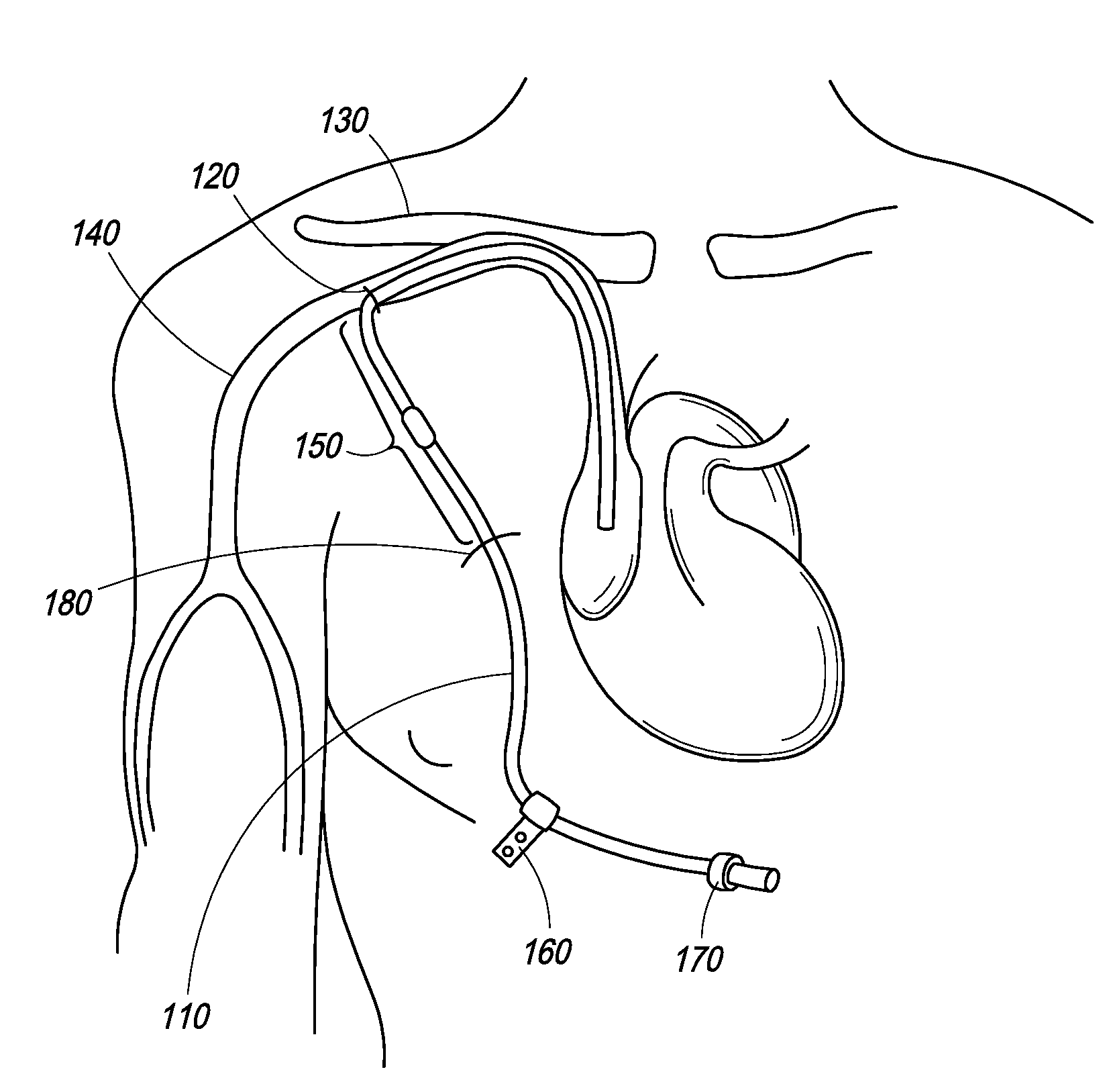
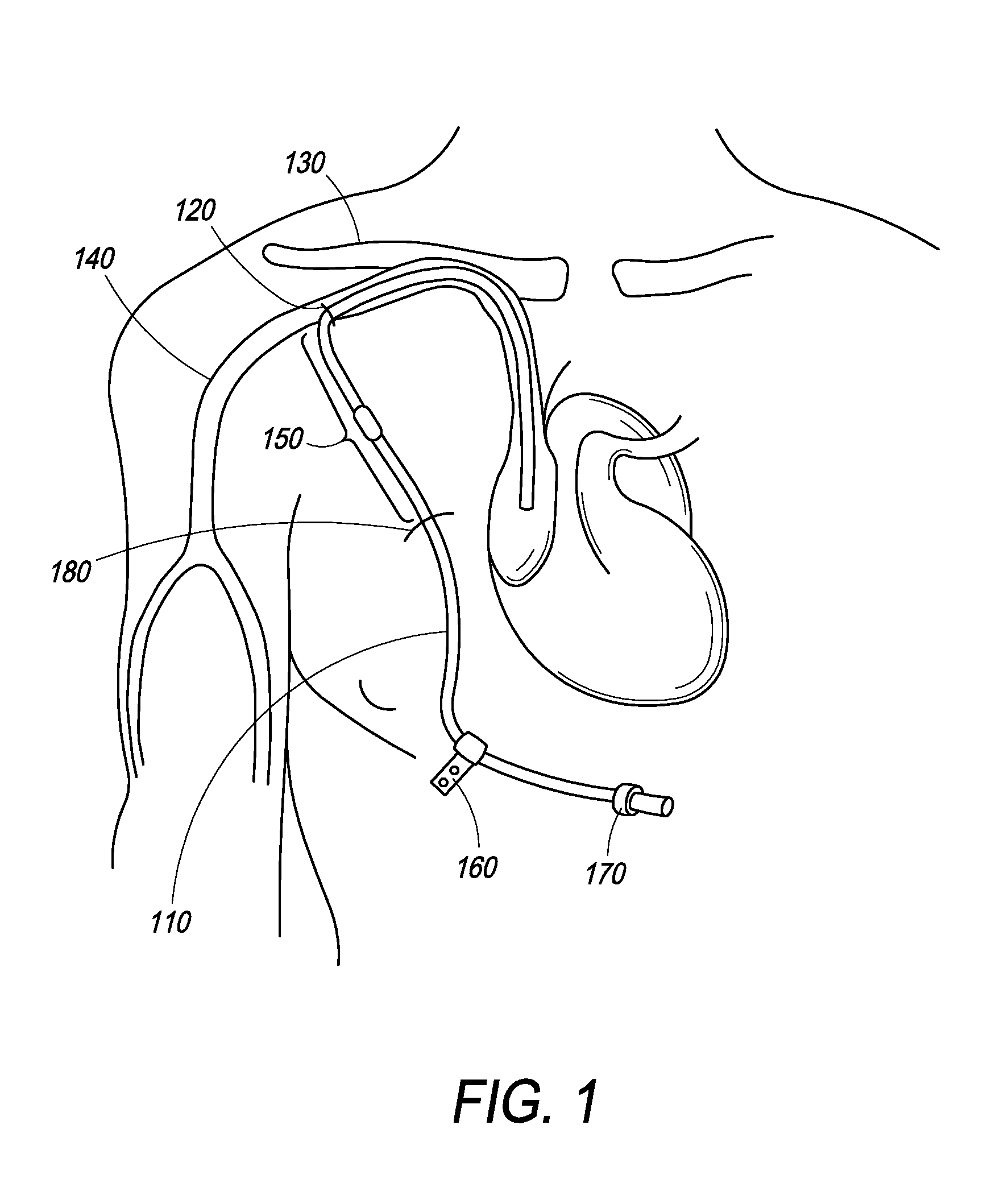
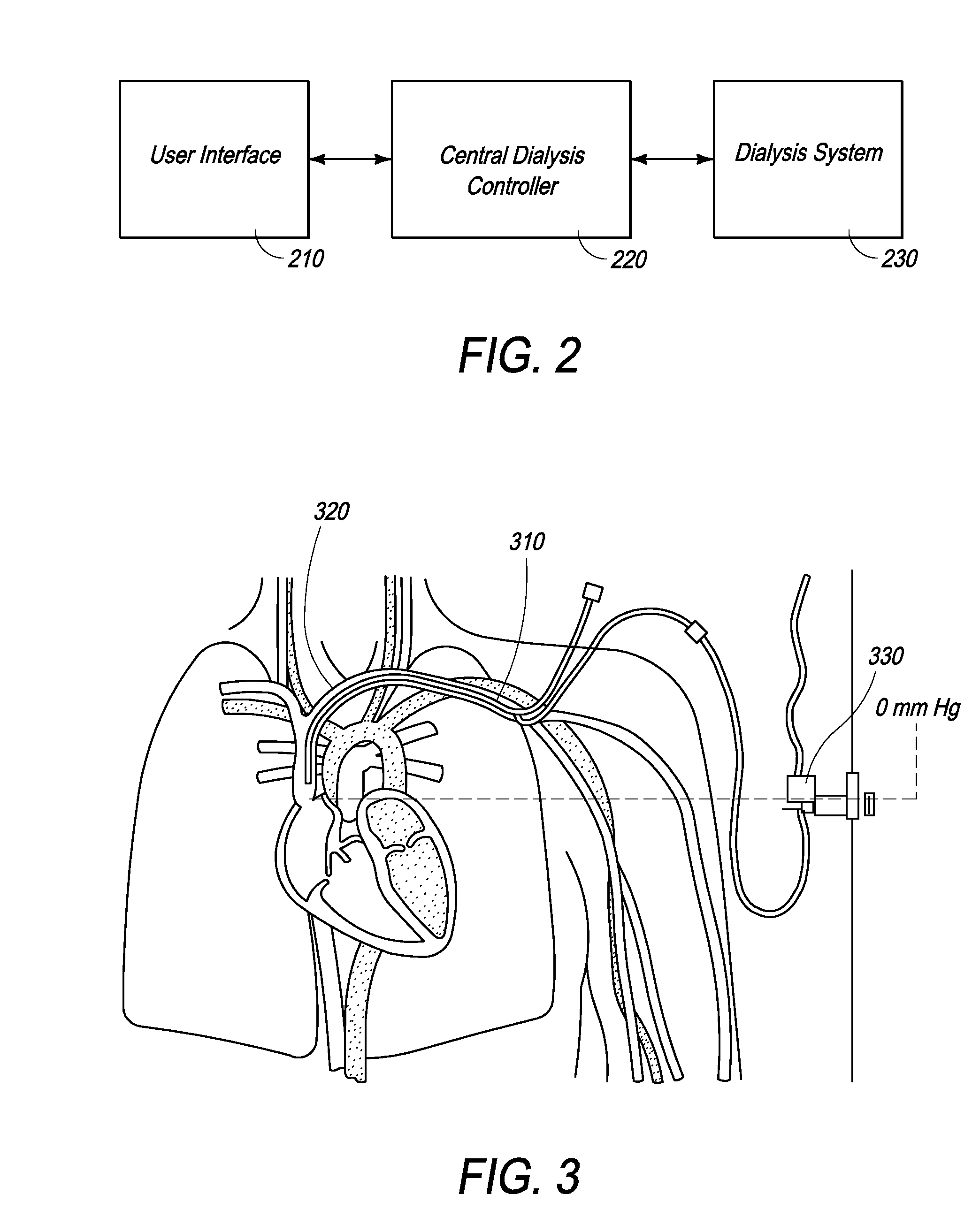
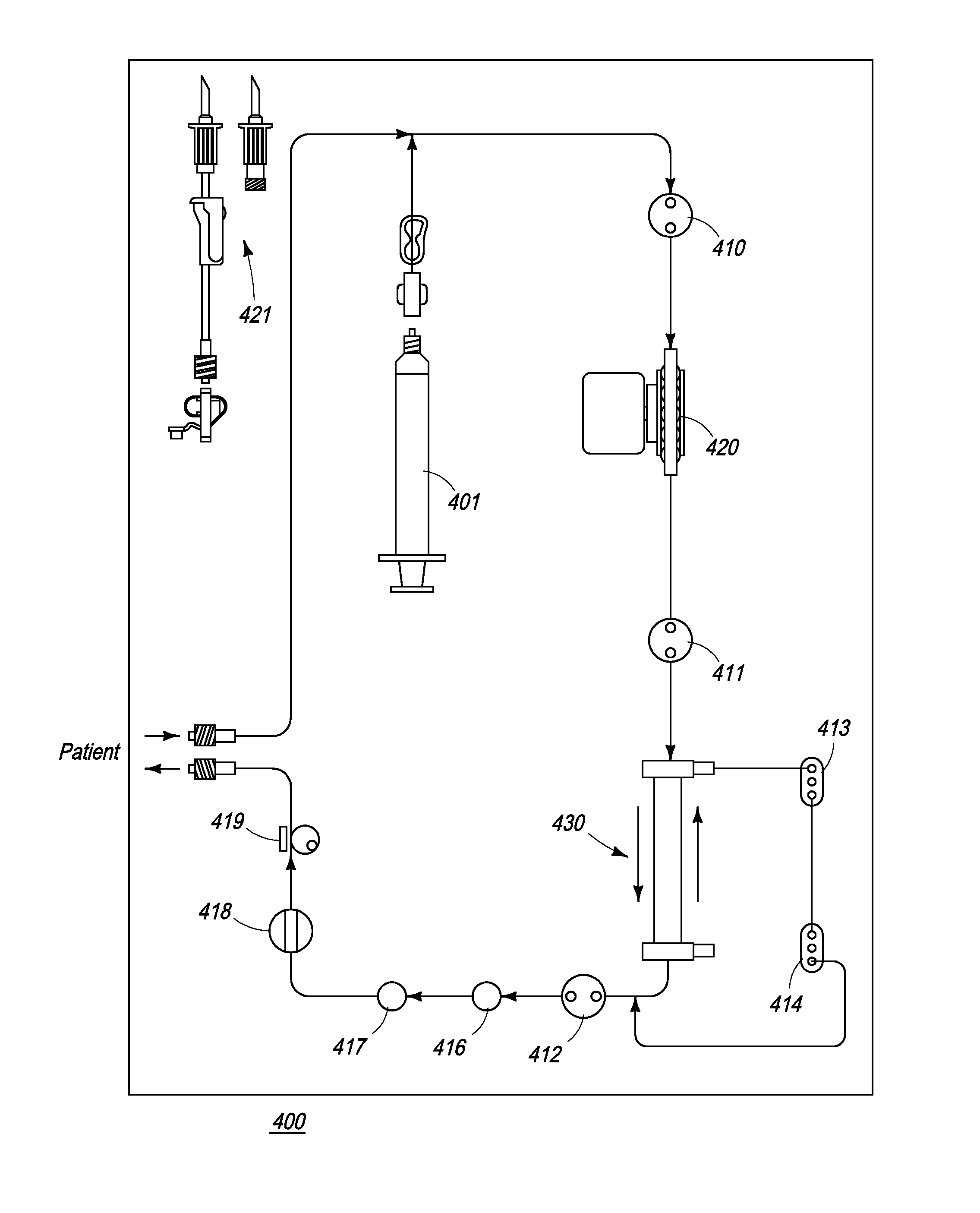
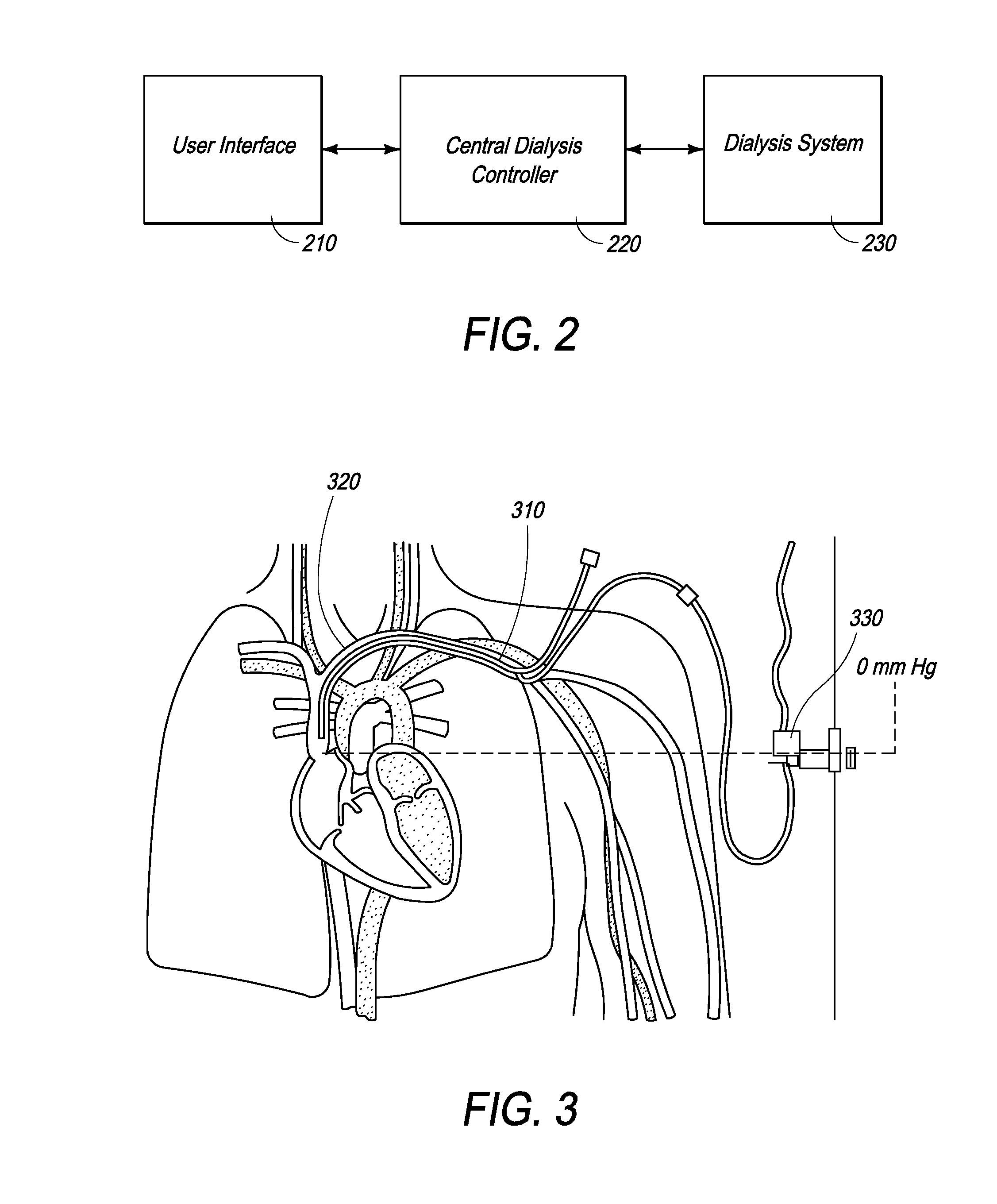
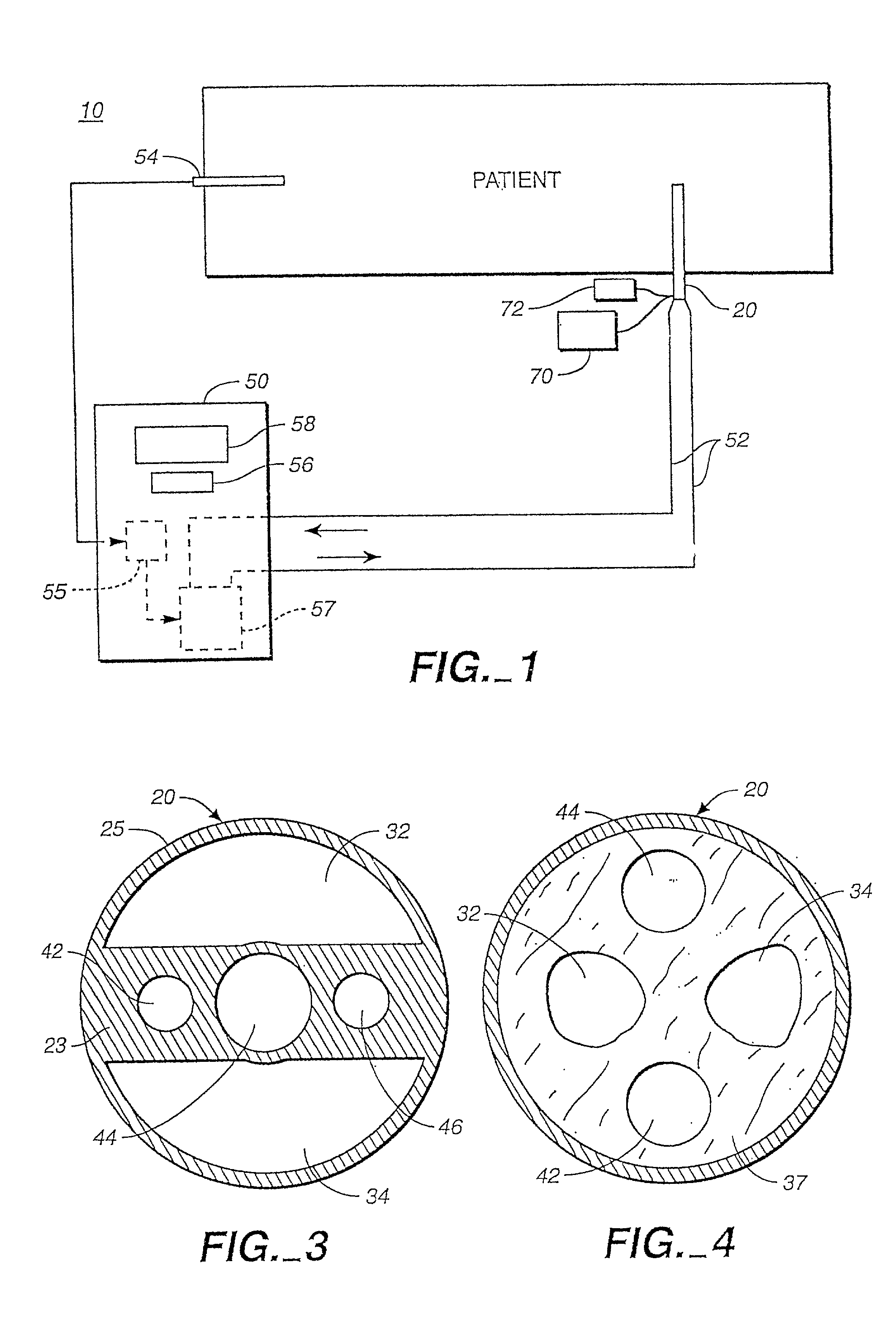
Methods and Systems for Controlling Ultrafiltration Using Central Venous Pressure Measurements
The volume of fluid removed from a patient during ultrafiltration is controlled automatically on the basis of central venous pressure (CVP) measurements. In one embodiment, a central venous catheter (CVC) is used for accessing blood during dialysis. A sensor located at the tip of the catheter or inside the dialysis machine is used to periodically measure CVP. CVP feedback data helps prevent the excessive removal of fluids from the patient.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
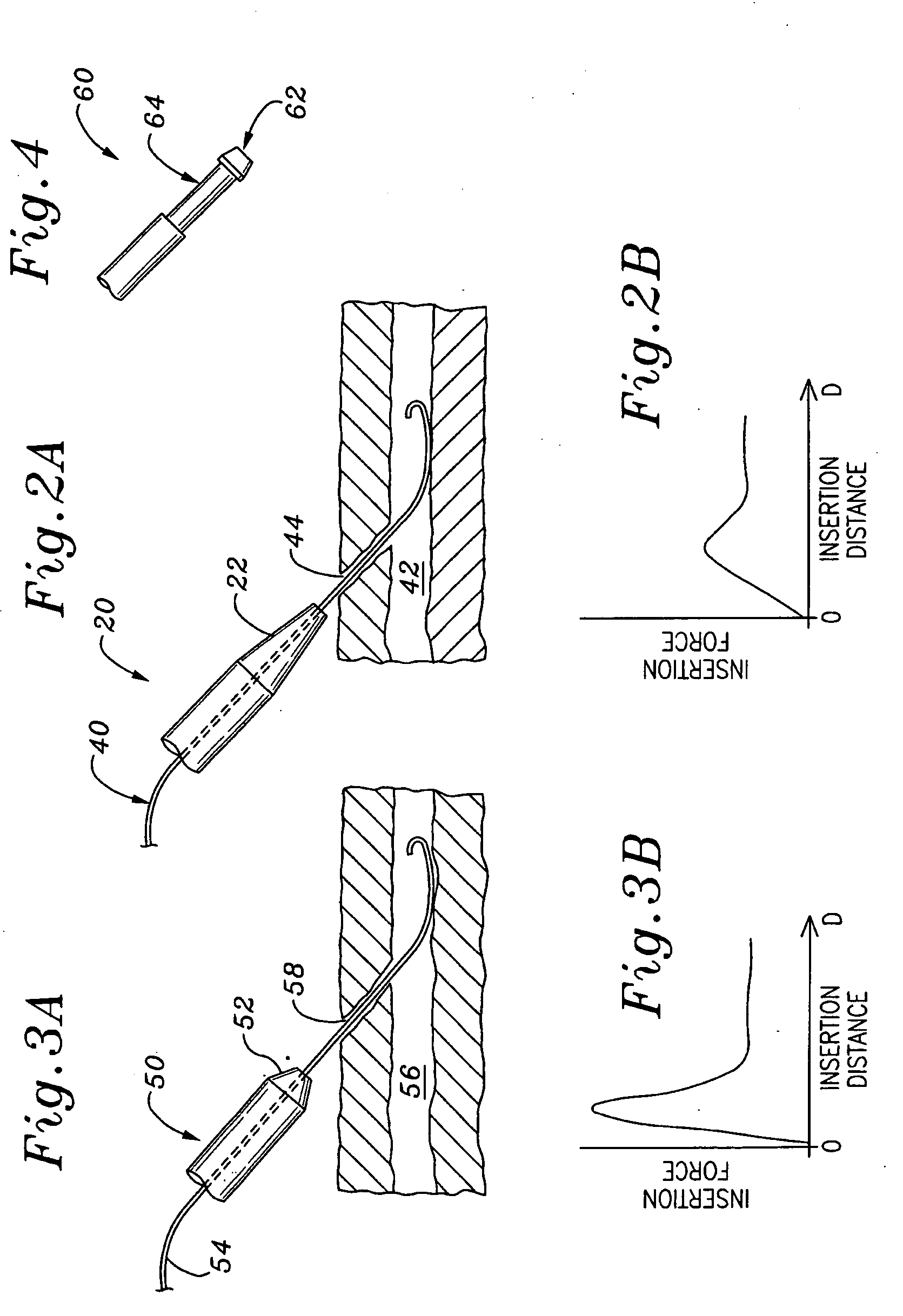
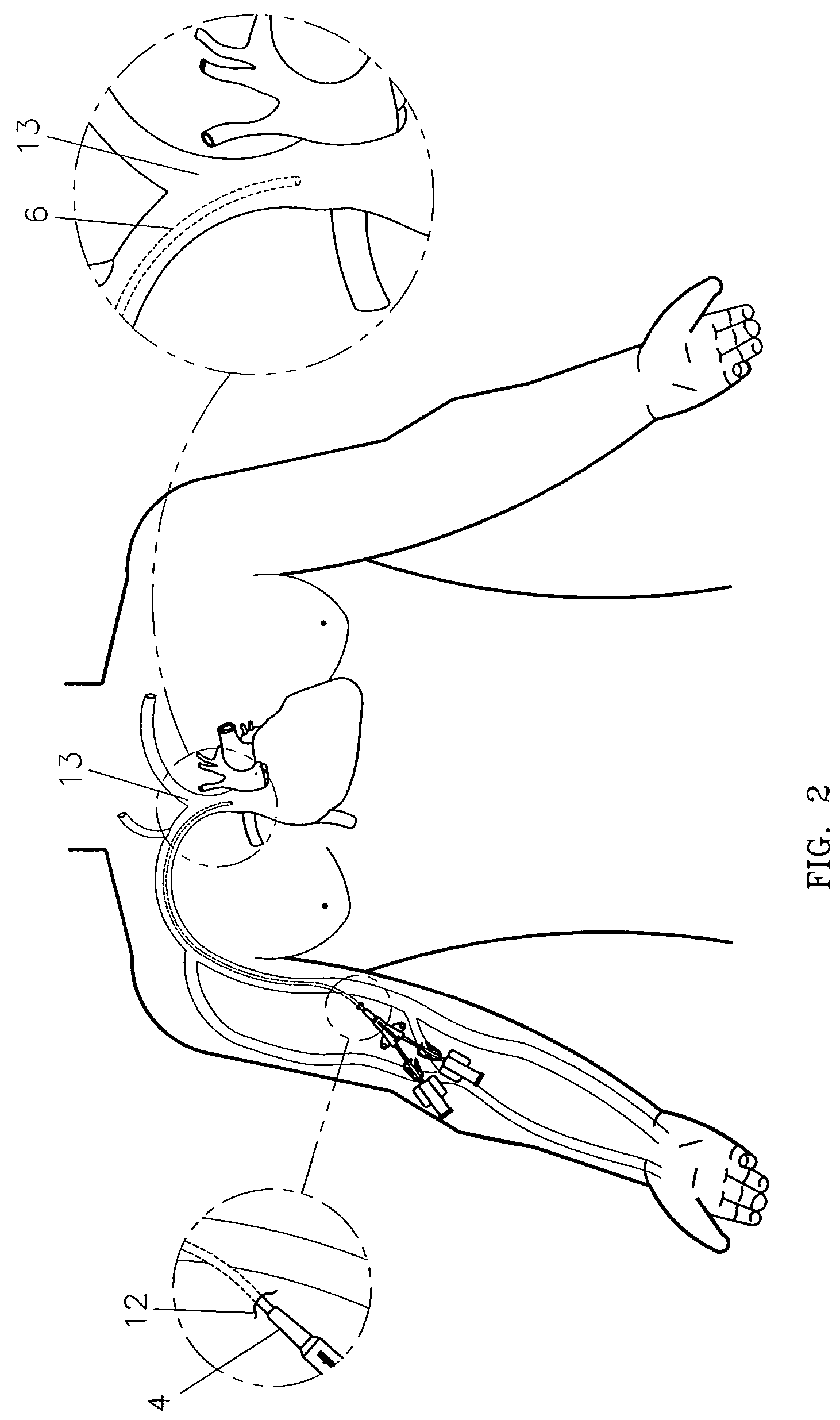
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
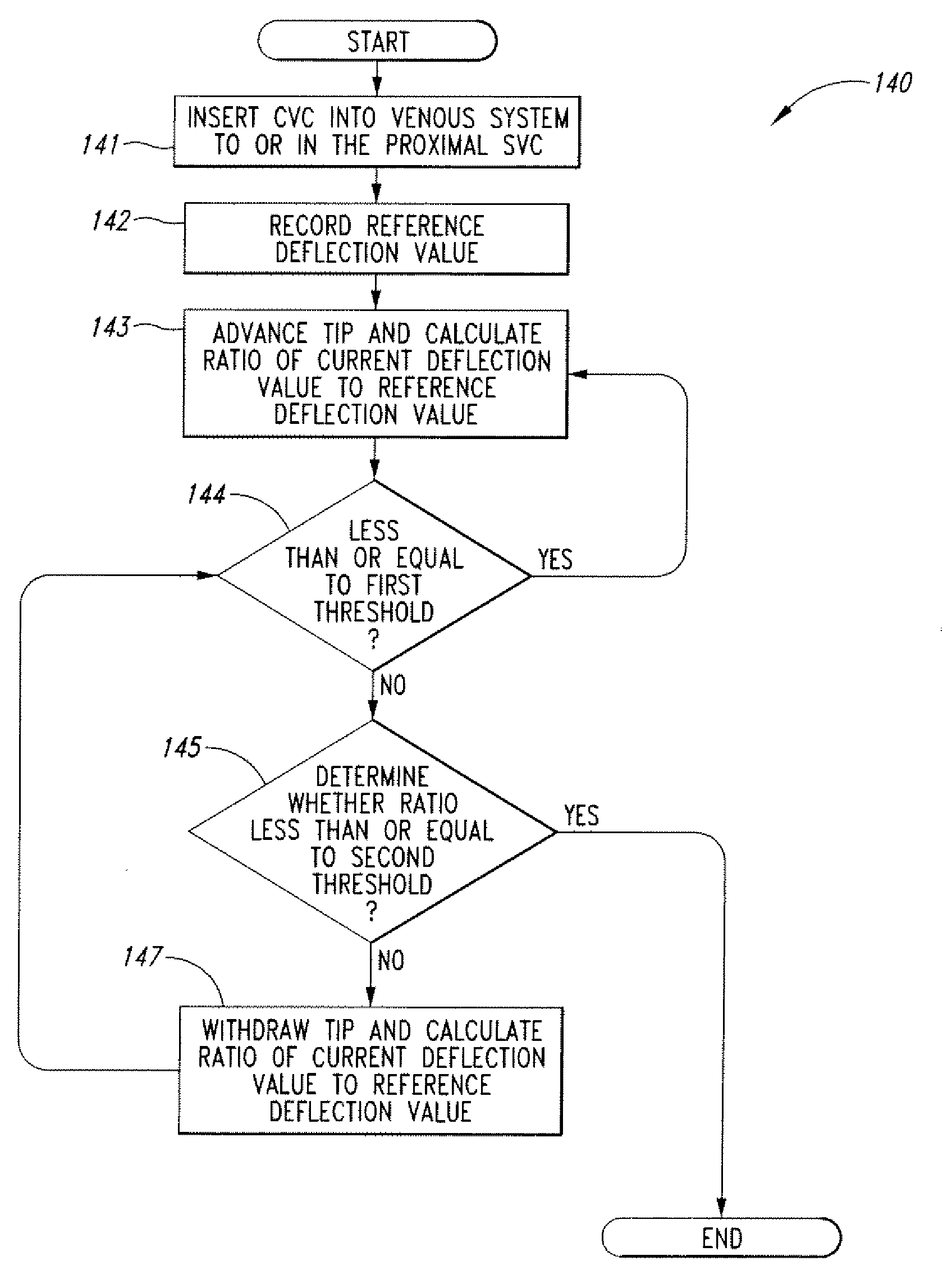
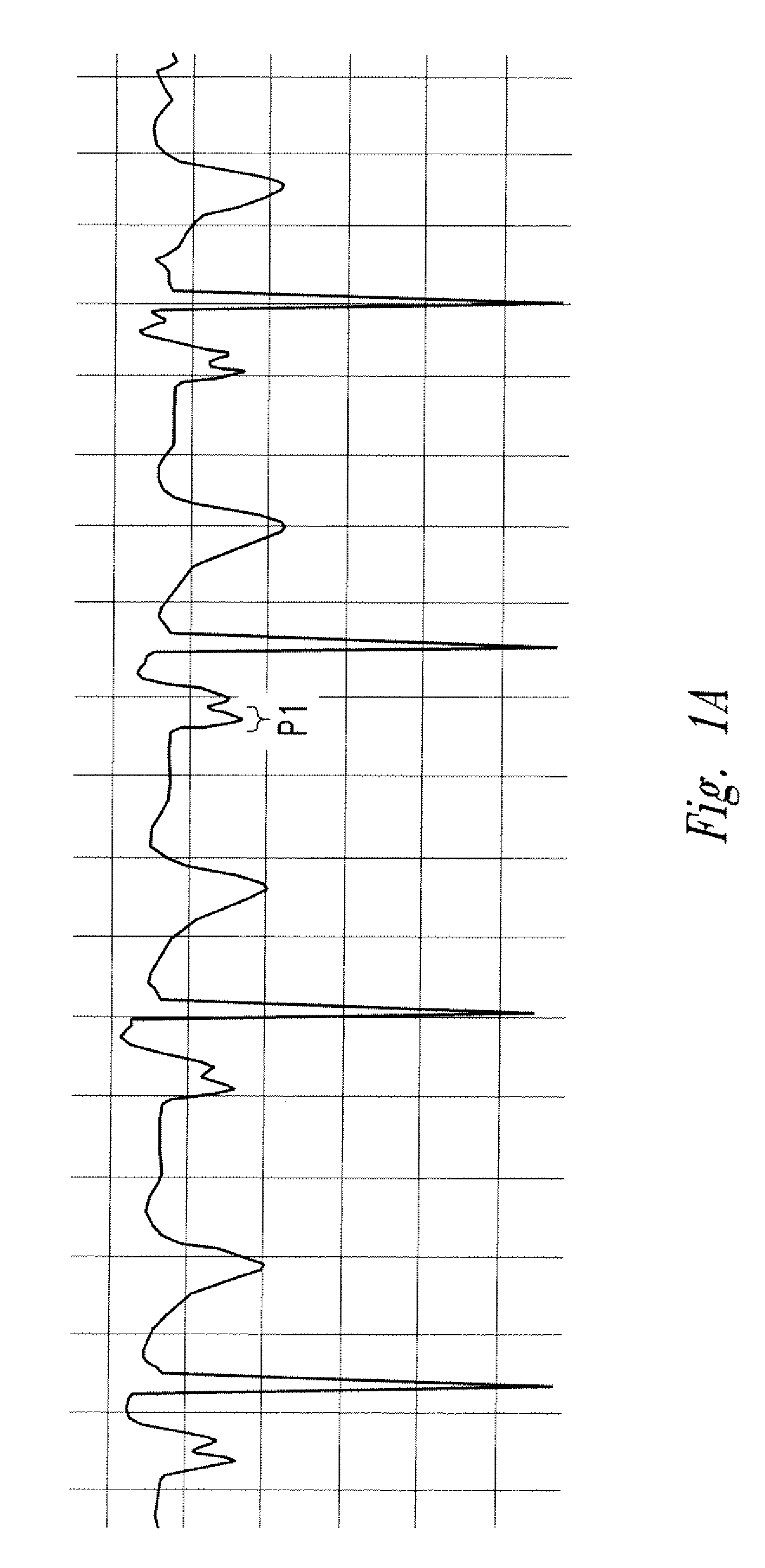
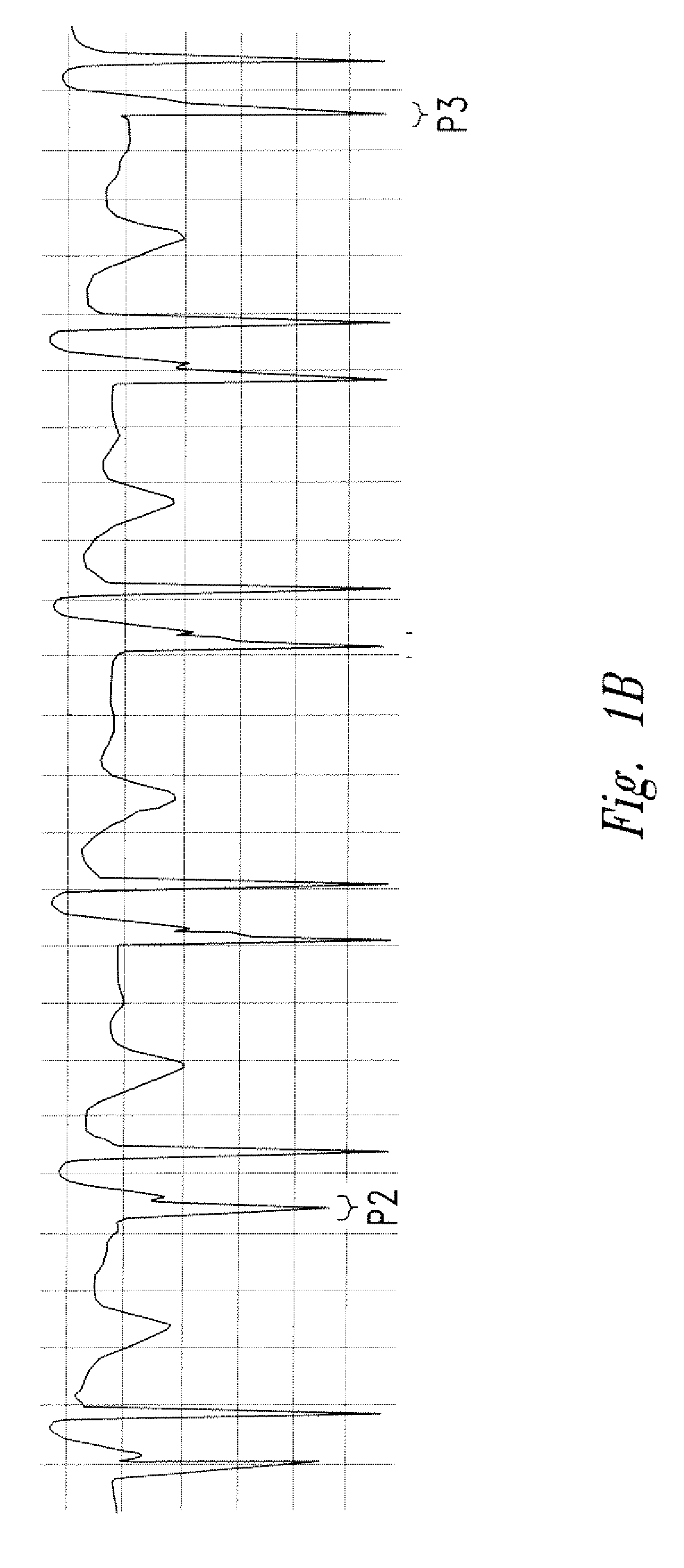
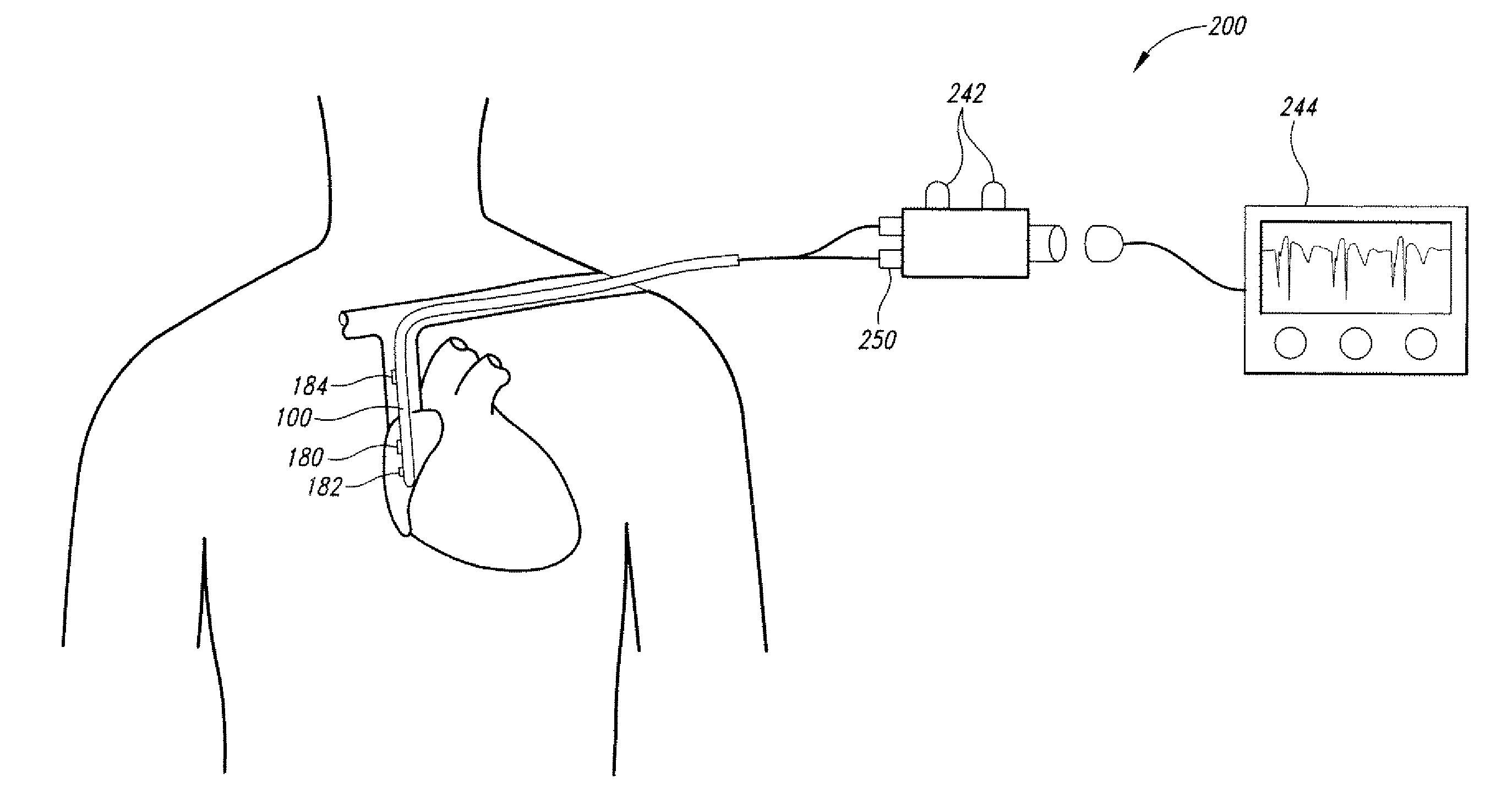
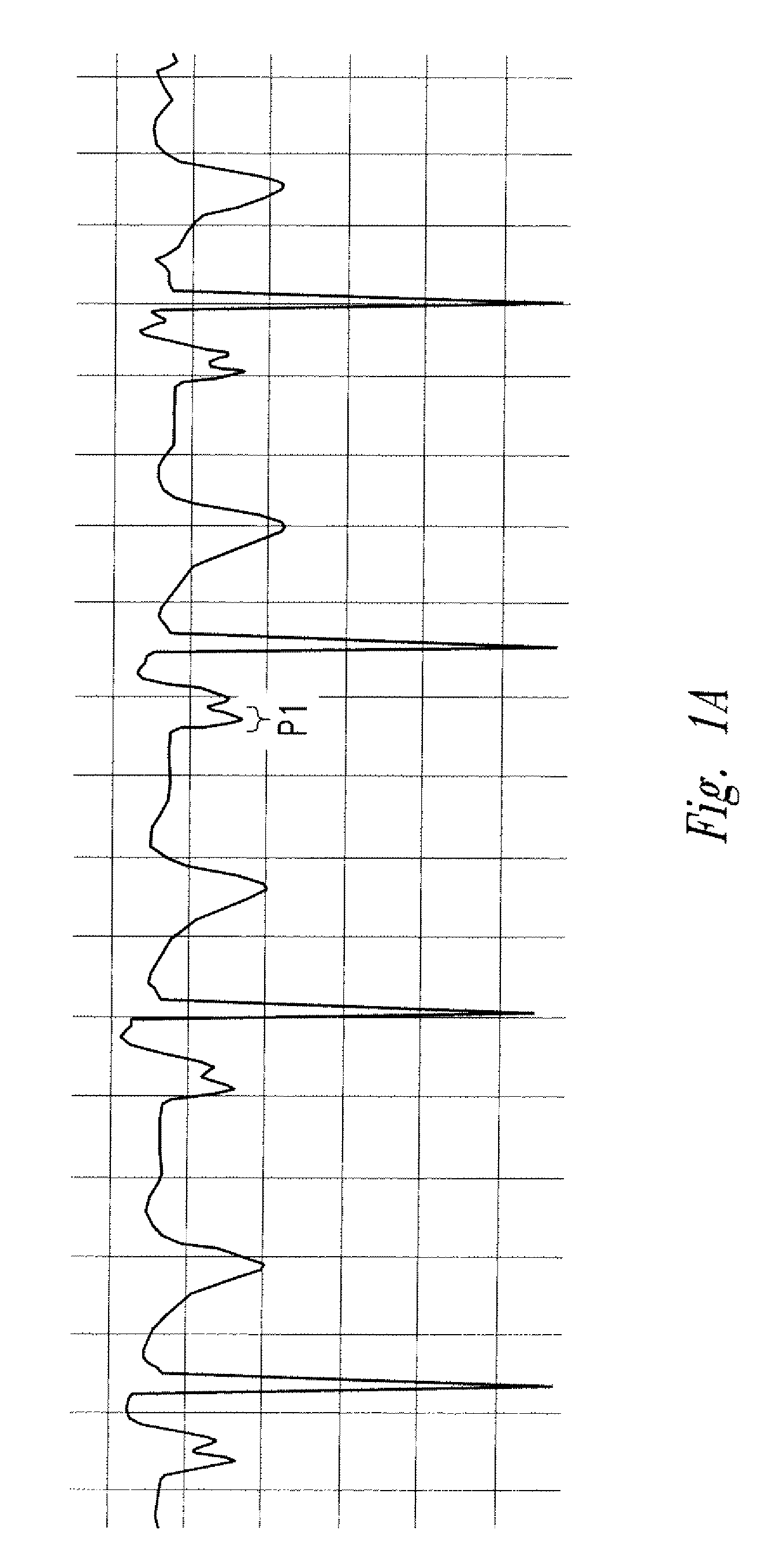
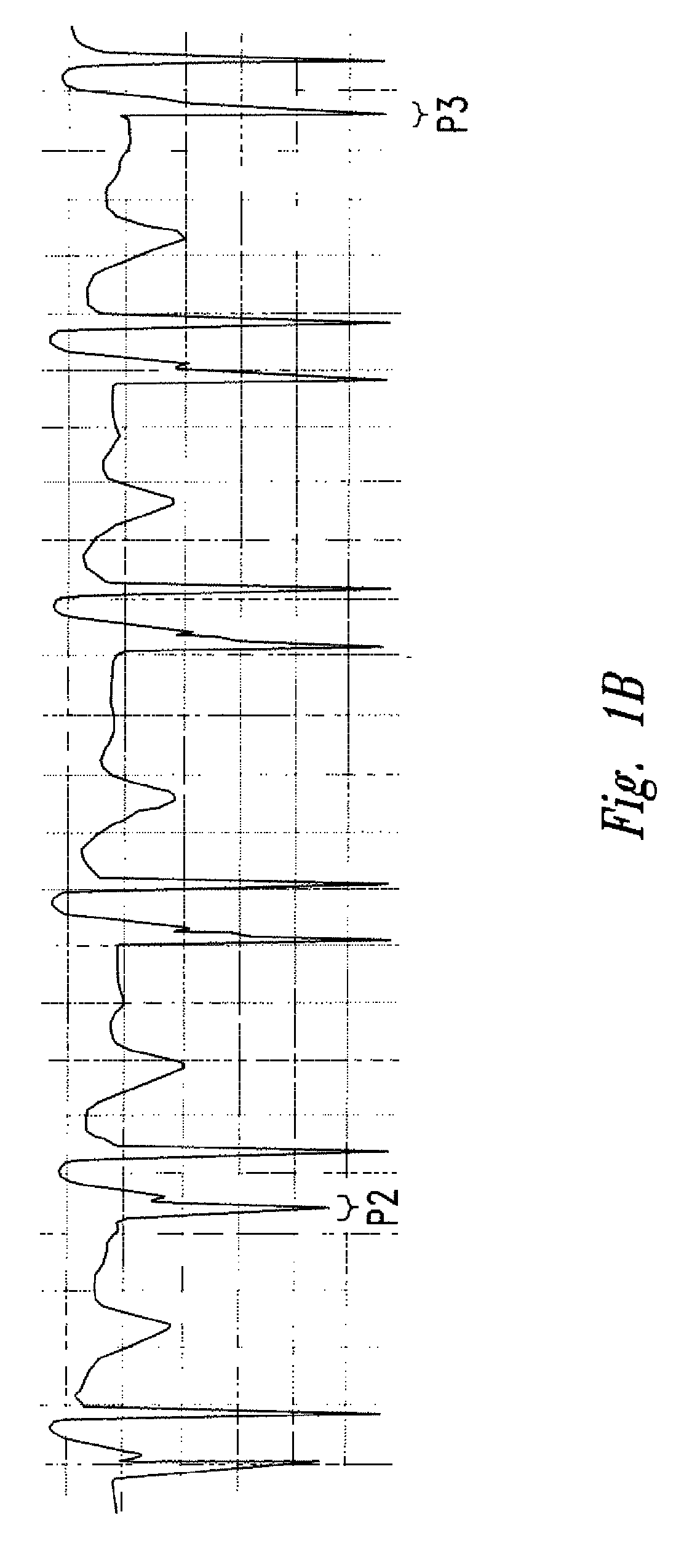
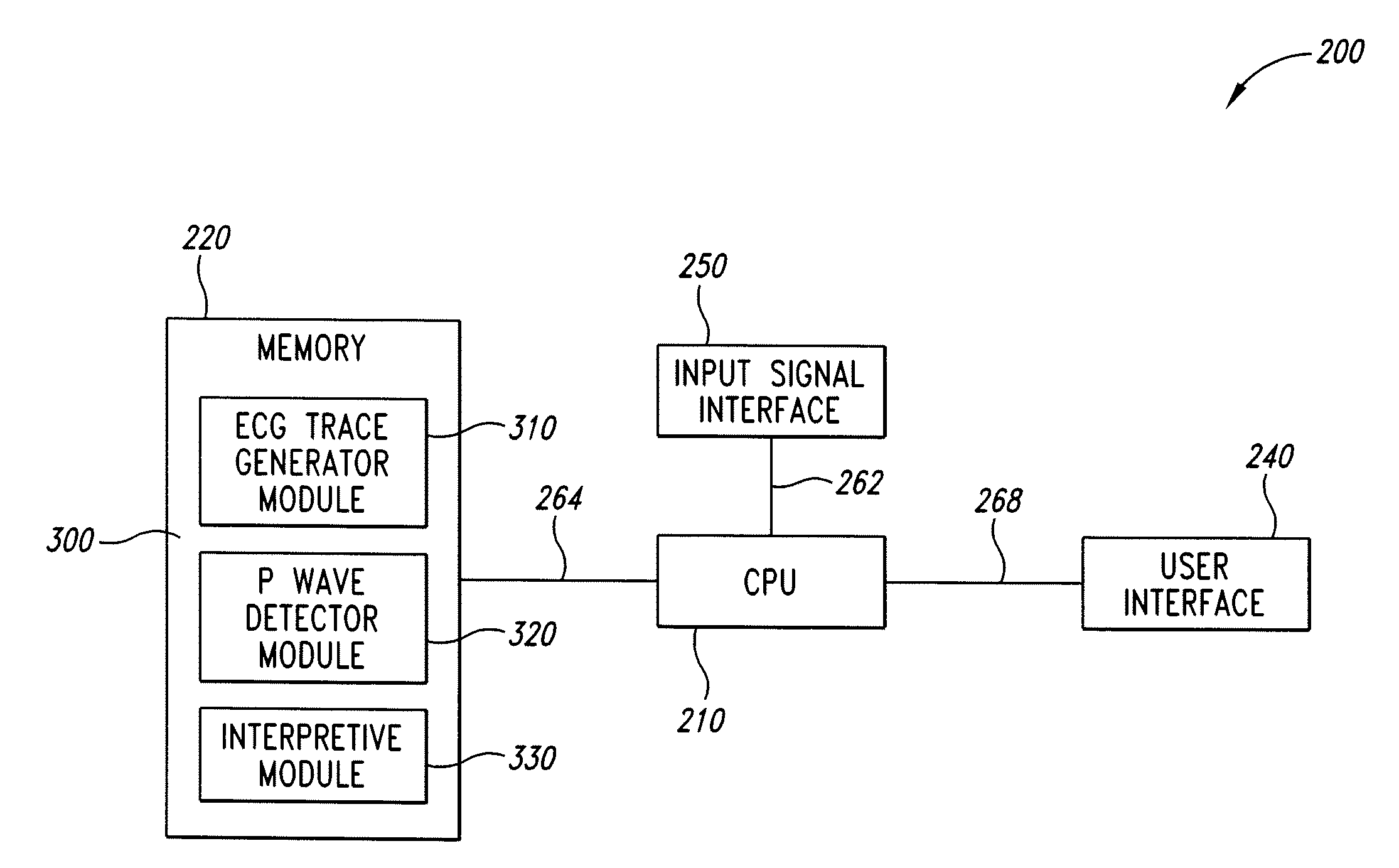
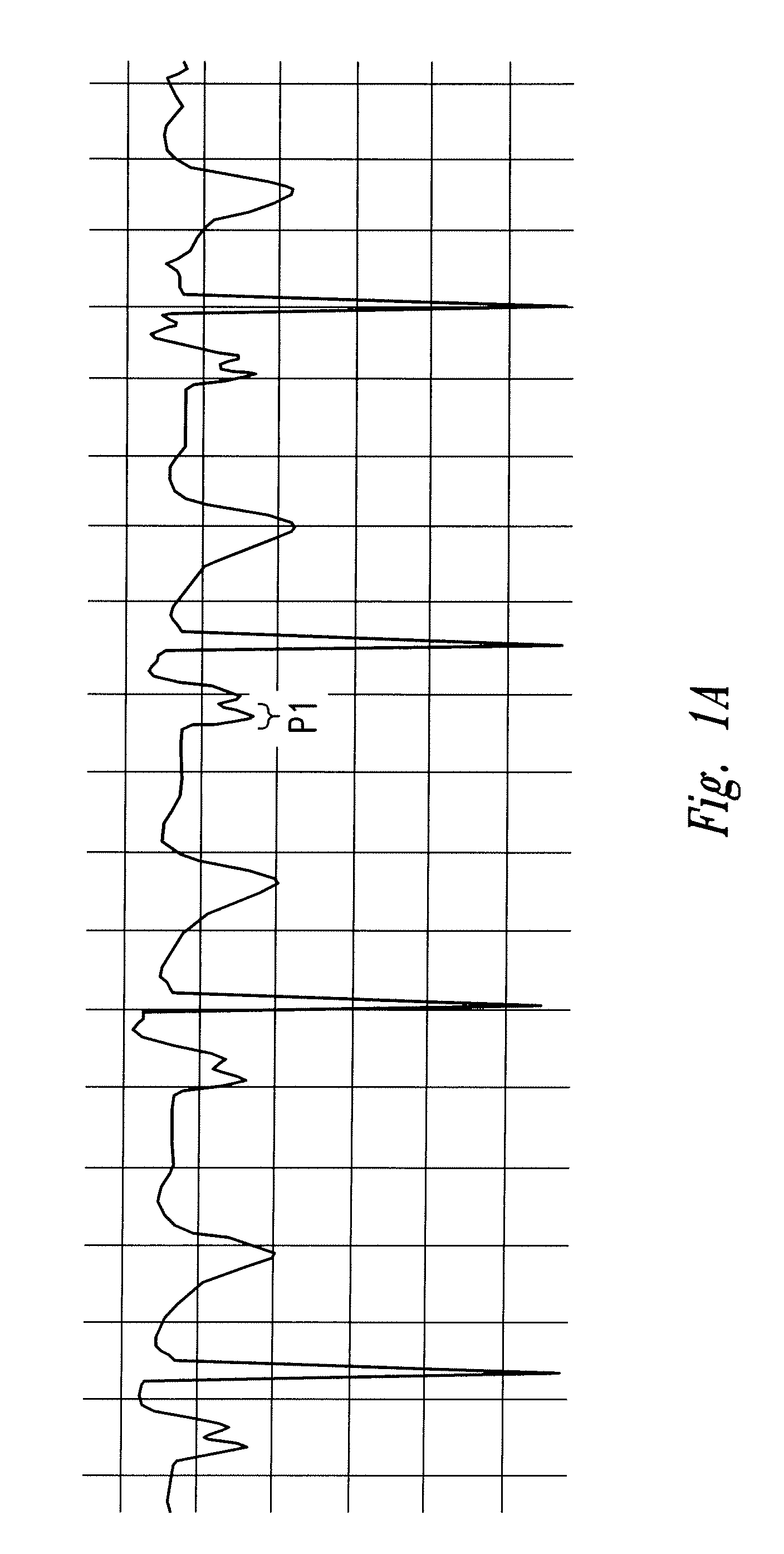
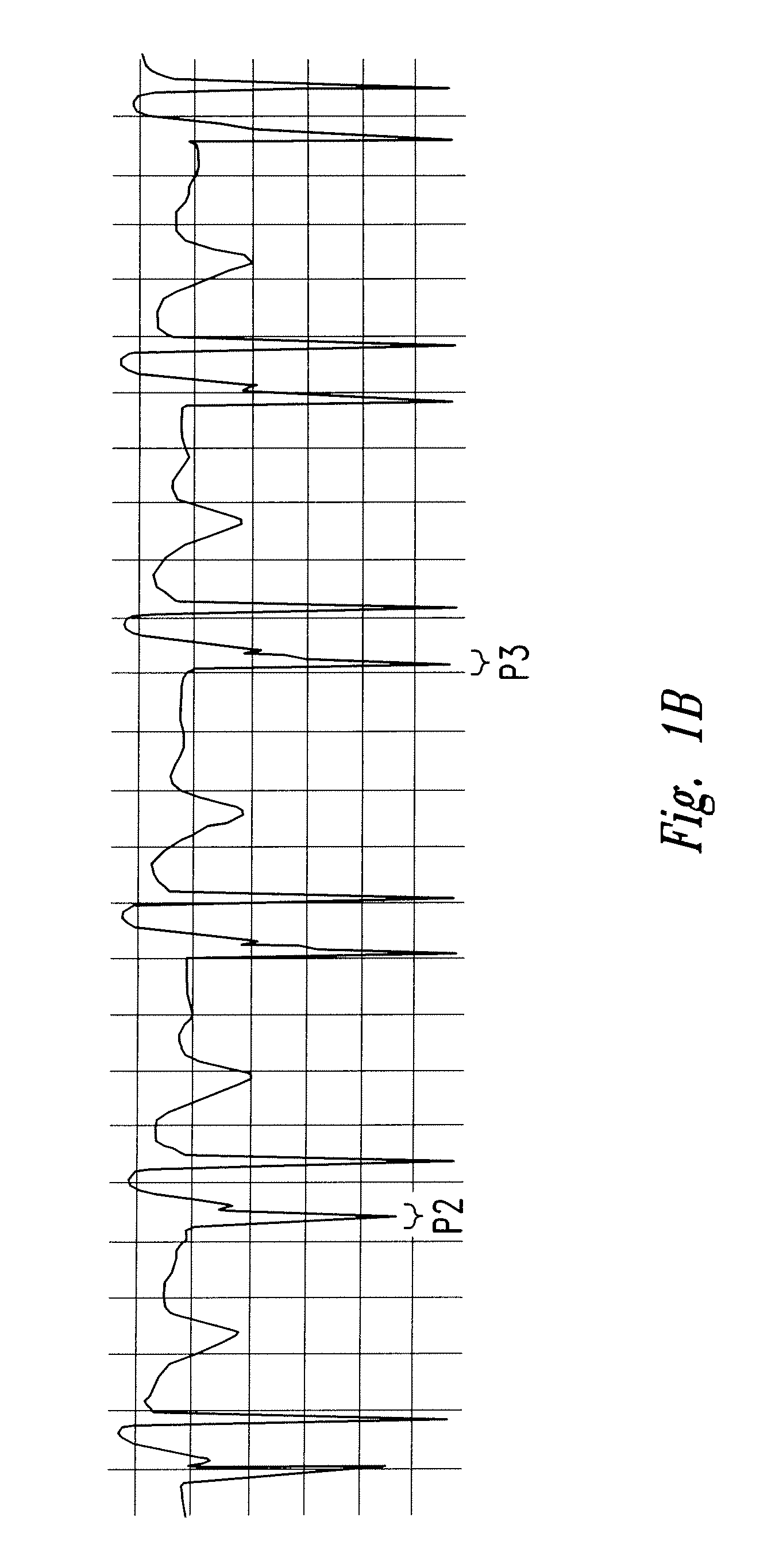
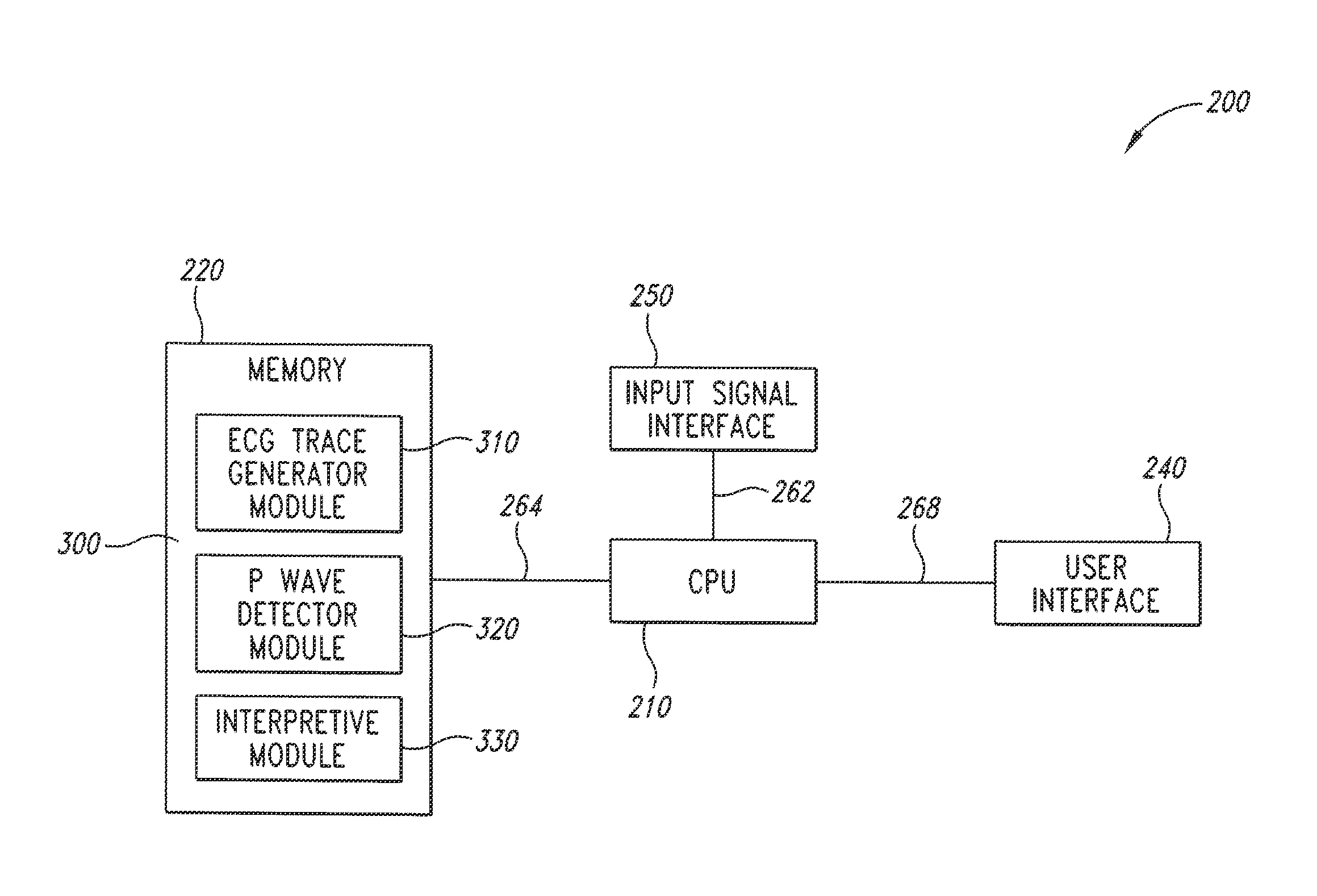
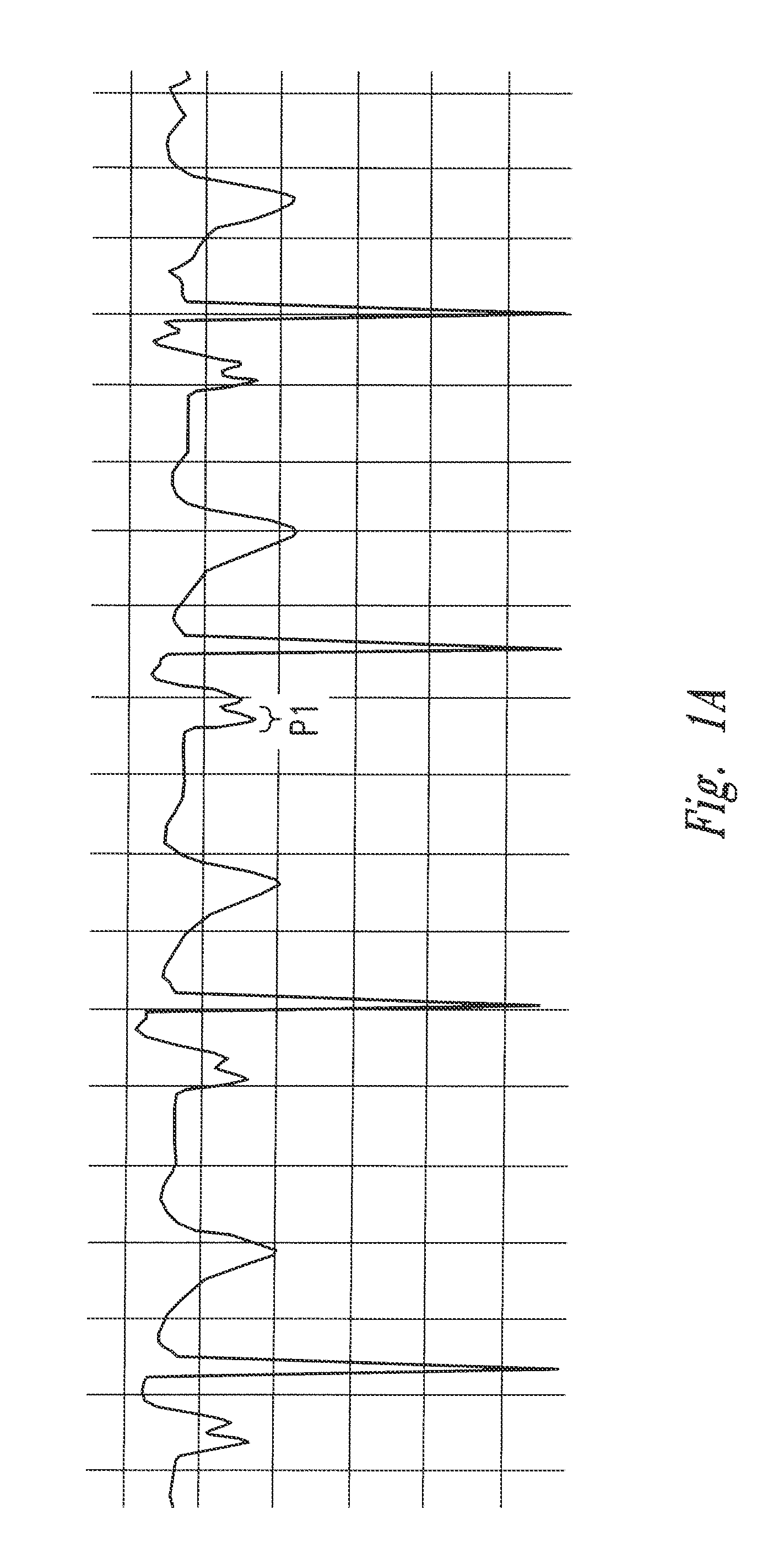
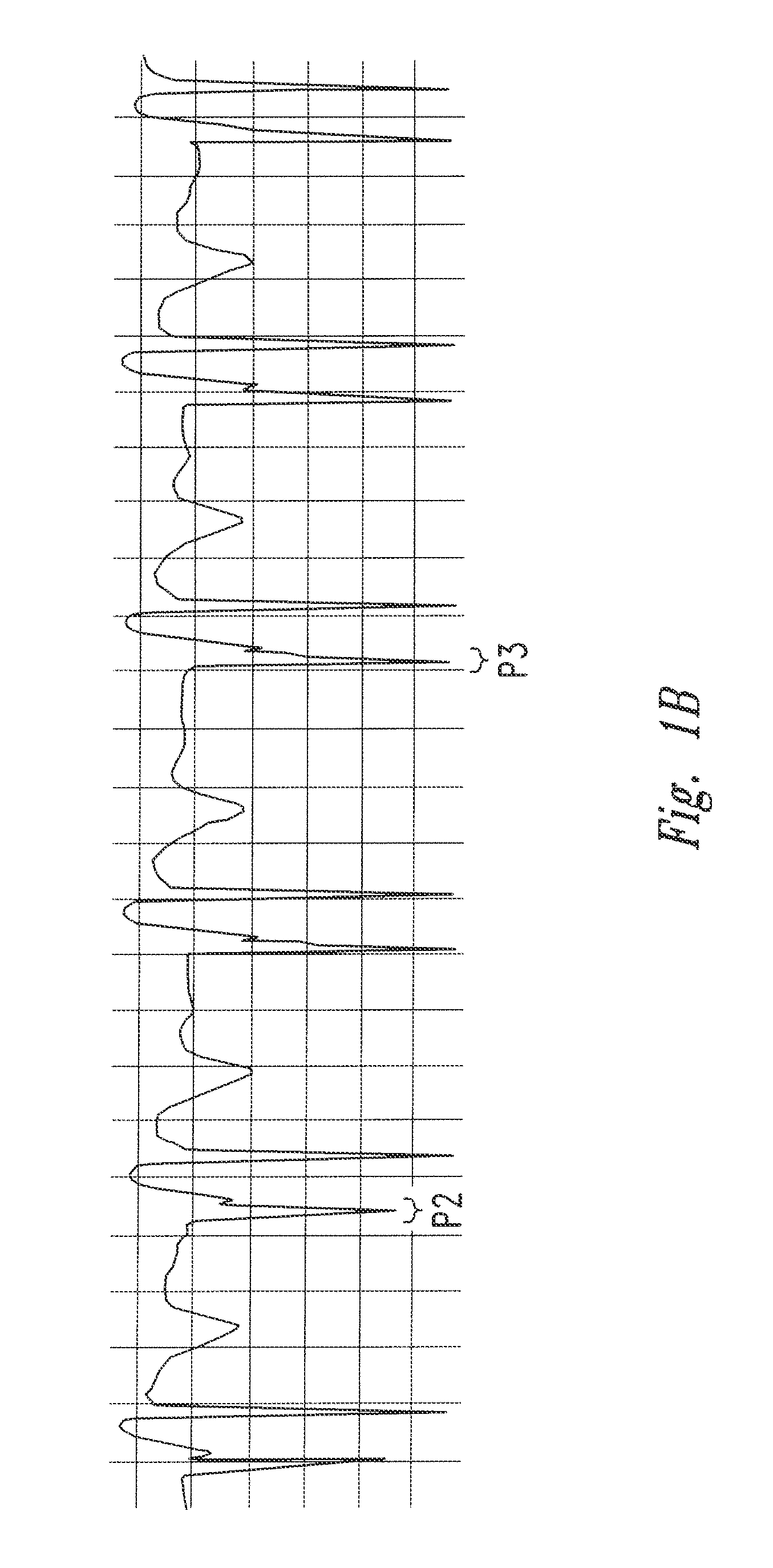
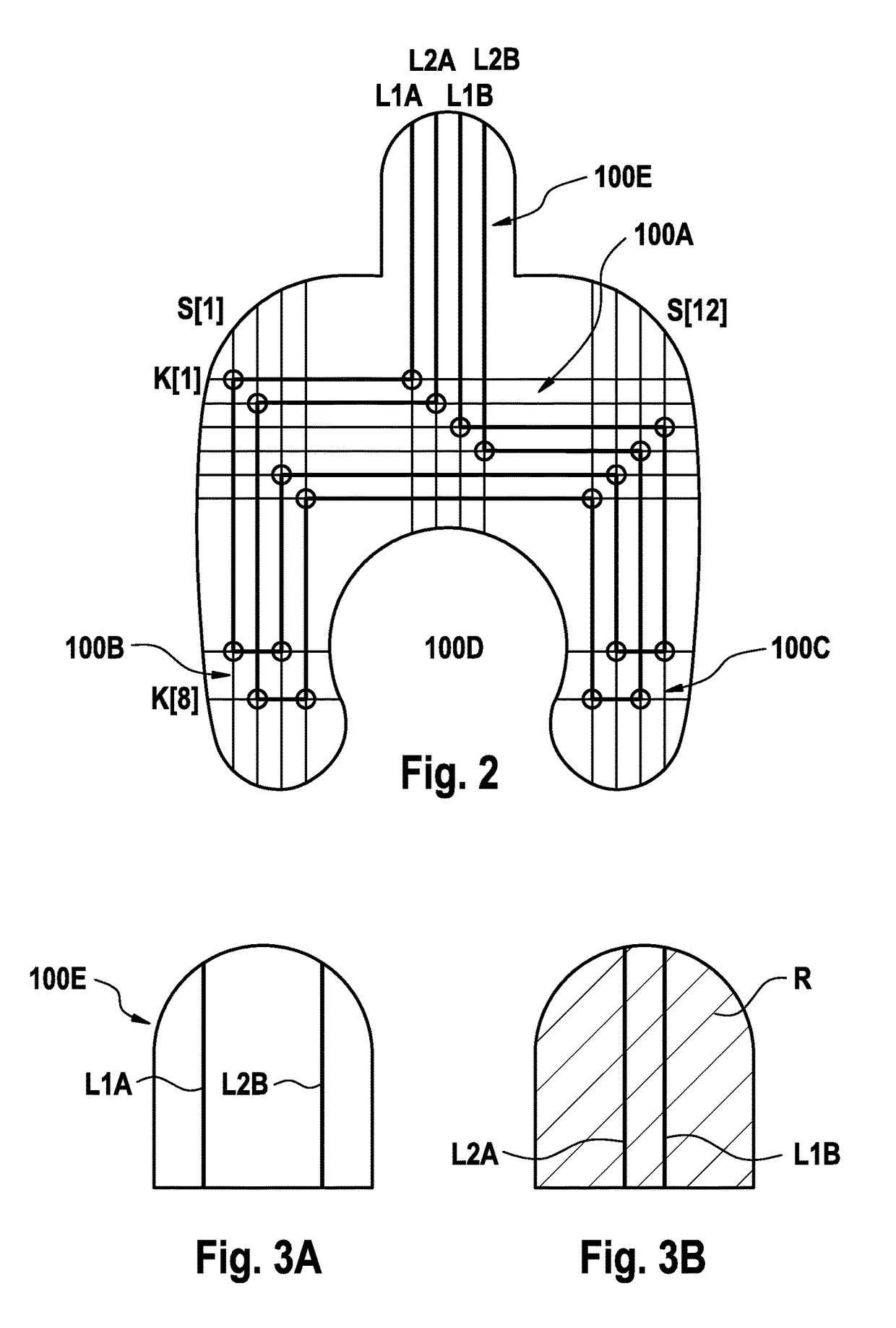
The invention includes a method of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) having a distal and proximal pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava, right atrium, and / or right ventricle. The method includes obtaining a distal and proximal electrical signal from the distal and proximal pair and using those signals to generate a distal and proximal P wave, respectively. A deflection value is determined for each of the P waves. A ratio of the deflection values is then used to determine a location of the tip of the CVC. Optionally, the CVC may include a reference pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava from which a reference deflection value may be obtained. A ratio of one of the other deflection values to the reference deflection value may be used to determine the location of the tip of the CVC.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
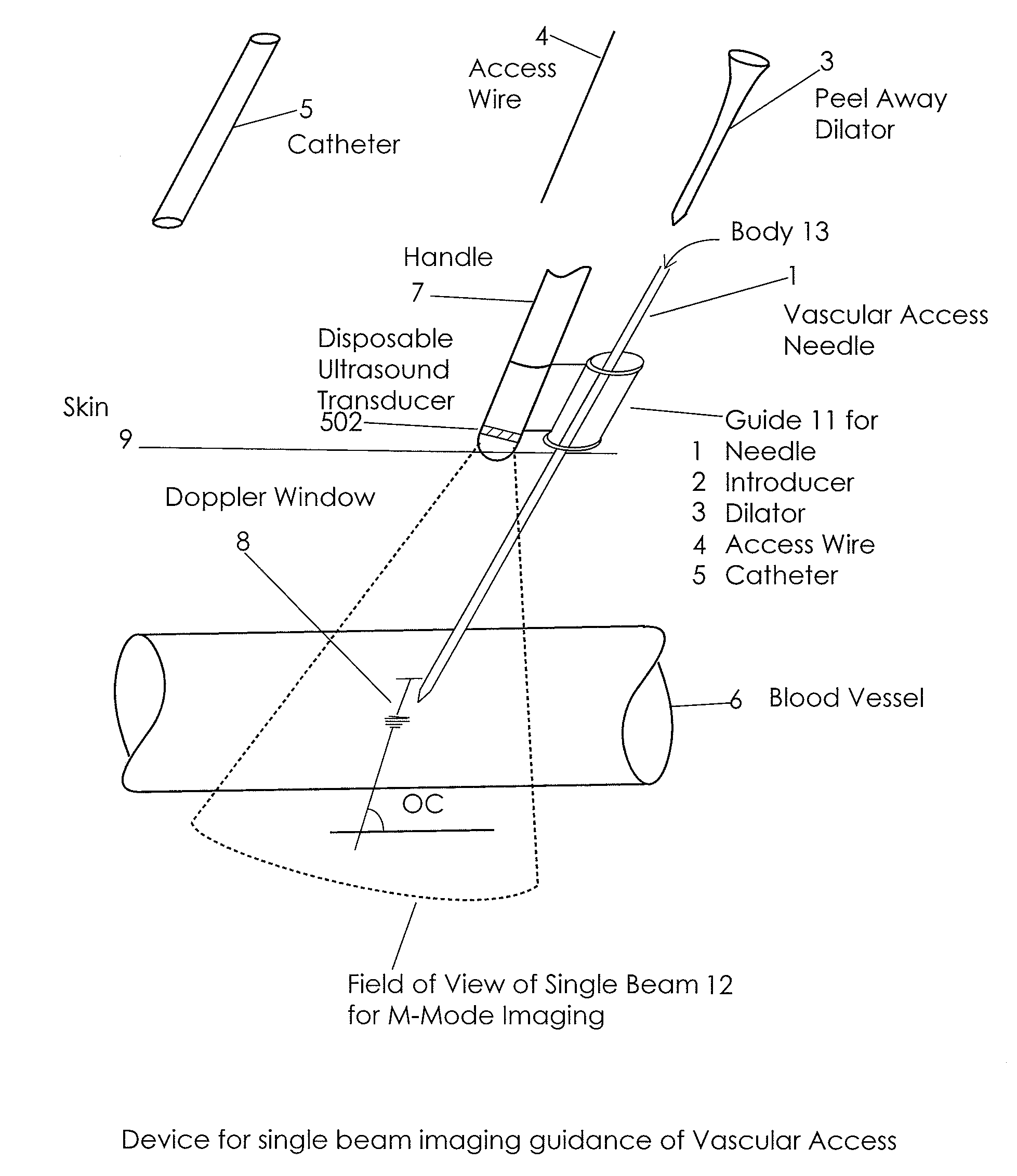
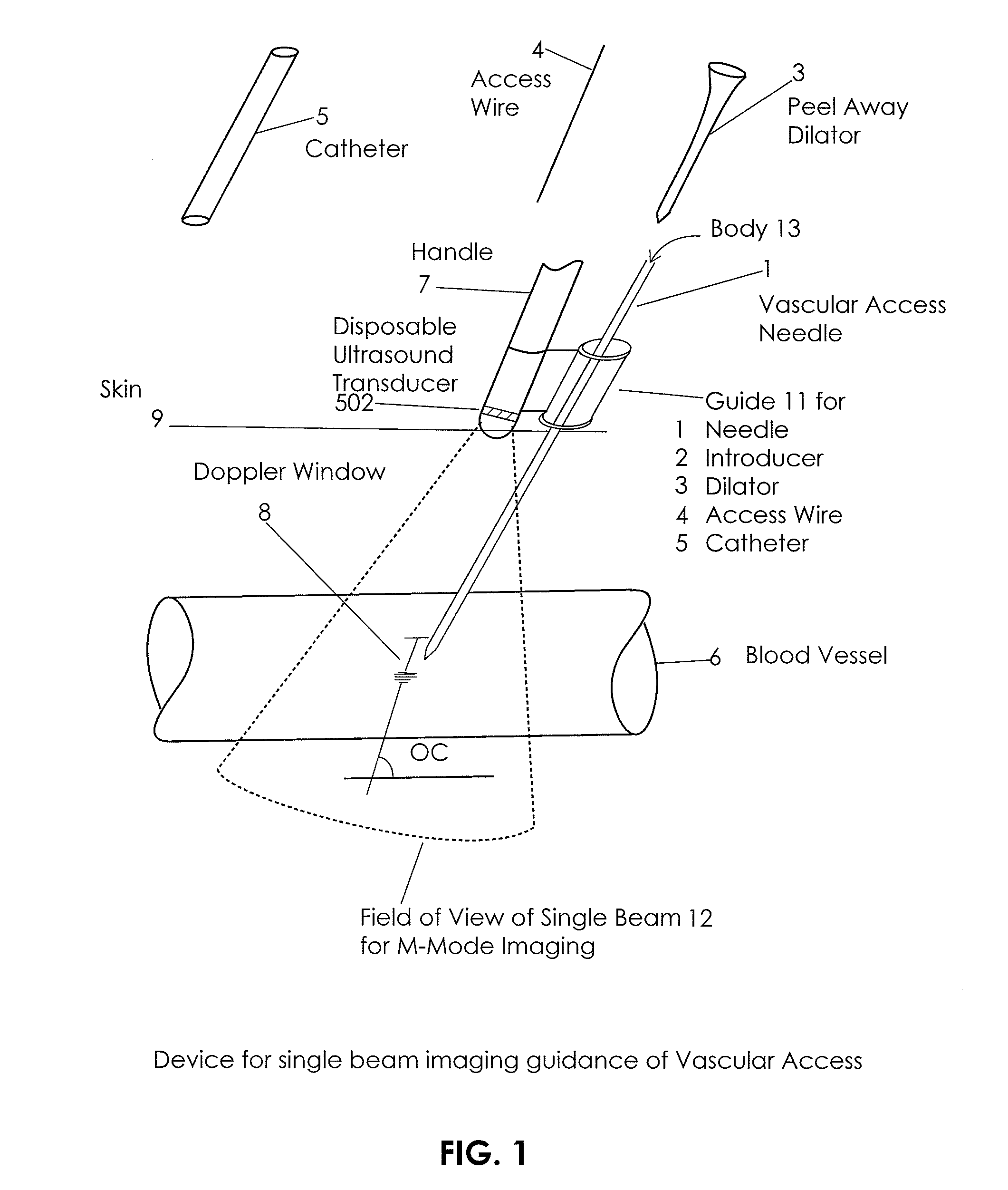
Apparatus and Method for Vascular Access
InactiveUS20090118612A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce needData processing applicationsMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesVeinX-ray
In an aspect, embodiments of the invention relate to the effective and accurate placement of intravascular devices such as central venous catheters, in particular such as peripherally inserted central catheters or PICC. One aspect of the present invention relates to vascular access. It describes devices and methods for imaging guided vascular access and more effective sterile packaging and handling of such devices. A second aspect of the present invention relates to the guidance, positioning and placement confirmation of intravascular devices without the help of X-ray imaging. A third aspect of the present invention relates to devices and methods for the skin securement of intravascular devices and post-placement verification of location of such devices. A forth aspect of the present invention relates to improvement of the workflow required for the placement of intravascular devices.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
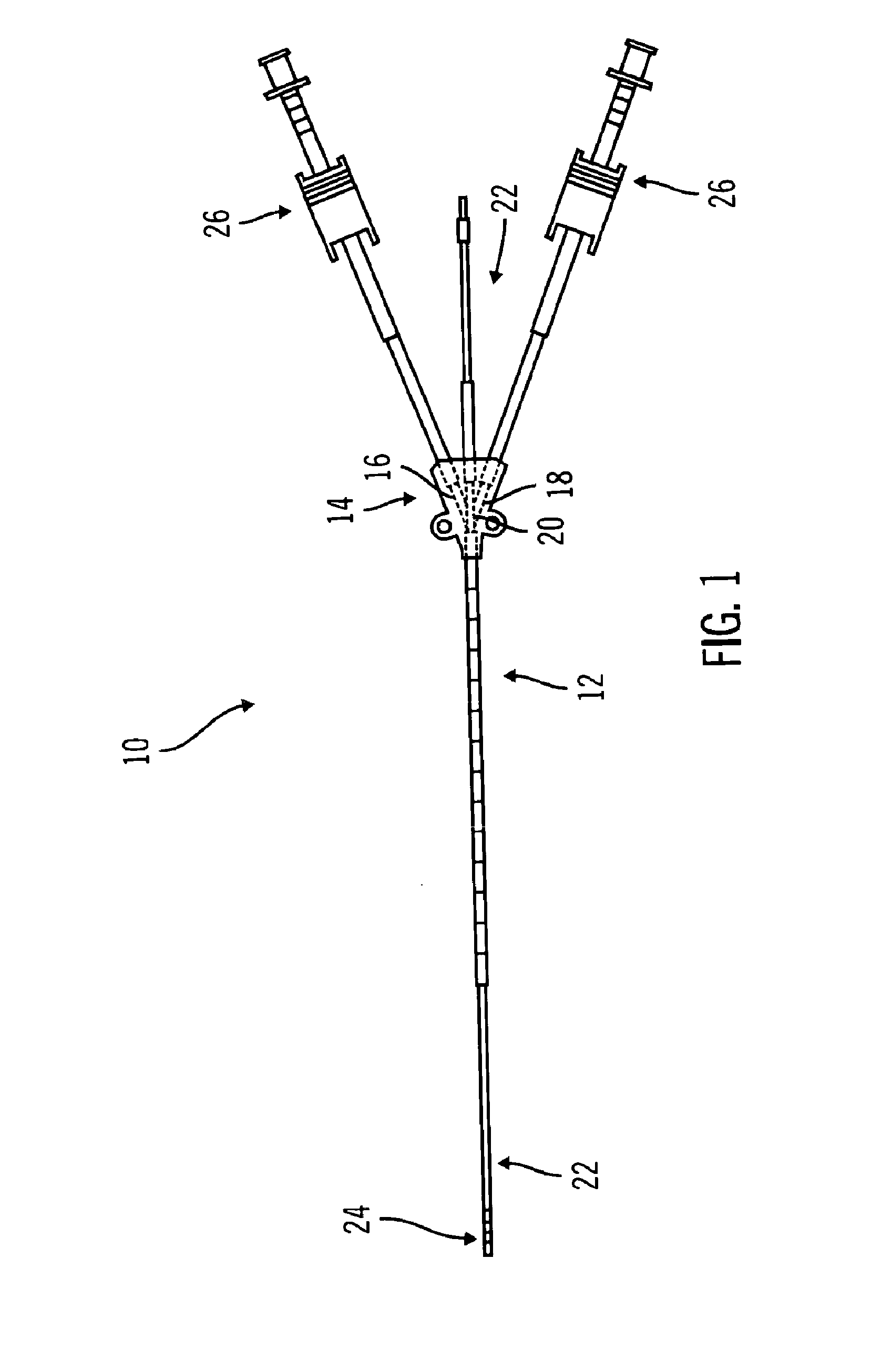
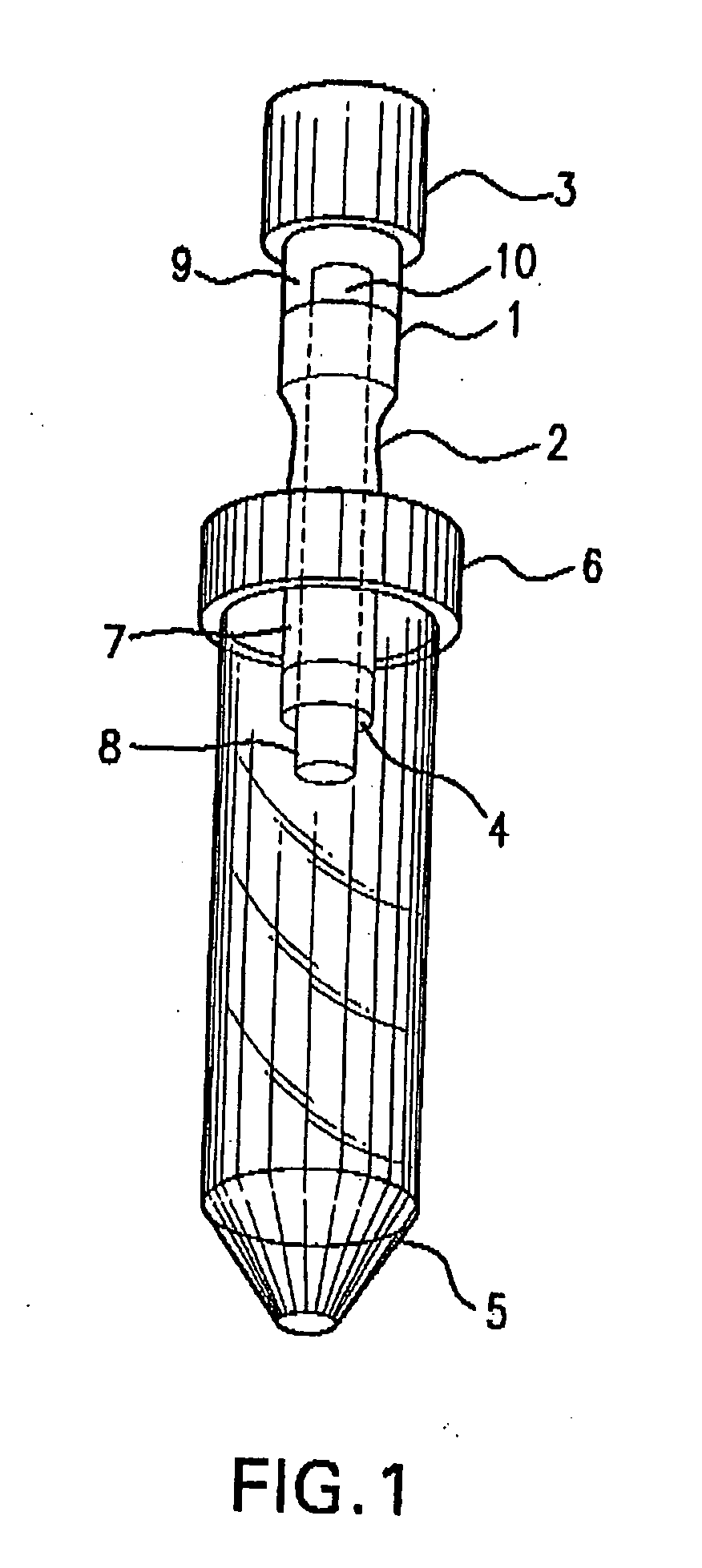
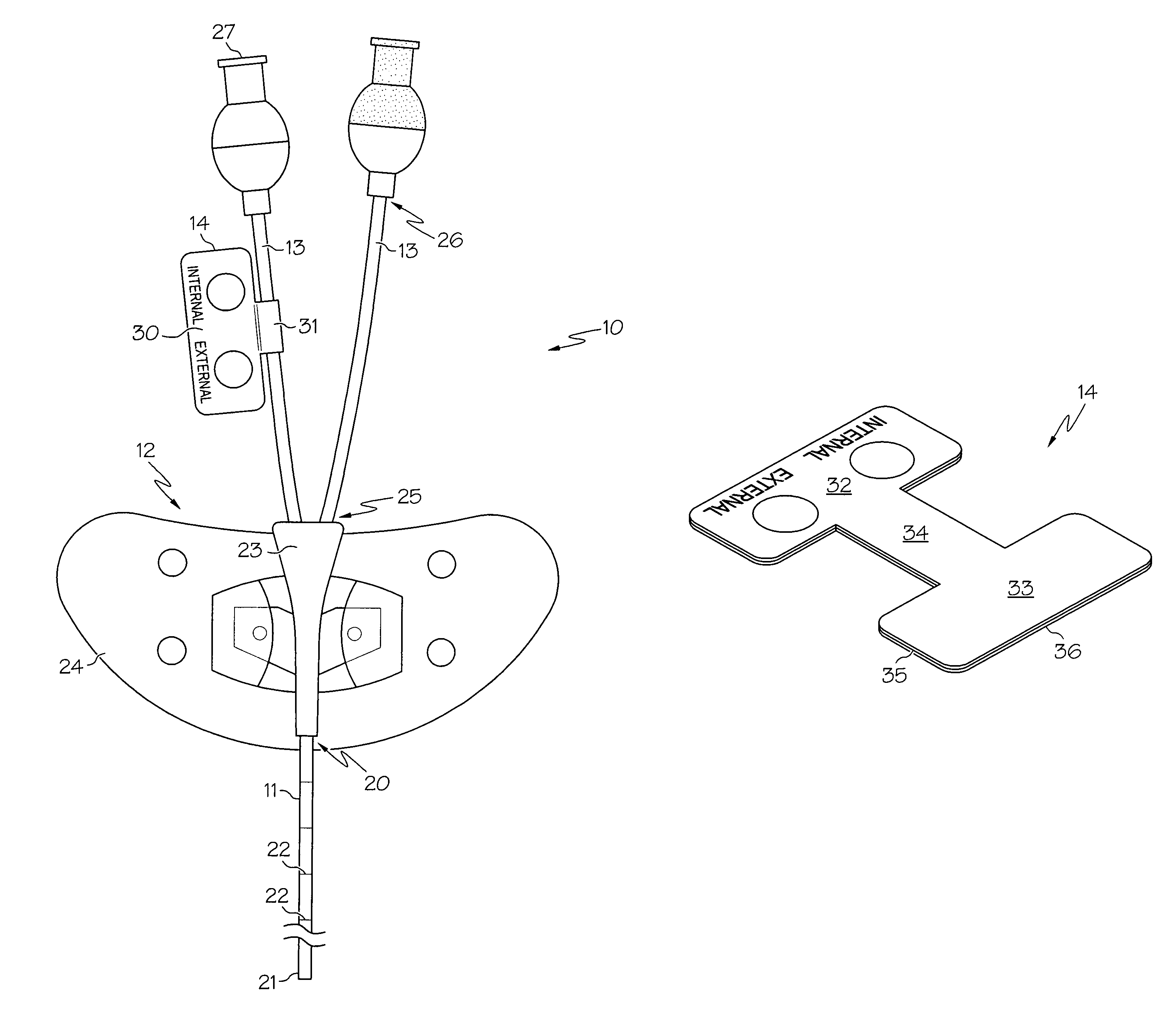
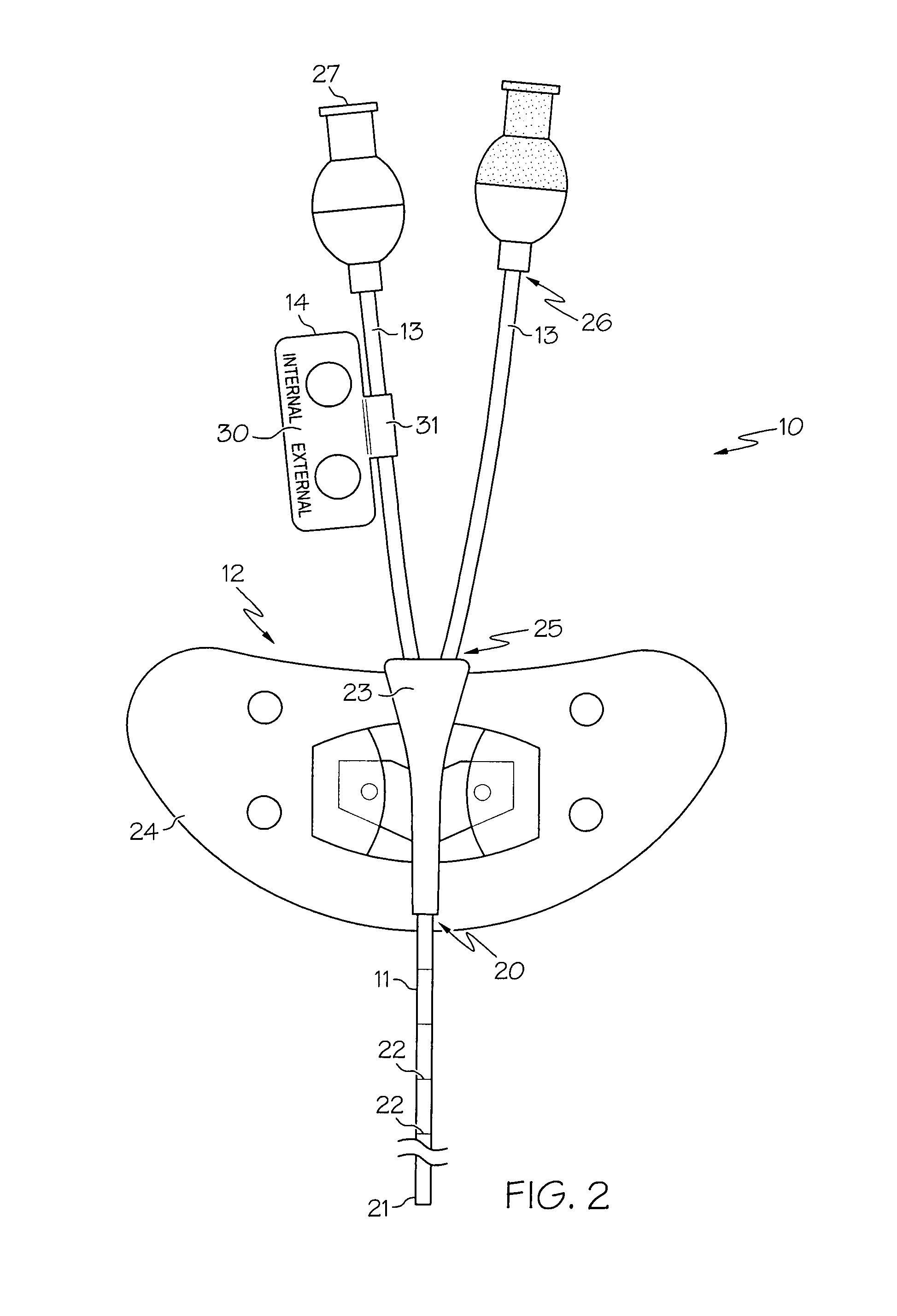
Multiple lumen catheter having a soft tip
A multiple lumen catheter having a soft, tapered multiple lumen distal tip for insertion into a body vessel. One of the lumens is sized to pass over a guidewire such that the catheter can be inserted into the body vessel using the Seldinger technique. At least one medical implement lumen is used for placement or positioning of a biomedical sensor or other medical implement. For example, at least one optical fiber passing through the medical implement lumen may transmit and receive light at the distal tip for measuring oxygen saturation of the blood. The catheter may have a cylindrical catheter body to which the soft distal tip attaches. The soft tip reduces the possibility of vessel or tissue puncture and abrasion. The tip is constructed of a soft plastic or pliable material that yields easily when force is applied. For example, the tip may be made of a softer material than the catheter body, or if made of the same material, the tip can be configured with thinner walls or a higher air-to-material ratio cross-section. Various geometrical configurations and combinations of materials can be used to decrease the flexible resistance of the tip to an applied load. One particular useful application for the catheter of the present invention is as a central venous catheter equipped with fibers for measuring oximetry. The fibers extend to the distal end of the tip and are preferably secured therein with minimal adhesive so as to limit the stiffness added to the tip. One particular useful construction is to secure the fibers within the medical implement lumen using adhesive only along a length of between about 0.5–3.5 mm.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
Methods of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) relative to the superior vena cava, sino-atrial node, right atrium, and / or right ventricle using electrocardiogram data. The CVC includes at least one electrode. In particular embodiments, the CVC includes two or three pairs of electrodes. Further, depending upon the embodiment implemented, one or more electrodes may be attached to the patient's skin. The voltage across the electrodes is used to generate a P wave. A reference deflection value is determined for the P wave detected when the tip is within the proximal superior vena cava. Then, the tip is advanced and a new deflection value determined. A ratio of the new and reference deflection values is used to determine a tip location. The ratio may be used to instruct a user to advance or withdraw the tip.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
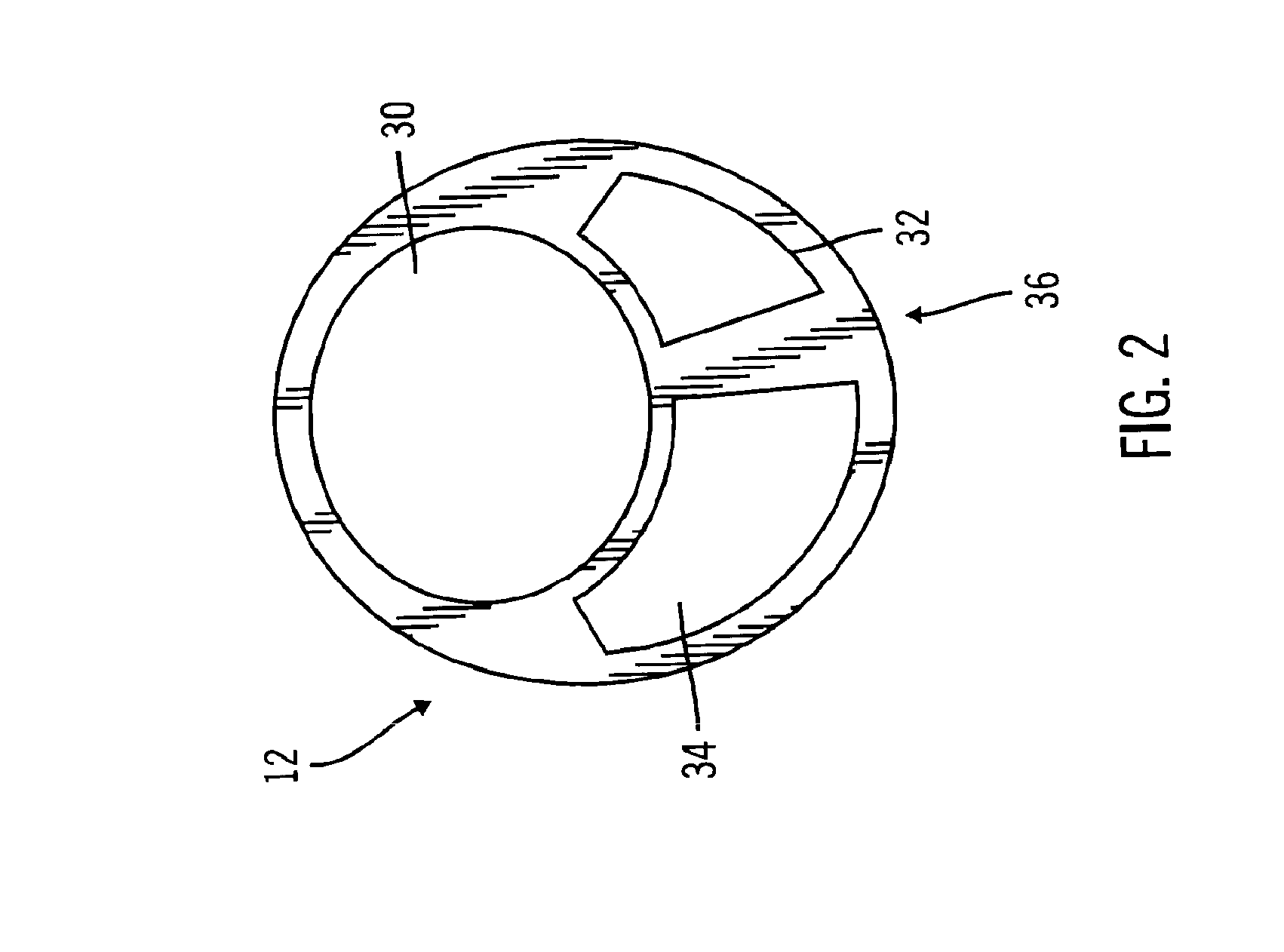
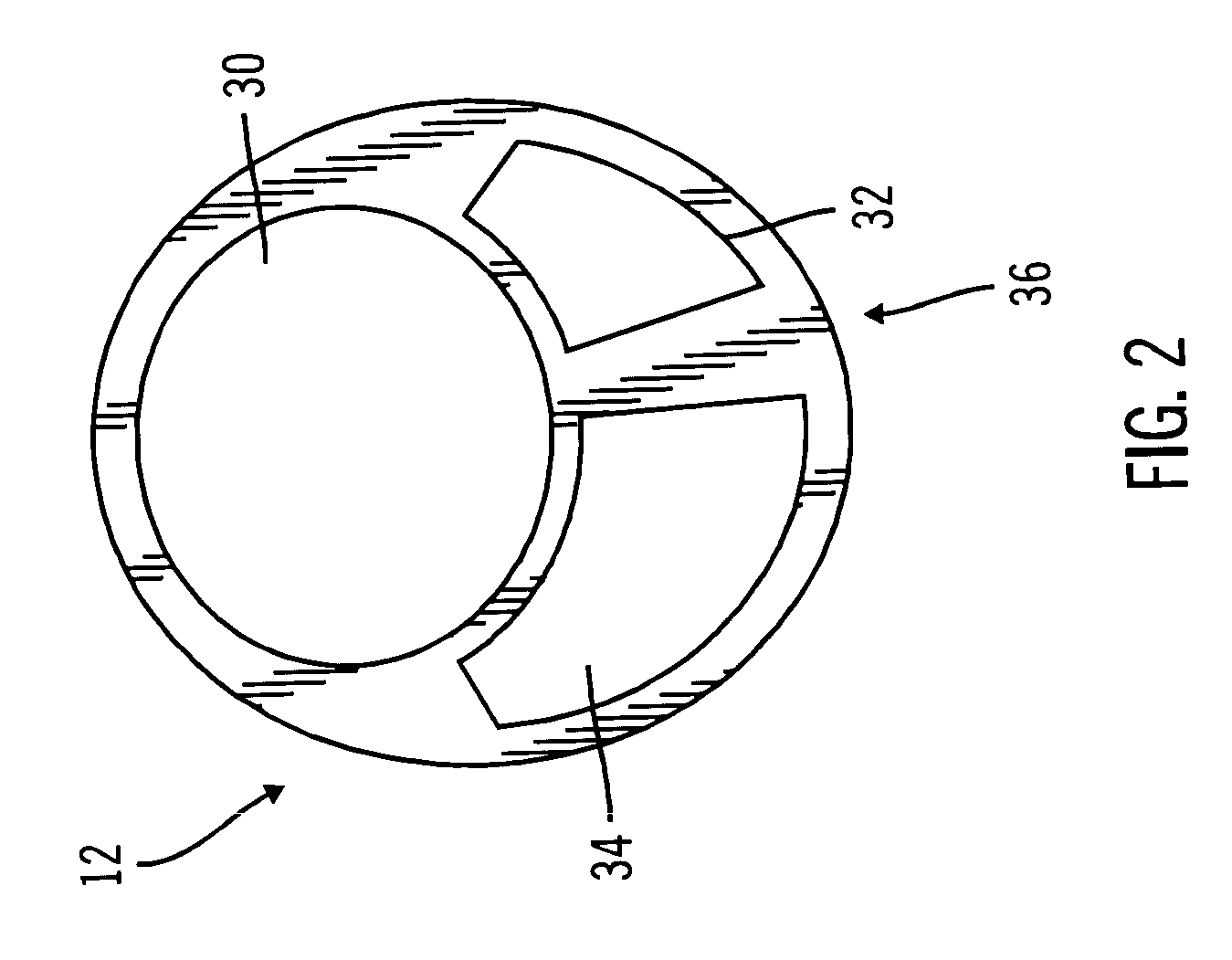
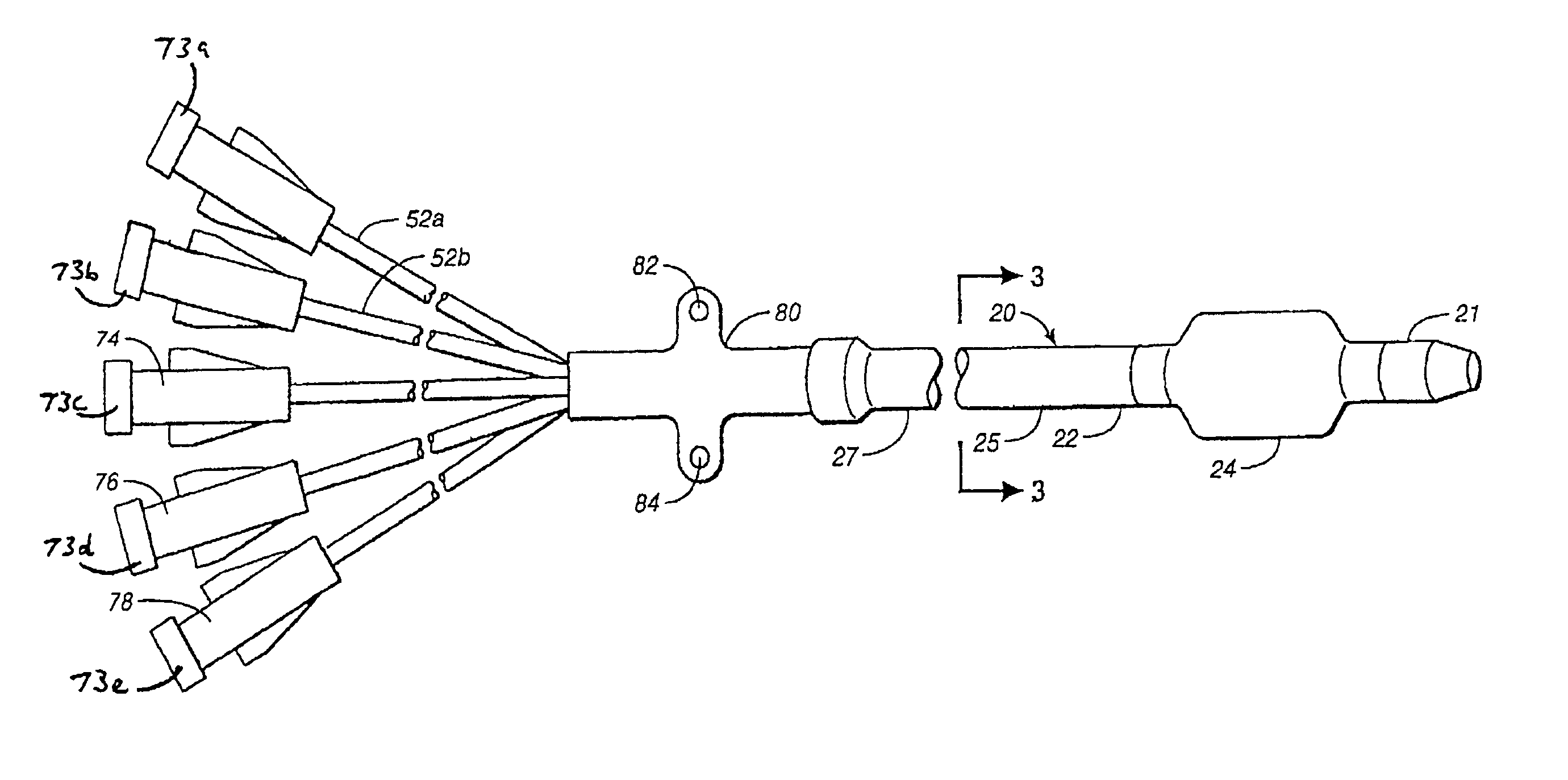
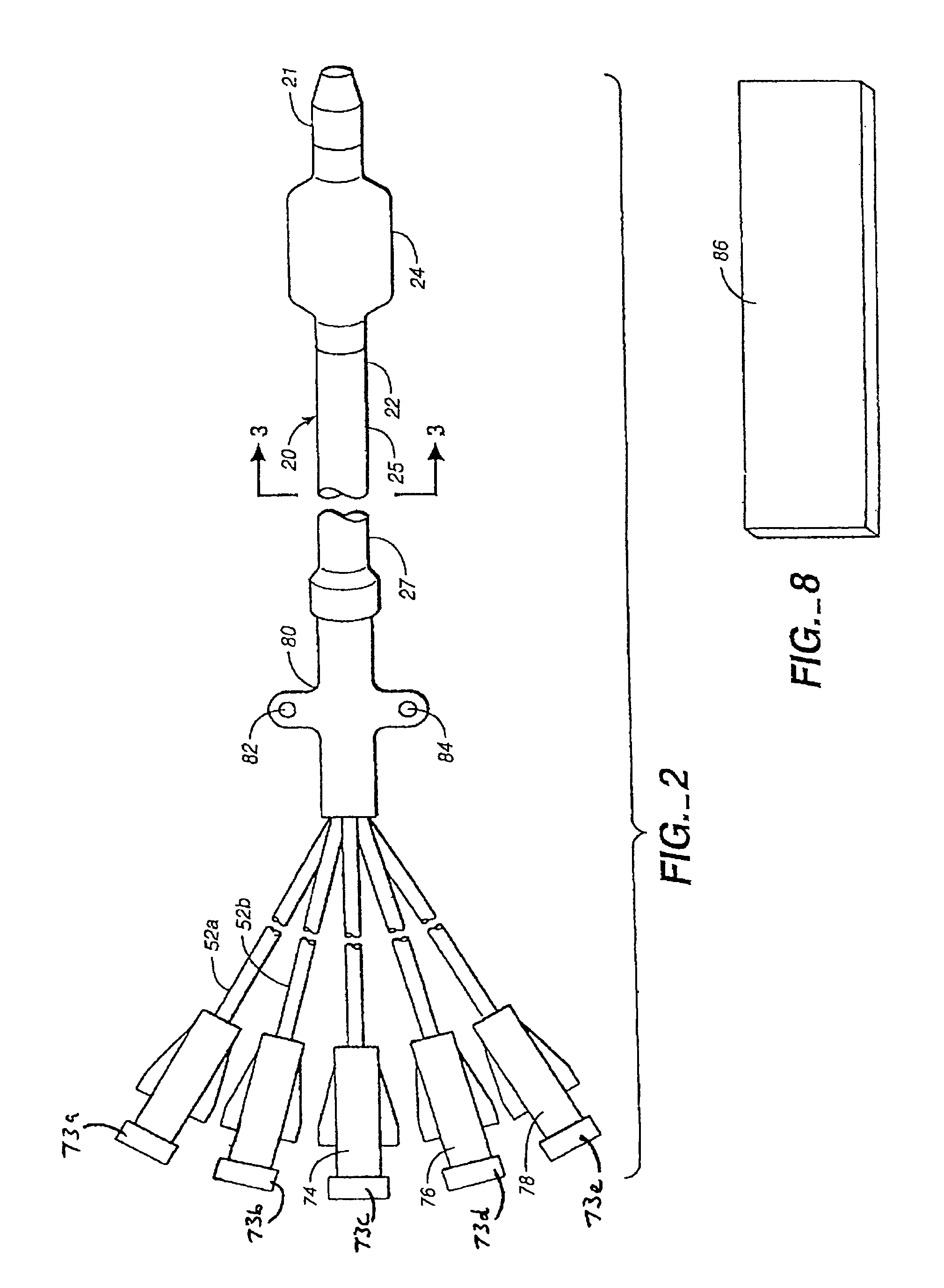
Multilumen catheter
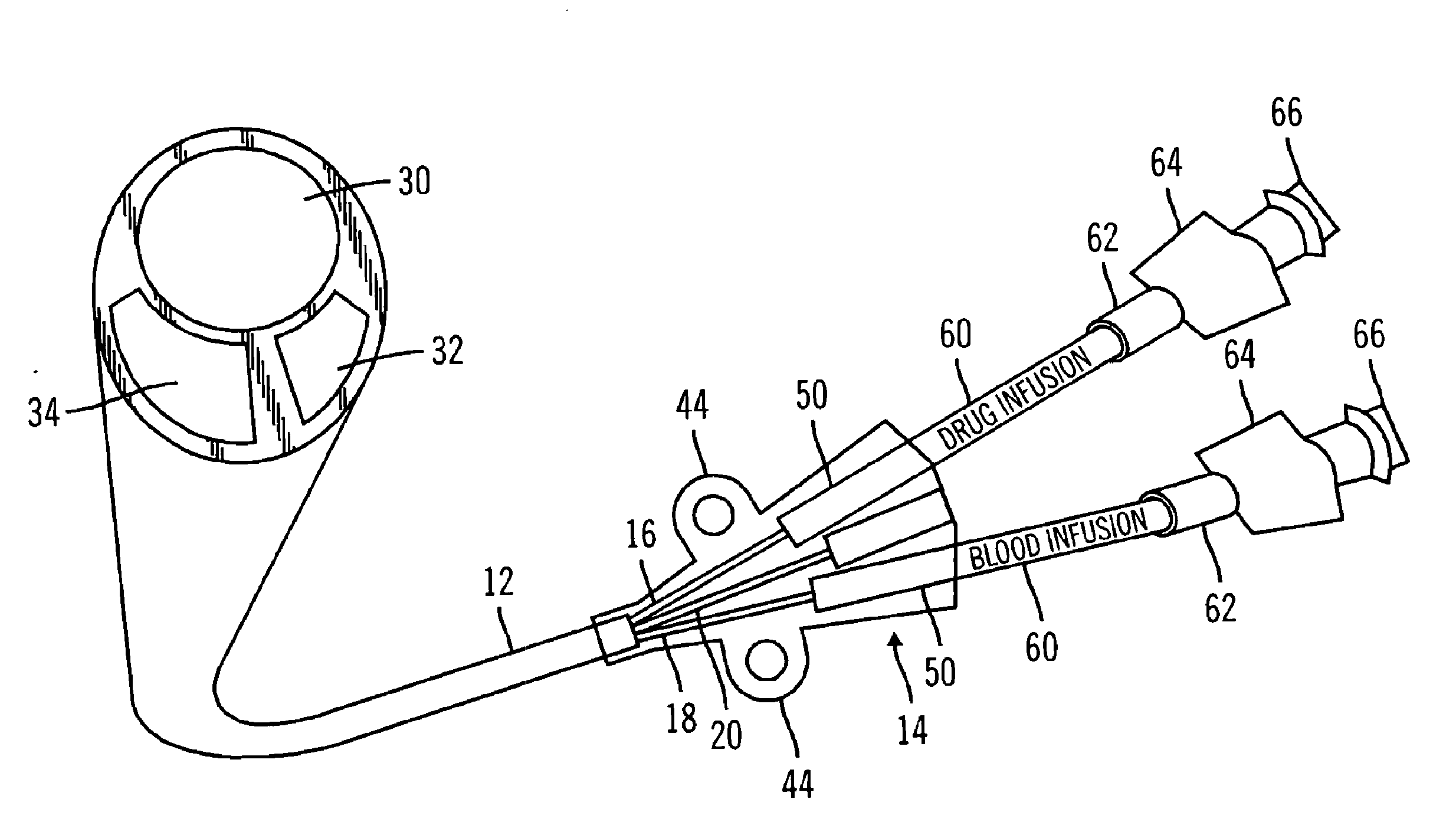
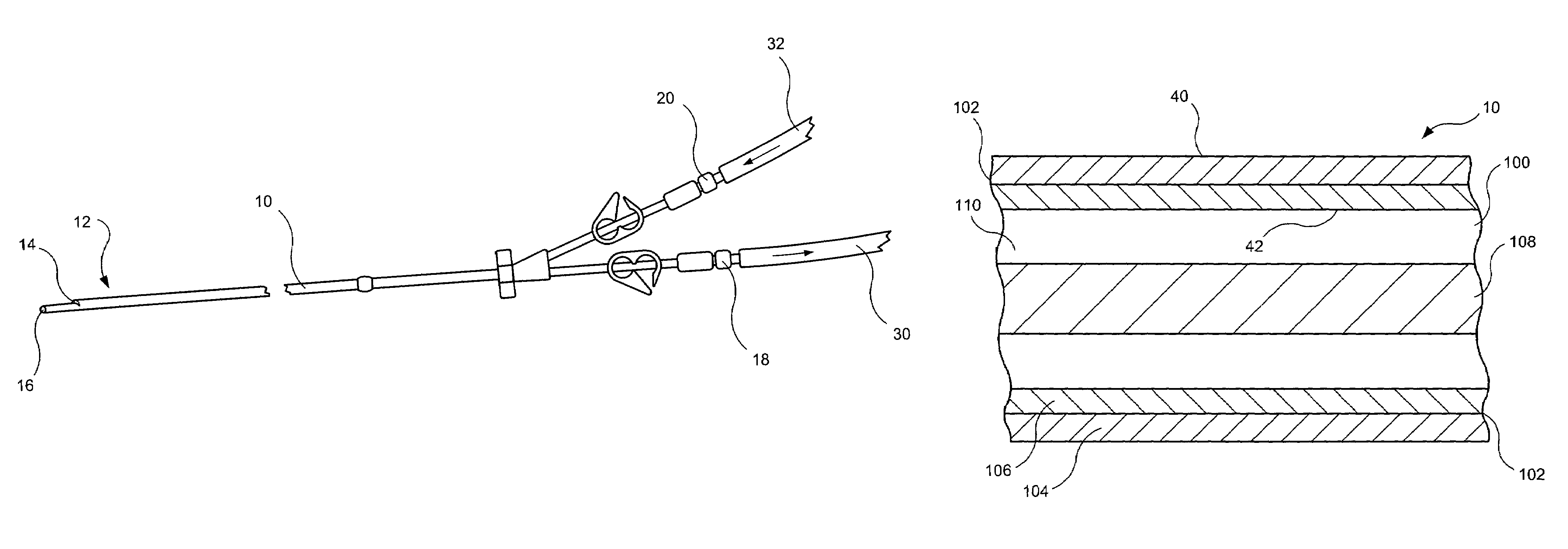
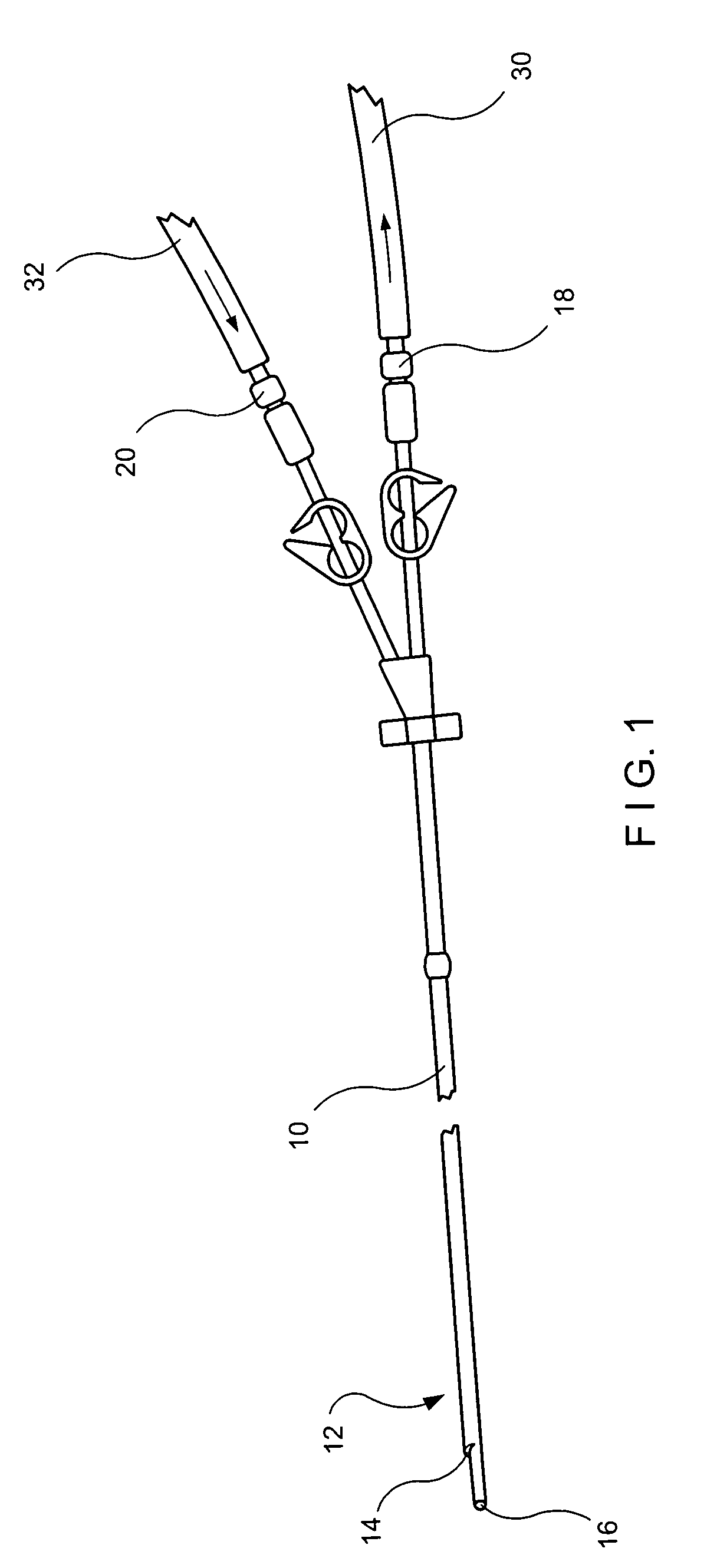
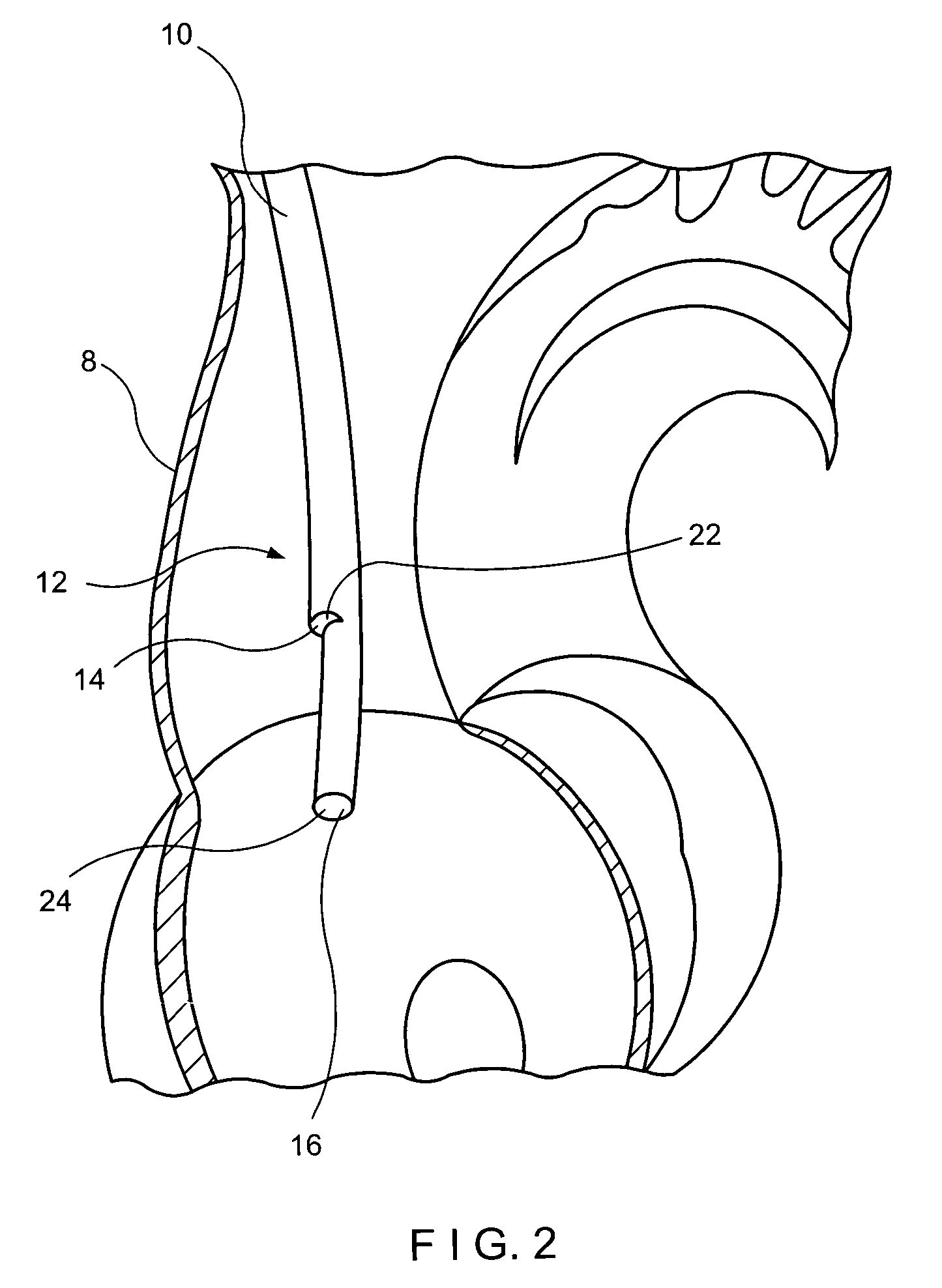
A multilumen catheter having tubings extending into lumens within the catheter. The lumens may be used for blood, drugs or other medicants. The lumens may also be used for sensors. The junction element, external to the patient, connects the tubings to the lumens. The tubings, also external to the patient, connect to infusion members, to which one or more infusion systems may be connected to deliver blood, drugs and other medicants to the patient. A sensor having a sensing element may extend through the sensor lumen and be positioned internal to the patient for physiological parameter sensing. An external portion of the sensor may be connected to associated electronics to provide automatic monitoring of the physiological parameters and automatic delivery and control of the infusants. Also, a central line catheter for delivering fluids directly into a main artery or vein near the heart, which contains a first lumen to deliver a fluid through the central line catheter and a second lumen containing a sensor capable indicating a characteristic level in blood. The first lumen delivers the fluid downstream of the sensor to prevent any interference between the fluid delivery and the sensor readings. In other versions, the central line catheter can have additional lumens for additional purposes. In addition, the central line catheter can further include a flush sleeve to remove debris around the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
Methods of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) relative to the superior vena cava, sino-atrial node, right atrium, and / or right ventricle using electrocardiogram data. The CVC includes at least one electrode. In particular embodiments, the CVC includes two or three pairs of electrodes. Further, depending upon the embodiment implemented, one or more electrodes may be attached to the patient's skin. The voltage across the electrodes is used to generate a P wave. A reference deflection value is determined for the P wave detected when the tip is within the proximal superior vena cava. Then, the tip is advanced and a new deflection value determined. A ratio of the new and reference deflection values is used to determine a tip location. The ratio may be used to instruct a user to advance or withdraw the tip.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
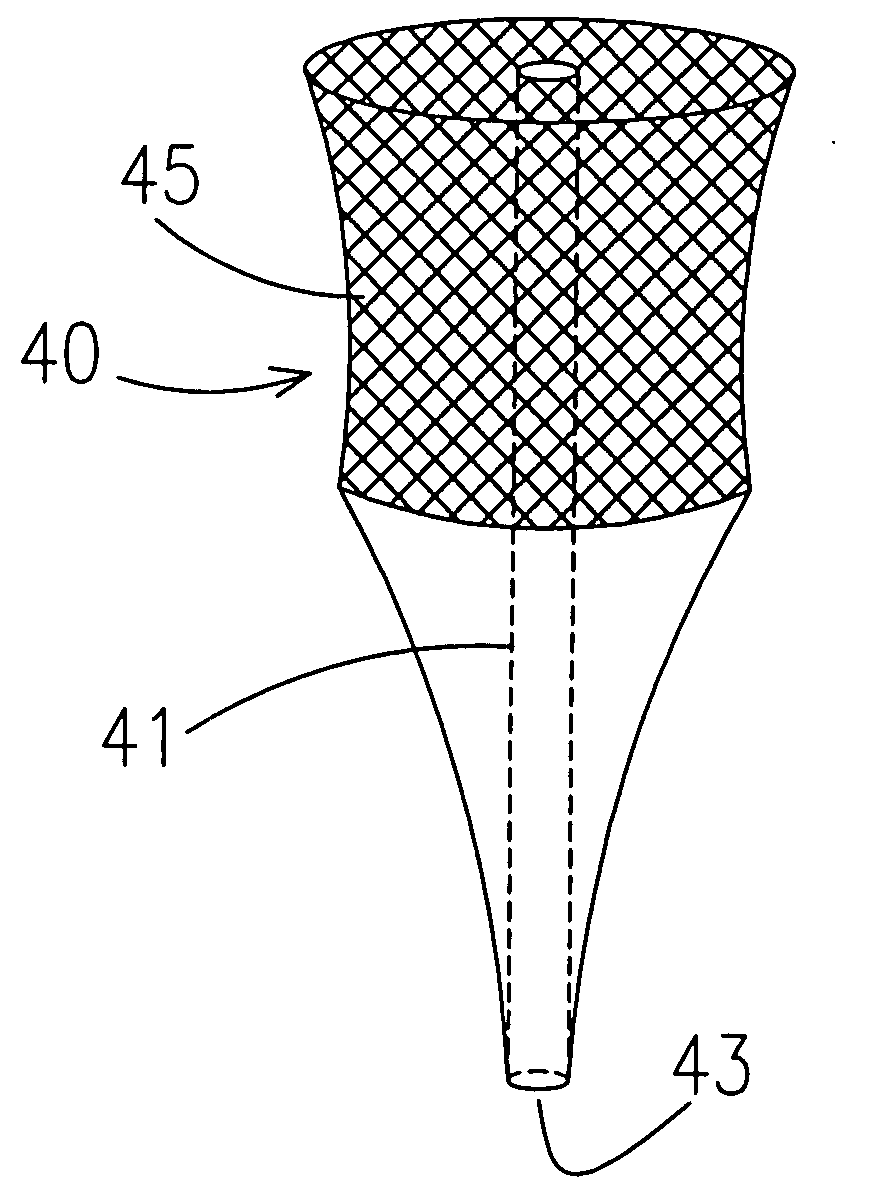
Central venous catheter having a soft tip and fiber optics
A multiple lumen catheter having a soft, tapered multiple lumen distal tip for insertion into a body vessel. One of the lumens is sized to pass over a guidewire such that the catheter can be inserted into the body vessel using the Seldinger technique. At least one medical implement lumen is used for placement or positioning of a biomedical sensor or other medical implement. For example, at least one optical fiber passing through the medical implement lumen may transmit and receive light at the distal tip for measuring oxygen saturation of the blood. The catheter may have a cylindrical catheter body to which the soft distal tip attaches. The soft tip reduces the possibility of vessel or tissue puncture and abrasion. The tip is constructed of a soft plastic or pliable material that yields easily when force is applied. For example, the tip may be made of a softer material than the catheter body, or if made of the same material, the tip can be configured with thinner walls or a higher air-to-material ratio cross-section. Various geometrical configurations and combinations of materials can be used to decrease the resistance of the tip to an applied load. One particular useful application for the catheter of the present invention is as a central venous catheter equipped with fibers for measuring oximetry. The fibers extend to the distal end of the tip and are preferably secured therein with minimal adhesive so as to limit the stiffness added to the tip. One particular useful construction is to secure the fibers within the medical implement lumen using adhesive only along a length of between about 0.5–3.5 mm.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
The invention includes a method of locating a tip of a central venous catheter (“CVC”) having a distal and proximal pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava, right atrium, and / or right ventricle. The method includes obtaining a distal and proximal electrical signal from the distal and proximal pair and using those signals to generate a distal and proximal P wave, respectively. A deflection value is determined for each of the P waves. A ratio of the deflection values is then used to determine a location of the tip of the CVC. Optionally, the CVC may include a reference pair of electrodes disposed within the superior vena cava from which a reference deflection value may be obtained. A ratio of one of the other deflection values to the reference deflection value may be used to determine the location of the tip of the CVC.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
Method of locating the tip of a central venous catheter
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
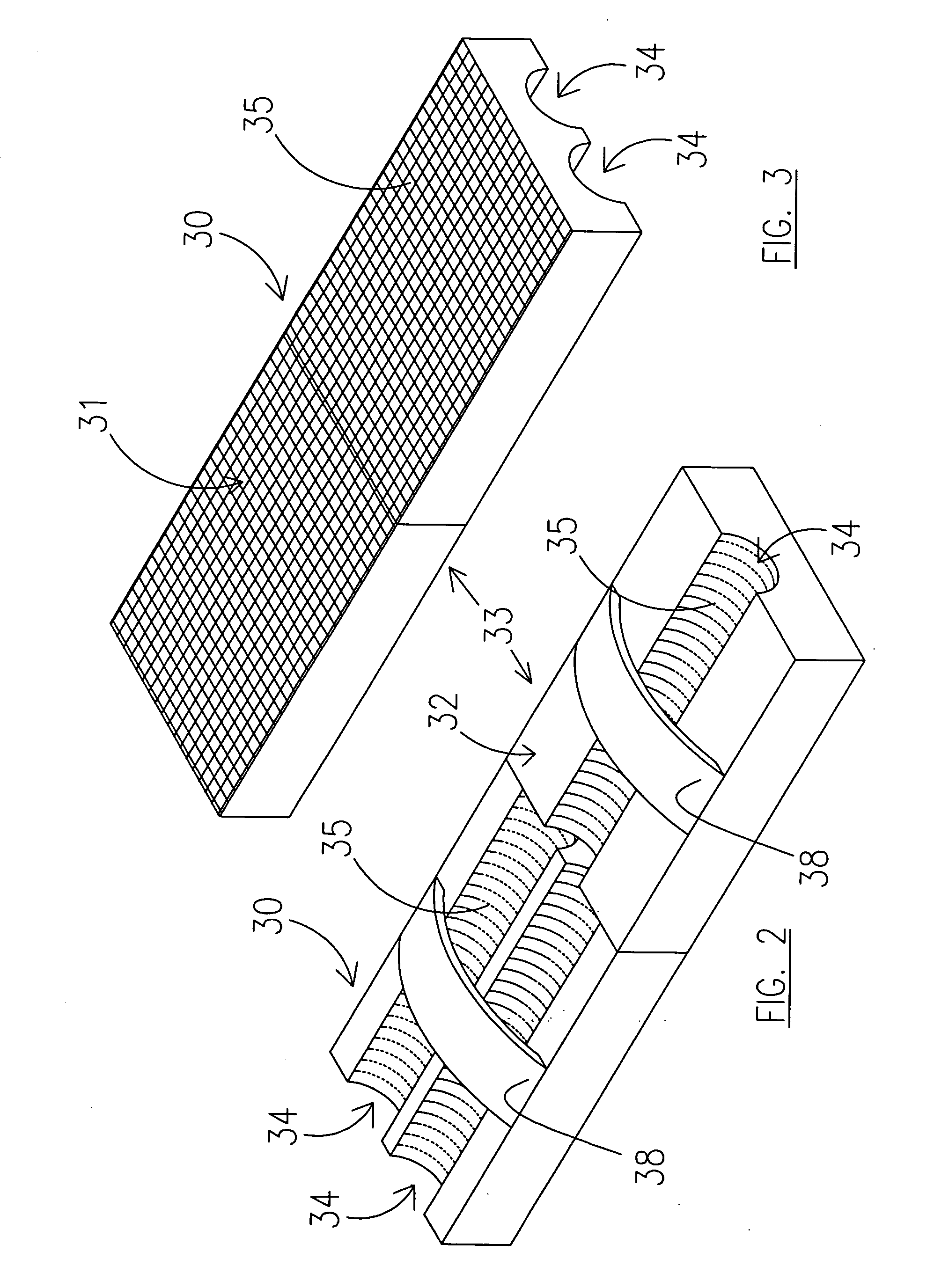
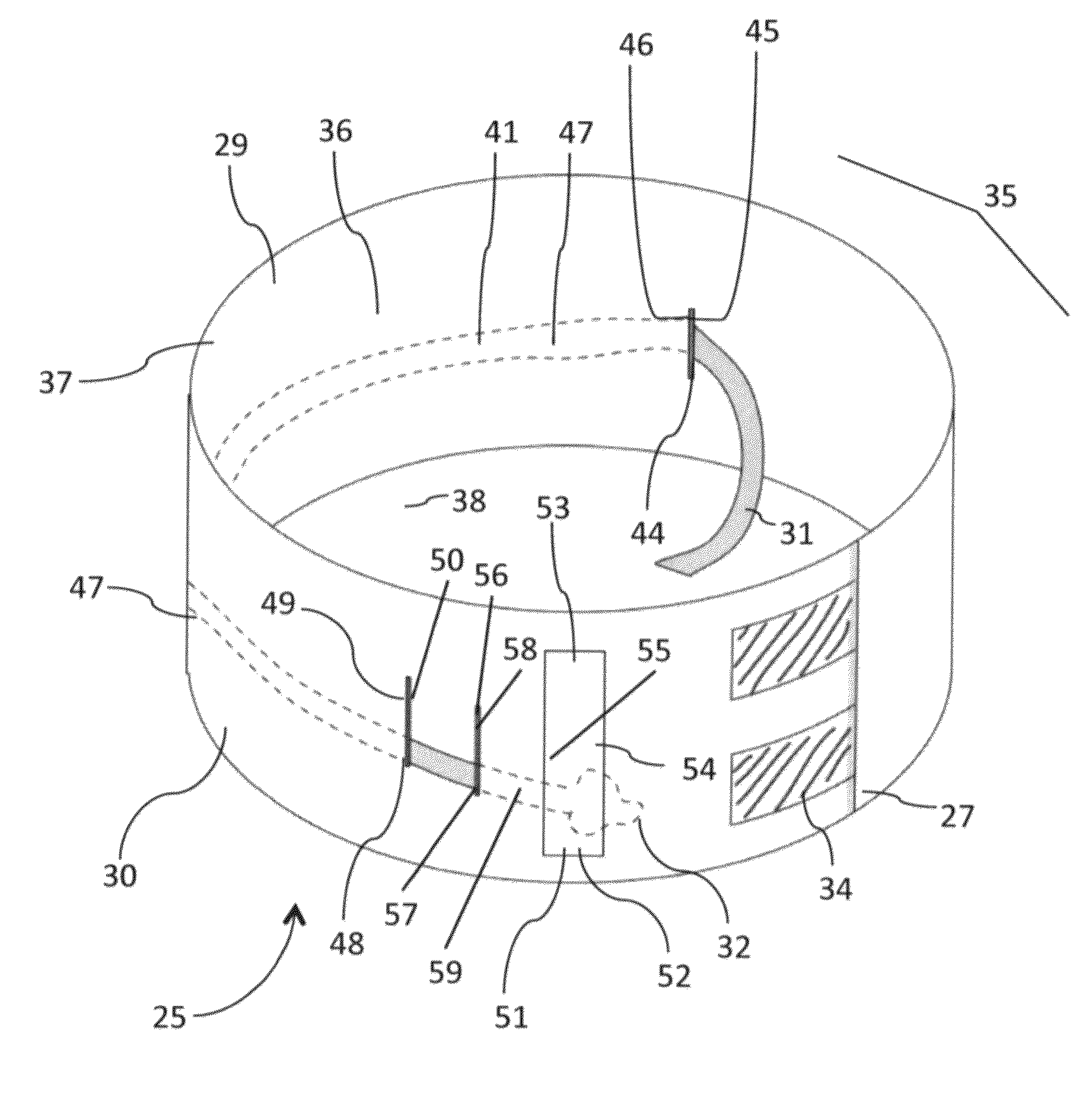
Multilumen catheter
A multilumen catheter having tubings extending into lumens within the catheter. The lumens may be used for blood, drugs or other medicants. The lumens may also be used for sensors. The junction element, external to the patient, connects the tubings to the lumens. The tubings, also external to the patient, connect to infusion members, to which one or more infusion systems may be connected to deliver blood, drugs and other medicants to the patient. A sensor having a sensing element may extend through the sensor lumen and be positioned internal to the patient for physiological parameter sensing. An external portion of the sensor may be connected to associated electronics to provide automatic monitoring of the physiological parameters and automatic delivery and control of the infusants. Also, a central line catheter for delivering fluids directly into a main artery or vein near the heart, which contains a first lumen to deliver a fluid through the central line catheter and a second lumen containing a sensor capable indicating a characteristic level in blood. The first lumen delivers the fluid downstream of the sensor to prevent any interference between the fluid delivery and the sensor readings. In other versions, the central line catheter can have additional lumens for additional purposes. In addition, the central line catheter can further include a flush sleeve to remove debris around the sensor.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Antimicrobial medical articles containing a combination of anti-infective compounds, octoxyglycerin, salicylic acid, and sesquiterpenoids
Medical articles impregnated with antimicrobial compositions containing synergistic combinations of octoxyglycerin and other anti-infective compounds are disclosed. Such medical articles may include urinary catheters, central venous catheters, tracheal catheters, arterial grafts, wound dressings, sutures, or any other medical articles derived from polymeric substrates such as biomedical polyurethane, biomedical polyvinylchloride (PVC), biomedical silicon, biodegradable polymers, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), etc. or from natural products including natural rubber, silk or cotton fiber. Antimicrobial compositions comprising salicylic acid and sesquiterpenoids are also disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Method and Systems for Controlling Ultrafiltration Using Central Venous Pressure Measurements
The volume of fluid removed from a patient during ultrafiltration is controlled automatically on the basis of central venous pressure (CVP) measurements. In one embodiment, a central venous catheter (CVC) is used for accessing blood during dialysis. A sensor located at the tip of the catheter or inside the dialysis machine is used to periodically measure CVP. CVP feedback data helps prevent the excessive removal of fluids from the patient.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
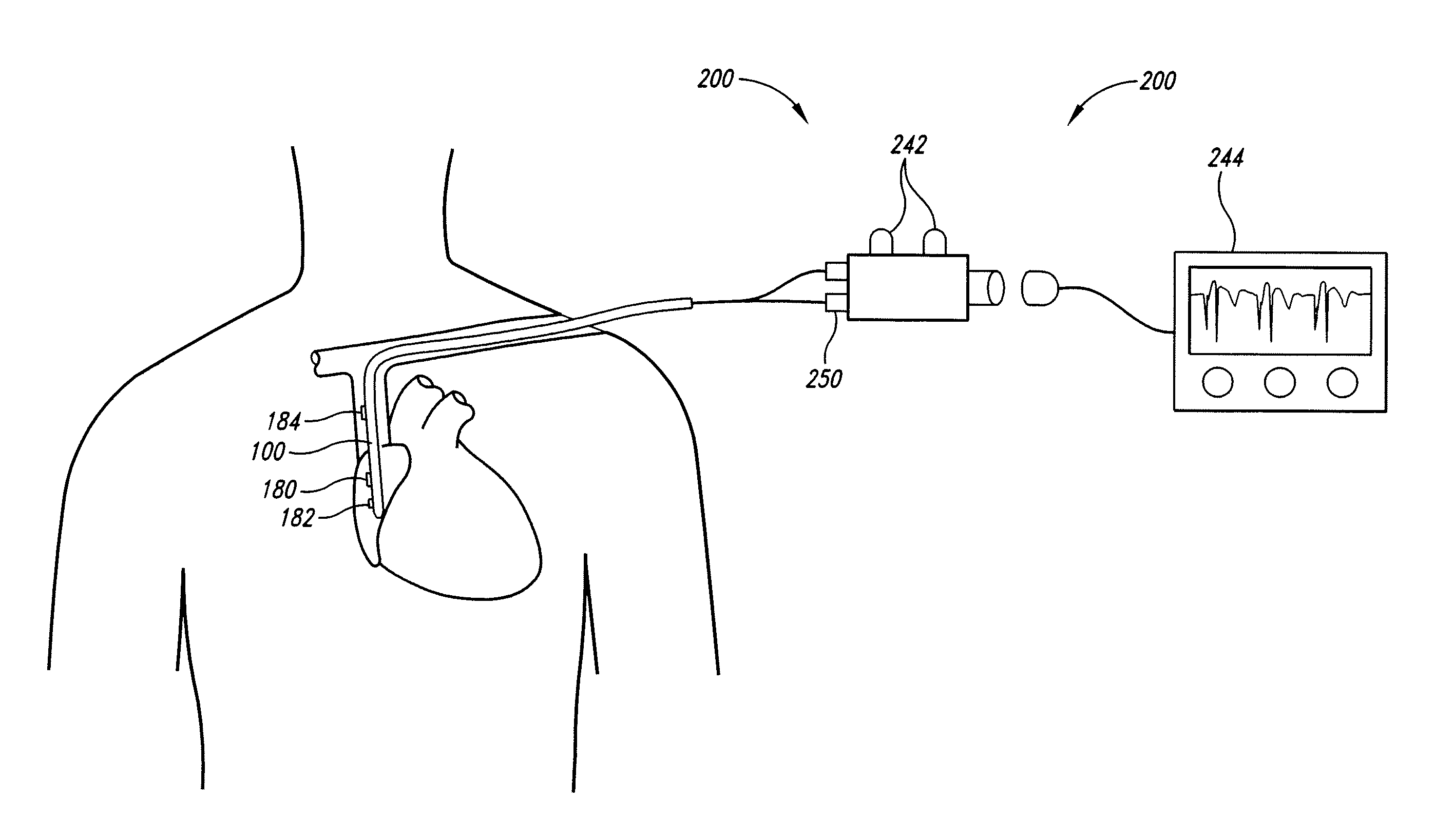
Catheter with position indicator
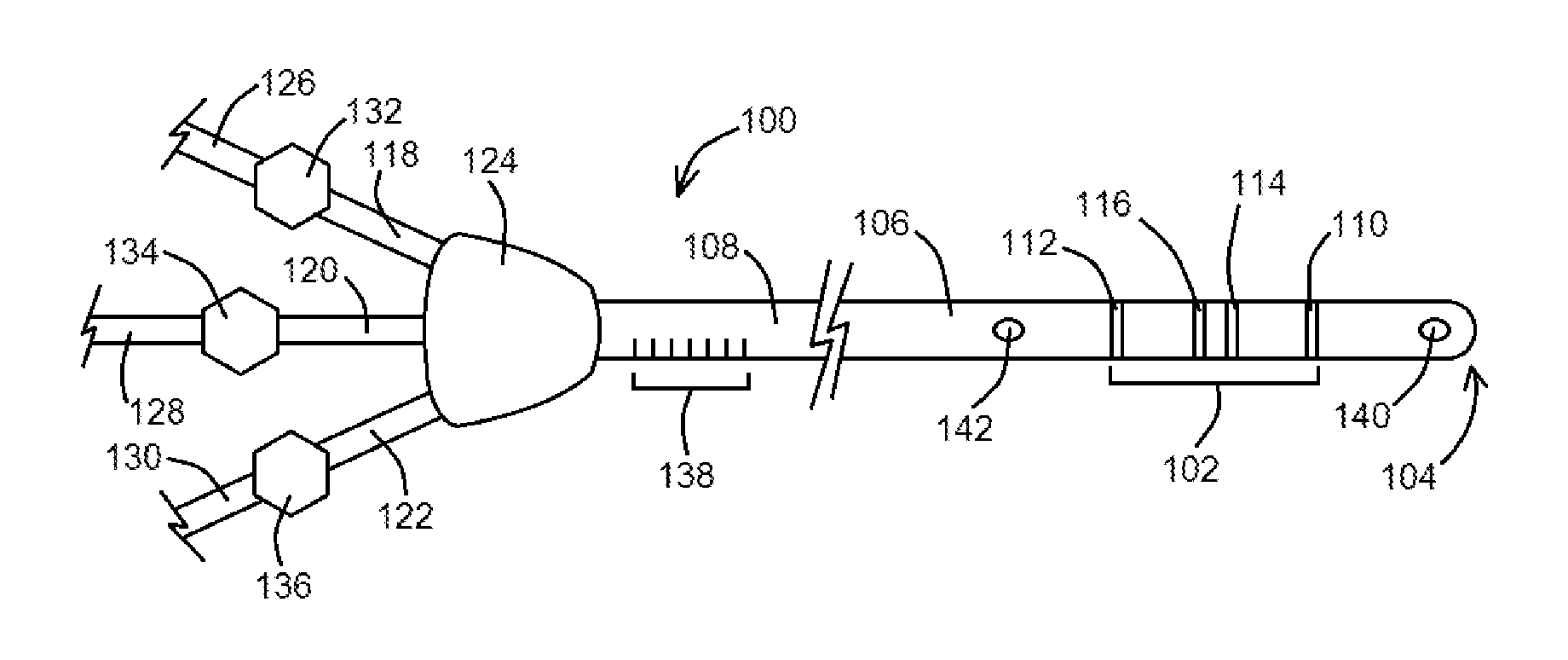
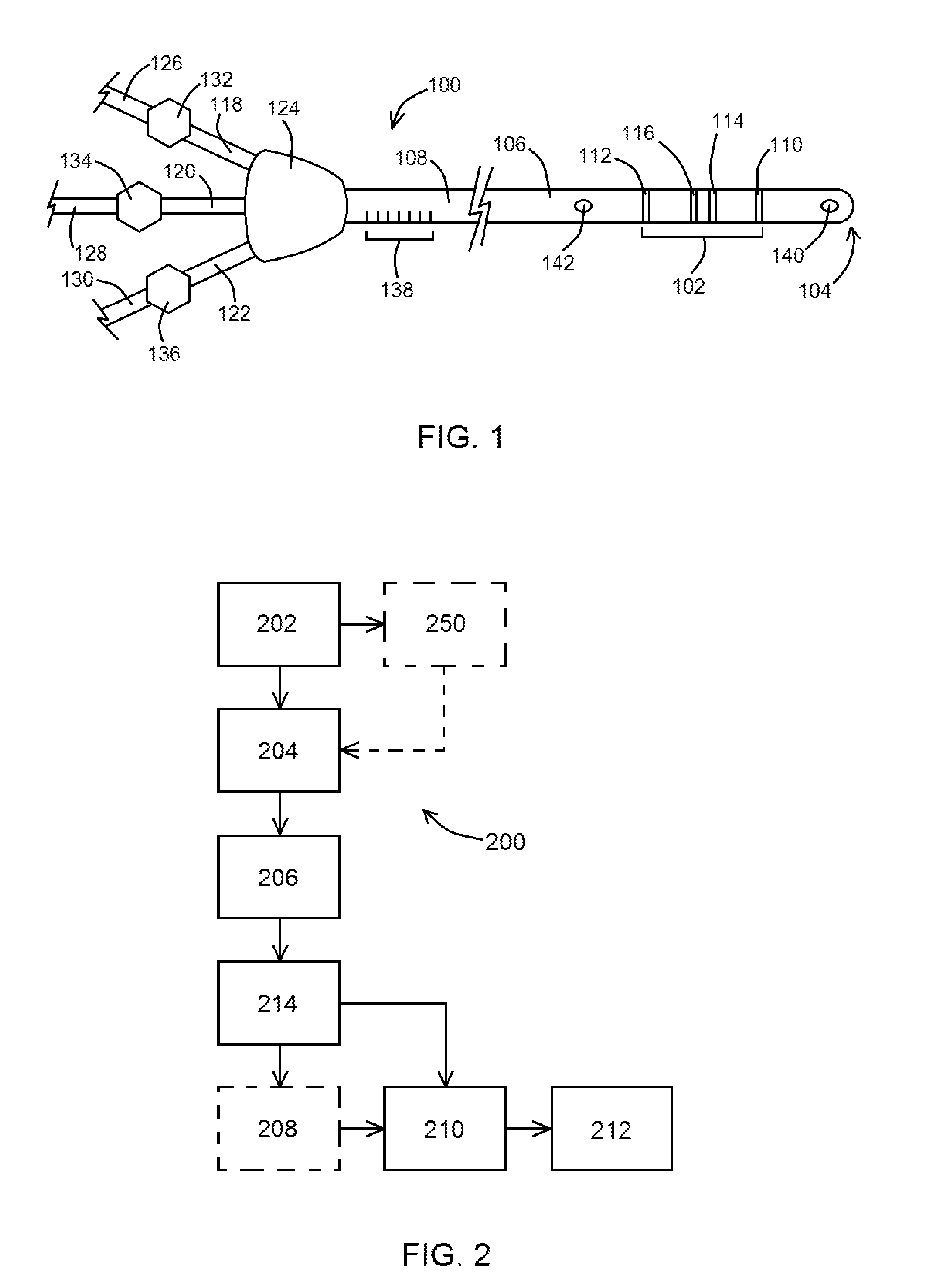
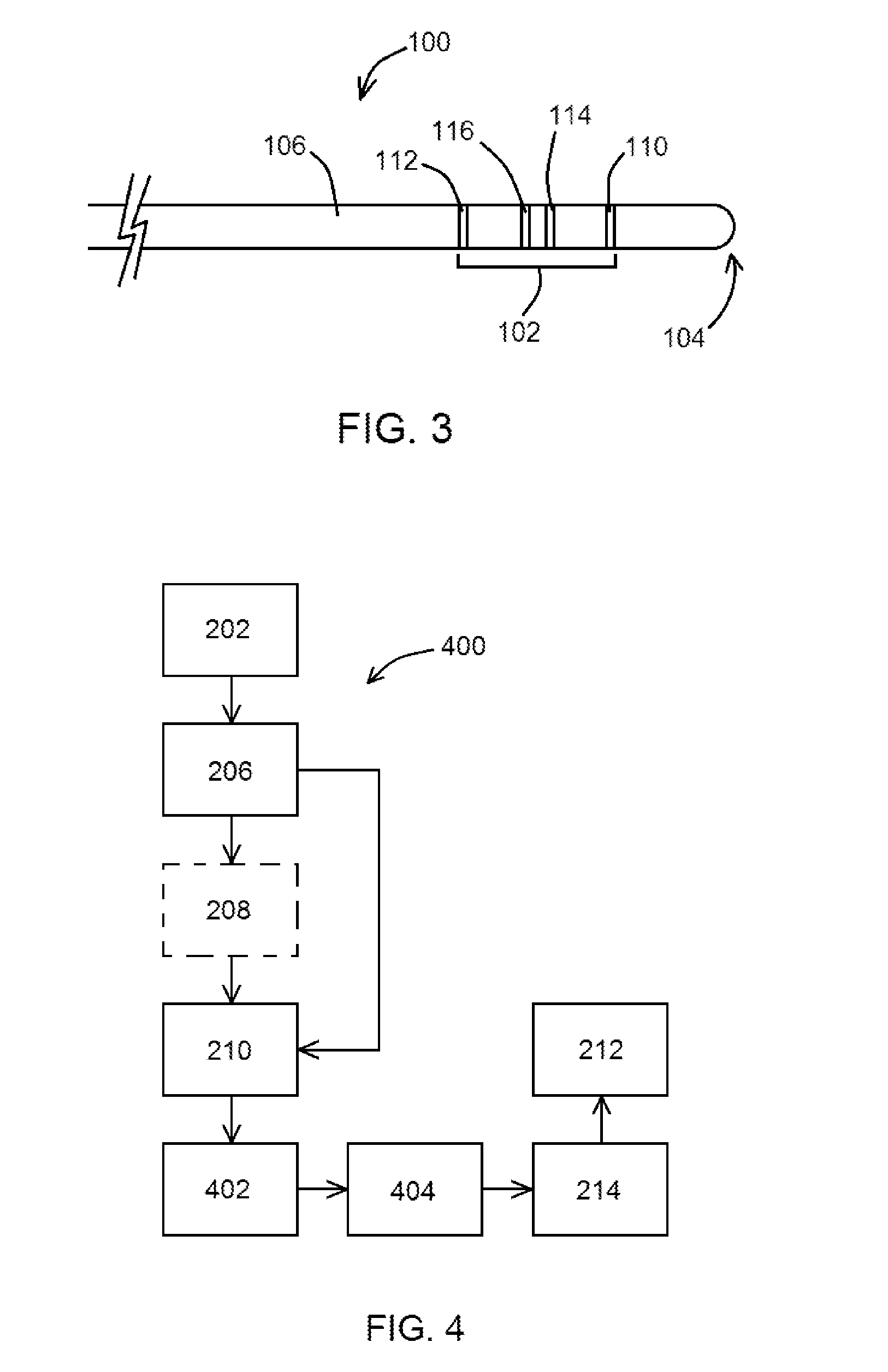
A peripherally inserted central venous catheter having a position indicator is used in a method of detecting movement of a catheter tip within a patient's superior vena cava. The PICC comprises a catheter having a proximal end with distance marks at measured intervals, an anchor wing system secured to the catheter's proximal end, at least one extension leg secured to the anchor wing system and the position indicator attached to the extension leg. The position indicator has an area for marking a distance signifying an initial external length of catheter which extends from the point the catheter enters the patient to the point it is attached to the anchor wing and / or marking an initial full length or the internal length of catheter which is fully within the patient. Any movement of the catheter's tip is detected by comparing the current external distance mark with the initial external distance mark.
Owner:DONOVAN GAIL MARIE
Apparatus and Methods Relating to Intravascular Positioning of Distal End of Catheter
Owner:CR BARD INC
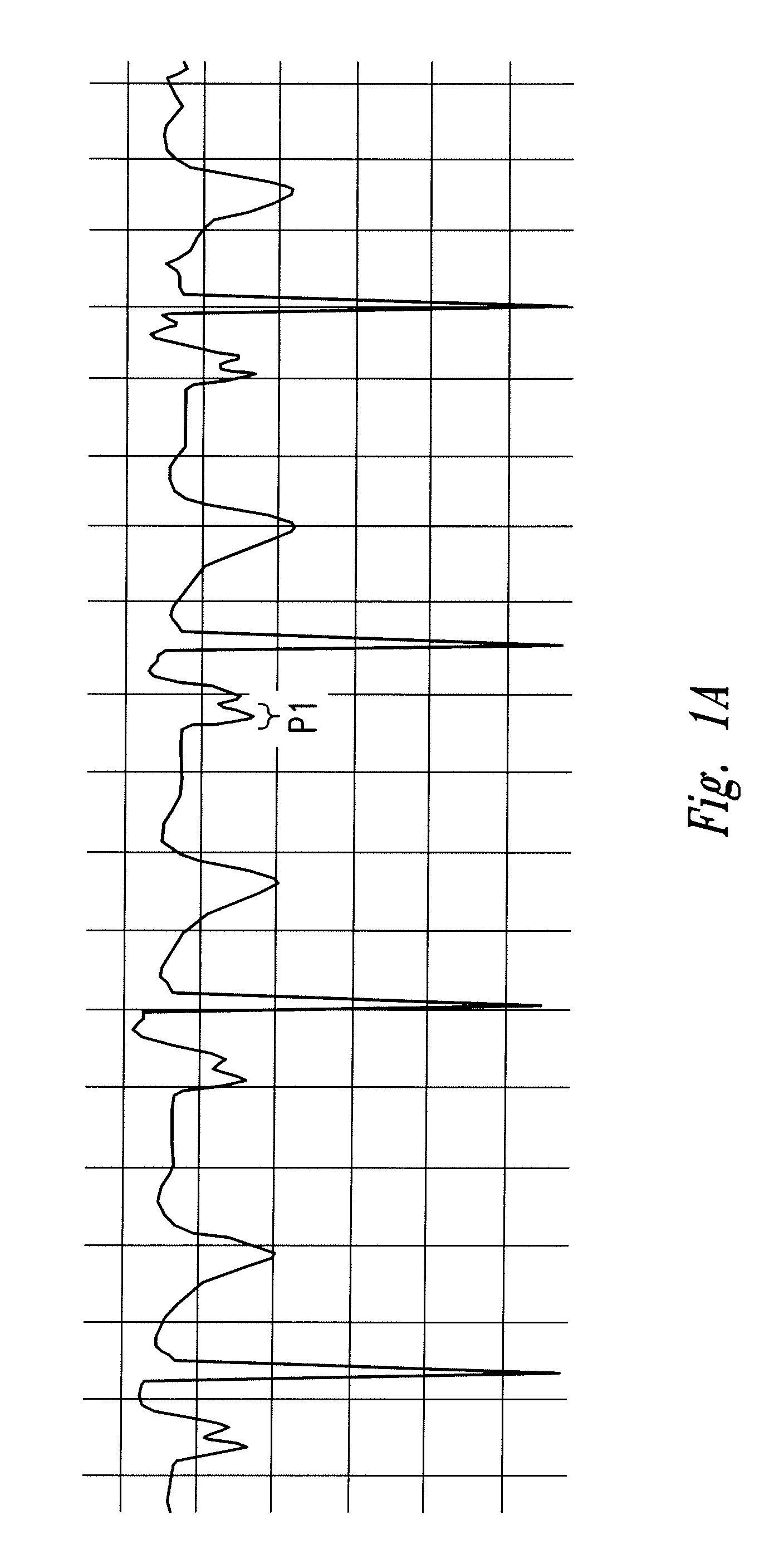
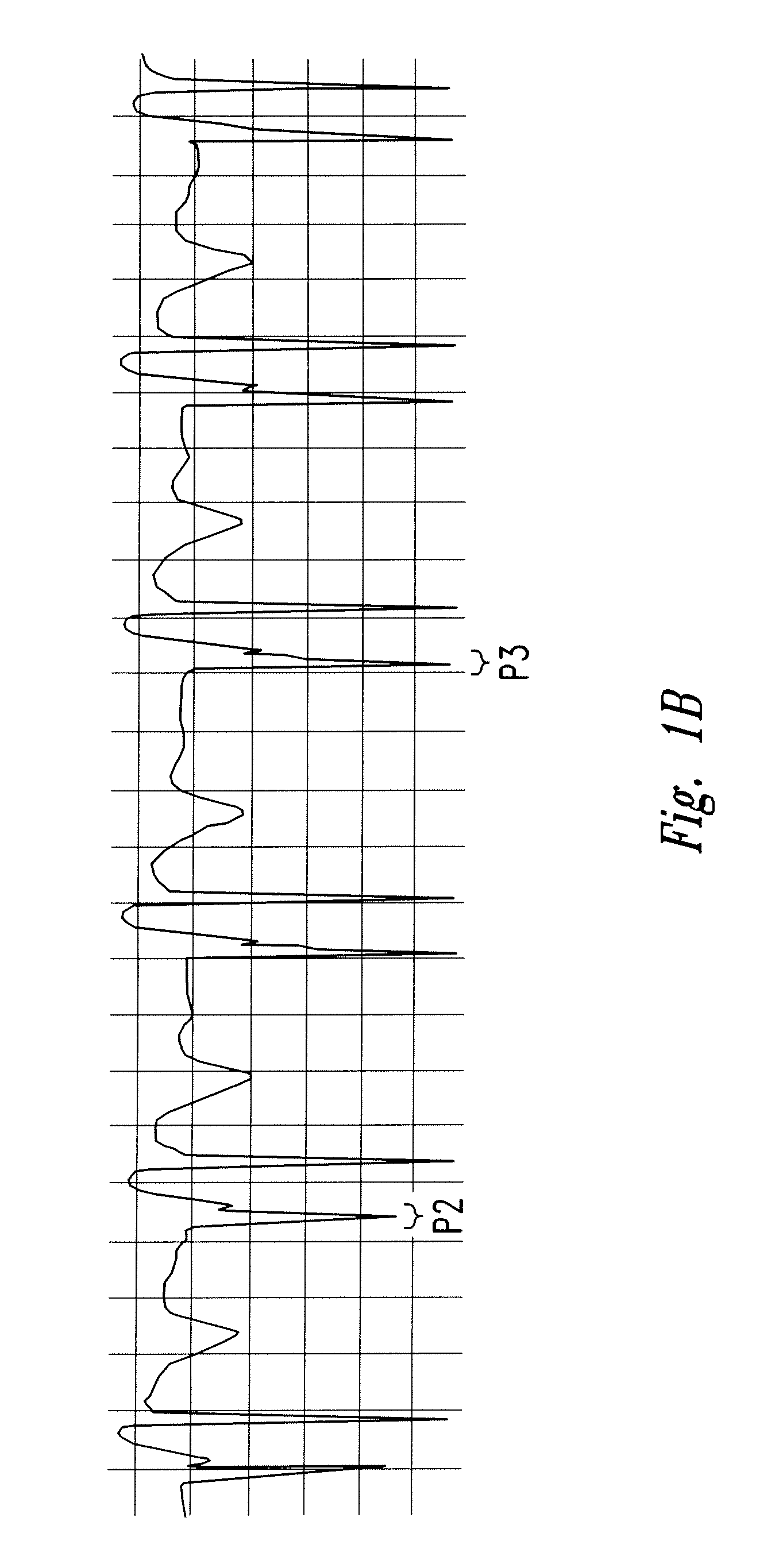
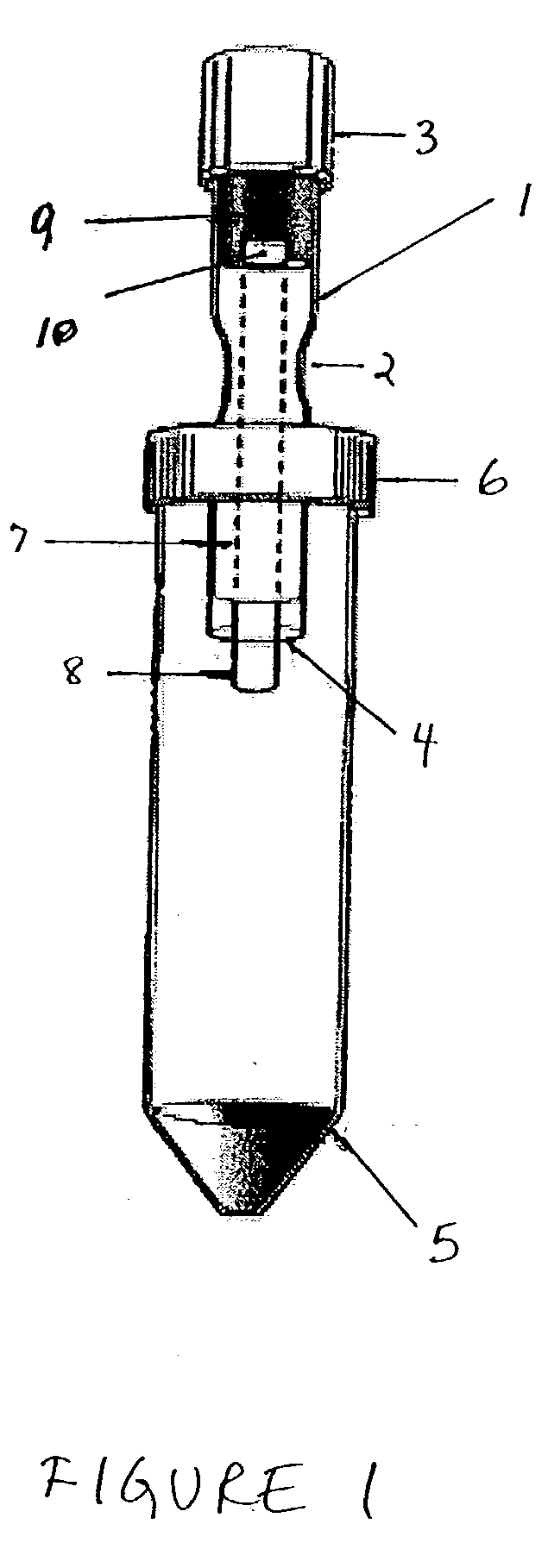
Central venous catheter kit with line gripping and needle localizing devices
ActiveUS8277417B2Improve health careUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfusion syringesVeinNeedle localization
A central venous catheter kit enables health care workers quickly and controllably gain ultrasound supported access to vascular tissue for catheterization. Ultrasound support requires gel for reducing acoustic impedance and reflectance loss, which gel is included in the kit, as well as at least two newly conceived devices, the first for gripping the guide wire in an otherwise gelled environment, and the second for marking the skin for proper needle localization. State of the art kit components are thus included in the kit, in addition to the scanning gel and the noted device(s). The devices each comprise certain finger- or digit-grippable structure, and textured surfacing for enhancing the frictional contact between the user's digits and the devices.
Owner:FEDINEC JAMES J
Multiple lumen catheter having a soft tip
A multiple lumen catheter having a soft, tapered multiple lumen distal tip for insertion into a body vessel. One of the lumens is sized to pass over a guidewire such that the catheter can be inserted into the body vessel using the Seldinger technique. At least one medical implement lumen is used for placement or positioning of a biomedical sensor or other medical implement. For example, at least one optical fiber passing through the medical implement lumen may transmit and receive light at the distal tip for measuring oxygen saturation of the blood. The catheter may have a cylindrical catheter body to which the soft distal tip attaches. The soft tip reduces the possibility of vessel or tissue puncture and abrasion. The tip is constructed of a soft plastic or pliable material that yields easily when force is applied. For example, the tip may be made of a softer material than the catheter body, or if made of the same material, the tip can be configured with thinner walls or a higher air-to-material ratio cross-section. Various geometrical configurations and combinations of materials can be used to decrease the flexible resistance of the tip to an applied load. One particular useful application for the catheter of the present invention is as a central venous catheter equipped with fibers for measuring oximetry. The fibers extend to the distal end of the tip and are preferably secured therein with minimal adhesive so as to limit the stiffness added to the tip. One particular useful construction is to secure the fibers within the medical implement lumen using adhesive only along a length of between about 0.5-3.5 mm.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Antimicrobial medical articles containing a synergistic combination of anti-infective compounds and octoxyglycerin
Medical articles impregnated with antimicrobial compositions containing synergistic combinations of octoxyglycerin and other anti-infective compounds are disclosed. Such medical articles may include urinary catheters, central venous catheters, tracheal catheters, arterial grafts, wound dressings, sutures, or any other medical articles derived from polymeric substrates such as biomedical polyurethane, biomedical polyvinylchloride (PVC), biomedical silicon, biodegradable polymers, polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), etc. or from natural products including natural rubber, silk or cotton fiber.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
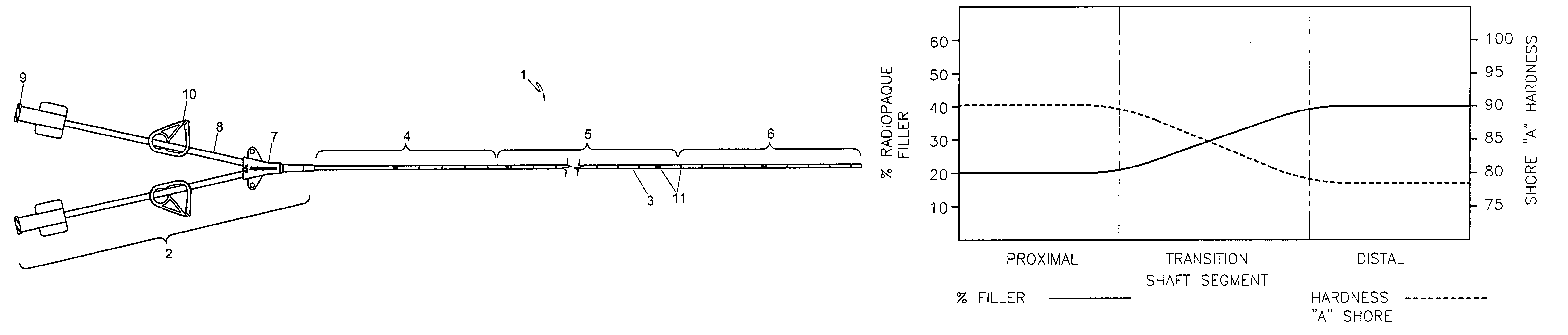
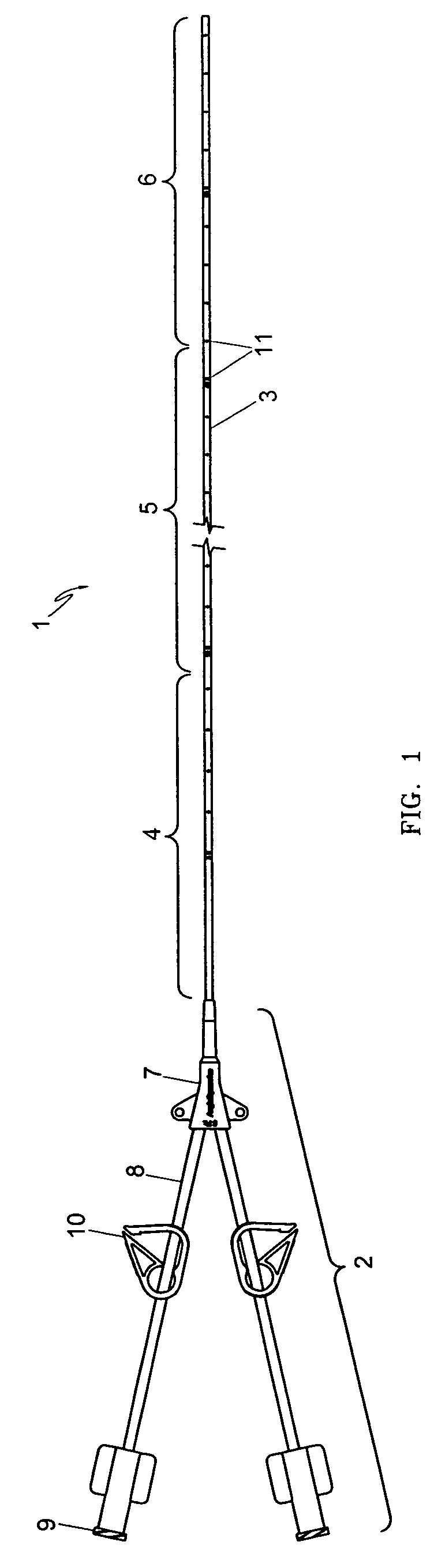
Variable characteristic venous access catheter shaft
InactiveUS7618411B2Increase weightOther blood circulation devicesCatheterVenous accessVariable Characteristic
A central venous catheter is provided having a proximal tube segment, a distal tube segment and a transition tube segment interposed between the proximal and distal tube segments which are preferably formed as a single integrated tube containing polymer material of different durometer and varying amounts of radiopaque filler material. The polymer durometer of the proximal segment is higher than the polymer durometer of the distal segment. By contrast, the percentage by weight of the filler material contained in the distal segment is higher than that of the proximal segment. The variation in the polymer durometer and the filler amount along the length of the tube provide the desired tensile strength, hardness, chemical resistance and fatigue resistance at the proximal segment and at the same time provide the desired flexibility and radiopacity at the distal segment.
Owner:ANGIODYNAMICS INC
Method for a central venous line catheter having a temperature control system
ActiveUS8128595B2Reduce riskEfficient cooling and warmingStentsBalloon catheterCentral venous lineFluid temperature
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Multi-lumen sheath central venous catheter with vena cava filter apparatus and method of using same
A combined multi-lumen sheath with a wire body and a filter. The filter may be removably coupled to the multi-lumen sheath within a filter capsule for temporary placement and retrieval.
Owner:BIO2MEDICAL
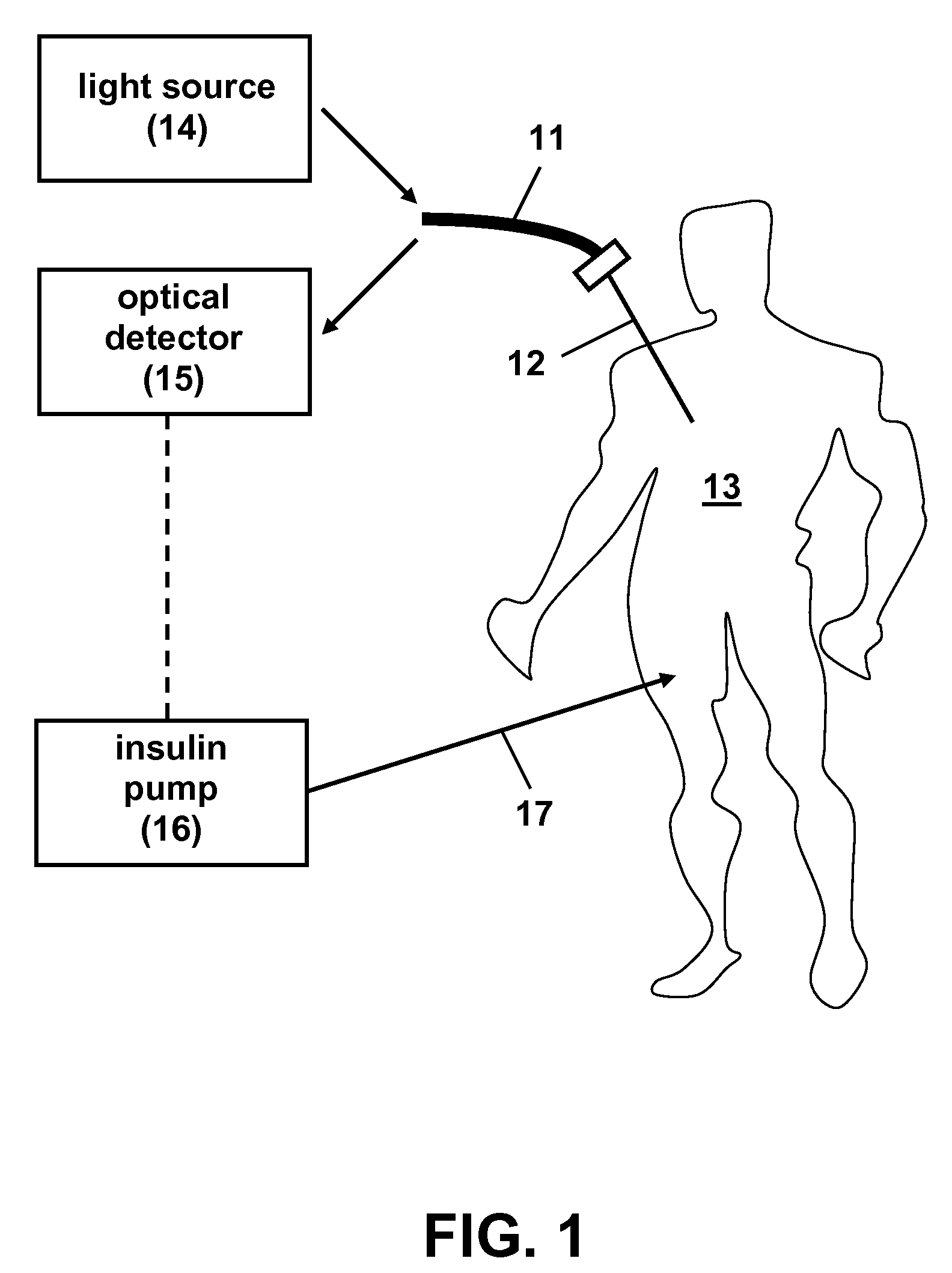
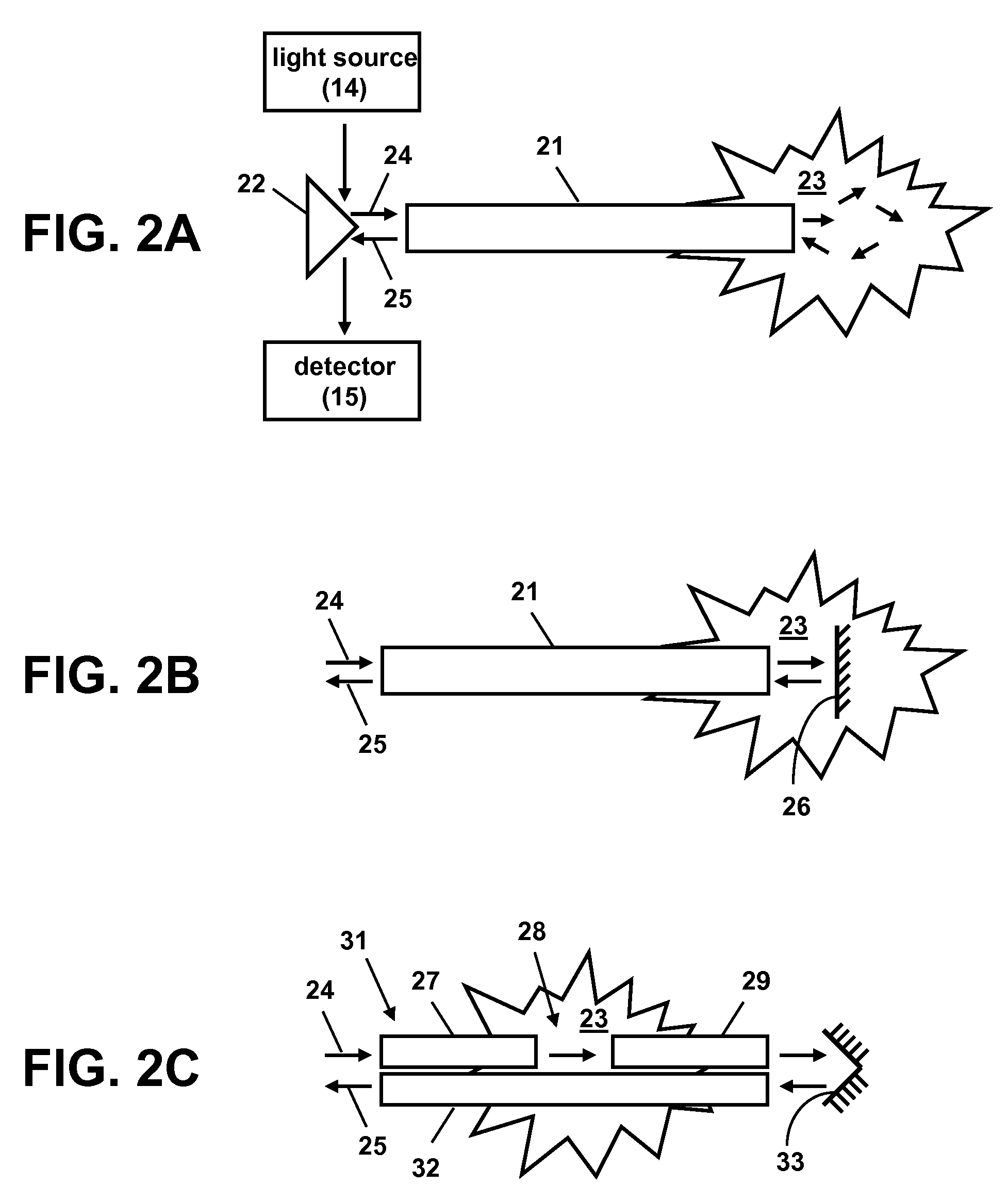
Indwelling Fiber Optic Probe for Blood Glucose Measurements
InactiveUS20090088615A1The instrumentation is simpleLong measurement timeMedical devicesPressure infusionFiberVein
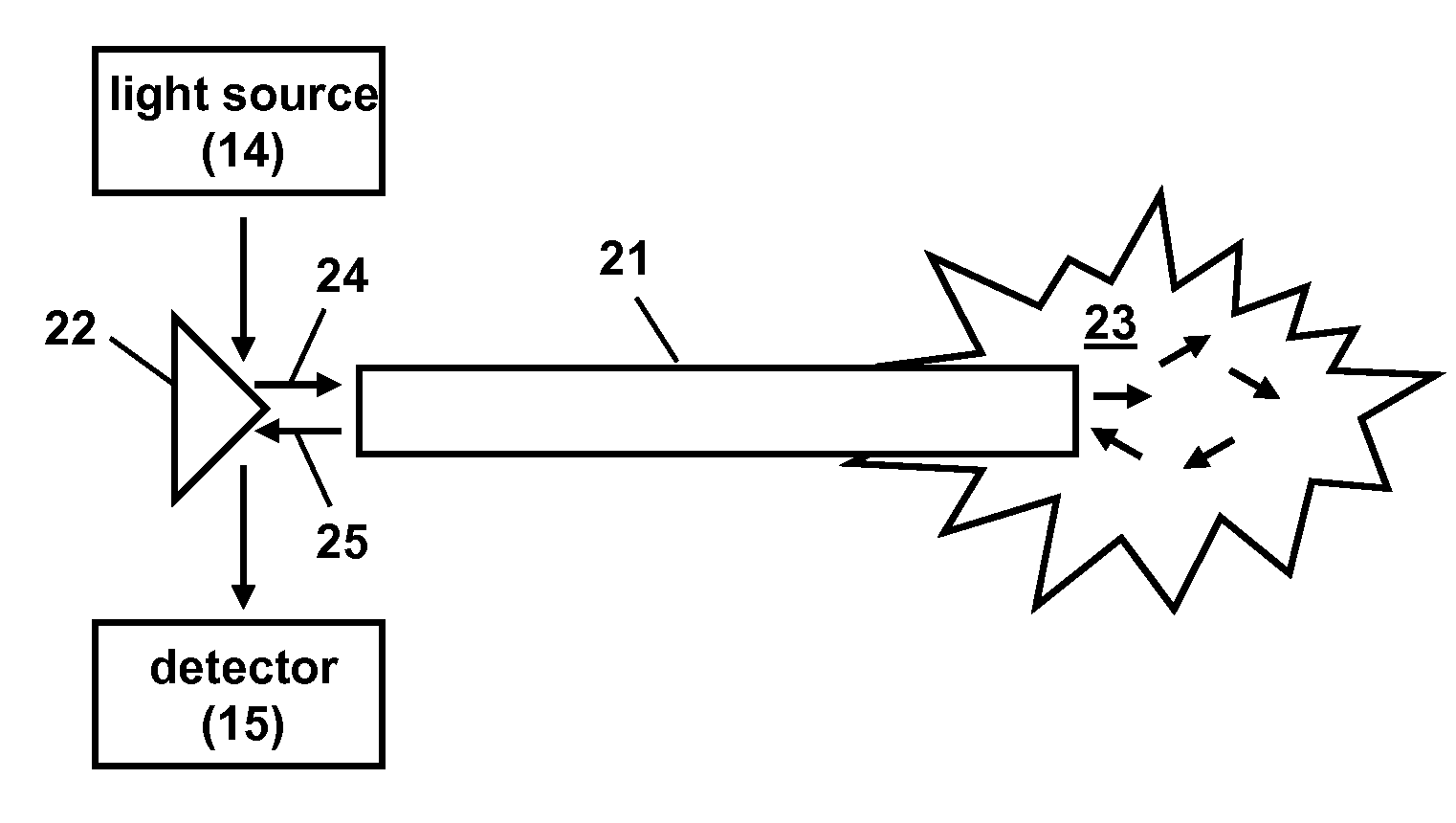
An indwelling fiber optic probe can be used to make in vivo blood glucose measurements through a central venous catheter. The fiber optic probe can operate in the near-infrared spectral region. The optical measurement can be backscattering, transmission, or a combination of both, depending on the optical configuration.
Owner:LUMINOUS MEDICAL
Moisture sensor for monitoring an access to a patient and method of producing the moisture sensor
ActiveUS9629964B2Low production costSimplify connectivity issuesDetection of fluid at leakage pointOther blood circulation devicesElectrical conductorEngineering
A moisture sensor for monitoring an access to a patient for a system by which, via a flexible line, a liquid is fed to and / or out from a patient, for monitoring the vascular access in extra-corporeal blood treatment or for monitoring a central venous catheter for acute dialysis, and a method of producing a moisture sensor are described. The moisture sensor has a substrate material with an electrically conductive structure having conductor paths arranged at a distance from one another and connected together across a terminating resistor. The terminating resistor is an electrically conductive film which is applied in a section of the substrate material on which are formed electrical contacting regions for connecting the terminating resistor to the conductor paths, such that an external terminating resistor is not required and the moisture sensor can be produced easily in large numbers complete with the terminating resistor.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
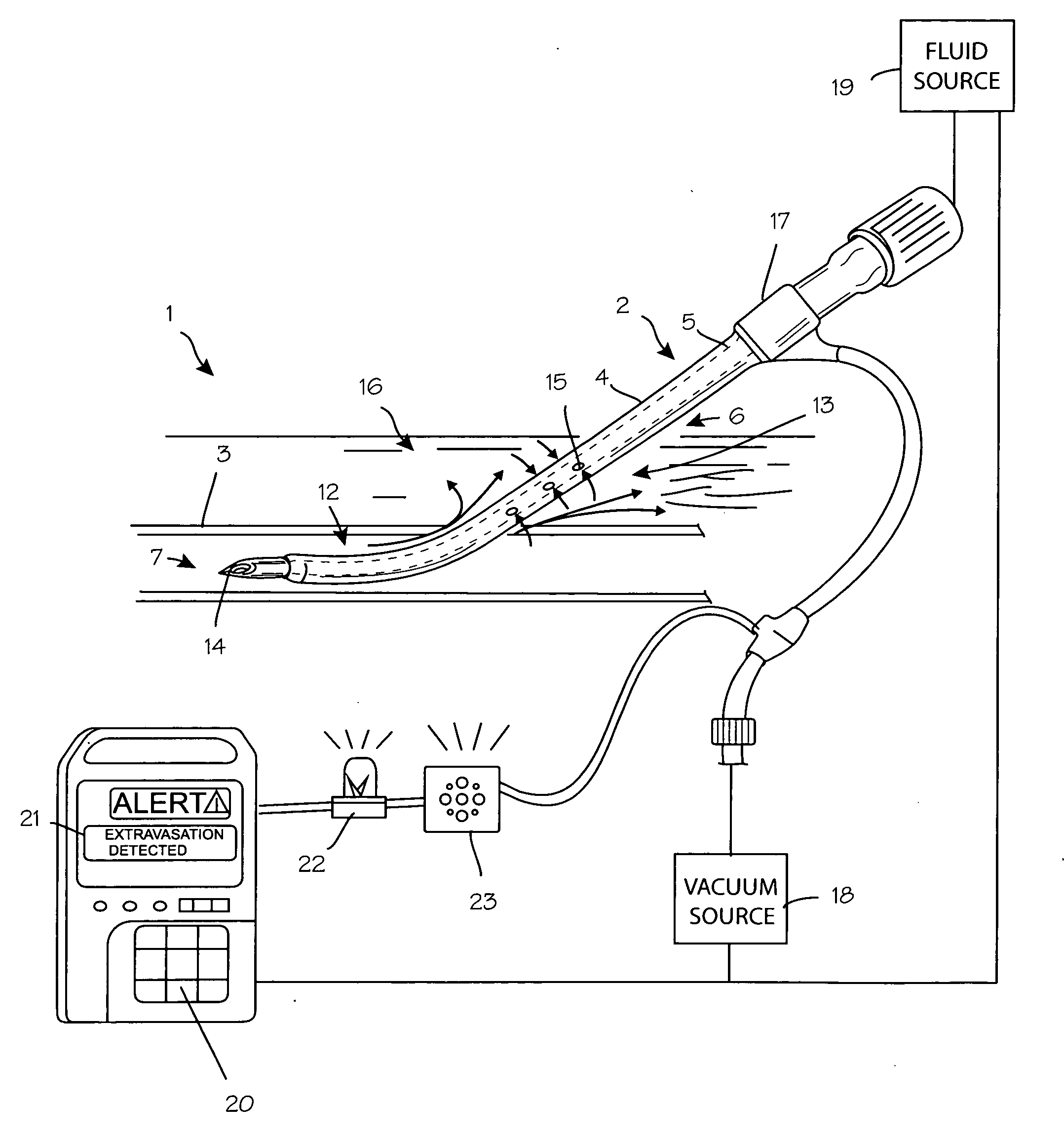
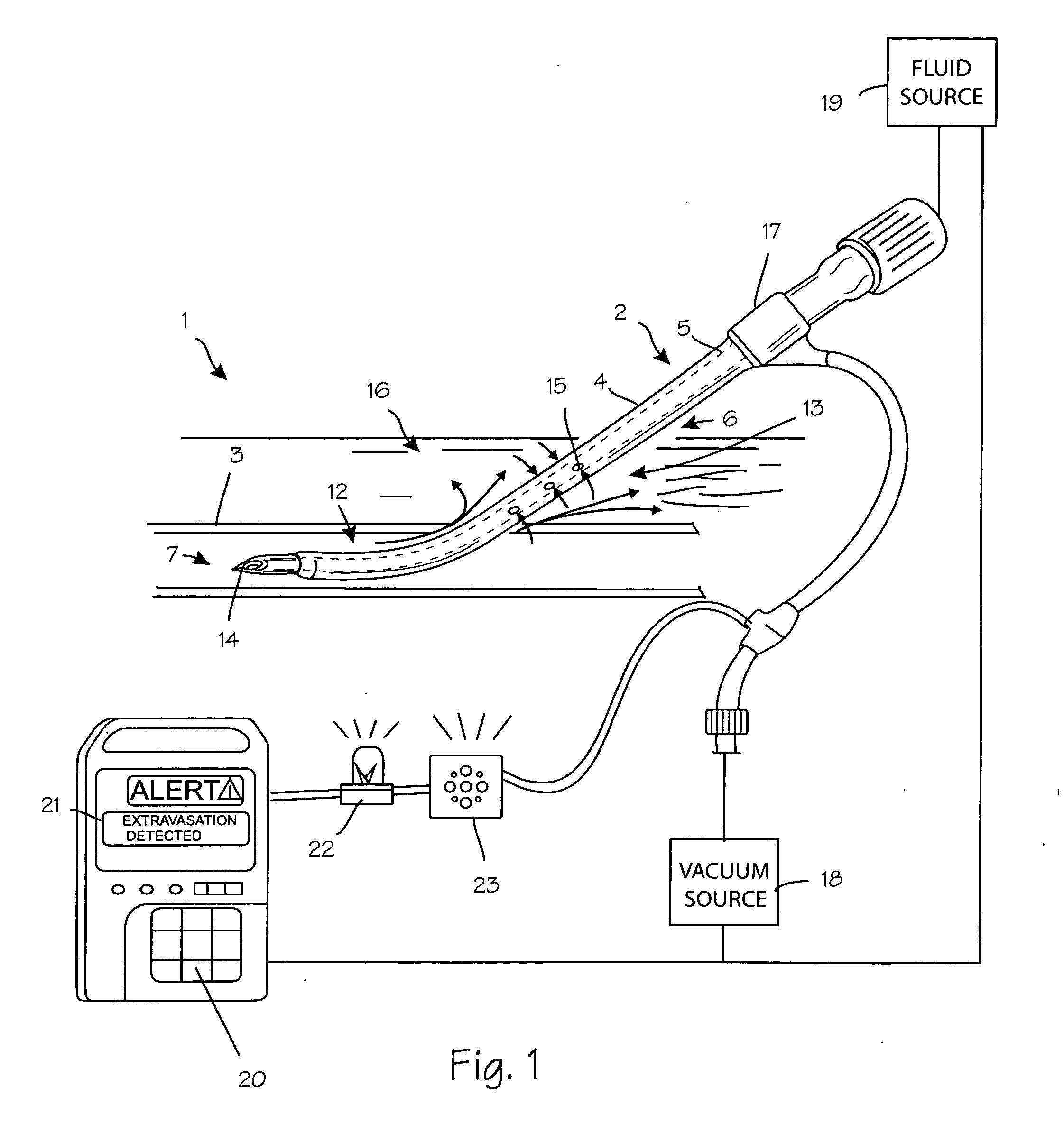
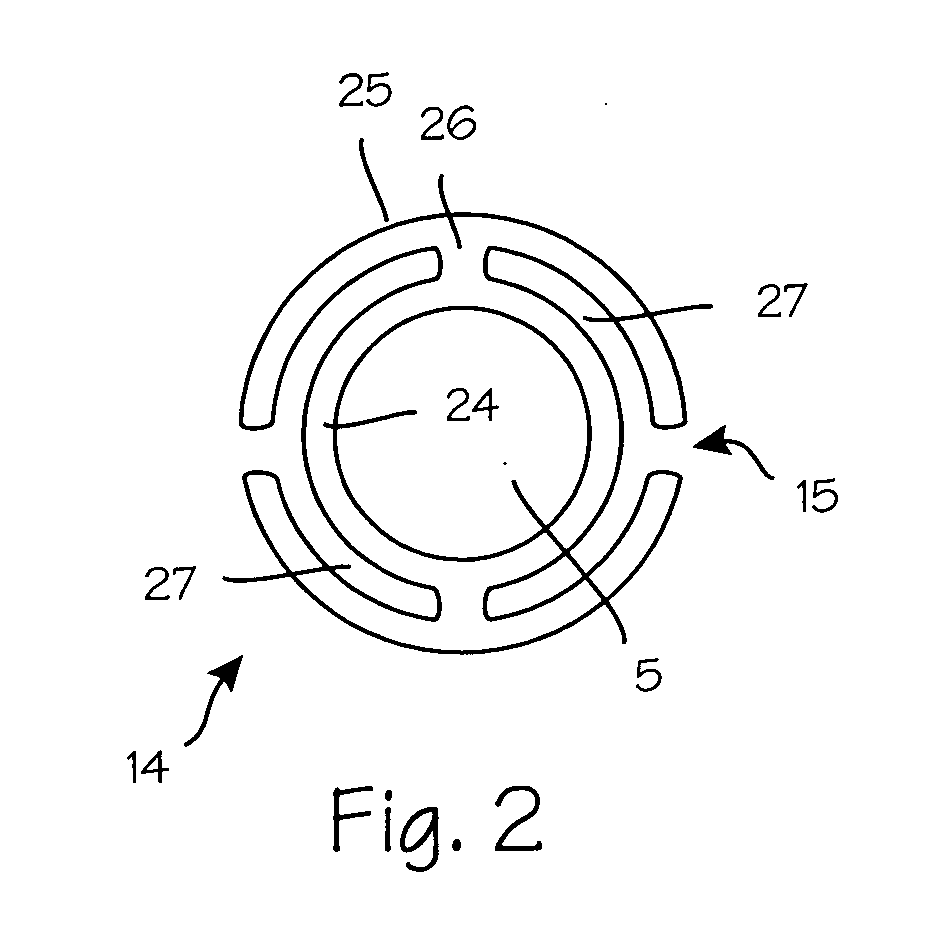
Anti-extravasation catheter
ActiveUS20080172013A1Reduce the amount requiredMulti-lumen catheterInfusion devicesInfusion catheterVein
The disclosed devices and methods provide for the minimization of fluid extravasation during use of infusion catheters such as peripherally inserted central catheters and central venous catheters. The anti-extravasation catheter allows a surgeon to drain fluids from soft tissue surrounding an infusion site while also providing fluid inflow to a patient.
Owner:CANNUFLOW INC
Central venous catheter kit with line gripping and needle localizing devices
ActiveUS20110071394A1Improve health careUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsGuide needlesVeinNeedle localization
A central venous catheter kit enables health care workers quickly and controllably gain ultrasound supported access to vascular tissue for catheterization. Ultrasound support requires gel for reducing acoustic impedance and reflectance loss, which gel is included in the kit, as well as at least two newly conceived devices, the first for gripping the guide wire in an otherwise gelled environment, and the second for marking the skin for proper needle localization. State of the art kit components are thus included in the kit, in addition to the scanning gel and the noted device(s). The devices each comprise certain finger- or digit-grippable structure, and textured surfacing for enhancing the frictional contact between the user's digits and the devices.
Owner:FEDINEC JAMES J
Stretchable Sleeve and Wrap for Protecting and Securing Catheter Dressings and Tubes on a Patient
ActiveUS20130012883A1Sufficient compressive forceFinger bandagesCatheterCentral venous catheterBlood draw
An easily removable, non-irritating stretchable sleeve or chest wrap for protecting and securing a PICC line or chest catheter tubing and cap extending externally from the insertion point. The sleeve or chest wrap is easily attached to a patient's arm or body, securing the small length of the external PICC line or the central venous catheter, protecting the tubing and cap from external contaminants, and allowing easy access to the PICC line or the central venous catheter for administration of drugs or nutrients, and access for blood draws. This sleeve allows the patient freedom of movement and is comfortable enough to prevent skin irritation over long-term usage.
Owner:FITZGERALD MICHAEL +1
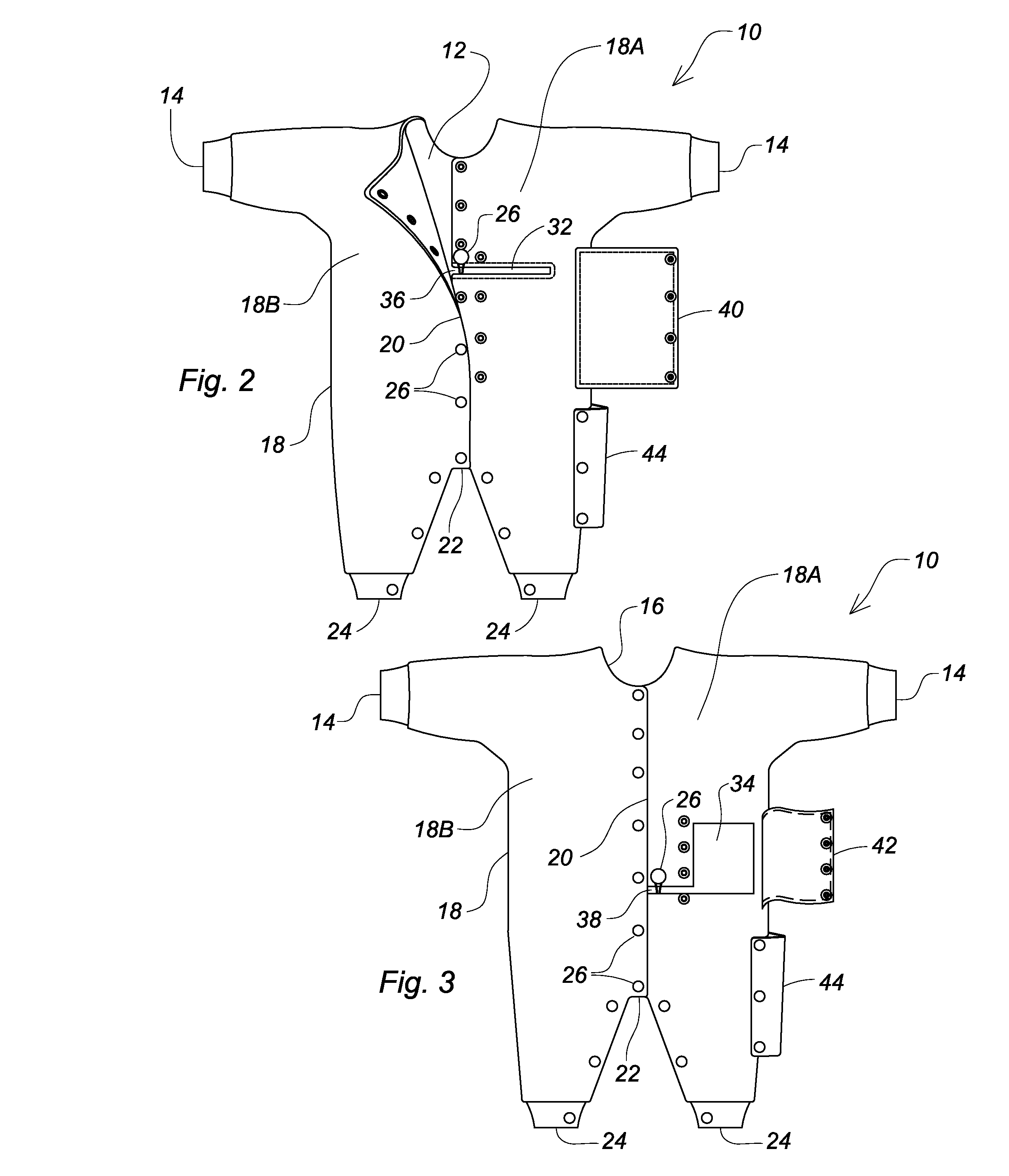
Garment for accommodating intravenous catheters and gastronomy tube
A garment for use with a patient requiring treatment with a central venous catheter and / or gastrostomy tube. Access openings are provided through which the catheter or tube may be reached from the outside of the garment and, in the case of the catheter, coiled on the outside of the garment. Flaps are attached to the garment for covering the access openings and securing the catheter or tube under the flaps. When the access openings are connected with an open ended slot to a central longitudinal opening in the front of the garment, the catheter or tube may be passed into the access opening and the garment put on and taken off without disturbing the medical appliance to which the catheter or tube is attached.
Owner:PARRIS NICOLE A
Anti-infective central venous catheter with diffusion barrier layer
A catheter extending from a distal end which, when in an operative position is inserted within a body of a patient, to a proximal end, the catheter comprising a charge holding cavity to which a therapeutic compound is to be supplied and a wall including inner and outer portions, an inner surface of the inner portion surrounding the charge holding cavity with an outer portion surrounding at least a portion of an outer surface of the inner portion, wherein the inner portion is formed so that a first diffusion rate of the therapeutic compound therethrough is different from a second diffusion rate through the outer portion.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Devices and Systems for Navigation and Positioning a Central Venous Catheter Within a Patient
ActiveUS20150297113A1Generate lotGuide wiresDiagnostic recording/measuringIntravenous catheterMarine navigation
Devices and systems for navigation and positioning a central venous catheter within a patient. In an exemplary embodiment of a system of the present disclosure, the system comprises a first pole and a second pole, the first pole and the second pole configured to generate an electric field within a mammalian body sufficient to obtain a plurality of field measurements therein, and an elongated body configured for at least partial insertion into a blood vessel of the mammalian body and advancement through a vasculature, said advancement dependent upon the plurality of field measurements indicative of one or more locations of a portion of the elongated body within the vasculature. In at least one embodiment, the elongated body is configured as a stylet.
Owner:BARD ACCESS SYST
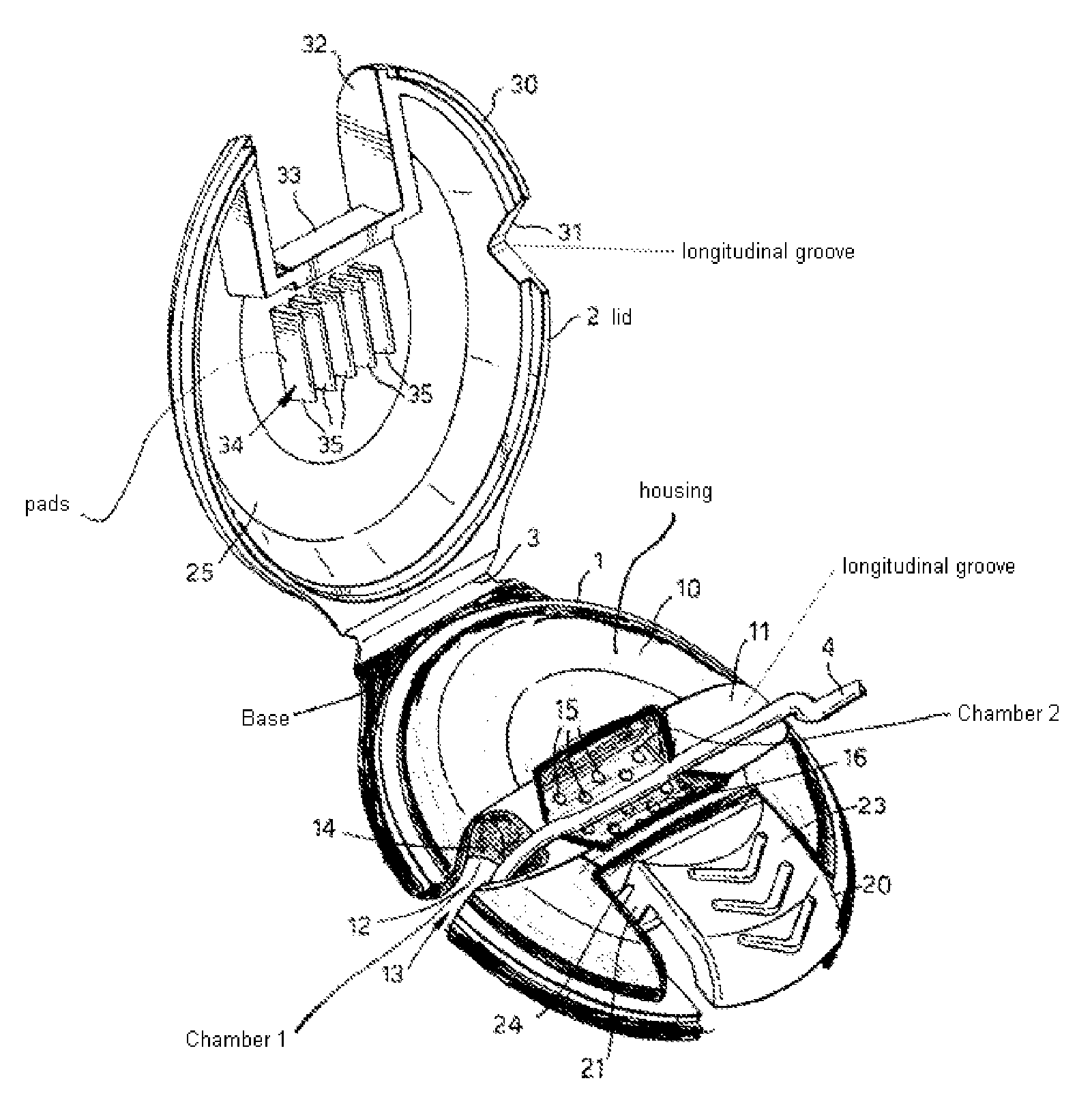
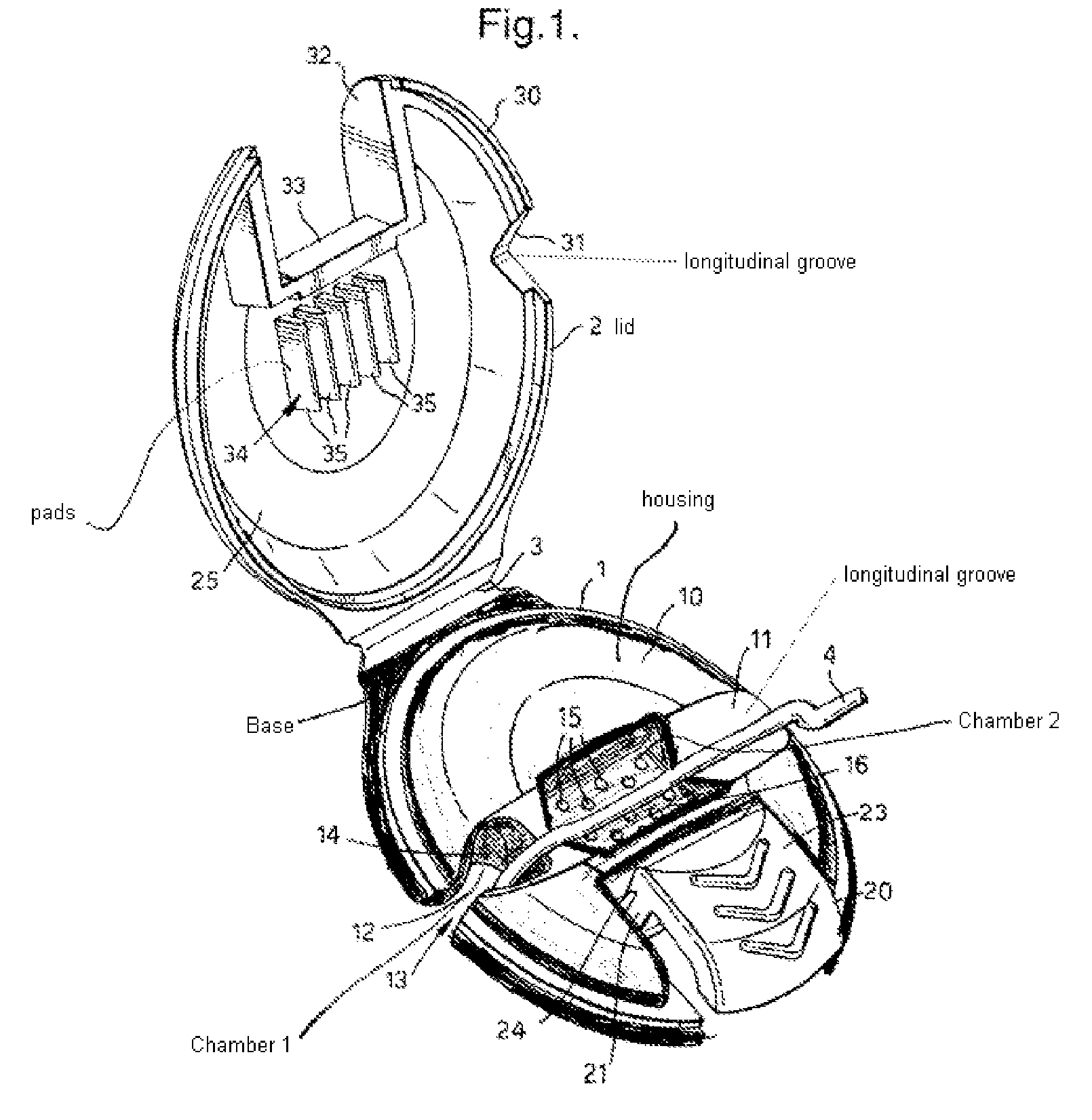
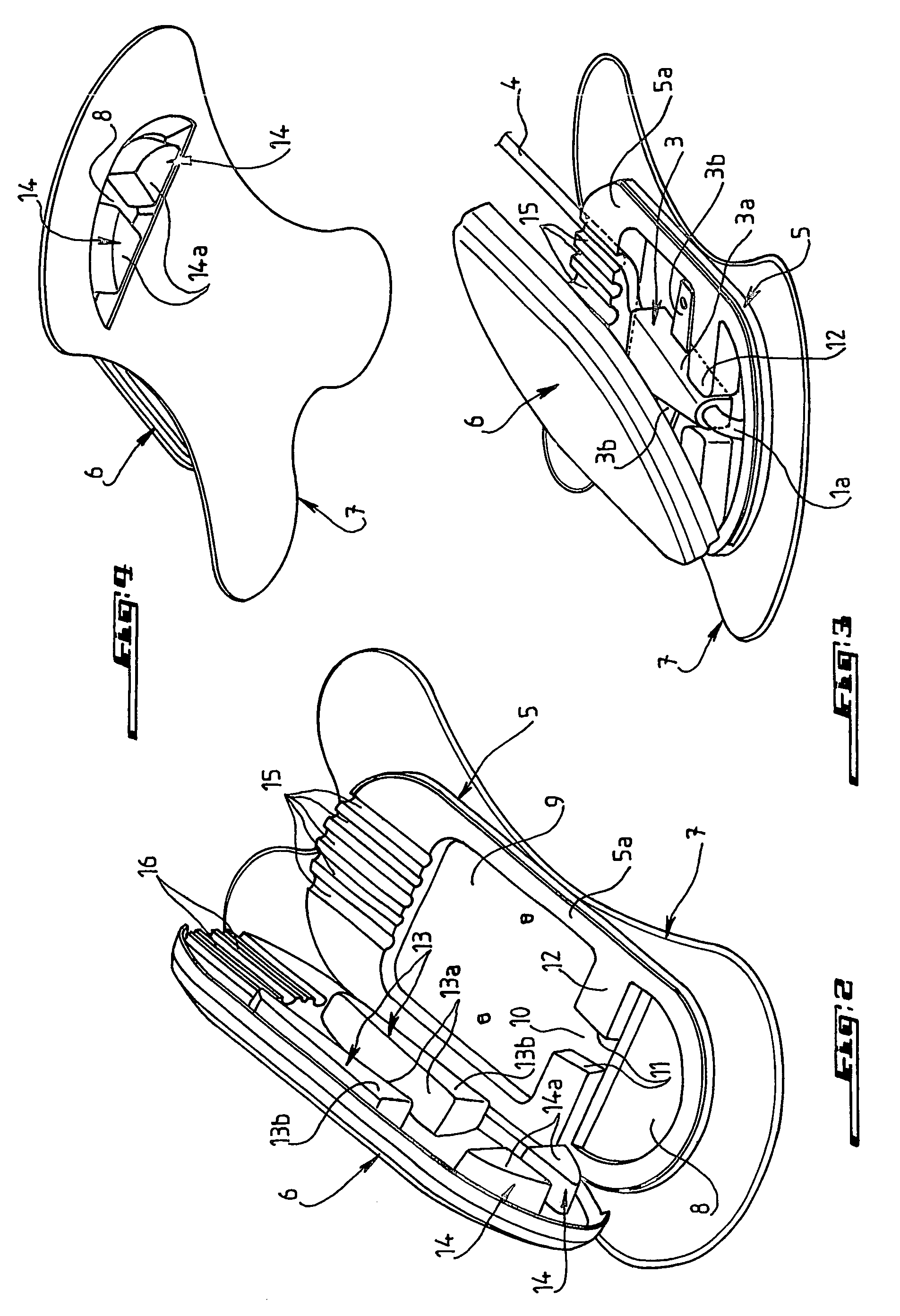
Device for fixing a catheter to the body of a patient
A device for fixing a catheter, such as a peripheral veinous catheter, a central veinous catheter or a central arterial catheter, to the body of a patient. The device includes a housing, which can be closed by a lid, and a base coupled to the housing, surrounding the housing and enabling the housing to be fixed to the skin of the patient. The housing includes a first chamber through which the outer part of the catheter, which is placed in the vein, passes and a second chamber for accommodating and maintaining the catheter.
Owner:NAVARRO +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com